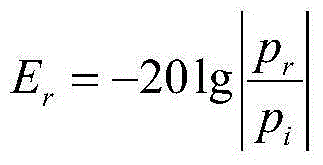Patents
Literature
227 results about "Inverse filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
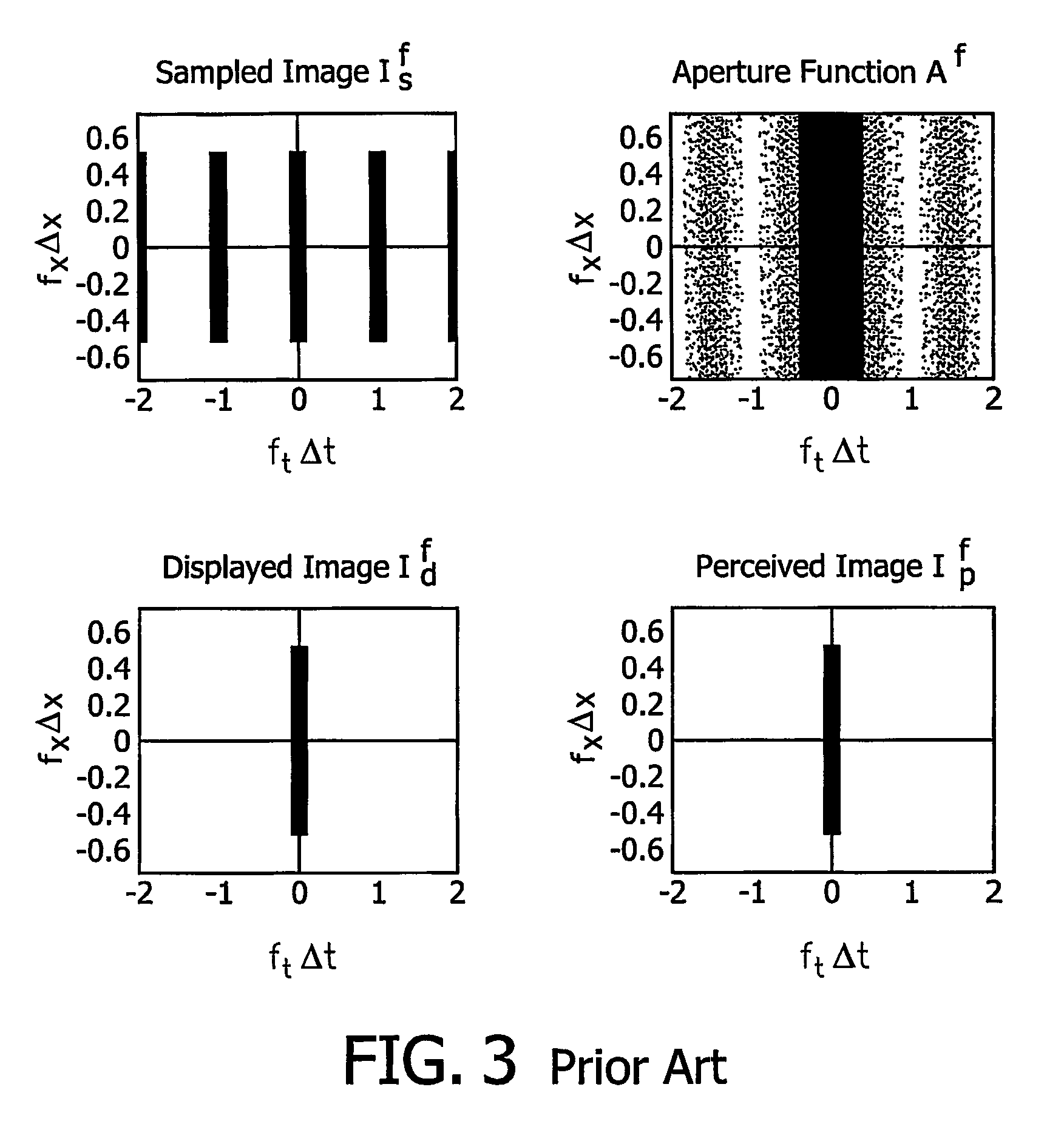
In signal processing, for a filter g, an inverse filter h is one such that the sequence of applying g then h to a signal results in the original signal. Software or electronic inverse filters are often used to compensate for the effect of unwanted environmental filtering of signals.
Spot-size effect reduction
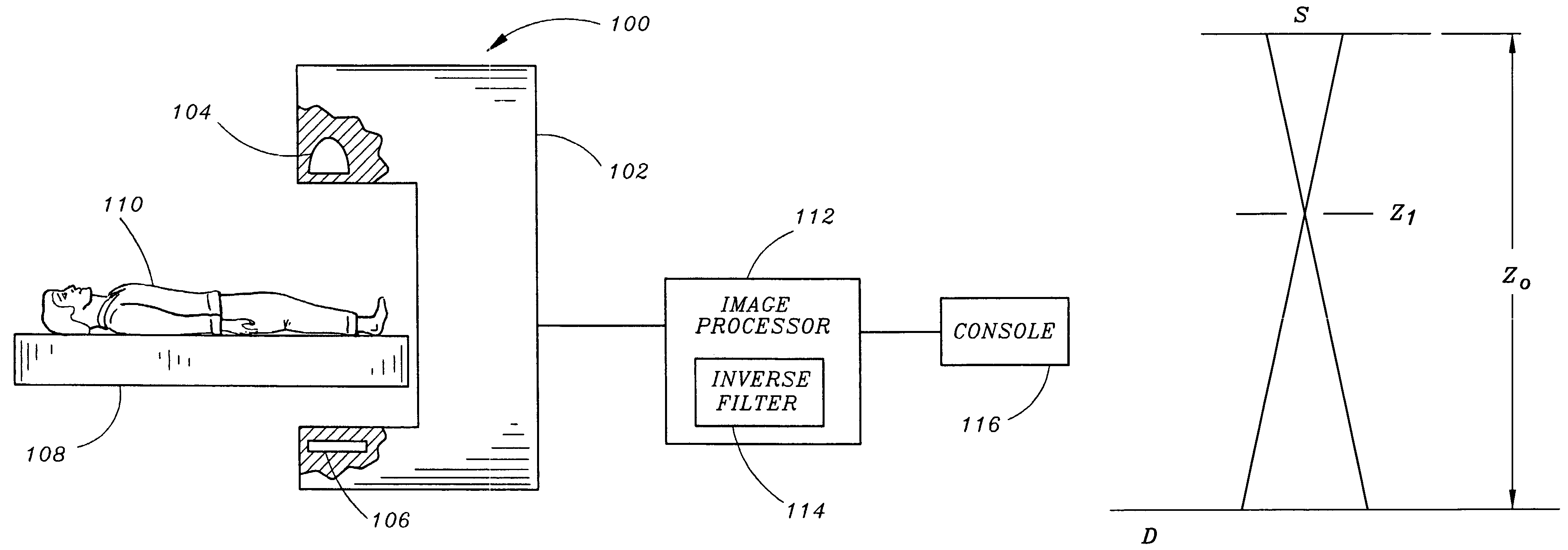
InactiveUS7418078B2Reduce adverse effectsImprove image qualityRadiation/particle handlingTomographyX-rayRadiography
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
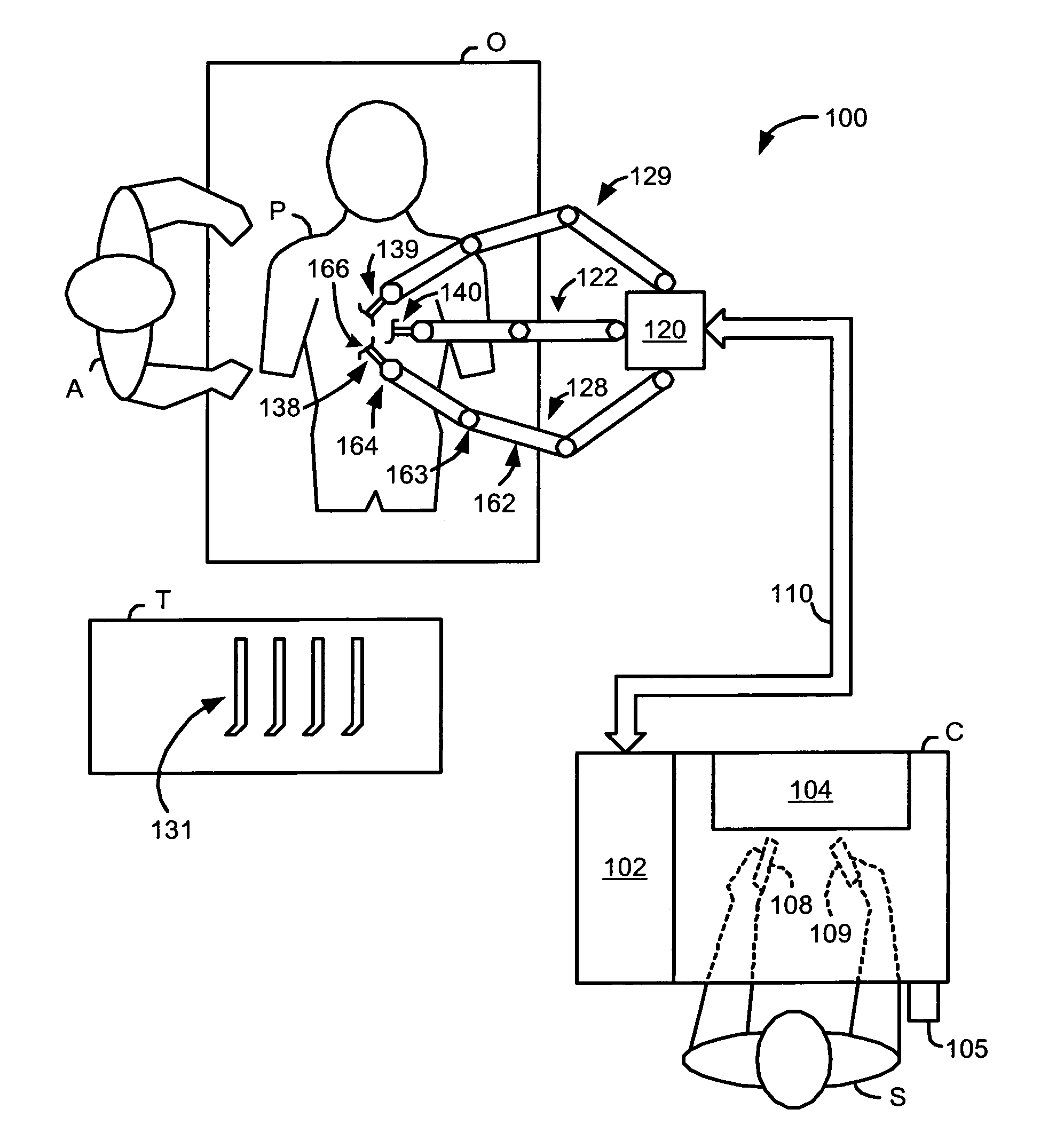
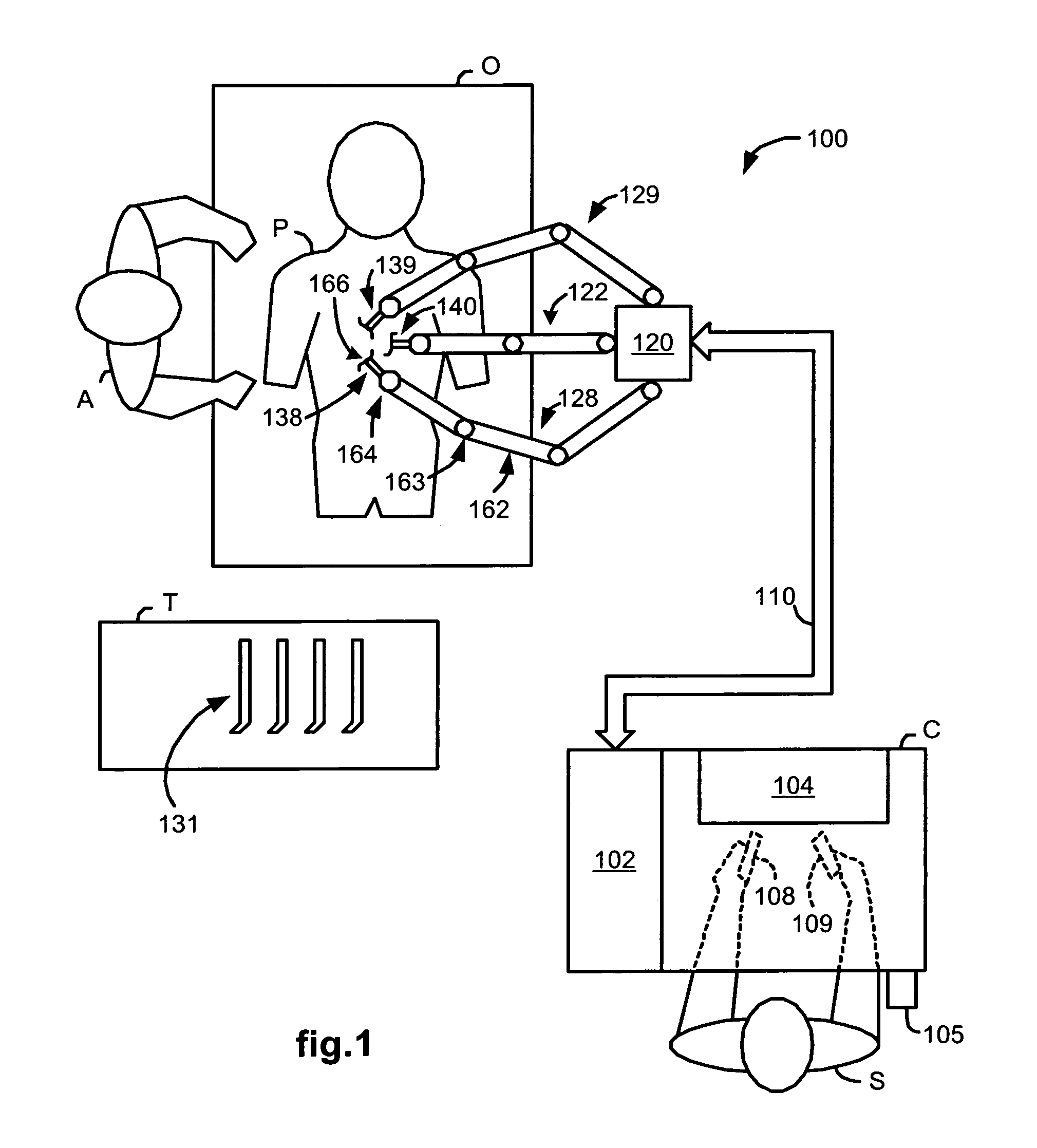
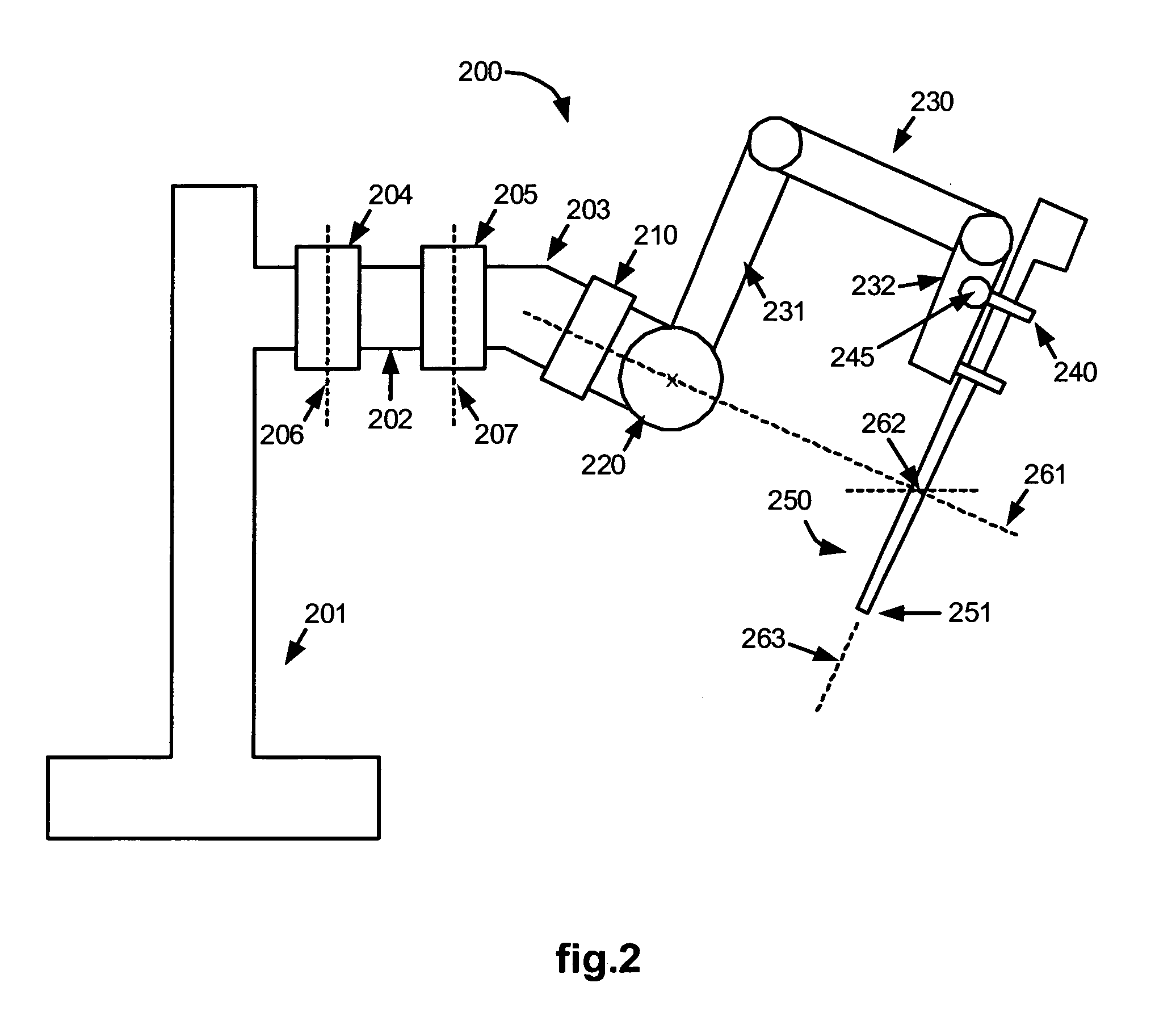
Robotic surgical system with joint motion controller adapted to reduce instrument tip vibrations
ActiveUS7689320B2Reduce vibrationWithout jeopardizing control system stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesControl systemJoints movement
A robotic surgical system has a robot arm holding an instrument for performing a surgical procedure, and a control system for controlling movement of the arm and its instrument according to user manipulation of a master manipulator. The control system includes a filter in its forward path to attenuate master input commands that may cause instrument tip vibrations, and an inverse filter in a feedback path to the master manipulator configured so as to compensate for delay introduced by the forward path filter. To enhance control, master command and slave joint observers are also inserted in the control system to estimate slave joint position, velocity and acceleration commands using received slave joint position commands and torque feedbacks, and estimate actual slave joint positions, velocities and accelerations using sensed slave joint positions and commanded slave joint motor torques.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
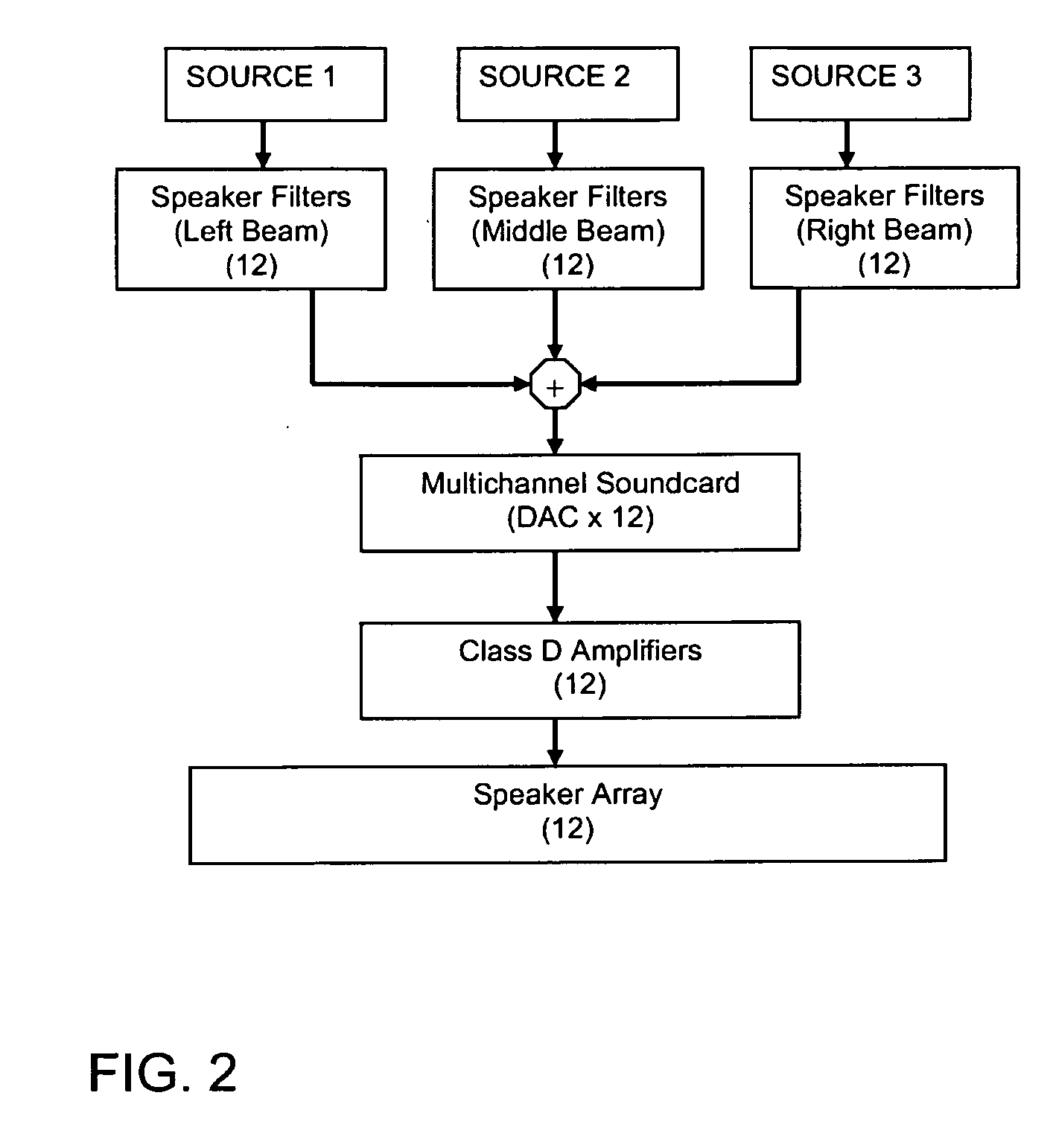
Method for controlling a speaker array to provide spatialized, localized, and binaural virtual surround sound
ActiveUS20140064526A1Superior speaker-based binaural sound imagingExisting technologyMicrophonesTransducer detailsSource materialCommon space
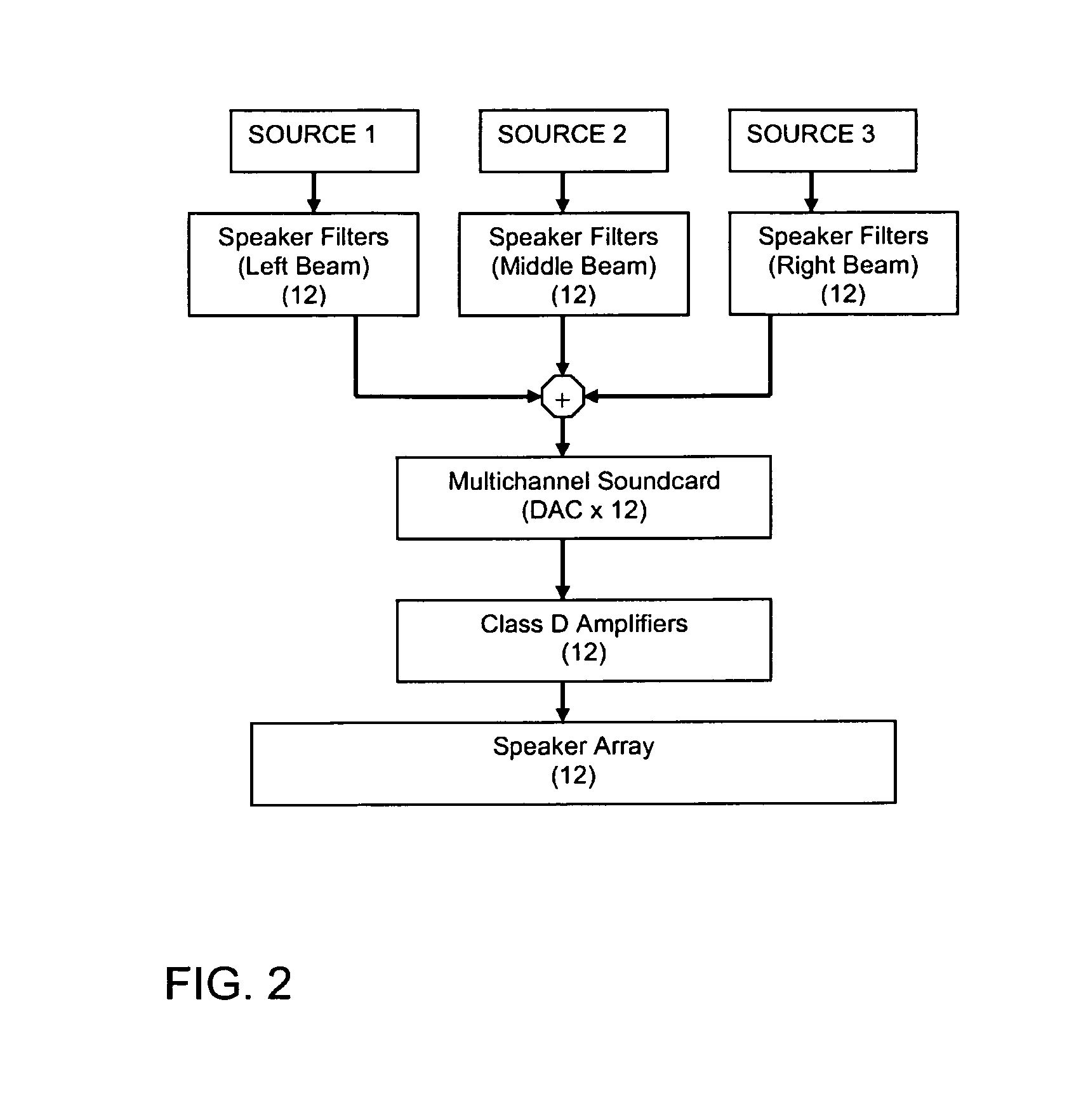
A system and method for producing a binaural and localized audio signal to a user is provided. A signal processing method is provided for delivering spatialized sound in various ways using highly optimized inverse filters to deliver narrow localized beams of sound from the included speaker array. The inventive method can be used to provide private listening areas in a public space and provide spatialization of source material for a single user to create a virtual surround sound effect. In a binaural mode, a speaker array provides two targeted beams aimed towards the primary user's ears—one discrete beam for the left ear and one discrete beam for the right ear. In a privacy mode, a privacy zone could be created in which a primary audio beam would deliver a signal of interest to the user while secondary beams would be aimed at different angles to provide a masking noise.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
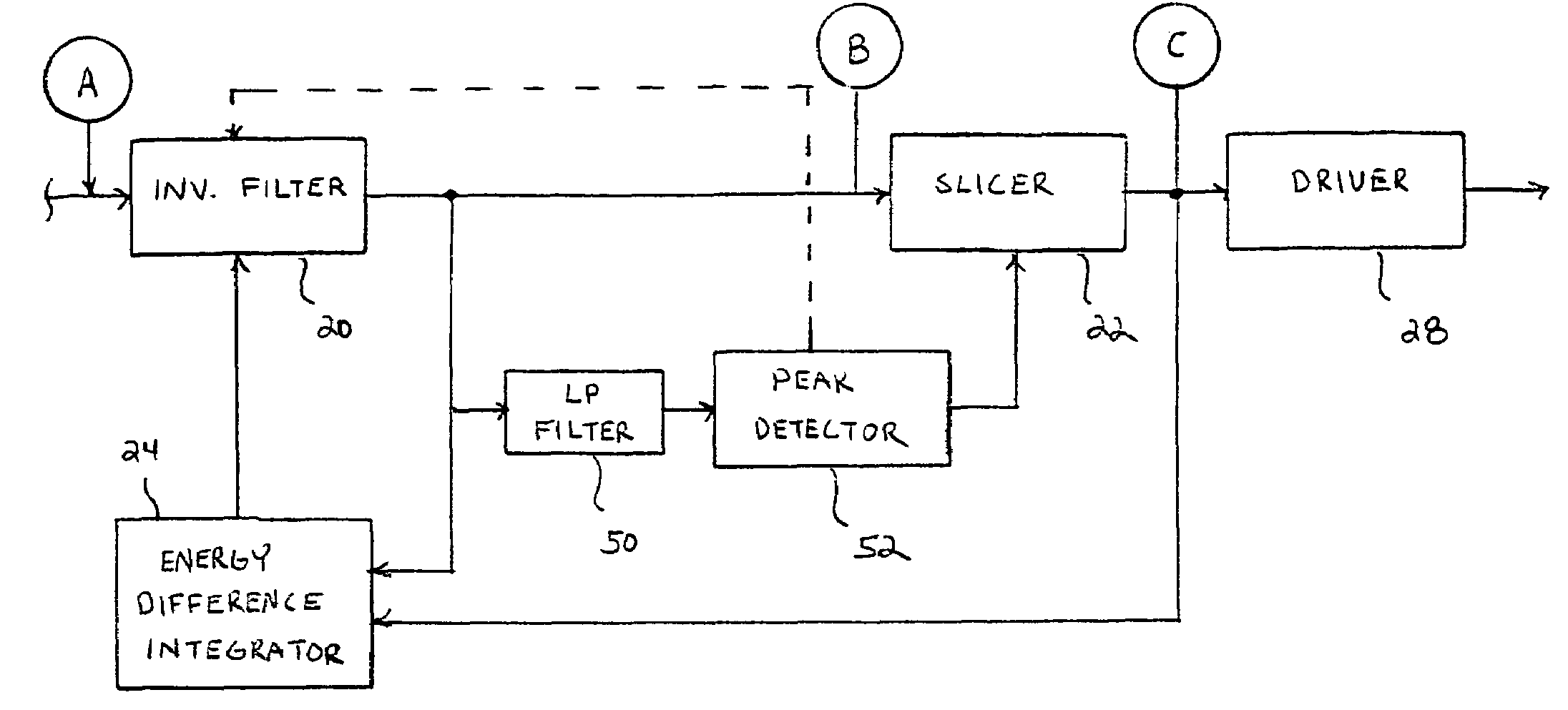
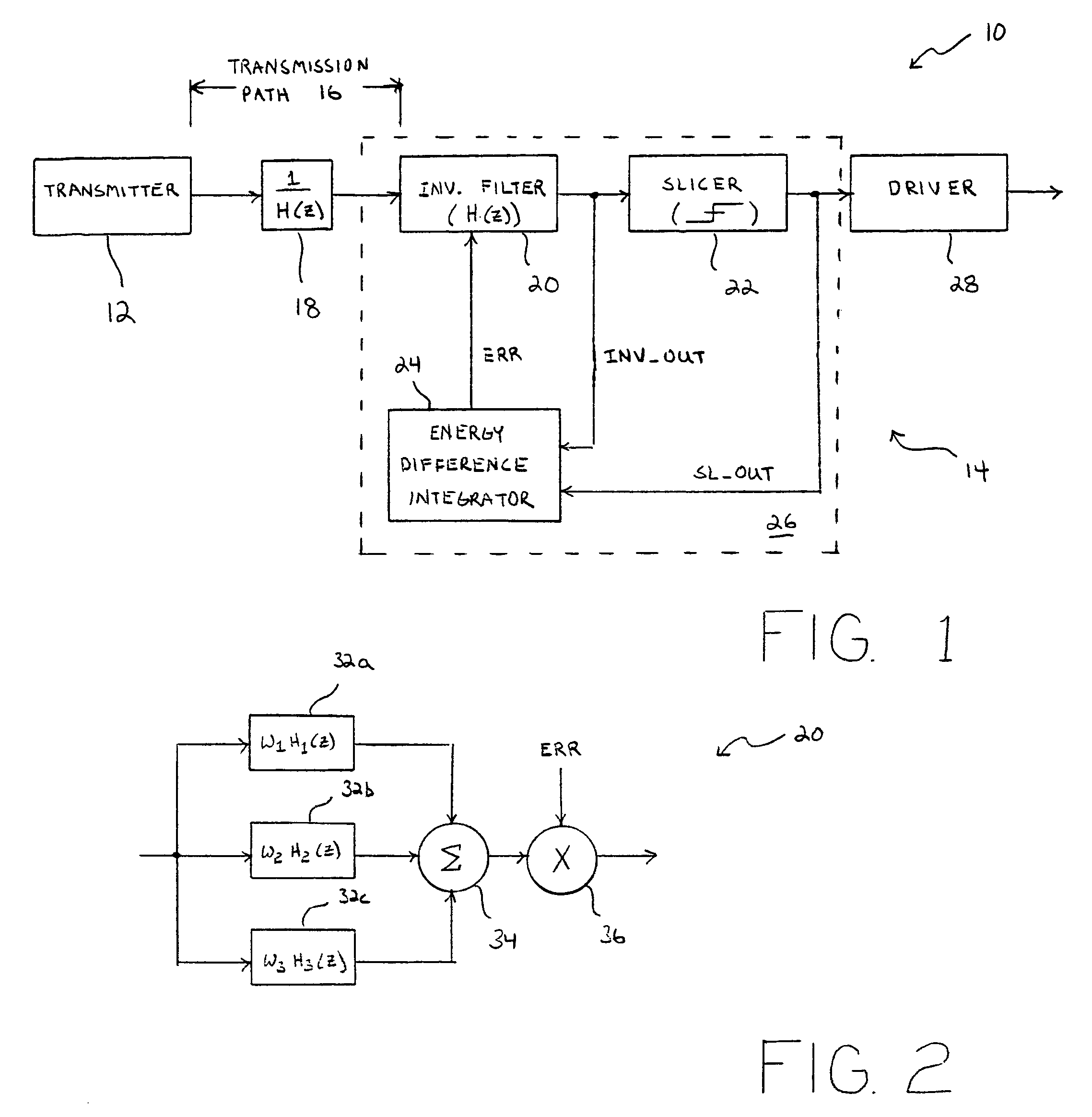
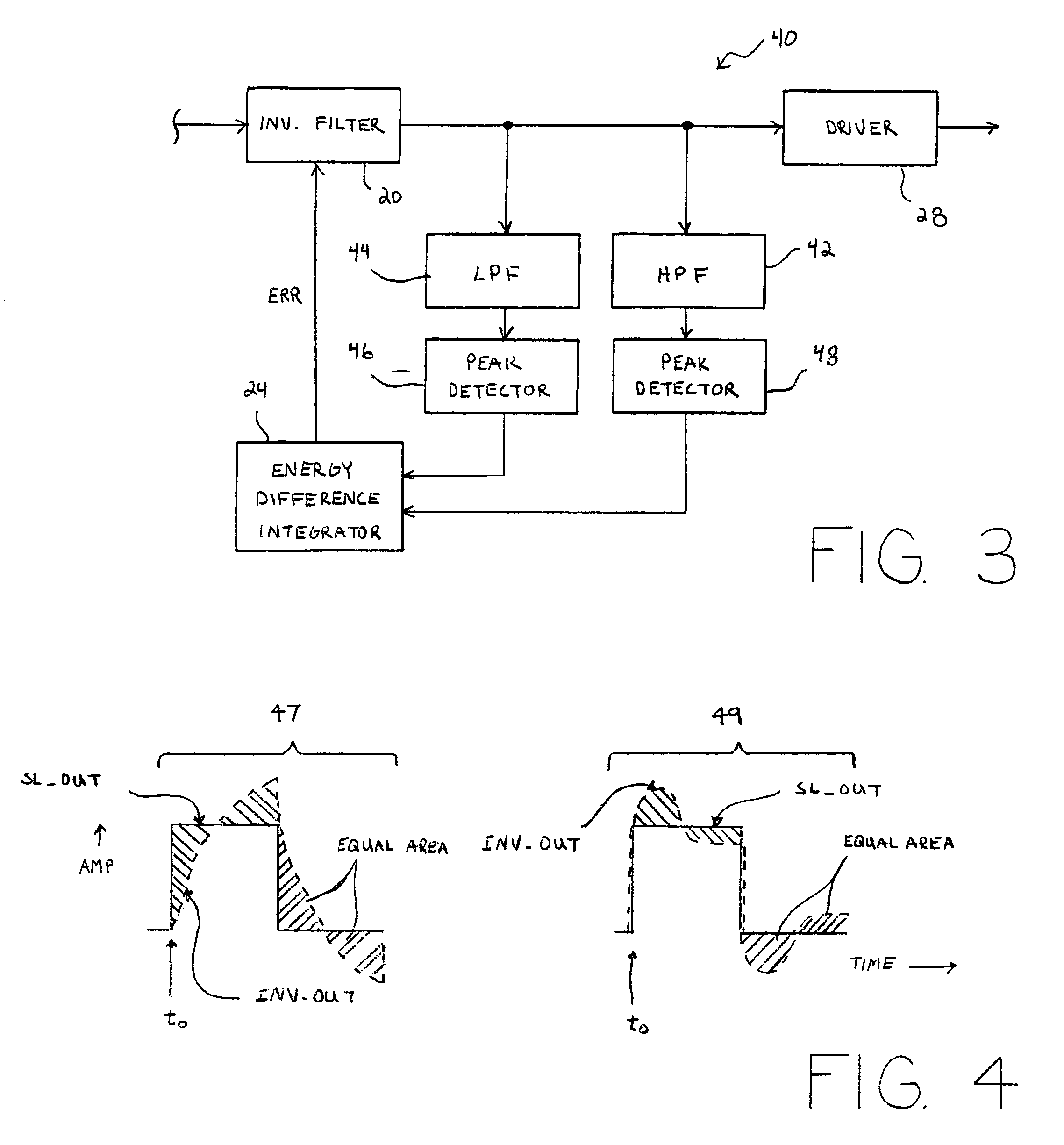
Equalizer circuit, communication system, and method that is adaptive to varying launch amplitudes for reducing receiver error
InactiveUS7620101B1Promote resultsMinimize signalingMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsIntegratorDual stage
A transmission line equalizer, communication system, and method are provided for adaptively compensating for changes in transmission path length and transmission path medium. Within the equalizer is a filter that exhibits a high pass characteristic and, more specifically, has an inverse frequency response to that of the transmission path. The inverse filter can include a pair of amplifier stages coupled in parallel, with a mixer chosen to adaptively select portions of one stage over than of the other. The dual stage inverse filter can, therefore, adapt to greater transmission path lengths and / or attenuation. A feedback architecture is used to set the inverse filter response by measuring the amplitude of a communication signal output from the inverse filter during periods of low frequency. A peak detector will capture a peak-to-peak voltage value during those periods, and adjust the output of the slicer to match a launch amplitude of the communication signal. The peak detector within the feedback architecture helps ensure the predicted amplitude matches the launch amplitude to minimize over-compensation or under-compensation even though a different integrator might register no difference in integrated voltage or energy at the output of the inverse filter compared to the output of the slicer.
Owner:RPX CORP
Speech separating apparatus, speech synthesizing apparatus, and voice quality conversion apparatus
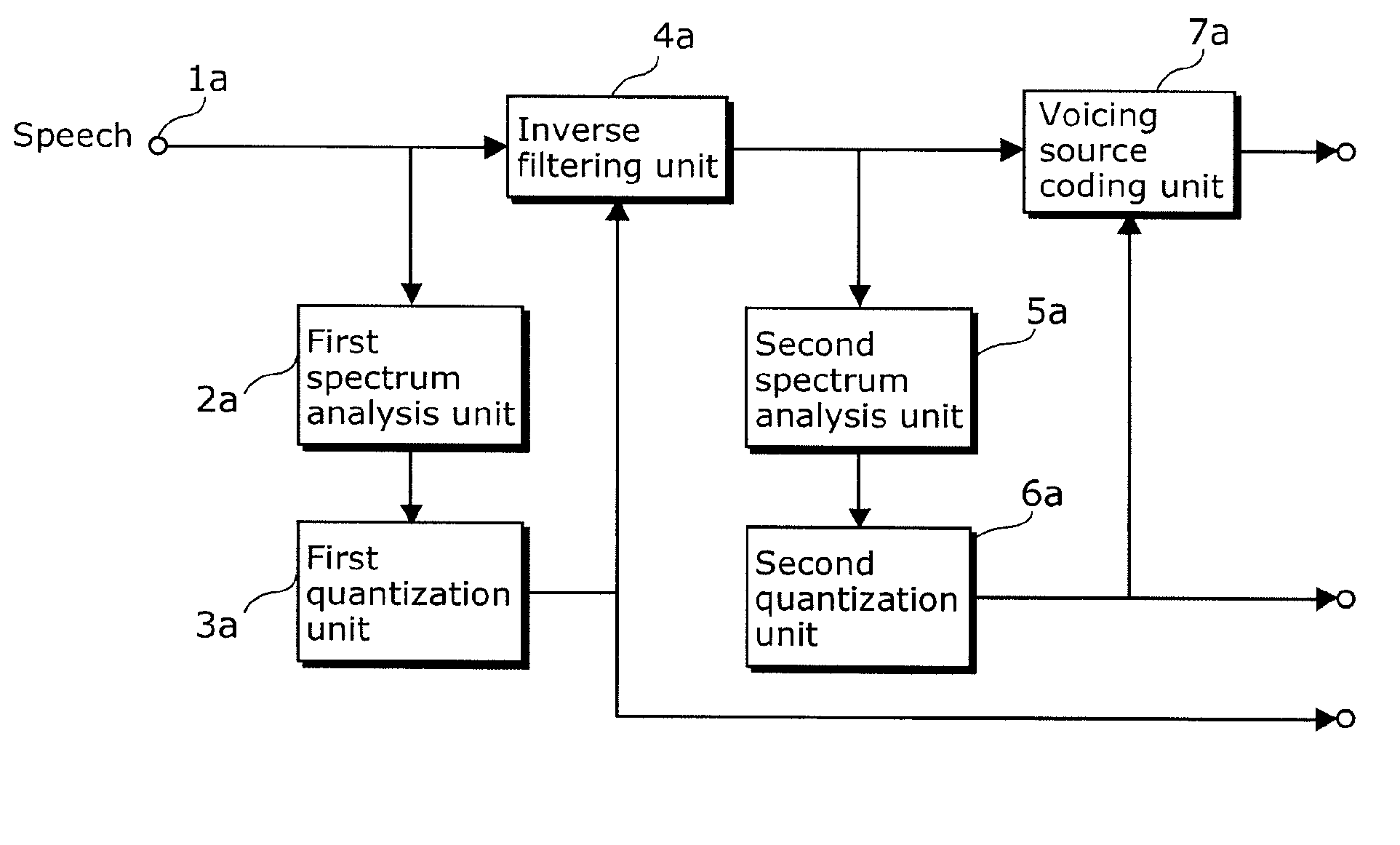
A speech separating apparatus includes: a PARCOR calculating unit (102) that extracts vocal tract information from an input speech signal; a filter smoothing unit (103) that smoothes, in a first time constant, the vocal tract information extracted by the PARCOR calculating unit (102); an inverse filtering unit (104) that calculates a filter coefficient of a filter having a frequency amplitude response characteristic inverse to the vocal tract information smoothed by the filter smoothing unit (103), so as to filter the input speech signal using the filter having the calculated filter coefficient; and a voicing source modeling unit (105) that cuts out, from the input speech signal filtered by the inverse filtering unit (104), a waveform included in a second time constant shorter than the first time constant, so as to calculate, for each waveform that is taken, voicing source information from the each waveform.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
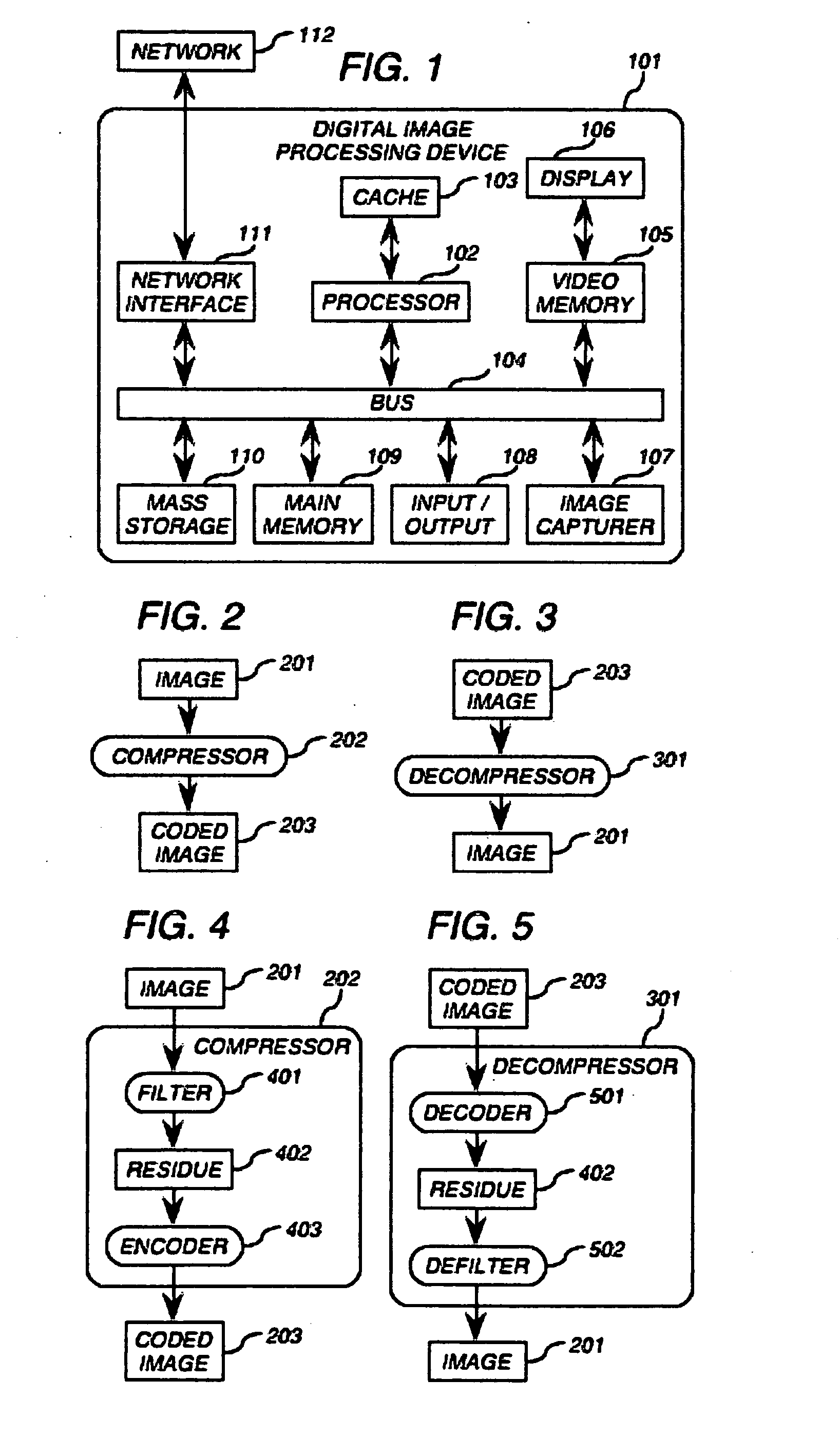
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS20080219575A1Maximize compression ratioMinimized on demandCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumContext independent
The present invention is a method and apparatus for compressing and decompressing data. In particular, the present invention provides for (de-)compressing naturalistic color-image and moving-image data, including high-precision and high-definition formats, with zero information loss, one-sample latency and in faster than real time on common computing platforms, resulting in doubled transmission, storage, and playback speed and doubled transmission bandwidth and storage capacity, and hence in doubled throughput for non-CPU-bound image-editing tasks in comparison with uncompressed formats. The present invention uses a nearly symmetrical compression-decompression scheme that provides temporal, spatial, and spectral compression, using a reversible condensing / decondensing filter, context reducer, and encoder / decoder. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the compression filter is implemented as a cascade of quasilinear feedforward filters, with temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral stages, where appropriate, in that order, whose support consists of adjacent causal samples of the respective image. The decompressor cascades quasilinear feedback inverse filters in the reverse order. The filters can be implemented with mere integer addition, subtraction, and either one-dimensional table lookup or constant multiplication and binary shifting, depending on the computing environment Tables permit the data precision to be constrained throughout to that of the image samples. The encoder uses a table of prefix codes roughly inversely proportional in length to their probability, while the decoder uses chunked decode tables for accelerated lookup. In the fastest and simplest mode, the code tables are context-independent. For greater power, at the cost of a reduction in speed, the code tables are based on the temporal, multidimensional spatial, and spectral adjacent causal residue samples, where contexts with similar probability distributions are incoherently collapsed by a context reducer using one-dimensional lookup tables followed by implicitly multidimensional lookup tables, to minimize the overall table size. The invention's minimal resource requirements makes it ideal for implementation in either hardware or software.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
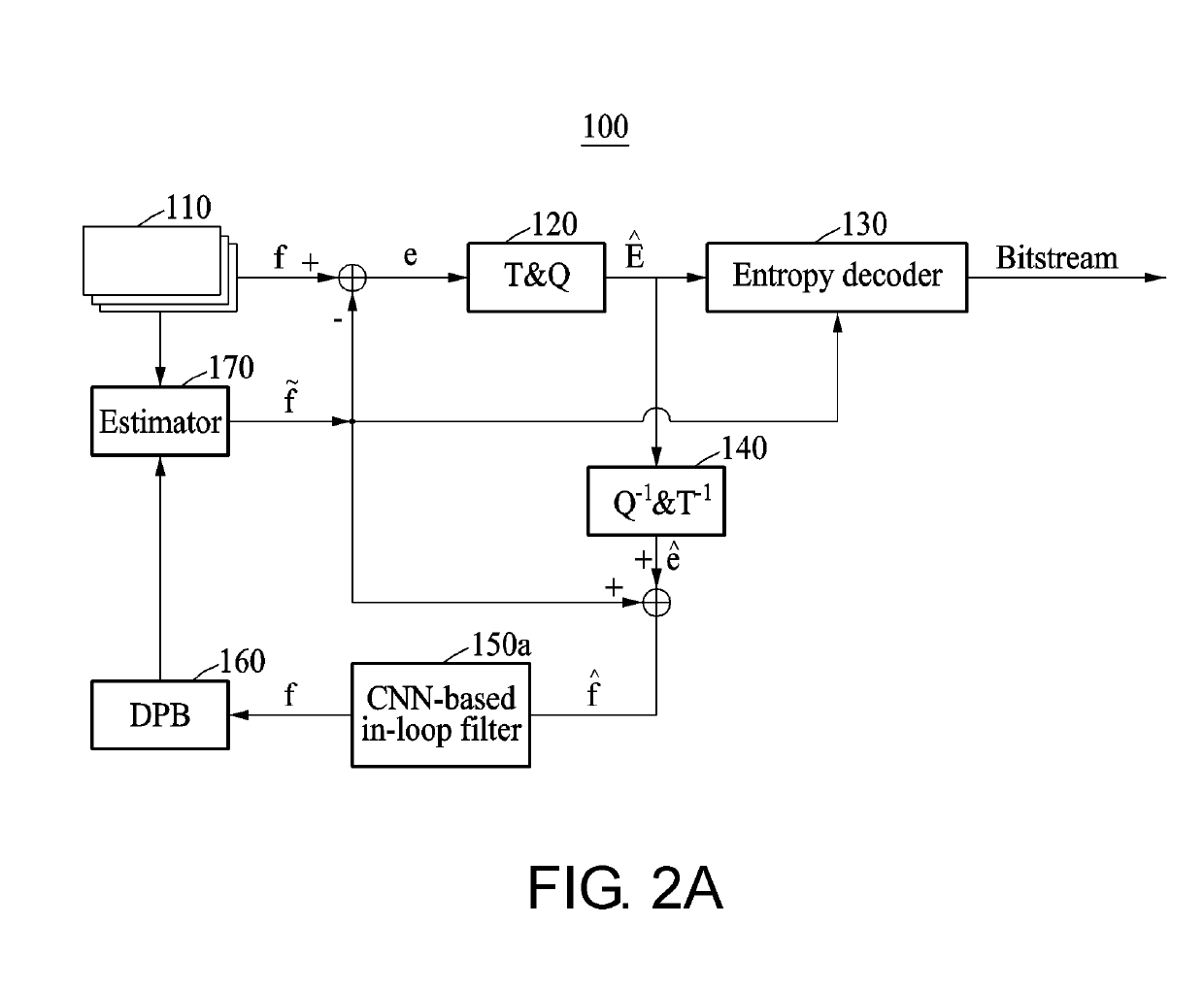
Encoding and decoding methods and devices including cnn-based in-loop filter
ActiveUS20190230354A1High-frequency blurringHigh frequency blurring artefactDigital video signal modificationNeural architecturesDecoding methodsLoop filter
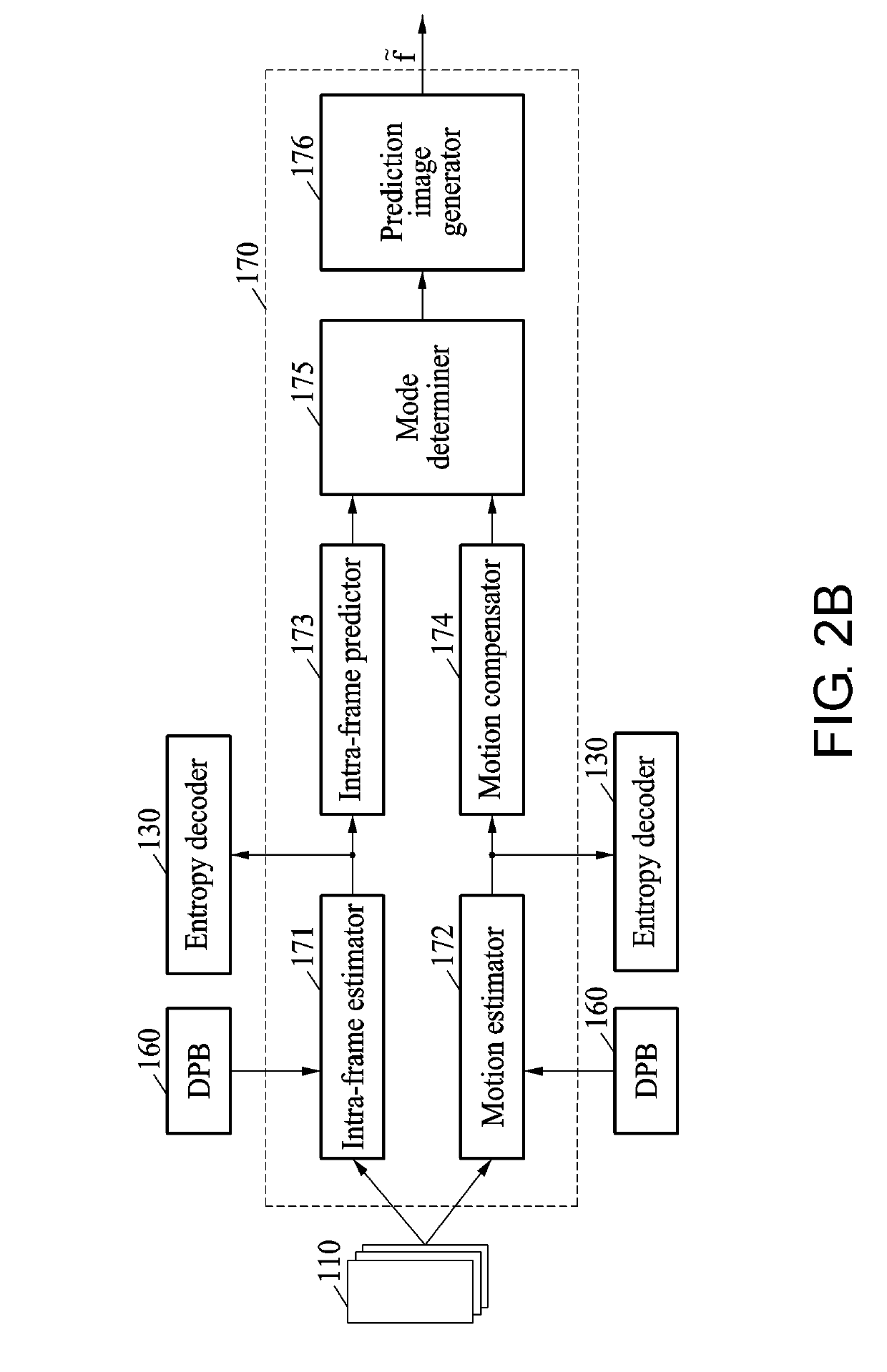
Disclosed are an encoding device and a decoding device, which include a CNN-based in-loop filter. The encoding device according to one embodiment comprises: a filtering unit for generating filtering information by filtering a residual image corresponding to a difference between an original image and a prediction image; an inverse filtering unit for generating inverse filtering information by inversely filtering the filtering information; a prediction unit for generating the prediction image on the basis of the original image and reconstruction information; a CNN-based in-loop filter for receiving the inverse filtering information and the prediction image so as to output the reconstruction information; and an encoding unit for performing encoding on the basis of the filtering information and information of the prediction image.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method, System and Program for Authenticating a User by Biometric Information
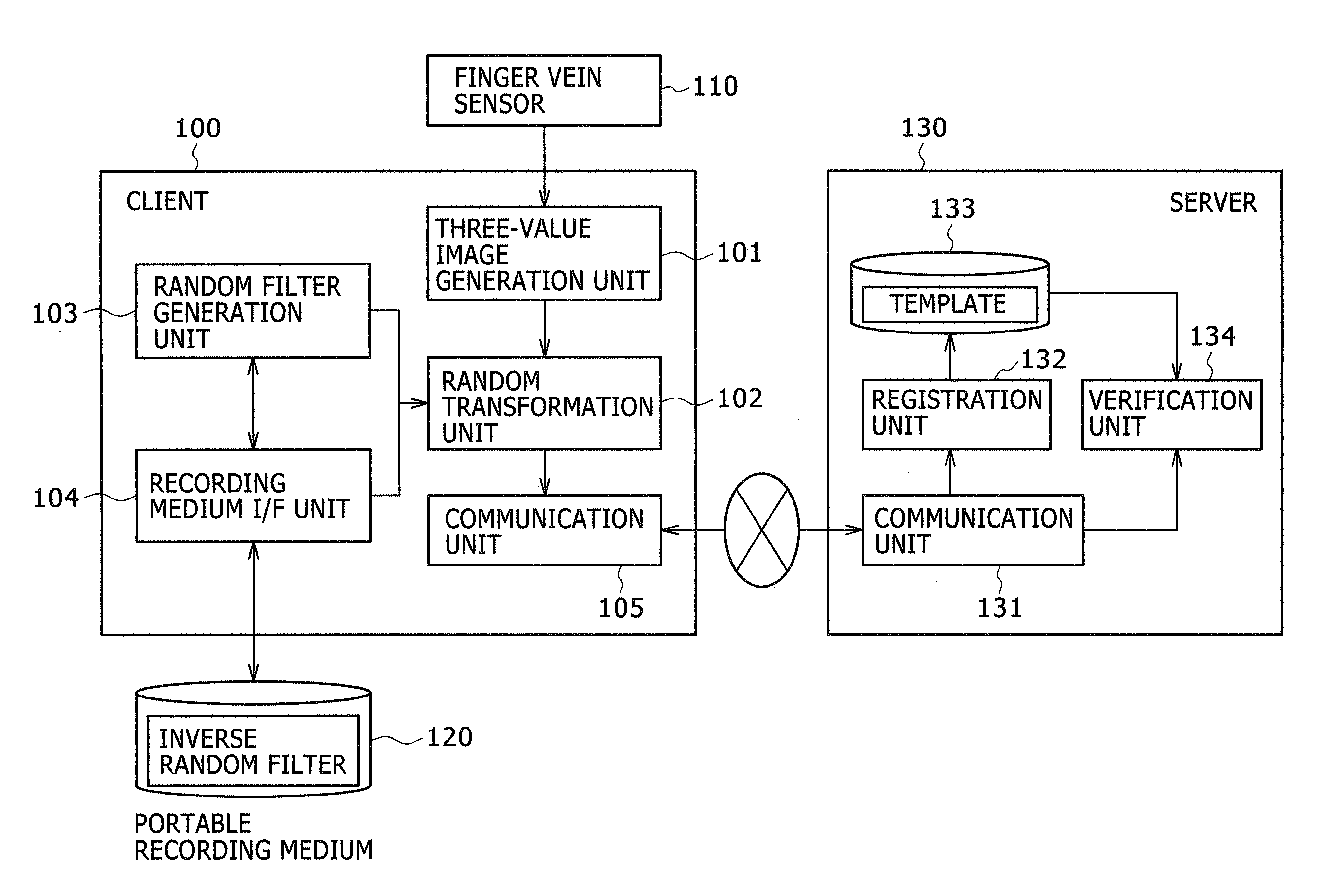
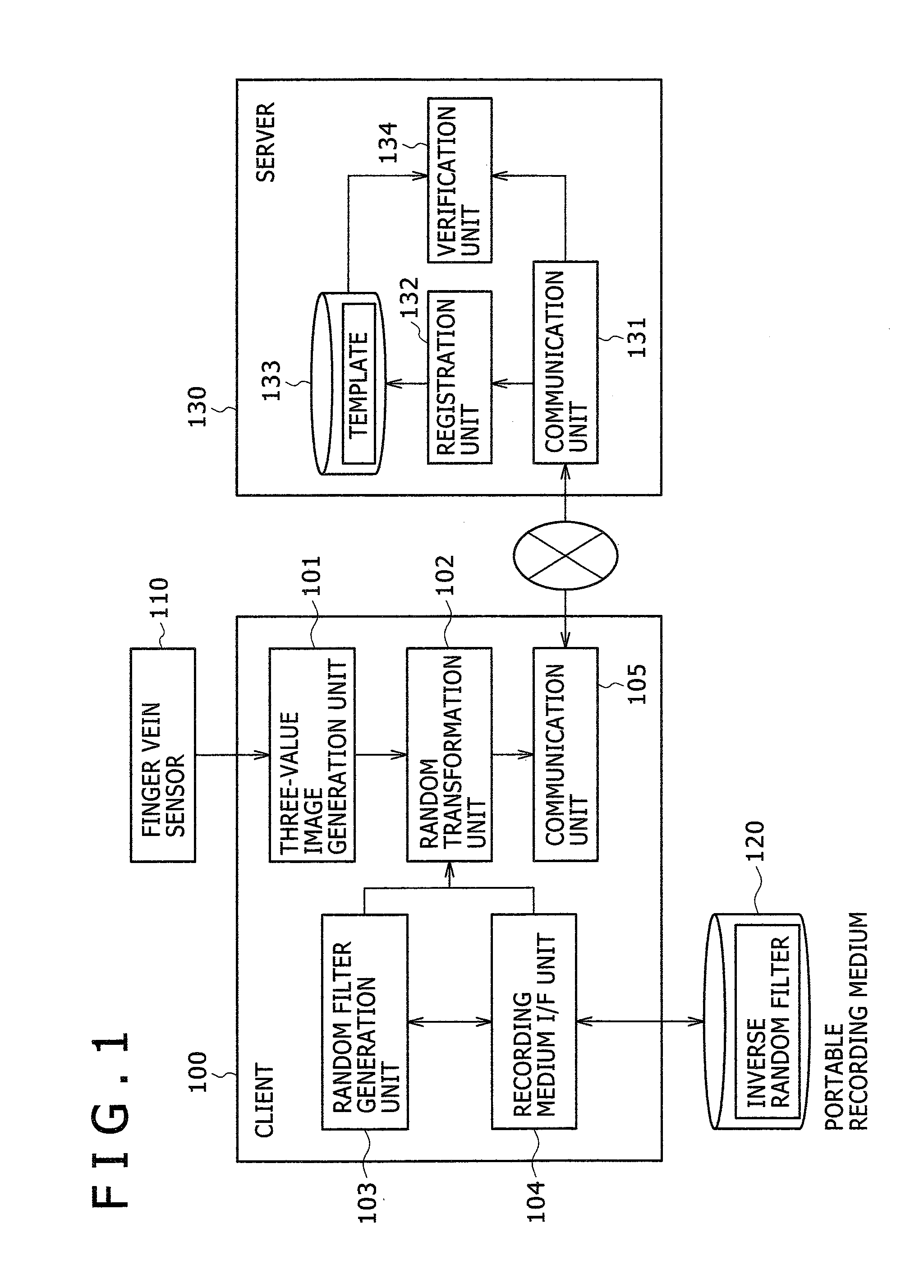
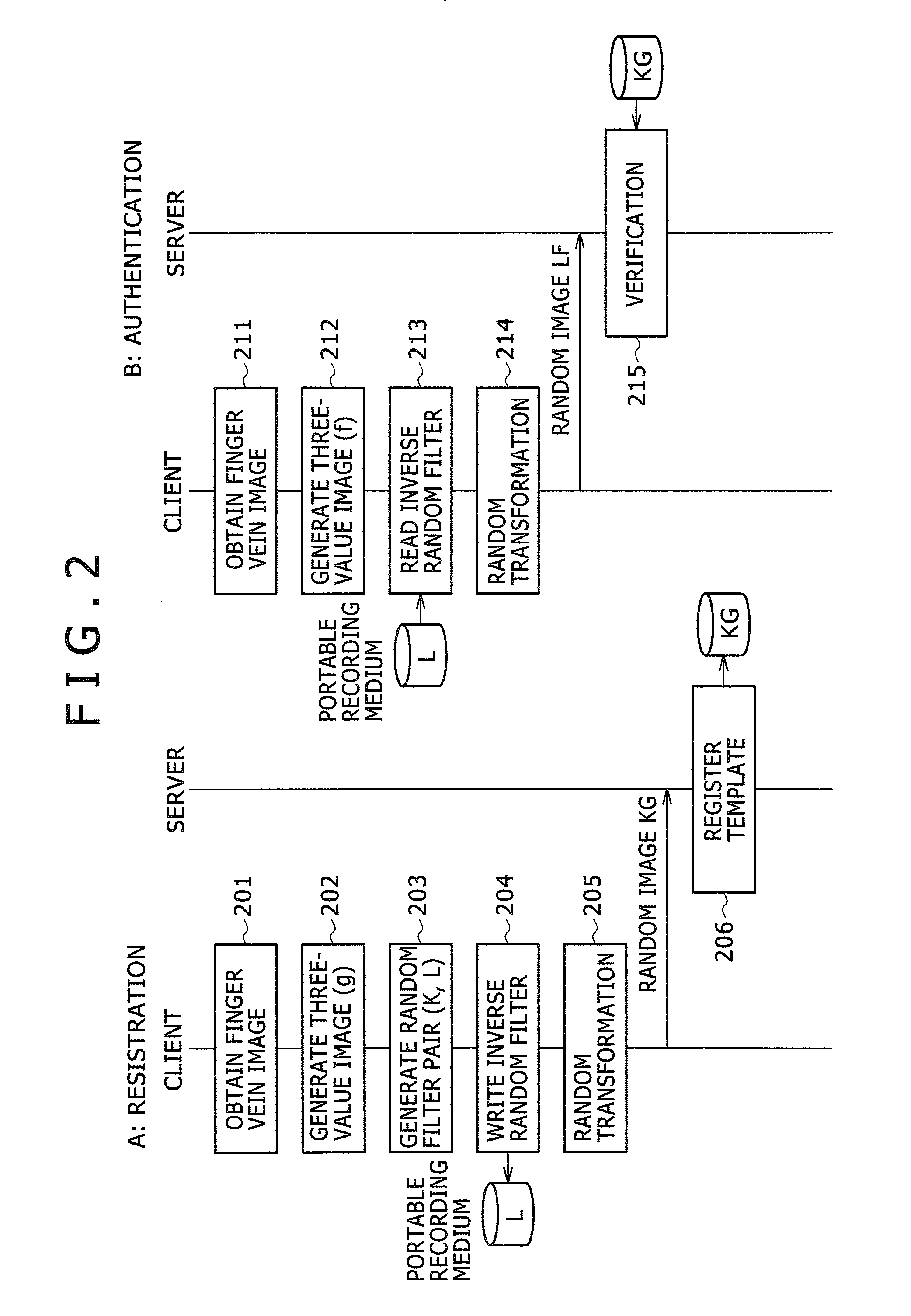
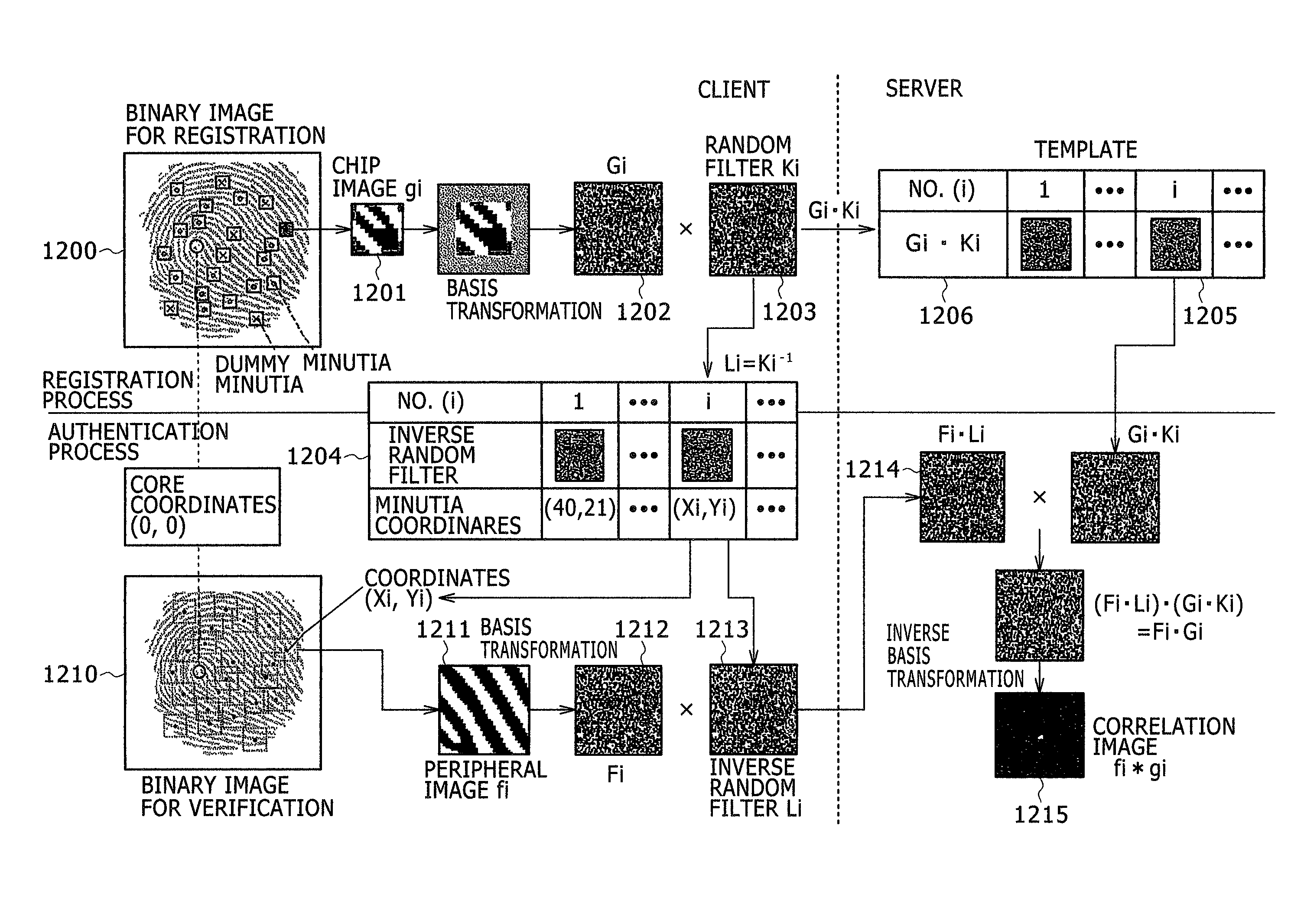
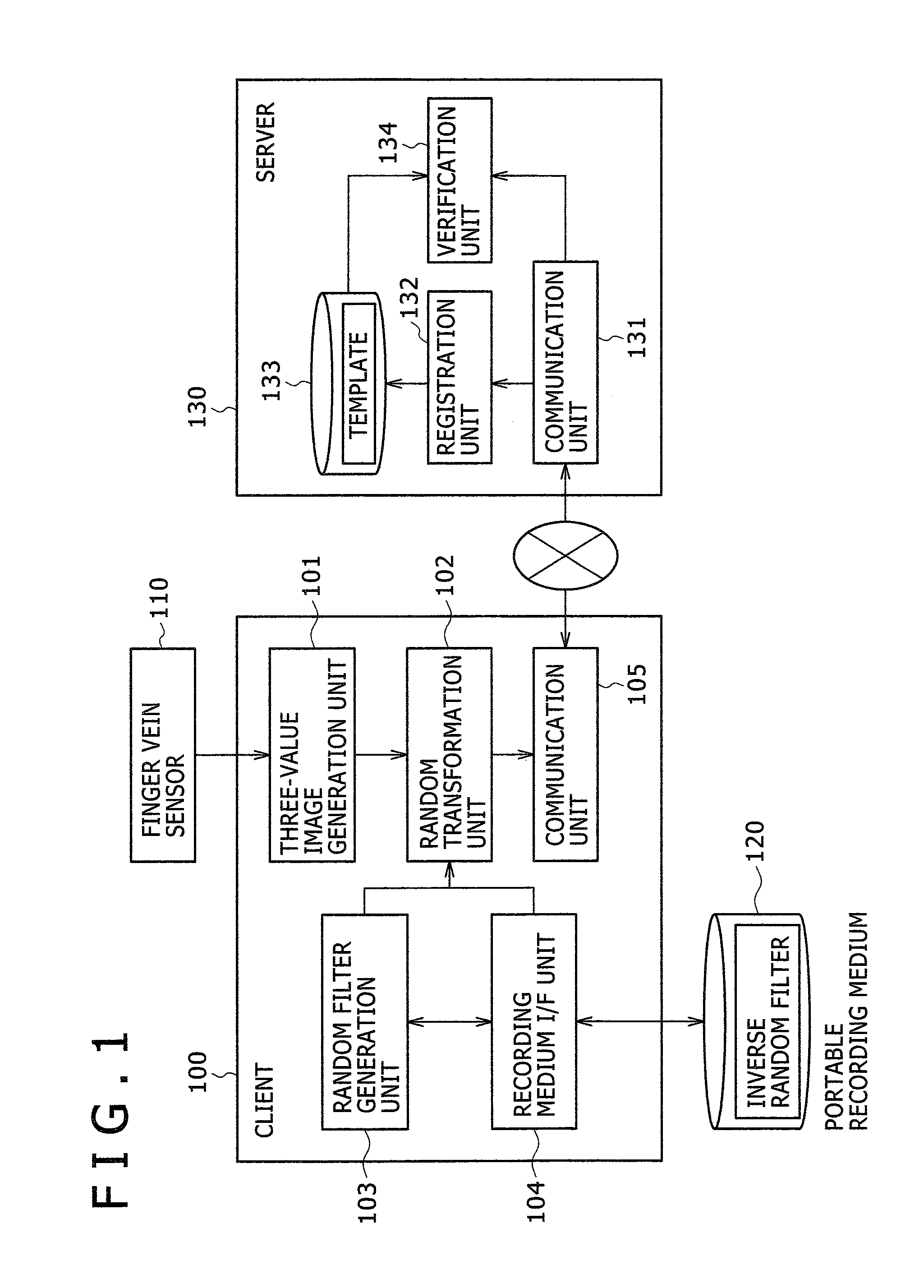
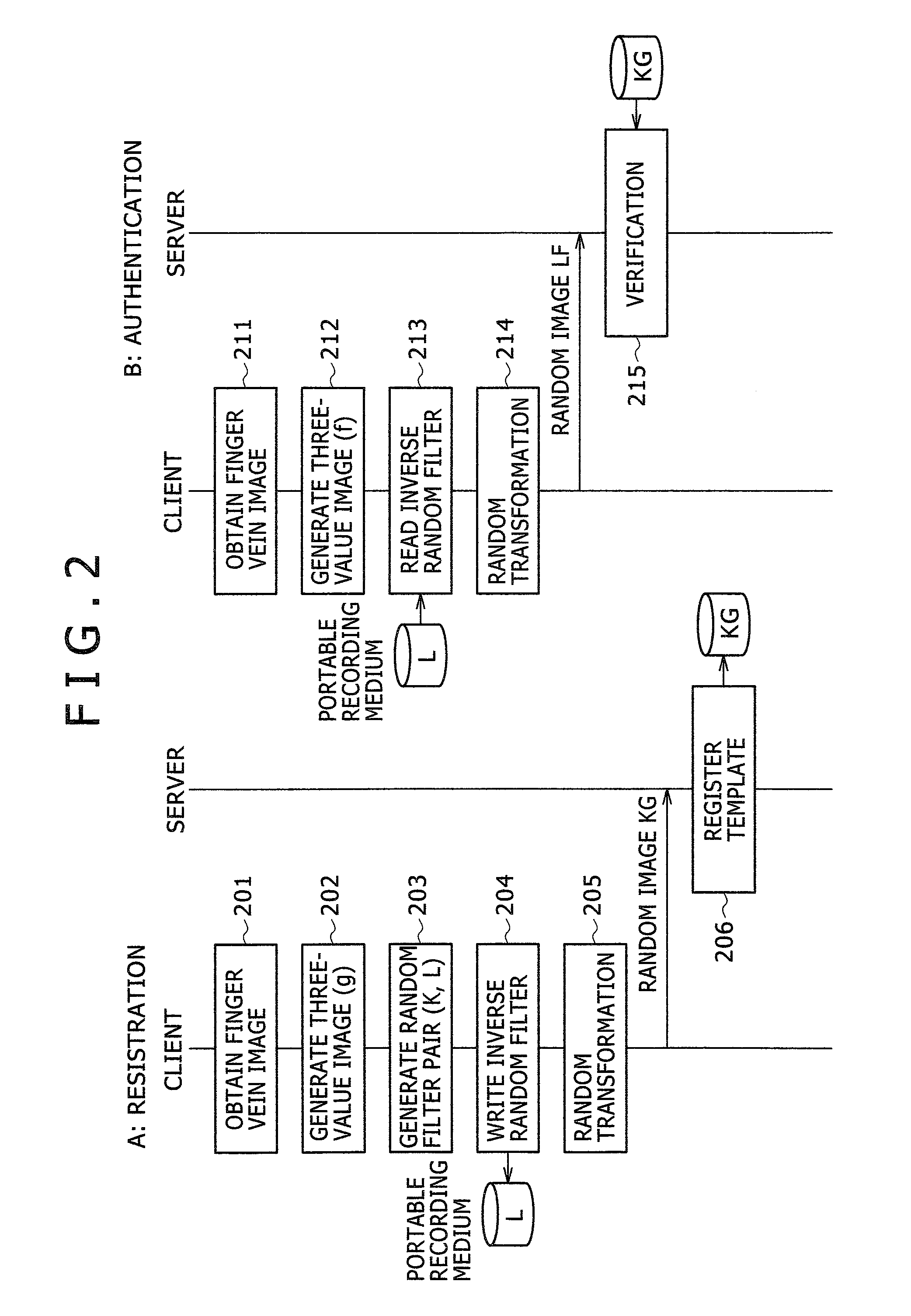
ActiveUS20080037833A1Difficult to reproduceWithout degrading verification accuracyDigital data authenticationSecret communicationUser authenticationInverse filter
A personal authentication method is provided for authenticating a user by cross-relation between an enrolled image and a verification image of biometric information of the user. Upon registration of the biometric information, the method generates a filter for scrambling the image and an inverse filter thereof, and applies the filter to the enrolled image generated from the biometric information to generate a registration template which is then stored to a memory. Upon authentication of the user, the method applies the inverse filter to the verification image generated from the biometric information collected from the user, and then verifies the identity of the user based on cross-relation between the verification image after application of the inverse filter and the registration template.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method, system and program for authenticating a user by biometric information
ActiveUS7936905B2Without degrading verification accuracyDigital data authenticationSecret communicationInverse filterAuthentication
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Simple noise suppression model
ActiveUS20050065792A1Reduce background noiseSuppress noiseSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumNoise suppression
An approach for efficiently reducing background noise from speech signal in real-time applications is presented. A noisy input speech signal is processed through an inverse filter when the spectrum tilt of the input signal is not that of a pure background noise model the noisy input signal is also filtered in order to reduce the spectrum valley areas of the noisy input signal when the background noise is present.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
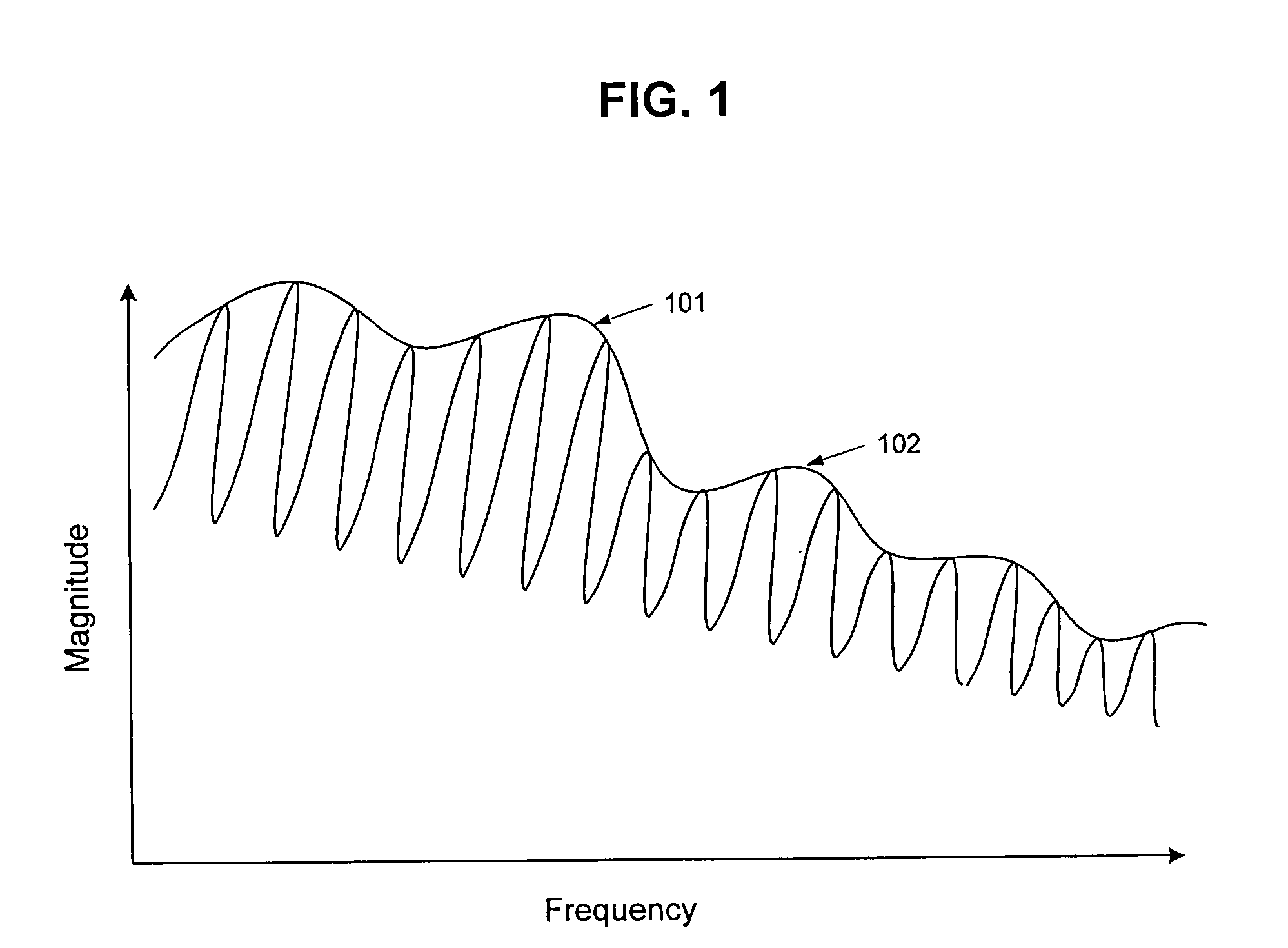
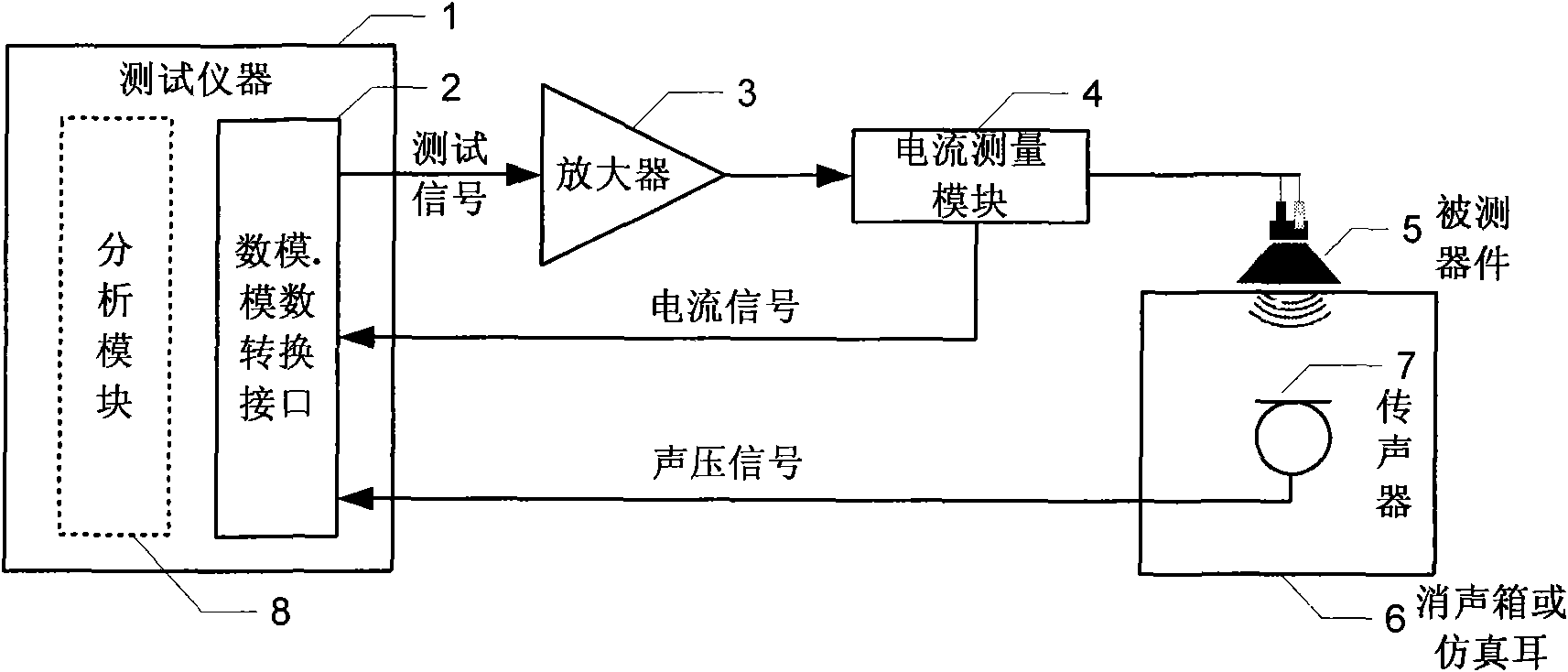
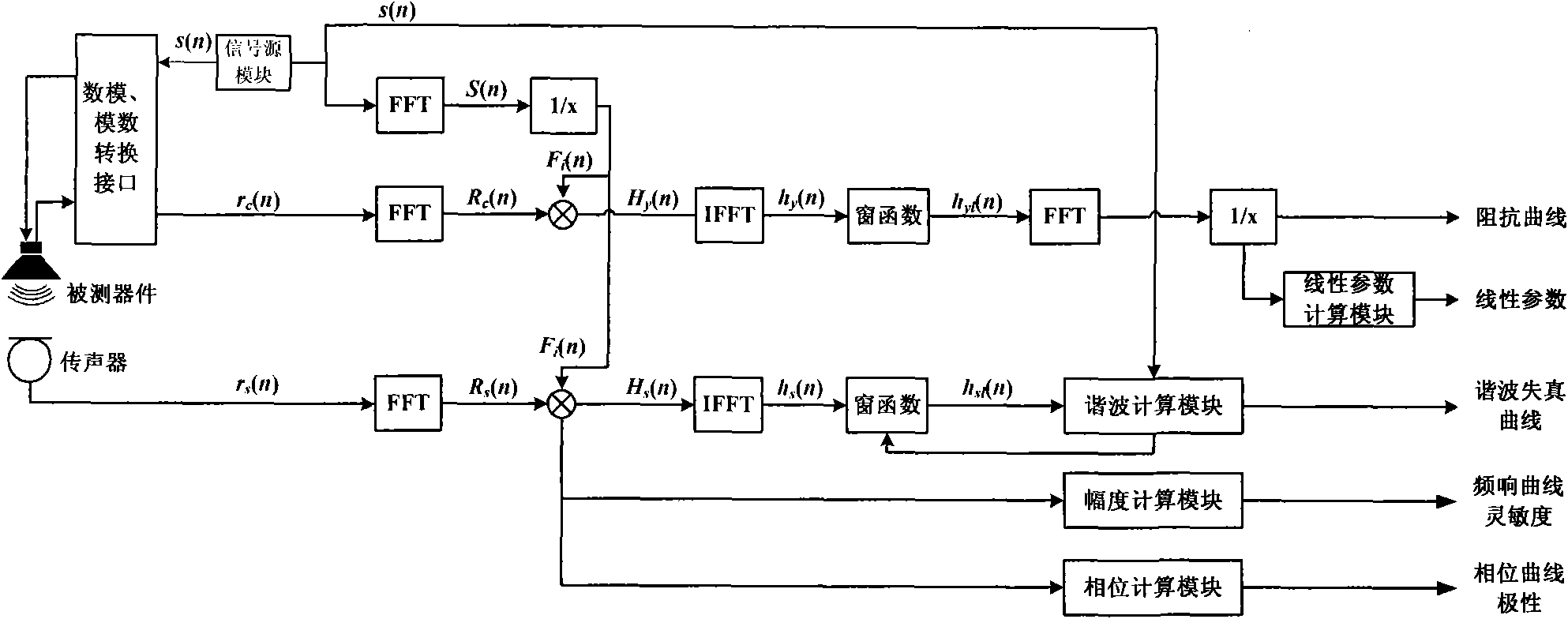
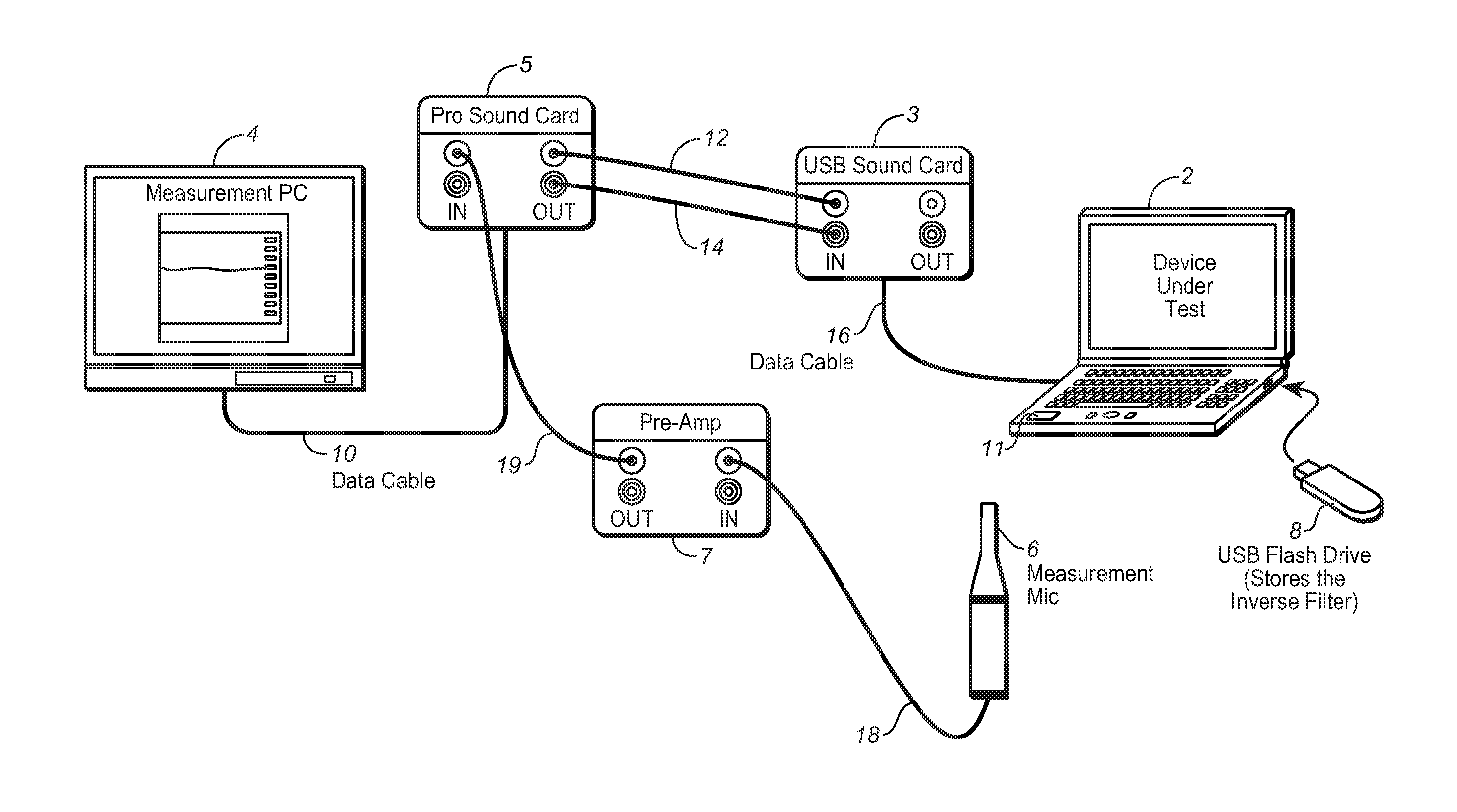
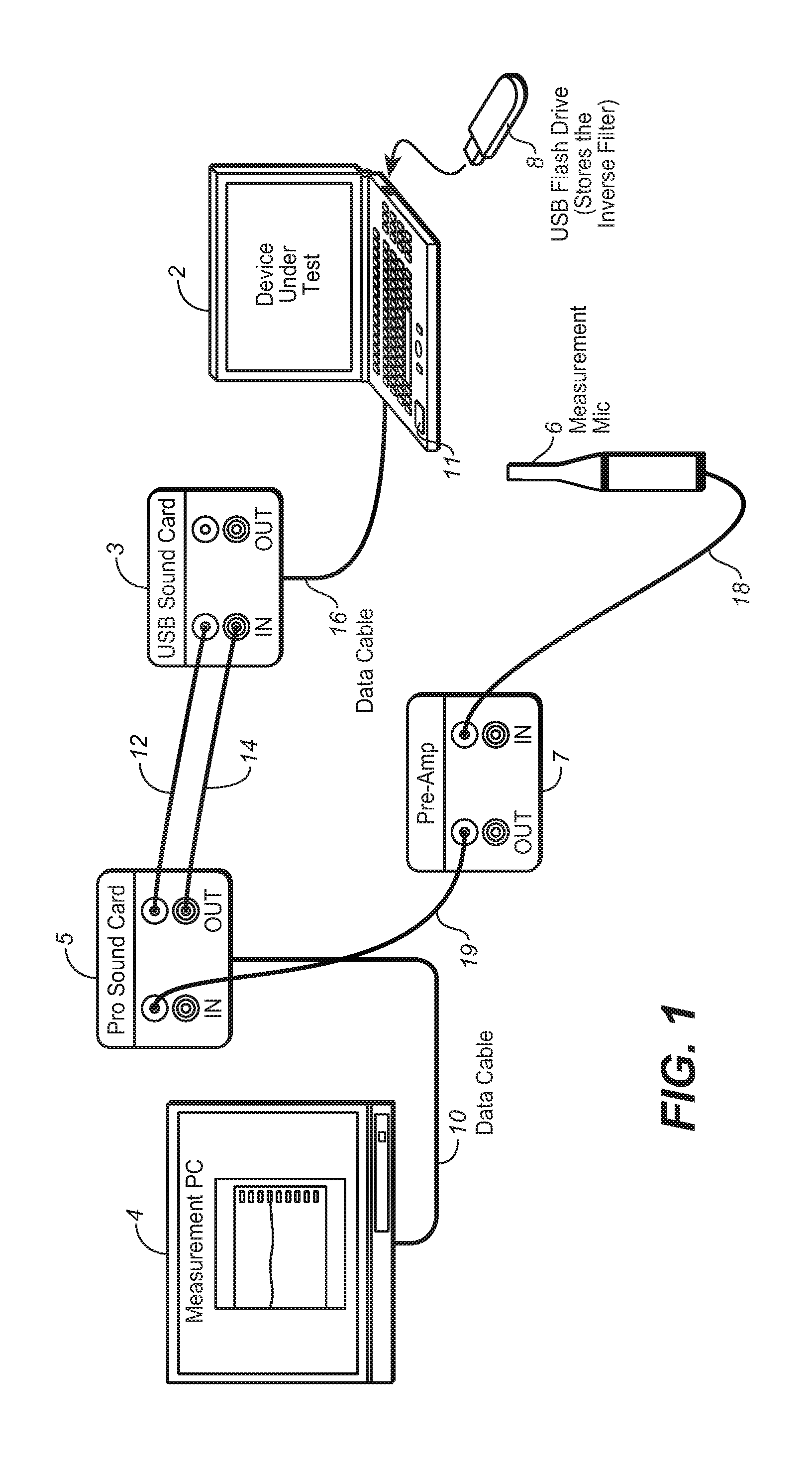
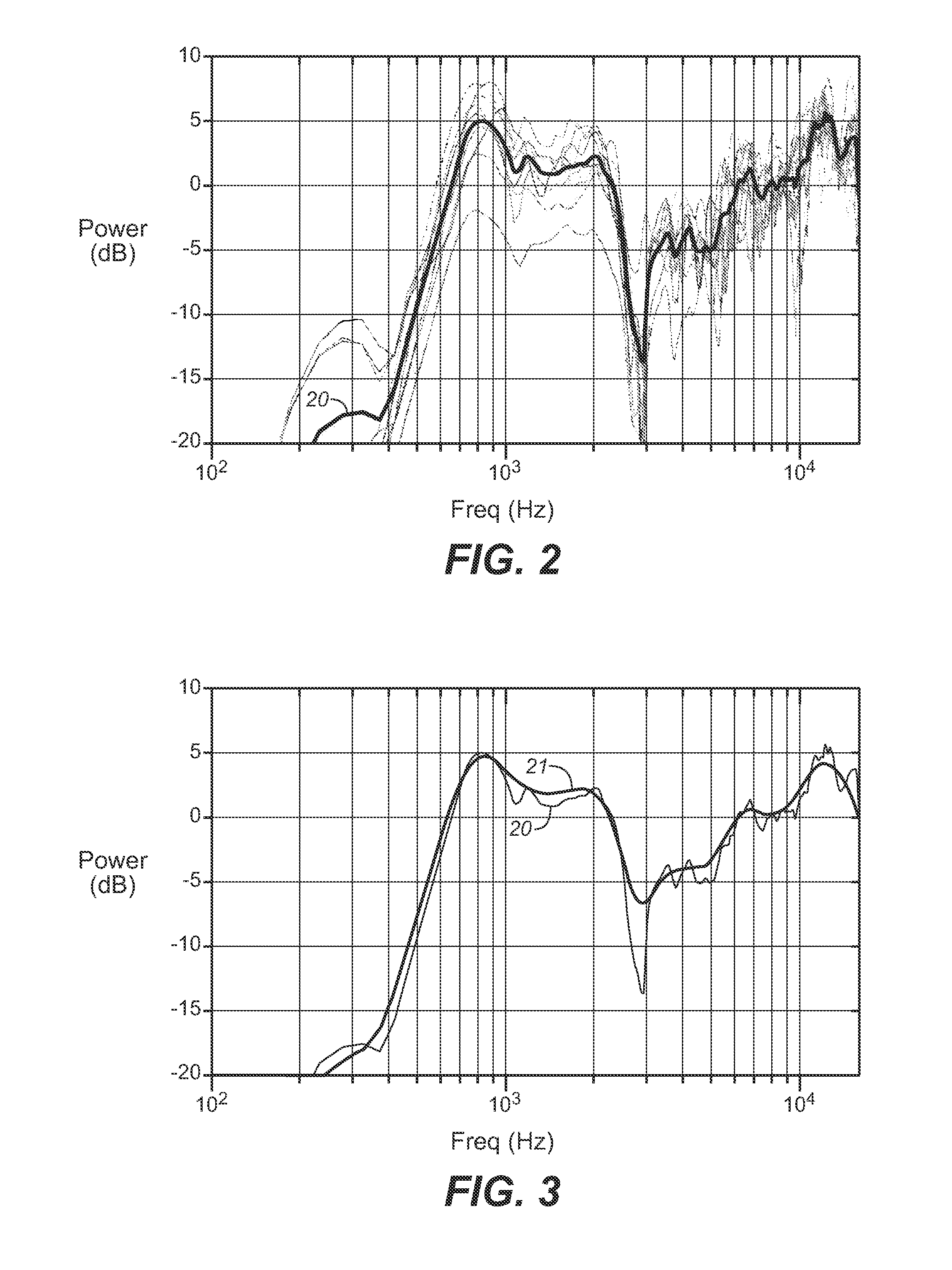
Method and system for obtaining a plurality of parameters of electro-acoustic product by adopting continuous logarithmic swept-frequency signal
The invention provides a method for rapidly measuring a plurality of parameters of an electro-acoustic product and also provides a test system realizing the method. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a continuous logarithmic swept-frequency signal to stimulate an electro-acoustic component and collecting an acoustic response signal transmitted by the electro-acoustic component to be tested and a current response signal flowing through the electro-acoustic component to be tested; obtaining a frequency response curve and a phase curve after the acoustic response signal is filtered by an inverse filter, and calculating and obtaining a harmonic distortion curve after time domain processing is carried out on the frequency response curve; calculating and obtaining an impedance curve after inverse filter and time domain processing are carried out on the current response signal; and further analyzing a result curve and obtaining results, such as sensitivity, polarity, rated impedance, linear parameters and the like. The test system comprises a test instrument, an amplifier, a current measurement module and a microphone.
Owner:嘉兴中科声学科技有限公司
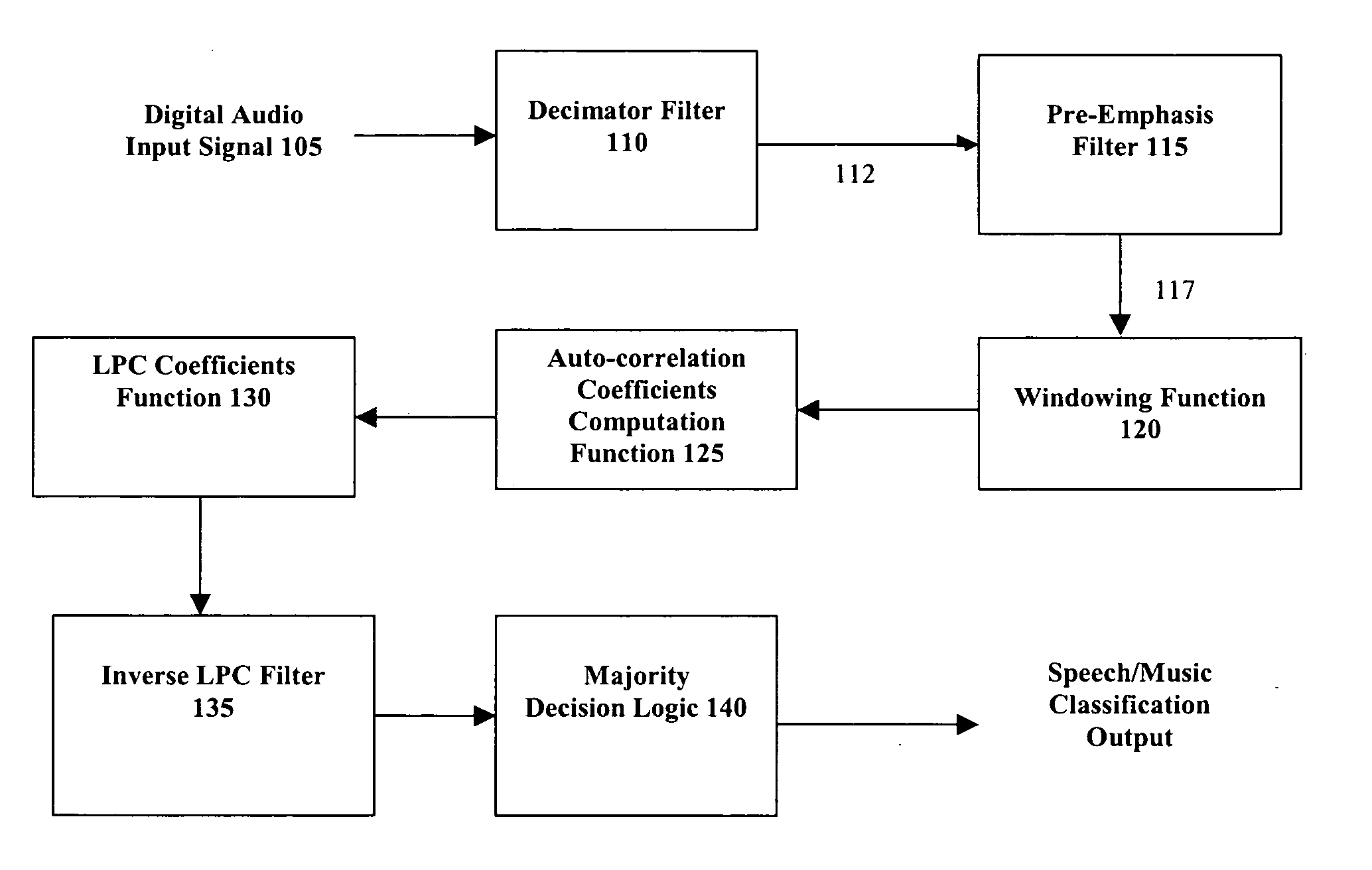
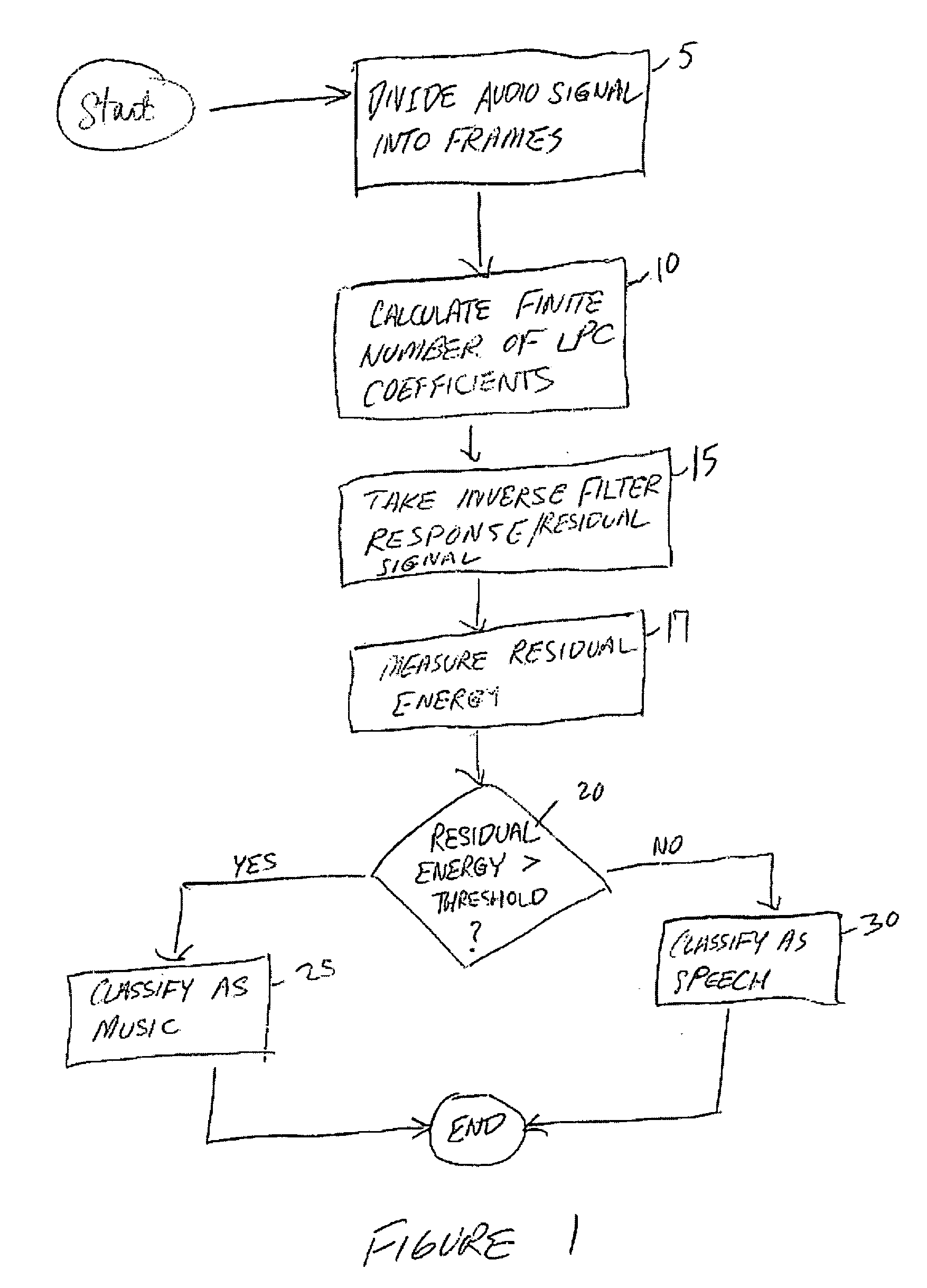
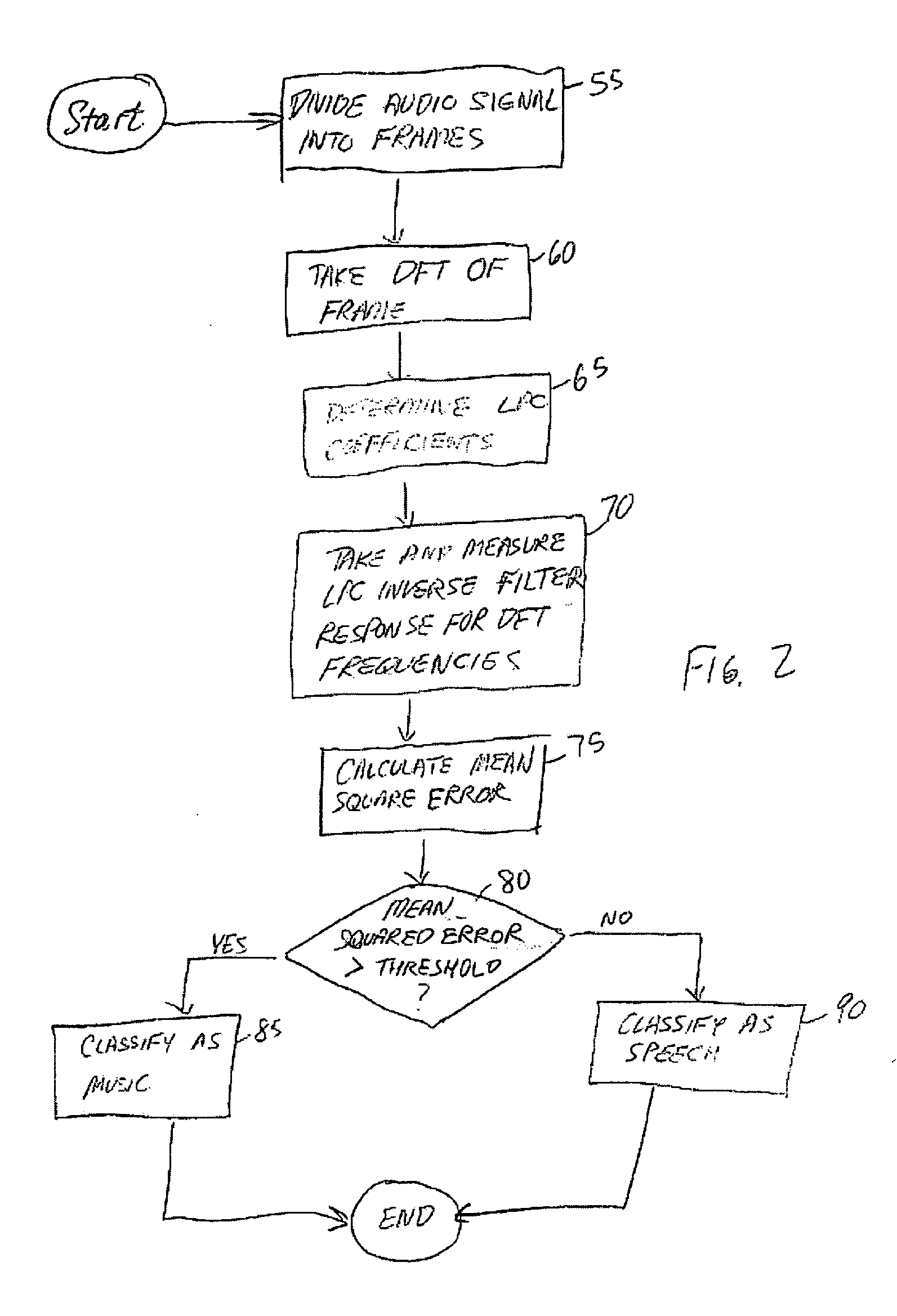
Classification of speech and music using linear predictive coding coefficients
InactiveUS20050159942A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisLinear predictive codingLinearity
Presented herein are systems and methods for classifying an audio signal. The audio signal is classified by calculating a plurality of linear prediction coefficients (LPC) for a portion of the audio signal; inverse filtering the portion of the audio signal with the plurality of linear prediction coefficients (LPC), thereby resulting in a residual signal; measuring the residual energy of the residual signal; and comparing the residual energy to a threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
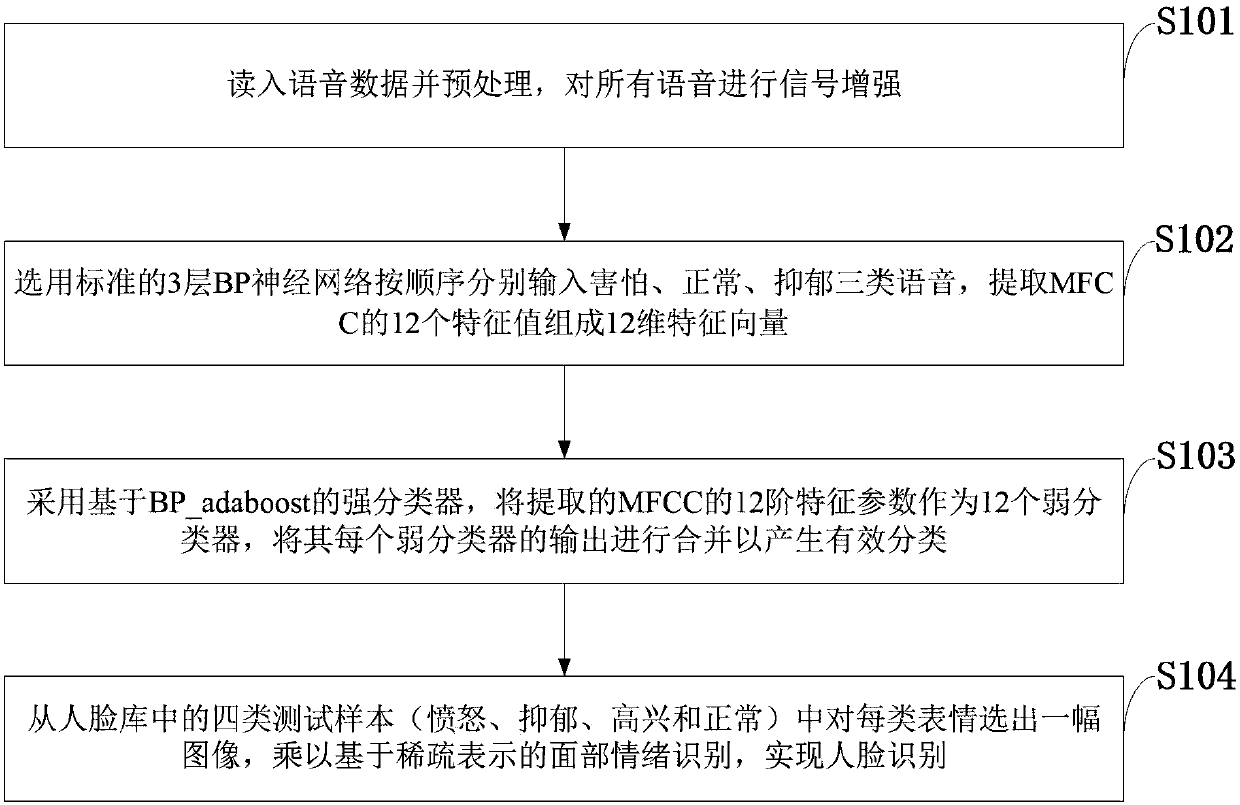
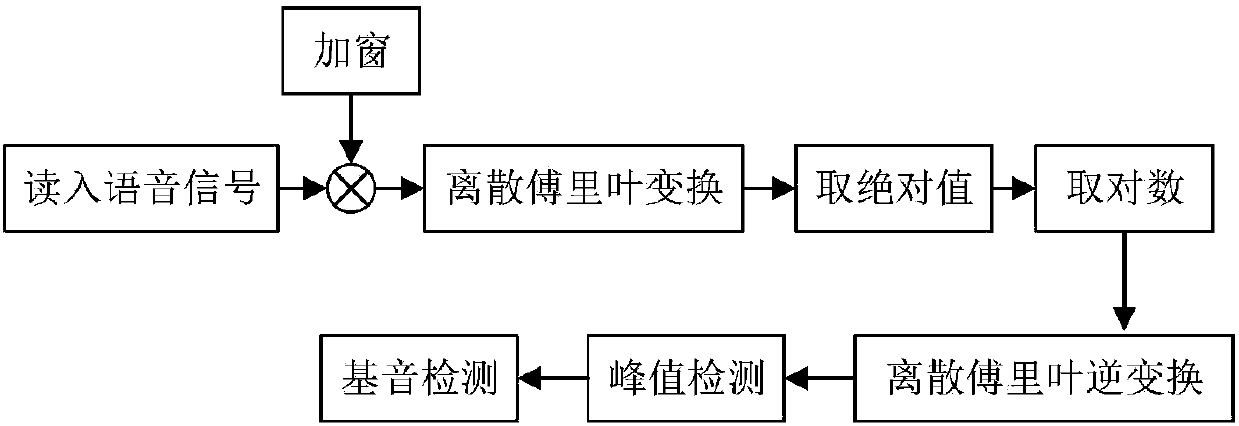
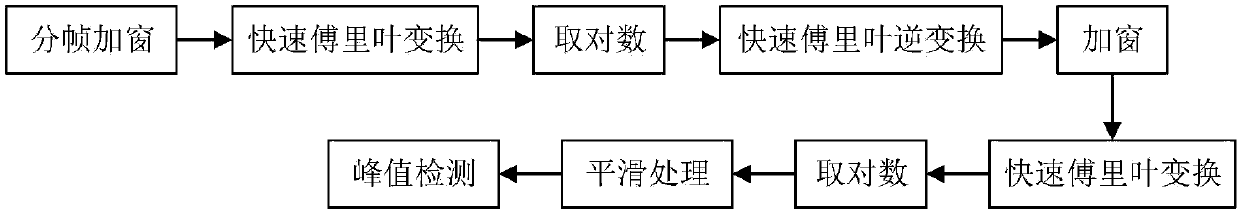
A depression auxiliary detection method based on acoustic characteristics and sparse mathematics and a classifier
ActiveCN107657964AImprove recognition rateEasy to implementPsychotechnic devicesSpeech recognitionImaging processingTest sample
The invention belongs to the technical field of speech processing and image processing and discloses a depression auxiliary detection method based on acoustic characteristics and sparse mathematics and a classifier. The method is characterized by carrying out depression diagnosis based on speech and facial emotion common identification; realizing estimation of a glottis signal through an inverse filter; carrying out global analysis on the speech signals to extract characteristic parameters, and analyzing timing and distribution features of the characteristic parameters to find out rhyme rulesof speeches in different emotions as basis of emotion recognition; using MFCC as a speech signal to be processed for analysis of the characteristic parameters, collecting data in records through a plurality of groups of training data, and establishing a neural network model for diagnosis; through an OMP-based sparse express algorithm, obtaining sparse linear combination of a test sample; and carrying out judgment and classification on facial emotions, and carrying out linear combination on the obtained result and the speech recognition result to obtain final probability for expressing each data. The depression recognition rate is improved greatly, and the cost is low.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV +1
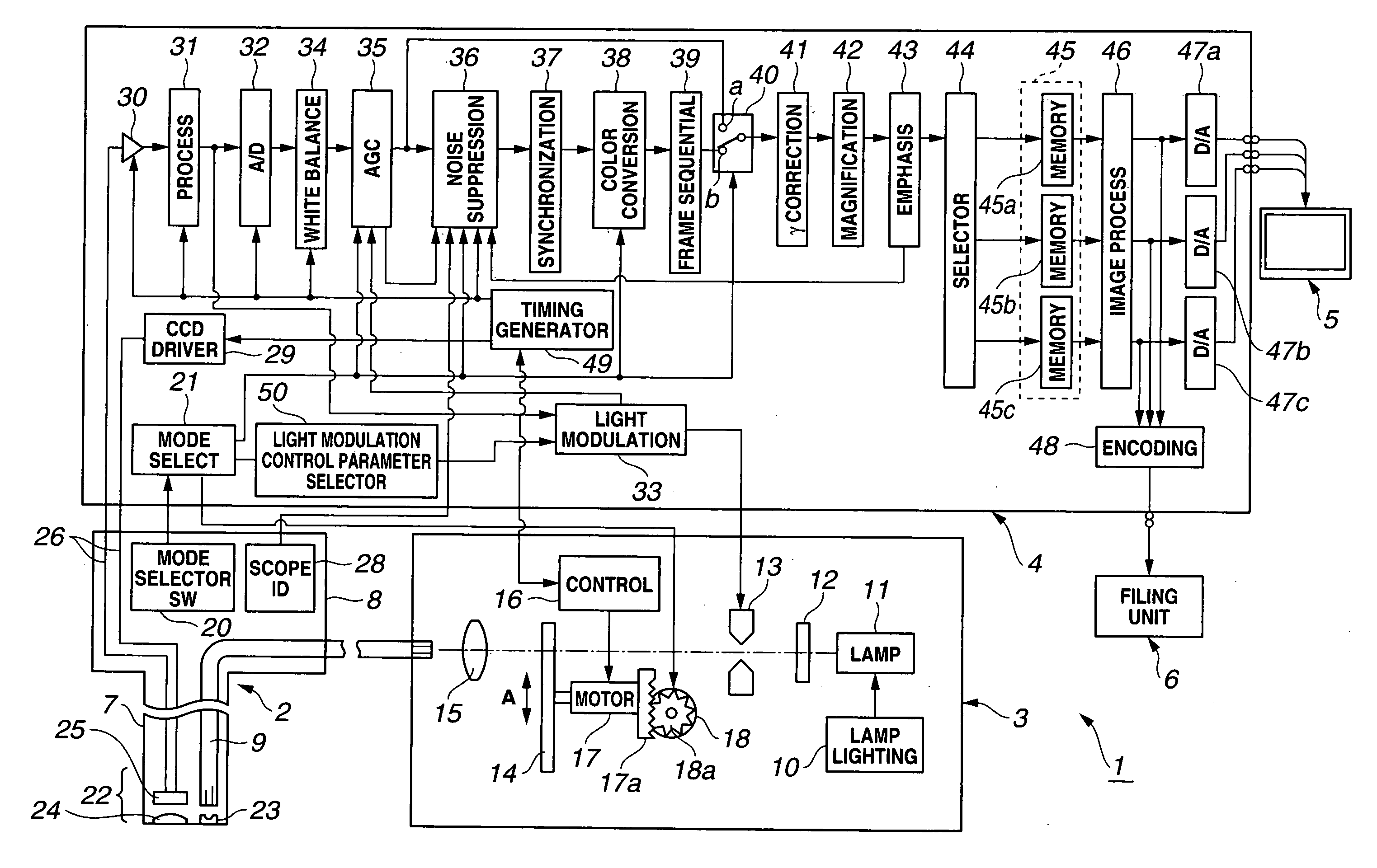
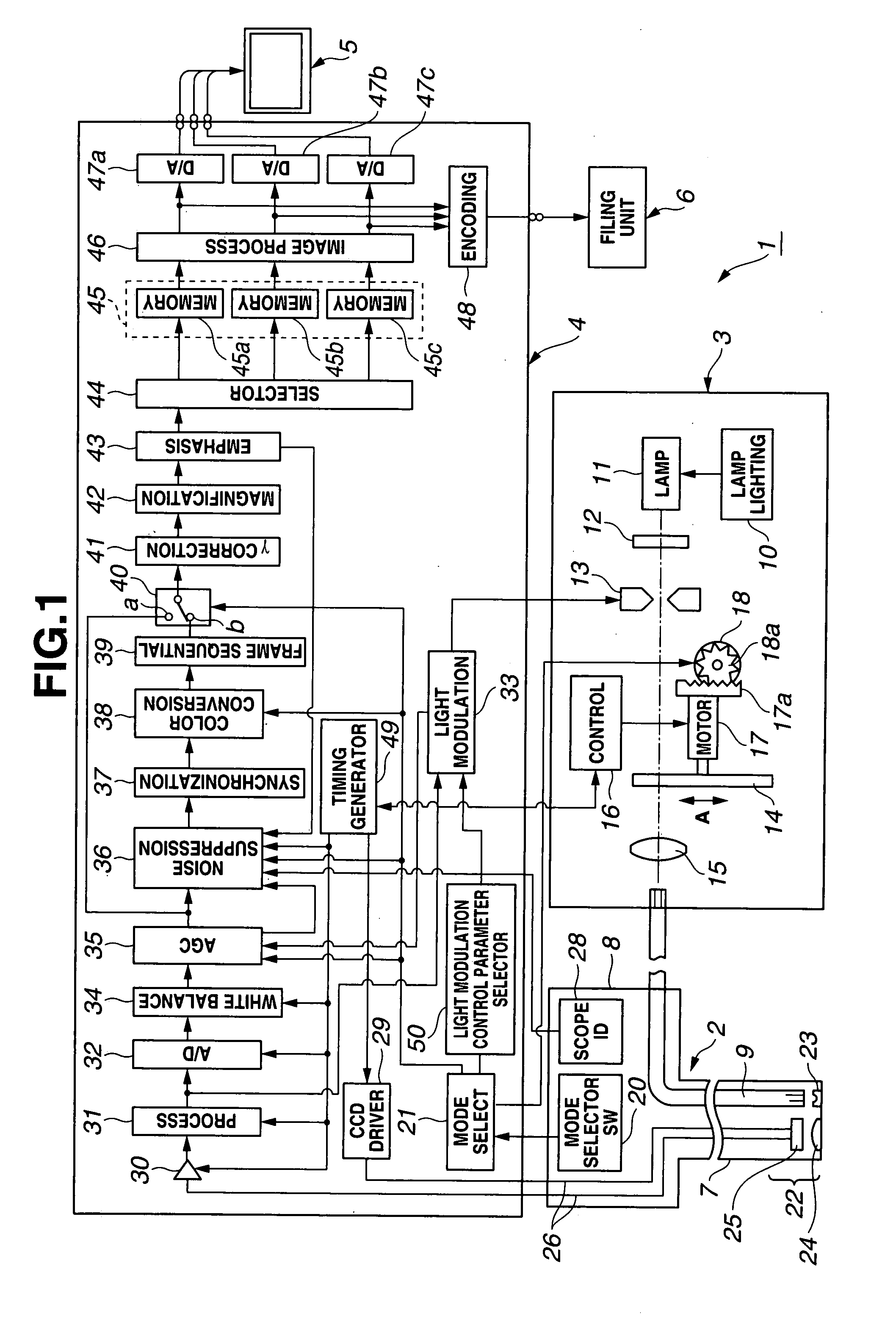
Image Processor and Endoscope Apparatus
ActiveUS20090021578A1Suppress noiseReduce contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer scienceBrightness perception
An image processor includes a filter process circuit for executing a filtering of image data picked up by an image pickup unit with a plurality of spatial filters, a brightness calculation circuit for calculating a brightness in a local area of the image data, a weighting circuit for weighting an output of the filter process circuit in accordance with an output of the filter process circuit and / or an output of the brightness calculation circuit, and an inverse filter process circuit for executing an inverse filter process with respect to an output of the weighting circuit to generate process image data.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method for controlling a speaker array to provide spatialized, localized, and binaural virtual surround sound
ActiveUS9578440B2Improve user interactionReduce leakageMicrophonesLoudspeakersSource materialLight beam
A signal processing method and system are provided for delivering spatialized sound using highly optimized inverse filters to deliver narrow localized beams of sound from the included speaker array. The inventive method can be used to provide private listening areas in a public space and provide spatialization of source material for individual users to create a virtual 3D audio effect. In a binaural mode, a speaker array provides two targeted beams aimed towards the primary user's ears—one discrete beam for the left ear and one discrete beam for the right ear.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +2
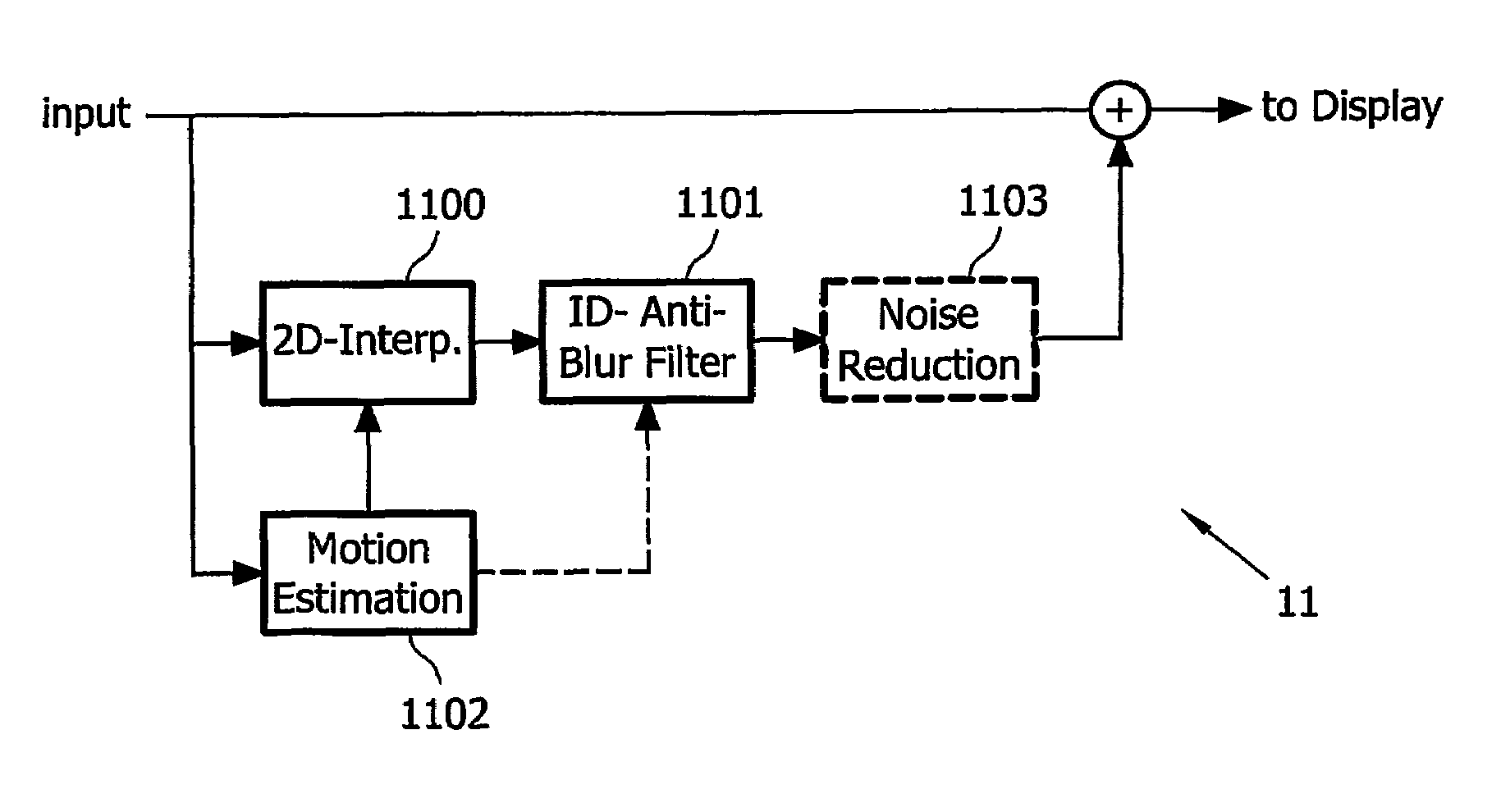
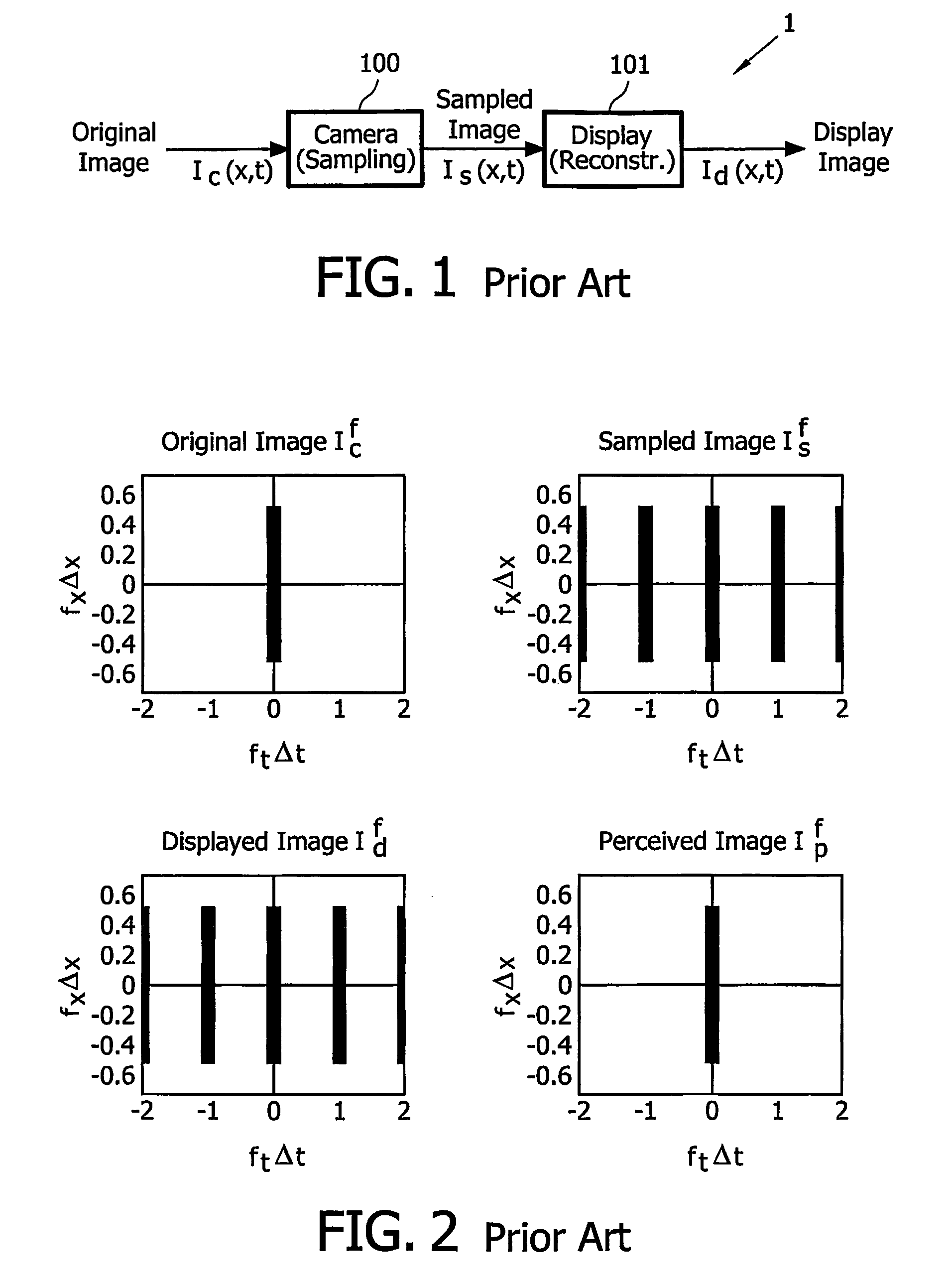
Motion-compensated inverse filtering with band-pass filters for motion blur reduction
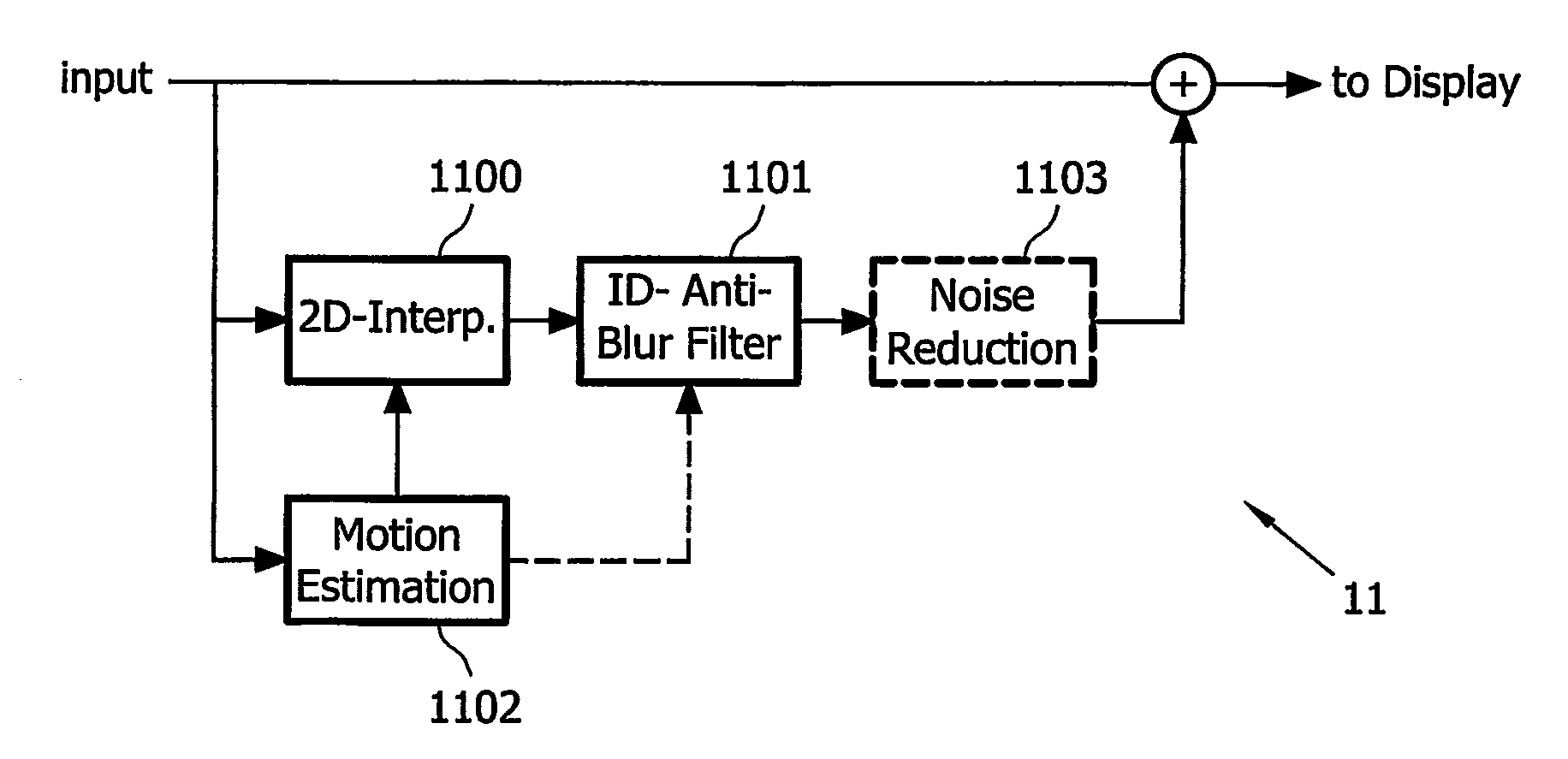
InactiveUS20070126928A1Reduce motion blurReduce relative motionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesBandpass filteringMotion vector
This invention relates to a method, a computer program, a computer program product, and a device for reducing motion blur of images of a video signal shown on a hold-type display (101), comprising estimating (1102) motion vectors of moving components in said images of said video signal; band-pass filtering (1100, 1101) said video signal with respect to a spatial frequency domain, wherein said band-pass filtering at least partially depends on said estimated motion vectors, and wherein with increasing length of said estimated motion vectors, the passband of said band-pass filtering adaptively shifts from high spatial frequencies to medium spatial frequencies; and combining (1104) said video signal and said band-pass filtered video signal to produce an input video signal for said hold-type display.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
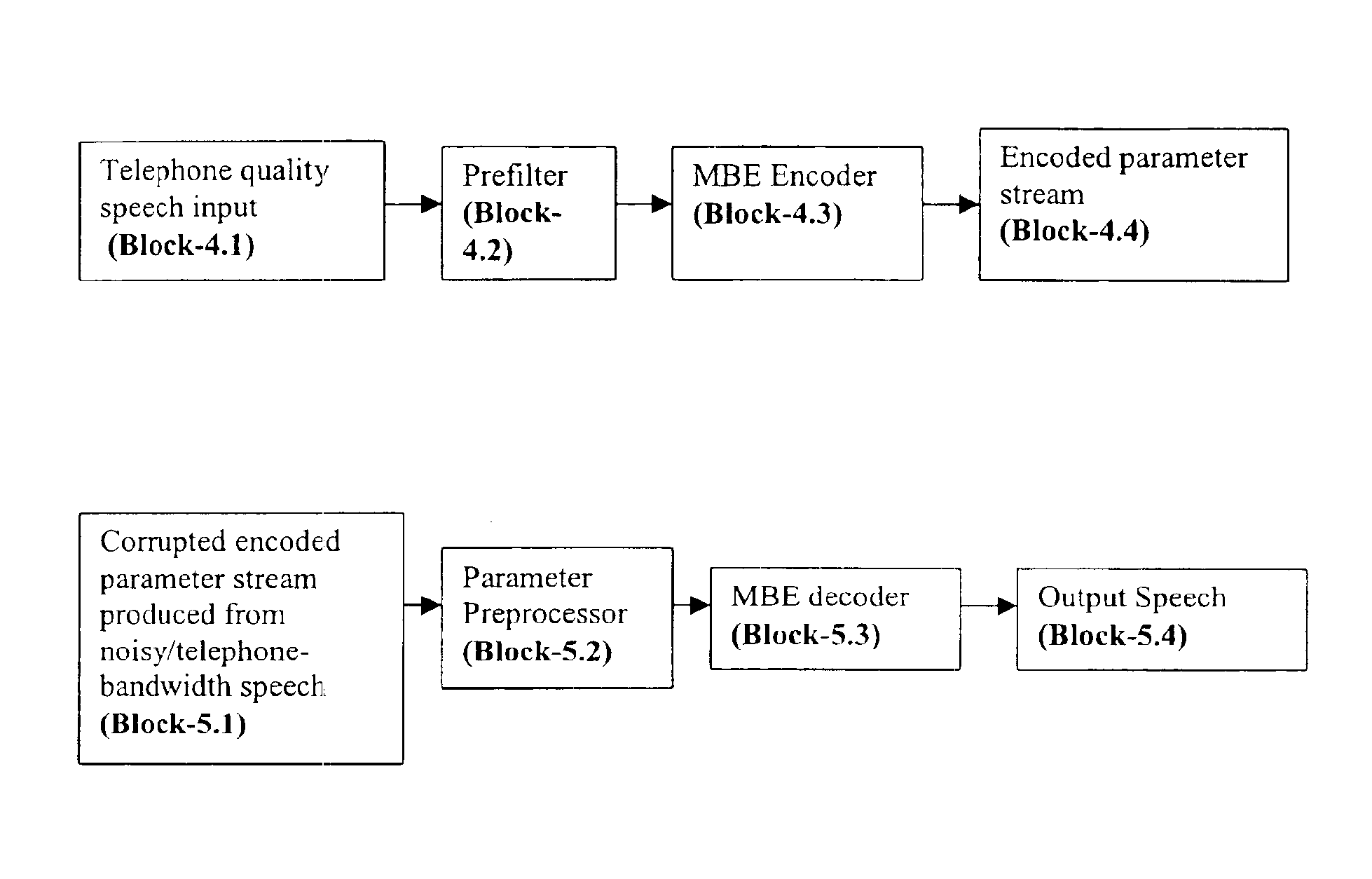
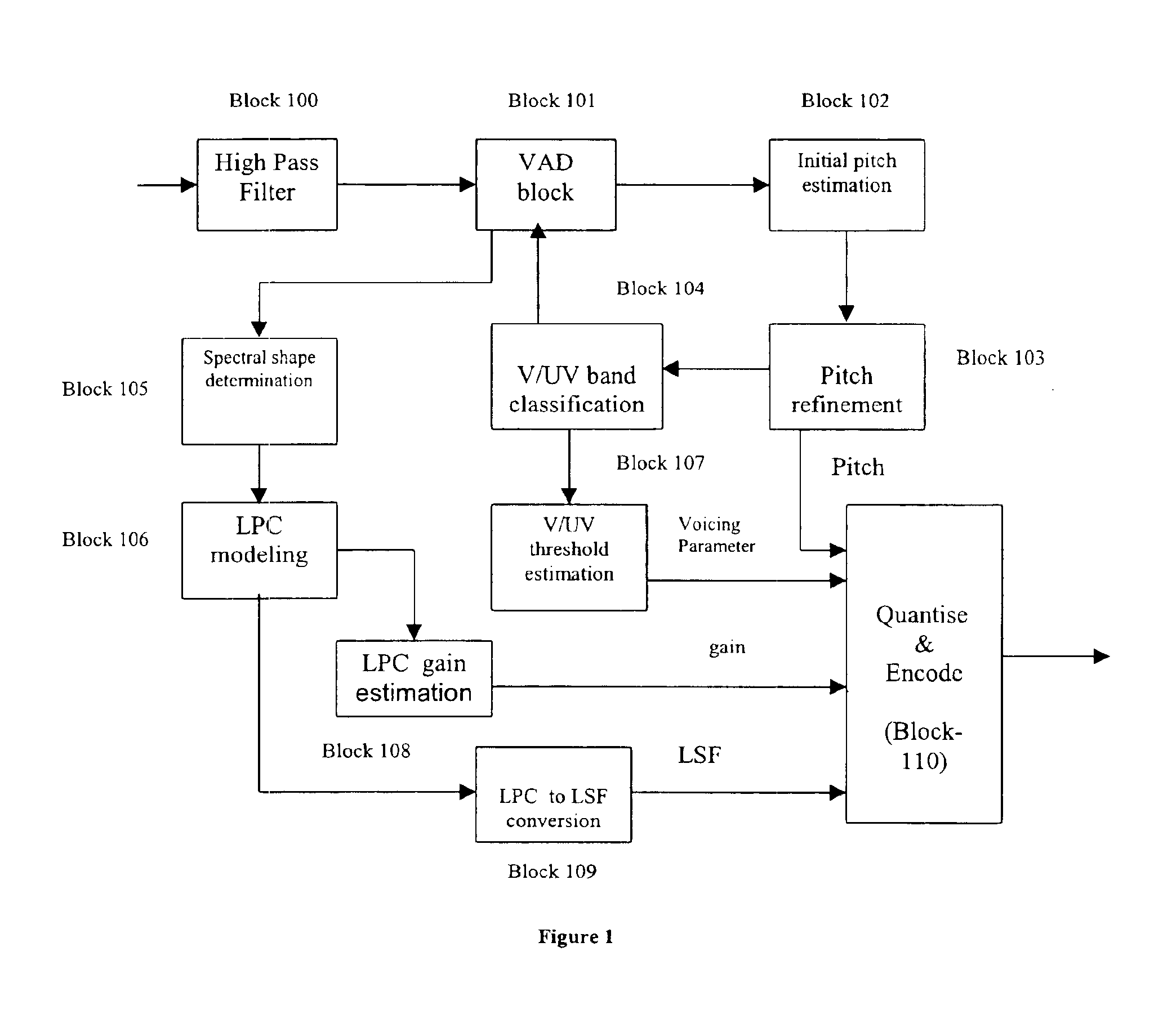
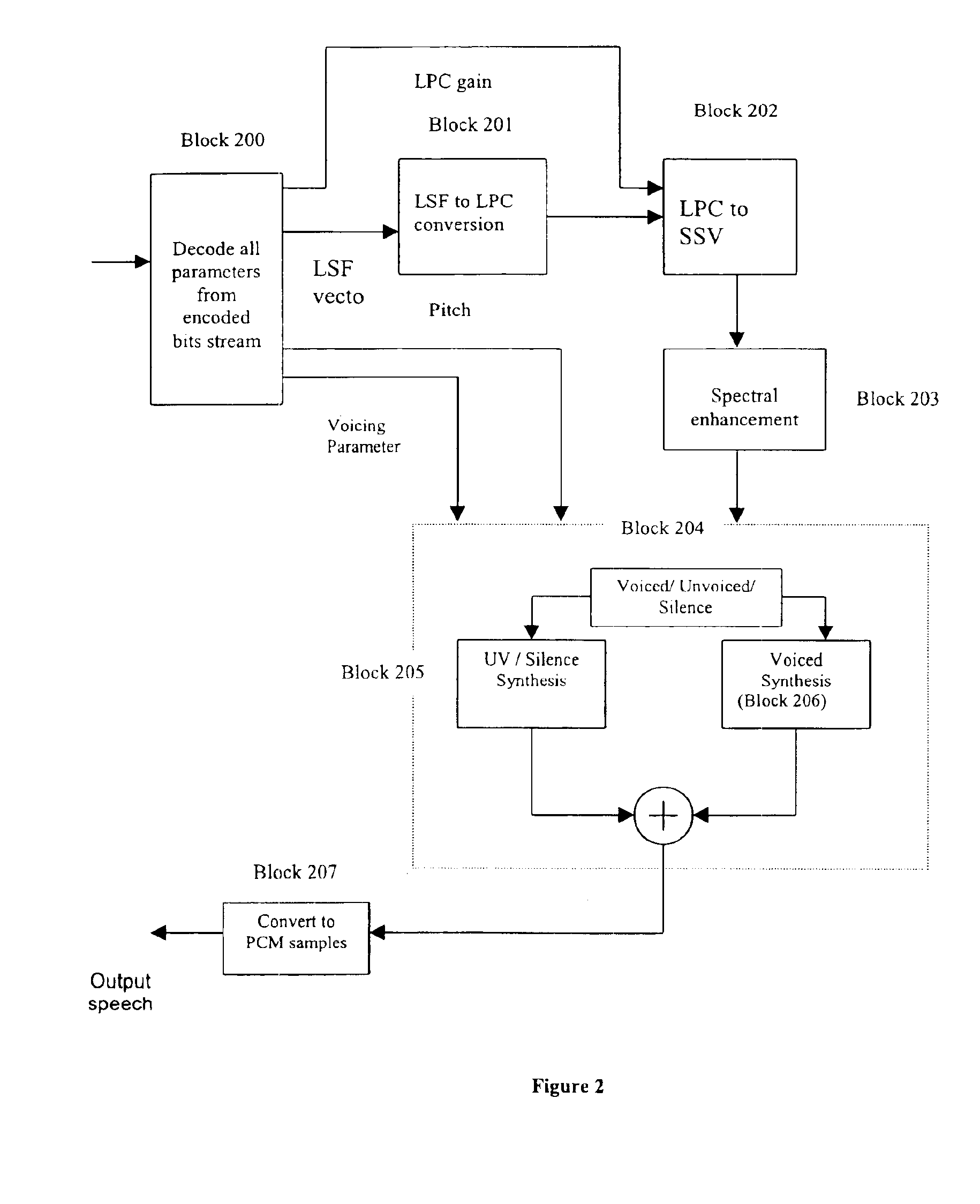
Preprocessing modules for quality enhancement of MBE coders and decoders for signals having transmission path characteristics
InactiveUS6912496B1Improve performanceClose to speech qualitySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumLinear filter
Pursuant to one aspect of the invention, a prefilter module that incorporates an inverse filter is used in conjunction with an encoder. The inverse filter has an inverse frequency response of a frequency response of a filter that simulates speech having transmission path characteristics, such as telephone-channel bandwidth speech, and / or noisy speech. The inverse filter is used to compensate transmission path characteristics of an input signal. The inverse filter can be designed using several methods, such as, for example, an autoregressive model or a moving average model. Pursuant to a second aspect of the invention, a parameter preprocessor is used in conjunction with a decoder. The parameter preprocessor performs pitch rectification through use of a medium and linear filter, and updates spectral amplitudes and voicing parameter depending on the pitch rectification. The inverse filter and parameter preprocessor, used in conjunction with an encoder and decoder, respectively, improve signal processing and parameter estimation.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
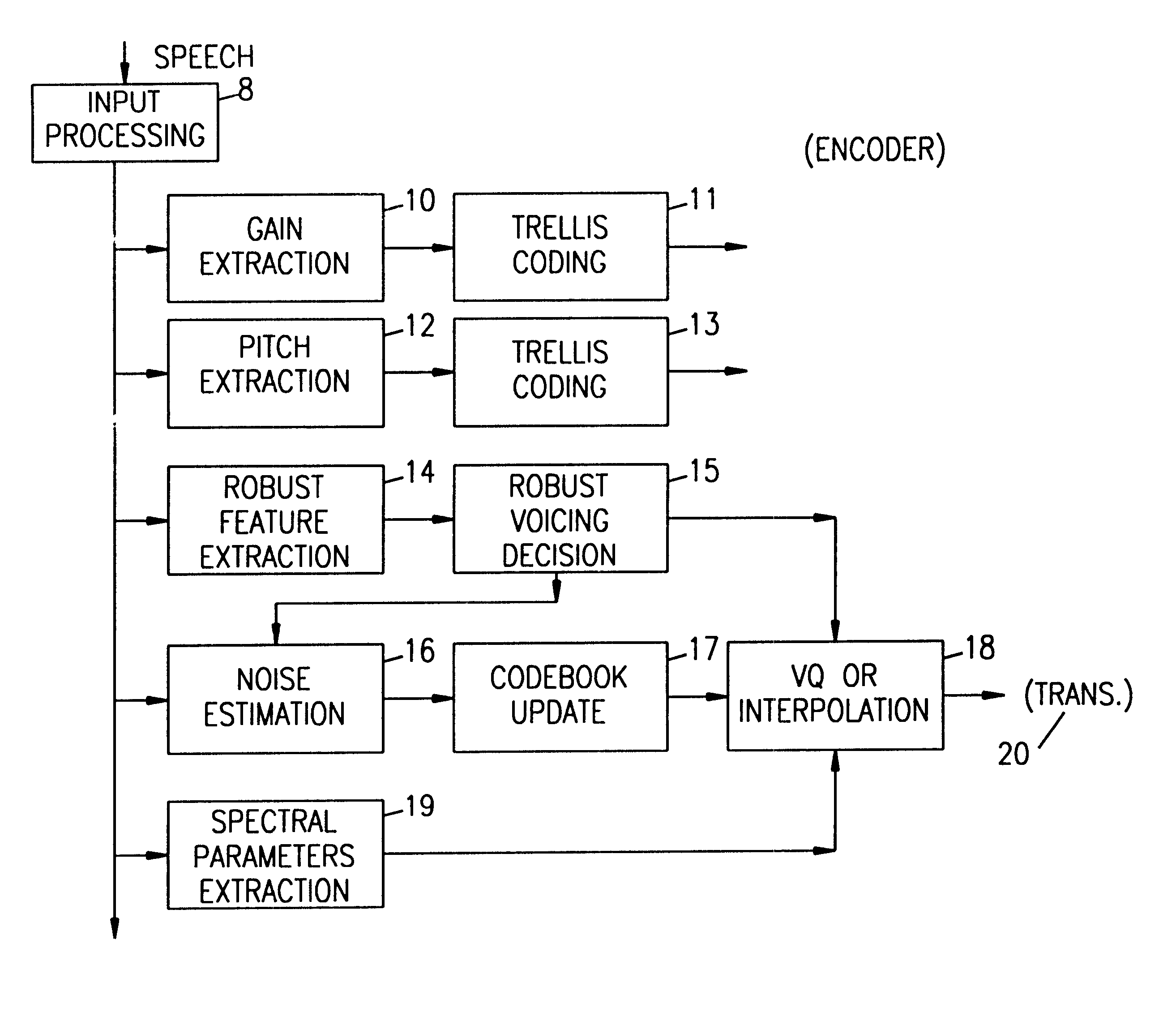
Enhancement of speech coding in background noise for low-rate speech coder
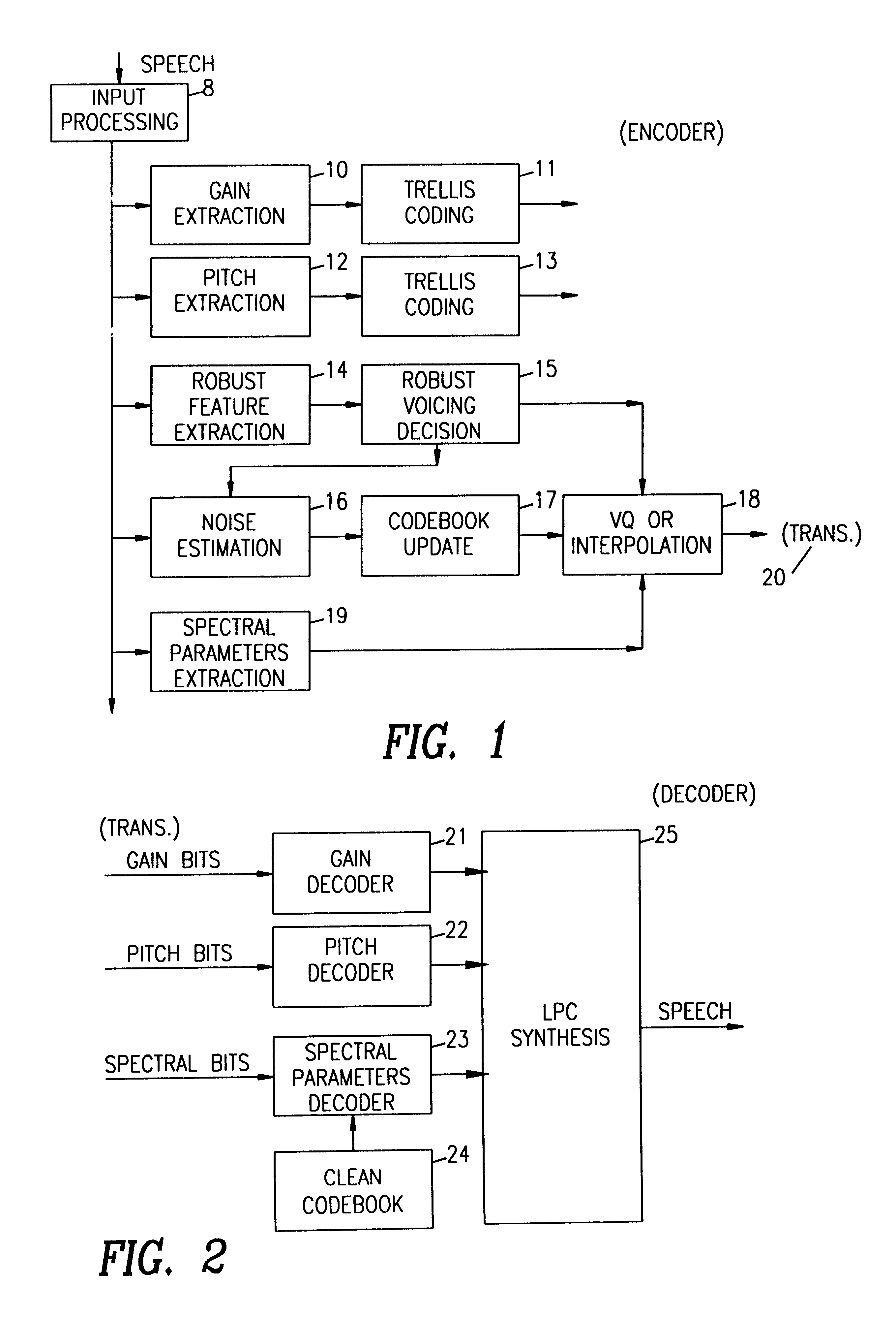
A speech coding system employs measurements of robust features of speech frames whose distribution are not strongly affected by noise / levels to make voicing decisions for input speech occurring in a noisy environment. Linear programing analysis of the robust features and respective weights are used to determine an optimum linear combination of these features. The input speech vectors are matched to a vocabulary of codewords in order to select the corresponding, optimally matching codeword. Adaptive vector quantization is used in which a vocabulary of words obtained in a quiet environment is updated based upon a noise estimate of a noisy environment in which the input speech occurs, and the "noisy" vocabulary is then searched for the best match with an input speech vector. The corresponding clean codeword index is then selected for transmission and for synthesis at the receiver end. The results are better spectral reproduction and significant intelligibility enhancement over prior coding approaches. Robust features found to allow robust voicing decisions include: low-band energy; zero-crossing counts adapted for noise level; AMDF ratio (speech periodicity) measure; low-pass filtered backward correlation; low-pass filtered forward correlation; inverse-filtered backward correlation; and inverse-filtered pitch prediction gain measure.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Motion-compensated inverse filtering with band-pass filters for motion blur reduction
InactiveUS7693343B2Reduce motion blurTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesBandpass filteringMotion vector
This invention relates to a method, a computer program, a computer program product, and a device for reducing motion blur of images of a video signal shown on a hold-type display (101), comprising estimating (1102) motion vectors of moving components in said images of said video signal; band-pass filtering (1100, 1101) said video signal with respect to a spatial frequency domain, wherein said band-pass filtering at least partially depends on said estimated motion vectors, and wherein with increasing length of said estimated motion vectors, the passband of said band-pass filtering adaptively shifts from high spatial frequencies to medium spatial frequencies; and combining (1104) said video signal and said band-pass filtered video signal to produce an input video signal for said hold-type display.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and means for creating prosody in speech regeneration for laryngectomees
InactiveUS20050049856A1Improve naturalnessAssist in intelligibilitySpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumGlottis
A device and a method to be used by laryngeally impaired people to improve the naturalness of their speech. An artificial sound creating mechanism which forms a simulated glottal pulse in the vocal tract is utilized. An artificial glottal pulse is compared with the natural spectrum and an inverse filter is generated to provide an output signal which would better reproduce natural sound. A digital signal processor introduces a variation of pitch based on an algorithm developed for this purpose; i.e. creating prosody. The algorithm uses primarily the relative amplitude of the speech signal and the rise and fall rates of the amplitude as a basis for setting the frequency of the speech. The invention also clarifies speech of laryngectomees by sensing the presence of consonants in the speech and appropriately amplifying them with respect to the vowel sounds.
Owner:BARAFF DAVID R
Method for realizing minimum phase of vibroseis seismic data zero-phase wavelet
ActiveCN101545981ADoes not change the amplitude spectrumAchieve minimum phasingSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingSection planeWavelet
The invention relates to the technologies of prospecting, development and exploration in an oil field, in particular to a method for realizing the minimum phase of a vibroseis seismic data zero-phase wavelet, which can provide a high-resolution seismic pattern. The realizing steps are as follows: seismic data is processed and transformed into vibroseis zero-phase wavelet seismic data, a vibroseis zero-phase wavelet and an autocorrelation function are calculated, an inverse filter factor is solved, phase-only factor, calibration factor and phase transformation factor are calculated, the phase transformation factor is used for transforming the zero-phase wavelet into a minimum-phase wavelet, and a phase-corrected seismic data section plane is drawn by corrected seismic data. The method can effectively transform the vibroseis zero-phase wavelet seismic data into the minimum-phase seismic data by a common seismic data processing system, thereby providing necessary input seismic data for seismic data processings such as deconvolution, and the like.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Audio enhancement system
An audio enhancement system is provided for compensating for distortions (e.g., linear distortions) of a sound signal reproduced by an audio system in a listening room. The audio enhancement system includes analysis filters that generate a plurality of analysis output signals from an audio signal to be enhanced. The system also includes synthesis filters that generate an enhanced audio signal from a number of synthesis input signals. The number of analysis output signals and the number of synthesis input signals preferably are equal. Signal processing elements between the analysis filters and the synthesis filters generate one of the synthesis input signals from a respective one of the analysis output signals to perform an inverse filtering for linearizing an unknown transfer function indicative of the audio system and the listening room in the respective frequency range.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
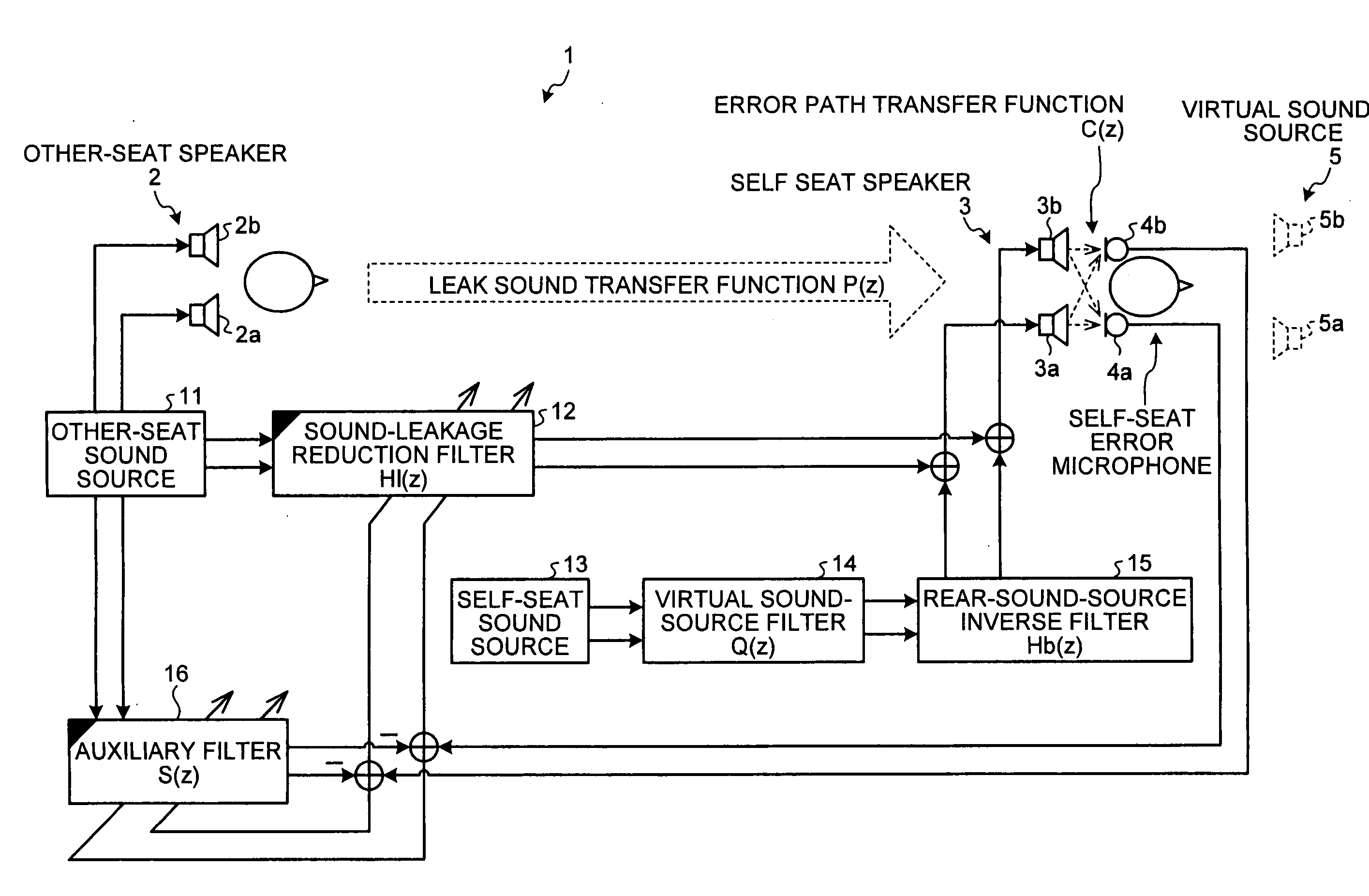
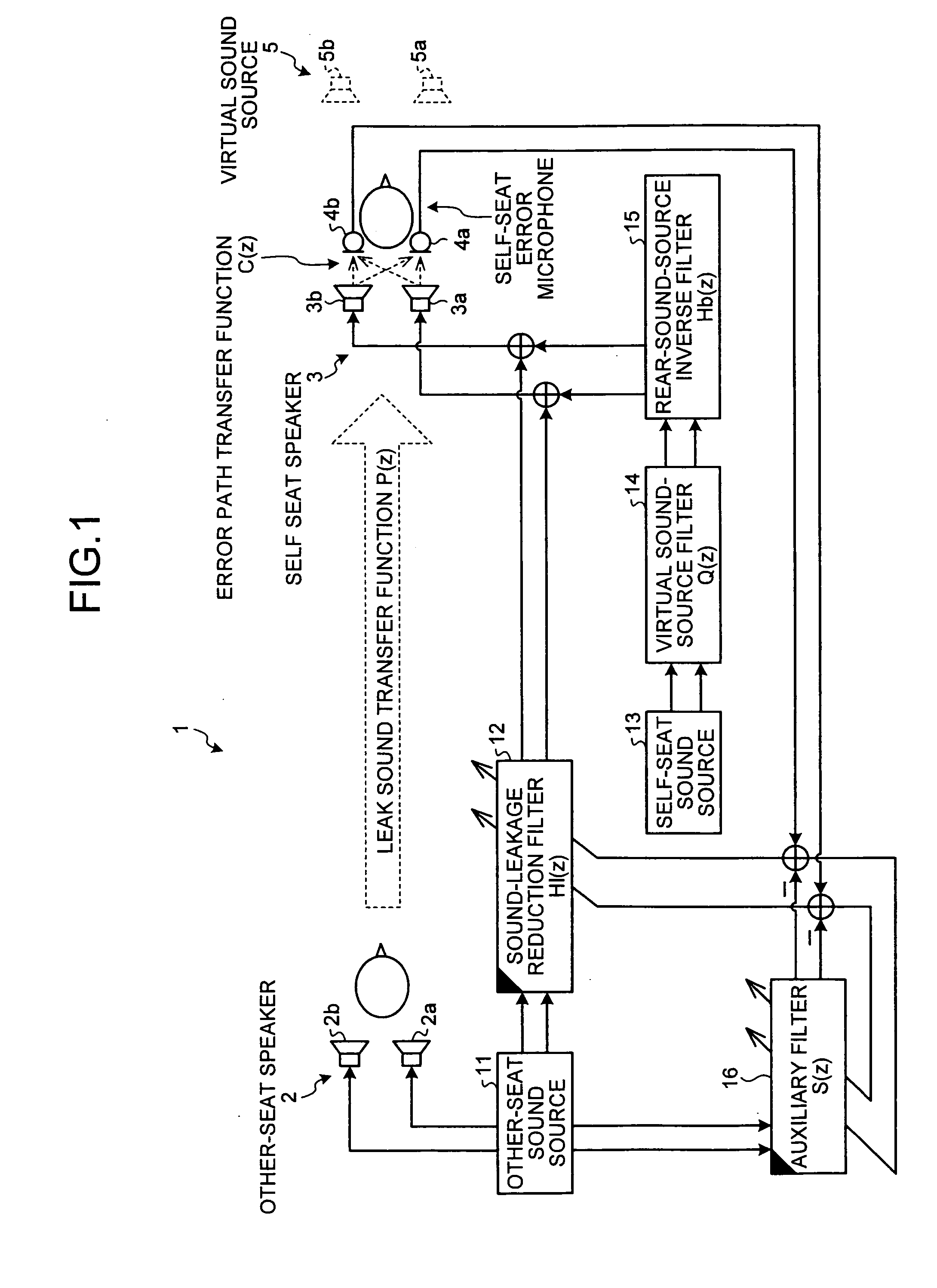
Acoustic system for providing individual acoustic environment
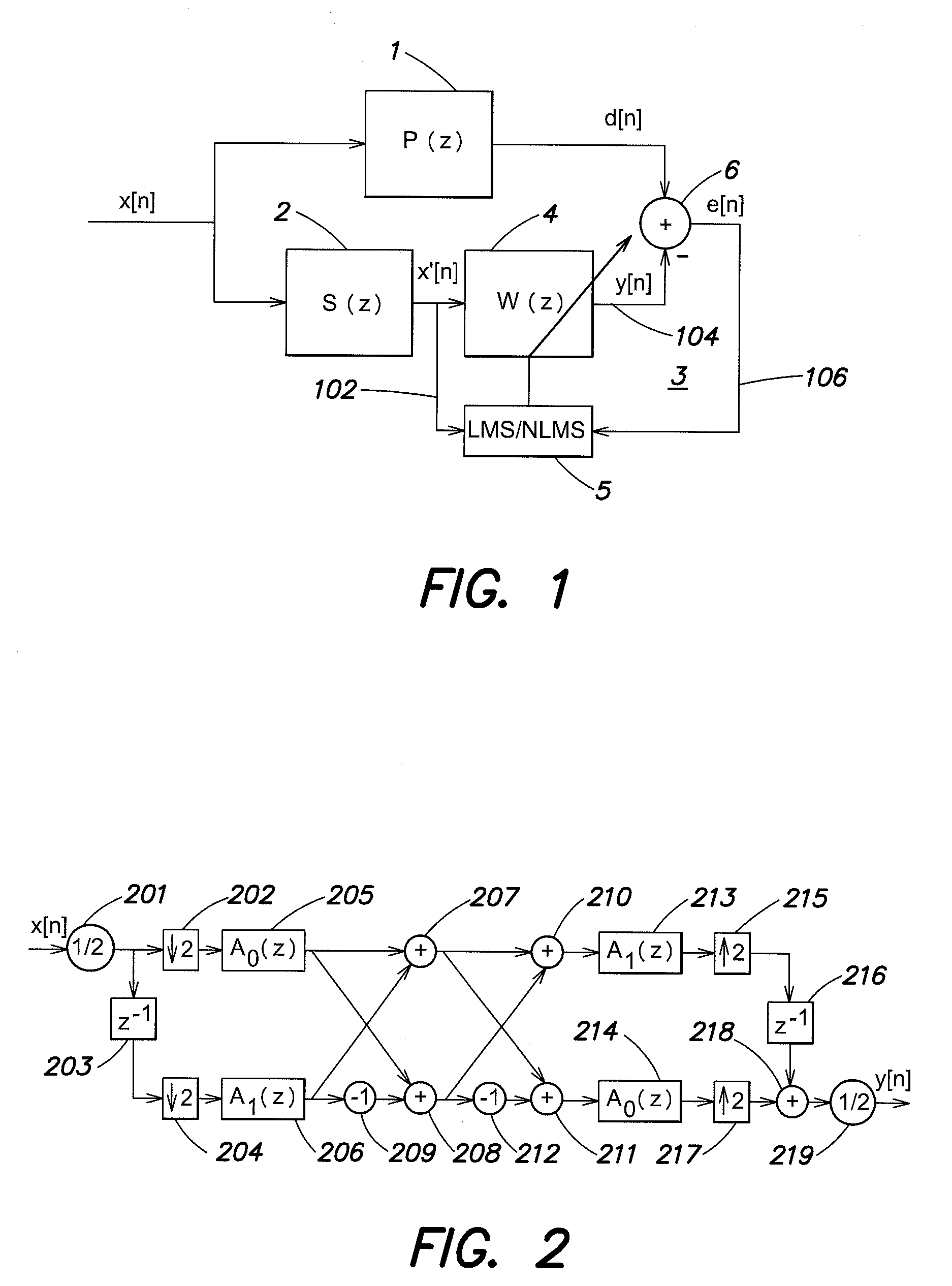
An acoustic system uses a self speaker installed to be at the back of a listener in a first individual space and an error microphone installed to be closer to the listener than the self speaker. A sound-leakage reduction filter generates control sound for negating sound leaked from another speaker installed in a second individual space to the first individual space, and provides the control signal to the self speaker. A virtual sound-source filter generates a virtual sound source, and a rear-sound-source inverse filter corrects rearward localization of a sound image toward the listener.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Method for Determining Inverse Filter from Critically Banded Impulse Response Data
ActiveUS20110274281A1Efficient executionEqual loudnessSignal processingFrequency response correctionMean squareEngineering
A method for determining an inverse filter for altering the frequency response of a loudspeaker so that with the inverse filter applied in the loudspeaker's signal path the inverse-filtered loudspeaker output has a target frequency response, and optionally also applying the inverse filter in the signal path, and a system configured (e.g., a general or special purpose processor programmed and configured) to determine an inverse filter. In some embodiments, the inverse filter corrects the magnitude of the loudspeaker's output. In other embodiments, the inverse filter corrects both the magnitude and phase of the loudspeaker's output. In some embodiments, the inverse filter is determined in the frequency domain by applying eigenfilter theory or minimizing a mean square error expression by solving a linear equation system.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
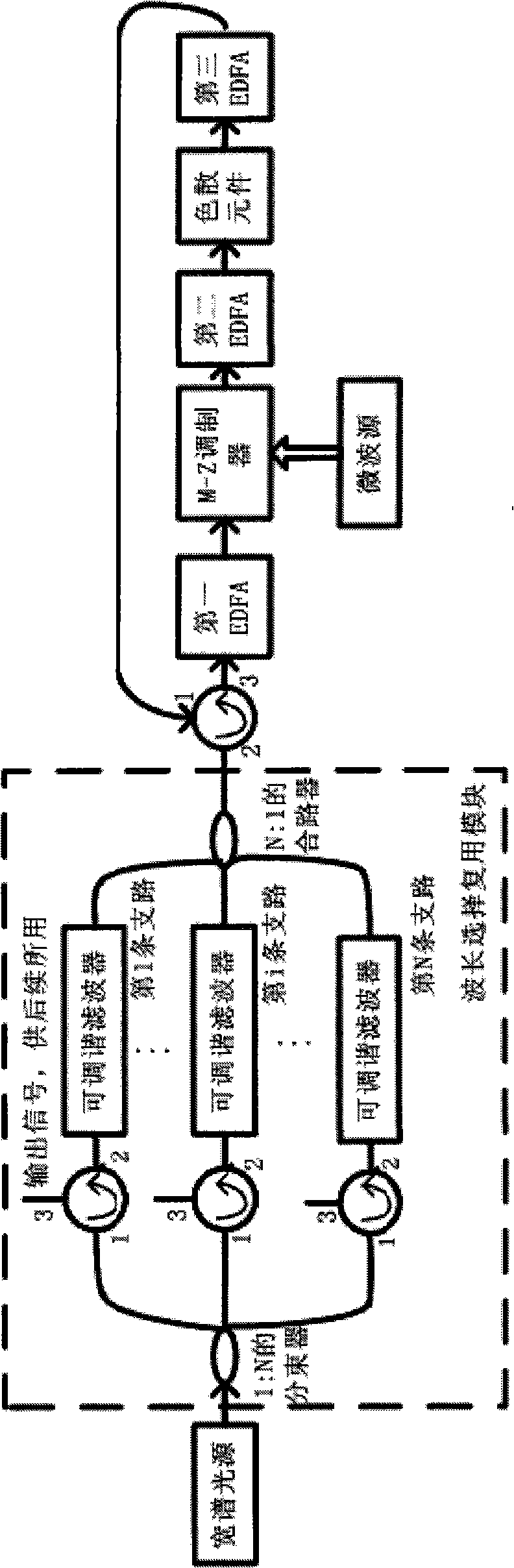
Filter feedback multiplexed millimeter wave subcarrier optical controlled microwave beam forming network
InactiveCN101359962AReduce unwanted spectral componentsIncrease optical powerFibre transmissionErbium dopingPeak value
The invention relates to a filter feedback reusable millimeter wave subcarrier light controlled microwave beam forming network, which belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave subcarrier optical controlled microwave beam forming, and is characterized in that a wavelength selecting reusable module transforms wide-spectrum light output by wide-spectrum light source to a comb-like spectrum; the comb-like spectrum is modulated by microwave signals which need to be transmitted, and the comb-like spectrum most energy of which is concentrated in the peak wavelength is formed after dispersive delay and amplification; then an adjustable filter in the wavelength selecting reusable module is utilized for inverse filtering to obtain each required signal; amplification efficiency of an erbium-doped optical fibre amplifier is greatly enhanced, and then the power level of useful spectra of the entire link is enhanced; and compared with that traditional wide-spectrum light passes through the light controlled microwave beam forming network, the invention enhances energy utilization.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
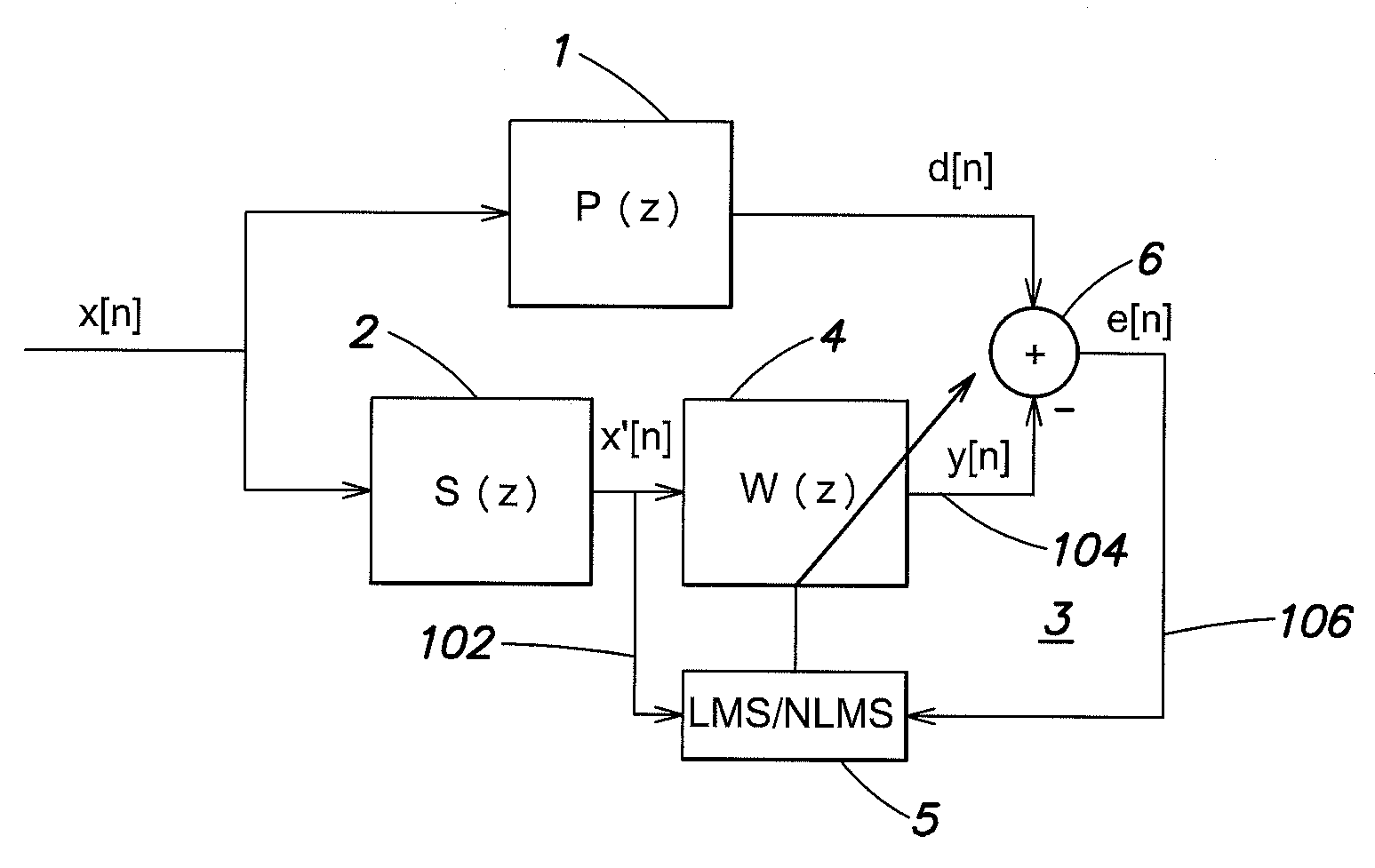
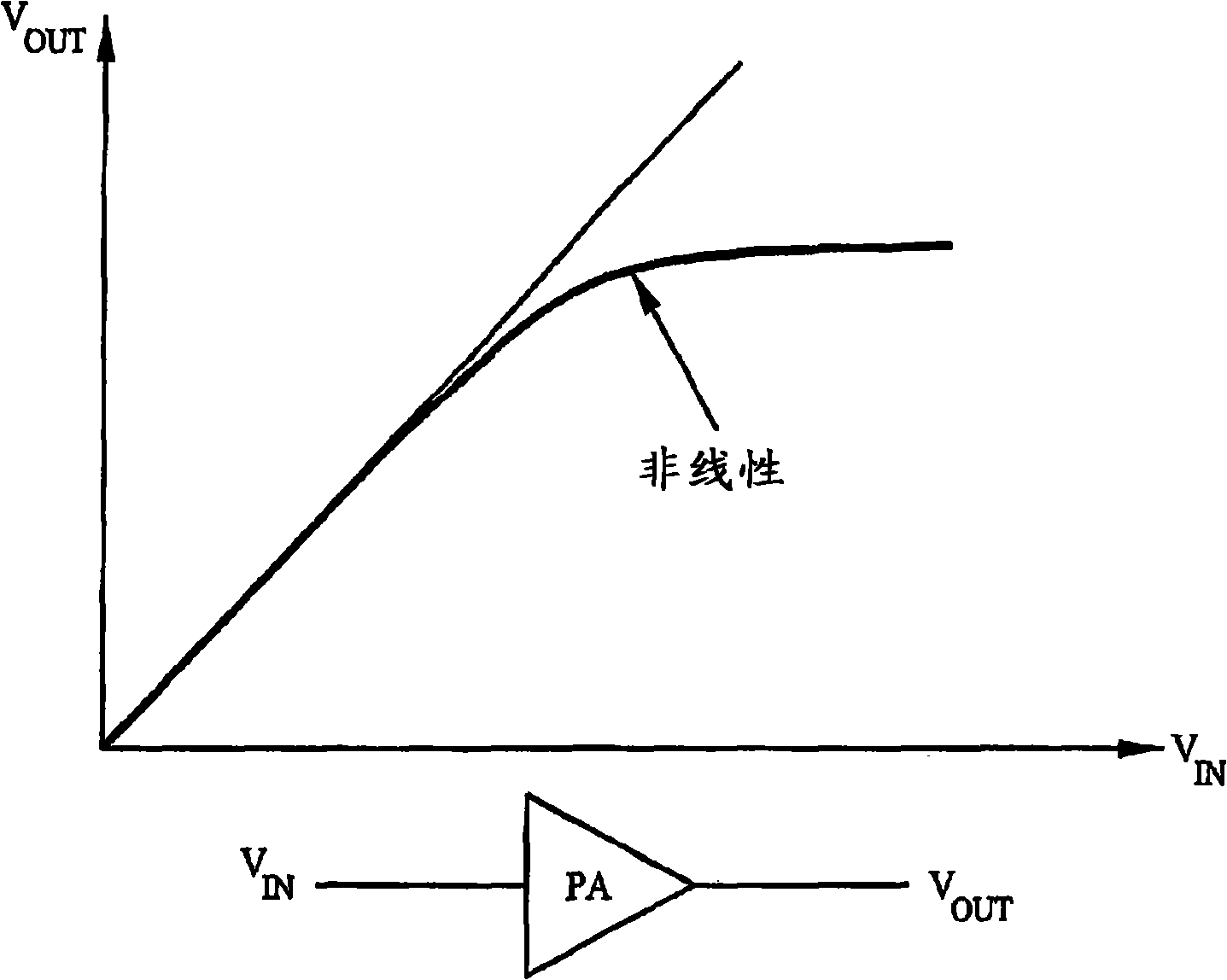
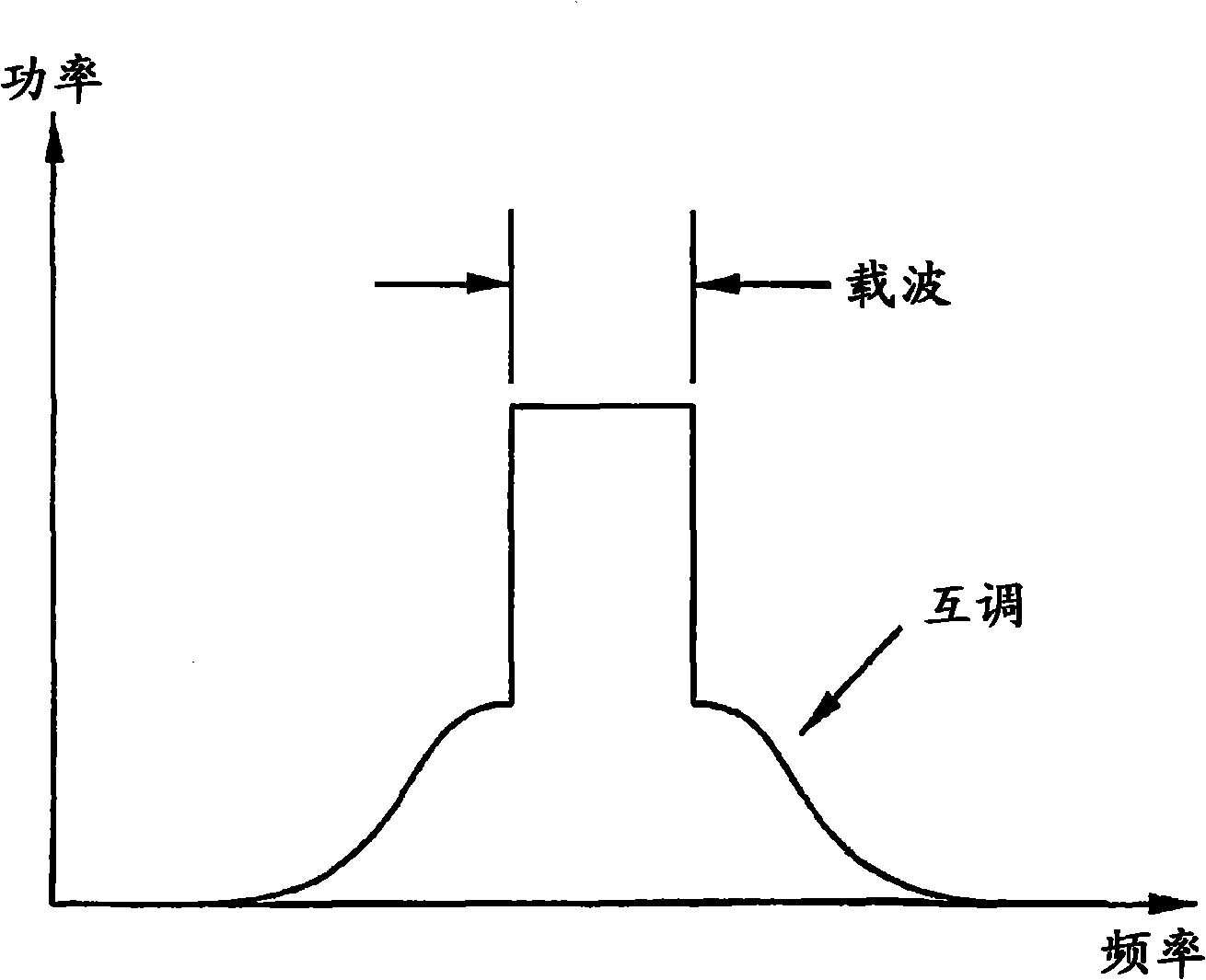
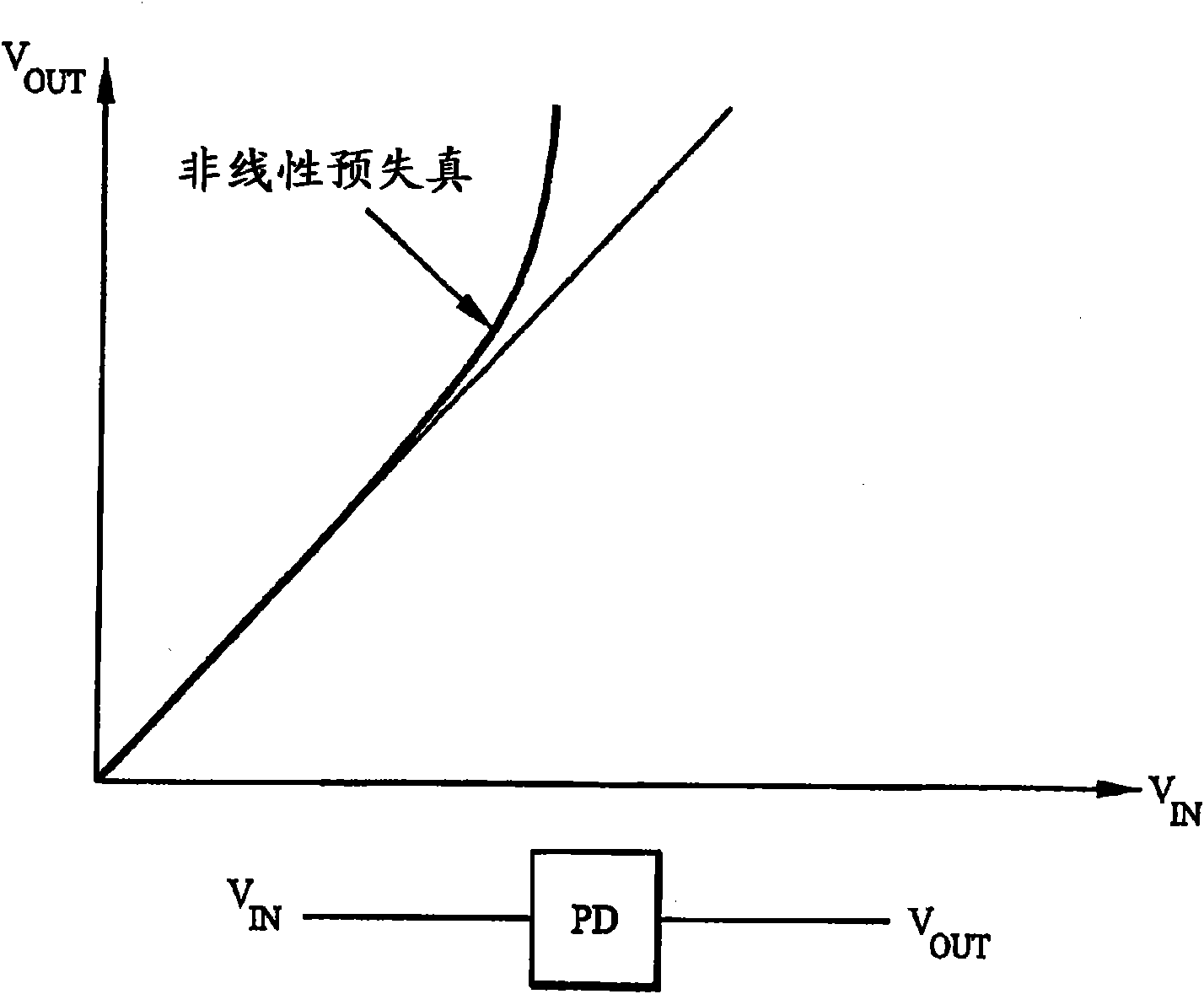
Device and method for identifying inverse characteristic of nonlinear system, power amplifier and predistorter thereof
InactiveCN101527544AAvoid numerical difficultiesNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention discloses a nonlinear system, in particular a device and a method for identifying inverse characteristic of a nonlinear power amplifier, a predistorter of the power amplifier and power amplification equipment using the device for identifying the inverse characteristic of the nonlinear system and the predistorter. The method for identifying the inverse characteristic of the nonlinear system according to an original input signal x(n) and a corresponding feedback output signal y<G>(n) of the nonlinear system comprises the following steps: according to an inverse filter signal x<F> (n) and the feedback output signal y<G>(n), calculating an inquiry form function Q[.]; according to the feedback output signal y<G>(n) and the inquiry form function Q[.], generating a middle predistortion signal z(n); according to the middle predistortion signal z(n) and the original input signal x(n), constructing a filter function F[.]; carrying out inverse filtering on the original input signal x(n) by using parameters of the filter function F[.] to generate an inverse filter signal x<F>(n); repeating each step through iteration till meeting the set condition, wherein the inquiry form function Q[.] and the filter function F[.] represent the inverse characteristic of the nonlinear system.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
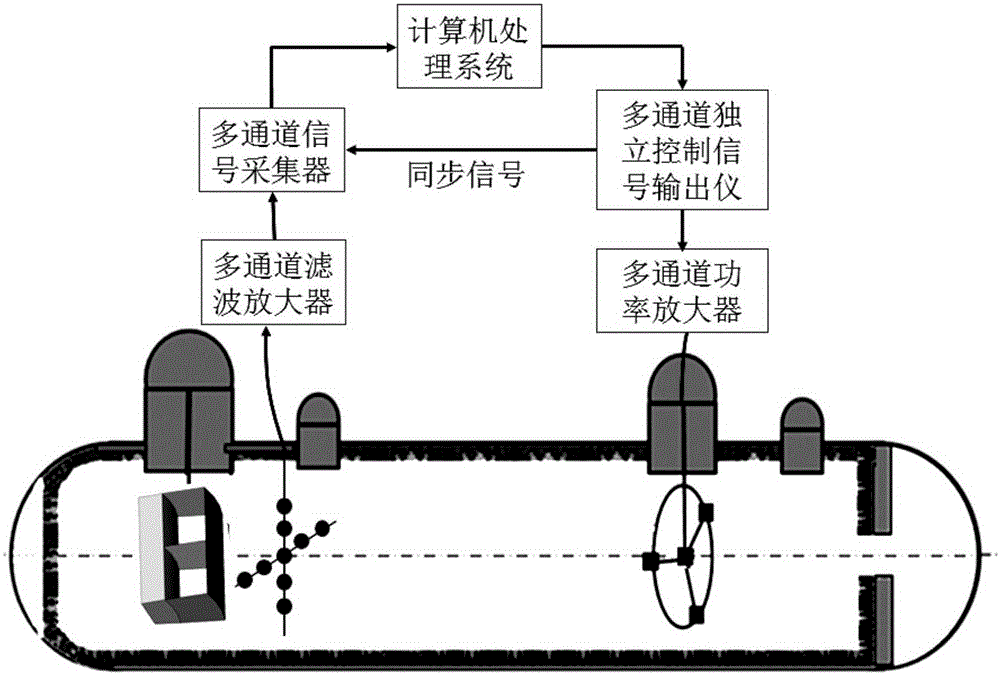
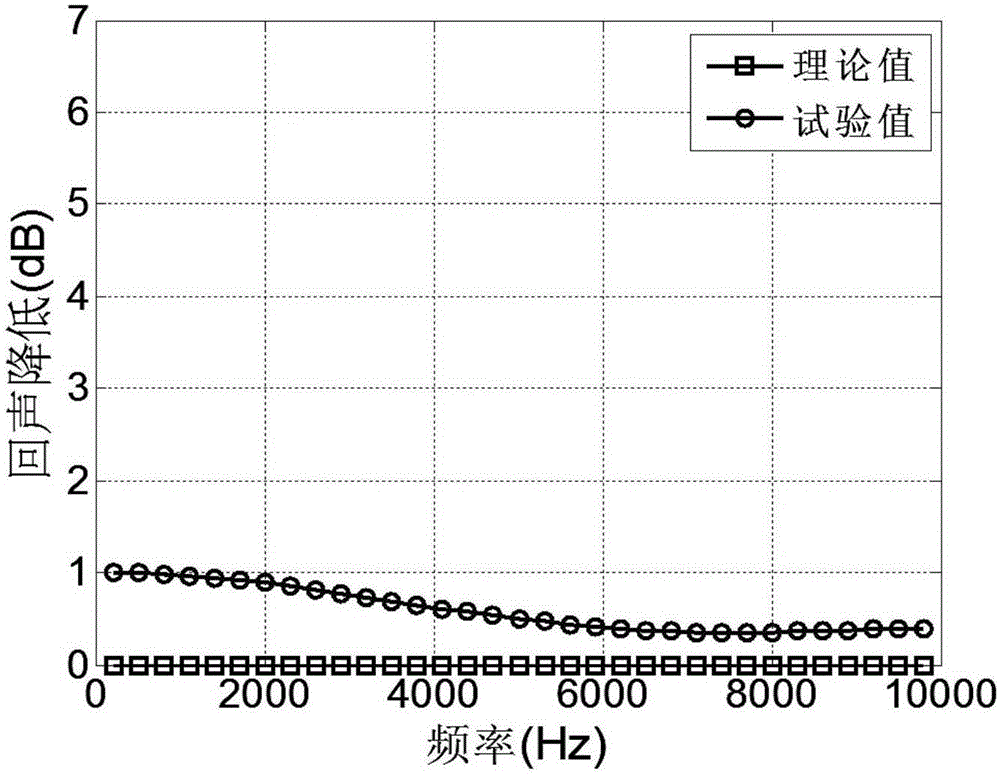
Acoustic covering layer echo reduction measuring method on basis of multichannel space-time inverse filtering technology
InactiveCN105181800ARealize time-domain pulse compressionEasy to separateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTime domainDirect path
The invention discloses an acoustic covering layer echo reduction measuring method on the basis of a multichannel space-time inverse filtering technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) generating a single channel space-time inverse filtering emission signal; (2) generating a multichannel space-time inverse filtering emission signal; (3) collecting a sample echo signal and an incident signal; (4) calculating the echo reduction measured value. By synchronously emitting the inversion signals of a circuit channel and underwater acoustic channel and multichannel inversion signals, the focusing of measuring signals in the space and time-domain pulse compression can be achieved, and the goals of reverberation inhibition, direct path wave separation, and multiple times of echoes of a multilayer sample can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Display device and control method for same
ActiveUS20160232857A1Increase valueTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesData acquisitionDisplay device
On the basis of the image data obtained by the image data acquisition section, a target luminance calculation section calculates a target luminance, which is a target value for the luminance of emitted light for each segment region. An inverse filter acquisition section acquires an inverse filter of a light emission distribution function which represents light emission distribution characteristics of the light source for each segment region. A setting value calculation section calculates a setting value for the luminance of emitted light of the light source for each segment region by performing a convolution operation on the target luminance for each segment region with the inverse filter. On the basis of the setting value for each segment region calculated by the setting value calculation section, a light source control section controls the luminance of emitted light of the light source for each segment region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Frequency response correction for a receiver having a frequency translation device
InactiveUS20080096489A1Receivers monitoringElectromagentic field characteristicsRunning timeMulti dimensional
A method of correcting the frequency response of an RF receiver having a frequency translation device and a fixed IF frequency section uses calibration data representing frequency responses over a wide frequency range for multiple center frequencies. The calibration data are based upon a multi-dimensional model for the frequency translation device that includes at least center frequency and offset frequency. The calibration data are stored in the RF receiver during factory calibration. A run-time normalization of the RF receiver produces a normalization frequency response at a reference frequency, and a relative frequency response at a desired center frequency is derived from the calibration data. The normalized and relative frequency responses are combined to produce an overall frequency response that is used by the RF receiver to configure an inverse filter to correct channel linear distortion produced by the frequency response of the frequency translation device at the desired center frequency.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Sidewalk pavement structure for water permeation, water storage and water discharging
InactiveCN106436528AEasy to collectHelp recycleClimate change adaptationSidewalk pavingsWater dischargeRoad surface
The invention discloses a sidewalk pavement structure for water permeation, water storage and water discharging. The sidewalk pavement structure comprises a sidewalk, a roadway and a rainwater port communicated with a municipal water discharging system and further comprises a transverse water permeation pipe, the sidewalk comprises a water-permeable surface layer, a water-permeable leveling layer, a water-permeable base layer and an inverse filtering cushion which are arranged sequentially from top to bottom, a groove paved with a filling material is formed in the bottom of the inner side of the inverse filtering cushion, and waterproof geotechnical cloth is arranged at the bottom of the inverse filtering cushion, on the left and right sides of the groove and at the bottom of the groove; first kerbs are arranged on two sides of the sidewalk, and the transverse water permeation pipe communicates the groove with the rainwater port. The sidewalk pavement structure has good water permeating, storing and discharging functions, can effectively prevent water accumulation on the surface of the sidewalk and can relieve pressure of the municipal water discharging system under extreme raining conditions to certain extent; rainwater is avoided permeating into roadbeds, so that long-time stability of the roadbeds is guaranteed; water permeability and air permeability of the sidewalk pavement structure can be improved, and urban 'heat island effect' is relieved to certain content.
Owner:中国市政工程西北设计研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com