Patents
Literature
3718 results about "Operating time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Operating time(Noun) The time interval between the instant of the occurrence of a specified input condition to a system and the instant of completion of a specified operation.
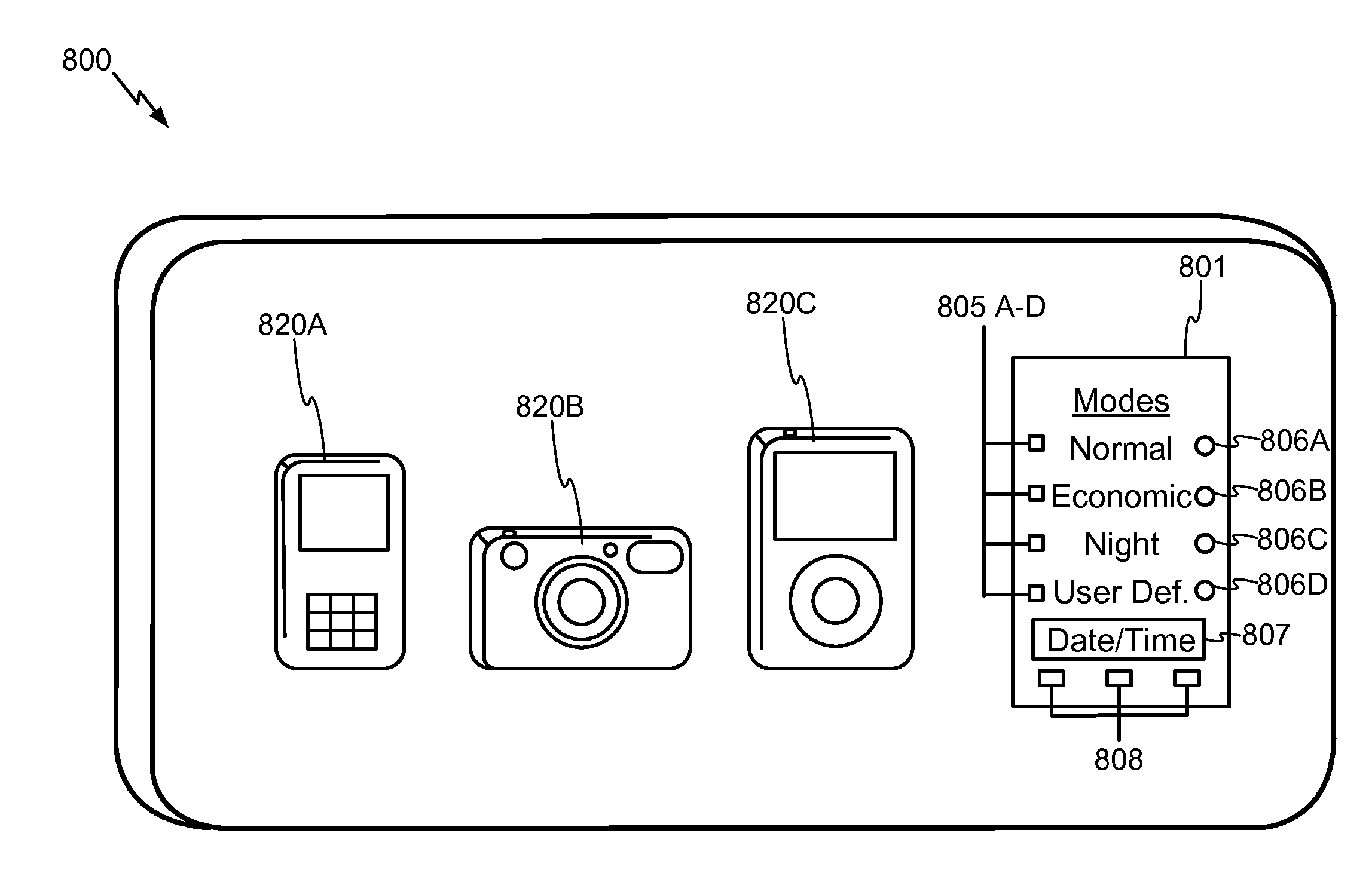
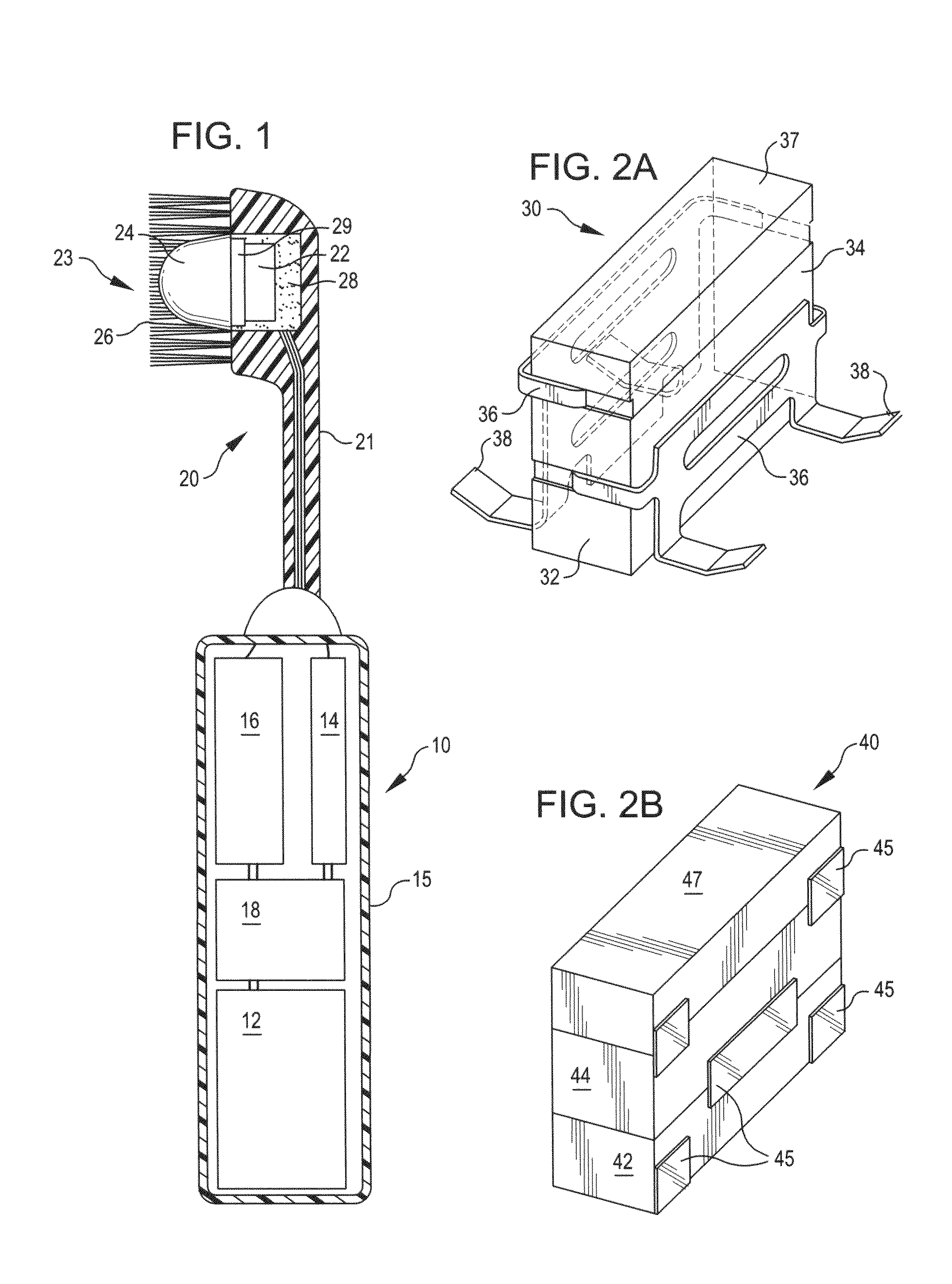
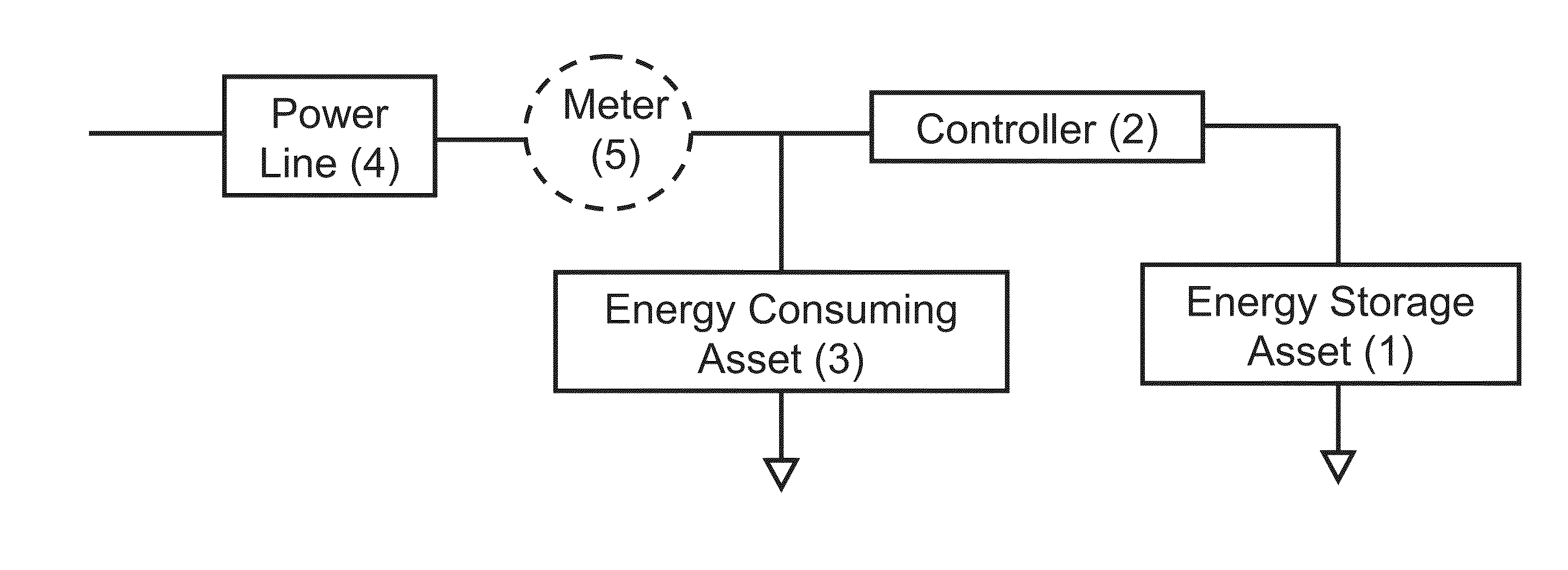
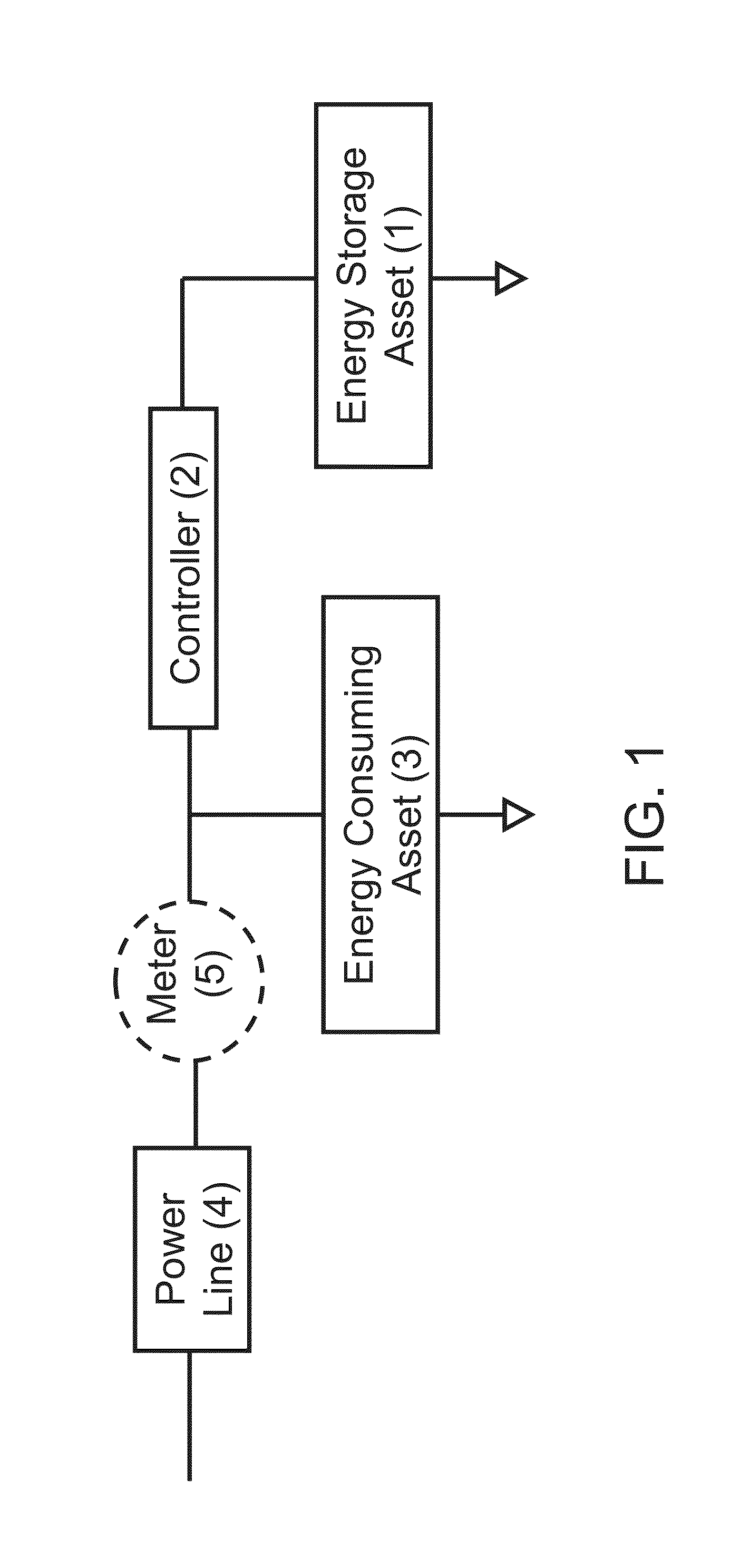
Wireless power charging timing and charging control
ActiveUS20100213895A1Control moreReduce energy costsElectromagnetic wave systemMobile unit charging stationsEnergy rateTime schedule
Exemplary embodiments are directed to timing and control of wireless power transfer. A wireless power charging device includes at least one transmitter and a processor in communication with the at least one transmitter. The transmitter is configured for transmitting wireless power to one or more electronic devices, and the processor is configured to deactivate the transmitter during a pre-determined time interval. The charging device may include charging modes that a user may select between from an interface of the charging device. Charging modes may be related to times of operation such as those based on a user schedule, based on energy rates, or with modes programmed by a user. A charging schedule may be created by a user through the interface of the charging device or from an external device in communication with the charging device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
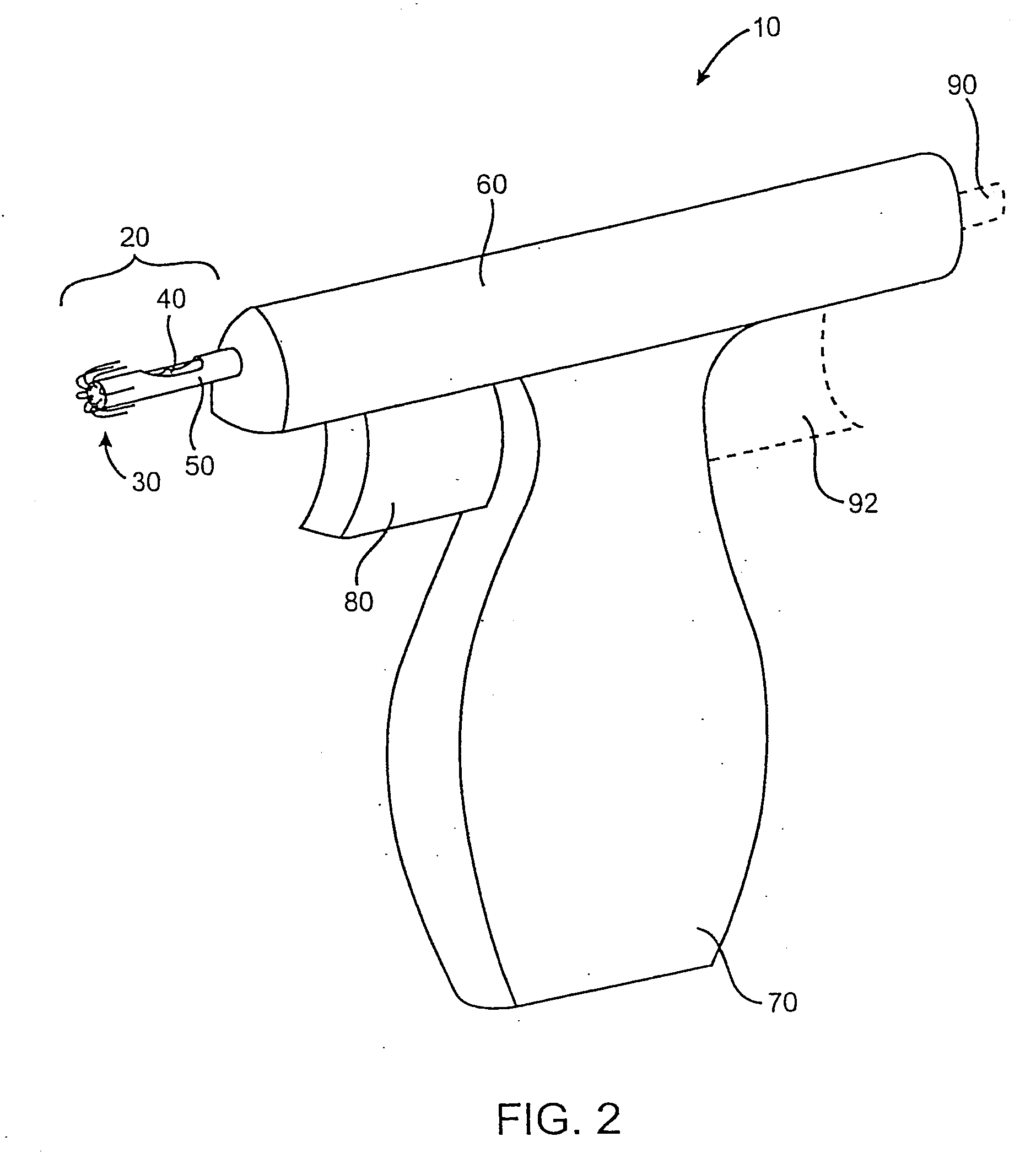
Electrical surgical instrument with optimized power supply and drive
ActiveUS20070270884A1Comfortably fit into a user's handReduce manufacturing difficultySuture equipmentsStapling toolsActuatorOperating time
A surgical instrument includes an end effector having an actuator effecting a surgical procedure when actuated, an electric motor operating the actuator, and a power supply actuating the actuator when power is supplied to the motor. The power supply has a battery cell with a given rated power for an operating period of over 15 seconds and for a total aggregate operating time of over 300 seconds. The motor and power supply are configured to utilize the battery cell at a power greater than the given rated power. The motor characteristics are selected to utilize the battery cell for periods of operation of less than 16 seconds and for a total aggregate operating time of less than 300 seconds. A one-handed handle contains all of the power supply, at least part of an anvil control assembly, and at least part of an electrically-powered stapler / cutter control assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
Atomic layer deposition apparatus
InactiveUS20060137608A1Uniform thicknessEasy to controlChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringAtomic layer deposition
An atomic layer deposition (ALD) apparatus is, suitable for thermal ALD and plasma-enhanced ALD of conductive and non-conductive films. The ALD apparatus can maintain electrical insulation of a gas dispersion structure, such as a showerhead assembly, which acts as an RF electrode to generate plasma inside a reaction chamber while depositing electrically conductive films in the reaction chamber. Fine tubules of micro-feeding tube assembly prevents plasma generation in them and reactive gases each have separate flow paths through the micro-feeding tube assembly. Process gases out of the micro-feeding tube assembly enter narrow grooves of a helical flow inducing plate and form helical flows which mix well each other. Symmetrically mounted pads on showerhead assembly and flow guiding plate maintain a symmetrical gap through which an inert gas flows continuously to keep reactive gases outside the gap and unwanted film deposition in the gap. Longer operating time before maintenance (cleaning) and thus higher productivity can be achieved.
Owner:ASM GENITECH KOREA
Communication device
ActiveUS20130310020A1Suppress power consumptionExtend continuous operation timePower managementCurrent supply arrangementsEngineeringLimit value
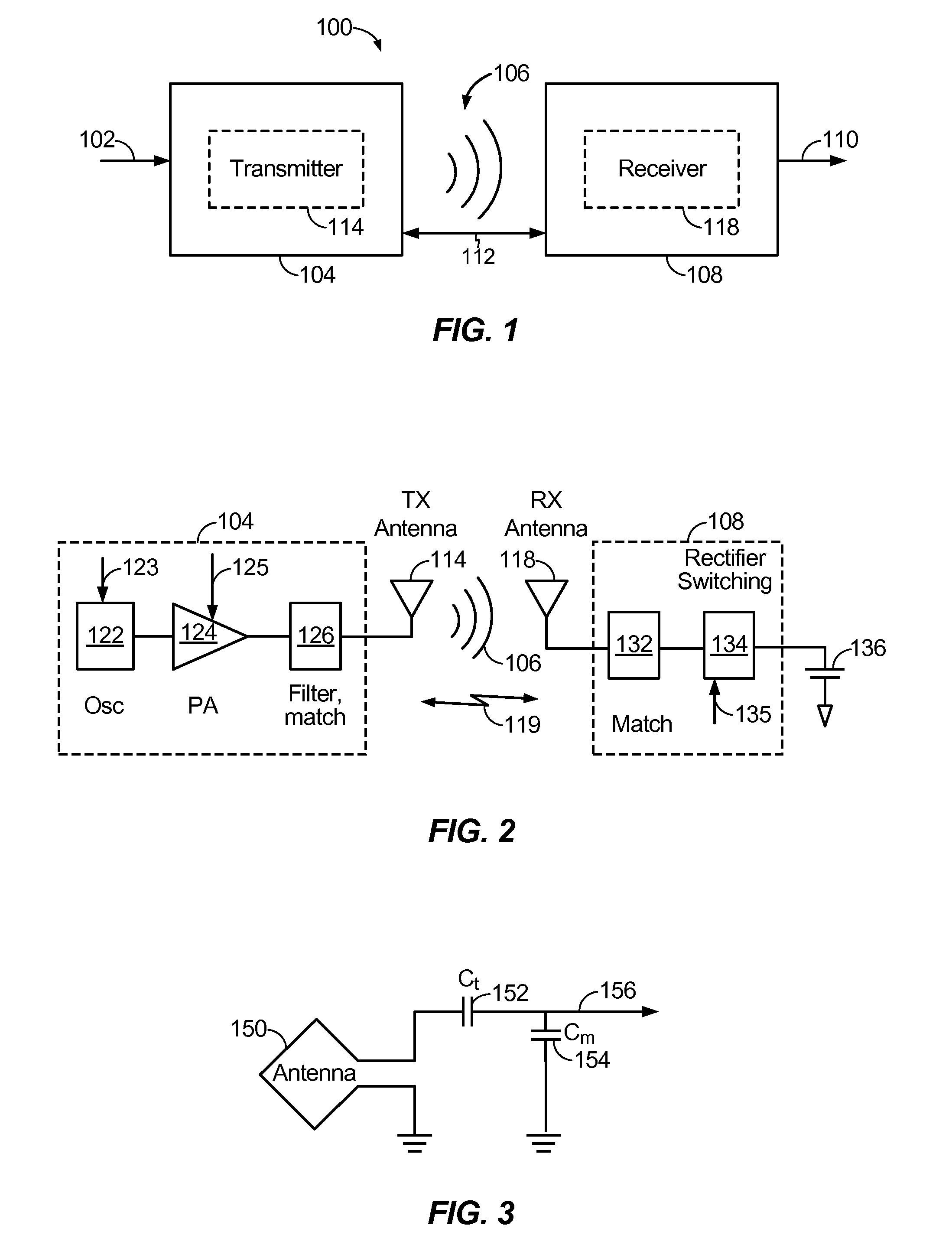
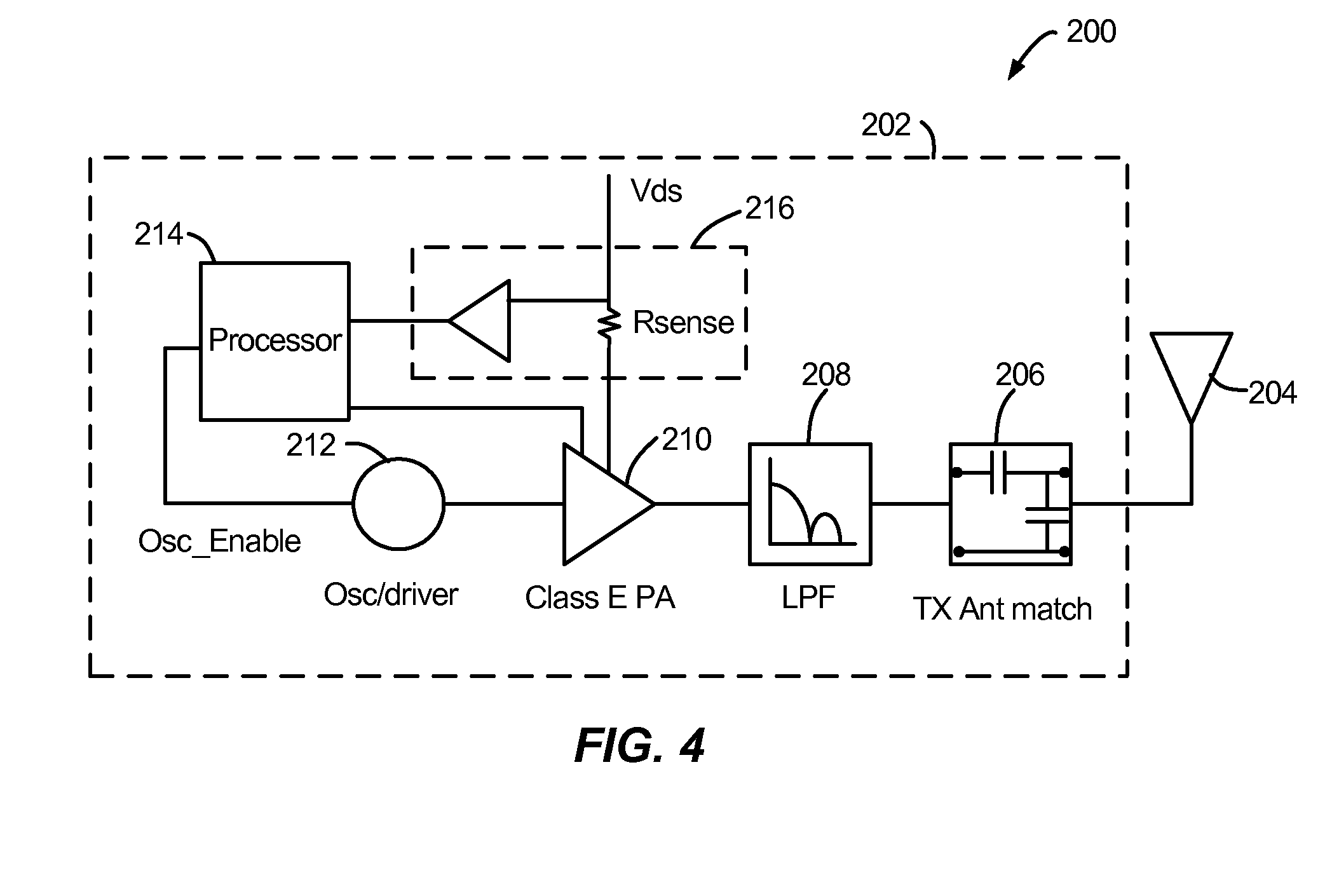
Provided is a wireless transmitter-receiver capable of suppressing undesirable power consumption and elongating the continuous operation time by operation of a user with the intention of controlling transmission power and also suitable to secure the “symmetry of communication”.The wireless transmitter-receiver decreases the upper limit value of transmission power by an operation of an operation means 114 and decreases the reception sensitivity in accordance with the decreased upper limit value of transmission power. Thereby, a user can determine the upper limit value of transmission power of the wireless transmitter-receiver and manage the transmission power to suppress power consumption and elongate a continuous operation time. Moreover, the wireless transmitter-receiver can eliminate the influence of radio frequency electromagnetic field on a human body. Furthermore, the degree of imbalance in the “symmetry of communication” can be minimized.
Owner:KAZUHIRO YAMAMOTO
Round-shank bit for a coal cutting machine
InactiveUS6199956B1Sufficient supportLess stressPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesMaximum diameterEngineering
A round-shank bit for a coal cutting machine or the like, having a bit head and a bit shank, wherein the bit head has a bit tip, maintained by a base element in a receptacle of the bit head. Starting at the base element, the bit tip tapers in a direction toward the free end of the bit tip, wherein the base element forms a maximum diameter of the bit tip, and wherein the bit tip has recesses on its outer contour. In order to assure good rotational behavior over the entire length of the operating time, the base element has the recesses on an outer circumference forming the maximum diameter.
Owner:BETEK BERGBAU UND HARTMETALLTECHN KARL HEINZ SIMON
Integrated multi-touch surface having varying sensor granularity
ActiveUS20080309631A1Easy inputFine granularityDigital data processing detailsSubstation equipmentGranularityComputer science
This relates to an event sensing device that includes an event sensing panel and is able to dynamically change the granularity of the panel according to present needs. Thus, the granularity of the panel can differ at different times of operation. Furthermore, the granularity of specific areas of the panel can also be dynamically changed, so that different areas feature different granularities at a given time. This also relates to panels that feature different inherent granularities in different portions thereof. These panels can be designed, for example, by placing more stimulus and / or data lines in different portions of the panel, thus ensuring different densities of pixels in the different portions. Optionally, these embodiments can also include the dynamic granularity changing features noted above.
Owner:APPLE INC
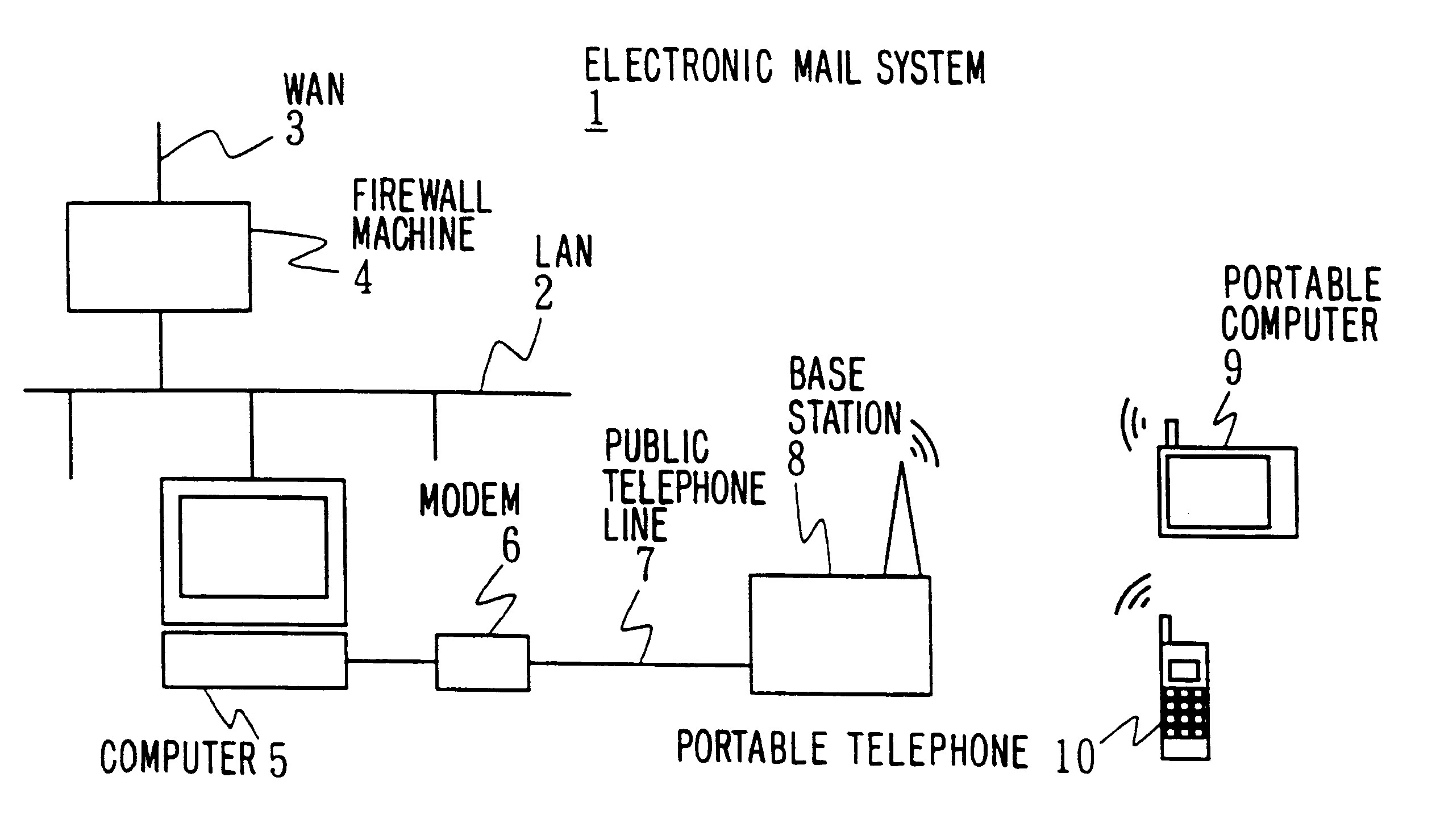
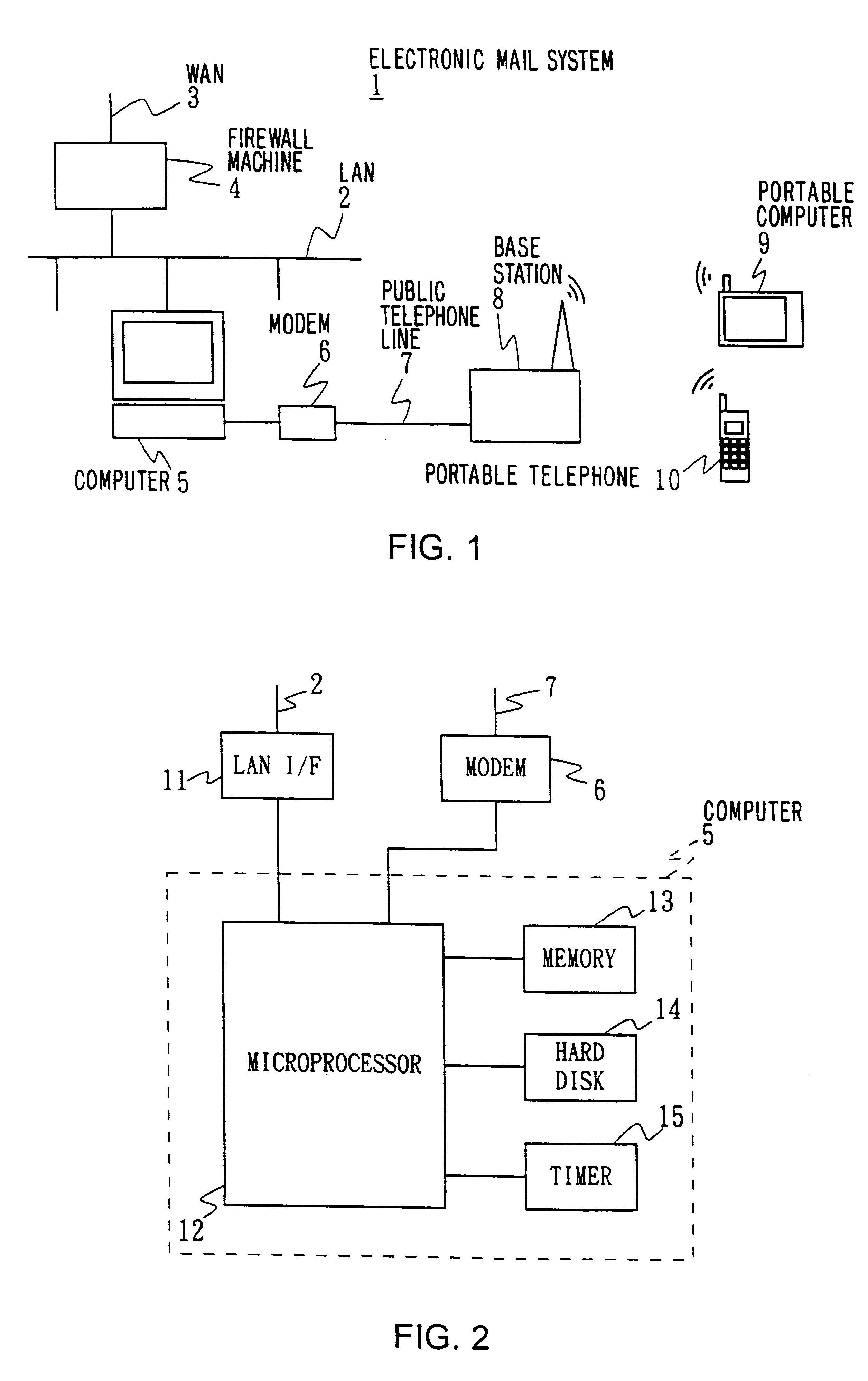
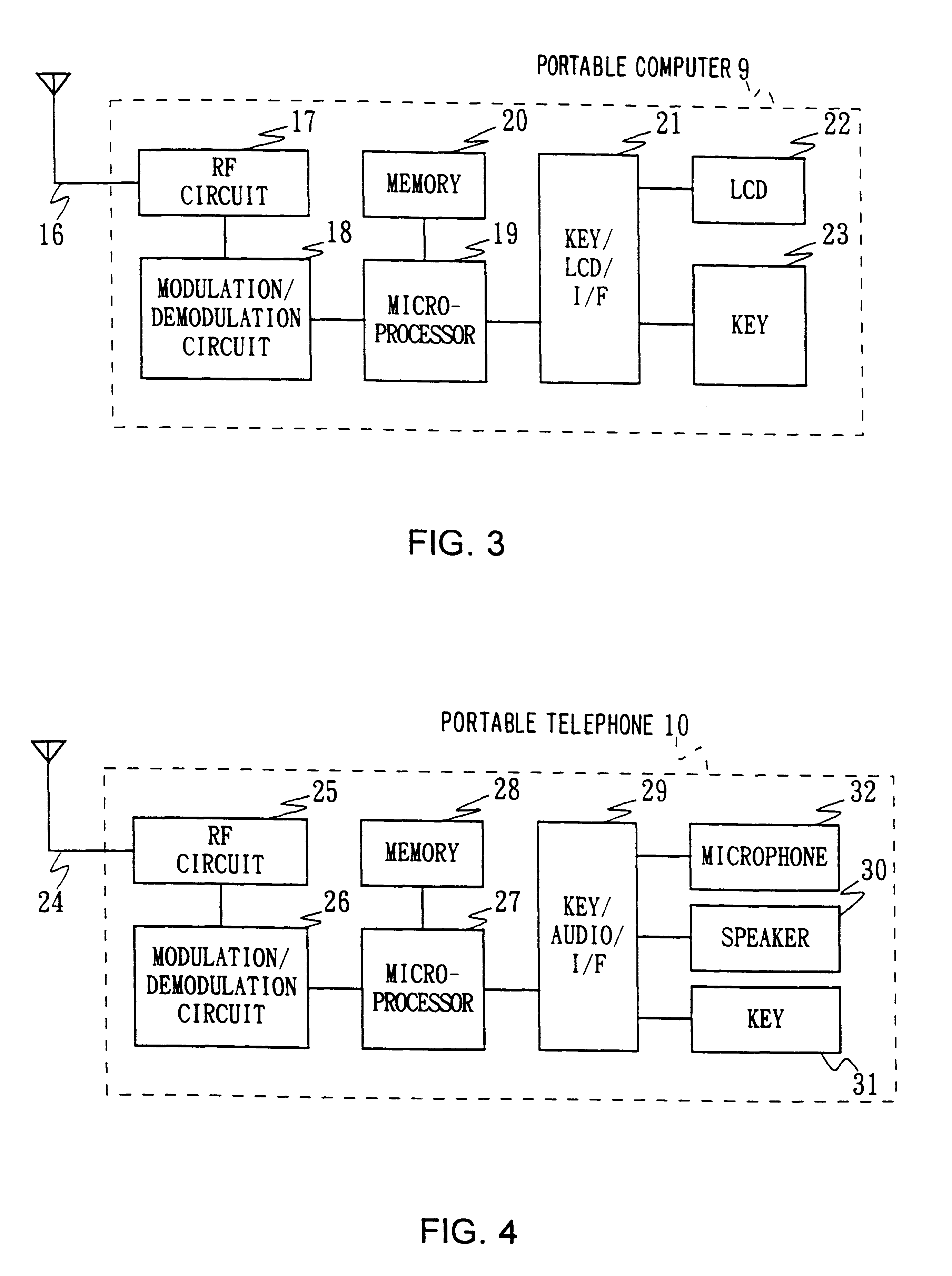
Electronic mail system, computer device, and remote notification method
InactiveUS6237027B1Wasteful consumption of battery powerUnnecessary accessPower managementNetwork topologiesCommunication unitTerminal equipment
In an electronic mail system, including a computer device and an arrival notification method, a user can confirm an arrival of electronic mail regardless of where he is and a drop in operating time of a portable information terminal device can be prevented. The computer device has a first communication unit for receiving and transmitting the electronic mail from / to other computer devices and detecting the arrival of electronic mail, a second communication unit for communicating with the portable information terminal device through a predetermined communication circuit, a memory wherein identification information of the portable information terminal device is stored, and a communication controller for informing the arrival of electronic mail to the portable information terminal device based on the identification information when the arrival of electronic mail is detected. Since the arrival of electronic mail is informed to the portable information terminal device side from the computer device side, the arrival of electronic mail can be informed to the user who is away from the computer device side, thus making the access from the portable information terminal device side unnecessary so that, wasteful consumption of battery power can be avoided.
Owner:SONY CORP
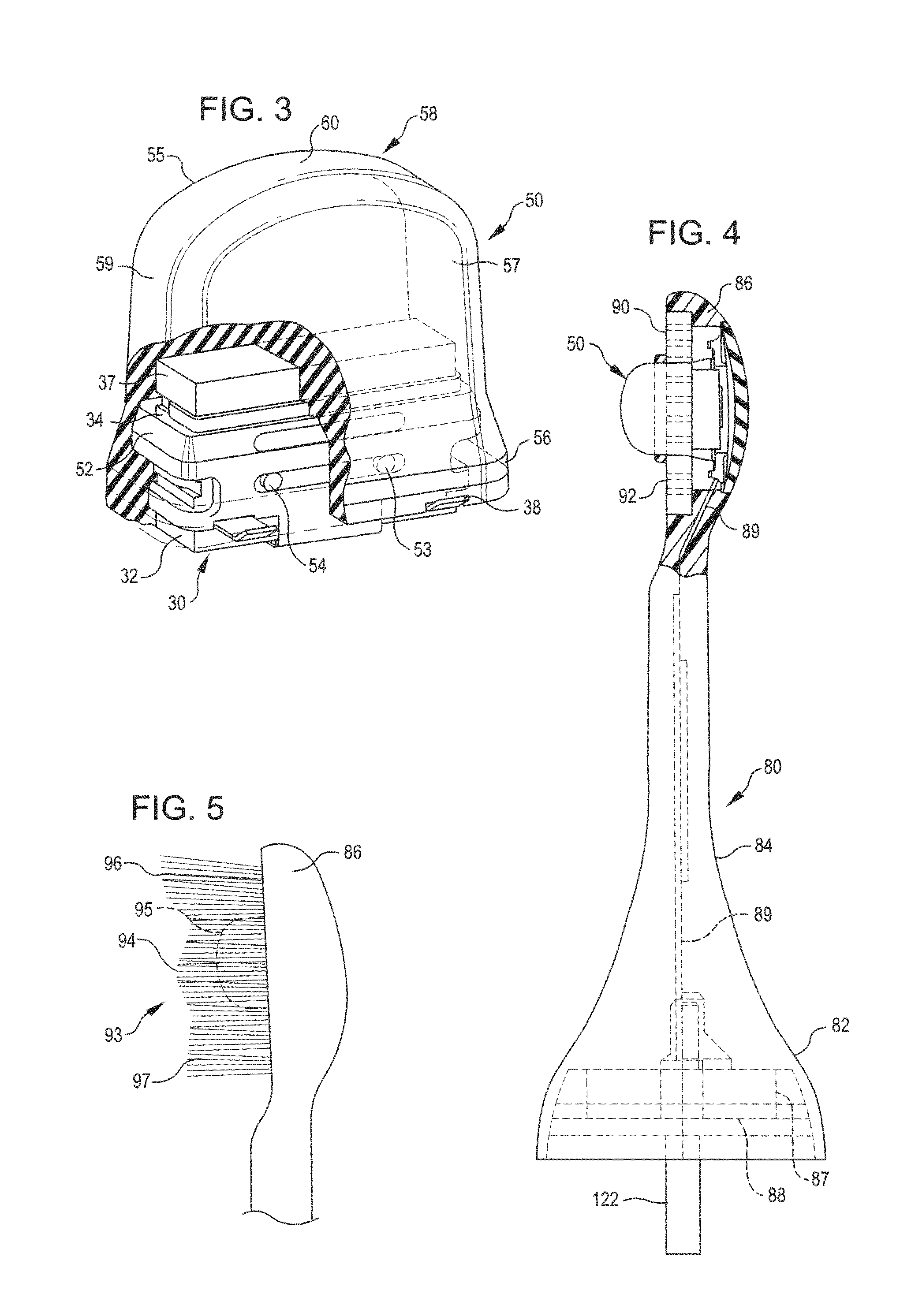
Remote camera relay controller method and apparatus
InactiveUS6400903B1Reduce transmit powerReduction in Eb/NoTelevision system detailsProjector film strip handlingModem deviceTelecommunications link
A remote camera relay method and apparatus for remotely operating a self-contained, unattended digital camera over a communications link. Format conversion means are included for transparently relaying control signals and remote image data between a local host processor and the remotely located digital camera, independently of specific camera command and image protocols. It thereby functions as a universal remote image transmission adapter, operable as an attachment for use with self-contained digital cameras. A portable enclosure is provided for accommodating the remote relay communications and control electronics and for attaching a hand-held digital camera thereto. Further means are included for remotely actuating the pan and tilt orientation of the camera in accordance with field-of-view selection commands. Data rate conversion and error correction coding are included for providing reliable, low power image forwarding. The communications channel could be a dial-up telephone system, a network connection, modem, an infra-red link or a wireless RF link, for example. Additional control means are provided for remotely selecting the camera field of view for image capture, and includes the ability to access only those subsets of image scenes for which viewing permissions are authorized. A further mode of operation includes protocol training whereby host photographing commands are captured by the remote relay invention during on-line operation, then replayed at programmed times resulting in automatic scheduled remote image capture. Power management is provided for maximizing operating time when used in low power, portable, battery operation.
Owner:CONOVAL PAUL
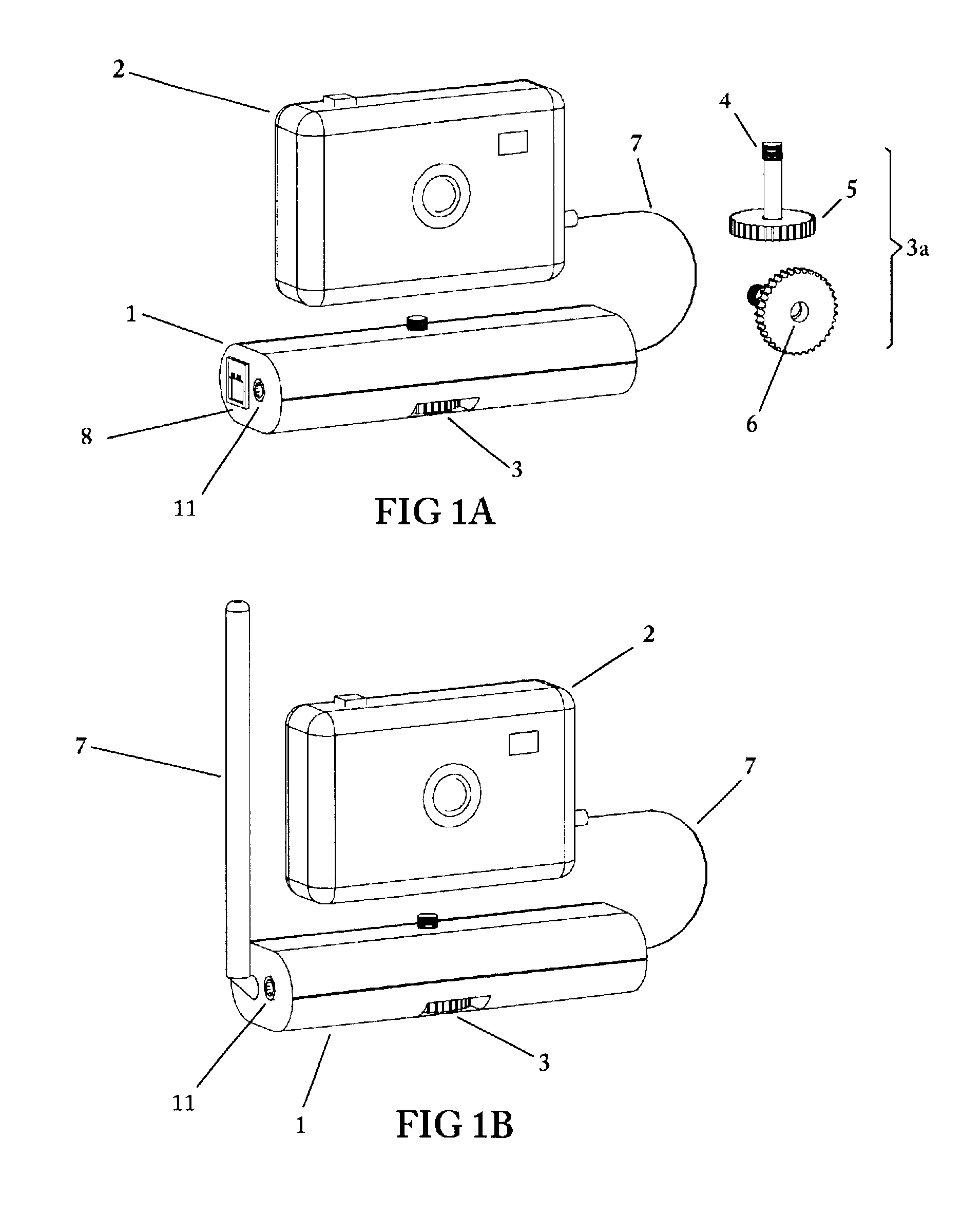
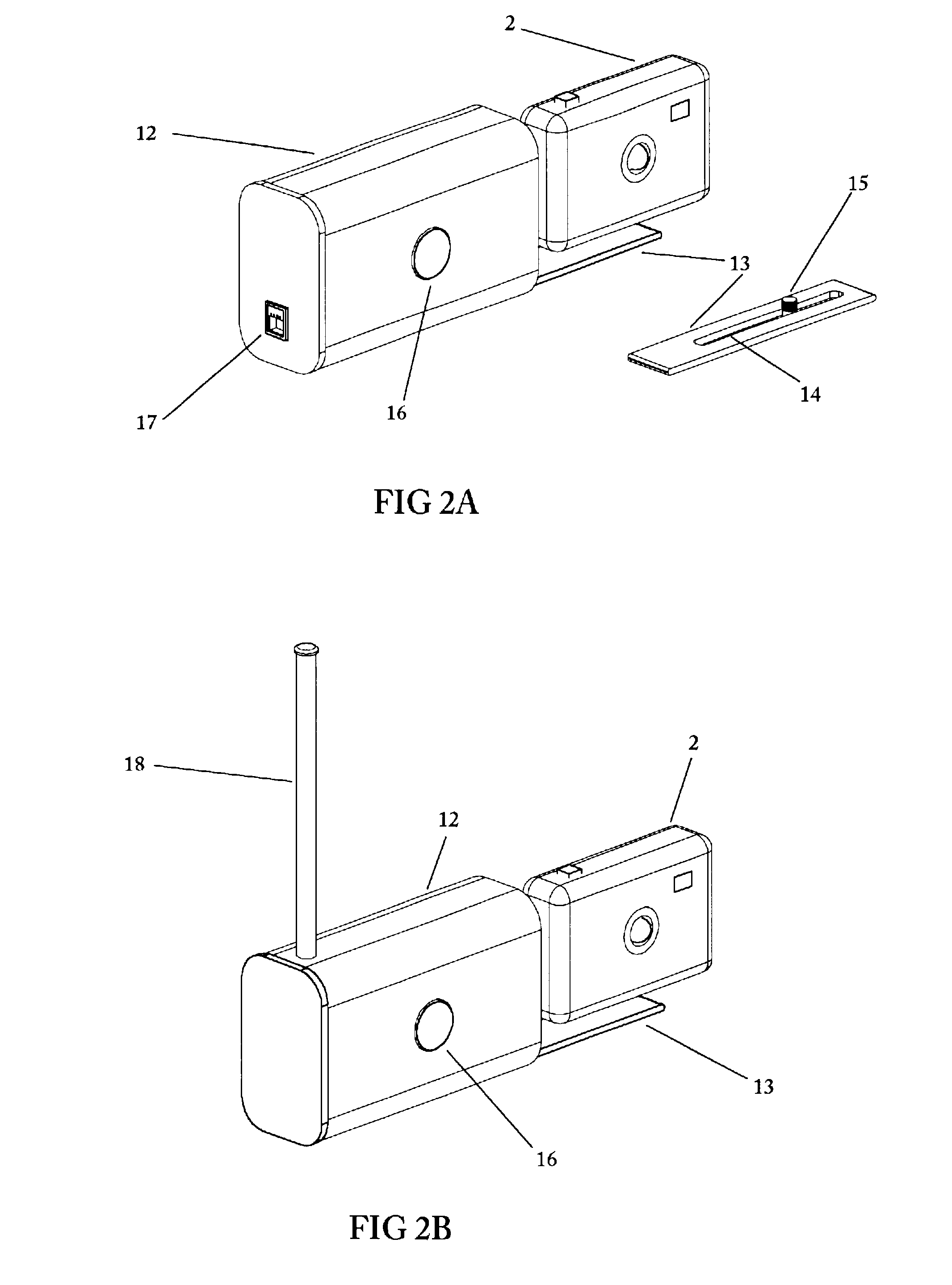
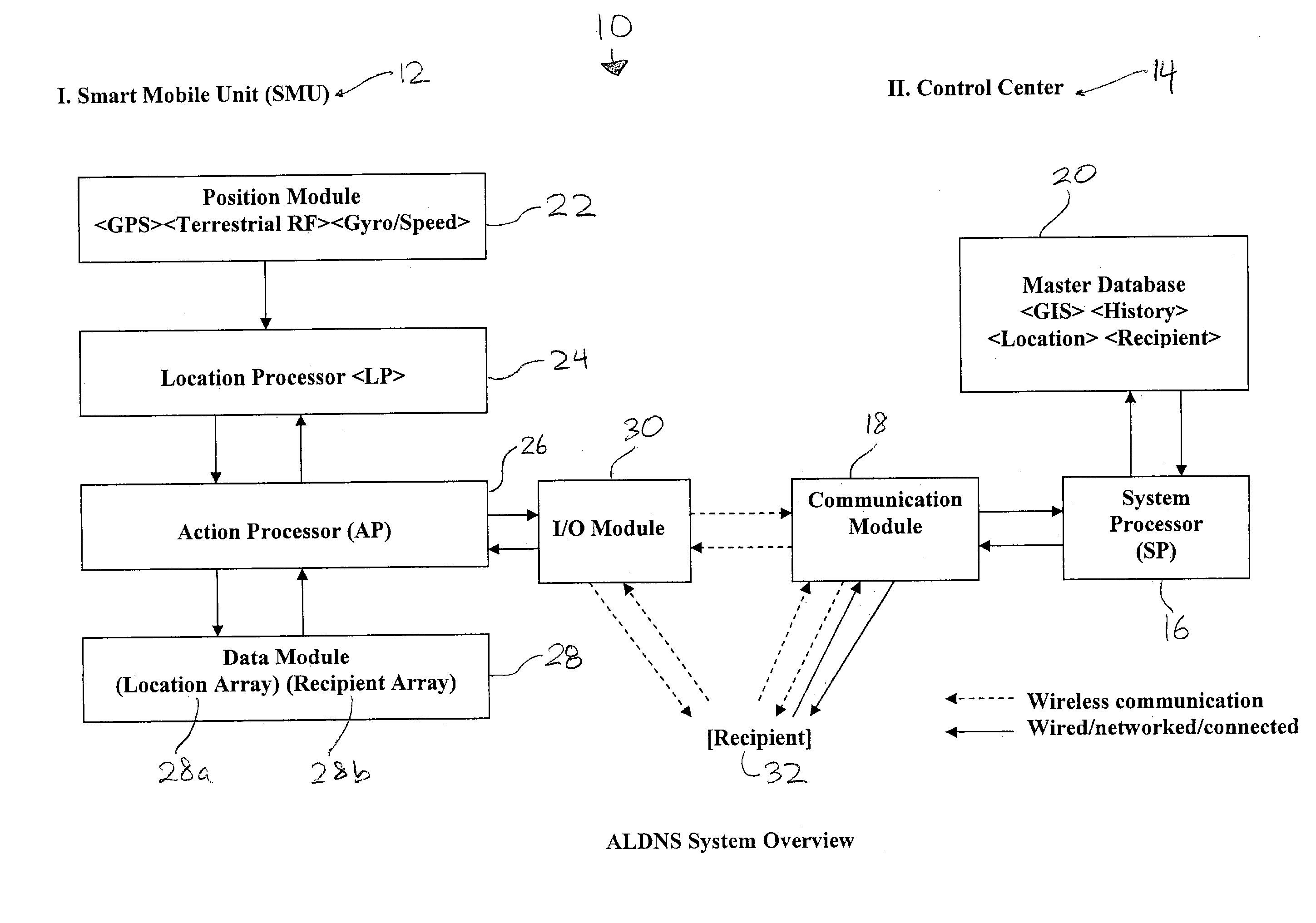
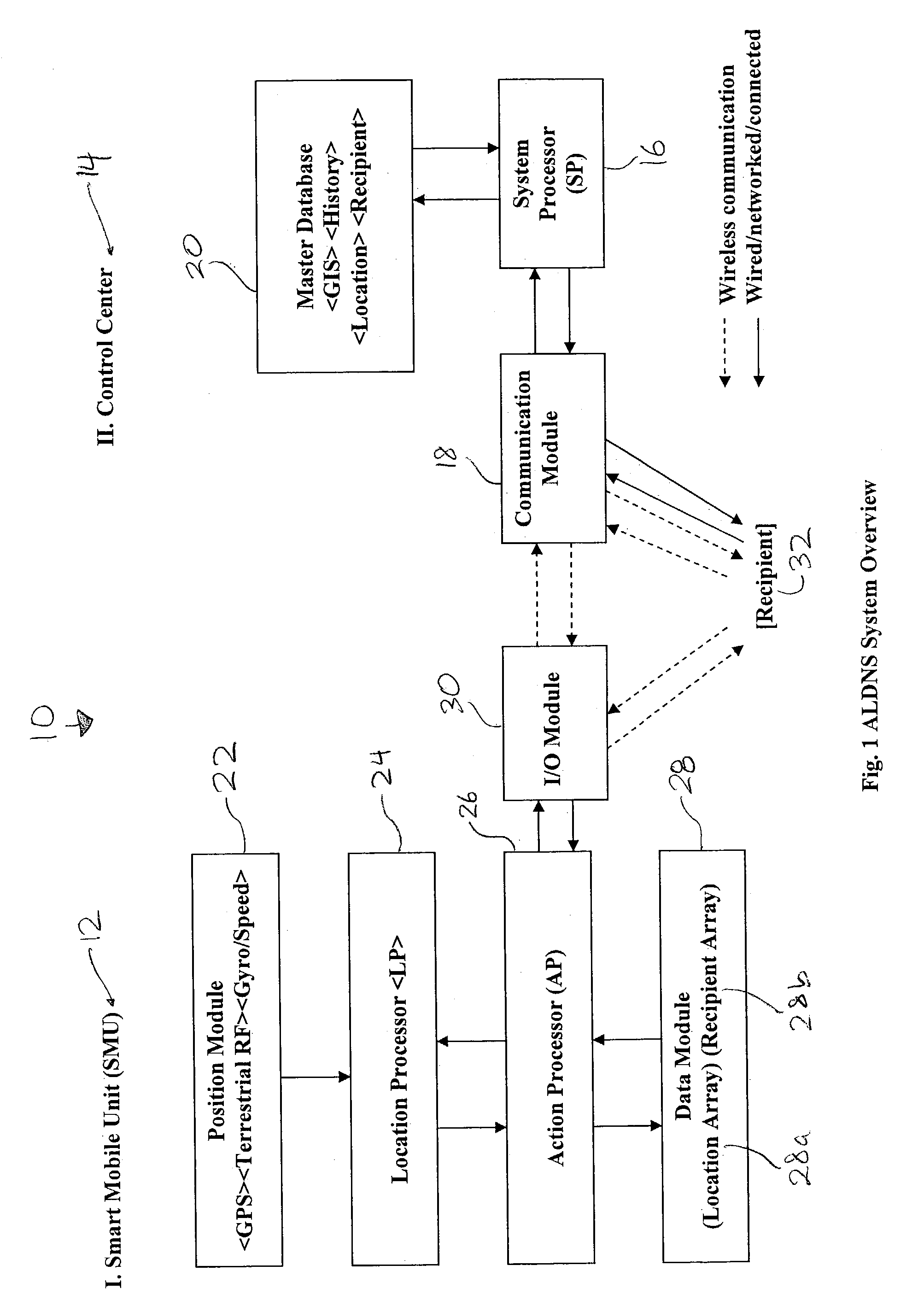
Method and apparatus for an automated location-based, dynamic notification system (ALDNS)
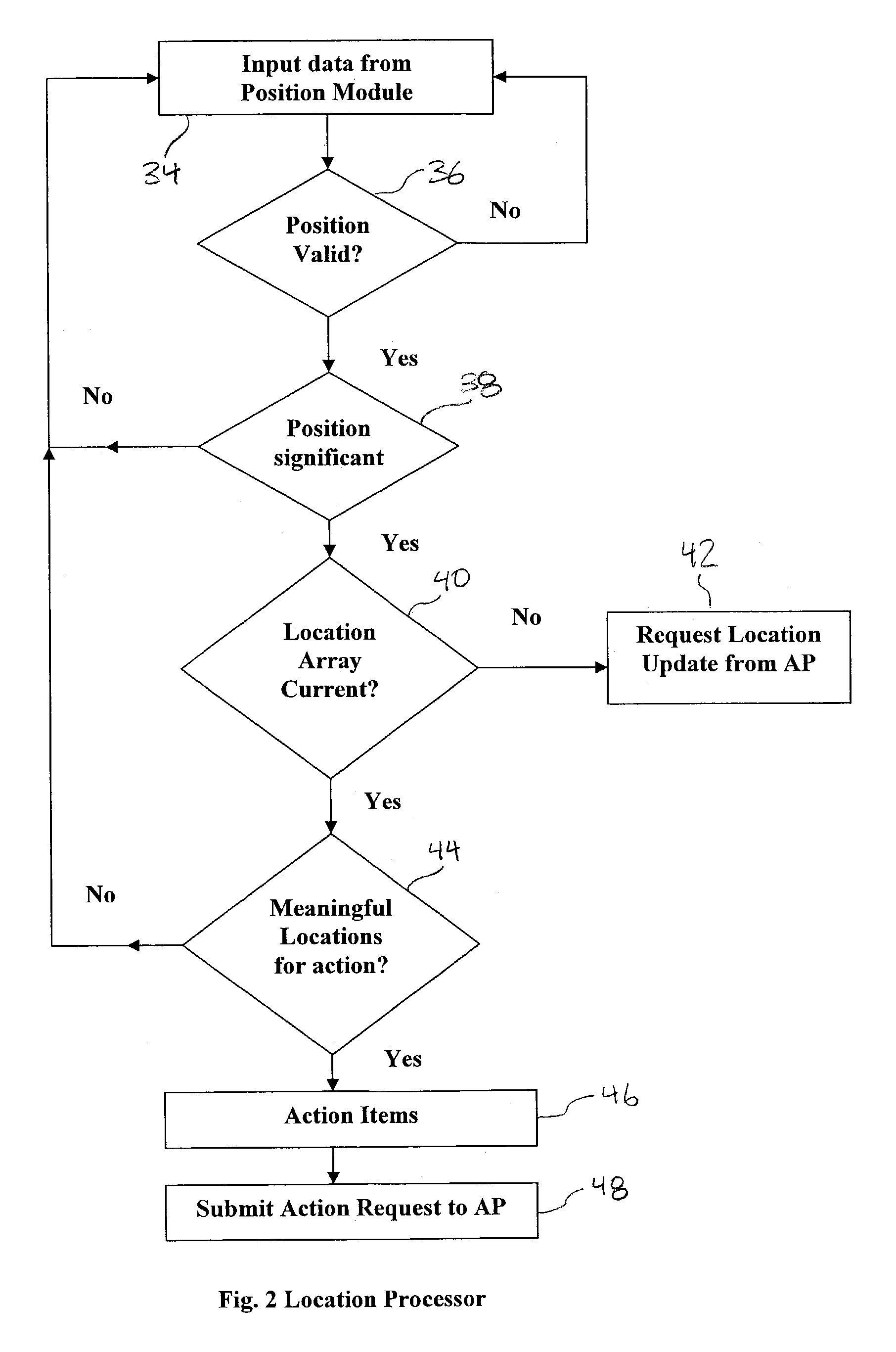
An automated, location-based, dynamic notification system comprises a mobile unit hardware device and a control center computer facility with communication capabilities. The mobile unit comprises a position module, a location processor, an action processor, a data module, and an I / O module. The control center comprises a system processor, a communication module, and a master database. The system provides notifications of arriving, approaching, leaving, entering, and any other types of location-related notifications, which are issued in an automatic, unattended manner. The illustrated embodiments of the invention are based on location and thus are used in a dynamic routing situation where both route patterns and stop locations change frequently while the object is moving. The system requires no interaction from the driver or the dispatcher, requires no on-board checking or manipulation of a schedule, and applies in many situations including special-education transportation, prisoner transportation, airport shuttle service.
Owner:GEOSPATIAL TECH
Multiradio control incorporating quality of service
InactiveUS20080291830A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceMessage flow
A system for managing the operation of one or more of wireless communication mediums supported by one or more radio modules integrated within a WCD. A control strategy may be employed to evaluate and manage pending communication activity down to the wireless message stream level through the creation of operational schedules. The operational schedules may be utilized by the one or more radio modules in the WCD in order to determine how resource usage should be allocated for supporting the communication activities conducted over a radio module.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System for Collecting Medical Data Using Proxy Inputs
PendingUS20170132374A1Reduce deliveryMedical data miningDrug and medicationsCommunity basedGlobal health
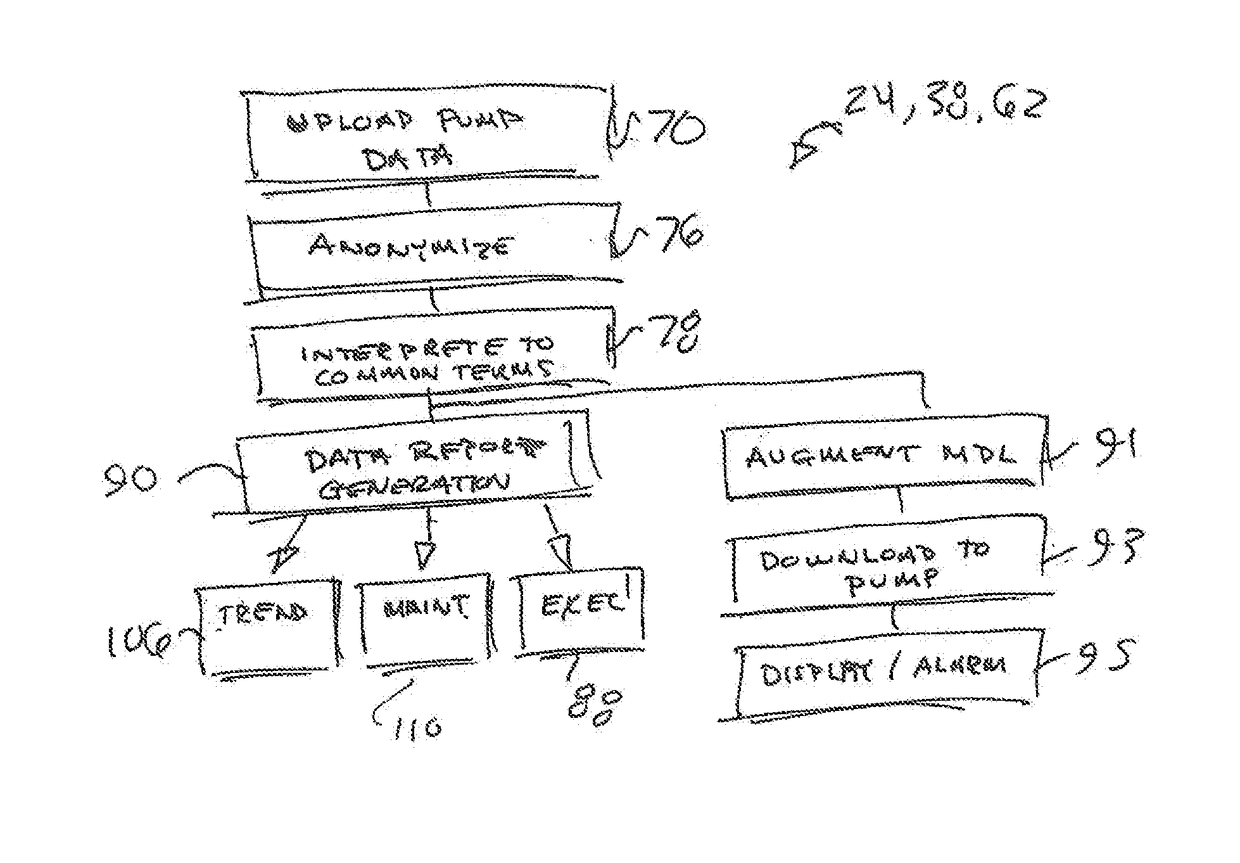
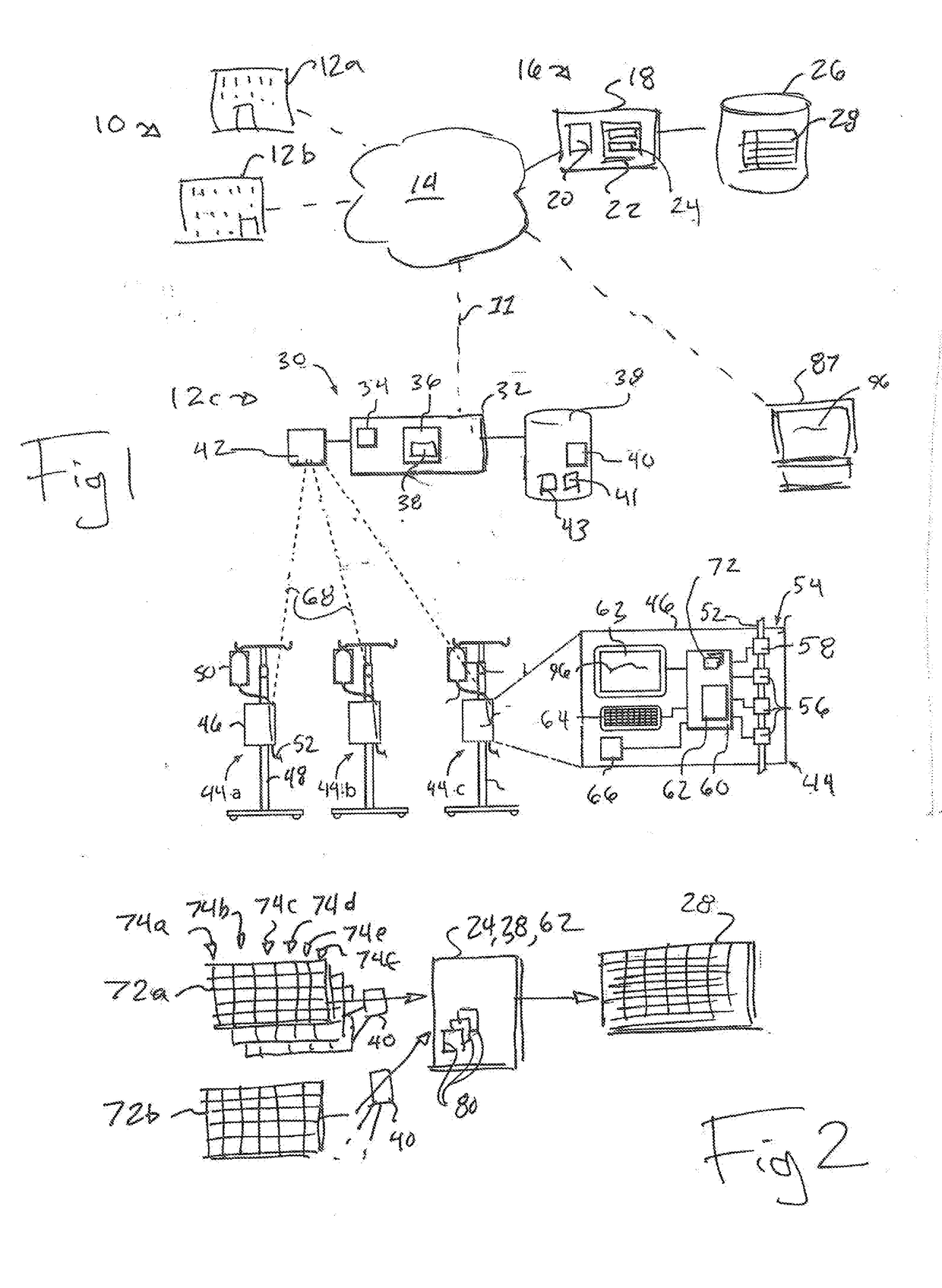
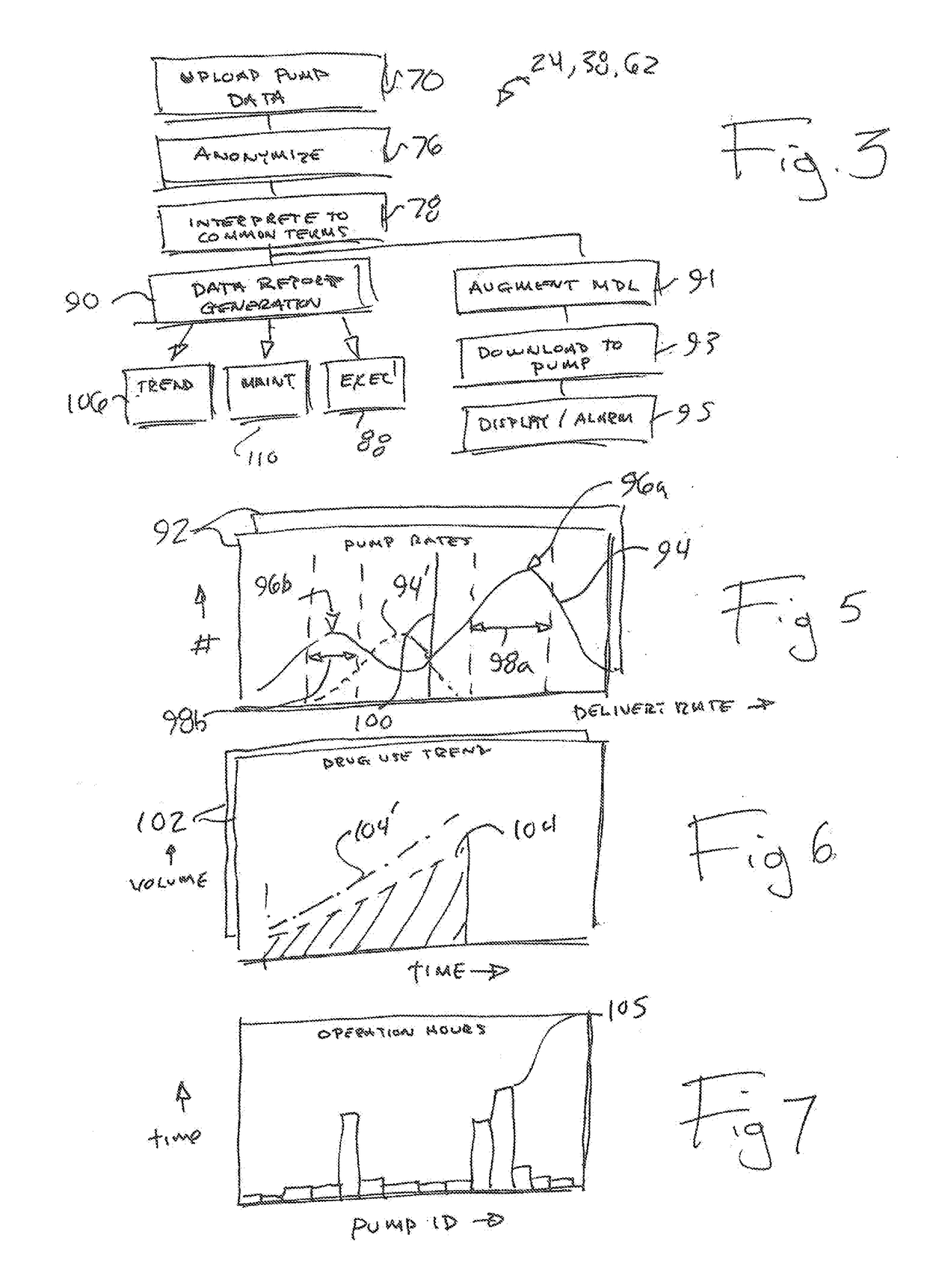
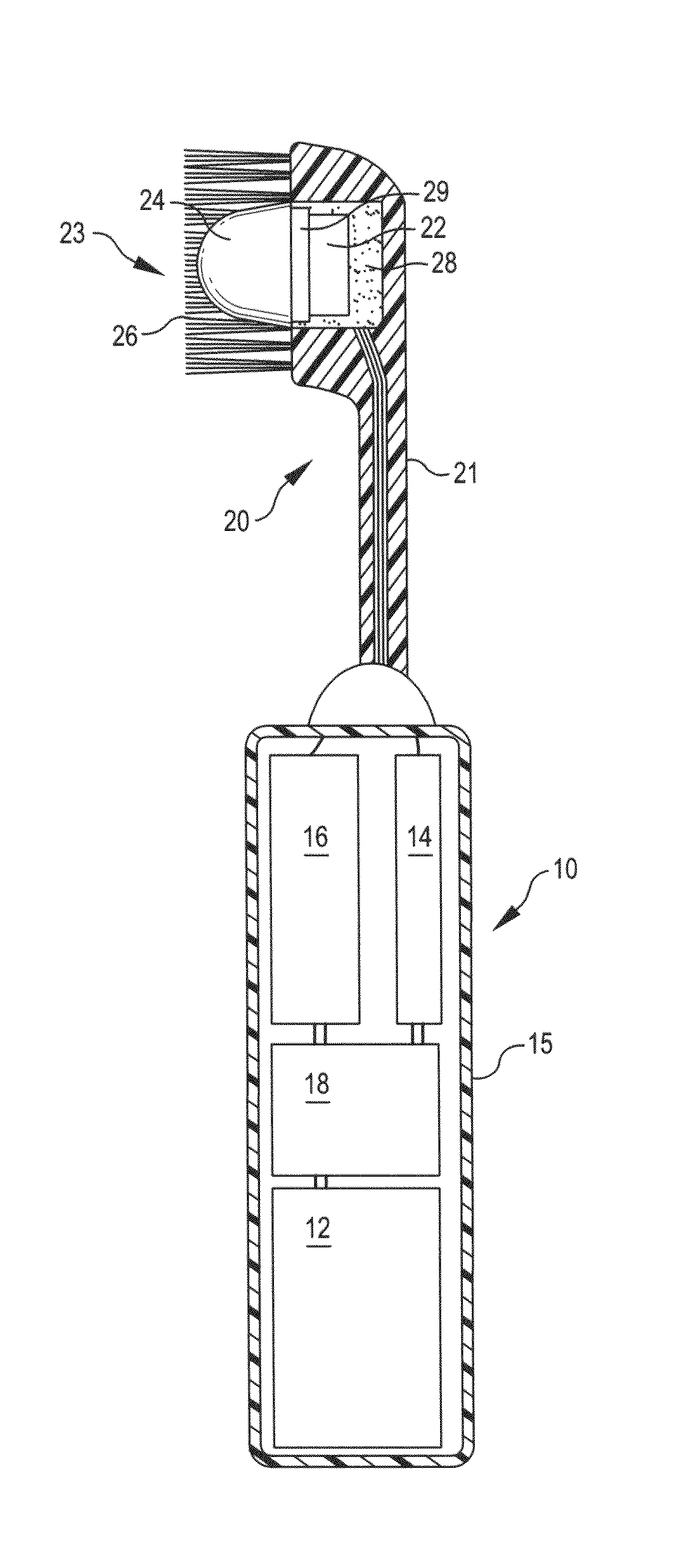
The present invention provides a system for collecting, anonymizing, and communicating information collected from medical pumps without the need for additional effort by medical care professionals. The pump / multi-pump derived information can be aggregated between hospitals and across healthcare institutions to provide global overviews of pump performance and drug use information. This information can assist with the delivery of healthcare by providing automatic guidance warnings, for example, deviating from established ranges for common delivery rates; trend monitoring to anticipate needs of the health care community based upon global health trends; and allocation of healthcare equipment by monitoring the total operating time and lifecycles of the pumps. Knowledge derived from this pump / multi-pump derived information can be used in an administrative capacity and to develop evolving advisory protocols for users of pumps comparing real-time pump protocols to those appropriate for a given drug.
Owner:ZYNO MEDICAL
Oral hygiene devices
InactiveUS20080209650A1Feel goodImprove experienceCarpet cleanersTooth pluggers/hammersSonificationUltrasonic sensor
Oral hygiene devices employing an ultrasound transducer are disclosed. The device is user-activatable to commence an operating cycle, and has a controller that may provide a timing function and may provide a variable level of ultrasound transducer output during an operating cycle. The controller may provide a monitoring function that is capable of detecting an ultrasound transducer fault condition and alert a user, through a user interface, when an ultrasound transducer fault condition is detected. The controller may be programmed to count the number of device operating cycles or accumulate the total device operating time and activate a transducer replacement signal following a predetermined number of uses or a predetermined accumulated operating time. The ultrasound transducer assembly may be provided in operative communication with an ultrasound drive circuit and power supply by means of a transformer assembly that inductively couples and transfers power from the ultrasound drive circuit to the ultrasound transducer.
Owner:GOLDMAN SACHS SPECIALTY LENDING GRP +1
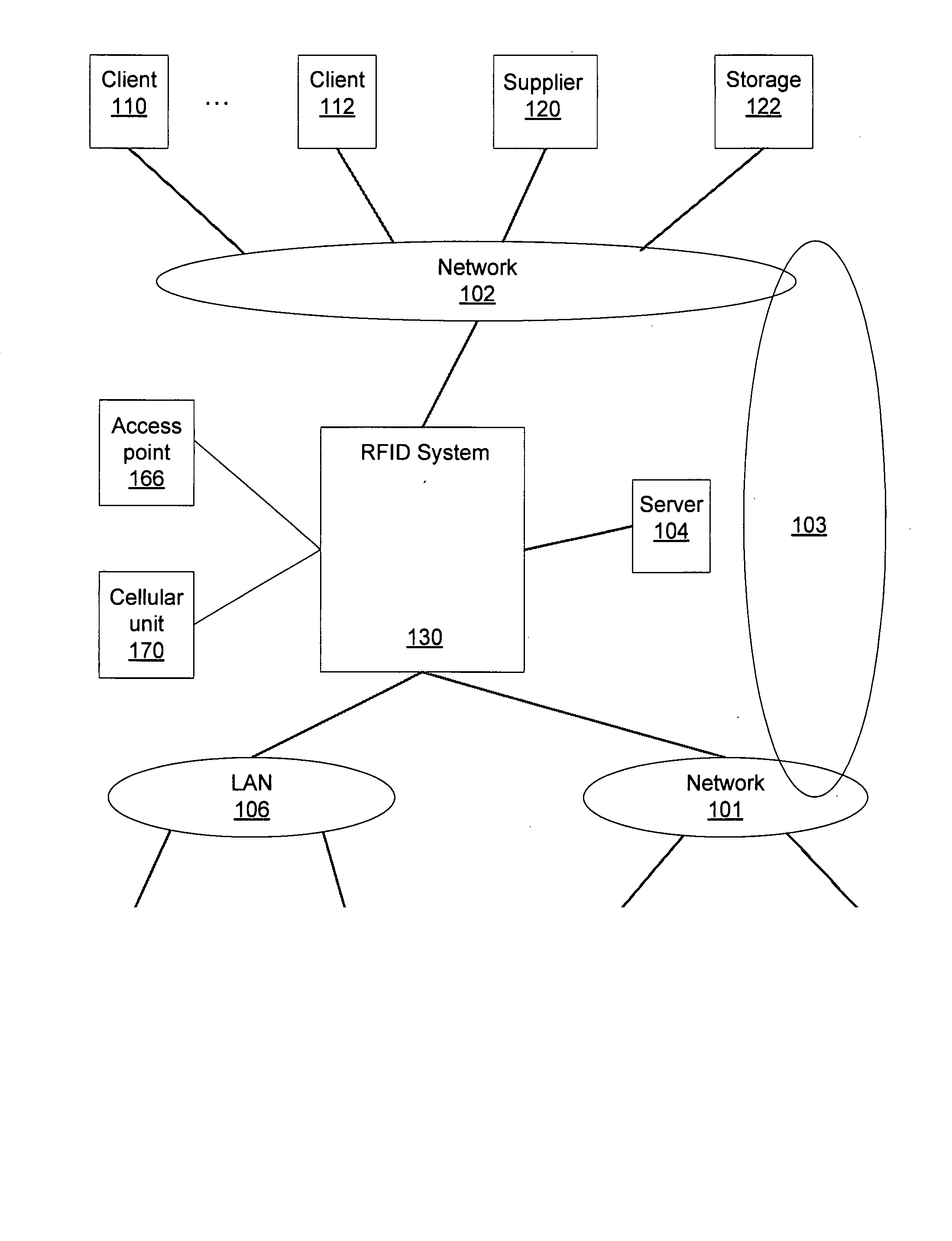
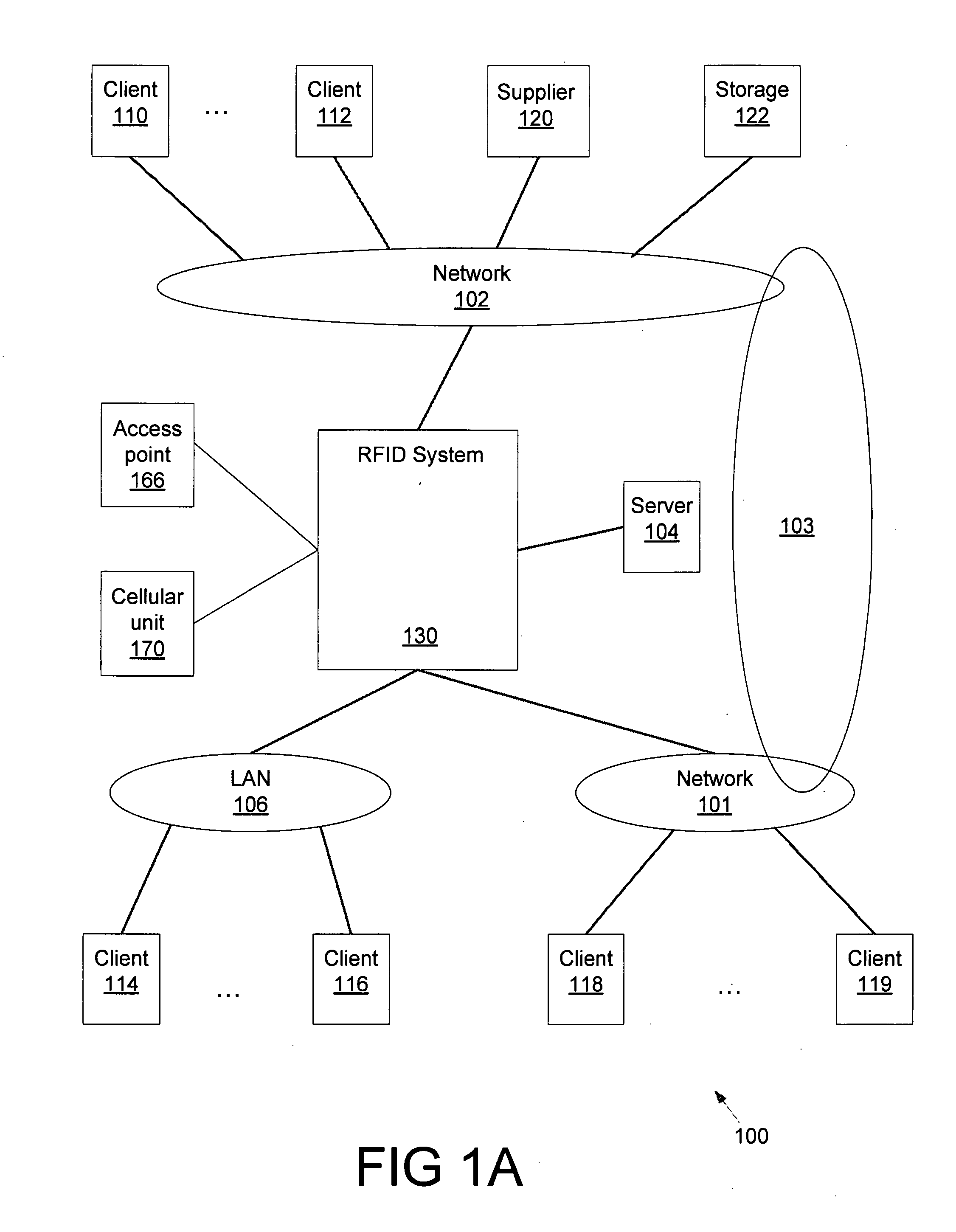
Method and apparatus for power management for a radio frequency identification system
A method and device of power management for a networked radio frequency identification (“RFID”) system are disclosed. The described power management methods reduce the power consumption of battery-operated RFID readers and RFID tags. These power conservation methods increase the RFID system's hours of operation and decrease the cost by allowing the RFID readers and tags to function for a longer period of time before requiring charging or replacement of their batteries.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
Apparatus and methods for energy management system
InactiveUS20130159153A1Facilitates power bill computationFacilitates power billLevel controlCircuit arrangementsElectricityEnergy management system
Apparatus for providing energy management with automation control features are invented. Power consumption details for building or household can be known as well as the expected power bill in advance. The operation status of specific appliance can also be monitored and controlled. Wireless technology is used as a communication medium with a plurality of appliances which facilitates the management of energy consumption with different applications, like checking the operation status, operating hours and consumption data. An advanced feature of communication with the utility provides power information and instant messaging to users. A consumption target can also be set to economize the electricity bill.
Owner:CITYGROW ENERGY SYST
Intelligent control method, device and system based on instant messaging
ActiveCN105471705AImprove interactive experienceData switching networksTotal factory controlIntelligent controlOperating time
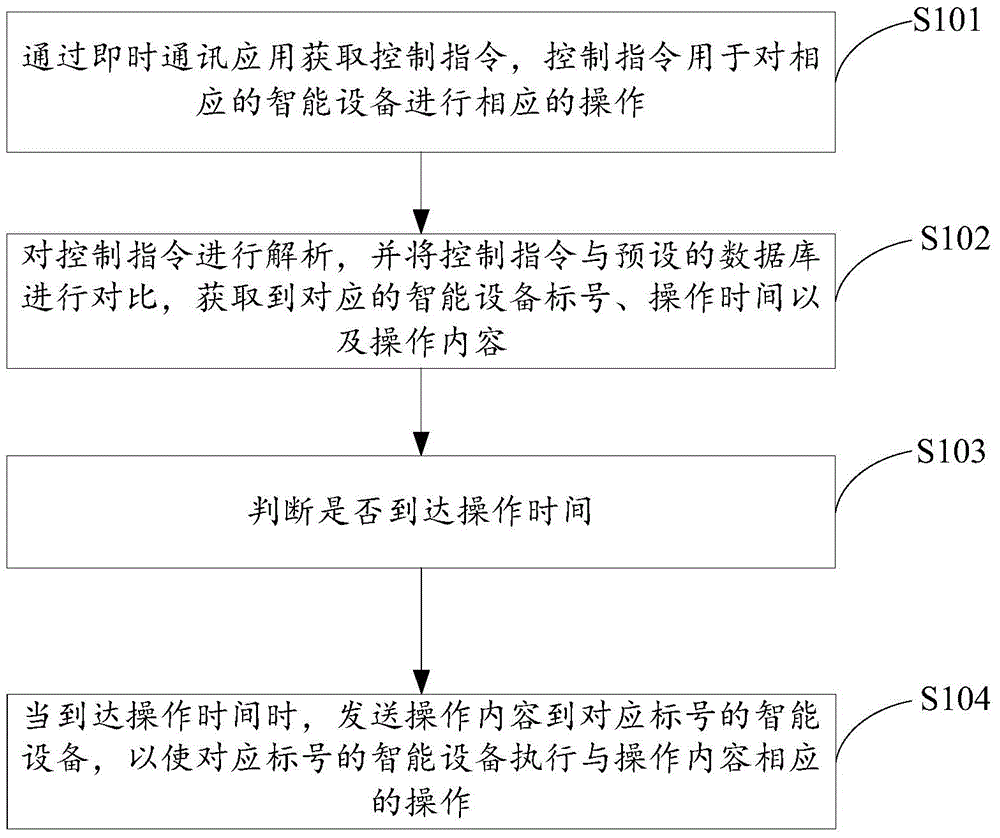
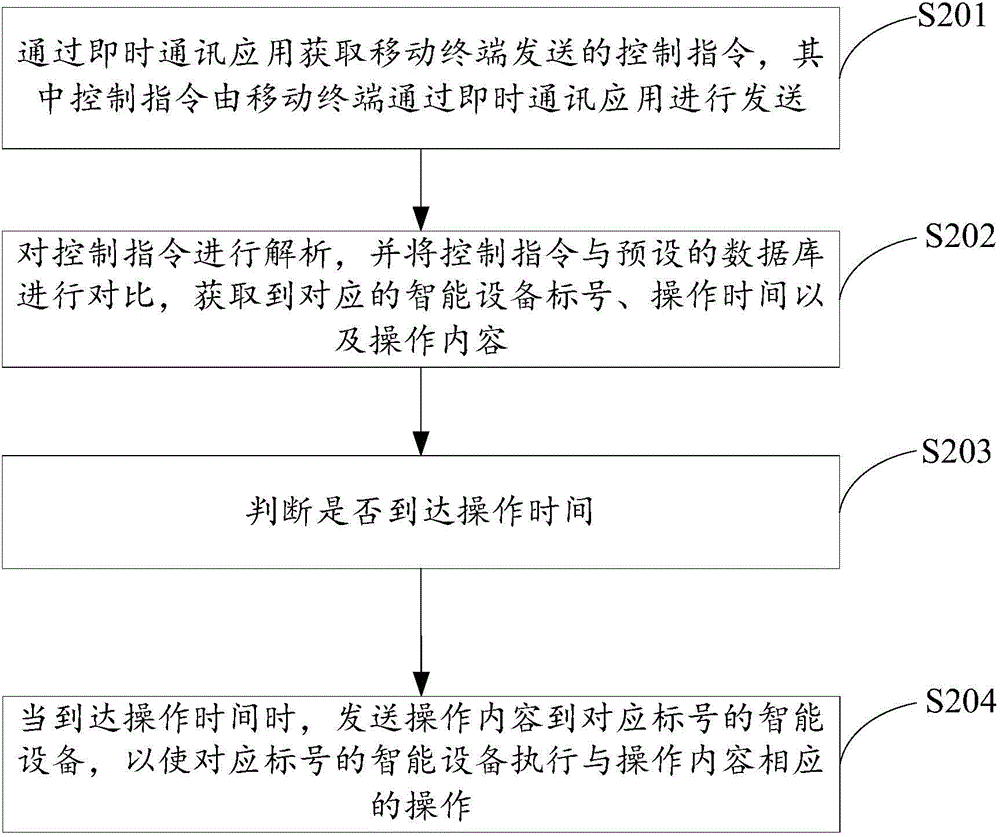
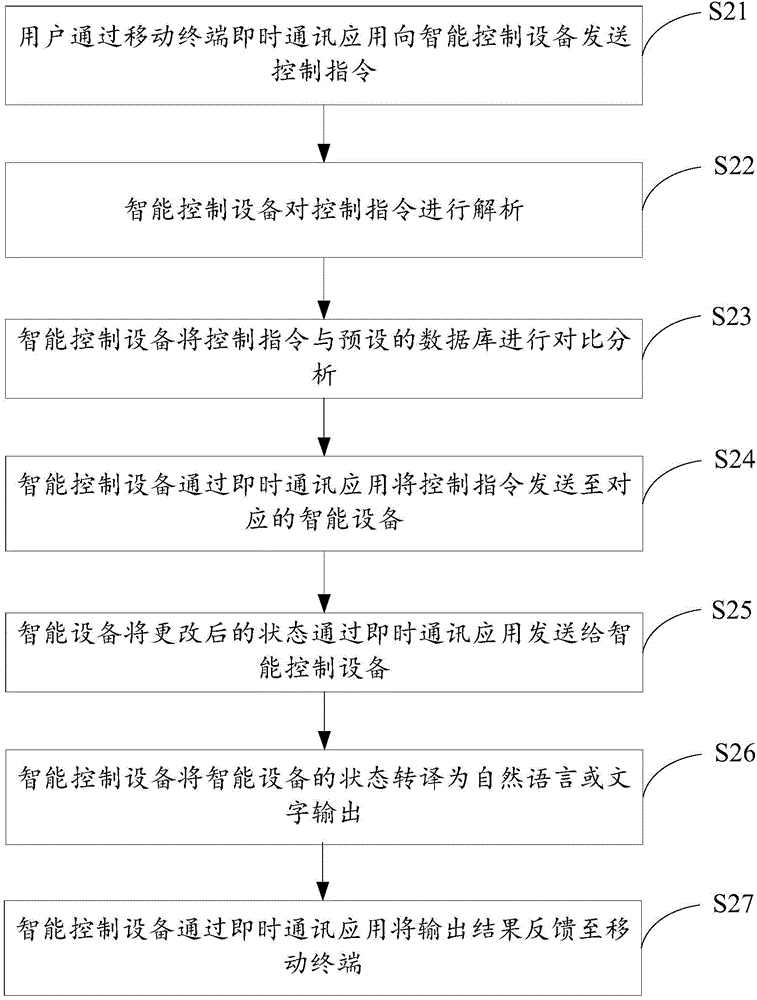
The invention discloses an intelligent control method, device and system based on instant messaging. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a control instruction through an instant messaging application, wherein the control instruction is used for carrying out corresponding operation on corresponding intelligent devices; analyzing the control instruction, and comparing the control instruction with a preset database to obtain corresponding intelligent device labels, operation time and operation content; judging whether the operation time arrives; and when the operation time arrives, sending the operation content to the intelligent devices of the corresponding labels to enable the intelligent devices of the corresponding labels to carry out operation corresponding to the operation content. The intelligent control device can manage different types of intelligent devices through instant messaging, thereby enhancing man-machine interaction experience and facilitating unified management of the intelligent devices.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Fuel vapor handling apparatus and diagnostic apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20020162457A1Desorption of fuel is facilitatedFuel can be purged efficientlyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel injection apparatusDesorptionVaporization
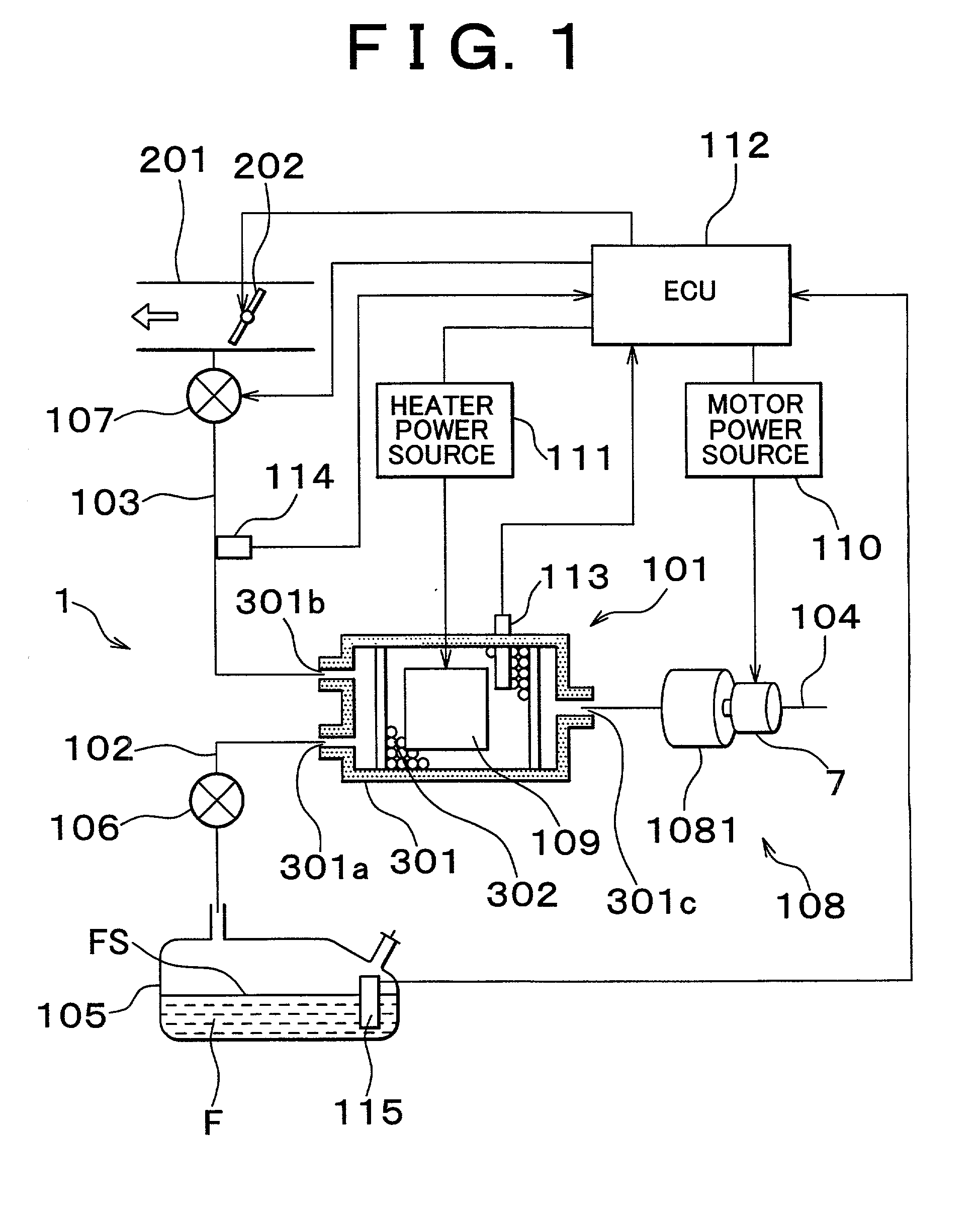
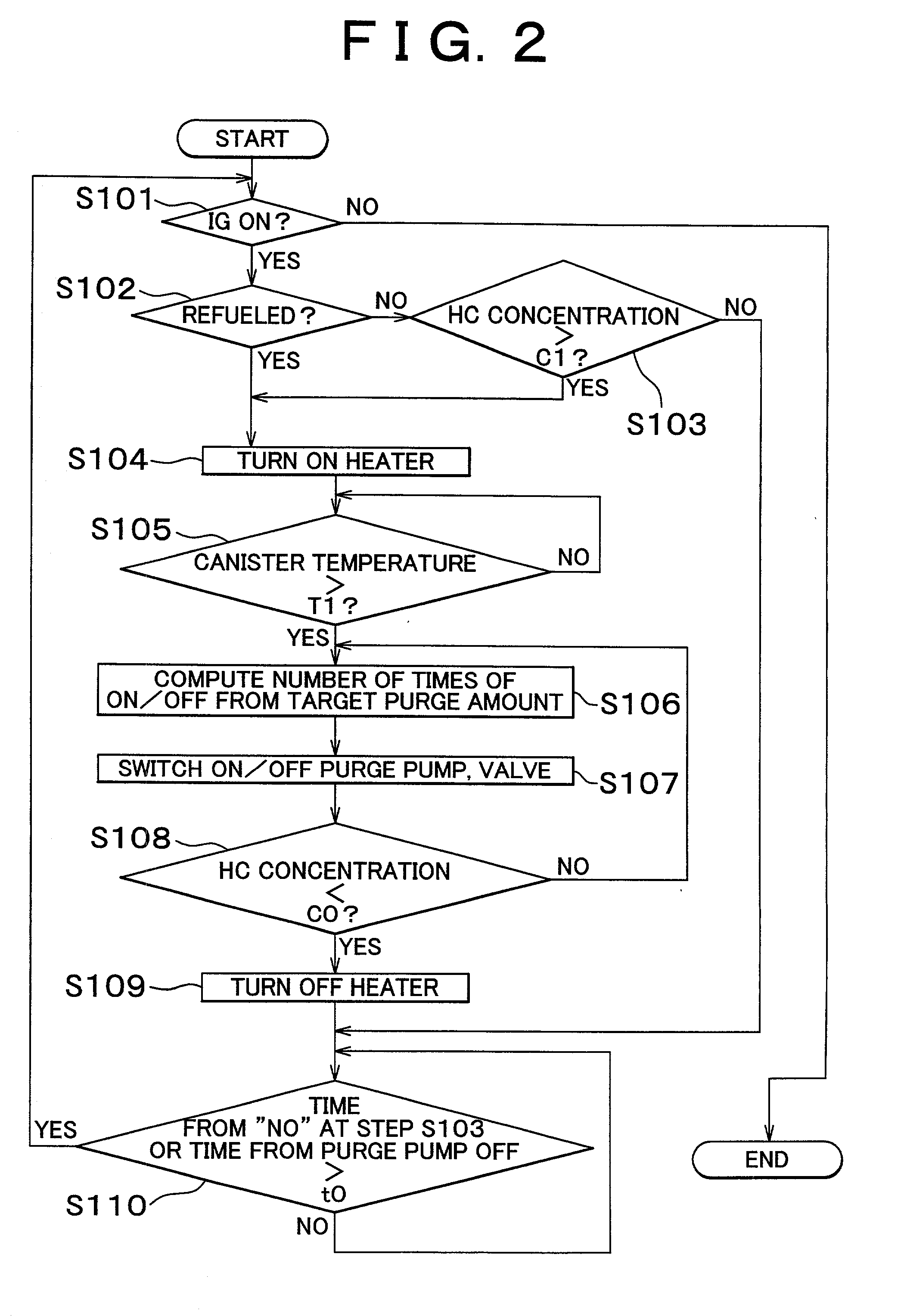
A fuel vapor handling apparatus supplies a purging air to a canister by using a purge pump and purges fuel desorbed from the canister into an intake pipe. A controller intermittently operates the purge so that the canister internal temperature recovers from a reduced level caused by the latent heat of vaporization of fuel during an operating period of the purge pump. Therefore, desorption of fuel from the canister during an operating period is facilitated. Since the actual operating time of the purge pump is reduced, the life of a motor that is a power unit of the purge pump becomes longer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
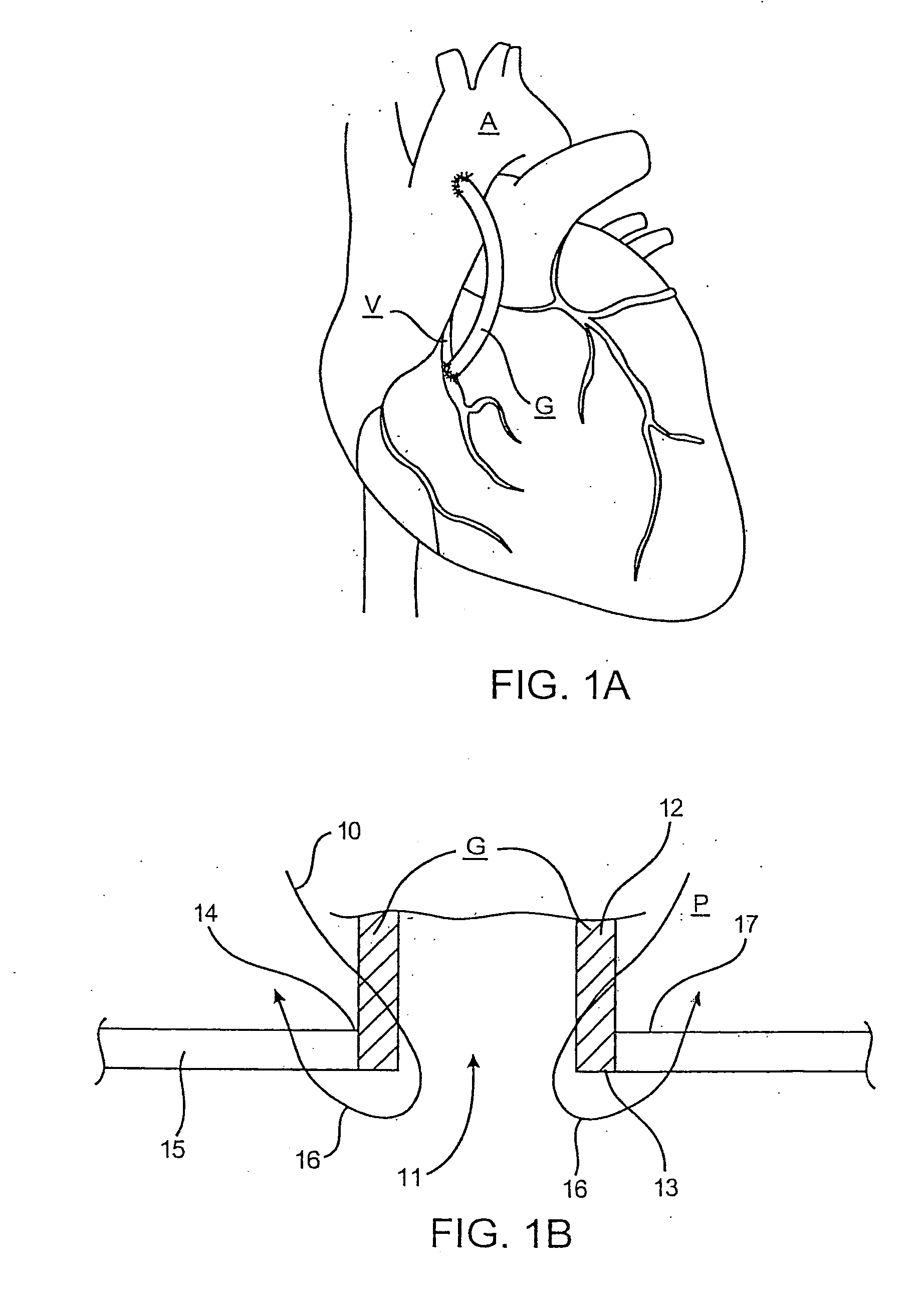
Device and method for performing end-to-side anastomosis
InactiveUS20060167477A1Simplifies suture deliveryAmount of timeSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEnd to side anastomosisCatheter
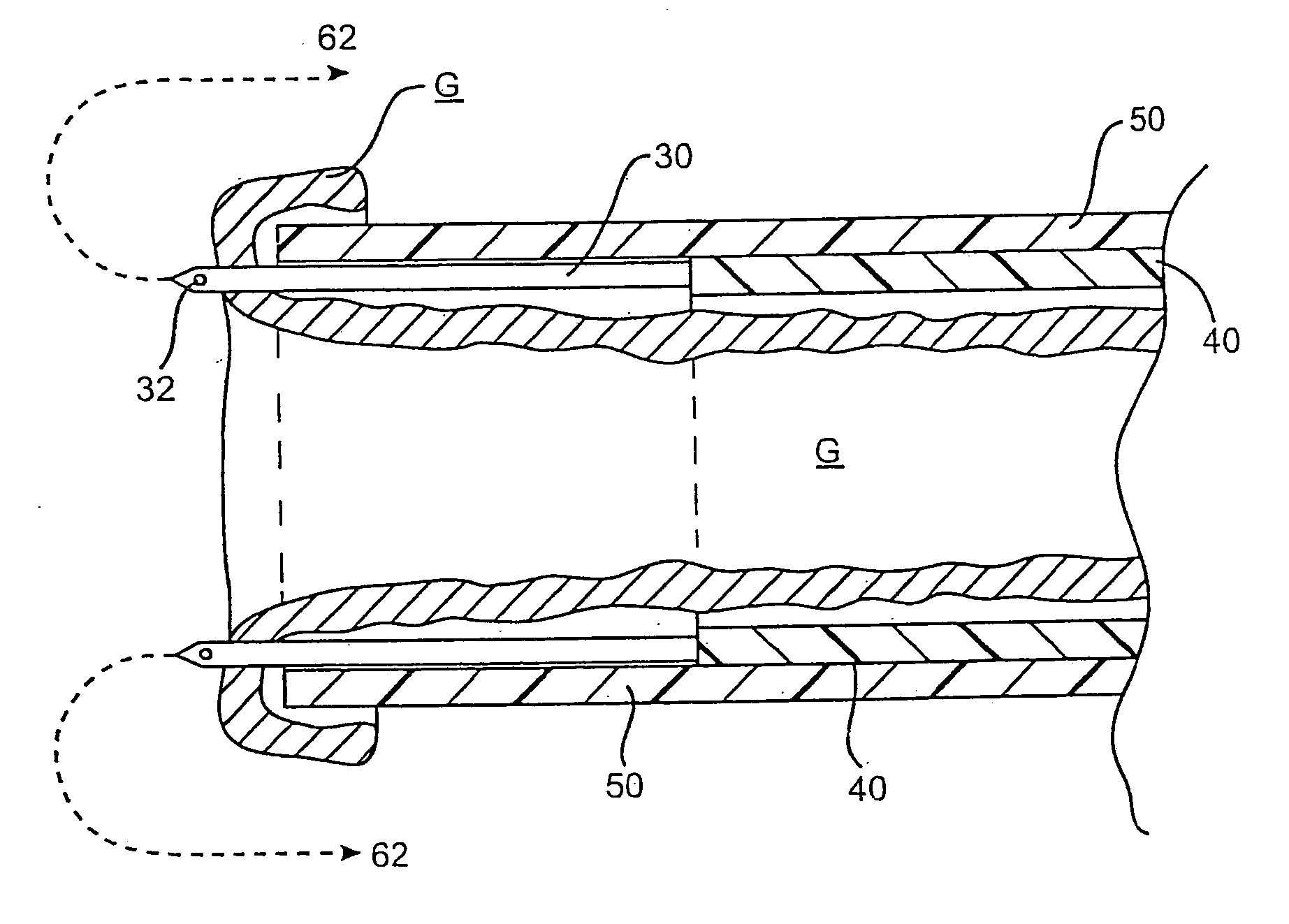
Devices, methods, and kits are provided for suturing an end of a first body duct to a hole in the side of a second body duct. The present devices and methods are used to simplify the suturing procedure and thus reduce operating time. In one embodiment, the present device includes a structure for holding the end of the first body duct and positioning the end adjacent to the hole in the side of the second body duct. The structure of the device is typically a shaft having a surface adapted to receive the first body duct. A plurality of needles are arranged on the structure to be advanced along a plurality of paths. Each needle path first passes radially into and forwardly out of the end of the first body duct and into the hole of the second body duct. The path then everts so that the needles and associated sutures will pass outwardly through tissue peripheral to the hole when the end of the first body duct is on the structure adjacent to the hole in the second body duct. The needles preferably travel along such paths when they are advanced forward. In one embodiment, the device uses a J-shaped tube for guiding one of the needles along the desired path. In another embodiment, shape-memory needles having an arcuate profile are used to create the desired path.
Owner:ARCIA ROVIL P +2
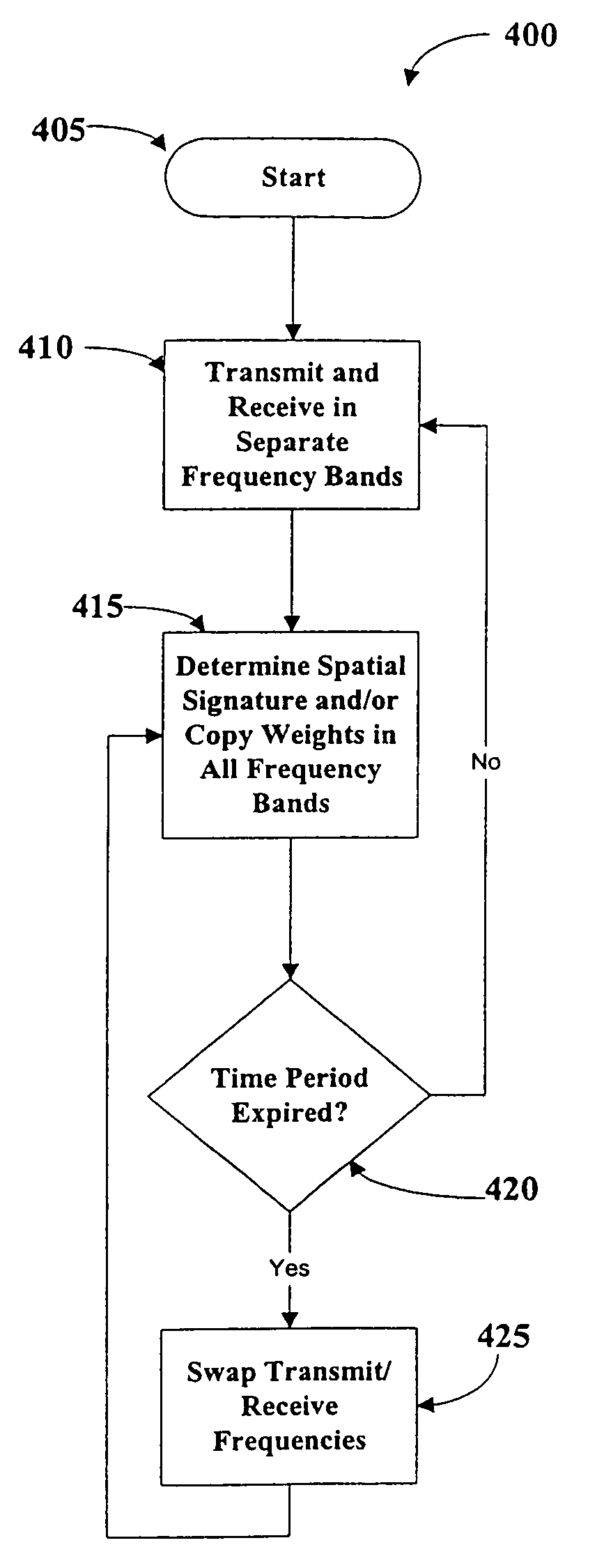
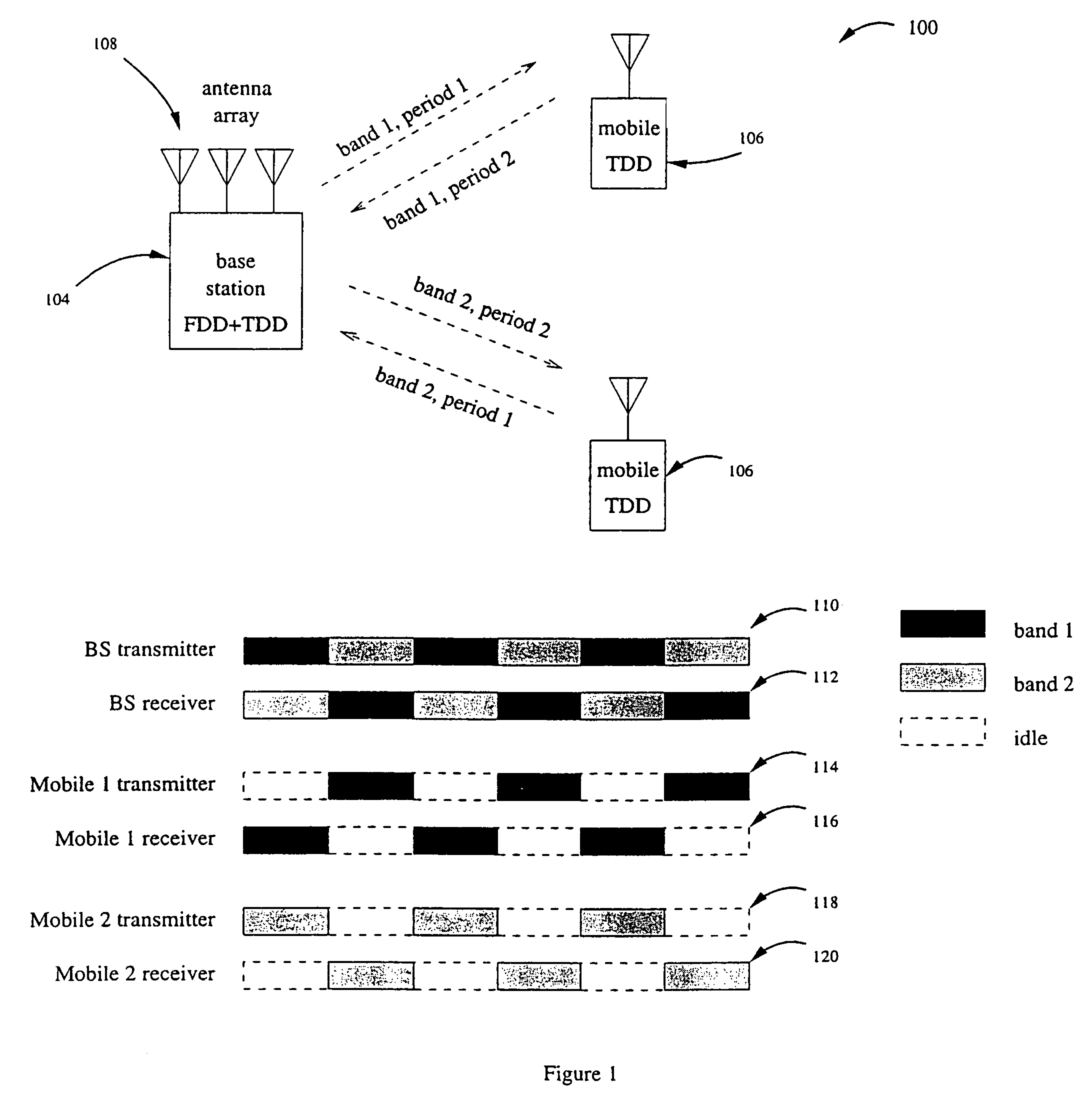
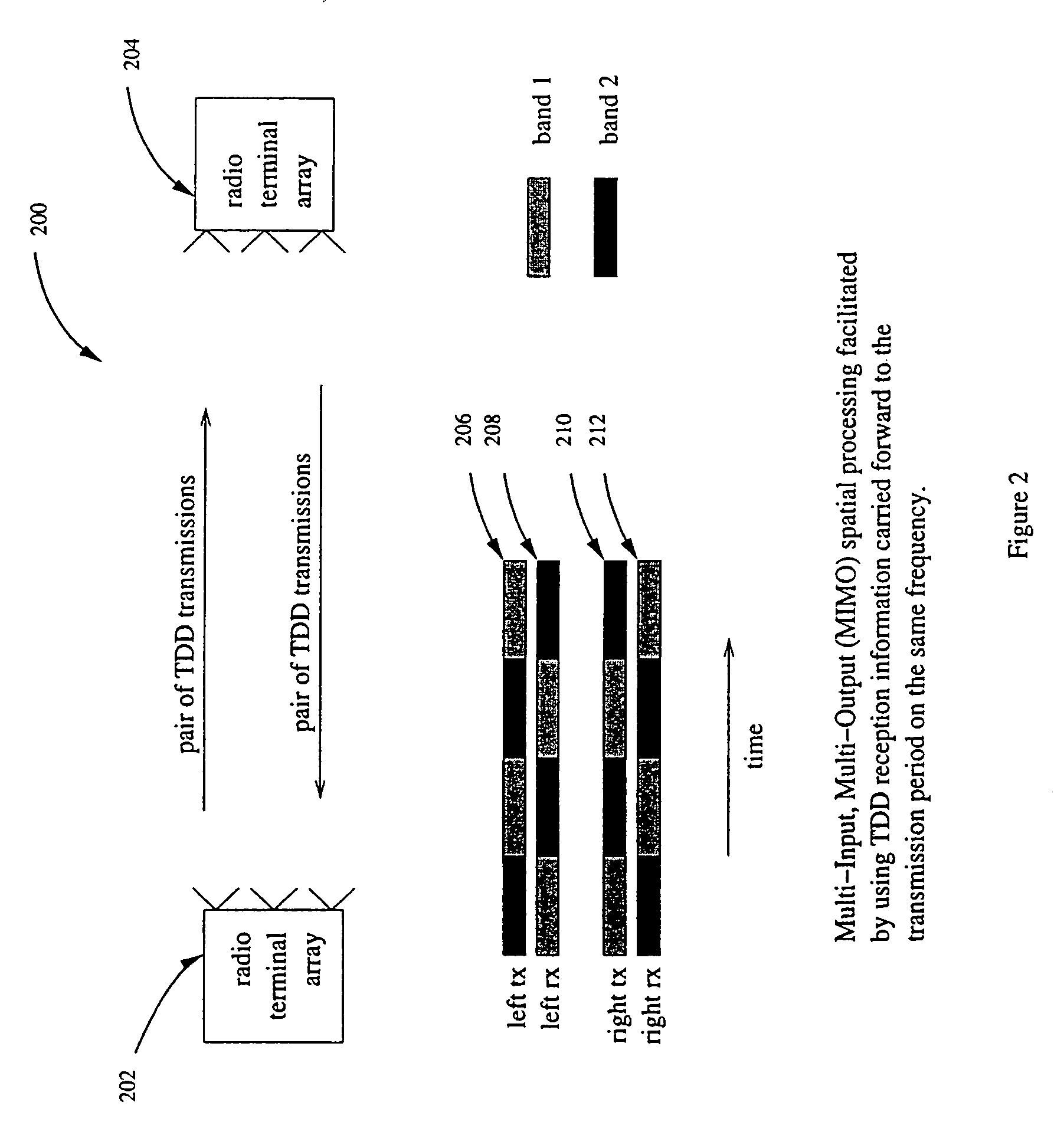
Operating time division duplex (TDD) wireless systems in paired spectrum (FDD) allocations
ActiveUS7336626B1Easy to copyIncrease profitFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency diversityCommunications systemTime segment
A wireless communication system operates in a combined FDD and TDD mode. During a first time period, data may be transmitted at a first frequency band and received at a second frequency band. During a second time period, data is transmitted at the second frequency band and received at the first frequency band. The first and second time periods may be of identical durations, thereby creating a 50% duty cycle. When the base station operates with multiple frequency bands, spatial processing parameters such as the spatial signature or copy weights of the mobile stations may be collected in all frequency bands, thereby allowing the full processing advantage of adaptive antenna.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
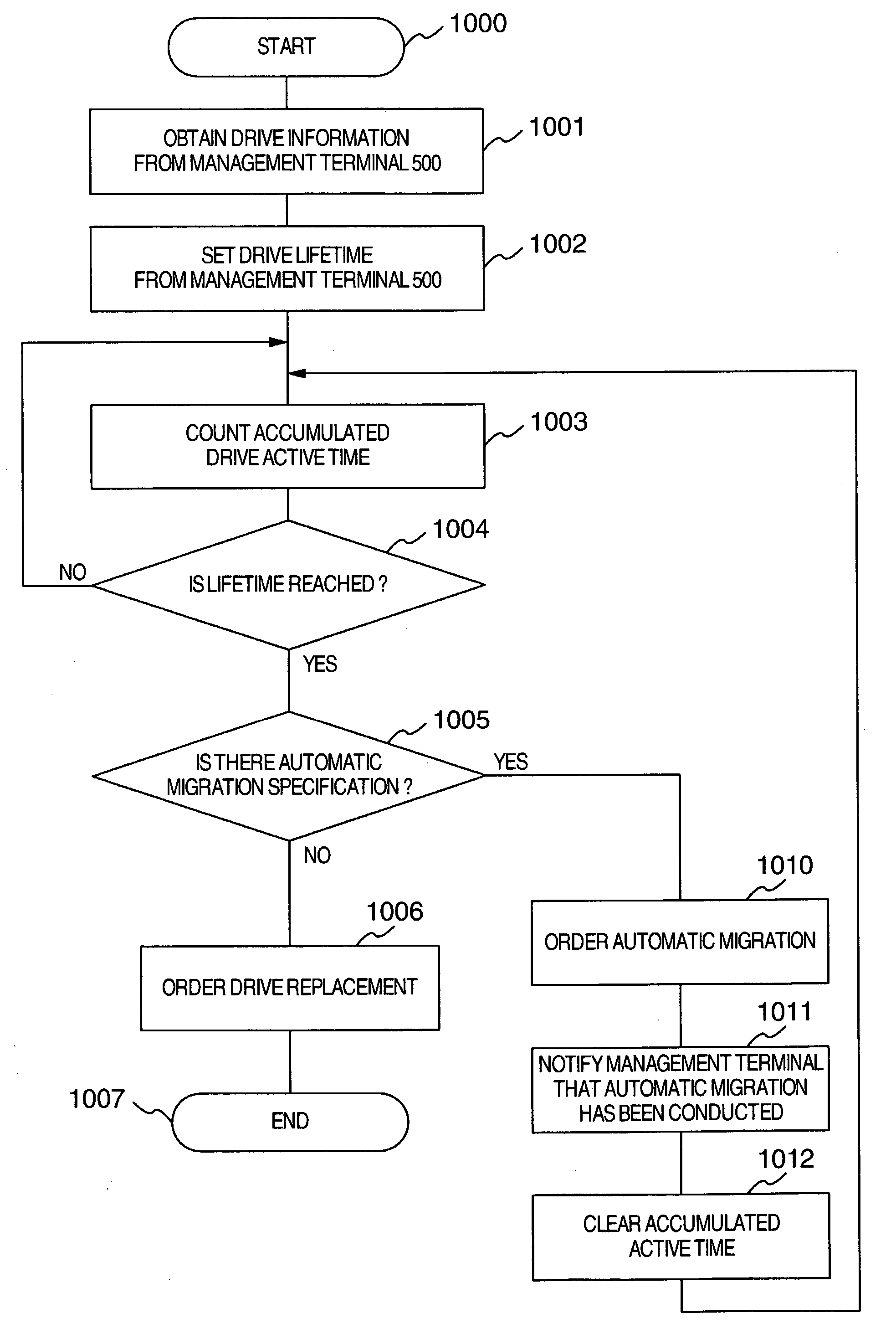
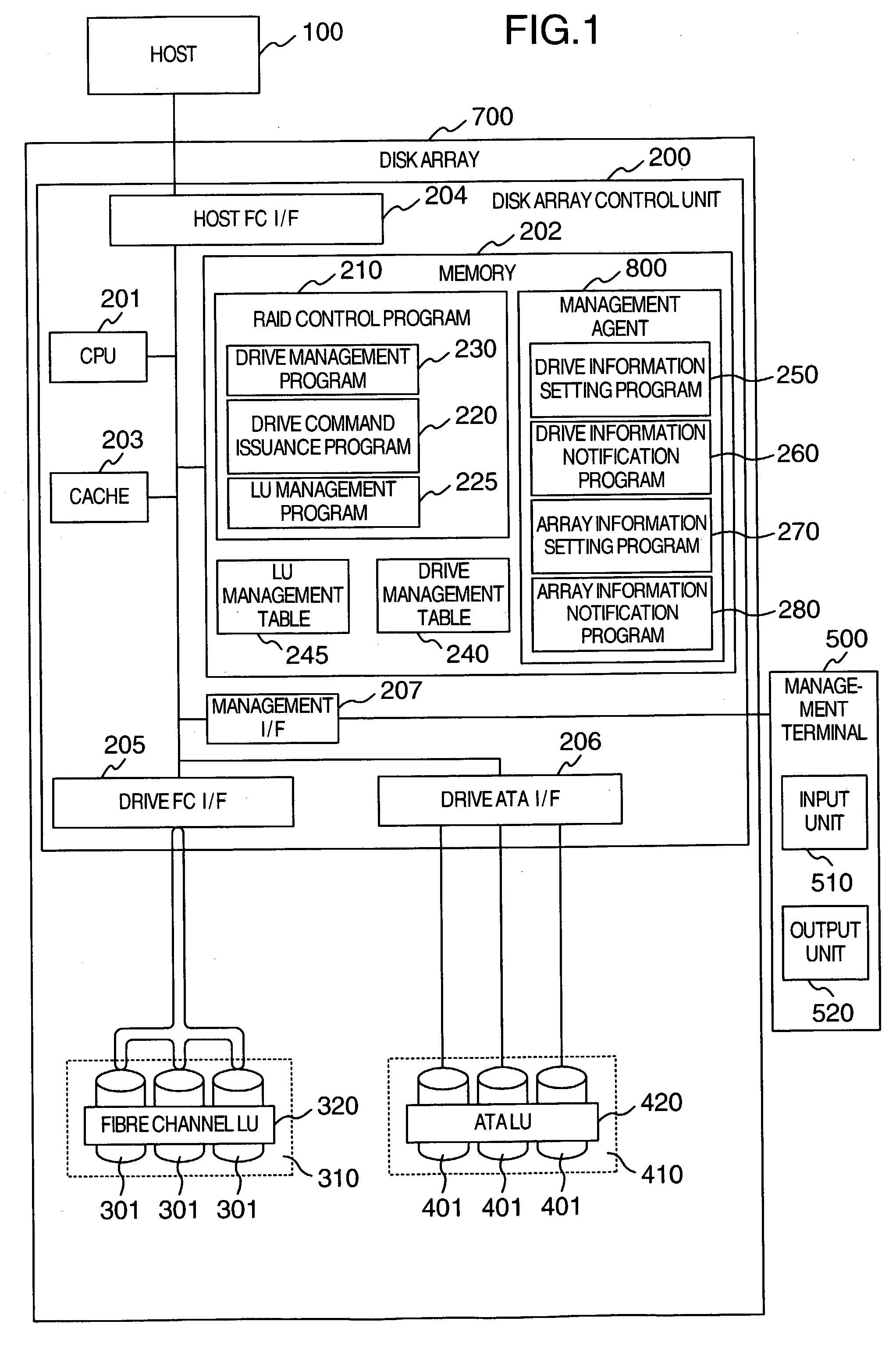
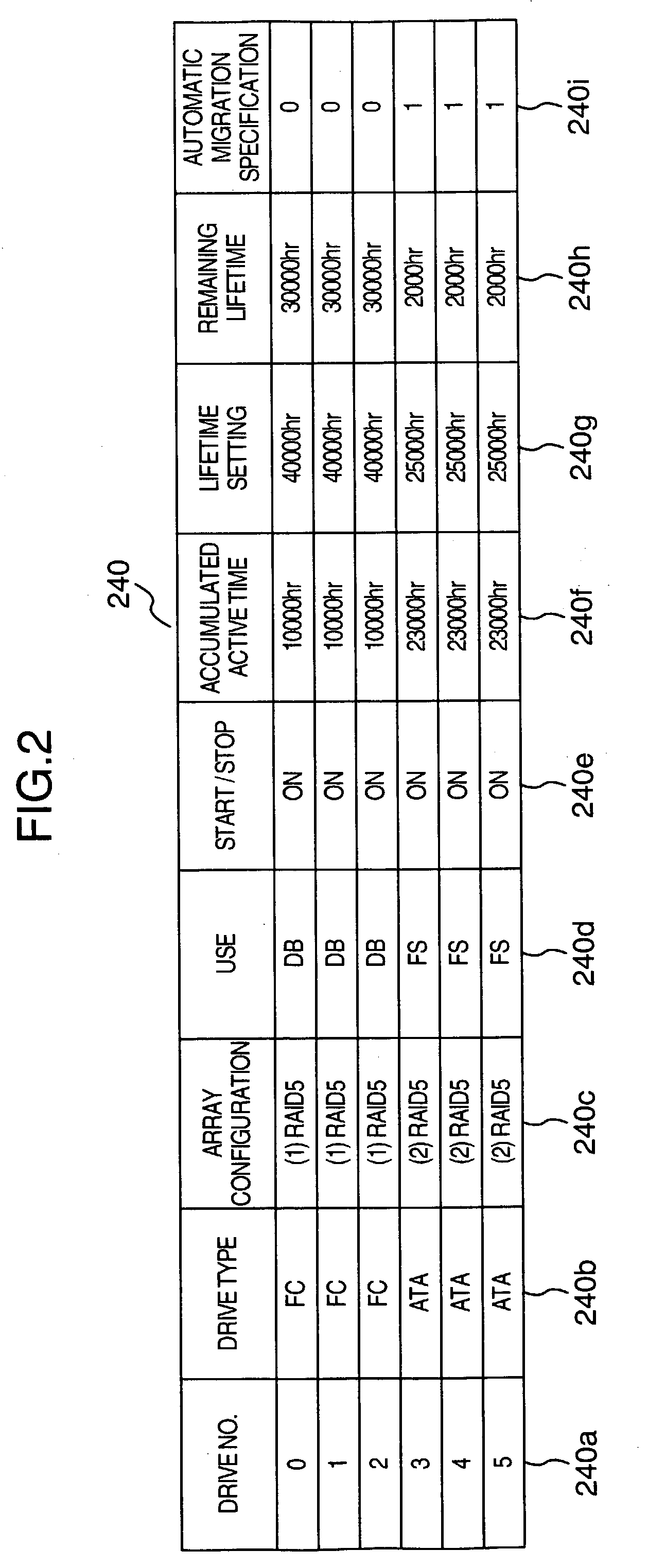
Storage system
A disk array includes a drive management unit, which is a program for identifying types of disk devices and managing different disk devices separately, and a drive management table for storing information to be utilized by the drive management unit. The disk array further includes a program for managing accumulated time of disk devices. The program includes a drive lifetime setting portion for setting lifetimes of drives, a drive start / stop portion for intentionally starting / stopping ATA disk devices, and an operation time measurement portion for measuring accumulated operation time. Since it is necessary to be conscious of difference in reliability and performance among disk devices when forming a RAID, a drive type notification unit, which is a program for notifying of the type of a disk device when forming the RAID, is provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
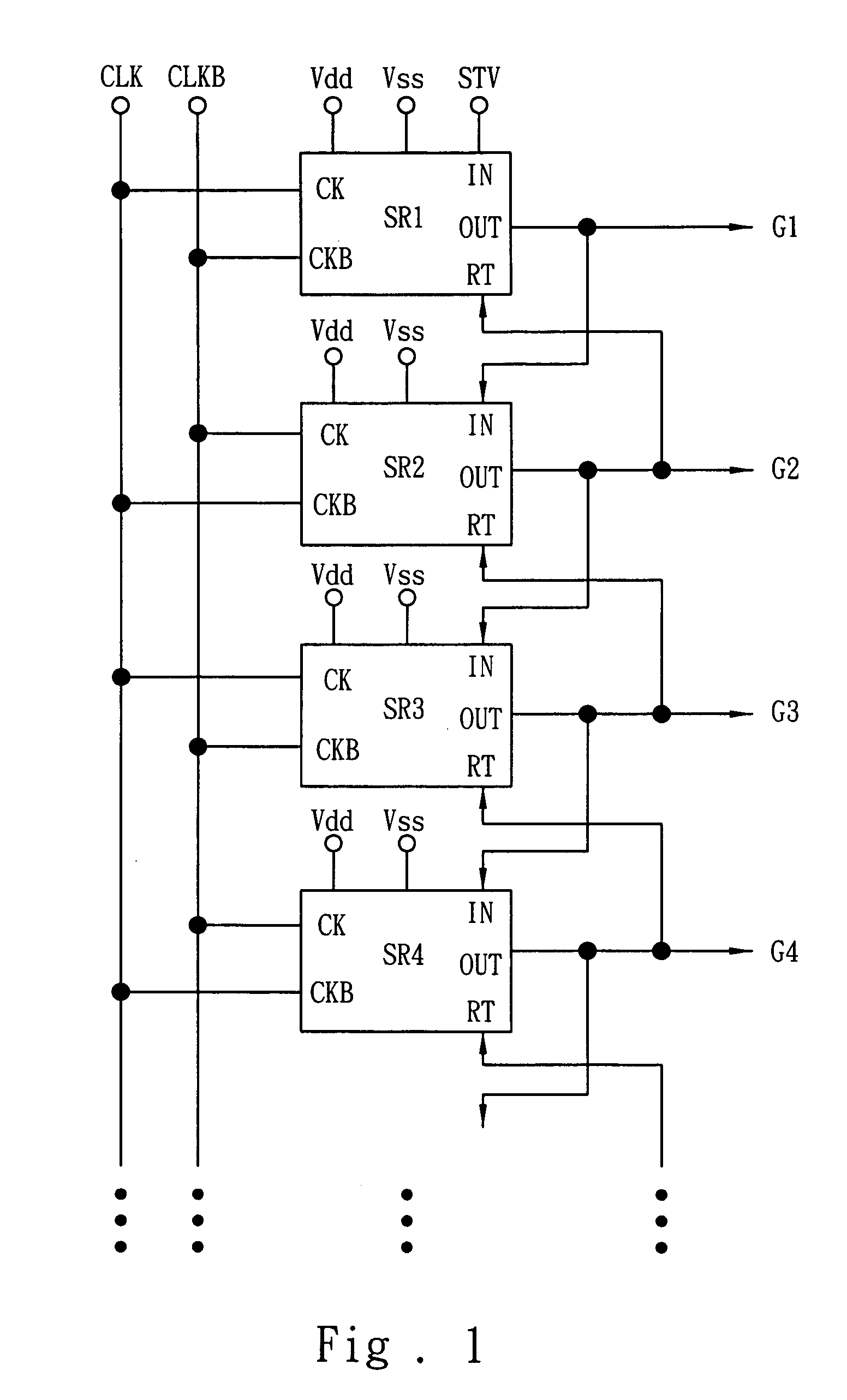
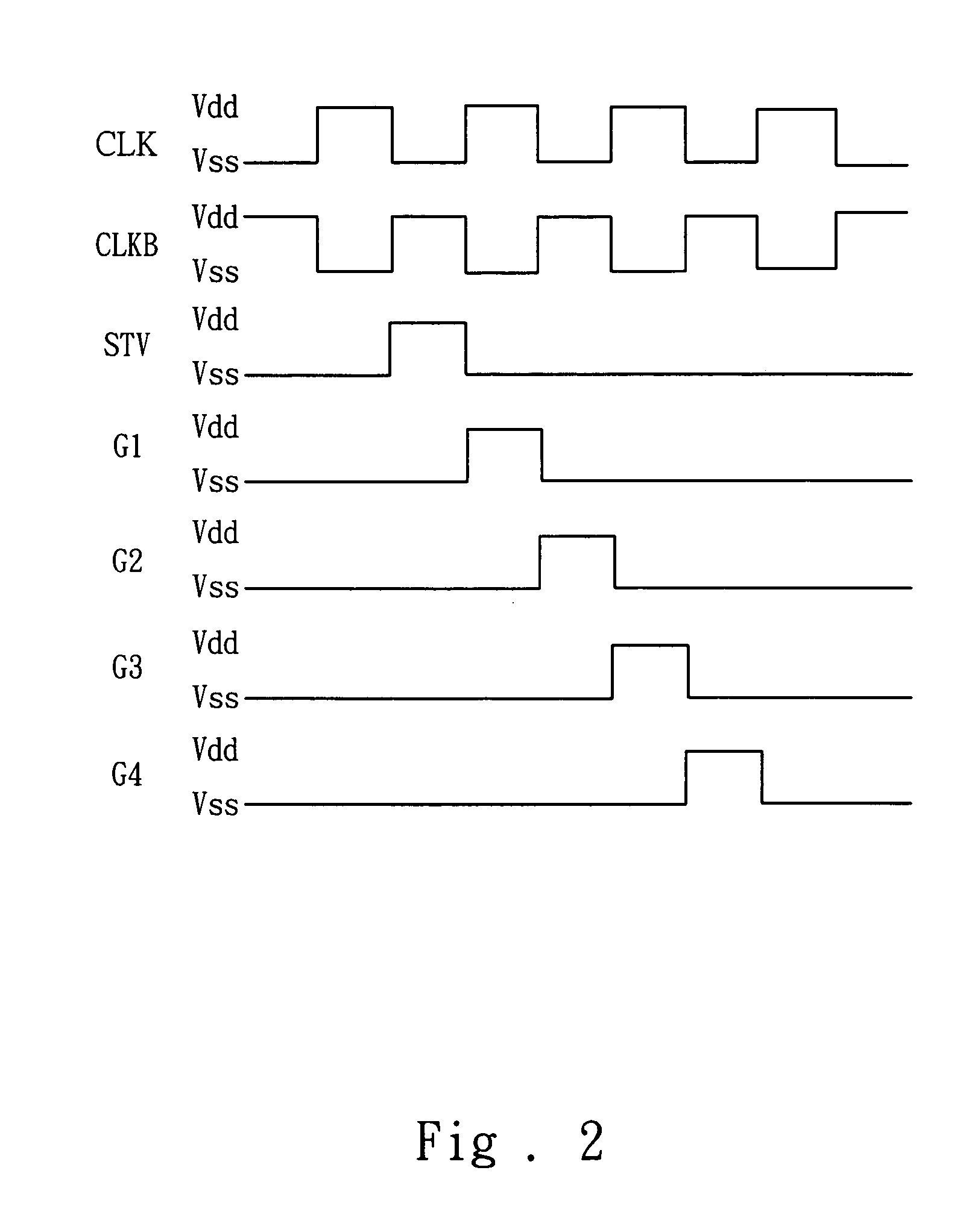
High-stability shift circuit using amorphous silicon thin film transistors
ActiveUS20060291610A1Prevent movementExtended operating timeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageWork periodAmorphous silicon
A high-stability shift circuit using amorphous silicon thin film transistors, which utilizes two out-of-phase pulses to control the operating mechanism and the bias-relations among transistors in the shift circuit. This makes the transistors under the driving conditions of positive / negative-alternating biases so as to restrain the voltage shift of the transistors such that the threshold voltage will not excessively increase along with the increasing operating time. This can not only increase the lifetime of the amorphous silicon thin film transistors but also extend the operating time of the shift circuit.
Owner:WINTEK CORP
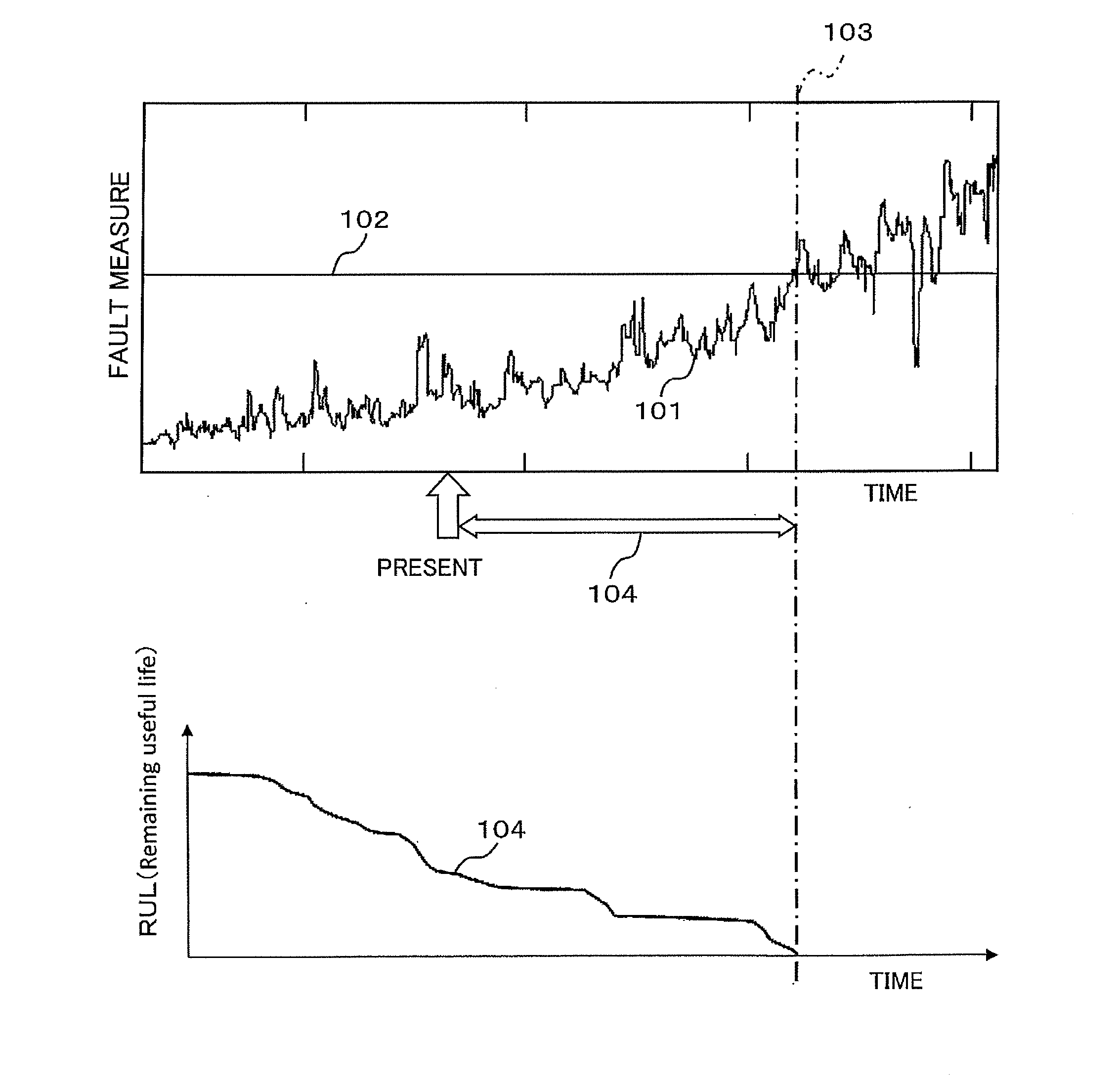
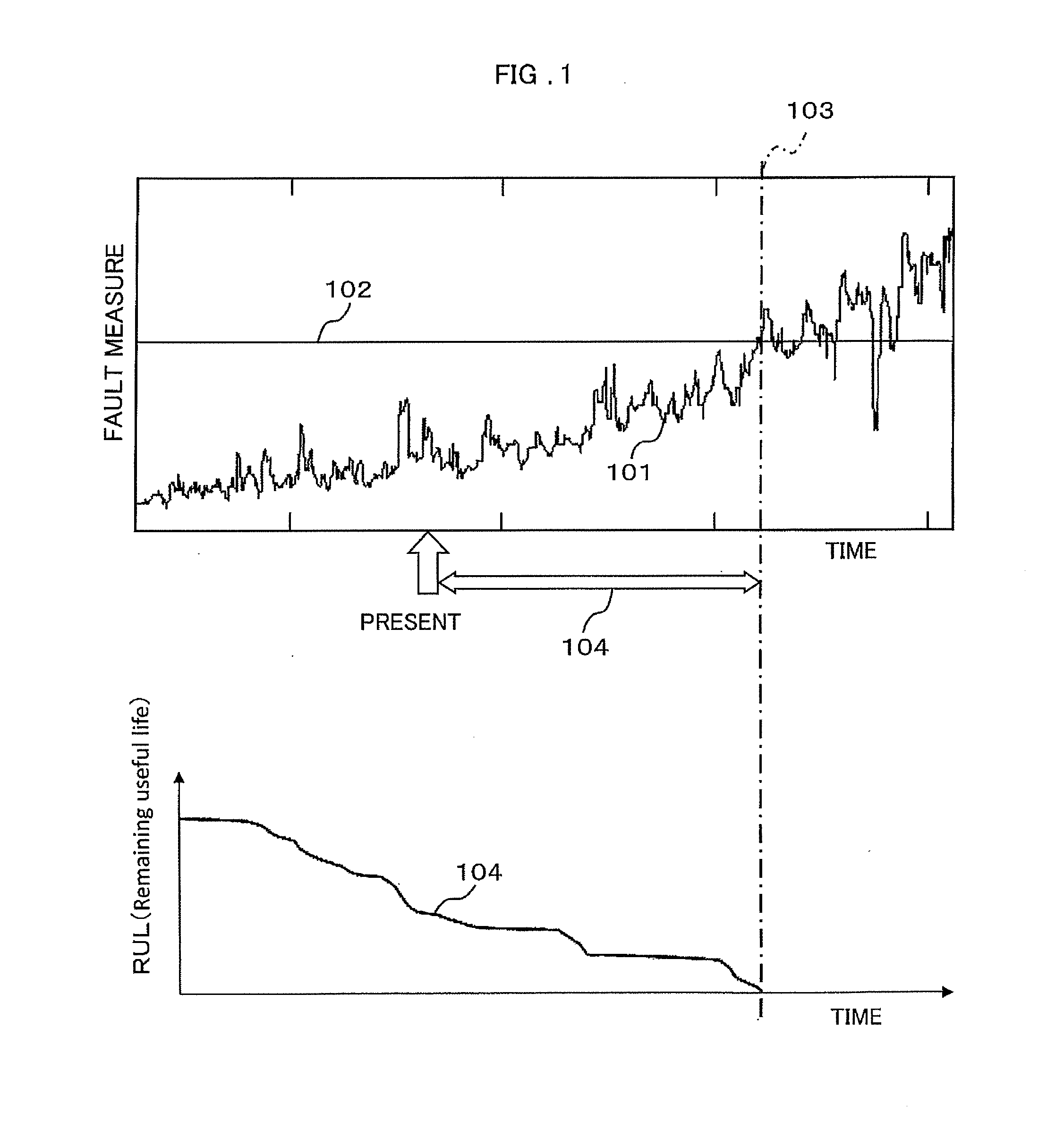
Health management system, fault diagnosis system, health management method, and fault diagnosis method
ActiveUS20150160098A1Easy to identifyTesting/monitoring control systemsStructural/machines measurementLearning dataMechanical equipment
An objective is to identify the health state of mechanical equipment and provide information usable for determining maintenance work timing or the like. A health management system includes a time-series data acquisition unit configured to acquire multi-dimensional sensor data and environmental data from mechanical equipment; a first discrimination unit configured to quantify the equipment state of the mechanical equipment by a statistical method using normal data as learning data; a second discrimination unit configured to quantify the health state indicating the performance or quality of the mechanical equipment by a statistical method using normal data; and an output unit configured to display and / or output to the outside the quantified equipment state and health state.
Owner:HIATACHI POWER SOLUTIONS CO LTD +1
Adaptive erase and soft programming for memory
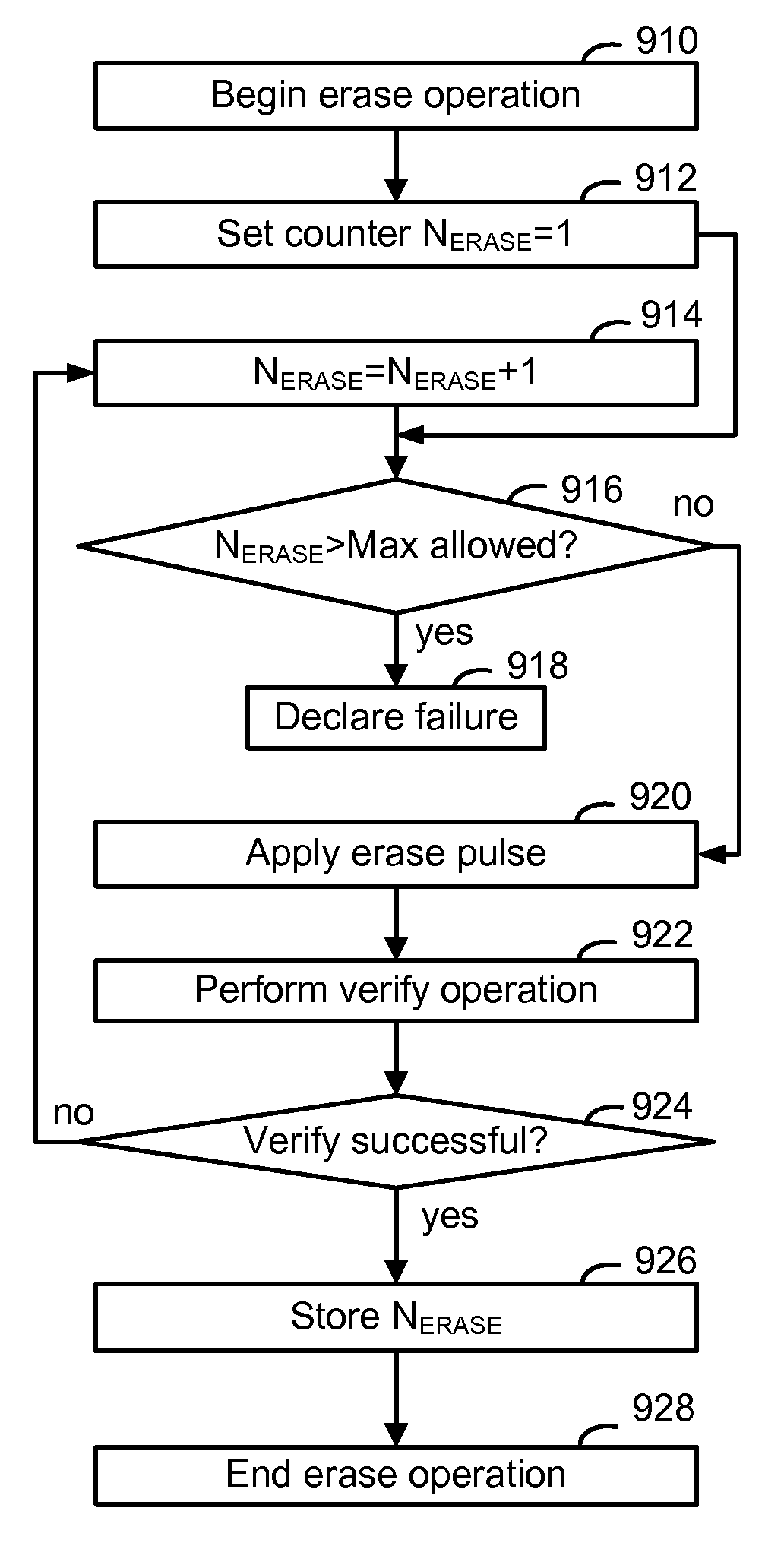
ActiveUS20100149881A1Improve memory performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storagePulse durationEmbedded system
An erase sequence of a non-volatile storage device includes an erase operation followed by a soft programming operation. The erase operation applies one or more erase pulses to the storage elements, e.g., via a substrate, until an erase verify level is satisfied. The number of erase pulses is tracked and recorded as an indicia of the number of programming-erase cycles which the storage device has experienced. The soft programming operation applies soft programming pulses to the storage elements until a soft programming verify level is satisfied. Based on the number of erase pulses, the soft programming operation time is shortened by skipping verify operations for a specific number of initial soft programming pulses which is a function of the number of erase pulses. Also, a characteristic of the soft programming operation can be optimized, such as starting amplitude, step size or pulse duration.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
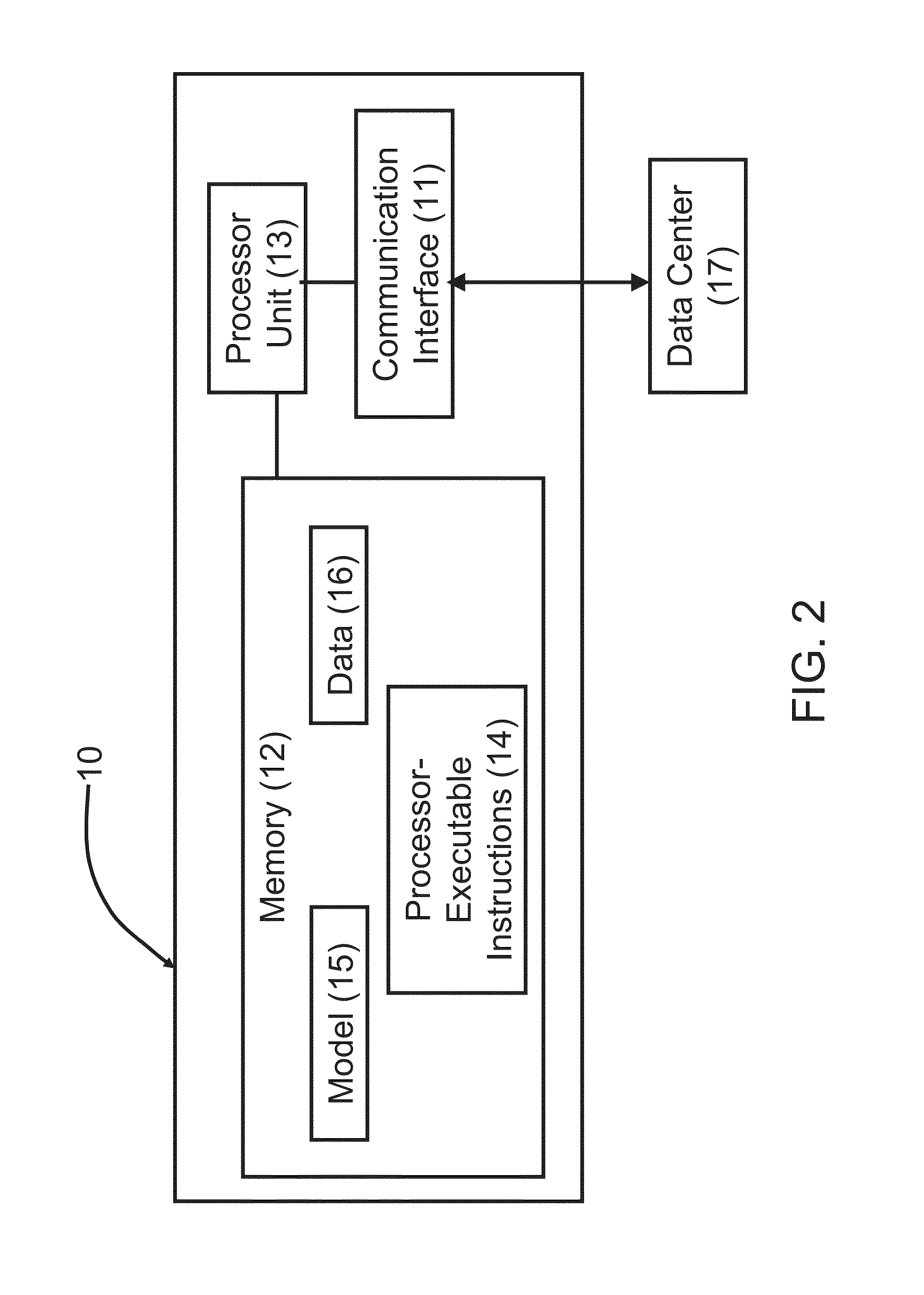
Facilitating Revenue Generation From Data Shifting By Data Centers
The disclosure facilitates management data center utilization for generating energy-related revenue from energy markets. Operating schedules are generated, over a time period T, for operation of an energy management system of energy assets of data center sites. Since CPU utilization (or computing load) can be correlated to energy consumption, the operating schedules can cause the energy management system to modulate the CPU utilization (or computing load) of energy assets within a data center, or to indicate shifting of CPU utilization (or computing load) from one data center site in a certain energy market price region to another data center site in a different energy market price region. When implemented, the generated operating schedules facilitates derivation of the energy-related revenue, over a time period T, associated with operation of the energy assets according to the generated operating schedule.
Owner:VIRIDITY ENERGY SOLUTIONS INC
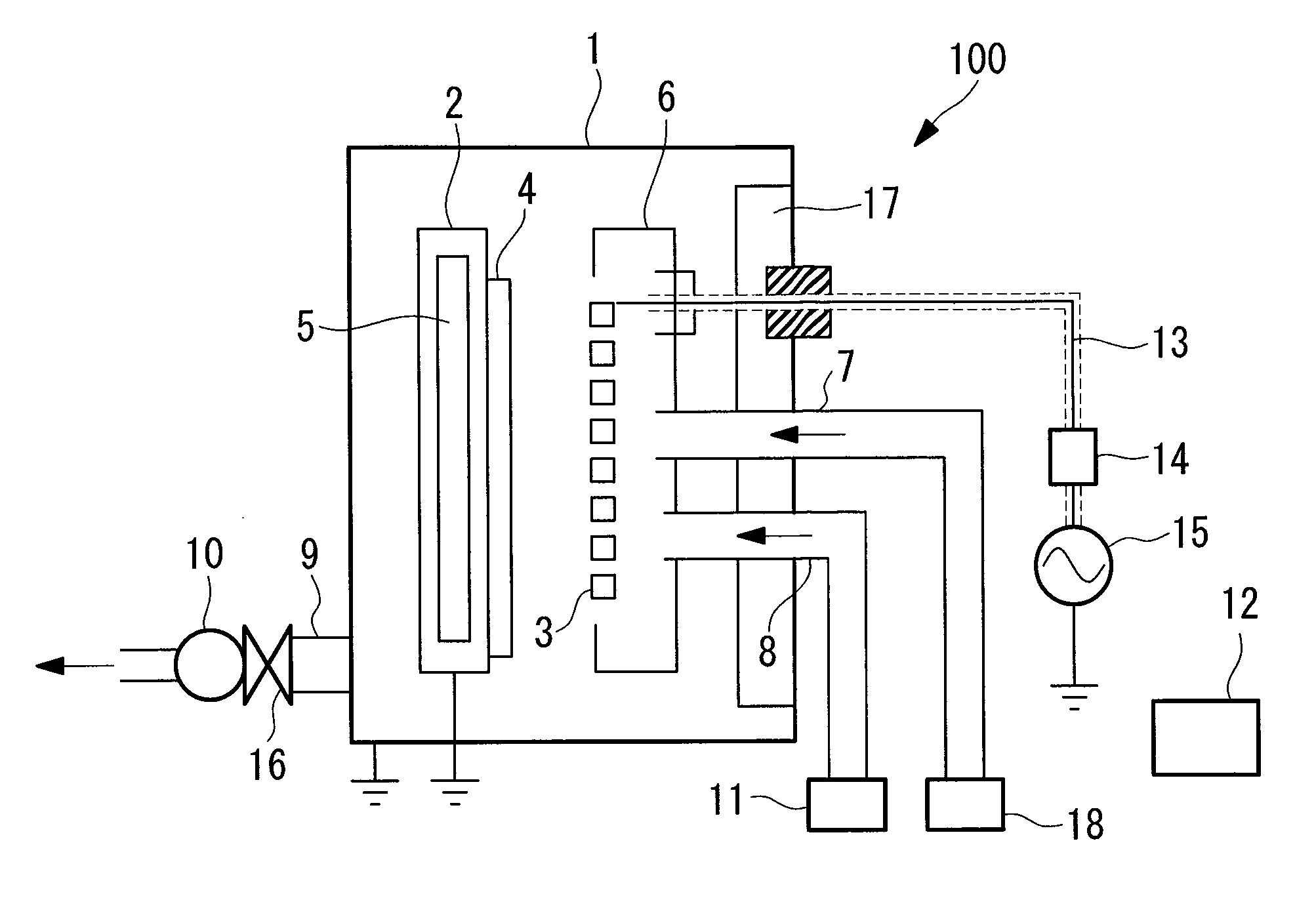
Vacuum processing apparatus and operating method for vacuum processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100310785A1Easy to set upEasy to changeElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningEngineeringOperational approach
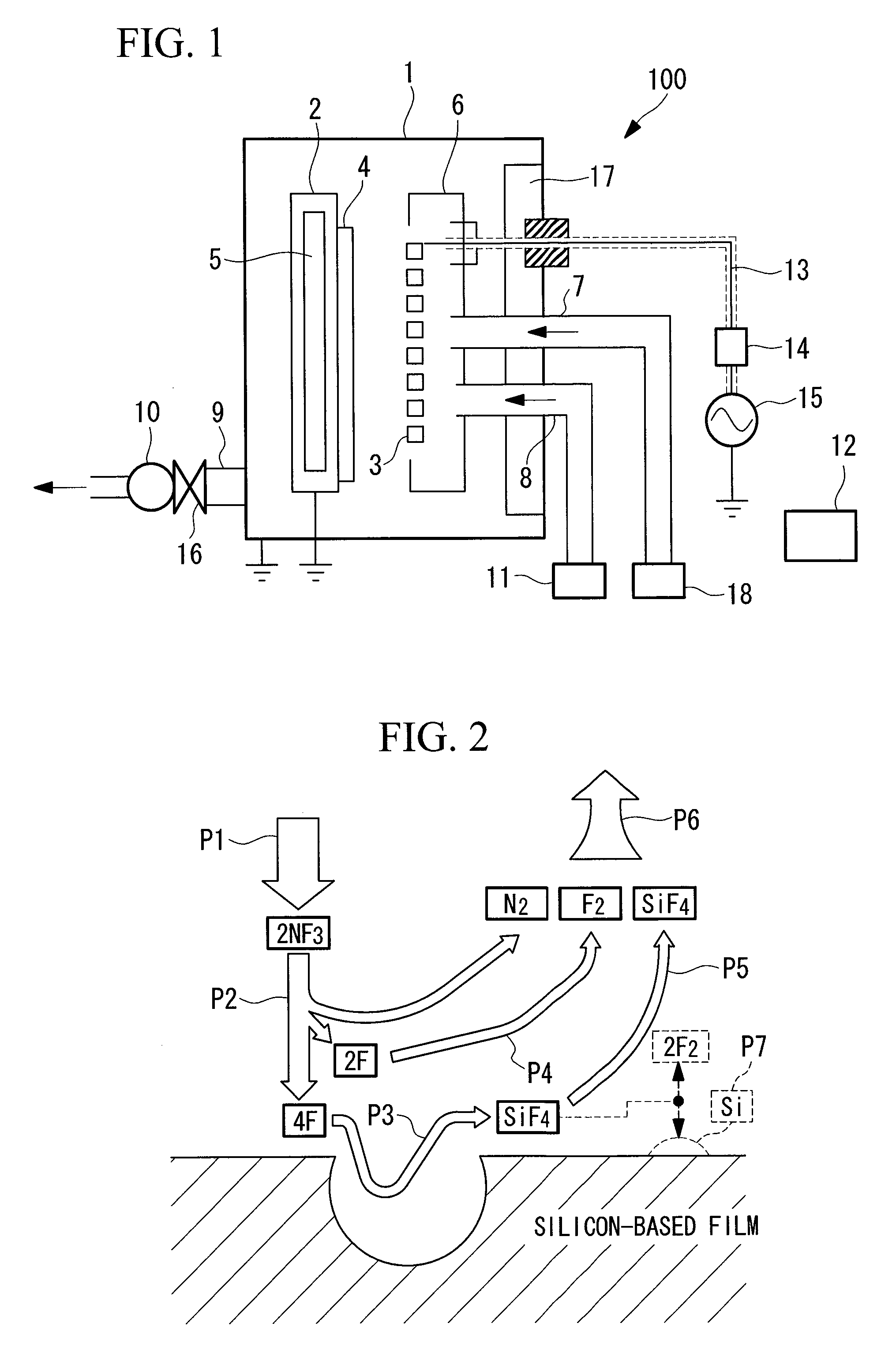
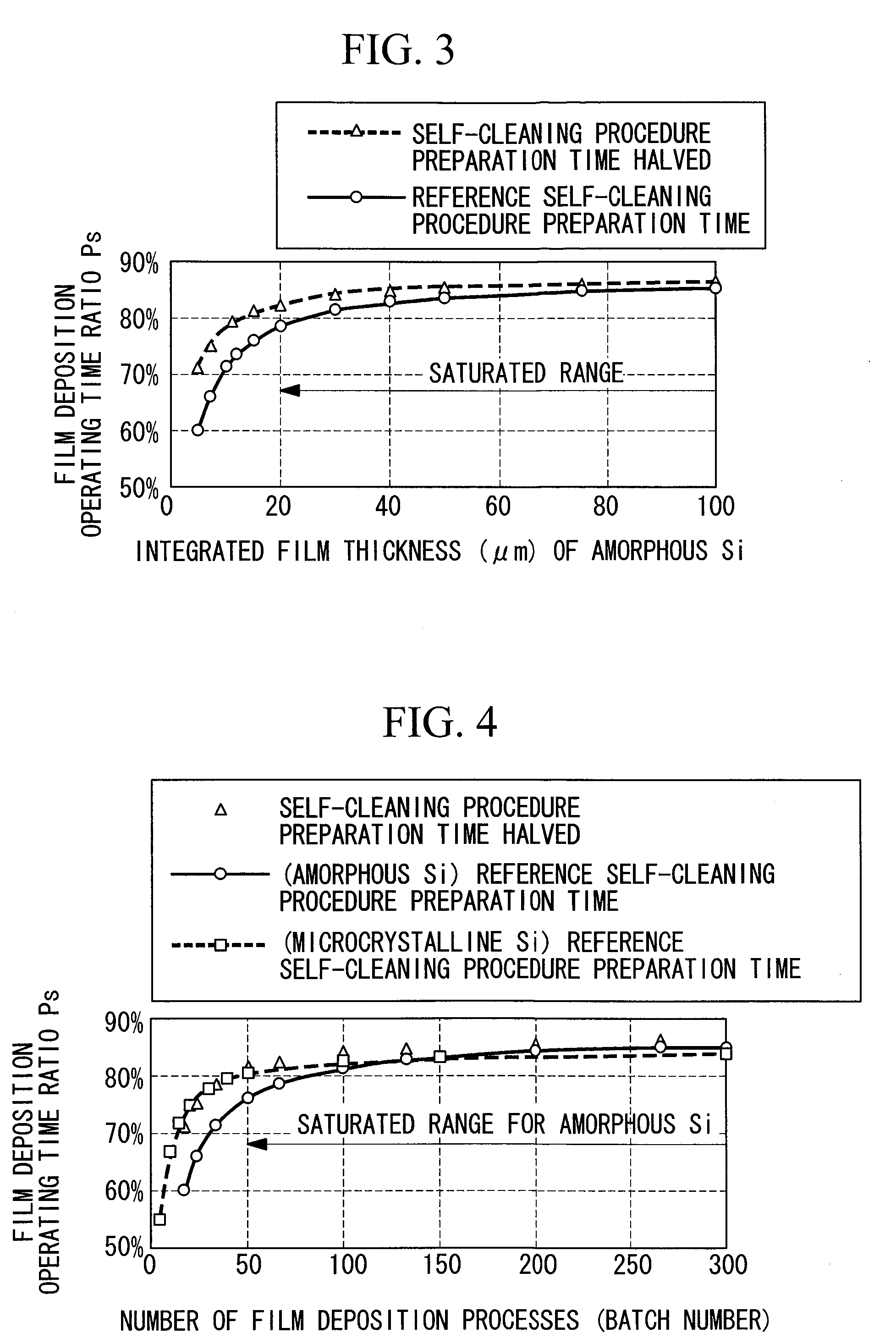
It is an object of the invention to provide a vacuum processing apparatus that enables setting a timing interval between self-cleaning procedures simply and so as to have general-use, enables significantly lengthening this timing interval, and improves the production efficiency. In a plasma CVD apparatus (100) that carries out self-cleaning procedure by feeding a cleaning gas into a film deposition chamber (1) in which film deposition processing is carried out on a substrate (4), the timing interval between self-cleaning procedures is set in a range in which a film deposition operating time ratio (Ps) is converged with respect to an increase in a film deposition process amount, where the film deposition operating time ratio (Ps) is represented by the proportion of a film deposition-related operating time (Tt) in the sum of the film deposition-related operating time (Tt) and a cleaning-related operating time (Tc).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
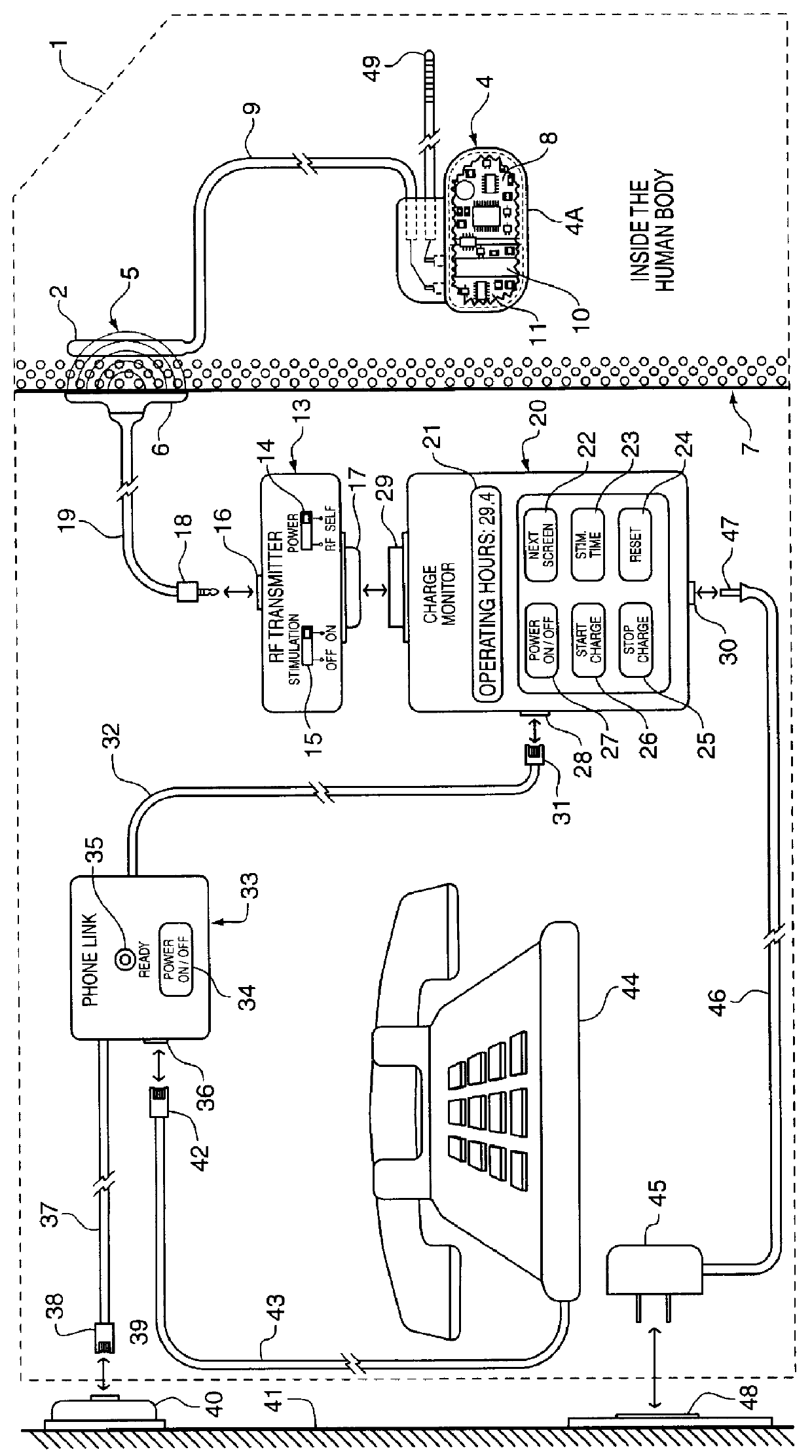
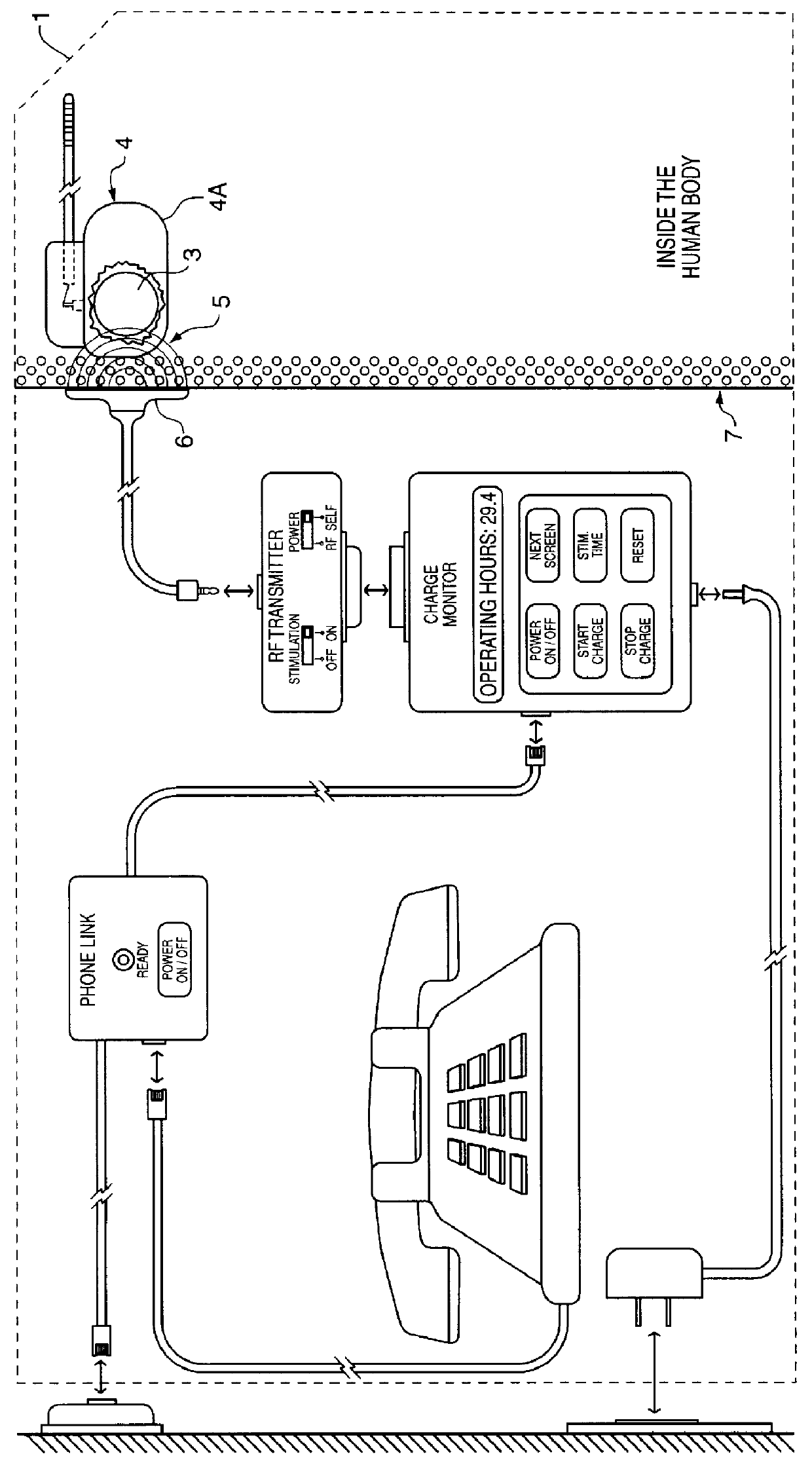
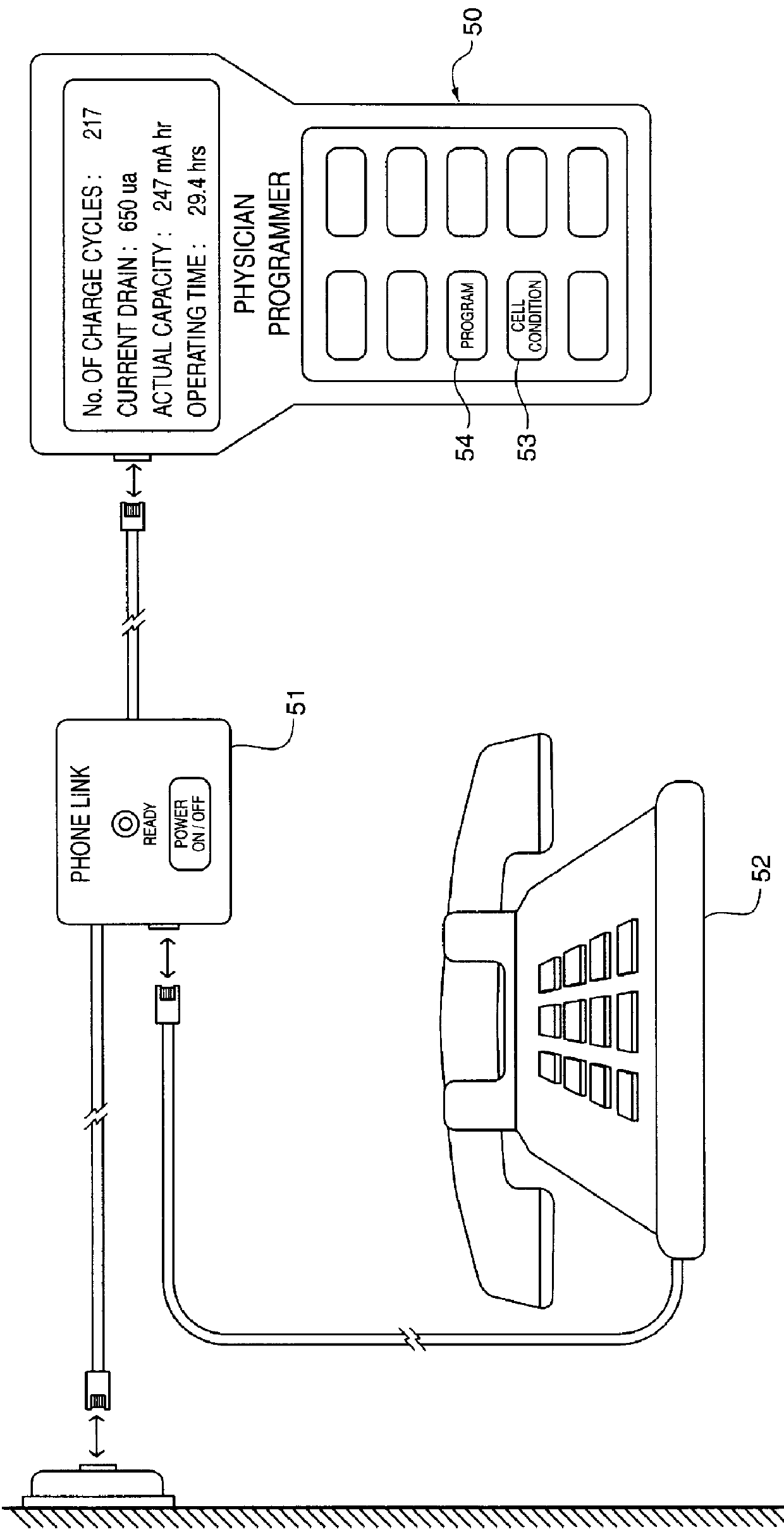
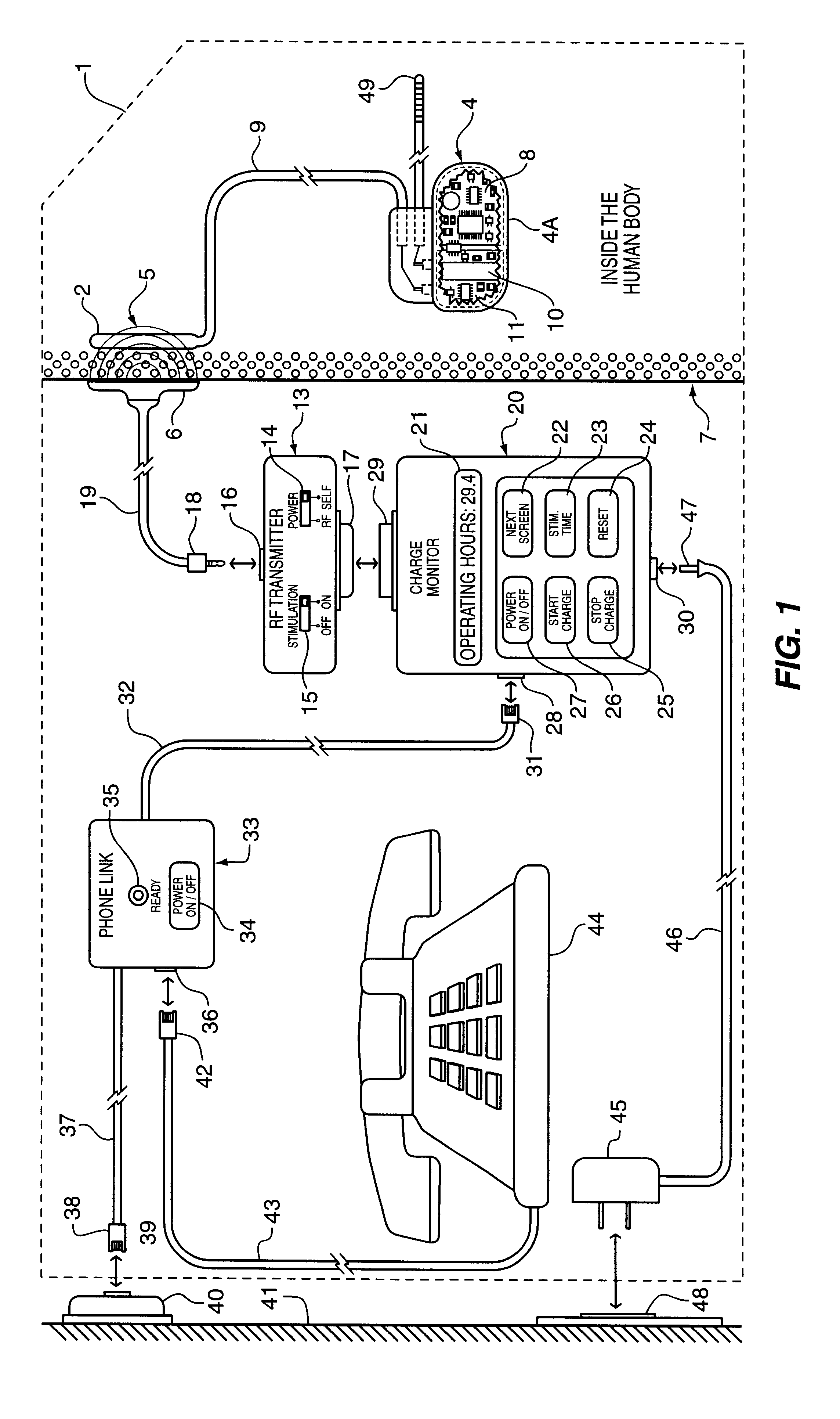
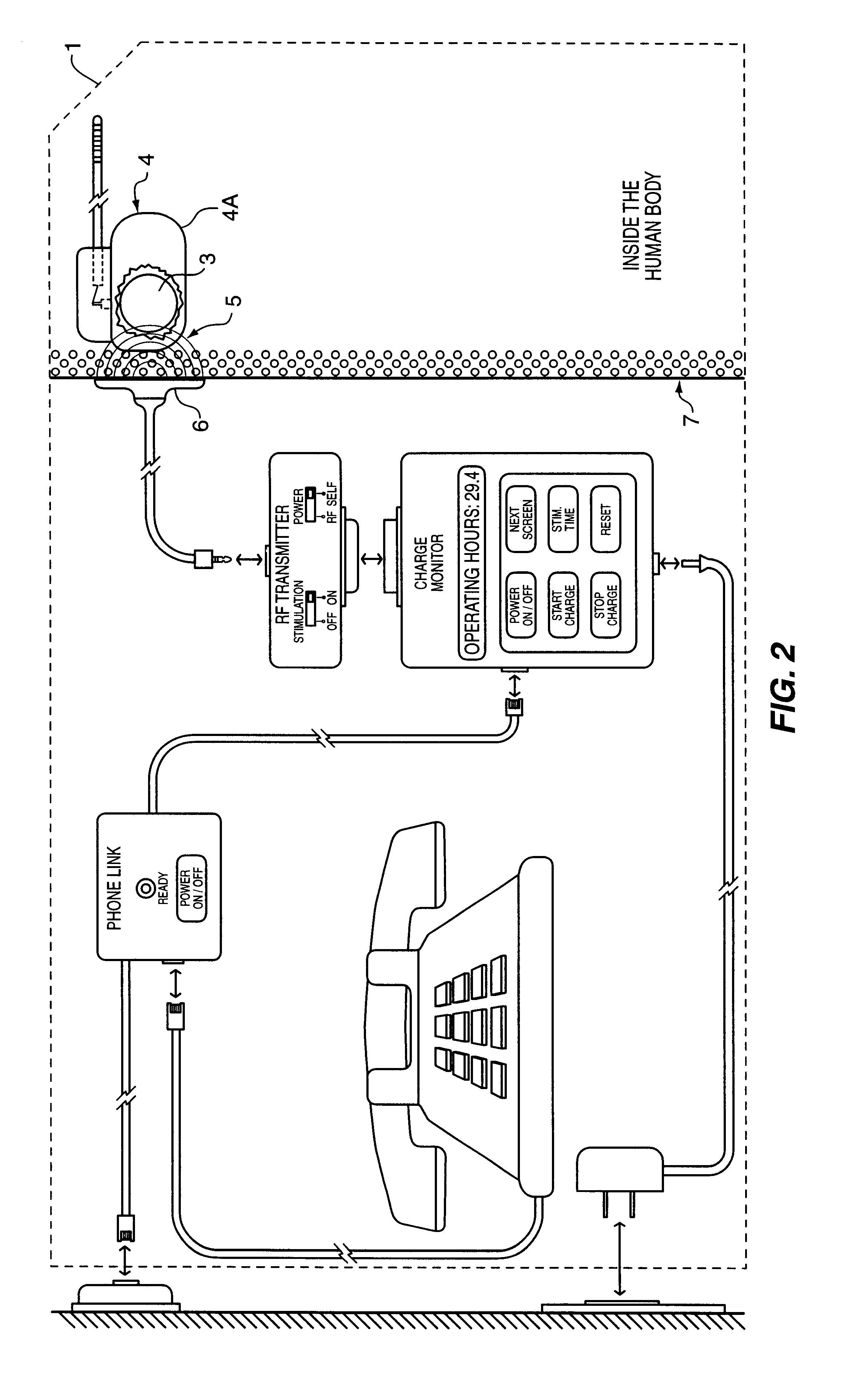
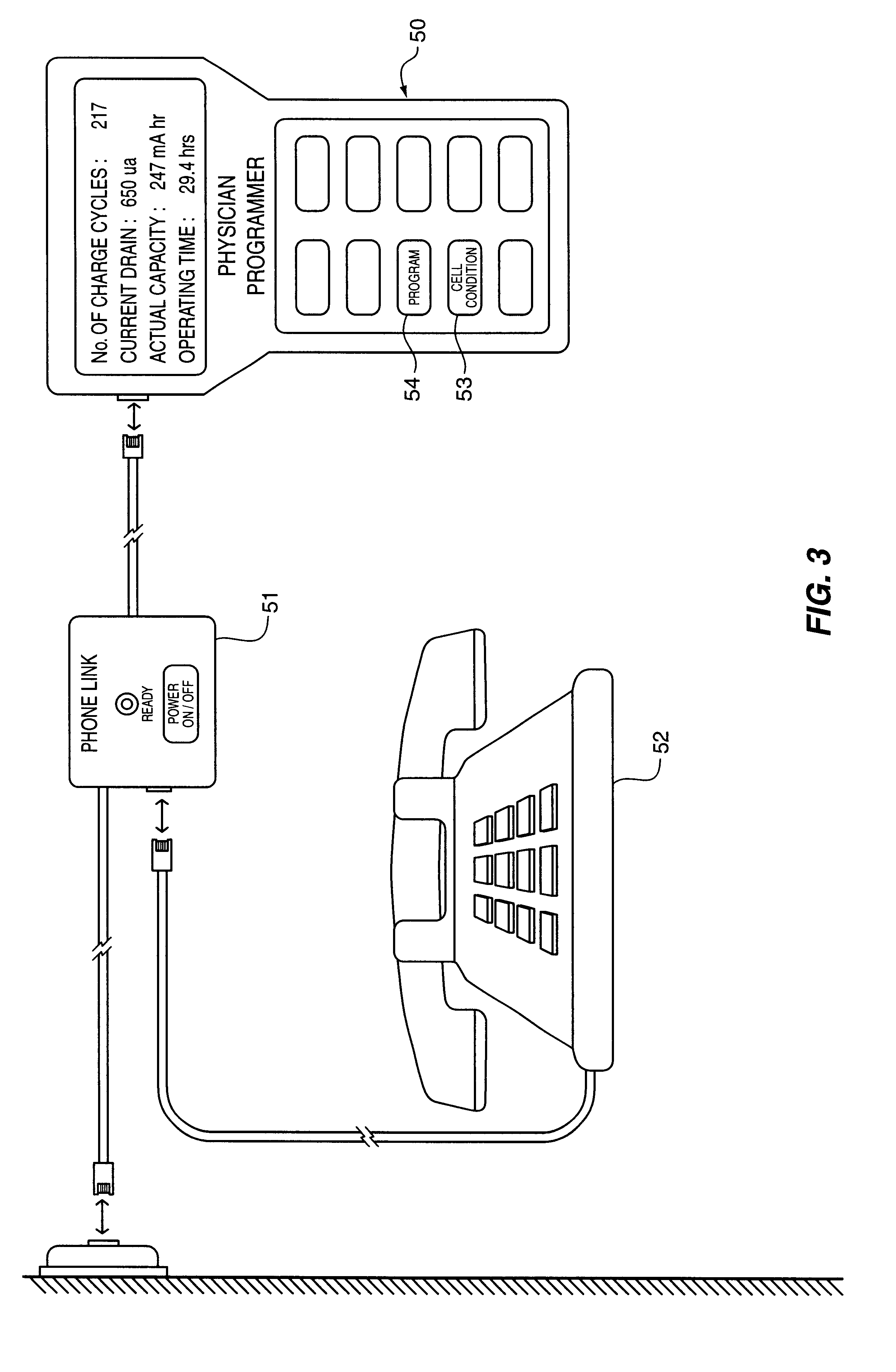
Implantable power management system
InactiveUS6166518AAccurately calculate and displayIncrease energy densityElectromagnetic wave systemHeart stimulatorsLow voltageElectric power
The method and system for managing power supplied from a charging circuit to a power source in an implantable medical device comprises the steps of and circuitry for: measuring the current drain of the medical device; measuring the elapsed time since the last full charge of a power source of the device; calculating the actual capacity of the power source (corrected for fade) based on the variable of current drain and the variable of elapsed time; calculating the operating time based on the variable of current drain and the variable of the actual capacity of the power source; measuring the voltage of the power source; signaling the medical device when the power source voltage has reached a certain low value which requires disconnection from the power source; disconnecting, during discharging, the power source from the medical device upon the power source reaching a certain low voltage in order to prevent deep discharging of the power source and subsequent damage; precisely limiting the charging voltage to the power source in order to prevent overcharging beyond safe limits; disconnecting, during charging, the power source from the charging circuit upon the power source reaching a certain high voltage in order to prevent overcharging of the power source and subsequent damage; sensing when the electromagnetic waves being transmitted by an RF transmitter / charger induce a voltage level above a certain value at an RF receiver of the implanted power management system; reconnecting power supply inputs of the medical device to the power source upon sensing this induced high voltage level; monitoring the temperature of the power source during charging and discharging; disconnecting the charging circuitry from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during charging; reconnecting the charging circuitry to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during charging; disconnecting the implanted medical device from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during discharging; and, reconnecting the medical device to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during discharging.
Owner:EXONIX
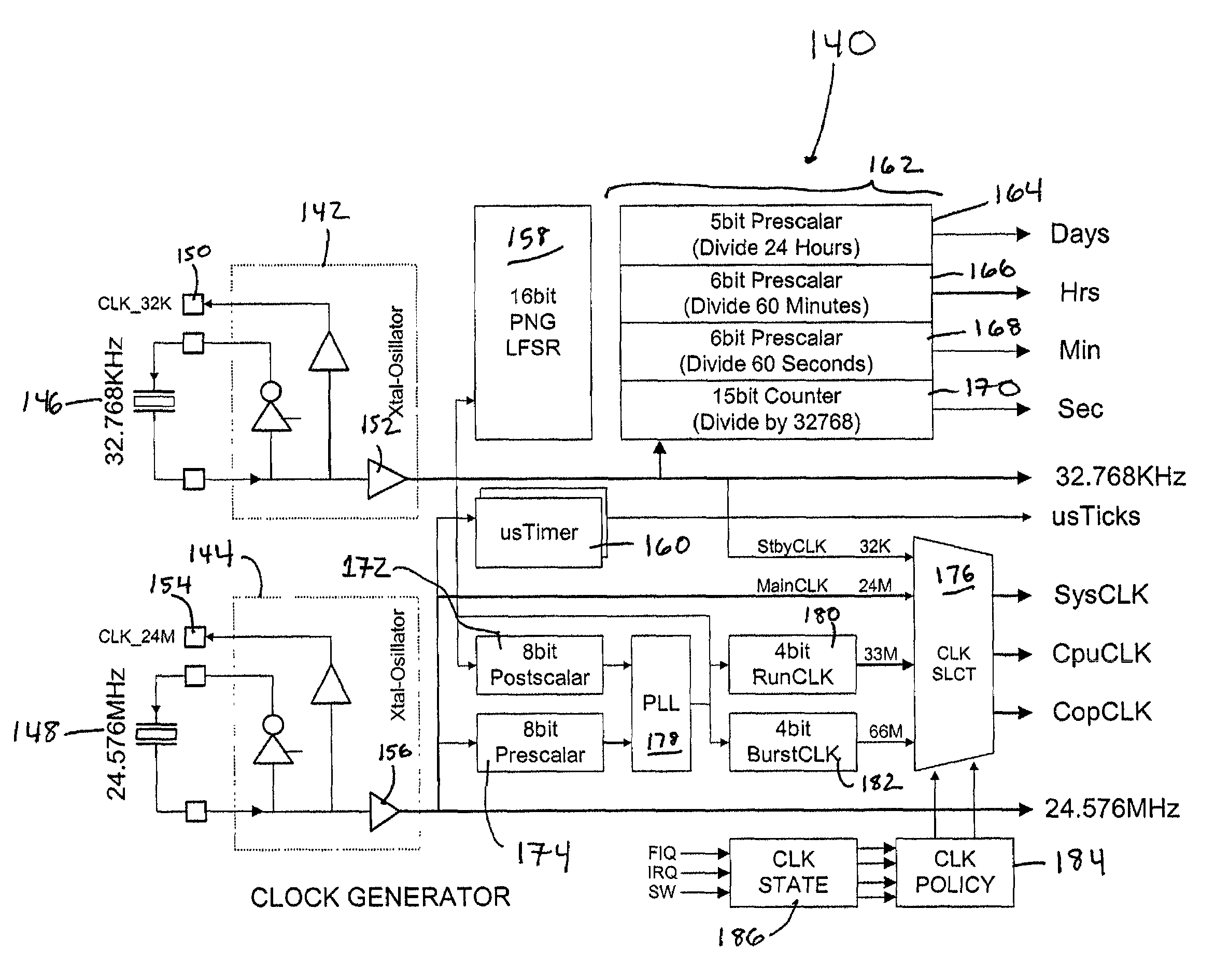
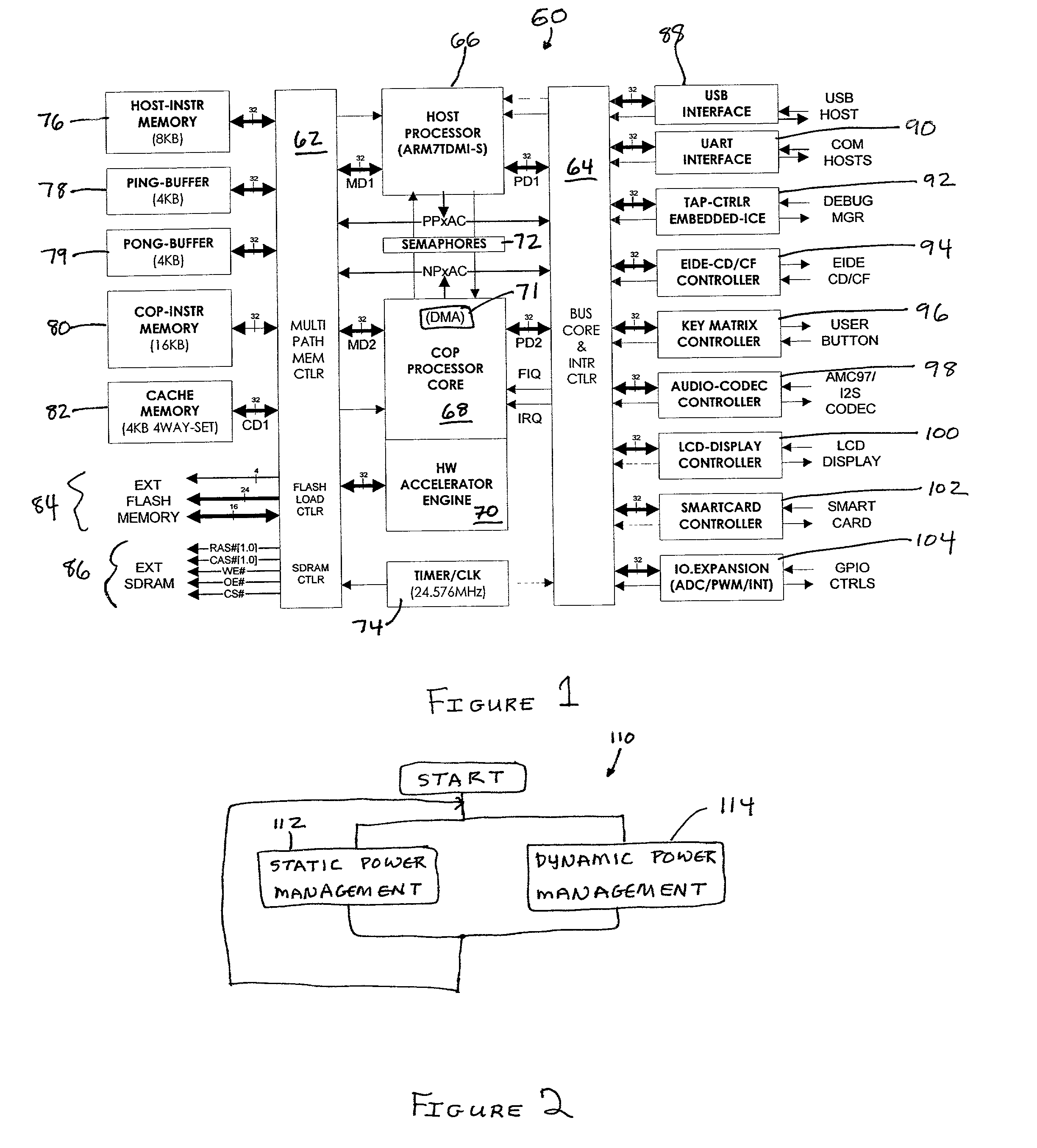
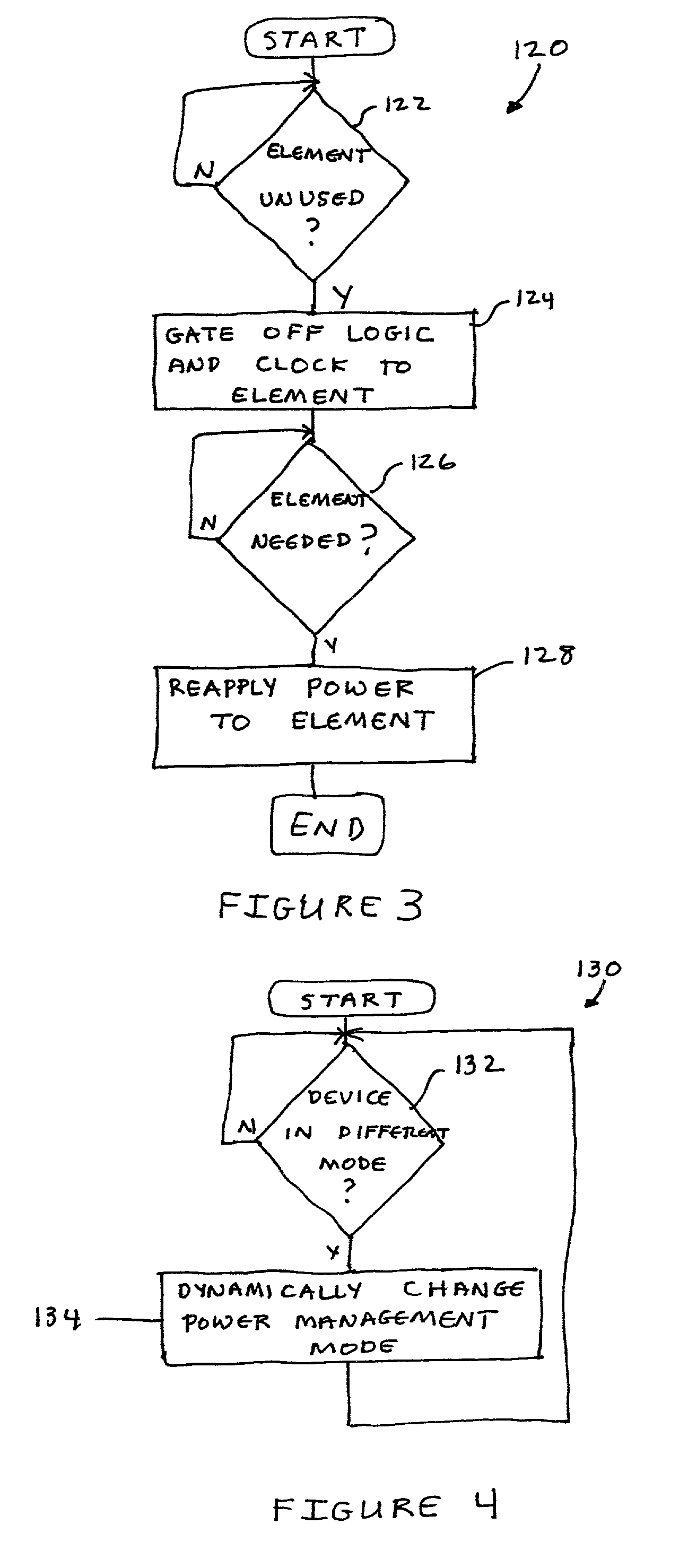
Dynamic power management of devices in computer system by selecting clock generator output based on a current state and programmable policies
InactiveUS6990594B2Maximize battery lifeMinimize powerEnergy efficient ICTCathode-ray tube indicatorsDynamic power managementElectrical battery
A power management system and method permit the total power consumption by a portable electronic device to be reduced so that the portable electronic device has a longer operating time on a limited power source, such as a battery. The system may also be used with devices that are powered by a more permanent source of power. The system may combine static power management techniques as well as dynamic power management techniques. The system may include a flexible clock generator.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Implantable power management system
InactiveUS6278258B1Accurately calculate and displayIncrease energy densityElectromagnetic wave systemSecondary cellsLow voltageElectric power
The method and system for managing power supplied from a charging circuit to a power source in an implantable medical device comprises the steps of and circuitry for: measuring the current drain of the medical device; measuring the elapsed time since the last full charge of a power source of the device; calculating the actual capacity of the power source (corrected for fade) based on the variable of current drain and the variable of elapsed time; calculating the operating time based on the variable of current drain and the variable of the actual capacity of the power source; measuring the voltage of the power source; signaling the medical device when the power source voltage has reached a certain low value which requires disconnection from the power source; disconnecting, during discharging, the power source from the medical device upon the power source reaching a certain low voltage in order to prevent deep discharging of the power source and subsequent damage; precisely limiting the charging voltage to the power source in order to prevent overcharging beyond safe limits; disconnecting, during charging, the power source from the charging circuit upon the power source reaching a certain high voltage in order to prevent overcharging of the power source and subsequent damage; sensing when the electromagnetic waves being transmitted by an RF transmitter / charger induce a voltage level above a certain value at an RF receiver of the implanted power management system; reconnecting power supply inputs of the medical device to the power source upon sensing this induced high voltage level; monitoring the temperature of the power source during charging and discharging; disconnecting the charging circuitry from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during charging; reconnecting the charging circuitry to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during charging; disconnecting the implanted medical device from the power source if the temperature of the power source raises above a certain level during discharging; and, reconnecting the medical device to the power source when the temperature of the power source drops below a certain low value during discharging.
Owner:EXONIX
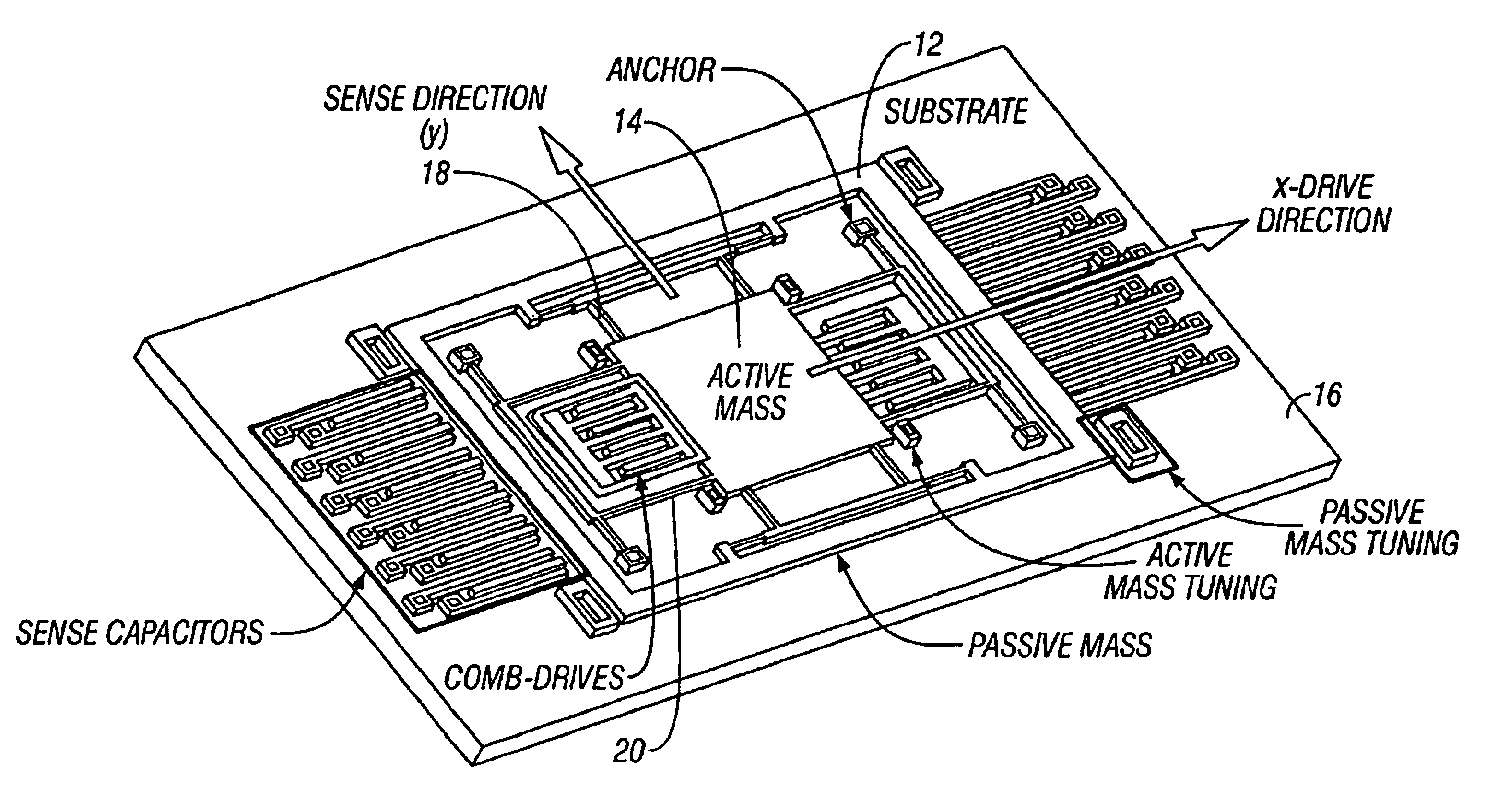
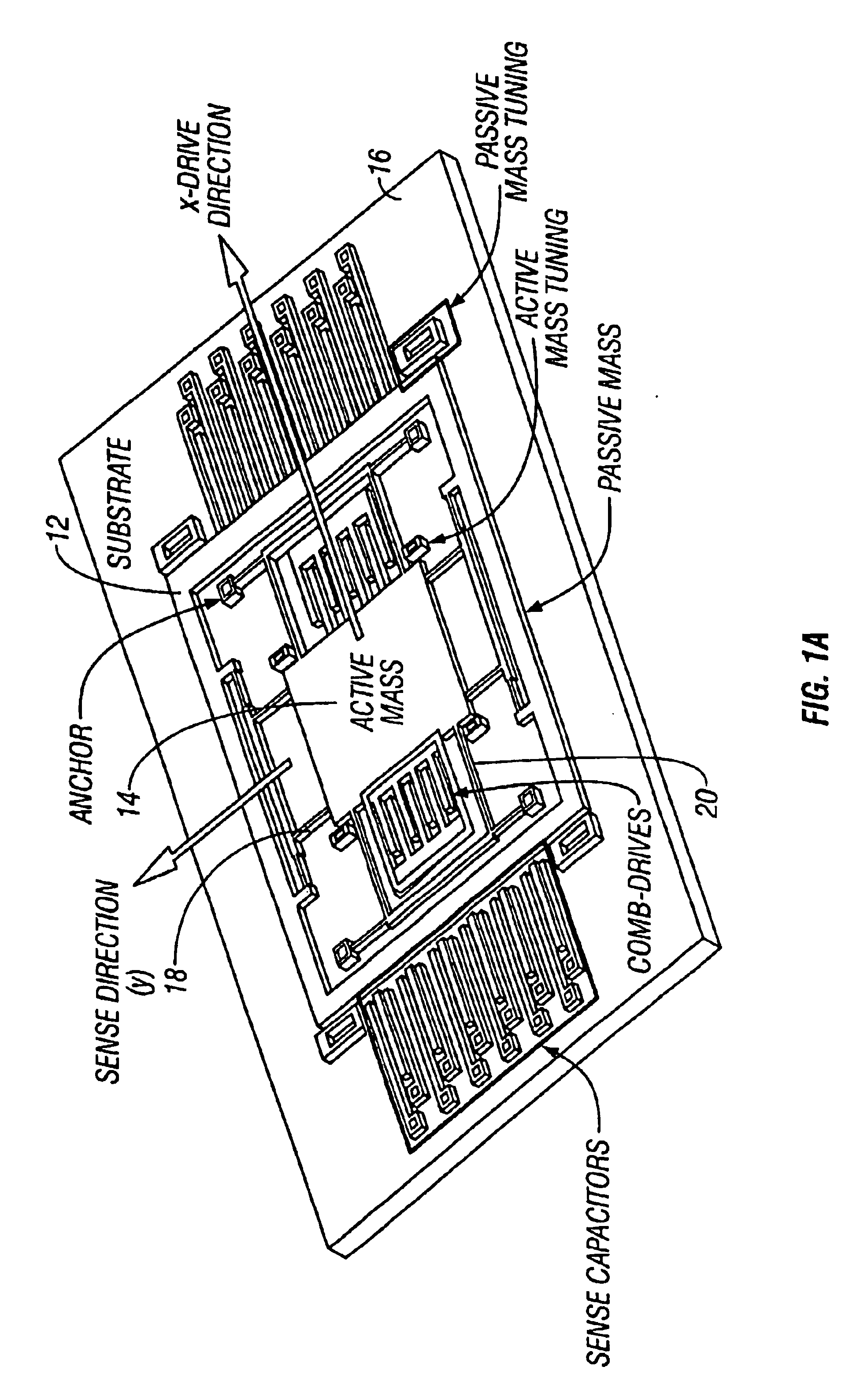
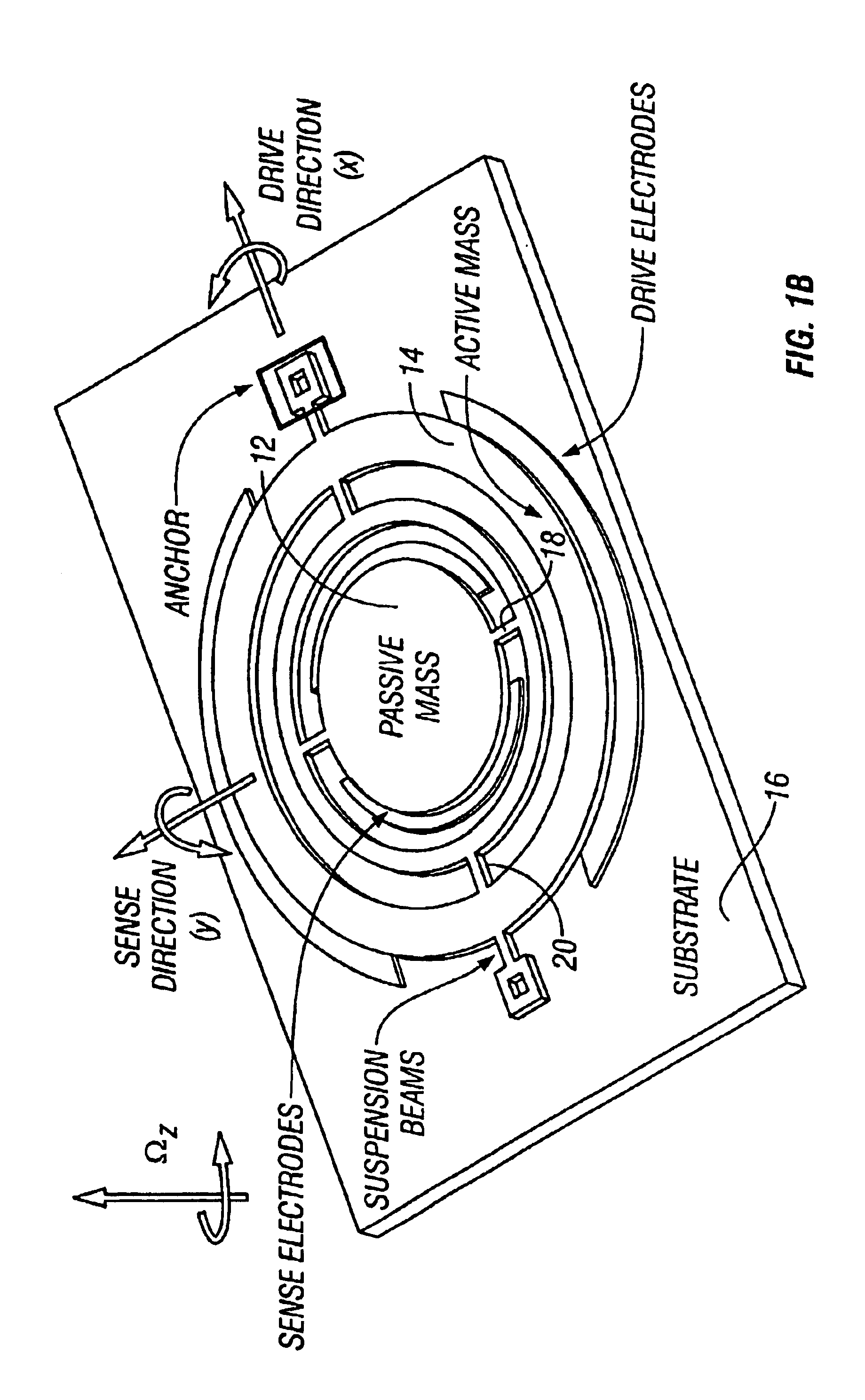
Non-resonant four degrees-of-freedom micromachined gyroscope
InactiveUS6845669B2WideOscillation amplitude is largeMechanical apparatusAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGyroscopeEngineering
A micromachined design and method with inherent disturbance-rejection capabilities is based on increasing the degrees-of-freedom (DOF) of the oscillatory system by the use of two independently oscillating proof masses. Utilizing dynamical amplification in the 4-degrees-of-freedom system, inherent disturbance rejection is achieved, providing reduced sensitivity to structural and thermal parameter fluctuations and damping changes over the operating time of the device. In the proposed system, the first mass is forced to oscillate in the drive direction, and the response of the second mass in the orthogonal direction is sensed. The response has two resonant peaks and a flat region between peaks. Operation is in the flat region, where the gain is insensitive to frequency fluctuations. An over 15 times increase in the bandwidth of the system is achieved due to the use of the proposed architecture. In addition, the gain in the operation region has low sensitivity to damping changes. Consequently, by utilizing the disturbance-rejection capability of the dynamical system, improved robustness is achieved, which can relax tight fabrication tolerances and packaging requirements and thus result in reducing production cost of micromachined methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Portable electronic device charger and method
InactiveUS20050231159A1Extended operating timeSelective utilizationBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerWork periodExternal energy
A method and apparatus for enabling extended operating time for a cellular telephone, pager, personal digital assistant, or the like, wherein the main battery of the portable electronic devices may be recharged from an auxiliary battery contained within a portable holder, and wherein the auxiliary battery is itself recharged by connecting to an external energy source.
Owner:JONES JAMES A SR +1
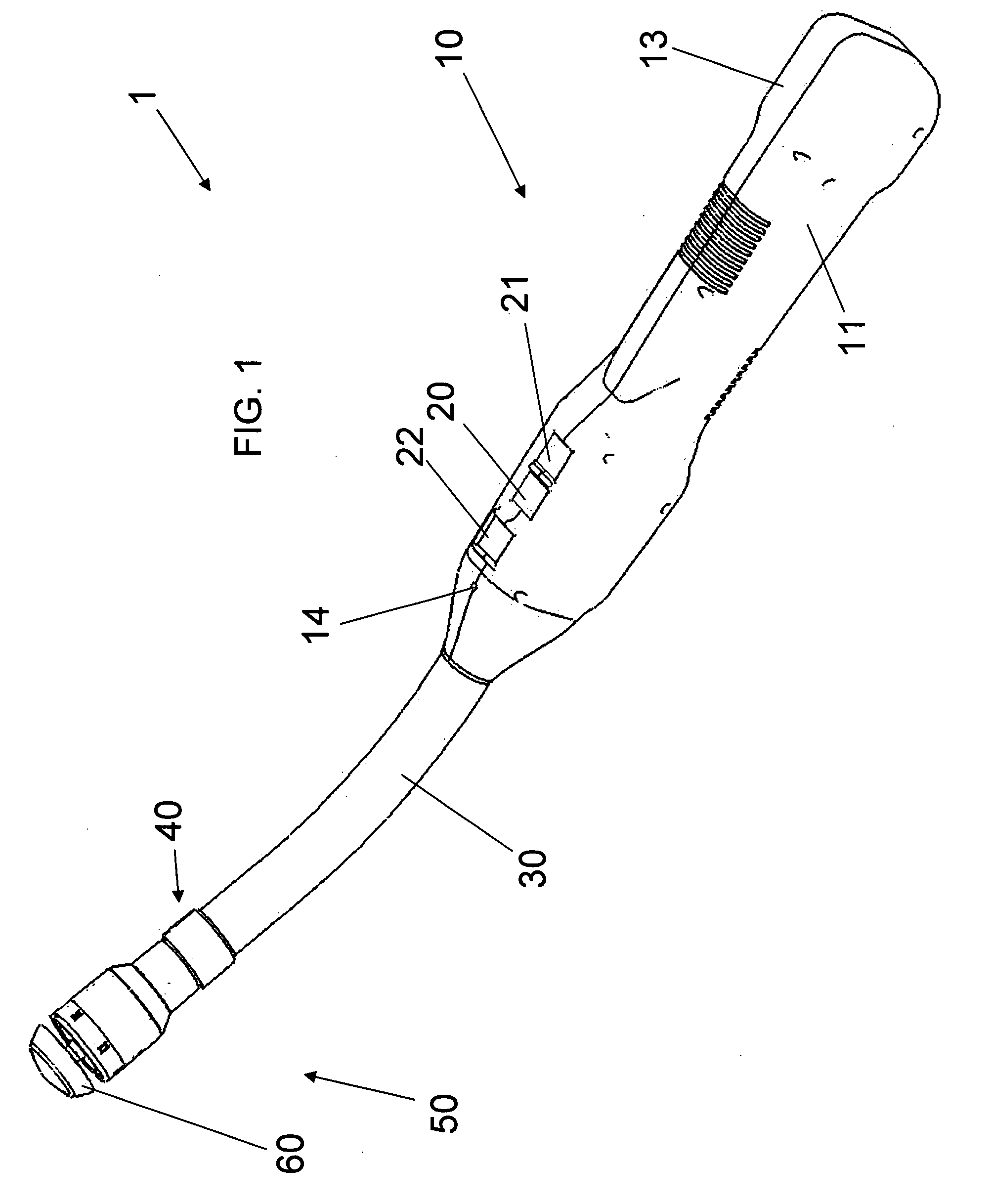
Ultrasonic probe
InactiveUS7308828B2Inhibit temperature riseAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsElectricityTransducer
An ultrasonic probe has a probe proper, a connector and a cable for electrically connecting between the probe proper and the connector. The probe proper includes a transducer that converts between ultrasonic wave and electricity, and a phase change member having a property to cause a phase change of from solid to liquid at a particular temperature reached in an operation time period of the transducer and a phase change of from liquid to solid at lower than the particular temperature.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com