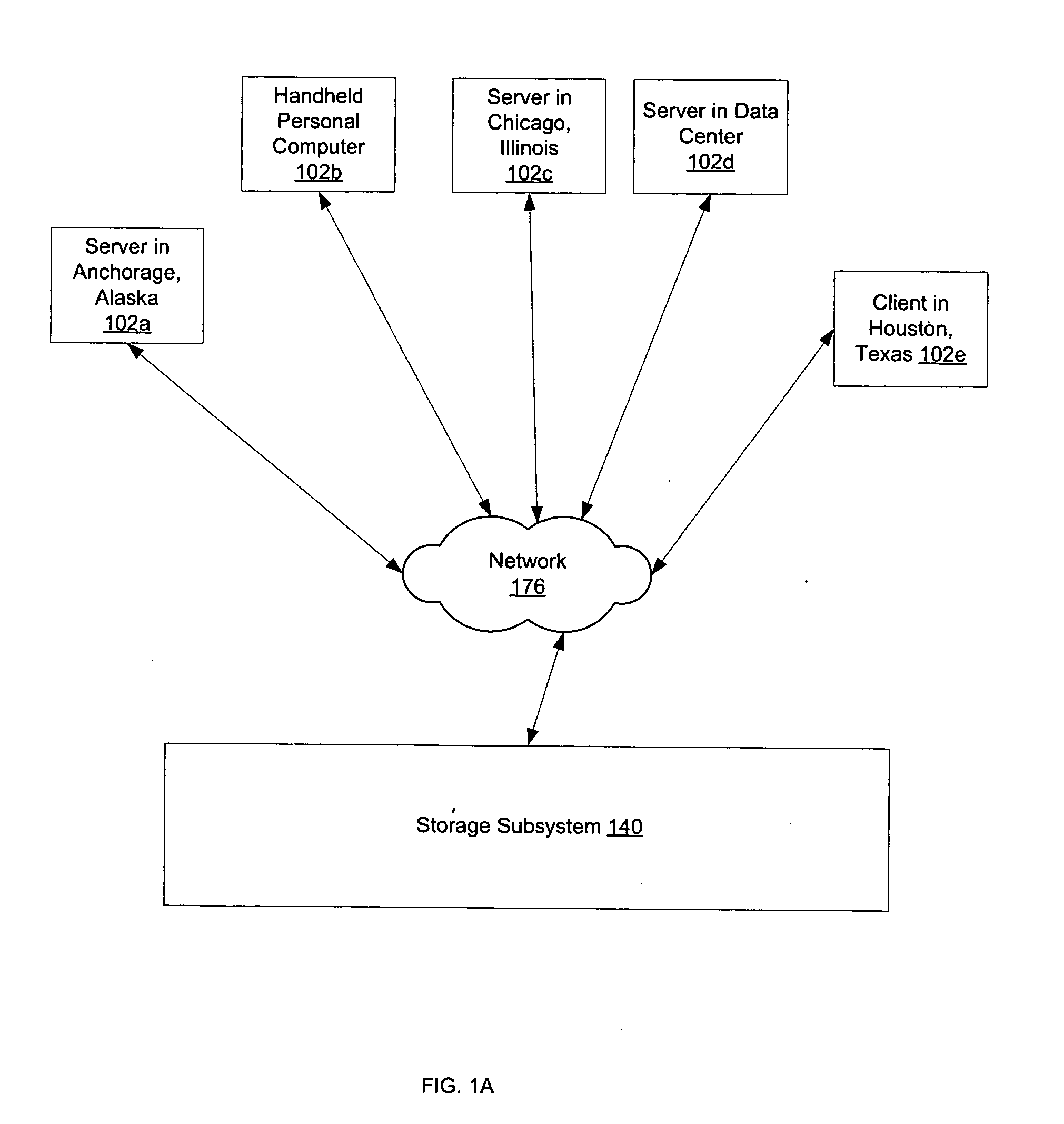
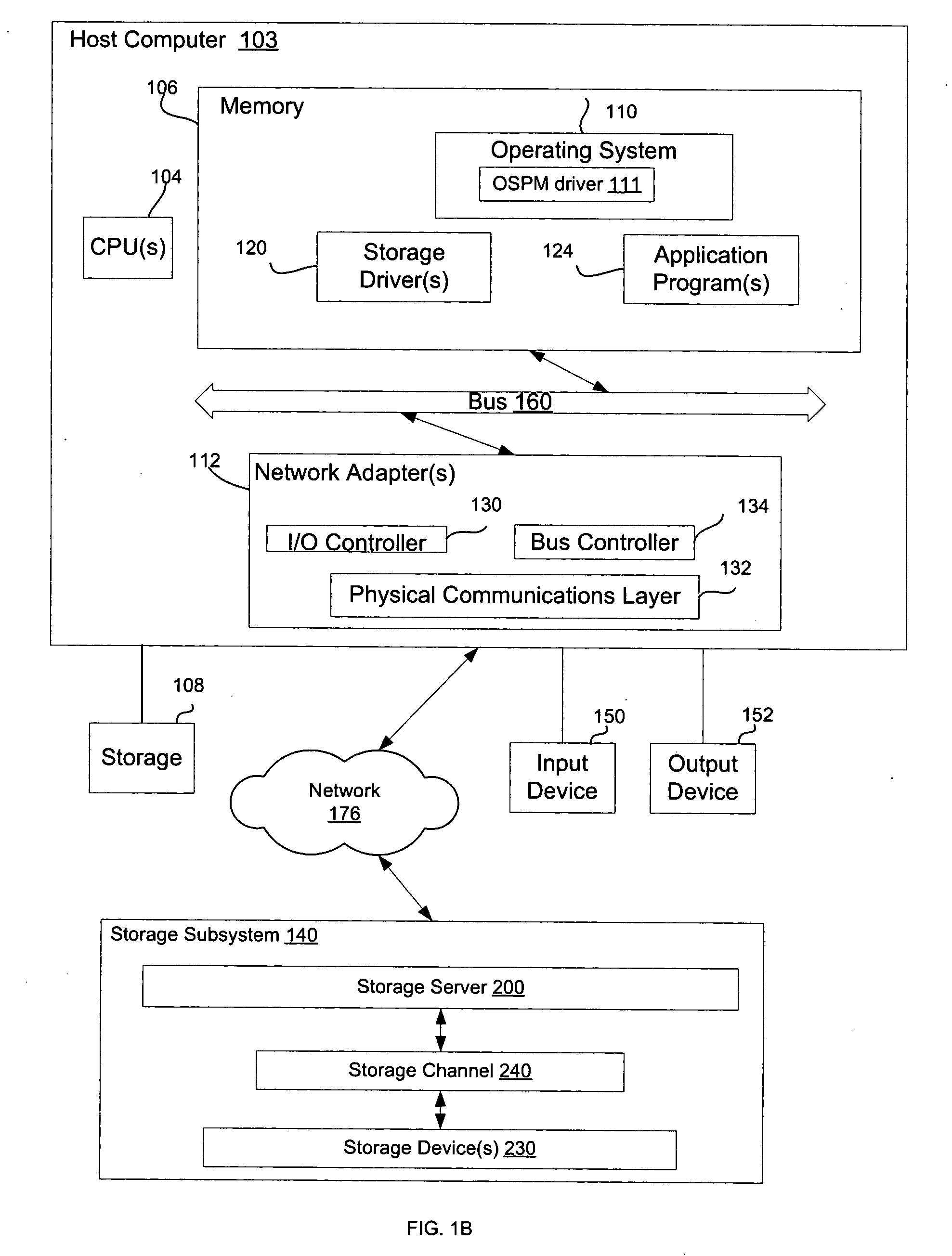
Patents
Literature
135 results about "Dynamic power management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
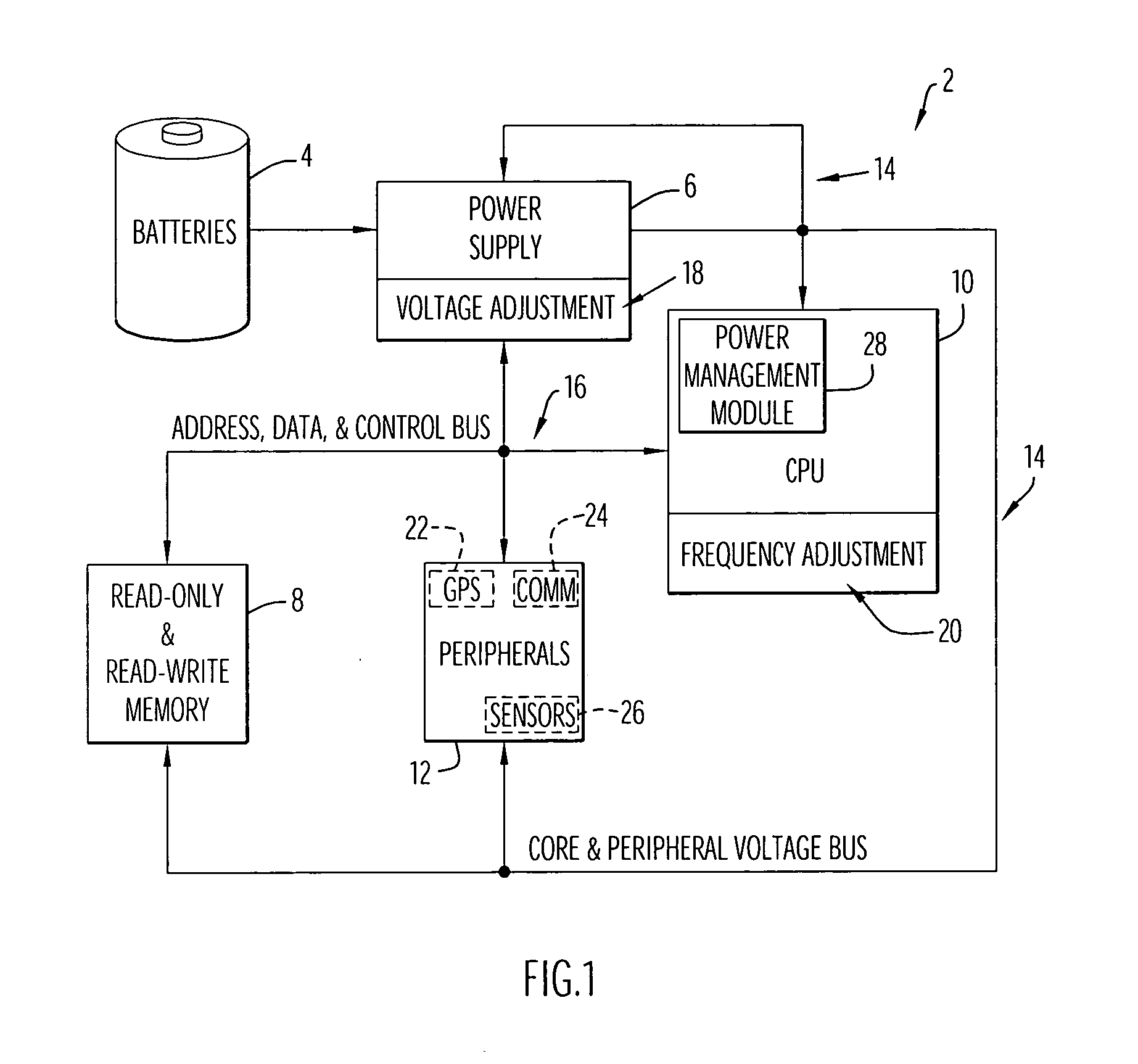
Method and apparatus for optimizing performance and battery life of electronic devices based on system and application parameters
InactiveUS7111179B1Reduce power consumptionExtending device operating lifeEnergy efficient ICTBatteries circuit arrangementsOperational systemElectrical battery
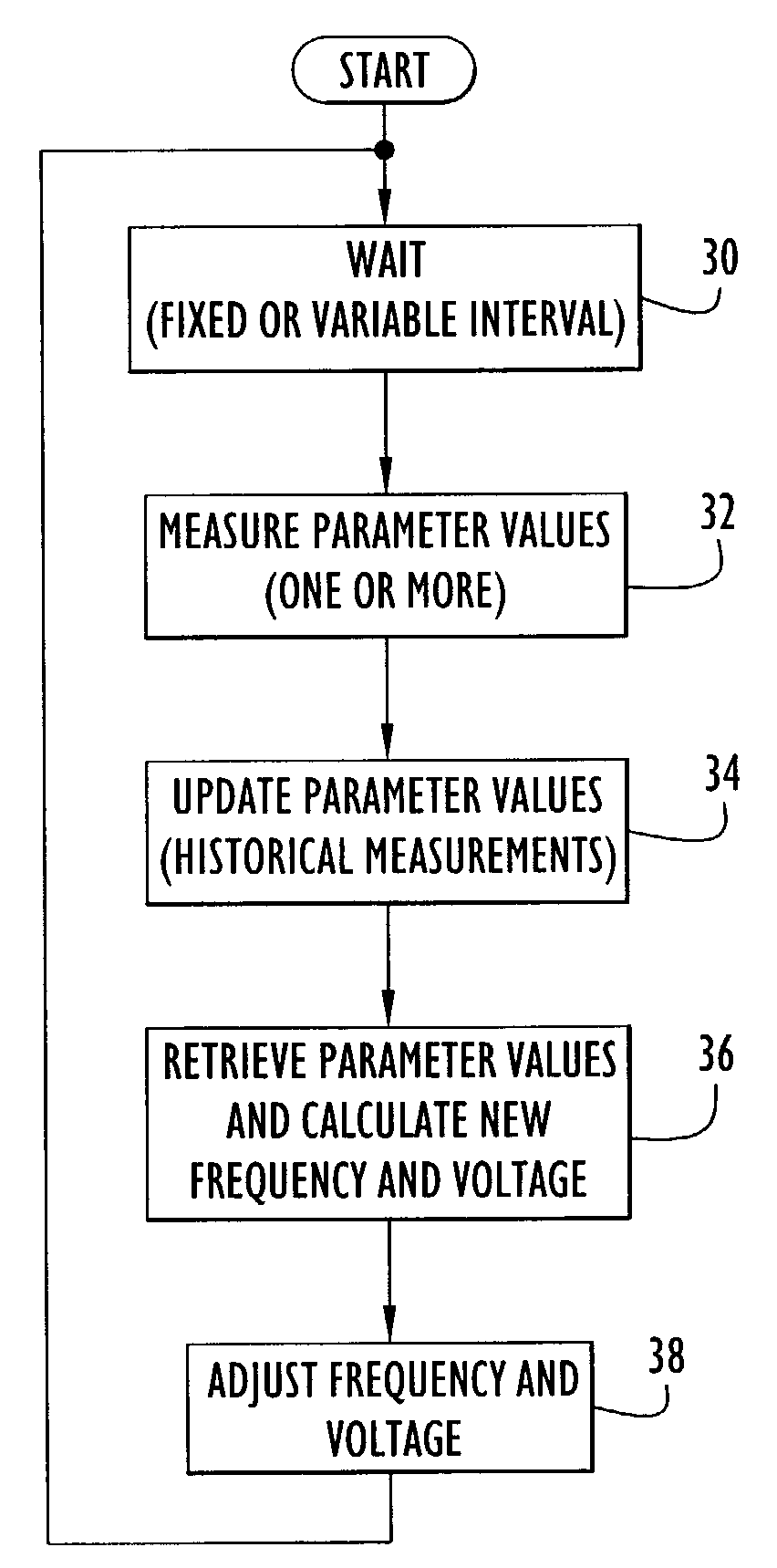
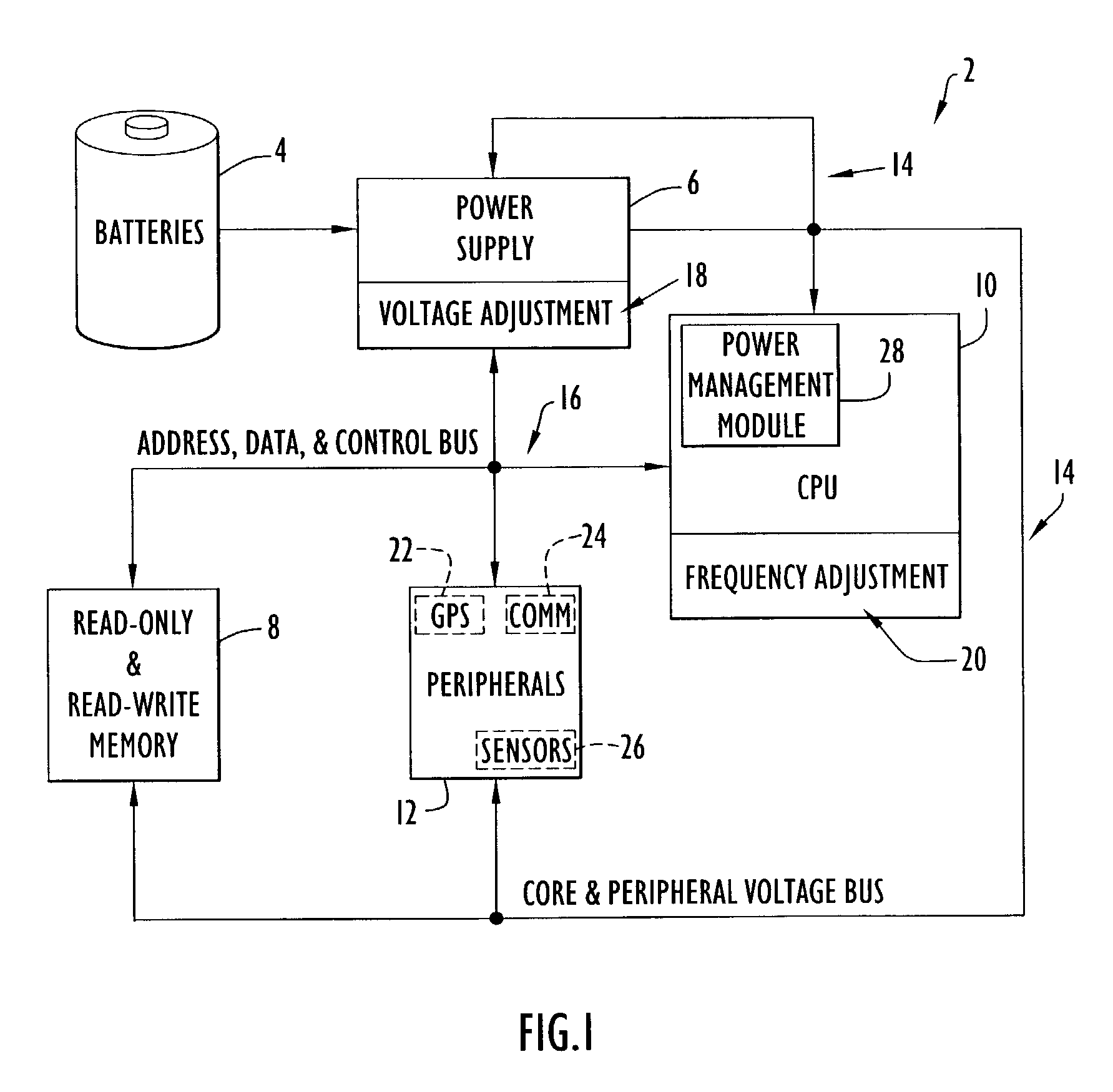
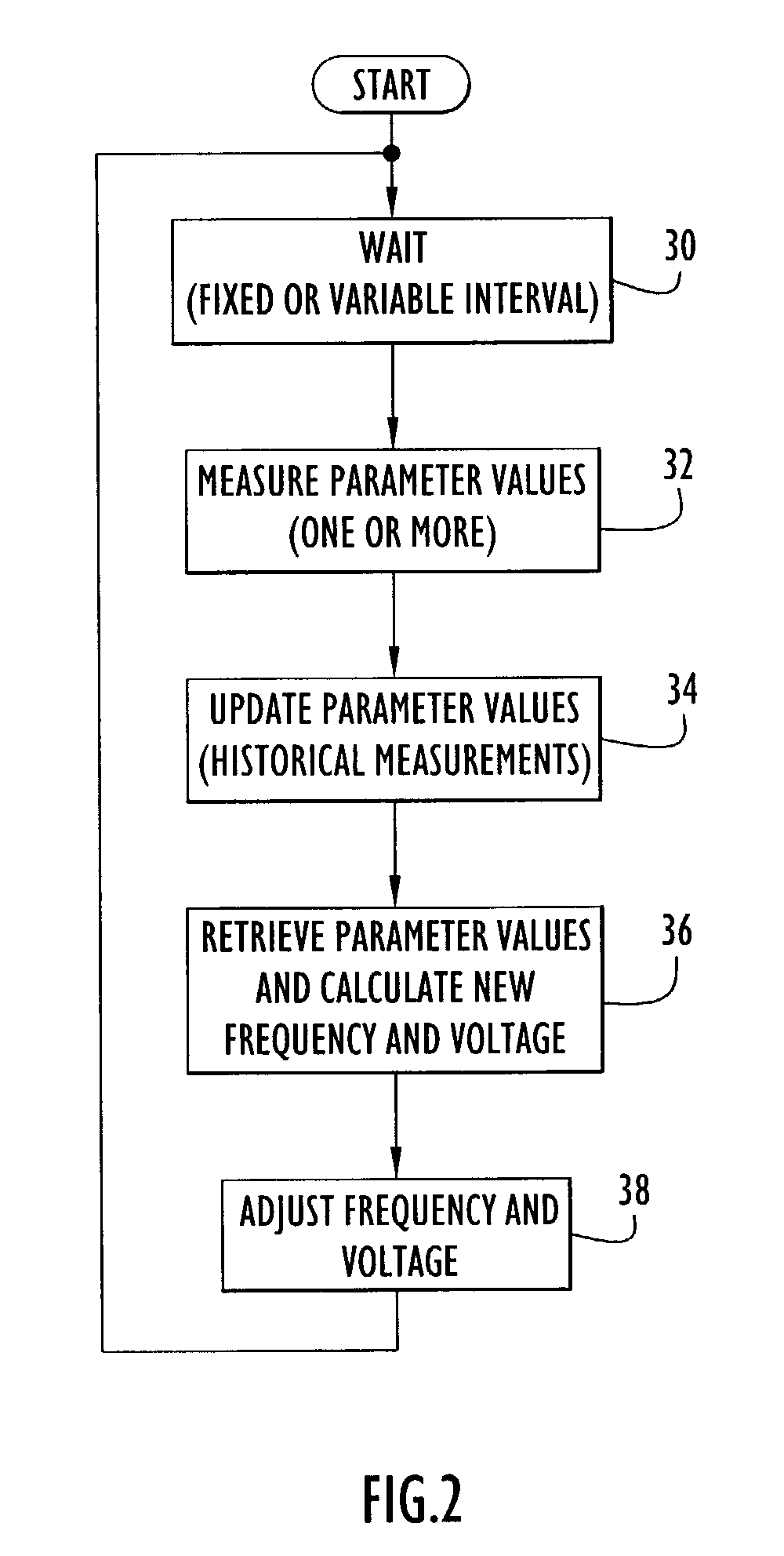
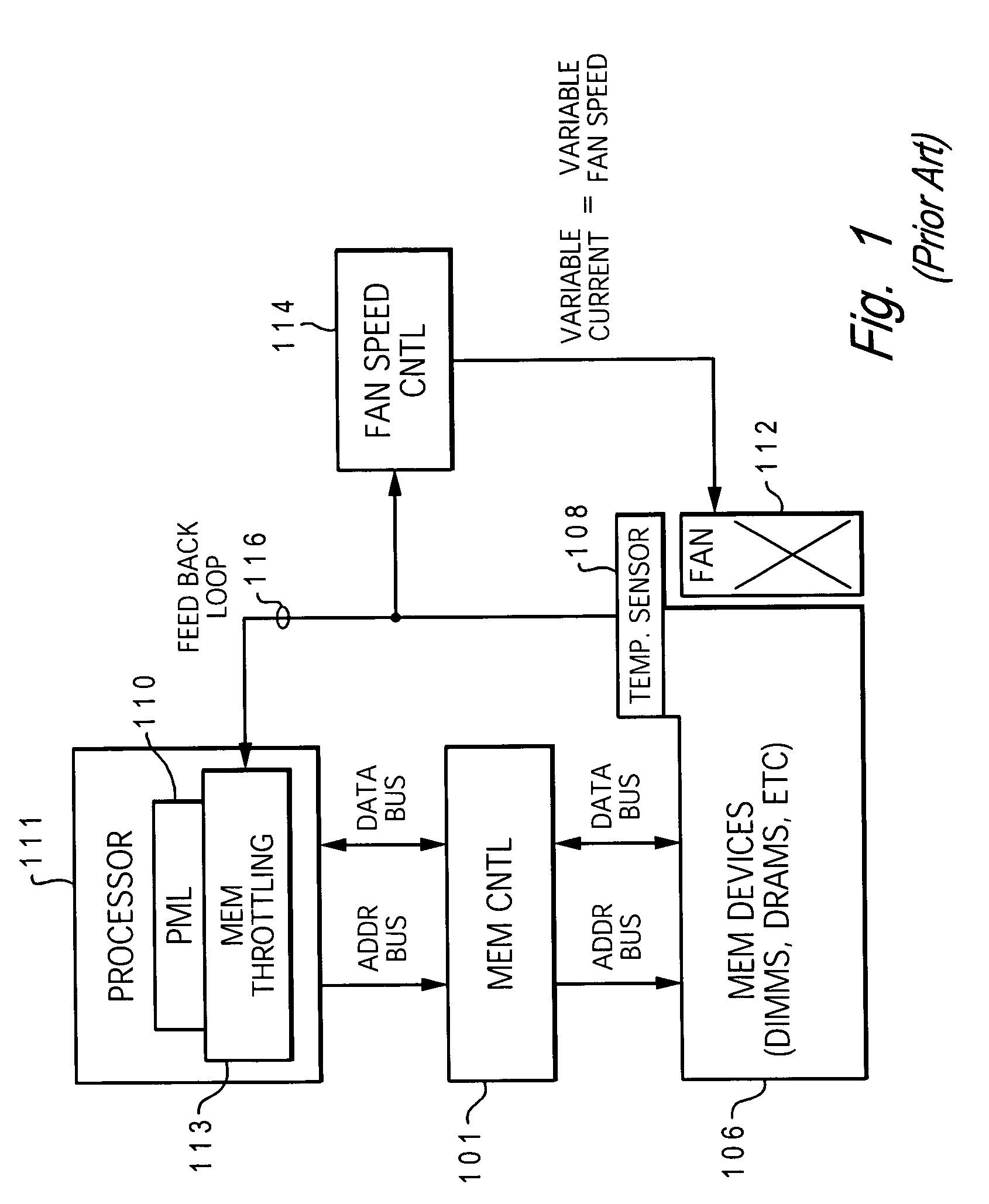
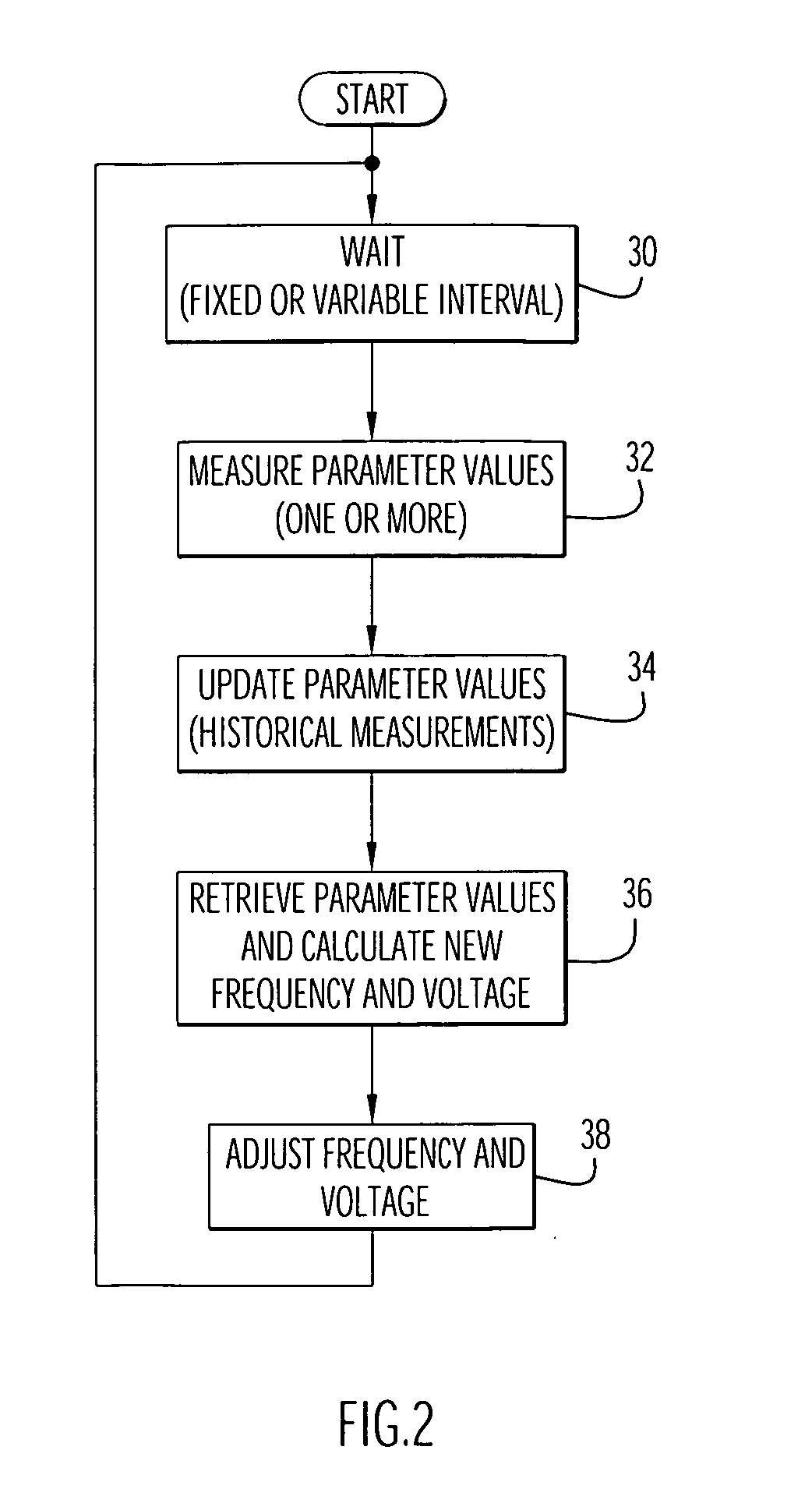
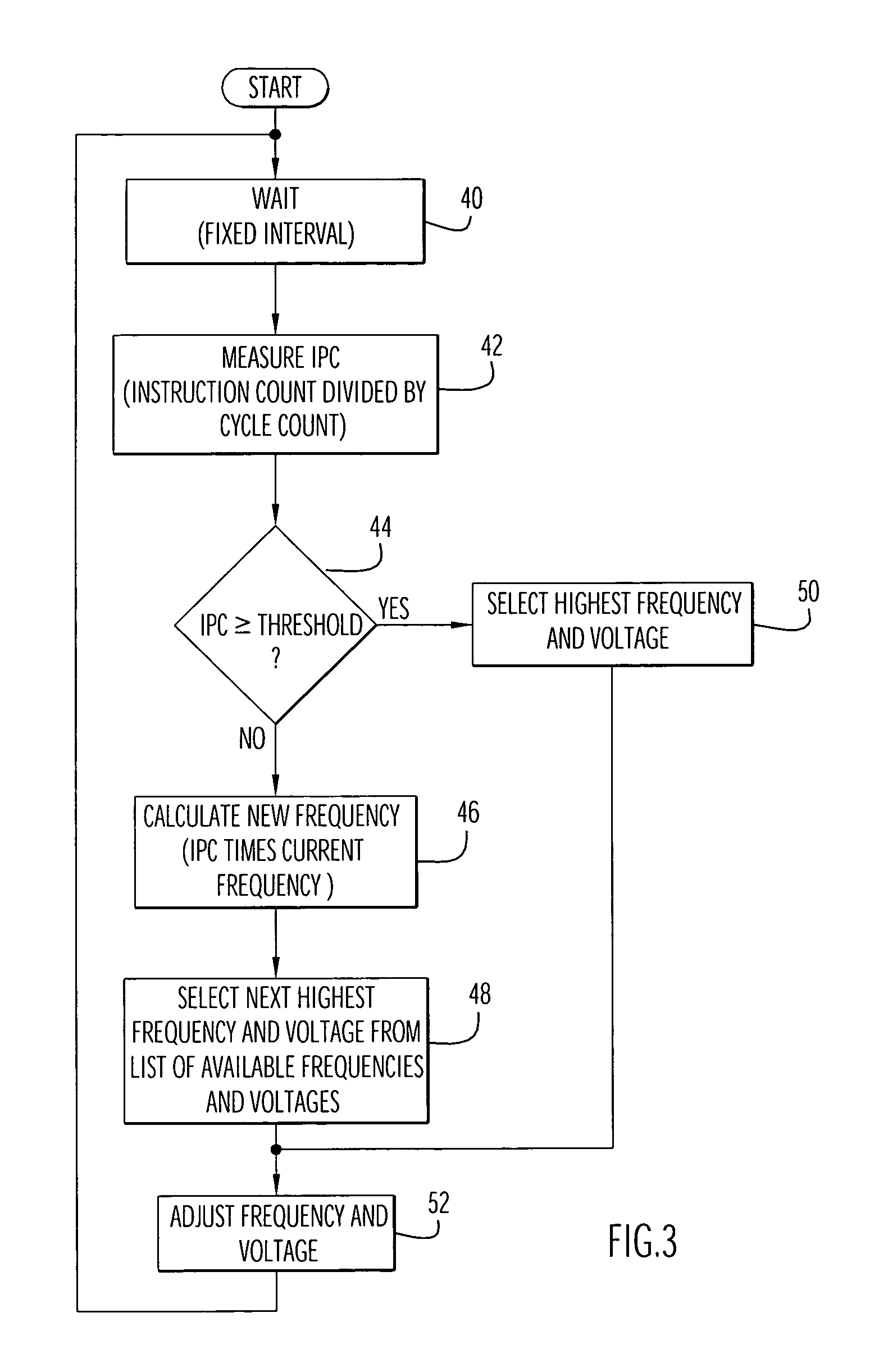
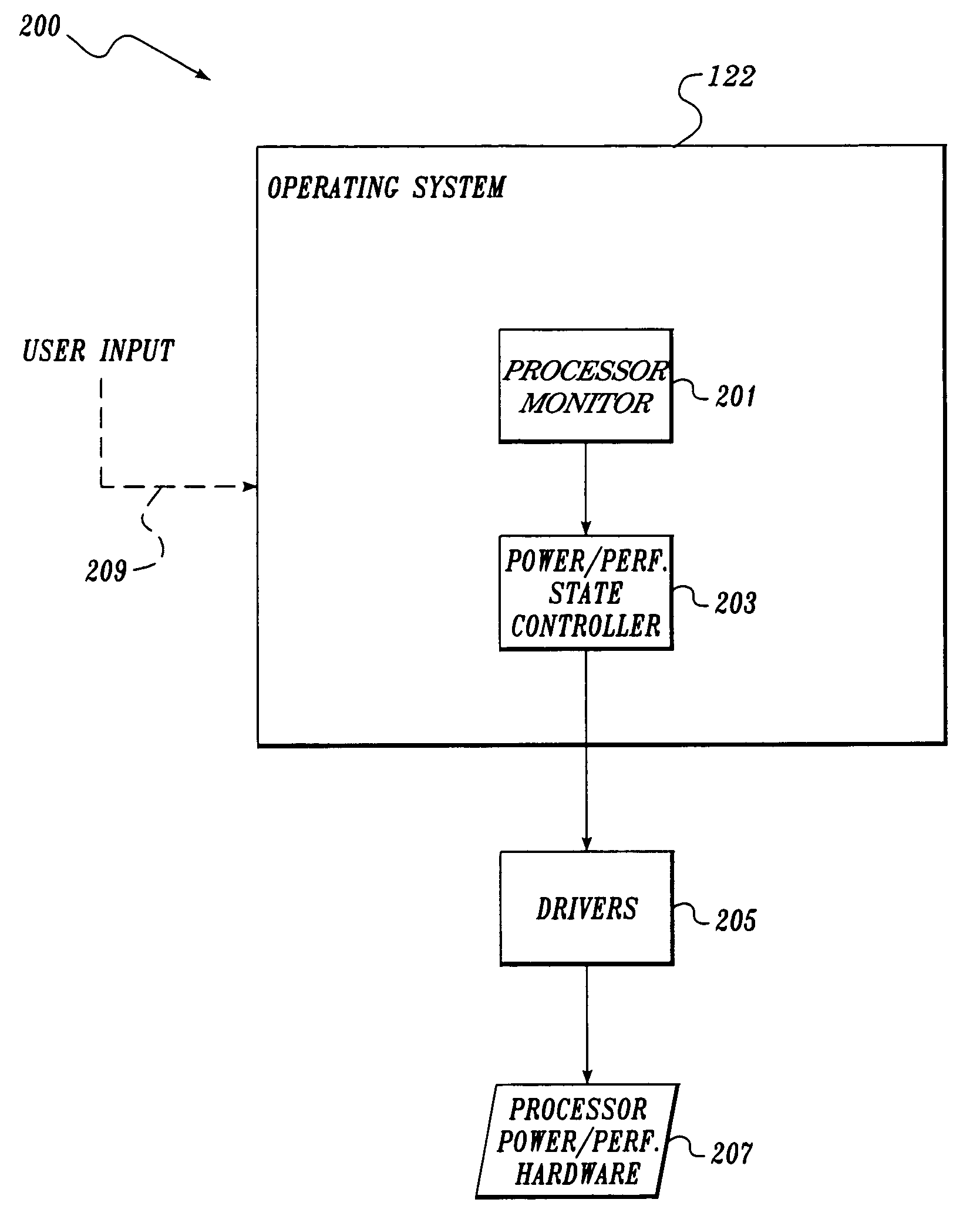
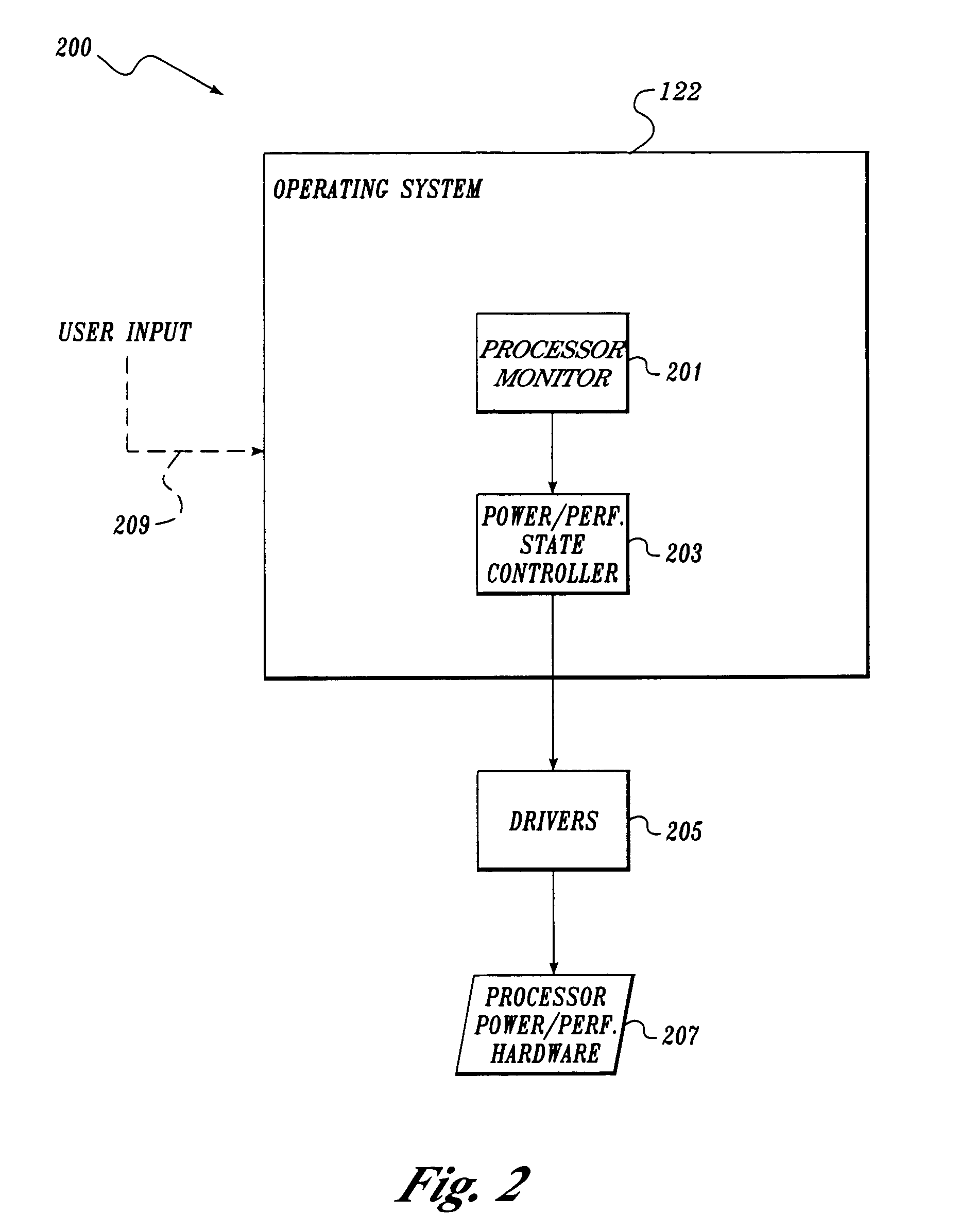
An electronic device (e.g., computer system, etc.) employing dynamic power management of the present invention adjusts power consumption in accordance with an analysis of parameters and events occurring over one or more time-periods. Preferably, the electronic device monitors microprocessor, operating system, peripheral and / or device-level events and adjusts run-time parameters, such as microprocessor clock frequency and voltage, to reduce power consumption with minimal perceived degradation in performance.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
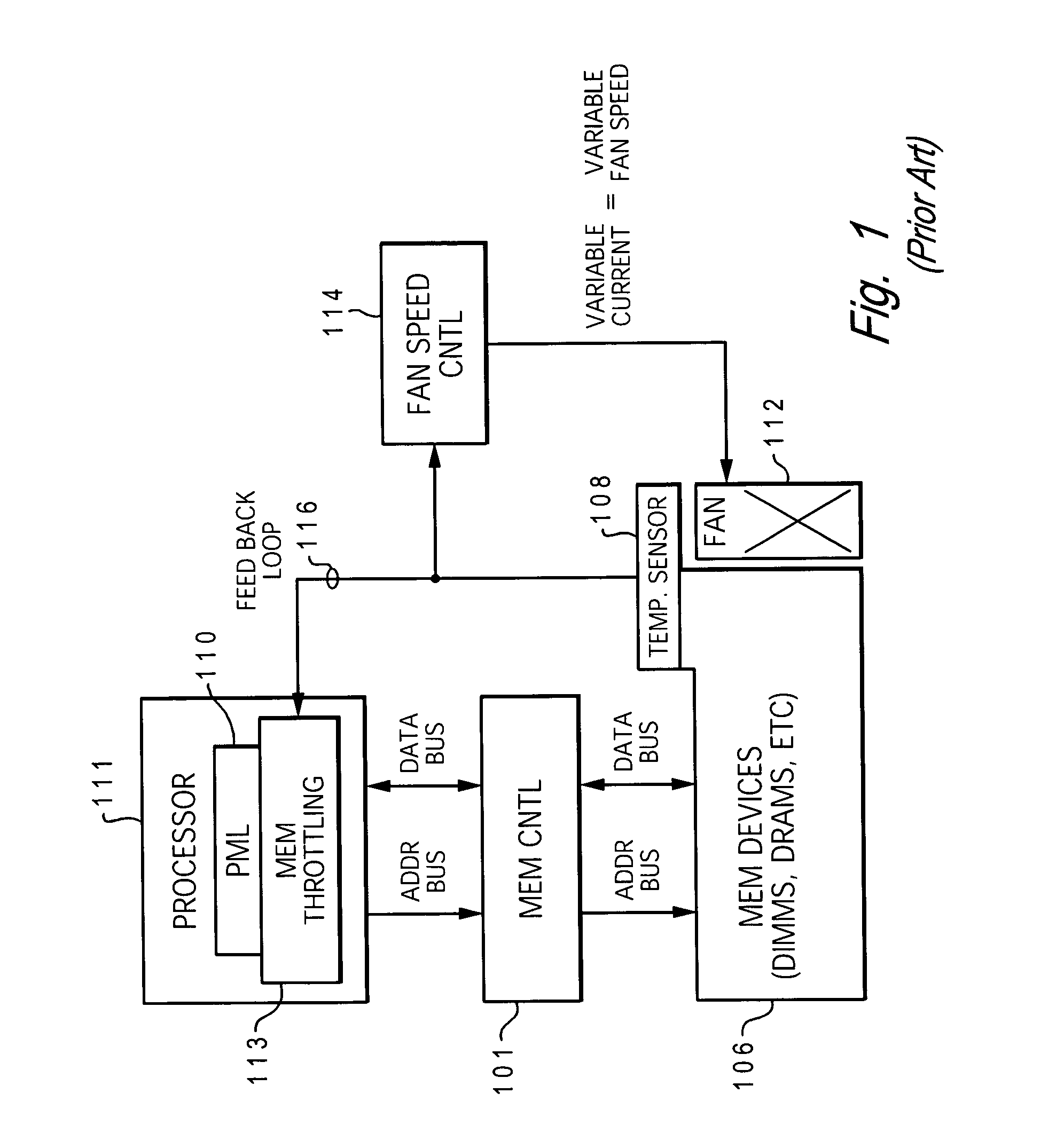
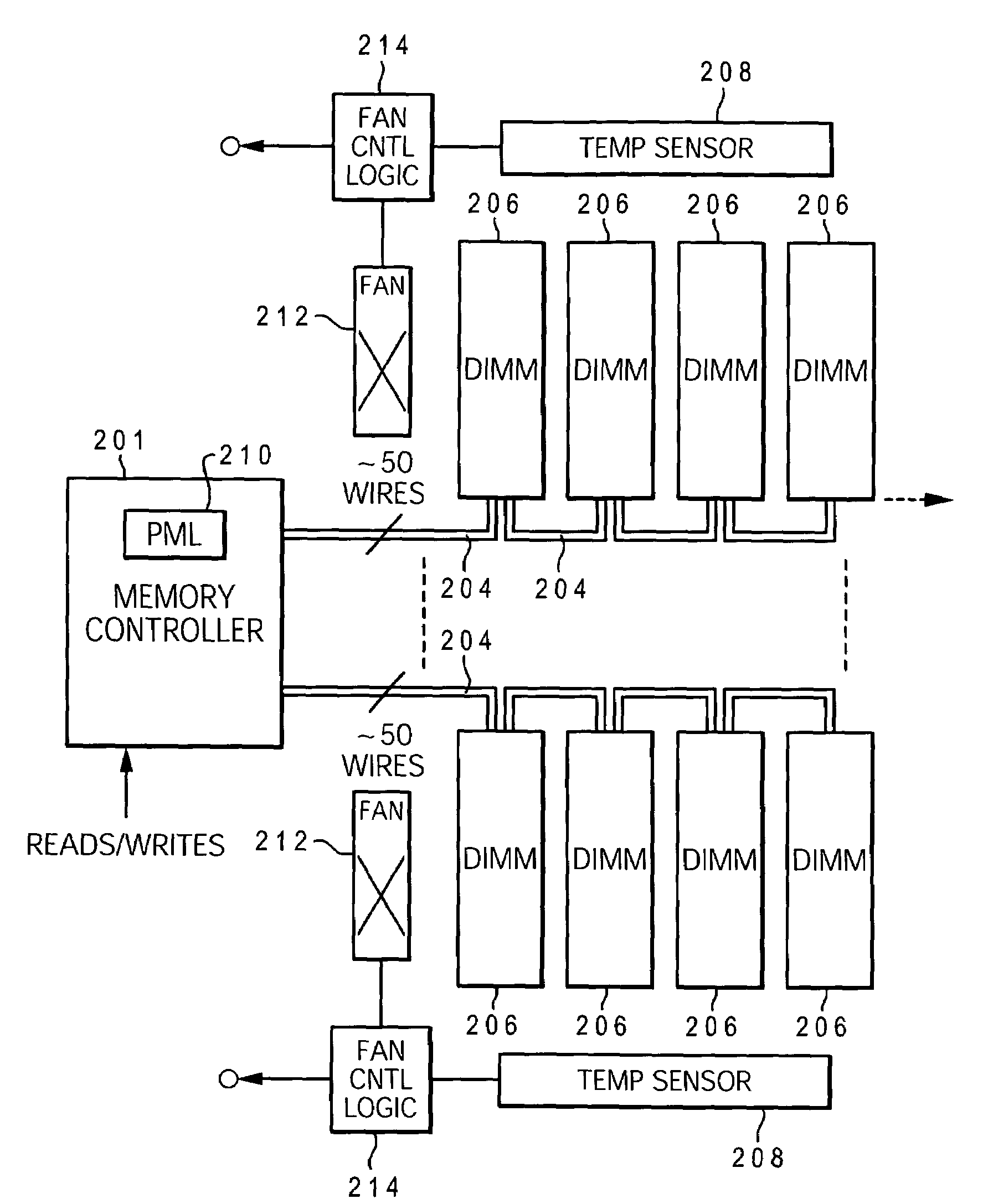
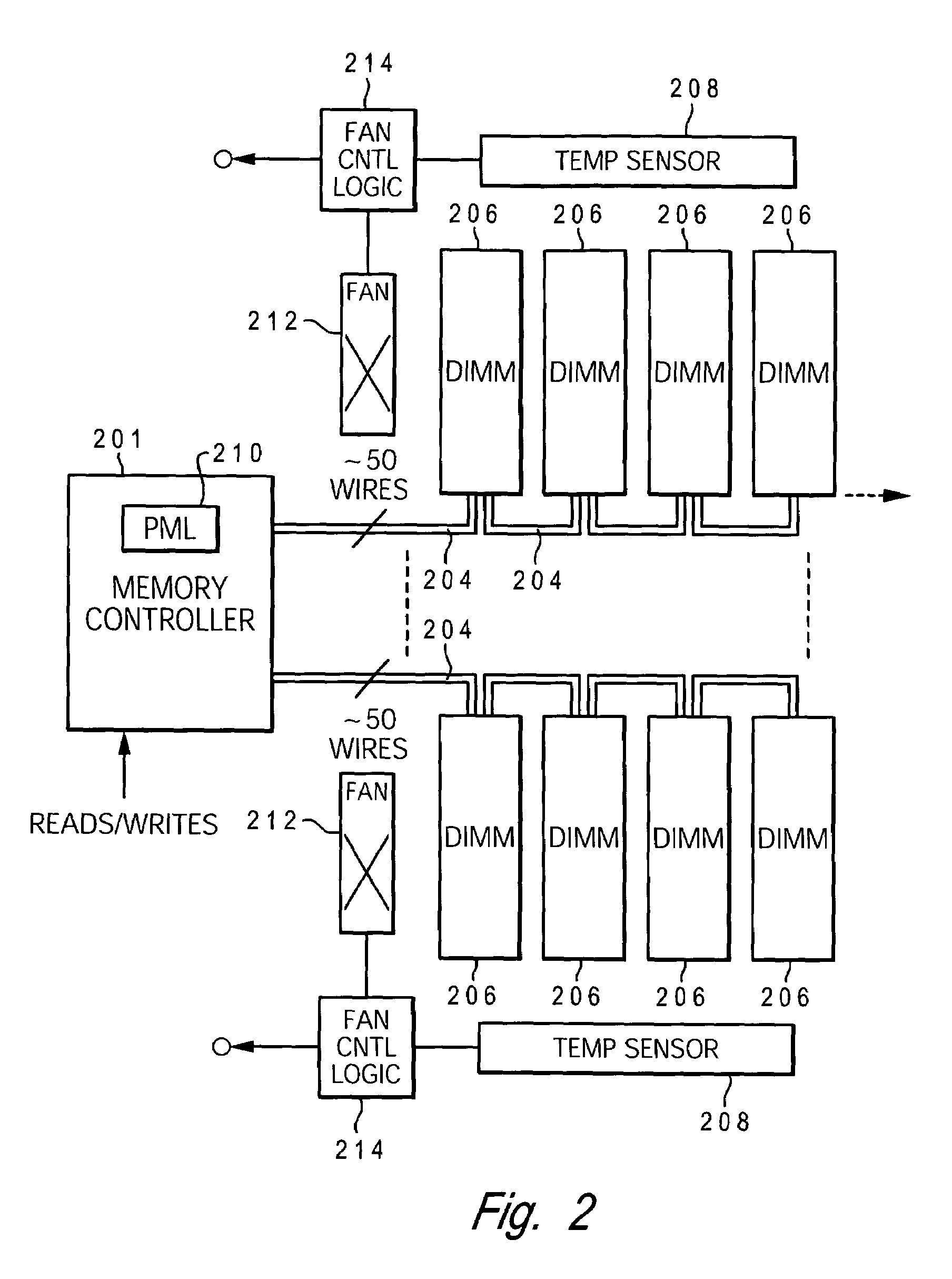
Dynamic power management via DIMM read operation limiter
InactiveUS20060179334A1Little or no usePower usageEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDIMMDynamic power management
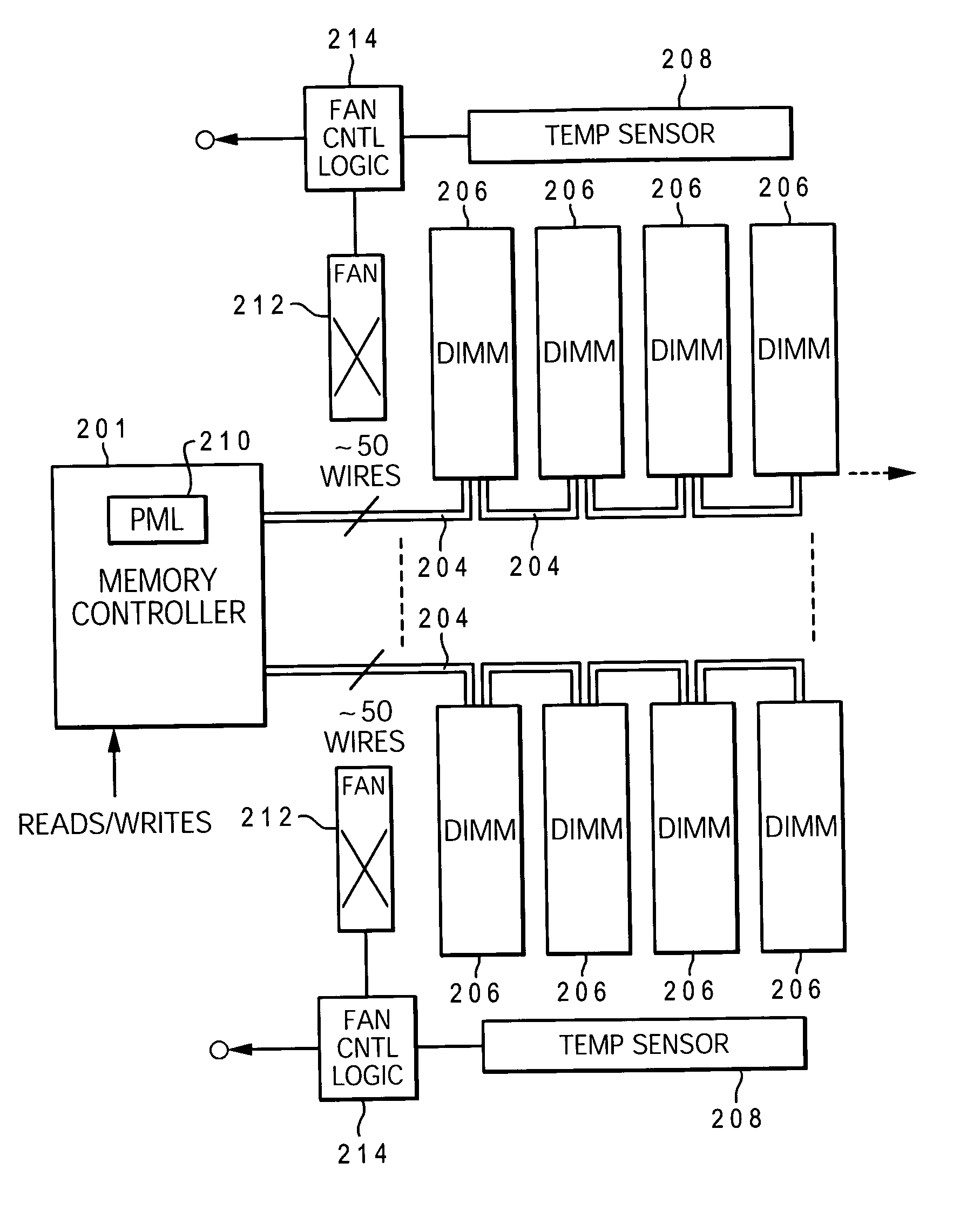
A method and system for enabling directed temperature / power management at the DIMM-level and / or DRAM-level utilizing intelligent scheduling of memory access operations received at the memory controller. Hot spots within the memory subsystem, caused by operating the DIMMs / DRAMs above predetermined / preset threshold power / temperature values for operating a DIMM and / or a DRAM, are avoided / controlled by logic within the memory controller. The memory controller logic throttles the number / frequency at which commands (read / write operations) are issued to the specific DIMM / DRAM based on feedback data received from the specific DIMM / DRAM reaching the preset threshold power usage value.
Owner:IBM CORP
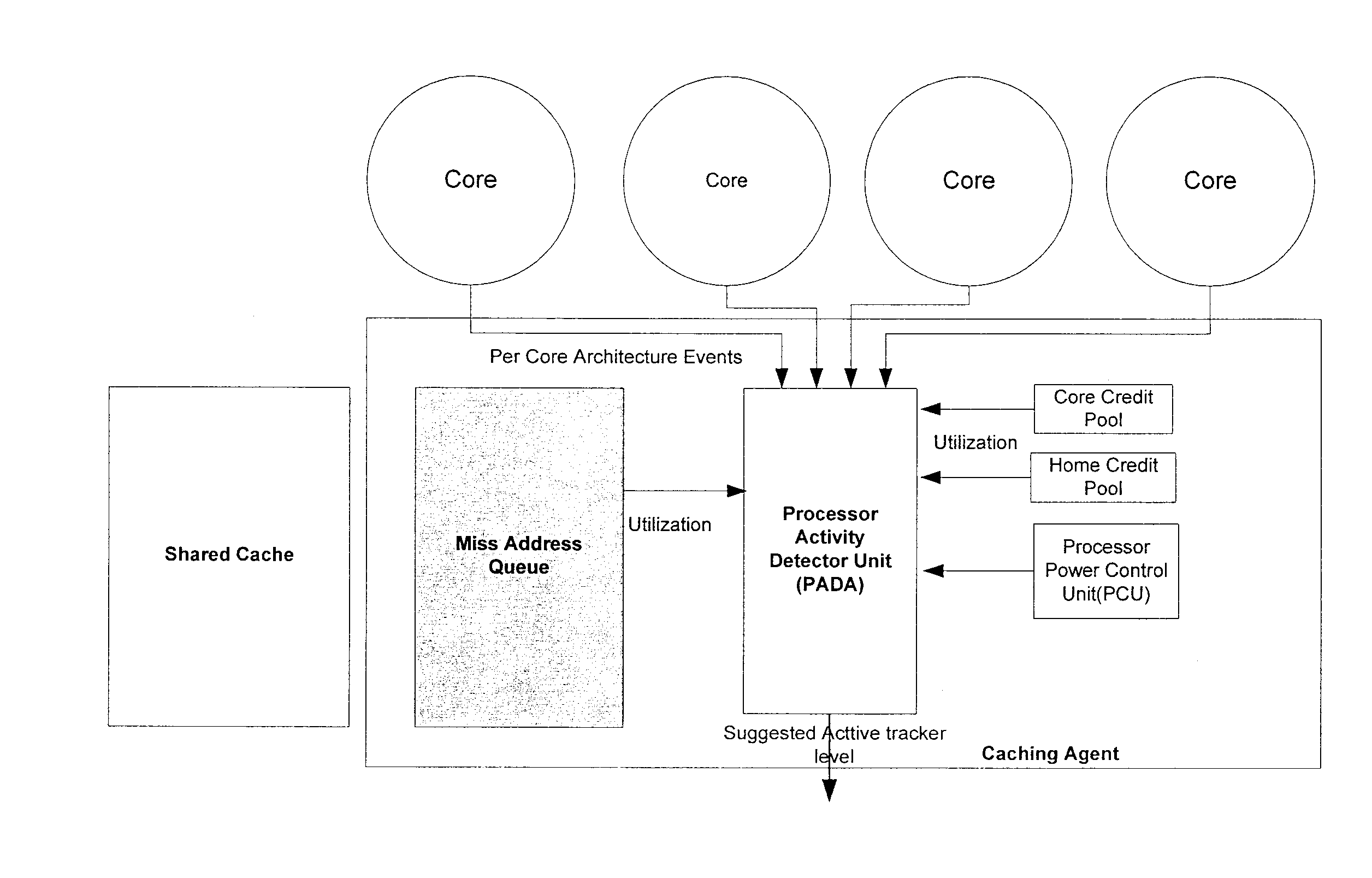
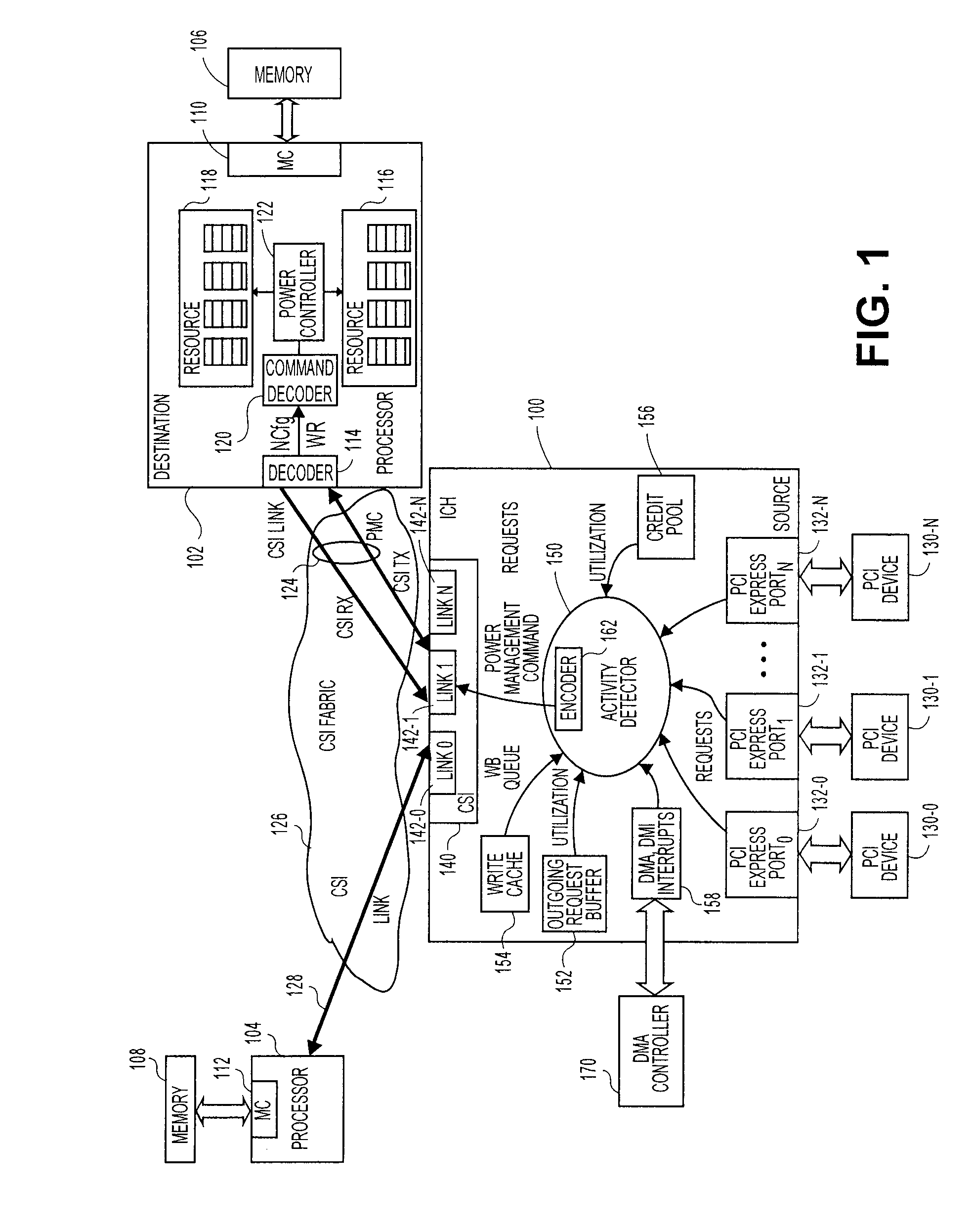
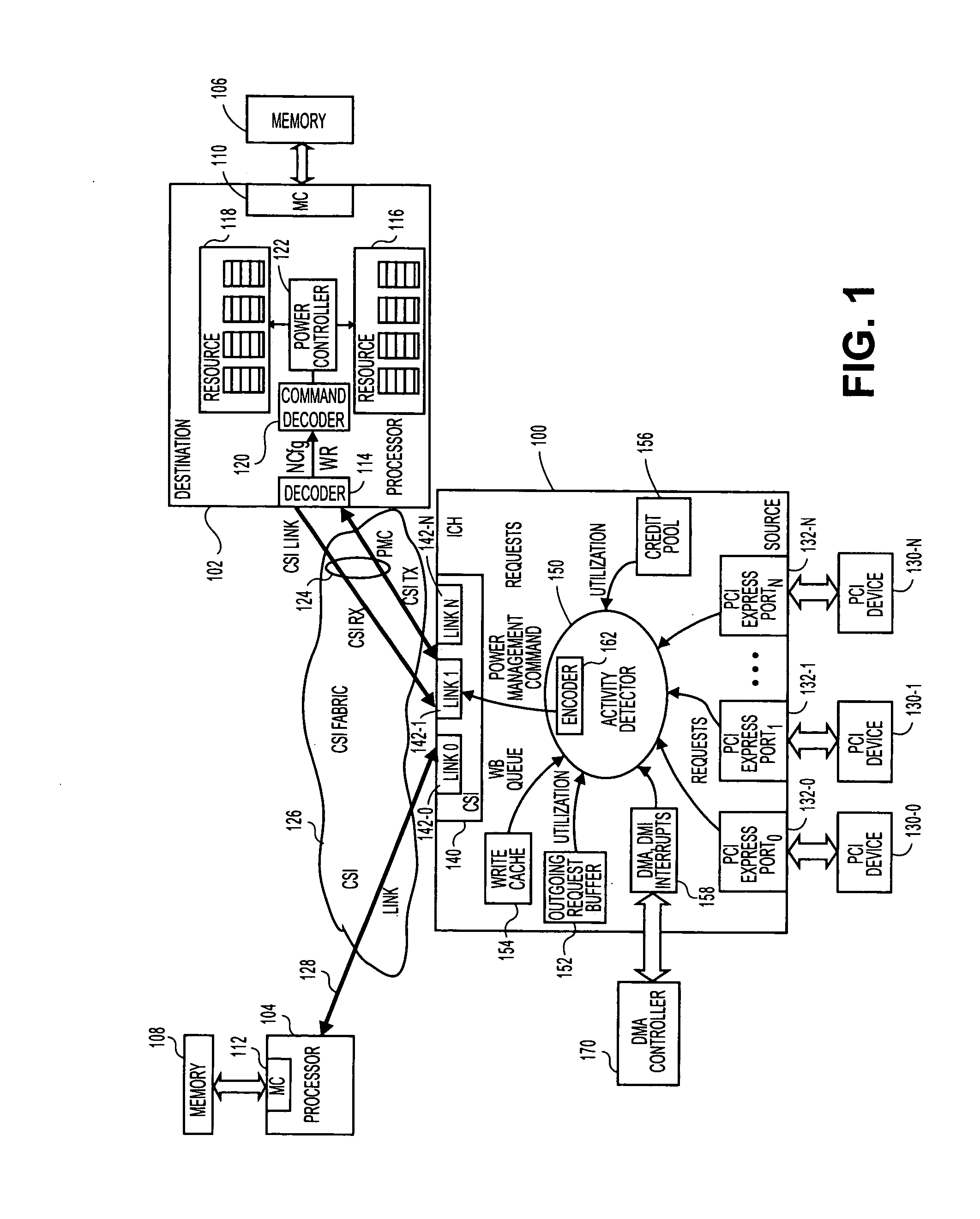
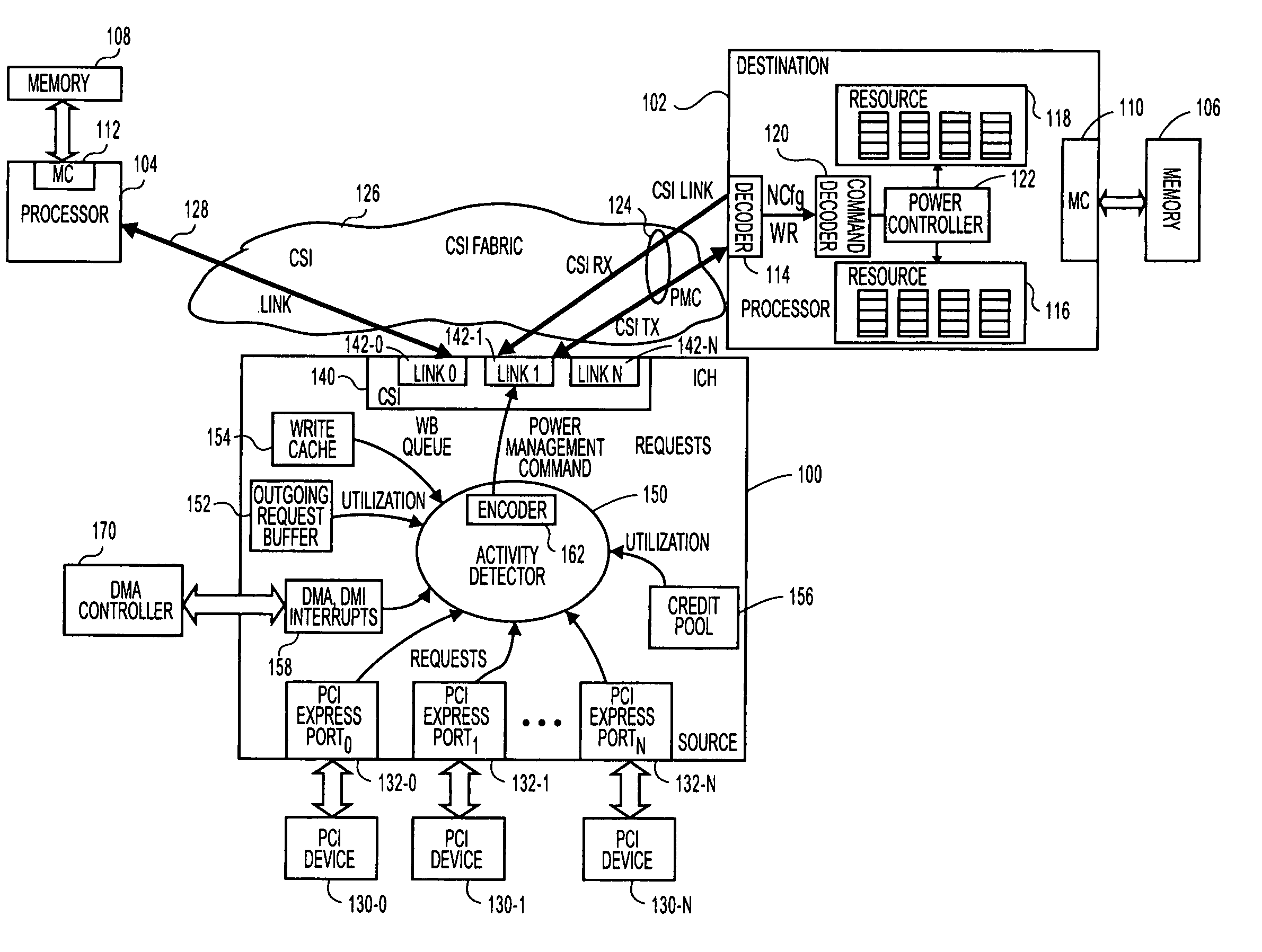
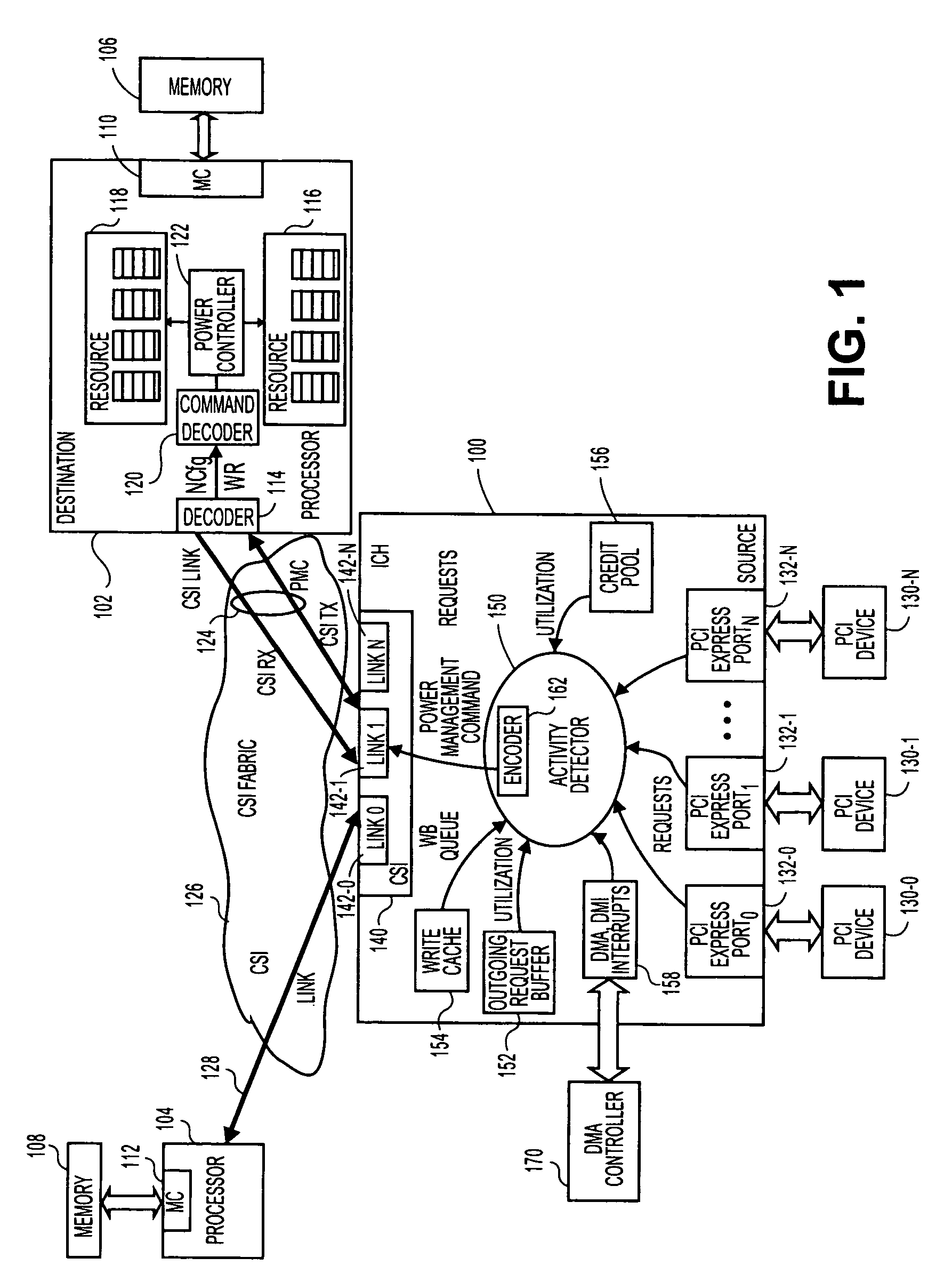
Method, system, and apparatus for a core activity detector to facilitate dynamic power management in a distributed system
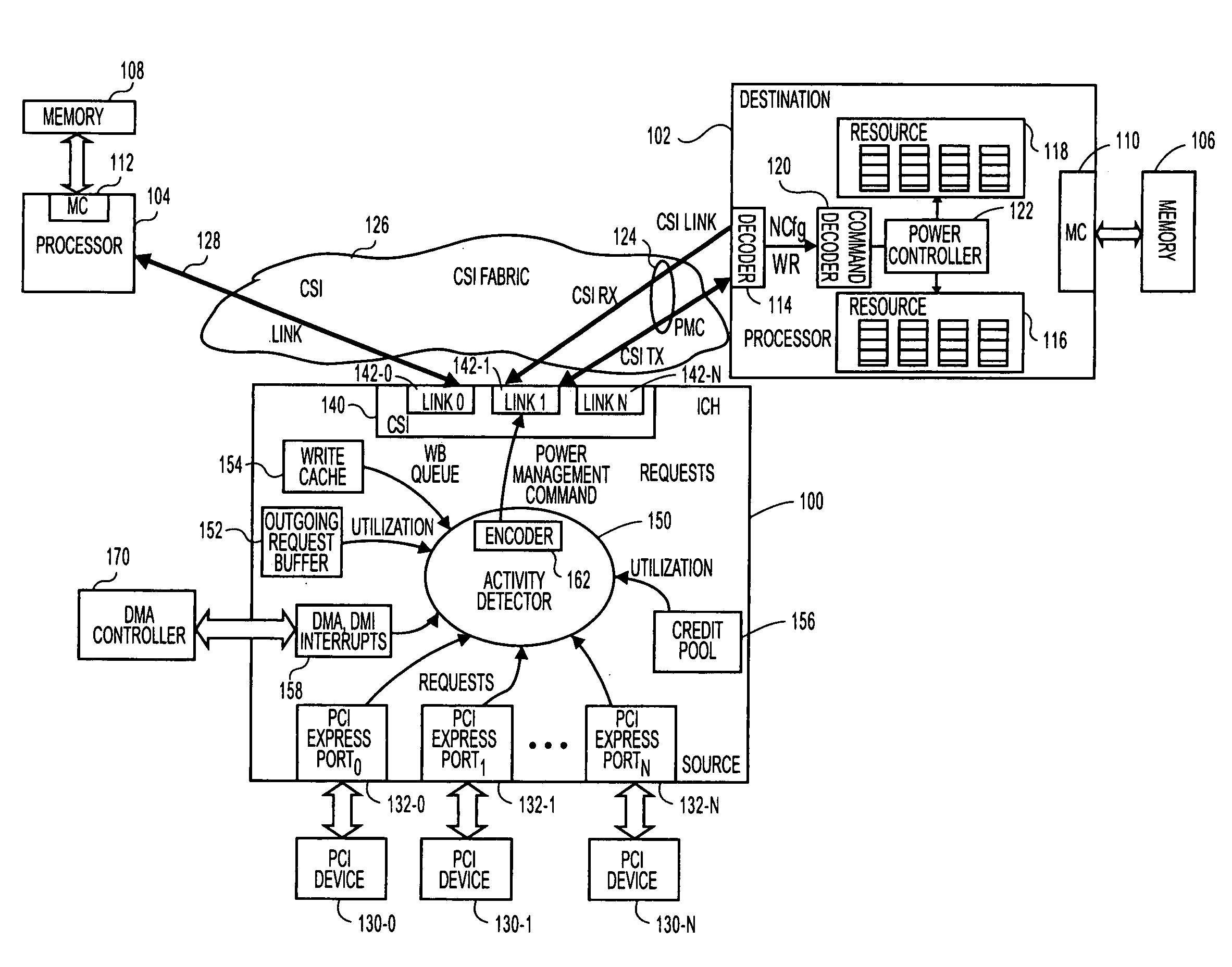
A system and method to provide source controlled dynamic power management. An activity detector in a source determines expected future resource usage. Based on that expected usage, the source generates a power management command and sends that command to a destination. The destination then adjusts the power level of the resource based in the command.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods and apparatus for static and dynamic power management of computer systems
InactiveUS6986069B2Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementComputerized system
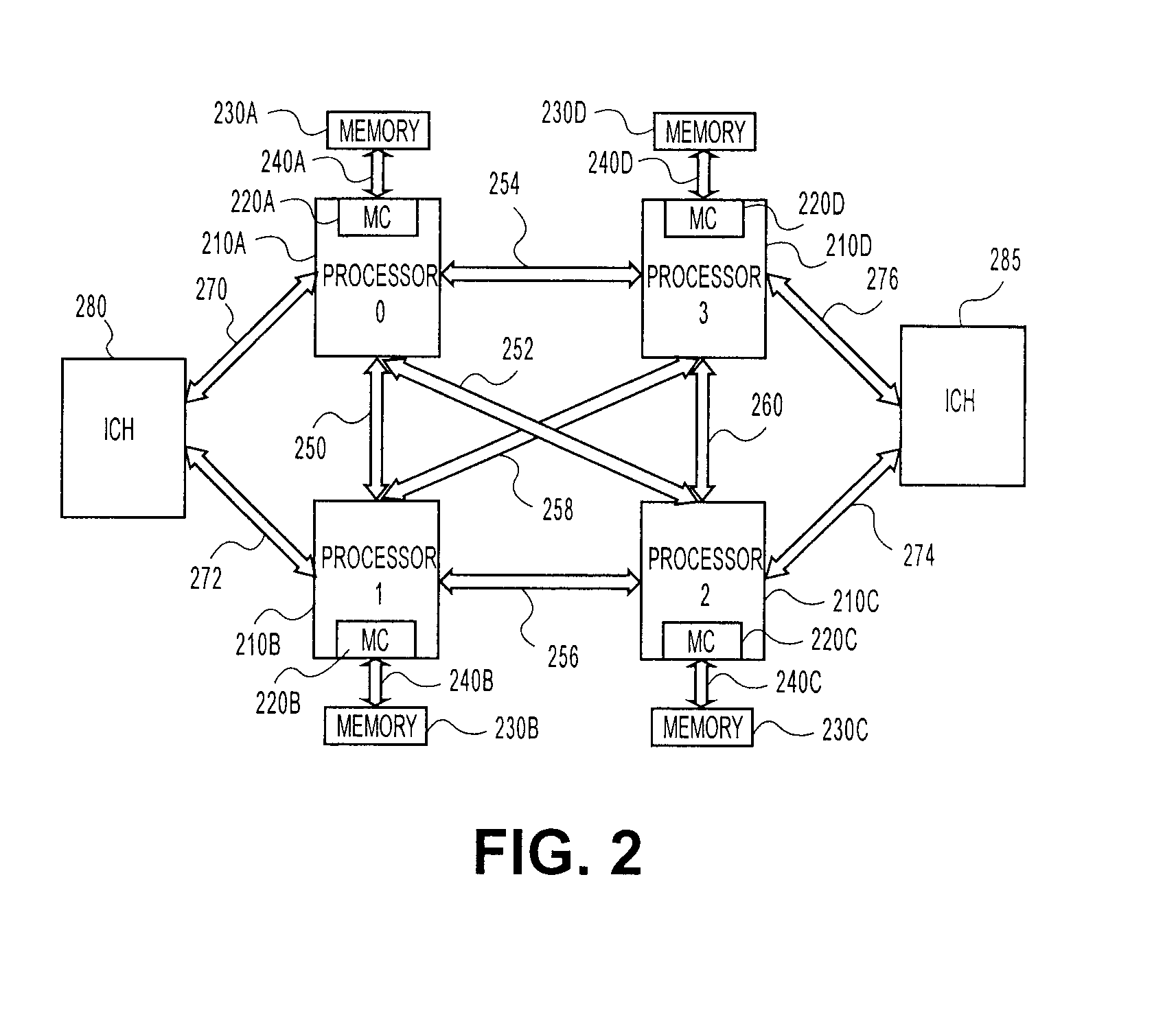
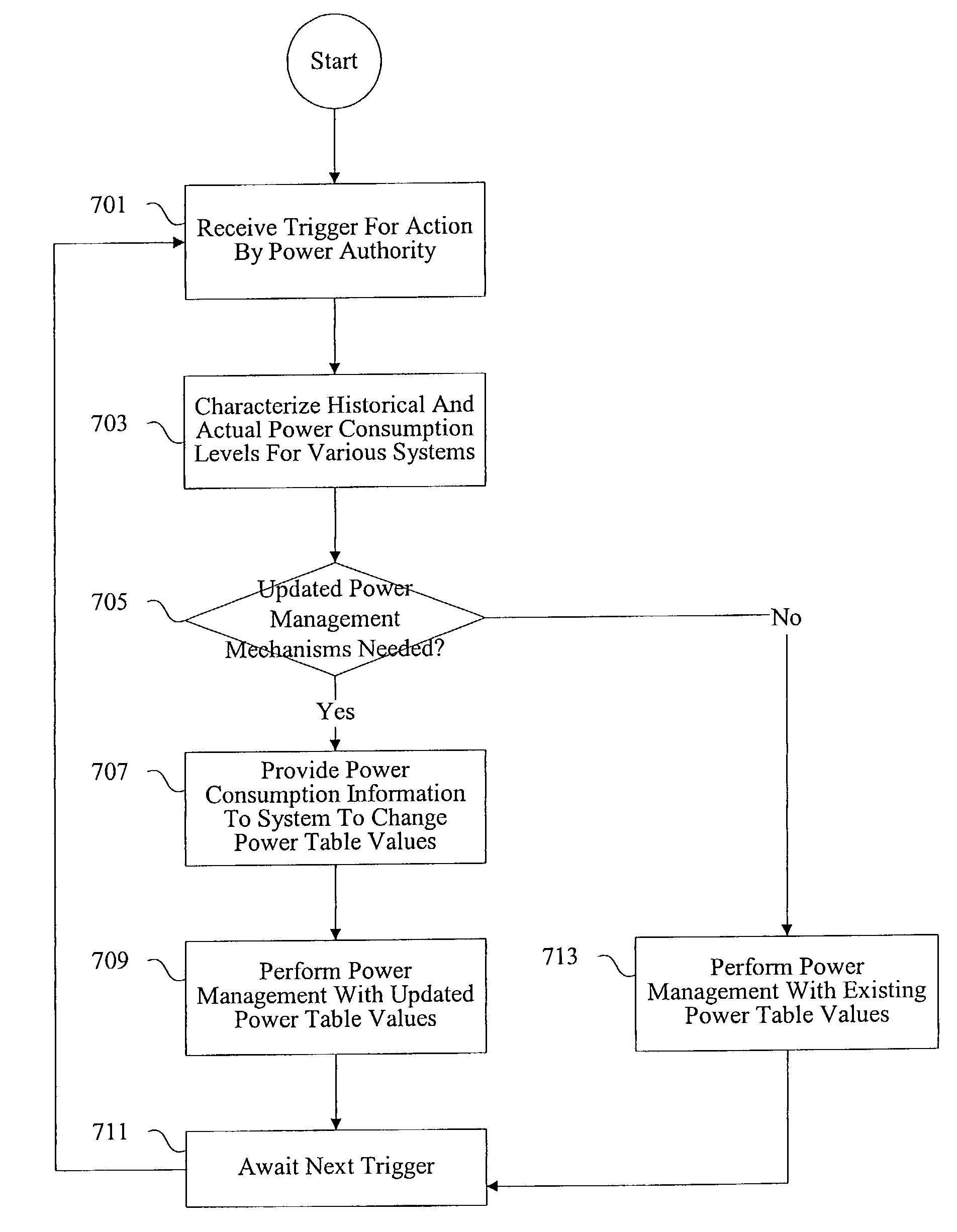
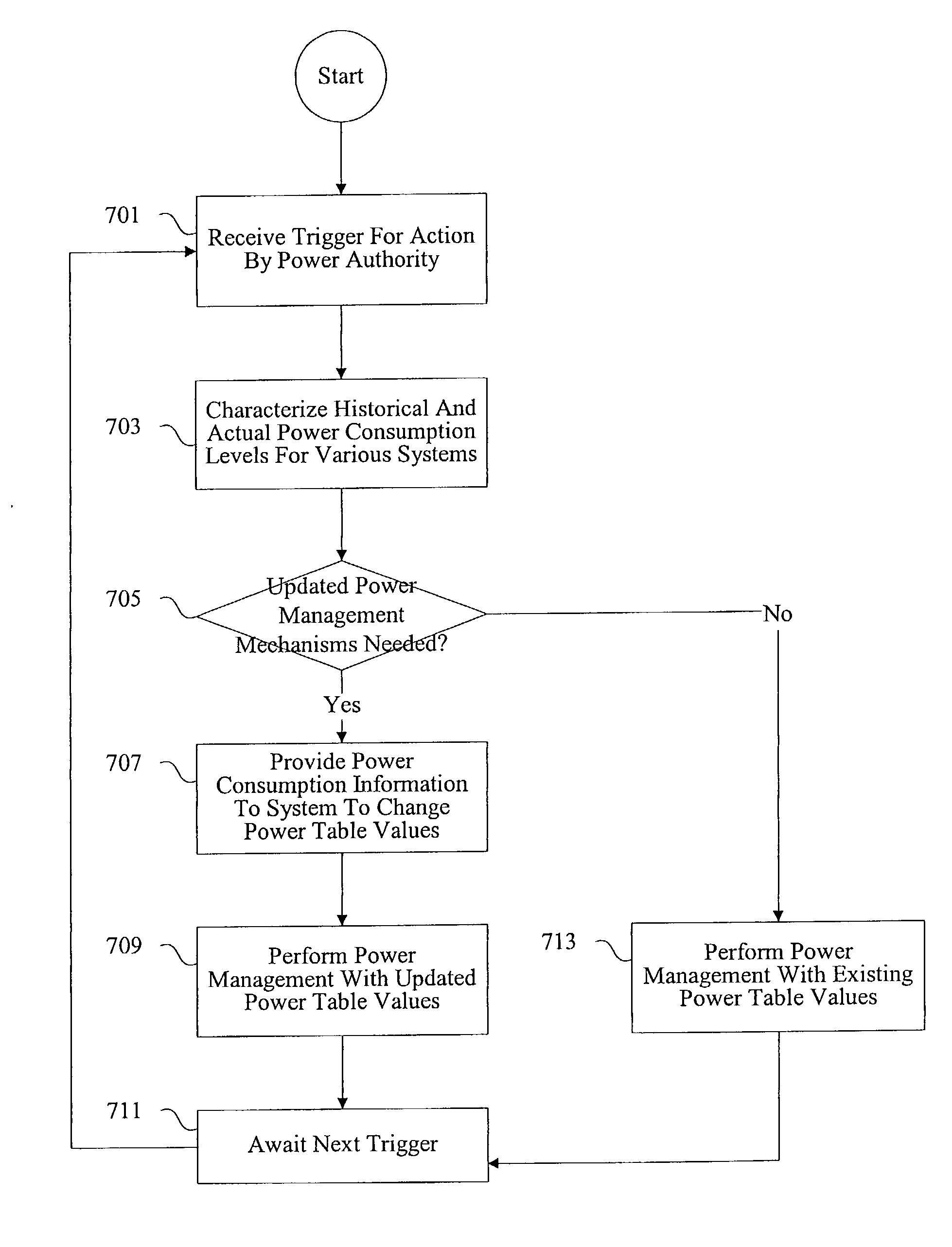
According to the present invention, methods and apparatus are provided for static and dynamic power management of computer systems. A power authority manages power usage levels in computer systems by monitoring power consumption levels and providing power consumption information to the various systems. In one example, the power authority updates power tables to vary aggregate power consumption levels.
Owner:SANMINA-SCI CORPORATION
Methods and apparatus for power management
InactiveUS20040003303A1Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementEngineering
According to the present invention, methods and apparatus are provided for static and dynamic power management of computer systems. A power authority manages power usage levels in computer systems by monitoring power consumption levels and providing power consumption information to the various systems. In one example, the power authority updates power tables to vary aggregate power consumption levels.
Owner:SANMINA-SCI CORPORATION
Dynamic power management of devices in computer system by selecting clock generator output based on a current state and programmable policies
InactiveUS6990594B2Maximize battery lifeMinimize powerEnergy efficient ICTCathode-ray tube indicatorsDynamic power managementElectrical battery
A power management system and method permit the total power consumption by a portable electronic device to be reduced so that the portable electronic device has a longer operating time on a limited power source, such as a battery. The system may also be used with devices that are powered by a more permanent source of power. The system may combine static power management techniques as well as dynamic power management techniques. The system may include a flexible clock generator.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
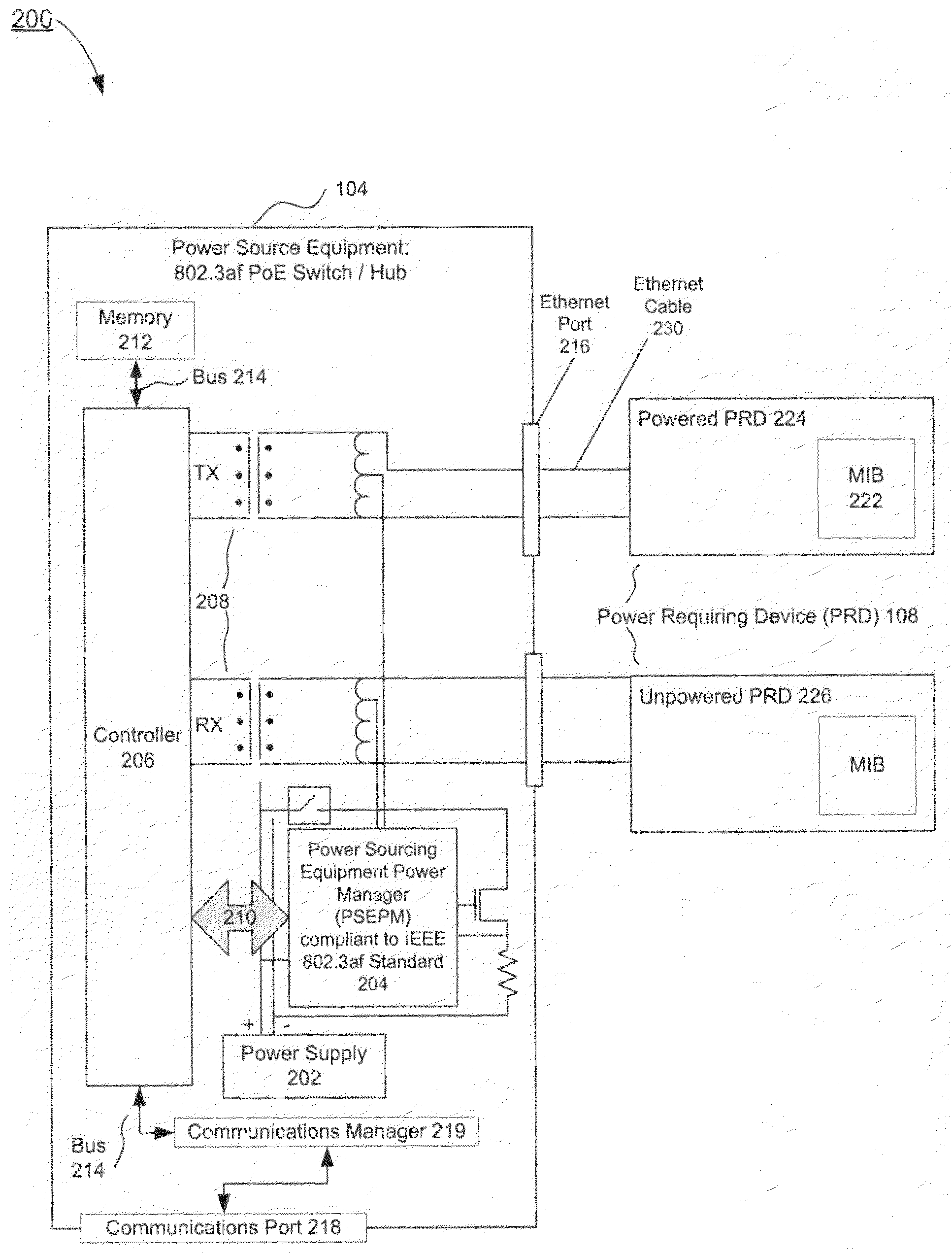
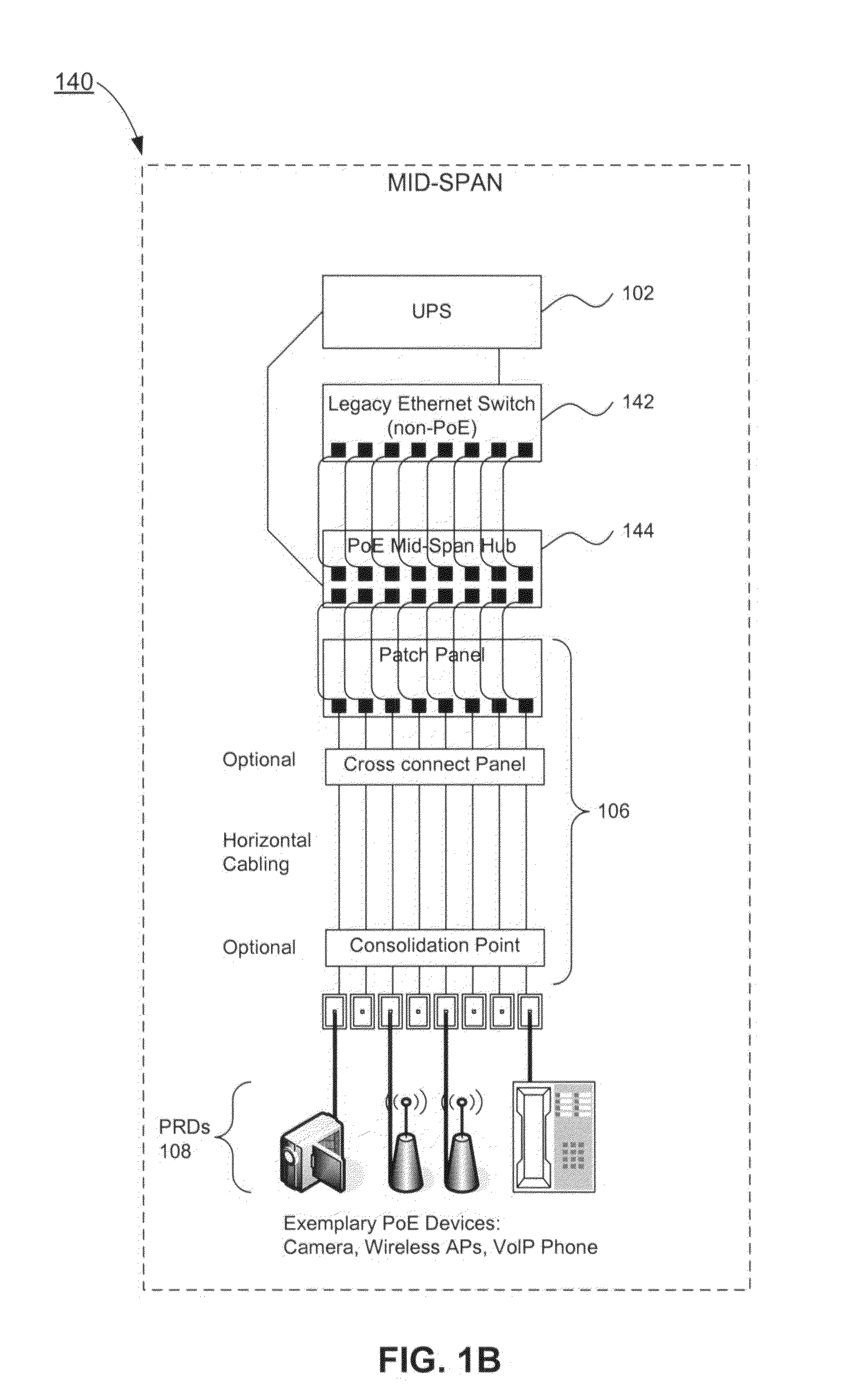
System and method of dynamic power management
ActiveUS20080114997A1Efficient use ofNumberVolume/mass flow measurementData switching current supplyCommunications systemDynamic power management
In a communications system, such as a Power-Over-Ethernet system, where power supply equipment (PSE) supplies power to powered requiring devices (PRDs), a system and method of dynamic power management is implemented. The system and method monitors the power consumed at each port by the PRDs. Based on this monitoring, the PSE dynamically determines the minimum power which can be allocated to each PRD, and so dynamically maximizes the available reserve power. The PSE maintains a queue or queues wherein PRDs are listed in order of a power allocation priority. When additional power is available, the PSE preferentially allocates power to a PRD or PRDs which have higher priority. The system and method of the present invention minimizes the power allocated to each individual network device, as a result of which the total number of network devices that can be supported with the available power may be maximized.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
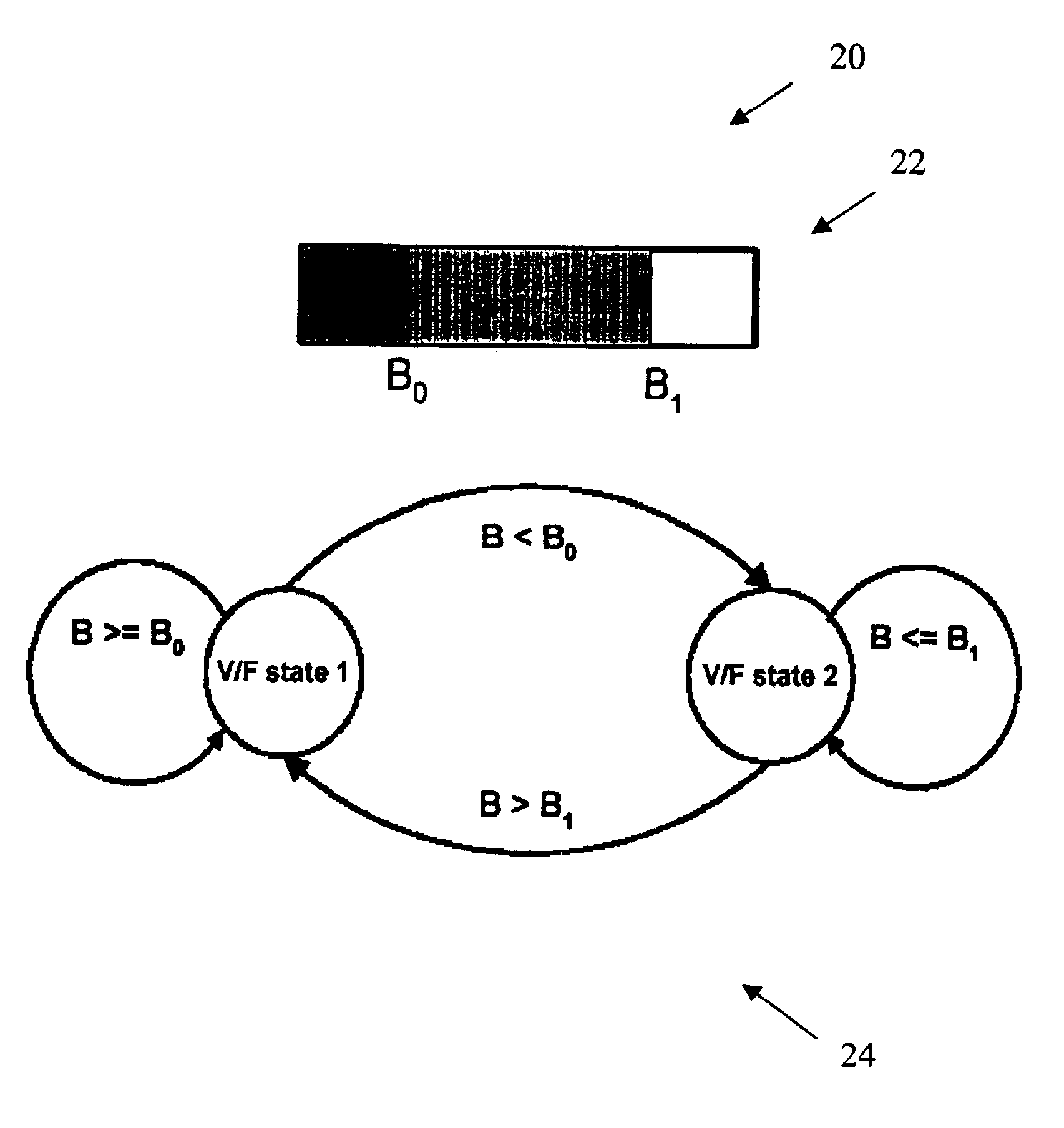
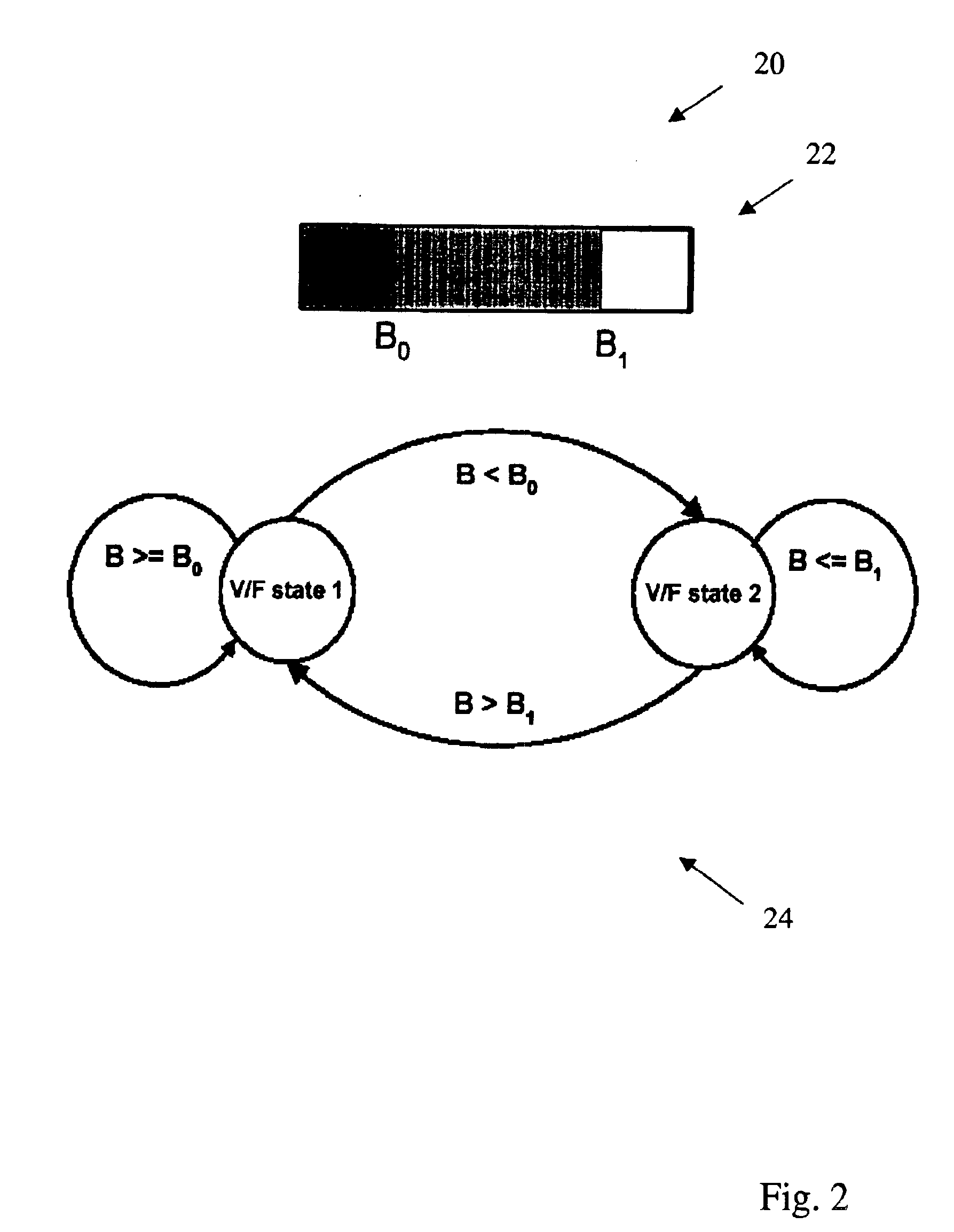
Methods and systems for performing dynamic power management via frequency and voltage scaling
ActiveUS7155617B2Significant latencyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementProcessing coreDynamic power management
Methods and systems are provided for dynamically managing the power consumption of a digital system. These methods and systems broadly provide for varying the frequency and voltage of one or more clocks of a digital system upon request by an entity of the digital system. An entity may request that the frequency of a clock of the processor of the digital system be changed. After the frequency is changed, the voltage point of the voltage regulator of the digital system is automatically changed to the lowest voltage point required for the new frequency if there is a single clock on the processor. If the processor is comprised of multiple processing cores with associated clocks, the frequency is changed to the lowest voltage point required by all frequencies of all clocks.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
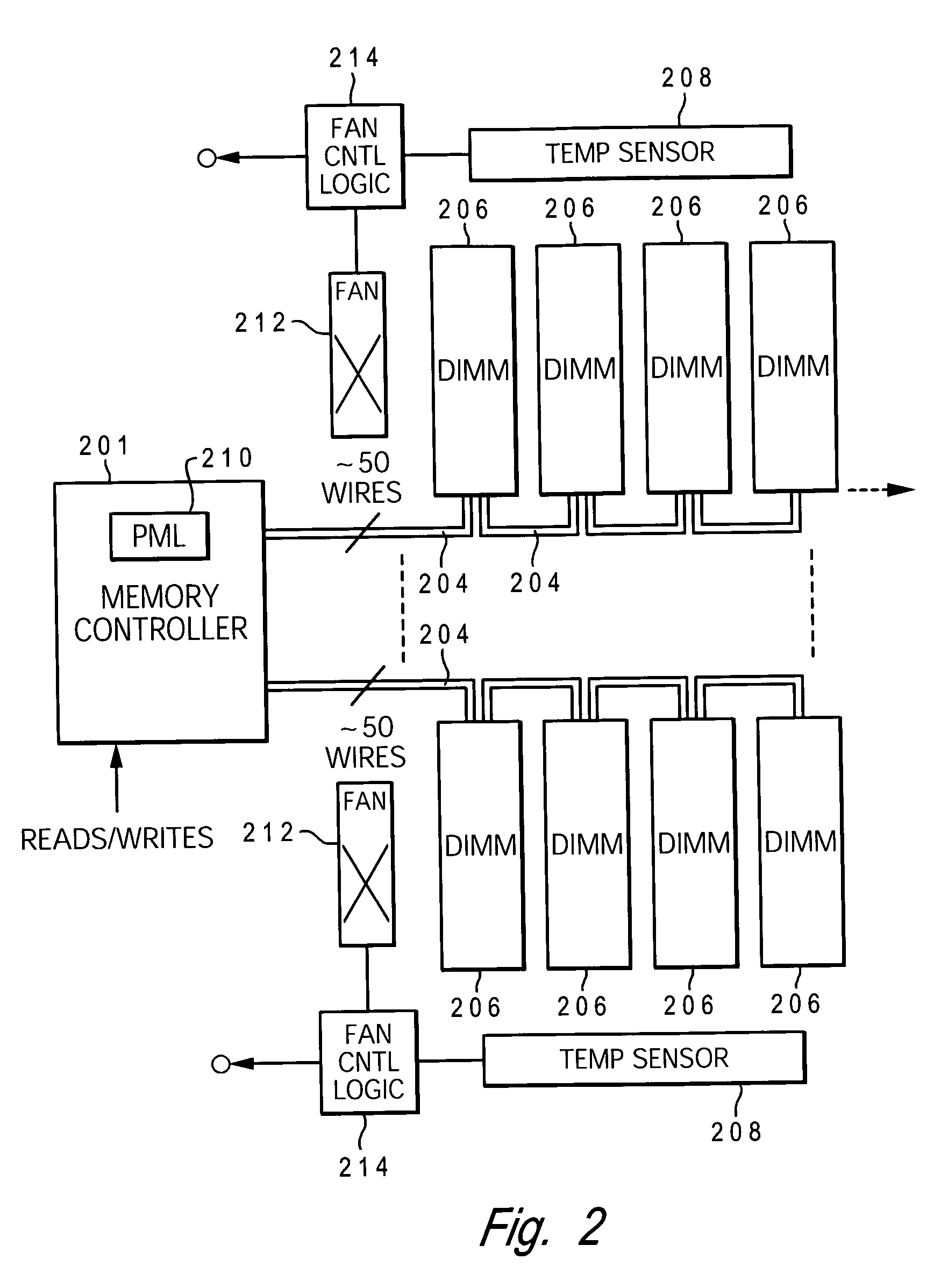
Dynamic power management via DIMM read operation limiter
InactiveUS7421598B2Little or no usePower usageEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDIMMDynamic power management
A method and system for enabling directed temperature / power management at the DIMM-level and / or DRAM-level utilizing intelligent scheduling of memory access operations received at the memory controller. Hot spots within the memory subsystem, caused by operating the DIMMs / DRAMs above predetermined / preset threshold power / temperature values for operating a DIMM and / or a DRAM, are avoided / controlled by logic within the memory controller. The memory controller logic throttles the number / frequency at which commands (read / write operations) are issued to the specific DIMM / DRAM based on feedback data received from the specific DIMM / DRAM reaching the preset threshold power usage value.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
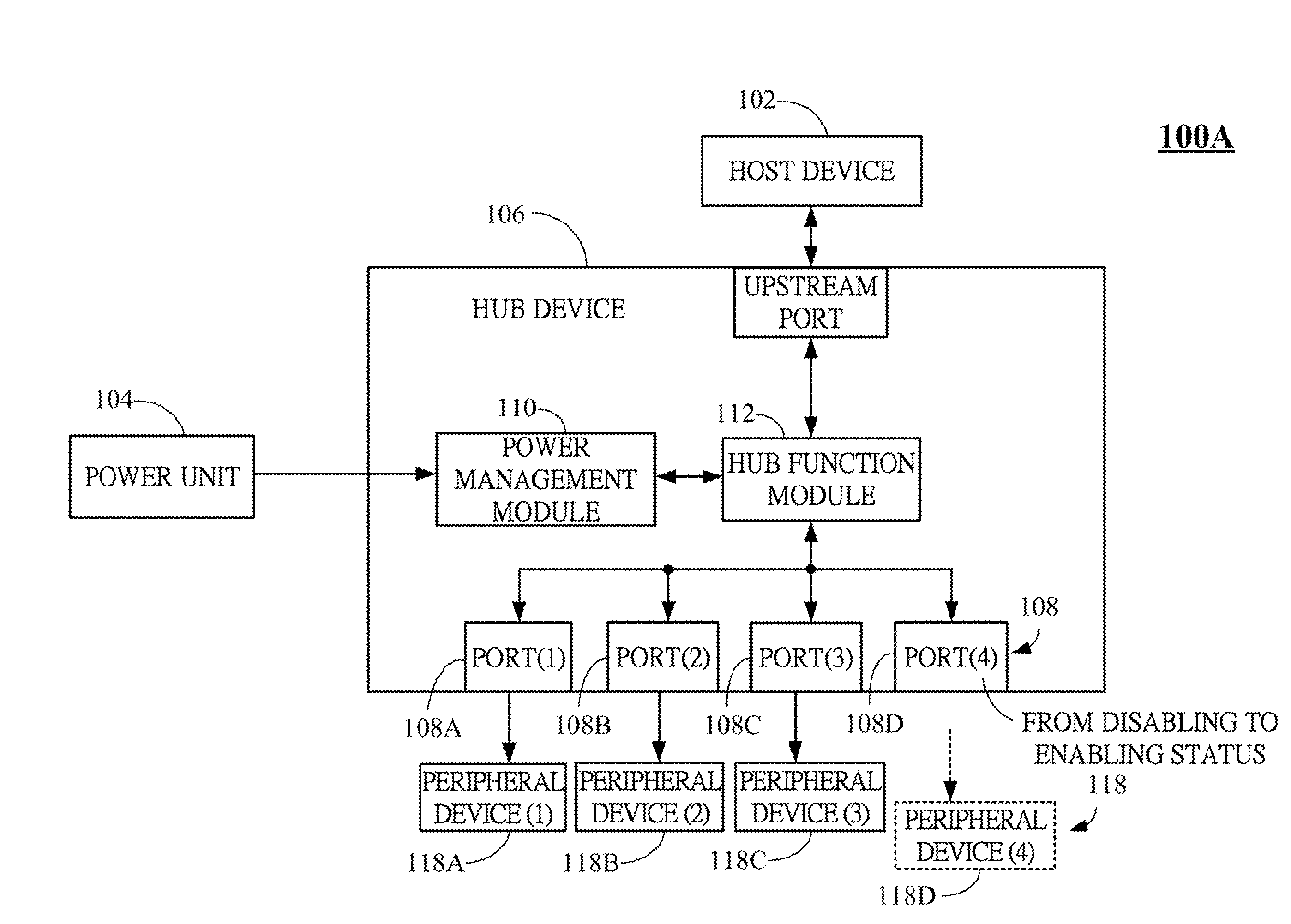
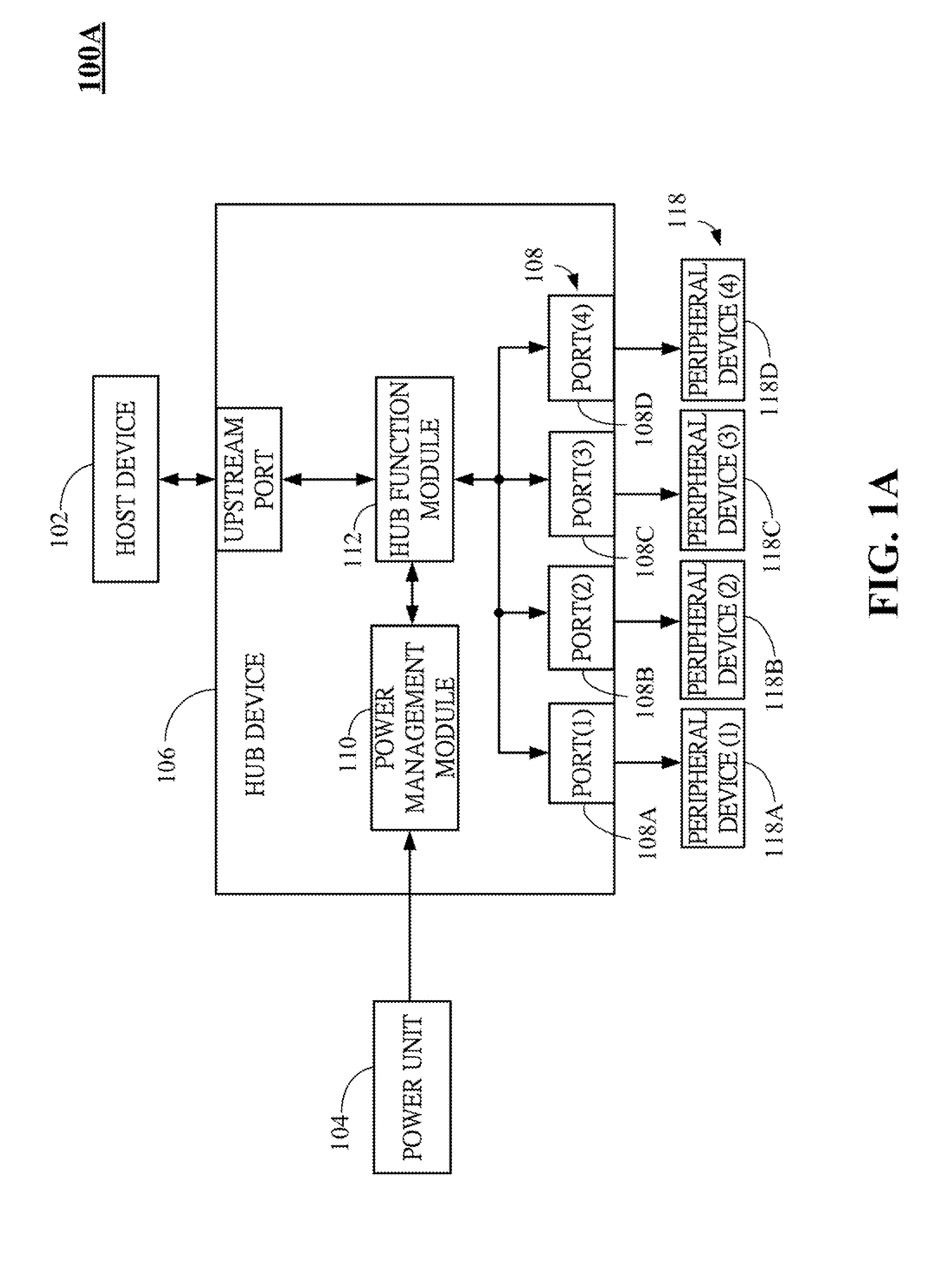
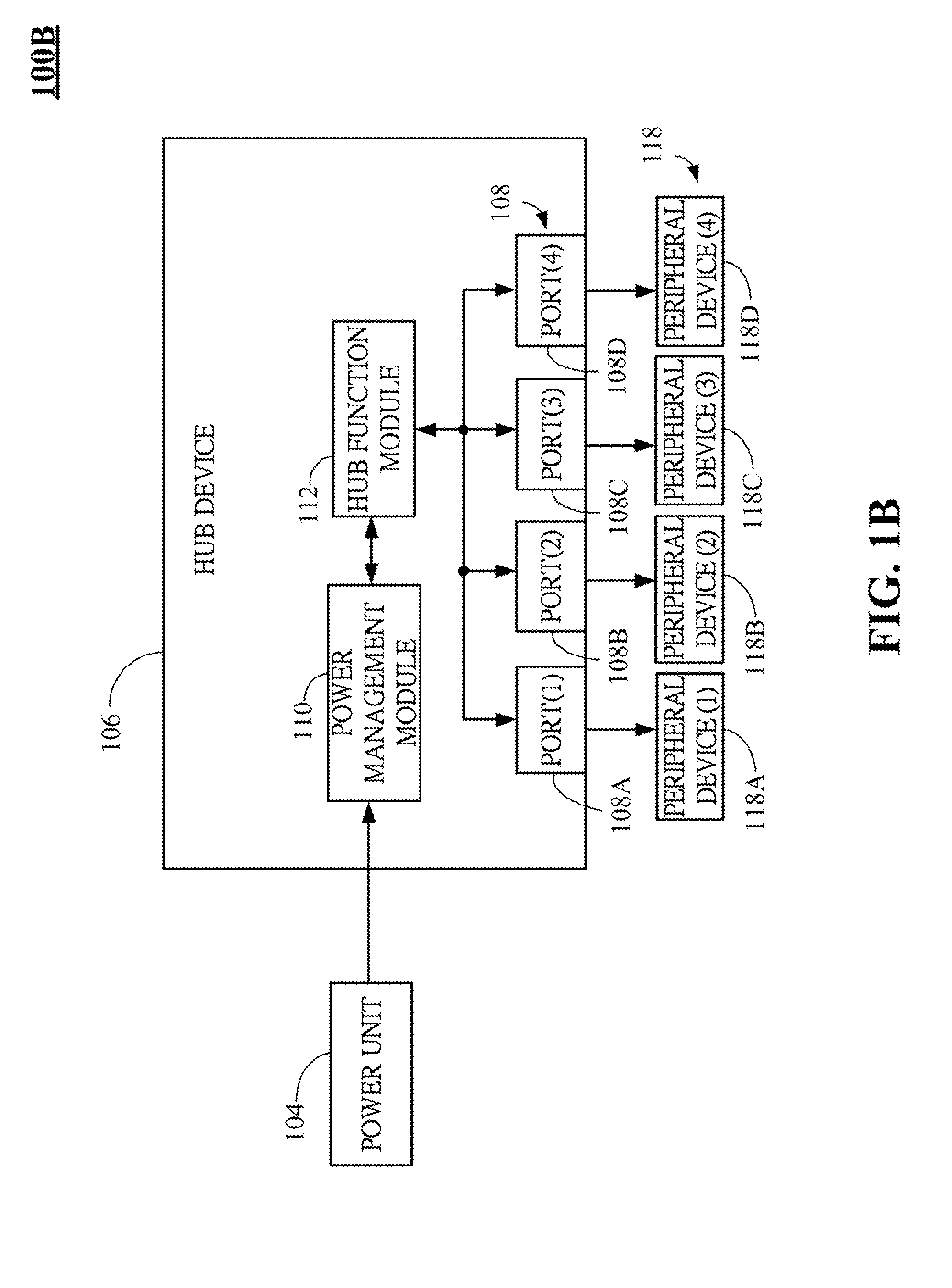
Dynamic power management system for universal serial bus (USB) hub and method thereof
ActiveUS20130013936A1Low costVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingDynamic power managementUSB hub
A dynamic power management system for USB hub and method thereof are described. The dynamic power management system includes a host device, a power unit and a hub device. A power management module disposed in the hub device dynamically adjusts the power-supplying statuses of ports in the hub device and further reduces the cost of power transformer externally connected to the hub device.
Owner:GENESYS LOGIC INC
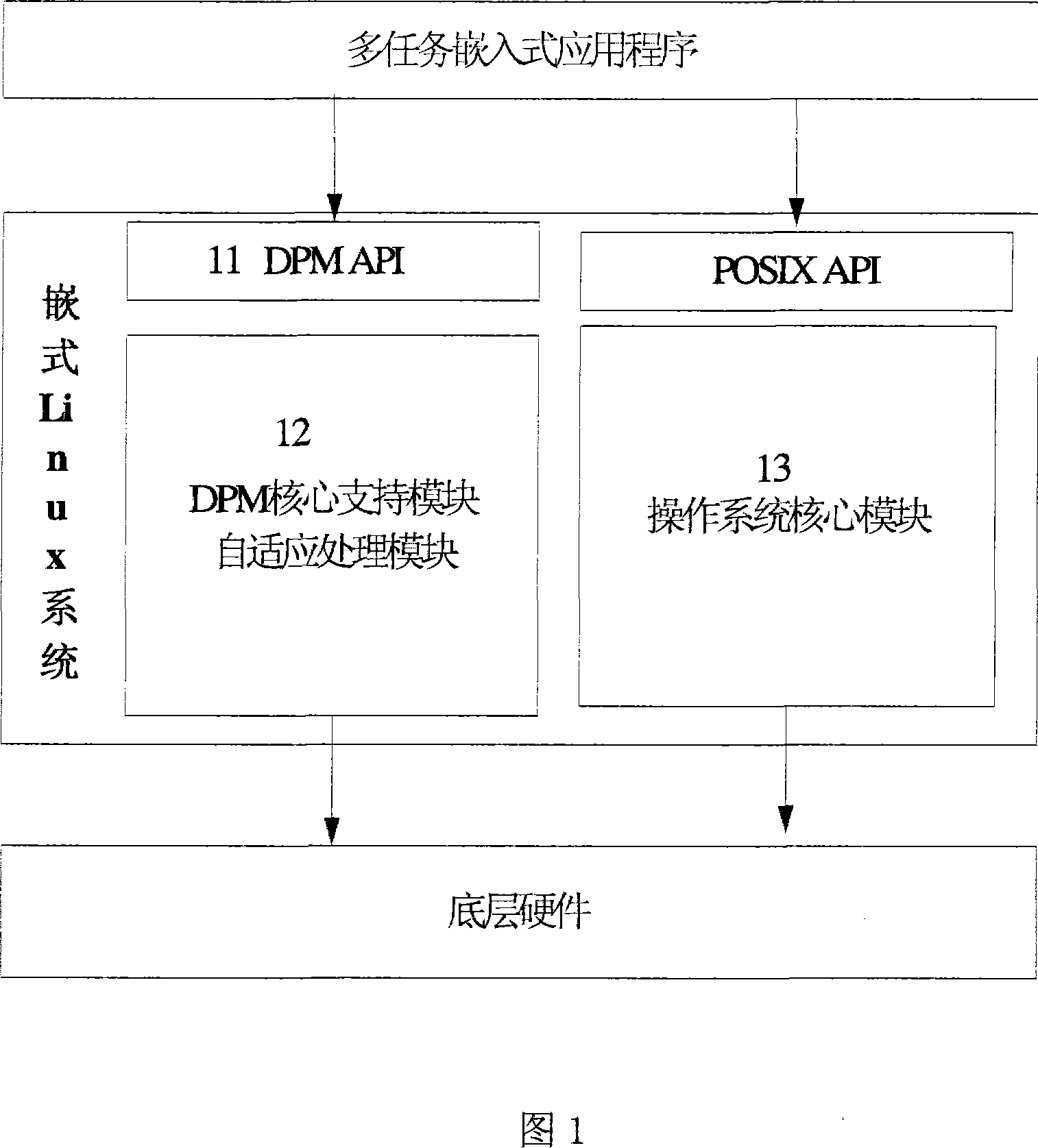
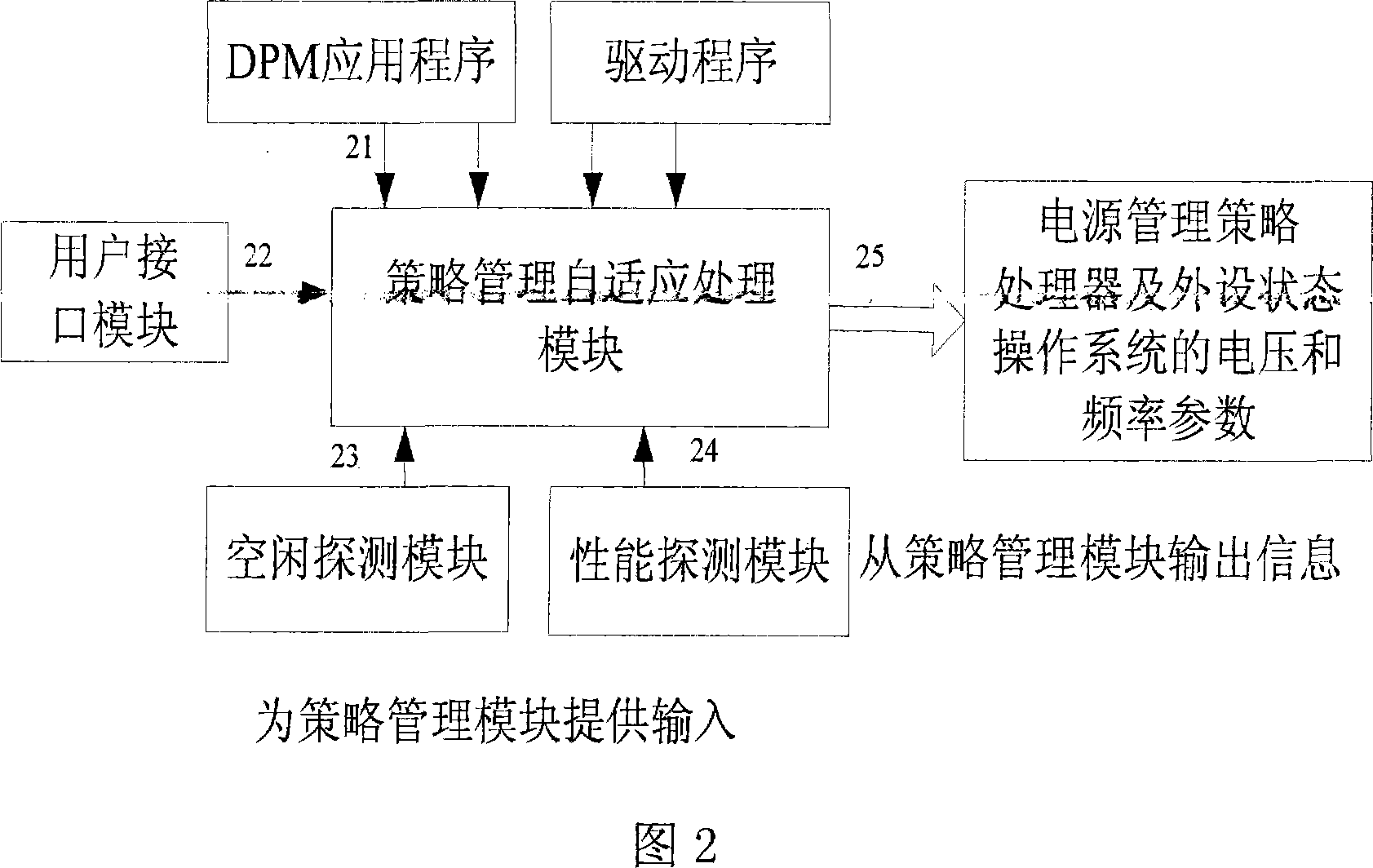
Energy consumption management method for inserting system
InactiveCN101067758AReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingEffective powerOperational system
The invention provides an energy consumption management method for an embedded system, implemented by dynamic power supply management support module, comprising: policy management module, idle detection module, and performance detection module, where the policy management module makes effective power supply management at system layer so as to implement system performance and power saving, and gives attention to idle state and executed load of system, and self-adaptively regulates equipment idle time according to system task executing state and makes the system enter a corresponding low-power state when the idle time continues to a certain extent; the idle detection module provides idle information of CPU and operating system and monitors the idle thread or activity of a given working load in the operating system and provides policy-making parameter information for the policy management module; and the performance detection module monitors CPU utilization ratio and utilization conditions of main memory and provides accurate executed load information for the policy management module.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
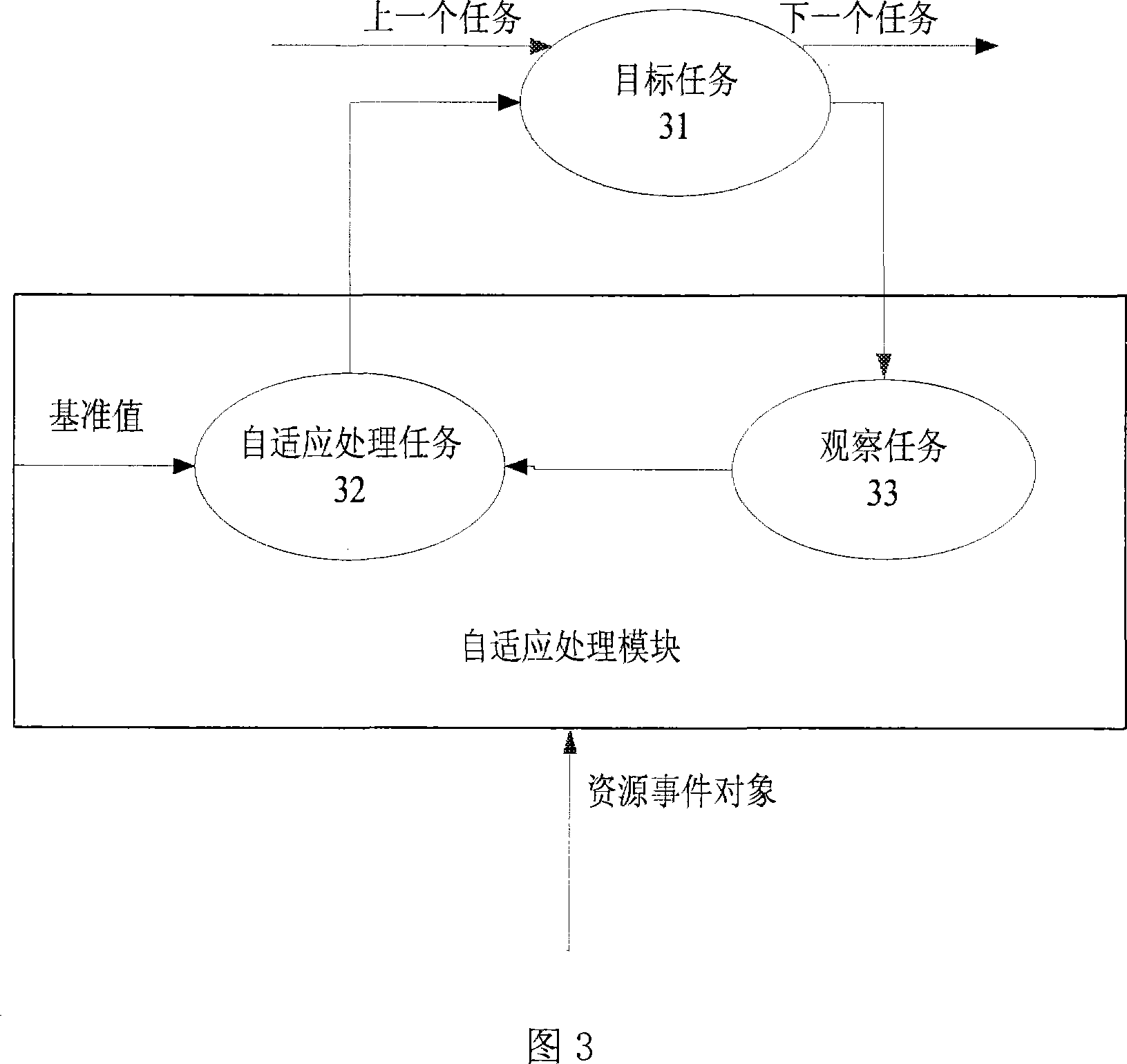
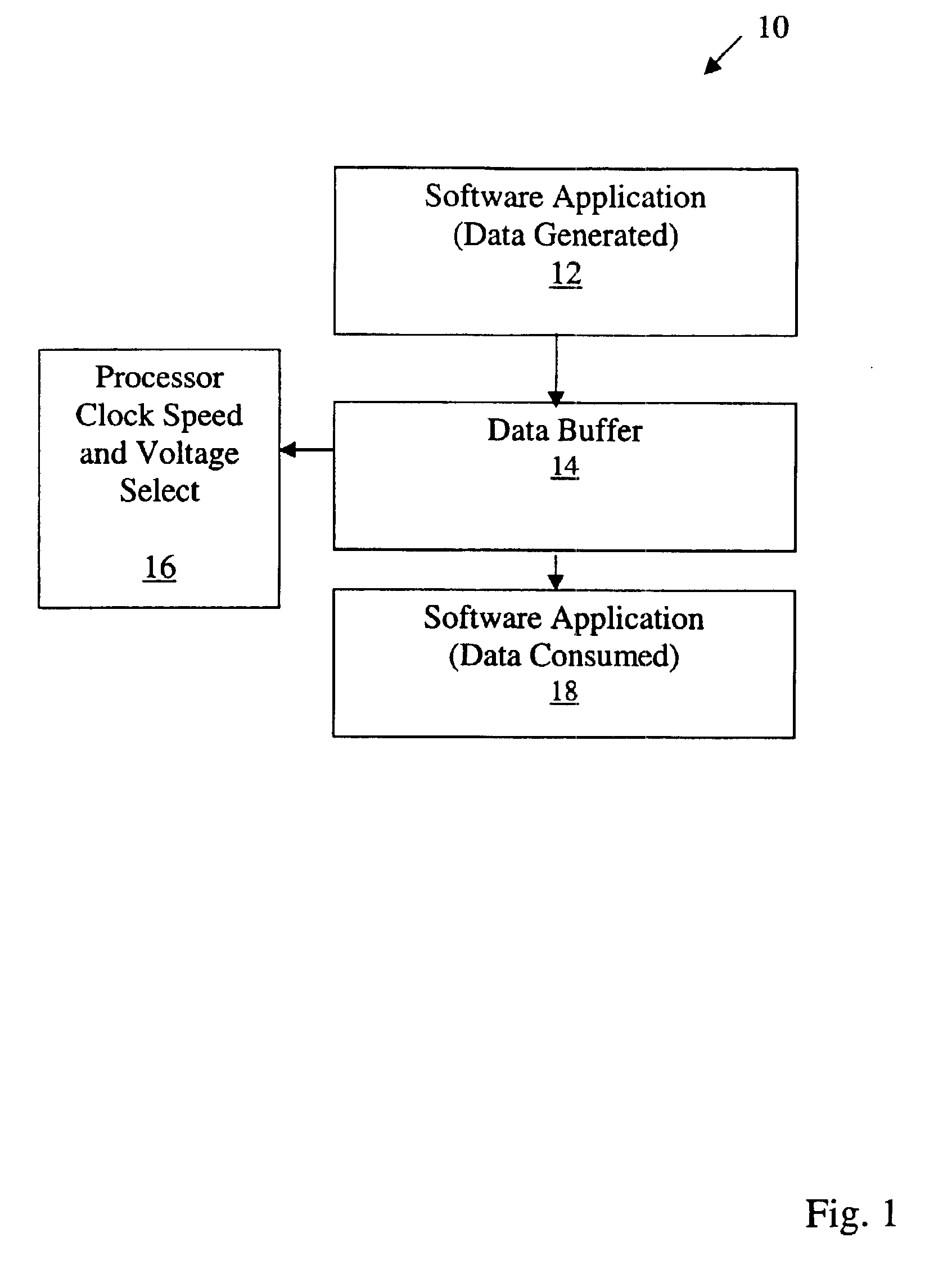
System and method for dynamic power management using data buffer levels
InactiveUS6865653B2Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementComputer science
A power management system for digital circuitry uses data buffer monitoring to determine appropriate processor clock speed or voltage. This allows a processor to be switched from a low power state to a high power state when a monitored data buffer level feeding data to a power intensive application is greater than a second memory buffer level. The processor is switched from a high power state to a low power state when the monitored data buffer level is less than a first memory buffer level.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for optimizing performance and battery life of electronic devices based on system and application parameters
InactiveUS20070139014A1Reduce power consumptionExtended service lifeEnergy efficient ICTBatteries circuit arrangementsOperational systemDynamic power management
An electronic device (e.g., computer system, etc.) employing dynamic power management of the present invention adjusts power consumption in accordance with an analysis of parameters and events occurring over one or more time-periods. Preferably, the electronic device monitors microprocessor, operating system, peripheral and / or device-level events and adjusts run-time parameters, such as microprocessor clock frequency and voltage, to reduce power consumption with minimal perceived degradation in performance.
Owner:GIRSON ANDREW +2
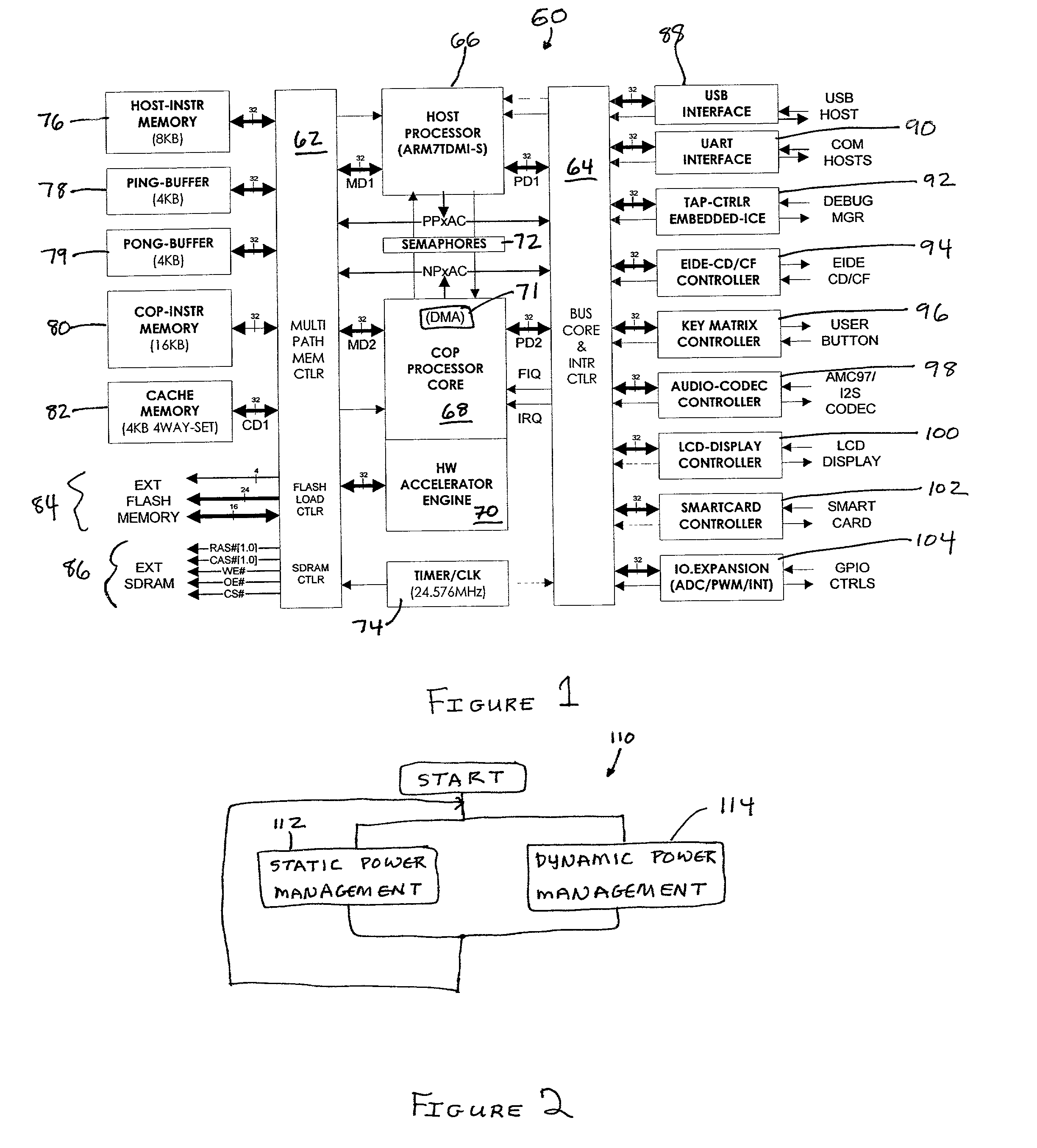
Dynamic power management
InactiveUS20050144486A1Energy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersDynamic power managementSet point
Provided is a technique for power and performance management of one or more storage devices. With a power and performance management agent, a power change notification identifying a power set point is received and a power state of at least one storage device is adjusted.
Owner:INTEL CORP
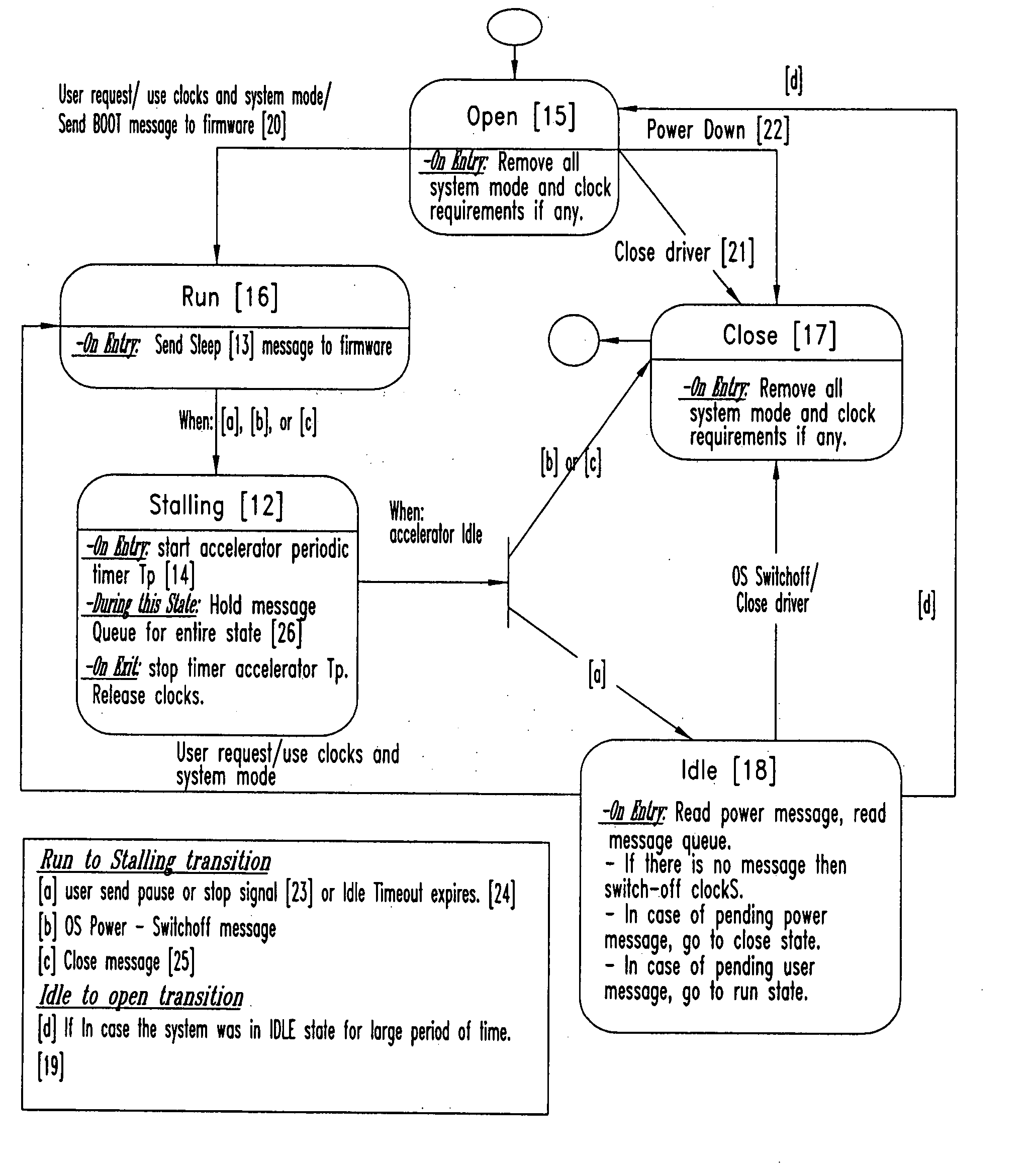
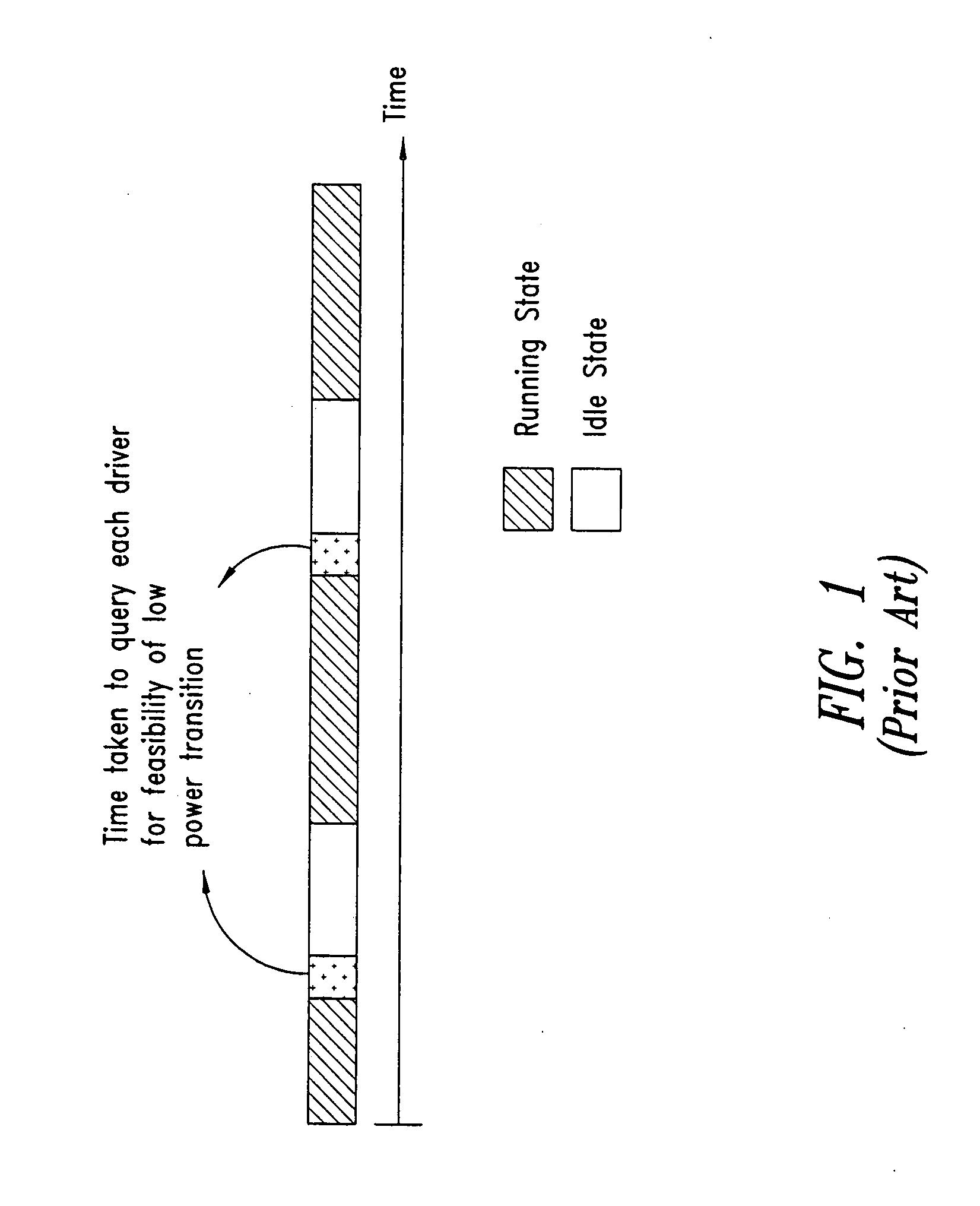
Dynamic power management in system on chips (SOC)
ActiveUS20070094525A1Effective dynamic power managementReduce total powerEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsPower modeDynamic power management
A system for dynamic power management in a distributed architecture system on chip, comprising a means for dynamically defining the feasibility of entering a low power mode of operation based on the status of components of the system, a means for entering or exiting safely from a low power state based on said feasibility, a means for decreasing the power centric communication between various processors and a means for increasing the low power mode time. Thus a framework is proposed in the instant invention wherein all the device drivers dynamically maintain the information on the feasibility of a low power transition at any point of time. Thus whenever an opportunity to enter a low power mode comes up one has to just check this feasibility variable to determine whether the low power mode entry is viable or not. For ensuring the safe transition to a low power mode, a stalling machine is proposed in case of DSPs. For further saving power, a power centric communication channel is established between various processors and to reduce the load on this communication channel techniques like quad-ring buffer and DSP feedback are proposed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
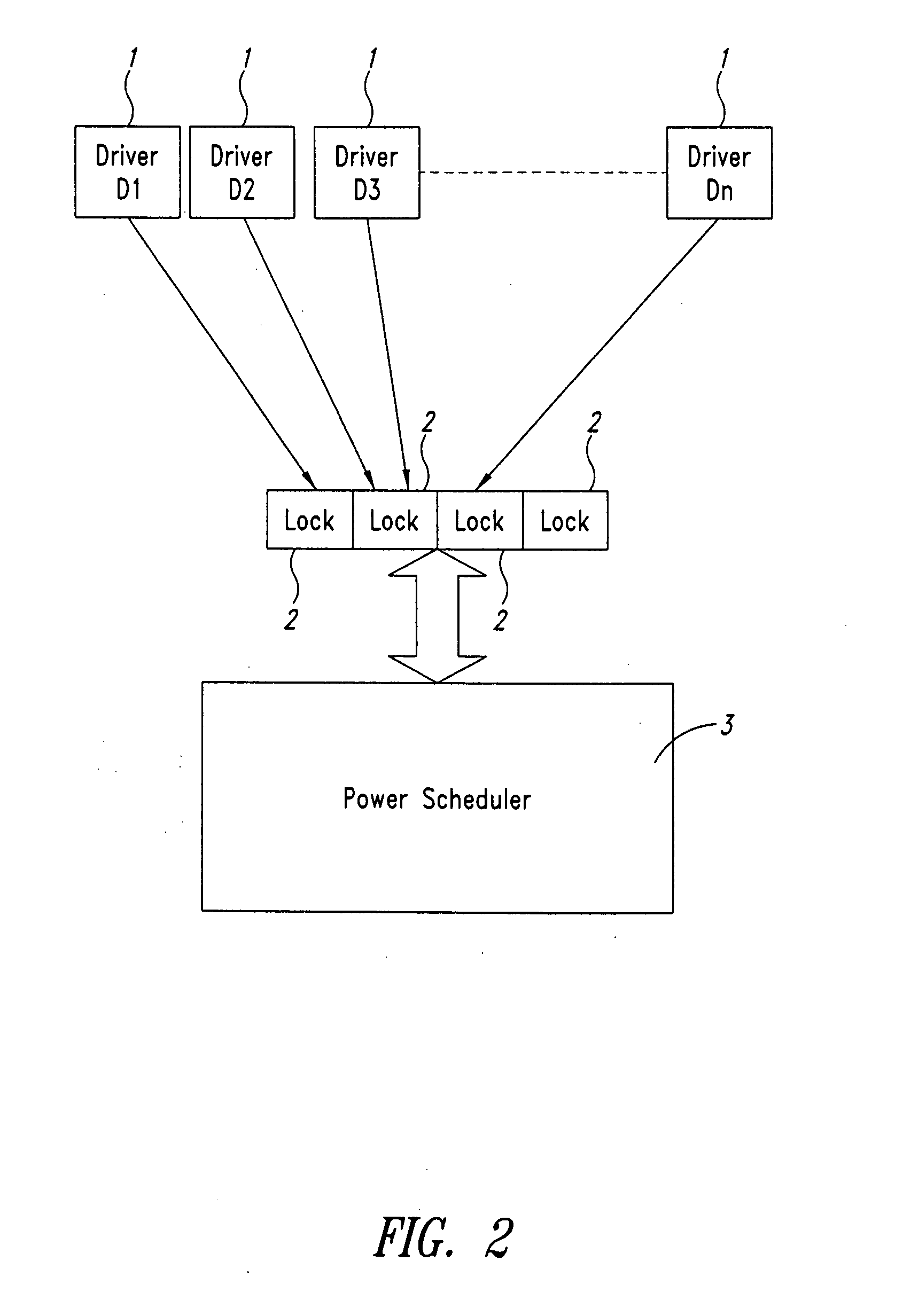
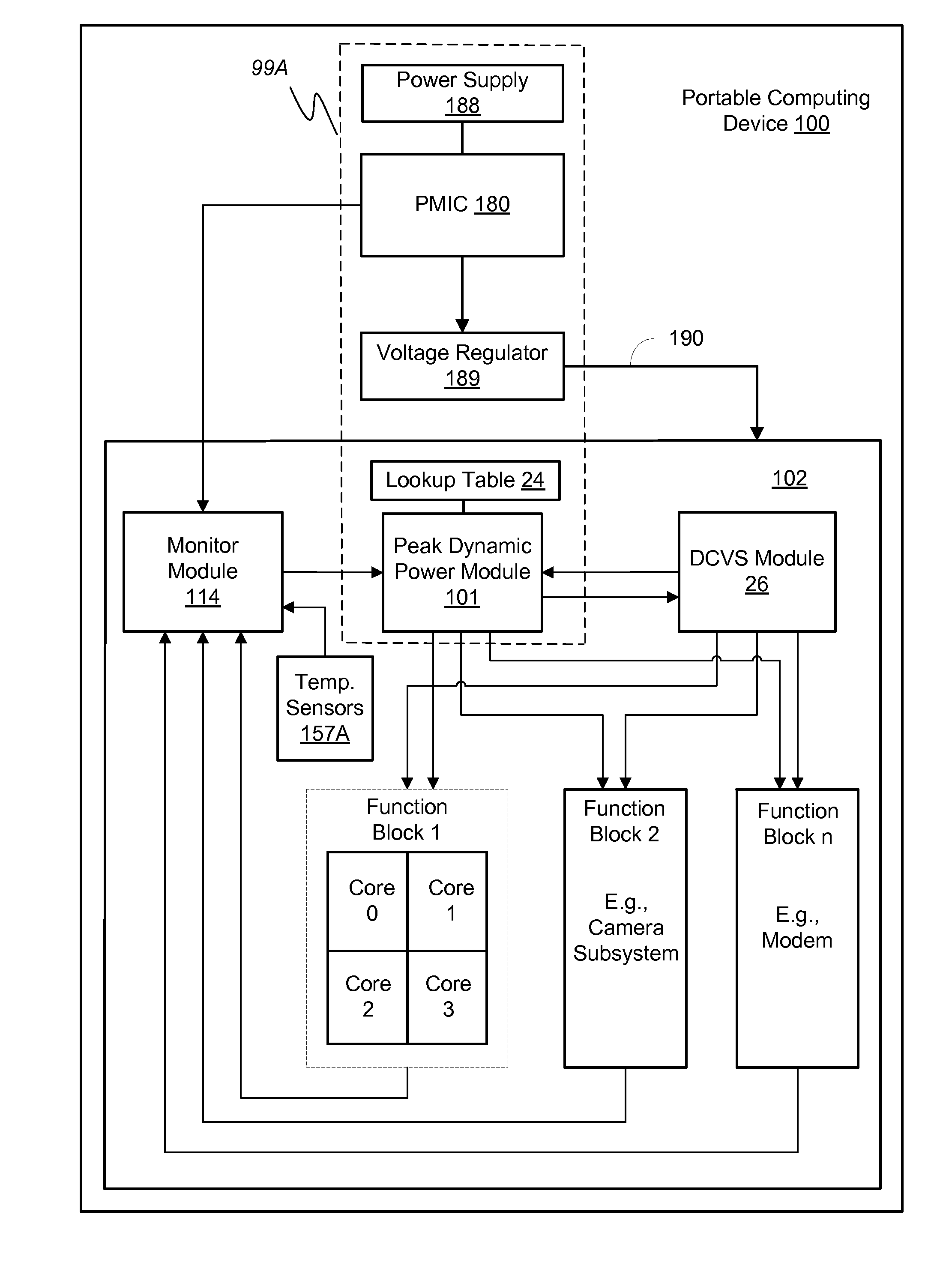
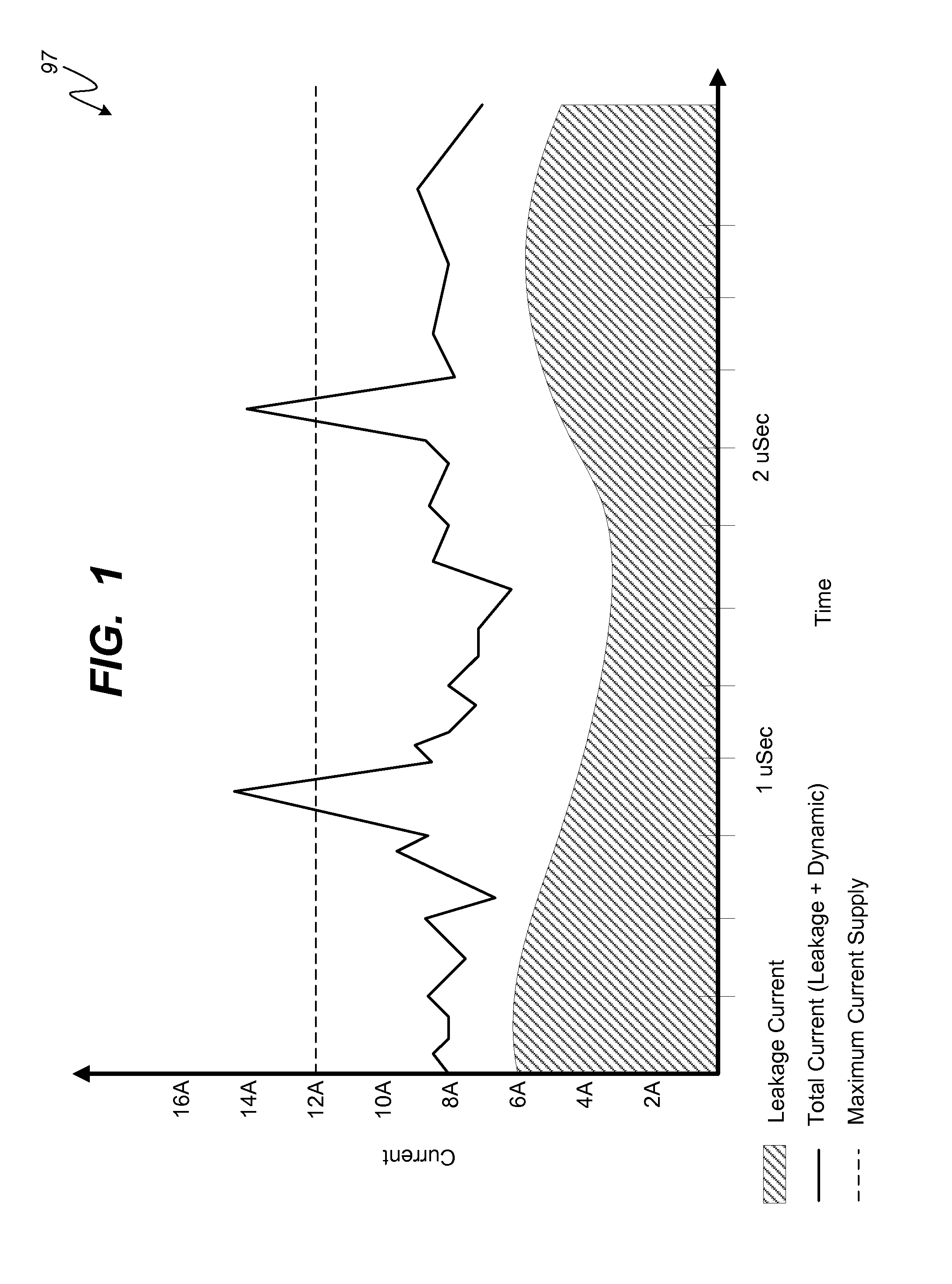
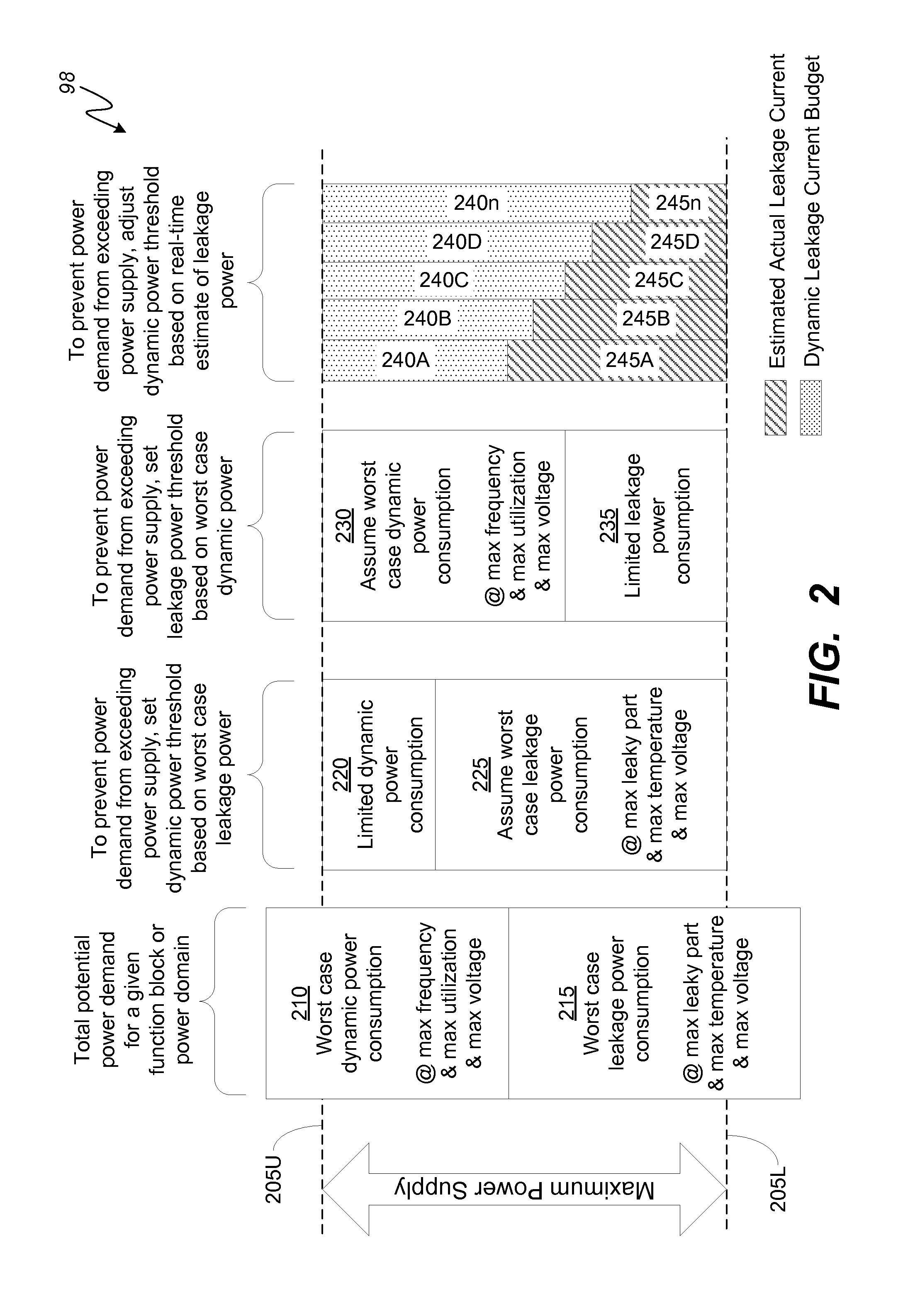
System and method for peak dynamic power management in a portable computing device
ActiveUS20160179164A1A large amountHardware monitoringPower supply for data processingQuality of serviceElectricity
Various embodiments of methods and systems for dynamically adjusting a peak dynamic power threshold are disclosed. Advantageously, embodiments of the solution for peak dynamic power management optimize a peak dynamic power threshold based on estimations of real-time leakage current levels and / or actual power supply levels to a power domain of a system on a chip (“SoC”). In this way, embodiments of the solution ensure that a maximum amount of available power supply is allocated to dynamic power consumption for processing workloads at an optimum performance or quality of service (“QoS”) level without risking that the total power consumption (leakage power consumption+dynamic power consumption) for the power domain exceeds the power supply capacity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for dynamic power management in a processor system
ActiveUS7240223B2Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingOperational systemDynamic power management
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus to dynamically adjust resource power usage in a distributed system
InactiveUS20080002603A1Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementResource based
A system and method to provide source controlled dynamic power management. An activity detector in a source determines expected future resource usage. Based on that expected usage, the source generates a power management command and sends that command to a destination. The destination then adjusts the power level of the resource based in the command.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic power management optimization
InactiveUS20160378168A1Wake-up intervalExtended durationPower supply for data processingEnergy efficient computingOperating pointSocial media
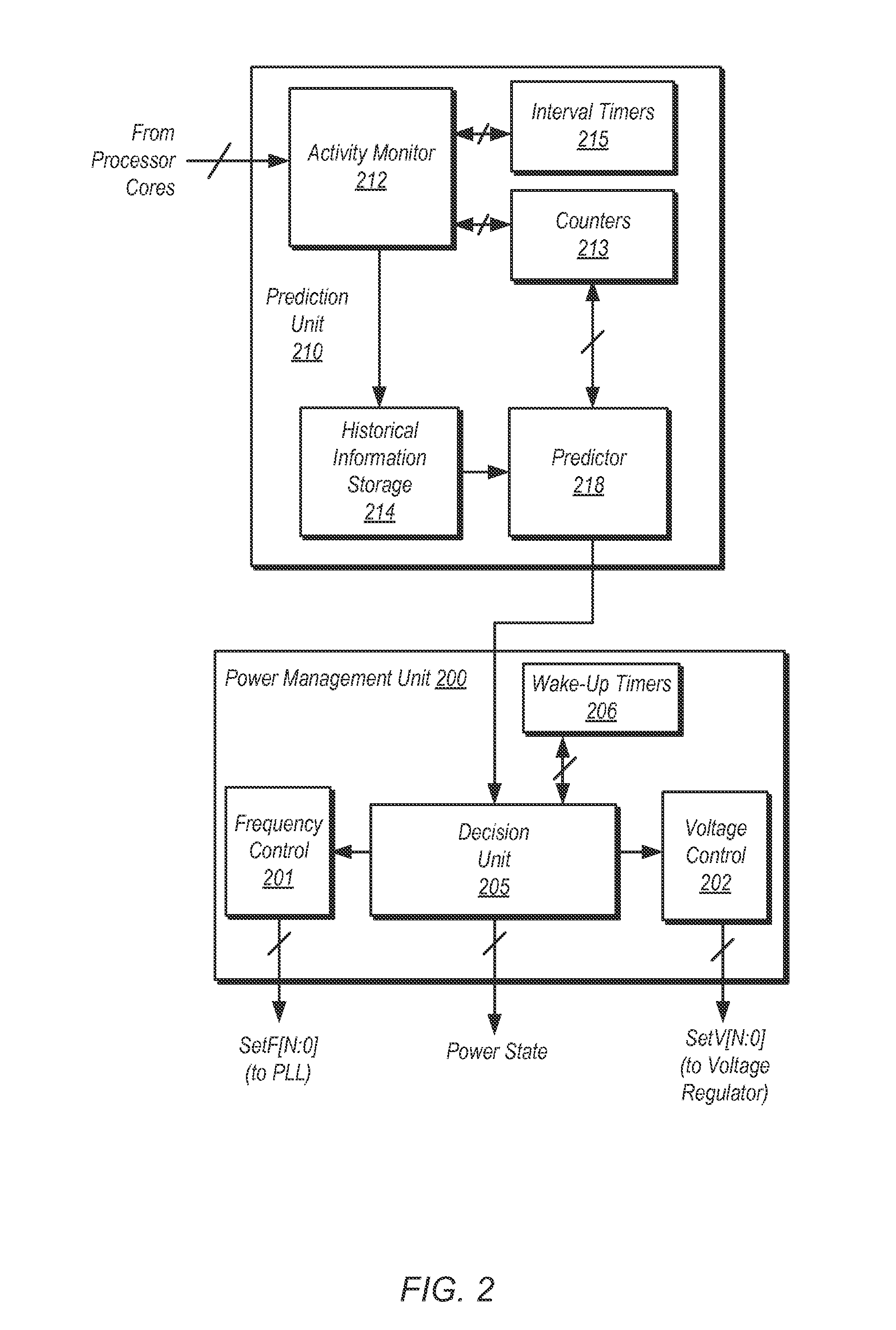
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for managing power usage of integrated circuits. One or more processor cores may be powered down when the system is idle. Even if there is no user activity, the processor core(s) may be woken up periodically for background downloads to retrieve the latest status for social media and other applications. Additionally, a power management unit may track the average number of active cores and the average core utilization. If the average number of active cores is less than a first threshold and the average core utilization is less than a second threshold, the power management unit may generate a request to offline one or more cores. Still further, when the processor's skin temperature is above a threshold and all of the cores are operating at the lowest acceptable operating point, one or more cores may be powered down.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting data based on OFDM
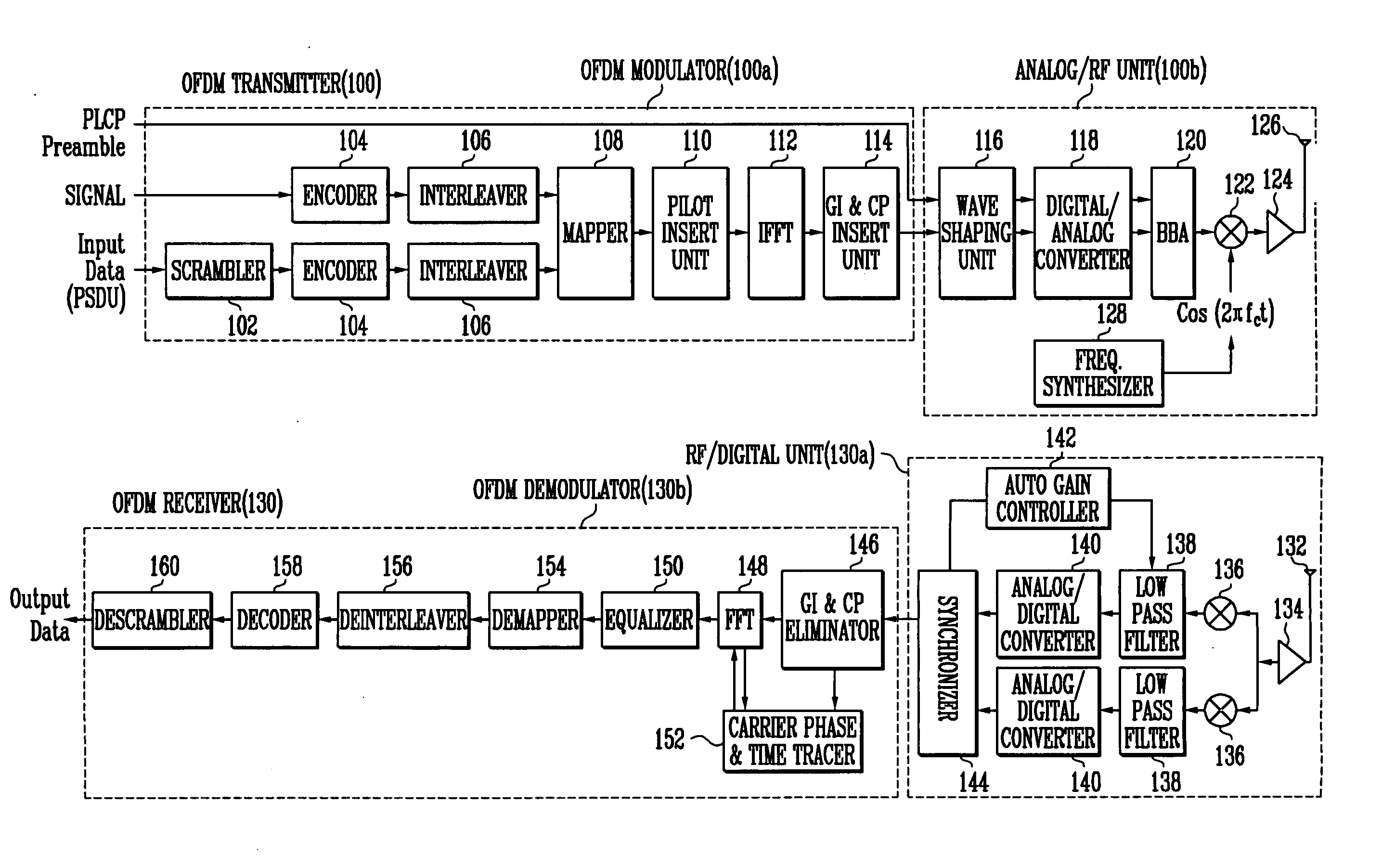
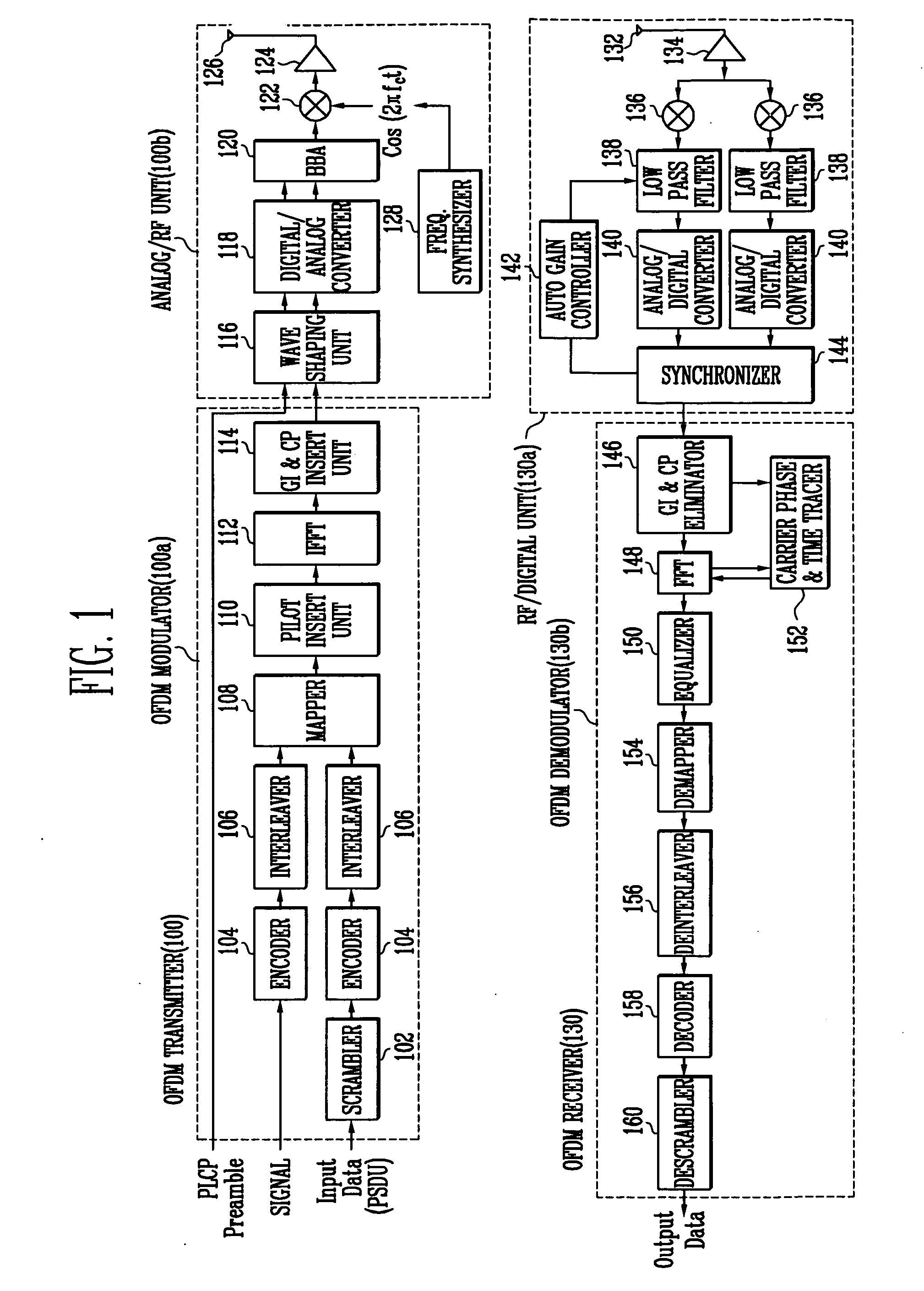
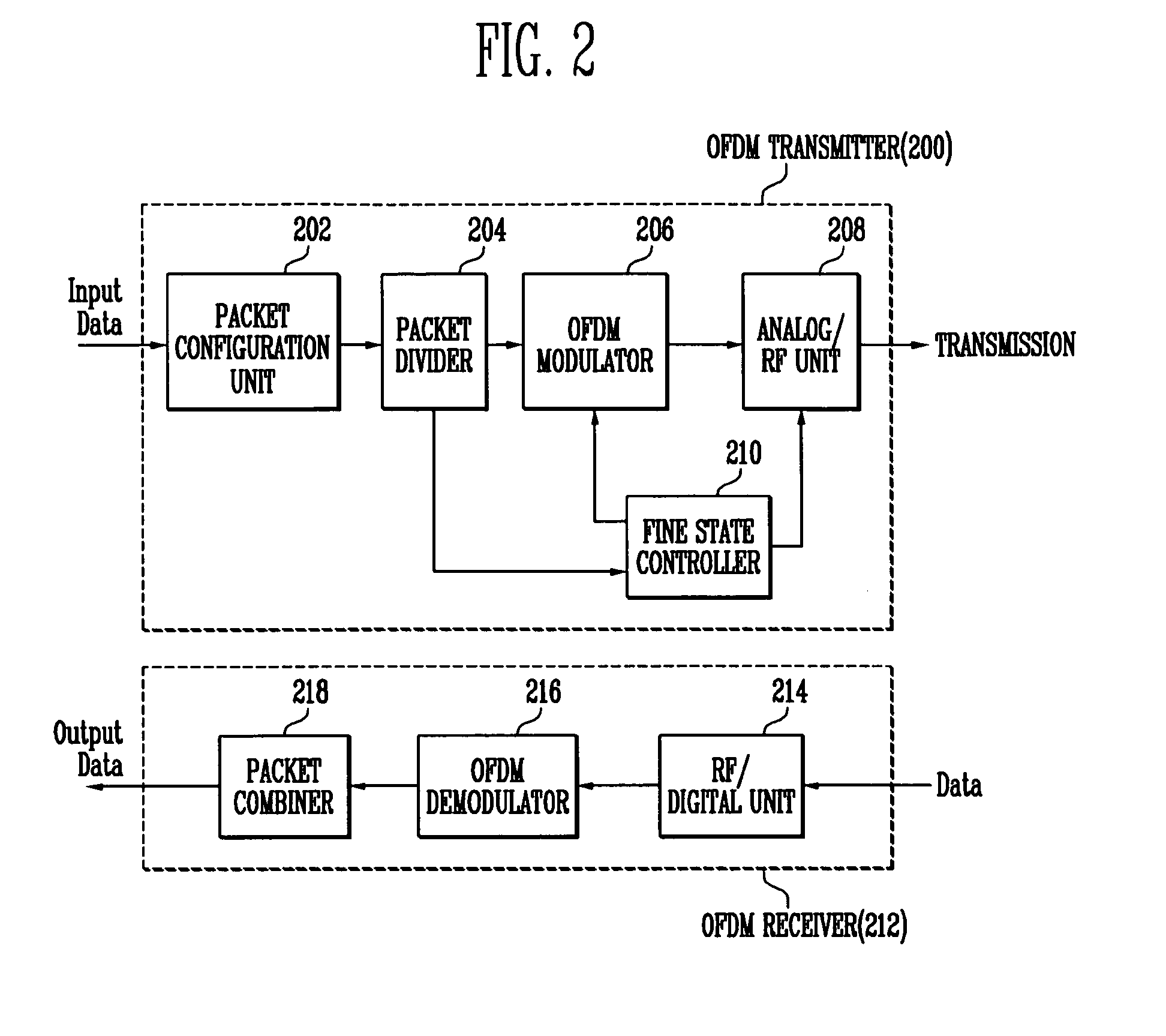
ActiveUS20060126492A1Easy to optimizeReduce power consumptionPower managementModulated-carrier systemsDynamic power managementTransfer mode
Provided is a method and apparatus for transmitting data based on OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing). The method includes: forming a plurality of packets suitable for a selected transmission mode from data input to a transmitter; determining a transfer rate of the data; when the data transfer rate is determined to be low and synchronous connection oriented link should be maintained, dividing each of the plurality of packets into a plurality of sub-packets; and transmitting the divided sub-packets, wherein when the divided sub-packets are transmitted, a power supply duration of the transmitter is reduced by using a DPM (dynamic power management) or fine state control unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
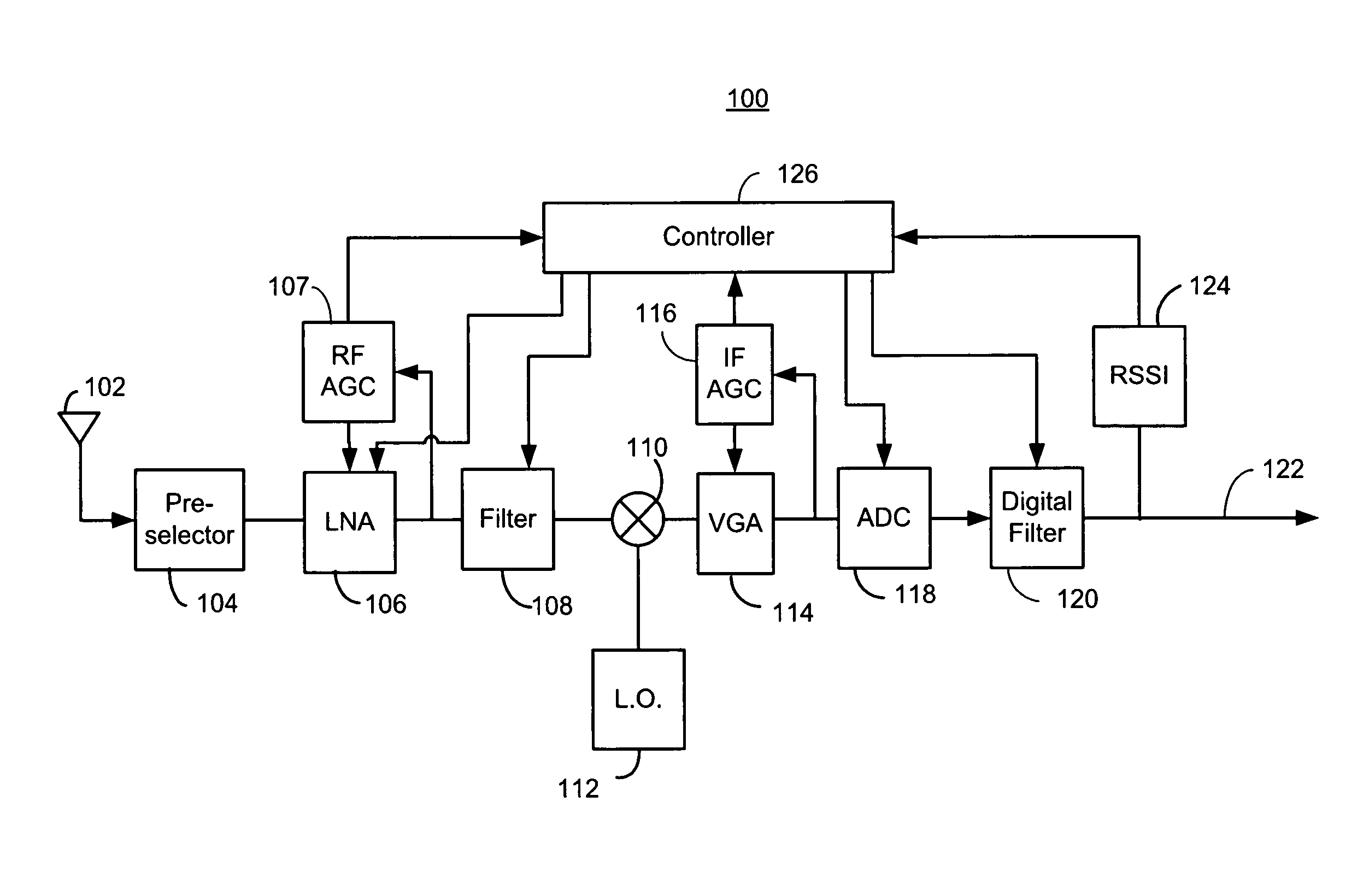
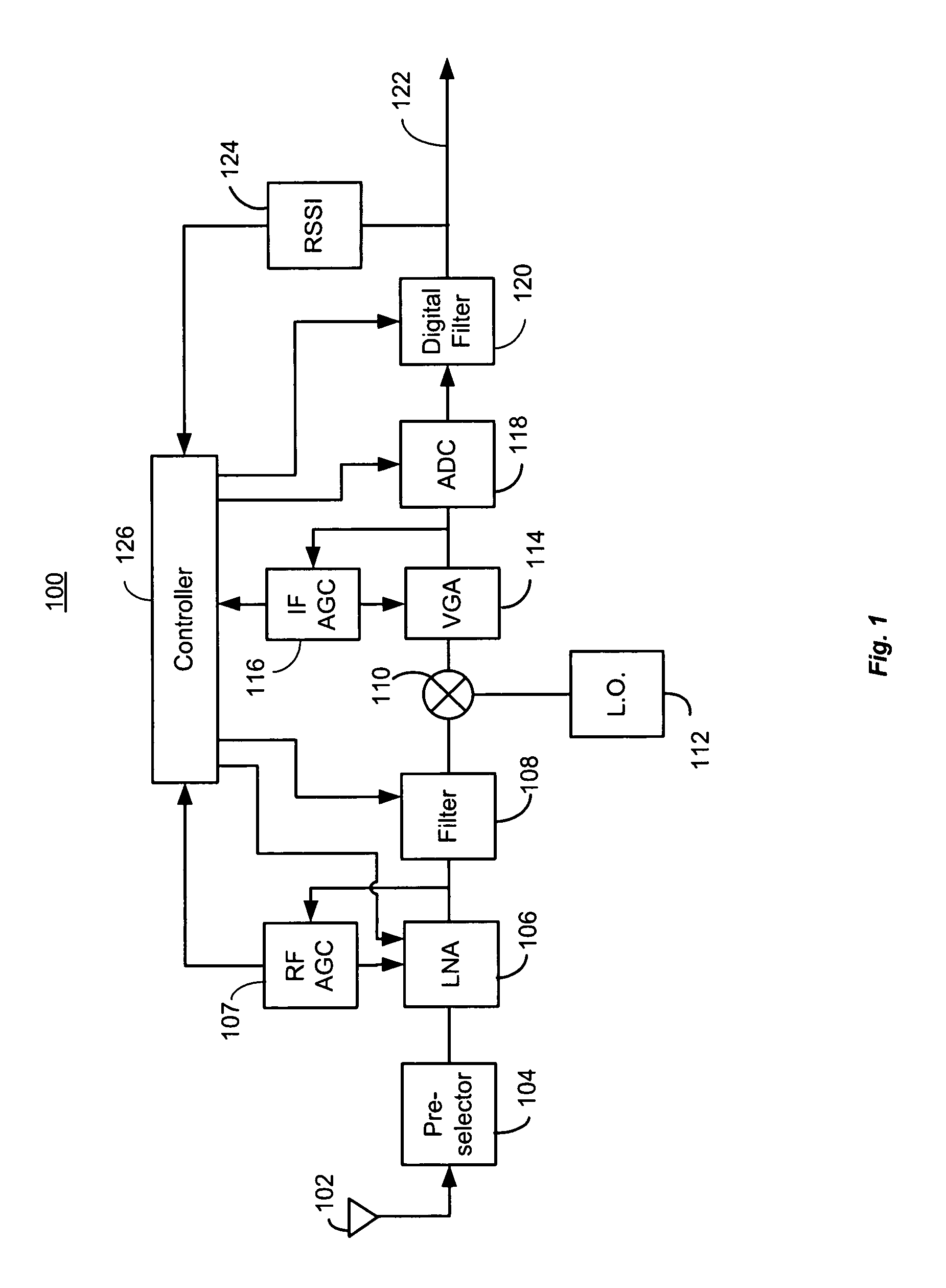
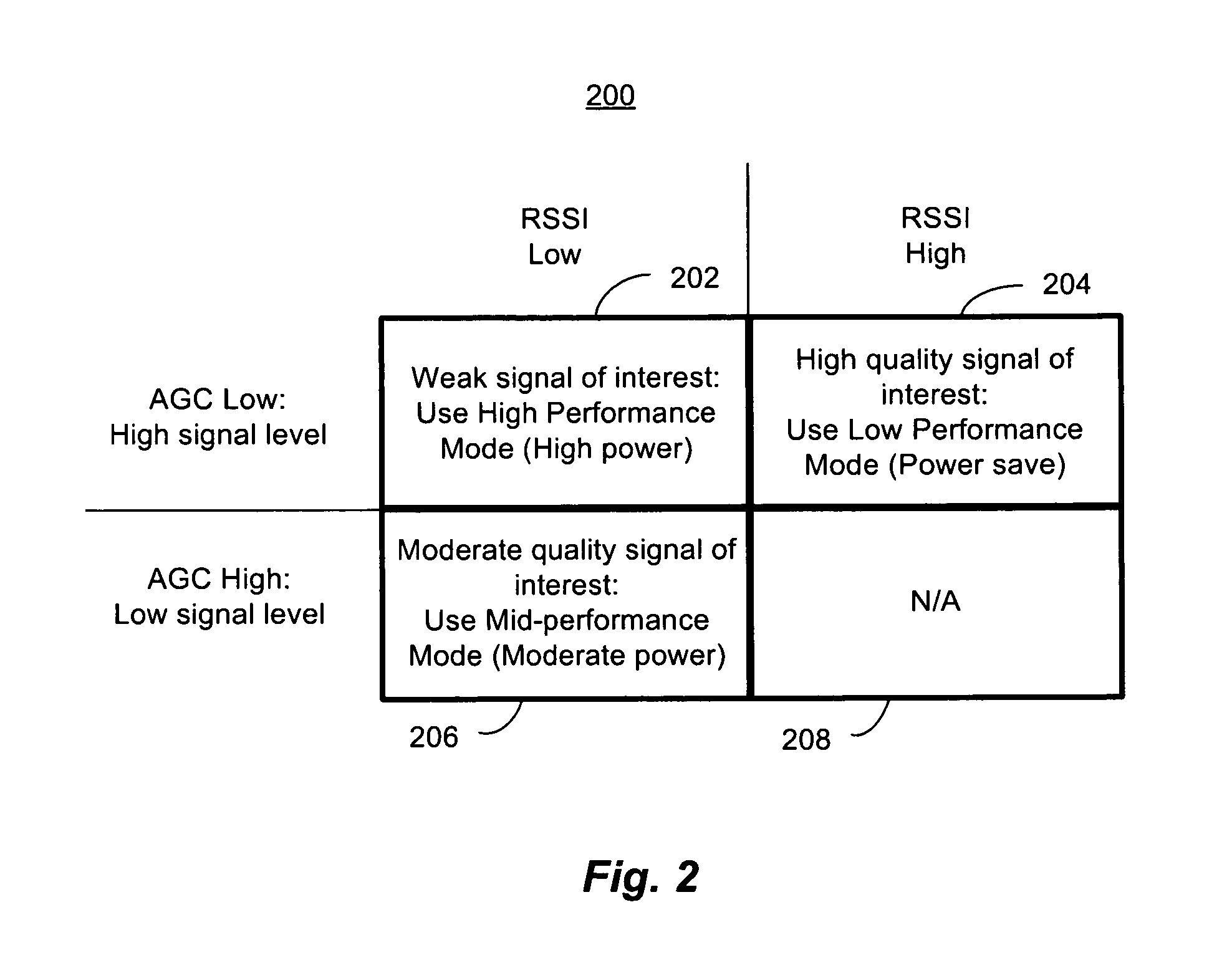
Receiver dynamic power management
ActiveUS8428535B1Improve performanceReduce the noise floorGain controlTransmission monitoringLow noiseAdaptive filter
A controller in a receiver monitors RSSI and AGC gain levels to determine signal conditions and adjust filter performance accordingly to optimize power consumption while providing acceptable signal quality. When RSSI level is high and AGC gain is low, a strong signal-of-interest is present. In this case, adaptive filter bias currents may be reduced raise the noise floor and degrade intermodulation to reduce power consumption because the strong signal-of-interest can tolerate the higher noise and distortion. When the RSSI level is low and AGC gain is high, a weak signal is present a low noise mode may be effected by increasing bias current to filters used to lower the noise floor, but intermodulation effects may still be tolerated so those filters may be cut back. Other cases are supported. RSSI and AGC gain level thresholds may be dynamically altered based on relative RSSI and AGC levels.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
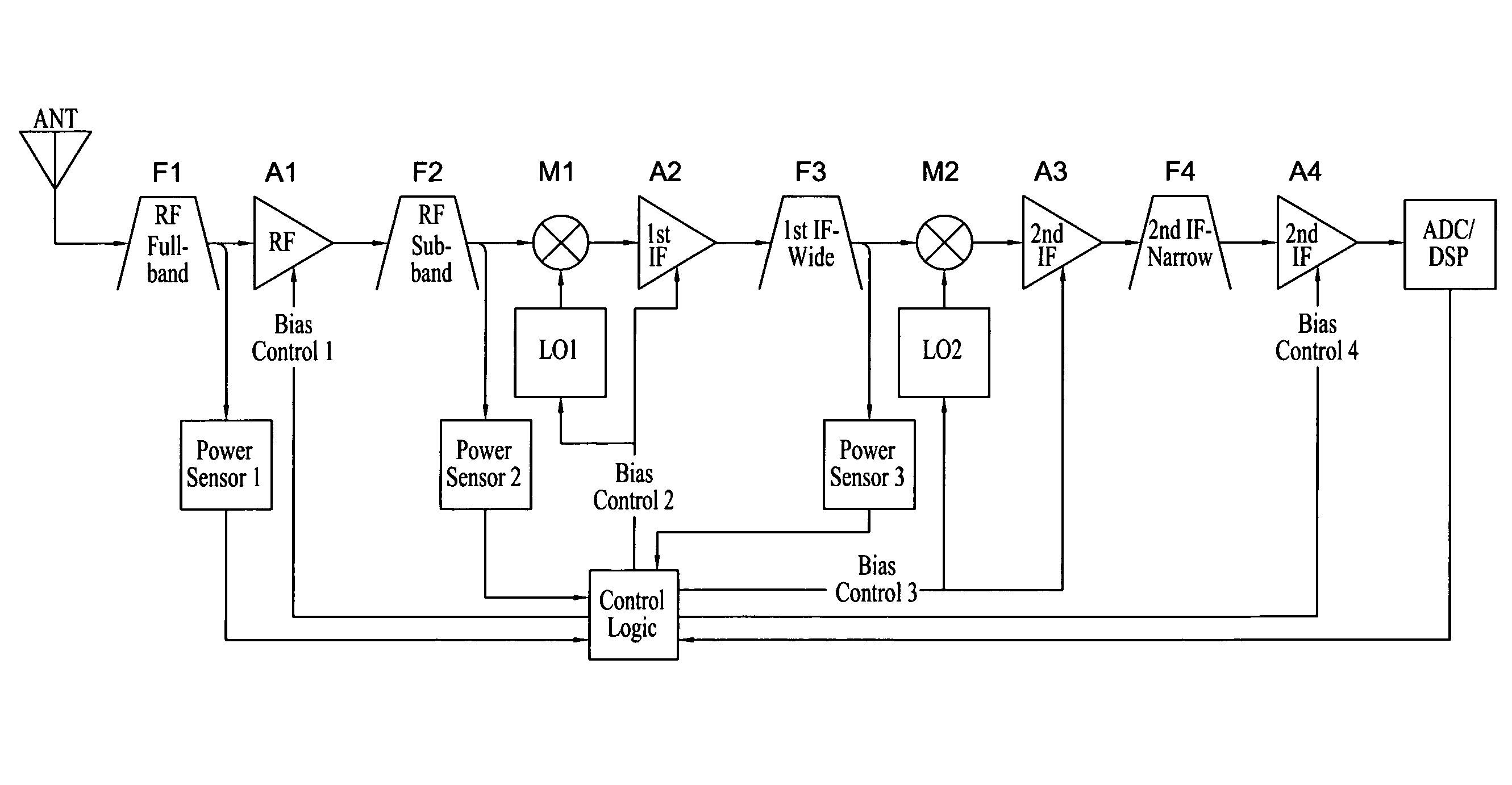
RF receiver utilizing dynamic power management
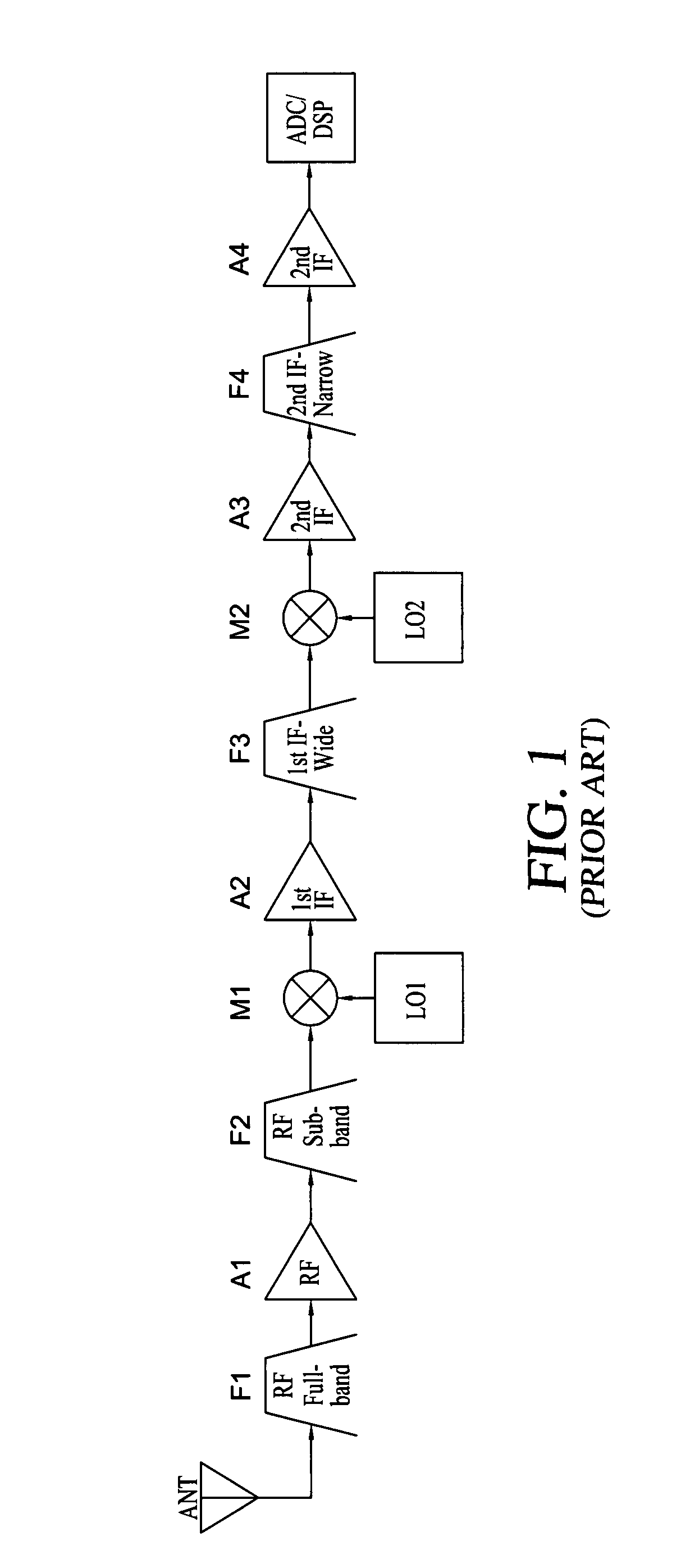
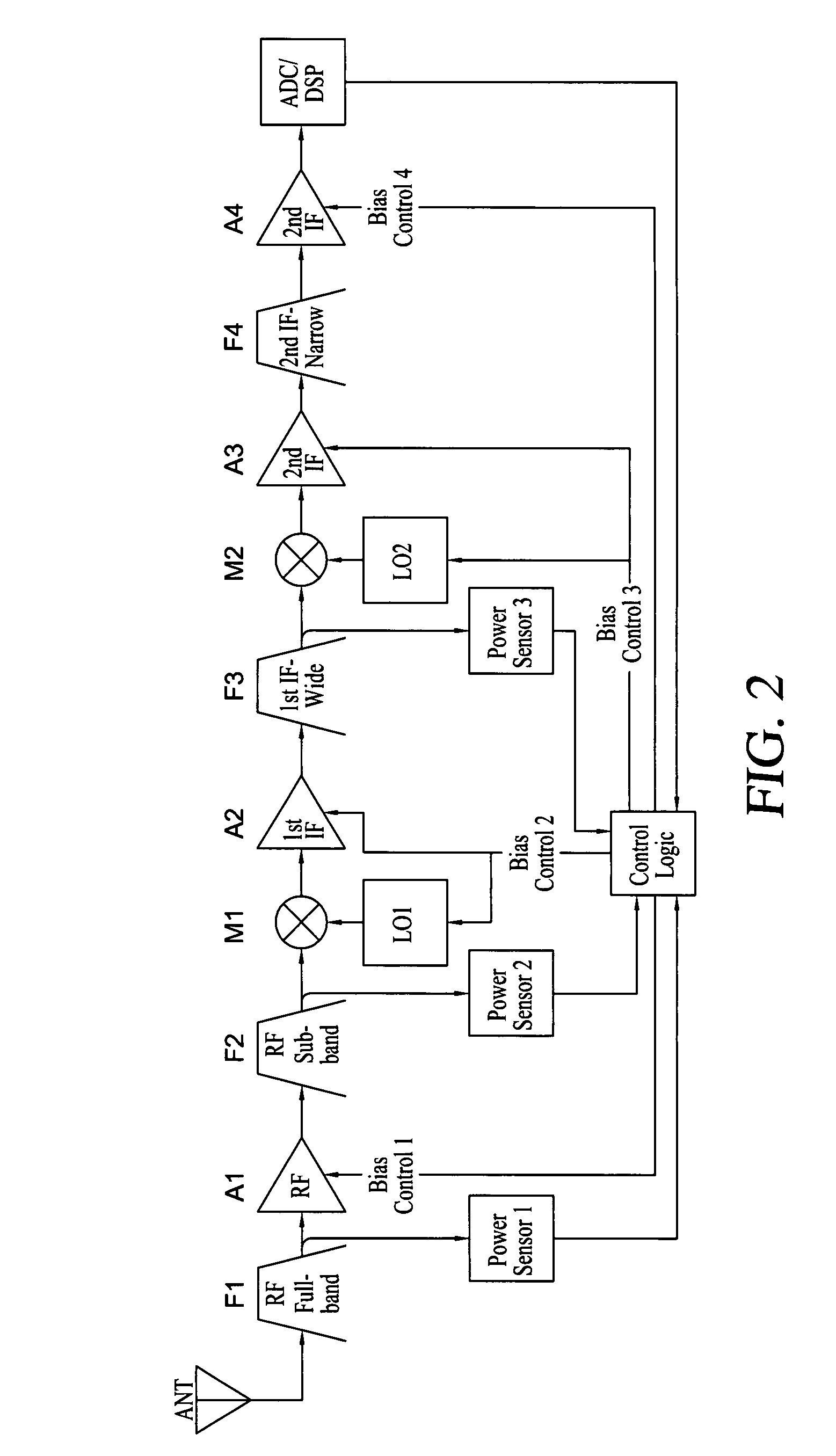
ActiveUS7639998B1Reduce power consumptionReduce thermal loadRadio transmissionAmplifier detailsPower sensorDigital signal processing
A radio frequency (RF) receiver utilizing dynamic power management for administration of power consumption. The RF receiver includes an RF antenna, an RF full band filter, an RF amplifier, an RF sub-band filter, a first local oscillator, an RF mixer, a first IF amplifier, an IF wide band filter, a second local oscillator, an IF mixer, two secondary IF amplifiers, an IF narrow band filter, a digital signal processing subsystem, three power sensors, and a control logic subsystem. Based on its location in the system, each power sensor has a unique threshold setting that is set just below a total RF power level where desired signal degradation might occur. The control logic subsystem utilizes outputs of the power sensors to detect a total RF power present due to interfering signals plus a desired signal within an entire bandwidth present at each stage and dynamically manages power by adjusting bias of each stage accordingly via its bias control outputs.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
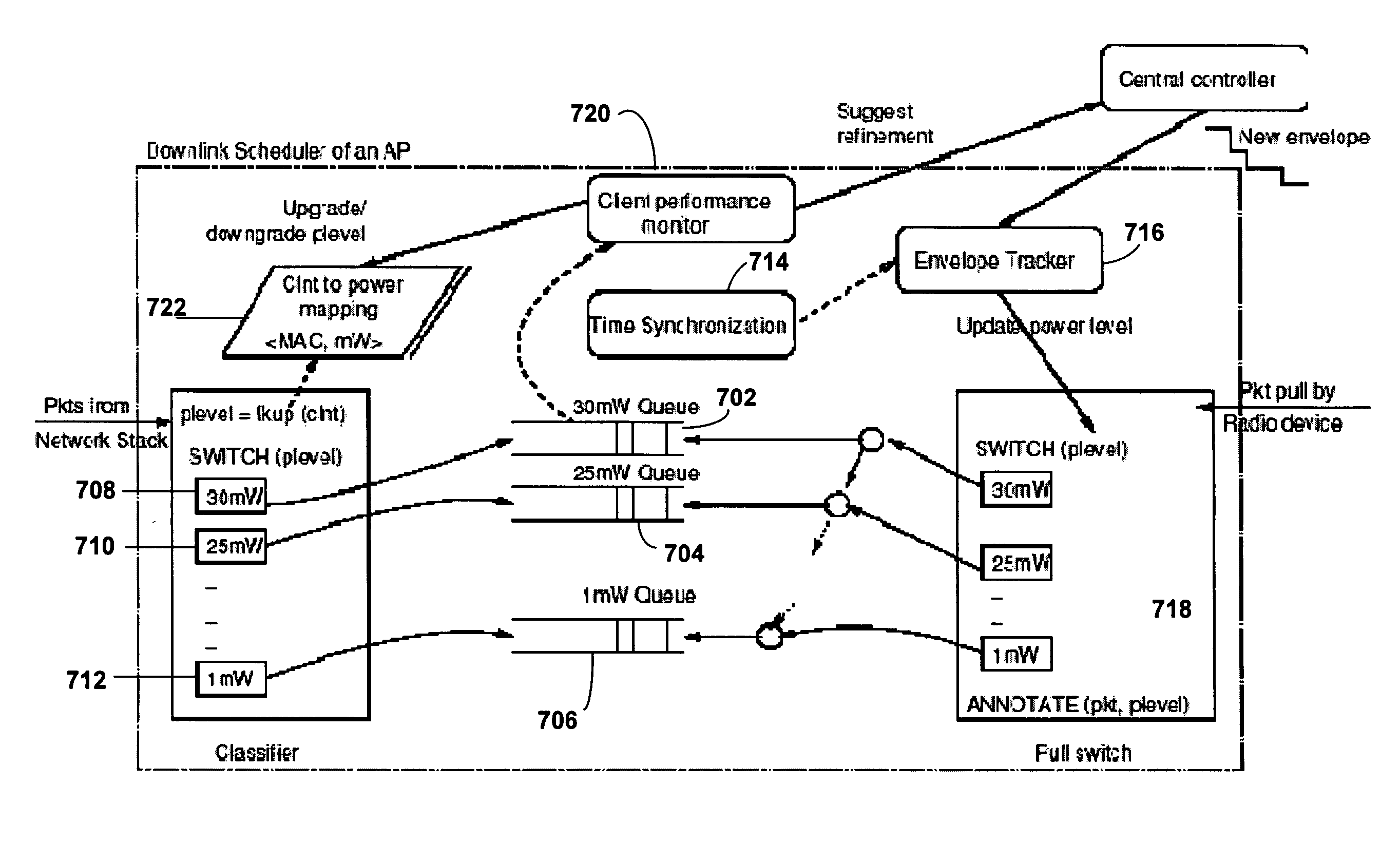
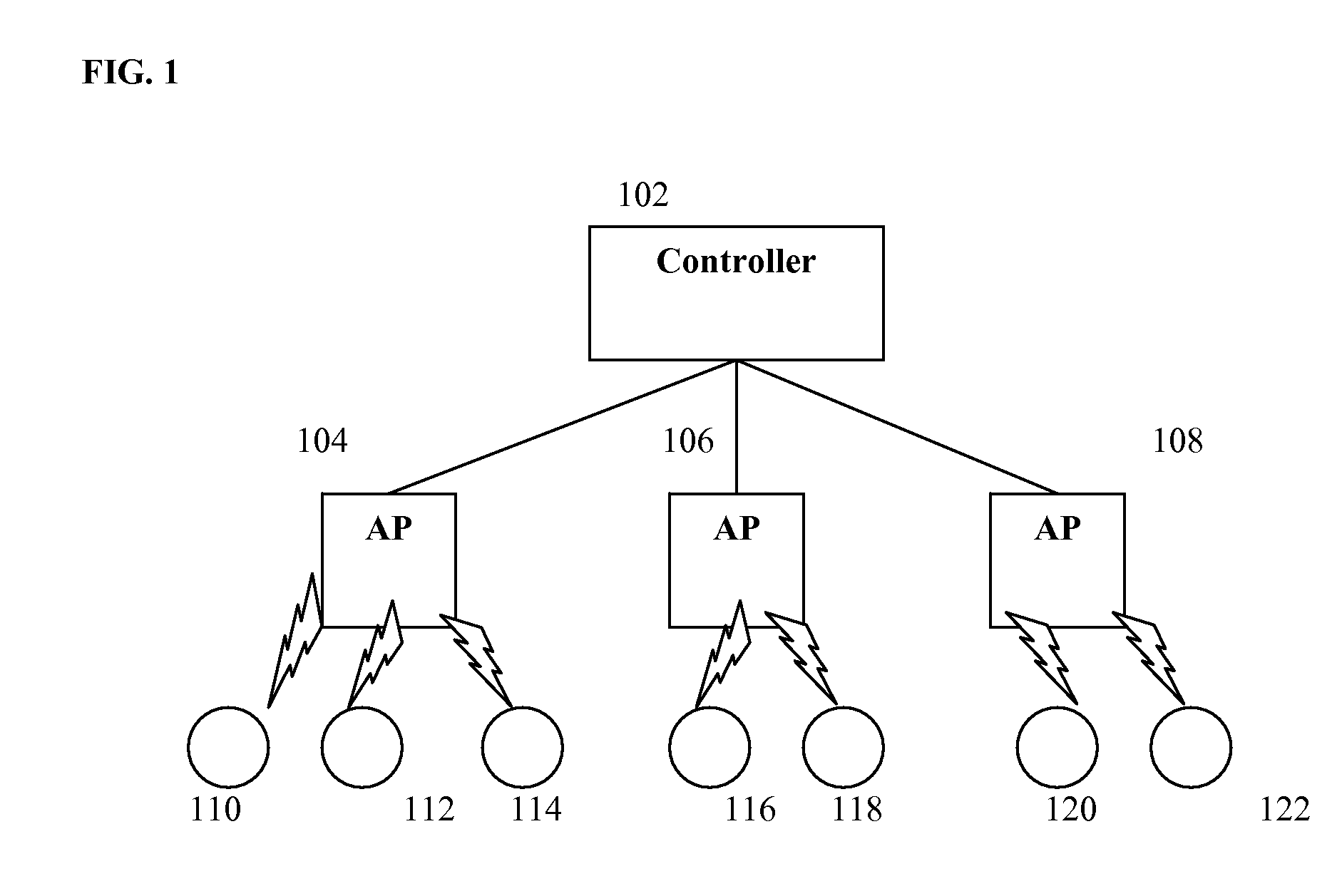
Method and System for Dynamic Power Management in Wireless Local Area Networks
ActiveUS20080130541A1Improve space reuseReduce transmit powerPower managementSynchronisation arrangementDynamic power managementEngineering
A method and system for improving spatial reuse in a wireless local area network (WLAN) by per-client dynamic power management. Each access point of the WLAN associates each of its clients with a minimum power level. A central controller of the WLAN generates a schedule for transmission at different power levels, and each access point varies its transmission power level based on the schedule. An access point transmits data packets, at the scheduled transmission power level, to clients associated with a minimum power level that is less than the scheduled power level.
Owner:NEC CORP
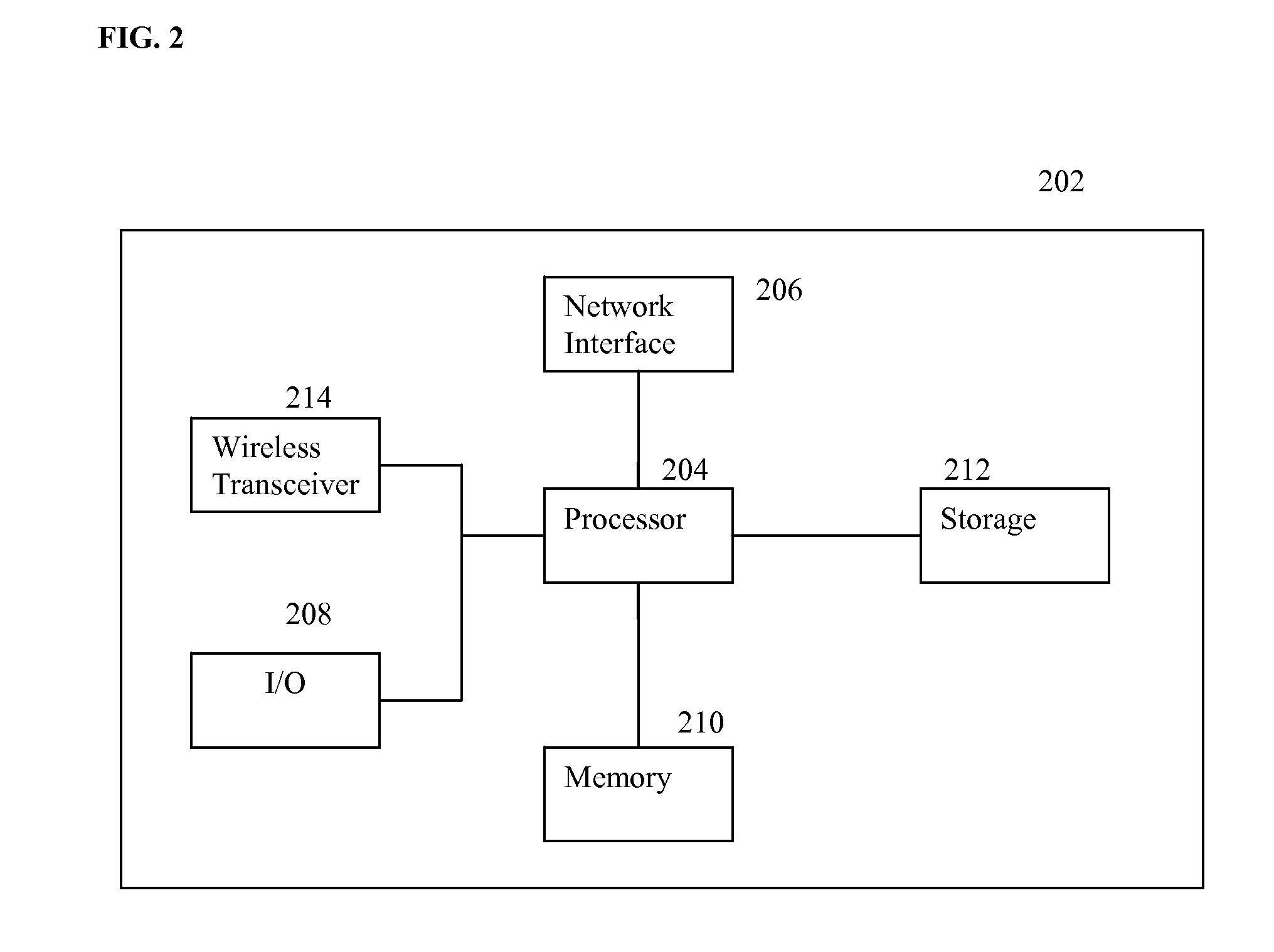
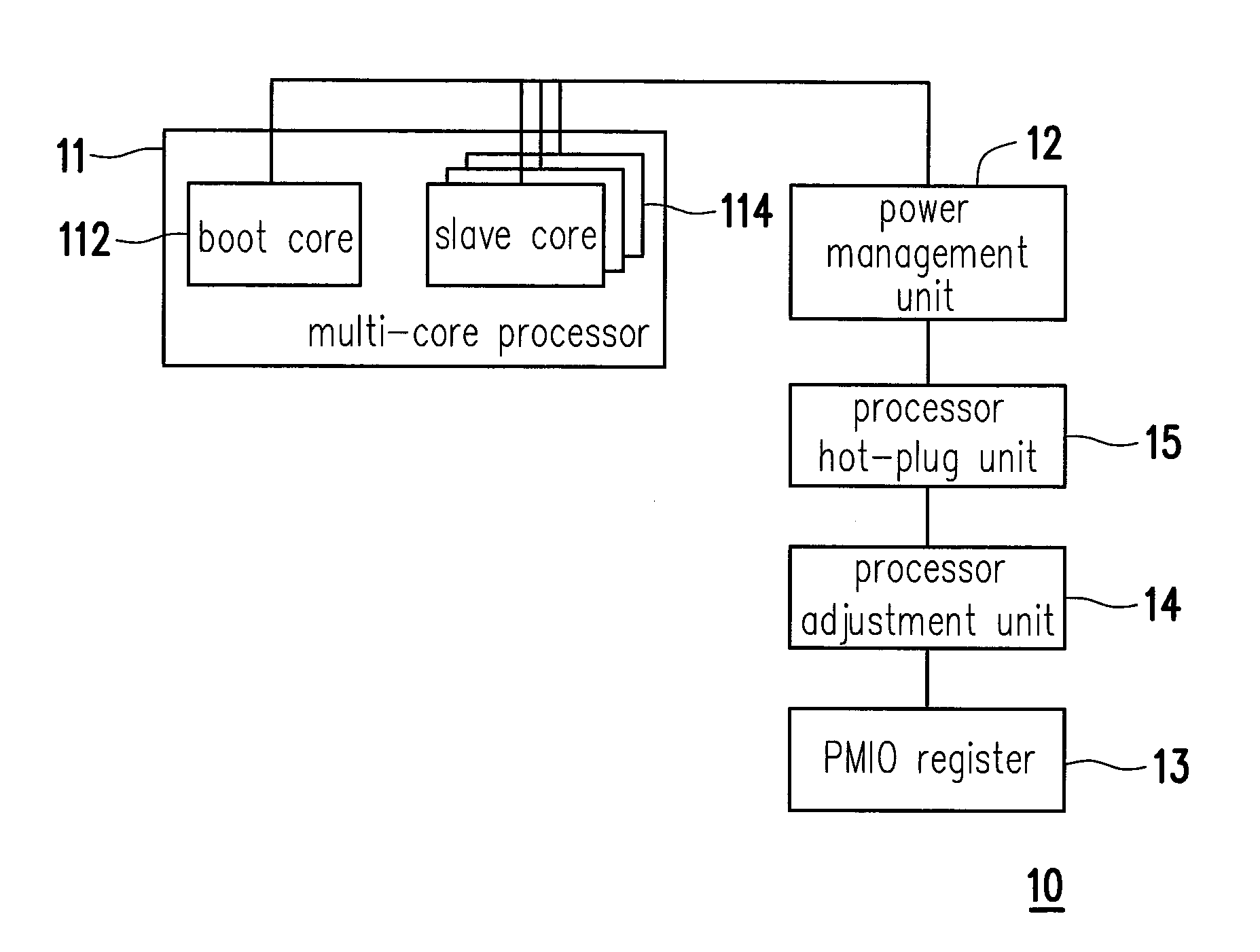
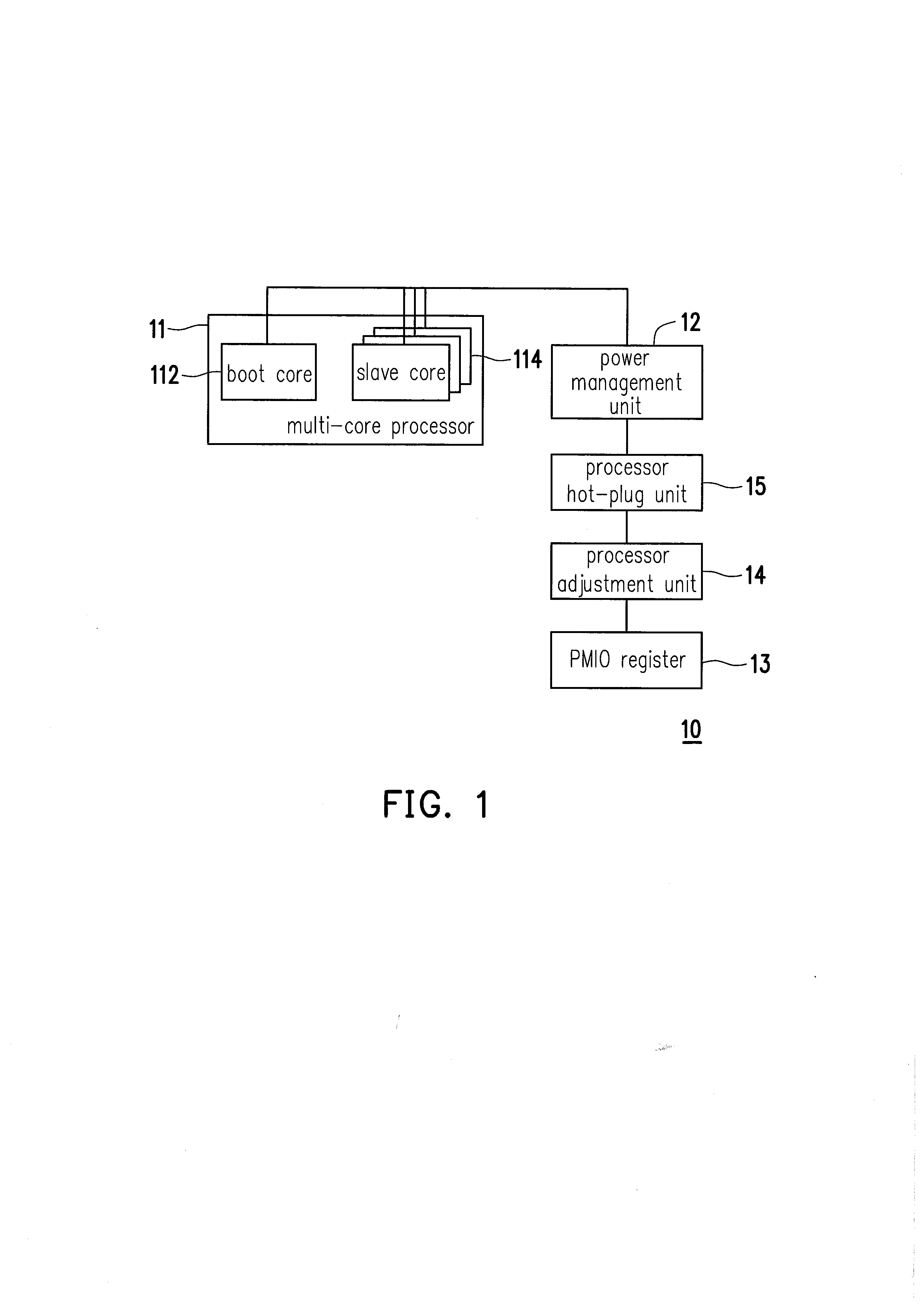
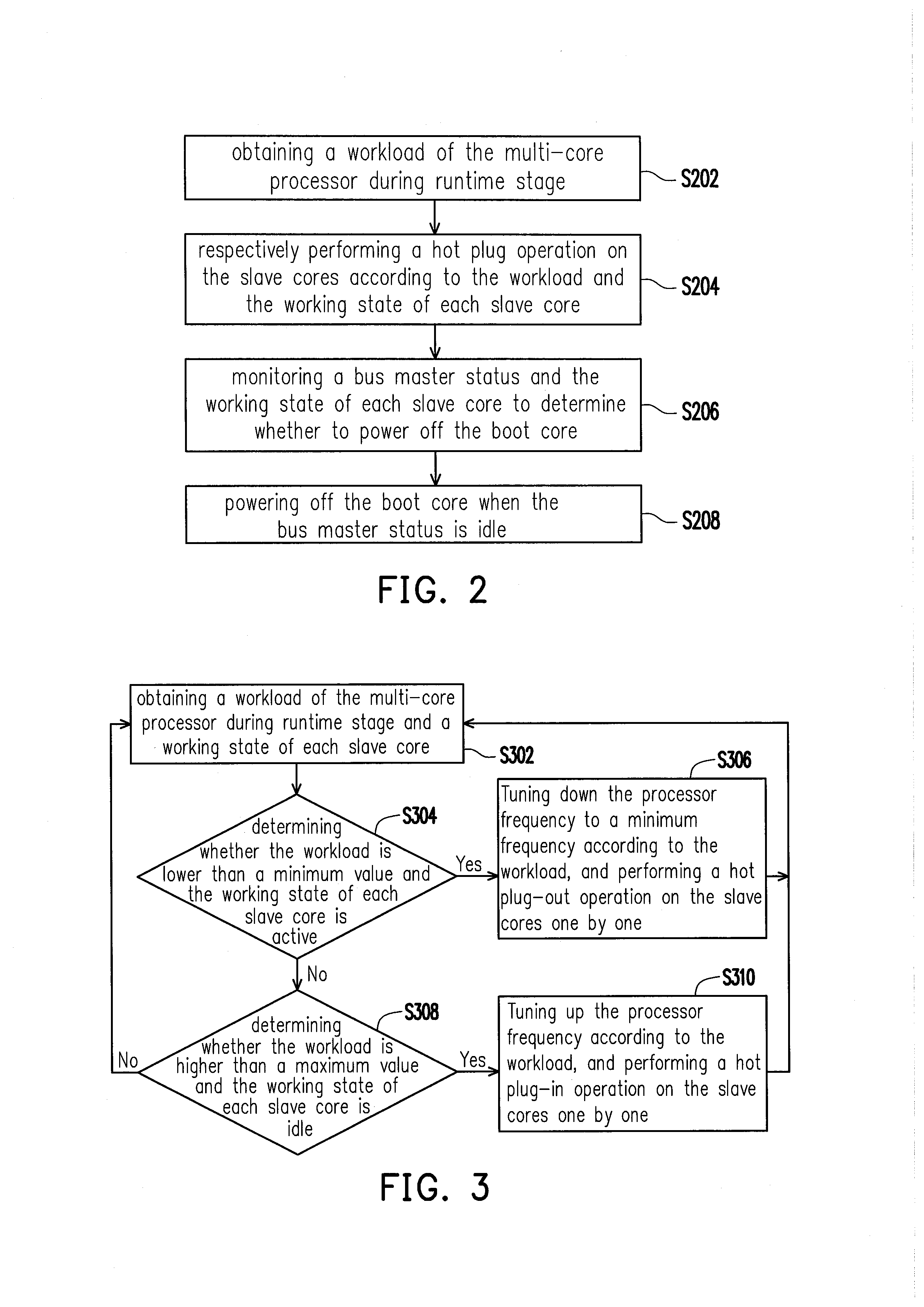
Multi-core processor system, dynamic power management method thereof and control apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20130179710A1Achieve effectEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementDevice status
A multi-core processor system, a dynamic power management method thereof and a control apparatus thereof are provided. In the method, a workload of a multi-core processor during a runtime stage is obtained. Next, a hot-plug operation is respectively performed on a plurality of slave cores according to the workload and a working state of each slave core. Then, a bus master status and the working state of a boot core are monitored to determine whether to power off the boot core, in which the bus master status is generated by combining a plurality of device statuses reflected by a plurality of peripheral devices. Finally, when the bus master status is determined as idle, the boot core is powered off.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
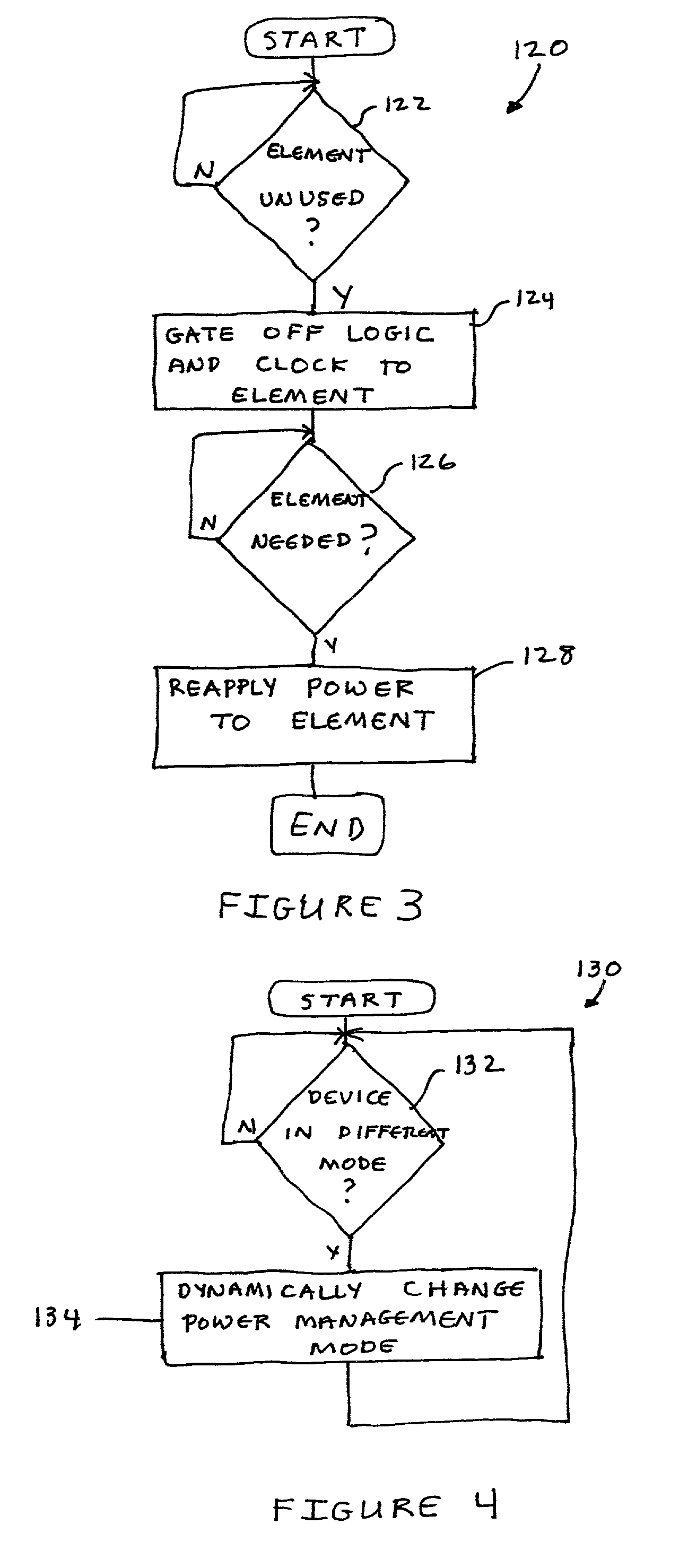
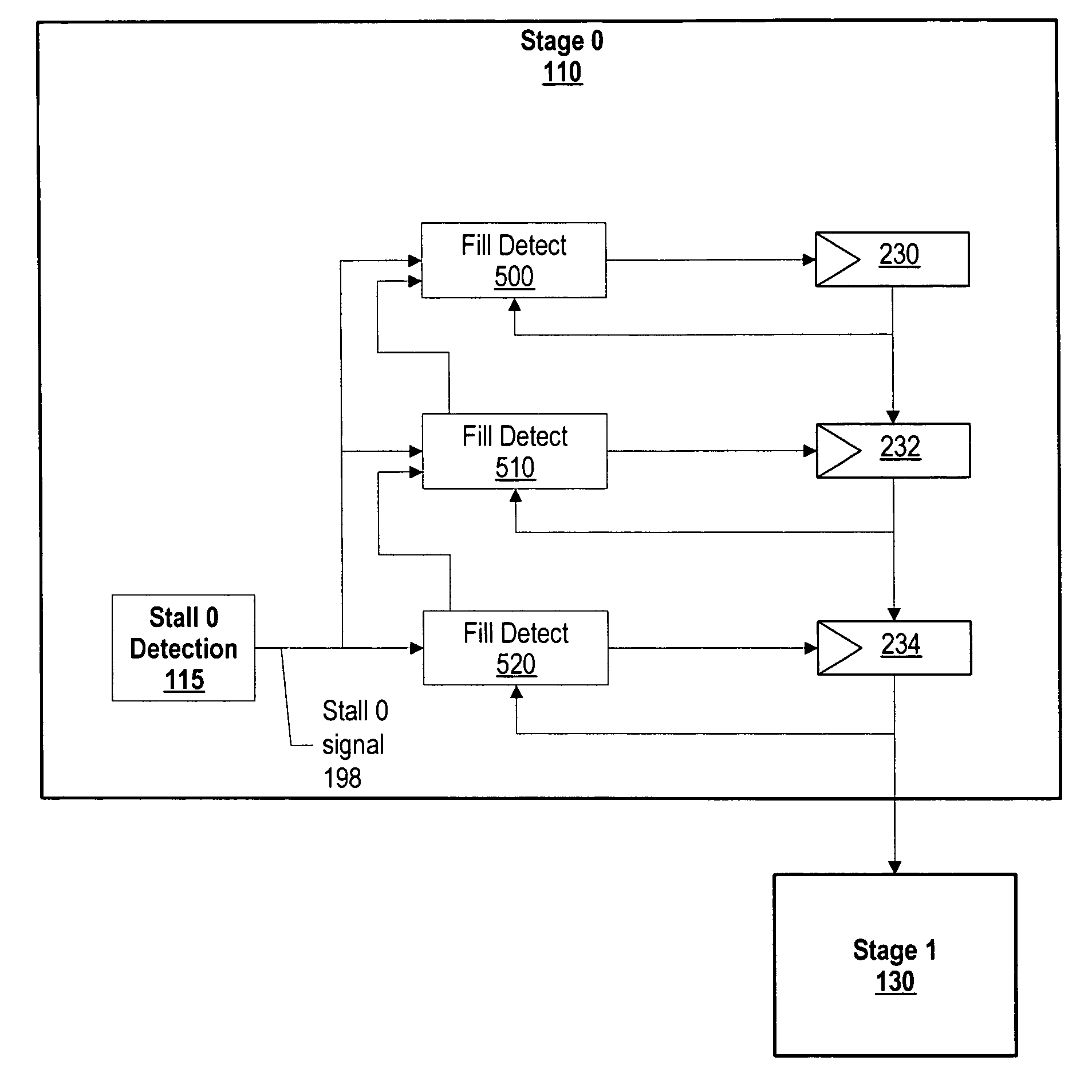
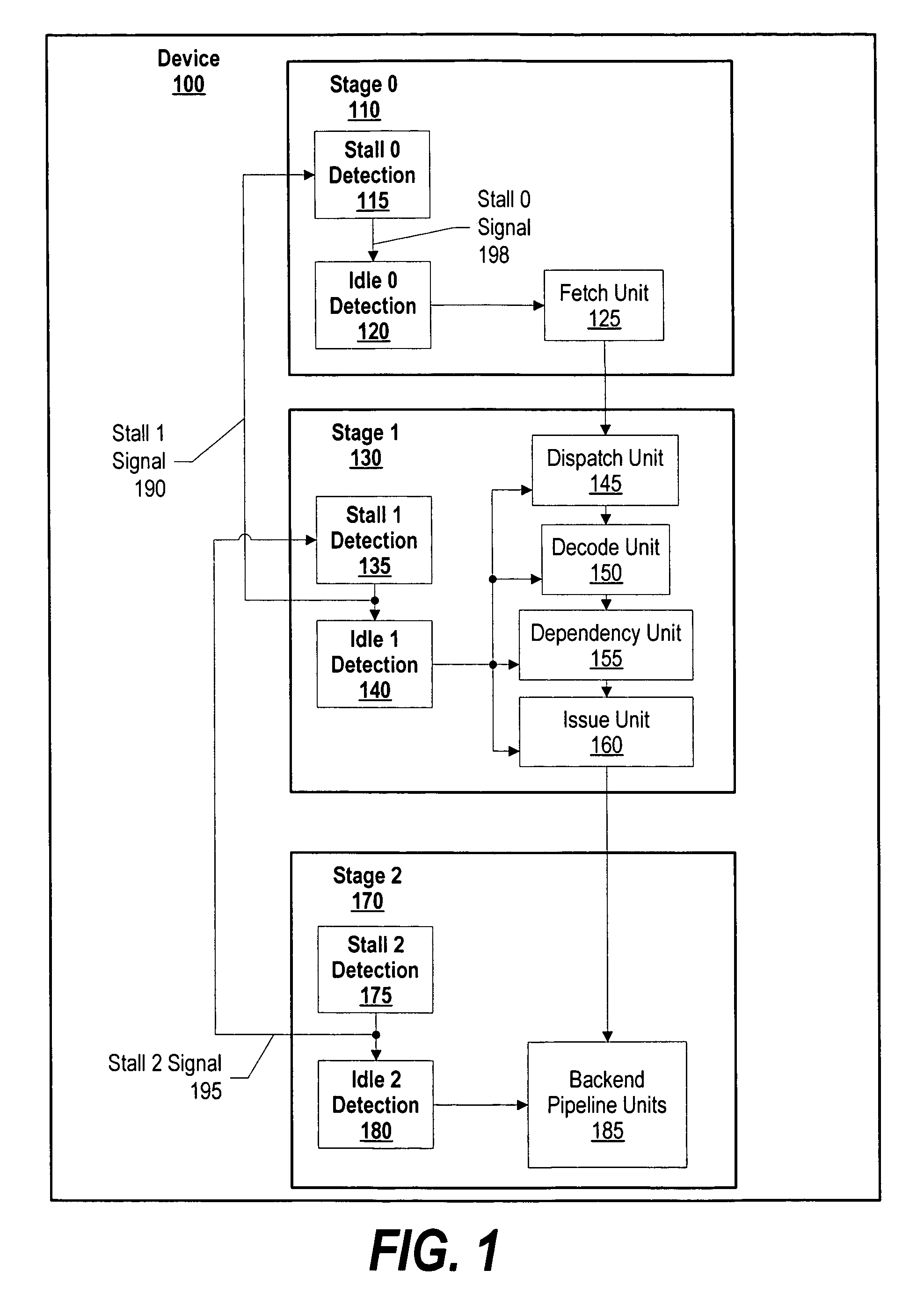
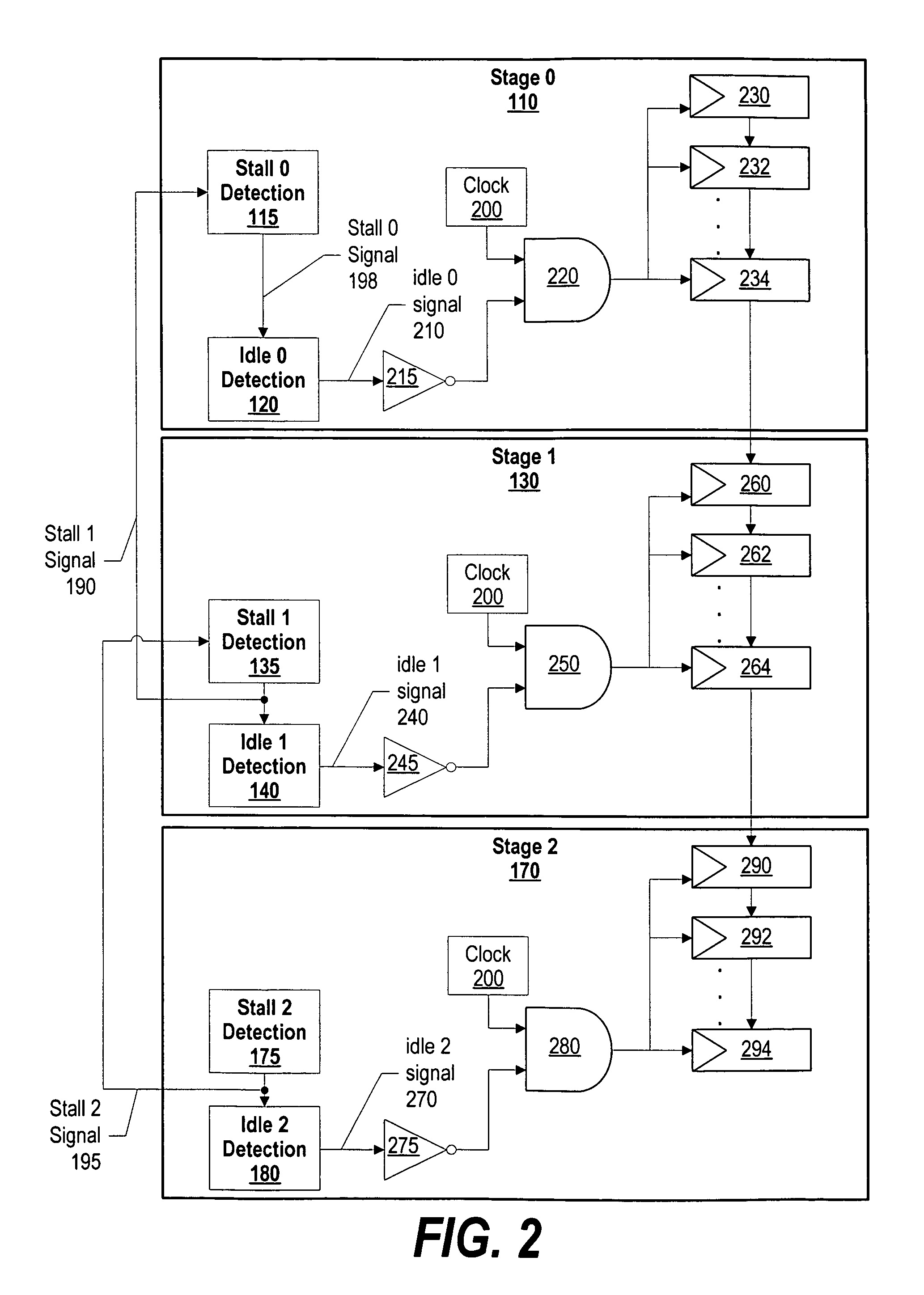
System and method for dynamic power management in a processor design
ActiveUS20070074059A1Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementProcessor design
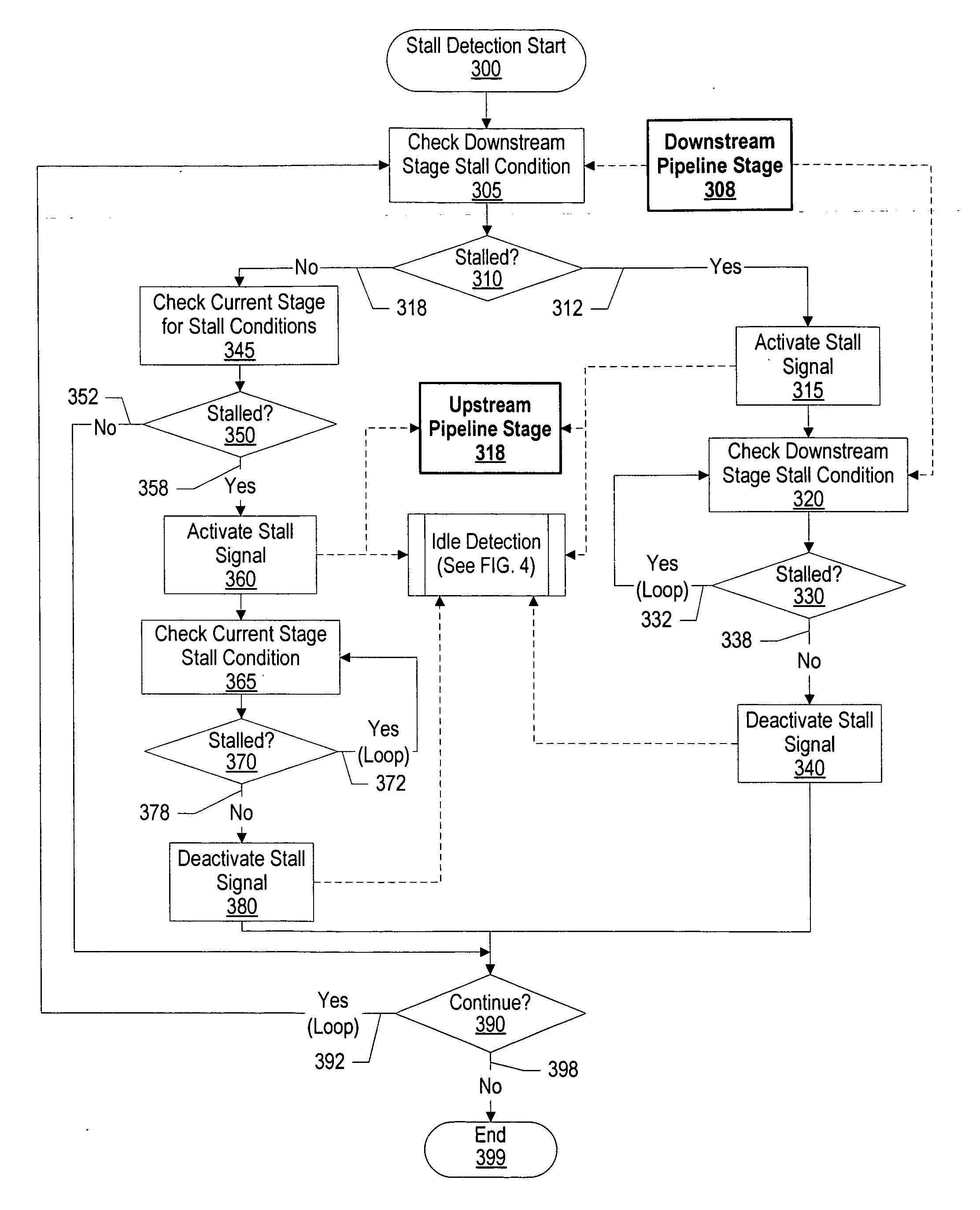
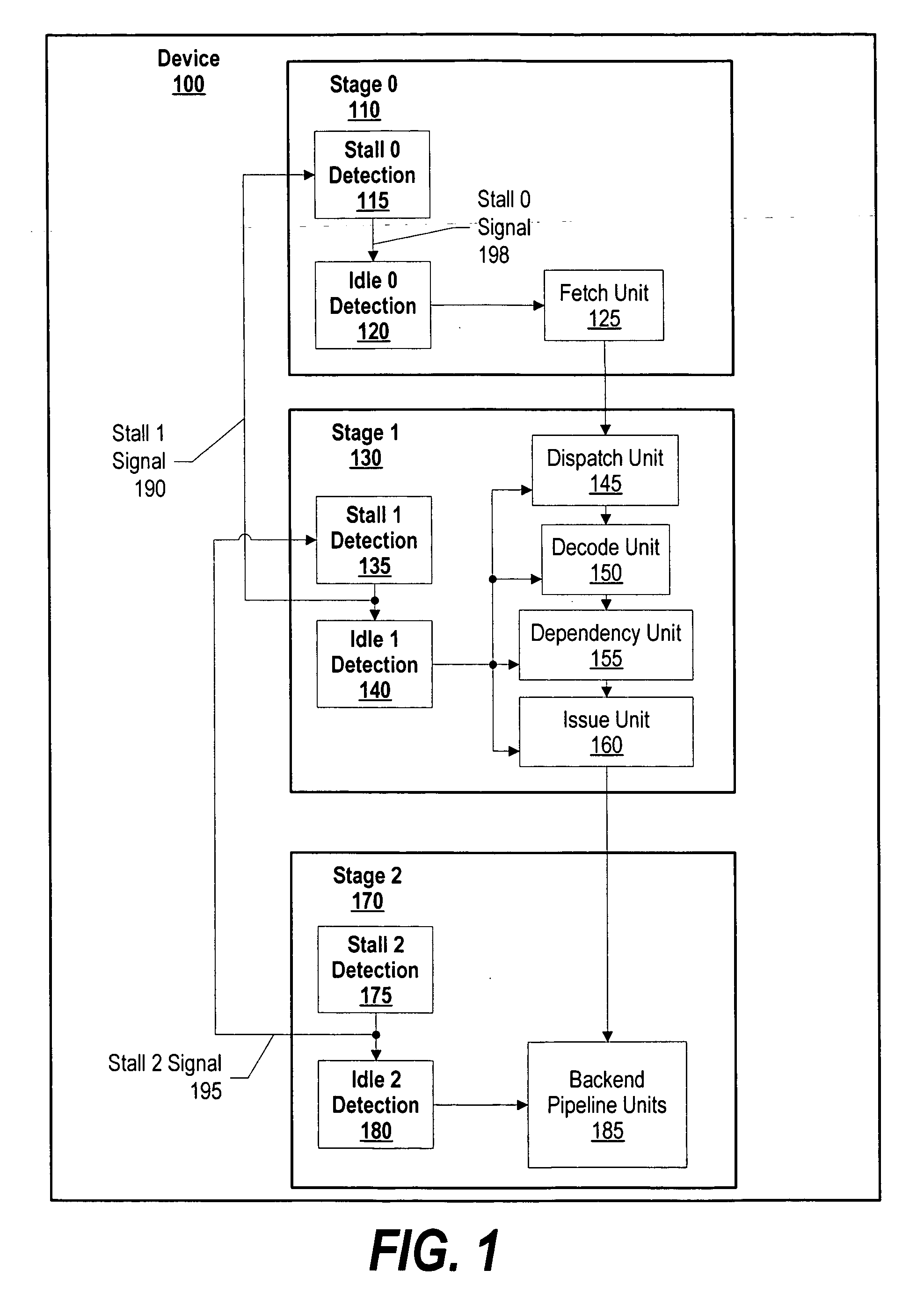
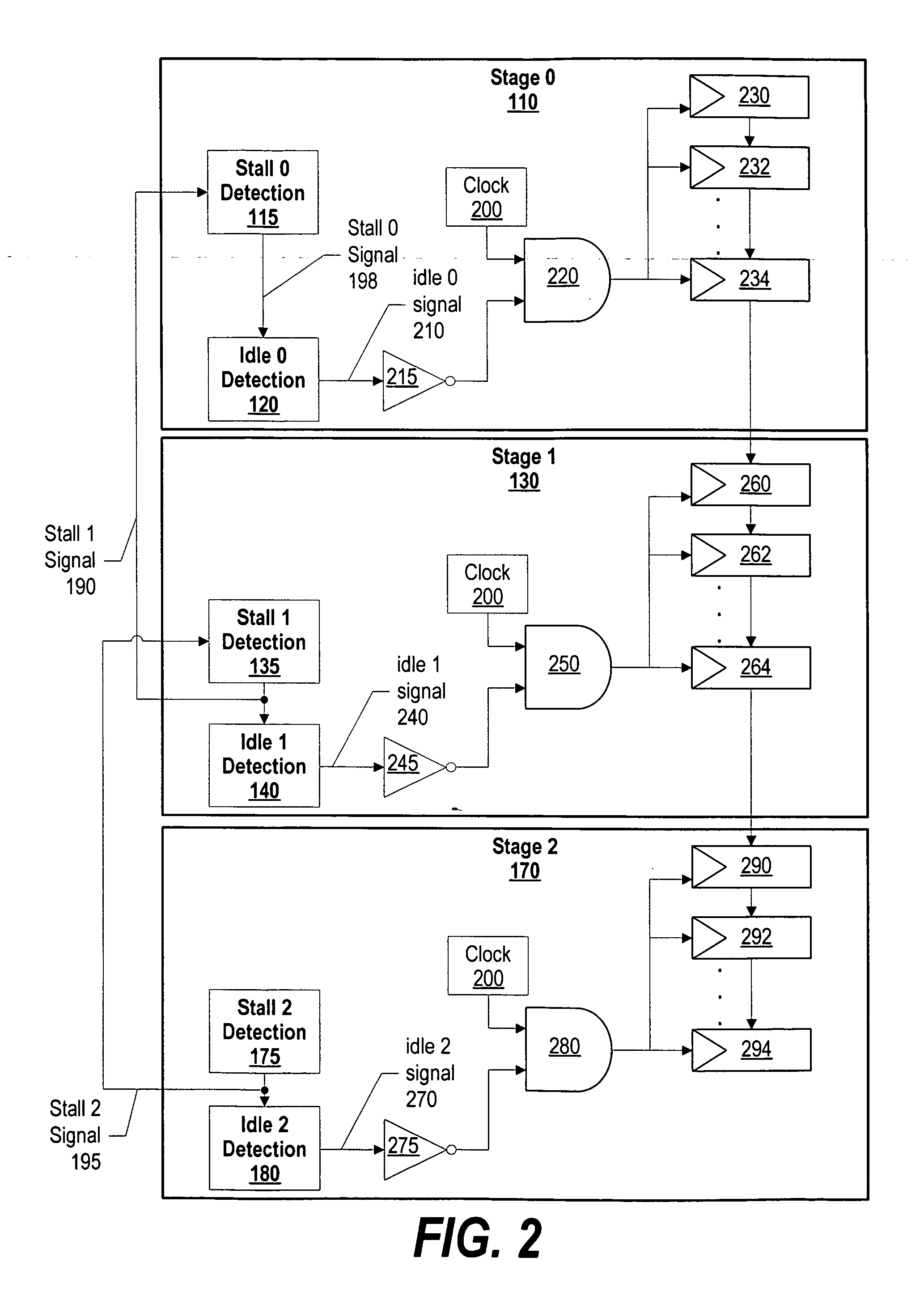
A system and method for dynamic power management in a processor design is presented. A pipeline stage's stall detection logic detects a stall condition, and sends a signal to idle detection logic to gate off the pipeline's register clocks. The stall detection logic also monitors a downstream pipeline stage's stall condition, and instructs the idle detection logic to gate off the pipeline stage's registers when the downstream pipeline stage is in a stall condition as well. In addition, when the pipeline stage's stall detection logic detects a stall condition, either from the downstream pipeline stage or from its own pipeline units, the pipeline stage's stall detection logic informs an upstream pipeline stage to gate off its clocks and thus, conserve more power.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC +1
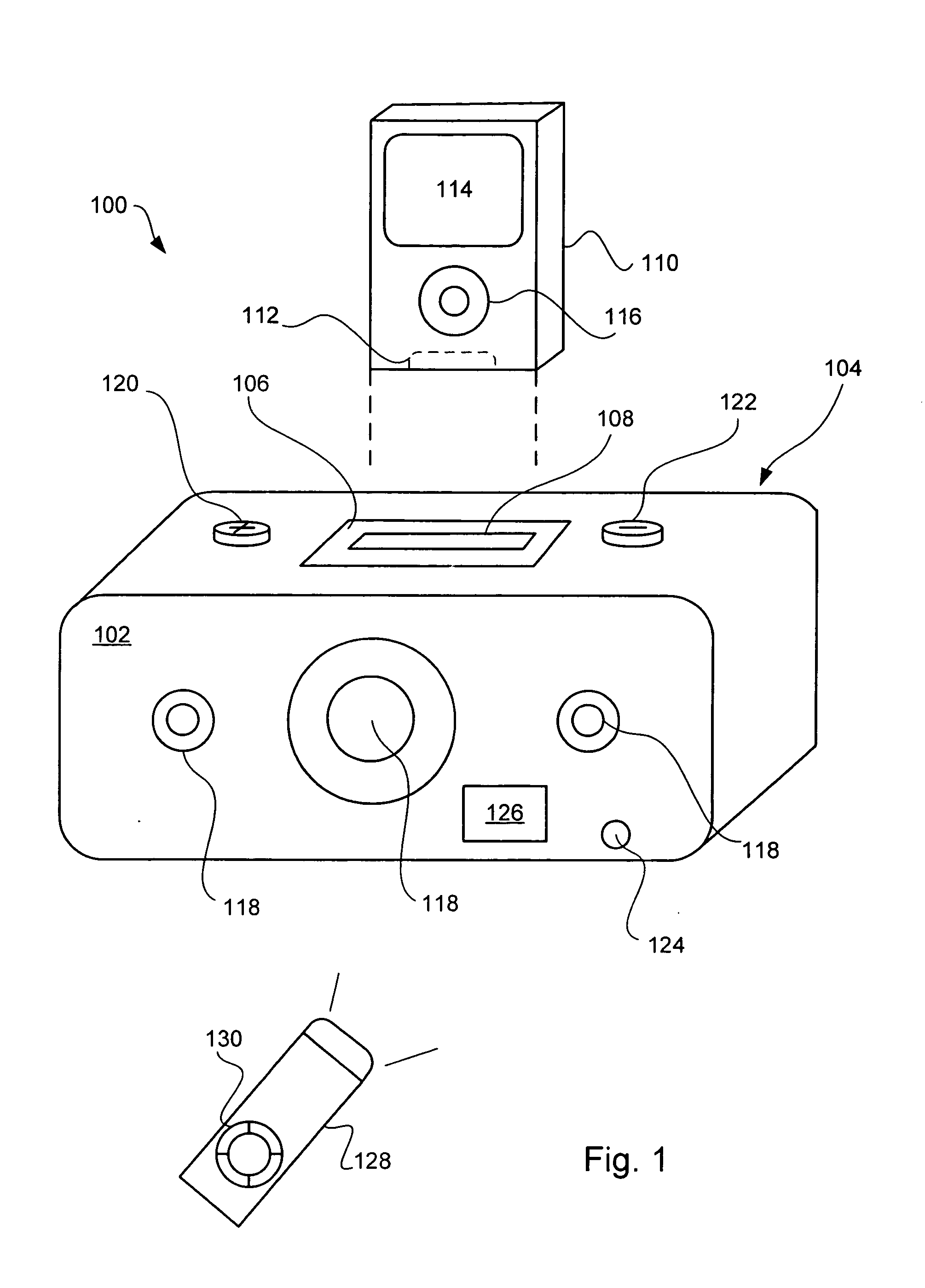
Dynamic power management in a portable media delivery system
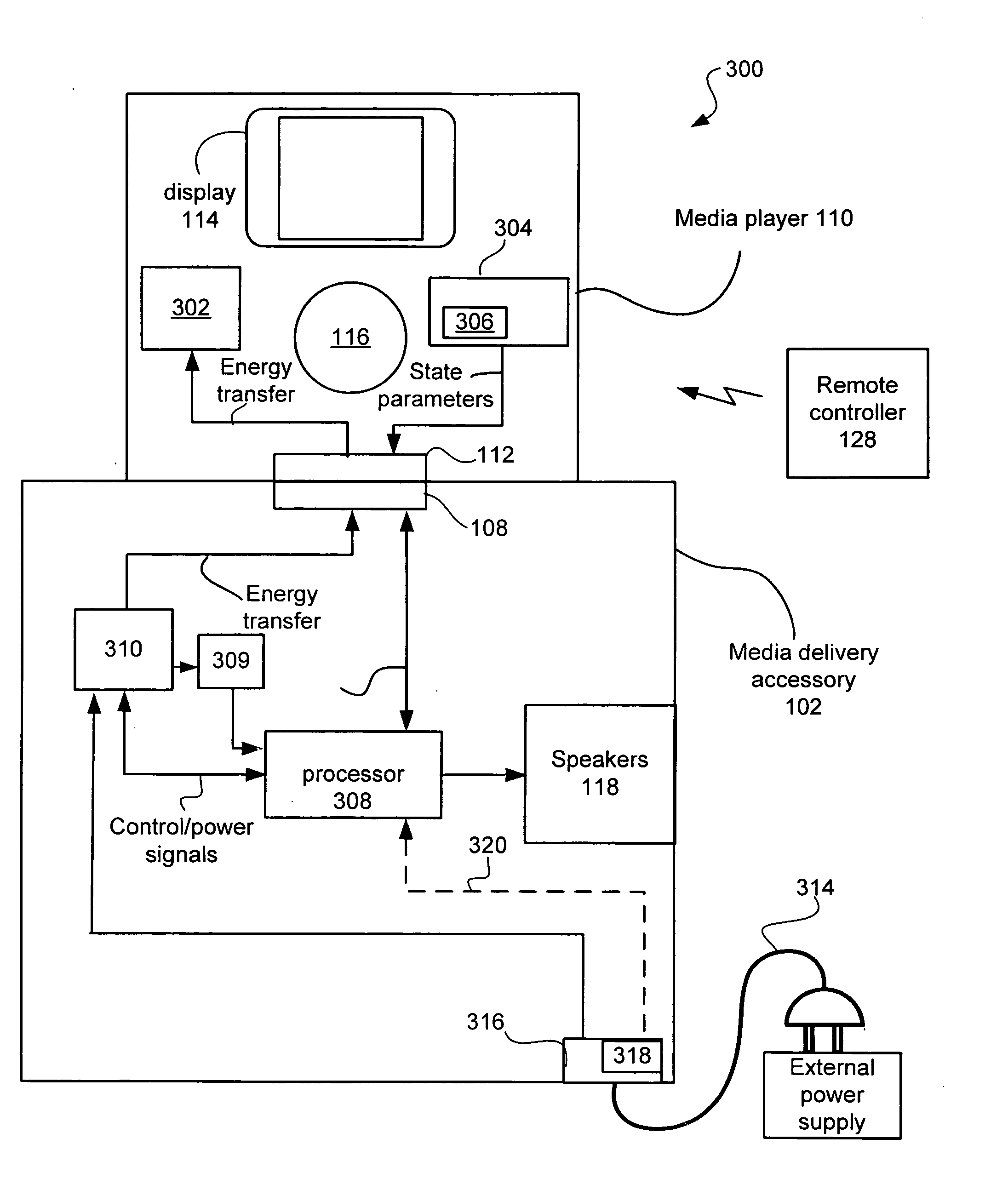
ActiveUS20070201703A1AdvertisingPower supply for data processingStored energyDynamic power management
A consumer electronic product (e.g., a portable media player ported to a media delivery accessory) is powered by a limited capacity DC power source (such as a battery or mini-fuel cell). The consumer electronic product limits the maximum allowable sound pressure level (SPL) that can be produced by the speakers. In one embodiment, the maximum allowable SPL is based upon an amount of stored energy available in the limited capacity DC power source.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic power management in a processor design
ActiveUS7401242B2Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementProcessor register
A pipeline stage's stall detection logic detects a stall condition, and sends a signal to idle detection logic to gate off the pipeline's register clocks. The stall detection logic also monitors a downstream pipeline stage's stall condition, and instructs the idle detection logic to gate off the pipeline stage's registers when the downstream pipeline stage is in a stall condition as well. In addition, when the pipeline stage's stall detection logic detects a stall condition, either from the downstream pipeline stage or from its own pipeline units, the pipeline stage's stall detection logic informs an upstream pipeline stage to gate off its clocks and thus, conserve more power.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC +1
Method and apparatus to dynamically adjust resource power usage in a distributed system
InactiveUS7827425B2Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementResource based
A system and method to provide source controlled dynamic power management. An activity detector in a source determines expected future resource usage. Based on that expected usage, the source generates a power management command and sends that command to a destination. The destination then adjusts the power level of the resource based in the command.
Owner:INTEL CORP
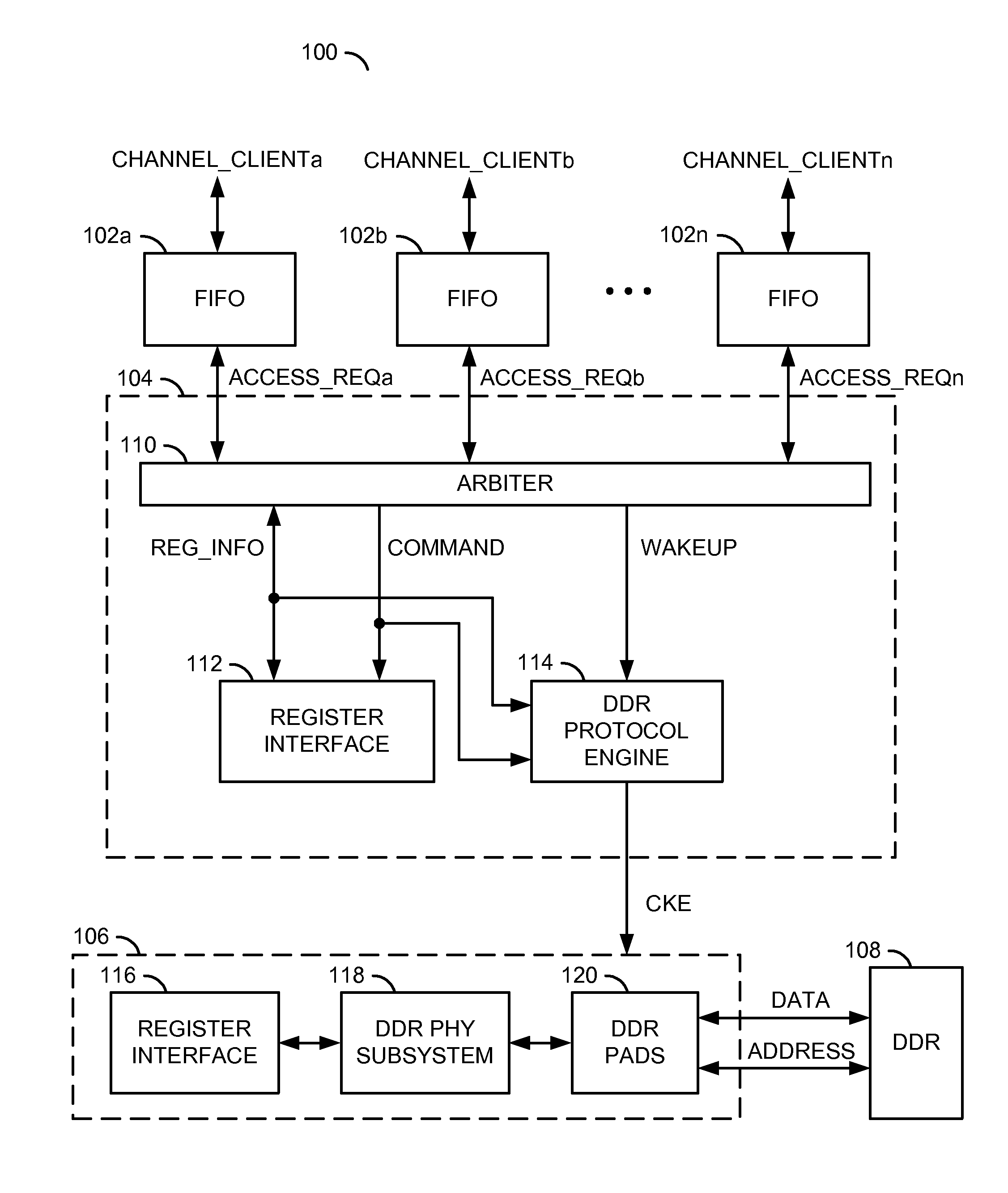
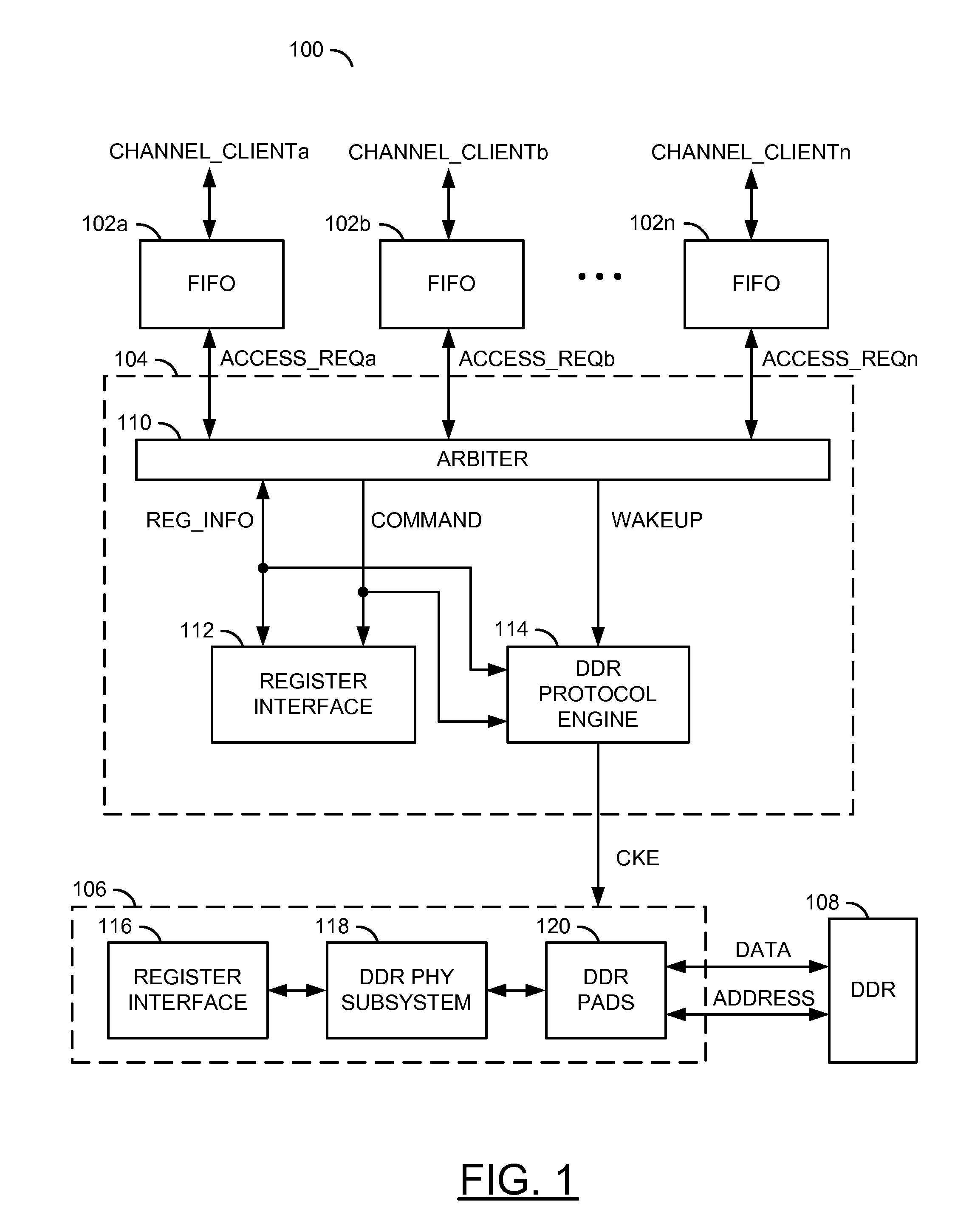
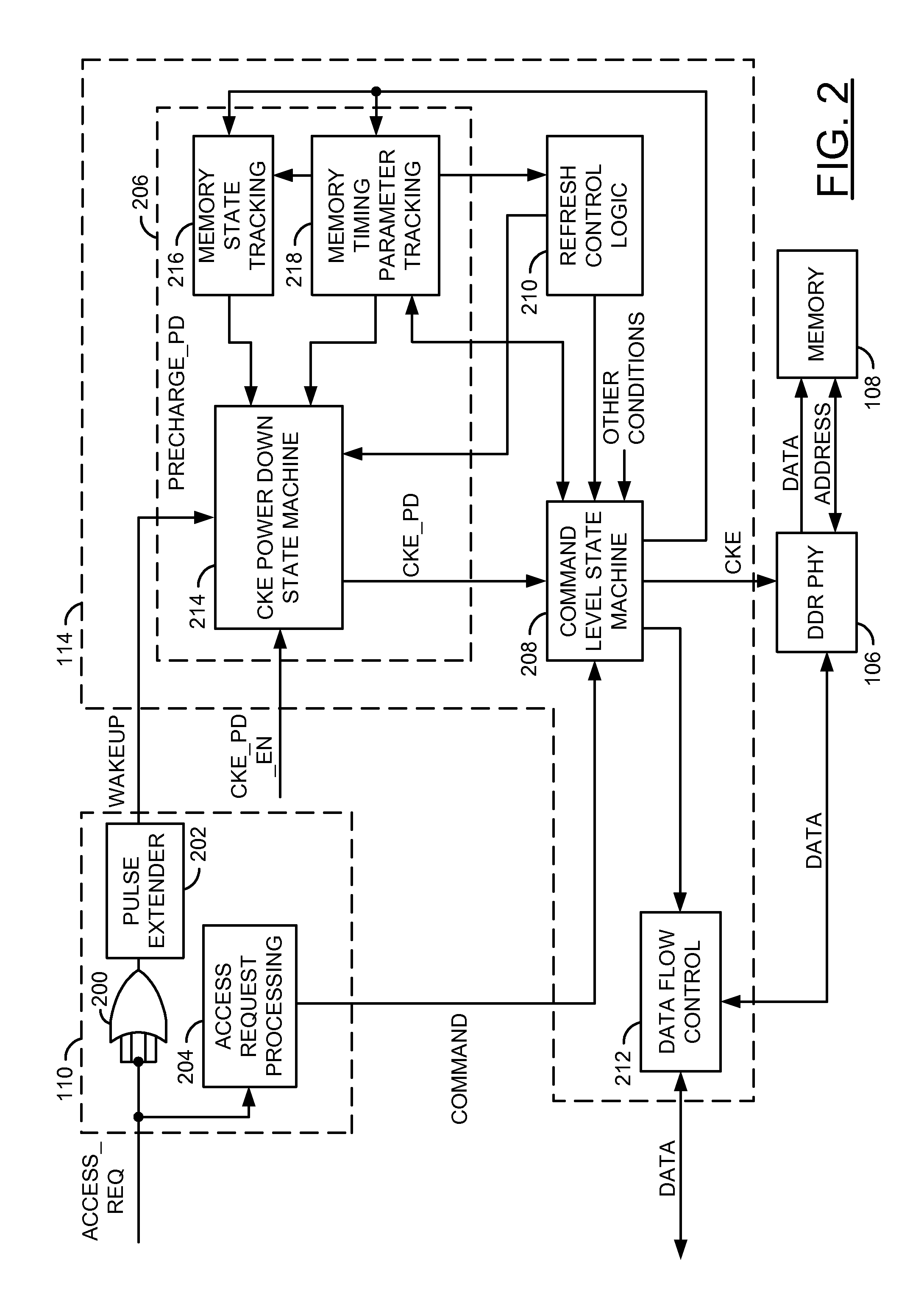
Power savings and/or dynamic power management in a memory
ActiveUS8339891B2Eliminate and minimize overheadEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDynamic power managementTerm memory
An apparatus comprising a plurality of buffers and a memory controller. The plurality of buffers may each be configured to generate an access request signal in response to a respective one of a plurality of channel requests received from a respective one of a plurality of clients. The memory controller circuit may be configured to generate a clock enable signal in response to the plurality of access request signals. The clock enable signal may be configured to initiate entering and exiting a power savings mode of a memory circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
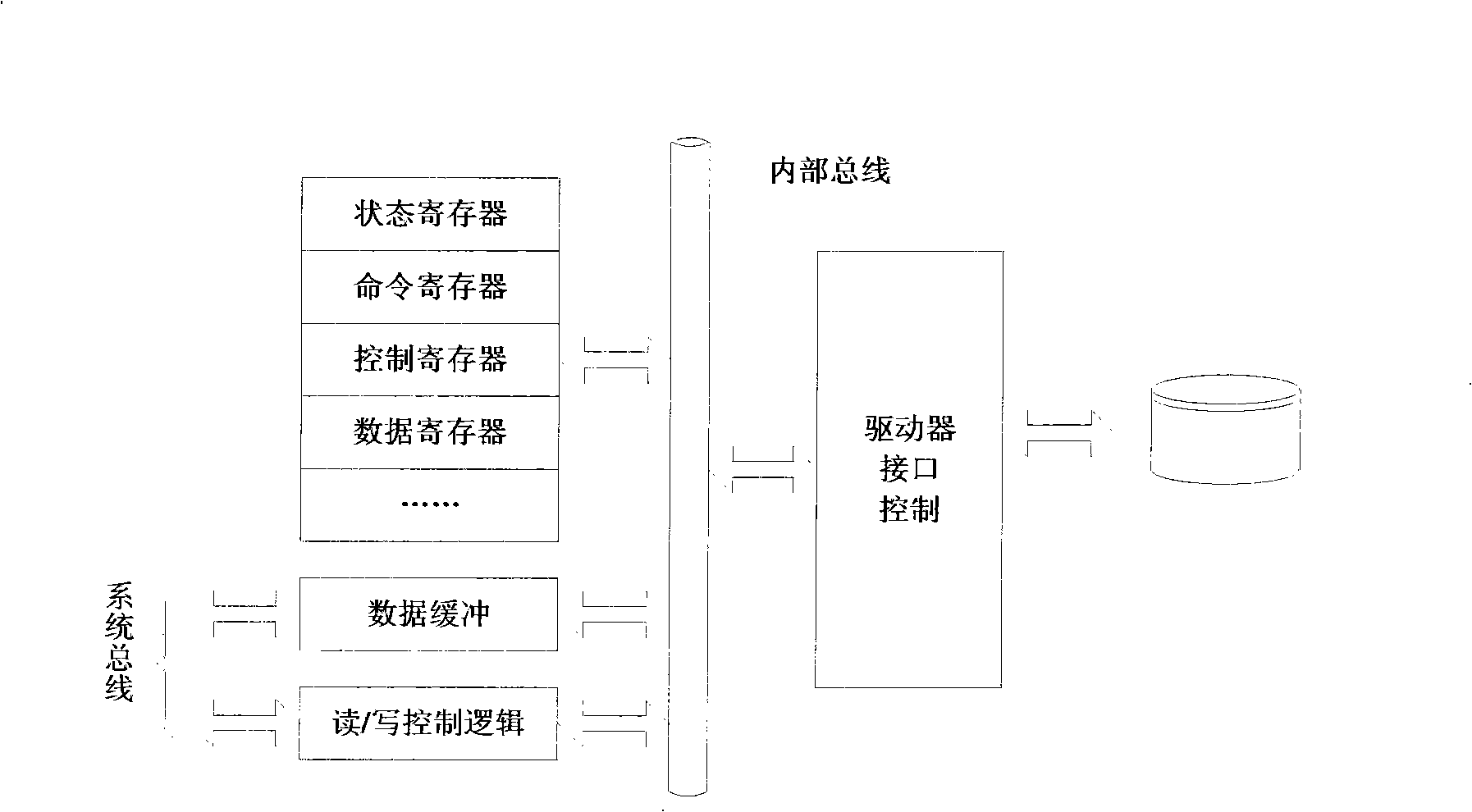
Magnetic disk dynamic power supply management method based on embedded system
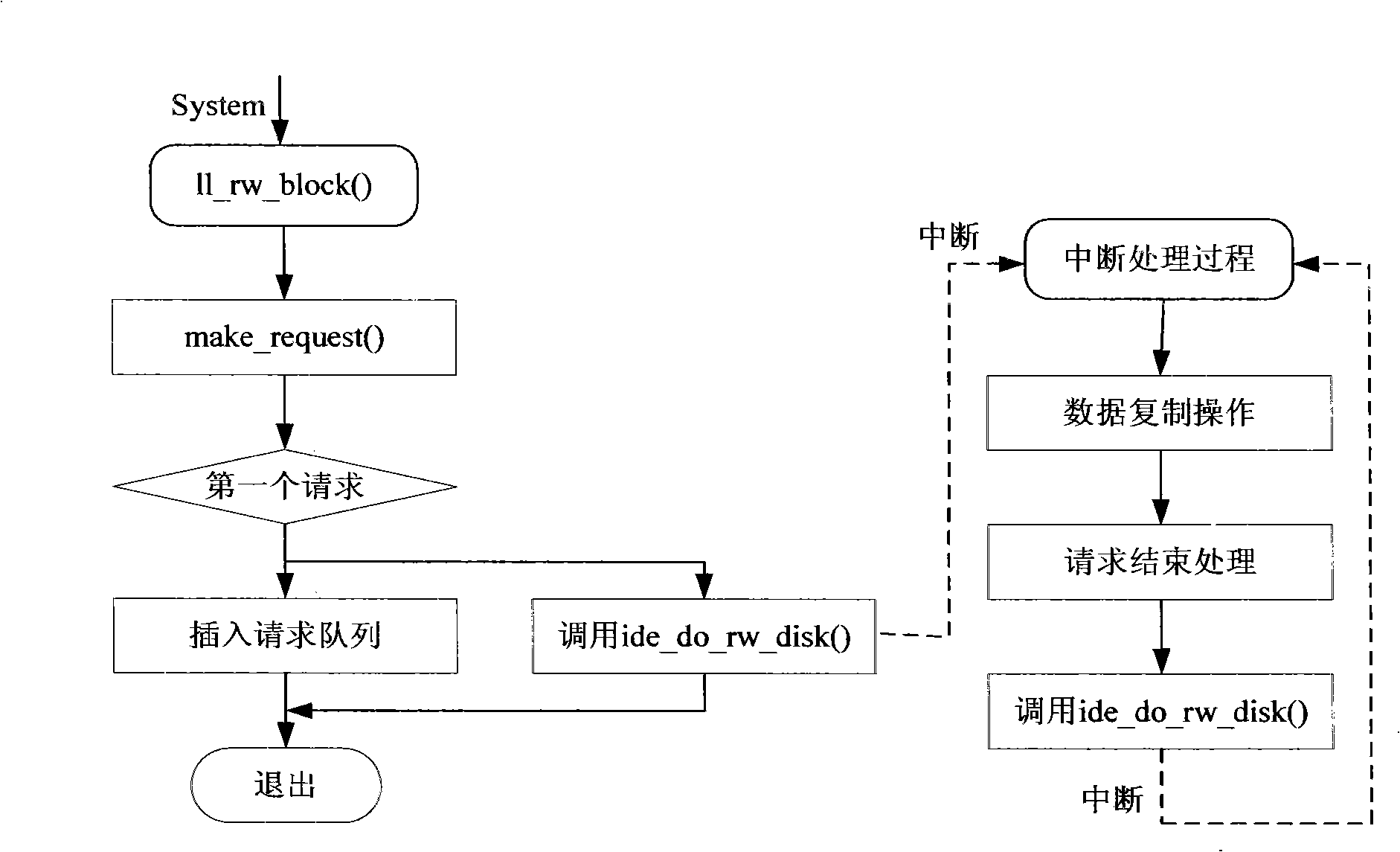
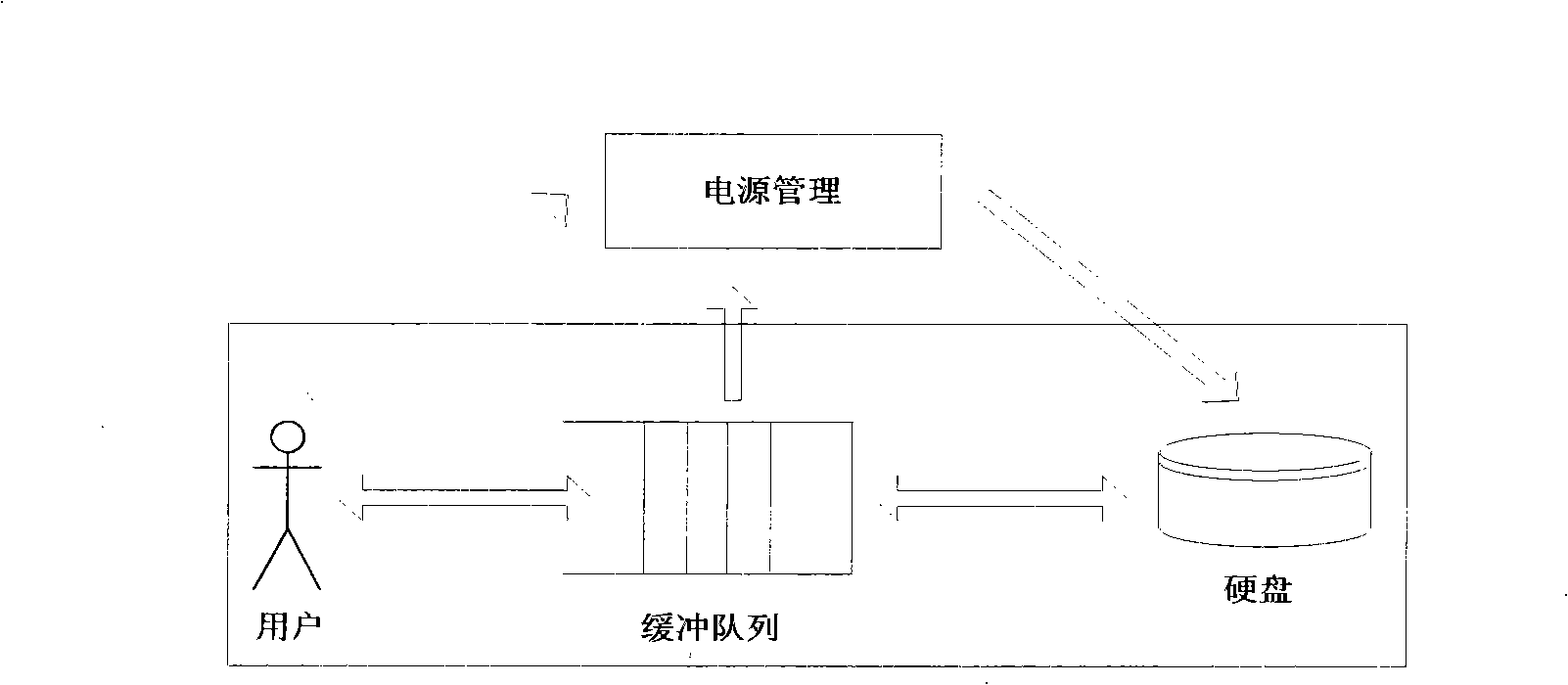
The invention provides an embedded system based dynamic disc power management method, which divides the state of a disc on a dynamic power management structure by expanding magnetic disc power management on the dynamic power management structure and sets contents in a command register of a disc controller by reading and writing I / O ports so that the magnetic disc is switched from a high power consumption state to a low power consumption state. The invention provides a method for changing disc state based on reading and writing the disc register and also a method for acquiring disc loading by reading and writing I / O requests; in addition, the invention realizes disc strategy optimization by using a renewed theory model algorithm and verifies the favorable performance thereof by experiments. Therefore, a method for realizing dynamic disc power management is completely provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com