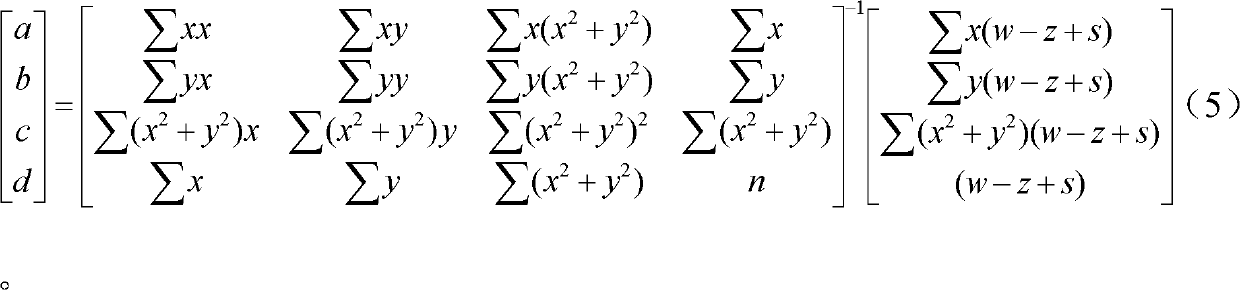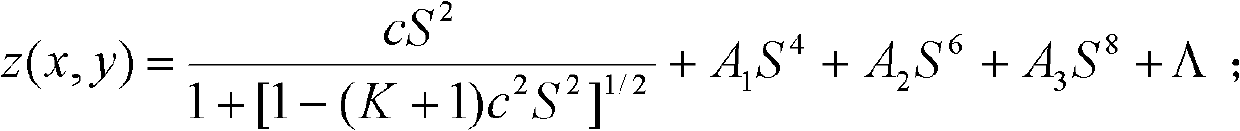Patents
Literature
607 results about "Spherical wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
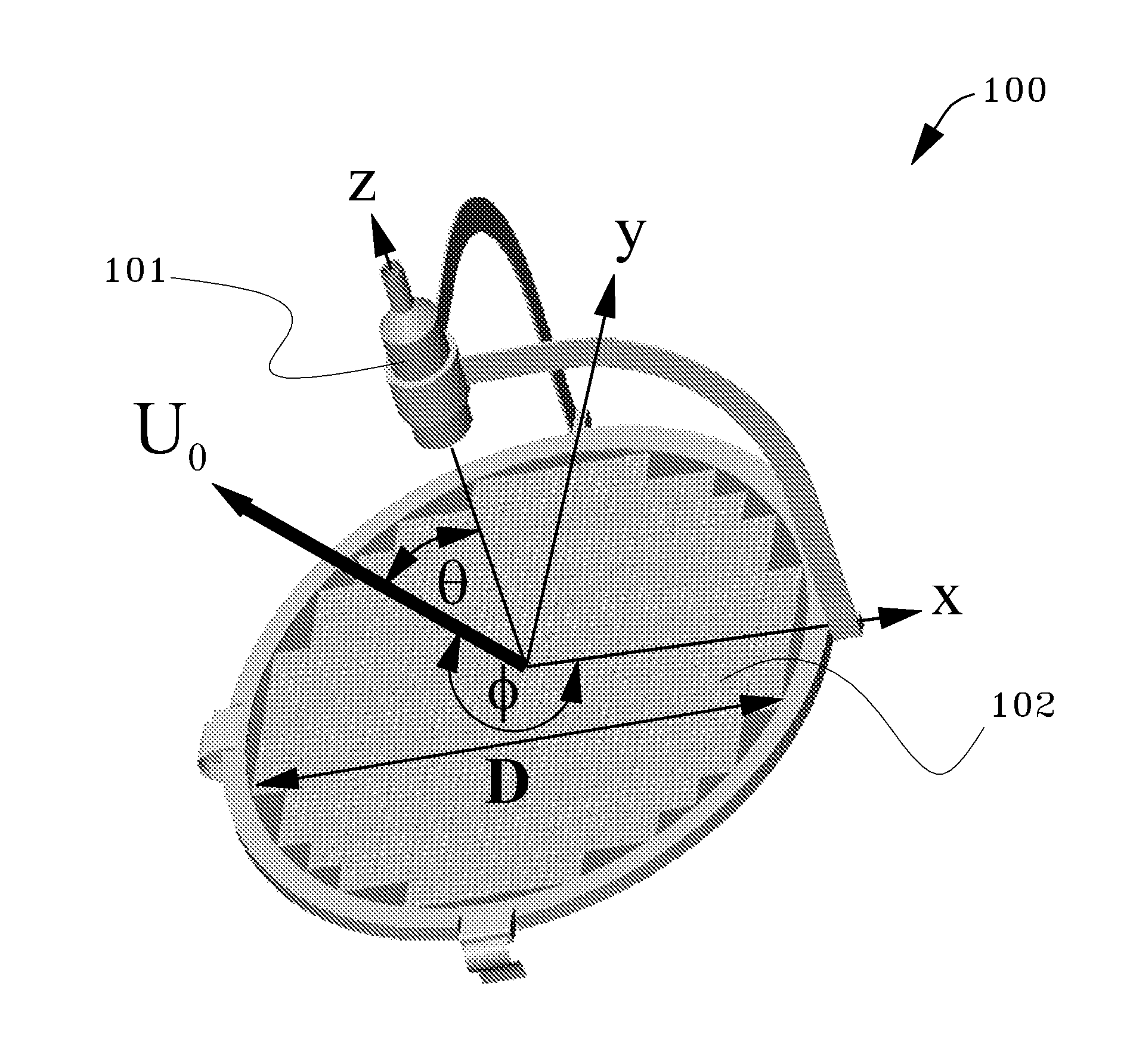
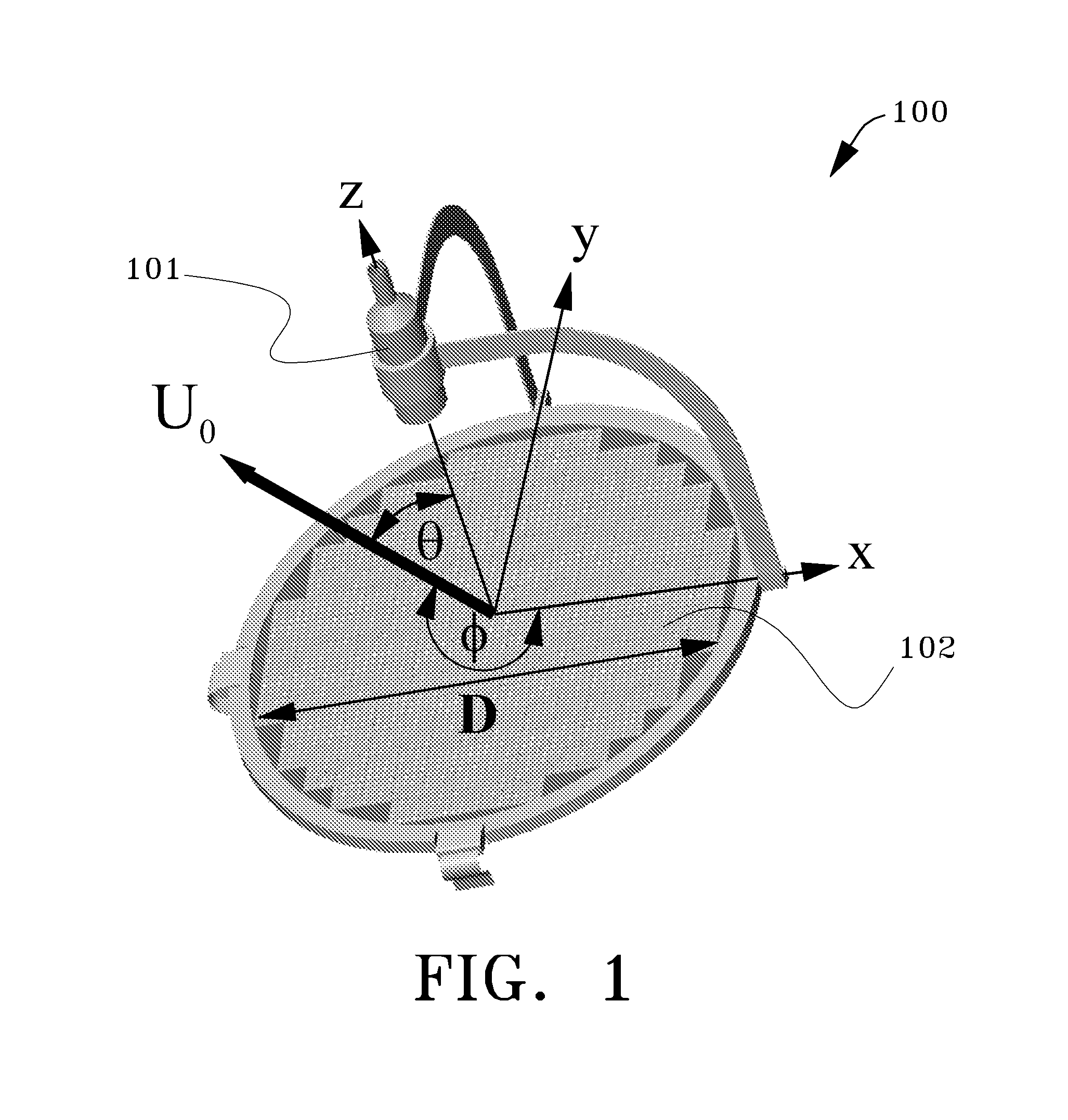
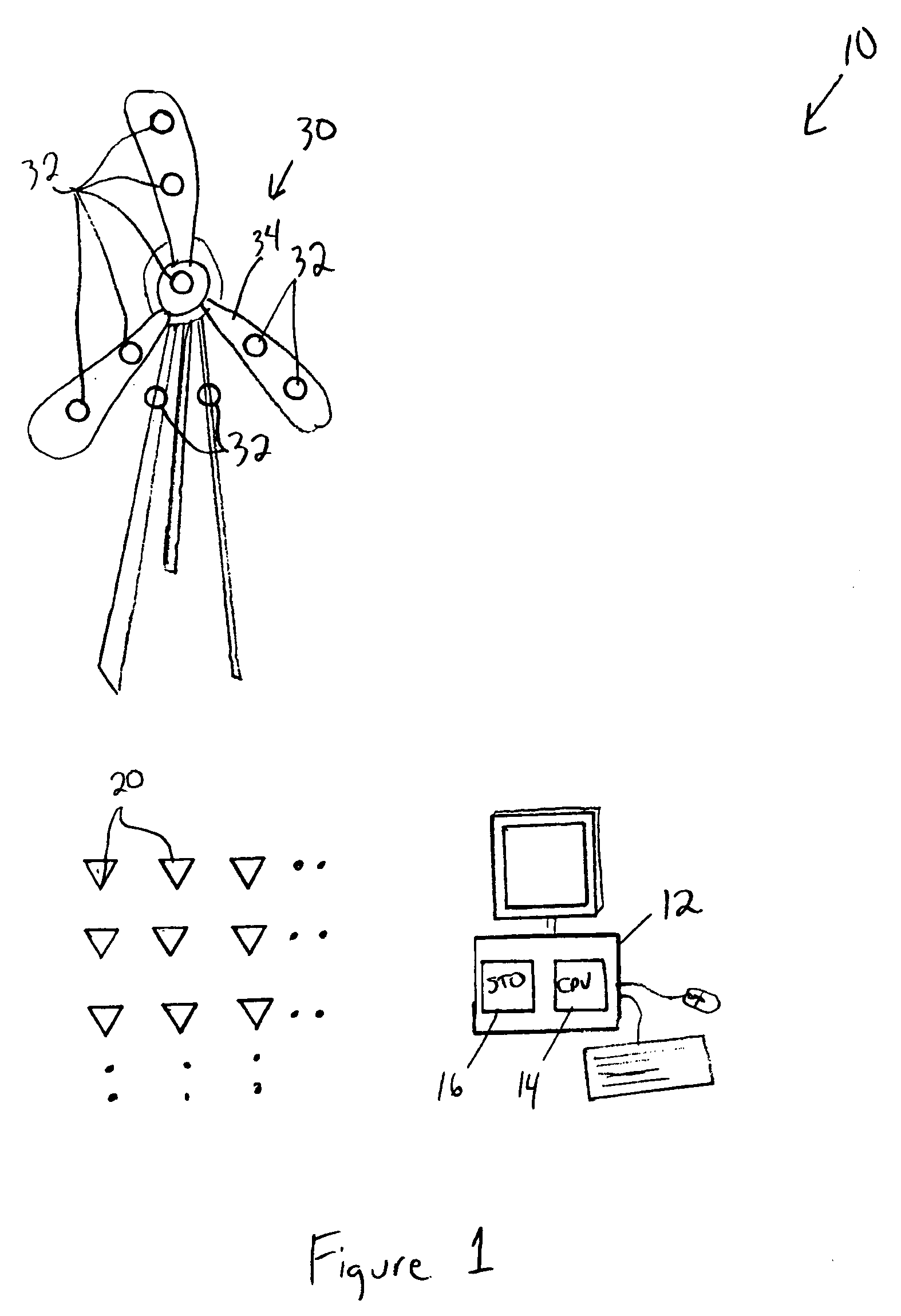
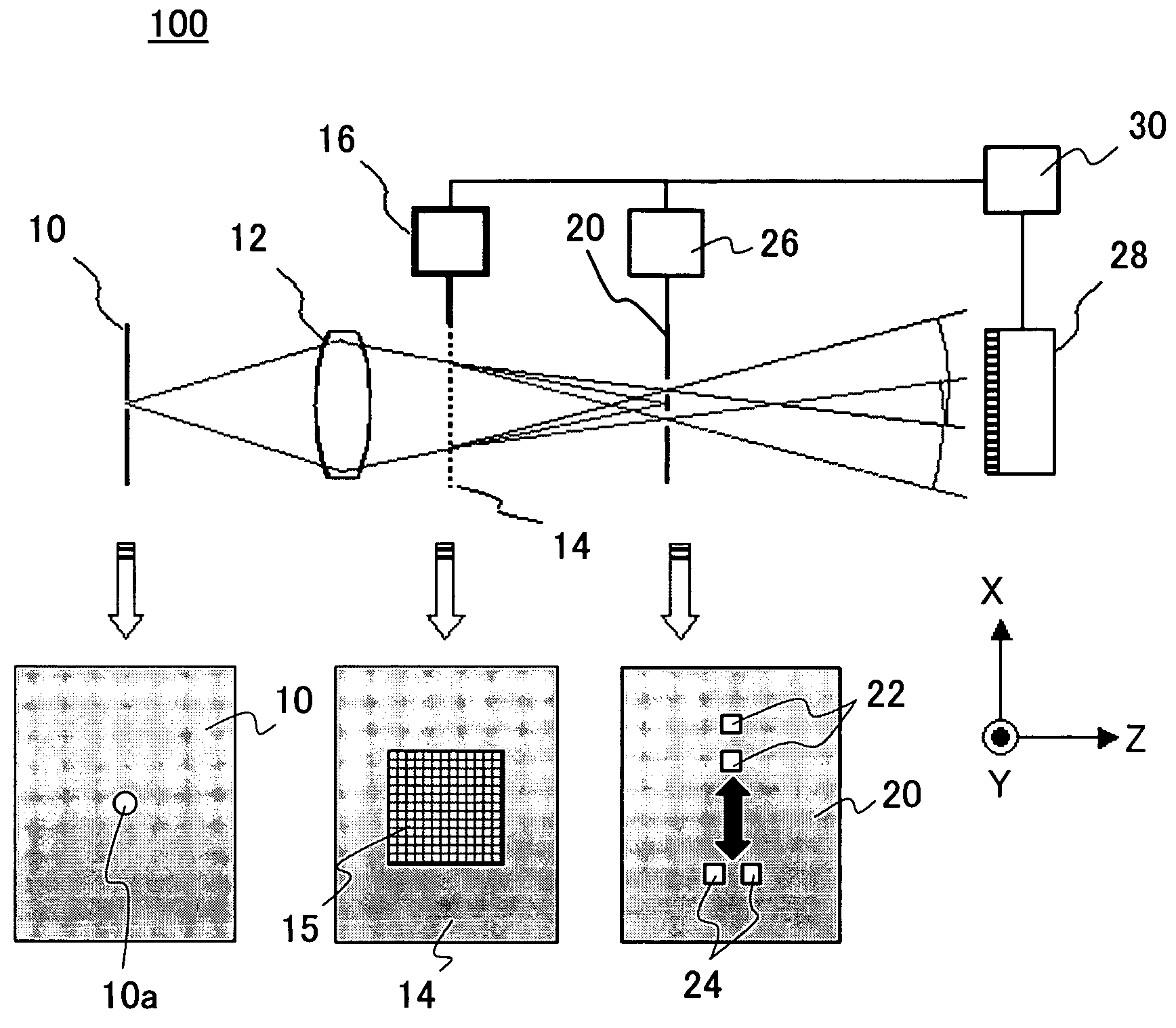
Such waves are generated by a point source, and they make possible sharp signals whose form is altered only by a decrease in amplitude as r increases (see an illustration of a spherical wave on the top right). Such waves exist only in cases of space with odd dimensions.
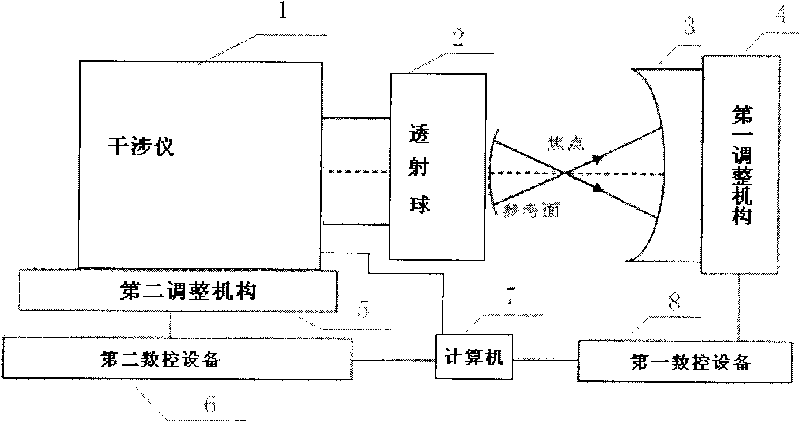
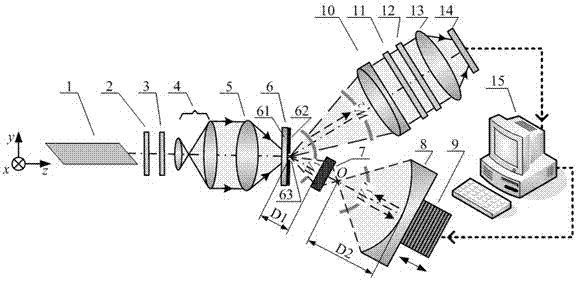
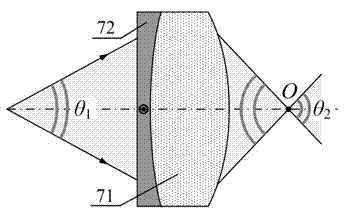
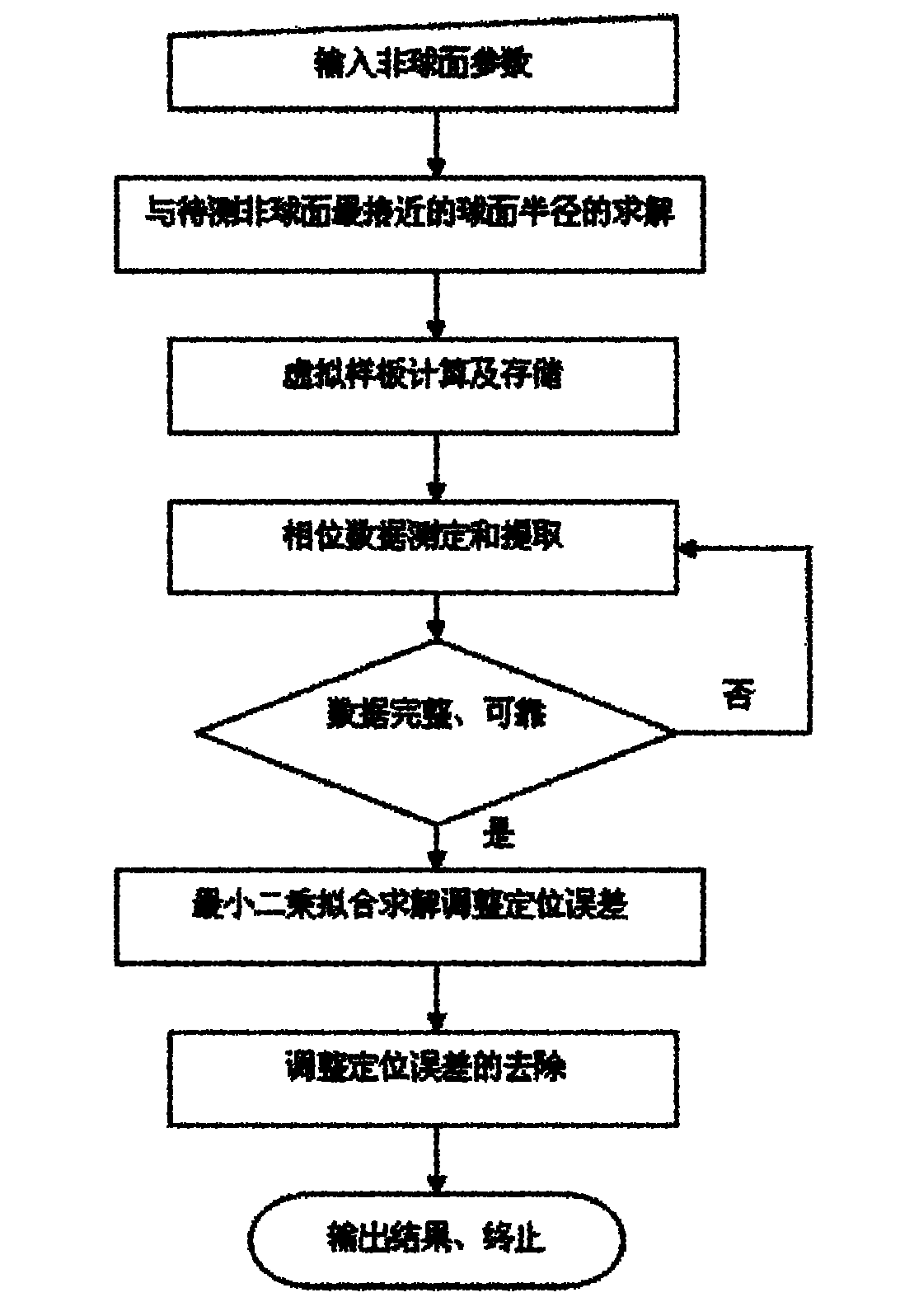
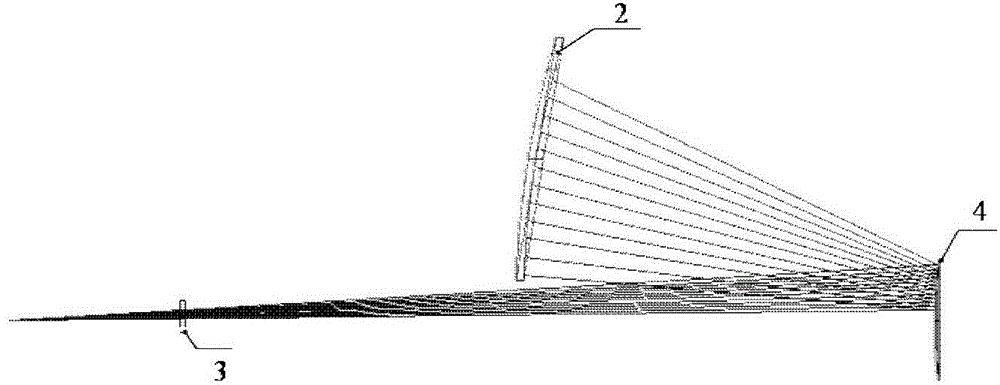
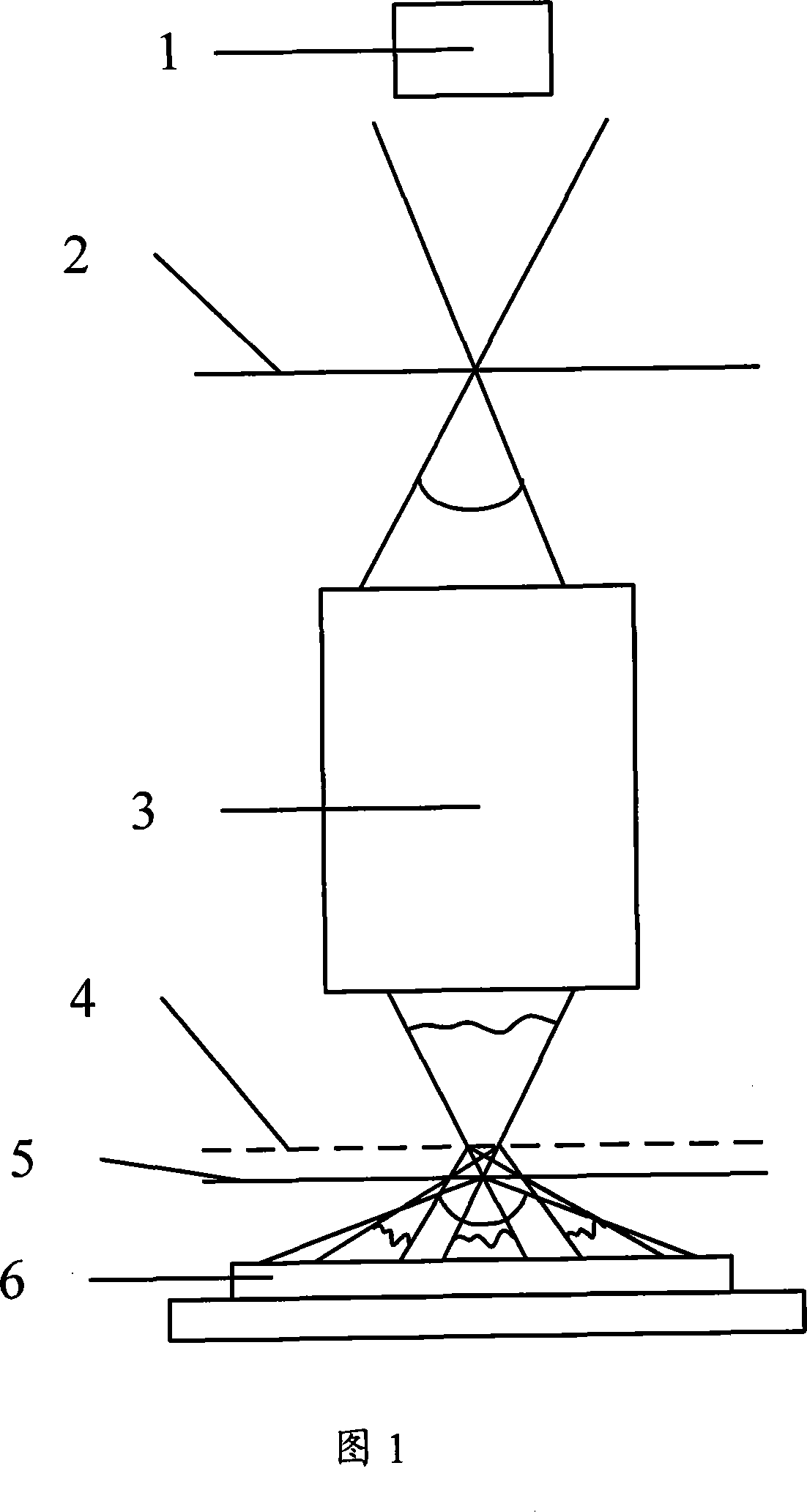
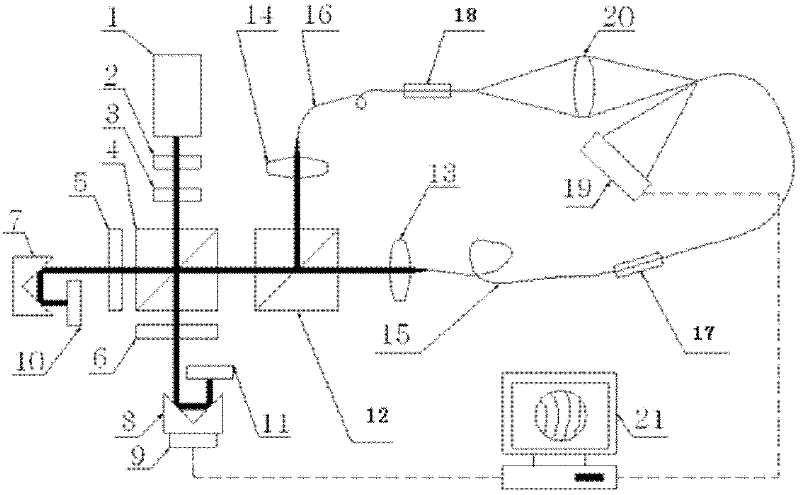
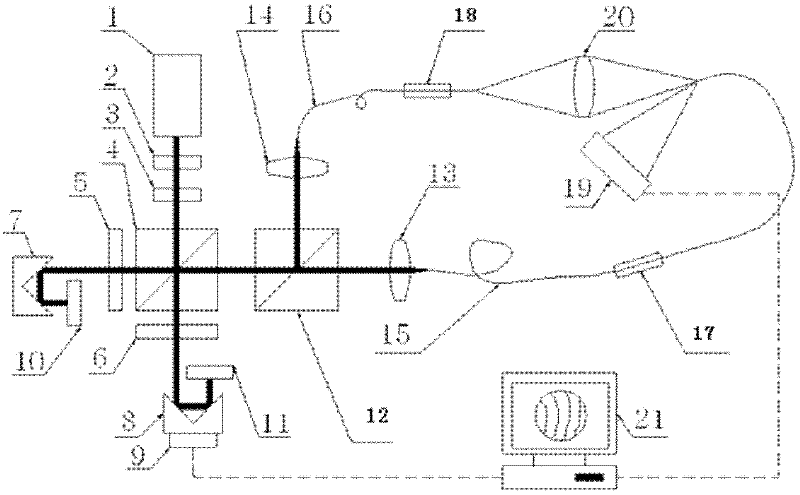
Device for detecting surface shape of optical aspheric surface by sub-aperture stitching interferometer
InactiveCN101709955AWiden horizontallyExpand the scope ofUsing optical meansNumerical controlFace shape
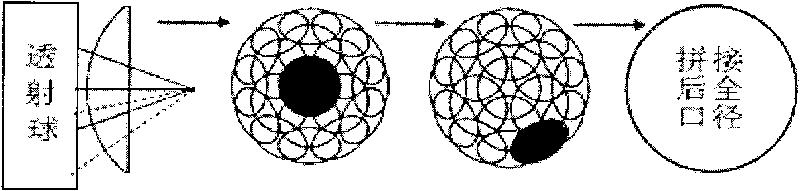
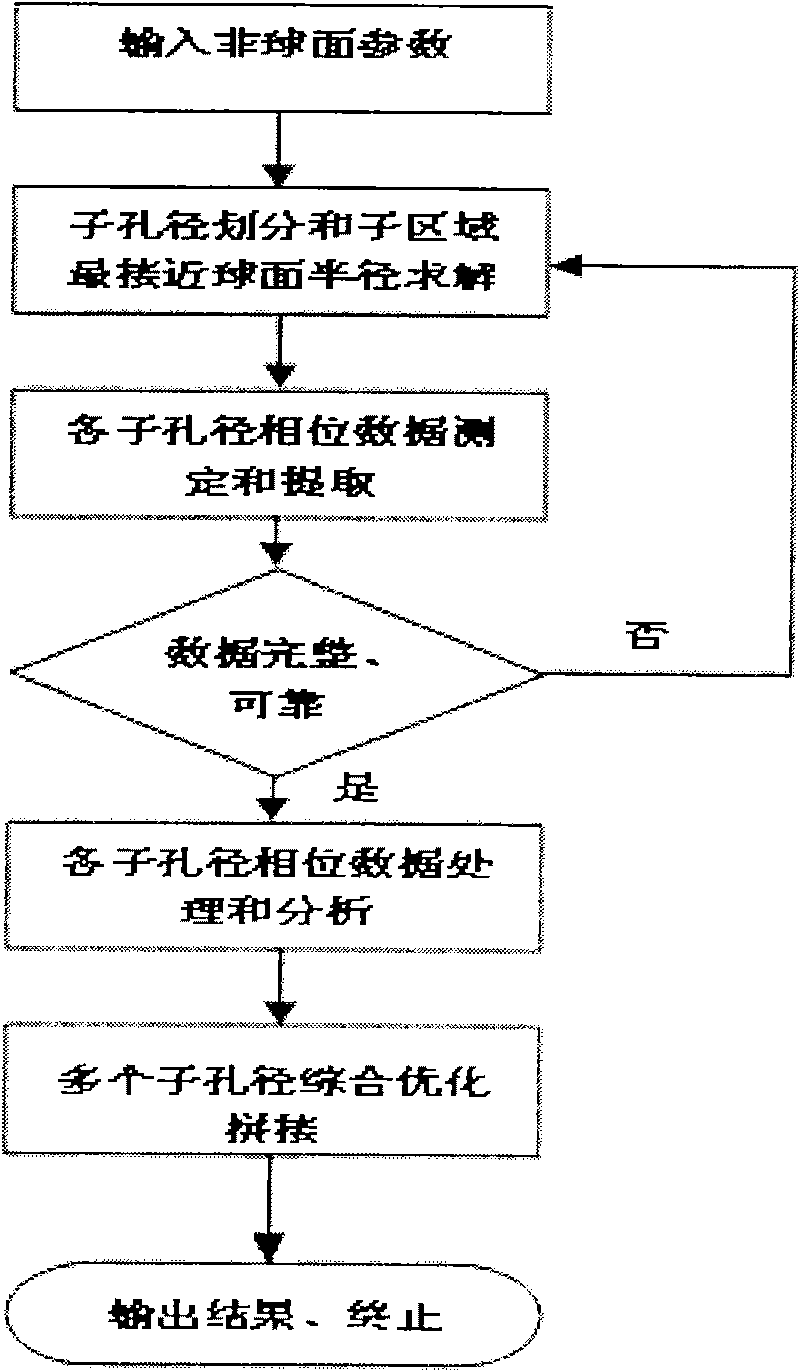
The invention relates to a device for detecting a surface shape of an optical aspheric surface by a sub-aperture stitching interferometer, which comprises an interferometer, a transmission sphere, an adjusting mechanism, a numerical control device and a computer, wherein parallel light emitted by the interferometer is changed into a standard spherical wave through the transmission sphere; the computer controls the action of the adjusting mechanism by the numerical control device to adjust the relative position of the interferometer and an aspheric surface to be detected so that the standard spherical wave is incided to each sub-aperture of the detected optical aspheric surface sequentially and returns to the interferometer; and the computer extracts phase distribution data of each sub-aperture measured by the interferometer for analysis and processing, and the error distribution of the surface shape of a full aperture of the detected optical aspheric surface is obtained by a stitching algorithm. The device broadens horizontal and vertical dynamic range tested by the interferometer, can detect surface shapes of large-aperture concave and convex aspheric surfaces and an off-axis aspheric surface in high resolution and high precision without other auxiliary optical elements, and has low testing cost and short construction period.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
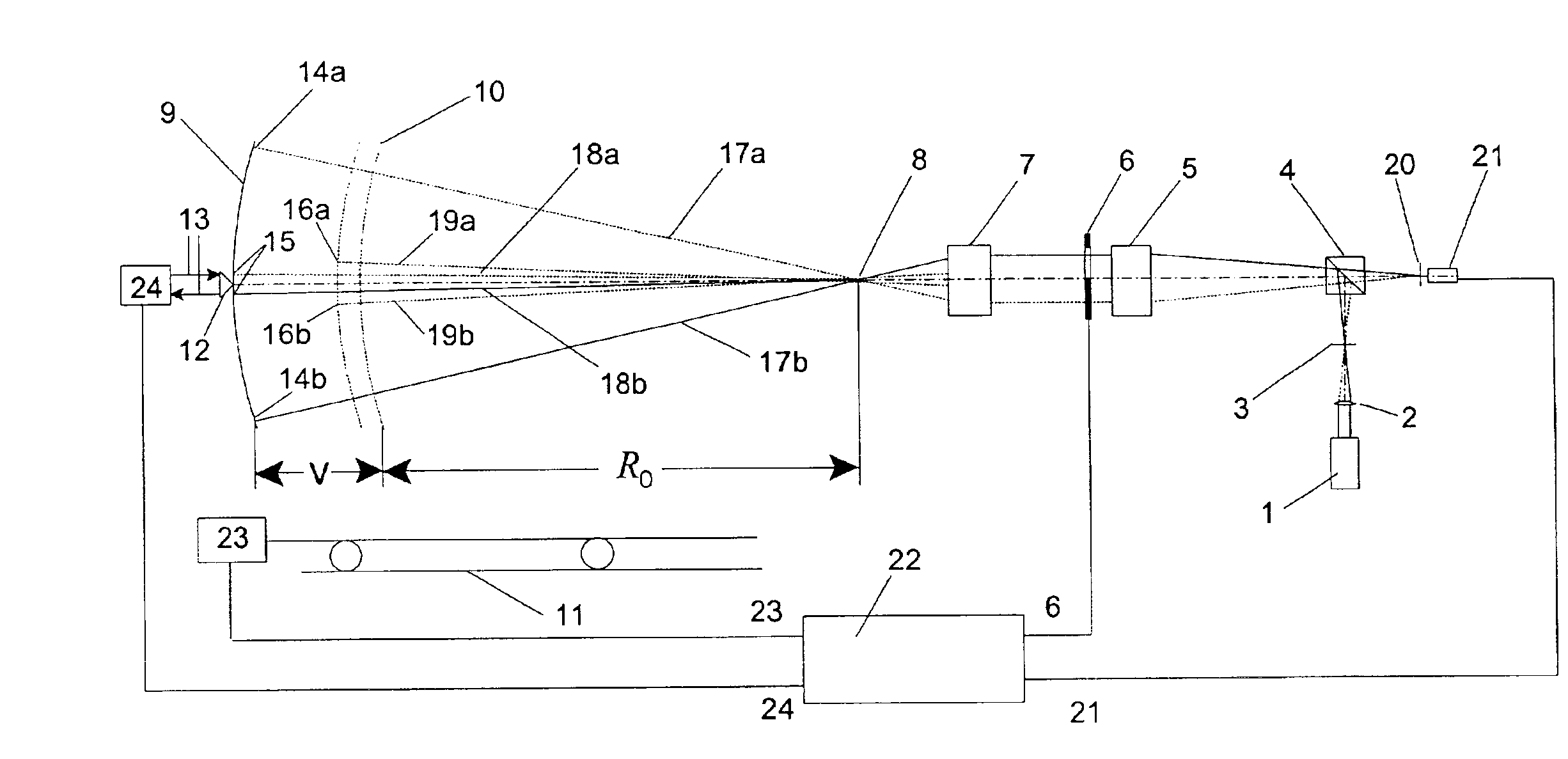
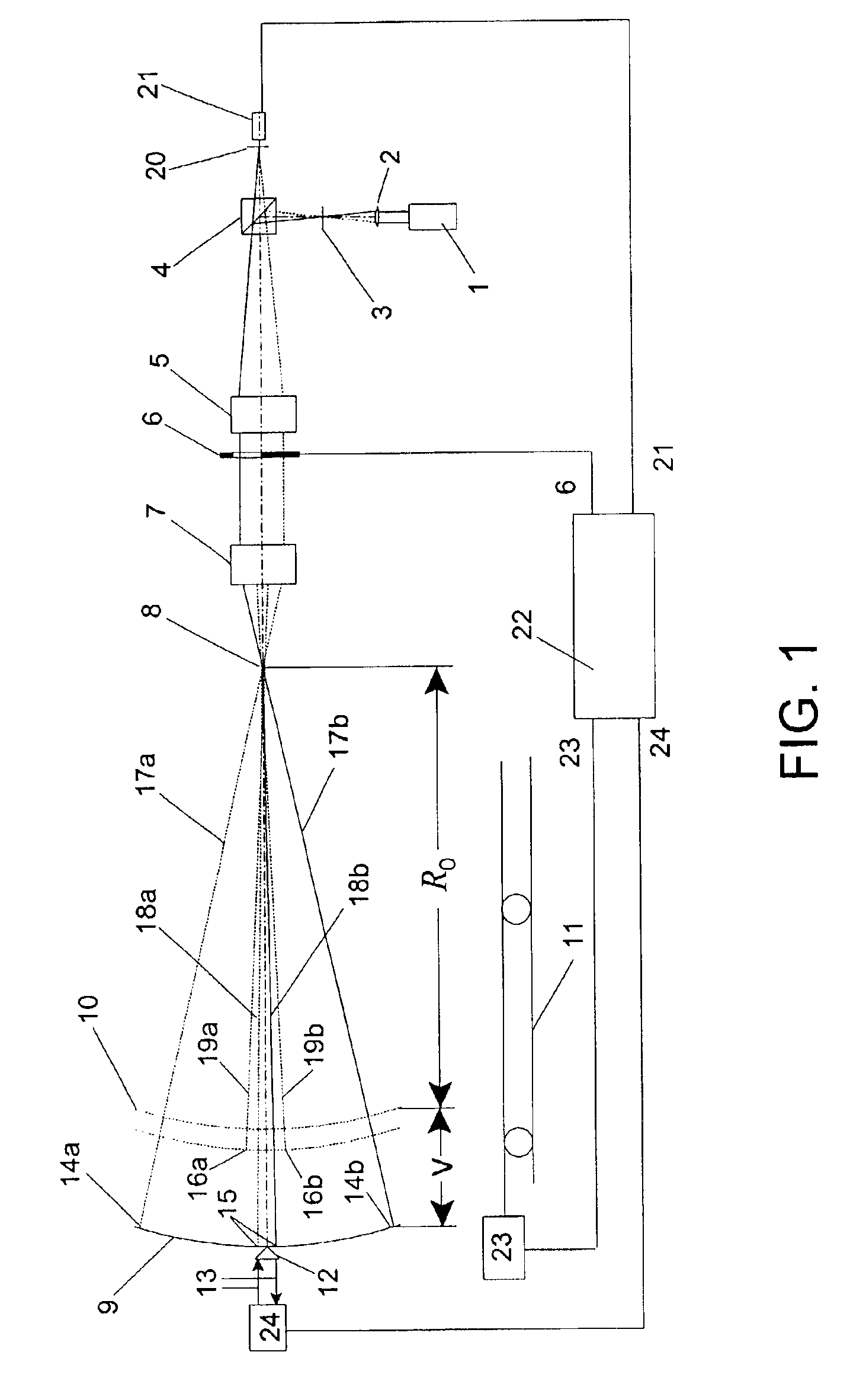
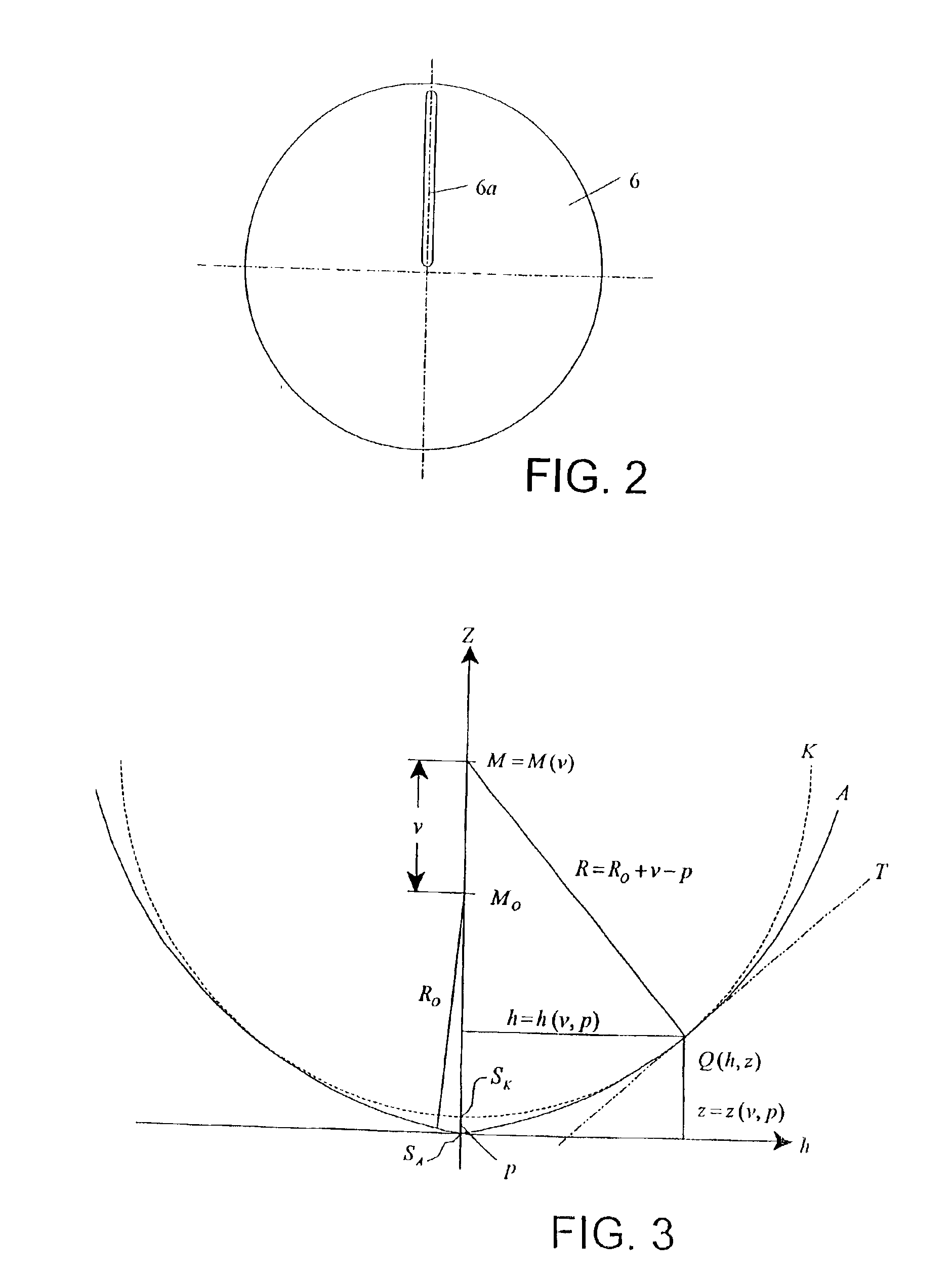
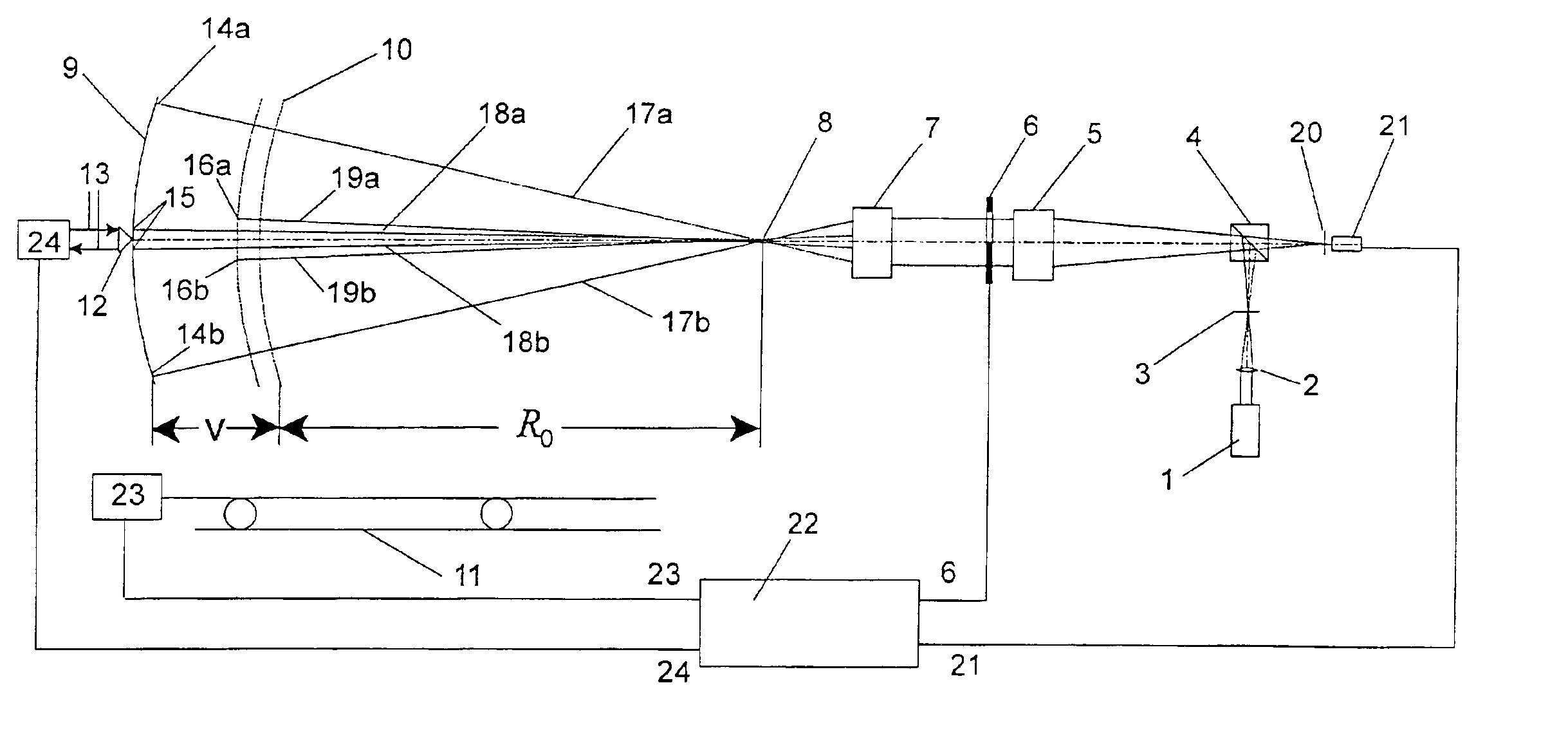
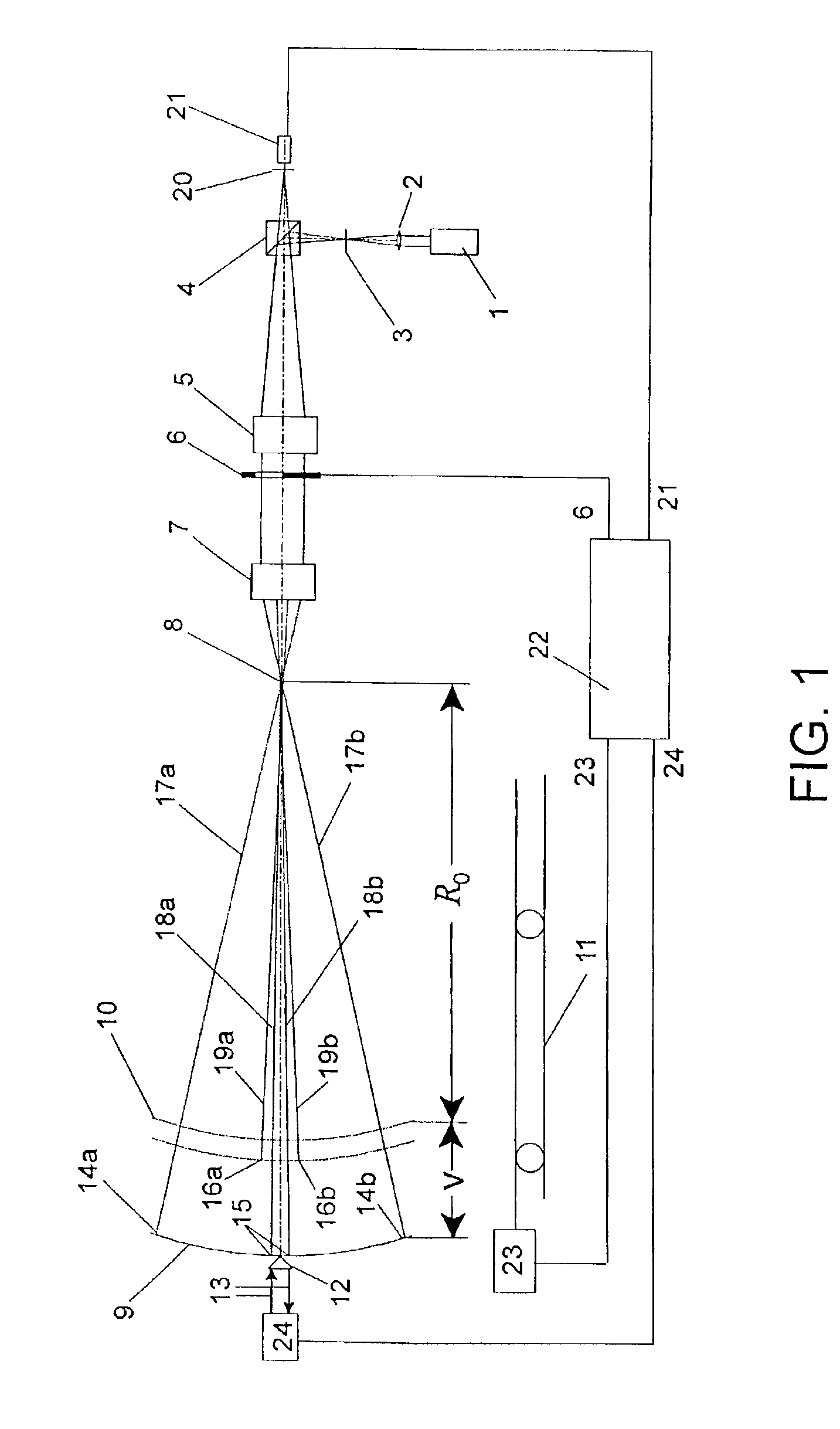
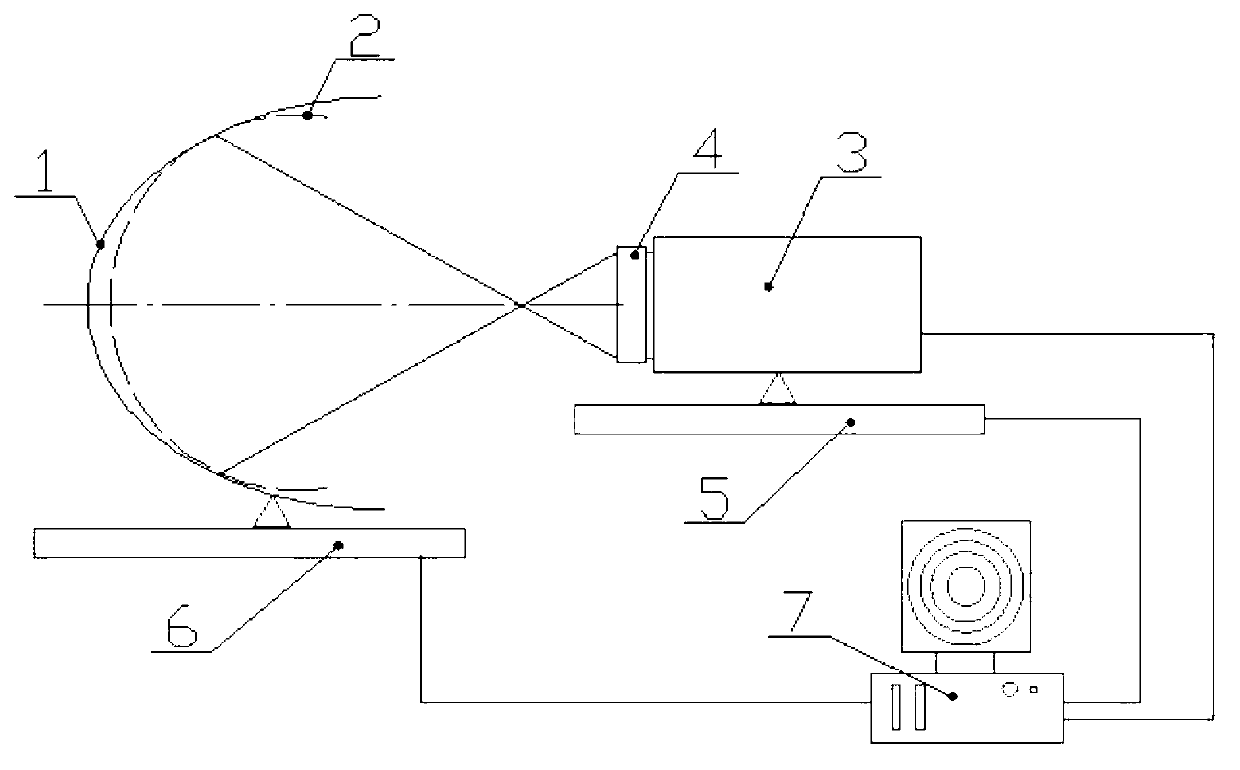
Scanning interferometer for aspheric surfaces and wavefronts
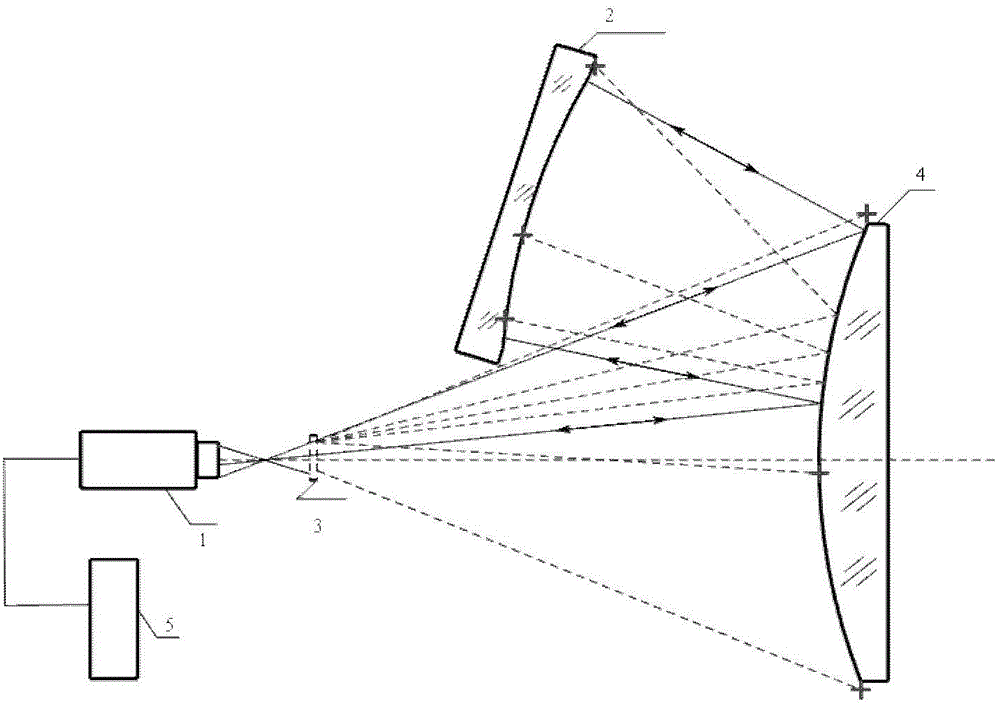
Interferometric scanning method(s) and apparatus for measuring rotationally and non-rotationally symmetric test optics either having aspherical surfaces or that produce aspherical wavefronts. A spherical or partial spherical wavefront is generated from a known origin along an optical axis. The test optic is aligned with respect the optical axis and selectively moved along it relative to the known origin so that the spherical wavefront intersects the test optic at the apex of the aspherical surface and at radial positions where the spherical wavefront and the aspheric surface intersect at points of common tangency. An axial distance, ν, and optical path length, p, are interferometrically measured as the test optic is axially scanned by the spherical wavefront where ν is the distance by which the test optic is moved with respect to the origin and p is the optical path length difference between the apex of an aspherical surface associated with the test optic and the apex of the circles of curvature that intersect the aspherical surface at the common points of tangency. Coordinates of the aspherical surface are calculated wherever the circles of curvature have intersected the aspherical surface and in correspondence with the interferometrically measured distances, ν and p. Afterwards, the shape of the aspheric surface is calculated. Where the test optic comprises a refracting optic a known spherical reflecting surface is provided upstream of the refracting optic for movement along the optical axis and a known wavefront is made to transit the refracting optic, reflects from the known spherical surface, again transits the refracting optic traveling towards the known origin after which the interferogram is formed. In another aspect of the invention, a spherical reference surface is provided to form a Fizeau that is used to generate phase information for measuring spheres, mild aspheres, and multiple mild aspheres.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
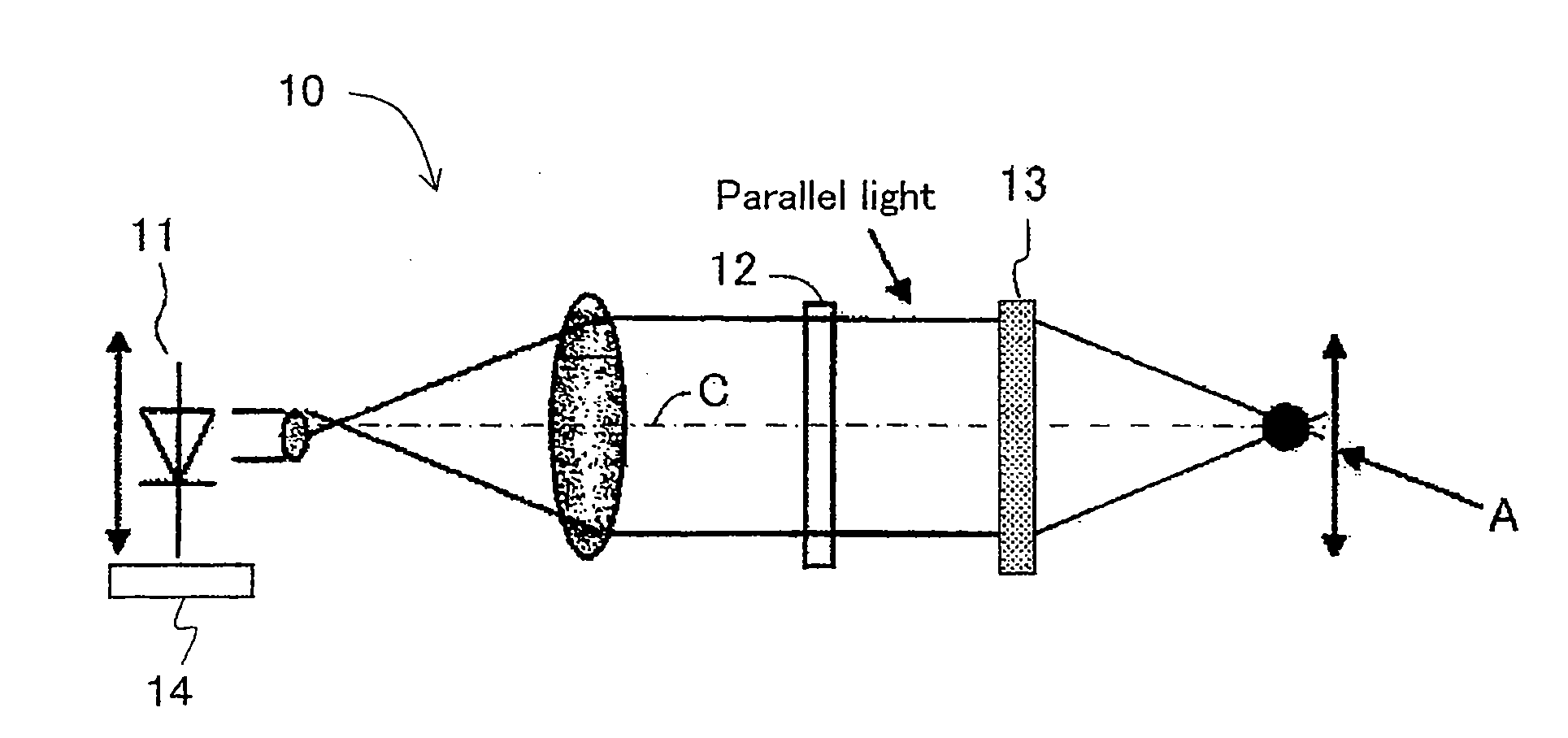
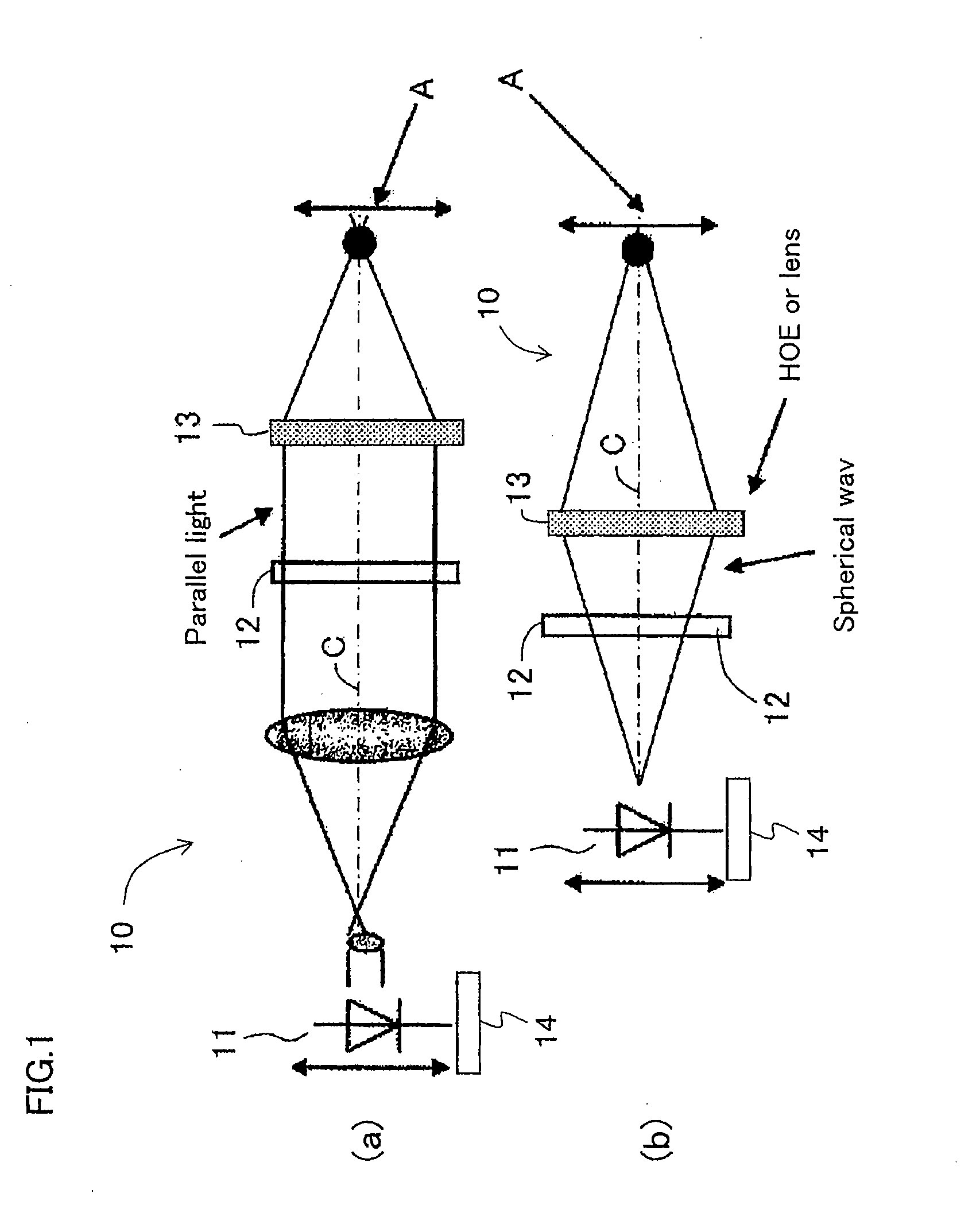
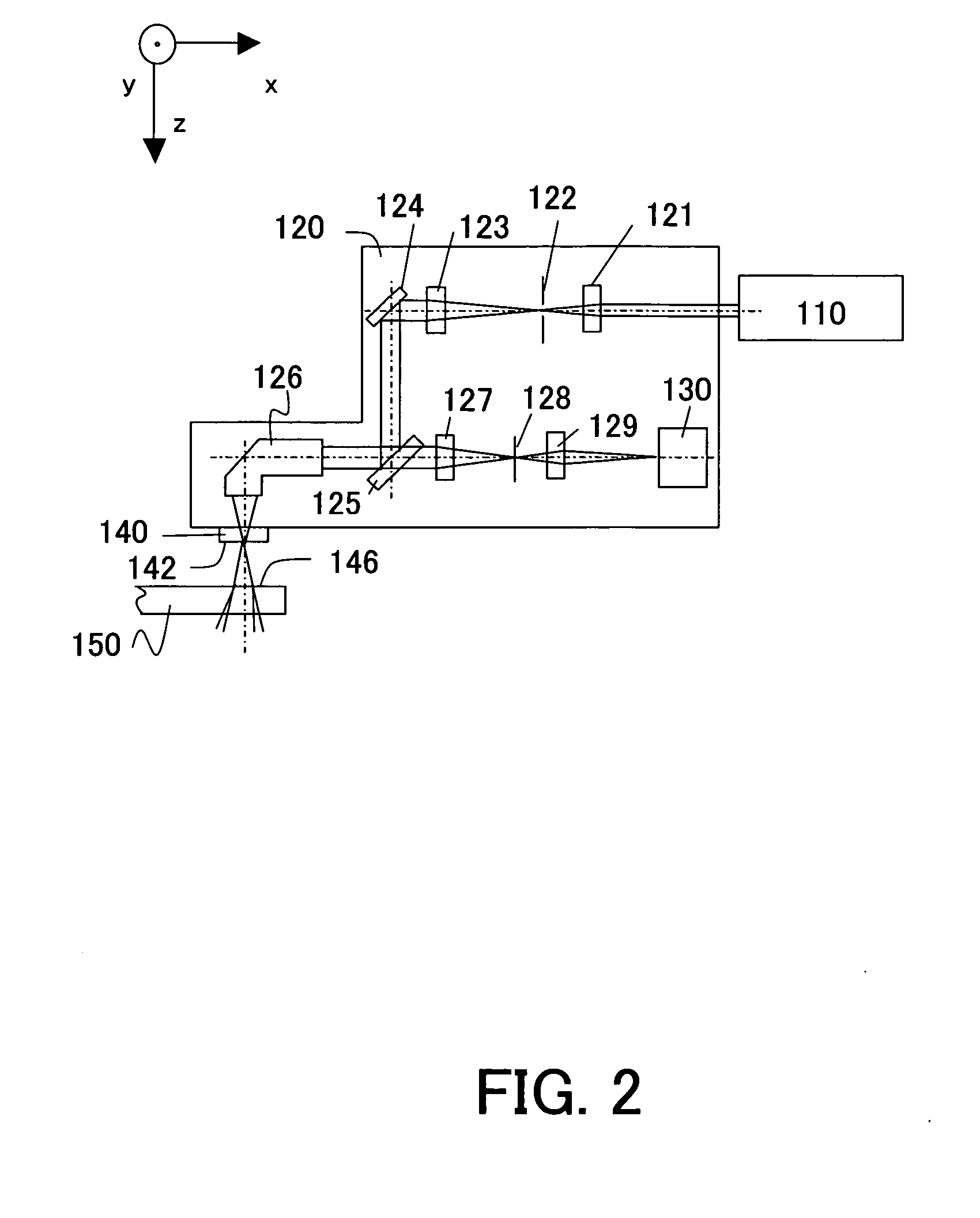
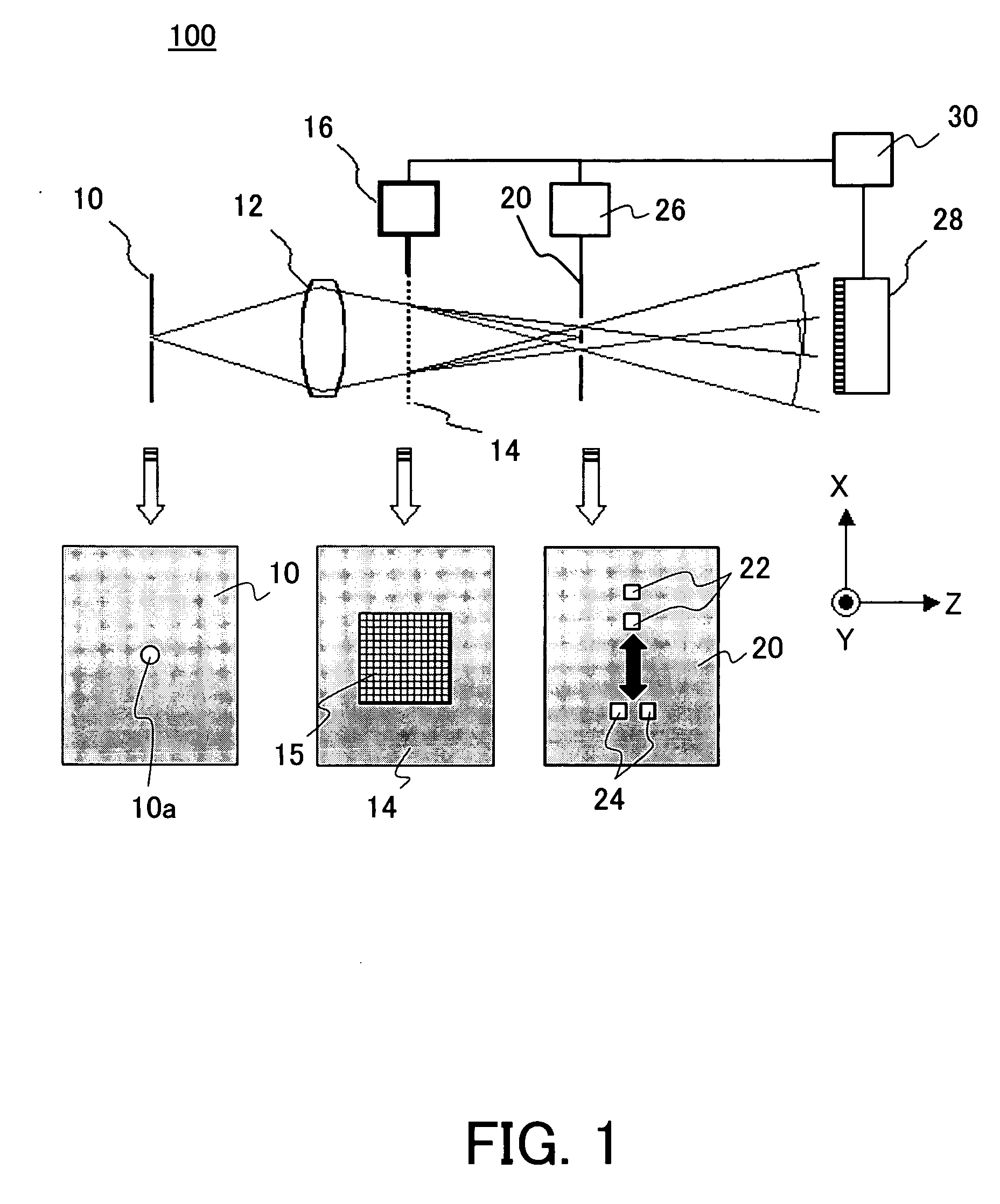
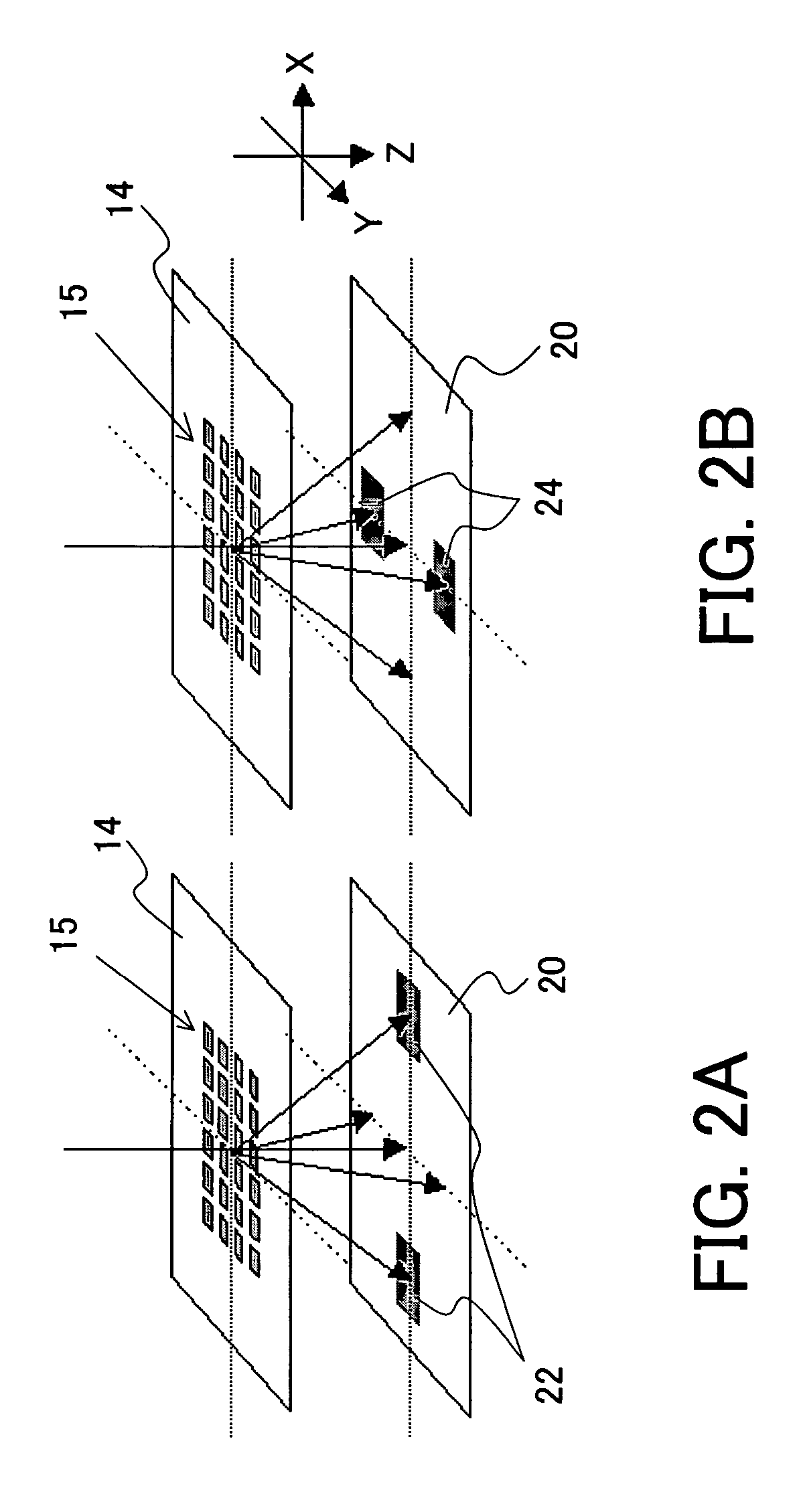
Image Display Unit and Electronic Glasses
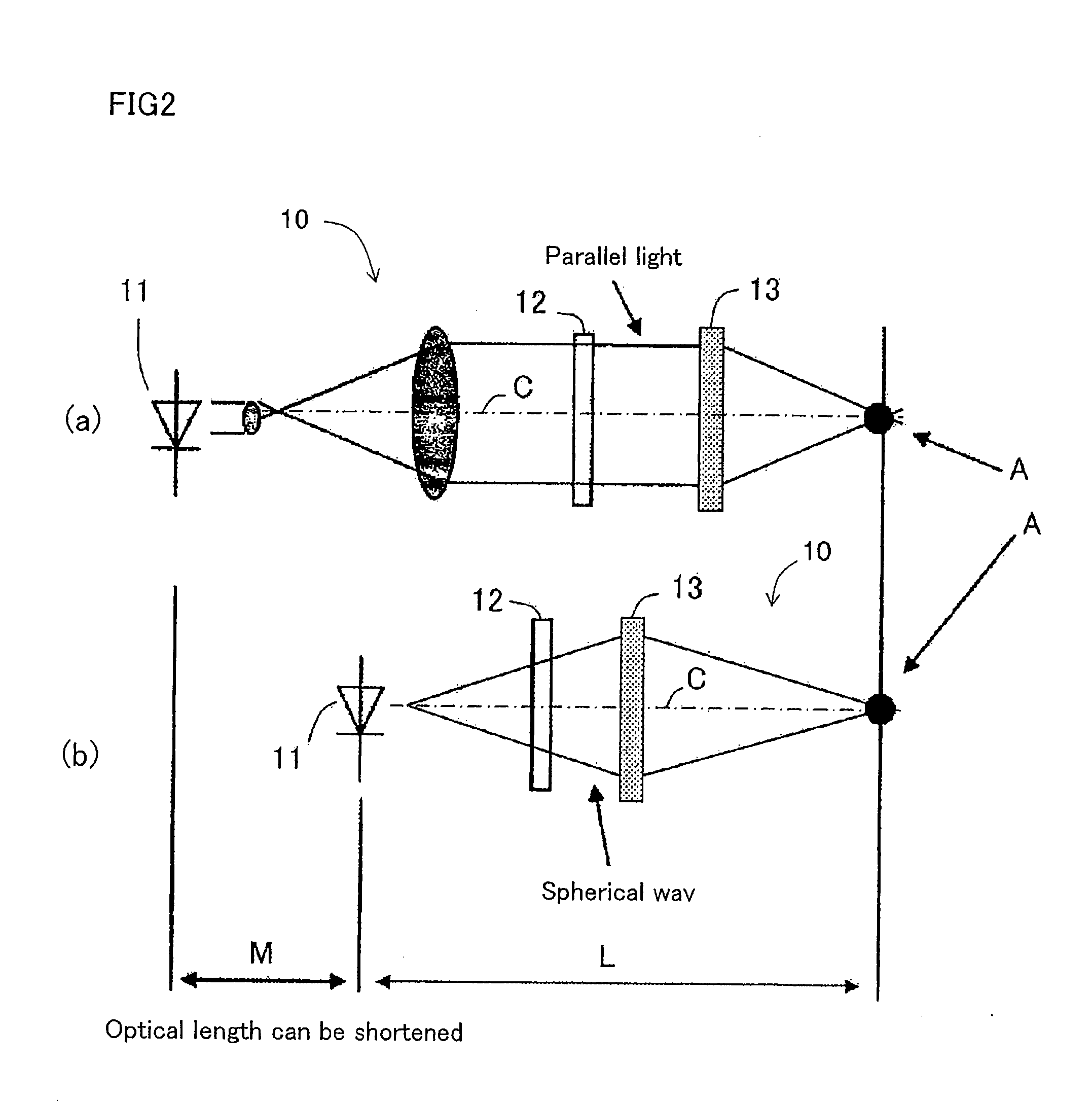
With a simple structure, the light focusing convergence point for the Maxwellian view and the position of the pupil can be easily and quickly matched to each other in a steady manner and thus it is possible to obtain a sharp image by the Maxwellian view. When the position of the point light source 11 is automatically adjusted by the light source driving apparatus 14 using the parallel light as shown in Portion (a) of FIG. 1 as the display image light incident on the convex lens 13 (or HOE) or using the spherical wave light instead of the parallel light as shown in Portion (b) of FIG. 1, the position of the light focusing convergence point A for the Maxwellian view with respect to the position of the pupil is easily and quickly adjusted in a steady manner. Further, as with an optical path length L of the entire optical system, as shown in Portion (b) of FIG. 2, which uses the spherical wave light, it is possible to shorten the entire optical system by distance M when compared to the case, shown in Portion (a) of FIG. 2, which uses the parallel light.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Tracking in Haptic Systems
ActiveUS20190196578A1Reduce noiseFast response timeInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementTransducerFull matrix
Described herein are techniques for tracking objects (including human body parts such as a hand), namely: 1) two-state transducer interpolation in acoustic phased-arrays; 2) modulation techniques in acoustic phased-arrays; 3) fast acoustic full matrix capture during haptic effects; 4) time-of-flight depth sensor fusion system; 5) phase modulated spherical wave-fronts in acoustic phased-arrays; 6) long wavelength phase modulation of acoustic field for location and tracking; and 7) camera calibration through ultrasonic range sensing.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Cellular reflectarray antenna and method of making same
InactiveUS7791552B1Quick installationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsLongitudeLength wave
A method of manufacturing a cellular reflectarray antenna arranged in an m by n matrix of radiating elements for communication with a satellite includes steps of determining a delay φm,n for each of said m by n matrix of elements of said cellular reflectarray antenna using sub-steps of: determining the longitude and latitude of operation, determining elevation and azimuth angles of the reflectarray with respect to the satellite and converting theta0 (θ0) and phi0 (φ0), determining Δβm,n, the pointing vector correction, for a given inter-element spacing and wavelength, determining Δφm,n, the spherical wave front correction factor, for a given radius from the central element and / or from measured data from the feed horn; and, determining a delay φm,n for each of said m by n matrix of elements as a function of Δβm,n and Δφm,n..
Owner:NASA
Farfield analysis of noise sources
ActiveUS20060080418A1Quick estimateVibration measurement in fluidSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementObject basedSound sources
An algorithm diagnoses the noise source strength distribution on an arbitrarily shaped object based on acoustic pressures measured in the far field, known as FANS. FANS enable one to acquire a quick estimate of the acoustic pressure at locations that are off limit to traditional measurement microphones. Generally, in the method of the present invention, the noise source is modeled in terms a plurality of virtual spherical wave sources distributed on an auxiliary surface conformal to a source boundary from the inside, but not on the source boundary itself. Sound is then measured at a plurality of measurement points external to the source boundary. The sound field is reconstructed on the source boundary surface itself.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna integrated with plane feed source
ActiveCN103490156AAvoid lossReduce thicknessRadiating elements structural formsPolarised antenna unit combinationsCommunications systemMiniaturization
The invention discloses a millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna integrated with a plane feed source. The millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna is of a layered structure and is sequentially provided with a polarization grid, a reflective array and the plane feed source from top to bottom. On the basis of a plane substrate integration waveguide structure, a substrate integration waveguide gap array antenna is used as the feed source for conducting feed on folding-type reflection, phase compensation is obtained on a reflection face, spherical waves are converted to plane waves, and therefore the antenna which is high in gain and efficiency and stable in beam pointing is realized. Under the Q-LINKPAN application background and directing at the development demands of a plane-integration and miniaturized long-distance wireless communication system, the low-section antenna which is high in gain and efficiency and capable of being integrated with a plane millimeter wave circuit is realized, the millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna has the advantages of being simple in structure, compact in size and low in cost, and the requirements for plane circuit integration are met.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Fringe contrast ratio-adjustable large-numerical value bore diameter point-diffraction interference device and method
ActiveCN102829733ASimplify adjustment difficultyLower performance requirementsUsing optical meansImaging lensReference wave
The invention discloses a fringe contrast ratio-adjustable large-numerical value bore diameter point-diffraction interference device and a fringe contrast ratio-adjustable large-numerical value bore diameter point-diffraction interference method. A linear polarization laser generates a parallel light through a 1 / 2 wave plate, a first 1 / 4 wave plate and a collimating and beam expanding system, the parallel light is focused on an interference pinhole of a point-diffraction plate through a microobjective, a detection wave front W1 is focused at an O point after passing through a second 1 / 4 wave plate to obtain a spherical wave front W1', a reflected light wave reflected by a spherical surface to be detected passes through the second 1 / 4 wave plate again to obtain a circularly polarized light of which the rotation direction is opposite to a reference wave front W2, and is reflected through a metal reflecting film on the point-diffraction plate, the detection wave front W1 and the reference wave front W2 are converged to change into a plane wave through a collimating lens, an interference fringe is obtained on a detector through a third 1 / 4 wave plate, a polarization analyzer and an imaging lens, and the detector timely acquires a corresponding interference pattern. The device and method simplify the point-diffraction interference adjusting difficulty, and provide a feasible method for the high-precision detection of a large-numerical value bore diameter spherical surface, particularly of a low-reflectivity spherical surface.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for detecting nonzero digit compensation light-degree optical aspheric surface profile
InactiveCN101949691AExtend existing functionalityImprove resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisGreek letter epsilon
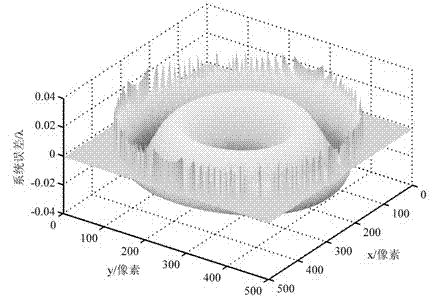
The invention relates to a method for detecting a nonzero digit compensation light-degree optical non-spherical profile. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating the value of z(x, y)-s(x, y, r), wherein z(x, y) is the rise distribution of an aspheric surface along the direction of an optical axis, and s(x, y, r) is the rise distribution of a spherical surface closest to the aspheric surface to be detected along the direction of the optical axis; converting emergent parallel light of an interferometer into standard spherical waves by utilizing a transmission ball and using the standard spherical waves as reference spherical waves; adjusting the position of the aspheric surface to be detected to ensure that the circle center of the spherical surface closest to the aspheric surface to be detected coincides with a focus point of converging the reference spherical waves; detecting phase distribution data of interference fringes formed by the optical waves reflected by the aspheric surface to be detected and the reference spherical waves by utilizing the interferometer; and rejecting the value of the z(x, y)-s(x, y, r) and an adjusting and positioning error epsilon (x, y) from the phase distribution data of the interference fringes to obtain the profile error distribution e(x, y) of the aspheric surface. The invention can realize the detection of large-caliber concave and convex light-degree aspheric surface profiles with high resolution and high precision and has the advantages of low detection cost and short detection cost.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Scanning interferometer for aspheric surfaces and wavefronts
ActiveUS6972849B2Reduce sensitivityRealize automatic adjustmentInterferometersUsing optical meansWavefrontPhase difference
Interferometric scanning method(s) and apparatus for measuring rotationally and non-rotationally symmetric test optics having spherical, mildly aspherical and multiple, mildly aspherical surfaces. At least a partial spherical wavefront is generated from a known origin along a scanning axis through the use of a spherical reference surface positioned along the scanning axis upstream of the known origin. A test optic is aligned with respect to the scanning axis and selectively moved along said scanning axis relative to the known origin so that the spherical wavefront intersects the test optic at the apex of the aspherical surface and at one or more radial positions where the spherical wavefront and the aspheric surface intersect at points of common tangency to generate interferograms containing phase information about the differences in optical path length between the center of the test optic and the one or more radial positions. The interferogram is imaged onto a detector to provide an electronic signal carrying the phase information. The axial distance, ν, by which said test optic is moved with respect to said origin is interferometrically measured and the optical path length differences, p, between the center of test optic and the one or more radial positions is calculated based on the phase differences contained in the electronic signal. The coordinates, z and h, of the aspherical surface are calculated wherever the circles of curvature have intersected the aspherical surface at common points of tangency and in correspondence with the interferometrically measured distance, ν and calculated optical path lengths, p. The shape of the aspheric surface is then determined based on the coordinate values and the optical path length differences.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Direct detection system for surface-shape errors in full-aperture optical aspheric surfaces
InactiveCN102997863ASimple structureReduce data processingUsing optical meansDimensional precisionNumerical control system
The invention relates to a direct detection system for surface-shape errors in full-aperture optical aspheric surfaces. The system comprises an interferometer, a standard spherical transmitting lens, a one-dimensional motorized translation stage, a five-dimensional precision motorized stage and a numerical control system. The position of the interferometer and the position of an aspheric surface to be detected are adjusted through the one-dimensional motorized translation stage and the five-dimensional precision motorized stage, the spherical wave generated by the interferometer is matched with a certain inscribed circle of the detected aspheric surface, and wave path difference between the detected aspheric surface and a comparison spherical surface is measured with the interferometer. Feature points of the wave path difference are extracted and subjected to circle fitting so as to obtain optimal matching point position, so that a comparison spherical rise equation is calculated. Finally, the wave path difference is subtracted by a theoretical rise difference between the aspheric surface and the comparison spherical surface so as to obtain the surface-shape error of the aspheric surface detected. A method for detecting surface-shape errors of aspheric surfaces is high in precision and efficiency and economical with no need of auxiliary lenses and compensators.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
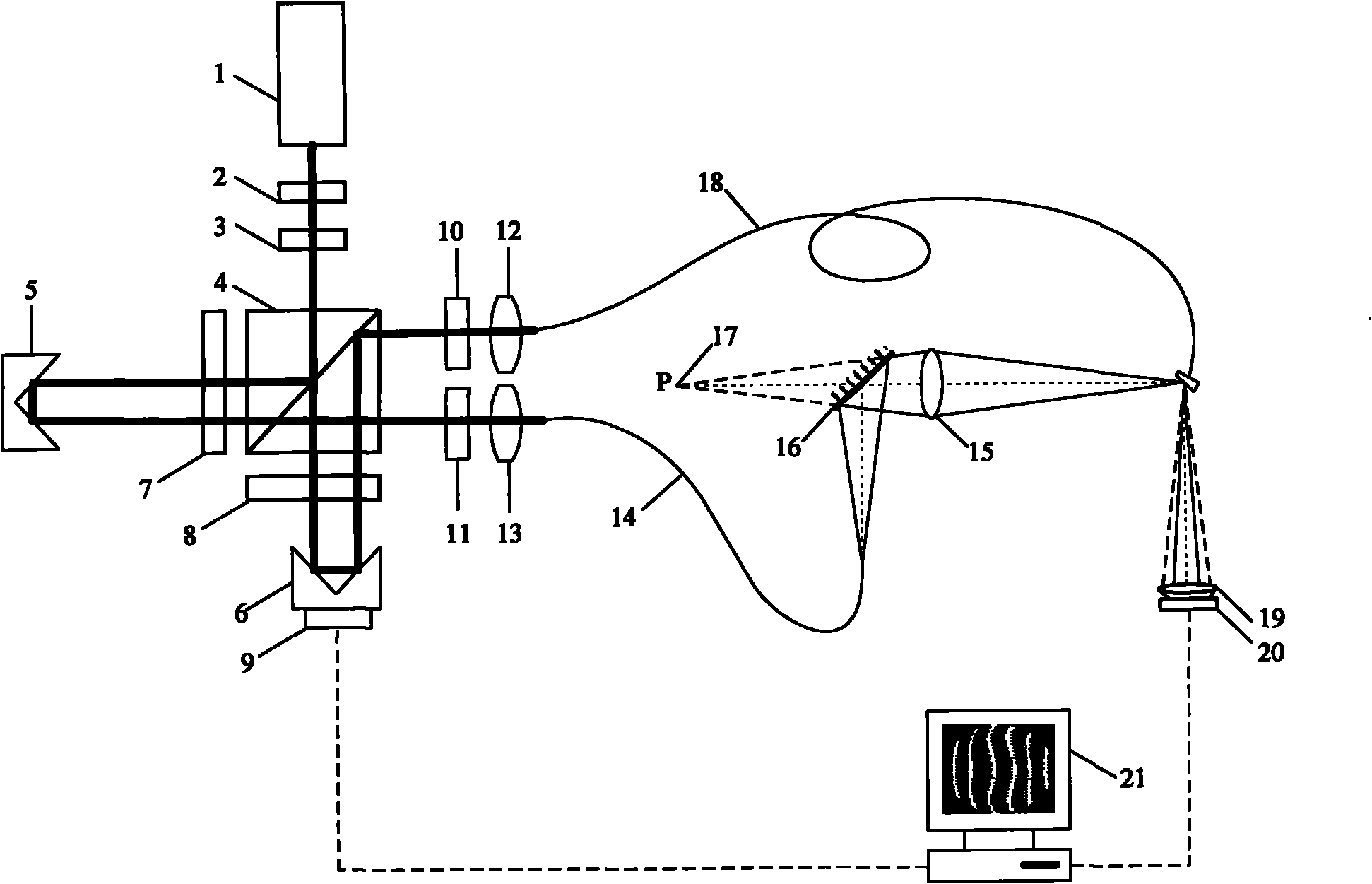
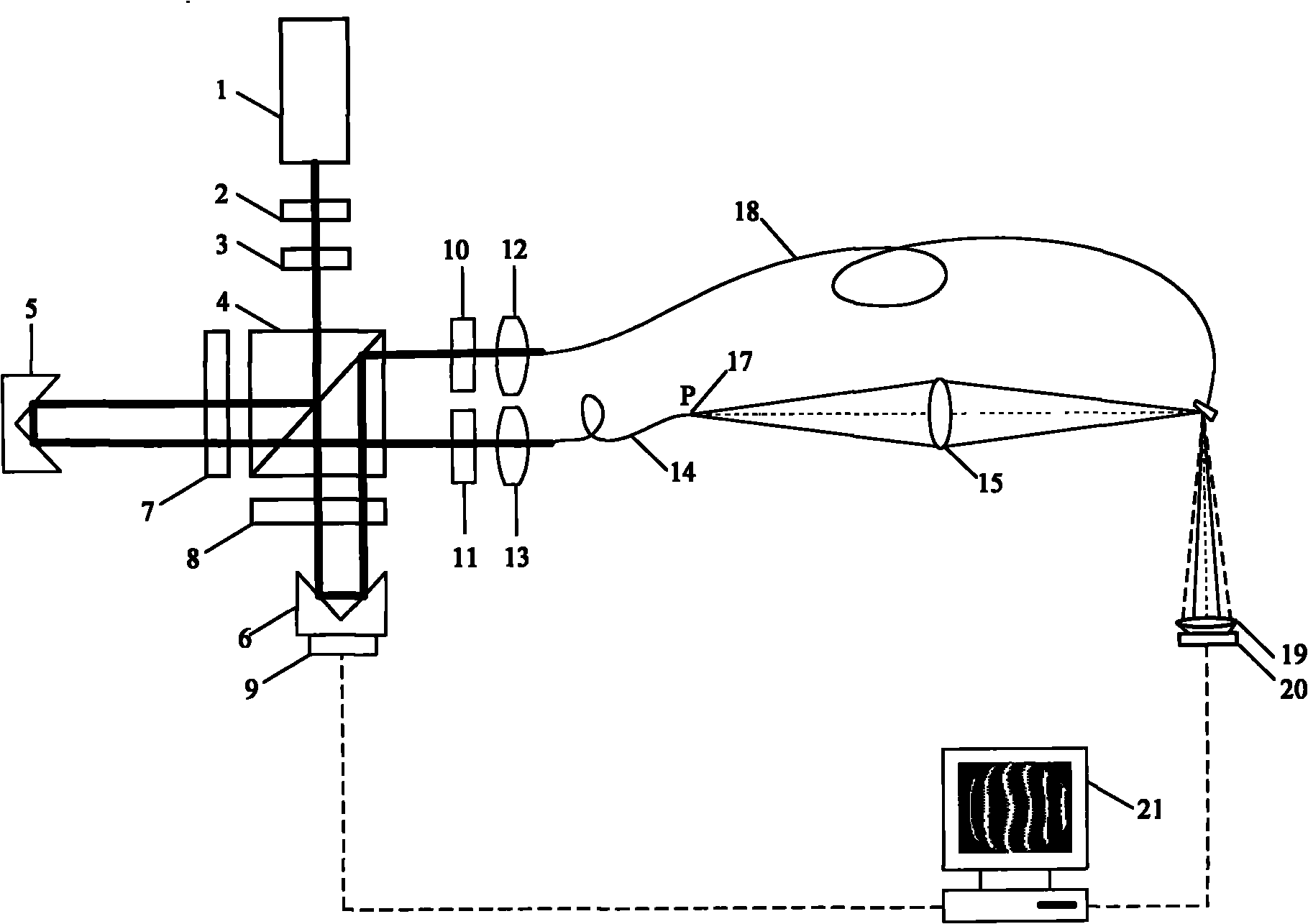
Calibration device for optical system wave aberration and calibration method for test error of the device
InactiveCN102261985AAchieve ultra-high precision detectionTesting optical propertiesFiberWavefront sensor
An optical system wave aberration calibration apparatus and a calibration method of using the apparatus to test an error relate to the optical measurement technology field. The current optical system can not evaluate whether the test error satisfies a detection precision requirement before detecting an optical element and the current optical system can not select an appropriate phase shifting algorithm to process collected data. The above problems can be solved by using the invention. The method comprises the following steps: a light splitting system emits two beams of common-optical-path orthogonal-line polarized lights and after being emitted by a polarization splitting prism, the polarized lights are coupled to a reference fiber through a coupling lens; two spherical waves diffracted by the reference fiber perform interference and an interferogram can be acquired; a photoelectric detector is used to collect the interferogram and to transmit to a computer; piezoelectric ceramics areused to carry out phase shifting and the photoelectric detector collects the interferogram several times; a thirteen step phase shifting algorithm is used to carry out data processing analysis so as to obtain the test error. By using the invention, ultrahigh precision testing of the optical system wave aberration can be realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Exposure apparatus mounted with measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20050190378A1Simple structureShort timeOptical measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPoint diffraction interferometerMeasurement device
An exposure apparatus for exposing a pattern of a mask onto an object using light from a light source, includes a projection optical system for projecting the pattern onto the object, and a measuring apparatus for measuring, as an interference fringe, optical performance of the projection optical system using the light, wherein the measuring apparatus is a point diffraction interferometer that has a pinhole to form an ideal spherical wave, a line diffraction interferometer that has a slit to form an ideal cylindrical wave or an ideal elliptical wave, or a shearing interferometer that utilizes a shearing interferometry.
Owner:CANON KK
Oxyopter type display device using holographic elements
The invention relates to an optical system comprising three holographic elements, which can be used for a helmet-mounted display or a spectacle-mounted display. By using the optical display system, an image projected from an image source element can be subject to beam expansion by the three holographic elements and can be converted into divergent or convergent spherical waves for emission, thereby facilitating the wear of a user having a certain oxyopter. Because the display is realized by the holographic elements instead of lenses, the optical system provided by the invention is especially applicable to an ultra-thin display device, has the advantage of low manufacturing cost and can be customized according to user requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
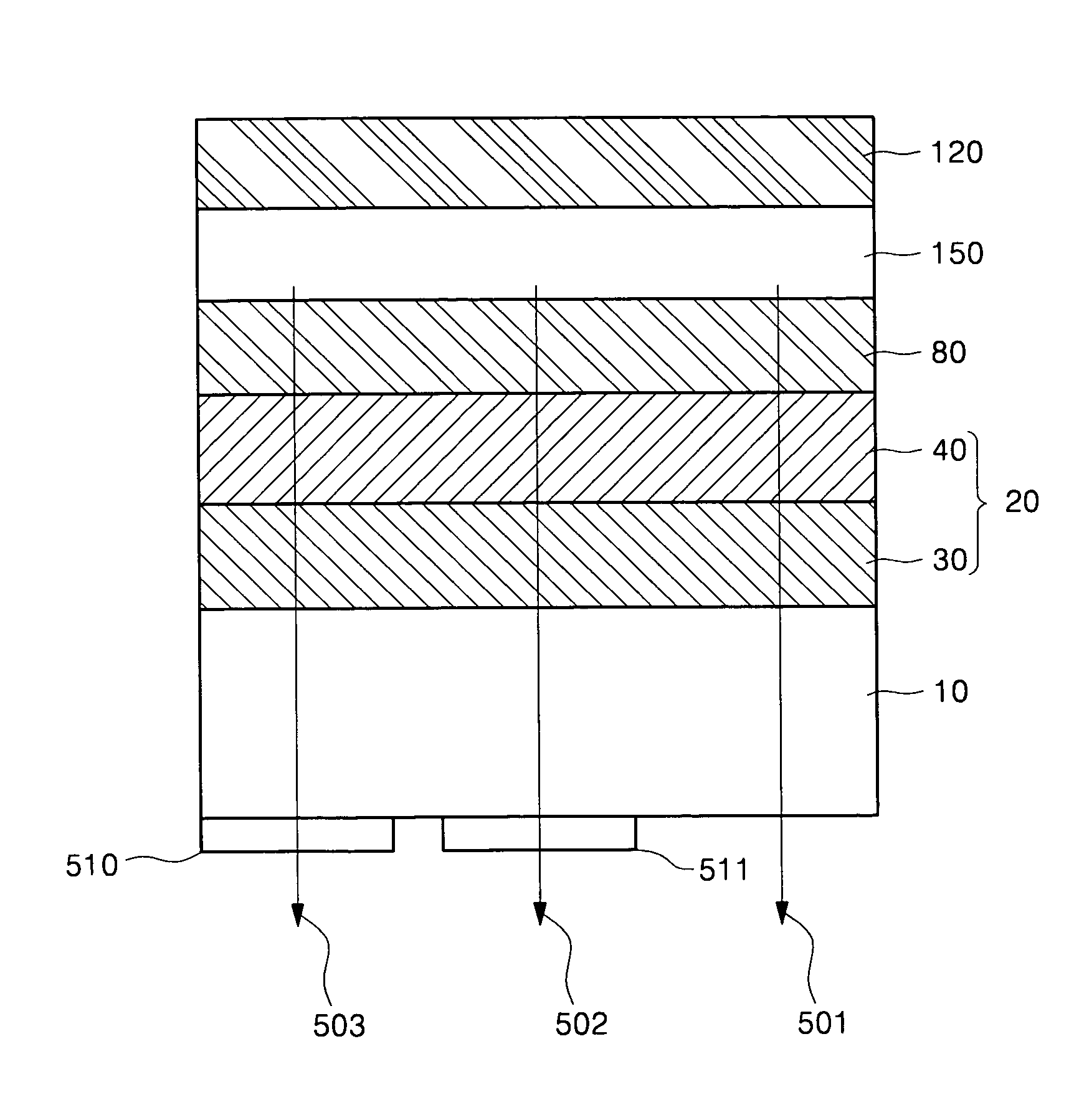
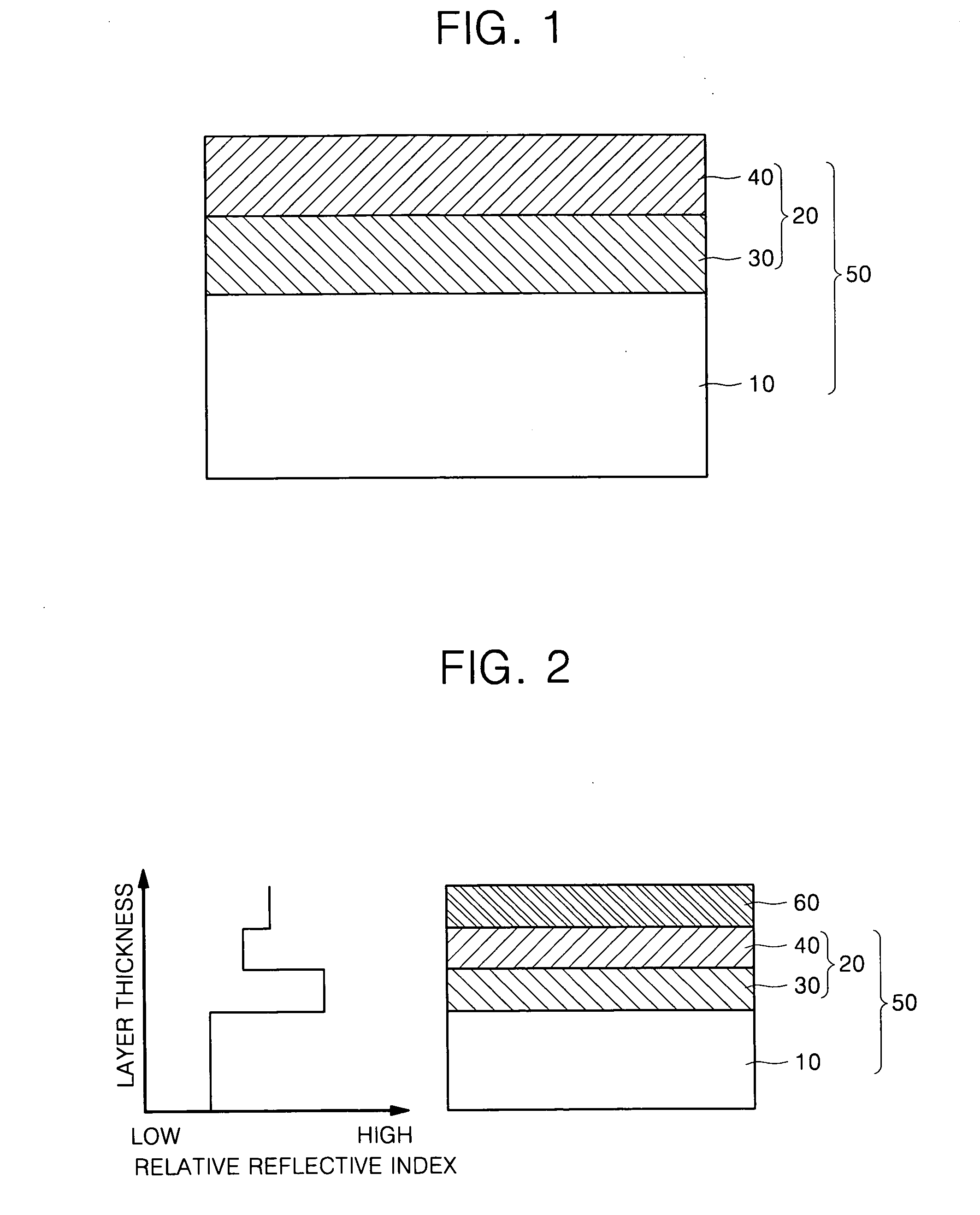
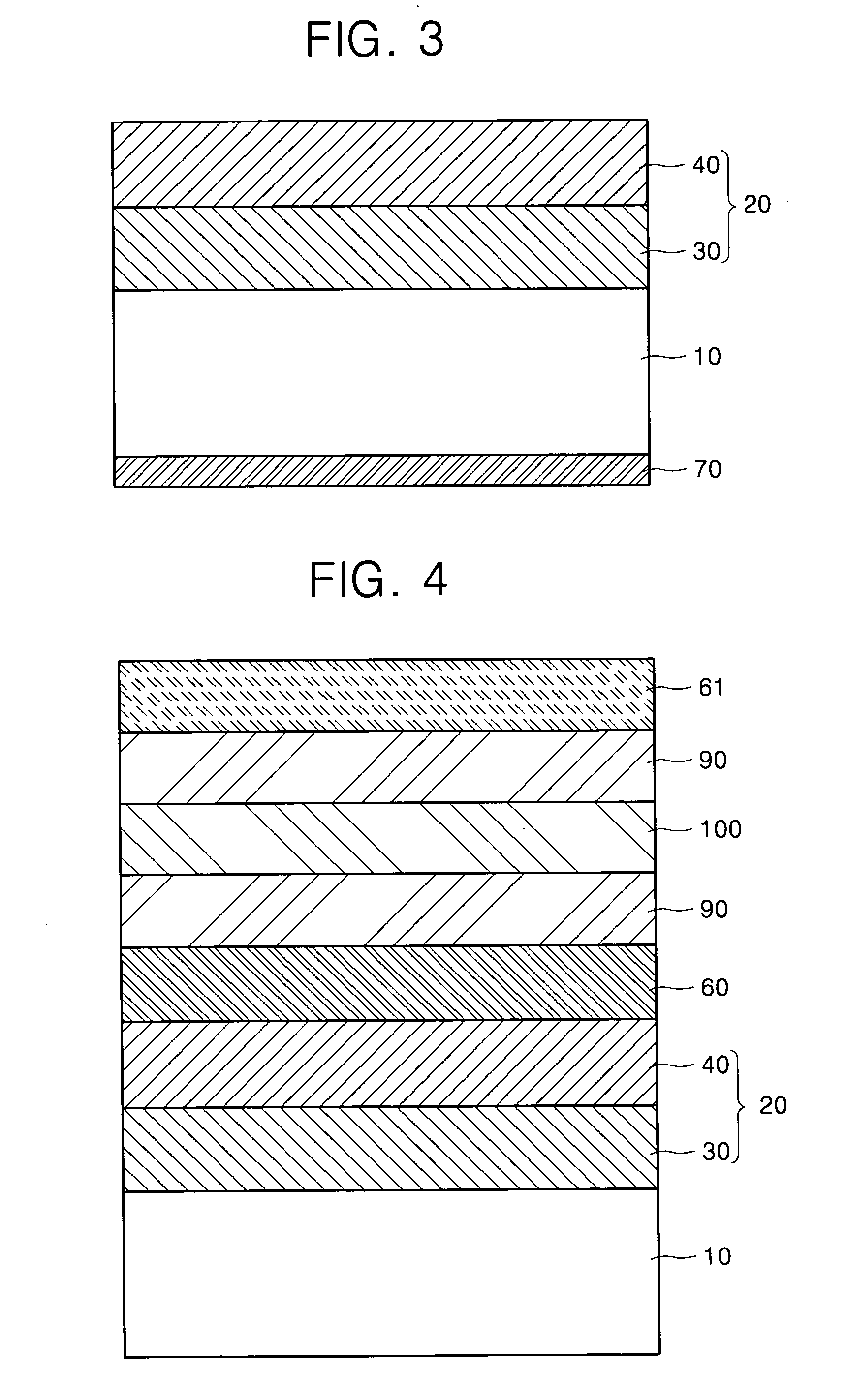
Substrate of emitting device and emitting device using the same
ActiveUS20050051791A1Shine wellSolve the real problemElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesRefractive indexLight emitting device
Provided is a substrate for a light-emitting device having good light emitting efficiency and light-emitting device using the substrate. A light transparent substrate 10 is layered with a first layer 30 having a refractive index higher than that of the light transparent substrate 10 and a s second layer 40 having a refractive index lower than that of the first layer. The refractive index of the first layer 30 is set to be 1.35 times as high as that of the second layer 40. With this layer structure, in an emitting layer of the light-emitting device, a wave front of a spherical wave form exited from a point light source in the front direction is converted into that of a plane wave form, and exited outside the substrate at a high efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
System for detecting large-aperture and high-order convex aspheric surface
ActiveCN103335610AReduce complexityReduce testing costsUsing optical meansReflective surface testingPhase shiftedAspheric lens
The invention relates to a system for detecting a large-aperture and high-order convex aspheric surface. The system comprises a phase shift interferometer, an auxiliary spherical reflector, a computer-generated hologram and a computer, wherein the computer is connected with the phase shift interferometer; a front focal point of an optical system comprising the computer-generated hologram and the high-order convex aspheric surface and a focal point of an optical wave sent by the phase shift interferometer coincide, and a rear focal point and a sphere center of the auxiliary spherical reflector coincide; after the optical wave sent by the phase shift interferometer passes through the computer-generated hologram, the optical wave is reflected by the high-order convex aspheric surface and becomes a standard spherical wave; after the standard spherical wave is reflected by the auxiliary spherical reflector, the standard spherical wave goes back in the same way to the phase shift interferometer, so that subaperture zero-crossing detection of the area corresponding to the high-order convex aspheric surface is realized; the phase shift interferometer obtains a subdomain, having overlapping areas, on the high-order convex aspheric surface; and a data processing unit in the computer processes data in the subdomain, and full-aperture surface-shaped distribution information of the high-order convex aspheric surface is obtained. The invention further provides a device for detecting a convex spherical mirror or a convex aspherical mirror.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plane surface shape measurement method of optical fiber point-diffraction phase-shifting interferometer
InactiveCN101865670AReduce aberrationImproving the Measurement Accuracy of Plane ShapeUsing optical meansFiberPlane mirror
The invention discloses a plane surface shape measurement method of an optical fiber point-diffraction phase-shifting interferometer, belonging to the technical field of optical measurement. The method comprises the following steps: firstly the spherical wave diffracted by a measuring fiber is reflected by a plane mirror to be measured, is focused on the slant end surface of a reference fiber by an auxiliary positive lens, is reflected again to combine with the spherical wave diffracted by the reference fiber and perform interference, the obtained interference pattern is analyzed and processed by the standard method to obtain the aberration caused by the plane mirror to be measured and the auxiliary positive lens; secondly, the plane mirror to be measured is removed, the end surface of the measuring fiber is moved to the conjugate position of the plane mirror to be measured, the spherical waves diffracted by the measuring fiber and the reference fiber are combined to interfere again; the aberration caused by the auxiliary positive lens is obtained through the measurement of the step; and the measurement result of the first step minus that of the second step is the aberration caused by the plane mirror to be measured, and the aberration is corrected according to the incident angle of the spherical wave to obtain the surface shape of the plane mirror to be measured. The method of the invention can be used to effectively increase the measurement precision of the plane surface shape of the optical fiber point-diffraction phase-shifting interferometer.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
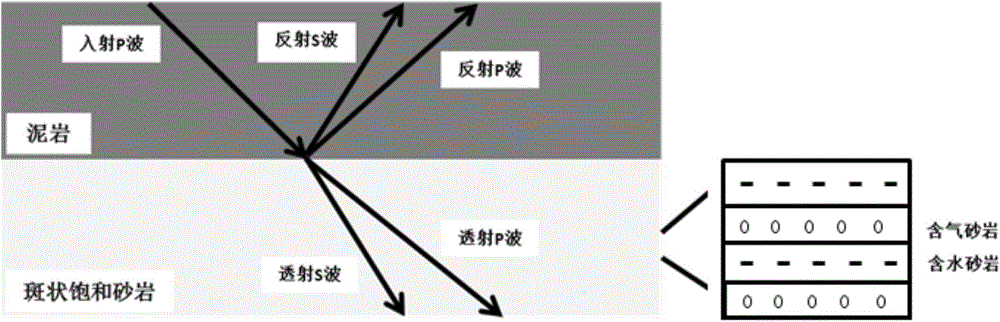
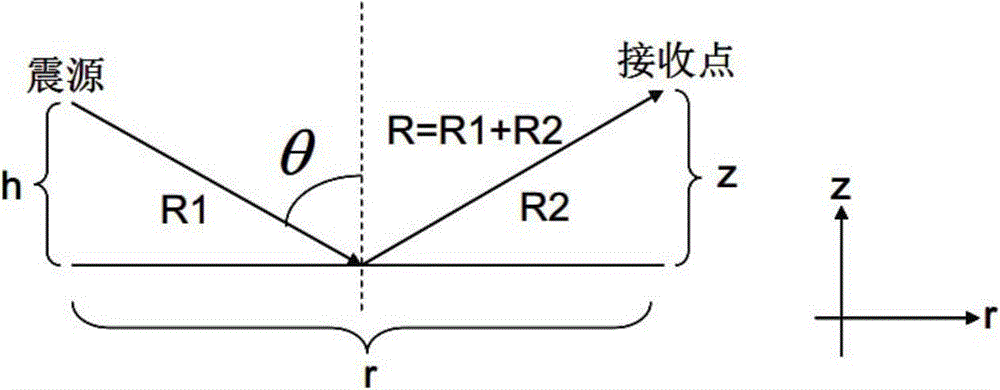
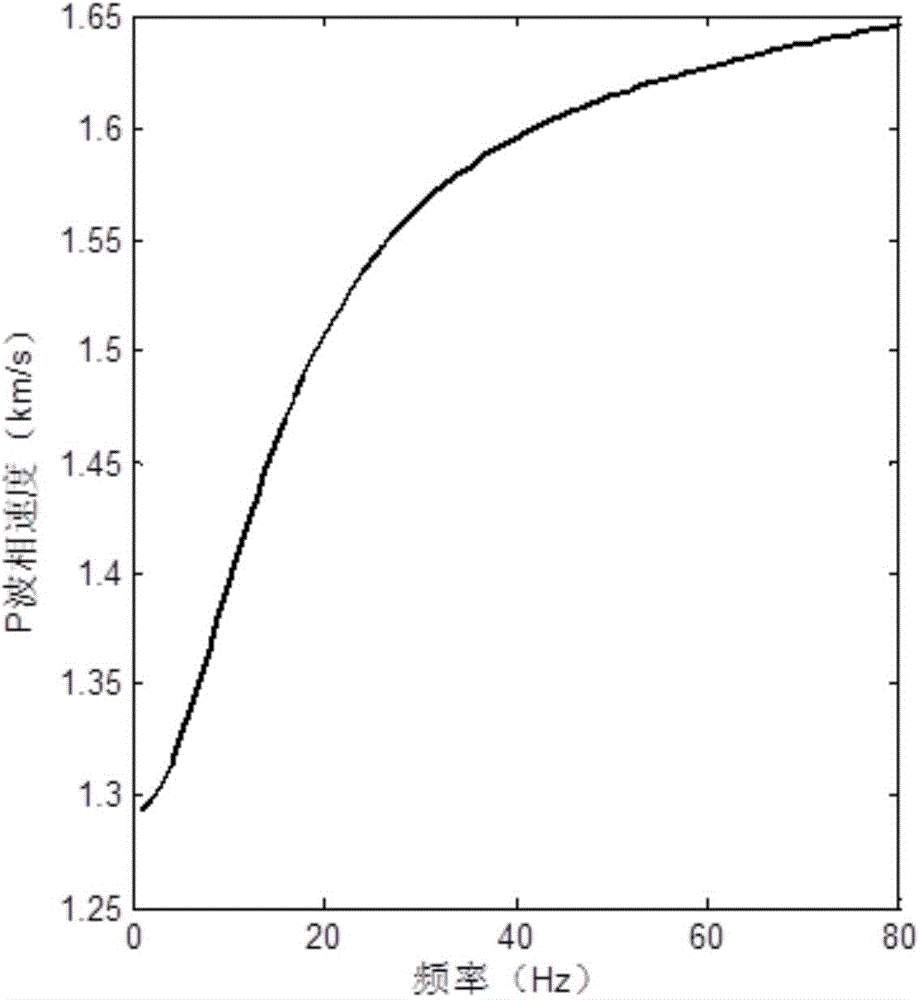
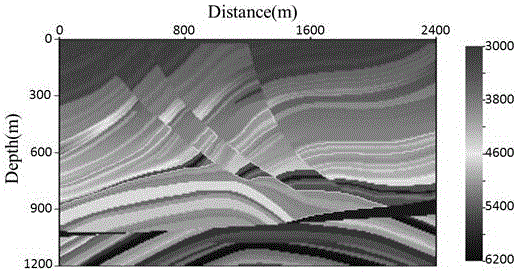
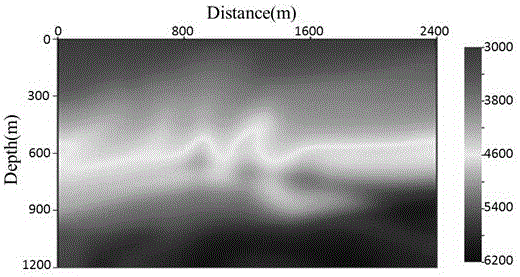
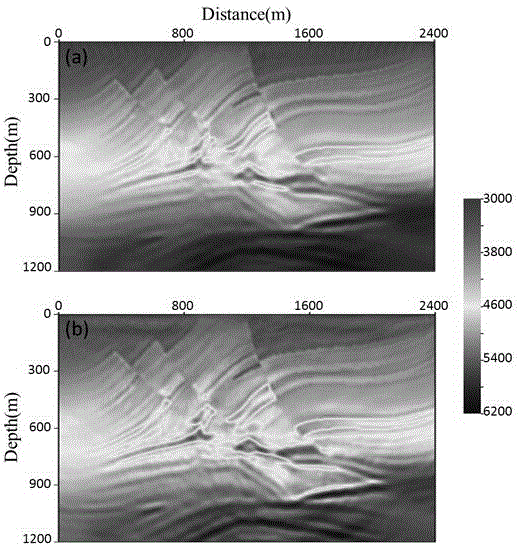
Method for modeling reflection coefficient of spherical PP wave in viscoelastic medium
The invention provides a method for modeling a reflection coefficient of a spherical PP wave in a viscoelastic medium and belongs to the field of geophysical prospecting for petroleum. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) a longitudinal wave phase velocity vp and a quality factor Q<-1> are calculated on the basis of a White model: the longitudinal wave phase velocity vp and the quality factor Q<-1> are calculated on the basis of the White model and reservoir parameters; (2) a reflection coefficient of a planar PP wave in a dispersive porous medium is calculated: the longitudinal wave phase velocity vp and the quality factor Q<-1> which are obtained in Step (1) are introduced in a Zoeppritz equation of the dispersive medium, and the reflection coefficient R<*>PP of the planar PP wave in the dispersive porous medium is calculated; (3) the reflection coefficient of the spherical wave is calculated: after the reflection coefficient R<*>PP of the planar PP wave is calculated in Step (2), the reflection coefficient of the spherical PP wave in the dispersive porous medium is modeled with a planar wave decomposition algorithm of the spherical wave, and the reflection coefficient R<spherical>PP of the spherical PP wave in the dispersive porous medium is calculated.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Frequency-control wave beam/focal point scanning plane reflective array/reflector
The invention discloses a frequency-control wave beam / focal point scanning plane reflective array / reflector. The basic structure of the plane reflective array and the basic structure of the reflector respectively comprise a printed patch array, a primary feed source and a corresponding supporting structure. The plane reflective array is irradiated by spherical waves, focusing of wave beams is realized in a far field, and the plane reflective array can be used in a modern wireless communication system and a modern radar system. The reflector is irradiated by plane waves or cylindrical waves or spherical waves, can realize wave beam focusing in a near field and can be applied to an imaging system. The plane reflective array and the reflector respectively enable the phase value actually obtained on each frequency point to meet the theoretically required value through selection of the size and freedom degree parameters of each unit, therefore, in-phase superposition, in different directions, of the array at different frequency points is realized, and the function of wave beam or focal point scanning is achieved. The frequency-control wave beam / focal point scanning plane reflective array / reflector has the advantages that electric wave beam / focal point scanning and high gain are realized through the simple array surface structure, and the cost, the loss and the complexity of a current scanning array / imaging system are greatly reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-mode signal source
ActiveUS20140266934A1Waveguide mouthsSimultaneous aerial operationsSignal sourceOrthomode transducer
A multimode radiation source is disclosed. One embodiment includes a waveguide radiator and an orthomode transducer coupled to the waveguide radiator to provide a first signal to the waveguide radiator. The waveguide radiator is configured to receive the first signal and to radiate the first signal at a first location as a first spherical wave signal with a first phase center. The multimode source also includes transmission medium coupled to the waveguide radiator and configured to radiate a second signal and a third signal from the first location as a second spherical wave and a third spherical wave with substantially the first phase center.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and system for extracting radar scattering feature data based on plasma near-field testing
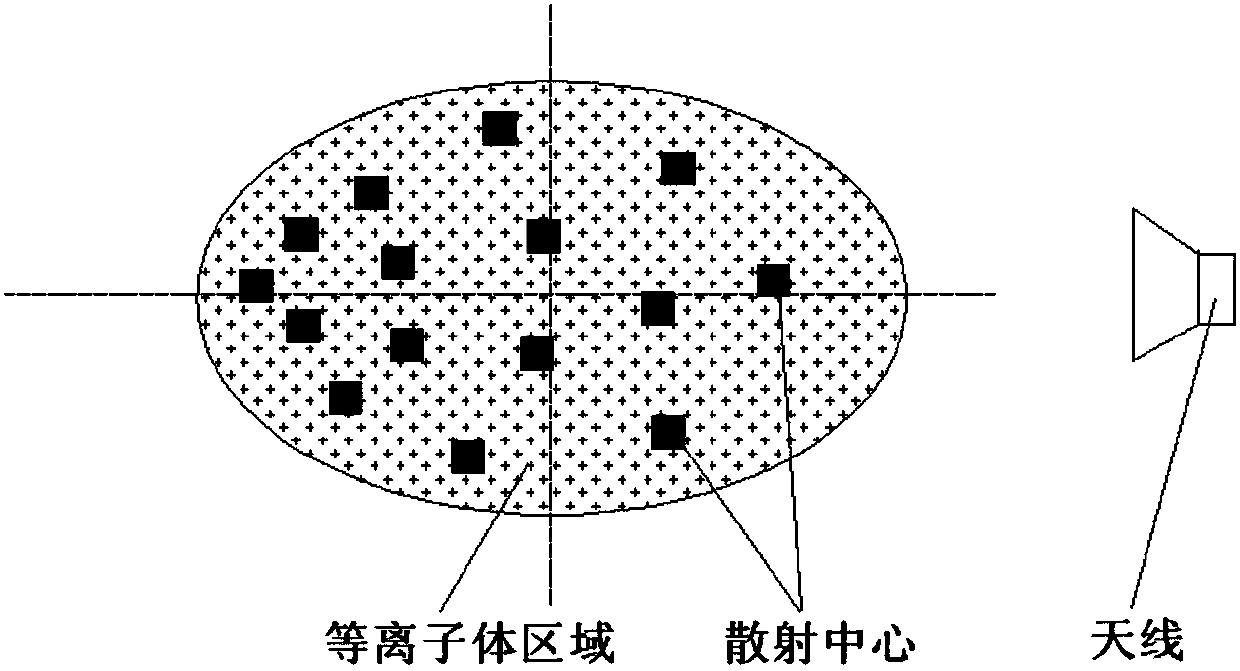
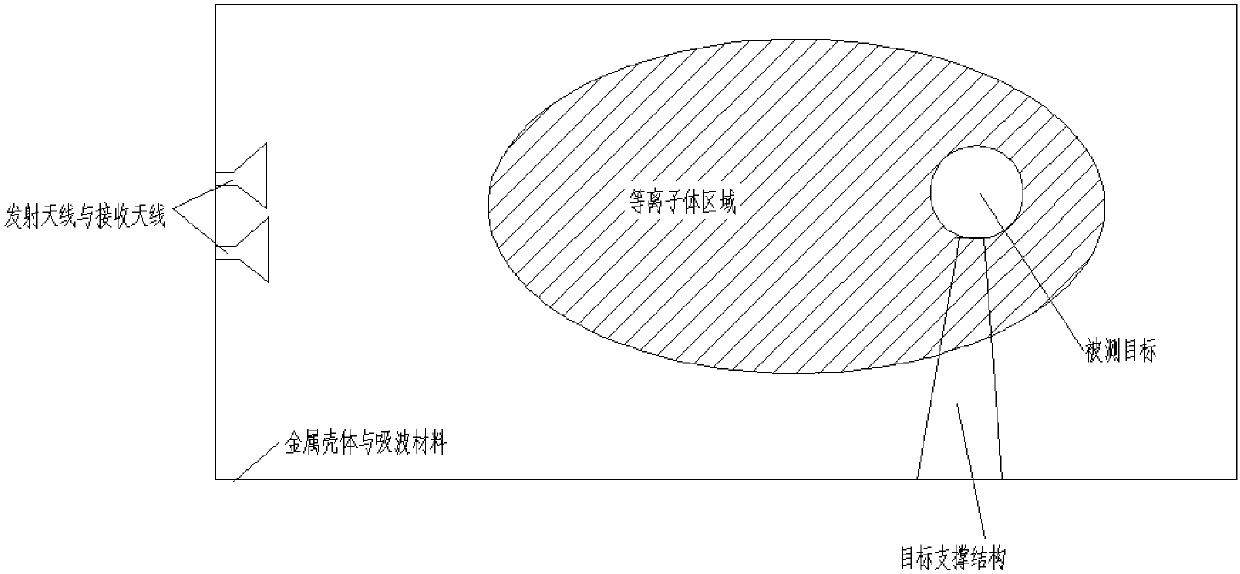
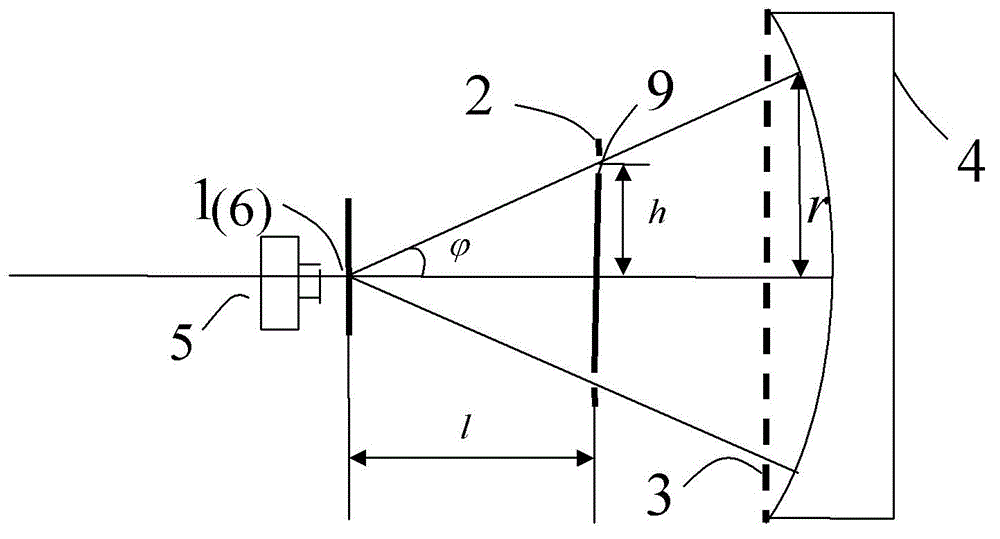
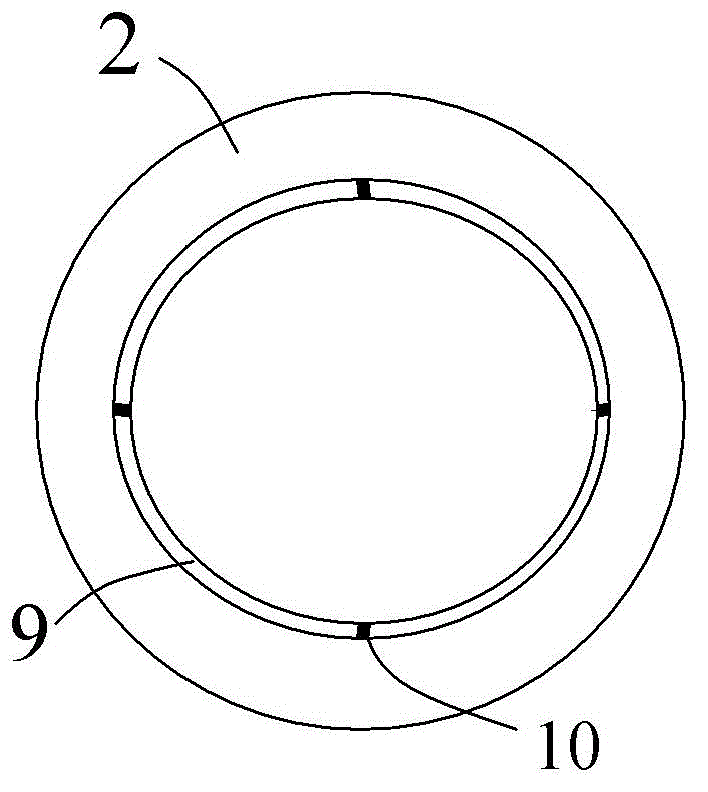
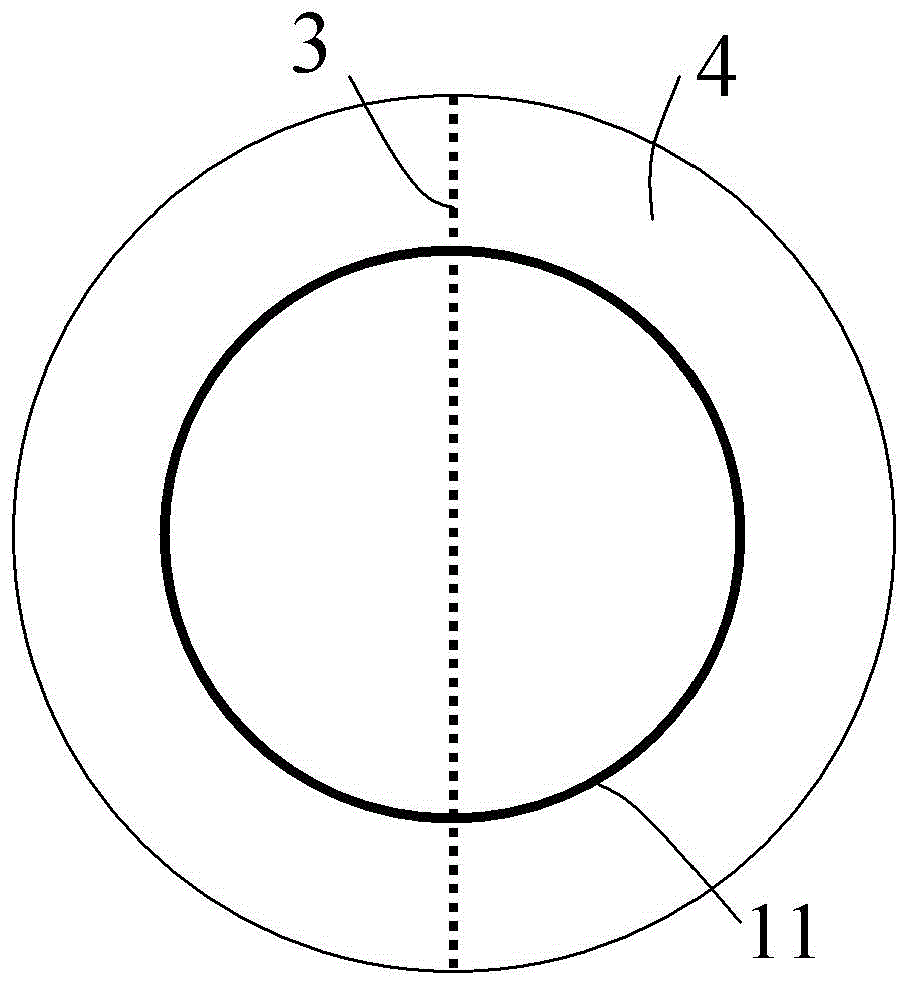
ActiveCN107942330ARealize generationImplementing Scattering Cross Section Performance TestingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionTechnology research
A method and system for extracting radar scattering feature data based on plasma near-field testing are disclosed. An ISAR imaging principle is adopted in a microwave anechoic chamber simulating vacuum environment, and a one-dimensional scanning near-field test method is employed to test scattering performance of a tested target. A near-field scattering 2D image of the tested target is obtained, and near-field correction techniques are used to correct errors of influence error exerted by spherical waves on RCS performance tests. A scattering center is adopted to achieve far-field RCS extrapolation of the tested target, and radar scattering cross section far field data of the test target is obtained. Via the test and the data extraction method, overall target radar cross section data of a plasma-coated aircraft can be provided for a special environment that generates plasma clouds and for peculiar diffusion and ionization characteristics of plasma. A test angle covers a wide angle rangeof -30 degrees to 30 degrees, test accuracy is higher than 2dB, and therefore a test method is provided for plasma stealth technology research and stealth performance evaluation.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST OF THE LONG MARCH VEHICLE +1
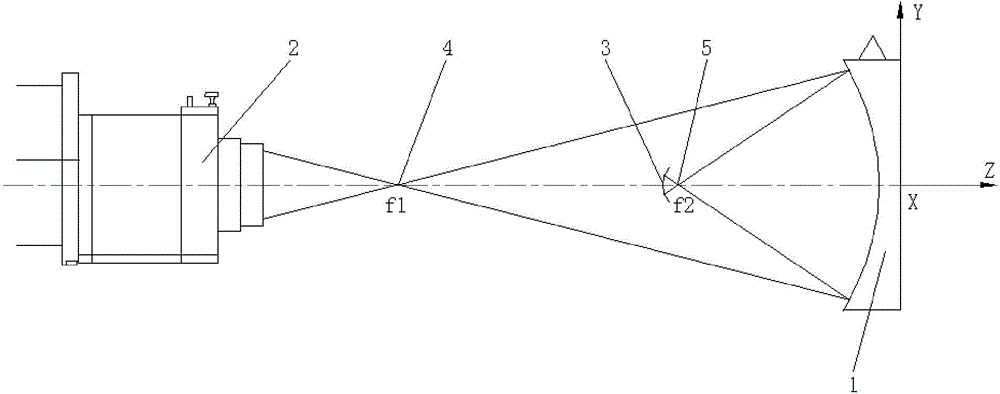
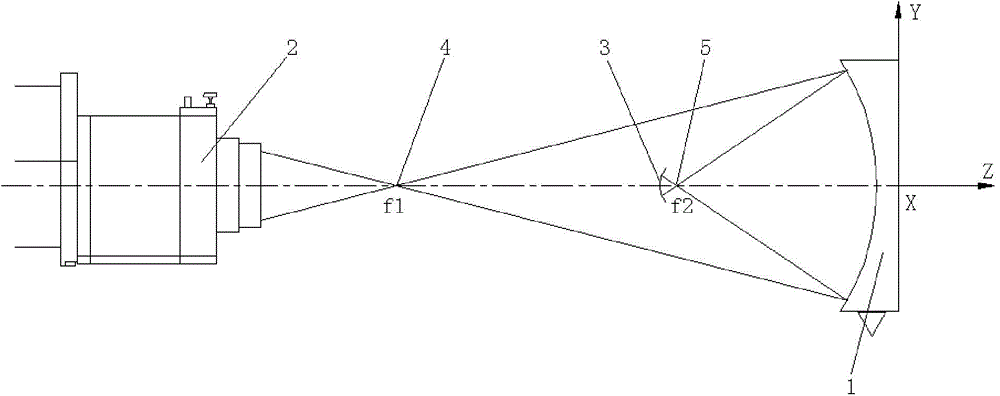
Large-caliber aspheric surface primary mirror detection device and method
ActiveCN103335613AAccurately determineAvoid Diffraction PhenomenaUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsSpecular reflection
The invention relates to a large-caliber aspheric surface primary mirror detection device and method. The device includes a point light source, a baffle, a measuring scale, a CCD (charge coupled detector) and a thin wire. According to the method, a spherical wave emitted by the point light source passes through an annular seam in the baffle and irradiates the mirror surface of a to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror; then the spherical wave is reflected by the mirror surface; the position of the baffle is adjusted, so that the light reflected by the mirror surface of the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror can pass through the annular seam in the baffle; a circle of bright ray is formed at the point light source; the thin wire is used for cutting at the point light source; observing from the back of the thin wire, a user can see that the bright ray disappears; the CCD positioned behind the point light source is used for shooting and recording images of the bright ray; the radius of the annulus of the bright ray and the distance from the light point source to the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror are measured. The position of the point light source or the baffle is adjusted, and the radius of the annulus of the bright ray and the distance from the light point source to the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror are measured, so that the radius of curvature of a vertex of the to-be-detected aspheric surface primary mirror, a secondary constant and a surface shape are figured out according to the aspheric surface primary mirror surface shape formula.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
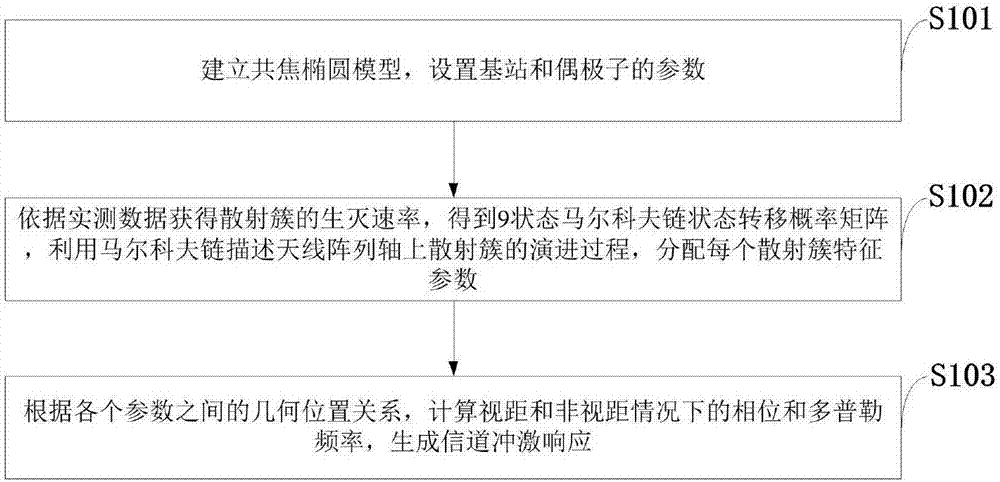
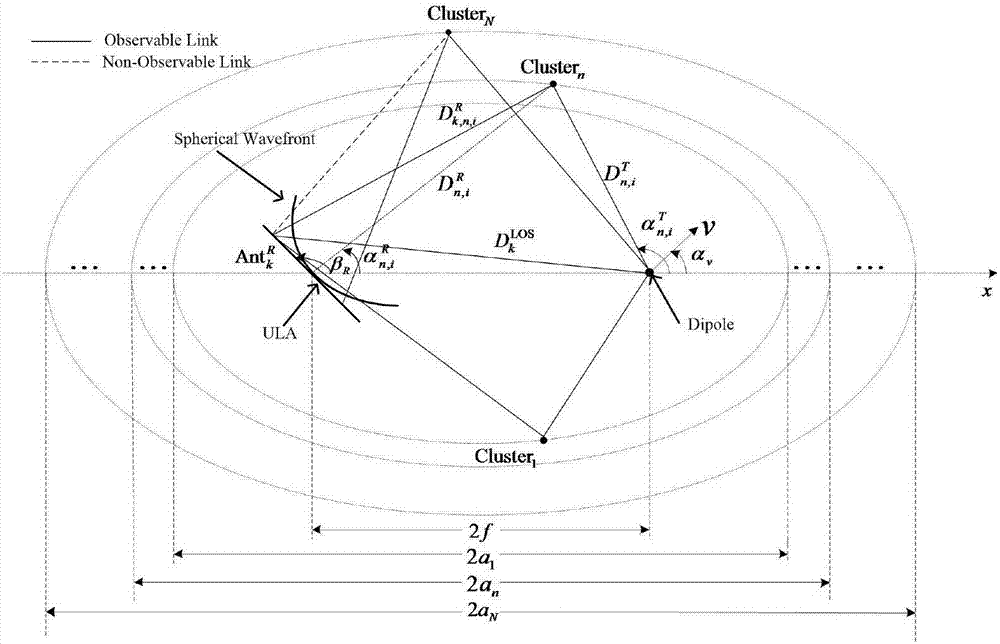
MassiveMIMO channel modeling method based on measured data
ActiveCN107248877AAccurate descriptionImprove Simulation EfficiencyTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionState markov chainBirth and death process
The invention belongs to the technical field of a multiple-input-multiple-output system and discloses a MassiveMIMO channel modeling method based on measured data. According to the method, a confocal elliptical model is established, and base station and dipole parameters are set; a birth and death rate of a scattering cluster is acquired according to the measured data to acquire a nine-state Markov chain state transfer probability matrix, an evolution process of the scattering cluster on an antenna array axis is described through utilizing a Markov chain, and characteristic parameters of each scattering cluster are distributed; and lastly, according to the geometric position relationships among the parameters, phase and Doppler frequency under the stadia and non-stadia conditions can be calculated, and channel impulse response is generated. The method is advantaged in that the birth and death process of the scattering cluster on the antenna array can be accurately described, non-stationary characteristics of a MassiveMIMO channel is reflected, spherical wave characteristics can be described, moreover, computational complexity is relatively low, the channel impulse response can be generated in relatively short time, and channel simulation efficiency is improved.
Owner:广州市埃特斯通讯设备有限公司
Point diffraction interferometer
ActiveCN101183042AAvoid motion errorsHigh sampling frequencyUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical diffractionPoint diffraction interferometer
The invention provides a point diffraction interferometer and comprises a light source module, a mask which can produce an ideal spherical wave, an optical diffraction component which can produce multi-level sub-diffraction light, an image sensor and an optical component. The measured optical component is arranged between the mask and the optical diffraction component and the diffraction light of some levels can permeate the optical component completely, wherein, the diffraction light of a certain level can permeate the optical component partly while being diffracted partly; the diffraction light of some levels can permeate the optical component completely, wherein, the diffraction light of a certain level can be diffracted or the optical component consists of a plurality of windows and a plurality of small holes; diffraction light of some levels can selectively permeate the window, however, the non-diffracted light can be diffracted through the small hole on the optical component. The point diffraction interferometer of the invention conducts measurement through a plurality of interference graphs which are produced at the same time and the sampling frequency is improved, moreover, the design and operation of the whole system is simplified and the motion error of a phase-shift component can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Holographic Microscope, Holographic Image Generation Method, and Method for Acquiring Data for Holographic Image
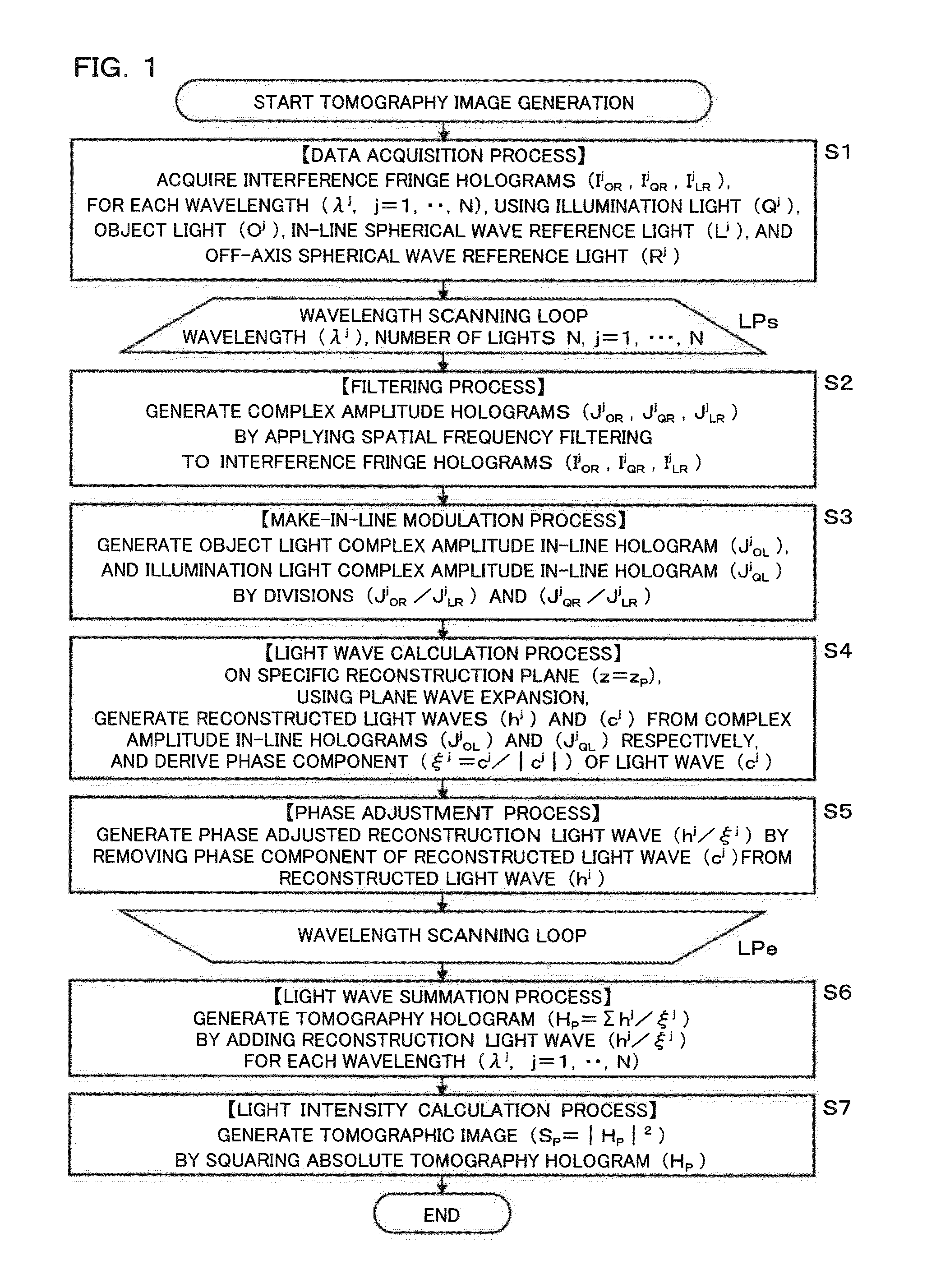
ActiveUS20150268628A1Increase speedShort timeHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesGeneration processPresent method
The present method includes a data acquisition process and tomographic image generation processes. In the data acquisition process, holograms of an object light and so forth are acquired for each light with a wavelength by changing the wavelengths of the illumination light, off-axis spherical wave reference light, and inline spherical wave reference light. In the tomographic image generation process, a reconstructed light wave of the object light and a reconstructed light wave of the illumination light on a reconstruction surface are generated from these holograms. A reconstruction light wave with adjusted phase is added up for each wavelength to generate a tomographic hologram. From this, an accurate and focused tomographic image without distortion can be generated.
Owner:UNIV OF HYOGO
Three-dimensional full waveform inversion energy weighted gradient preprocessing method
ActiveCN106526674AVelocity Depth Accuracy ImprovementsImprove build precisionSeismic signal processingTime correlationPretreatment method
The invention relates a three-dimensional full waveform inversion energy weighted gradient preprocessing method. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out time second-order space finite difference method 3D forward simulation, storing a boundary wave field, and storing the maximum amplitude of reaching each speed grid point at the same time, (2) carrying out source wavefield reconstruction and residual wave field backward spreading at the same time, and carrying out corresponding time correlation to obtain a gradient, (3) reading the information stored in the step (1) and obtaining an energy weighted operator to carry out preprocessing of the gradient, and (4) obtaining the gradient operator of an appropriate step length action after preprocessing, and obtaining speed update quantity iterative update speed. According to the method, in the premise of not increasing computing amount, the problem of gradient operator deep and shallow layer energy imbalance caused by spherical wave spreading geometric diffusion and the like is solved, and the precision of deep layer speed imaging by full waveform inversion is improved effectively.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Optical system wave aberration detection device
InactiveCN102289152AAchieve ultra-high precision detectionEliminate errorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPlane mirrorWave aberration
The invention discloses an optical system wave aberration detection device, relates to the technical field of optical measurement and solves the problem that the existing optical system wave aberration detection device has deflection error and translation error in the phase shift process. Two beams of common-path orthogonal line polarized light emitted from a light splitting system are split by asecond polarization splitting prism, a reference light and a testing light are coupled to a reference optical fiber and a testing optical fiber with a motor-driven polarization controller through a first coupling lens and a second coupling lens; a light emitted from the testing optical fiber is irradiated to a coated end face of the reference optical fiber by a detected optical system and is reflected, a first pyramid prism is adjusted so that a test spherical wave and a reference spherical wave generate interference, a second pyramid lens which is insensitive to the deflection error is movedby a piezoelectric ceramic so as to realize the phase shift process; a second plane mirror enables the wave aberration detection device to be insensitive to the translation error in the phase shift process; an interference image is acquired by using a photoelectric detector, and is input into the computer to be processed and analyzed by using a phase shift algorithm; therefore, the optical systemwave aberration is obtained.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aberration-free absolute inspection method of ellipsoidal surface
The invention discloses an aberration-free absolute inspection method of an ellipsoidal surface. The method comprises the steps of firstly, performing aberration-free zero detection on the confocal position of the ellipsoidal surface by use of a spherical wave interferometer and a spherical reflector to obtain detection results W1 and W2, secondly, performing twice detection on the cat eye position of the spherical reflector to obtain detection results W3and W4, and finally, calculating the absolute surface shape error inspection result T of ellipsoidal surface according to the formula T=(W1-W2+2W3-2W4) / 4. According to the aberration-free absolute inspection method, the system error of the spherical wave interferometer and the surface shape error of the spherical reflector are completely separated out by use of four inspection positions and the absolute inspection result of the ellipsoidal surface is obtained; the method has the advantages of simple operations and high accuracy.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Optical transmission spherical surface detector
InactiveCN101545760AOvercoming spherical templateOvercome the disadvantage of one-to-one correspondence of radiiUsing optical meansCoatingsSurface finishOptical processing
The invention discloses an optical transmission spherical surface detector for inspecting the surface shape quality of lens convex-concave spherical surfaces, which is characterized by adopting a spherical surface non-contact interference method to obtain a standard spherical wave of which the curve radius changes continuously in certain range by a standard transmission spherical surface instrument consists of a group of positive lenses so as to achieve the detection of the convex-concave spherical surfaces with different curve radiuses, wherein the relative aperture detection coverage of a detected piece can reach F / 0.75 to 11. The optical transmission spherical surface detector has the characteristics of multiple functions, no damage to the surface finishment of a detected spherical surface and high test precision, and overcomes the disadvantage of contact measurement of the prior spherical surface sample plate; and if the optical transmission spherical surface detector is used together with a length-measuring linear scale, a length-measuring interferometer, and the like, the curve radiuses of the spherical surfaces can be measured precisely. The optical transmission spherical surface detector can be extensively applied to the optical manufacturing industry to inspect the surface shape quality of various lens convex-concave spherical surfaces.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Measuring method and apparatus using shearing interferometry, exposure method and apparatus using the same, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050117170A1Improve accuracySimple signal processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceInterferometry
A measuring apparatus includes a first mask having a pinhole for generating a spherical wave as measuring light, a second mask provided subsequent to the first mask in a light traveling direction, the second mask having a selecting window that allows the measuring light that has passed a target optical system to transmit through the selecting window, and a two-dimensional light divider, located between the first and second masks, for two-dimensionally dividing light, wherein the measuring apparatus calculating optical performance of the target optical system from an interference fringe formed by the measuring light that has passed the selecting window.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com