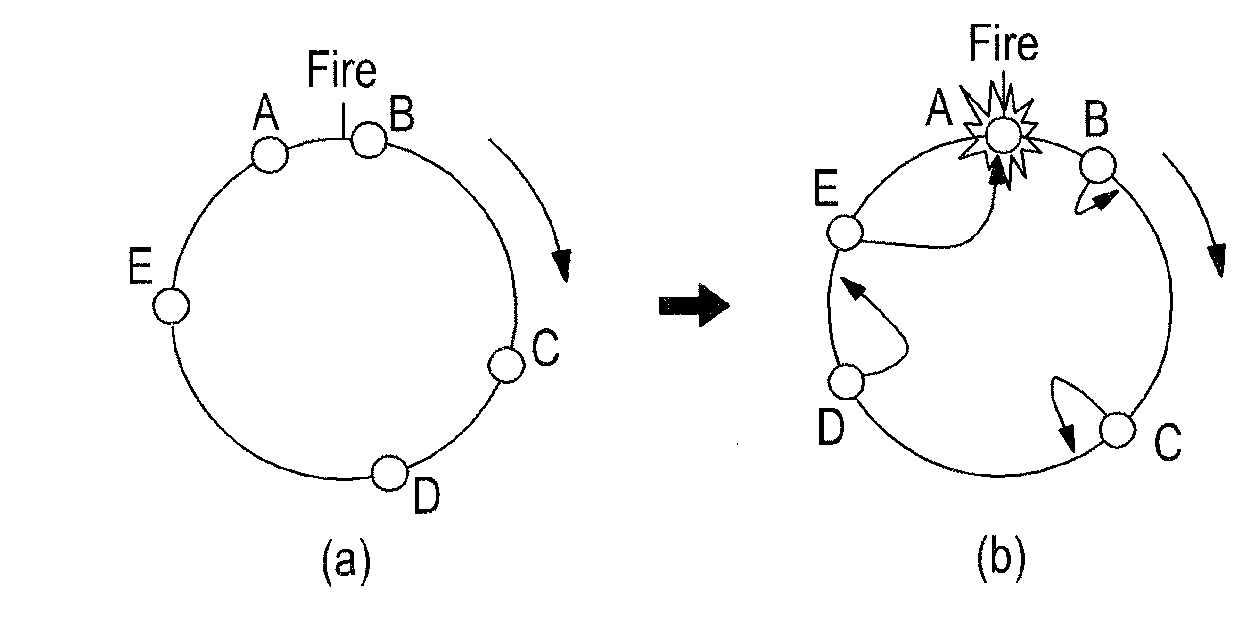
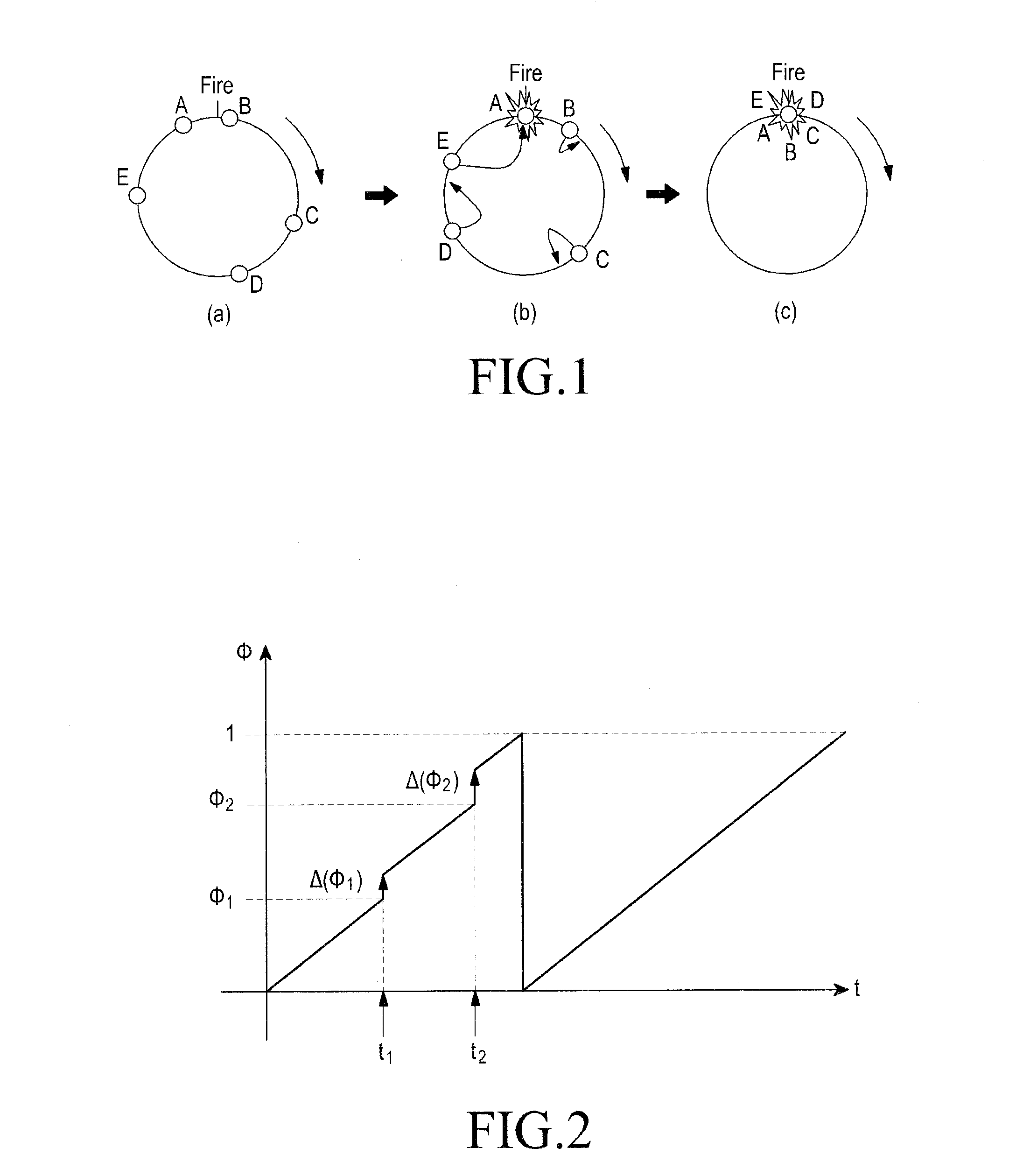
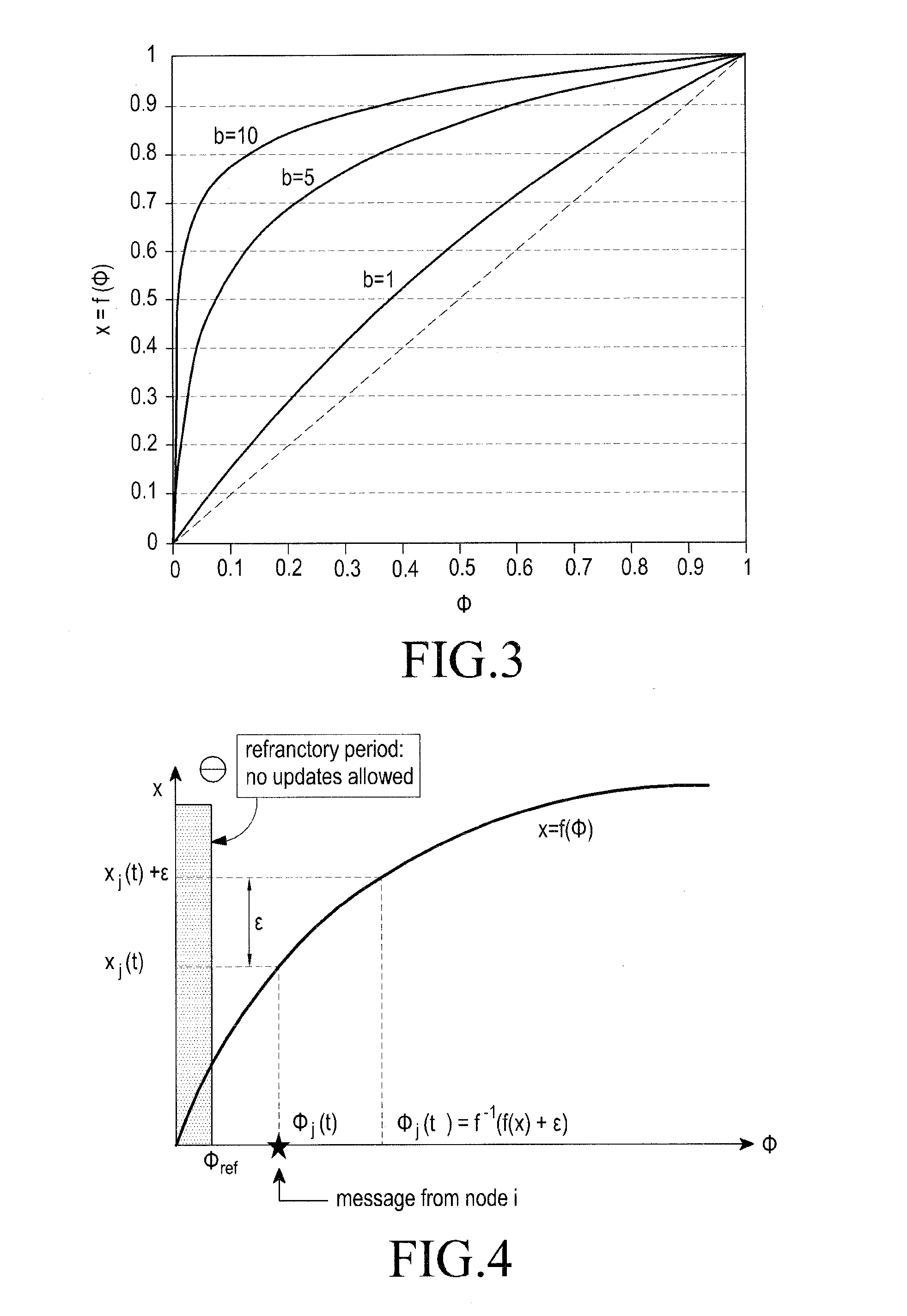
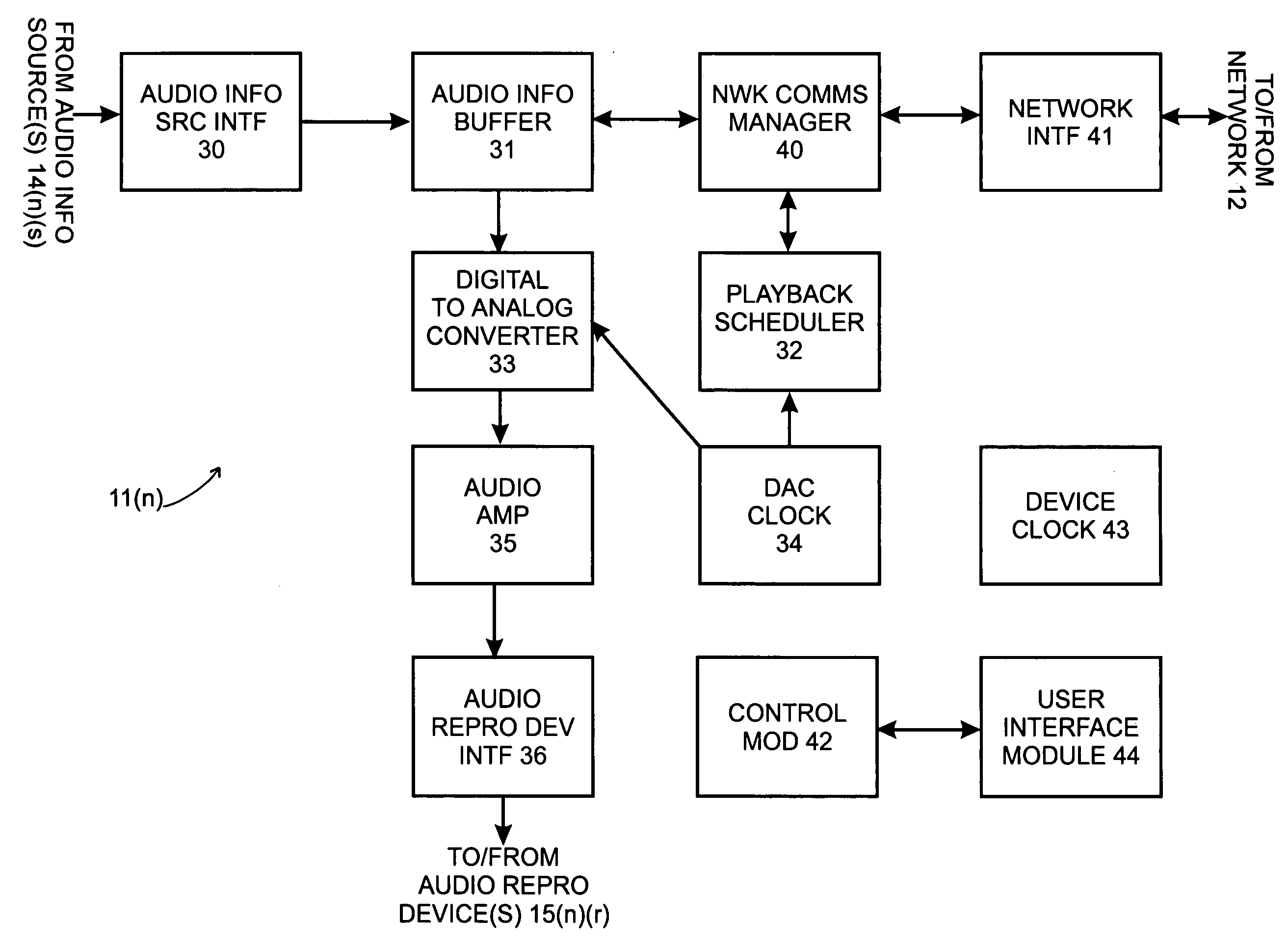
Patents
Literature
15603results about "Synchronisation arrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
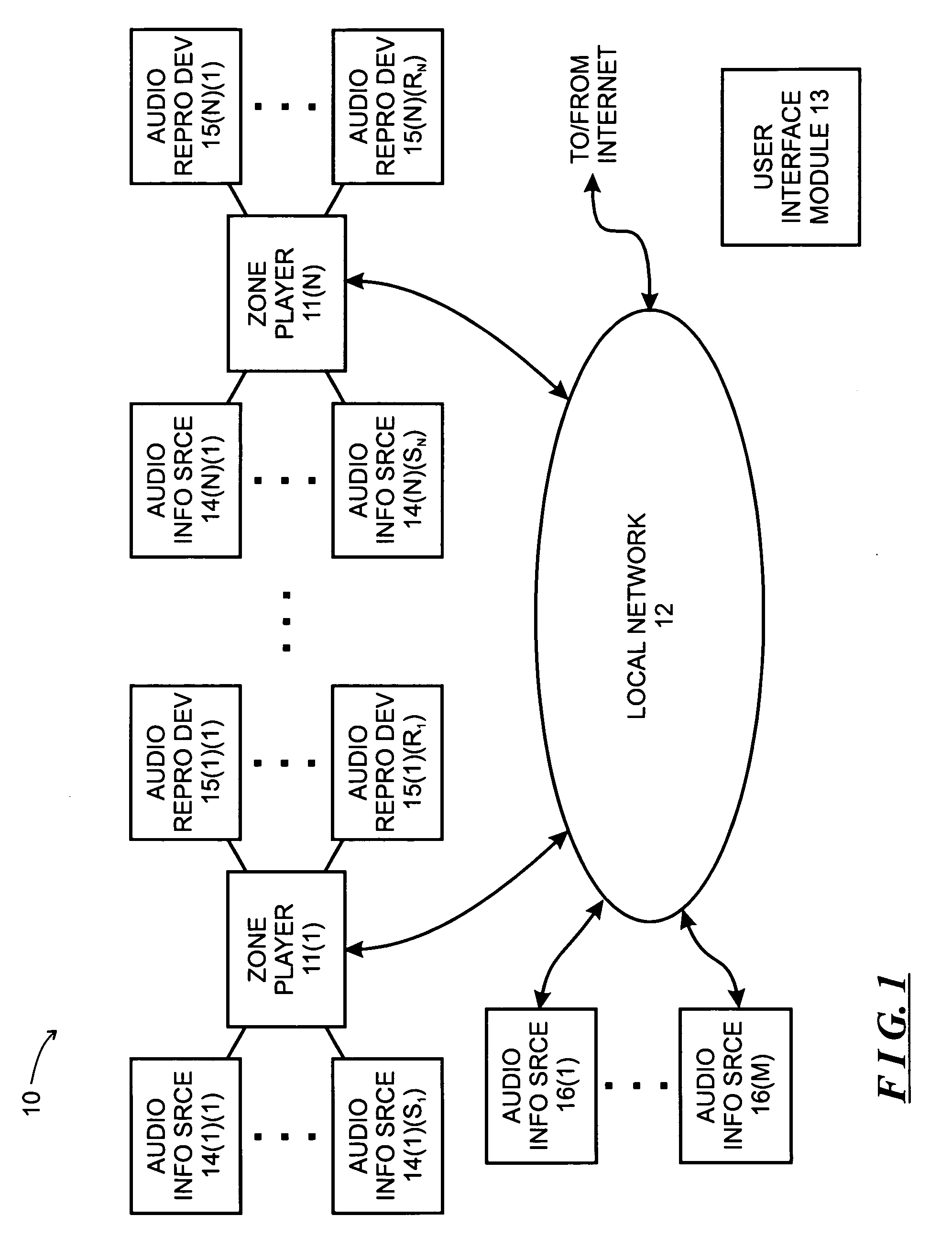
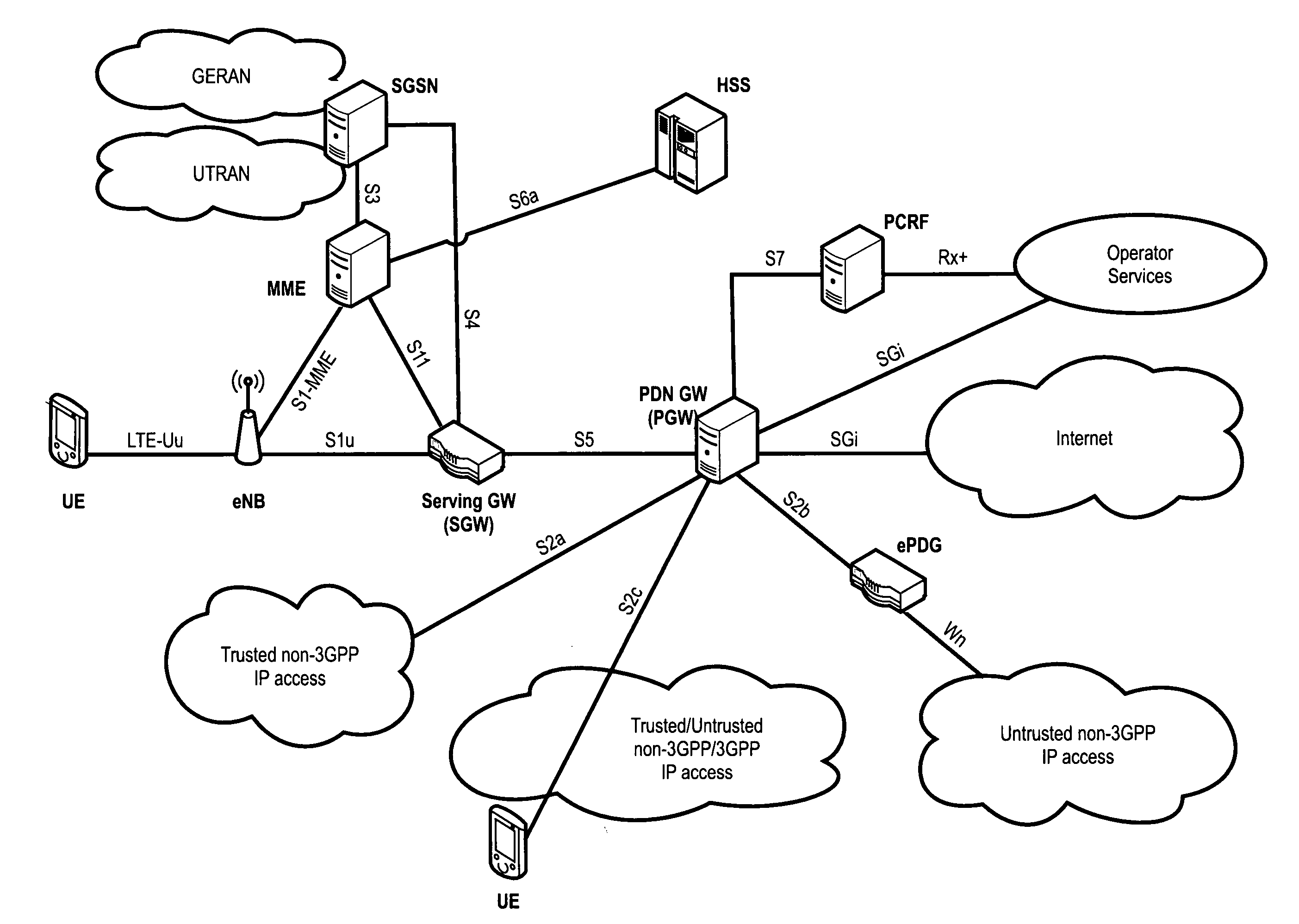
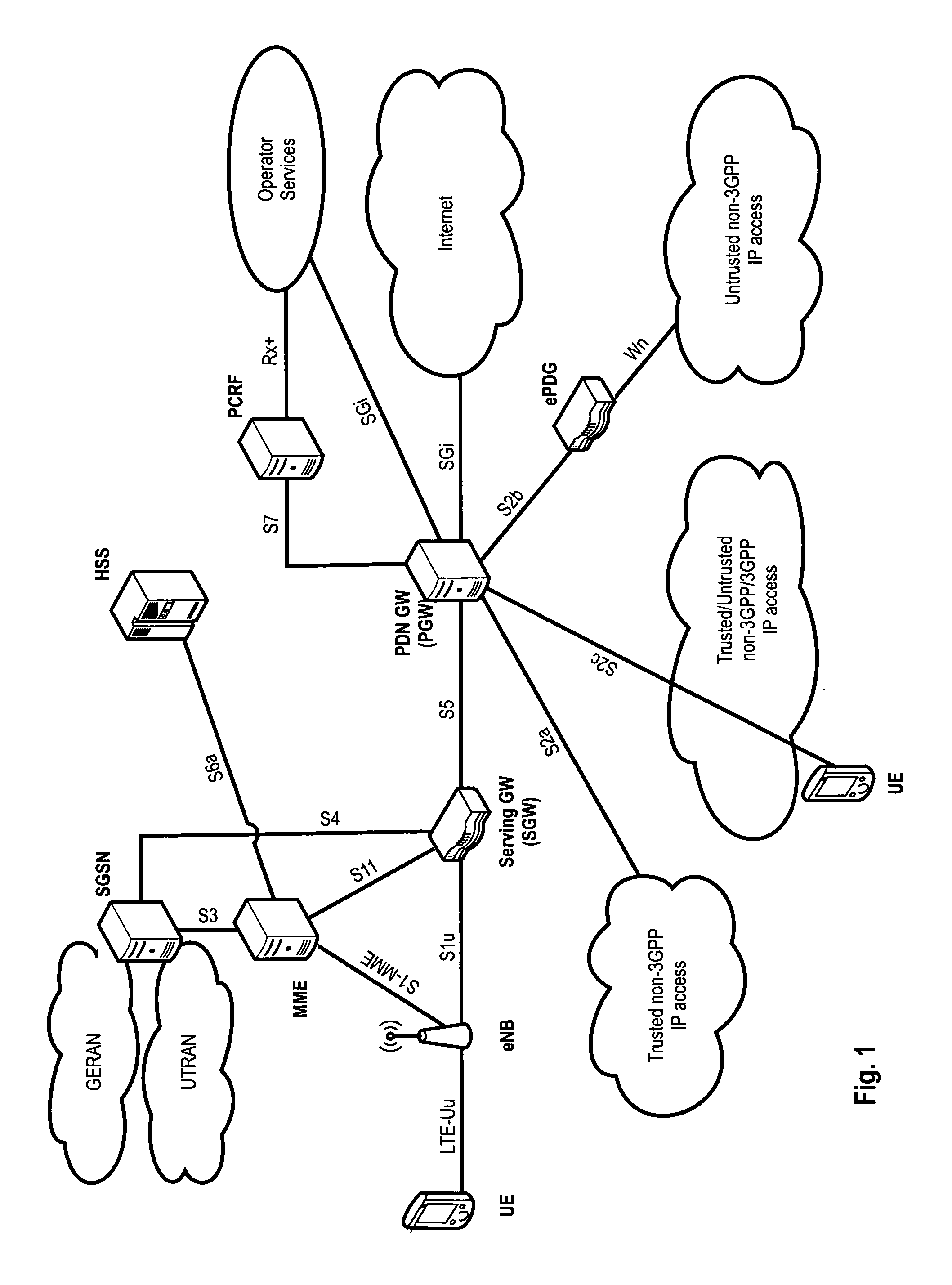
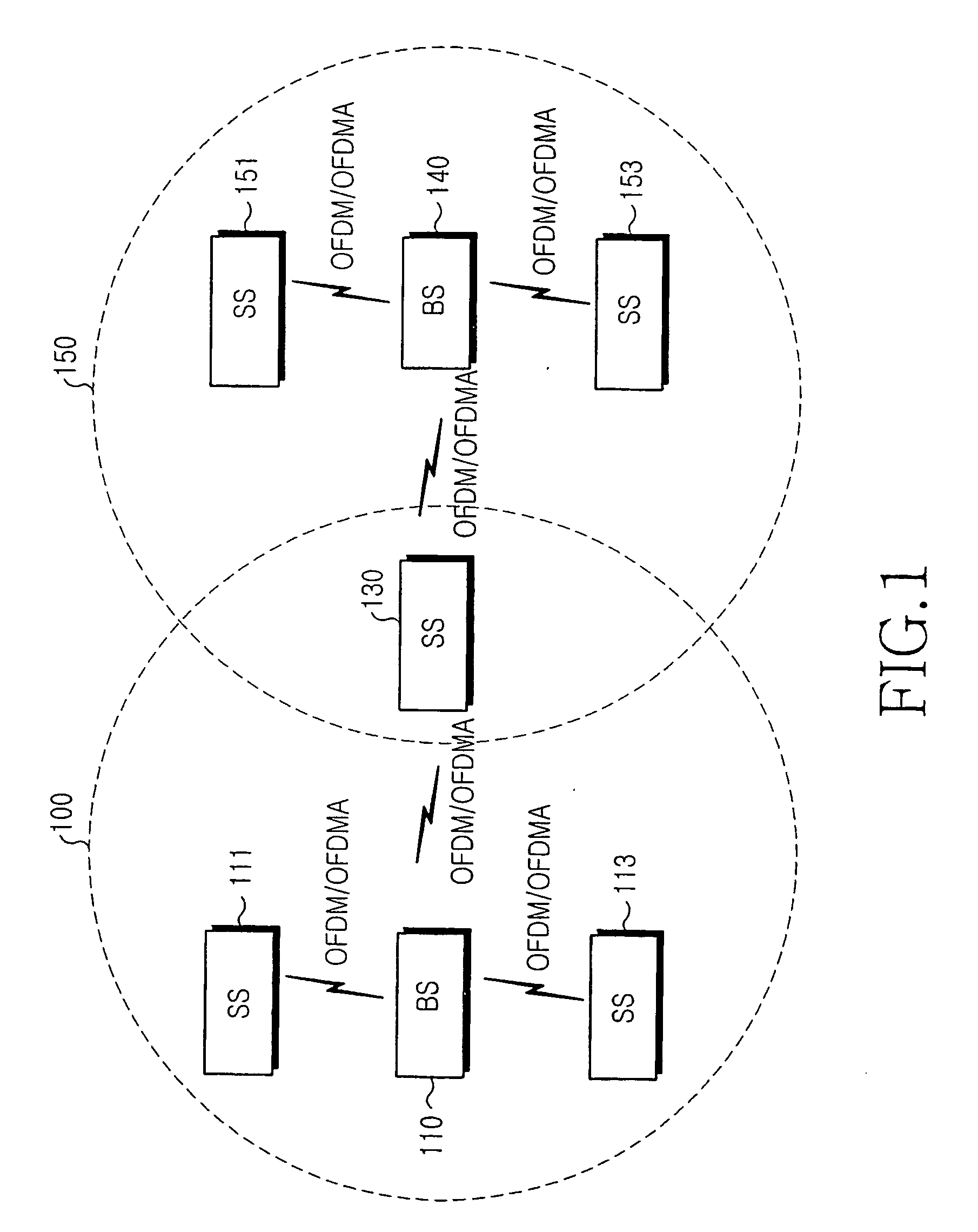
Method and apparatus for performing synchronization in device-to-device network
ActiveUS20130308625A1Perform synchronizationSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexComputer sciencePhase adjustment
A method and an apparatus for performing synchronization by a first device in a Device-to-Device (D2D) network are provided. The method includes detecting a synchronization signal from at least one second device during one period, determining a phase adjustment value depending on a number of synchronization signals, which have been detected from the at least one second device during the one period, adjusting a phase value of a first device using the phase adjustment value, and transmitting a synchronization signal if the phase value of the first device reaches a predetermined specific value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
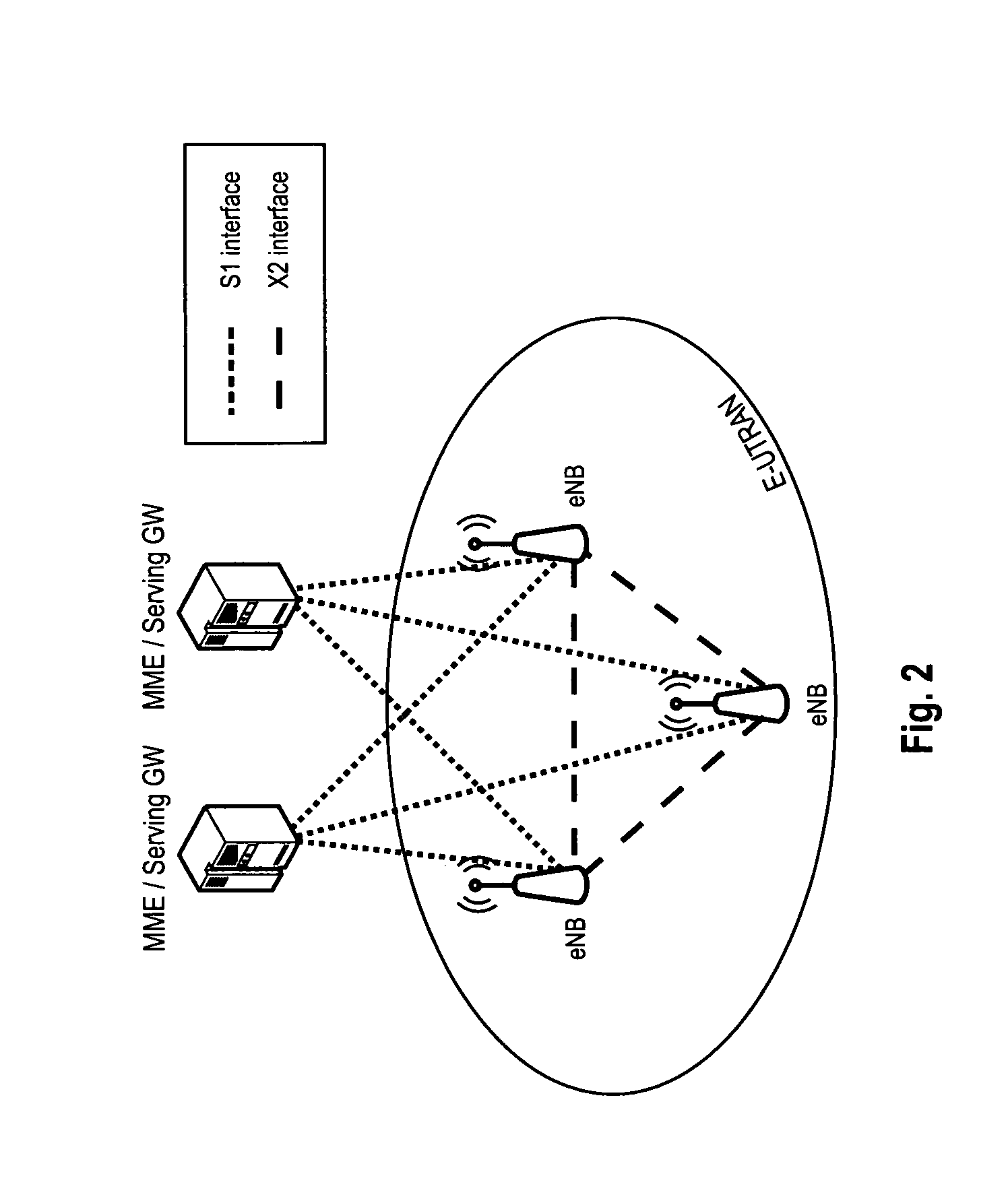
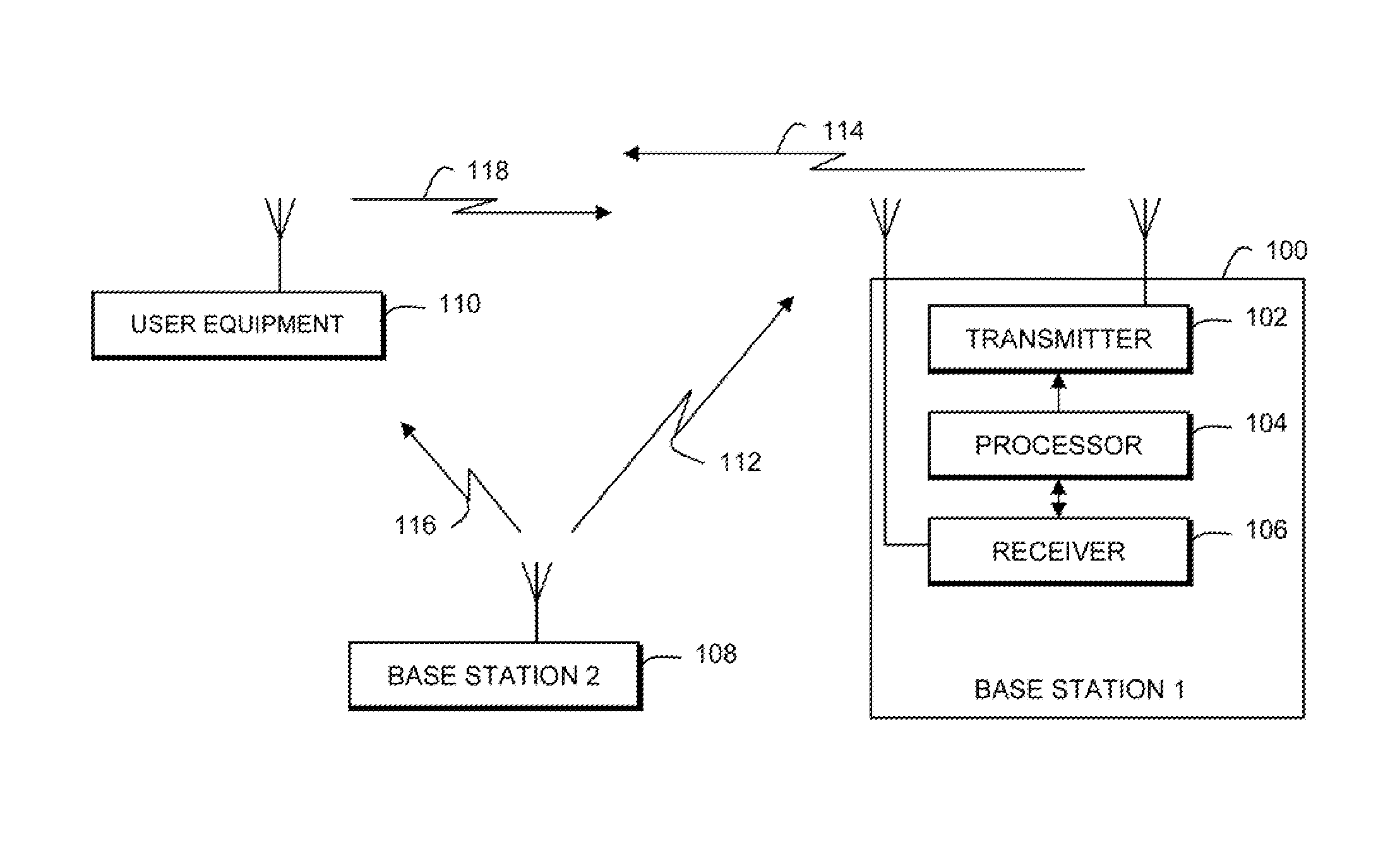
System and method for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices
ActiveUS20070038999A1Maintenance operationTelevision system detailsGain controlElectronic data processingIndependent clock
A system is described for maintaining synchrony of operations among a plurality of devices that have independent clocking arrangements. The system includes a task distribution device that distributes tasks to a synchrony group comprising a plurality of devices that are to perform the tasks distributed by the task distribution device in synchrony. The task distribution device distributes each task to the members of the synchrony group over a network. Each task is associated with a time stamp that indicates a time, relative to a clock maintained by the task distribution device, at which the members of the synchrony group are to execute the task. Each member of the synchrony group periodically obtains from the task distribution device an indication of the current time indicated by its clock, determines a time differential between the task distribution device's clock and its respective clock and determines therefrom a time at which, according to its respective clock, the time stamp indicates that it is to execute the task.
Owner:SONOS
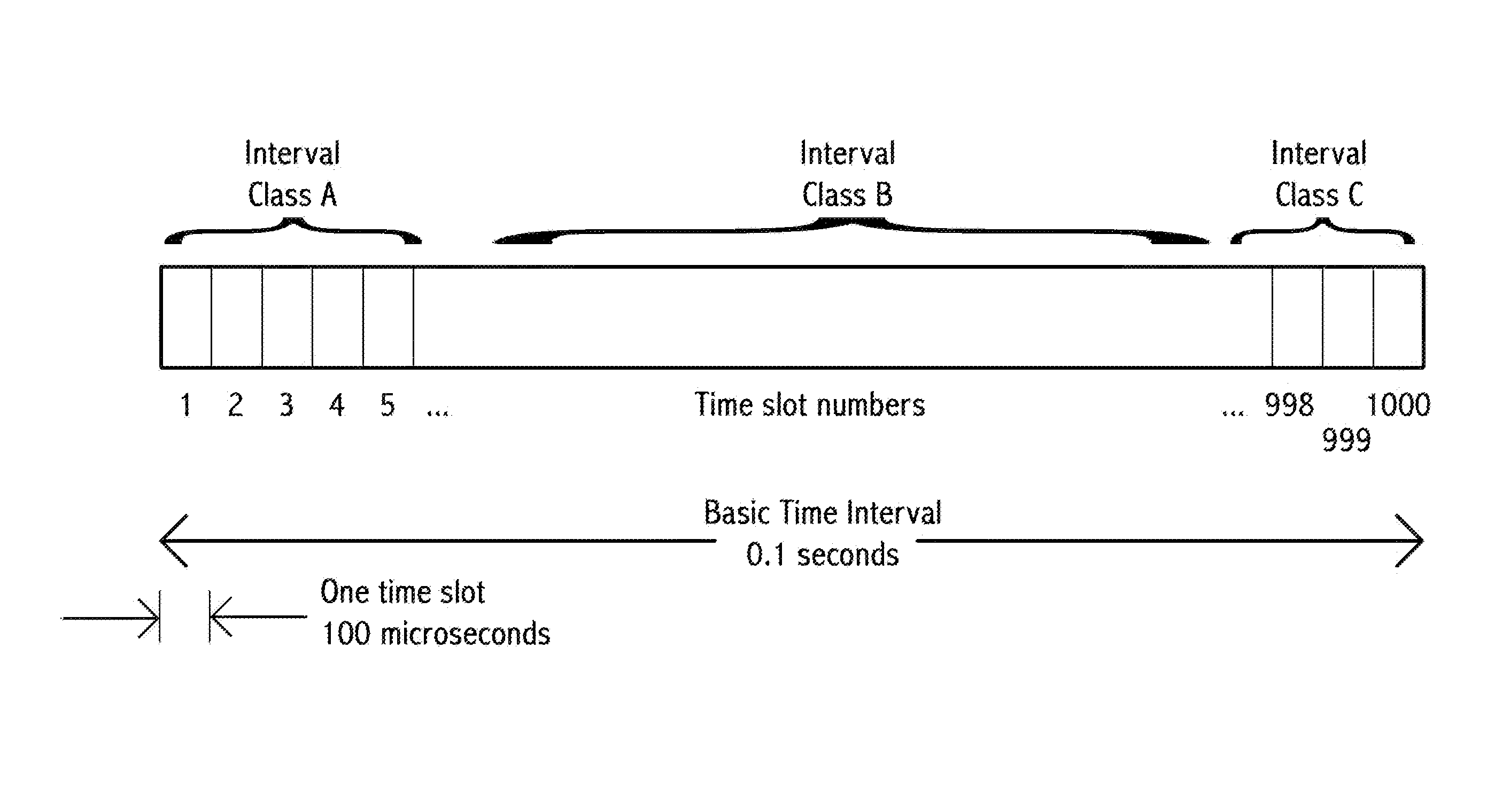
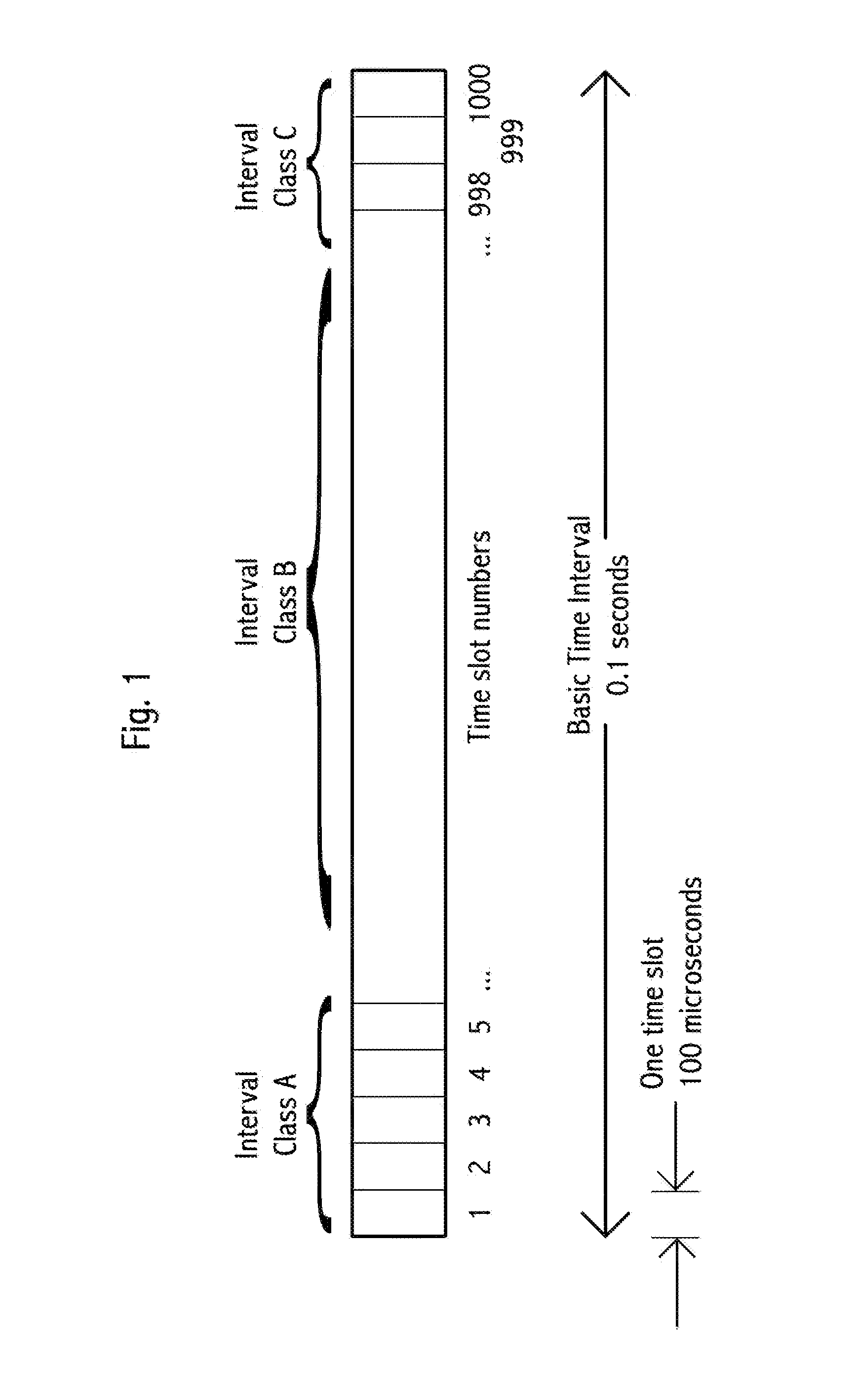
Time-slot-based system and method of inter-vehicle communication
ActiveUS8520695B1Efficient communicationEfficient codingInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsWireless transmissionCommunications system
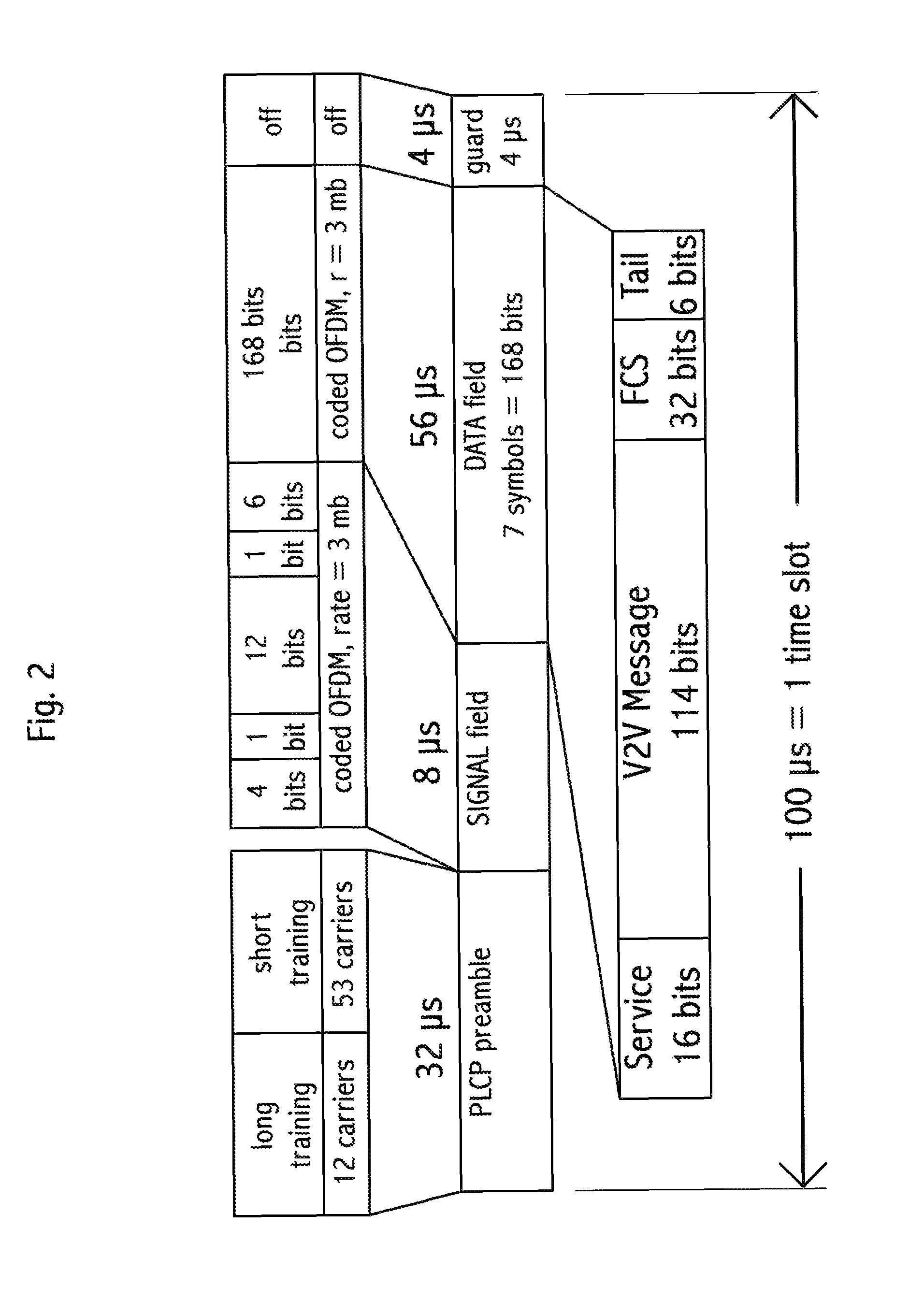
Device, system and method, in a vehicle communication system, to transmit wirelessly a message comprising the position, heading and speed of a vehicle or other moving object, wherein the transmission is repeated at regular intervals in a temporarily fixed time slot within a predetermined basic time interval. In a key embodiment the message duration is equal to or less than a predetermined time slot duration. Embodiments use generally the same time slot in a contiguous sequence of basic time intervals. Algorithms are described to resolve wireless interference within a time slot. Embodiments divide the basic time interval in multiple durations, “class regions,” for different message classes. Embodiments use different wireless bandwidth allocation algorithms for the class regions.
Owner:ZETTA RES & DEV - FORC SERIES
Method for optimizing the random access procedures in the cdma cellular networks
InactiveUS20030076812A1Limit collisionSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCellular networkSystem information
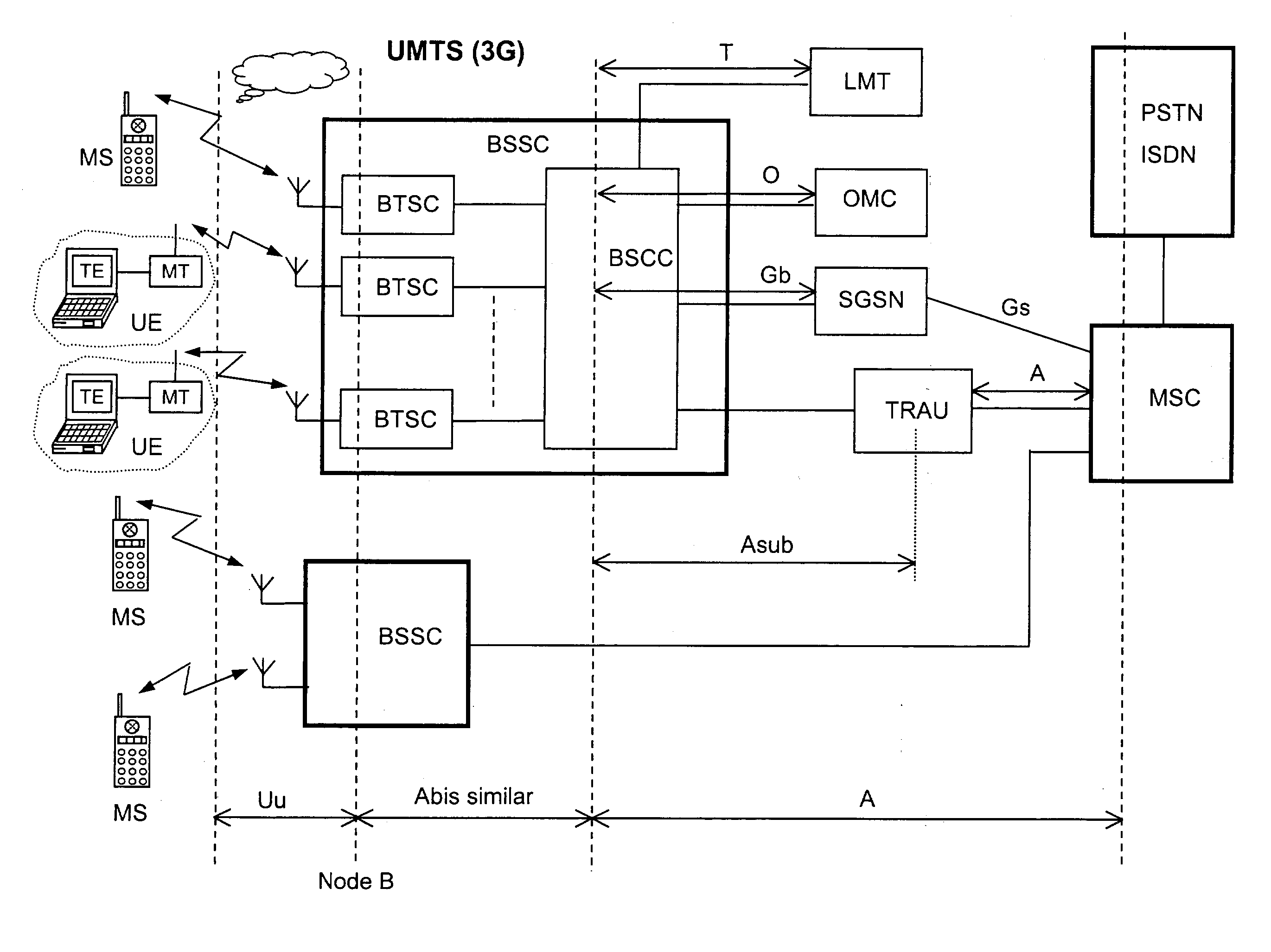
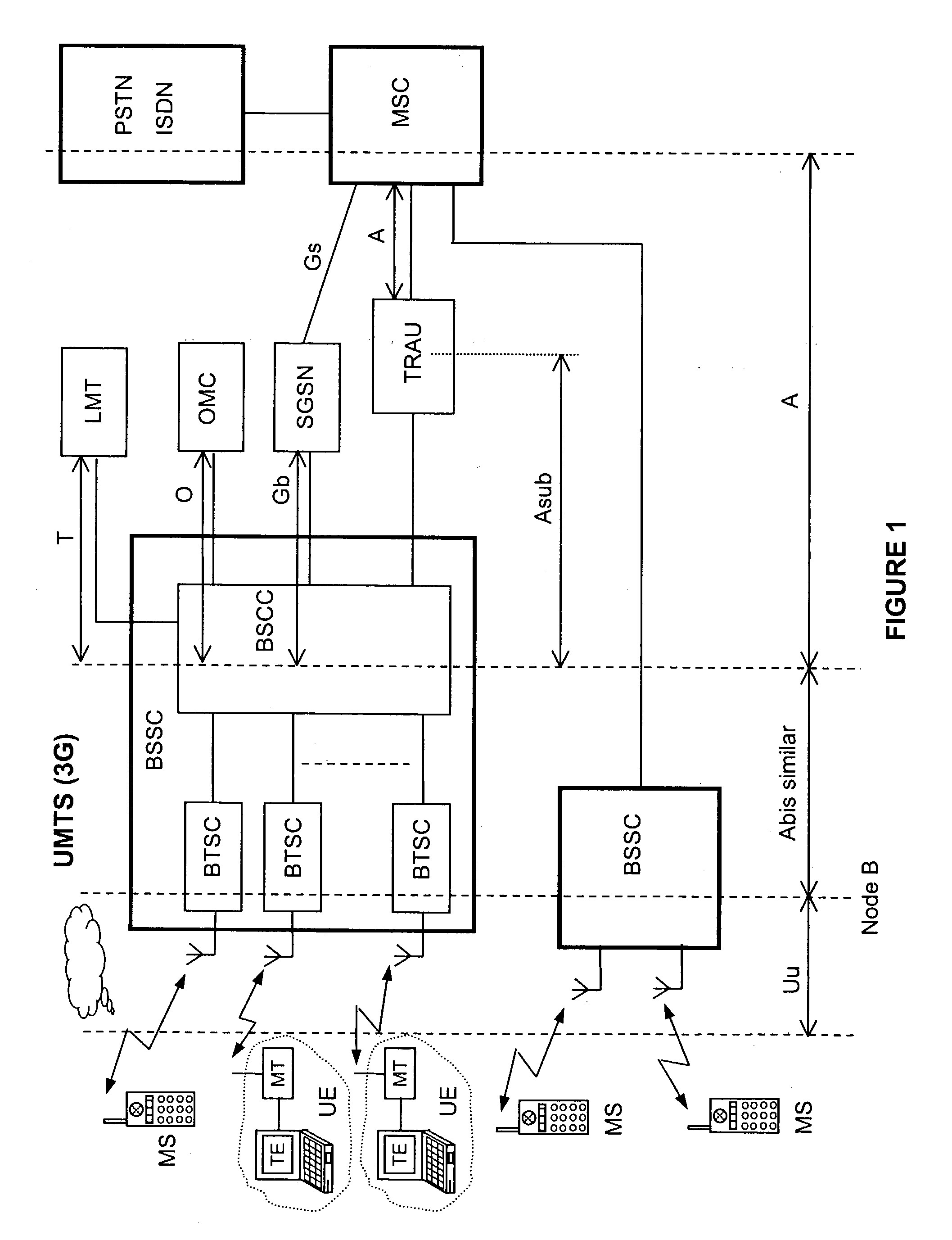
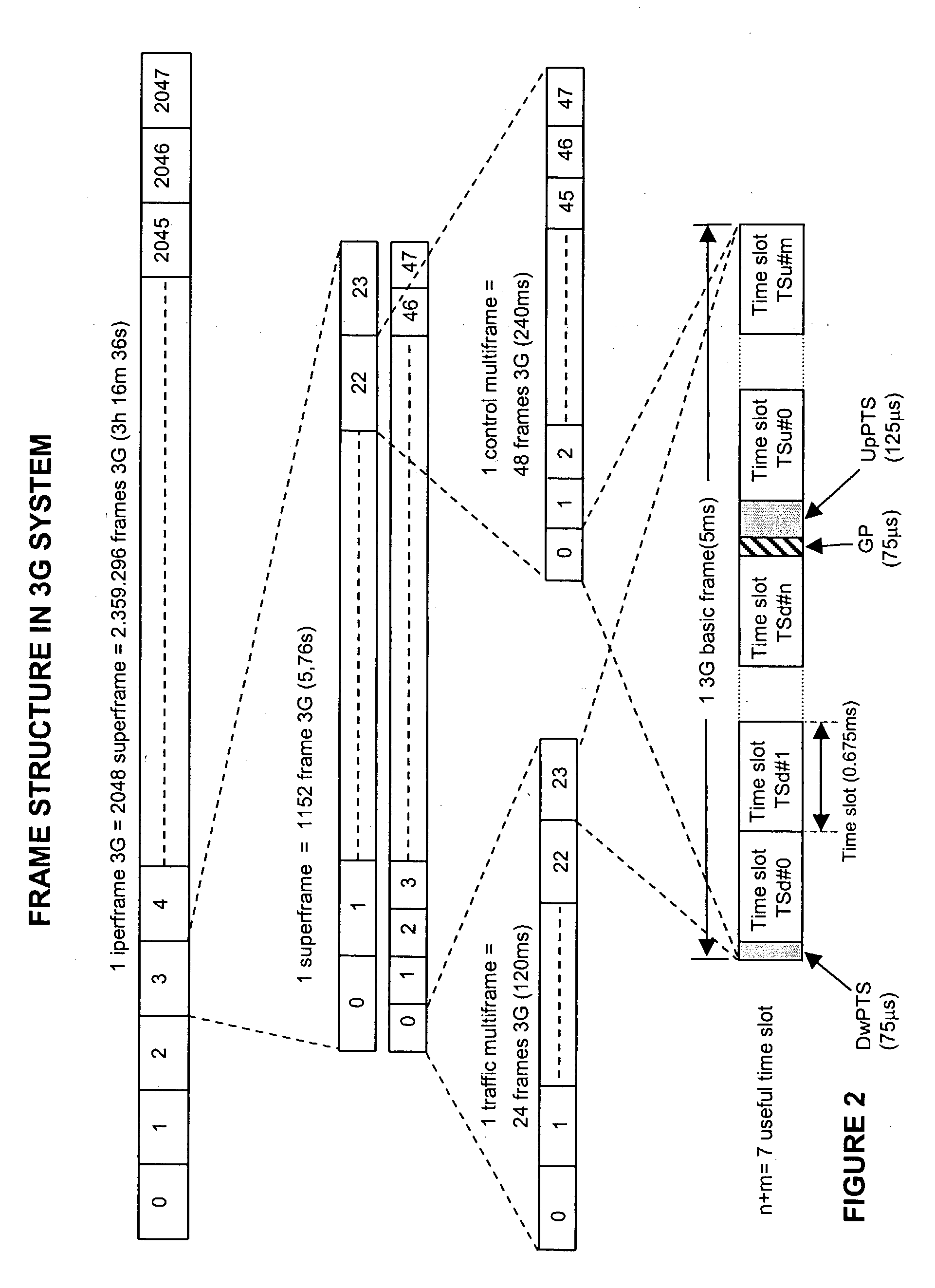
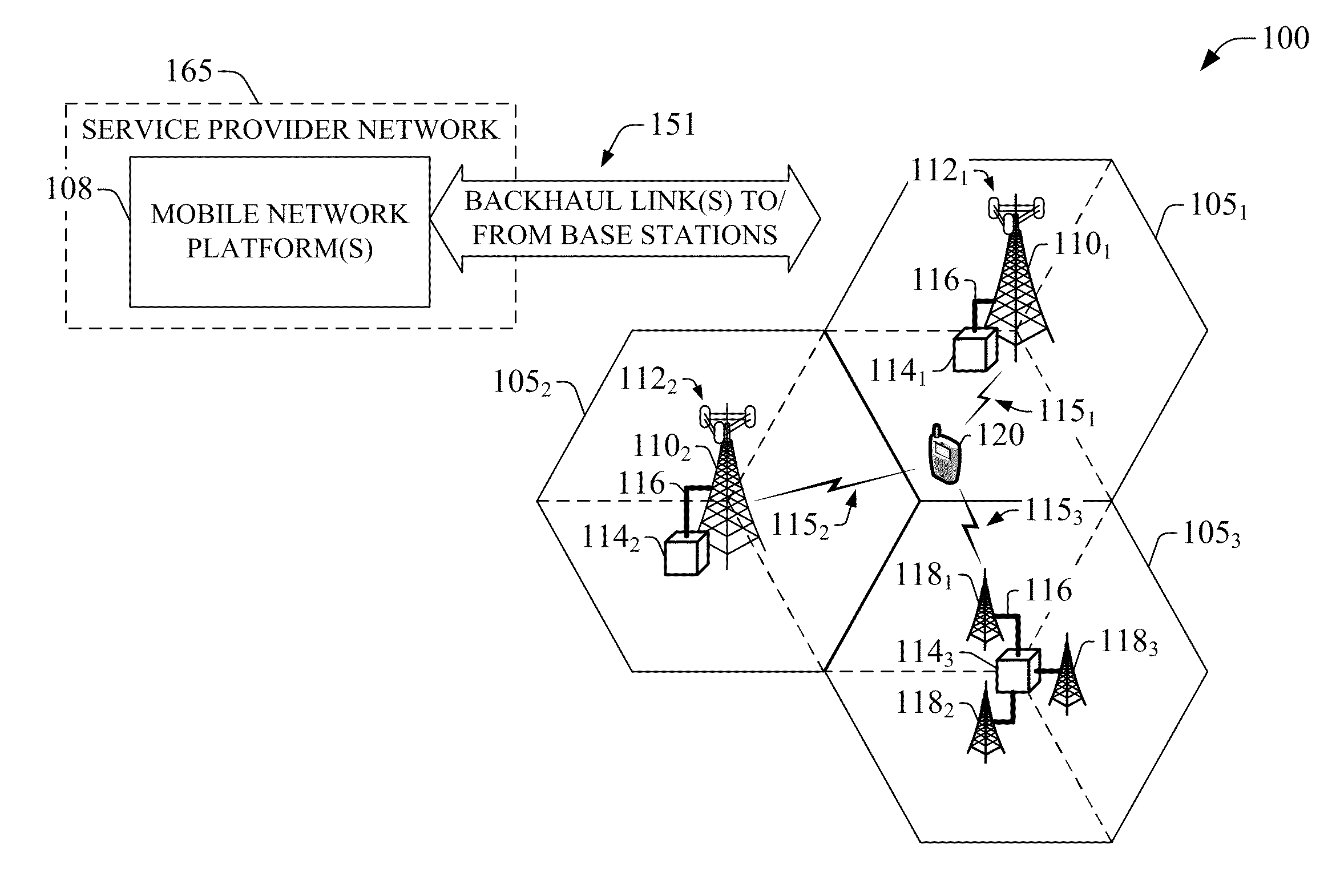
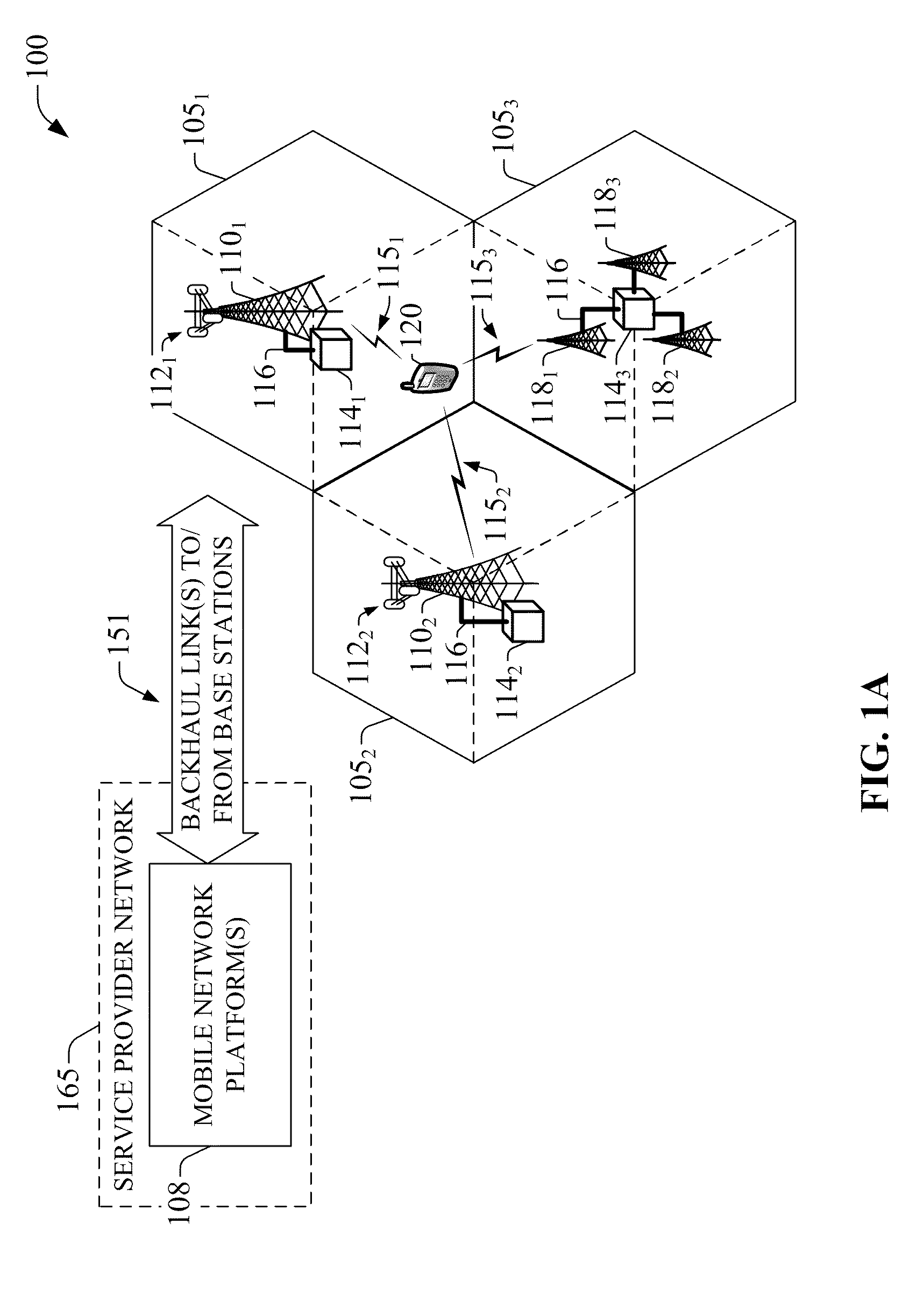
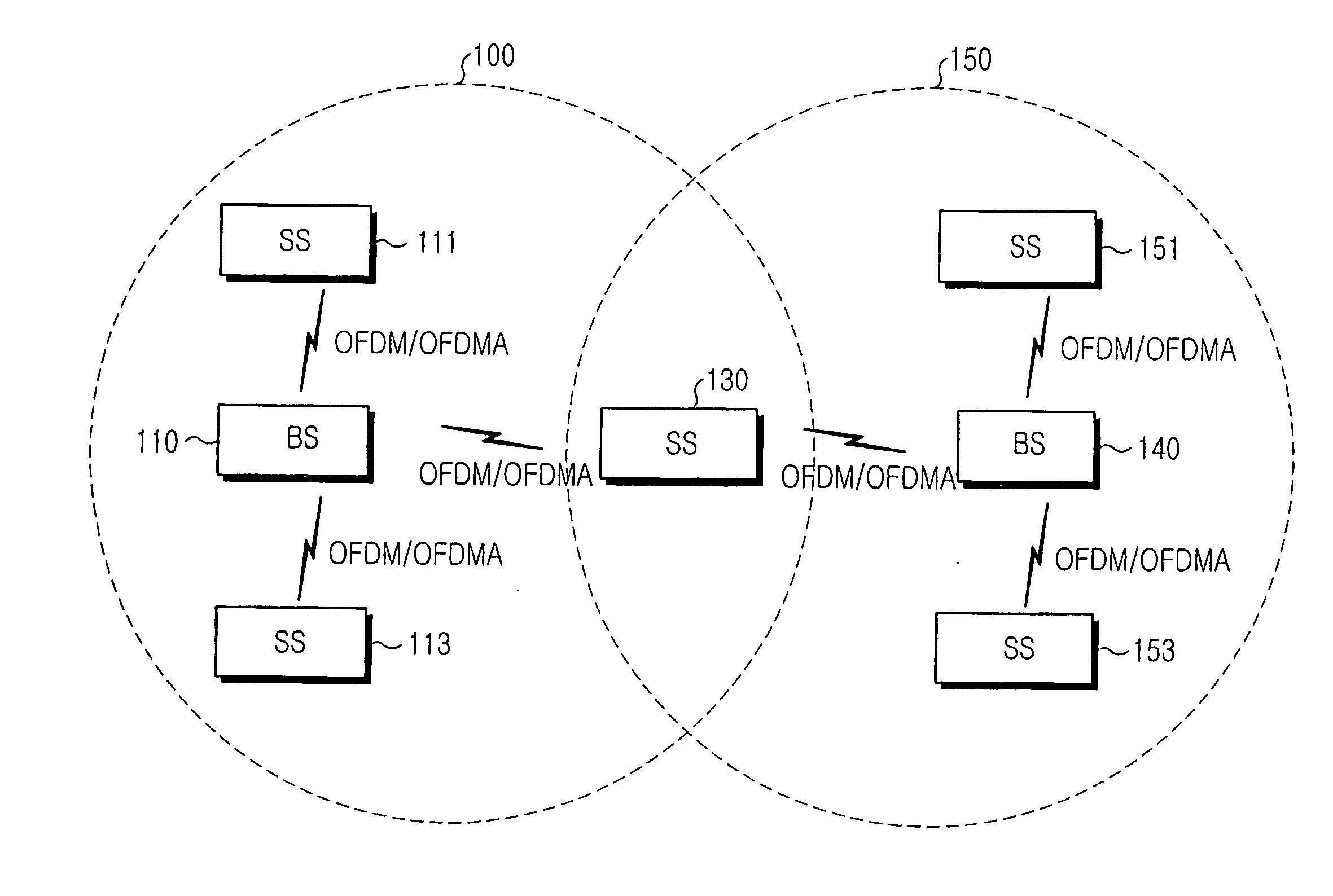
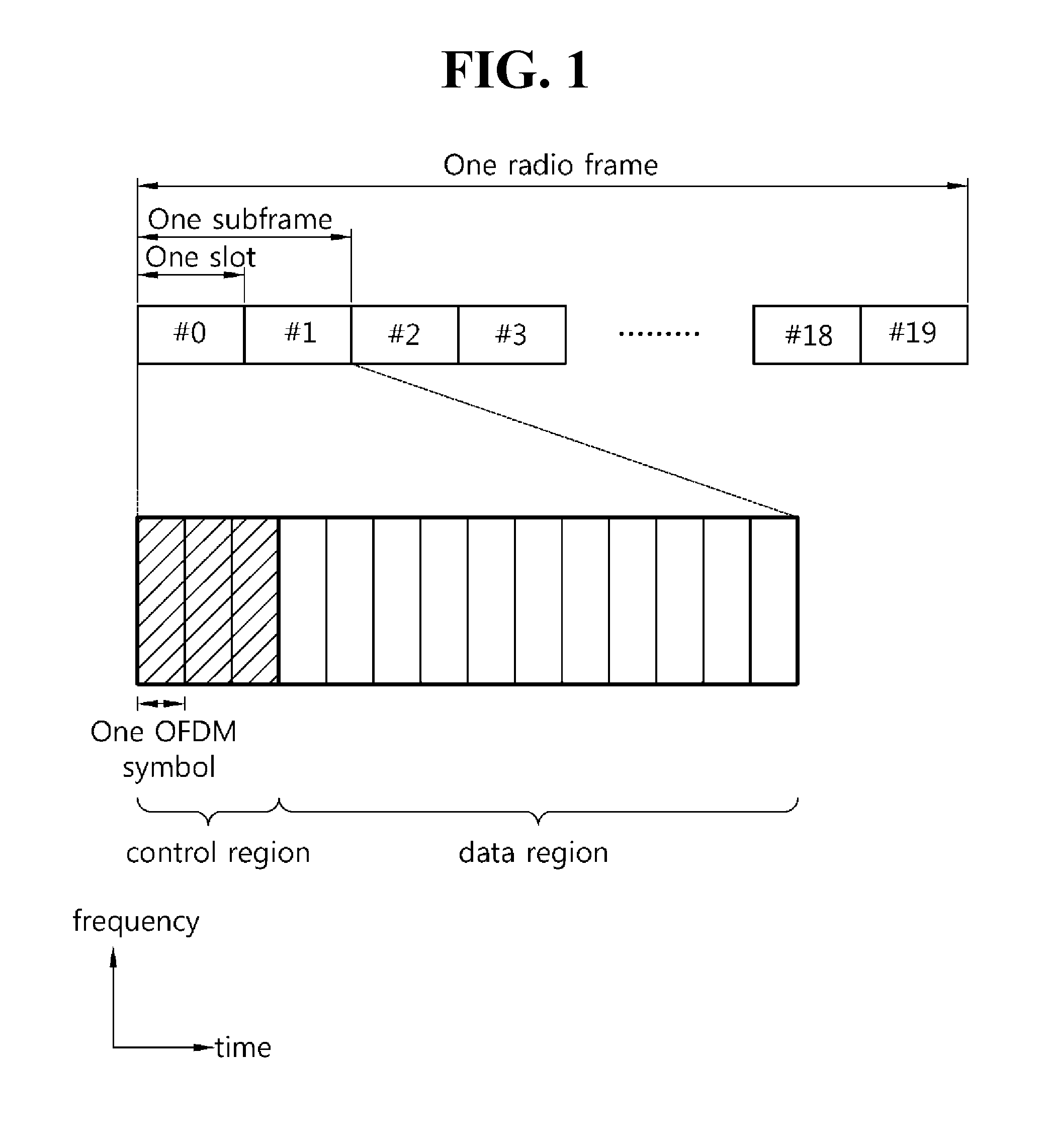
The disclosed invention is referred to a method for optimising the random access procedures in third generation CDMA cellular telephony systems. The particular embodiment of the example concerns a TD-SCDMA-TDD synchronous realization. The disclosed procedure includes a preliminary part charged to the network (BSSC, MSC) only for establishing the following associations between the configuration parameters of the involved physical channels: one signature burst (SYNC1) is associated to one forward access channel (P-FACH) only, in order to avoid any, ambiguity in the mobile stations about where to look for the expected acknowledgement from the network; one random access common channel (P-RACH) is associated to one forward access channel (P-FACH) only, in order to reduce collision on the latter (P-RACH); one access grant channel (P / S-CCPCH, AGCH) only is associated to one random access common channel (P-RACH), in order to avoid any ambiguity in the mobile stations about where to look for the expected answer from the network with the indication of the dedicated service channels (DPCH); and each complete associative link binding the involved physical channels is included in the system information and broadcasted into the serving cell to be read by the mobile stations (MS, UE) when entering an actual part of the procedure charged to exchange protocol messages with the network (BSSC, MSC) through said associative links that being signalling at once to the mobile stations the route towards the services offered by the network, simplifying the access procedure consequently. Suitable groupings among: Downlink pilot sequences, Uplink pilot sequences, scrambling codes, basic midambles, are carried out in a cell-discriminating way and broadcasted into the cell to simplify the serving cell selection procedure (<cross-reference target="DRAWINGS">FIG. 1< / cross-reference>).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Apparatus and method for dynamic communication resource allocation for device-to-device communications in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20120093098A1Facilitate communicationPower managementSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemDirect device
An apparatus, system and method to dynamically manage an allocation of communication resources for direct device-to-device communications between a plurality of wireless communication devices in a wireless communication system. In one embodiment, the apparatus (410) includes a communication resource allocator (420) configured to: (1) select a master communication device of a plurality of wireless communication devices that form a device-to-device group, (2) provide an allocation of communication resources for device-to-device group that facilitate direct device-to-device communications therebetween. The apparatus (410) also includes a message generator (430) configured to assemble messages that include the allocation of the communication resources.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
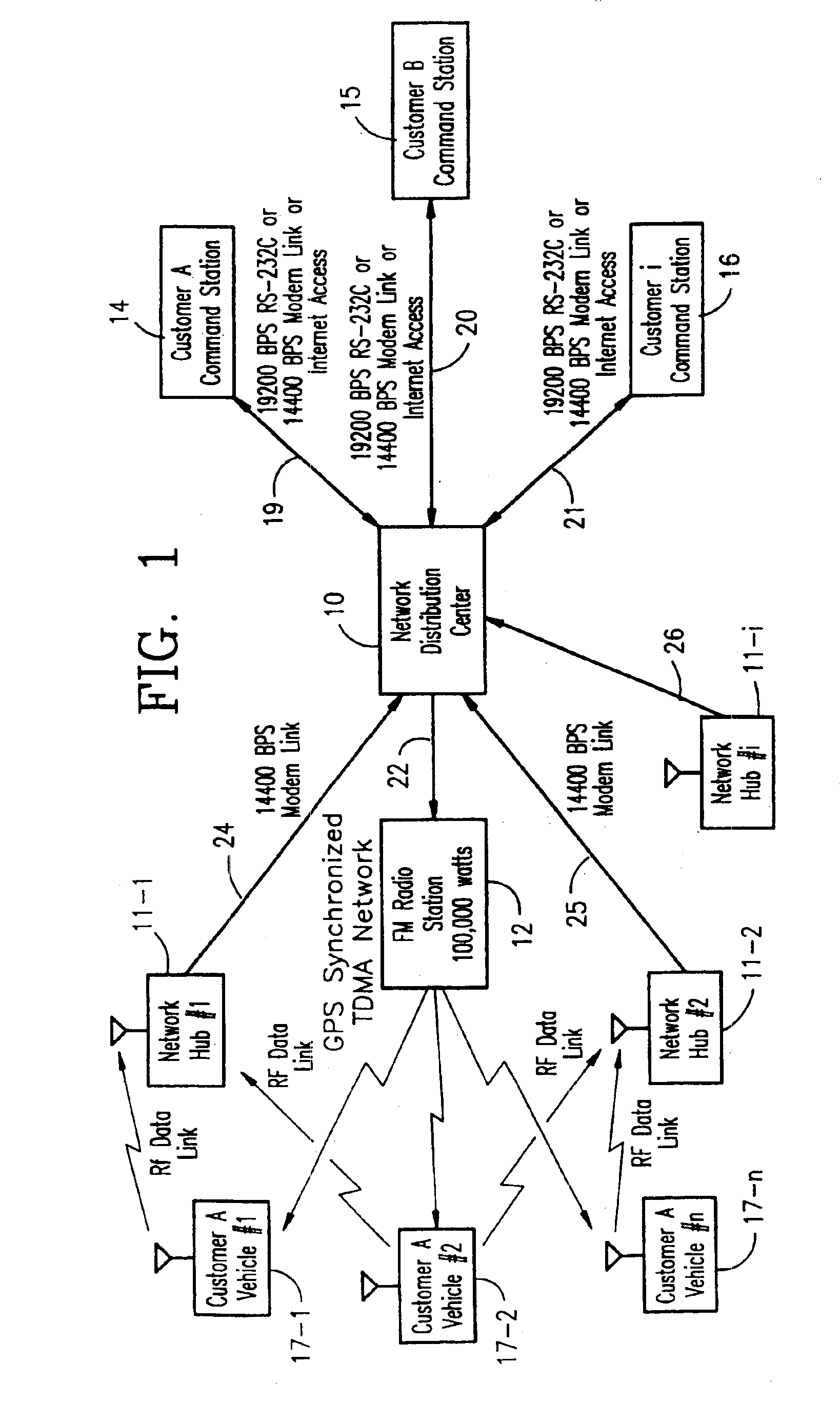
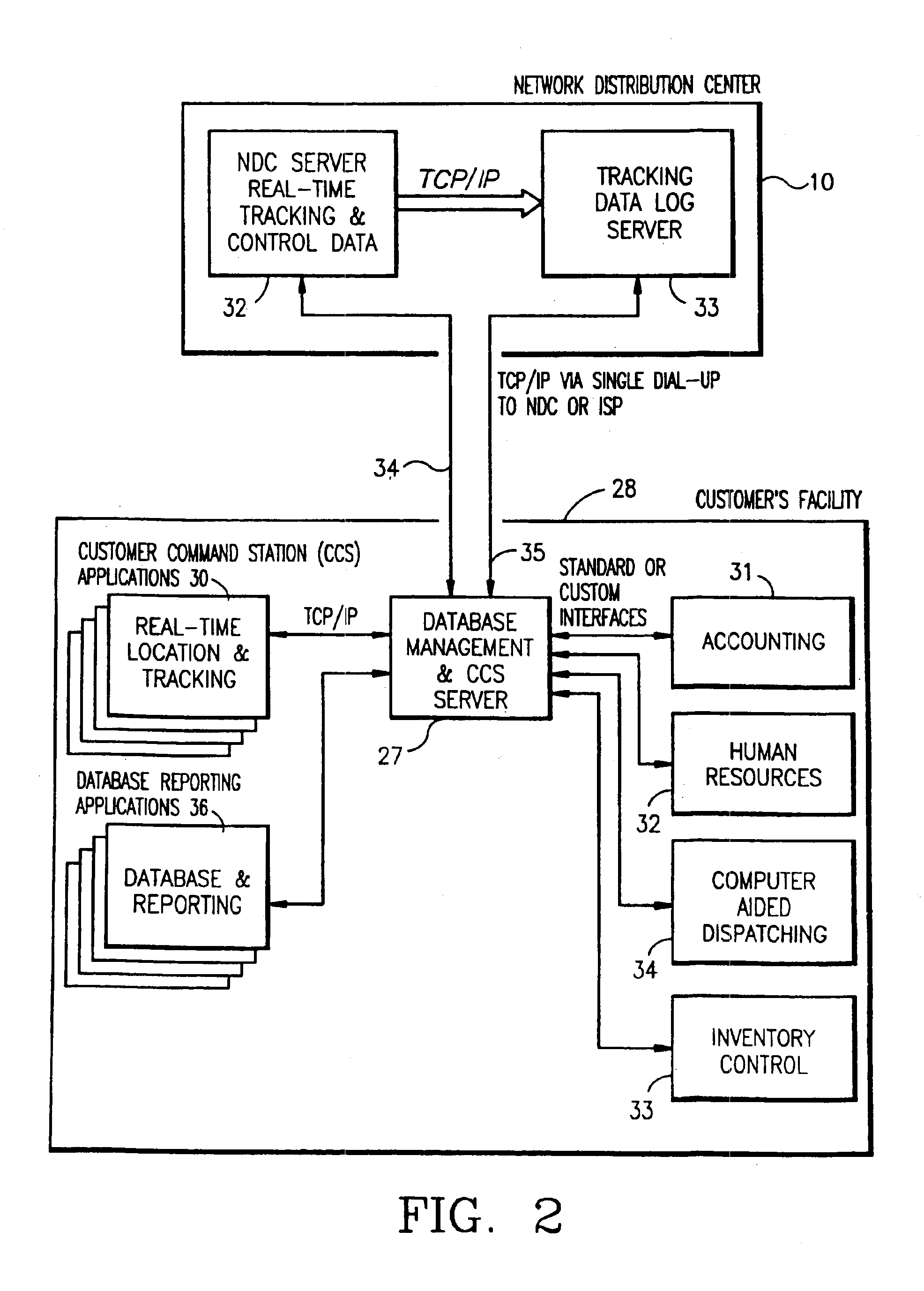
Vehicle tracking, communication and fleet management system
InactiveUS6892131B2Management moreEfficient and reliableVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesFleet managementTruck
A vehicle fleet management information system for identification of location and direction of movement of each vehicle in the fleet in real-time and automatic communication directly with management offices to report its location and heading, and status of predetermined events in which the vehicle may be engaged. One example is a cement delivery truck which monitors location, speed and status information such as start pour, pouring, end pour, wash and leave job, and automatically transmits this information with a management office without requiring affirmative action by the vehicle operator.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
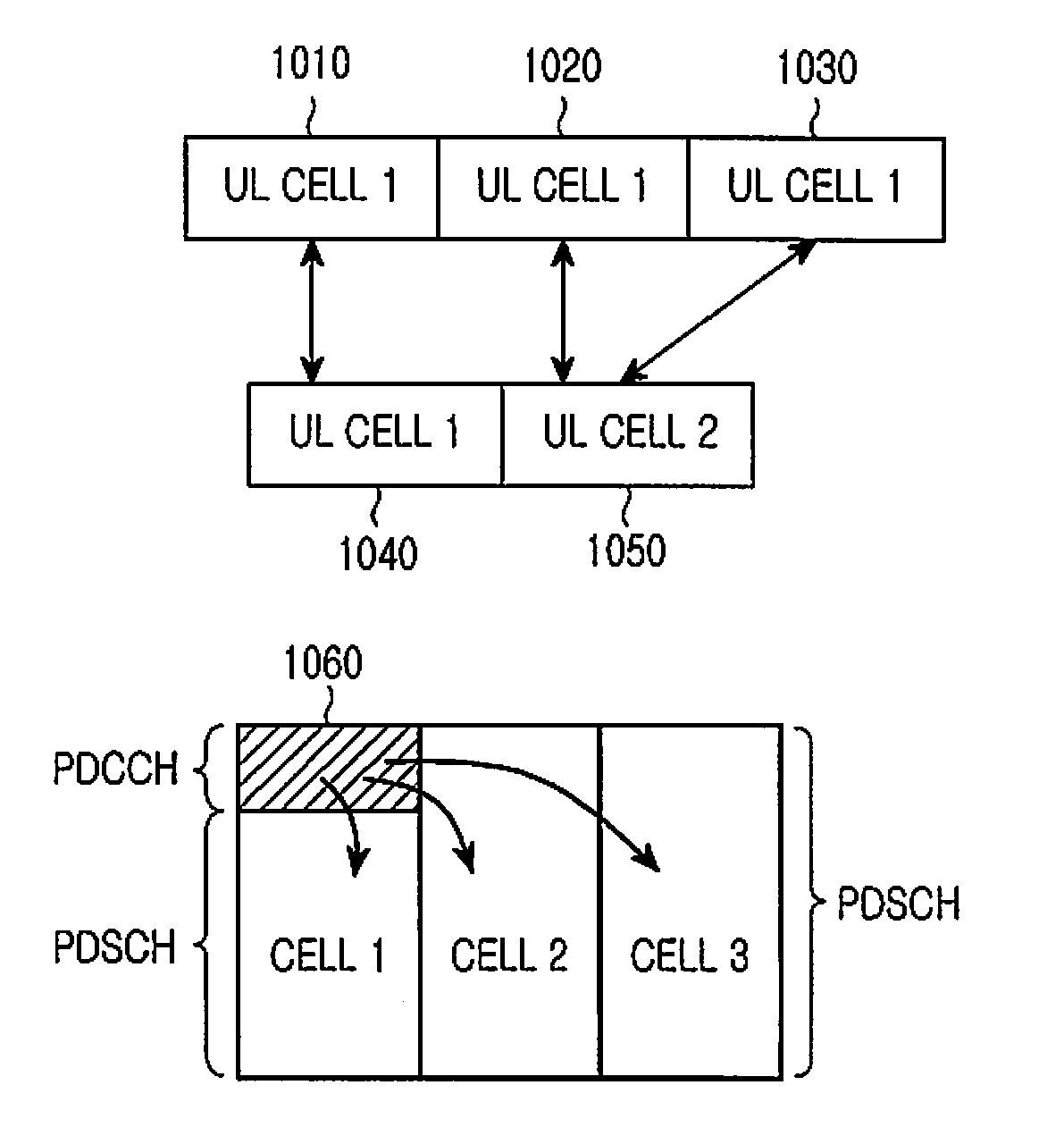
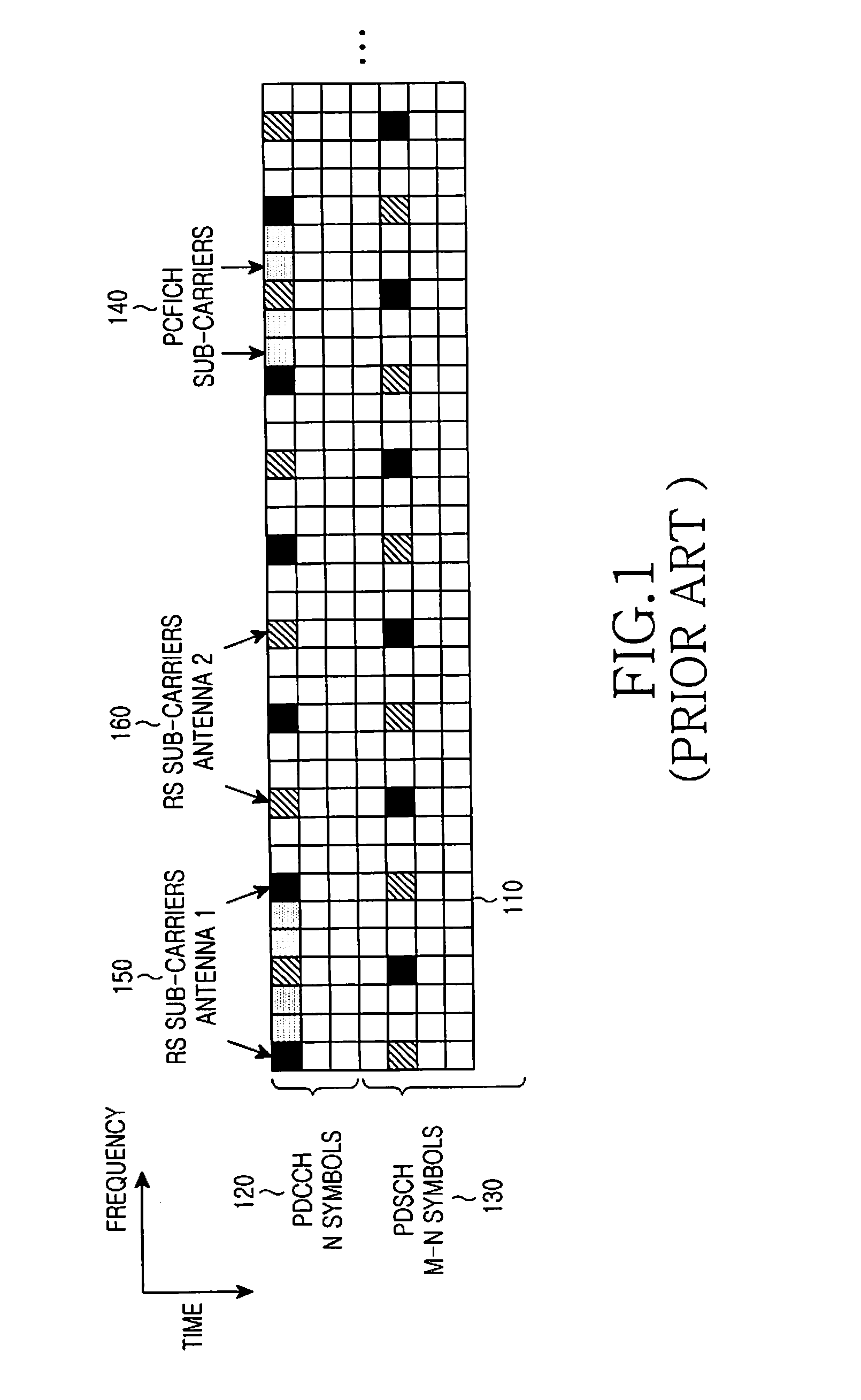
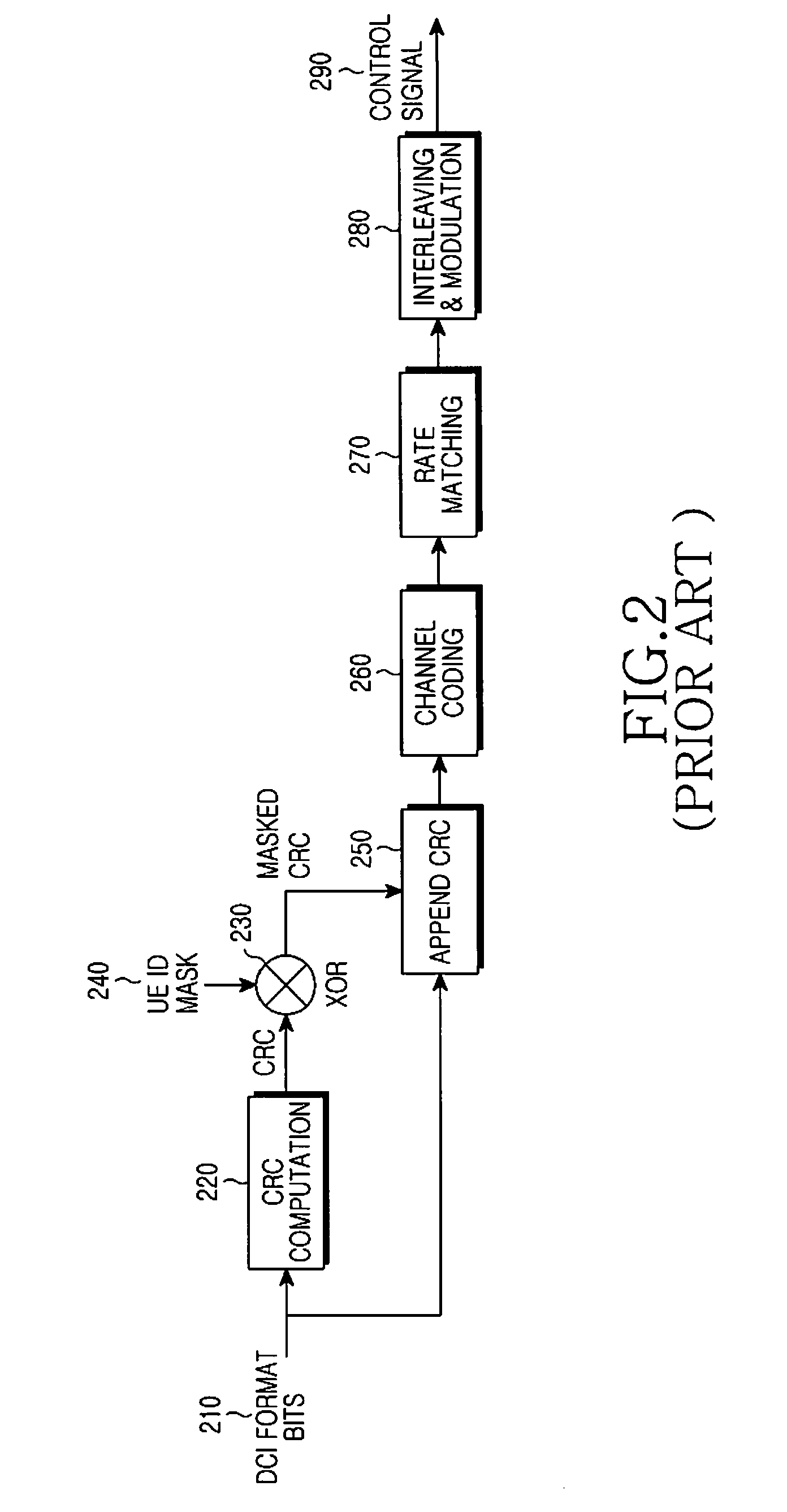
Extending physical downlink control channels
ActiveUS20110075624A1Limit regionSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionTelecommunicationsControl channel
Methods and apparatus for transmitting and receiving Downlink Control Information (DCI) in a single cell in order to support communication over multiple cells. The DCI is conveyed by DCI formats transmitted through Physical Downlink Control CHannels (PDCCHs) in a UE-Common Search Space (UE-CSS) and in a UE-Dedicated Search Space (UE-DSS). A distinct UE-DSS is defined in the single cell for each of the multiple cells. Each distinct UE-DSS has the same structure as a conventional UE-DSS and a location that is determined by the same parameters as the location of the conventional UE-DSS and by the respective cell identity (Cell_ID).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmit power control for physical random access channels
ActiveUS20130058315A1Increase the likelihood of successAvoid low successPower managementSynchronisation arrangementUplink transmissionTransmitted power
The invention relates to methods for adjusting the transmit power utilized by a mobile terminal for uplink transmissions, and to methods for adjusting the transmit power used by a mobile terminal for one or more RACH procedures. The invention is also providing apparatus and system for performing these methods, and computer readable media the instructions of which cause the apparatus and system to perform the methods described herein. In order to allow for adjusting the transmit power of uplink transmissions on uplink component carriers, the invention suggests introducing a power scaling for uplink PRACH transmissions performing RACH procedures on an uplink component carrier. The power scaling is proposed on the basis of a prioritization among multiple uplink transmissions or on the basis of the uplink component carriers on which RACH procedures are performed.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Compensation of propagation delays of wireless signals
ActiveUS20100190509A1Weakening rangeImprove accuracySynchronisation arrangementLocation information based servicePropagation delayRadio networks
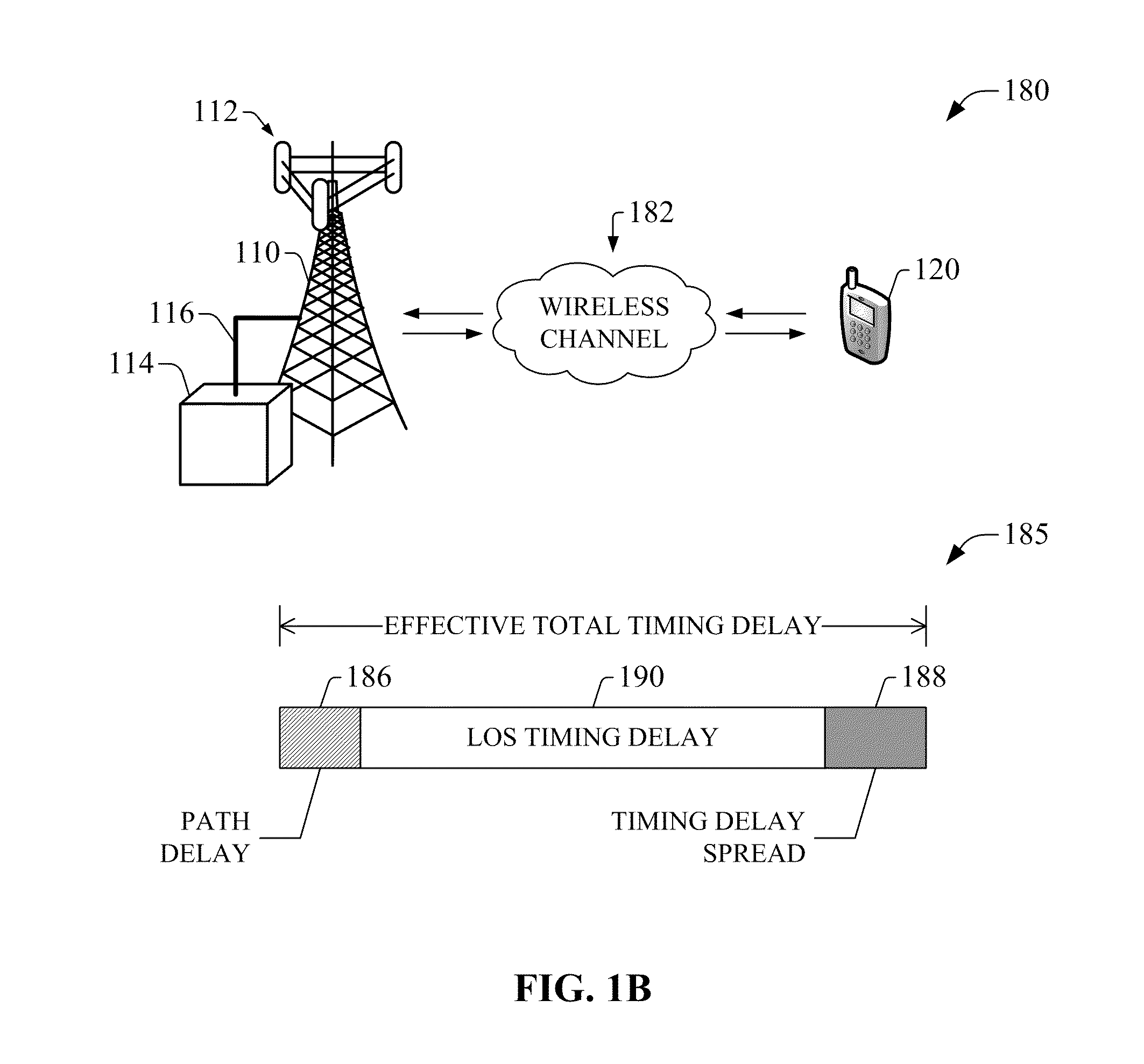
System(s) and method(s) for compensation of propagation delay offsets of wireless signals. Compensation is accomplished through determination of an effective wireless signal propagation delay that accounts for signal path delay and propagation delay over the air. Such determination is based at least in part on statistical analysis of accurate location estimates of reference positions throughout a coverage sector or cell, and location estimates of the reference positions generated through time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of wireless signals. Determination of propagation or signal path delay offset also is attained iteratively based at least in part on reference location estimates and TOF location estimates. High-accuracy location estimates such as those obtained through global navigation satellite systems are employed as reference location estimates. Position of probes or wireless beacons, deployed throughout a sector or cell, also are employed as reference locations. Compensation of propagation delay offset improves accuracy of conventional TOF location estimates and radio network performance.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Tiered contention multiple access (TCMA): a method for priority-based shared channel access
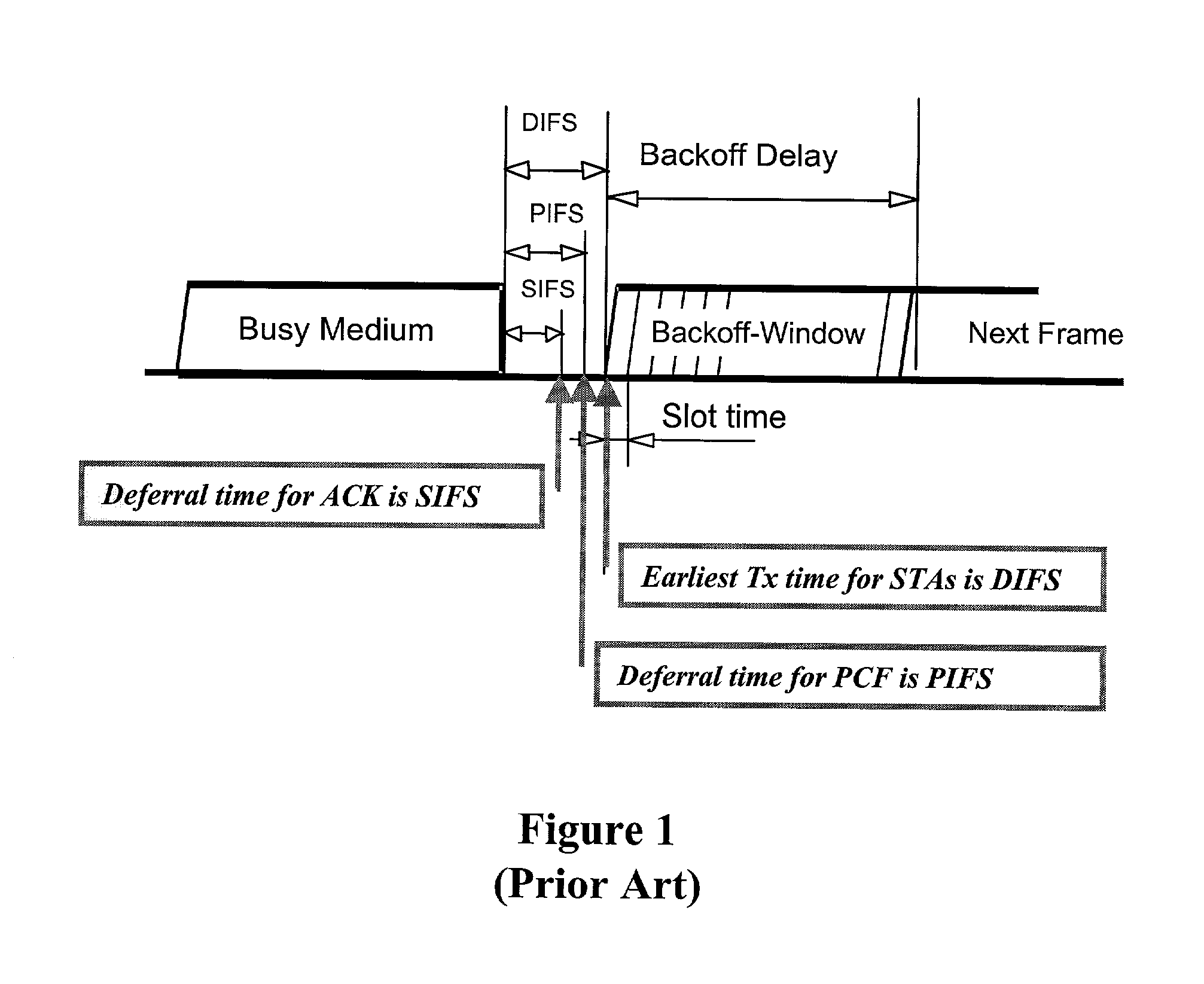
ActiveUS7095754B2Minimizing chanceLower latencySynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementService-level agreementIdle time
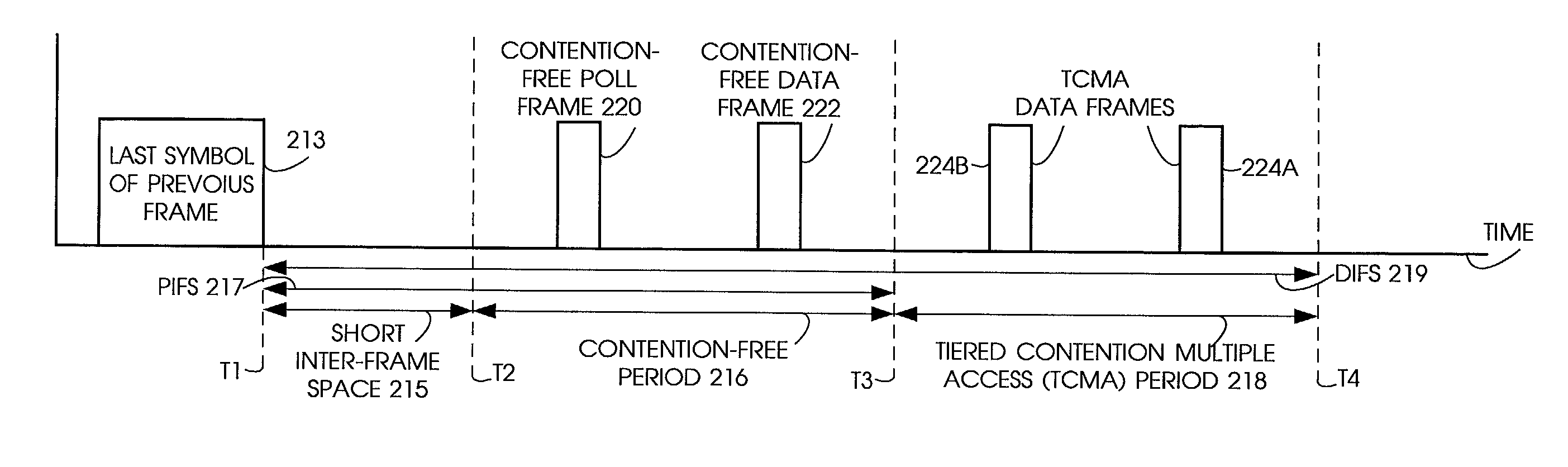
Quality of Service (QoS) support is provided by means of a Tiered Contention Multiple Access (TCMA) distributed medium access protocol that schedules transmission of different types of traffic based on their service quality specifications. In one embodiment, a wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a lower QoS priority QoS(A), such as file transfer data. Another wireless station is supplied with data from a source having a higher QoS priority QoS(B), such as voice and video data. Each wireless station can determine the urgency class of its pending packets according to a scheduling algorithm. For example file transfer data is assigned lower urgency class and voice and video data is assigned higher urgency class. There are several urgency classes which indicate the desired ordering. Pending packets in a given urgency class are transmitted before transmitting packets of a lower urgency class by relying on class-differentiated urgency arbitration times (UATs), which are the idle time intervals required before the random backoff counter is decreased. In another embodiment packets are reclassified in real time with a scheduling algorithm that adjusts the class assigned to packets based on observed performance parameters and according to negotiated QoS-based requirements. Further, for packets assigned the same arbitration time, additional differentiation into more urgency classes is achieved in terms of the contention resolution mechanism employed, thus yielding hybrid packet prioritization methods. An Enhanced DCF Parameter Set is contained in a control packet sent by the AP to the associated stations, which contains class differentiated parameter values necessary to support the TCMA. These parameters can be changed based on different algorithms to support call admission and flow control functions and to meet the requirements of service level agreements.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Energy Efficient Wireless Sensor Network, Node Devices for the Same and a Method for Arranging Communications in a Wireless Sensor Network
ActiveUS20080253327A1Reduce power consumptionAvoiding prohibitively network scanning timeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementLine sensorTelecommunications
A wireless sensor network, a node device thereof and a method for arranging communications therein are presented. A first frequency is used in wireless communication of information between a headnode and subnodes of a first cluster (103) using a time slotted channel access scheme. A headnode of a second cluster (113) known the first frequency and selects a second, different frequency for use in wireless communication of information within said second cluster (113) using a time slotted channel access scheme. The headnode of the first cluster (103) is informed about the second frequency selected for the second cluster (113). Information from the headnode of said first cluster (103) to the headnode of said second cluster (113) is communicated on said second frequency, using the same time slotted channel access scheme as other nodes in said second cluster (113).
Owner:WIREPAS
Propagation delay difference reporting for multiple component carriers
The invention relates to methods for reporting on downlink timings by a mobile terminal in a mobile communication system. In order to allow for an aggregation access point to obtain information on propagation delay differences of downlink transmissions on aggregated serving cells, the invention suggests the mobile terminal to report timing information based on reception time difference information for a the target / reference cell. The mobile terminal performs measurements relating to transmission and / or reception time differences on the target / reference cell, and reports same to the eNodeB. The eNodeB compares the measurement result to a predefined maximum propagation delay time difference. Alternatively, the mobile terminal performs the measurements, compares same to the predefined maximum propagation delay time difference and then report the comparison result to the eNodeB.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Logical channel prioritization procedure for generating multiple uplink transport blocks
ActiveUS20120057547A1Promote generationEfficient schedulingPower managementTransmission path divisionComputer hardwareUplink transmission
The invention relates to methods for scheduling of uplink transmission and generating transport blocks according to multiple received uplink assignments Furthermore, the invention is also related to the implementation of these methods in hardware and software. To propose strategies for generating plural transport blocks within a given time constraint, the invention introduces prioritization of the uplink assignments, so that multiple uplink assignments can be ranked in the mobile terminal in a priority order. The prioritization of the uplink assignments is used to determine the order in which the individual transport blocks corresponding to the uplink assignments are filled, respectively how the data of different logical channels is multiplexed to the transport blocks for transmission in the uplink. Another aspect of the invention is to suggest joint logical channel procedures that operate on virtual transport blocks accumulated from the received uplink assignments. One or more such joint logical channel procedure can be performed in parallel.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Synchronization for femto-cell base stations
Timing synchronization between base stations of uncoordinated communication networks includes obtaining timing synchronization information from one base station, and adjusting a clock of the other station in response to the synchronization information. The timing synchronization information can be identified from a strongest synchronization signal from nearby uncoordinated base stations. The timing synchronization can accommodate clock offsets and frequency offsets.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
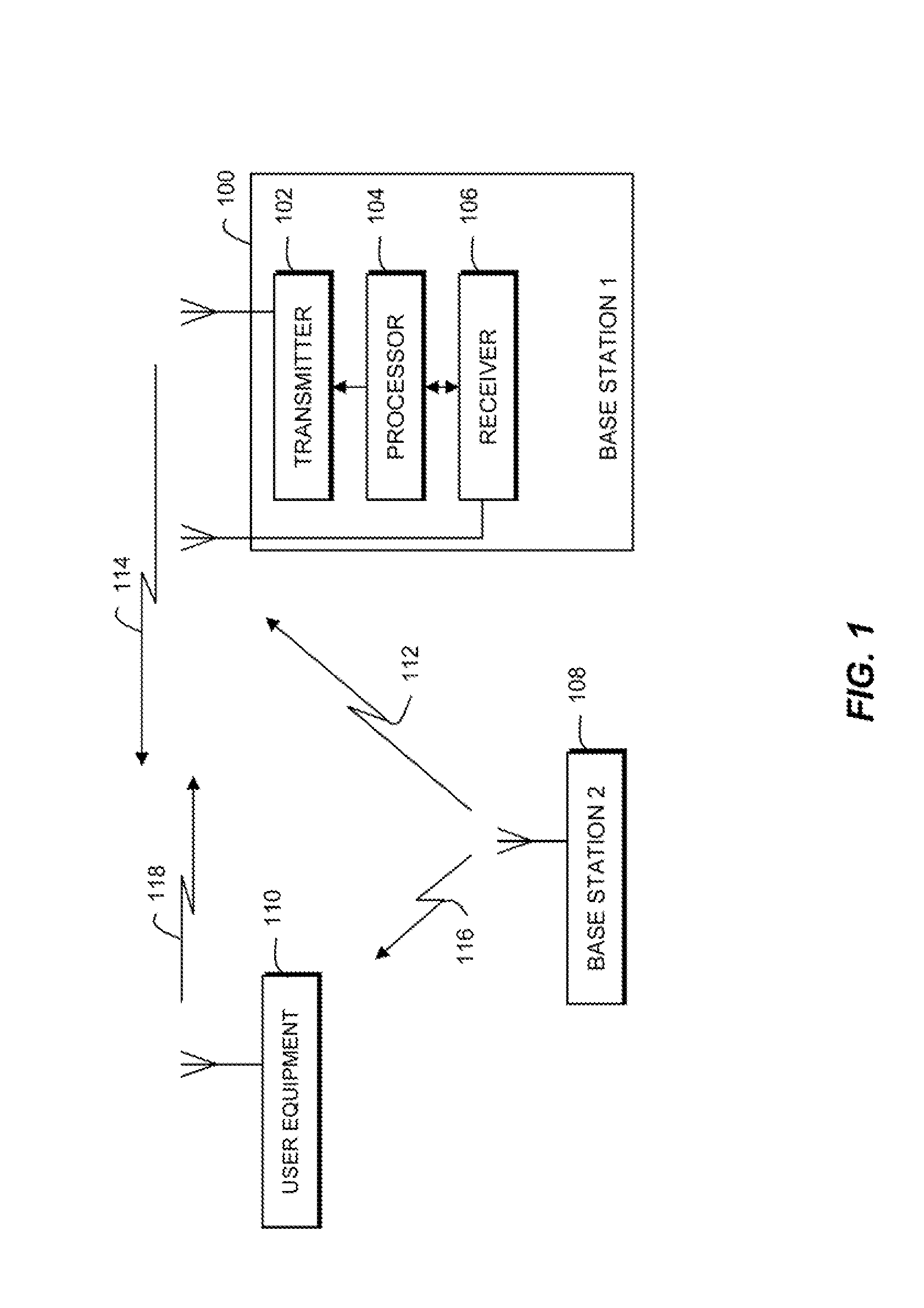
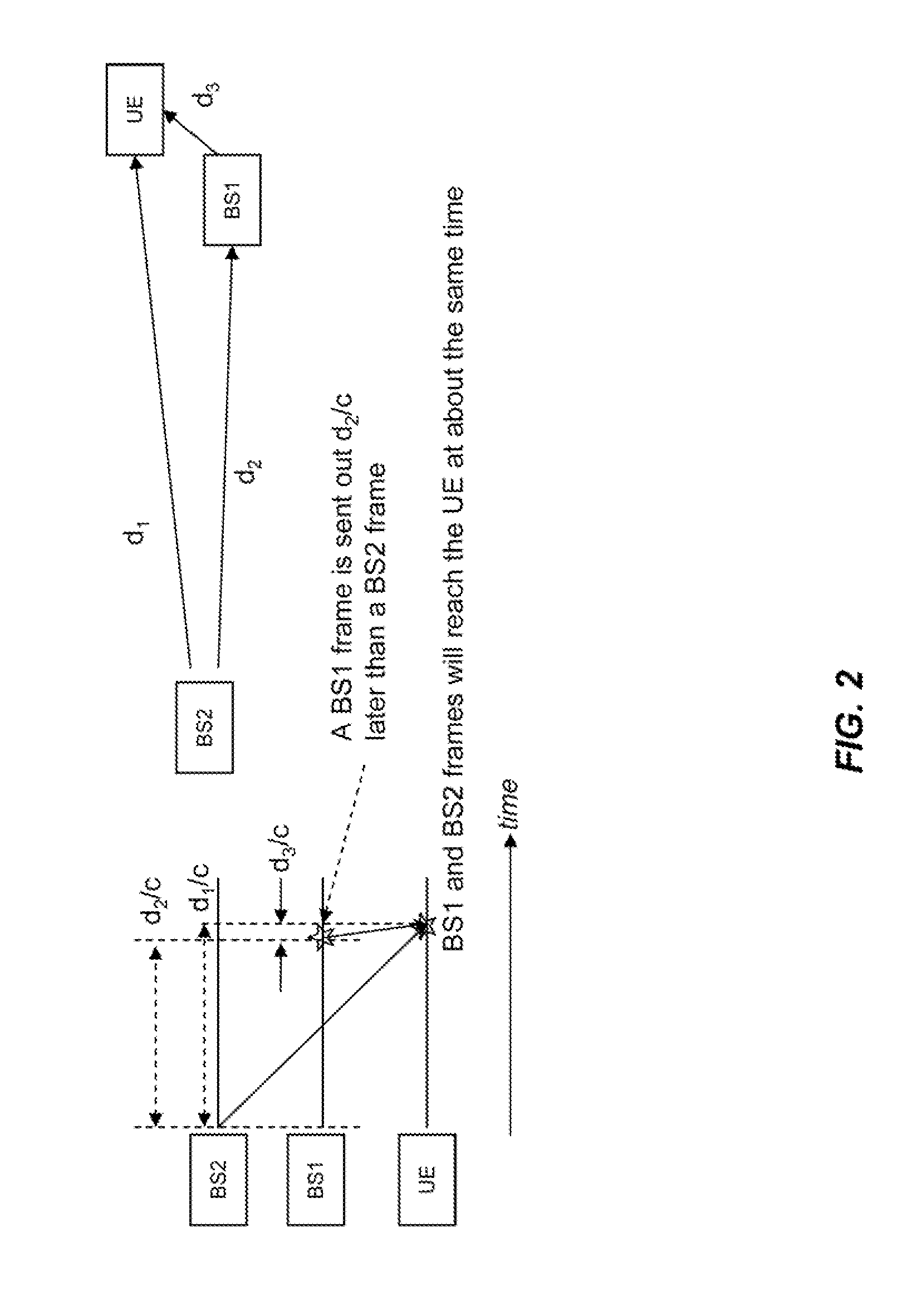
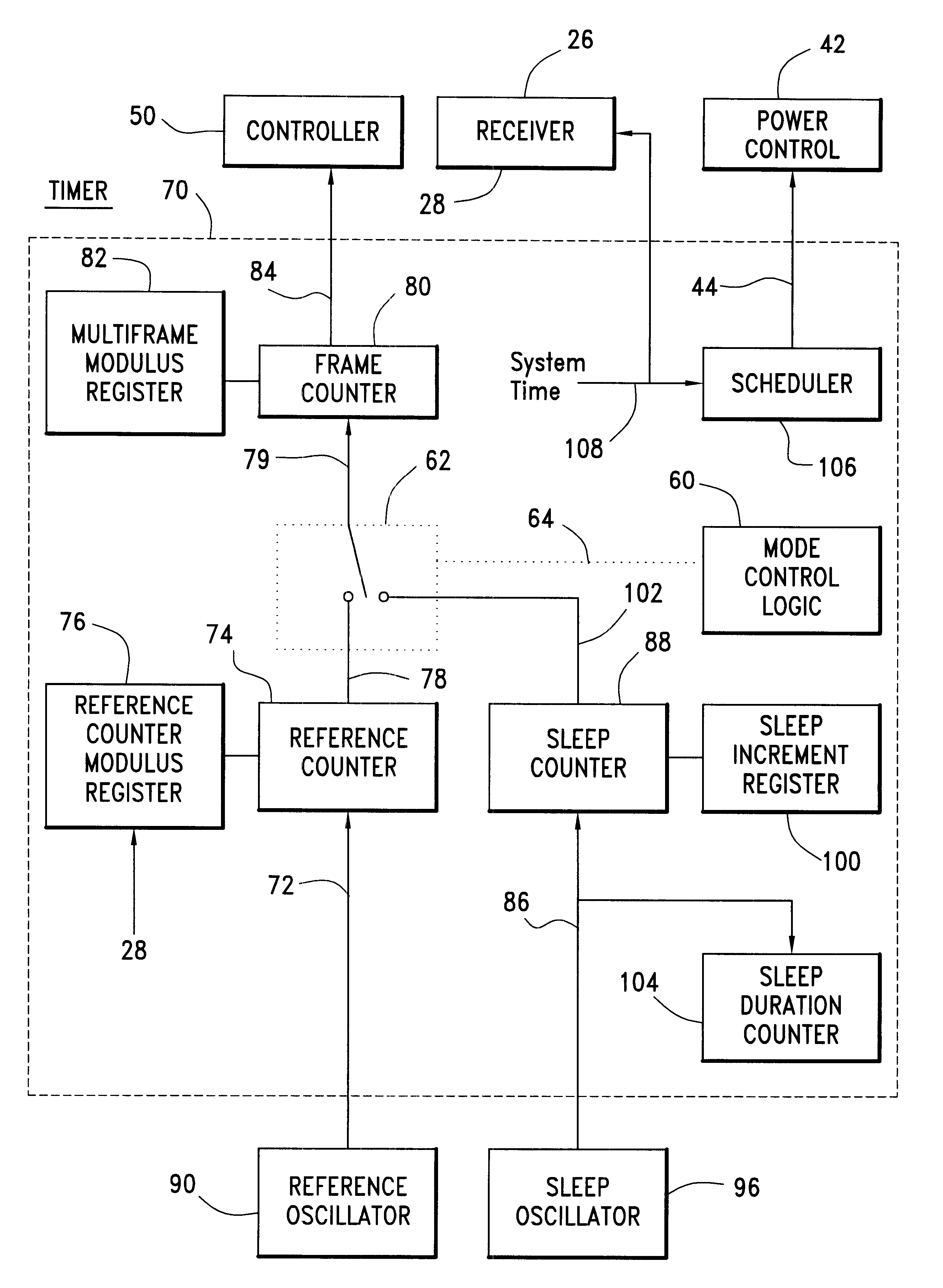
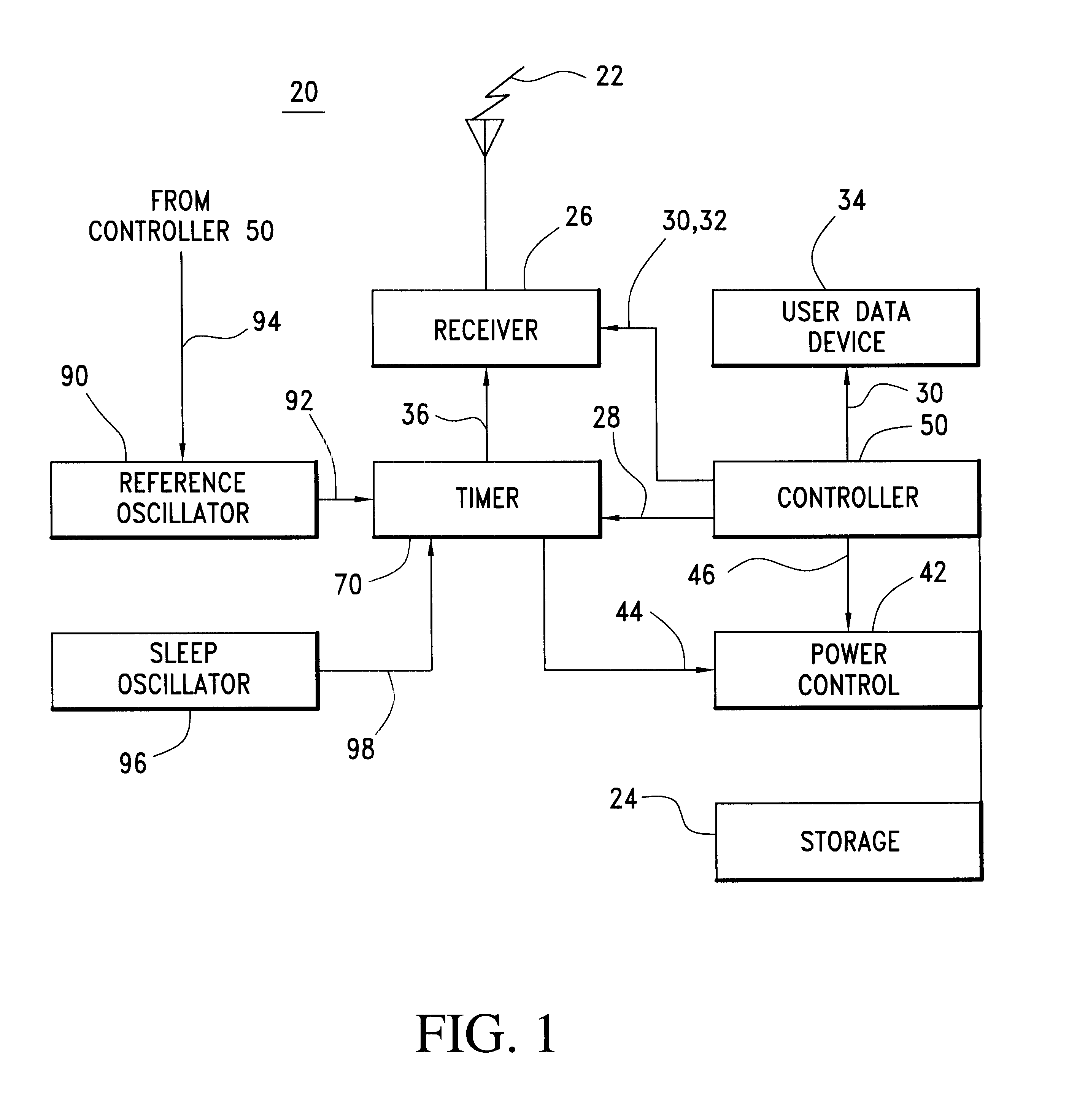
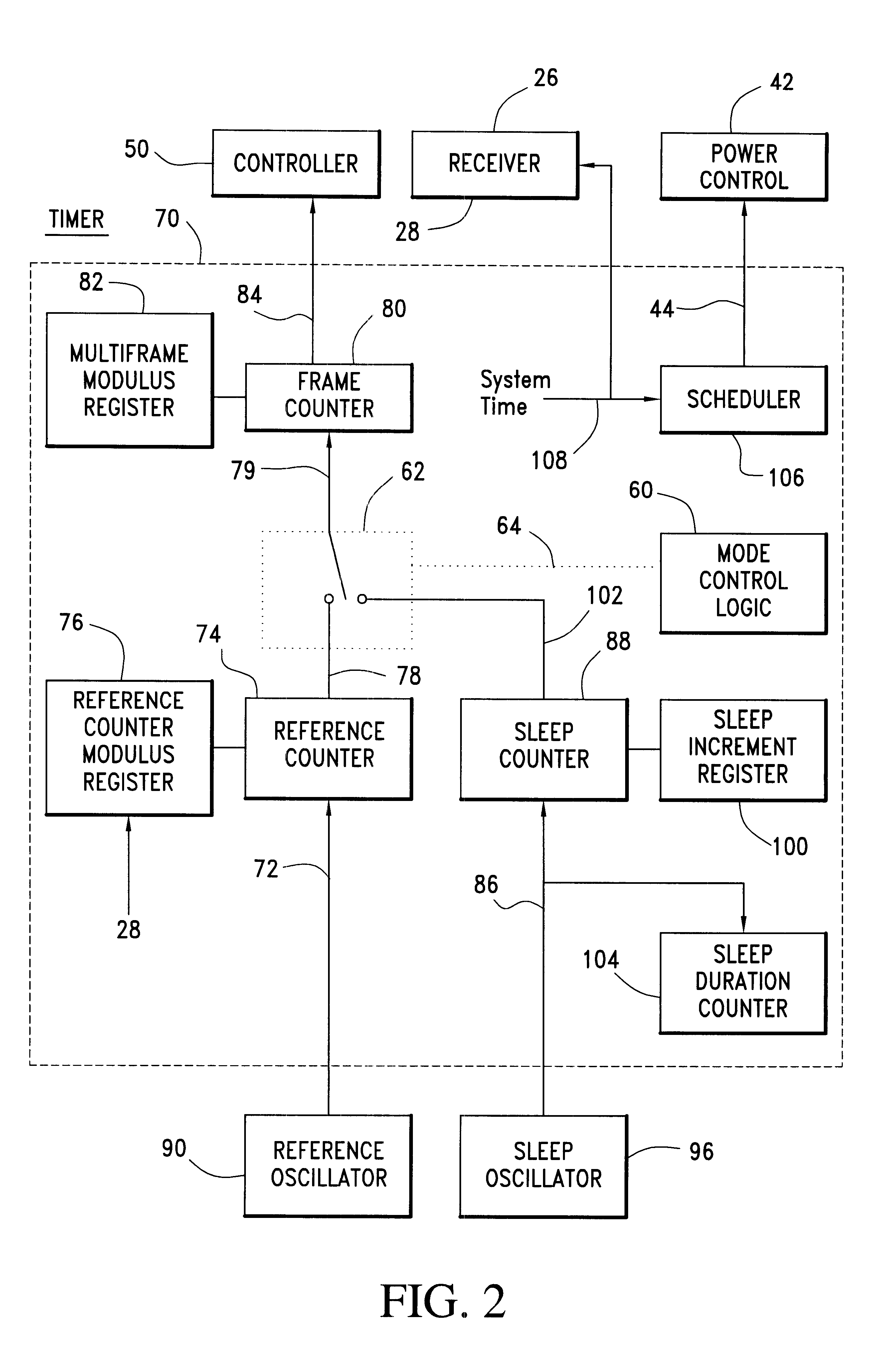
Communication device with a self-calibrating sleep timer
The present invention provides for a system for operating a communication device (20) for reception of scheduled intermittent information messages (22) with a dual mode timer (70) that extends battery life. A controller (50) schedules the timer (70) to power down all idle components of the device (20) between message receptions in a power saving sleep mode to conserve battery power. During active mode when the device is fully active in reception of messages, the timer (70) uses a reference oscillator (90) with a relatively high frequency to support digital processing by the receiver (26). During sleep mode when only the timer is powered on, a much lower frequency sleep oscillator (96) is used to maintain the lowest possible level of power consumption within the timer itself. The timer (70) has provision for automatic temperature calibration to compensate for timing inaccuracies inherent to the low-power low-frequency crystal oscillator (96) used for the sleep mode. The resultant improvement in timer accuracy during sleep mode eliminates the need for an initial reacquisition period following wake up in active mode, thereby reducing battery drain in active mode as well.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method of performing random access procedure in wireless communication system
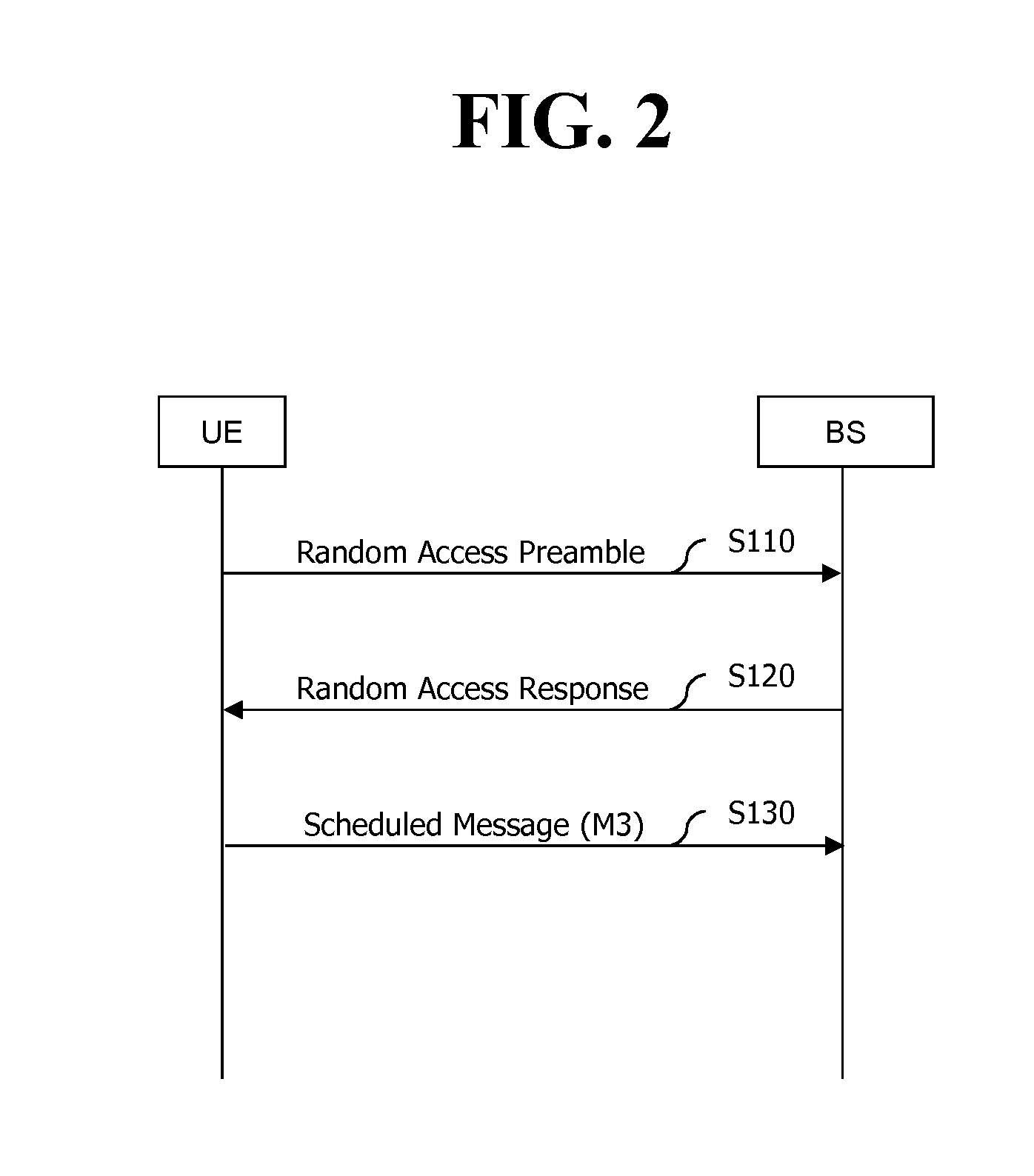
ActiveUS20090186613A1Reliable data transmissionSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource allocation
A method includes transmitting a random access preamble, receiving a random access response as a response of the random access preamble, wherein the random access response comprises an uplink resource assignment and a request for transmission of a Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), and transmitting the CQI in the uplink resource assignment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS20010036810A1Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Method for providing multi-level access services in common access channel
ActiveUS20070032255A1Easy to useSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesMobile communication systems
The present invention relates to a method for performing a ranging operation according to the priority order in a mobile communication system using a BWA (Broadcast Wireless Access) scheme. The method according to the invention for performing a range operation by a subscriber terminal in a mobile communication system using the BWA (Broadcast Wireless Access) scheme comprises steps of: receiving backoff domains having the start and end values of the backoff corresponding to each ranging operation, the backoff domains being determined from a base station according to the priority order of the ranging operations between the base station and subscriber terminals; performing a ranging operation and, if it is determined that the step of performing the ranging operation fails, selecting backoff domains among the received backoff domains according to the priority order of the performed ranging operations; and, re-performing the ranging operation according to the selected backoff domains.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
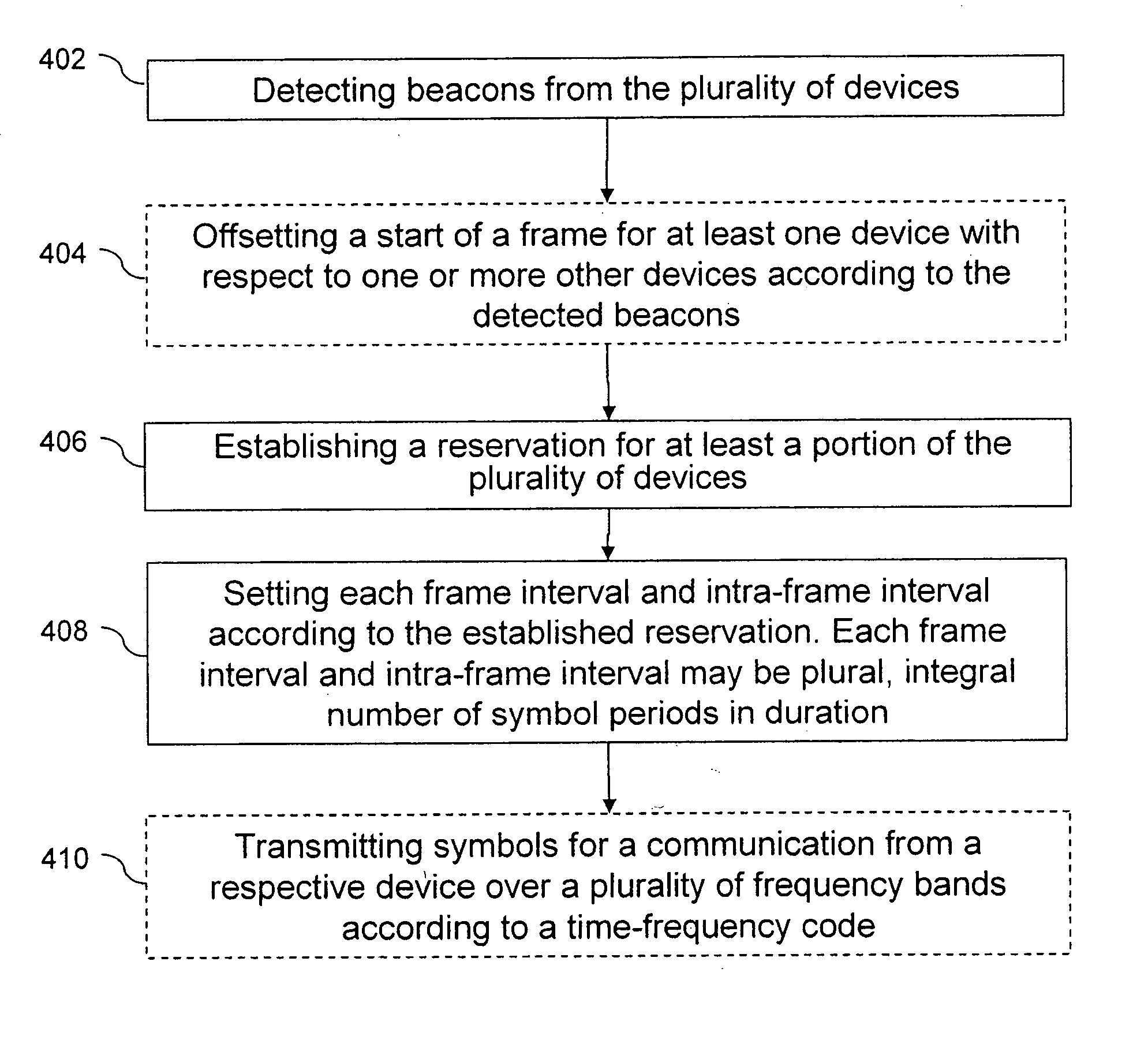
Method of band multiplexing to improve system capacity for a multi-band communication system
ActiveUS20070054680A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMulti bandCommunications system
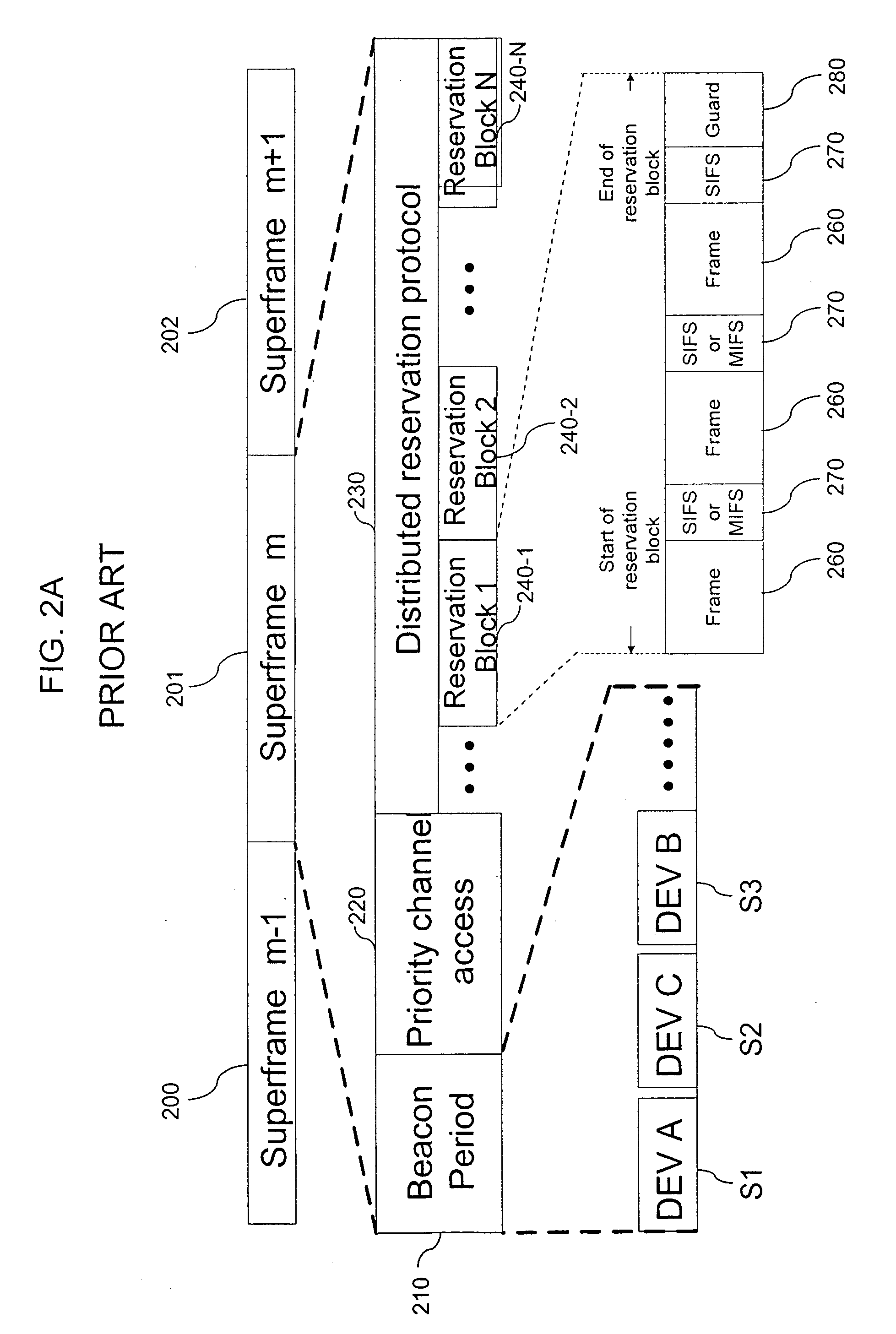
A control method of synchronizing communications between or among a plurality of devices in a communication system includes detecting beacons from the plurality of devices in the communication system, and establishing a reservation for at least a portion of the plurality of devices in the communication system. Each reservation is a frame interval in which to transmit symbols from one device to one or more of the other devices in the communications system. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is set according to the established reservation. Each frame interval and intra-frame interval is a plural, integral number of symbol periods in duration.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Apparatus and method for performing random access in multi-carrier system
InactiveUS20110249641A1Synchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsResponse generationCarrier signal
A method for performing a random access in a multi-carrier system includes transmitting a random access preamble on an uplink component carrier to a base station, and receiving a random access response on a first downlink component carrier. The random access response includes information regarding a second downlink component carrier used to transmit a contention resolution message indicating that a random access collision with other mobile stations are resolved. A base station to perform the method includes a preamble reception unit to receive the random access preamble, a response generation unit to generate the random access response, and a response transmission unit to transmit the random access response. A mobile station to perform the method includes a preamble transmission unit, a response reception unit, a carrier configuration unit, and a message reception unit.
Owner:PANTECH CO LTD
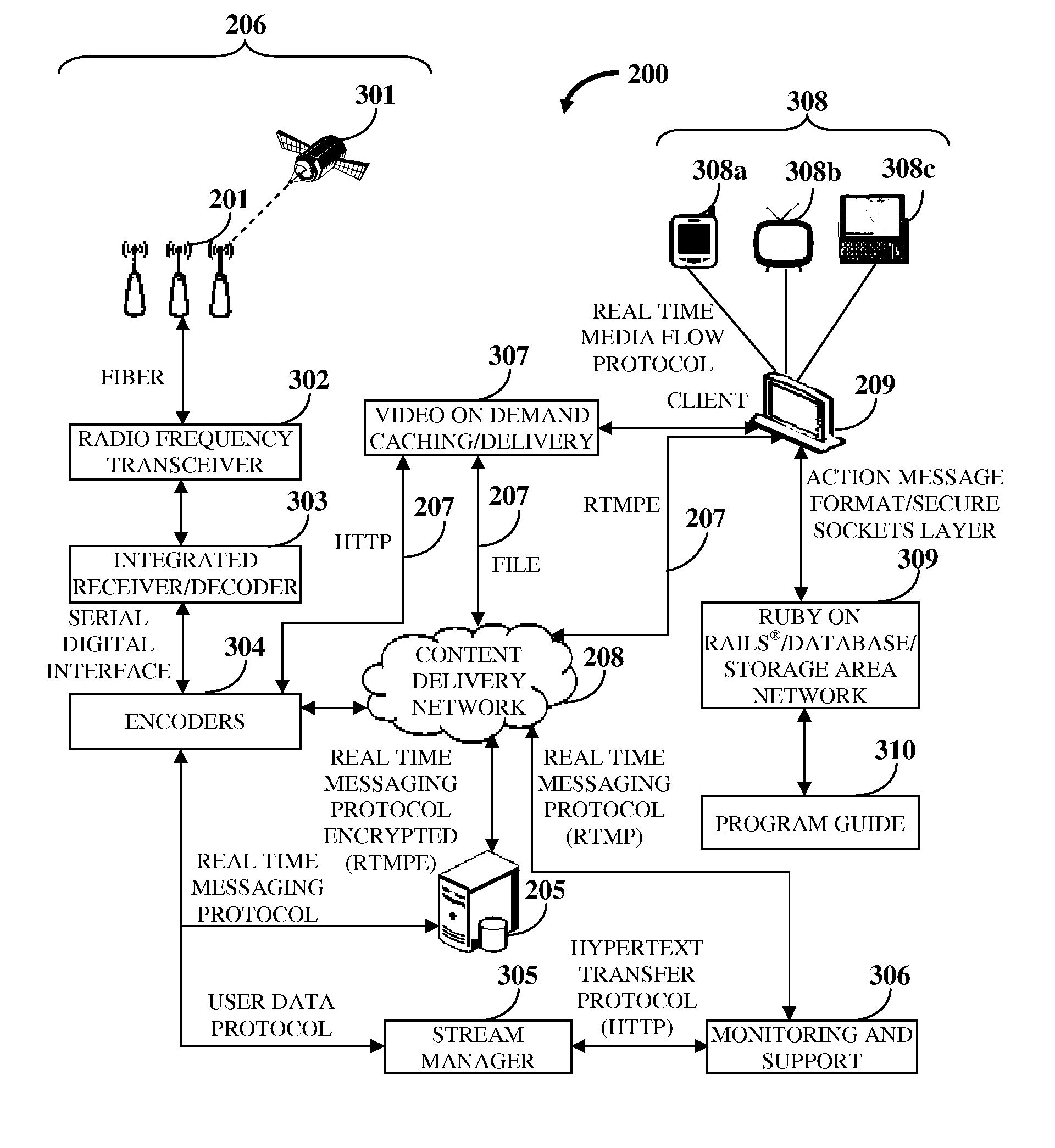
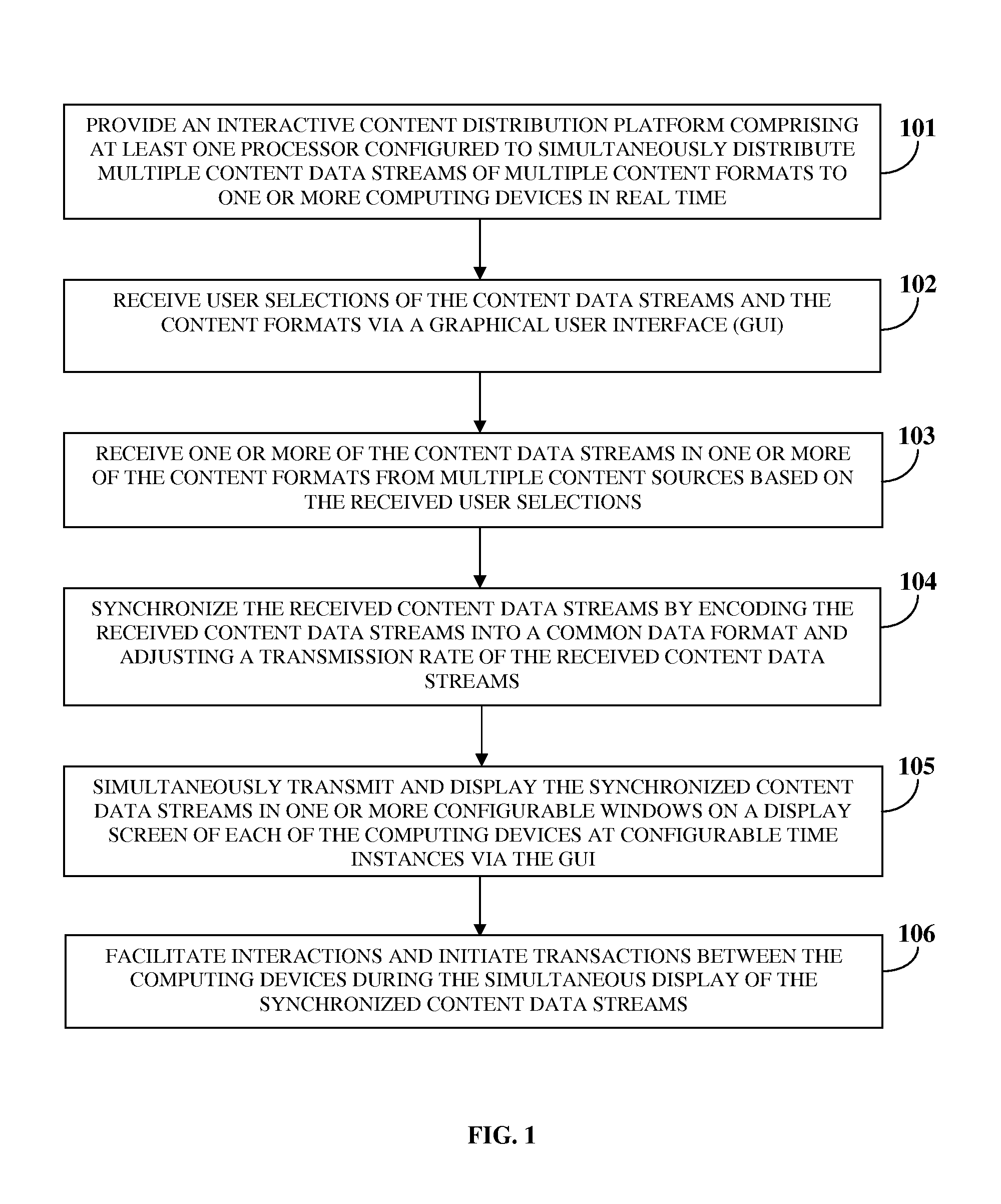
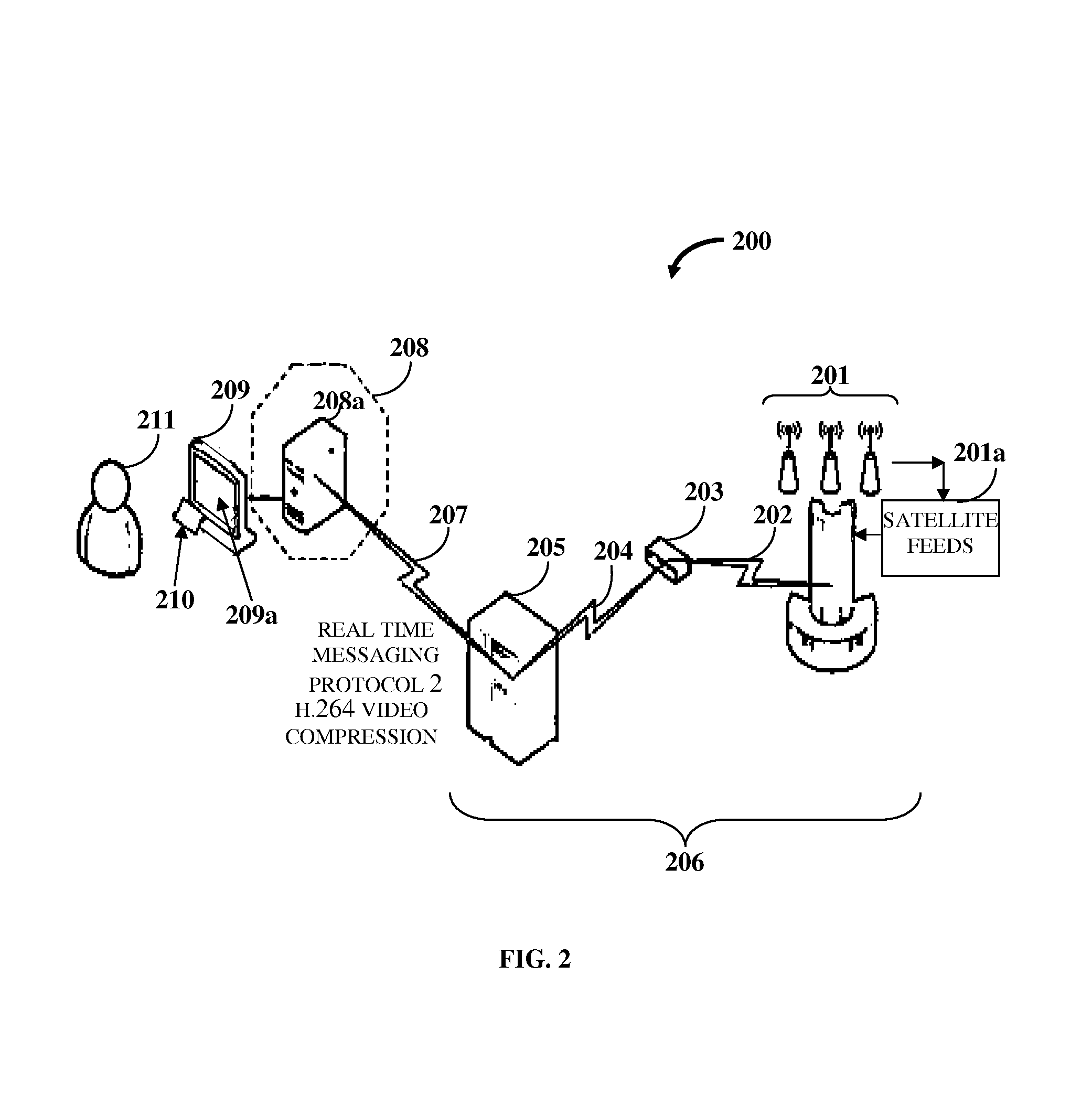
Simultaneous Content Data Streaming And Interaction System
InactiveUS20140195675A1Enhanced interactionSimple waySynchronisation arrangementBroadcast transmission systemsInteraction systemsContent distribution
A computer implemented method and system simultaneously distributes content data streams (CDSs) of multiple content formats, for example, live cable television content, gaming content, social media content, user generated content, etc., to one or more computing devices. An interactive content distribution platform (ICDP) receives user selections of the CDSs and the content formats via a graphical user interface (GUI) and receives one or more CDSs in one or more content formats from multiple content sources based on the user selections. The ICDP synchronizes the CDSs by encoding the CDSs into a common data format and adjusting a transmission rate of the CDSs. The ICDP simultaneously transmits and displays the synchronized CDSs in one or more configurable windows on a display screen of each computing device at configurable time instances via the GUI. The ICDP facilitates interactions and initiates transactions between computing devices during the simultaneous display of the synchronized CDSs.
Owner:GIGA ENTERTAINMENT MEDIA
Method for controlling uplink transmission power and wireless device using same
ActiveUS20140050205A1Power managementSynchronisation arrangementTelecommunicationsUplink transmission
Provided are a method for controlling uplink transmission power and a wireless device. The wireless device decides a first transmission power of a first uplink channel, which is transmitted through a first wireless resource from a first serving cell, and decides a second transmission power of a second uplink channel, which is transmitted through a second wireless resource from a second serving cell. The first serving cell belongs to a first timing advance (TA) group, and the second serving cell belongs to a second TA group that differs from the first TA group. All or a portion of the first wireless resource and the second wireless resource overlap, wherein the sum of the first and second transmission powers in the overlapping portion is decided so as not to exceed a maximum transmission power.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
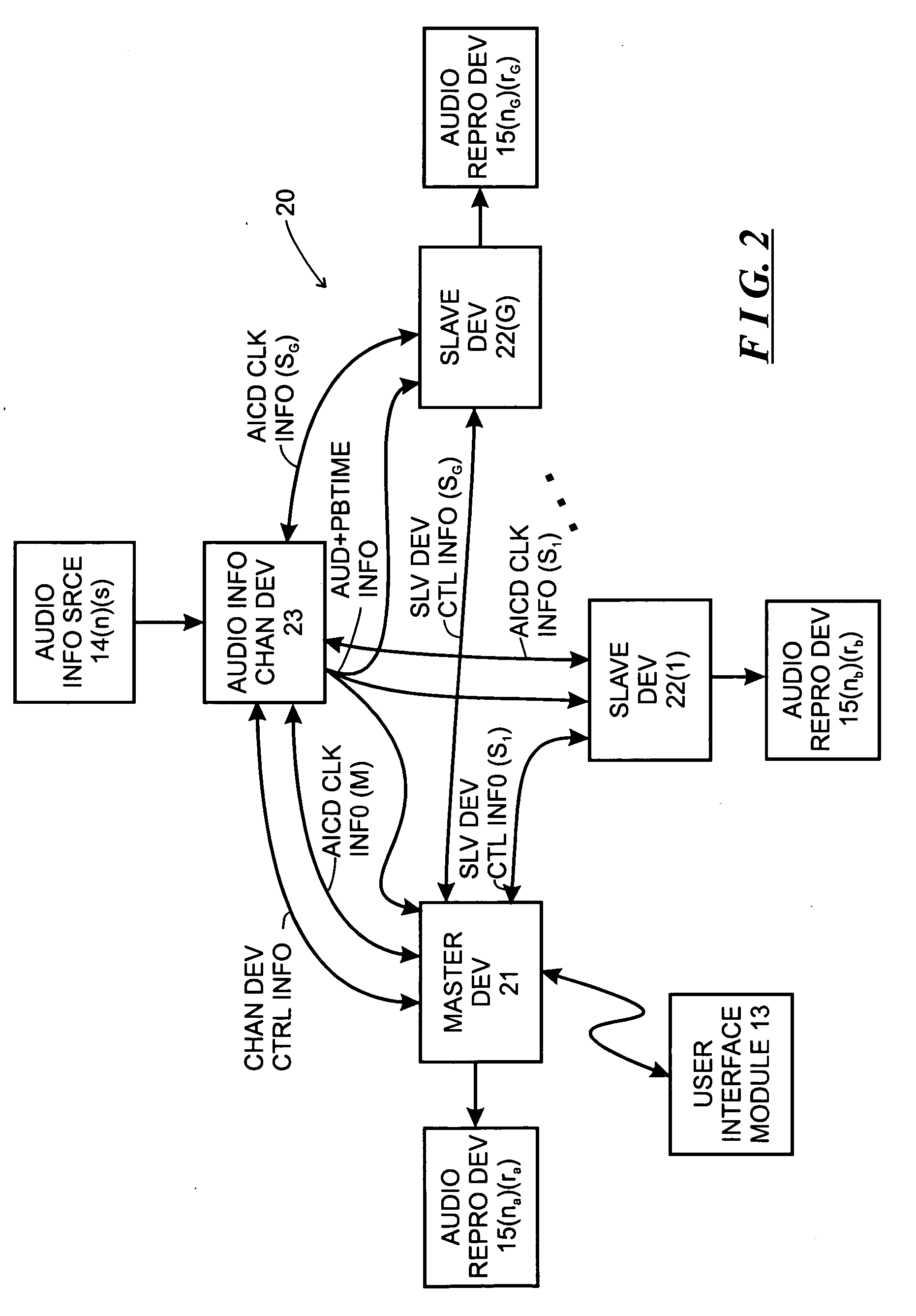
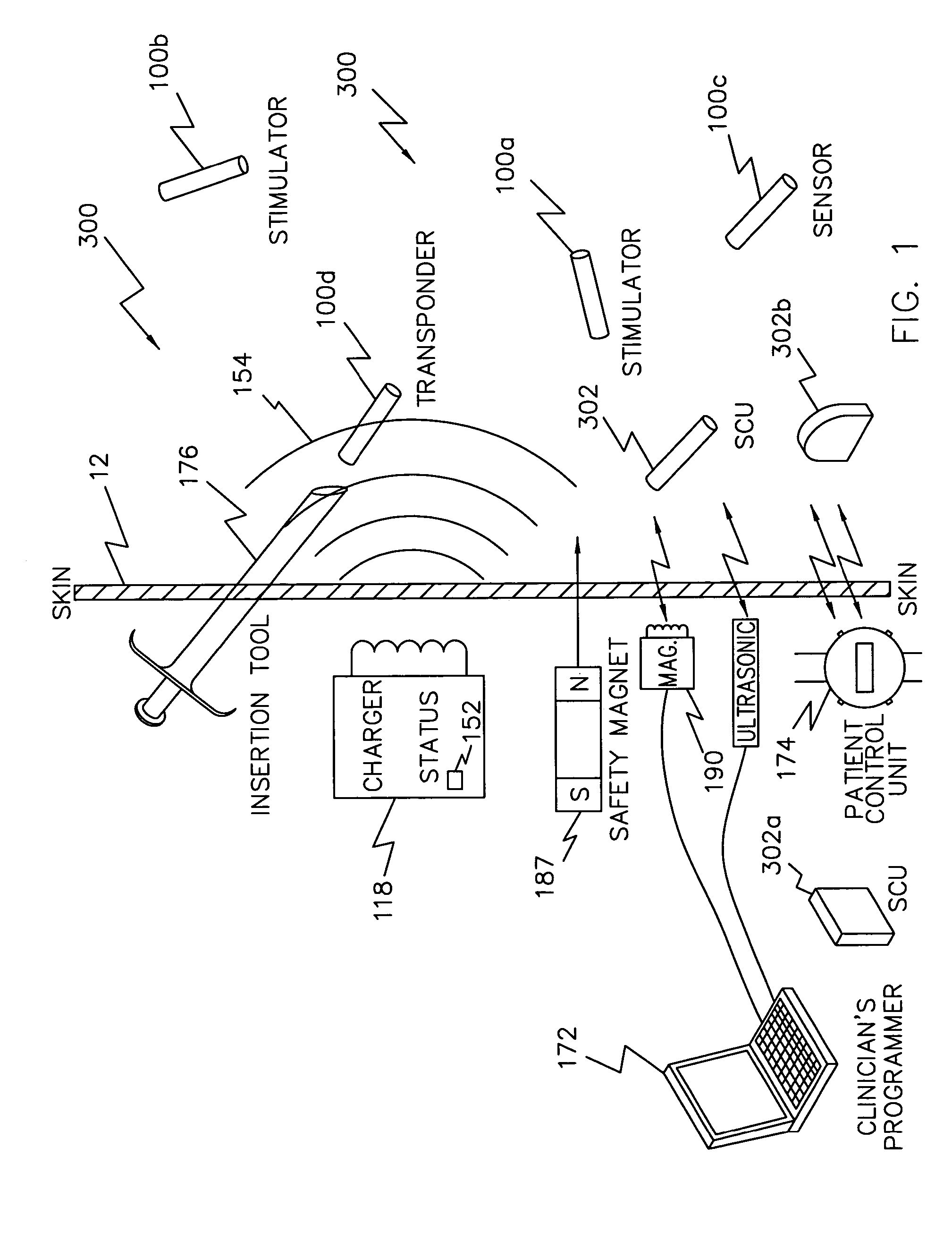
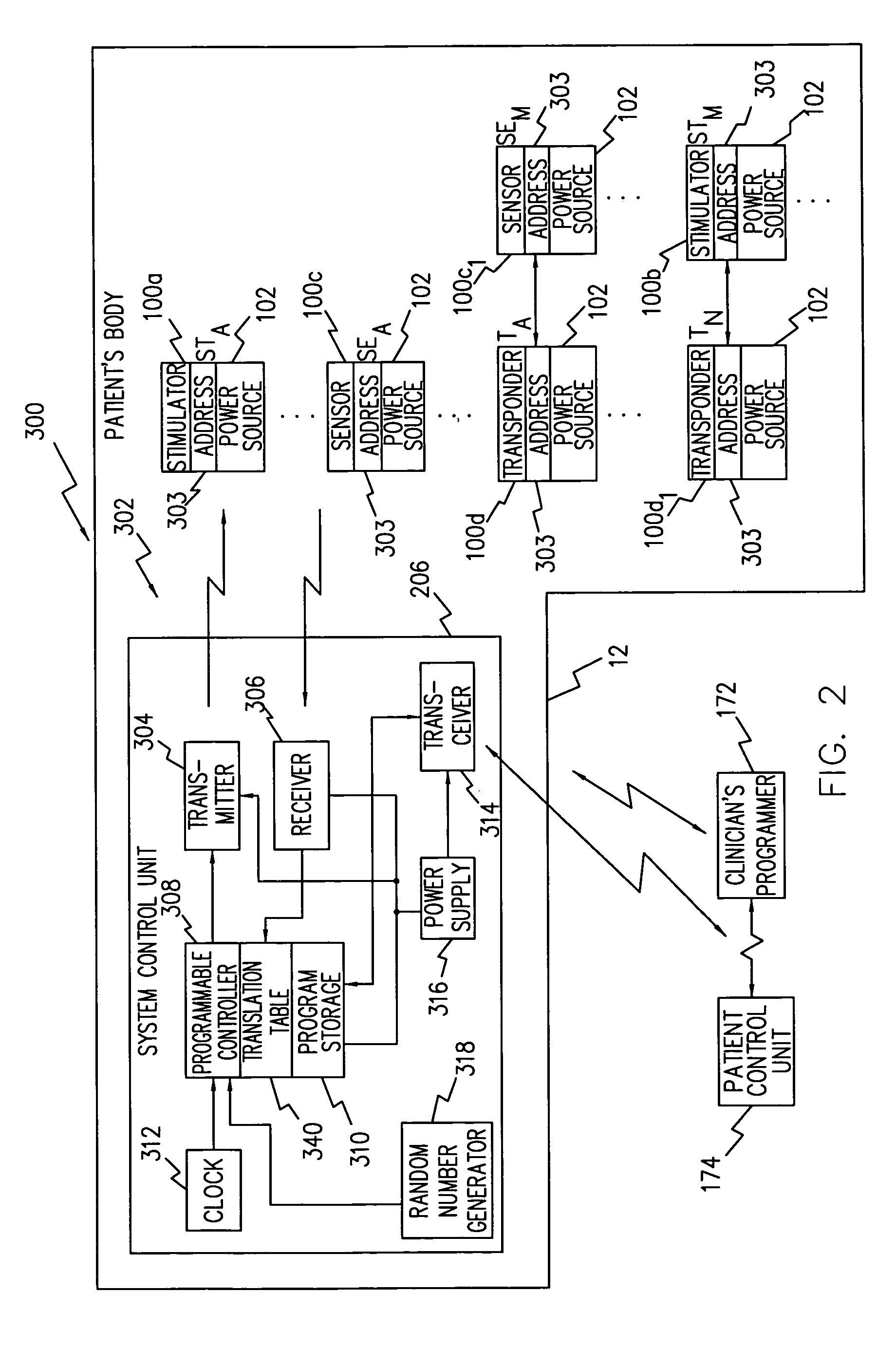
System and method for sharing a common communication channel between multiple systems of implantable medical devices
ActiveUS7406105B2Facilitates multiple systems of communicating devicesNear-field transmissionElectrotherapyComputer scienceMedical device
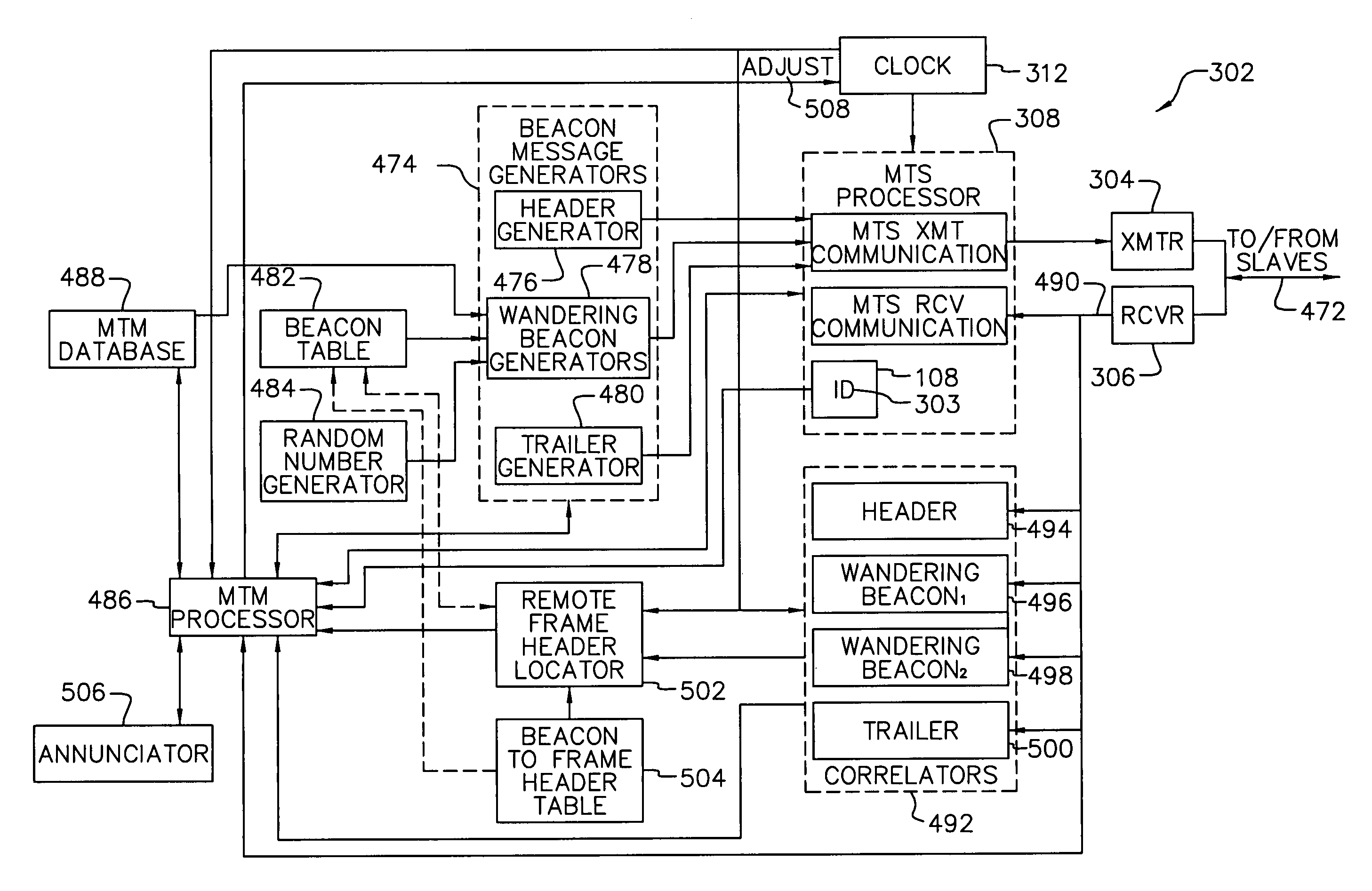
A system and method that facilitates multiple systems of communicating devices, i.e., a master device and one or more implantable slave devices, to coexist on a common, e.g., RF, communication channel having a limited temporal bandwidth while maintaining the required update rate between each master device and its associated slave devices. In embodiments of the present invention, master devices periodically transmit one or more beacon messages that are suitable for identification by other such master devices at a communication range greater than the communication range that may cause interference between systems and thus enabling one or more systems to cause the position of its frame periods to be interleaved with the frame periods of other such systems in anticipation of systems moving in closer proximity and actually interfering with each other.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
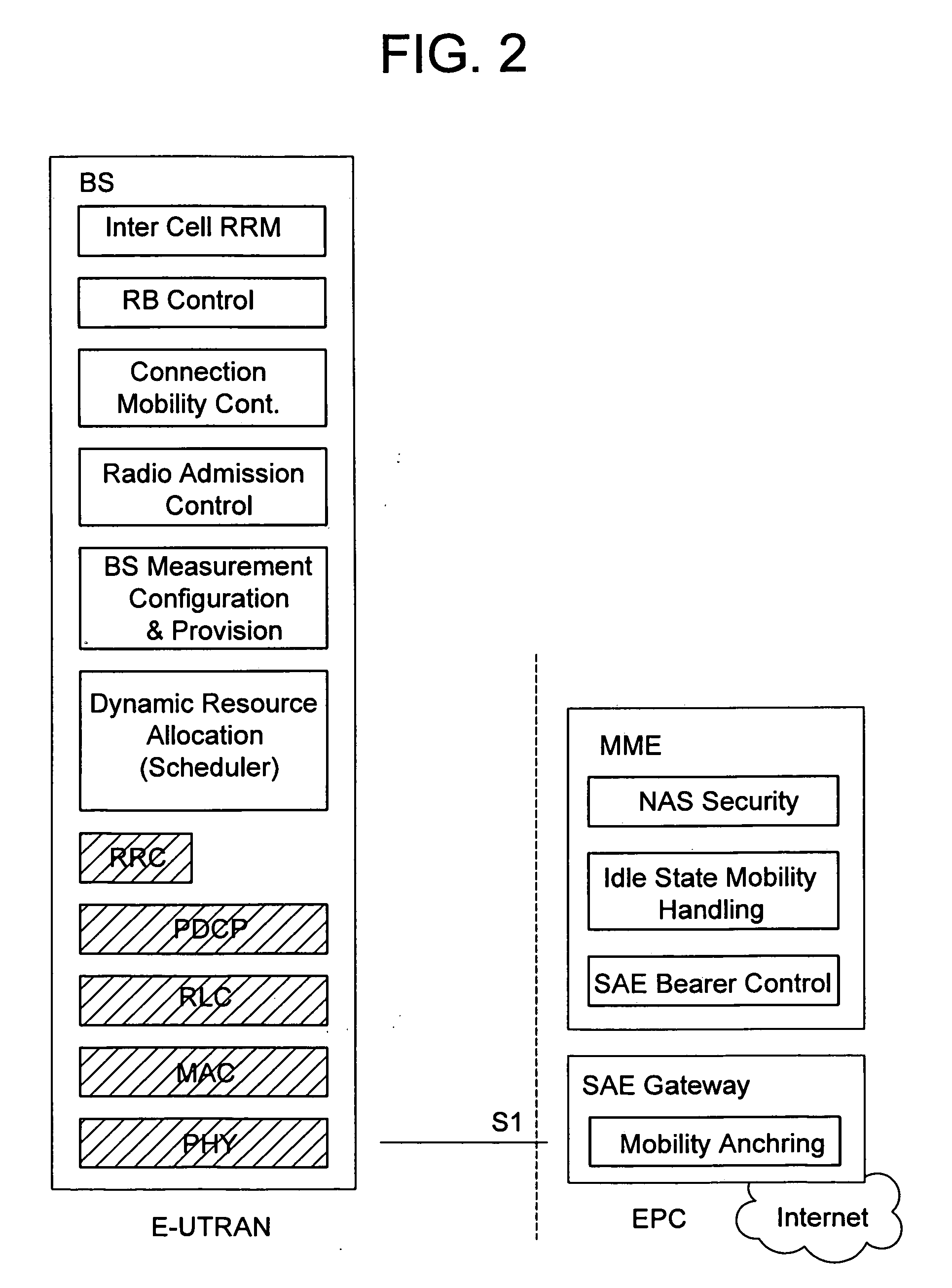
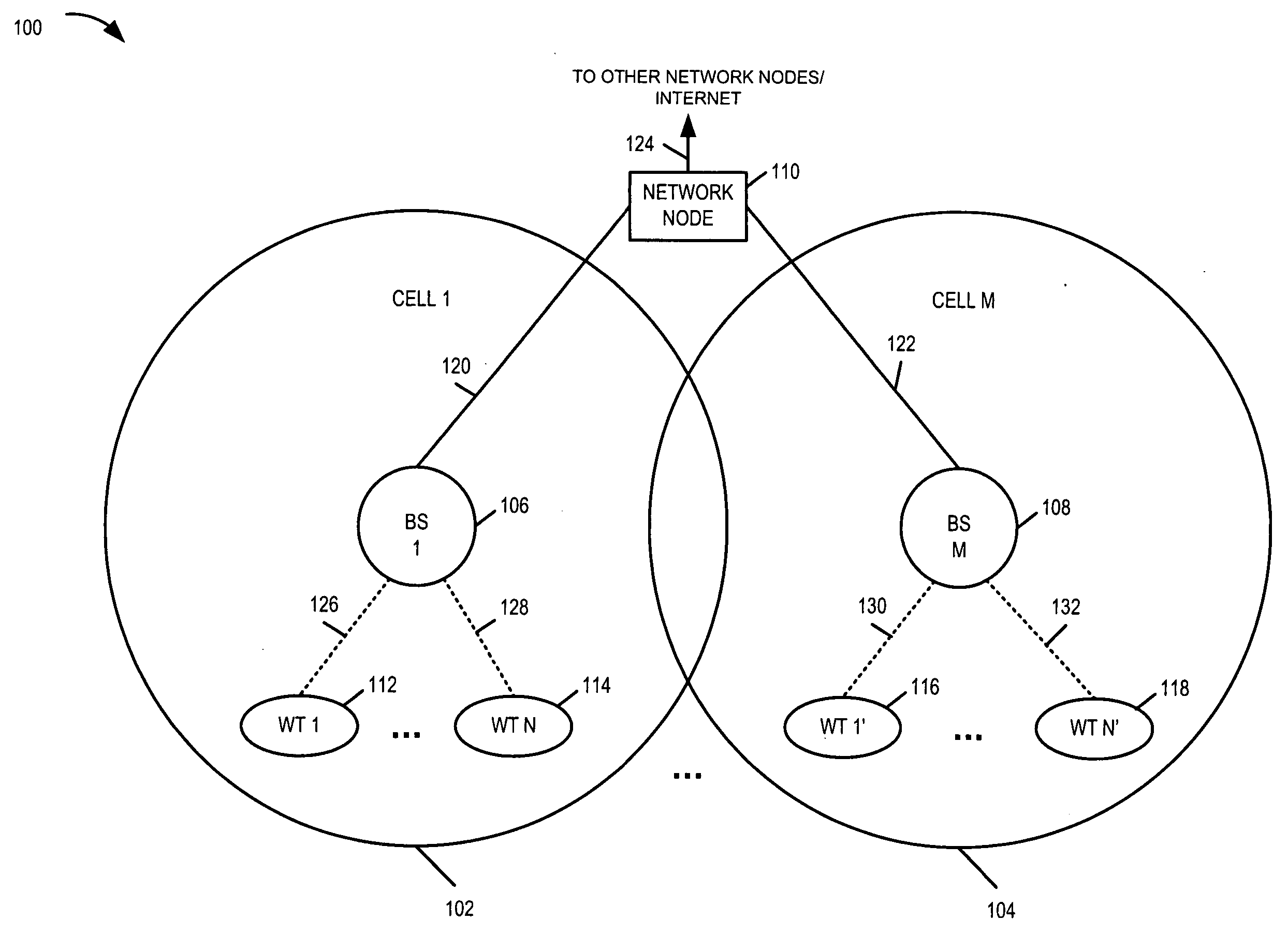
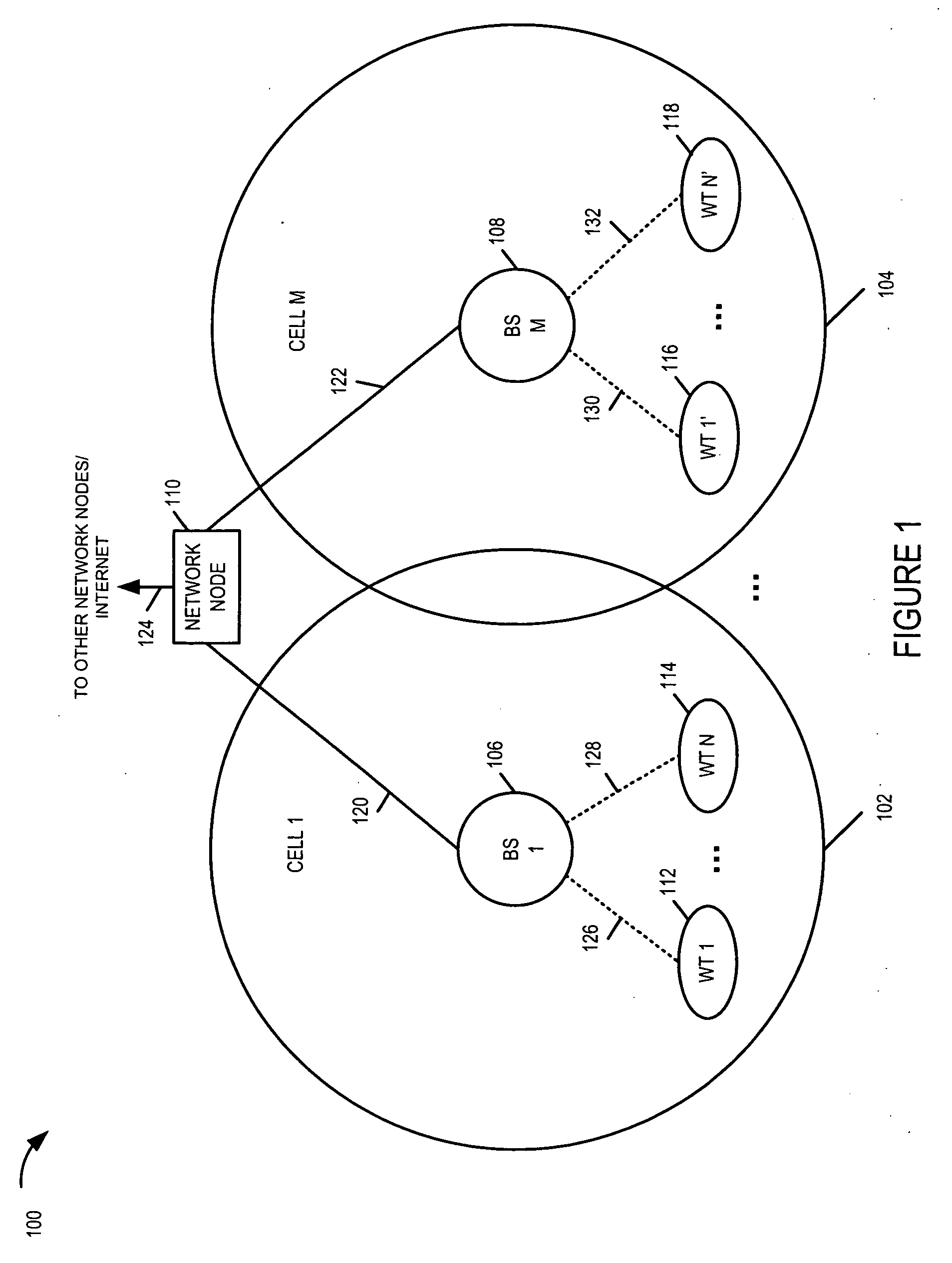
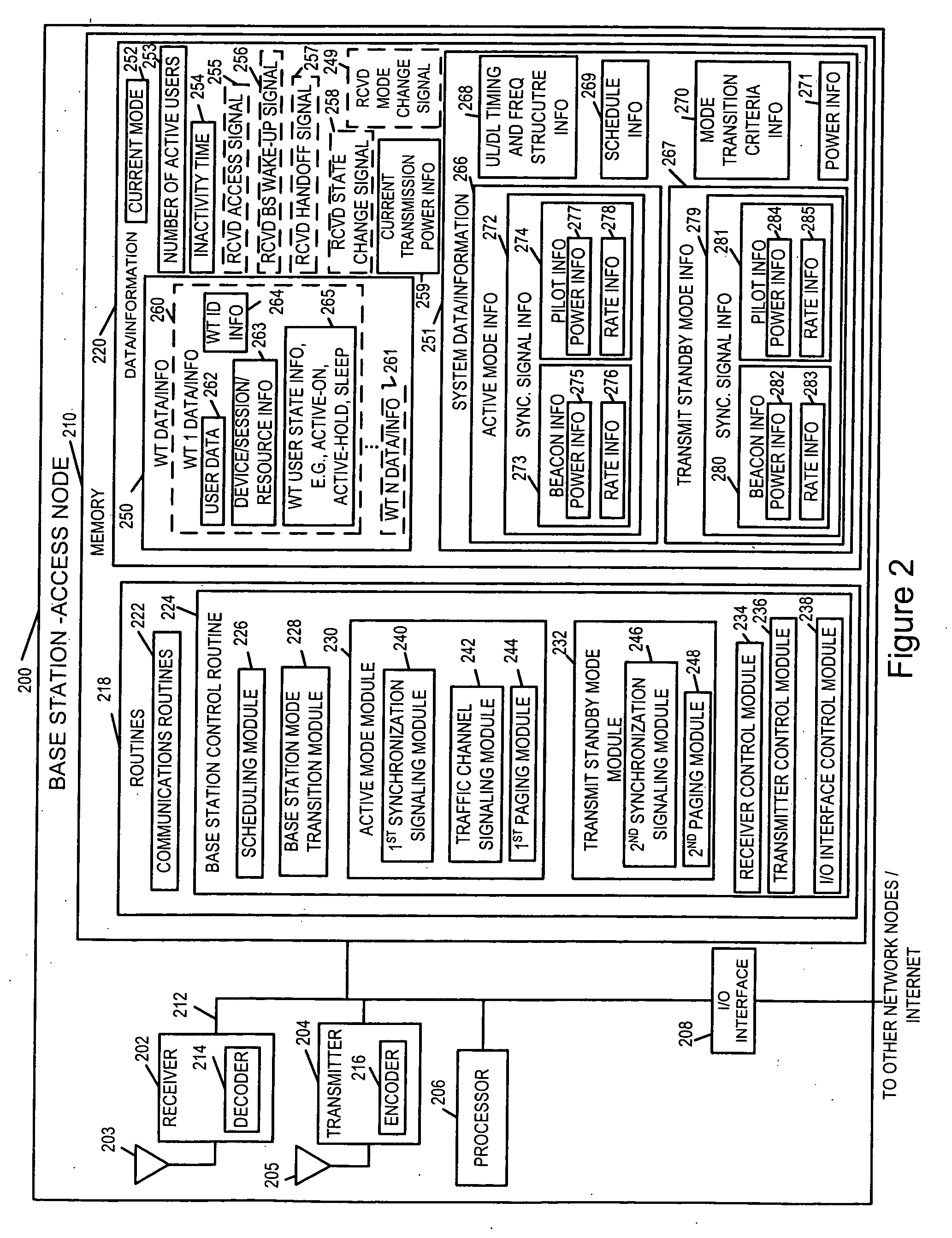
Methods and apparatus for use in a wireless communications system that uses a multi-mode base station
ActiveUS20070066329A1Improve throughputReducing base stationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemSleep state
A multi-mode base station includes a transmit standby mode and an active mode. Transmit standby mode of base station operation is a low power / low interference level of operation as compared to active mode. In transmit standby mode at least some of the synchronization signaling such as pilot tone signaling is reduced in power level and / or rate with respect to the active mode. In transmit standby mode, the base station has no active state registered wireless terminals being serviced but may have some sleep state registered wireless terminals being serviced. Mode transitions from active to transmit standby may be in response to: a detected period of inactivity, scheduling information, base station mode change signals, and / or detected wireless terminal state transition. Mode transitions from transmit standby to active may be in response to: scheduling information, access signals, wake-up signals, hand-off signals, wireless terminal state change signals, and / or base station mode change signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for handover in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080267127A1Effectively contention-freeEliminates and minimizes timeSynchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemMobile equipment identifier
A method and apparatus for handover in a wireless communication system. A handover indication can be received from a source base station (120) that is connected with a mobile station (110). The handover indication can include a random access channel preamble. The random access channel preamble can include a temporary mobile equipment identifier. The random access channel preamble can be received from the mobile station. A timing advance message can be sent in response to receiving random access channel preamble. The timing advance message can be addressed by the random access channel preamble and a source base station identifier. The connection with the mobile station can be switched from the source base station to a target base station (130).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
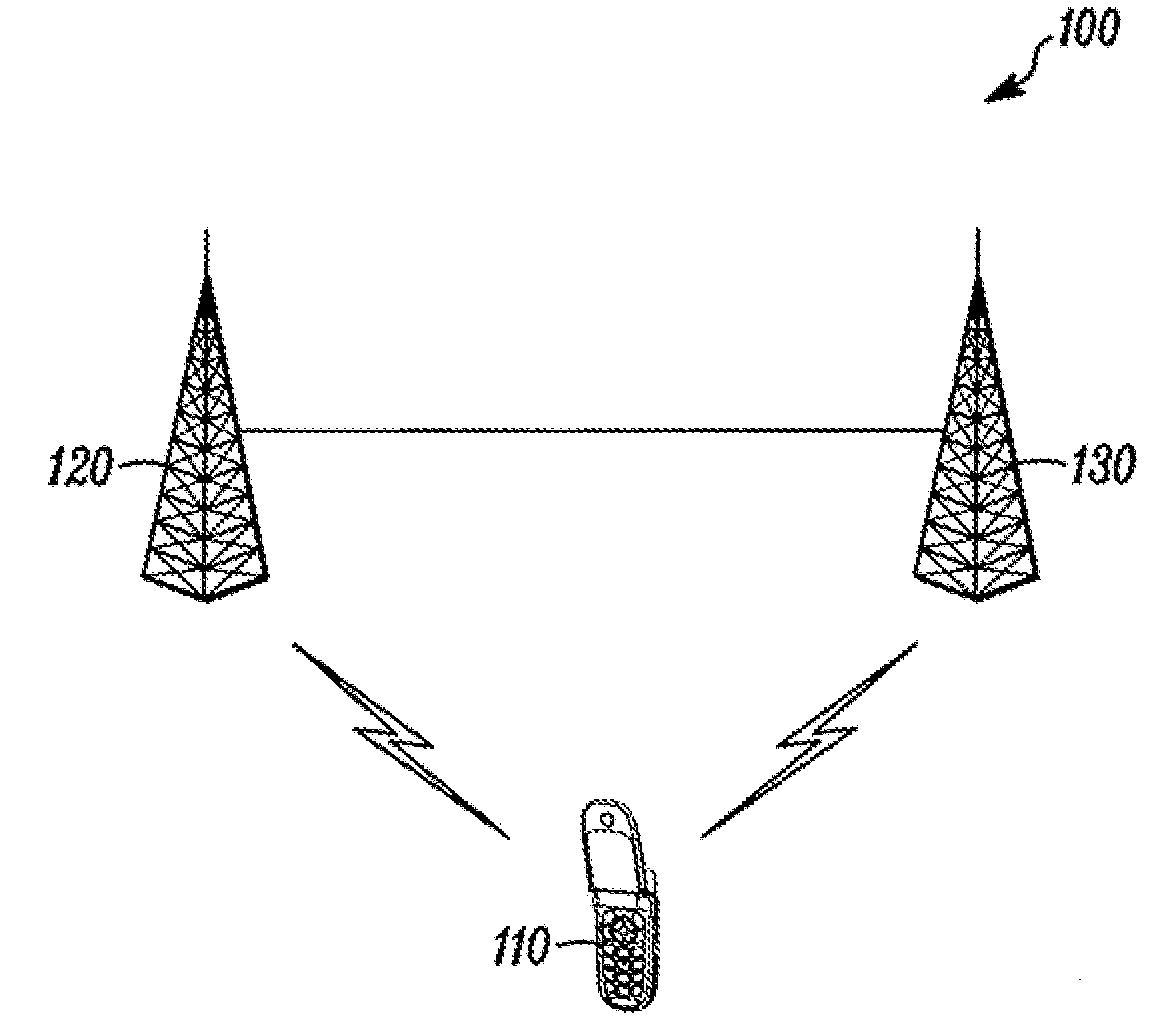
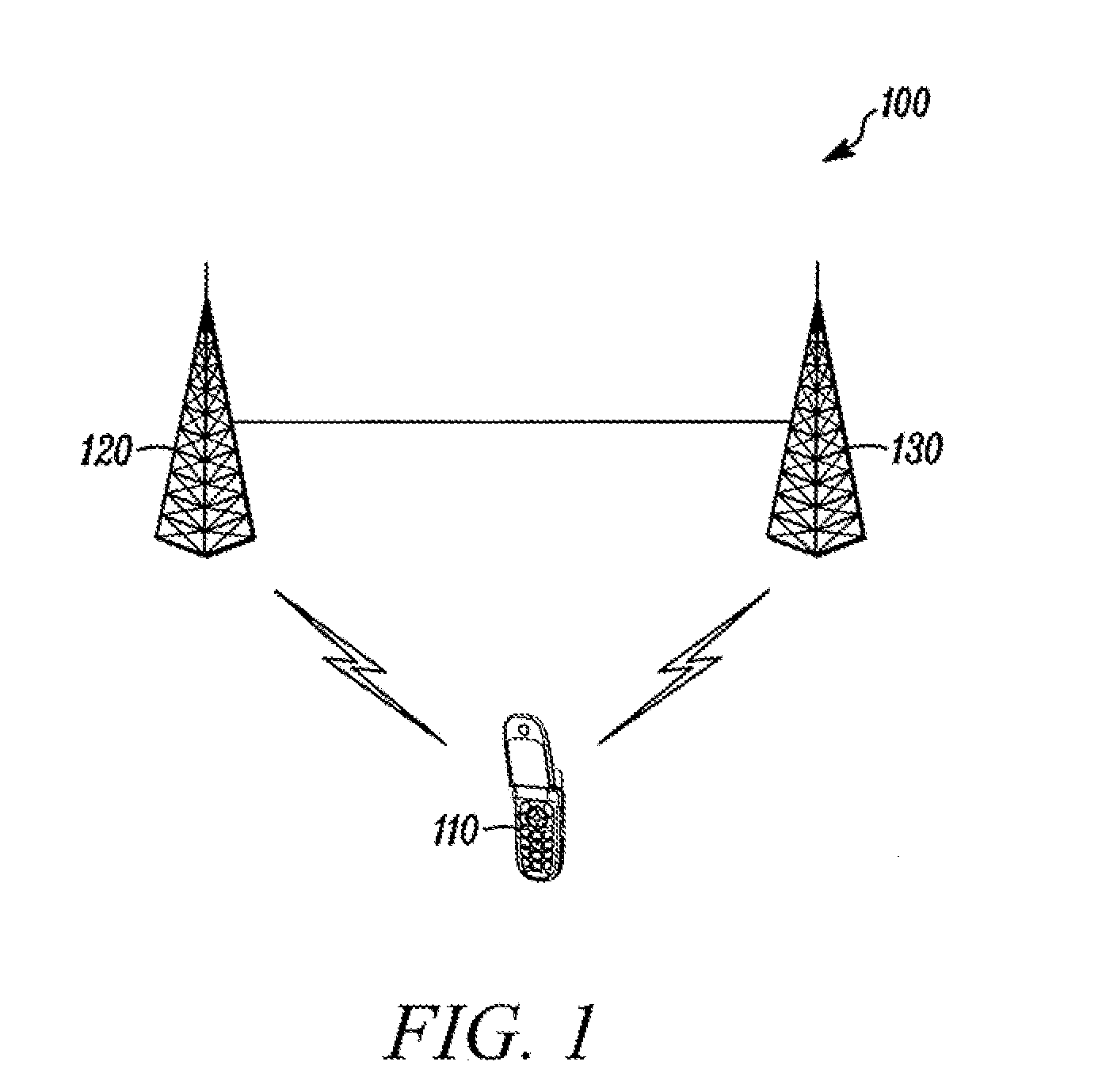
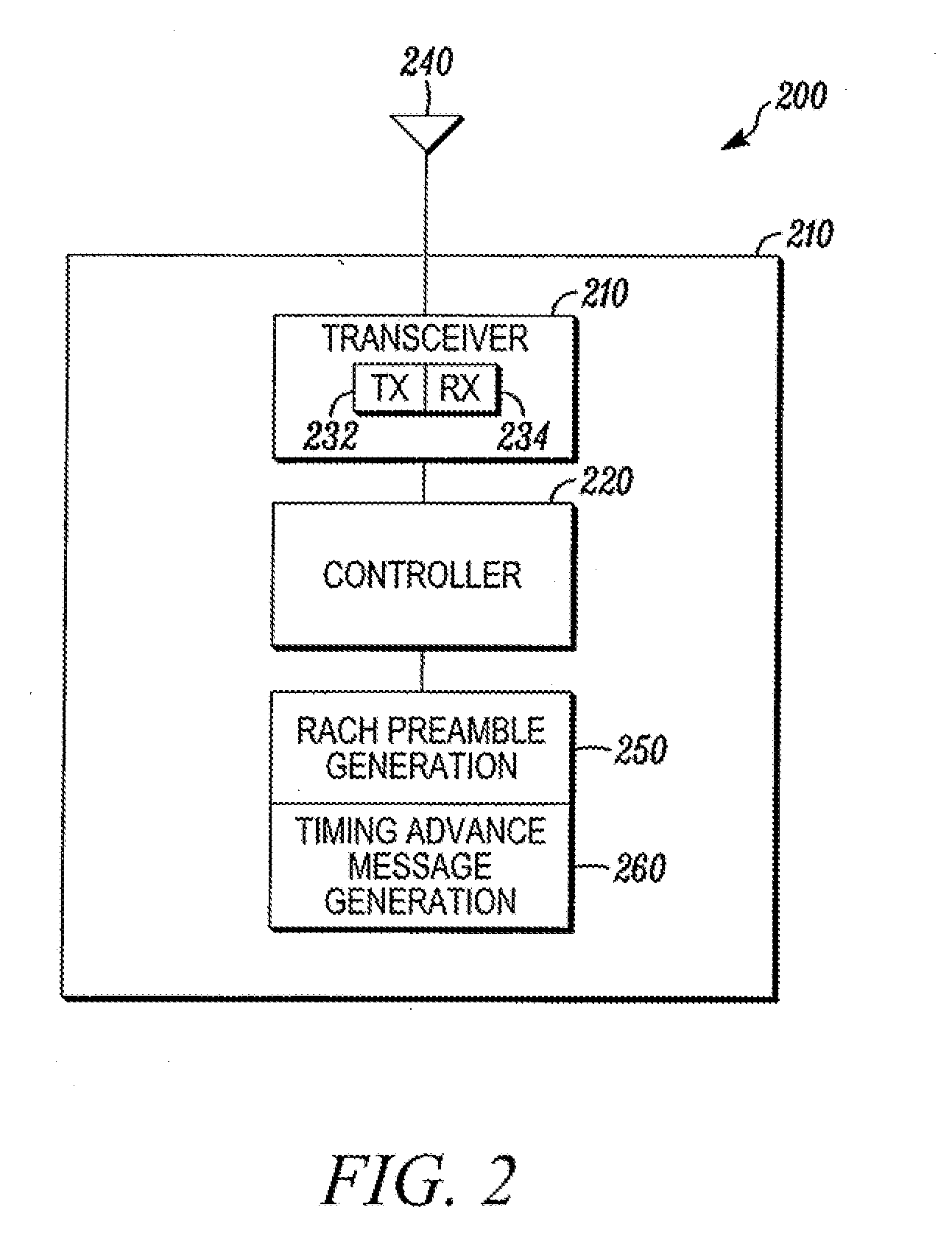
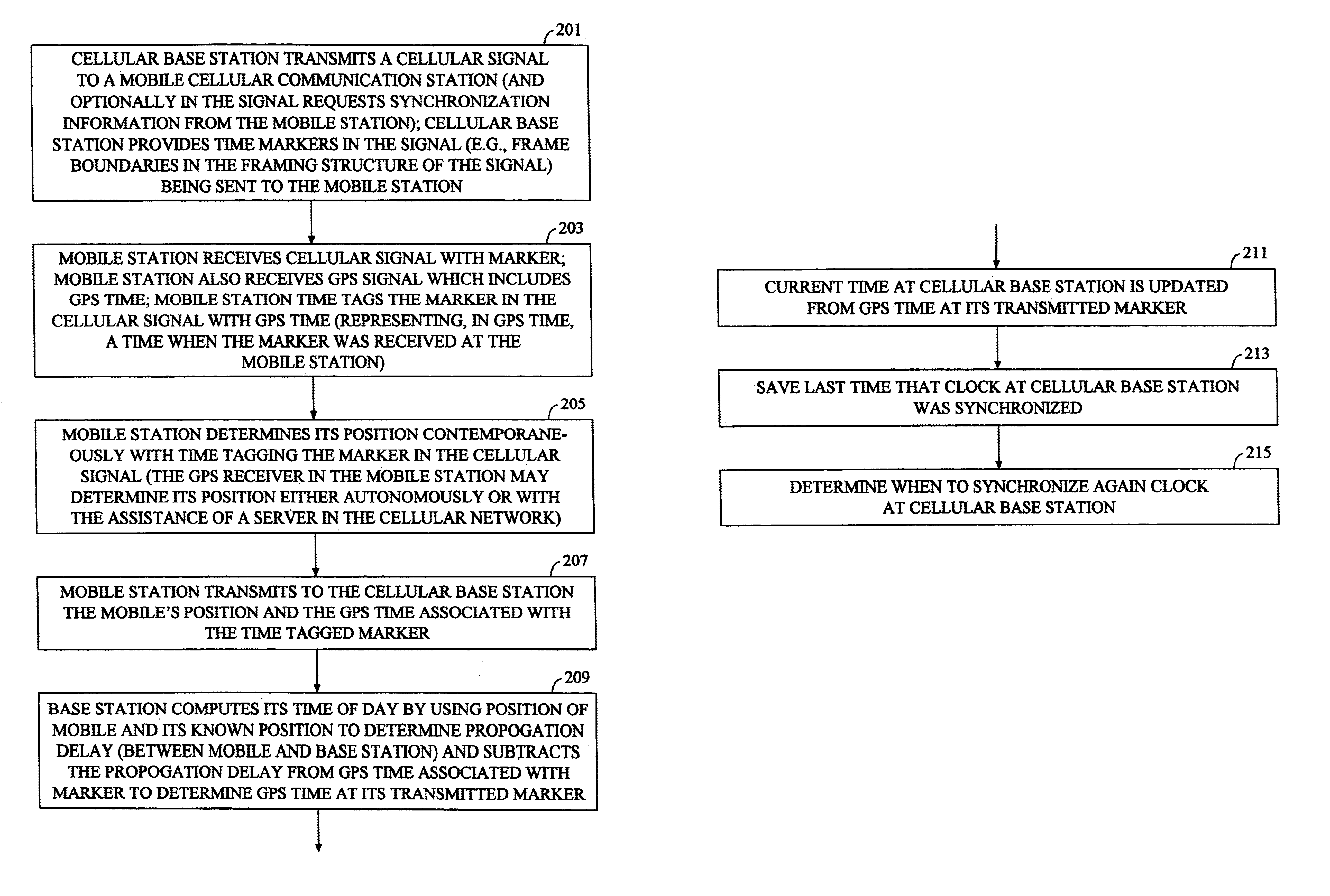
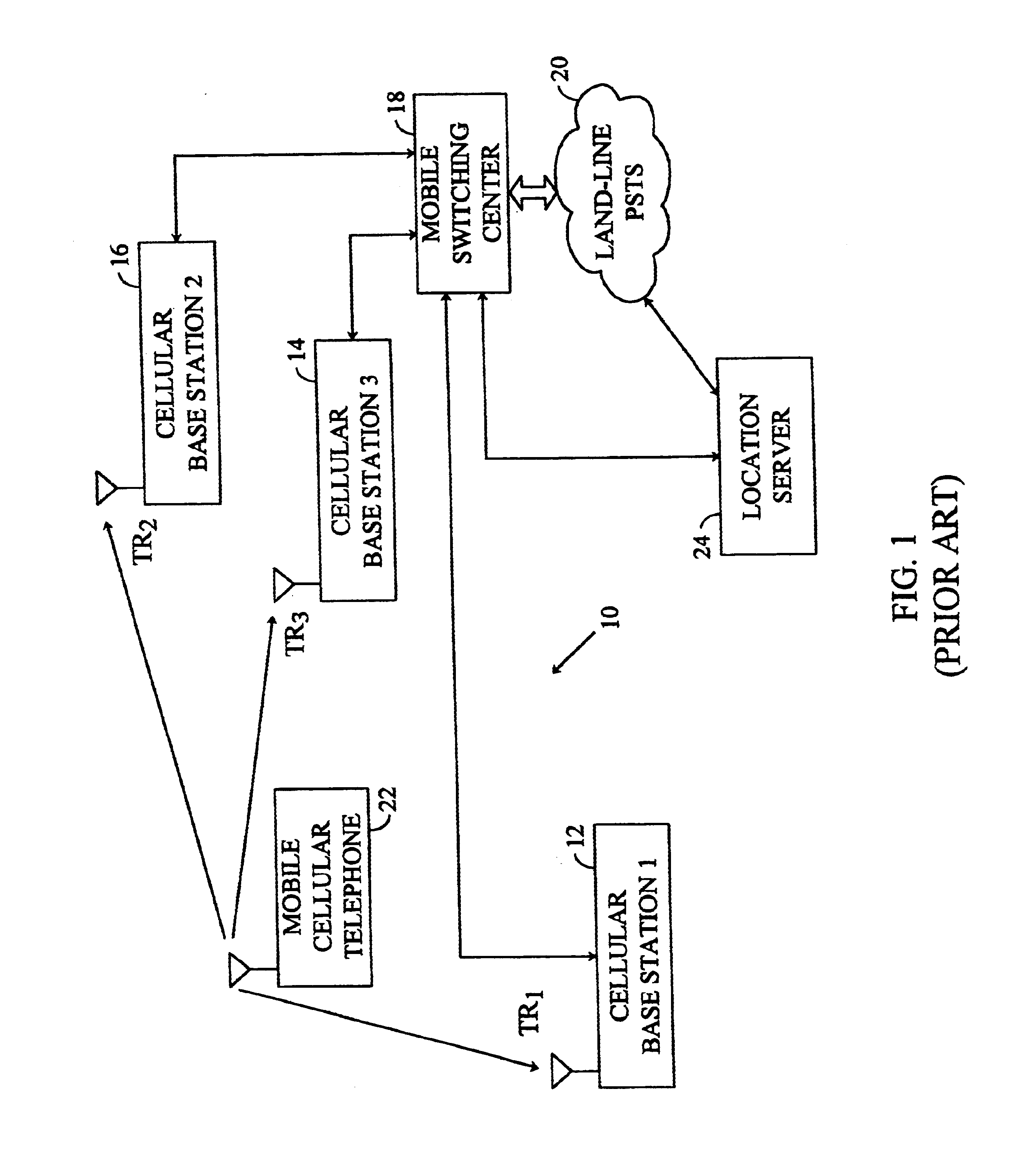
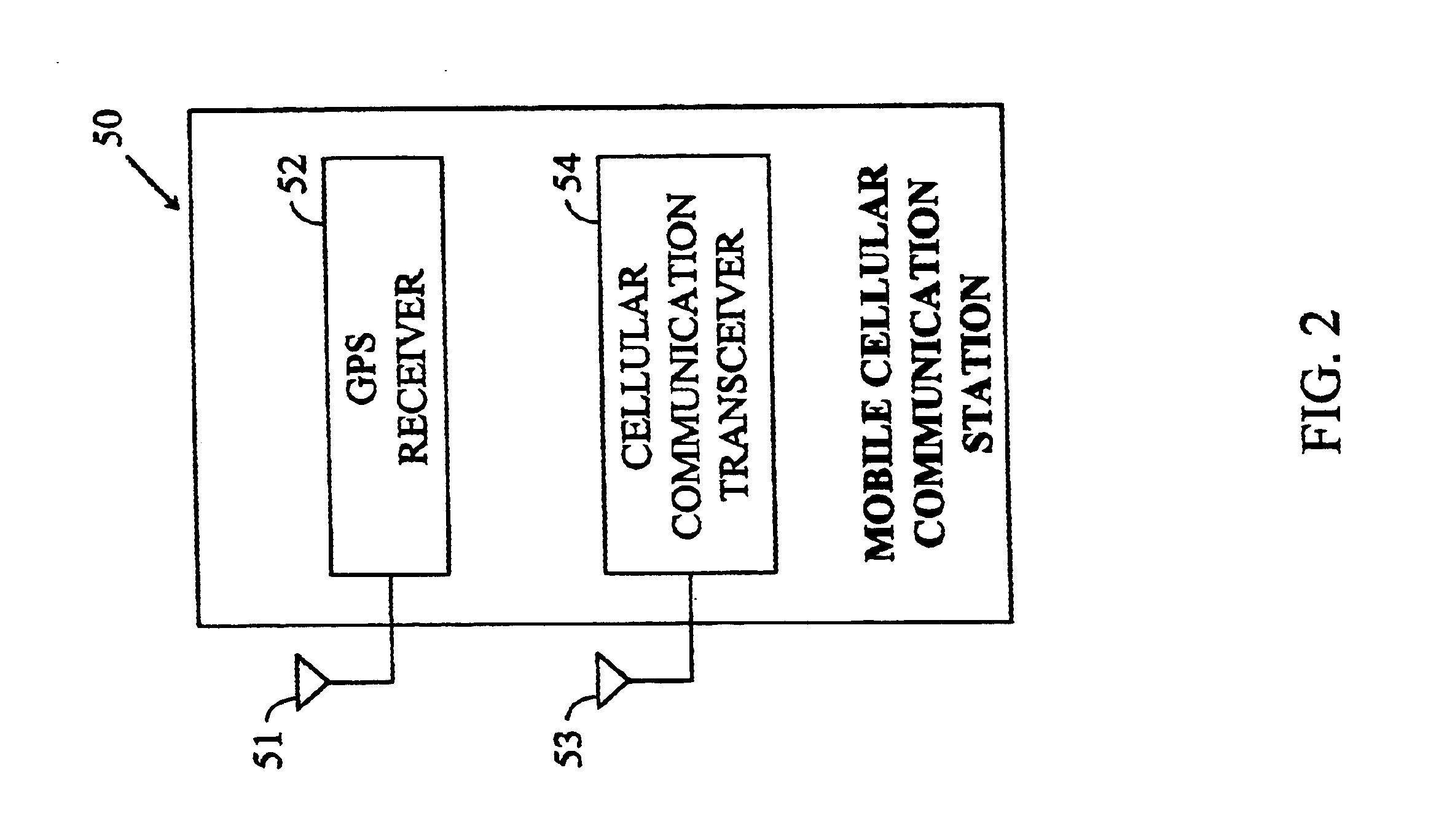
Methods and apparatuses for using mobile GPS receivers to synchronize basestations in cellular networks
InactiveUS6665541B1Low costSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexGeolocationGps receiver
Methods and apparatuses for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network. One exemplary method performs time synchronization between at least two basestations, a first basestation and a second basestation, of a cellular communication system. In this exemplary method, a first time-of-day and a first geographical location of a first mobile cellular receiver station (MS) are determined from a first satellite positioning system (SPS) receiver which is co-located with the first MS, and the first time-of-day and first location are transmitted by the first MS to a first basestation which determines a time-of-day of the first basestation from the first time-of-day and first location and from a known location of the first basestation. Also in this exemplary method, a second time-of-day and a second geographical location of a second MS are determined from a second SPS receiver which is co-located with the second MS, and the second time-of-day and the second location are transmitted to a second basestation which determines a time-of-day of the second basestation from the second time-of-day and the second location and a known location of the second basestation. Other methods and apparatuses are also described for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
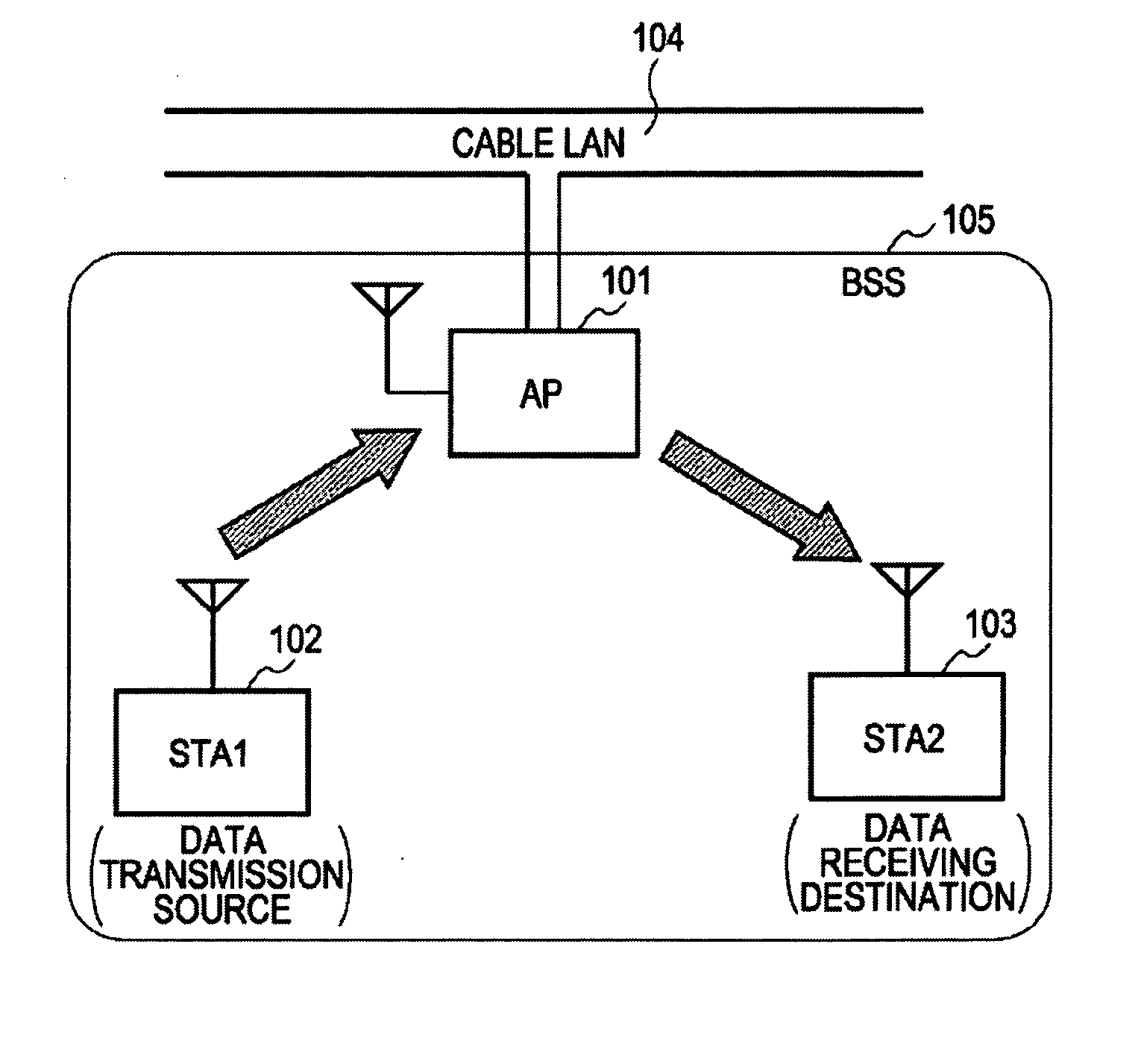
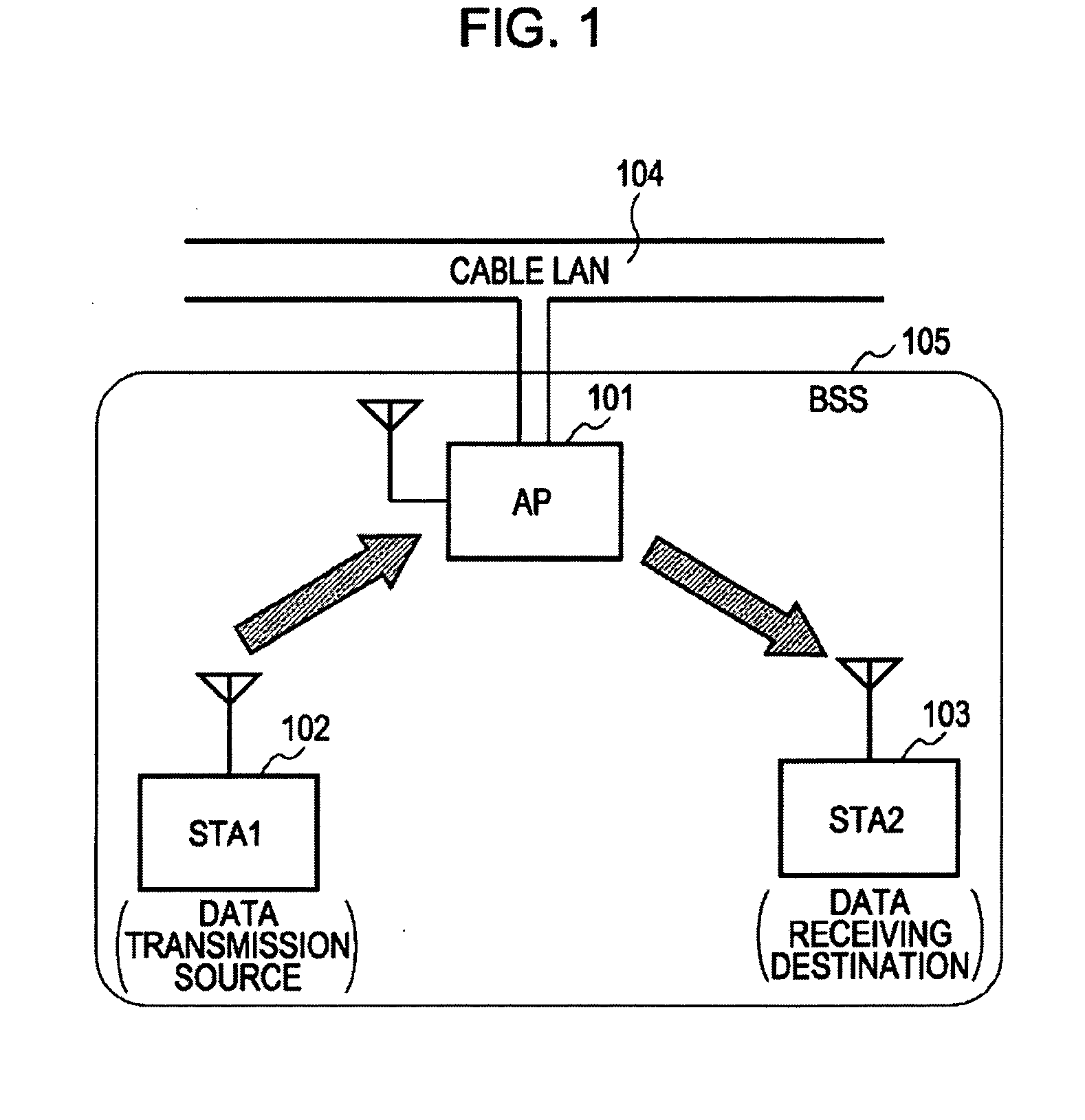
Wireless Communication System, Wireless Communication Device and Wireless Communication Method, and Computer Program
ActiveUS20080186901A1Reduce transmission efficiencyReduce throughputSynchronisation arrangementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemTime segment
A wireless communication system, wherein packet transmission operations are carried out in an infrastructure mode, includes: a first terminal station serving as a data transmission source; a second terminal station serving as a data receiving destination; and a control station configured to contain each terminal station and relay a packet transmitted between the two terminal stations; wherein the first terminal station transmits a packet addressed to the second terminal station via the control station, and detects that the second terminal station is within range capable of a direct link, based on the first terminal station receiving a confirmation response packet replied from the second terminal station, the confirmation response packet being replied from the second terminal station upon a predetermined period of time having passed from the time of the control station transferring the packet to the second terminal station address.
Owner:SONY CORP
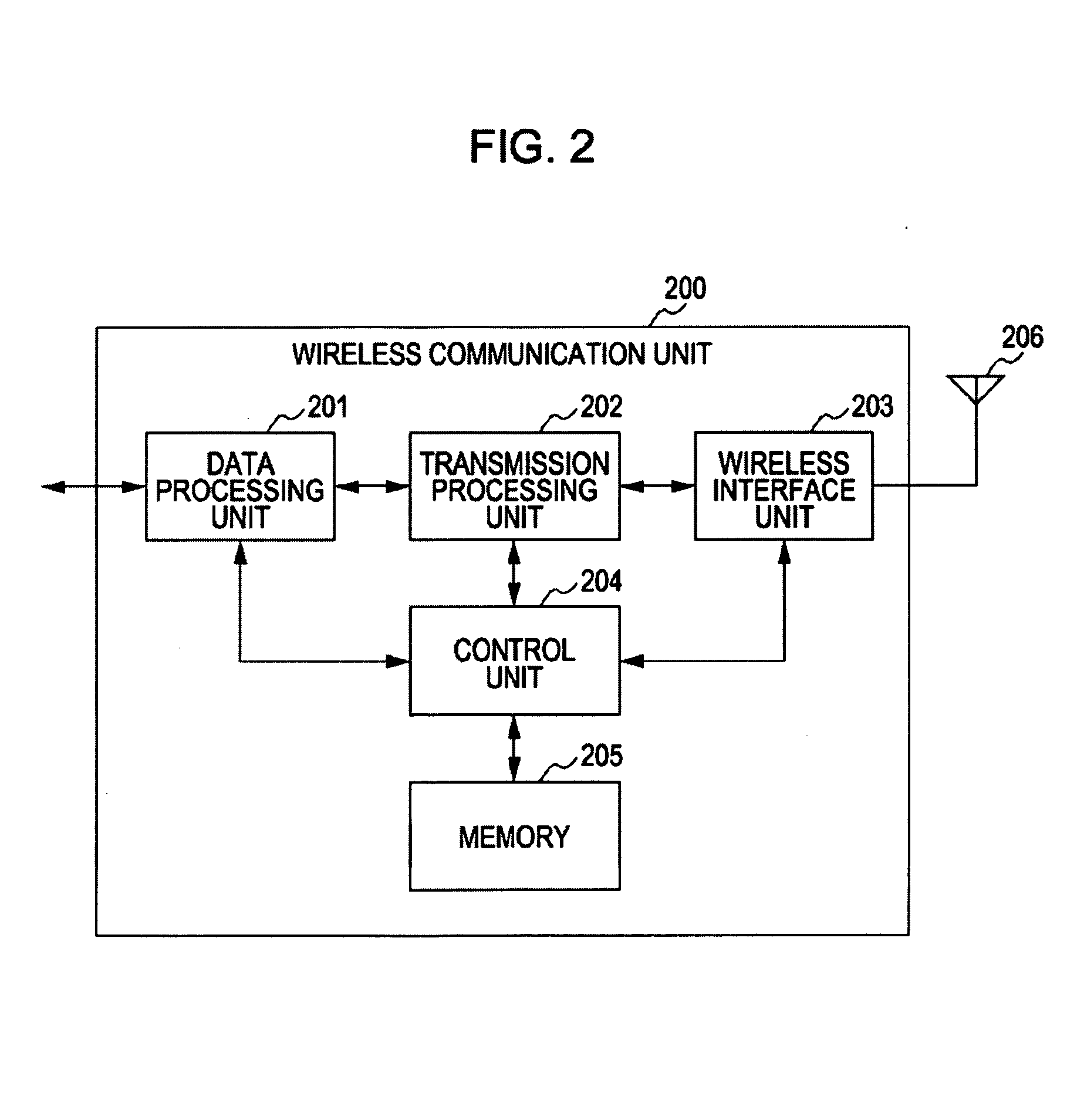
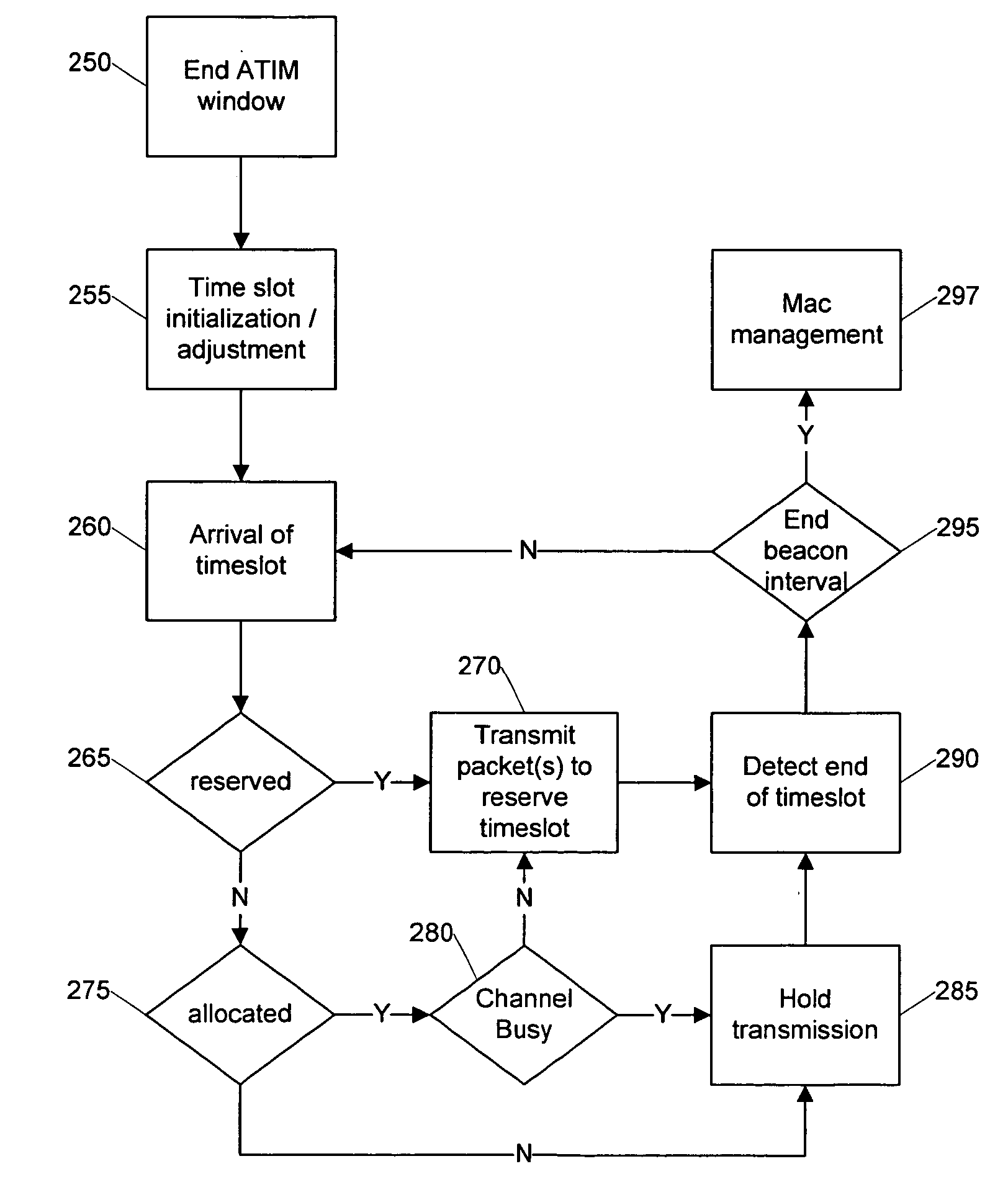
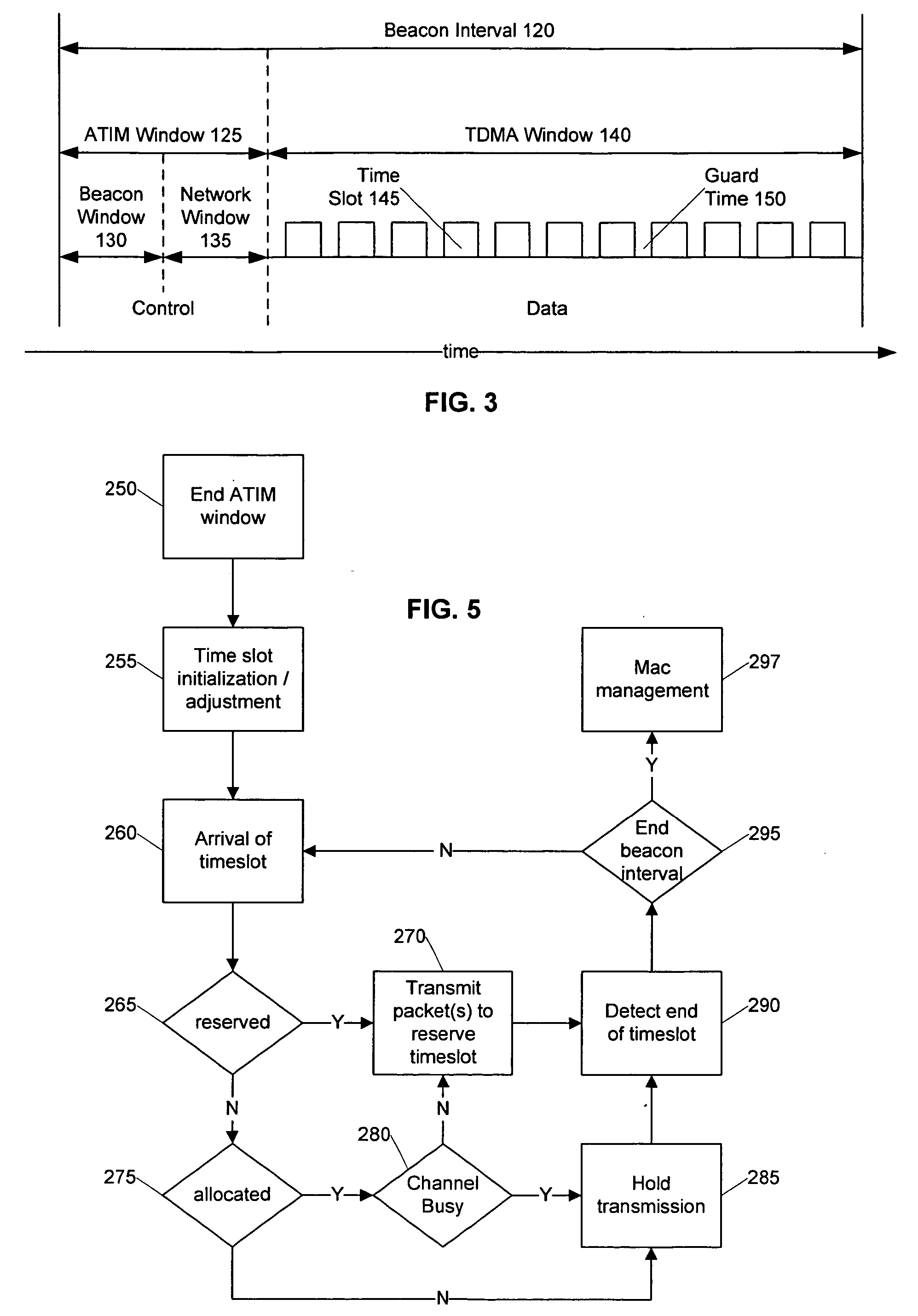
Distributed TDMA for wireless mesh network
InactiveUS20050201340A1Optimizing bandwidth usageFree communicationSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceWireless mesh network
Systems and methods are provided that facilitate distributed TDMA communication amongst nodes in an ad hoc wireless network without the need for centralized management and control. A wireless communication device includes a MAC layer that is configured to synchronize its local clock from a beacon frame that is sent by another node in the ad hoc network. After synchronizing its clock to the ad hoc network, the device identifies a timeslot for transmission. When the timeslot arrives, the device senses the channel to determine if there is traffic and if there is no traffic, the device reserves the timeslot by transmitting. In this fashion, a plurality of timeslots can be divided amongst the devices in the ad hoc wireless network for optimized collision free communication using distributed TDMA. This distributed TDMA communication can also be applied across multiple channels in a wireless network to significantly increase bandwidth and quality-of-service.
Owner:COMMWORKS SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Wireless Data Networking
ActiveUS20080291855A1Low powerBetter read rateEnergy efficient ICTPower managementWireless dataNetwork mapping
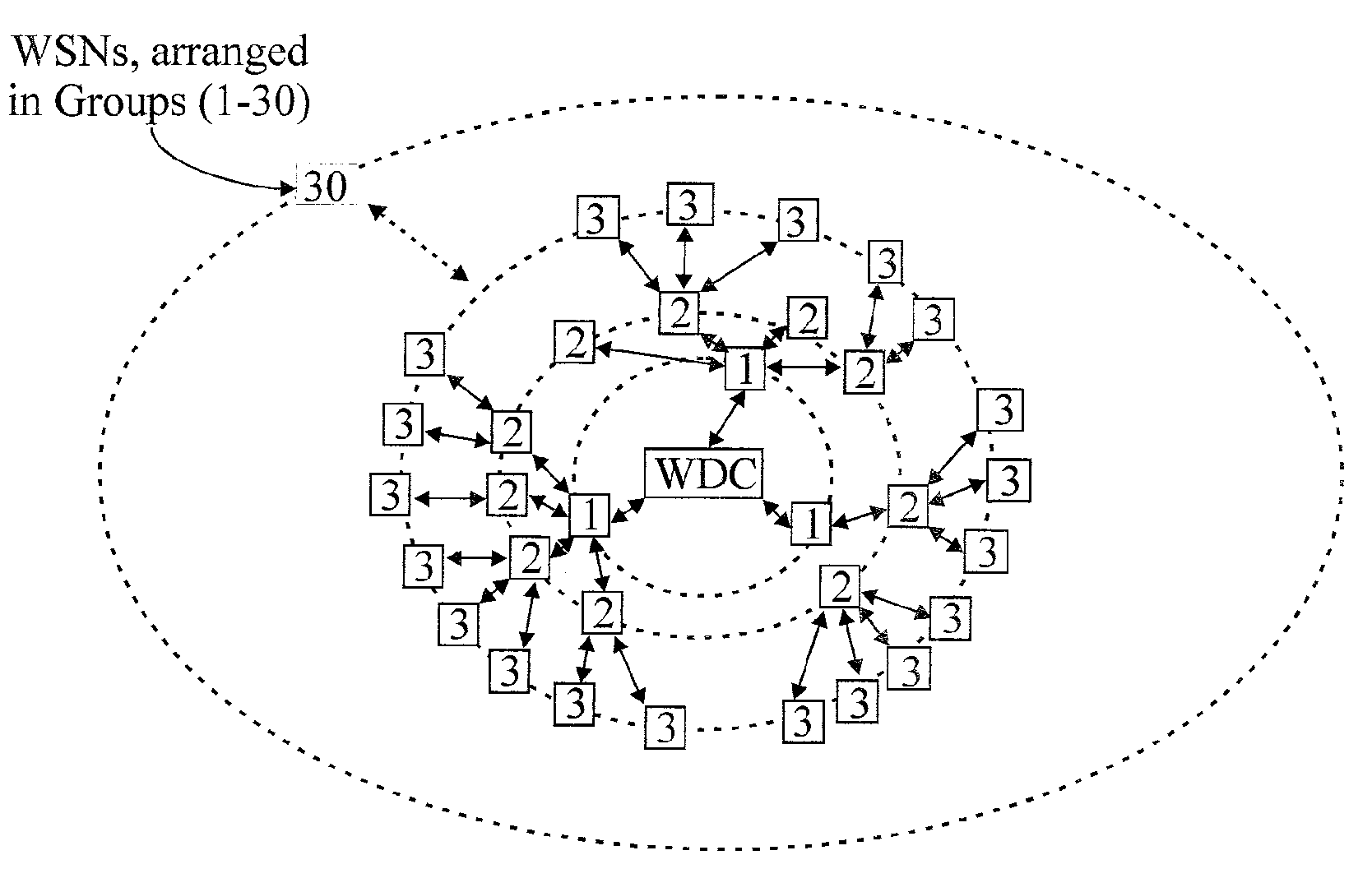
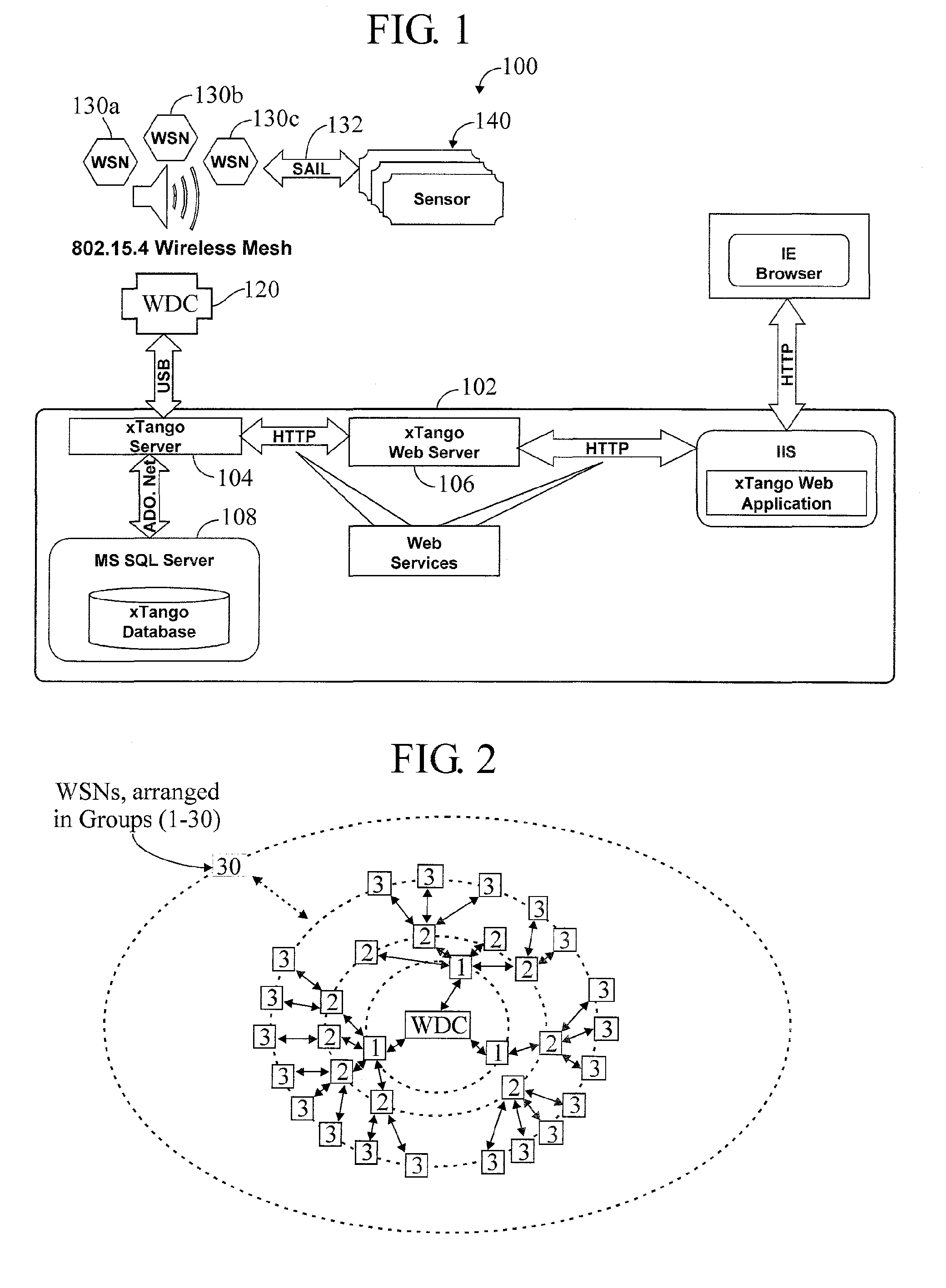
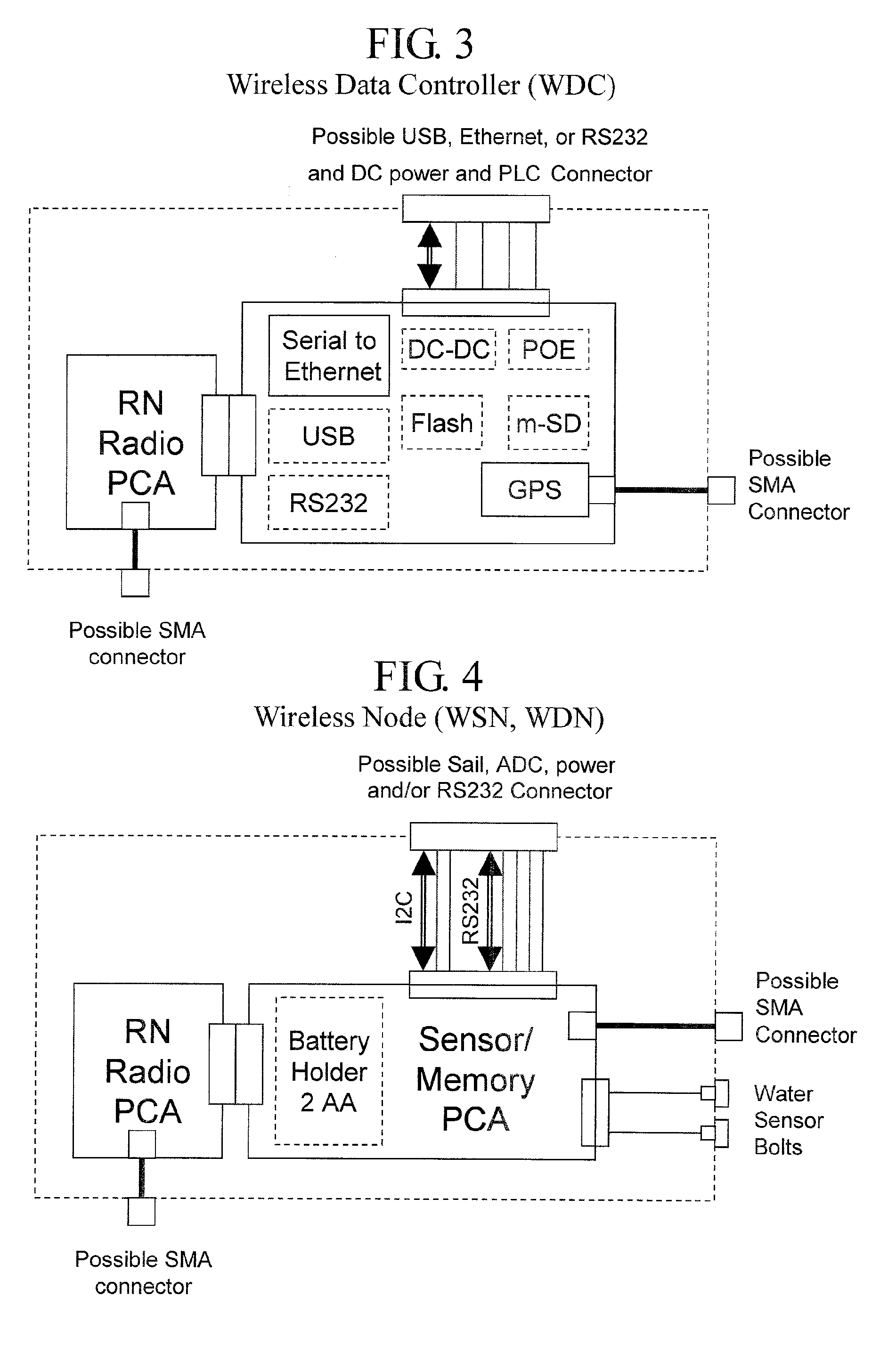
A meshing network comprising one full function controller (WDC) and a plurality of nodes (WDN, WSN), that is RF quiet capable with very low power consumption and the ability to quickly heal itself and create new network paths. The network uses an addressing scheme that allows for each node to not have a network map but still be able to route messages. A piping scheme allows a mesh to become a high throughput network. A sensor rail protocol definition allows sensor devices to connect to nodes and route messages through the network.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Routing in a multi-station network
InactiveUS6785510B2Effective expansionReduce data rateSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemHybrid system
A method of relaying data between mobile stations in a cellular communications system is provided. The system comprises a number of mobile stations and base stations. Each base station makes synchronization transmissions within its area of covers, which define a broadcast control channel for the transmission of broadcast data from the base station to mobile stations within the area of coverage. The synchronization transmissions are received at mobile stations within the area of coverage, which extracts data defining the broadcast control channel, and at least one calling channel on which mobile stations can transmit probe data to one another. The probe data is used by the mobile stations to obtain connectivity information relating to the availability of other mobile stations. The synchronization transmissions also contain data which is used to define at least one traffic channel which is used by the mobile stations to relay message data between themselves. Effectively, the method of the invention provides a hybrid system which combines conventional cellular technology with opportunistic relaying technology.
Owner:IWICS INC
Popular searches
Synchronisation signal speed/phase control Generating/distributing signals Line-transmission Machine-to-machine/machine-type communication service Digital data processing details Broadcast information switching/replacement Record information storage Color television details Recording signal processing Program control
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com