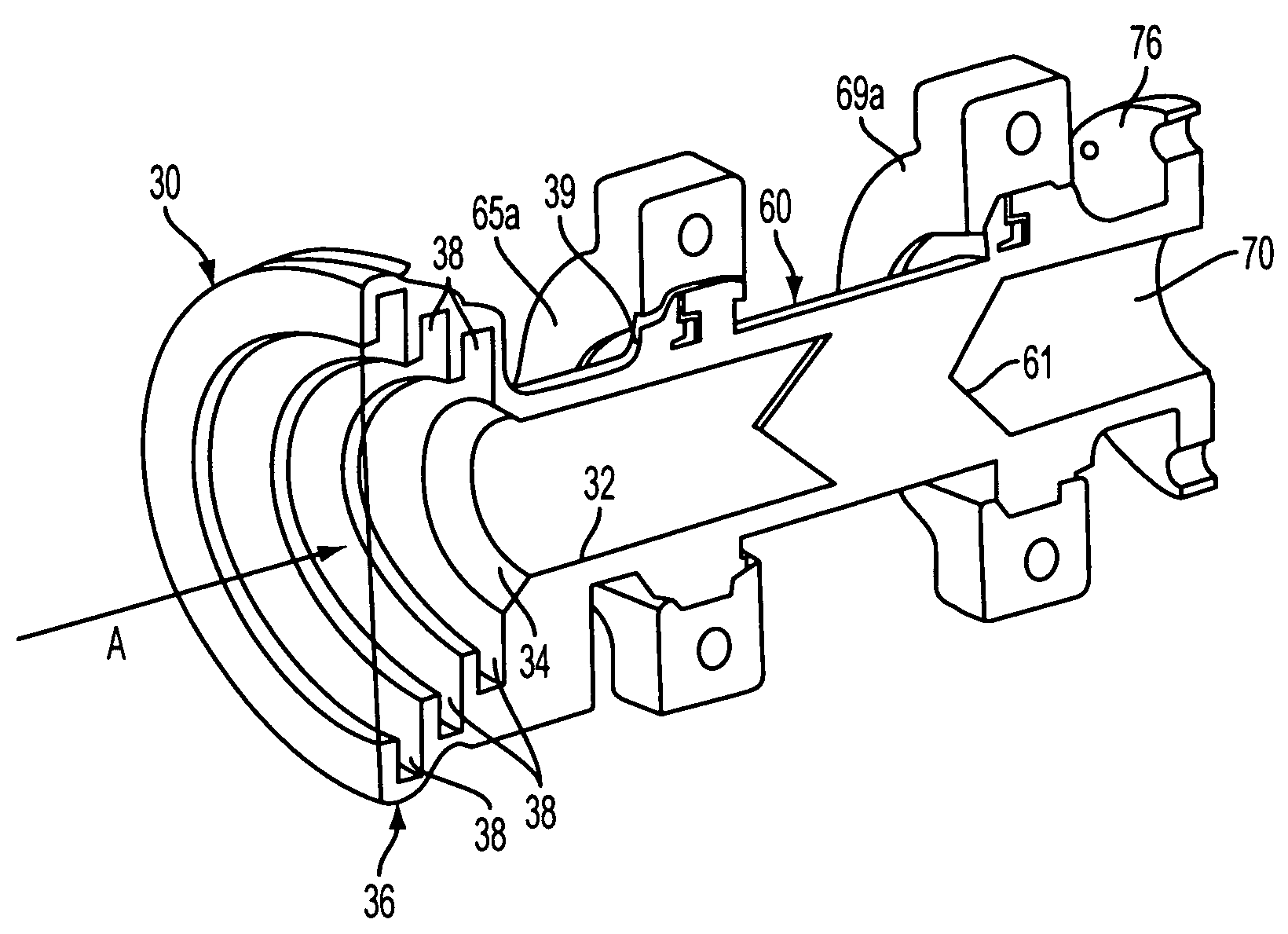
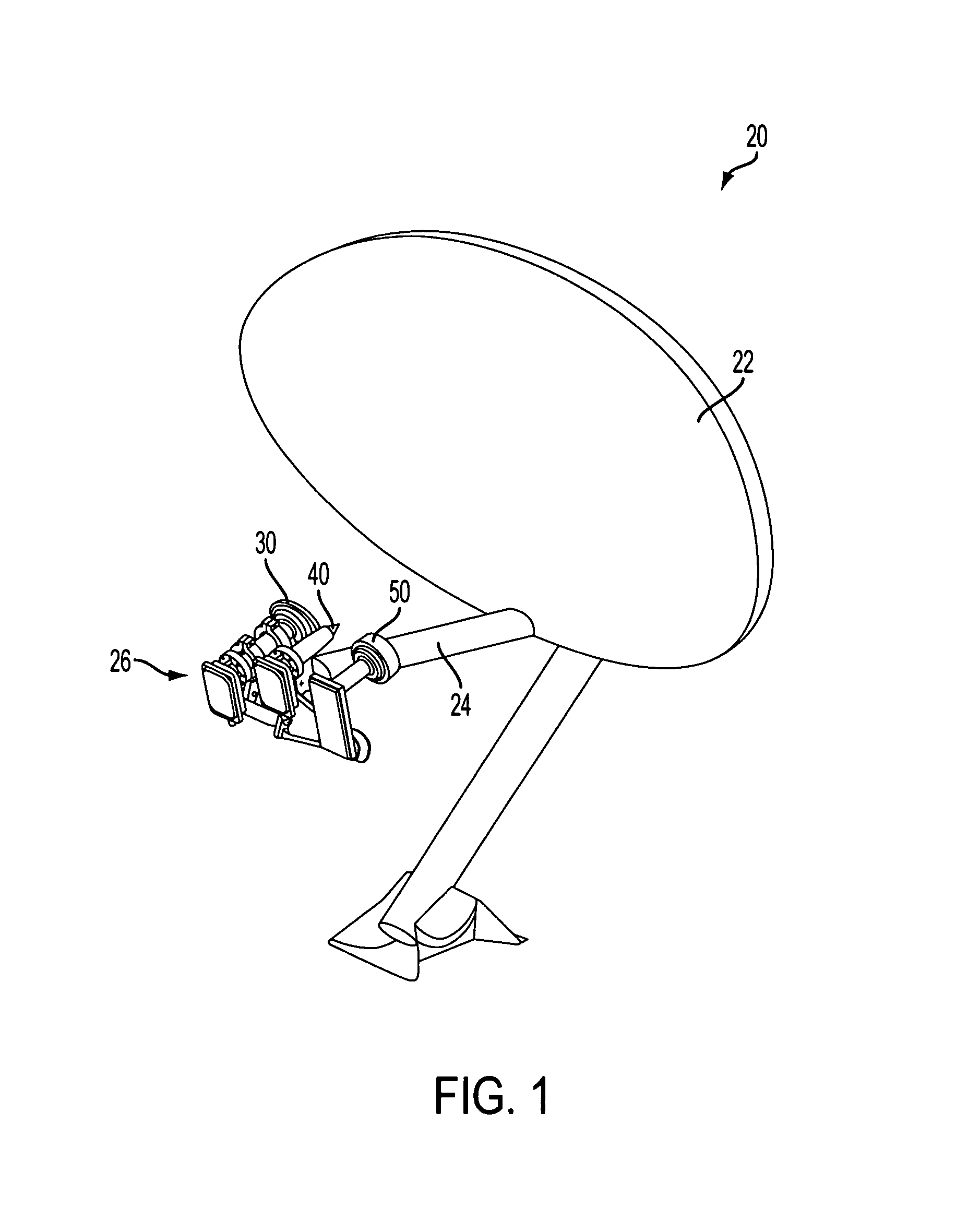
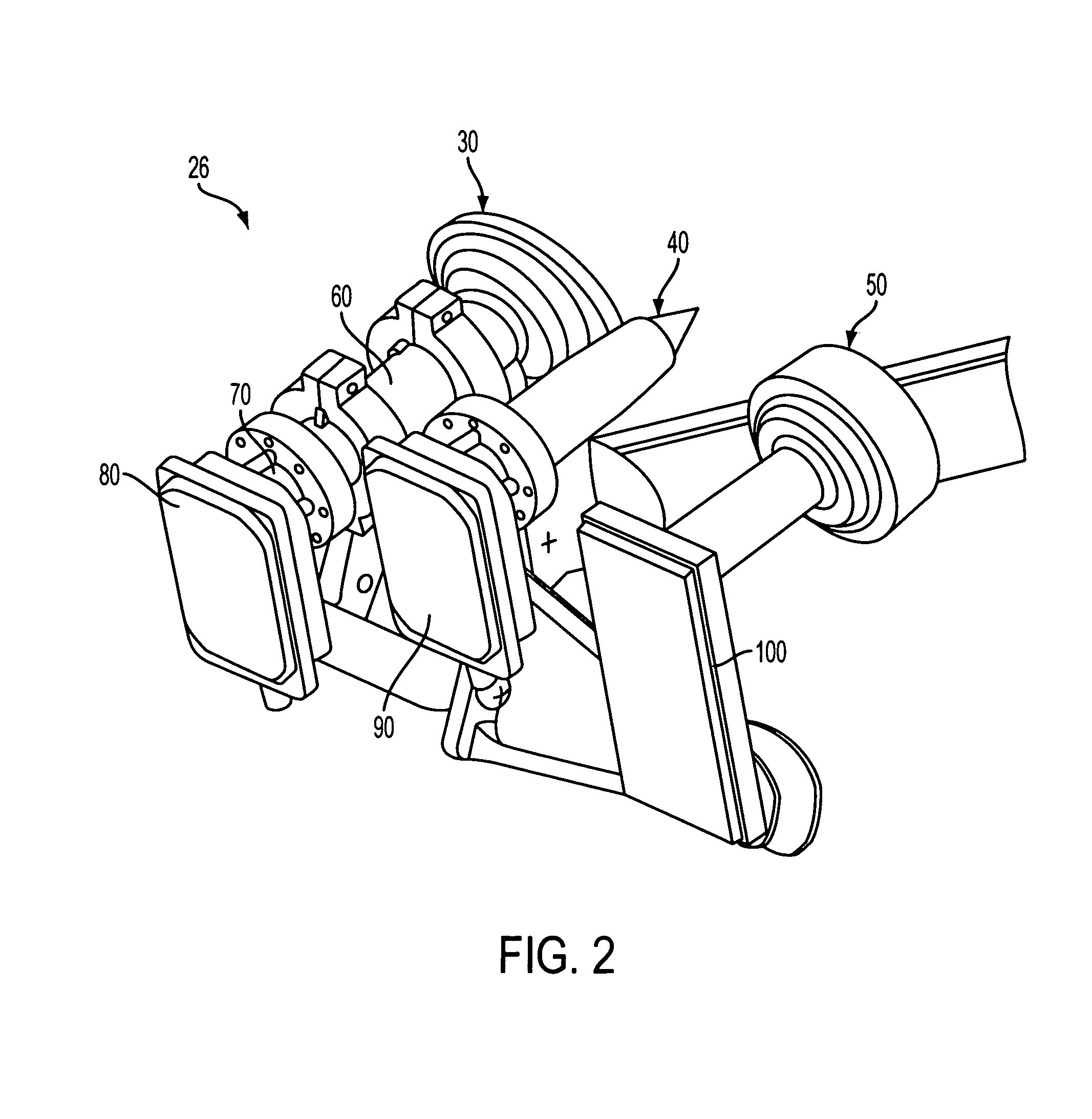
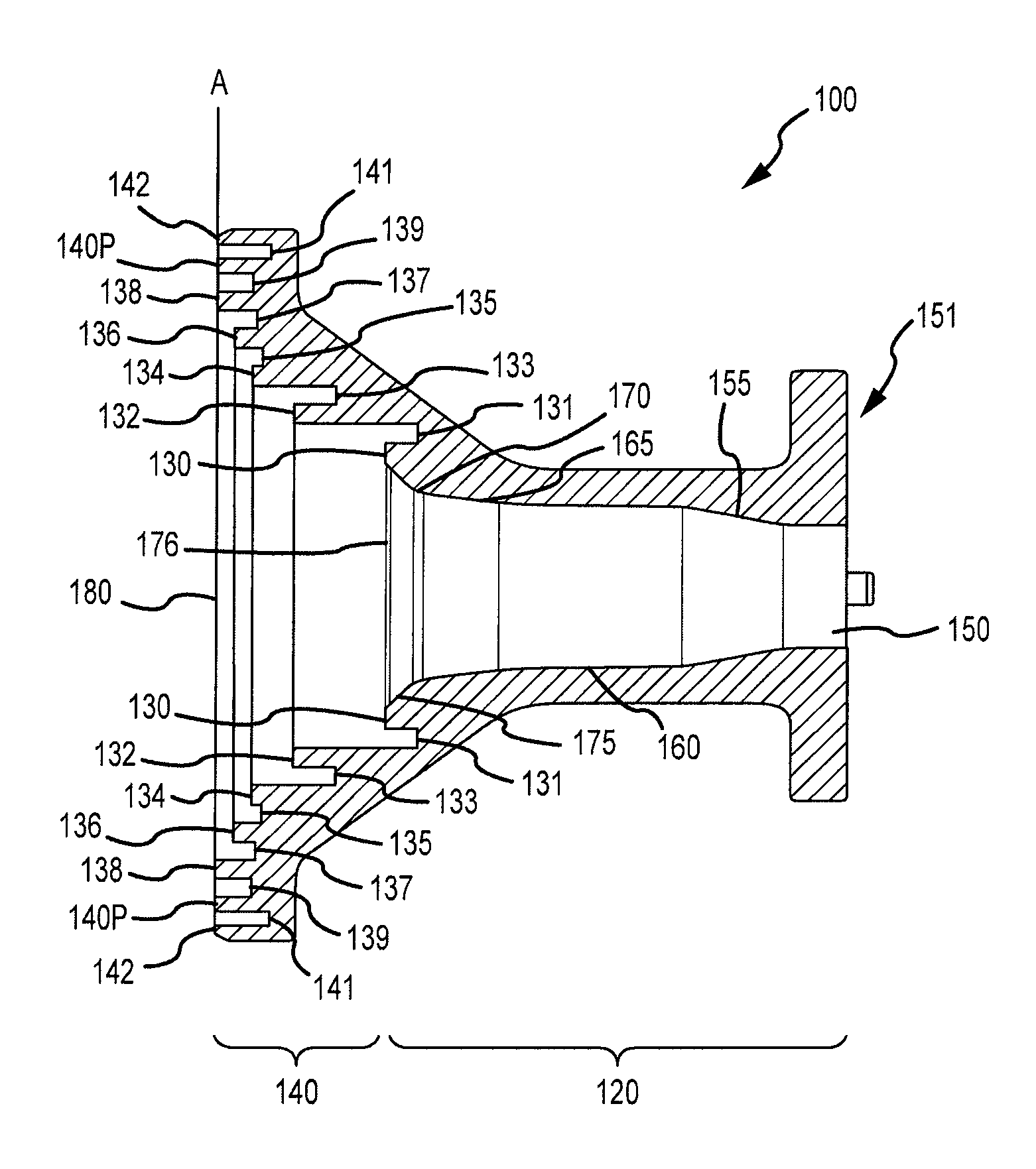
Patents
Literature
177 results about "Feed horn" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
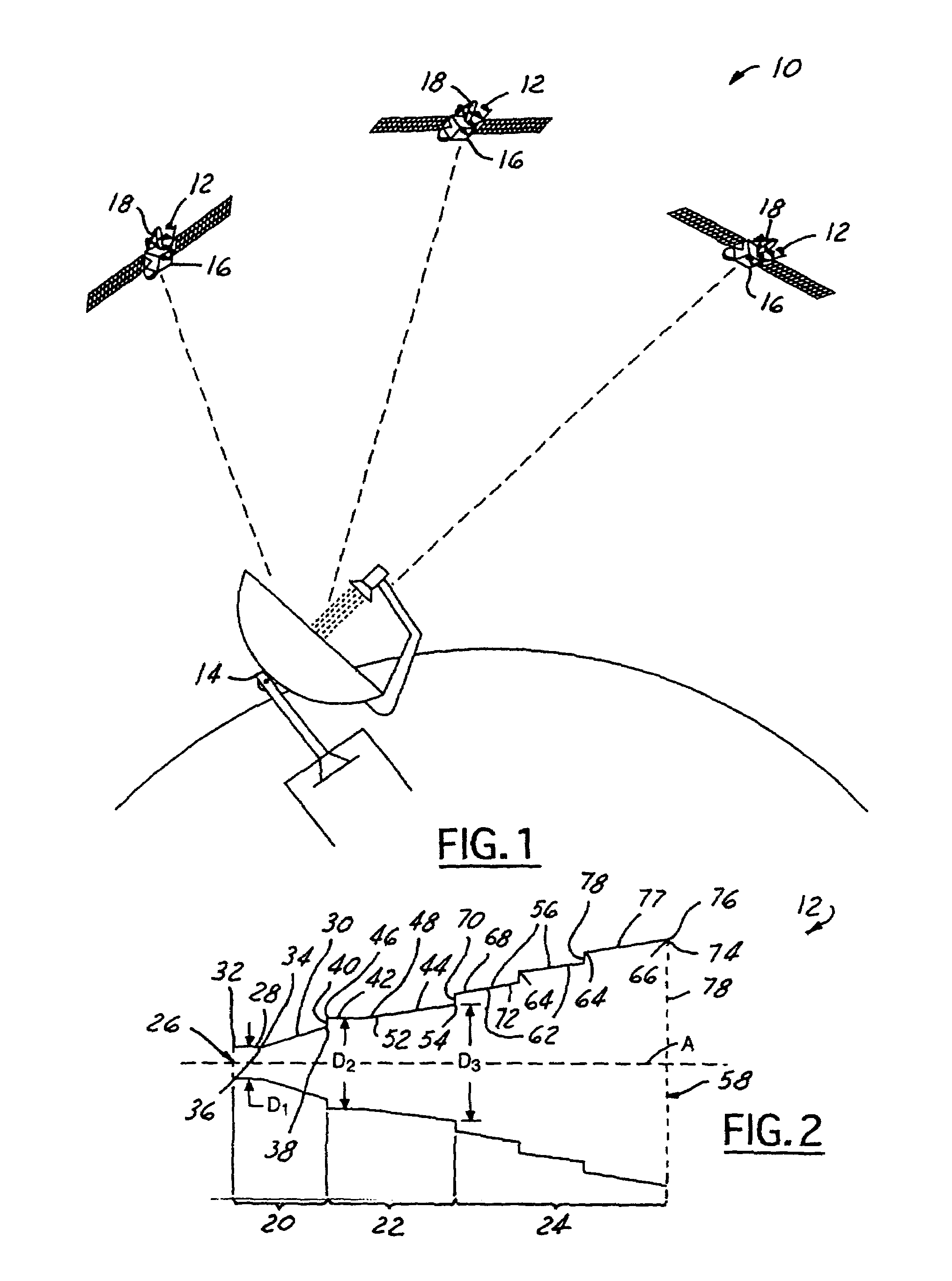
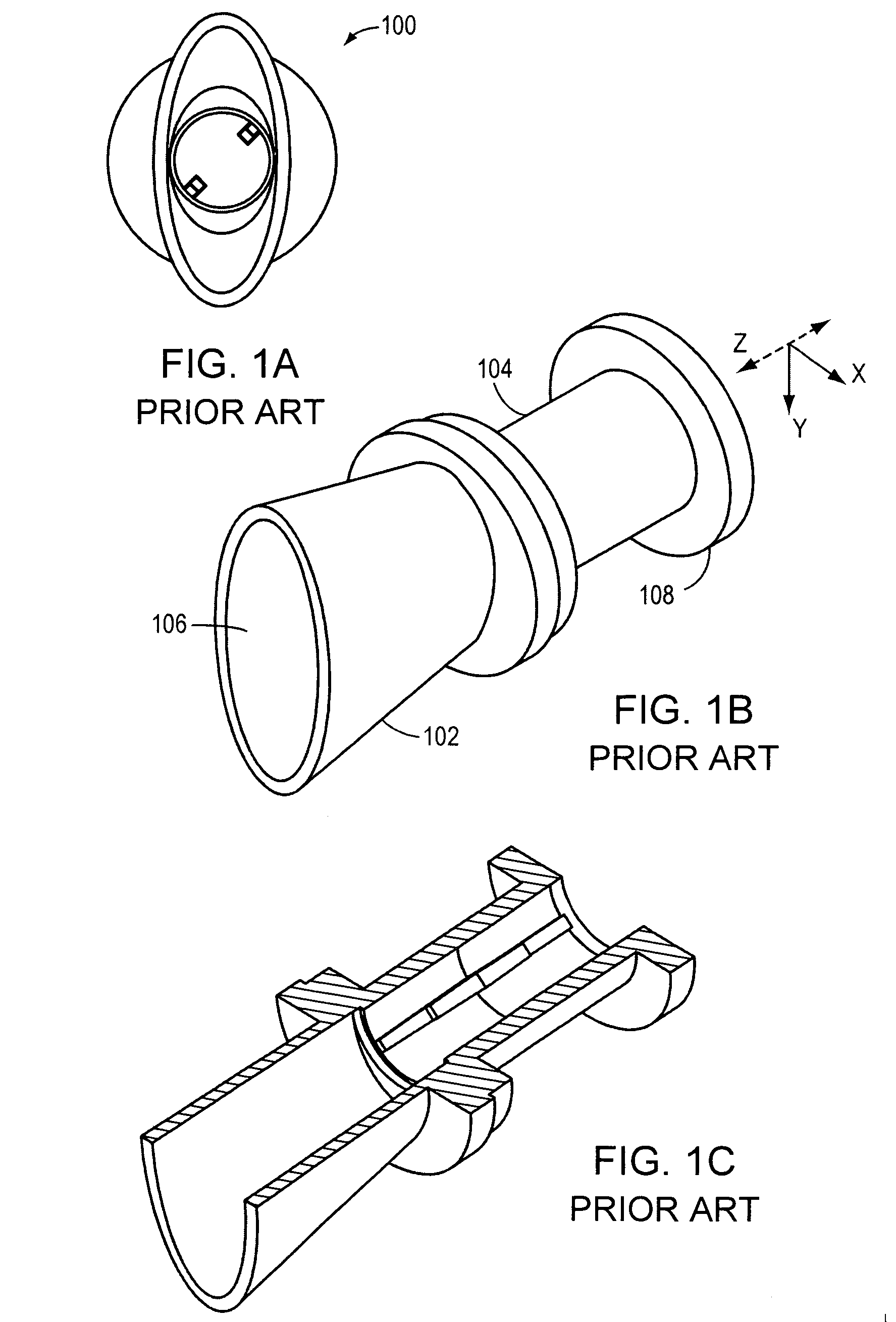
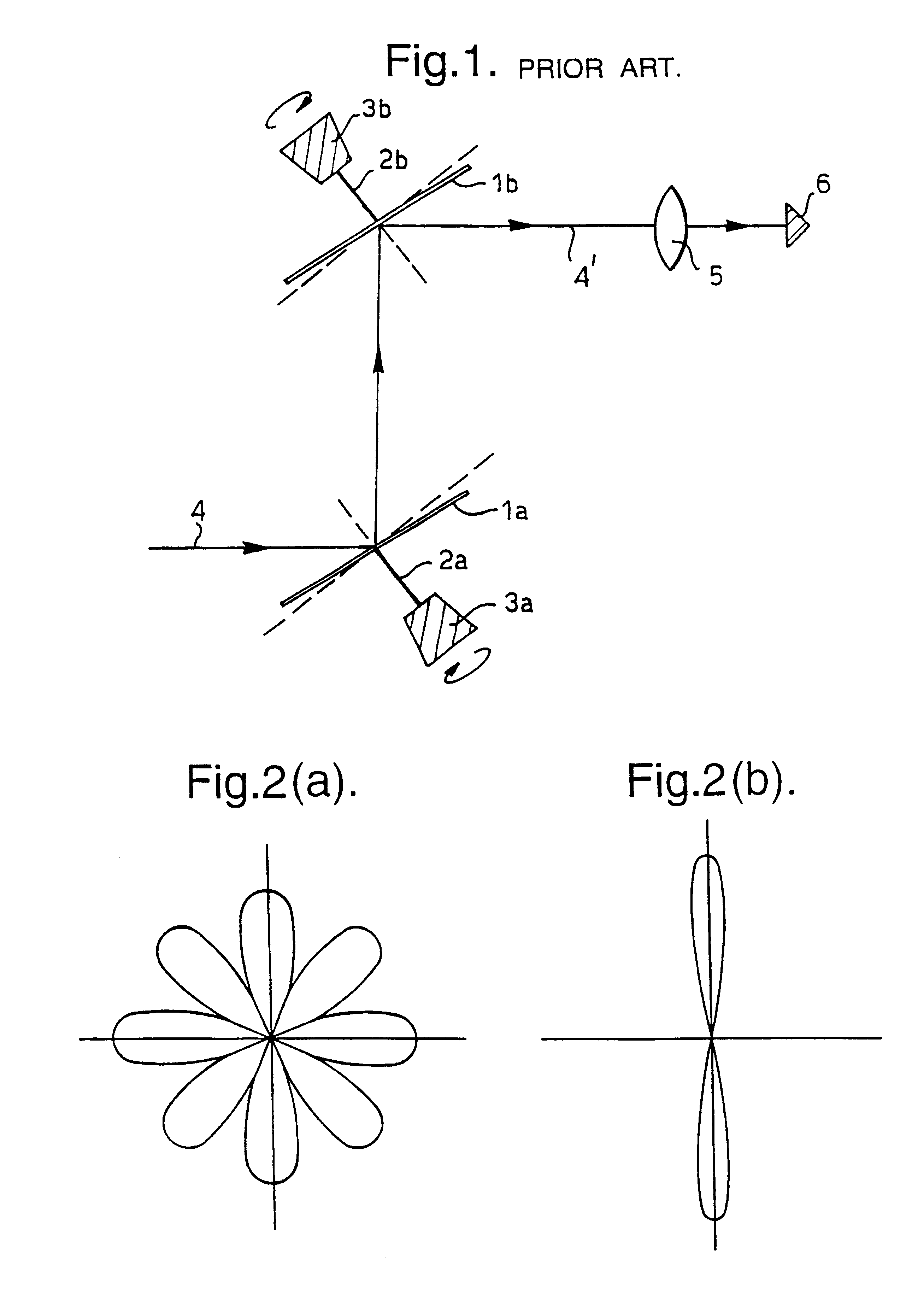
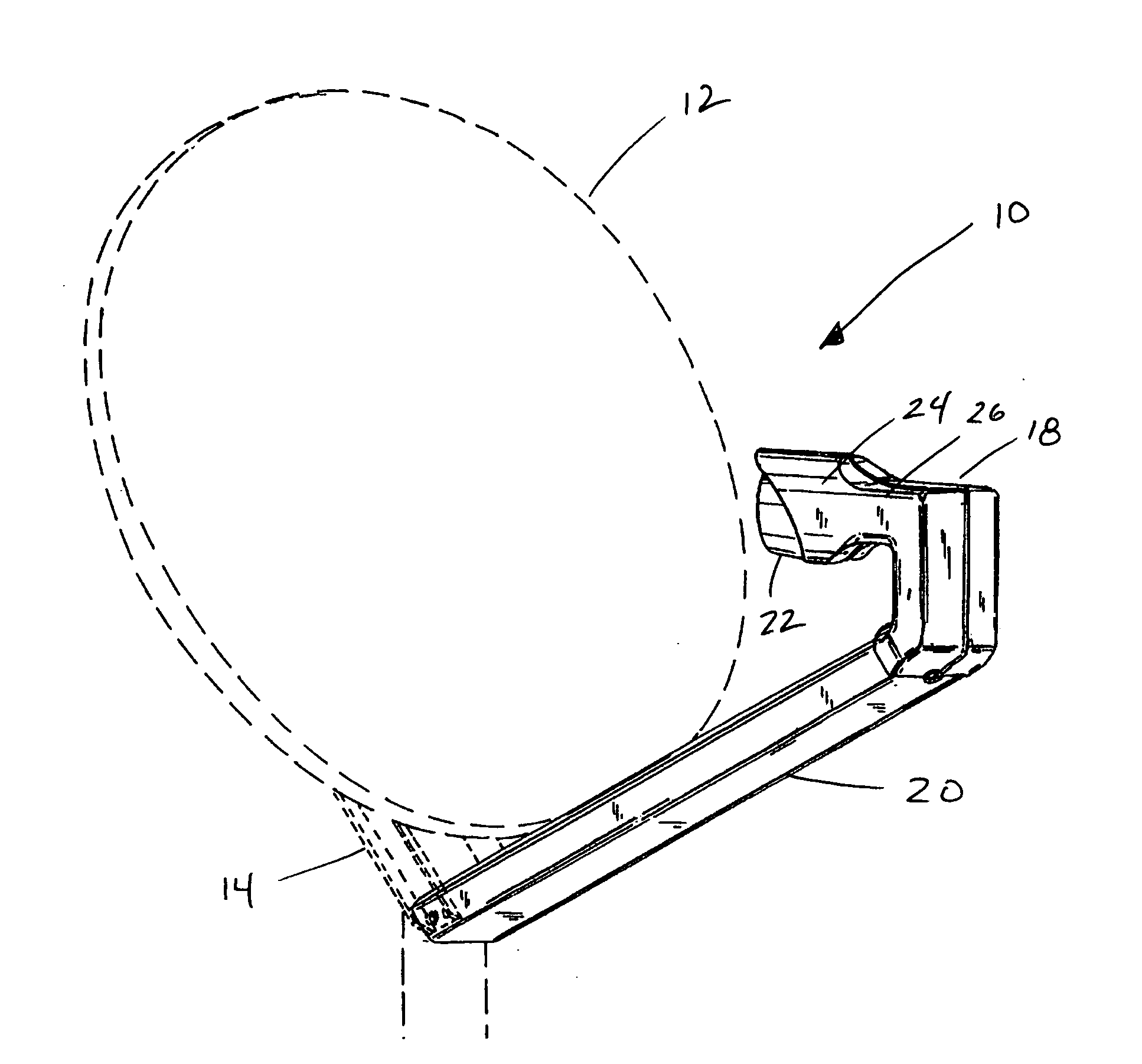
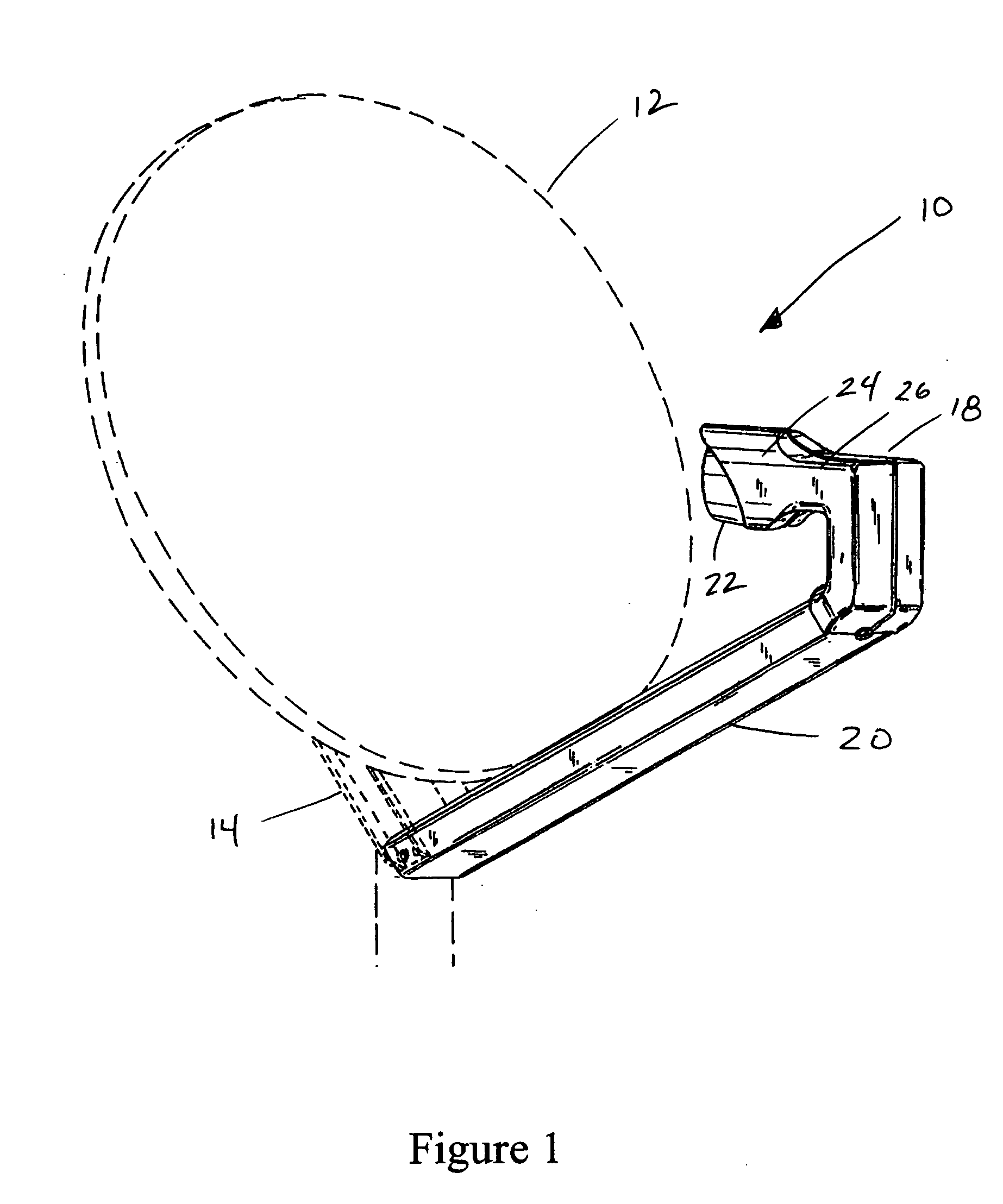
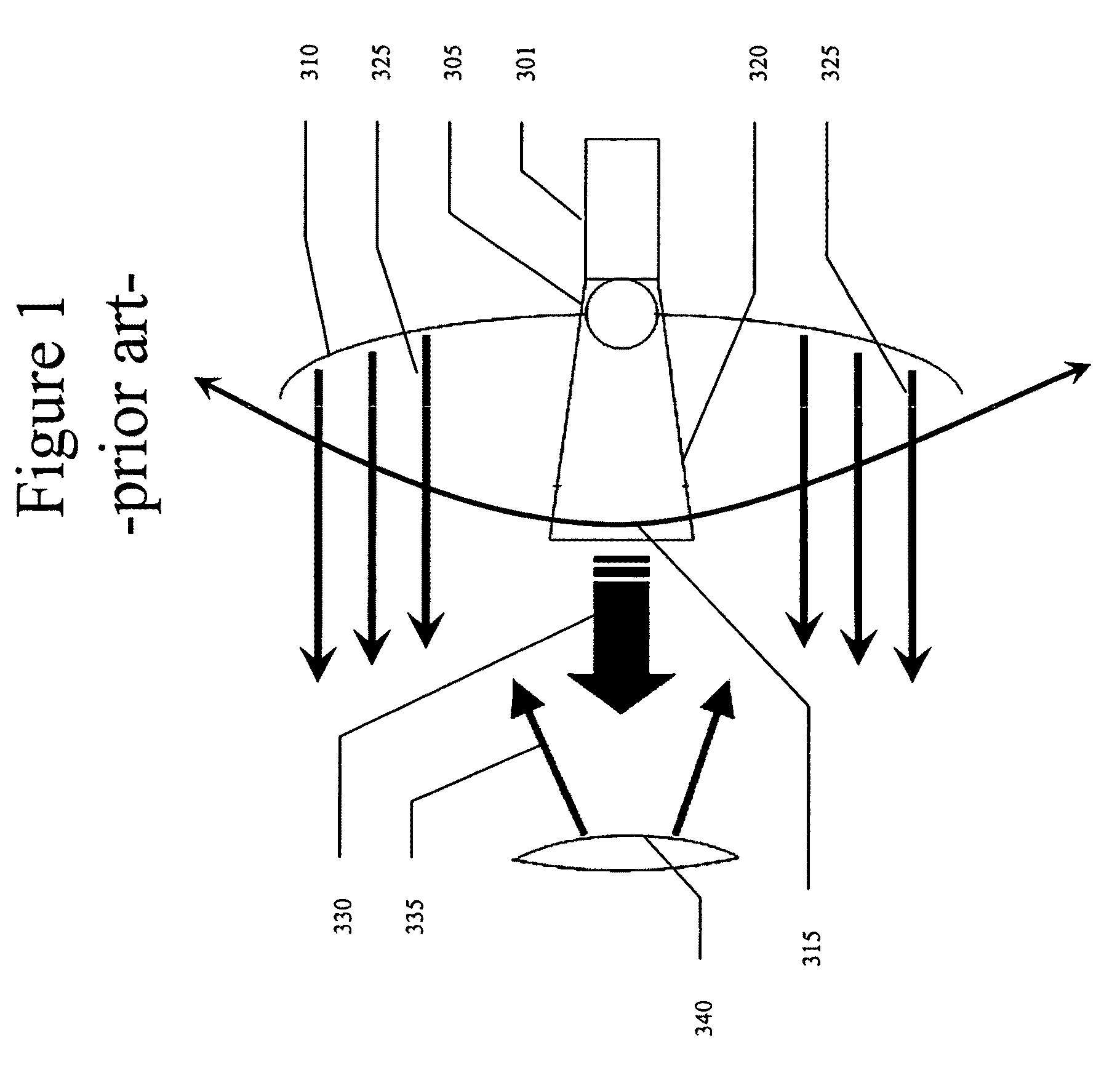
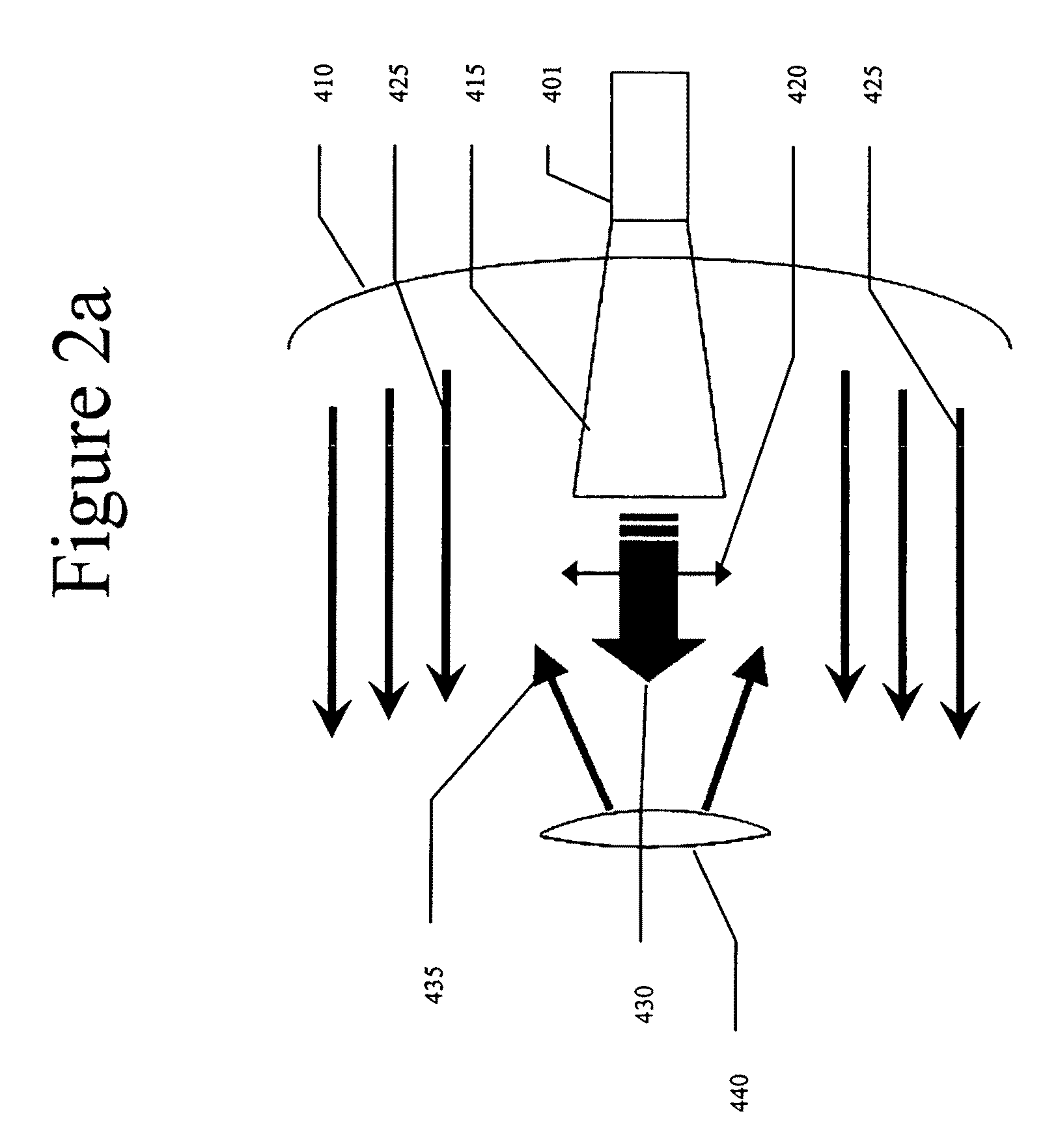
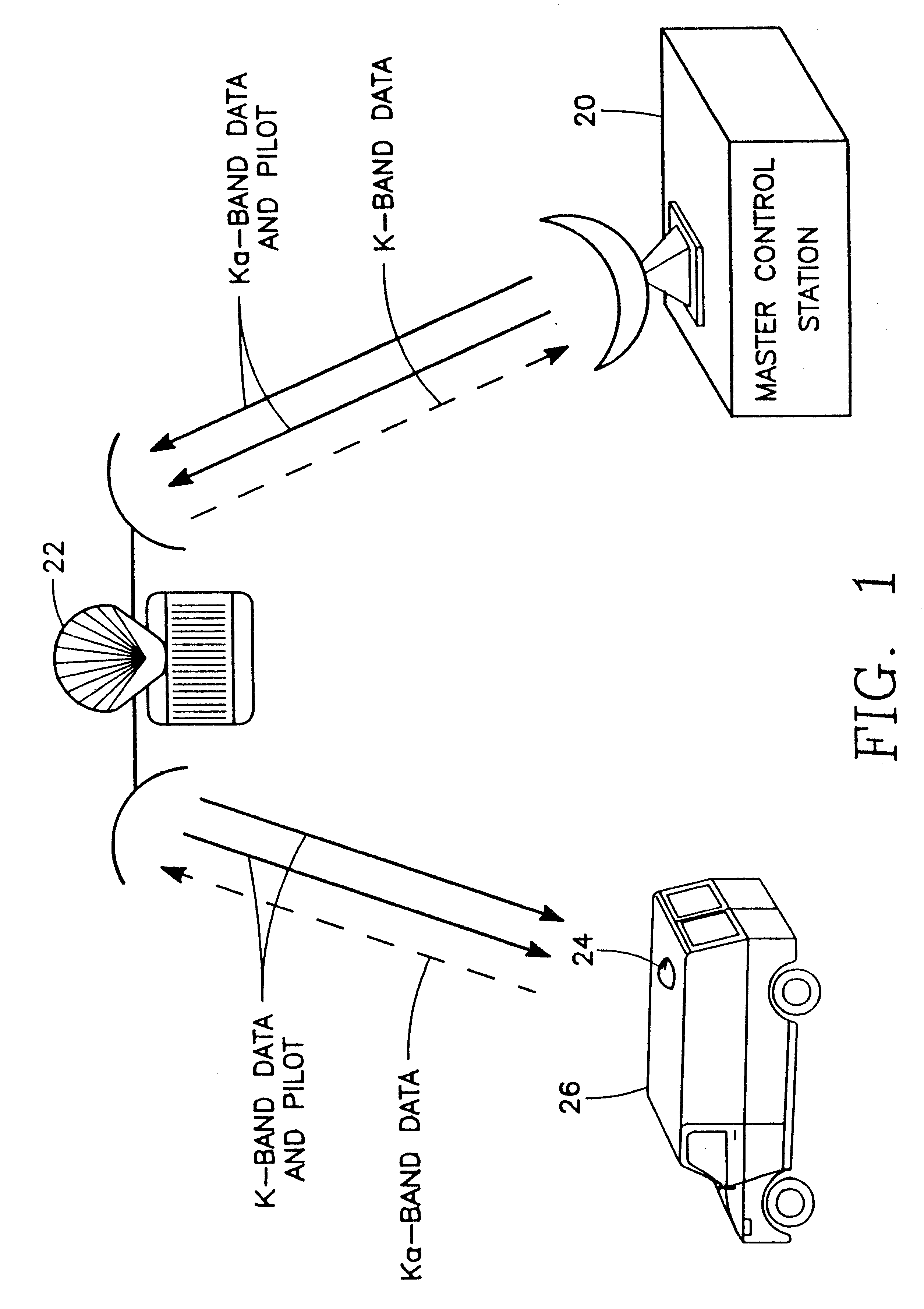
In parabolic antennas such as satellite dishes, a feed horn (or feedhorn) is a small horn antenna used to convey radio waves between the transmitter and/or receiver and the parabolic reflector. In transmitting antennas, it is connected to the transmitter and converts the radio frequency alternating current from the transmitter to radio waves and feeds them to the rest of the antenna, which focuses them into a beam. In receiving antennas, incoming radio waves are gathered and focused by the antenna's reflector on the feed horn, which converts them to a tiny radio frequency voltage which is amplified by the receiver. Feed horns are used mainly at microwave (SHF) and higher frequencies.
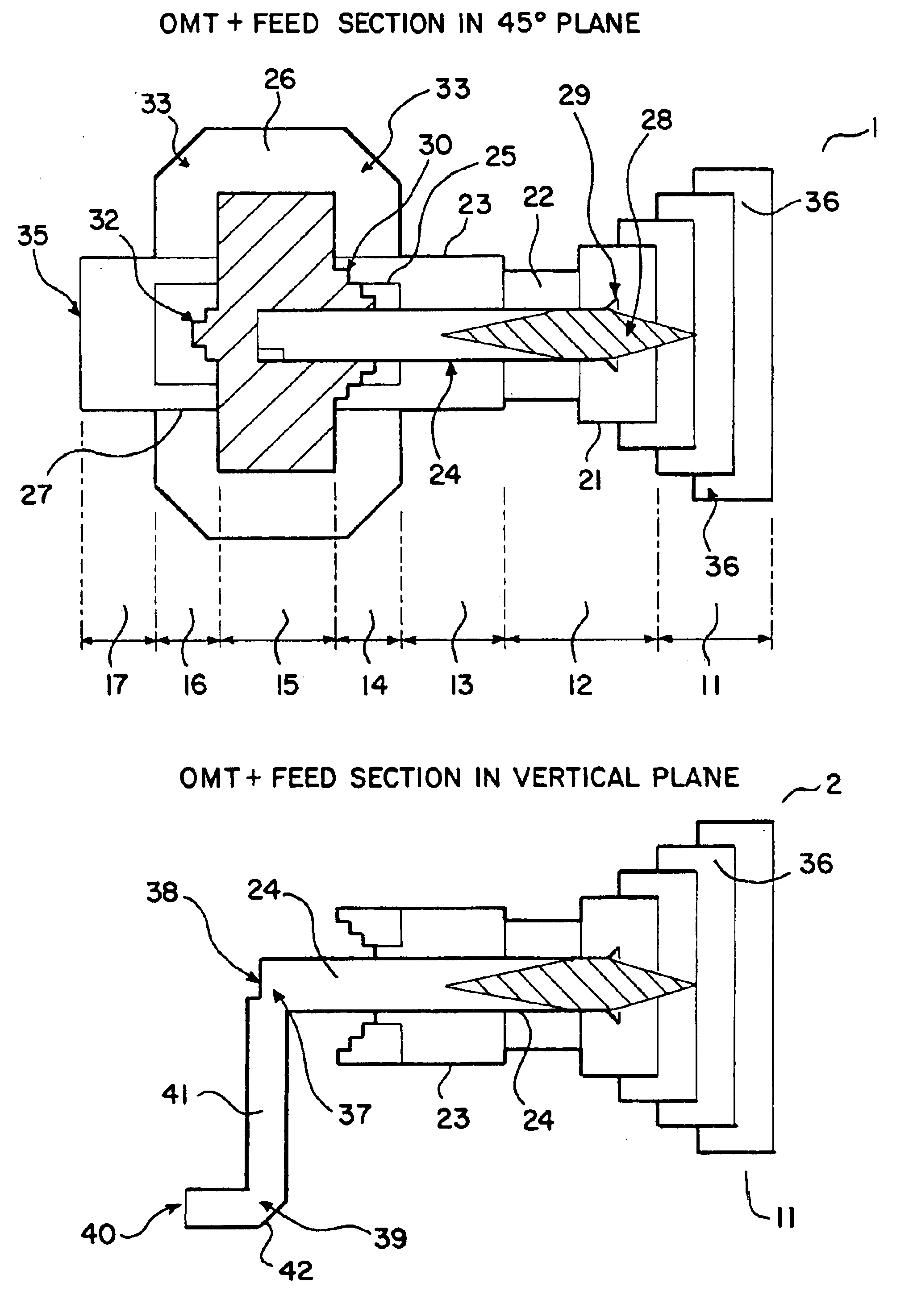
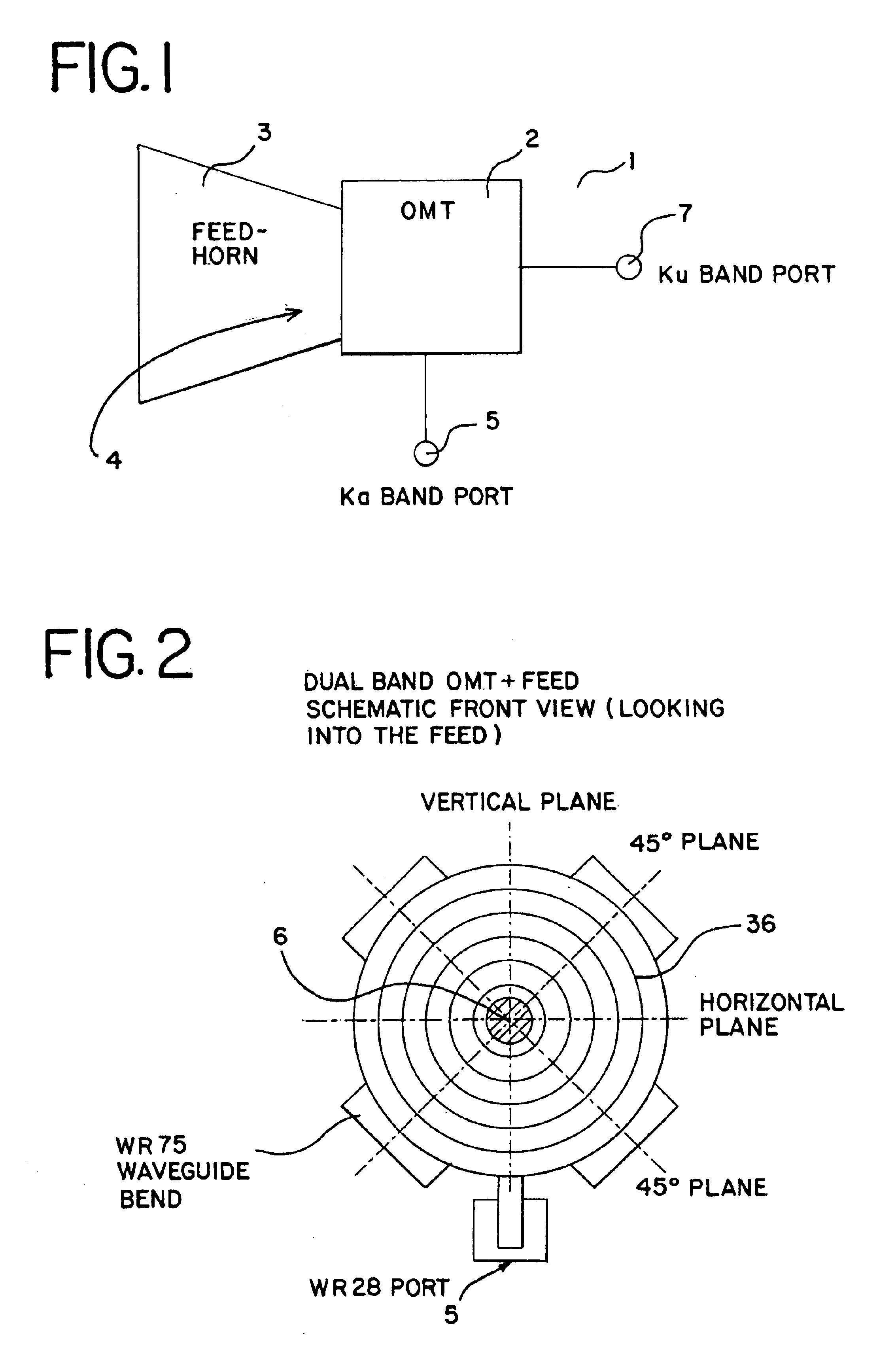
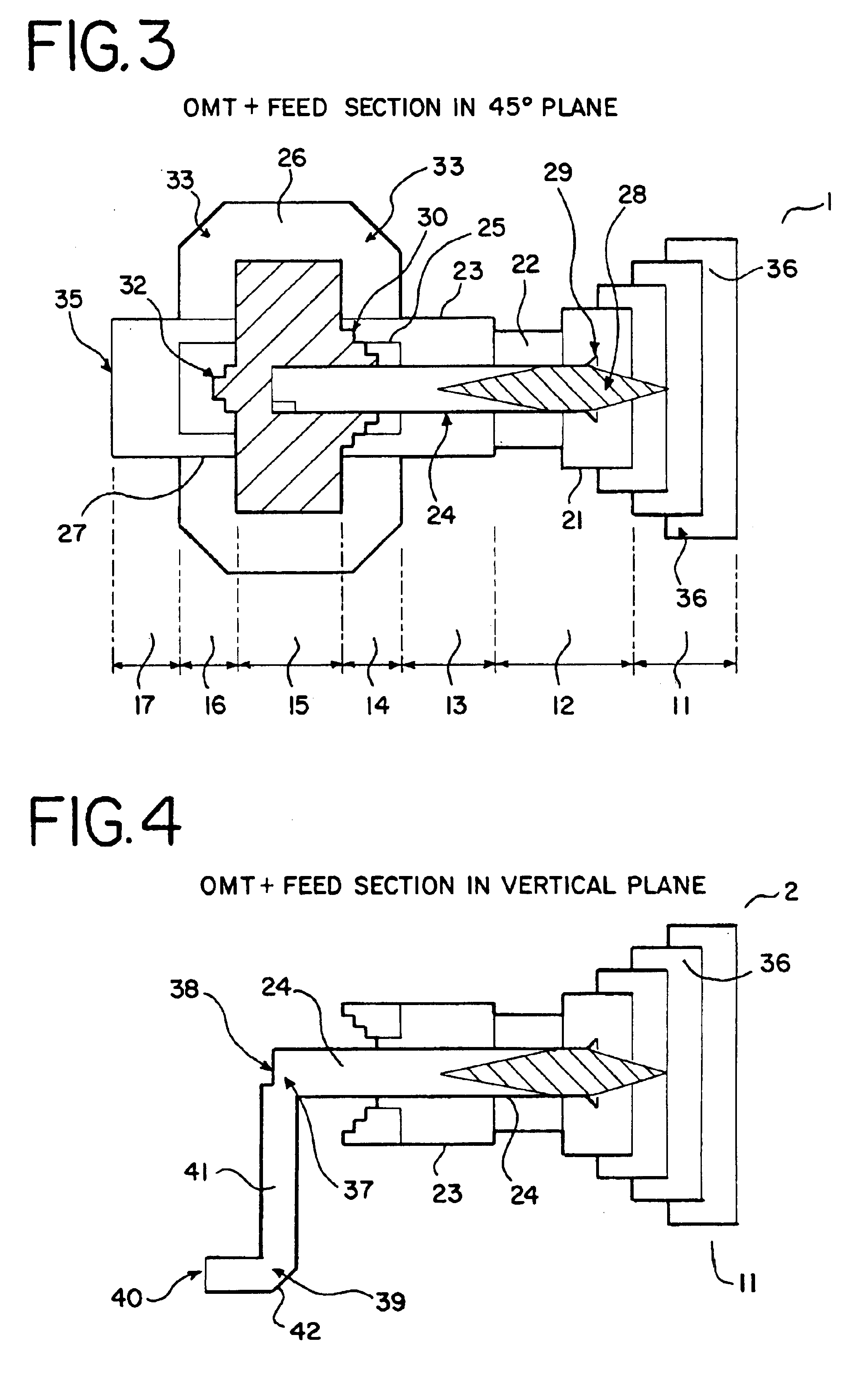
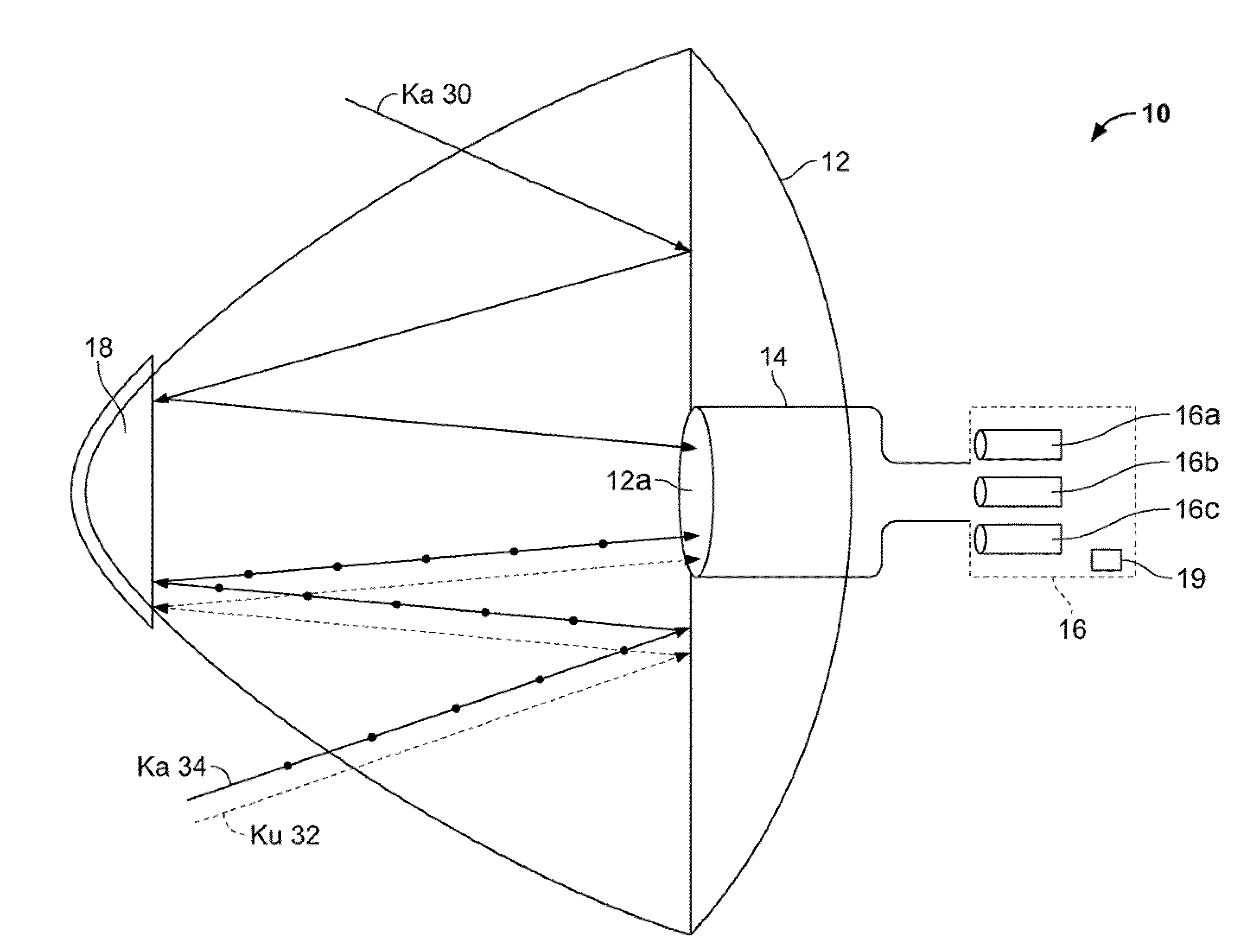
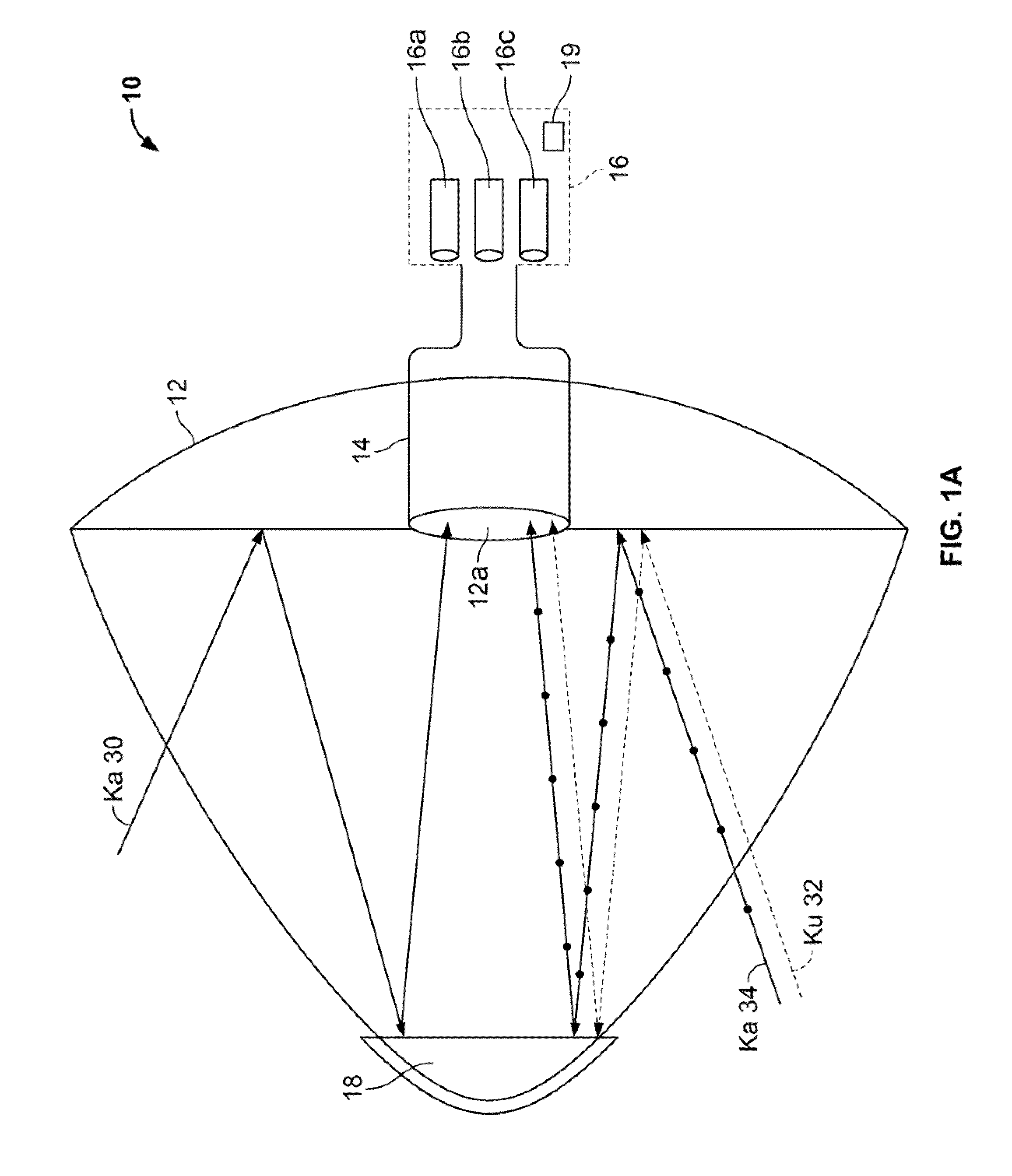
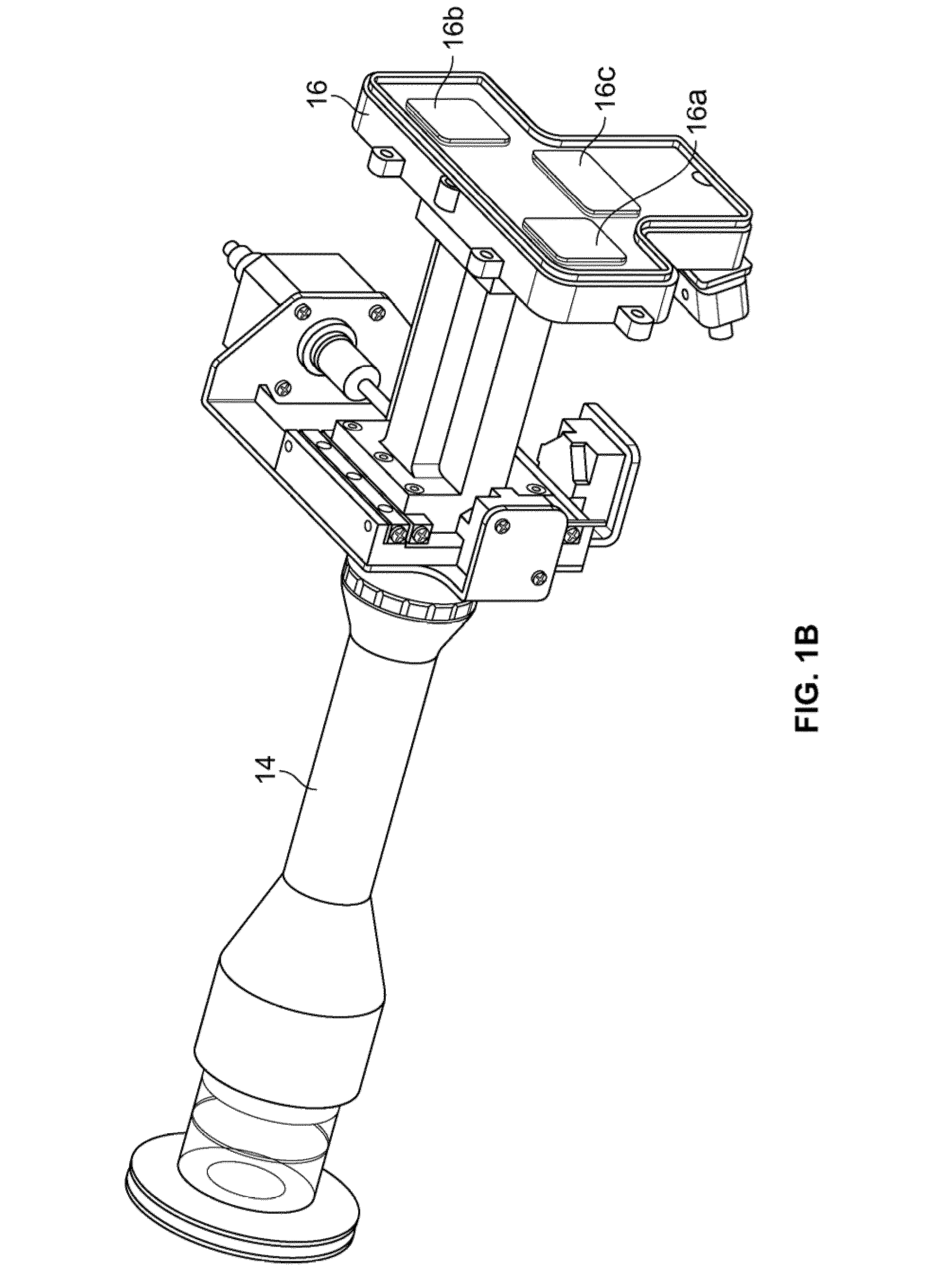
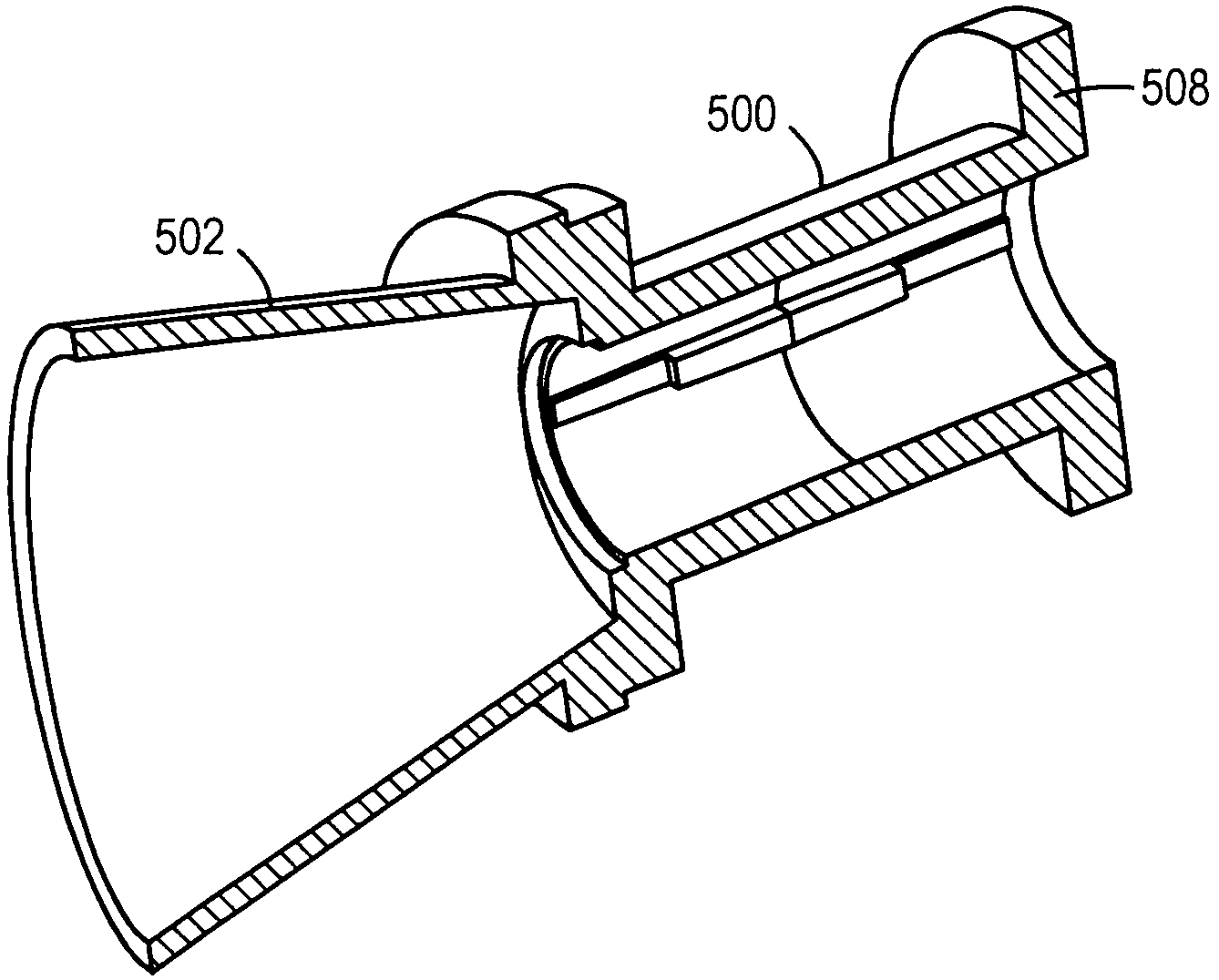
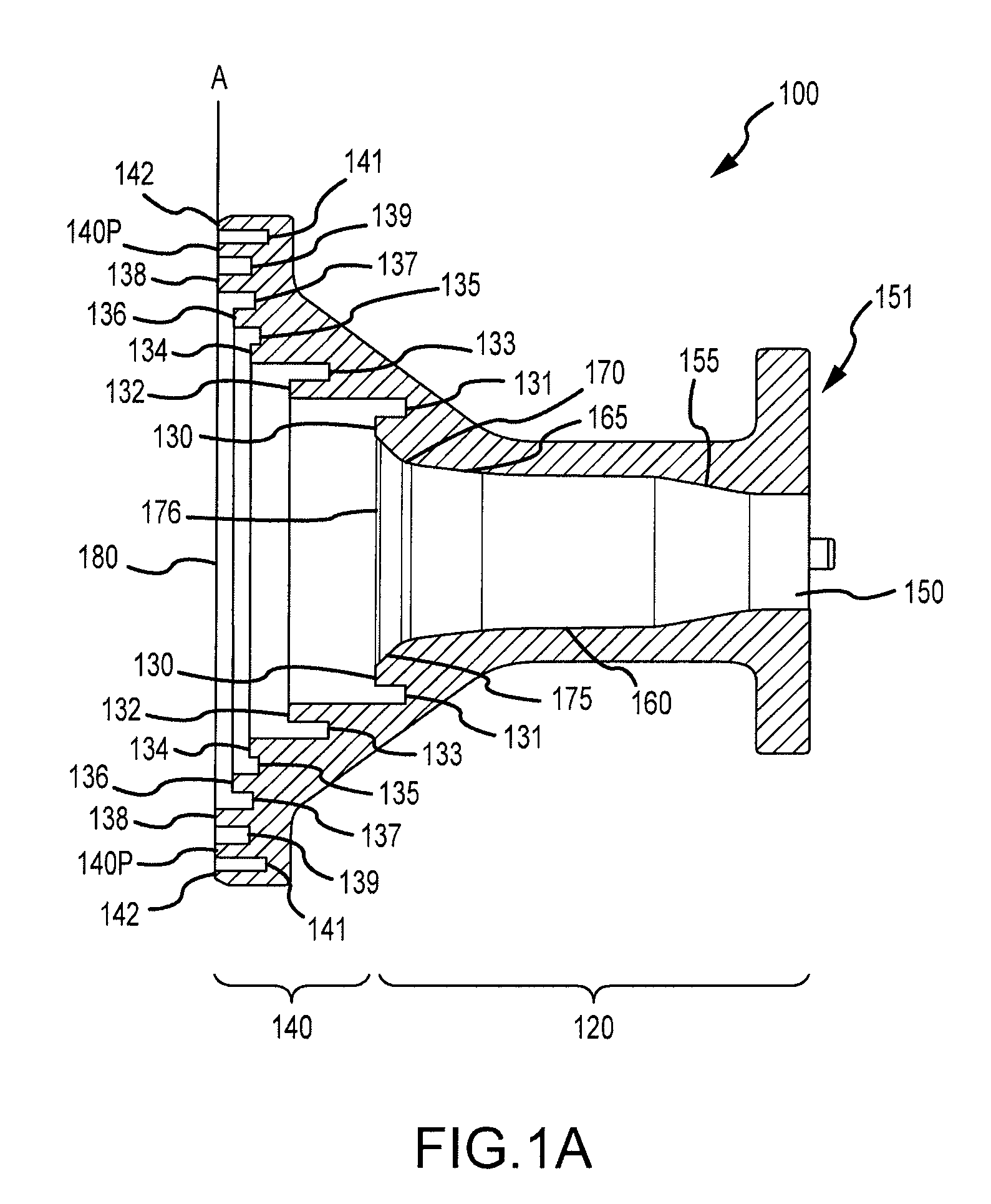
Ka/Ku dual band feedhorn and orthomode transduce (OMT)
InactiveUS6714165B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntennas earthing switches associationRidge waveguidesTransducer
A dual band, higher and lower frequency range transducer with a circular coaxial waveguide feed is described having a first junction for connection of a lower frequency range outer waveguide of the coaxial waveguide feed to at least two rectangular or ridge waveguides offset from the longitudinal axis of the transducer and a second junction for connection of the at least two rectangular or ridge waveguides to a further waveguide. A third junction is provided for connecting an inner waveguide of the coaxial waveguide feed to a higher frequency range waveguide. The transducer comprises at least first and second parts joined across a first plane substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and including at least a portion of the higher frequency range waveguide extending within the first plane of the join. A seal such as an "O" ring seal may be placed easily in the plane of the join thus preventing moisture ingress. Similarly, a feed horn and input and output ports may be sealingly attached to the first and second parts of the transducer. The first and second junctions are preferably impedance matched turnstile junctions.
Owner:NEWTEC CY
Coaxial horn antenna system
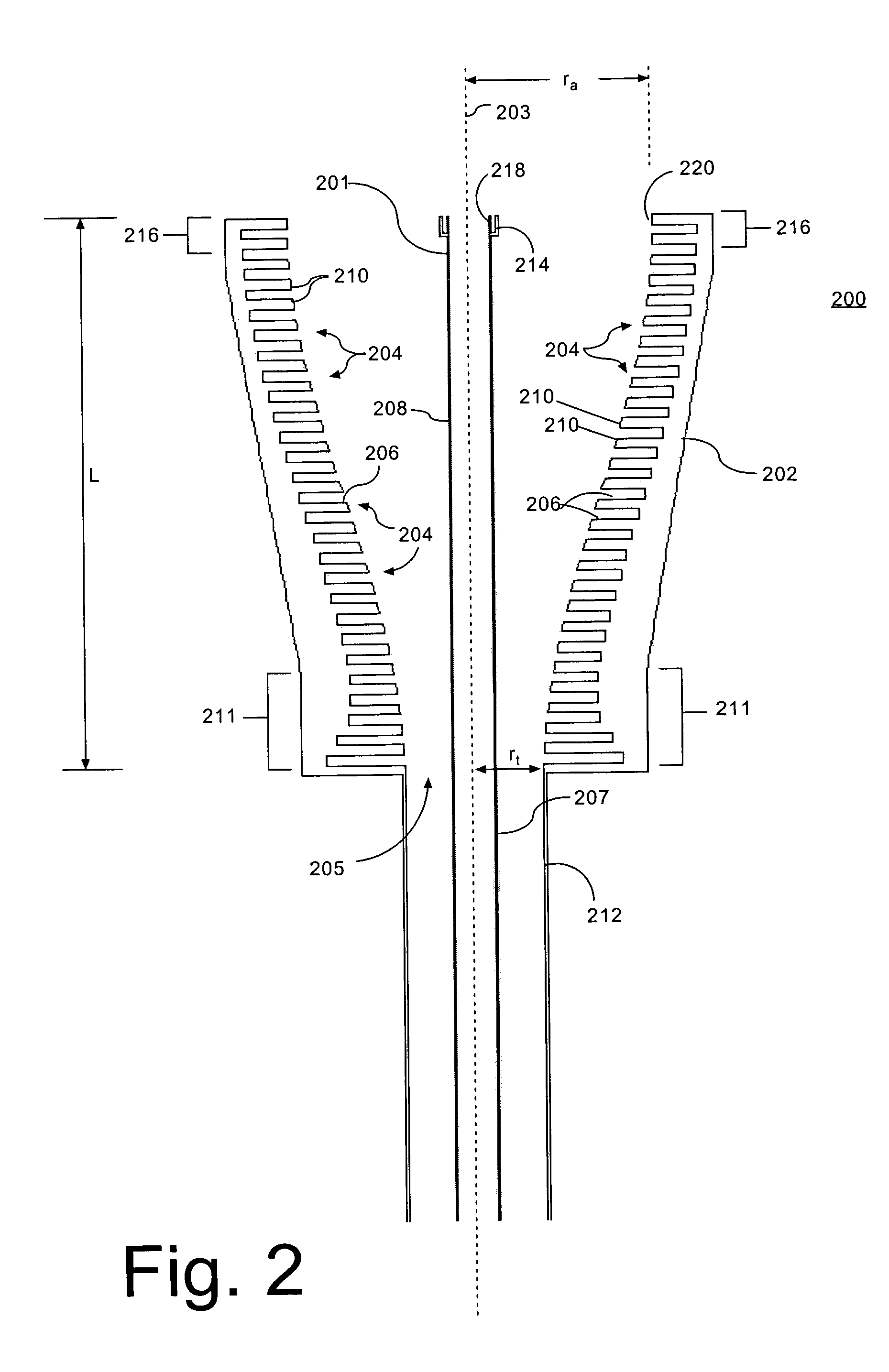
An antenna feed system includes a plurality of RF horn antennas (201, 202) for operating on a plurality of RF frequency bands. A first one of the feed horns (202) can have a boresight axis and is configured for operating at a first one of the frequency bands. A second one of the feed horns (201) is positioned coaxially within the first one of the feed horns (202) and is configured for operating at least at a second one of the frequency bands. Further, the first one of the feed horns (202) is a corrugated horn that has a plurality of corrugations (204) formed on an interior surface defining a profile. The profile extends substantially from a throat (205) of the first feed horn and along a tapered portion of the first feed horn. The profile substantially minimizes an interaction of the corrugations with the second feed horn.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Small wave-guide radiators for closely spaced feeds on multi-beam antennas
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
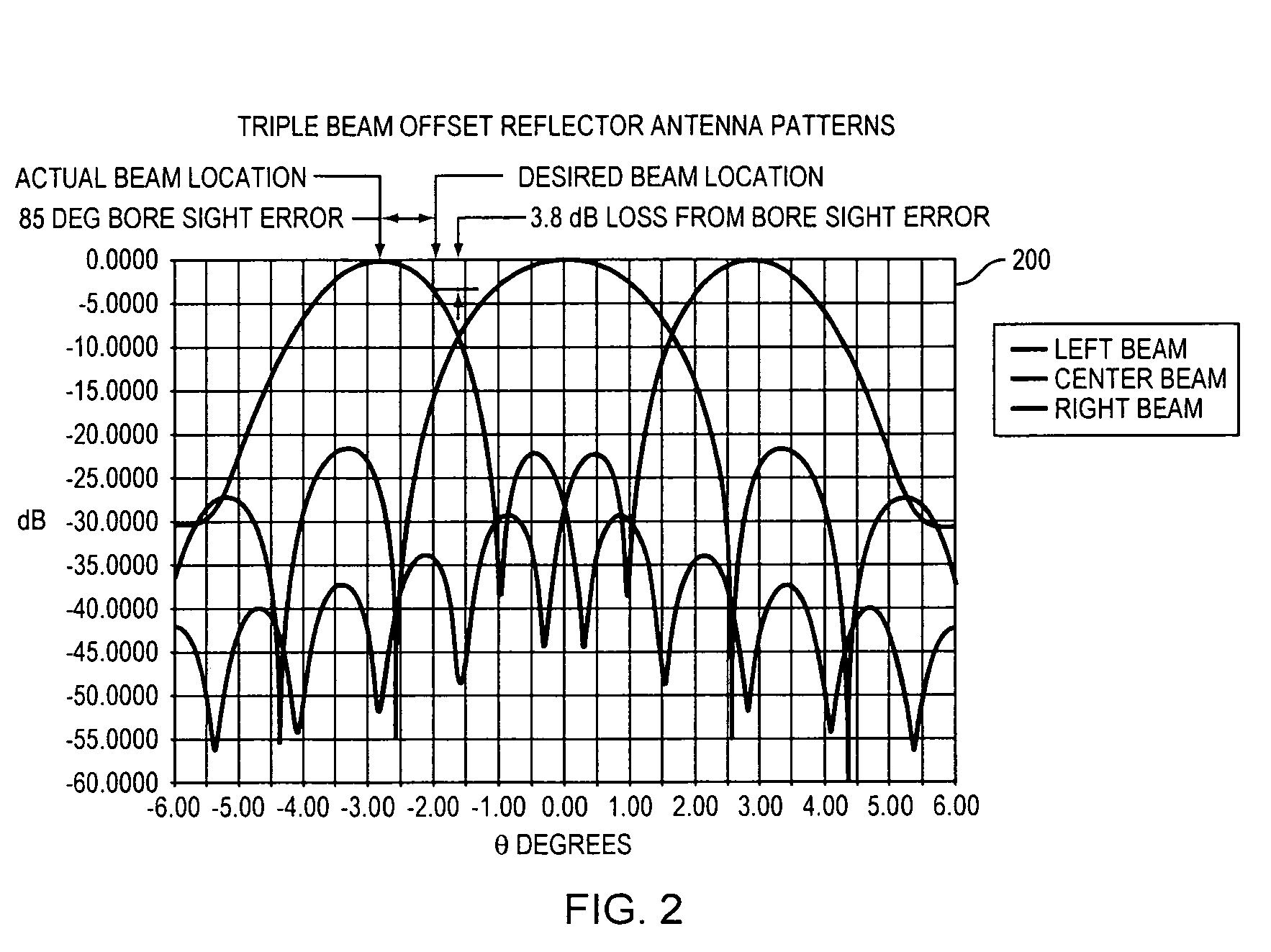
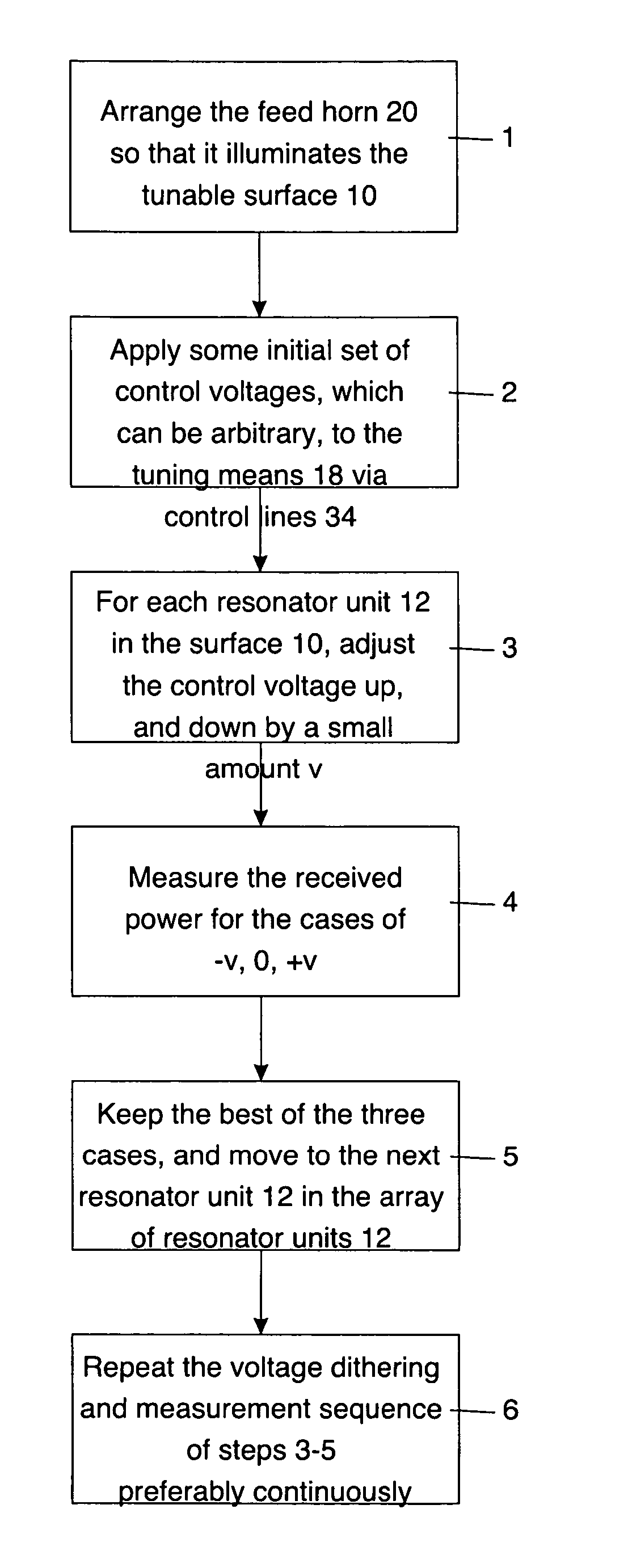
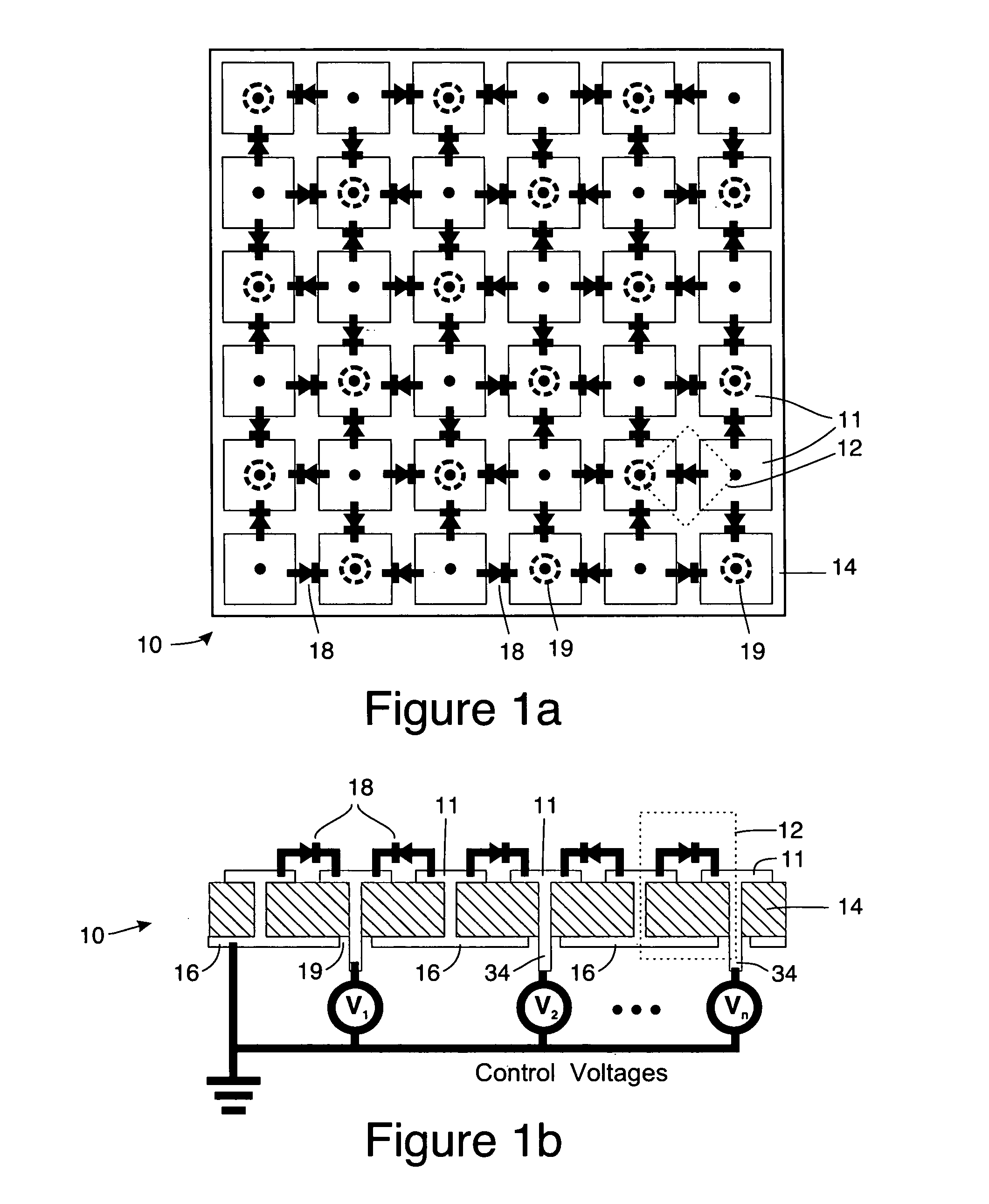
Adaptive beam forming antenna system using a tunable impedance surface
A method of and apparatus for beam steering. A feed horn is arranged so that the feed horn illuminates a tunable impedance surface comprising a plurality of individually tunable resonator cells, each resonator element having a reactance tunable by a tuning element associated therewith. The tuning elements associated with the tunable impedance surface are adjusted so that the resonances of the individually tunable resonator cells are varied in a sequence and the resonances of the individually tunable resonator cells are set to values which improve transmission of information via the tunable impedance surface and the feed horn.
Owner:HRL LAB
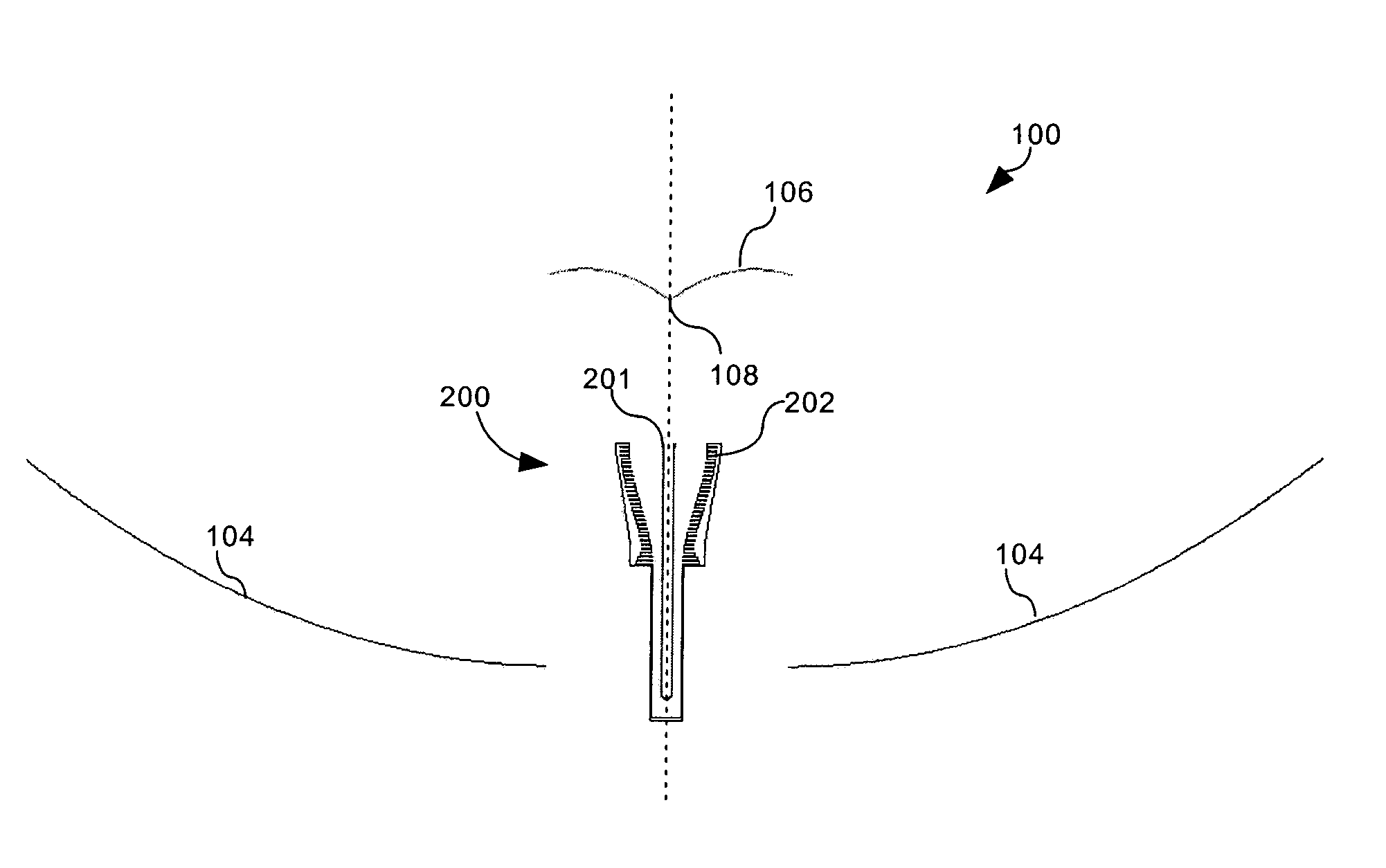
Antenna with Shaped Asymmetric Main Reflector and Subreflector with Asymmetric Waveguide Feed
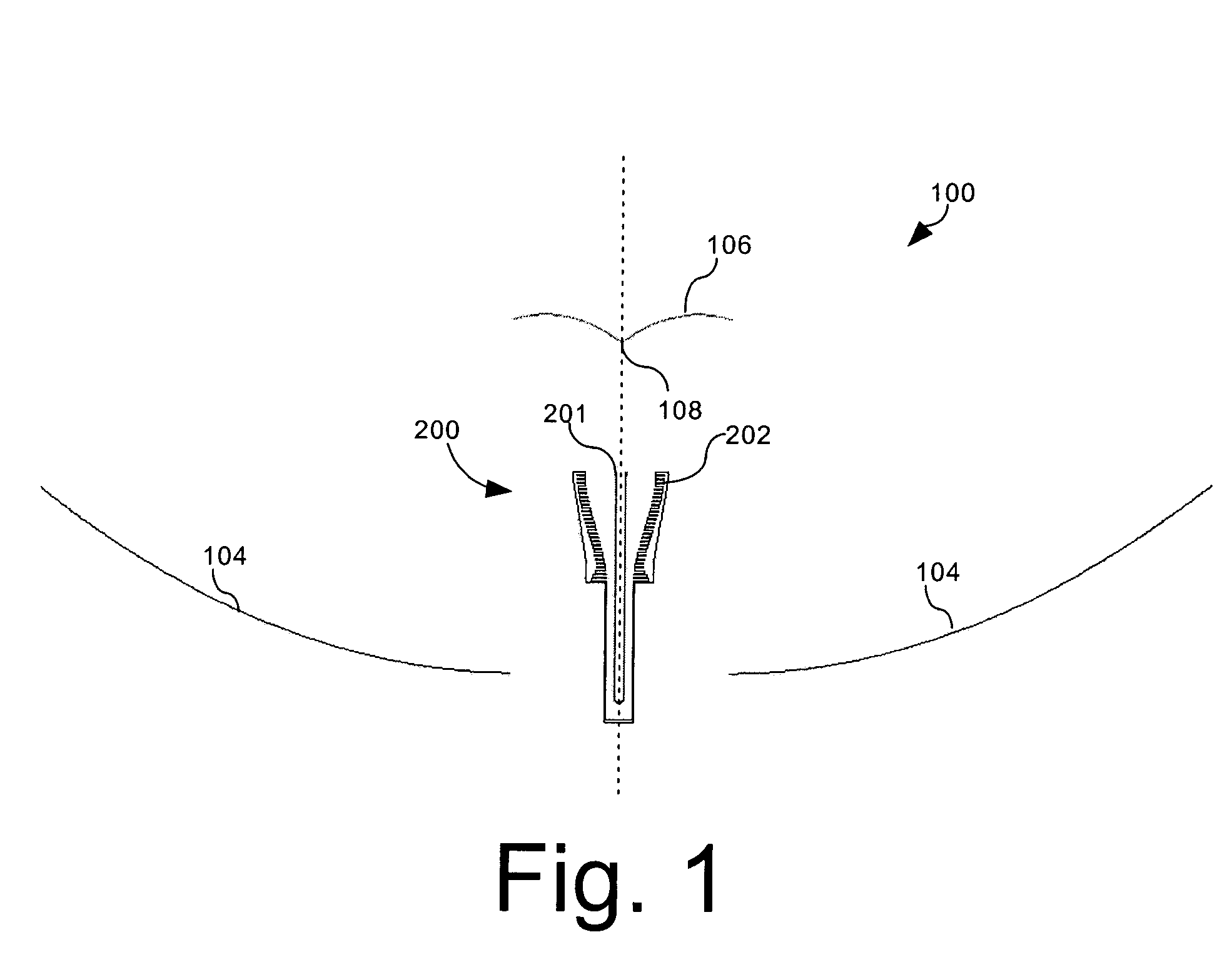
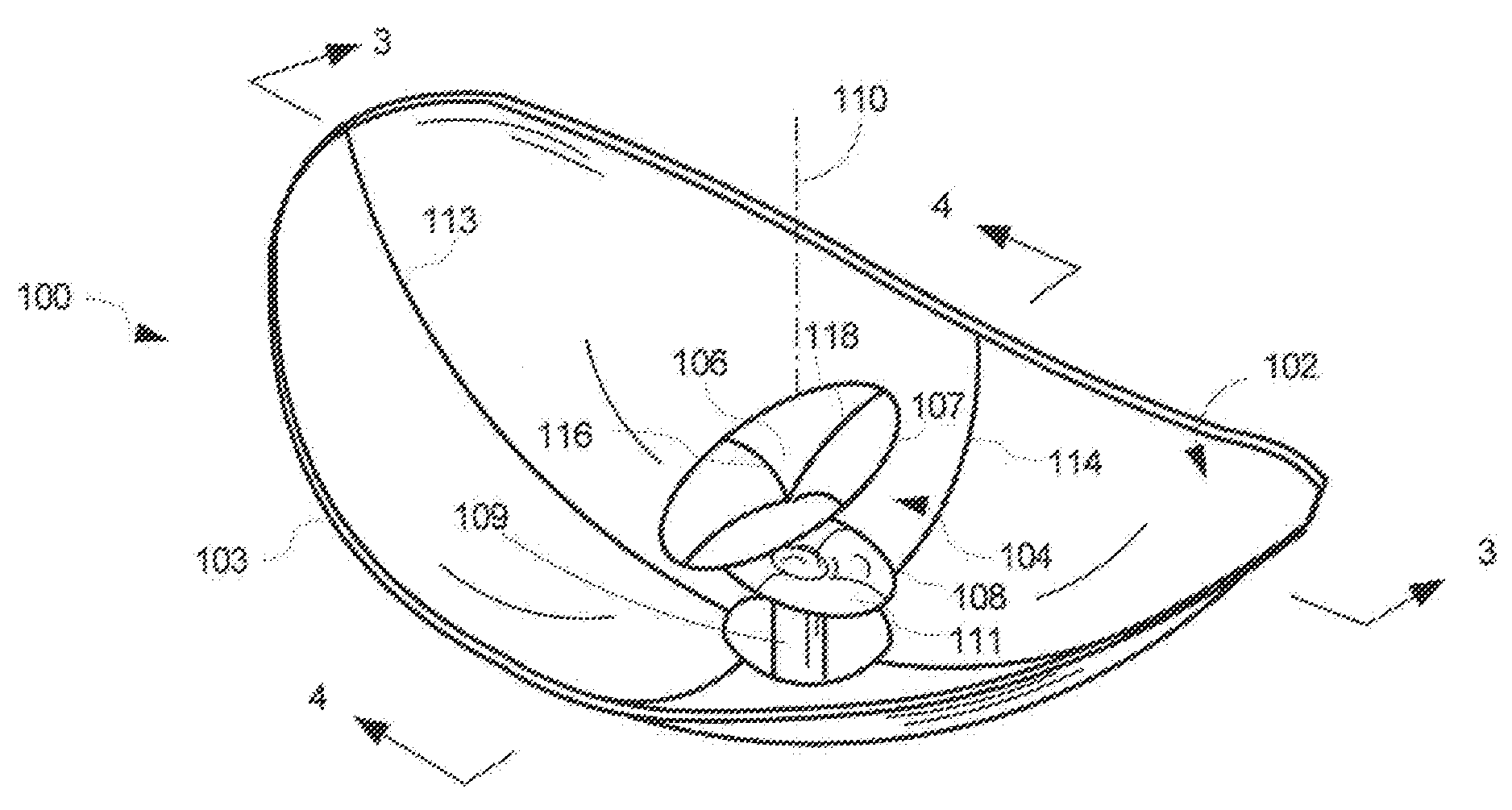
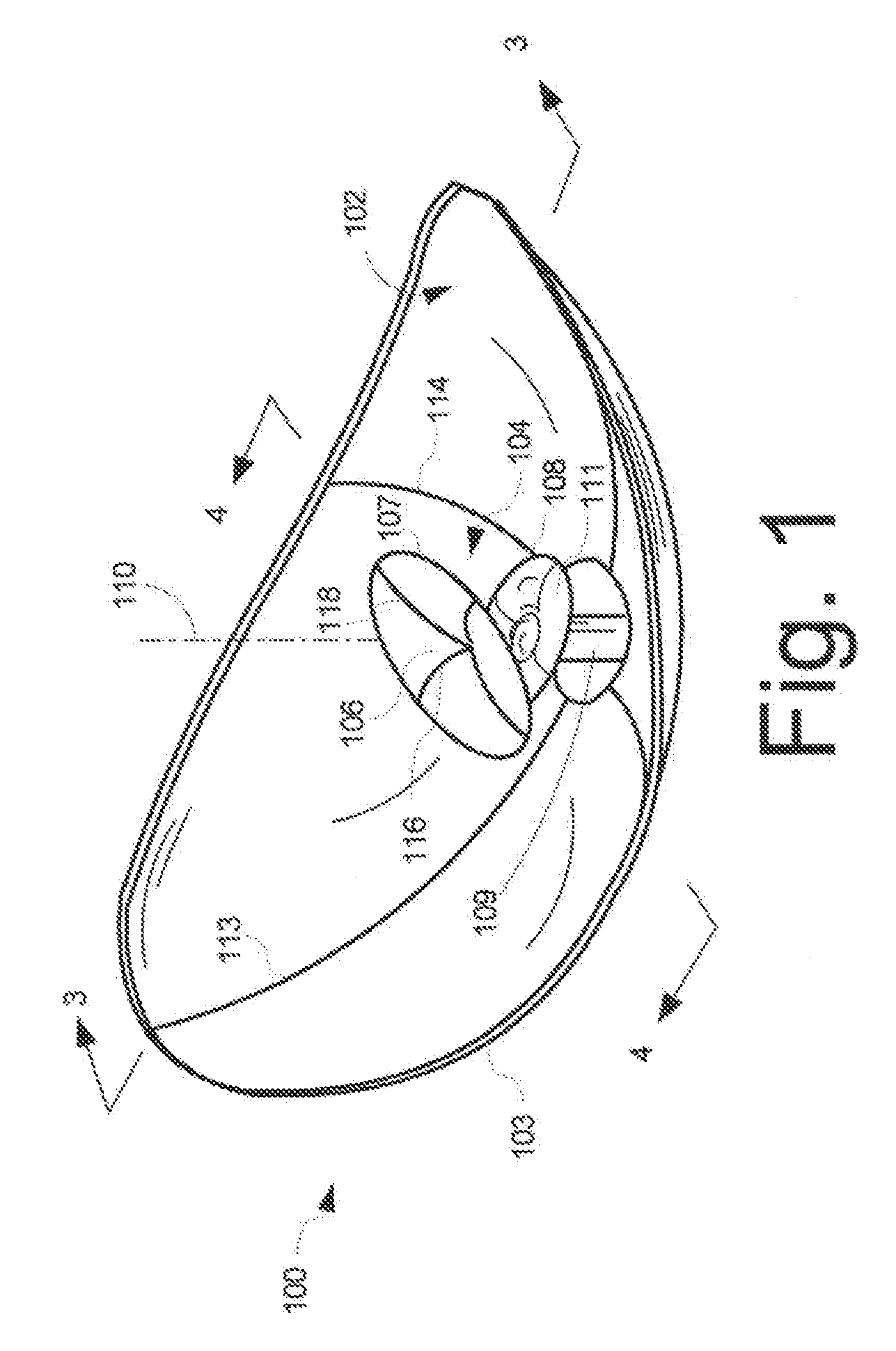
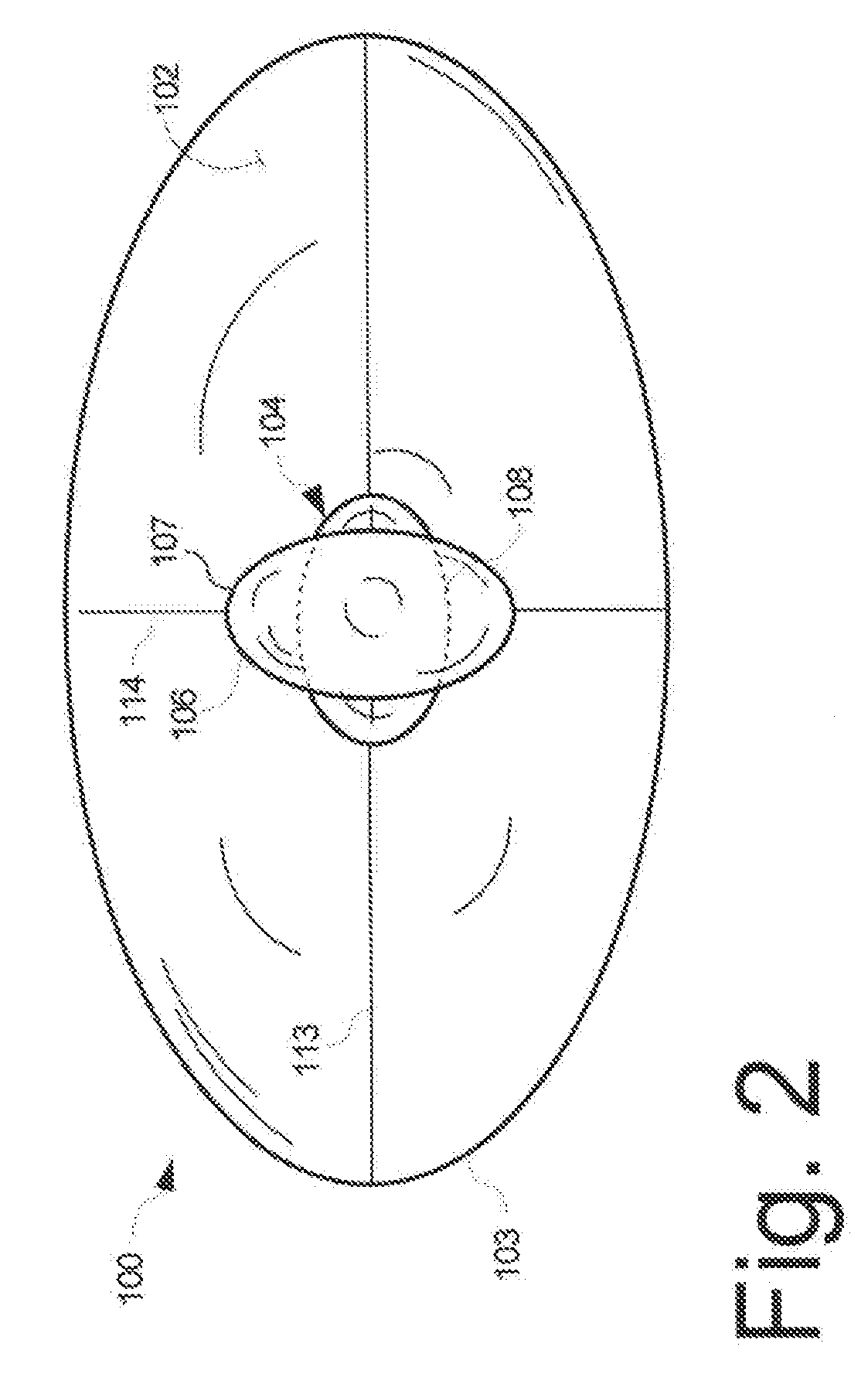
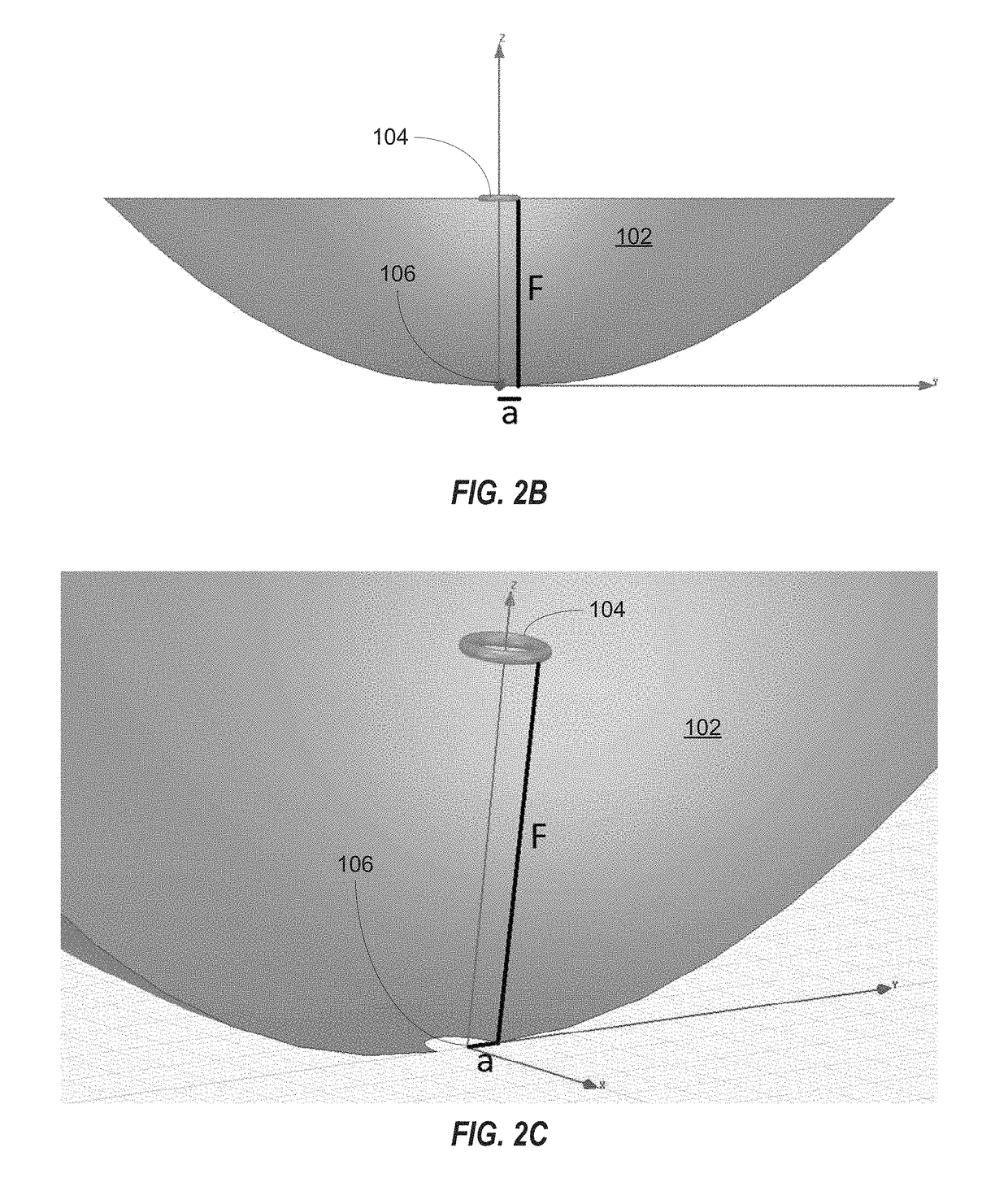
A low-profile antenna system includes a main reflector (102) formed as a shaped main reflector surface that is approximately, but not precisely, parabolic. The main reflector (102) has a main reflector edge configuration (103) that is asymmetric. A feed system (104) for the main reflector includes a subreflector (106) formed as a shaped subreflector surface that is approximately, but not precisely, elliptical. The subreflector has a subreflector edge configuration (107) that is also asymmetric. An RF feed horn (108) associated with the feed system 104 has an aperture profile which also has an asymmetric shape.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
High radiation efficient dual band feed horn
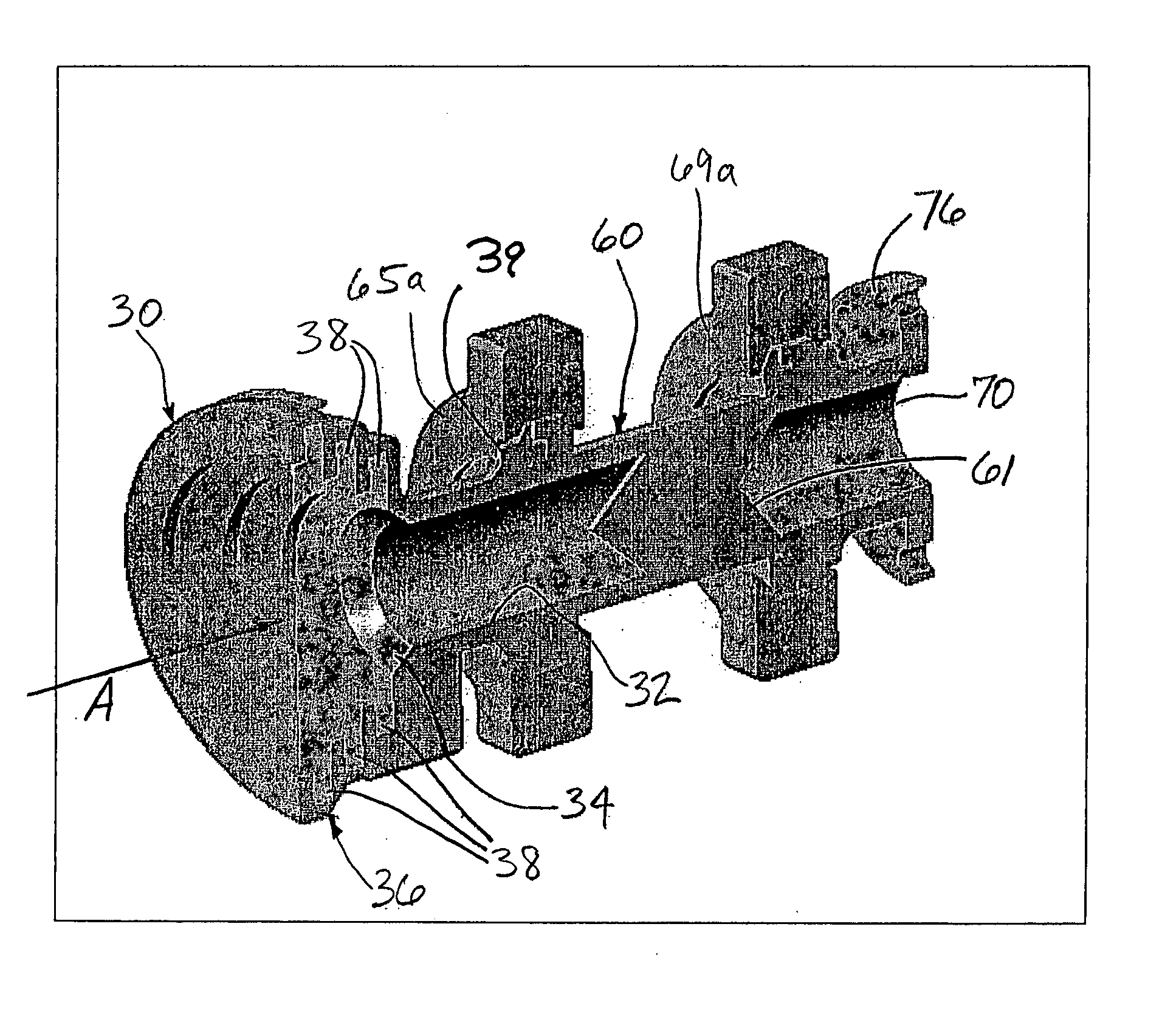
InactiveUS6967627B2MiniaturizationEasy to operateWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsDouble frequencyHigh radiation
A multiple mode feed horn is provided for transmitting and receiving signals. The feed horn includes a transverse electric throat section, a transverse electric profile section, and a transverse electric aperture section. The transverse electric profile section propagates a first transverse electric (TE) mode. The transverse electric aperture section propagates a second TE mode. The multiple mode feed horn prevents propagation of traverse magnetic modes from said throat section to said aperture section.
Owner:KEENE BUILDING PRODS CORP
Adaptive beam forming antenna system using a tunable impedance surface
ActiveUS7245269B2Improve communication qualitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsResonanceBeam steering
A method of and apparatus for beam steering. A feed horn is arranged so that the feed horn illuminates a tunable impedance surface comprising a plurality of individually tunable resonator cells, each resonator element having a reactance tunable by a tuning element associated therewith. The tuning elements associated with the tunable impedance surface are adjusted so that the resonances of the individually tunable resonator cells are varied in a sequence and the resonances of the individually tunable resonator cells are set to values which improve transmission of information via the tunable impedance surface and the feed horn.
Owner:HRL LAB
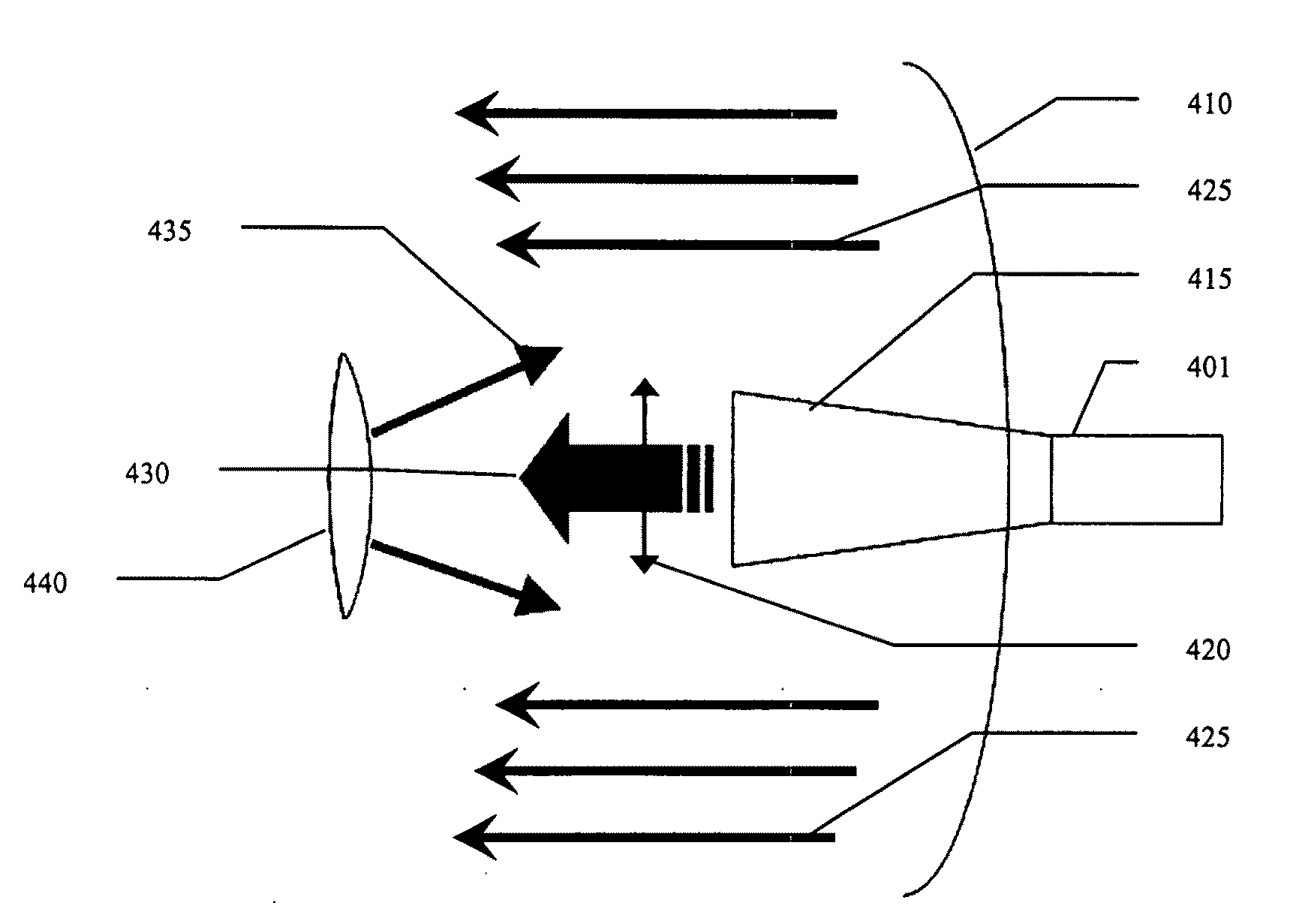
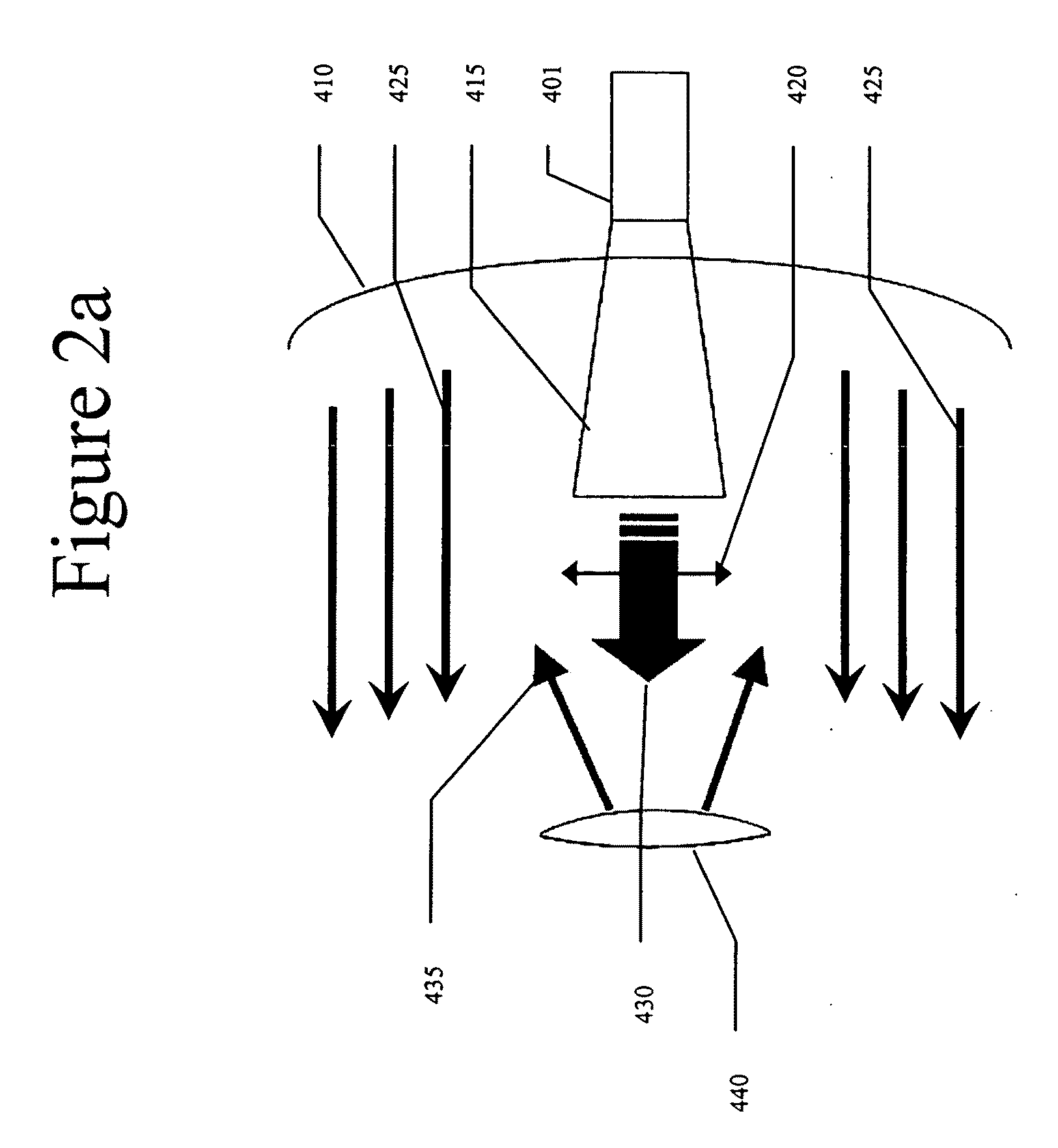
Multi-Feed Antenna System for Satellite Communicatons
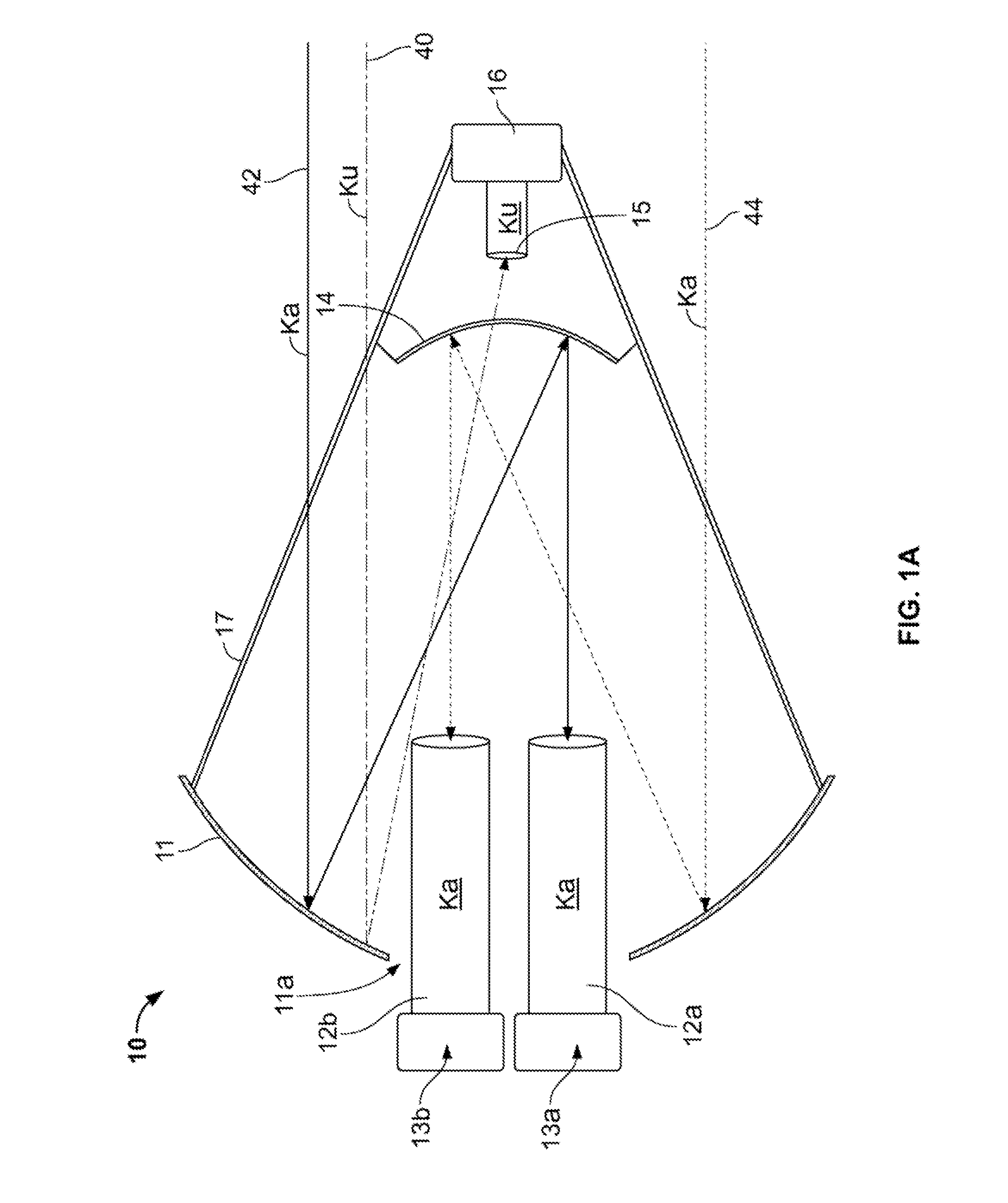
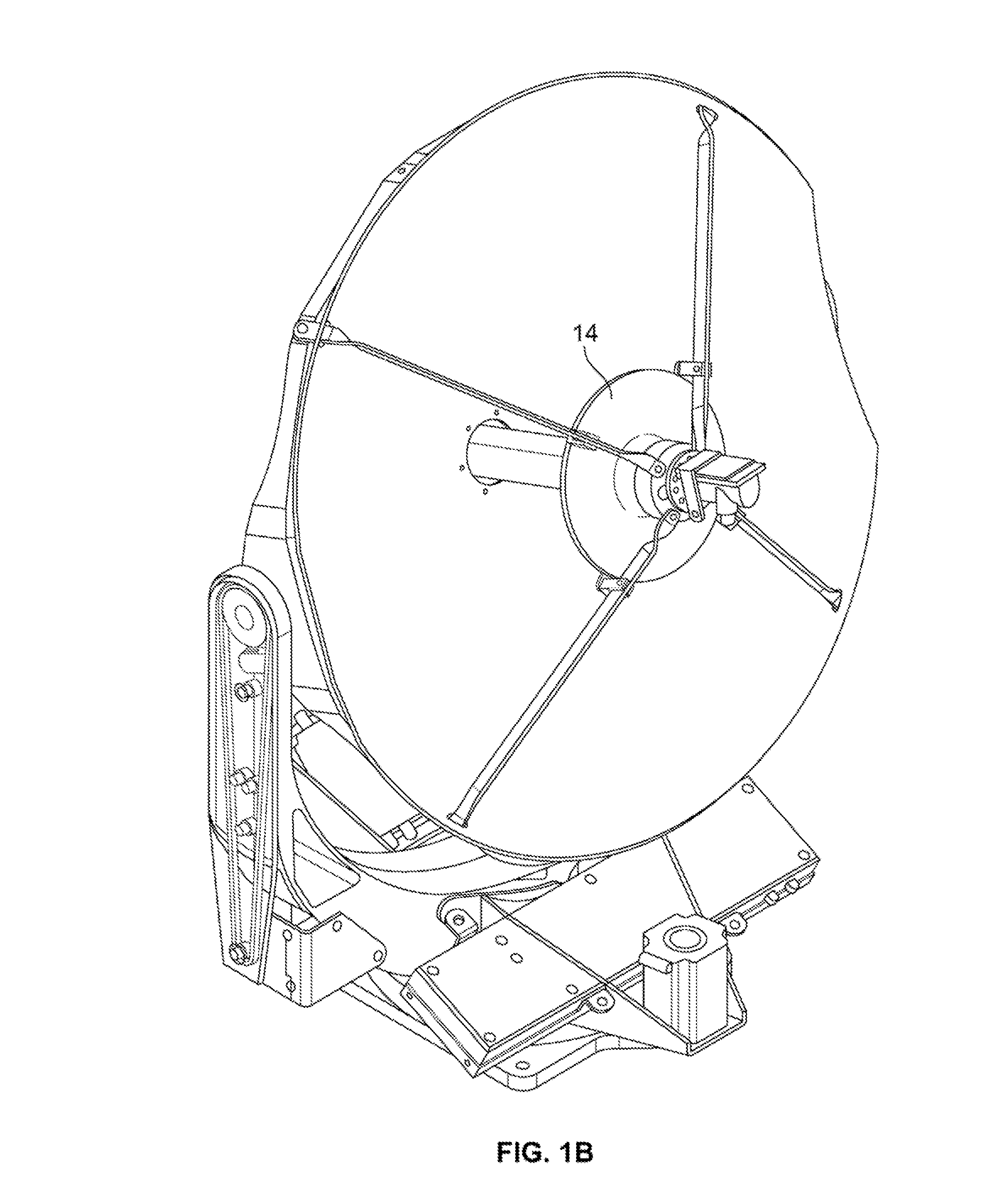
The present invention provides an improved single antenna system that allows reception of RF energy at multiple frequencies. In one embodiment, the antenna is implemented as a multi-beam, multi-feed antenna having a primary reflector fitted with a dual mode feed tube and a switchable LNB that supports both Ka band and Ku band reception. In another embodiment, the antenna is implemented as a multi-beam, multi-feed antenna having a primary reflector fitted with a feed horn and a LNB that is capable of providing movement such that the feed horn with the LNB is at a focal point with the primary reflector for both Ka and Ku band reception. In another embodiment, the antennae is implemented as a multi-beam, multi-feed antenna having a primary reflected fitted with a feed horn assembly and a switchable LNB that supports both Ka band and Ku band reception.
Owner:KVH IND INC
Circular polarity elliptical horn antenna
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
Multi-Band Antenna System for Satellite Communications
The present invention provides an improved antenna system on moving platform that is in communication with multiple satellites for simultaneous reception and transmission of RF energy at multiple frequencies. The antenna is implemented as a multi-beam, multi-band antenna having a main reflector with multiple feed horns and a sub-reflector having a reflective surface defining an image focus for a Ka band frequency signal and a prime focus for a Ku band frequency signal.
Owner:KVH IND INC
Scanning apparatus
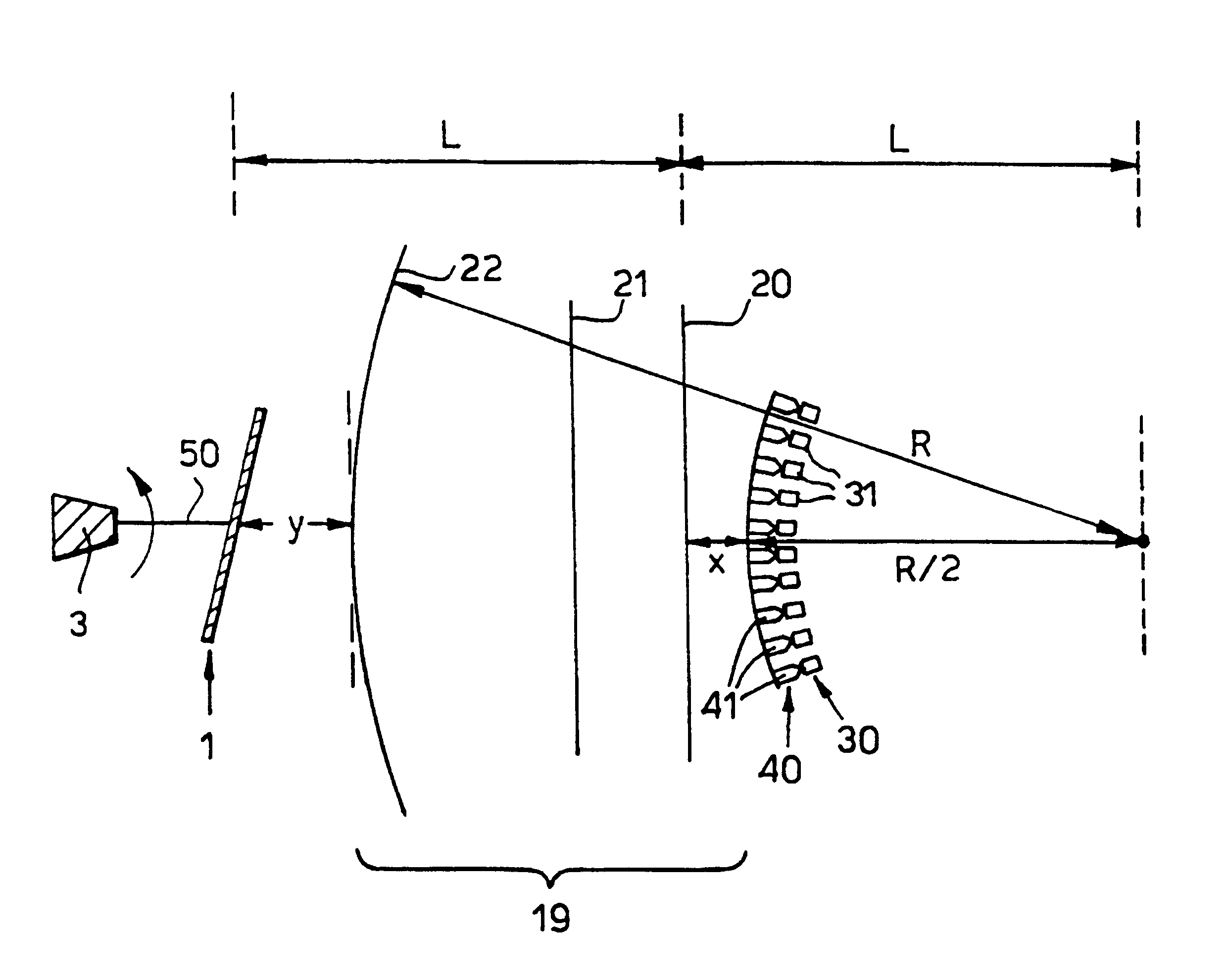
InactiveUS6587246B1Limited power requirementMinimum inertiaTelevision system detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRadarDetector array
Scanning apparatus which may be used in a real-time passive millimeter wavelength imaging system or in other radiometry systems. The apparatus scans input radiation from a scene and output radiation is transmitted to a receiver system, for example a millimeter wave imaging camera or a radar receiver. The apparatus comprises a rotatable reflective plate having an axis of rotation passing through the centre of its surface and a lens arrangement for selectively transmitting and focusing radiation having a particular direction of polarisation. The apparatus may also comprise a feed horn array comprising a plurality of feed horns, the feed horns forming part of a spherical surface having a radius of curvature substantially equal to R / 2 and being concentric with the third substantially spherical polarising element. The apparatus may further comprise a detector array comprising a plurality of detector elements. The detector array may form part of a millimeter wave imaging camera.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Cellular reflectarray antenna and method of making same
InactiveUS7791552B1Quick installationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsLongitudeLength wave
A method of manufacturing a cellular reflectarray antenna arranged in an m by n matrix of radiating elements for communication with a satellite includes steps of determining a delay φm,n for each of said m by n matrix of elements of said cellular reflectarray antenna using sub-steps of: determining the longitude and latitude of operation, determining elevation and azimuth angles of the reflectarray with respect to the satellite and converting theta0 (θ0) and phi0 (φ0), determining Δβm,n, the pointing vector correction, for a given inter-element spacing and wavelength, determining Δφm,n, the spherical wave front correction factor, for a given radius from the central element and / or from measured data from the feed horn; and, determining a delay φm,n for each of said m by n matrix of elements as a function of Δβm,n and Δφm,n..
Owner:NASA
Feed assembly for multi-beam antenna with non-circular reflector, and such an assembly that is field-switchable between linear and circular polarization modes
InactiveUS7236681B2Improve approachFacilitate close spacingWaveguide hornsOptical waveguide light guidePolarizerMulti beam
A feed assembly for an antenna having a non-circular reflector, in which the feed assembly includes a feed horn capable of correcting the distortions of circularly polarized signals caused by the non-circular reflector profile, and wherein the feed horn is coupled with a polarizer that is field-switchable between linear and circular polarization modes of operation. The feed assembly can include a second receive-only feed located in close proximity to the feed horn for communication with adjacent satellites.
Owner:CPI SATCOM & ANTENNA TECH INC
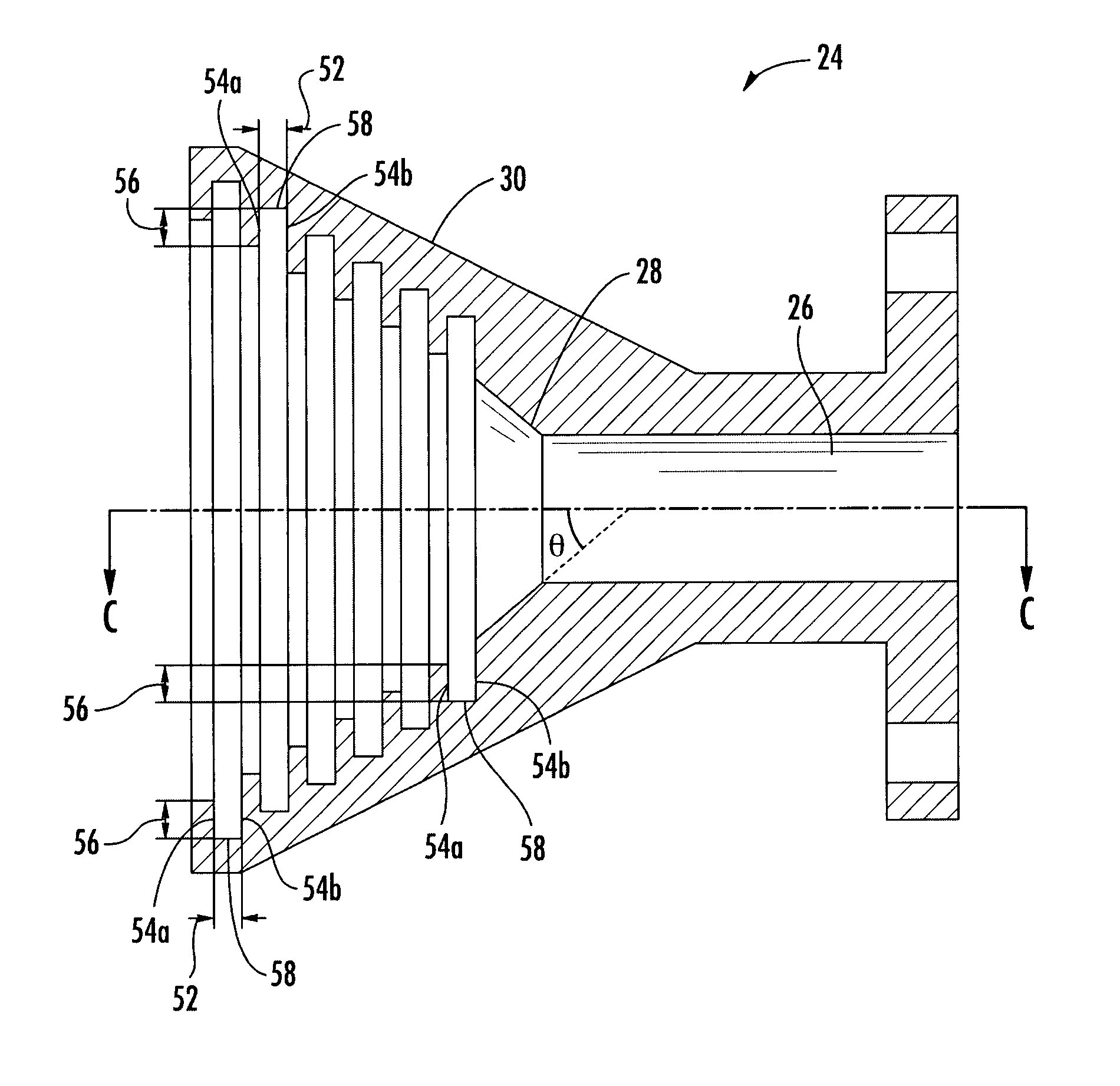
System and method for hybrid geometry feed horn
A feed horn and systems and methods of making and using the feed horn are presented. Exemplary feed horns include a first portion comprising a dual mode geometry and a second portion comprising an axial corrugation geometry. The feed horn may operate simultaneously in a plurality of separate frequency bands (e.g., from about 18.3 GHz to about 20.2 GHz and from about 29.1 GHz to about 30.0 GHz) and a plurality of separate waveguide modes (e.g., TE11, TM11 or HE11 modes); simultaneously operating over two bandwidth segments of at least 1900 MHz that are separated by at least 5000 MHz. The feed horn may have a short axial length (e.g. less than 4 wavelengths at 18.3 GHz), and it may be configured to operate in a prime fed offset reflector antenna system. In addition, the feed horn may be formed as a single piece via a single casting pull.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Low index metamaterial
ActiveUS20100078203A1Facilitate propagationReduce applicationsWaveguide hornsPrinted circuitsElectrical conductorRefractive index
Various aspects of the disclosure provide low index metamaterials. The low index metamaterials may be used to form soft and / or hard electromagnetic (EM) boundaries to facilitate desired EM performance or propagation in applications including feed horns, spatial feed / combiners, isolation barriers between antennas or RF modules, and reduced radar cross-section applications. In one aspect, a low index metamaterial comprises a dielectric layer and a plurality of conductors on a surface of the dielectric layer, embedded in the dielectric layer or both, wherein the low index metamaterial appears as a medium having a dielectric constant less than one with respect to electromagnetic waves at predetermined frequencies and propagating at grazing angles with respect to a surface of the low index metamaterial.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Antenna systems for reliable satellite television reception in moisture conditions
InactiveUS7342551B2Reliable receptionMinimize impactRadiating element housingsTransmittanceEngineering
More reliable satellite television reception in moisture conditions is provided by recognizing the critical relationship between satellite signal transmissivity and the effects of superhydrophobocity. Instead of trying to use a hydrophobic or superhydrophobic coating or material to shed water from a satellite antenna, superhydrophobic materials and coatings are strategically utilized to minimize the impact of water on the transmissivity of the satellite signal through transmissive surfaces in the antenna system. In a preferred embodiment, an exterior surface of a feed horn cover is coated with a superhydrophobic material to maintain a more consistent satellite signal reception. In an alternate embodiment, an exterior surface of a dome covering a small dish DBS satellite television antenna system is coated with a superhydrophobic material to minimize the overall satellite signal loss during moisture conditions so as to permit a dome to be effectively used over a small dish DBS satellite television antenna system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS CONTROLLED SYST
Antenna systems for reliable satellite television reception in moisture conditions
InactiveUS20050225495A1Increase coverageReliable receptionRadiating element housingsTransmittanceEngineering
More reliable satellite television reception in moisture conditions is provided by recognizing the critical relationship between satellite signal transmissivity and the effects of superhydrophobocity. Instead of trying to use a hydrophobic or superhydrophobic coating or material to shed water from a satellite antenna, superhydrophobic materials and coatings are strategically utilized to minimize the impact of water on the transmissivity of the satellite signal through transmissive surfaces in the antenna system. In a preferred embodiment, an exterior surface of a feed horn cover is coated with a superhydrophobic material to maintain a more consistent satellite signal reception. In an alternate embodiment, an exterior surface of a dome covering a small dish DBS satellite television antenna system is coated with a superhydrophobic material to minimize the overall satellite signal loss during moisture conditions so as to permit a dome to be effectively used over a small dish DBS satellite television antenna system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS CONTROLLED SYST
Wireless millimeter wave communication system
InactiveUS20080153549A1Minimized in sizeDivergence of beam is maximizedRepeater circuitsSubstation equipmentMillimeter wave communication systemsTransceiver
A lens-based millimeter wave transceiver for use in wireless communication systems operating in the E-band spectrum consistent with the FCC rules regulating the 71-76 GHz and 81-86 GHz bands. The transceiver includes a single lens adapted for transmission of millimeter radiation to form communication beams in one band of either a band of about 71-76 GHz or a band of 81-86 GHz and for collection and focusing of millimeter wave radiation from communication beams in the other of the two bands. It includes a feed horn adapted to broadcast millimeter radiation through said single lens and to collect incoming millimeter wave radiation collected and focused by said single lens. A millimeter wave diplexer separates incoming and outgoing millimeter wave radiation.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Integrated single-piece antenna feed
The invention is an integrated single-piece antenna feed, turnstile polarizer and antenna system suitable for satellite communications. One embodiment of the integrated single-piece antenna includes a circular waveguide input, a circular polarizer, a coaxial feed horn, subreflector and subreflector support. One embodiment of the circular polarizer features four branches of wrapped-single-ridged waveguide.
Owner:OPTISYS INC
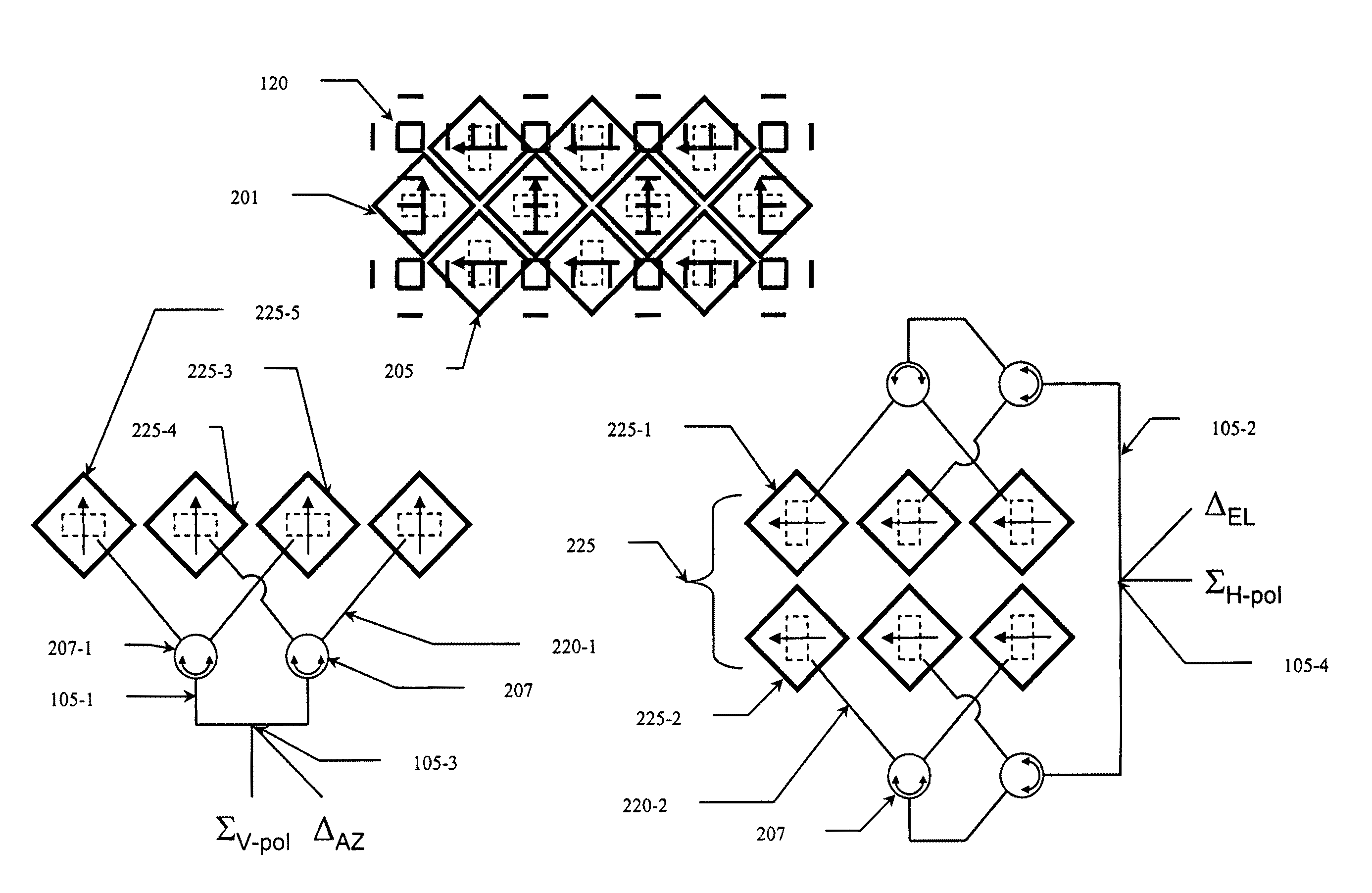
Electronically steered, dual-polarized, dual-plane, monopulse antenna feed
InactiveUS20100052987A1Reduce weight and costSmall sizePolarised antenna unit combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna feedElectron
A method and apparatus for electronically steering a RADAR beam across an array of feed horns by moving the phase center of the beam to different origination points on the array—each origination point being the phase center of a feed horn pair. Variations include polarized beams, polarized feed horns, dual-beam systems, dual direction steering, diagonal steering, and cross-polarized wire grids to control beamwidth.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Circularly polarized receive/transmit elliptic feed horn assembly for satellite communications
The present invention provides a feed horn for use in an antenna assembly having a non-circular reflector. The feed horn is capable of transmitting and receiving circularly polarized signals. The feed horn includes a circular waveguide section for connection to a transmitter and receiver of the antenna assembly. A conical waveguide section is connected to an opposed end of the circular waveguide section for creating a smooth transition from the circular waveguide section to a non-circular corrugated waveguide section. The corrugated waveguide section includes a plurality of corrugations that transition for a circular shape adjacent to the conical waveguide section to an increasing non-circular shape at an end proximal to the reflector of the antenna assembly. The corrugations have individuals depths defined in the inner wall of the corrugated waveguide section. These depths compensate circularly polarized signals propagating in the feed horn for distortions due to the non-circular reflector.
Owner:CPI SATCOM & ANTENNA TECH INC
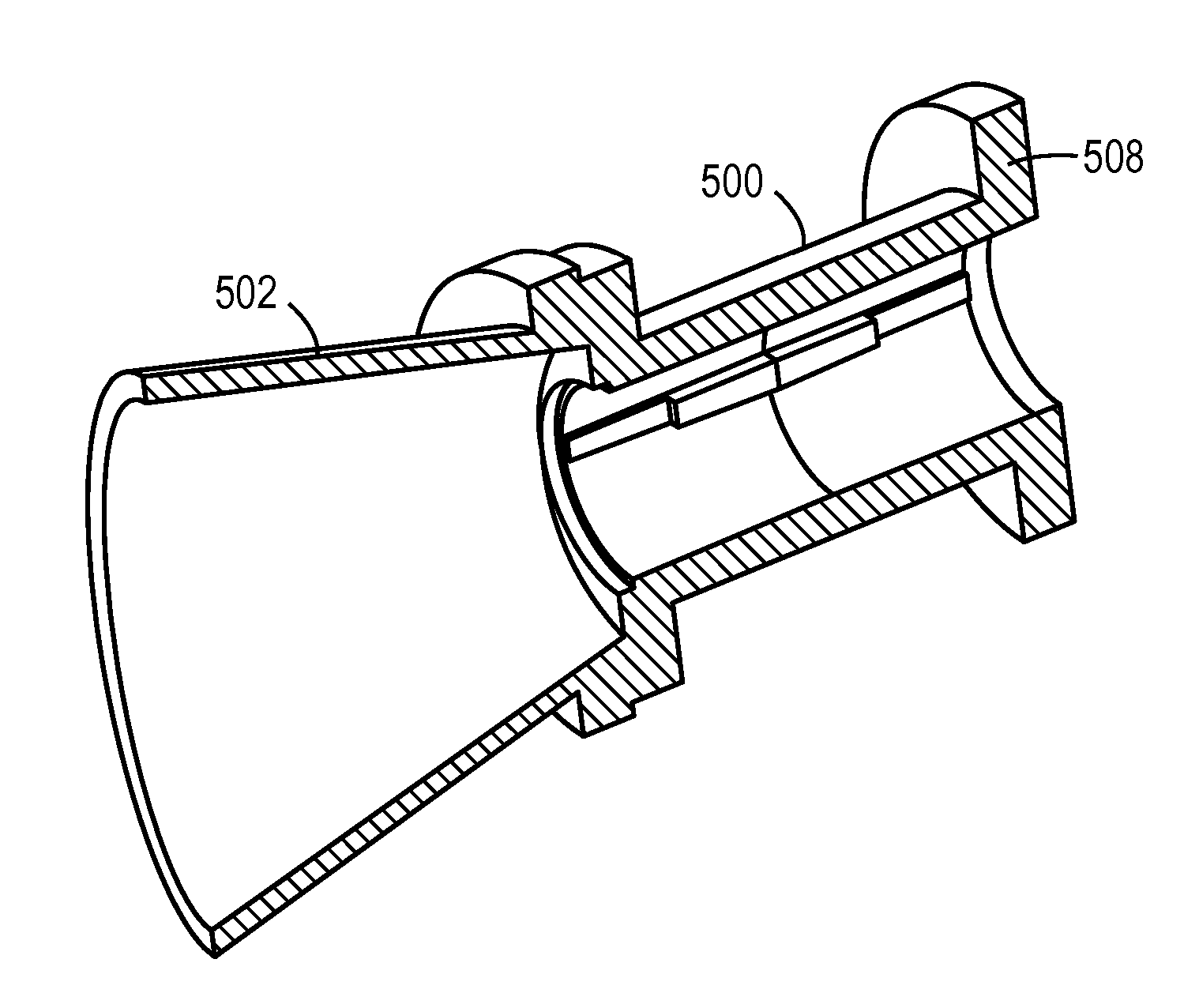
Modular waveguide feed horn
A modular waveguide feed horn is provided that includes an assembly having a waveguide plate section. The modular waveguide feed horn assembly also includes a feed horn section having at least one feed horn. The feed horn section is separately provided from and removably coupled to the waveguide plate section.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
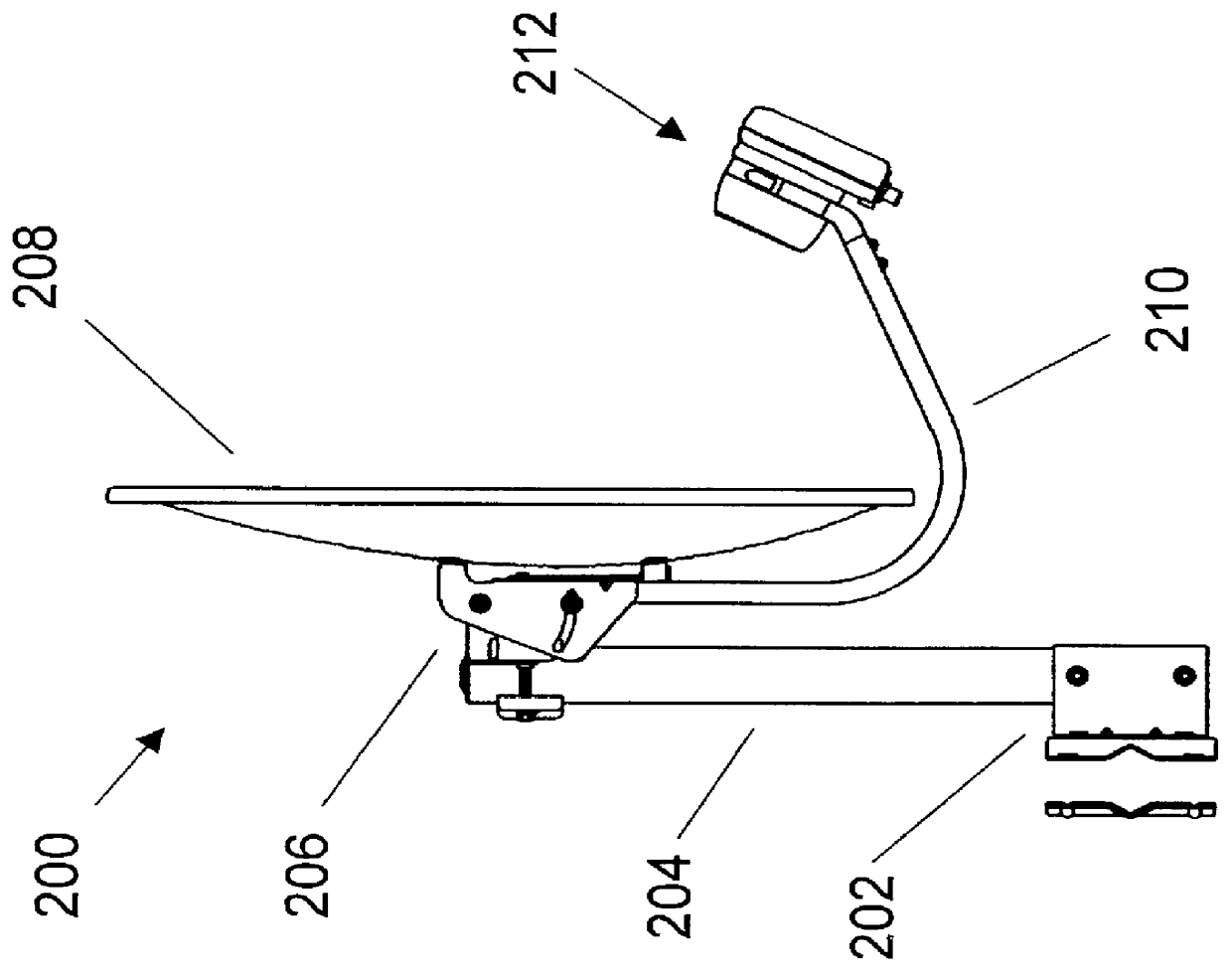
Satellite dish antenna mounting system
InactiveUS7385564B2Quick and efficient alignmentAccurate settingAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
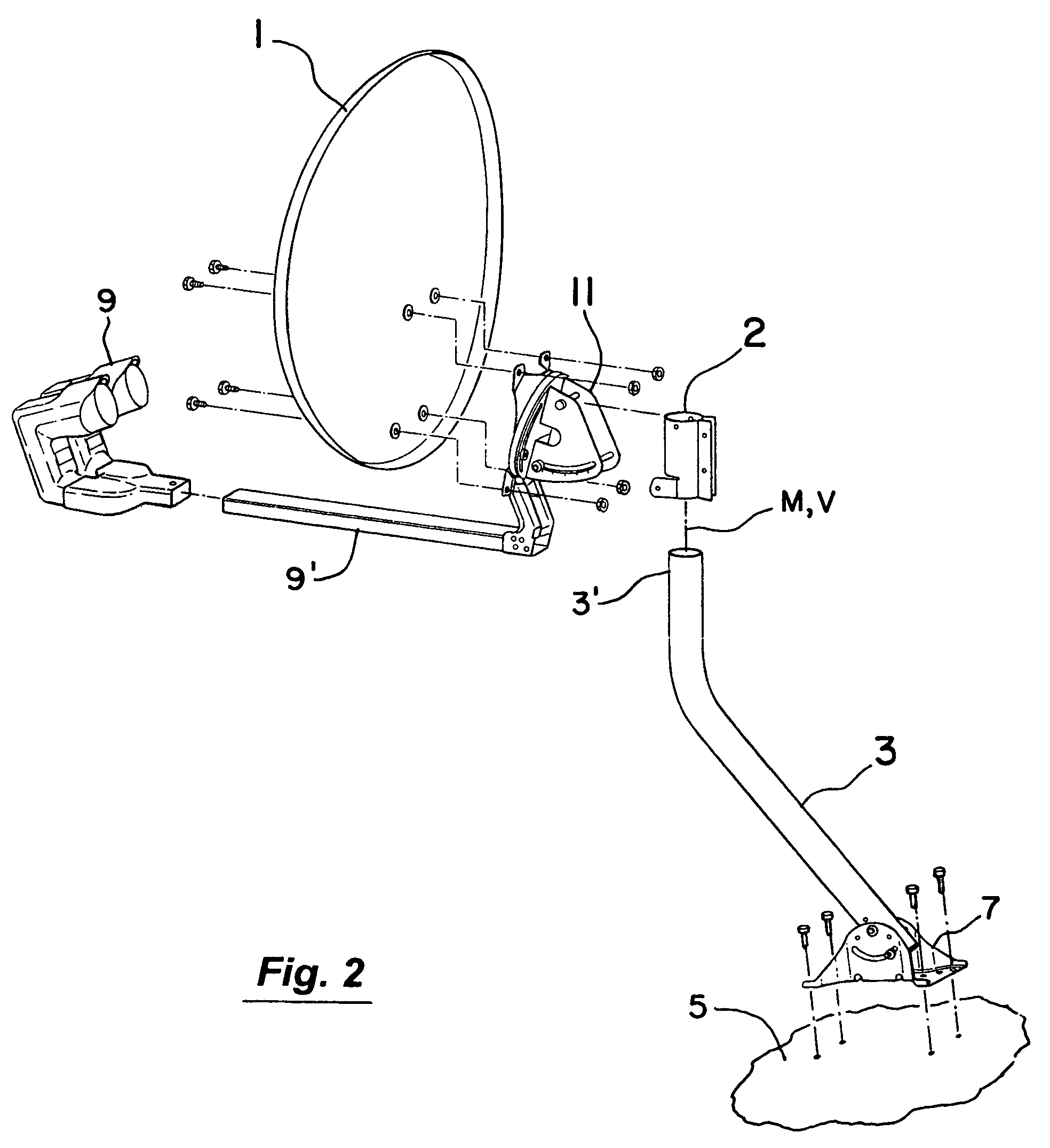
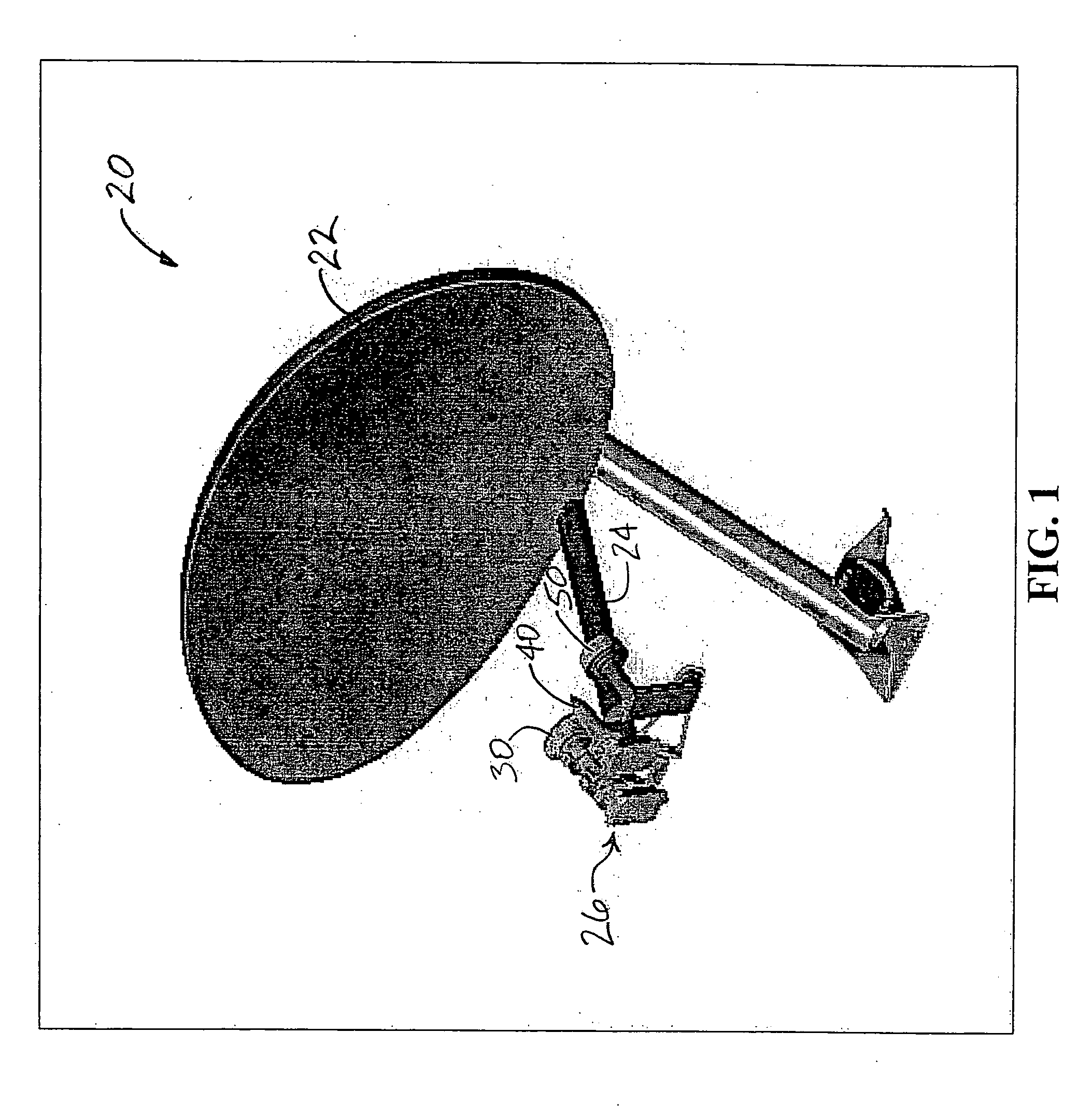
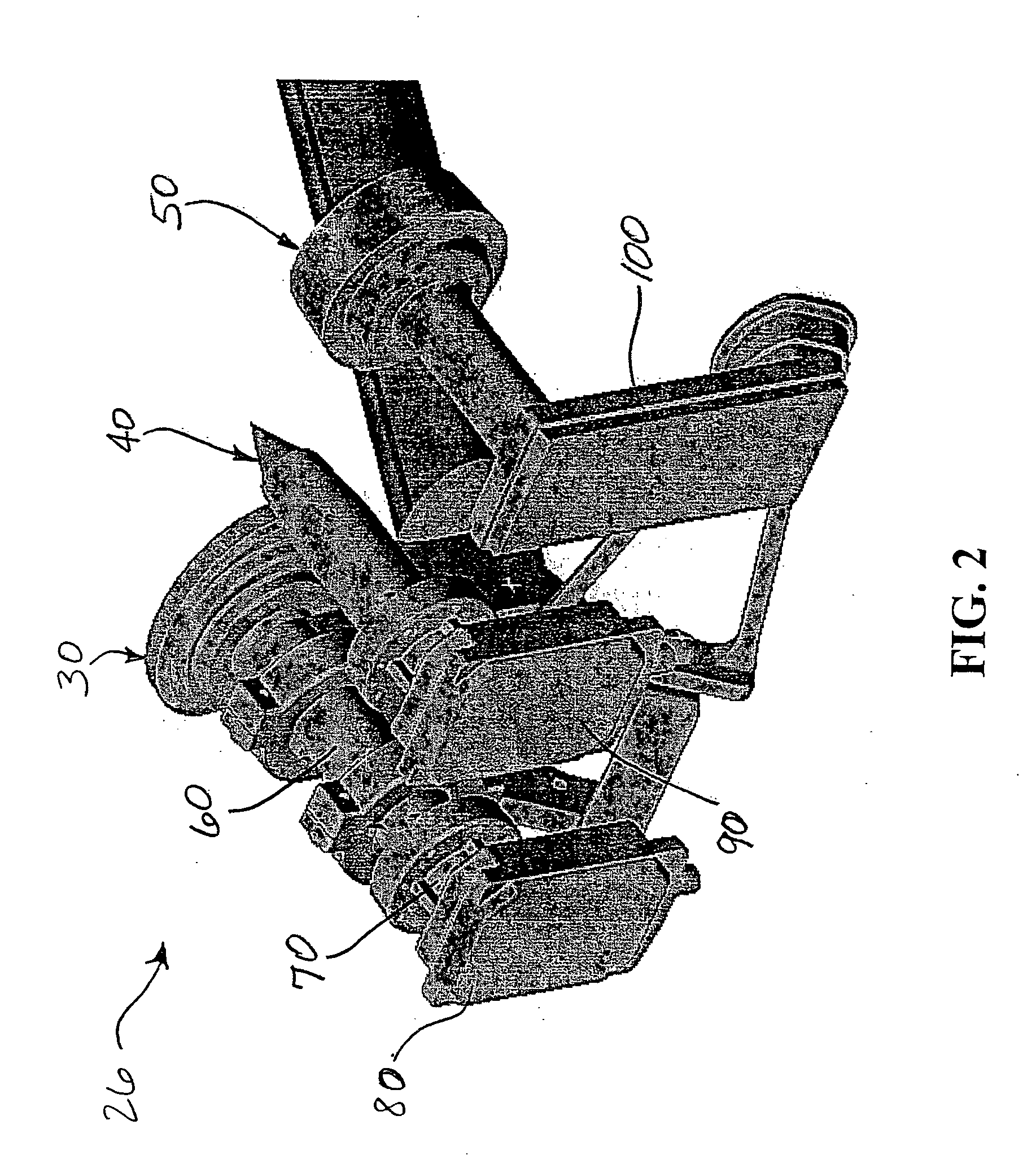
A satellite antenna mounting system primarily for residential homes including a dish, feed horn, elevation, clamp, and mast. The main body of the clamp to which the assemblage of the dish, feed horn, and elevation bracket are attached is provided with a downwardly inclined tab or clip member. In operation, the clamp of the assemblage can be lowered to receive the upper portion of the mast which is affixed to the roof or other part of the house. In doing so, the clip member engages the upper rim of the mast and firmly attaches or clips the assemblage to the mast with the dish in its desired elevation. Thereafter, the loose clamp can be tightened about the upper portion of the mast at the desired azimuth without affecting the set elevation of the dish.
Owner:WINEGARD
Feed assembly for multi-beam antenna with non-circular reflector, and such an assembly that is field-switchable between linear and circular polarization modes
InactiveUS20050116871A1Improve approachSmall sizeWaveguide hornsOptical waveguide light guidePolarizerMulti beam
A feed assembly for an antenna having a non-circular reflector, in which the feed assembly includes a feed horn capable of correcting the distortions of circularly polarized signals caused by the non-circular reflector profile, and wherein the feed horn is coupled with a polarizer that is field-switchable between linear and circular polarization modes of operation. The feed assembly can include a second receive-only feed located in close proximity to the feed horn for communication with adjacent satellites.
Owner:CPI SATCOM & ANTENNA TECH INC
Electronically steered, dual-polarized, dual-plane, monopulse antenna feed
InactiveUS7834803B2Reduce weight and costSmall sizePolarised antenna unit combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna feedElectron
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Multi-band circular polarity elliptical horn antenna
InactiveUS20070296641A1Good circular polarity performanceWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysMulti bandDigital video
A relatively low cost, easy to install and aesthetically pleasing multi-band, multi-port digital video broadcast from satellite (DVBS) elliptical horn antenna designed as part of a reflector antenna system to simultaneously receive satellite television broadcast signals with circular polarity on two frequency channels. This type antenna may be implemented with a single antenna feed horn with multiple feed horns that may be arranged separately or in one or more integral feed horn blocks. The antennas may be designed to achieve acceptable circular polarity performance over broad and multiple frequency bands through the use of oppositely sloped differential phase differential sections.
Owner:COOK SCOTT J
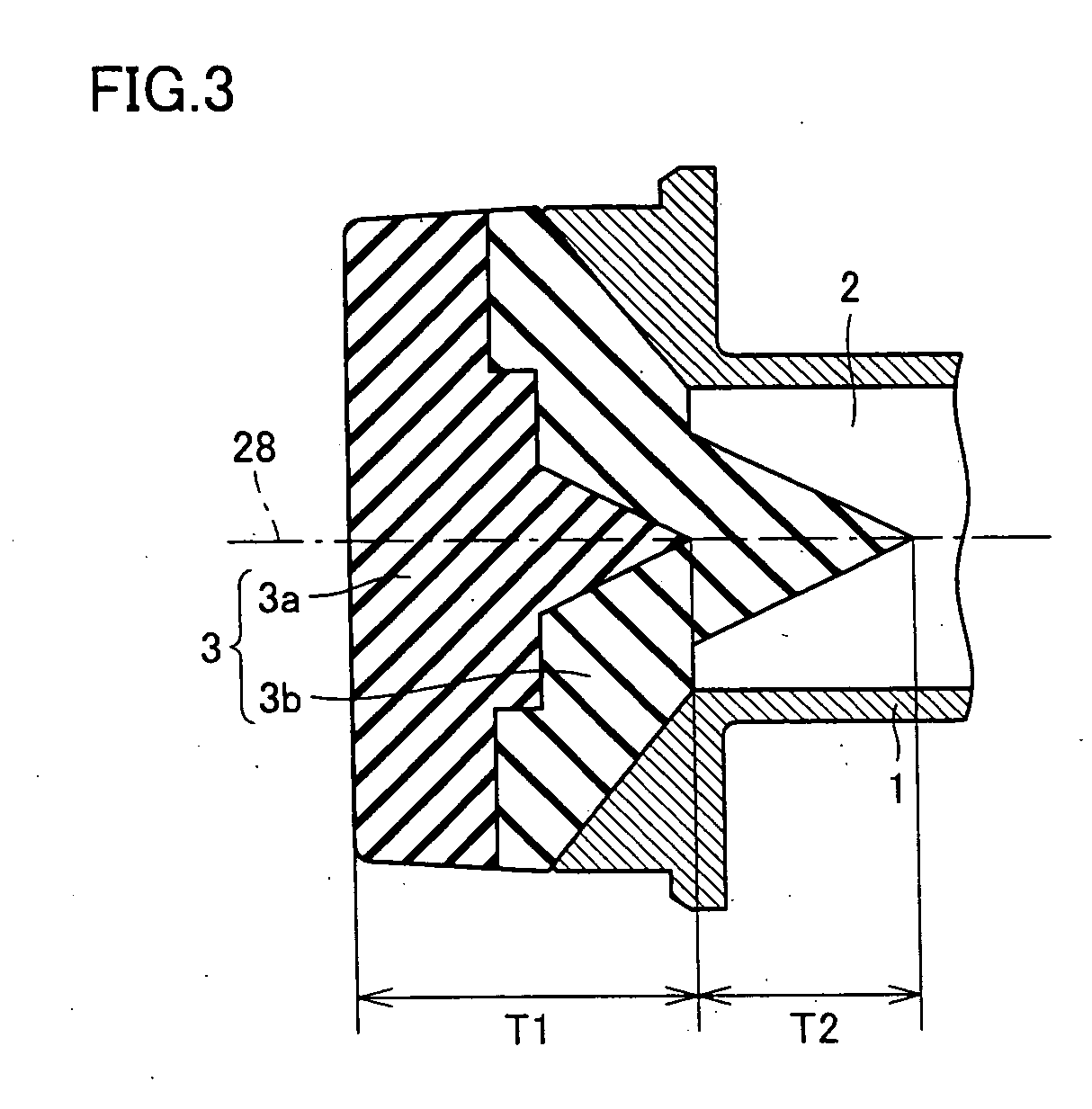
Feedhorn, radio wave receiving converter and antenna
InactiveUS20050140560A1Suppression of manufacturing cost increaseWaveguide hornsDe-icing/drying-out arrangementsDielectricEngineering
A dielectric feedhorn as a feedhorn according to the present invention, with which a feedhorn, a radio wave receiving converter and an antenna capable of suppressing an increase in manufacturing costs can be obtained, includes a chassis body including a waveguide having an opening, and a dielectric member. The dielectric member is connected to the opening of the waveguide, and constituted by dielectrics as a plurality of members.
Owner:SHARP KK
Dual elliptical corrugated feed horn for a receiving antenna
This invention is a compact and cost effective signal receiver for use in conjunction with a parabolic reflector to receive electromagnetic signals from two satellites. The signal receiver has a dual elliptical corrugated feed horn to increase C / N ratio and reduce the spill over loss of the energy of signals receiving from two satellites, and to provide a sufficient rejection for preventing interference coming from the other satellite.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Satellite-tracking millimeter-wave reflector antenna system for mobile satellite-tracking
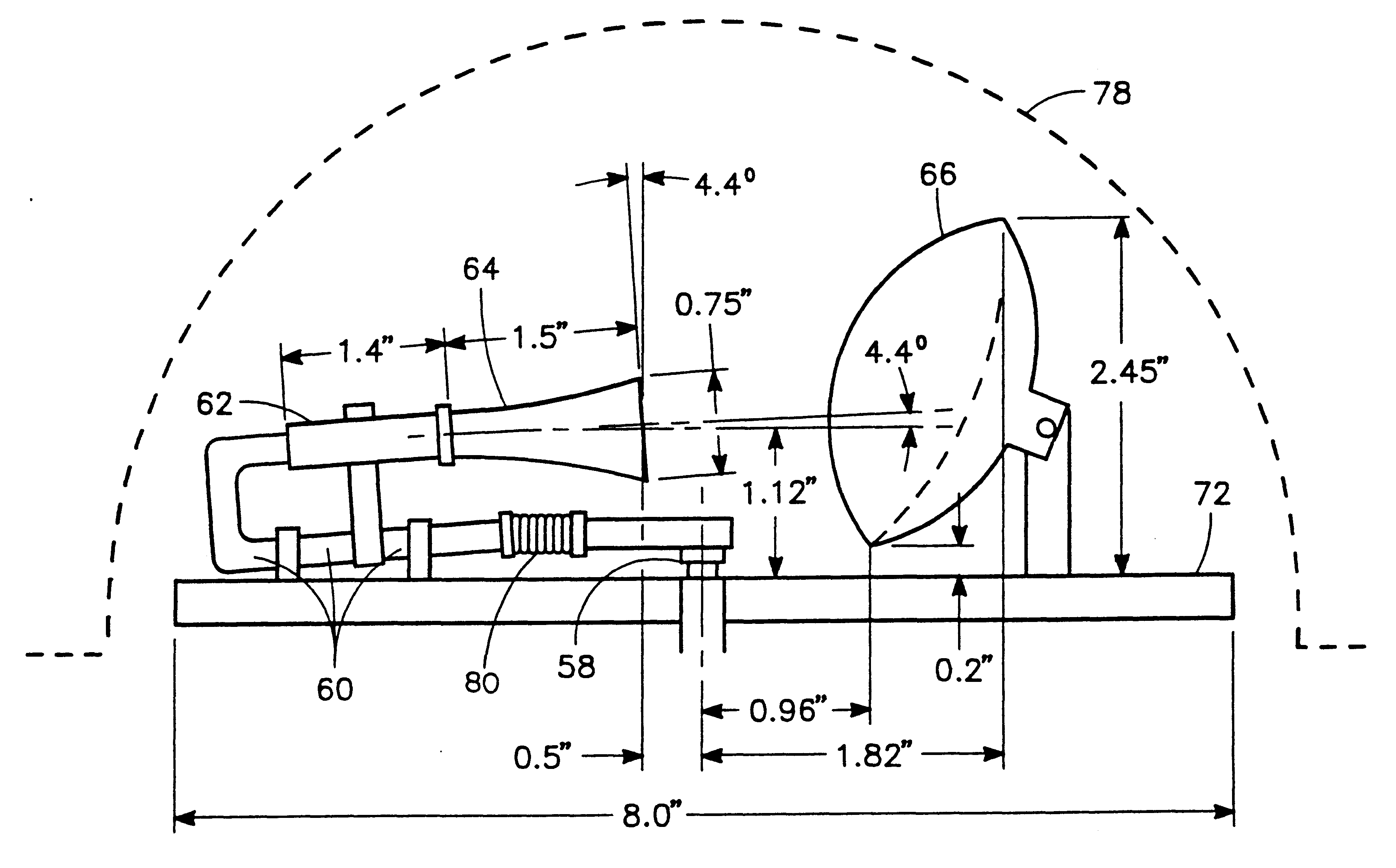
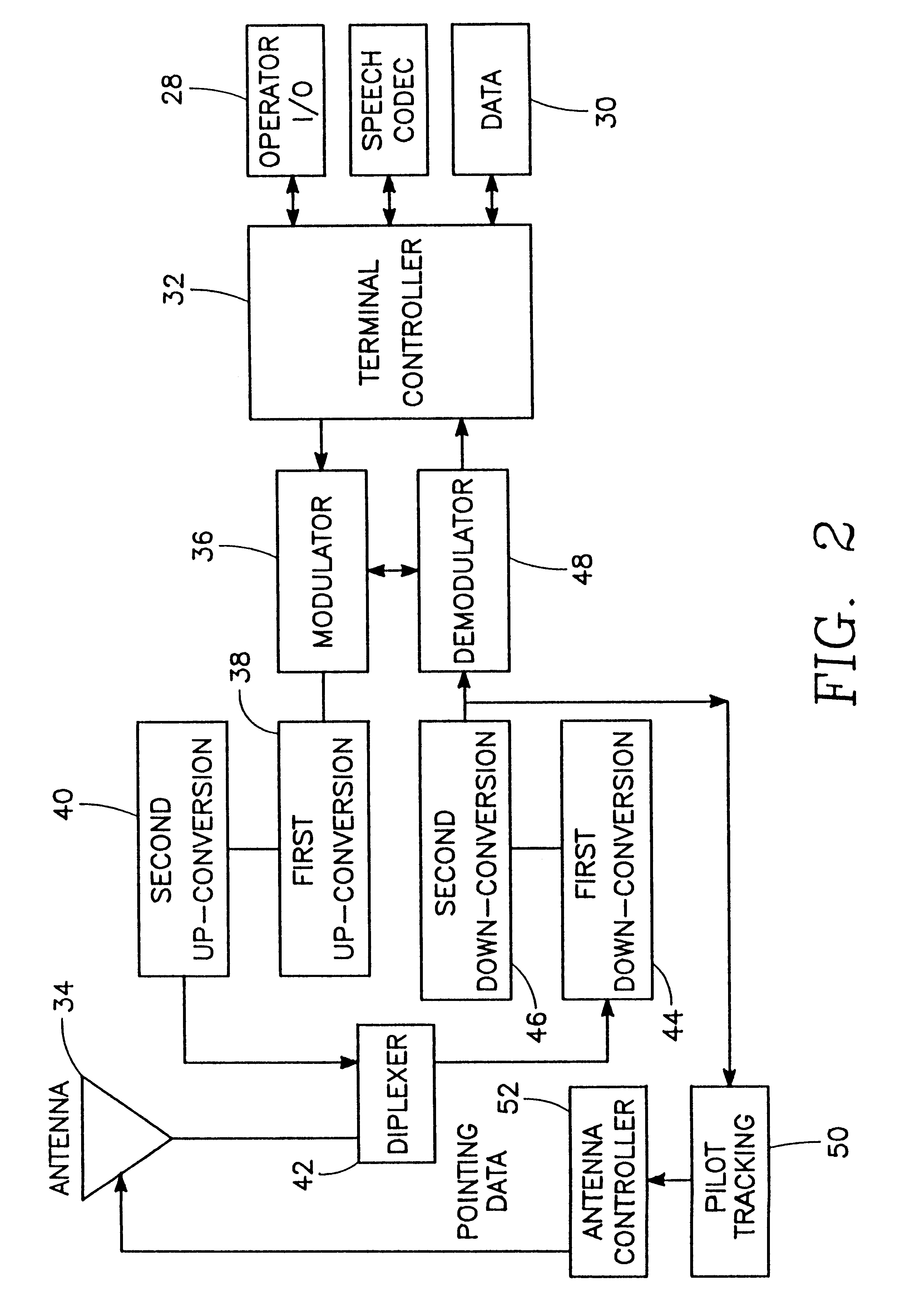
A miniature dual-band two-way mobile satellite-tracking antenna system mounted on a movable vehicle includes a miniature parabolic reflector dish having an elliptical aperture with major and minor elliptical axes aligned horizontally and vertically, respectively, to maximize azimuthal directionality and minimize elevational directionality to an extent corresponding to expected pitch excursions of the movable ground vehicle. A feed-horn has a back end and an open front end facing the reflector dish and has vertical side walls opening out from the back end to the front end at a lesser horn angle and horizontal top and bottom walls opening out from the back end to the front end at a greater horn angle. An RF circuit couples two different signal bands between the feed-horn and the user. An antenna attitude controller maintains an antenna azimuth direction relative to the satellite by rotating it in azimuth in response to sensed yaw motions of the movable ground vehicle so as to compensate for the yaw motions to within a pointing error angle. The controller sinusoidally dithers the antenna through a small azimuth dither angle greater than the pointing error angle while sensing a signal from the satellite received at the reflector dish, and deduces the pointing angle error from dither-induced fluctuations in the received signal.
Owner:NASA
Electronically scanned antenna
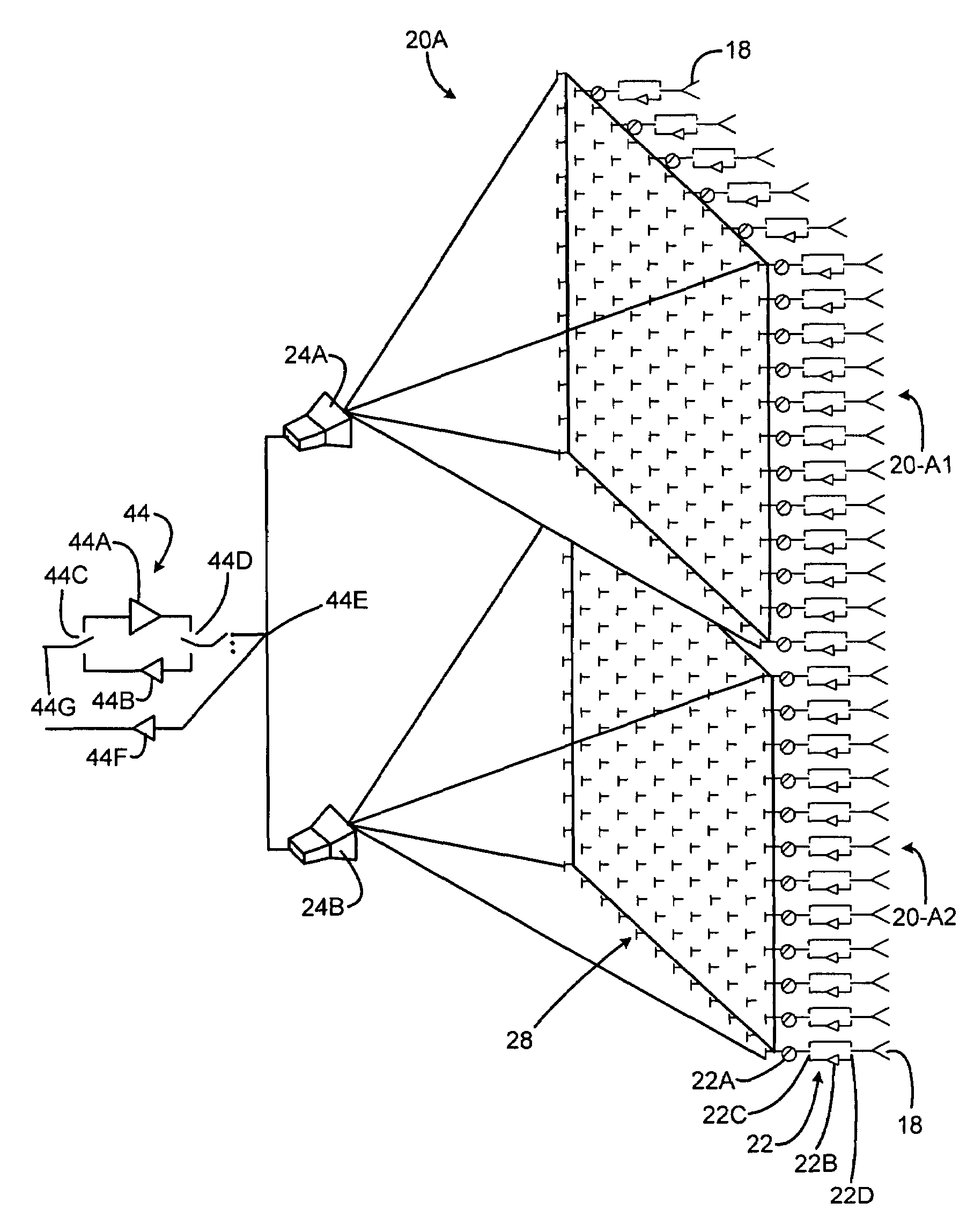
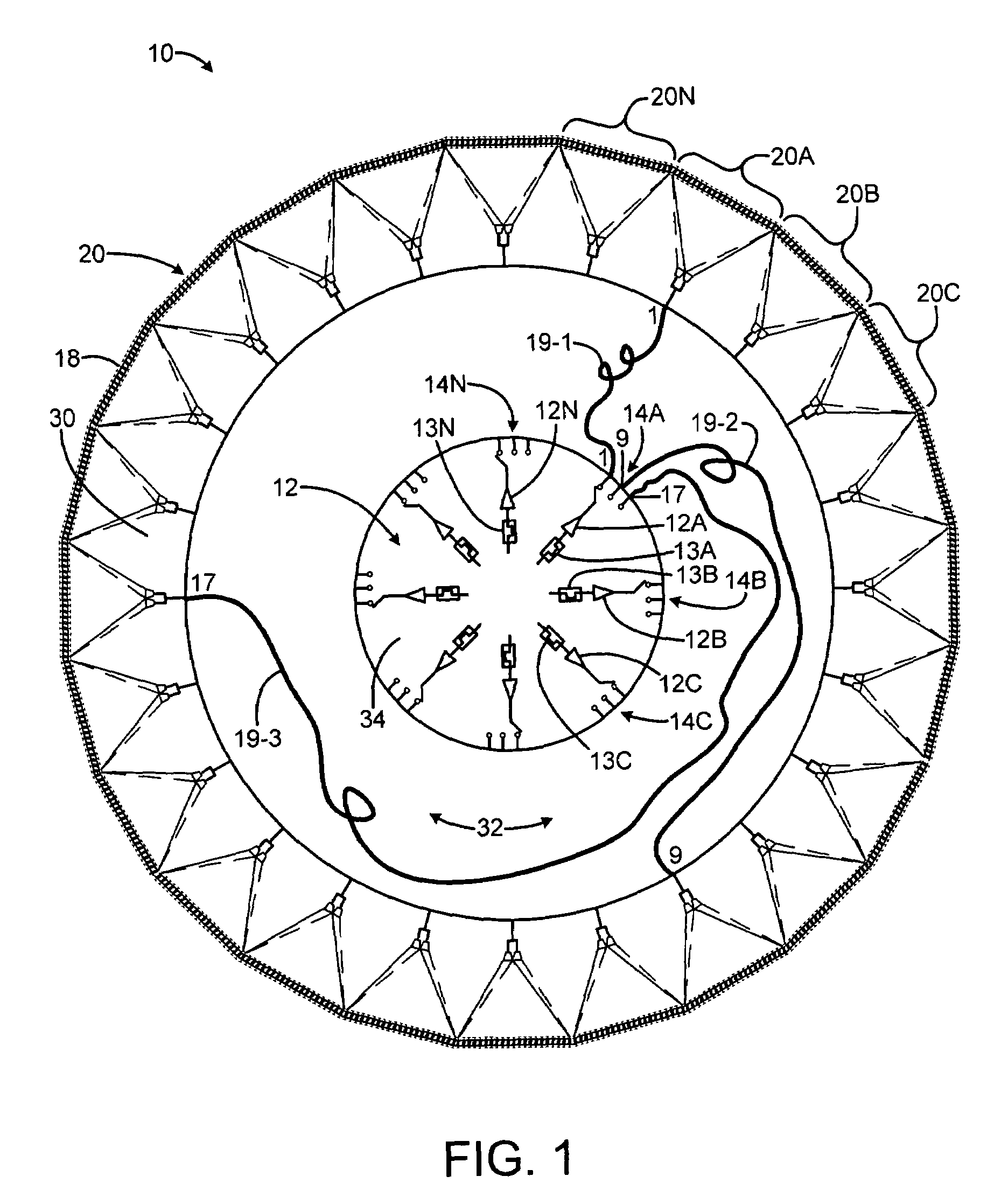
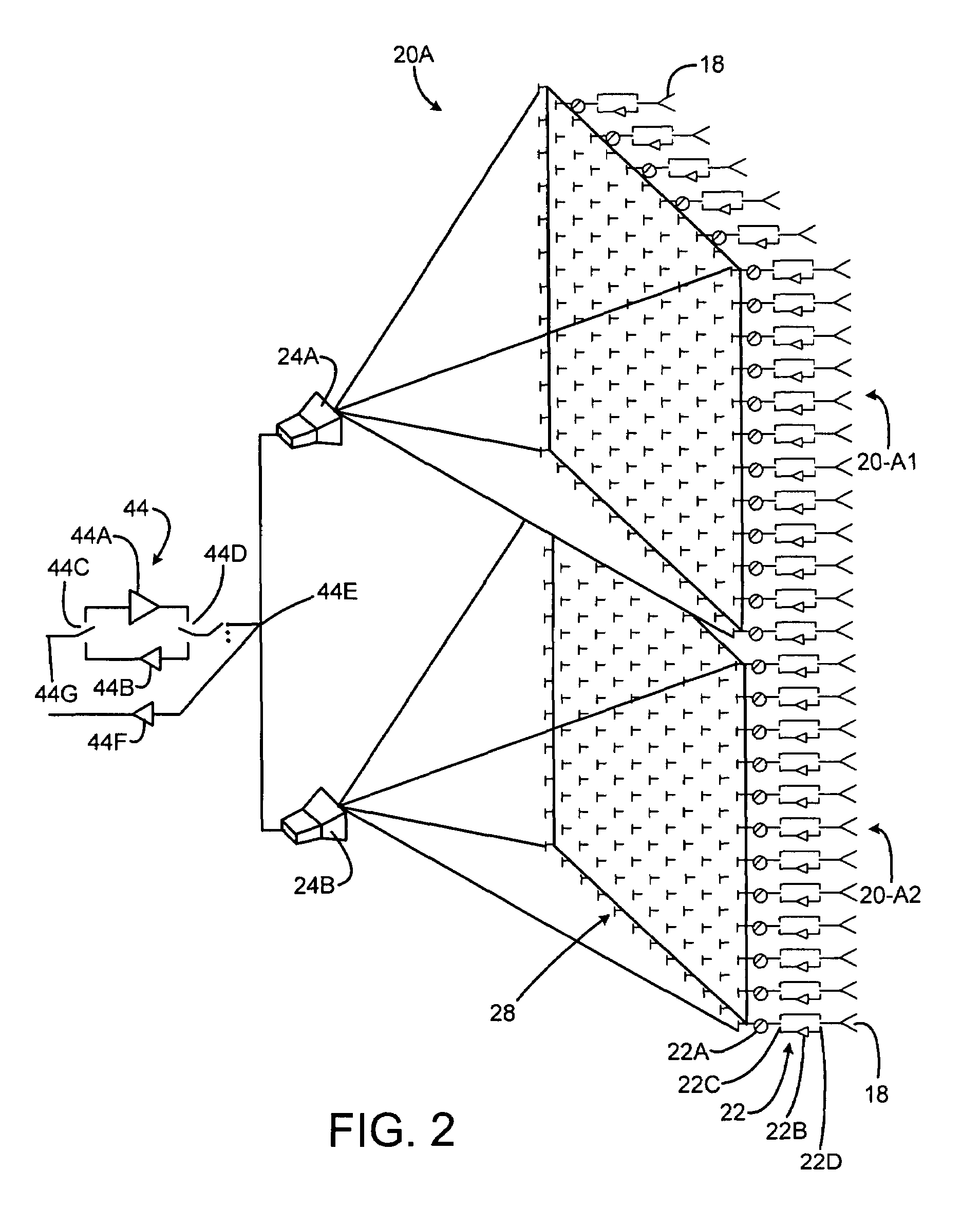
An electronically scanned antenna may include a plurality of space-fed, contiguous subarrays arranged in an annular region, each subarray including an inner set of radiating elements facing inwardly, an outer-facing set of radiating elements, and a feed system for illuminating the inner set of radiating elements. A plurality of RF amplifiers are coupled through a commutation switch matrix to selected ones of the subarray feed horn systems to illuminate a desired sector with RF energy.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com