Patents
Literature
92results about How to "More capacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
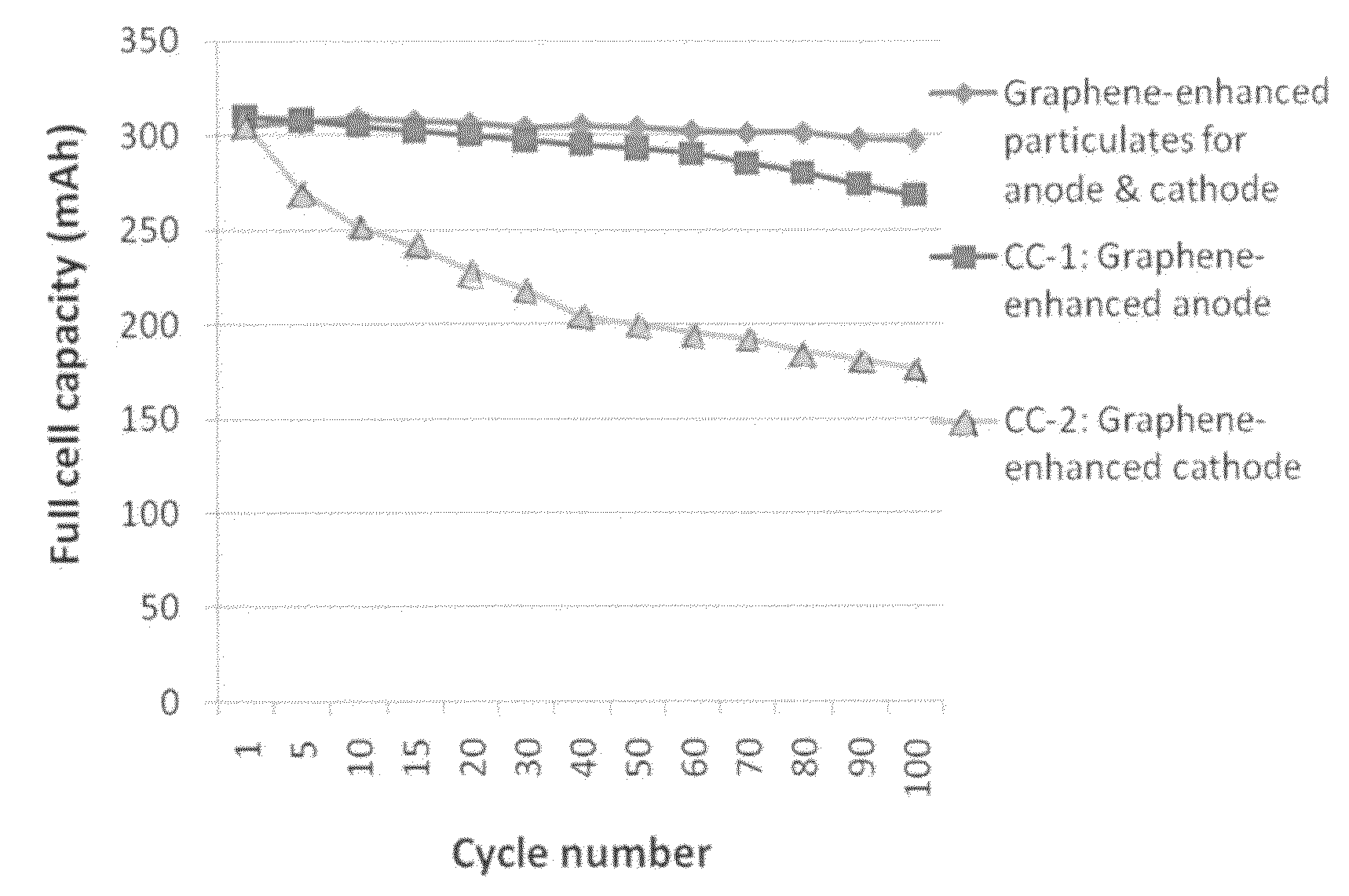
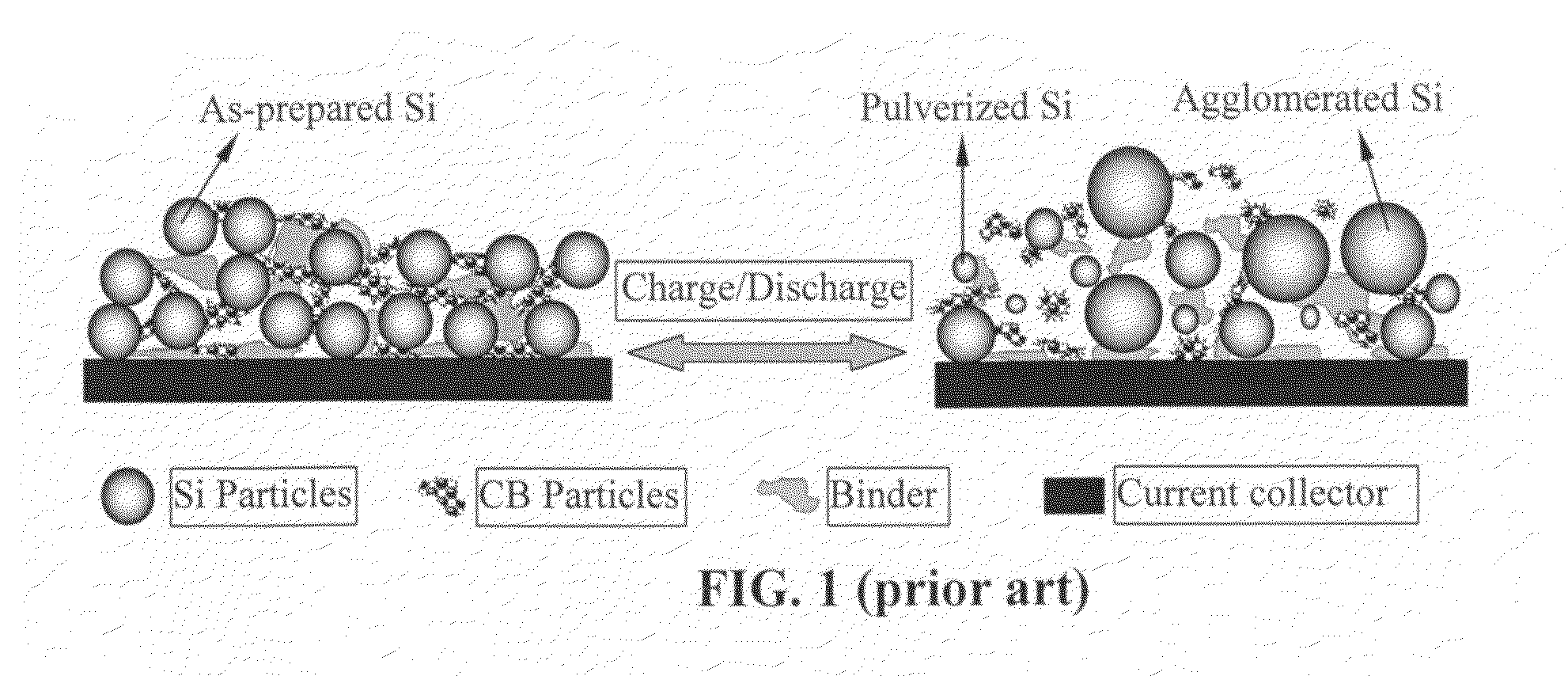
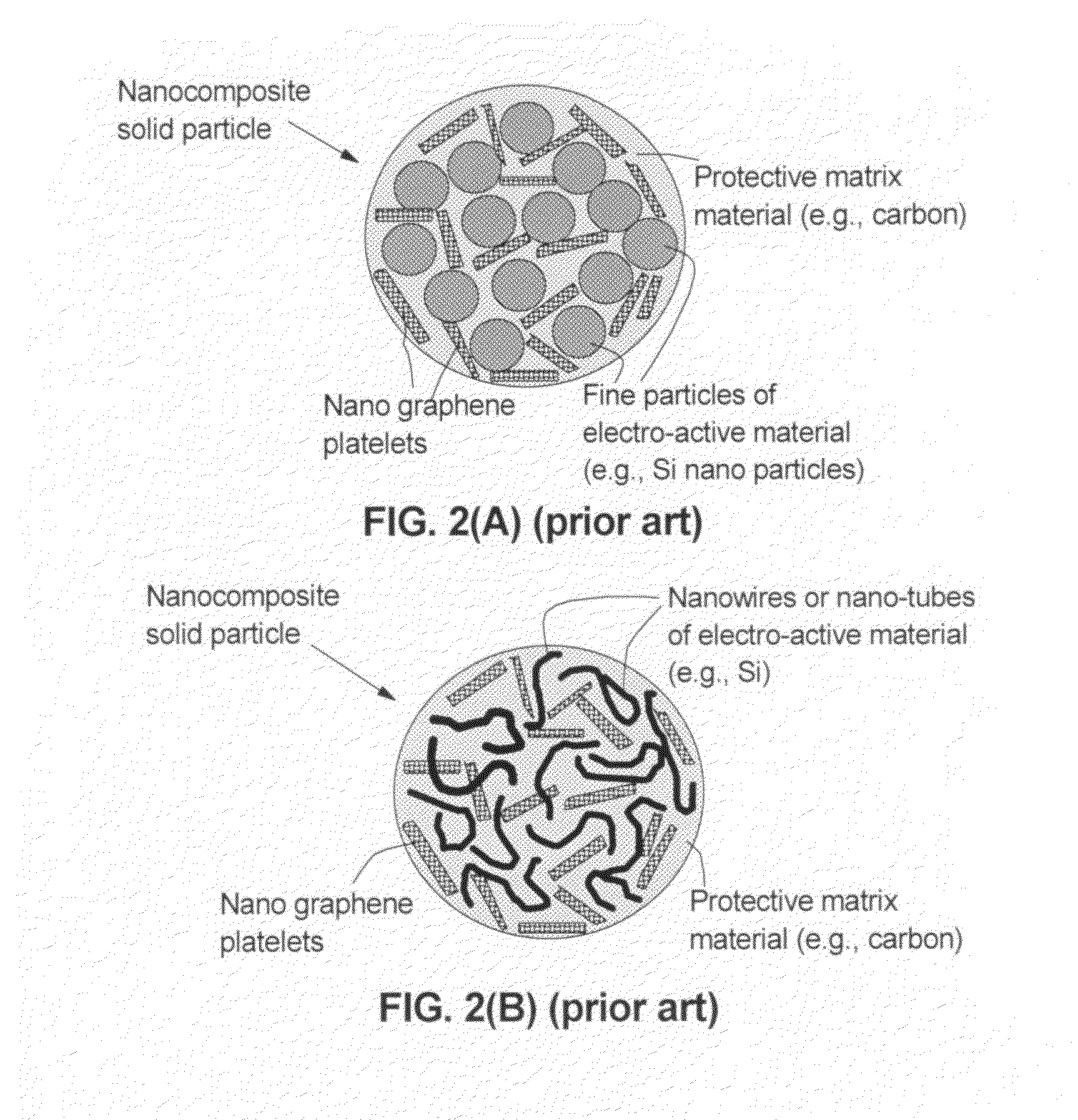
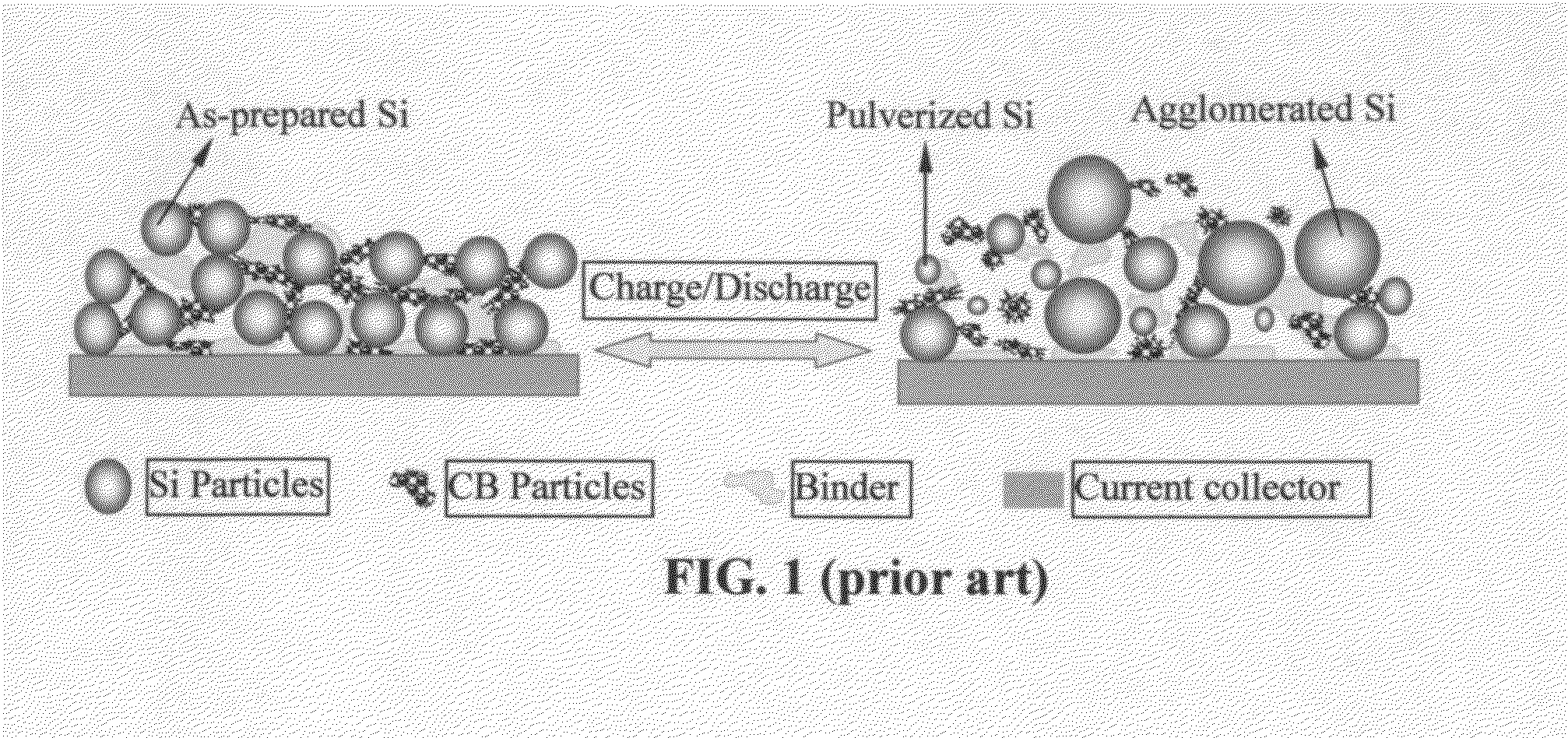
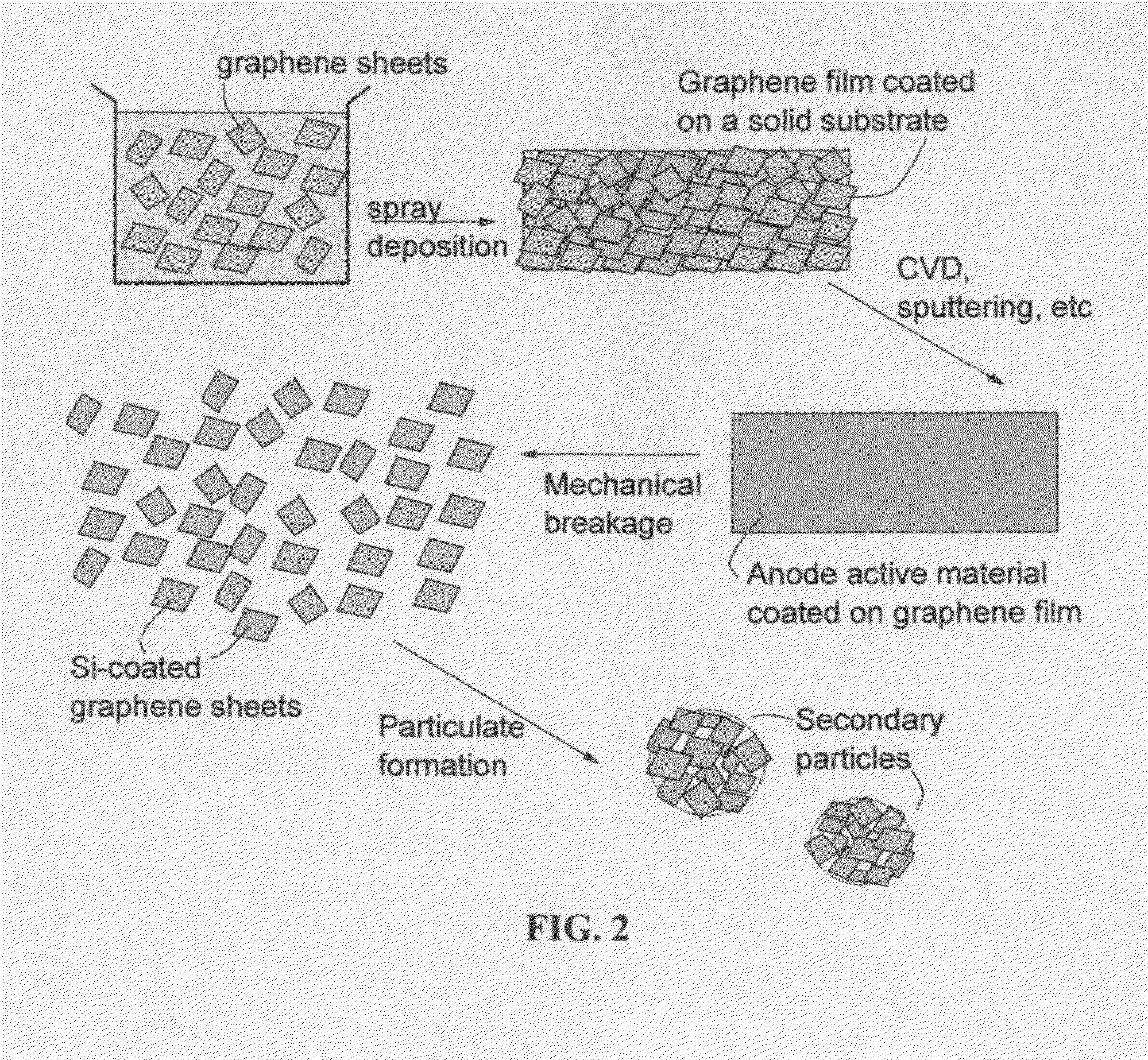
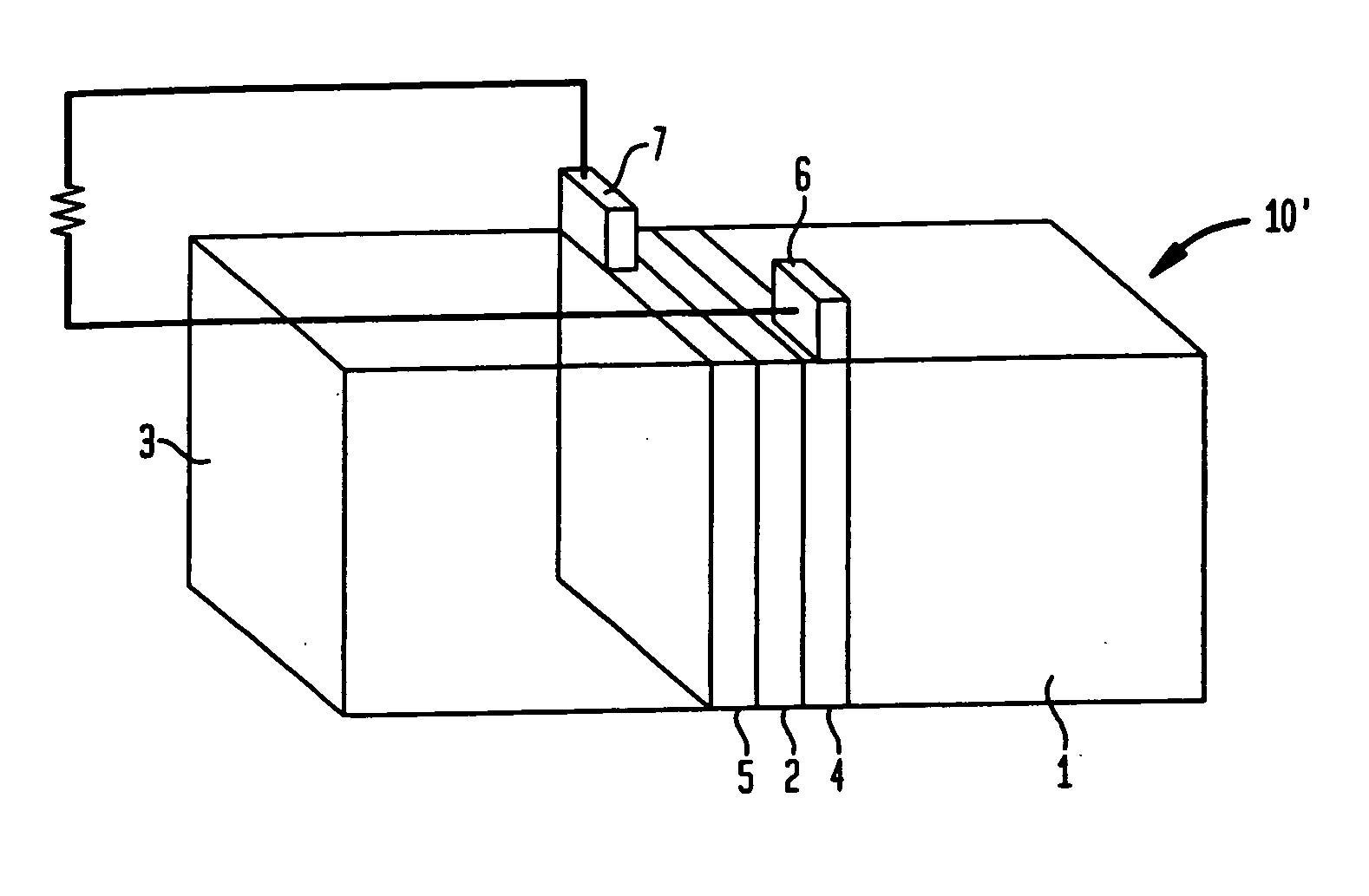
Graphene-enhanced anode particulates for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20120064409A1Enhanced Li-ion insertionIncrease capacityNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesMicroparticle
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium-ion battery anode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single sheet of graphene or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine anode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm. The graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into the particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the anode active material particles. The amount of graphene is at least 0.01% by weight and the amount of the anode active material is at least 0.1% by weight, all based on the total weight of the particulate. A lithium-ion battery having an anode containing these graphene-enhanced particulates exhibits a stable charge and discharge cycling response, a high specific capacity per unit mass, a high first-cycle efficiency, a high capacity per electrode volume, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
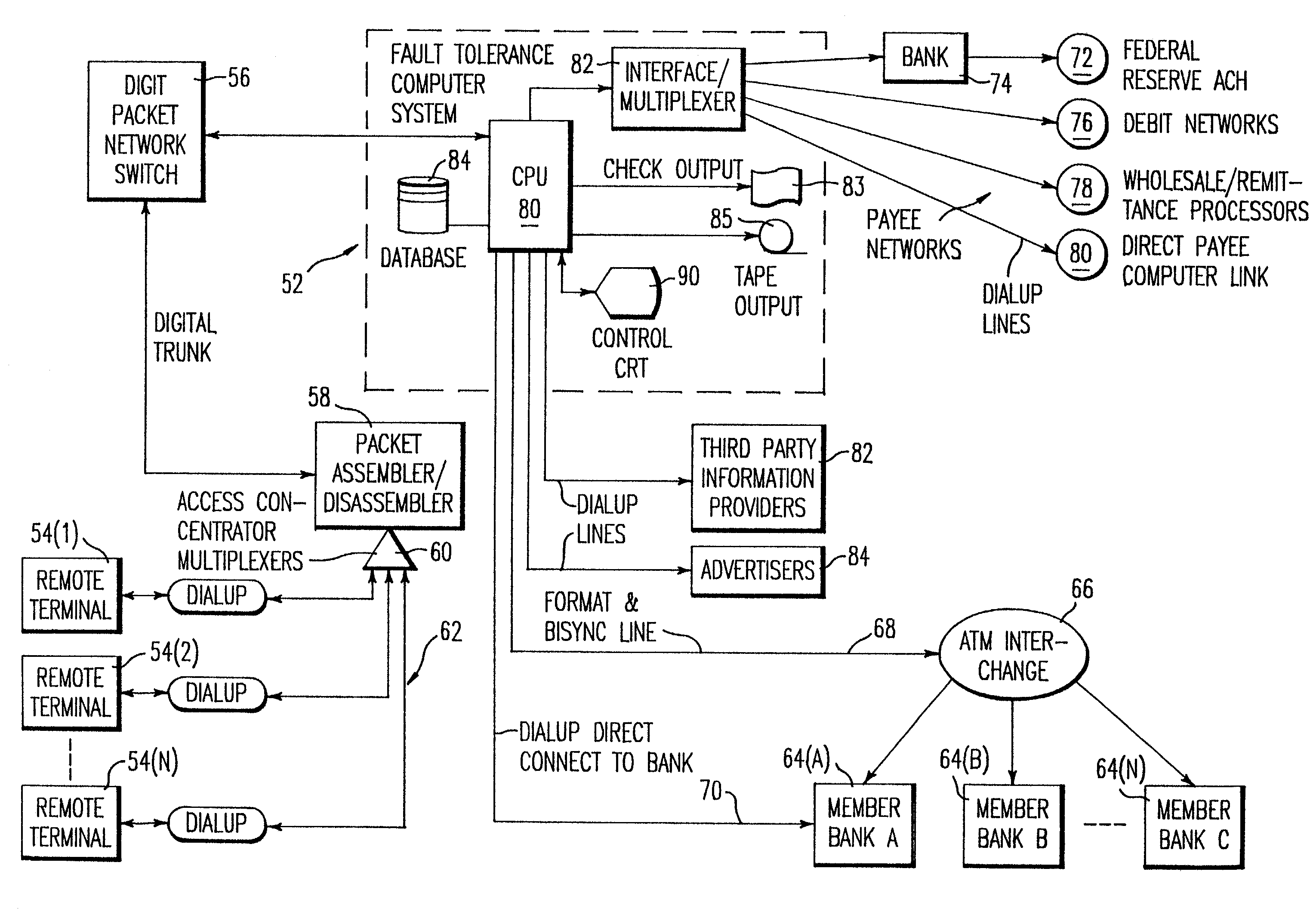
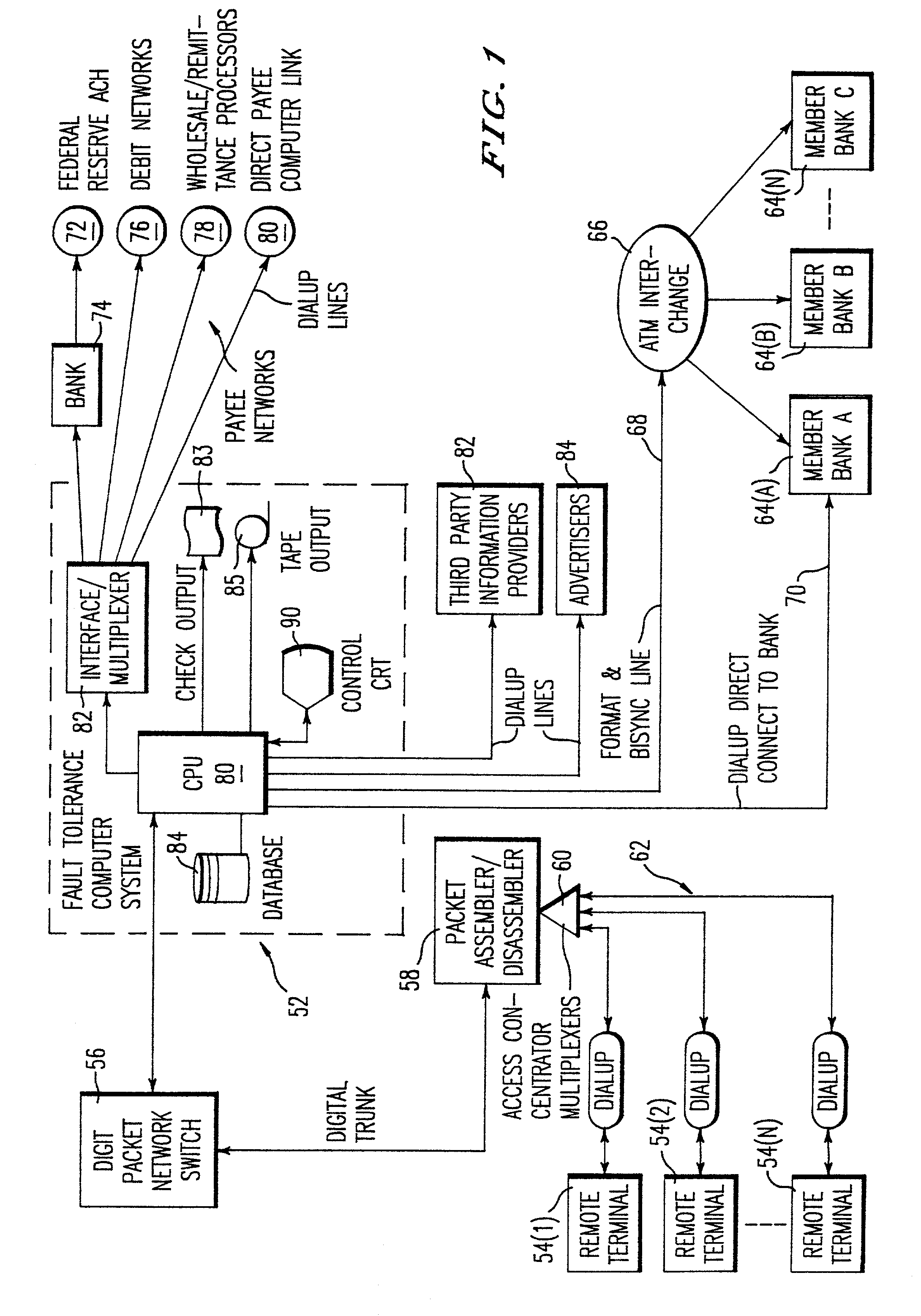
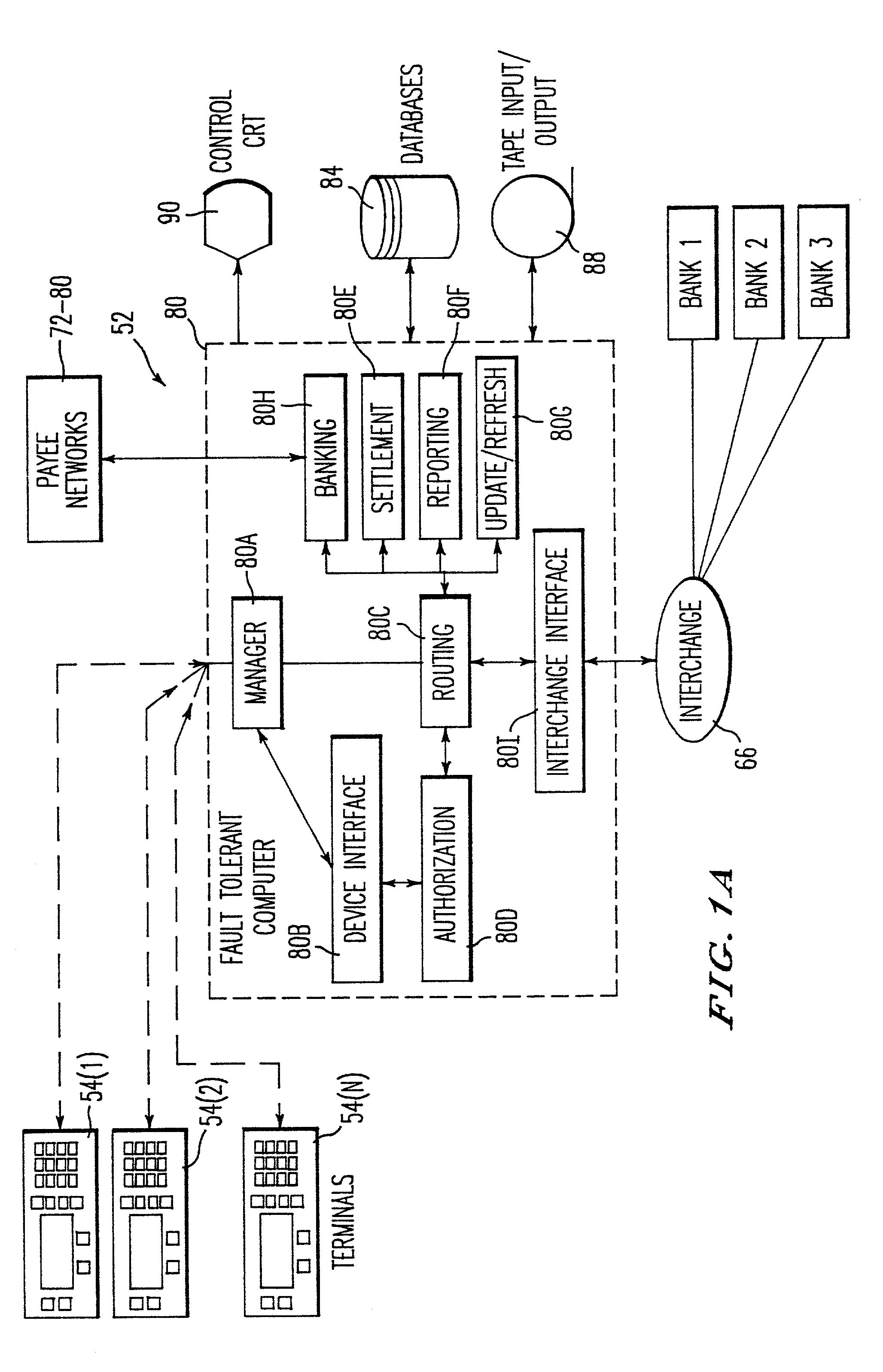
Method and system for remote delivery of retail banking services
A practical system and method for the remote distribution of financial services (e.g., home banking and bill-paying) involves distributing portable terminals to a user base. The terminals include a multi-line display, keys “pointing to” lines on the display, and additional keys. Contact is established between the terminals and a central computer operated by a service provider, preferably over a dial-up telephone line and a packet data network. Information exchange between the central computer and the terminal solicits information from the terminal user related to requested financial services (e.g., for billpaying, the user provides payee selection and amount and his bank account PIN number). The central computer then transmits a message over a conventional ATM network debiting the user's bank account in real time, and may pay the specified payees the specified amount electronically or in other ways as appropriate. Payments and transfers may be scheduled in advance or on a periodic basis. Because the central computer interacts with the user's bank as a standard POS or ATM network node, no significant software changes are required at the banks' computers. The terminal interface is extremely user-friendly and incorporates some features of standard ATM user interfaces so as to reduce new user anxiety.
Owner:OFFICIAL PAYMENTS
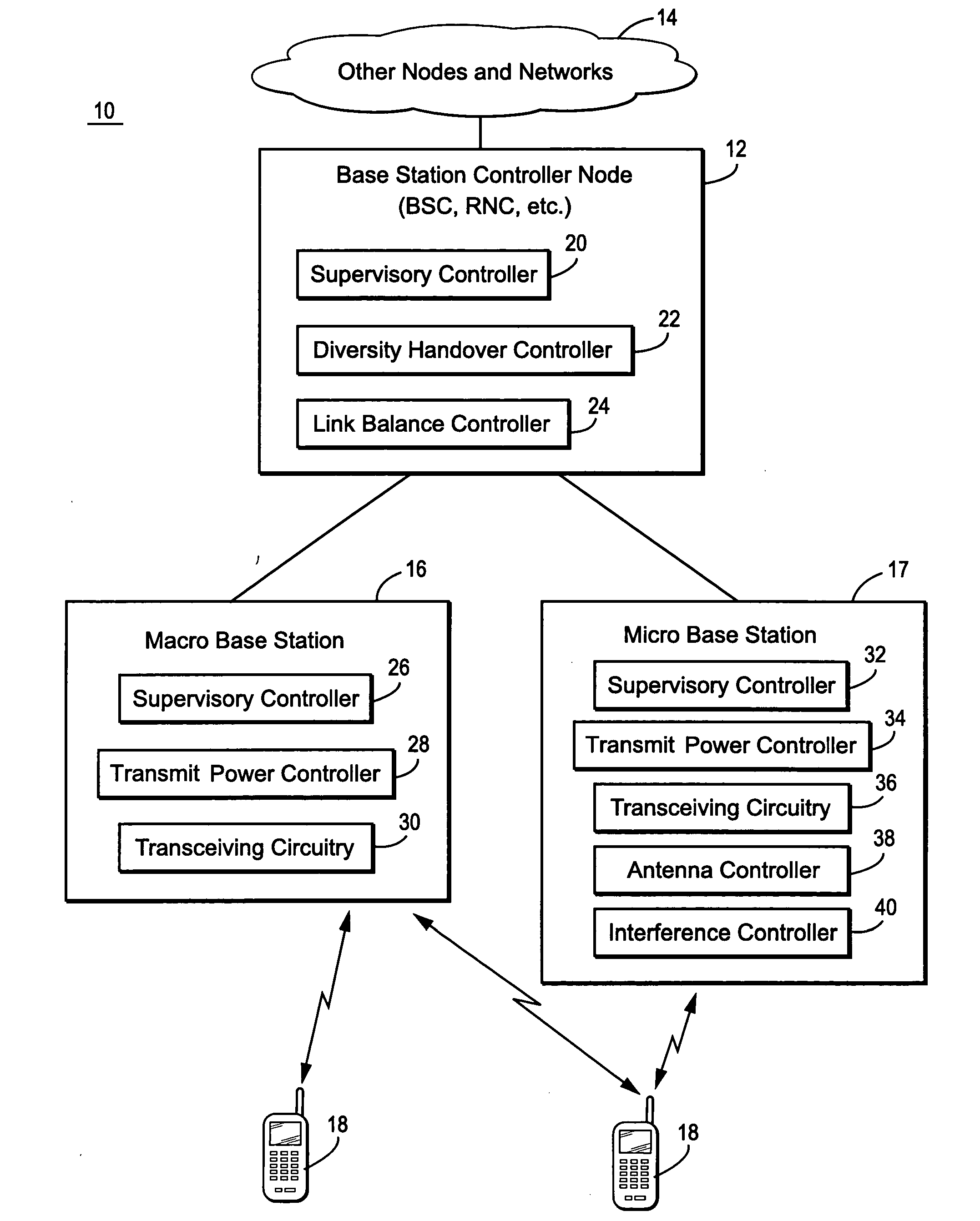
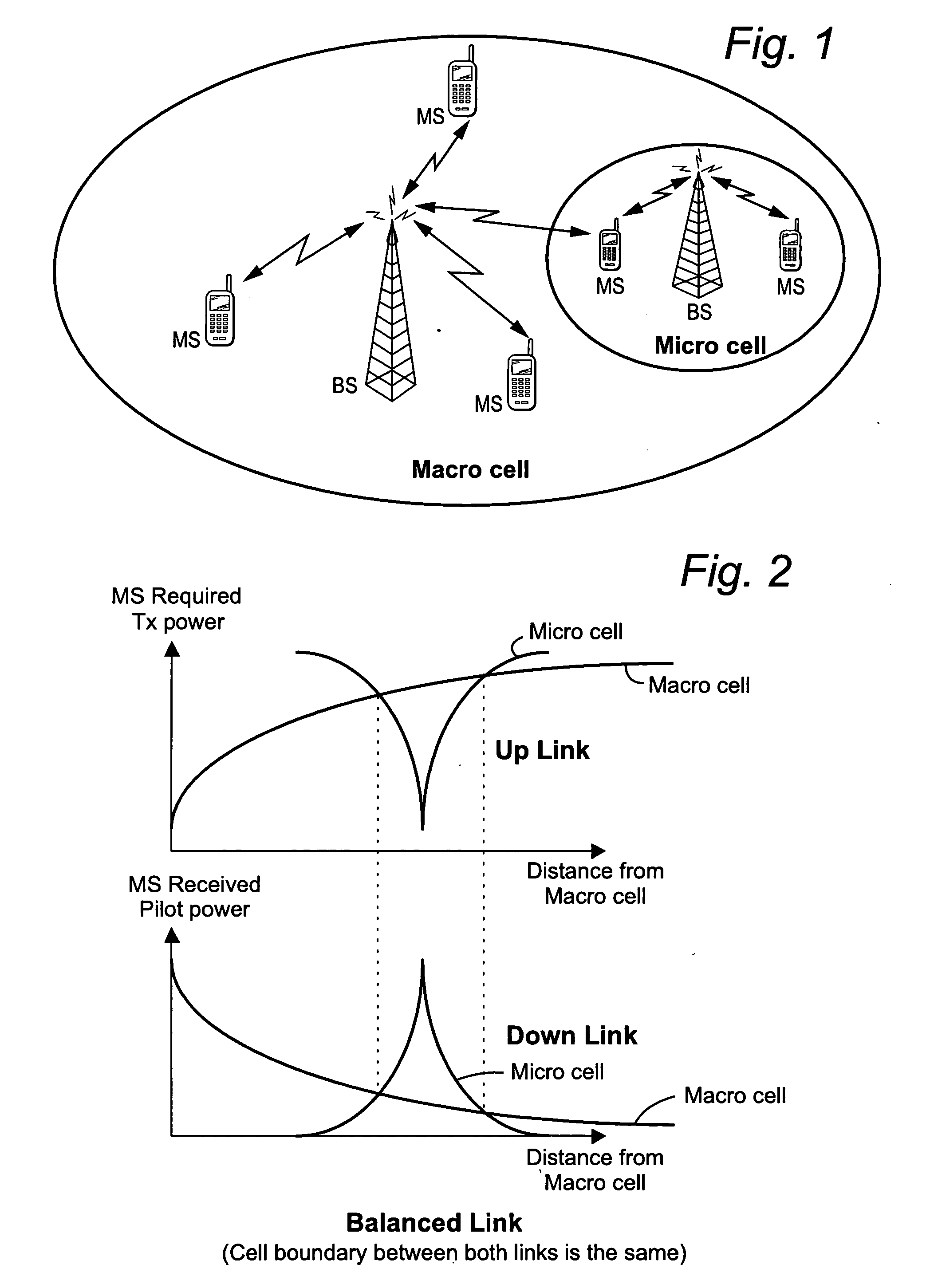
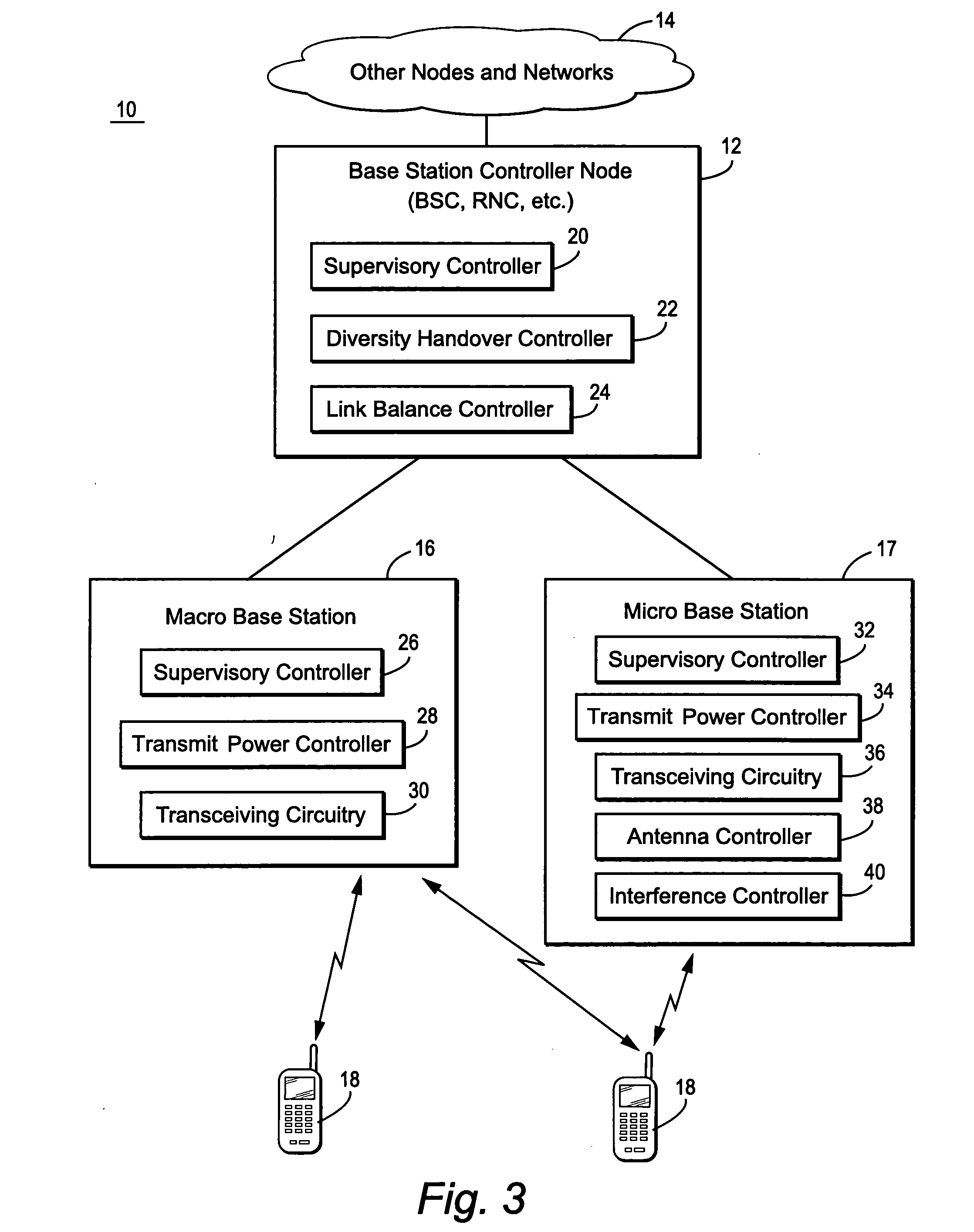
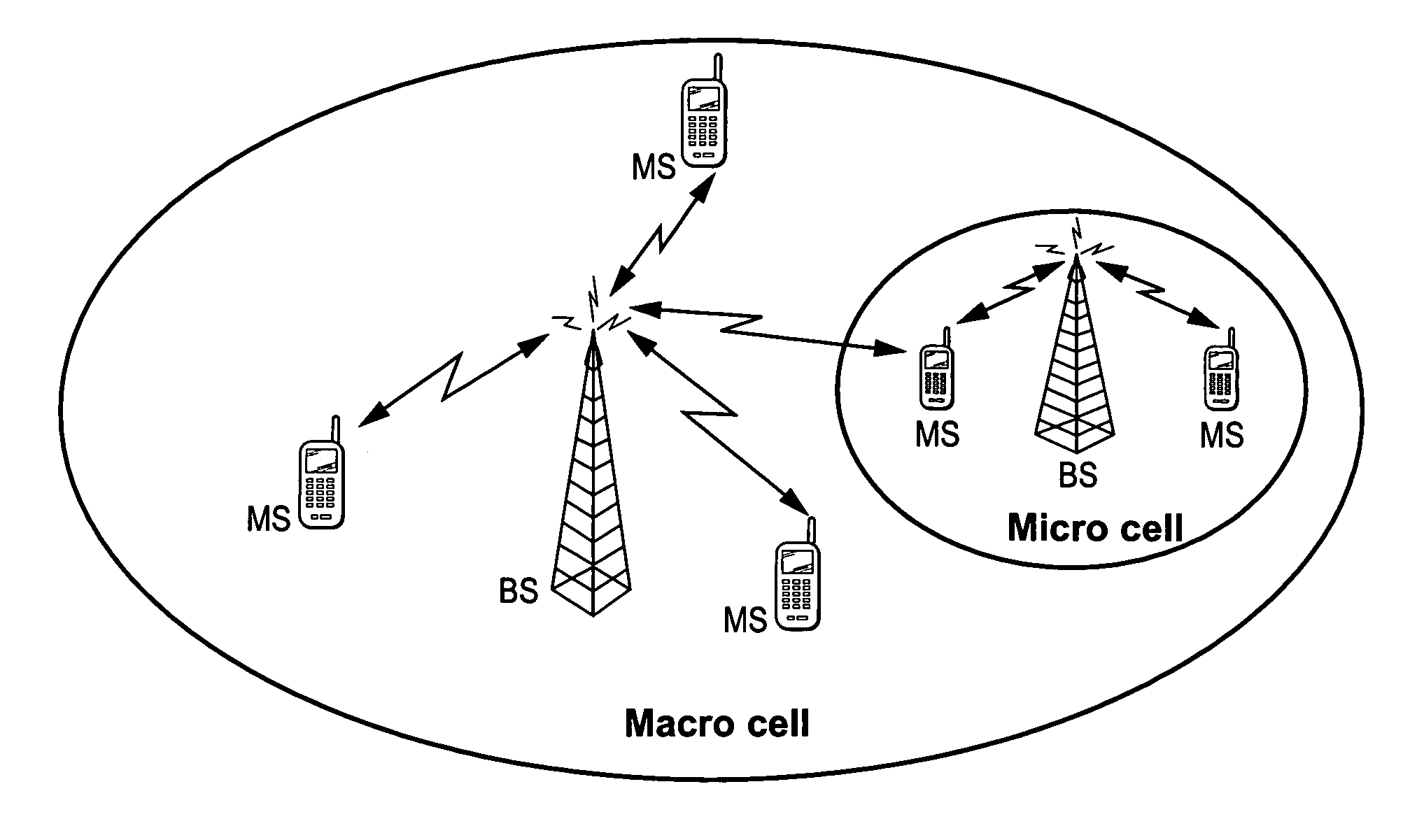
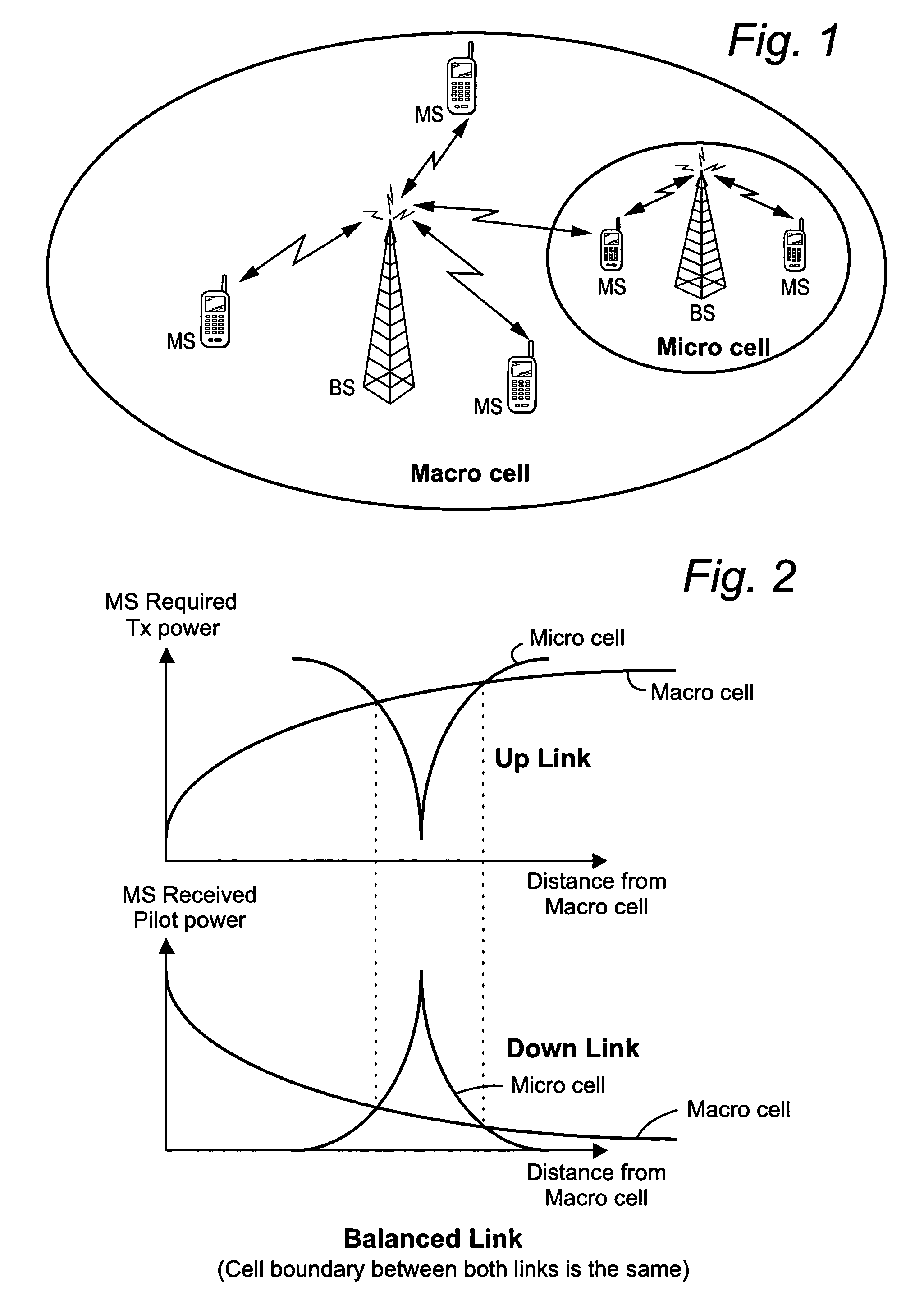
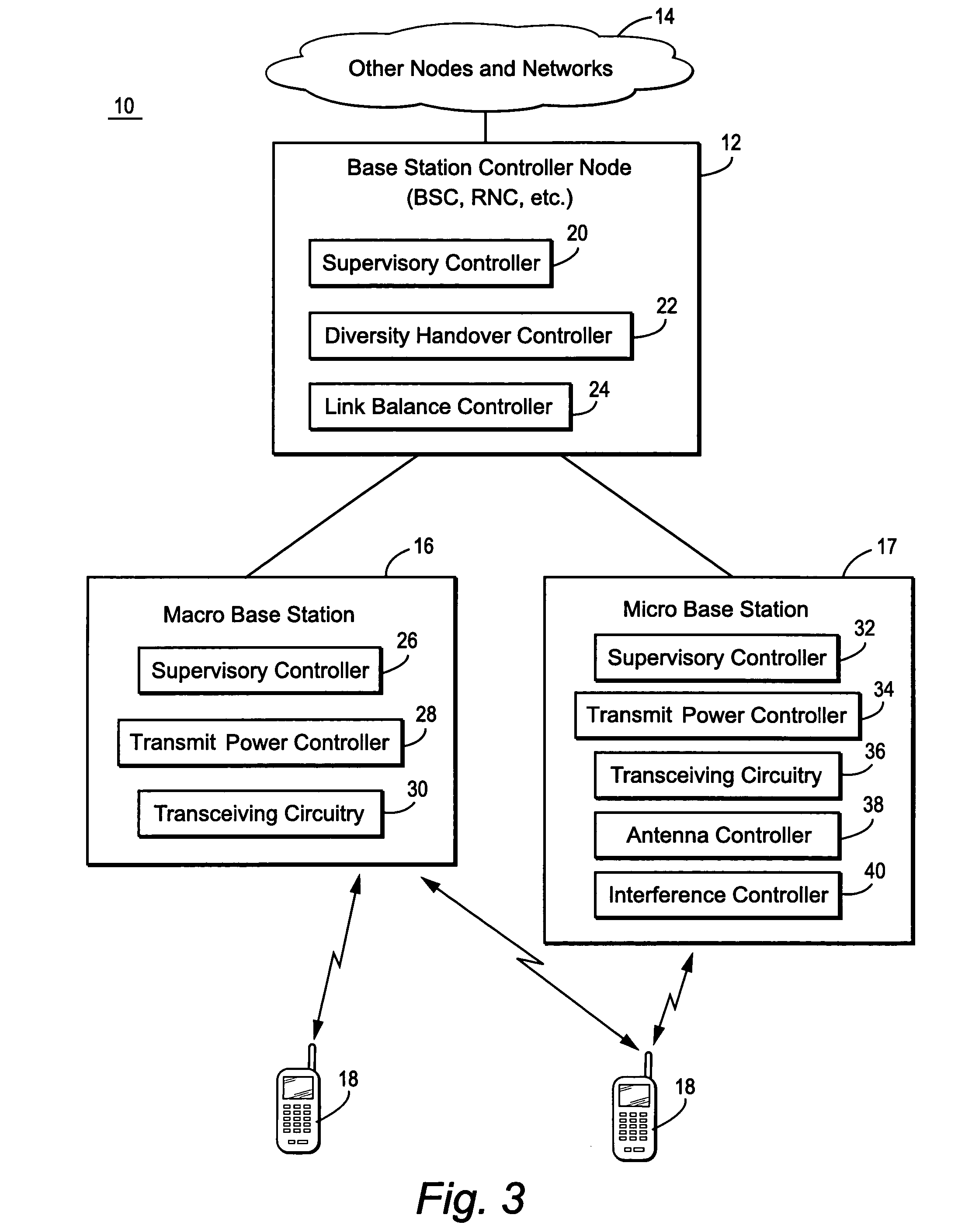
Mobile communications in a hierarchical cell structure
InactiveUS20050130662A1Prevent handoverIncrease speedCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio networksFrequency band
A hierarchical cell structure (HCS) cellular communications system includes a macro cell encompassing a smaller micro cell that employ the same frequency band. The macro cell includes a macro cell base station, and the micro cell includes a micro cell base station. An uplink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established, and a downlink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established. A radio network controller determines whether a condition exists in the HCS system which indicates that the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries should be unbalanced. If the condition is met or exists, the power and / or antenna beam tilt of a downlink transmission from the micro cell base station is reduced to unbalance the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries. Alternatively, the radio network controller may employ an offset value to mathematically reduce mobile detected pilot power levels associated with the micro base station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Mobile communications in a hierarchical cell structure
InactiveUS7142861B2Long talk timeIncrease capacityCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio networksCommunications system
A hierarchical cell structure (HCS) cellular communications system includes a macro cell encompassing a smaller micro cell that employ the same frequency band. The macro cell includes a macro cell base station, and the micro cell includes a micro cell base station. An uplink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established, and a downlink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established. A radio network controller determines whether a condition exists in the HCS system which indicates that the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries should be unbalanced. If the condition is met or exists, the power and / or antenna beam tilt of a downlink transmission from the micro cell base station is reduced to unbalance the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries. Alternatively, the radio network controller may employ an offset value to mathematically reduce mobile detected pilot power levels associated with the micro base station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Medium access control protocol for data communications
InactiveUS6879579B1Maximize their success probabilityMore capacityNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsMedia access control
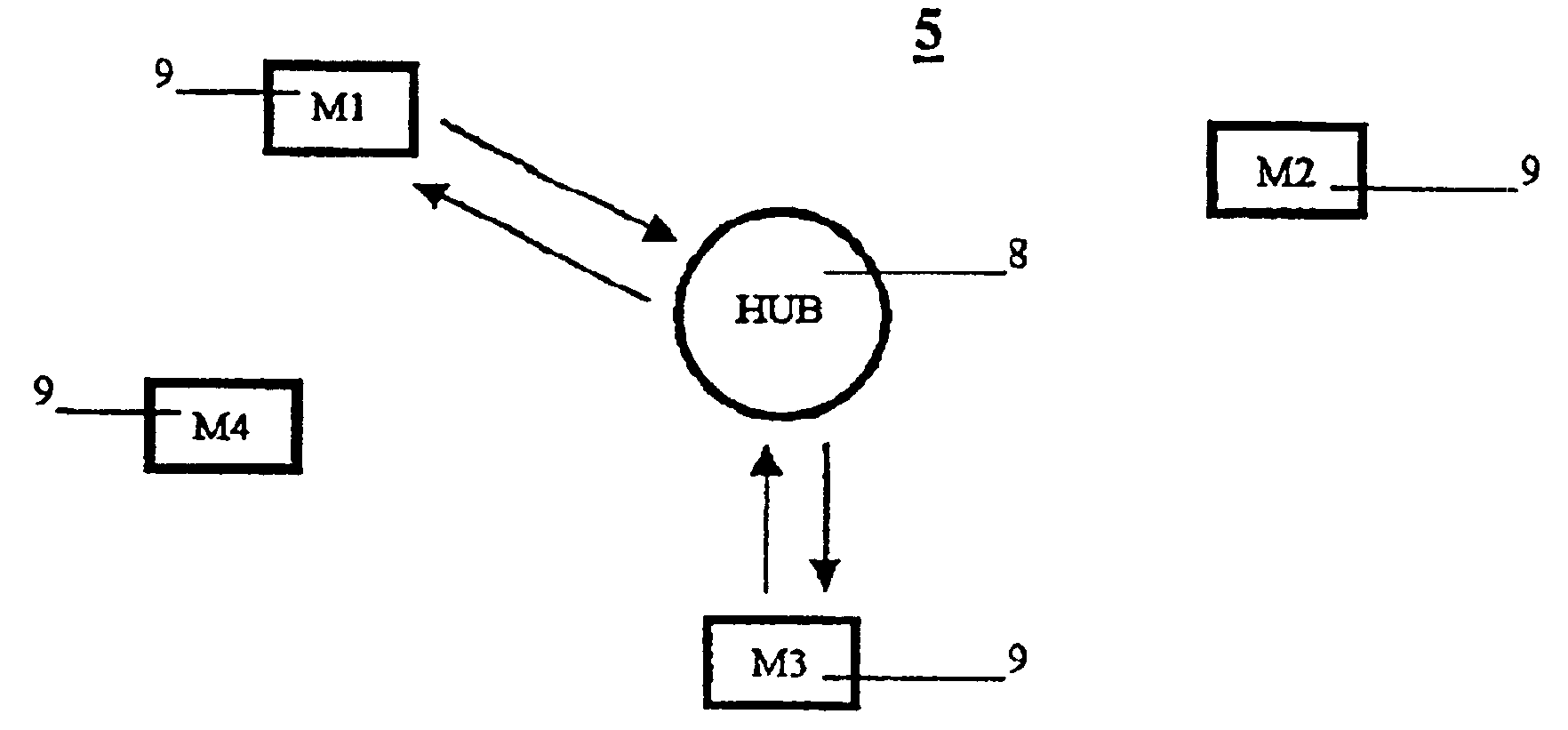
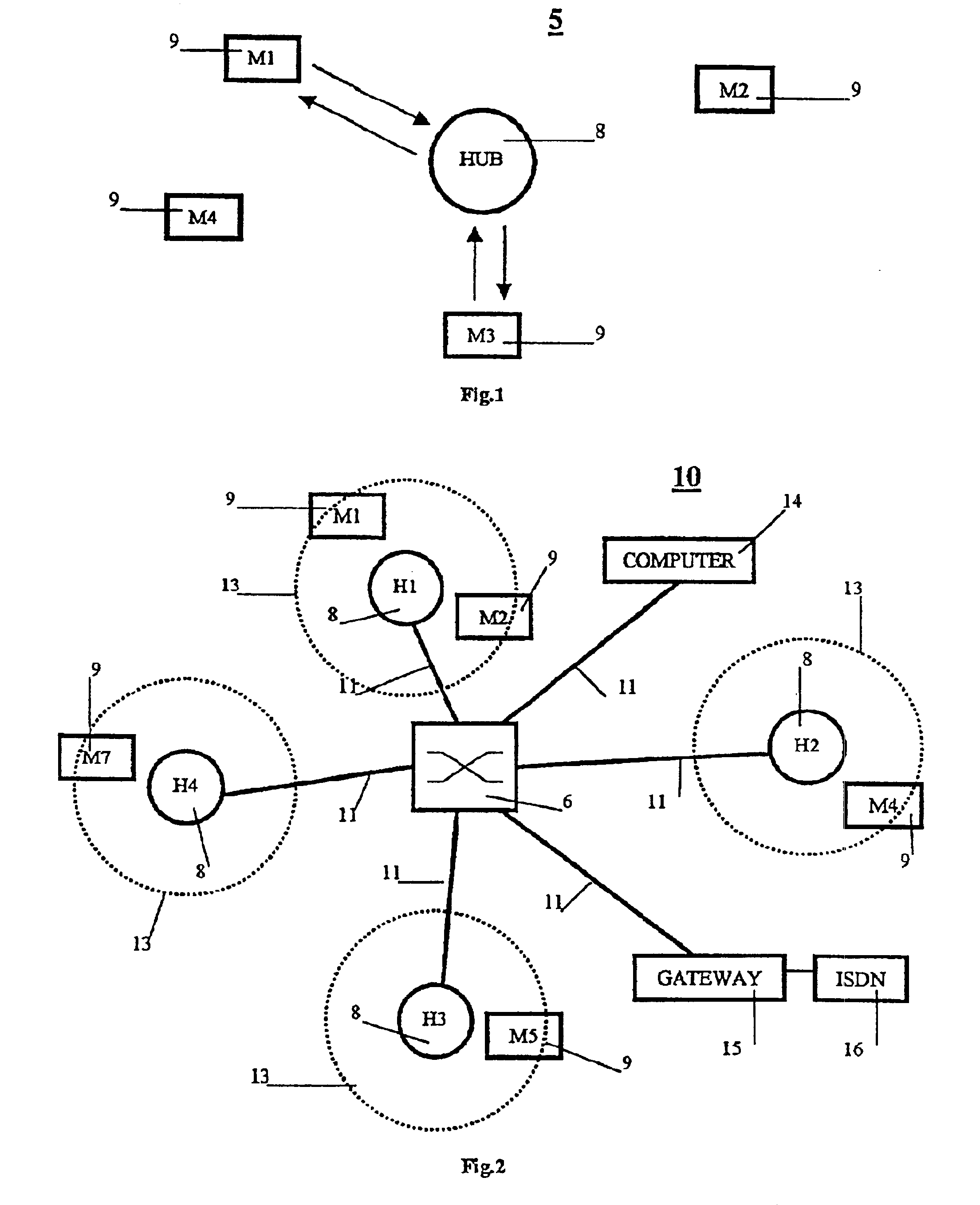
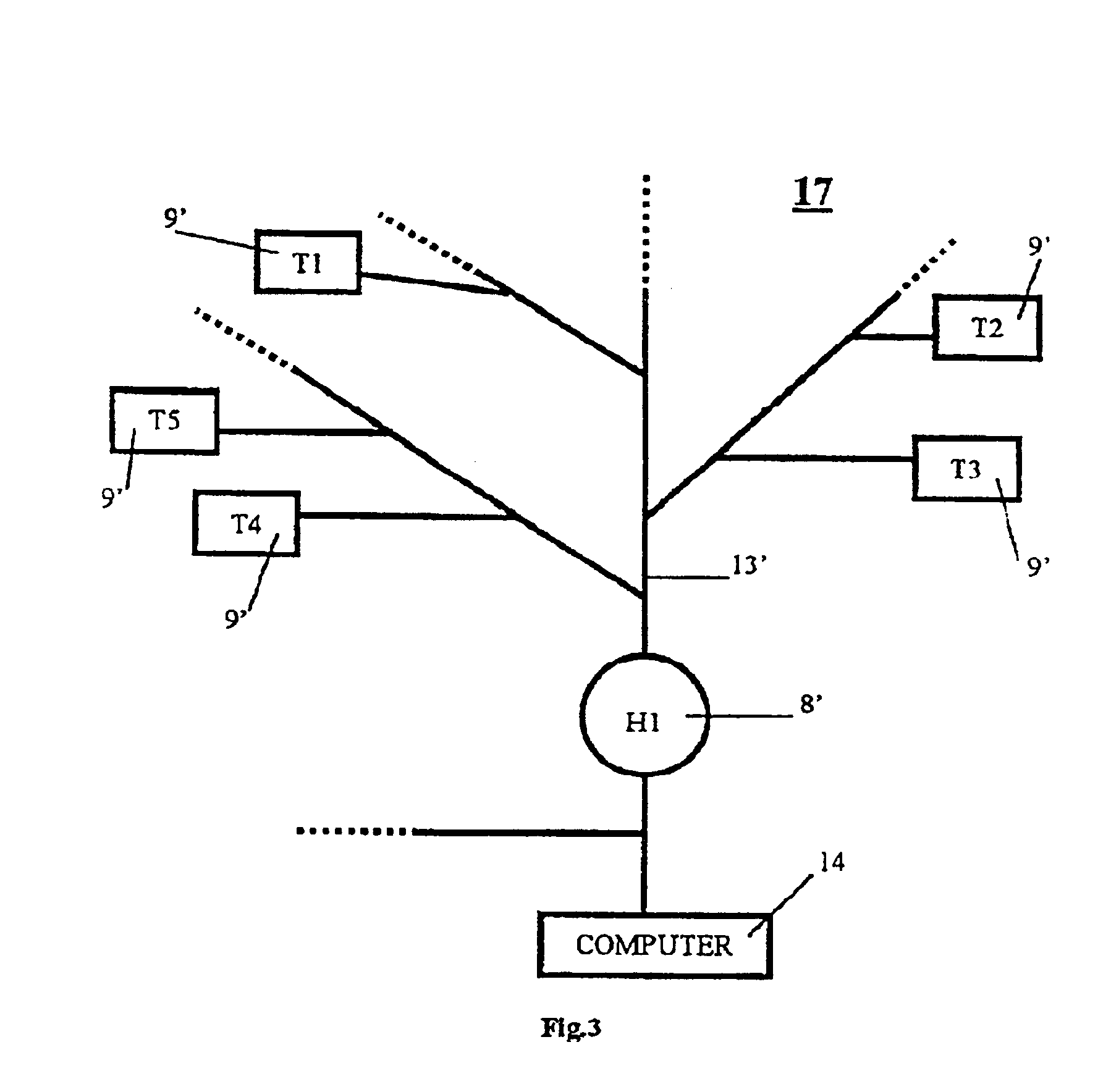
A method for controlling communication between a hub and a plurality of distributed stations over a medium is disclosed. The method comprising the steps of a method for controlling communications access between a hub (8) and a plurality of distributed stations (M1-M7) over a medium, the method comprising the steps of (a) allocating a plurality of channels for data communications between the station (M1-M7) and the hub (8), the number of channels being at least equal to the number of stations, (M1-M7) and each station owning at cast one channel, each channel being varyingly in one of an empty-, a reserved, or an owner-state, and whereby (i) the empty-state provides a channel to which any station (M1-M7) can have access; (ii) the reserved-state provides a channel to which a station (M1-M7) having made a reservation with the hub (8), but not owning the channel, can have access; and (iii) the owner-state provides a channel to which only the owning station (M1-M7) has access; and (b) allocating the respective state and / or the number of channels over time an the basis of each station's data requirements.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Organic data network having a dynamic topology
InactiveUS7065548B2Reduce failureReduced flexibilityRoad vehicles traffic controlMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetMobile phone
The invention relates to a method and system of growing a network and distributing data using the network including one or more production nodes that send data and a plurality of consumer nodes that receive data from one or more production nodes or at least one other consumer node. The first software resides on each of the consumer nodes and the second software resides on each of the production nodes wherein a data request is not relayed and routed through several intermediate nodes in a path way but only is made to a logically adjacent node and where the logically adjacent nodes take no action to retrieve data from another node if the logically adjacent node is unable to fulfill the request itself. The invention can be implemented for mobile phones, streaming internet applications and cable television.
Owner:NONEND INVENTIONS NV
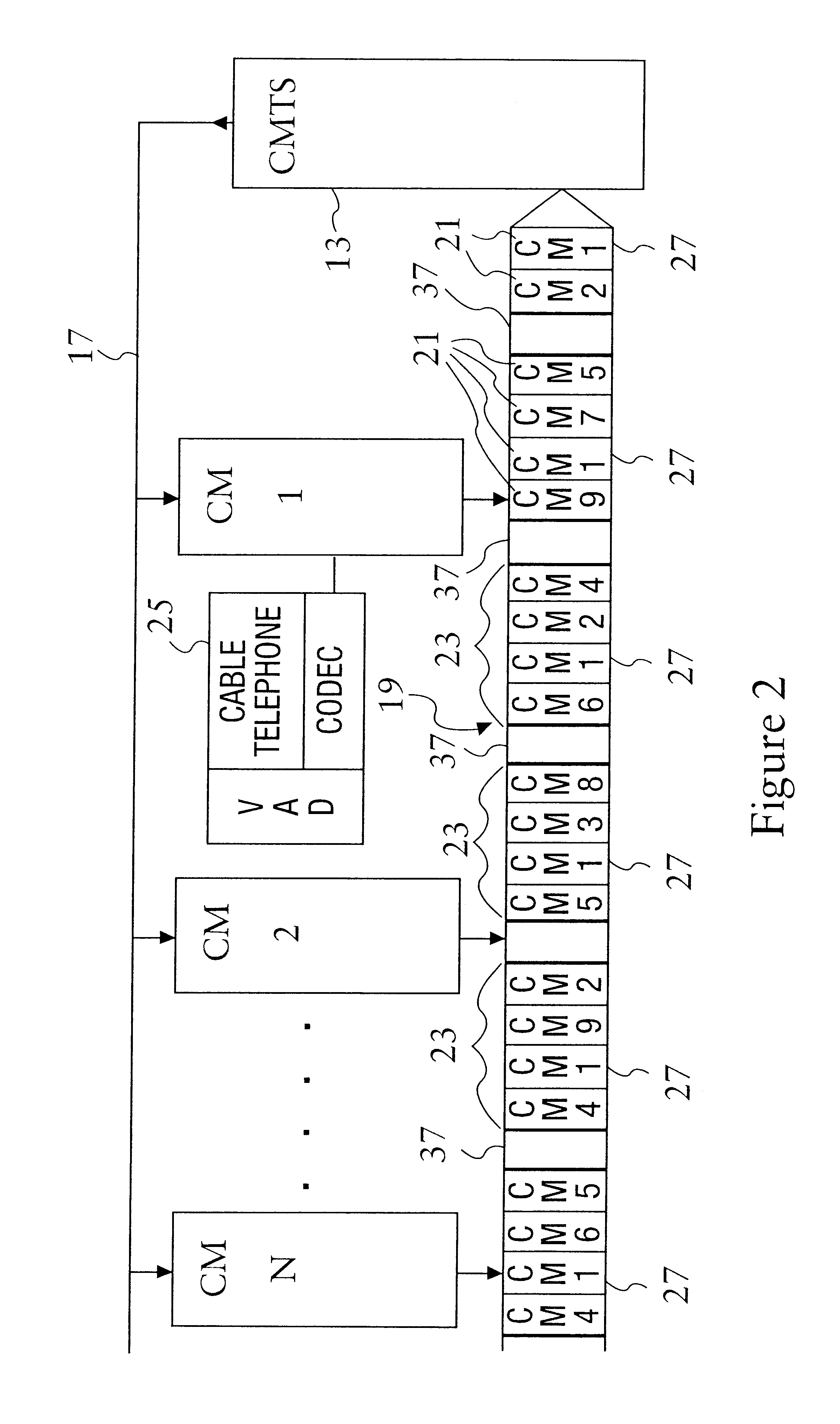
Method to transmit silence compressed voice over IP efficiently in DOCSIS cable networks
InactiveUS6847635B1Accurately and quickly transmitSent very quickly and very accuratelyBroadband local area networksTwo-way working systemsModem deviceNetwork packet
A method to use the data packet carrying ability of cable TV networks as described in DOCSIS to accurately and quickly transmit a voice call from a cable user to another user over a cable TV cable. The cable telephone, or cable modem, is given the ability to detect when voice activity from the subscriber is above and below a predetermined value. When the cable modem has voice activity, the cable modem knows that it will have a continuous stream of voice data packets which need to be sent very quickly and very accurately to the CMTS. Therefore, the cable modem requests a periodic stream of time slots from the CMTS. When the cable modem detects no voice activity or a silence period from the subscriber, the cable modem indicates that the periodic stream of time slots is no longer needed and the CMTS stops providing the periodic stream of time slots. When voice activity of the subscriber resumes, the cable modem again request the periodic stream of time slots, and transmits the voice data packets or cells in these time slots.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
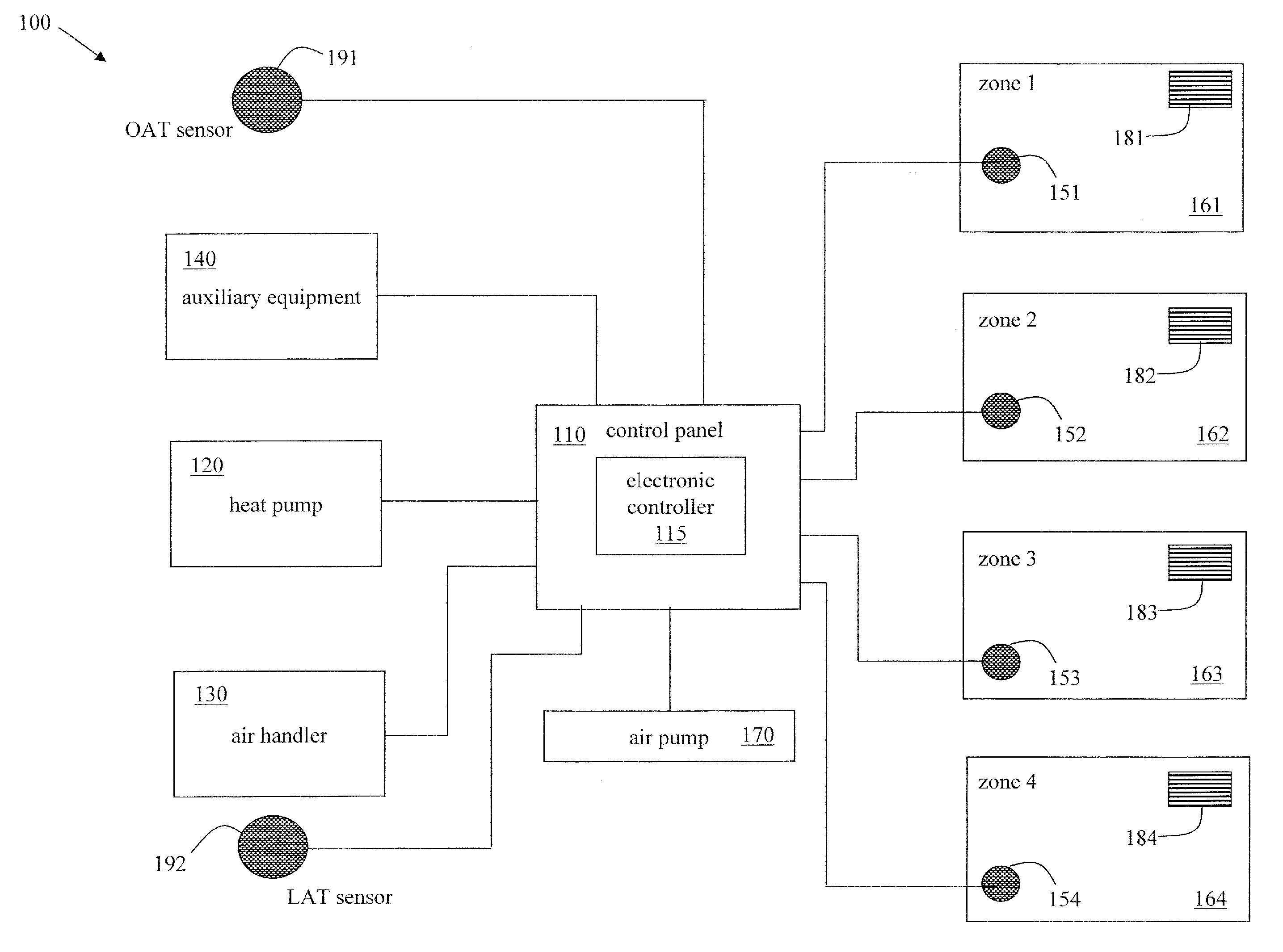
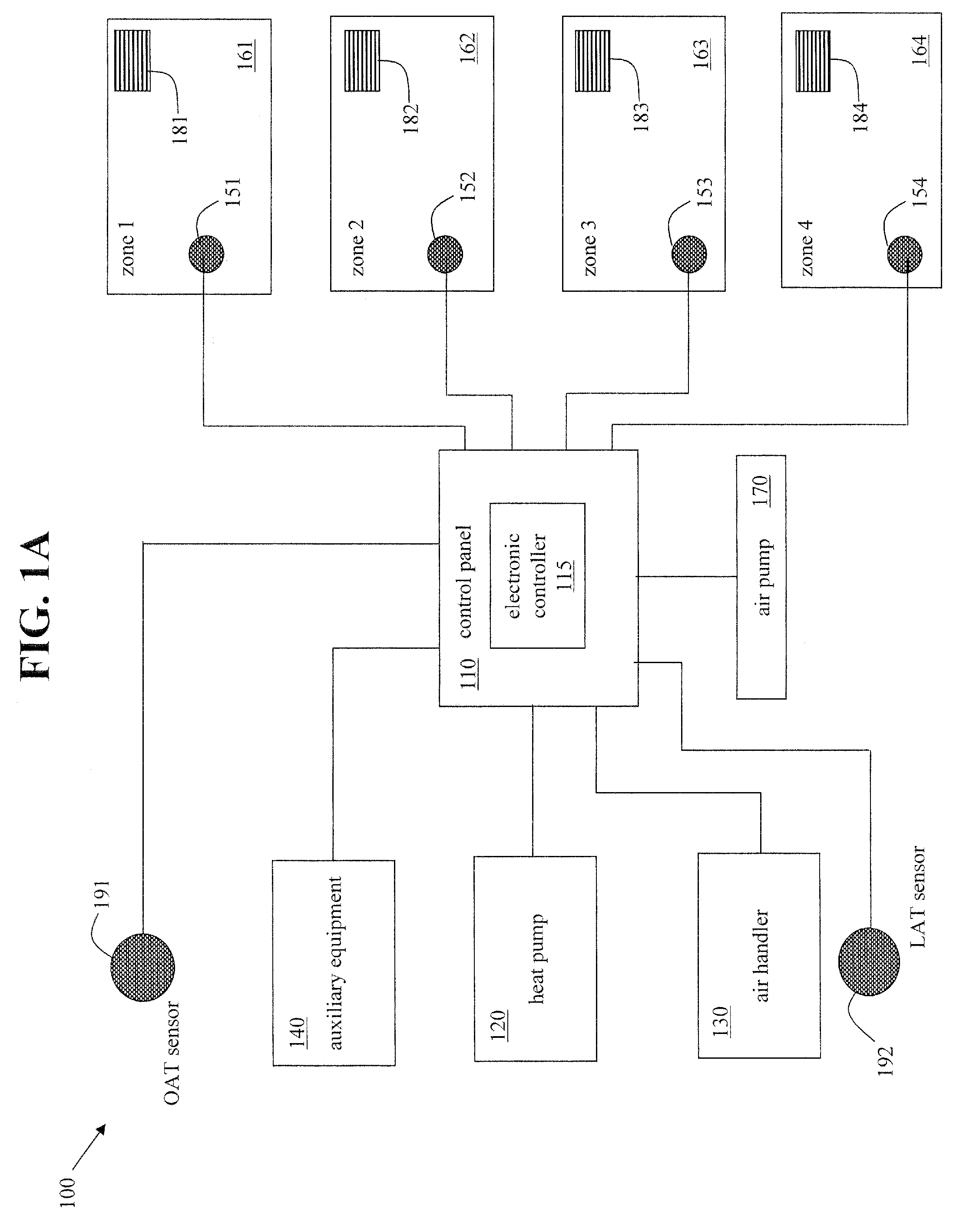
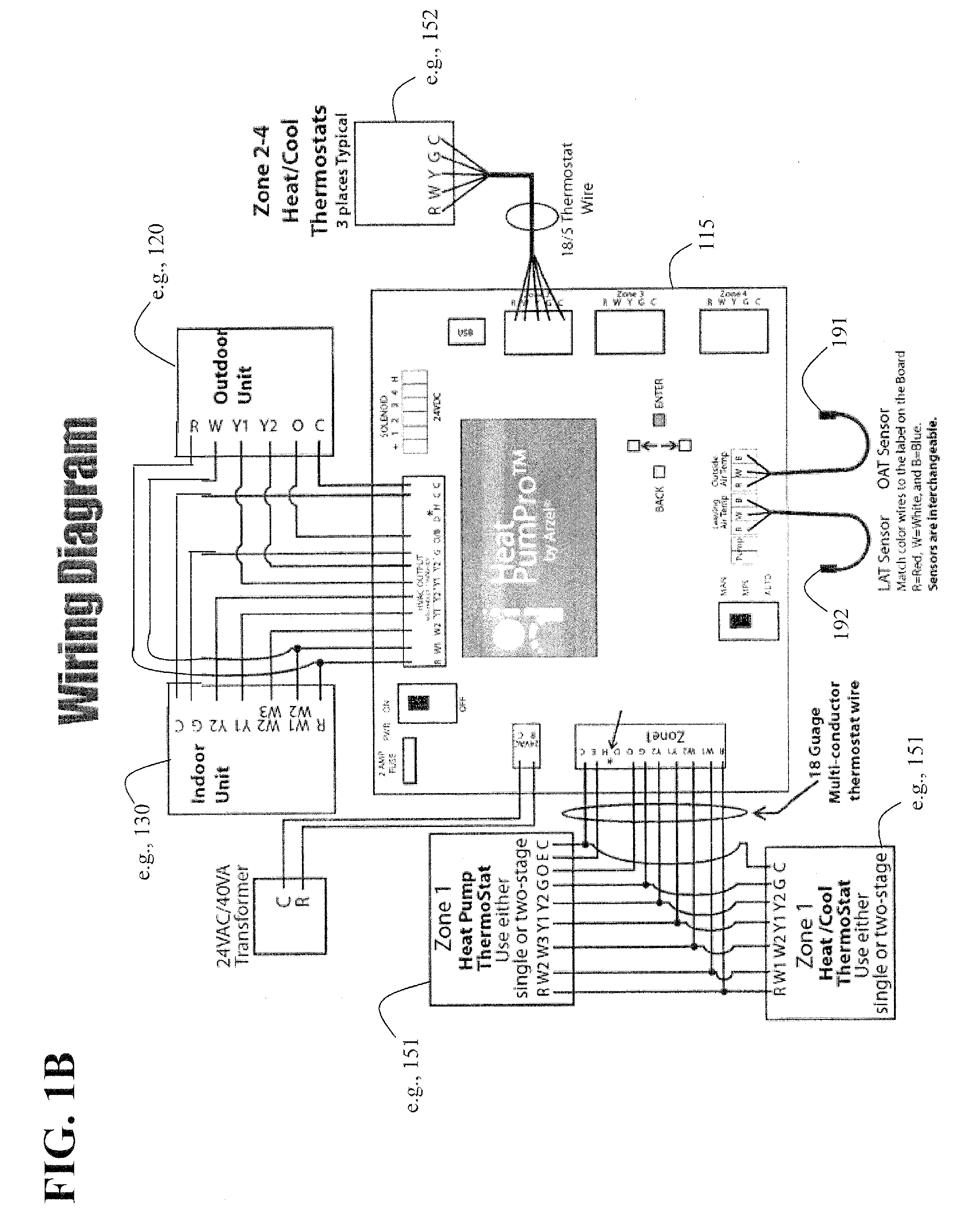
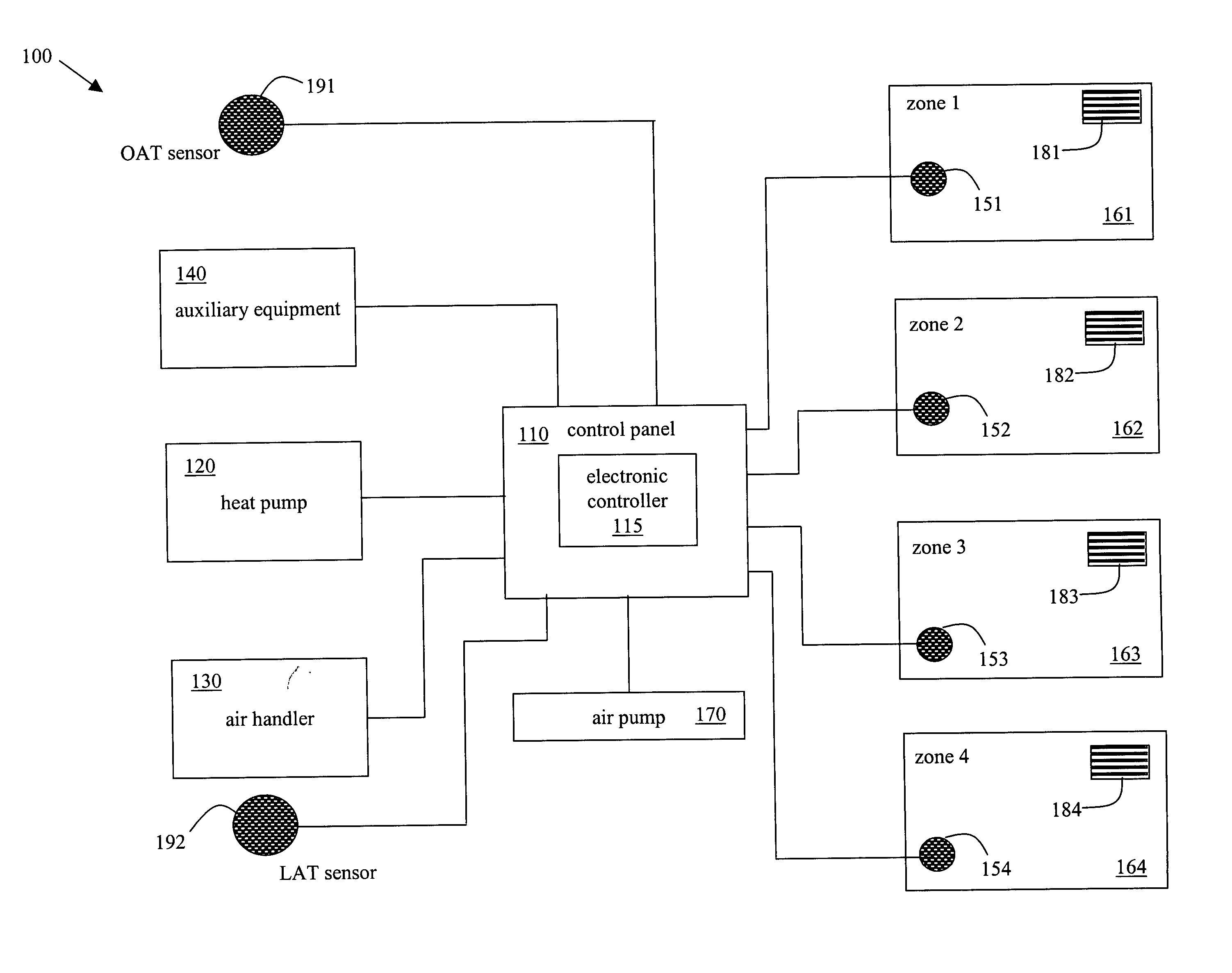
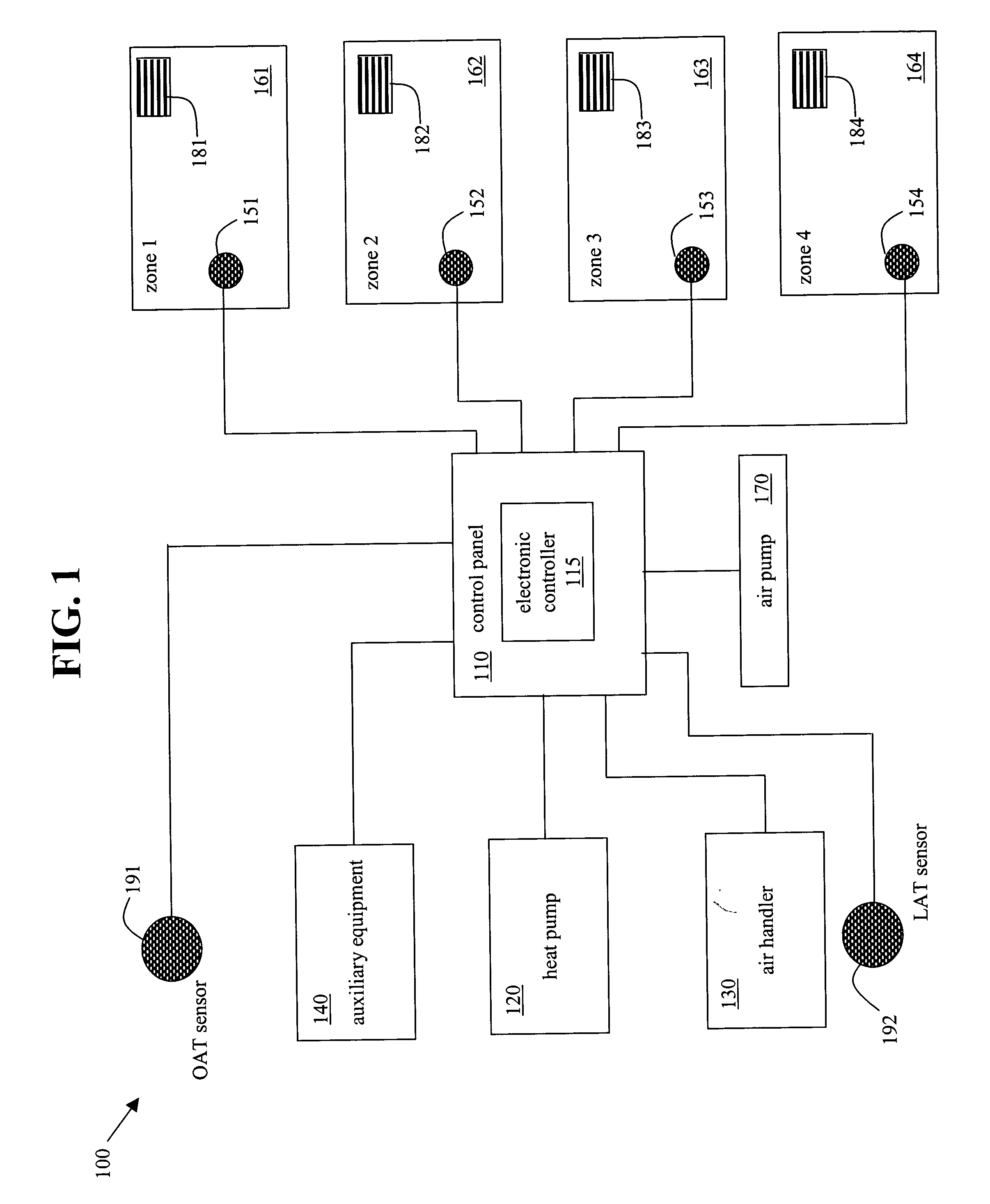
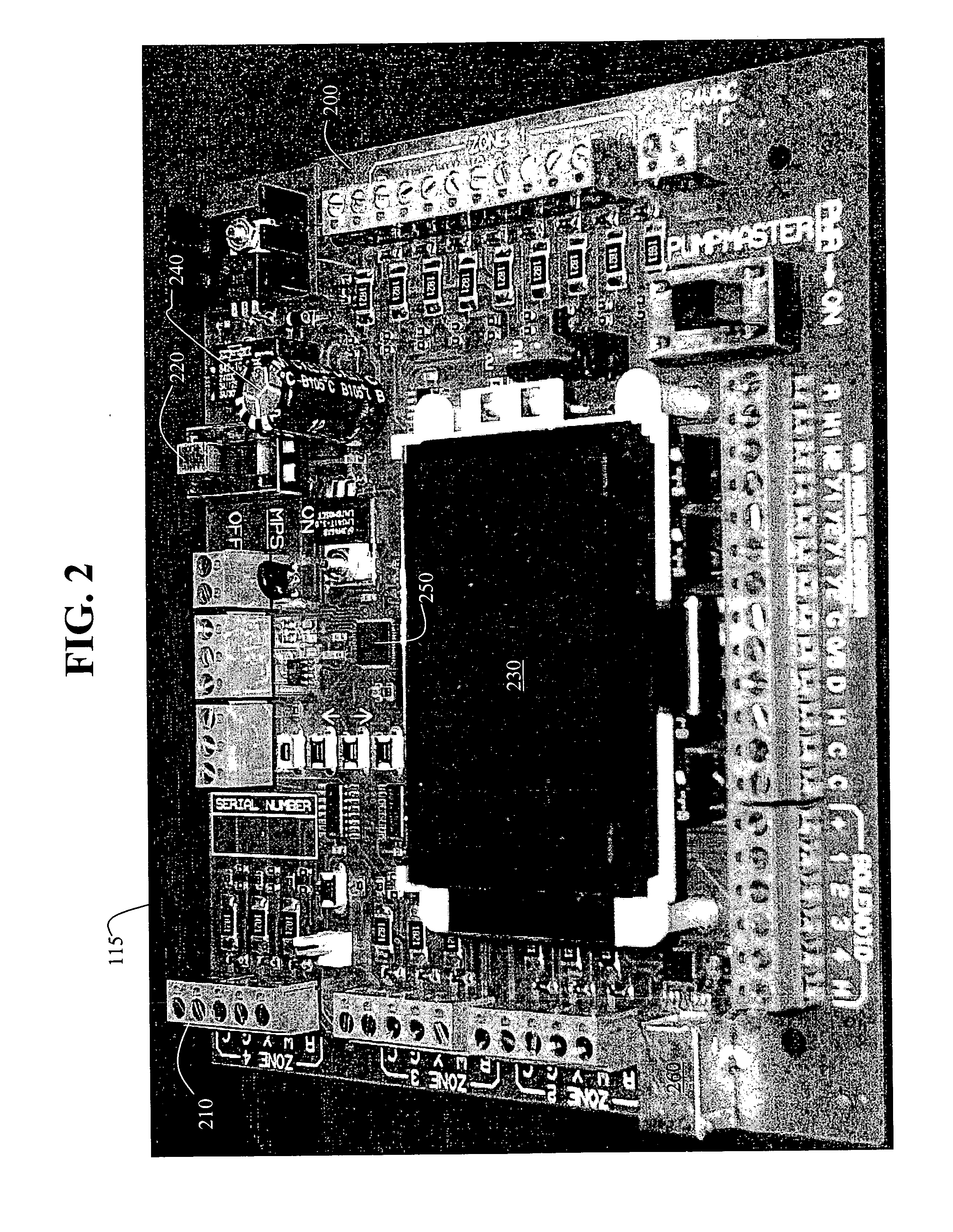
System and method for heat pump oriented zone control
ActiveUS20070063059A1Easy to operateEasy to controlMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsElectronic controllerAir handler
A system and method to control environmental parameters of pre-defined zones within an environment using an electronic controller are disclosed. The system includes a non-proprietary electronic controller which enables a weighting value to be assigned to each zone within the environment. The electronic controller also detects any zone service calls from sensor devices associated with each of the zones and determines a cumulative weighting value in response to the detected zone service calls. The electronic controller selects an equipment staging combination from at least two possible equipment staging combinations in response to thermal capacity, and an air handler stage is selected in response to at least the cumulative zone weighting value.
Owner:ARZEL ZONING TECH
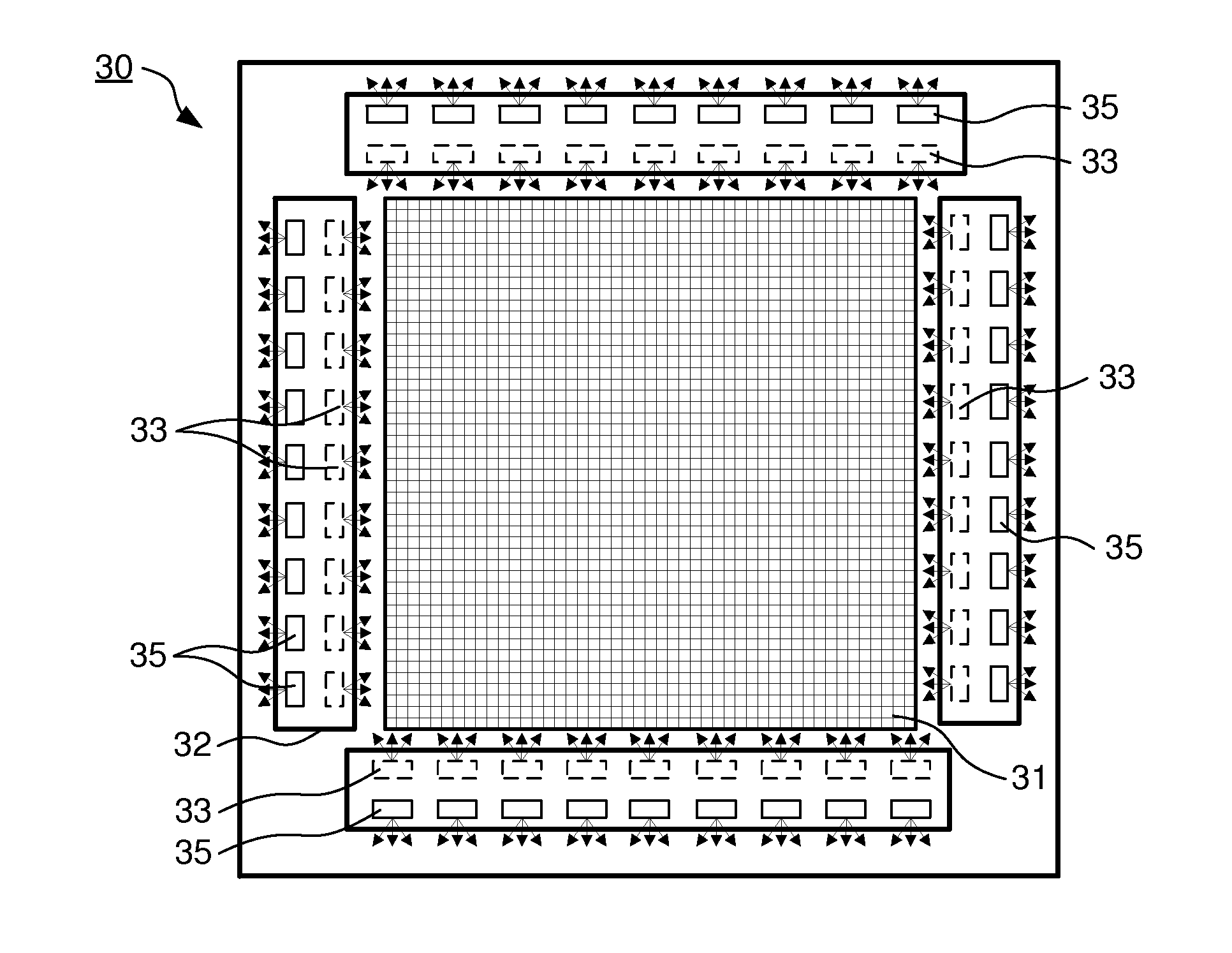
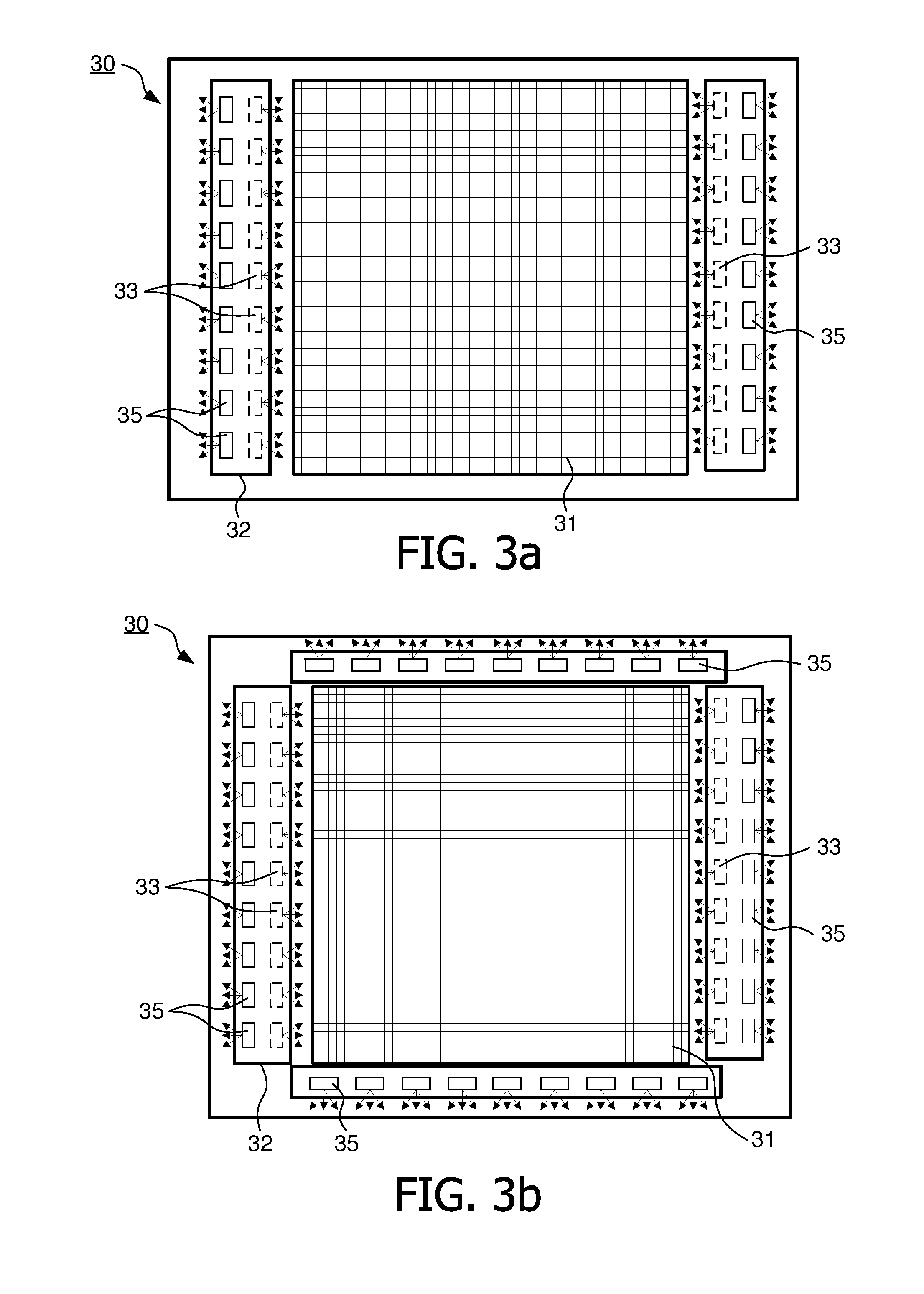
Display device, method of controlling a light emitting diode array of the display device, and computer program product
ActiveUS20110194047A1Reduce in quantityMore capacityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLed arrayEngineering
A display device (10, 20, 30) is provided, the display device (10, 20, 30) comprising an LED array (33, 35, 12) working both as a backlight source for an LCD panel (31) and as an ambient light source providing ambient light with properties dependent on the image content presented by the LCD panel (31). A corresponding method and computer program product is also provided.
Owner:TOP VICTORY INVESTMENTS
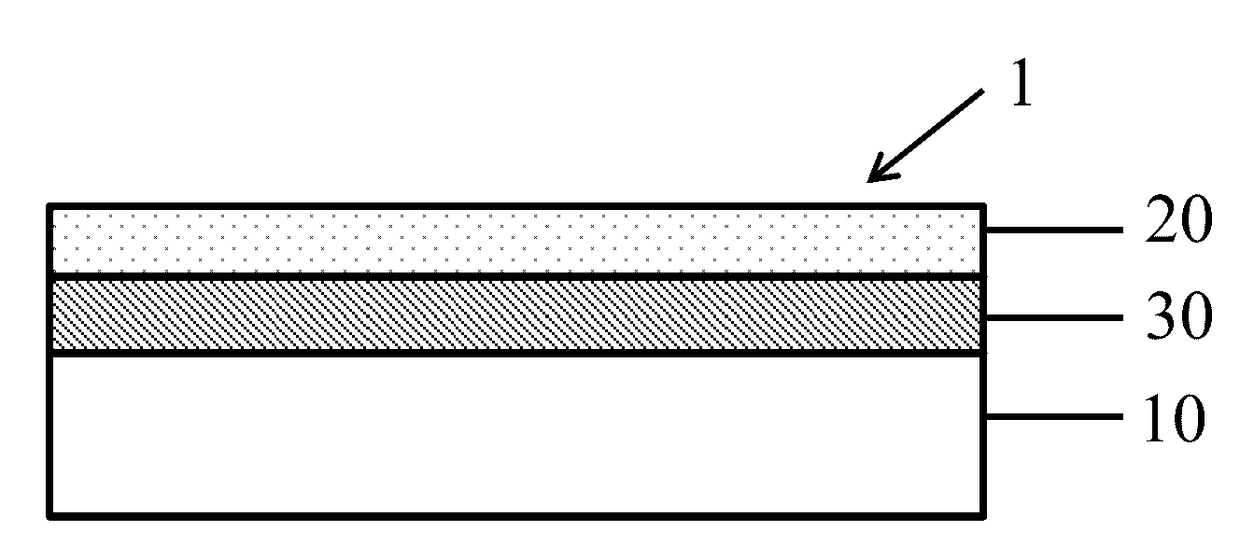
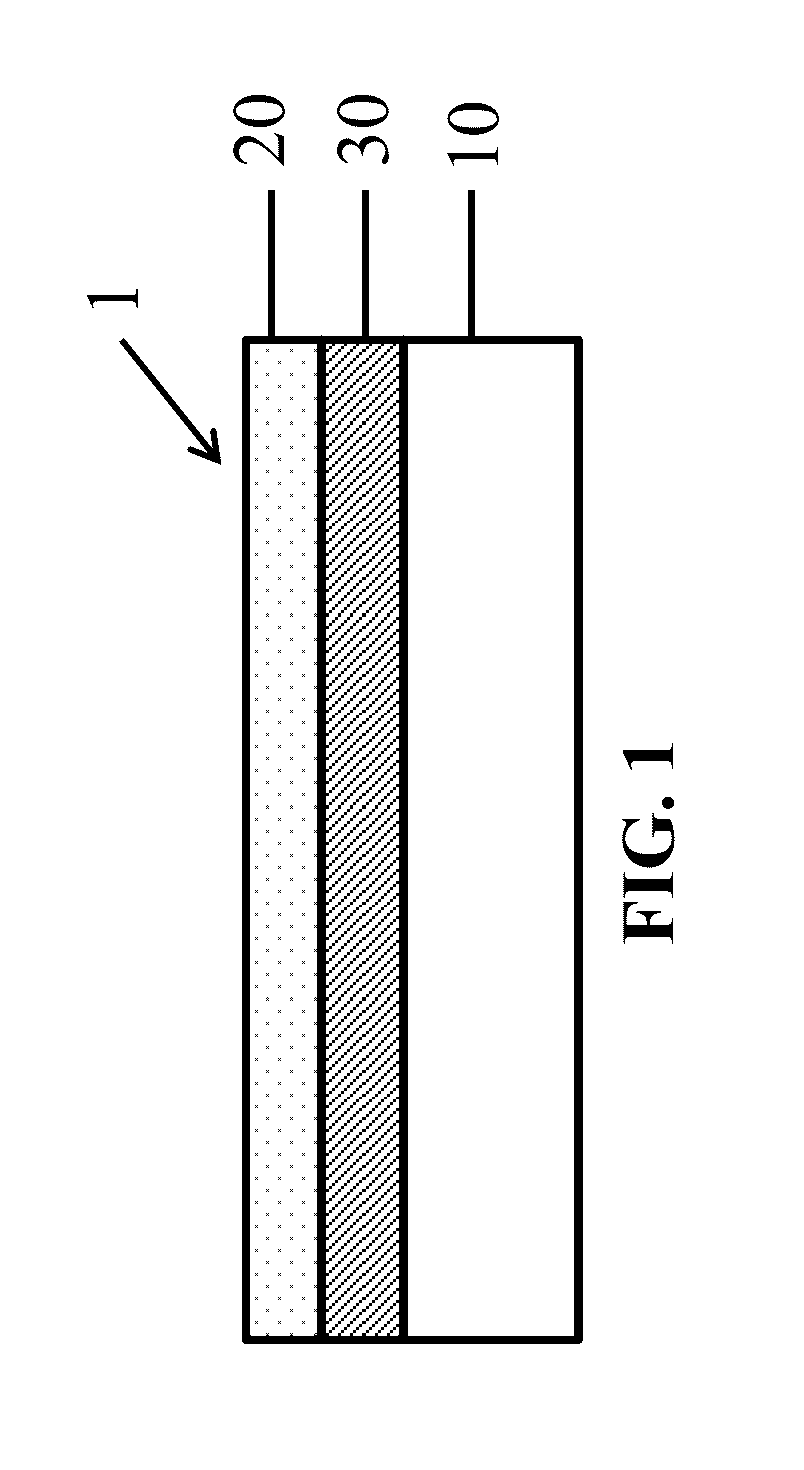
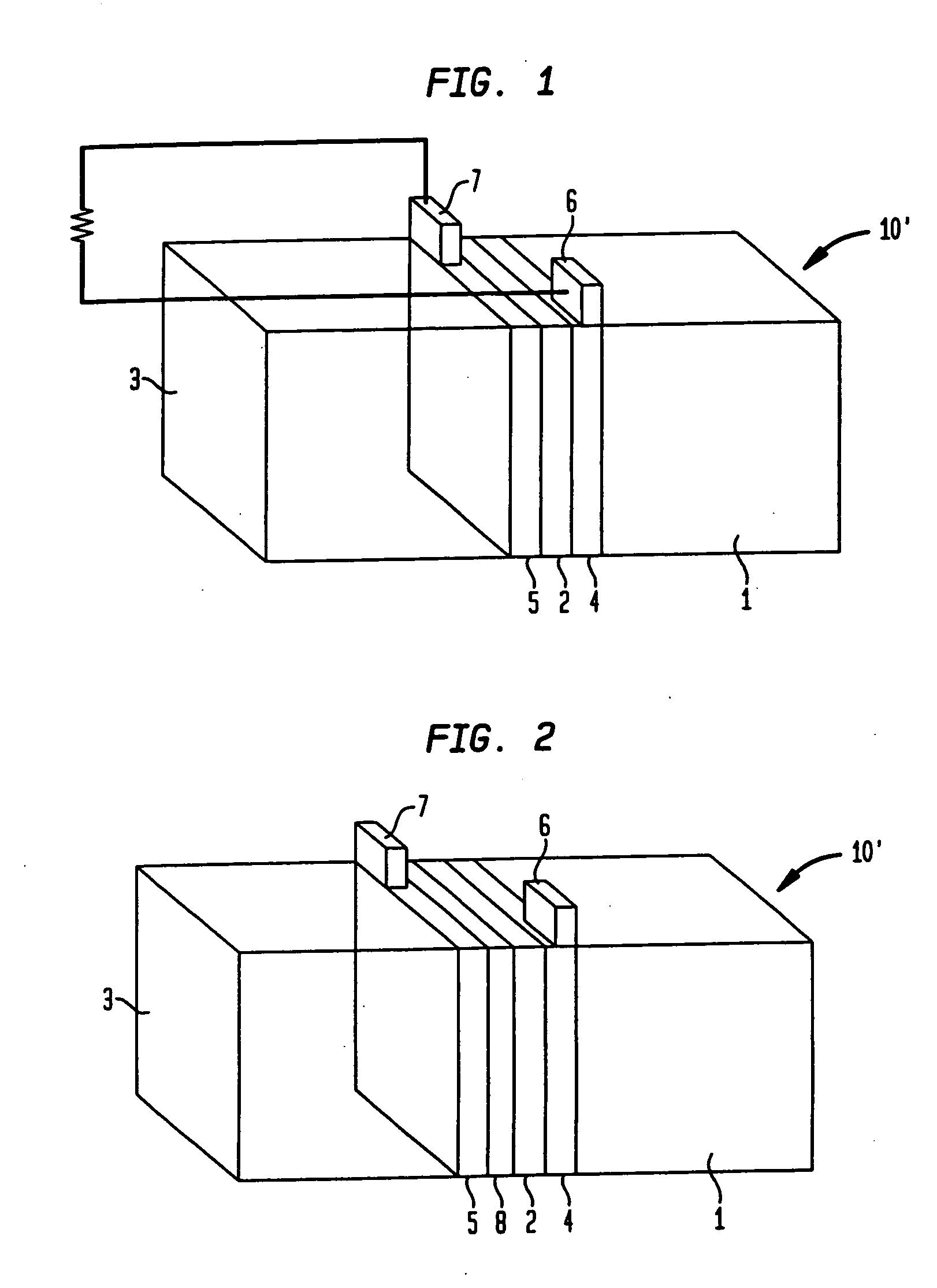
Anode containing active material-coated graphene sheets and lithium-ion batteries containg same
ActiveUS20150044564A1Enhanced Li-ion insertionIncrease capacityNegative electrodesSecondary cellsGrapheneLithium-ion battery
The present invention provides an anode electrode of a lithium-ion battery, comprising an anode active material-coated graphene sheet, wherein the graphene sheet has two opposed parallel surfaces and at least 50% area of one of the surfaces is coated with an anode active material and wherein the graphene material is in an amount of from 0.1% to 99.5% by weight and the anode active material is in an amount of at least 0.5% by weight (preferably at least 60%), all based on the total weight of the graphene material and the anode active material combined.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Coated stacks for batteries and related manufacturing methods
PendingUS20170098857A1Less complexIncrease speedFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsOptoelectronicsMetal particle
Provided is a battery stack for use in an electric current producing cell, wherein the coated stack comprises a porous separator, an electrode layer adjacent the porous separator, and a current collector layer coated on the electrode layer, wherein the current collector layer comprises sintered metal particles. Also provided are methods of manufacturing such coated stacks.
Owner:META MATERIALS INC
Telecommunications system power supply
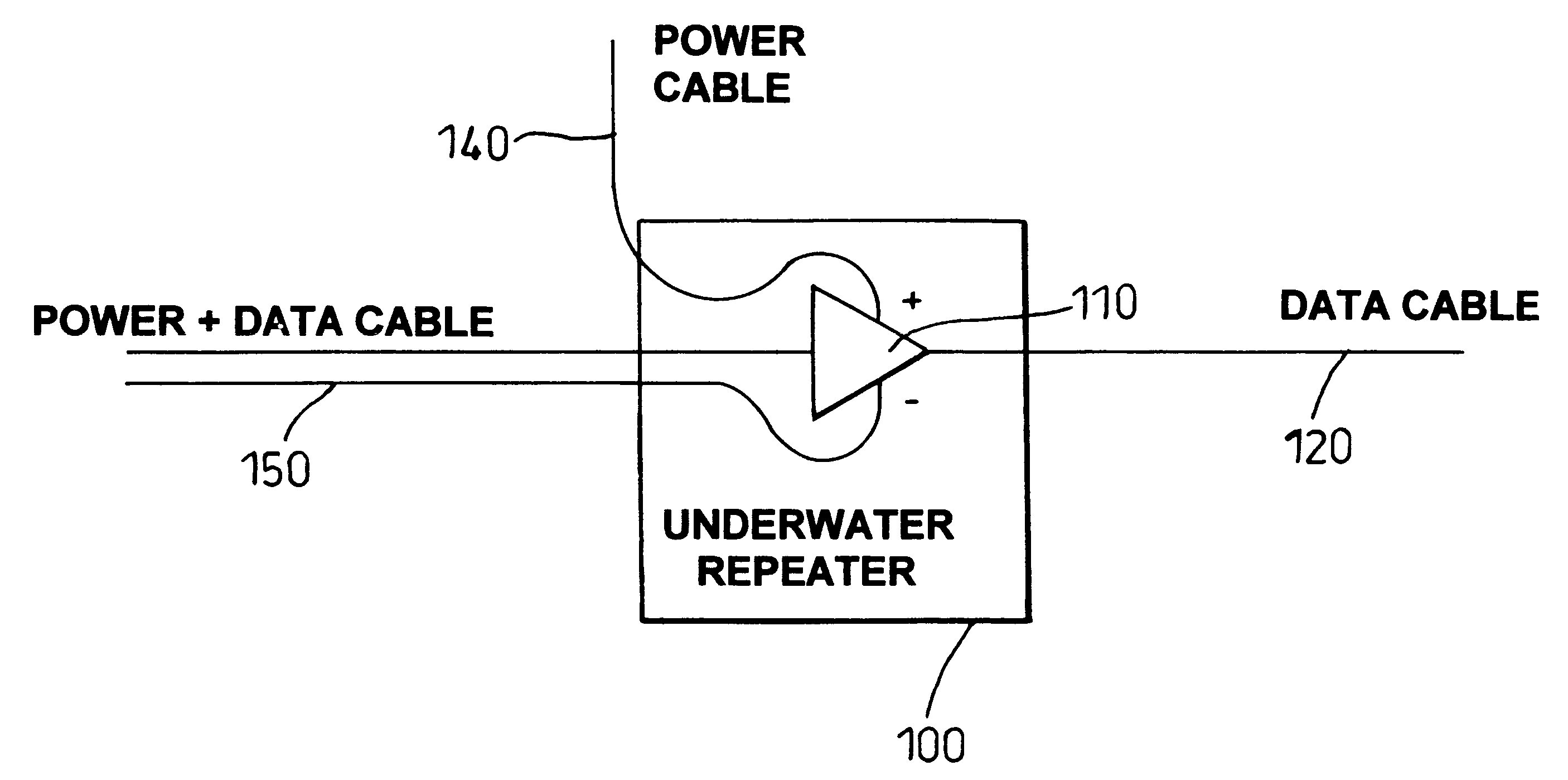
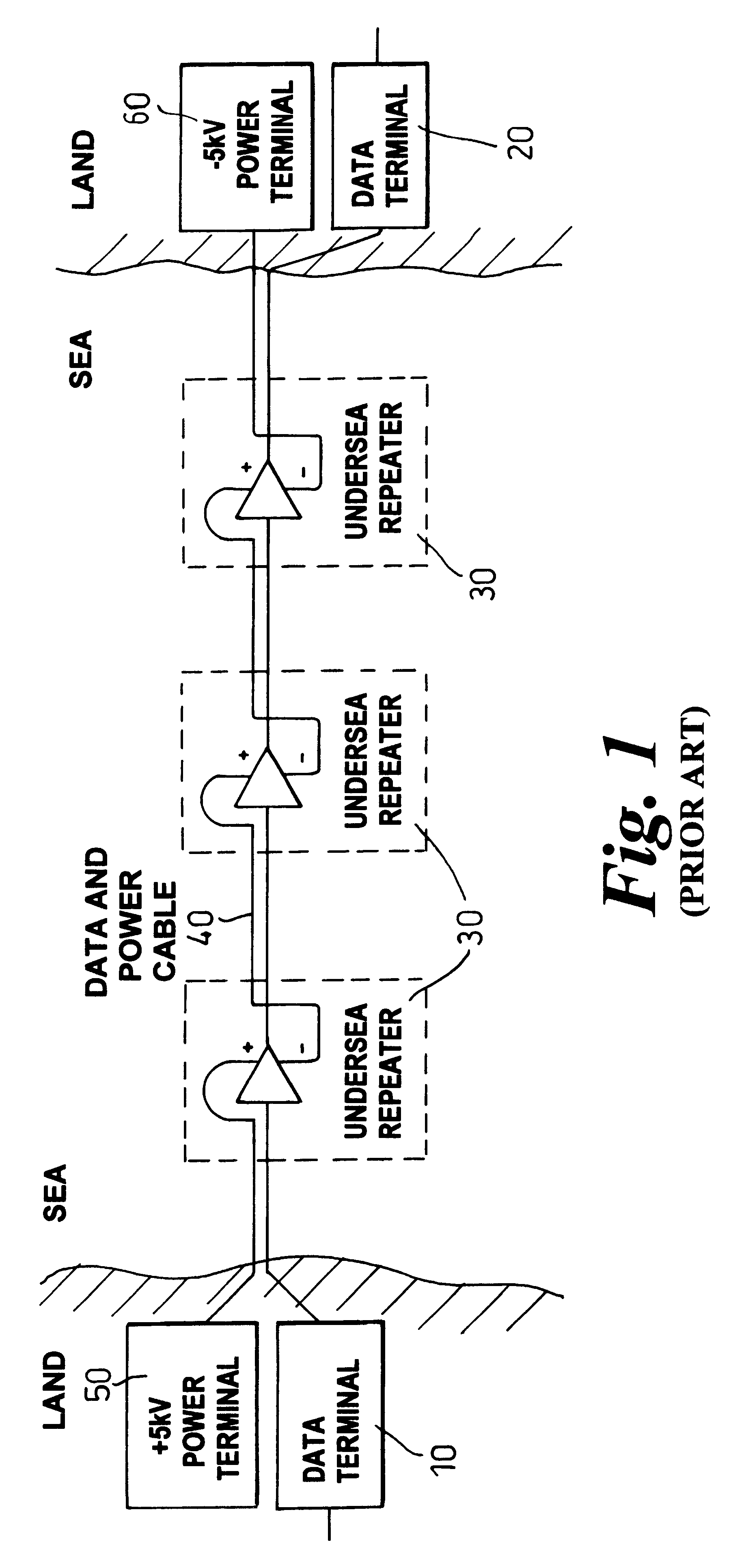
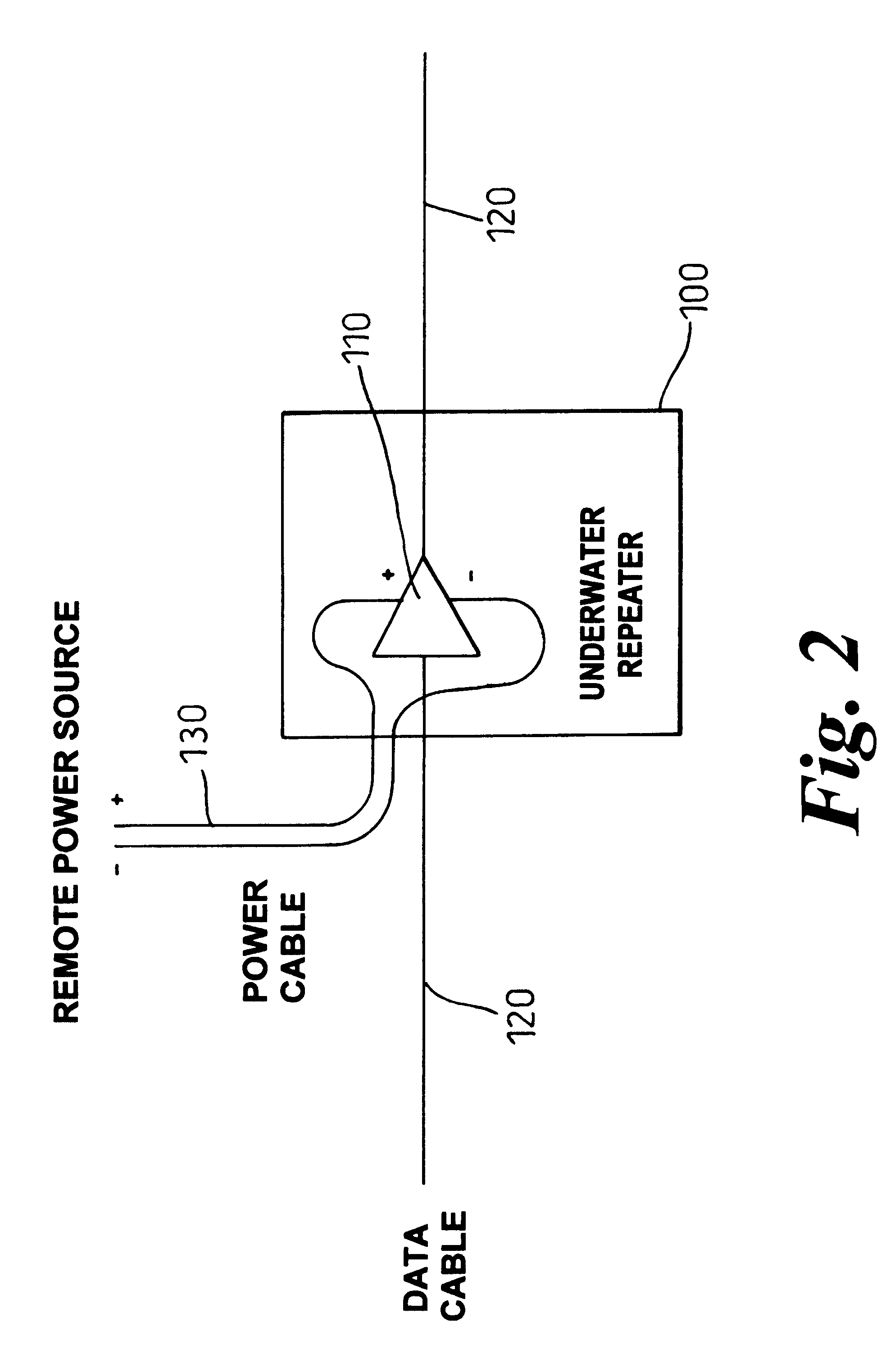
InactiveUS6496626B2More repeaterMore functionalityBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsWelding electric supplyFiberPower grid
An underwater telecommunications system has a first underwater cable for carrying data traffic, one or more underwater repeaters, and an underwater power network for supplying power to the repeaters. By providing a separate cable for some or all of the power supply, the power route may be made shorter, thus more power can be delivered, therefore more repeaters can be used, which enables more fiber pairs to be laid, and thus the capacity to be increased.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
System and method for heat pump oriented zone control
ActiveUS20070057075A1Easy to operateEasy to controlMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsElectronic controllerControl theory
A system and method to control environmental parameters of pre-defined zones within an environment using an electronic controller are disclosed. The system includes an electronic controller which enables a weighting value to be assigned to each zone within the environment. The electronic controller also detects any zone service calls from sensor devices associated with each of the zones and determines a cumulative weighting value in response to the detected zone service calls. The electronic controller selects a staging combination from at least two possible staging combinations in response to at least the cumulative zone weighting value.
Owner:ARZEL ZONING TECH
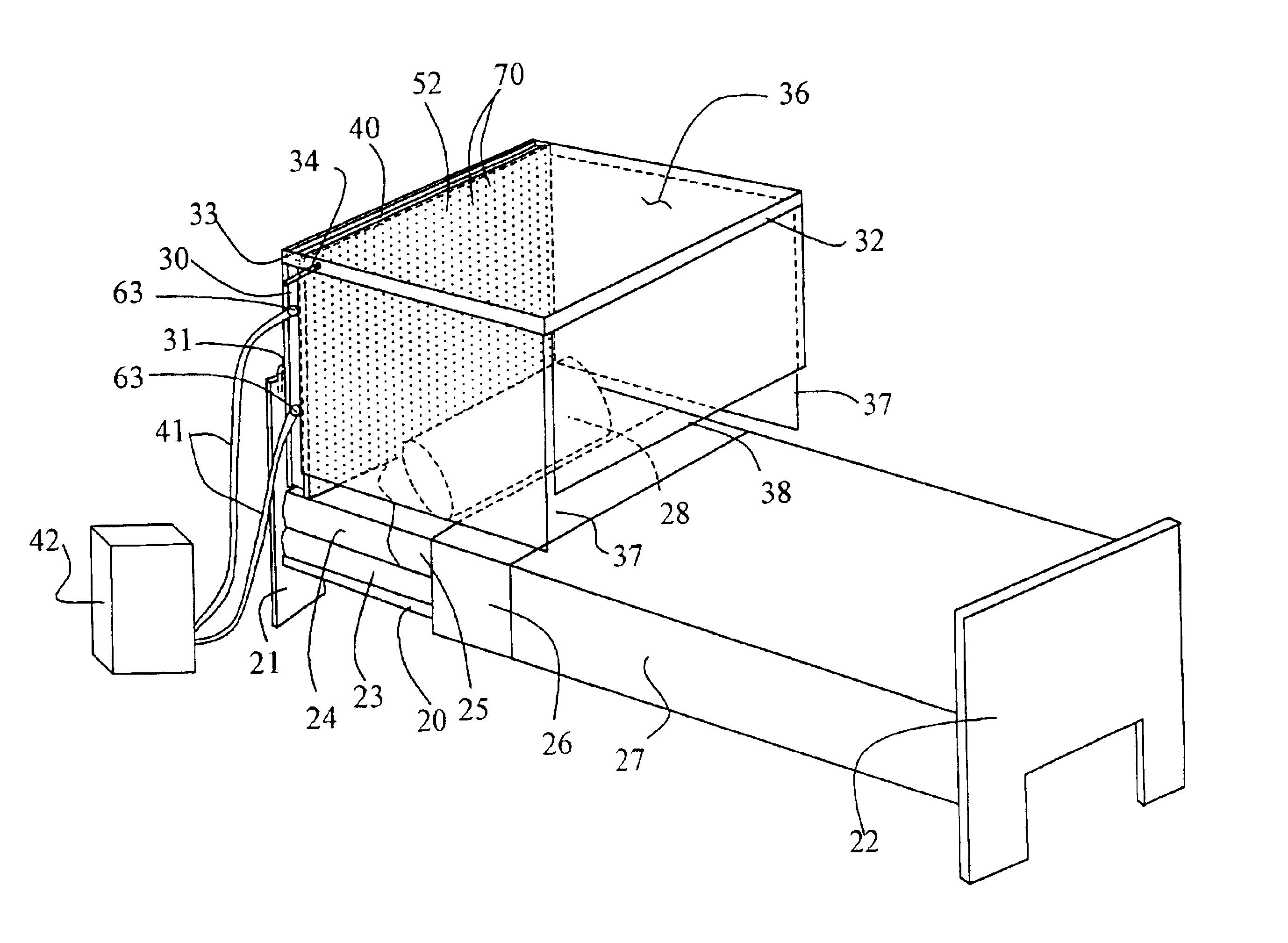
Canopy air delivery system
InactiveUS6916238B2Minimize and limit contactMore capacityBreathing protectionCombination devicesMaterial PerforationDelivery system
An area air delivery system for delivery of filtered air to an area occupiable by a user who can enter and leave the area, such as the head end of a bed, includes a canopy for at least partially surrounding the area to which air is to be supplied and defining the area which a user can enter and leave. An air diffuser positioned in the canopy includes a housing having an air impervious rear wall, air impervious side walls, and a perforated front wall forming a plenum in which a filter bag resides. The plenum is connected to a source of pressurized, preferably prefiltered, air so that pressurized air is supplied to the interior of the filter bag to diffuse through the filter bag into the plenum. Perforations in a predetermined area of the perforated front wall of the housing allow air to flow through the perforations and provide a substantially even flow of air from the perforated front wall of the diffuser into the canopy.
Owner:NAT BUSINESS CONSULTANTS
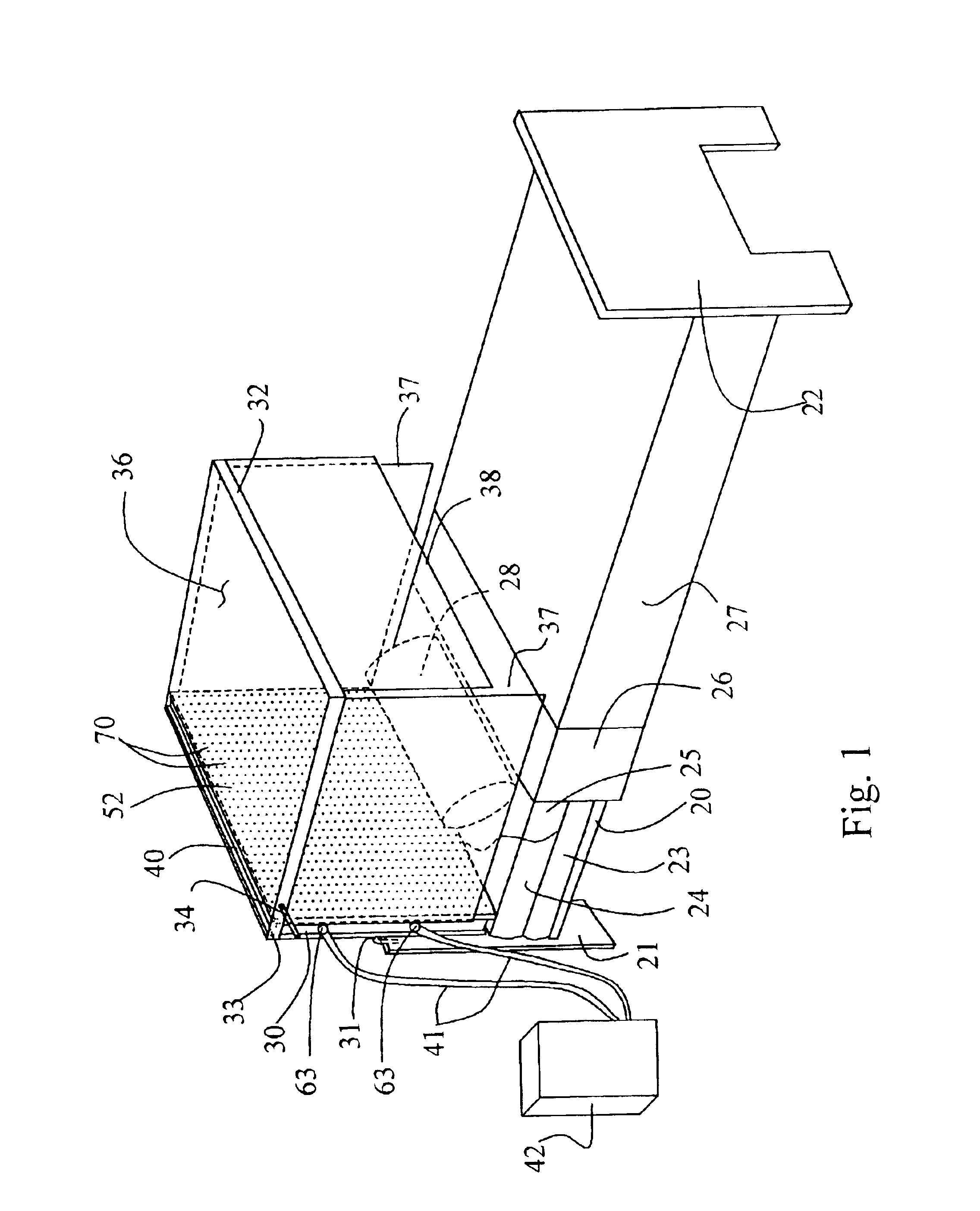
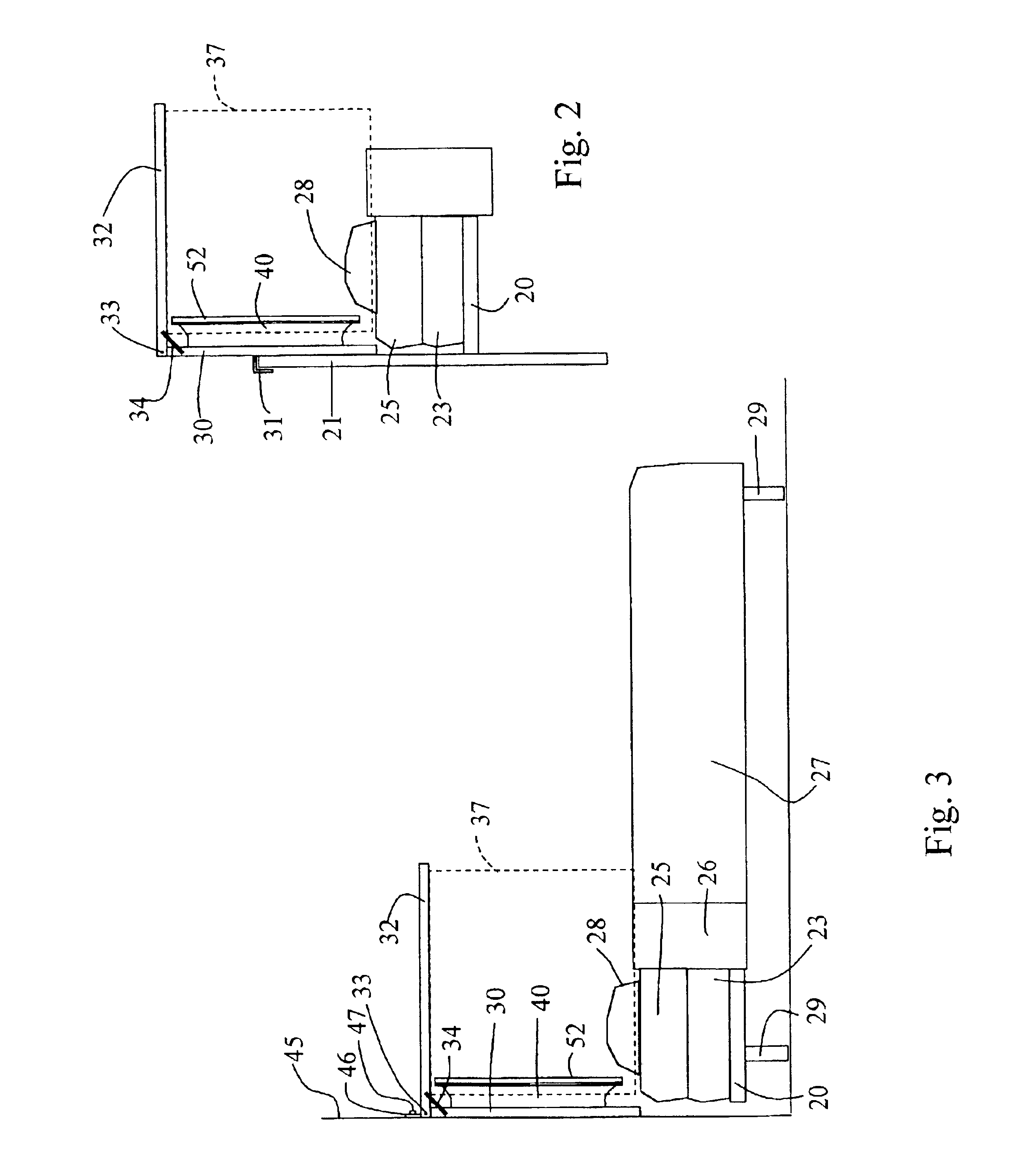
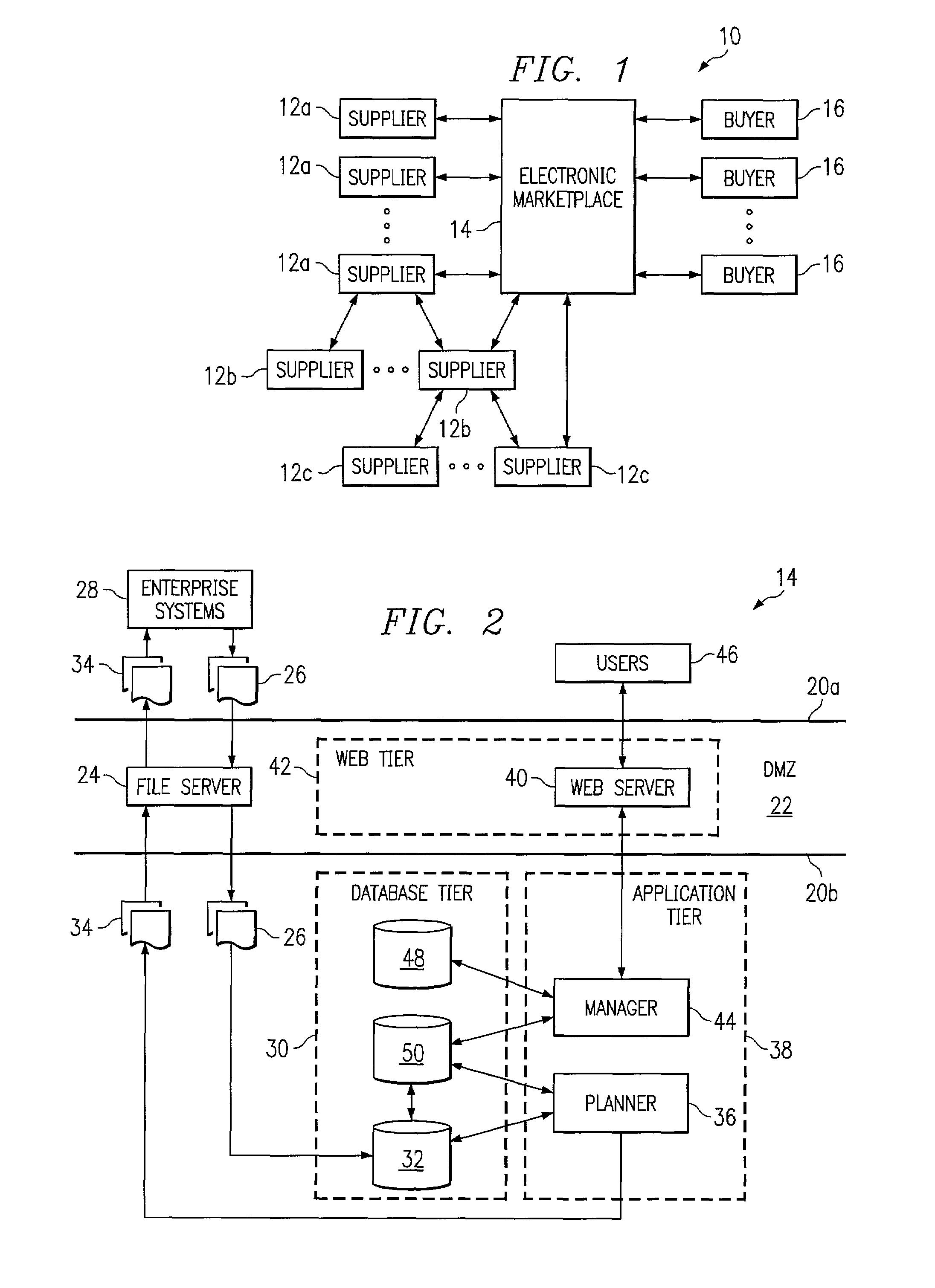
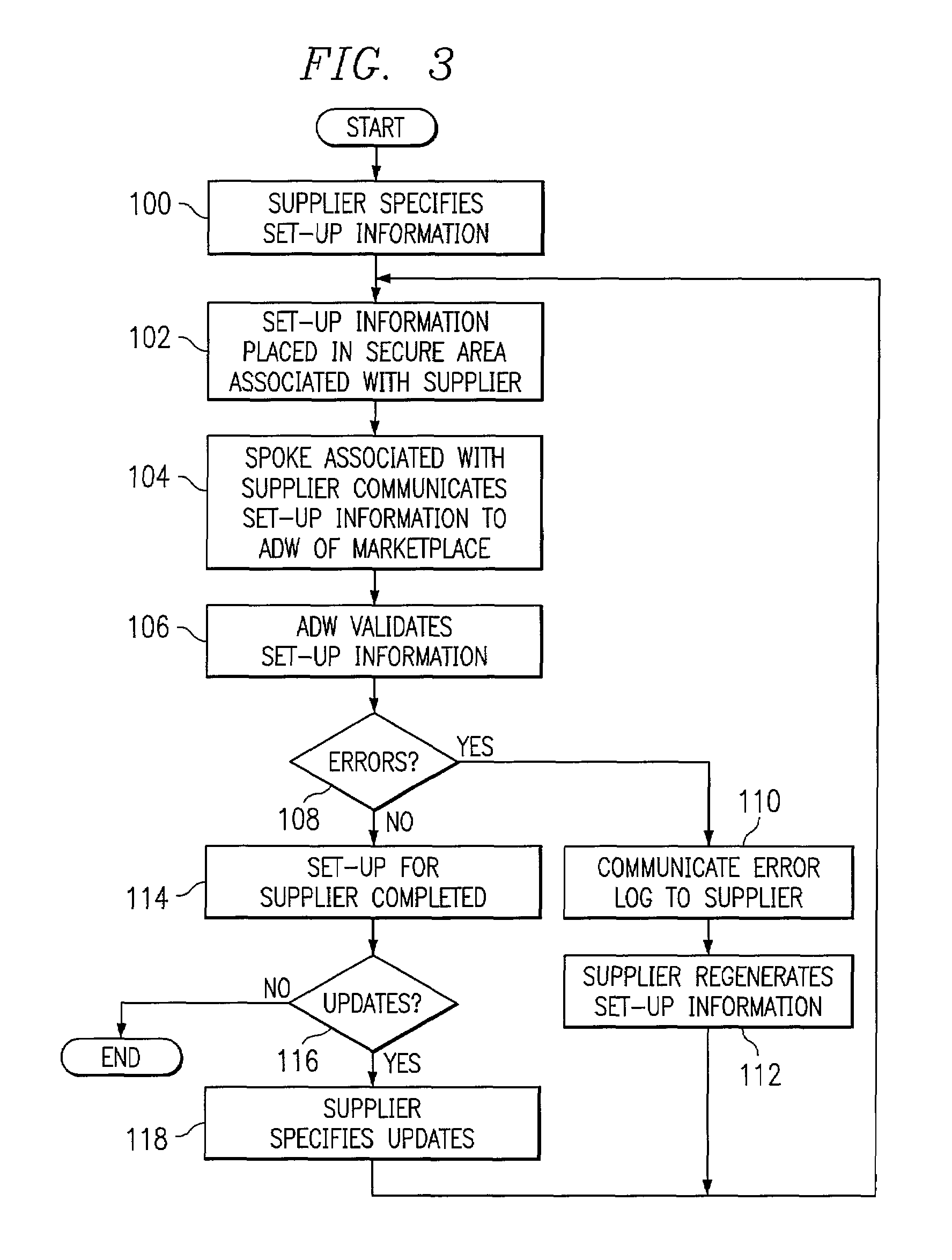
Extreme capacity management in an electronic marketplace environment
InactiveUS7370009B1Addressing extremes in capacity have been substantially reduced or eliminatedEasy to operateAnimal feeding devicesBuying/selling/leasing transactionsImage resolutionEngineering
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
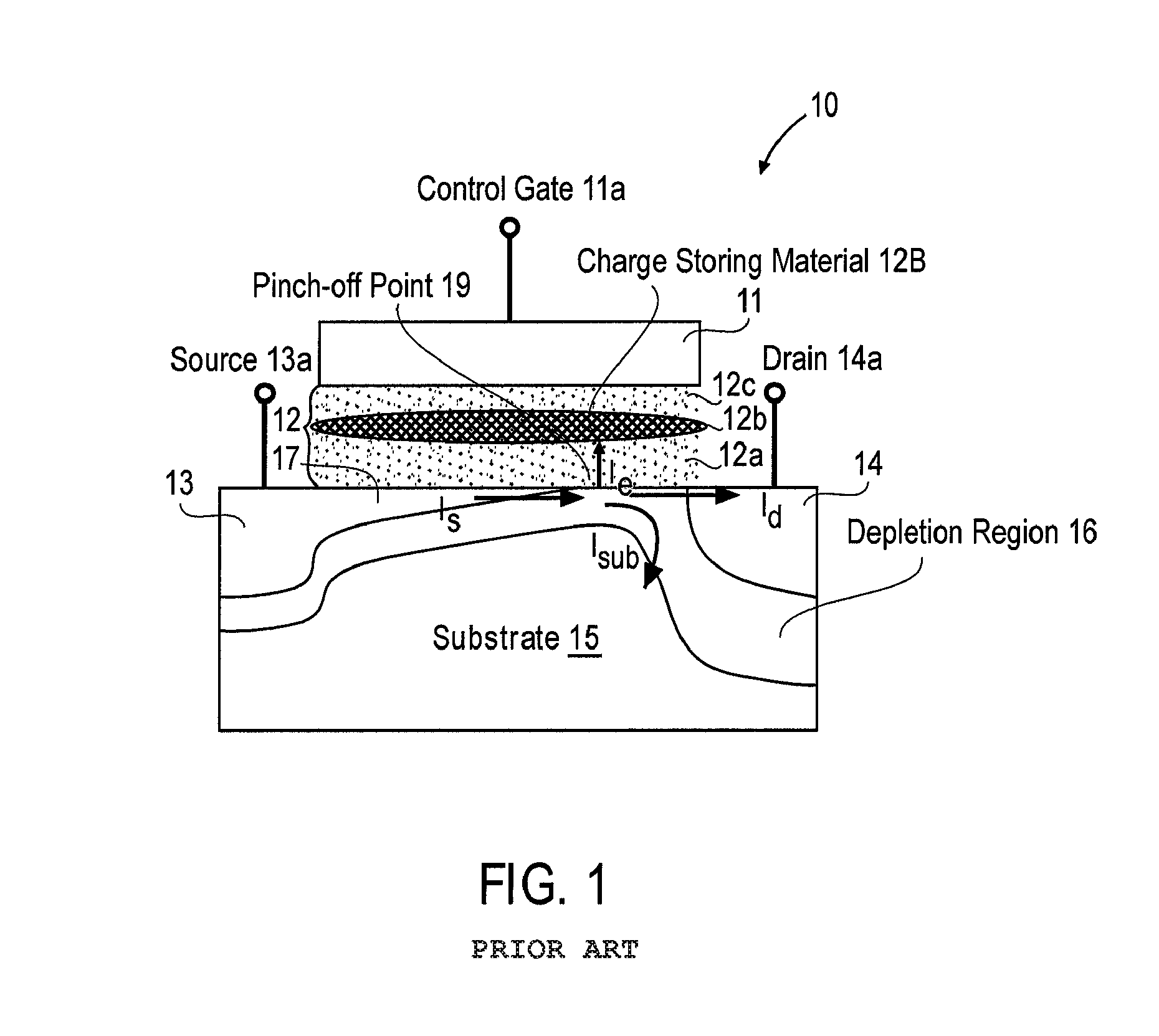
Methods and structures for highly efficient hot carrier injection programming for non-volatile memories
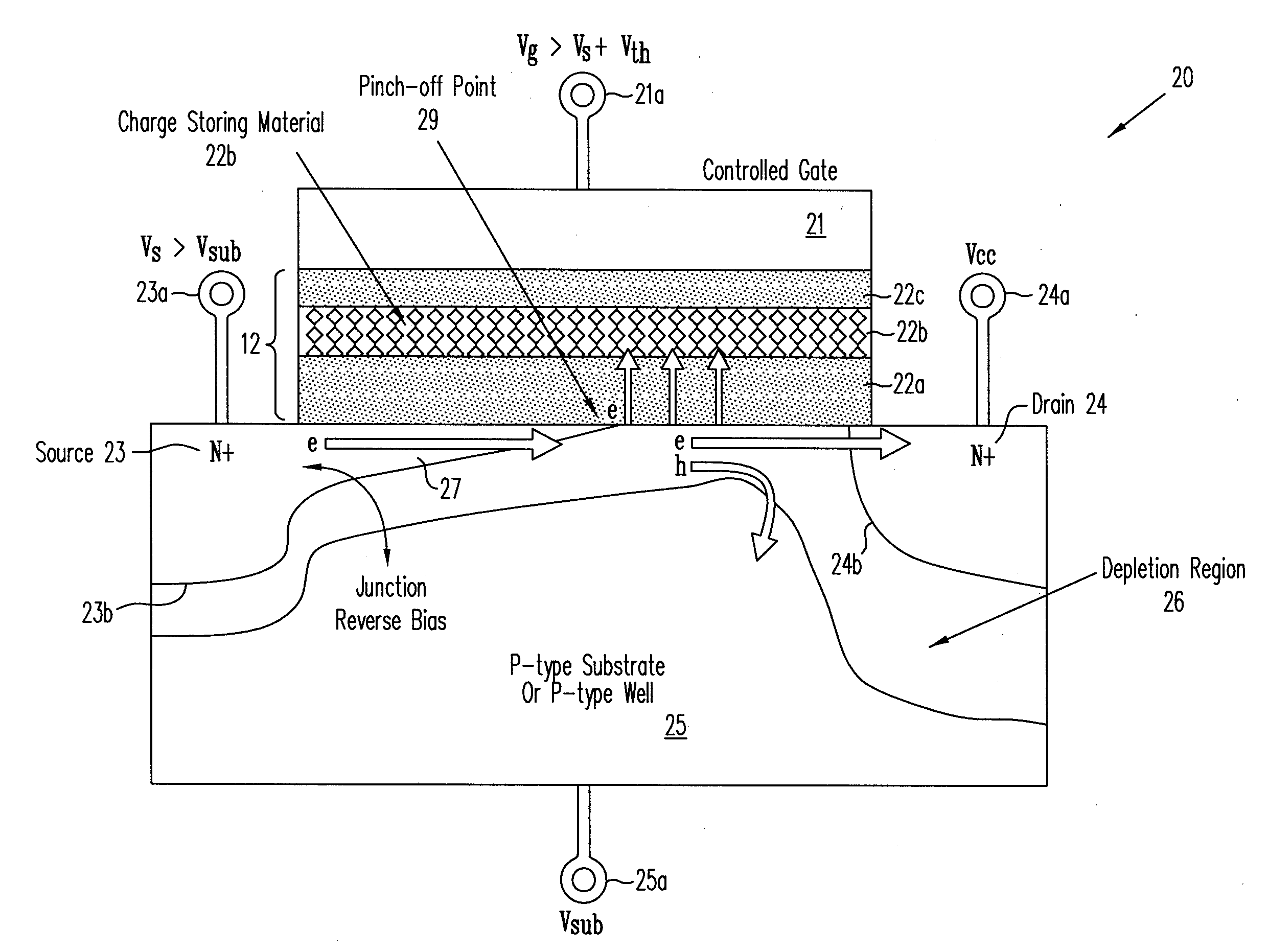
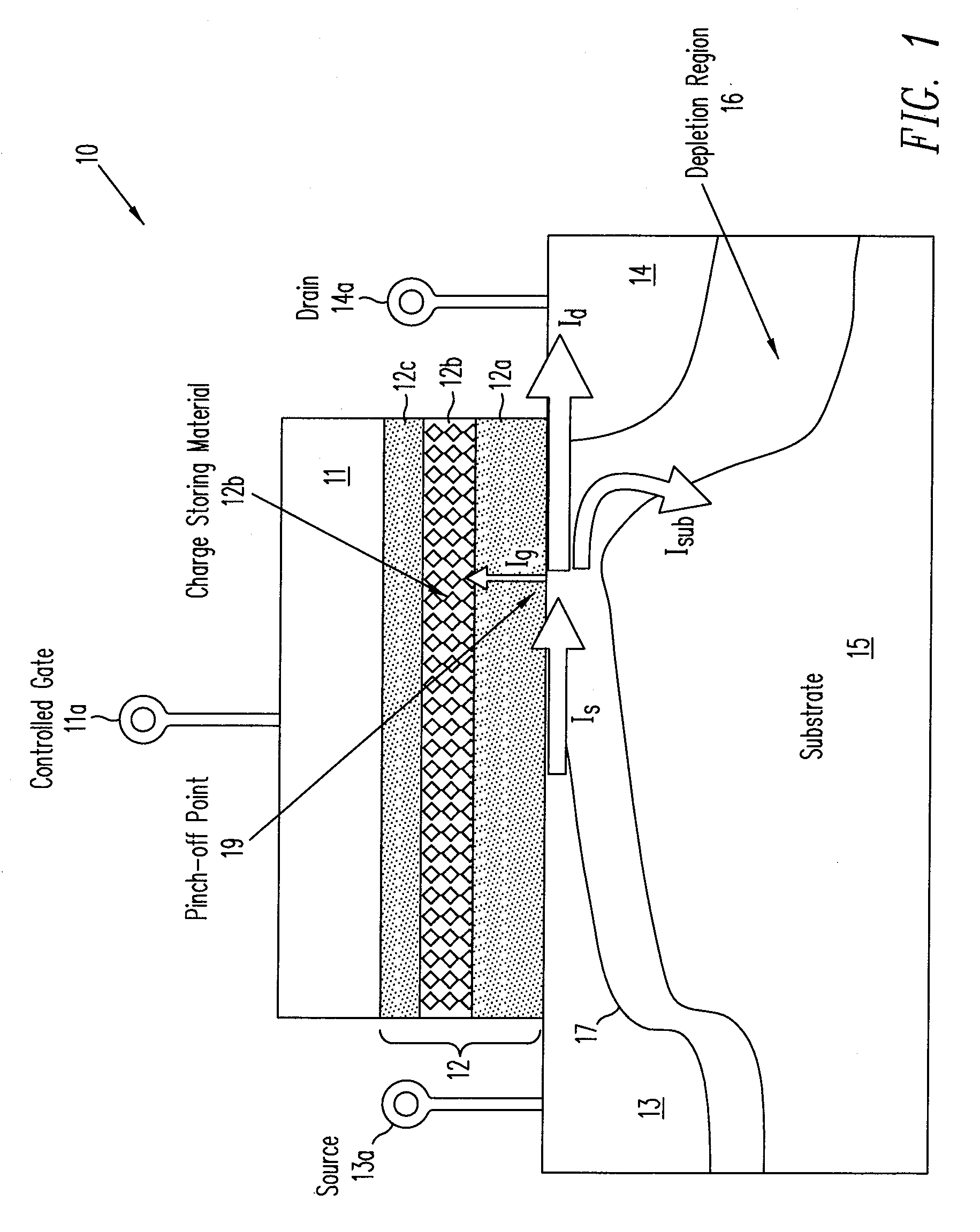
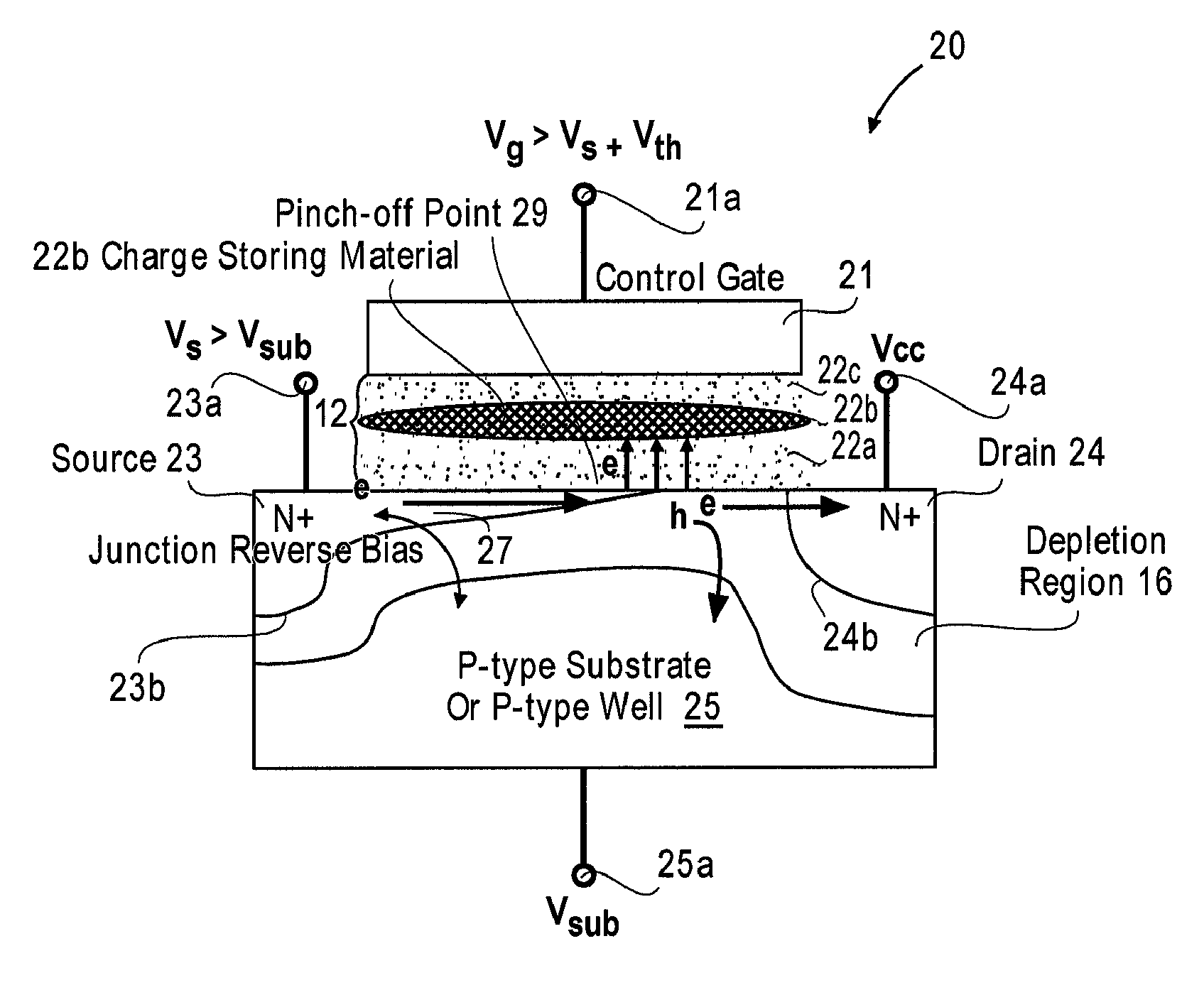
ActiveUS20090021984A1Improve programming efficiencyHigh injection rateRead-only memoriesDigital storageMOSFETVoltage amplitude
A metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) in a non-volatile memory cell has a source, a drain and a channel region between the source and the drain, all formed in a substrate of opposite conductivity type to the conductivity type of the source and drain. The MOSFET is programmed by connecting the drain electrode to the supply source of the main voltage, Vcc, provided to said non-volatile memory cell and supplying selected voltages to the source and substrate so as to invert a portion of the channel region extending from the source toward the drain. The inverted portion of the channel region ends at a pinch-off point before reaching the drain. By controlling the reverse bias across the PN junction between the source and the substrate, the pinch-off point of the inversion region is pulled back toward the source thereby to increase the programming efficiency of the MOSFET.Methods and structures for highly efficient Hot Carrier Injection (HCI) programming for Non-Volatile Memories (NVM) apply the main positive supply voltage Vcc to, the drain electrode of the NVM cell from the chip main voltage supply in contrast to the conventional method using a higher voltage than Vcc. The source electrode and substrate are reverse biased with a differential voltage relative to the drain, while a voltage pulse is applied to the control gate of the NVM cell to turn on the NVM cell for programming. To optimize the programming condition, the source voltage and the substrate voltage are then adjusted to achieve the maximum threshold voltage shifts under the same applied gate voltage pulse condition (i.e. using a gate pulse with the same voltage amplitude and duration regardless of the source voltage and the substrate voltage). The substrate voltage to the drain voltage can not exceed the avalanche multiplication junction breakdown for a small programming current during the bias voltage adjustment.
Owner:PEGASUS SEMICON SHANGHAI CO LTD
Enzymatic fuel cell
InactiveUS20050158618A1No longer operatesReadily availableCell electrodesSolid electrolyte cellsFuel cellsBiomedical engineering
Owner:POWERZYME
Gas turbine electric powerplant
InactiveUS7461510B1Low costImprove powerTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEngine fuctionsReduction driveControl system
A gas turbine electric powerplant, preferably driven by an aeroderivative turbine engine of split shaft design. The gas turbine engine is coupled to a speed reducer, which is in turn coupled to an electric generator. An engine mount is provided that ensures that the gas turbine engine will remain in proper alignment with the speed reducer and generator, even during the thermal expansion or contraction thereof. Preferably, the components comprising the powerplant are mounted to a common, transportable base, so that the powerplant can be delivered to various locations. An overspeed control system is provided for ensuring that a runaway condition of the gas turbine engine does not occur should the gas turbine engine become disconnected from the speed reducer or generator. Sensors are used to monitor multiple operating conditions of the powerplant. A microprocessor-based control system communicates with the sensors, and is further adapted to activate the overspeed control system if an overspeed condition is detected.
Owner:ALTEK POWER CORP
Distributor power line communication system
InactiveUS20100204850A1Reliable powerReduce recurring operating and maintenance costMechanical power/torque controlSystems using filtering and bypassingFrequency bandCommunications server
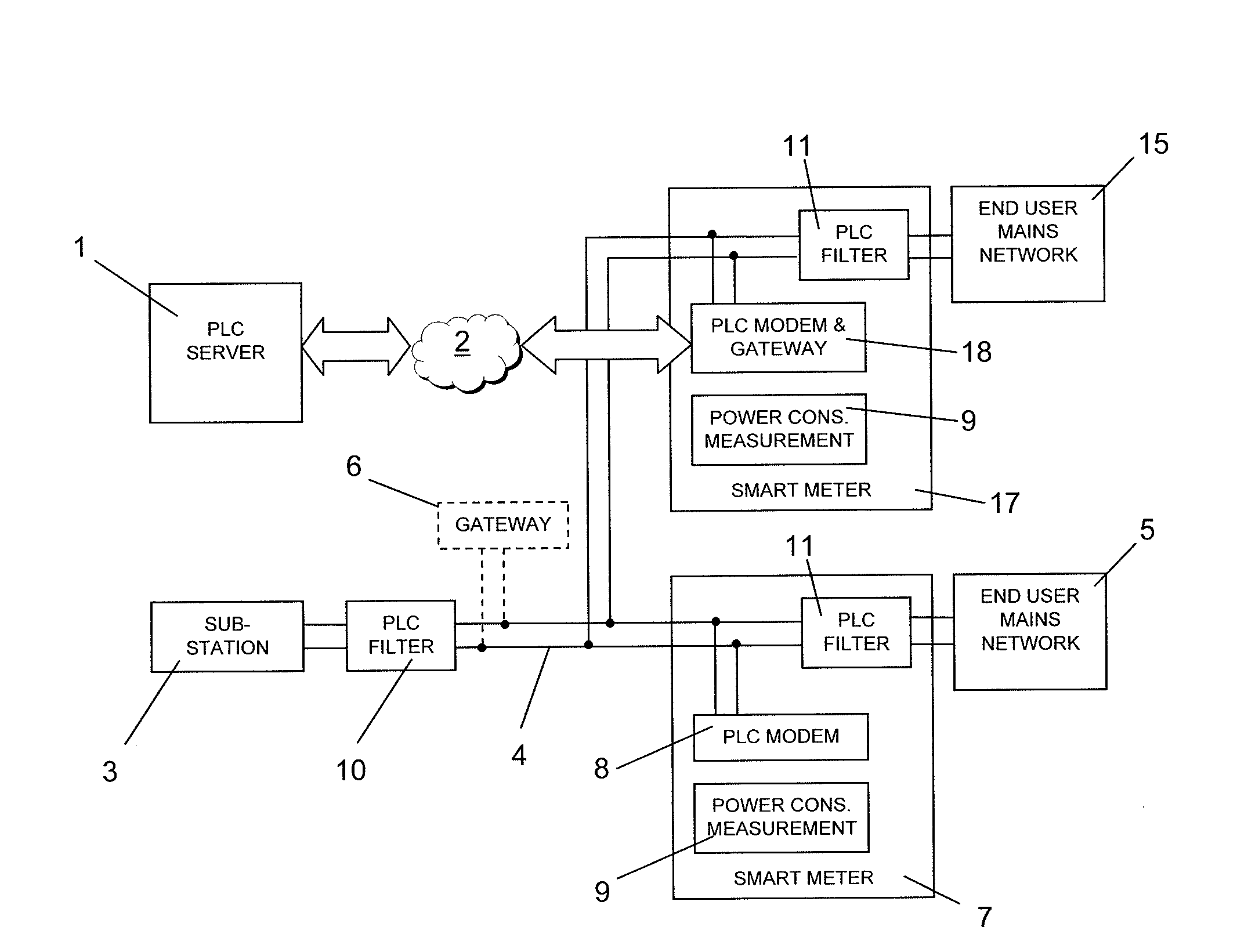
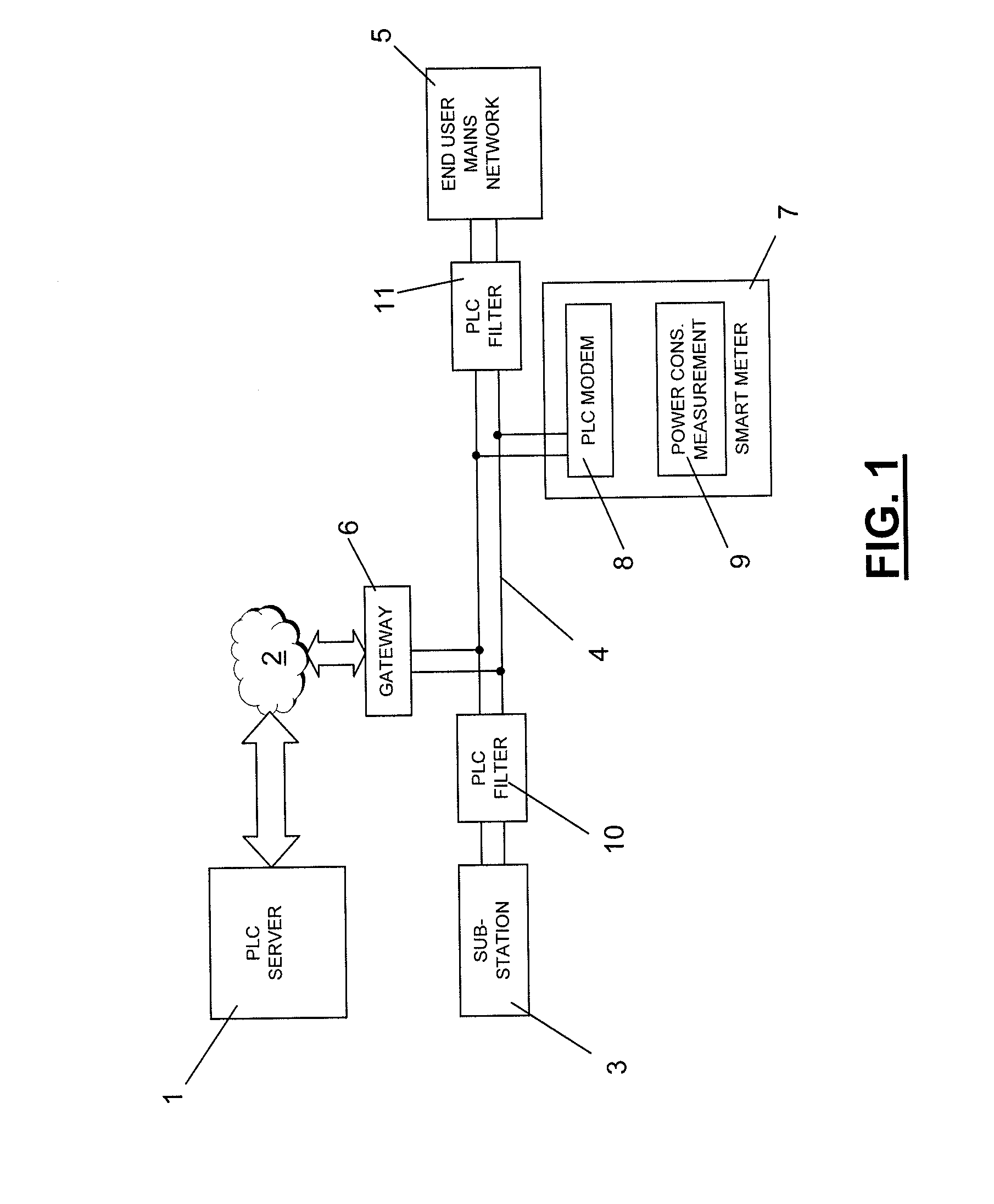
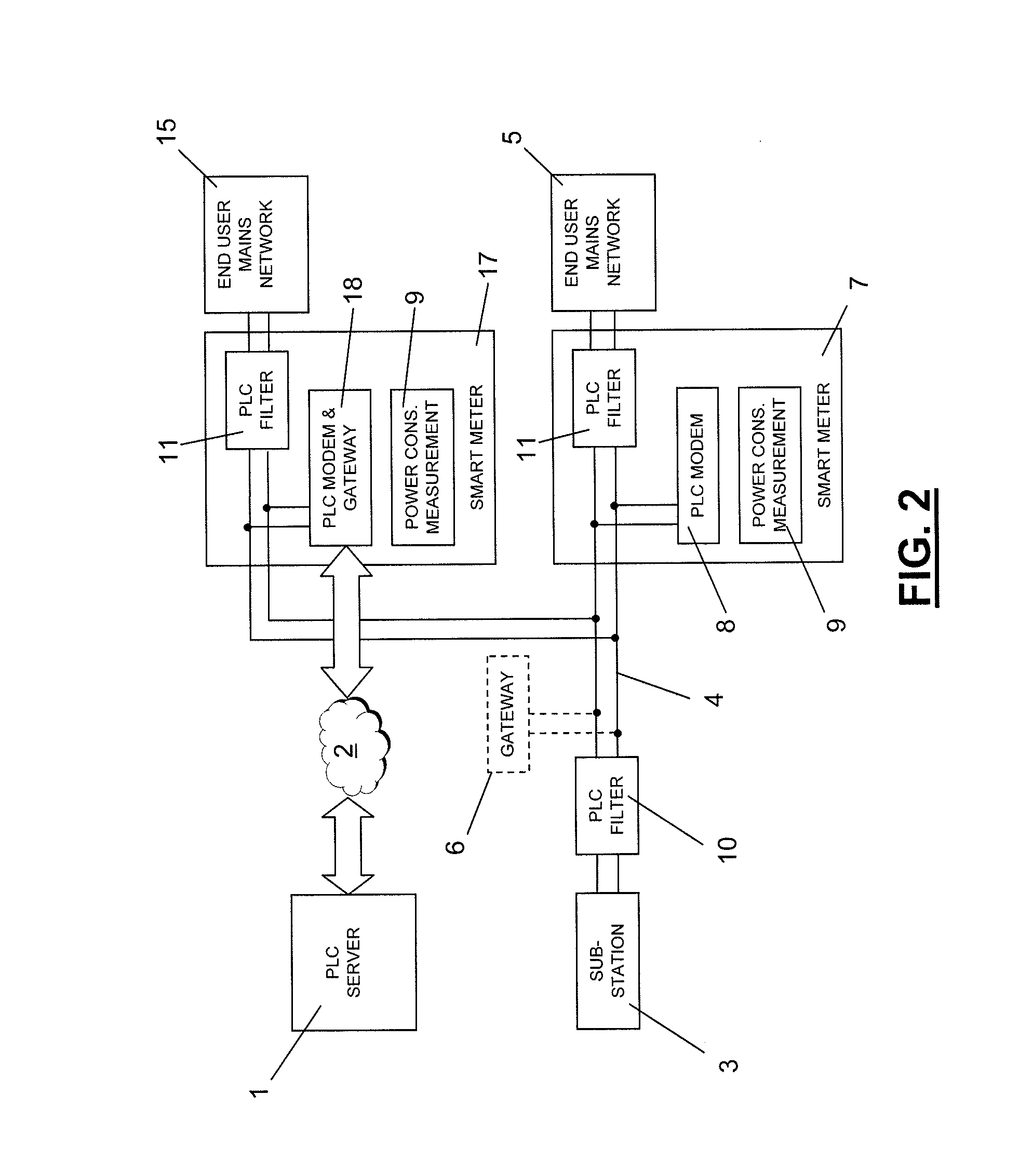
Distributor power line communication system comprising a communication server (1) sending and receiving messages over a telecommunication network (2), a power distribution substation (3) to which a power distribution network (4) towards end users (5) is connected, at least one gateway (6; 18) transferring messages from the telecommunication network (2) onto the power distribution network (4) in a predetermined frequency band, a plurality of smart metering devices (7; 17; 27) at end user mains networks for measuring power consumption and comprising a power line communication modem (8; 18) sending and receiving messages within the predetermined frequency band over the power distribution network (4), power line communication filters (10, 11) on power lines connecting the power distribution network and the end user mains networks and on power lines connecting the power distribution network to the power distribution substation, each filter blocking frequencies within the predetermined frequency band.
Owner:EANDIS
Method for Opportunistically Balancing Charge Between Battery Cells
ActiveUS20140049222A1Accurately determineAccurate balanceCharge equalisation circuitSecondary cellsImage resolutionEngineering
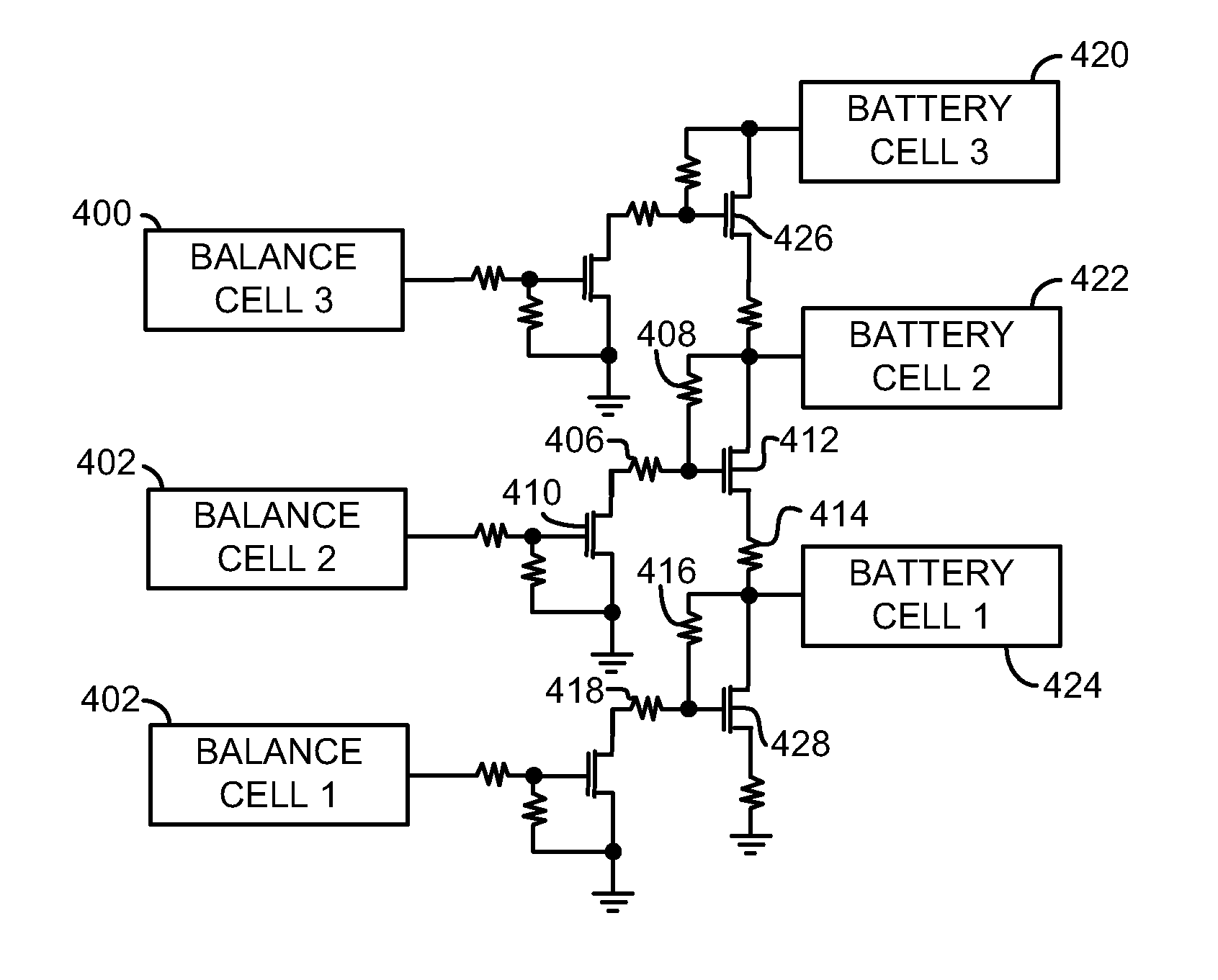
Systems and methods for balancing battery cells of a battery pack are disclosed. In one example, a charge imbalance is determined while battery cells operate in a high charge resolution voltage range. The charge imbalance determined during operation in the high charge resolution voltage range may be removed when the battery cells are operated in a low charge resolution voltage range. The system and method may be particularly useful for balancing battery cells that operate in the low charge resolution voltage range for a large portion of their operating time.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
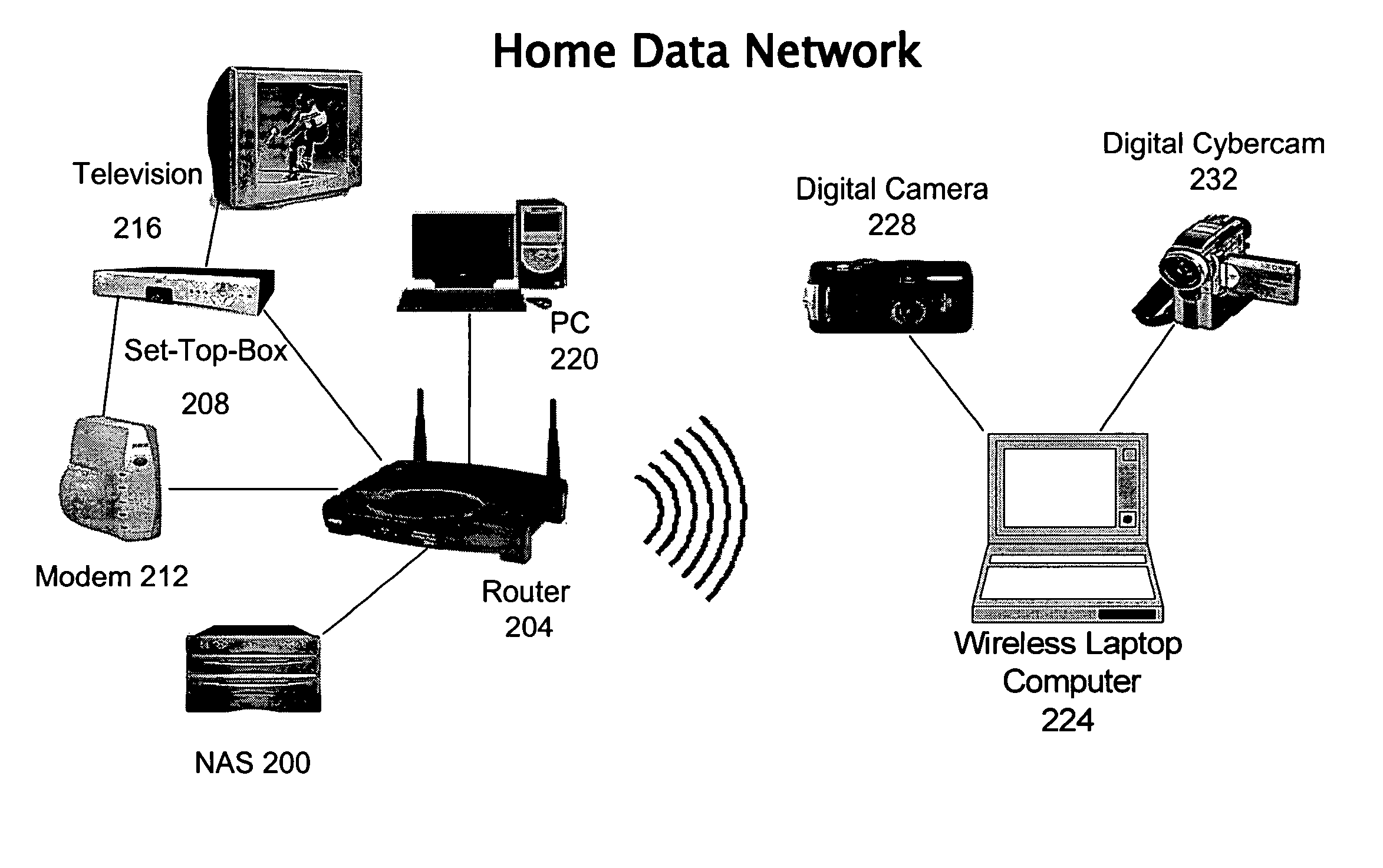
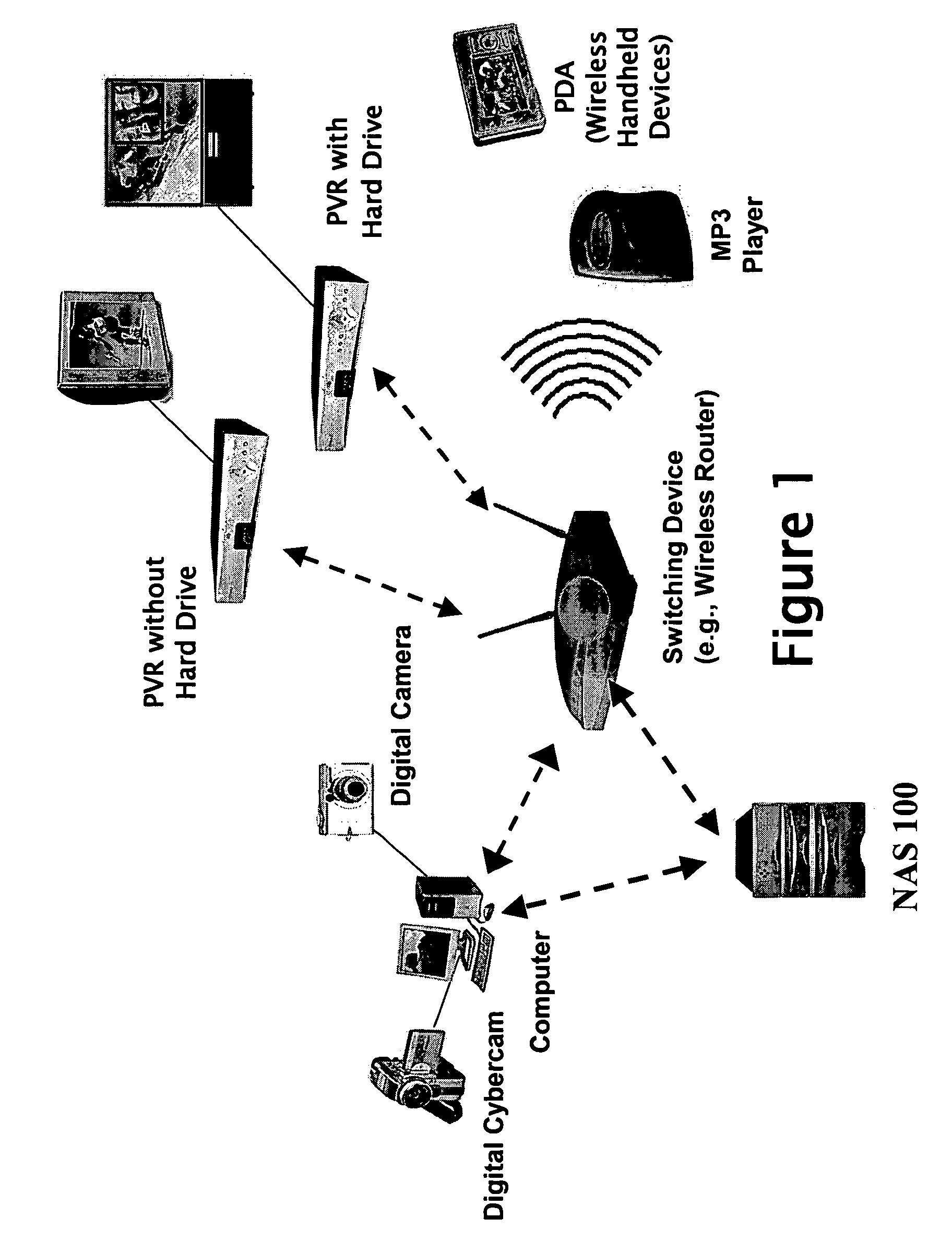
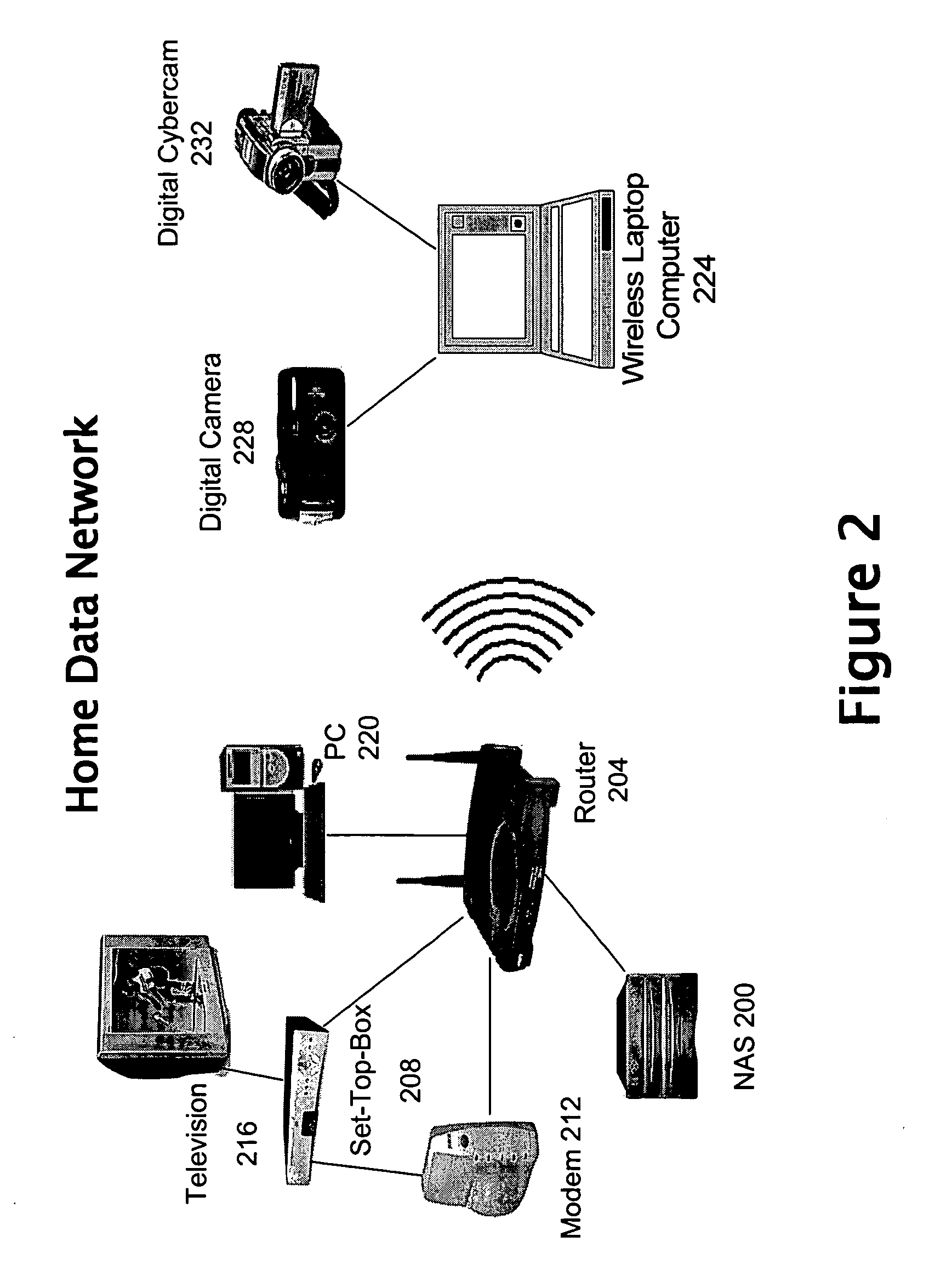
Data storage system and method that supports personal video recorder functionality
InactiveUS20050235336A1More capacityTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingComputer hardwareCoupling
Various aspects of the invention provide a system, apparatus, and method of storing data in a storage device for use by one or more data processing devices, such as person video recorders, communicatively coupled to the data storage device. In a representative embodiment, the method comprises receiving data from the one or more personal video recorders, and storing the received data in the storage device, wherein the storage device acts as a centralized facility for storing data provided by the one or more personal video recorders. In a representative embodiment, a system for implementing a centralized storage mechanism used by one or more personal video recorders comprises a storage device comprising one or more storage drives and one or more switching devices that provides communicative coupling between the storage device and the one or more personal video recorders.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
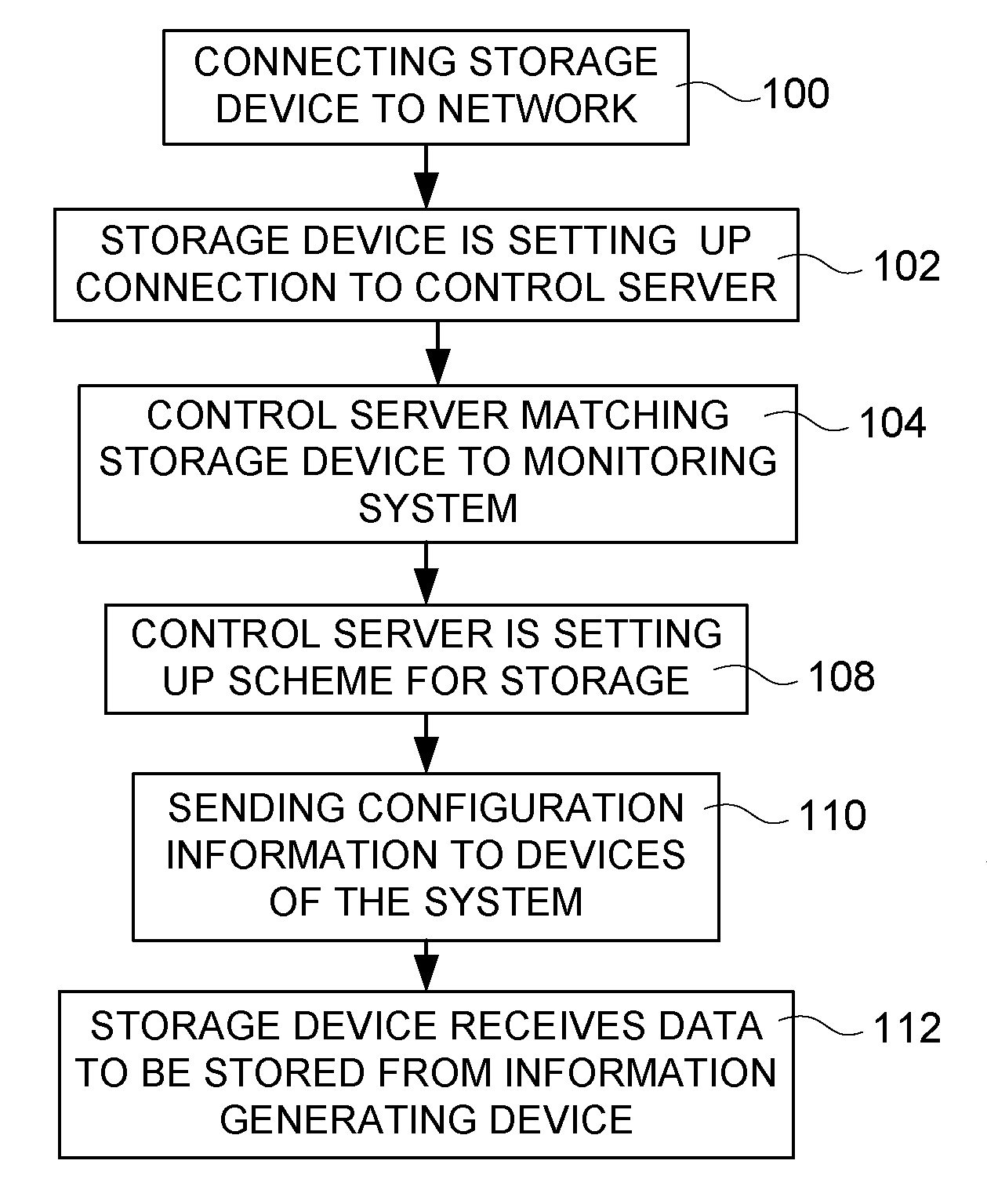
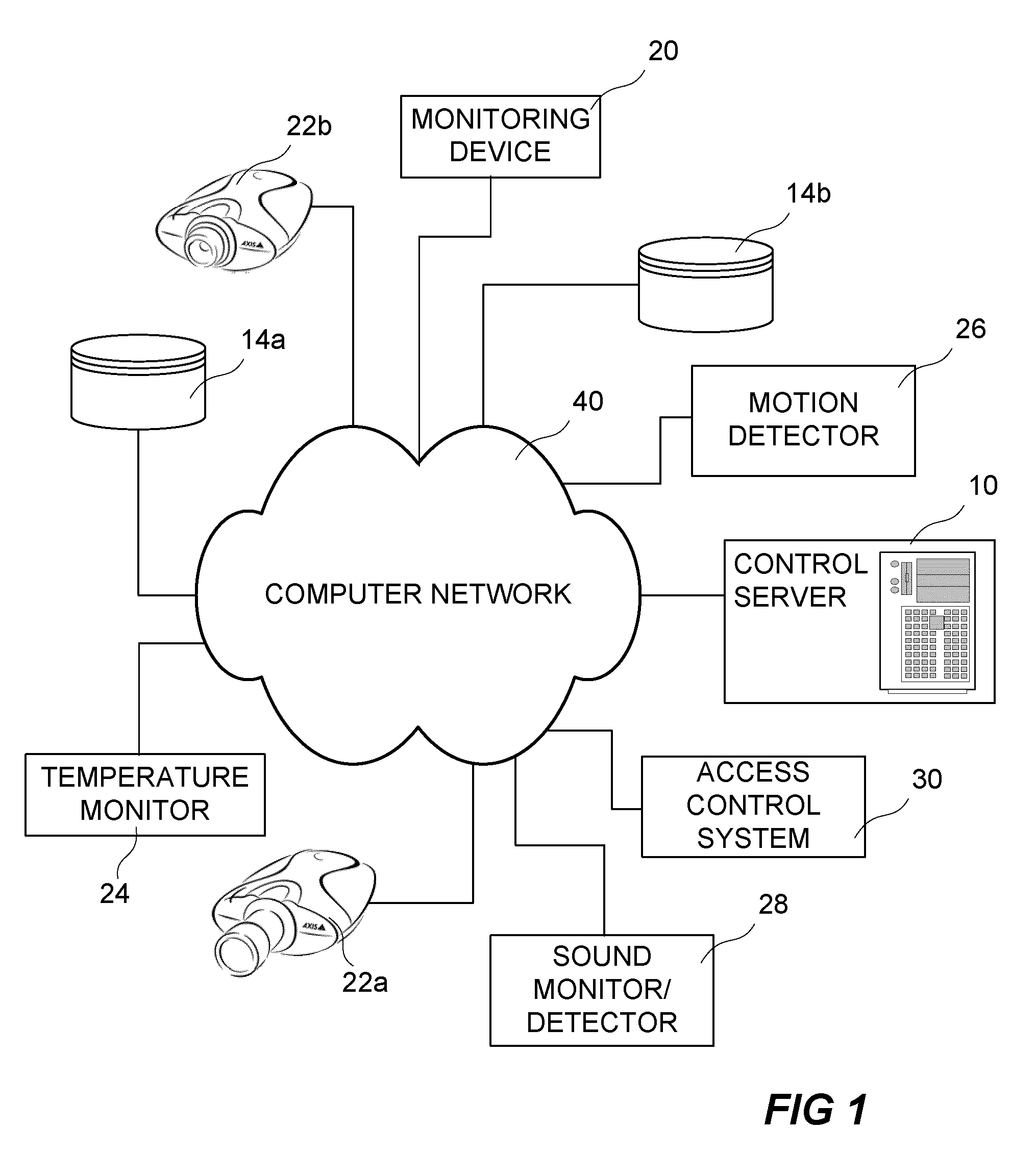
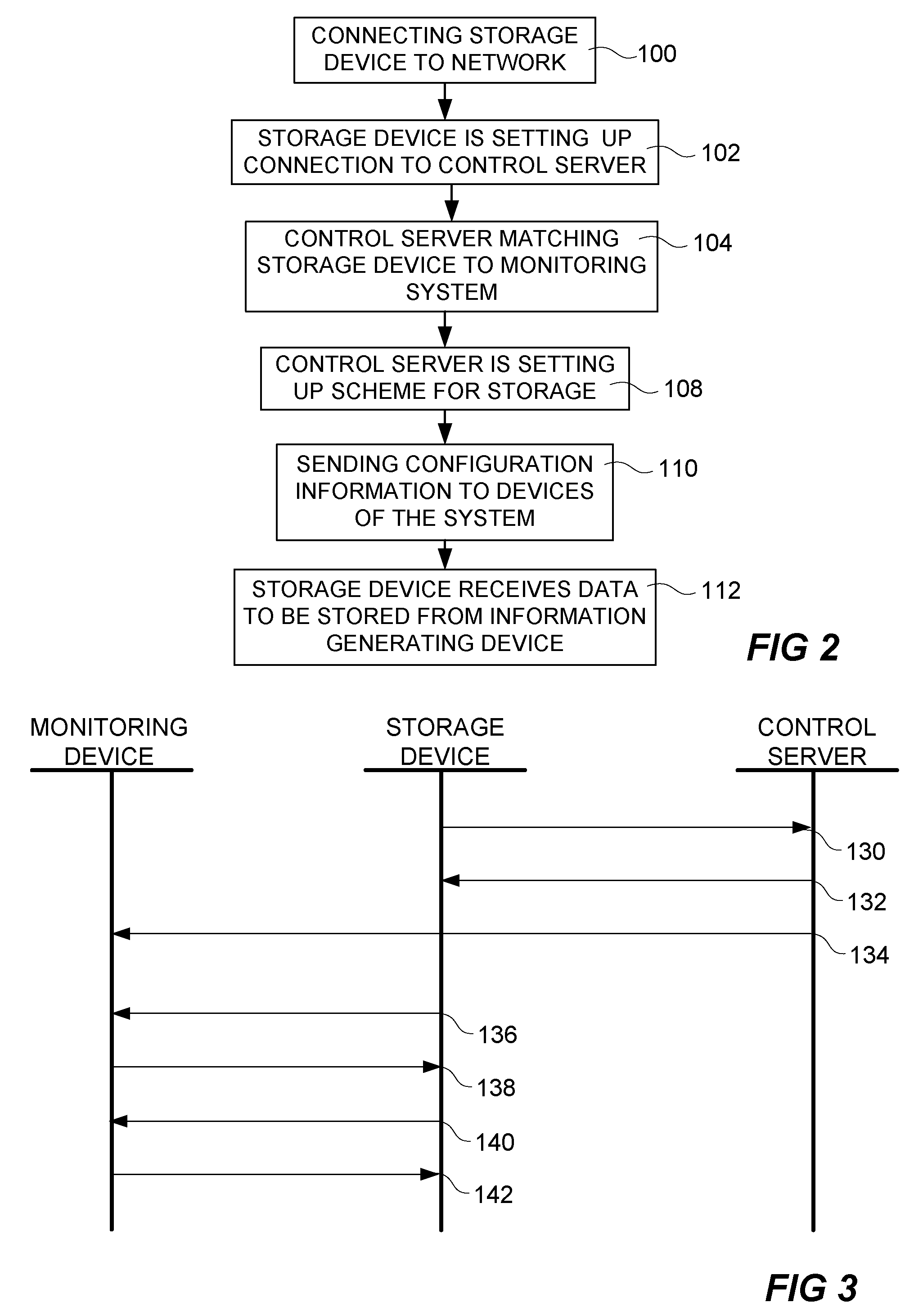
Information collecting system
ActiveUS20090259747A1Increase capacityAdditional of to pluralityTelevision system detailsDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareUnique identifier
A method for connecting a storage device to an information generating device includes transferring an identifying message from the storage device to a control server via a computer network. The identifying message includes a unique identifier uniquely identifying the storage device, matching a registered information generating system to the unique identifier, and identifying at least one information generating device included in the matched information generating system. A configuration message is transferred from the control server to the storage device, and the configuration message includes an address to the identified at least one information generating device and instructions of interaction. The instructions of interaction are arranged to define how the transfer of generated information is to be performed.
Owner:AXIS
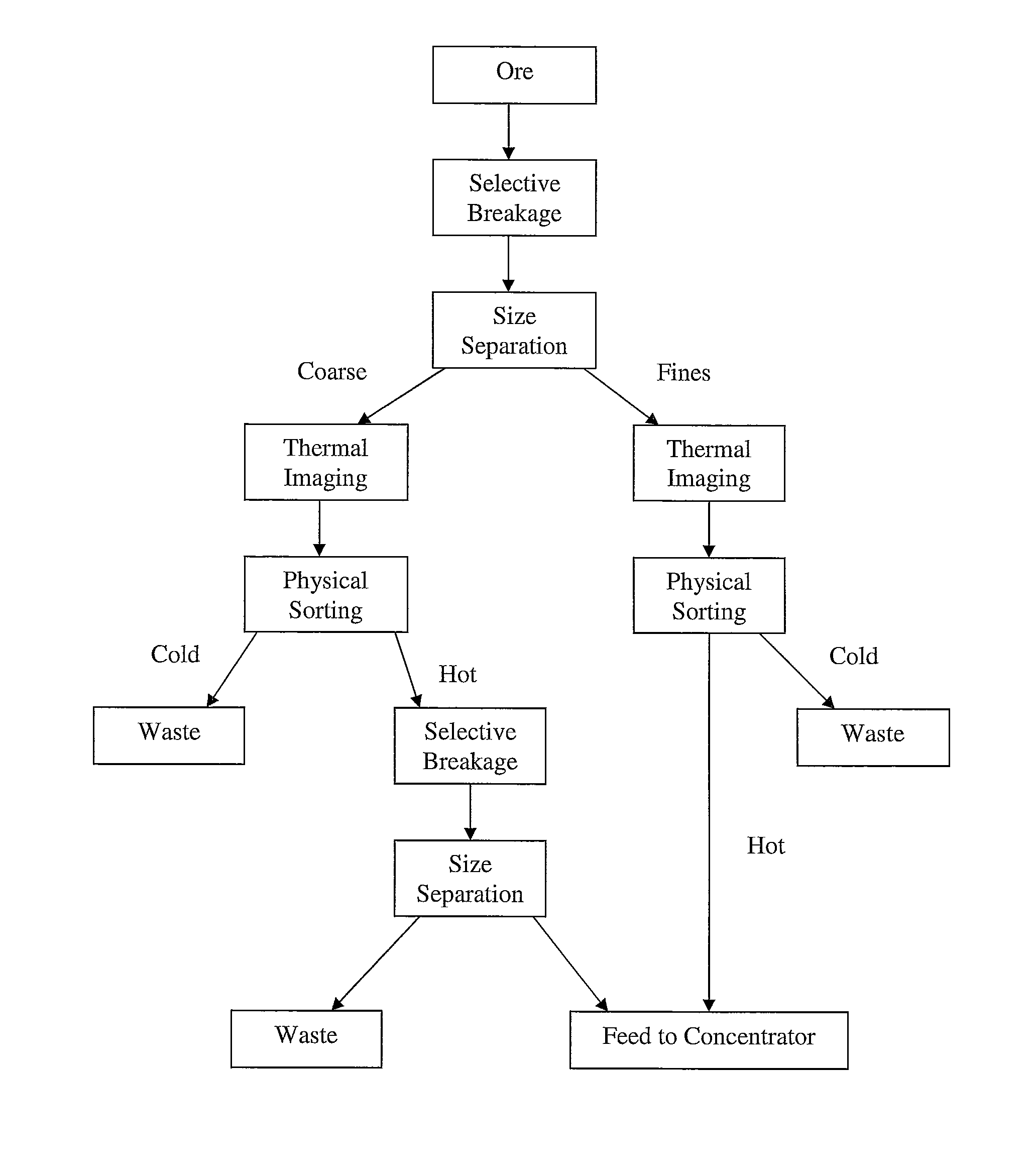
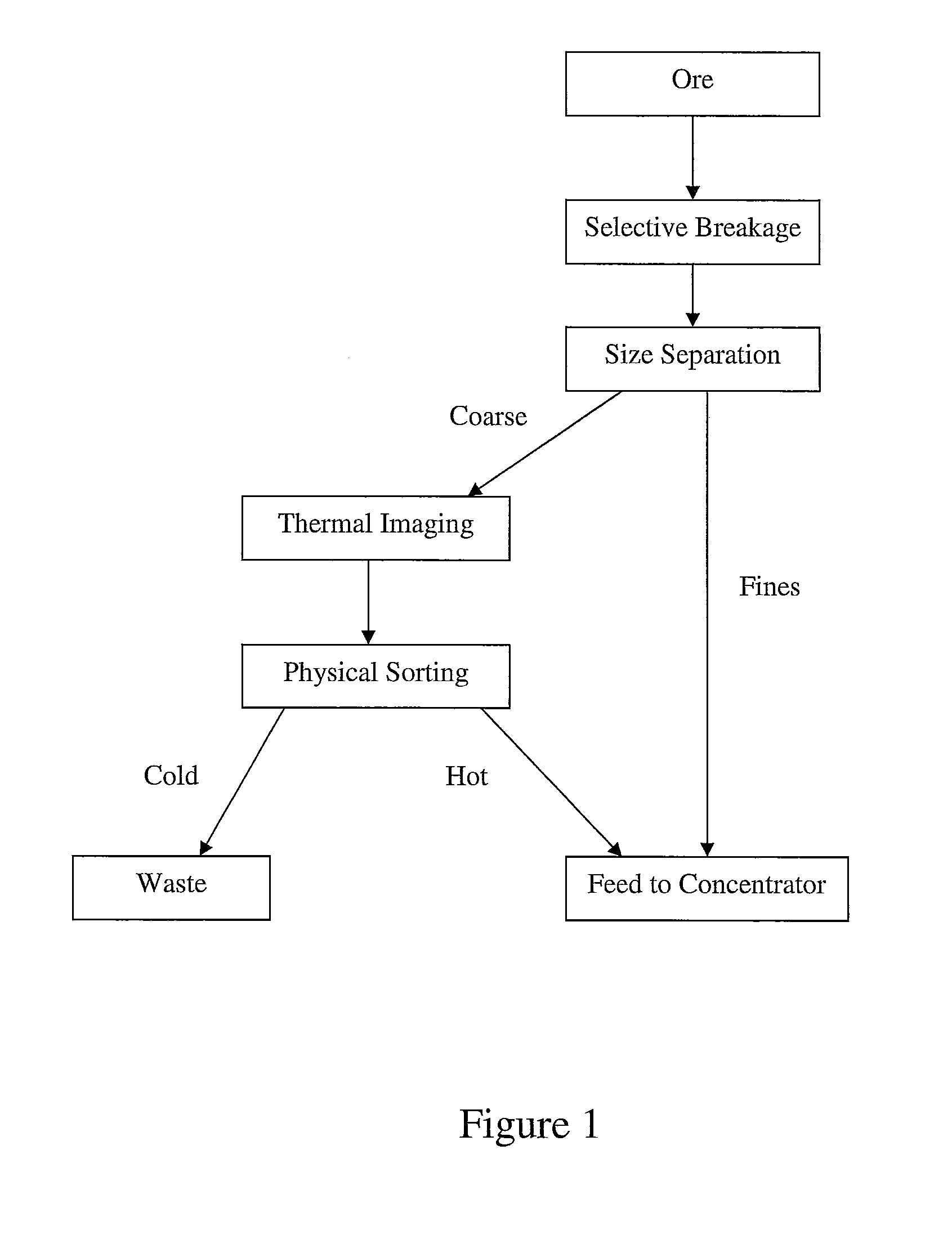
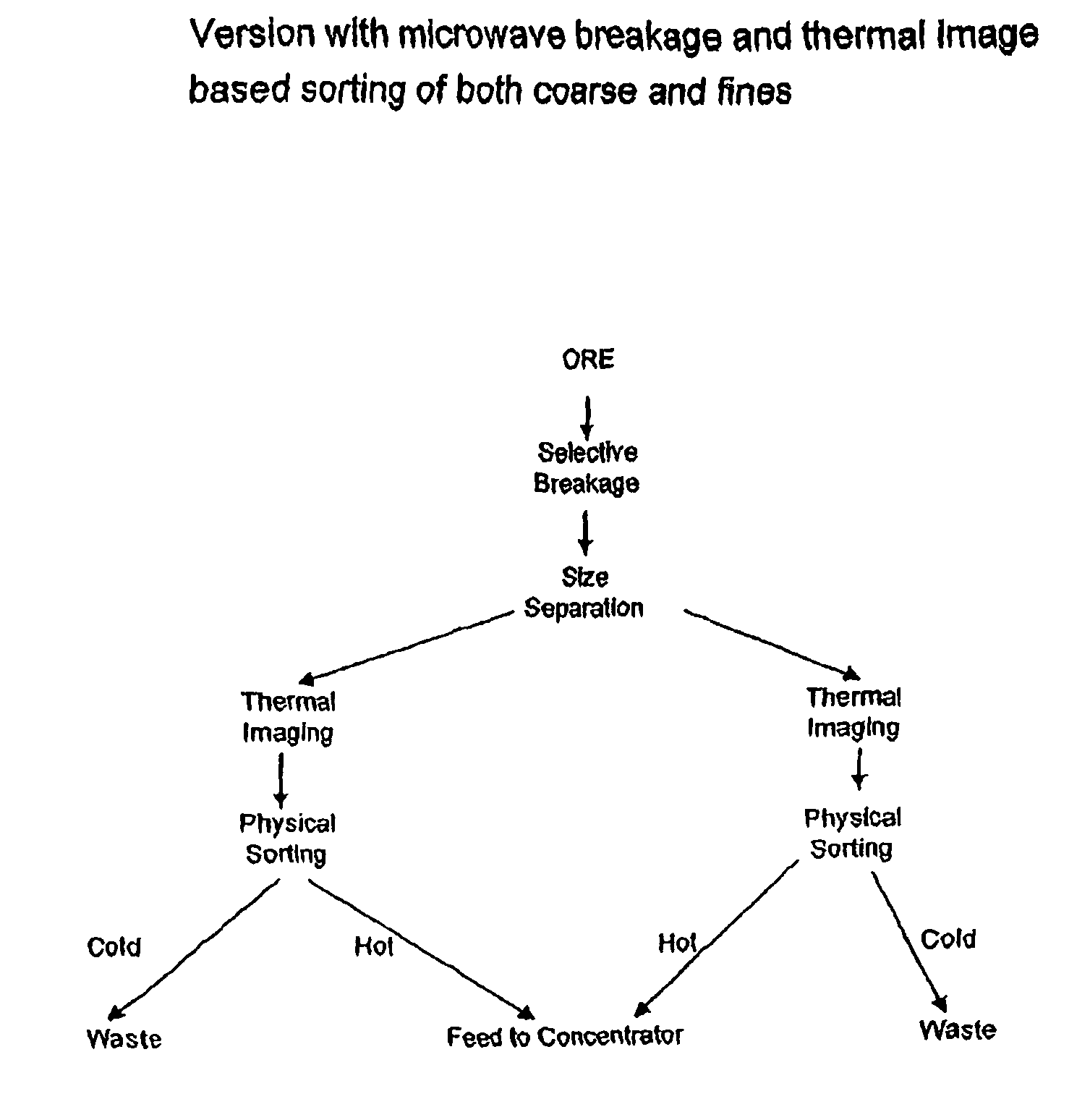
Sorting mined material
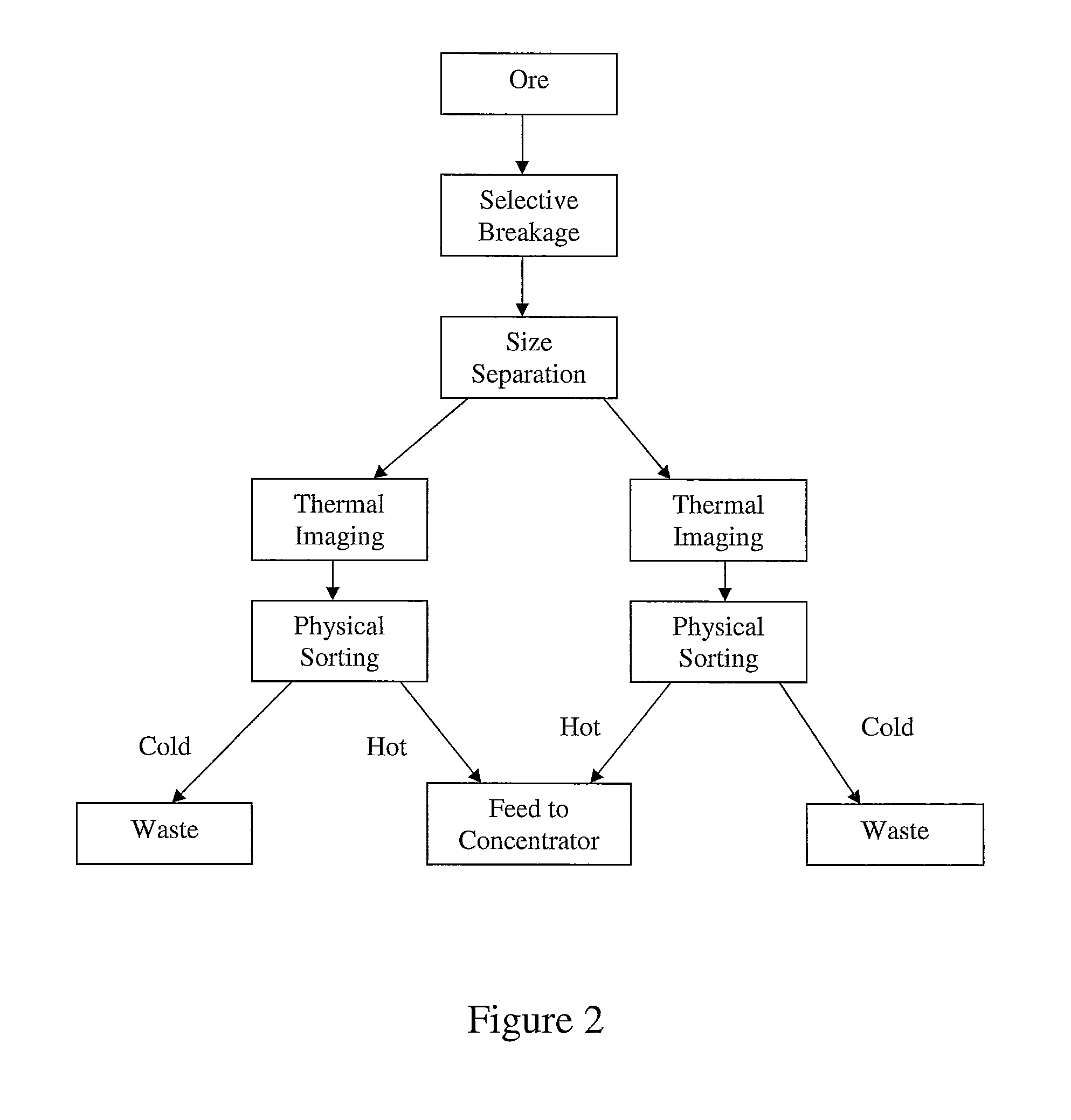
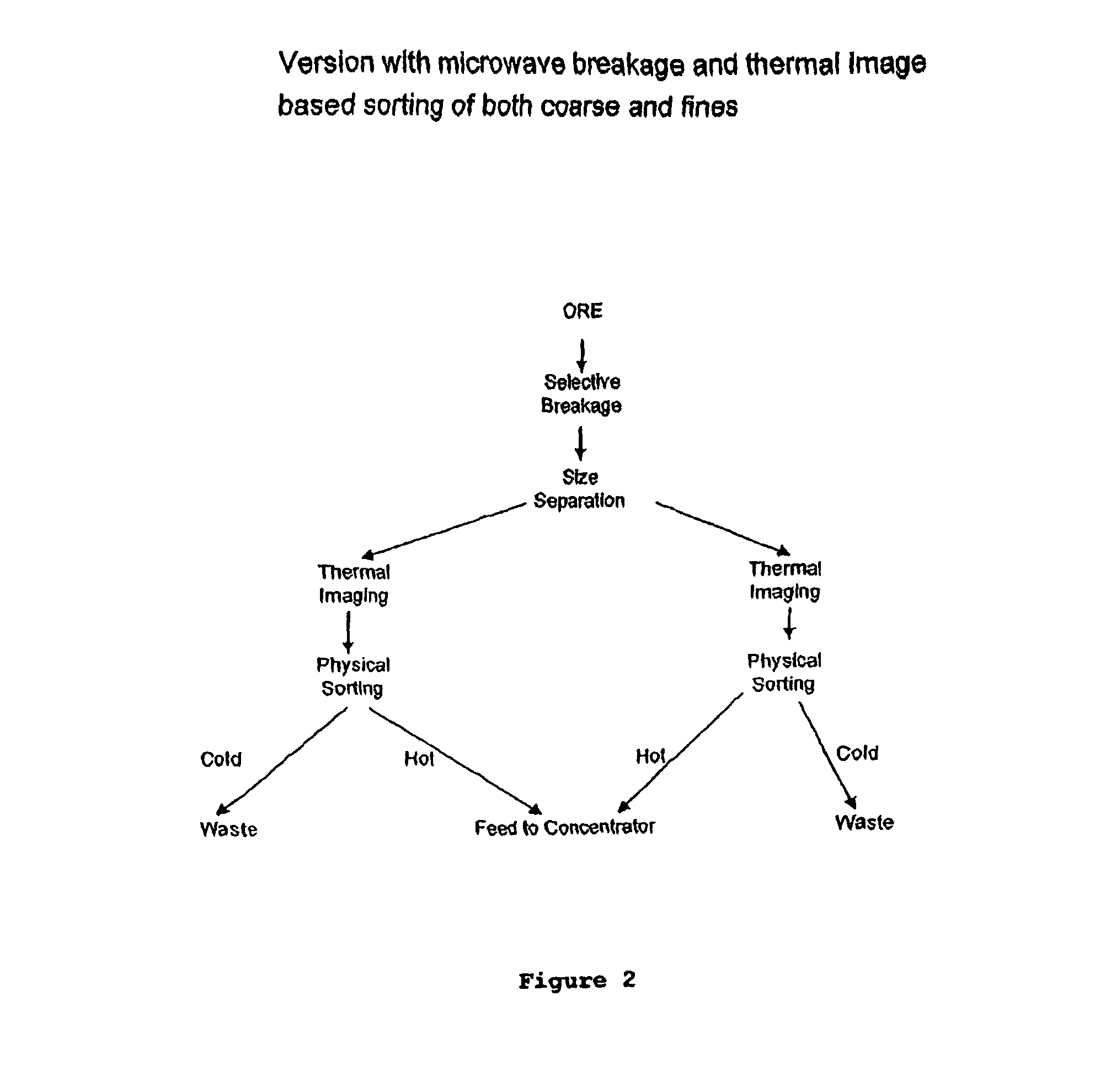
ActiveUS8820533B2Reduce the amount requiredMore capacityEarth material testingDifferential sedimentationMechanical engineeringThermography
A method of sorting mined material for subsequent processing to recover valuable material, such as valuable metals, from the mined material is disclosed. The method includes a combination of selective breakage of mined material, for example, by using microwaves and / or high pressure grinding rolls, subsequent size separation, and then particle sorting of a coarse fraction of the separated material based on differential heating and thermal imaging.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
Smart charging algorithm of lithium ion battery
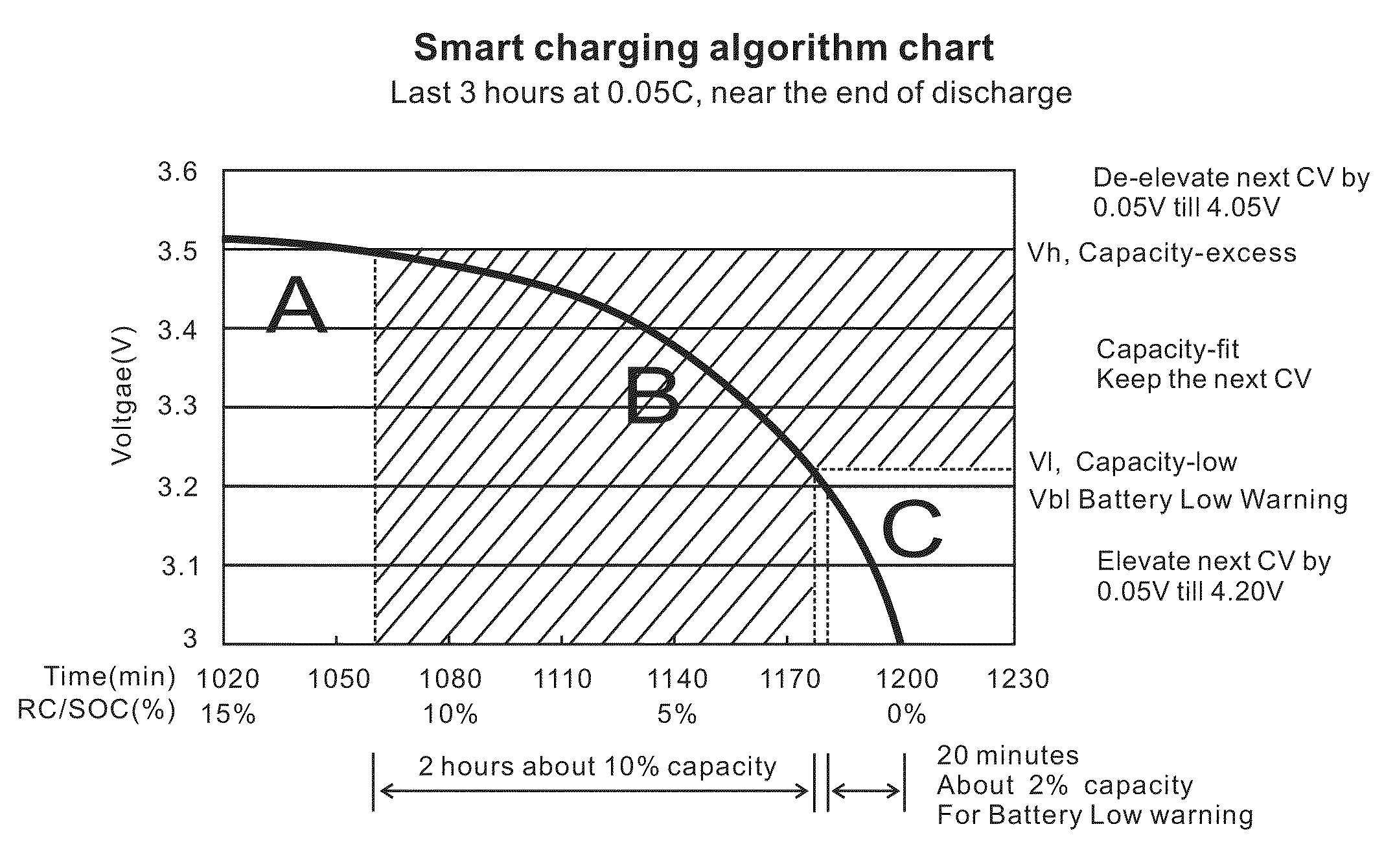
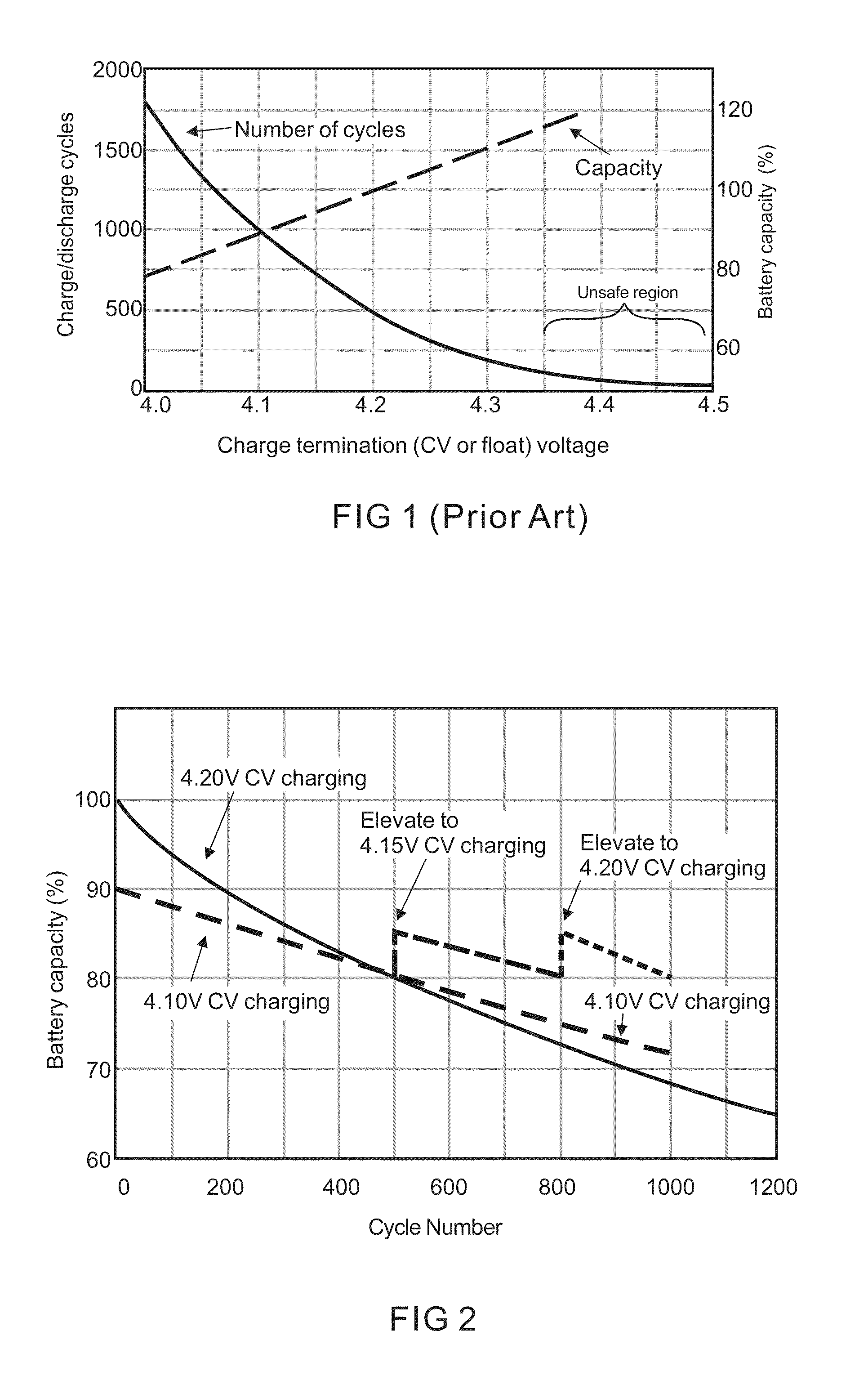
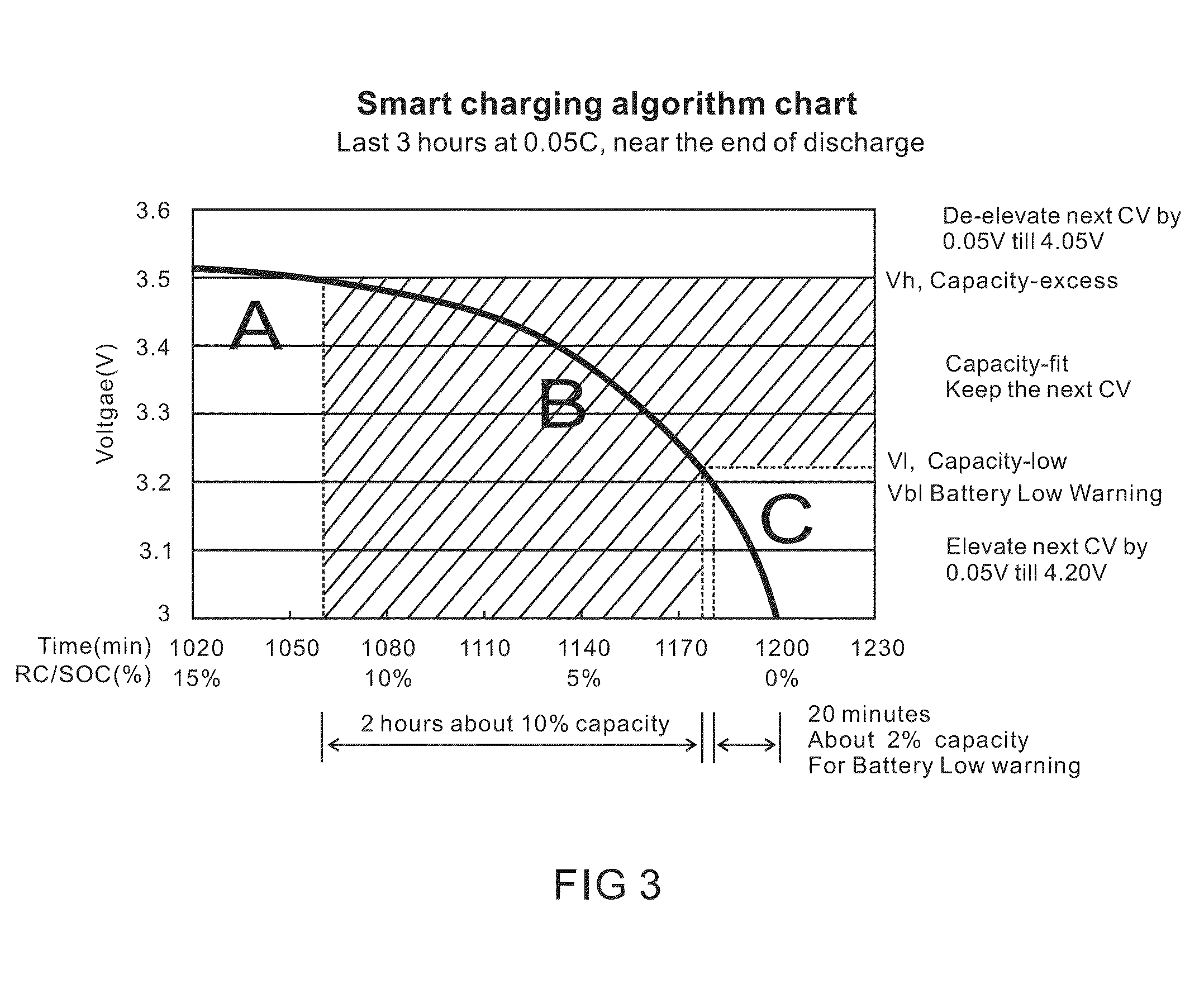
InactiveUS20140320089A1Increase demandImprove cycle lifeCircuit monitoring/indicationSecondary cellsState of chargeEngineering
A charging algorithm of lithium ion battery comprises at least one final stage wherein a maximum charging voltage is reached and the charging stops at said voltage. The state of charge or remaining capacity at the end of last discharging is measured and recorded, and said maximum charging voltage of last charging is also recorded. The maximum charging voltage of a new charging will be determined by said state of charge of last discharging and said maximum charging voltage of last charging. This novel charging algorithm provides longest possible cycle life for the daily used electronic devices while fully utilizes the battery capacity, and also fits the individual user's battery capacity consumption.
Owner:ZHUHAI ZHI LI BATTERY
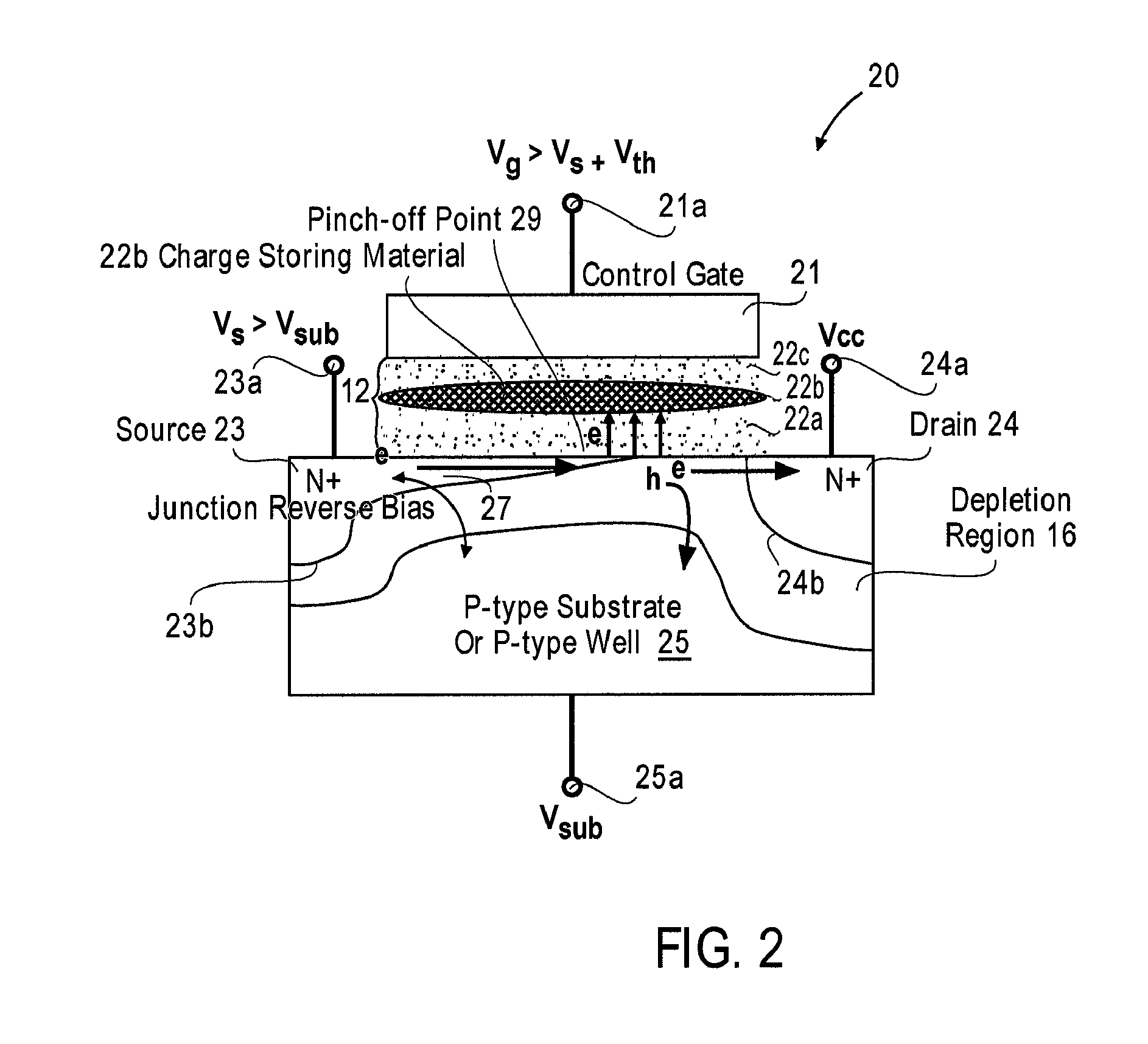
Method and structures for highly efficient hot carrier injection programming for non-volatile memories
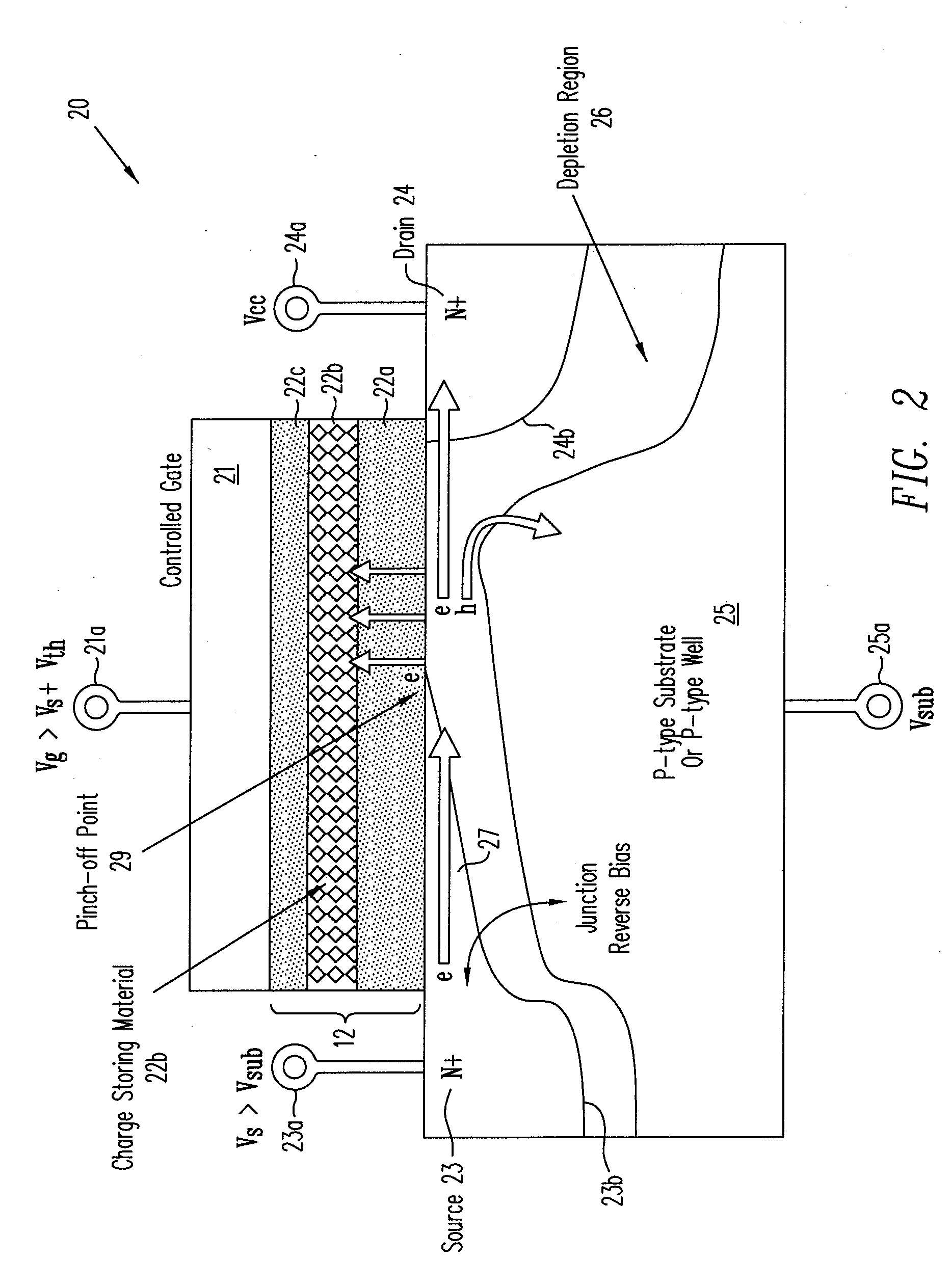
ActiveUS7733700B2High rateReduce voltage dropRead-only memoriesDigital storageMOSFETVoltage amplitude
A method programs a memory cell by controlling a reverse bias voltage across the PN junction between a source electrode of a MOSFET in the memory cell and the substrate, and pulling back the pinch-off point of the inversion region toward the source electrode, thereby increasing the programming efficiency of the memory cell. The method applies the main positive supply voltage Vcc to, the drain electrode of the memory cell from the chip main voltage supply, rather than the conventional method of using a higher voltage than Vcc. To optimize the programming condition, the source voltage and the substrate voltage are adjusted to achieve the maximum threshold voltage shifts under the same applied gate voltage pulse condition (i.e. using the gate pulse with the same voltage amplitude and duration regardless of the source voltage and the substrate voltage). The substrate voltage to the drain voltage can not exceed the avalanche multiplication junction breakdown for a small programming current during the bias voltage adjustment.
Owner:PEGASUS SEMICON SHANGHAI CO LTD
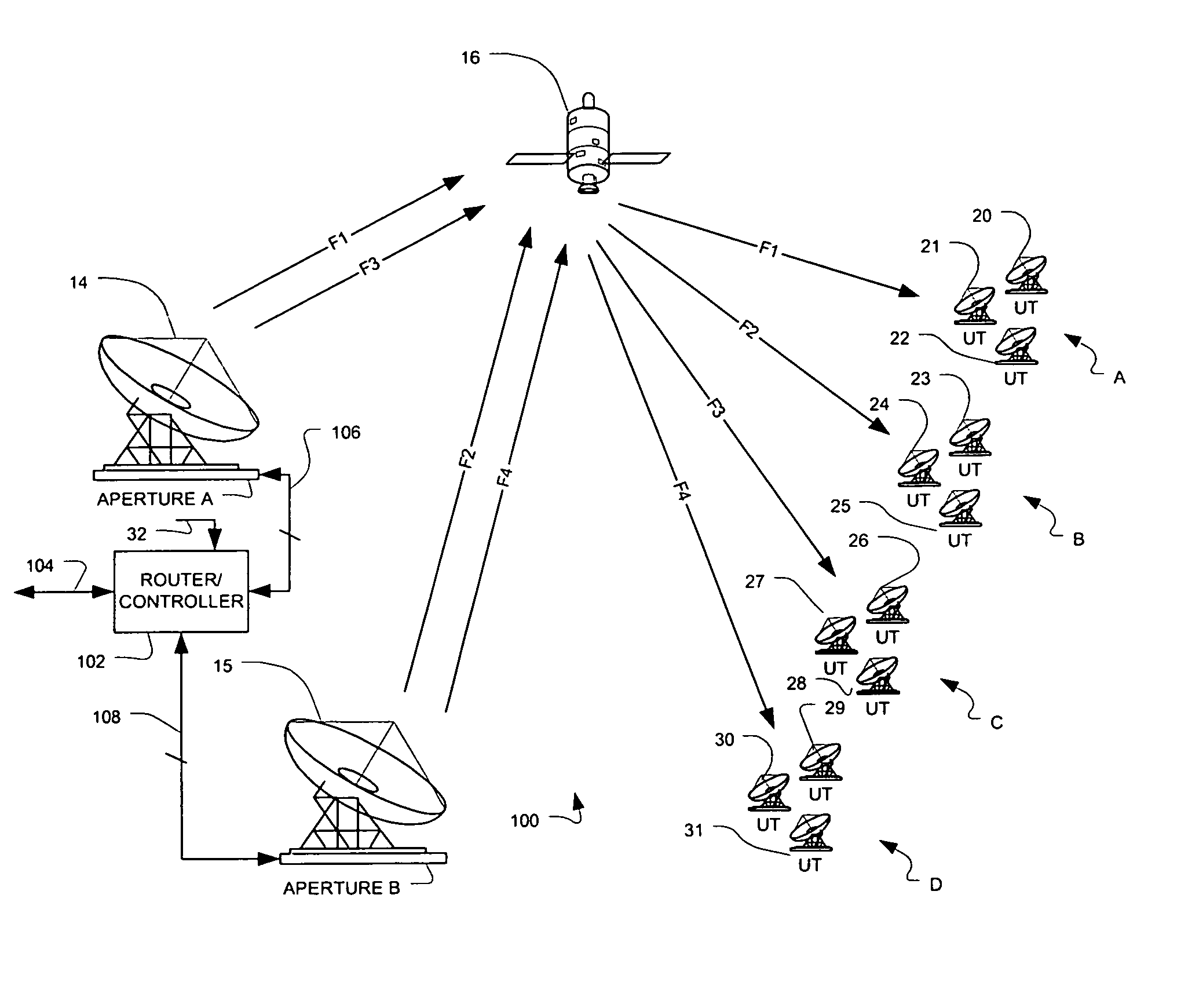
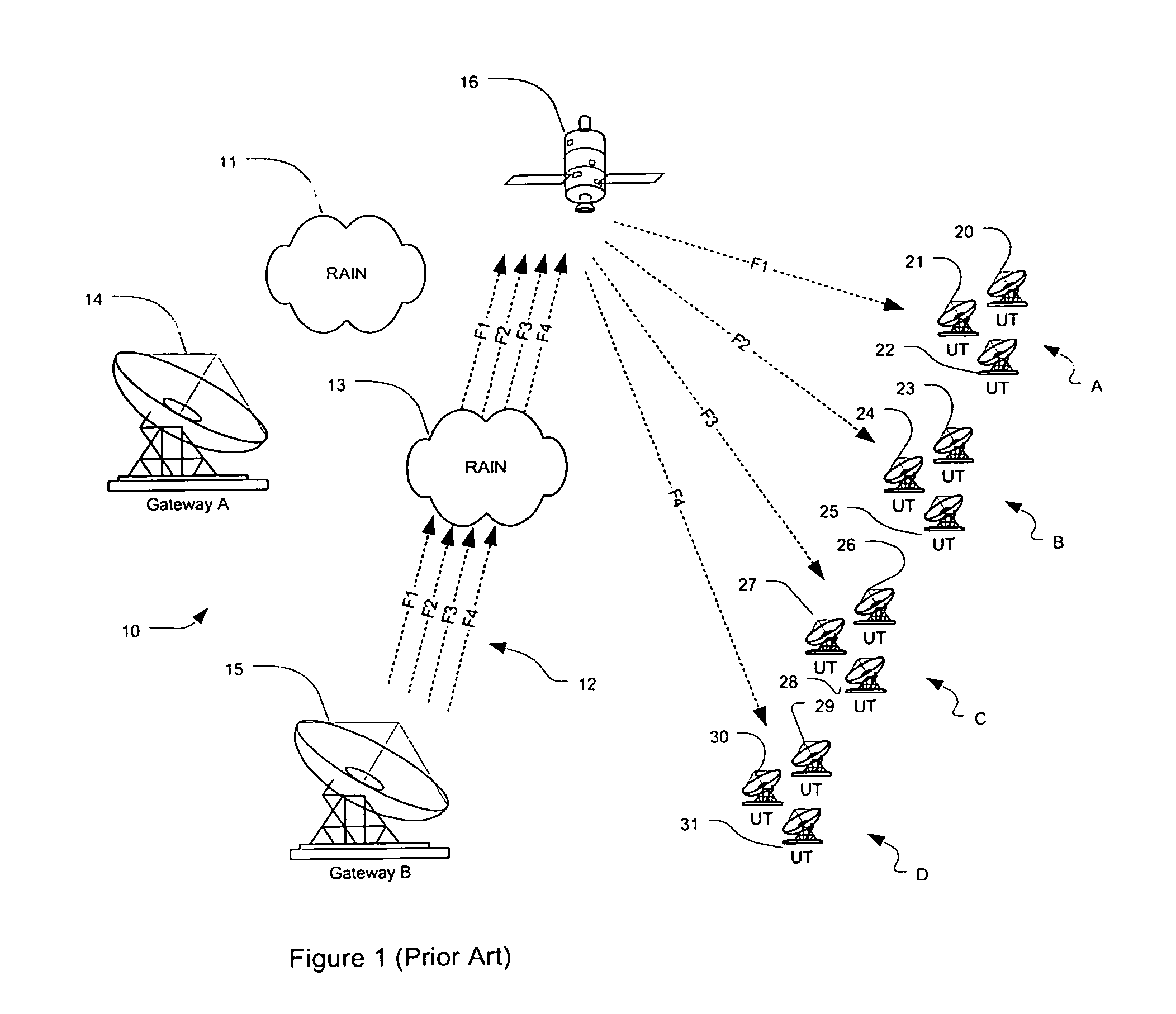
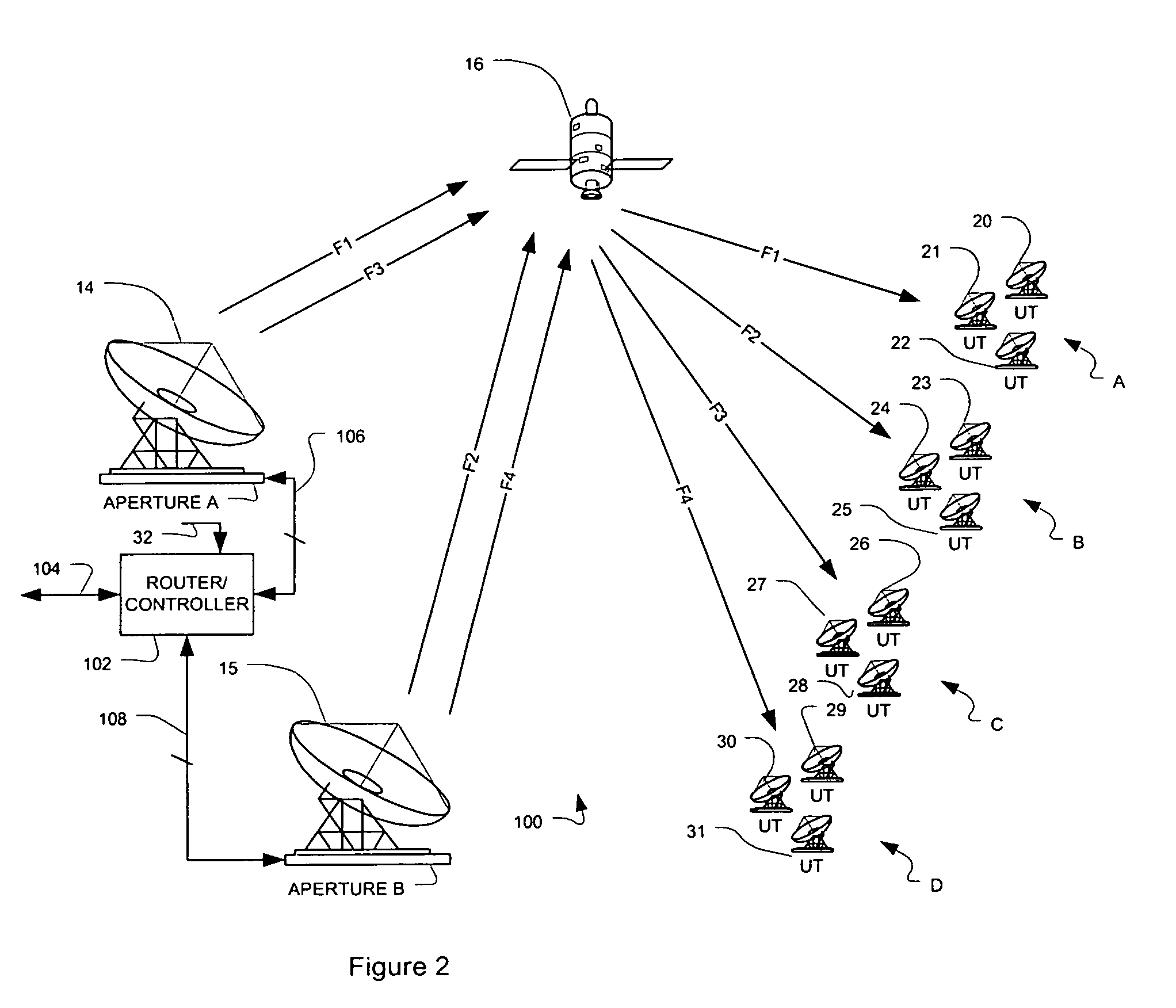
Soft diversity satellite gateway architecture
ActiveUS7584297B1Reduces gateway costImprove effectivenessNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsTelecommunicationsData rate
Methods and systems are provided for satellite communication wherein a plurality of geographically-separated apertures are controlled by a central controller that analyzes link availability of each aperture and then user connectivity is prioritized above a minimum user data rate, whereupon the gateway-established data rate of lower priority users is reduced to allocate more capacity to highest priority users, which are routed through available links in order to better optimize a gateway architecture, to reduce gateway costs and to improve effective performance in the presence of atmospheric interference events.
Owner:VIASAT INC
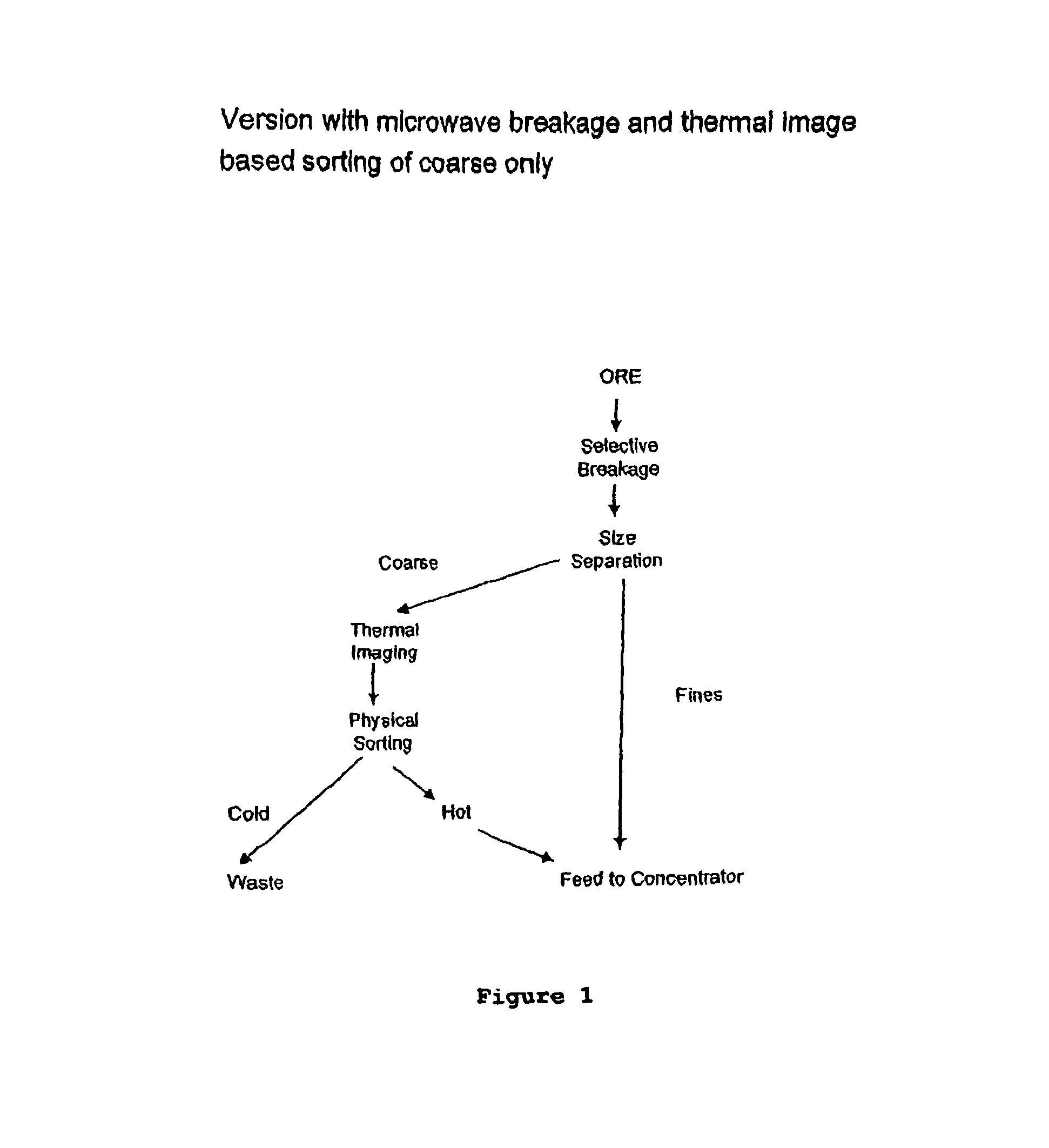
Sorting mined material
ActiveUS8240480B2Minimize powerMaximises thermal cyclingRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsEarth material testingMicrowaveParticle sorting
A method of sorting mined material for subsequent processing to recover valuable material, such as valuable metals, from the mined material is disclosed. The method includes a combination of selective breakage of mined material, for example, by using microwaves and / or high pressure grinding rolls, subsequent size separation, and then particle sorting of a coarse fraction of the separated material based on differential heating and thermal imaging.
Owner:TECHNOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Refrigerant Dehumidification System with Variable Condenser Unloading
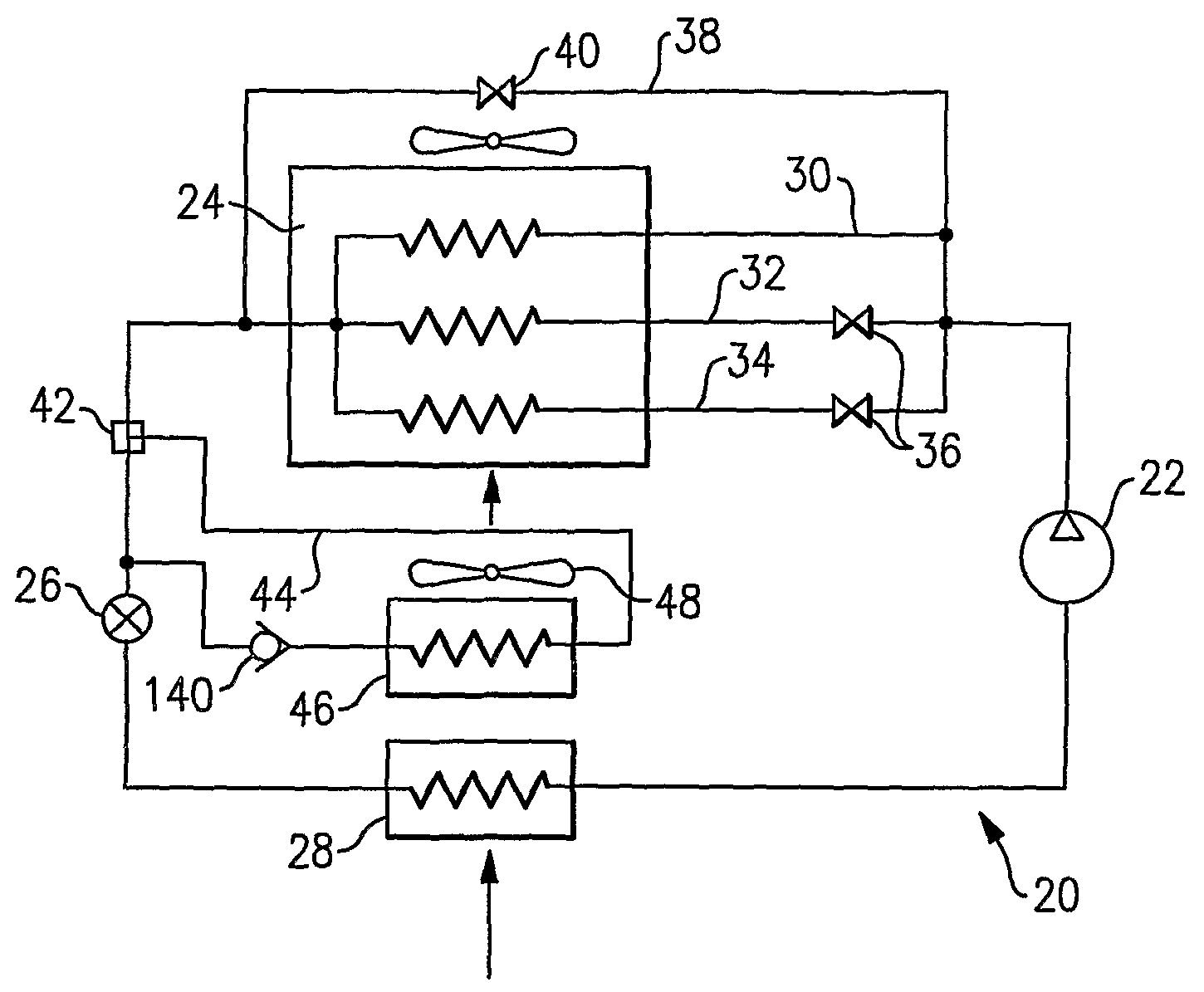
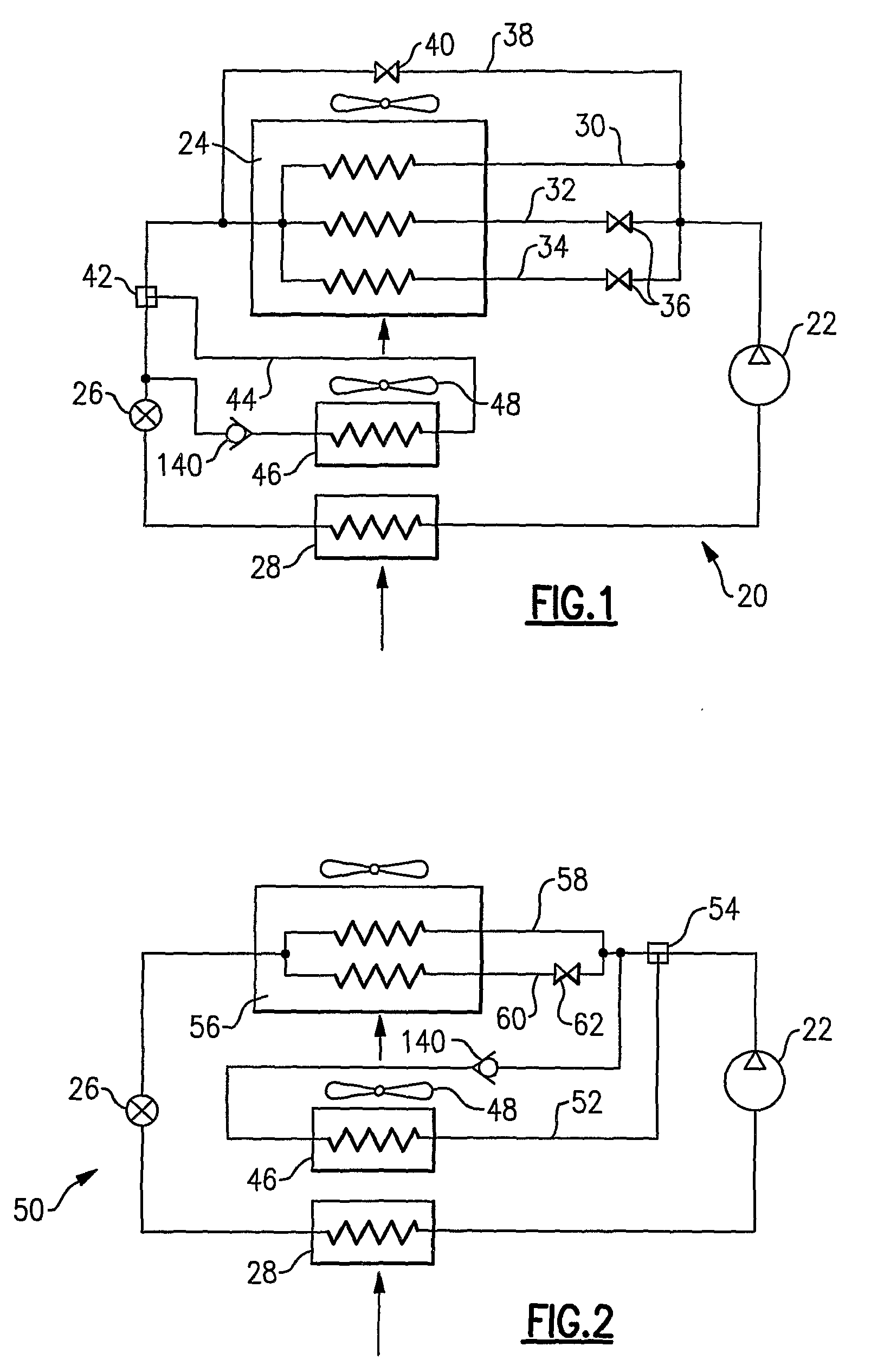
InactiveUS20080229764A1More reheat capacityLess heatCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCompression machines with several condensersEngineeringRefrigerant
A condenser in a refrigerant system is provided with a plurality of refrigerant circuits, with at least one of the plurality of circuits being equipped with a shut off device. A reheat coil is also incorporated into the refrigerant system to provide enhanced dehumidification functionality. By selectively shutting off at least one of the active refrigerant circuits in the condenser, the amount of heat rejected by the condenser as well as by the reheat coil can be controlled shifting the heat load between the condenser and reheat coil. In this manner, and in combination with operation of the reheat cycle, incremental dehumidification and cooling / heating can be provided and humidity and temperature can be precisely controlled.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Method to optimize the communication parameters between an access point and at least one client device
ActiveUS20140307571A1Increase volumeWide bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsClient-side
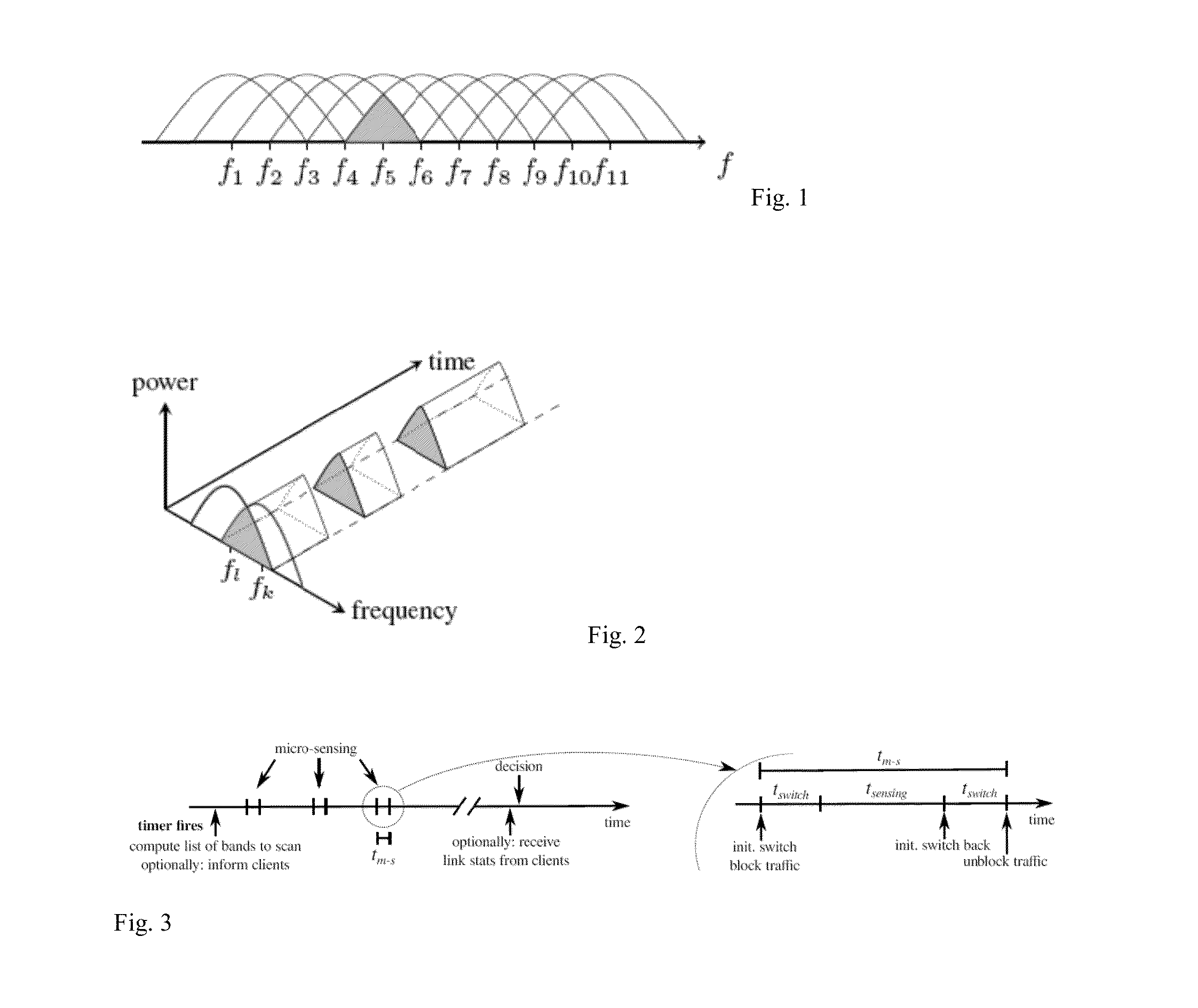
A method to optimize the communication on a channel between an access point and at least one client device, said channel being characterized by a center frequency and a bandwidth, comprises: establishing a connection on a first channel according to a first center frequency and a first bandwidth; exchanging data through this first channel between the access point and the client device; monitoring a first interference level on the first channel; the access point, while the data are exchanged, executes: informing the client device to switch to a second channel having a different center frequency and / or a different bandwidth; determining a second interference level on the second channel; comparing the first interference level with the second interference level; deciding to switch back or keep the second channel based on the comparison.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Drive System For An Aircraft And Method For Supplying Drive Power For An Aircraft
InactiveUS20190241274A1Improve electrical reliabilityReduce failure rateBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power distributionElectricityFlight vehicle
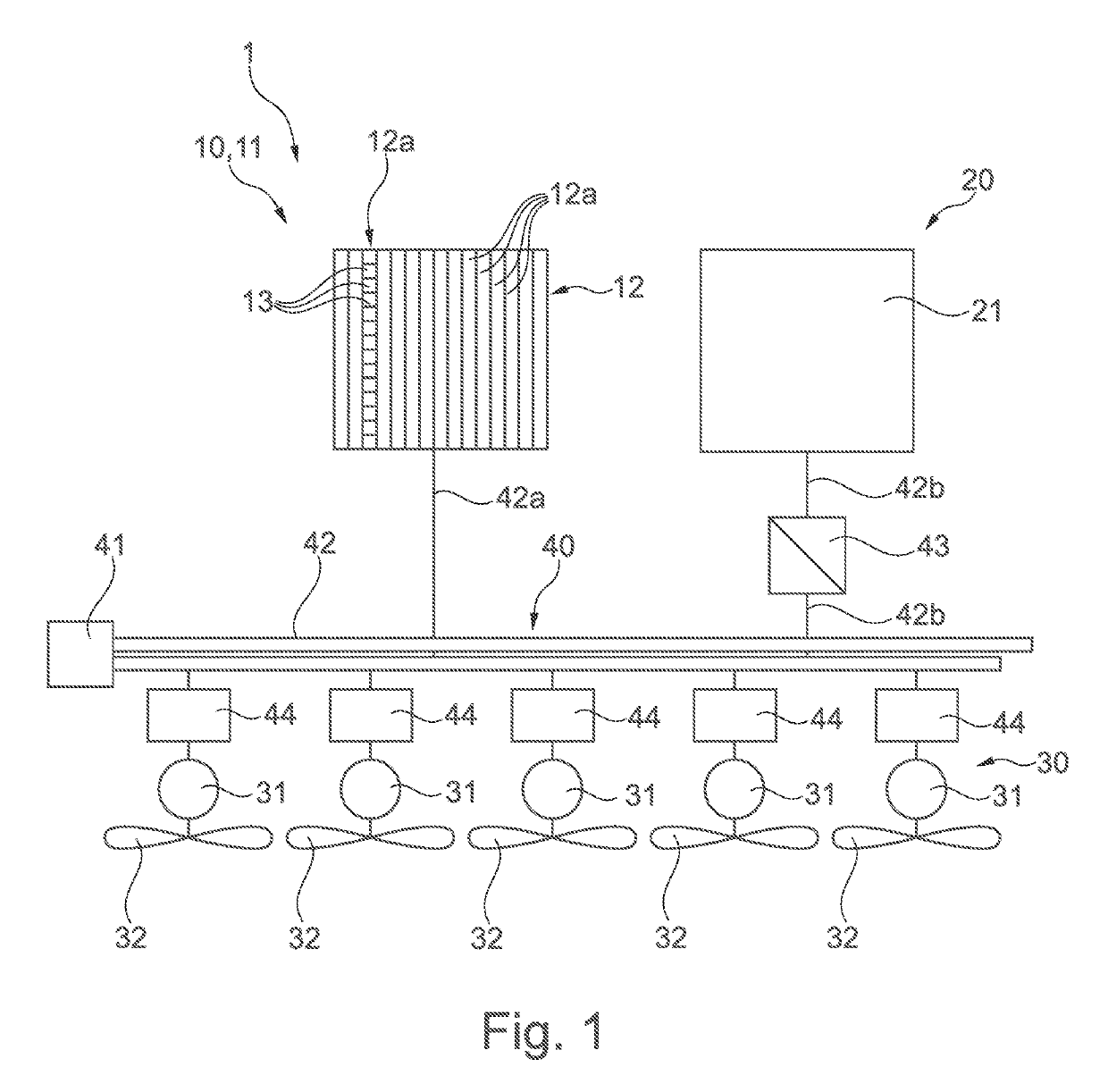
A drive system for an aircraft has a first energy store for supplying electrical energy, a second energy store for supplying electrical energy, and an electric drive for supplying drive power for the aircraft. An energy distribution unit of the drive system is designed to transmit the supplied electrical energy of the first energy store and the supplied electrical energy of the second energy store to the electric drive. The energy distribution unit is also designed to charge the second energy store using a first portion of the energy supplied by the first energy store and at the same time to transmit a second portion of the energy supplied by the first energy store to the electric drive, in order to supply the drive power for the aircraft. An aircraft having a drive system and a method for supplying drive power for an aircraft are disclosed.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com