Patents
Literature
144 results about "Microwave beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
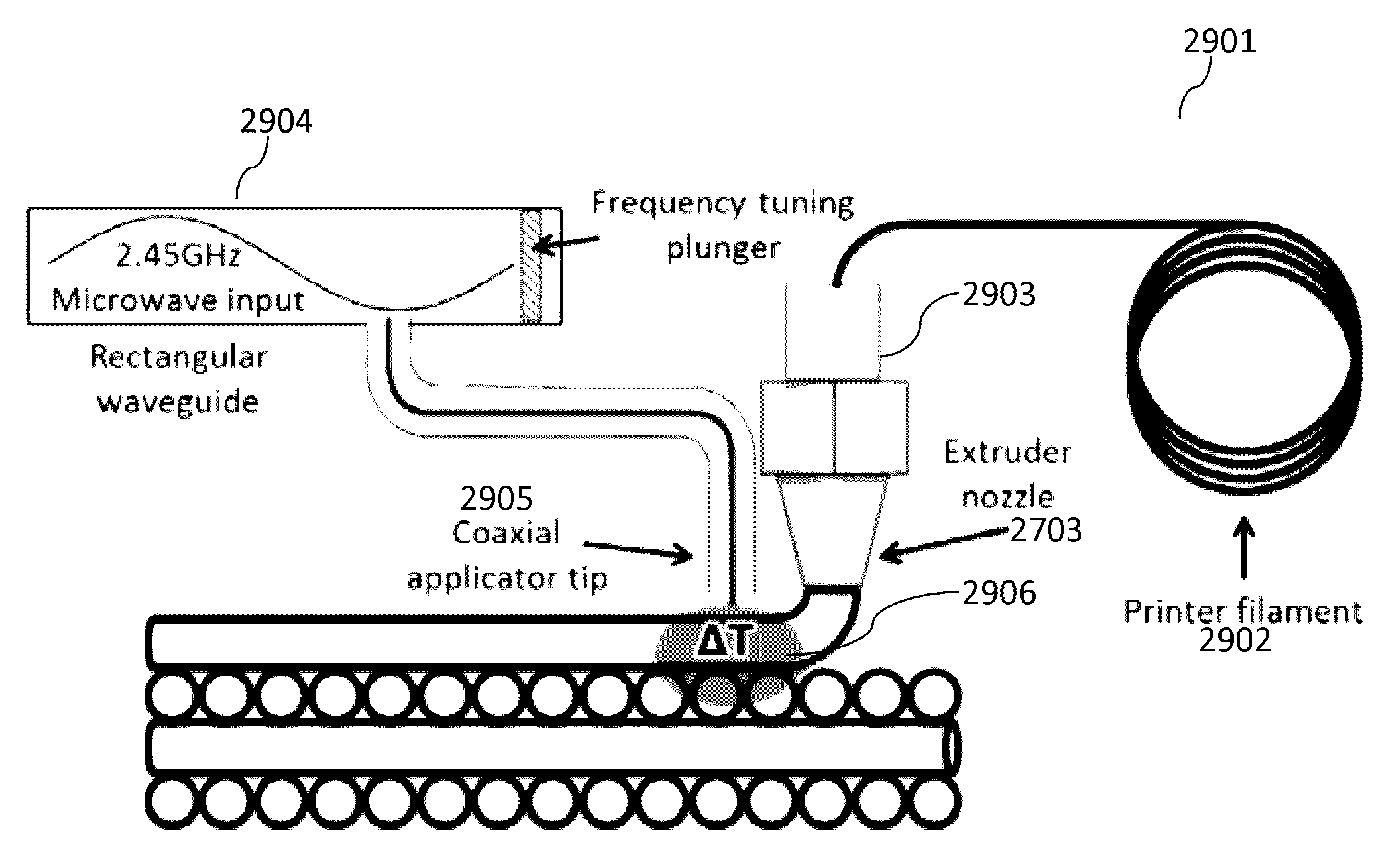
Microwave-induced localized heating of cnt filled polymer composites for enhanced inter-bead diffusive bonding of fused filament fabricated parts
ActiveUS20160325491A1Increase inter-bead bond strengthImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufacture3d printCarbon nanotube
A microwave-induced heating of CNT filled (or coated) polymer composites for enhancing inter-bead diffusive bonding of fused filament fabricated parts. The technique incorporates microwave absorbing nanomaterials (carbon nanotubes (CNTs)) onto the surface or throughout the volume of 3D printer polymer filament to increase the inter-bead bond strength following a post microwave irradiation treatment and / or in-situ focused microwave beam during printing. The overall strength of the final 3D printed part will be dramatically increased and the isotropic mechanical properties of fused filament part will approach or exceed conventionally manufactured counterparts.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
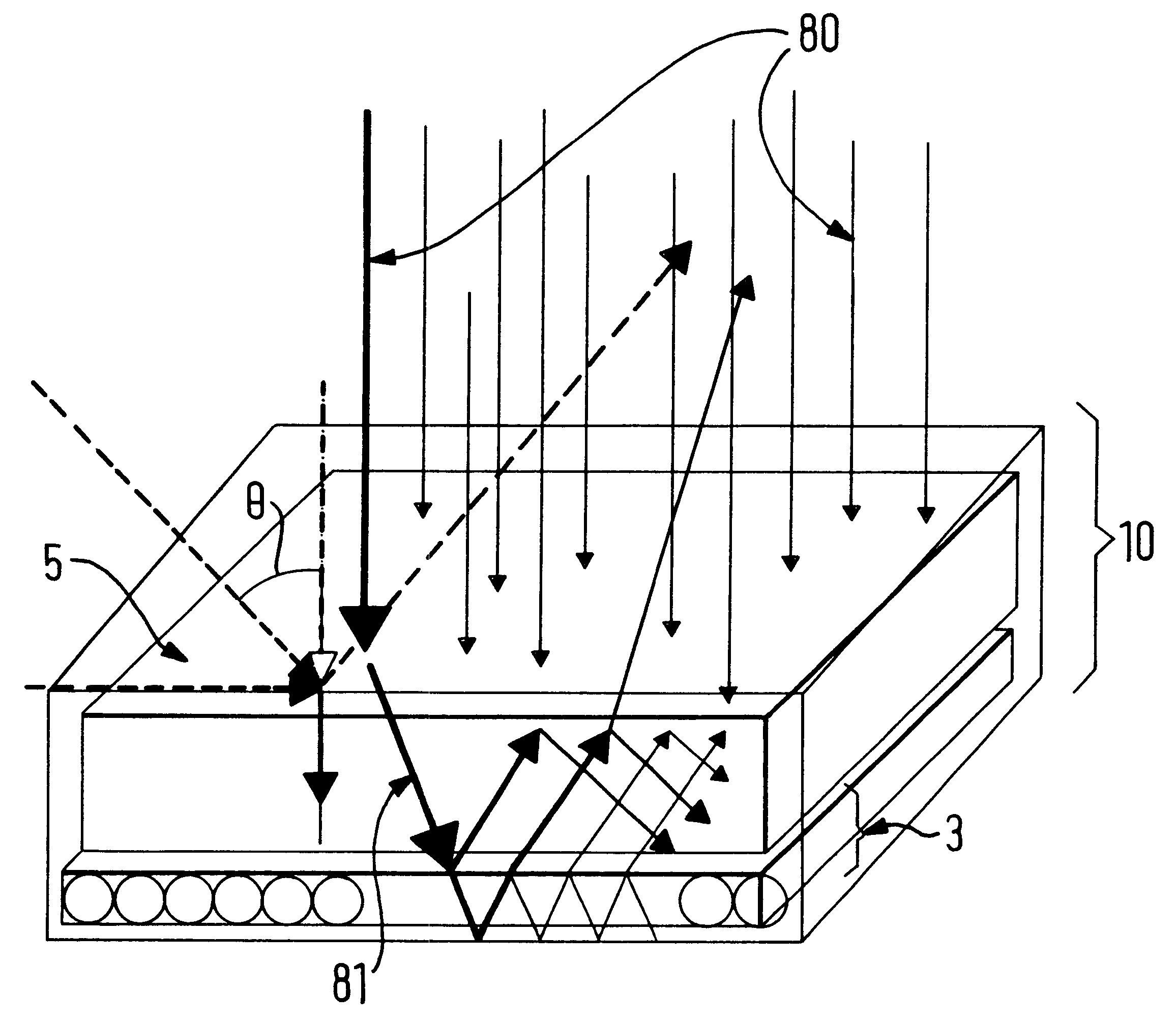
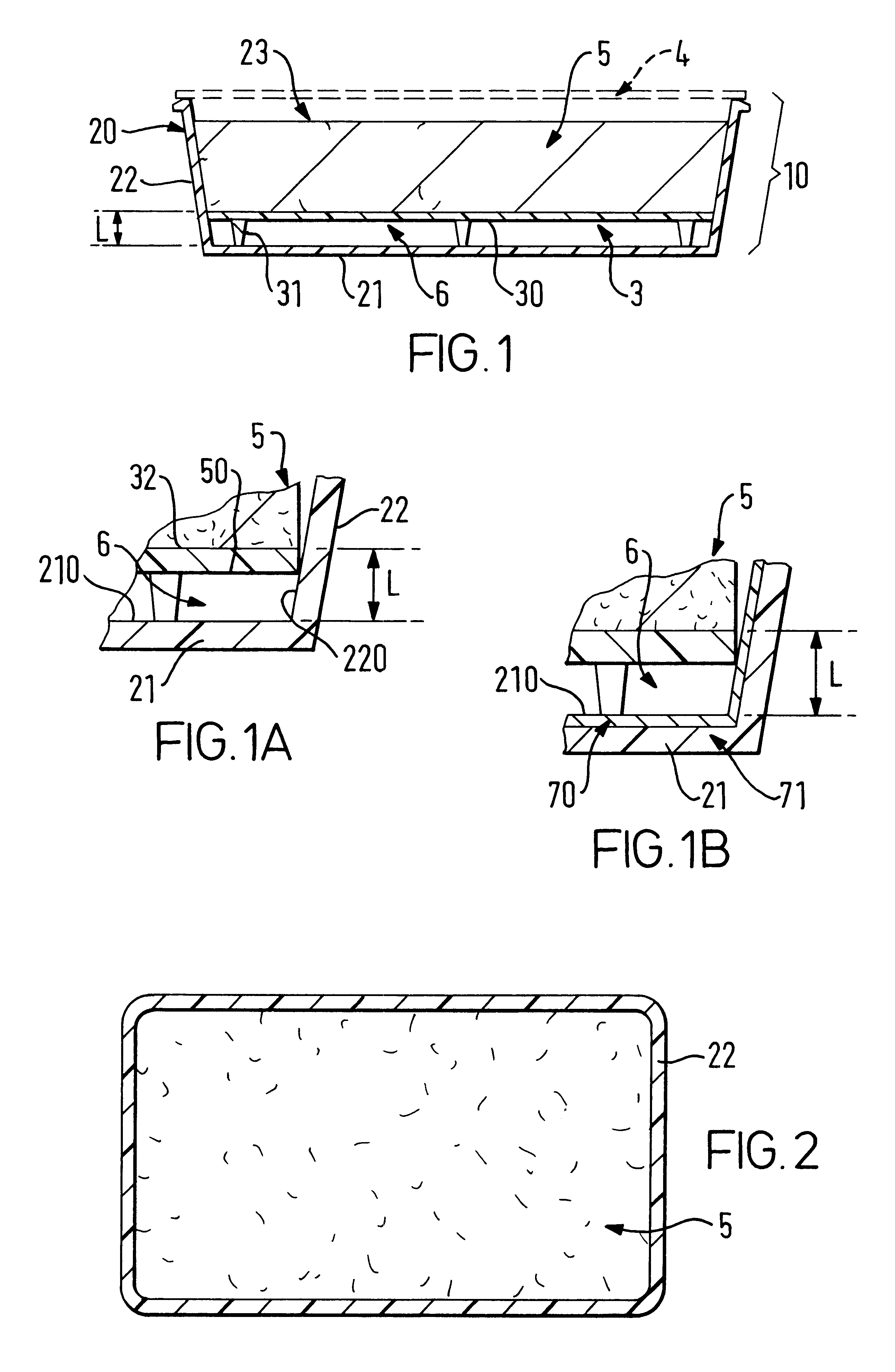
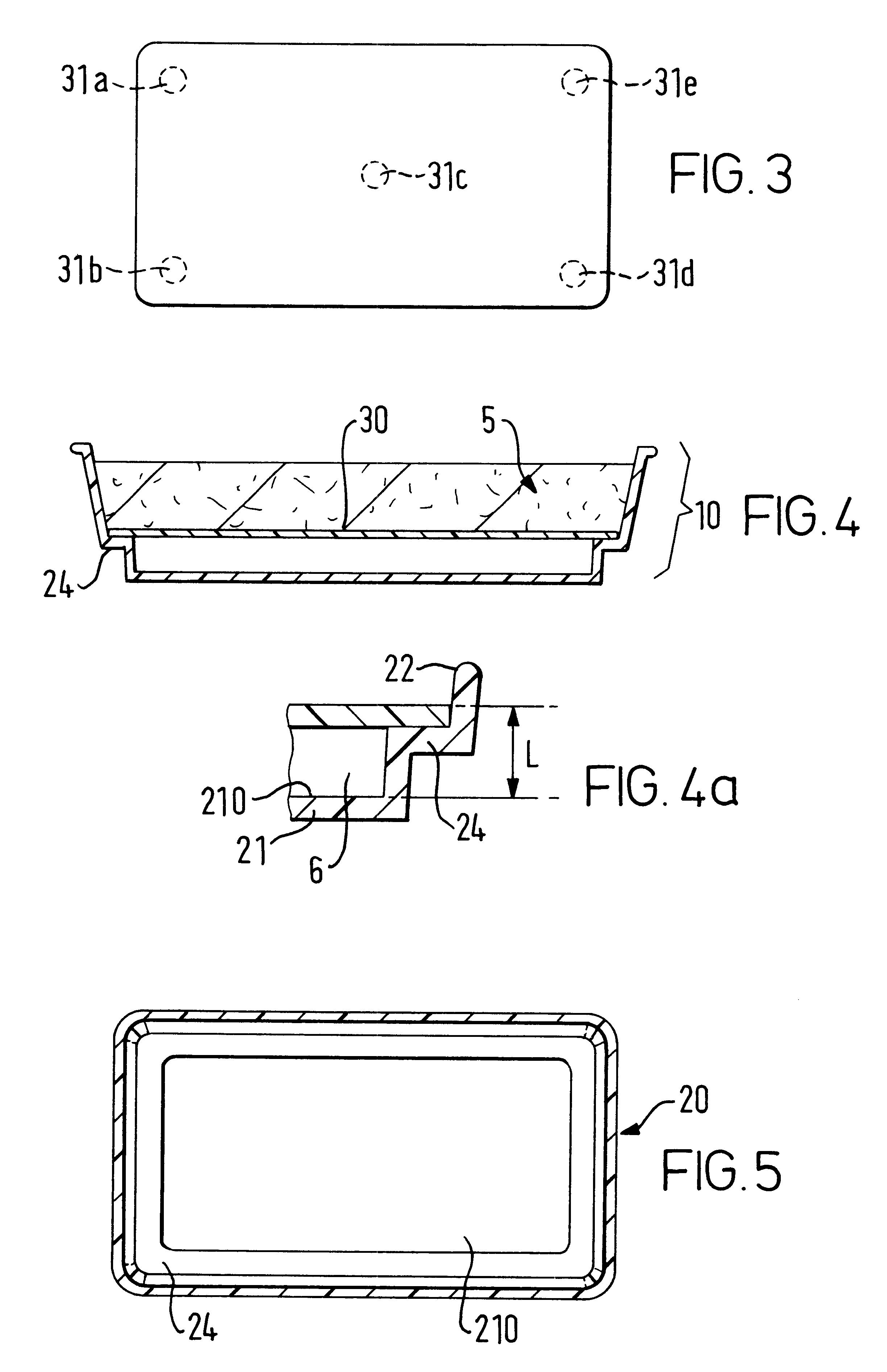
Container for heating rapidly and evenly frozen foods in a microwave oven
The present invention relates to a container for cooking food in a microwave oven. The container includes a tray having a bottom wall and a side wall that is attached to the bottom wall and extends upwardly from the bottom wall to define an interior cavity and a support means to provide support for a food product and elevate the food product with respect to the bottom wall. A continuous shielding layer is provided in the bottom wall and the side wall of the tray. The bottom wall and side wall of the tray along with the bottom of the food product define a free space under the food product that totally reflects microwave beams that pass through the food product back in the direction of the food product. The container of the invention reduces the formation of temperature gradients in the food product when it is heated and accelerates the microwave reheating of the food product. The container is particularly useful for reheating large blocks of frozen food.
Owner:NESTEC SA
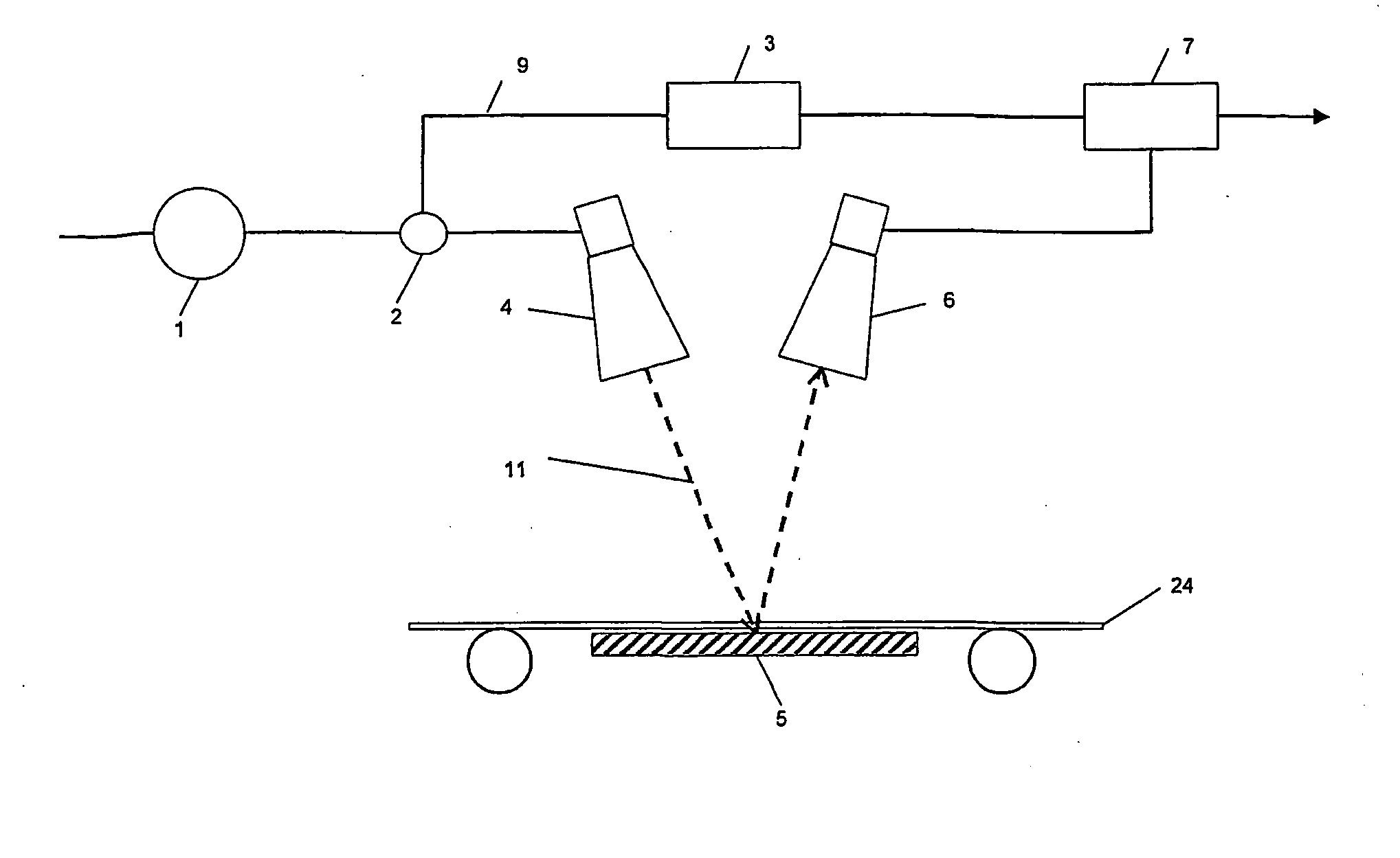
Apparatus and method for microwave determination of least one physical parameter of a substance
InactiveUS20040239338A1High sensitivityImprove accuracySamplingResistance/reactance/impedenceRest positionSalt content
A method and an apparatus is described to measure at least one physical parameter of a substance such as moisture and salt content. This is done by transmitting a microwave beam through the material to be measured and detect only a reflection of a predetermined polarity of the transmitted waves. To accomplish this a polarizing plate is used so that only cross-polarised microwaves, which pass through the substance are detected and the co-polar reflections from surrounding structures are excluded. The object can either be moving as on a conveyer belt or in a rest position.
Owner:INTELSCAN ORBYLGJUTAEKNI EHF
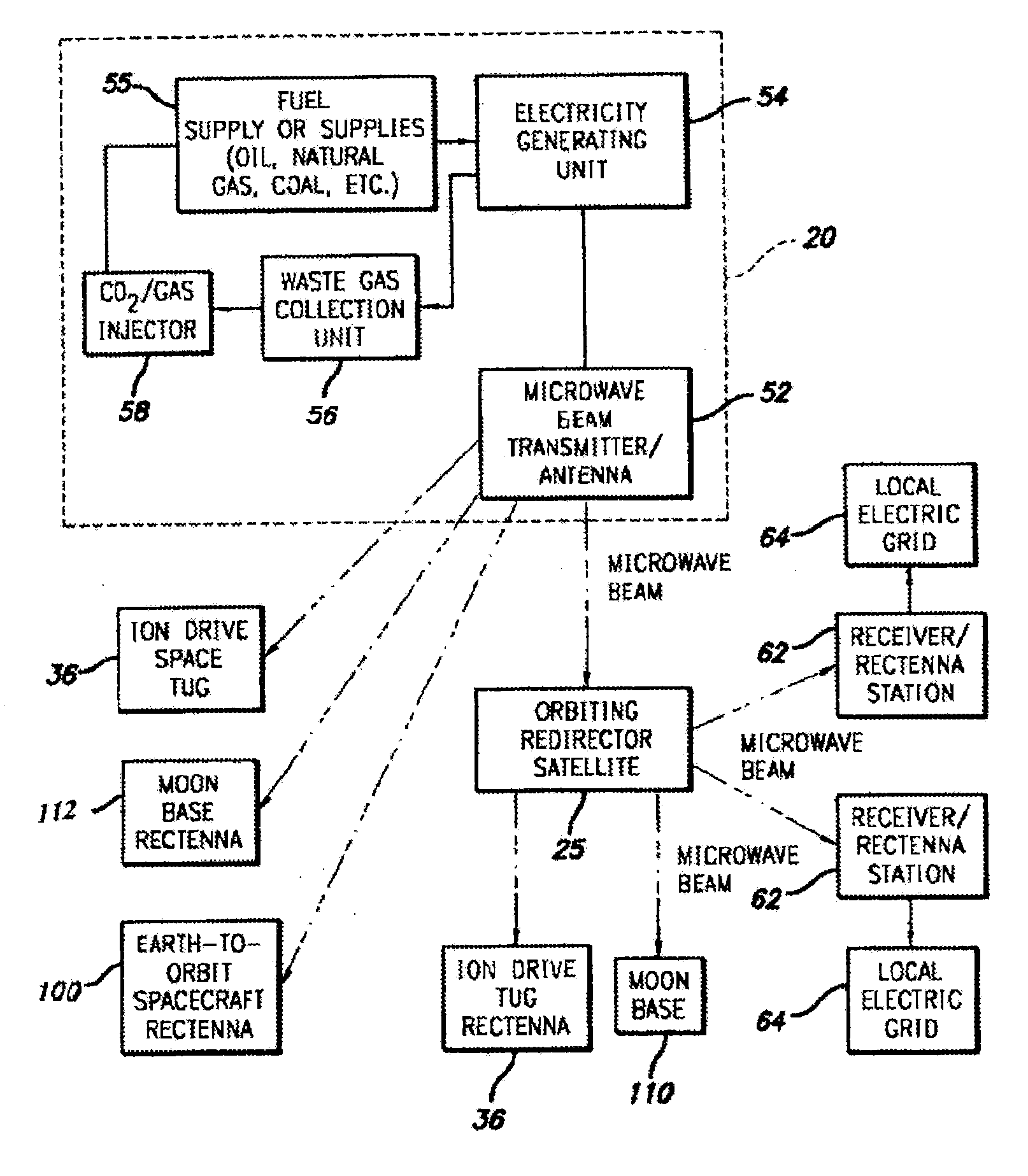
Power Generating and Distribution System and Method
ActiveUS20120153744A1Reduce and eventually eliminate dependenceLess expensiveElectromagnetic wave systemCosmonautic vehiclesDistribution systemEngineering
A power distribution network is provided comprising ground-based microwave transmitters, receivers and microwave redirectors. The ground-based microwave transmitters have their own directional, focus and amplitude controllers for aiming a focused microwave beam at a microwave redirector. The microwave redirectors each have a receiving antenna and a plurality of transmitting antennae such that the redirectors transmit focused microwave beams to at least two different stations (for example, being either ground-based microwave receivers or other microwave redirectors).
Owner:CRISWELL DAVID R DR
Uniform radiation microwave heating method and device
InactiveCN1826026AOvercome the defect of uneven microwave field distributionOvercome the defect of uneven distributionDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusImpedance ConverterRadiation heating
This invention relates to a heating method with uniform radiated microwaves and a device, in which, said method includes: a microwave device generates microwaves transmitted by a waveguide impedance converter and output to a corresponding couple cavity from the waveguide port to be reflected and scattered to output multiple microwave beams to the heating cavity uniformly from multiple couple holes on a sidewall of the couple cavity and these microwave beams enter into the heating cavity to radiate on the heated object, which greatly improves the un-uniform distribution of microwave energies in the heating cavity.
Owner:TSANN KUEN CHINA ENTERPRISE
Multi Beam Photonic Beamformer
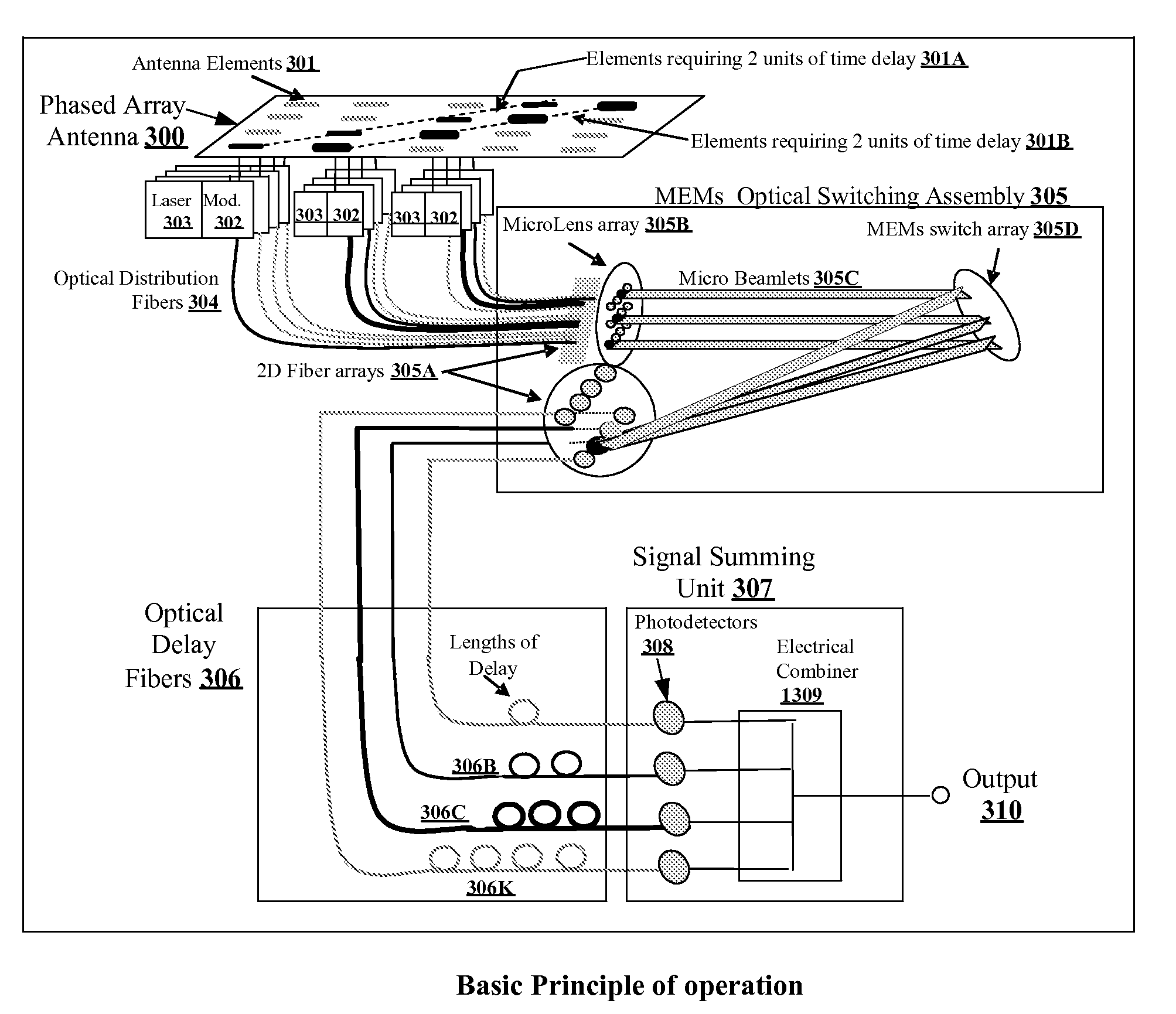
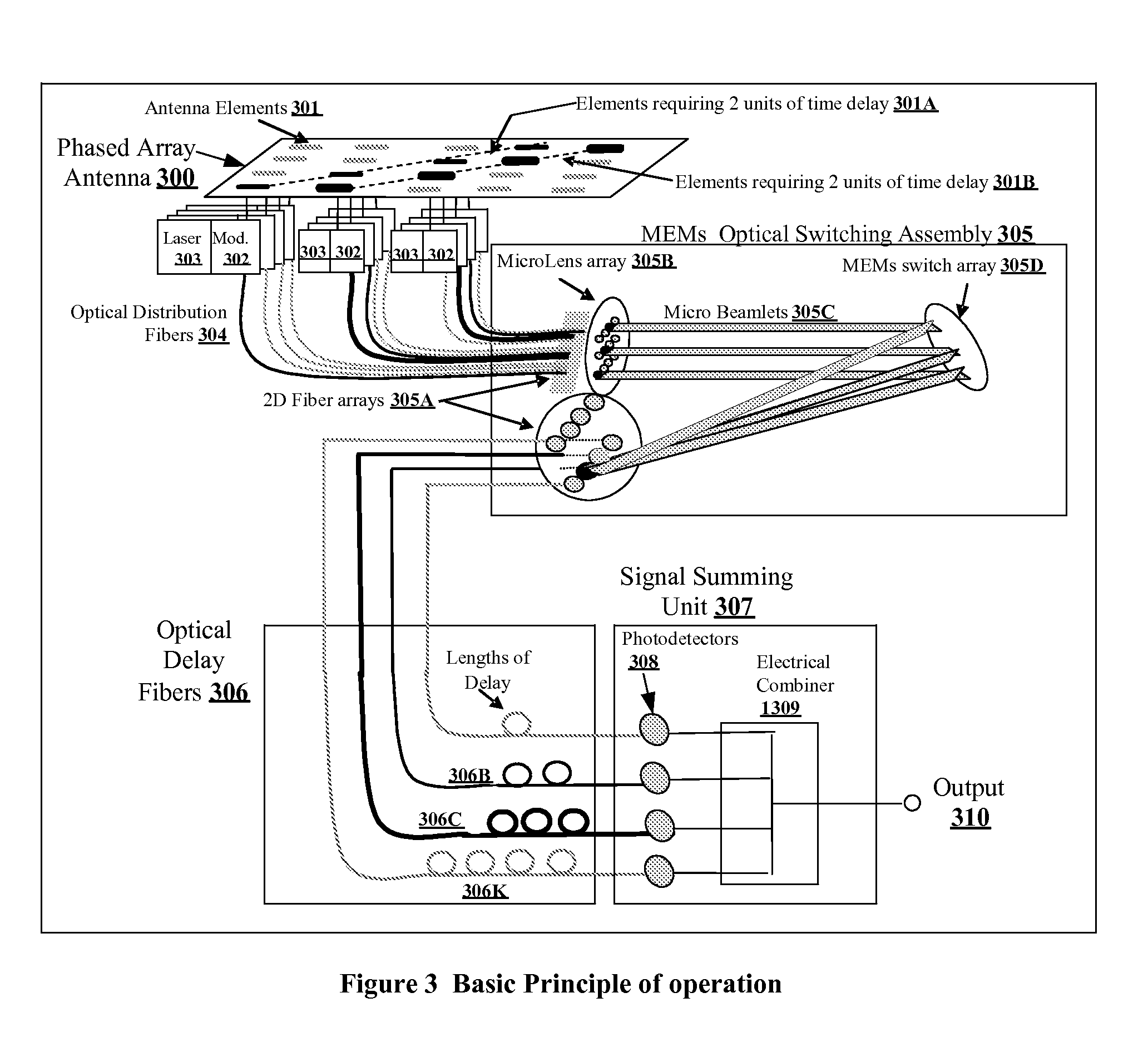
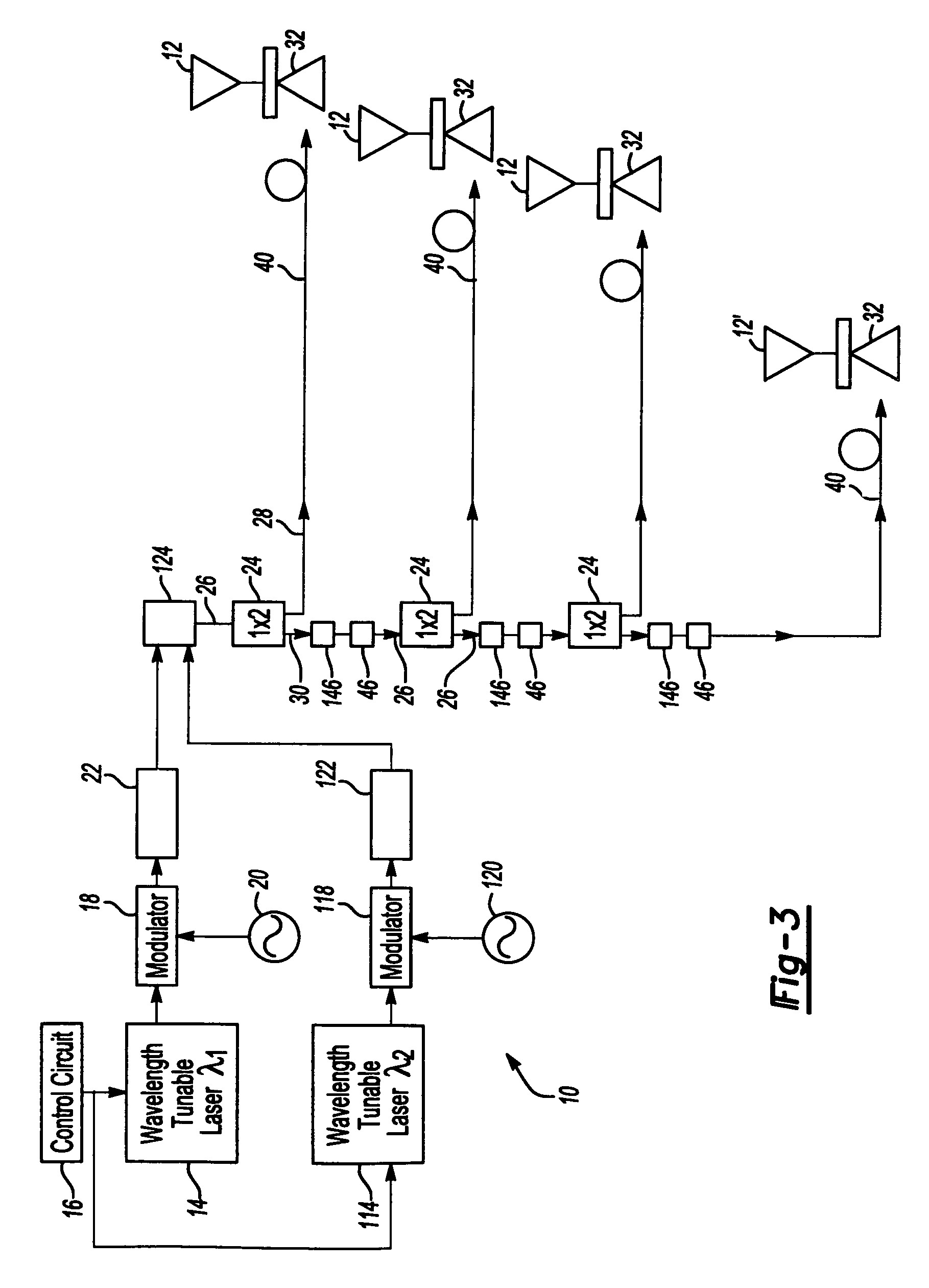
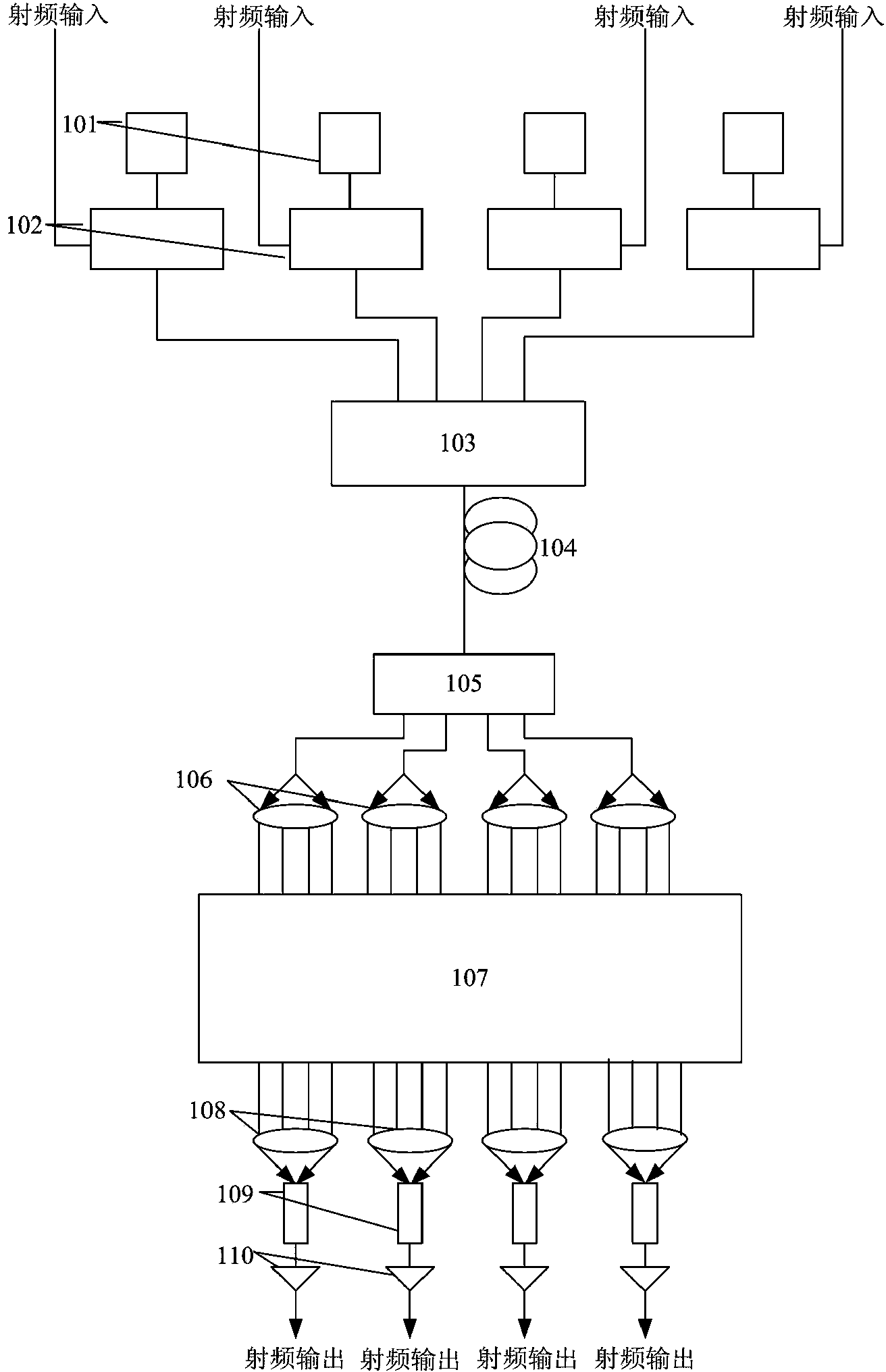
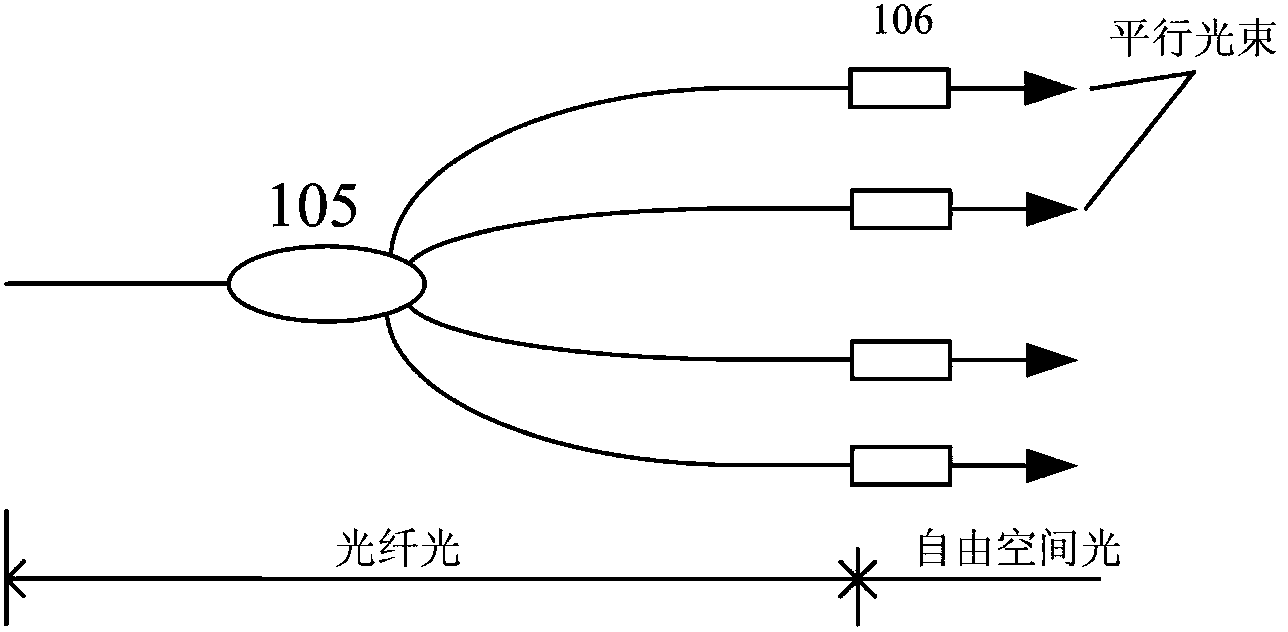
A true time delay beamformer for RF / microwave phased array antenna systems using multiple laser sources, optical modulators to convert the electrical signal to a modulated optical signal, standard optical fiber for creating time delays, dispersive optical fiber for creating delays, optical splitting and / or switching section, photodetectors to convert the modulated optical signal to an electrical signal, and a signal combining section. The true time delay beamformer has the capability to create multiple simultaneous RF / microwave antenna beams. One (more lasers) is used to source one (or more) wavelengths of light to the optical modulator. The signal from one (or more) antenna elements drive the optical modulator. The light from the optical modulator passes through the standard optical fibers and / or the dispersive optical fibers to create time delay variation for one optical modulator relative to another allowing for the formation of RF / microwave beams. Fixed location RF / microwave beams can be generated by a static network of standard and / or dispersive optical delay fibers. Steering of the location of the RF / microwave beams can be accomplished by an optical switching mechanism which could be based on MEMs and / or wavelength routing based switching. Finally, all the signals for a RF / microwave beam are summed to form a single output. The summing can occur either optically before the photodetectors and / or electrically after the photodetectors.
Owner:COWARD JAMES F
Microwave oven with antenna array
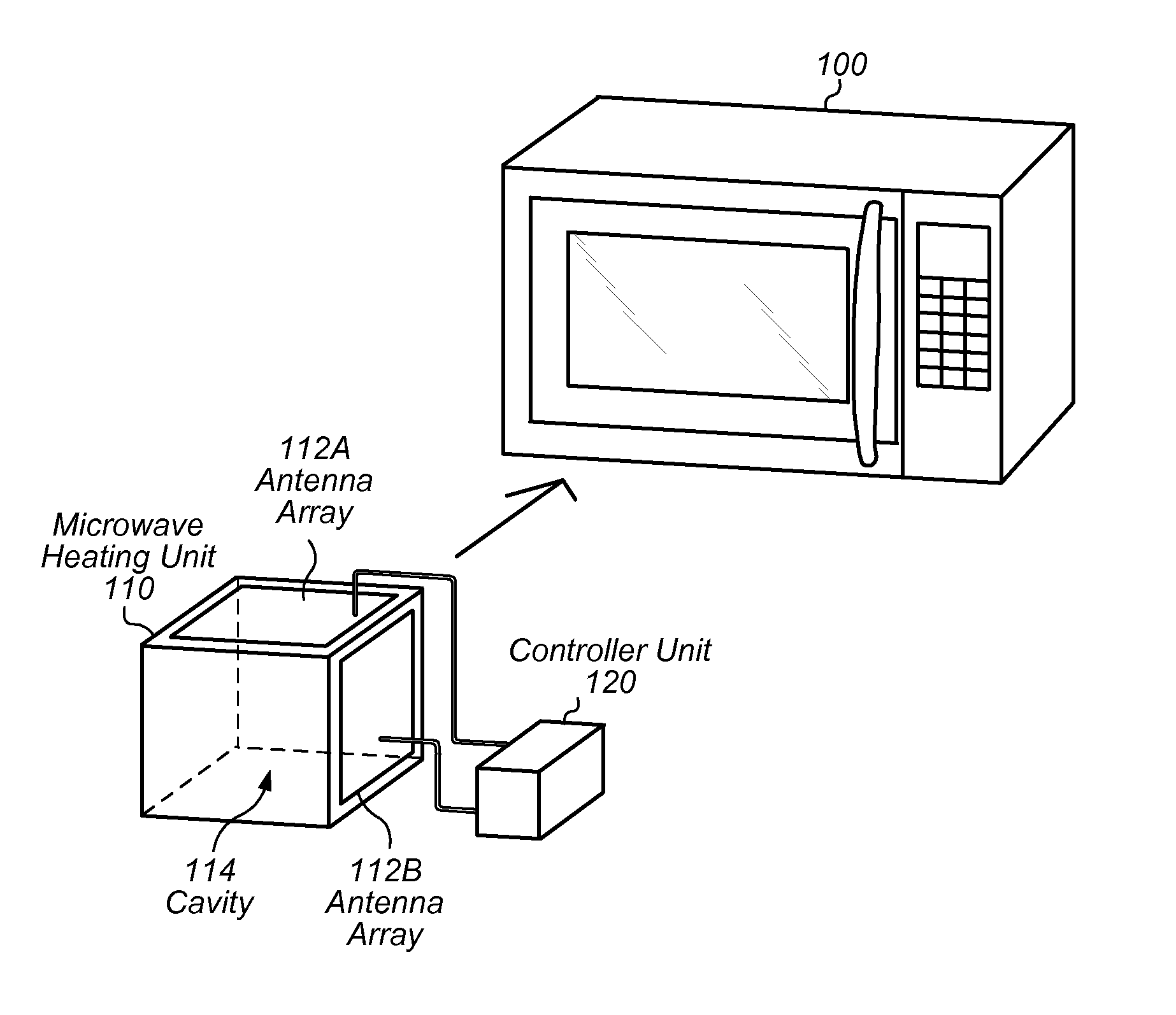
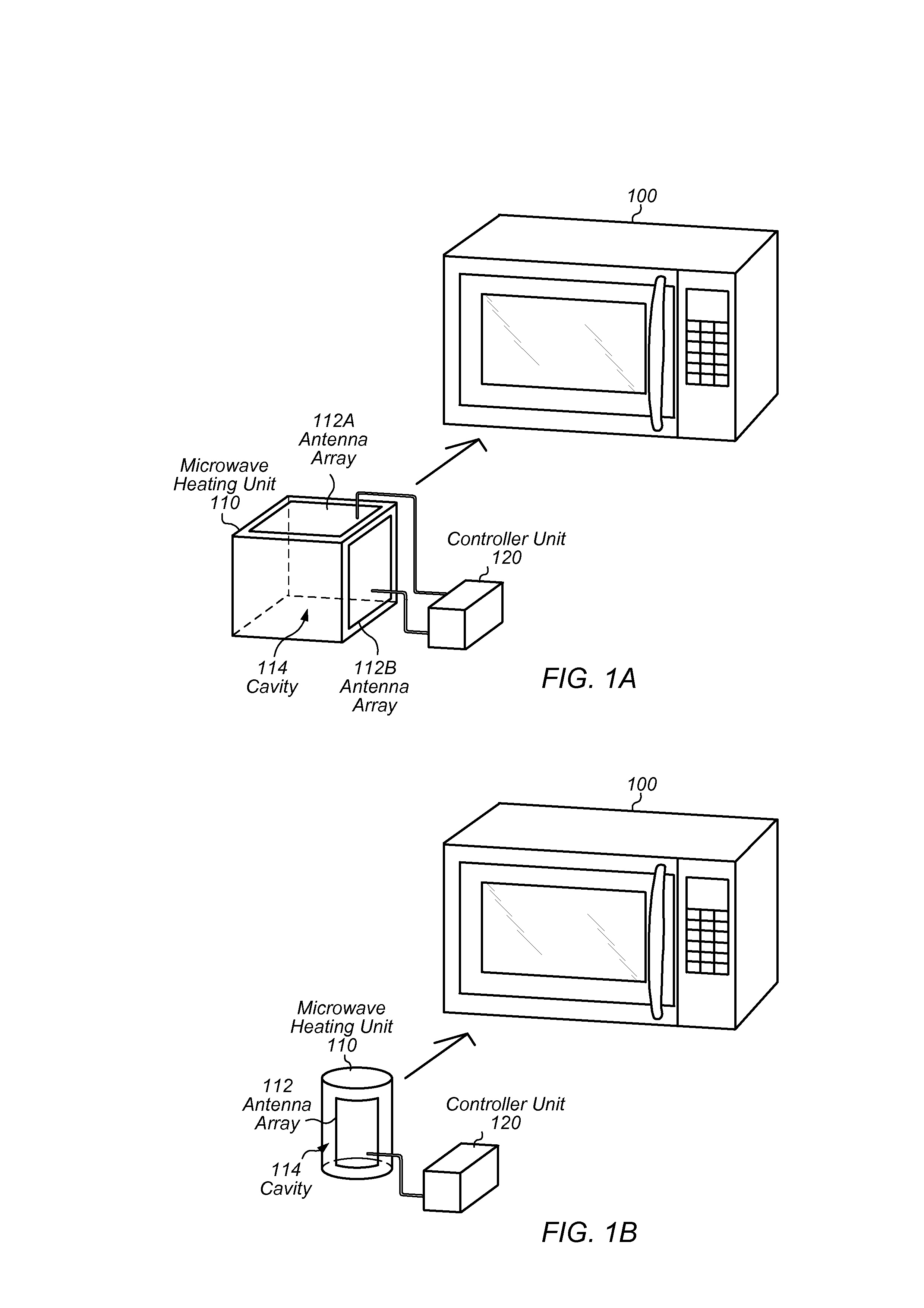
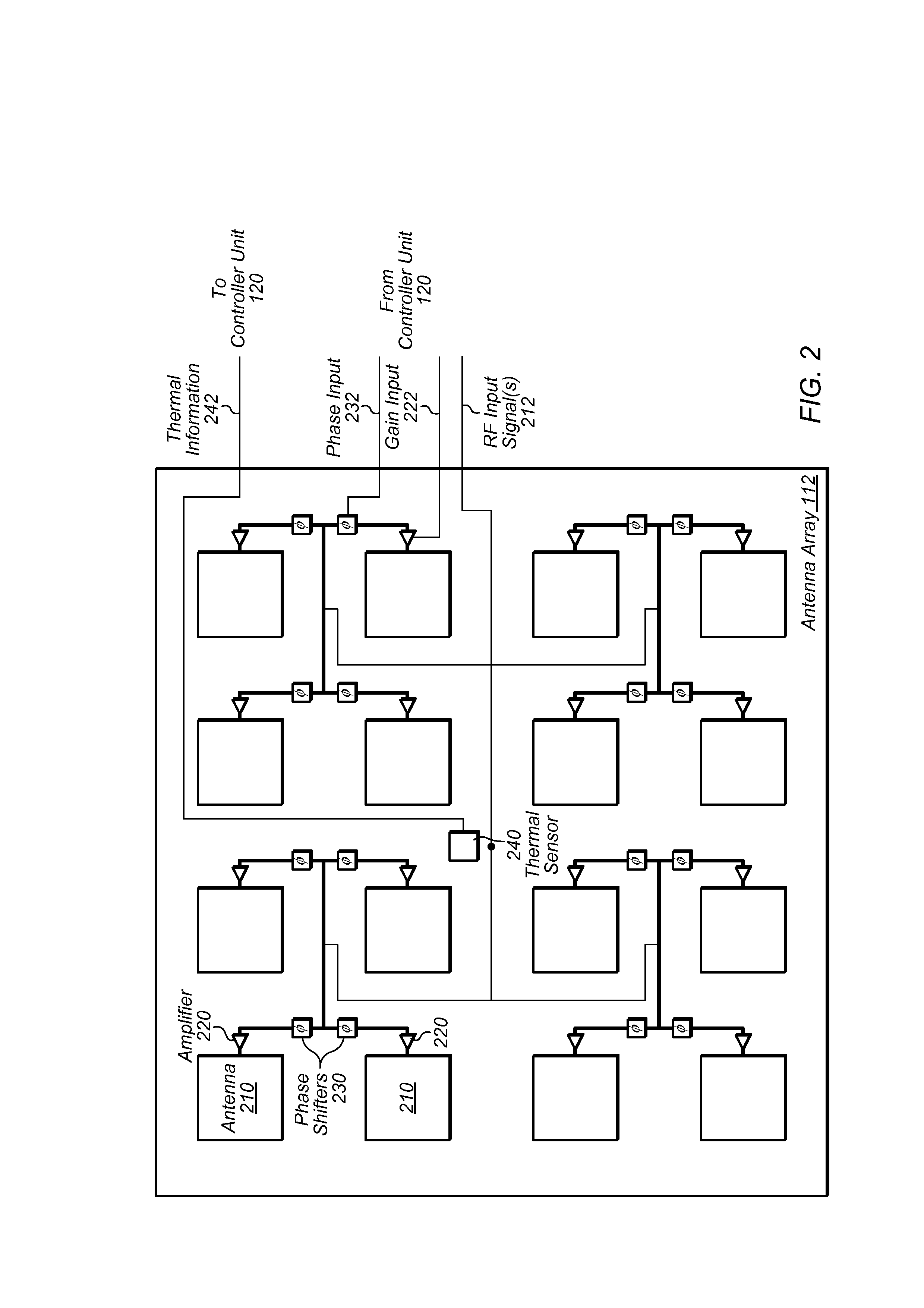
InactiveUS20130175262A1Efficient heatingConsuming less powerMicrowave heatingMicrowave ovenAudio power amplifier
Techniques are disclosed relating to microwave ovens. In one embodiment, an apparatus is disclosed that includes a microwave heating unit. The microwave heating unit is configured to radiate microwaves into a cavity and includes an antenna array coupled to one or more amplifiers. The antenna array is configured to generate the radiated microwaves. In some embodiments, the microwave oven is configured to measure temperatures of a item within the cavity, and to steer a microwave beam produced by the antenna array based on the measured temperatures.
Owner:GHARPUREY RANJIT +1
Optical communications system with back-up link
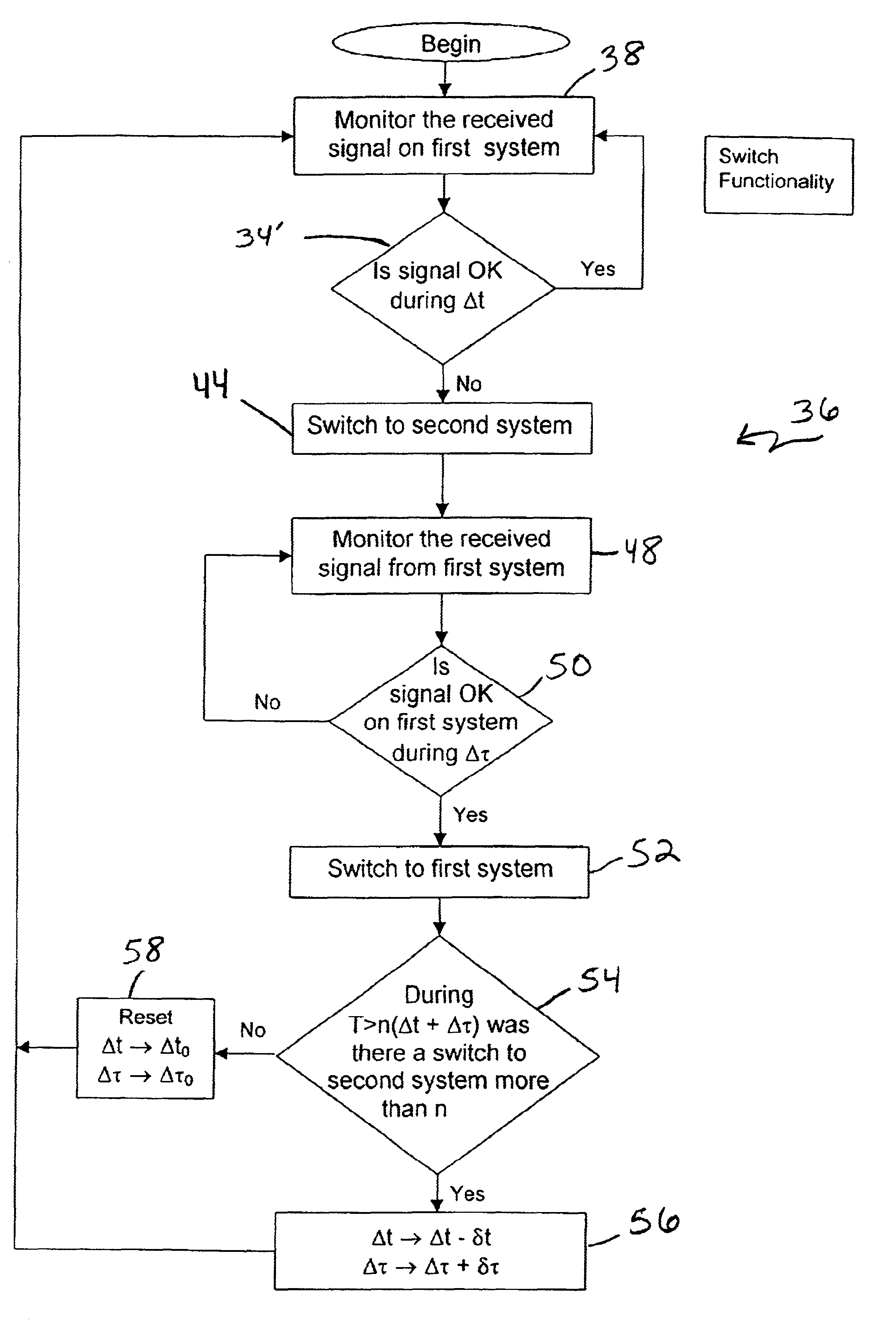
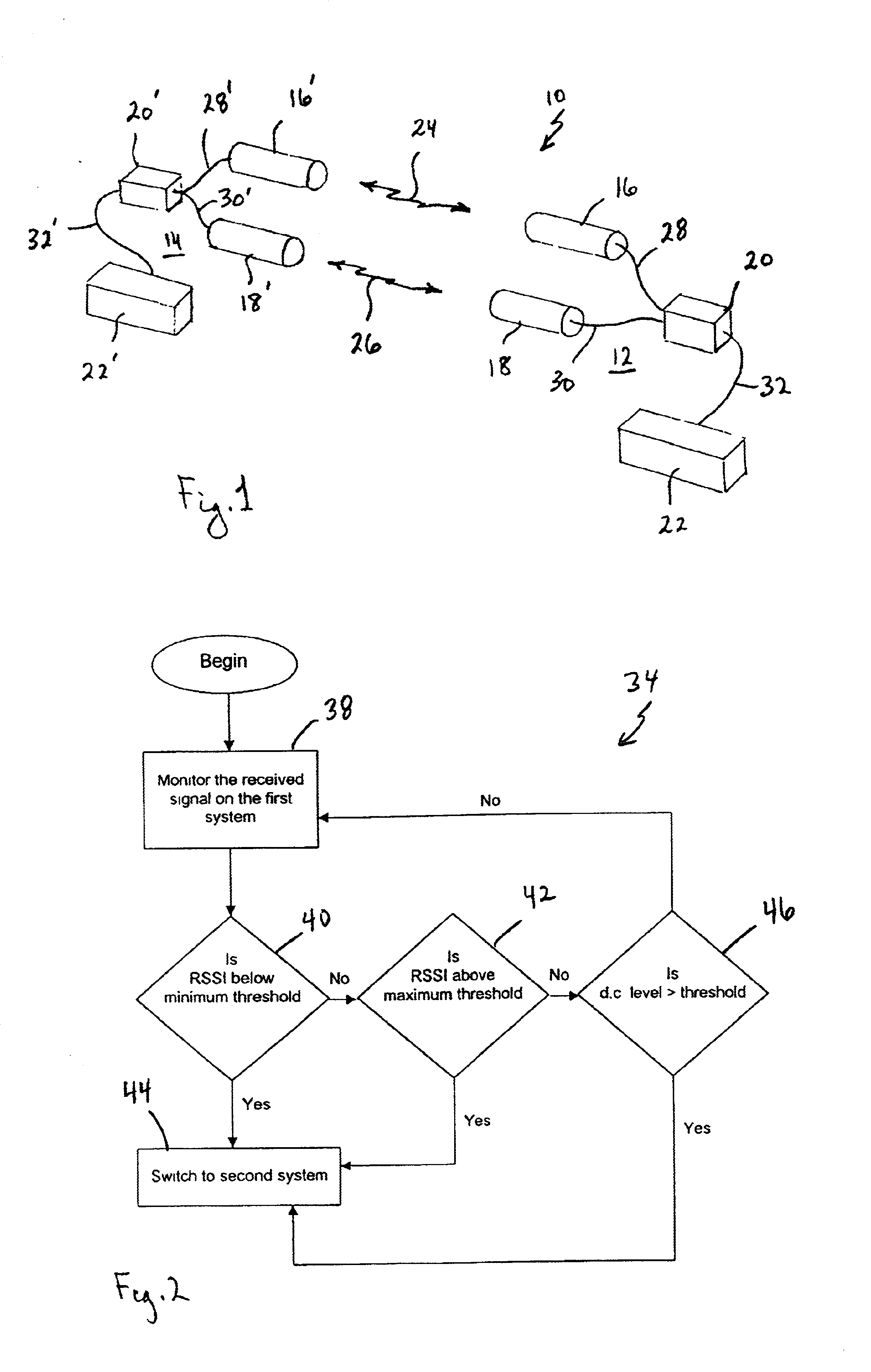
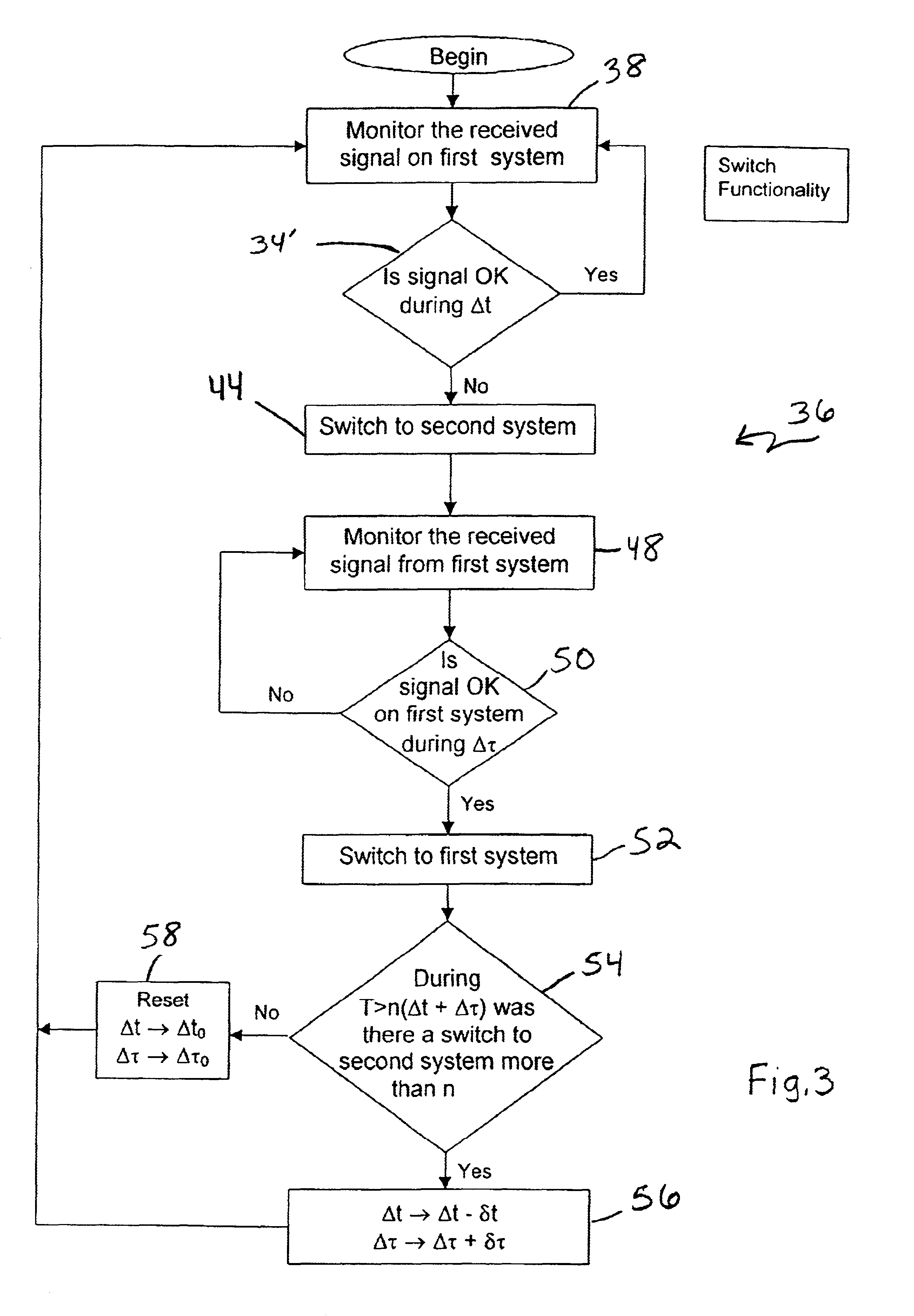
InactiveUS6928248B2Improve noise levelLaser detailsTransmission monitoringCommunications systemTransceiver
A device and method for operational switching between line-of-sight wireless communications transceivers requires evaluating a useful received signal strength intensity (RSSI) for a first transceiver, and switching to a second transceiver when the consequent bit error rate (BER) is not useful for the first transceiver. Subsequent switching between the first and second transceivers is accomplished in accordance with a timed sequence regimen that involves variable time delays, and considerations of RSSI changes within determined time periods. Preferably, the first transceiver transmits and receives on a laser beam and the second transceiver transmits and receives on a microwave beam.
Owner:MRV COMM - BOSTON DIV
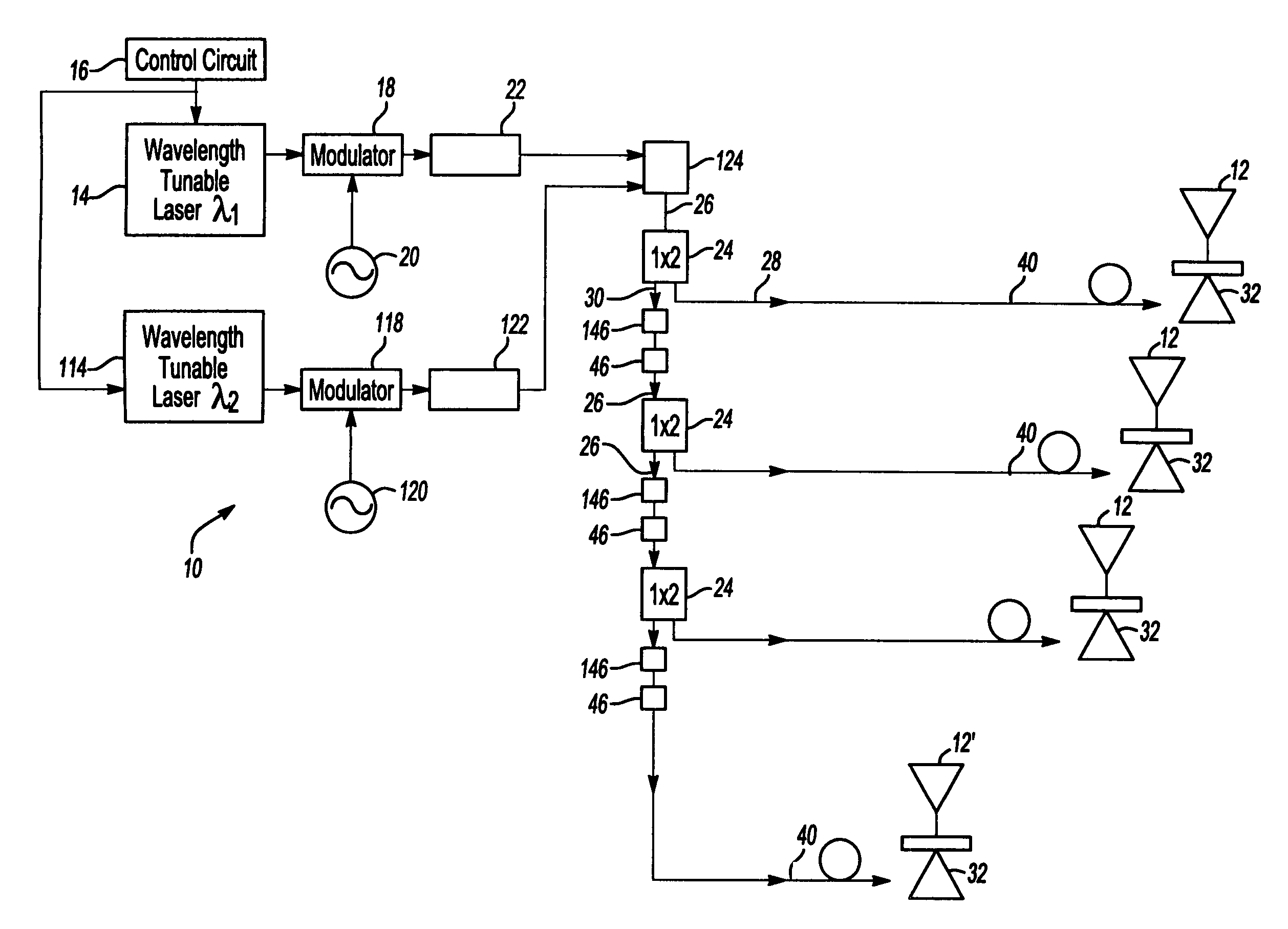
Electro optical scanning multi-function antenna
InactiveUS7609971B1Direct controlEliminate needElectromagnetic transmissionAntennasBeam splitterTime delays
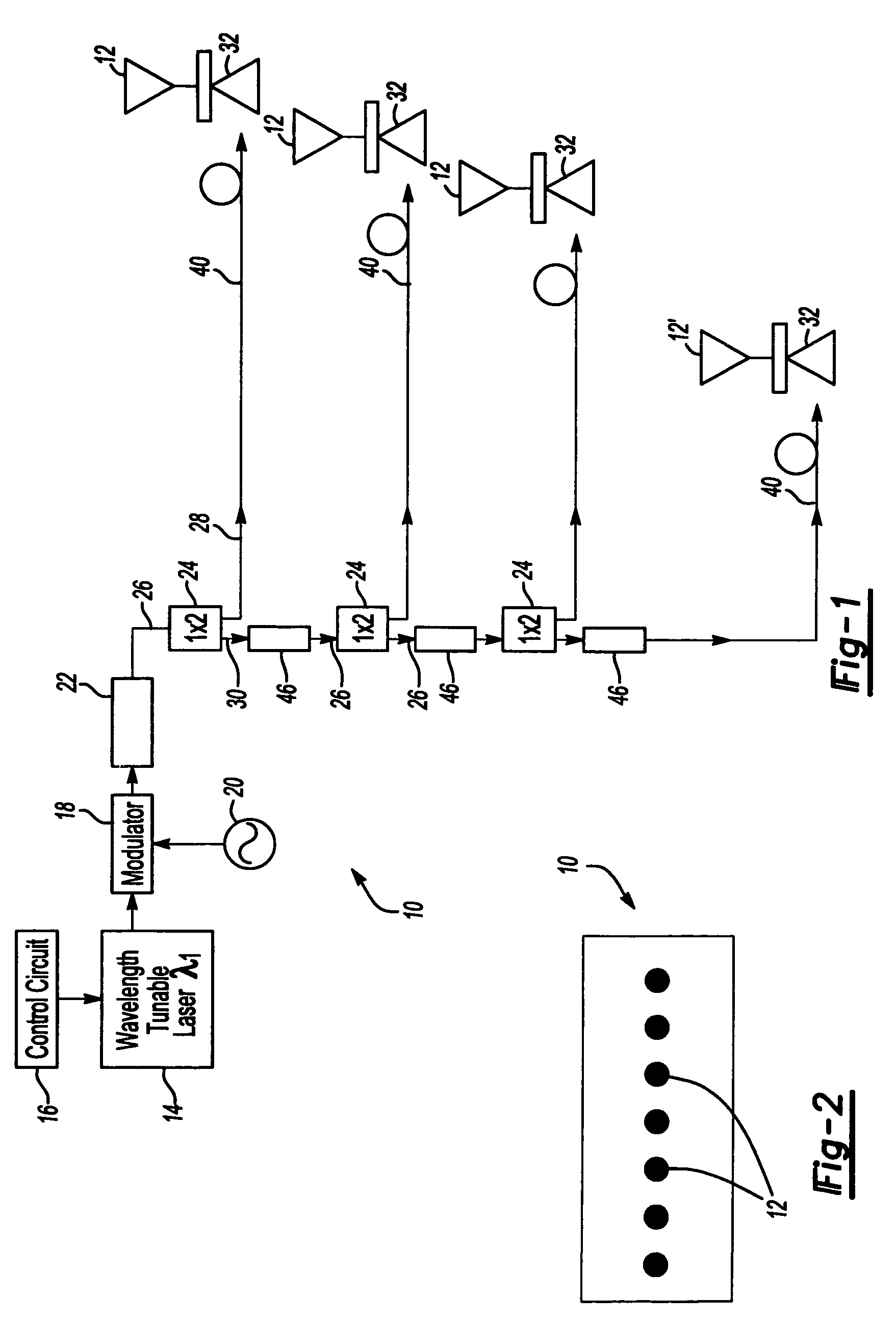
An multi-beam multifunction electro optical scanning antenna having a first variable wavelength tunable laser having an output wavelength variable within a first range and a second variable wavelength tunable laser having an output wavelength variable within a second range, different from the first range. The outputs from both lasers are modulated by independent microwave sources and the modulated outputs from both lasers are combined by an optical combiner into a combined output signal. An antenna array includes a plurality of radiators and a photodetector is associated with each radiator which converts the combined optical output from the lasers to microwave signals. Beam splitters divide the combined output signals to each of the antenna radiators while first and second wavelength-dependent time delay elements are optically connected in series between each sequential beam splitter. Each first time delay element is operable within the first wavelength range, while each second time delay element is operable within the second wavelength range. The antenna can generate two or more RF microwave beams simultaneously and independently scan / steer them.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Free-space phase shifter having one or more columns of phase shift devices
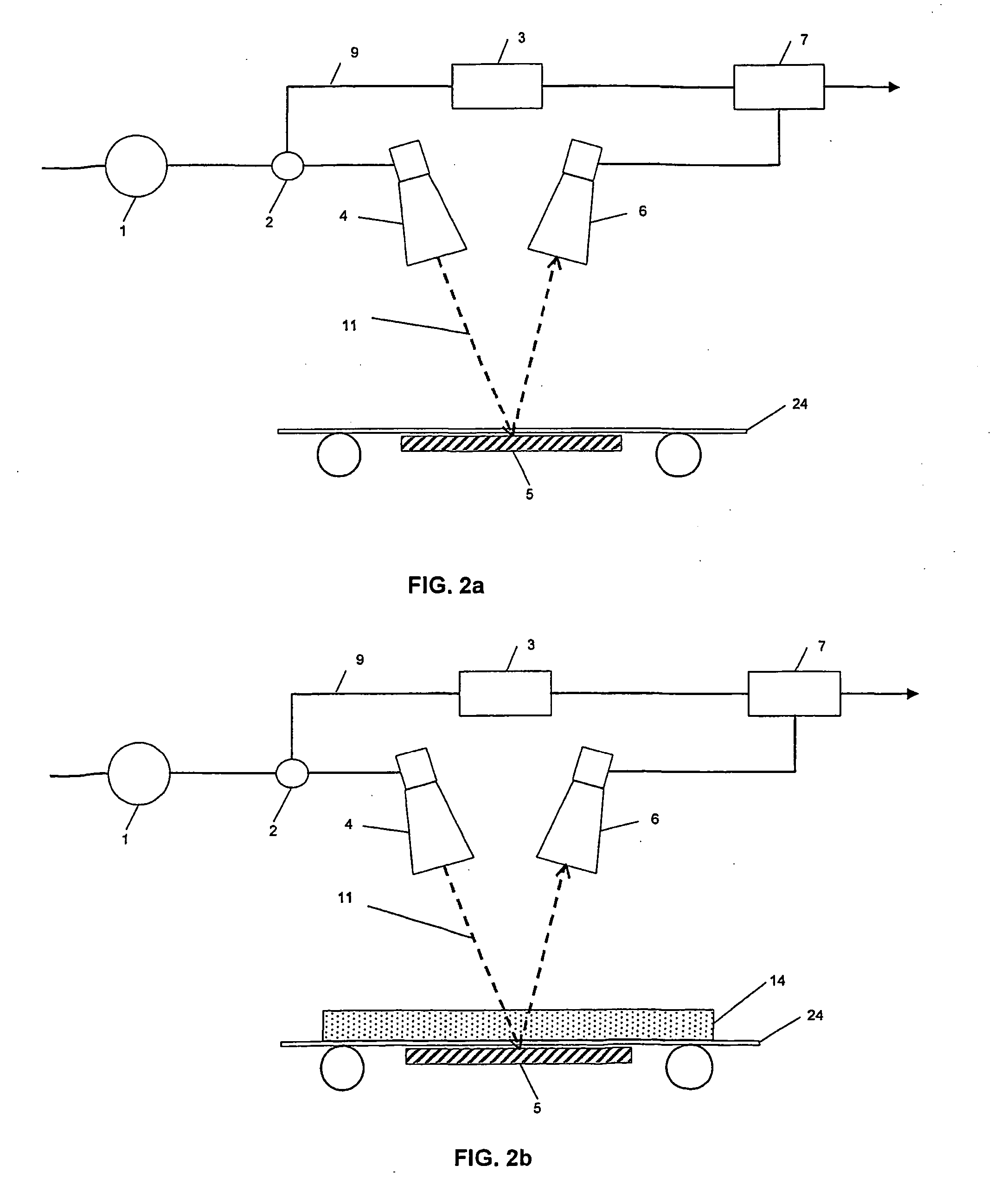
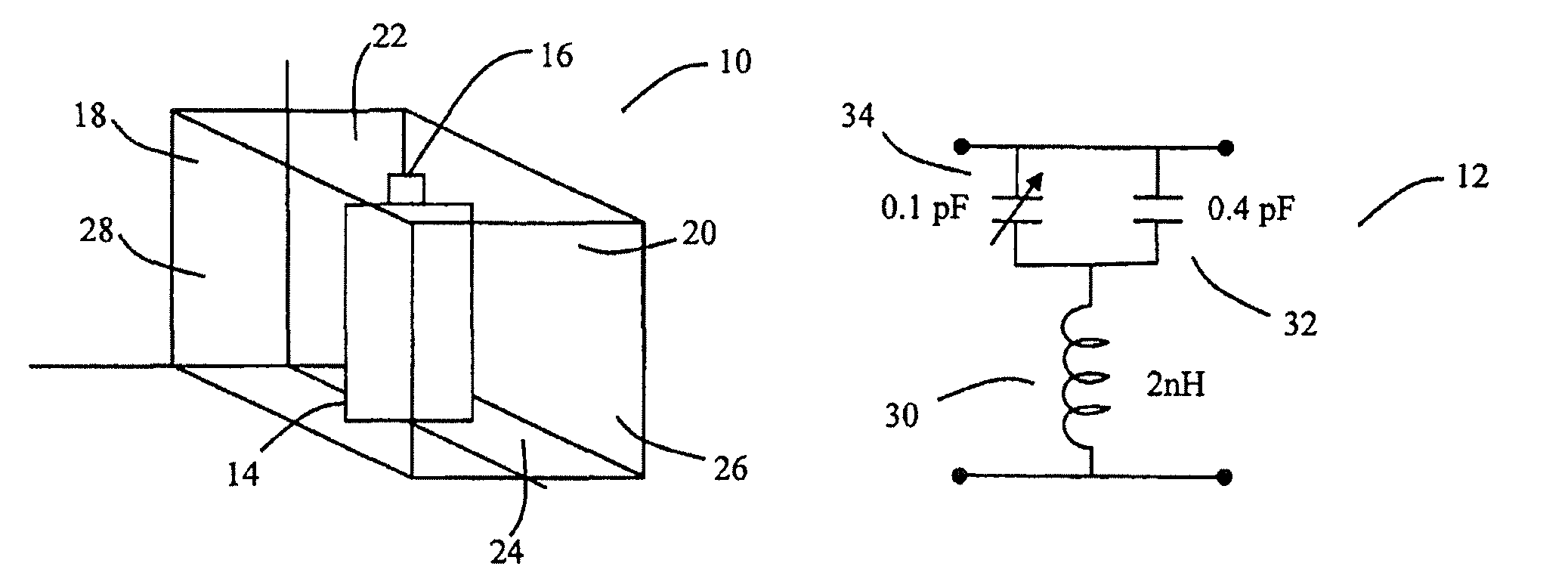
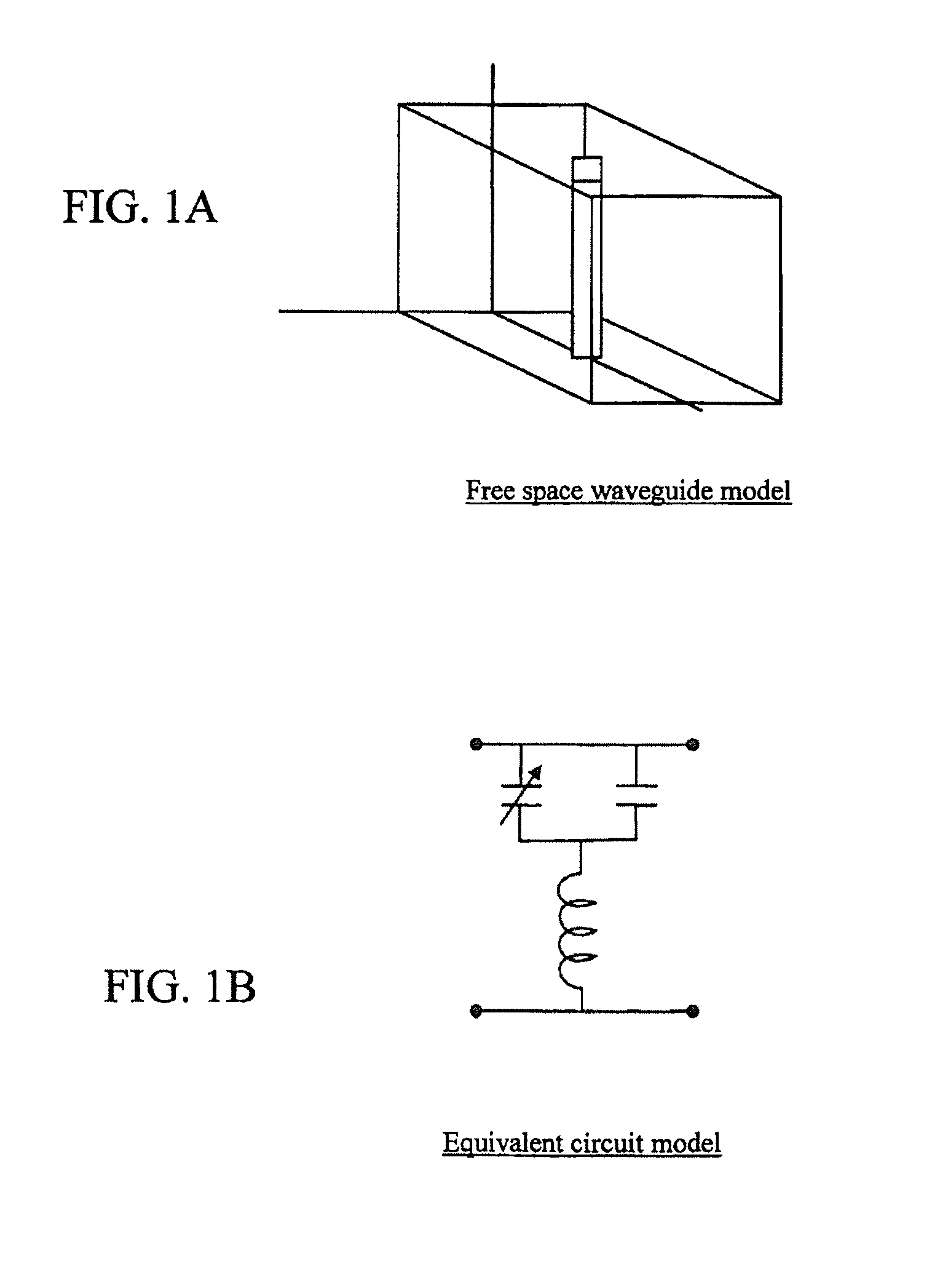
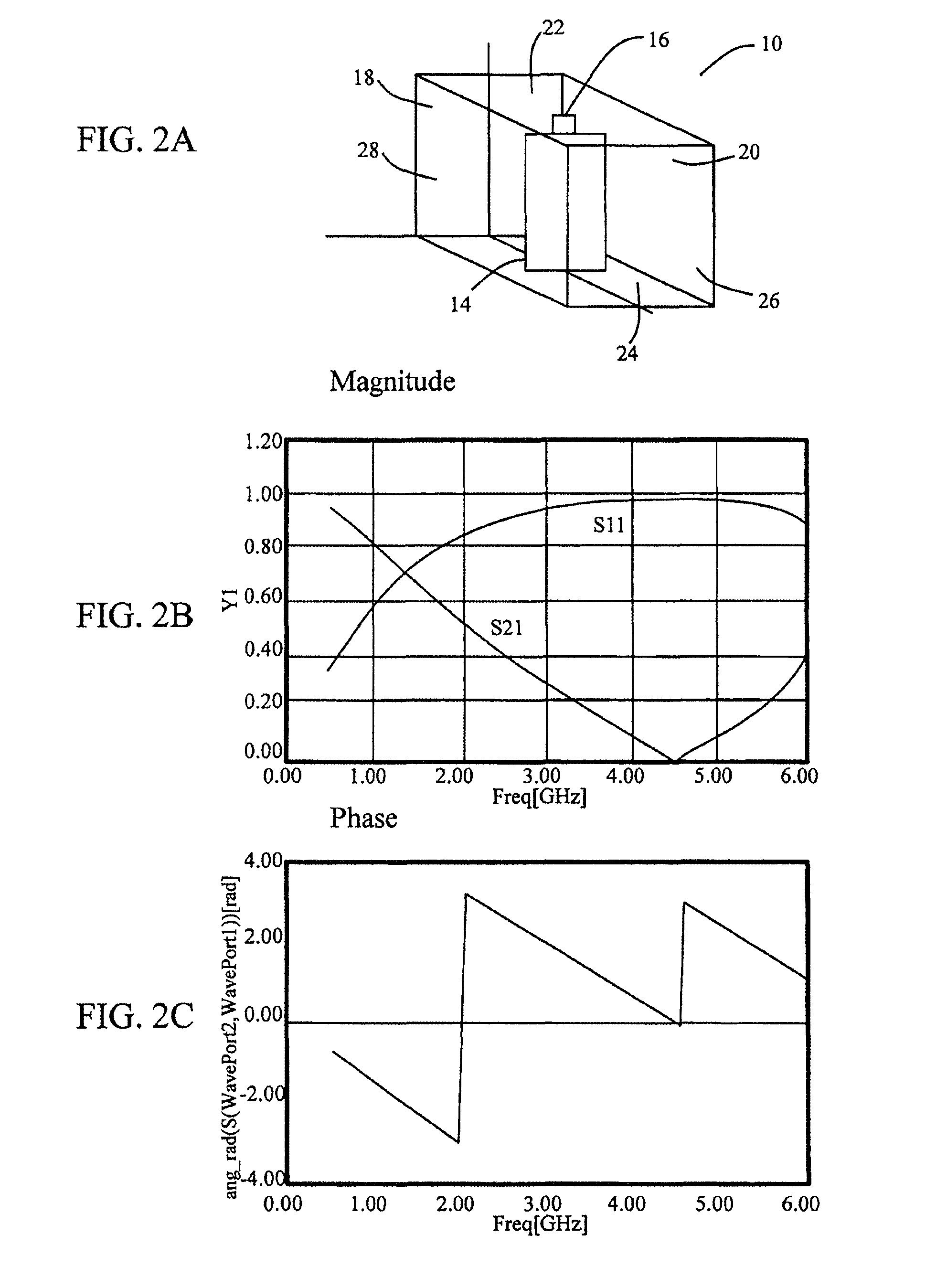
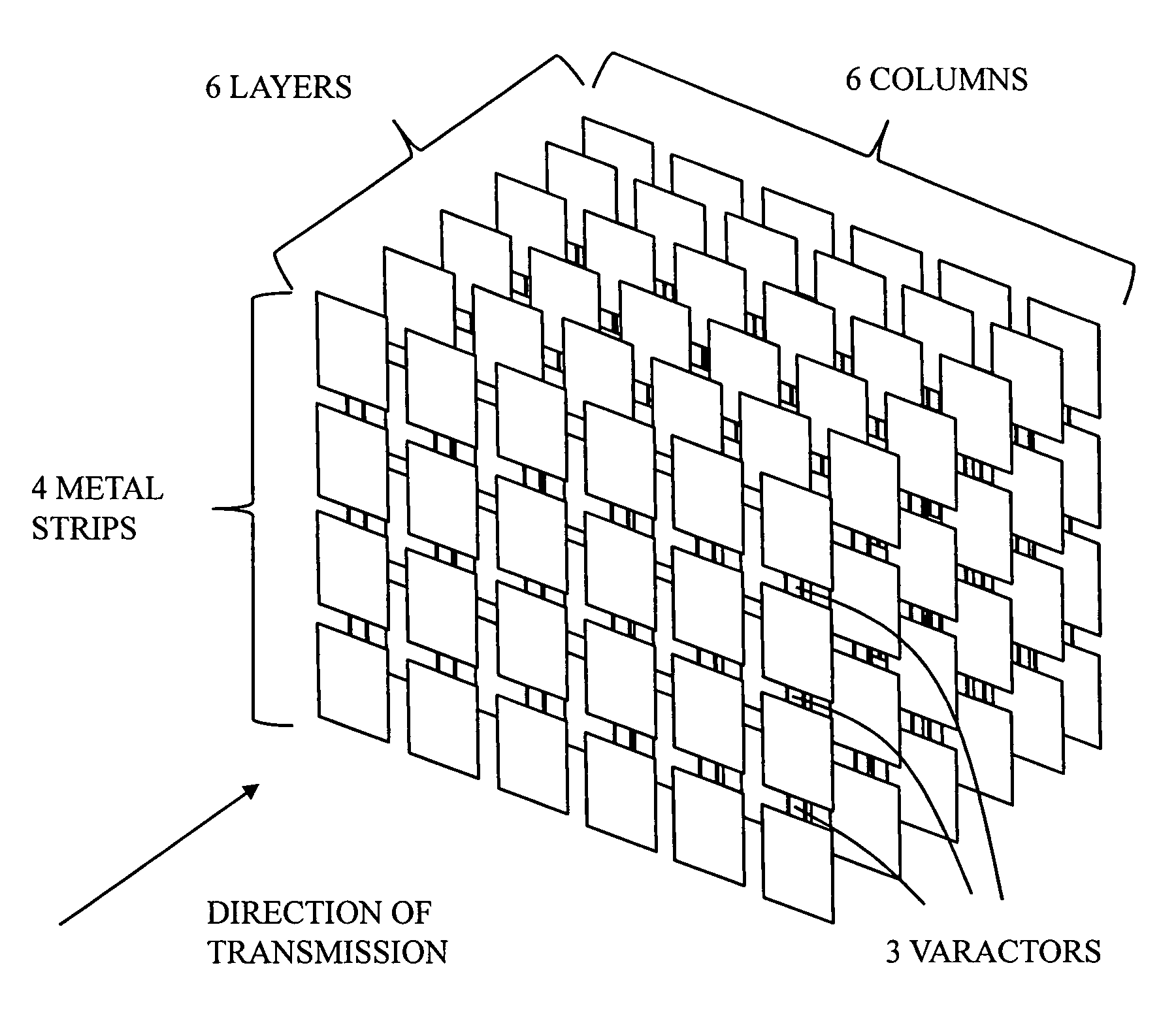
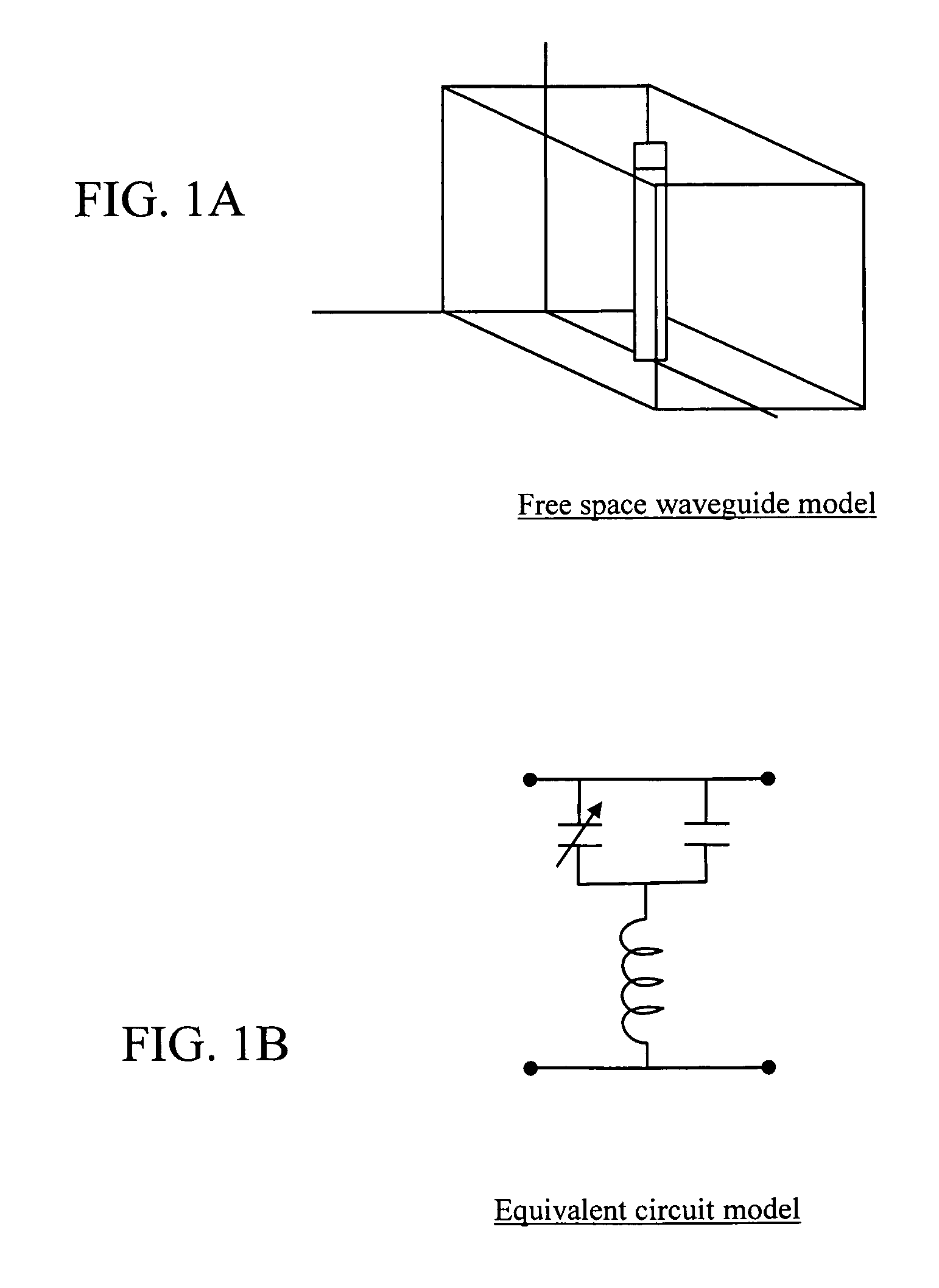
A method of changing phase of a microwave electromagnetic beam in free space is provided wherein a cascade of device layers is located transverse to a path of the microwave beam. Each of the device layers have one or more columns. Each column has a device combination series-coupled to an adjacent device combination in the column. Each device combination has a first device having inductive characteristics at microwave frequencies and a second device series-coupled to the first device. The second device has at microwave frequencies characteristics of a fixed capacitance in parallel with a variable capacitance. The capacitance of one or more of the second devices is variable to establish a desired phase shift and a desired frequency band edge within a desired frequency pass band.
Owner:HRL LAB
Ocean surface wind and wave feature retrieval method based on echo of spaceborne laser height indicator
InactiveCN102759731AHigh precisionImprove spatial resolutionWave based measurement systemsWave fieldDivergence angle
The invention relates to an ocean surface wind and wave feature retrieval method based on an echo of a spaceborne laser height indicator. The method comprises the steps of preprocessing and extracting the features of echo waveform of the spaceborne laser height indicator, and then establishing a mathematic relation between the extracted echo waveform and the ocean surface wind field and wave field, thus calculating the slope and the height of the ocean surface wave and the wind speed of ocean surface through a retrieval way according to the echo parameters. On the basis that laser beam has the characteristics that the divergence angle is far less than that of a microwave beam, the method for inverting the ocean surface wind speed under the echo pulse width by adopting the spaceborne laser height indicator has foot positioning precision and space resolution ratio higher than those of currently commonly used method for inverting the wind speed through the scattering section of a radar of a microwave radar height indicator.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Microwave cavity with dielectric region and method thereof
InactiveUS20130063158A1Small sizeReduce the overall diameterResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansDielectricElectricity
A method and apparatus for obtaining dielectric constant and other measurements of a sample, comprising an open cavity resonator; a microwave energy generator for creating a resonating microwave in the open cavity resonator; a predetermined dielectric material having a high dielectric constant in the range of 2 to 100,000 substantially filling the region in which a microwave resonates; the dielectric material adapted to receive a sample for measurement of the dielectric properties of the sample; whereby during operation the resonating microwave beam is substantially immersed in the predetermined dielectric material such that the effective electrical spot size and beam cross-section along the cylindrical axis of the resonating microwave is reduced as a function of the inverse of the square root of the predetermined dielectric material dielectric constant. The dielectric constant or loss tangent of the sample may be determined based upon the change in the cavity's resonant frequency modes.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE THE
Dual-band antenna using high/low efficiency feed horn for optimal radiation patterns
ActiveUS8514140B1Reduces pointing requirementLow efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsDual frequencyRadiation mode
A dual-band antenna system configured to transmit and / or receive microwave beams over two or more frequency bands with substantially similar beam widths and substantially similar sidelobe levels is disclosed. The antenna system includes at least one reflector and at least one feed horn, the horn configured to provide a first efficiency over a first frequency band and lower efficiencies over one or more second frequency bands. The horn includes a substantially conical wall having an internal surface with a variable slope. The internal surface includes one or more slope discontinuities, wherein the slope discontinuities are configured to generate primarily TE1,m modes within the first frequency band and within the second frequency bands and generate TM1,n modes substantially only within the second frequency bands.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Microwave zoom antenna using metal plate lenses
A zoom antenna includes an ordinary pyramidal horn antenna with either a coaxial or waveguide feed and two parallel plate waveguide lenses (commonly referred to as “metal plate lenses”) positioned with their optical axes collinear with the boresight of the pyramidal horn antenna and aligned with their plates parallel to the electric field vector. The zoom antenna outputs a collimated microwave beam having a diameter varied by translation of the lenses along boresight relative to each other and relative to the phase center of the horn antenna. The zoom antenna can be rotated to vary the azimuth and elevation angles of the collimated microwave beam produced therefrom, to thereby aim the beam in any direction.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE AIR FORCE
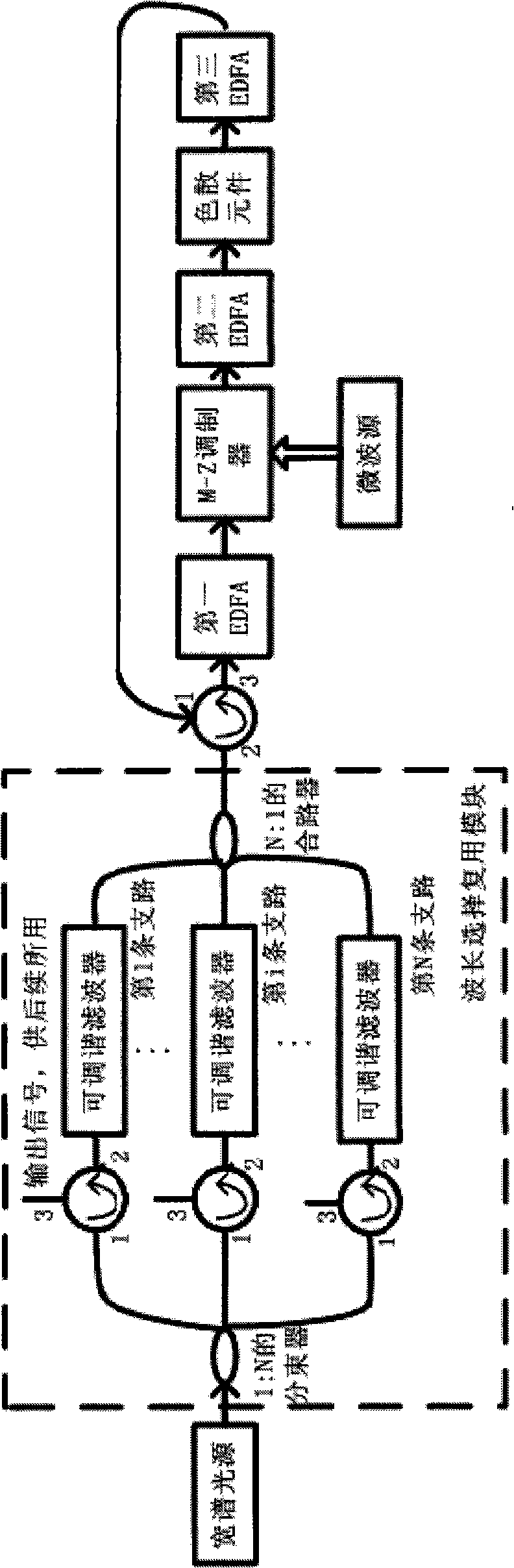
Filter feedback multiplexed millimeter wave subcarrier optical controlled microwave beam forming network
InactiveCN101359962AReduce unwanted spectral componentsIncrease optical powerFibre transmissionErbium dopingPeak value
The invention relates to a filter feedback reusable millimeter wave subcarrier light controlled microwave beam forming network, which belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave subcarrier optical controlled microwave beam forming, and is characterized in that a wavelength selecting reusable module transforms wide-spectrum light output by wide-spectrum light source to a comb-like spectrum; the comb-like spectrum is modulated by microwave signals which need to be transmitted, and the comb-like spectrum most energy of which is concentrated in the peak wavelength is formed after dispersive delay and amplification; then an adjustable filter in the wavelength selecting reusable module is utilized for inverse filtering to obtain each required signal; amplification efficiency of an erbium-doped optical fibre amplifier is greatly enhanced, and then the power level of useful spectra of the entire link is enhanced; and compared with that traditional wide-spectrum light passes through the light controlled microwave beam forming network, the invention enhances energy utilization.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
One-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna capable of scanning
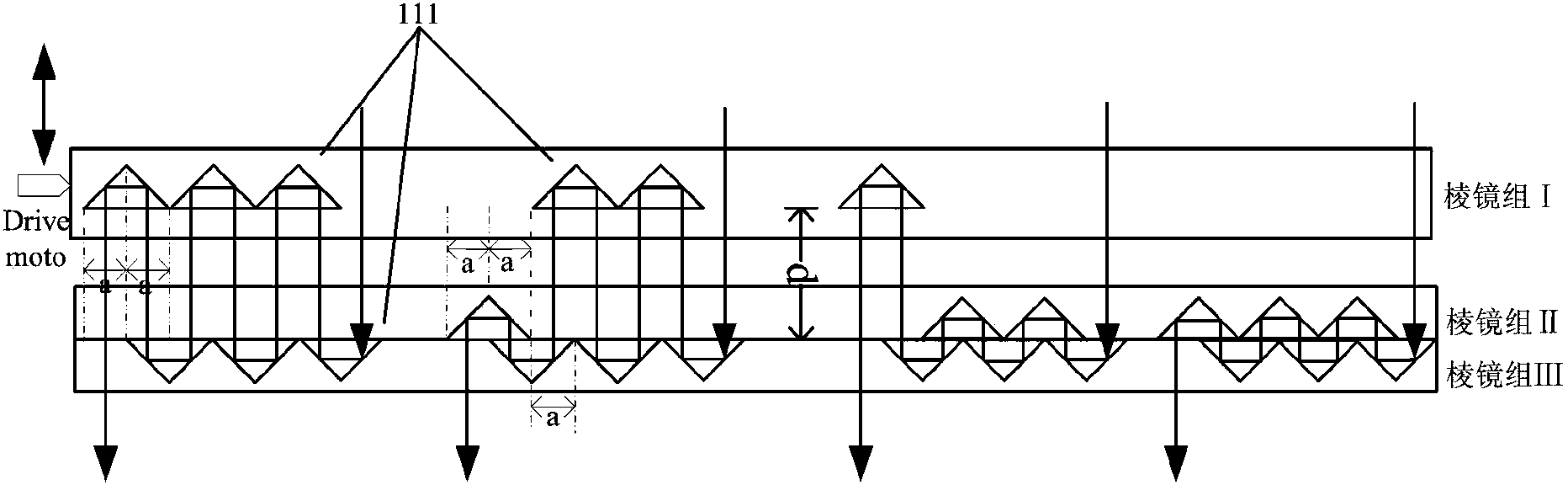
ActiveCN103326125AUniform radiationSimple structureWaveguide mouthsRadiating element housingsSlot-waveguideBeam scanning
The invention discloses a one-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna capable of scanning in order to solve the problems that an existing waveguide narrow slot array antenna unit is not even in radiation, difficult to achieve beam scanning in the single frequency condition, not high in power capacity and the like. The one-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna capable of scanning is composed of a rectangular slot waveguide, a sliding panel and a stepping motor. The rectangular slot waveguide is composed of a first narrow wall, a second narrow wall and two wide walls, one end of the rectangular slot waveguide is provided with a microwave feed-in port, the other end of the rectangular slot waveguide is connected with a matched load, n slots are formed in the first narrow wall of the rectangular slot waveguide, and the stepping motor is fixedly arranged on the second narrow wall. The sliding panel is embedded between the first narrow wall and the second narrow wall, and the sliding panel can slide in the direction perpendicular to the second narrow wall of the waveguide. According to the one-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna cable of scanning, each slot unit basically achieves even radiation, the purpose that the microwave beams scan in the one-dimensional direction under the single frequency working condition is achieved, large-scale array arranging capacity and high-power microwave field application potential are achieved, the structure is simple, and operating is convenient.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
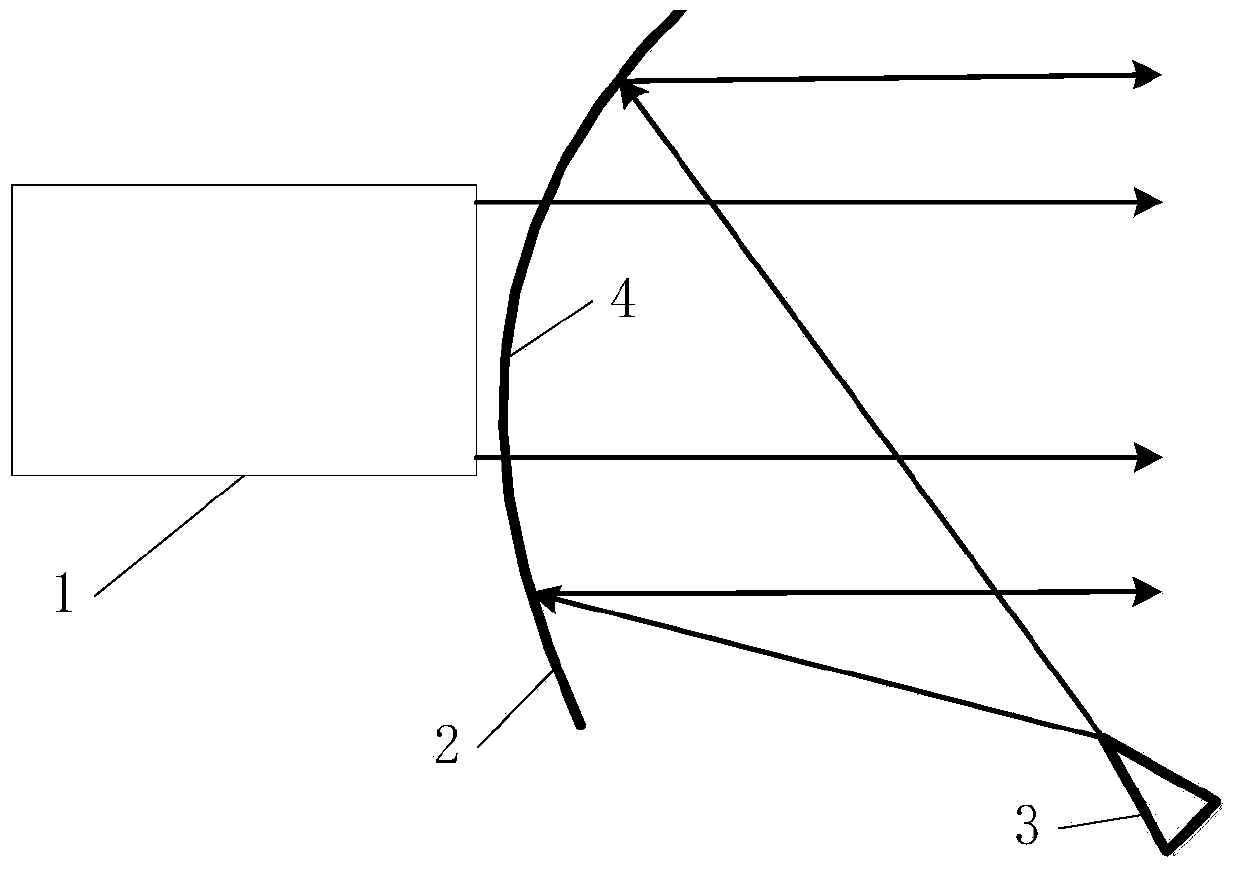
Microwave beam focusing rotary scanning device
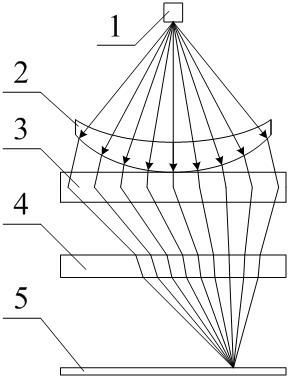
InactiveCN102508242AEasy to moveSimple structureWaveguide hornsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHorn antennaPhysics
The invention discloses a microwave beam focusing rotary scanning device, which comprises a horn antenna (1), a crescent lens (2), an offset focusing antenna (3) and a focus adjustment board (4) which are arranged coaxially, wherein the horn antenna (1) is arranged above the crescent lens (2); the bottom of the crescent lens (2) is contacted with the upper end face of the offset focusing antenna (3); and the focus adjustment board (4) is arranged below the offset focusing antenna (3). By adoption the structure, the whole microwave beam focusing rotary scanning device has a simple structure and a small volume, and is easy to implement; and according to the microwave beam focusing rotary scanning device, electromagnetic waves can be moved conveniently in a focus offsetting manner, a focusing manner and a focal point manner.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method, device and method for forming infrared-microwave beam
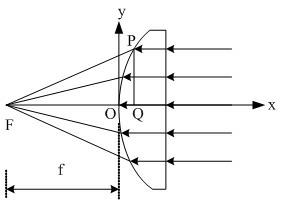
InactiveCN104215950AIncrease in sizeReduce volumeWave based measurement systemsOptical axisFocal position
The invention discloses a method for forming an infrared-microwave beam. A metal mesh is arranged in the center position of a rotationally parabolic reflecting surface in a matching manner; the metal mesh allows an infrared signal to pass through, and the metal mesh and the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface reflect a microwave signal simultaneously, and therefore, the infrared signal and the microwave signal are synthesized. The invention also discloses a system for forming an infrared-microwave beam; the system comprises an infrared light source, a feed source and the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface; an infrared target simulation system is located on the back of the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface, and the optical axis of the infrared target simulation system is coincident with the optical axis of the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface; the feed source is located in the focal position of the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface; a hole is formed in the central position of the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface; the metal mesh is inlaid in the hole of the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface, and the metal mesh is matched with the curvature of the rotationally parabolic reflecting surface. The device for forming the infrared-microwave beam, namely a simulation device for synthesizing infrared and microwave with the structure, is small in volume and light in weight, and can be mounted on two outer frame shafts of a five-axis turntable.
Owner:BEIJING SIMULATION CENT
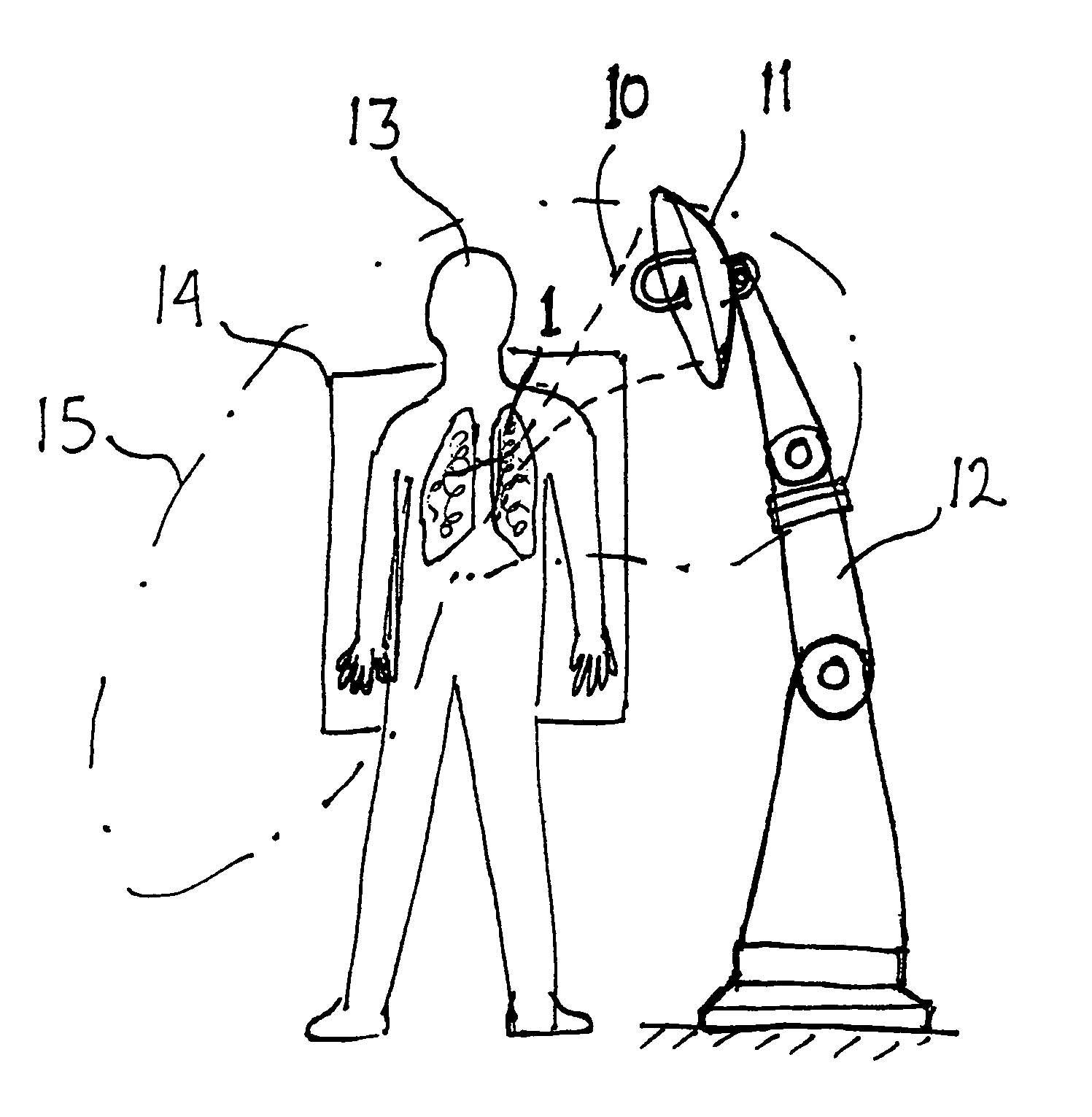
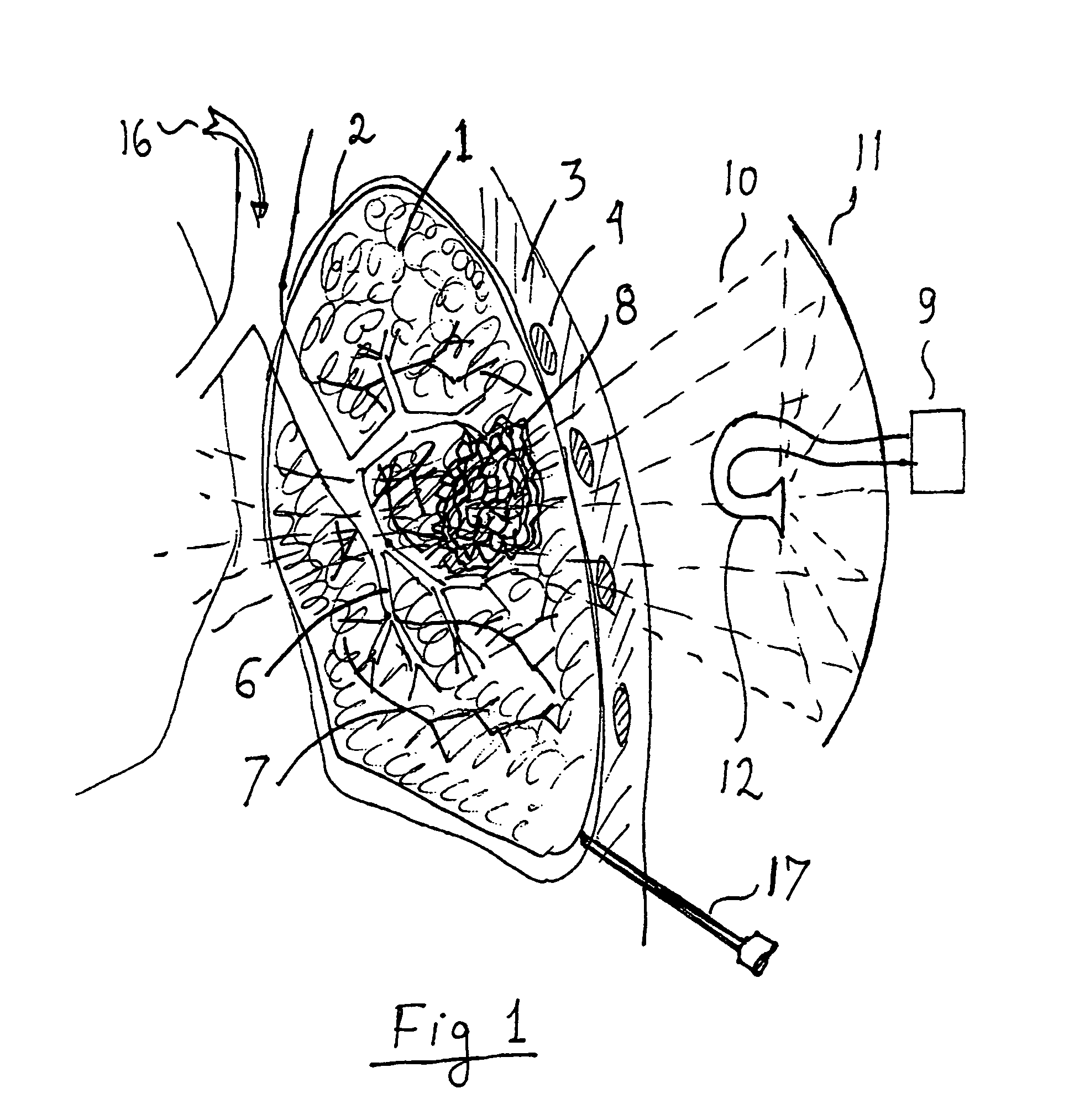
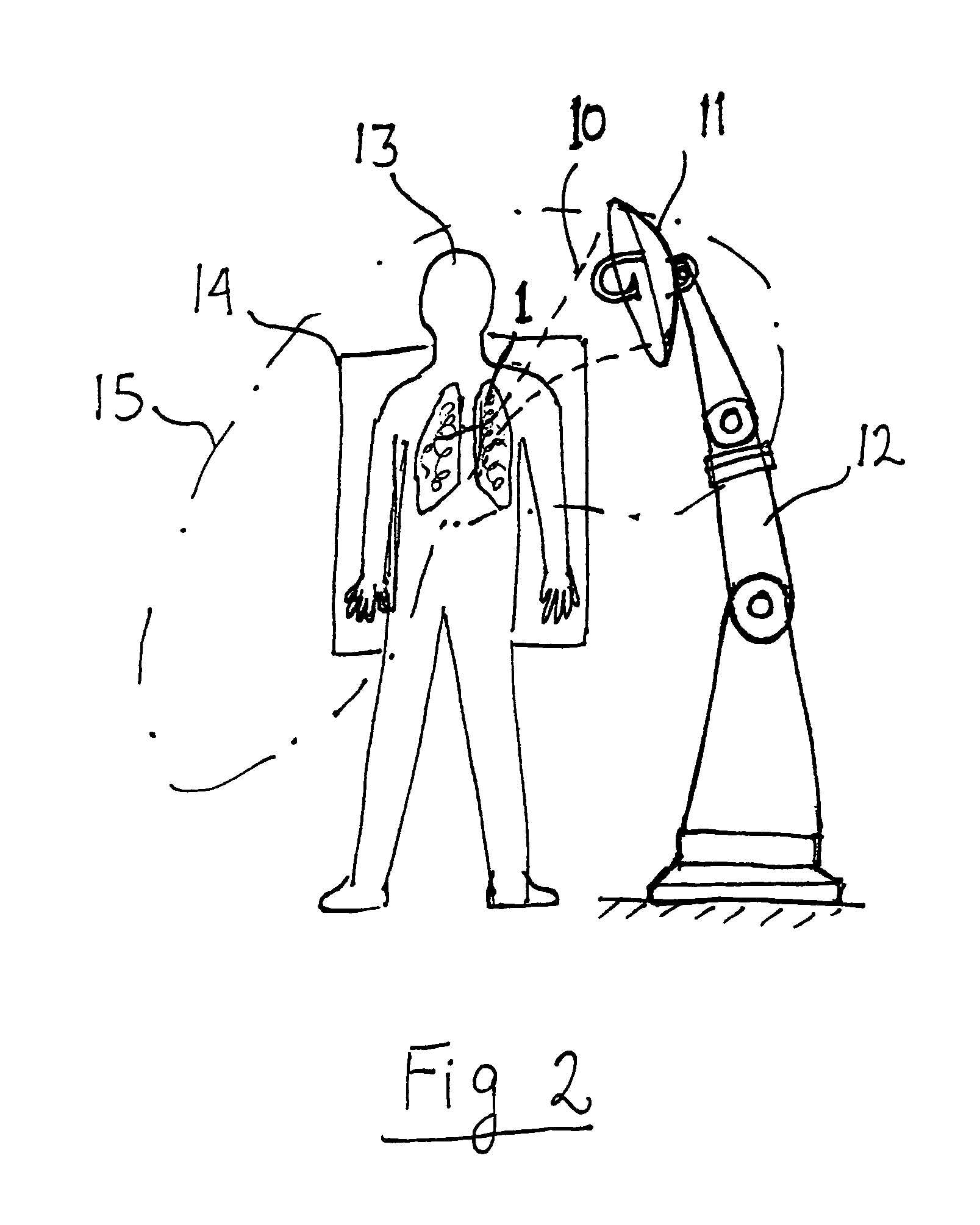
Methods for selectively heating tissue
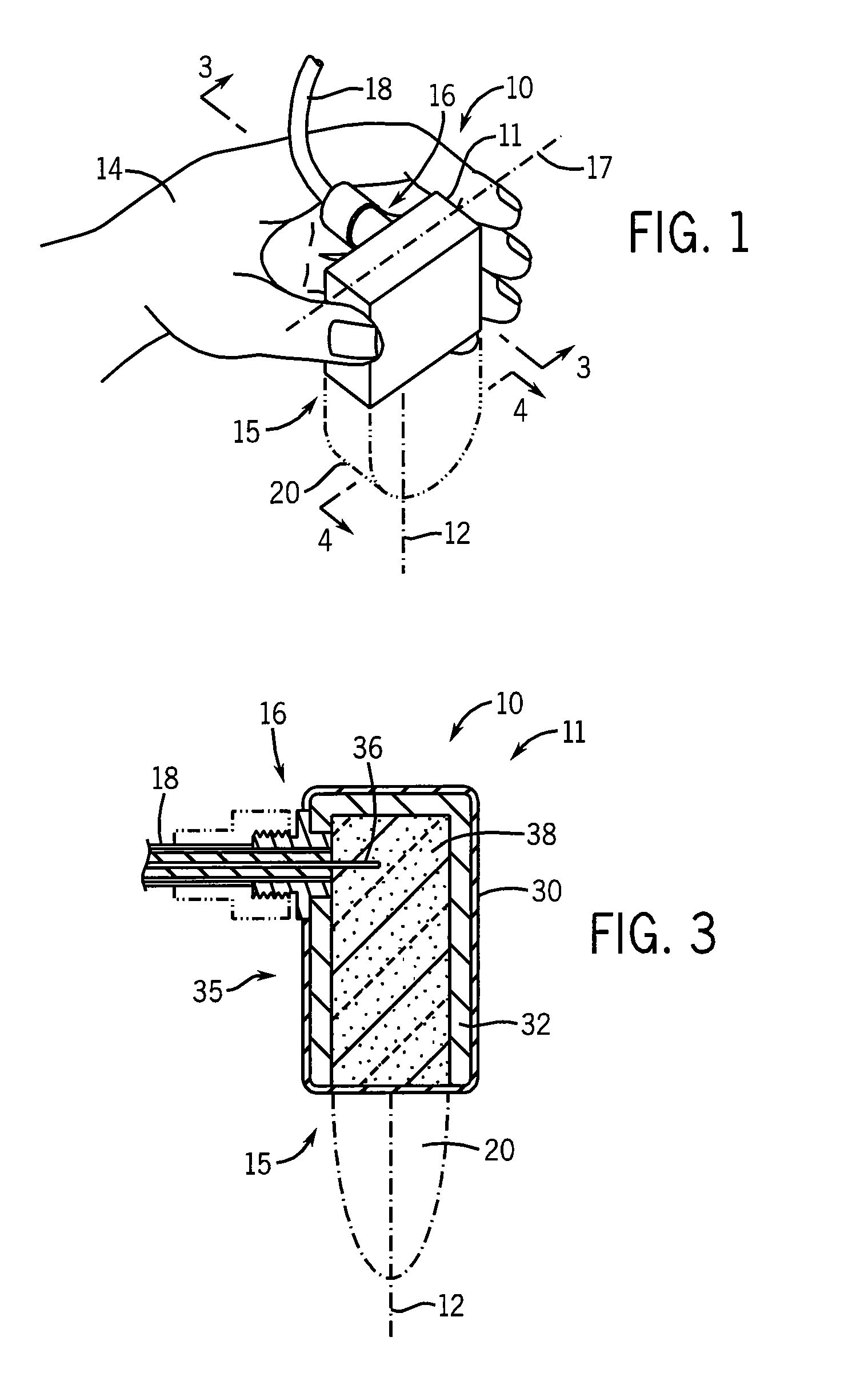
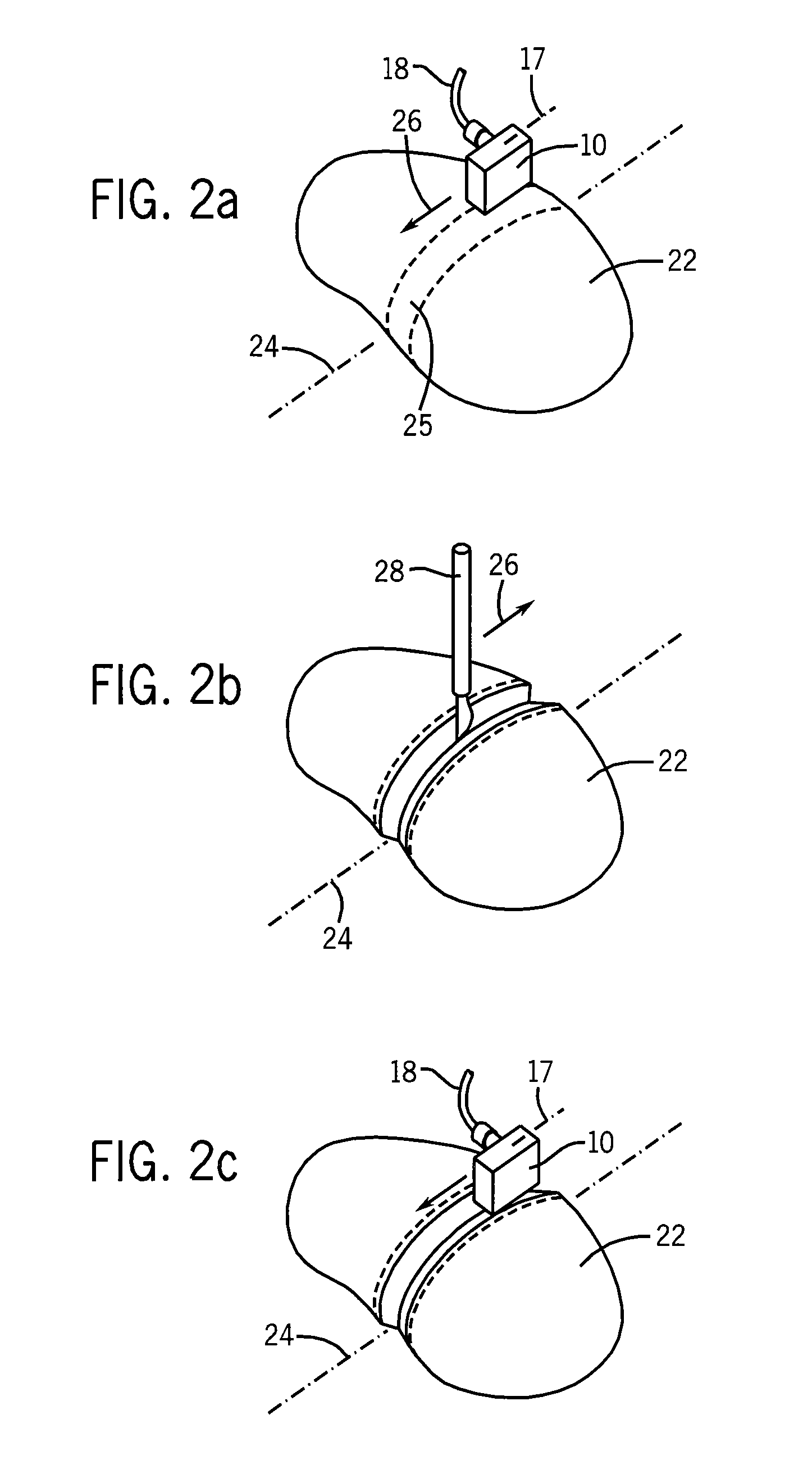
ActiveUS8444635B2Selective heatingReduce heatDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingHigh blood flowHealthy tissue
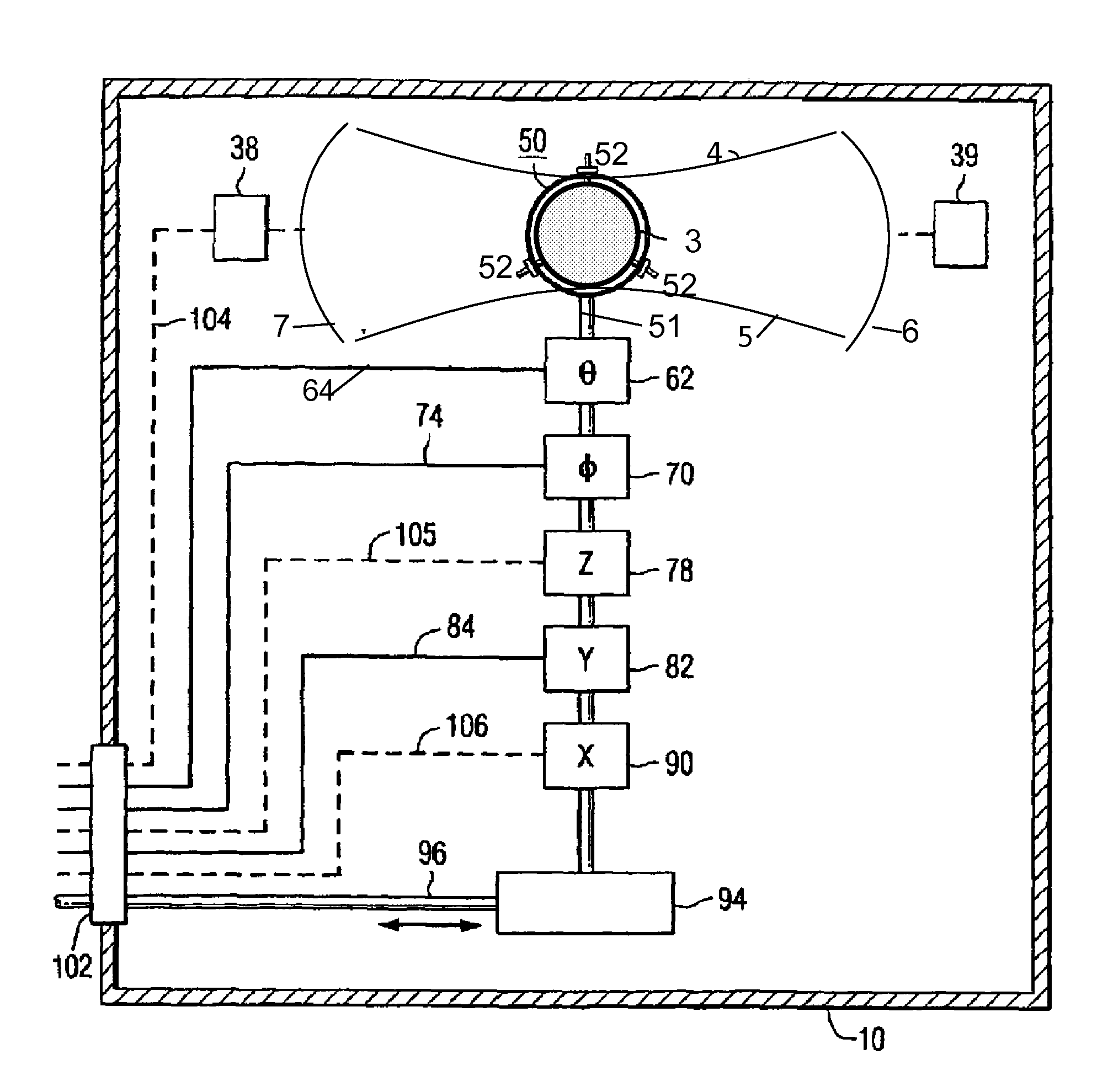
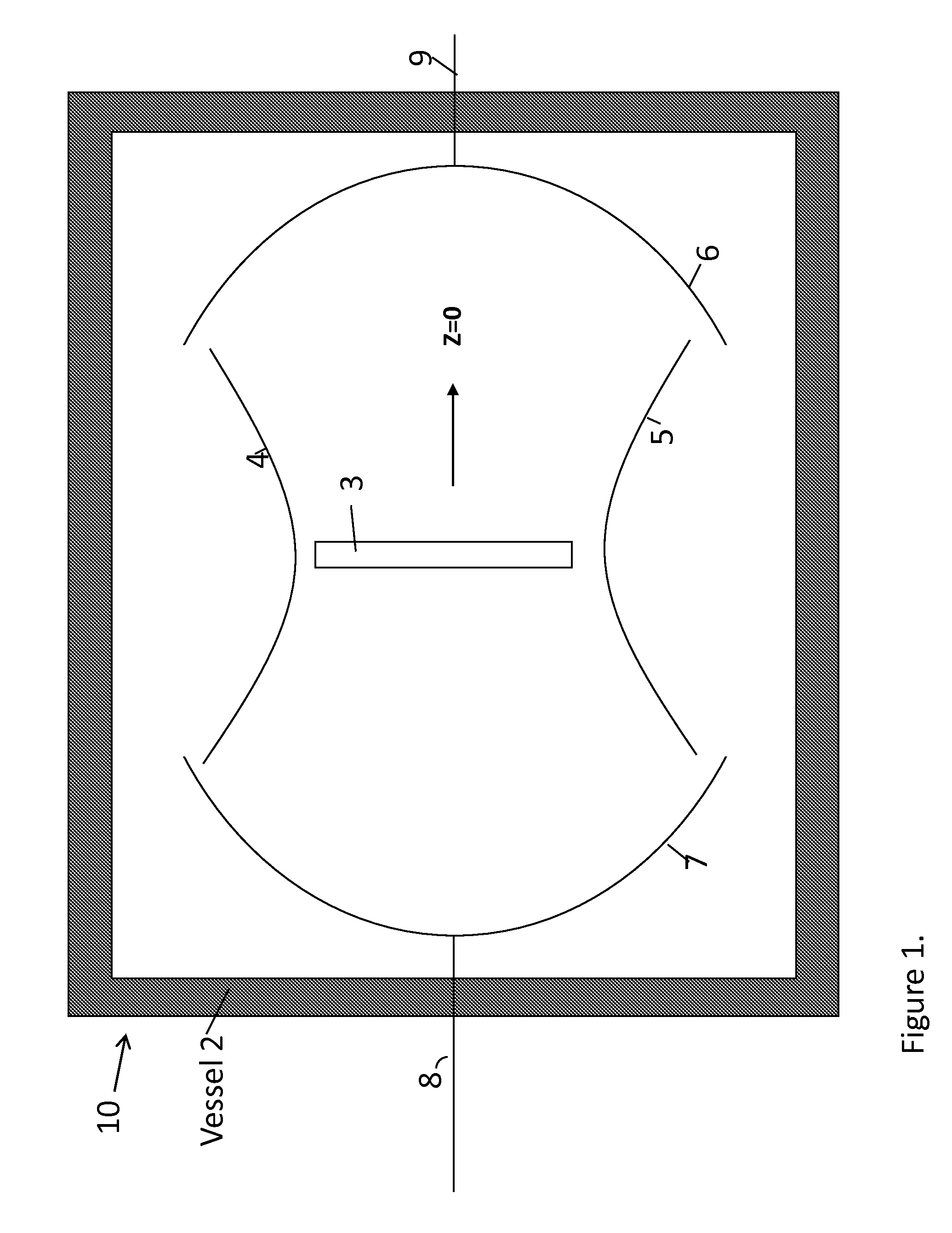
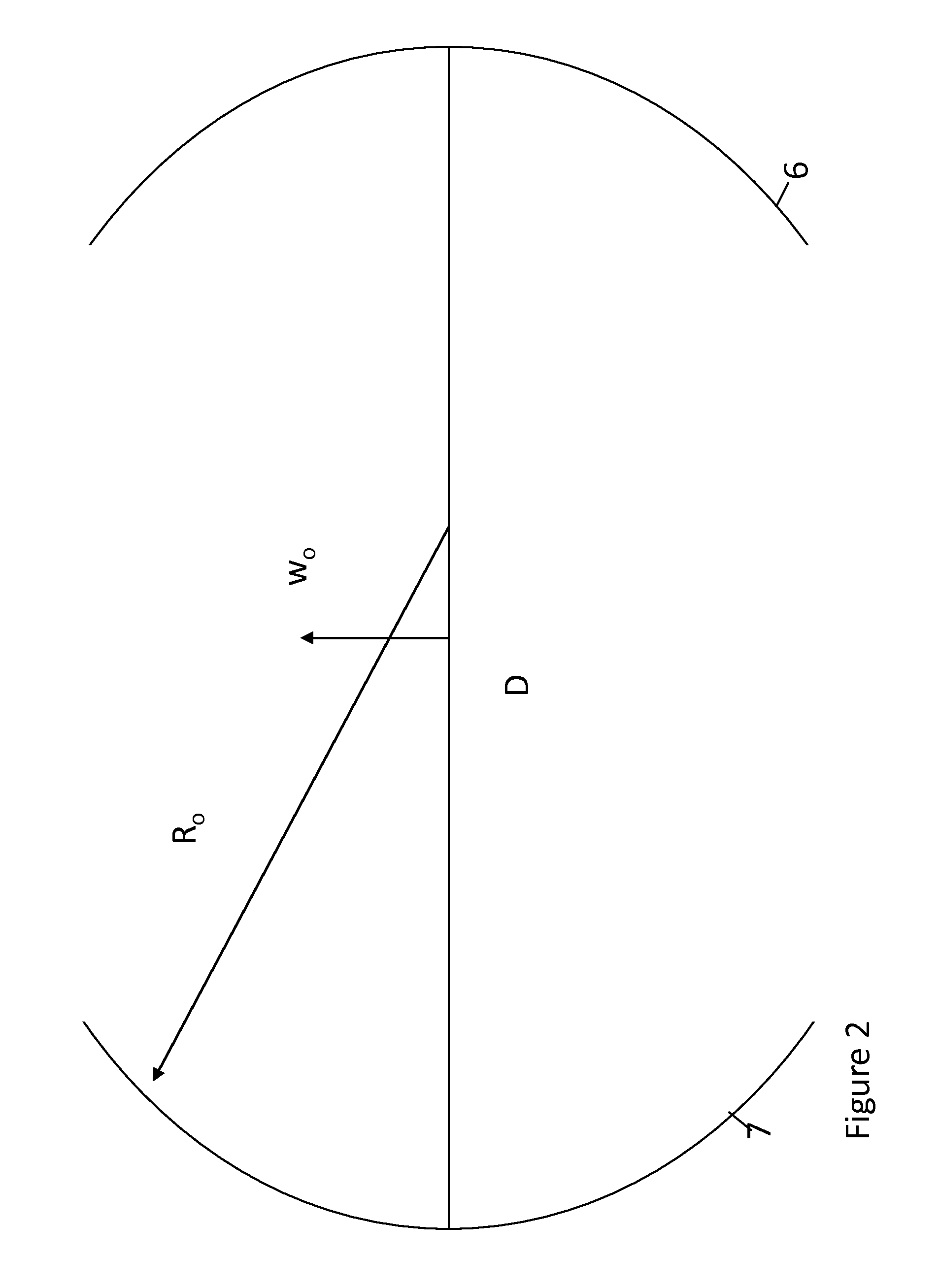
The invention can selectively heat a diseased area or undesired tissue in the body while minimizing heating to the healthy area and surrounding tissue. This is done by exposing the undesired tissue to a scanning focused microwave beam arriving from different directions, all directions passing through the undesired tissue. The invention is particularly useful for heating tissues in which the undesired tissue has reduced blood flow. The undesired area will heat up rapidly while the healthy tissue will be cooled by the blood flow. This is particularly effective for treating emphysema because of the low mass of the lungs and the high blood flow.
Owner:IKOMED TECH
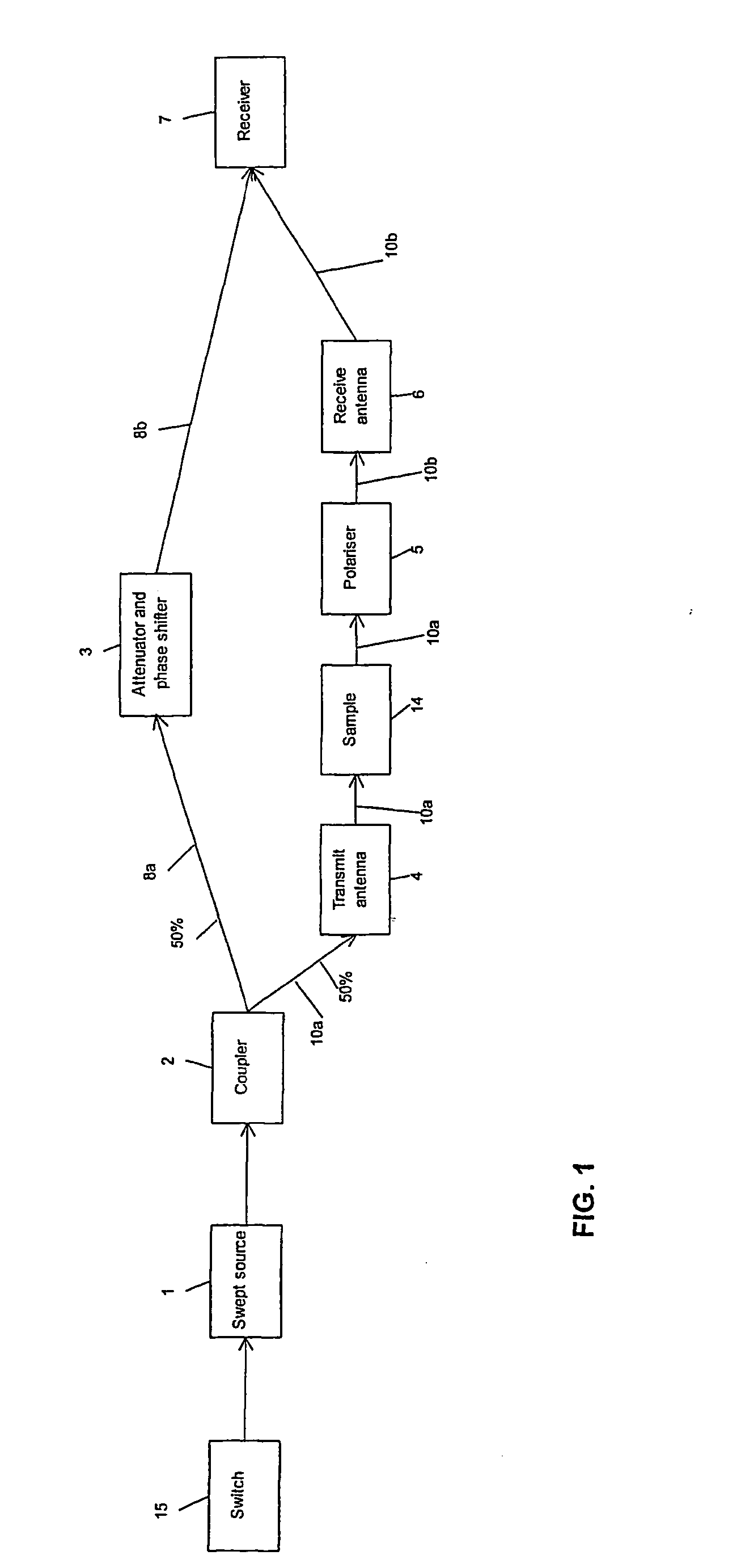
Optically-controlled microwave beam forming networks
ActiveCN103414519AReduced stabilityUniform gainAntenna arraysWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberLow noise
Optically controlled microwave beam forming networks comprise 2N single frequency DFB lasers of different wavelengths, , 2N electro-optic intensity modulators, 2N *1 passive wavelength division multiplexers, an optical fiber, 1*2N optical beam splitter, 2N fiber collimator, a time delay network module, 2N coupled lenses, 2N photoelectric detectors and 2N low noise amplifiers, wherein N is an integer larger than 2. The optically controlled microwave beam forming networks have the advantages of the high signal to noise ratio, good dynamic performance, high time delay precision, continuous adjustability, and good stability, and are easy to be extended in the system array size.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
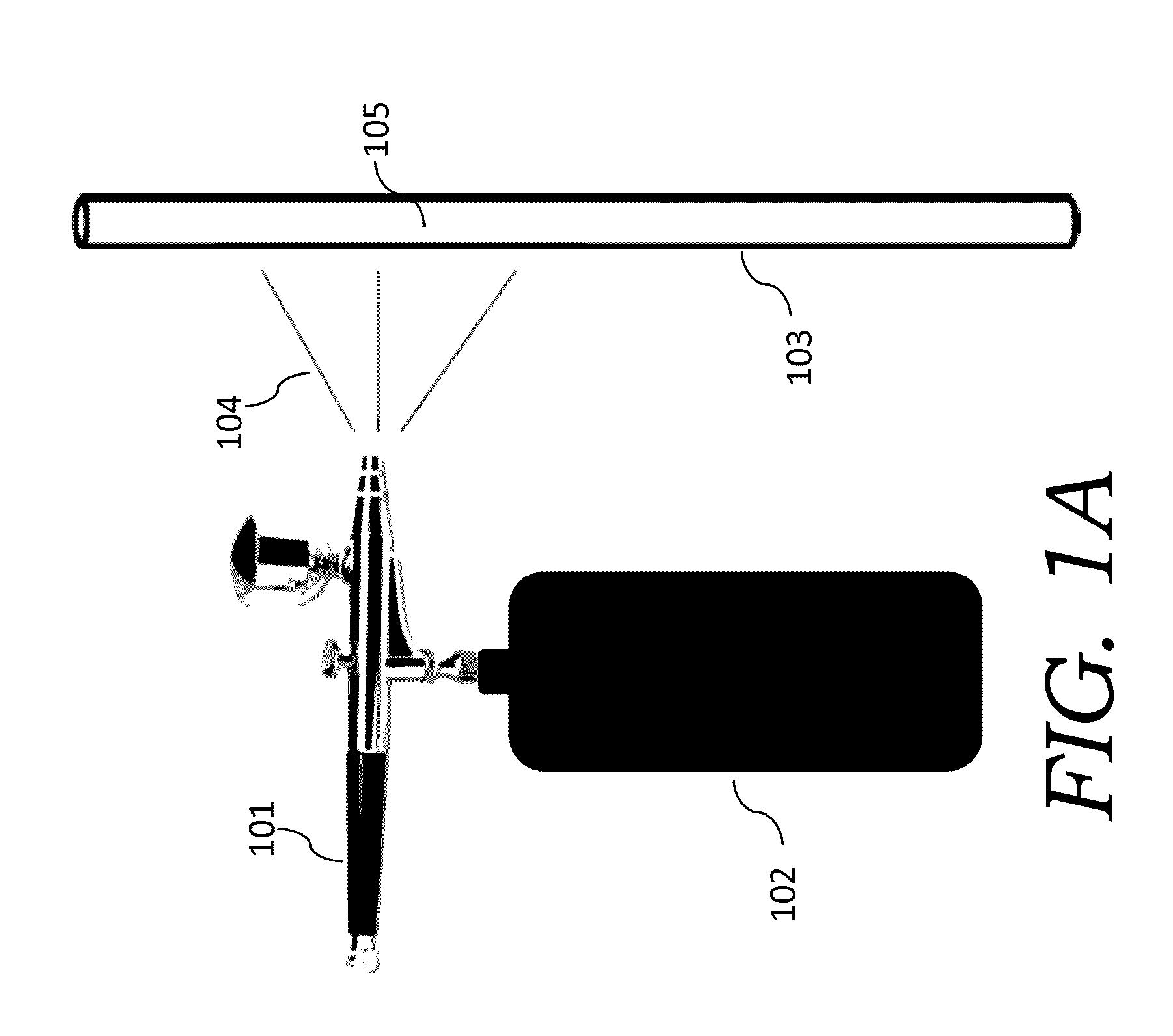
Fan-beam microwave horn for bloodless resection
ActiveUS20100312234A1MinimizationEasy to shapeSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesMedicineHand held
A handheld microwave waveguide provides a planar microwave beam for rapid coagulation of a strip of tissue in an organ providing a barrier against blood loss during resection operations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
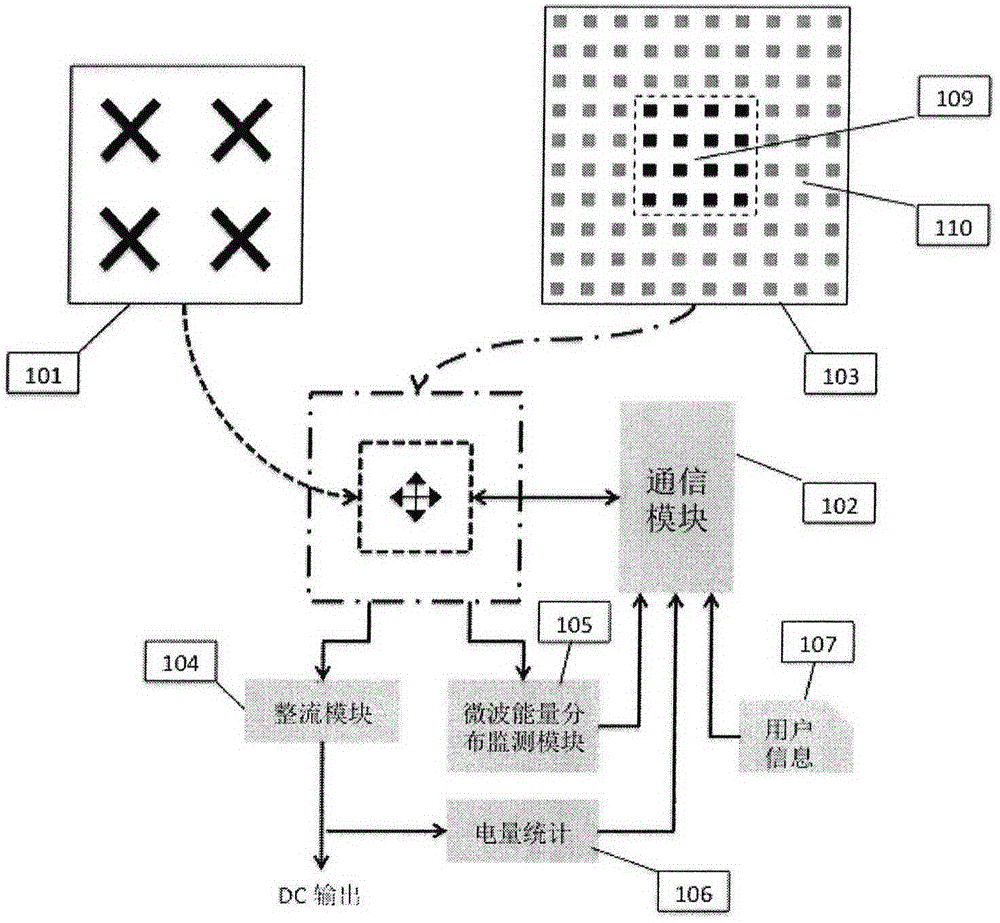
Vehicle road mobile charging system
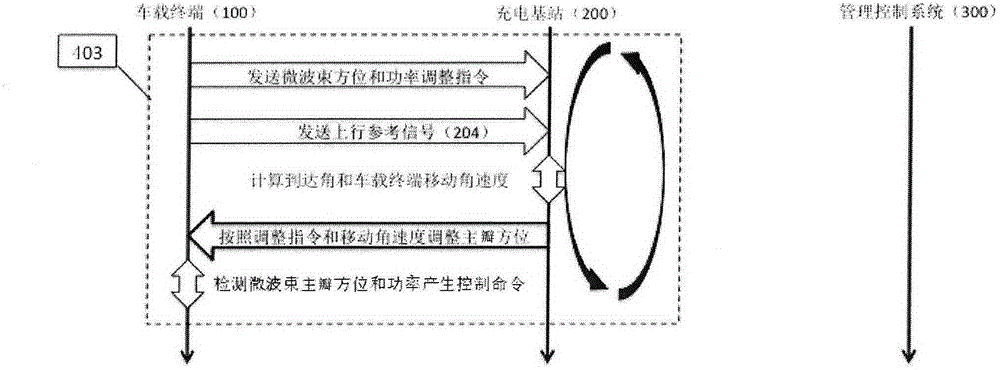
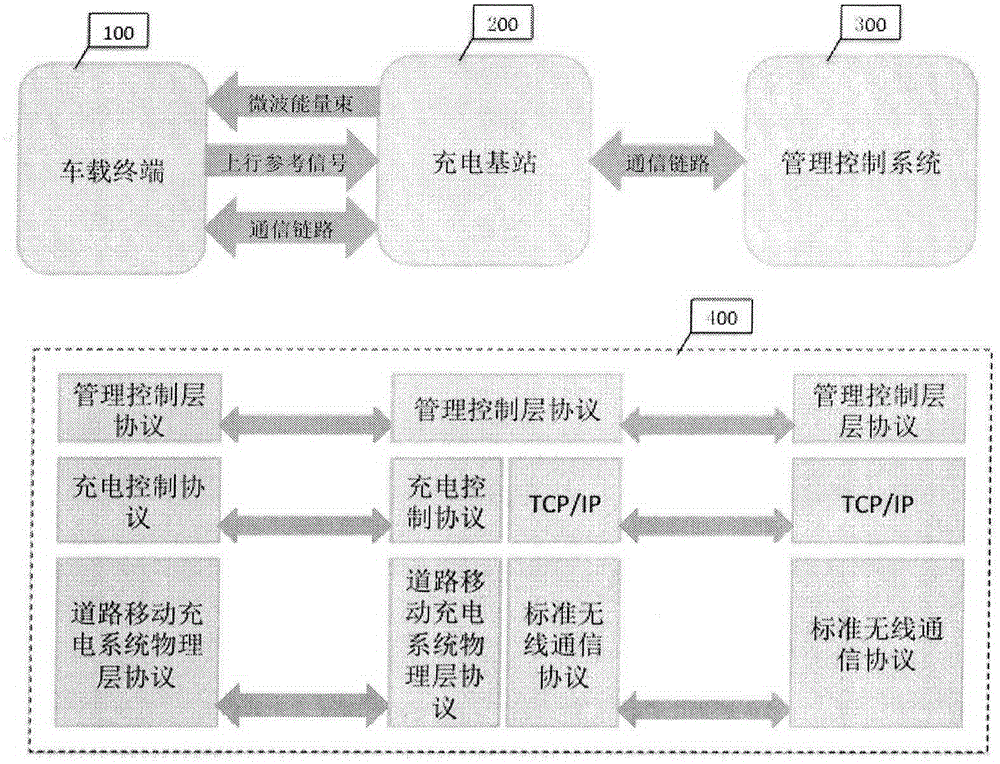
InactiveCN104967155ABatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionDriver/operator
A vehicle road mobile charging system is an innovative system combining wireless microwave electric power transmission technologies and wireless communication technologies. The system makes up for the defect that electric vehicles are charged by fixed charging facilities. By means of the system, electric vehicles can be charged through microwave energy beams in a driving state. The means effectively increases the driving distance of pure electric vehicles, prevents defects of multi-time charging and long consumed time during a long distance trip and further makes a driver no longer worry about the mileage. The system comprises a vehicular terminal, a charging base station and a management control system. After successfully accessing to a charging network and being authorized, the vehicular terminal sends uplink reference signals. The charging base station receives the uplink reference signals through an antenna array and processes the signals to determine the orientation of vehicles. The microwave antenna array is further controlled according to the orientation information to send electric energy to a vehicle energy collecting and converting device in a microwave beam means. Closed-loop wave beam control technologies are adopted to guarantee that the energy beams are constantly aligned with the vehicular energy collecting device; and harm to surrounding objects is prevented.
Owner:李高山
Method for the production of a visible, UV or IR radiation with a lamp without electrodes, and lamp that carries out this method
A lamp capable of emitting electromagnetic radiation (9), for example visible, IR or UV radiation, exploiting the activation of substances (4) triggered with an antenna (6) irradiating microwaves (8) located inside and insulated, in focal position. Advantageously, the substances (4) are put into a chamber (3) obtained by introduction of a first bulb (1) in a second bulb, in order to form the chamber (3) closed between the walls of the first (1) and of the second bulb (2), the walls of the first bulb defining the recess (5) which houses the antenna (6). A better energy efficiency and a better economy is obtained with respect to the conventional techniques which require introduction of the lamp in a metal vessel crossed by microwaves, or under external microwaves beams. It belongs to the category of lamps without electrodes, because the atoms or the other particles that emit the radiation (8) are neither in contact with the antenna nor with other metal parts. It characterized by a high duration and by the possibility of emitting radiation of modulated wavelength in continuous or pulsed way.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
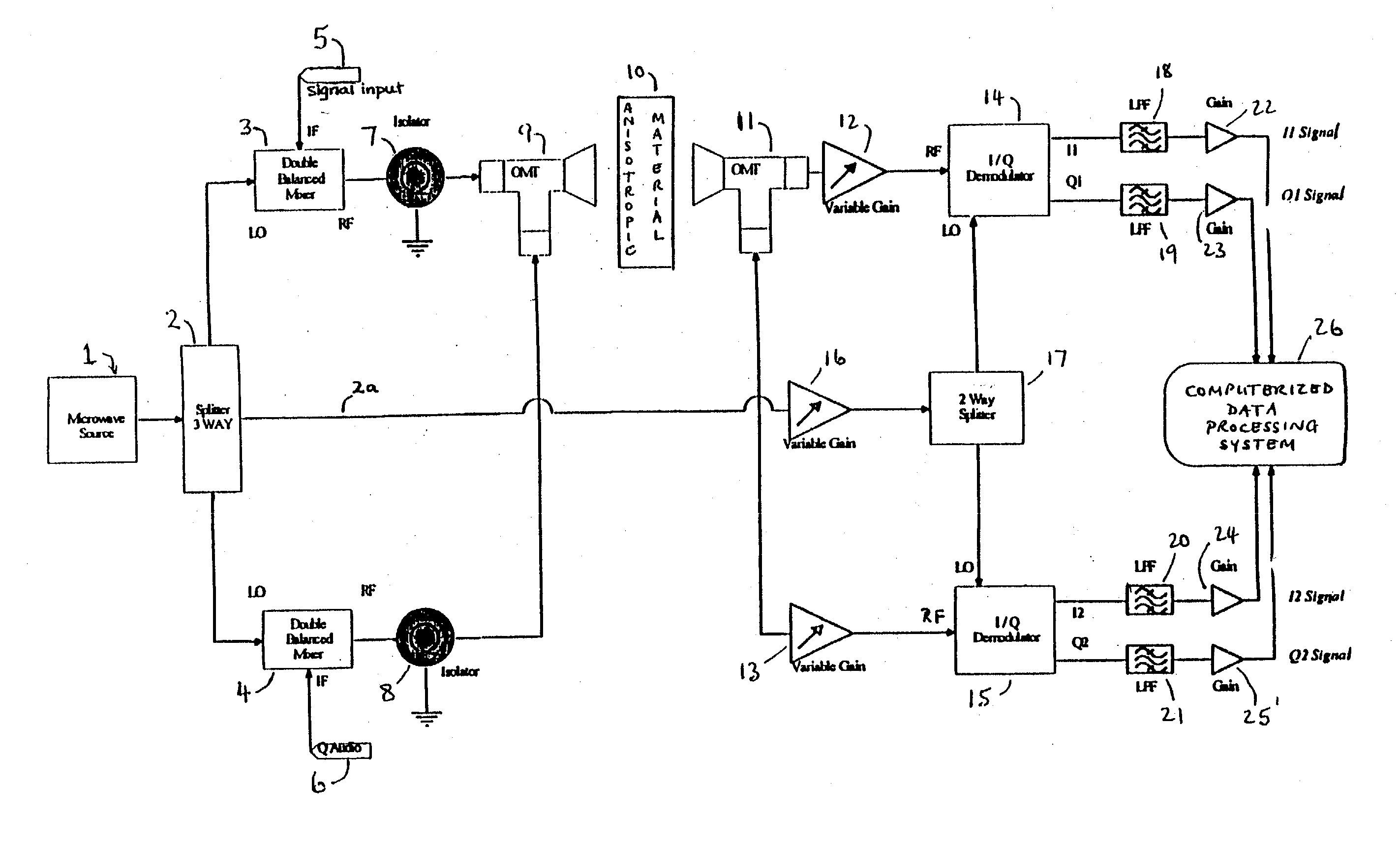
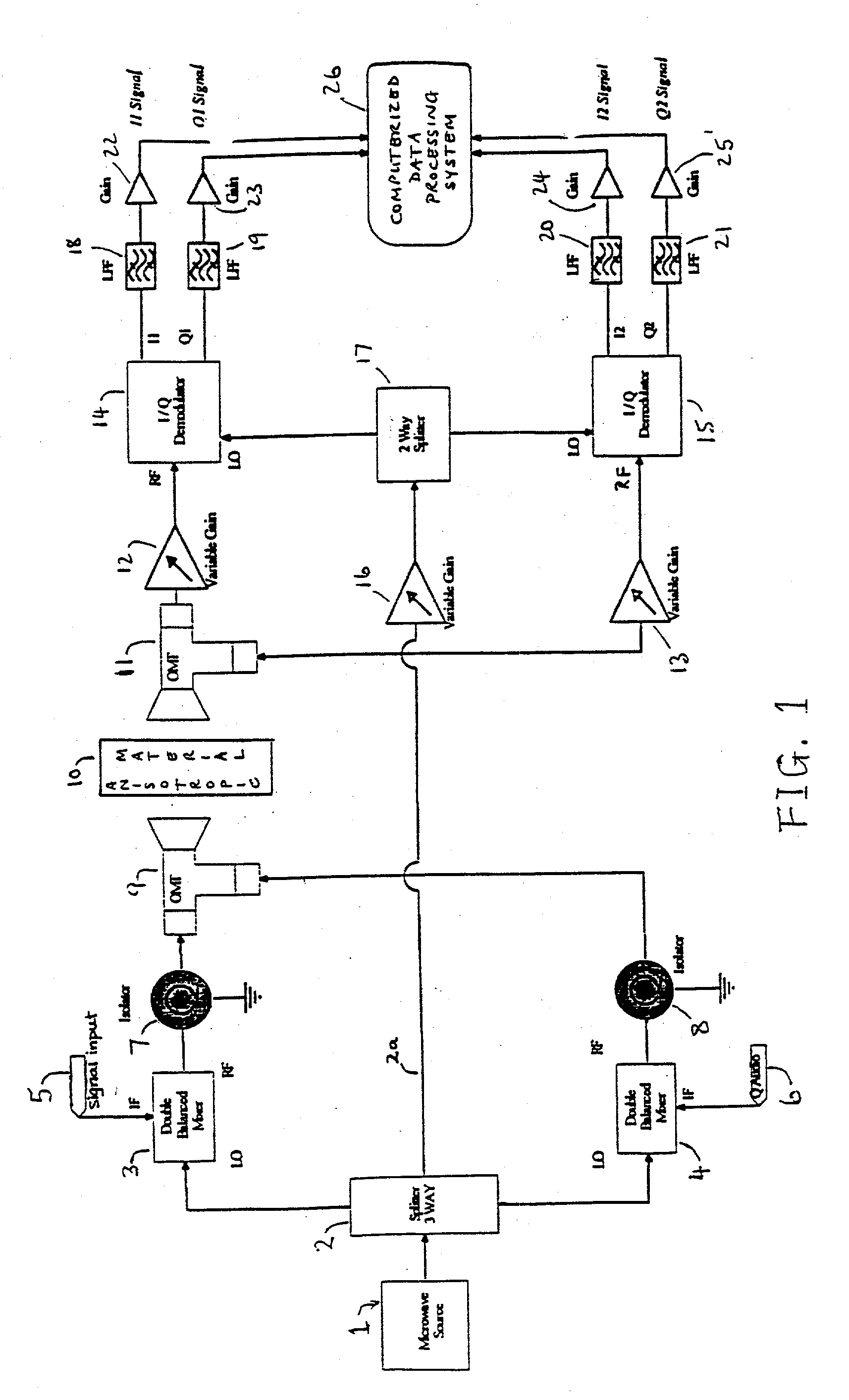
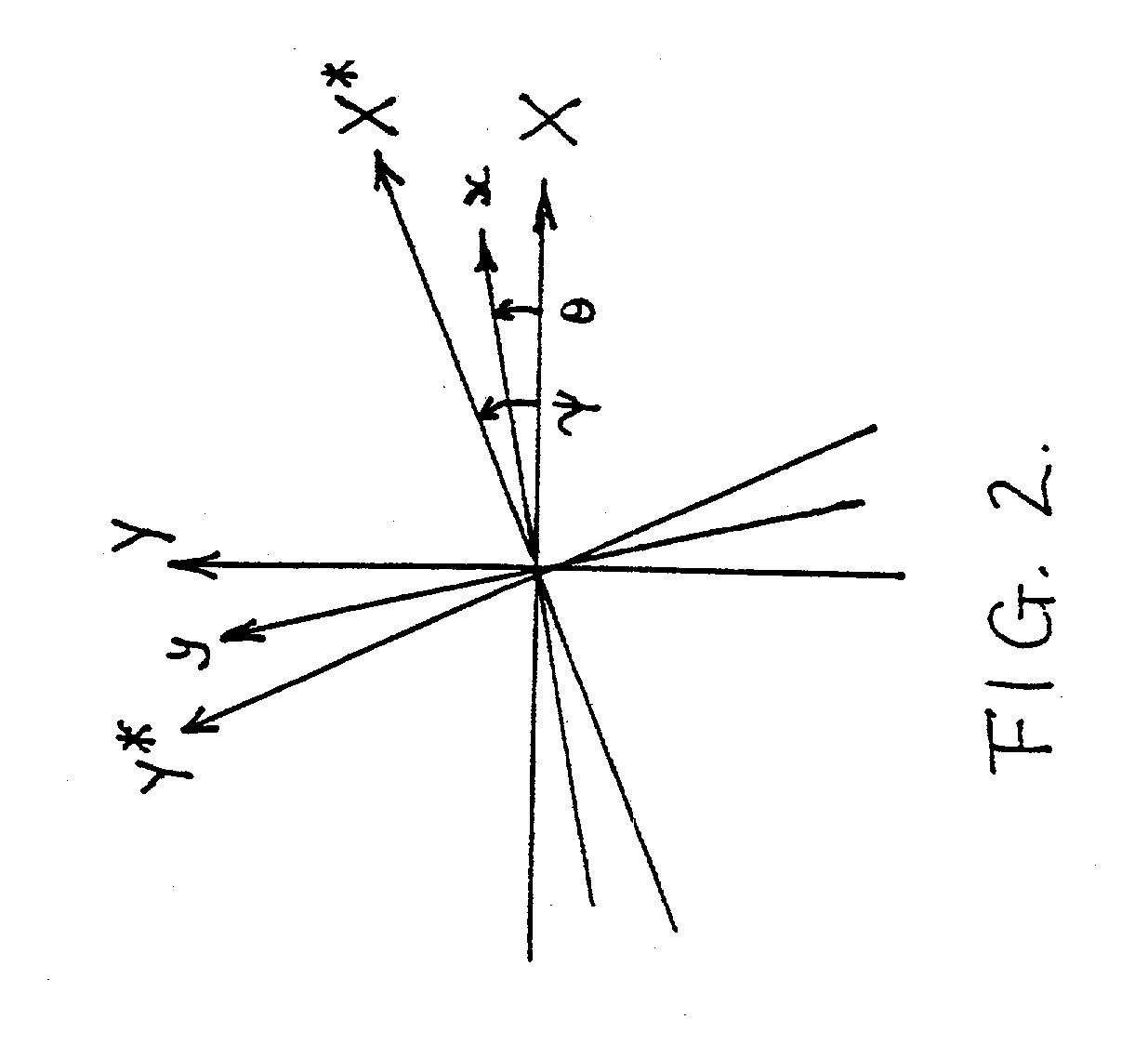
Method and apparatus for evaluating anisotropic materials
InactiveUS20030222658A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansUltrasound attenuationPhase shifted
An apparatus for evaluating dialectically-anisotropic materials comprising a plurality of microwave transmitters with differing planes of polarization, and a plurality of microwave receivers with differing planes of polarization, wherein each transmitter includes a means of modulating the microwave beam to be transmitted, the transmitters and receivers arranged, relative to a workpiece to be measured, so as to cooperate in communication therebetween, and wherein connected to each receiver is a processor to identify the received amplitude and phase of a component of the transmitted microwave beam, and to analyze by Fourier analysis the received signals to identify the principal axes, attenuations and phase shifts of the received microwave beam without requiring the phases of the transmitted microwave beams to be synchronized.
Owner:USNRKOCKUMS CANCAR
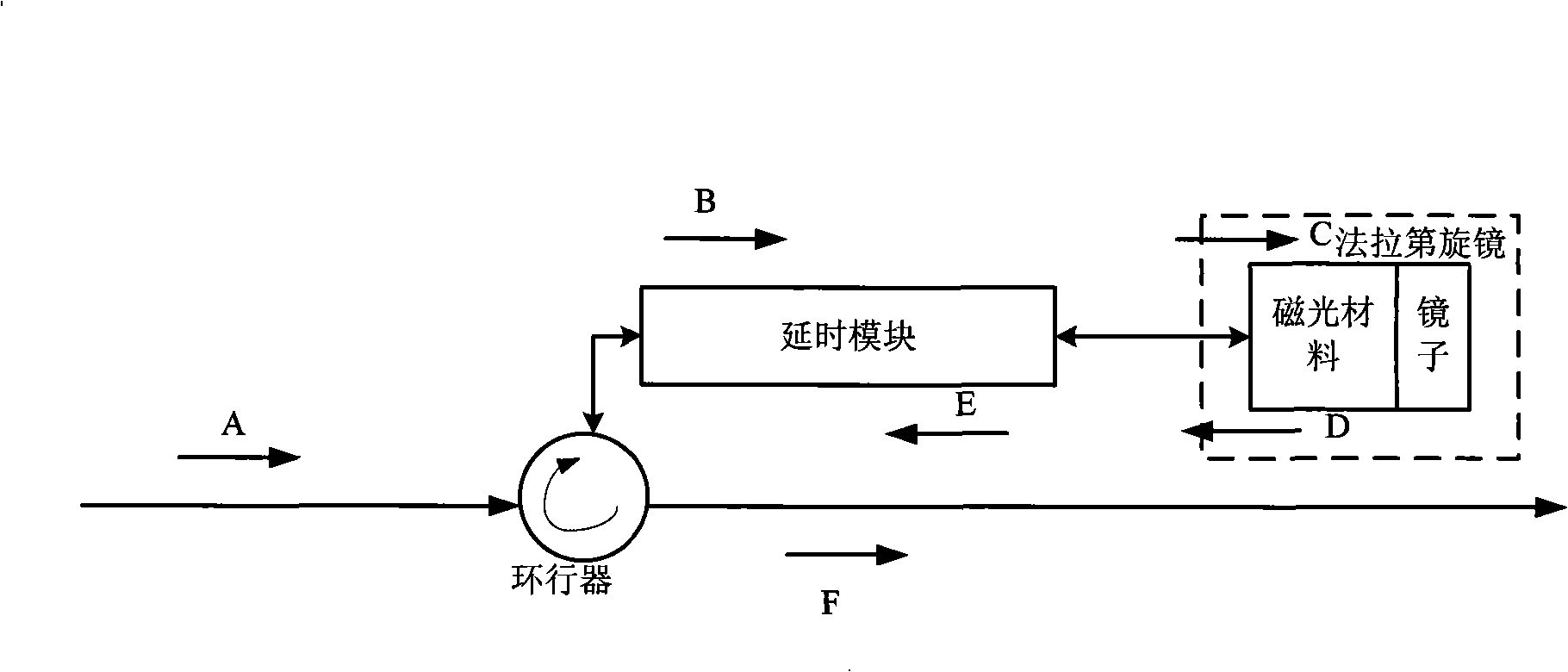
Apparatus and method for compensating polarization membrane dispersion in network for forming light control microwave beam
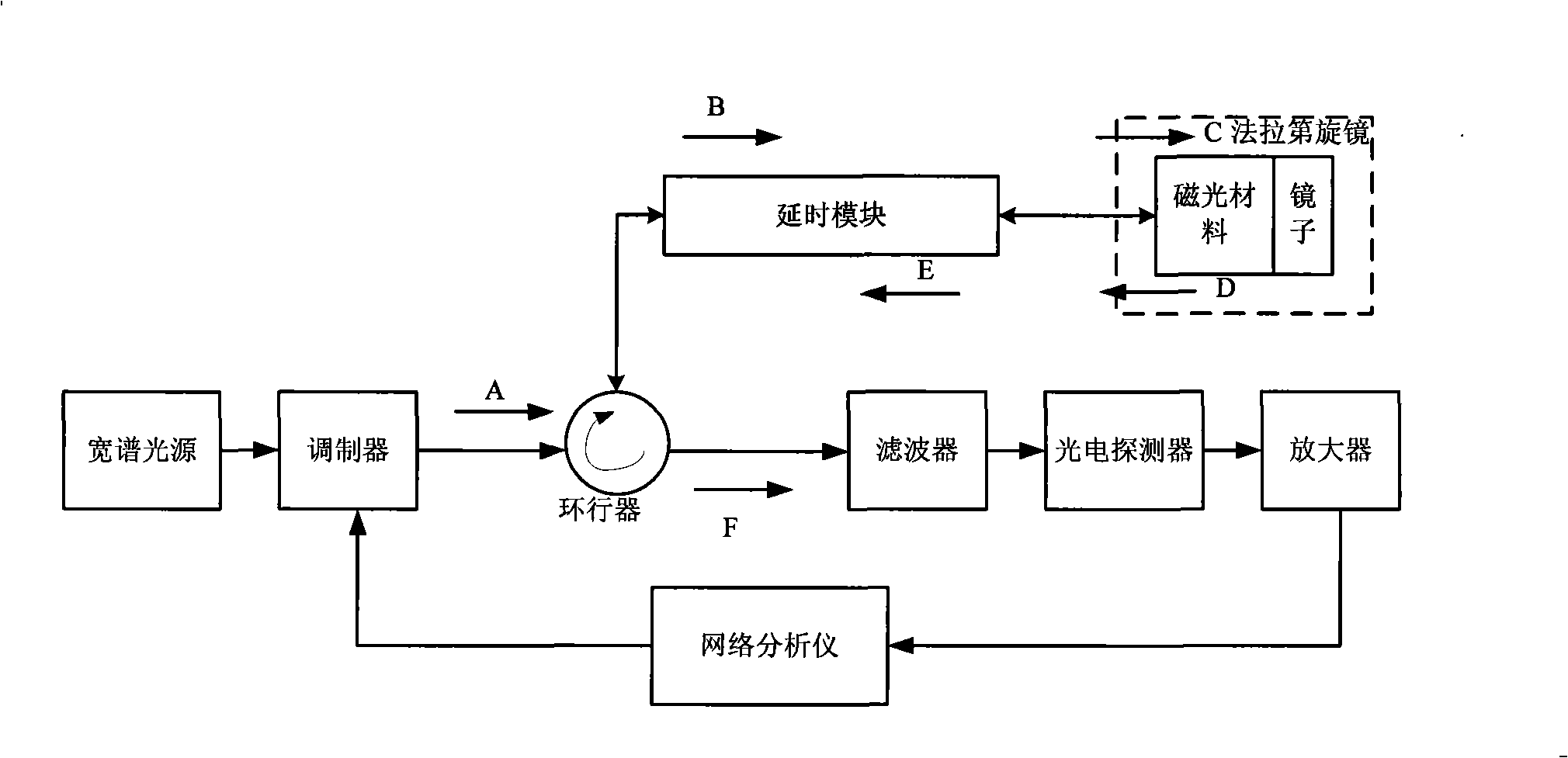
The present invention relates to a compensation device of polarization module dispersion in the optically controlled microwave beam forming network, and a method thereof, belonging to the technical field of compensation of the polarization module dispersion. The compensation device is characterized by comprising a circulator, a delay module, and a 90-degree Faraday rotating mirror; the circulator is used for transmitting the input light of modulated signals; the delay module adopts the principle of Jones matrix to polarize the input light of the circulator so as to realize the delay with the influence of polarization module dispersion; the 90-degree Faraday rotating mirror adopts the Jones matrix to transform the signal light transmitted from the delay module into a reflective electric field; the signal light is transmitted reversely to realize the compensation of the polarization module dispersion, and is transmitted outwards by an analyzer after entering an optical link, so as to compensate the corresponding polarization module dispersion. The compensation device has the advantages of simple structure and low costs.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of heat treating coatings by using microwave
InactiveUS20050221017A1Quality improvementLower cost of capitalPretreated surfacesInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureCeramicHeat treated
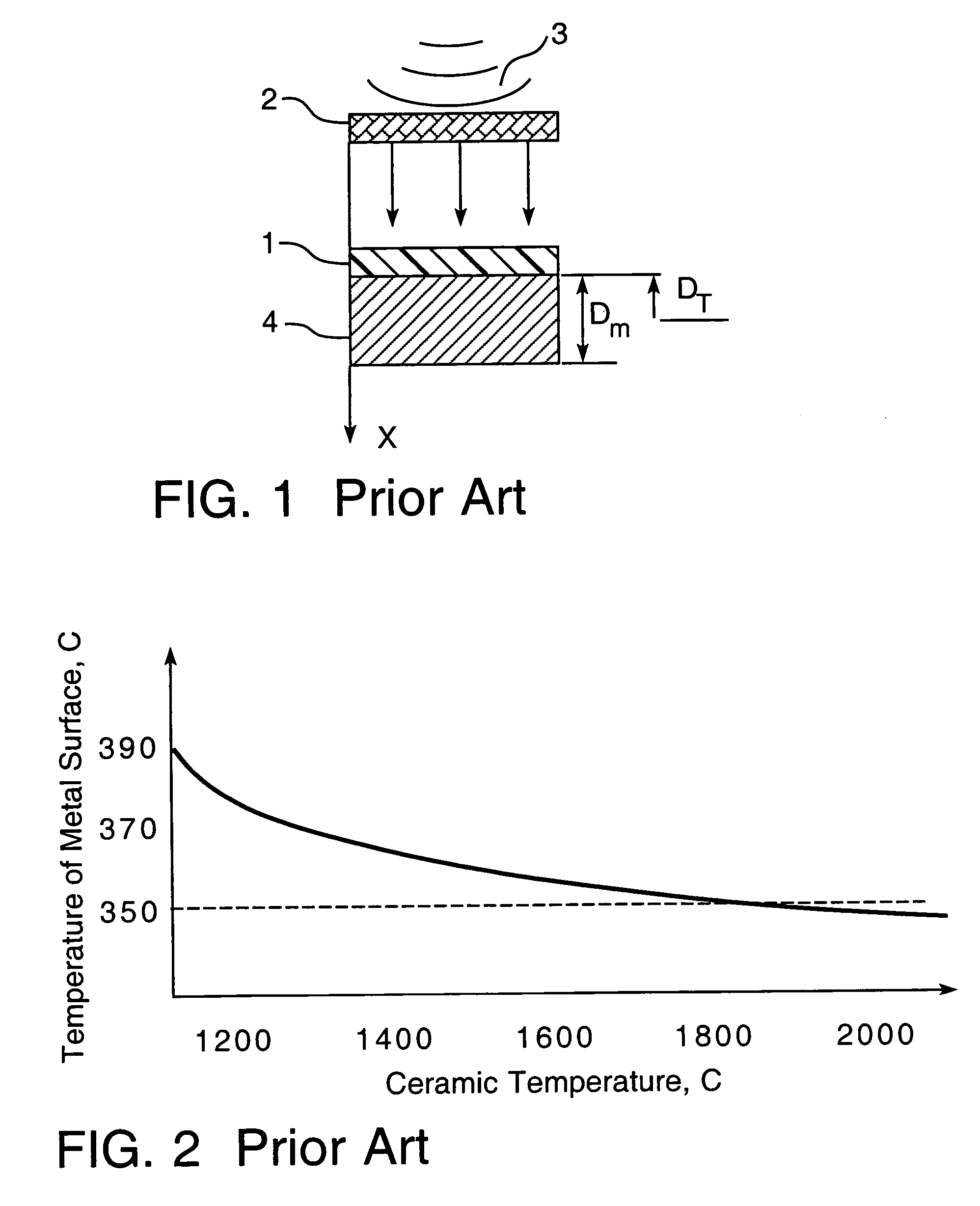
A method for heat treatment of coatings for application to metal surfaces wherein a ceramic is positioned adjacent to the coating to be treated and the ceramic is exposed to a microwave beam having a predetermined frequency and power density which are sufficient to heat the ceramic to a desired temperature whereby the coating is adhered to an applied metal surface without temperature degradation of the metal.
Owner:GYROTRON TECH
Apparatus and method for microwave determination of at least one physical parameter of a substance
InactiveUS7187183B2High sensitivityImprove accuracySamplingResistance/reactance/impedenceRest positionSalt content
A method and an apparatus is described to measure at least one physical parameter of a substance such as moisture and salt content. This is done by transmitting a microwave beam through the material to be measured and detect only a reflection of a predetermined polarity of the transmitted waves. To accomplish this a polarizing plate is used so that only cross-polarized microwaves, which pass through the substance are detected and the co-polar reflections from surrounding structures are excluded. The object can either be moving as on a conveyer belt or in a rest position.
Owner:INTELSCAN ORBYLGJUTAEKNI EHF
Aluminized BSF secondary sintering technology for crystal silicon solar cell
InactiveCN101540349AFacilitated DiffusionImprove collection efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesThermal impactBack surface field
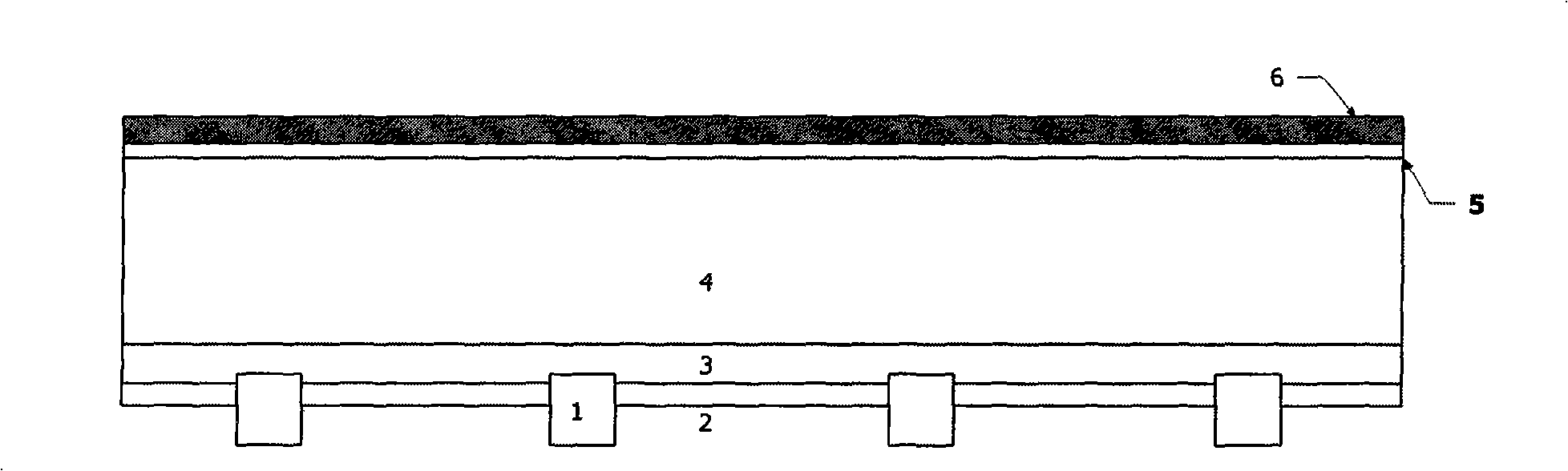
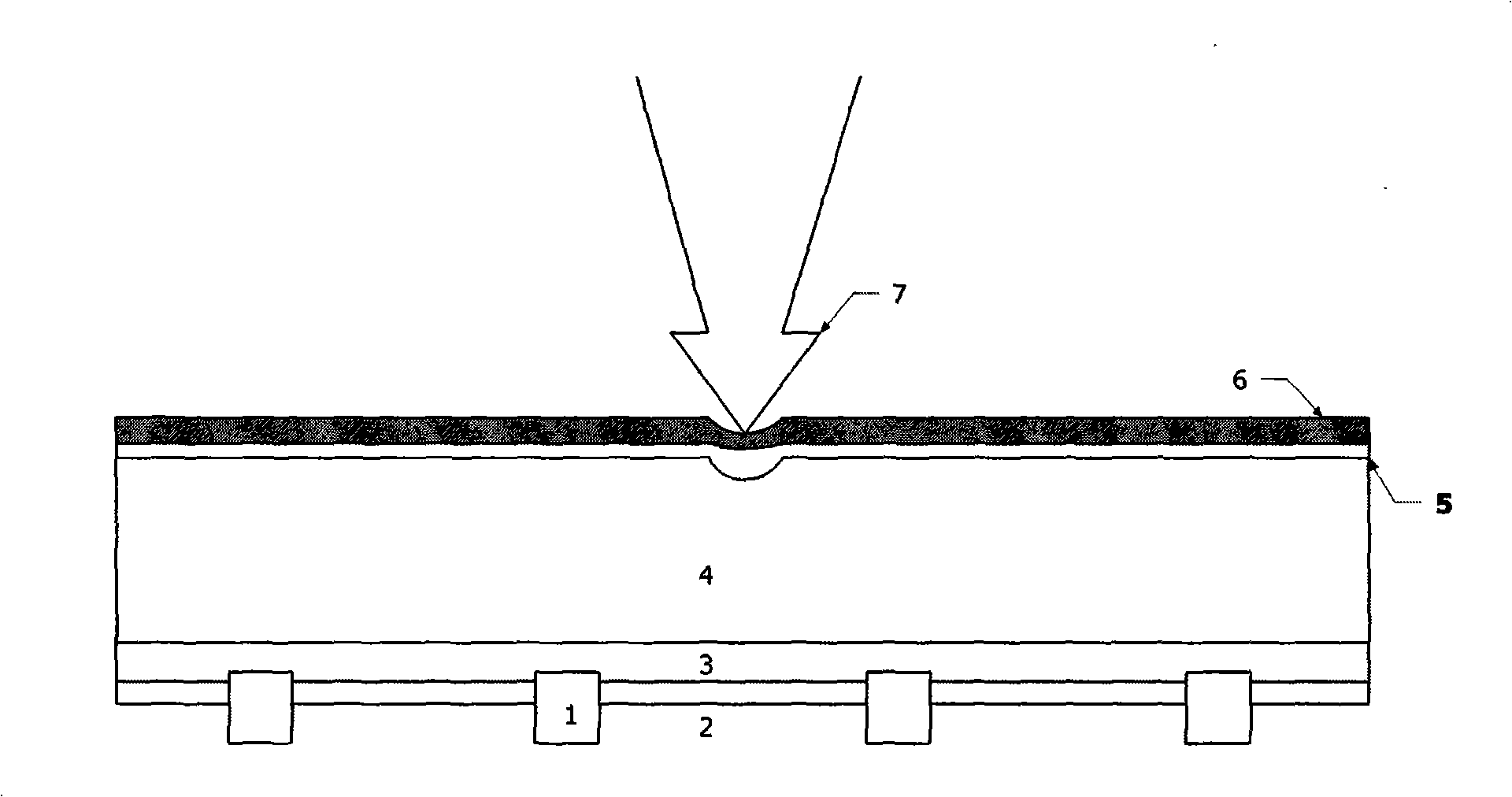
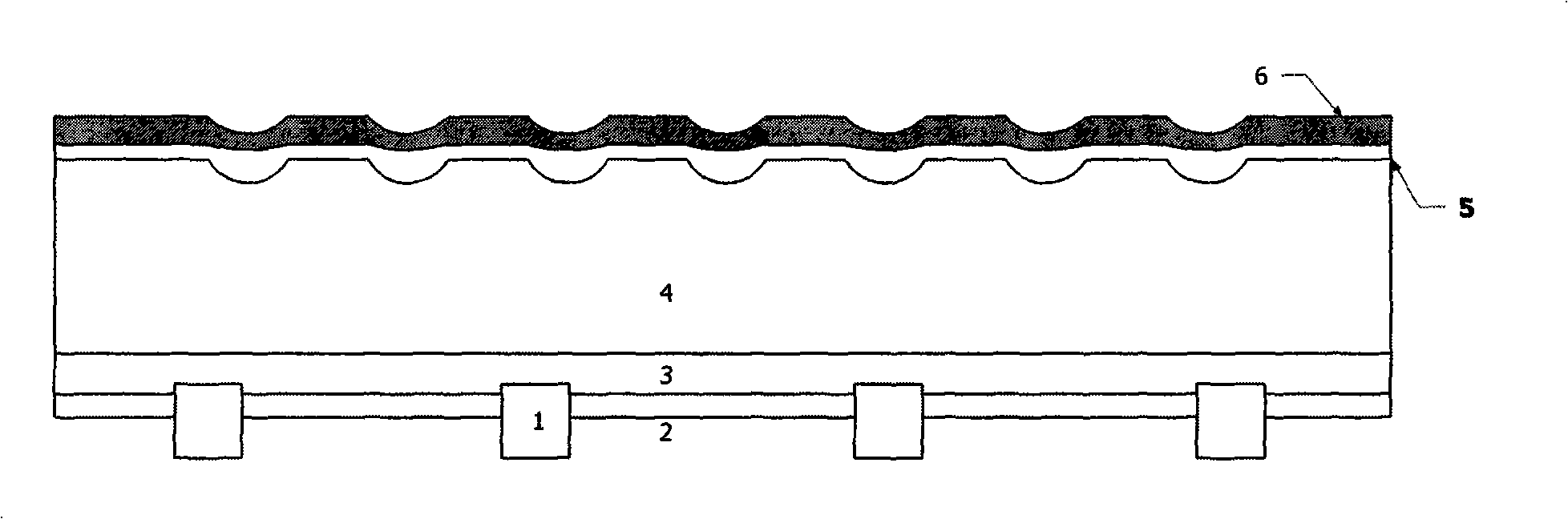
The invention discloses an aluminized BSF secondary sintering technology for a crystal silicon solar cell. The technology utilizes a laser beam or a microwave beam in a pulse mode to scan or integrally scan an aluminized BSF region at the back of the cell so that aluminum in a scanning region is instantaneously heated and melted and diffuses to a silica body; and a whole or partial aluminum heavily-doped region is formed at the back of the solar cell so as to form a BSF with excellent performance, thereby accelerating the diffusion of minority carriers, improving the collection ratio of the minority carriers, improving the long-wave response of the cell and further improving the whole efficiency of the cell. The technology can control the thermal influence of secondary sintering on the periphery of an aluminum layer so as not to generate obvious adverse influence on other parts of the cell, has various flexible laser sintering design modes, is simple, convenient and rapid to manufacture and can be rapidly combined with the prior industrial production.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
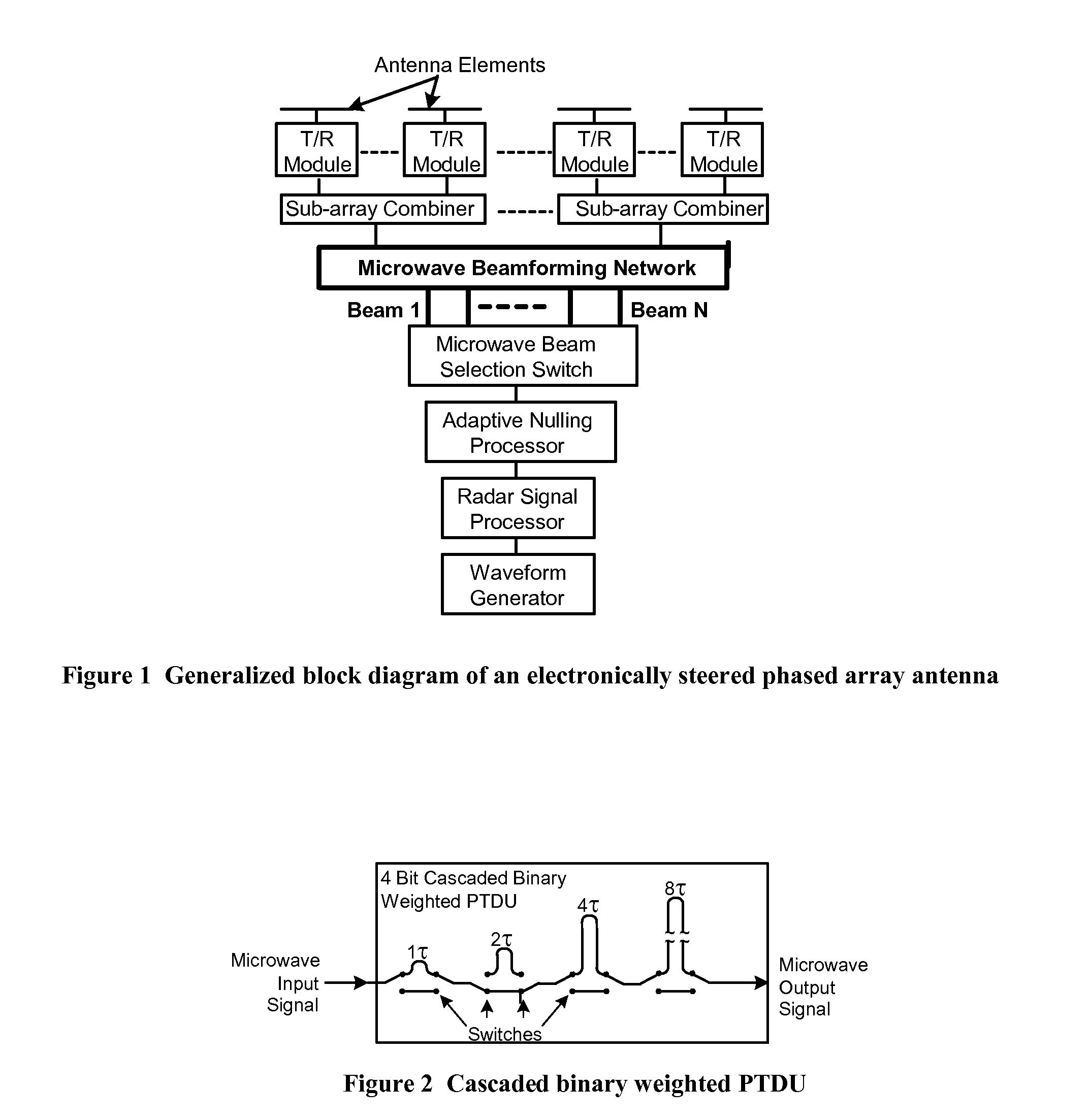
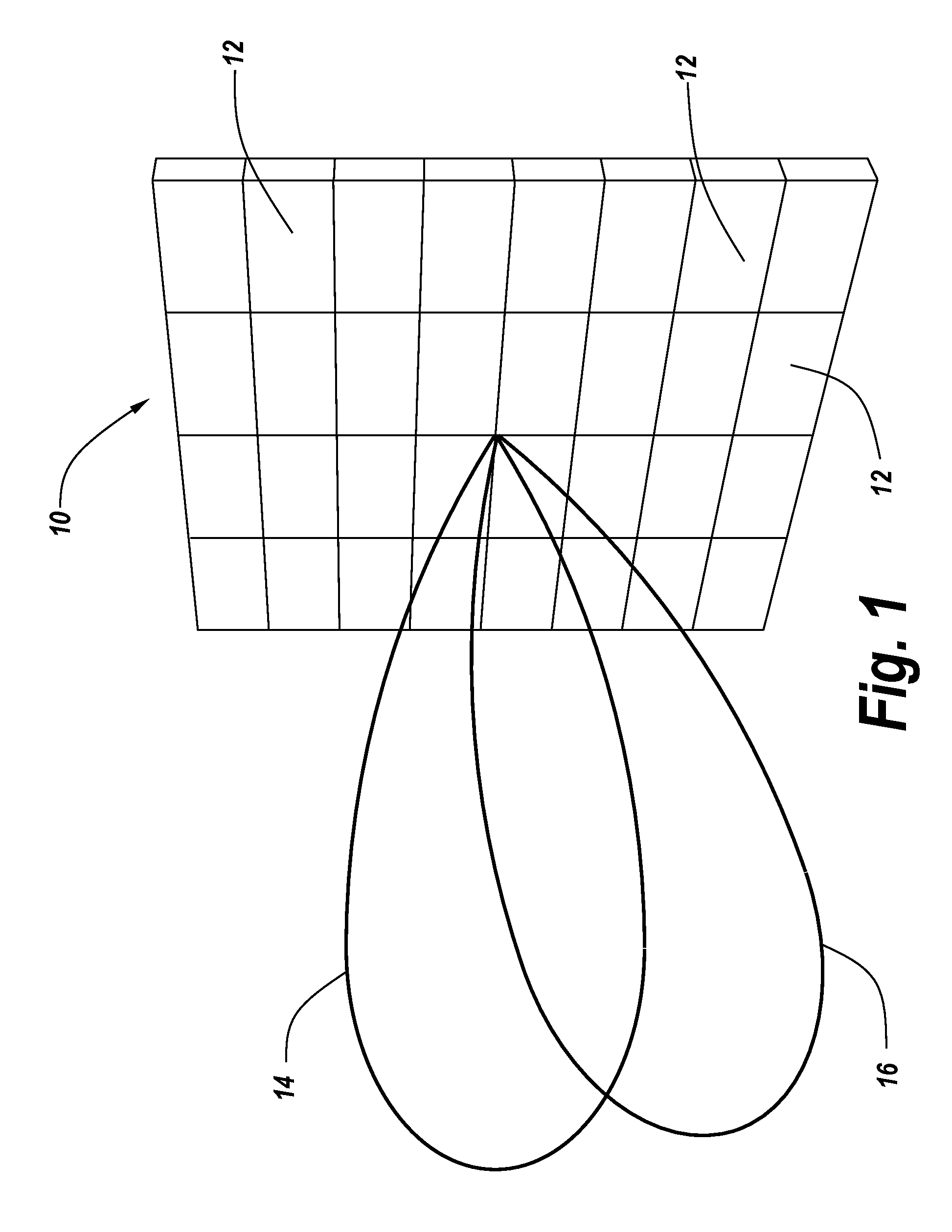
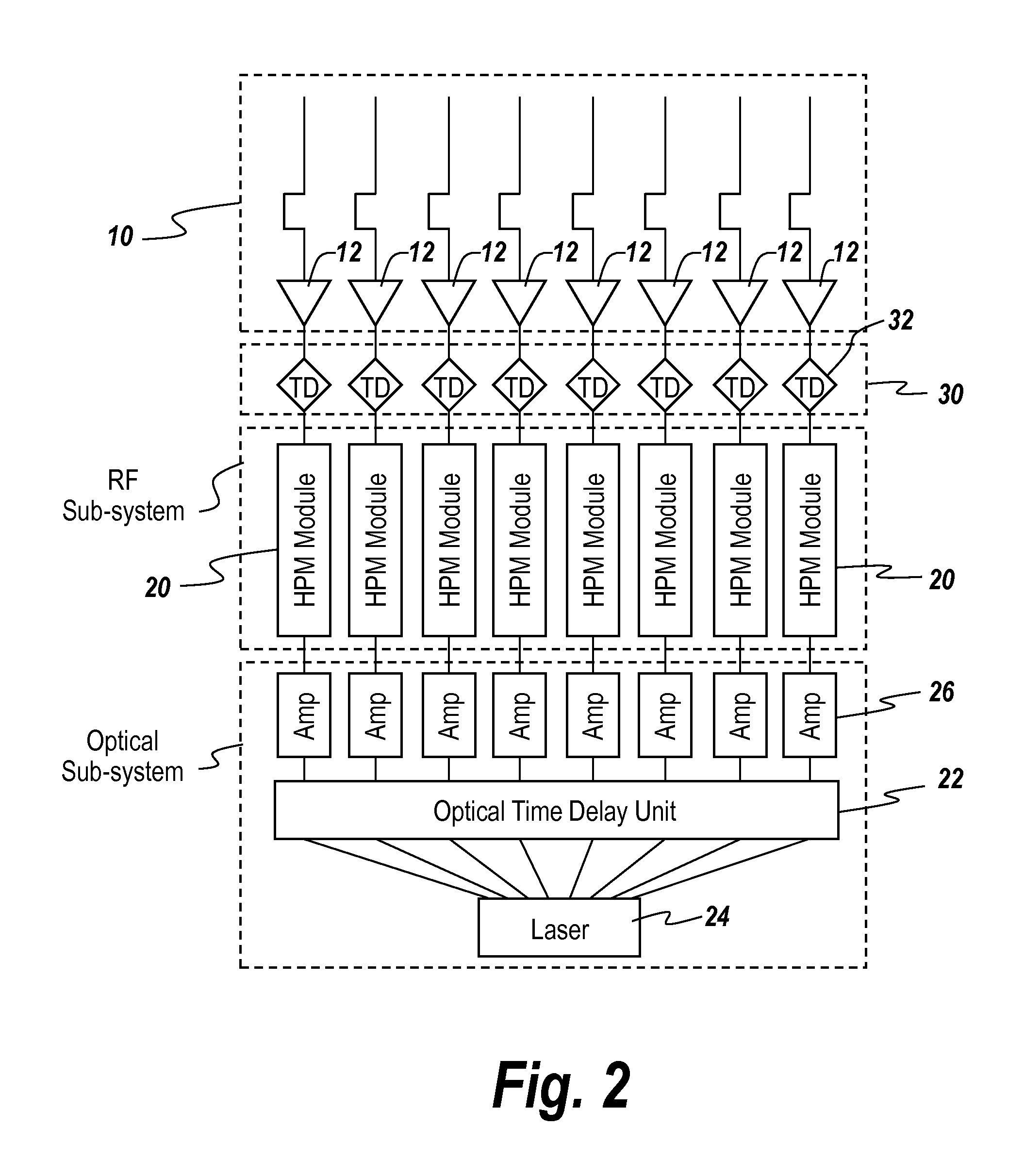
High-Power Microwave Beam Steerable Array and Related Methods
ActiveUS20160126628A1Increase the number ofWave based measurement systemsCommunication jammingTime delaysAntenna element
A steerable high-power microwave beam array includes an optical sub-system comprising a laser and an optical time delay unit and a parallel set of RF time delay units. The optical system and / or the RF delay subsystem are utilized to precisely delay the pulses from the microwave antenna elements to provide steerable beam forming.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com