Patents
Literature
1930 results about "Telephone line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A telephone line or telephone circuit (or just line or circuit within the industry) is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. This is the physical wire or other signaling medium connecting the user's telephone apparatus to the telecommunications network, and usually also implies a single telephone number for billing purposes reserved for that user. Telephone lines are used to deliver landline telephone service and Digital subscriber line (DSL) phone cable service to the premises. Telephone overhead lines are connected to the public switched telephone network.
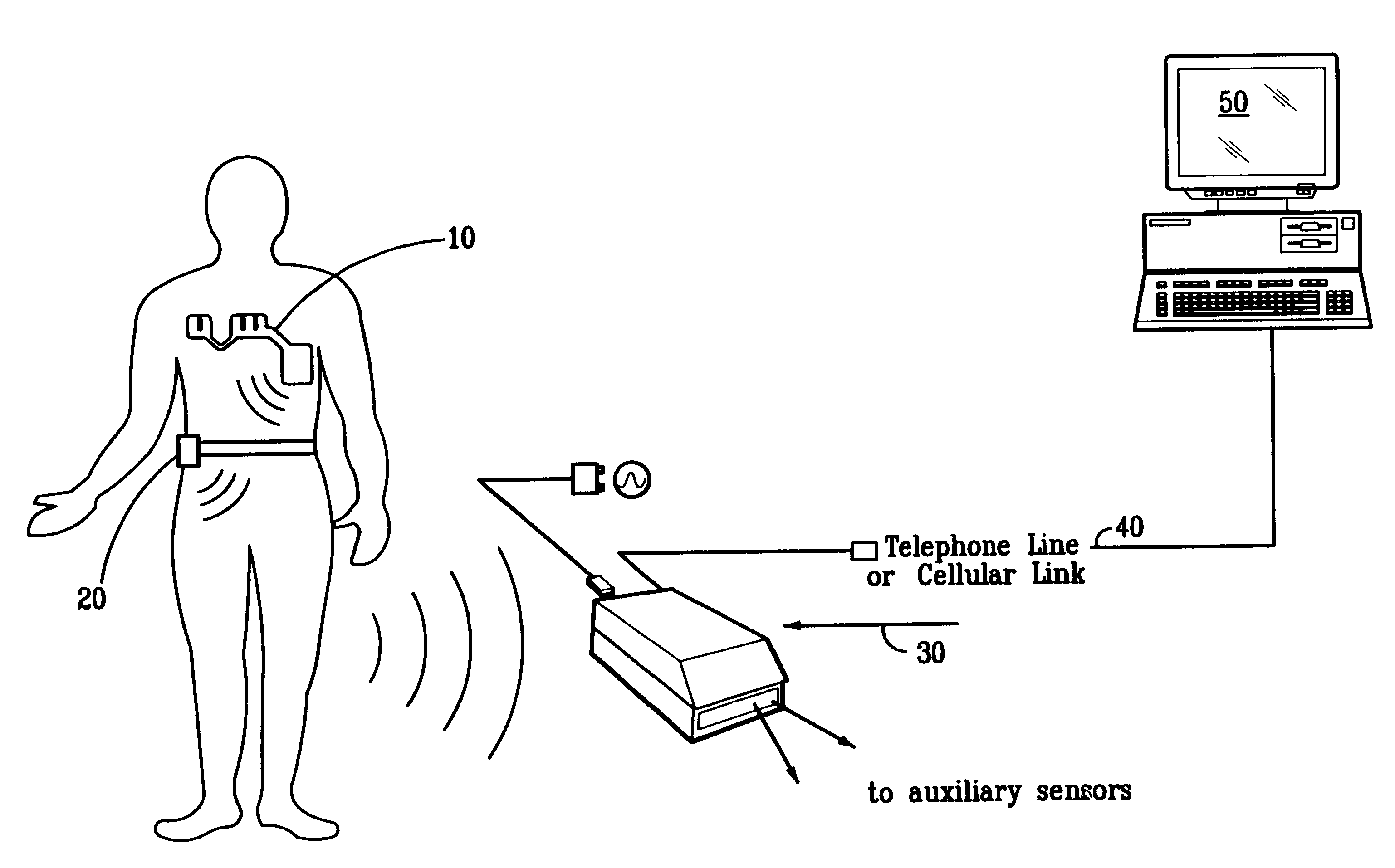
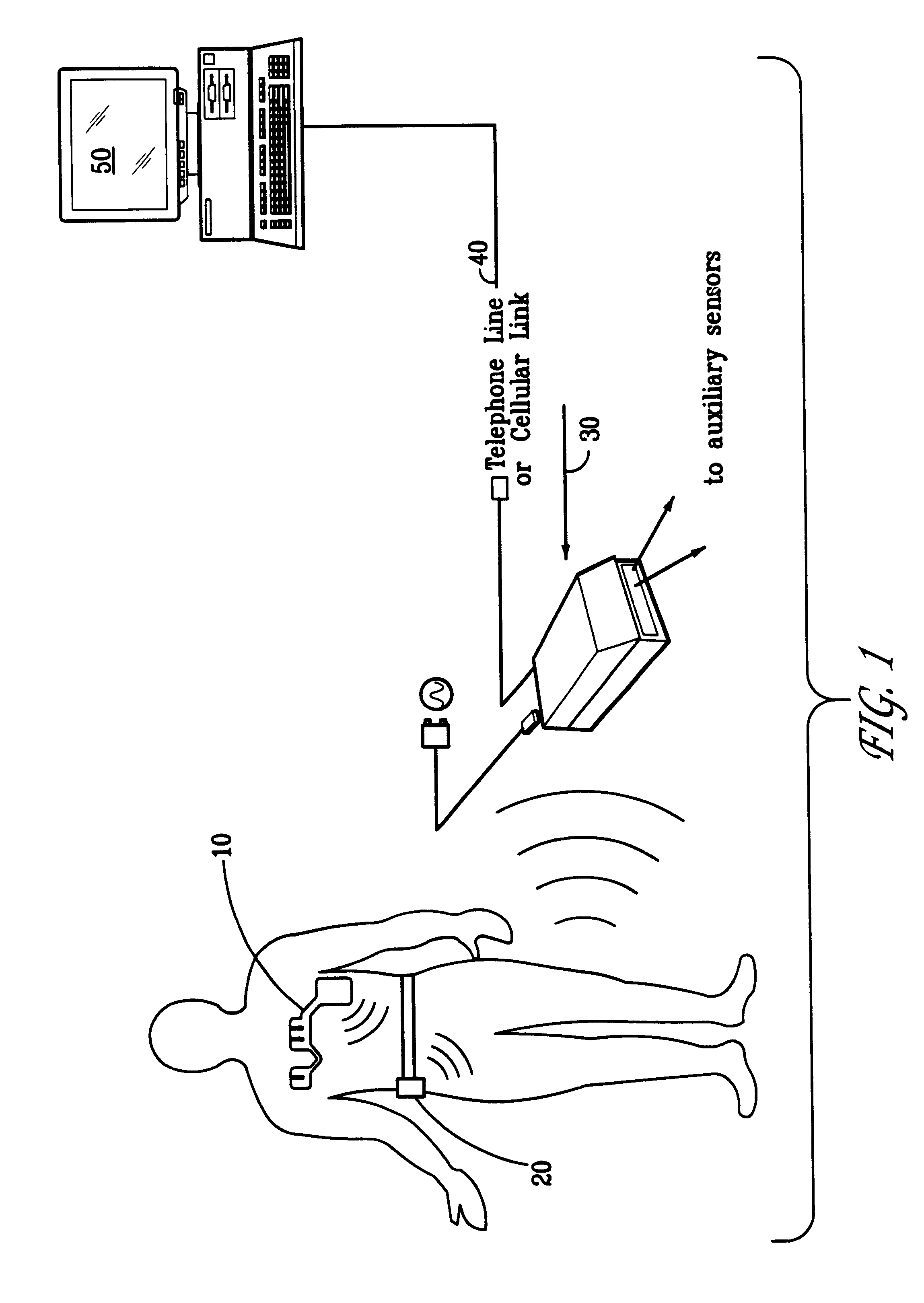
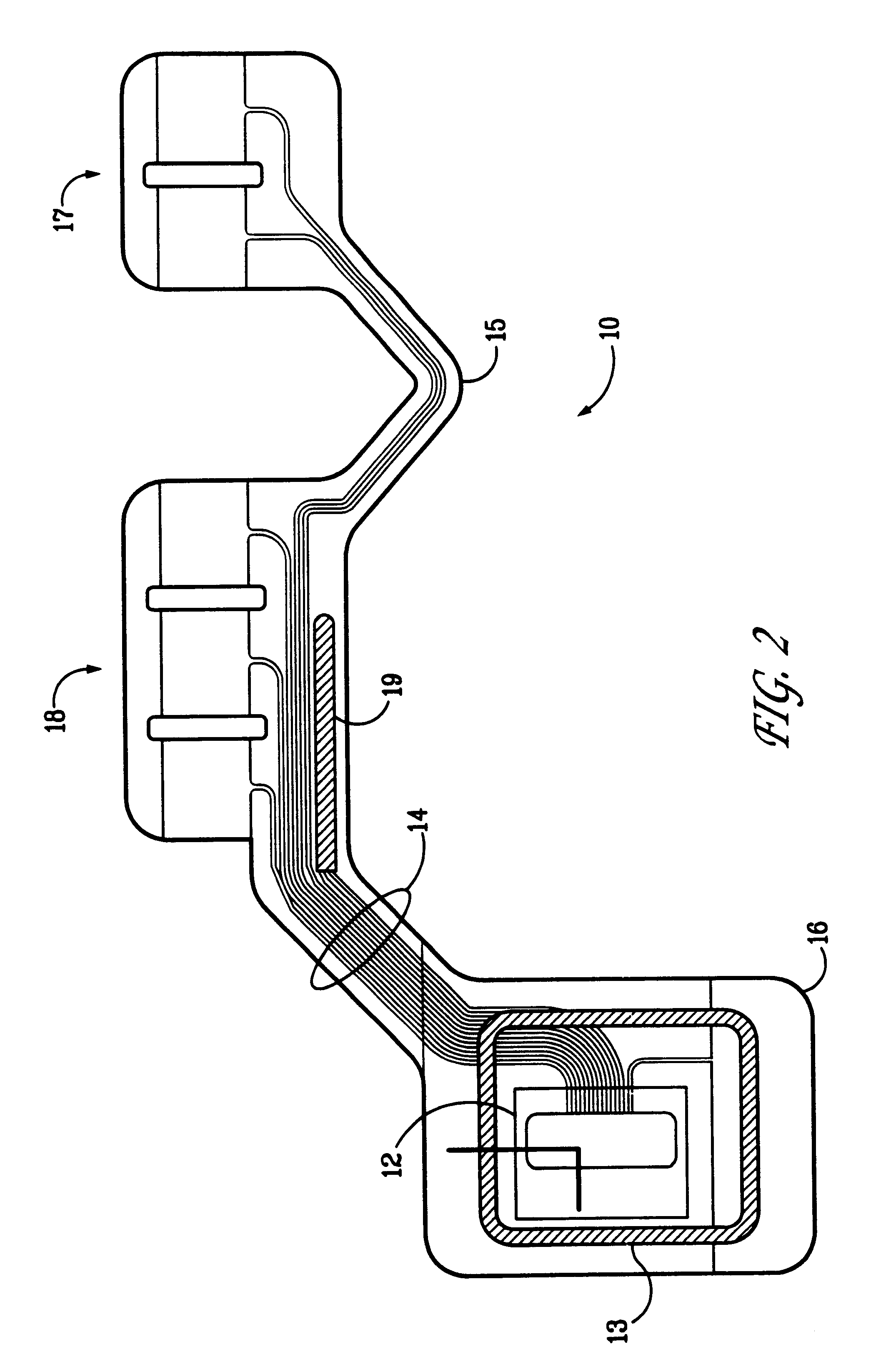
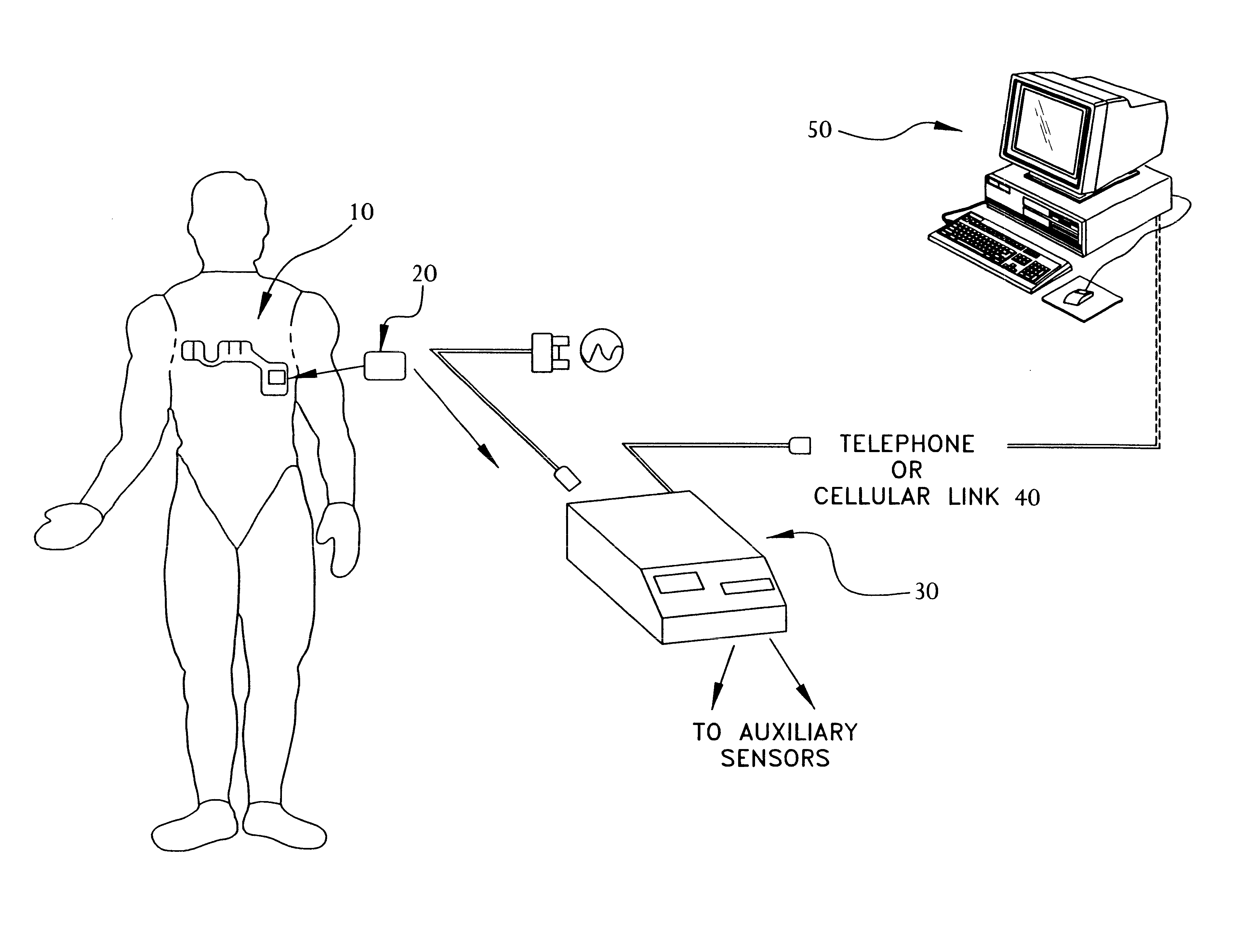
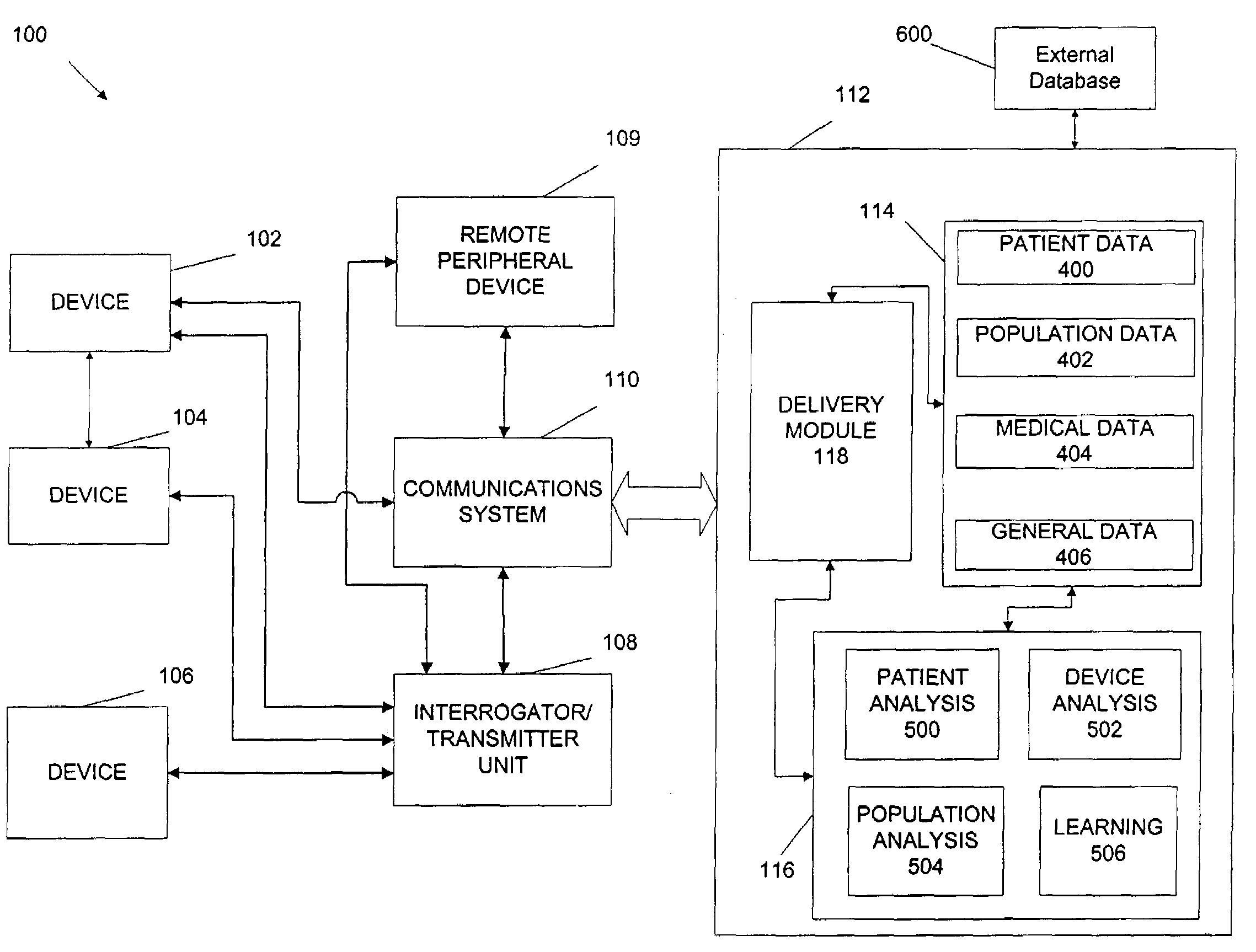
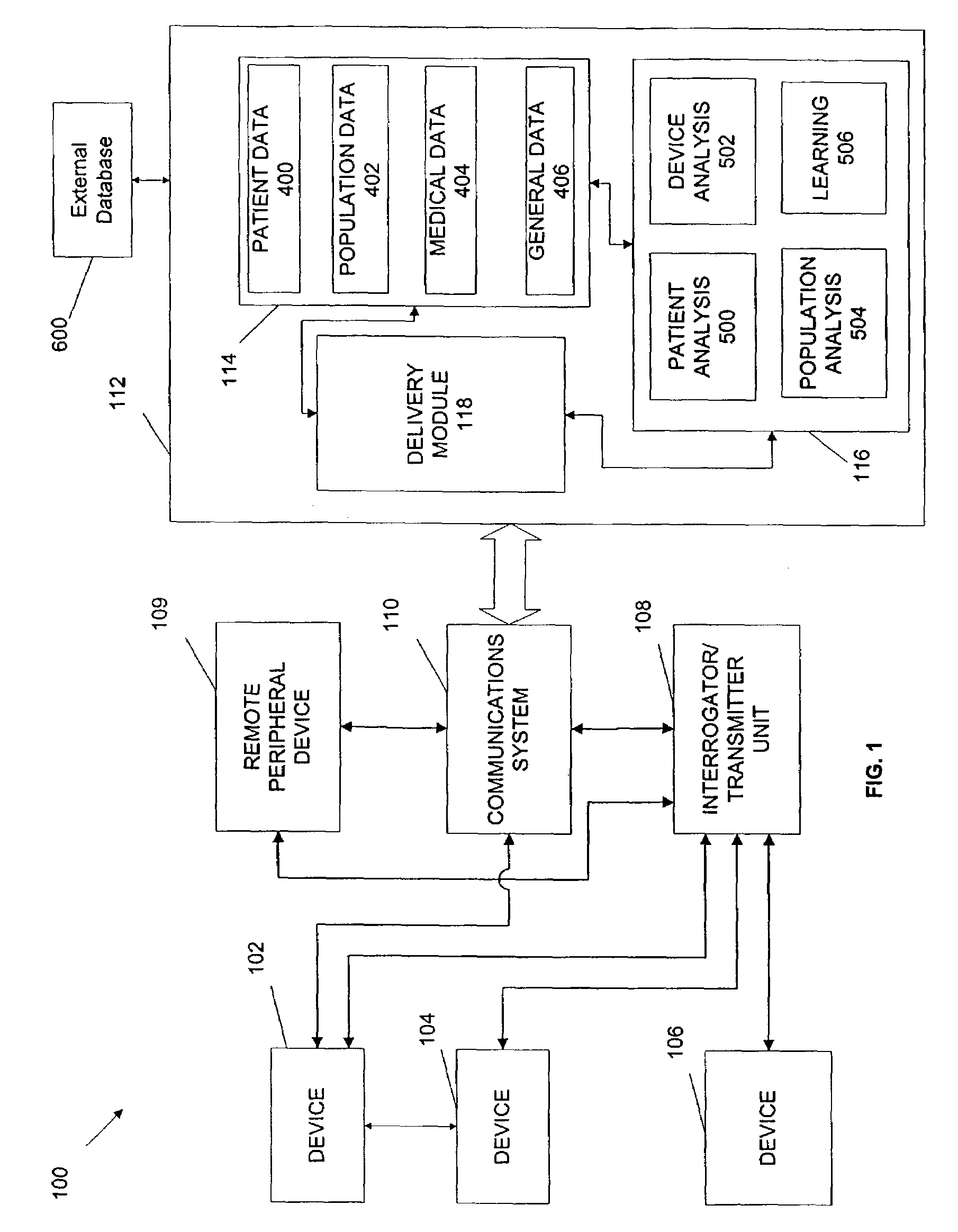
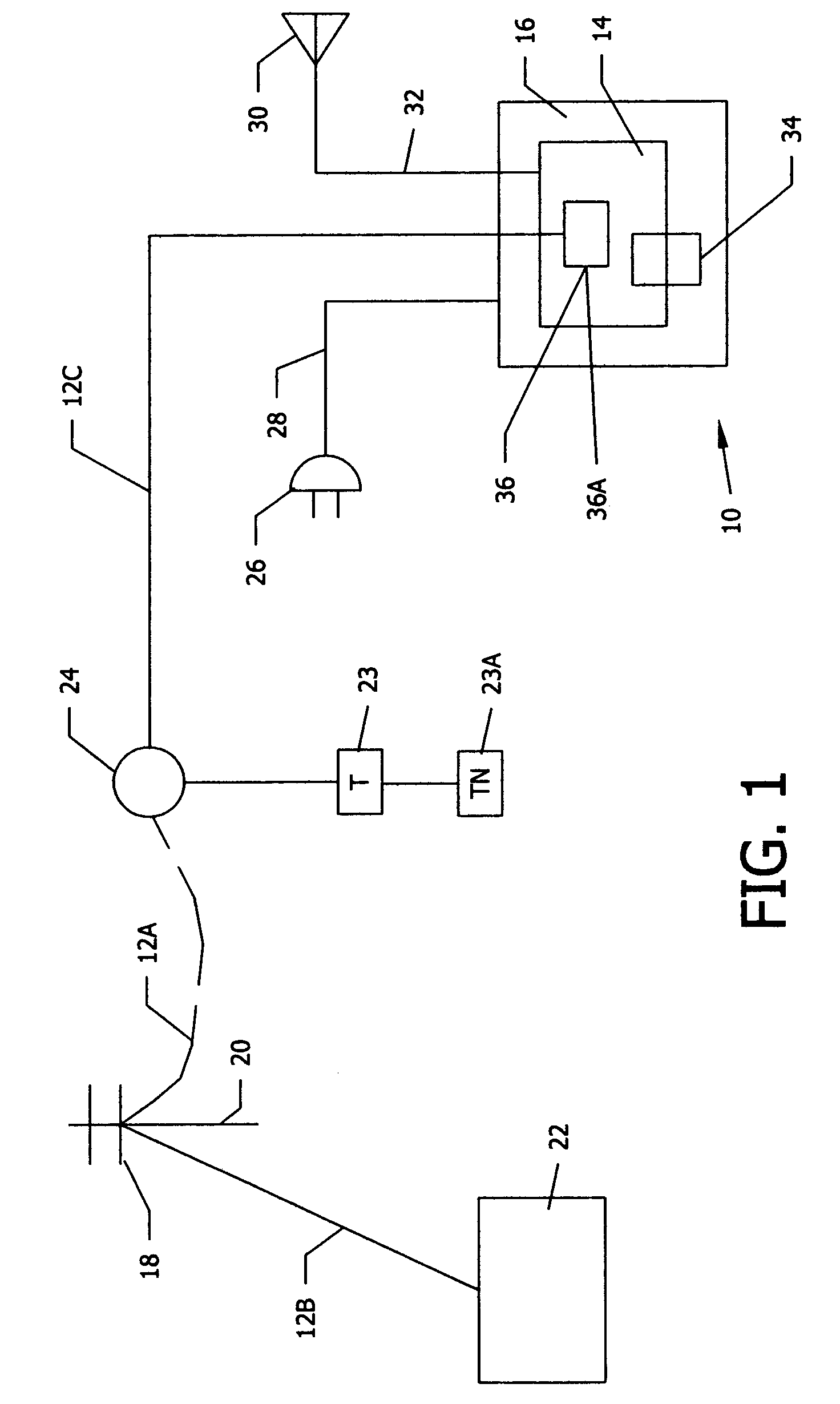
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system
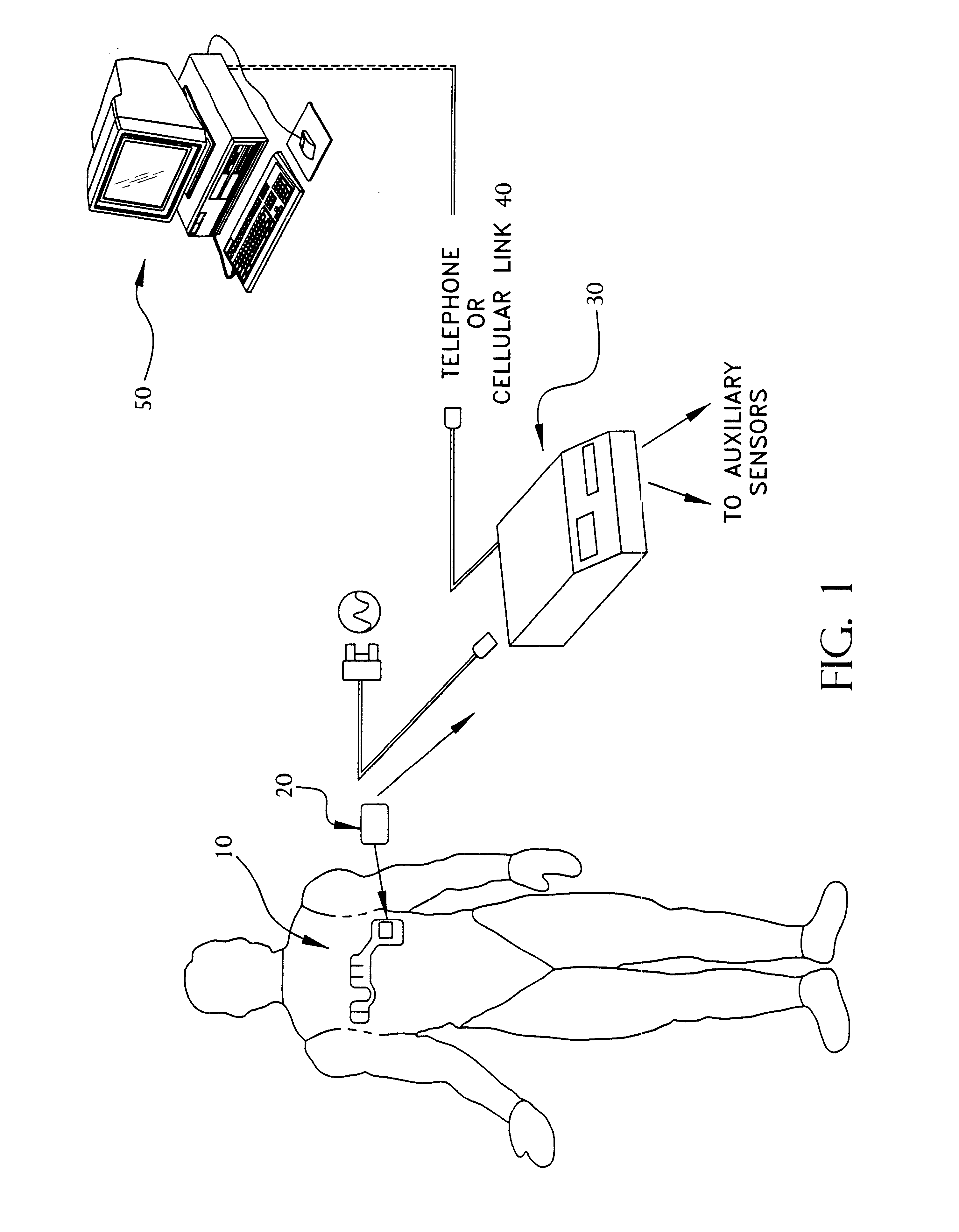
A system and method for monitoring vital signs and capturing data from a patient remotely using radiotelemetry techniques. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors form measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and transmission circuitry for the detection and transmission of vital signs data of the patient. A small signal transfer unit that can either be worn by the patient, e.g., on his or her belt, or positioned nearby receives data from the sensor band, which it then forwards by e.g., radio transmission to a base station that can be located up to 60 meters away. The base station receives data transmissions from the signal transfer unit and is designed to connect to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Patient safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g., ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. Such events are indicated to the physician and could be indicated to the patient by reverse transmission to the signal transfer unit. A remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of patient clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of patients with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
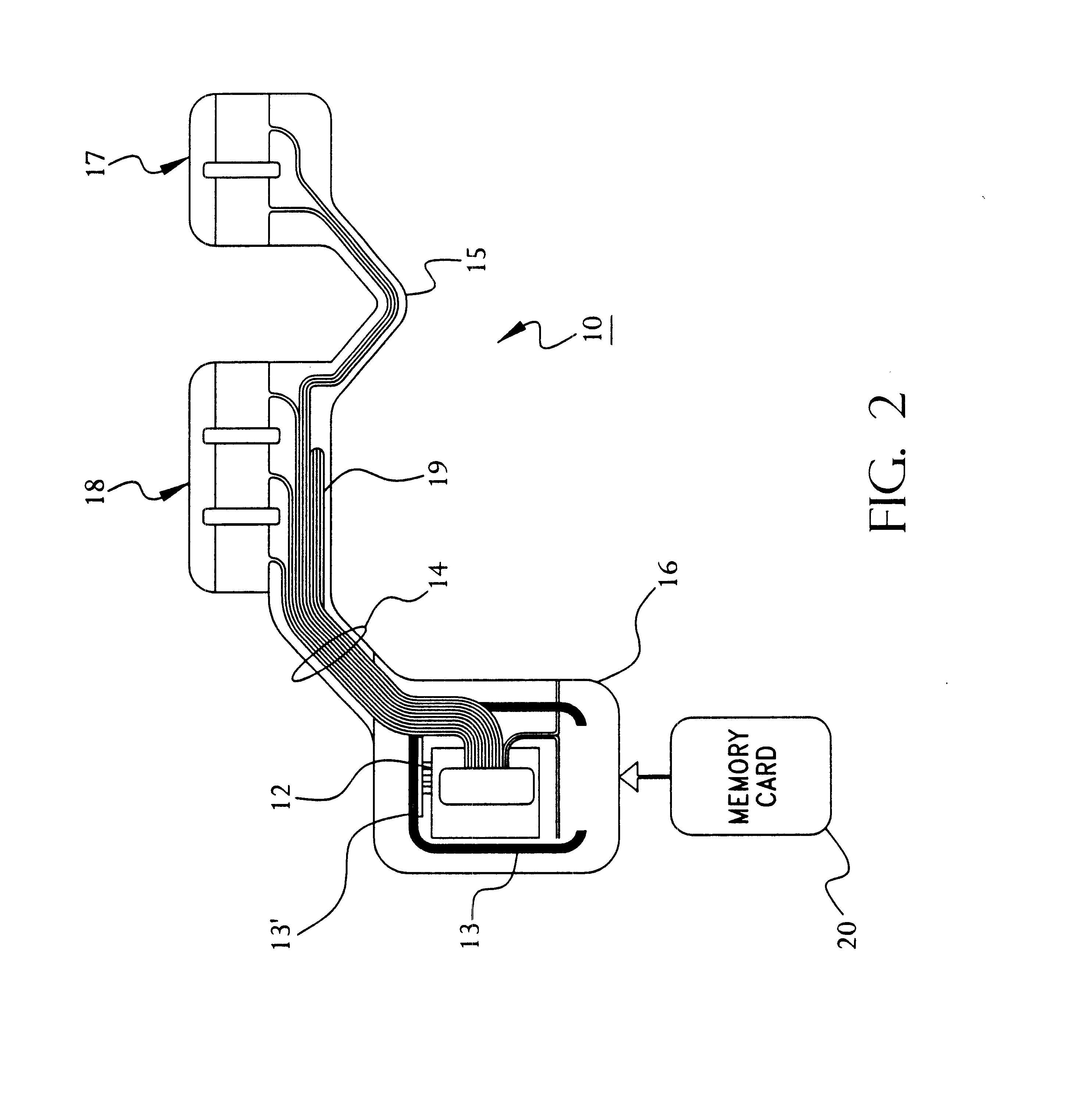
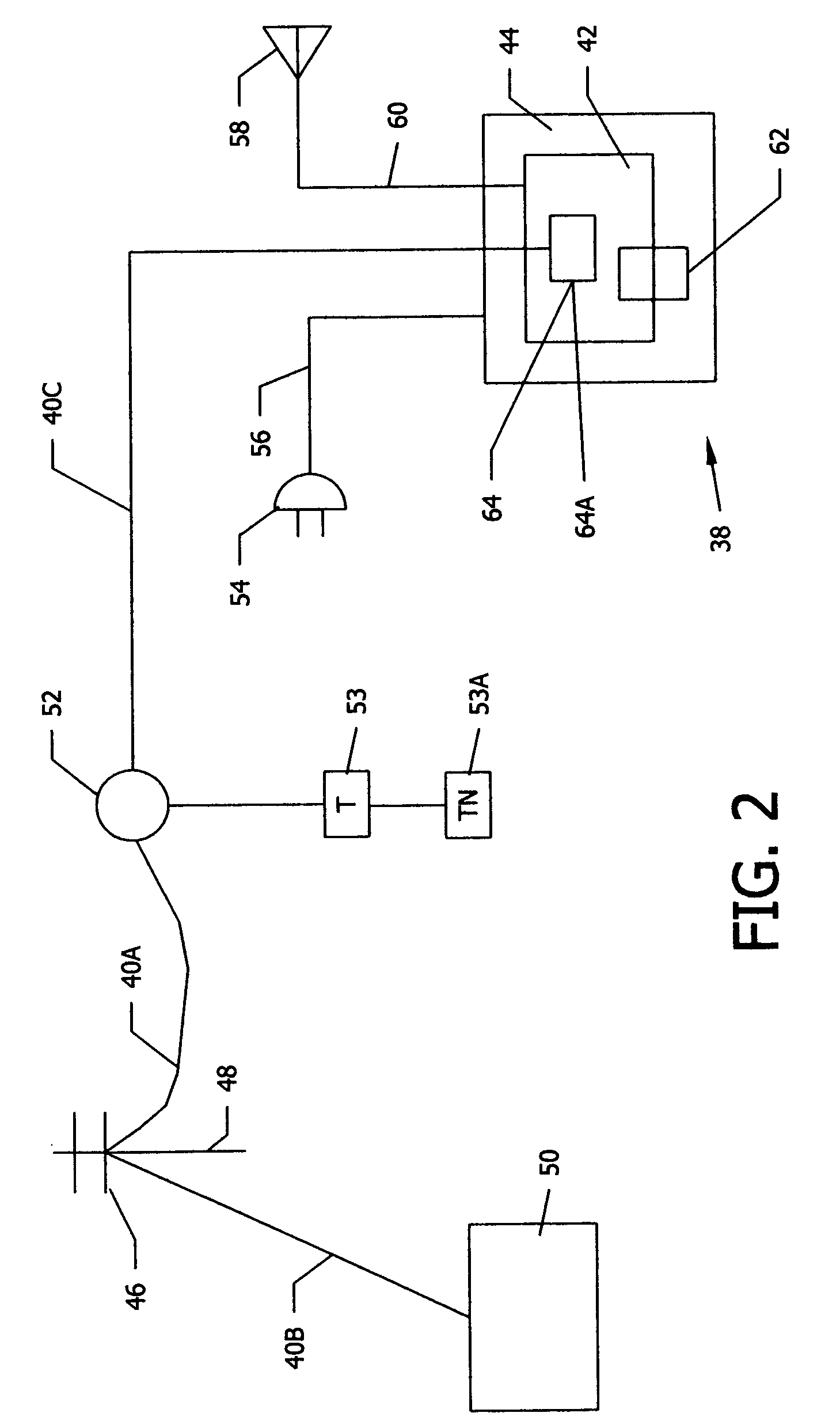
Portable remote patient telemonitoring system using a memory card or smart card
InactiveUS6454708B1Low costIncrease the number ofSurgeryRespiratory organ evaluationSmart cardFull waveform
A system and method for monitoring health parameters and capturing data from a subject. The system is characterized by a cordless, disposable sensor band with sensors for measuring full waveform ECG, full waveform respiration, skin temperature, and motion, and a connector which accepts a memory card or a smart card for storage of the measured data. After a predetermined period of time, such as when the sensor band is removed, the memory card or smart card is removed and inserted into a monitoring device which reads the stored health parameter data of the subject. The monitoring device includes a base station that includes a memory / smart card reader and is connected to conventional phone lines for transferring the collected data to a remote monitoring station. The base station may also capture additional clinical data, such as blood pressure data, and to perform data checks. Subject safety is enhanced by the ability of the base station to compare clinical data, e.g. ECG, against given profiles and to mark events when appropriate or when the base station is programmed to do so. The remote monitoring station allows the presentation and review of data (including events) forwarded by the sensor band. ECG analysis software and a user-friendly graphical user interface are provided to remotely analyze the transmitted data and to permit system maintenance and upkeep. In alternative embodiments, a smart card includes the sensor band's electronics and / or signal transmission circuitry in conjunction with a portable data logger so that the electronics may be reused from one disposable sensor band to the next without limiting the patient's range of movement. The system of the invention has useful application to the collection of subject clinical data during drug trials and medical testing for regulatory approvals as well as management of subjects with chronic diseases.
Owner:CLEARPATH PARTNERS
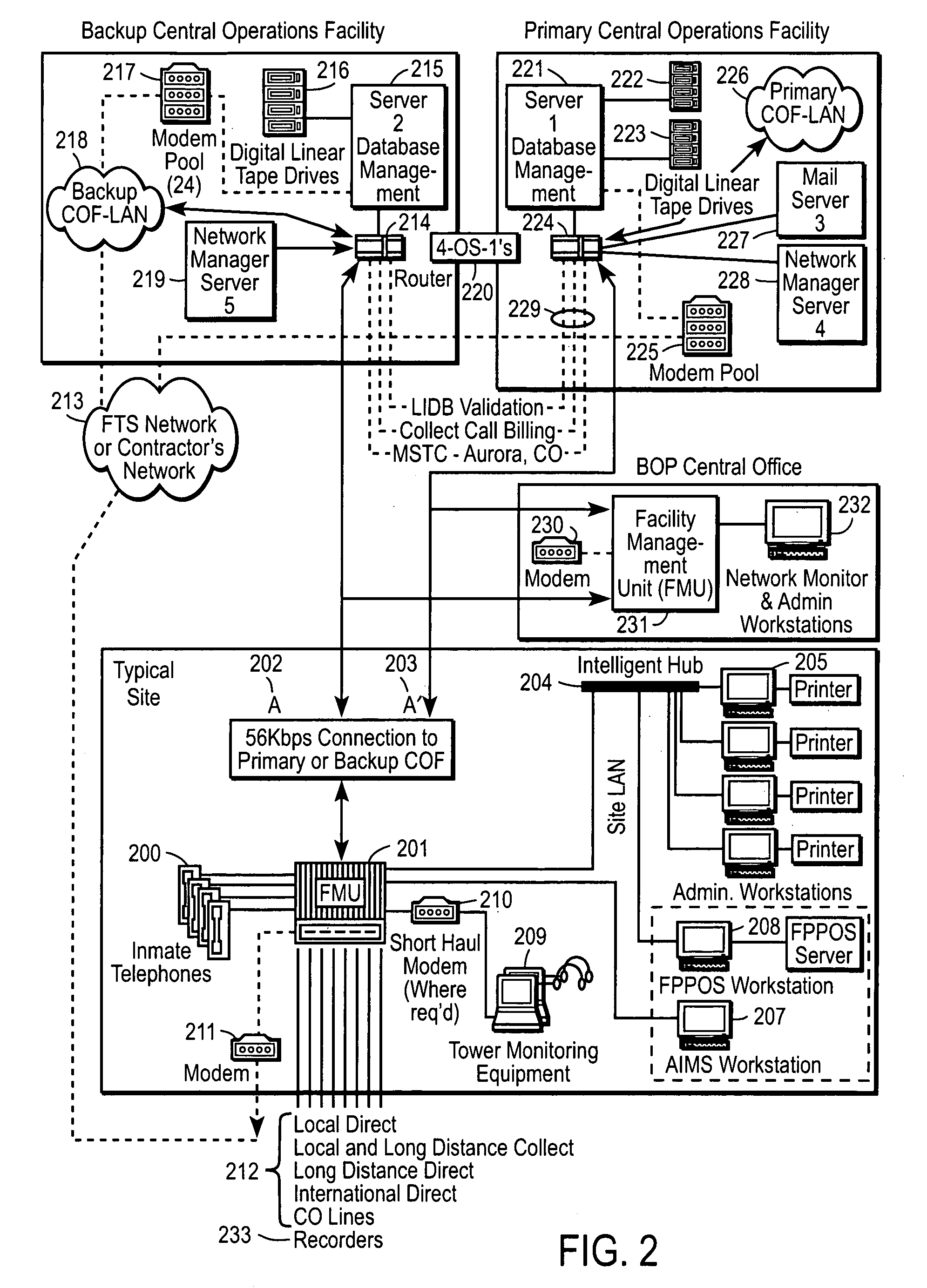
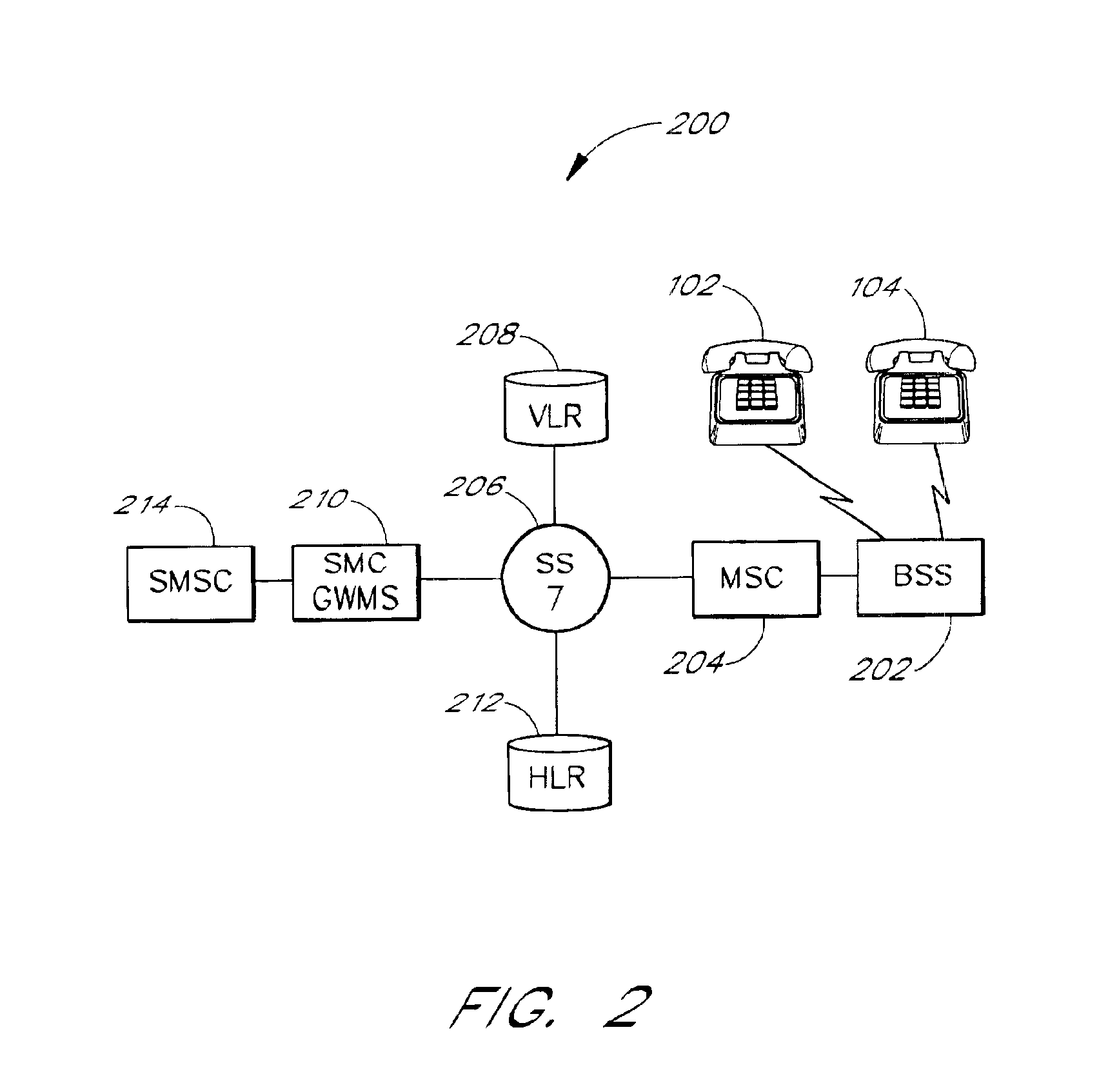
Computer-based method and apparatus for controlling, monitoring, recording and reporting telephone access
InactiveUS7106843B1Improve securityLow costUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsManagement unitCentralized management
A method and apparatus for managing institutional telephone activity utilizing a computer-based telephony management unit to connect institutional telephones with outside telephone lines. The unit provides institutional users with fully automated, direct dial and collect calling privileges for local, long distance, and international calls. The unit contains a database for storing the calling privileges and restrictions of institutional users, for recording calling transactions made by the users, and for managing user monetary accounts. The unit can record up to 400 hours of conversation in a digital format. The unit provides various administrative capabilities, including user account management, audit trails, transaction reports, centralized management and report capabilities, and detection of fraudulent calling.
Owner:AMERICAN CAPITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES +1
Repeater device for communications with an implantable medical device
A repeater device for an advanced patient management system communicates with a medical device coupled to a patient to obtain data about the medical device and / or patient's condition. The repeater device maintains the data while if considers various factors when coordinating transfer of the data to a repository of the advanced patient management system. The repeater device may be configured to analyze the data to determine a degree of urgency, such as whether an emergency exists, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the degree of urgency. The repeater device may also be configured to test the condition of the communication medium being used to transfer the data to the repository, such as determining whether a telephone line is in use, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the condition of the of the communication medium.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
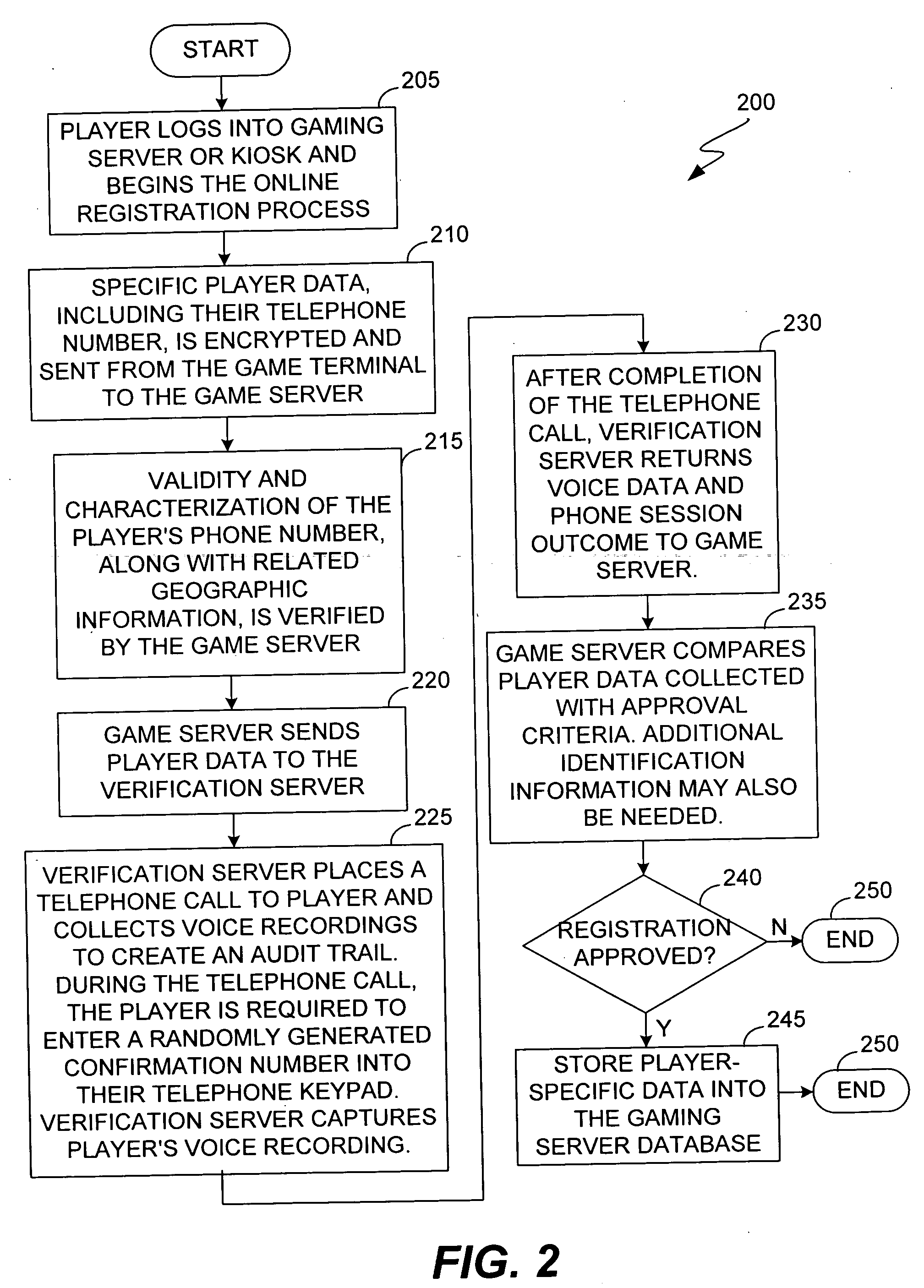
Location and user identification for online gaming
ActiveUS20060095790A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsUser inputTelephone network
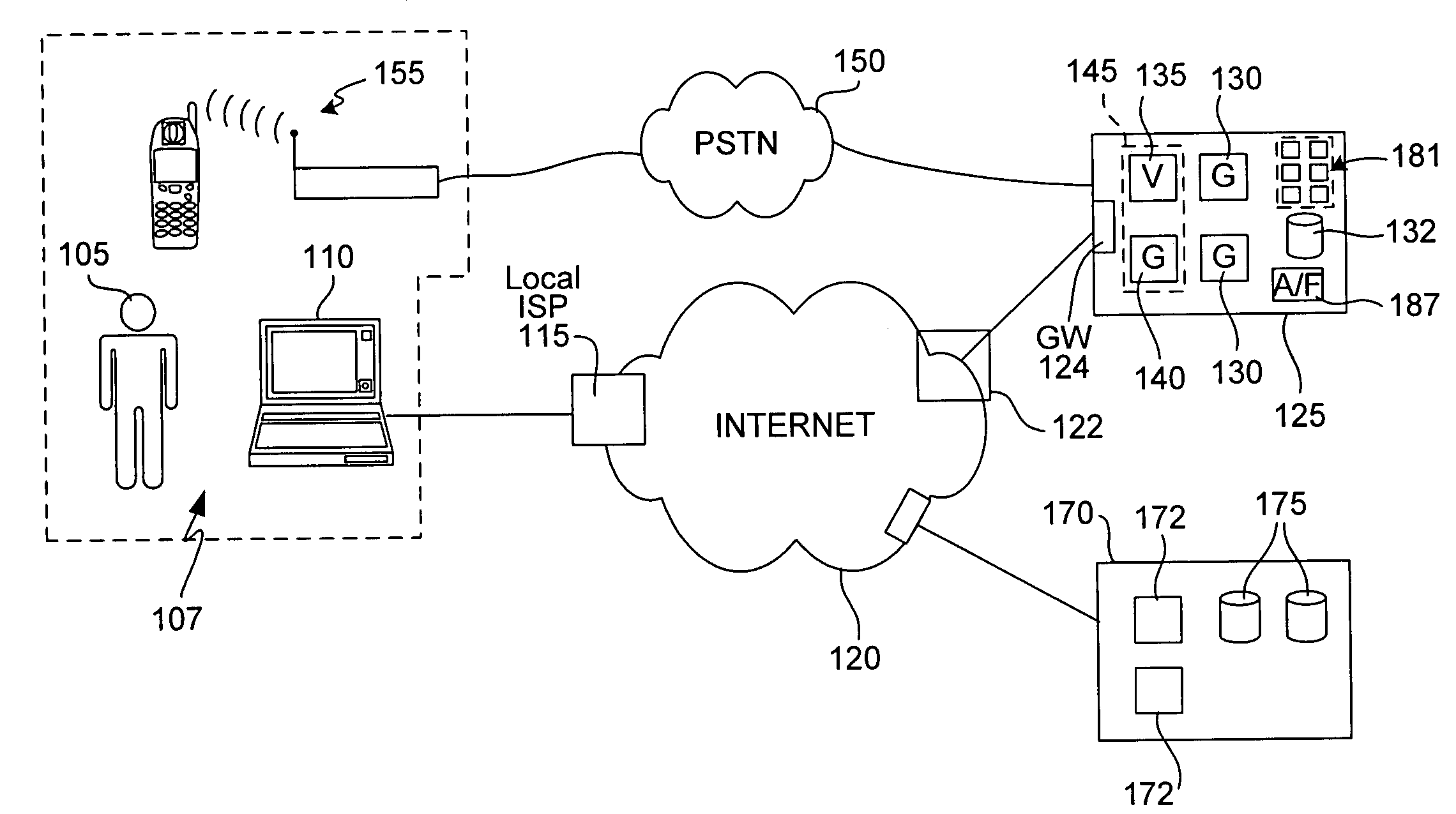
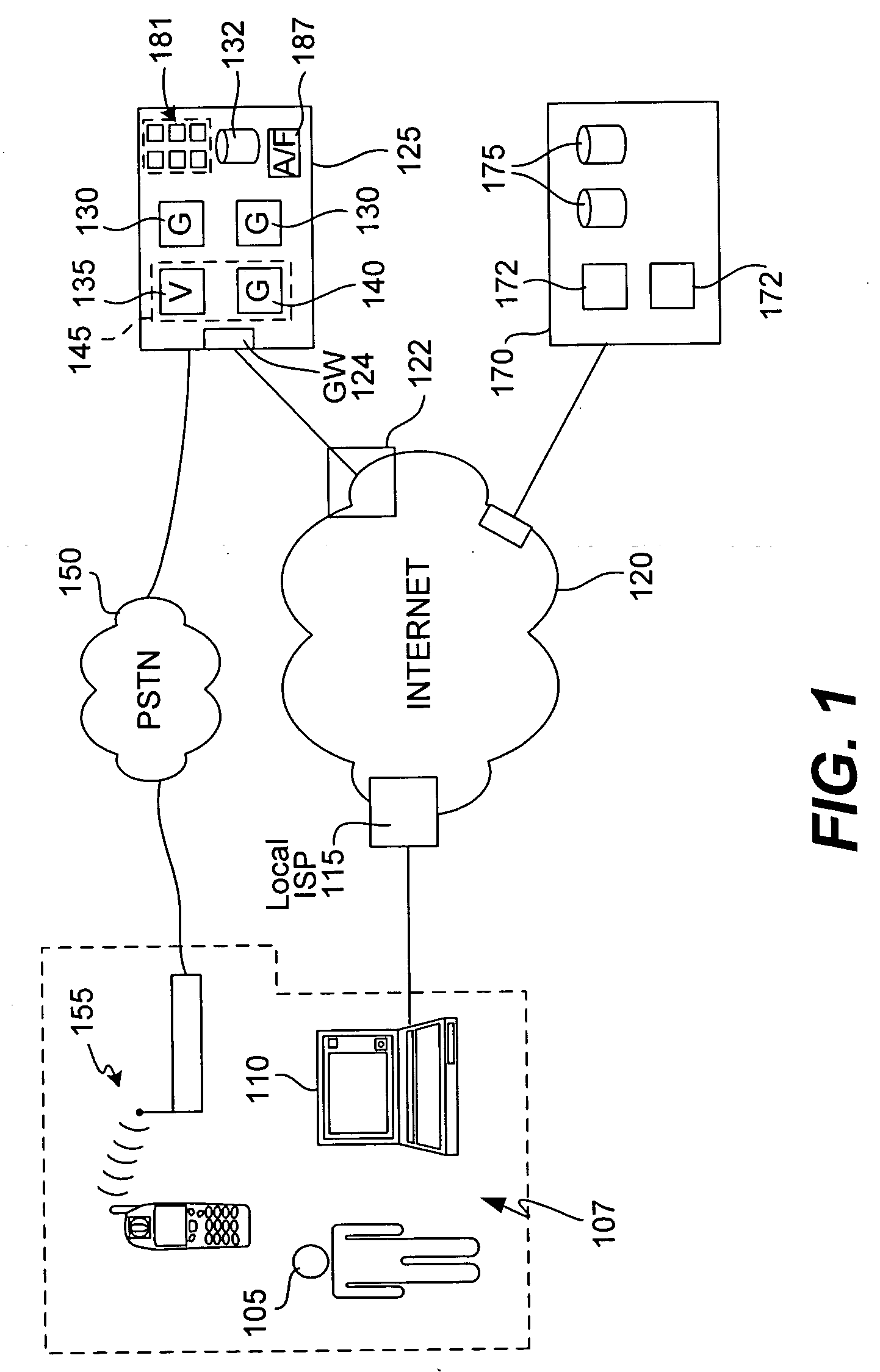
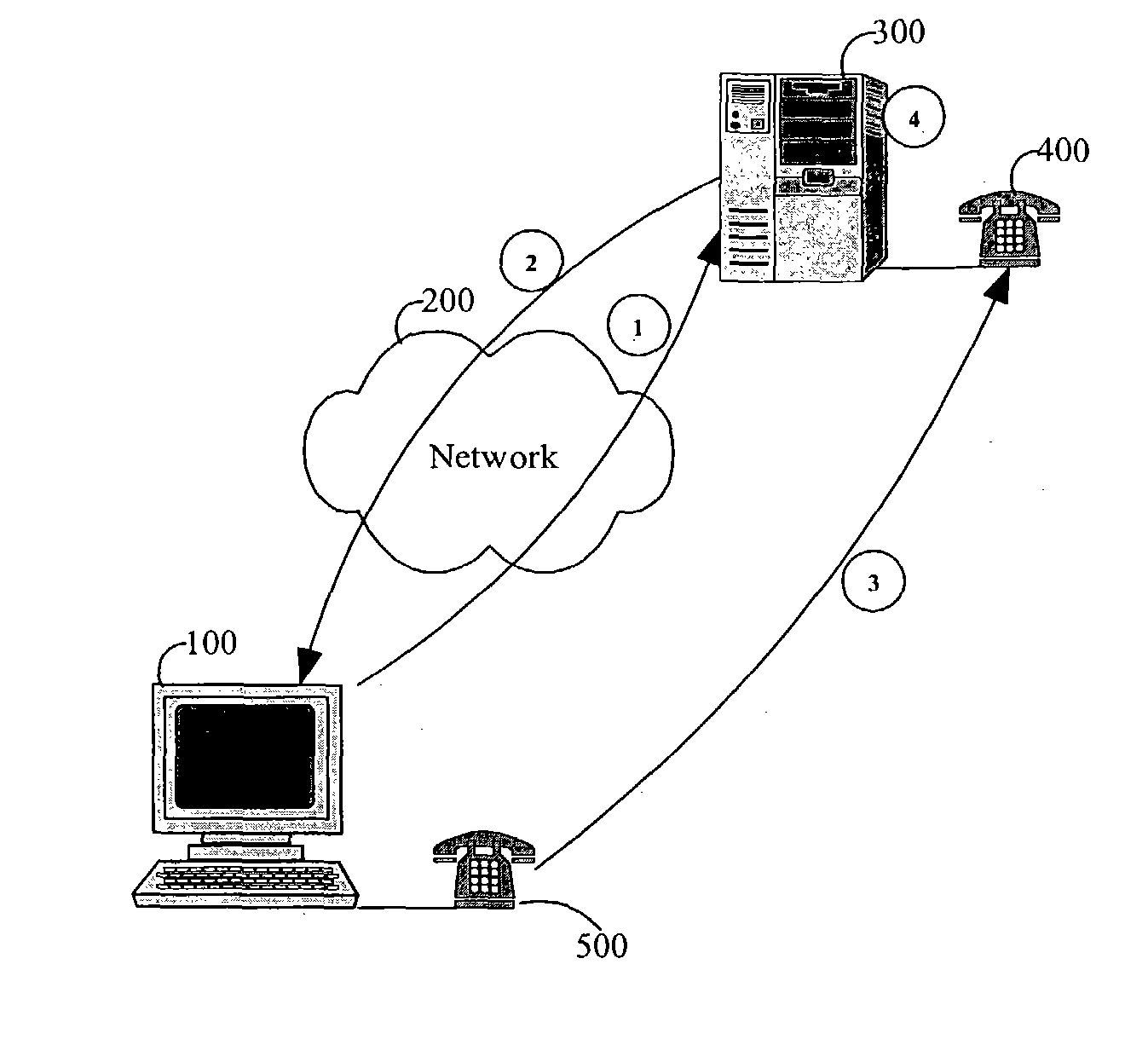
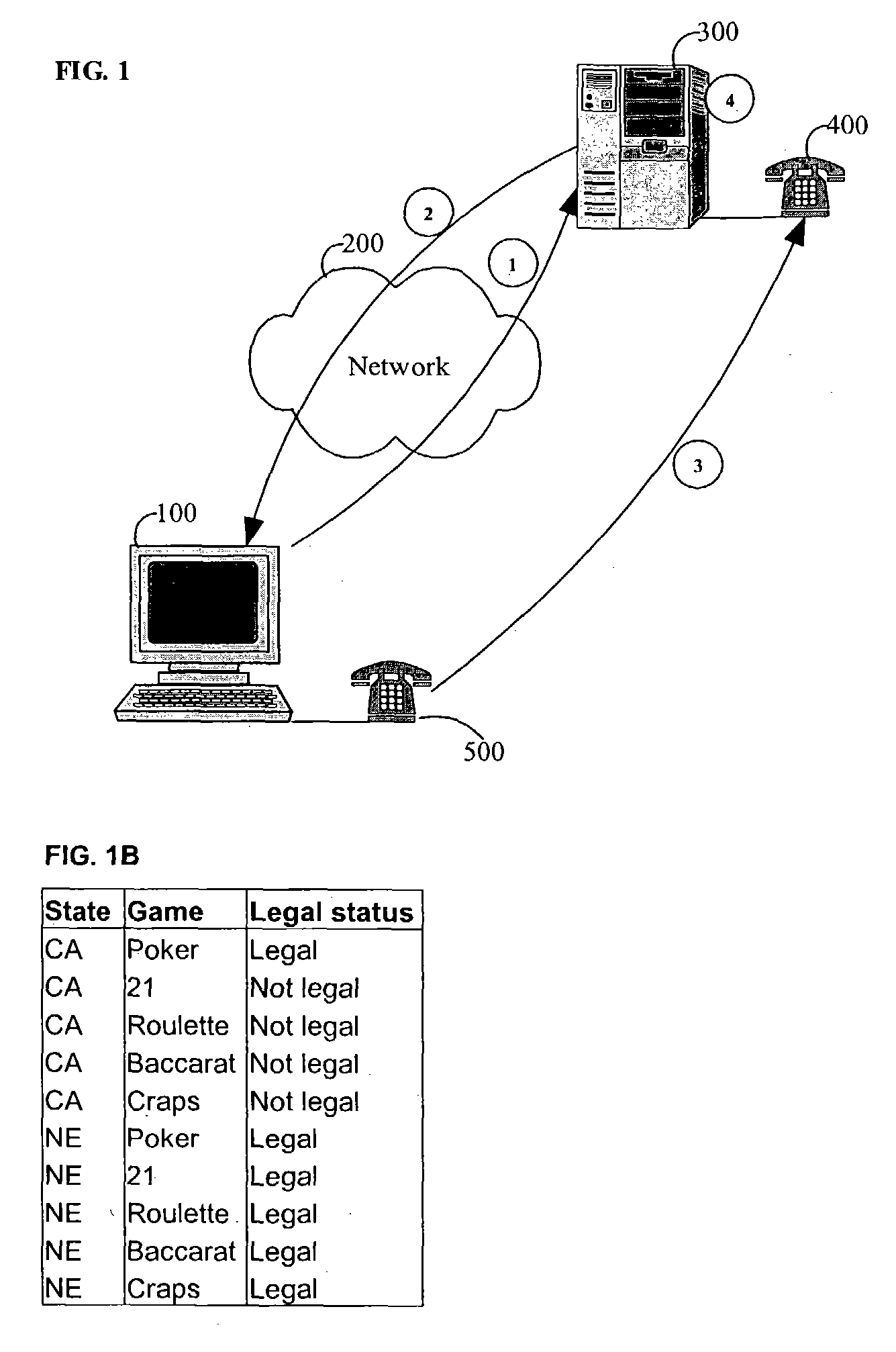
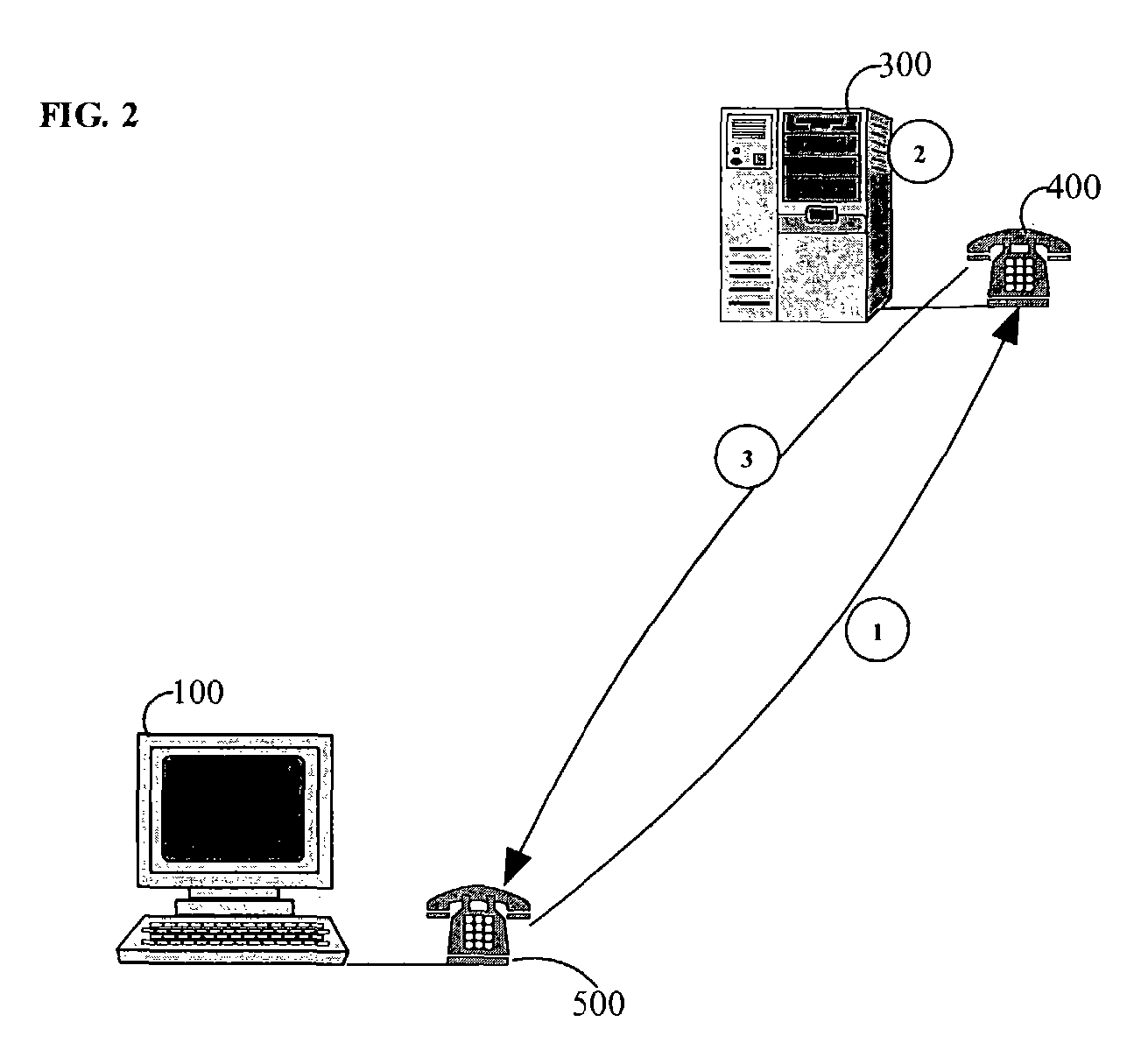
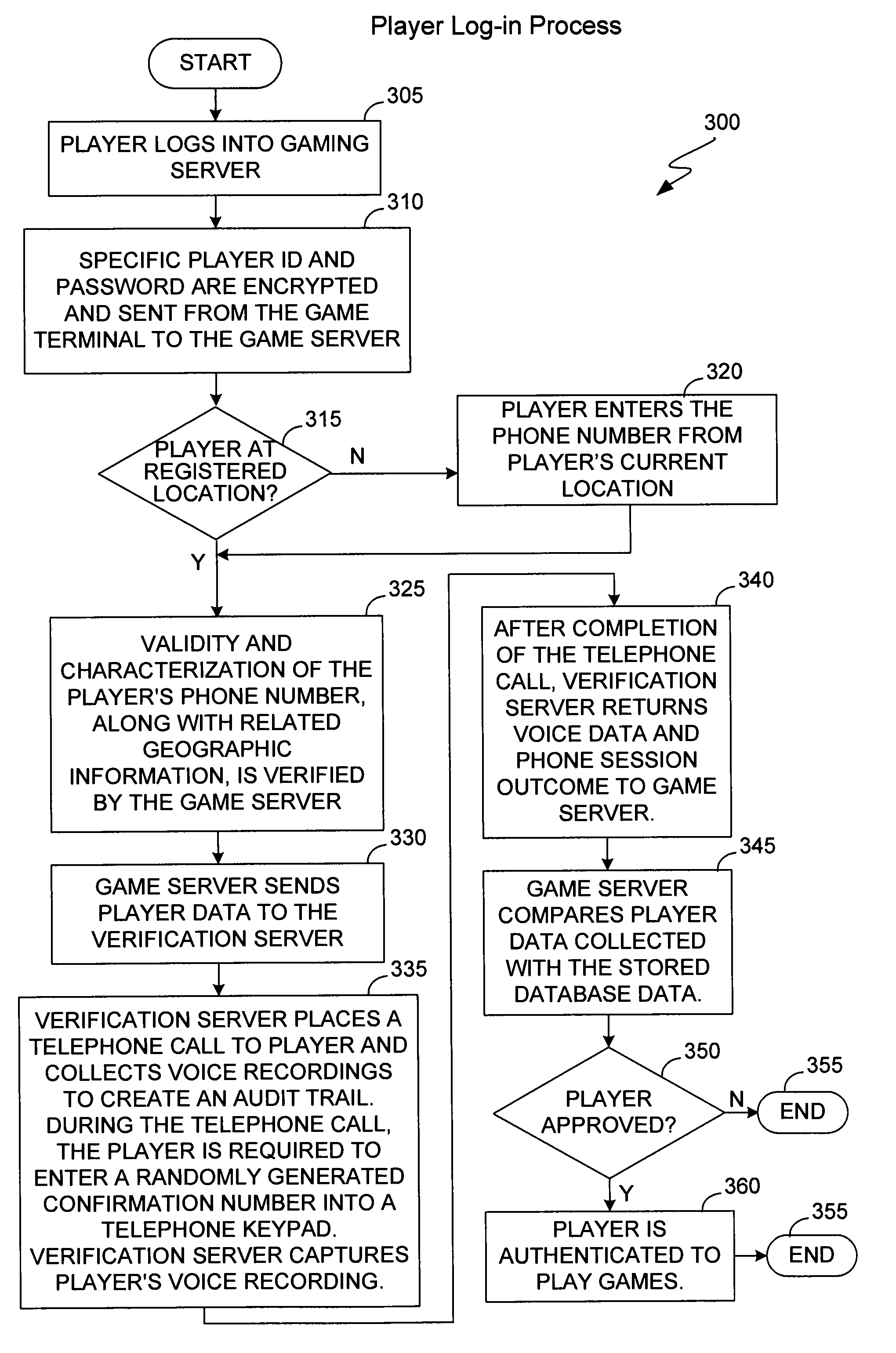
The present invention provides methods and devices for determining the location, identity and age of a user who desires to initiate a gaming session from an uncontrolled environment such as a home, a gaming kiosk or a hotel room. In some implementations, the user's location is determined in part by reference to a database of land telephone lines and corresponding addresses. The location may be verified by reference to a location determined by other methods, e.g., by determining the location of an Internet service provider's network device that is near a user's host device. In other implementations, the user's location is determined by information provided by a cellular telephone network. The user may be asked to input a confirmation number and / or make an oral response during a telephone call to a telephone number associated with the uncontrolled environment. These the oral response may be analyzed to verify the user's identity. The user may also be prompted to make statements verifying his or her identity, age, a maximum amount available for wagering or other statements, which are preferably recorded and stored.
Owner:IGT
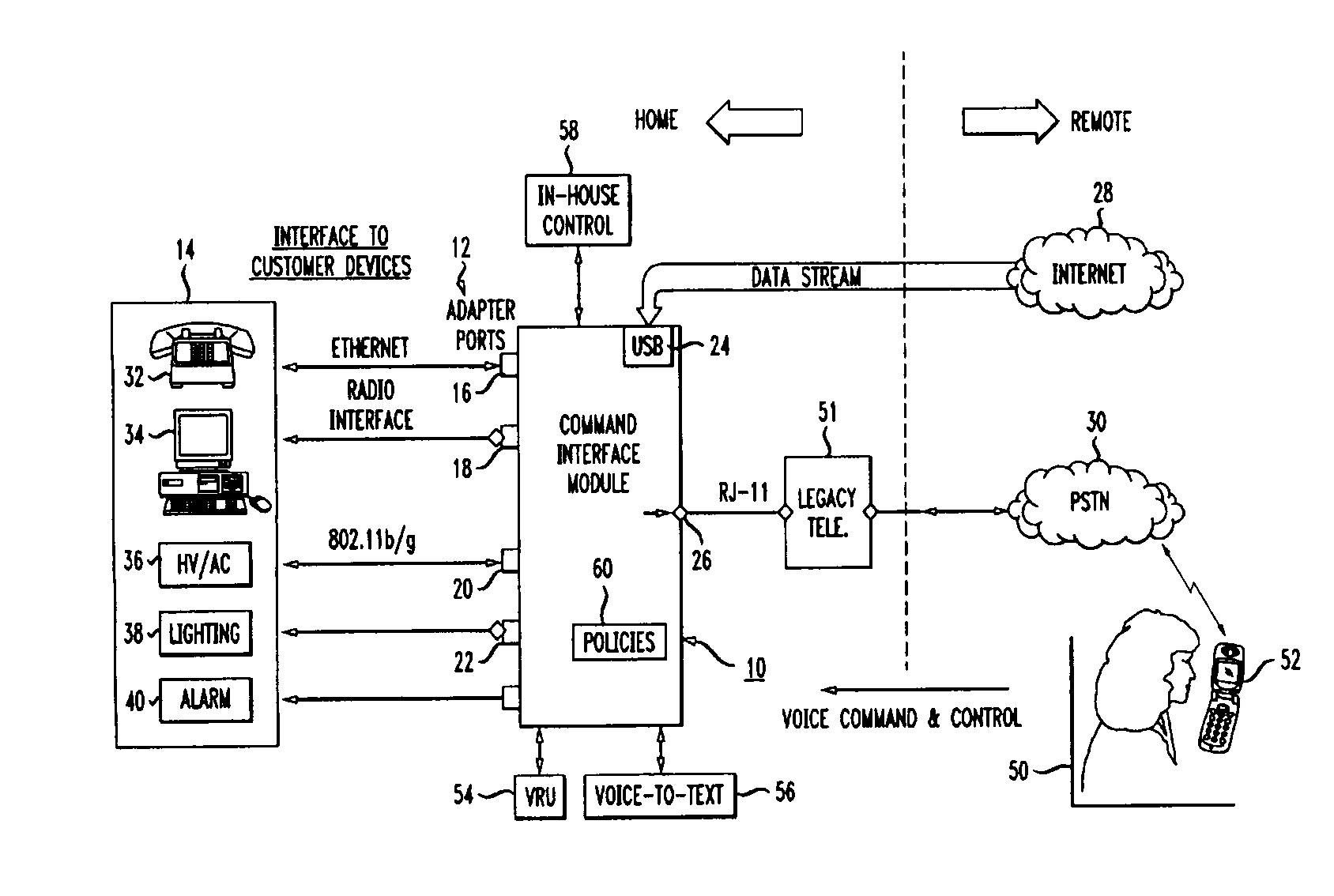
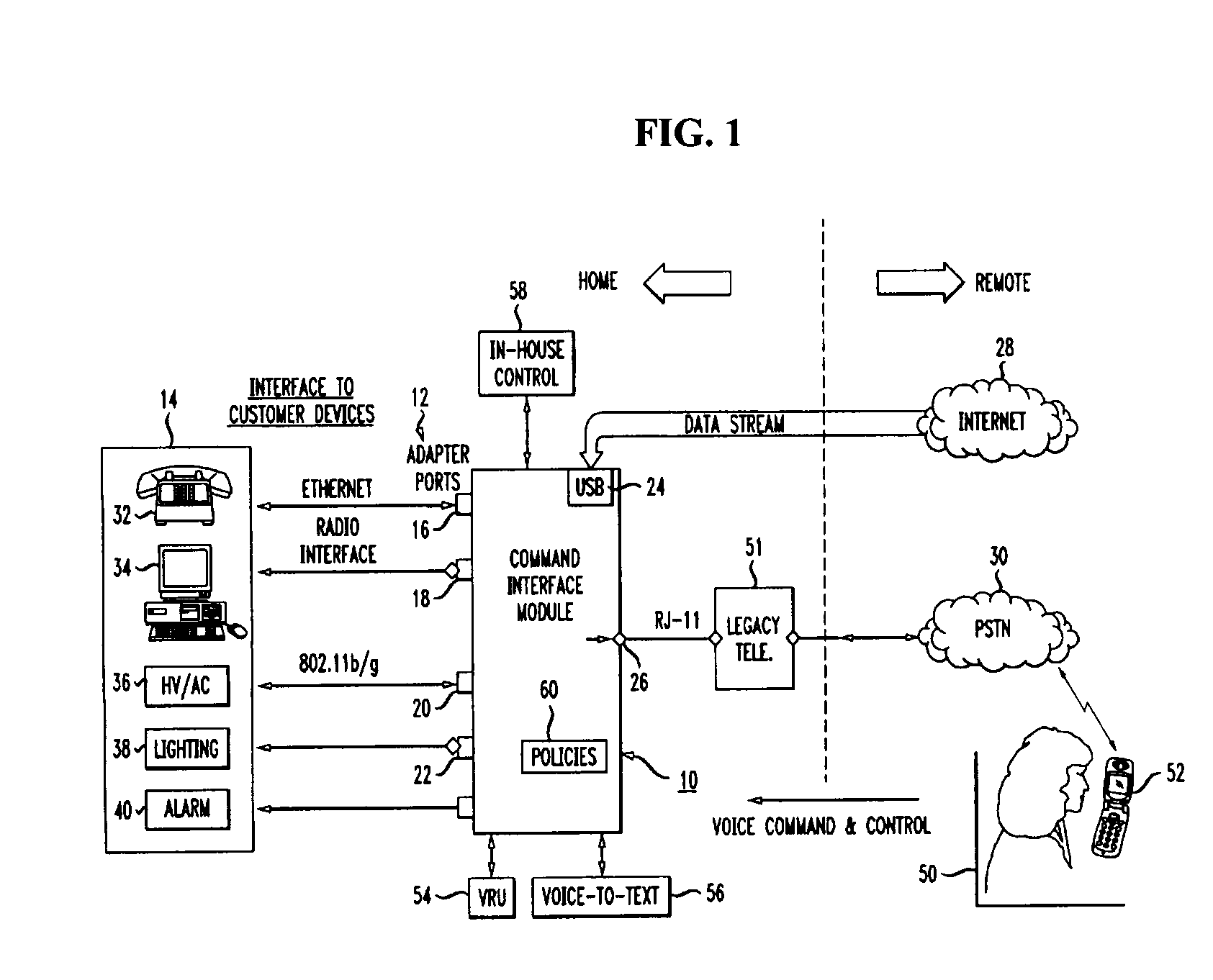
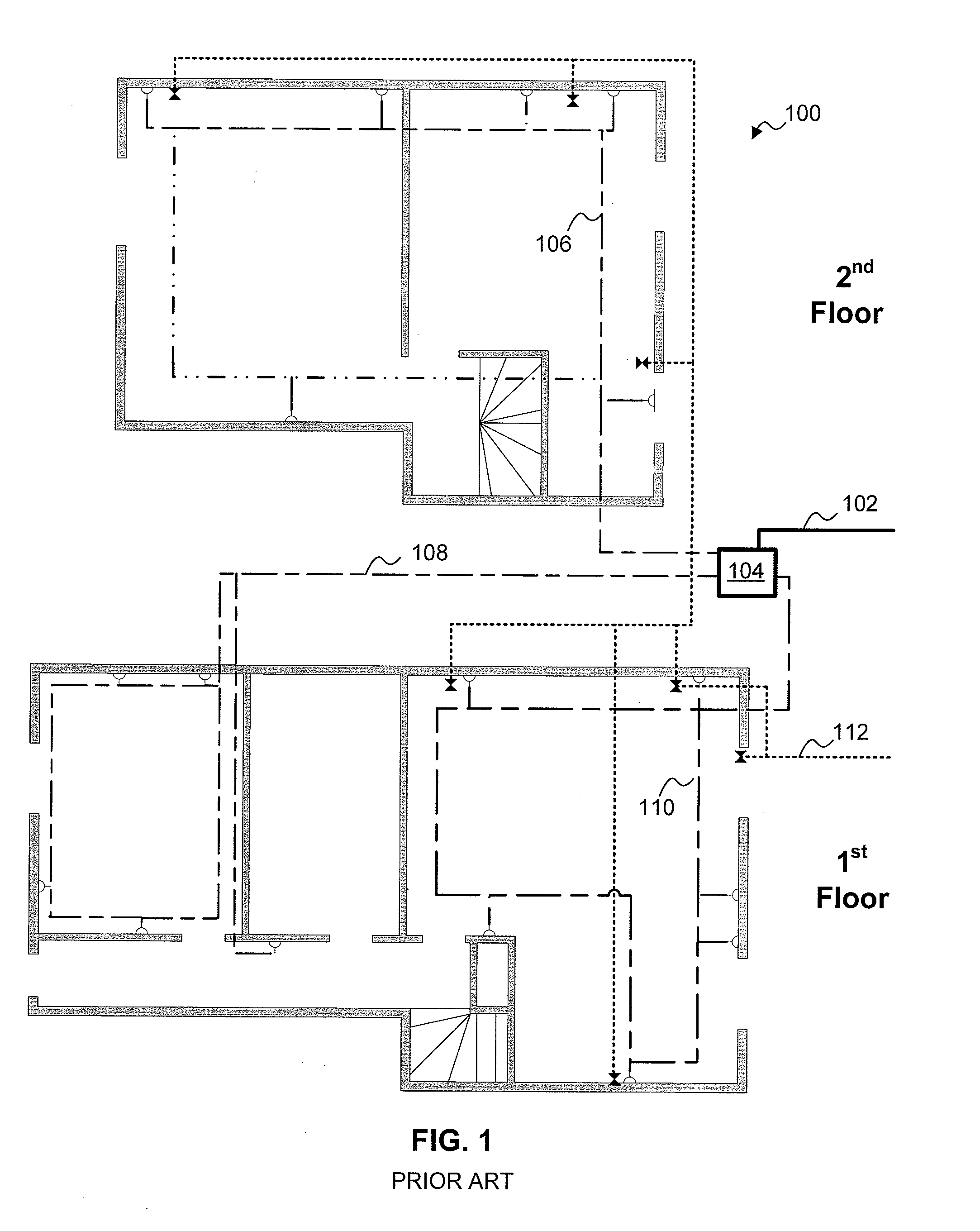
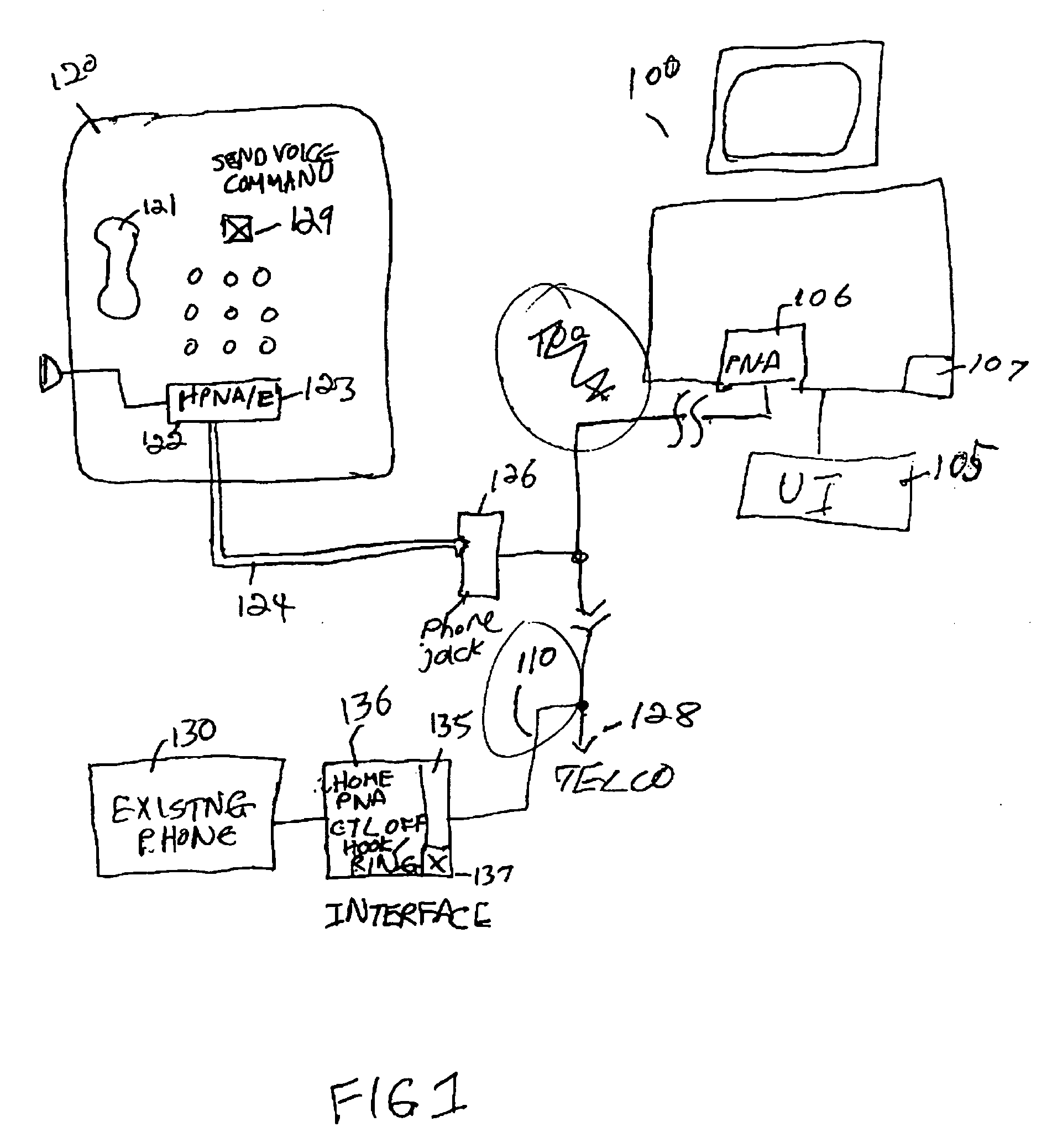
Home control, monitoring and communication system using remote voice commands
ActiveUS8654936B1Devices with voice recognitionAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingCommunication interfaceCommunications system
A voice-activated command interface module for interacting with a plurality of home-based electronic devices so as to allow for a remotely-located home owner to communicate with, command and control various ones of the electronic devices. The module includes a plurality of communication ports, each communication port associated with a different type of communication interface for providing communications to and from the plurality of electronic devices. The module also includes a voice network communication port for receiving the voice commands from the home owner and a data network communication port for transmitting monitoring and control information between the plurality of electronic devices and the home owner. In operation, the command interface module is responsive to voice commands received from a remote user via an incoming telephone line (either data or voice). A voice recognition unit within the command interface module is utilized to translate the received voice signal into an “action / control” signal and then perform the desired activity.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
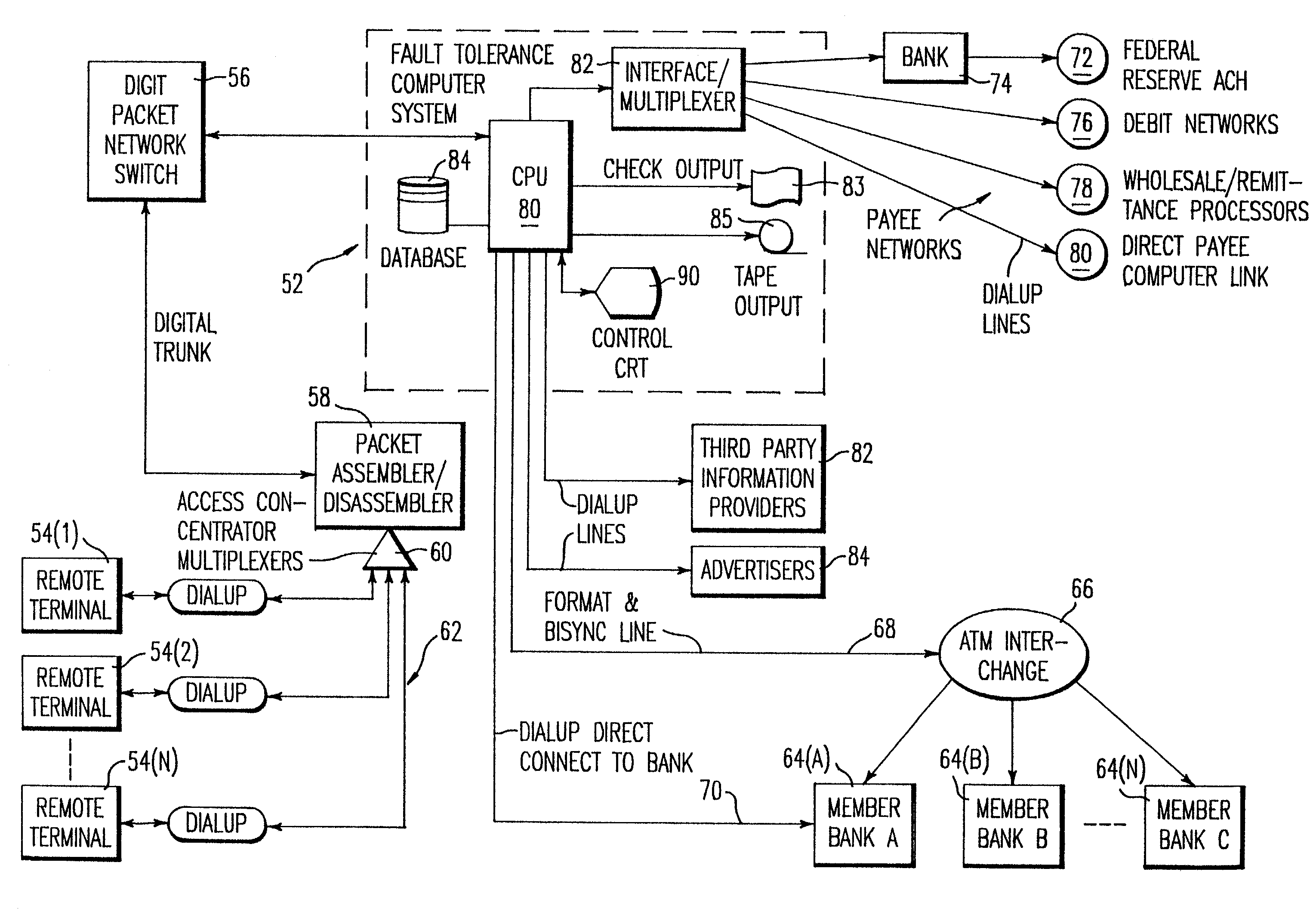
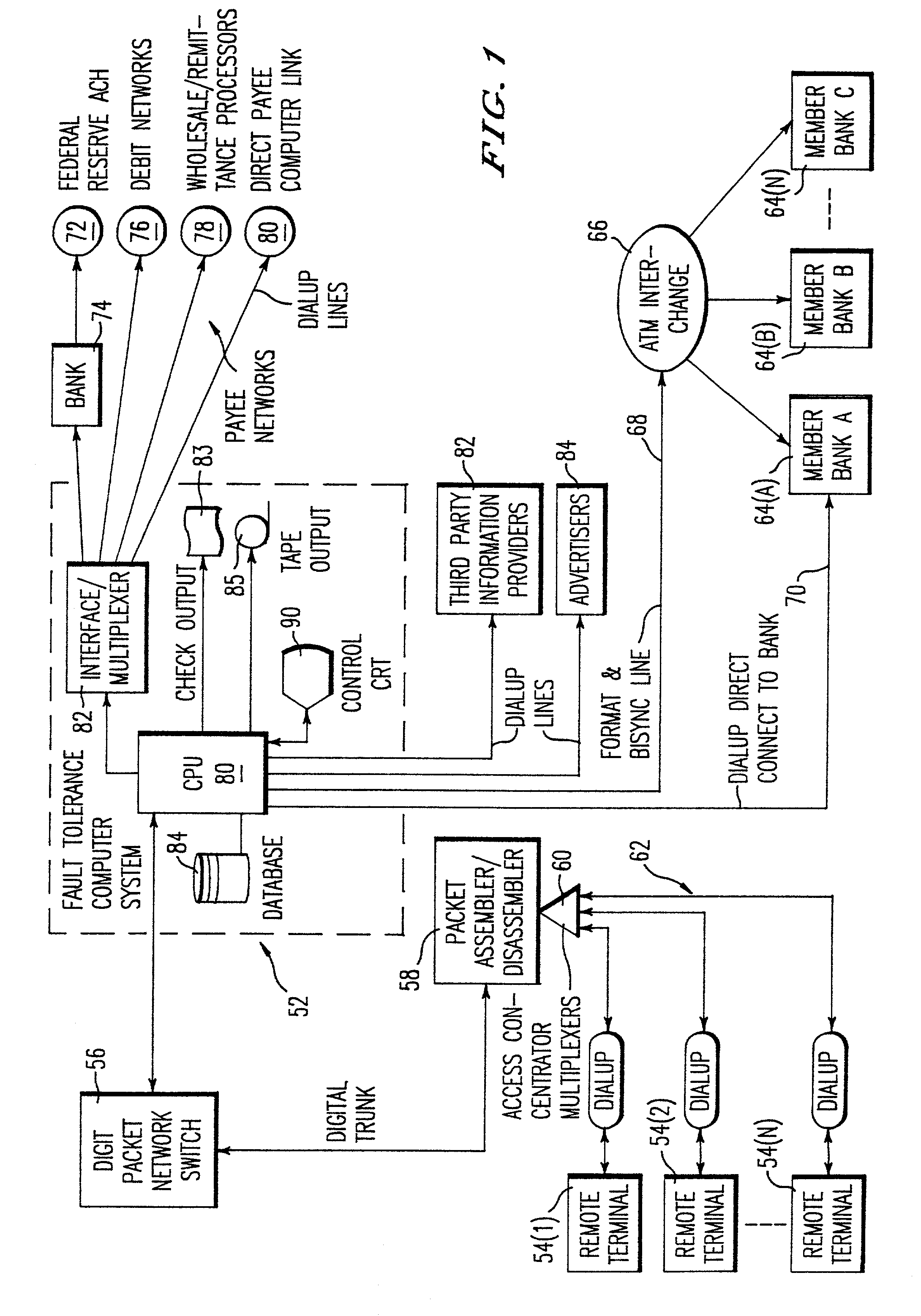
Method and system for remote delivery of retail banking services
A practical system and method for the remote distribution of financial services (e.g., home banking and bill-paying) involves distributing portable terminals to a user base. The terminals include a multi-line display, keys “pointing to” lines on the display, and additional keys. Contact is established between the terminals and a central computer operated by a service provider, preferably over a dial-up telephone line and a packet data network. Information exchange between the central computer and the terminal solicits information from the terminal user related to requested financial services (e.g., for billpaying, the user provides payee selection and amount and his bank account PIN number). The central computer then transmits a message over a conventional ATM network debiting the user's bank account in real time, and may pay the specified payees the specified amount electronically or in other ways as appropriate. Payments and transfers may be scheduled in advance or on a periodic basis. Because the central computer interacts with the user's bank as a standard POS or ATM network node, no significant software changes are required at the banks' computers. The terminal interface is extremely user-friendly and incorporates some features of standard ATM user interfaces so as to reduce new user anxiety.
Owner:OFFICIAL PAYMENTS
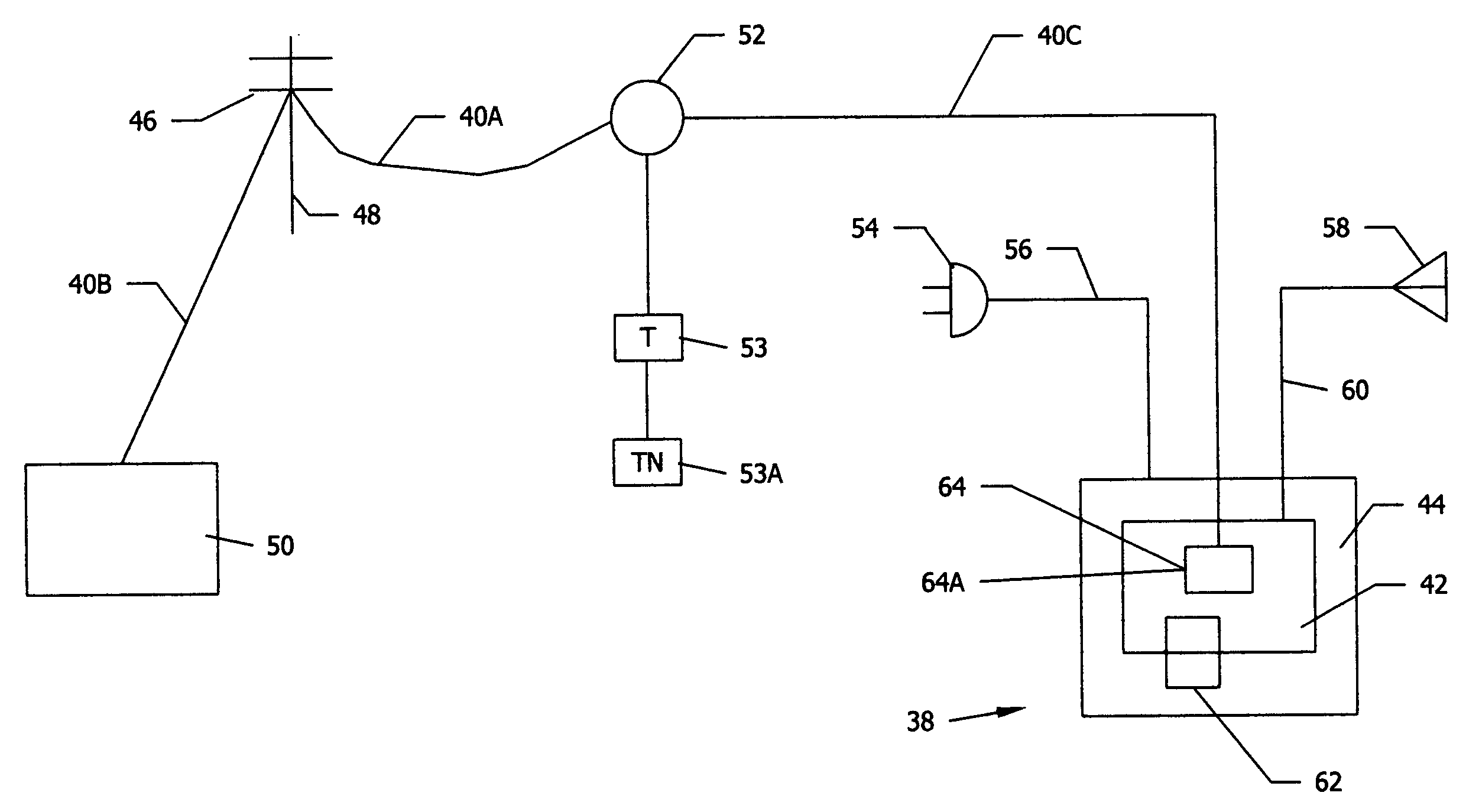
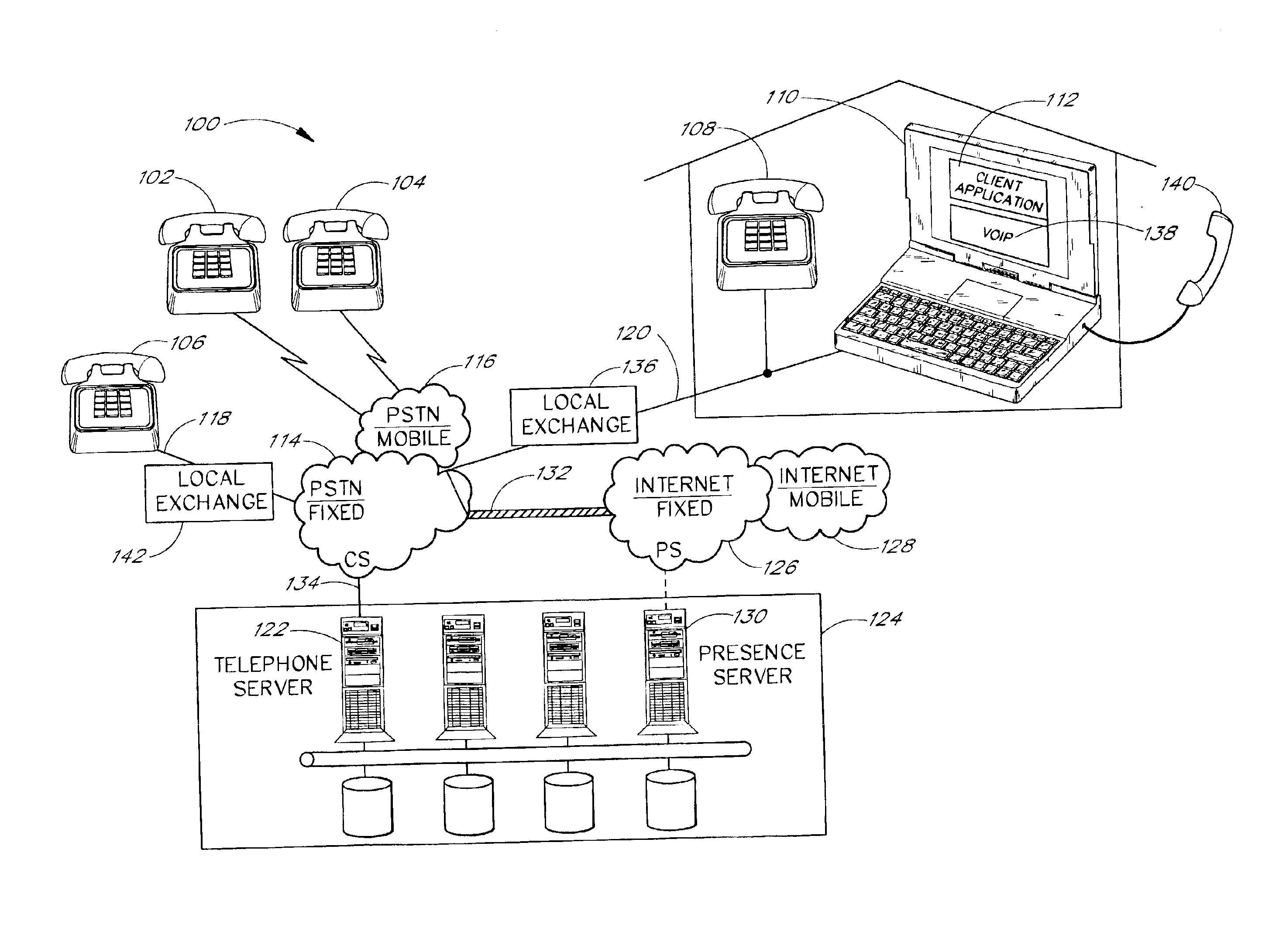
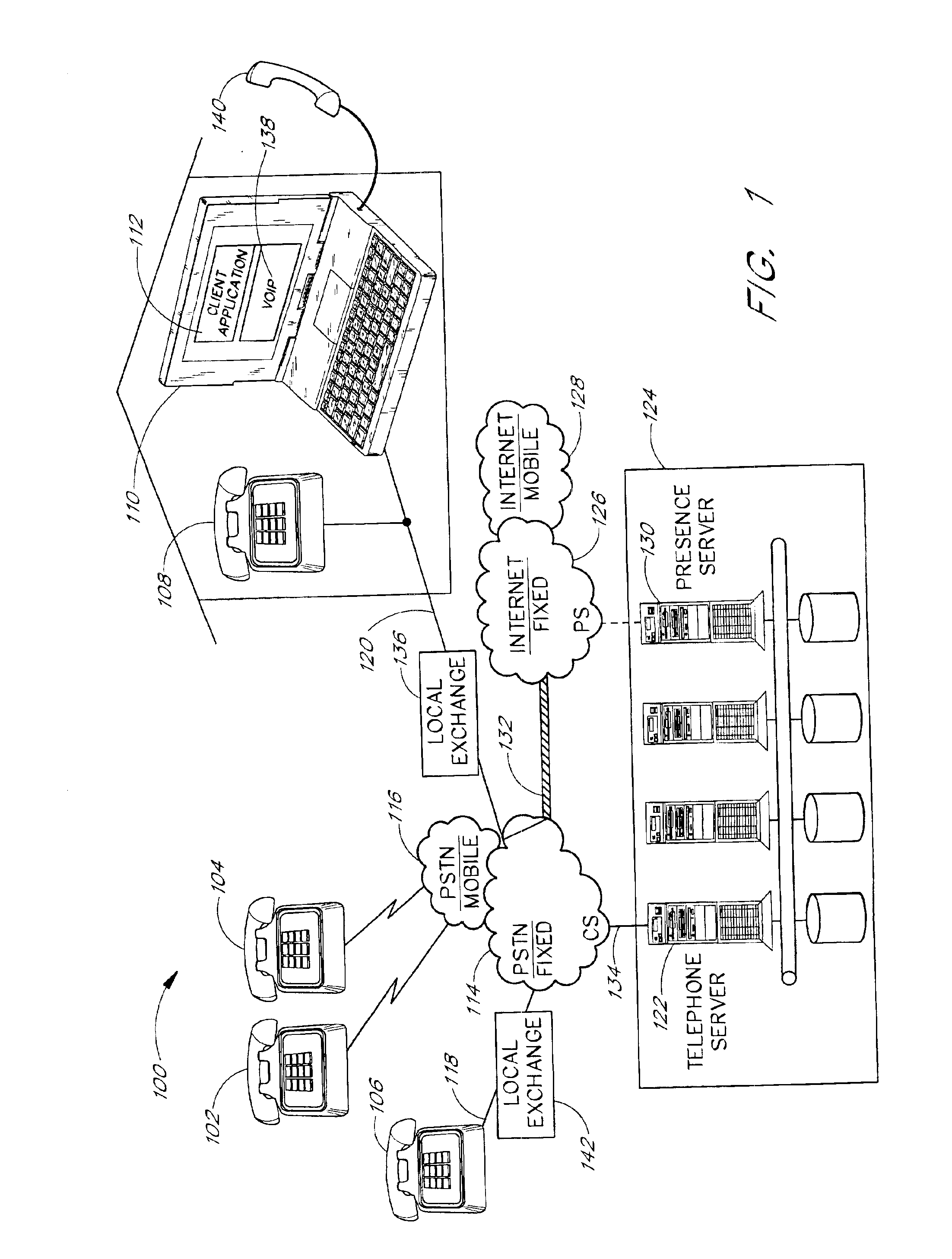
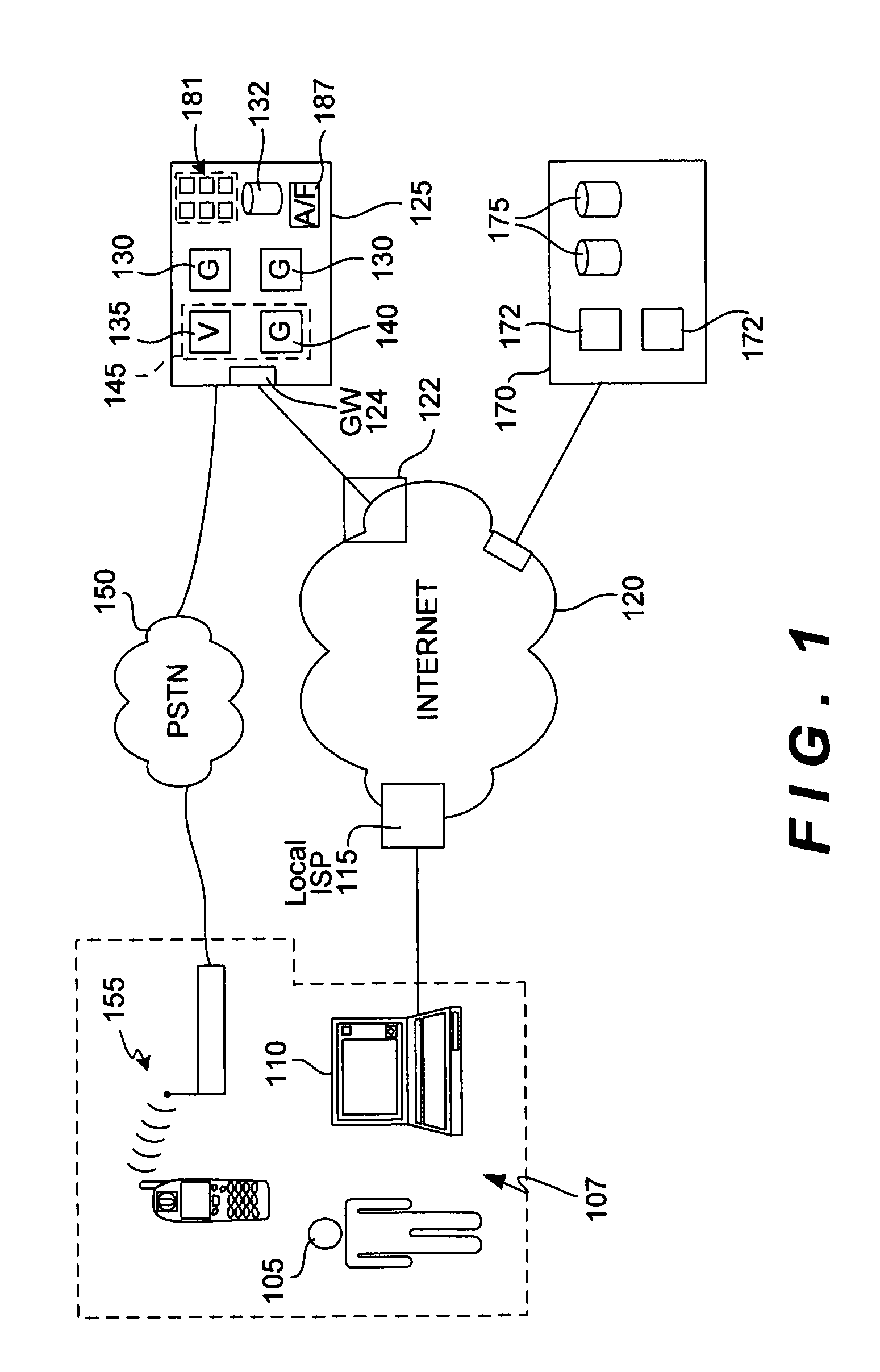
Picture transmission and display between wireless and wireline telephone systems
InactiveUS20060033809A1Accurate operationInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentCamera phoneImage transfer
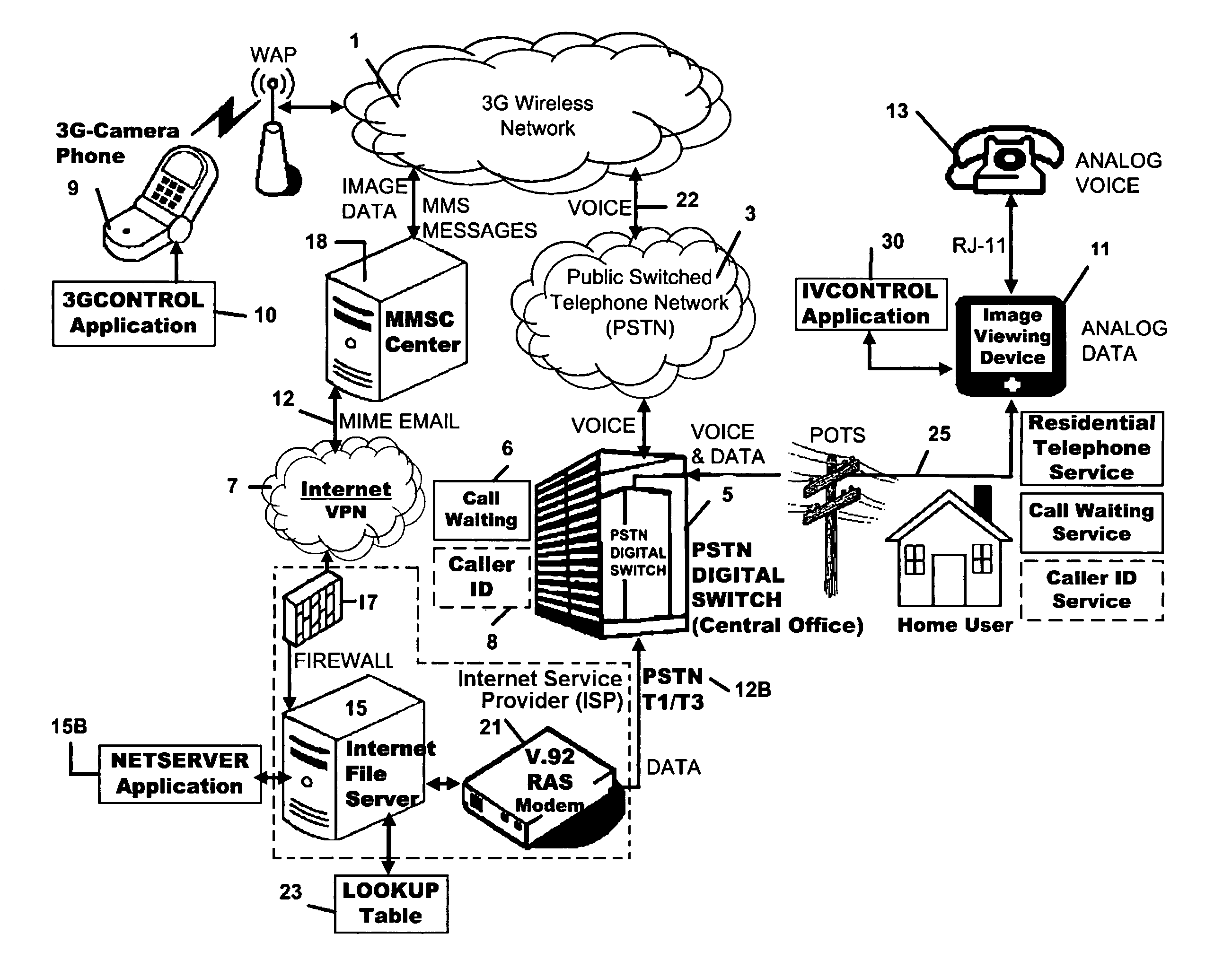
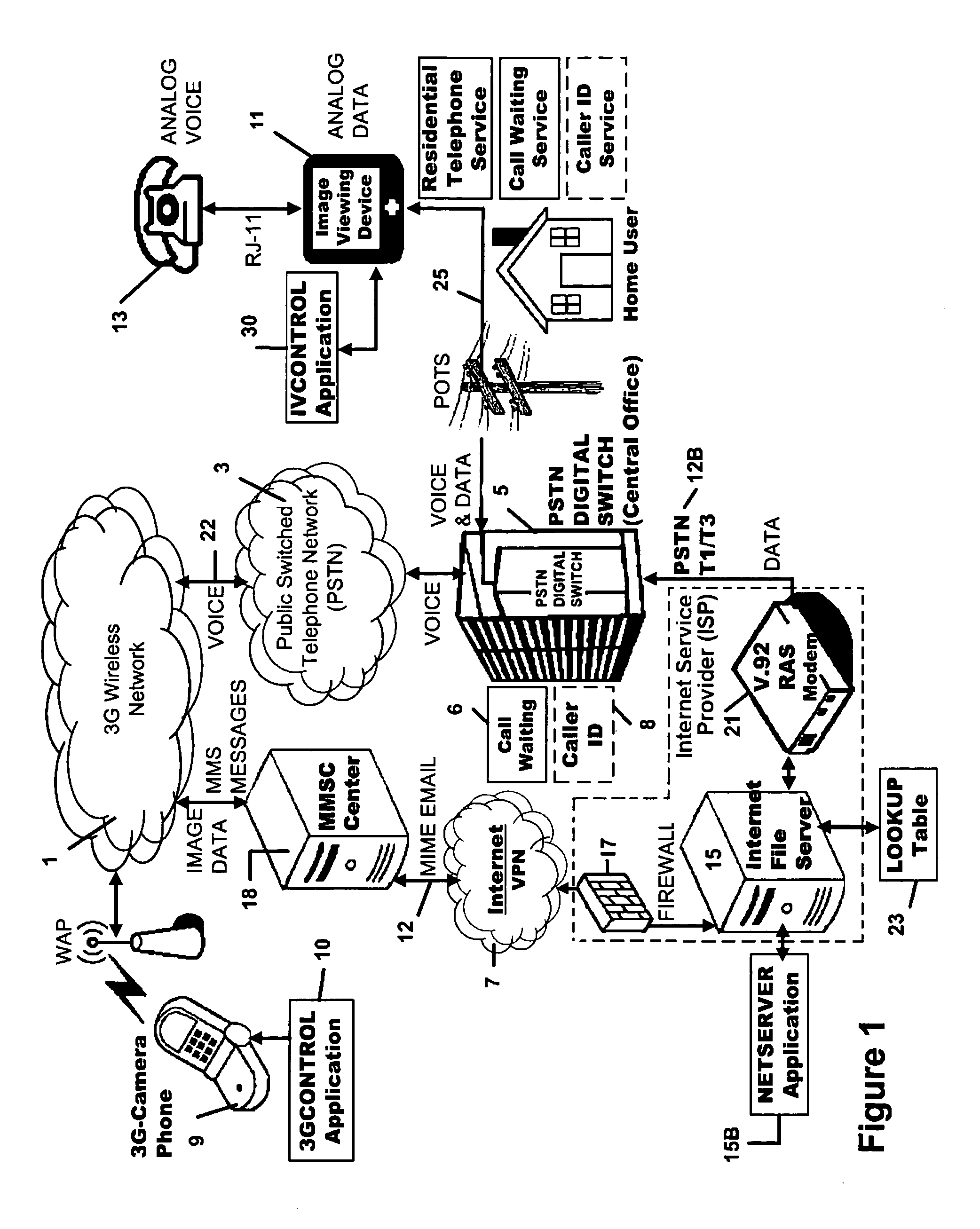
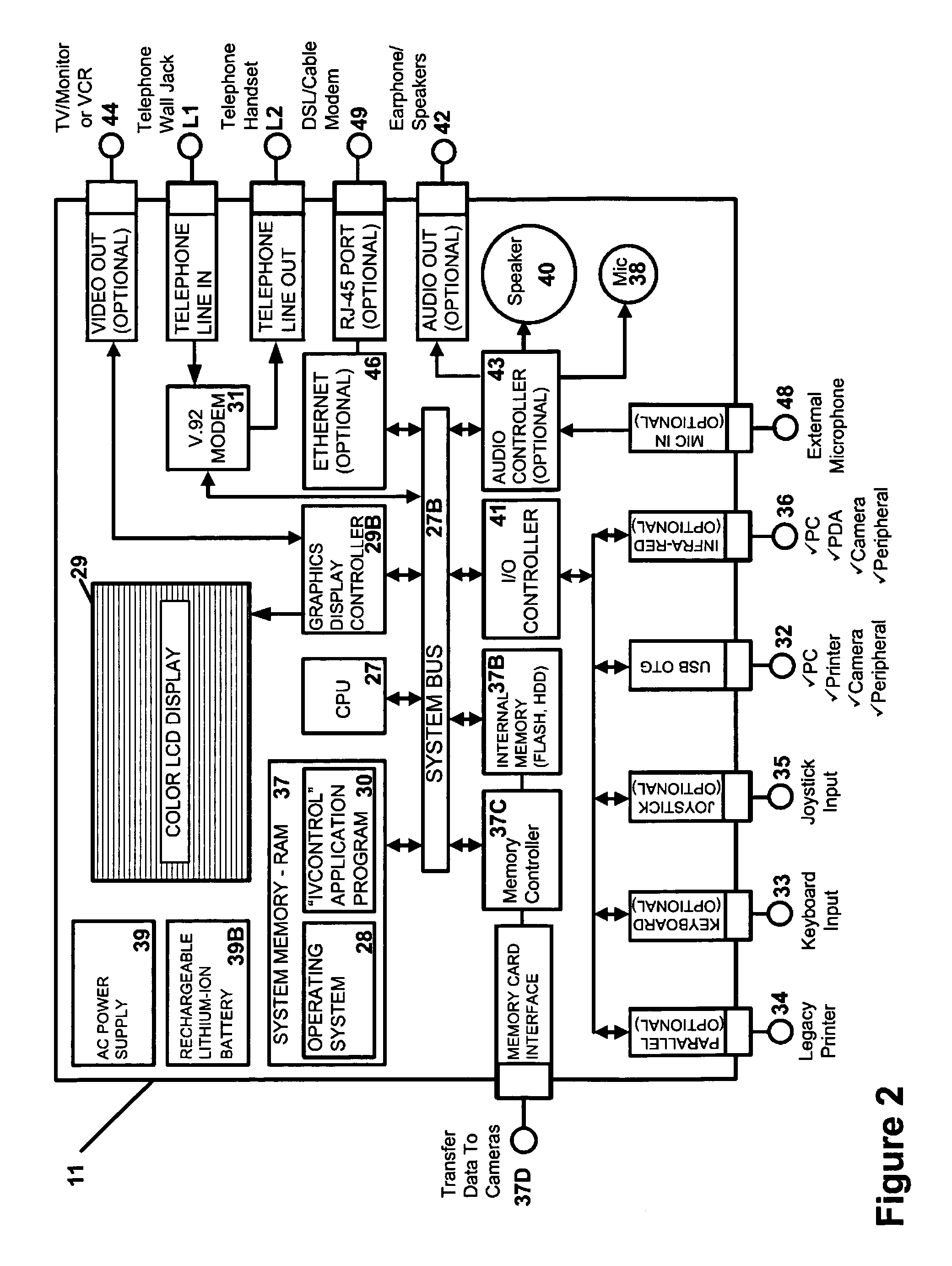
A 3G-camera phone (9) user may transfer photographic images from 3G-camera phone to an image viewing device (11) associated with a residential telephone (13) accessible on the PSTN telephone network (3). Both the image viewing device (11) and telephone (13) are connected to narrowband PTSN POTS telephone line (25). Through use of a call waiting (6) feature of the networks, data transfer is performed over a single narrowband PTSN POTS line with the voice conversation put on hold. Reciprocal image transmission is also possible. Like data transfers may also be made to telephone users having broadband DSL (45, 47 FIGS. 8 &10) or CATV (54, 57 FIGS. 9 &11) or VoIP (82, FIGS. 10 &11) services. An Internet (7) connected fileserver (15) uses a lookup table (23) to determine the kind of line to which the image viewing device is connected and select the appropriate routing for the image transfer.
Owner:FARLEY MARK A +1
Satellite TV security system
InactiveUS20050198673A1Transmission becomes disabledGHz frequency transmissionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsIntegrated receiver/decoderOperability
A satellite TV security system including a TV satellite operated by a satellite TV provider directed to a television set of a satellite TV subscriber that defends the satellite TV provider from illegal reception of TV signals from a TV satellite. An addressable integrated receiver / decoder (IRD) positioned in the TV set top box has an assigned identification number and a smart card positioned in the IRD has an assigned identification number. A security module is provided that is integrated with the IRD. Upon command of the satellite TV provider or automatically, the security module makes a periodic verification of a match of the two identification numbers. Lack of verification of a match triggers a signal from the security module to the IRD to stop transmitting TV signals to the subscriber television. As an alternative verification, the security module initiates periodic verifications of the operability of the telephone line connection between the satellite TV provider and the IRD of the subscriber. Lack of verification of the operability of the telephone line triggers a signal from the security module to the IRD to stop transmitting TV signals to the subscriber TV. The two systems of verification can be operated independently or simultaneously. The subscriber telephone number can be added as an assigned identification number, so that a three-way verification of identification numbers by the security module is required for continued transmission of TV signals to the subscriber television.
Owner:KIT JOHN +2
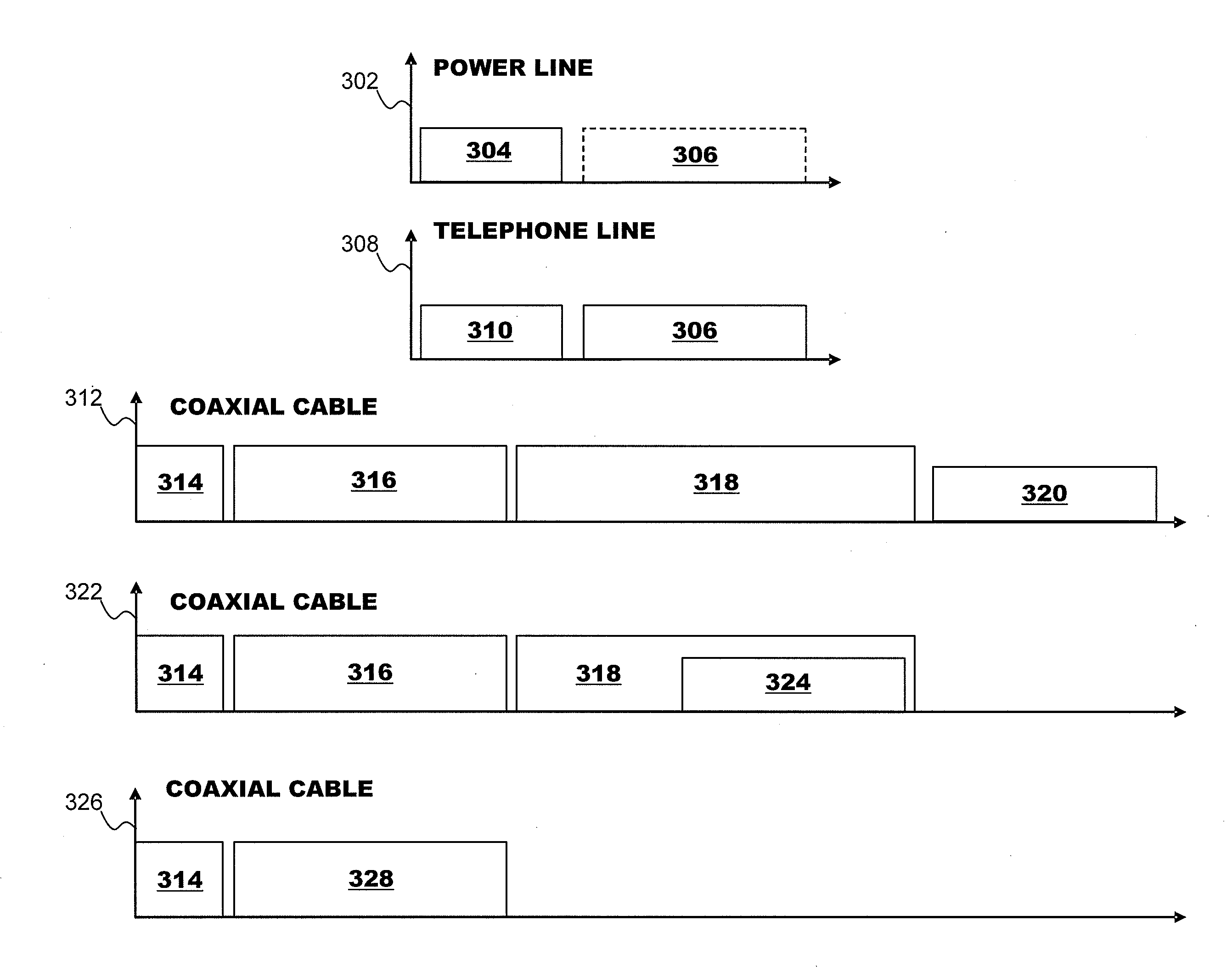
Multi-Wideband Communications over Multiple Mediums within a Network
ActiveUS20070229231A1Systems using filtering and bypassingInterconnection arrangementsQuality of serviceMultiple frequency
A powerline communications device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other communications interface configured to communicate over a computing network. The powerline communications interface is further configured to receive electrical power. The computing network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. In some embodiments, the powerline communications interface may communicate with a network apparatus, such as a personal computer, via an Ethernet interface. The powerline interface, the telephone line interface, and / or the coaxial cable interface may all be associated with the same media access control (MAC) address. The powerline communications device may receive a message via a first medium and repeat the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric. In some embodiments, the powerline communications device may communicate using multiple frequency bands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
A telephone using a connection network for processing data remotely from the telephone
ActiveUS20090104898A1Special service for subscribersSubstation equipmentNetwork connectionSpeech sound
A system of connection between computers. First and second computers are connected over a network. The network preferably uses an existing channel, such as a wireless connection or a telephone line. The first computer may be a PDA or a cell phone. One aspect may take speech into the telephone, send it over the network connection to the second computer, where it is recognized, and return the recognized speech to the first computer.
Owner:LOSCH +2
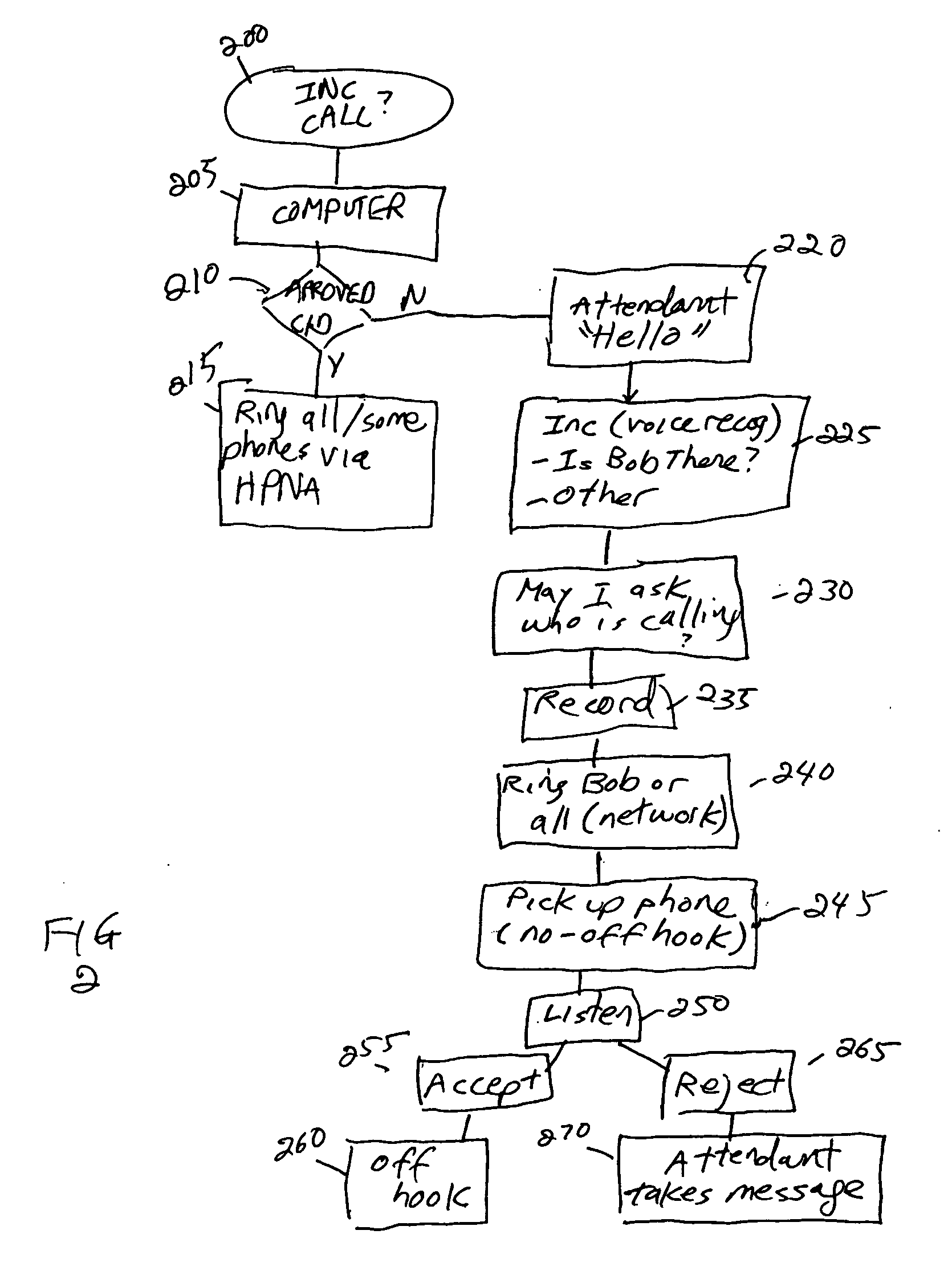
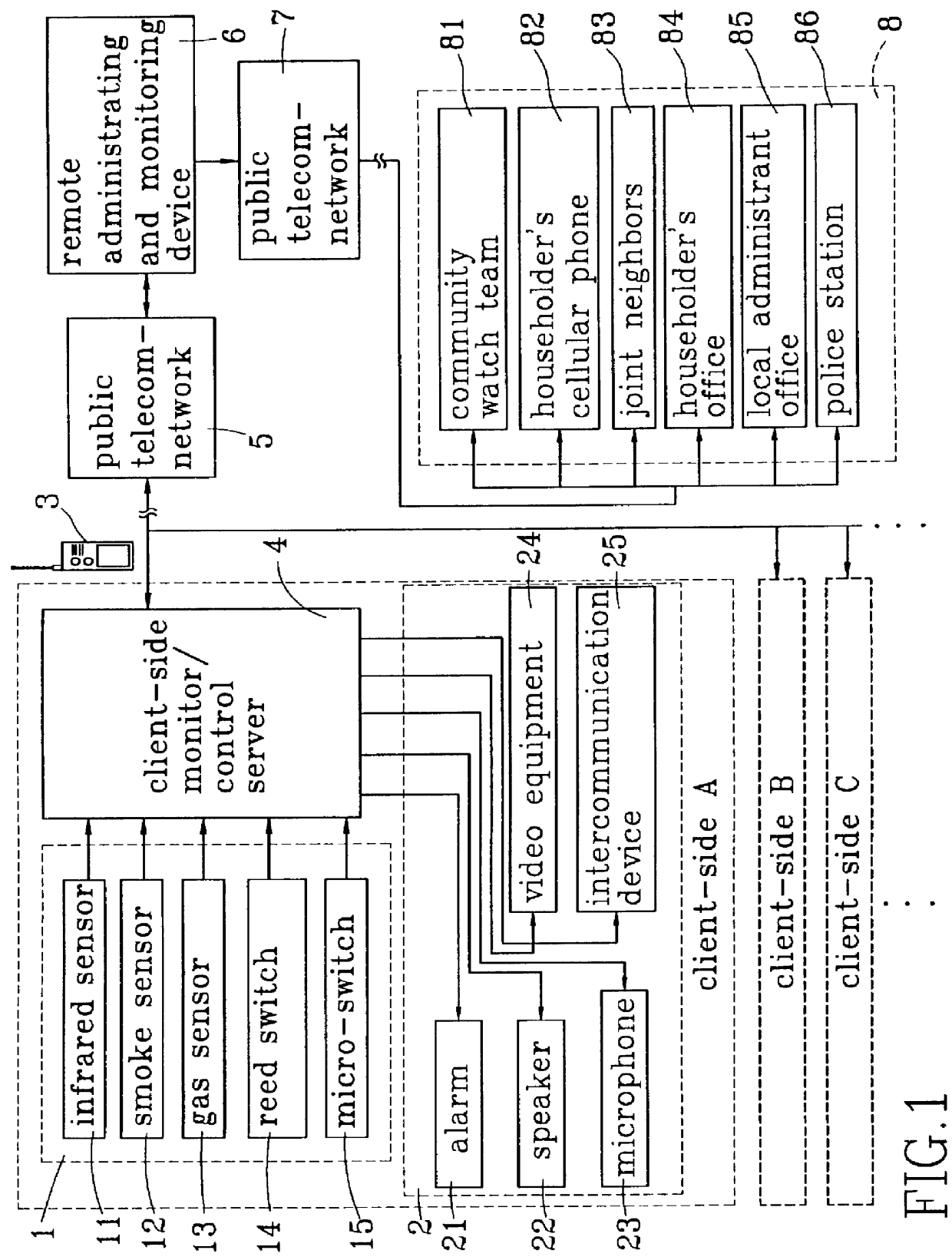
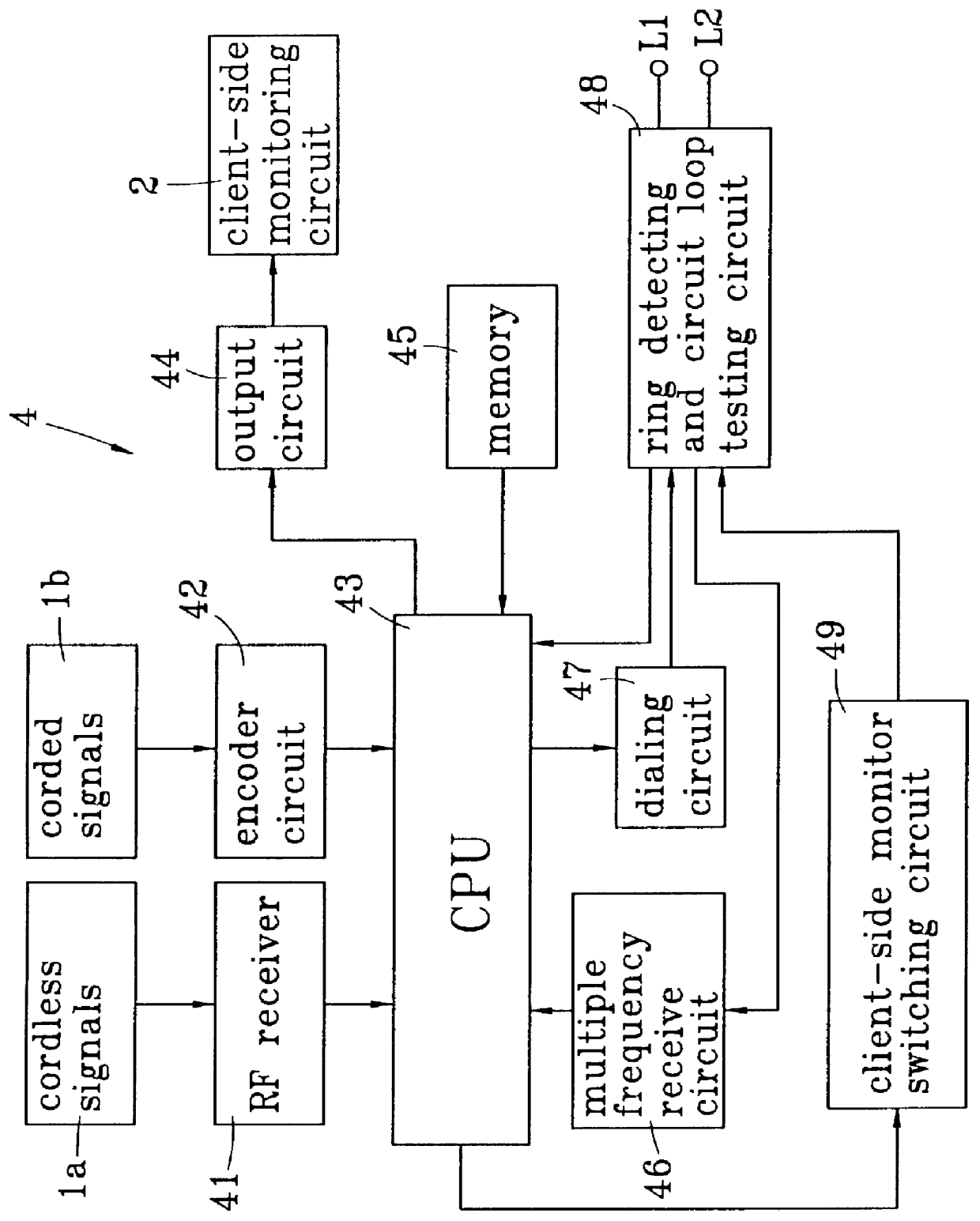
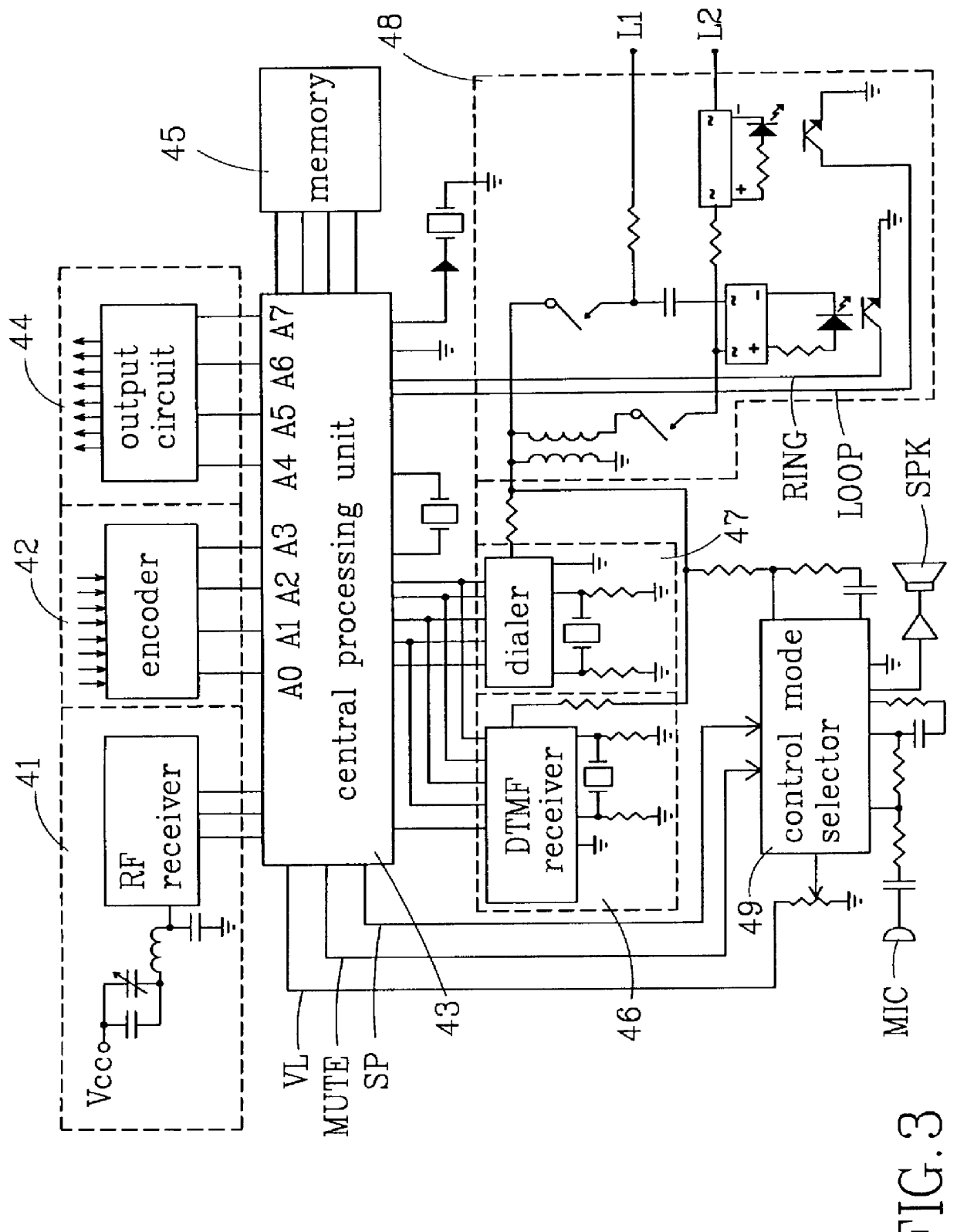
Subscriber control unit for united home security system
A subscriber control circuit adapted to be incorporated in an united home security system is disclosed. The control circuit includes a plurality of client-side monitor / control servers, each serving to detect and control the situation at the subscriber and connected to a remote administrating and monitoring device via a public telephone network. The remote administrating and monitoring device is capable of transmitting alarm signal to an alarm transmitting network. The client-side monitor / control server also includes a central processing unit, a radio frequency receiver for receiving a detection signal from wireless sensing elements and an encoder for receiving and processing a detection signal from cabled sensing element. A DTMF based receiver connects the central processing unit to the remote administrating and monitoring device to receive a DTMF signal transmitted through the telephone line and transmit the received DTMF signal to the central processing unit. A dialer circuit is coupled to the central processing unit for performing automatic dialing operation.
Owner:FORMOSA ELECTRONICS IND INC
Multi-function general purpose transceiver
InactiveUS7397907B2Controlling coin-freed apparatusUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionGeneral purposeTransceiver
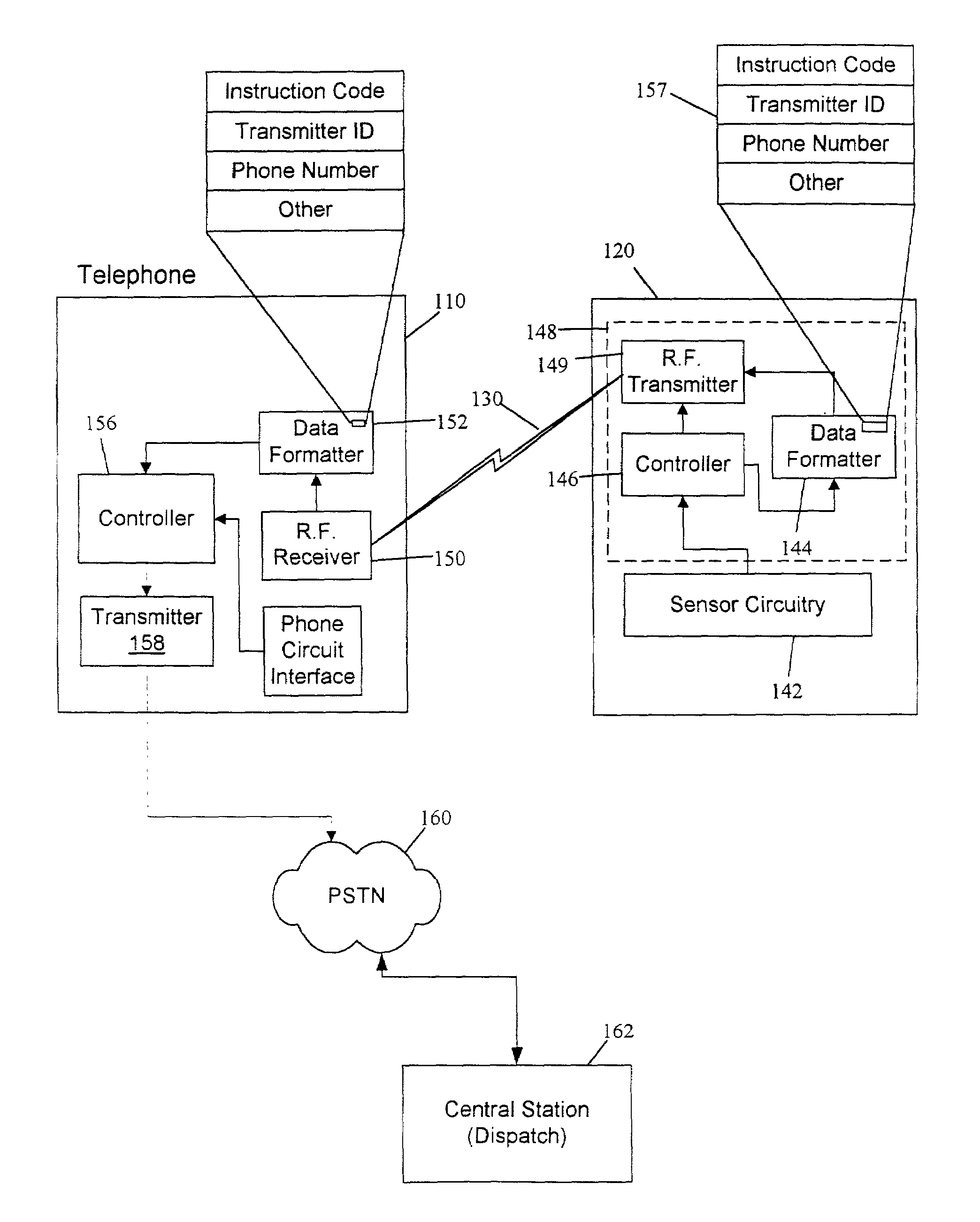
The present invention is generally directed to a system and associated method for communicating information to a predetermined location. The system includes a transmitter disposed at a first location and configured to transmit a signal containing an instruction code that uniquely identifies an instruction to be carried out. The system further includes a transceiver disposed remotely from the transmitter and configured to receive the transmitted signal. The transceiver circuit includes a line interface circuit configured to interface with a telephone line that is part of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and initiate a phone call over the telephone line. Finally, the system includes a central station remotely located from said transceiver but being in communication with said transceiver via the PSTN The central station further include a decoder configured to decode the instruction code. In accordance with a broader aspect, the invention is directed to a general purpose transceiver having a receiver for receiving an information signal and a transmitter configured to transmit an outgoing signal over a phone line to a central station A portion of the information signal includes an instruction code, which may be decoded by the central station and acted upon accordingly Consistent with the general purpose nature of the transceiver, the phone number of the central station may be transmitted to the transceiver as part of the information signal.
Owner:STATSIGNAL IPC
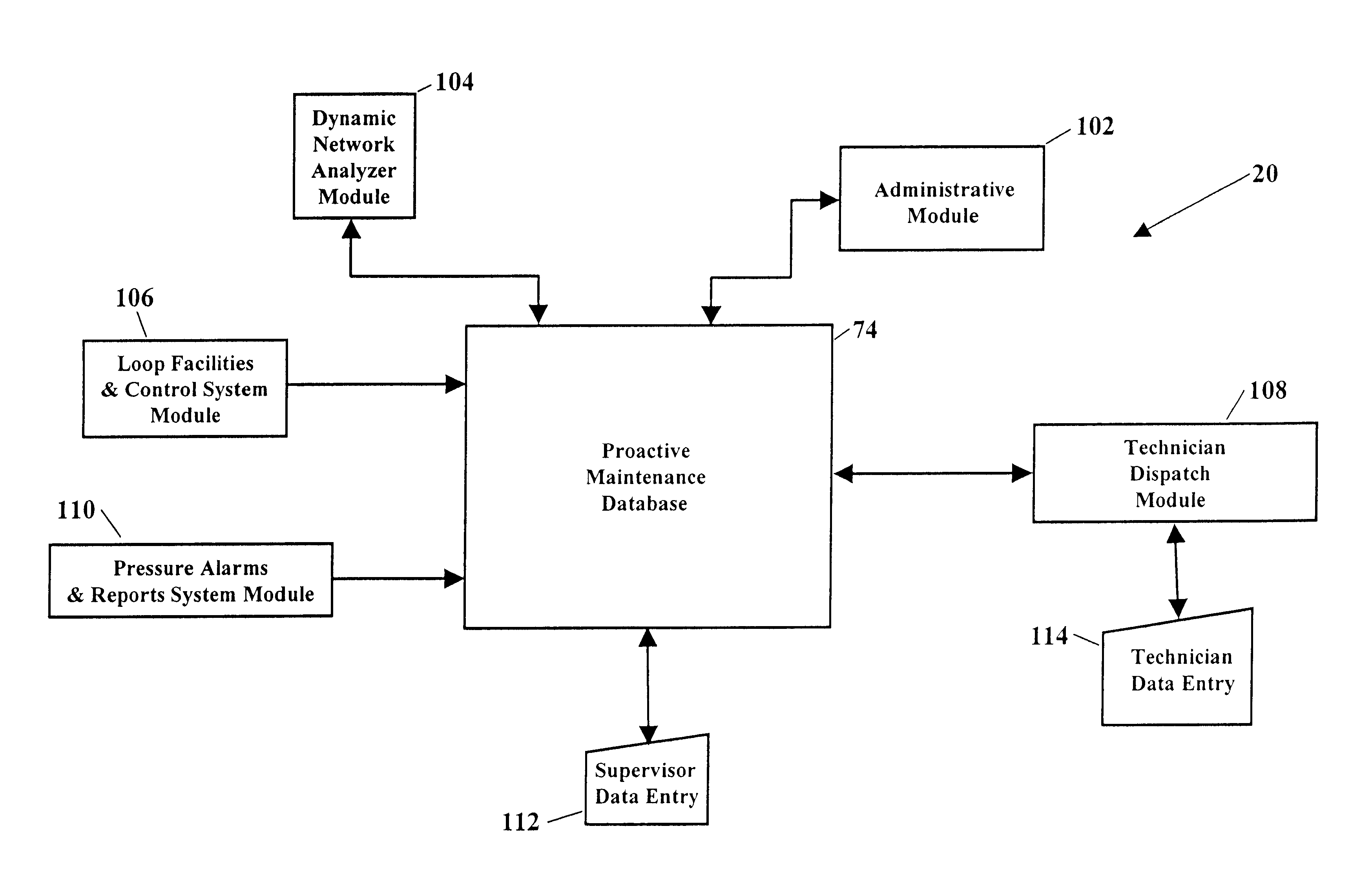
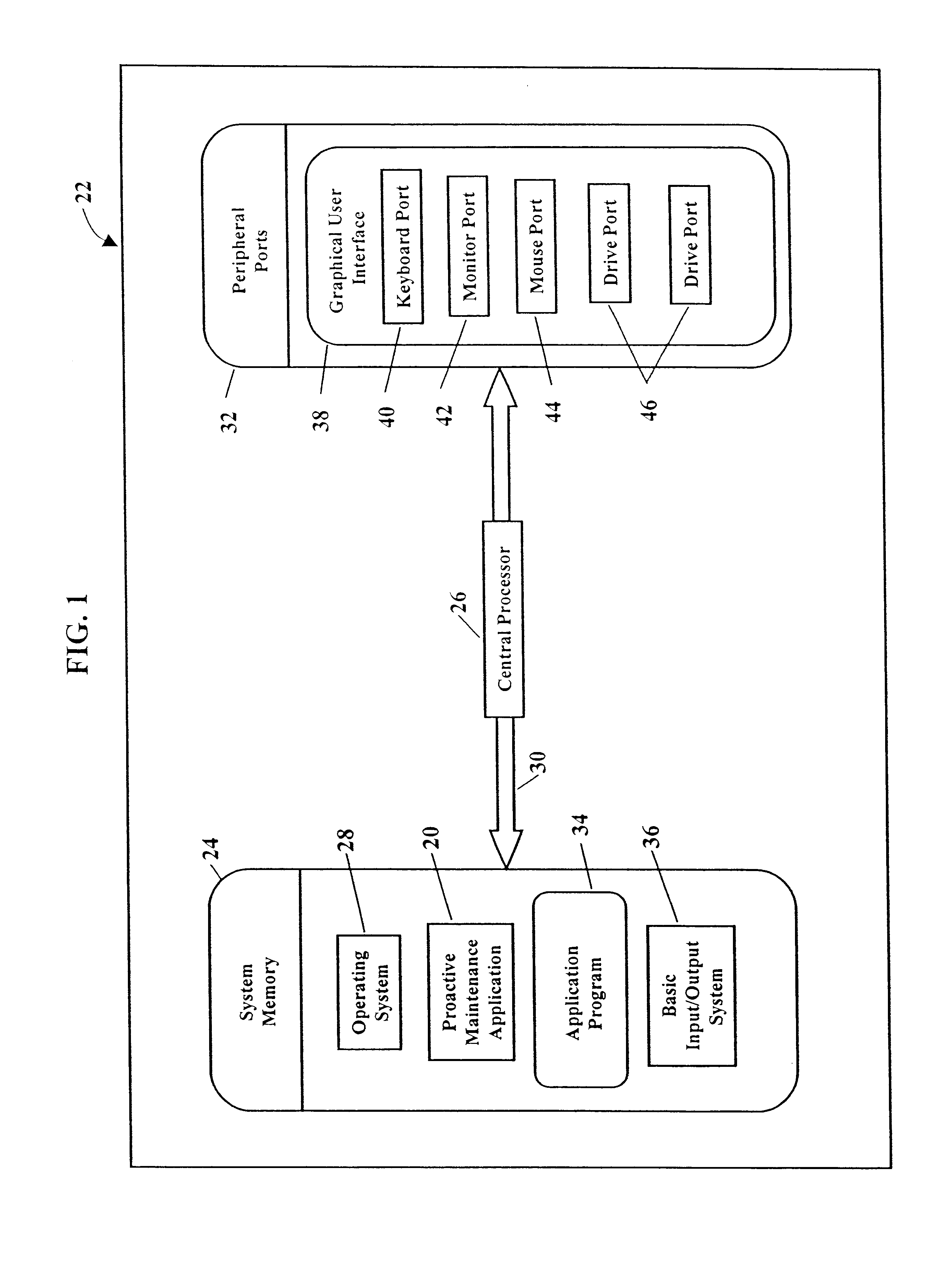
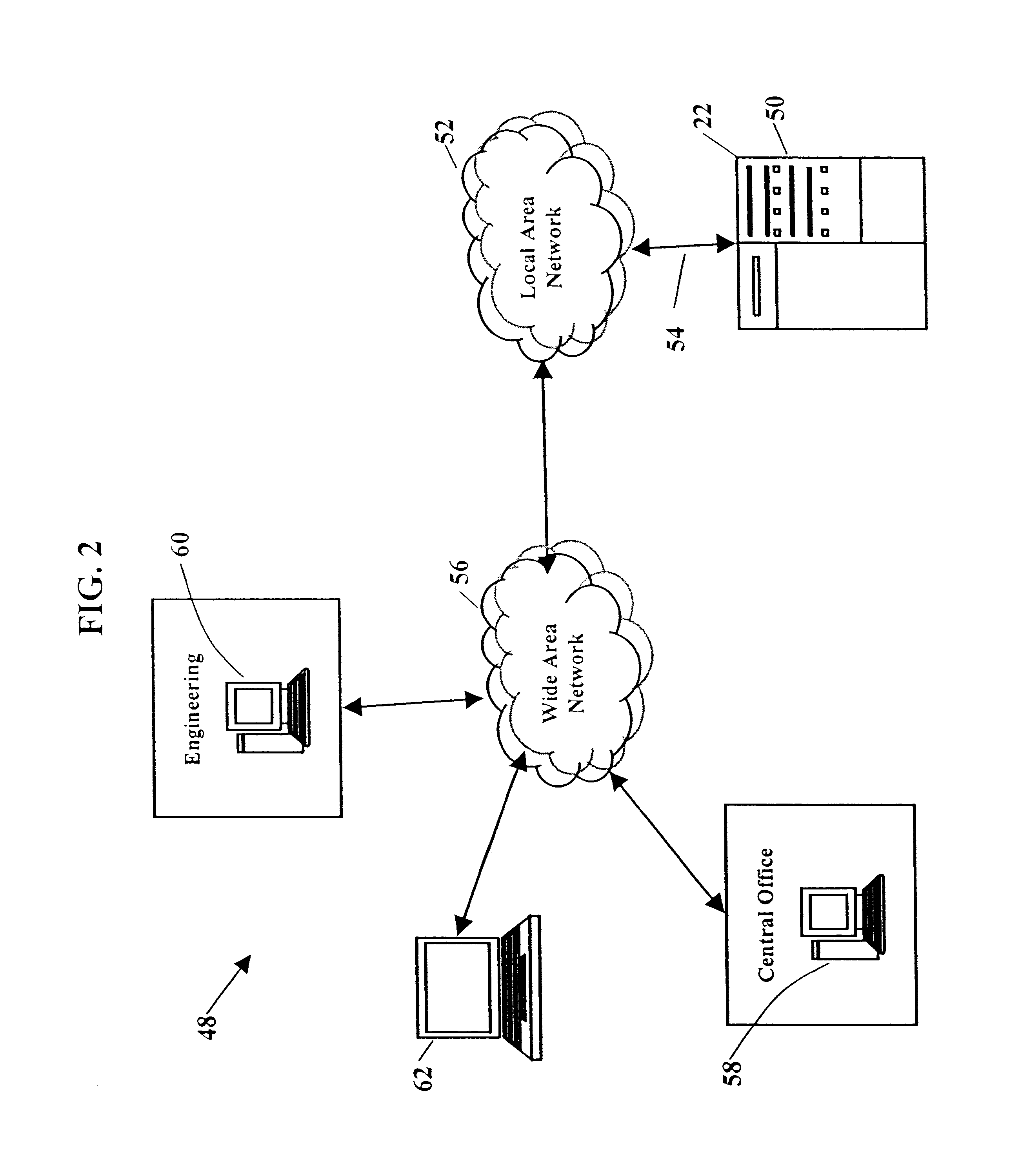
Pressure alarms and reports system module for proactive maintenance application
InactiveUS6771739B1Supervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentFiberNetwork analytics
Methods and systems for proactively maintaining a telephone system local loop. One embodiment includes communicating with a communications network and acquiring information associated with pressure or flow sensors along fiber optic cables. Proactive maintenance of the fiber optic cables is predicted using the information associated with pressure or flow sensors. The embodiment may further include generating and dispatching work order information describing the predicted proactive maintenance. The embodiment may also include predicting proactive maintenance of telephone lines using information from a Dynamic Network Analyzer and using information from a Loop Facilities and Control System. Another embodiment includes a system for predicting proactive maintenance of a telephone system local loop. This embodiment includes a Pressure Alarms and Reports System Module, a database stored in memory, and a processor. The Pressure Alarms and Reports System Module communicates with a communications network and acquires at least one of i) pressure information associated with fiber optic cables and ii) flow information associated with fiber optic cables. The database stores the acquired information. The processor processes information stored in the database and generates predicted proactive maintenance.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Multi-wideband communications over multiple mediums
InactiveUS8406239B2Electric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceMultiple frequency
A powerline communications device comprises a powerline communications interface and at least one other communications interface configured to communicate over a computing network. The powerline communications interface is further configured to receive electrical power. The computing network may comprise mediums including powerlines, telephone lines, and / or coaxial cables. In some embodiments, the powerline communications interface may communicate with a network apparatus, such as a personal computer, via an Ethernet interface. The powerline interface, the telephone line interface, and / or the coaxial cable interface may all be associated with the same media access control (MAC) address. The powerline communications device may receive a message via a first medium and repeat the message via a second medium based on a quality of service (QoS) metric. In some embodiments, the powerline communications device may communicate using multiple frequency bands.
Owner:GIGLE SEMICON
Private VoIP network for security system monitoring
InactiveUS20060067484A1Reduce errorsShort response timeInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications securityPrivate network
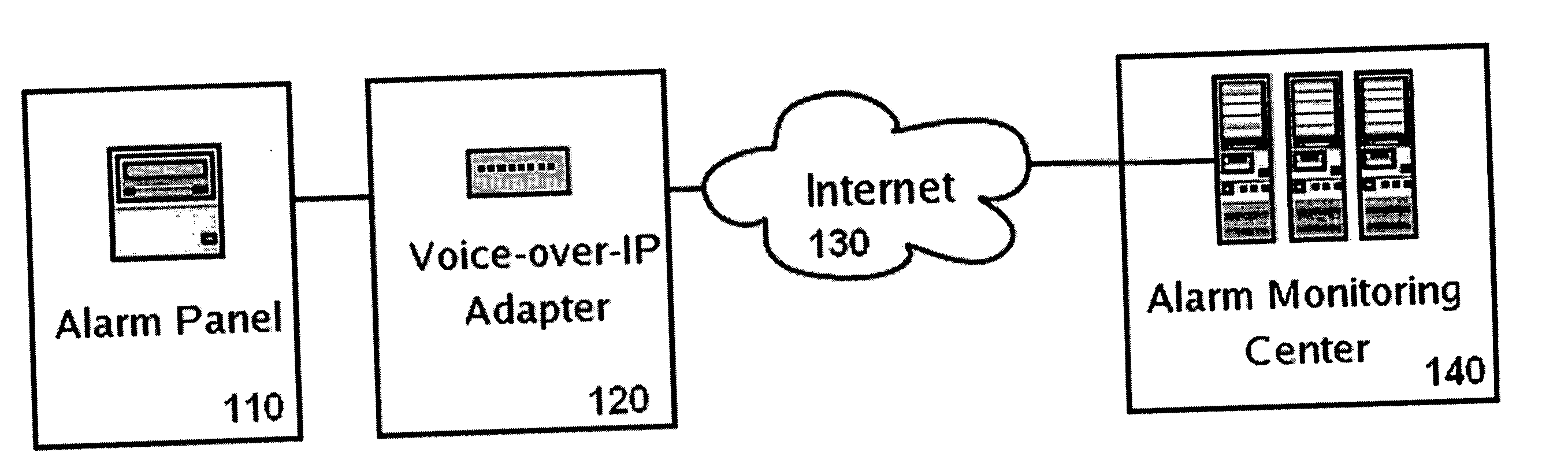
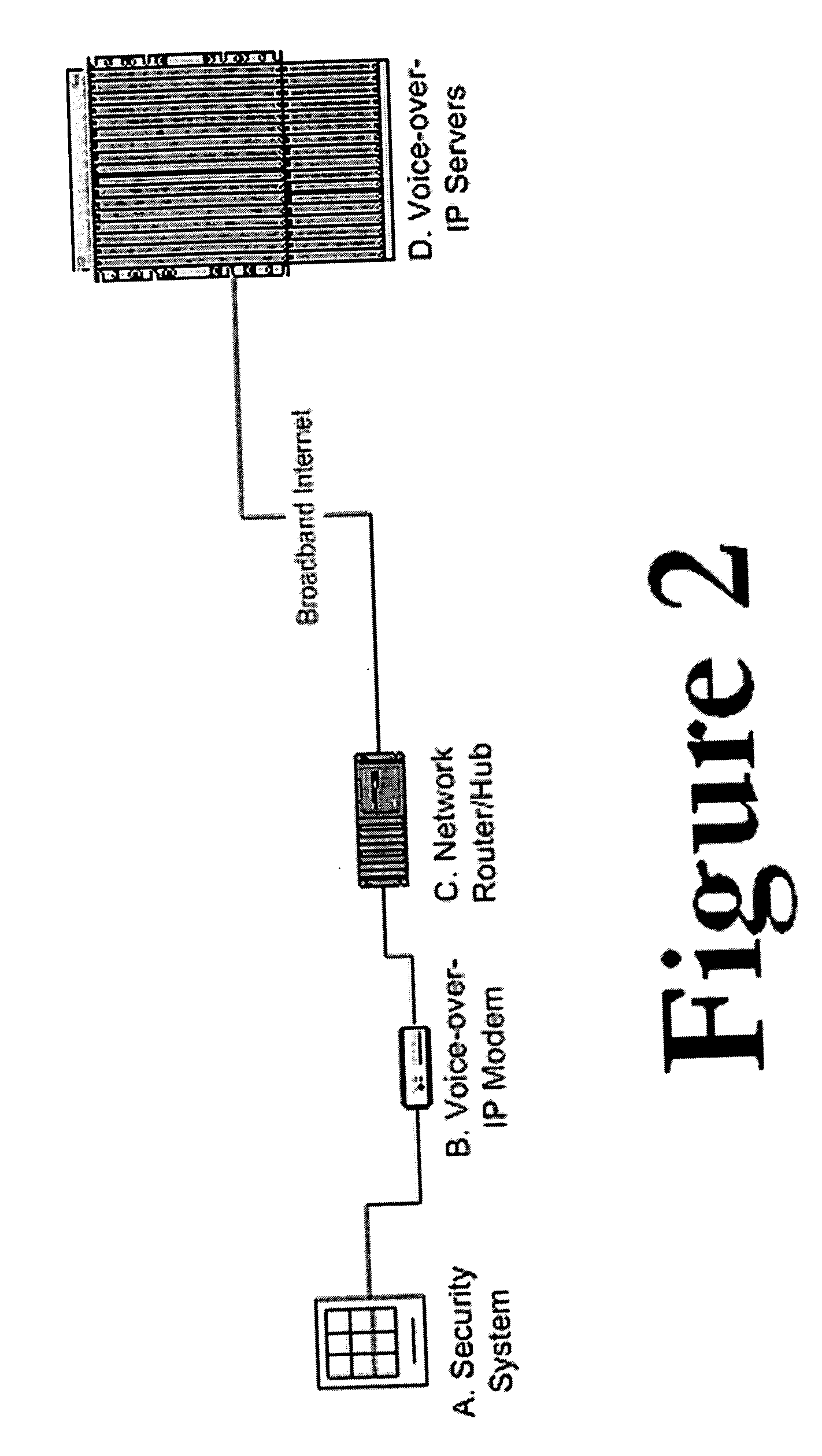
Security systems typically communicate with alarm monitoring centers using a telephone connection. Security systems will check in with the alarm monitoring center with a diagnostic signal at a predetermined interval—typically once per day. When a security system is connected to a Voice-over-IP service (using Broadband Internet), rather than a standard telephone line, the opportunity exists to poll in real-time the status of the connection, and alert the owner (or alert the alarm monitoring center) that the customer's connection has been broken. The present invention offers a system and technique for monitoring a security system connected using a Voice-over-IP connection, in real time, and alerting the owner of the security system, or the alarm-monitoring center, when the connection is broken. This alert can be used, for example, to issue a telephone call to the police, informing them of the breach of line integrity and possible compromise of the premise.
Owner:NUMEREX CORP
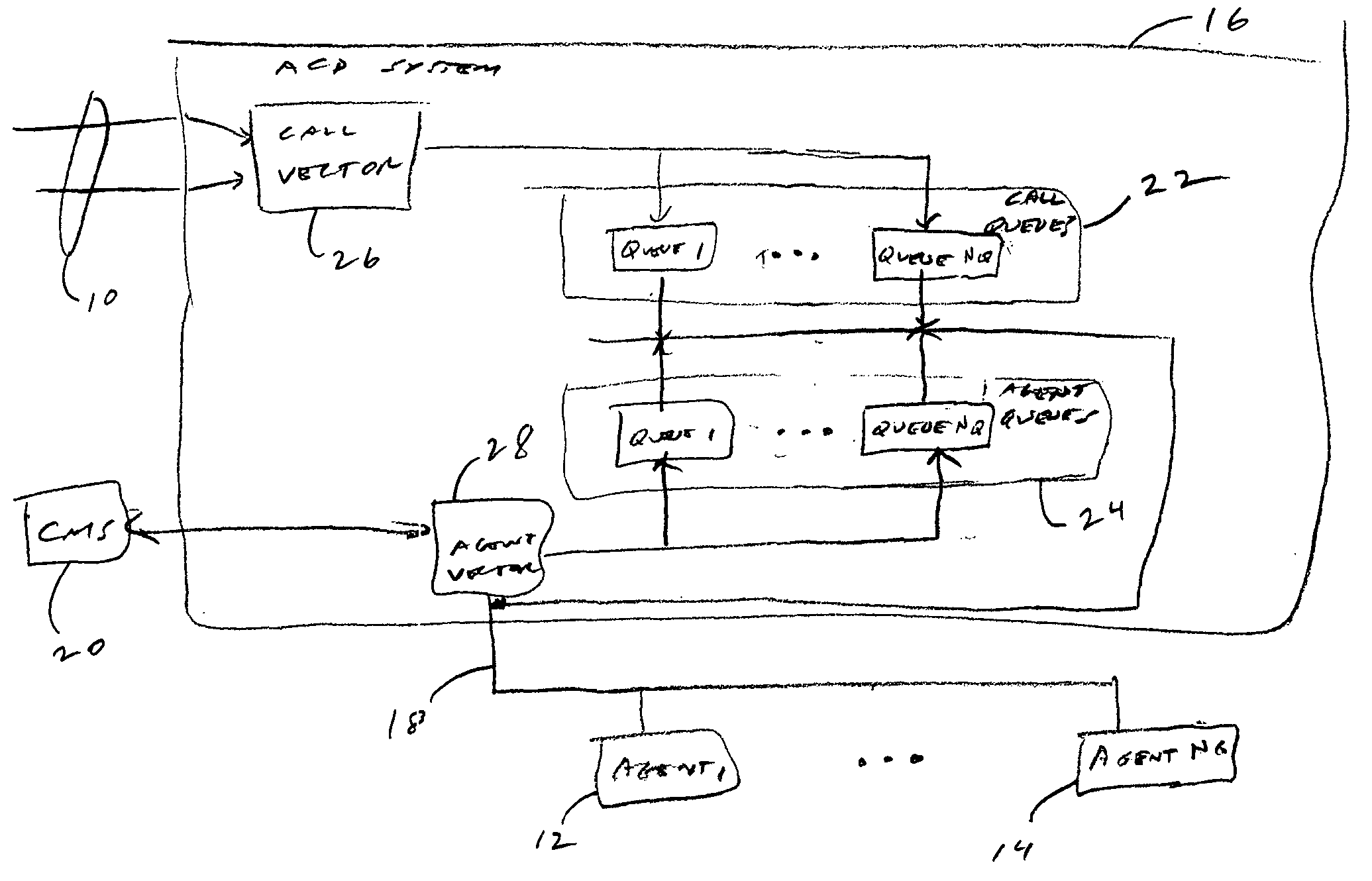
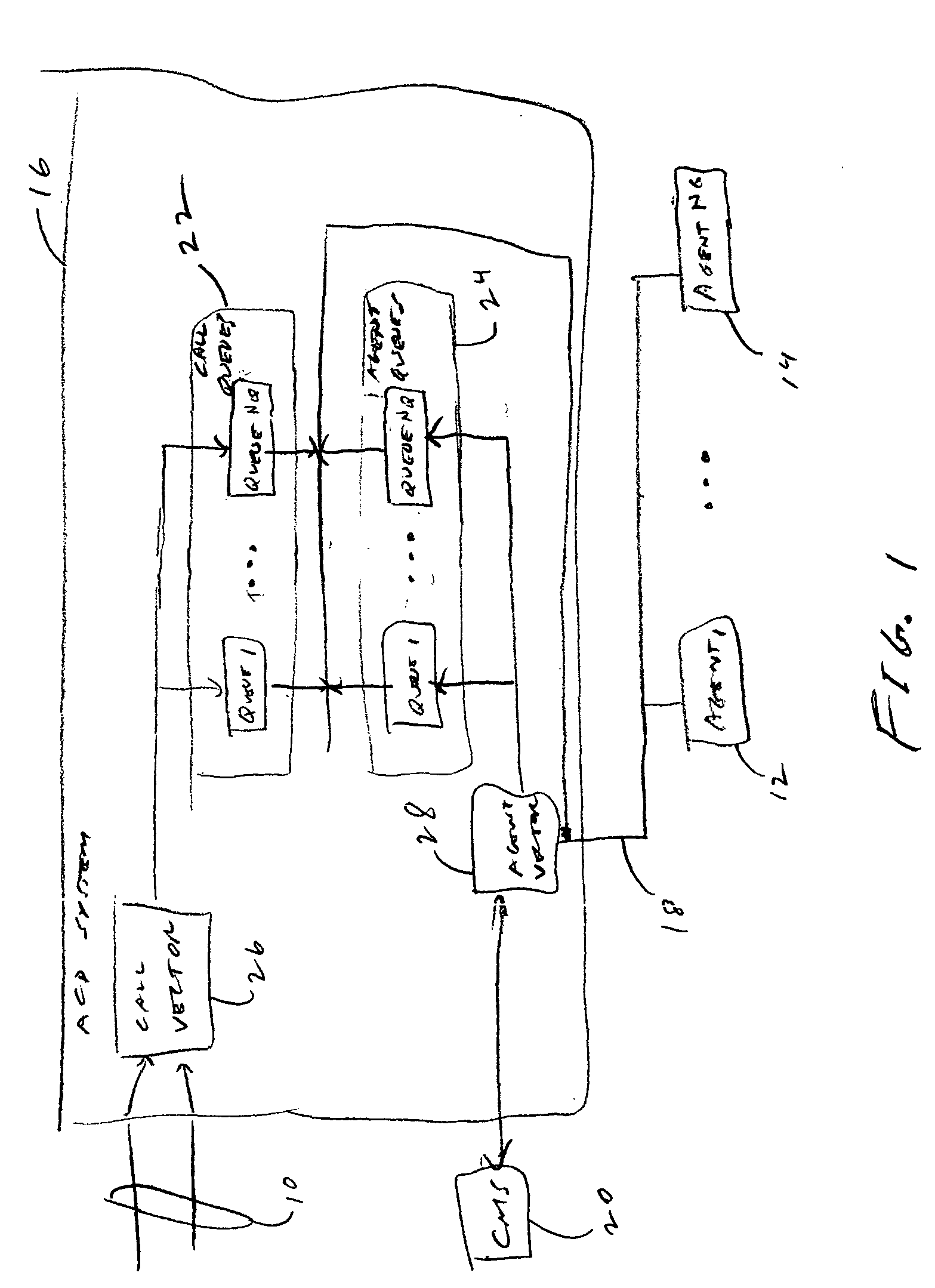
High availability multi-tenant feature
InactiveUS20050025303A1Special service for subscribersDigital computer detailsConfigfsHigh availability
A multi-tenant call-center system and method of configuring and monitoring. The system includes a plurality of telephone lines, a plurality of agent positions, a call distribution system connecting the plurality of agent positions to the telephone lines, a call management system connected to the call distribution system. The call management system includes a storage system of storing database files, processes and configuration files, a memory system for processing the database files and configuration files and running selected processes stored on the storage system, a configuration server for reading the configuration file and starting selected processes according to multi-tenant inter-process dependencies and process priorities, and a monitor process for monitoring each of the started processes according to a respective monitor frequency in the configuration file.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
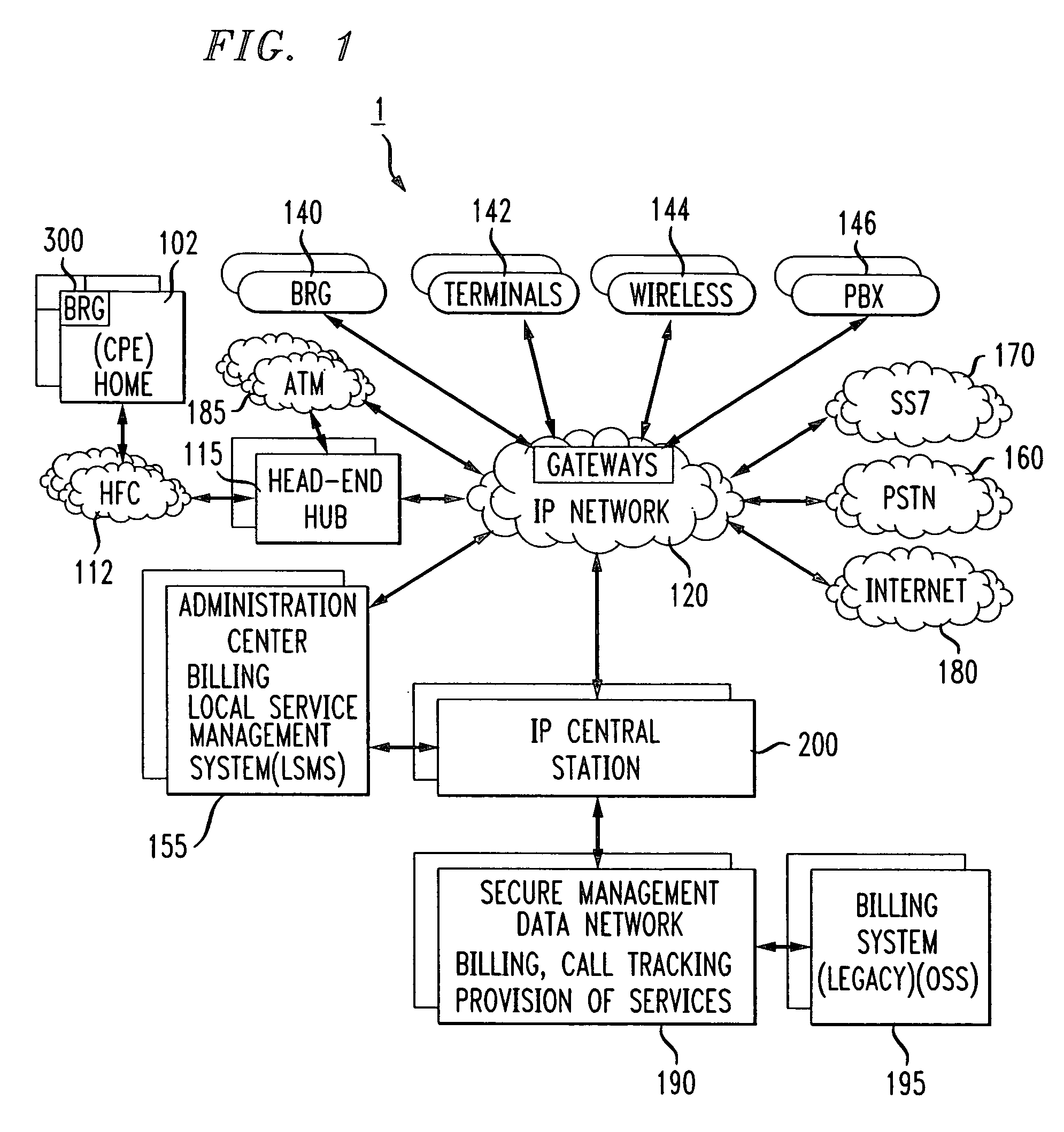
Personal control of address assignment and greeting options for multiple BRG ports
InactiveUS7180889B1Enhanced greetingEnhanced message featureInterconnection arrangementsAutomatic exchangesDirectory numberUser interface
A method and apparatus for providing multiple telephone lines using a single directory number. A method and apparatus for associating multiple directory numbers with multiple telephone lines. A broadband residential gateway (BRG) is a user interface to a broadband communication system providing packetized telephone service and other media services. The BRG has multiple ports, and each port is connected to one or more telephones. The multiple ports may be mapped to a single directory number, or the multiple ports may be mapped to multiple directory numbers. The BRG can provide greeting and message features. A greeting may instruct a caller to select a port which is associated with a party the caller is attempting to reach. Also, a message, played after the greeting, may further instruct the caller.
Owner:SHORETEL
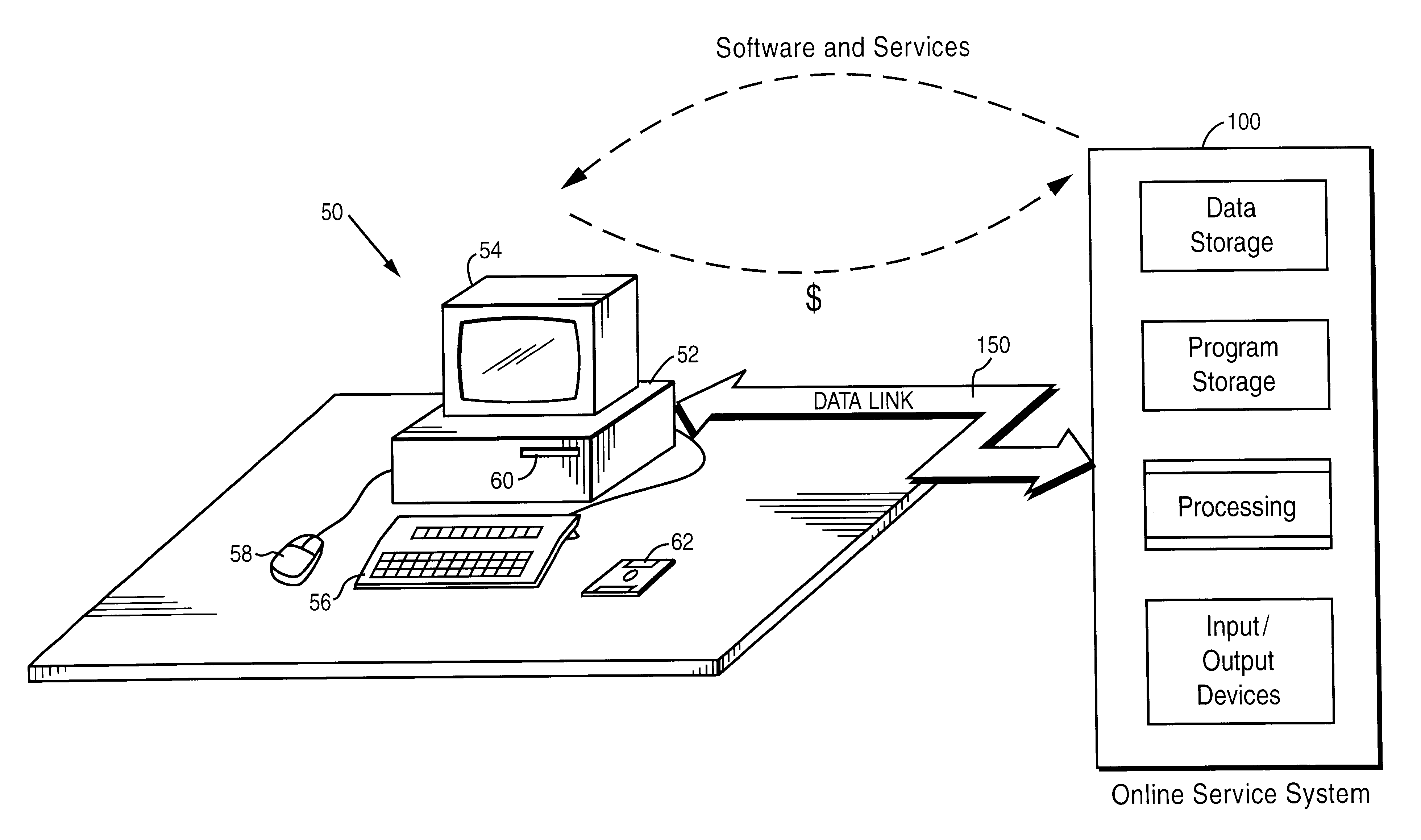
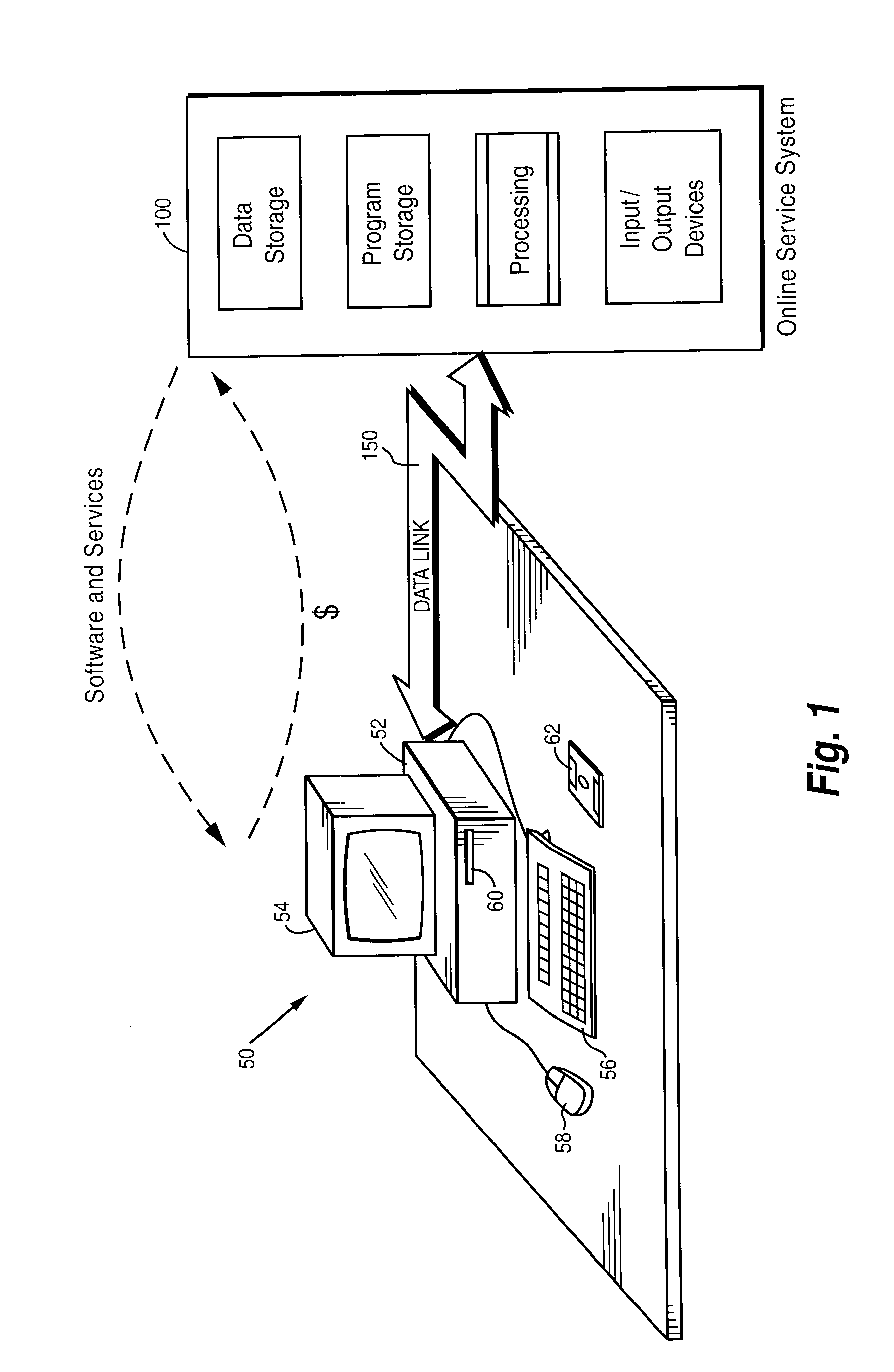
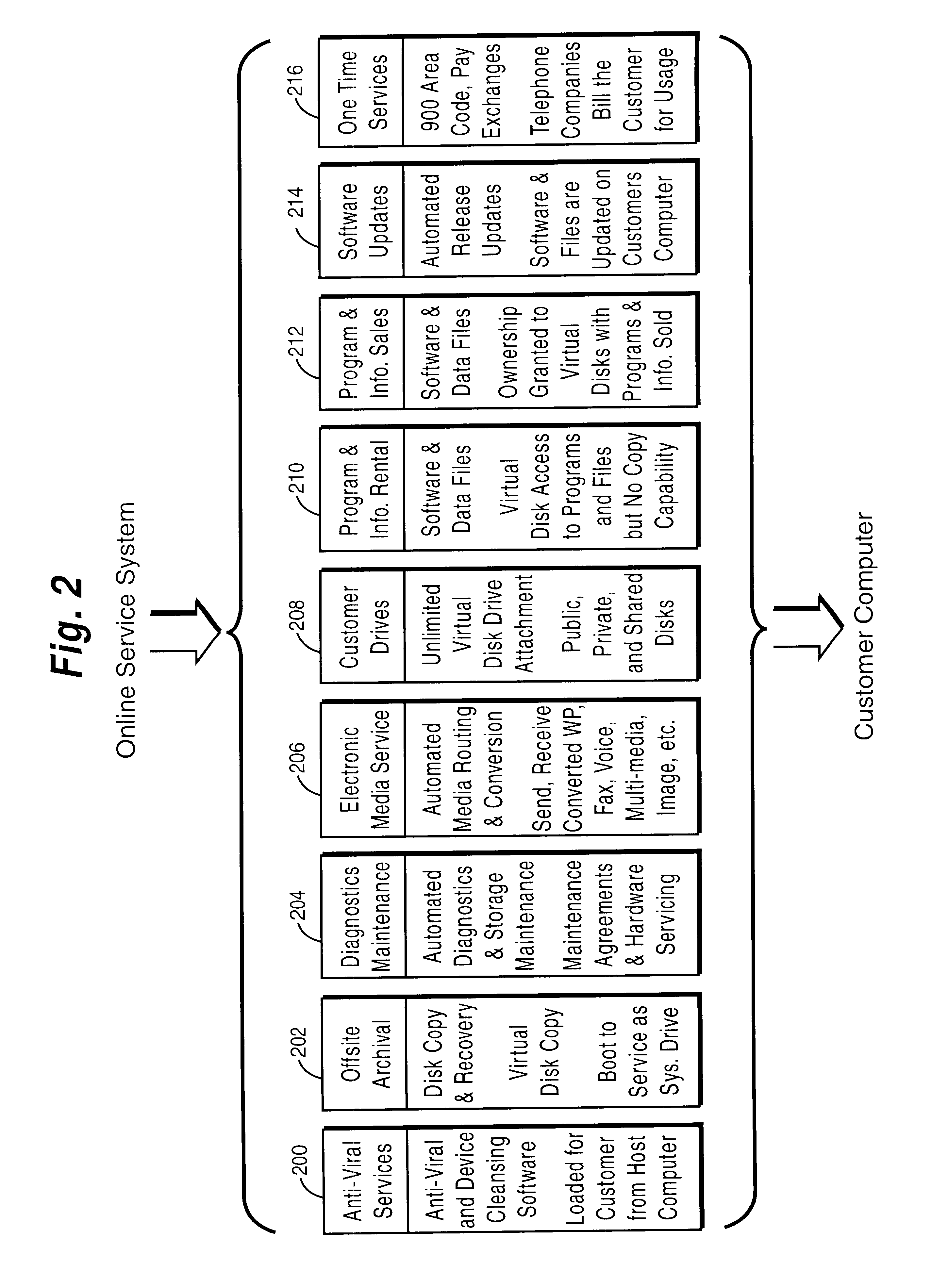
Internet online backup system provides remote storage for customers using IDs and passwords which were interactively established when signing up for backup services
InactiveUS6411943B1Guaranteed uptimeRelieving userComplete banking machinesFinanceTelecommunications linkPassword
A user can use his personal computer to call up an on-line service system over a telecommunications link such as a telephone line. The On-line system provides all sorts of useful services to the personal computer such as antiviral protection, auxiliary processing capabilities, and other features that are impractical or inconvenient to provide locally.
Owner:EMC CORP +6
Repeater device for communications with an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7292139B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRespiratory organ evaluationPatient managementAnalysis data
A repeater device for an advanced patient management system communicates with a medical device coupled to a patient to obtain data about the medical device and / or patient's condition. The repeater device maintains the data while if considers various factors when coordinating transfer of the data to a repository of the advanced patient management system. The repeater device may be configured to analyze the data to determine a degree of urgency, such as whether an emergency exists, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the degree of urgency. The repeater device may also be configured to test the condition of the communication medium being used to transfer the data to the repository, such as determining whether a telephone line is in use, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the condition of the of the communication medium.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and systems for telephony call completion
InactiveUS6879677B2Facilitate call completionEasy to manageSpecial service for subscribersAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingTelephone lineCall management
The present invention is directed to processing calls to busy telecommunications lines. In one embodiment, the presence of a subscriber accessing a computer network over a first telephone line via a first computer terminal is detected, wherein the subscriber also has a first telephone station connected to the first line. When a caller calls the first line and the first line is busy, the call is forwarded to a second telephone line associated with a call manager system. The call manager system determines when the subscriber is no longer accessing the computer network. At least partly in response to determining that the subscriber is no longer accessing the computer network, the call manager system transmits a text message to the caller, the message including the subscriber's phone number. The caller can then call back the first line using the transmitted phone number.
Owner:CALLWAVE COMM
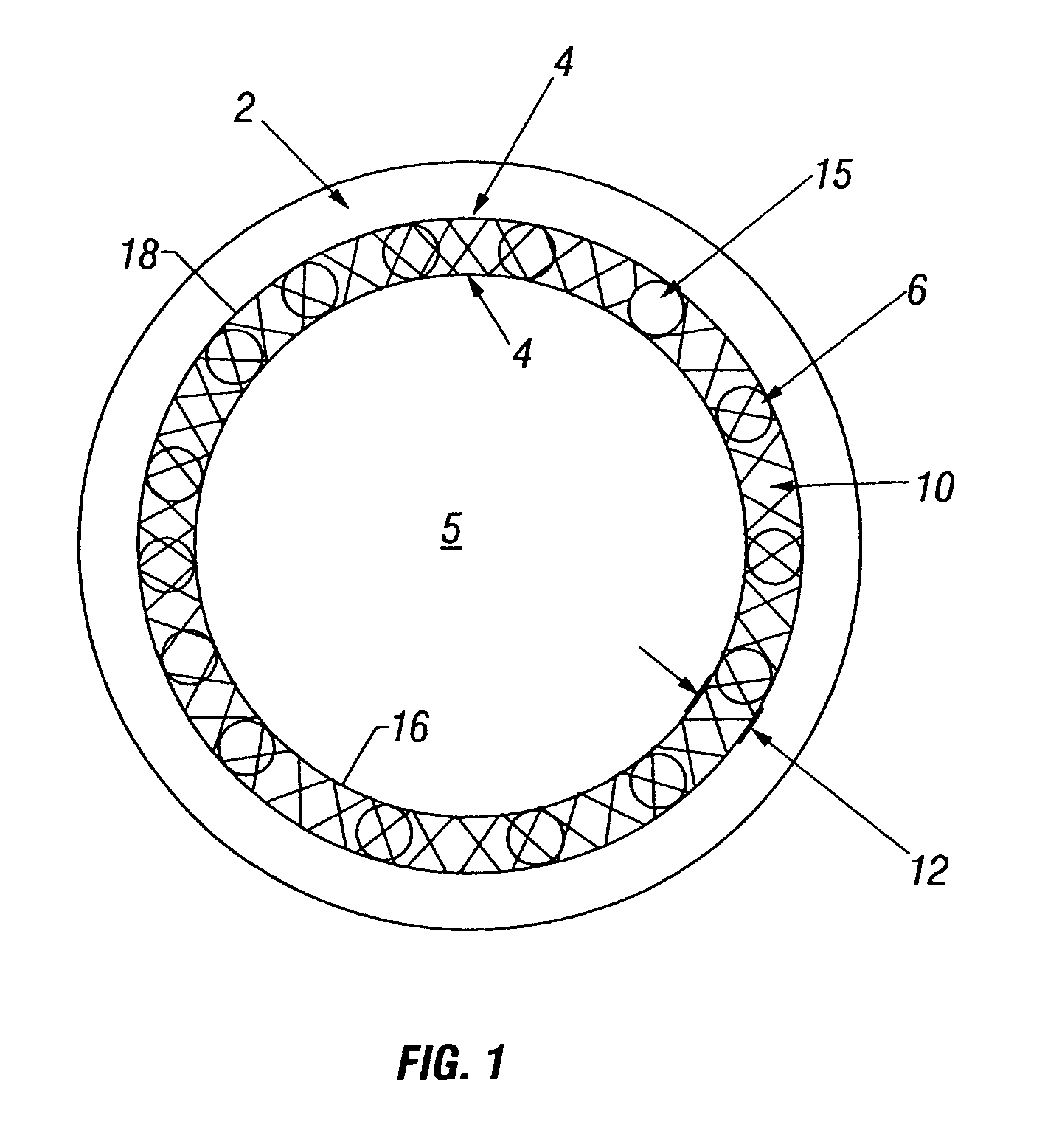
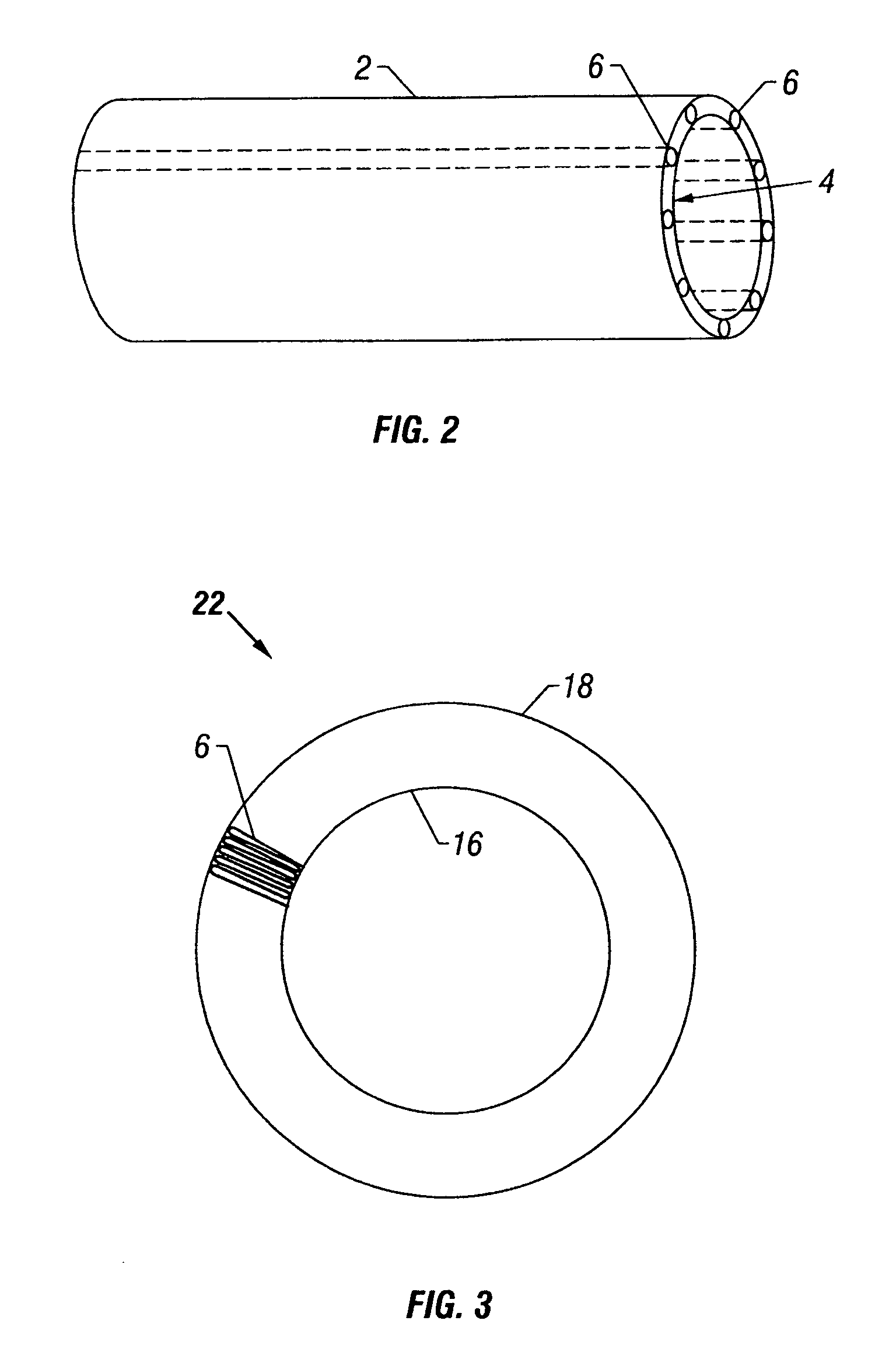
Method and apparatus for lining a conduit
Owner:HEAGY RICHARD T +3
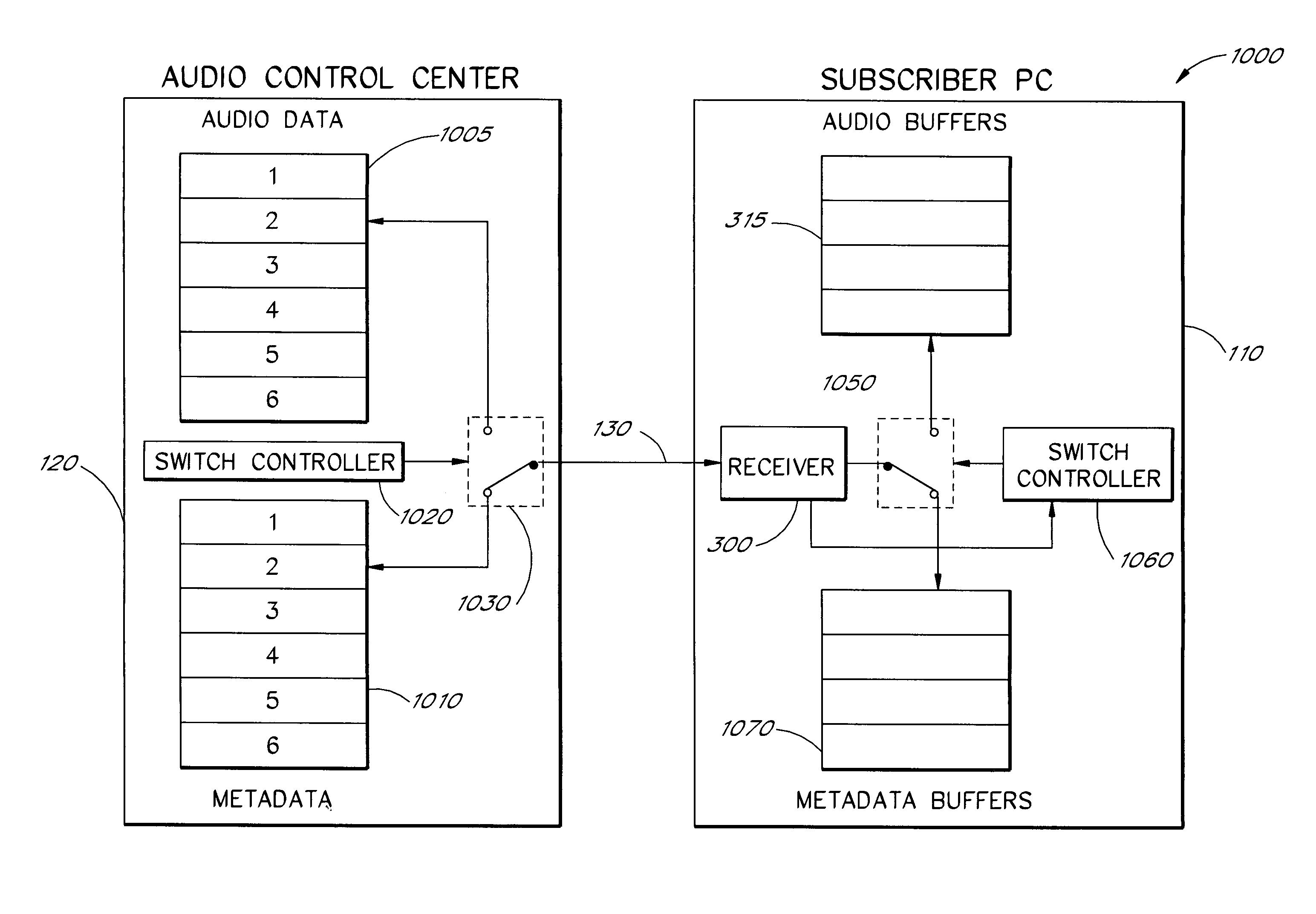
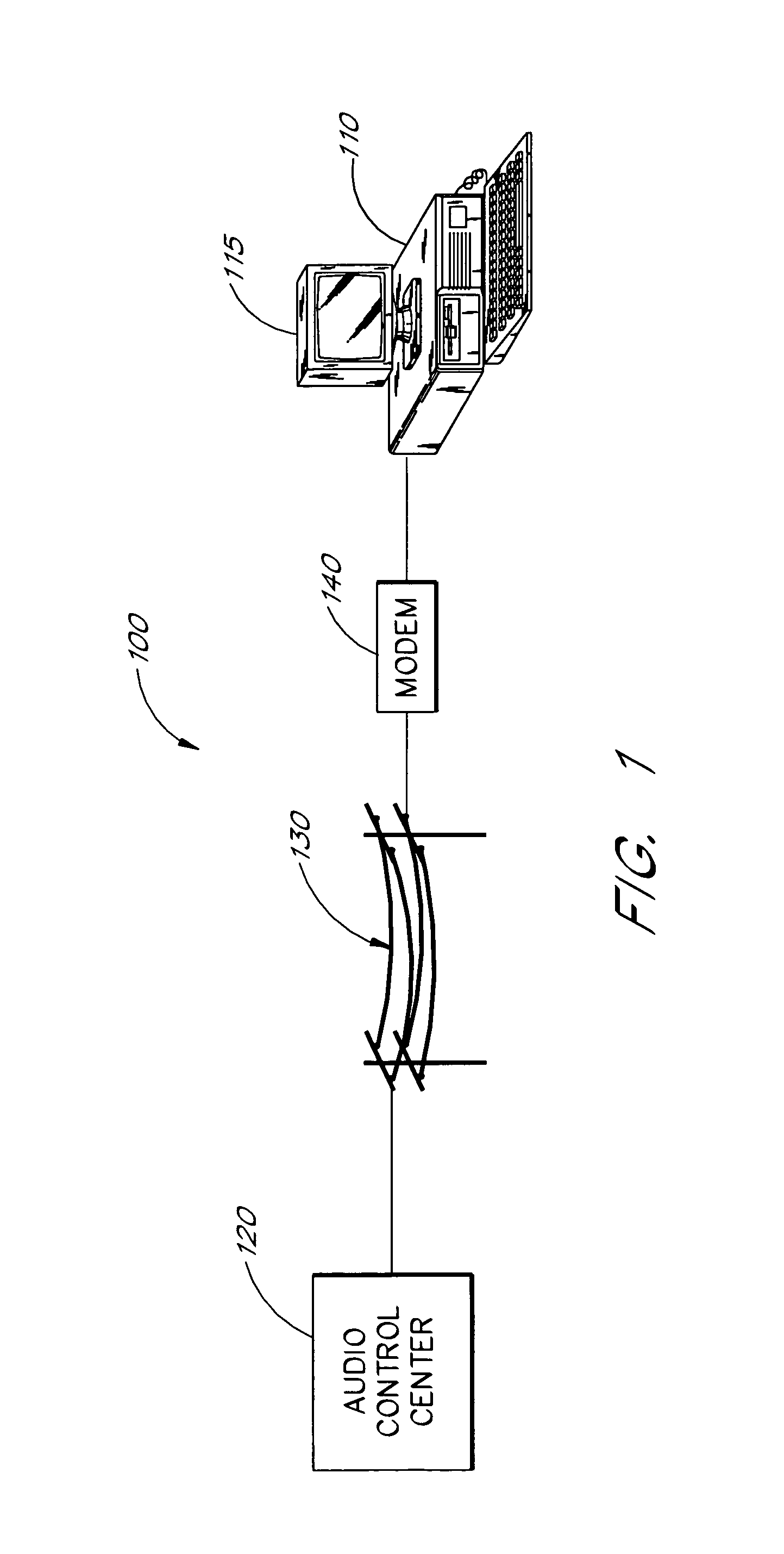
Multimedia communications system and method for providing audio on demand to subscribers
InactiveUS6985932B1Quality improvementHigh audio signalSpecific information broadcast systemsBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemTelecommunications link
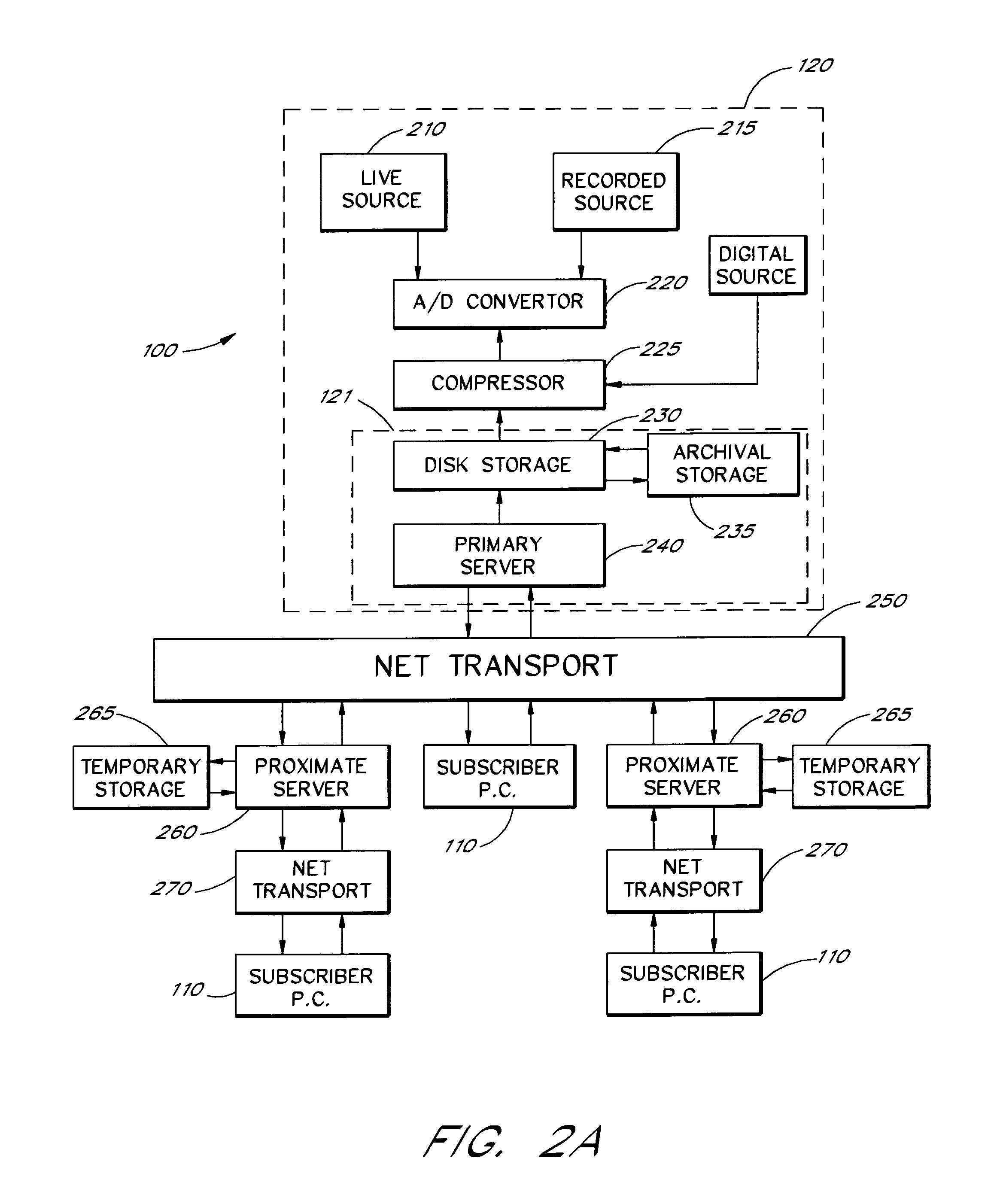
An audio-on-demand communication system provides real-time playback of audio data transferred via telephone lines or other communication links. One or more audio servers include memory banks which store compressed audio data. At the request of a user at a subscriber PC, an audio server transmits the compressed audio data over the communication link to the subscriber PC. The subscriber PC receives and decompresses the transmitted audio data in less than real-time using only the processing power of the CPU within the subscriber PC. According to one aspect of the present invention, high quality audio data compressed according to lossless compression techniques is transmitted together with normal quality audio data. According to another aspect of the present invention, metadata, or extra data, such as text, captions, still images, etc., is transmitted with audio data and is simultaneously displayed with corresponding audio data. The audio-on-demand system also provides a table of contents indicating significant divisions in the audio clip to be played and allows the user immediate access to audio data at the listed divisions. According to a further aspect of the present invention, servers and subscriber PCs are dynamically allocated based upon geographic location to provide the highest possible quality in the communication link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
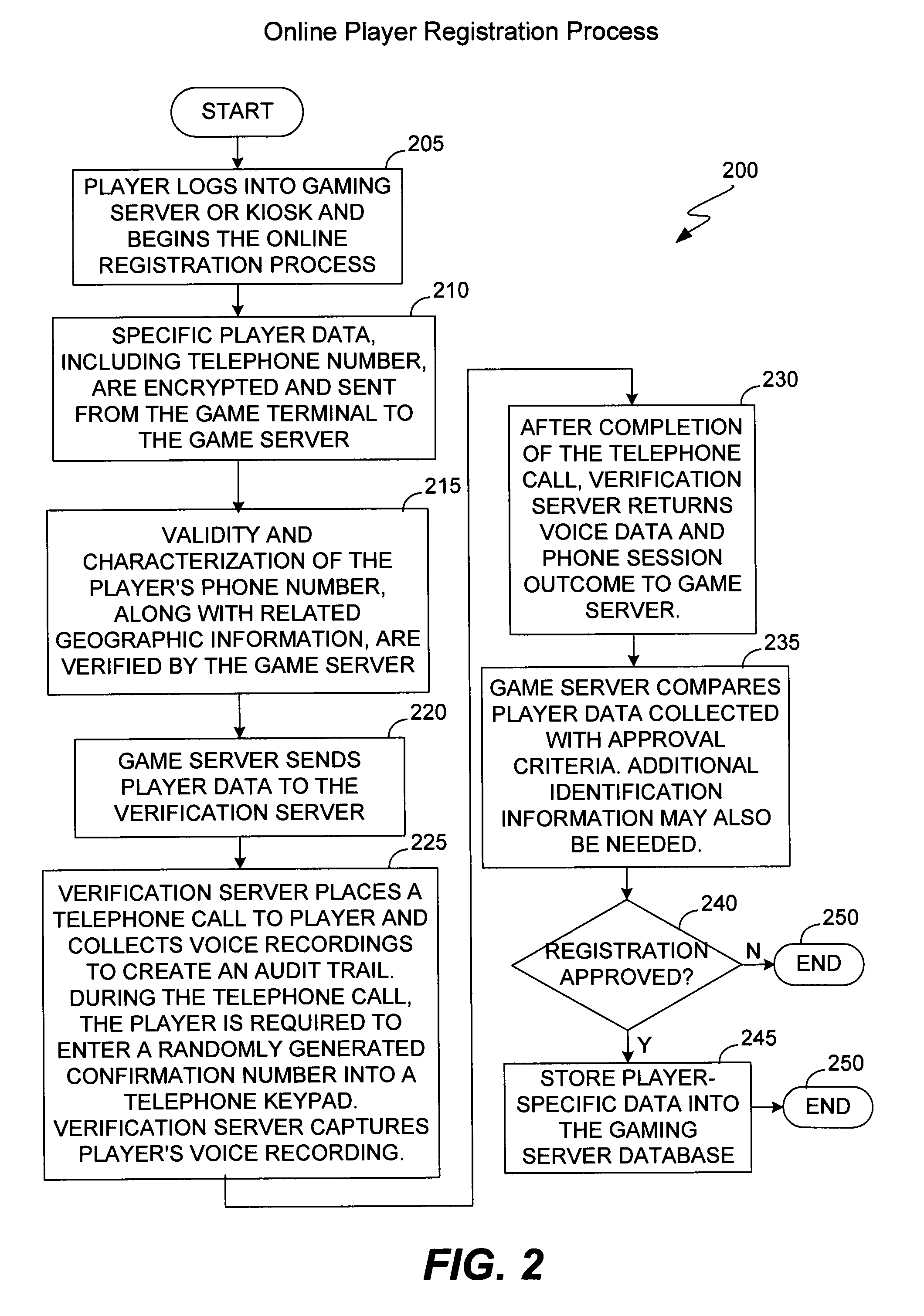
Method and apparatus using geographical position and universal time determination means to provide authenticated, secure, on-line communication between remote gaming locations
InactiveUSRE39644E1Facilitates denialAccurately determineSecret communicationApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingGeolocationThe Internet
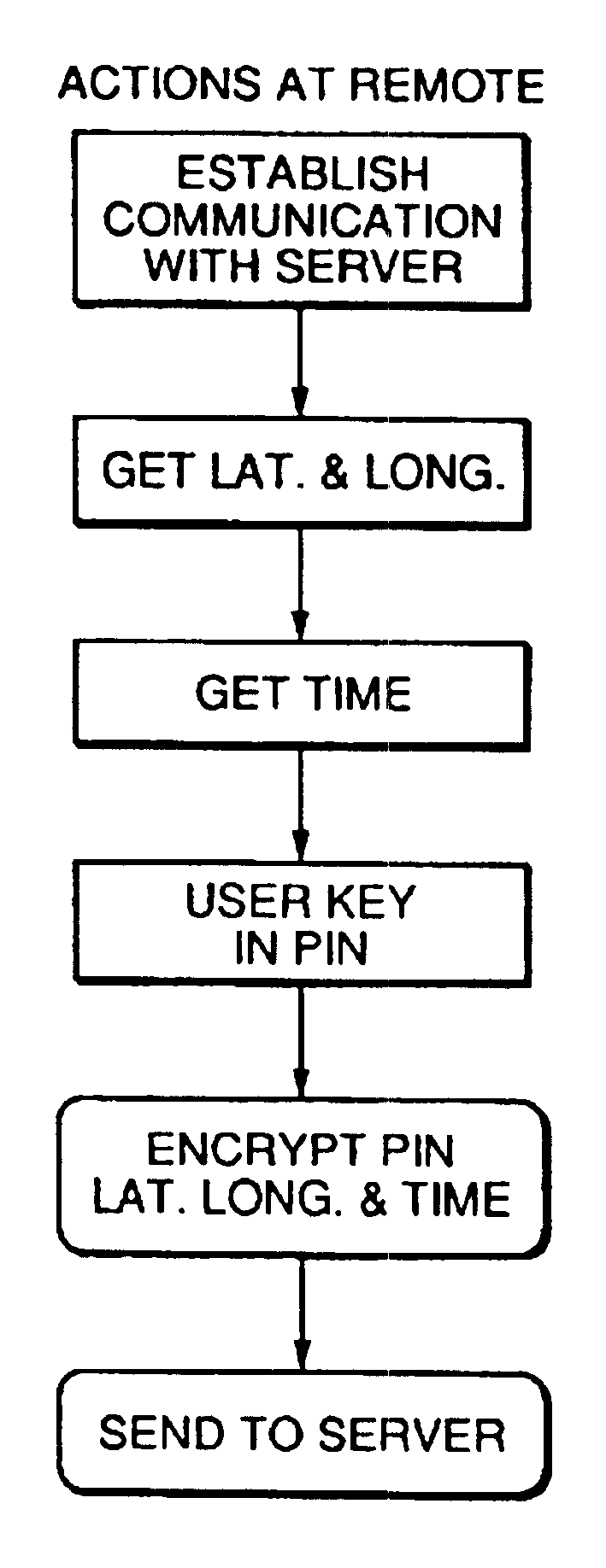
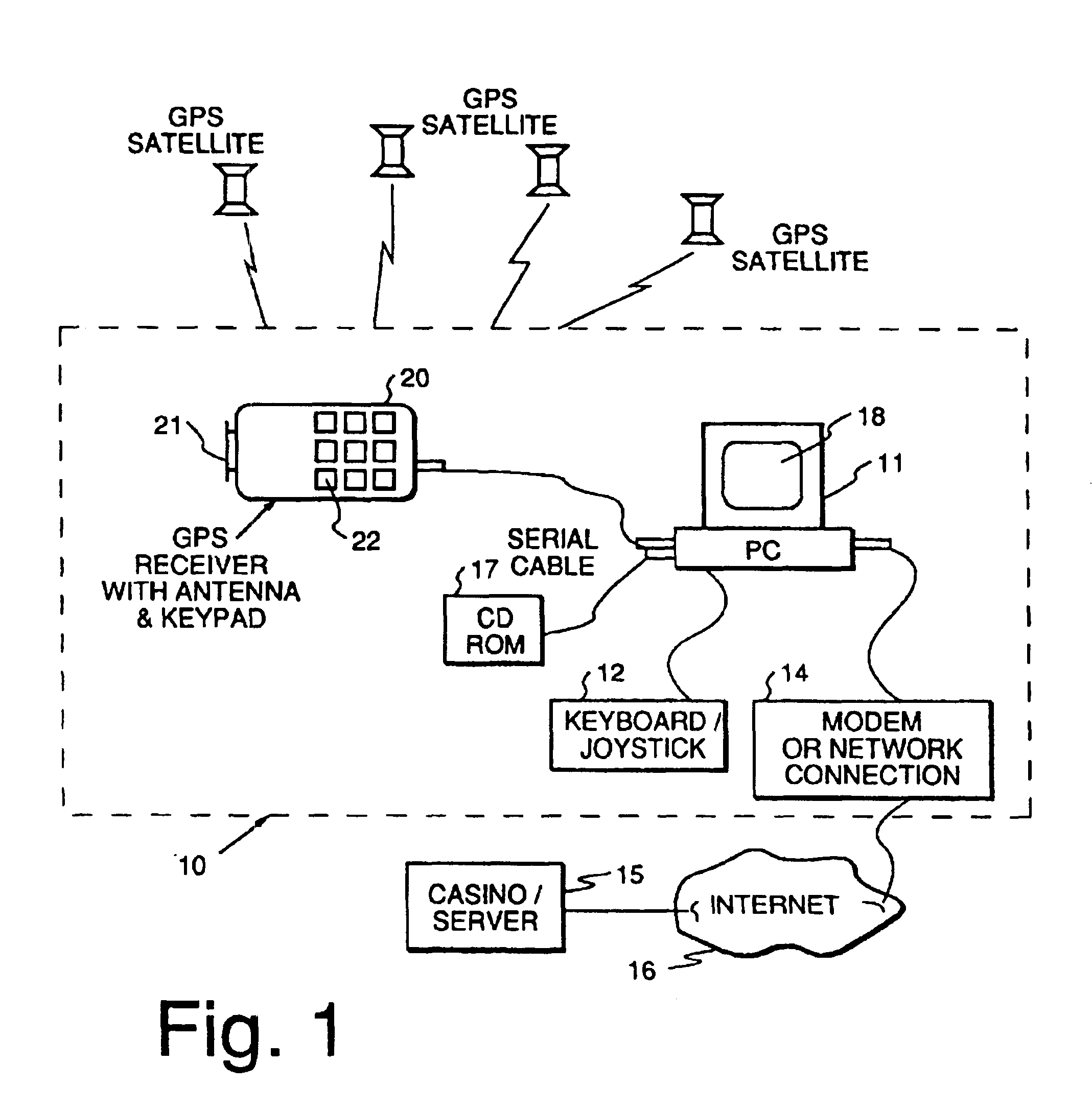
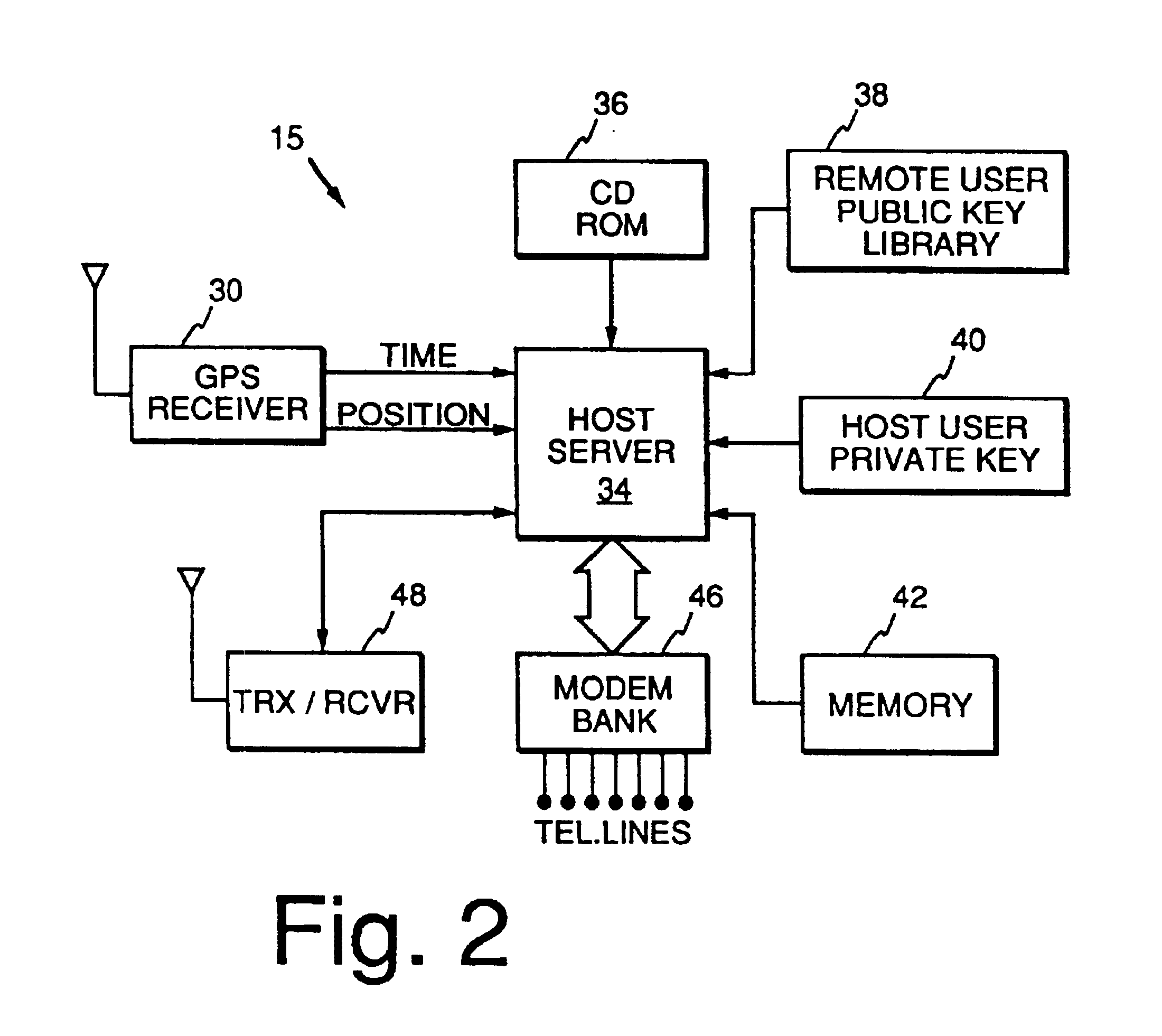
Method and apparatus for providing authenticated, secure, on-line communication between remote locations including a user terminal adapted to enable a player in one location to remotely communicate via a communications medium such as the Internet with a gaming host in another location. Location of the remote user terminal, the host server and universal time are determined using means for accessing signals generated by geostationary navigational transmitters, such as in the global positioning satellite (GPS) system. Player authentication (identity verification) is determined by use of a personal identification number (PIN) and an electronic signature verification service. Security of communication is accomplished through use of a public-key / private-key encryption system. The remote user terminal may be comprised of one or more discreet components adapted to be used with a laptop or desktop personal computer (PC), or may be embodied in a stand alone or self-contained single unit that is portable and communicates via radio waves, telephone lines or the Internet to a host server.
Owner:IGT
Method and device for determining the physical location and identity of a user
InactiveUS20030236120A1Selection is limitedPayment architectureApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingSession IDRestricted activity
A method and a device is described for determining the physical location and / or identity of network users and for preventing certain undesired users for participating in-or getting access to restricted activities, services or information. When a user accesses a service provider's website, an encrypted session ID is stored on the user's electronic device or computer. The user's electronic device or computer is then coupled to the service provider's server through a phone connection and the session ID is transferred to the service provider over the phone line for verification. By using Caller ID technology the user's telephone number is identified, and by analyzing the phone number the location of the player is determined. If the location satisfied the service provider's and any official regulator's requirements the available service options are then determined depending on the user's specific location. The available service options-if any-are then displayed on the user's electronic device or computer.
Owner:REECE KENNETH +1
Location and user identification for online gaming
ActiveUS7577847B2Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsHotel roomCellular telephone
The present invention provides methods and devices for determining the location, identity and age of a user who desires to initiate a gaming session from an uncontrolled environment such as a home, a gaming kiosk or a hotel room. In some implementations, the user's location is determined in part by reference to a database of land telephone lines and corresponding addresses. The location may be verified by other methods, e.g., by determining the location of an Internet service provider's network device that is near a user's host device or via a cellular telephone network. The user may be asked to input a confirmation number and / or make an oral response during a telephone call to a telephone number associated with the uncontrolled environment. The user may also be prompted to make statements verifying his or her identity, age, a maximum amount available for wagering or other statements.
Owner:IGT
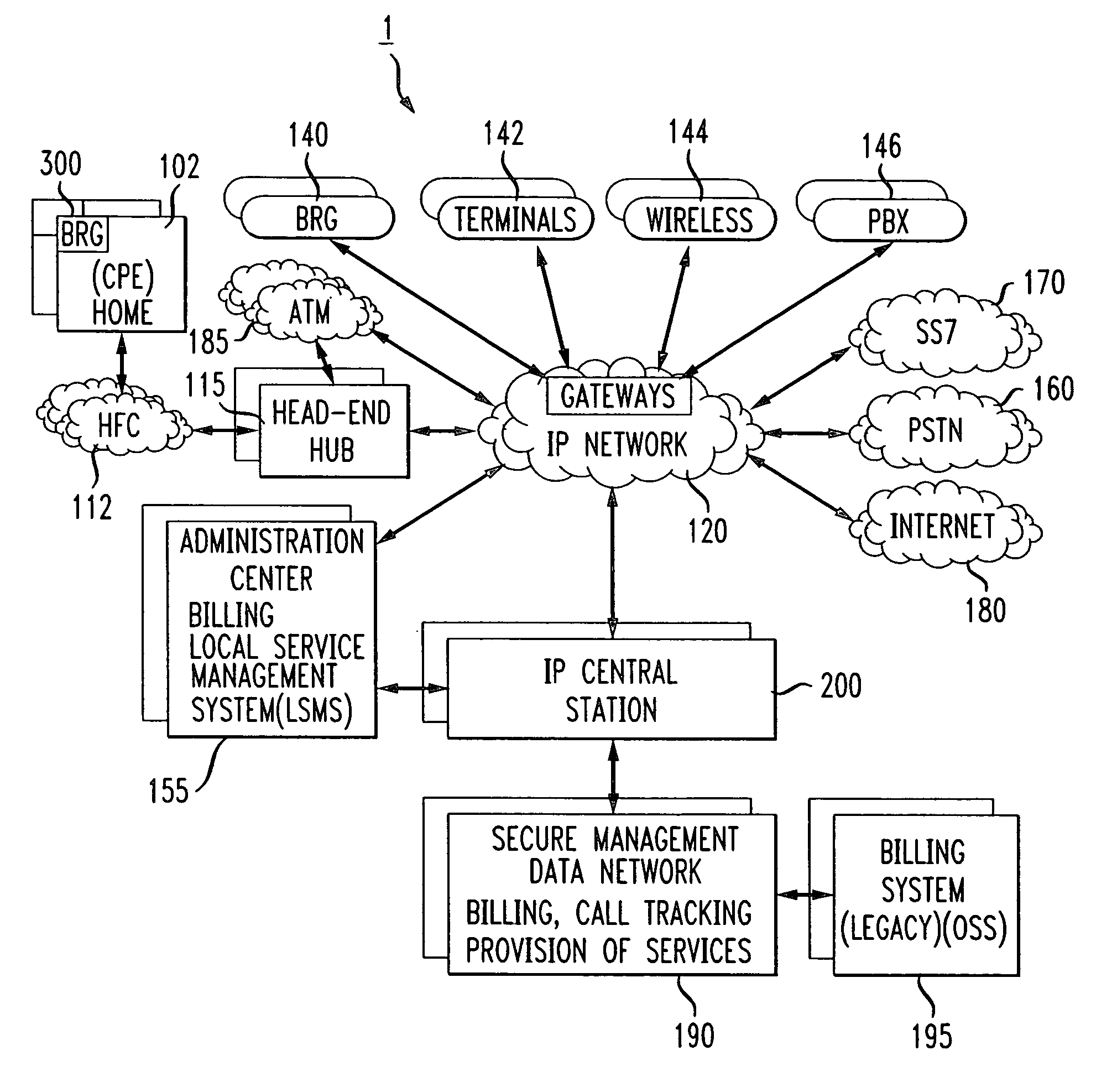
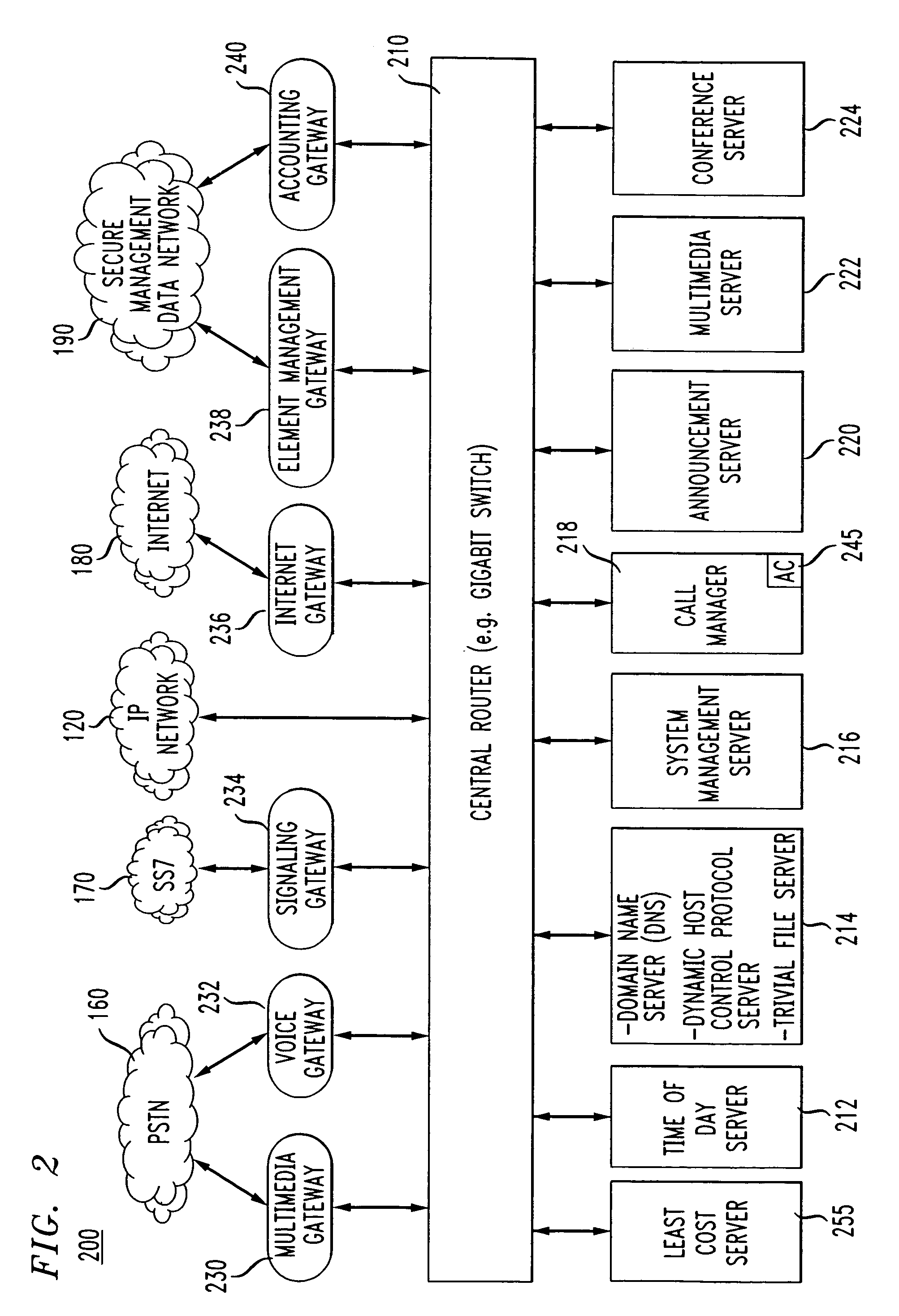
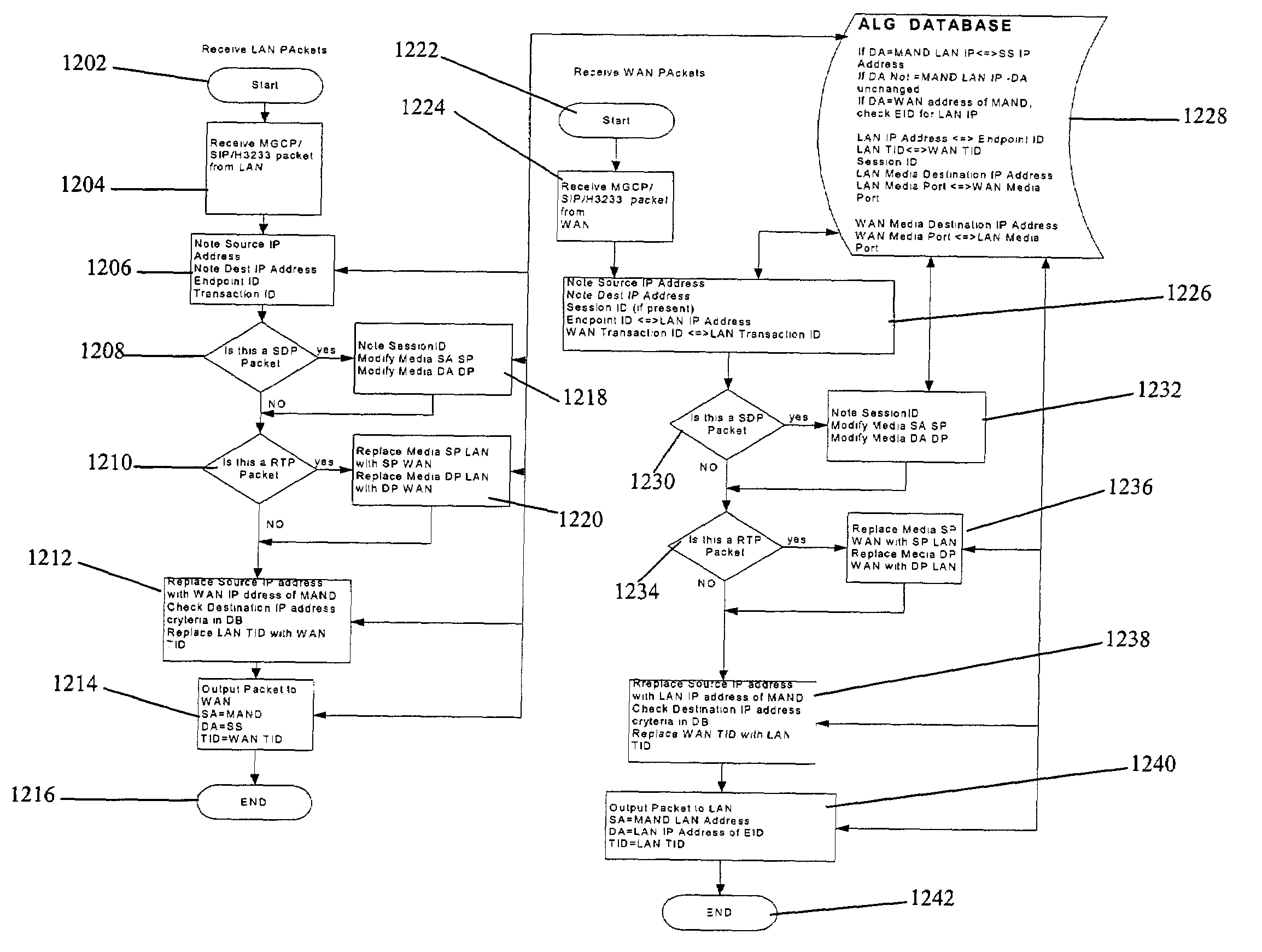
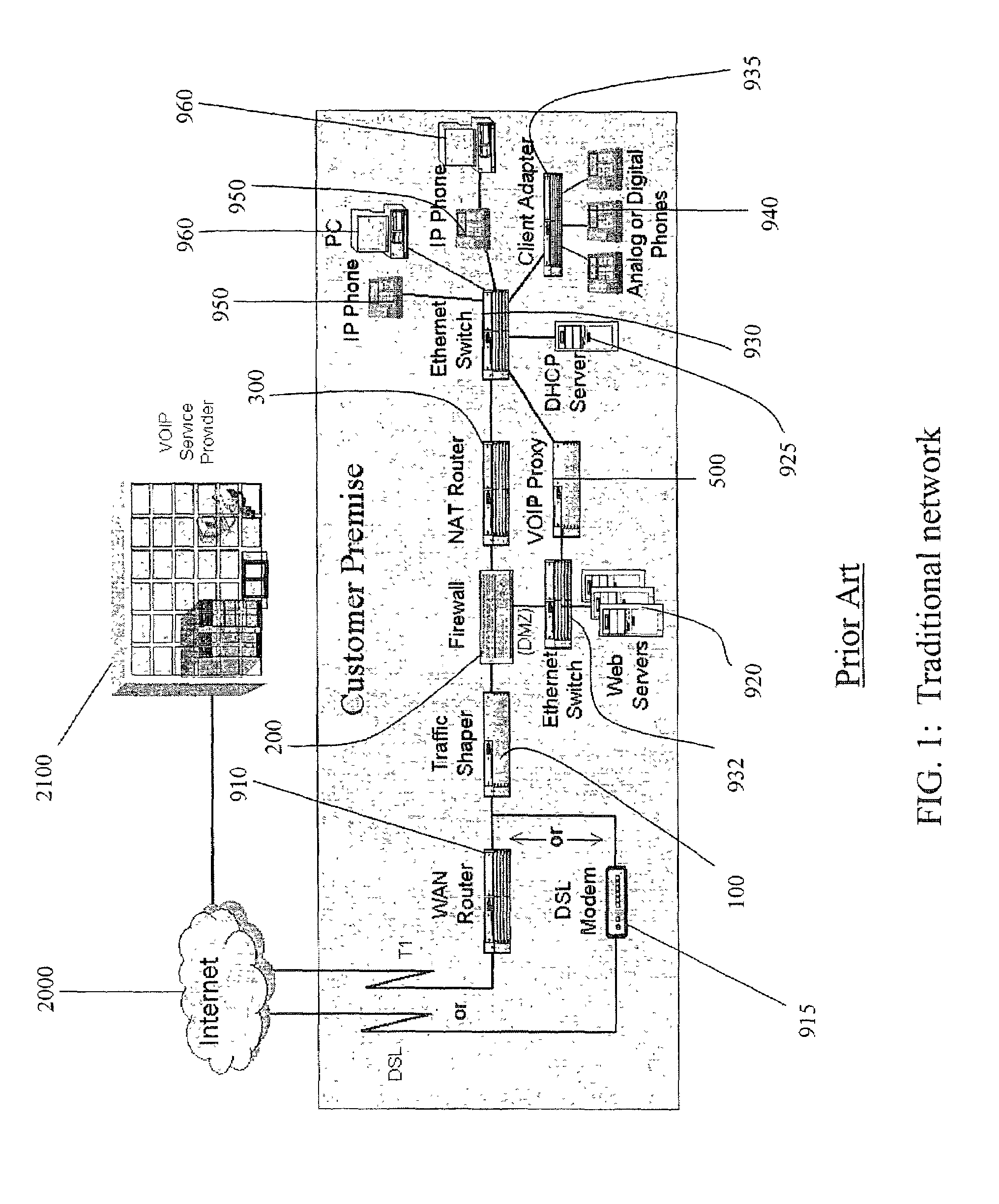
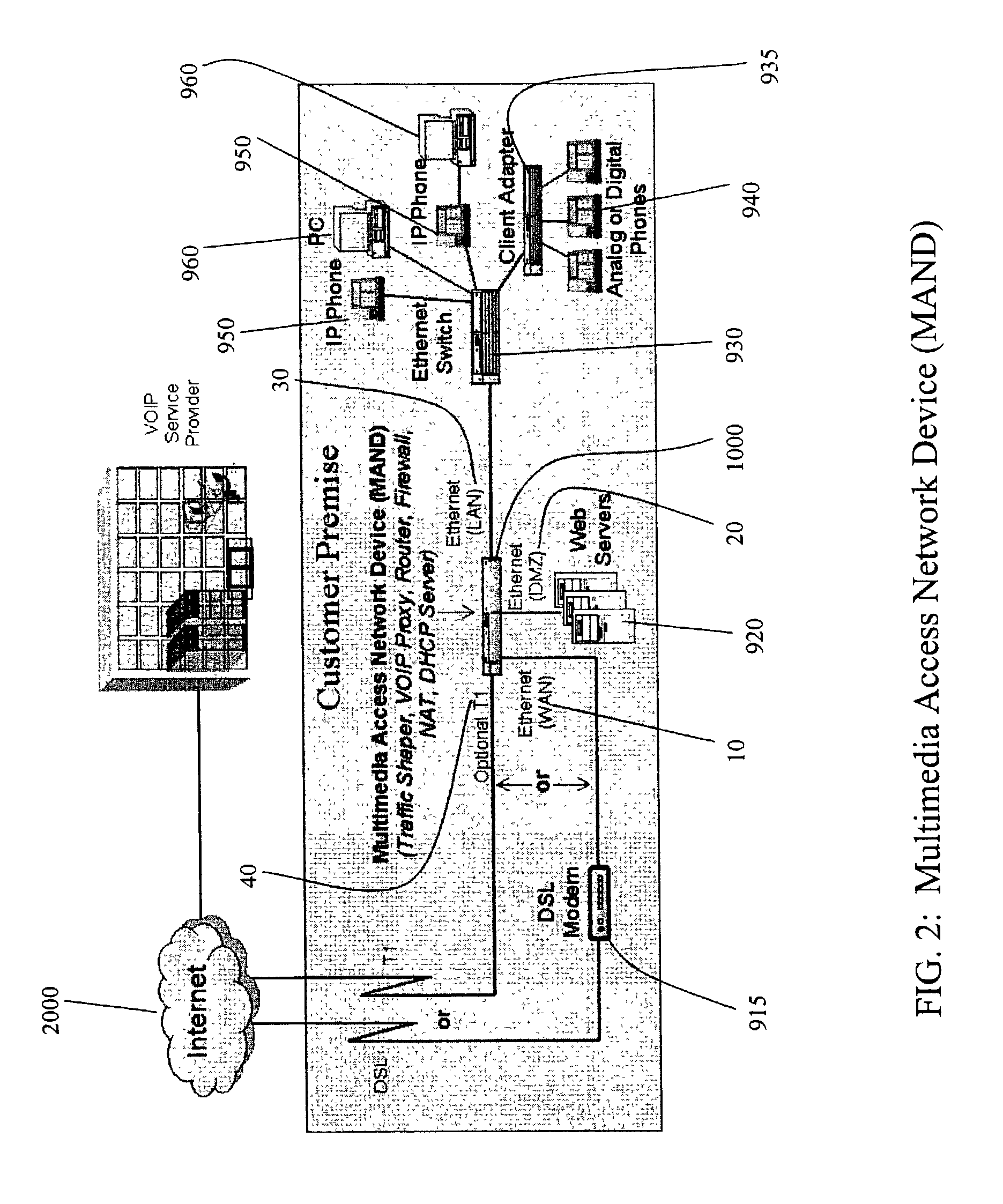
Method and system for implementing and managing a multimedia access network device
ActiveUS7274684B2Telephonic communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address translationAuthentication
In a complete network-in-a-box system acting as an enterprise network demarcation point, packets such as voice, video and data packets, are routed over common network connections, such as LAN and WAN. The packets are mapped from a public address field (such as an IP address) and port number to a private address field and port number, the mapping process typically being handled by a NAT (Network Address Translation). The packets are also prioritized, by marking the packets for priority queuing and routing, and configuring the bandwidths of the WAN traffic and the voice traffic to predetermined quantities and configuring the address fields of the voice devices. Simultaneous transmission of the various packets can be limited to predetermined quantities, typically by utilizing a CAC (Client Access Control). Secure firewalls are also included as well as a performance test client application that provides a defined workload generated across the WAN interface for capacity planning measurements and allows remote monitoring of the QoS (Quality of Service) data, such as latency, jitter, lost packets and MOS scores. Optionally, a simple, common remote management interface is included, allowing service providers to configure, upgrade and manage the system. Additionally, address fields can be provided to voice, video or data devices attached to a LAN port. VPN authentication and encrypted sessions can be tunneled through the firewall for access to an internal network by using a VPN terminator. For power outages and other emergency purposes, additional ports that connect to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) analog telephone lines as well as other analog telephones or devices, can be provided. Another advantageous element is that most of the above components or features may be enabled or disabled.
Owner:EDGEWATER NETWORKS
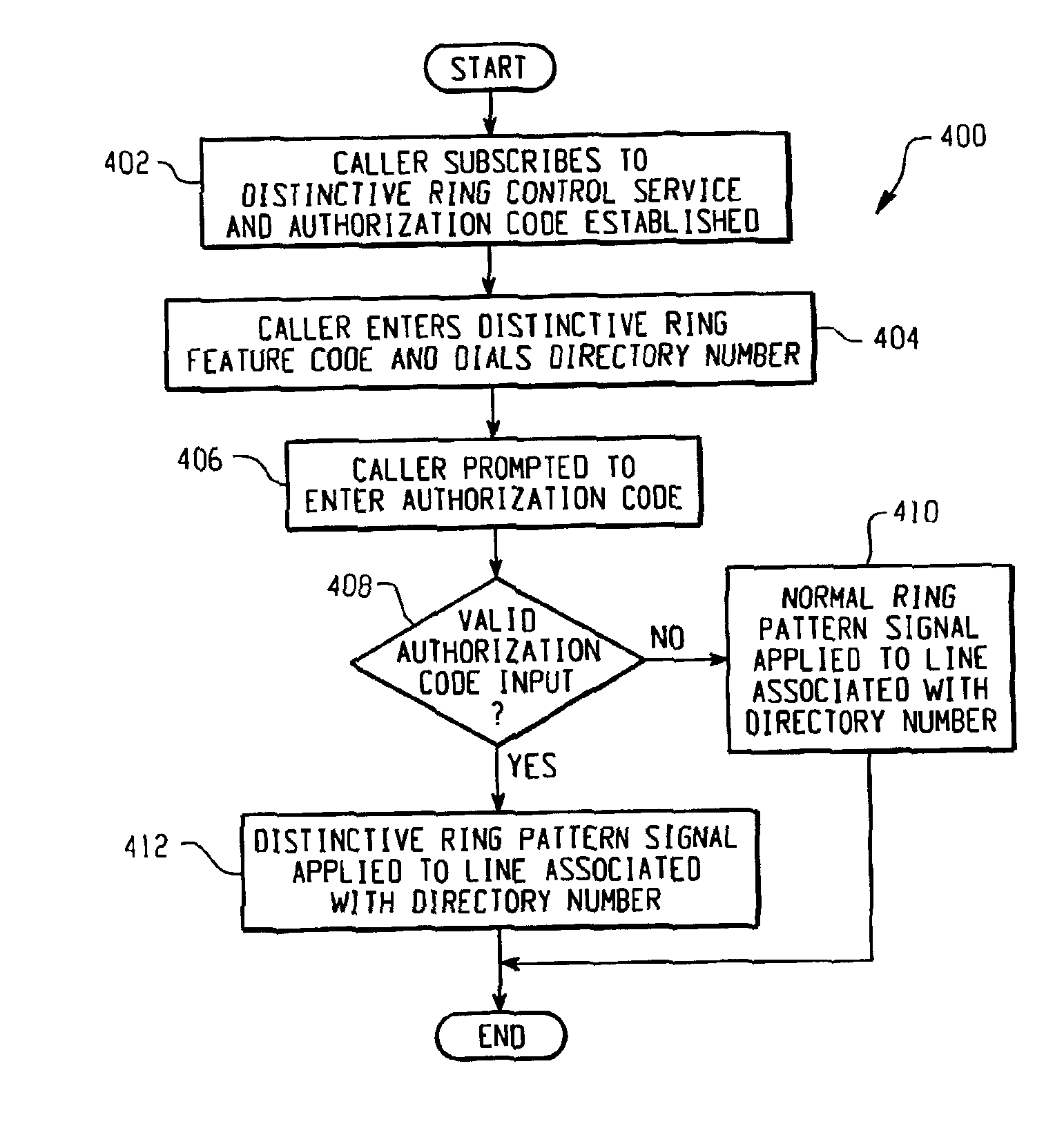
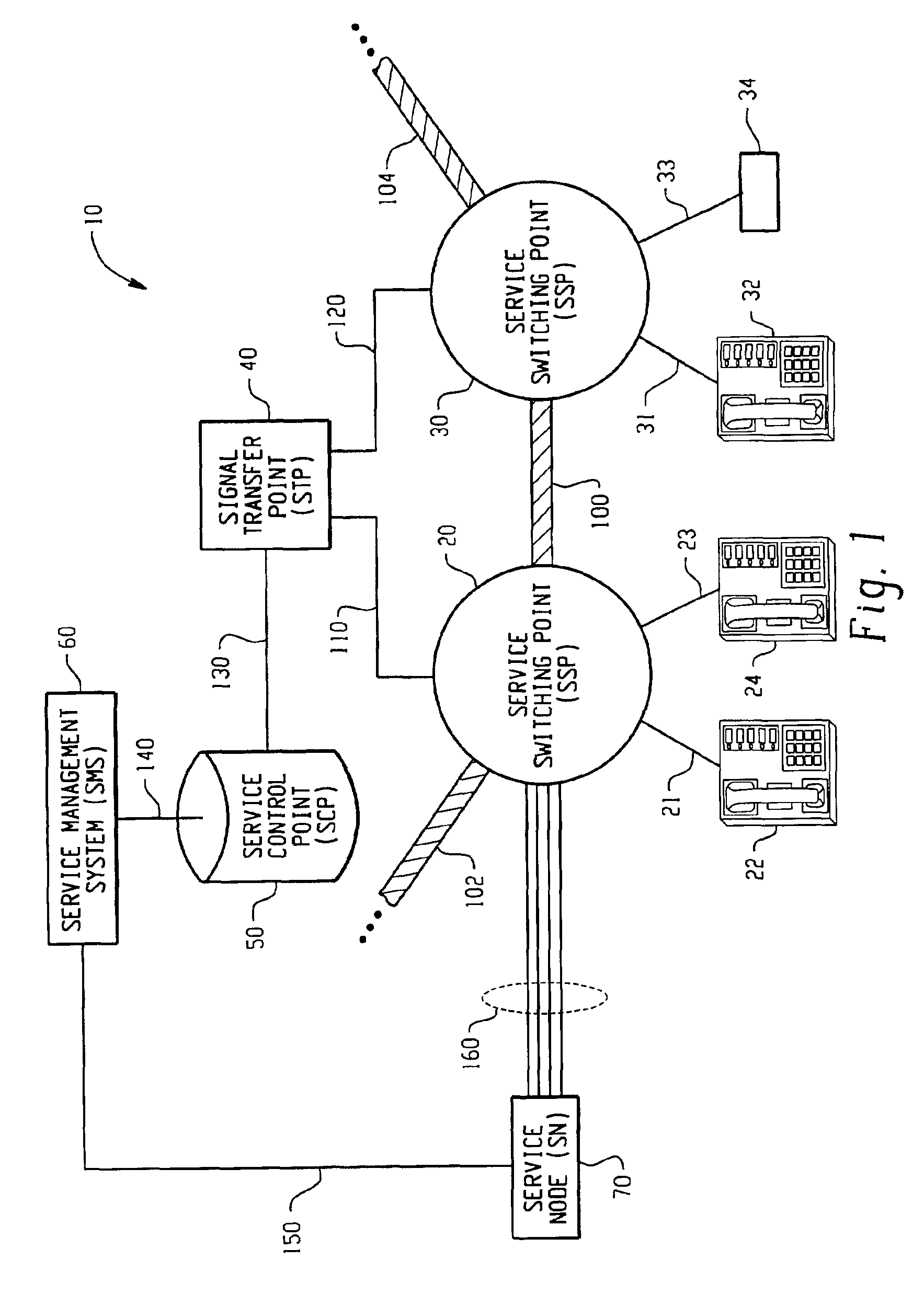
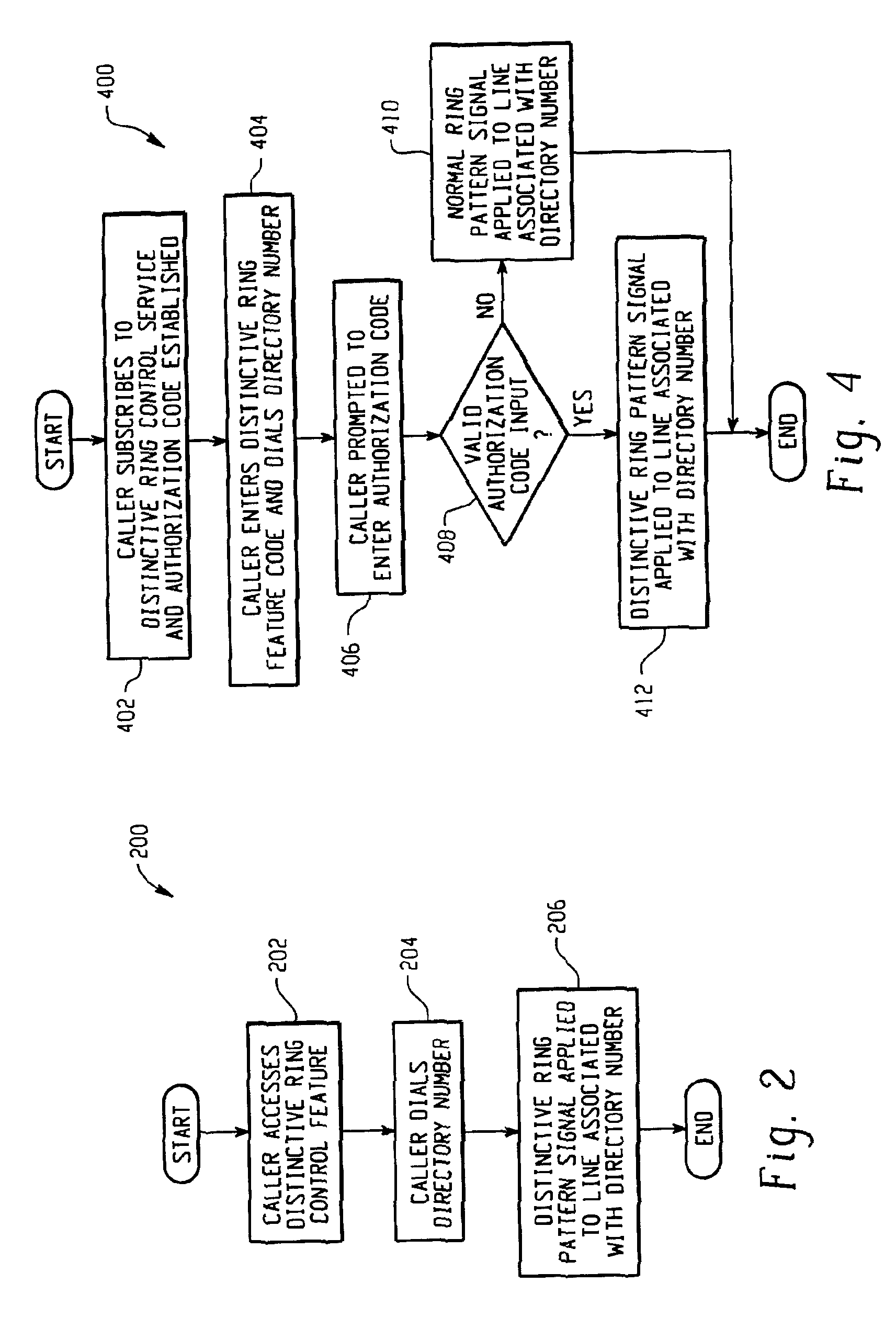
System and method for caller control of a distinctive ring
InactiveUS7106846B2Special service for subscribersCurrent supply arrangementsService controlDirectory number
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
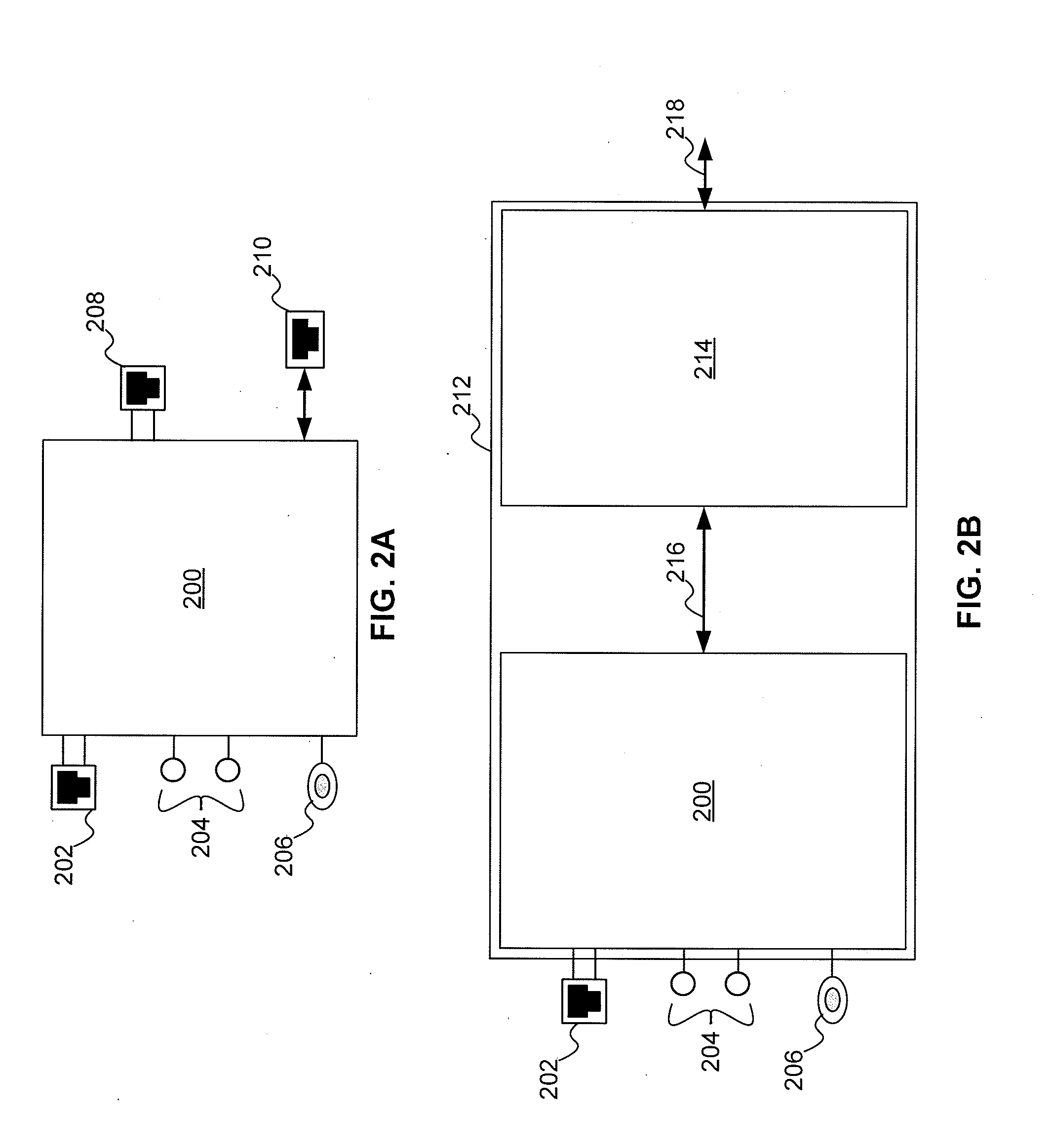
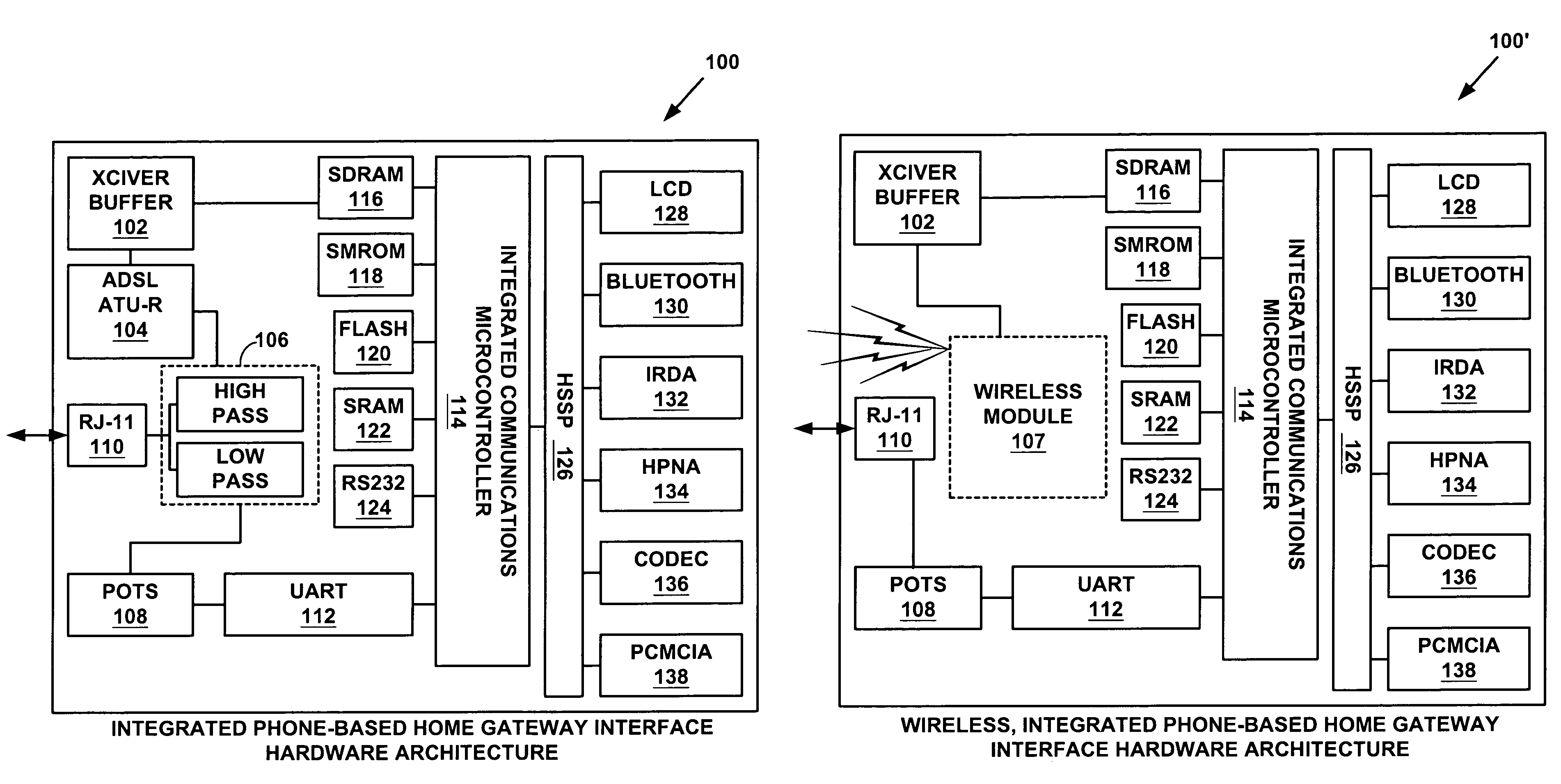
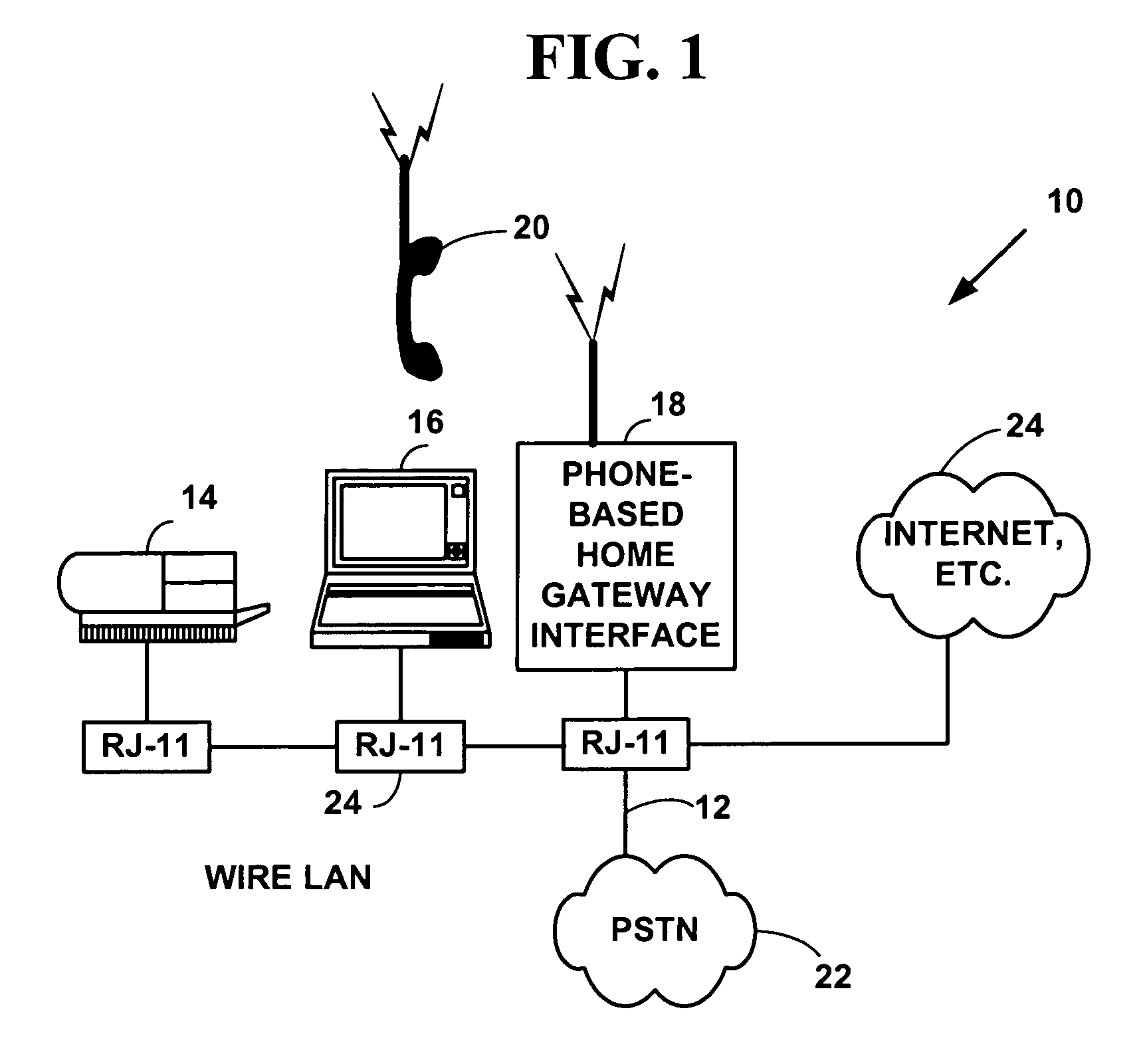
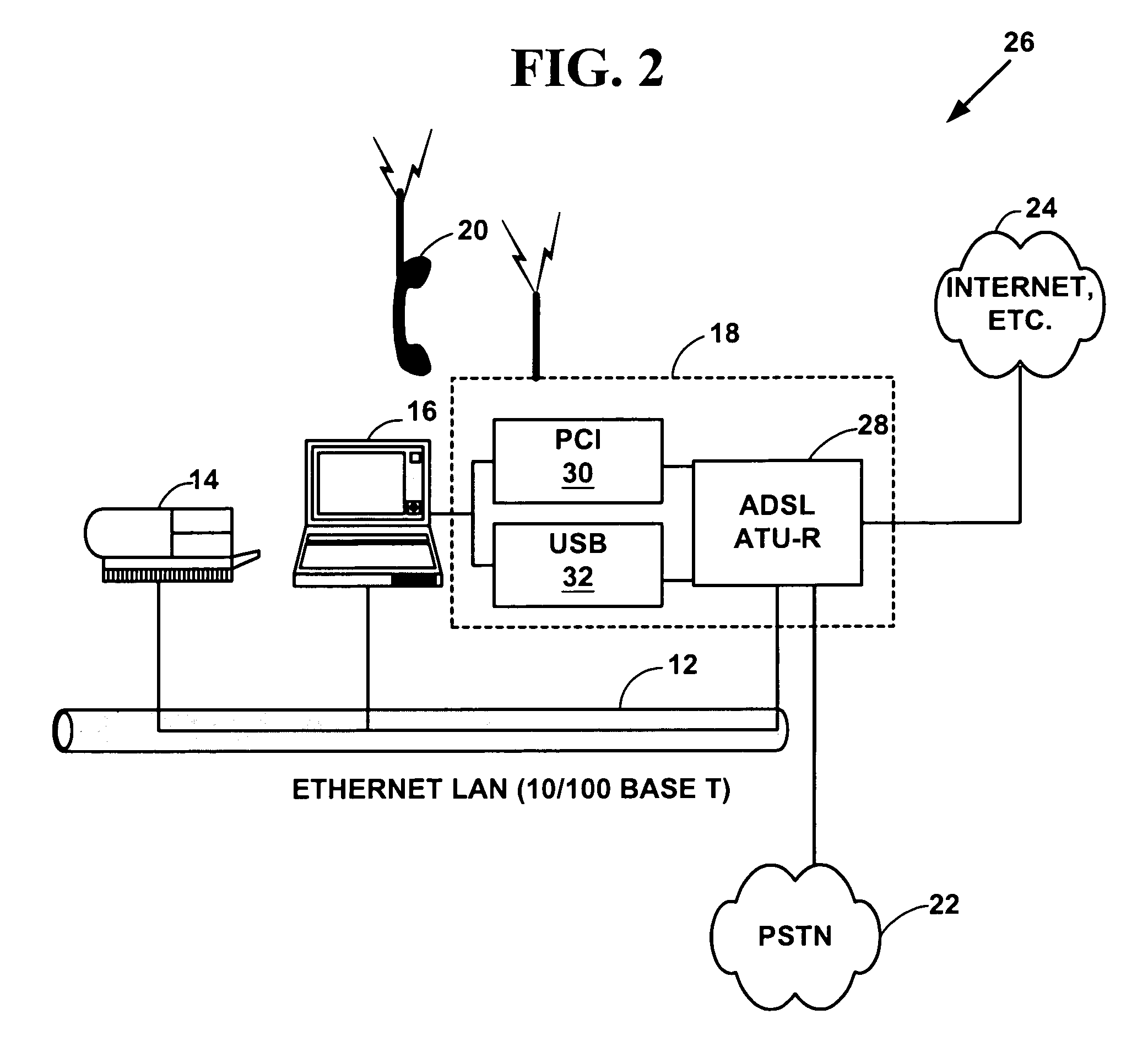
Integrated phone-based home gateway system with a broadband communication device
A integrated phone-based home gateway system is disclosed. The integrated phone-based home gateway system includes a broadband communication device, such as digital subscriber line (“DSL”) device, an analog modem, a wireless interface, integrated into a screen-phone for providing broadband communication service to home users. Multiple home users are able to access the Internet and the content services for conducting e-commerce, receiving content news, entertaining on-demand, making audio or video communications, and telecommuting or working at home. This screen-phone based, modular, plug-n-play home gateway interface allows in-home as well as to-home networking, provides automatic data and broadband initialization, configuration and service provisioning, routing and bridging functionality and allows resource sharing among home devices via the existing phone wire, wireless, coaxial or optical cable connections.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
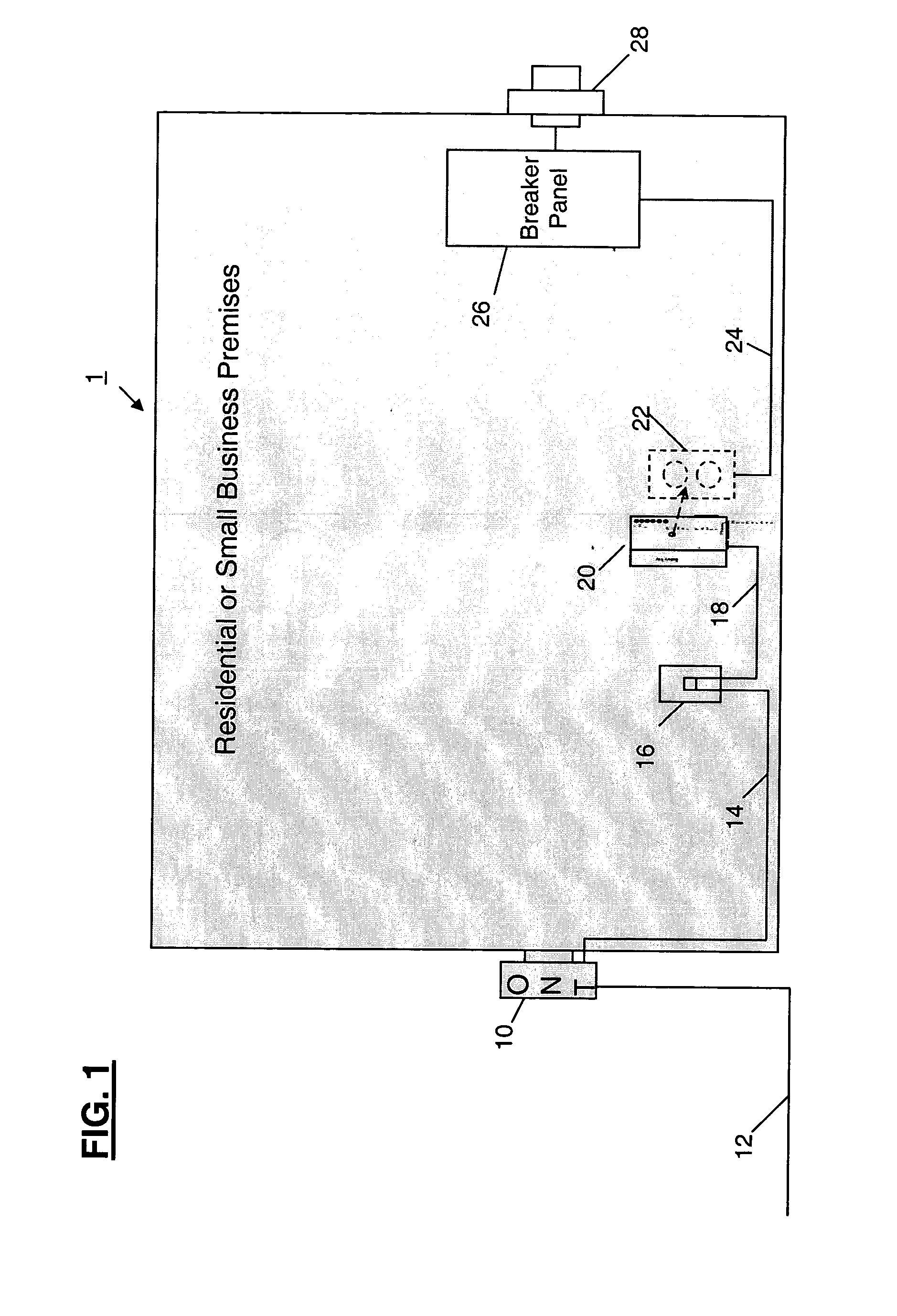
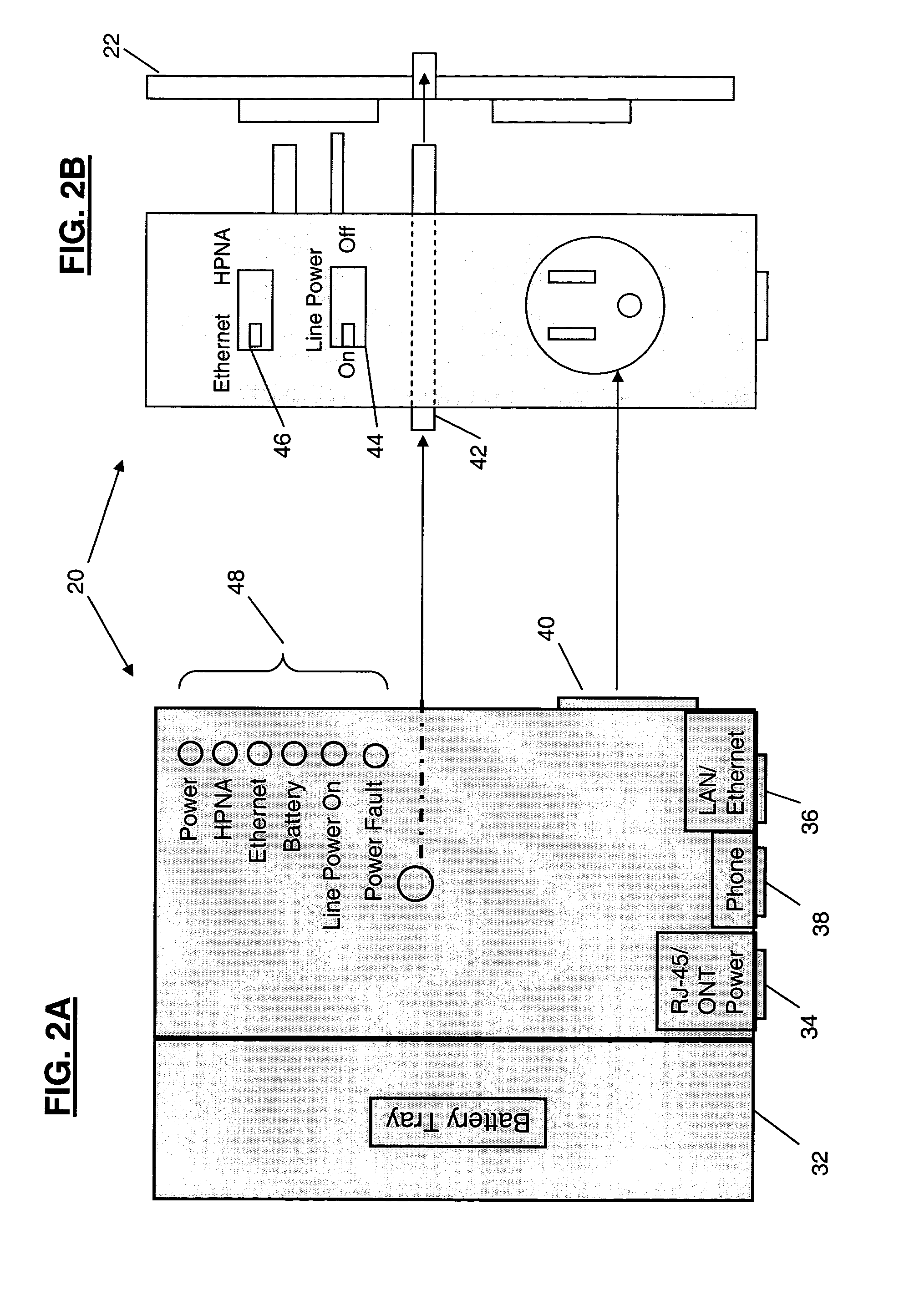
Power adapter and broadband line extender system and method
ActiveUS20040268160A1Volume/mass flow measurementTwo-part coupling devicesNetwork terminationData port
A power adapter, in a presently preferred embodiment, includes a power converter and multiple data ports, and is configured for ease of coupling the power converter into pre-existing premises power connectors. Thus, premises power can be supplied from the power converter and a first data port, via data cabling, to a network terminating device for an external network. Multi-protocol adapters, such as an HPNA (Home Phoneline Network Alliance protocol compliant) / Ethernet adapter, may also be included to provide extension of a protocol (such as Ethernet) over pre-existing premises wiring. A back-up battery is optionally provided, as well as appropriate switches and indicators. Specialized male-female connectors may also be used.
Owner:TELLABS VIENNA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com