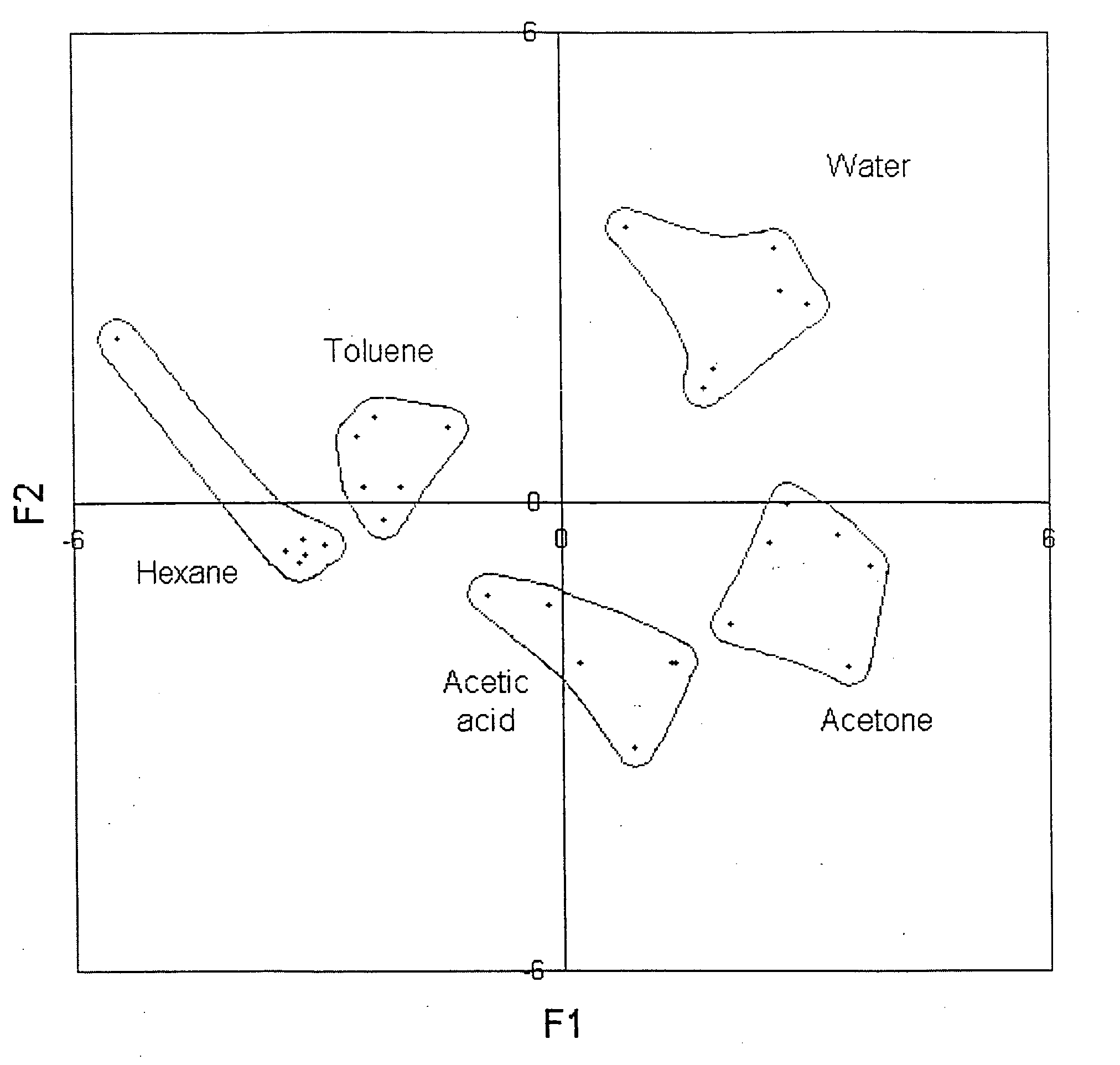
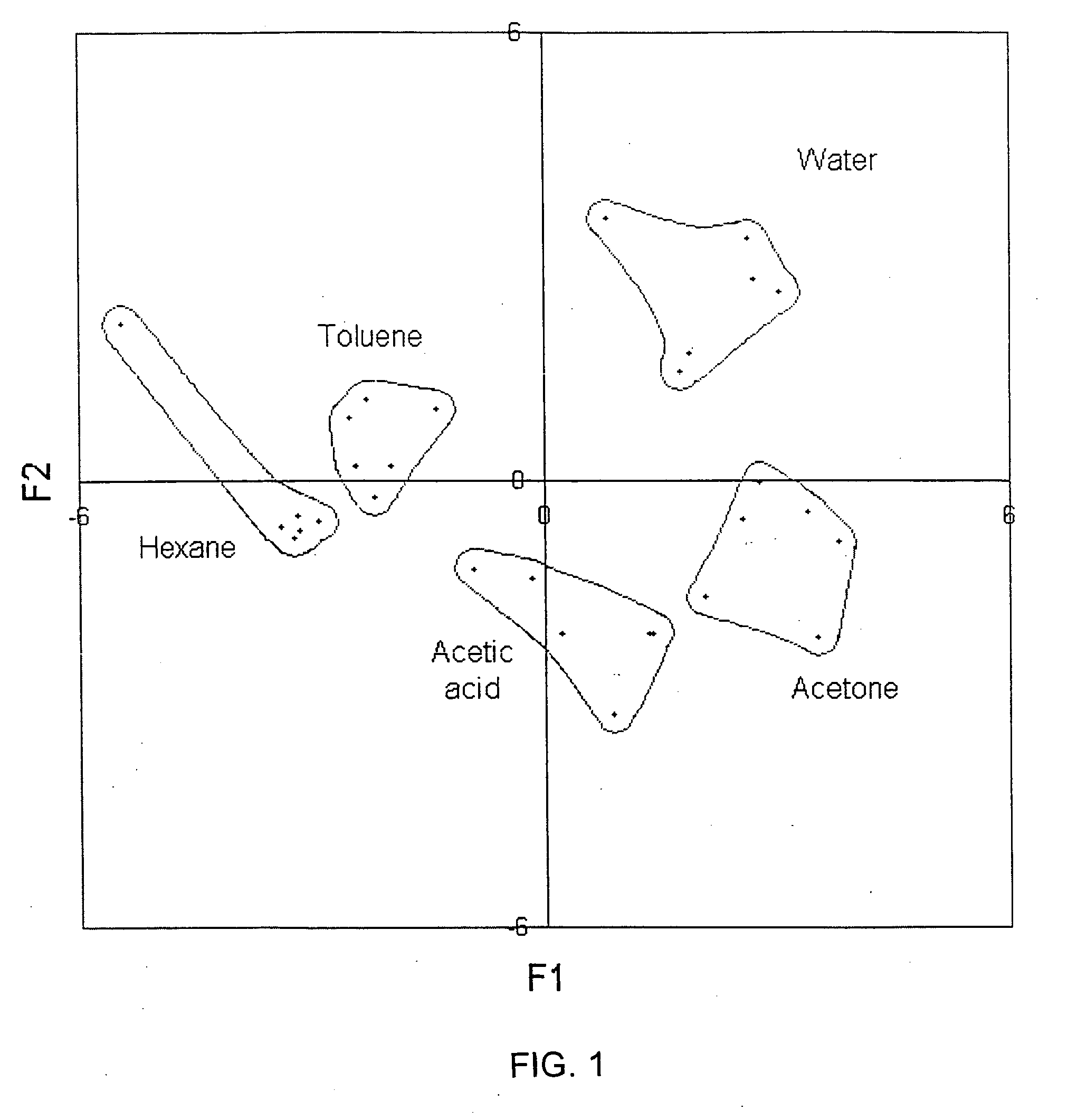
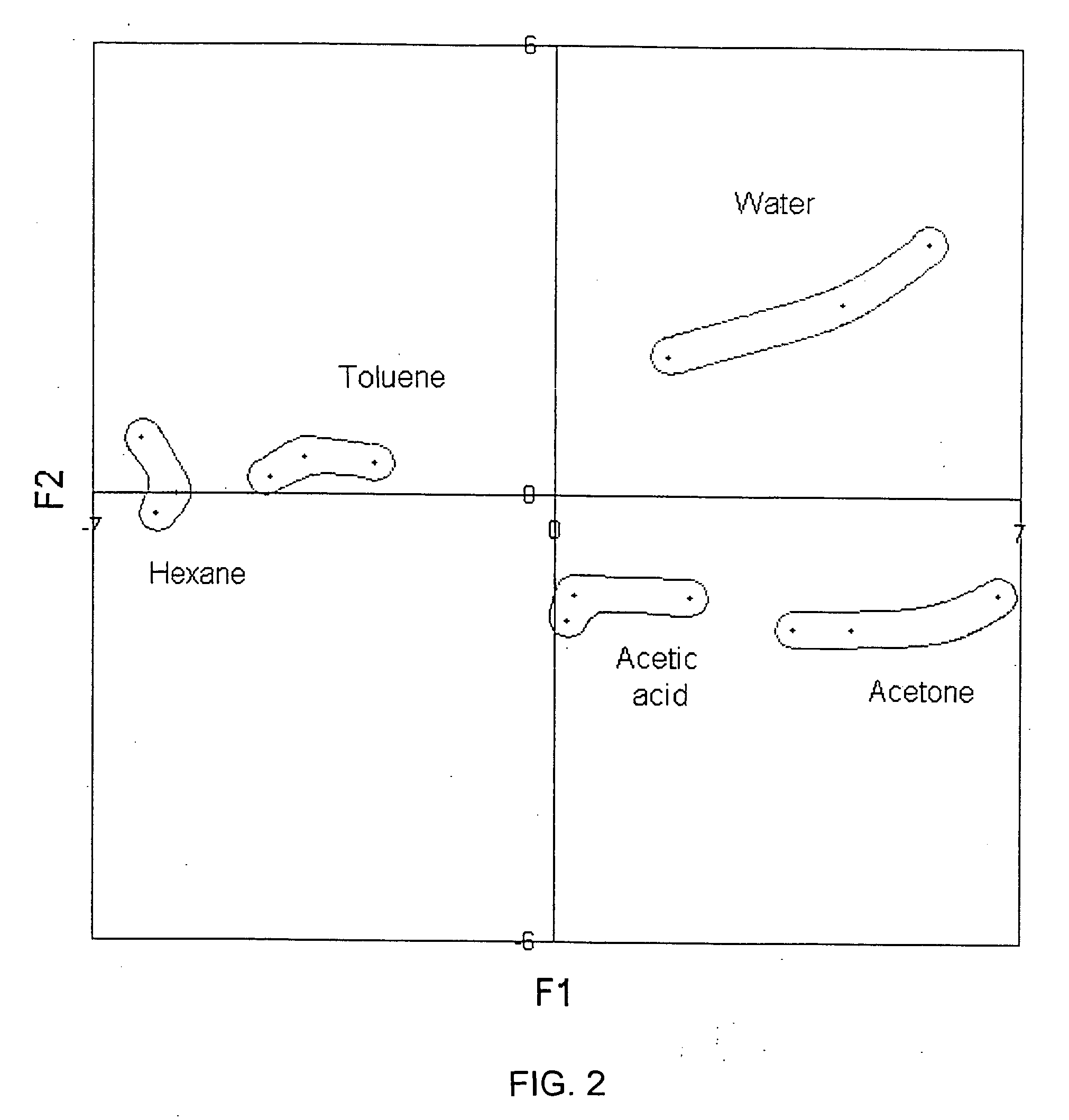
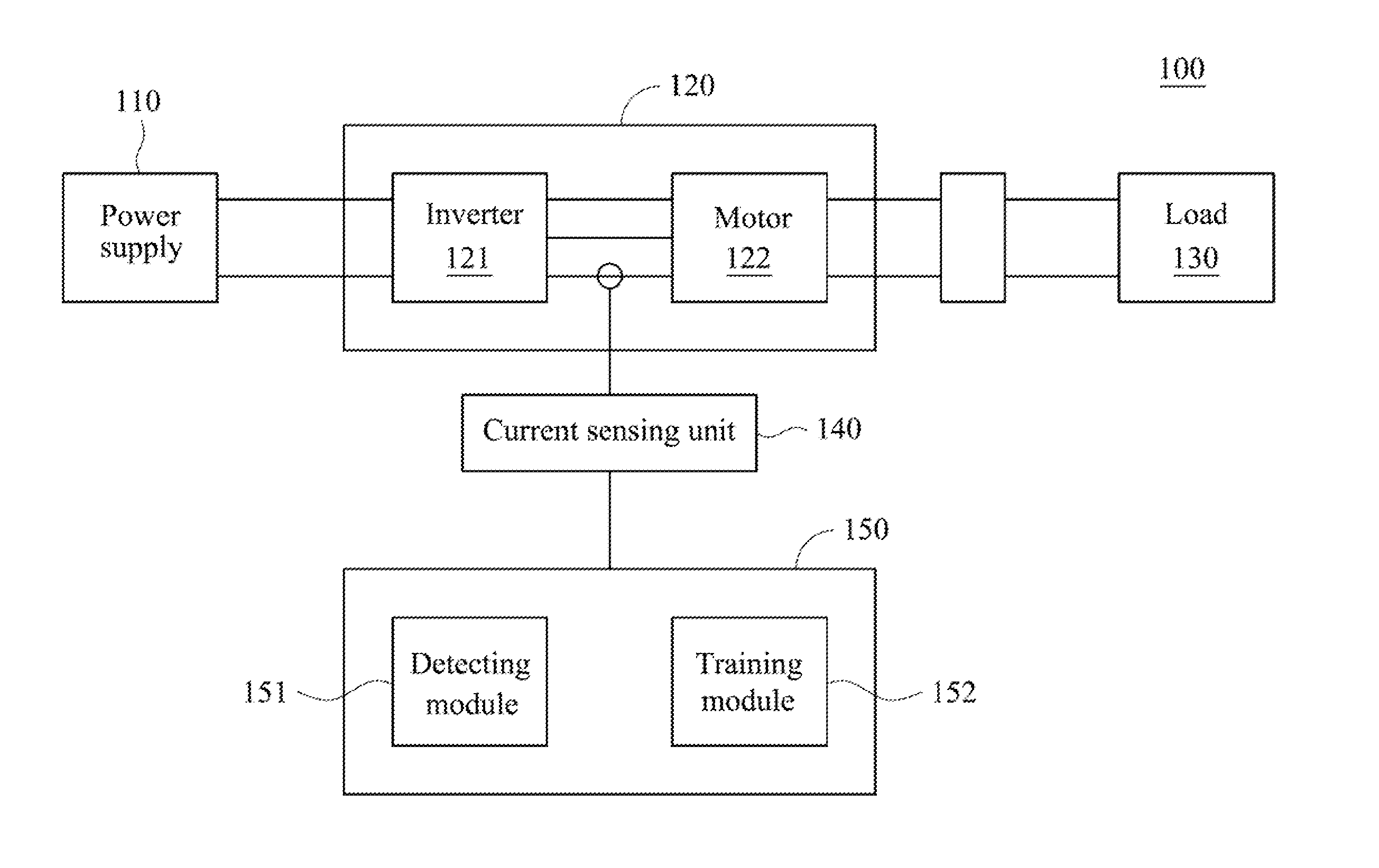
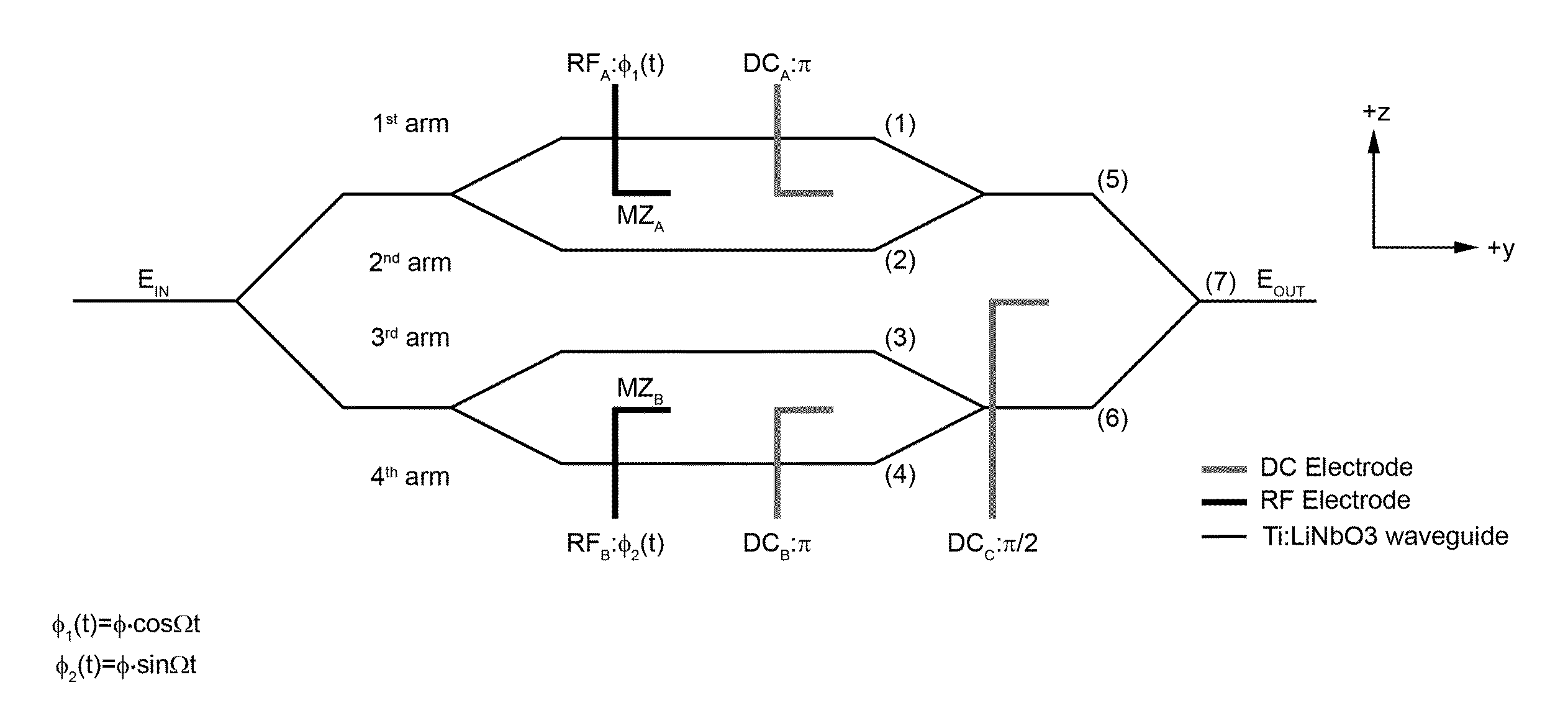
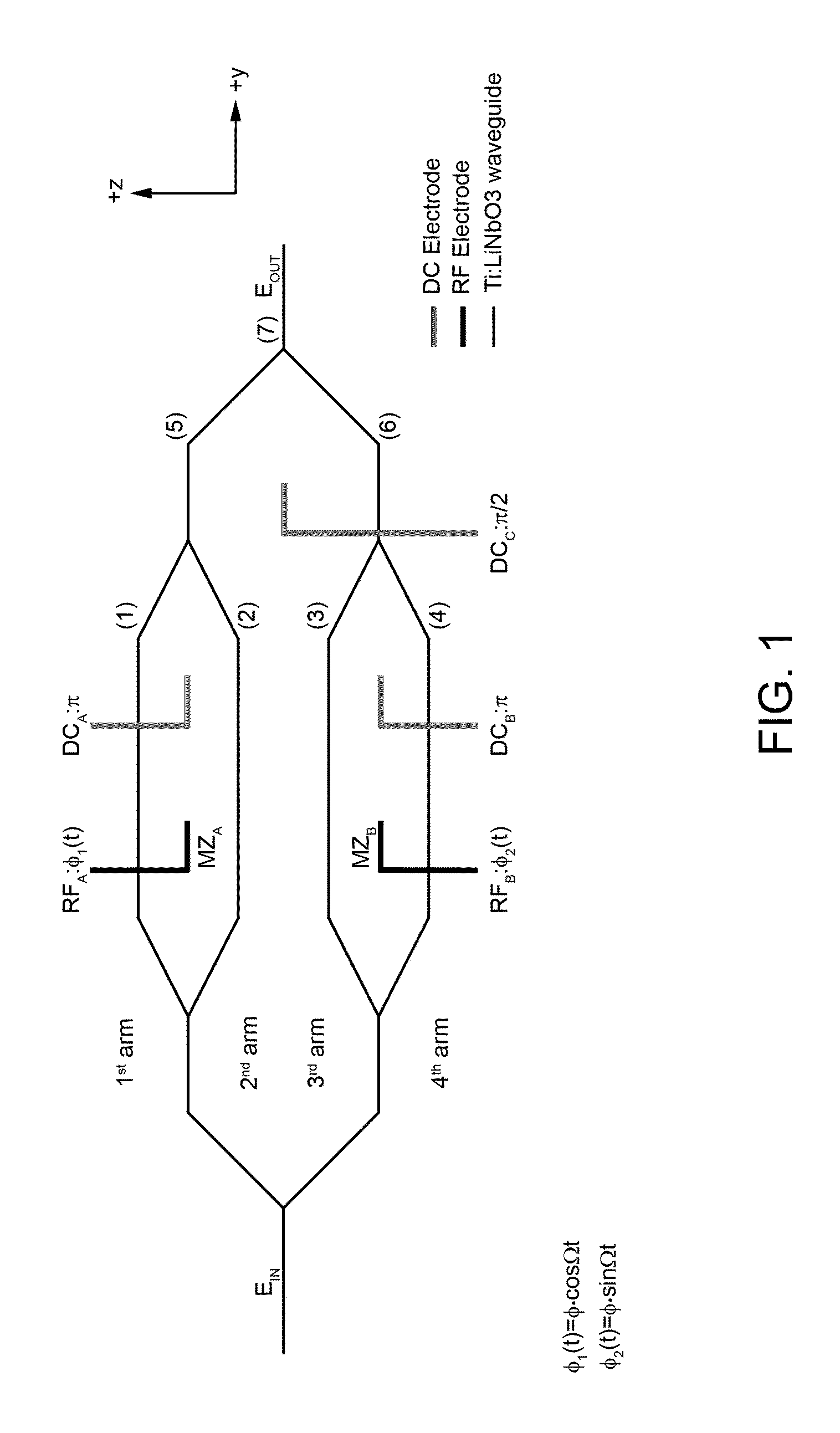
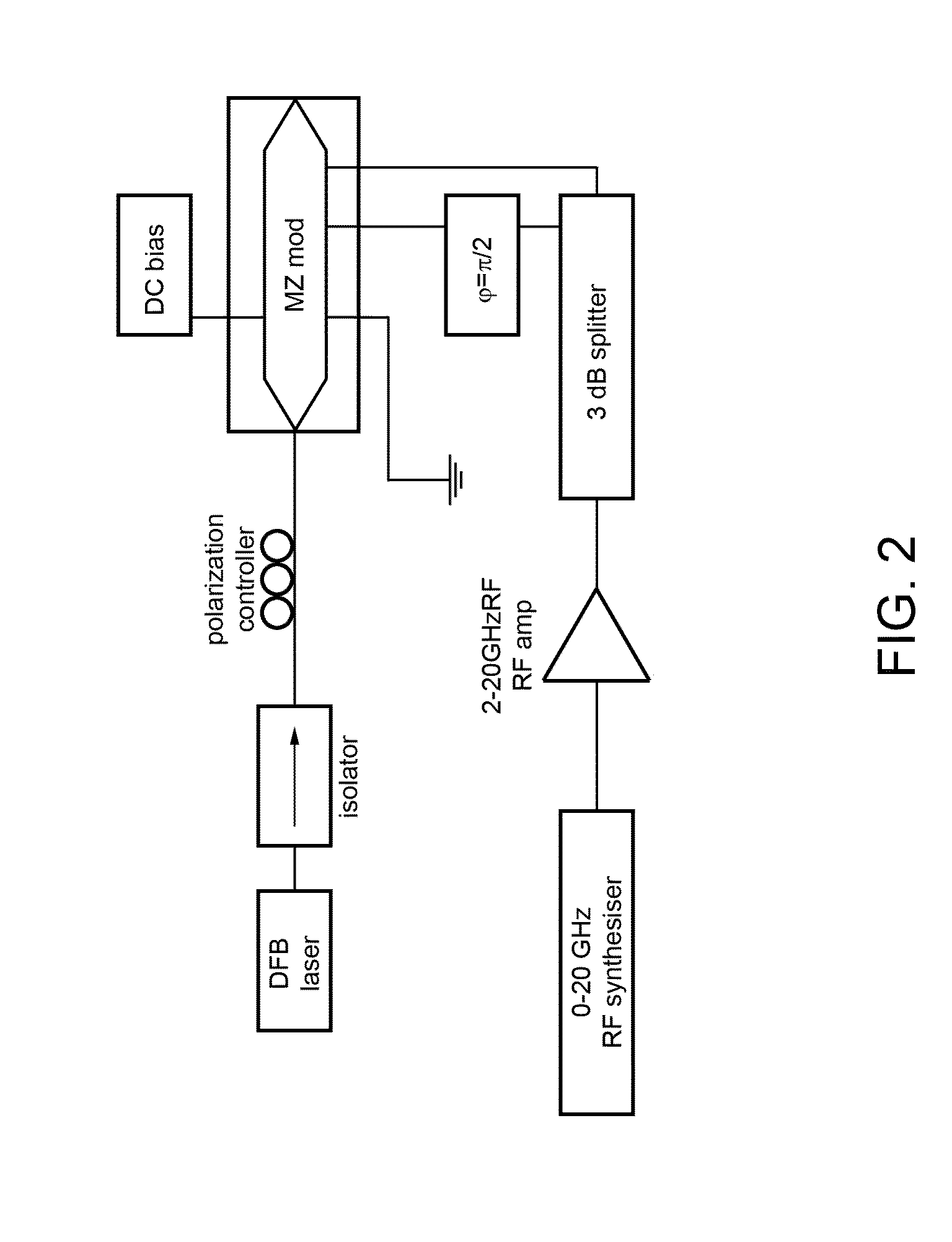
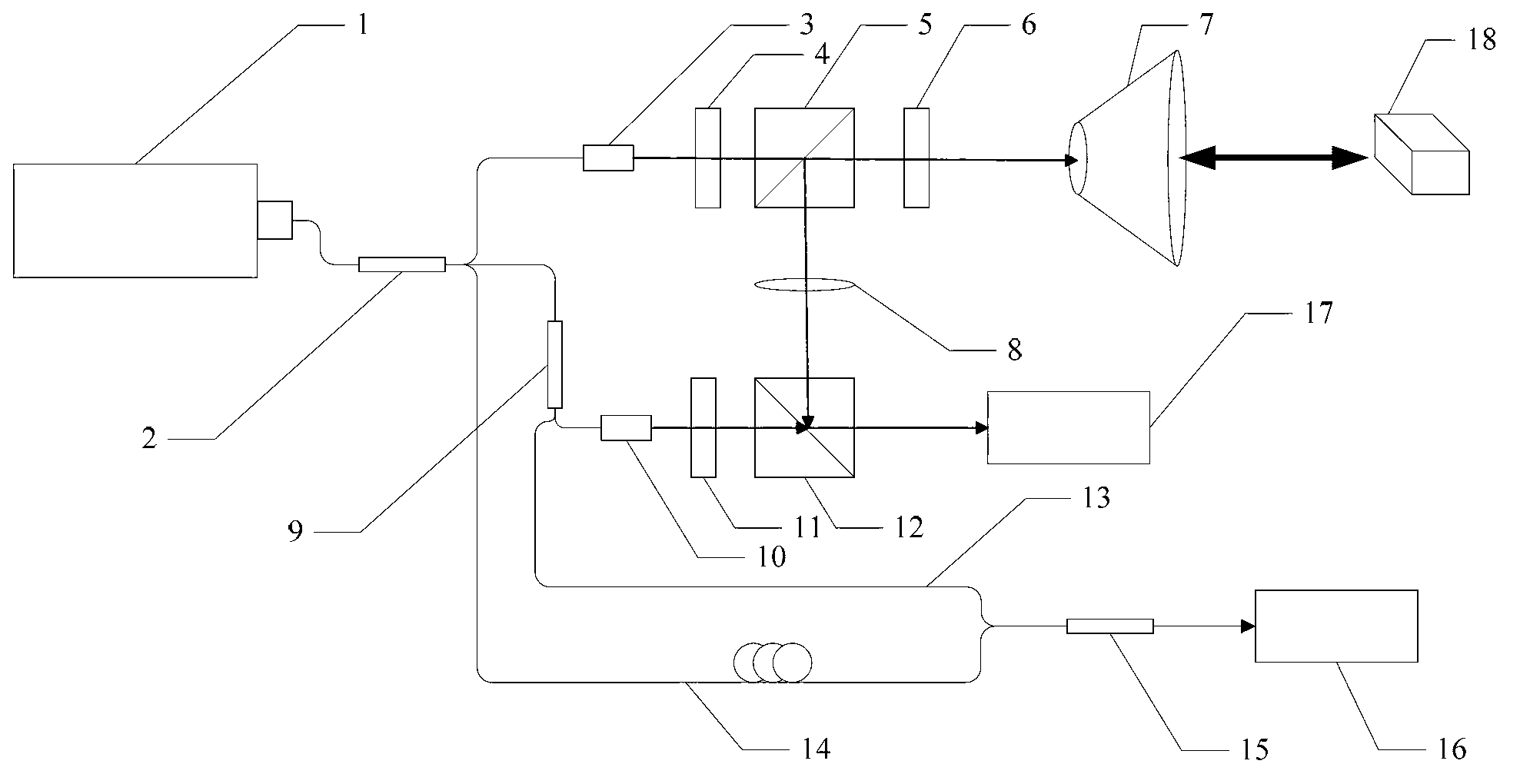Patents
Literature
118 results about "Electrical frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
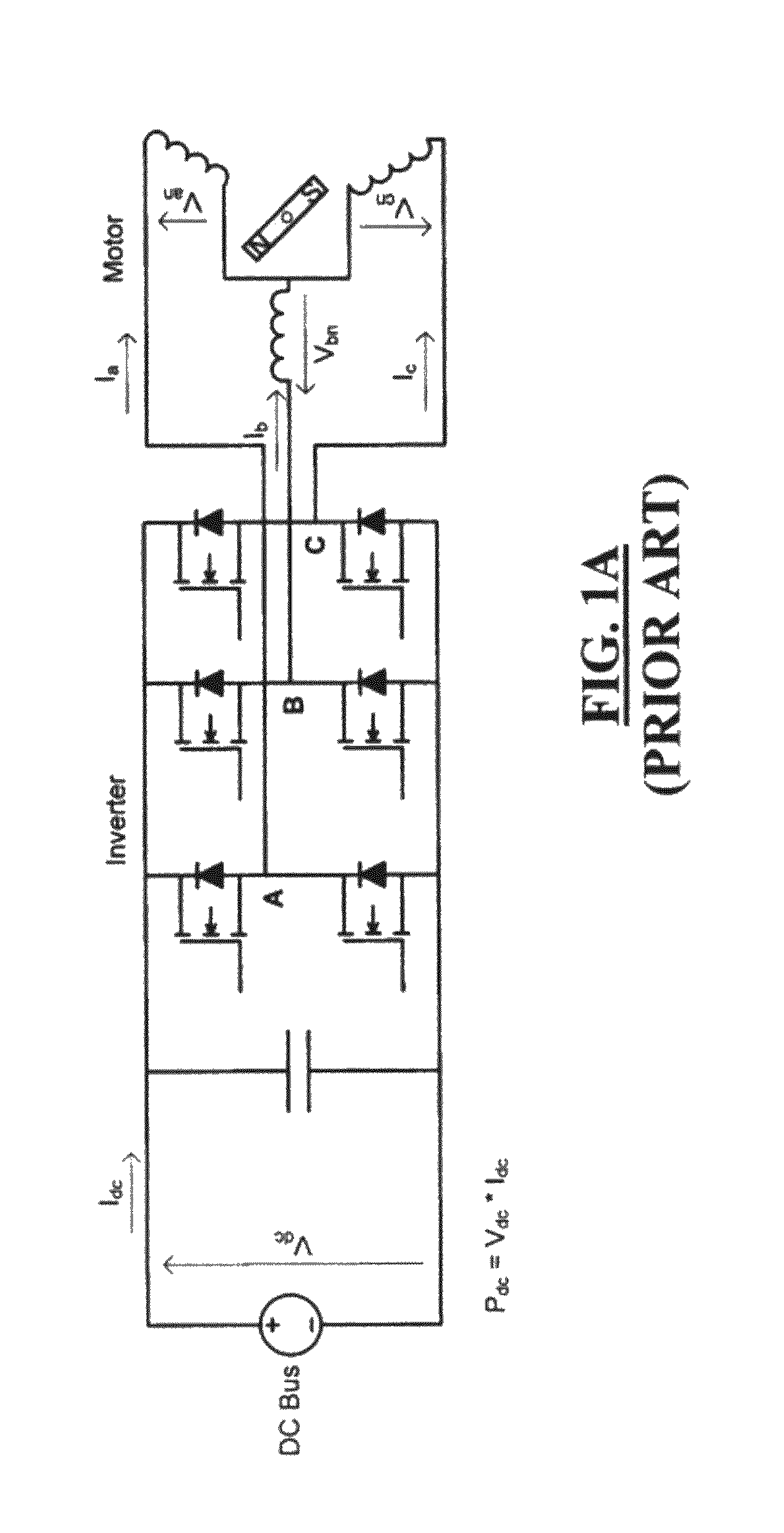
Railroads in many countries use current with a frequency of 16⅔ Hz (for electric traction) as well as frequencies of 25 and 75 Hz (for automatic block signaling, for example, on track circuits). In aviation, the current used has a frequency of 400 Hz (for independent power-supply systems).
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveUS8449824B2Novel and uniqueSimple designLaboratory glasswaresNanosensorsTransceiverHydrogen selectivity
A sensor instrument system for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region contains a local sensor instrument and remote central station. The instrument includes a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement, a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station connects to a network means connected to a plurality of local receiving sites equipped with including the respective transceivers, so that the local analyte electrical information and geographic position information transmitted by the instrument can be wirelessly and remotely received and processed by the central station. The core technology further includes a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivities including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:SUN YIZHONG
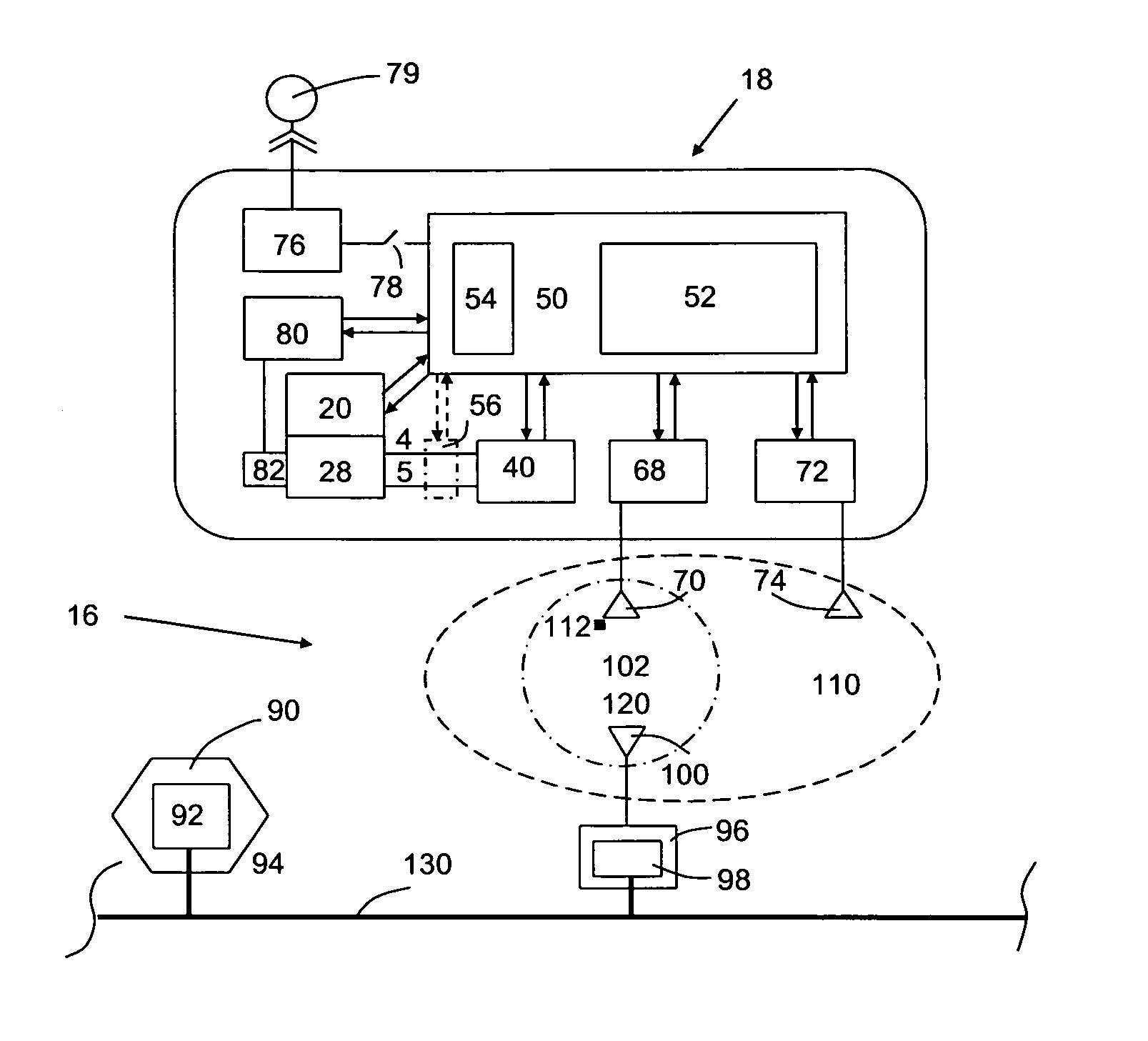
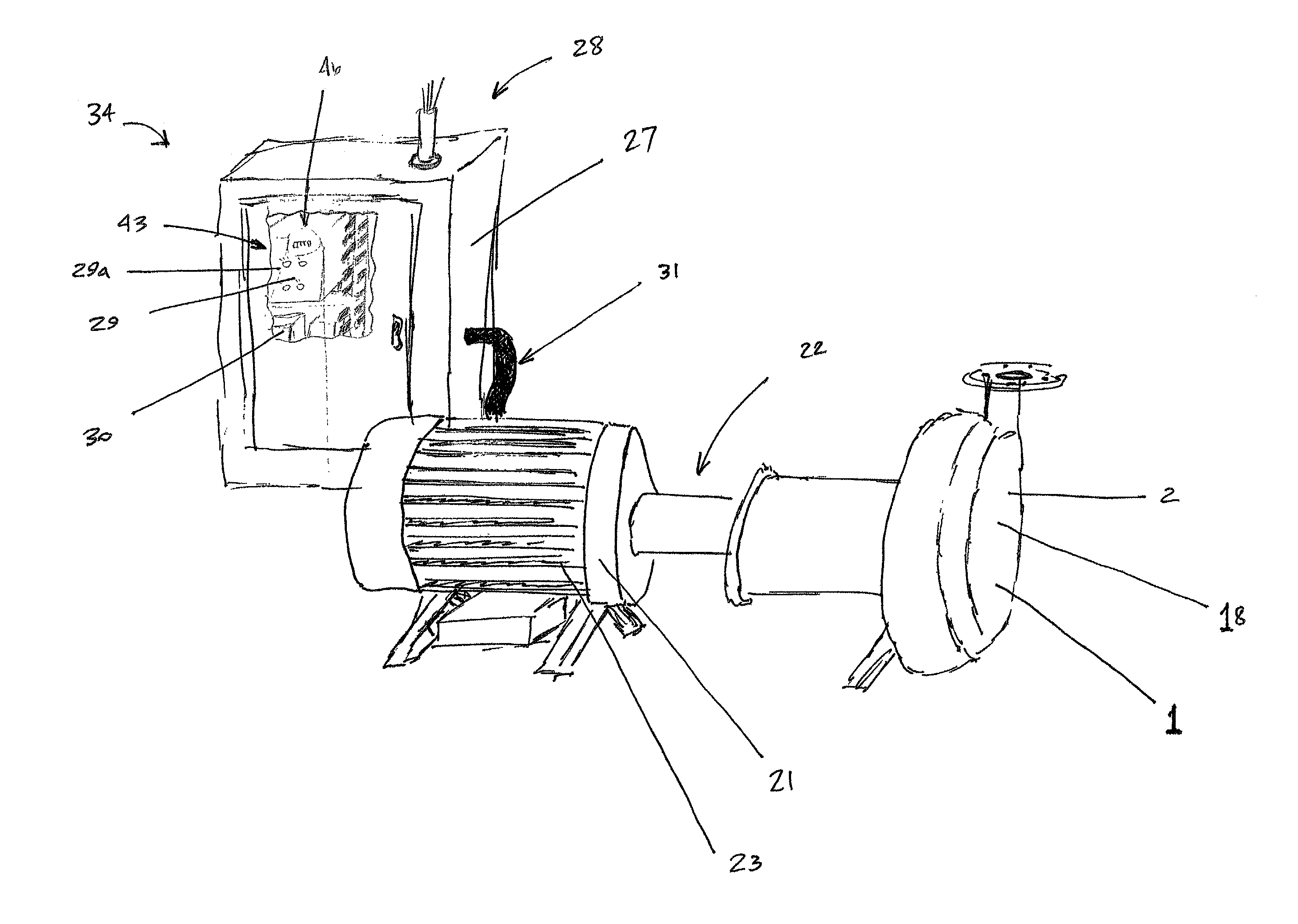
Speed control for a pumping system
A wastewater pumping system includes a centrifugal pump operatively connected to an electric motor via a coupling. The speed of the electric motor is automatically varied responsive to the head or load realized by the pump of the system as it varies with the composition of the slurry mixture. A variable frequency drive is operatively connected to the motor and the electrical power supply that affects a shift or change in electrical frequency delivered to the electrical motor so that the speed of the motor and consequently the pump is varied. This allows the electrical power deliver to the system to remain substantially unchanged for varying loads realized by the pump.
Owner:F E MEYERS
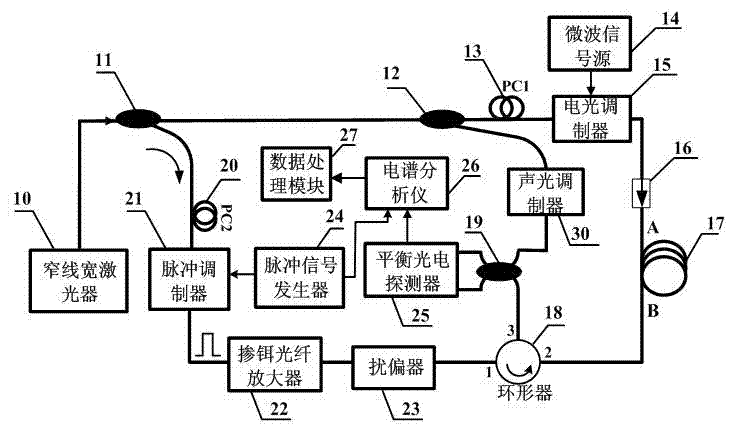
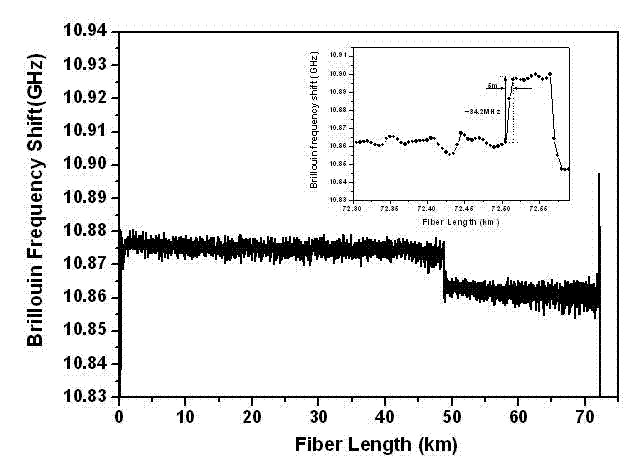
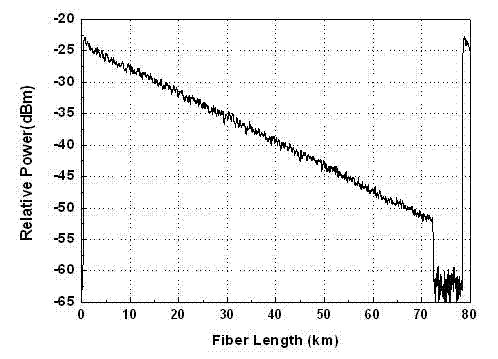
COTDR (coherent detection based optical time-domain reflectometry) fused long-distance coherent detection brilouin optical time-domain analyzer
InactiveCN102759371AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove dynamic rangeThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansSpectrum analyzerLine width
The invention discloses a COTDR (coherent detection based optical time-domain reflectometry) fused long-distance coherent detection brilouin optical time-domain analyzer which comprises a narrow-linewidth laser, two couplings, a microwave signal source, an electro-optic modulator, an isolator, a long-distance sensing optical fiber, an optical circulator, a 3 db coupling, a pulse modulator, an Er-doped fiber amplifier, a scrambler, a pulse signal generator, a balancing photoelectric detector, an electrical frequency spectrum analyzer, a data processing module and an acousto-optic modulator. According to the invention, the signal-to-noise ratio of BOTDA (brilouin optical time domain analysis) is improved by using a coherent detection method, a non-local effect of a BOTDA system is reduced in a double-sideband detection mode, and the sensing distance is more than 70 km under the condition of no light amplification such as raman; and according to the invention, the COTDR is fused to a coherent detection based BOTDA system, and the system can run in a breakpoint testing mode, so that the defect that the traditional BOTDA can not run when a sensing fiber has breakpoints and can not carry out positioning on breakpoints is effectively overcome, thereby enhancing the adaptability and practicability of the sensing system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
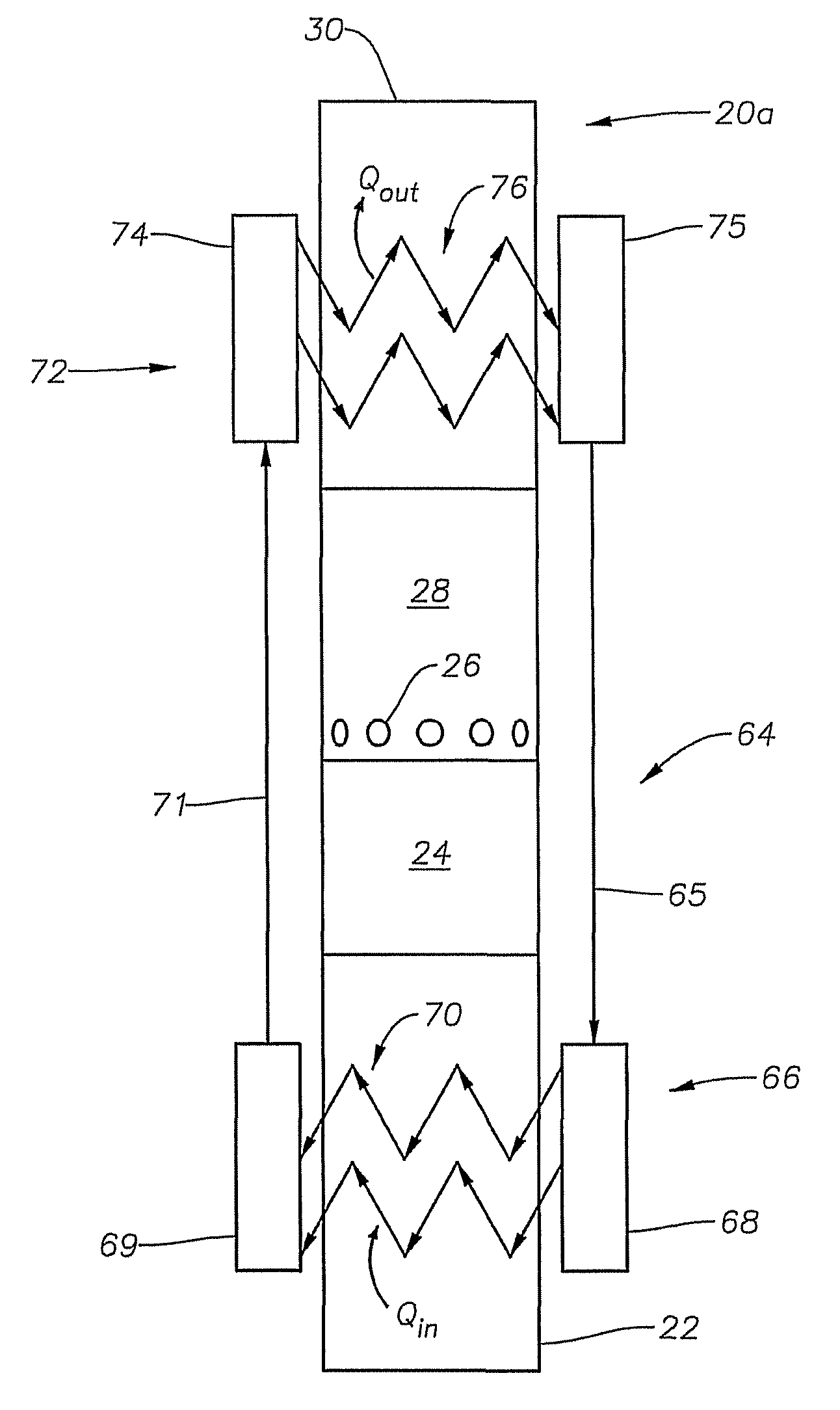
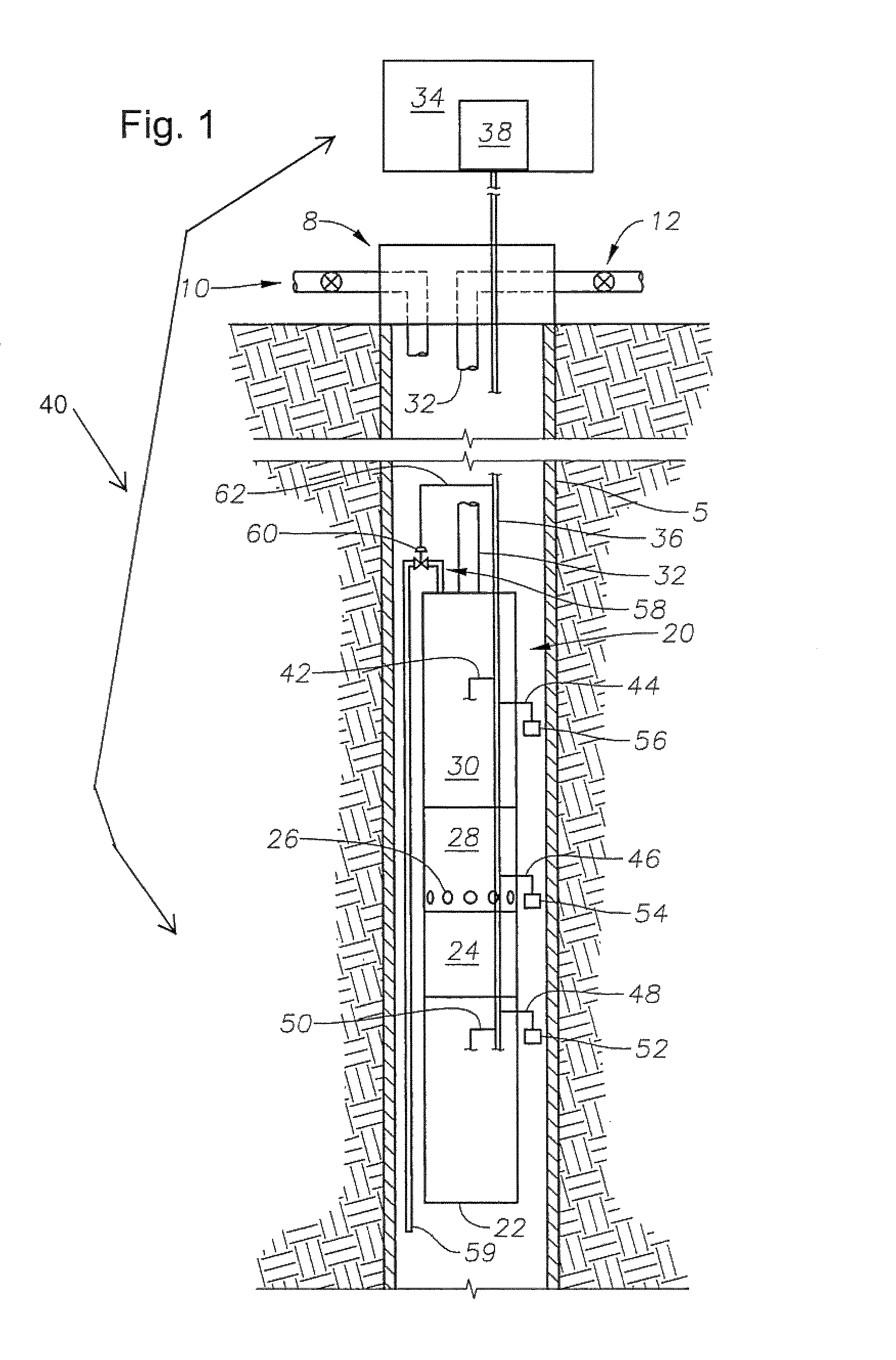
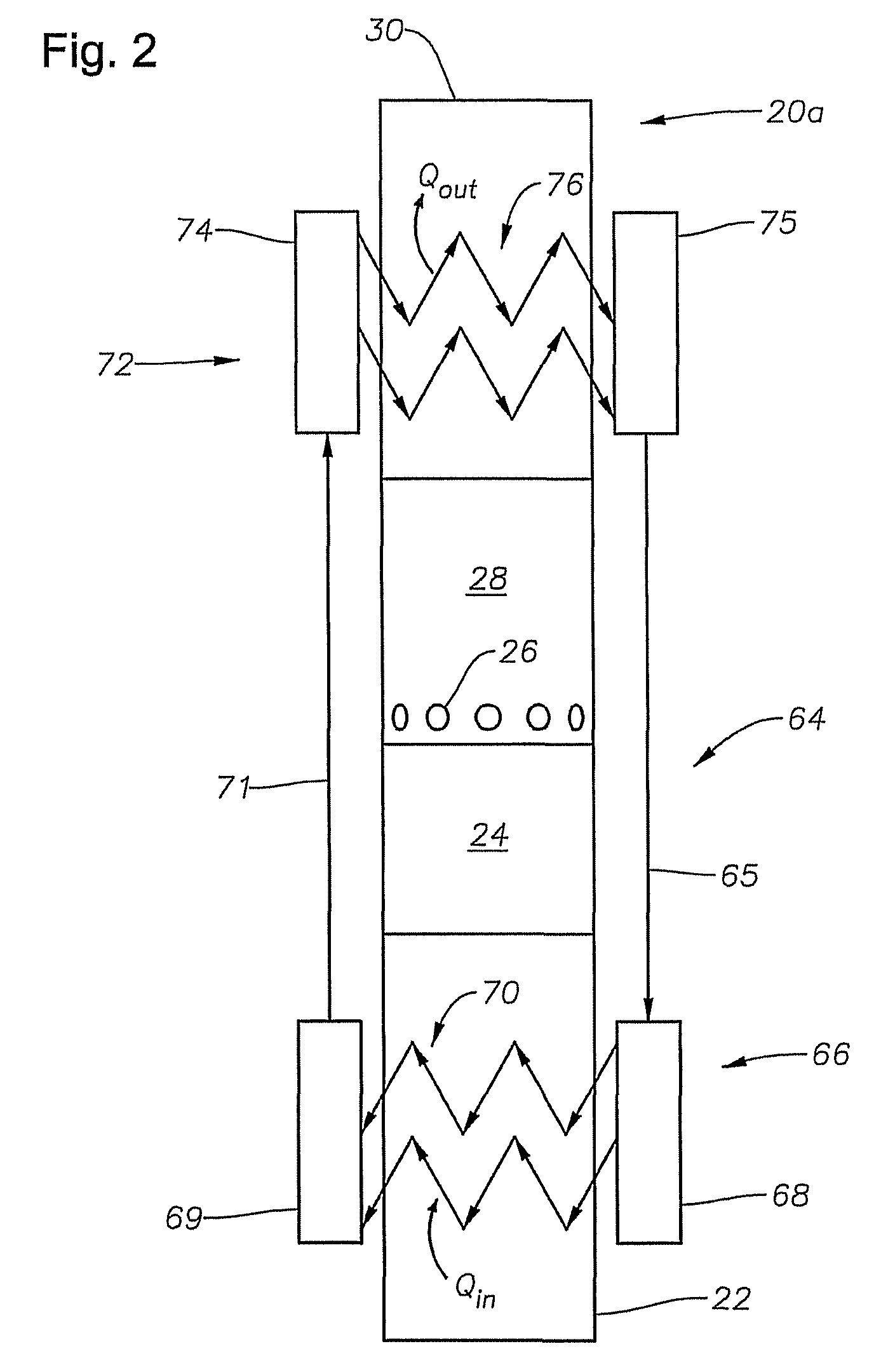
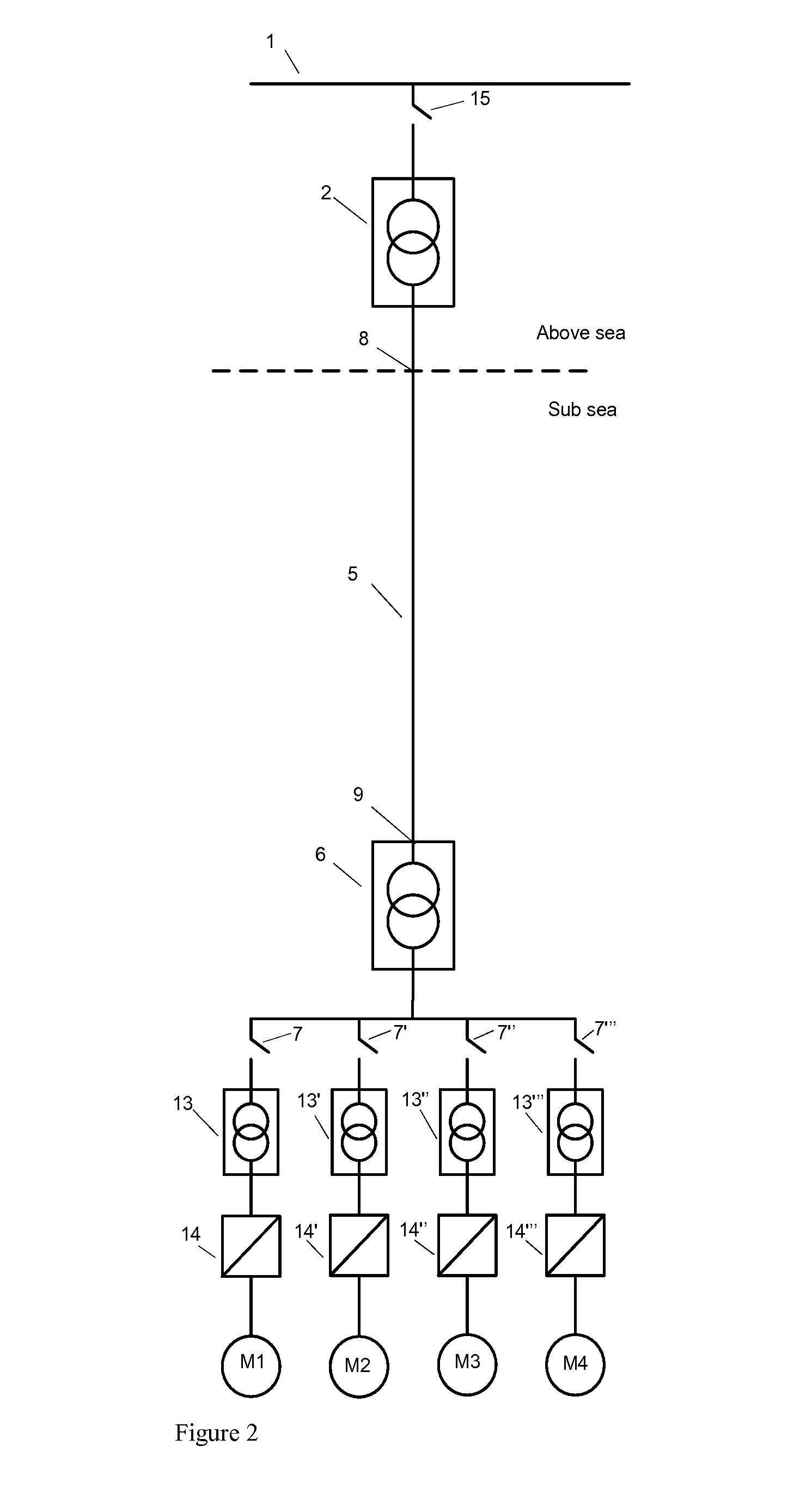
Method of heating sub sea ESP pumping system
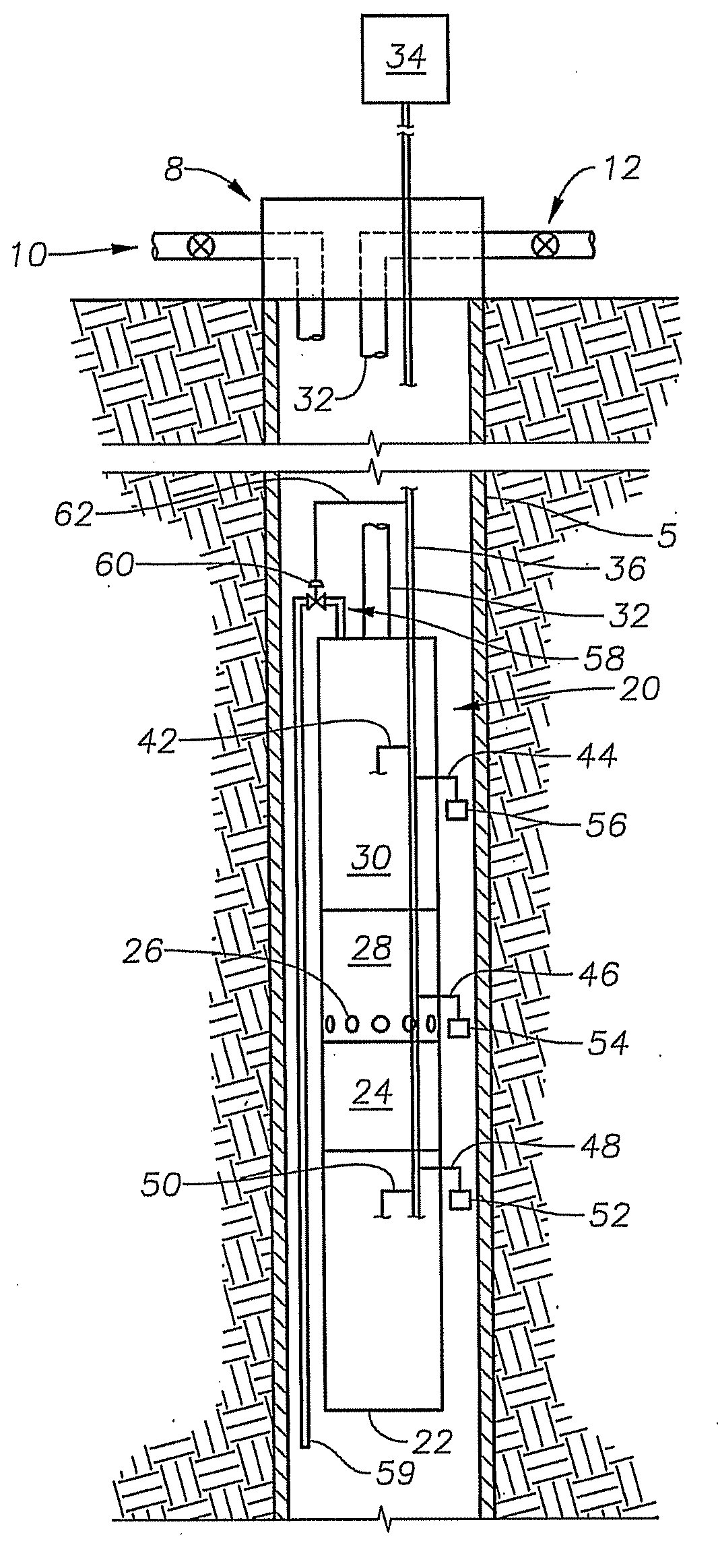
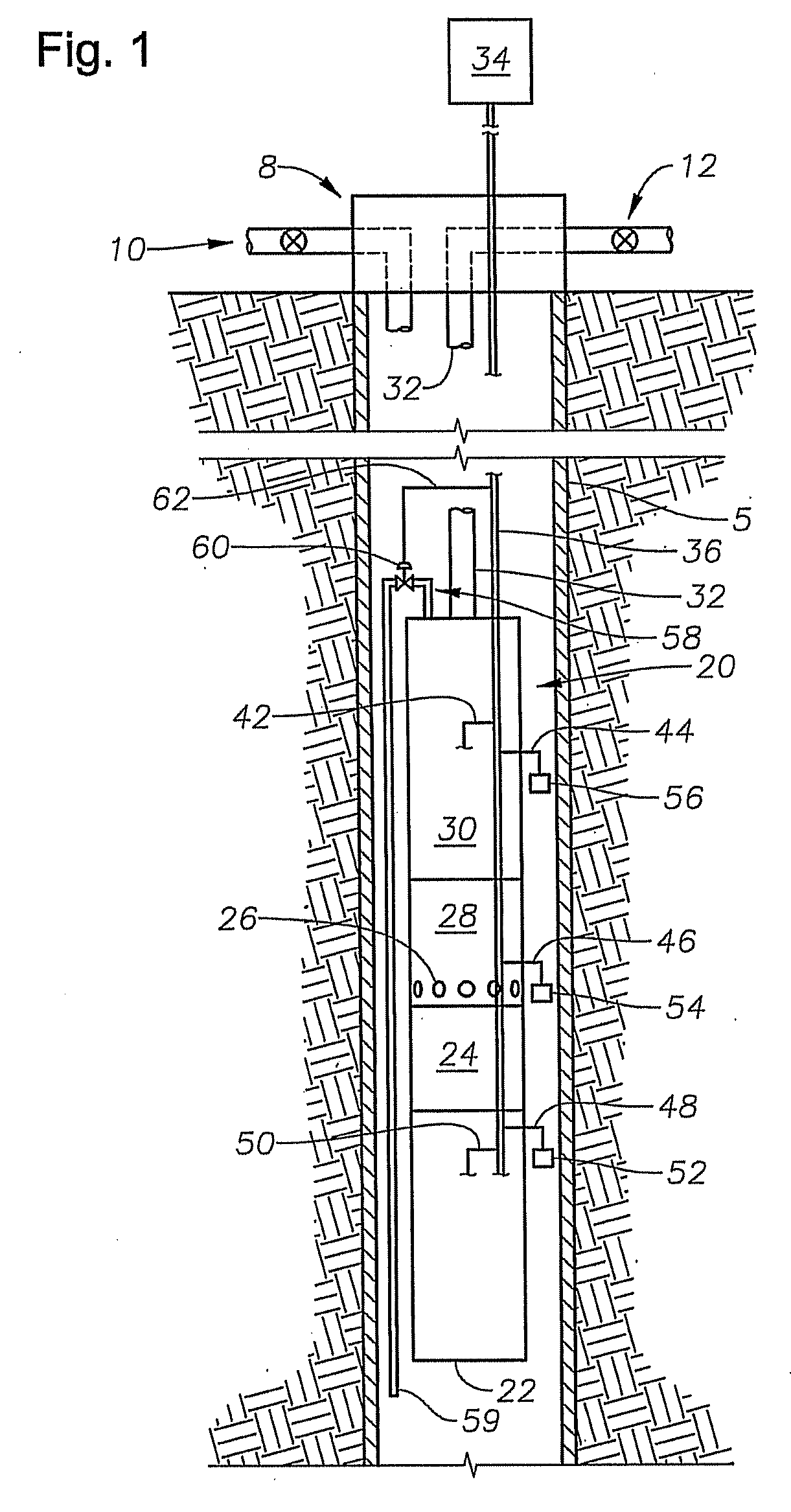
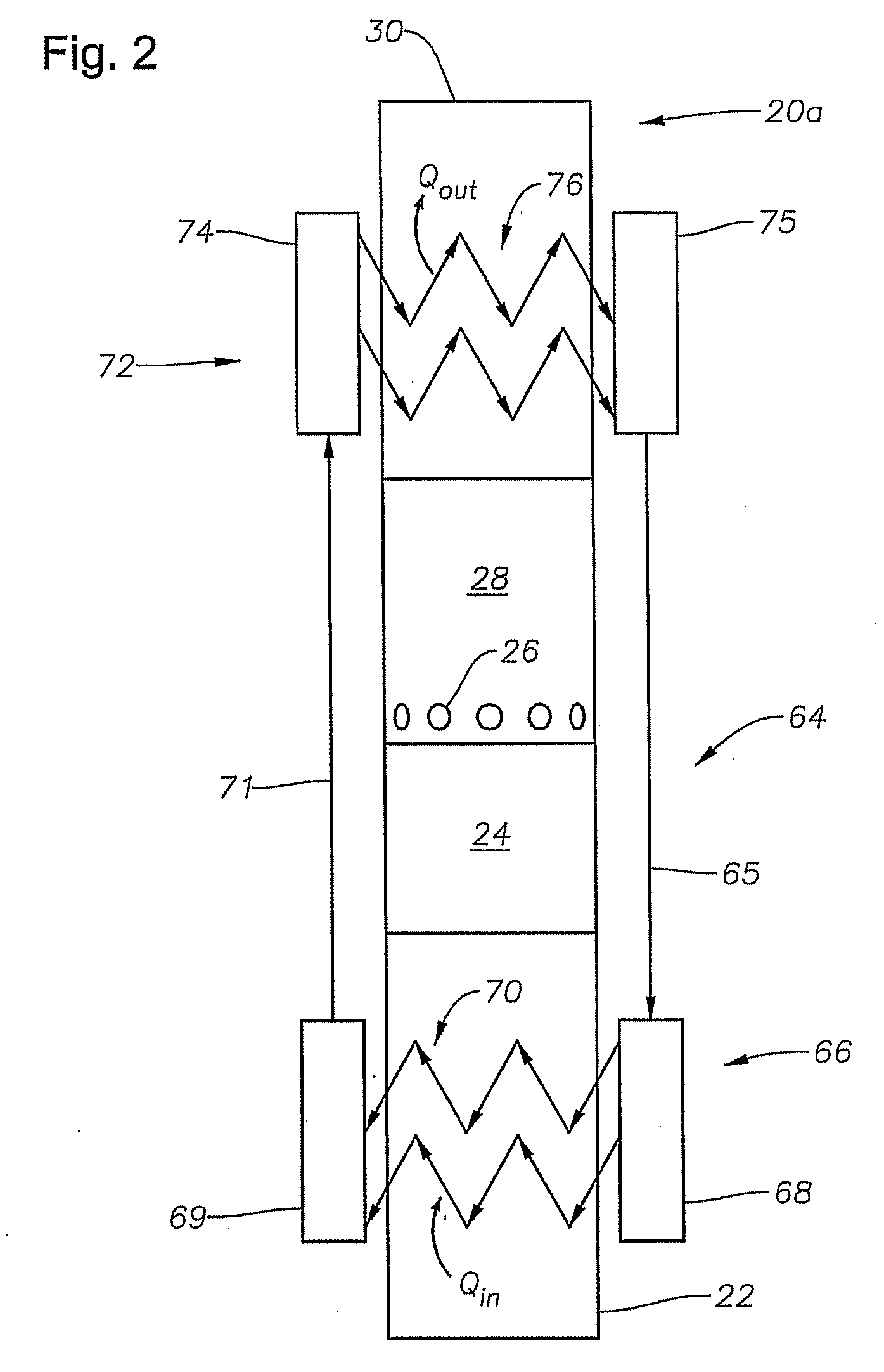
A system and method is provided for heating fluid to be pumped by an electrical submersible pumping system. Heat for heating the fluid may be inductively generated by adjusting the power delivered to the motor of the pumping system. In one example, the power adjustment includes supplying the voltage applied to the pump motor to a value less than voltage applied during normal operations. While lowering the voltage the electrical frequency may be varied as well as the electrical waveform.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveUS20090261987A1Improves analyte detectionEasy to identifyElectric signal transmission systemsLaboratory glasswaresTransceiverDesorption
A sensor instrument system for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region comprising a local sensor instrument and remote central station. The instrument is comprised of a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement, a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station connects to a network means connected to a plurality of local receiving sites equipped with including the respective transceivers, so that the local analyte electrical information and geographic position information transmitted by the instrument can be wirelessly and remotely received and processed by the central station. The core technology is further comprised of a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivity including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:SUN YIZHONG
Motor fault detecting method and motor fault detecting system
InactiveUS20160011268A1Efficient detectionDynamo-electric machine testingBrushless motorsElectrical resistance and conductance
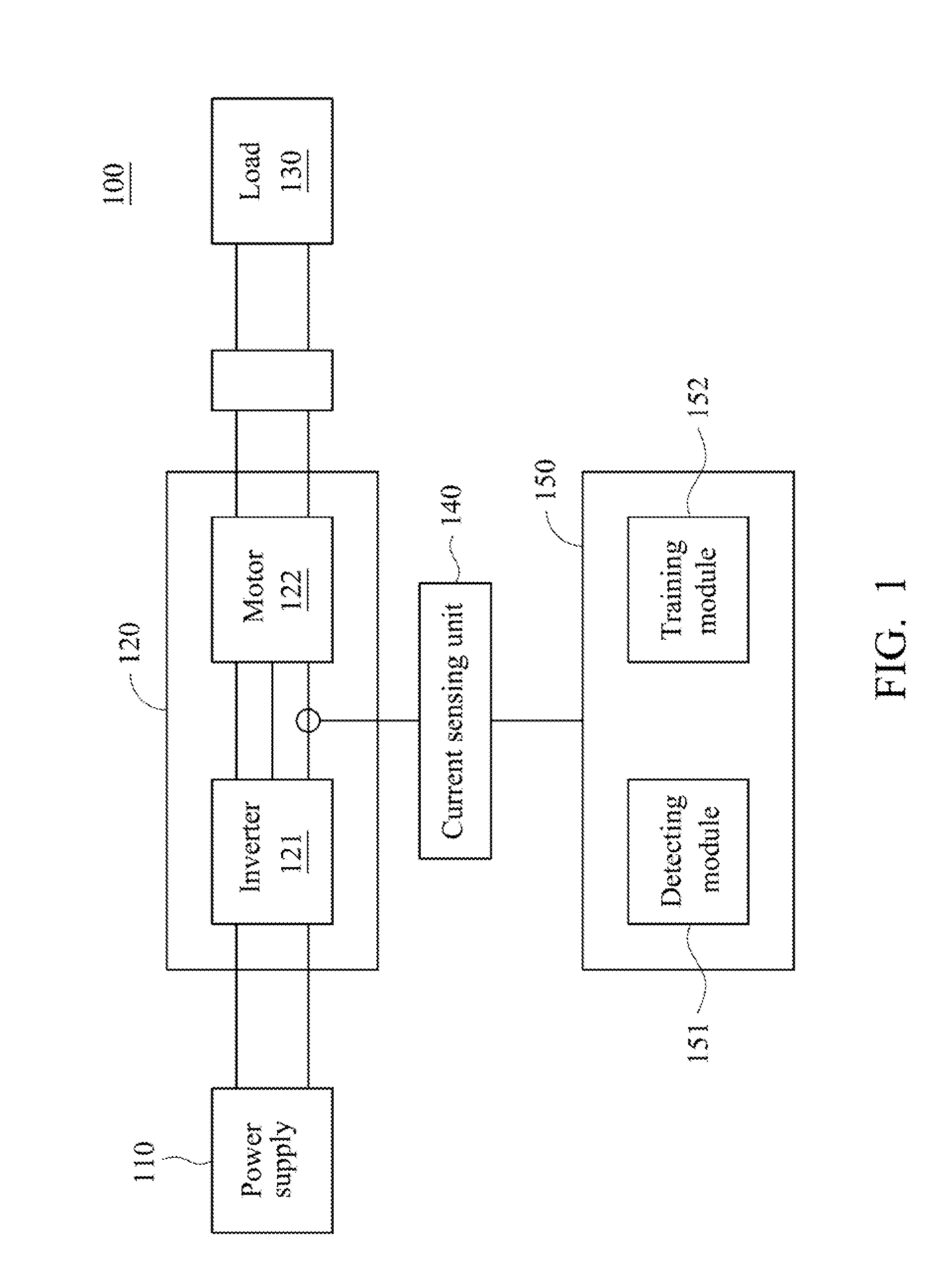
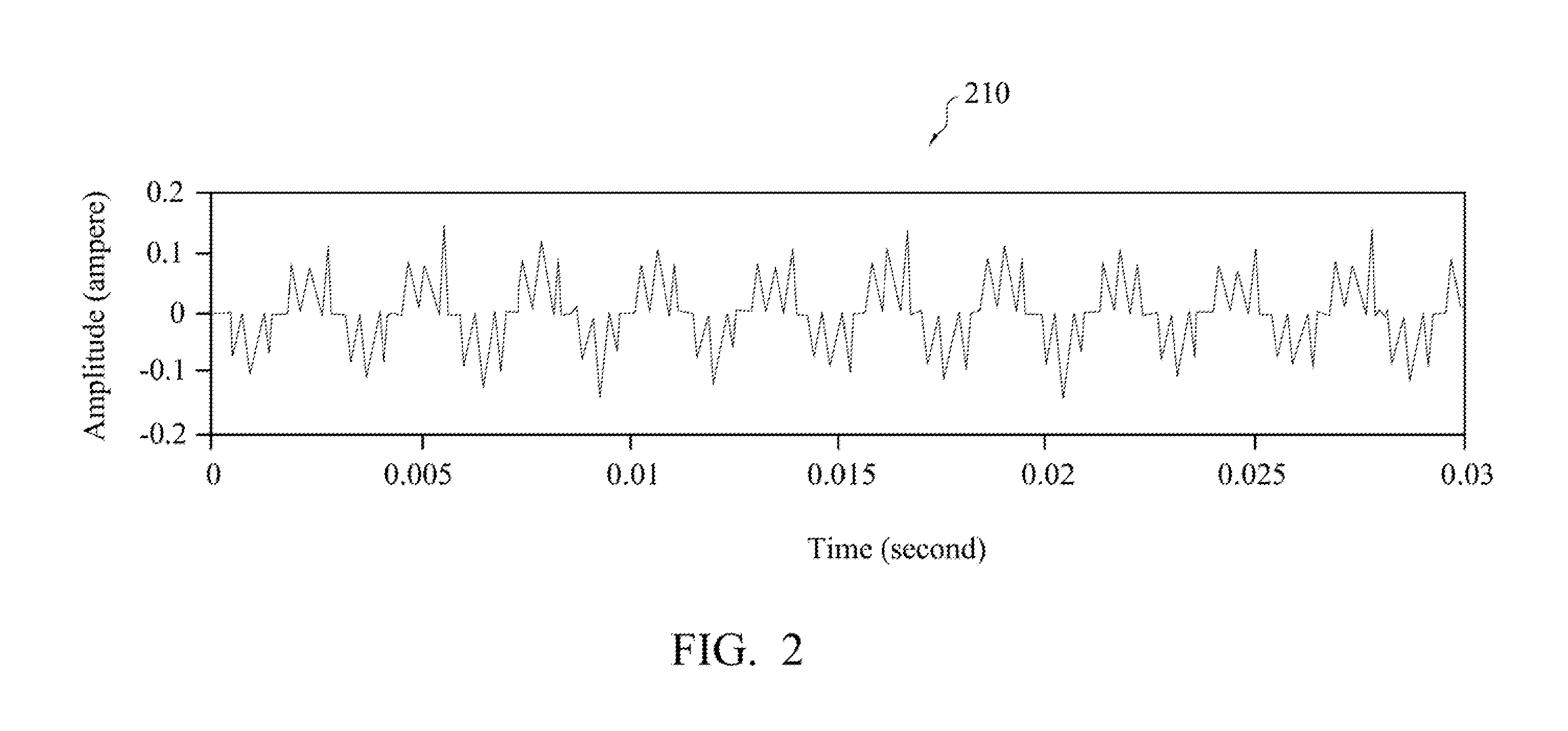
A motor fault detecting method and a motor fault detecting system are provided. An electrical frequency and sensing current data of a brushless motor is obtained. An empirical mode decomposition (EMD) is performed on the sensing current data to obtain intrinsic mode functions (IMF). A feature IMF is obtained from the IMFs, in which the feature IMF is feature current data, and a frequency of the feature current data complies with the electrical frequency of the brushless motor. An electrical impedance is calculated according to an input voltage of the brushless motor and the feature current data. The electrical impedance is compared with a reference electrical impedance to determine if the brushless motor is abnormal. The reference electrical impedance is calculated according to training sensing current data of a training brushless motor which is in a healthy state. Accordingly, whether the brushless motor is abnormal is effectively determined.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
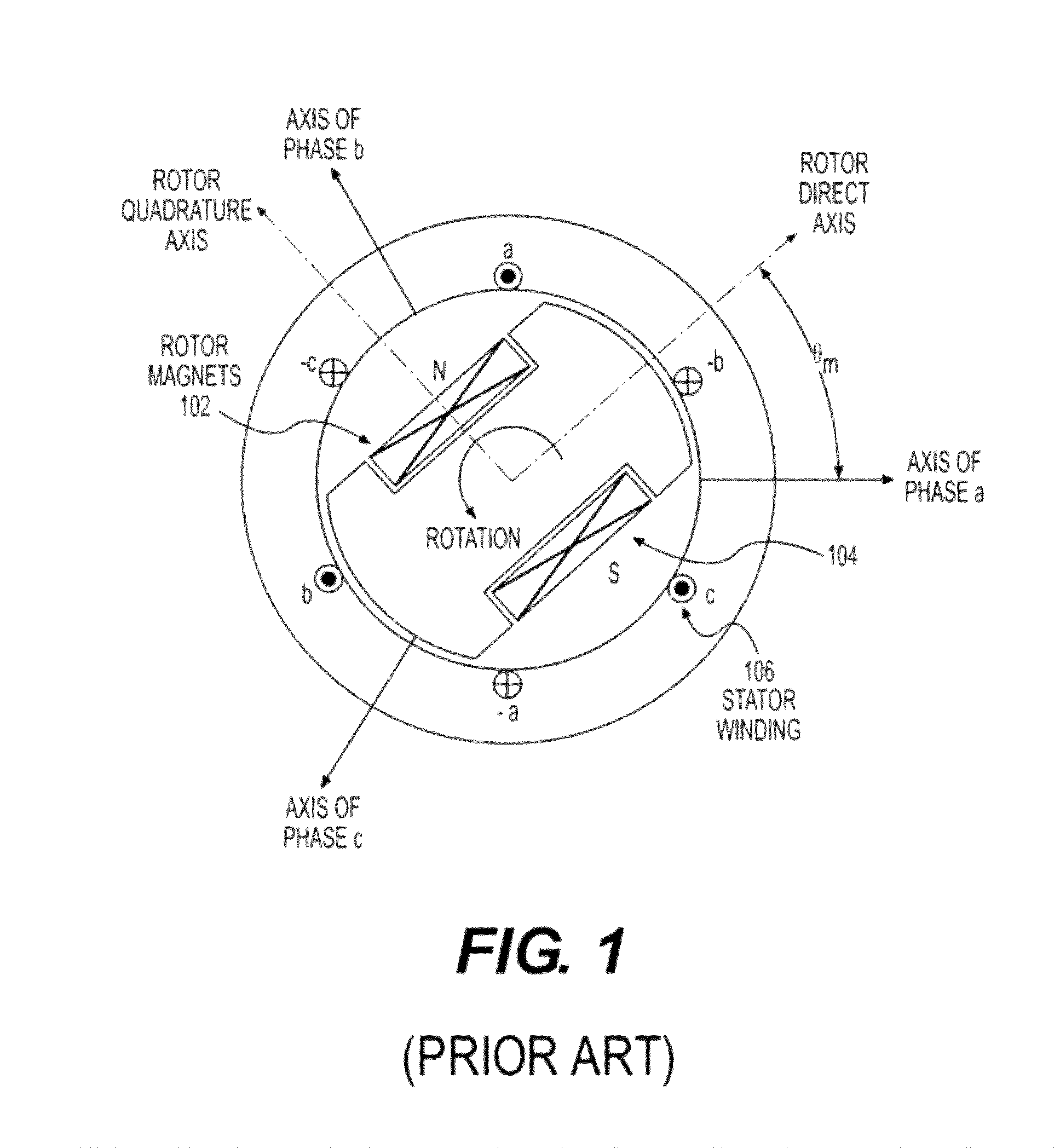
Angular position and velocity estimation for synchronous machines based on extended rotor flux
ActiveUS20070194742A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersCorrection algorithmIntegrator
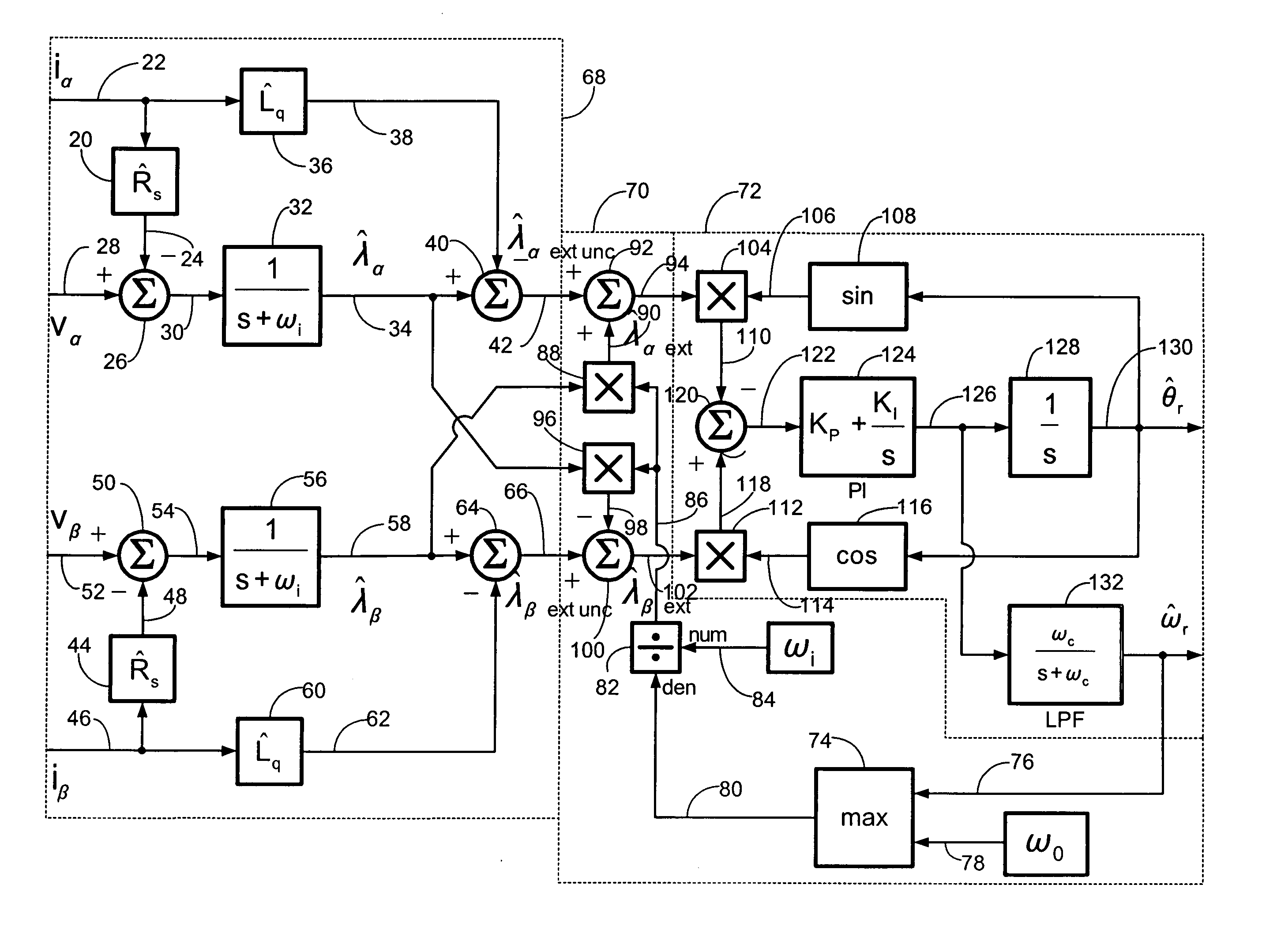
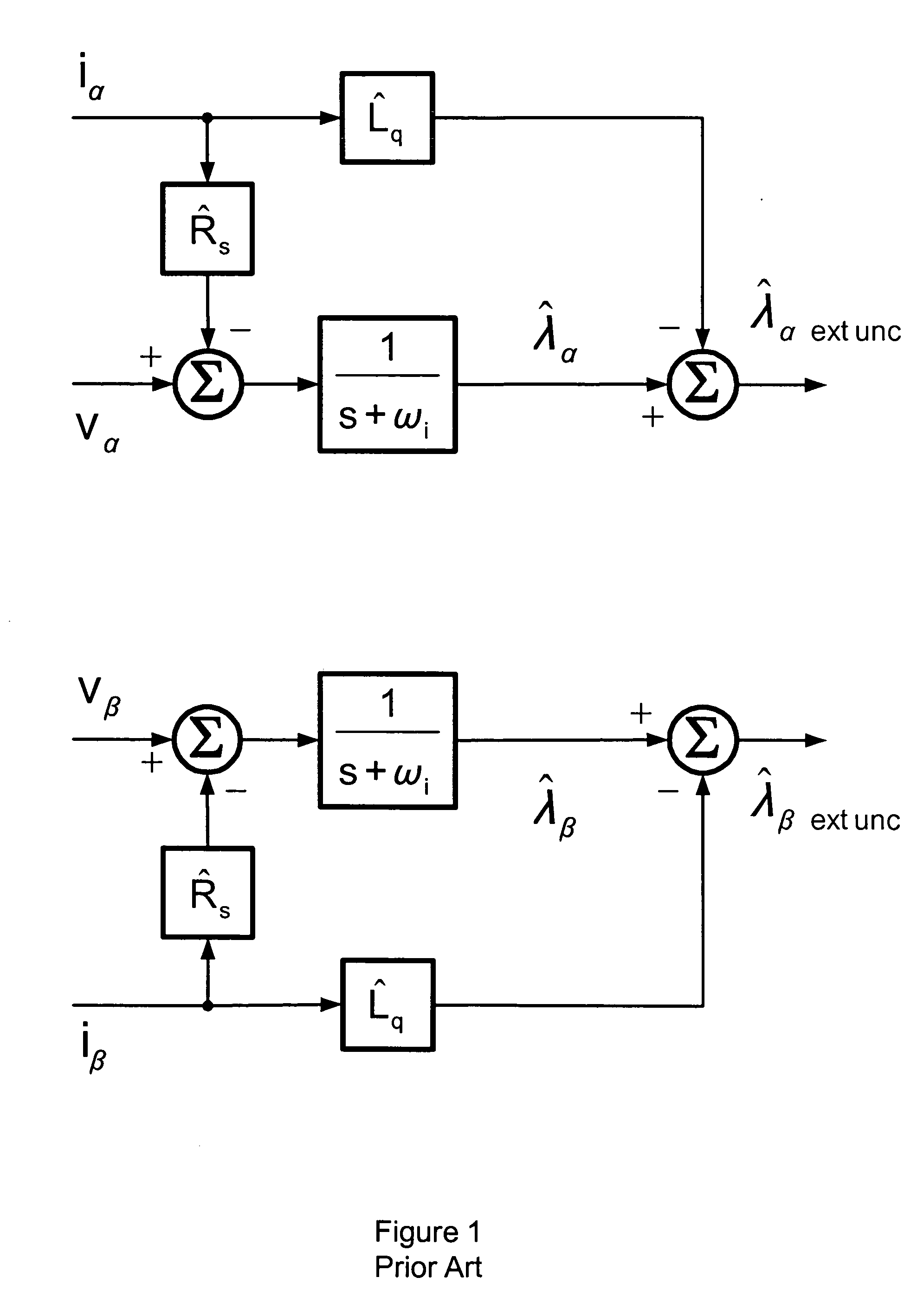
A method of correcting the determination of extended rotor flux using a lag function and a correction algorithm that closely approximates a pure integrator function to correct for lag function errors that can extend the EFS control down to dynamoelectric machine speeds corresponding to as low as 10 Hz electrical frequency.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Linear synchronous motor with multiple time constant circuits, a secondary synchronous stator member and improved method for mounting permanent magnets
ActiveUS6930413B2Accurate pole pitch spacingReduce frequencyDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMagnetic circuitElectricitySynchronous motor
The linear synchronous motor consists of a specific primary and secondary part. The secondary portion is a ferromagnetic back plate. An array of permanent magnets are attached to the back plate so that a fixed or variable pole pitch occurs in a precise manner between at least two magnets of alternating polarity which improves existing methods for attaching, guiding, protecting and enhancing the overall flux array produced and emitted by the permanent magnets. A one-piece electrically synchronous linear secondary stator member accompanies a primary member, the synchronous linear permanent magnet motor. The stator electrical frequency is customizeable to allow for a wide variety of braking applications.
Owner:VELOCITY MAGNETICS
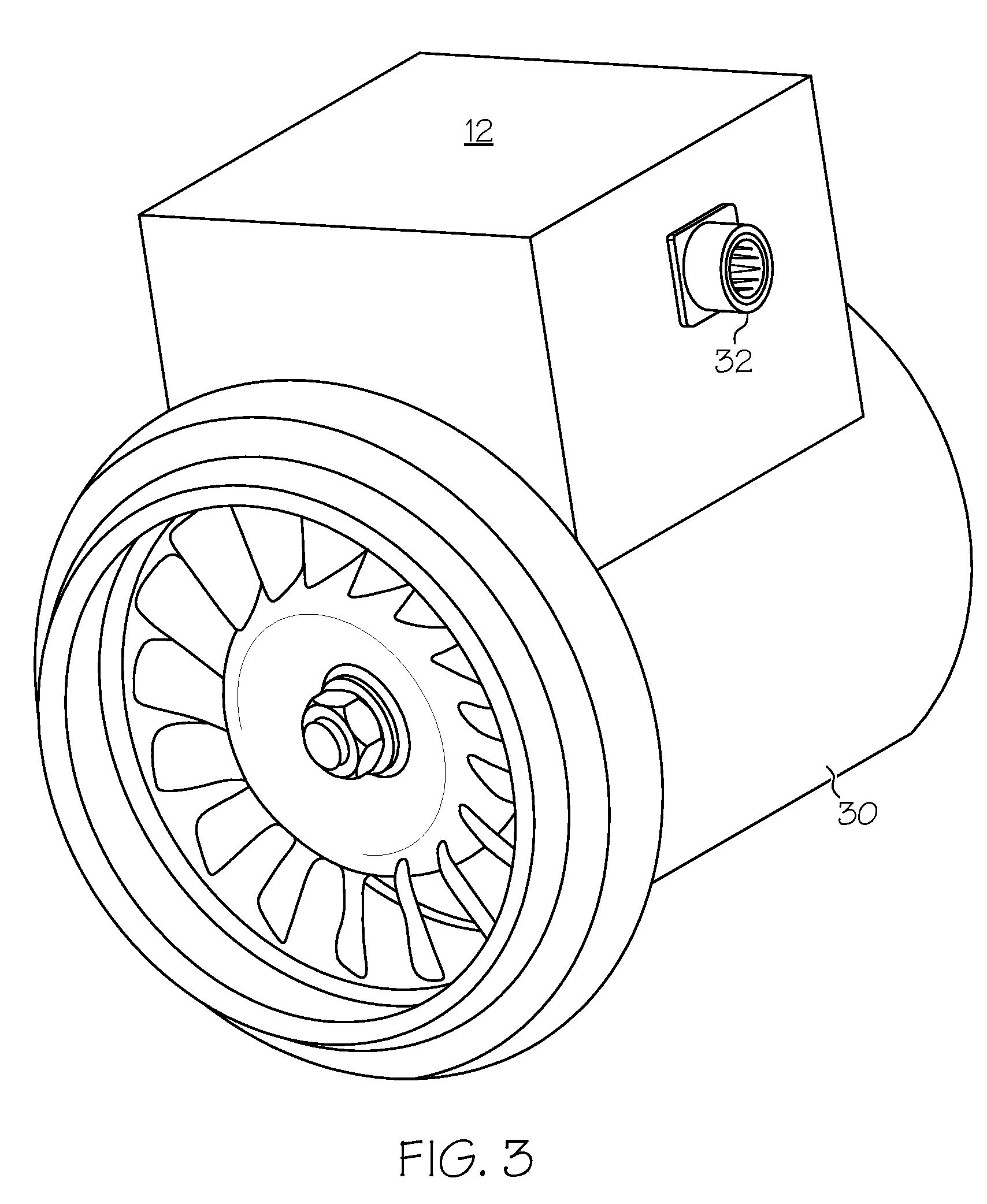
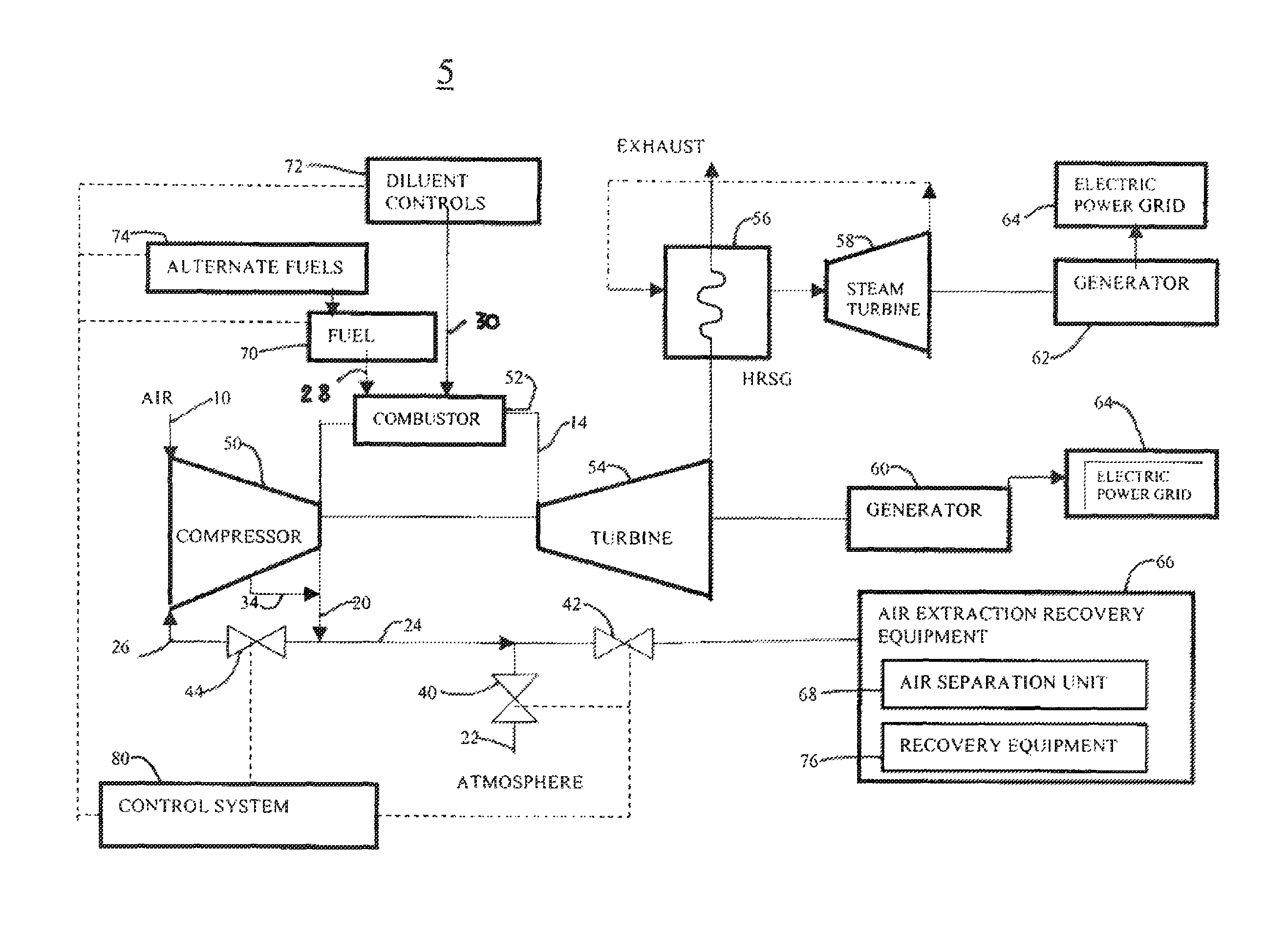
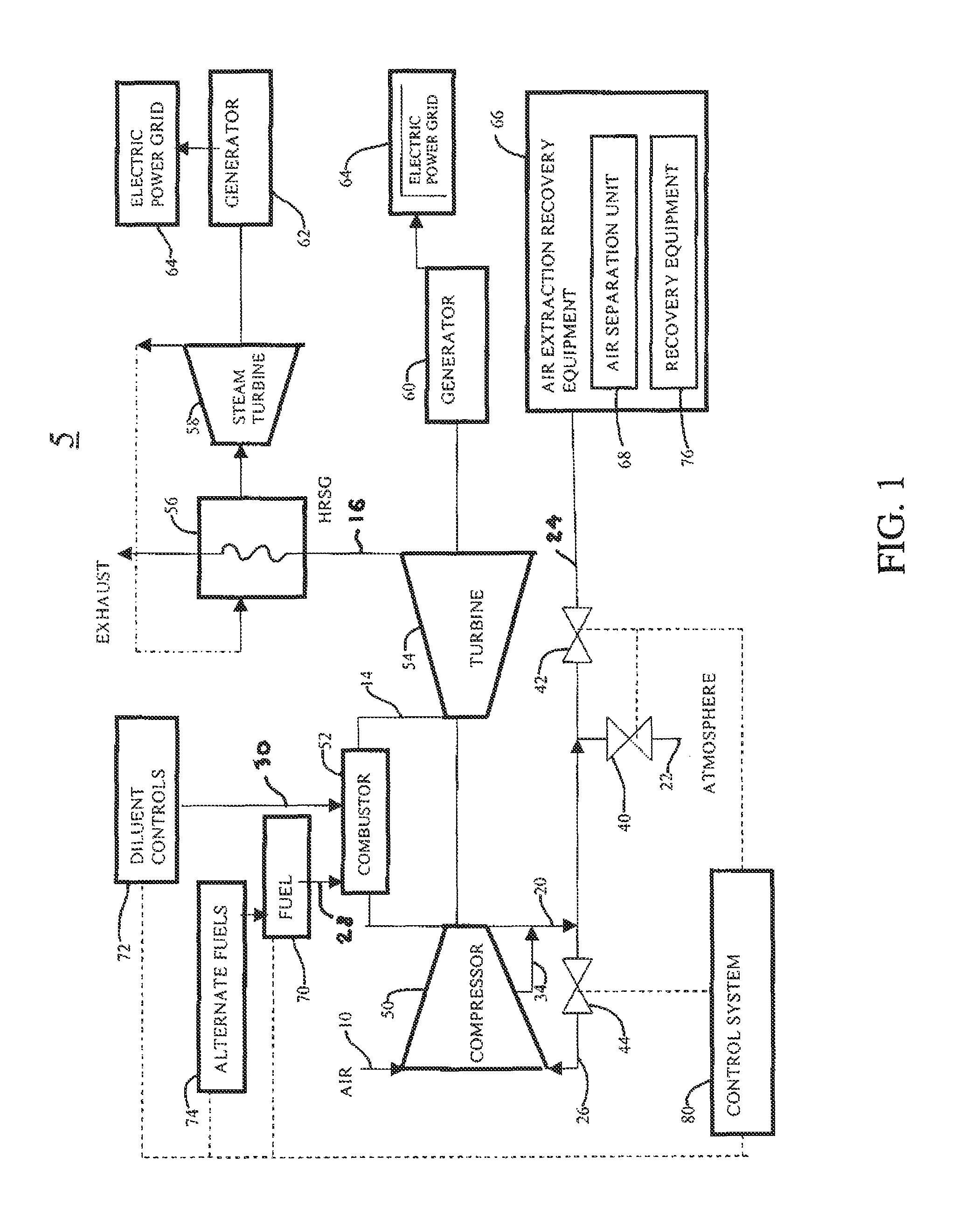
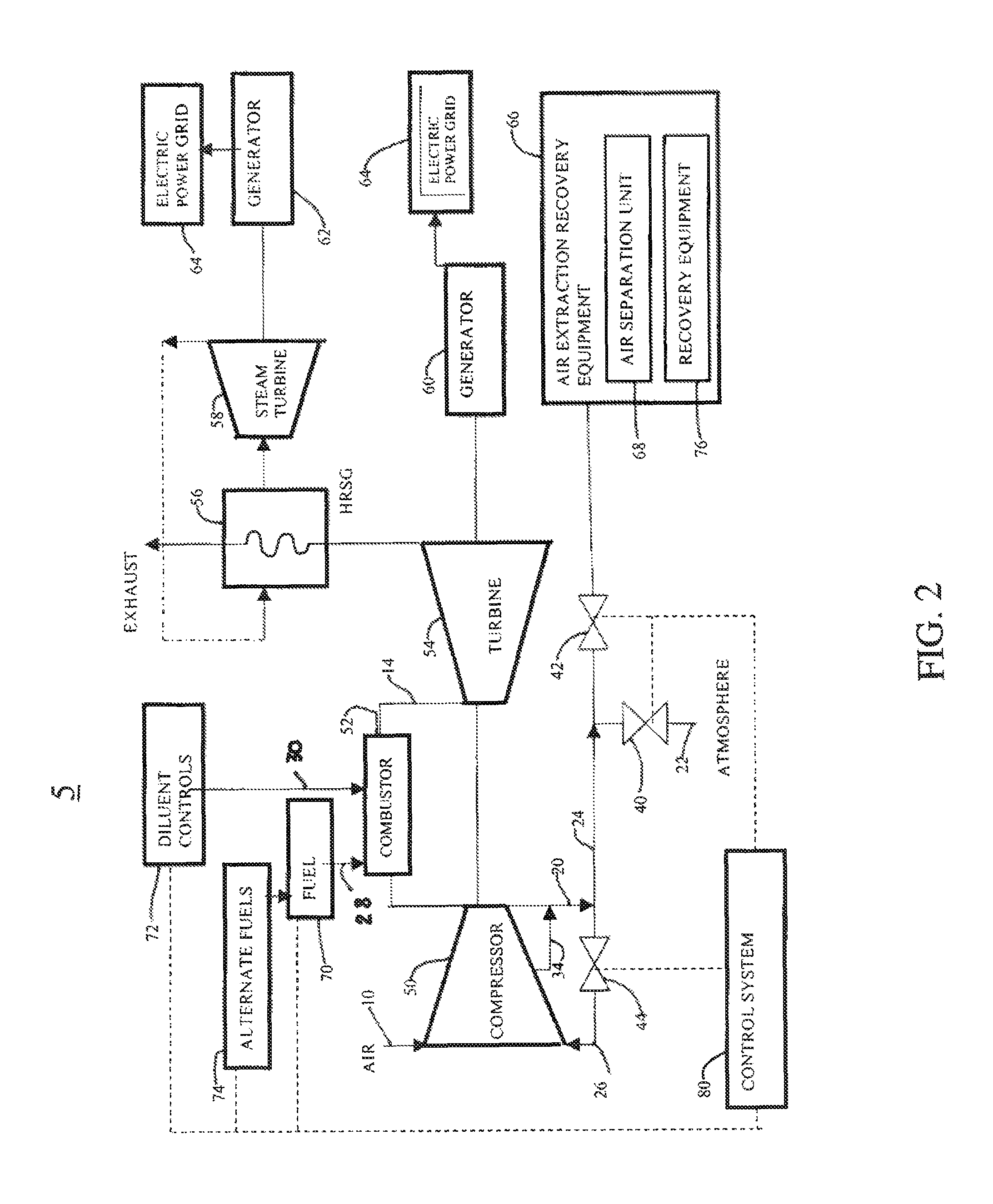
Method for gas turbine operation during under-frequency operation through use of air extraction
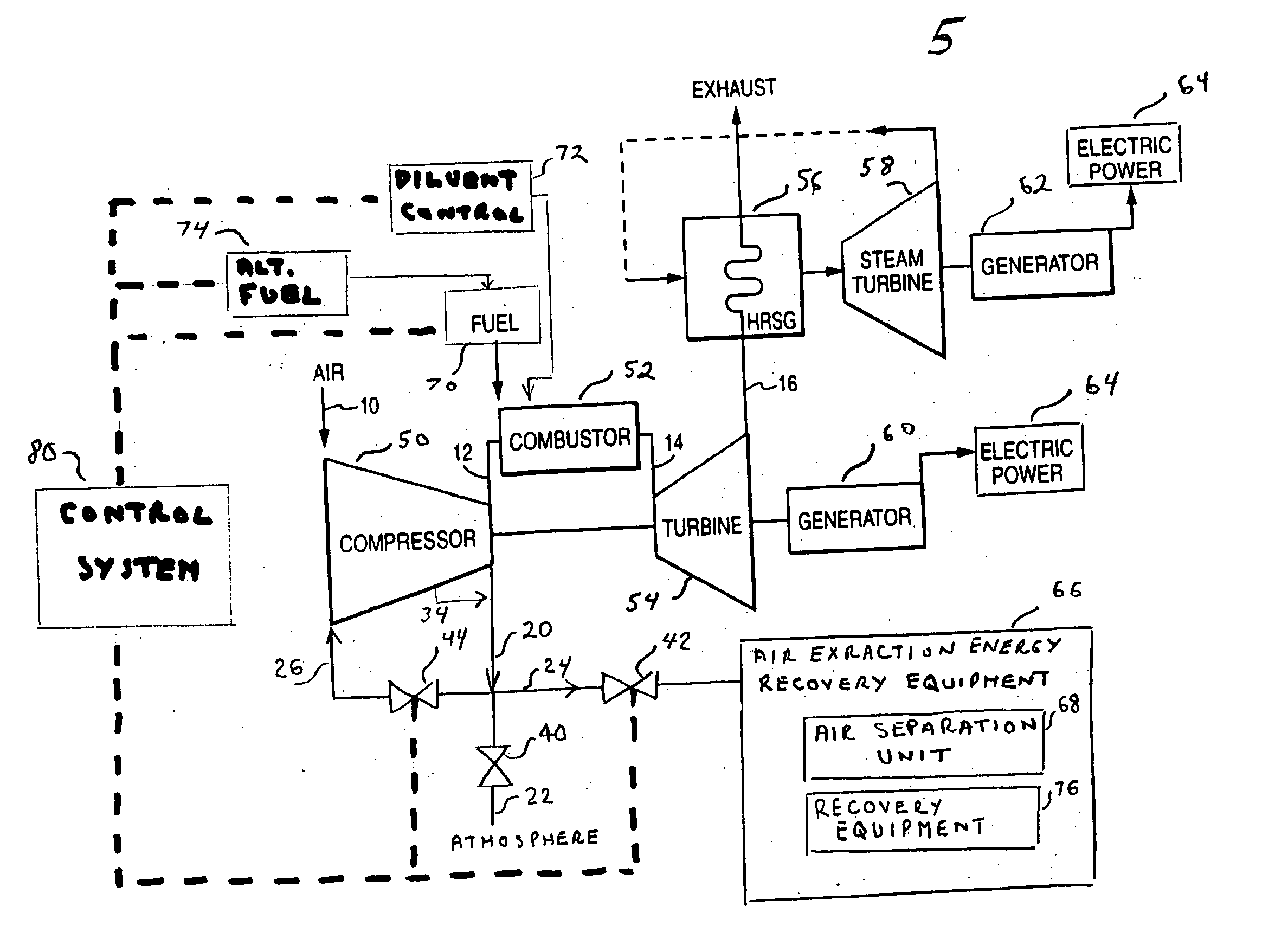
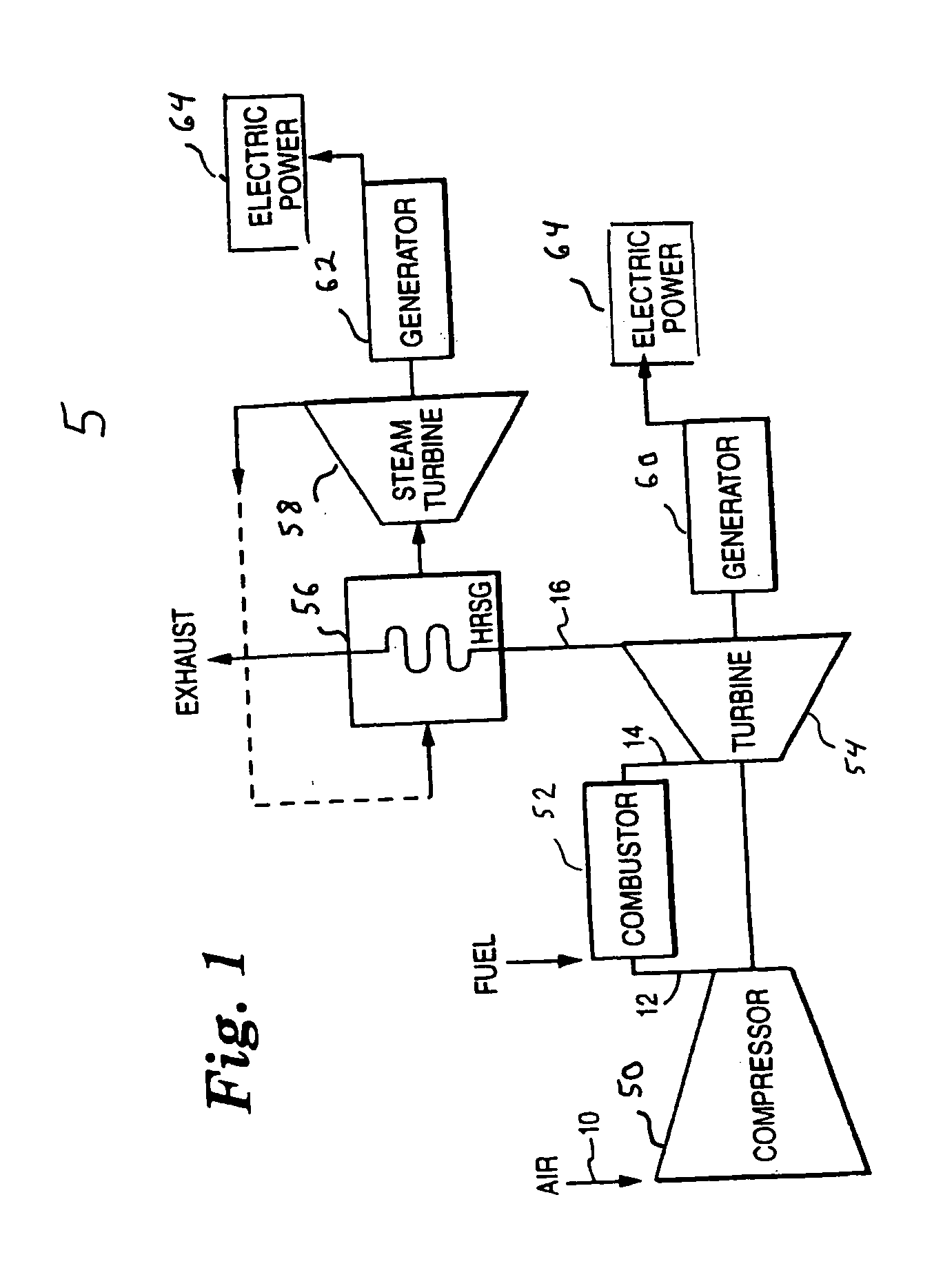
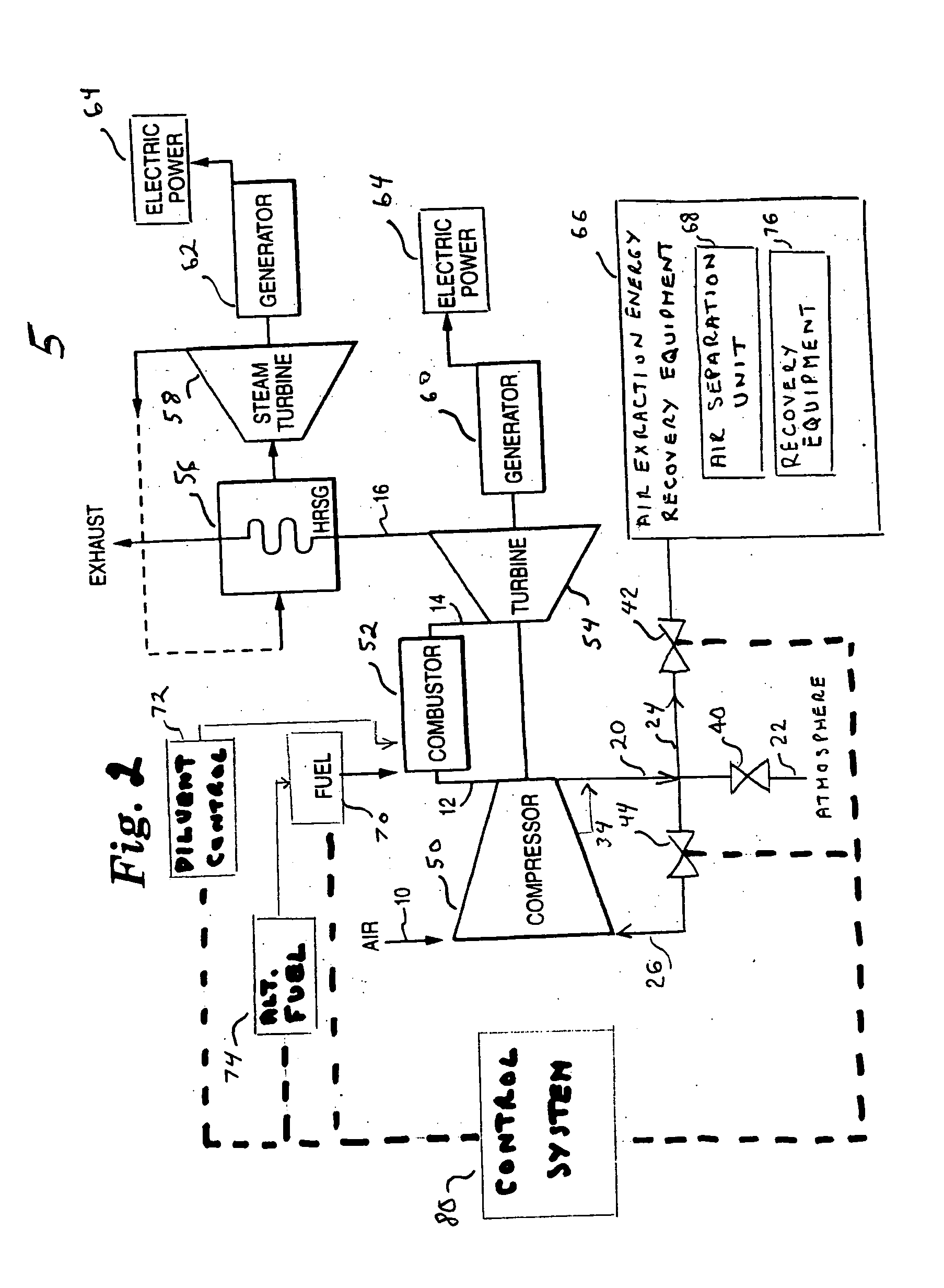
ActiveUS20070271929A1Reducing diluent flowRaise the firing temperatureGas turbine plantsEngine componentsElectricityPower grid
In a gas turbine electric power generator where rotational speed of the gas turbine is synchronized to the electrical frequency of a power grid and the gas turbine includes a compressor component, an air extraction path, and means for controlling an amount of compressor air extraction, a method is provided for controlling output power produced by a gas turbine. The method includes initiating compressor air extraction and controlling the amount of compressor air extraction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Brushless DC motor and brushless DC motor controller
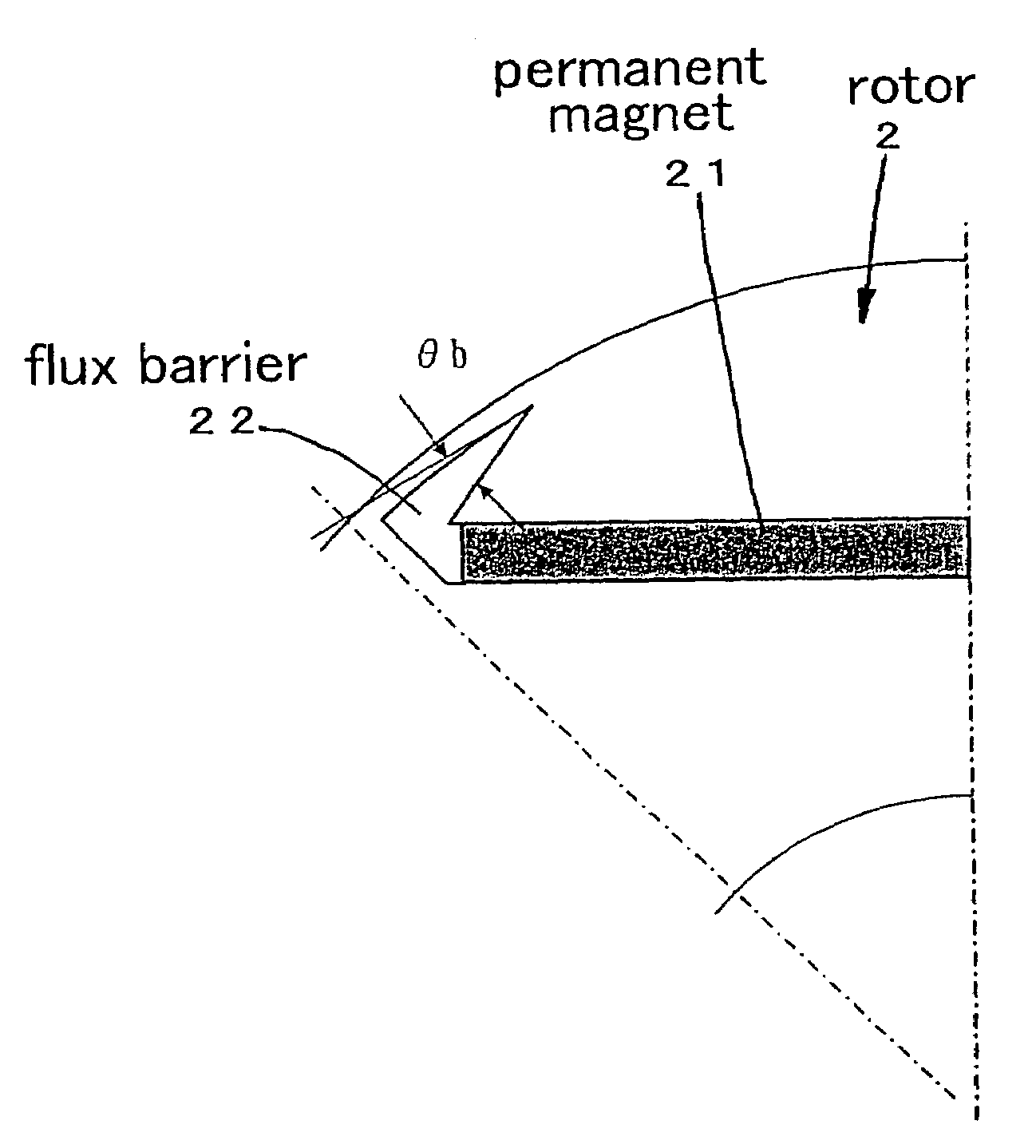
ActiveUS7119507B2Efficient preparationReduce noiseTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersMagnetic polesDC motor
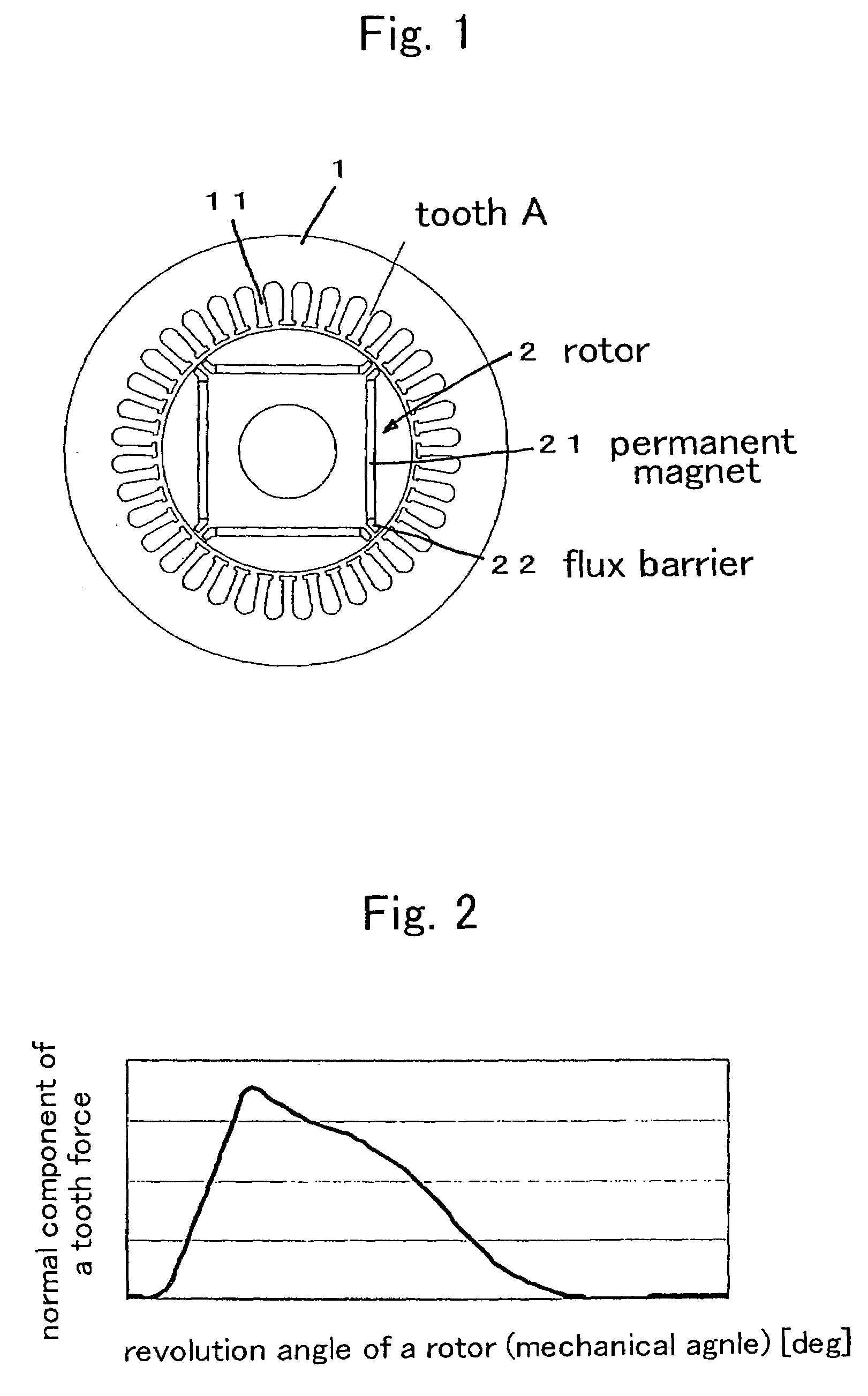
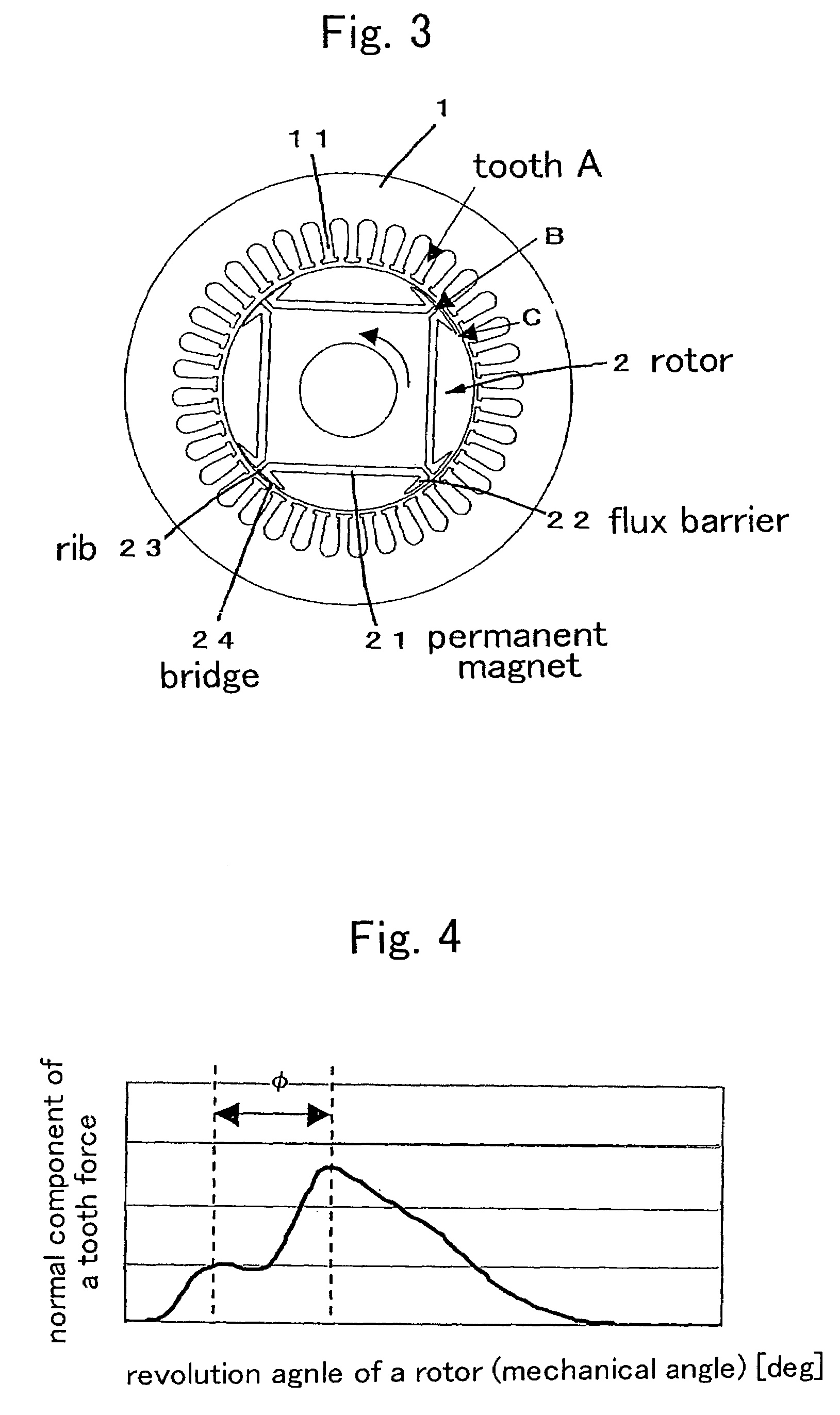
A brushless DC motor has a stator and a rotor. An angle θ0 between an edge section of the flux barrier on a magnetic pole center side and an edge section on a side for coming in contact with the rib of adjacent flux barrier, with respect to the rotor center, is determined to be equal to or greater than an angle satisfying a following relationshipθ0=180°*m / (Pn*f / f0) (provided 2θ0−θr<90°)wherein, a frequency of vibration which is to be reduced is represented with f, a pole pair number is represented with Pn, an electrical frequency is represented with f0=Pn*N, a motor revolution is represented with N, m=1, 3, 5, . . . , an angle of the rib with respect to the rotor center is represented with θr, therefore making of motor highly effective and decreasing of the motor acoustic noise are coped with.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
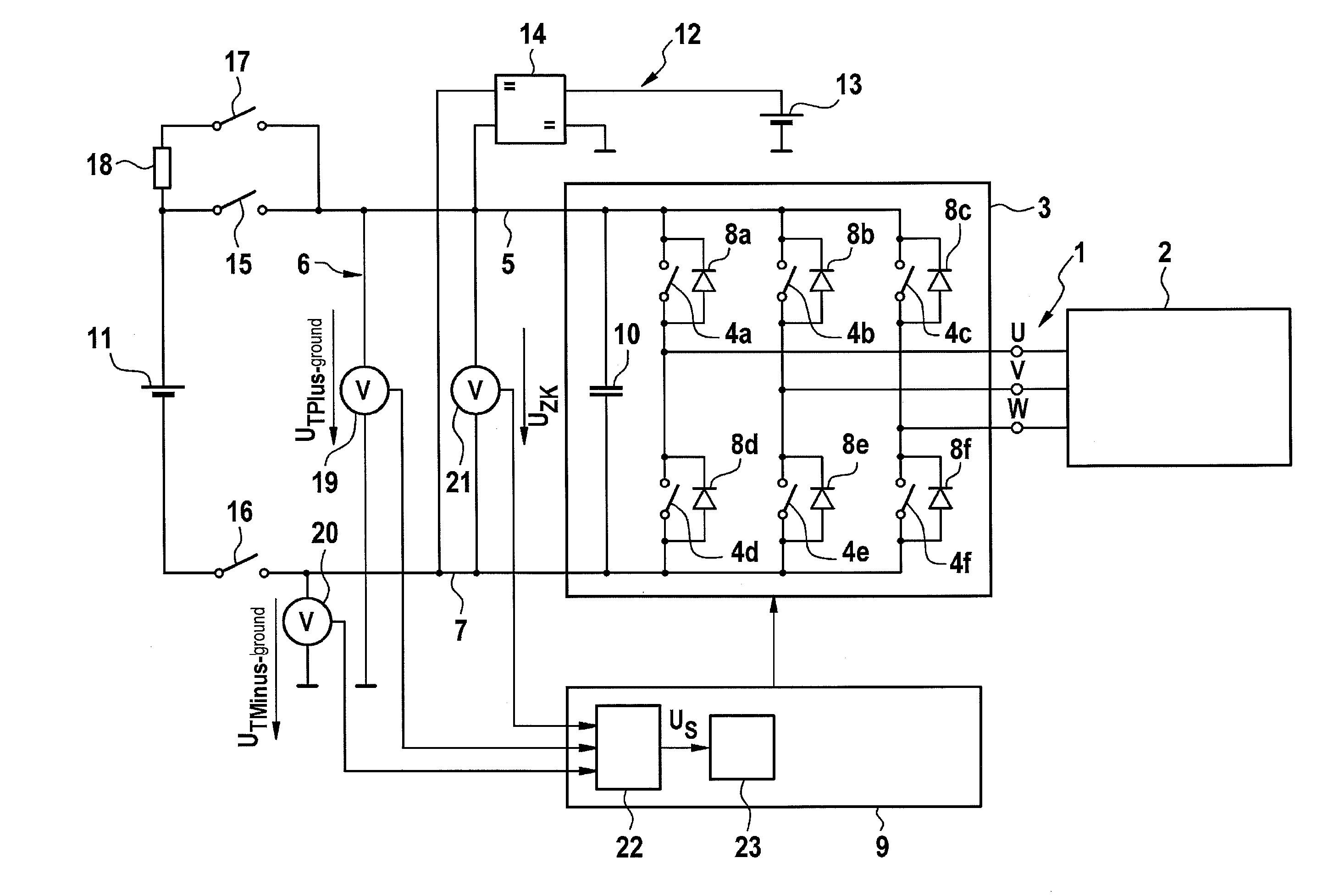
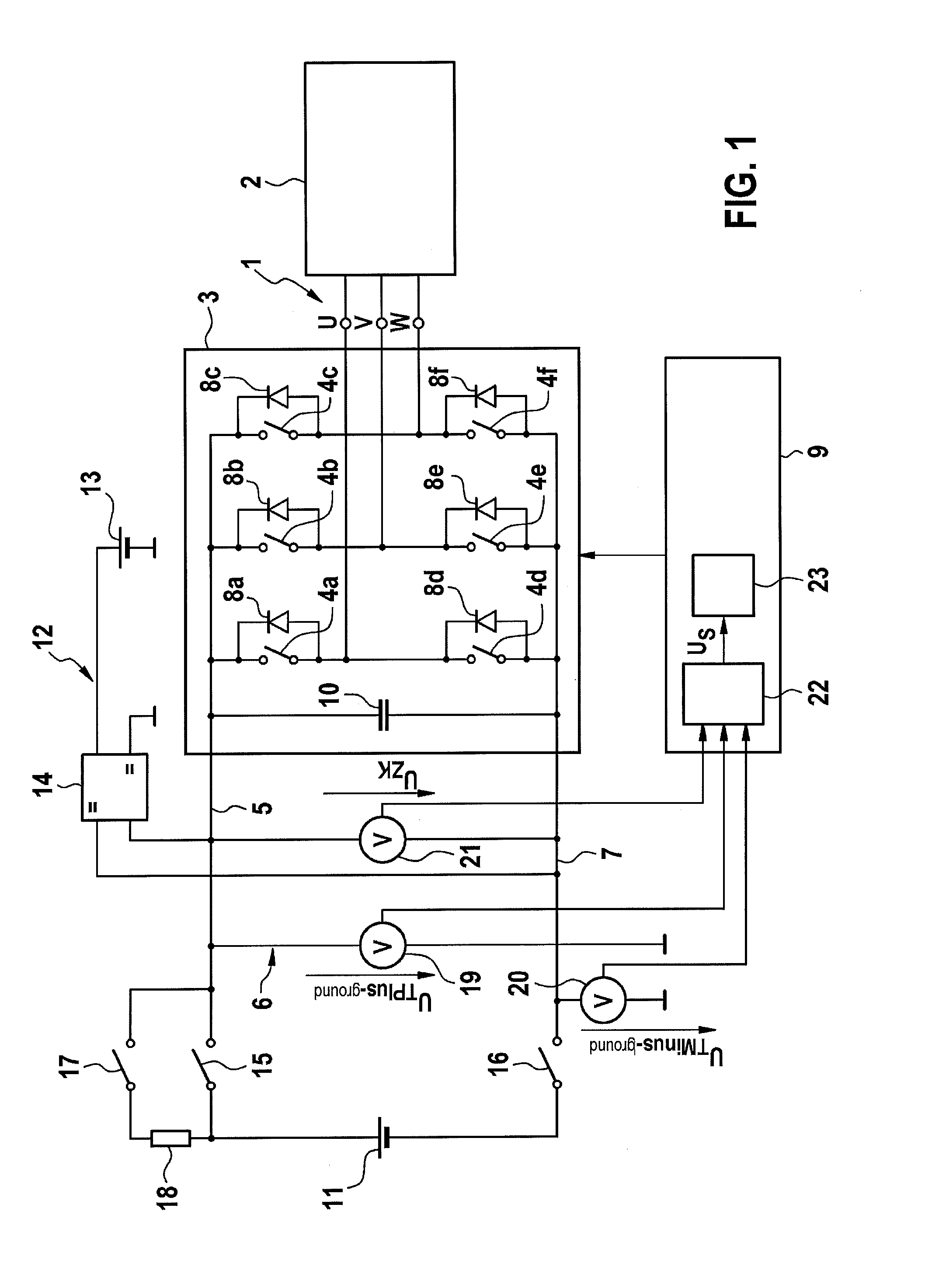
Method and device for monitoring the insulation resistance in an ungrounded electrical network
InactiveUS20130221997A1High measurement accuracyElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceElectric networkPower usage
A method and a device for monitoring the insulation resistance in an ungrounded electrical network having a constant-voltage d.c. link and at least one inverter, connected to it, for controlling an n-phase electrical consumer in an n-phase network. A voltage to be monitored, is determined during operation of the consumer, which represents a voltage fluctuation of supply voltage potentials of the constant-voltage d.c. link with respect to a reference potential. In addition, a variable characterizing an electrical frequency of the electrical consumer is determined, particularly an electrical angular speed of the electrical consumer. A first spectral amplitude of the voltage to be monitored at the n-fold electrical frequency of the electrical consumer, is compared to a first reference value, and detects a symmetrical insulation error in the constant-voltage d.c. link or the n-phased network, if the comparison yields a deviation of the first spectral amplitude from the first reference value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Optical transmission apparatuses, methods, and systems
InactiveUS6891981B2Overcome problemsLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal onCarrier signal
Apparatuses, methods, and systems are disclosed for controlling optical signal wavelength spacing by providing for simultaneous upconversion of a plurality of electrical signal on subcarrier frequencies of an optical carrier frequency with or without modulation of an electrical data signal onto the optical carrier frequency. The optical carrier lightwave is split into a plurality of split lightwaves upon which one or more electrical frequencies carrying information can be upconverted onto optical subcarriers of the lightwave carrier frequency. The relative spacings of the optical subcarrier lightwaves will thus be unaffected by variation in the carrier frequency. The optical subcarrier lightwaves can then be recombined to form the optical data signal carrying the plurality of information carried by the electrical frequencies.
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
Method of heating sub sea esp pumping system
A system and method is provided for heating fluid to be pumped by an electrical submersible pumping system. Heat for heating the fluid may be inductively generated by adjusting the power delivered to the motor of the pumping system. In one example, the power adjustment includes supplying the voltage applied to the pump motor to a value less than voltage applied during normal operations. While lowering the voltage the electrical frequency may be varied as well as the electrical waveform.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
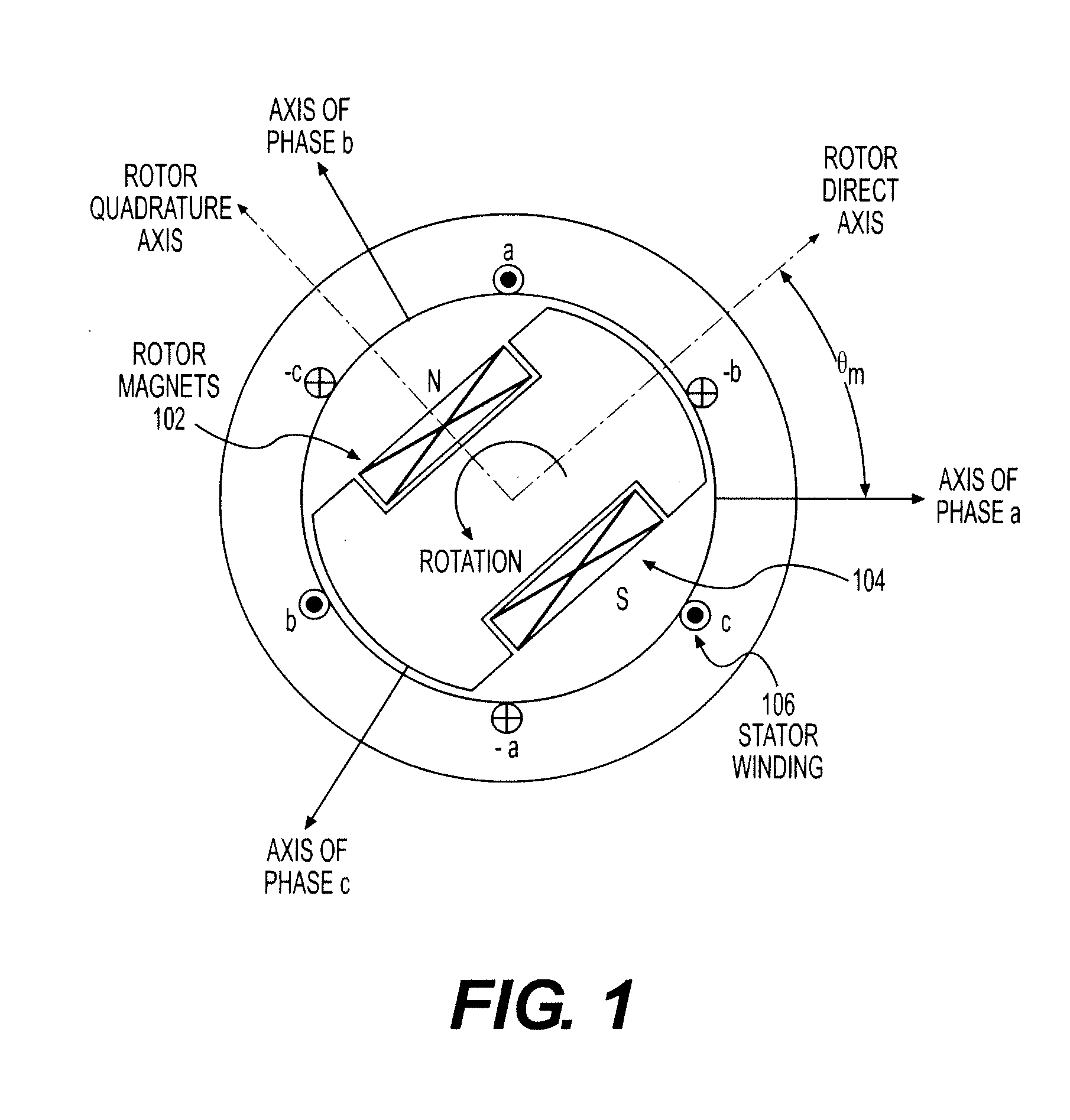
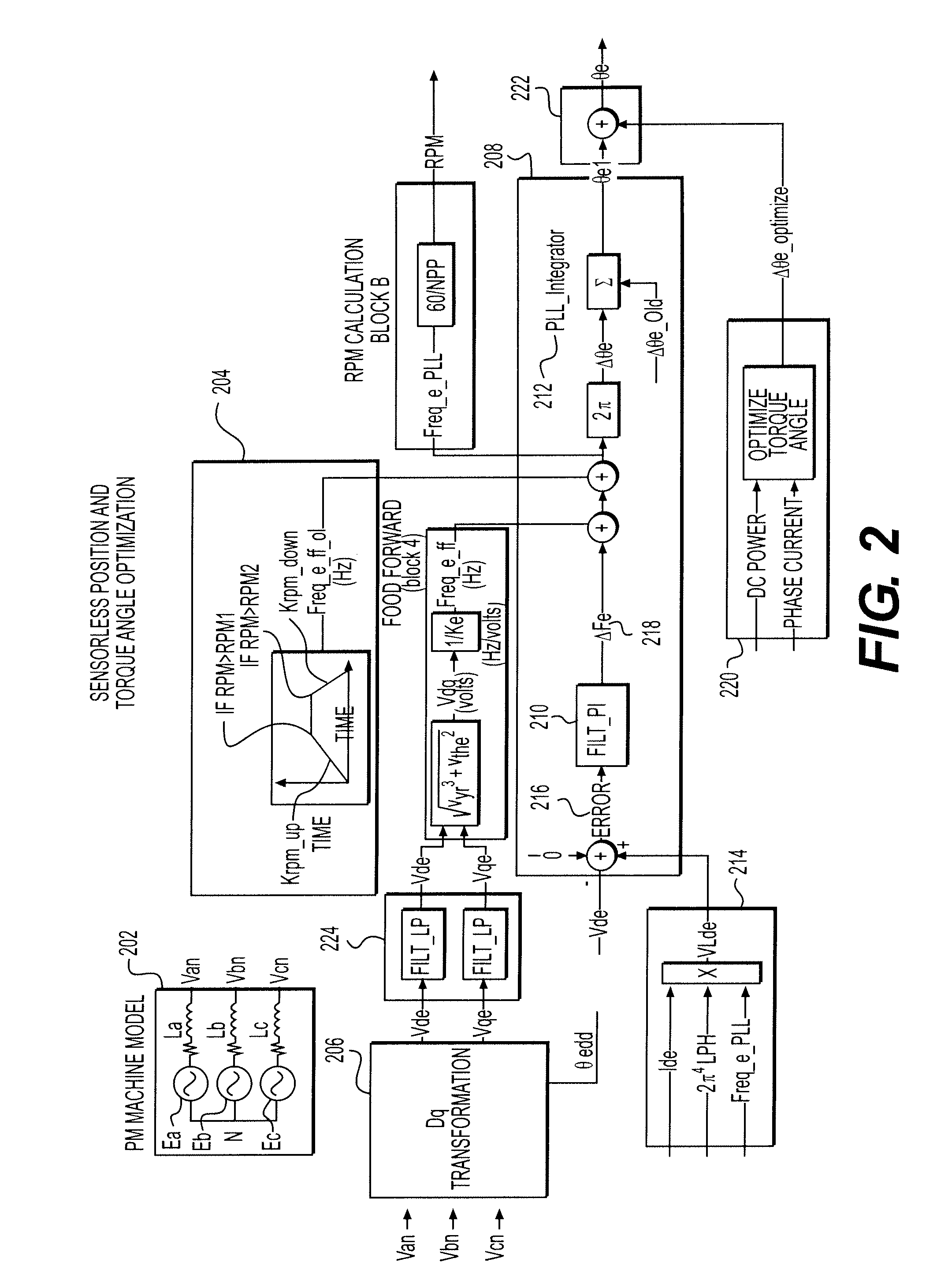
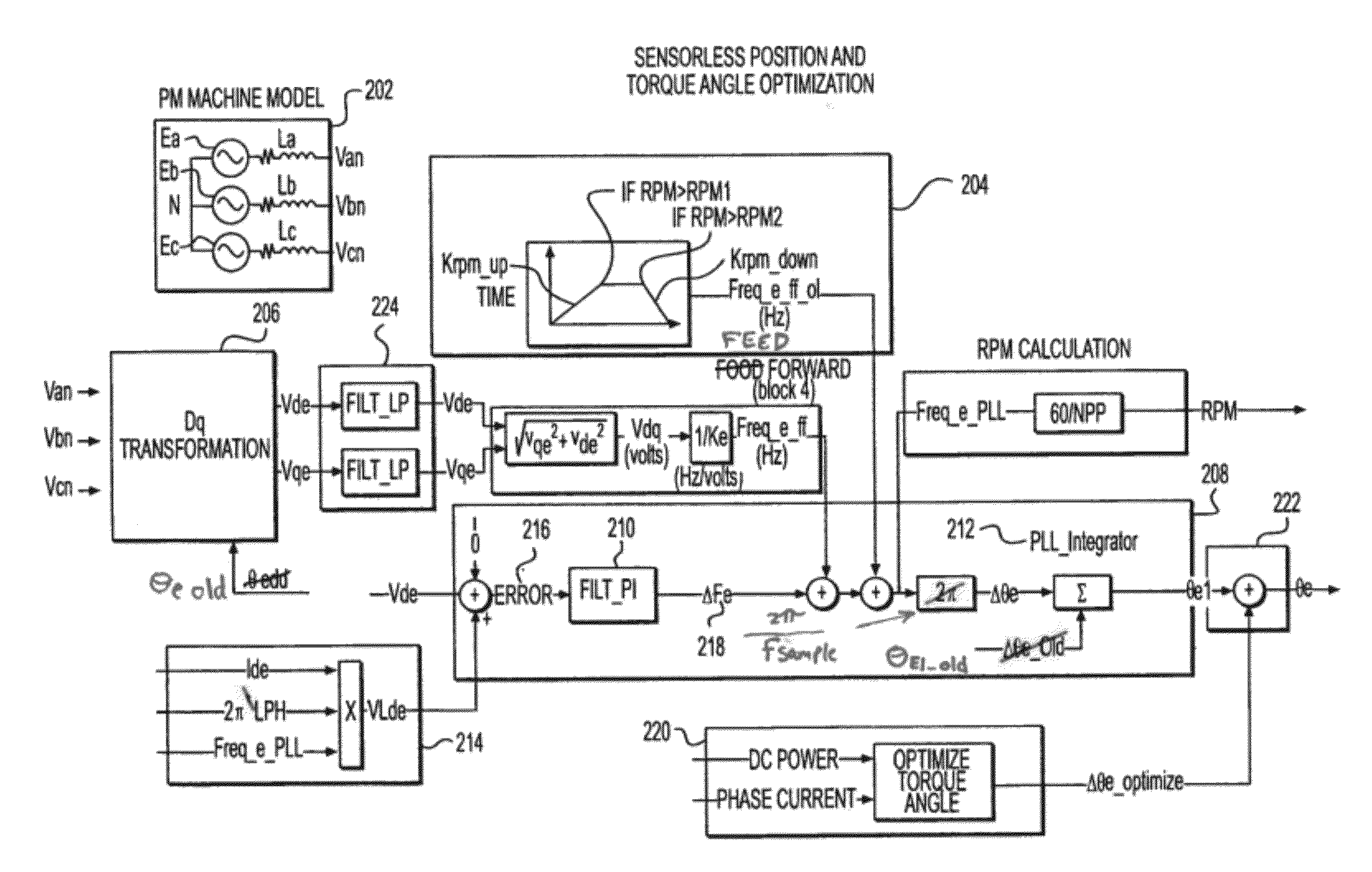
Sensorless optimum torque control for high efficiency ironless permanent magnet machine
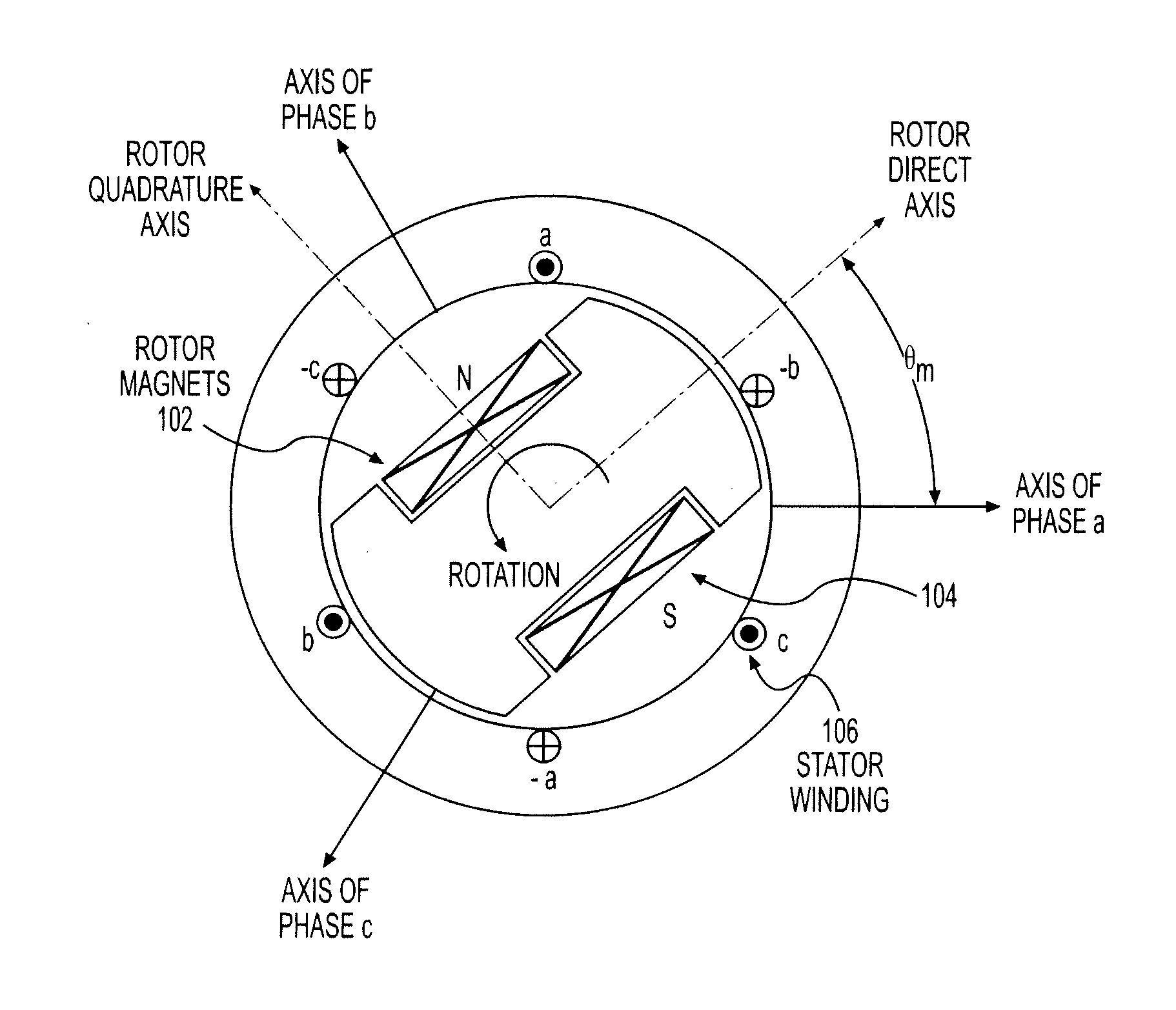
ActiveUS20100188033A1Commutation monitoringMotor/generator/converter stoppersIntegratorTerminal voltage
Embodiments of the present invention permit the optimization of torque control of a permanent magnet machine including obtaining instantaneous terminal voltages of the machine, transforming the instantaneous terminal voltages to a zero direct axis voltage and a non-zero quadrature axis voltage, using a mathematical transformation, regulating the electrical frequency of the permanent-magnet machine such that the zero direct-axis voltage is adjusted to have a value of zero, determining a non-final electrical angle of the permanent-magnet machine by applying an integrator to the regulated electrical frequency of the machine, determining a final electrical angle of the of the machine by integrating the non-final electrical angle and an electrical angle from a previous calculation cycle, and regulating the current vector of the machine such that the current vector is perpendicular to the final electrical angle of the machine, thereby optimizing the torque of the machine.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
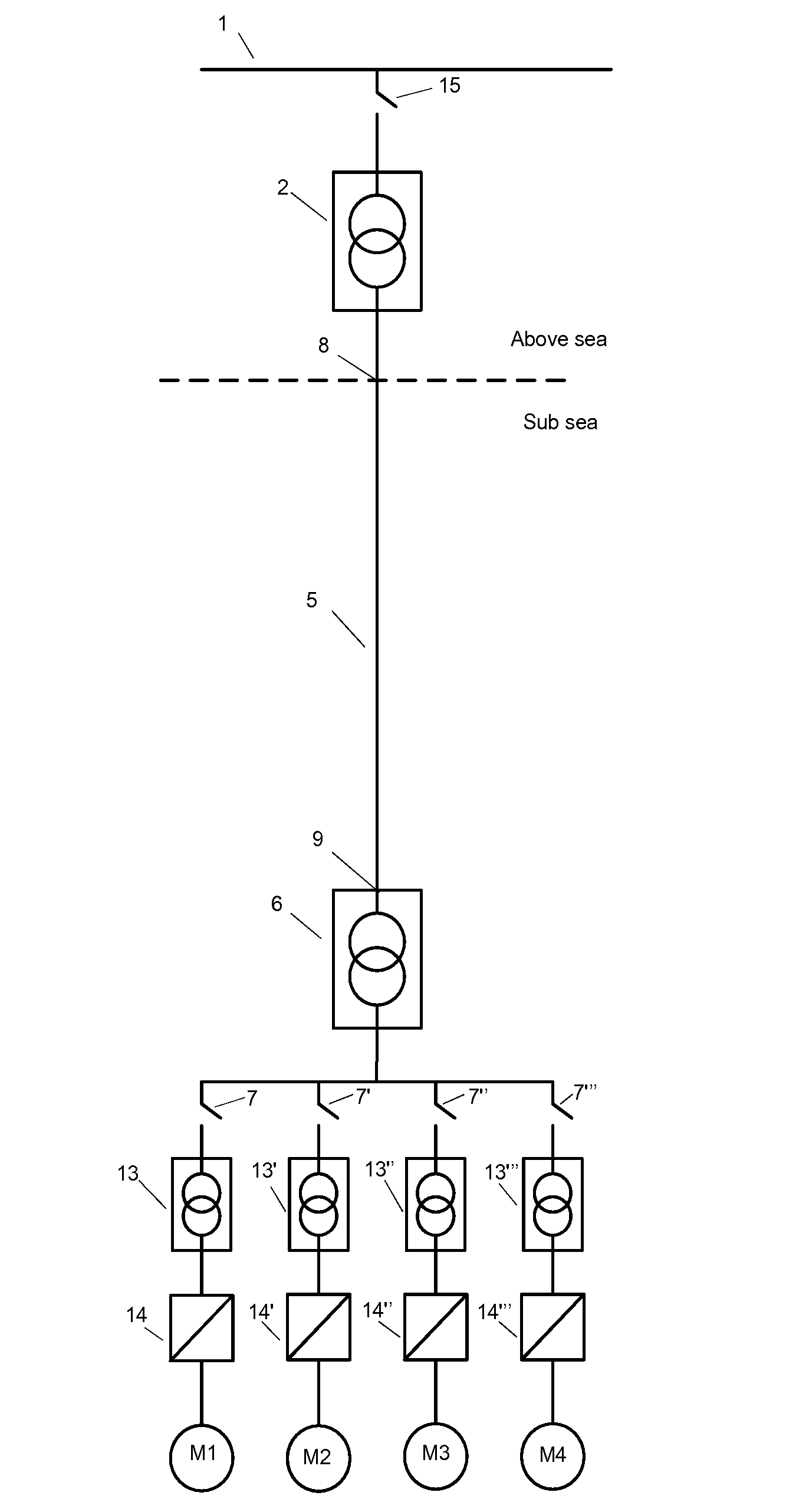
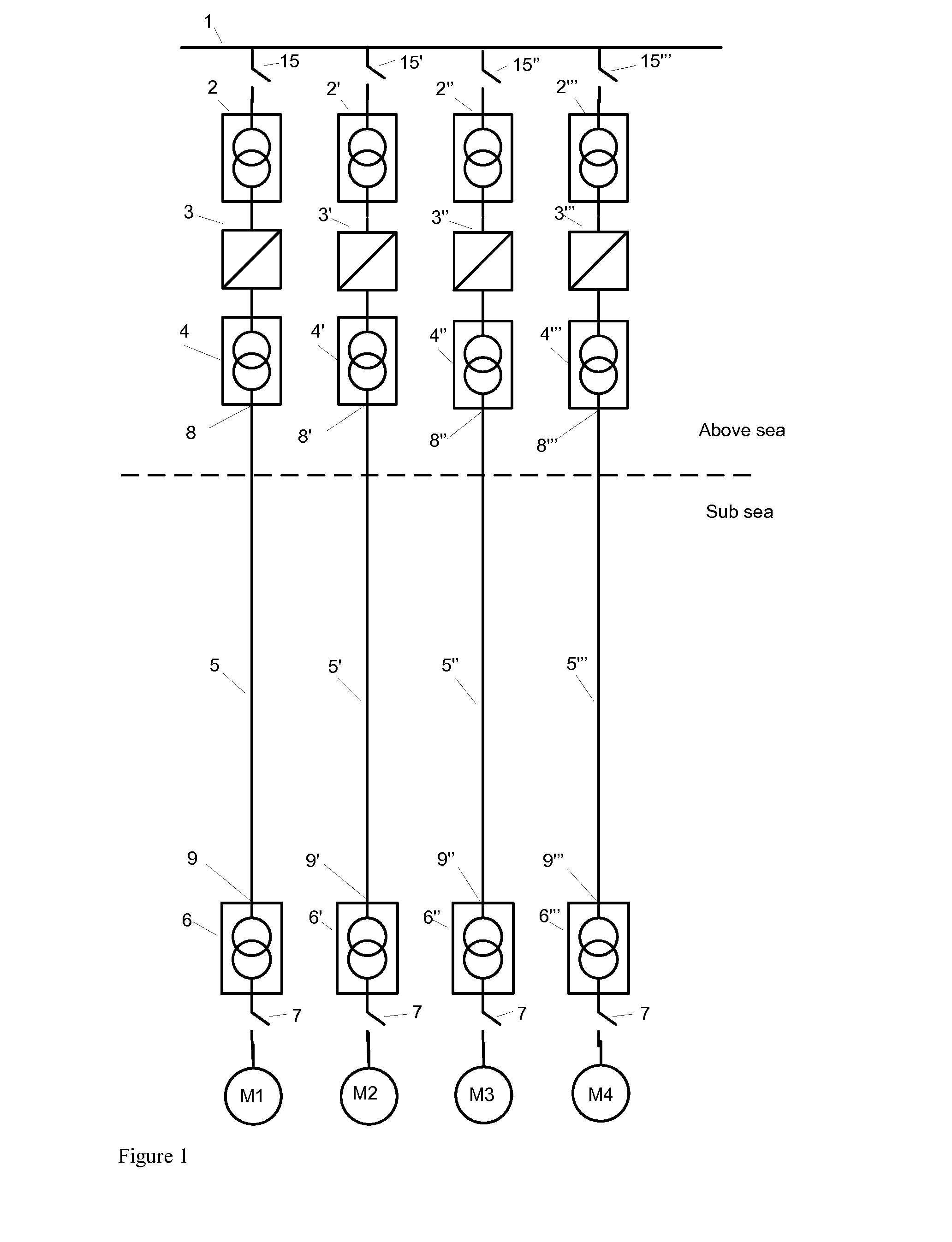
Device for stable subsea electric power transmission to run subsea high speed motors or other subsea loads
ActiveUS20140203640A1Compensation effectReduce investmentDc network circuit arrangementsMultiple ac dynamo-electric motors controlElectric power transmissionOcean bottom
The invention provides a device for operative connection between a subsea step out cable far end and subsea loads such as pumps, compressors and control systems, distinctive in that the device is a rotating frequency stepper device, more specifically a rotating step up or step down device, and it comprises: a motor and a generator operatively connected so that the motor drives the generator, at least one gas and / or liquid filled vessel into which at least one of the motor and generator are arranged, and the step out length is long, which means long enough to cause problems due to the Ferranti effect at frequency and power levels feasible for subsea pump and compressor motors, and where the device via the step out cable receives input electrical power at a low enough frequency to have stable transmission and the device, operatively connected to the subsea motor, delivers an output electrical frequency, amperage and voltage feasible for operation of the connected motors. System for pressure boosting of hydrocarbon fluid or other fluid subsea, comprising the device.
Owner:AKER SOLUTIONS AS
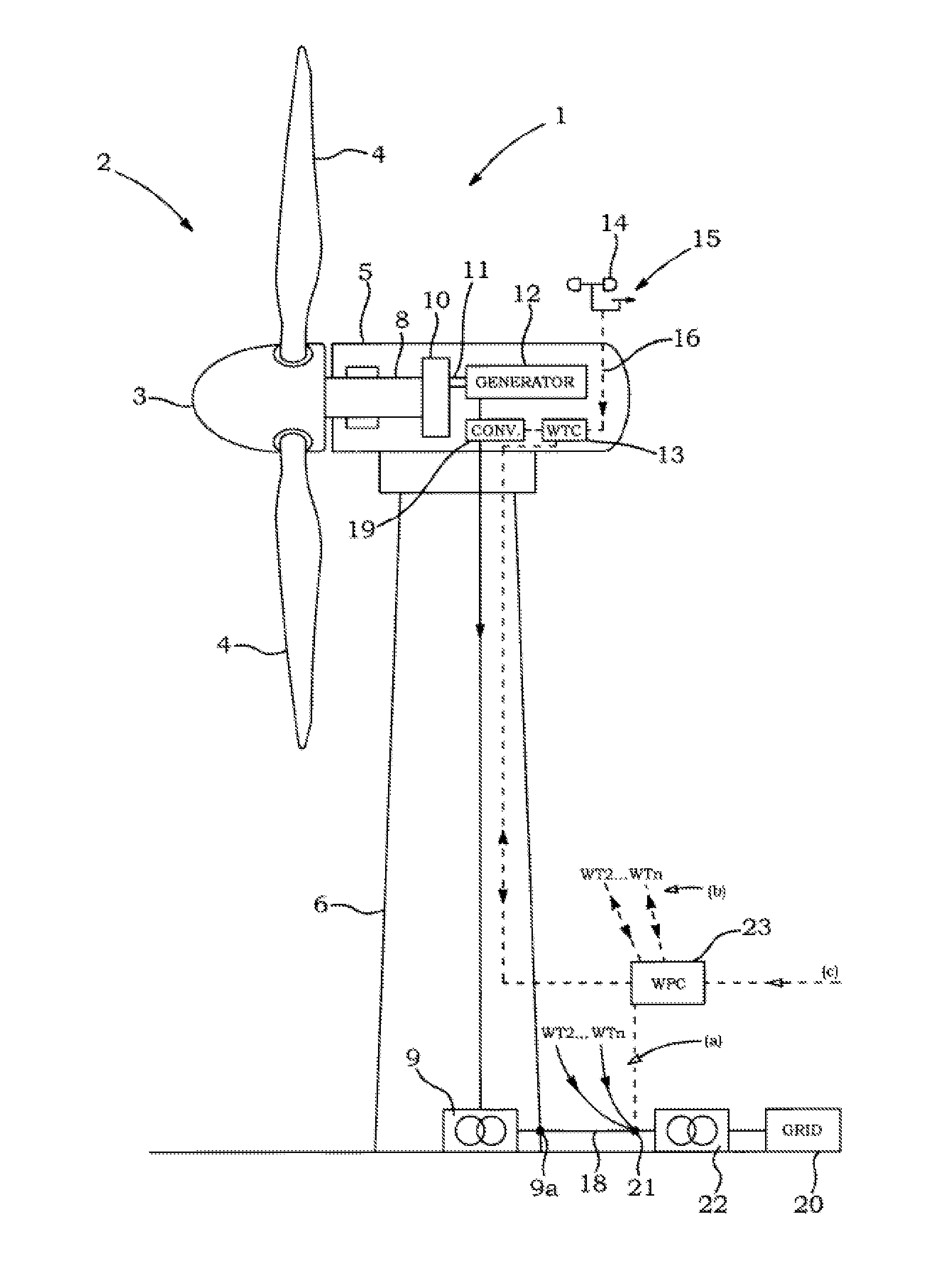
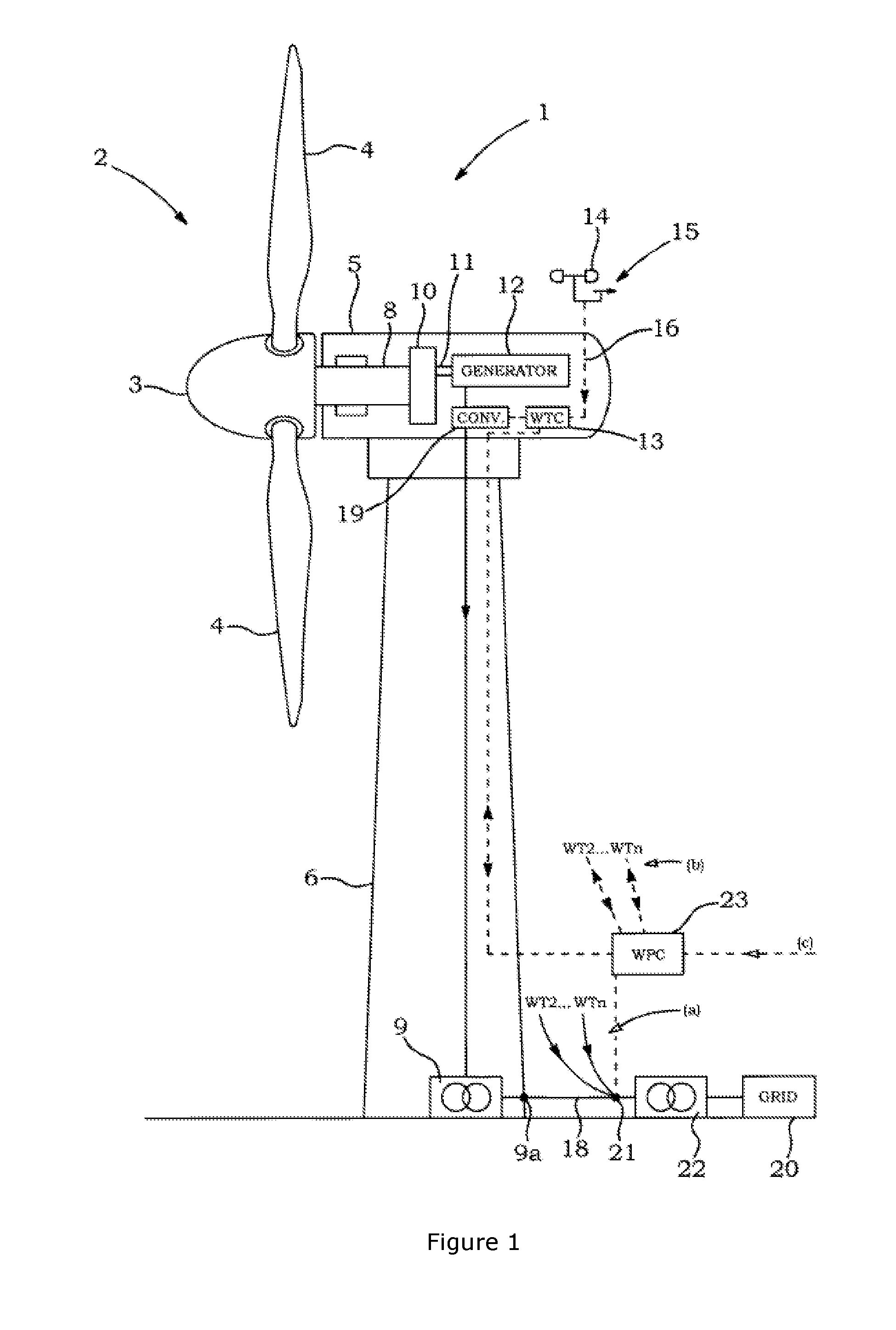
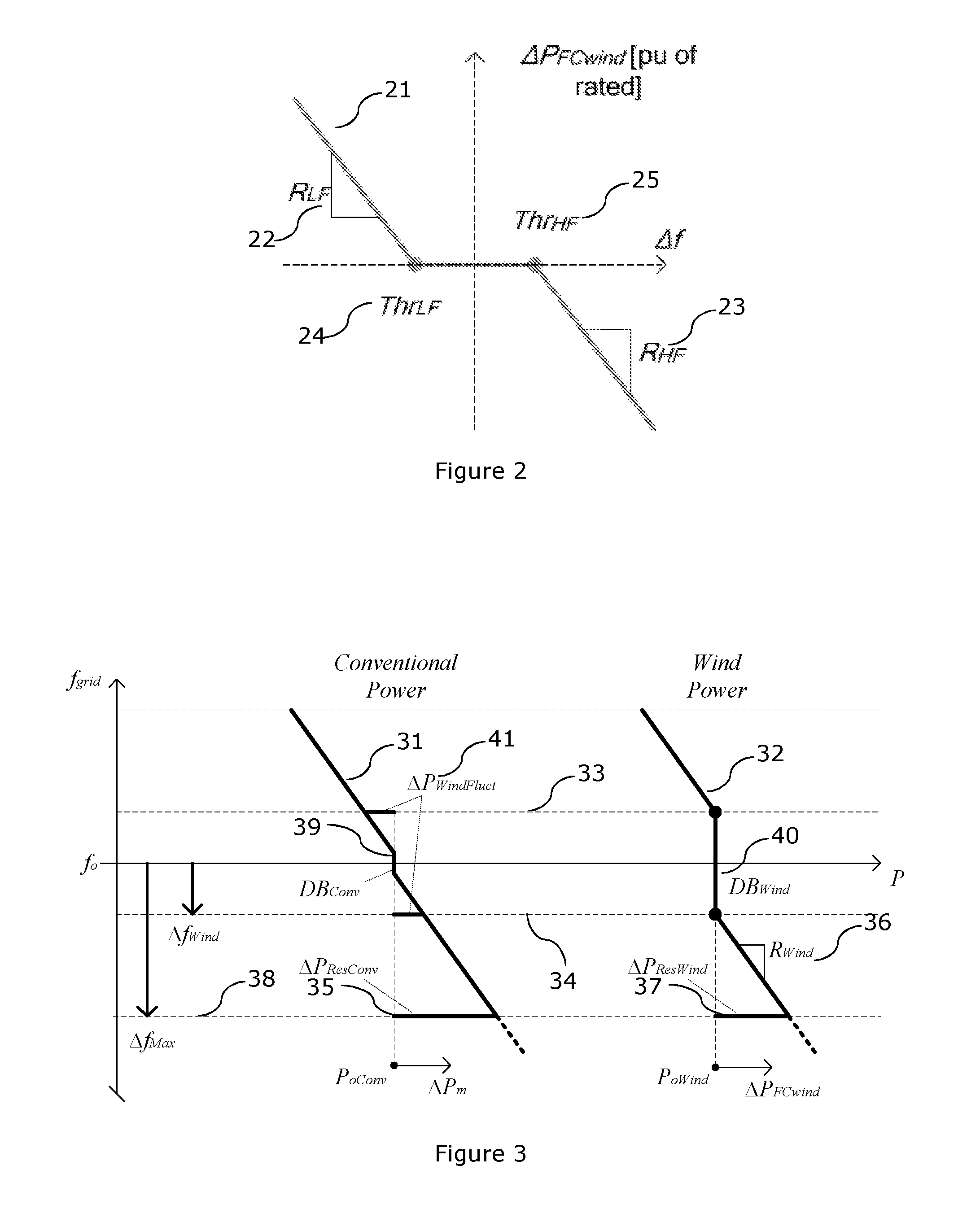
Method for coordinating frequency control characteristics between conventional plants and wind power plants
ActiveUS20150120070A1Stable grid operationMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectricityPower station
The present invention relates to a method for operating an electrical power system, comprising at least one wind turbine generator and at least one other power source, the method comprises the steps of, setting a set of technical requirements and limits for the electrical power system, including a total power reserve and at least one of: maximum electrical frequency deviation and allowable wind power electrical frequency fluctuations, distributing the total power reserve between the at least one other power source and a total wind power capacity available from the at least one wind turbine generator, and calculating in response thereto an amount of power reserve from the at least one wind turbine generator, and providing settings for a wind power controller, the settings comprising the set of technical requirements and the amount of power reserve from the at least one wind turbine generator. The invention also relates to a power plant operating according to the method.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveCN101581685ADetectableTo achieve the purpose of identificationMaterial resistanceTransceiverDesorption
A sensor instrument system and a method for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region comprising a local sensor instrument and remote central station are disclosed. The instrument is comprised of a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement, a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station connects to a network means connected to a plurality of local receiving sites equipped with including the respective transceivers, so that the local analyte electrical information and geographic position information transmitted by the instrument can be wirelessly and remotely received and processed by the central station. The core technology is further comprised of a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivity including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:孙一慧 +1
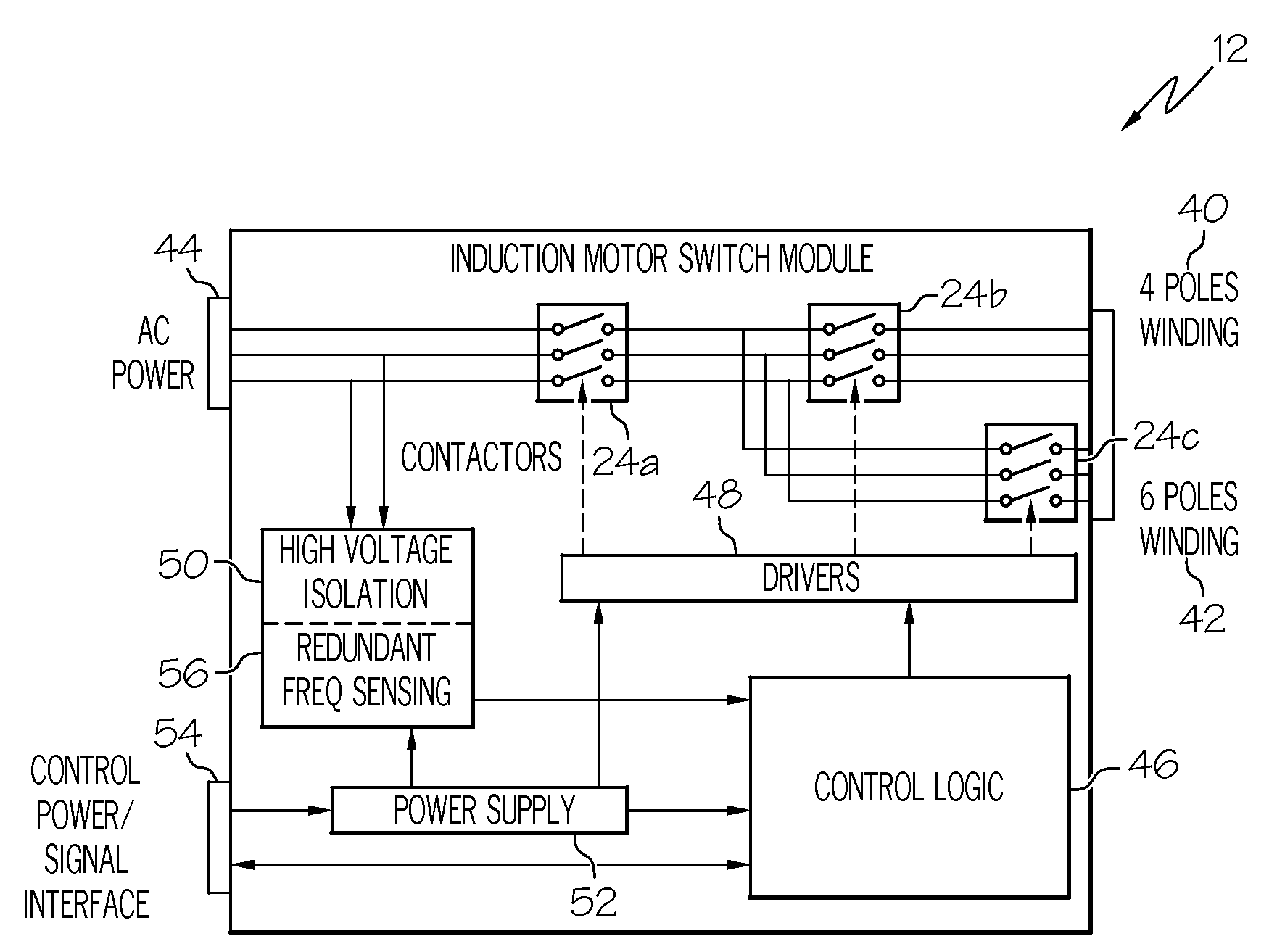
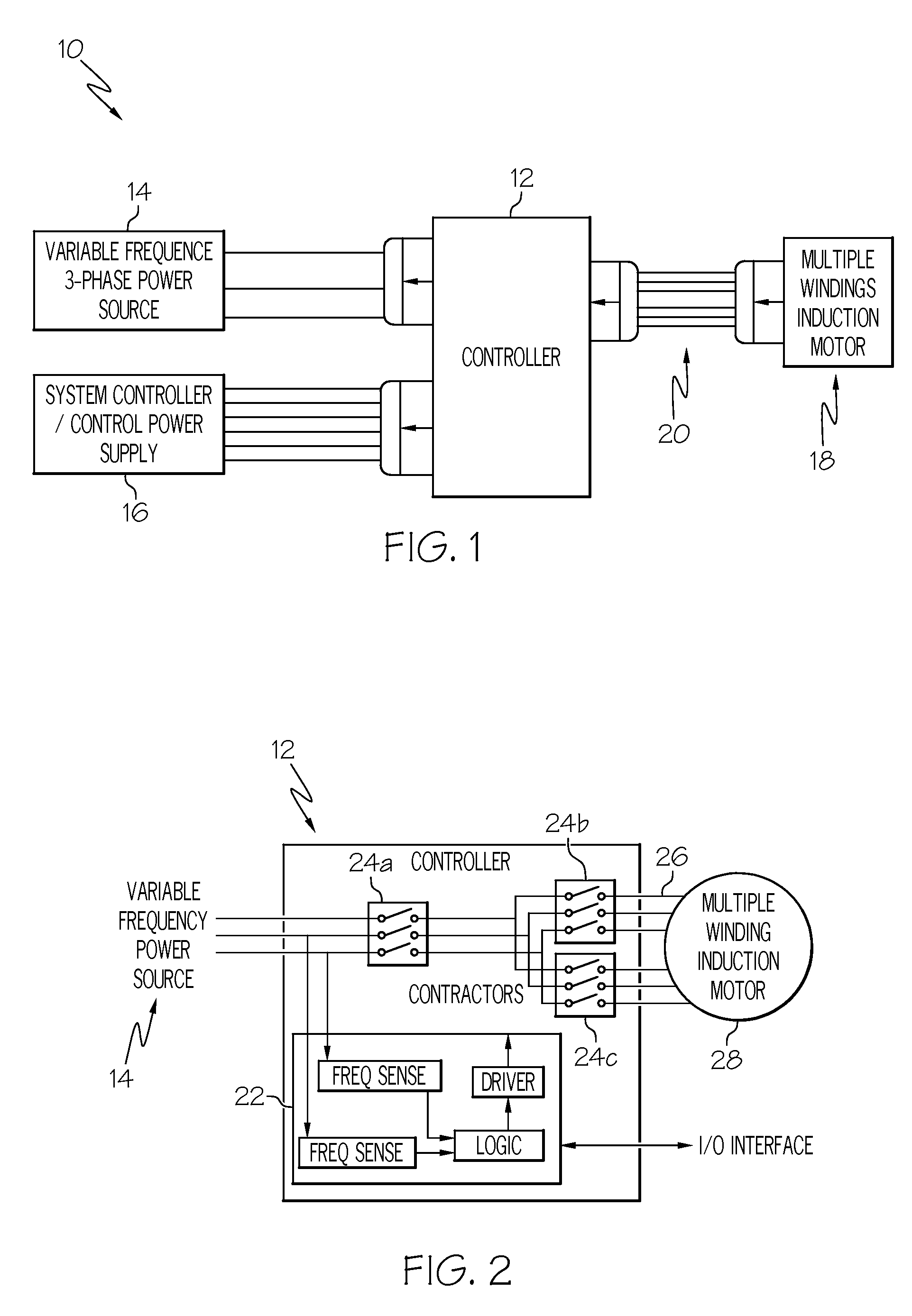
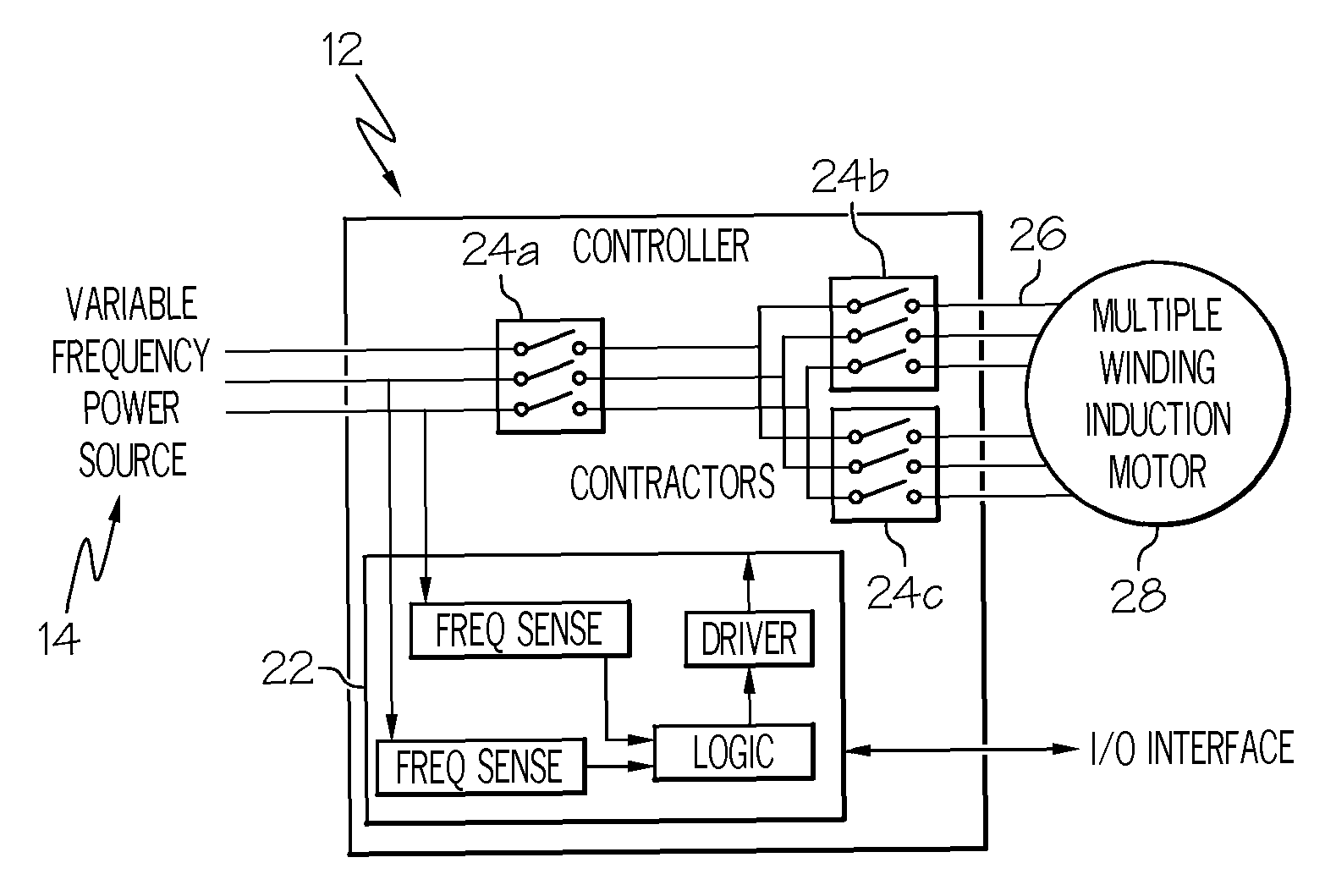
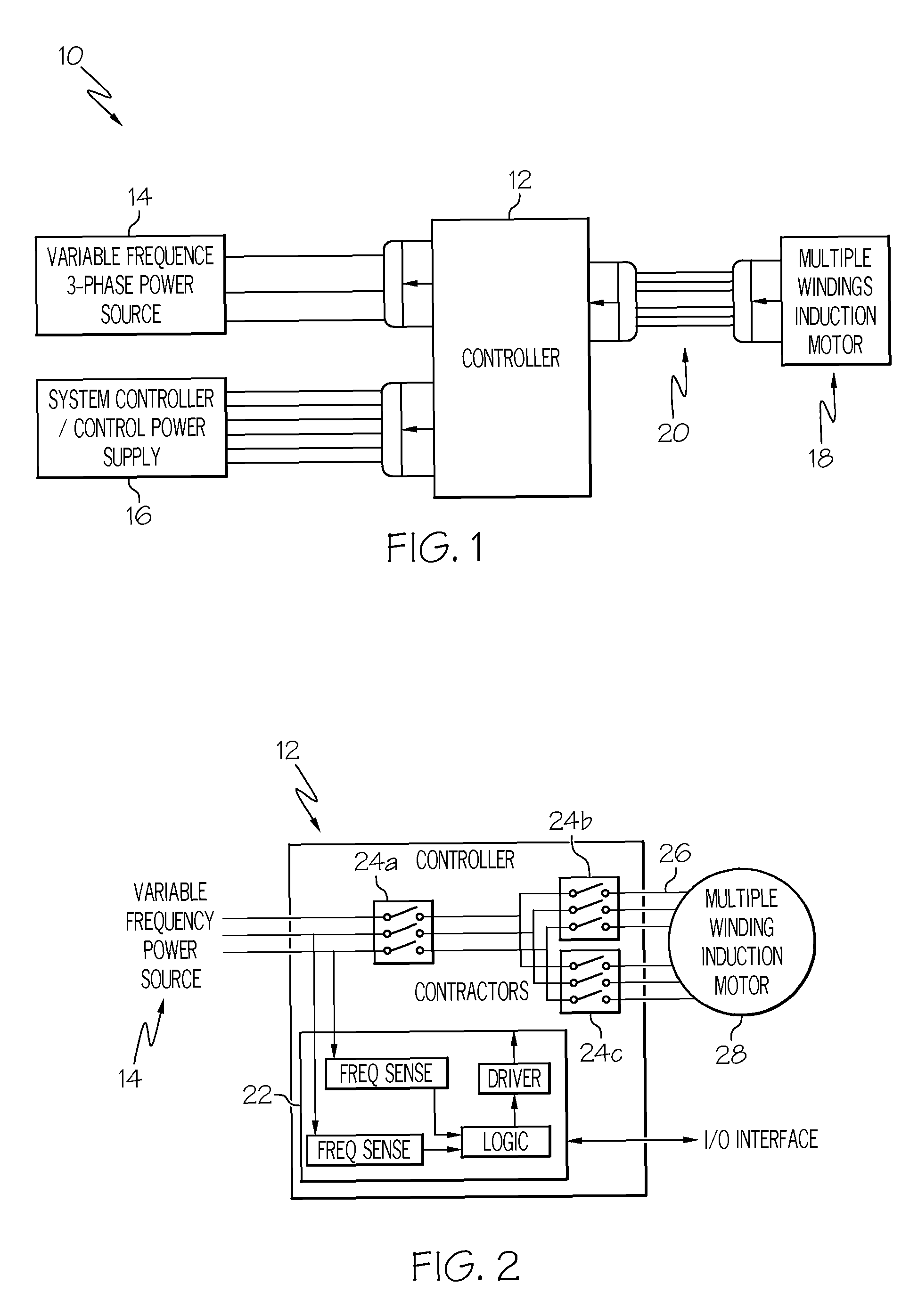
Variable frequency reduced speed variation electric drive
InactiveUS20080265828A1Minimizing speed variationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlElectricityIntermediate frequency
A multiple-winding induction machine may be used to obtain a reduced-speed-variation electric drive when using a variable-frequency power distribution system. Each winding may have a different number of poles. The winding with the smallest number of poles may operate the machine at the lowest bus frequency, while the winding with the largest number of poles may operate the machine at the highest bus frequency. In one embodiment, a third winding, with a middle number of poles, may operate the machine at the middle frequency ranges. The speed of the induction machine is a function of the electrical frequency and the number of the winding poles. Therefore, the operating speed range can be reduced by switching from one winding to another. According to the present invention, windings with different numbers of poles can be designed to achieve different reductions in speed variation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Variable frequency reduced speed variation electric drive
InactiveUS7952316B2Minimizing speed variationMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlElectricityIntermediate frequency
A multiple-winding induction machine may be used to obtain a reduced-speed-variation electric drive when using a variable-frequency power distribution system. Each winding may have a different number of poles. The winding with the smallest number of poles may operate the machine at the lowest bus frequency, while the winding with the largest number of poles may operate the machine at the highest bus frequency. In one embodiment, a third winding, with a middle number of poles, may operate the machine at the middle frequency ranges. The speed of the induction machine is a function of the electrical frequency and the number of the winding poles. Therefore, the operating speed range can be reduced by switching from one winding to another. According to the present invention, windings with different numbers of poles can be designed to achieve different reductions in speed variation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for gas turbine operation during under-frequency operation through use of air extraction
ActiveUS8479523B2Reducing diluent flowRaise the firing temperatureGas turbine plantsEngine componentsElectricityControl system
In a gas turbine electric power generator where rotational speed of the gas turbine is synchronized to the electrical frequency of a power distribution grid and the gas turbine includes a compressor component, an air extraction path, and a control system for controlling an amount of compressor air extraction, a method is provided for controlling output power produced by a gas turbine. The method includes initiating compressor air extraction and controlling the amount of compressor air extraction.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Microwave photonic down-conversion apparatus and method based on bidirectional cyclic frequency shift
ActiveCN108809437ADown conversionDown conversion is flexible and variableOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingPhotonic quantum communicationSignal onBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a microwave photonic down-conversion apparatus and method based on a bidirectional cyclic frequency shift, and relates to the field of microwave photonics. The microwave photonic down-conversion apparatus and method aim to solve the defects of small bandwidth, large loss and the like confronted by a traditional electrical frequency converter and the defect that high-frequency electrical local oscillation is needed by an optical frequency conversion technology. The apparatus provided by the invention consists of a laser, a cyclic frequency shift module and a photoelectric detector; and the cyclic frequency shift module includes a 2*2 optical coupler, a polarization controller, a dual-drive electro-optical intensity modulator, an electrical local oscillation source, an optical amplifier, an optical band pass filter and an optical adjustable delay line. In the cyclic frequency shift module, first-order optical sidebands of a to-be-converted radio-frequency signal and an electrical local oscillation signal on an optical carrier simultaneously perform opposite optical sideband movement step by step at a same frequency shift, and at last photoelectric detection isperformed on two opposite frequency shift optical sidebands having nearest frequencies to implement down-conversion of the radio-frequency signal; and with the characteristic of opposite frequency shift of the cyclic frequency shift module, by changing a frequency of the electrical local oscillation source, the wide frequency range under low-frequency electrical local oscillation and the down-conversion of a tunable microwave signal are implemented.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Soft decoding system of resolver
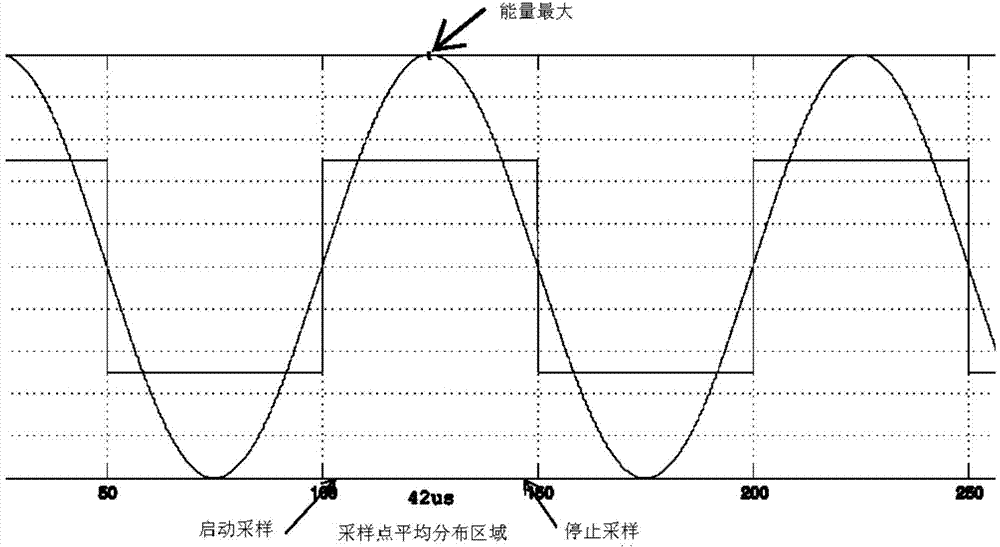
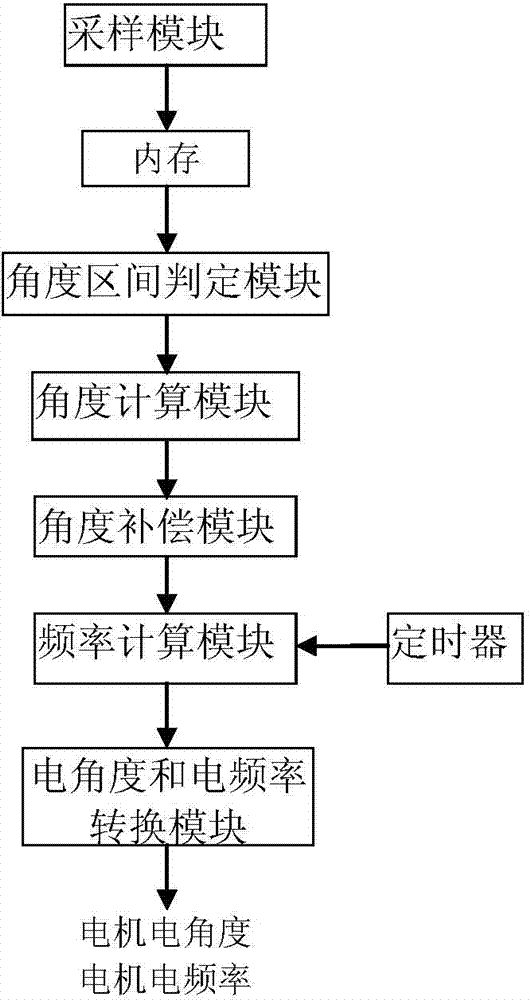
ActiveCN103762912ASoft decoding implementationReduce complexityTransformersInductancesElectricityMotor controller
The invention discloses a soft decoding system of a resolver. The soft decoding system of the resolver comprises an angle interval judgment module, an angle calculation module, an angle compensation module, a frequency calculation module and an electrical angle and electrical frequency conversion module, wherein the angle interval judgment module is used for judging the angle interval where the angle at the DMA interruption moment is located according to sampling values of sin differential signals and sampling values of cos differential signals, the angle calculation module is used for calculating the angle at the DMA interruption moment according to the angle interval where the angle at the DMA interruption moment is located, the angle compensation module is used for carrying out compensation on the angle at the DMA moment to obtain the angle at the soft decoding interruption moment, the frequency calculation module is used for calculating the frequency of the resolver, and the electrical angle and electrical frequency conversion module is used for converting the current angle at the soft decoding interruption moment into the electrical angle of a motor, and converting the current frequency of the resolver into the electrical frequency of the motor. According to the soft decoding system of the resolver, a decoding chip is not needed, and the cost of a motor controller can be reduced.
Owner:UNITED AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS SYST
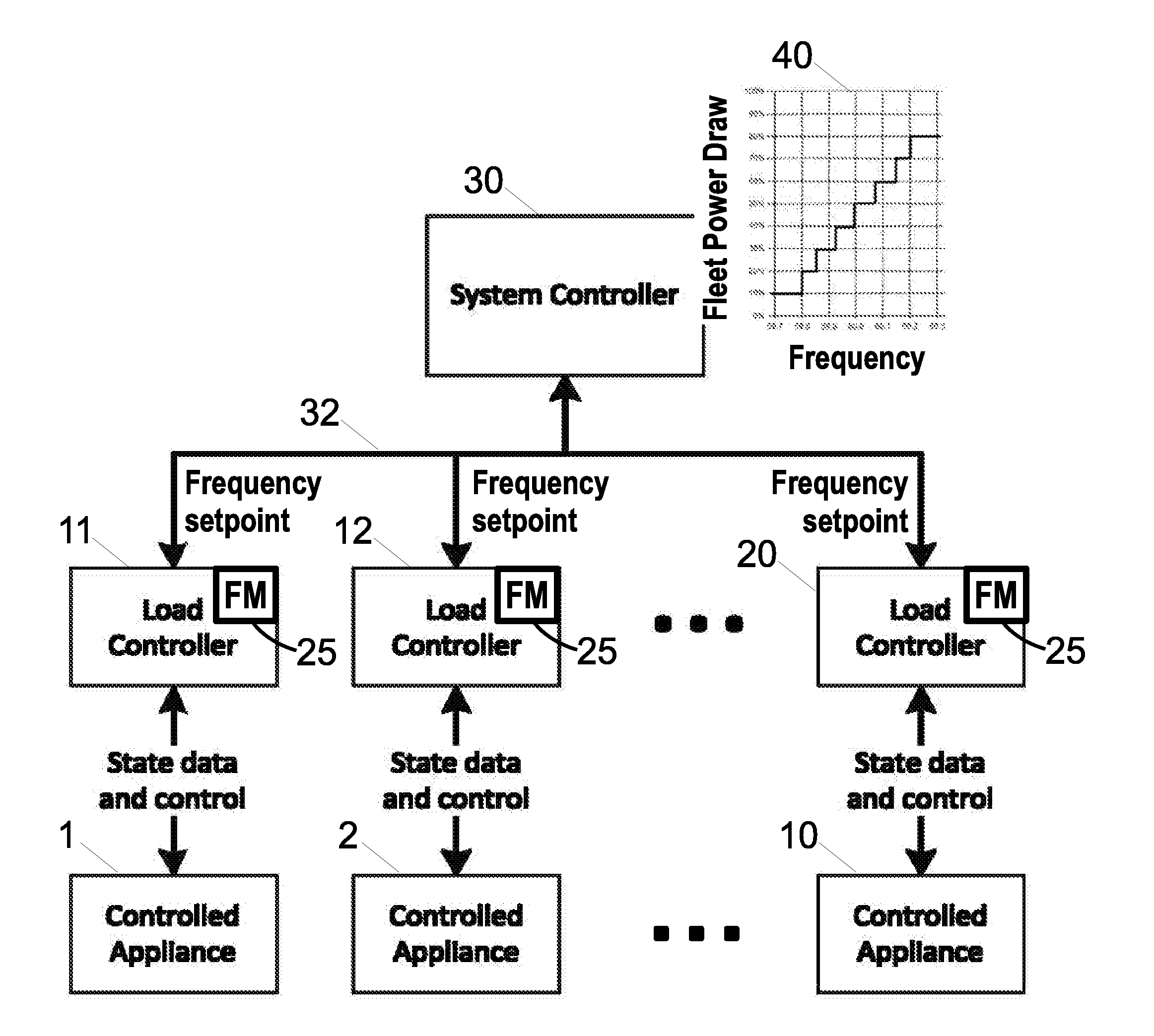
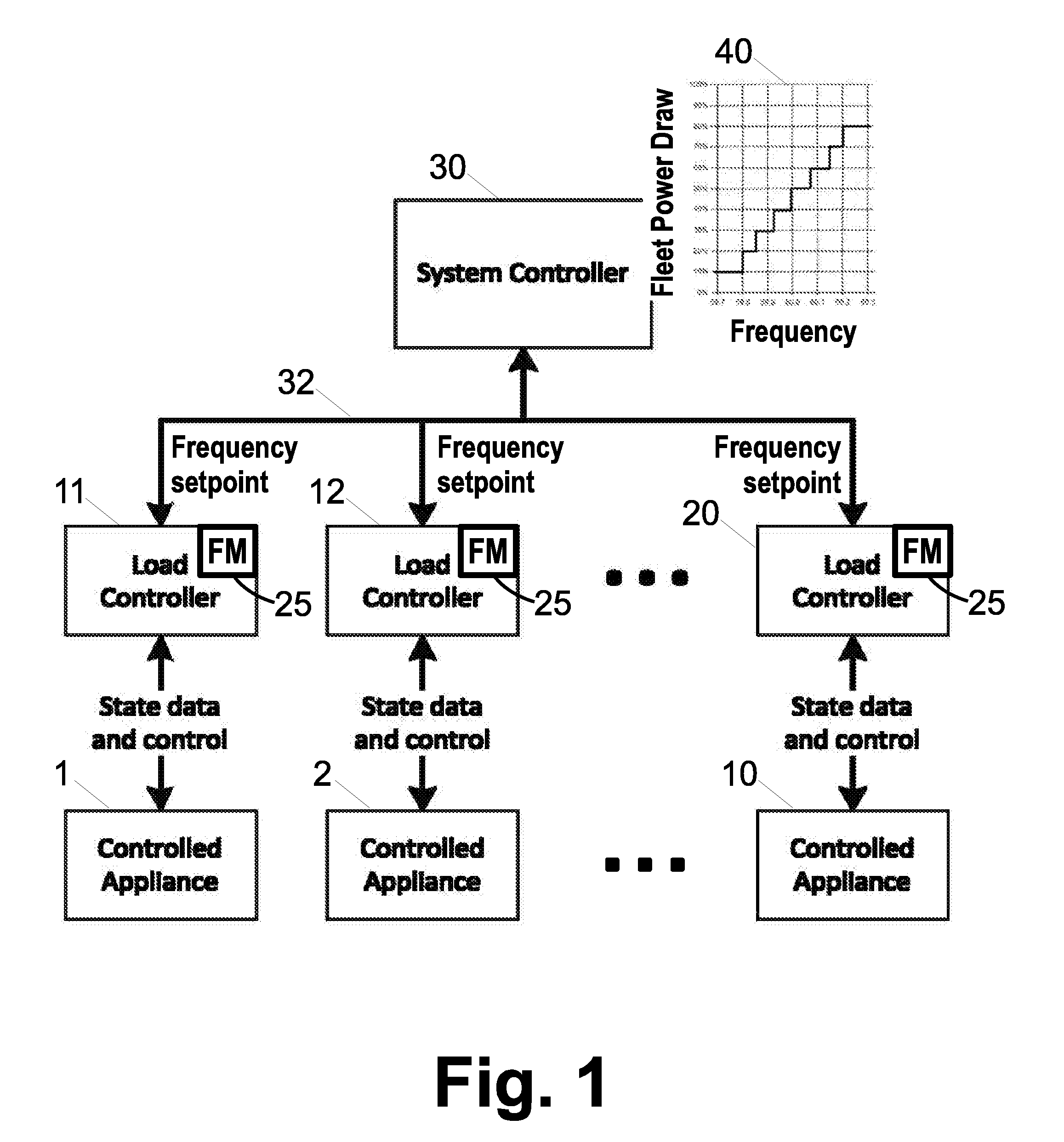
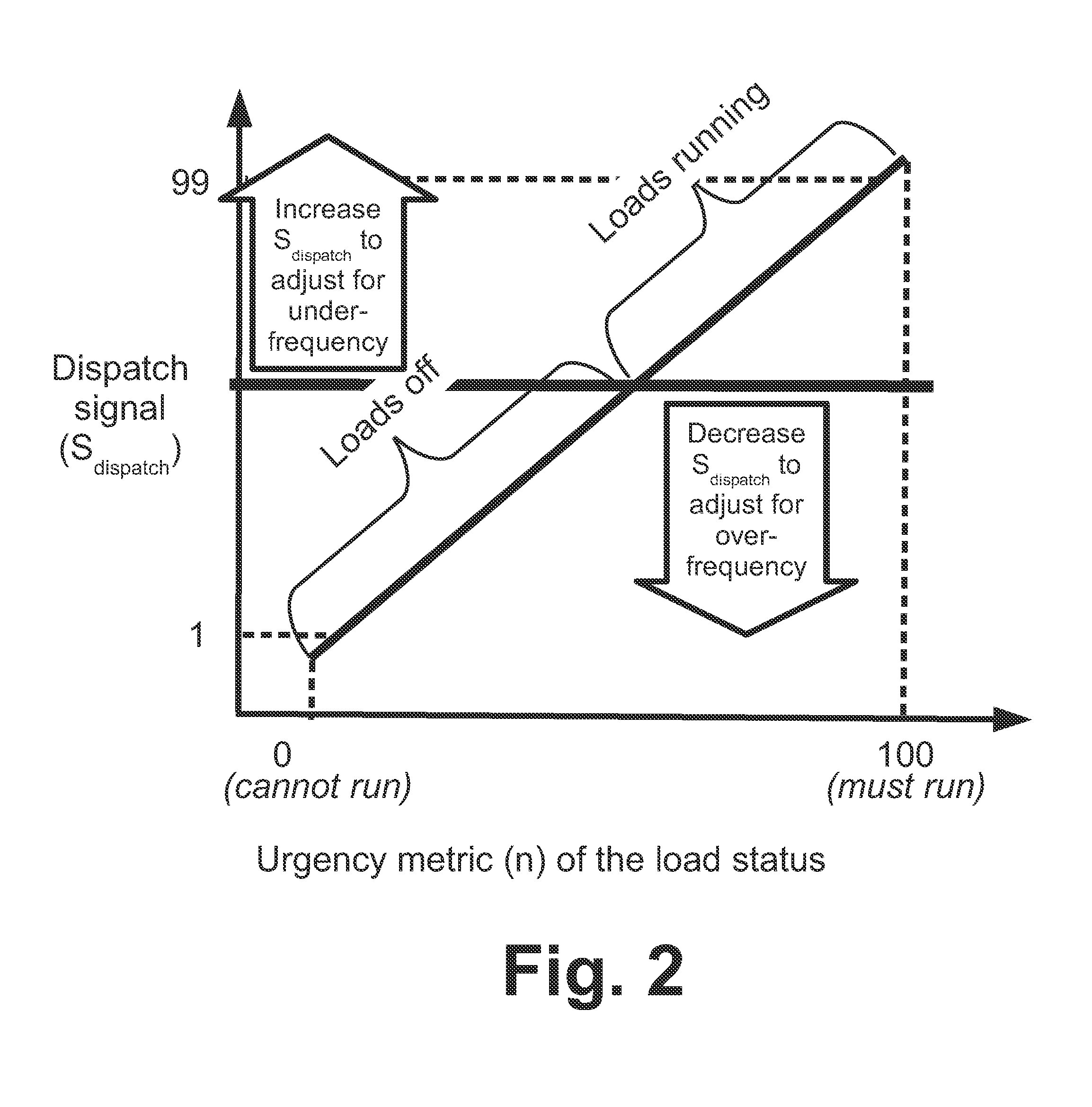
Primary frequency control through simulated droop control with electric loads
ActiveUS20160276834A1Computer controlPower network operation systems integrationDroop speed controlElectricity
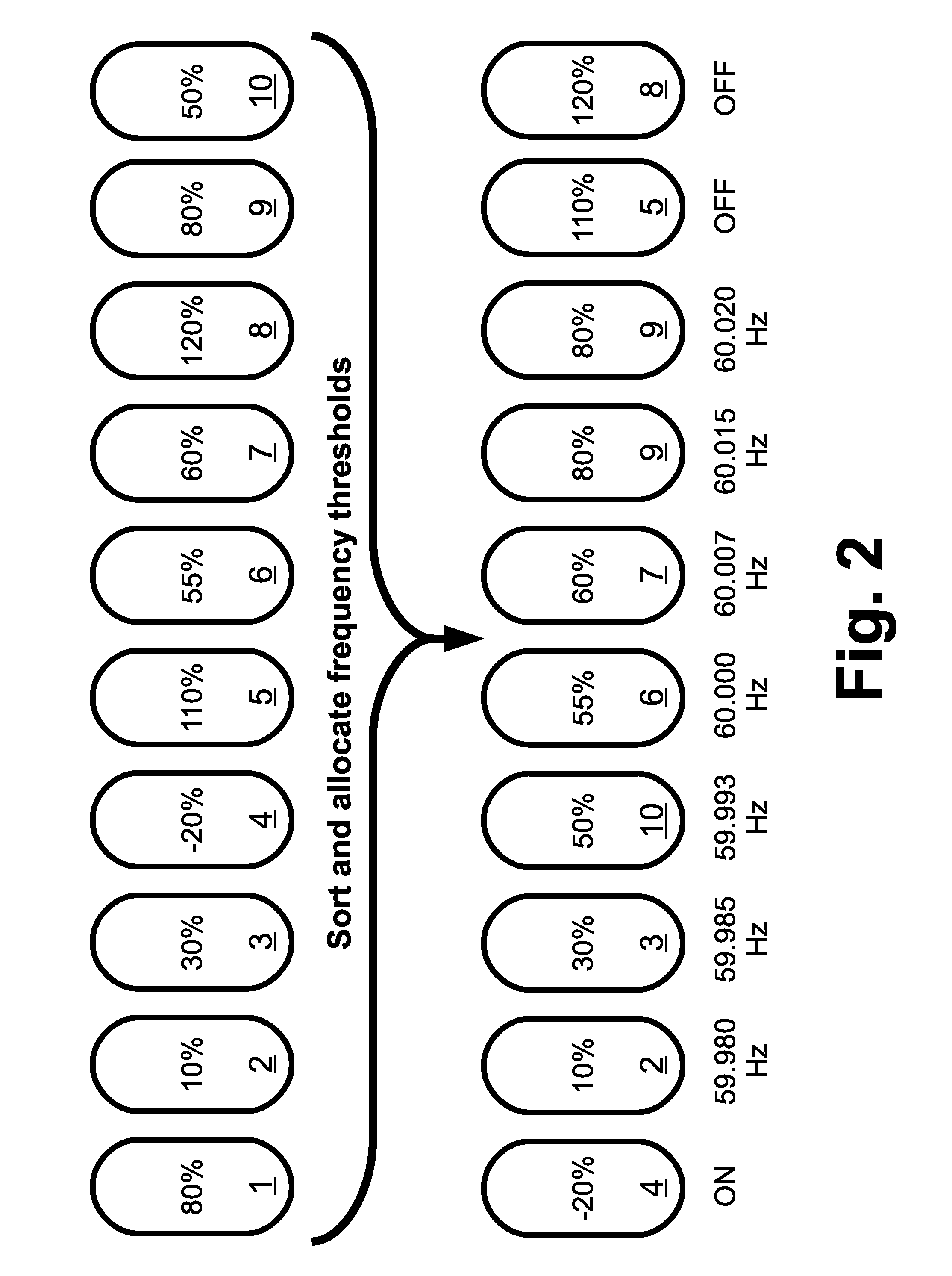
In a frequency control system, a system controller assigns load-specific threshold frequencies to electrical loads of a fleet of electrical loads. Load controllers perform load monitoring and control operations for controlled electrical loads of the fleet including (i) comparing a measurement of the electrical frequency with the threshold frequency assigned to the controlled electrical load and (ii) operating the controlled electrical load based on the comparison. For example, each load controller may perform operation (ii) by turning the controlled electrical load on if the measurement of the electrical frequency is greater than the threshold frequency assigned to the controlled electrical load, and turning the controlled electrical load off if the measurement of the electrical frequency is less than the threshold frequency assigned to the controlled electrical load. The threshold frequencies may be assigned based on State of Charge (SOC) values for the loads.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Sensor instrument system including method for detecting analytes in fluids
ActiveCN103293198AReduce manufacturing costOverall small sizeMaterial resistanceDesorptionHydrogen selectivity
A sensor instrument system and a method for detecting and identifying analytes in fluids of a region comprising a local sensor instrument and remote central station are disclosed. The instrument is composed of a core technology employing a single sensor having two electrodes operated by an electrical frequency sweeping to generate two sets of patterned electrical information from a single measurement. The instrument further includes a data transmission module and a GPS receiver module. The central station is connectd with a plurality of local information sites which can wirelessly transmit and receive information in different areas in the region, so that information transmitted by the sensor instrument can be received by the central station through the local sites. The core technology further comprises a reference sensor for eliminating background influence, a temperature programming to control adsorption and desorption of analytes, and usage of all kinds of adsorbent materials having chemical selectivity including the hydrogen selectivity to enhance detection and identification of analytes in fluids.
Owner:孙一慧 +1
Heterodyne optical network analysis that utilizes signal modulation
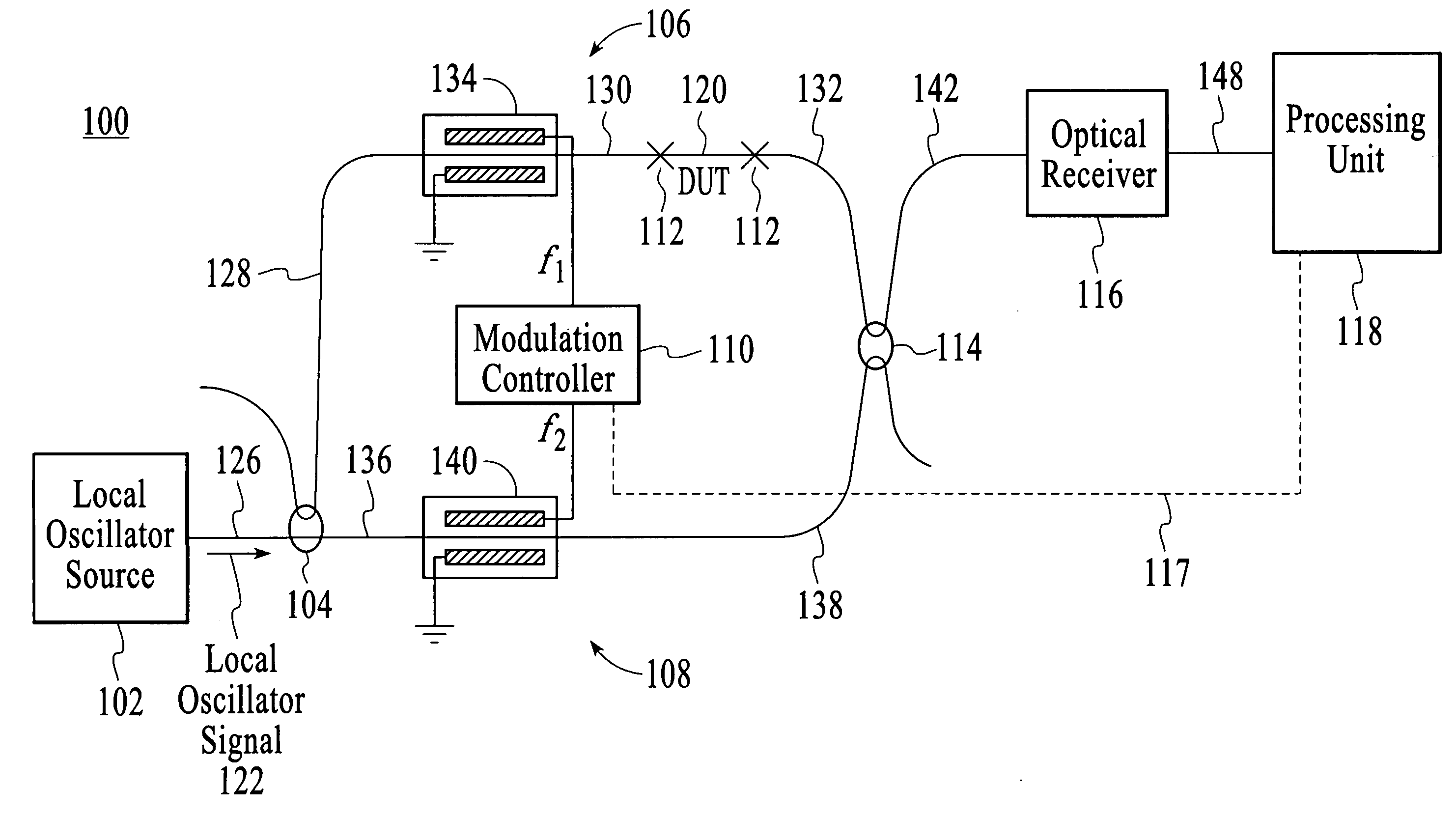
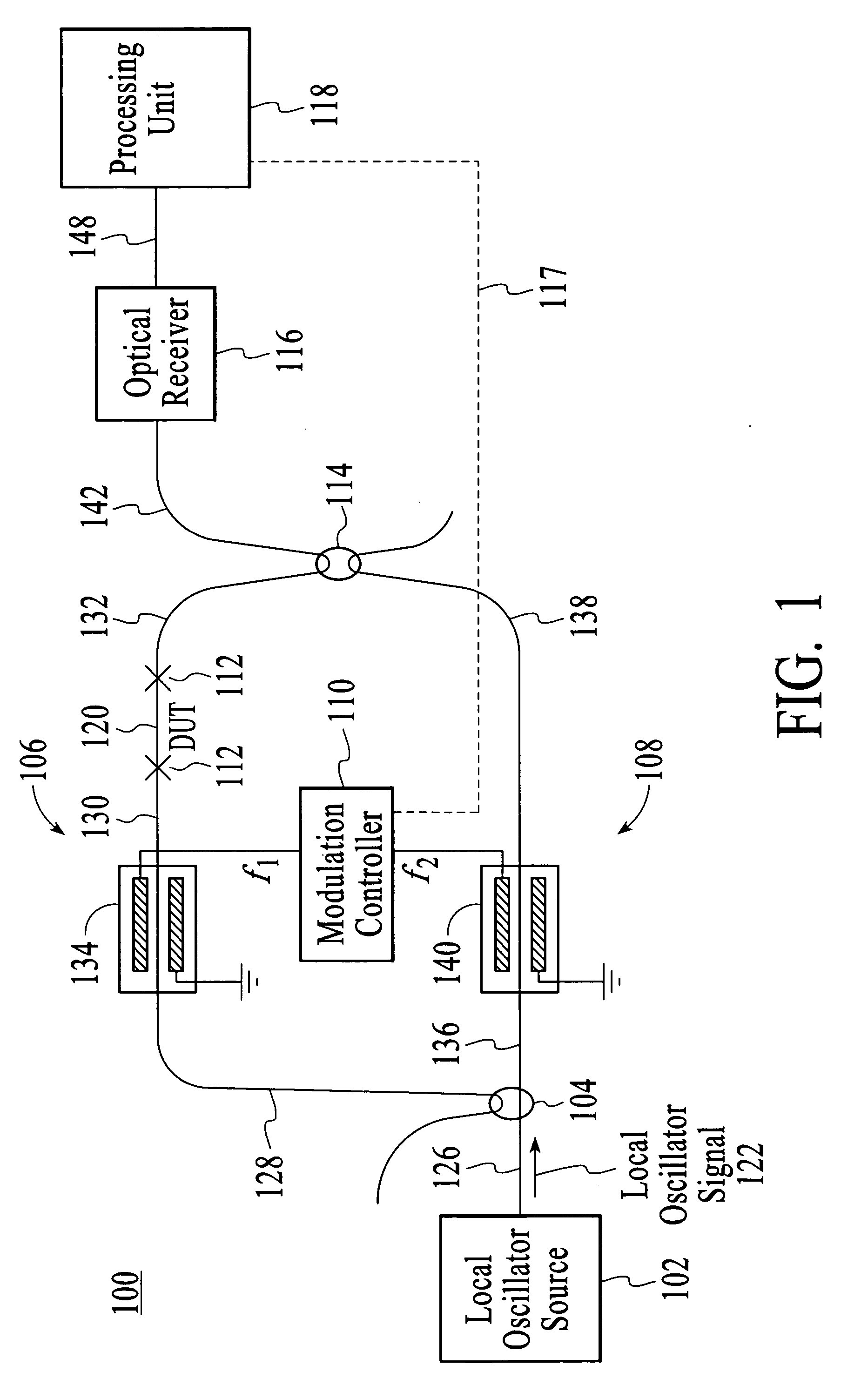
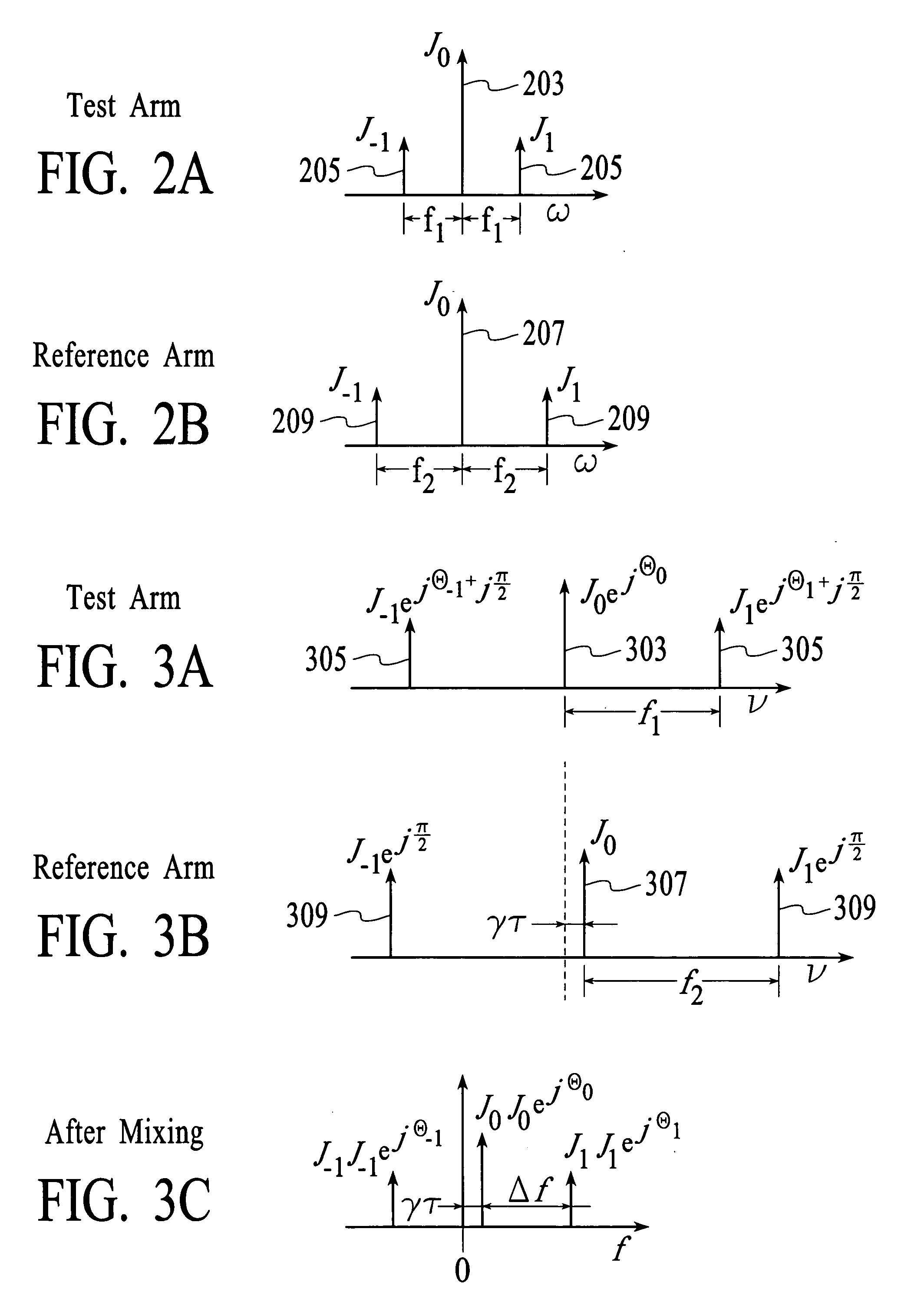
InactiveUS20050174577A1Material analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansLocal oscillator signalPhase difference
The group delay of a DUT is measured by modulating test and reference portions of a local oscillator signal at different frequencies to create modulation sidebands, applying the modulated test portion of the local oscillator signal to the DUT, and then optically mixing the two modulated signals. Optically mixing the two modulated signals translates the optical frequencies down to electrical frequencies. Phase changes that are caused by the DUT are determined by measuring the phase differences between modulation sidebands of the test portion of the local oscillator signal. Frequency translation can be achieved by electrical mixing instead of optical mixing.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
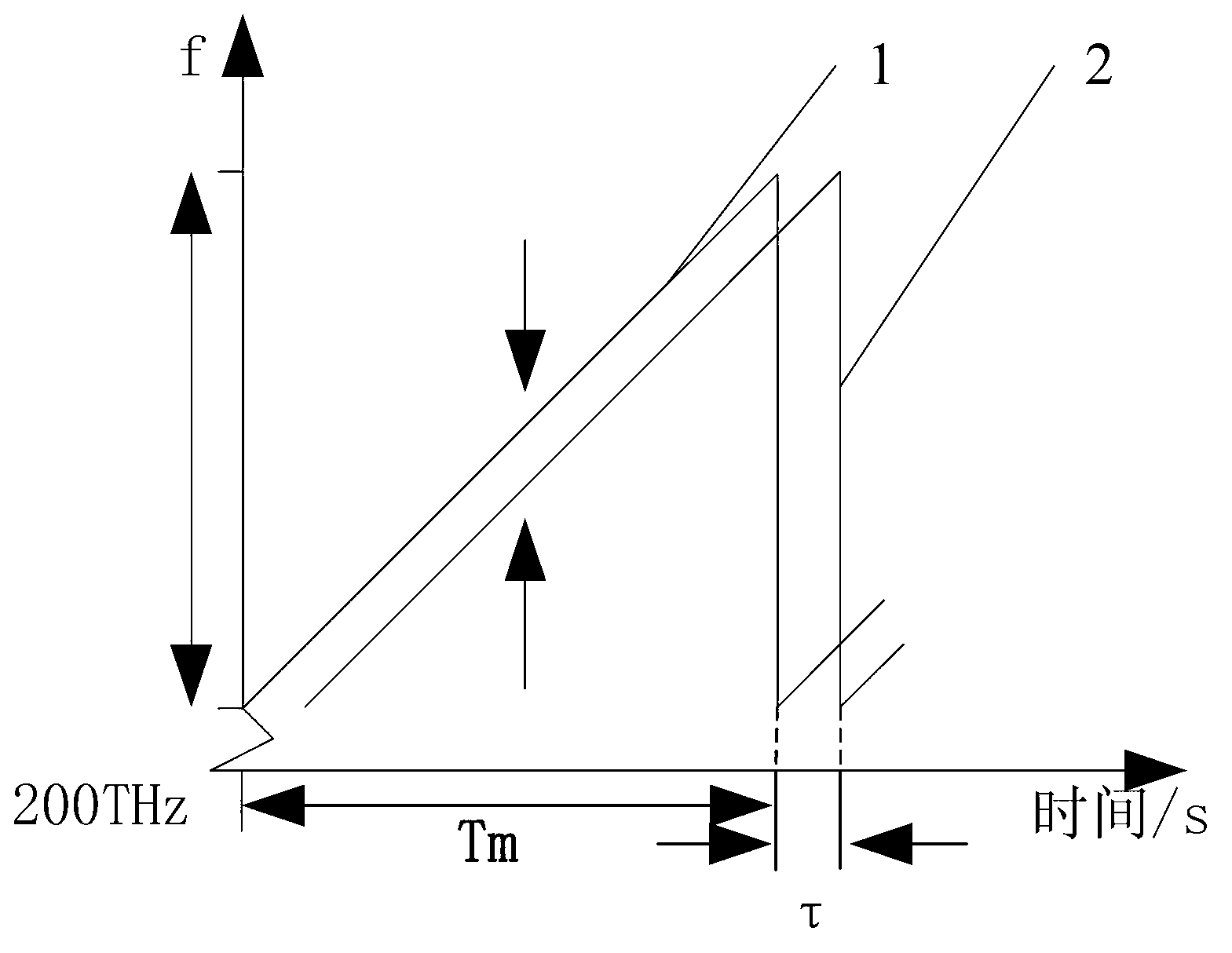
Non-linear correction method for LFMCW (linear frequency modulated continuous wave) laser radar frequency modulation based on optical fiber sampling technology
ActiveCN103176173AEliminate the effects ofSimple structureWave based measurement systemsLight beamContinuous wave
The invention discloses a non-linear correction method for LFMCW (linear frequency modulated continuous wave) laser radar frequency modulation based on an optical fiber sampling technology, and relates to the technical field of LFMCW laser radar frequency modulation and non-linear correction. The method solves the problems that non-linear correction cannot be performed when frequency modulation curve changes are not gradual. Lengths of a first optical fiber and a second optical fiber in a correction optical path are calibrated in advance, the length difference of the first optical fiber and the second optical fiber is the maximum measuring distance of an LFMCW laser radar, namely the measuring range upper limit, a third coupler combines beams of the first optical fiber and the second optical fiber, and correction light is received by a first probe to form a beat frequency signal. After the beat frequency signal is subjected to electrical frequency doubling, beat frequency signals in an interferometry optical path are sampled, and then the sampled signals are subjected to signal processing, so that influences, of frequency modulation non-nonlinearity of a frequency modulation laser, on measuring results are eliminated. The method is suitable for laser radar frequency modulation non-linear correction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sensorless optimum torque control for high efficiency ironless permanent magnet machine
Embodiments of the present invention permit the optimization of torque control of a permanent magnet machine including obtaining instantaneous terminal voltages of the machine, transforming the instantaneous terminal voltages to a zero direct axis voltage and a non-zero quadrature axis voltage, using a mathematical transformation, regulating the electrical frequency of the permanent-magnet machine such that the zero direct-axis voltage is adjusted to have a value of zero, determining a non-final electrical angle of the permanent-magnet machine by applying an integrator to the regulated electrical frequency of the machine, determining a final electrical angle of the of the machine by integrating the non-final electrical angle and an electrical angle from a previous calculation cycle, and regulating the current vector of the machine such that the current vector is perpendicular to the final electrical angle of the machine, thereby optimizing the torque of the machine.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
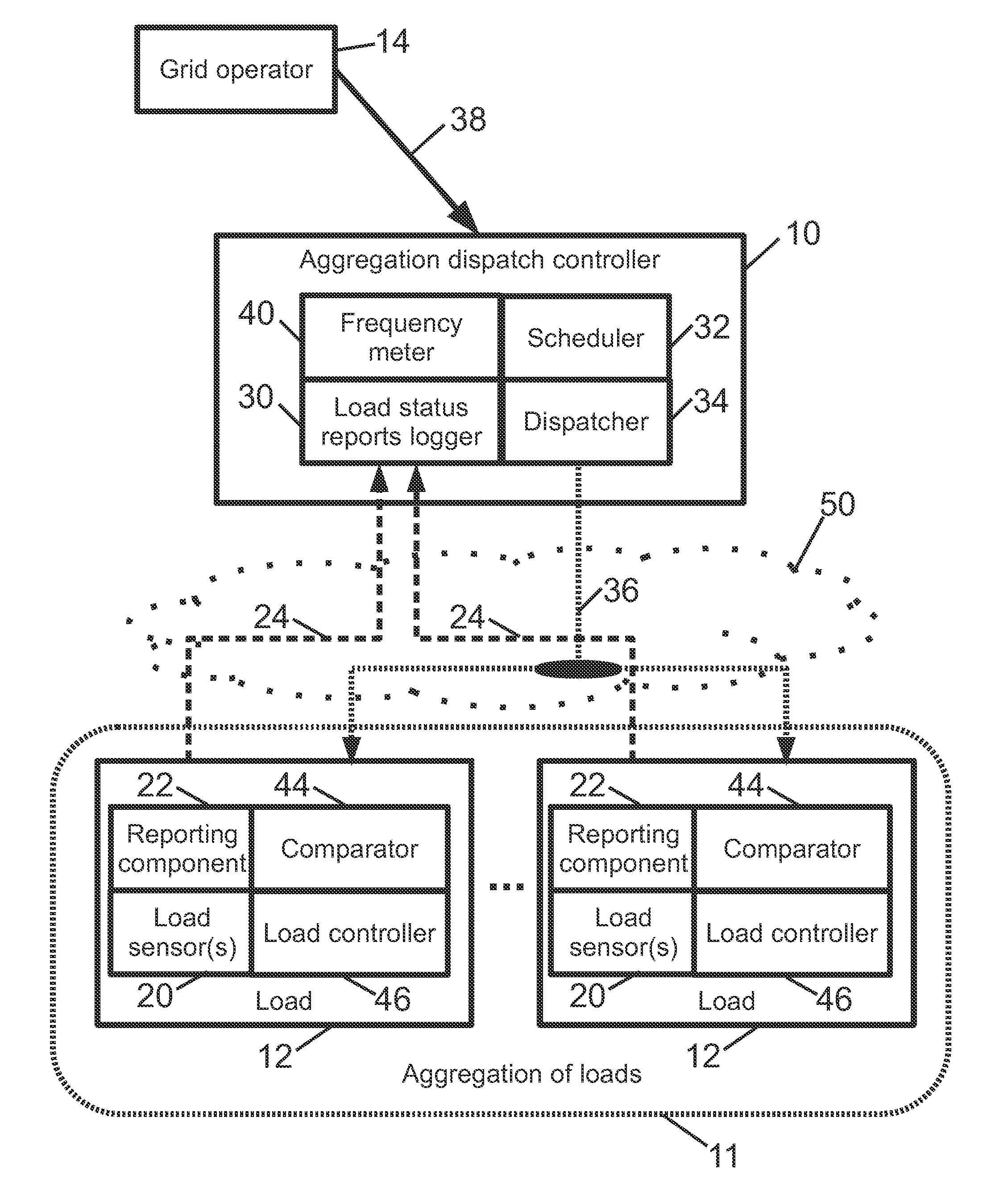
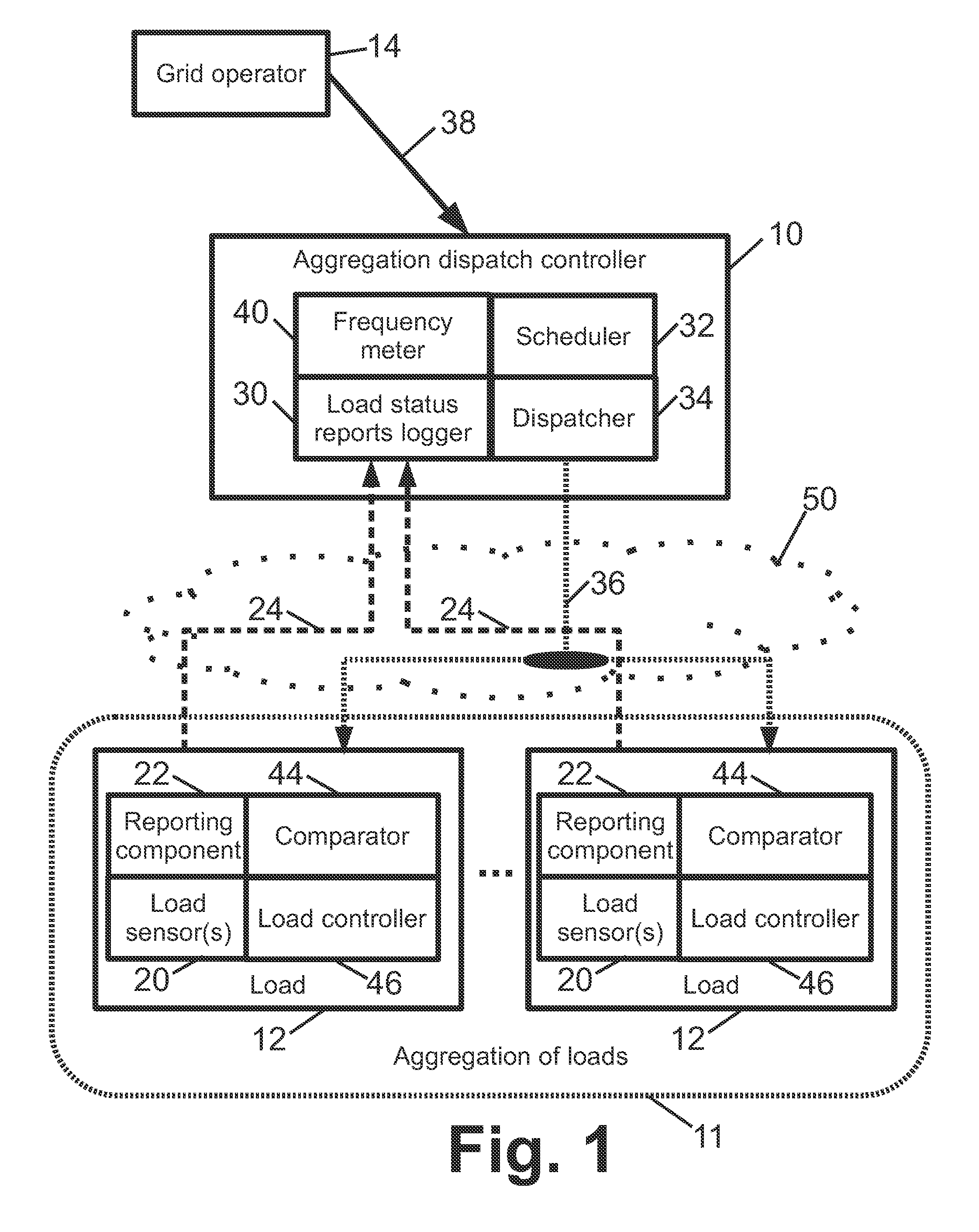
Using demand side resources to provide frequency regulation
In a direct load control system supporting frequency control of an electrical grid, at each electrical load of an aggregation of loads, a load status report is generated comprising an urgency value and a power level. At an aggregation dispatch controller, a dispatch signal is generated based on the generated load status reports and information indicative of electrical frequency. At each electrical load of the aggregation, the load is operated at the reported power level if the reported urgency value satisfies the dispatch signal and is not operated at the reported power level if the reported urgency value does not satisfy the dispatch signal.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Electro-Optical Single-Sideband Modulator
ActiveUS20130142521A1Simpler in terms of both overall optical patternElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsOptical propagationElectricity
An electro-optical single-sideband modulator comprising:an electro-optical substrate;a bimodal optical waveguide structure formed in the substrate to support different optical modes having associated optical frequencies and optical propagation constants and comprising an optical input to receive an input optical carrier signal having an optical frequency, and a pair of optical outputs to output corresponding SSB modulated optical signals, each having an optical frequency spectrum with a single side lobe; andan electrode structure formed on the substrate to receive an input electrical modulating signal having an associated electrical frequency and electrical propagation constant, and to responsively apply an electrical field to the bimodal optical waveguide structure.
Owner:SELEX SISTEMI INTEGRATI
Arrangement for steering a ship and for supplying power to its propulsion system
InactiveCN103347780AReduce electricity lossPropulsion based emission reductionPropulsion power plantsElectricityPropeller
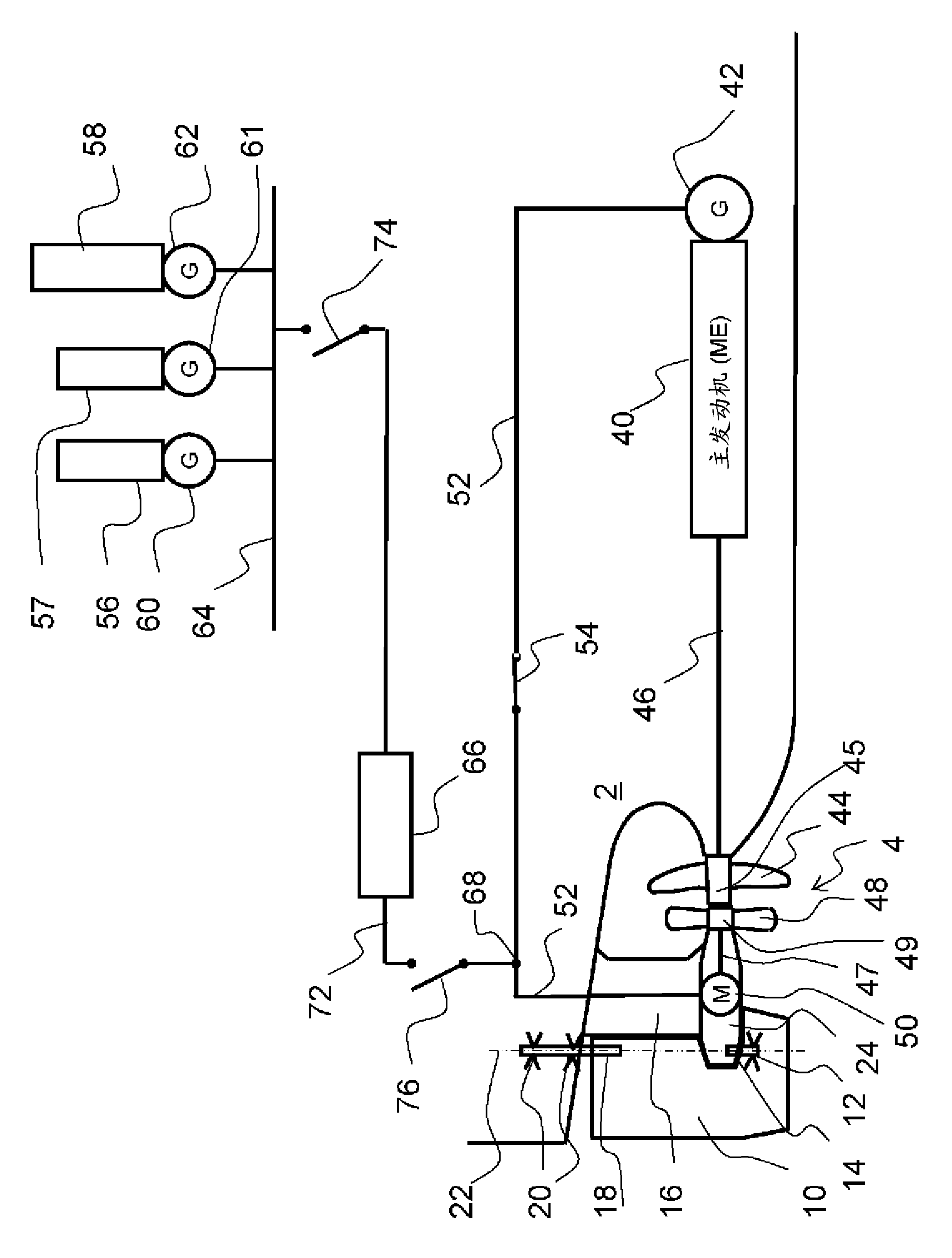
Arrangement for steering and supplying propulsion power to a contra rotating propellers (CRP) propulsion system in a marine vessel, which arrangement comprises a first propeller (44) driven by a rotating power unit (40) and a second propeller (48) driven by an AC motor (50) whereby the second propeller (48) is rotated in the opposite direction as the first propeller (44), and an AC generator (42) coupled to mechanical output shaft of the power unit (40) and driven by a rotating power unit, whereby the AC generator (42) is electrically connected to the AC motor (50). According the arrangement the AC motor (50) and the AC generator (42) have the same electrical frequency, another electrical power source (60,61,62) is electrically connectable to the AC motor (50) parallel to the AC generator (42), the shaft (47) of the second propeller is mounted rotatable in a support structure (16,24) which is attached to a hull of the marine vessel (2), and a rudder (10), which is supported in a manner allowing pivotal movement of the rudder (10) relative to the support structure (16, 24).
Owner:ABB AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com