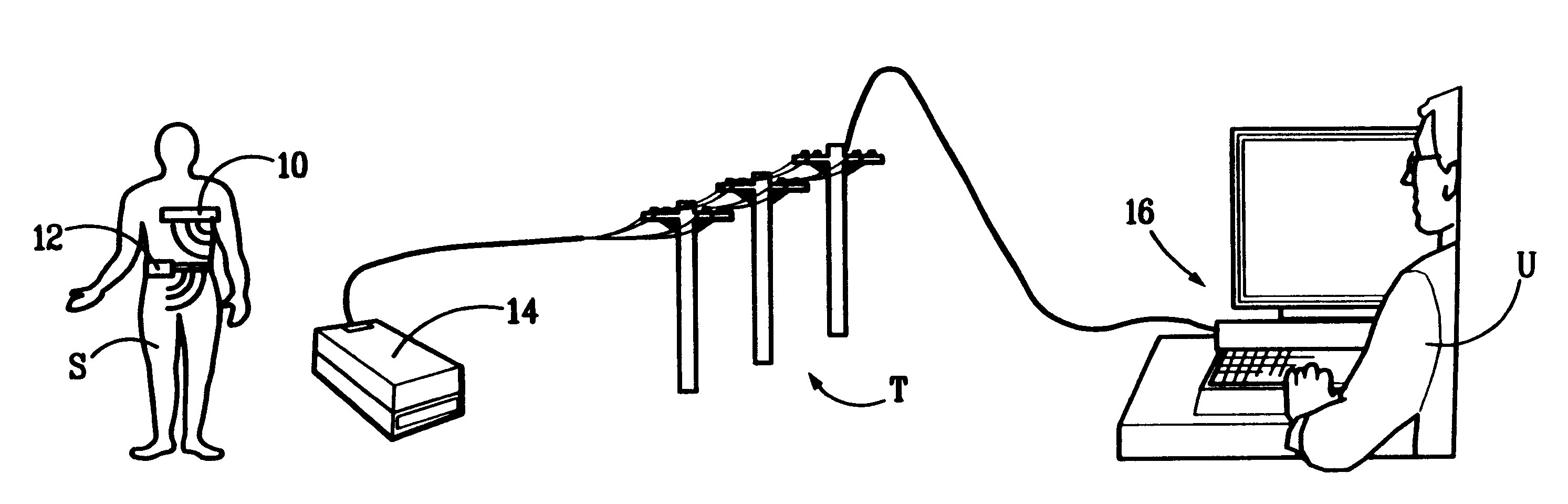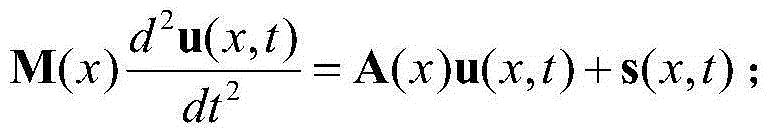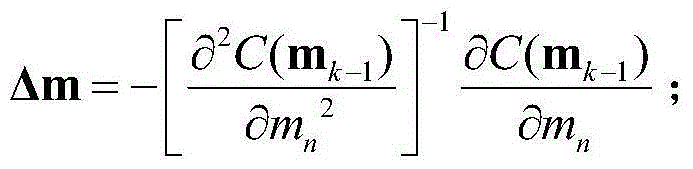Patents
Literature
428 results about "Full waveform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
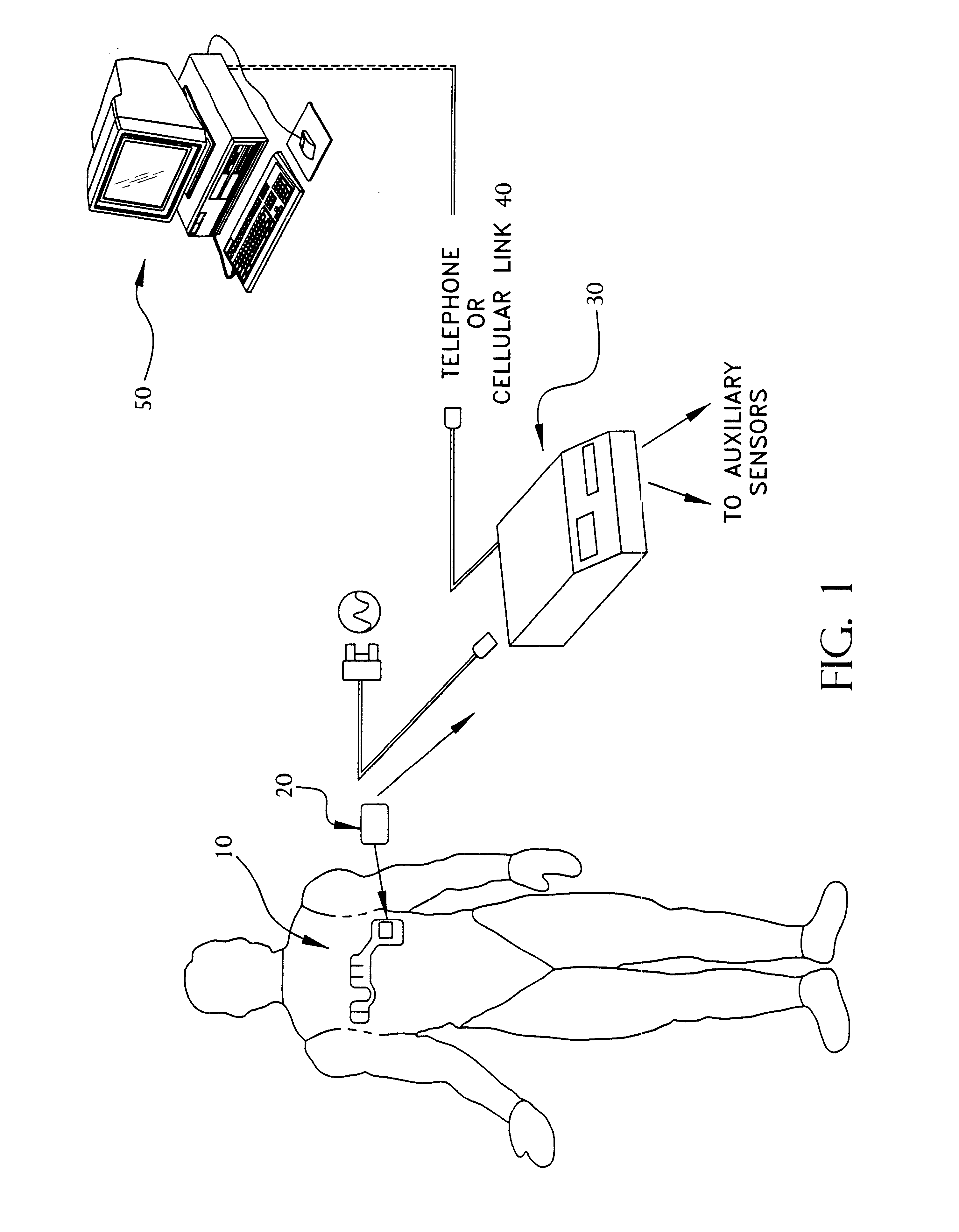
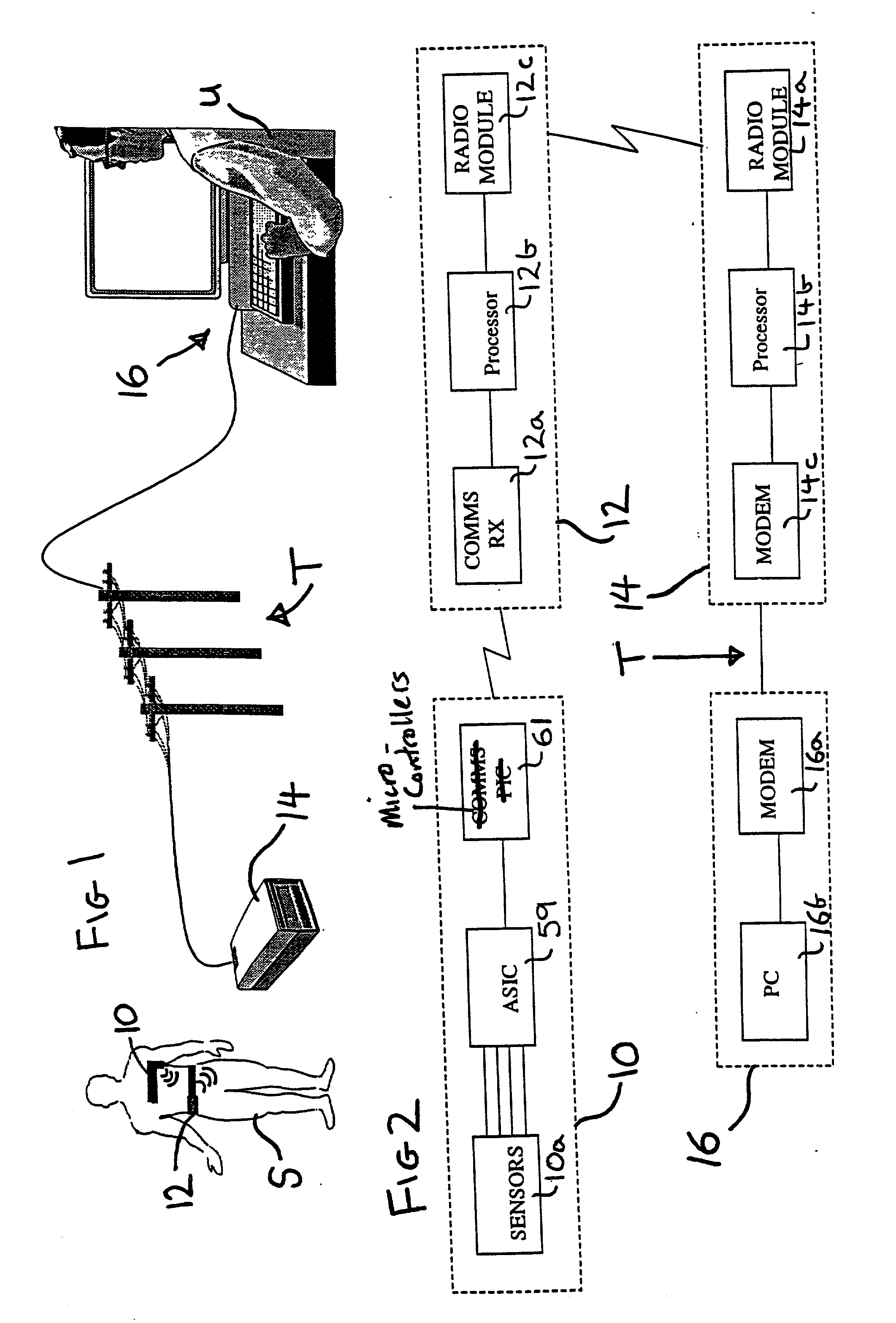
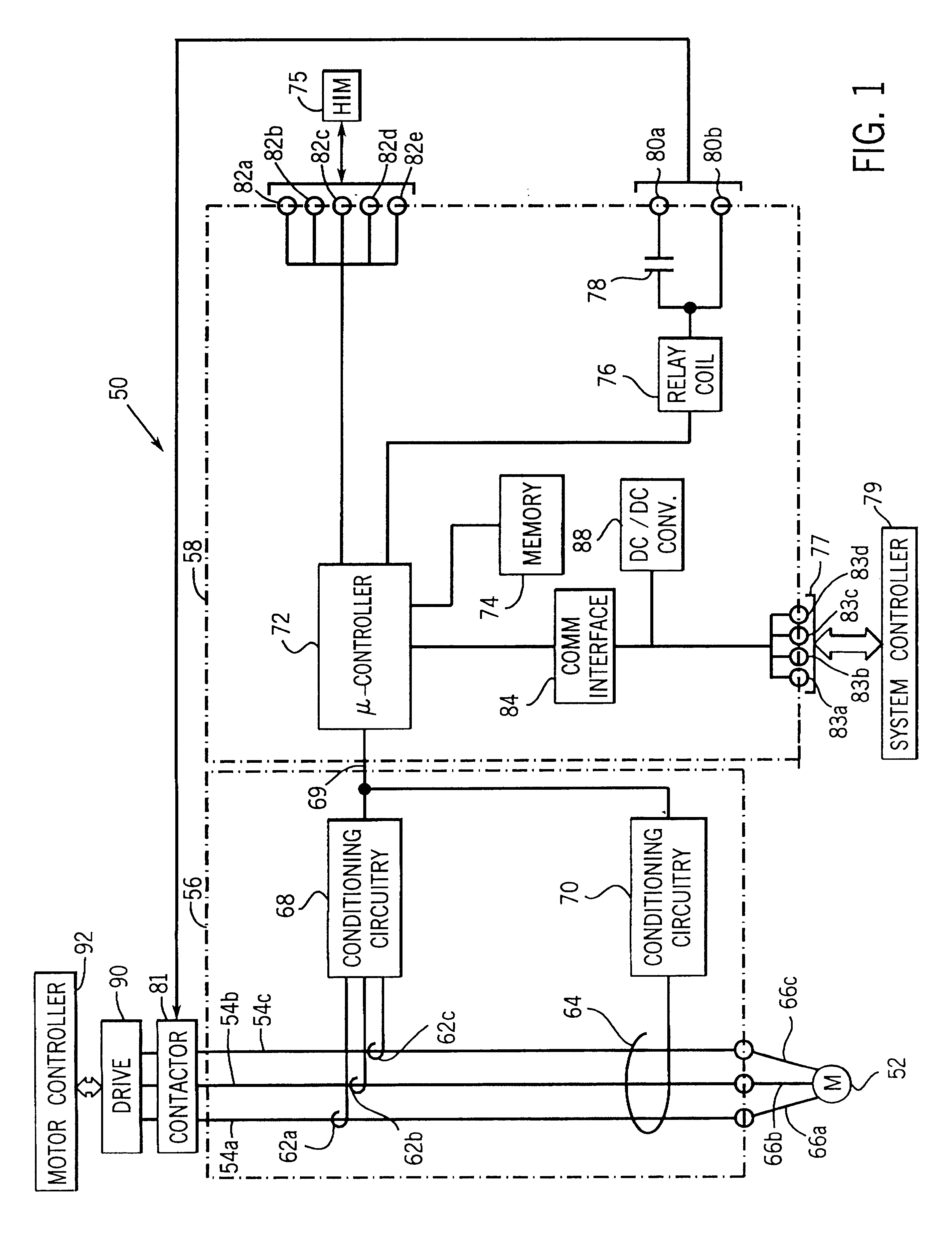
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system
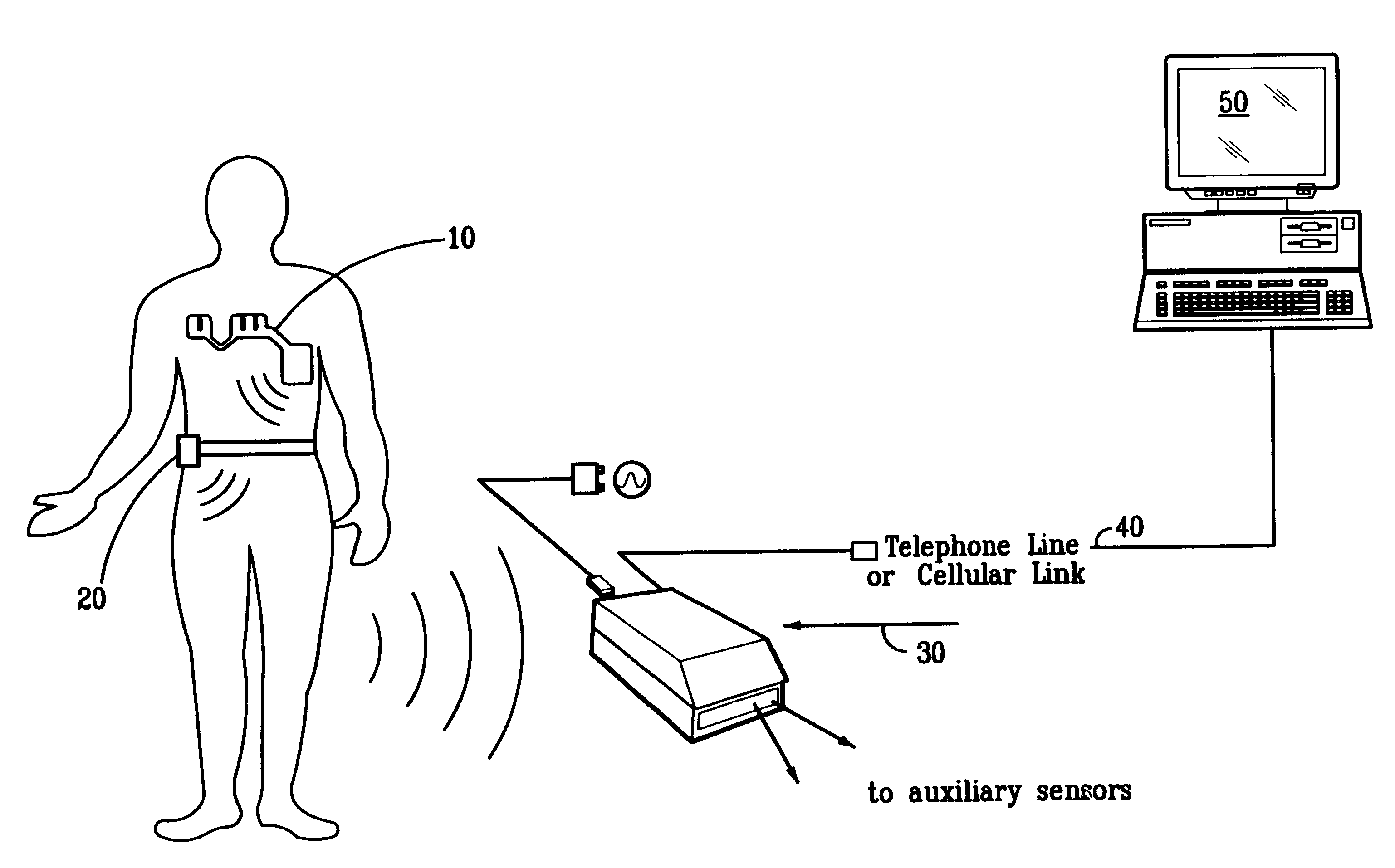
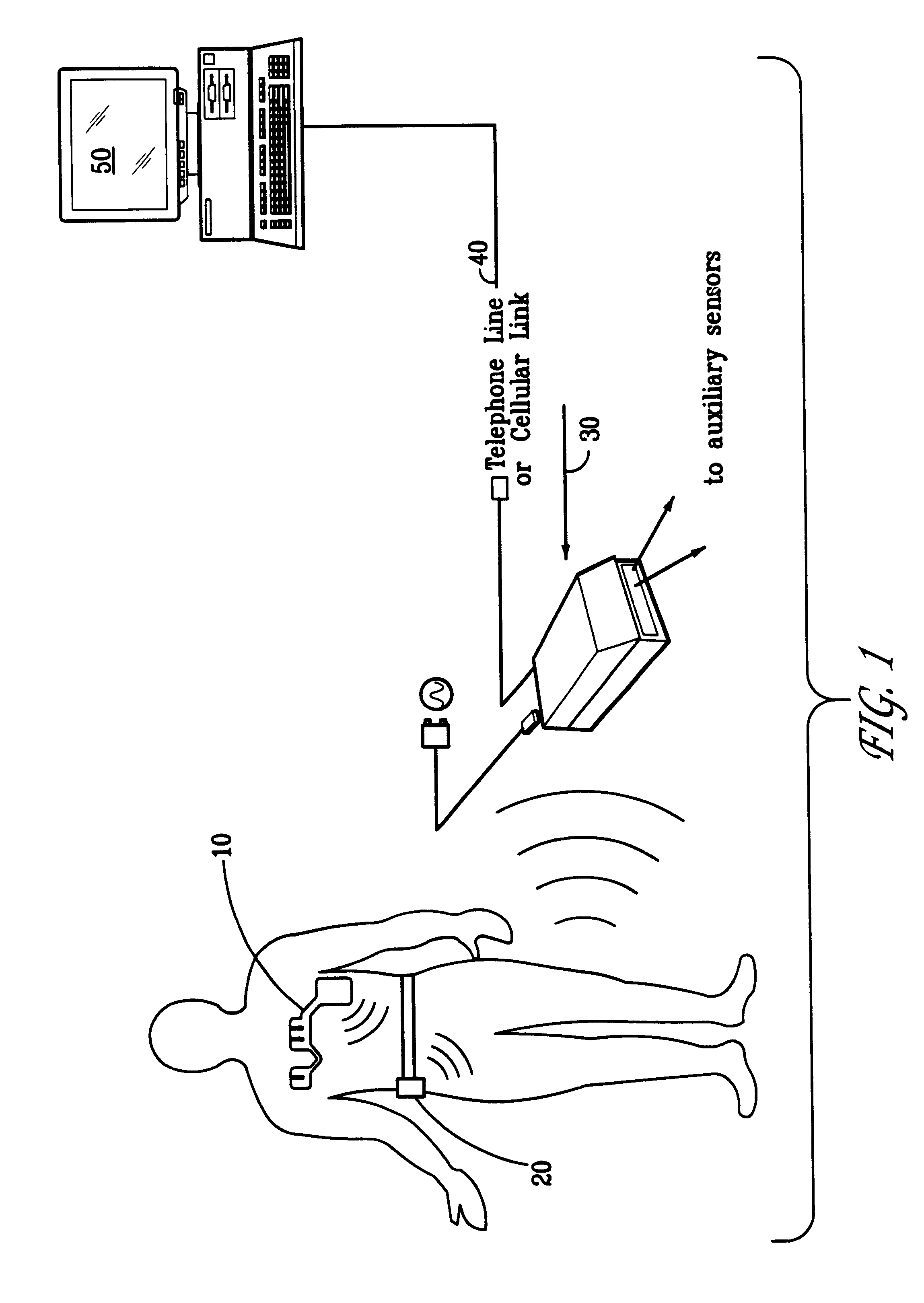
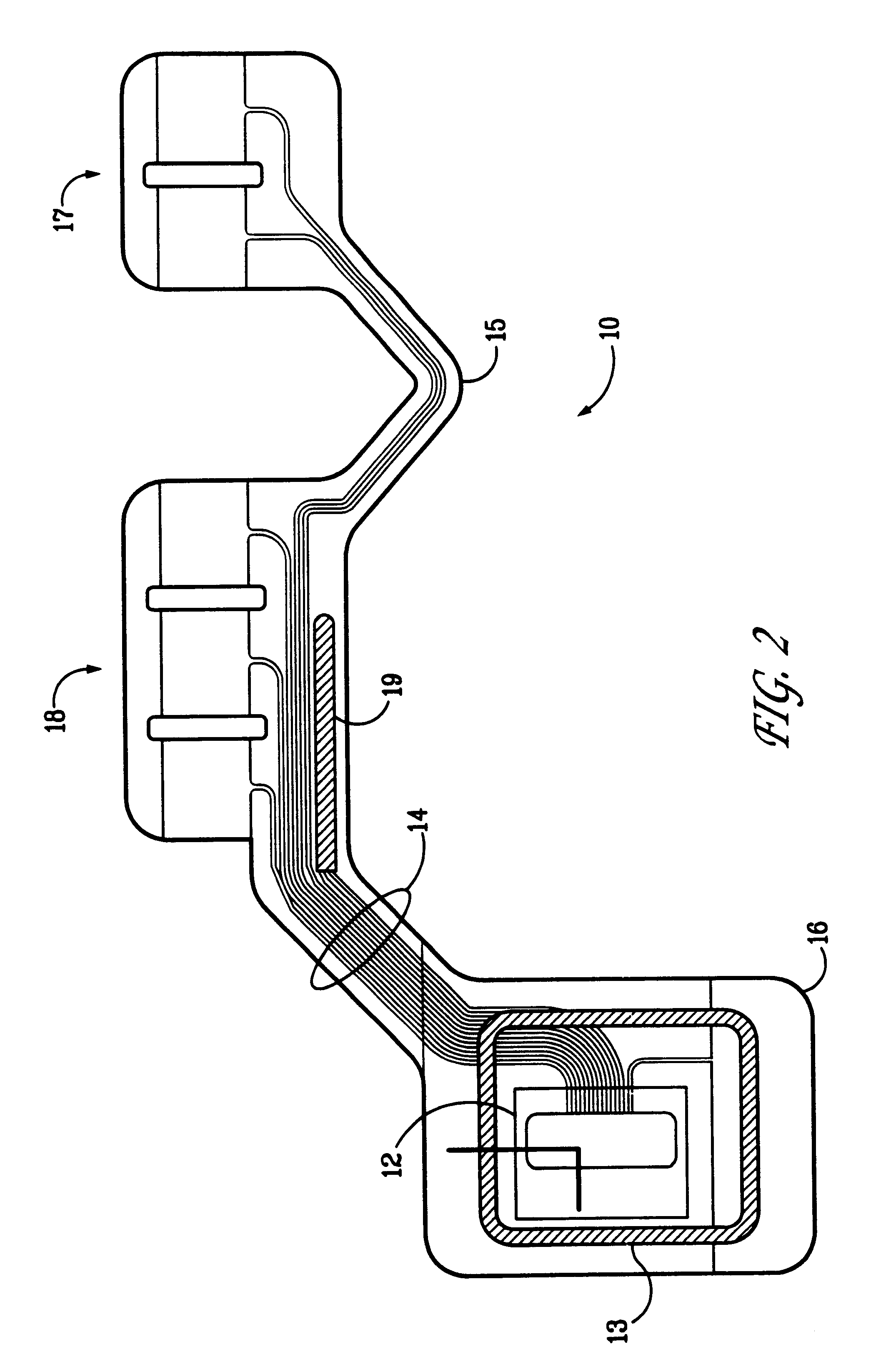
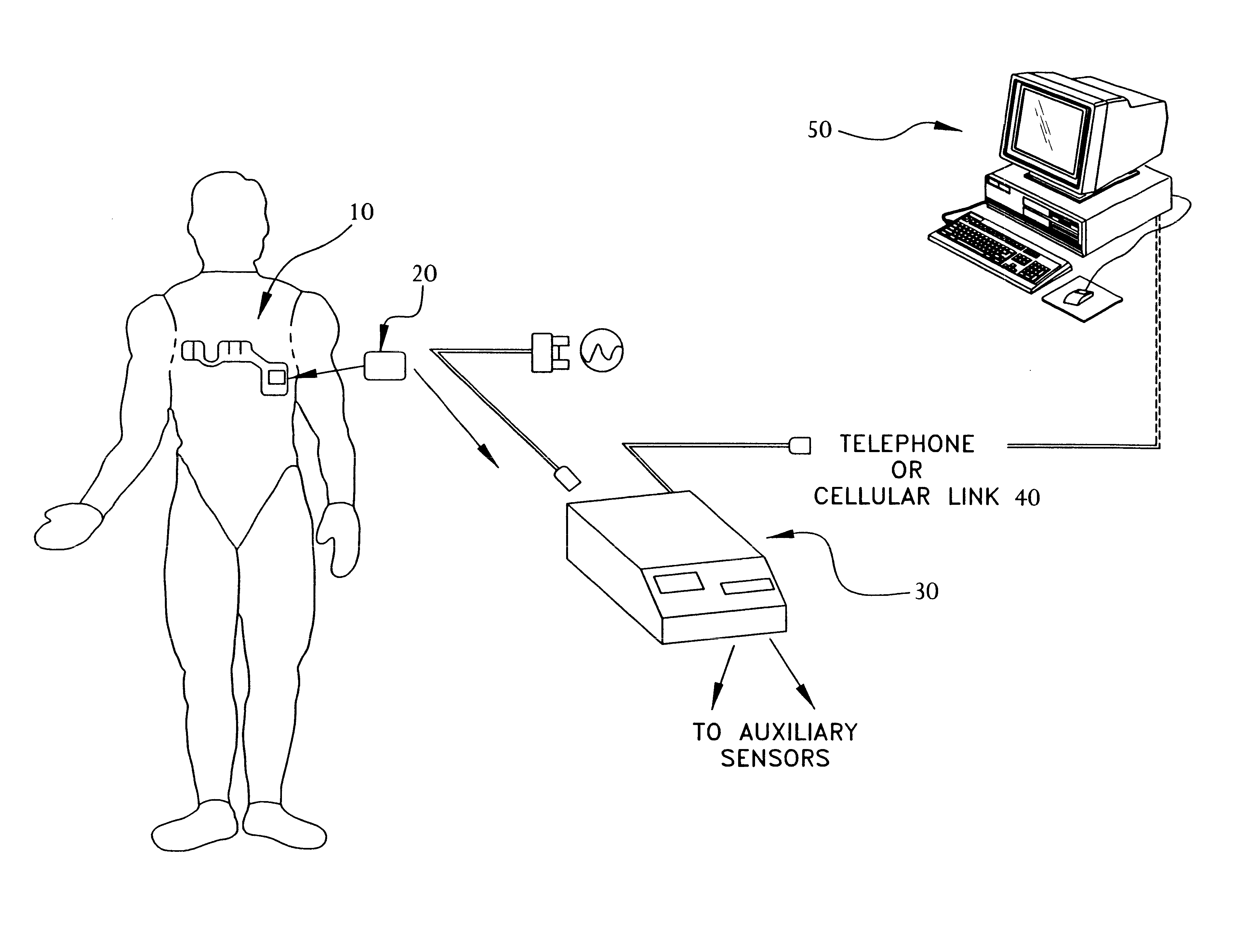
A system and method for monitoring vital signs and capturing data from a patient remotely using radiotelemetry techniques. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors form measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and transmission circuitry for the detection and transmission of vital signs data of the patient. A small signal transfer unit that can either be worn by the patient, e.g., on his or her belt, or positioned nearby receives data from the sensor band, which it then forwards by e.g., radio transmission to a base station that can be located up to 60 meters away. The base station receives data transmissions from the signal transfer unit and is designed to connect to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Patient safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g., ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. Such events are indicated to the physician and could be indicated to the patient by reverse transmission to the signal transfer unit. A remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of patient clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of patients with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
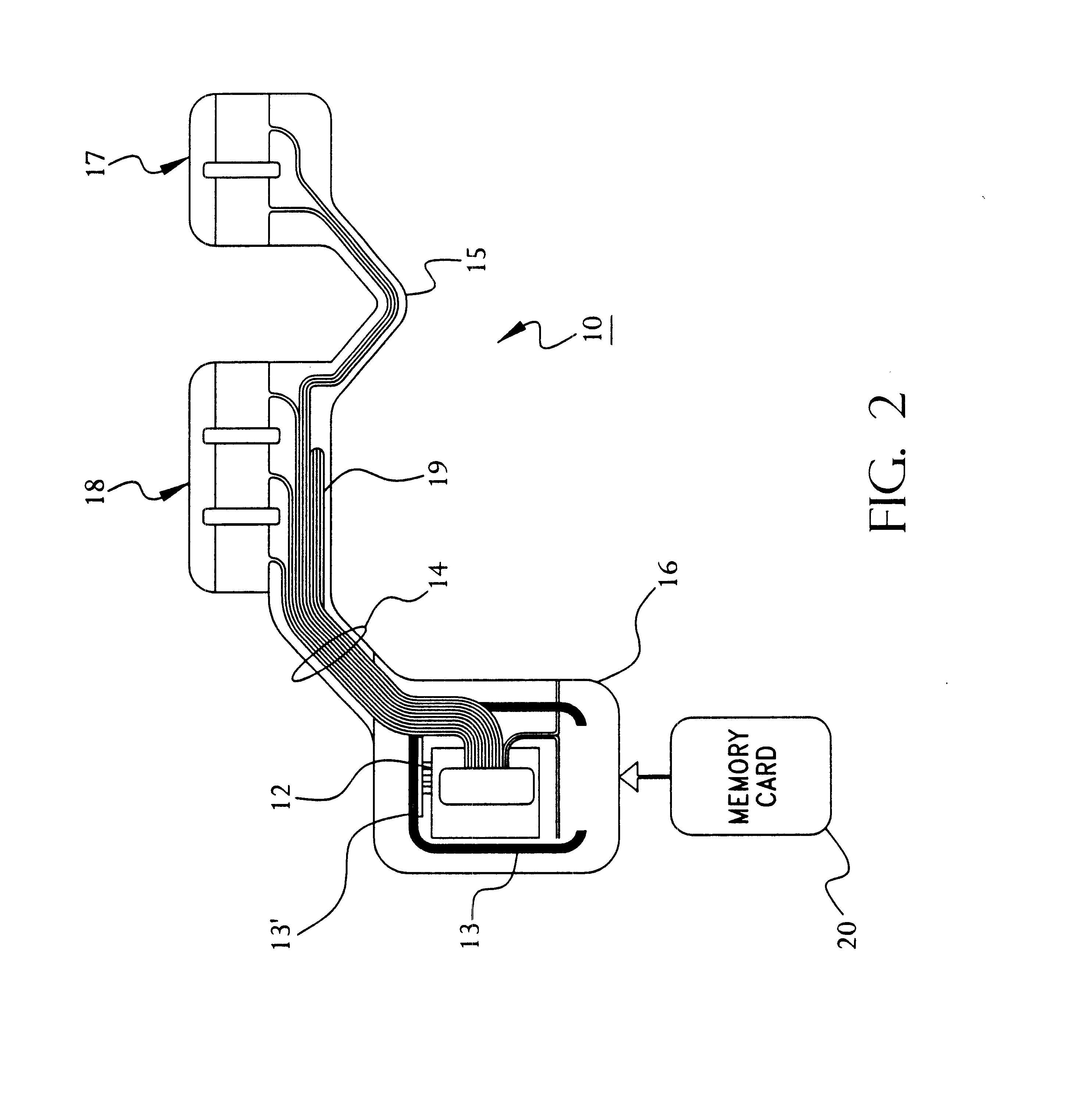
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system using a memory card or smart card
InactiveUS6454708B1Low costIncrease the number ofSurgeryRespiratory organ evaluationSmart cardFull waveform
A system and method for monitoring health parameters and capturing data from a subject. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors for measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and a connector which accepts a memory card or a smart card for storage of the measured data. After a predetermined period of time, such as when the sensor band is removed, the memory card or smart card is removed and inserted into a monitoring device which reads the stored health parameter data of the subject. The monitoring device includes a base station that includes a memory / smart card reader and is connected to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Subject safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g. ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. The remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. In alternative embodiments, a smart card includes the sensor band's electronics and / or signal transmission circuitry in conjunction with a portable data logger so that the electronics may be reused from one disposable sensor band to the next without limiting the patient's range of movement. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of subject clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of subjects with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
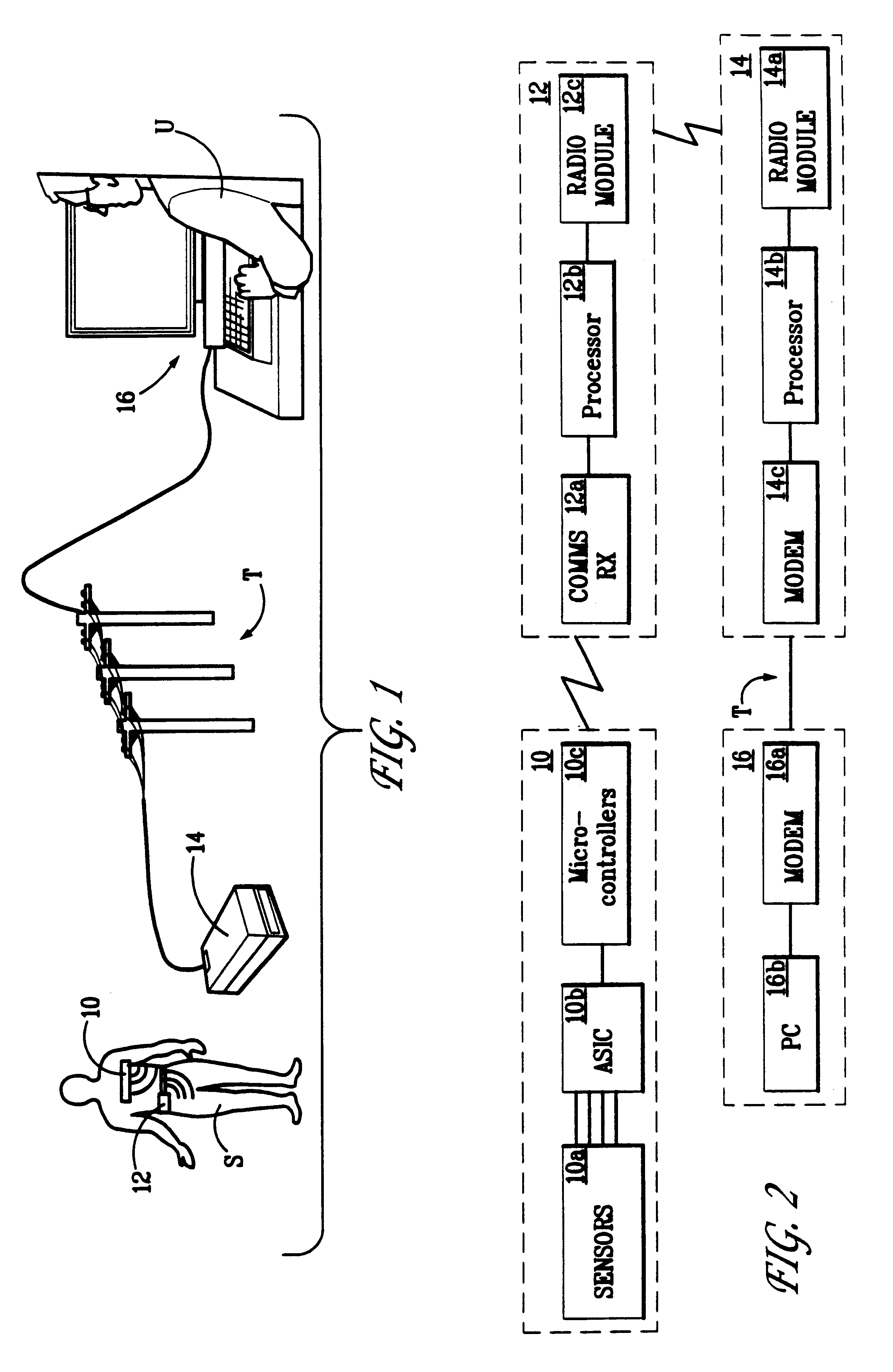
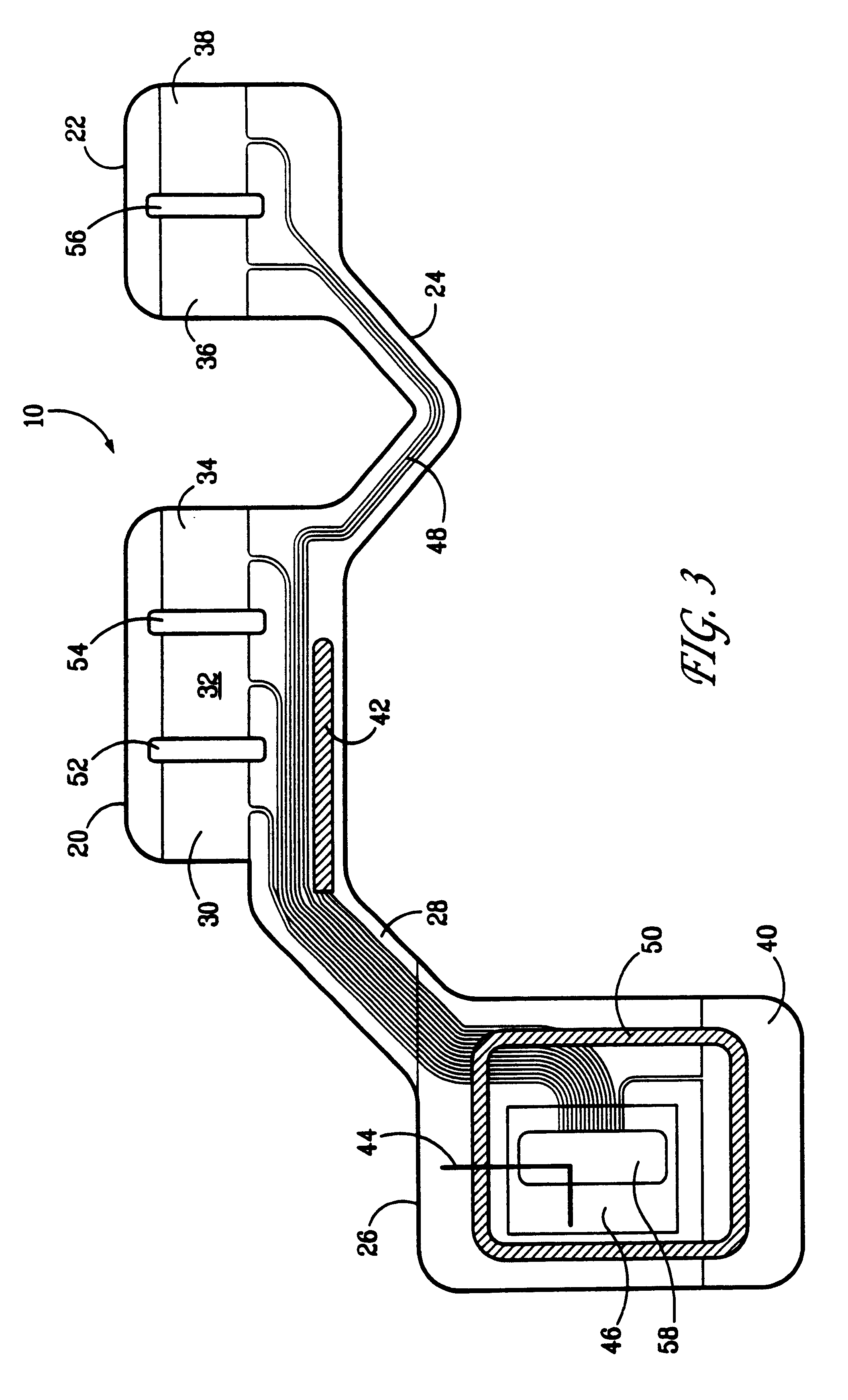
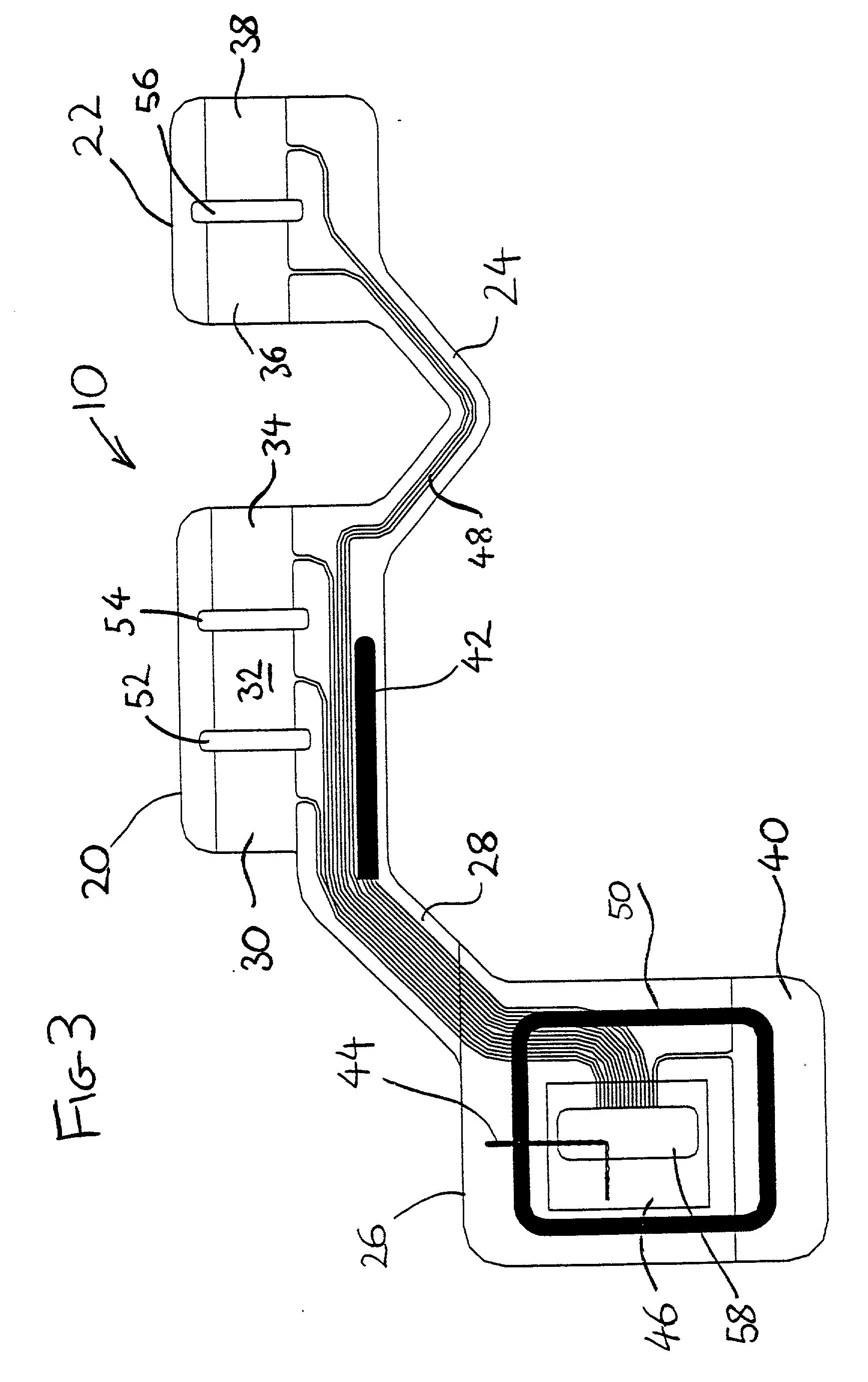
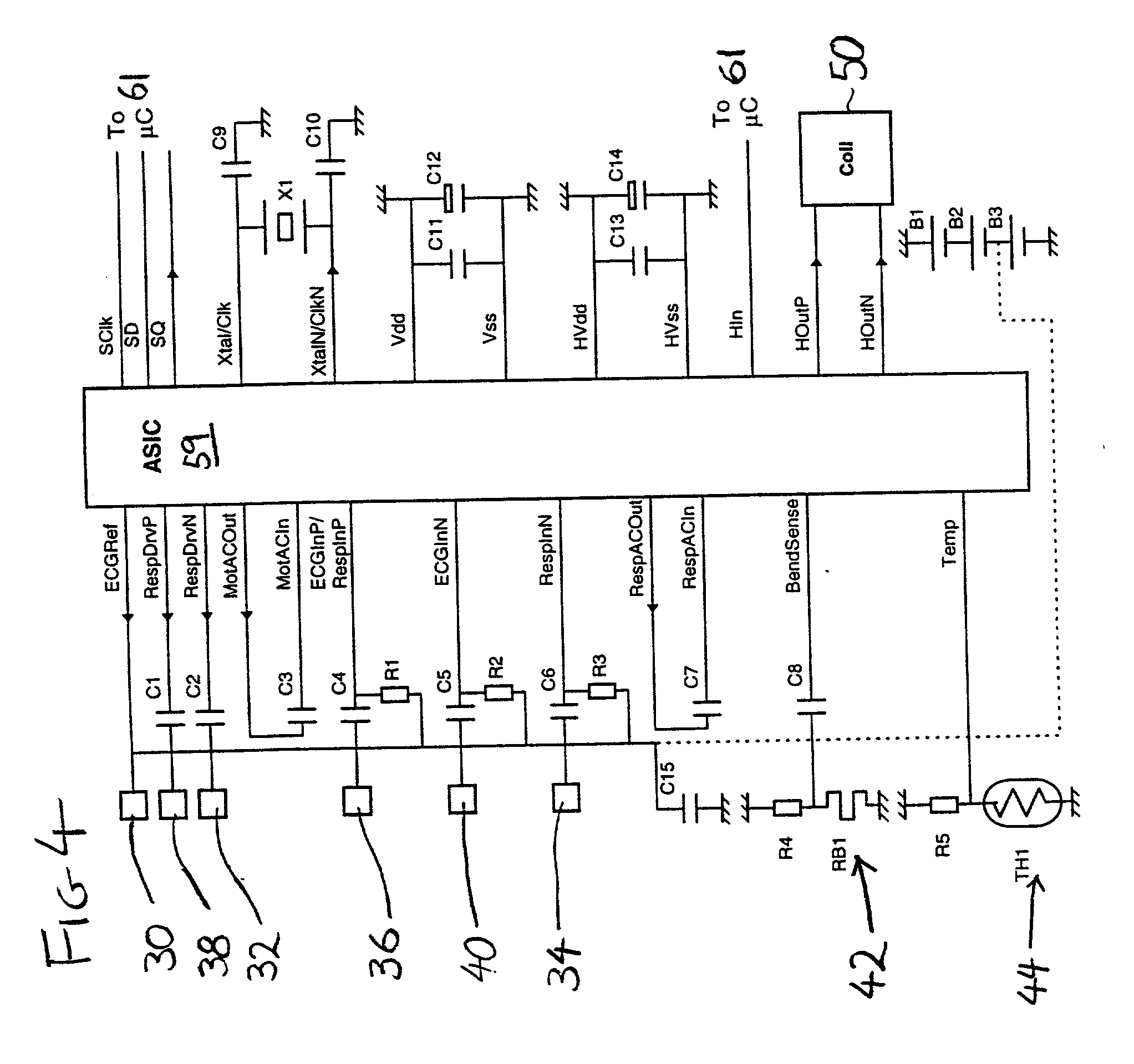
Physiological sensor array
InactiveUS6494829B1Efficient low powered transfer of dataImprove power efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsElectrocardiographySensor arrayMultiplexer
A physiological sensor device for attachment to a mammalian subject comprising an output transmitter, at least two physiological sensors each for sensing one of the subject's physiological parameters, and a controller operably in communication with the physiological sensors which controller communicates a signal comprising data representative of both the sensed physiological parameters to the output transmitter which operably transmits the signal to a remote location, wherein the controller comprises a multiplexer which operably switches the data from both the physiological sensors into a serial output signal. Respiration may be detected by a bend sensor including an elongate member and an electrical component mounted thereon which electrical component has an electrical property which varies in dependence on the extent of bending of the elongate member. Other parameters such as temperature and full waveform ECG may also be measured.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
Physiological sensor array
InactiveUS20010047127A1Efficient low powered transfer of dataReduce power lossElectric signal transmission systemsElectrocardiographySensor arrayMultiplexer
A physiological sensor device for attachment to a mammalian subject comprising an output transmitter, at least two physiological sensors each for sensing one of the subject's physiological parameters, and a controller operably in communication with the physiological sensors which controller communicates a signal comprising data representative of both the sensed physiological parameters to the output transmitter which operably transmits the signal to a remote location, wherein the controller comprises a multiplexer which operably switches the data from both the physiological sensors into a serial output signal. In a preferred embodiment, respiration is detected by a bend sensor including an elongate member and an electrical component mounted thereon which electrical component has an electrical property which varies in dependence on the extent of bending of the elongate member. Other parameters such as temperature and full waveform ECG may also be measured.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
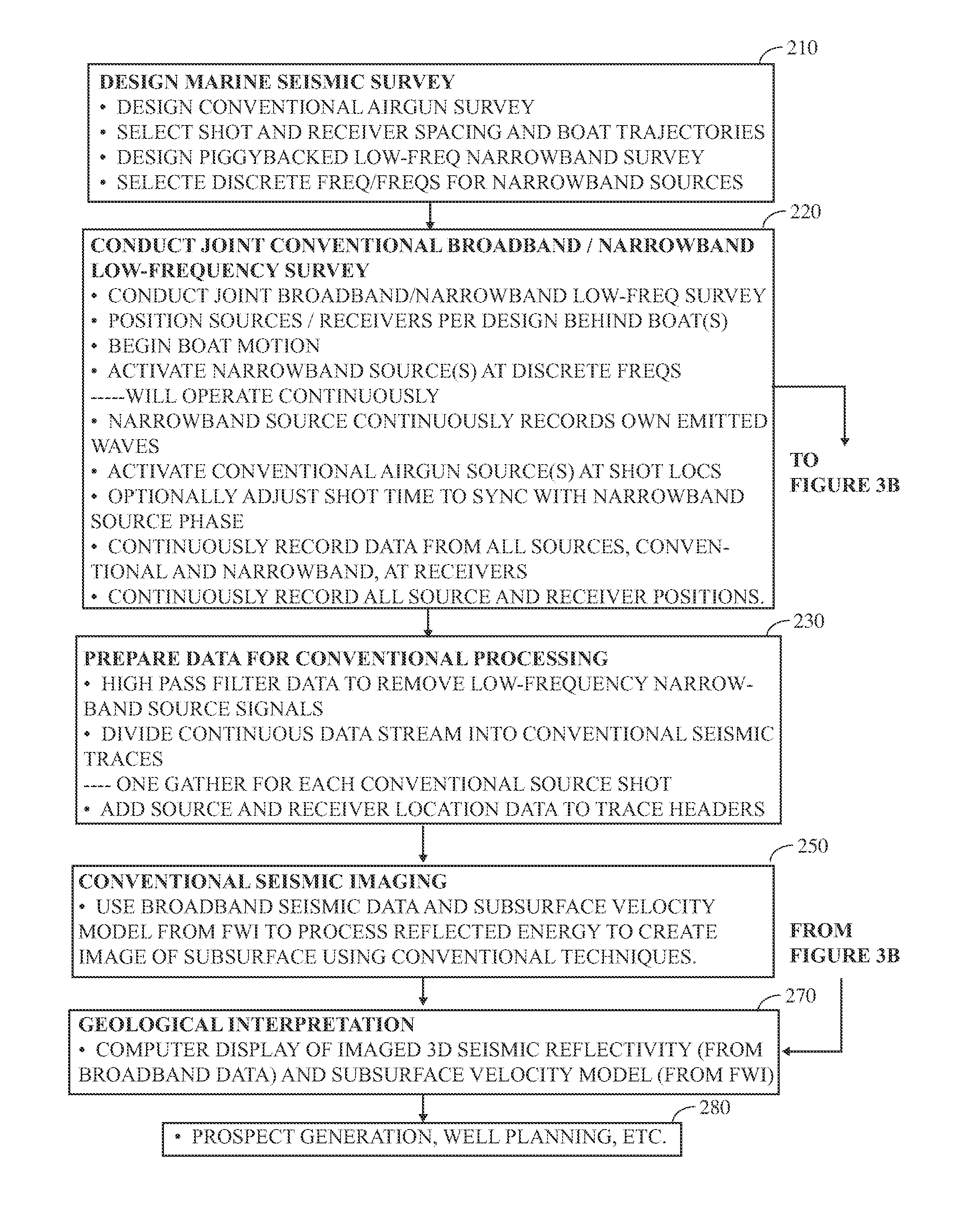
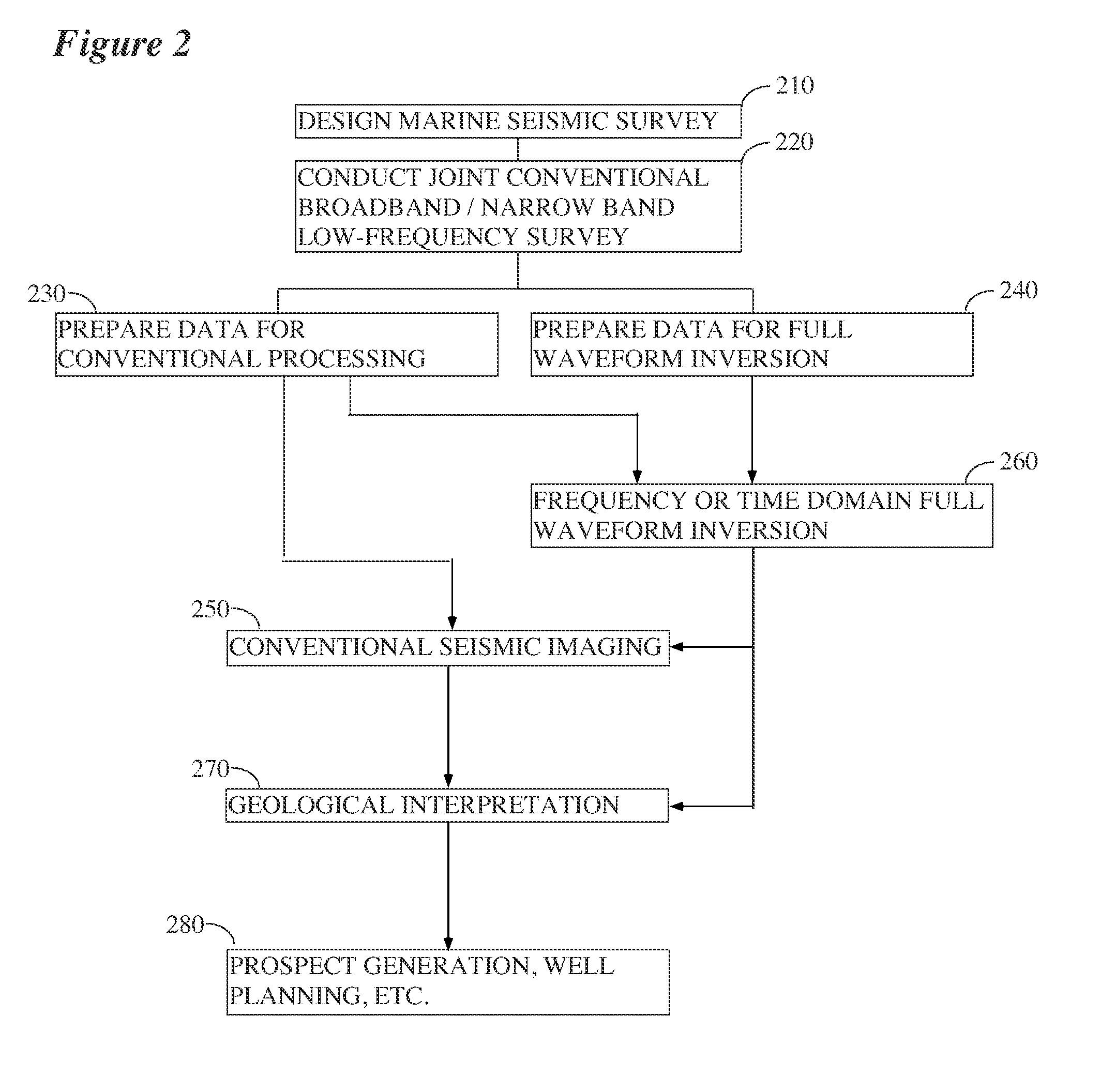
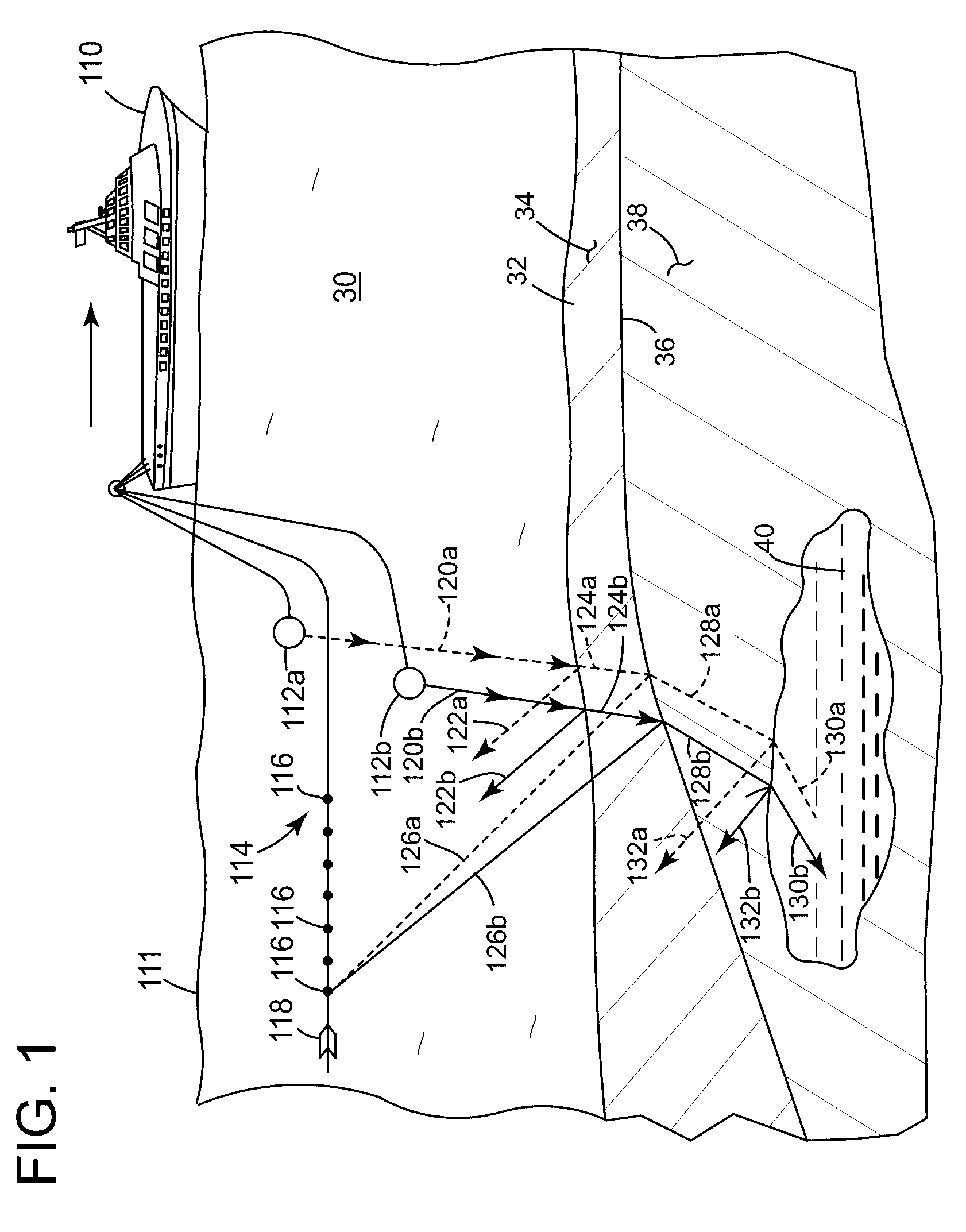
Seismic acquisition using narrowband seismic sources
ActiveUS20120155217A1Reduce crosstalkSpeed up the processSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingMonochromatic colorFull waveform
There is provided herein a system and method of seismic data collection for land and marine data that utilizes narrowband to monochromatic low-frequency non-impulsive sources designed to optimize the ability of migration / inversion algorithms to image the subsurface of the Earth, in particular, full-waveform inversion.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Dip guided full waveform inversion
InactiveUS20110131020A1Reduce difficultyLow costSeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationImaging qualityFull waveform
A method of determining seismic data velocity models comprising dip-guided full waveform inversion that obtains a better velocity model with less computational requirements. DG-FWI quickly converges to provide a better image, obtains better amplitudes, and relies less on lower frequencies. Improved image quality allows detailed seismic analyses, accurate identification of lithological features, and imaging near artifacts and other anomalies.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
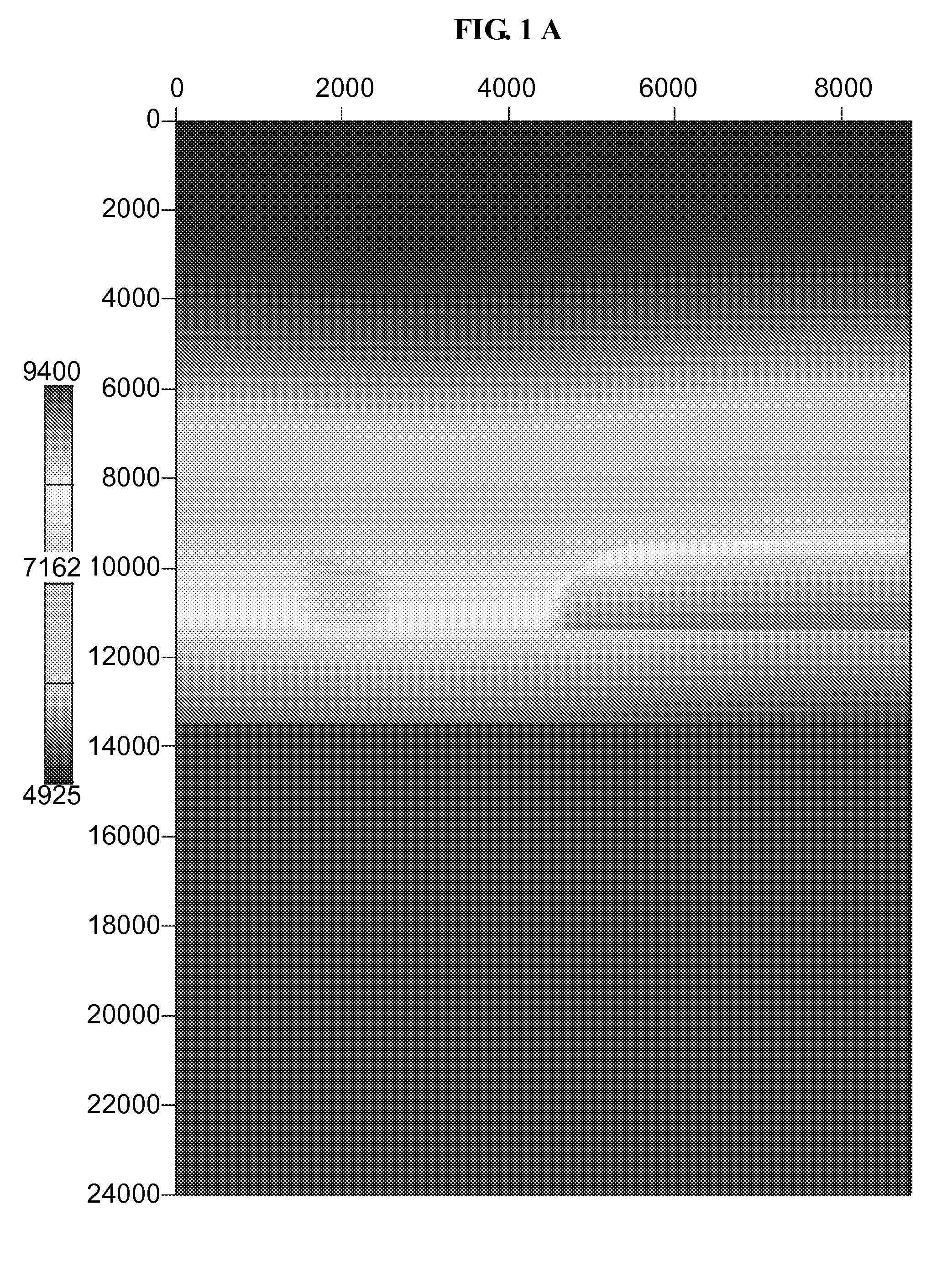
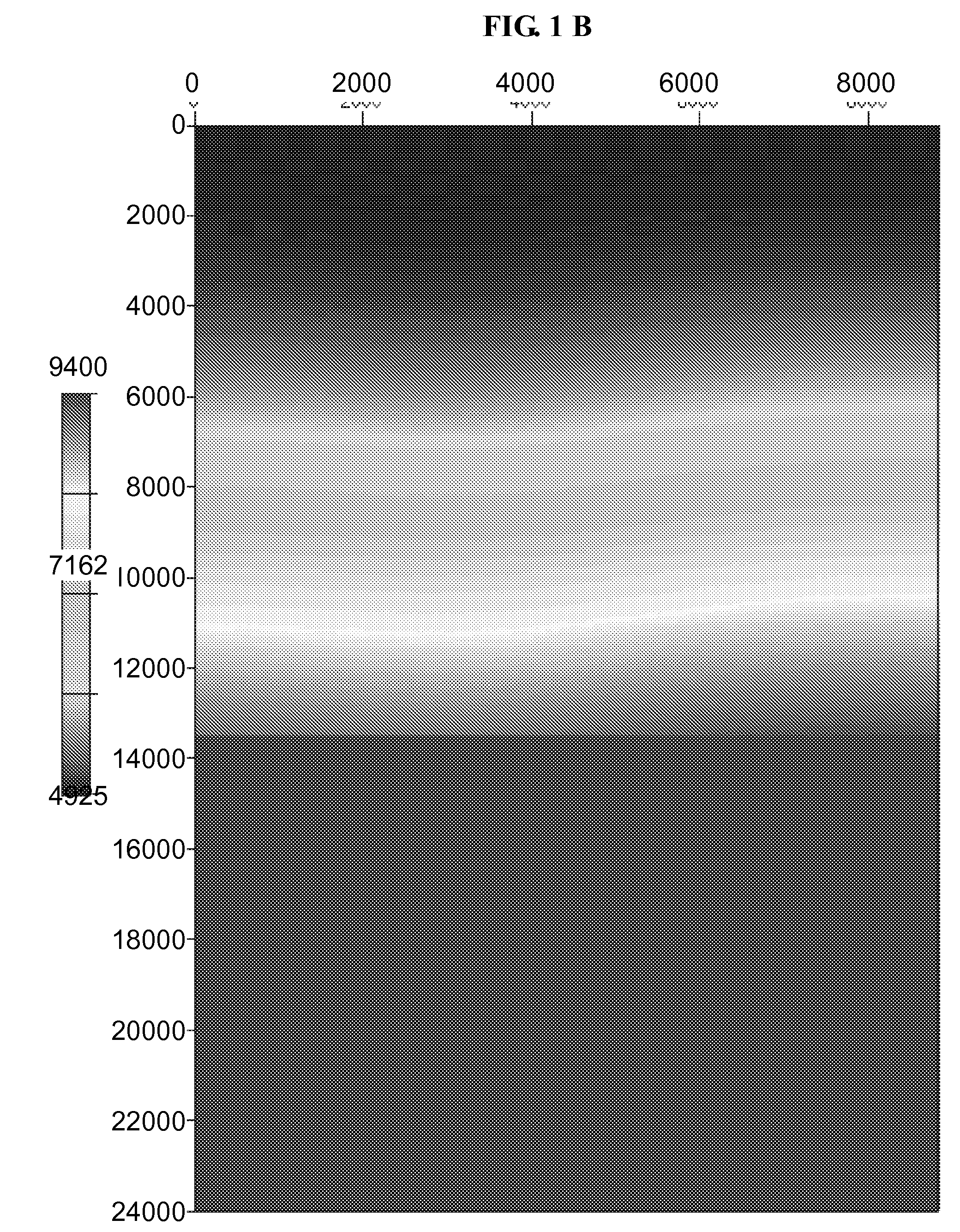
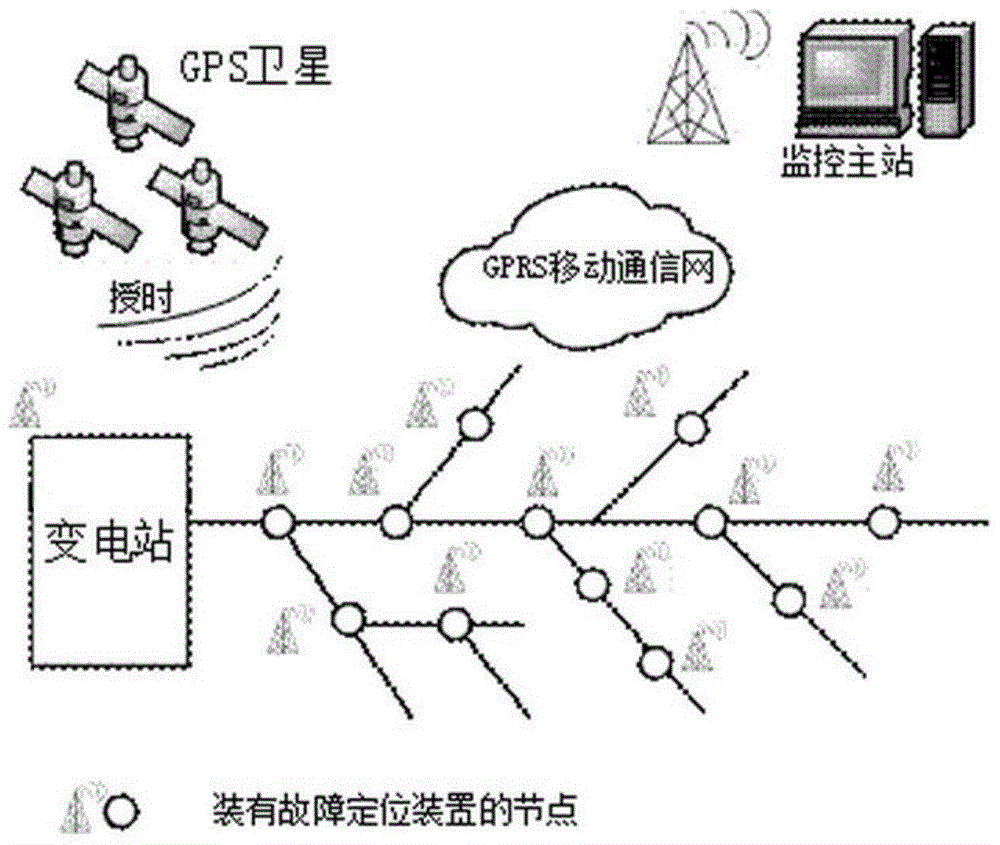
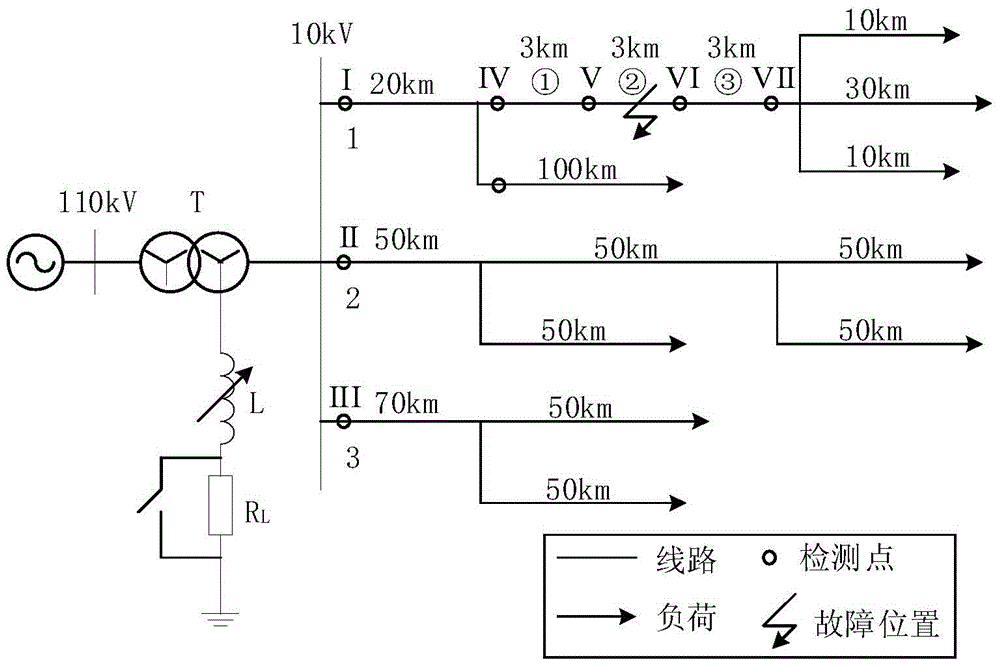
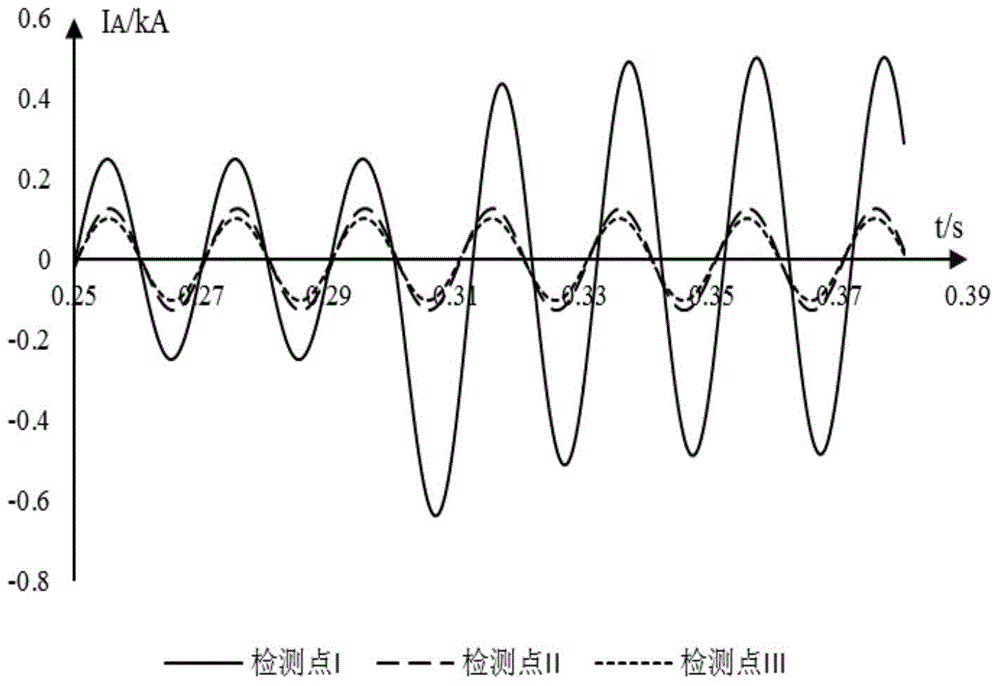
Distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information
ActiveCN104155582AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesPhase currentsCorrelation function
The invention discloses a distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information. For the grounding fault, line selection is carried out through extreme value points of a cross-correlation function of the bus zero-sequence voltage and all outgoing line zero-sequence currents, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point zero-sequence current waveform standard drift rate of the whole action process of a fault occurrence and compensation device; for the interphase fault, line selection is carried out according to the overcurrent information obtained before action of a relay protection device, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point fault phase current waveform standard drift rate. The waveform data of the whole action process of a fault and arc extinction device are utilized, the current ubiquitous problems that when a small current grounding system encounters the single-phase grounding phase, the fault current is weak, the reliability is poor, and the sensitivity is low can be well solved, and meanwhile the system cannot get interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAINE ENERGY TECH CO LTD
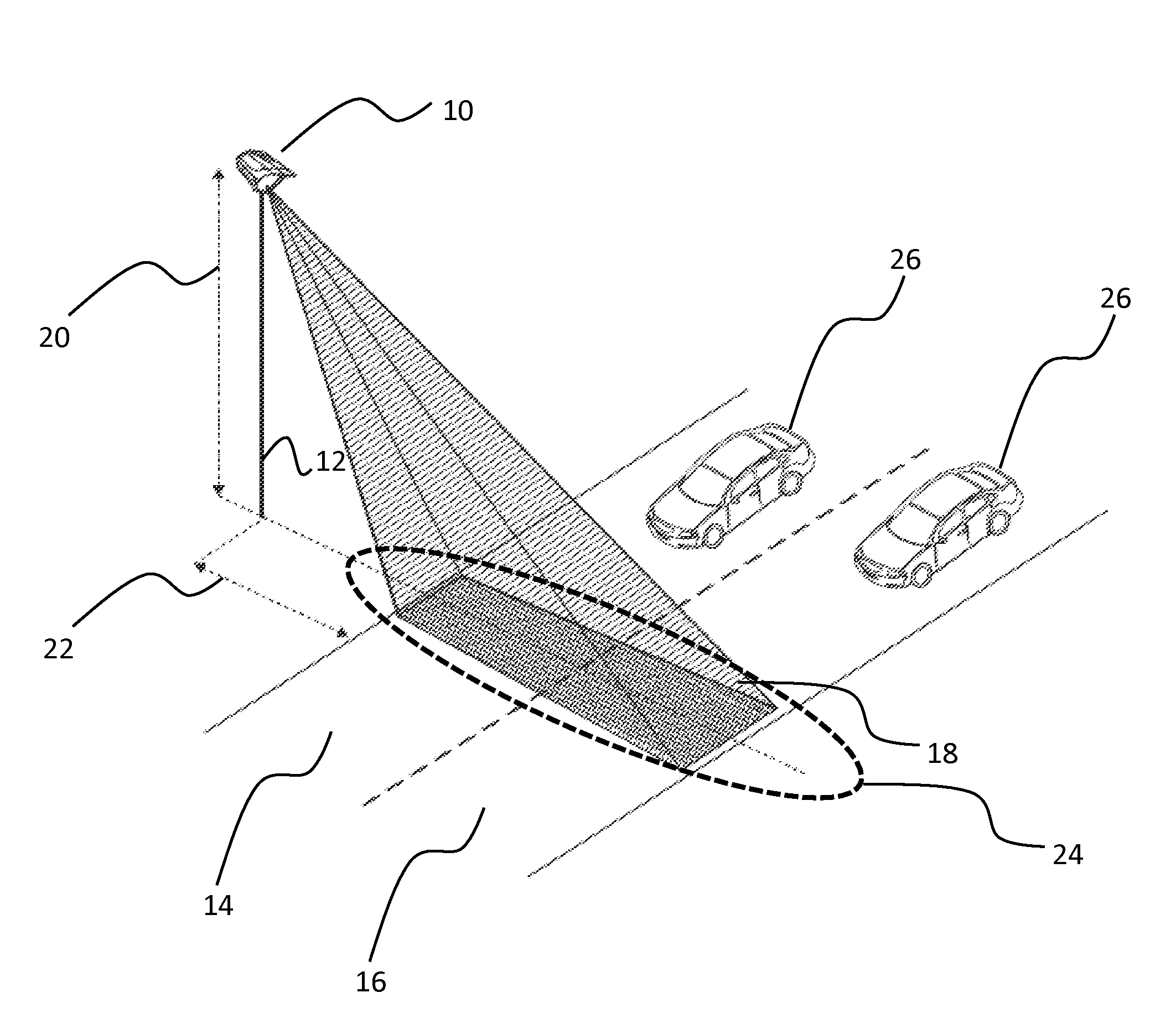
System and method for traffic side detection and characterization
ActiveUS20140232566A1High repetition rateDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionRadarFull waveform
A method for detecting a vehicle comprising: providing a multi-channel scannerless full-waveform lidar system operating in pulsed Time-Of-Flight operation oriented towards a surface of the roadway to cover the detection zone; providing at least one initialization parameter; emitting pulses at an emission frequency; receiving reflections of the pulses from the detection zone; and acquiring and digitalizing a series of individual complete traces at each channel of system; identifying at least one detection in at least one of the traces; obtaining a height and an intensity for the detection; determining a nature of the detection to be one of an environmental particle detection, a candidate object detection and a roadway surface detection; if the nature of the detection is the candidate object detection, detecting a presence of a vehicle in the detection zone.
Owner:LEDDARTECH INC
Earth model estimation through an acoustic full waveform inversion of seismic data
InactiveUS20130311151A1Optimize timingExtend depth of investigationComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationFull waveformEarth model
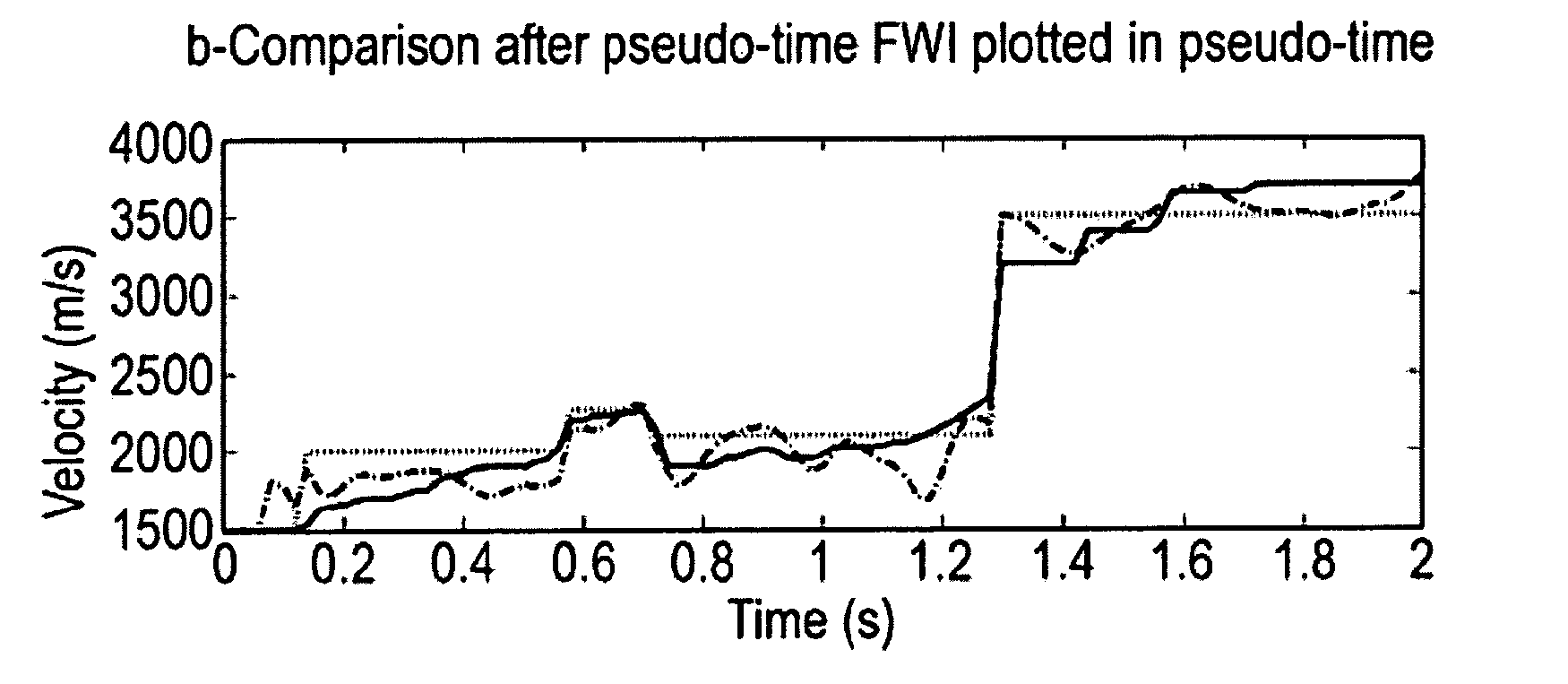
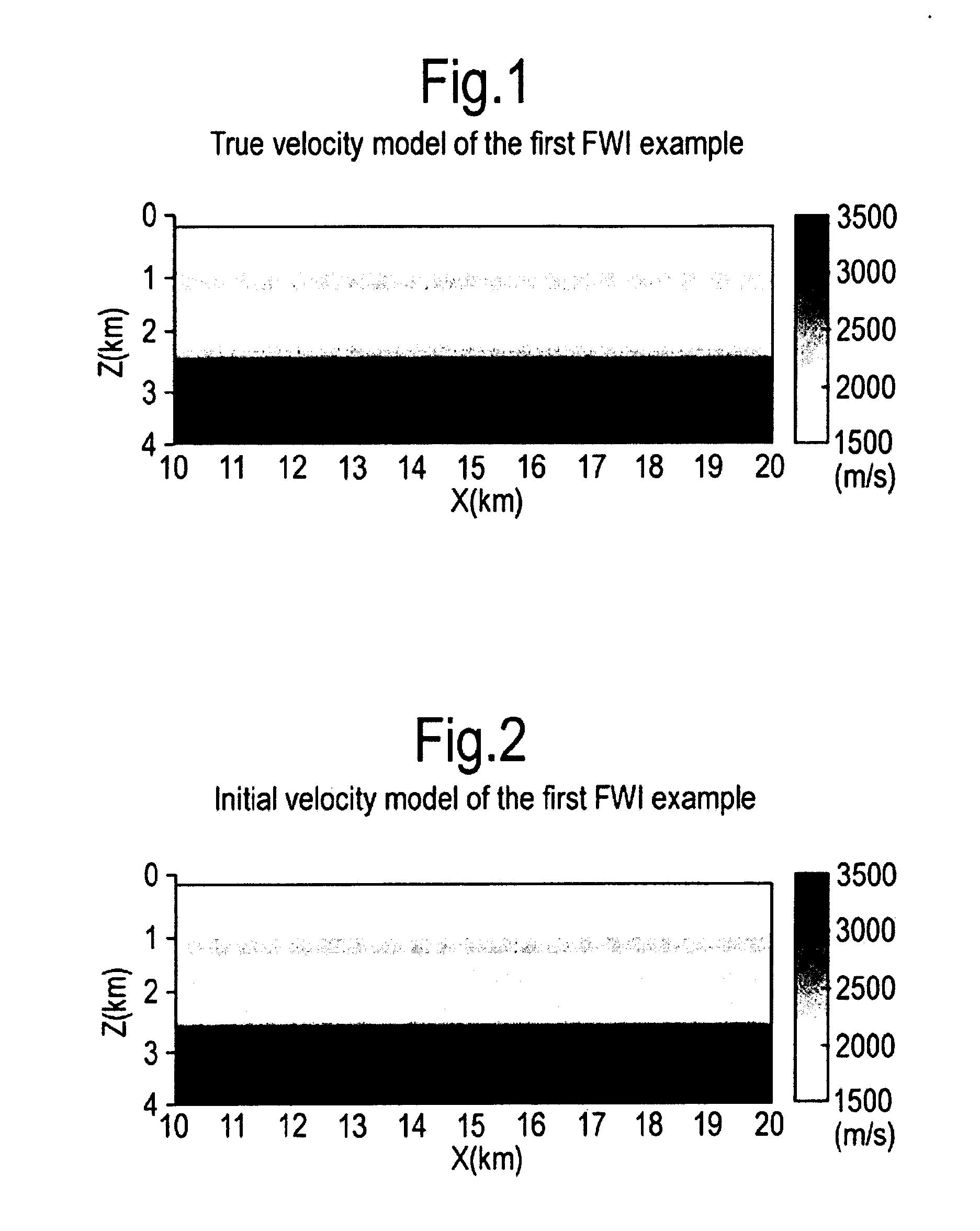
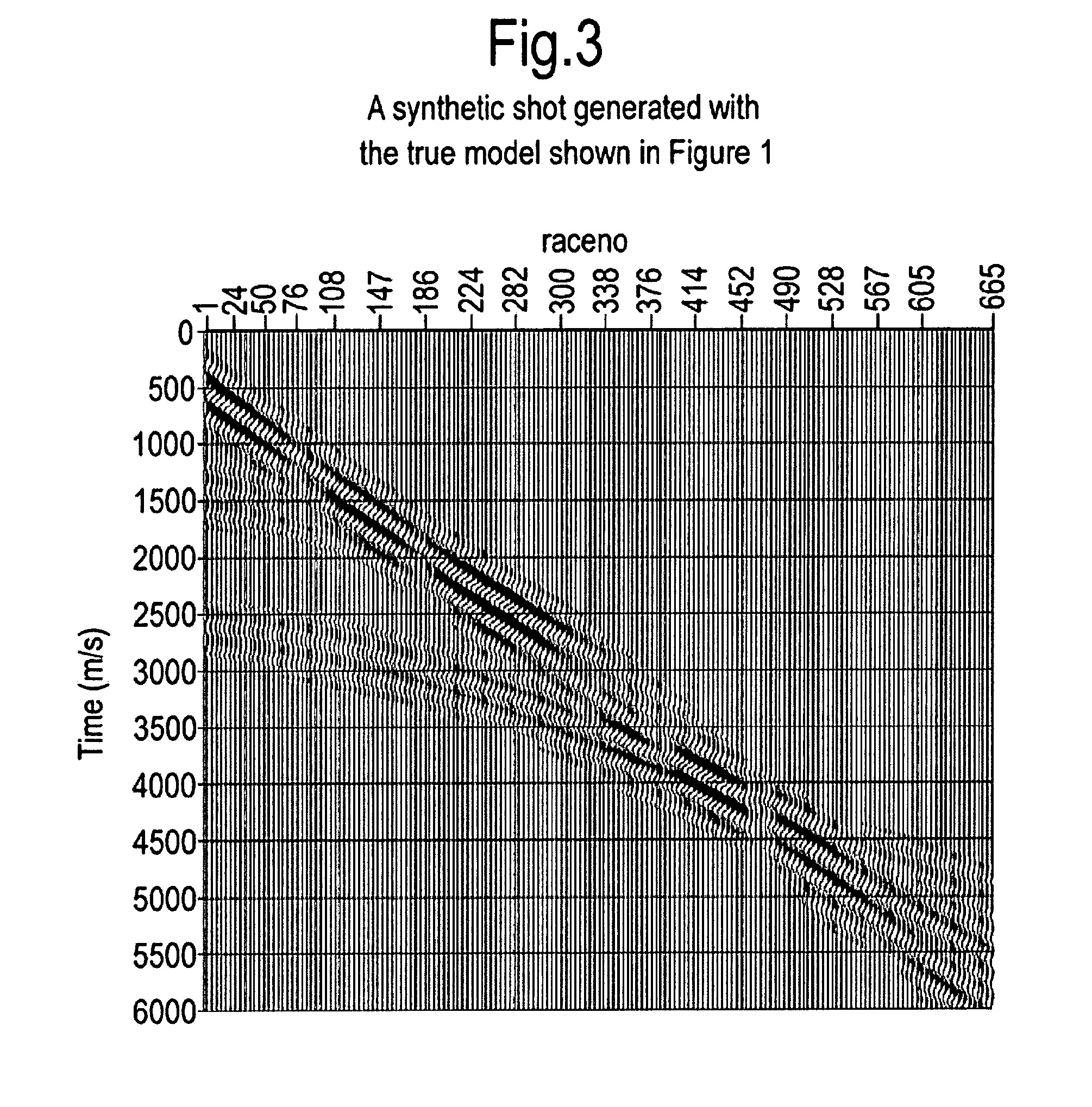
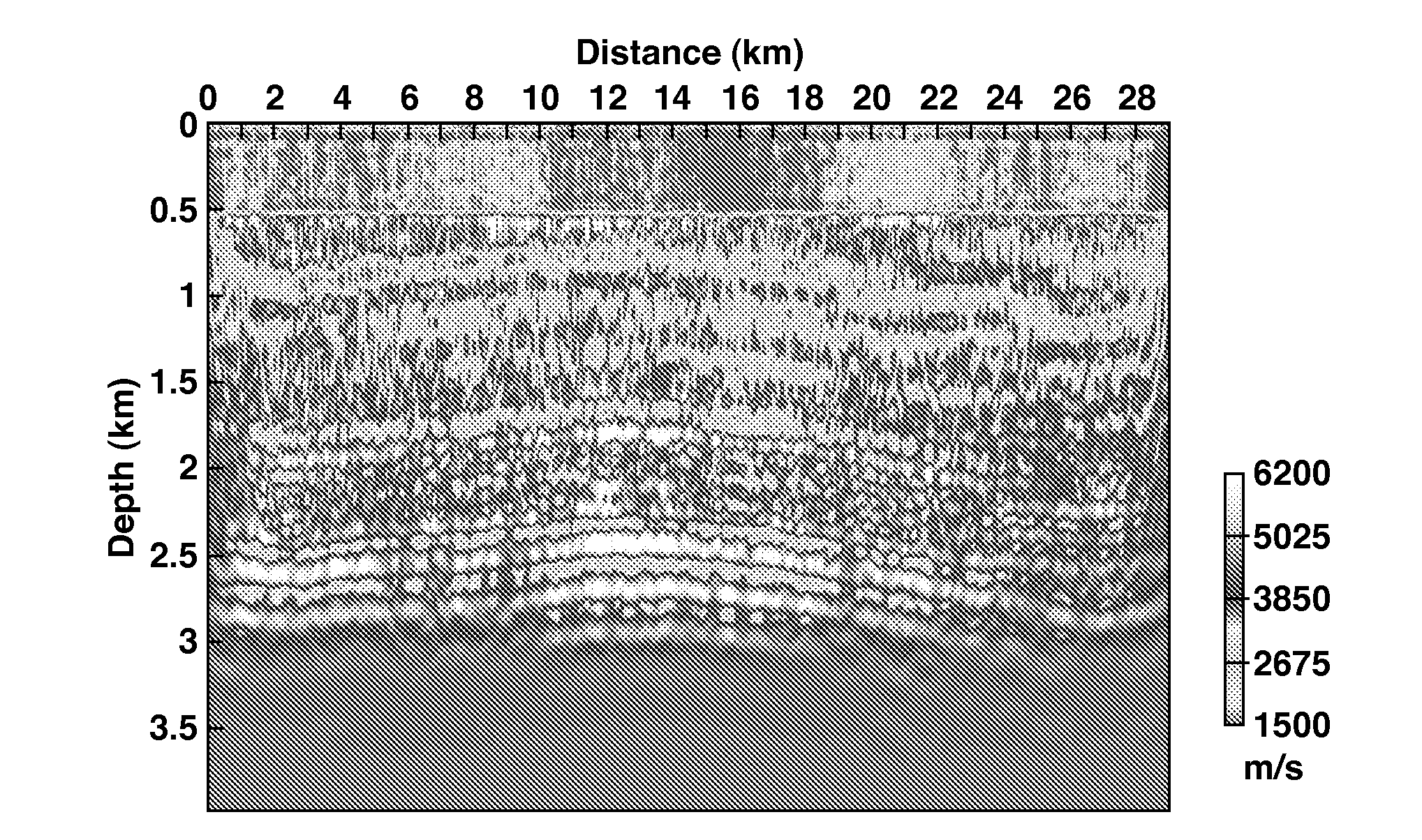
An improved method of estimating an earth model utilizes an acoustic Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) of seismic data in a pseudo-time coordinate system, in which the earth model m({tilde over (m)}) is parameterized with two lateral coordinates (x,y) and a vertical coordinate ({tilde over (z)}) which expresses vertical travel time of acoustic signals used to generate the seismic data.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Hybride Method For Full Waveform Inversion Using Simultaneous and Sequential Source Method
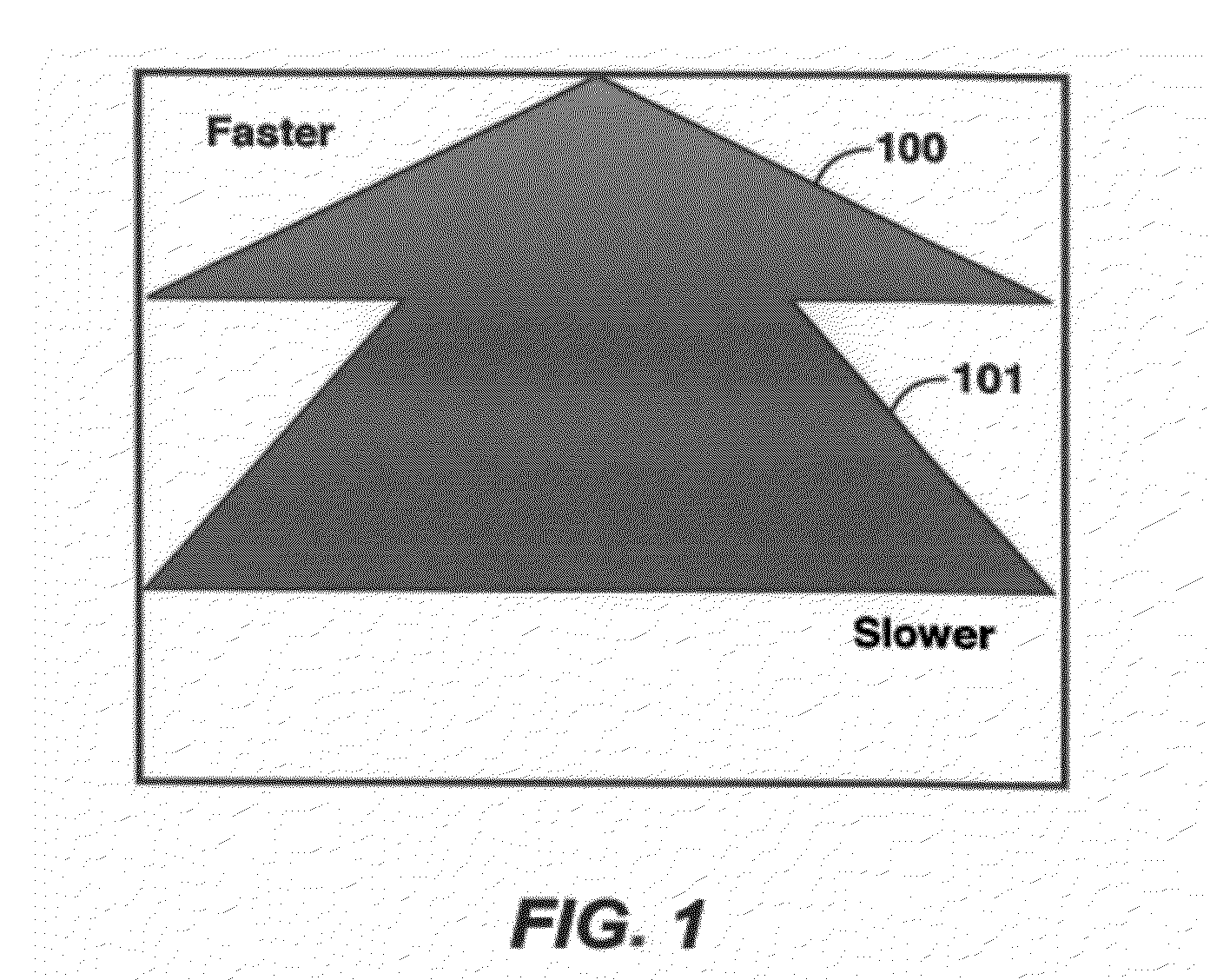
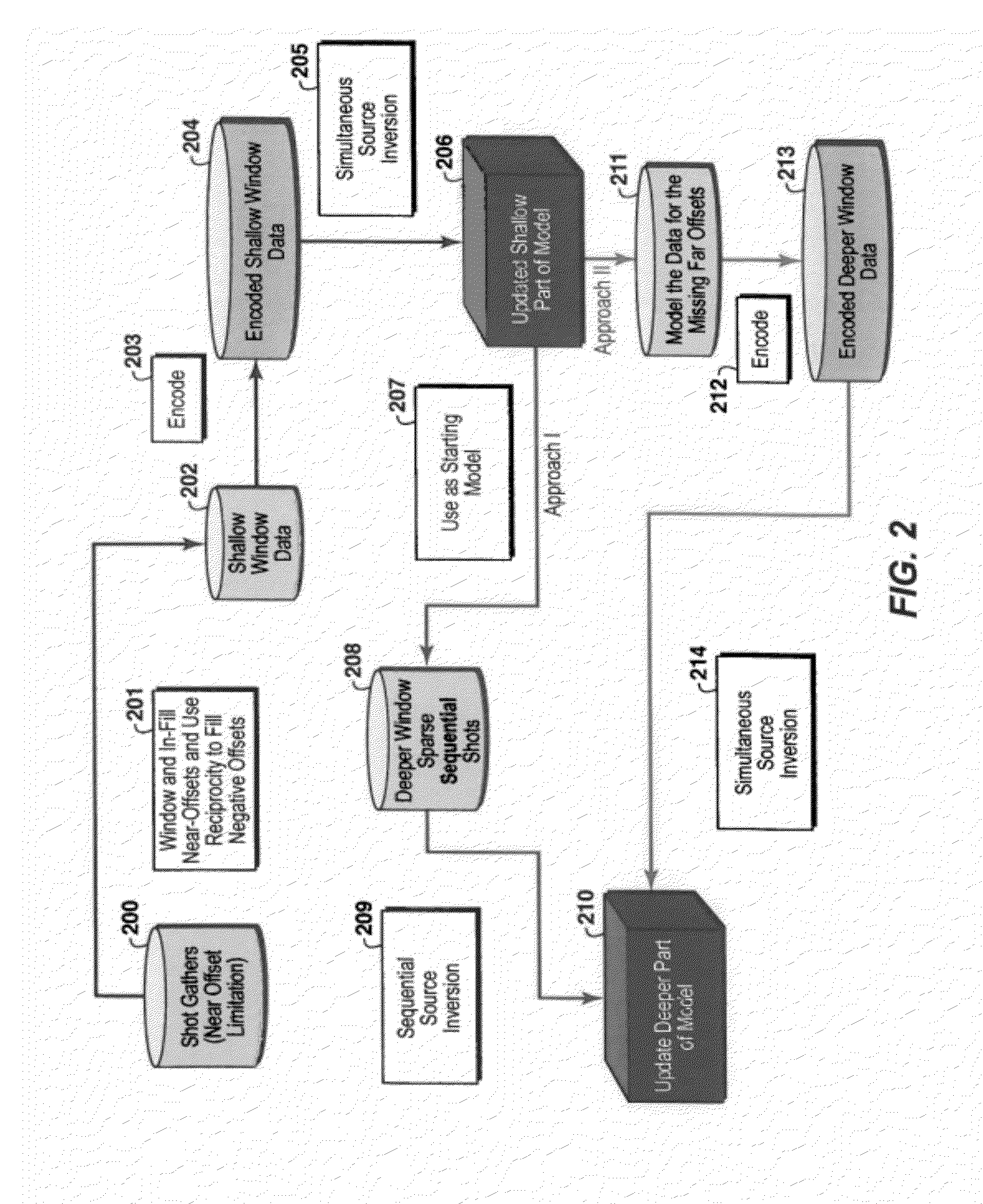
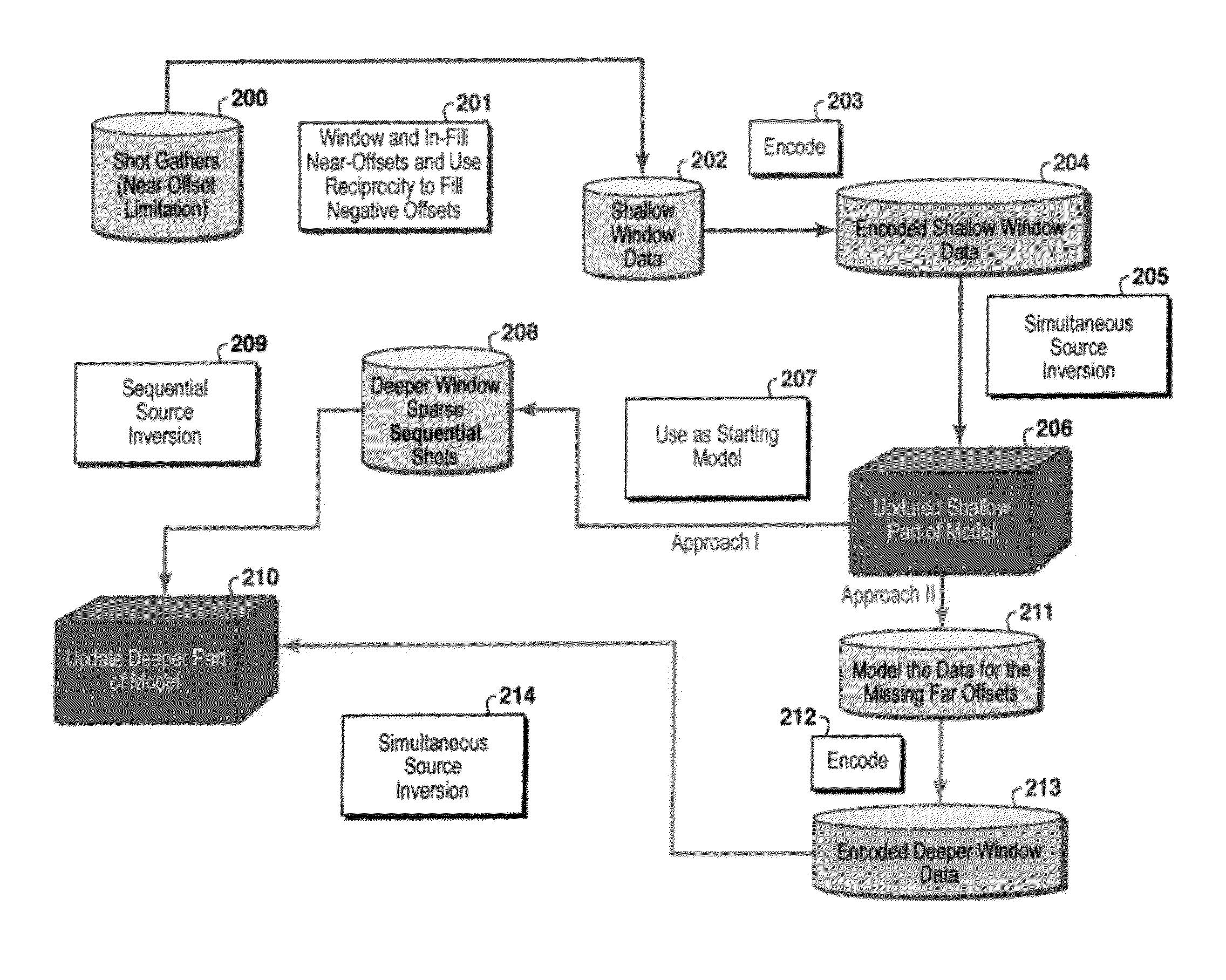
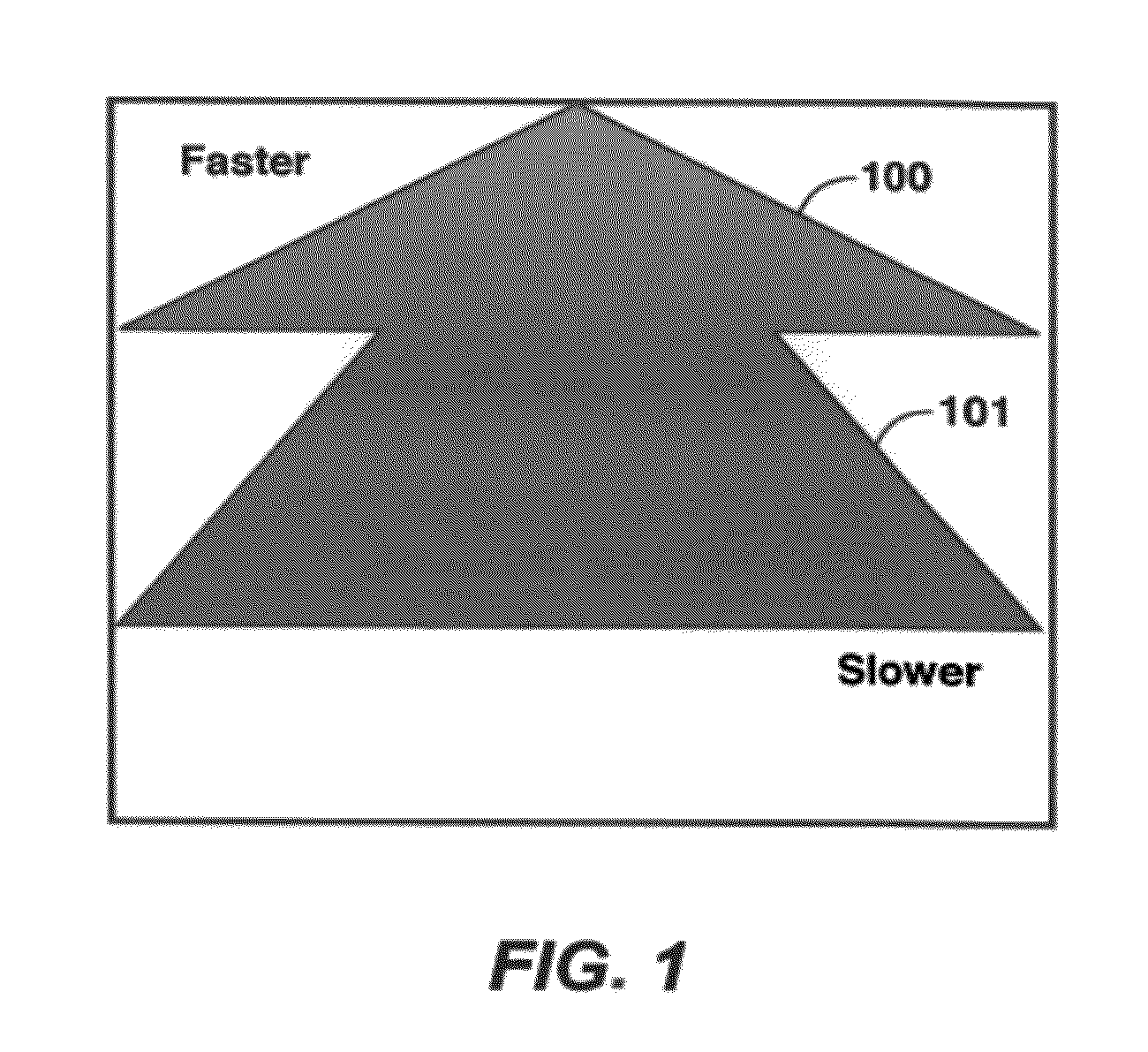
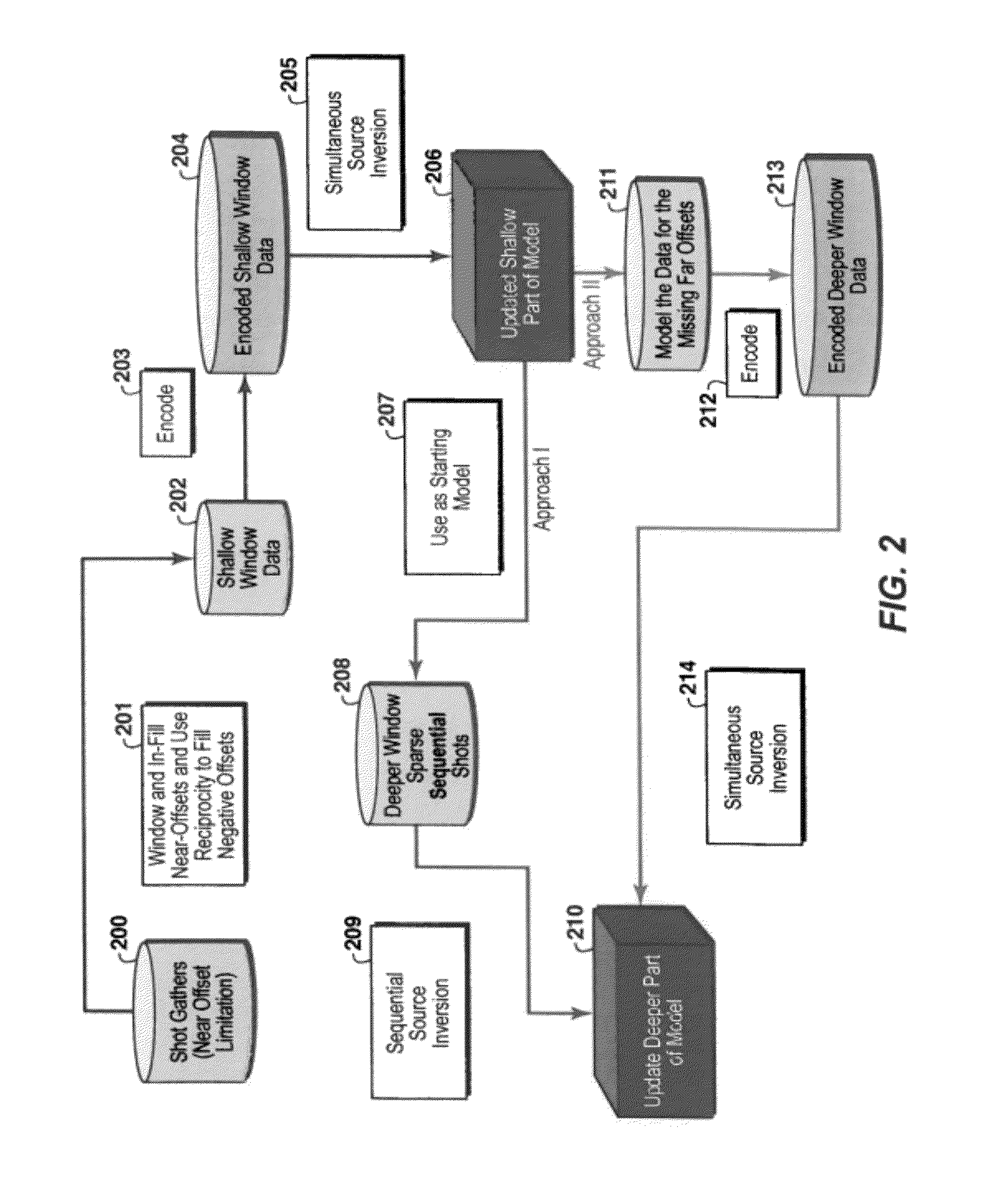
Method for simultaneous full-wavefield inversion of gathers of source (or receiver) encoded geophysical data to determine a physical properties model for a subsurface region, especially suitable for surveys where fixed receiver geometry conditions were not satisfied in the data acquisition. First, a shallow time window of the data (202) where the fixed receiver condition is satisfied is inverted by simultaneous encoded (203) source inversion (205). Then, the deeper time window of the data (208) is inverted by sparse sequential source inversion (209), using the physical properties model from the shallow time window (206) as a starting model (207). Alternatively, the shallow time window model is used to simulate missing far offset data (211) producing a data set satisfying the stationary receiver assumption, after which this data set is source encoded (212) and inverted by simultaneous source inversion (214).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Hybrid method for full waveform inversion using simultaneous and sequential source method
Method for simultaneous full-wavefield inversion of gathers of source (or receiver) encoded geophysical data to determine a physical properties model for a subsurface region, especially suitable for surveys where fixed receiver geometry conditions were not satisfied in the data acquisition. First, a shallow time window of the data (202) where the fixed receiver condition is satisfied is inverted by simultaneous encoded (203) source inversion (205). Then, the deeper time window of the data (208) is inverted by sparse sequential source inversion (209), using the physical properties model from the shallow time window (206) as a starting model (207). Alternatively, the shallow time window model is used to simulate missing far offset data (211) producing a data set satisfying the stationary receiver assumption, after which this data set is source encoded (212) and inverted by simultaneous source inversion (214).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Two stage seismic velocity model generation
InactiveUS20150120200A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic velocityFeature data
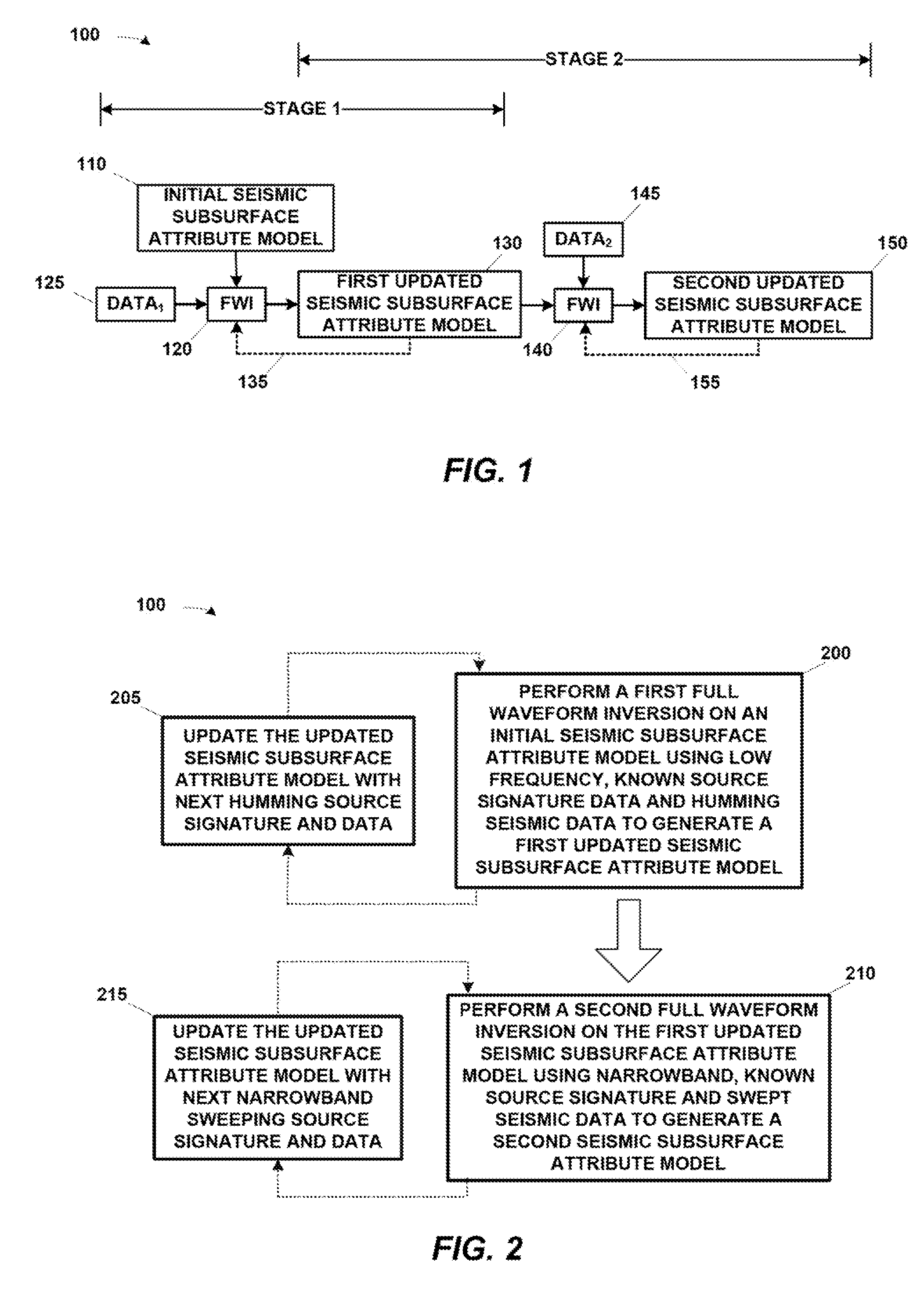
A computer-implemented process includes: performing a first foil waveform inversion on an initial subsurface attribute model using low frequency, known source-signature data and low frequency humming seismic data to generate a first updated subsurface attribute model; and performing a second full waveform inversion on the first updated subsurface attribute model using low-frequency, narrowband sweeping known source-signature data and low-frequency, swept seismic data to generate a second updated subsurface attribute model. The process may be performed by a suitably programmed computing apparatus, the program residing on some form of non-transitory program storage medium.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Hybrid-domain full wave form inversion method of central processing unit (CPU)/graphics processing unit (GPU) synergetic parallel computing
InactiveCN103135132ASolving Convergence ProblemsAvoid the problem of insufficient storage and occupancySeismic signal processingInternal memoryFull wave
The invention discloses a hybrid-domain full wave form inversion method of central processing unit (CPU) / graphics processing unit (GPU) synergetic parallel computing. Compared with a traditional method, the method can be adopted to conduct the CPU / GPU synergetic parallel computing so as to obviously improve computing efficiency. The method enables a forward part of full wave form inversion to be placed to a time domain, namely forward is conducted in the time domain, the forward is converted to be conducted as the inversion in a frequency domain by the discrete fourier transform (DFT) being utilized, namely the DFT is adopted to pick wave field components corresponding to inversion frequency, and the inversion is conducted in the frequency domain from low frequency to high frequency. The method effectively resolves the problem of astringency of a standard time domain method, and avoids the problem that internal memory of wave form inversion of a standard three-dimensional frequency domain and a Laplace domain cannot be satisfied. The method is few in step, reduces computing expenses, and due to the fact the method can be adopted to conduct the CPU / GPU synergetic parallel computing, largely improves speed-up ratio of the computing method.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
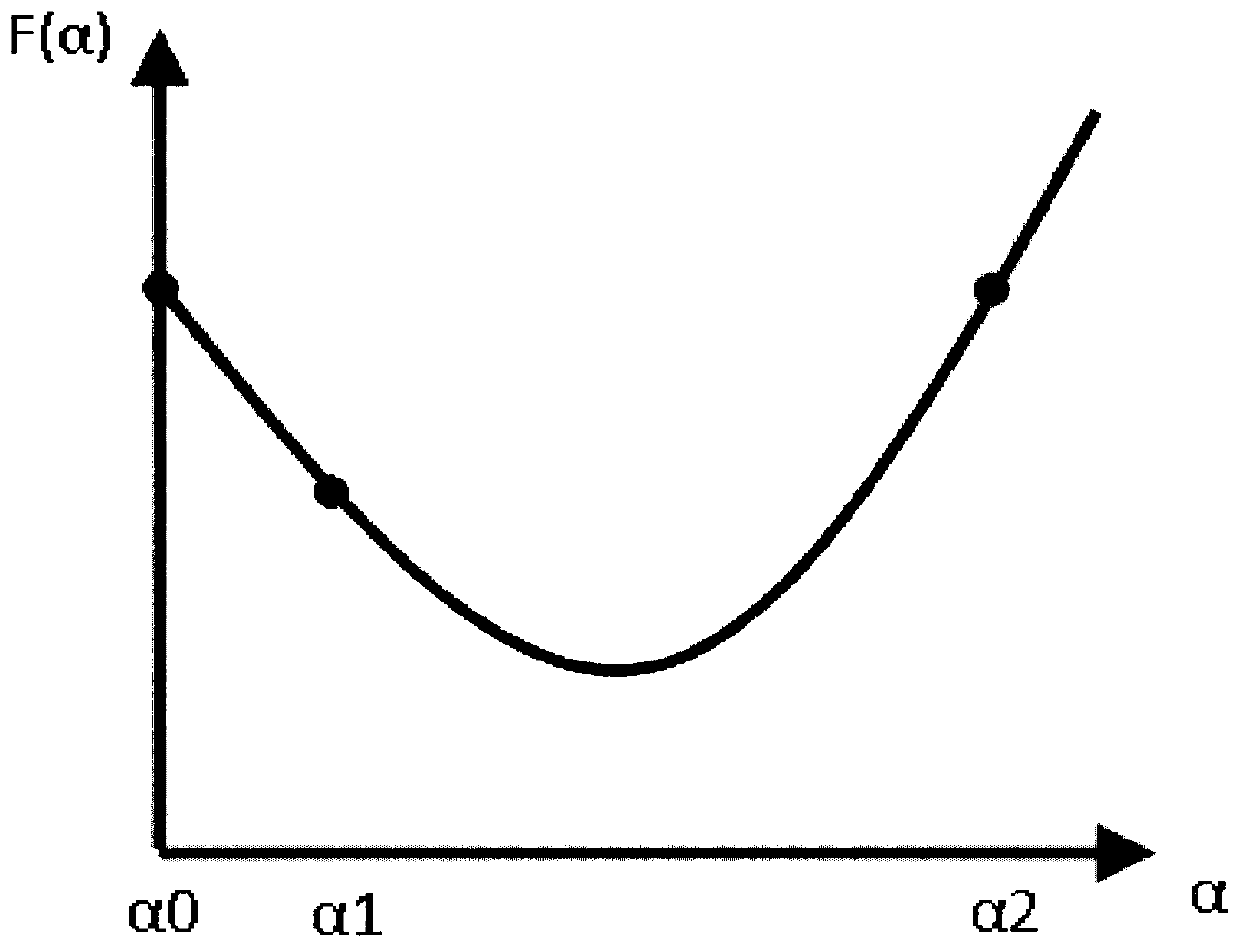
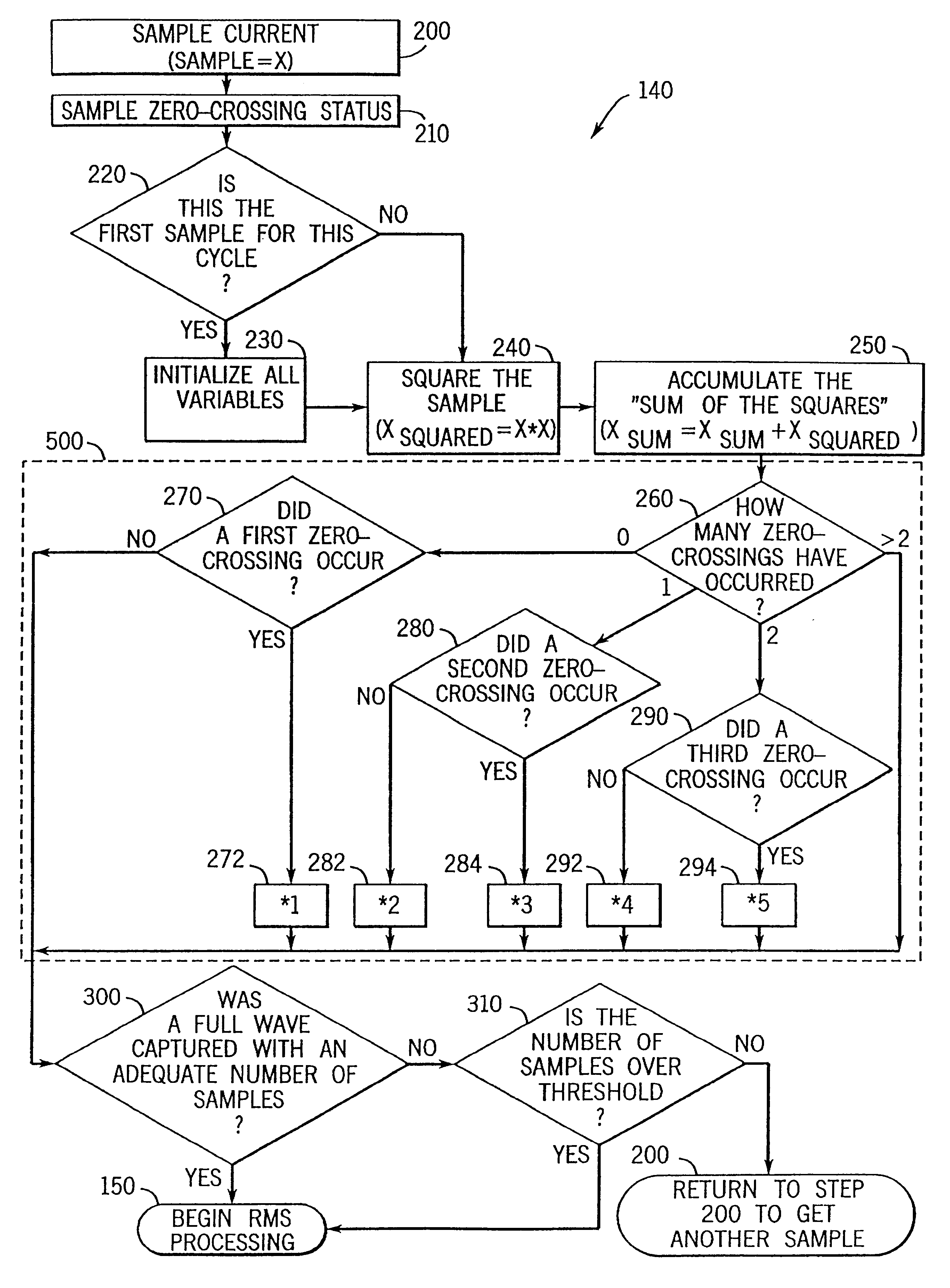
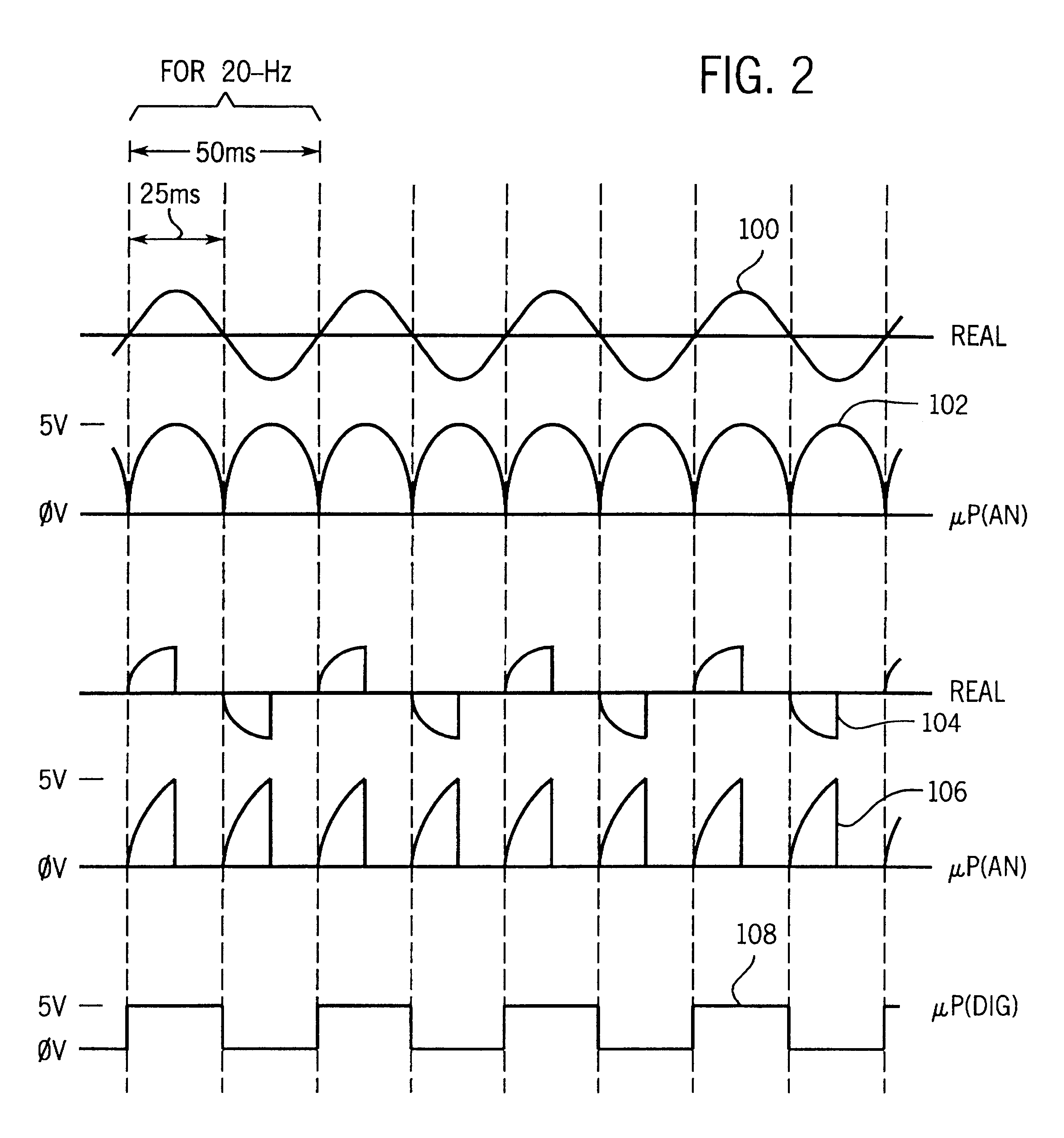
Method and apparatus for calculating RMS value
InactiveUS6516279B1Sampled-variable control systemsNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementReal-time dataFull waveform
A technique for computing RMS values for sampled waveforms. More specifically, a technique for computing RMS values for periodic waveforms, using data taken from a full waveform, a half waveform or some other portion of a waveform is described. Each RMS calculation is based on a different algorithm and provides accurate, real time data.
Owner:ROCKWELL TECH
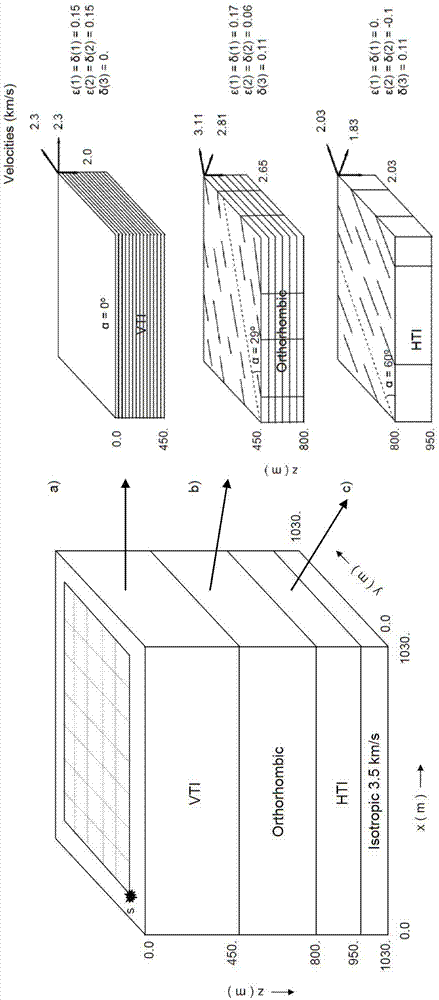
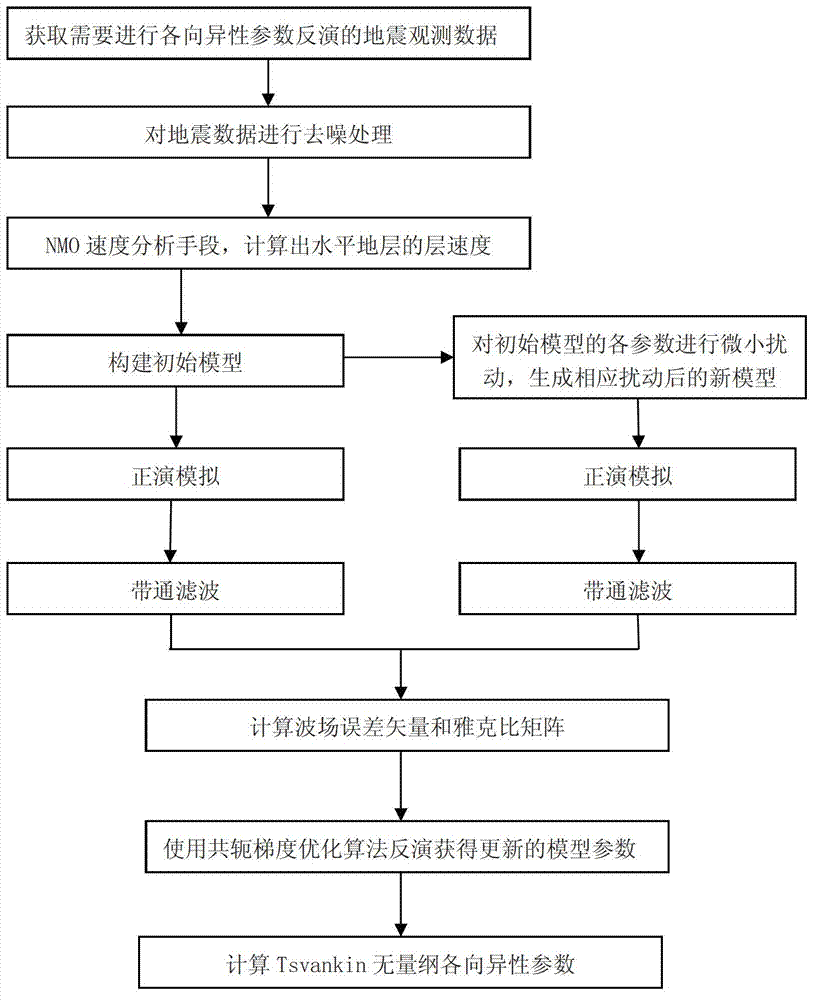
Seismic anisotropy parameter full waveform inversion method and device
ActiveCN103713315AHigh accuracy of inversion resultsHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismic anisotropyWave field
The invention provides a seismic anisotropy parameter full waveform inversion method and device, and belongs to the field of seismic anisotropy parameter prediction in oil geophysical exploration. The method comprises the steps that (1) seismic data which are going to carry out anisotropy parameter inversion are acquired, namely observation wave field data; (2) denoising processing is carried out on the seismic data acquired in the step (1) to acquire denoised data; (3) by using the denoised data acquired in the step (2), and according to shot point and receiver point coordinates, a common midpoint gather is extracted to acquire seismic CMP gather information, and then the seismic CMP gather information is used to calculate the interval velocity of a horizontal stratum; (4) by using the interval velocity, which is acquired in the step (3), of the horizontal stratum, an initial model used for inversion is constructed in an interpolation mode; and (5) small perturbation is carried out on each parameter of the initial model to generate a model after parameter perturbation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
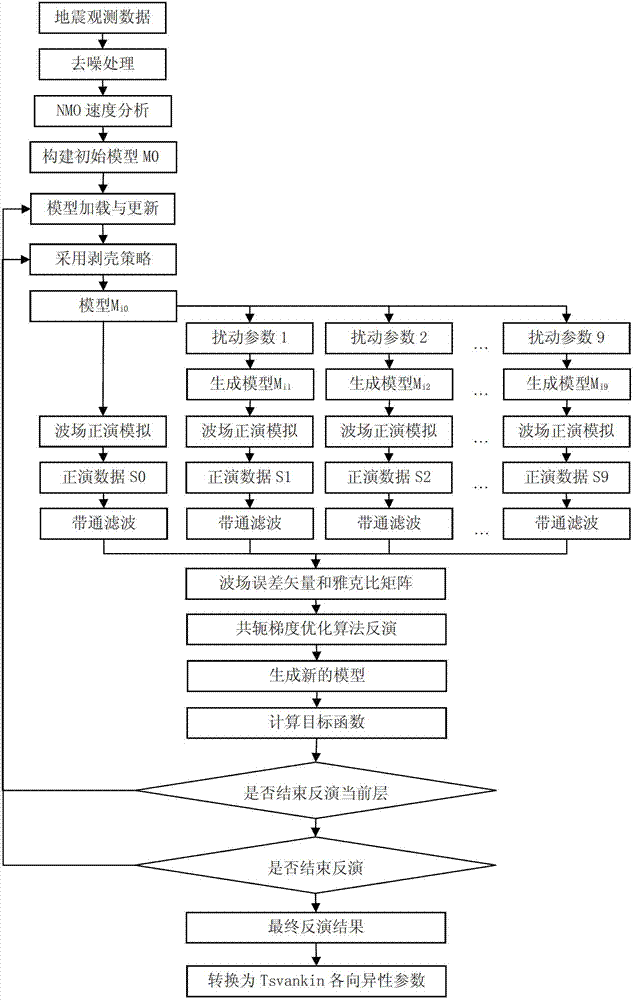
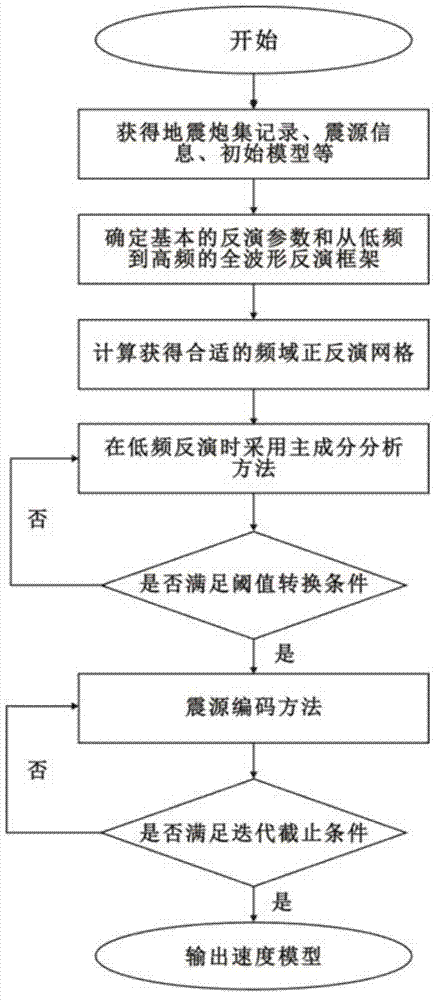
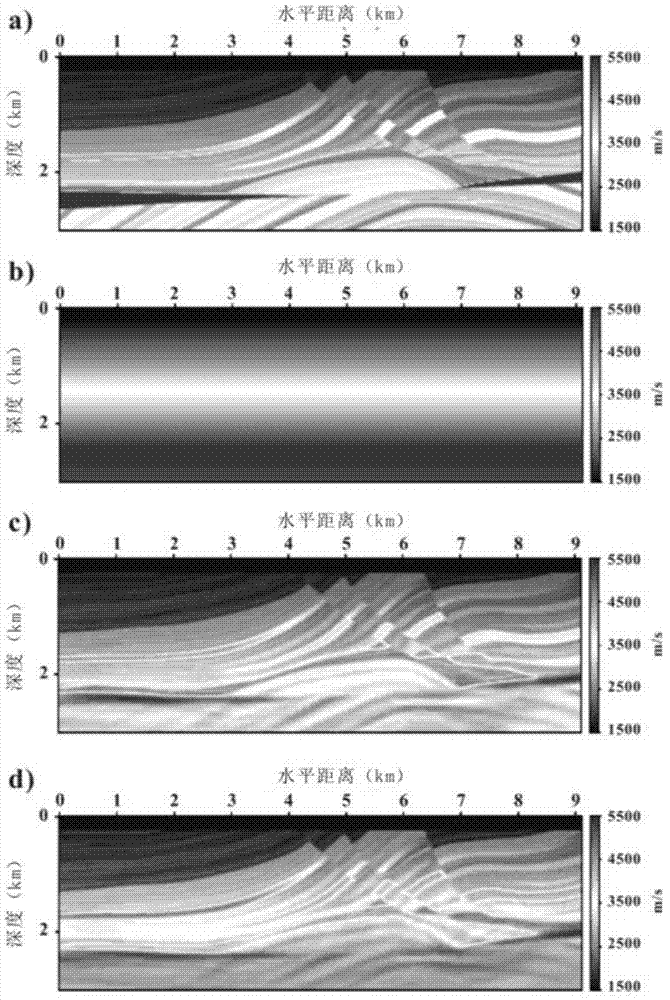
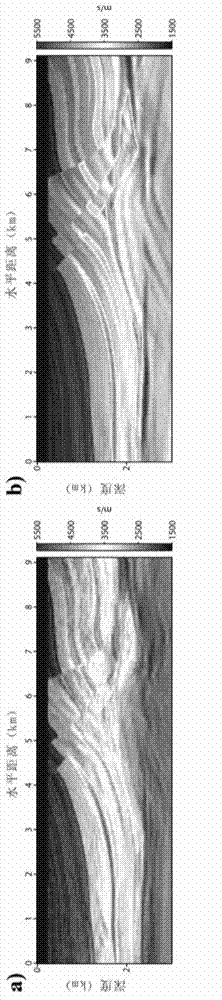
Frequency domain full-waveform inversion seismic velocity modeling method
The invention relates to a frequency domain full-waveform inversion seismic velocity modeling method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring an original seismic shot gather record, focus wavelet information and an initial model used by inversion; 2) analyzing information acquired in the step 1), and determining basic inversion parameters and a full-waveform inversion frame from low frequency to high frequency based on a forward modeling algorithm and an optimization algorithm; 3) calculating to acquire the most appropriate forward and inversion model network for different frequencies; 4) compressing data dimensions which participate in inversion by a principal component analysis method during low-frequency inversion; 5) judging whether projection matrix dimensions corresponding to different frequencies meet the threshold value conversion standard, if the conversion standard is met, performing a next step, and if the conversion standard is not met, returning to the step 4); 6) introducing a focus encoding method, and pressing crosstalk noise by a random phase encoding method; 7) judging whether an iteration stopping condition is met, if the iteration stopping condition is met, performing a next step, and if the iteration stopping condition is not met, returning to the step 6); and 8) if the inversion of all the frequencies is not finished, returning to the step 3) until the inversion of all the frequencies is finished, acquiring the final velocity model, and outputting the velocity model.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Multi-scale seismic full-waveform inversion method based on local adaptive convexification method
ActiveCN107422379AAvoid skippingSolve the problem of inaccurate estimatesSeismic signal processingWave fieldSource function
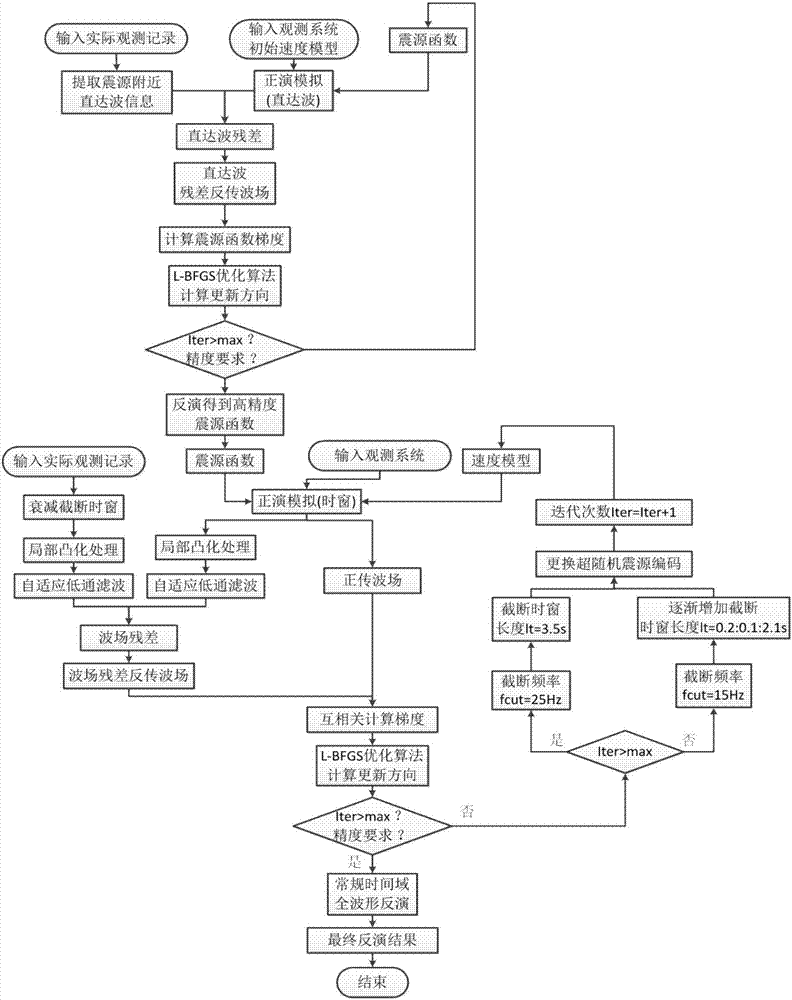
The invention relates to a multi-scale seismic full-waveform inversion method based on a local adaptive convexification method. The method comprises steps: pre-processing is carried out, a zero value sequence serves as an initial value, and an initial speed model serves as a starting value; direct wave information is intercepted; forward modeling direct waves are obtained; an objective function inverted by a seismic source function is built; a direct wave residual and a direct wave residual back propagation wave field are obtained; an updating gradient and an updating direction of the seismic source function are calculated, and a step length is searched; the high-precision seismic source function obtained through inversion is outputted; attenuation time window processing is carried out; seismic data in the time window are simulated; local convexification processing and separation processing are carried out; a high-frequency component in an observation record is removed; a least square objective function is built, and a wave field residual is obtained; a residual back propagation wave field of the model space is obtained; the model updated gradient is obtained; the model updated direction is calculated, and the step length is searched; a multi-scale seismic full-waveform inversion result is outputted; and a final inversion result is outputted. The method is widely applied in the technical field of seismic exploration.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Full Waveform Inversion Using Perfectly Reflectionless Subgridding
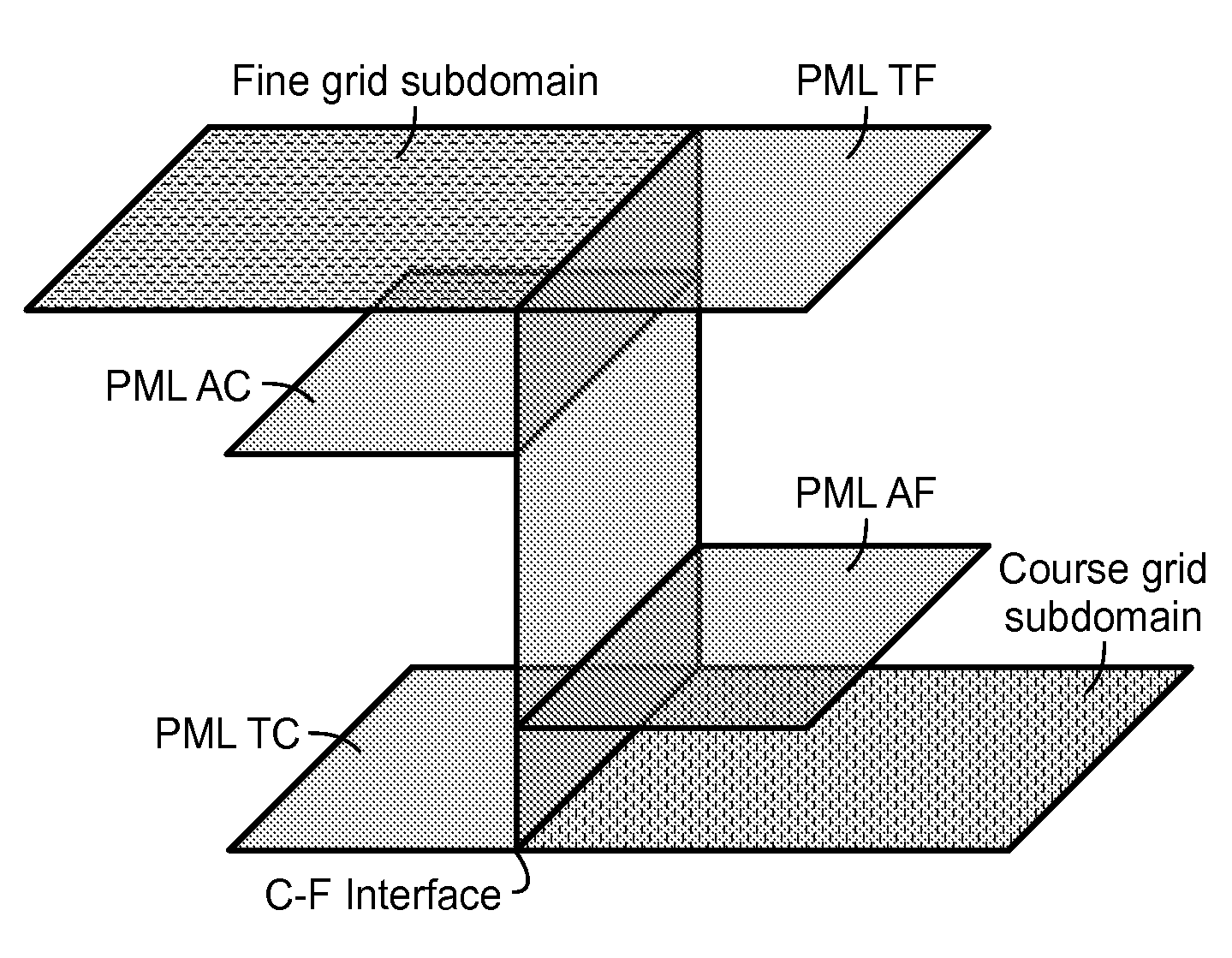
InactiveUS20140372043A1Improve efficiencySignificant computational expenseSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic velocityPerfectly matched layer
Method for reconstructing subsurface profiles for seismic velocity or other geophysical properties from recorded seismic data. In one embodiment, a starting model of seismic velocity is assumed (10). The computational domain is divided into two (or more) subdomains by horizontal planes based on an analysis of velocity model (30), and the allowed maximum grid size for each subdomain is determined (50). Auxiliary perfectly matched layers (PML's) are attached to each planar interface between subdomains (80), e.g. two PML's on each side of the interface between the coarse and fine subdomains. Simulated seismic data are computed using the SG-DO technique (100-230). The simulated seismic data are compared to the recorded seismic data, then the residual is calculated (240) and used to update the model (320). The method may be iterated until the model is suitably converged (260).
Owner:HU WENYI +3
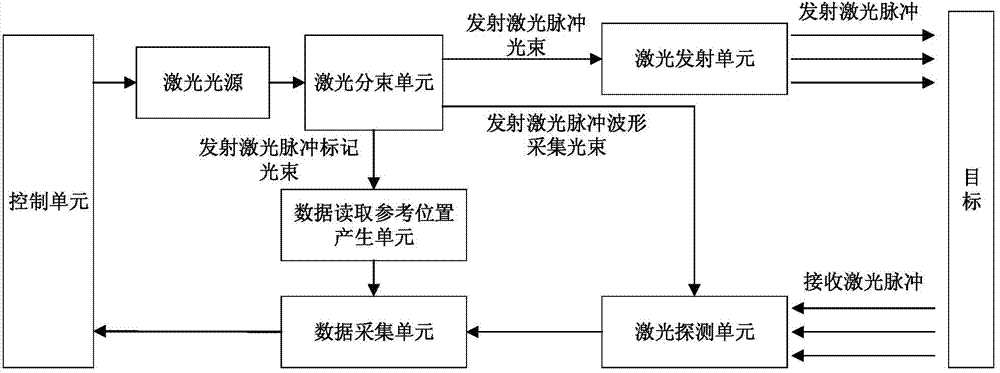
Full-fiber optical path full-waveform laser radar system
The invention discloses a full-fiber optical path full-waveform laser radar system. The laser radar system comprises a control unit, a laser source, a laser beam splitting unit, a laser emitting unit, a data reading reference position generating unit, a laser detecting unit, a data acquiring unit and a software unit. The control unit controls a pulse laser to emit laser pulses, and the laser pulses are divided into an emitted laser pulse beam, an emitted laser pulse waveform acquisition beam and an emitted laser pulse marking beam through the laser beam splitting unit; after being subjected to target scattering, the emitted laser pulse beam enters the data acquiring unit through the laser detecting unit to serve as the received laser pulse waveform to be acquired, and a human-computer interaction interface is provided by the software unit. The laser radar system breaks through the limitation that a convectional laser radar can only measure a limited amount of distance and intensity data, complete fiberization of a full-waveform laser radar optical path is achieved through fiber components, and the debugging flexibility and the system integration simplification of a full-waveform laser radar are effectively enhanced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
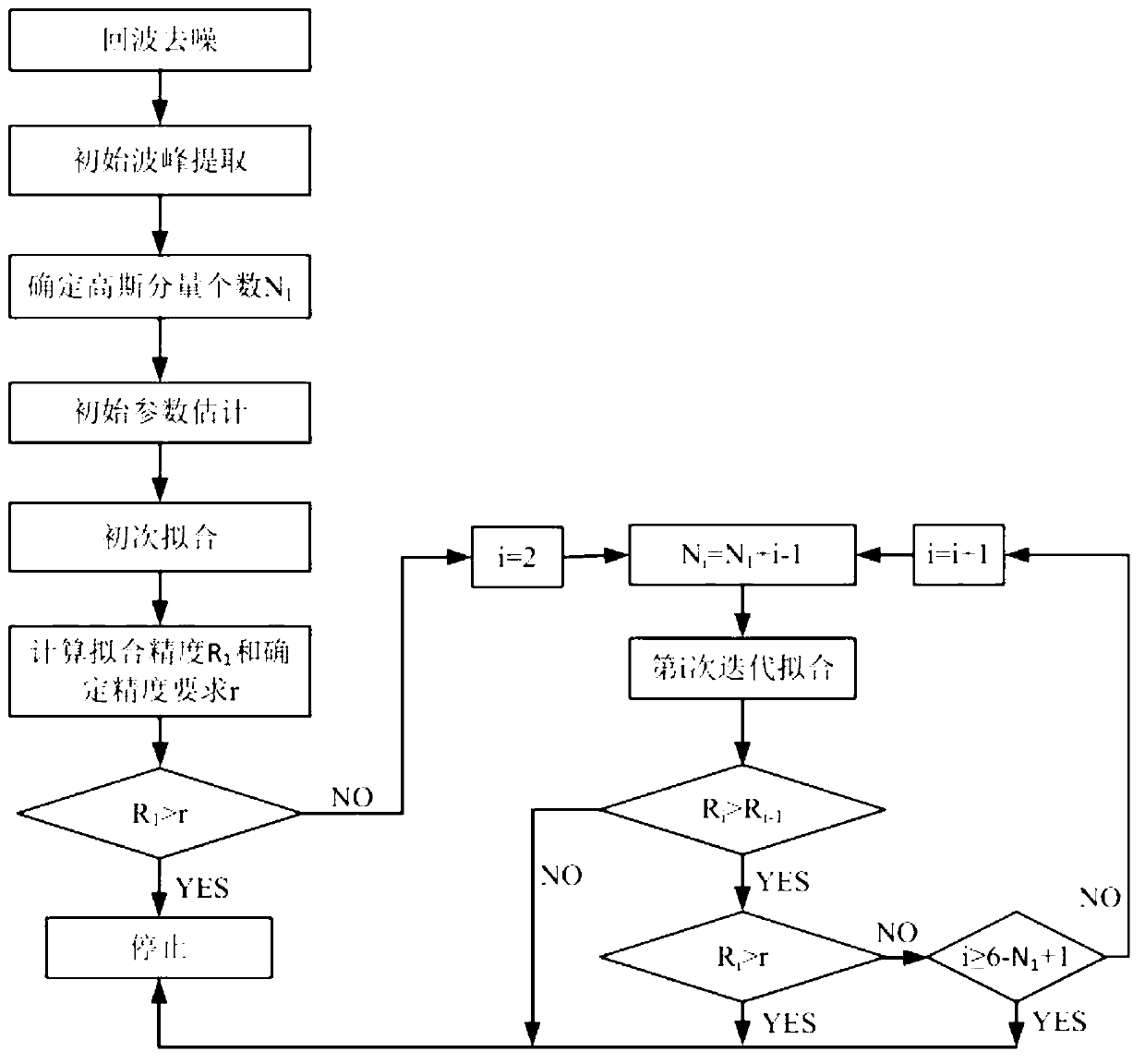
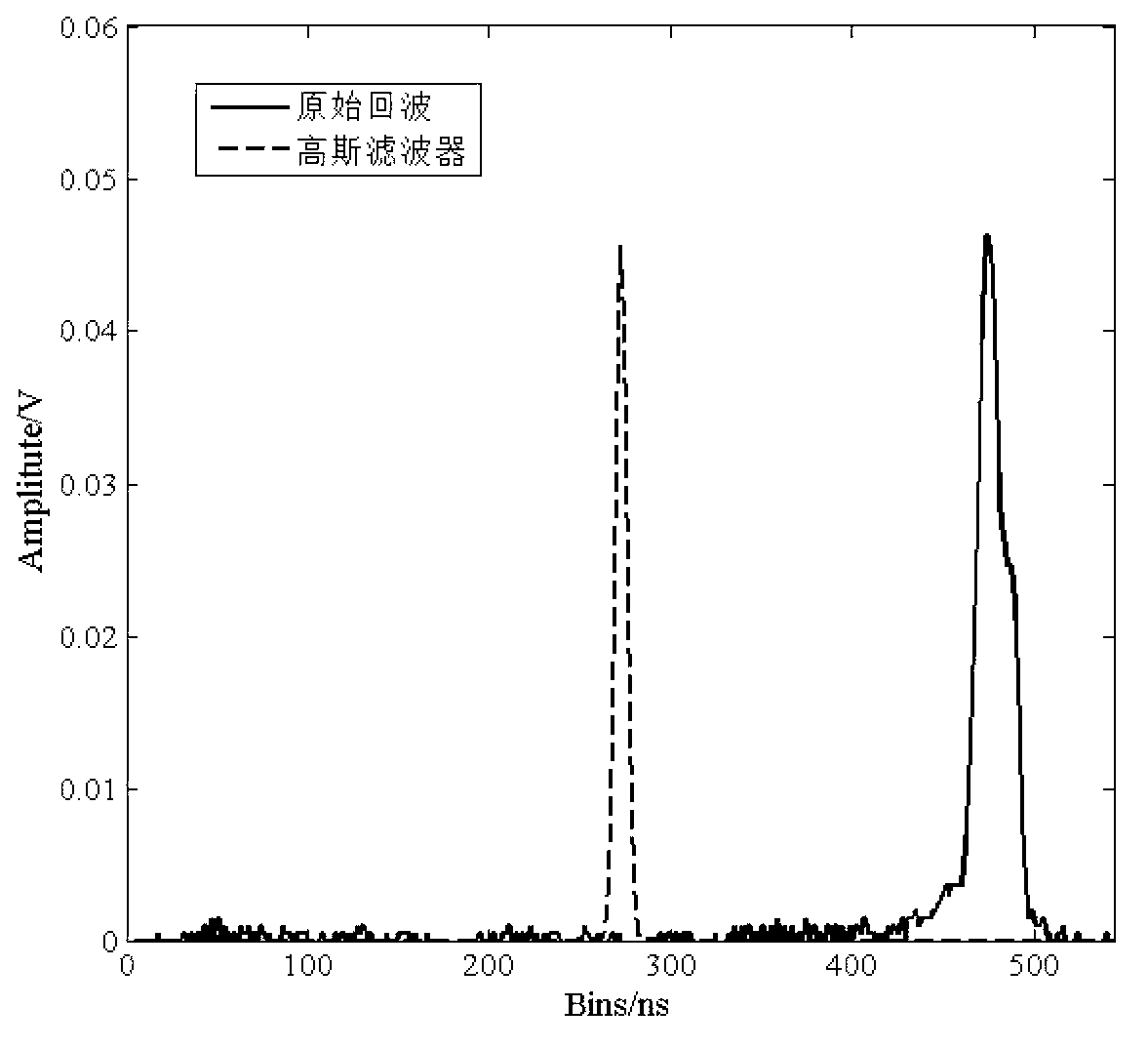
Full-waveform laser radar echo data gaussian decomposition method based on genetic algorithm
The invention discloses a full-waveform laser radar echo data gaussian decomposition method based on a genetic algorithm. The method is mainly formed by five steps including echo denoising, initial wave crest extracting, initial parameter estimating, waveform fitting and precision judging; when the precision of initial fitting meets the requirements, second fitting is not carried out, when the precision of the initial fitting does not meet the requirements, iteration fitting is carried out, and in each iteration, the fitting precision is improved by a method of increasing a gaussian component until a stopping condition is met; a gaussian function is used for fitting echo data of a full-waveform laser radar; and a gaussian filter method is adopted to filter noise of the echo data of the full-wave form laser radar, the number of initial gaussian components is confirmed by extracting a peak value point, an initial parameter range is estimated, fitting and precision adjusting are carried out on the echo data of the full-waveform laser through the genetic algorithm, an echo gaussian decomposition software system based on the genetic algorithm is manufactured, and echo decomposition operation is simplified.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Lidar three-dimensional imaging system based on virtual instrument
ActiveCN104049259AAchieve seamless integrationShorten the development cycleElectromagnetic wave reradiationMirror reflectionFull waveform
A lidar three-dimensional imaging system based on a virtual instrument comprises a three-dimensional scene modeling module, a lidar testing system simulation environment modeling module, a full-waveform signal processing module and a three-dimensional reconstruction module. The three-dimensional scene modeling module comprises a three-dimensional model loading element used for setting background colors, visual angle control, illumination, a projection mode, a display model and other basic scene projects. The lidar testing system simulation environment modeling module comprises four modeling sub-modules which are a laser pulse model, an atmospheric transmission model, an object interaction model and a receiving unit model. The laser pulse model is used for simulating a laser source according to the wavelength, pulse width, energy and other characteristics of a laser. The atmospheric transmission model is used for simulating a tested atmospheric environment, so that a noise model is generated for acting on the laser. The object interaction model is used for simulating effects of the laser and a detected object, and the effects comprise mirror reflection, diffuse reflection, surface reflection and speckles. The receiving unit model is used for simulating detector noise and amplifier noise which are generated after sensing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
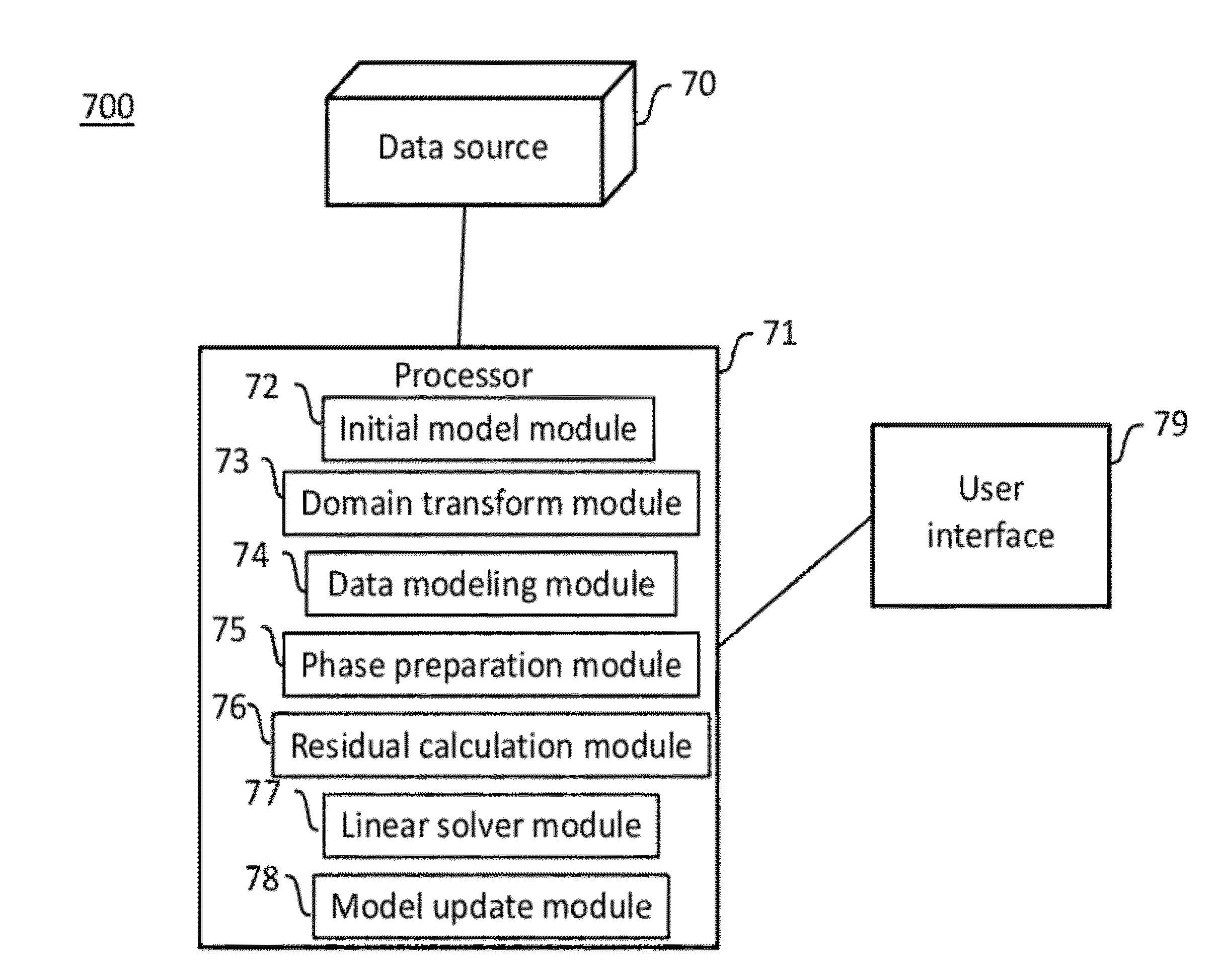
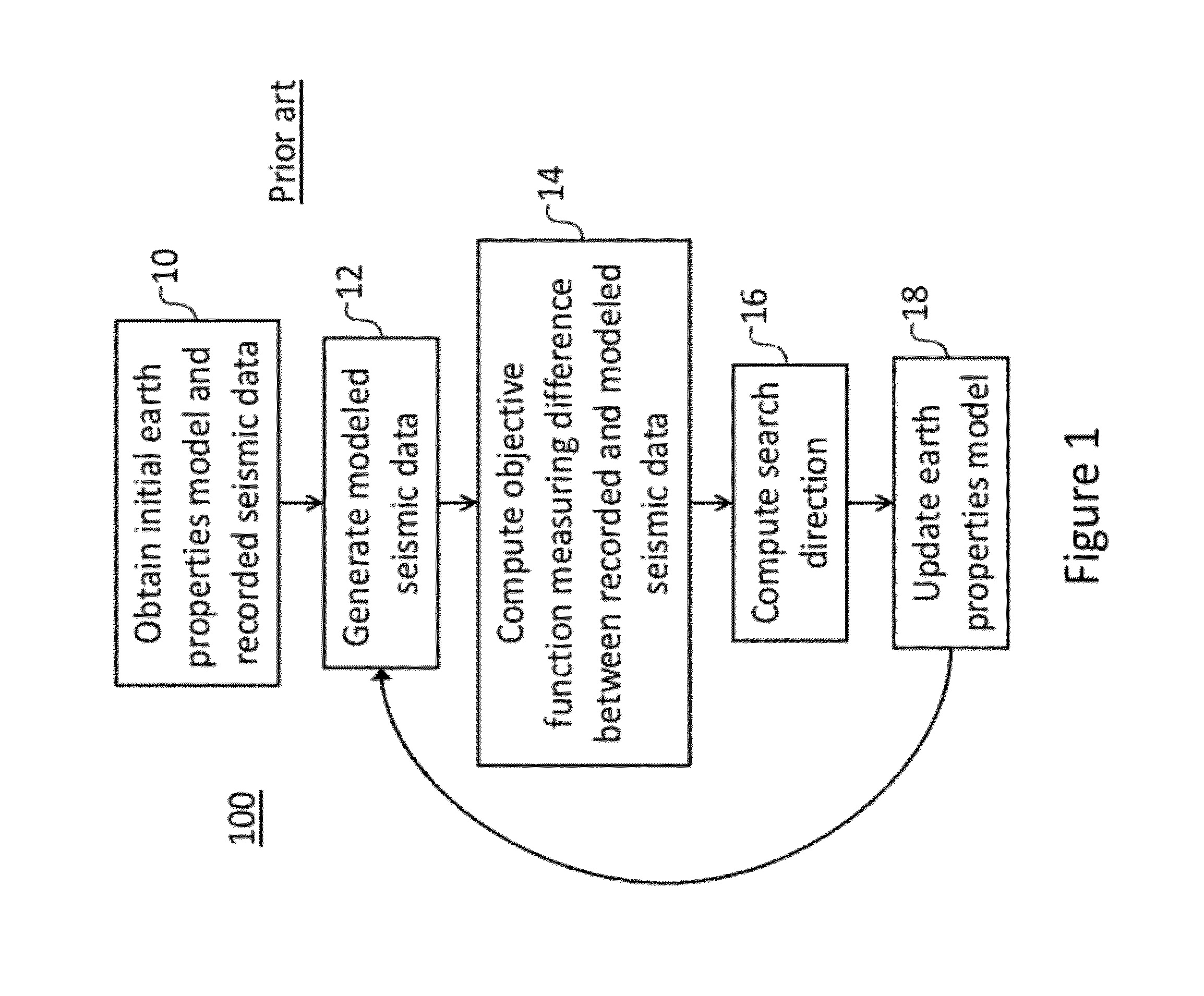
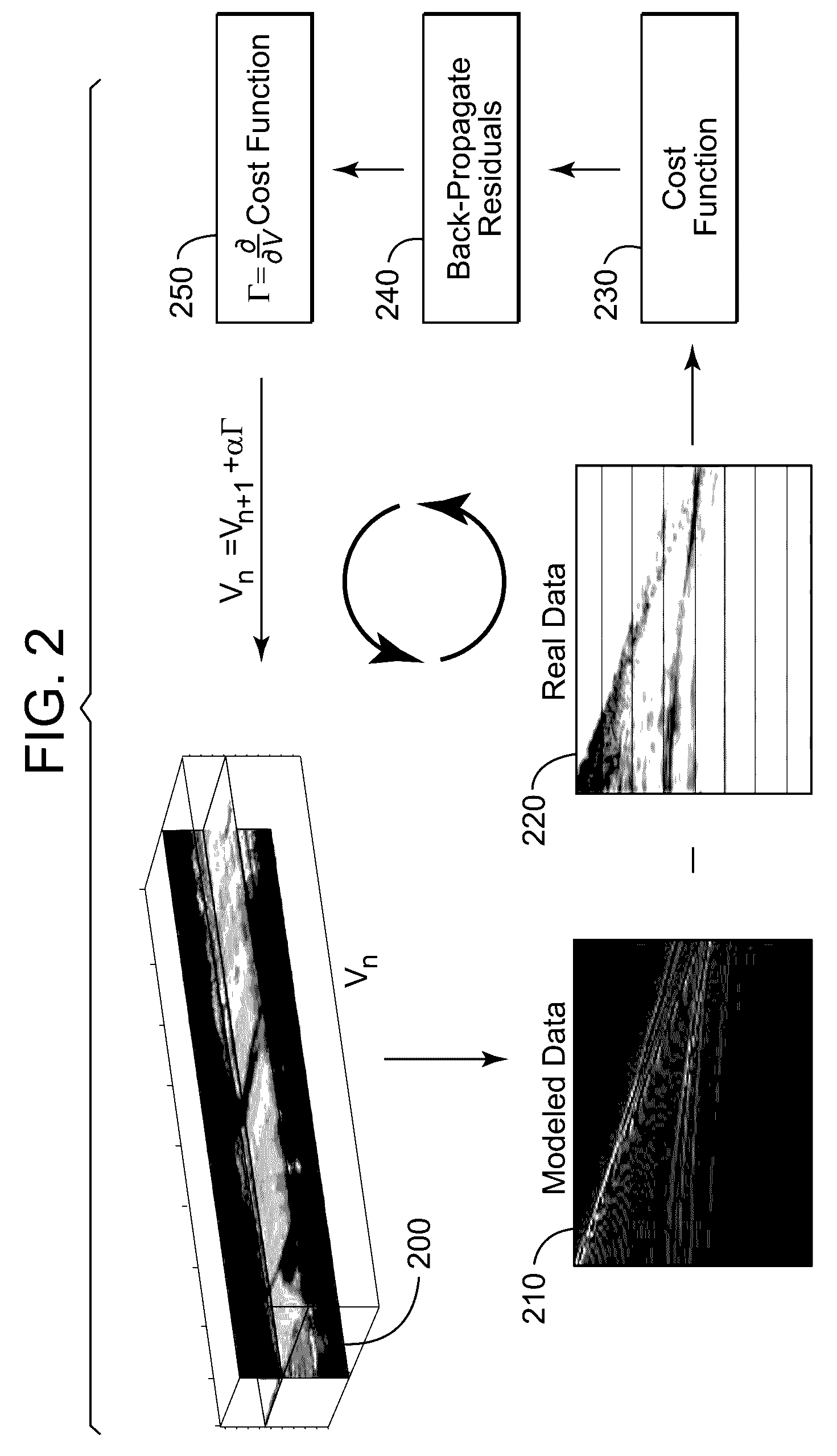
System and method for seismic data inversion by non-linear model update
InactiveUS20120316791A1Well formedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsData sourceFull waveform
A system and computer-implemented method for determining properties of a subsurface region of interest from seismic data is disclosed. An embodiment of the method performs full waveform inversion by non-linear model update to compute a velocity model. The method includes obtaining actual seismic data representative of the subsurface region and an initial earth property model for the subsurface region, performing forward modeling using the initial earth property model to create modeled seismic data with similar acquisition specifications as the actual seismic data, calculating a residual between the actual seismic data and the modeled seismic data in a time or transform domain, and inverting the residual to generate a model produced by non-linear model update components. The system includes a data source, user interface, and processor configured to execute computer modules that implement the method.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for inverting near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms
The invention discloses a method for inverting a near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms. The method comprises acoustic wave equation-based wave field forward modeling and steepest descent-based waveform inversion technologies, and comprises the following steps of 1, extracting time-domain preliminary waveform records and an initial model; 2, calculating a simulated wave field and a wave field residual by utilizing acoustic wave equation staggered grid finite-difference forward modeling simulation; 3, reversely propagating the wave field residual to obtain a retransmission wave field; 4, calculating a gradient of a target function by utilizing the retransmission wave field and a forward propagation wave field, and calculating an updating step length; 5, updating a speed model; 6, inspecting whether the speed model is consistent with an iteration stopping condition, outputting the speed model if the speed model is consistent with the iteration stopping condition, otherwise returning to the step 2, and continuing iterative updating. According to the method, a wave equation theory-based full-waveform inversion technology is used as reference, and preliminary waves with higher energy and more stable waveforms are used for inversion, so that the multiplicity of solutions of full-waveform inversion is reduced, and the inversion stability and the calculation efficiency are improved; the accuracy of static correction and shallow depth imaging is improved.
Owner:中国石油集团西北地质研究所有限公司
Multi-parameter inversion through offset dependent elastic fwi
ActiveUS20140350861A1Robust and efficient computer-implementedConvergence can be speededSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsModel parametersFull waveform
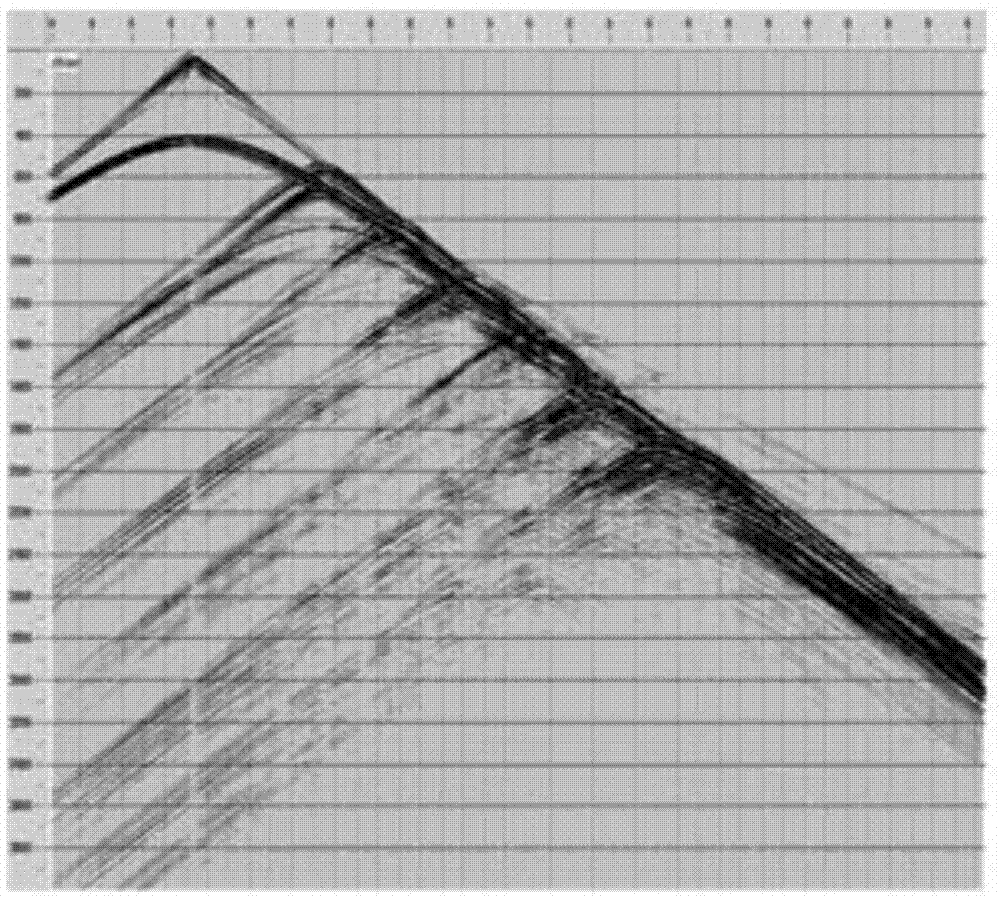
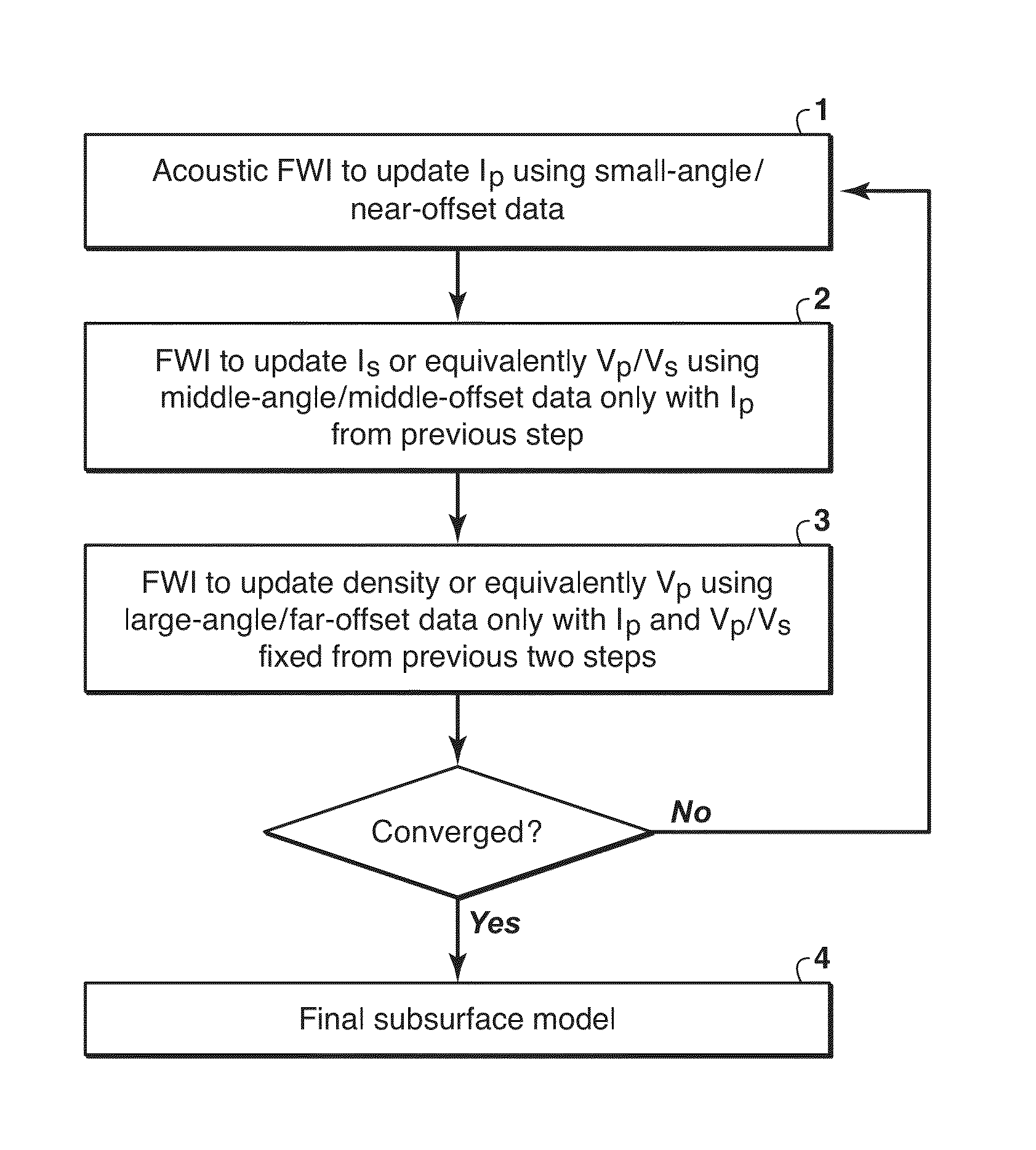
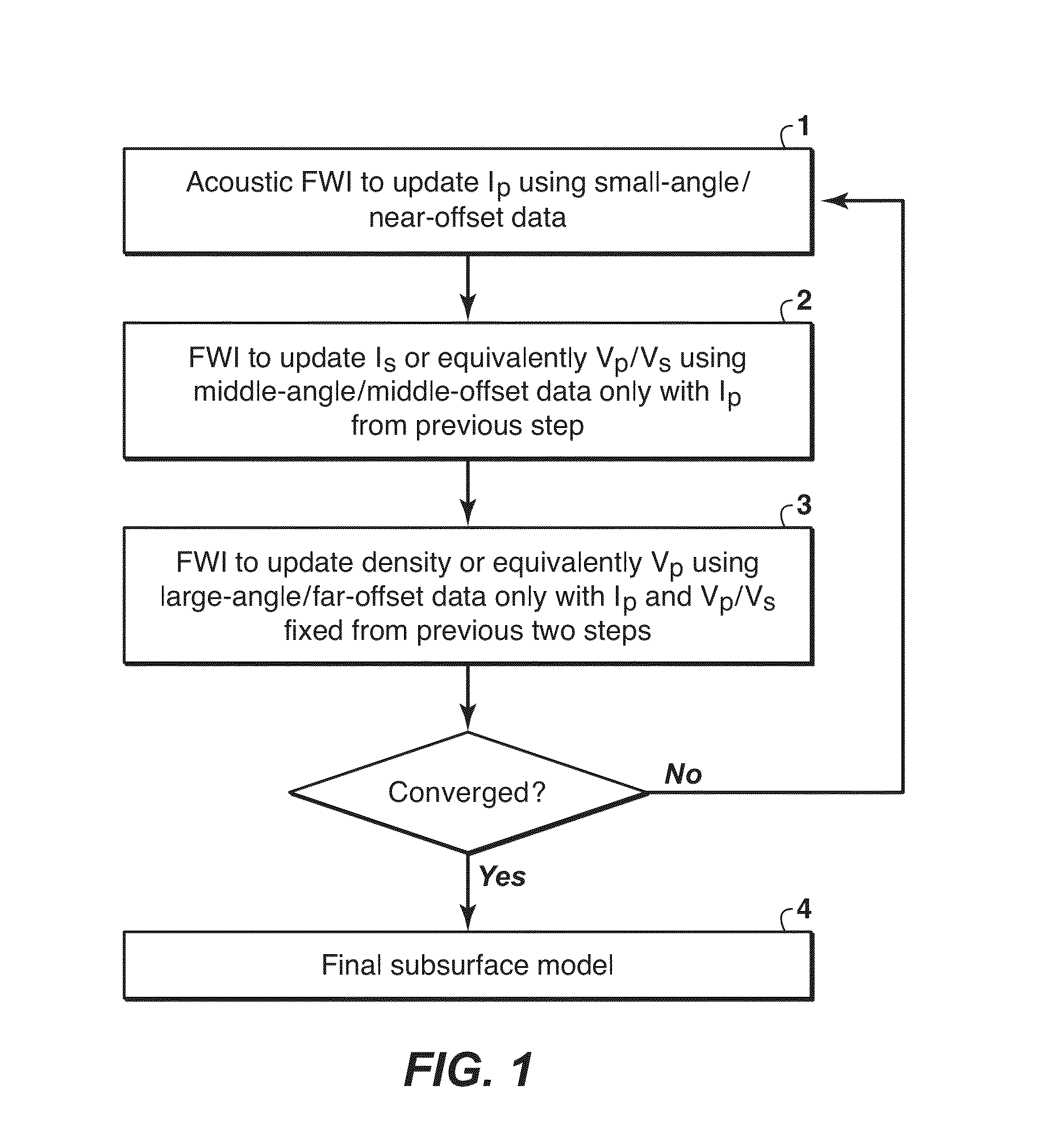
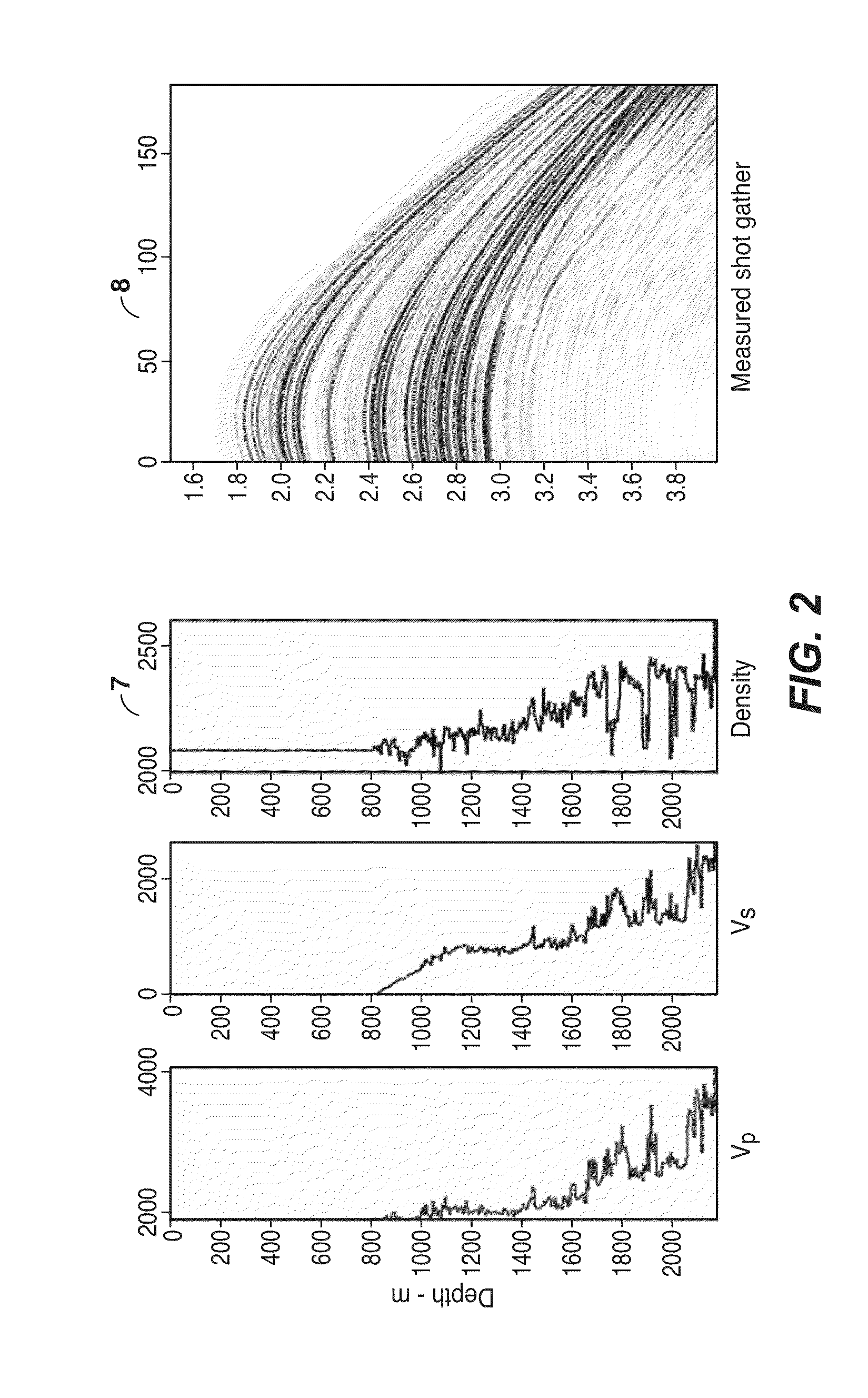
Method for multi-parameter inversion using elastic inversion. This method decomposes data into offset / angle groups and performs inversion on them in sequential order. This method can significantly speed up convergence of the iterative inversion process, and is therefore most advantageous when used for full waveform inversion (FWI). The present inventive approach draws upon relationships between reflection energy and reflection angle, or equivalently, offset dependence in elastic FWI. The invention uses recognition that the amplitudes of small angle (near offset) reflections are largely determined by acoustic impedance alone (1), independent for the most part of Vp / Vs. Large angle (middle and far offset) reflections are affected by Ip, Vp / Vs (2) and other earth parameters such as density (3) and anisotropy. Therefore, the present inventive method decomposes data into angle or offset groups in performing multi-parameter FWI to reduce crosstalk between the different model parameters being determined in the inversion.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Beat tone full waveform inversion
A full wave inversion (FWI) may utilize an Amplitude-Frequency-Differentiation (AFD) or a Phase-Frequency-Differentiation (PFD) operation to form a velocity model of a subterranean formation utilizing recovered low wavenumber data. Received seismic data is processes to isolate two data signals at different frequencies. In an AFD operation, the two data signals are summed and the data of the envelope of the summed function is used for the FWI. In a PFD operation, the phase data of the quotient of the two data signals is used for the FWI. The FWI proceeds iteratively utilizing either the AFD or PFD data or with single frequency data until the cost function of the AFD or PFD is satisfied.
Owner:ADVANCED GEOPHYSICAL TECH
Full waveform inversion method for seismic data processing using preserved amplitude reverse time migration
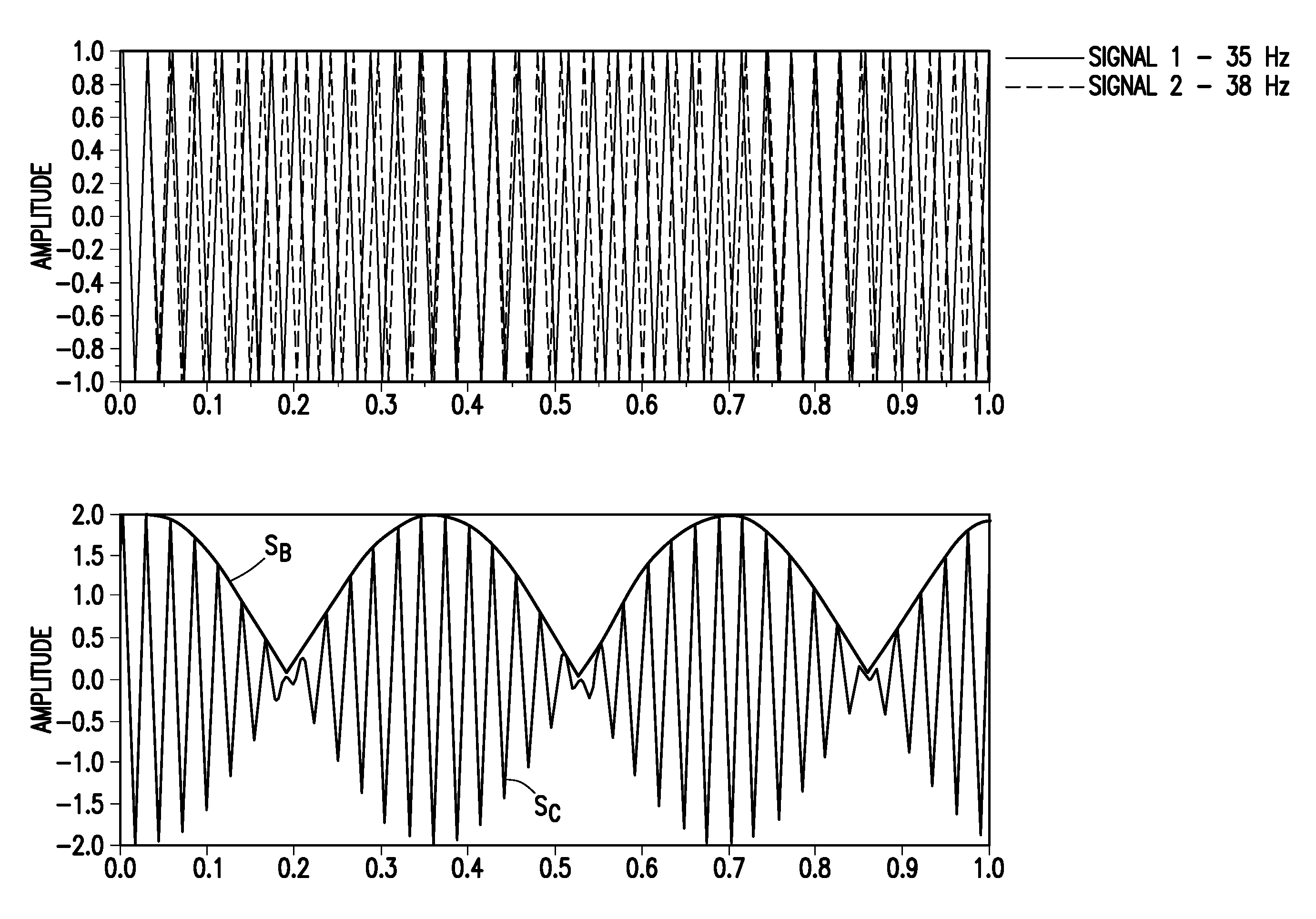
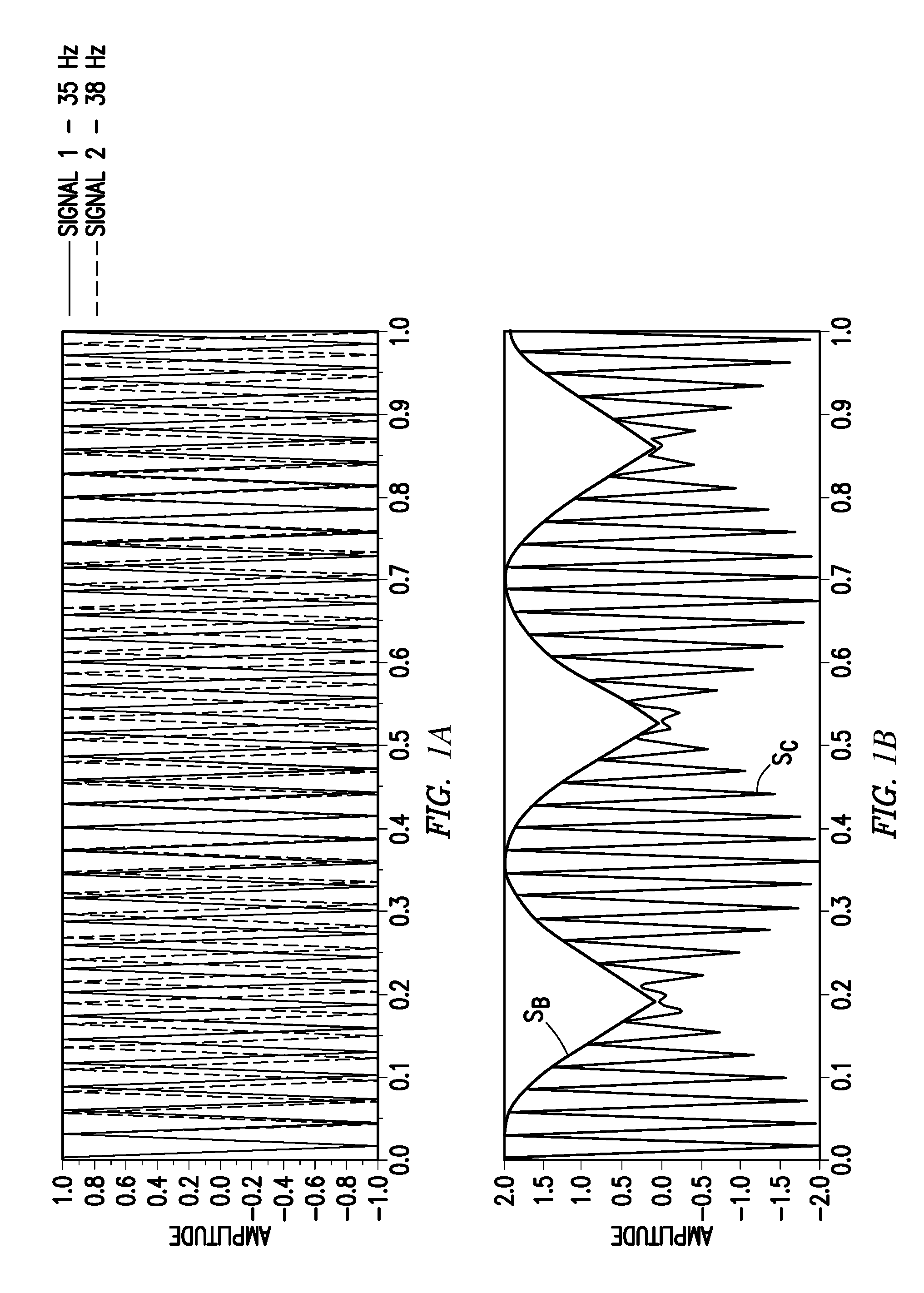
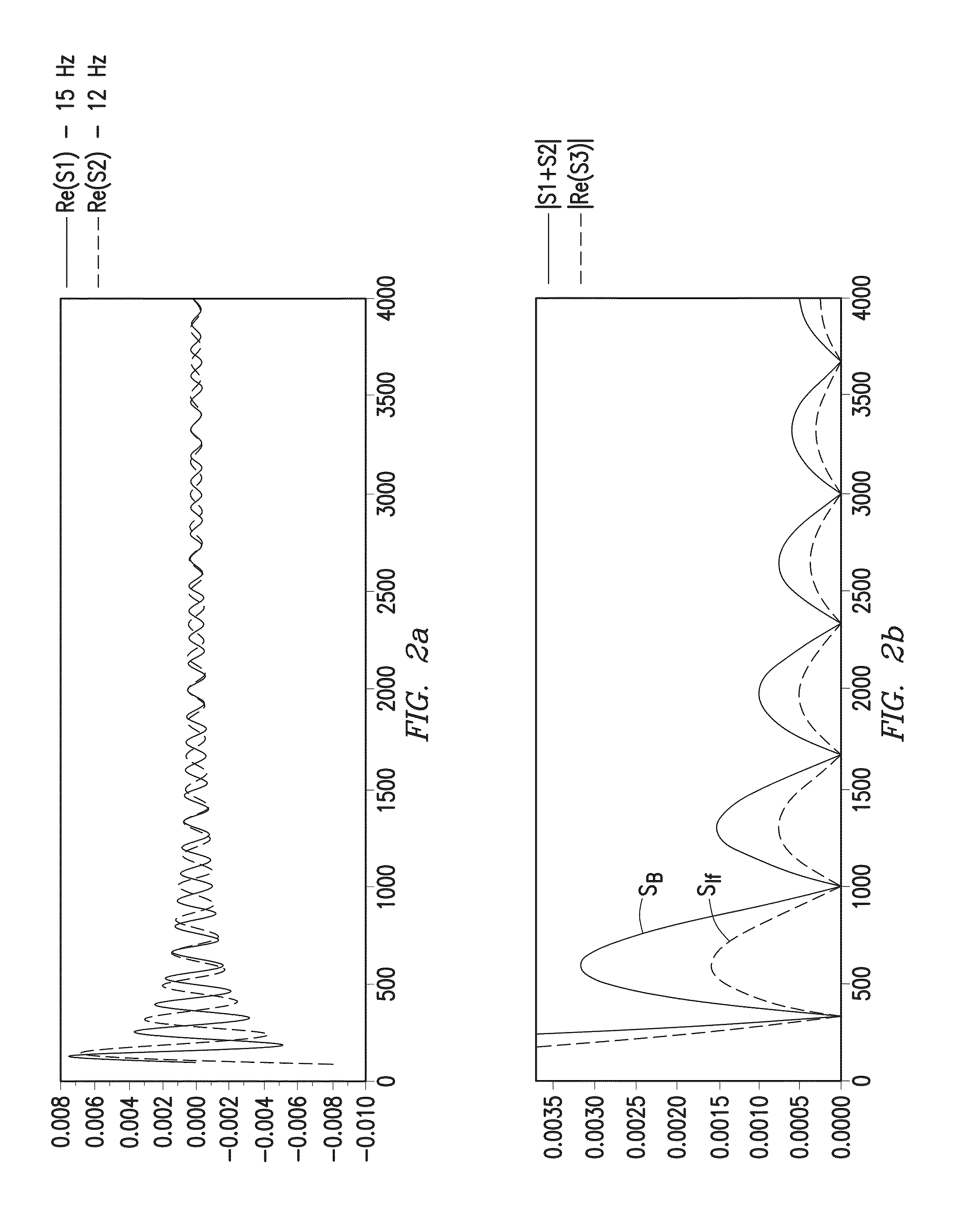
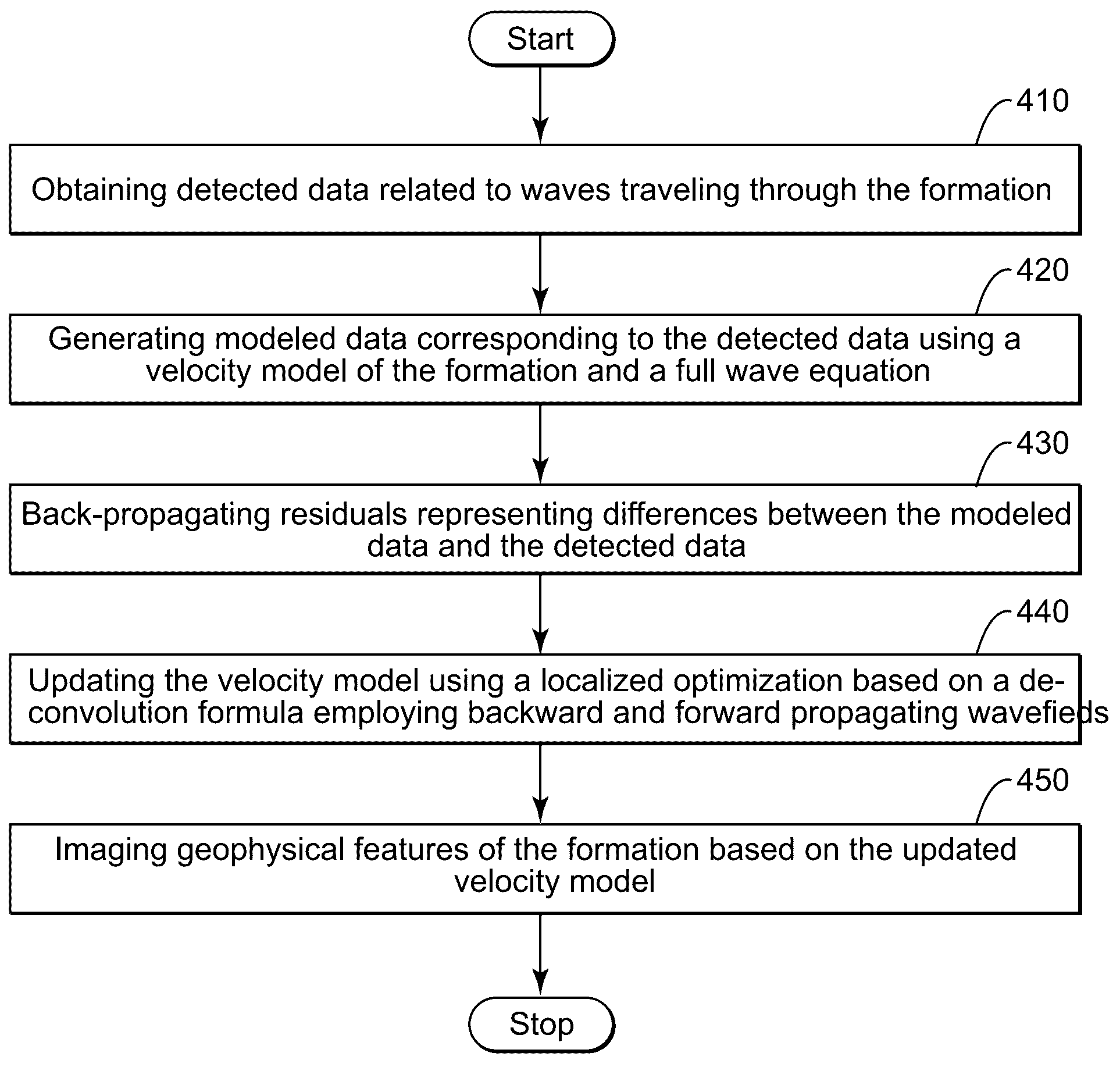
A preserved-amplitude RTM-based FWI method is used to obtain an image of an explored subsurface formation. Model data corresponding to detected data is generated using a velocity model of the formation. Residuals representing differences between the modeled data and the detected data are back-propagated to then update the velocity model a local optimization based on a deconvolution formula employing a backward propagating wavefield and a forward propagating wavefield. Geophysical features of the formation are imaged based on the updated velocity model.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
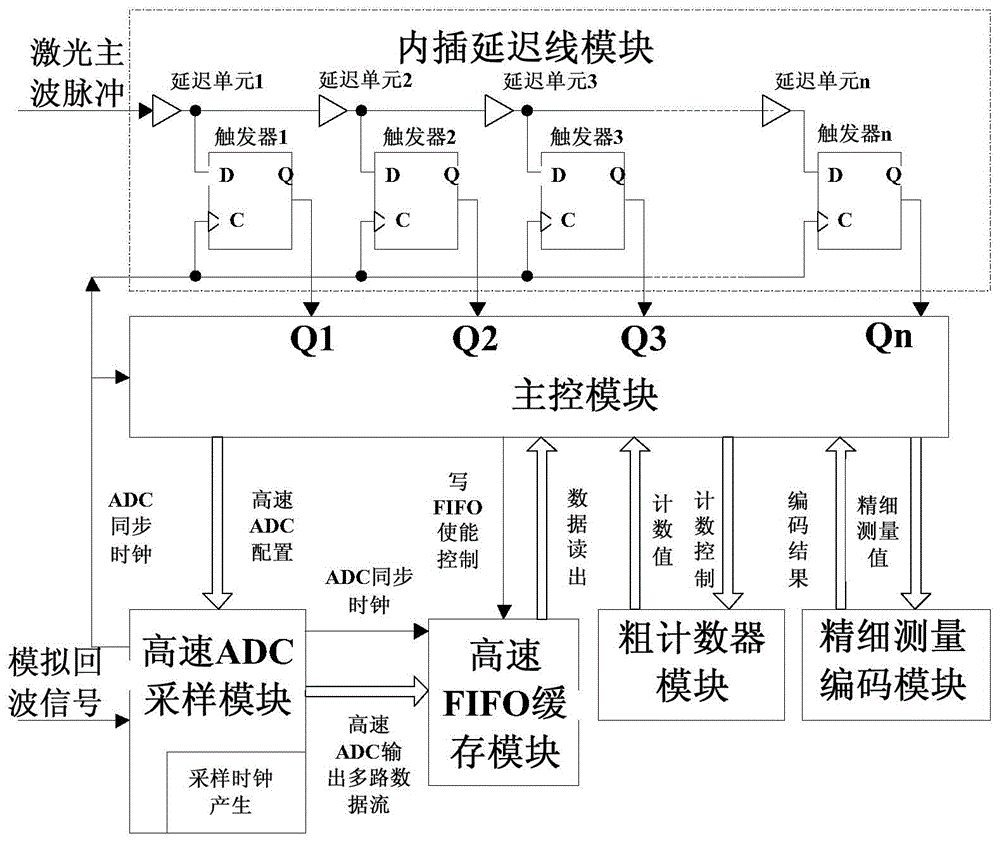
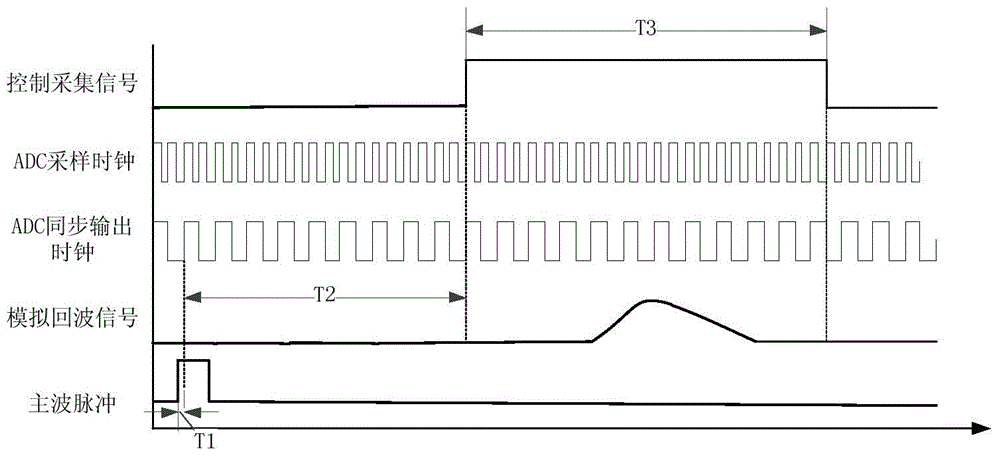
Laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device with sampling point time location
ActiveCN104155640AEasy to implementFlexible configurationElectromagnetic wave reradiationCode moduleEarth observation
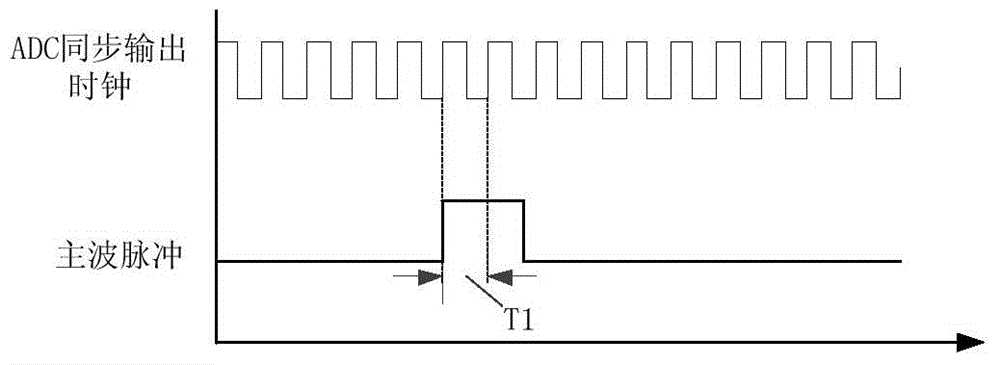
The invention discloses a laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device with sampling point time location, and belongs to the technical field of earth observation laser radar remote sensing. The full-waveform acquisition device comprises a main control module, a high-speed ADC sampling module, a high-speed FIFO cache module, an interpolation delay line module, a high-speed coarse counter module, and a fine measurement coding module. All the modules except the high-speed ADC sampling module are implemented inside an FPGA. The invention aims to provide a laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device for acquiring sampling point time location by a simple method. A frequency division clock synchronous with a high-speed ADC sampling clock is used as a rough counting clock, echo sampling point data is stored in a certain time interval under control, and the time interval between a main wave pulse and a coarse counting clock edge is finely measured by use of an interpolation delay chain, thereby obtaining an echo sampling point which has precise time location relative to laser transmitting main wave pulse. The laser radar echo full-waveform acquisition device with sampling point time location has the advantages of simple peripheral circuit, concise means of realization, flexible function interface configuration, and high cost performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Seismic wave full waveform inversion method based on least square gradient update speed model
ActiveCN105005076AImprove update gradient accuracyQuick updateSeismic signal processingWave fieldFull waveform
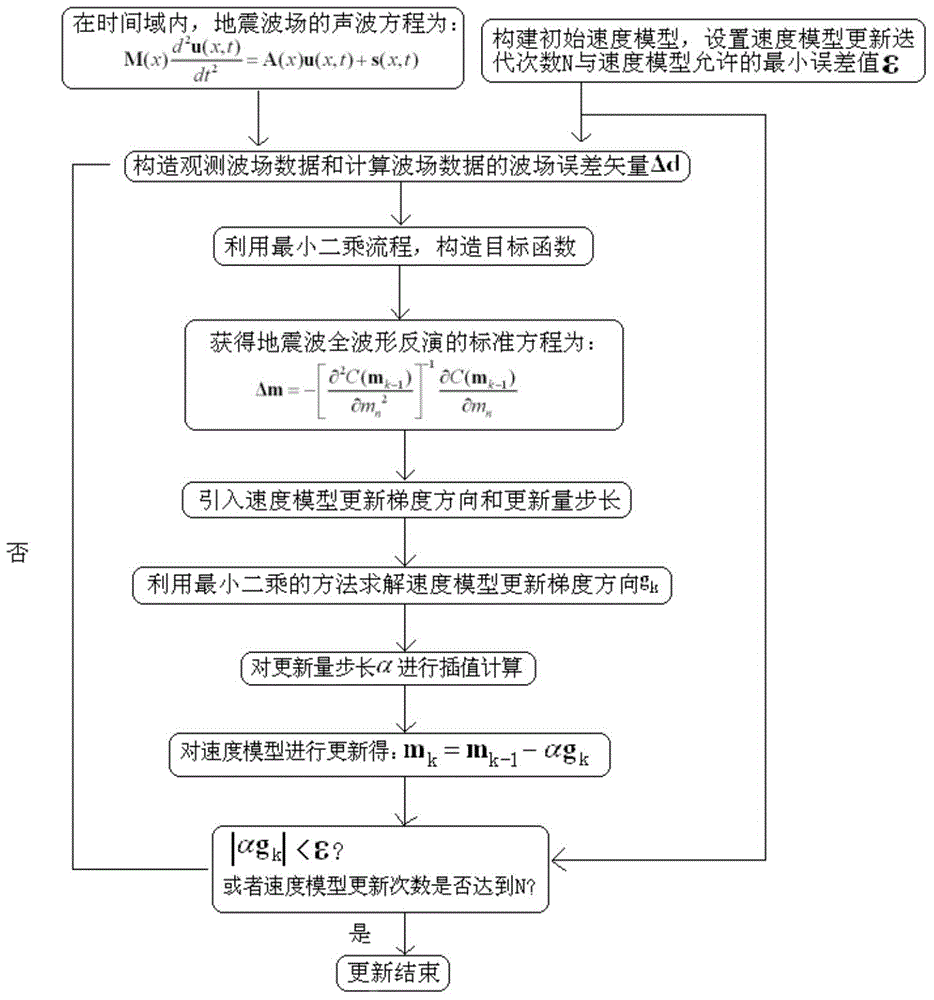
The present invention relates to a seismic wave full waveform inversion method based on a least square gradient update speed model, comprising the following steps: 1) obtaining a sound wave equation of a seismic wave field in time domain; 2) constructing an initial speed model, setting a speed model update iteration number N and an allowed minimum error value epsilon; 3) constructing observation wave field data and calculating a wave field error vector of the wave field data; 4) constructing an object function; 5) calculating the object function to obtain a standard equation of seismic wave full waveform inversion; 6) introducing a speed model update gradient direction g<k> and an update amount step length alpha; 7) solving the speed model update gradient direction g<k> by using a least square method; 8) performing interpolation calculation for the update amount step length alpha; and 9) updating the speed model, wherein m<k>=m<k-1>+alpha*g<k>; when |alpha*g<k>| < epsilon or the update number of the speed model reaches the speed model update iteration number N, ending the update of the speed model; otherwise, entering into the step 3). The seismic wave full waveform inversion method of the present invention can quickly achieve update of the speed model, and can be widely applied in seismic wave full waveform inversion.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
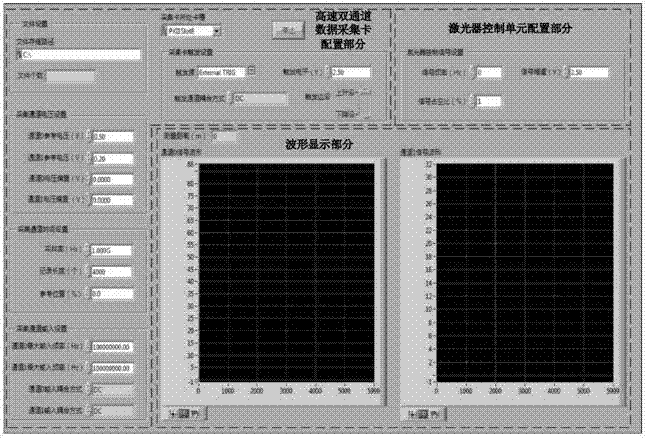
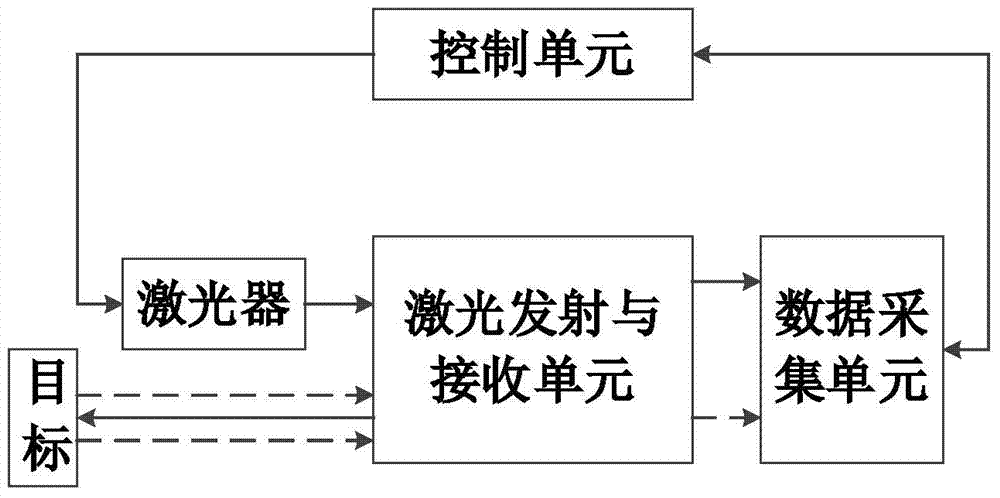
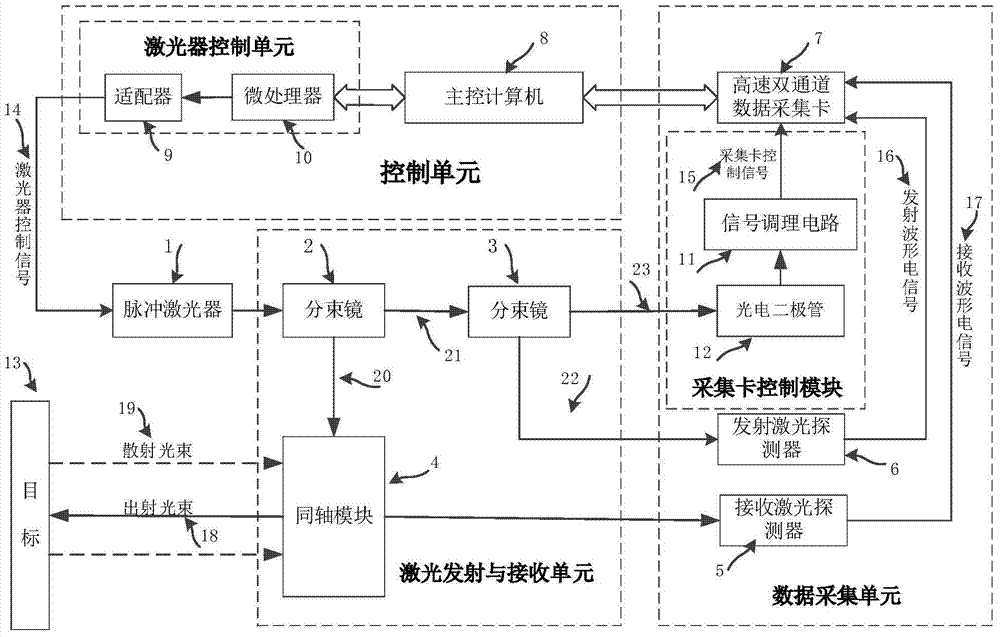
Full-waveform laser radar system based on coaxial two-channel data acquisition
ActiveCN103576134AEliminate measurement blind spotsImprove detection distanceElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsControl signal
The invention discloses a full-waveform laser radar system based on coaxial two-channel data acquisition, breaks through the limit that a conventional laser radar can only measure a limited number of distance and strength data, and simultaneously solves the dead zone problem of non-coaxial laser radar detection. The full-waveform laser radar system based on coaxial two-channel data acquisition comprises a pulse laser, a laser transmitting and receiving unit, a data acquisition unit, a control unit and a software unit, wherein the control unit controls the pulse laser to transmit laser pulse; the laser pulse is divided into outgoing beam, acquisition card control signal generation beam and transmitted waveform recording beam after passing by the laser transmitting and receiving unit; the outgoing beam is scattered by a target, then collected into the data acquisition unit by the transmitting and receiving unit and collected as a receiving signal; and the software unit is used for providing a man-machine interaction interface. The system can store a complete waveform for transmitting and receiving the laser pulse, so that the detectivity of the full-waveform laser radar is effectively enhanced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
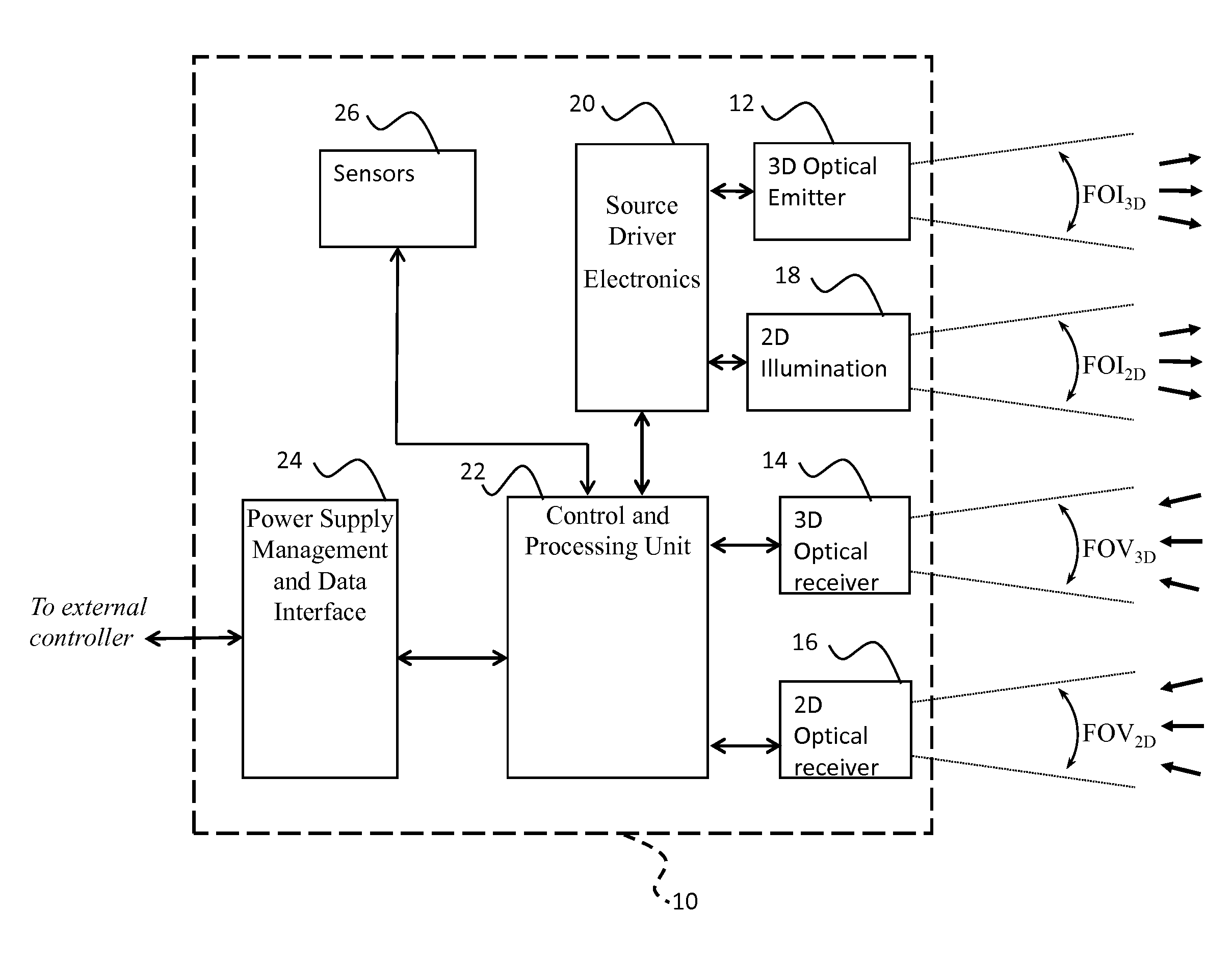
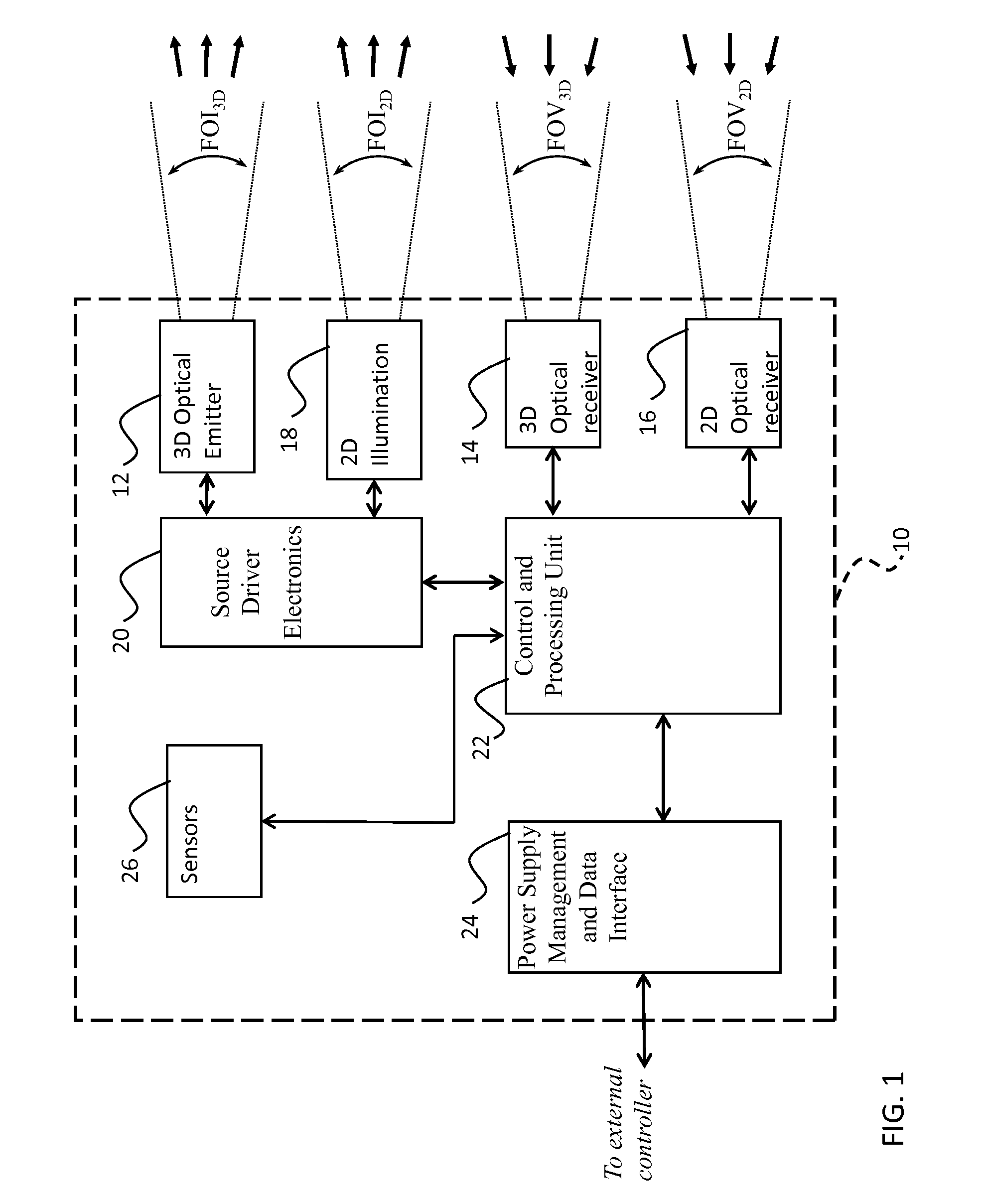
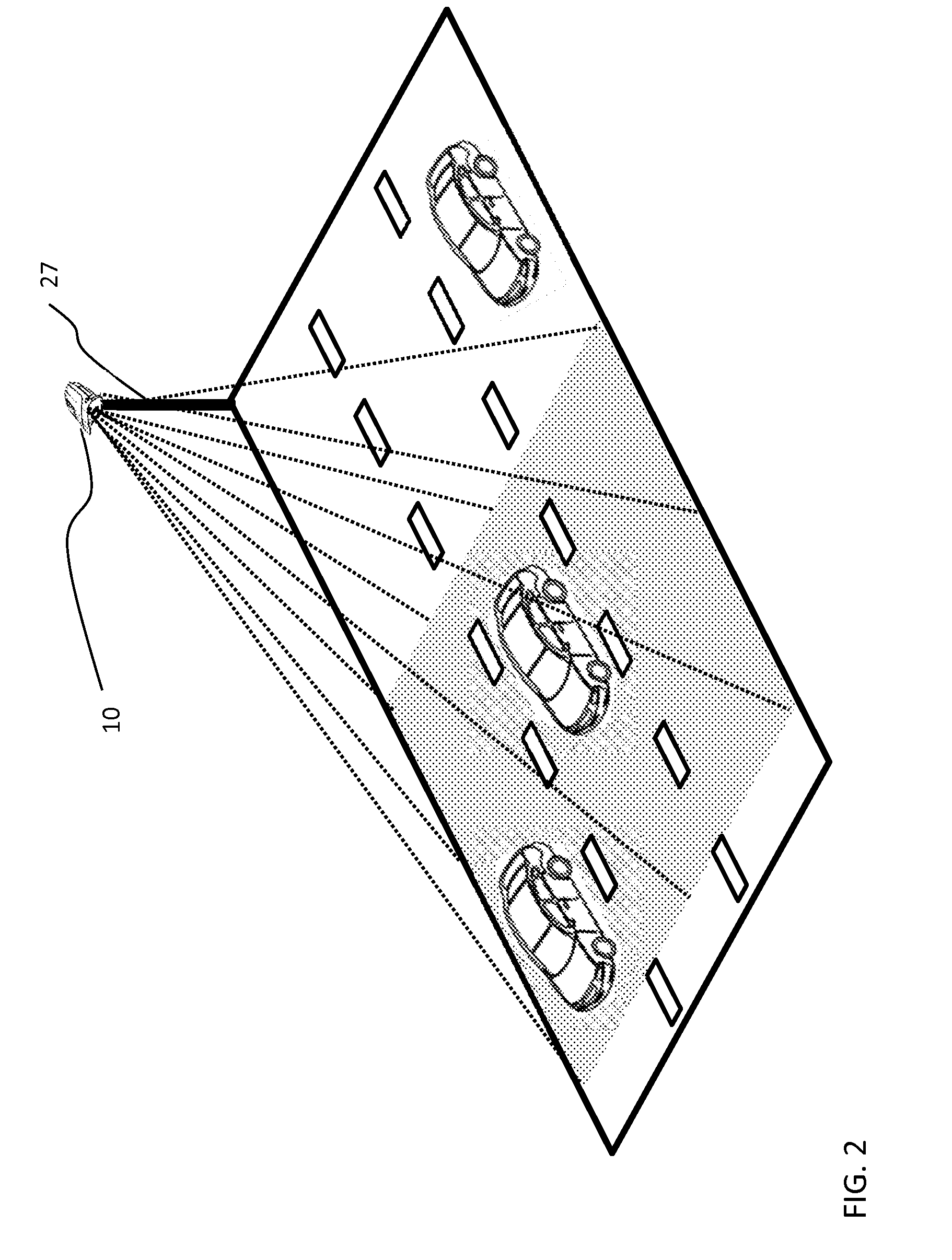
System and method for multipurpose traffic detection and characterization
A method for tracking and characterizing a plurality of vehicles simultaneously in a traffic control environment, comprising: providing a 3D optical emitter; providing a 3D optical receiver with a wide and deep field of view; driving the 3D optical emitter into emitting short light pulses; receiving a reflection / backscatter of the emitted light, thereby acquiring an individual digital full-waveform LIDAR trace for each detection channel of the 3D optical receiver; using the individual digital full-waveform LIDAR trace and the emitted light waveform, detecting a presence of a plurality of vehicles, a position of at least part of each vehicle and a time at which the position is detected; assigning a unique identifier to each vehicle; repeating the steps of driving, receiving, acquiring and detecting, at a predetermined frequency; tracking and recording an updated position of each vehicle and an updated time at which the updated position is detected.
Owner:LEDDARTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com