Patents
Literature
3577results about "Synchronisation signal speed/phase control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
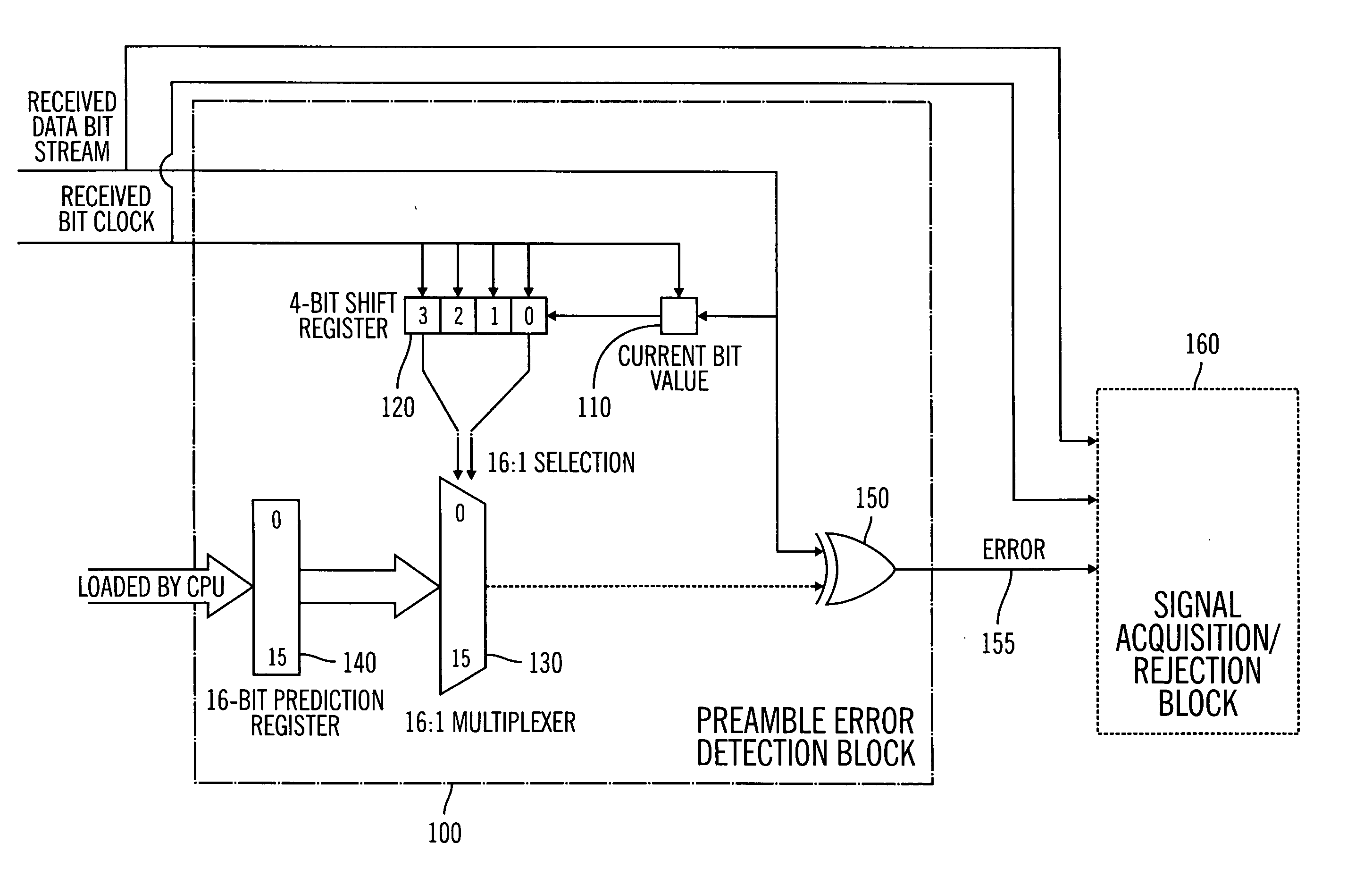
Rapid discrimination preambles and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20050195930A1Sync fastLess power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTElectrotherapyComputer hardwareSystems approaches
A system, method and program are disclosed for achieving rapid bit synchronization in low power medical device systems. Messages are transmitted via telemetry between a medical device and a communication device. The synchronization scheme uses a portion of a unique preamble bit pattern to identify the communication device allowing for economical communications with a minimum expenditure of energy. A special set of preamble bit patterns are utilized for their unique synchronization properties making them particularly suited for rapid bit synchronization. These unique preamble bit patterns further provide simplification to the preamble error detection logic.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Method and apparatus for performing synchronization in device-to-device network
ActiveUS20130308625A1Perform synchronizationSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexComputer sciencePhase adjustment
A method and an apparatus for performing synchronization by a first device in a Device-to-Device (D2D) network are provided. The method includes detecting a synchronization signal from at least one second device during one period, determining a phase adjustment value depending on a number of synchronization signals, which have been detected from the at least one second device during the one period, adjusting a phase value of a first device using the phase adjustment value, and transmitting a synchronization signal if the phase value of the first device reaches a predetermined specific value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for synchronizing device information
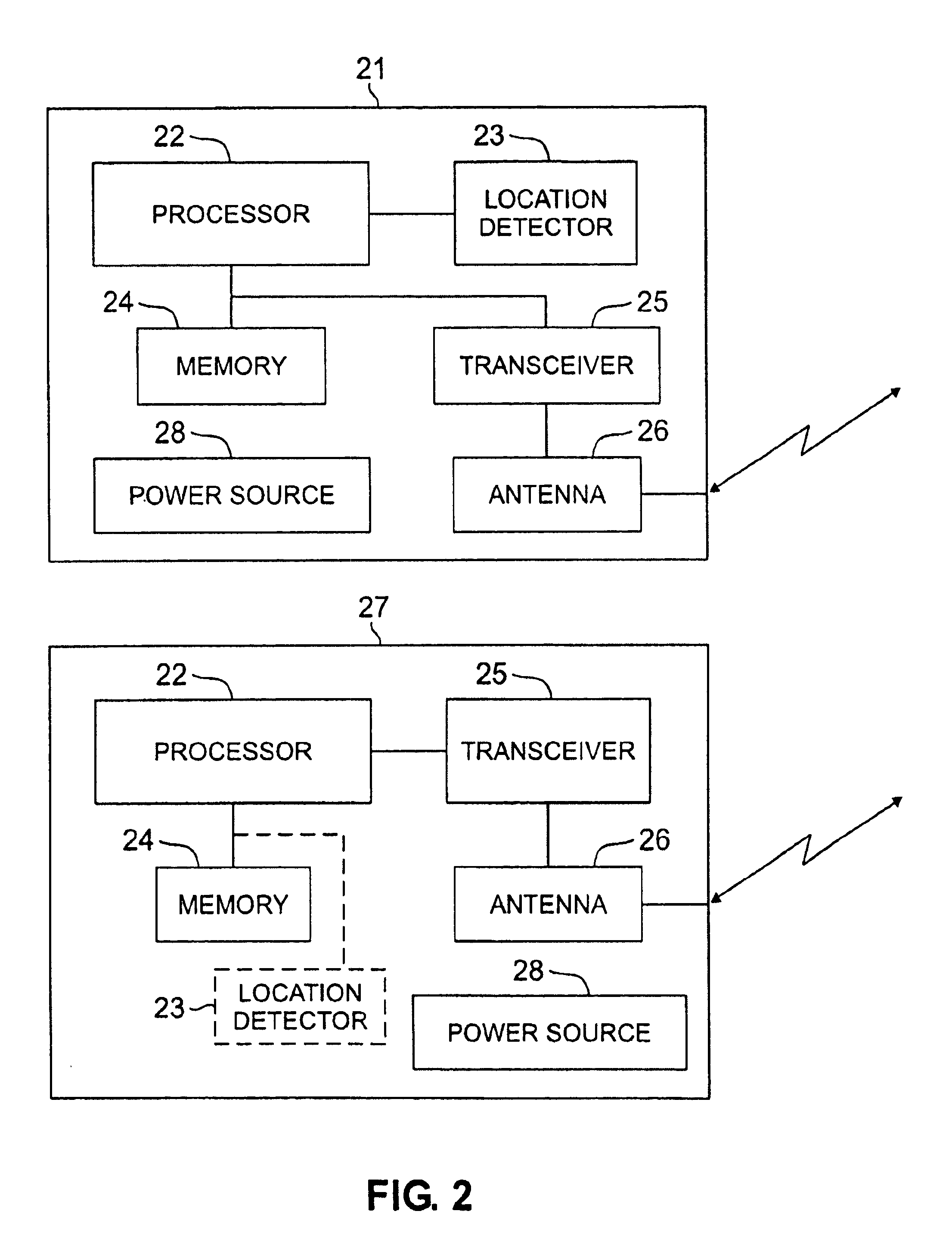
InactiveUS6874037B1Enabling of informationMultiple digital computer combinationsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPositioning technologyComputer science
Two electronic devices automatically perform a synchronization session when one of the electronic devices is brought in proximity to the other electronic device. The synchronization session is initiated without user intervention based simply on the fact that the two devices have recently been brought within a predetermined distance of each other. The two electronic devices communicate in a wireless manner. The two devices may determine that they are within a predetermined distance of each other using global positioning technology, via which one of the devices determines its own position and compares it to a known position of the other electronic device. Alternatively, one of the electronic devices may output a low level signal that can be received by the other electronic device when within a certain range. Once the low level signal is received, the recipient of the low level signal outputs a stronger signal to ensure that it is received by the other electronic device requesting a synchronization session, which once established enables synchronization of information between the two devices.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC +2
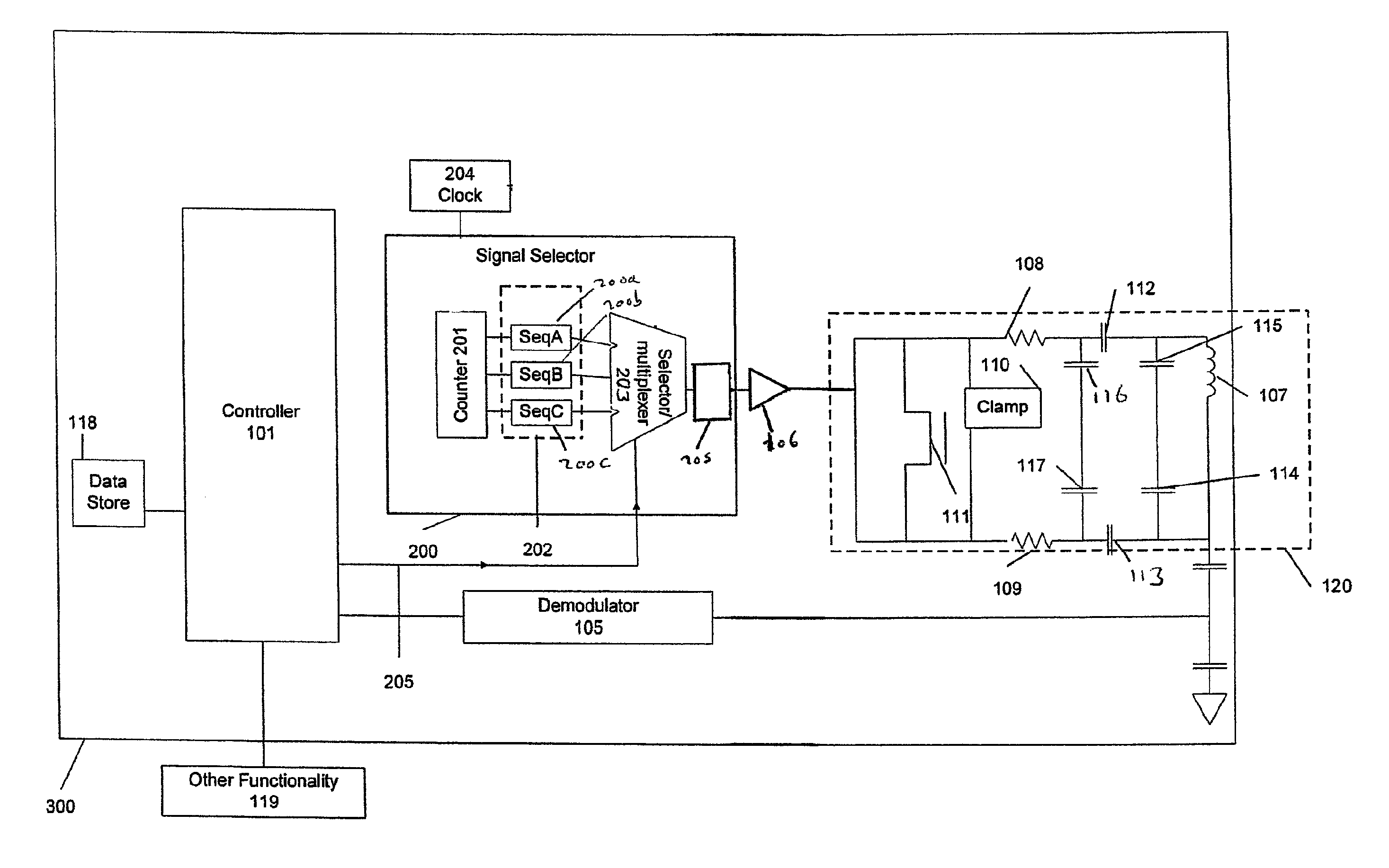
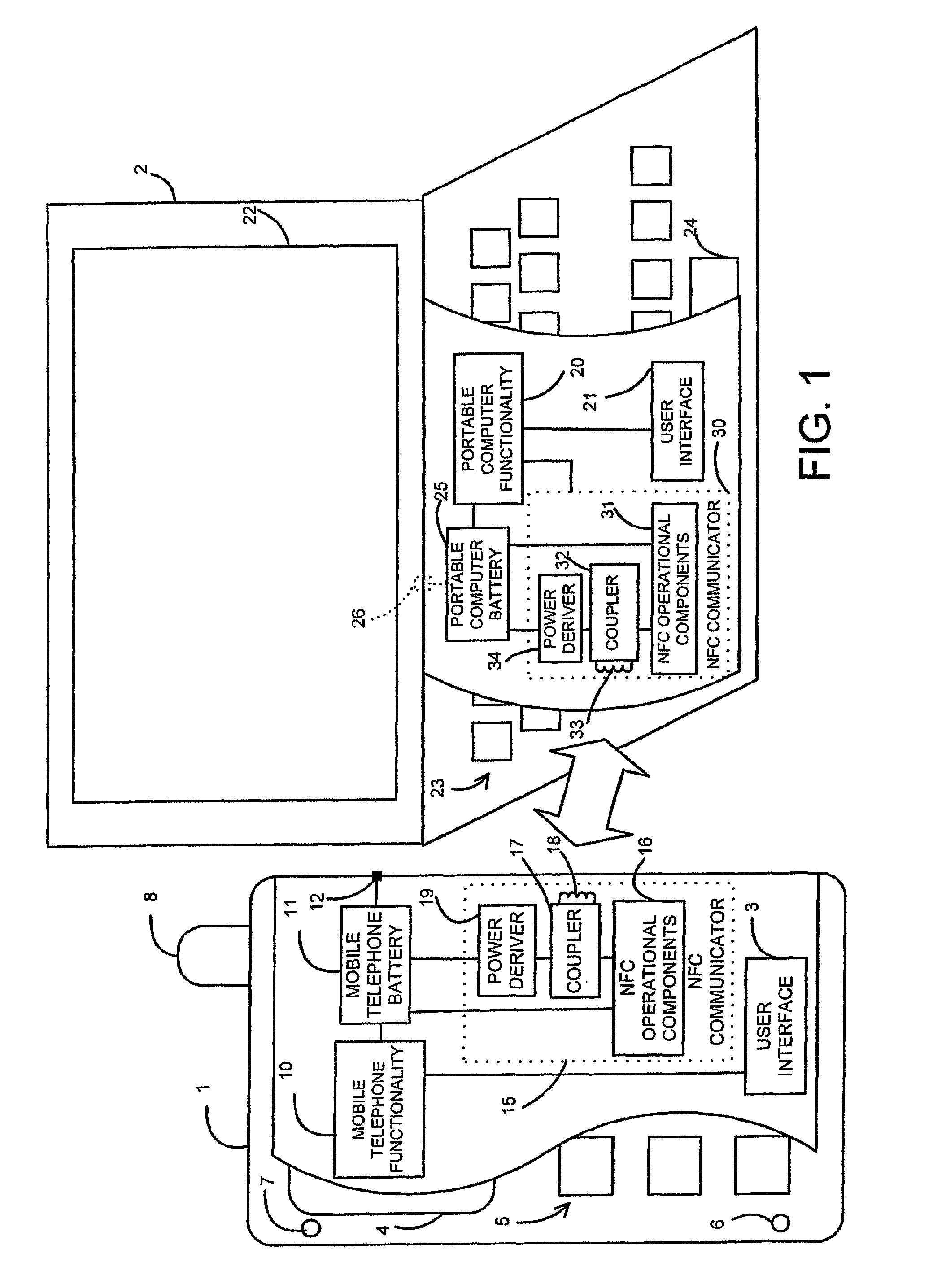
Near field RF communicators and near field communications enabled devices
ActiveUS8150321B2Near-field systems using receiversNear-field in transpondersEngineeringSignal generator
A near field RF communicator has: an antenna operable to generate an RF signal to enable inductive coupling via the magnetic field of the RF signal between the antenna and another near field RF communicator or RF transponder in near field range; and a signal generator operable to generate a multi-level digital sine wave drive signal to drive the antenna to generate the RF signal, wherein the signal generator comprises a selector operable to select one or more digital sequences to provide one or more digital signals from which the digital sine wave drive signal is generated.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
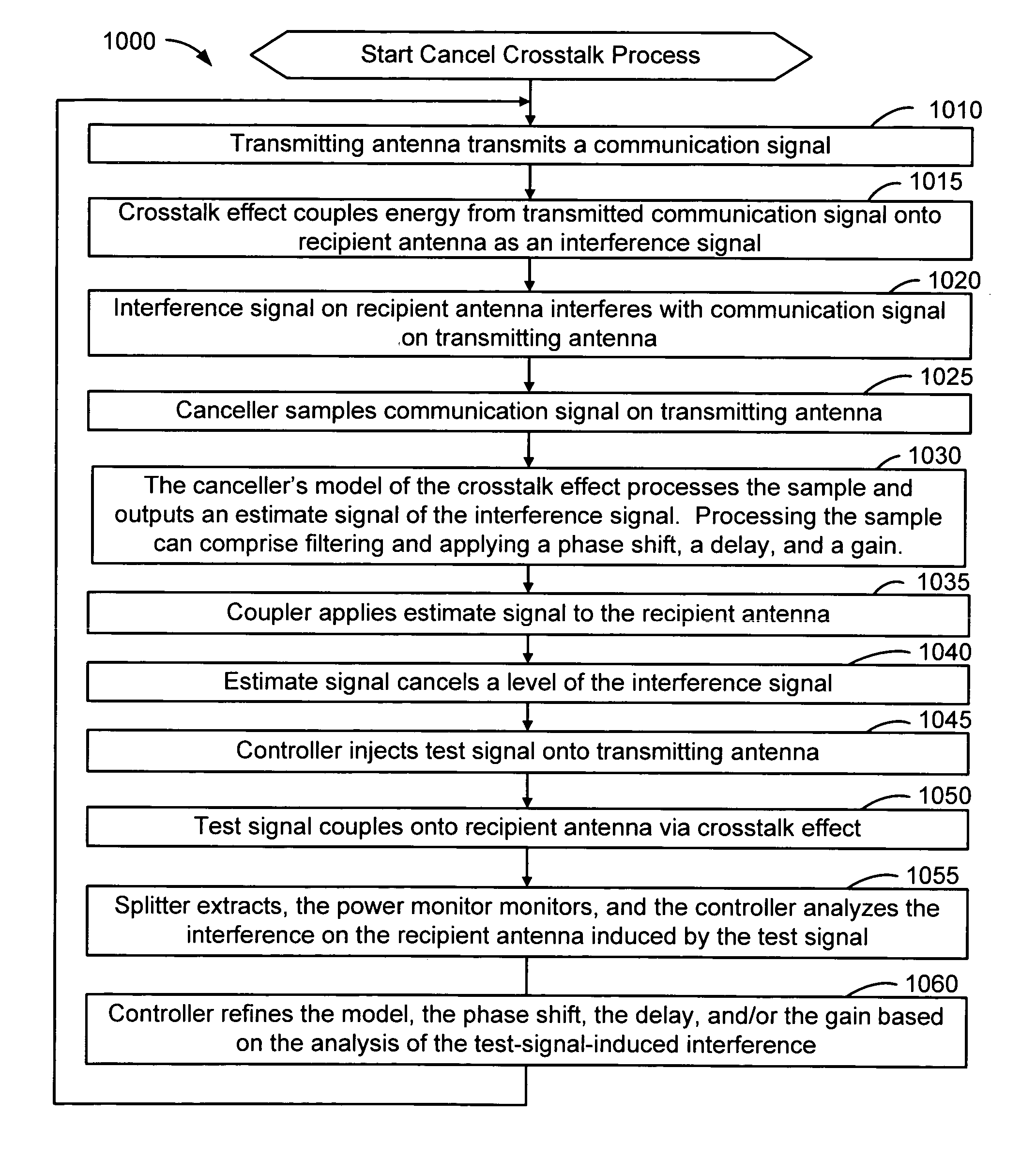
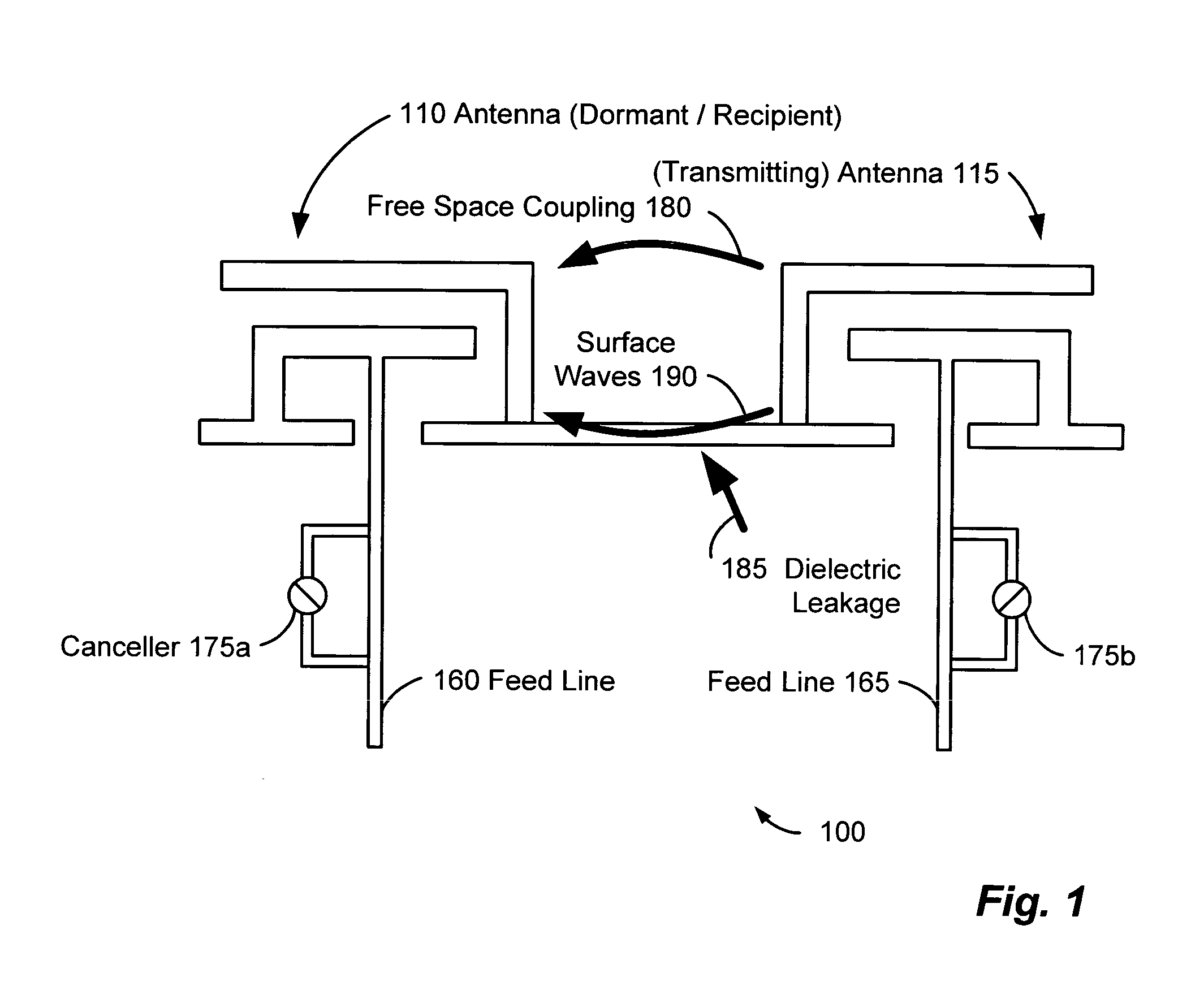
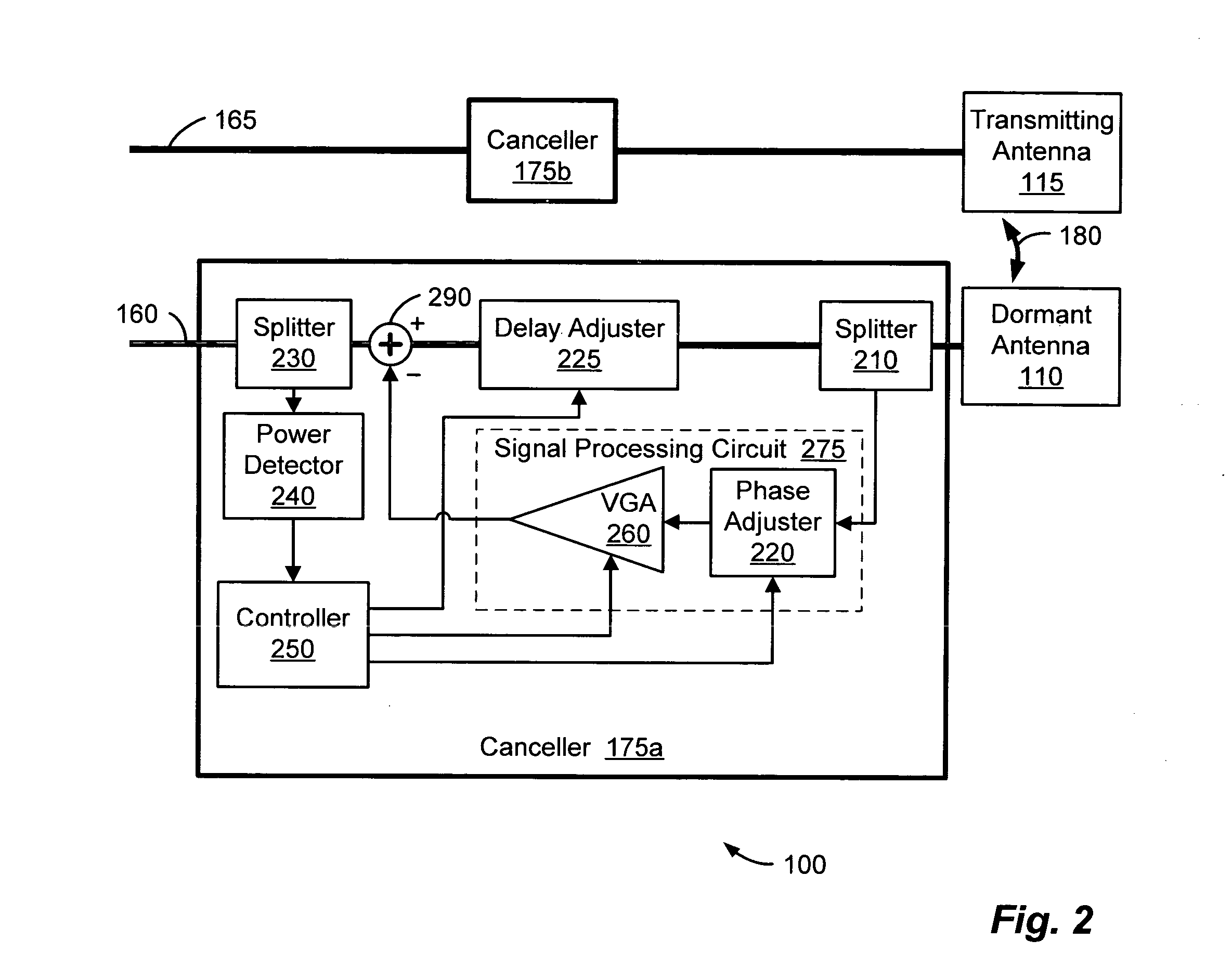
InactiveUS20050226353A1Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthCorrect operation testingLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignal on
A wireless communication system can comprise two or more antennas that interfere with one another via free space coupling, surface wave crosstalk, dielectric leakage, or other interference effect. The interference effect can produce an interference signal on one of the antennas. A cancellation device can suppress antenna interference by generating an estimate of the interference signal and subtracting the estimate from the interference signal. The cancellation device can generate the estimate based on sampling signals on an antenna that generates the interference or on an antenna that receives the interference. The cancellation device can comprise a model of the crosstalk effect. Transmitting test signals on the communication system can define or refine the model.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
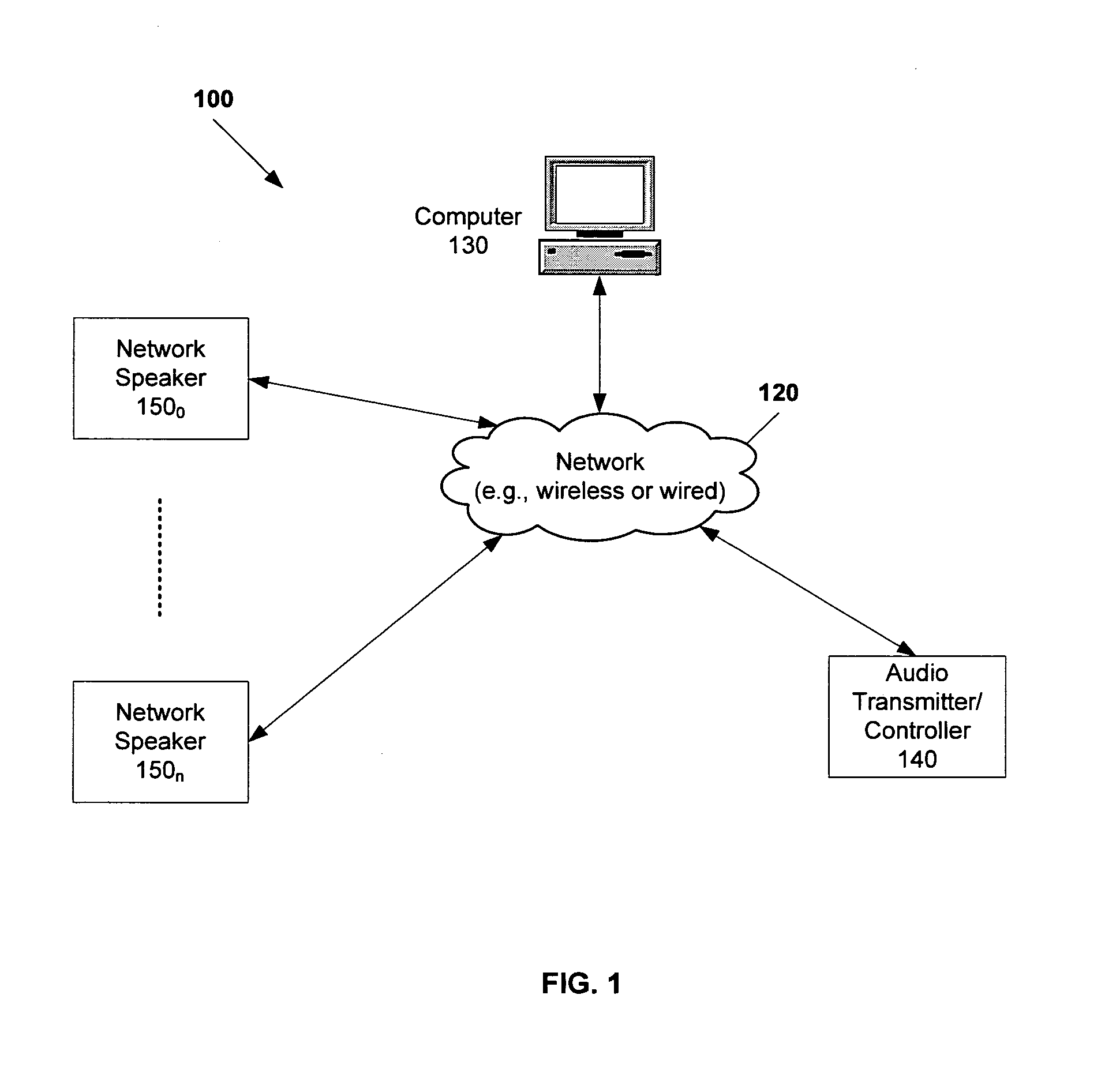
Apparatus and method to synchronize multimedia playback over a network using out-of-band signaling
InactiveUS7206367B1Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexData transmissionComputer science
An apparatus and method to synchronize devices in a network to a sub-millisecond timing accuracy. In a first embodiment, the transmission of data is synchronized between a first source device and destination devices communicatively coupled to a network. In a second embodiment, data is deterministically transmitted between a first source device and destination devices communicatively coupled to a network. In a third embodiment, a deterministic network synchronizes the transmission of data between a first source device and destination devices coupled to a network.
Owner:APPLE INC
Synchronization for femto-cell base stations
Timing synchronization between base stations of uncoordinated communication networks includes obtaining timing synchronization information from one base station, and adjusting a clock of the other station in response to the synchronization information. The timing synchronization information can be identified from a strongest synchronization signal from nearby uncoordinated base stations. The timing synchronization can accommodate clock offsets and frequency offsets.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Protocol and method for multi-chassis configurable time synchronization
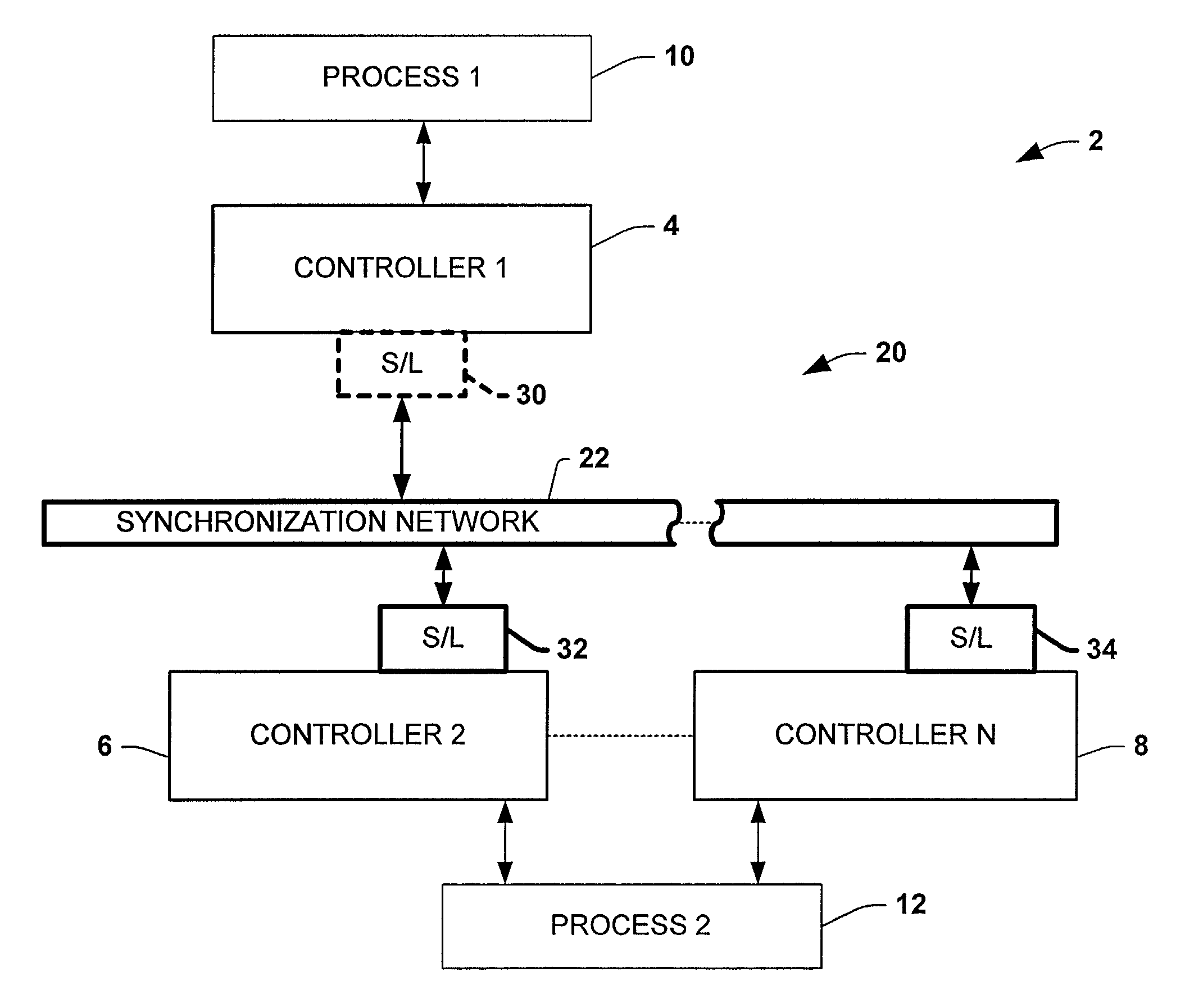
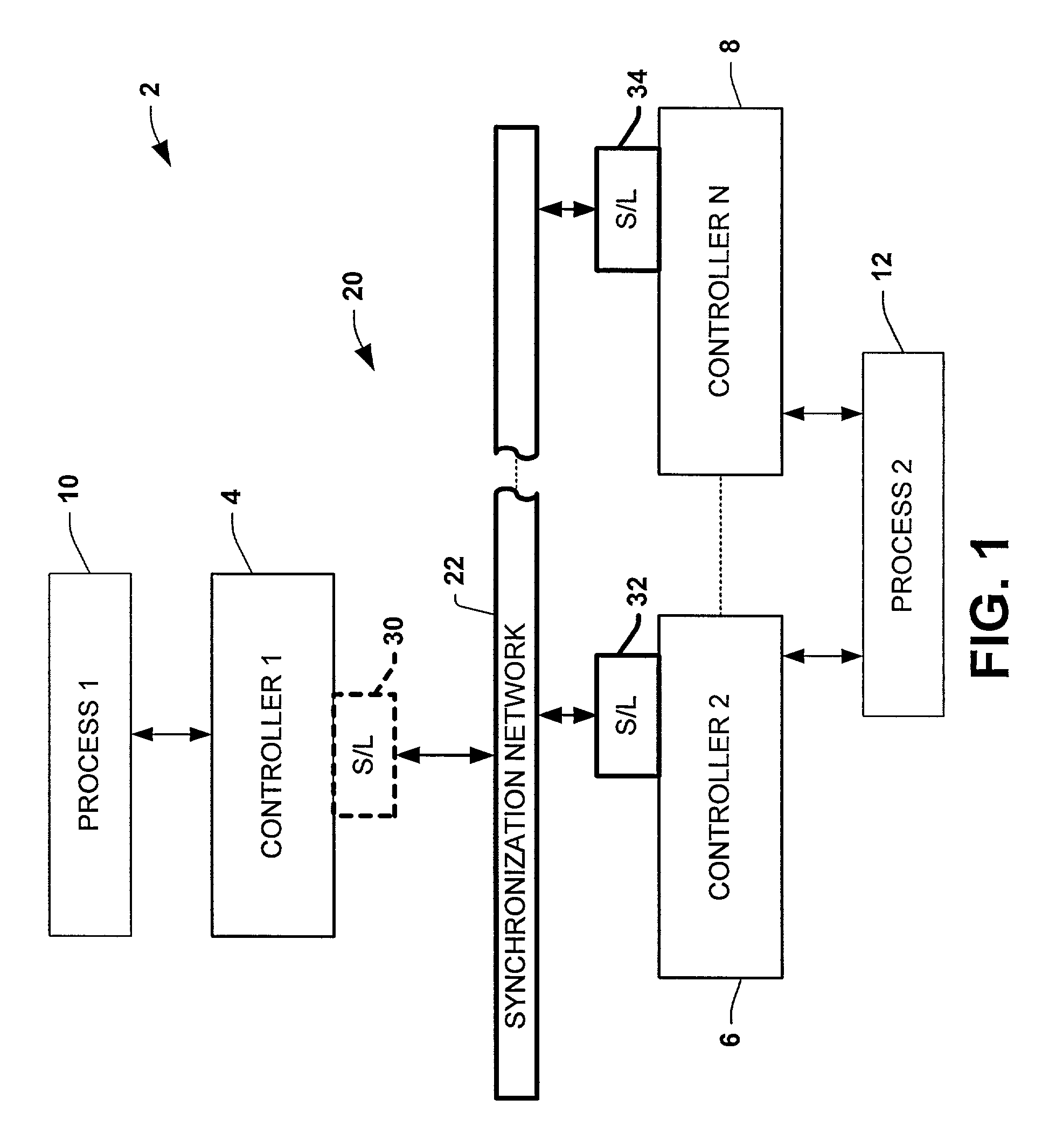
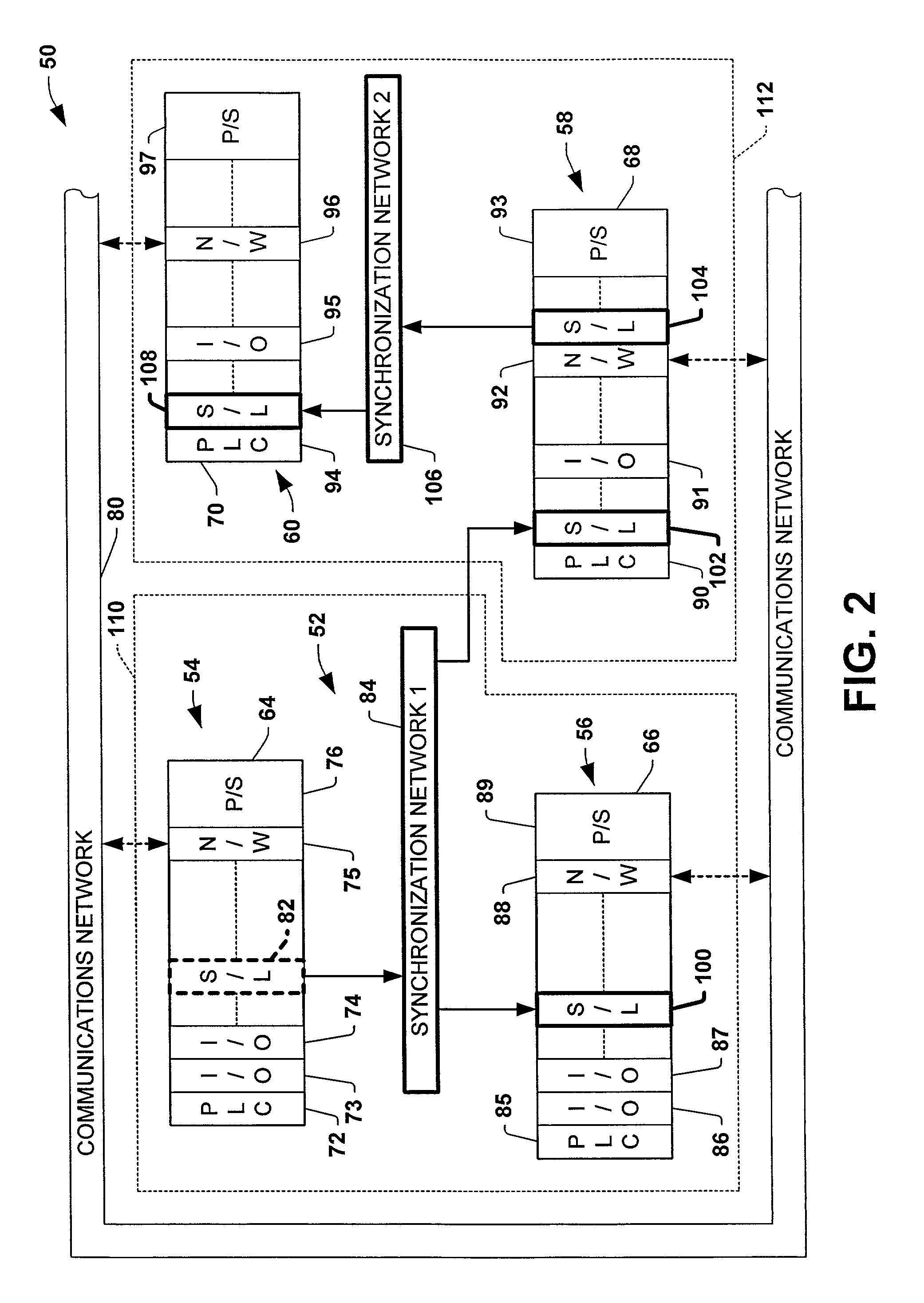
ActiveUS7007106B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionSynchronous controlControl system
Systems and methods are disclosed for time synchronization of operations in a control system. Synchronization networks and devices are provided for transferring synchronization information between controllers in a distributed or localized control system, which is employed in order to allow operation of such controllers to be synchronized with respect to time. Also disclosed are synchronization protocols and hardware apparatus employed in synchronizing control operations in a control system.
Owner:ROCKWELL TECH
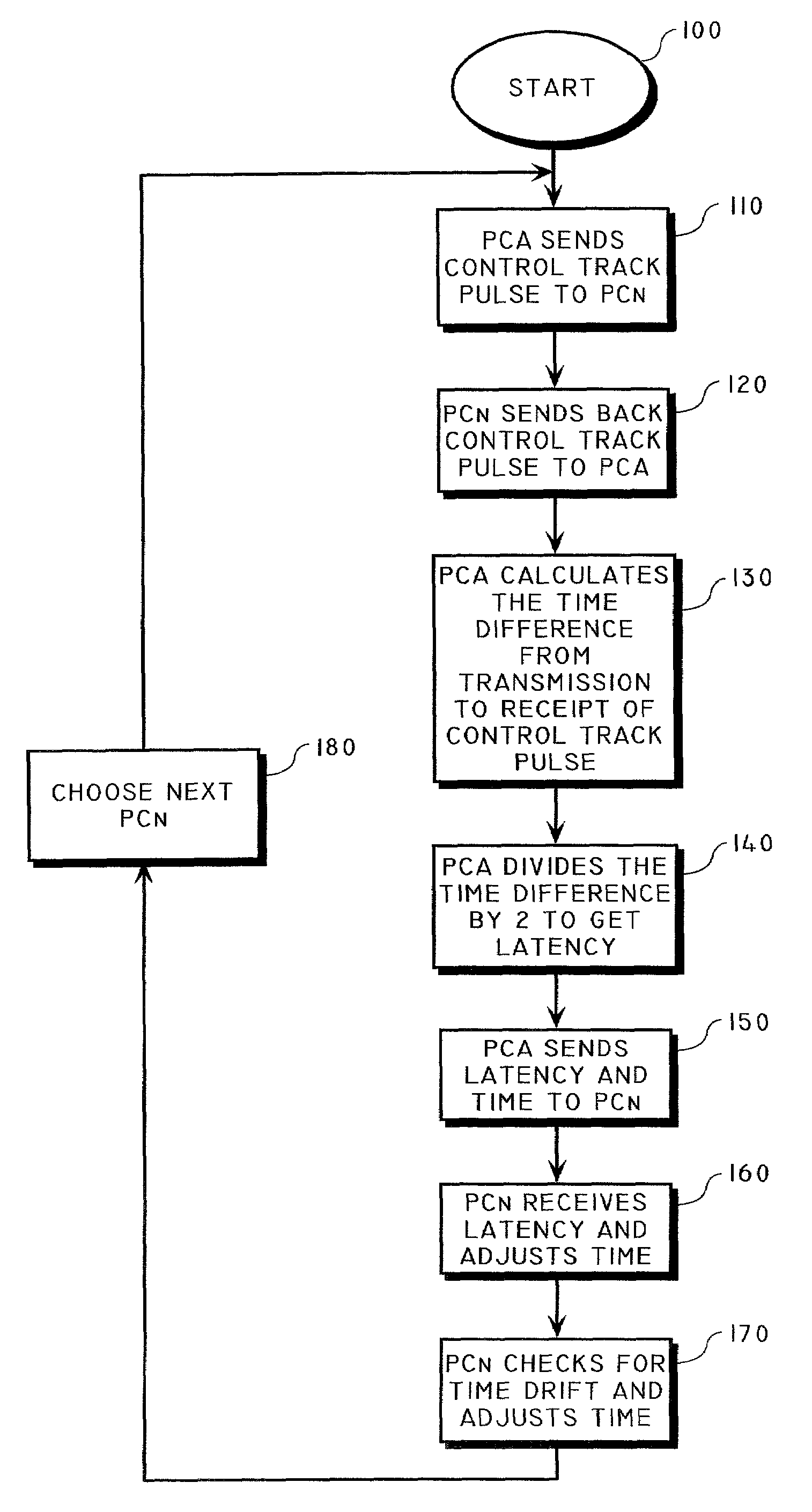
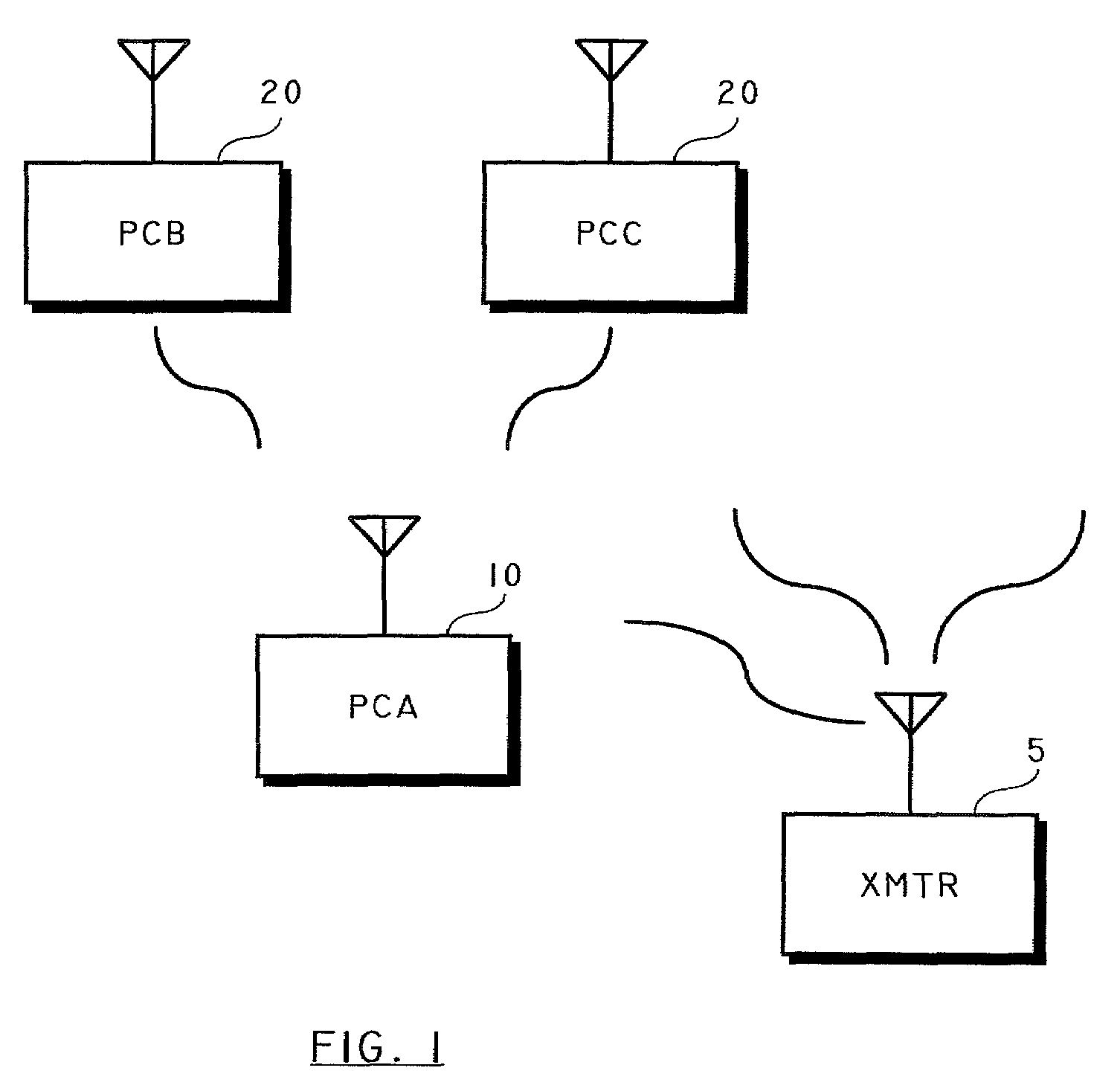
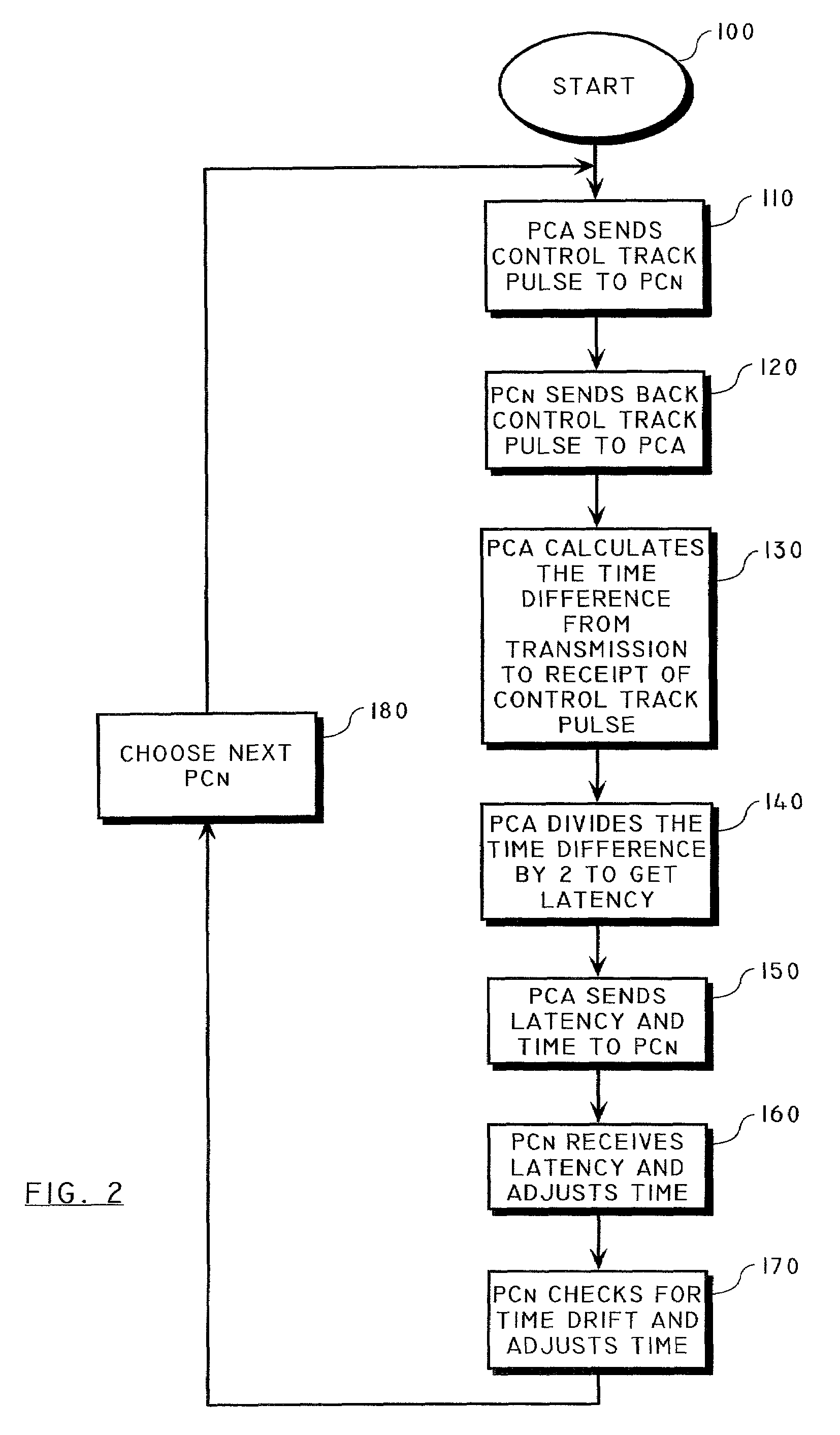
Method of synchronizing the playback of a digital audio broadcast by inserting a control track pulse
ActiveUS7209795B2Broadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexNetwork outputDigital audio broadcasting
A method is provided for synchronizing the playback of a digital audio broadcast on a plurality of network output devices by inserting a control track pulse in an audio stream of the digital audio broadcast. The method includes the steps of outputting a first control track pulse as part of an audio signal which has unique identifying characteristics and is regularly occurring, outputting a second control track pulse so that the time between the first and second control track pulses must be significantly greater than the latency between sending and receiving devices, and coordinating play of audio at the time of the occurrence of the transmission of the second control track pulse assuring the simultaneous output of the audio signal from multiple devices. The control track pulses have a value unique from any other portion of the audio stream. The digital audio broadcast from multiple receivers does not present to a listener any audible delay or echo effect.
Owner:GATEWAY
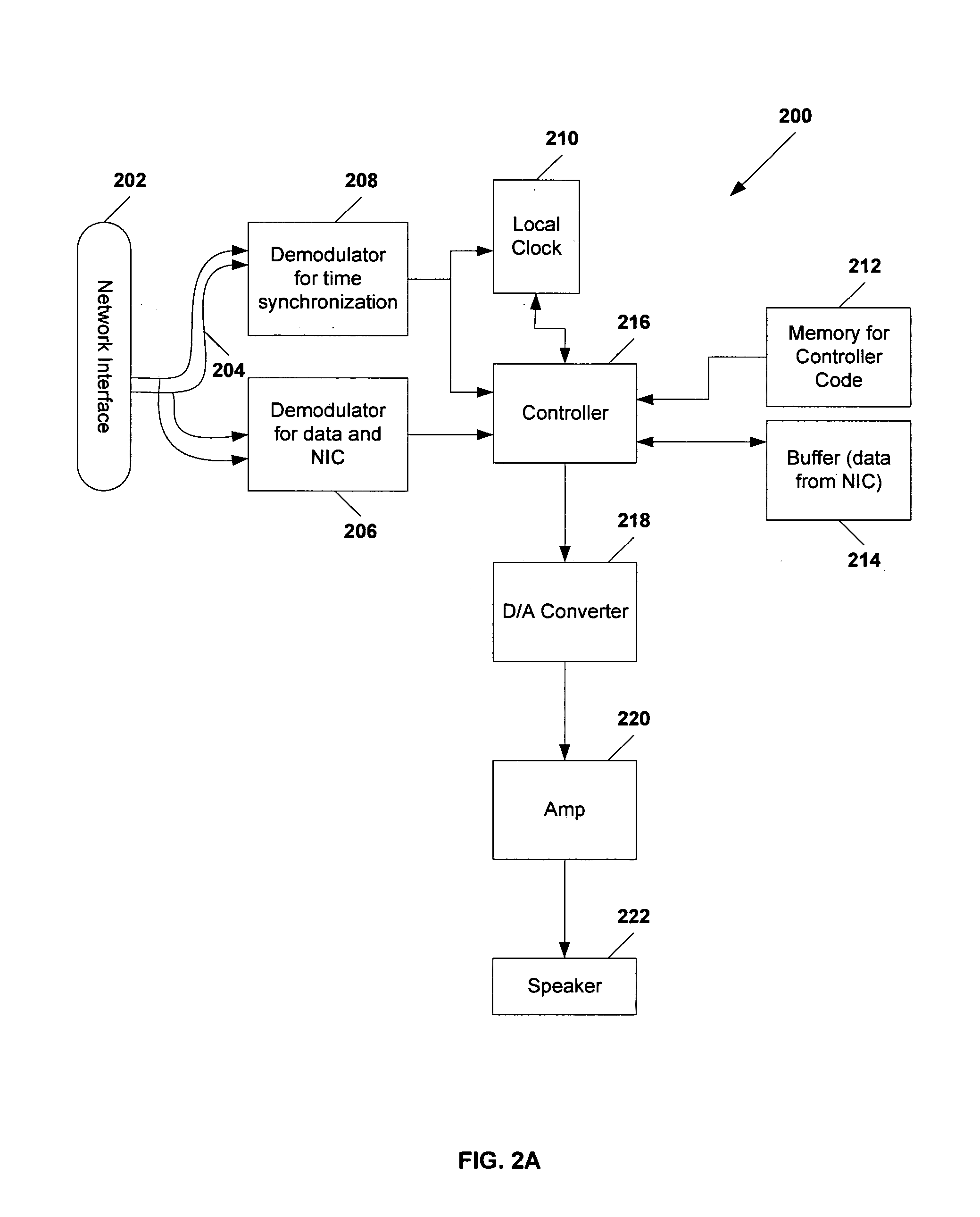
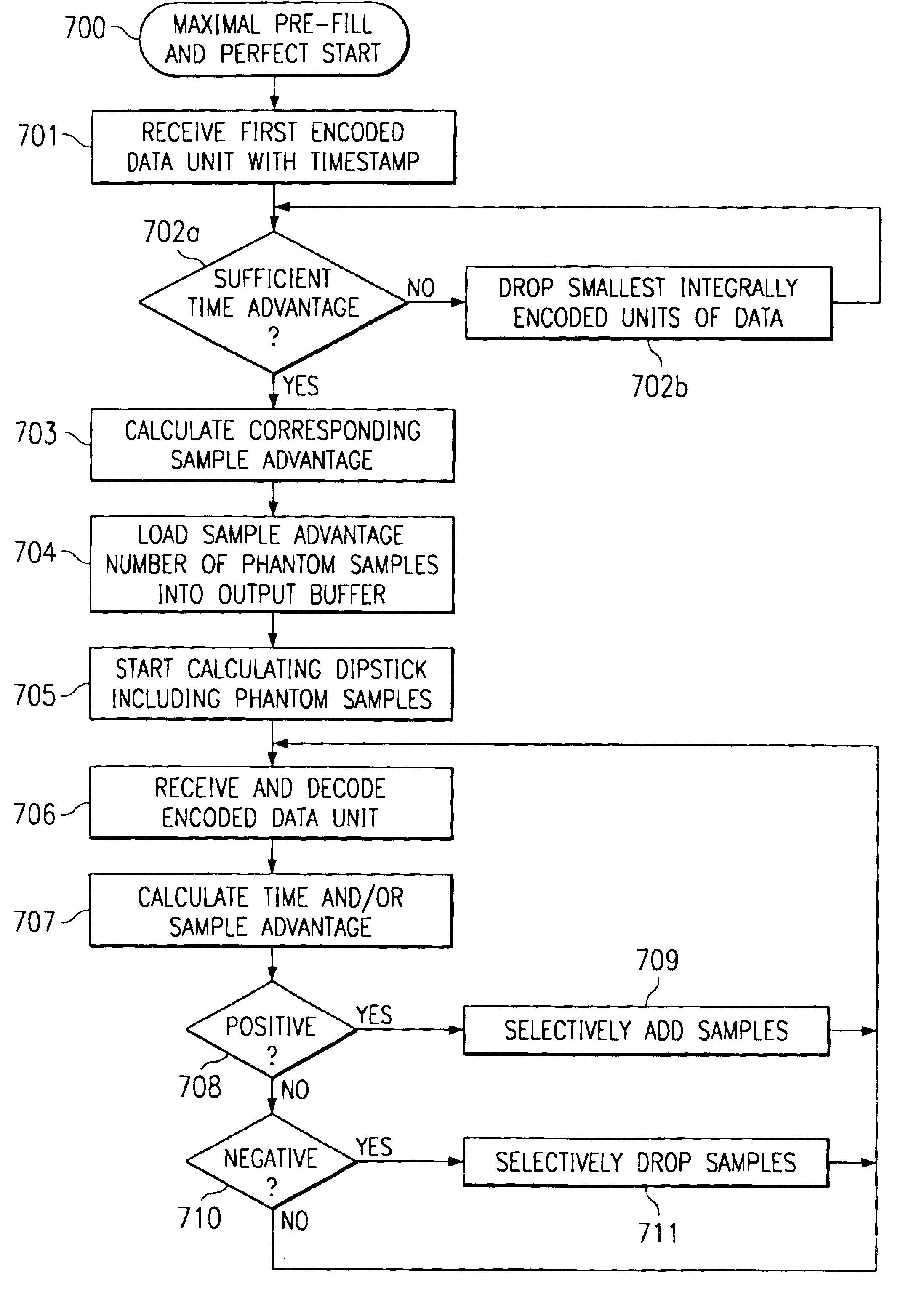
Methods and systems for prefilling a buffer in streaming data applications
ActiveUS6937988B1Accurately presentedSpeech analysisSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlReference sampleAlgorithm
A method of processing a stream of encoded units of data samples includes the step of calculating a sample advantage using timing information embedded in selected ones of the encoded units, the sample advantage representing a time difference in number of samples between the presentation of a reference sample and the availability of the reference sample. A number of phantom samples substantially equal to the number of samples represented by the calculated sample advantage are queued and then output from the queue at a selected rate. Substantially simultaneous with the outputting of the phantom samples from the queue, at least some data samples of at least one encoded unit are decoded and queued behind the phantom samples.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Signal construction, detection and estimation for uplink timing synchronization and access control in a multi-access wireless communication system
InactiveUS6922388B1Improve estimation accuracyGreat rangeTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexFourier transform on finite groupsCyclic prefix
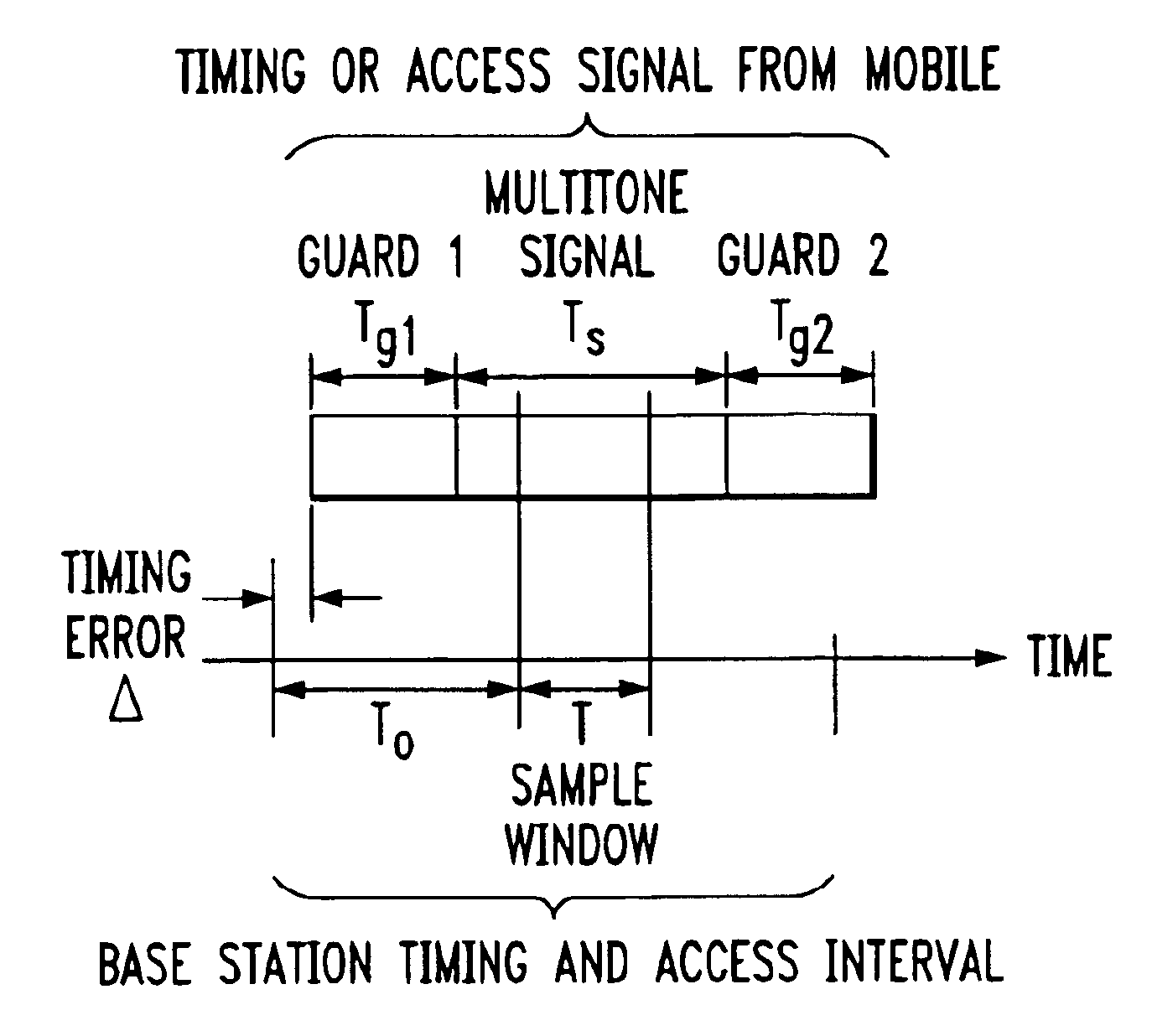
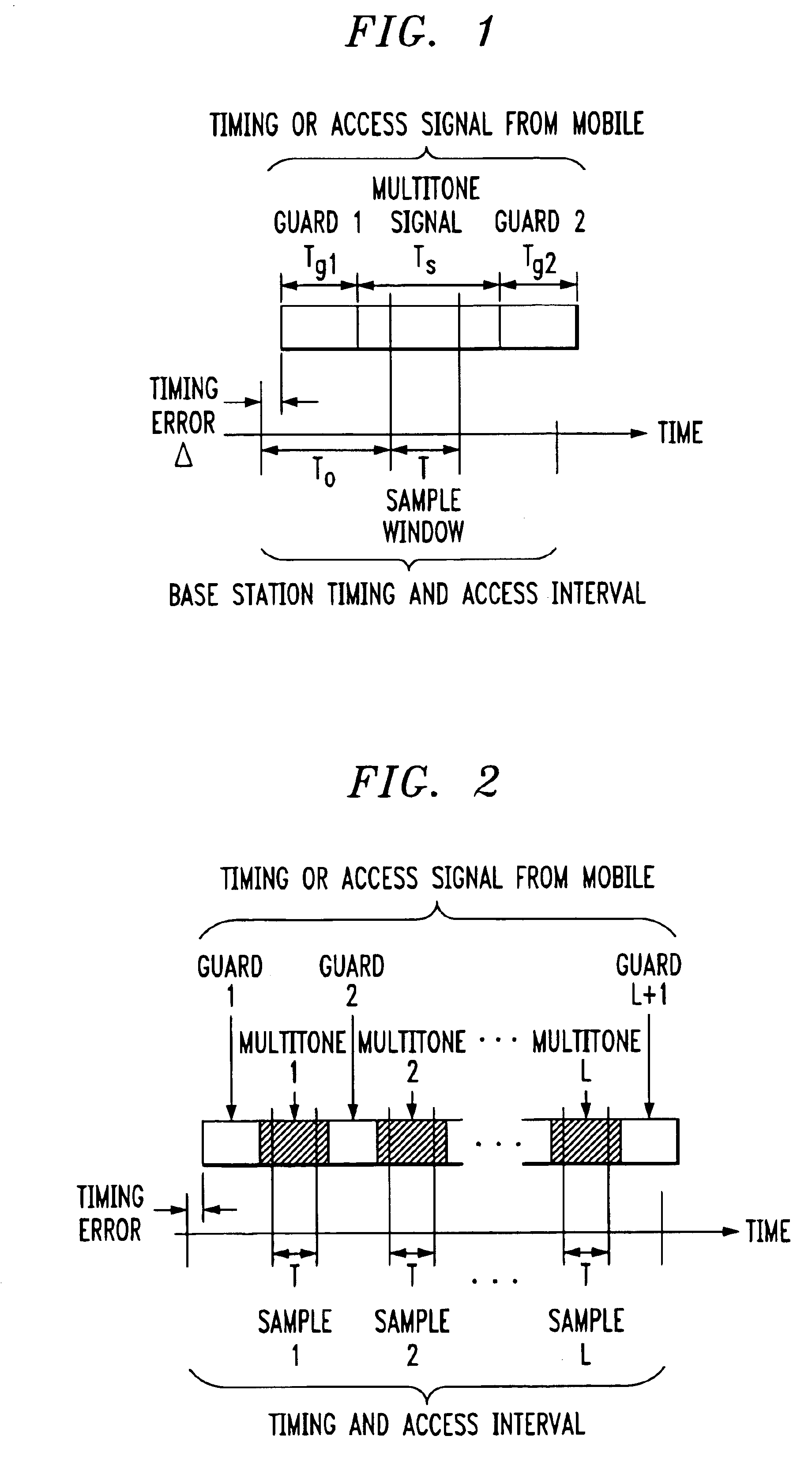
Signal construction, detection and estimation techniques for use in uplink timing synchronization and access control in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) wireless system or other type of wireless communication system. In accordance with an illustrative embodiment of the invention, timing and access signals to be transmitted in designated timing and access intervals are constructed from orthogonal multitone signals. The multitone signals may be similar to multitone signals used in OFDM data transmission, except that a cyclic prefix associated with reception of the signals in a base station is extended to cover the timing errors of mobile stations not yet synchronized. The invention also provides design techniques which optimize the time resolvability and peak-to-average ratio of the multitone signals, an efficient fast Fourier transform (FFT) based technique for maximum likelihood timing estimation, and a robust linear filtering technique for averaging timing estimates from different synchronizations.
Owner:GEMPLU
Transmitting and receiving methods
This invention describes a wireless system comprising a plurality of transmitters and receivers, wherein each transmitter has between 1 and n antennas and each receiver has between 1 and m antennas wherein one of said transmitter is arranged to transmit to one of the receivers, said one transmitter is controlled in dependence on at least one of at least one parameter of said transmitters, at least one parameter of said receiver, and at least one parameter of a wireless environment between said transmitter and said receiver.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Digital broadcasting transmission and/or reception system to improve receiving performance and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20050249300A1Increase receiving capacityResource management arrangementsBroadcast transmission systemsData streamMultipath channels
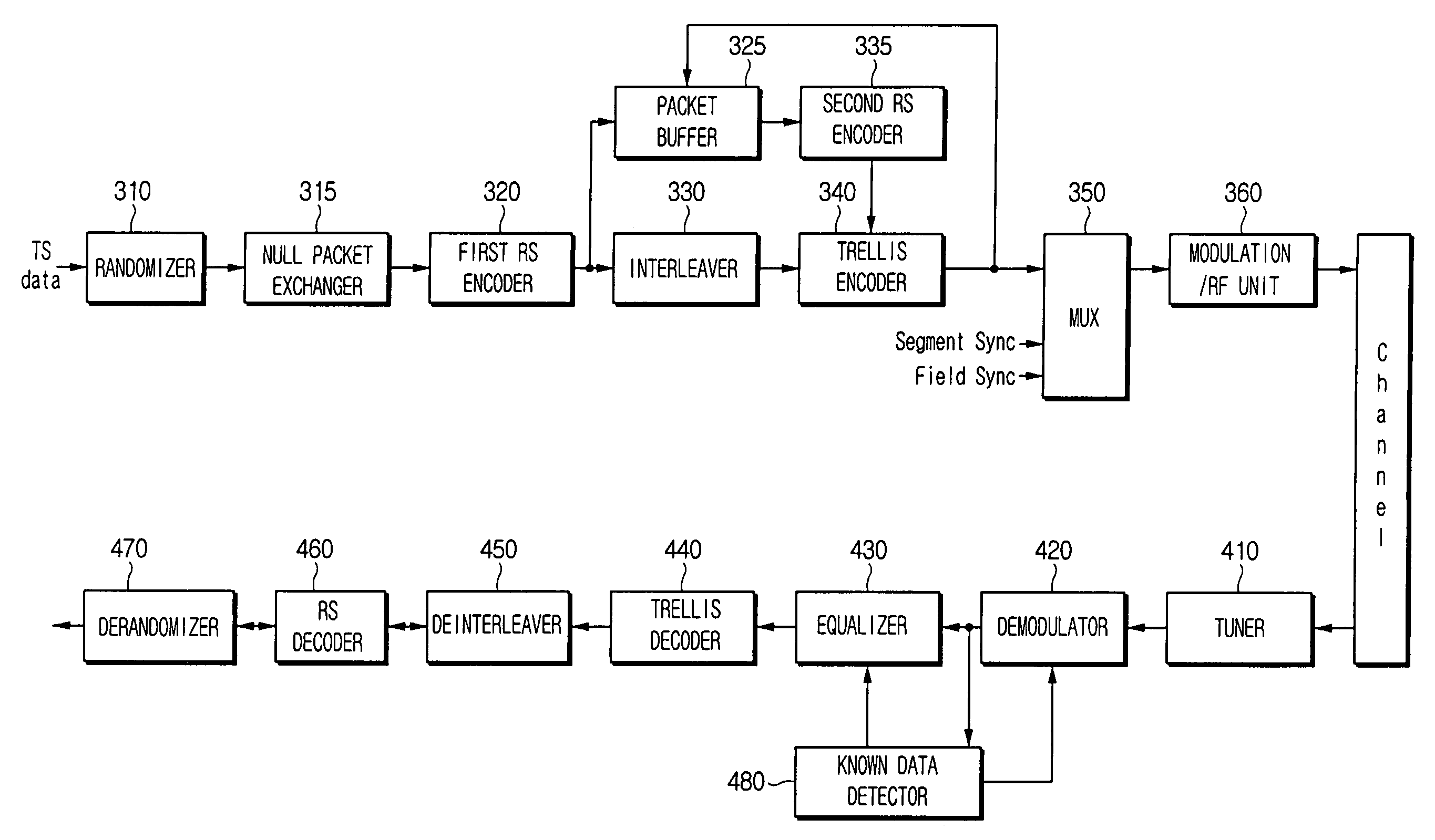
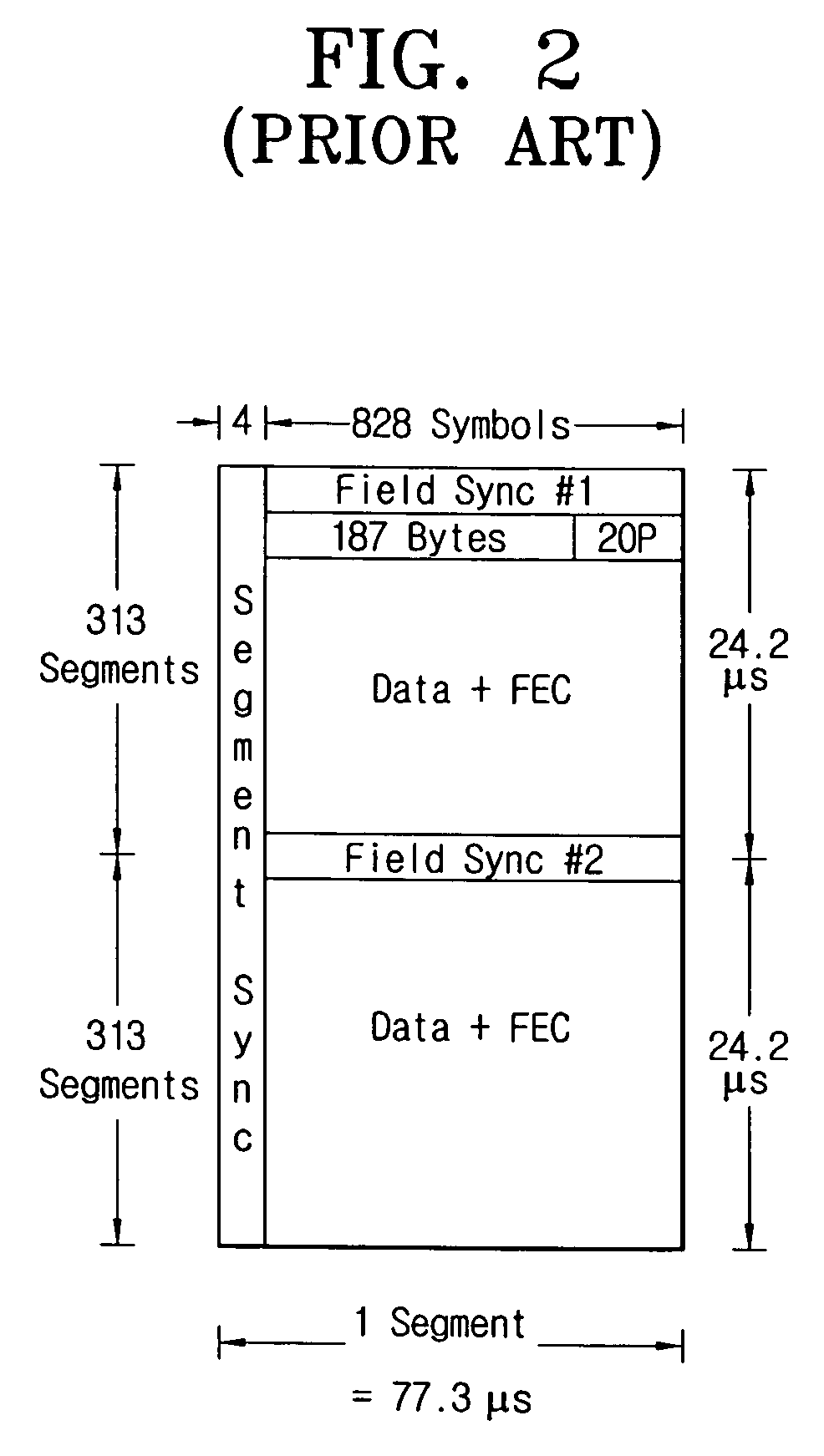
A digital broadcasting transmission and / or reception system having an improved reception performance and a signal-processing method thereof. A digital broadcasting transmitter comprises a randomizer to input and randomize data streams including a plurality of segments having at least one segment having one or more null packets, a null packet exchanger to create known data having a predetermined pattern and to replace the null packets at positions of the segments having the null packets of the randomized data streams to insert the known data, an encoder to encode the data streams to which the known data is inserted, and a modulation / RF unit to modulate, RF-modulate, and transmit the encoded data streams. A digital broadcasting receiver detects the known data from a signal received from the digital broadcasting transmitter and uses the detected known data for synchronization and equalization, so that a digital broadcasting reception performance of the digital broadcasting receiver can be improved at poor multipath channels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Generating and implementing a signal protocol and interface for higher data rates
ActiveUS20050021885A1Increase data rateEnergy efficient ICTPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital dataDisplay device
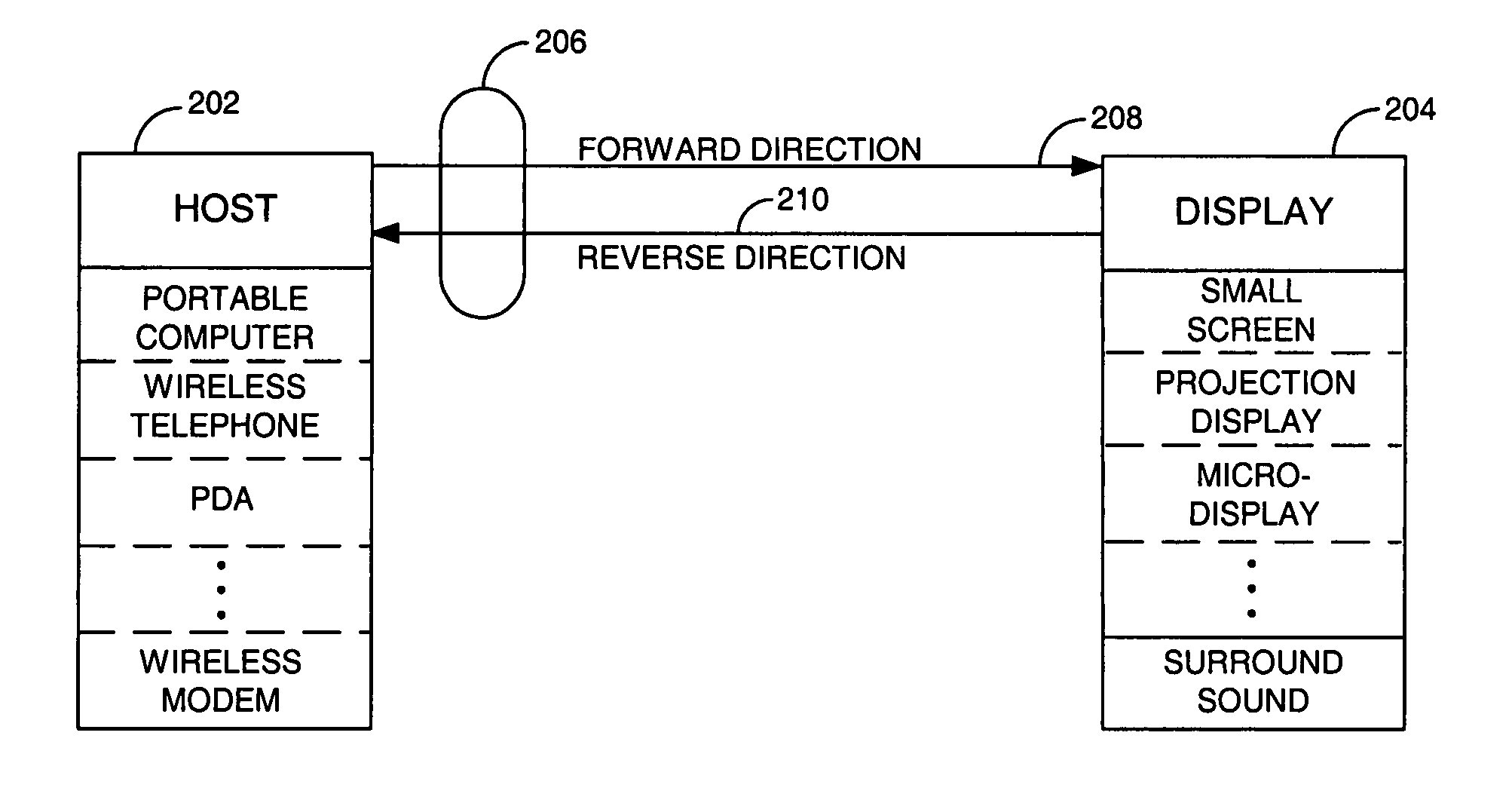
A data Interface for transferring digital data between a host and a client over a communication path using packet structures linked together to form a communication protocol for communicating a pre-selected set of digital control and presentation data. The signal protocol is used by link controllers configured to generate, transmit, and receive packets forming the communications protocol, and to form digital data into one or more types of data packets, with at least one residing in the host device and being coupled to the client through the communications path. The interface provides a cost-effective, low power, bi-directional, high-speed data transfer mechanism over a short-range “serial” type data link, which lends itself to implementation with miniature connectors and thin flexible cables which are especially useful in connecting display elements such as wearable micro-displays to portable computers and wireless communication devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
High-speed chip-to-chip communication interface
ActiveUS7180949B2Improve scalabilitySynchronisation information channelsModulated-carrier systemsCommunication interfaceCMOS
A high-speed parallel interface for communicating data between integrated circuits is disclosed. The interface is implemented by a transmitter and receiver pair and a single-ended parallel interconnect bus coupling to the transmitter and receiver pair. As opposed to transmitting small swing signals over differential signal lines, the transmitter transmits data to the receiver at full swing over the single-ended parallel interconnect bus. The invention can be implemented with simple CMOS circuitry that does not consume large die area. Accordingly, many link interfaces can be implemented on a single chip to provide a large data bandwidth.
Owner:RIVERSTONE NETWORKS +1
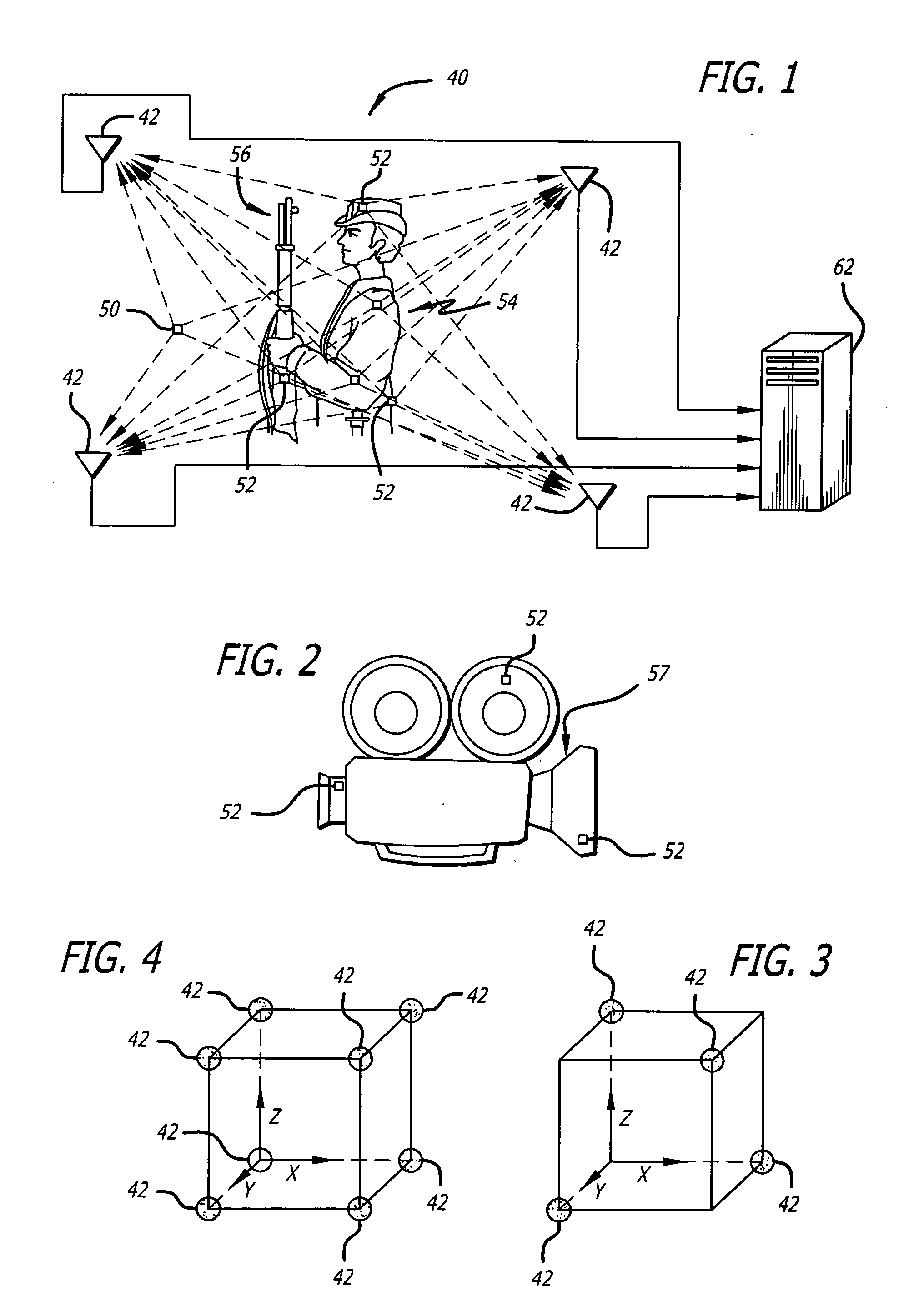
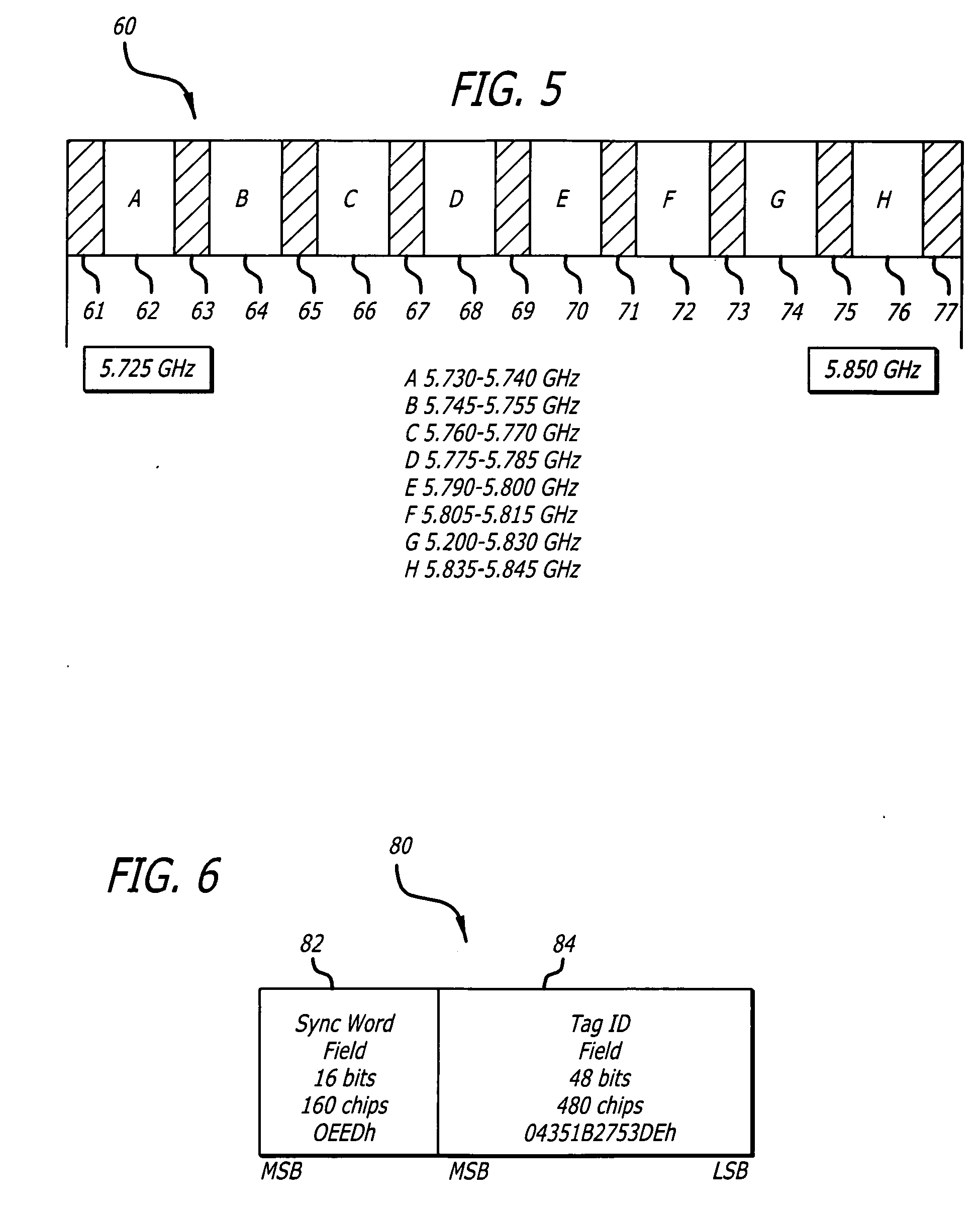
Radio frequency motion tracking system and method
InactiveUS7009561B2Desirable effectReducing manual correlatingDirection finders using radio wavesCode conversionDouble differenceHandling system
A radio frequency (RF) motion capture system includes stationary sensor receivers, one or more transmitter marker tags on one or more objects to be tracked within a capture zone, at least one stationary reference tag transmitter, and a processing system for processing the received signals. The individual tags transmit burst of spread-spectrum RF signals. The transmitted signals include a common sync code, and a tag identification code that is unique to each tag. By computing double differences of pseudoranges, clock terms are cancelled out allowing the processing system to precisely determine the location of each tag as it moves through the capture zone without the need to synchronize clocks between sensors and tags. The system can be used for RF match moving.
Owner:MENACHE
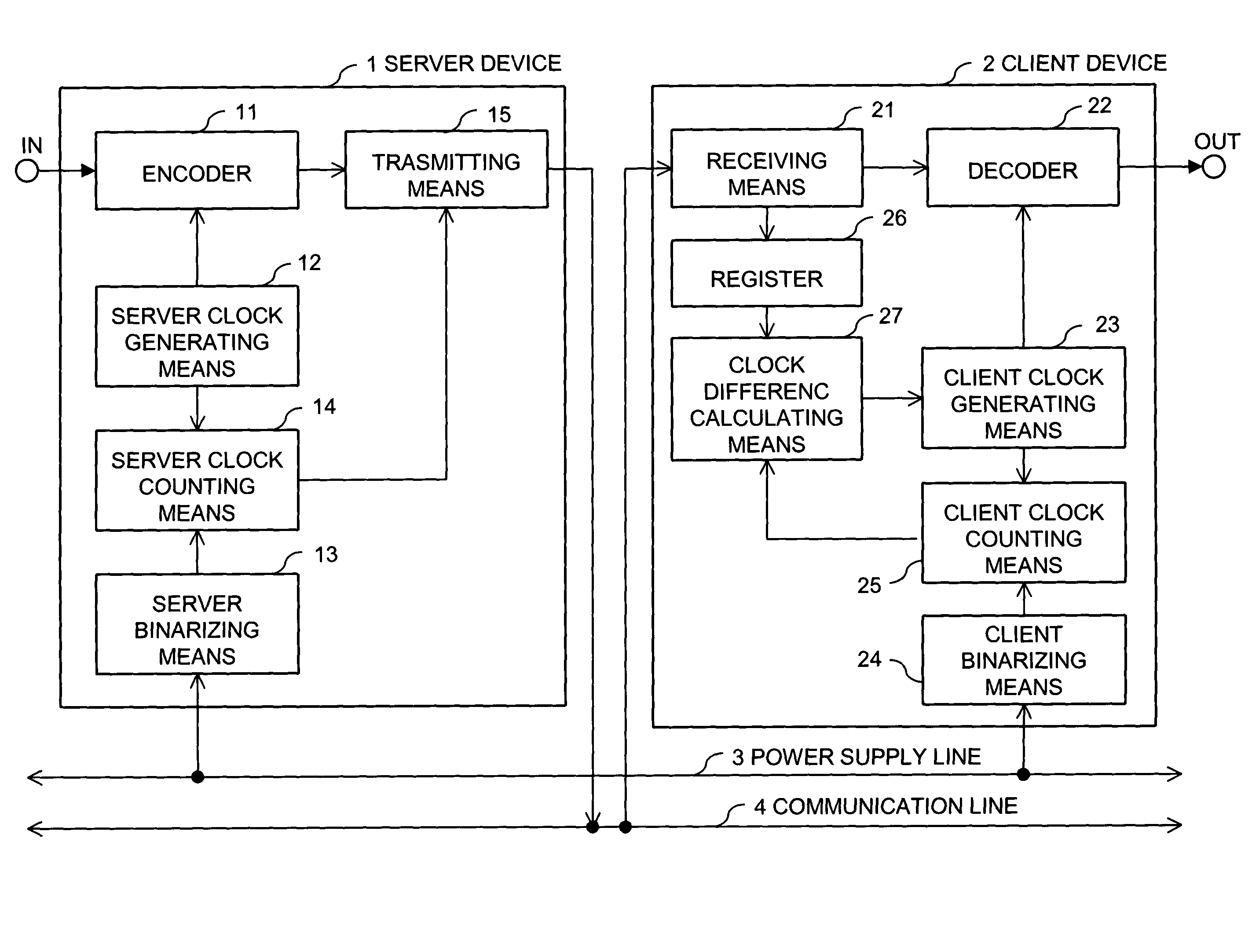
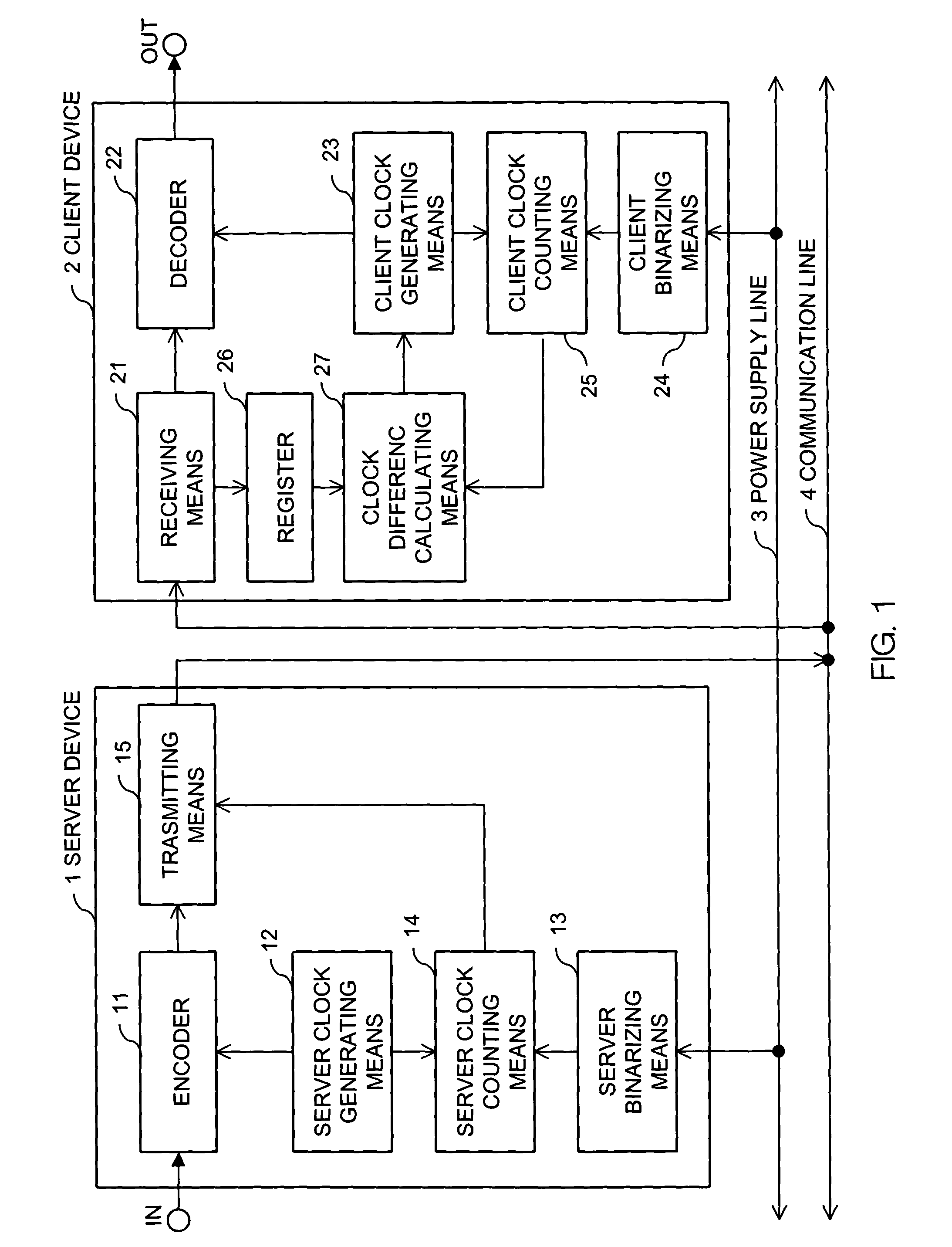
Synchronizing clock signals of server and client devices in a network system based on power source synchronous pulse signal
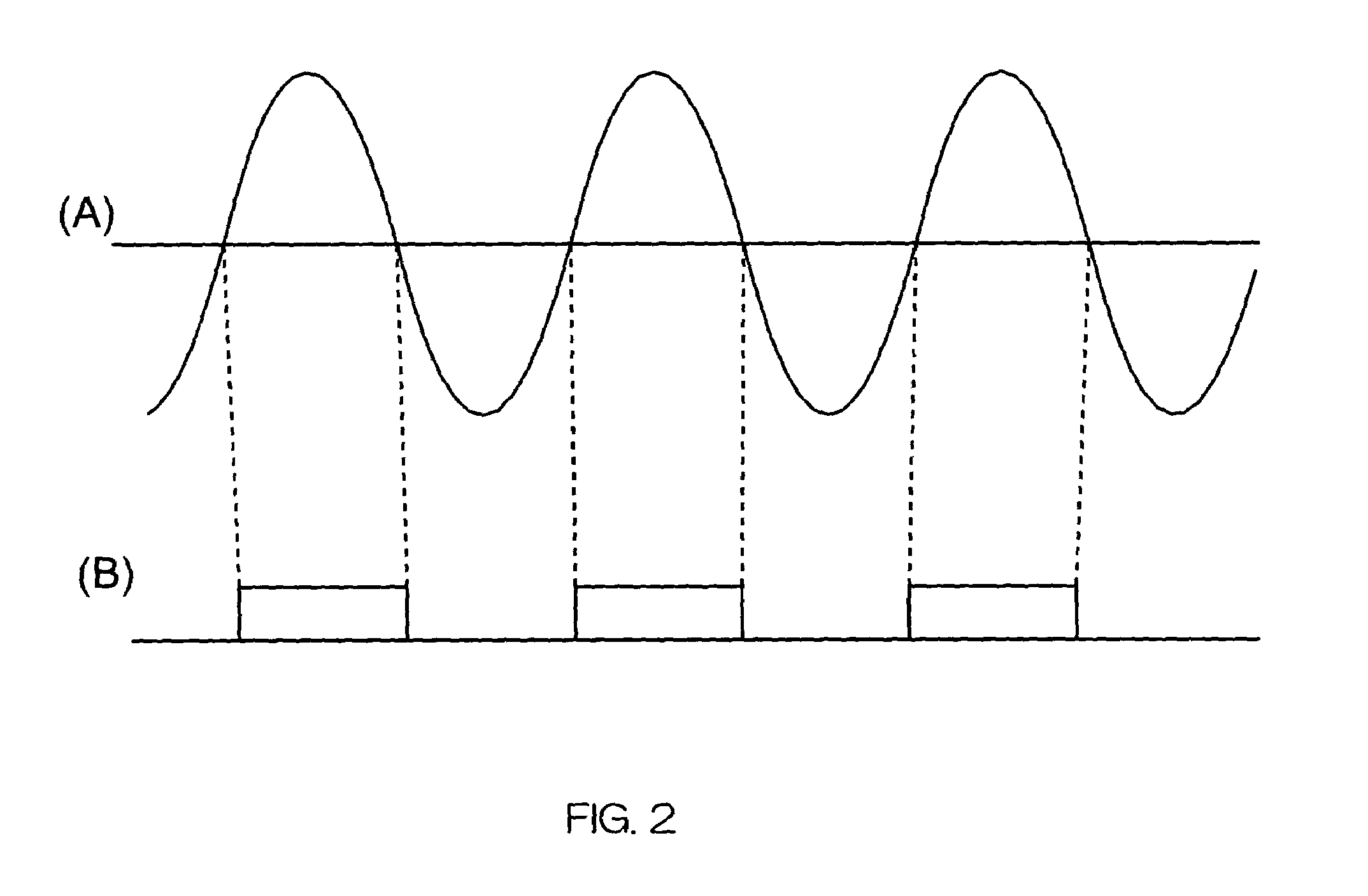
InactiveUS7263110B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData transmission timeNetworked system
In a network system, clock signals of a server device and a client device are synchronized with each other without having any influence of a change and a delay of the transmission time of data. Therefore, in the network system in which the client device receives and reproduces information transmitted from the server device, the server device counts the number of clock pulses of a server clock signal used to compress and encode information on the basis of a power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with a power source frequency. The server device outputs information showing the counted clock pulse number and the compressed and encoded information to the client device. The client device counts the number of clock pulses of a client clock signal used to decode and decompress the compressed and encoded information on the basis of the power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with the power source frequency. The client device conforms the frequency of the client clock signal to the frequency of the server clock signal on the basis of the clock difference between the clock pulse number received from the server device and the counted clock pulse number.
Owner:D & M HOLDINGS INC
Radio frequency tags for use in a motion tracking system
InactiveUS20060125691A1High precisionGood autocorrelation propertiesDirection finders using radio wavesLaminationHuman bodyOxygen sensor
Small radio frequency tags for use in a motion capture system include a power source, circuitry for generating radio frequency identification signals, an antenna for transmitting the signals, and means for automatically activating the tags so that the tags begin transmitting the signals including a tag identification code when a cover is removed. The activation means may include a release strip that, when removed, opens or closes an electrical circuit that activates the tag and also exposes an adhesive covered surface of the tag so that the tag can then be adhered to a clothed or unclothed human body or other object to be tracked. The activation means can also include an optical sensor, an oxygen sensor, or other sensors. The battery and the antenna may be printed or constructed of film, thus allowing the tag to be small, thin, and flexible.
Owner:MENACHE
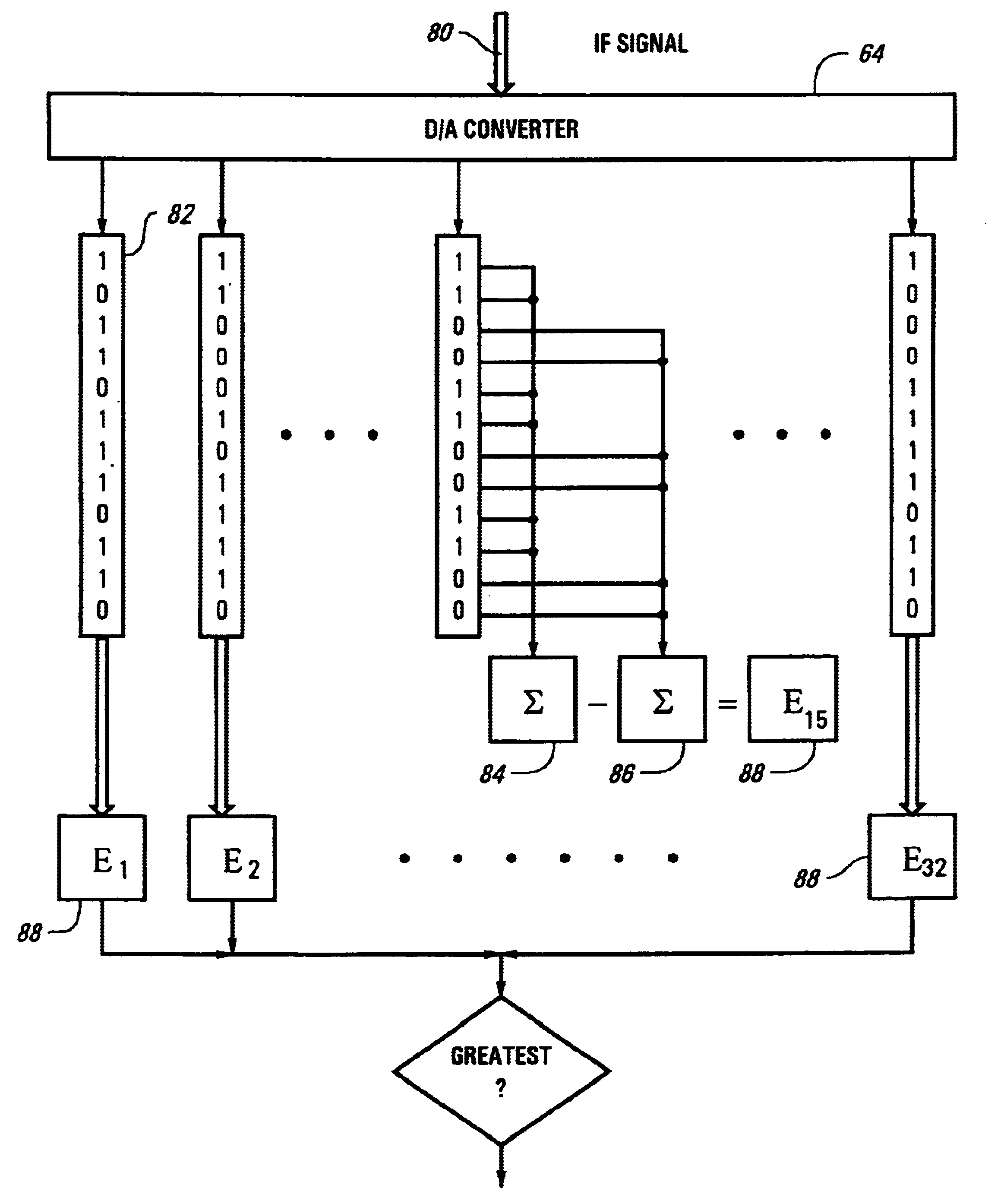
Frequency hopping spread spectrum system with high sensitivity tracking and synchronization for frequency unstable signals
InactiveUS6934316B2Improve dynamic rangeReduce sensitivityData switching by path configurationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlFrequency-hopping spread spectrumFast Fourier transform
A wireless spread spectrum communication system for transmitting data includes a plurality of end point transmitters and at least one receiver. The end point transmitters transmit data via a frequency hopped spread spectrum signal where the transmitting signal is sent without the benefit of frequency stabilization. The receiver is responsive to the frequency hopping spread spectrum signals and includes a correlator and a signal processor. The correlator samples at least a first portion of a preamble of the signal and correlates the portion of the preamble with a known preamble pattern to determine a probability of correlation. The signal processor applies a Fast Fourier Transform algorithm to the signal in response to the probability of correlation to track a narrowband frequency of the signal based on at least a second portion of the preamble and to decode data encoded within the signal subsequent to the preamble.
Owner:ITRON
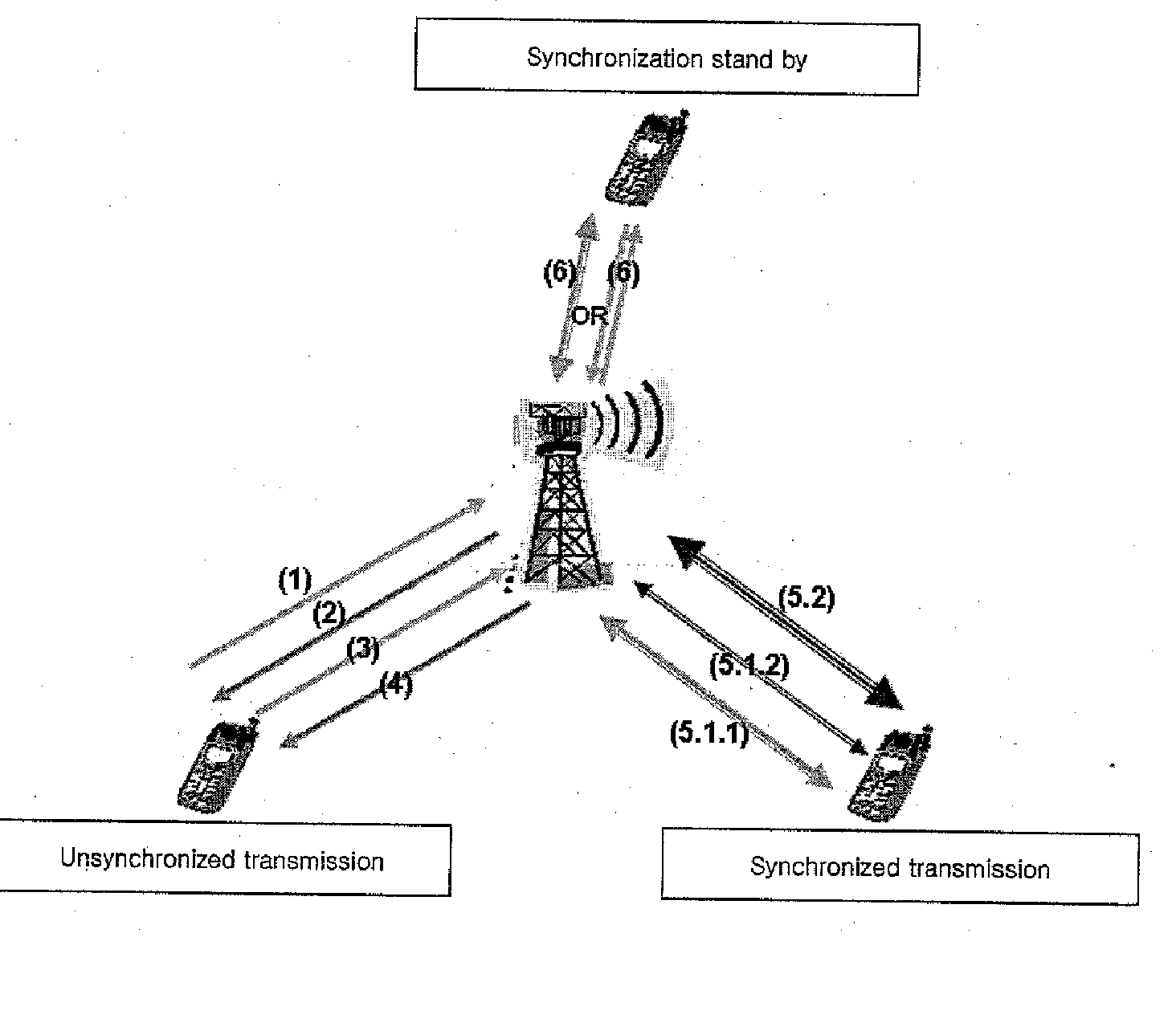
Method and procedures for unsynchronized, synchronized, and synchronization stand by communications in e-utra systems
ActiveUS20090252125A1Allocation is fastMaintain the given level of performancesSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsImproved method
An improved method of processing random access procedures, wherein the network receives at least one access burst to allow a network to estimate uplink received timing, the access burst containing at least a preamble, and transmits information for responding to the at least one access burst, while the mobile terminal configures at least one access burst containing at least a preamble and transmits the at least one access burst to allow a network to at least estimate uplink received timing.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
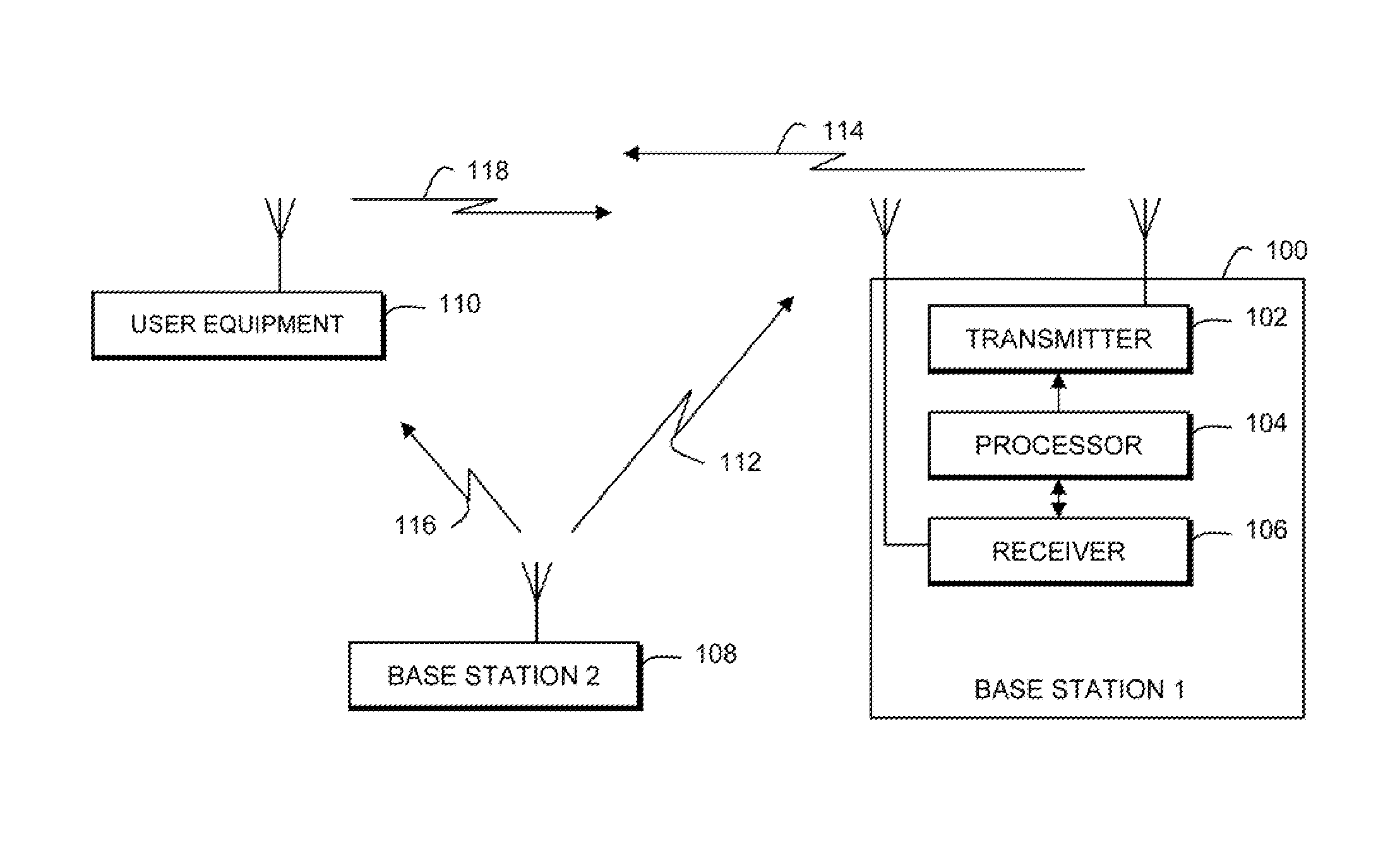
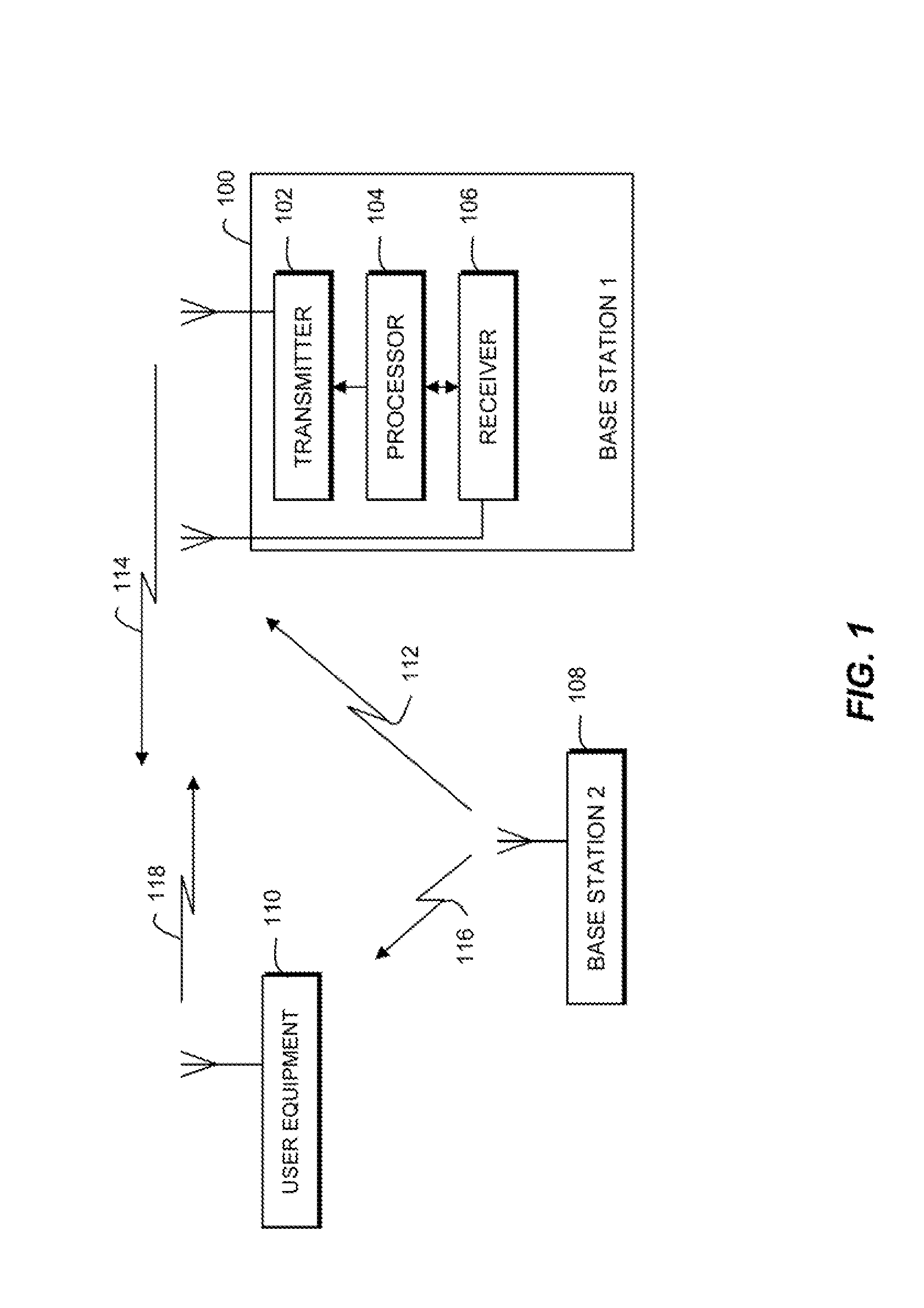
Method for synchronizing a base station with a mobile station, a base station and a mobile station
InactiveUS7062002B1Sure easyEasy to useCode division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMobile stationComputer science
Method for forming and determining a signal sequence, a synchronization method, a transmitting unit and a receiving unit, including the formation of signal sequences that are based on partial signal sequences, the second partial signal sequence being repeated and modulated in the process by the first partial signal sequence, and at least one of the signal sequences being a Golay sequence, and use of these partial signal sequences for the purpose of simplified calculation of correlation sums in a two-stage calculation method, with one partial correlation sum sequence being calculated first.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
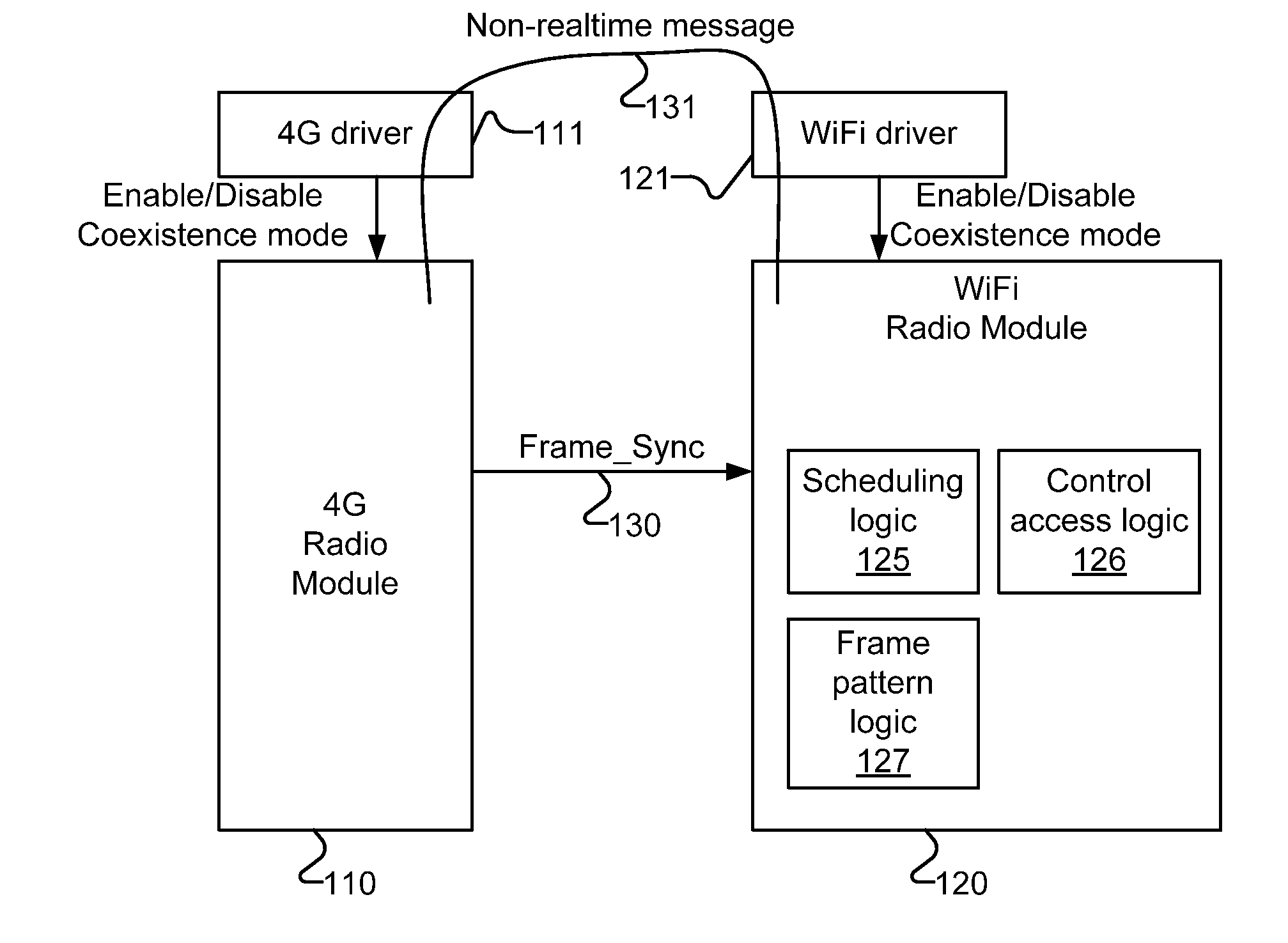
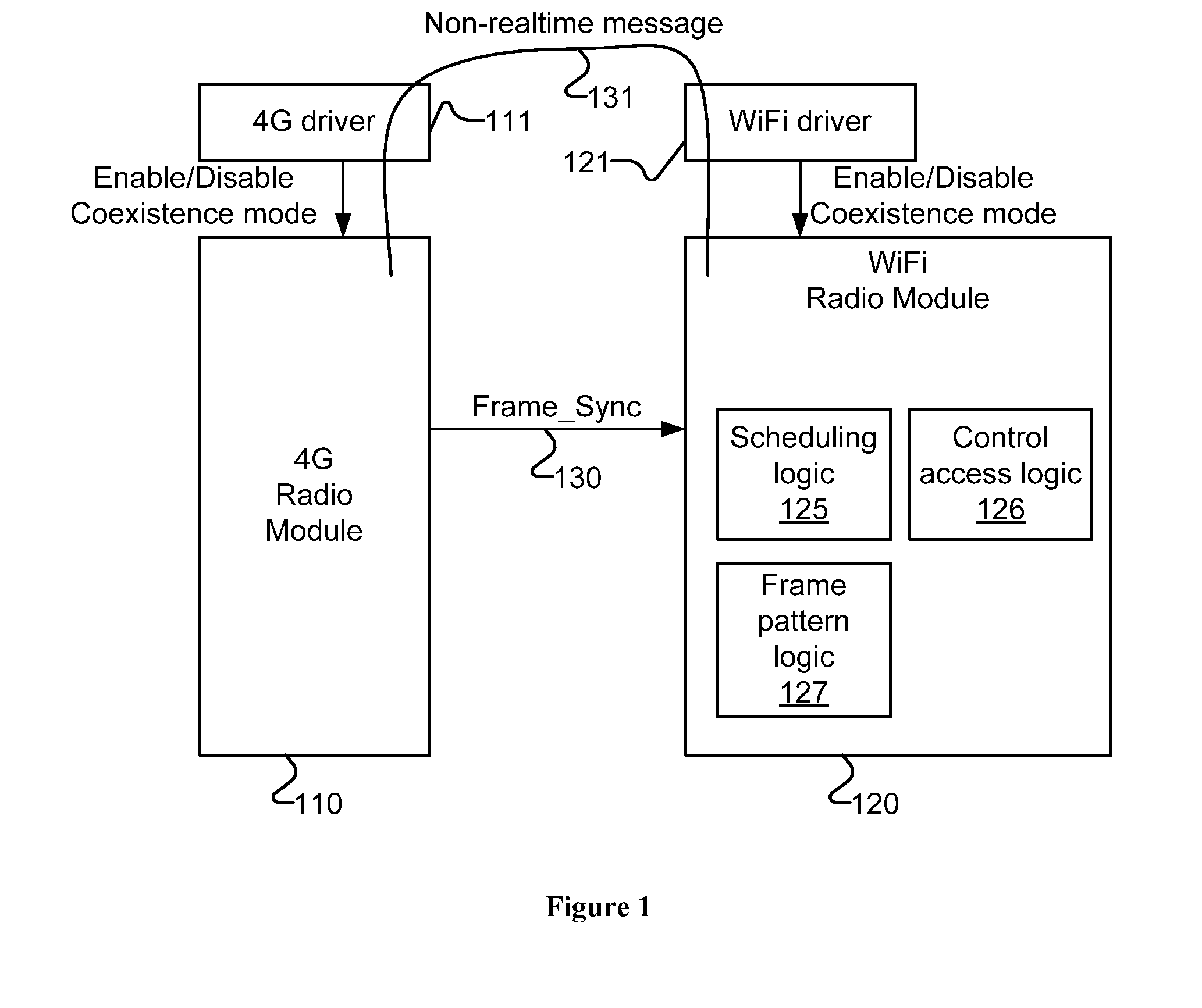
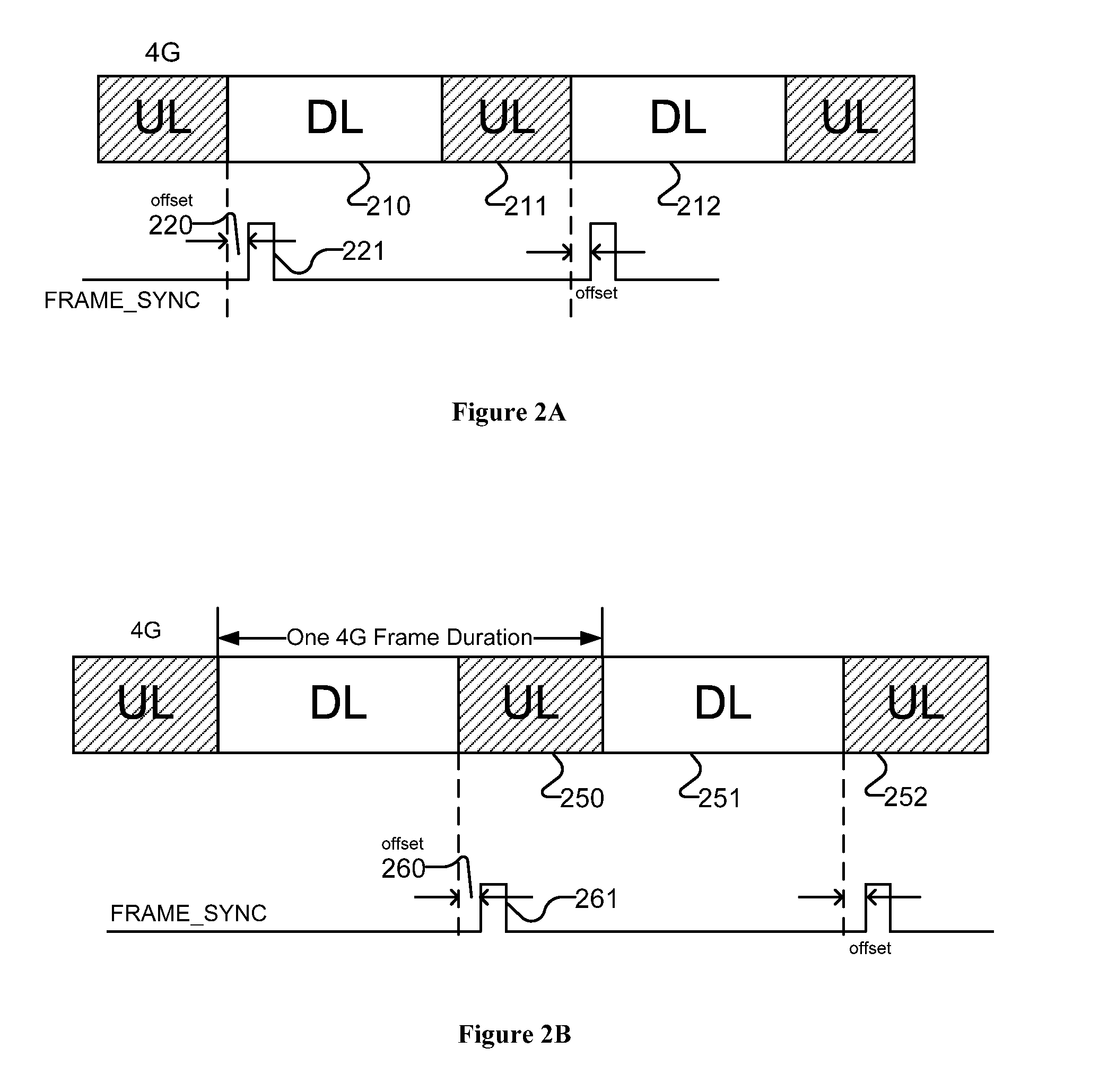
Methods and apparatuses for multi-radio coexistence
InactiveUS20120120944A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemVIT signals
A method for coexistence radio communication systems is presented. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving a realtime frame synchronization signal and receiving one or more frame parameters. The method further includes determining, based at least on the frame synchronization signal and the frame parameters, estimated frame timing information and scheduling transmission based on the estimated frame timing information to avoid collision of the transmission and reception.
Owner:INTEL CORP
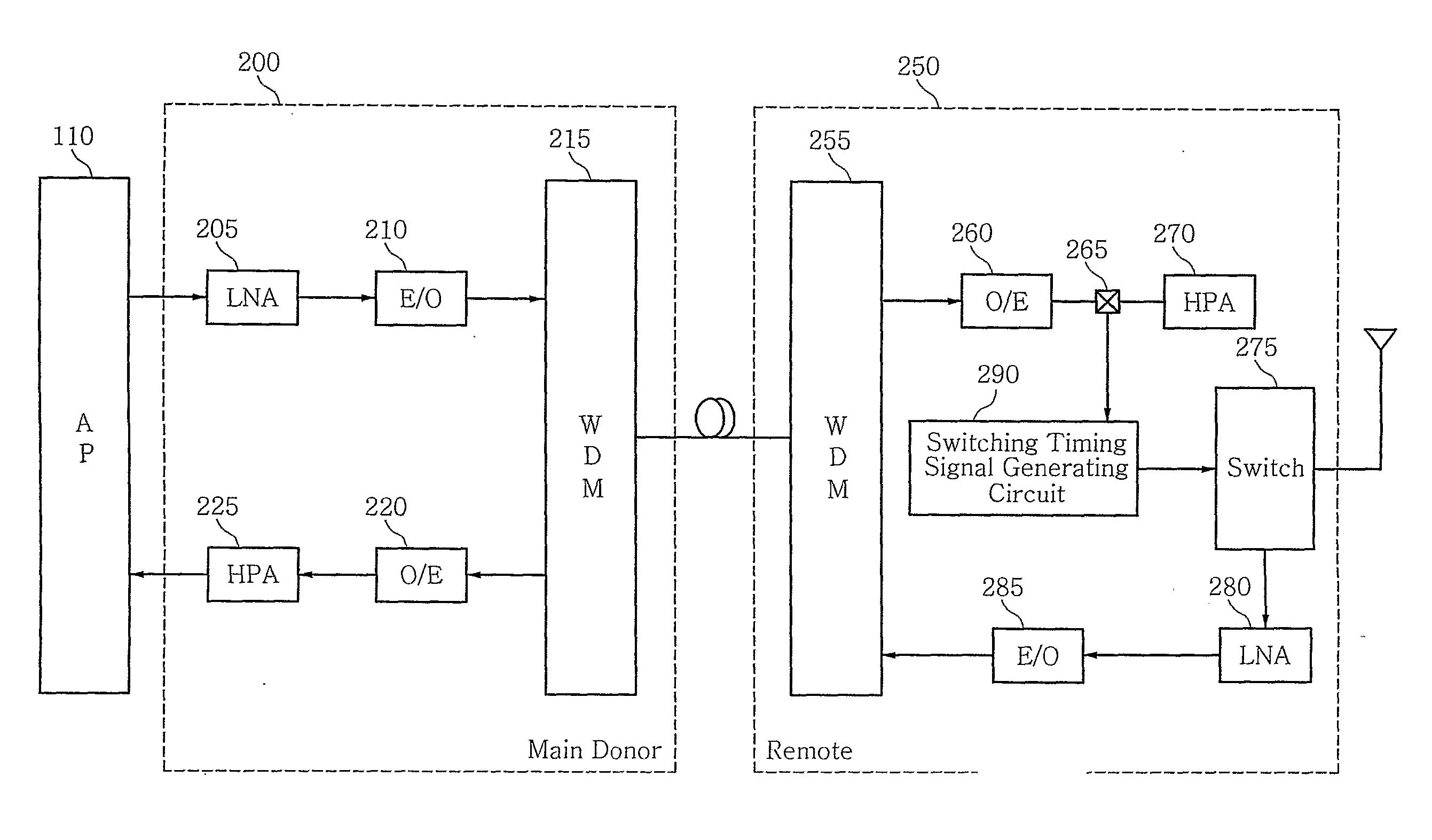
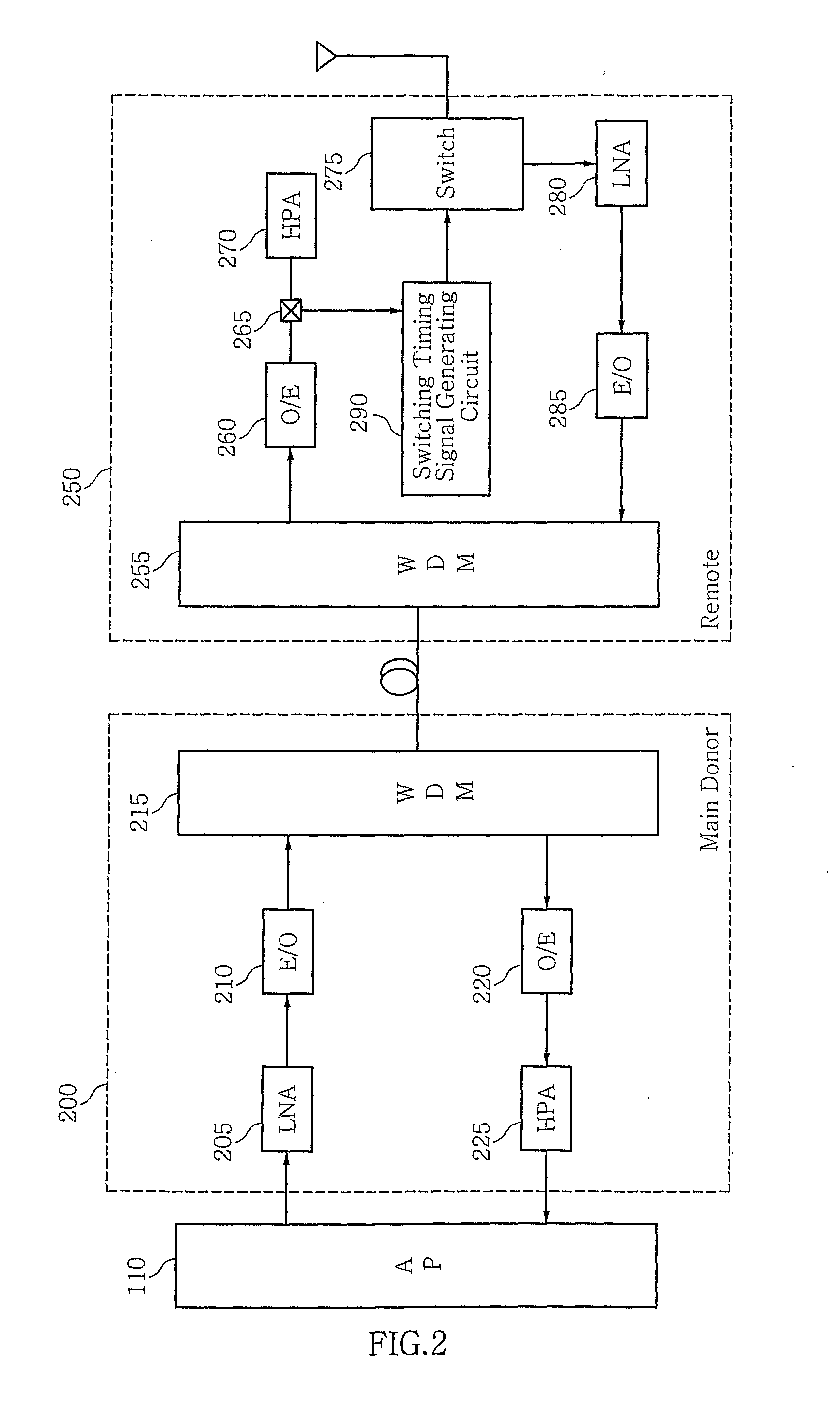
Method and System for Generating Switching Timing Signal for Separating Transmitting and Receiving Signal in Optical Repeater of Mobile Telecommunication Network Using Tdd and Ofdm Modulation
InactiveUS20070237181A1Pulse transformerWavelength-division multiplex systemsTelecommunications networkSignal on
Disclosed are a method and system for generating switching a timing signal for separating a transmitting and receiving signal in an optical repeater of a mobile telecommunication network by using a Time Division Duplex (hereinafter, referred to as “TDD”) scheme and an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (hereinafter, referred to as “OFDM”) modulation scheme, which transmits a part of a RF signal extracted from a coupler included in a remote of an optical repeater to a switching timing signal generating circuit, locates a frame start position of a RF signal by correlating a reference signal generated in a switching timing signal generating circuit with a RF signal extracted from a coupler, and is capable of transmitting a RF signal by distinguishing between a downlink signal and a uplink signal by using a switching timing signal in a switch when calculating a starting point of a downlink signal and a uplink signal included in an RF signal on the basis of a frame starting location, generating a switching timing signal by using it, and transmitting to a remote's switch.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
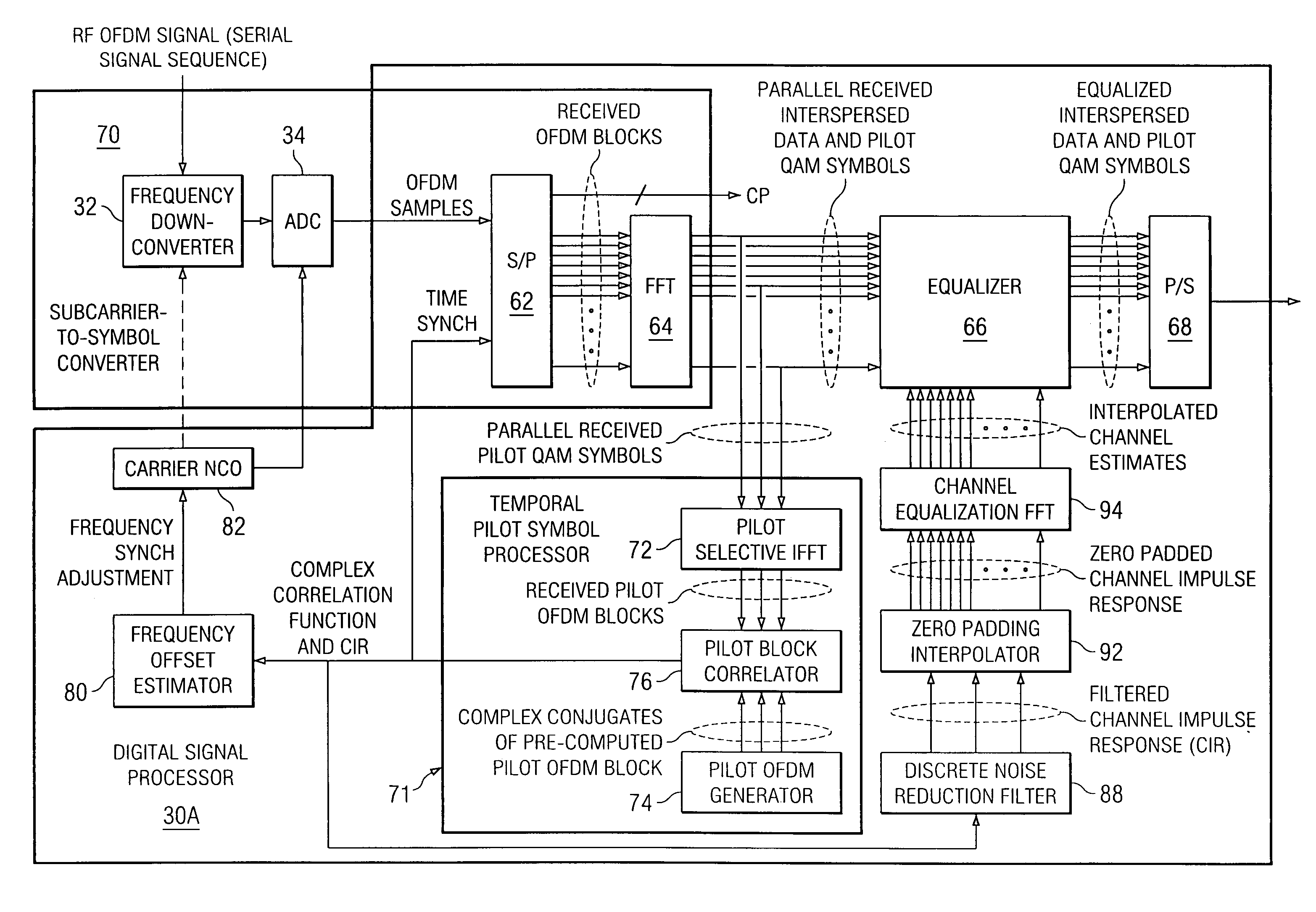
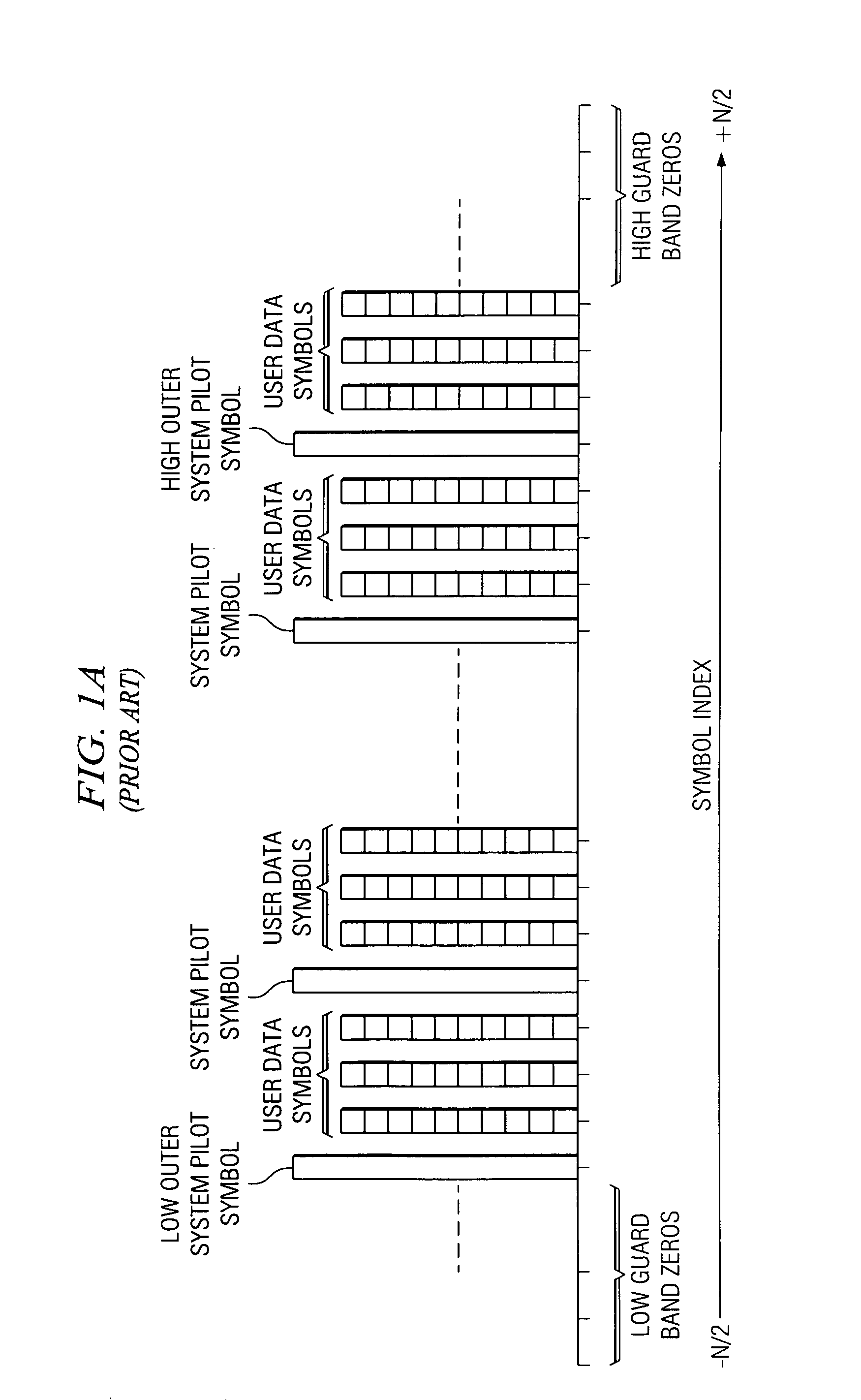
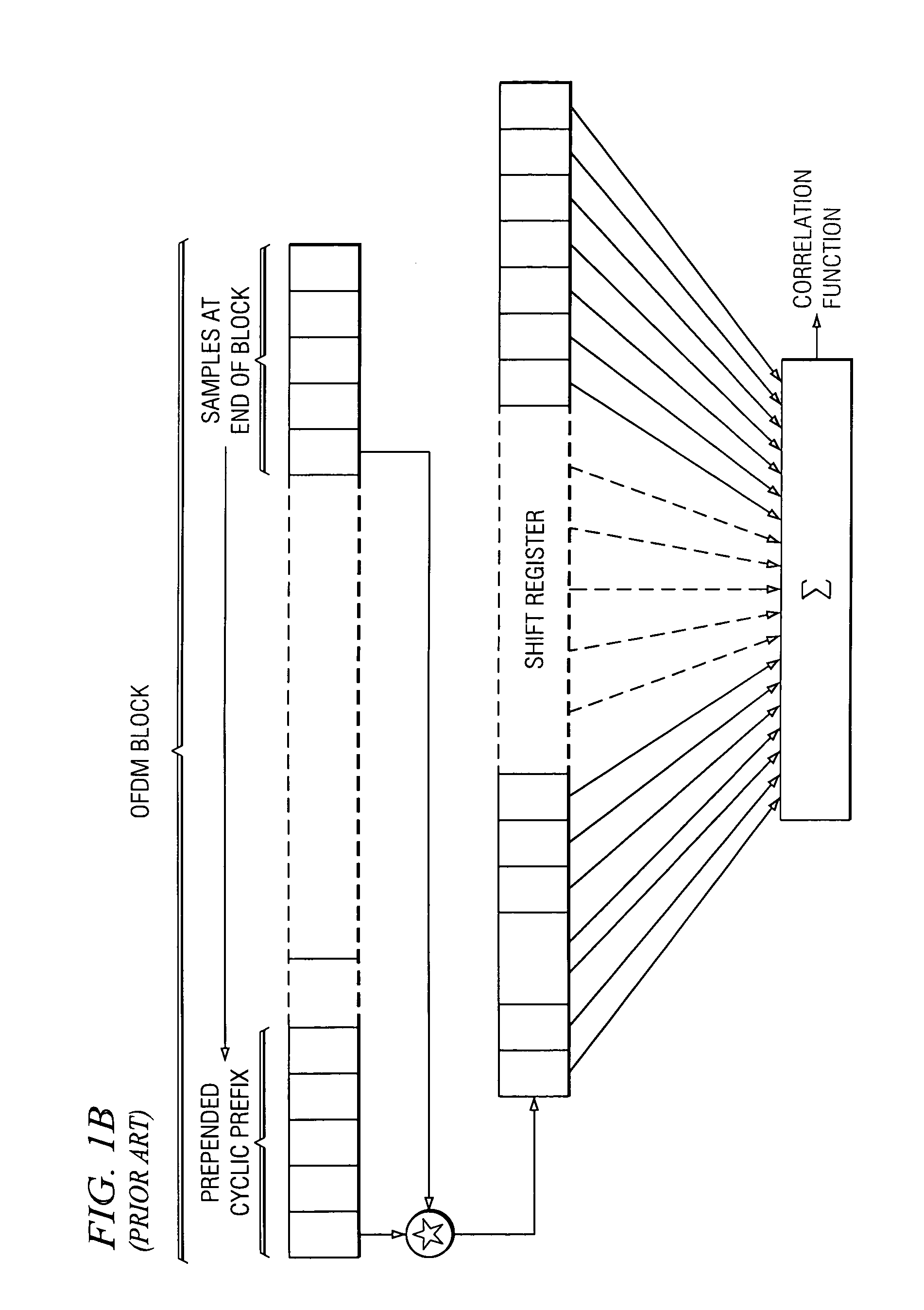
Method and apparatus for multicarrier channel estimation and synchronization using pilot sequences
ActiveUS7139320B1Extension of timeTransmission path divisionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPilot systemChannel impulse response
Method and apparatus for OFDM synchronization and channel estimation. In a temporal embodiment, received embedded system pilot symbols are inverse Fourier transformed at expected index locations and correlated with computed complex conjugates of inverse Fourier transforms of pilot symbols for providing a correlation function for the channel impulse response. In a frequency domain embodiment, embedded system pilot symbols are augmented with pilot-spaced inferred guard band symbols, multiplied by scaled complex conjugates of computed pilot systems, and inverse Fourier transformed into the channel impulse response. Time and frequency are synchronized in feedback loops from information in the channel impulse response. The channel impulse response is filtered, interpolated, and then Fourier transformed for determining channel estimates for equalization.
Owner:RADIA COMM
Methods and arrangements in a radio communications system
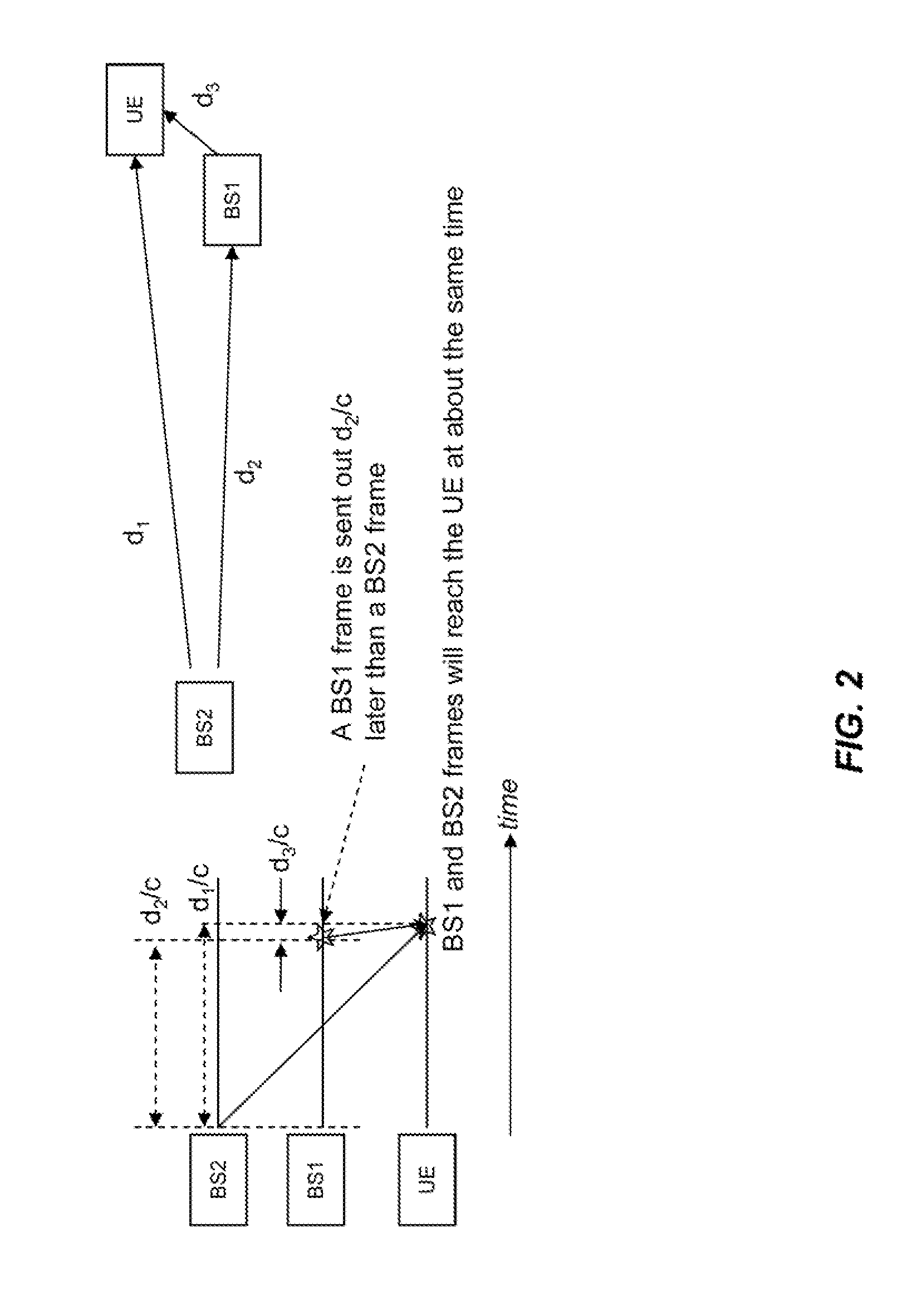
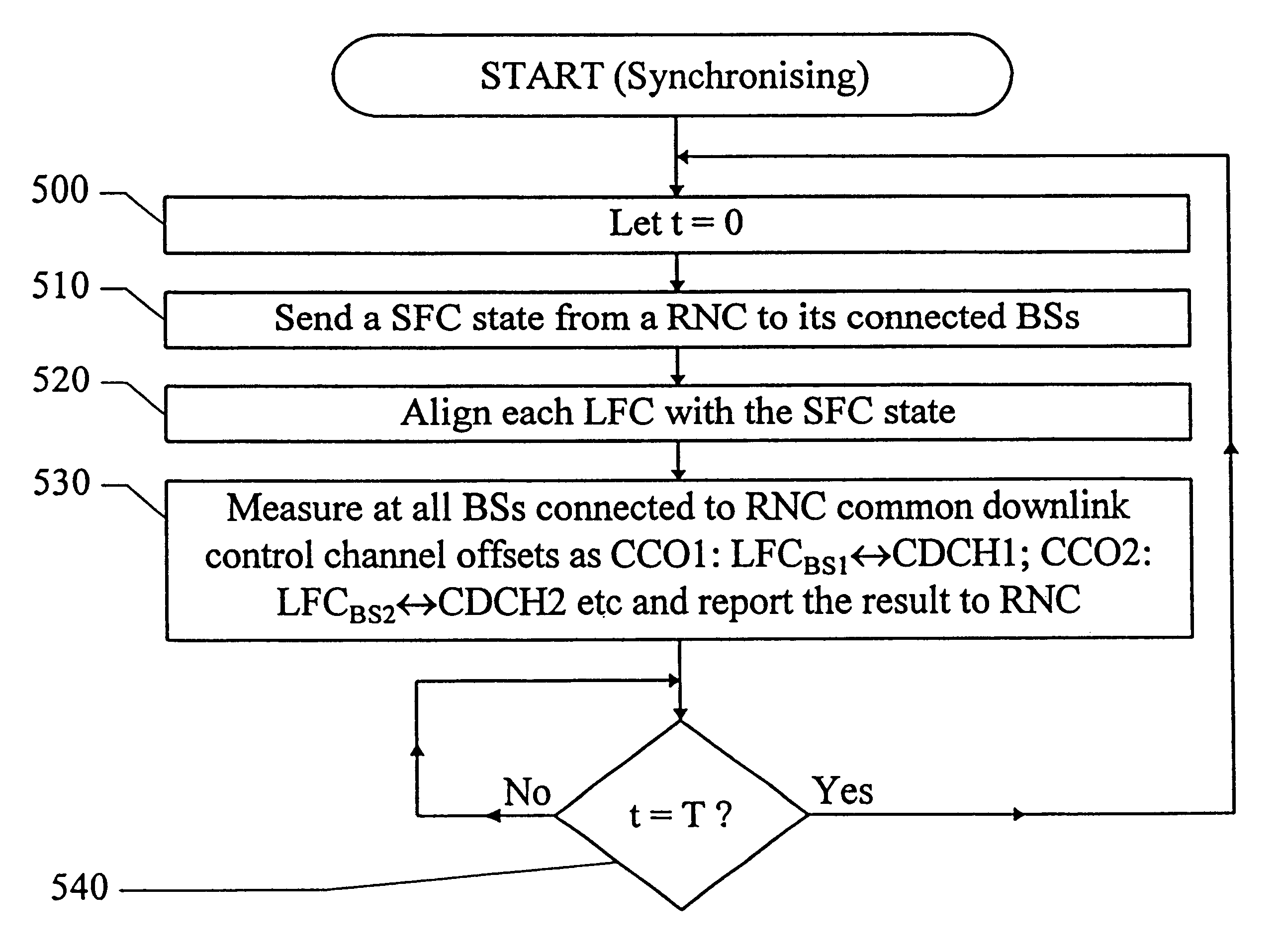
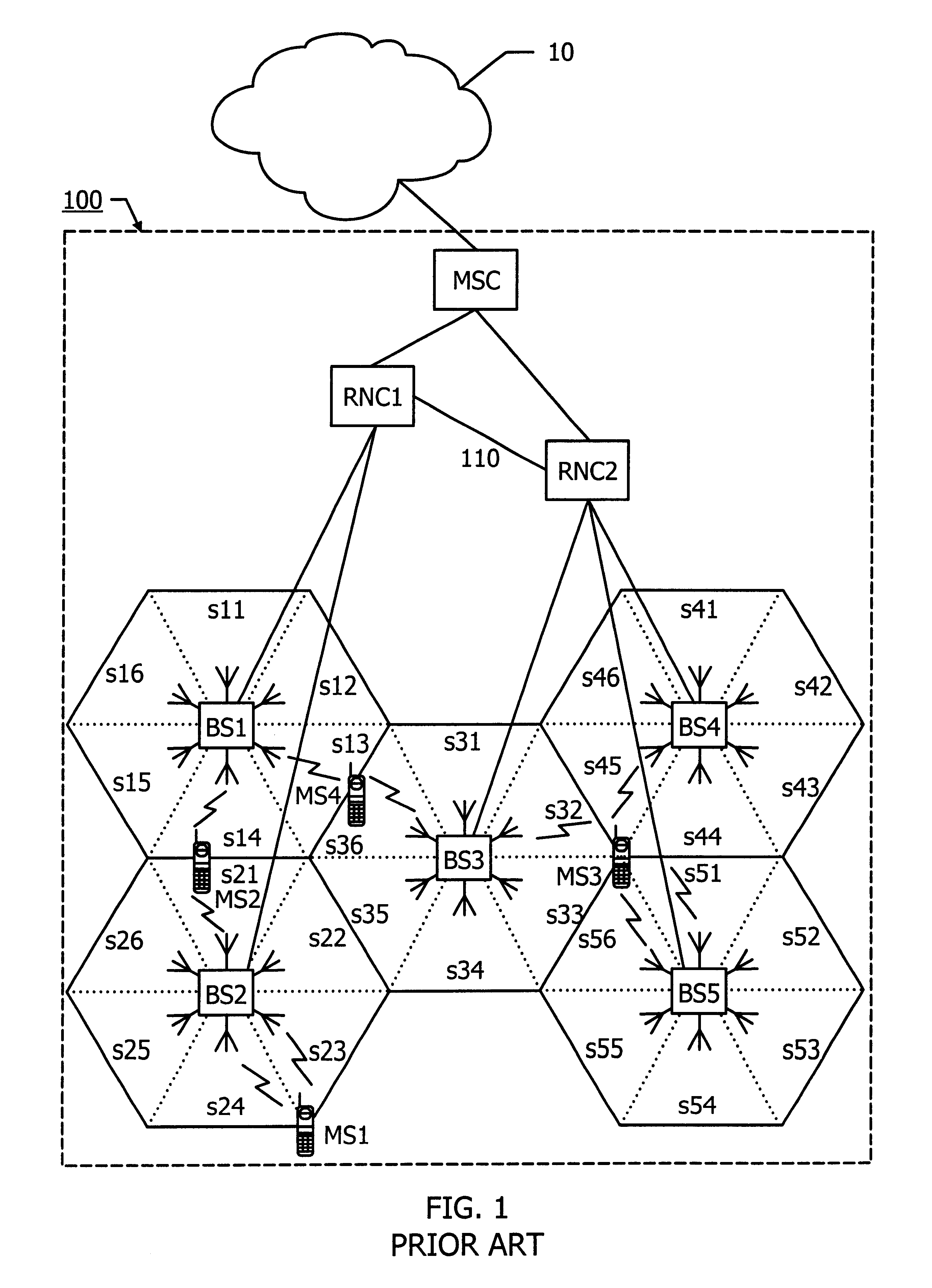
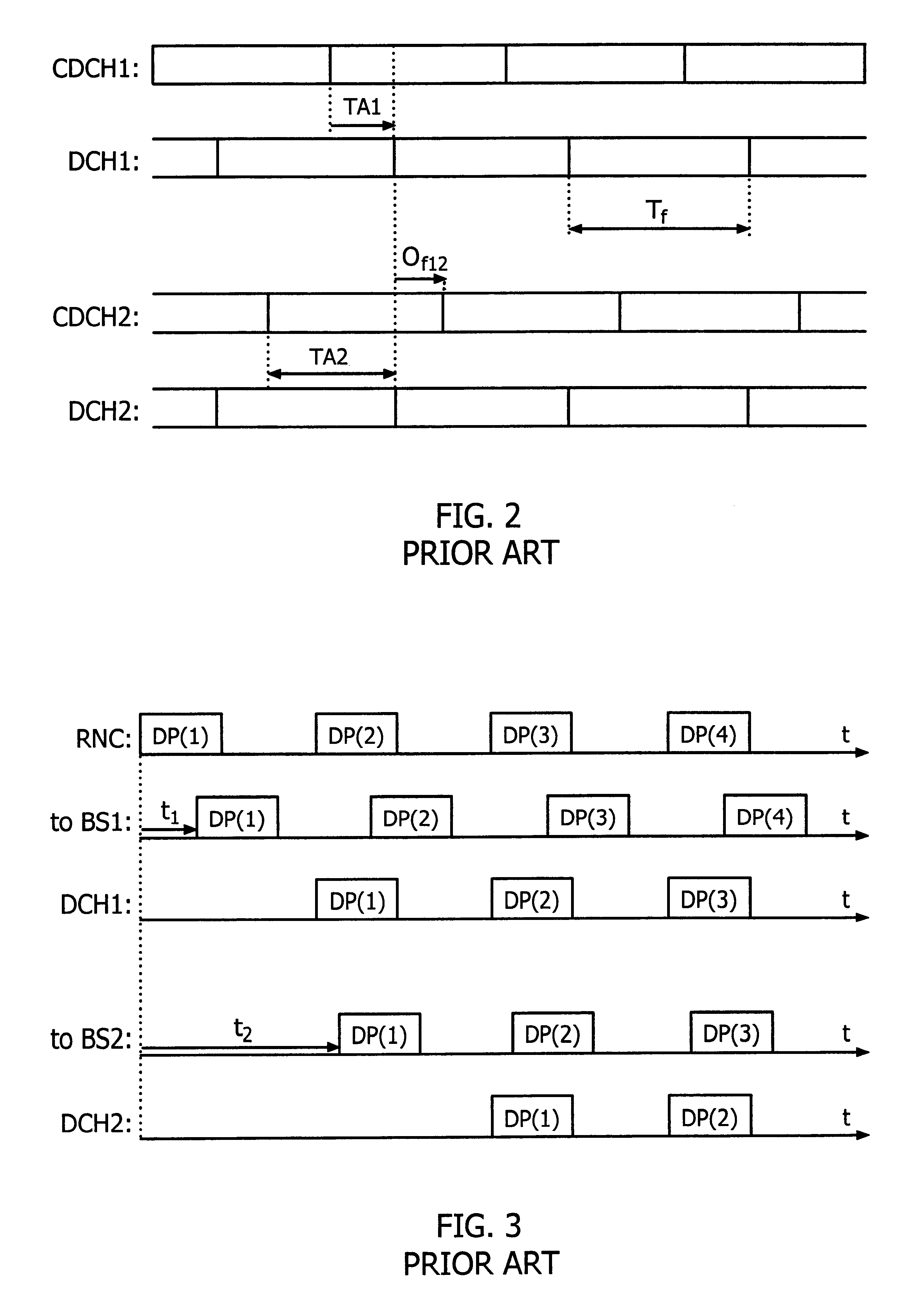
InactiveUS6449290B1Low round-trip delayLess complexSite diversitySynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemCellular communication systems
Methods and an arrangement for synchronizing communication of framed data via asynchronous base stations (BS1, BS2) in a cellular communication system are presented. The synchronization methods are performed continuously by sending out certain system frame counter states from a central node in the system to all its connected base stations (BS1, BS2). Each base station (BS1, BS2) includes a local frame counter (LFCBS1, LFCBS2), which generates local frame counter states (t1(1)-t1(4), t2(1)-t2(4)) correlated to the system frame counter states. Transmission of information via the base stations (BS1, BS2) is synchronized by assigning each data frame (DR(1)-DR(4)) a particular frame number, which is given by the local frame counter states (t1(1)-t1(4), t2(1)-t2(4)), so that data framed (DF(1)-DF(4)) having identical numbers contain copies of a certain data packet. Correct frame numbers are derived from common downlink channel offset measurements (CCO1, CCO2) carried out in the base stations (BS1, BS2), and timing advance values (TA2) and downlink channel offsets (DCO1, DCO2) calculated in the central node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
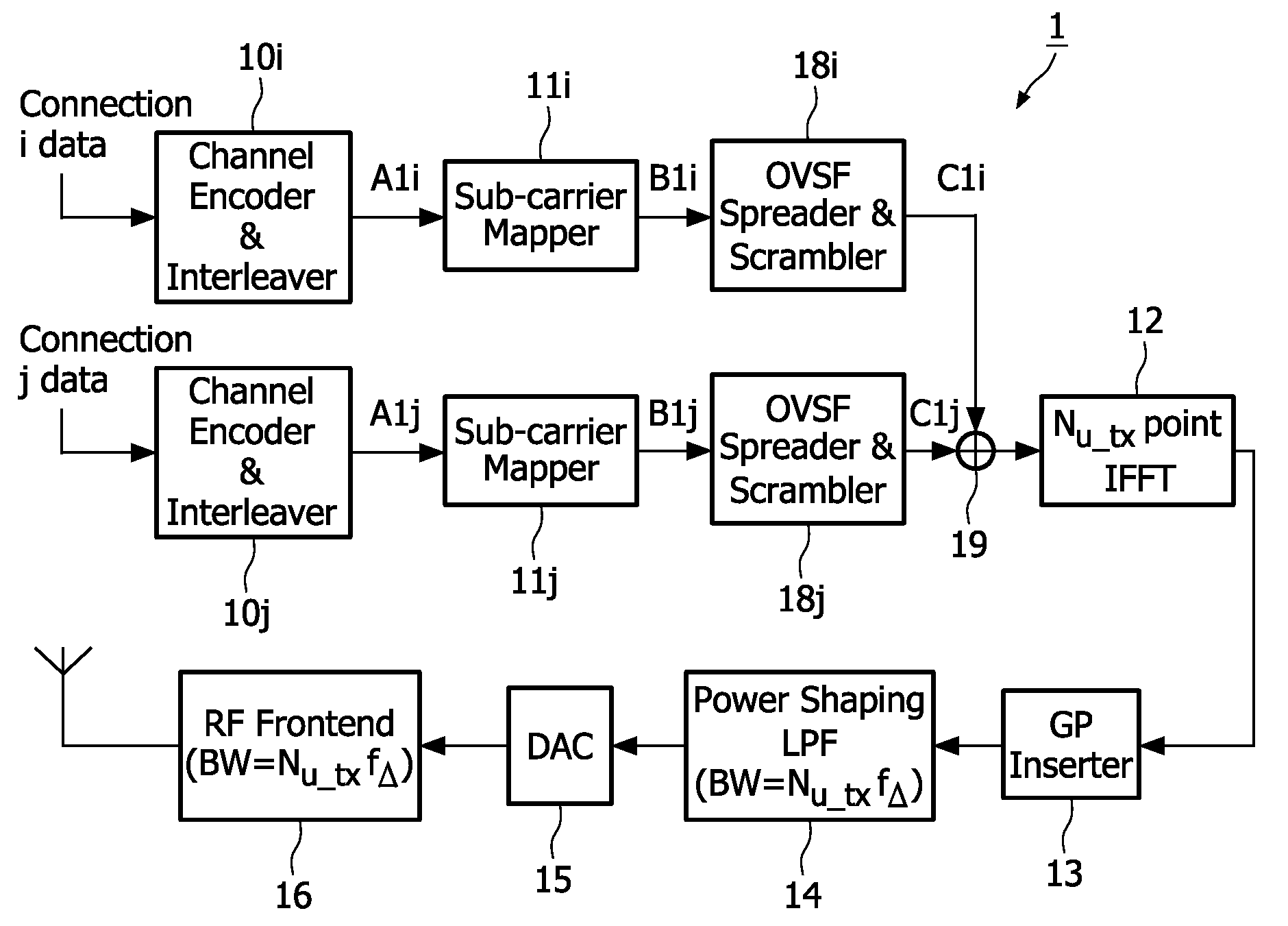
Bandwidth asymmetric communication system
InactiveUS20090232234A1Reduce complexityCutting synchronizationSignal allocationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlCommunications systemUplink transmission
The present invention relates to a communication system comprising a plurality of terminals each having an uplink transmission unit (1) for transmitting radio frequency OFDM signals at a radio frequency and an access point having an uplink receiving unit (4) for concurrently receiving said radio frequency OFDM signals from at least two terminals, said OFDM signals being Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) modulated, wherein the bandwidth of said uplink transmission units and of the transmitted radio frequency OFDM signals is smaller than the bandwidth of said uplink receiving unit and that the bandwidth of at least two uplink transmission units and of their transmitted radio frequency OFDM signals is different. The present invention relates further to a communication system wherein the access point has a downlink transmission unit (7) for transmitting radio frequency OFDM signals at a radio frequency and that the at least two terminals each have a downlink receiving unit (11) for receiving said radio frequency OFDM signals, wherein the bandwidth of said downlink transmission unit is larger than the bandwidth of said downlink receiving units and that the downlink transmission unit is adapted to generate and transmit radio frequency OFDM signals having a bandwidth that is smaller than or equal to the bandwidth of the downlink transmission unit and that is equal to the bandwidth of the downlink receiving unit by which the radio frequency OFDM signals shall be received. Still further, the present invention relates to a communication method, to a terminal and to an access point for use in such a communication system.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
GPS receiver with efficient signal acquisition
InactiveUS6118808AReduce power consumptionShorten the timePosition fixationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlMemory bankGps receiver
A direct sequence spread spectrum receiver samples an incoming signal and translates the signal to an IF signal. The IF signal is sampled and stored in memory. In one embodiment, the memory consists of two memory banks which alternately receive sample segments. During a write period to one of the memory banks, the other memory bank supplies its output to a processor. This continues in a ping-pong manner. In another embodiment, a single memory bank is filled and read as necessary, the receiver ignoring incoming signal until the processor has completed processing the sample available at the output of the memory. Such a receiver is useful in global positioning satellite (GPS) signal processing where the incoming signal contains several satellite transmissions encoded with CDMA encoding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Maximum likelihood synchronization for a communications system using a pilot symbol
ActiveUS20040081205A1Time-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase offsetFrequency offset
A method and apparatus for detecting and synchronising packets of data with a repeated sequence as a pilot symbol received by a communications system are provided. The method and apparatus include receiving data, detecting a packet within the received data, producing an estimate of the time-varying frequency offset of the received data, estimating the start of the packet of the received data, estimating the time-varying phase offset of the received data and estimating the time-varying time offset of the received data. Methods for assessing each one of the time-varying frequency offset, the time-varying phase offset, the time-varying time offset and the start of packet are also provided.
Owner:CALLAGHAN INNOVATION
Method and system for frequency synchronization
The present invention provides a method of synchronising the frequency of a slave clock to that of a master, preferably using a packet network. An aspects of the invention provide a method of synchronizing the frequency of a slave clock in a slave device to a master clock in a master device, the method including the steps of: a) receiving in the slave device a first message from said master device having a first time-stamp which is a time-stamp of said master clock indicating the time of sending of said first message; b) extracting said time-stamp from said message and initializing a counter in the slave device which counts an output of said slave clock; c) receiving in the slave device a further message from said master device and reading the value of said counter at the time of receipt of said further message; d) extracting a further time-stamp which is the precise time of sending of the further message according to said master clock; e) determining an error signal which is representative of the difference between said value of the counter and the difference between said first and further time-stamps; and f) adjusting the frequency of said slave clock based on said error signal. An apparatus for synchronizing the frequency of a clock in a slave device which is communicatively coupled to a master device is also provided.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
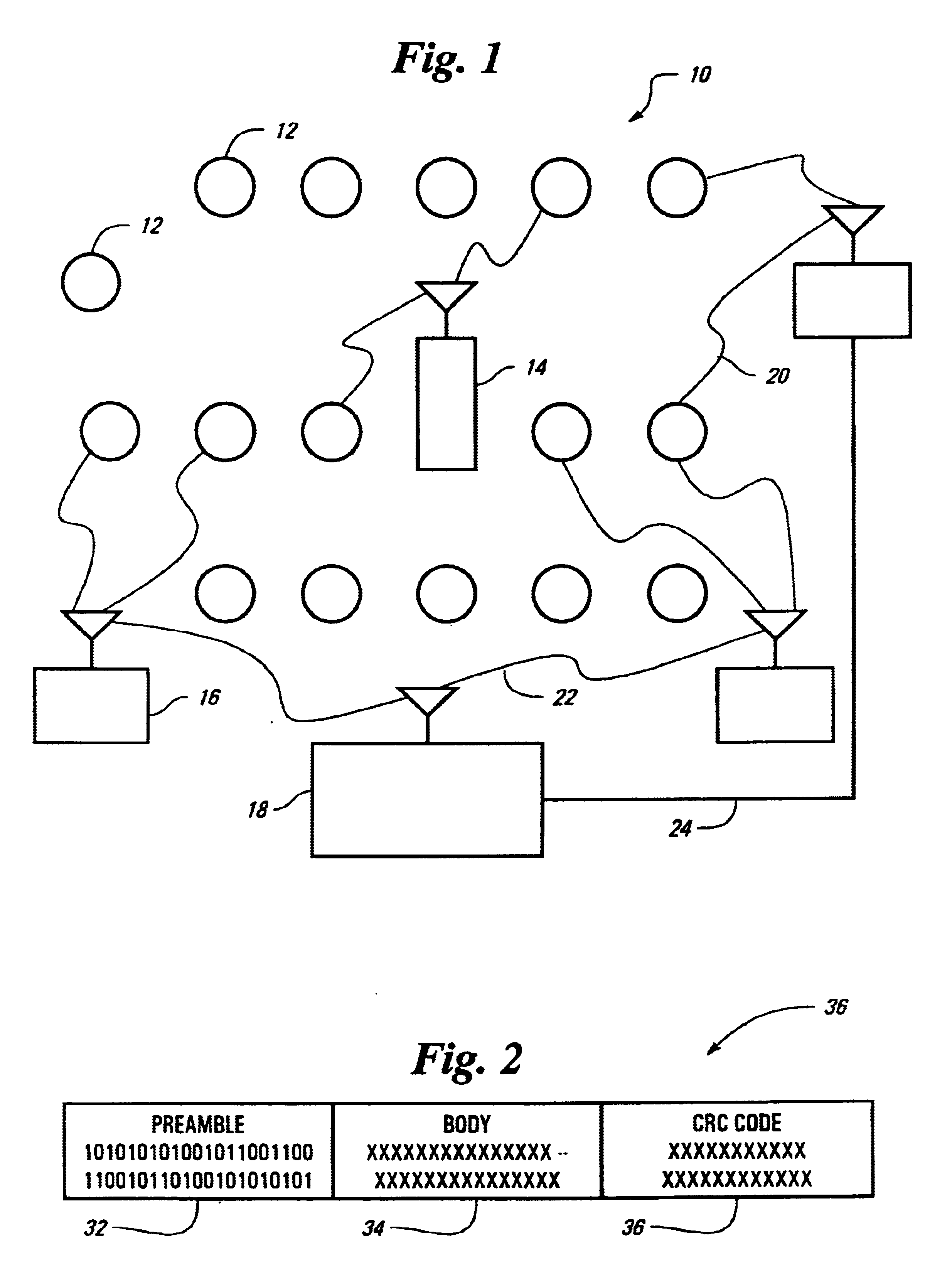
Method and device for exchanging data between at least two stations connected via a bus system
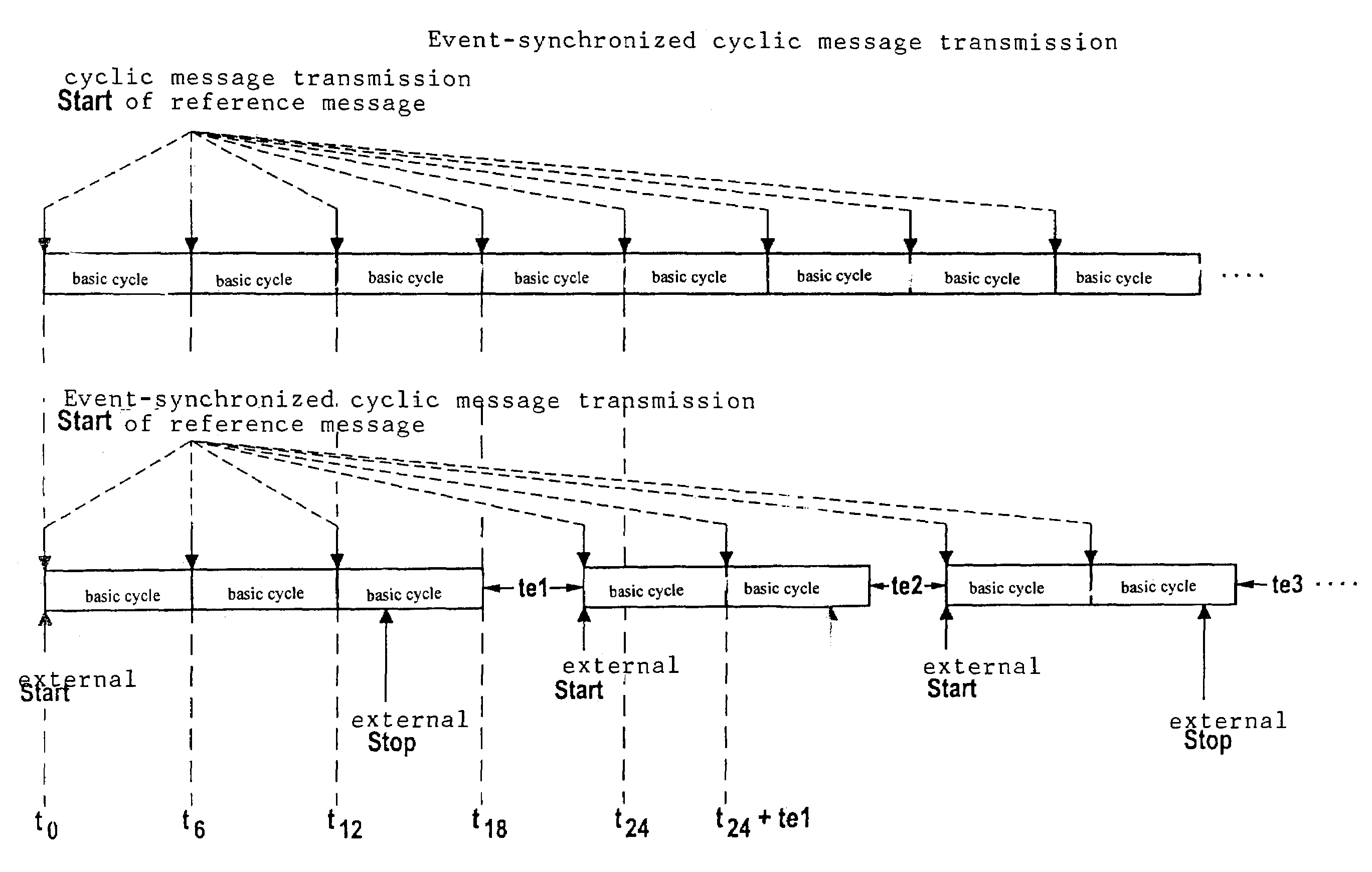
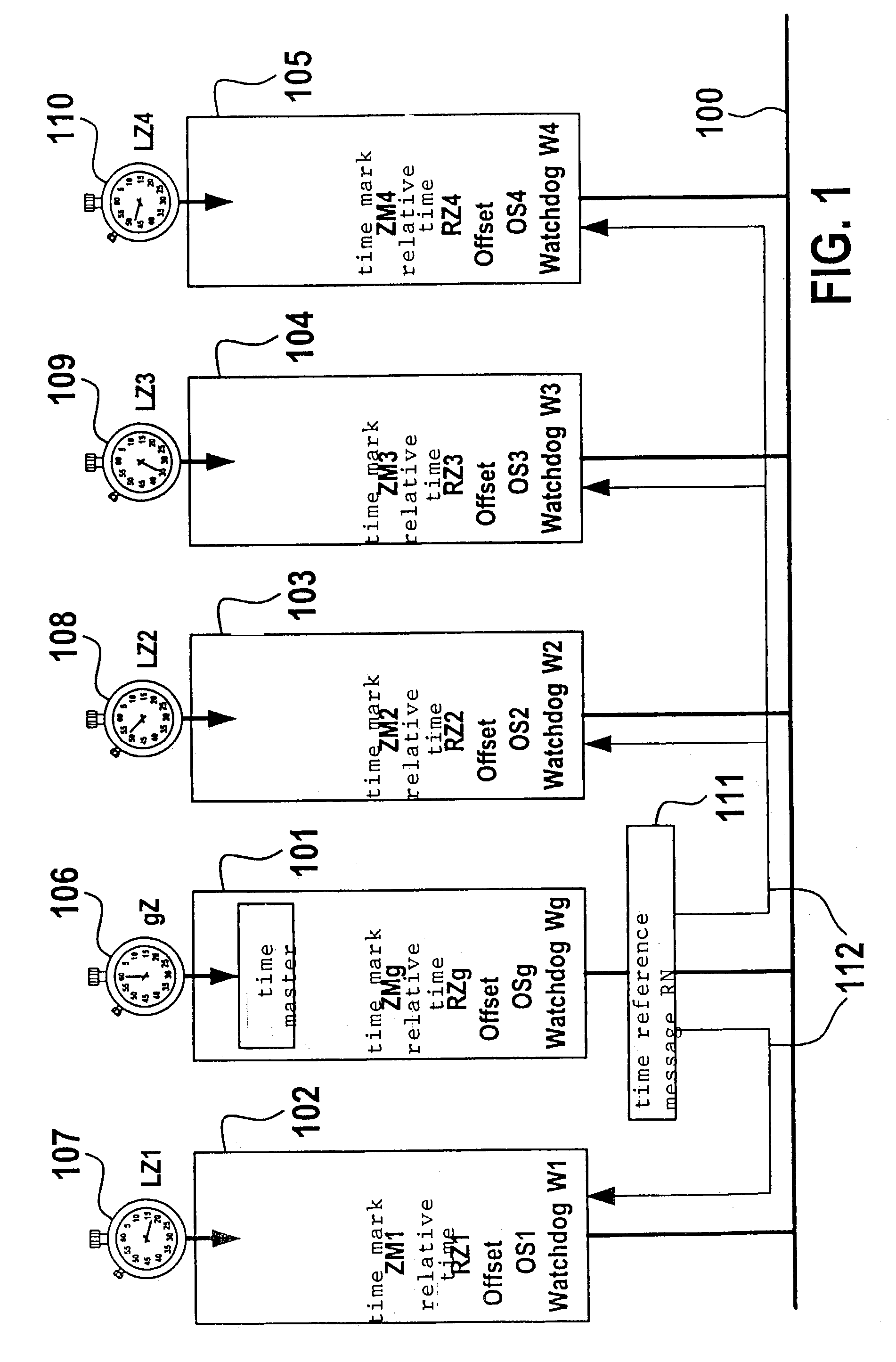
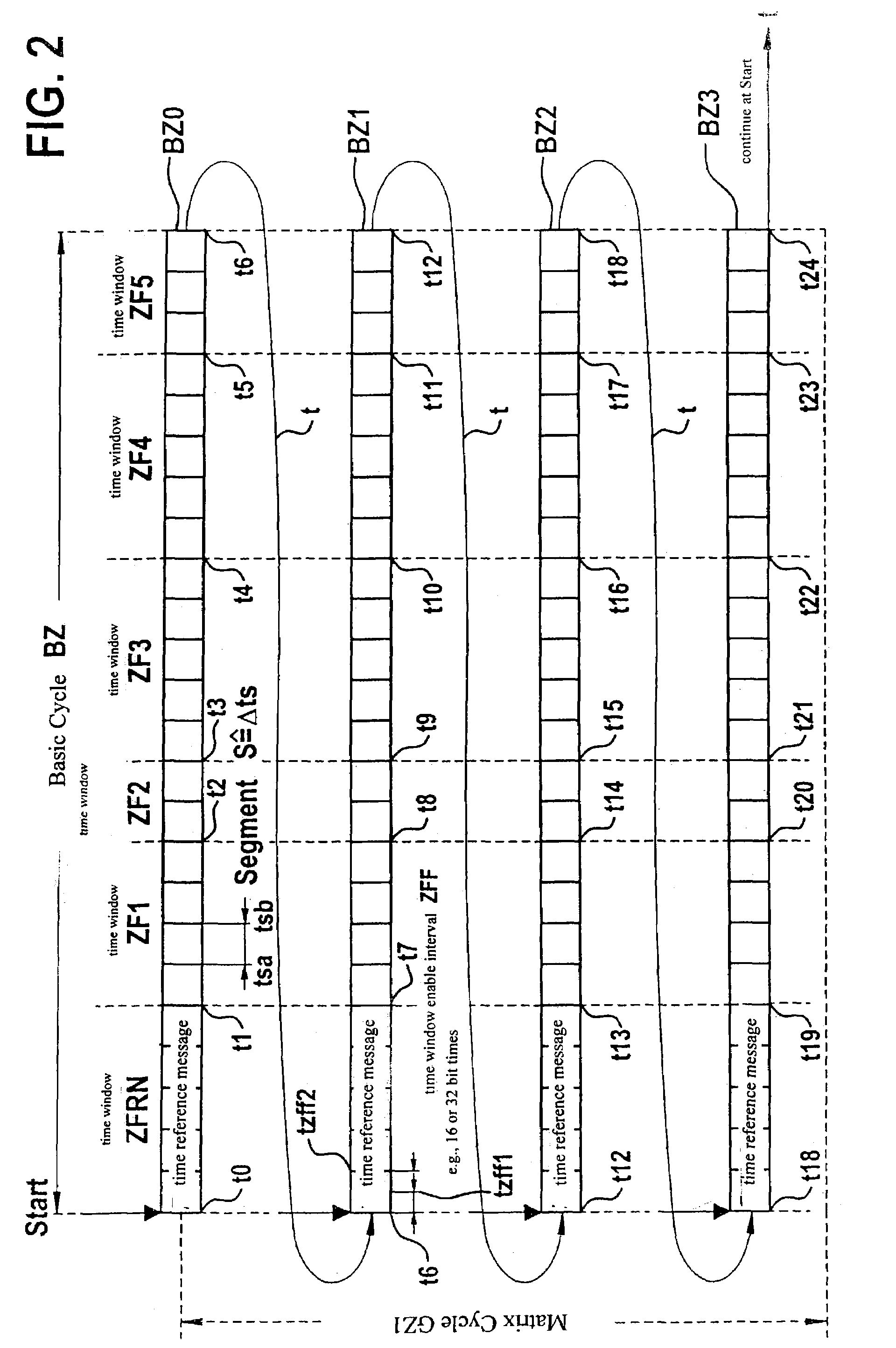
InactiveUS7171579B2Quick checkBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexTime controlTime windows
A method and a device for exchanging data in messages between at least two stations connected via a bus system, the messages containing the data being transmitted by the stations over the bus system and the messages being controlled over time by a first station in such a manner that the first station repeatedly transmits a reference message over the bus at at least one specifiable time interval and the time interval is divided into time windows of specifiable length, the messages being transmitted in the time windows, a reference message and the subsequent time windows until the next reference message being combined into a first cycle, and the first station interrupting the transmission at the end of a first cycle due to a stop request, in particular, a message of the at least second station.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com