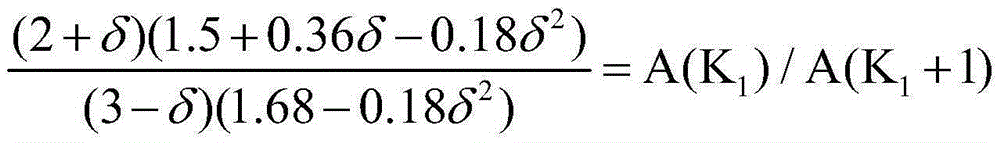Patents
Literature
128 results about "Spectral amplitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Power is proportional to the square of amplitude, so squaring the amplitude spectral density gives you a power spectral density, or how much power is in each frequency.
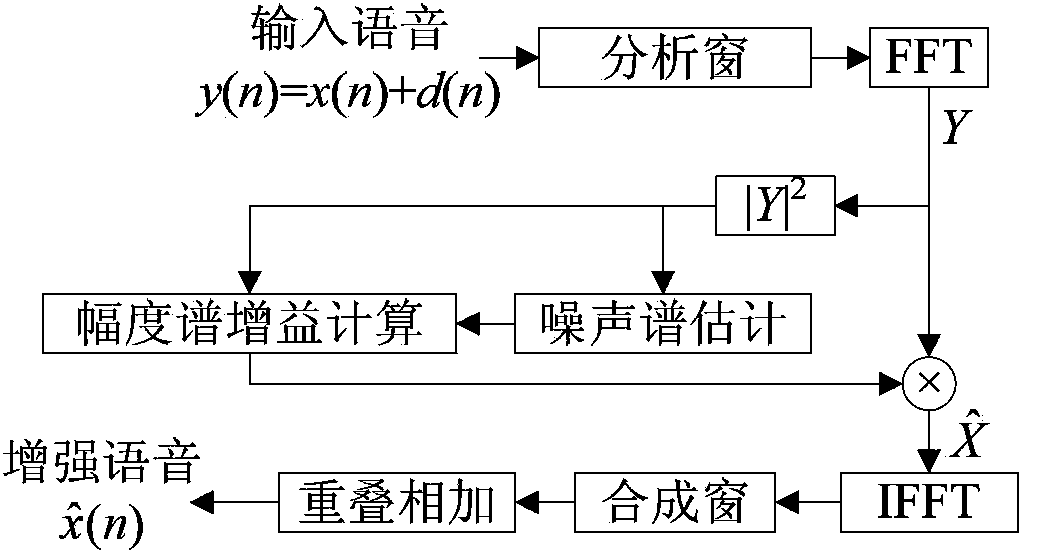
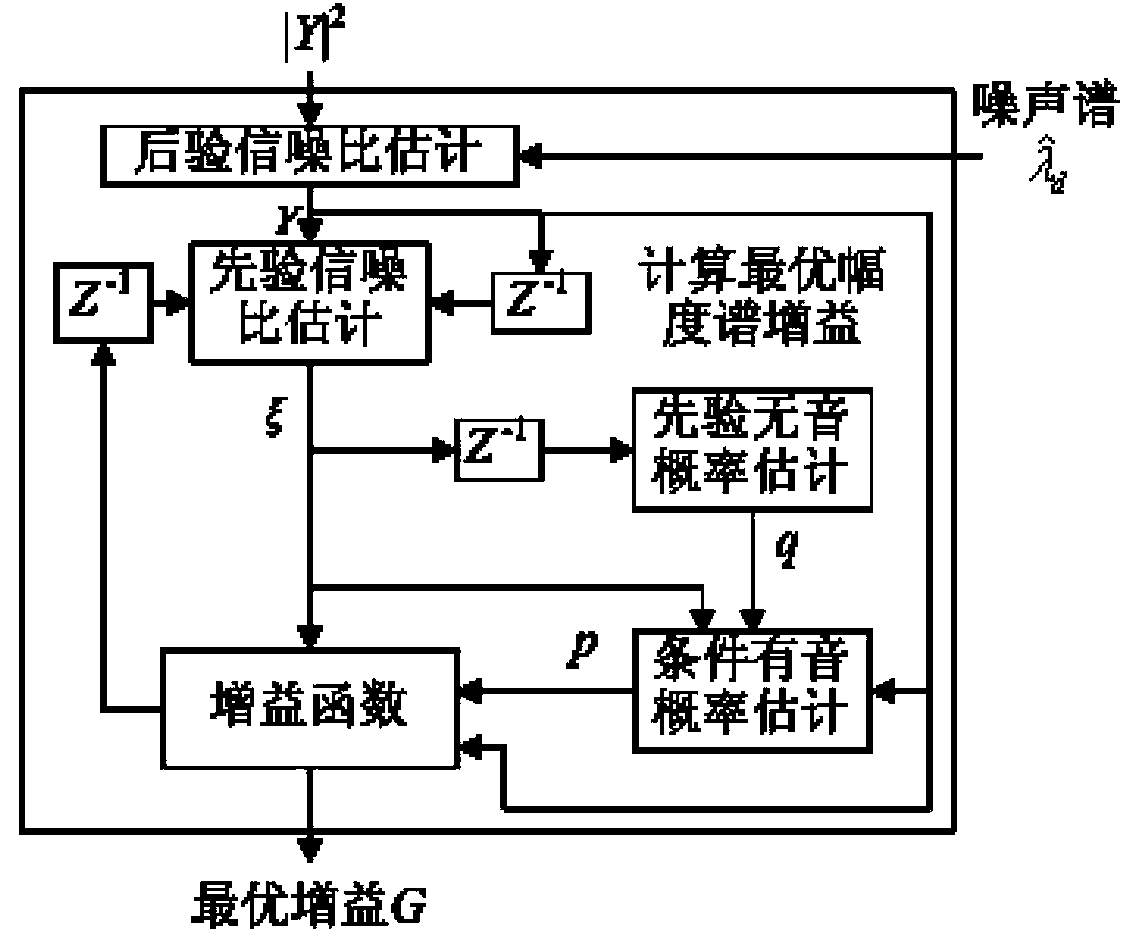
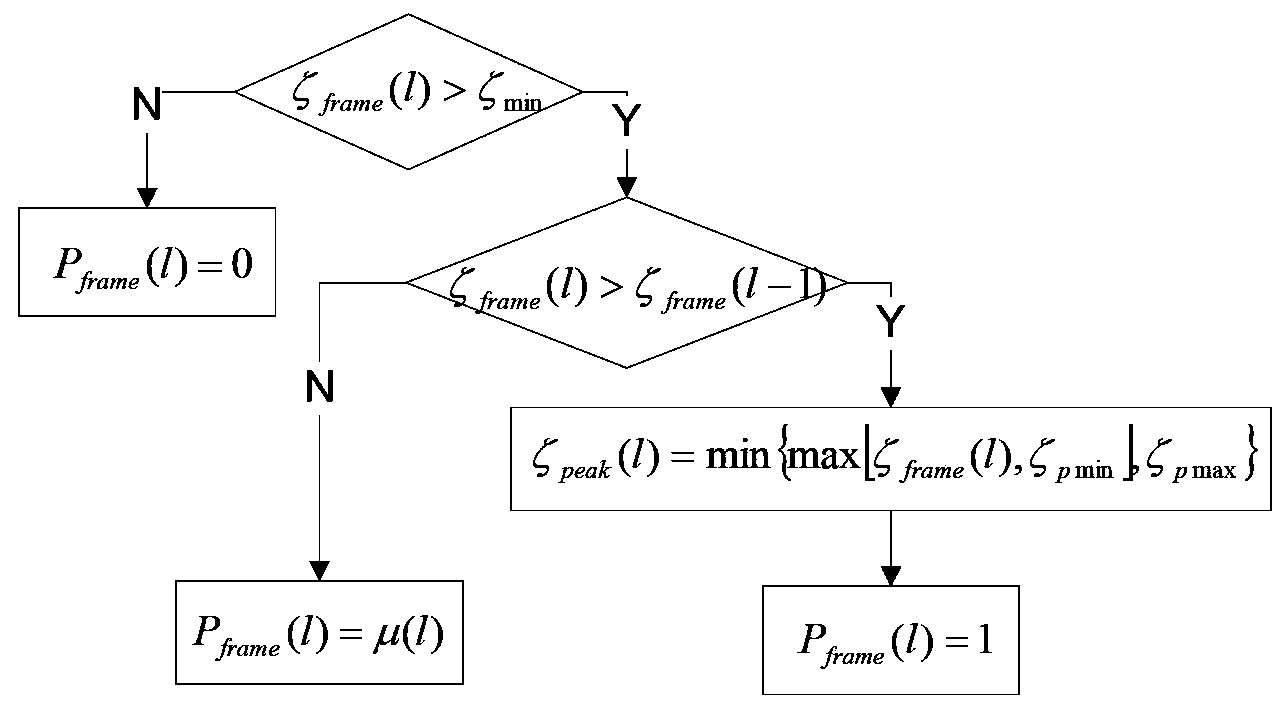
Transient noise suppression method based on spectrum estimation
ActiveCN103456310AEnhanced Speech Magnitude SpectrumSpeech analysisDigital signal processingNoise suppression
The invention discloses a transient noise suppression method based on spectrum estimation and belongs to the technical field of digital signal processing. The method includes the following steps of firstly, conducting non-transient background noise power spectrum estimation based on modified minima controlled recursive averaging; secondly, conducting transient noise power spectrum estimation based on the modified minima controller recursive averaging and the optimally modified log spectral amplitude estimator; thirdly, conducting voice noise suppression based on the optimally modified log spectral amplitude estimator and the transient noise spectrum estimation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
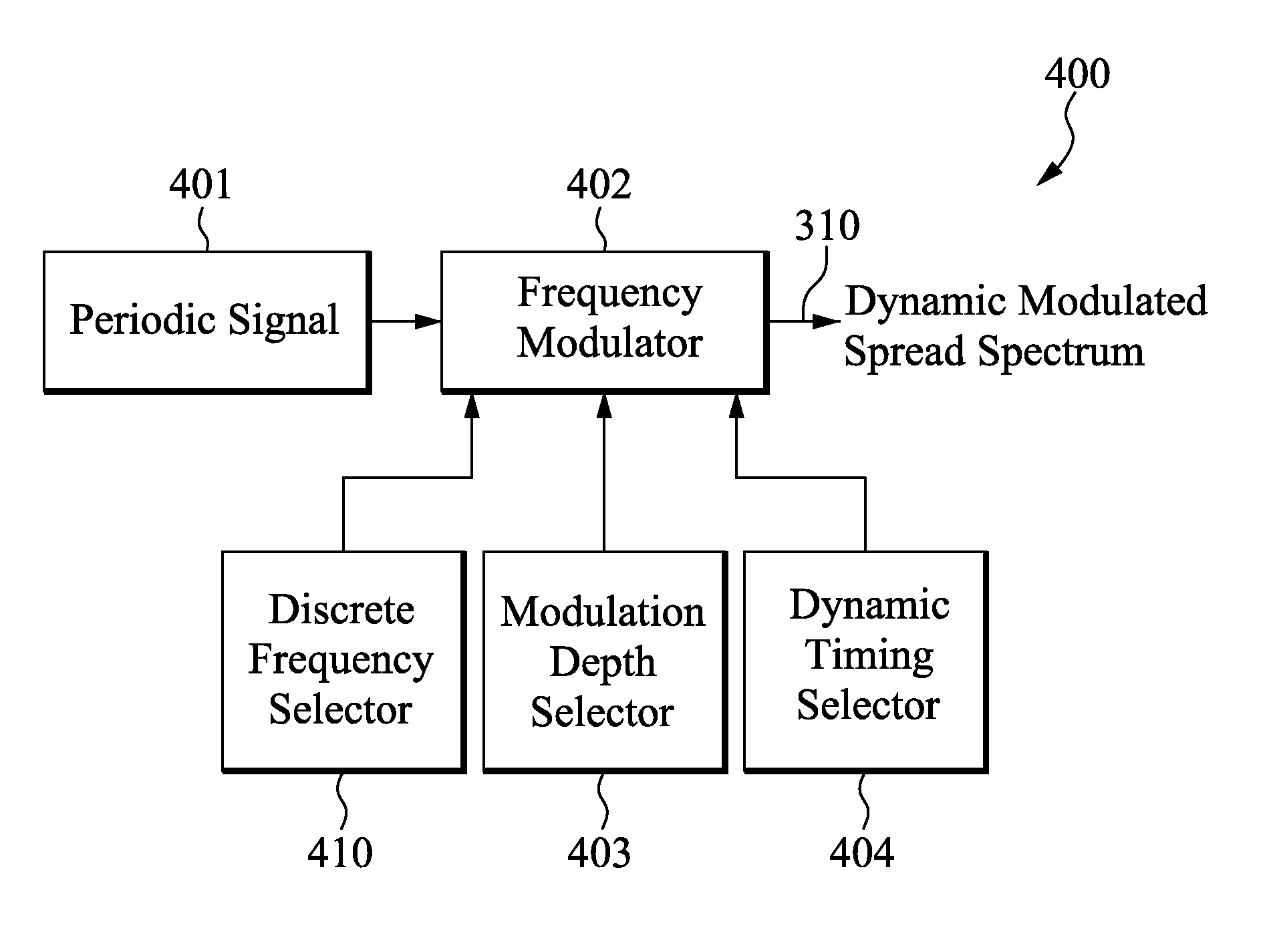
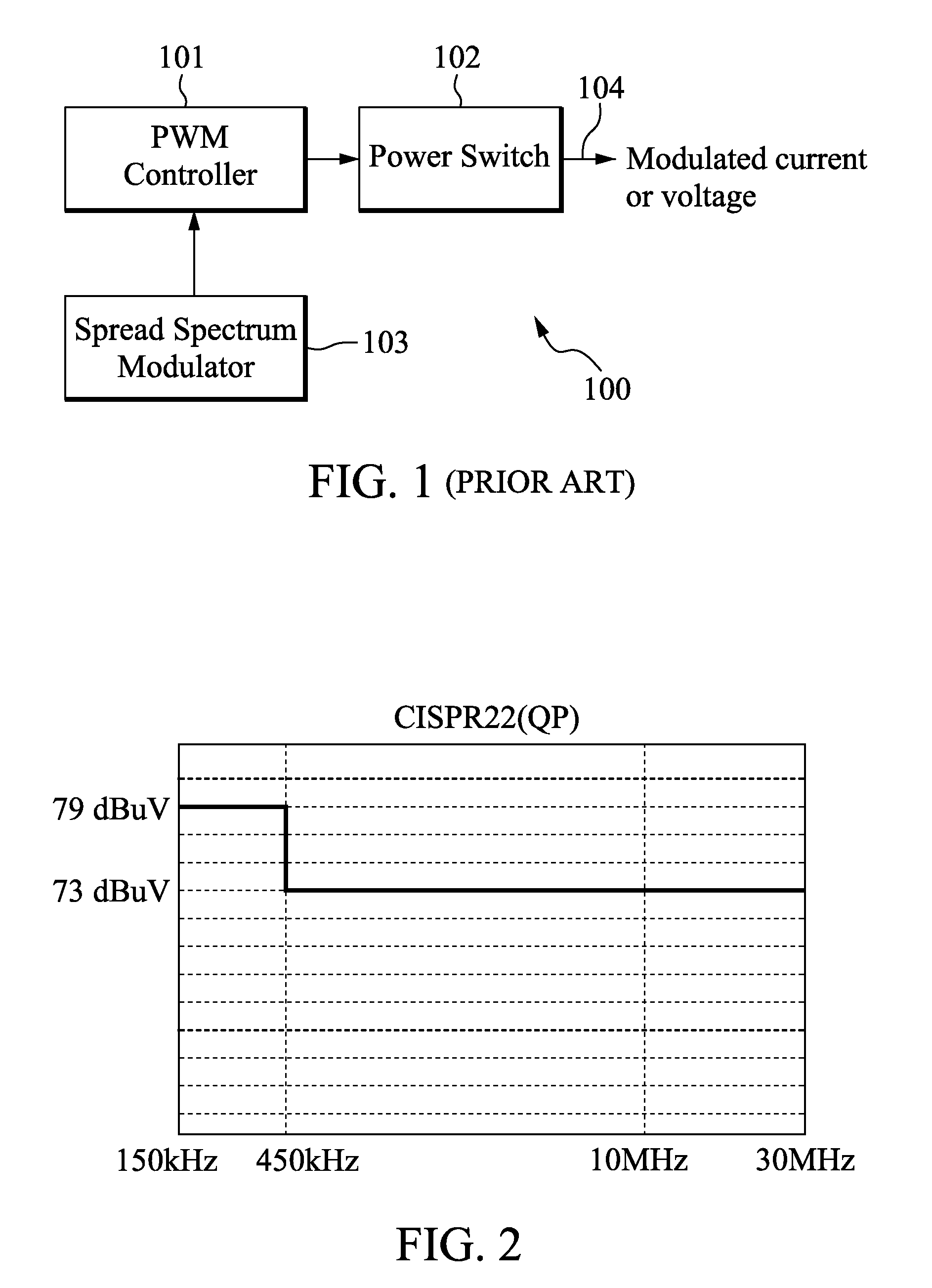
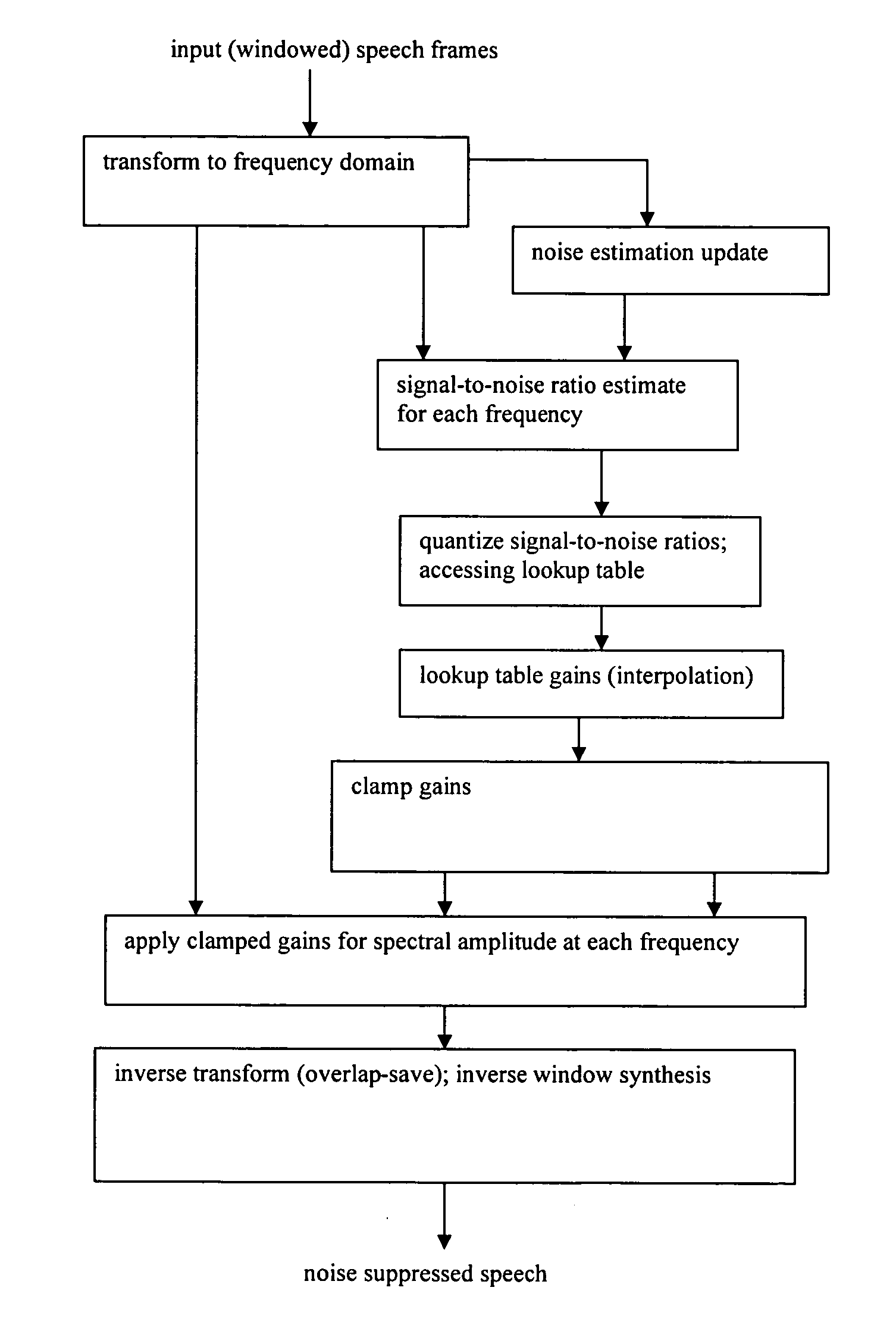
Method and apparatus for dynamic modulation
InactiveUS8085106B2Angle modulation detailsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency spectrumHarmonic
Circuits and methods of dynamic modulation are disclosed. A dynamic modulator is used to reduce measurable conducted and / or radiated electromagnetic interference (EMI). The dynamic modulator is configured to generate either a set of optimal frequency modulation depths or discrete frequencies or both, and dynamically selects them to use over a series of programmable time durations (dwell time). Together with the utilization of Peak, Average or Quasi-Peak (QP) method of measurement, the dynamic modulator can reduce the spectral amplitude of EMI components, in particular the lower harmonics, to effectively pass regulatory requirements. In alternative embodiments, the dynamic modulator is used in a closed loop system to continuously adjust the frequency and the duty cycle of a PWM signal to reduce conducted and / or radiated EMI.
Owner:HUDA MUZAHID BIN +1
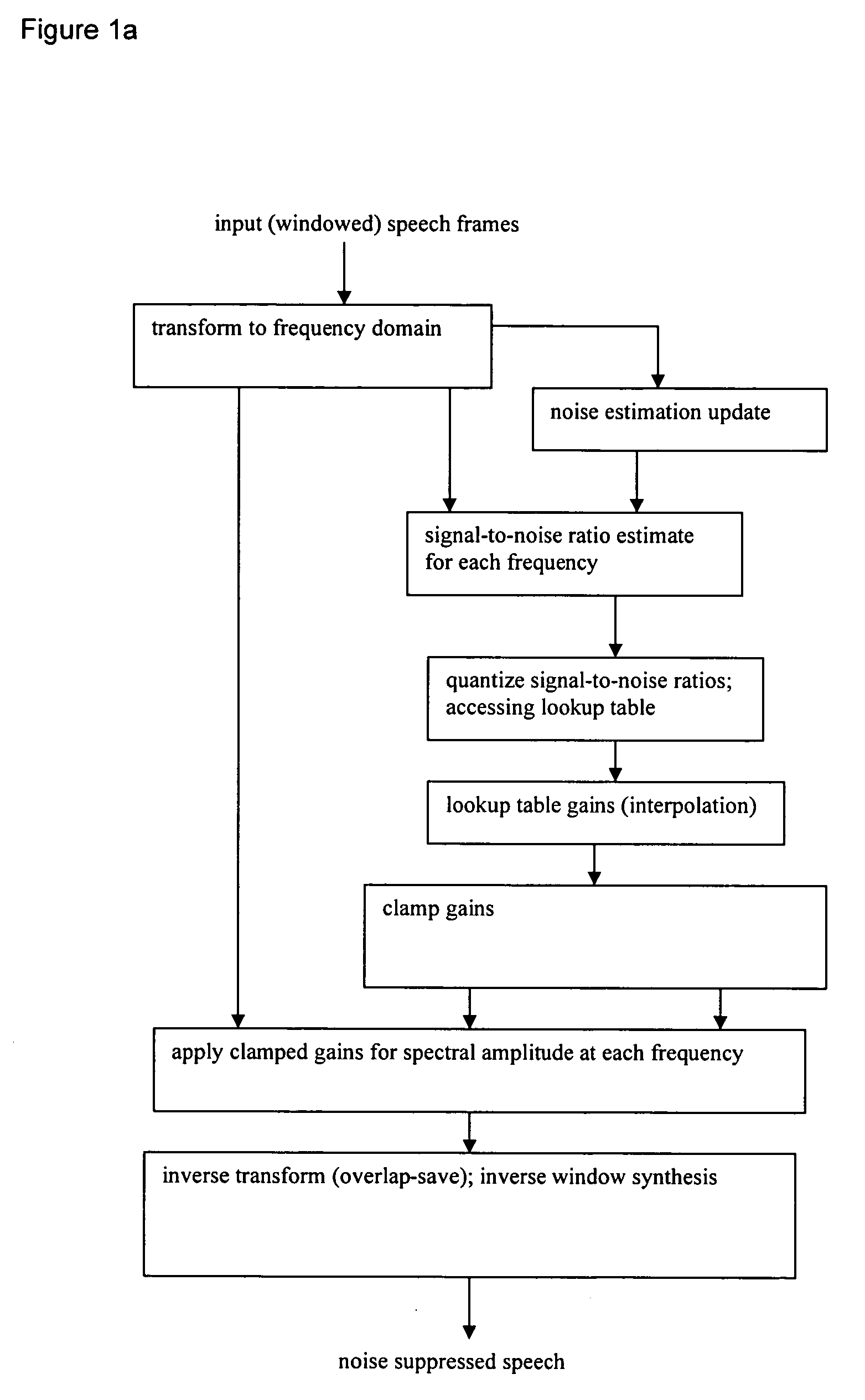
Noise suppression
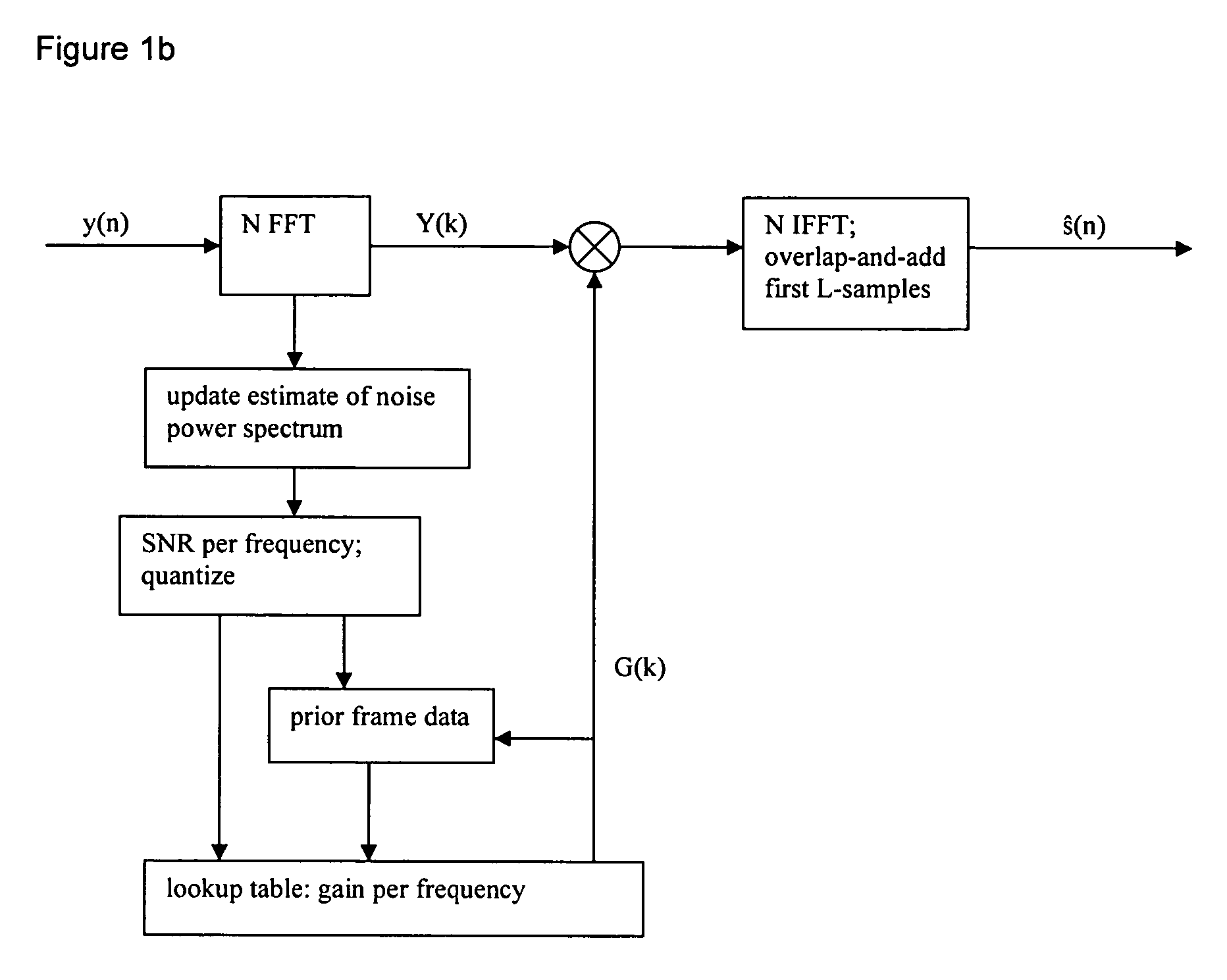
InactiveUS20060184363A1Improve performanceReduce computational complexitySpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumFilter gain
Noise suppression (speech enhancement) by spectral amplitude filtering using a gain determined with a quantized estimated signal-to-noise ratio plus, optionally, prior frame suppression. The relation between signal-to-noise ratio and filter gain derives from a codebook mapping with a training set constructed from clean speech and noise conditions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
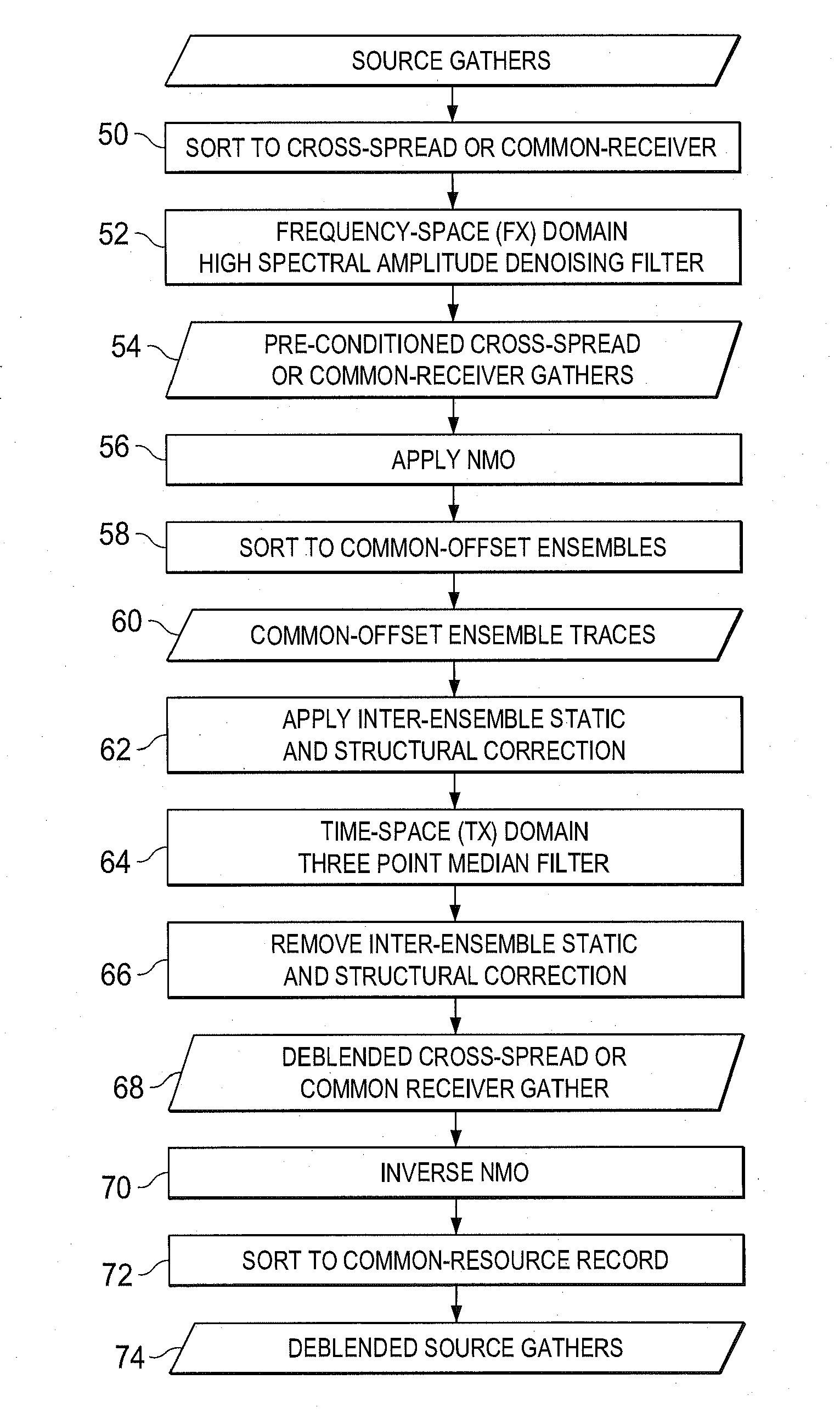
Coupled time-distance dependent swept frequency source acquisition design and data de-noising
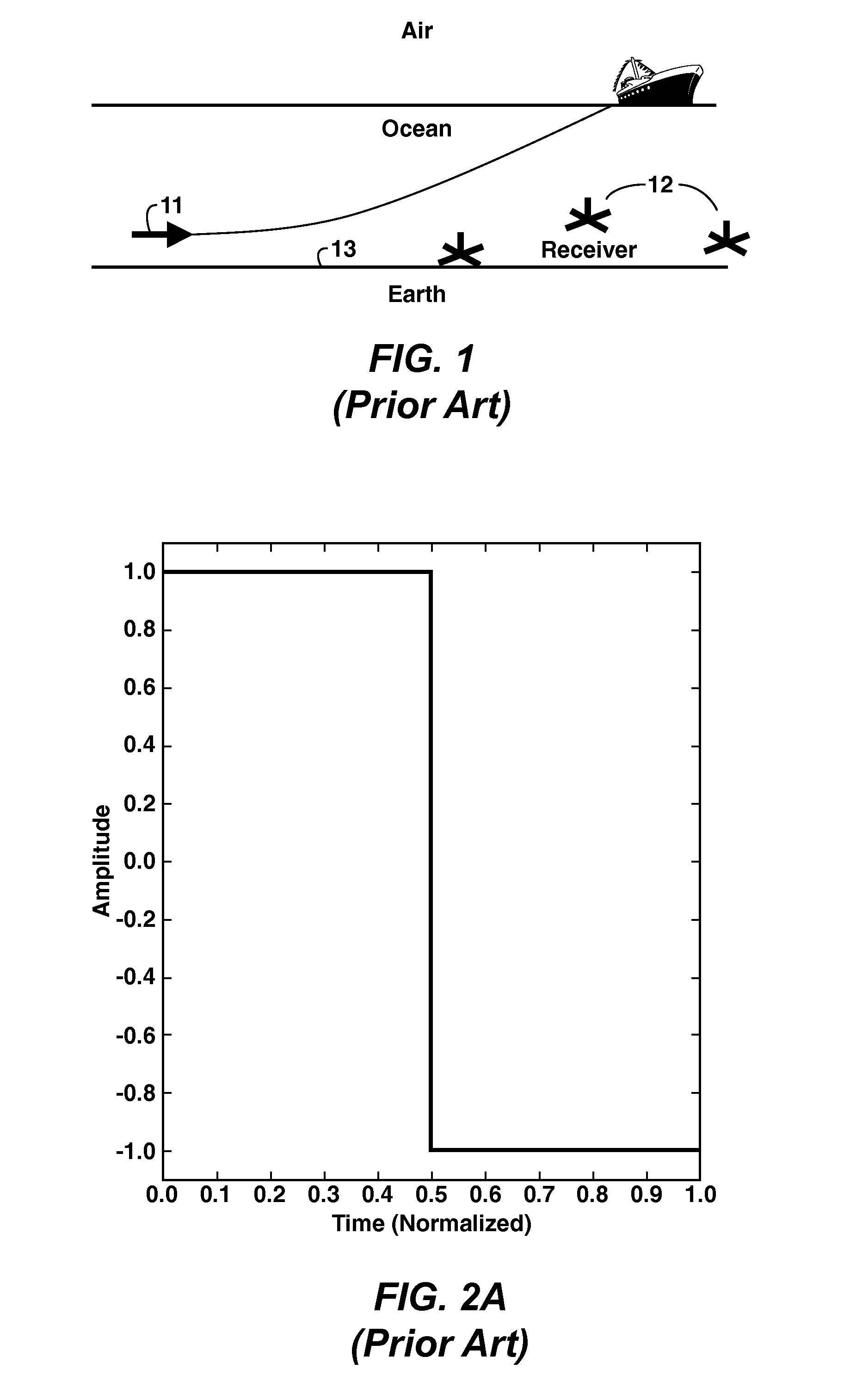
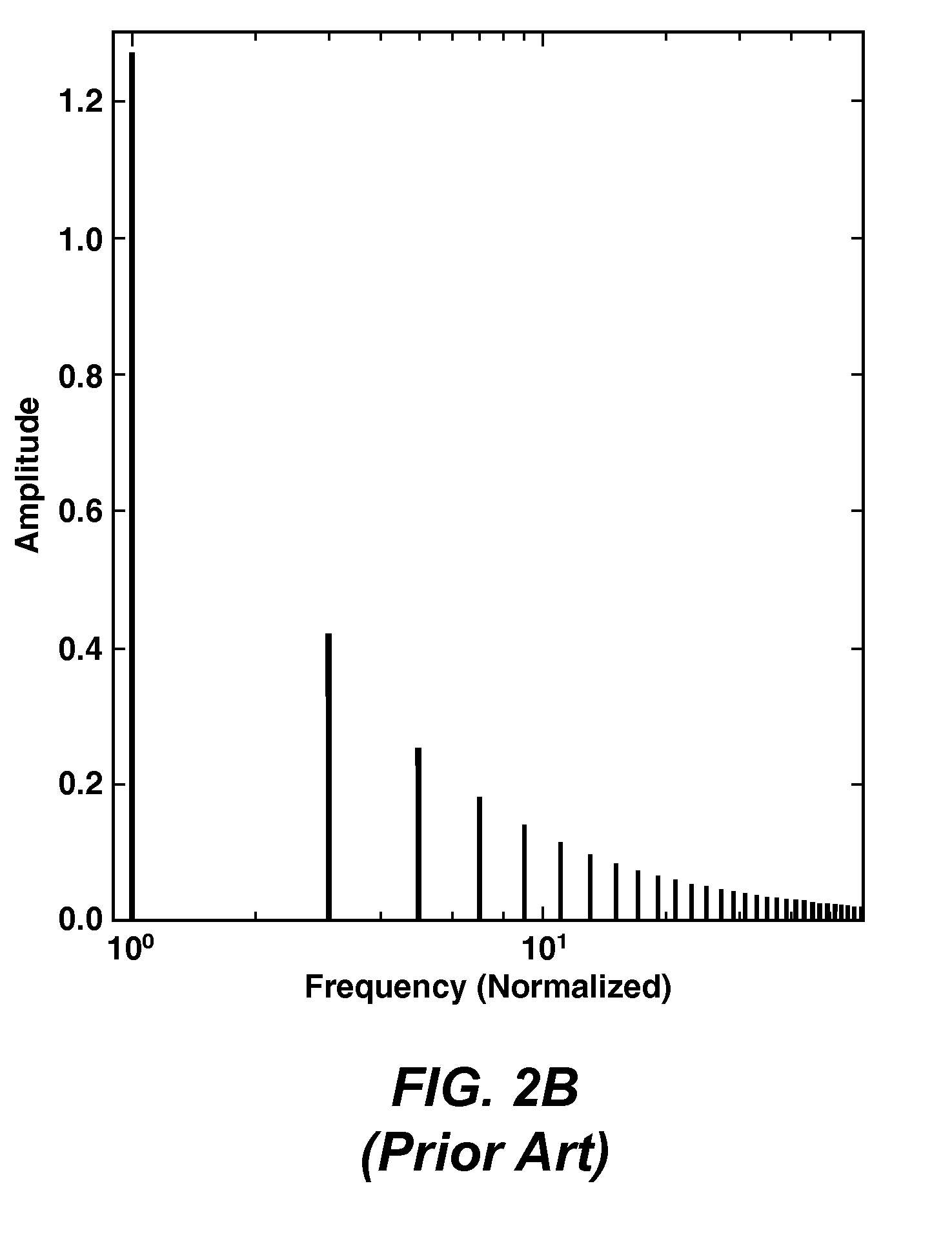
Acquisition of data by managing crosstalk interference with sector designs and unique sweeps is conducted and the resultant data are processed in 3D common receiver domain to attenuate crosstalk noise while preserving the signals for high source and receiver density acquisition designs. High-amplitude spectral amplitudes are attenuated and inter-ensemble statics or structural time delays are applied to achieve optimum filter performance. If the spectral amplitudes have been attenuated to a level consistent with non-simultaneous acquisition, conventional surface consistent processing can be performed to correct for statics and amplitude variations. A 3-point filter in different frequency bands may then be applied to remove any remaining residual crosstalk noise.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
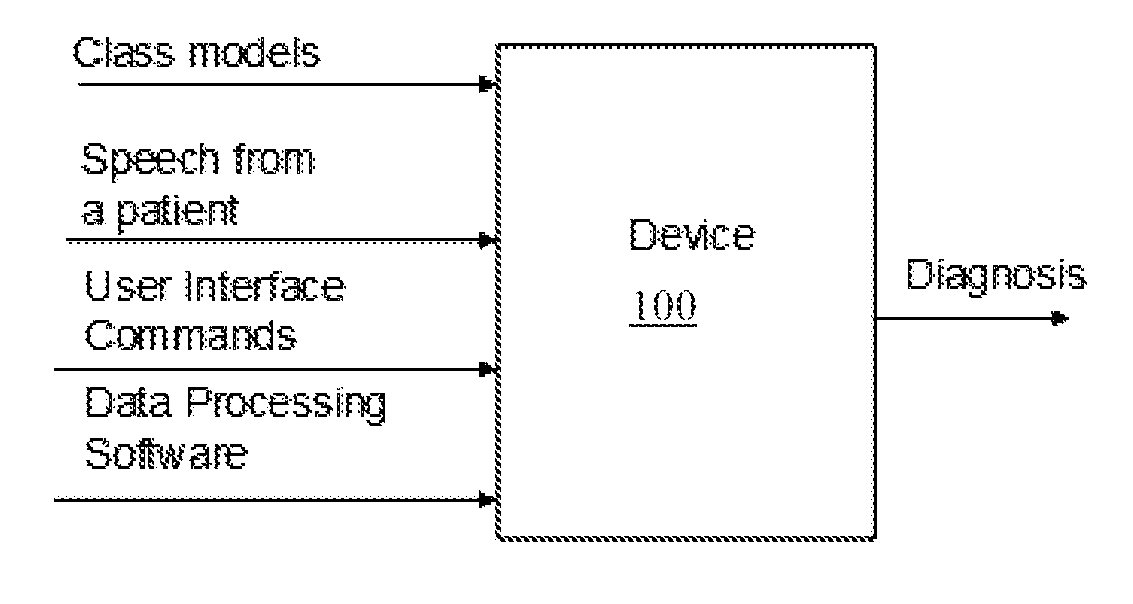
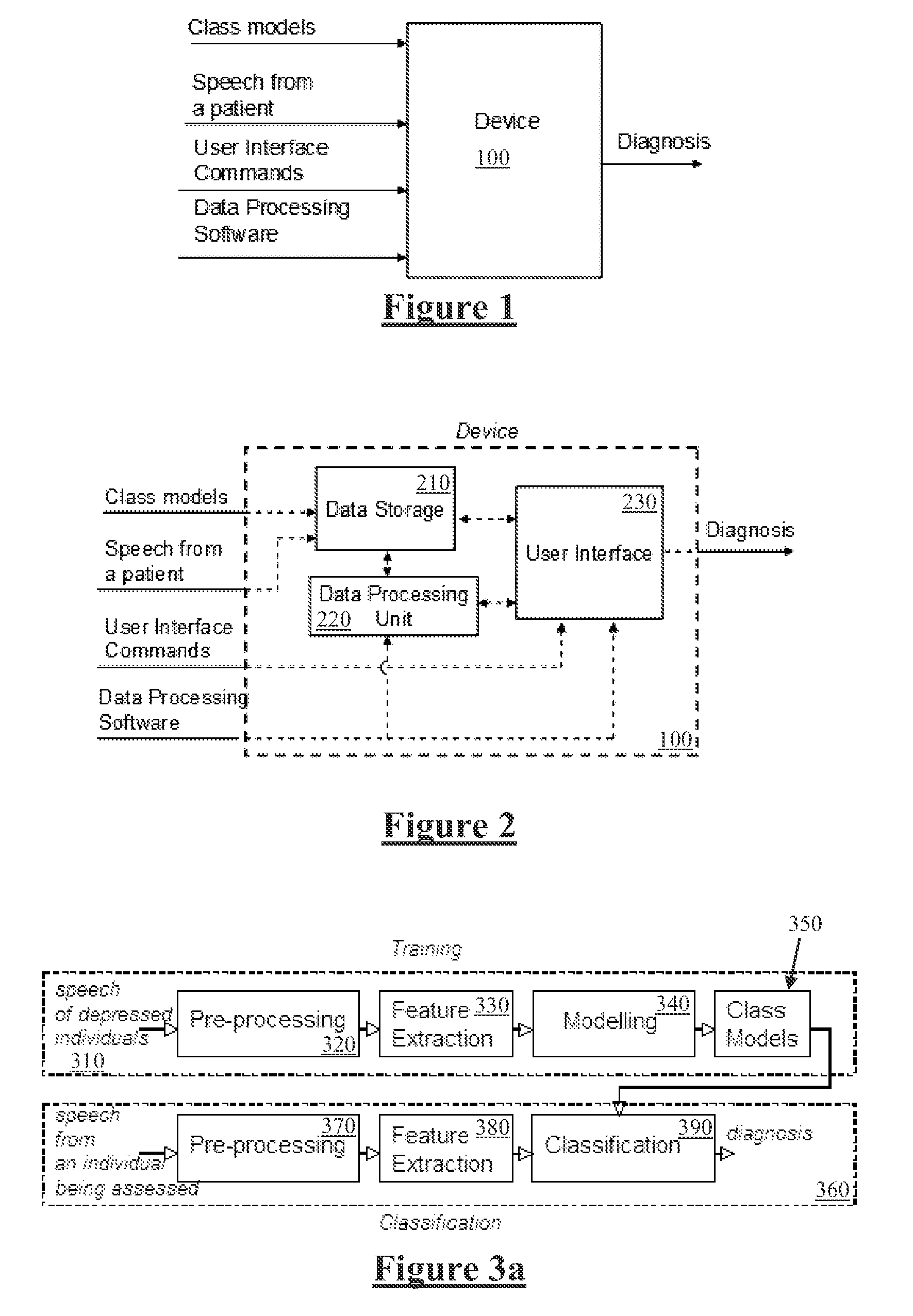
Emotional and/or psychiatric state detection
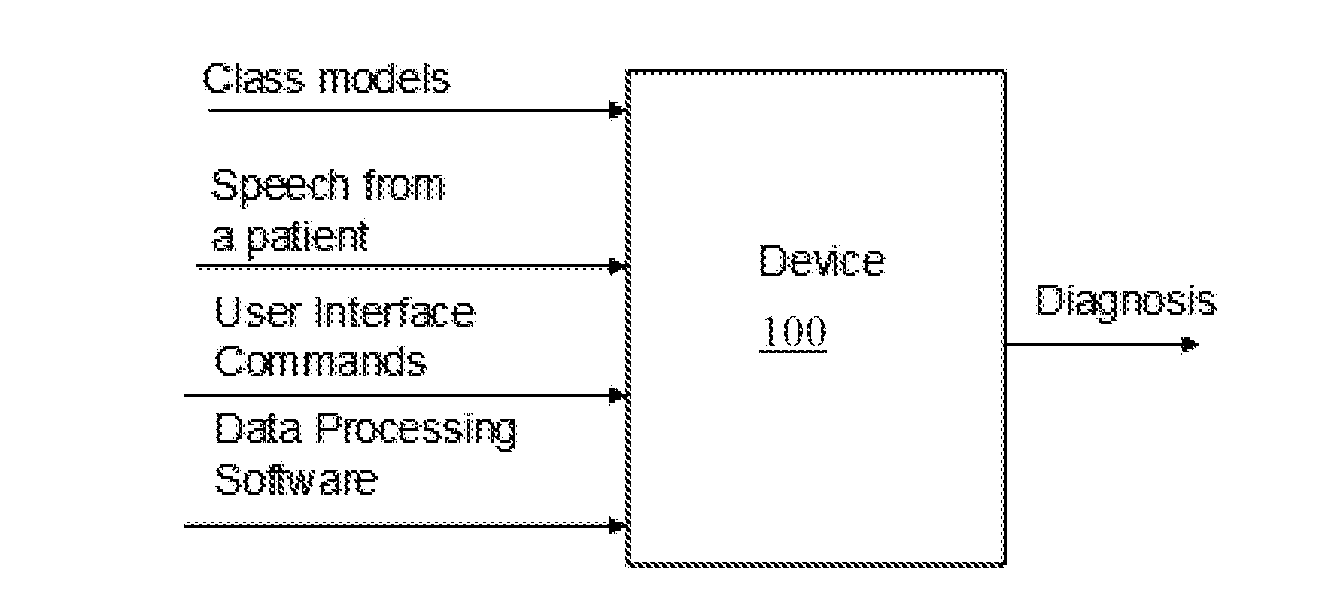
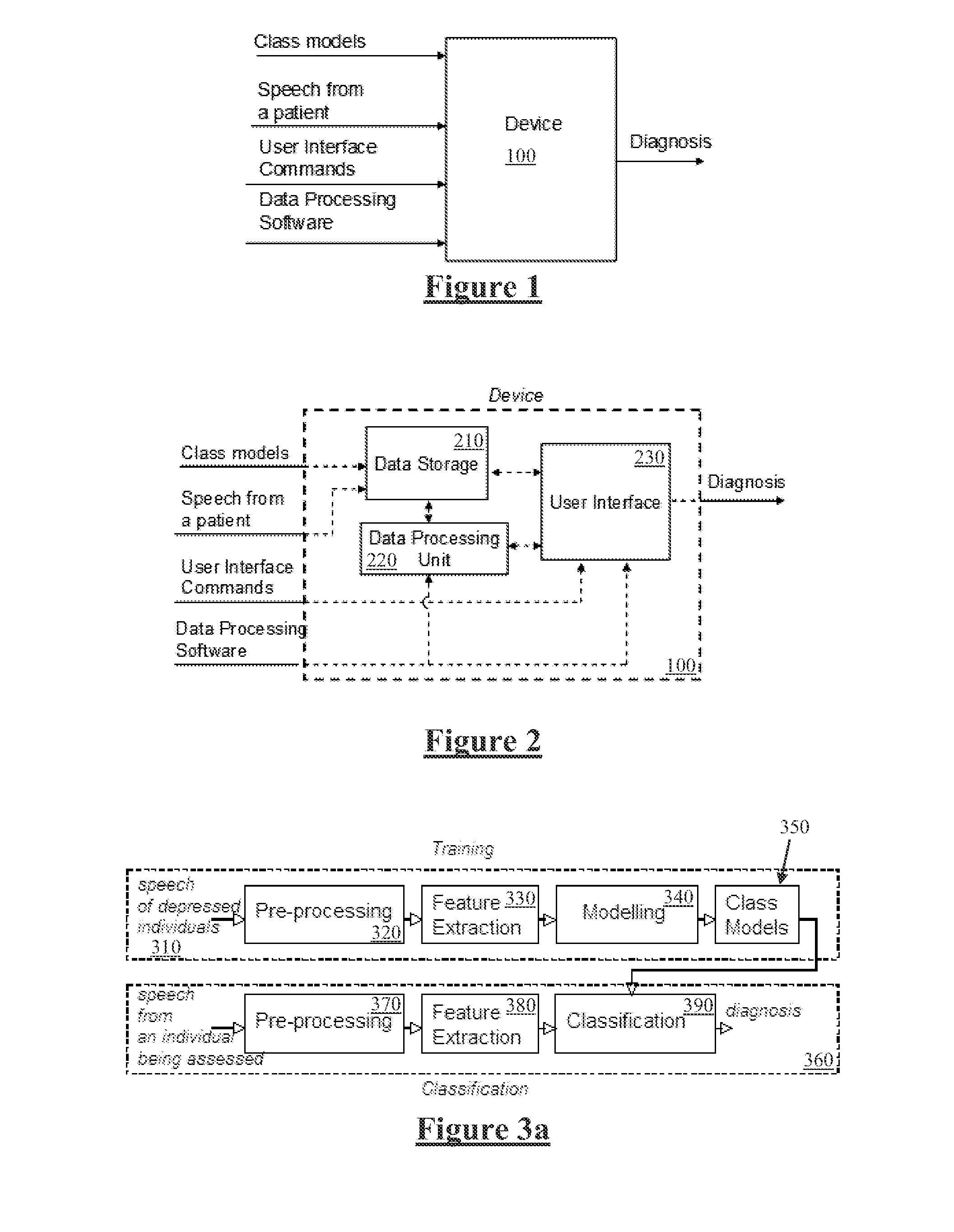
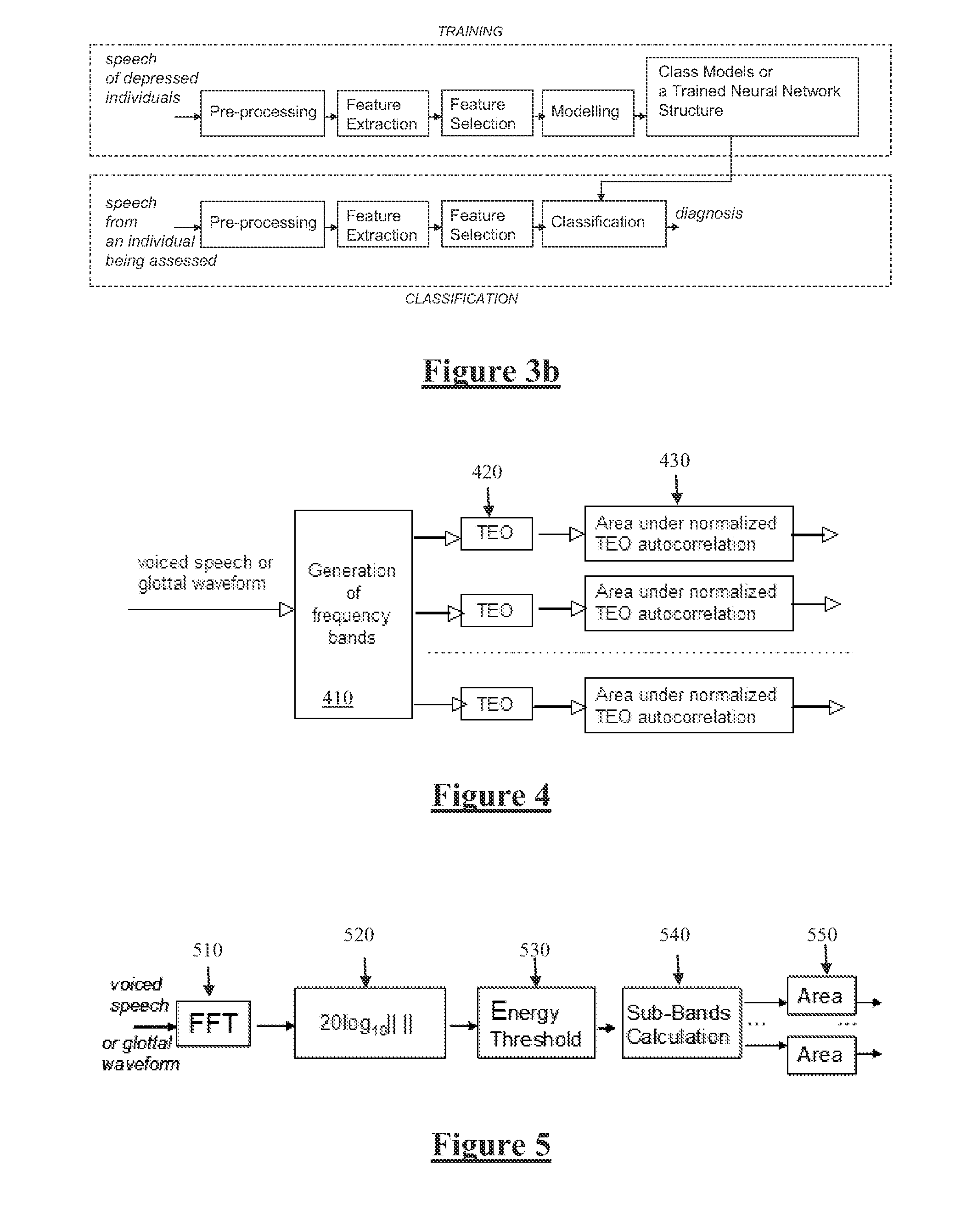
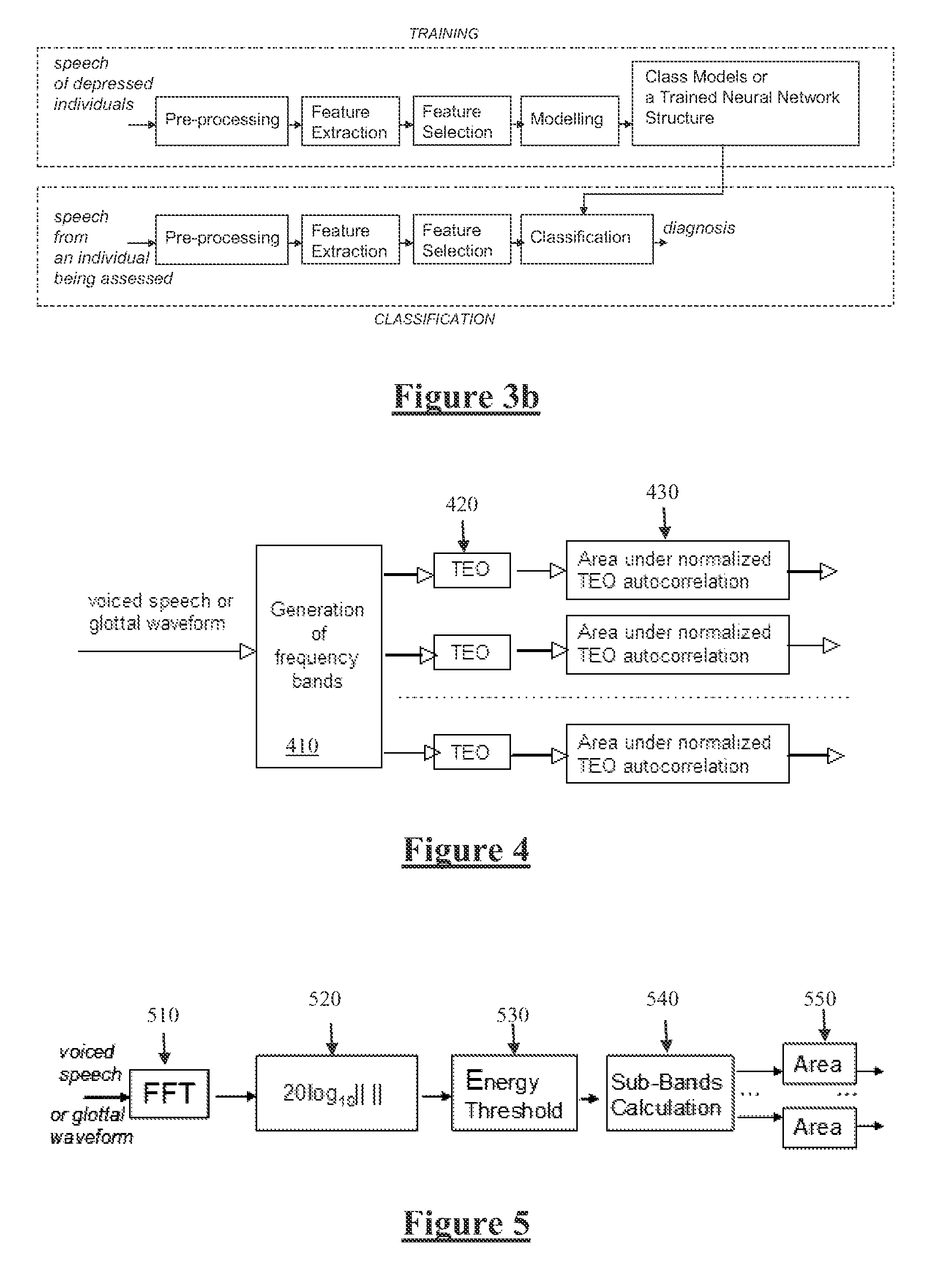
ActiveUS20130166291A1Rapid quantitative assessmentImprove accurate classificationMedical data miningSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumPsychological status
Mental state of a person is classified in an automated manner by analysing natural speech of the person. A glottal waveform is extracted from a natural speech signal. Pre-determined parameters defining at least one diagnostic class of a class model are retrieved, the parameters determined from selected training glottal waveform features. The selected glottal waveform features are extracted from the signal. Current mental state of the person is classified by comparing extracted glottal waveform features with the parameters and class model. Feature extraction from a glottal waveform or other natural speech signal may involve determining spectral amplitudes of the signal, setting spectral amplitudes below a pre-defined threshold to zero and, for each of a plurality of sub bands, determining an area under the thresholded spectral amplitudes, and deriving signal feature parameters from the determined areas in accordance with a diagnostic class model.
Owner:RMIT UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving encoding-decoding speech
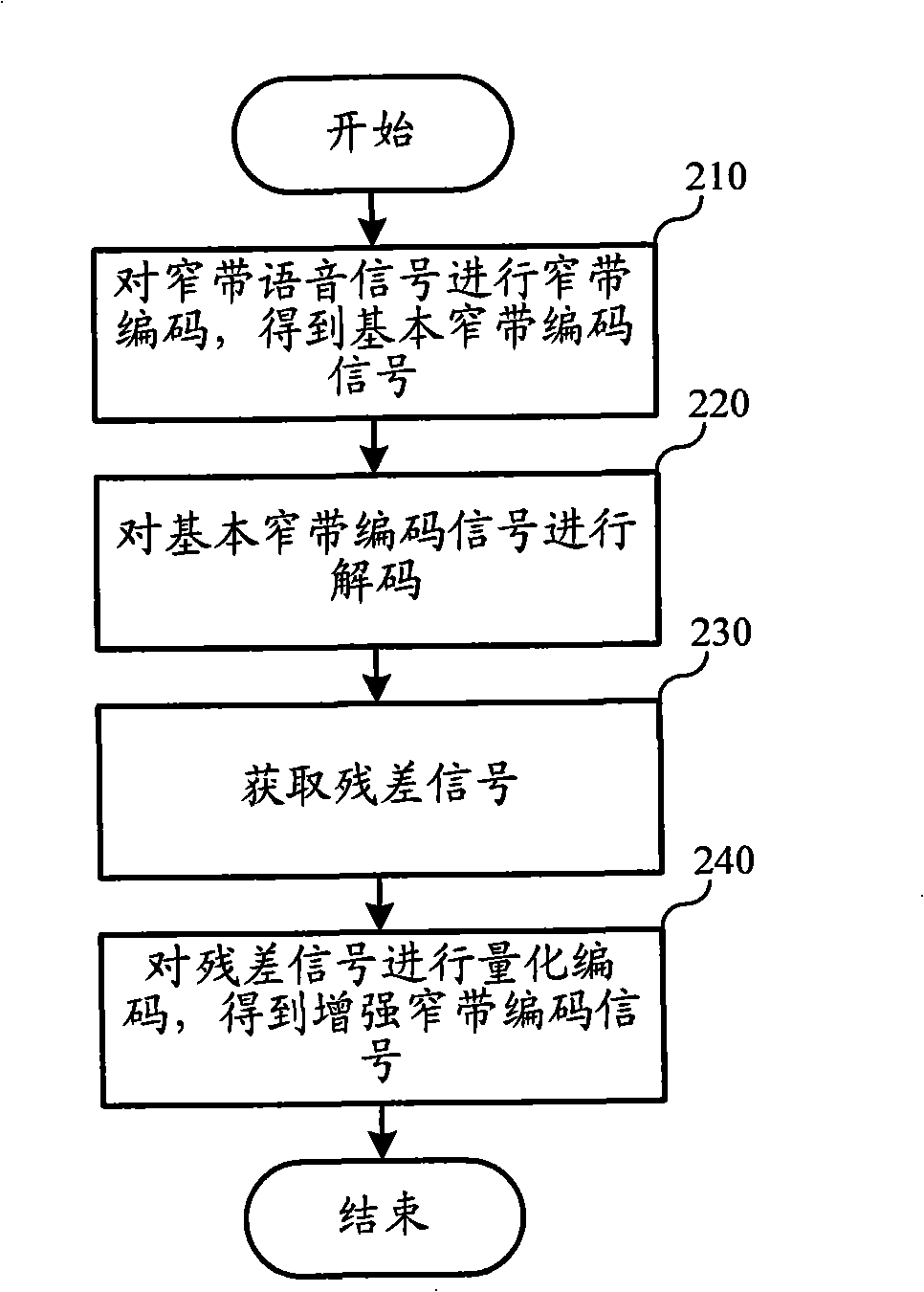
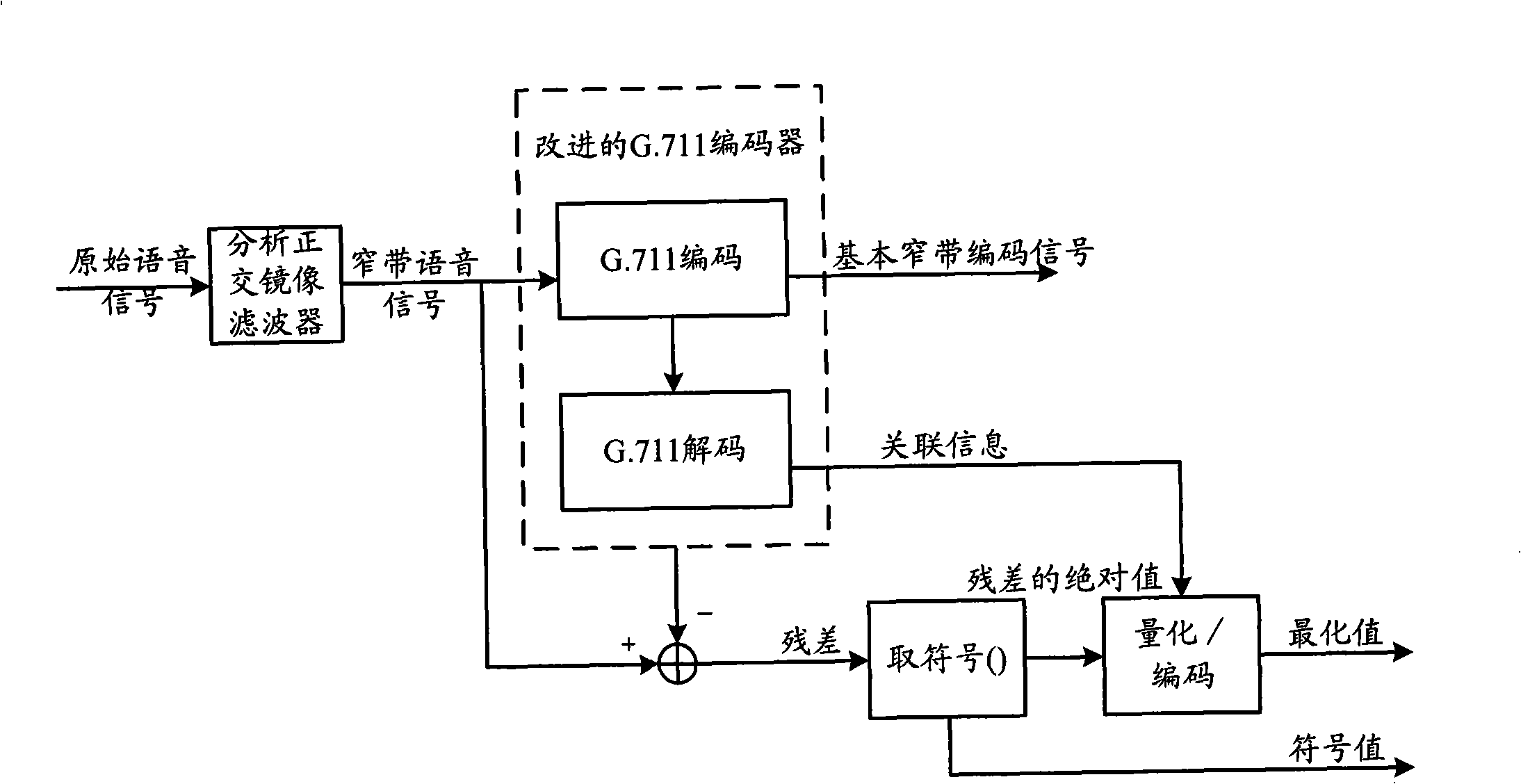
InactiveCN101325059AImprove coding efficiencyReduce subjective auditory distortionSpecial service provision for substationInterconnection arrangementsFrequency spectrumFrequency conversion
The invention relates to the communication field, and discloses a method for receiving and sending the voice coding and decoding and a device thereof, so as to allow the code efficiency of voice signals to be enhanced and the voice quality to be enhanced. The time-frequency conversion is performed to voice signals to obtain X frequency domain conversion coefficients, the X frequency domain conversion coefficients are quantified to obtain the broad-band coded signals, wherein, Y frequency domain conversion coefficients which are relatively important are quantified with a first codebook, the other X-Y frequency domain conversion coefficients are quantified with a second codebook, the code word quantity of the first codebook is higher than the code word quantity of the second codebook, Y is smaller than or equal to X and larger than or equal to 1, and the acquired broad-band coded signals are sent. According to the ratio of the average spectrum amplitude and the maximum spectrum amplitude of each quantified block, fine spectrum structures of the frequency domain quantified signals in the quantified block are reduced, wherein, the smaller the ratio is , the larger the reducing extent of the fine spectrum structures are.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
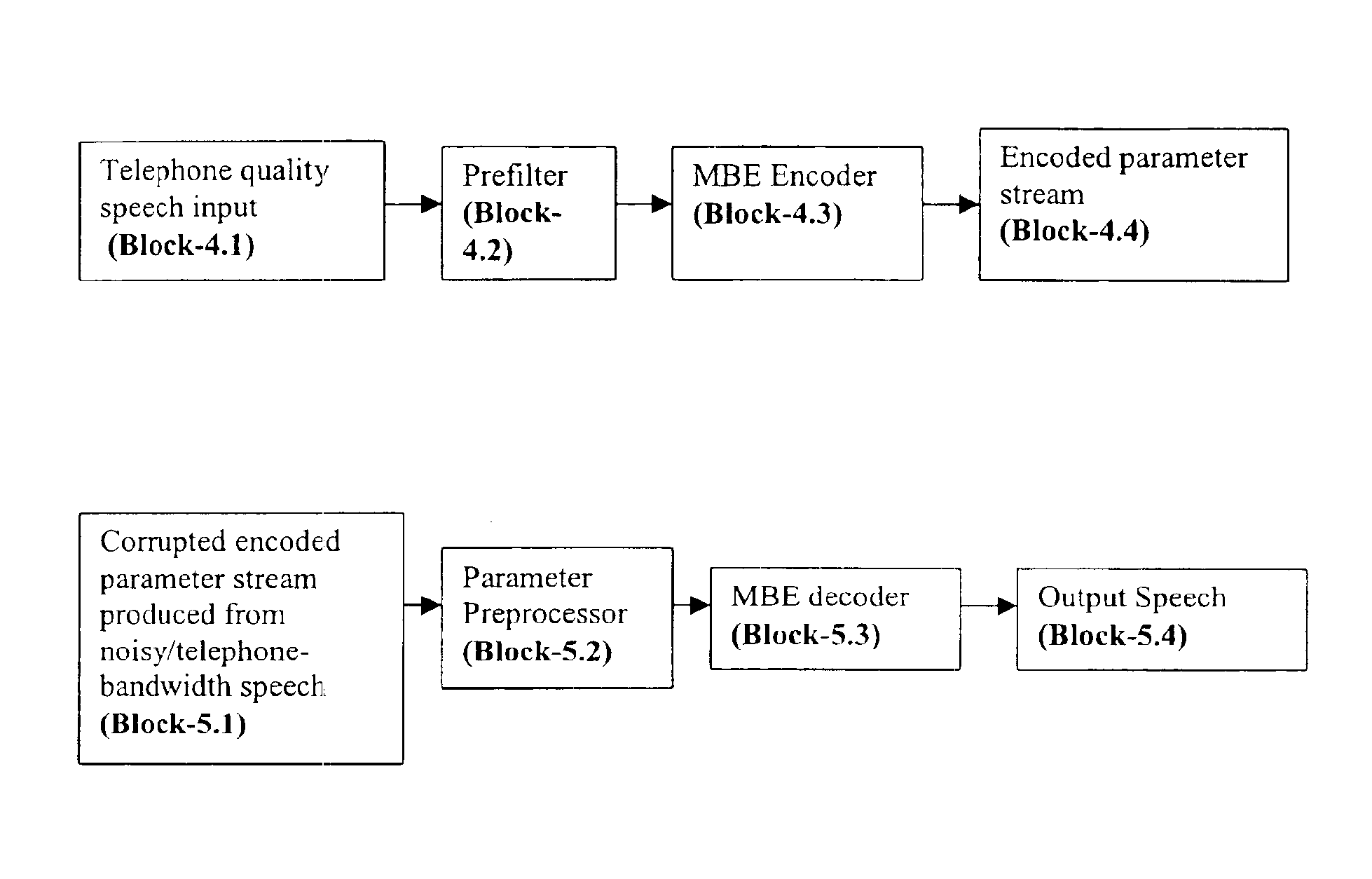
Preprocessing modules for quality enhancement of MBE coders and decoders for signals having transmission path characteristics
InactiveUS6912496B1Improve performanceClose to speech qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumLinear filter
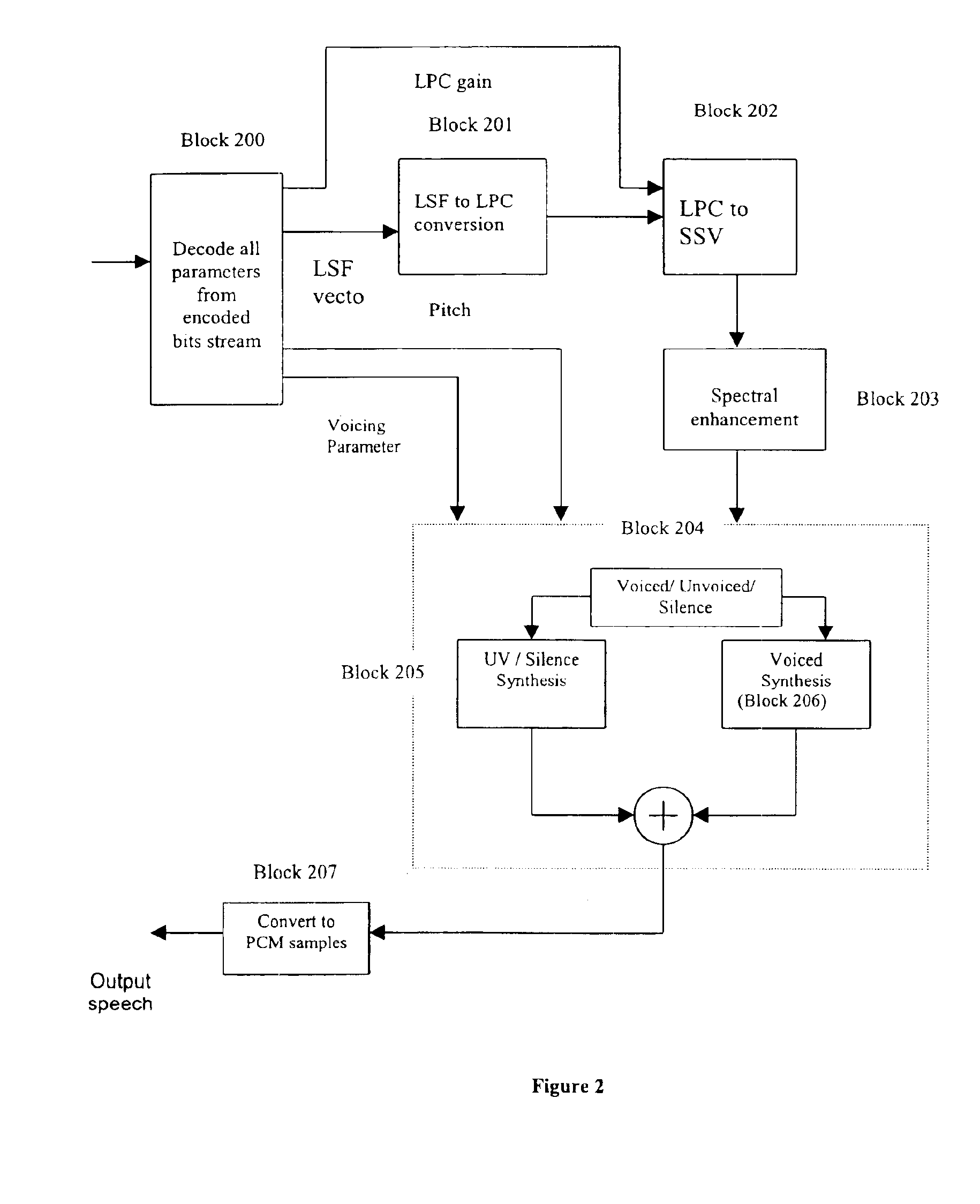
Pursuant to one aspect of the invention, a prefilter module that incorporates an inverse filter is used in conjunction with an encoder. The inverse filter has an inverse frequency response of a frequency response of a filter that simulates speech having transmission path characteristics, such as telephone-channel bandwidth speech, and / or noisy speech. The inverse filter is used to compensate transmission path characteristics of an input signal. The inverse filter can be designed using several methods, such as, for example, an autoregressive model or a moving average model. Pursuant to a second aspect of the invention, a parameter preprocessor is used in conjunction with a decoder. The parameter preprocessor performs pitch rectification through use of a medium and linear filter, and updates spectral amplitudes and voicing parameter depending on the pitch rectification. The inverse filter and parameter preprocessor, used in conjunction with an encoder and decoder, respectively, improve signal processing and parameter estimation.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Method and device for monitoring the insulation resistance in an ungrounded electrical network
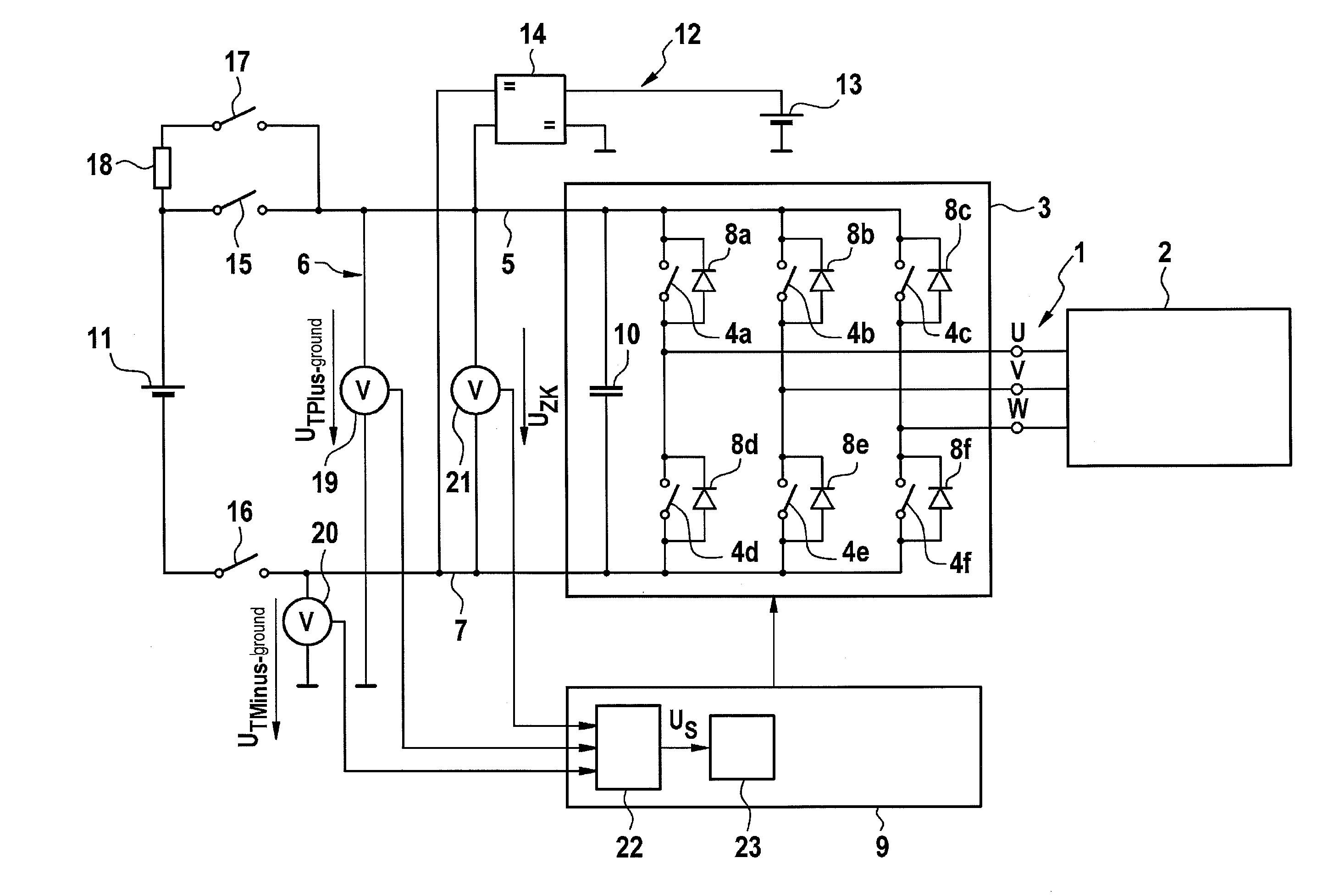
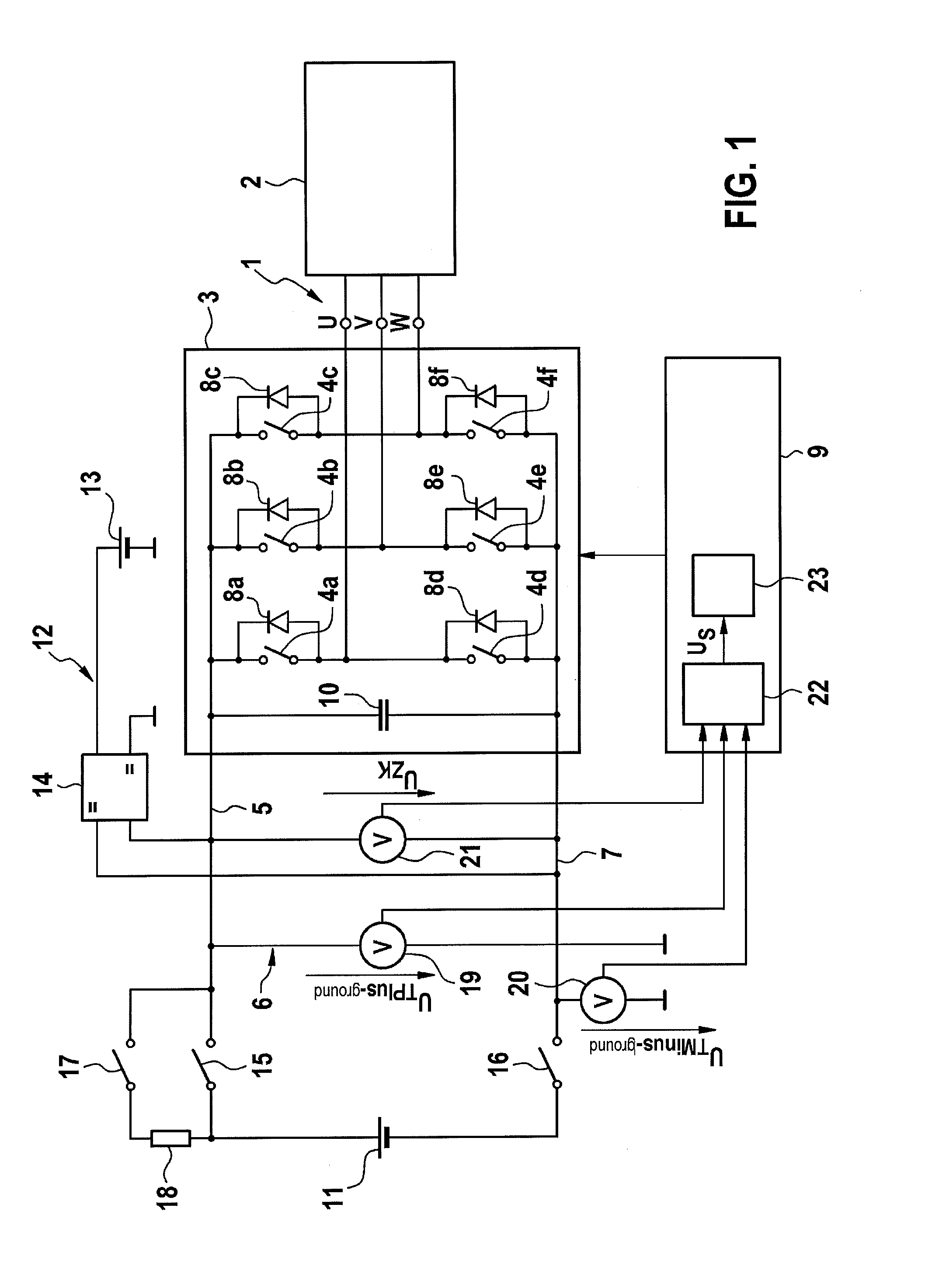
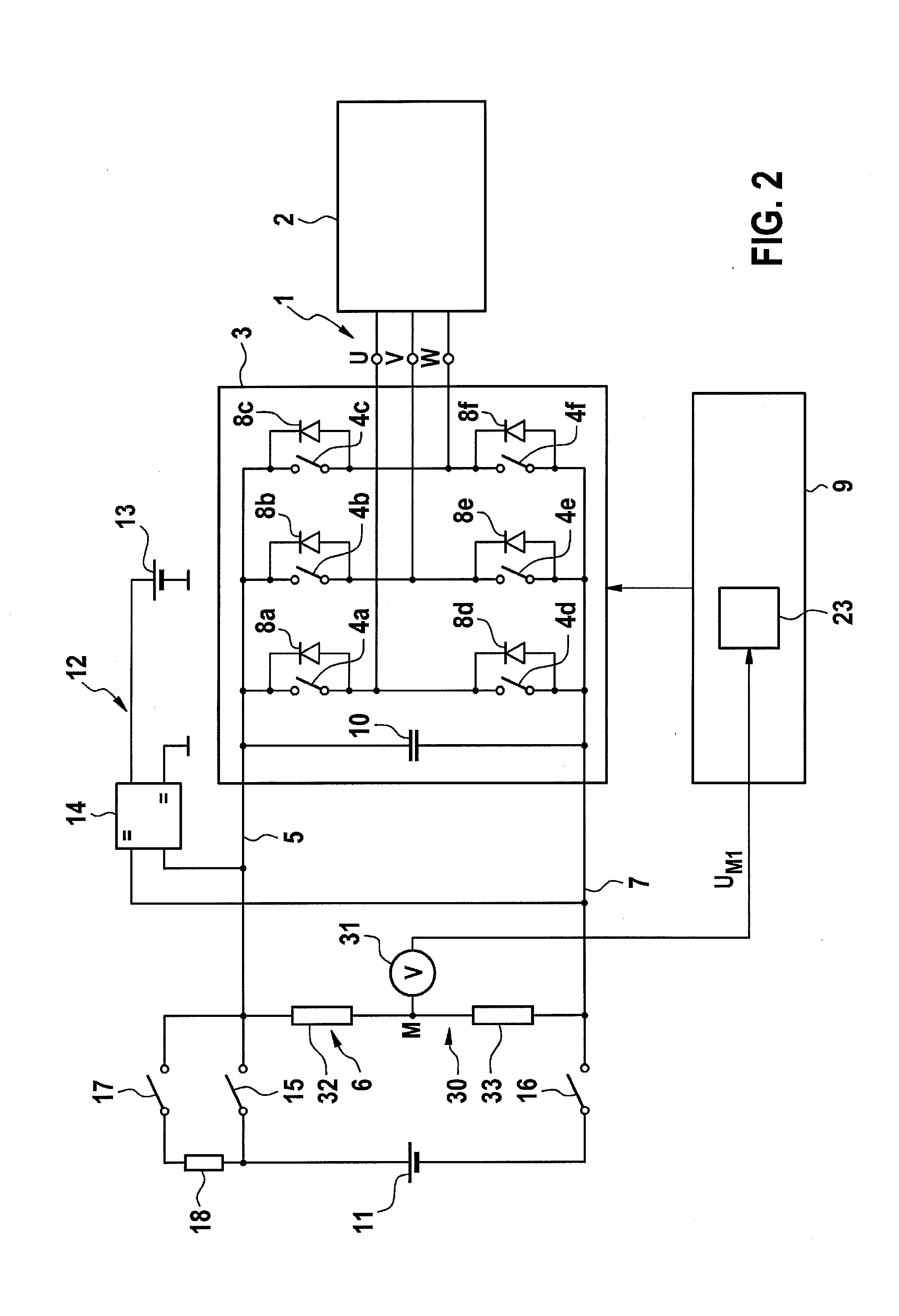
InactiveUS20130221997A1High measurement accuracyElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceElectric networkPower usage
A method and a device for monitoring the insulation resistance in an ungrounded electrical network having a constant-voltage d.c. link and at least one inverter, connected to it, for controlling an n-phase electrical consumer in an n-phase network. A voltage to be monitored, is determined during operation of the consumer, which represents a voltage fluctuation of supply voltage potentials of the constant-voltage d.c. link with respect to a reference potential. In addition, a variable characterizing an electrical frequency of the electrical consumer is determined, particularly an electrical angular speed of the electrical consumer. A first spectral amplitude of the voltage to be monitored at the n-fold electrical frequency of the electrical consumer, is compared to a first reference value, and detects a symmetrical insulation error in the constant-voltage d.c. link or the n-phased network, if the comparison yields a deviation of the first spectral amplitude from the first reference value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Automatic equalization using adaptive frequency-domain filtering and dynamic fast convolution
InactiveUS9084049B2Less sensitive to temporal alignment errorDigital technique networkNoise generationFrequency spectrumBlock transform
Frequency-domain techniques are used for adaptive equalization that is responsive to spectral magnitude characteristics but not sensitive to phase characteristics of system response. Signal correlation may be used to improve adaptation accuracy when significant levels of ambient sounds are present. A preferred filter implementation uses convolution-based block transforms and cross-fade windows.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for noise filtering
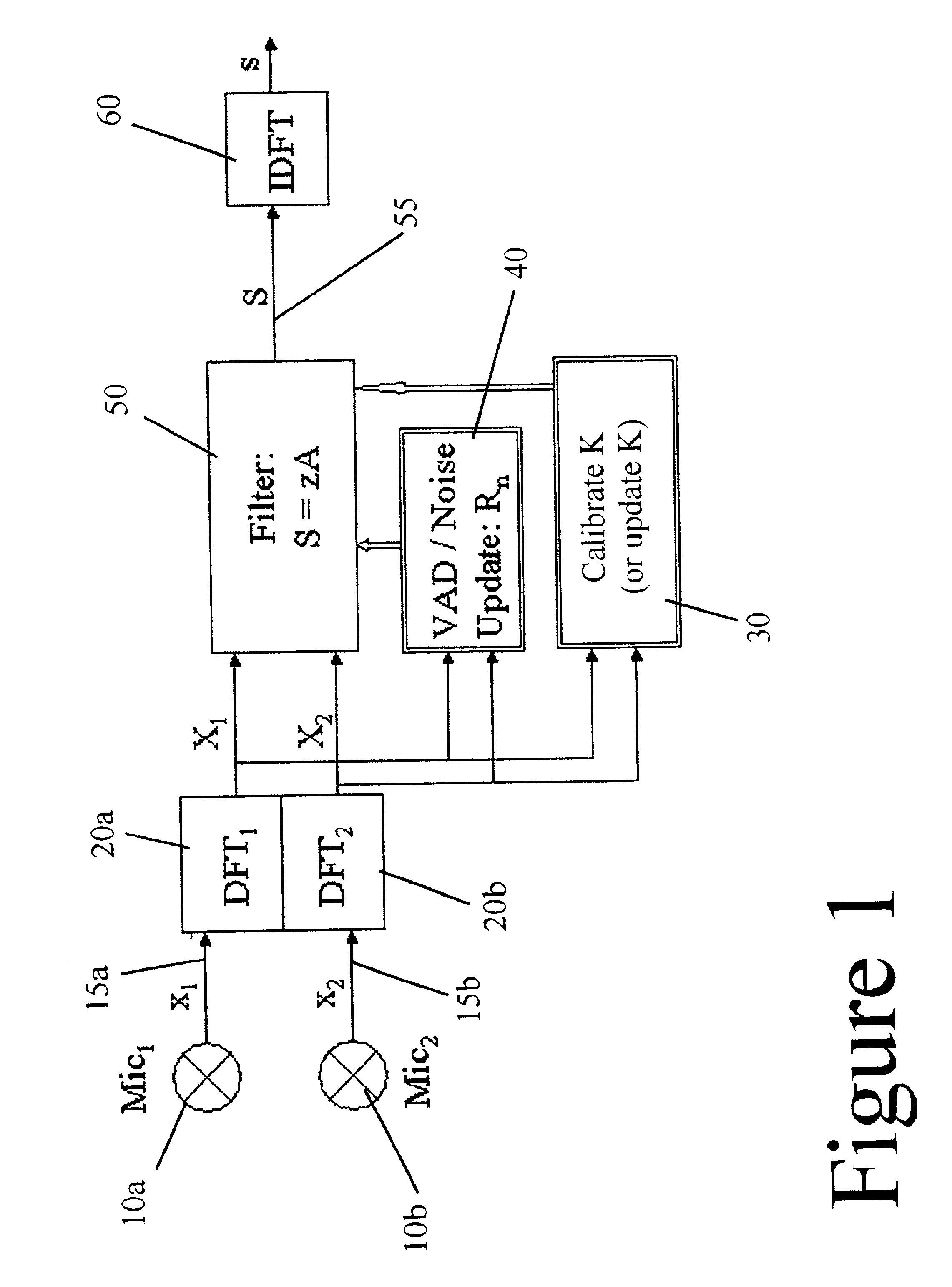
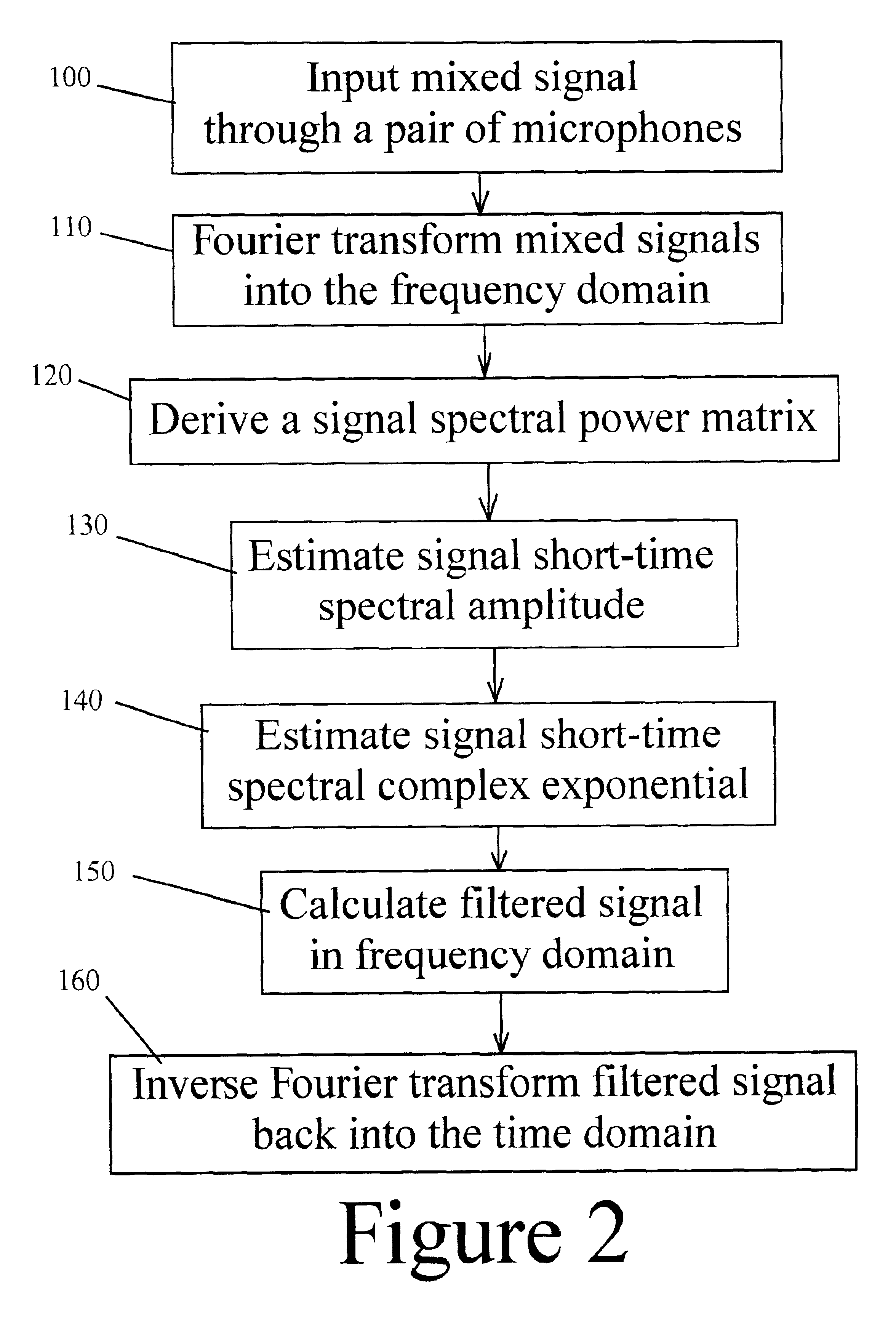
Disclosed is an apparatus for and a method of filtering noise from a mixed sound signal to obtained a filtered target signal, comprising the steps of inputting the mixed signal through a pair of microphones into a first channel and a second channel, separately Fourier transforming each said mixed signal into the frequency domain, computing a signal short-time spectral amplitude |Ŝ| from said transformed signals, computing a signal short-time spectral complex exponential ei arg(S) from said transformed signals, where arg(S) is the phase of the target signal in the frequency domain, computing said target signal S in the frequency domain from said spectral amplitude and said complex exponential.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Compressed spectrum sensing method based on autocorrelation matrix reconstitution
InactiveCN102946288ADownsamplingSave storage spaceTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSignal classification
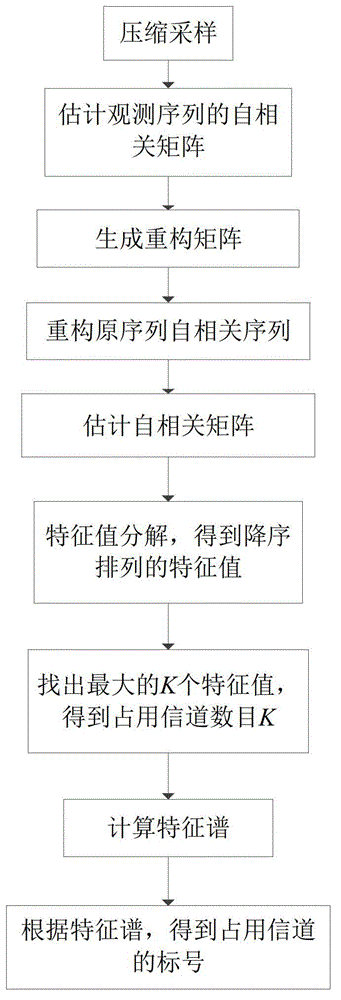
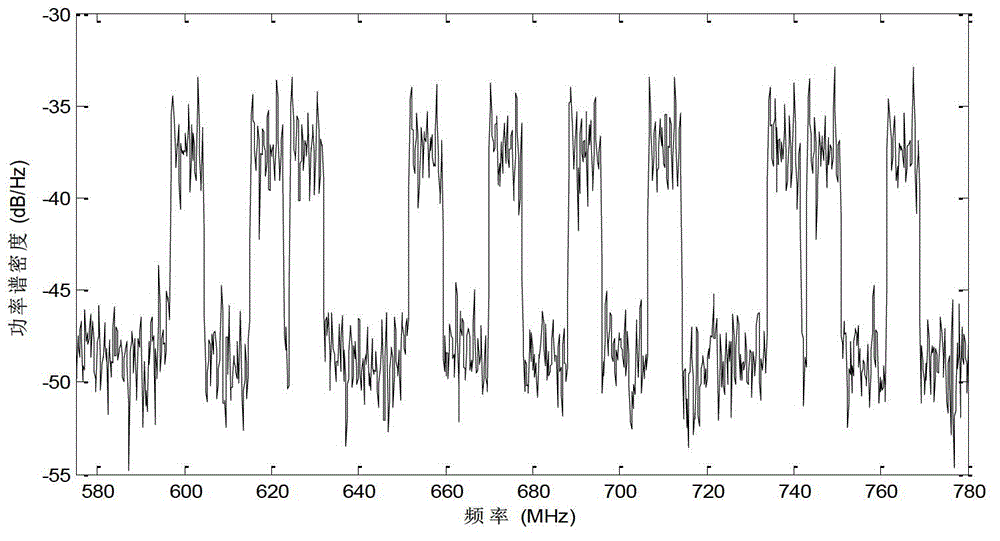
The invention provides a compressed spectrum sensing method based on autocorrelation matrix reconstitution and mainly solves the problem that an existing sensing algorithm is high in sampling speed and large computation overhead. The compressed spectrum sensing method comprises that a secondary user obtains an observation sequence of a frequency spectrum environment through compressed sensing and obtains an autocorrelation matrix estimated value of Nyquist sampling by utilizing autocorrelation vector quantity of a autocorrelation matrix reconstitution Nyquist sample sequence of the observation sequence; a multi-signal classification MUSIC algorithm is adopted to obtain an estimated value of occupied channel number according to a characteristic value of the autocorrelation matrix estimated value; a characteristic spectrum is constructed according to the characteristic value and the estimated value of the occupied channel number, spectral amplitude values corresponding to characteristics of channels are added to obtain a sum, and mark numbers of the occupied channels are judged. By means of the compressed spectrum sensing method, the sampling speed of a secondary user receiving machine can be reduced, algorithm complexity at the reconstitution end is low, and spectral amplitude occupying situation in a cognitive radio system can be judged quickly.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Device for dispersing light pulses of which the spectral amplitude is programmable
InactiveUS20070103778A1Overcome disadvantagesPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLight beamAcoustic wave
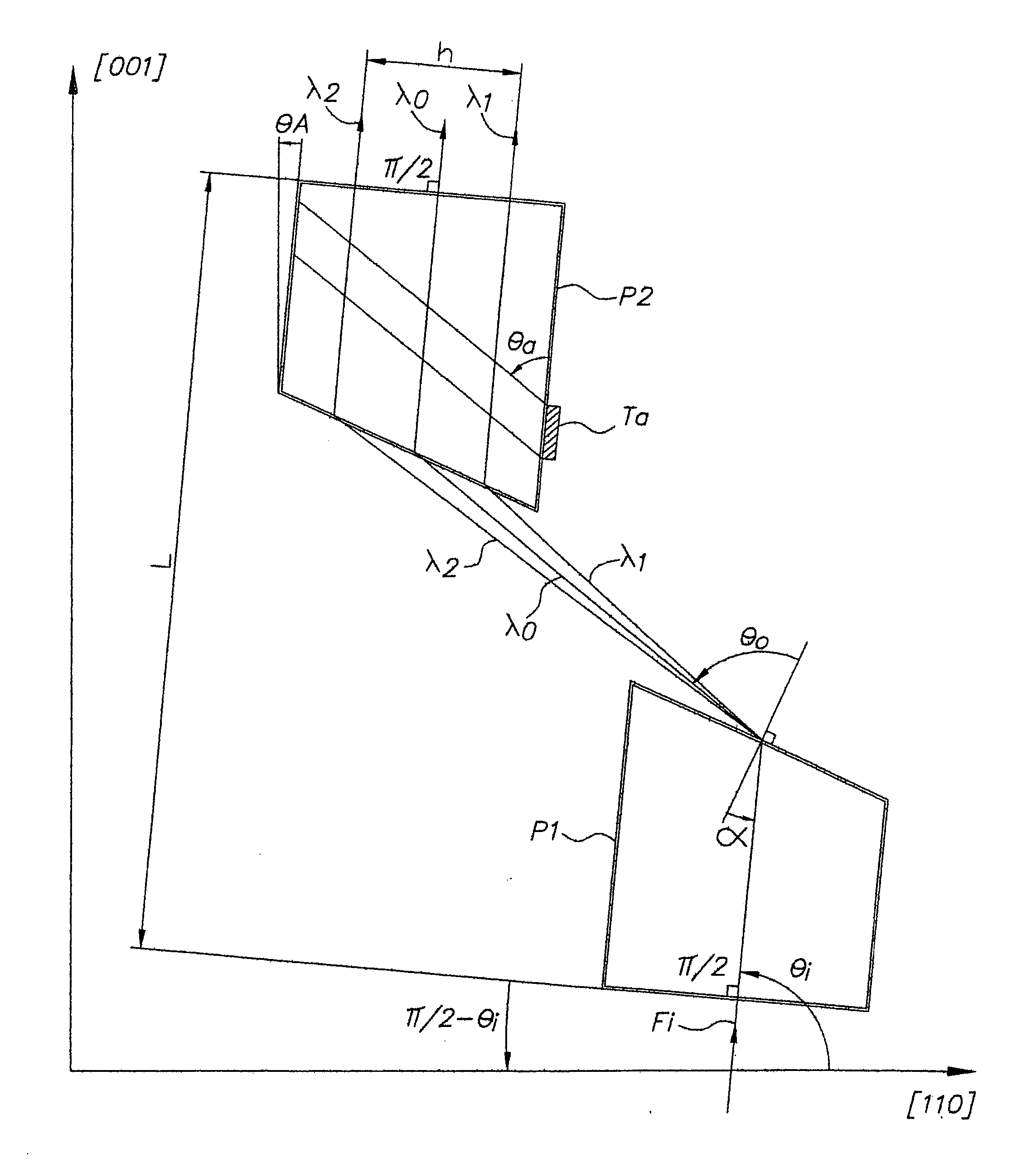
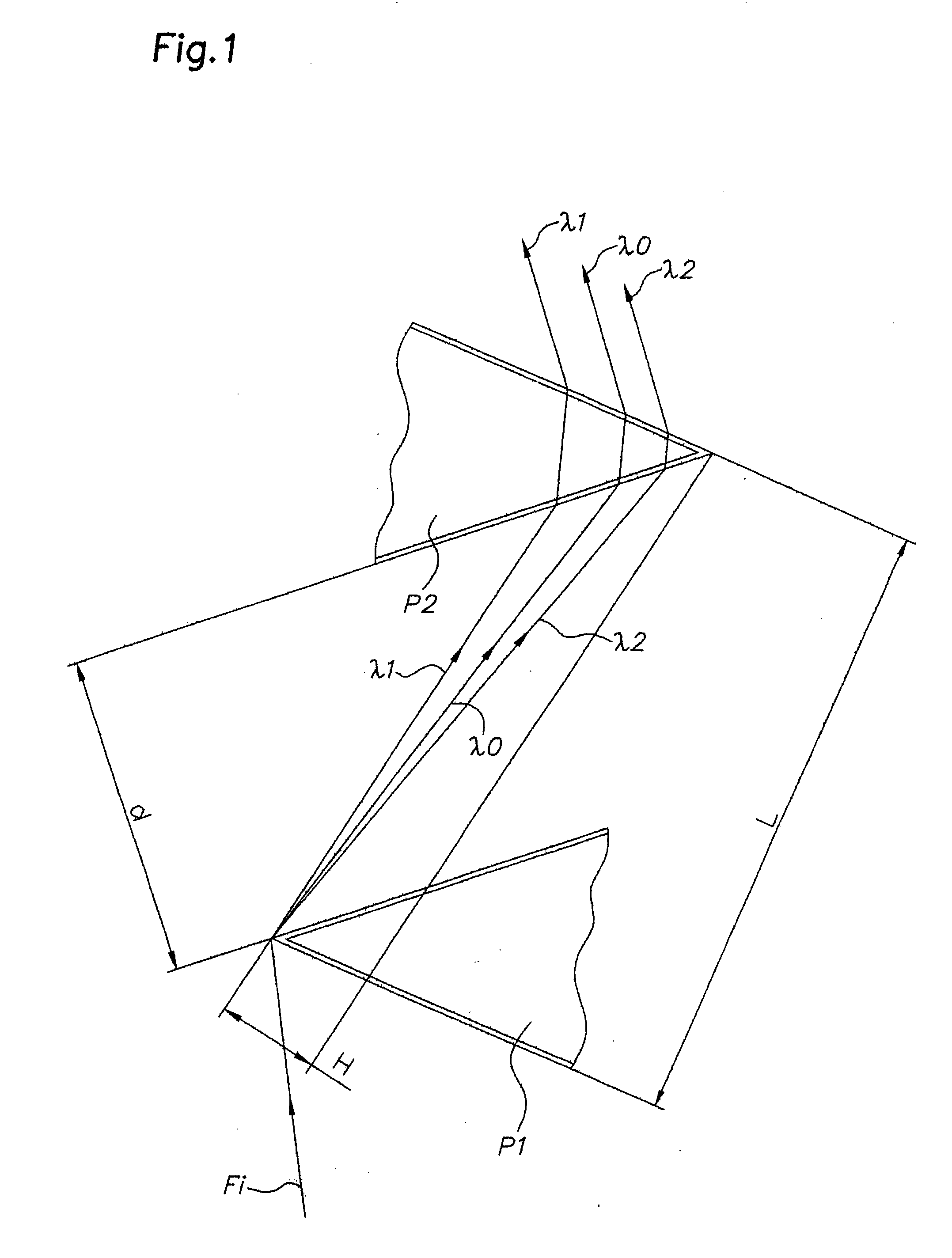
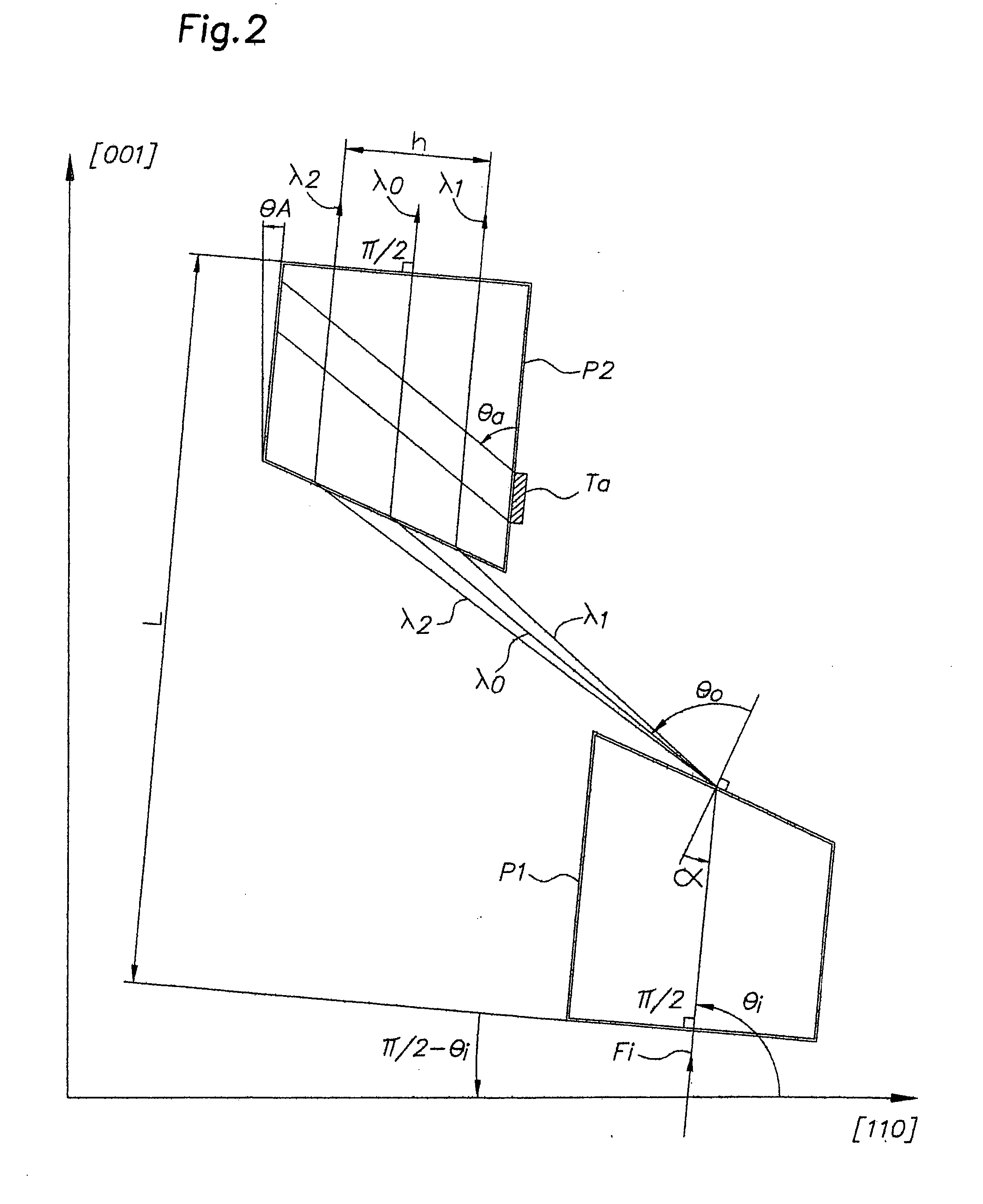
Device for dispersion of light pulses of an optical beam (Fi) constituted by two dispersive prisms (P1, P2), with the same vertex angle (α), mounted head to tail, the optical input surface of the first prism (P1) being parallel to the optical output surface of the second prism (P2), the distance (L) separating said optical input surface of the first prism (P1) and said optical output surface of the second prism (P2) being adjustable, given that the material constituting at least one of said first and second prisms (P1, P2) is an acousto-optic material allowing for acousto-optic interaction between said optical beam and an acoustic beam, the acoustic wave of said acoustic beam generating, in at least one of said first and second prisms (P1, P2), an integrated deflective Bragg cell.
Owner:FASTLITE
Method For Electromagnetic Prospecting Waveform Design
InactiveUS20110087435A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisControlled source electro-magneticNoise level
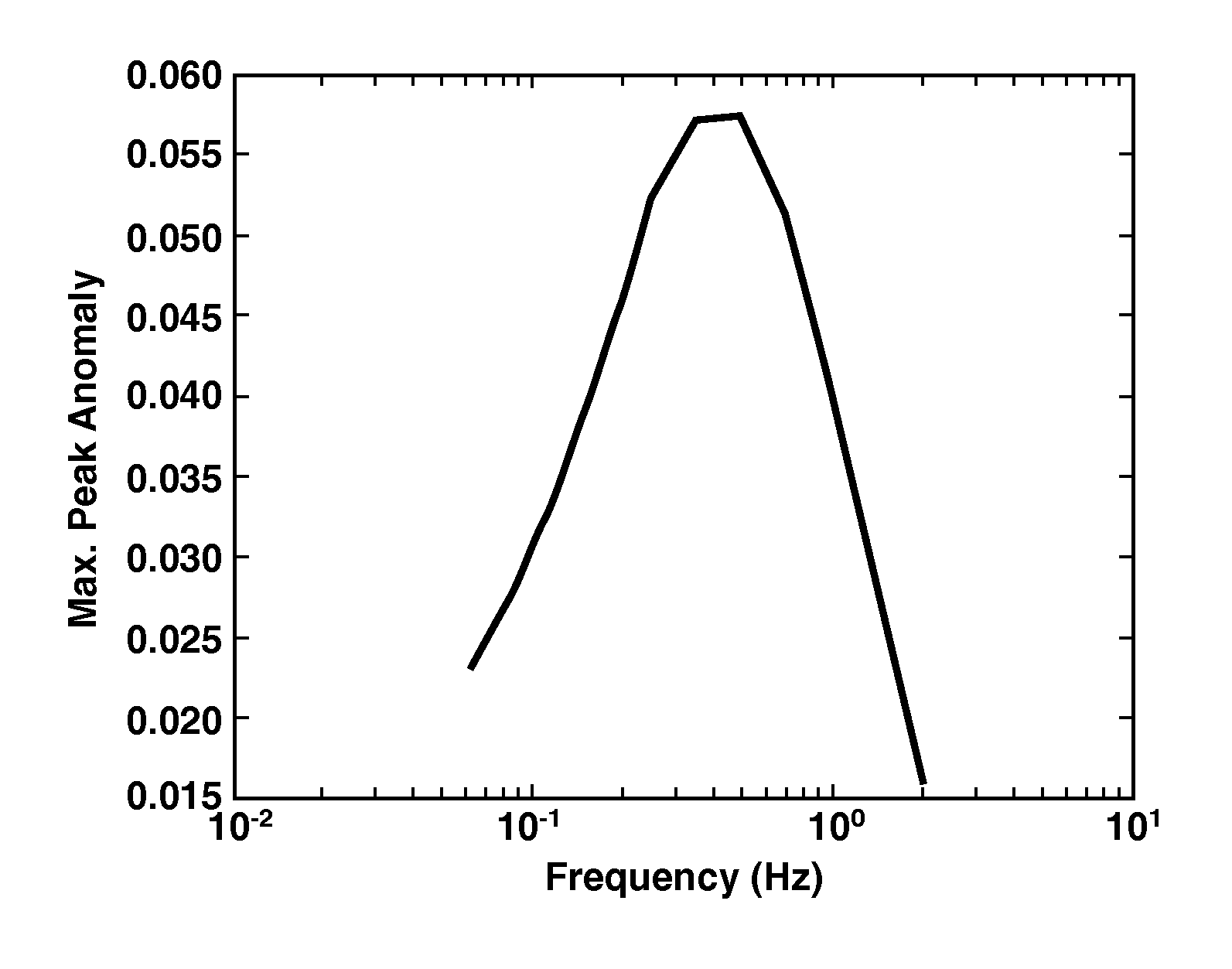
A waveform design method is presented for controlled source electromagnetic surveying. A desired source spectrum (82) is specified based on a desired resistivity depth image resolution (81) with spectral amplitudes determined by expected noise levels (83). Techniques are disclosed for designing a source waveform to match the desired source spectrum. When better resolution is desired at a target zone, this leads to a required clustering of frequency components. A modulated waveform can be used to provide this clustering of frequency components.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
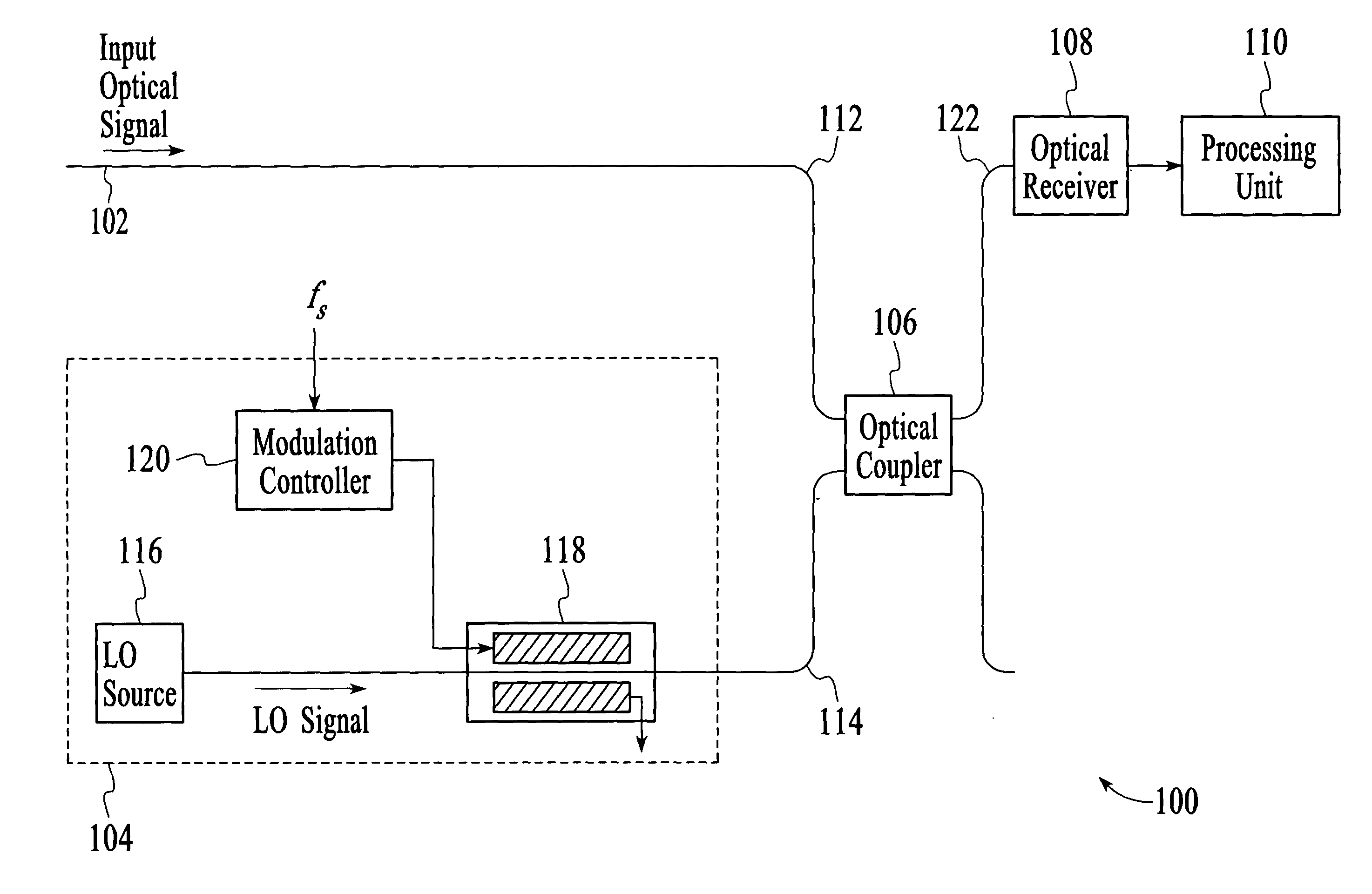
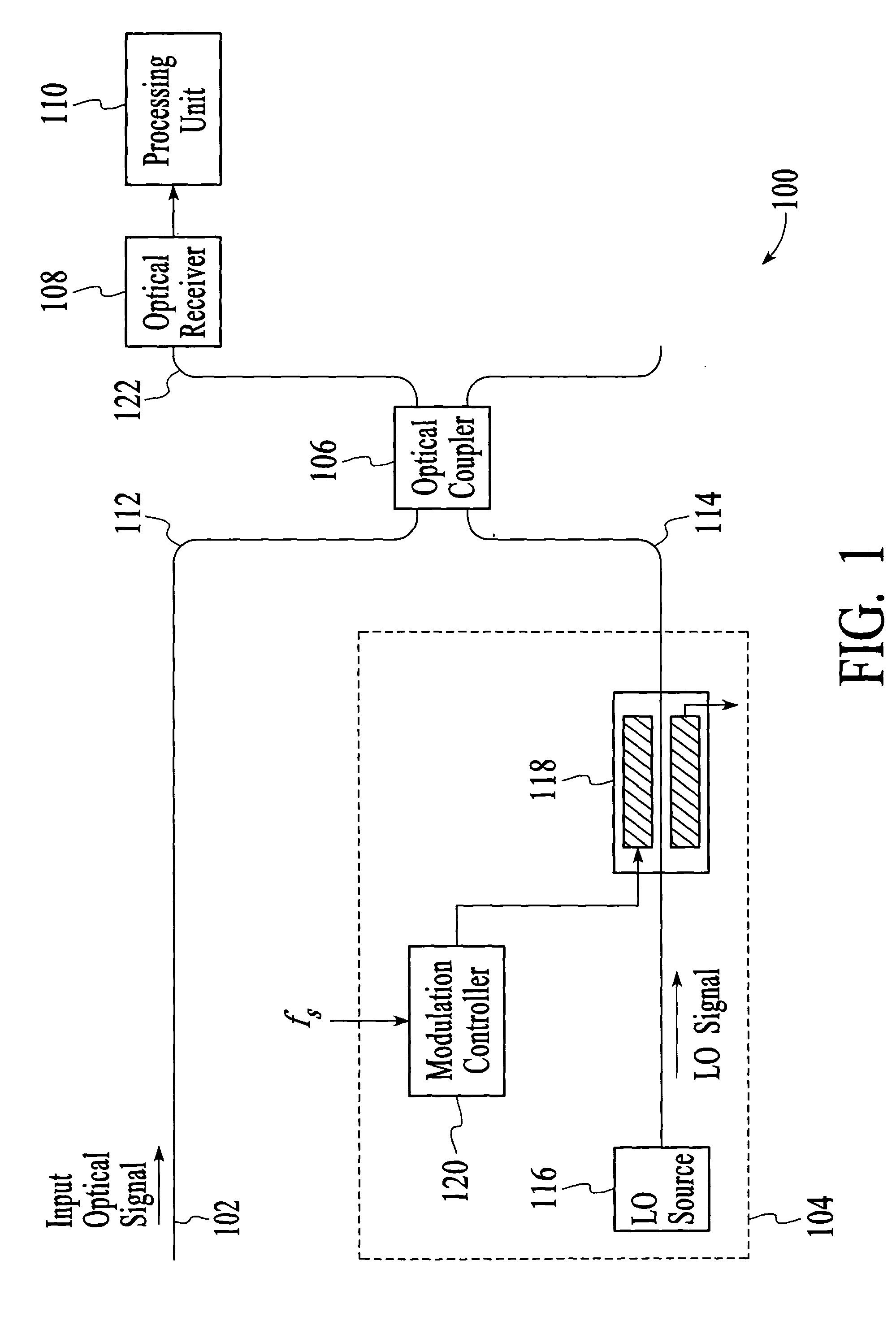
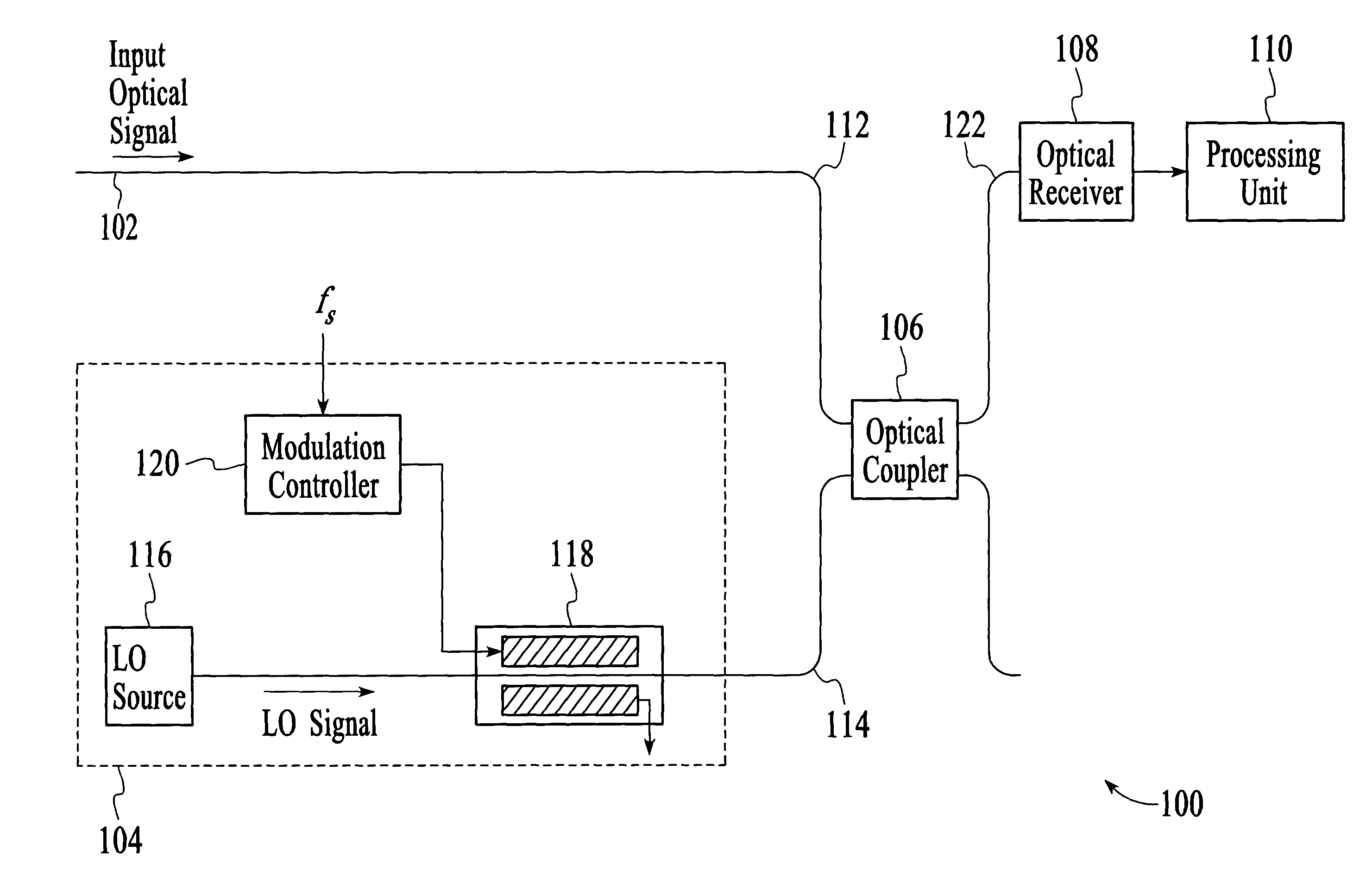
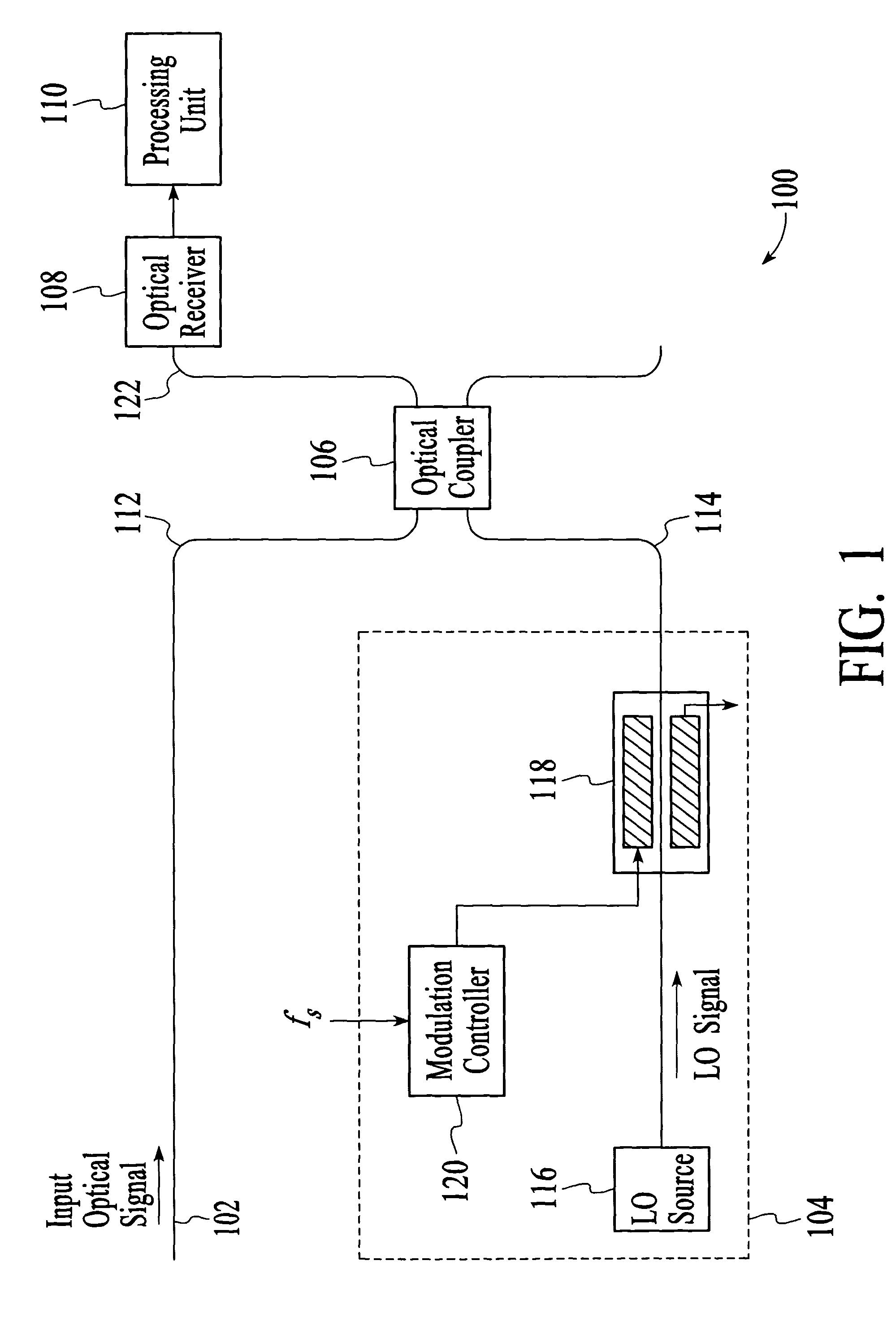
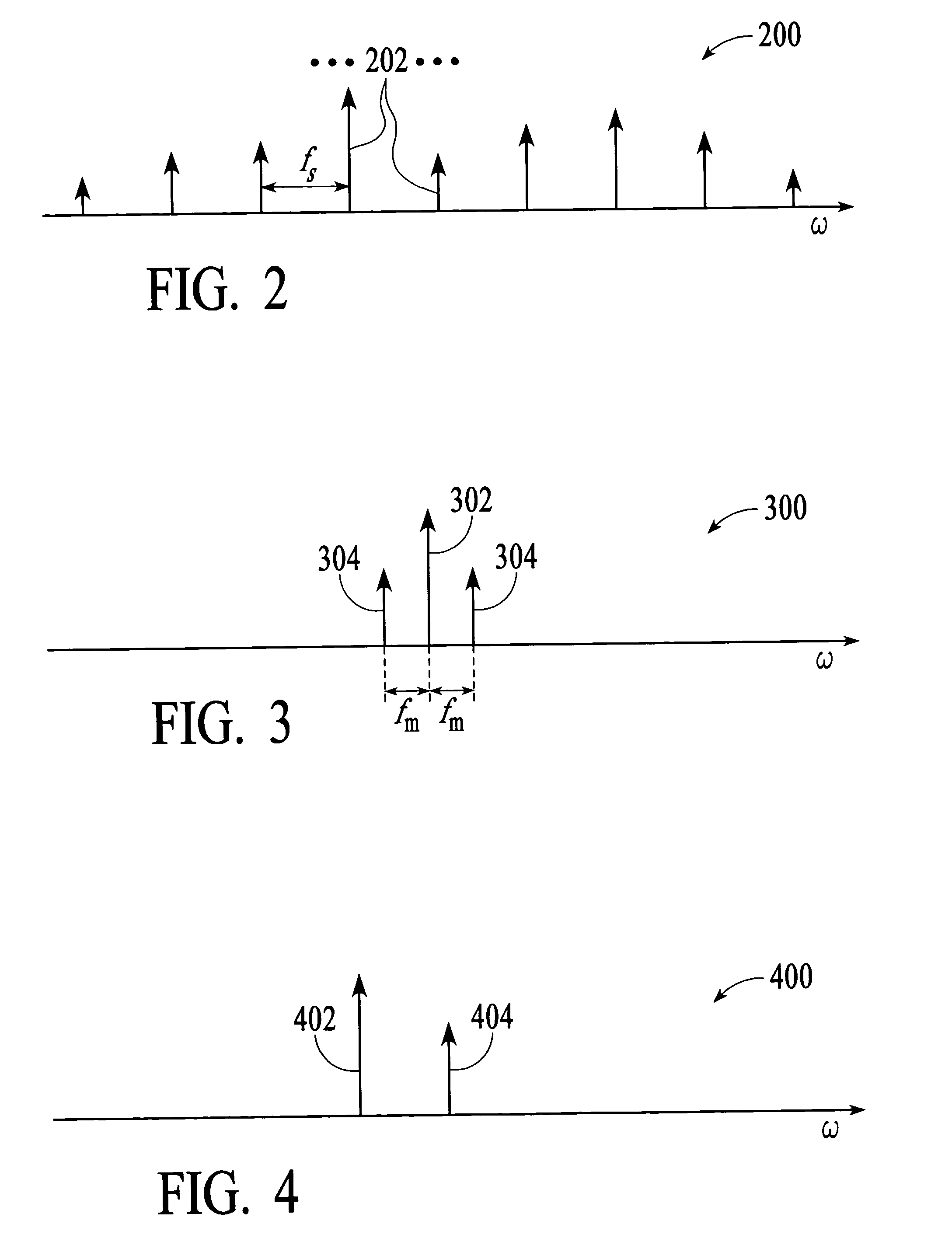
Optical analyzer and method for measuring spectral amplitude and phase of input optical signals using heterodyne architecture
InactiveUS20050012934A1Calculation is complexOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryDistributed feedback laserFrequency spectrum
An optical analyzer and method for measuring optical properties of optical signals utilizes a heterodyne architecture to measure spectral amplitude and phase of a periodically modulated input optical signal, such as an optical signal from a periodically modulated distributed feedback (DFB) laser. The spectral amplitude and phase measurements are derived from a heterodyne signal, which is produced by combining and mixing the input optical signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal. The optical spectrum that is reconstructed from the heterodyne signal includes “inner” spectral peaks that contain phase information of the input optical signal. The inner spectral peaks may be produced by an optical or electrical mixing technique. The spectral phase of the input optical signal is recovered from the inner spectral peaks of the reconstructed optical spectrum.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Emotional and/or psychiatric state detection
ActiveUS9058816B2Improve classification resultsRapid quantitative assessmentMedical data miningSpeech recognitionPsychological statusFeature extraction
Mental state of a person is classified in an automated manner by analysing natural speech of the person. A glottal waveform is extracted from a natural speech signal. Pre-determined parameters defining at least one diagnostic class of a class model are retrieved, the parameters determined from selected training glottal waveform features. The selected glottal waveform features are extracted from the signal. Current mental state of the person is classified by comparing extracted glottal waveform features with the parameters and class model. Feature extraction from a glottal waveform or other natural speech signal may involve determining spectral amplitudes of the signal, setting spectral amplitudes below a pre-defined threshold to zero and, for each of a plurality of sub bands, determining an area under the thresholded spectral amplitudes, and deriving signal feature parameters from the determined areas in accordance with a diagnostic class model.
Owner:RMIT UNIVERSITY
System for managing feedback
ActiveUS20100111339A1Eliminate and minimize false positiveTransmission noise suppressionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency spectrumConcentration ratio
Owner:ZOUNDS LLC FORMERLY ZOUNDS ACQUISITION
Method and system for speech coding
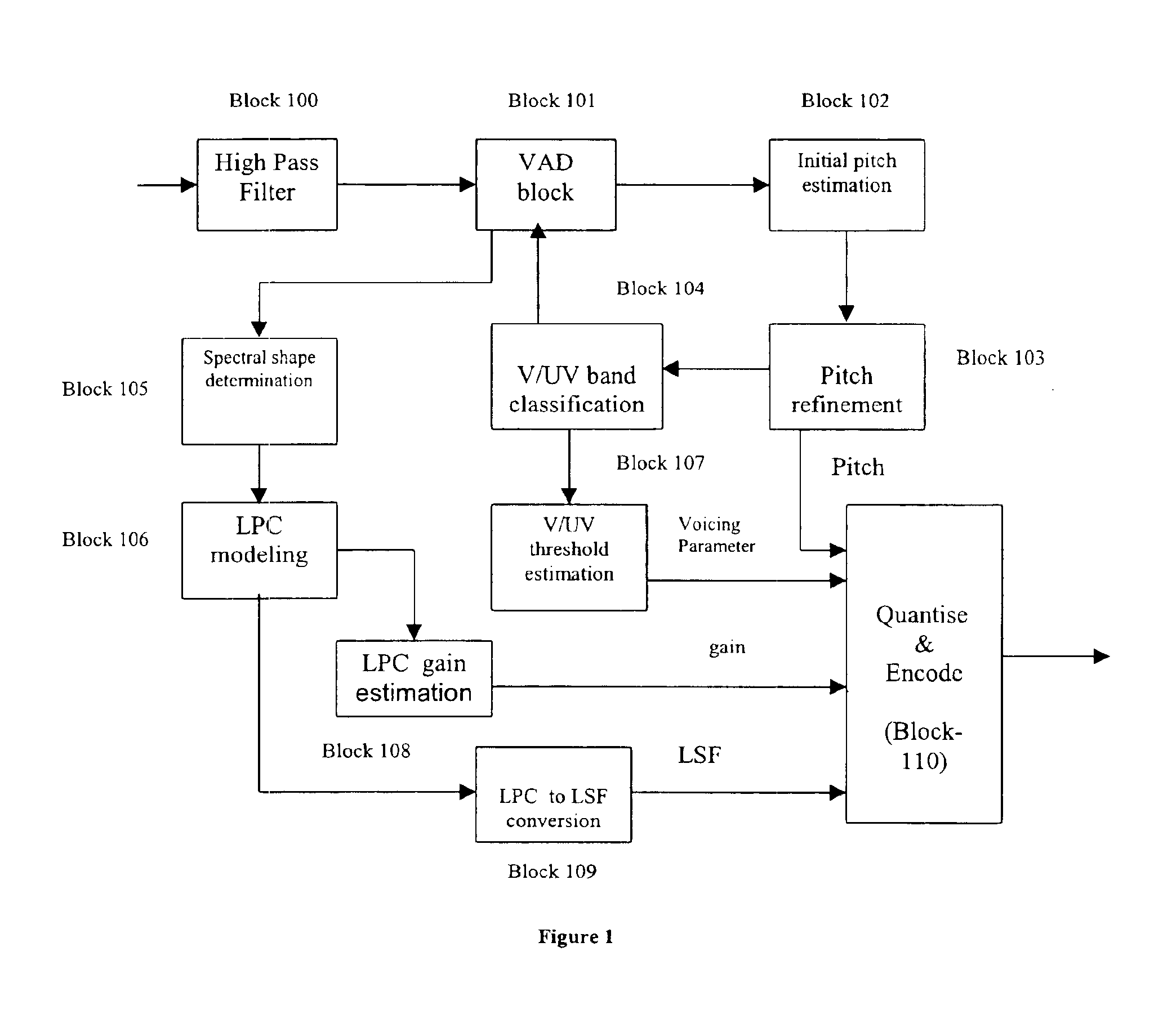
InactiveUS20050091041A1Improve coding efficiencySpeech analysisTelephonic communicationFrequency spectrumPitch contour
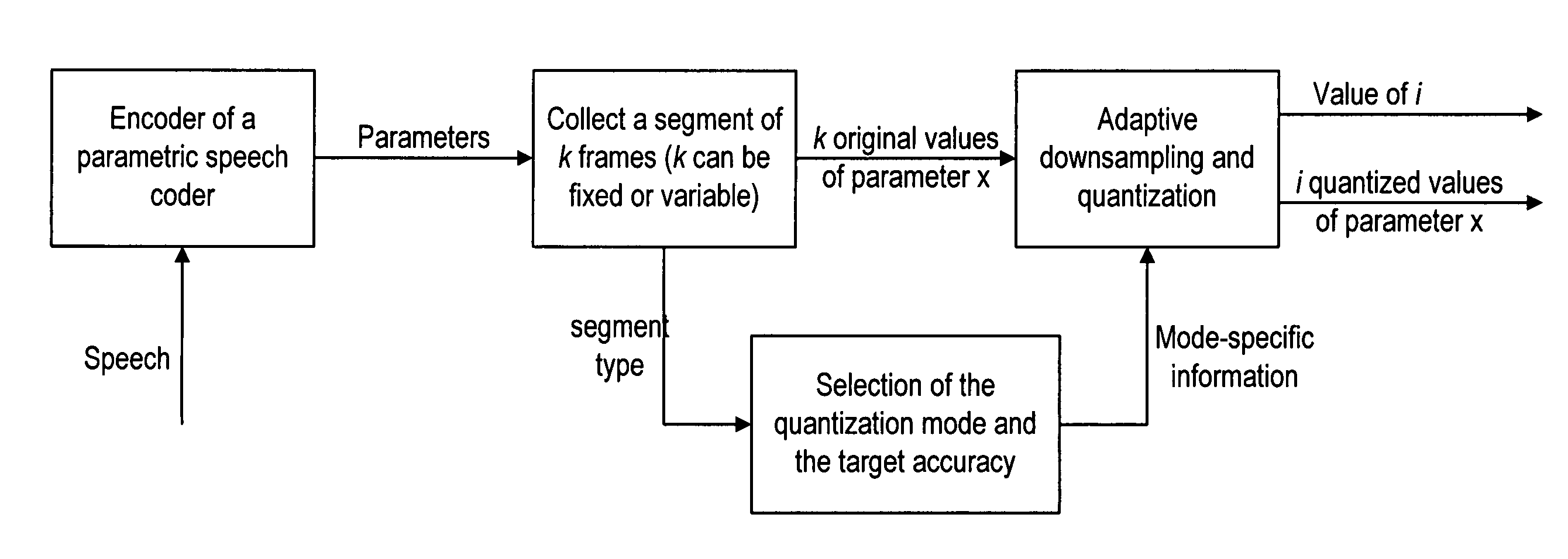
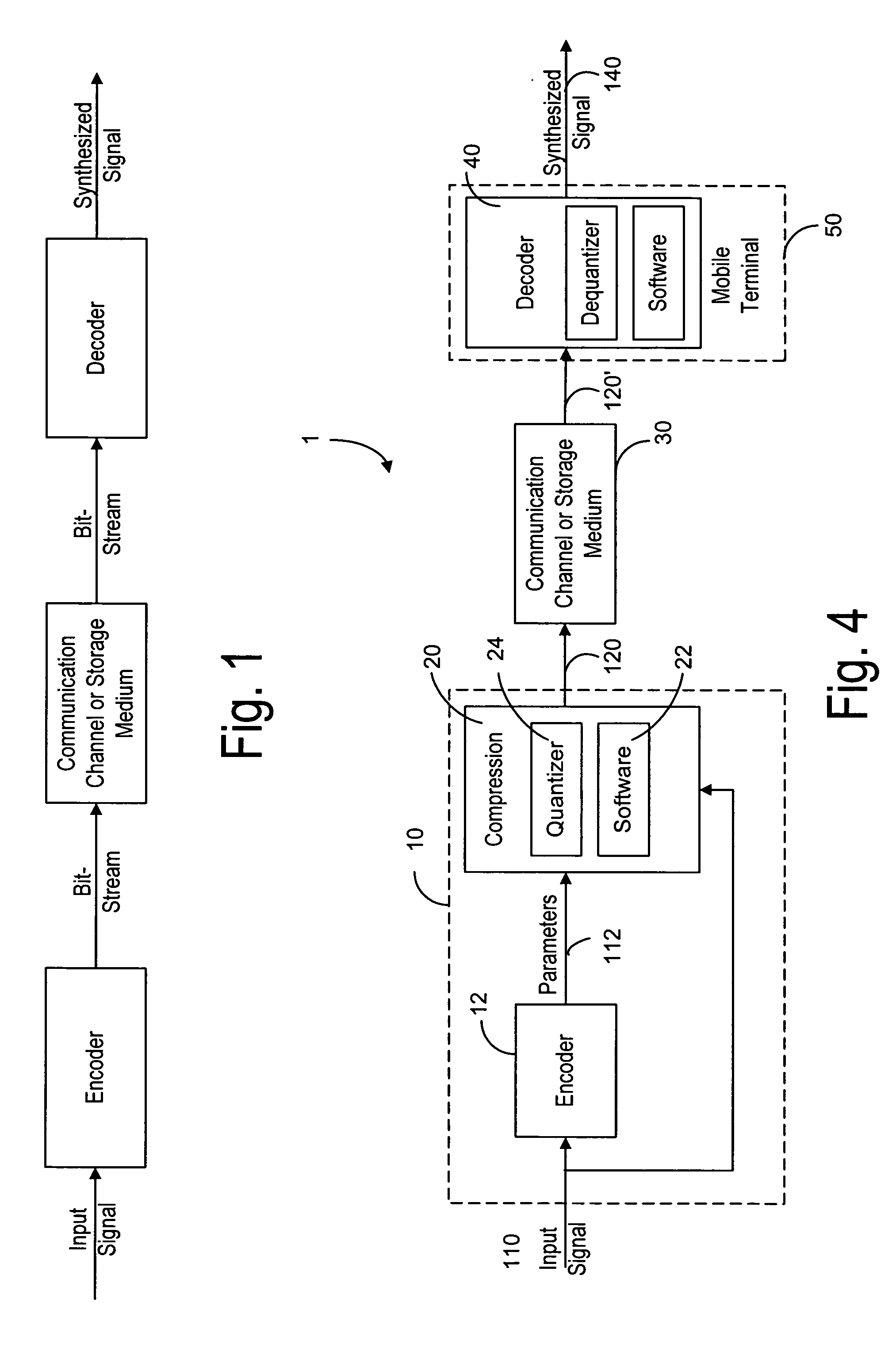
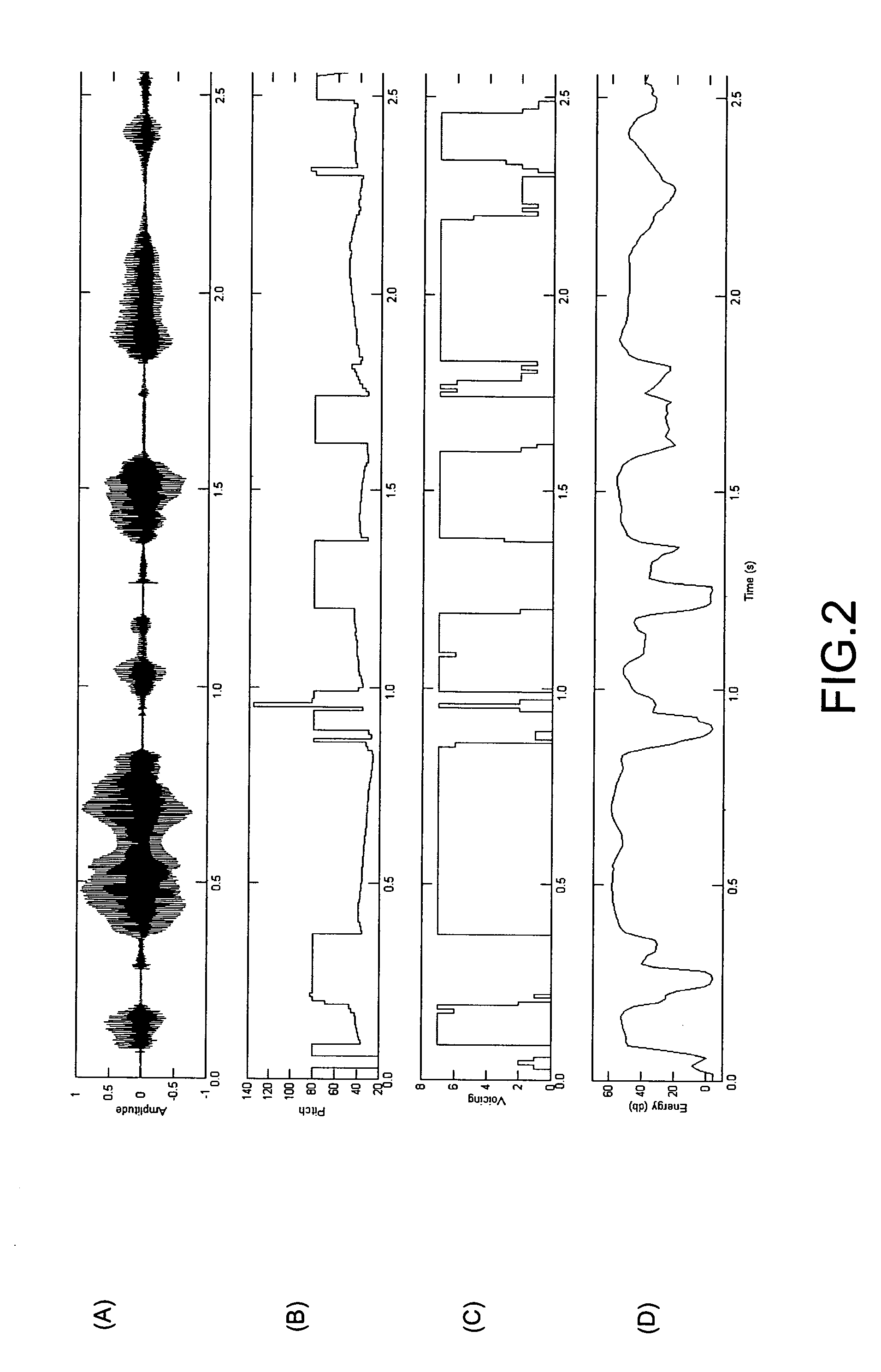
A method and device for use in conjunction with an encoder for encoding an audio signal into a plurality of parameters. Based on the behavior of the parameters, such as pitch, voicing, energy and spectral amplitude information of the audio signal, the audio signal can be segmented, so that the parameter update rate can be optimized. The parameters of the segmented audio signal are recorded in a storage medium or transmitted to a decoder so as to allow the decoder to reconstruct the audio signal based on the parameters indicative of the segment audio signals. For example, based on the pitch characteristic, the pitch contour can be approximated by a plurality of contour segments. An adaptive downsampling method is used to update the parameters based on the contour segments so as to reduce the update rate. At the decoder, the parameters are updated at the original rate.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Capacity controlled numerical frequency modulation circuit
InactiveCN101197531AIncrease the areaIncrease the number of digitsFrequency selective two-port networksPower conversion systemsCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a capacity control digital frequency adjusting circuit which belongs to the frequency adjusting technology in the electronic technology field. The invention comprises a capacitance charge-discharge circuit and a variable capacitance circuit. In the variable capacitance circuit, the switching on-off of the switch tube is controlled by the output signal of the counter and thus the total capacitance value of the charge-discharge capacitance; therefore, the dither output of frequency can be achieved, the frequency spectrum of the former higher harmonic is extended to a new frequency range which lowers the frequency spectrum amplitude and thus the electromagnetic interference of the switch power supply is reduced. Compared with flow control digital frequency adjusting circuit, the invention can achieve the dither function of frequency much better and lower the peak value of the switch frequency higher harmonic frequency spectrum and thus inhibit electromagnetic interference, besides, the chip area is reduced greatly, the production costs are reduced efficiently and thus the invention can be applied widely in the switch power supply chip field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Resistance, inductance and capacitance measurement method based on damping oscillatory wave in oscillation circuit
ActiveCN105277790ANo need to change hardware configurationSimple structureResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a resistance, inductance and capacitance measurement method based on damping oscillatory wave in an oscillation circuit. According to the method, an improved discrete Fourier algorithm is used to realize high-precision measurement of resistance, inductance and capacitance parameters; window function processing is carried out on a detection voltage signal; the influence of a truncation effect in standard discrete Fourier transformation can be effectively suppressed; the accuracy of Fourier transformation is improved; the measurement accuracy of resistance, inductance and capacitance parameters is improved; on the basis that window function processing is carried out on the detection voltage signal, a single spectral line interpolation algorithm is further used; frequency calculation errors caused by non-integer number cycle sampling are corrected; spectral amplitude errors caused by the truncation effect are corrected; and the accuracy of the measurement method is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Noise suppressor
InactiveUS7302065B2Reduce deteriorationPreferable feelingSpeech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionFrequency spectrumSpectral subtraction
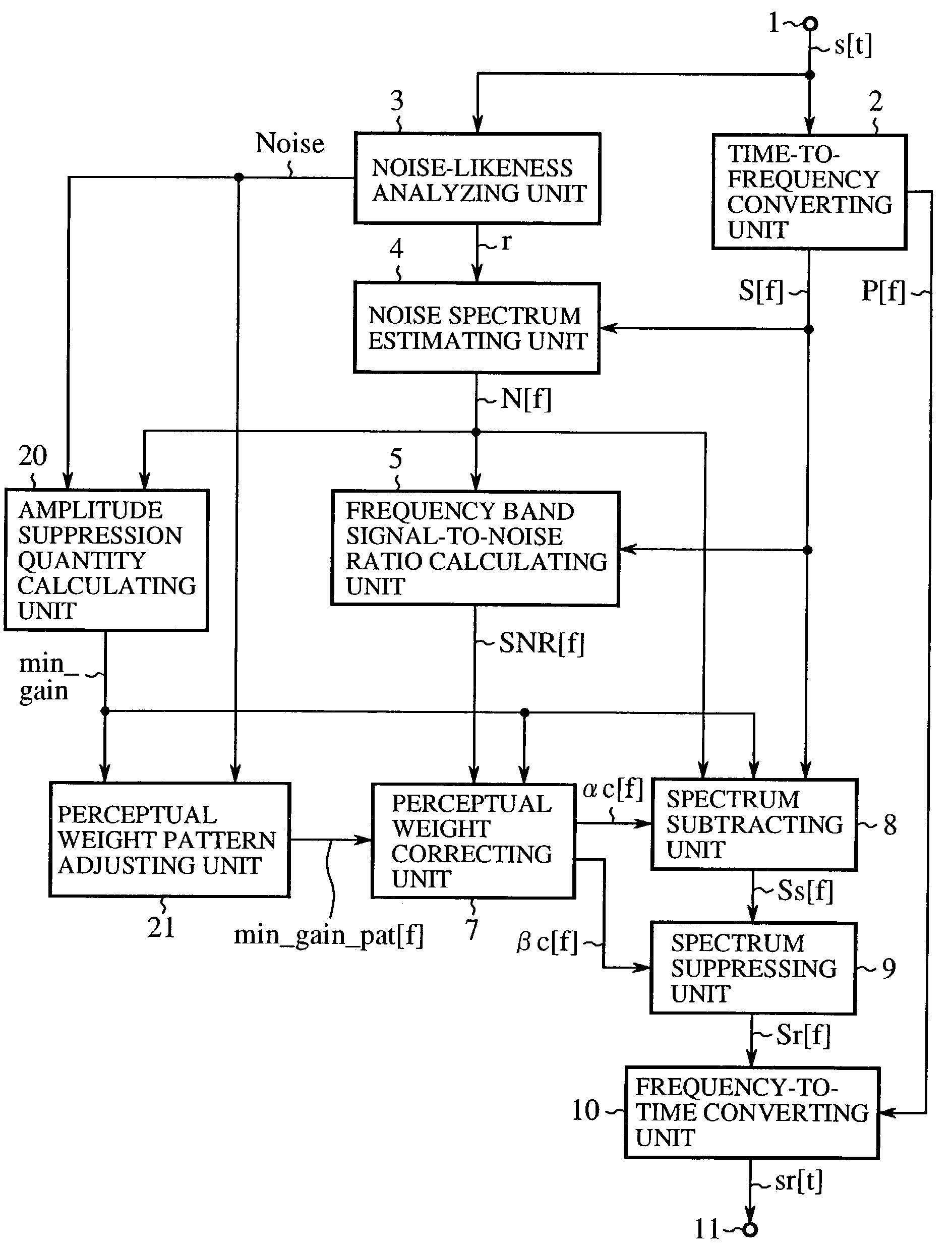
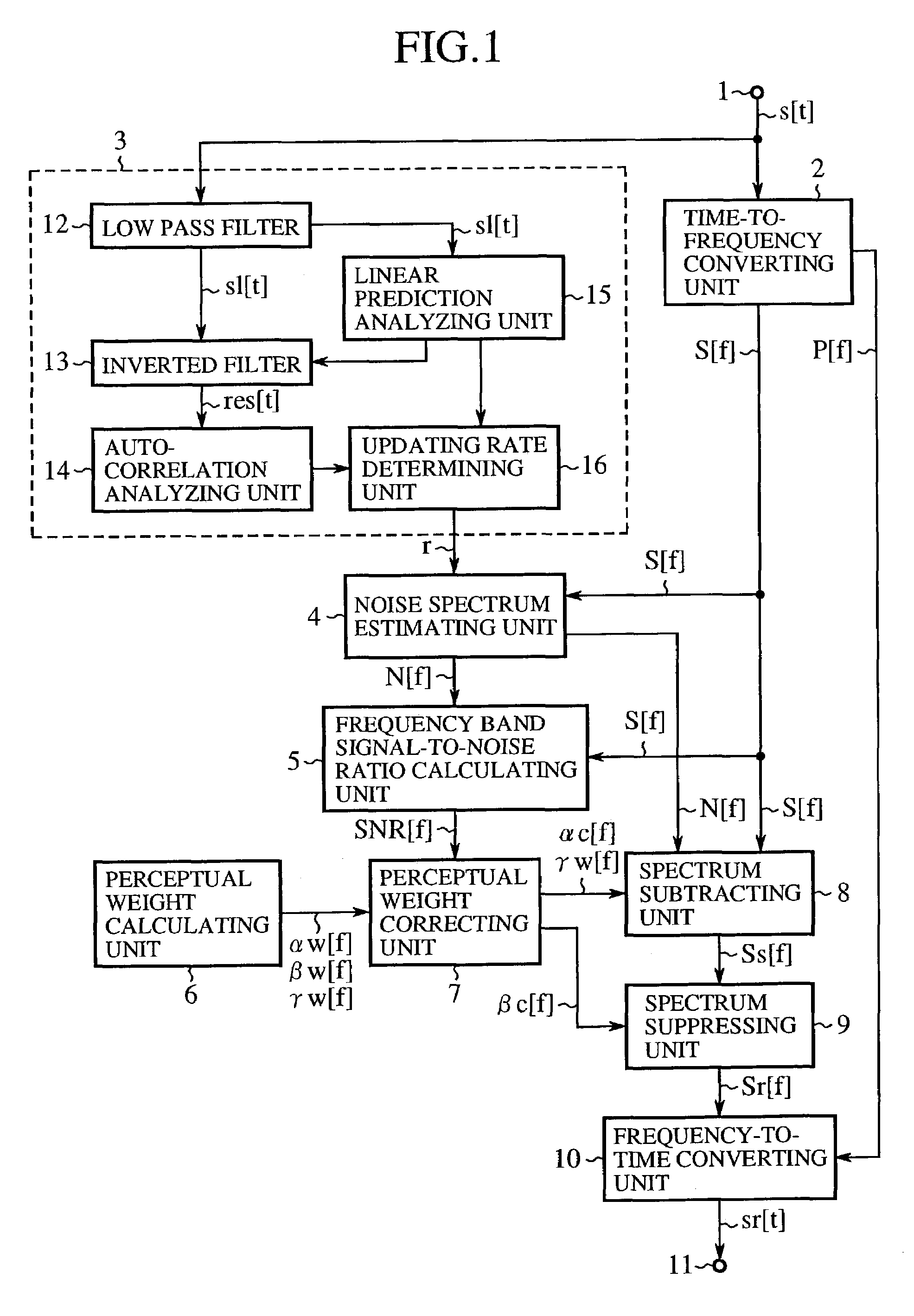
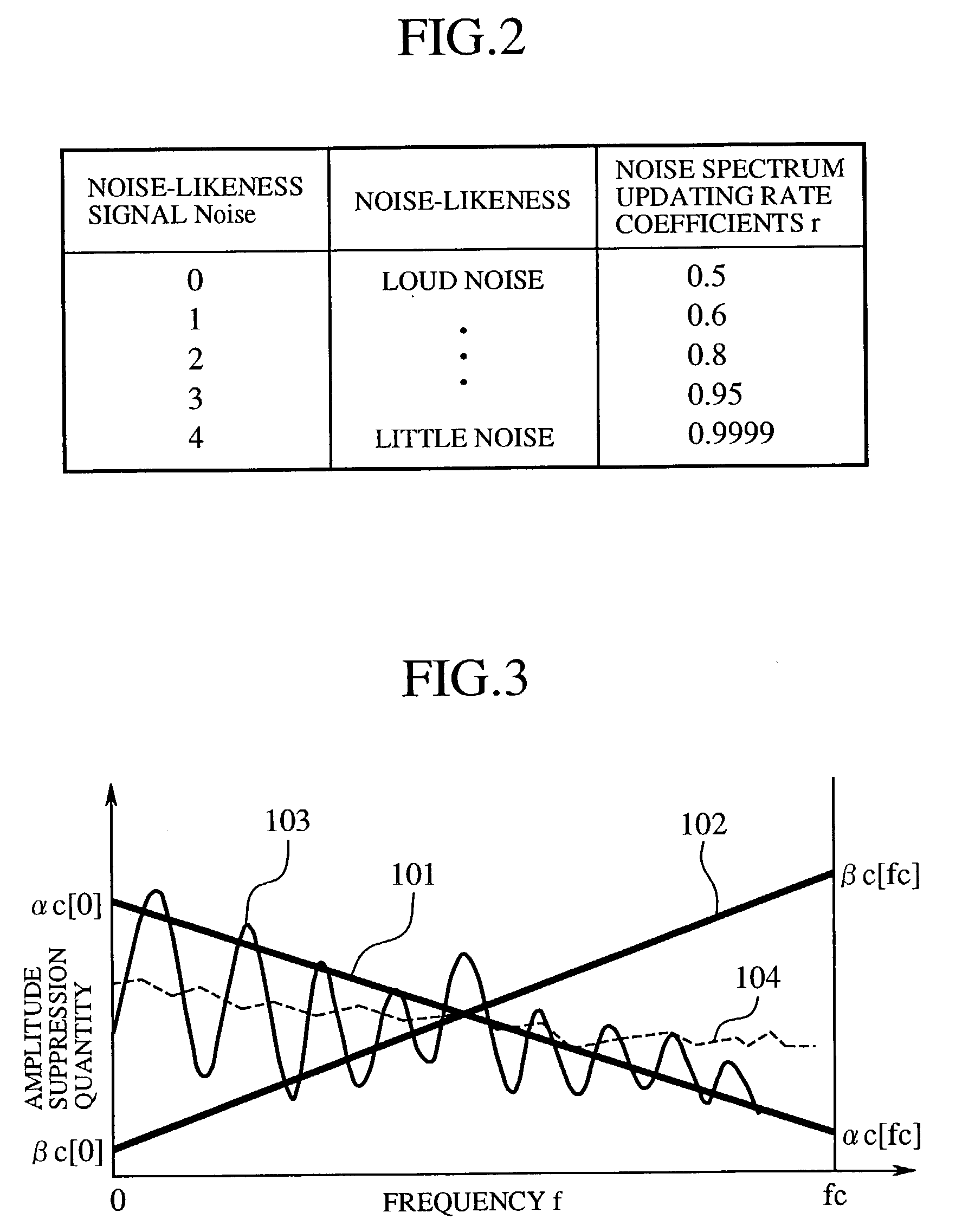
An amplitude suppression quantity denoting a noise suppression level of a current frame is calculated in an amplitude suppression quantity calculating unit (20), a perceptual weight distributing pattern of both a spectral subtraction quantity and a spectral amplitude suppression quantity is determined in a perceptual weight pattern adjusting unit (21), the spectral subtraction quantity and the spectral amplitude suppression quantity given by the perceptual weight distributing pattern are corrected according to a frequency band SN ratio in a perceptual weight correcting unit (7), a noise subtracted spectrum is calculated from an amplitude spectrum, a noise spectrum and a corrected spectral subtraction quantity in a spectrum subtracting unit (8), and a noise suppressed spectrum is calculated from the noise subtracted spectrum and a corrected spectral amplitude suppression quantity in a spectrum suppressing unit (9).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
System and method for agile remote generation of a broadband tunable short-pulse emission
ActiveUS20120243564A1Agile remote generationLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierFilamentation
A method comprising using a pulse shaper in the spectral domain to generate multiple-color pulses directly at the output of the laser amplifier. The delay can thus be controlled directly in the spectral domain and there is no need for an optical delay line. The method allows reducing the number of optical components and insures insensitivity to alignment, vibrations and turbulence on long distance propagation and filamentation, particularly in air. The method allows programmable and tunable interaction, since the pulse shaper is able to control the laser spectral amplitude and phase.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
Special up channel frequency deviation estimating method in code division multiplexing address system
InactiveCN1741395AReduce computationImprove performanceBaseband system detailsCode division multiplexFrequency spectrumLow-pass filter
A method for estimating frequency deviation of uplink special channel in CDMA system includes carrying out large dimension frequency deviation estimation then carrying out estimation for small dimension frequency deviation after calibration, using signal in special channel to remove off high frequency interference through low - pass filter and carrying out Fourier transform for partial data, carrying out mode sampling calculation on spectrum value for obtaining spectrum amplitude value being low -pass filtered, searching out frequency corresponding to data peak value.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for measuring harmonic waves of power system rapidly
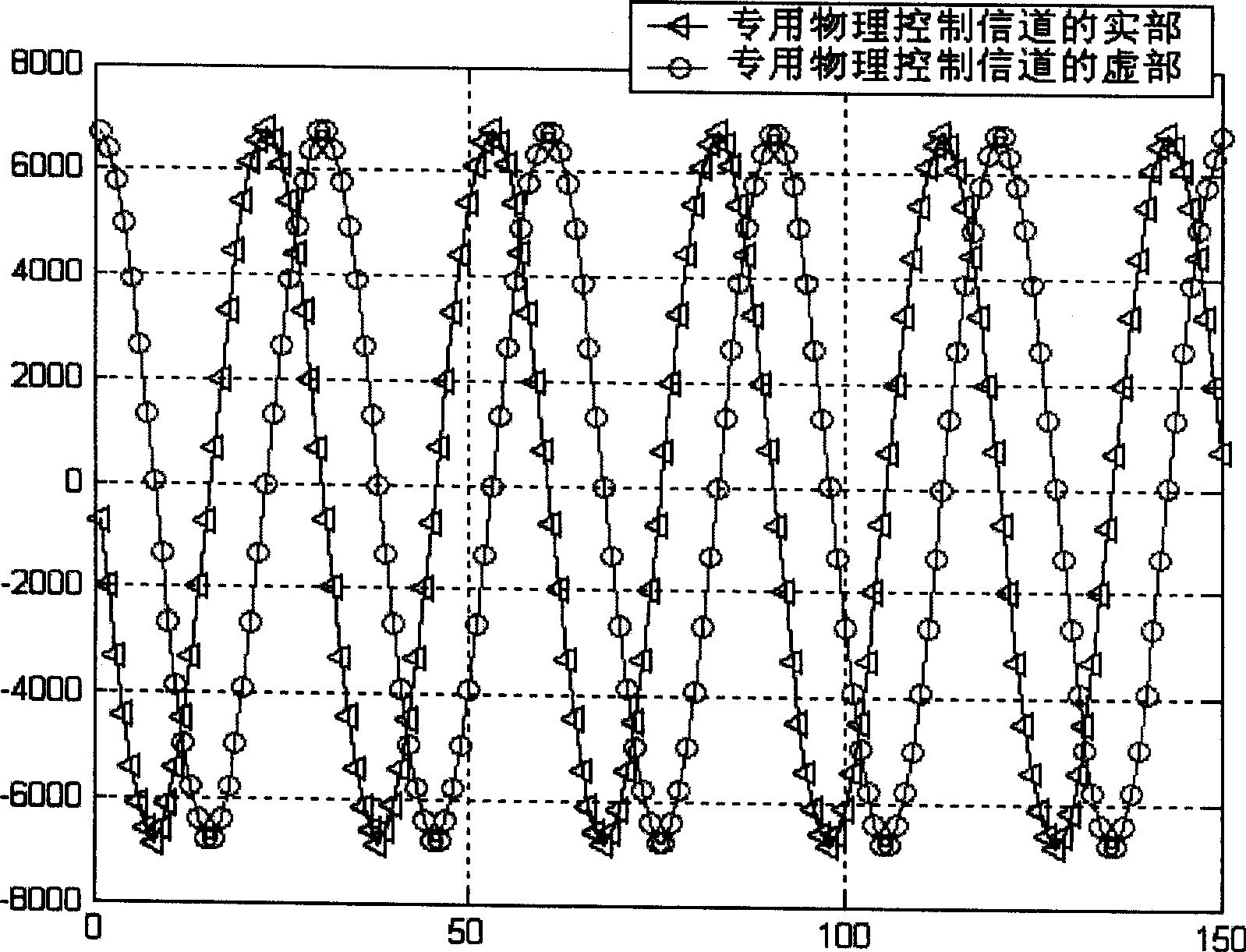
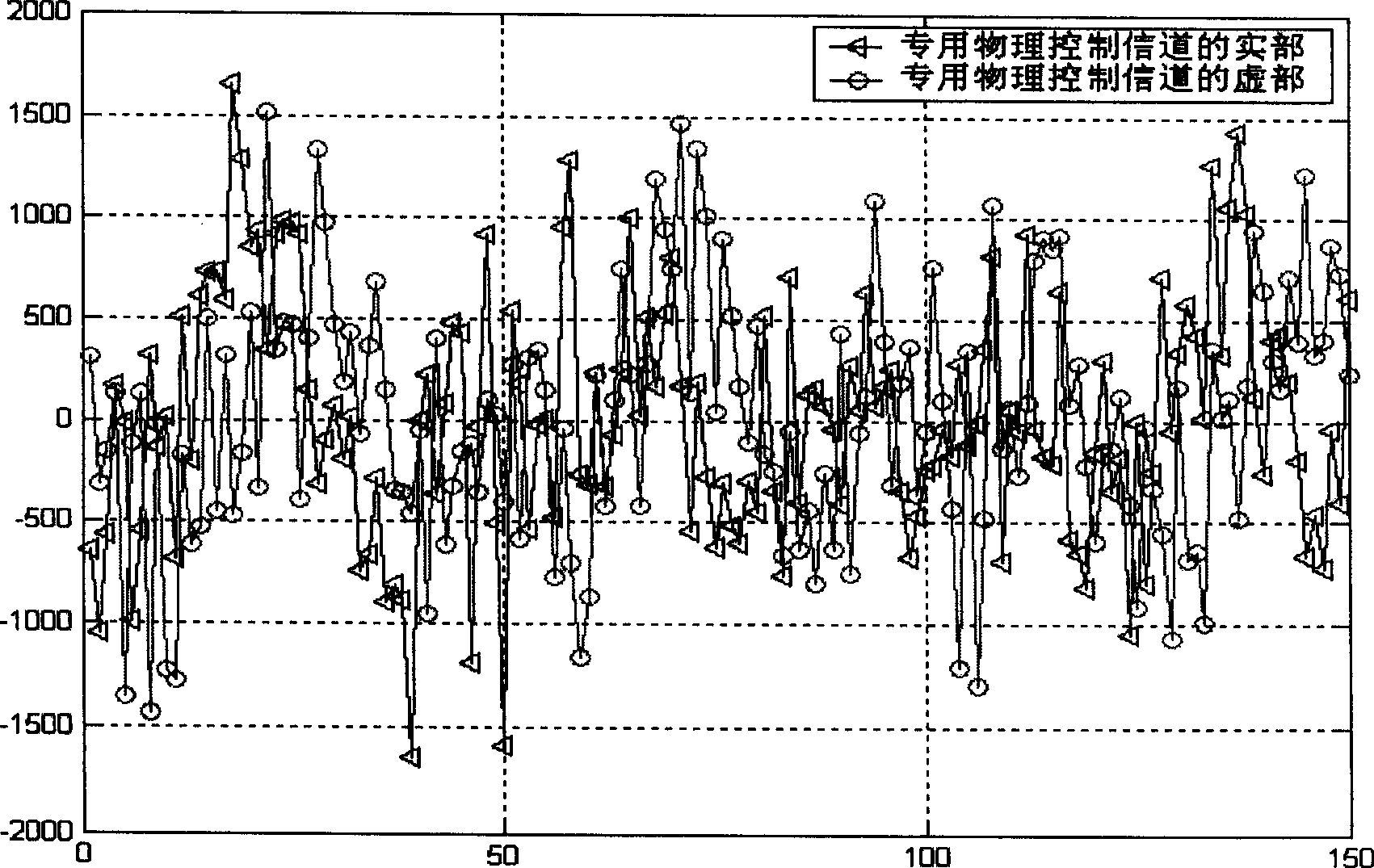
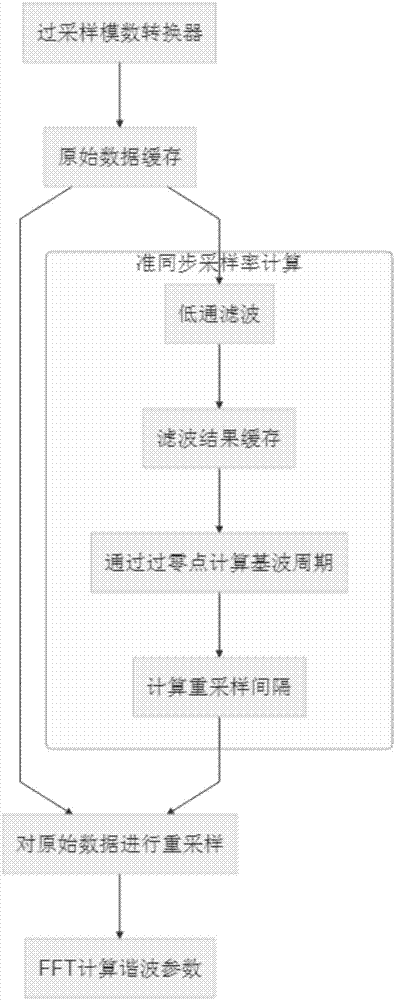
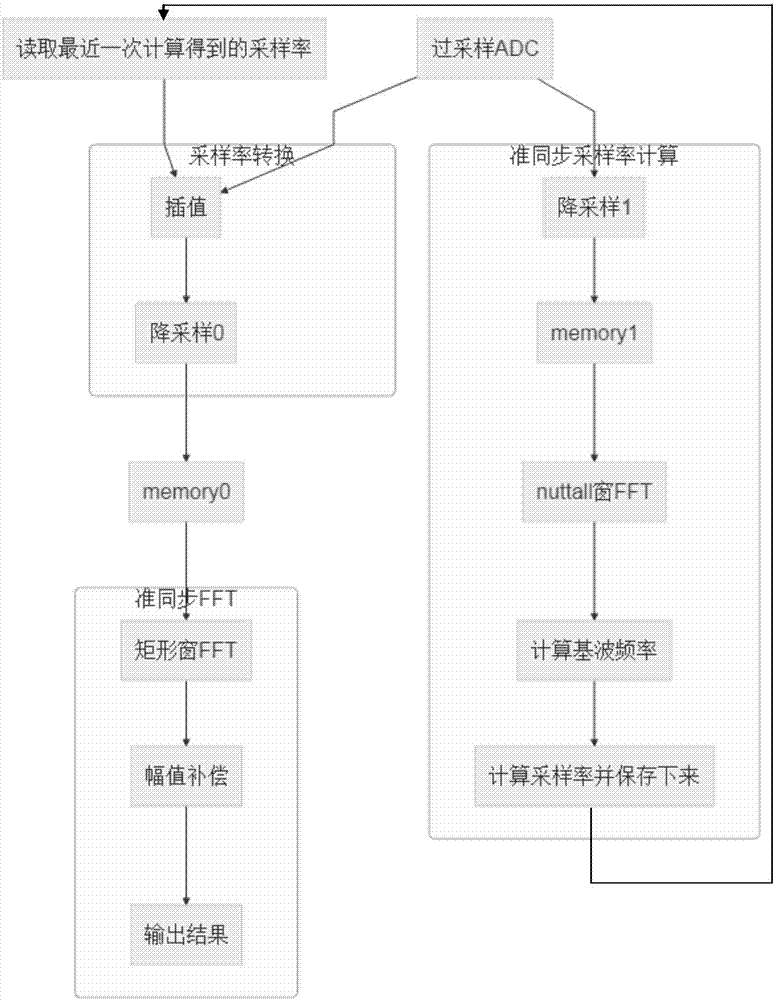
ActiveCN107085144AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove accuracyFrequency analysisComputation complexityFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method for measuring harmonic waves of a power system rapidly. The method comprises the following steps that an oversampling ADC oversamples signals to obtain original sampling data; the original sampling data output by the oversampling ADC is down-sampled and stored; windowing FFT is carried out on the down-sampled data; a fundamental wave frequency is calculated; a quasi-synchronization sampling rate is calculated and stored; the calculated quasi-synchronization sampling rate is used to carry out interpolation on the original sampling data output by the oversampling ADC; the data after interpolation is down-sampled and stored; rectangular window FFT is used to process the data; and FFT spectral amplitudes after rectangular window FFT are multiplied by a compensation coefficient, amplitude compensation is carried out, and a result is output. The method can be used to improve the signal to noise ratio of in-band signals via an oversampling technology, on the premises that the frequency and resolution are ensured, the computing complexity is reduced greatly, the accuracy of fundamental wave frequency calculation is improved, and less buffer memory is occupied by down-sampling.
Owner:珠海泰为电子有限公司
Method for suppressing noise in an acoustic signal for a multi-microphone audio device operating in a noisy environment
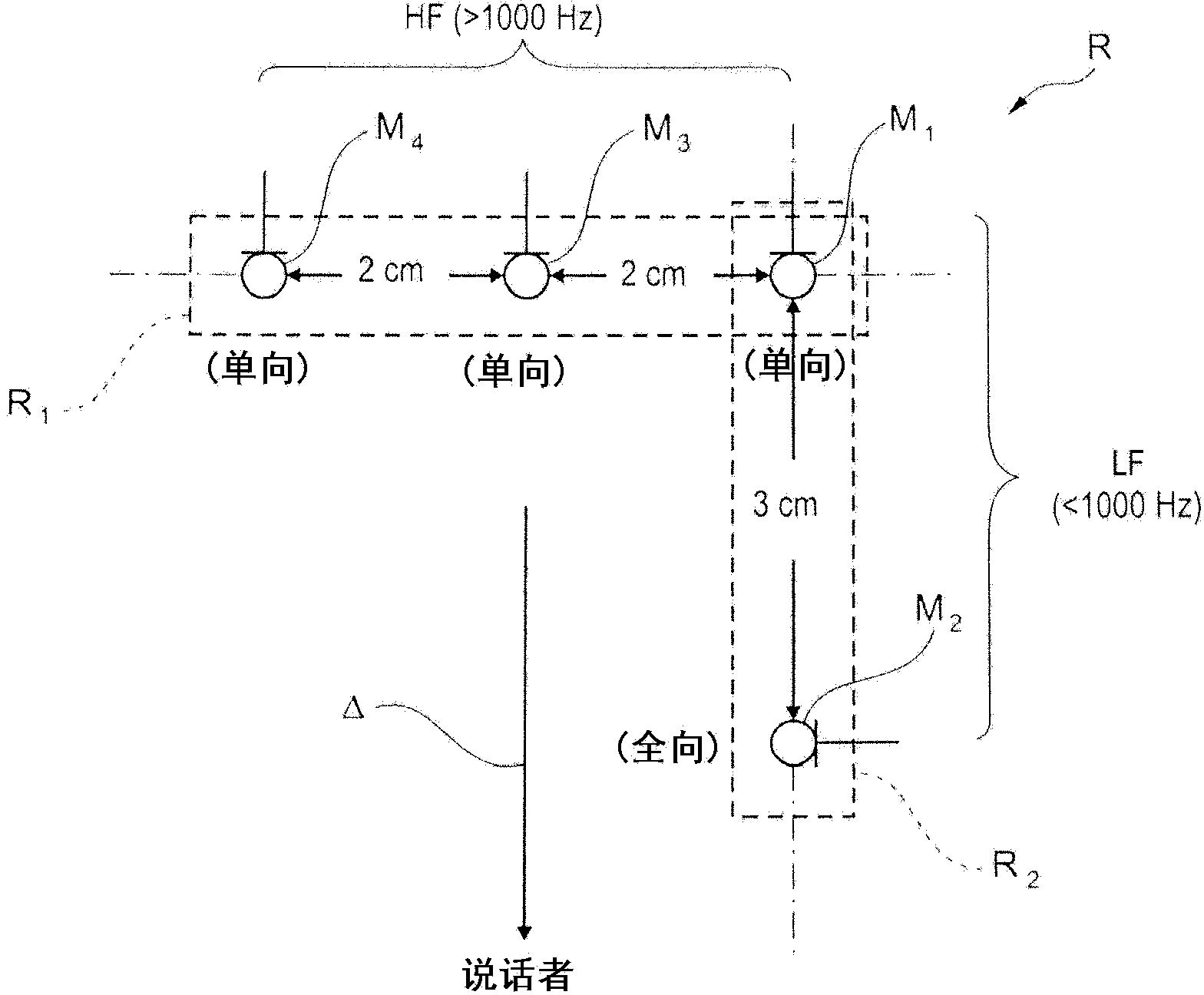
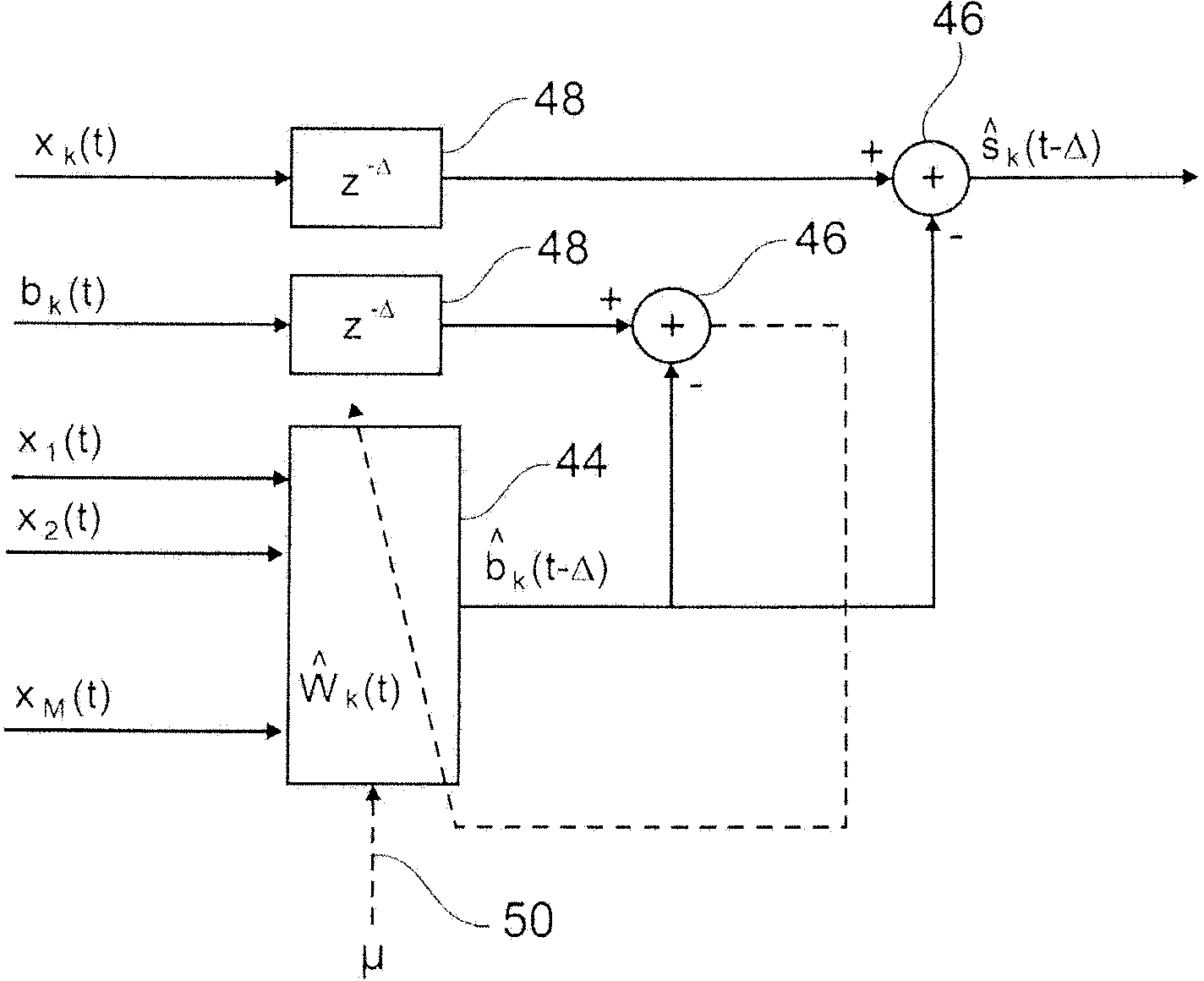
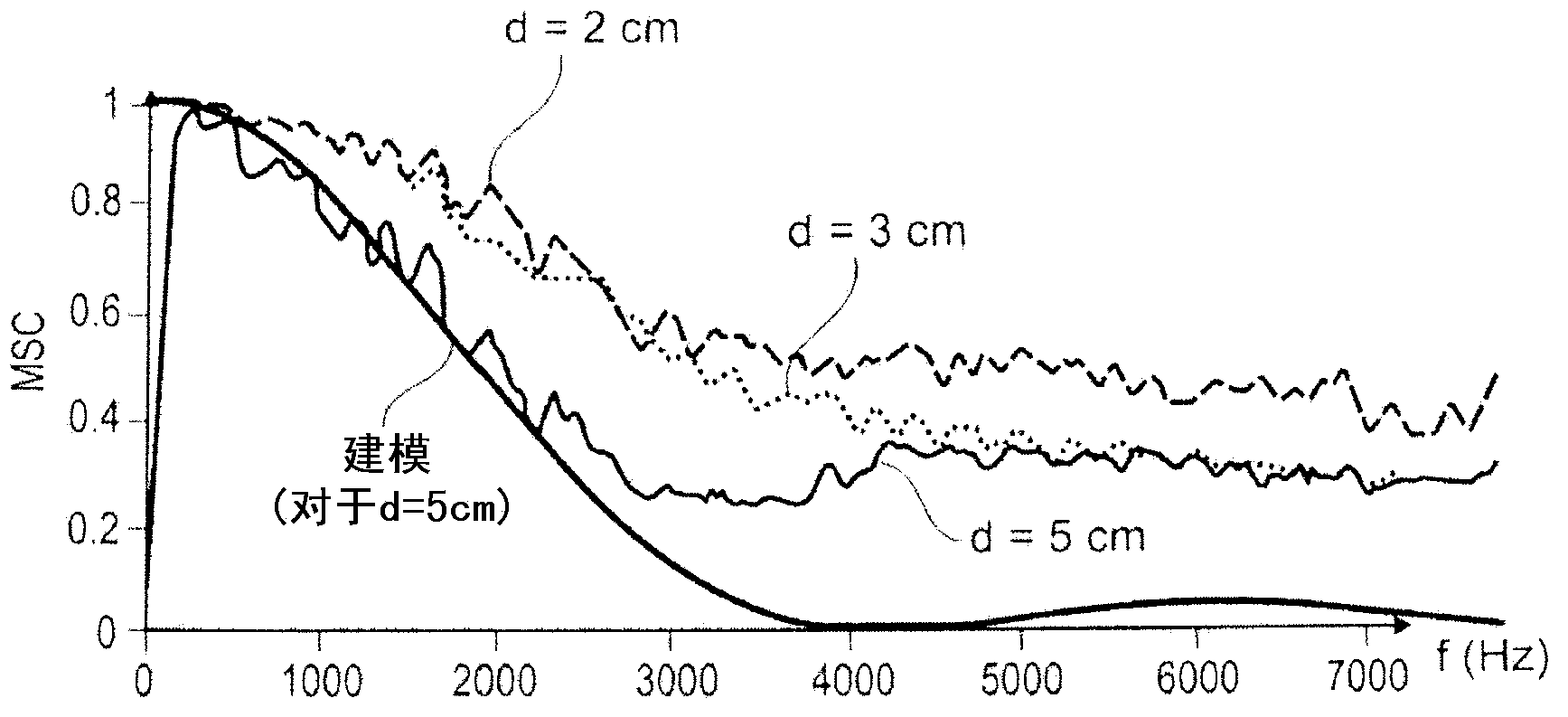
Provided is a method for suppressing noise in an acoustic signal for a multi-microphone audio device operating in a noisy environment. The method comprises steps of: a) partitioning (10, 16) the spectrum of the noisy signal into a HF part and a LF part; b) operating denoising processes in a differentiated manner for each of the two parts of the spectrum with, for the HF part, a denoising by prediction of the useful signal from one sensor to the other between sensors of a first sub-array (R1), by means of a first adaptive algorithm estimator (14), and, for the LF part, a denoising by prediction of the noise from one sensor to the other between sensors of a second sub-array (R2), by means of a second adaptive algorithm estimator (18); c) reconstructing the spectrum by combining together (22) the signals delivered after denoising of the two parts of the spectrum, respectively; and d) selectively reducing the noise (24) by an Optimized Modified Log-Spectral Amplitude gain, OM-LSA, process.
Owner:PARROT AUTOMOTIVE
Noise filtering utilizing non-Gaussian signal statistics
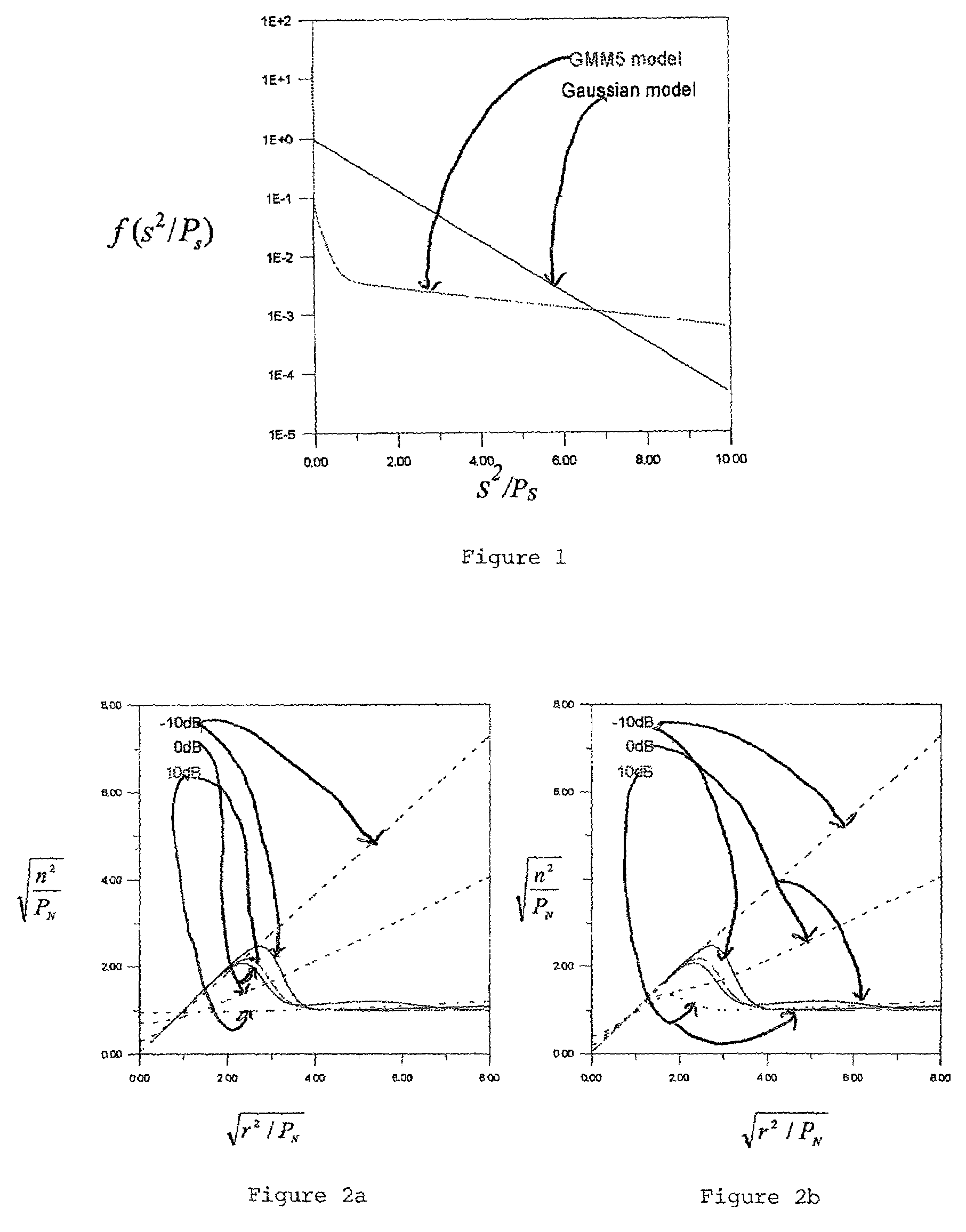
The present invention is directed to a method and system for capturing an information signal from within a noisy background utilizing a non-Gaussian model for the a priori statistics of the information signal conditioned on other a priori quantities. A specific implementation utilizing a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) is described. The GMM implementation includes Wiener filtering as a special case, and includes methods for adaptively tracking multiple properties of the input noise and the information signal, including noise PSD, information signal PSD, information signal spectral amplitude, and probability of information signal presence versus time and frequency.
Owner:DEFENSE GROUP INC
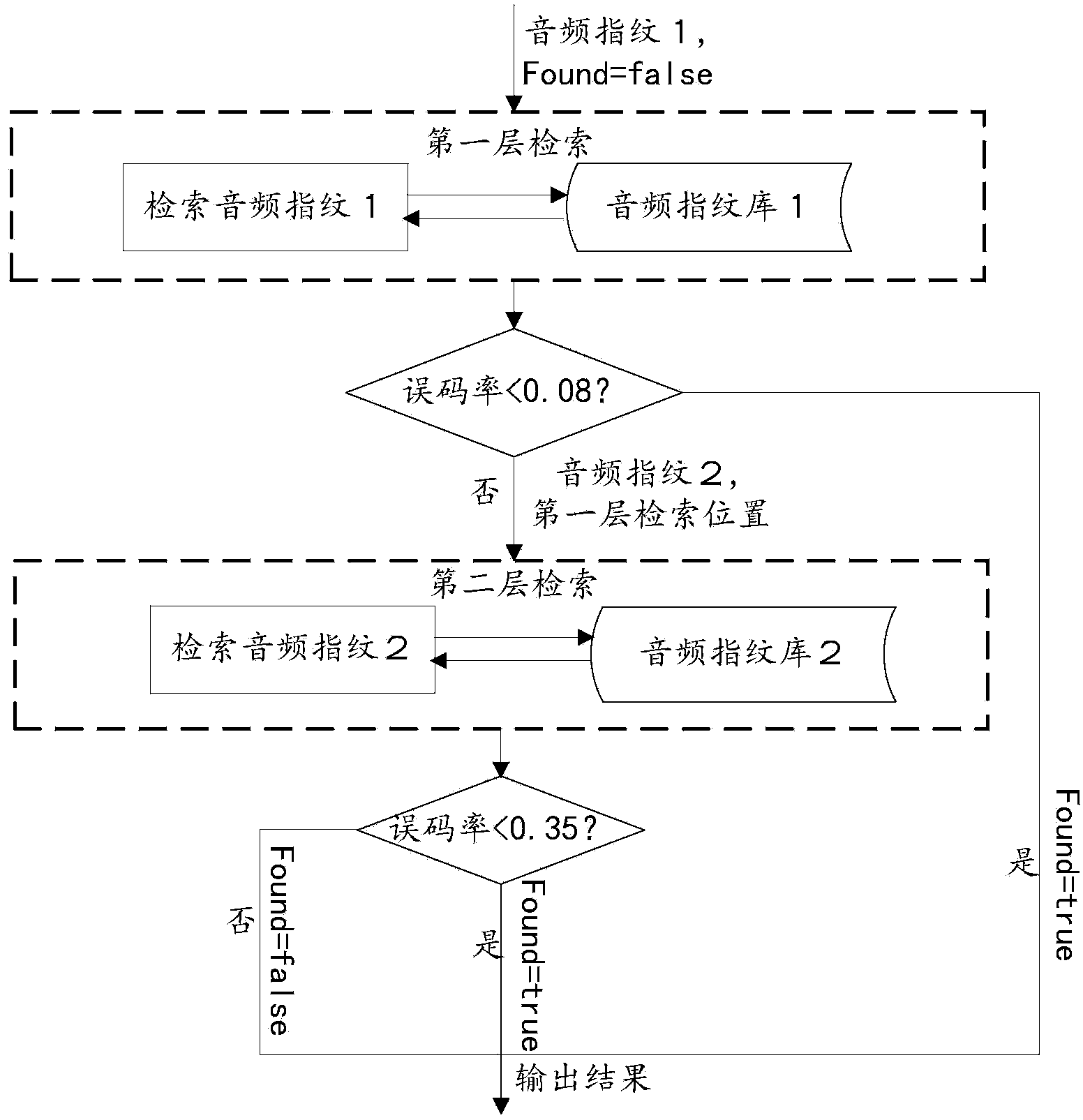
Two-layer advertisement audio retrieval method based on audio fingerprints
InactiveCN104317967AImprove noise immunityExact matchSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumSpectral amplitude
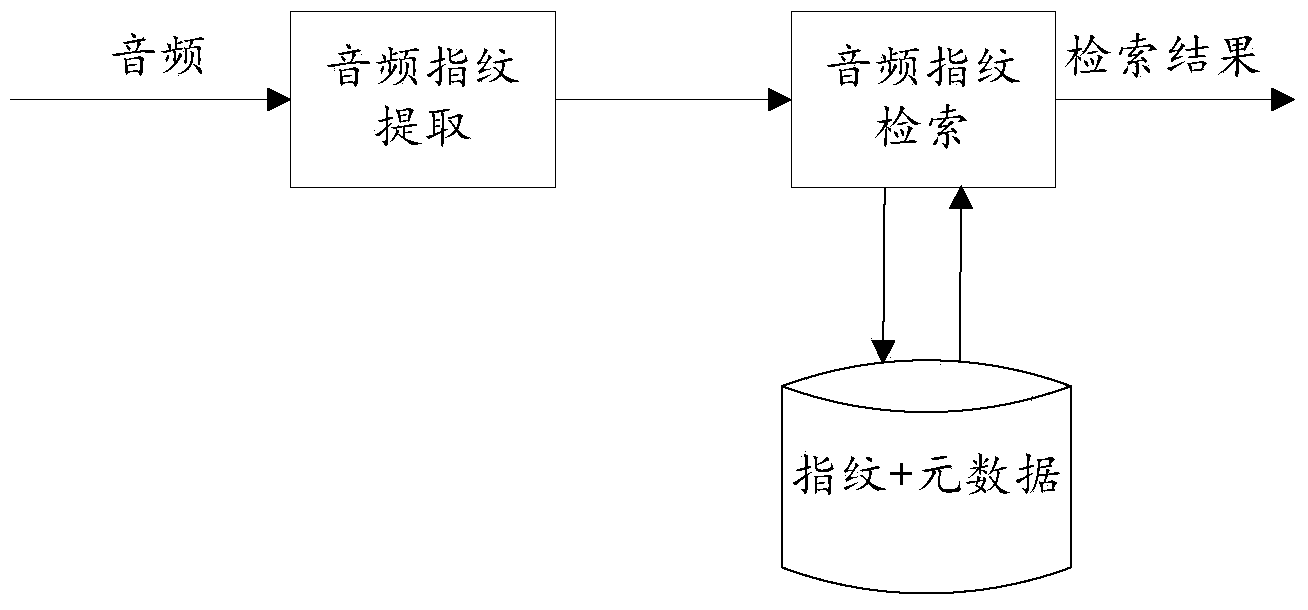
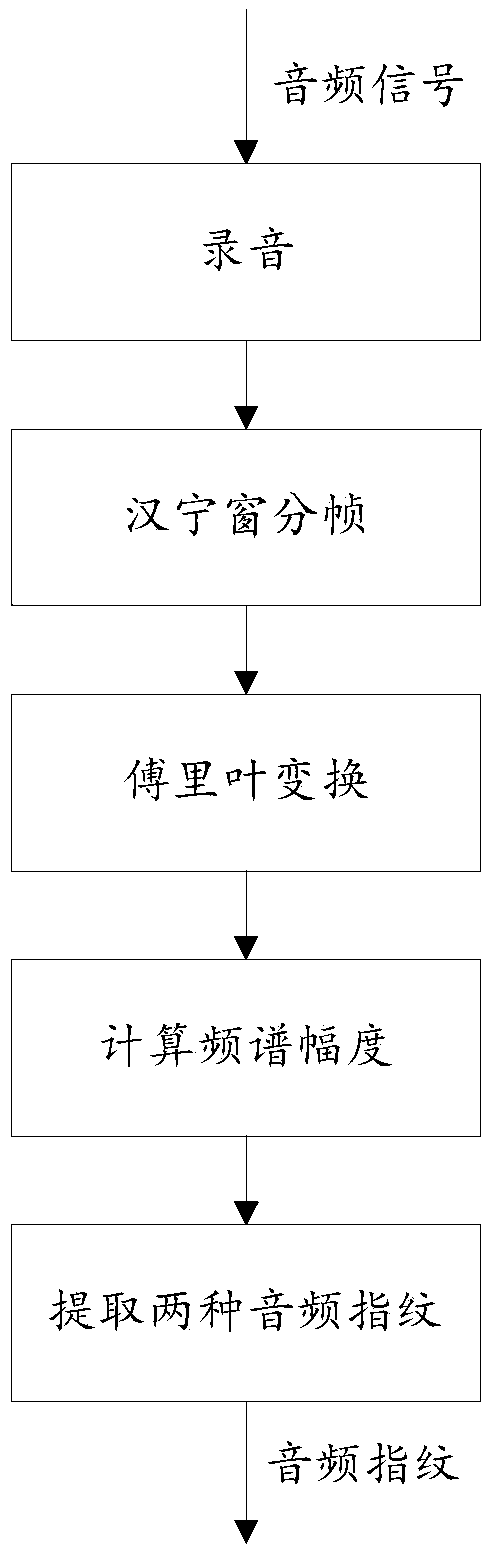
The invention relates to a two-layer advertisement audio retrieval method based on audio fingerprints. The method includes the steps: firstly, extracting two different-dimensional audio fingerprints based on spectral amplitude features of audios; secondly, performing two-layer retrieval based on the two audio fingerprints. Advertisements are accurately matched based on audio fingerprint technology. On one hand, the extracted audio fingerprints have excellent anti-noise property, and advertisement matching accuracy is high. On the other hand, the audio fingerprints are much smaller than original audio data, and retrieval can be rapidly performed by the two-layer retrieval method. Therefore, the method has wide practical values and application prospects in the field of commercial application and scientific research.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Optical analyzer and method for measuring spectral amplitude and phase of input optical signals using heterodyne architecture
An optical analyzer and method for measuring optical properties of optical signals utilizes a heterodyne architecture to measure spectral amplitude and phase of a periodically modulated input optical signal, such as an optical signal from a periodically modulated distributed feedback (DFB) laser. The spectral amplitude and phase measurements are derived from a heterodyne signal, which is produced by combining and mixing the input optical signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal. The optical spectrum that is reconstructed from the heterodyne signal includes “inner” spectral peaks that contain phase information of the input optical signal. The inner spectral peaks may be produced by an optical or electrical mixing technique. The spectral phase of the input optical signal is recovered from the inner spectral peaks of the reconstructed optical spectrum.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Pulse noise suppression method for power line communication system
ActiveCN106936743AReduce complexityAccurate estimatePower distribution line transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumDiscrete-time signal
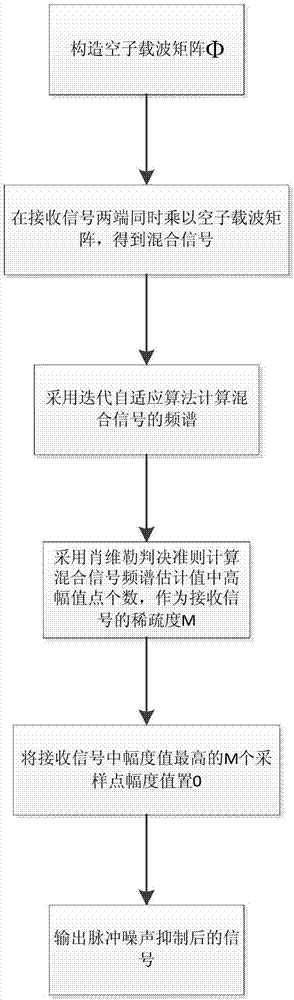
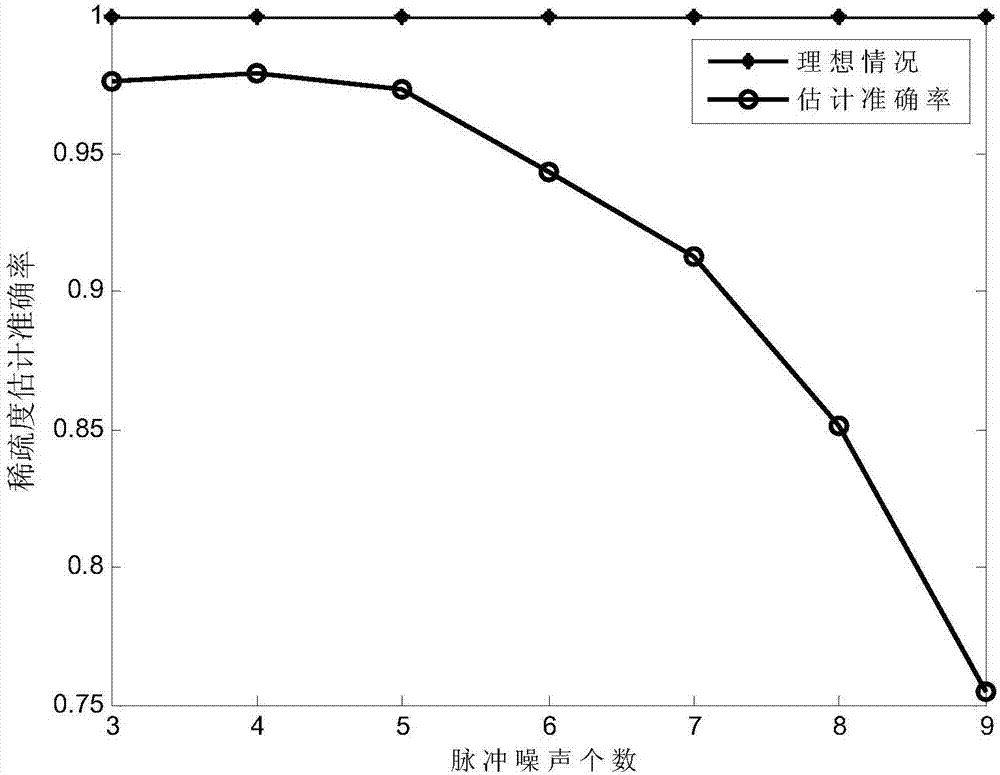
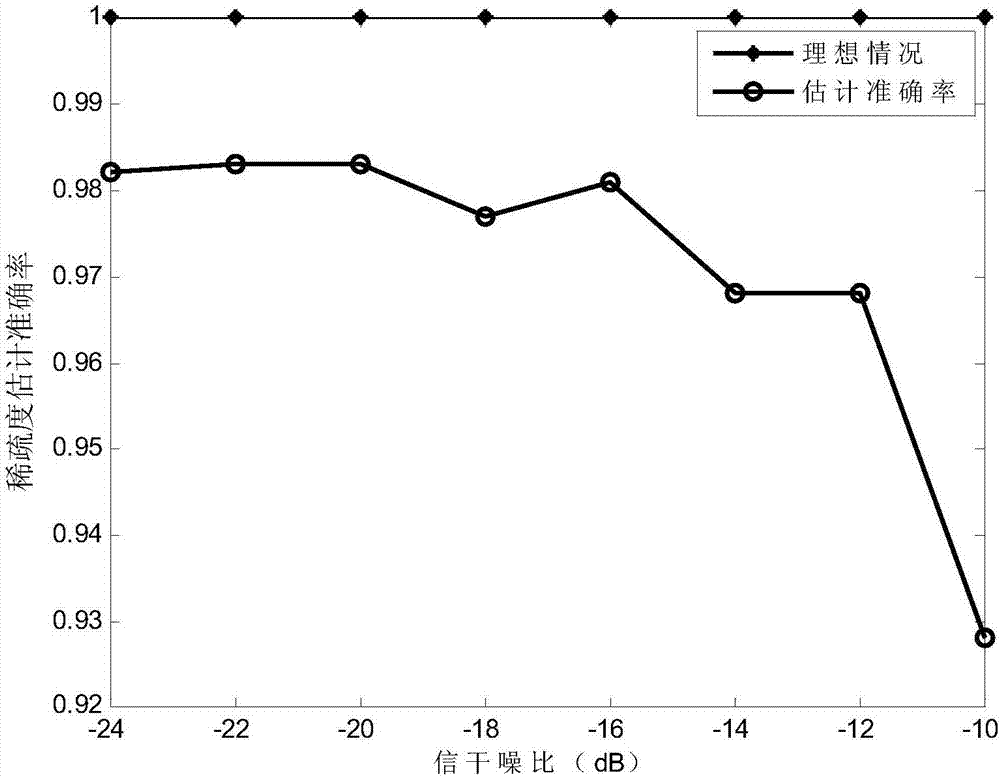
The invention discloses a pulse noise suppression method for a power line communication system. The method comprises the following steps: transmitting a discrete time domain signal added with a cyclic prefix by a transmission end; acquiring a mixed signal only including asynchronous pulse noise and colored background noise by a receiving end according to a discrete time domain signal from which the cyclic prefix is removed and which carries asynchronous pulse noise interference; then, estimating a spectrum amplitude of the mixed signal by an iteratively adaptive algorithm; finding high amplitude points in the spectrum amplitude of the mixed signal through calculation of a mean value and a standard difference of the spectrum amplitude of the mixed signal and by use of a Chauvenet decision criterion; and setting a plurality of maximum amplitude values in the discrete time domain signal from which the cyclic prefix is removed and which carries the asynchronous pulse noise interference as 0 by counting the total quantity of the high amplitude points in the spectrum amplitude of the mixed signal in order to finish suppression of the asynchronous pulse noise and obtain a valid signal. The pulse noise suppression method has the advantages of high pulse noise suppression performance and relatively high robustness, and can be implemented well in the power line communication system.
Owner:安徽融兆智能有限公司
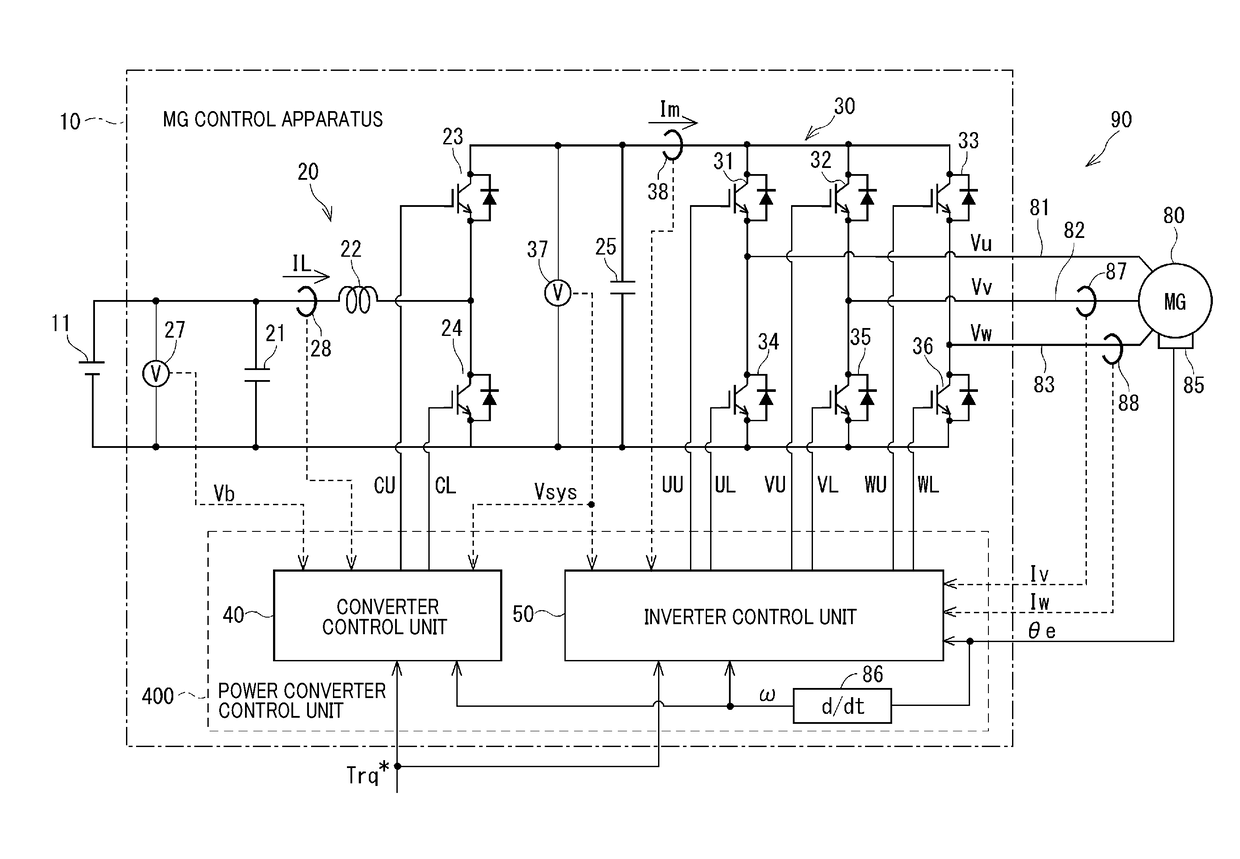
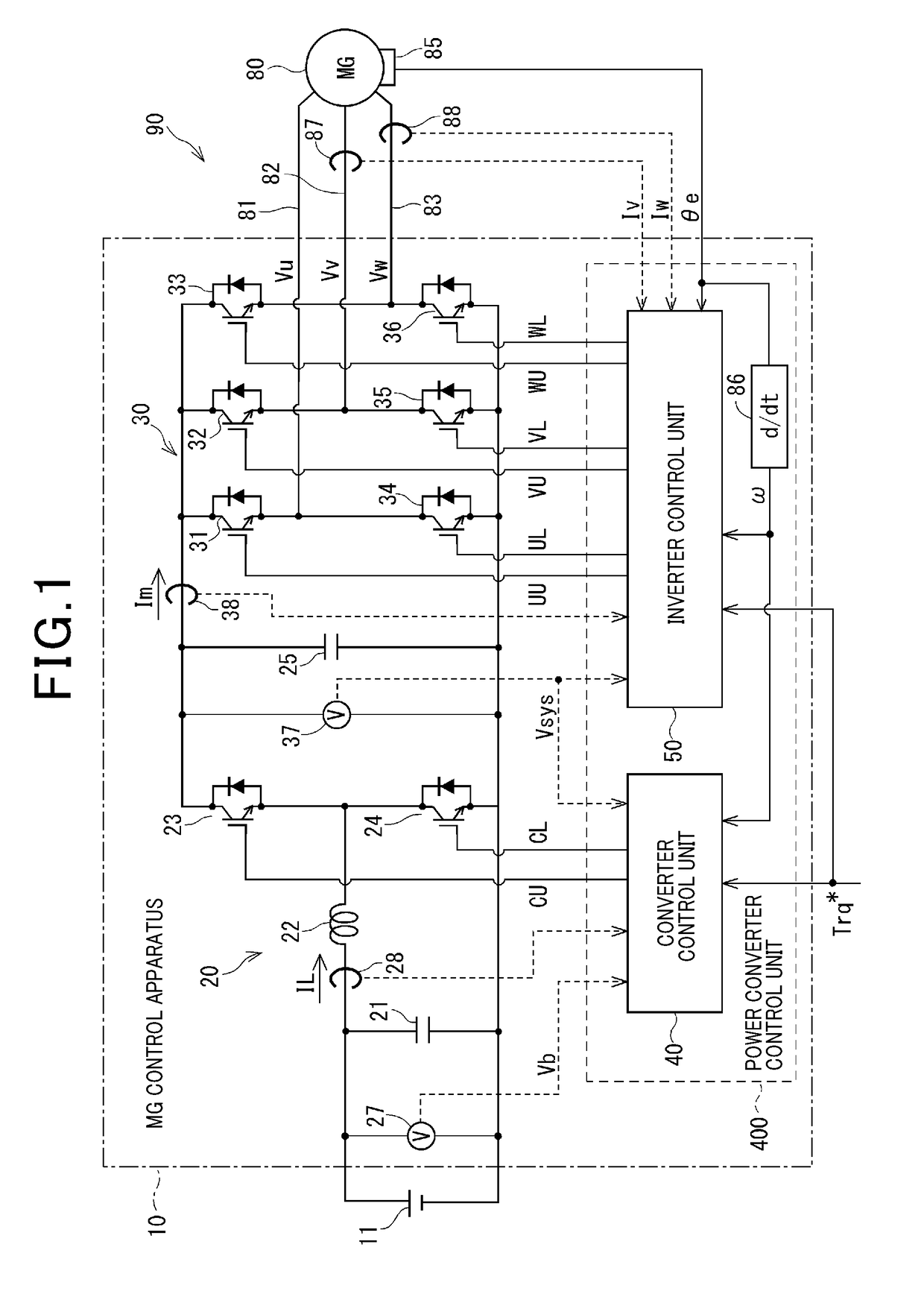
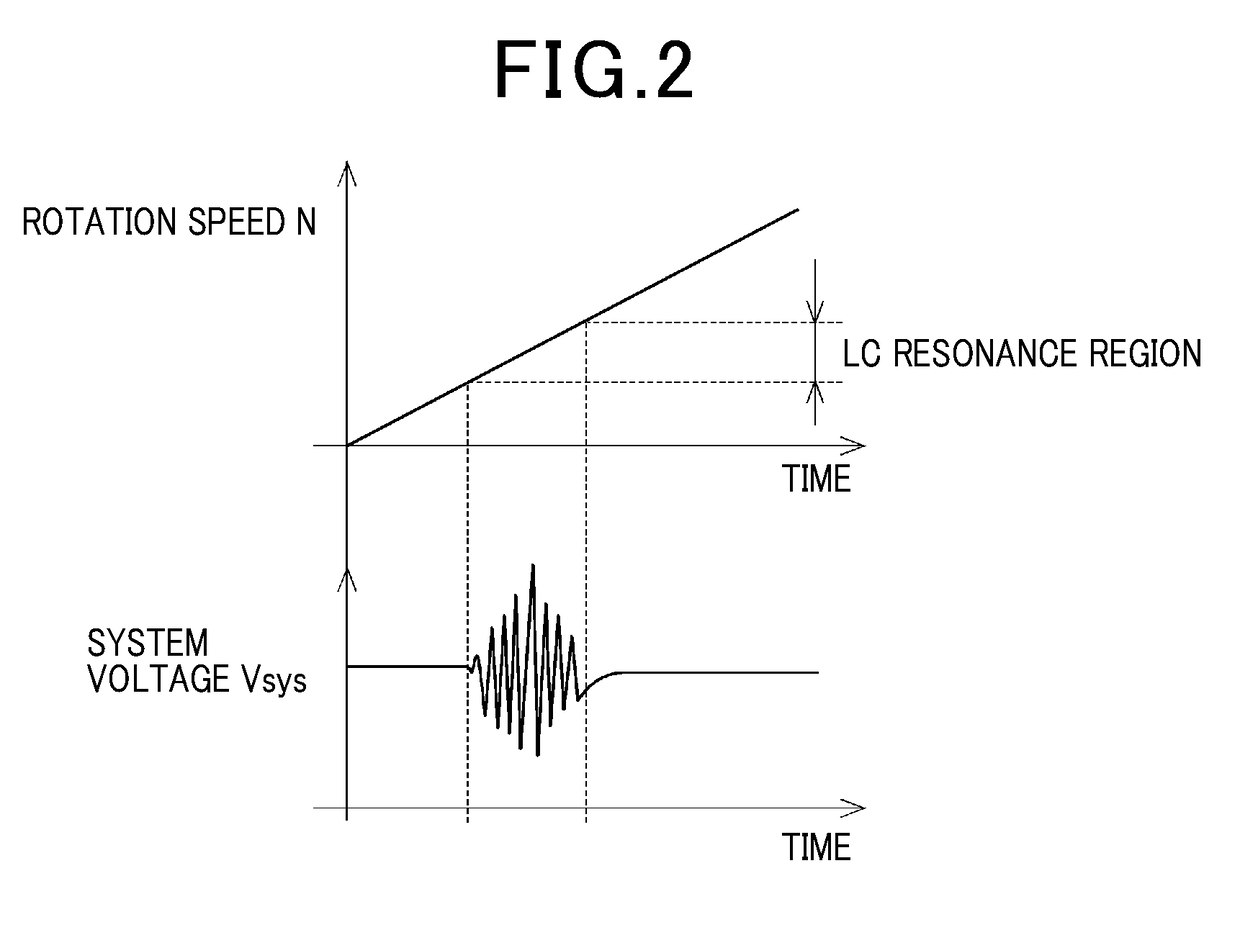
Control apparatus for ac motor
ActiveUS20170294862A1Suppresses fluctuations in output voltageIncreasing system lossElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorFrequency spectrum
In a control apparatus for an AC motor, a voltage waveform specifying unit of an inverter control unit specifies a voltage waveform for operating the inverter, based on a voltage vector calculated by a voltage command calculation unit. A spectrum amplitude extraction unit acquires values of bus current of the inverter and extracts the spectrum amplitude of the specific frequency that corresponds to the LC resonance frequency of the converter. A boost / non-boost state judgement unit of a converter control unit determines whether the state required by the converter in the next control cycle is the boost state or the non-boost state. When the spectrum amplitude of the specific frequency, correlated with the voltage waveform, is higher than the judgement threshold value and the converter is in the non-boost state, a voltage command value alteration unit changes the voltage command reference value such that the converter transitions to the boost state.
Owner:DENSO CORP
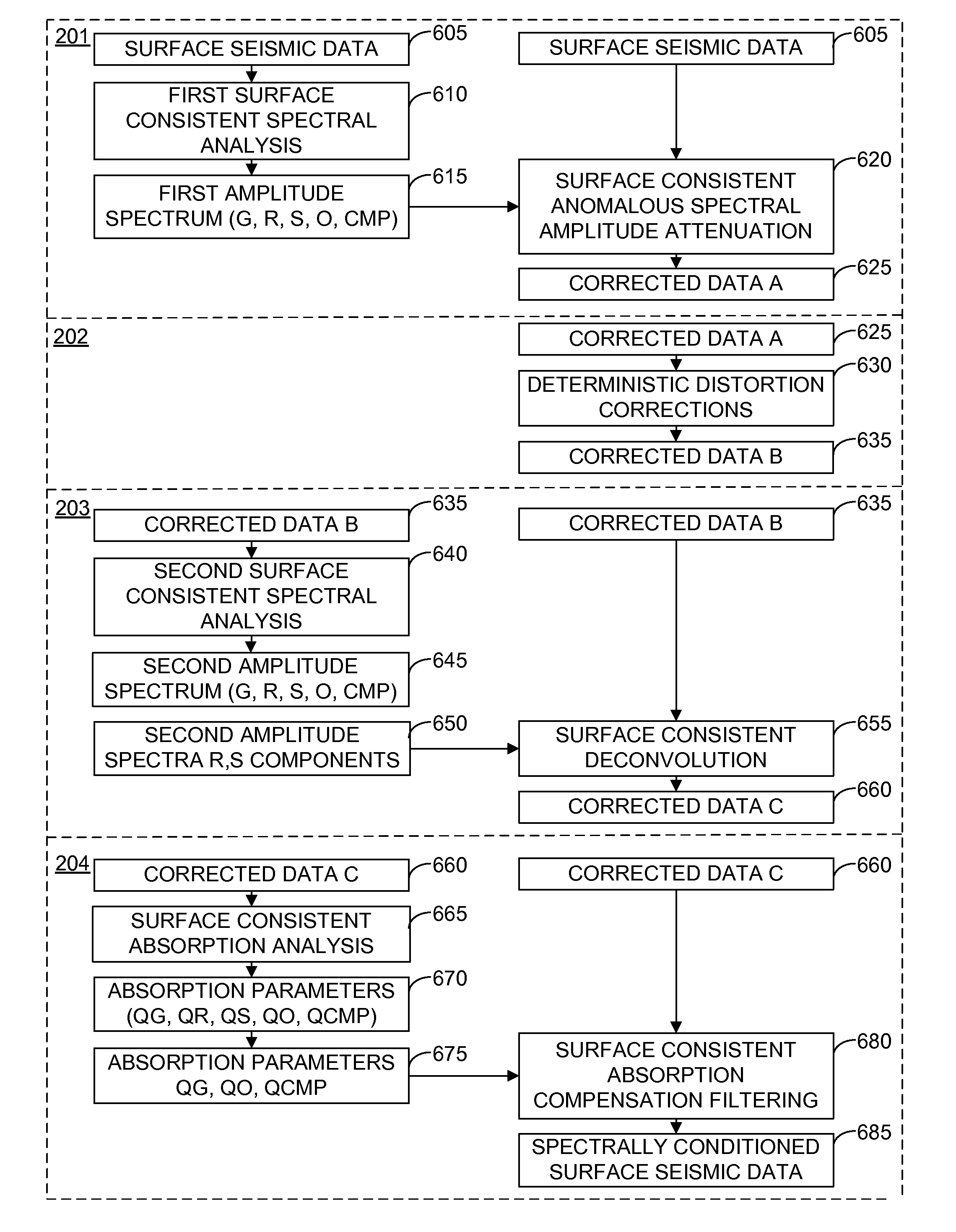
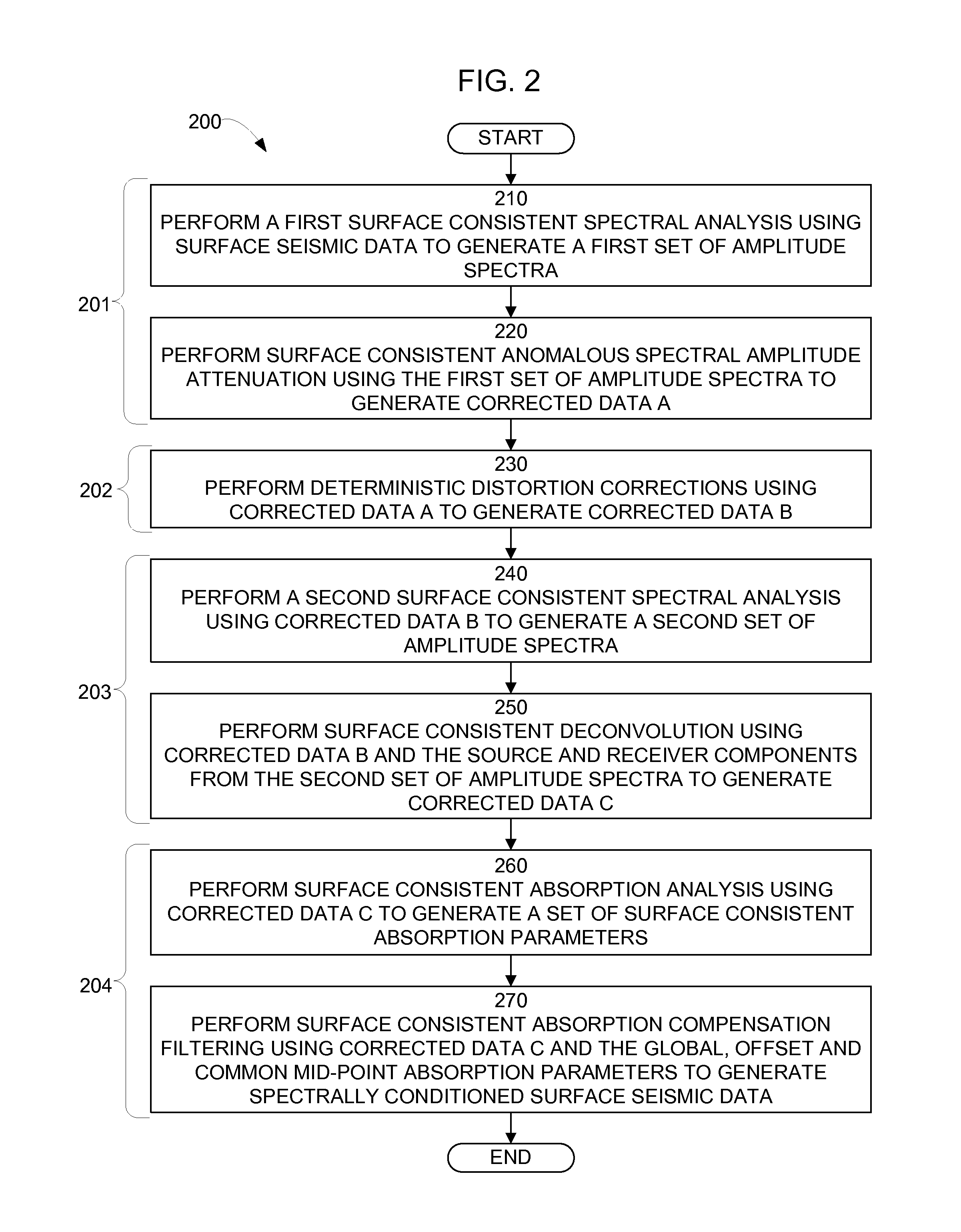
Spectral conditioning for surface seismic data
InactiveUS8139440B2Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasFrequency spectrumSpectral distortion
A method for spectrally conditioning surface seismic data. In one implementation, the method may include correcting surface seismic data for distortions due to anomalous spectral amplitudes, thereby generating a first set of corrected data; correcting the first set of corrected data for deterministic distortions, thereby generating a second set of corrected data; correcting the second set of corrected data for spectral distortions due to the seismic waves traveling through the near-surface, thereby generating a third set of corrected data; and correcting the third set of corrected data for spectral distortions due to the seismic waves traveling through deeper strata.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com