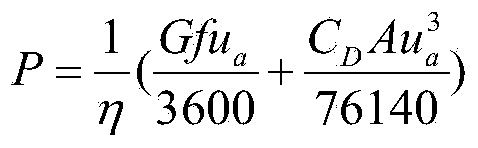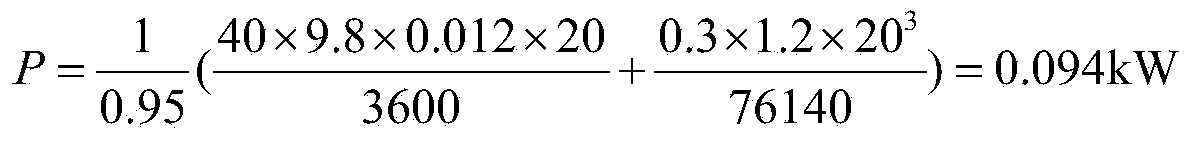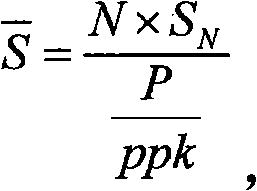Patents
Literature
1312 results about "Pulse number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Your pulse, or heart rate, is the number of times your heart beats each minute. When at rest, a normal heart rate ranges between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
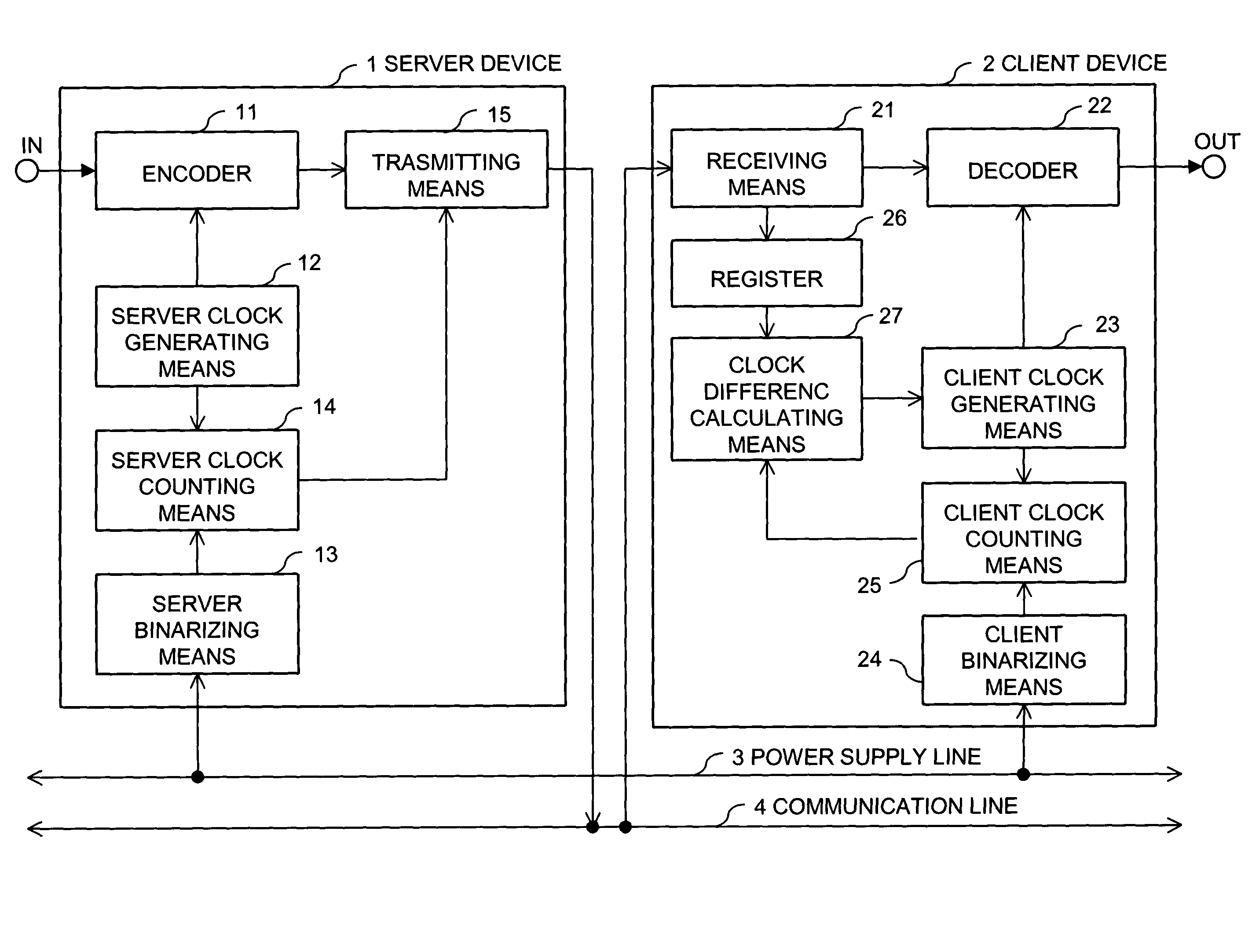
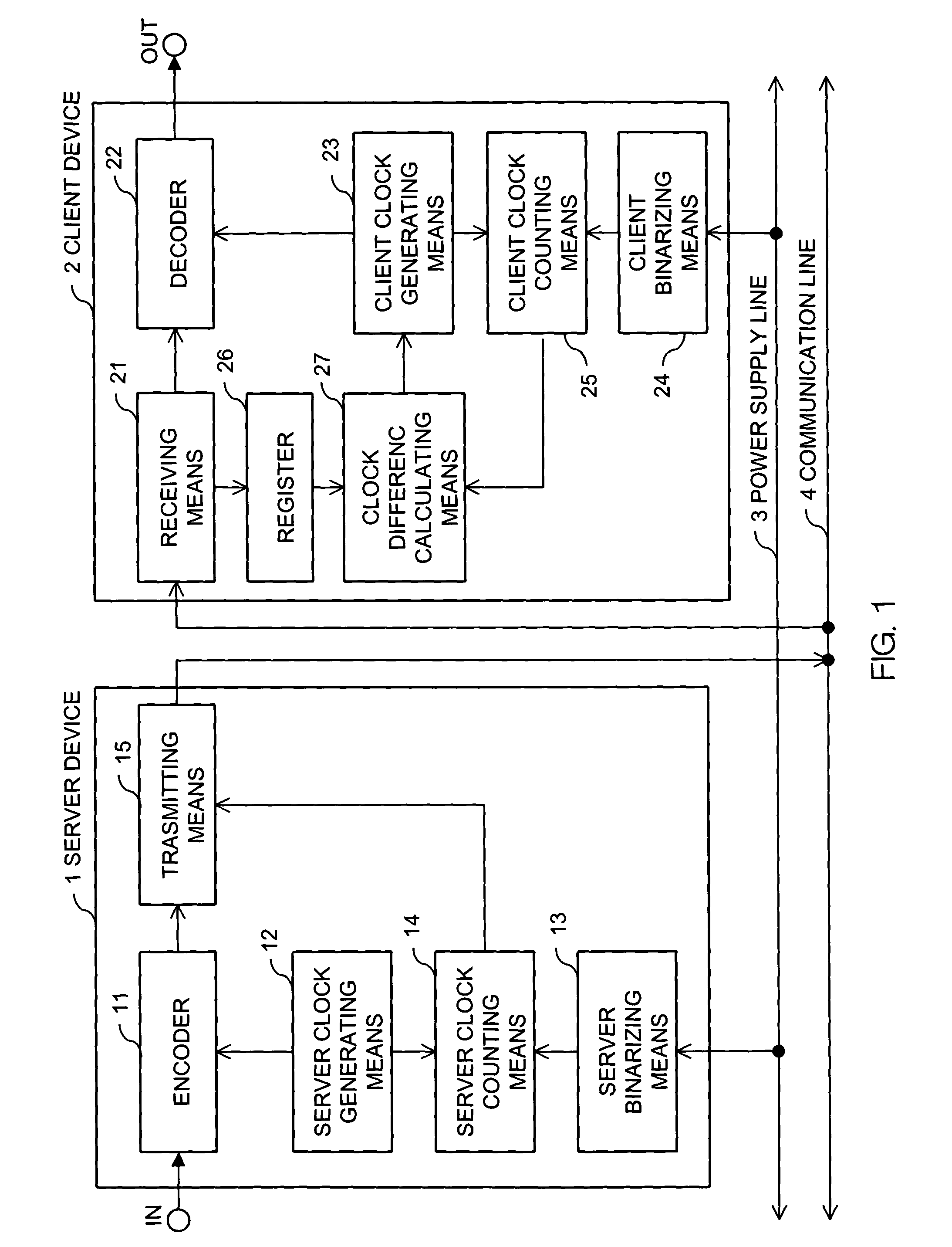
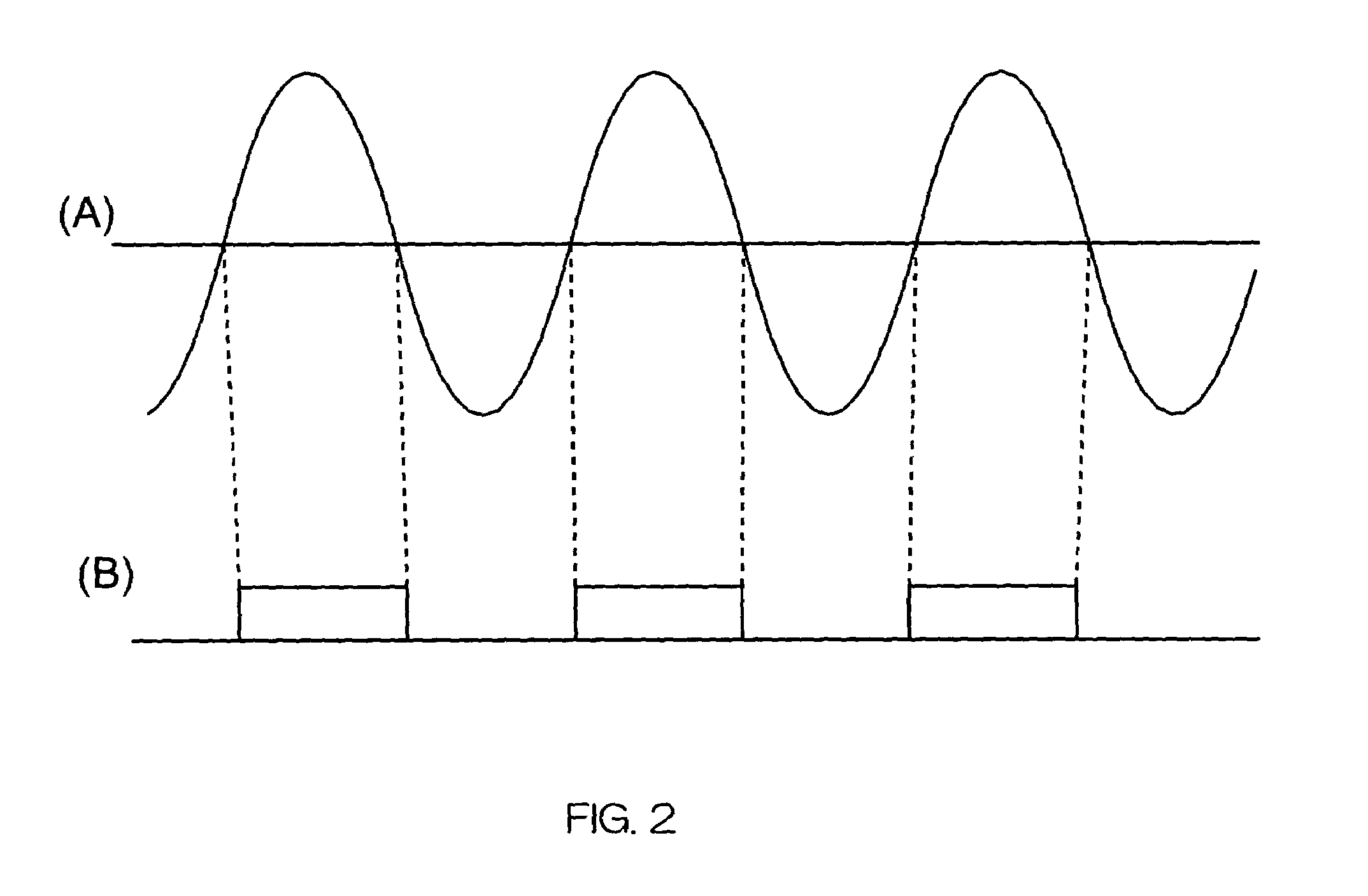
Synchronizing clock signals of server and client devices in a network system based on power source synchronous pulse signal
InactiveUS7263110B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData transmission timeNetworked system
In a network system, clock signals of a server device and a client device are synchronized with each other without having any influence of a change and a delay of the transmission time of data. Therefore, in the network system in which the client device receives and reproduces information transmitted from the server device, the server device counts the number of clock pulses of a server clock signal used to compress and encode information on the basis of a power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with a power source frequency. The server device outputs information showing the counted clock pulse number and the compressed and encoded information to the client device. The client device counts the number of clock pulses of a client clock signal used to decode and decompress the compressed and encoded information on the basis of the power source synchronous pulse signal synchronized with the power source frequency. The client device conforms the frequency of the client clock signal to the frequency of the server clock signal on the basis of the clock difference between the clock pulse number received from the server device and the counted clock pulse number.
Owner:D & M HOLDINGS INC
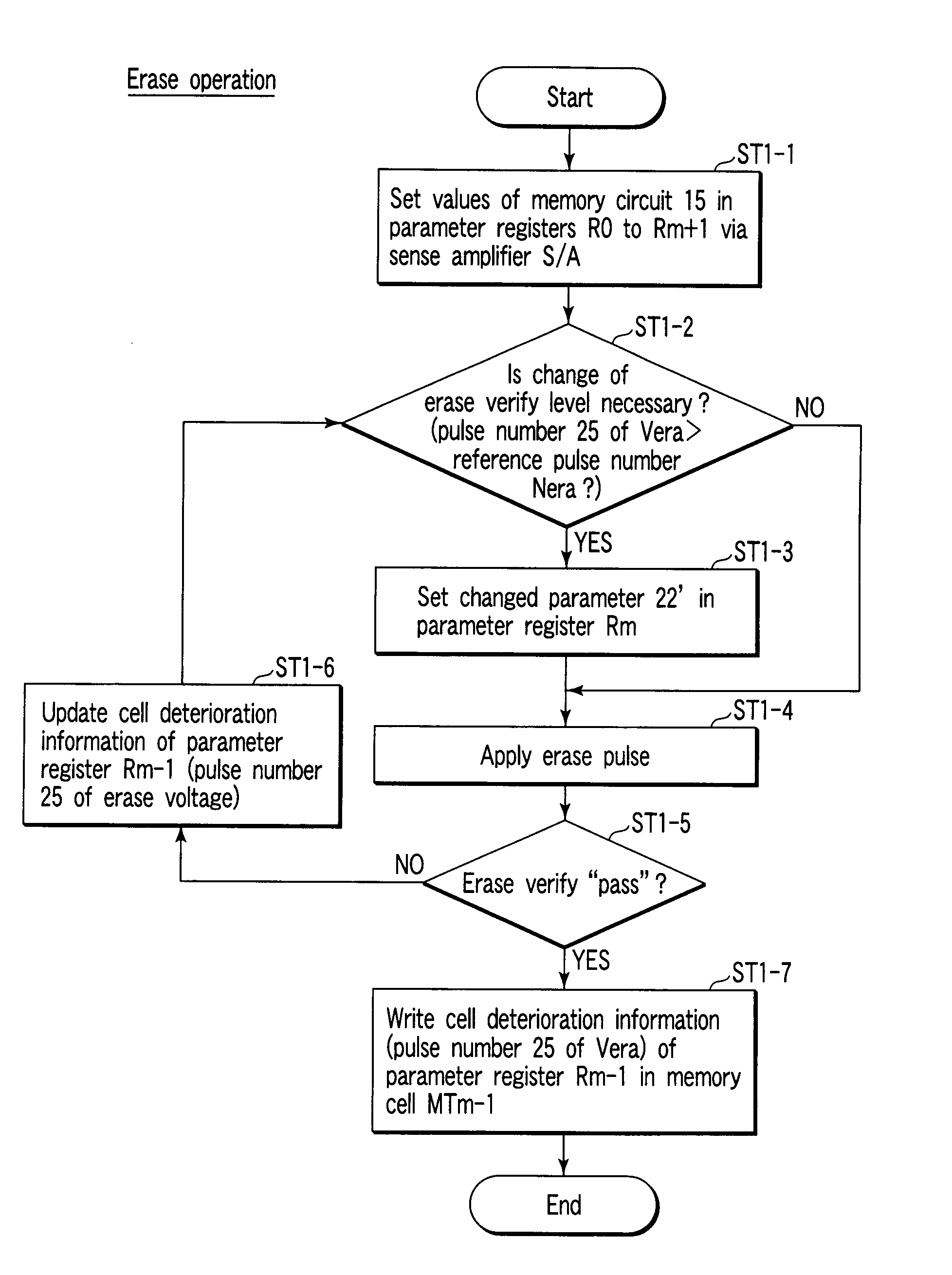
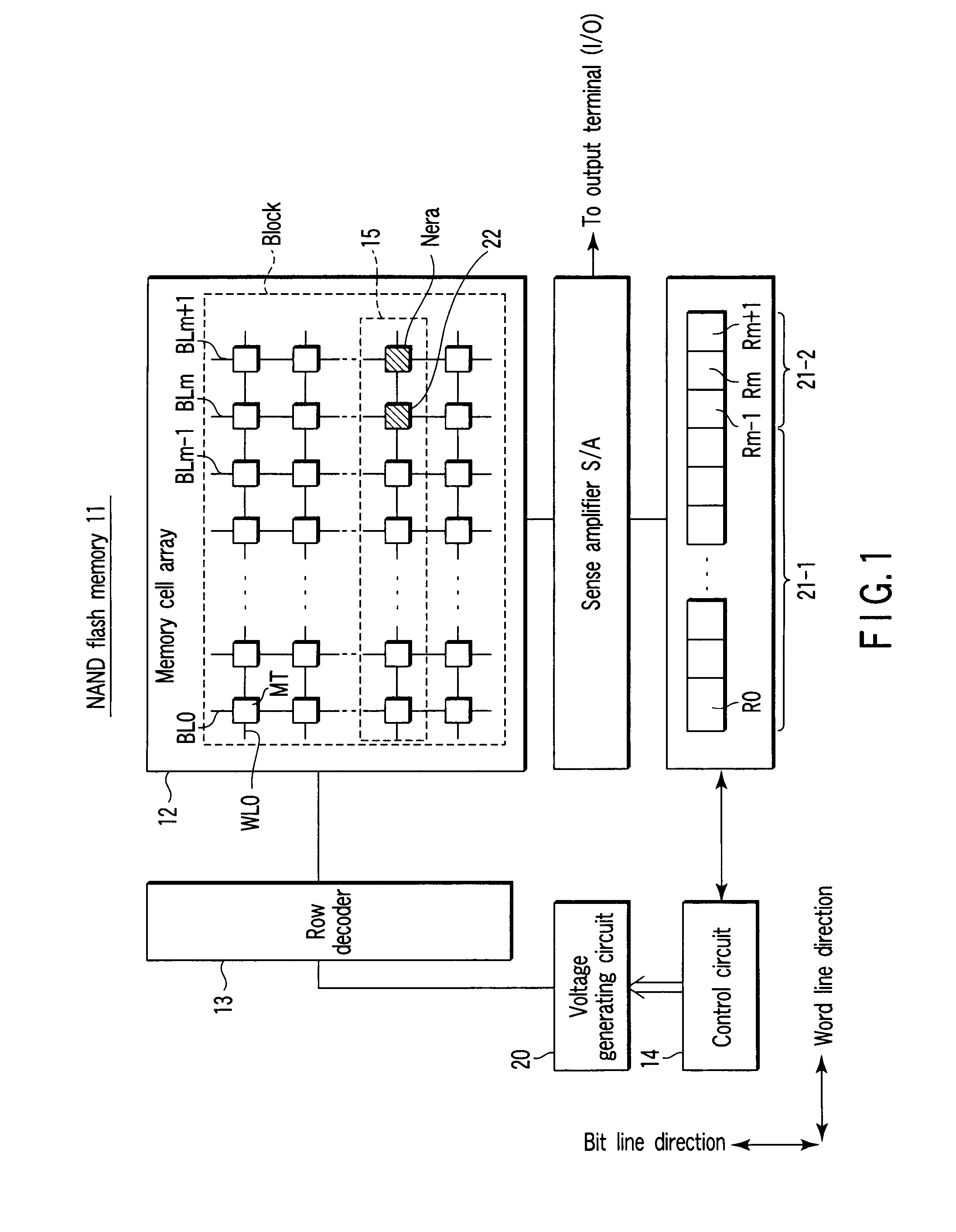
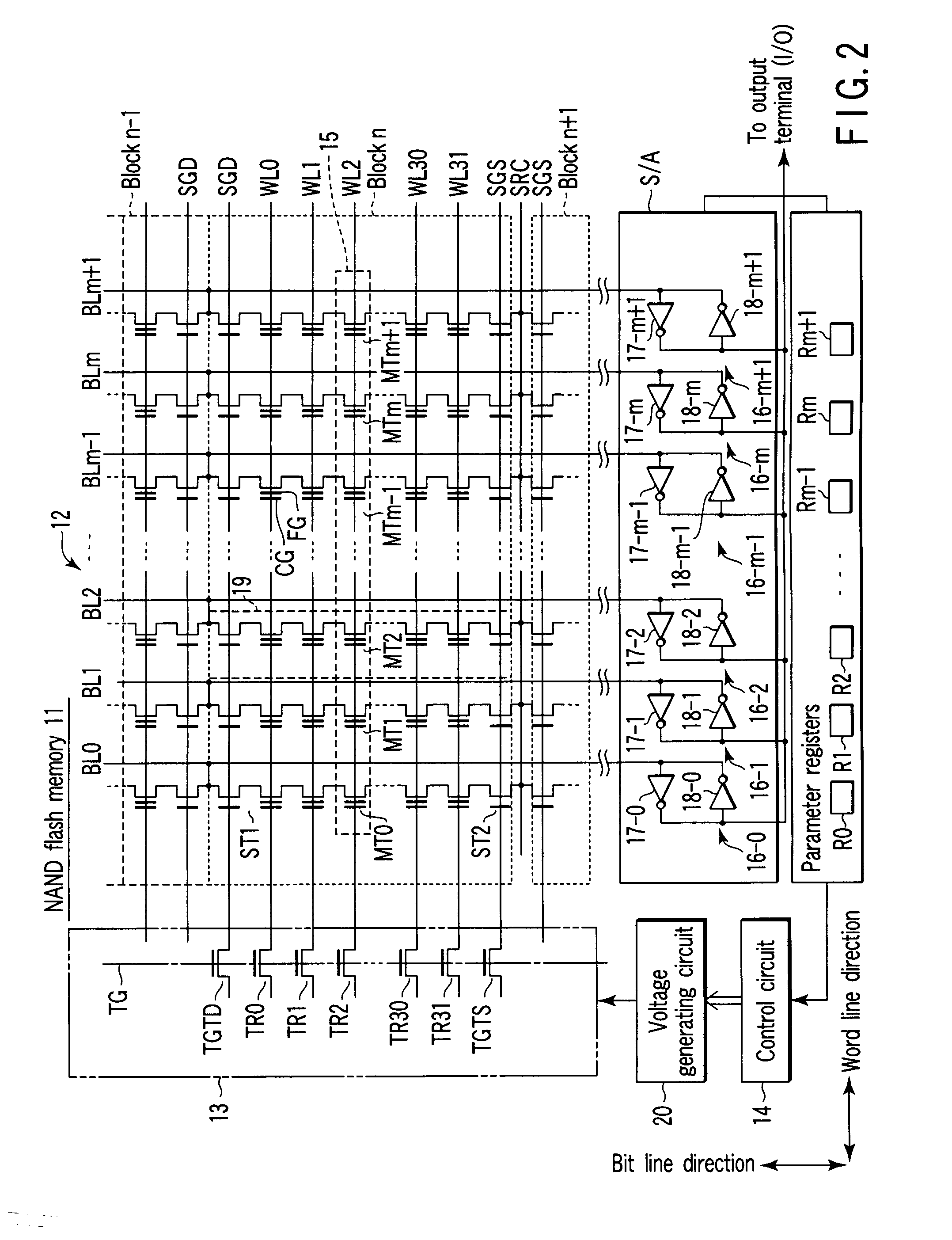
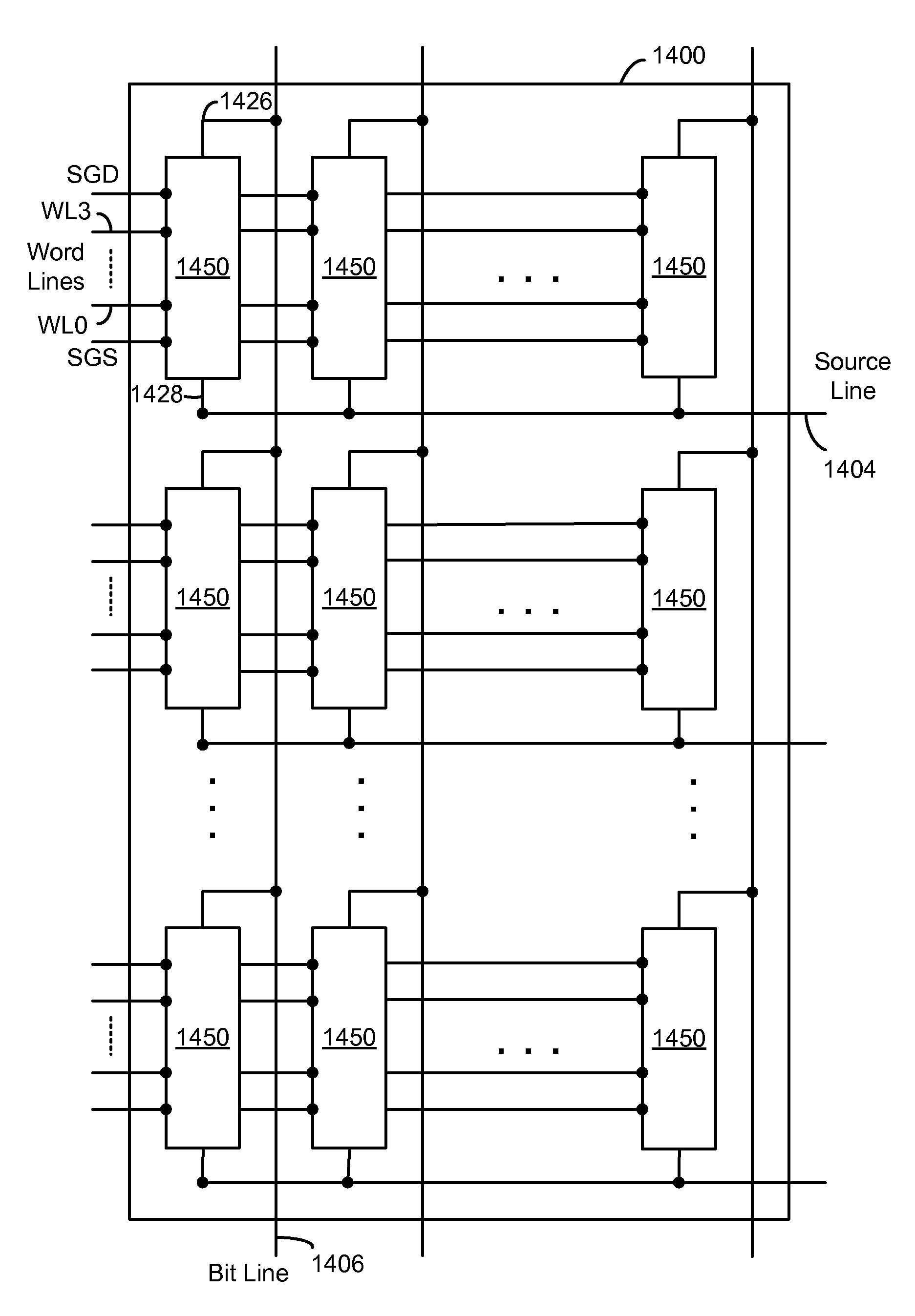
Semiconductor memory device and control method of the same
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array, a voltage generating circuit, a memory circuit which stores a reference pulse number of an erase voltage of the memory cell array and a parameter, and a control circuit which controls, when a pulse number of the erase voltage exceeds the reference pulse number of the erase voltage, the voltage generating circuit in a manner to increase at least an erase verify level in accordance with the parameter.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
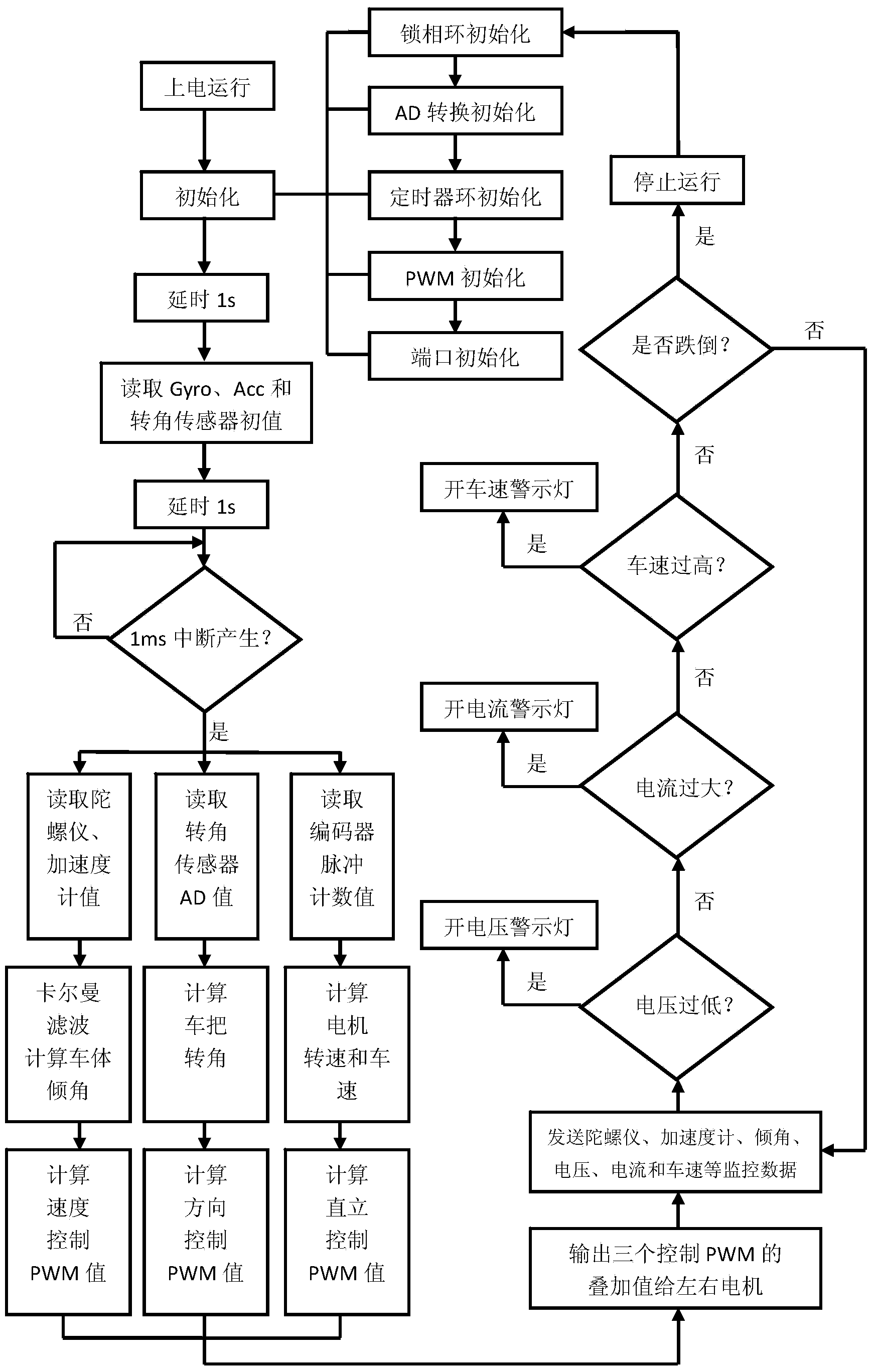
Control method of two-wheeled self-balance vehicle
InactiveCN103529850AShort correction timeShorten the timeAttitude controlMotorcyclesMotor speedAccelerometer
A control method of a two-wheeled self-balance vehicle comprises the steps as follows: (1), performing initialization: (2), reading values of a gyroscope, an accelerometer and a rotation angle sensor as well as the pulse number of an encoder respectively; (3), obtaining a vehicle body inclination, a handlebar turning angle, motor speeds and a vehicle speed; (4), then calculating PWM (pulse width modulation) values of vertical control, direction control and speed control respectively through a PID (proportion integration differentiation) control algorithm; (5), superposing the three PWM values together and outputting the three PWM values to left and right motors; (6), then sending data of the gyroscope, the accelerometer, the vehicle body inclination, a battery voltage, motor currents and the vehicle speed to an upper computer so as to monitor the operating status of the whole vehicle; (7), when the battery voltage is monitored to be smaller than a preset value, and the motor currents or the vehicle speed is monitored to be larger than the preset value through monitoring, turning on corresponding LED warning lights; and (8), when the vehicle body inclination is larger than a preset angle through monitoring when the vehicle body inclination is monitored to be larger than a preset angle, determining that the vehicle body falls down, stopping the operation and returning to an initializer. According to the control method, a more accurate operational method is adopted.
Owner:GUANGZHOU COLLEGE OF SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pulse measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20070191718A1CatheterTime-pieces with integrated devicesMeasurement deviceMeasuring instrument
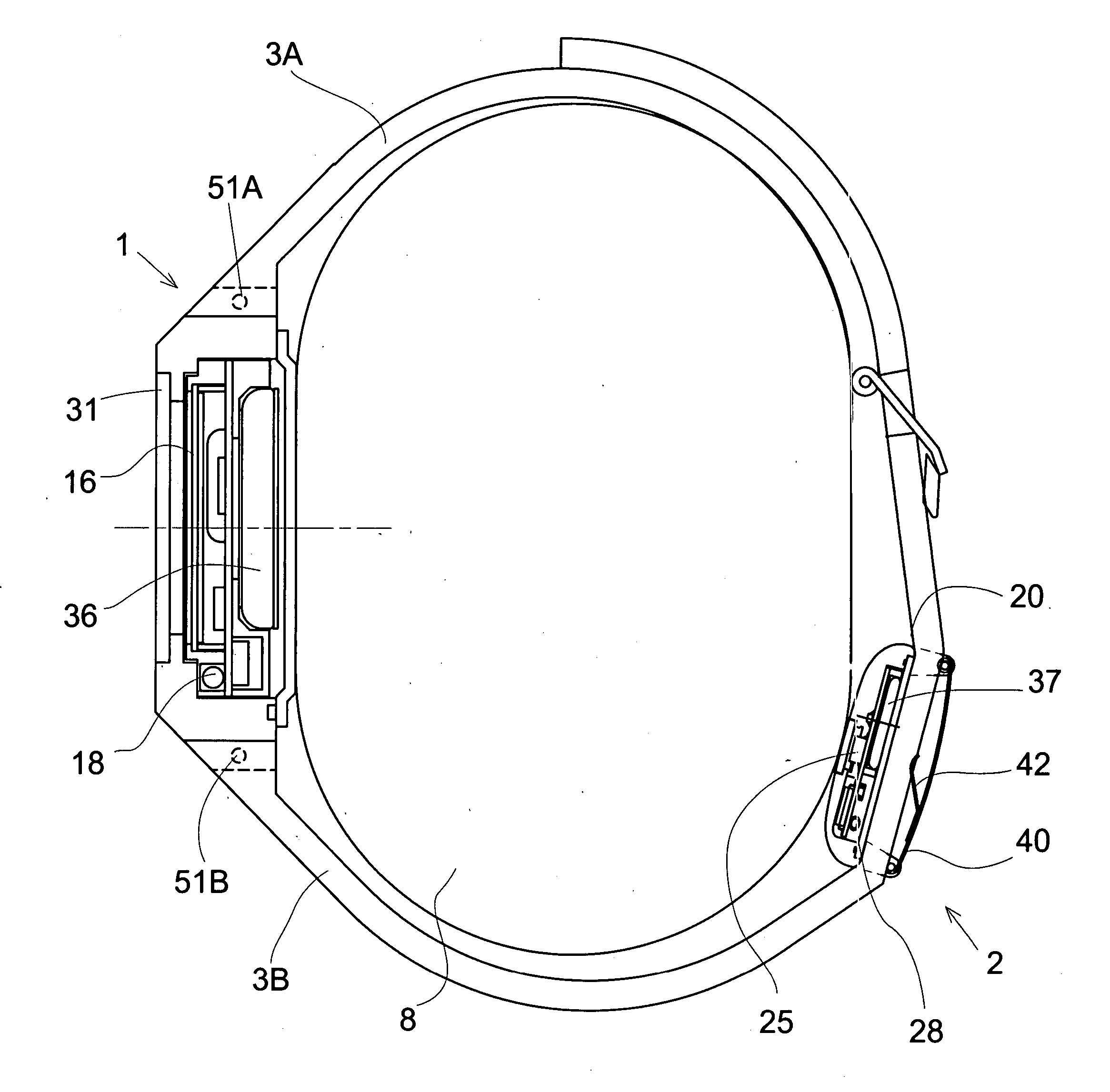
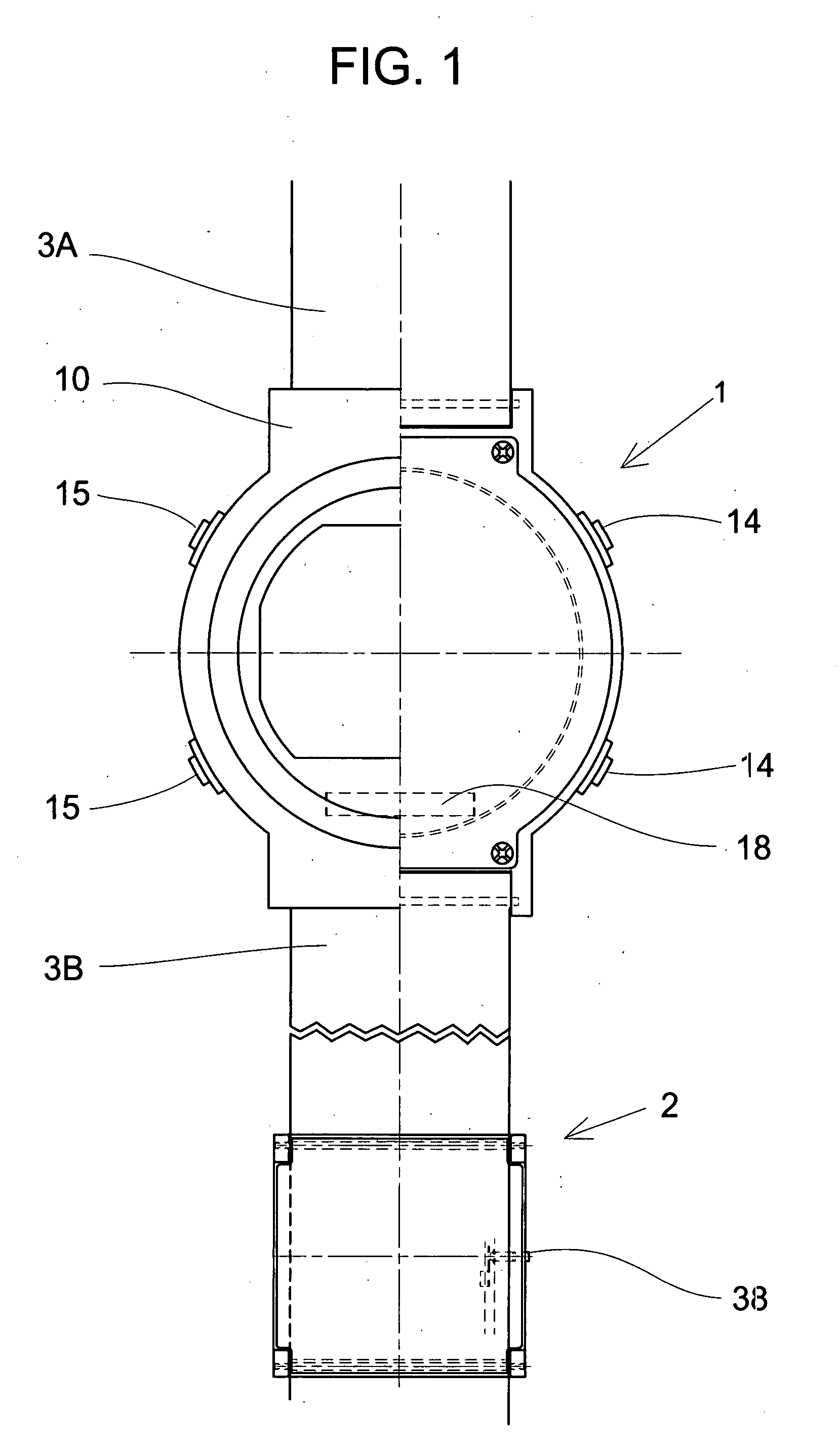
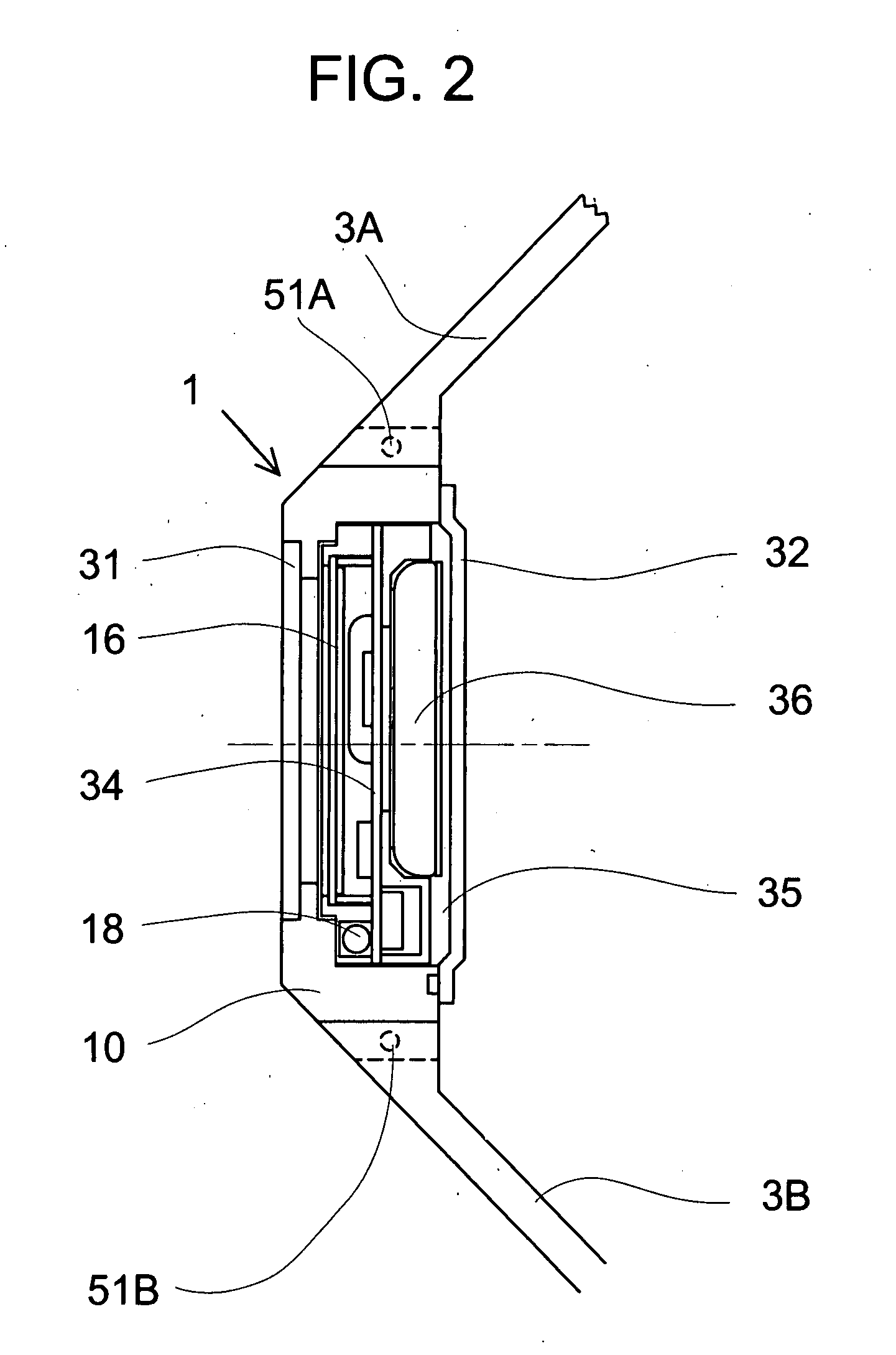
A pulse measuring apparatus comprises a pulse sensor unit having a pulse sensor, a pulse measuring instrument having a display section for displaying a pulse number, and an arm wearing band fixed to the pulse measuring instrument and to which the pulse sensor unit is attached so as to be capable of adjusting its position in a longitudinal direction. A radio transmission section is disposed in the pulse sensor unit and a radio reception section is disposed in the measuring instrument, whereby data can be radio-transmitted from the pulse sensor unit to the measuring instrument. The data to be radio-transmitted is a pulse detection signal of the pulse sensor of the pulse sensor unit, or a pulse number obtained by calculation-processing the pulse detection signal by a signal processing section of the pulse sensor unit.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
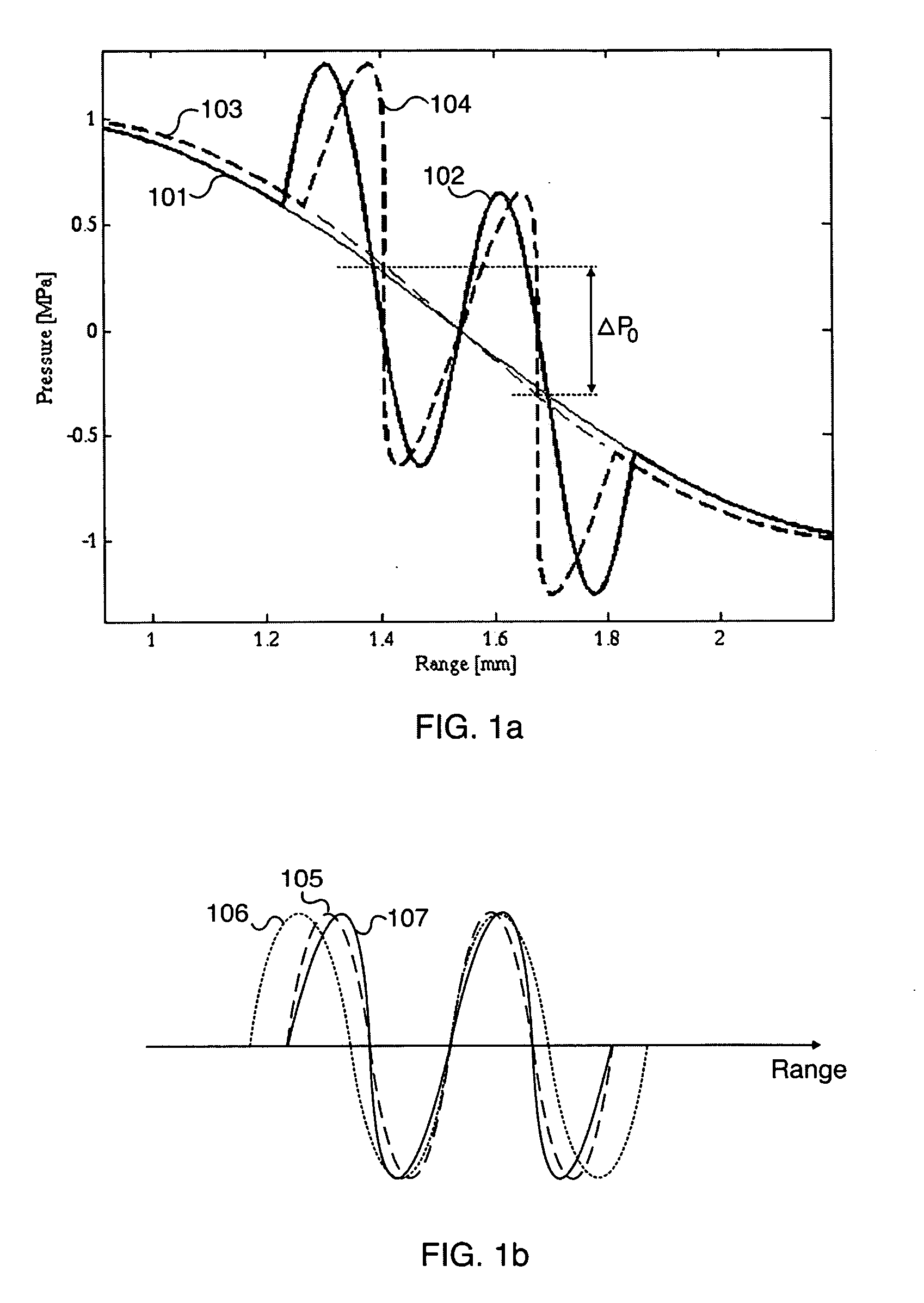
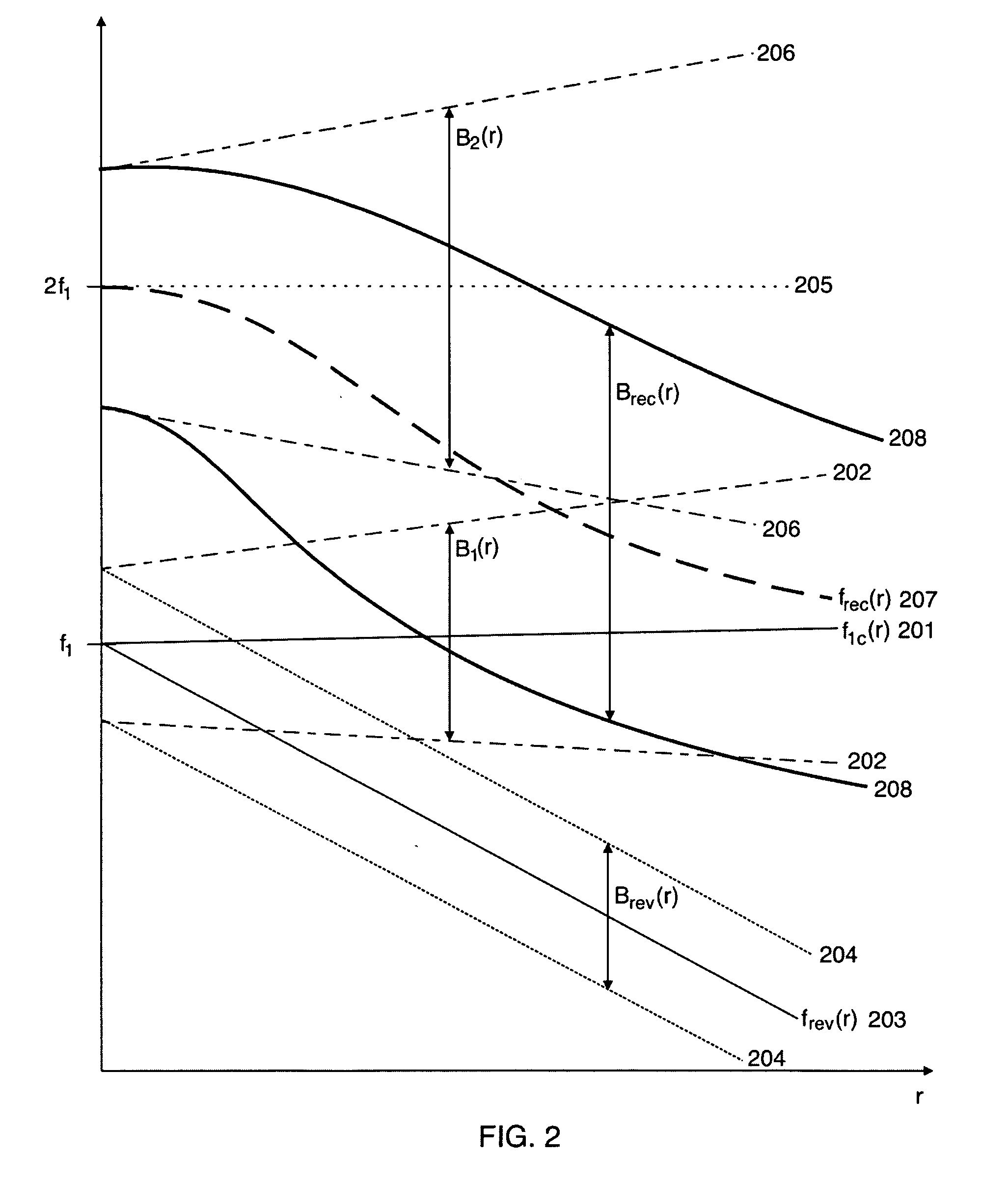
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
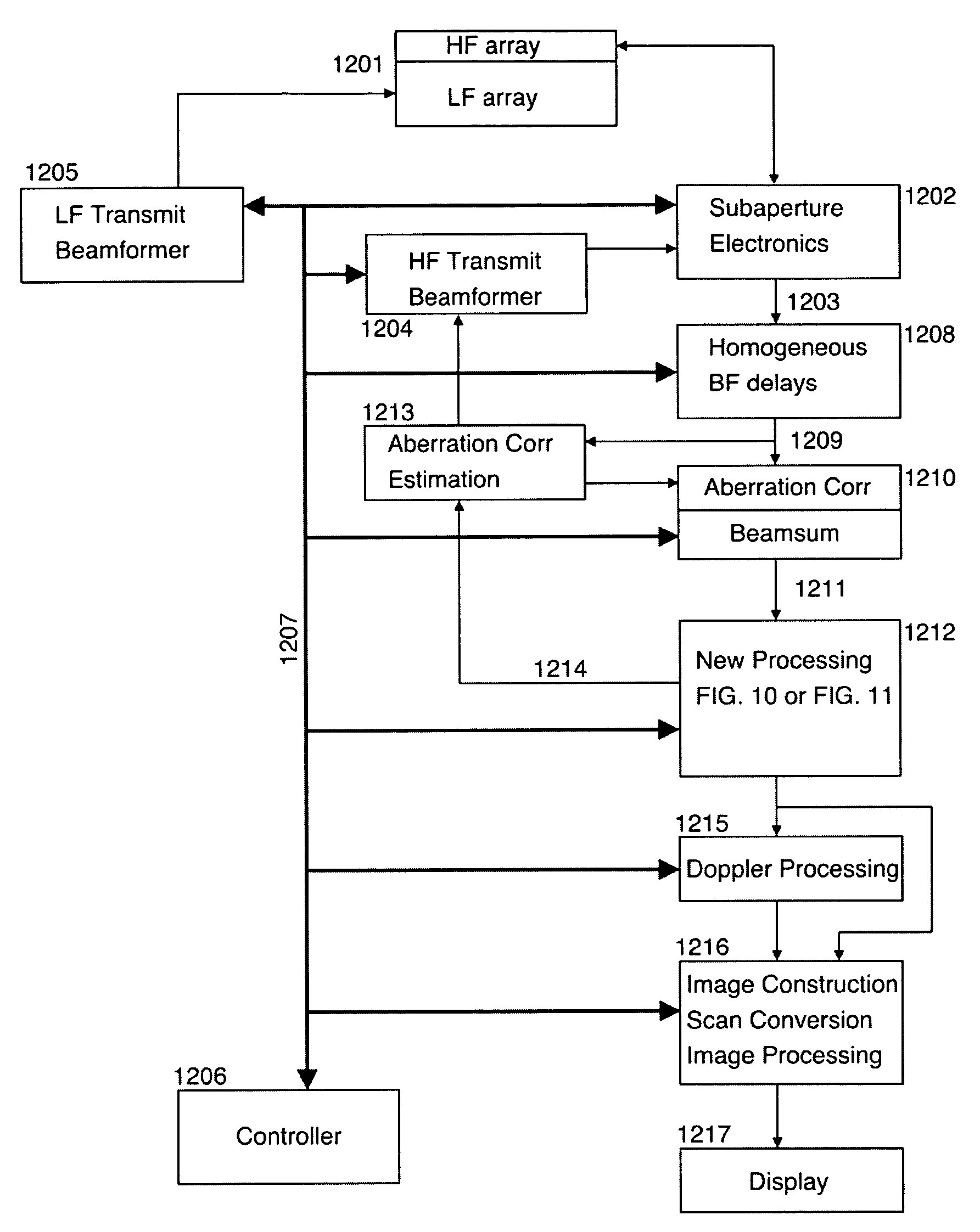
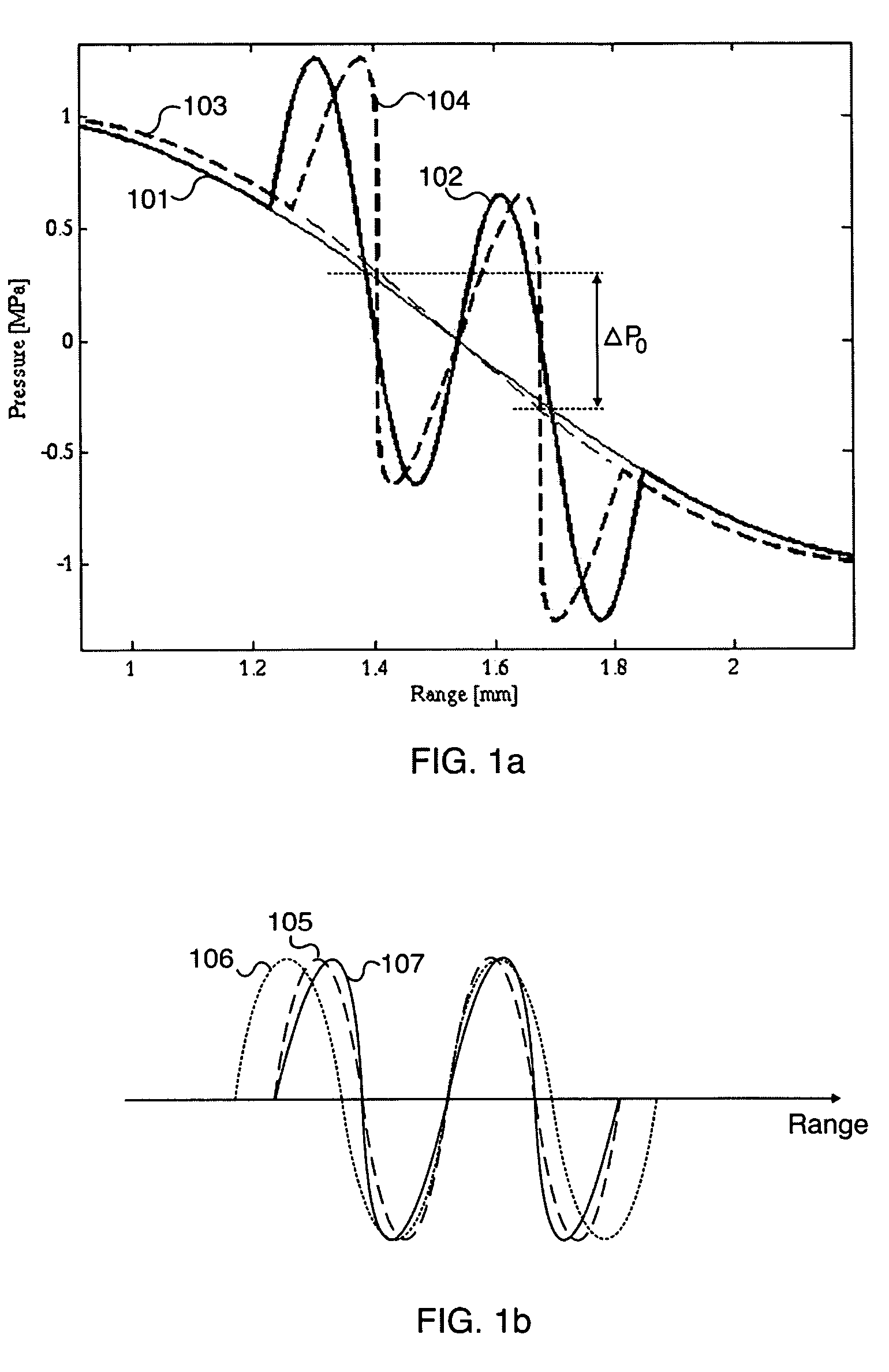
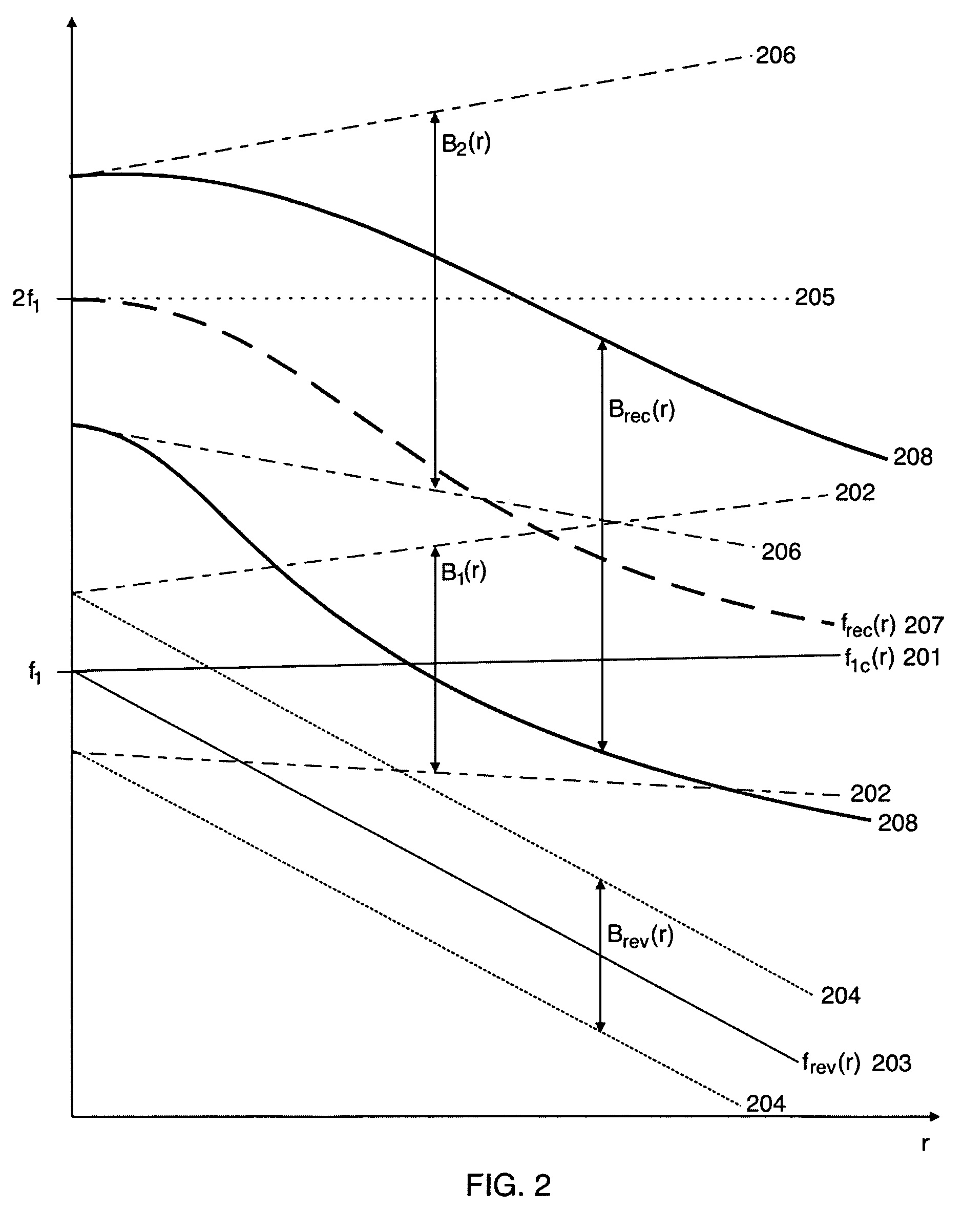
ActiveUS20060052699A1Easy to measureFrame rateOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryLinearityAcoustical imaging
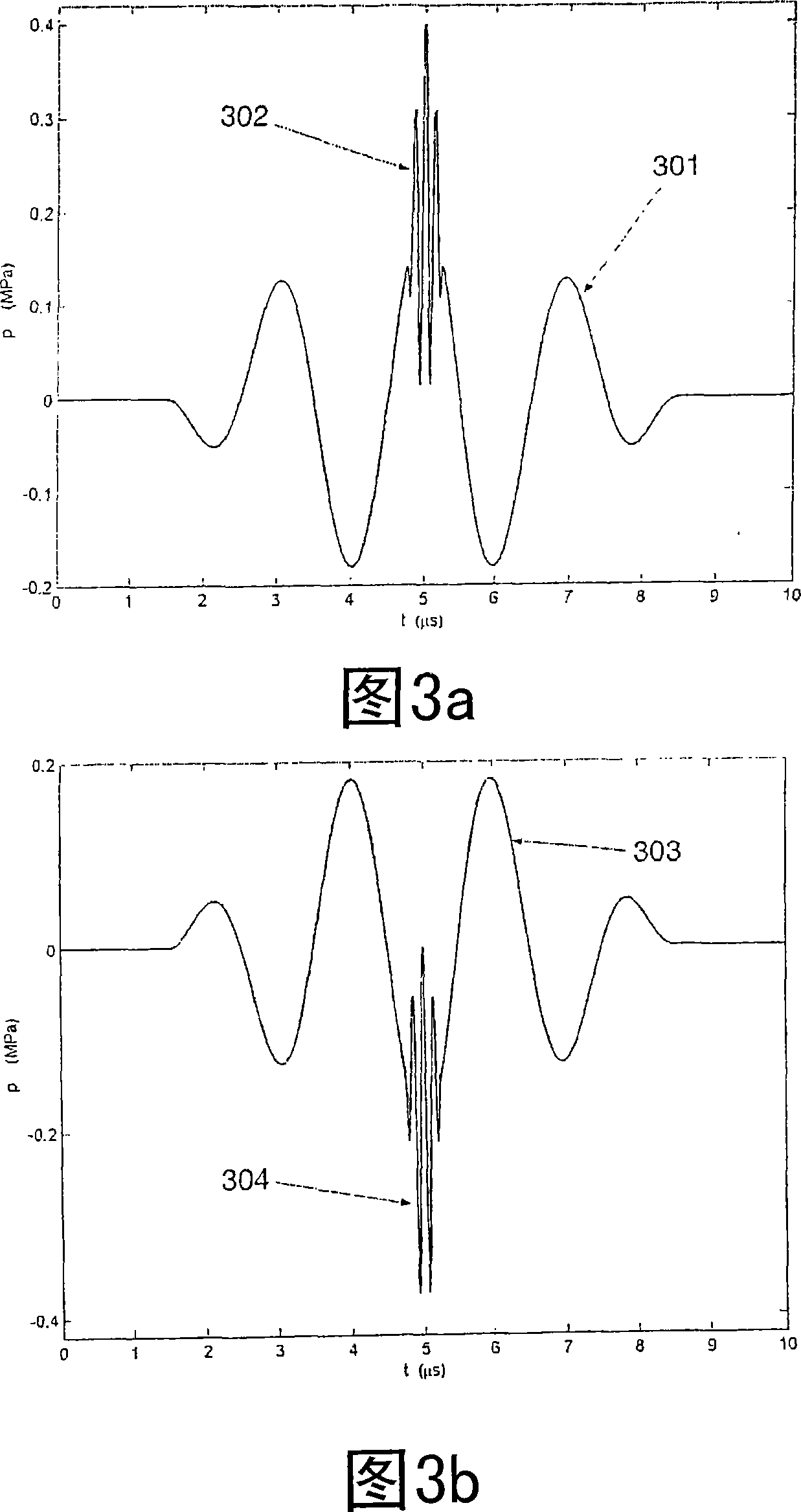
Acoustic imaging provides images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object. The received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes is processed with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. The scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) domain provides a signal with suppression of reverberation noise with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
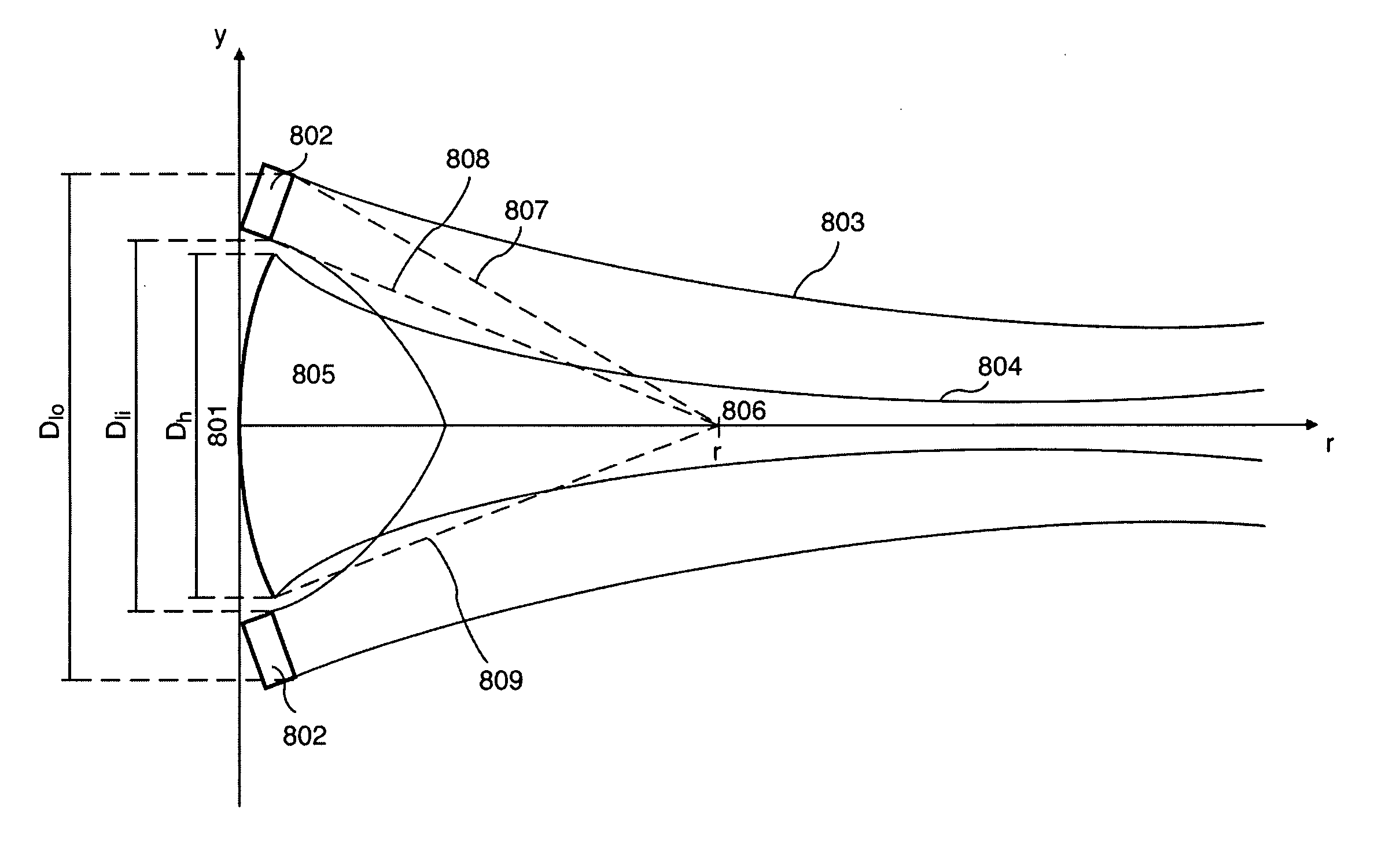
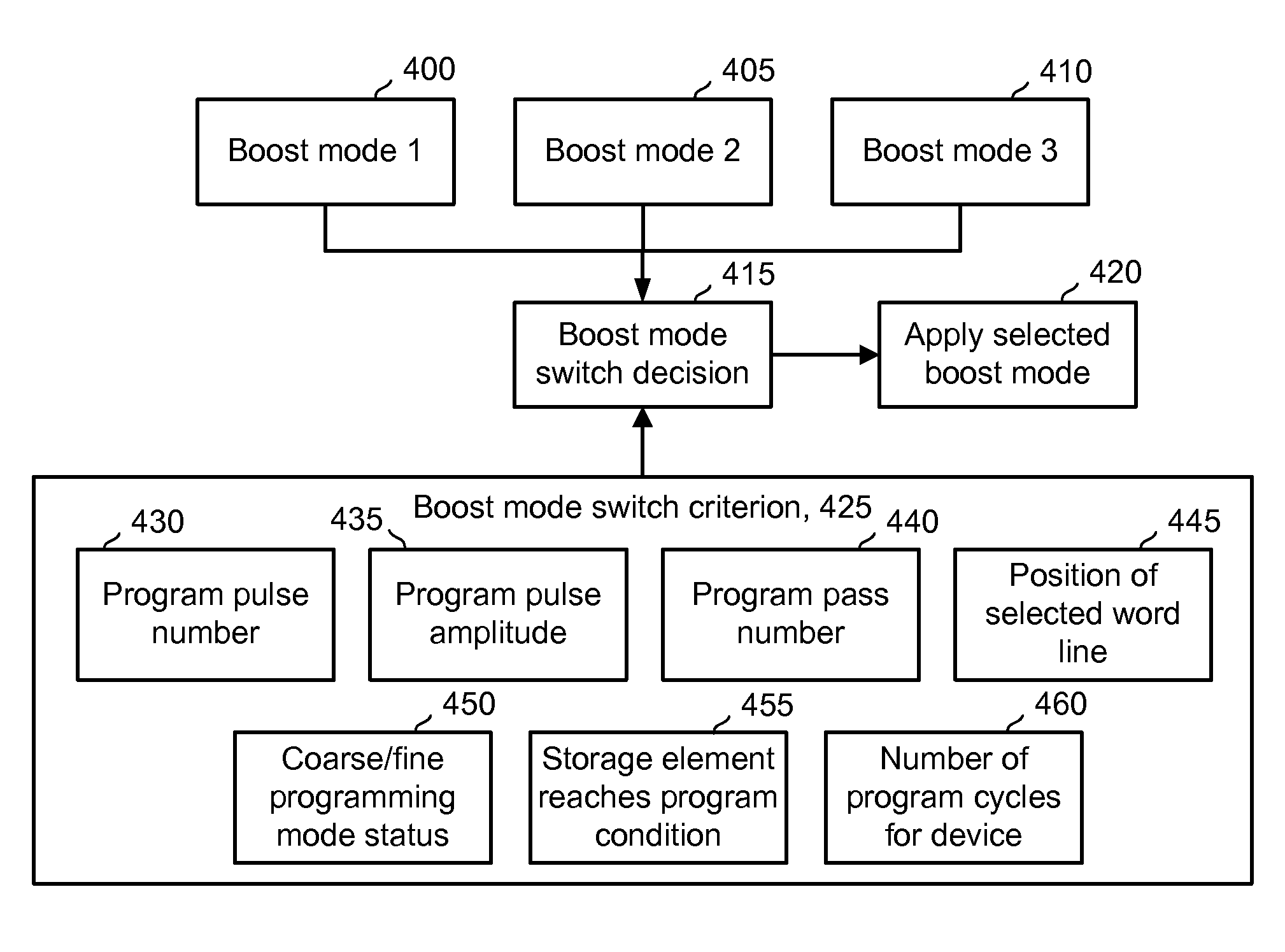
Non-volatile memory using multiple boosting modes for reduced program disturb
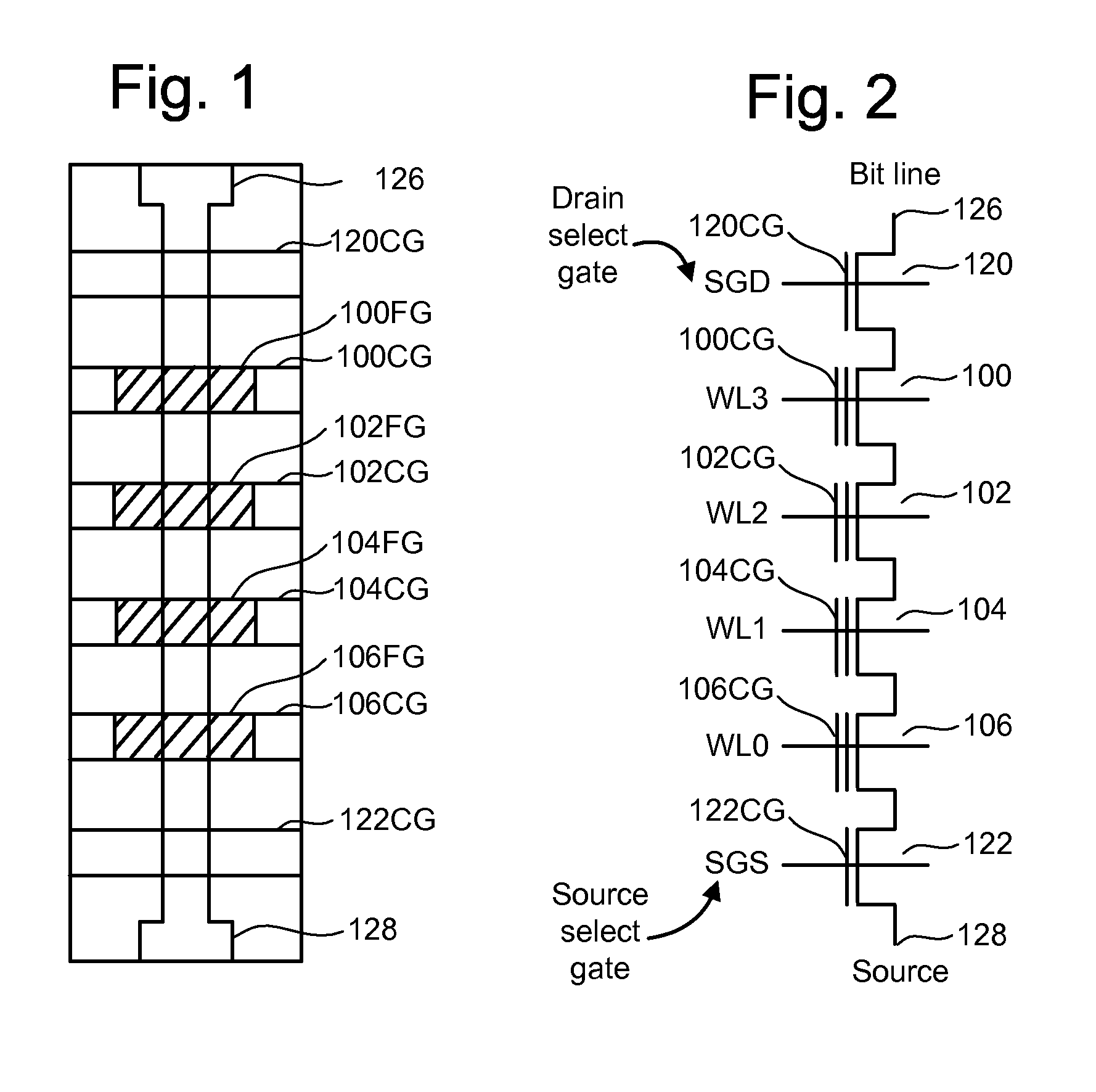
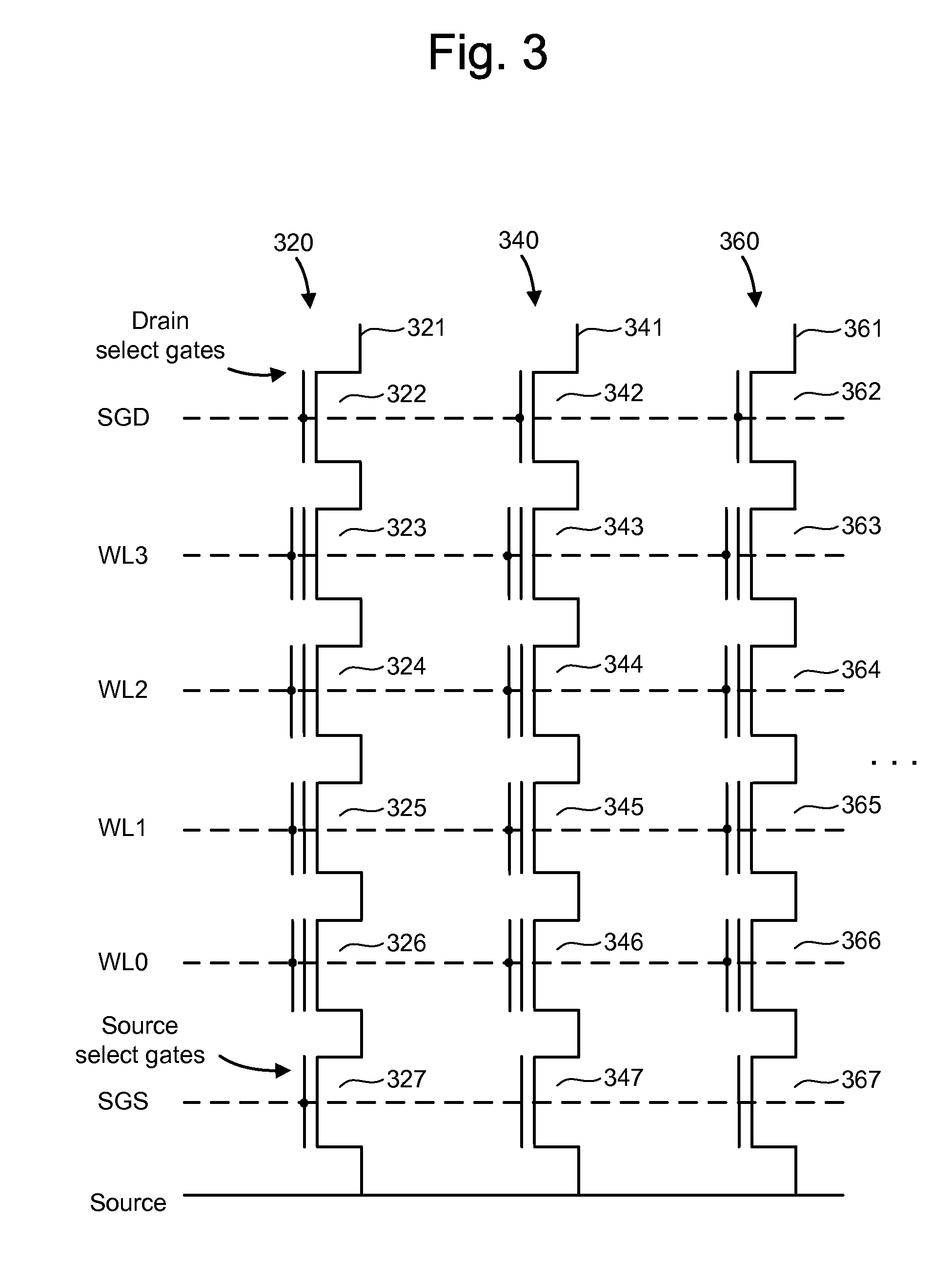
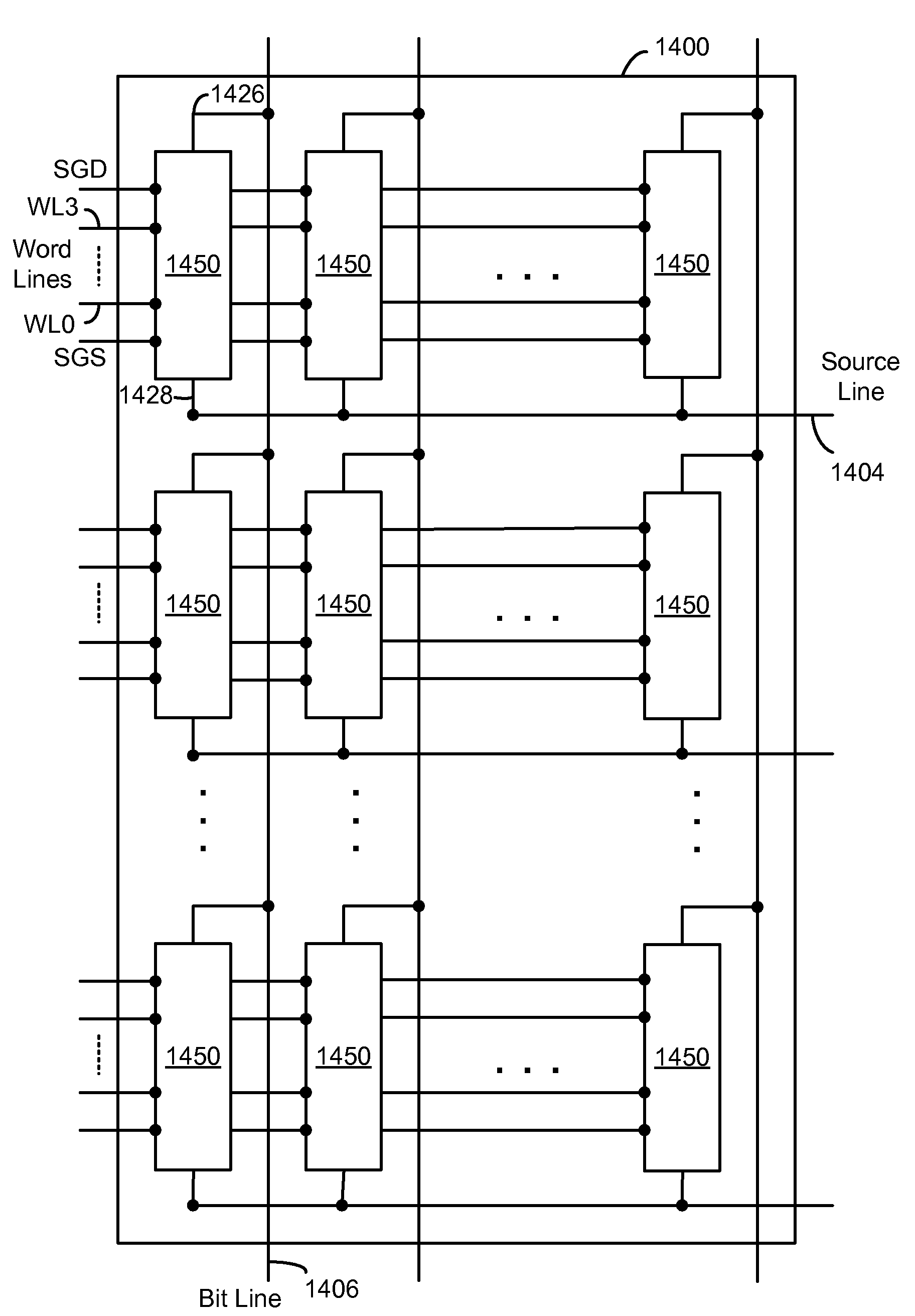
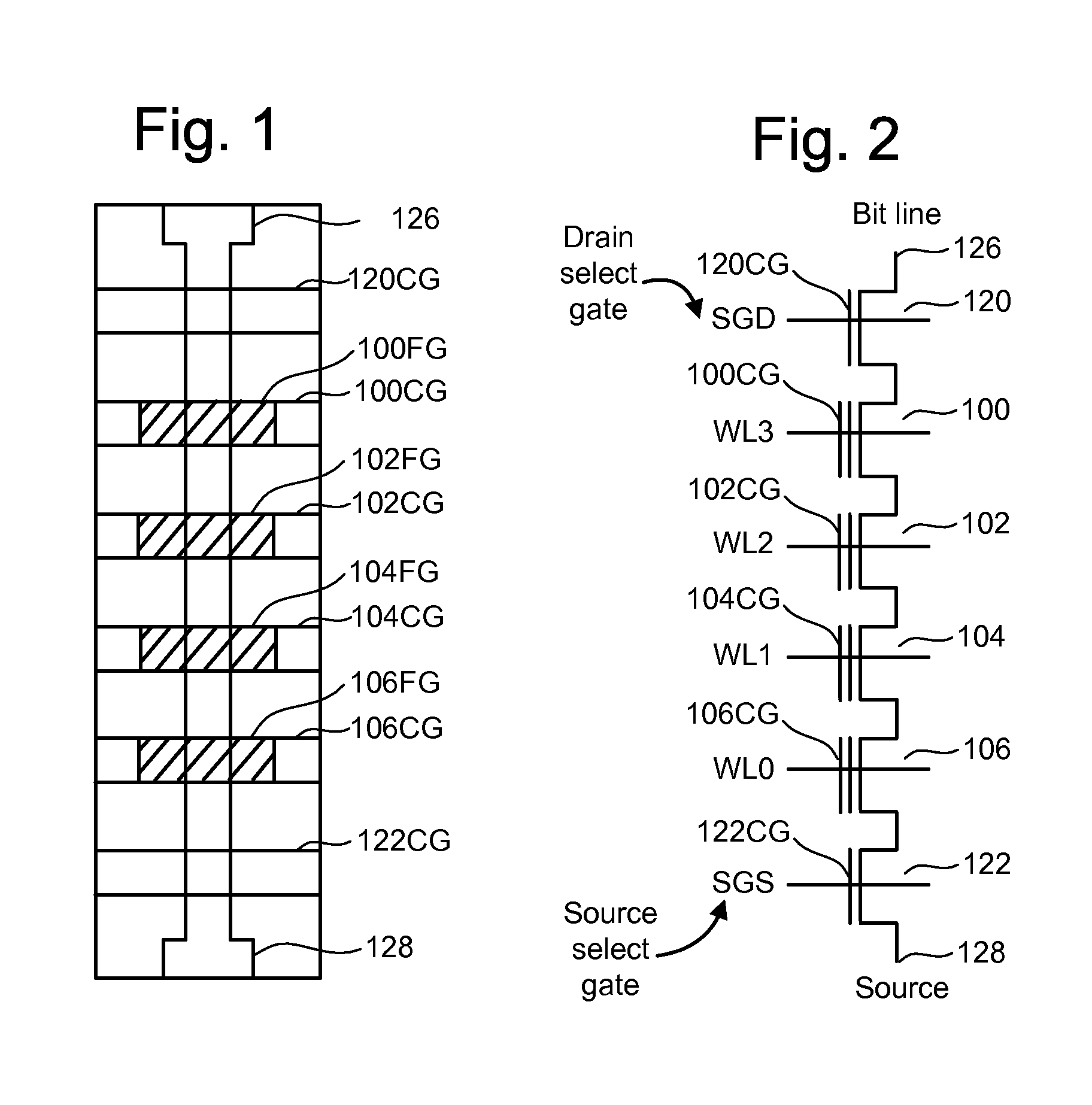
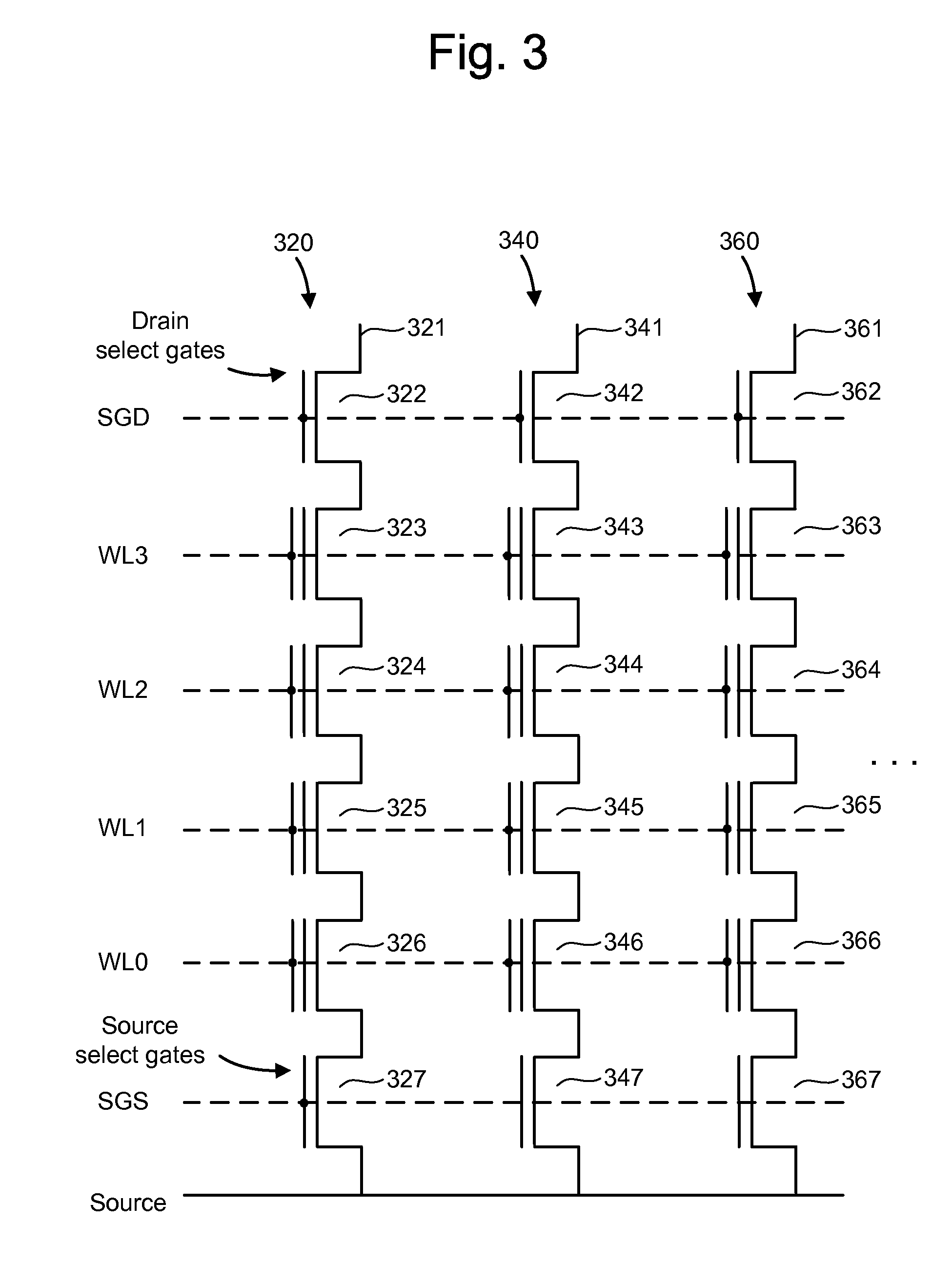
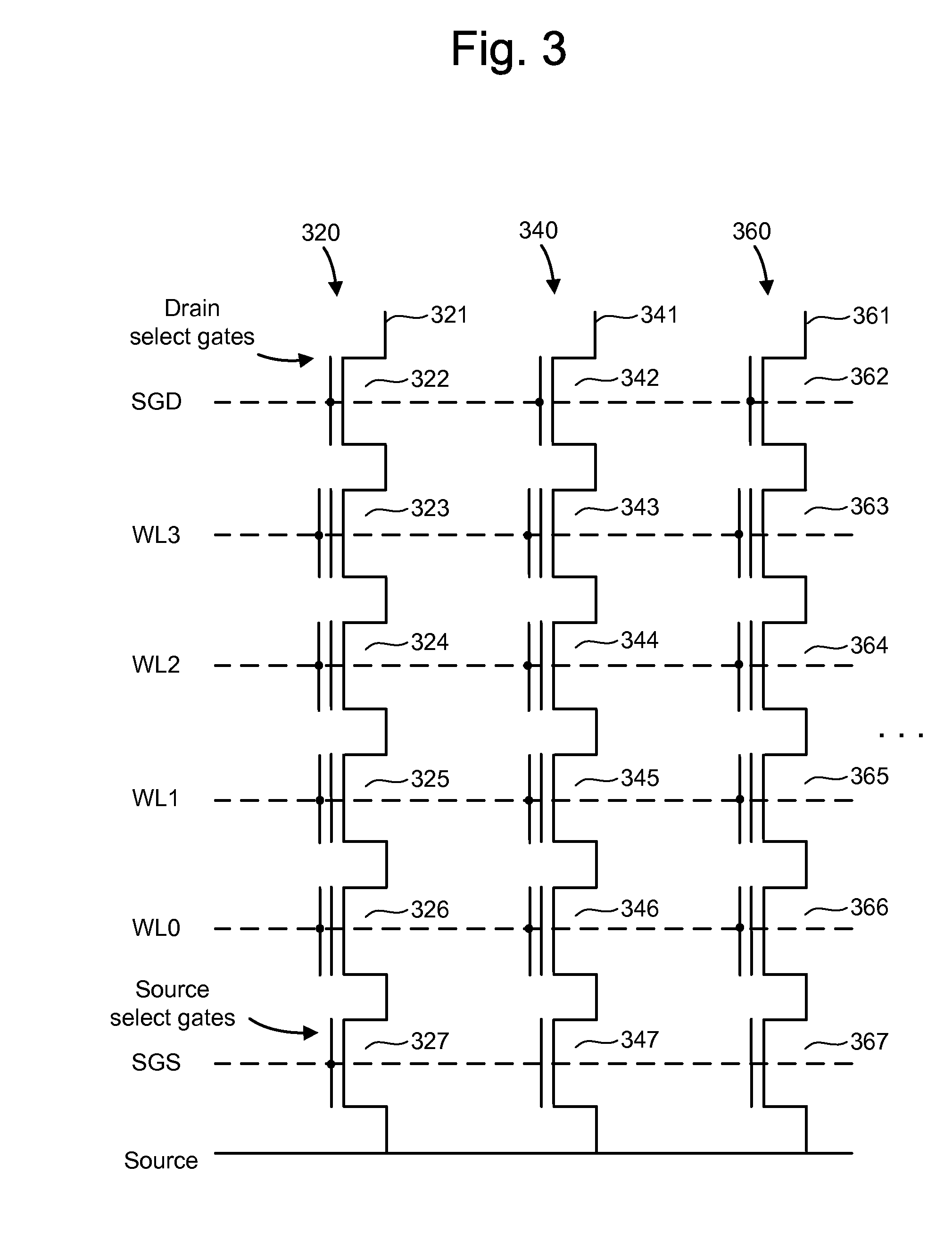
ActiveUS7468911B2Reduces program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePulse numberNon-volatile memory
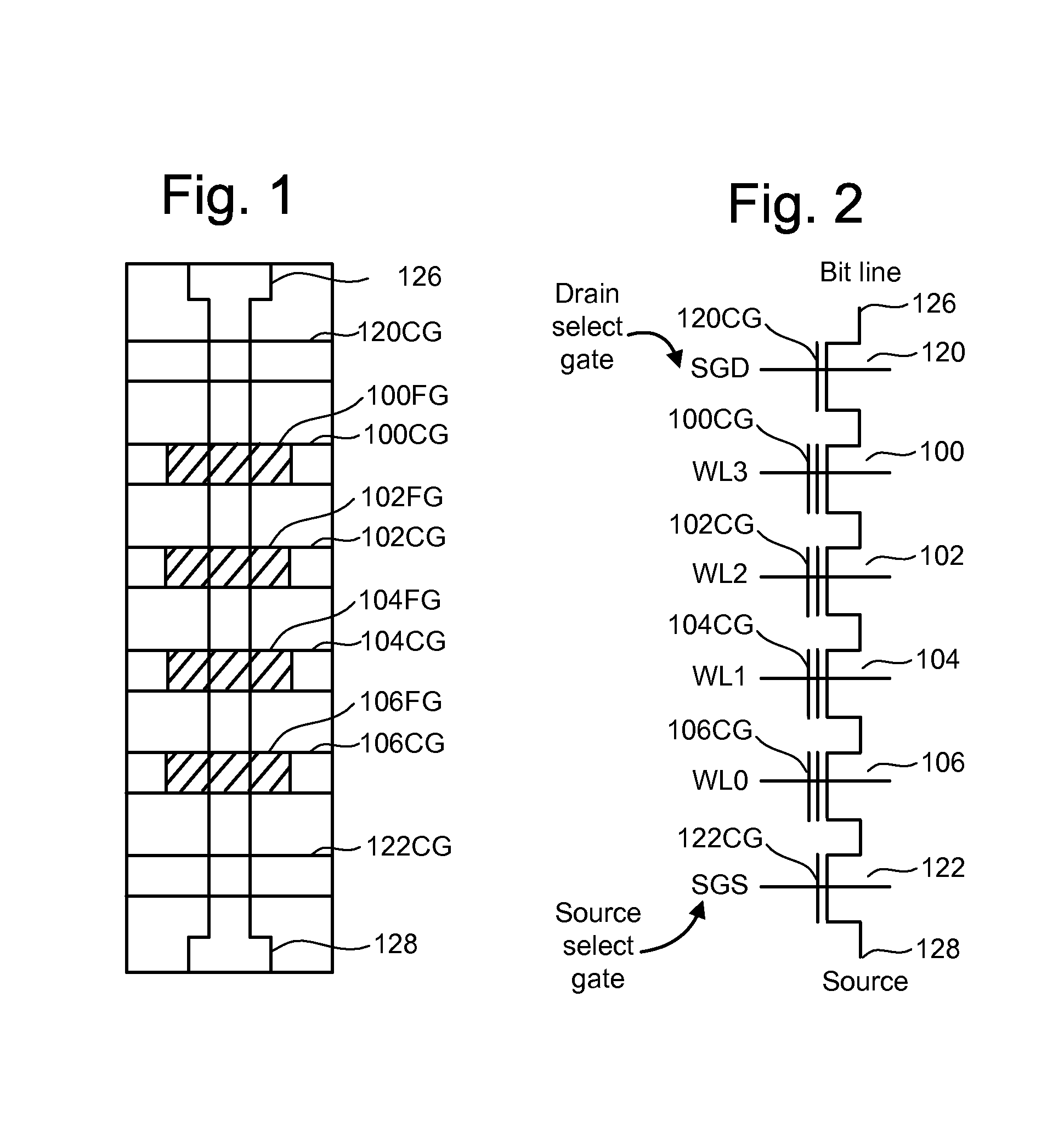
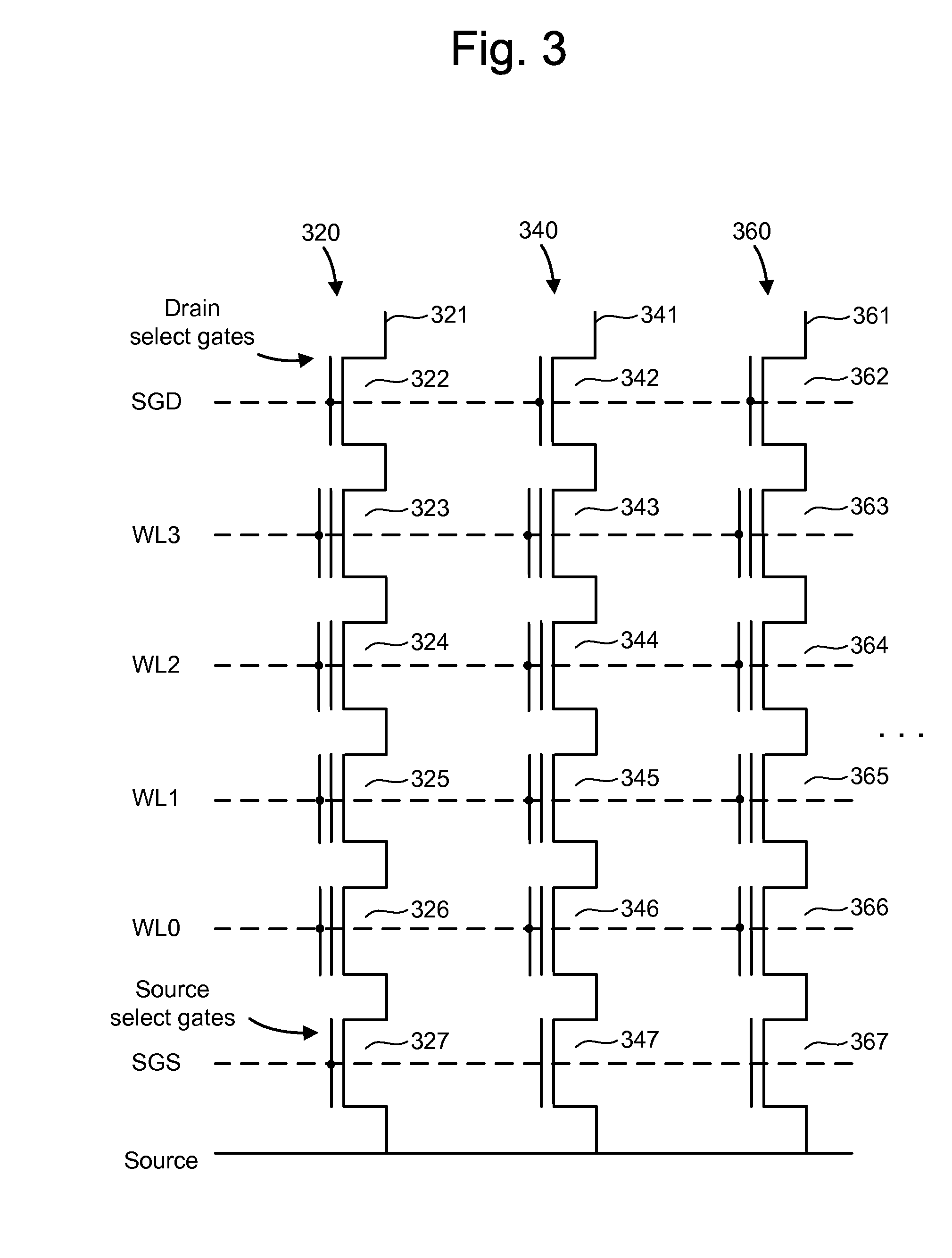
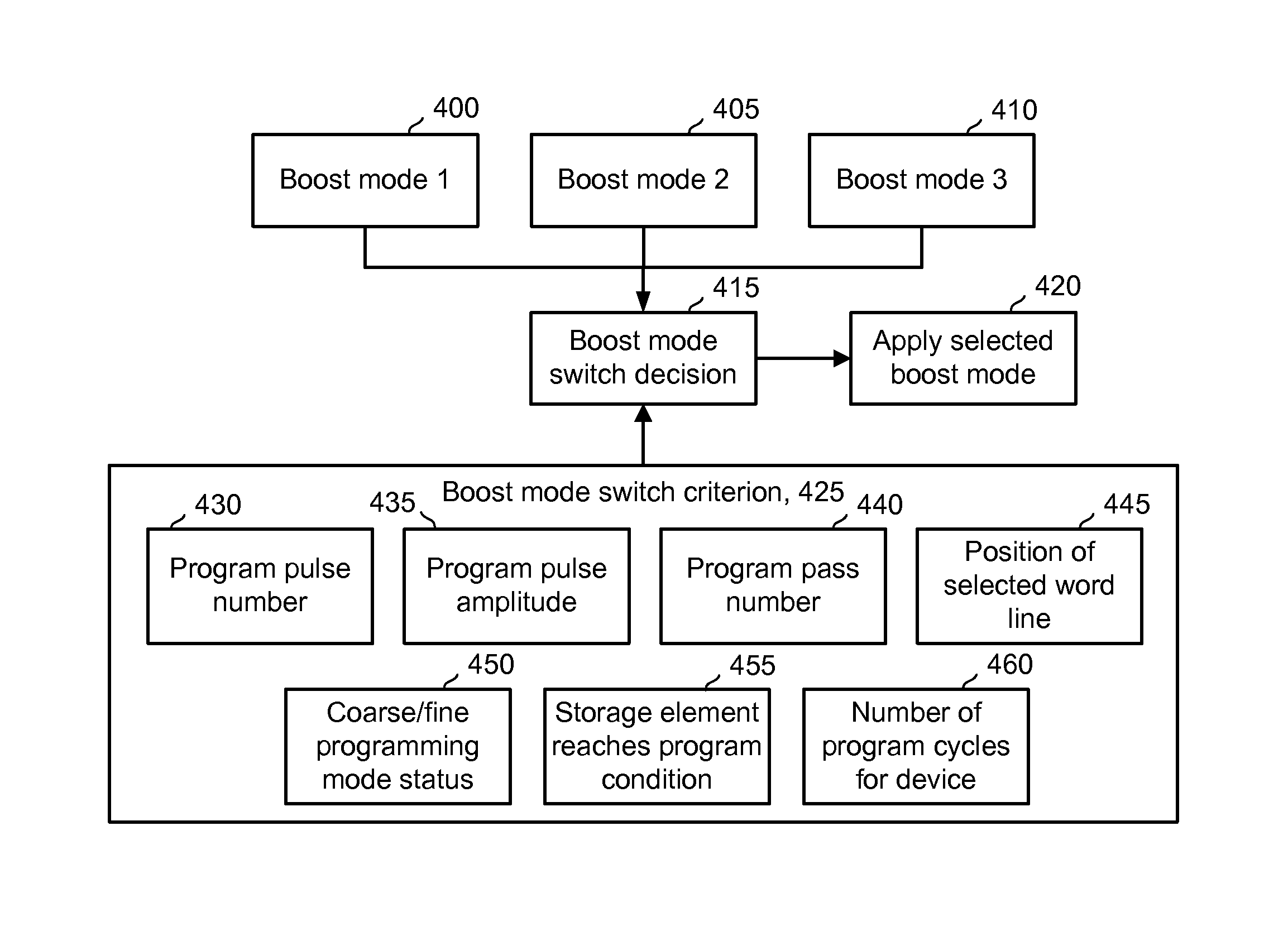
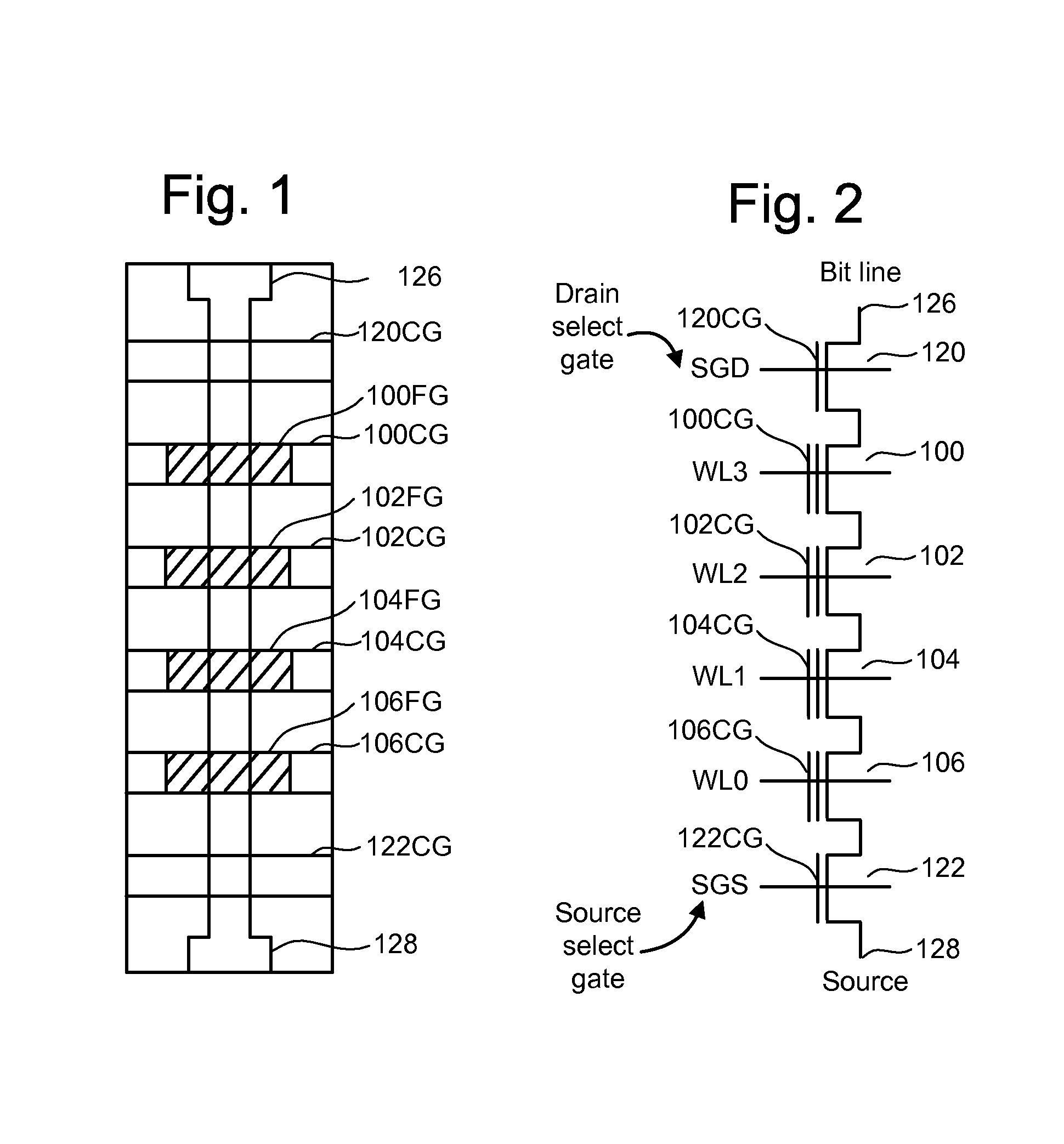
A non-volatile storage system which reduces program disturb. Multiple boosting modes are implemented while programming non-volatile storage. For example, self-boosting, local self-boosting, erased area self-boosting and revised erased area self-boosting may be used. One or more switching criteria are used to determine when to switch to a different boosting mode. The boosting mode may be used to prevent program disturb in unselected NAND strings while storage elements are being programmed in selected NAND strings. By switching boosting modes, an optimal boosting mode can be used as conditions change. The boosting mode can be switched based on various criteria such as program pulse number, program pulse amplitude, program pass number, the position of a selected word line, whether coarse or fine programming is used, whether a storage element reaches a program condition and / or a number of program cycles of the non-volatile storage device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory using multiple boosting modes for reduced program disturb
ActiveUS20080123426A1Reduces program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePulse numberNon-volatile memory
A non-volatile storage system which reduces program disturb. Multiple boosting modes are implemented while programming non-volatile storage. For example, self-boosting, local self-boosting, erased area self-boosting and revised erased area self-boosting may be used. One or more switching criteria are used to determine when to switch to a different boosting mode. The boosting mode may be used to prevent program disturb in unselected NAND strings while storage elements are being programmed in selected NAND strings. By switching boosting modes, an optimal boosting mode can be used as conditions change. The boosting mode can be switched based on various criteria such as program pulse number, program pulse amplitude, program pass number, the position of a selected word line, whether coarse or fine programming is used, whether a storage element reaches a program condition and / or a number of program cycles of the non-volatile storage device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Acoustic imaging by nonlinear low frequency manipulation of high frequency scattering and propagation properties
ActiveUS8038616B2Easy to measureFrame rateMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionWavefront aberrationApproximation property
Methods of acoustic imaging provide images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object, and estimation methods of corrections for wave front aberrations produced by spatial variations in the acoustic propagation velocity. The methods are based on processing of the received signal from transmitted dual frequency band acoustic pulse complexes with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for the image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse is used to manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections for nonlinear propagation delays and optionally also amplitudes, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear forward propagation and scattering parameters are extracted.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
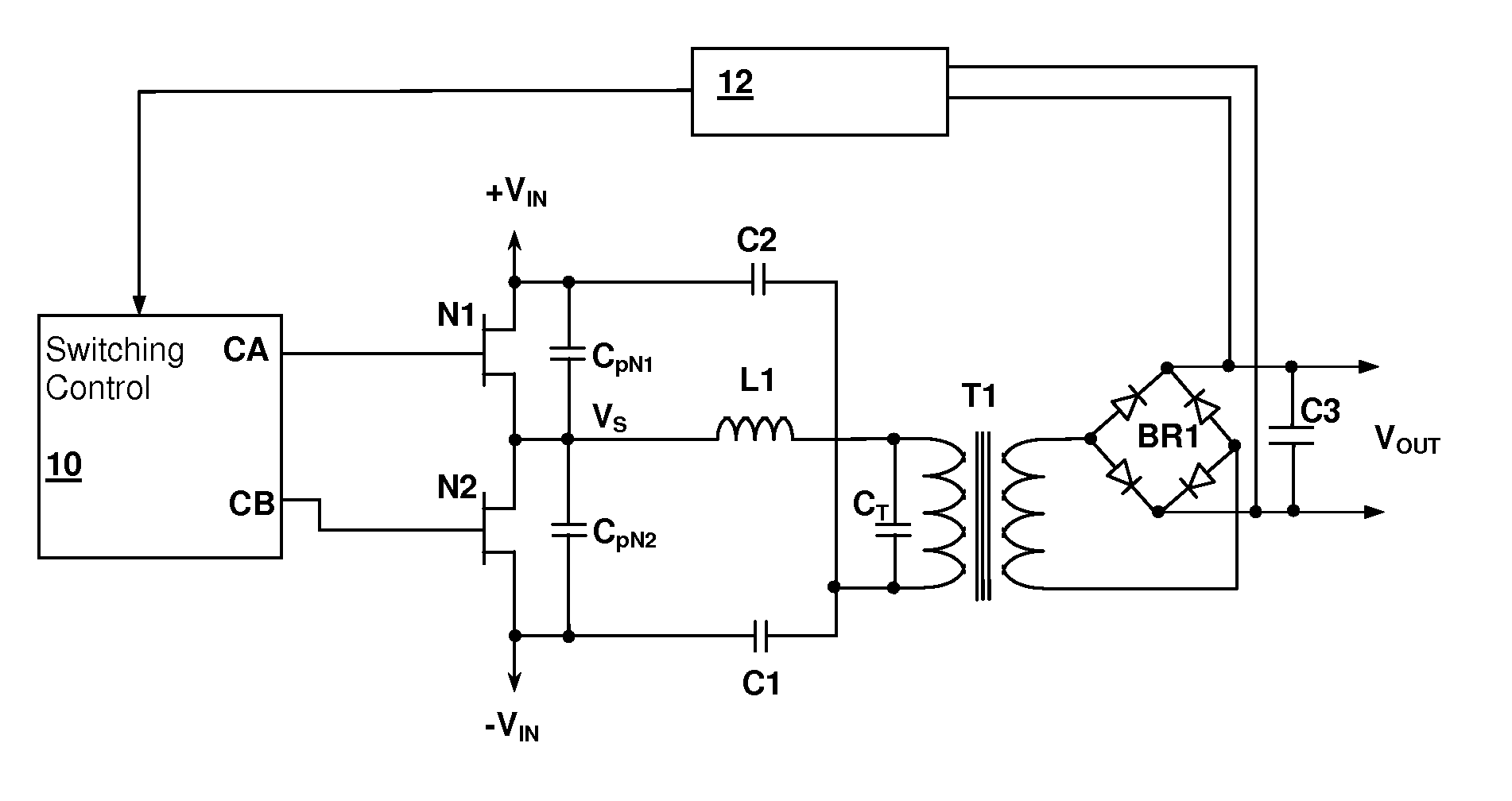
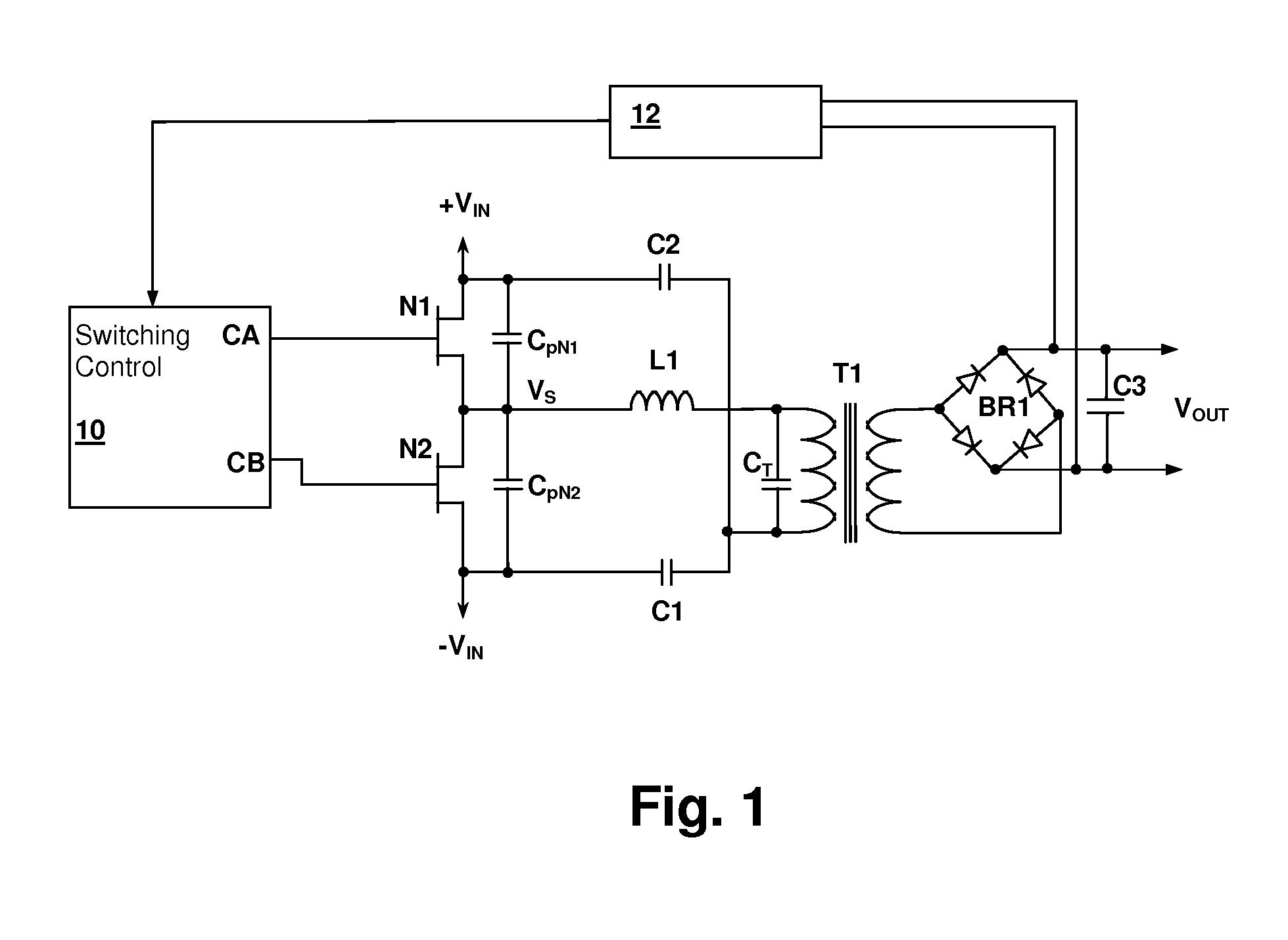
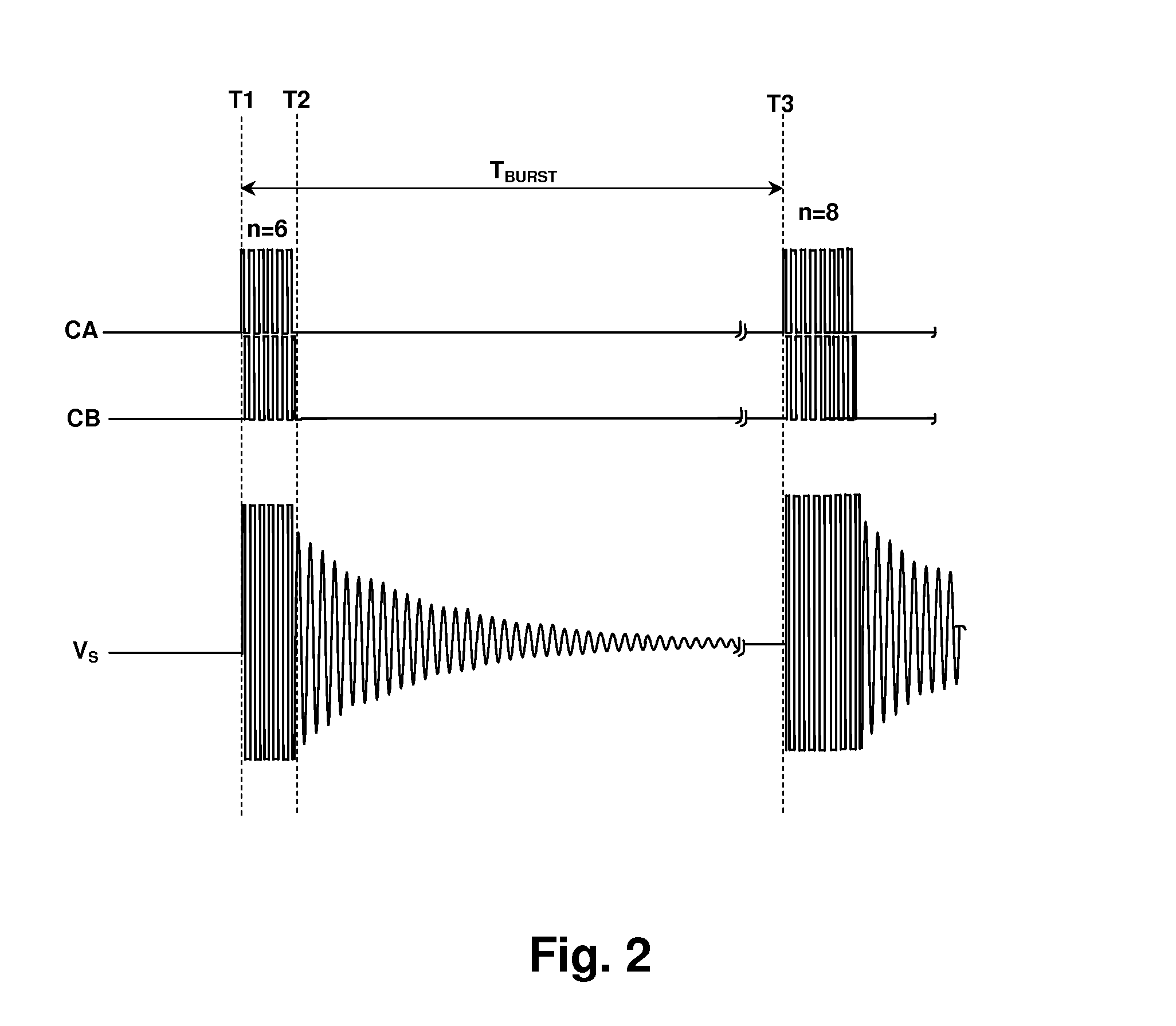
Audible noise suppression in a resonant switching power converter
InactiveUS20100020573A1Spreads audible noiseWeaken energyTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionFrequency spectrumNoise
Audible noise in resonant switching power converter during low-power burst mode operation is reduced by spreading the spectrum generated by the bursts, thereby reducing the amplitude of audio spectrum peaks in the current supplied through the resonant tank from a switching circuit. The spreading can be accomplished by varying the intervals between the bursts and / or by varying a pulse pattern within the bursts. The pulse pattern within the bursts can be varied by varying the number of pulses in the bursts, the polarity of the initial pulse of the bursts, and / or the duration of pulses within the bursts either uniformly or randomly. The burst pulse pattern may also be selected in alternation from a set of pulse patterns stored in a memory and the selection may be made randomly or systematically.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
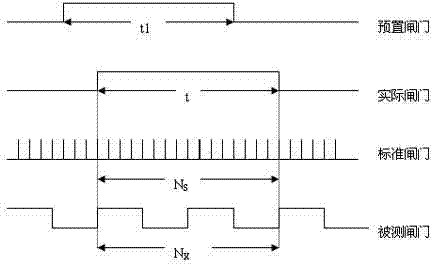
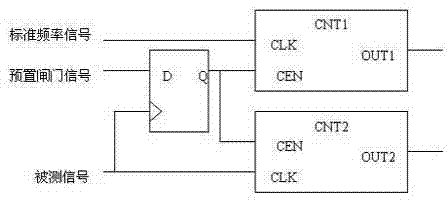
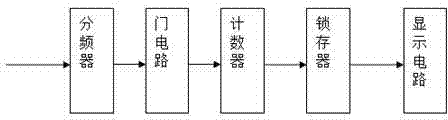
Frequency measurement method based on FPGA
InactiveCN103499739ASolve inaccurateImprove accuracyFrequency to pulse train conversionFrequency measurementsLow frequency band
The invention provides a frequency measurement method based on an FPGA. A standard reference clock is adopted to count the number of pulses of a measured signal in a unit time (1s) and the number of the pulses of the measured signal in the unit time (1s) is the frequency of the signal. Due to the fact that the starting moment of a gate and the finishing moment of the gate are random for the signal, a pulse period quantization error can be produced, and measurement accuracy needs to be analyzed further: the pulse period of a signal to be measured is set to be Tx, the frequency is set to be Fx, and when the measuring time T equals to 1s, the measurement accuracy & meets the equation that &=Tx / T=1 / Fx. The fact that measurement accuracy in a direct frequency measurement method is relevant to the frequency of the signal is known, the higher the frequency of the signal to be measured is, the higher the measurement accuracy is, and otherwise, the lower the frequency of the signal to be measured is, the lower the measurement accuracy is. The direct frequency measurement method is only suitable for measurement of the signal at the higher frequency and can not meet the demand that the measurement accuracy remains unchanged in the whole measurement frequency band. In order to overcome the defect of inaccuracy in low-frequency-band measurement, gating signals and the measured signal are used for carrying out dual control on enable signals of the counter, and therefore accuracy is improved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Ultrasound imaging
ActiveCN101023376AImprove the contrast-to-noise ratioSuppression of linear scatter signalsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationCalcification
New methods of ultrasound imaging are presented that provide images with reduced reverberation noise and images of nonlinear scattering and propagation parameters of the object, and estimation of corrections for wave front aberrations produced by spatial variations in the ultrasound propagation velocity. The methods are based on processing of the received signal from transmitted dual frequency band ultrasound pulse complexes with overlapping high and low frequency pulses. The high frequency pulse is used for the image reconstruction and the low frequency pulse is used to manipulate the nonlinear scattering and / or propagation properties of the high frequency pulse. A 1st method uses the scattered signal from a single dual band pulse complex for filtering in the fast time (depth time) to provide a signal with suppression of reverberation noise and with 1st harmonic sensitivity and increased spatial resolution. In other methods two or more dual band pulse complexes are transmitted where the frequency and / or the phase and / or the amplitude of the low frequency pulse vary for each transmitted pulse complex. Through filtering in the pulse number coordinate and corrections of nonlinear propagation delays and optionally also amplitudes, a linear back scattering signal with suppressed pulse reverberation noise, a nonlinear back scattering signal, and quantitative nonlinear scattering and forward propagation parameters are extracted. The reverberation suppressed signals are further useful for estimation of corrections of wave front aberrations, and especially useful with broad transmit beams for multiple parallel receive beams. Approximate estimates of aberration corrections are given. The nonlinear signal is useful for imaging of differences in tissue properties, such as micro-calcifications, in-growth of fibrous tissue or foam cells, or micro gas bubbles as found with decompression or injected as ultrasound contrast agent.
Owner:比约恩・A・J・安杰尔森 +2
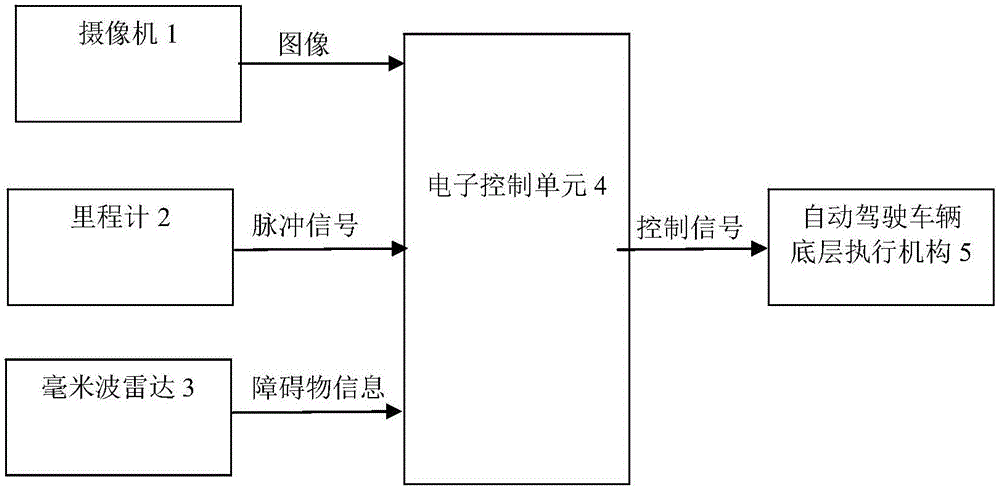
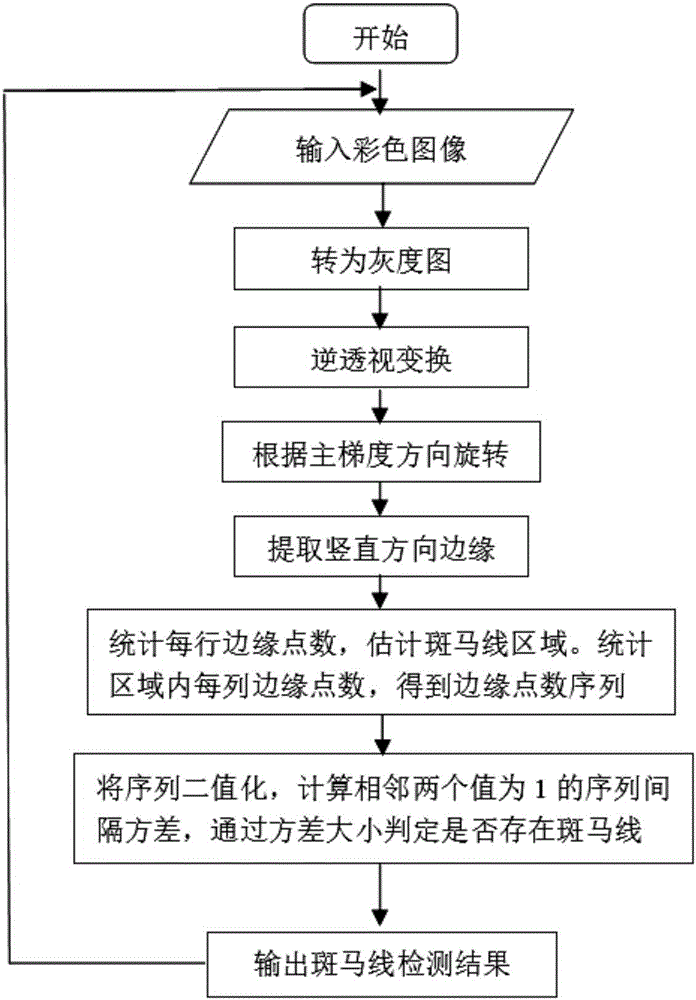
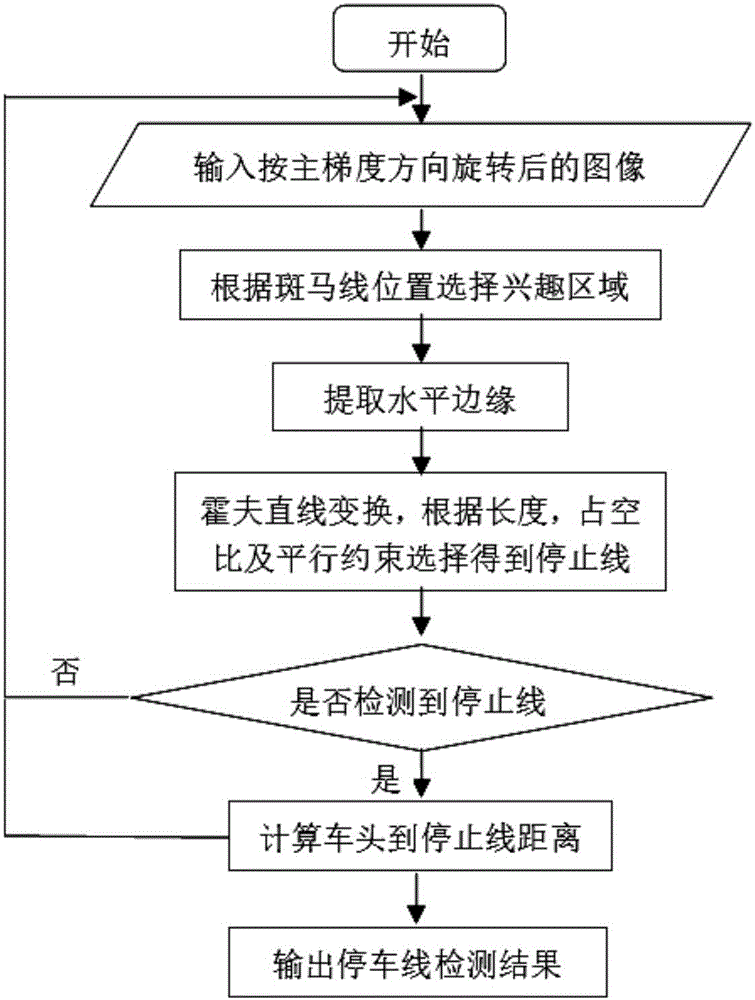
Intersection precise parking device and method used for automatic driving
ActiveCN106205170AAccurate parkingSolve the problem of precise parkingRoad vehicles traffic controlPulse numberField of view
The invention provides an intersection precise parking device and method used for automatic driving. The device comprises an image acquisition device, an electronic control unit, millimeter-wave radar and a speedometer. A camera is used for acquiring images of zebra crossing and a stop line in a road and traffic lights above the road. The millimeter-wave radar is used for detecting front vehicle information. The electronic control unit can detect the zebra crossing, the stop line and the traffic lights and can estimate the distance between a vehicle and the stop line according to pulse number fed back by the speedometer when the stop line enters a camera view dead zone, and the automatically driven vehicle can be precisely parked at the stop line of an intersection. When a vehicle is in front of the current vehicle, the electronic control unit can achieve precise parking according to data detected by the millimeter-wave radar, the position of the front vehicle and the states of the traffic lights. The device and method solve the problem about how to precisely park the automatically driven vehicle at the stop line at the intersection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
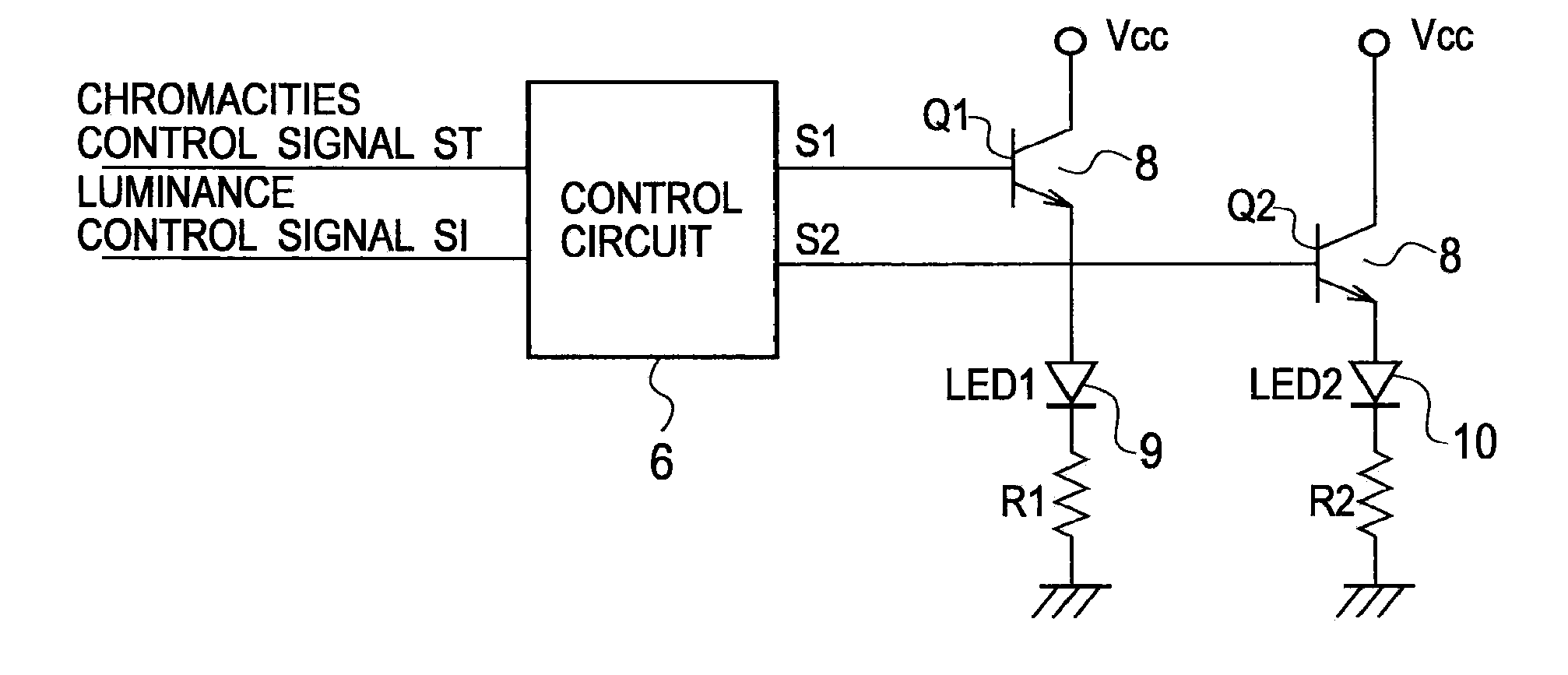
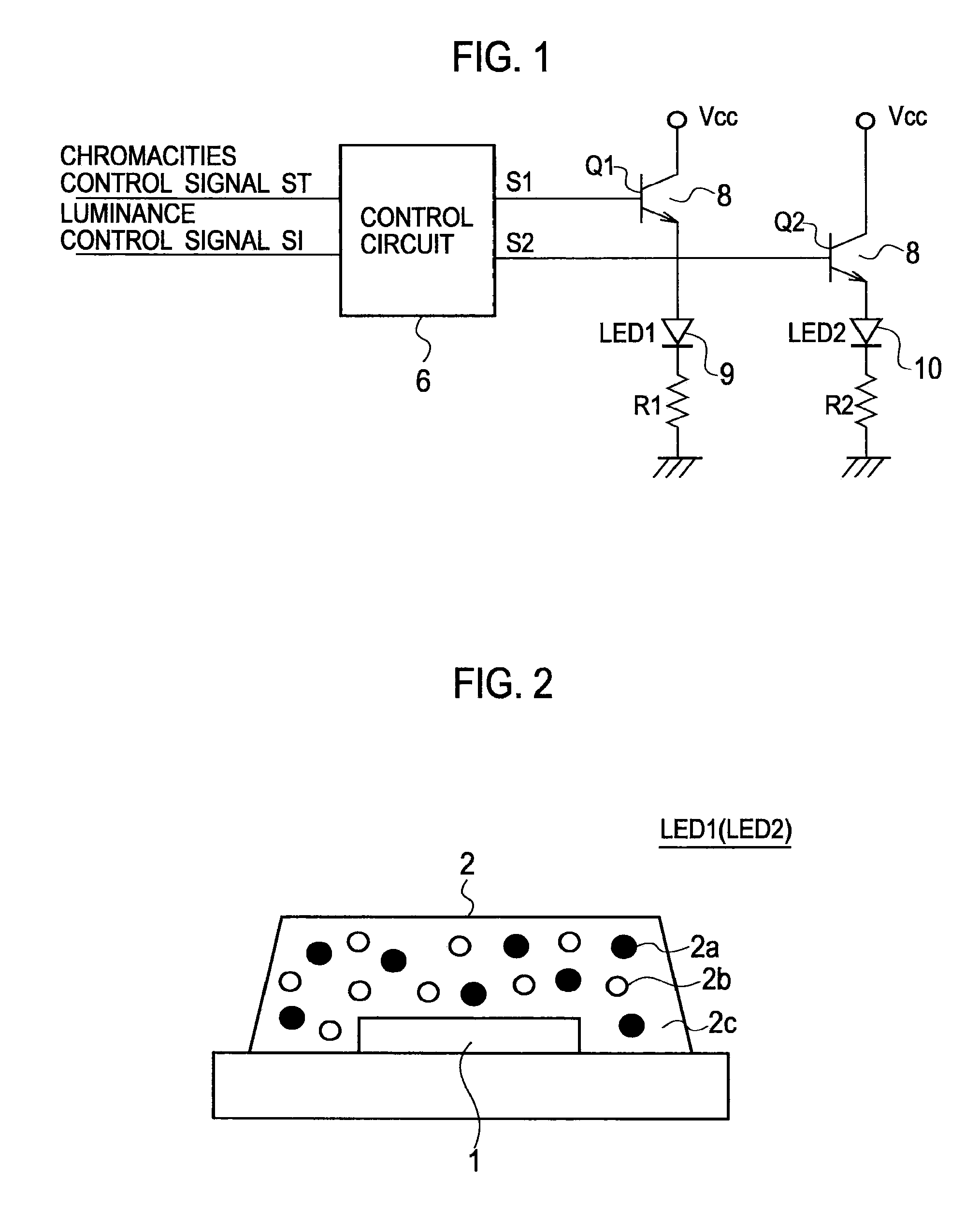
LED lighting device and driving method for the same
It is provided an LED lighting device calibratable to 0 to 100% of wide range about a chromaticity and luminance of a illumination light by a simple configuration, and a driving method for the LED lighting device. The LED lighting device is provided with a first light-emitting unit and a second light-emitting unit differing a color temperature mutually, and a control circuit for executing a cyclic light / quench control of the first light-emitting unit and the second light-emitting unit, and for executing a light control of the first light-emitting unit and the second light-emitting unit by a PNM (Pulse Number Modulation) control in a fixed cycle so as to have a lighting period Ton for lighting / quenching the first light-emitting unit and the second light-emitting unit complementarily, and a quenching period Toff for quenching both the first light-emitting unit and the second light-emitting unit.
Owner:IRIS OHYAMA
Reducing program disturb in non-volatile memory using multiple boosting modes
ActiveUS20080123425A1Reduces program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePulse numberNon-volatile memory
A method for operating a non-volatile storage system which reduces program disturb. Multiple boosting modes are implemented while programming non-volatile storage. For example, self-boosting, local self-boosting, erased area self-boosting and revised erased area self-boosting may be used. One or more switching criteria are used to determine when to switch to a different boosting mode. The boosting mode may be used to prevent program disturb in unselected NAND strings while storage elements are being programmed in selected NAND strings. By switching boosting modes, an optimal boosting mode can be used as conditions change. The boosting mode can be switched based on various criteria such as program pulse number, program pulse amplitude, program pass number, the position of a selected word line, whether coarse or fine programming is used, whether a storage element reaches a program condition and / or a number of program cycles of the non-volatile storage device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Reducing program disturb in non-volatile memory using multiple boosting modes
ActiveUS7440323B2Reduces program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storagePulse numberNon-volatile memory
A method for operating a non-volatile storage system which reduces program disturb. Multiple boosting modes are implemented while programming non-volatile storage. For example, self-boosting, local self-boosting, erased area self-boosting and revised erased area self-boosting may be used. One or more switching criteria are used to determine when to switch to a different boosting mode. The boosting mode may be used to prevent program disturb in unselected NAND strings while storage elements are being programmed in selected NAND strings. By switching boosting modes, an optimal boosting mode can be used as conditions change. The boosting mode can be switched based on various criteria such as program pulse number, program pulse amplitude, program pass number, the position of a selected word line, whether coarse or fine programming is used, whether a storage element reaches a program condition and / or a number of program cycles of the non-volatile storage device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Malfunction detection method of incremental encoder
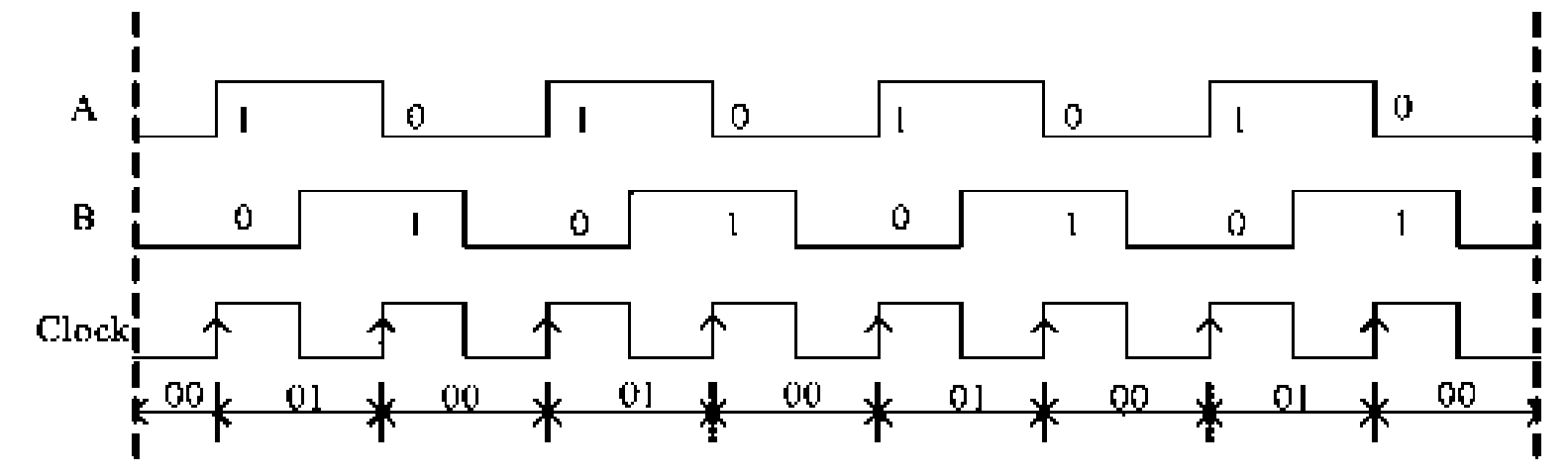
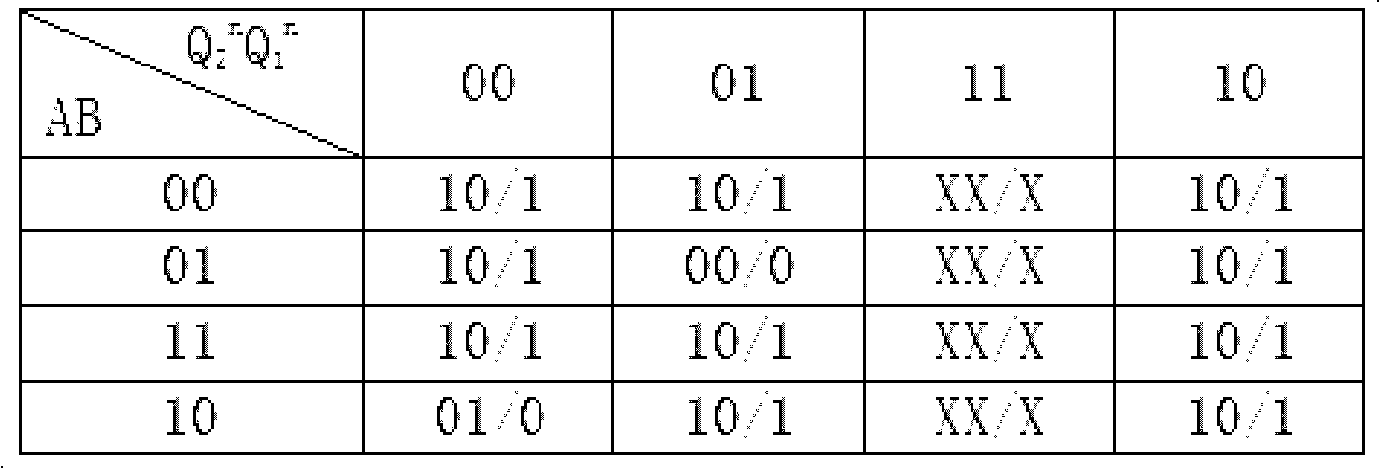
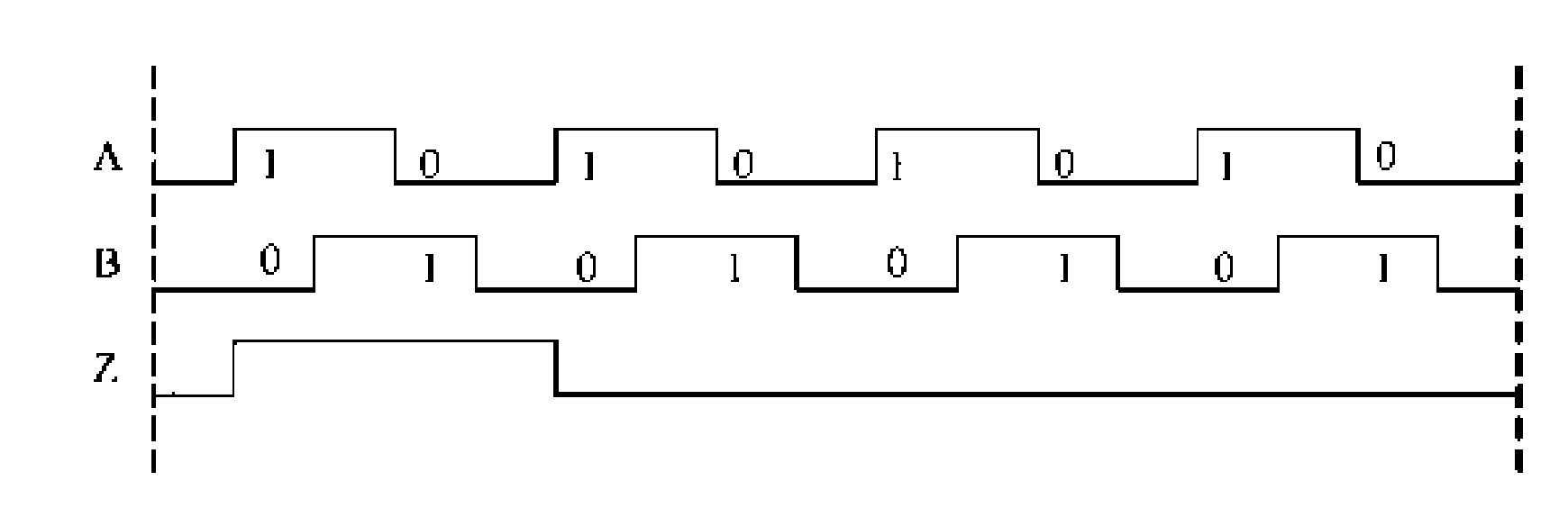
The invention relates to a malfunction detection method of an incremental encoder, which belongs to the malfunction detection field of the encoder, and solves the problems of the prior art that the non-wire-break malfunction of the incremental encoder cannot be detected. An electric pulse signal A and an electric pulse signal B of the incremental encoder, phase difference of which is 90 degrees, are exclusive or to obtain a synchronic clock signal Clock, circuit output states Q2 and Q1 of two JK triggers FF2 and FF1 which are triggered by two rising edges are determined according to the state of the electric pulse signals A and B at the rising edge time of every two adjacent periods of the Clock, and the malfunction of the incremental encoder is judged according to the output state Q2 and Q1. The method also comprises the detection of a Z pulse signal of the incremental encoder: a Z pulse signal is adopted to preset a cascaded counter so as to count the pulse number which is outputted by the synchronic clock signal Clock when incremental encoder rotates a circle, and the malfunction of the Z pulse signal is judged according to the overflow of the cascaded counter. The method is applicable to the malfunction detection of the incremental encoder.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Note width and distance detecting and quantity calculating method and device
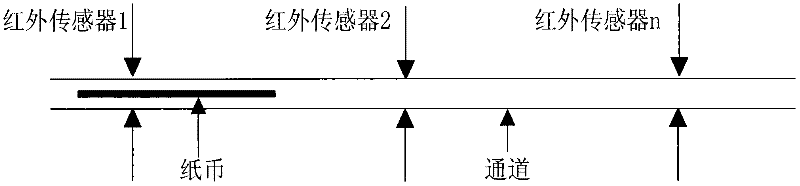
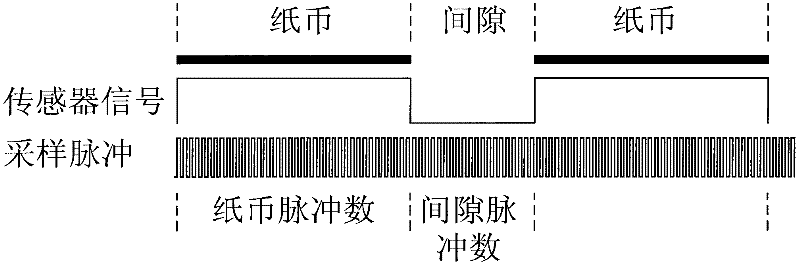
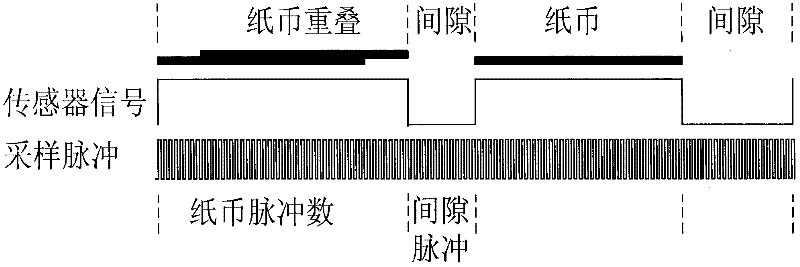
InactiveCN102254370AAccurate statisticsAvoid financial disputesPaper-money testing devicesCoin/currency accepting devicesClock ratePulse number
The invention relates to a note width and distance detecting and quantity calculating method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: a. charging notes into a transmission passage for running; b. carrying out data sampling on an infrared sensor in the transmission passage according to fixed clock frequency and respectively recording high level frequency and low level frequency of a sampled infrared sensor signal by a detecting unit; c. calculating the note width and distance through pulse number; and d. carrying out note calculation of the calculated pulse number in the range of the preset note width pulse number. The device comprises a plurality of infrared sensors, a multi-channel selector, an analog-to-digital converting circuit, a timer and a data processing and logic control chip.
Owner:SHENZHEN YIHUA COMP +2
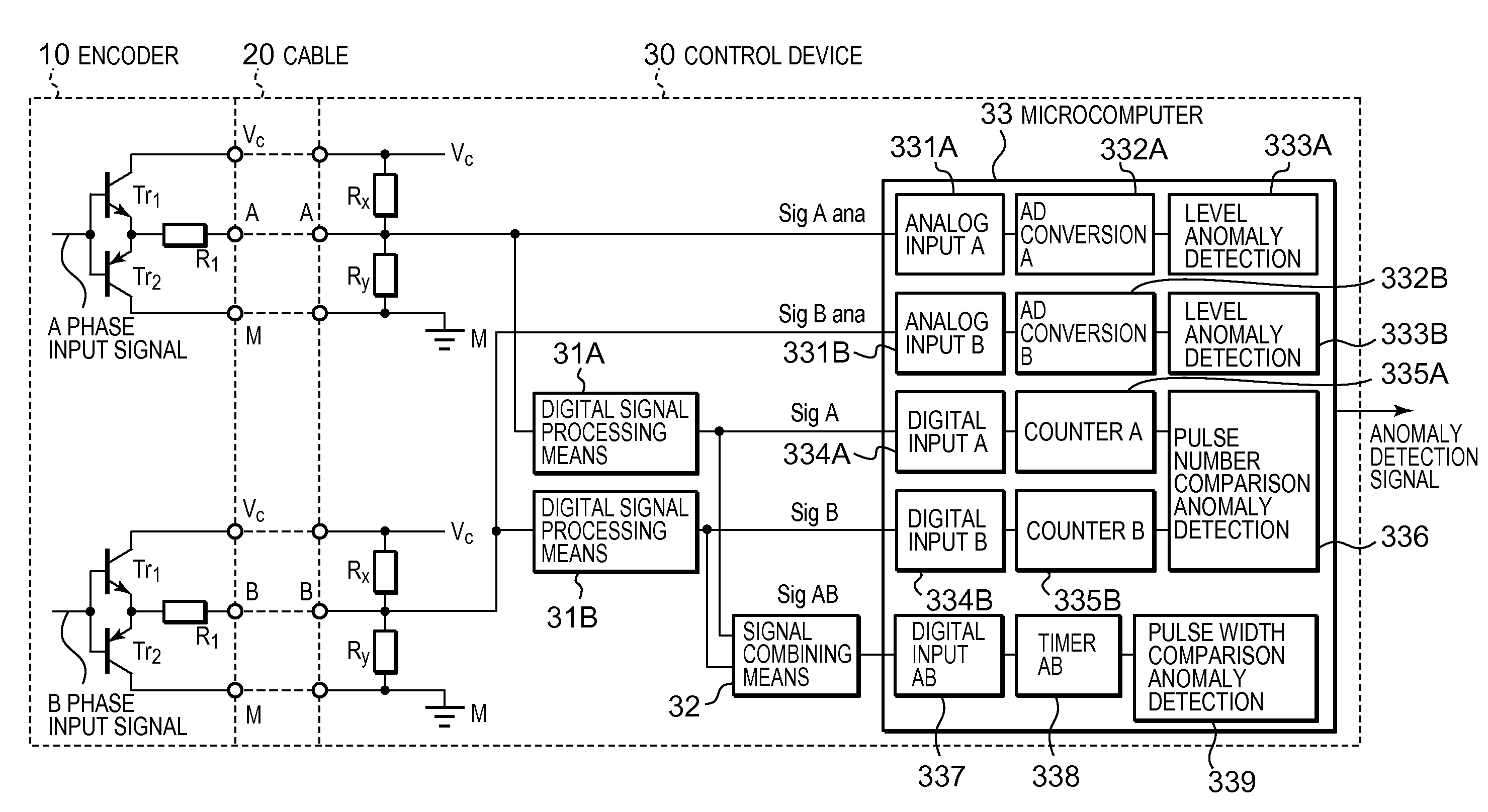
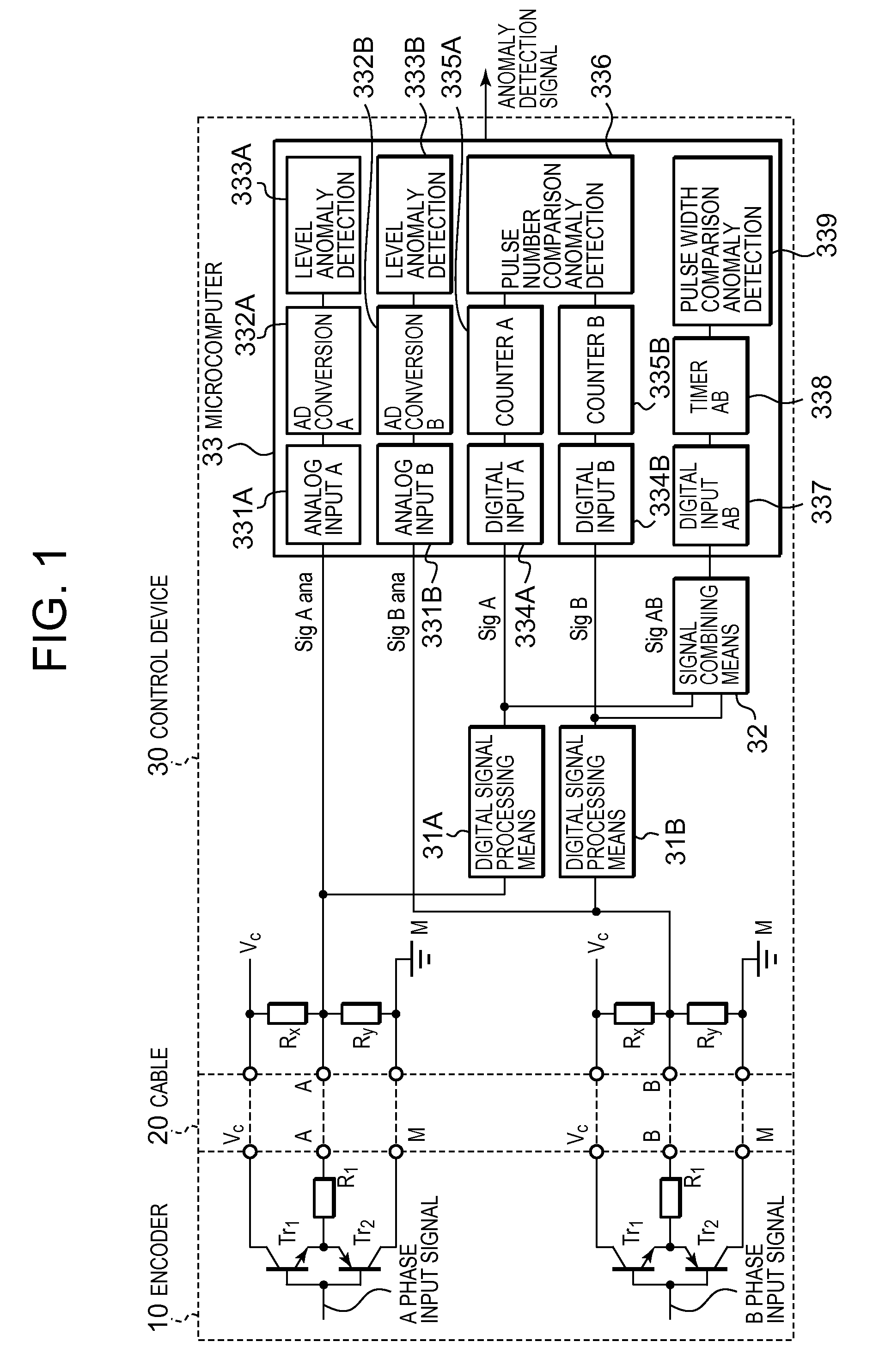
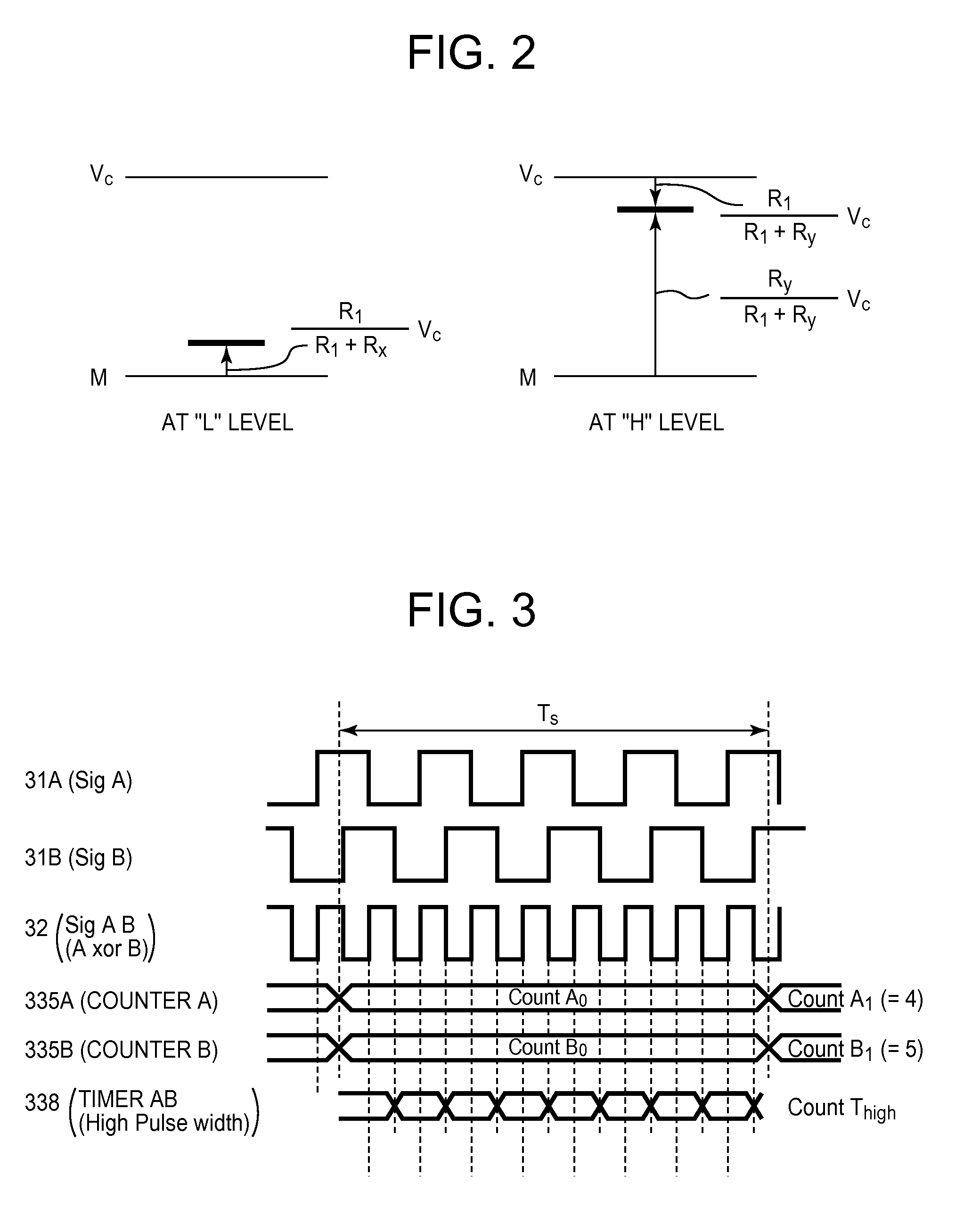
Anomaly monitoring device
ActiveUS20100201373A1Improve reliabilityIncreased costElectrical testingConverting sensor outputPulse numberAnalog signal
In an anomaly monitoring device, in which an output signal from an encoder is input as an analog input signal via a wiring system, for detecting anomalies in the encoder or the wiring system, provided are a voltage level based device, a pulse number based device and a pulse width based device. The voltage level based device detects anomalies when the voltage level of the analog input signal exists within a prescribed range. The pulse number based device detects anomalies when the difference in the numbers of pulses of digital signals corresponding to the analog input signals is equal to or greater than a prescribed threshold value. The pulse width based device detects anomalies when the pulse width of the digital signals, measured from a combined signal of the digital signals or each of the digital signals, is different from the pulse width in a past control period.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
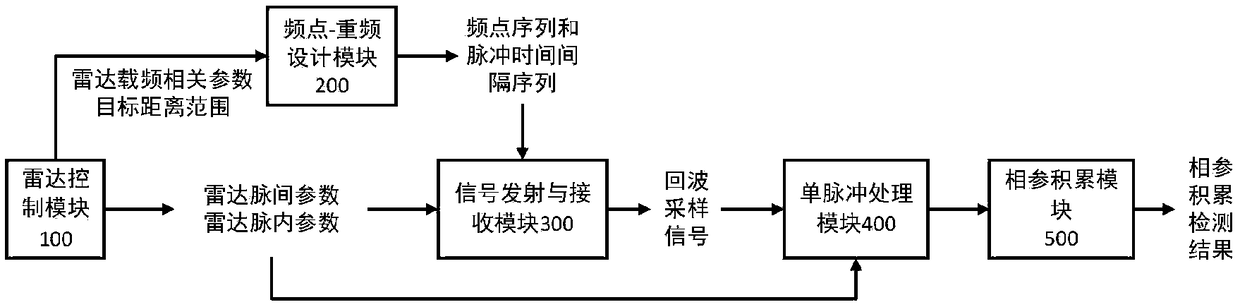
Signal processing method and device for frequency-agile radar based on variable repetition frequency technology
ActiveCN109143179AReal-time processingReduce processingWave based measurement systemsBasebandEcho signal
The invention provides a signal processing method and device for frequency-agile radar based on a variable repetition frequency technology. The method includes the following steps: designing a frequency point sequence of random hopping according to a random number and the carrier frequency related parameters of radar, and designing a pulse time interval sequence according to the frequency point sequence and the distance range of a target to be detected; emitting a radar pulse signal according to the designed frequency point sequence and the designed pulse time interval sequence, receiving an echo signal of the radar pulse signal, and sampling and preprocessing the echo signal to obtain a baseband echo sampling signal; processing the baseband echo sampling signal by a single pulse to obtaina time-domain echo signal after pulse compression; and coherently accumulating the time-domain echo signal after pulse compression in the two dimensions of frequency point and pulse number, and obtaining the fine resolution distance and Doppler velocity values of the target to be detected through threshold decision. Accurate detection of the distance and velocity of a moving target by coherent frequency-agile radar is realized, and the amount of computation for the processing of coherent frequency-agile signals can be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
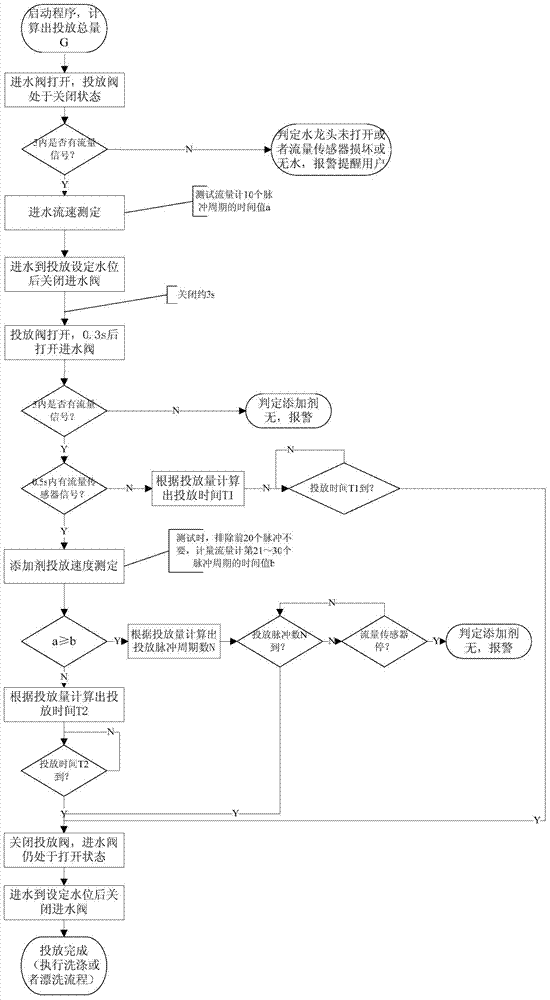
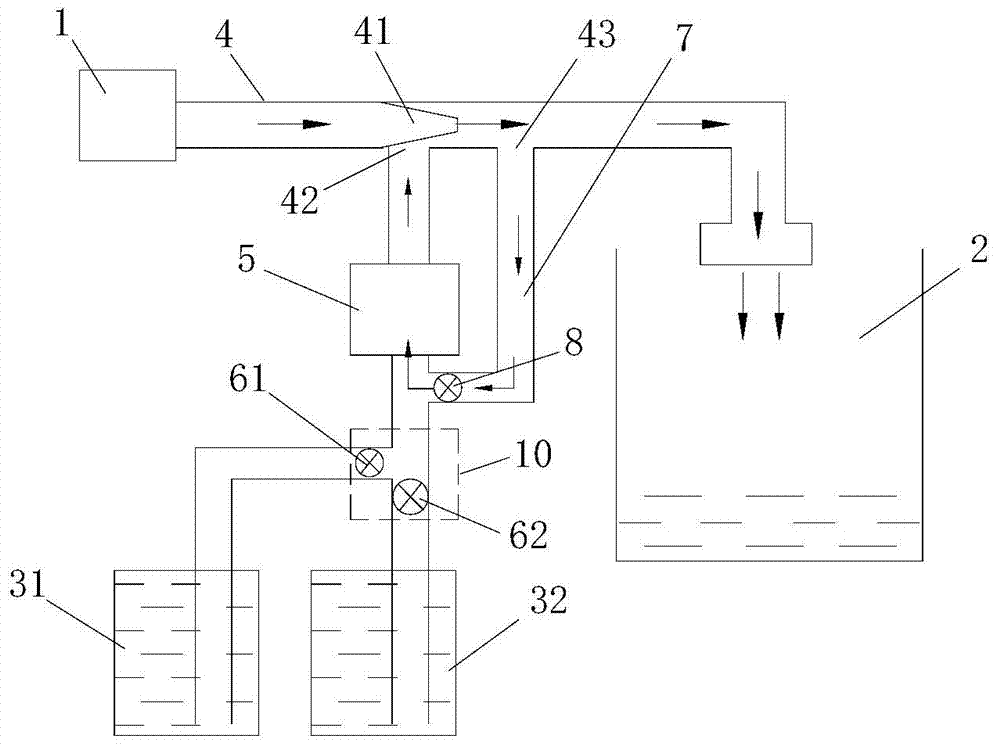
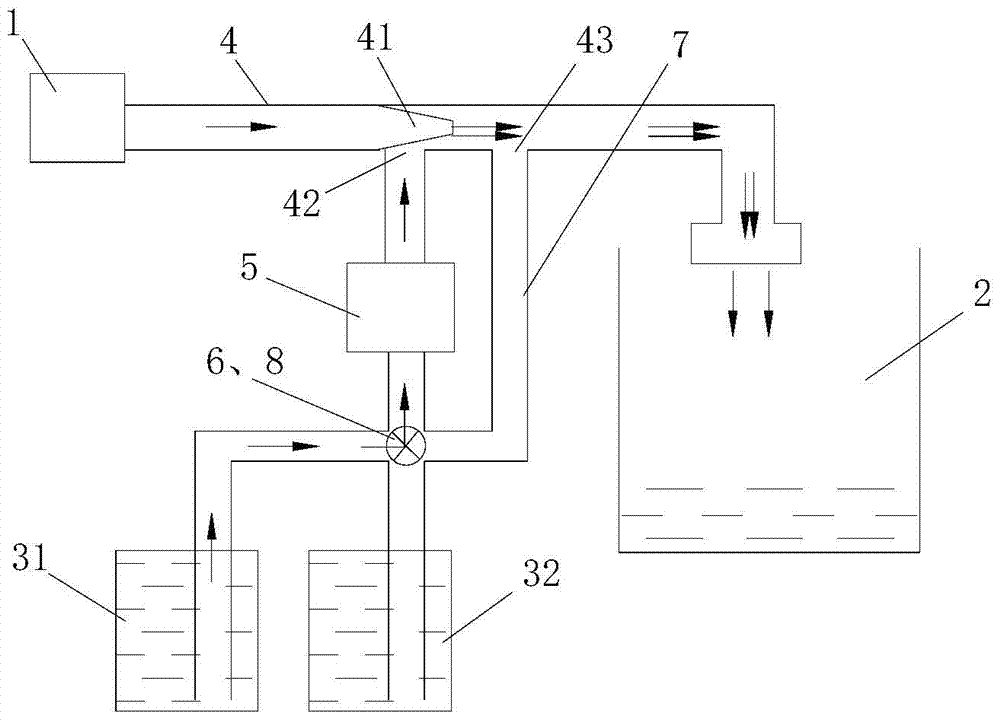
Control method of automatic additive adding
ActiveCN104727099AEasy to washImprove rinsing performanceOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusInlet valvePulse number
The invention discloses a control method of automatic additive adding. The method includes: opening an additive adding control valve, opening a water inlet valve, using negative pressure generated by water inlet to extract additives, measuring water pressure, additive viscosity and additive adding speed, selecting adding time or adding pulse number to judge whether a total adding amount reaches the required additive amount G, and closing the additive adding control valve when the additive adding amount reaches G to complete additive adding. The control method has the advantages that a flow sensor and a negative pressure structure are used in coordination, precise adding of various liquid additives is achieved by combining the on and off of the adding control valve, the influence of the water pressure and the precise detection of the flow sensor and by precise judgement, washing and rising effects are increased, and the control method is simple and practical.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER WASHING MASCH CO LTD
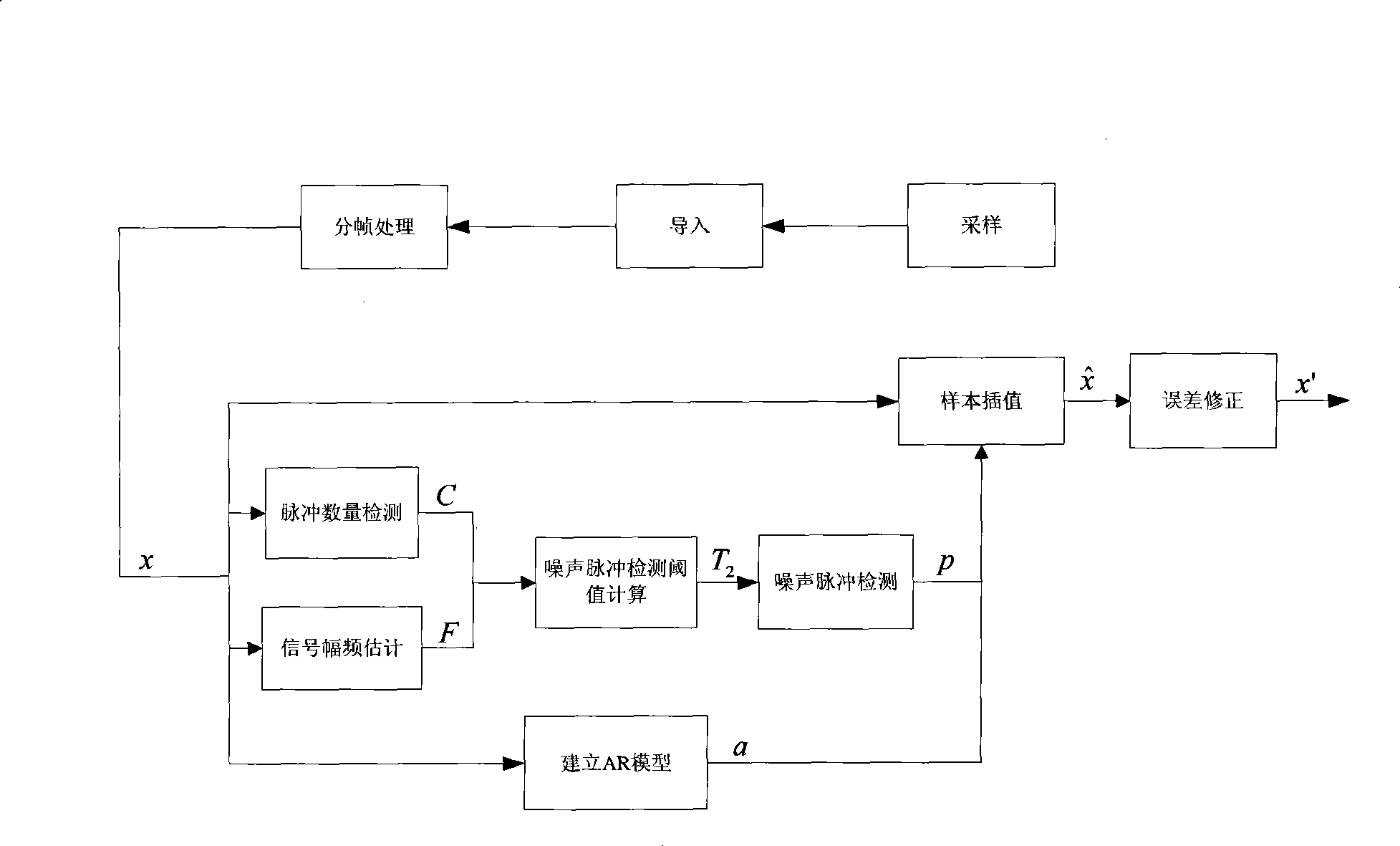
Method for detecting and eliminating pulse noise in digital audio signal
The invention provides a method for detecting and removing pulse noise in a digital audio signal, which comprises the following steps: utilizing weighted difference vectors of adjacent signal samples in a certain neighbor in the signals to detect pulse number and determine detection thresholds of the noise pulse according to the estimation value of the change degree of the amplitude and frequency of the signal; utilizing the envelope based on the weighted difference vectors of the signal samples to evaluate the width of the noise pulse and establish an autoregressive model of the signal; according to the correlation of voice frequency signals, utilizing adjacent signal samples which are repaired or not contaminated to repair a signal section which is contaminated by the pulse noise and recover original signals. The invention has the advantages that a normal signal which is changed abruptly and the noise pulse can be separated, and the width of the pulse can be calculated; and meanwhile, by adopting the envelop which is formed by the weighted difference vectors of the signal, the position and the width of the noise pulse are detected, so that a single noise pulse, a plurality of contiguous noise pulses or a plurality of overlapping noise pulses can be processed.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Method monitoring air pressure of automobile tire in running
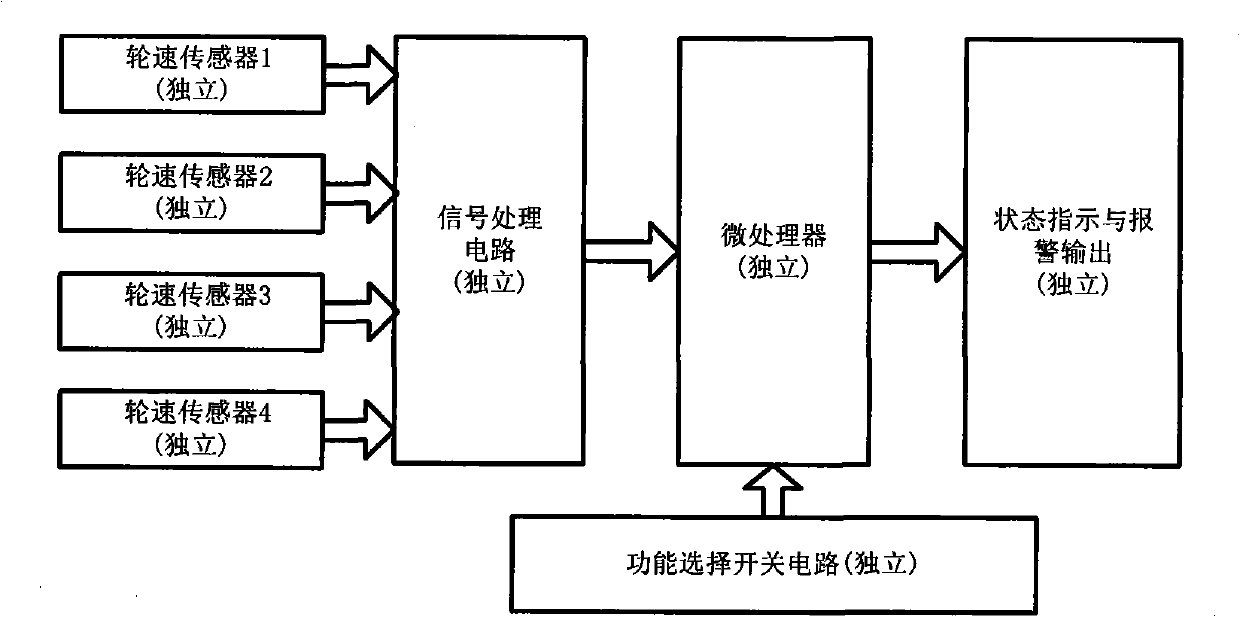
InactiveCN101306638AAccurate forecastEffective forecastFluid pressure measurementTyre measurementsDrive wheelPulse number
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
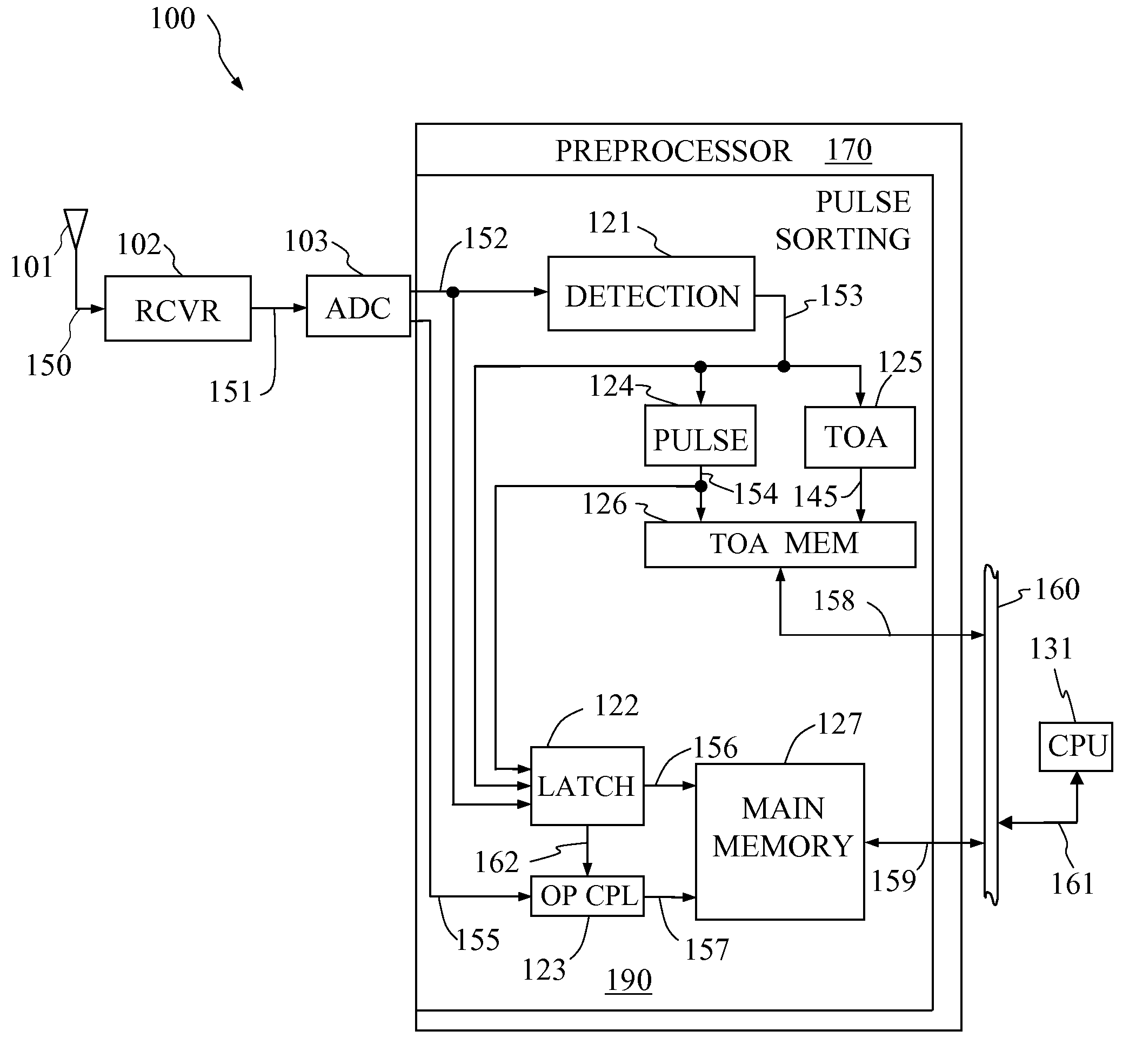
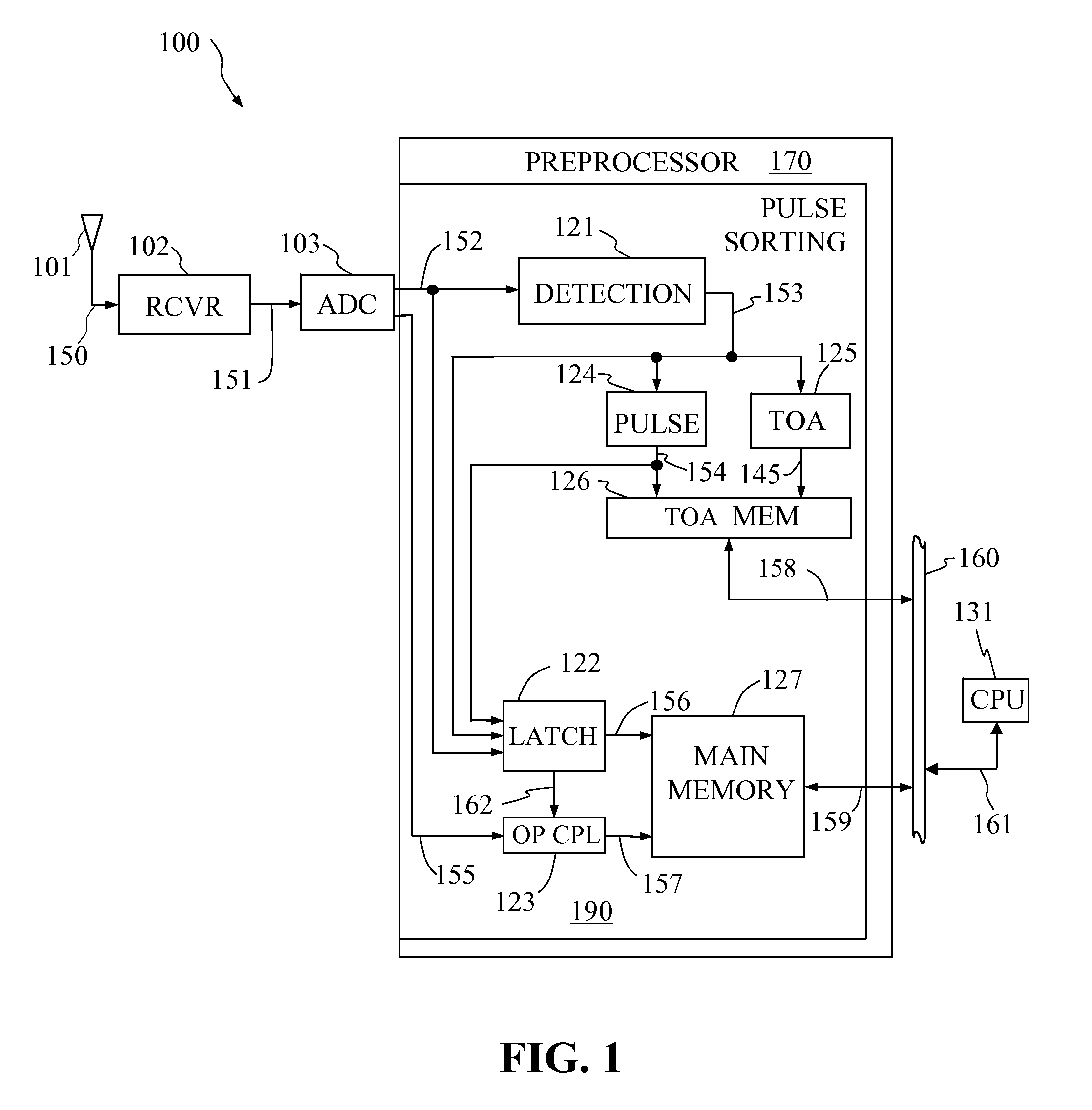
Pulse sorting apparatus for frequency histogramming in a radar receiver system
ActiveUS7184493B1Frequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunication jammingDigital dataPulse radiation
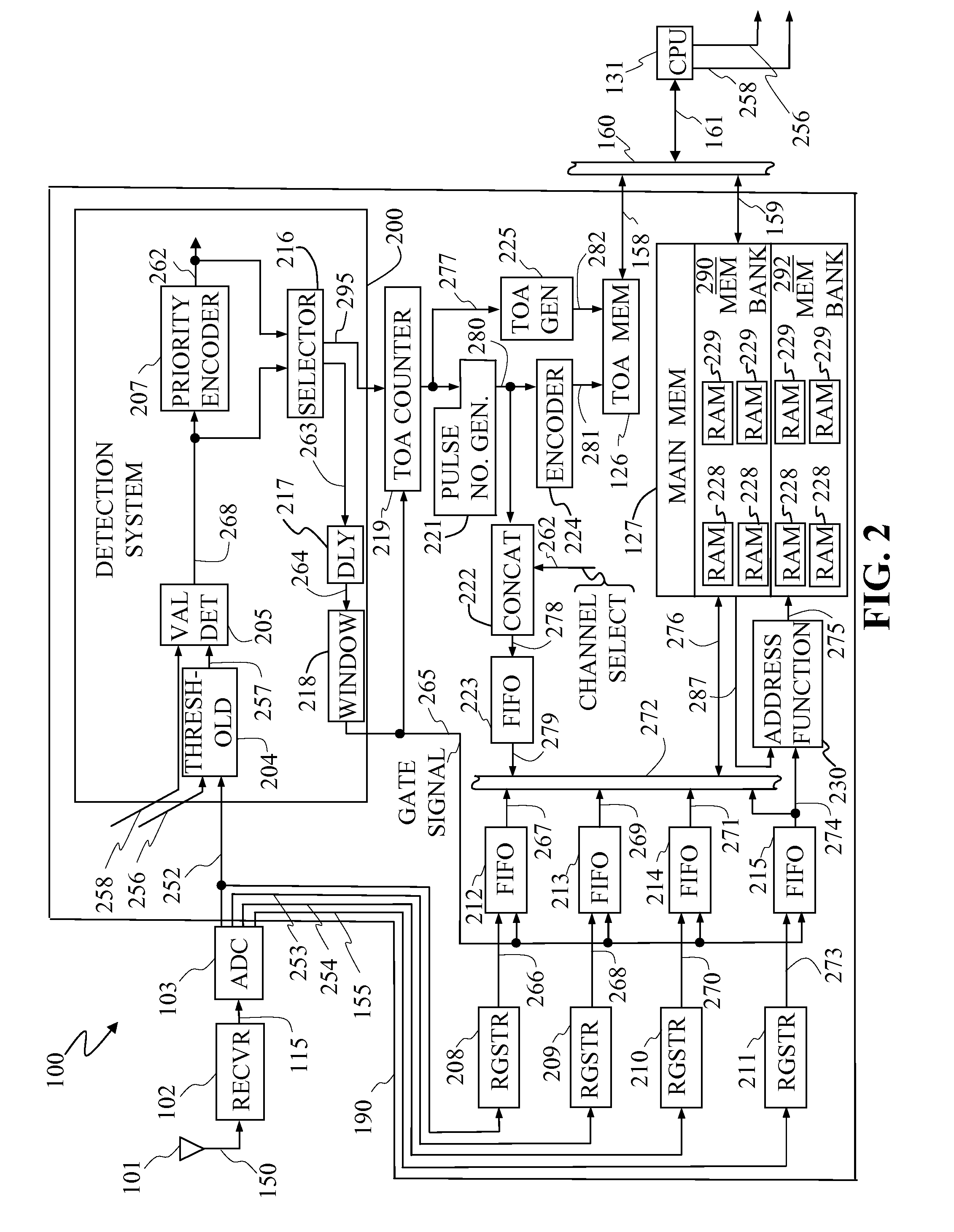
Disclosed is a real-time pulse sorting apparatus of a preprocessor in a pulsed radiation detection system. The apparatus, responsive to digital signals generated by a system receiver, uses the instantaneous frequency as the address input to store discrete data groups in main memory. Each data group, comprising the digital data corresponding to a single analog-to-digital converter sample point, includes the RF signal amplitude, inter-channel phase difference, instantaneous frequency as well as a unique pulse number generated by the pulse sorting apparatus. The present invention further includes a TOA memory for storing the time-of-arrival of each pulse at an address given by the pulse number. The main memory, organized in the form of a frequency-based histogram, together with the TOA memory, linked to the main memory by means of the pulse number pointer, sorts and records RF signal data with minimal processor control and intervention.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
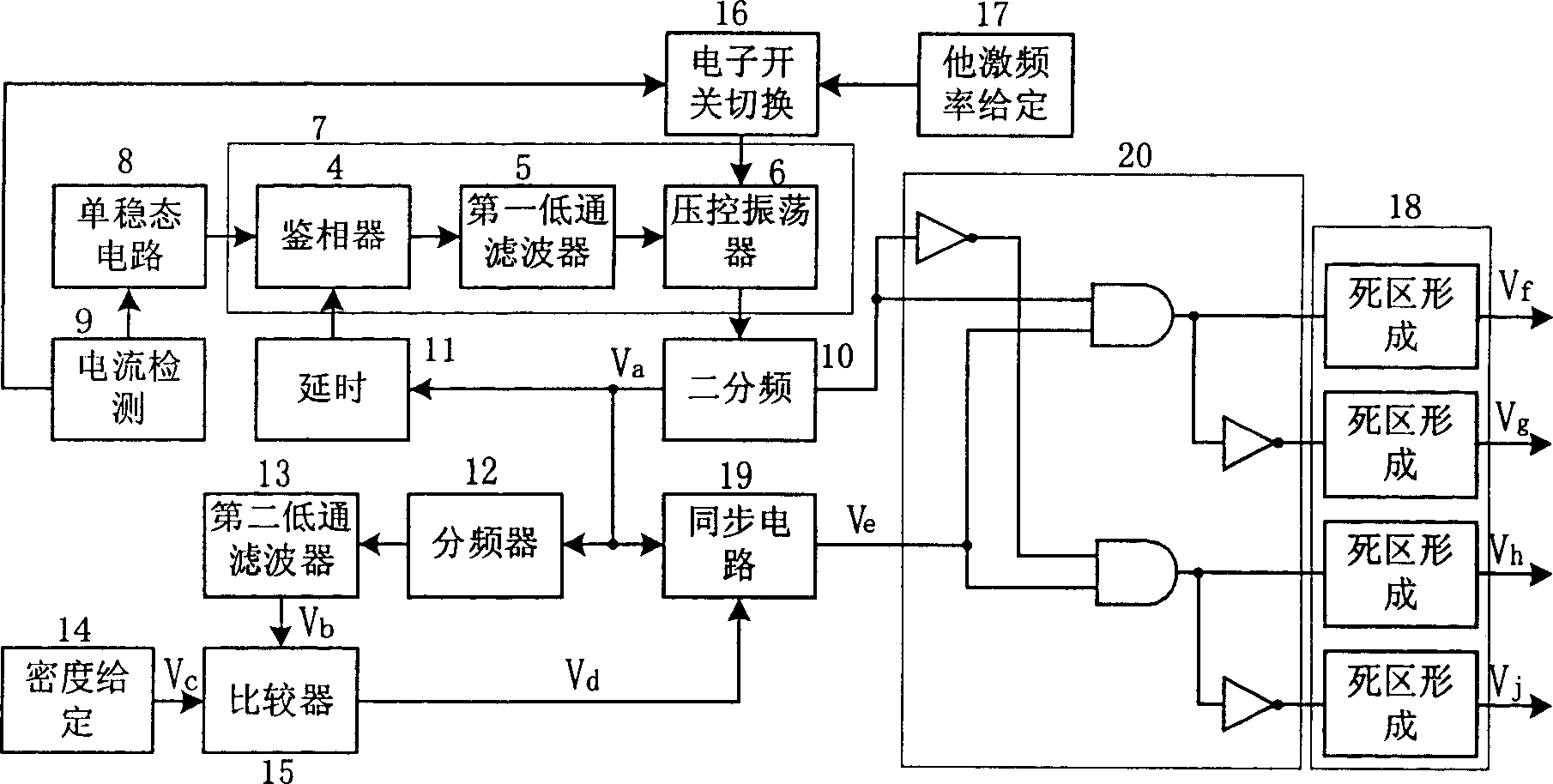
Atmospheric pressure glow discharge control method and its circuit based on pulse density modulation
Present invention discloses pulse number modulation based atmospheric pressure glow discharge control method and circuit. Control method adopts pulse density modulation to generate alternate presented square wave pulsing signal to control inversion circuit switch tube on / off in glow discharge main circuit, each working period containing fixed quantitative square wave pulse, through keeping working period unchanged and changing working period square wave pulse number to control inversion circuit feeding energy time to load, realizing atmospheric pressure glow discharge load fixed frequently constant voltage control. The present invention can realize frequency follow-up control and linear power regulation to atmospheric pressure glow discharge type nonlinear variational capacitive loading.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
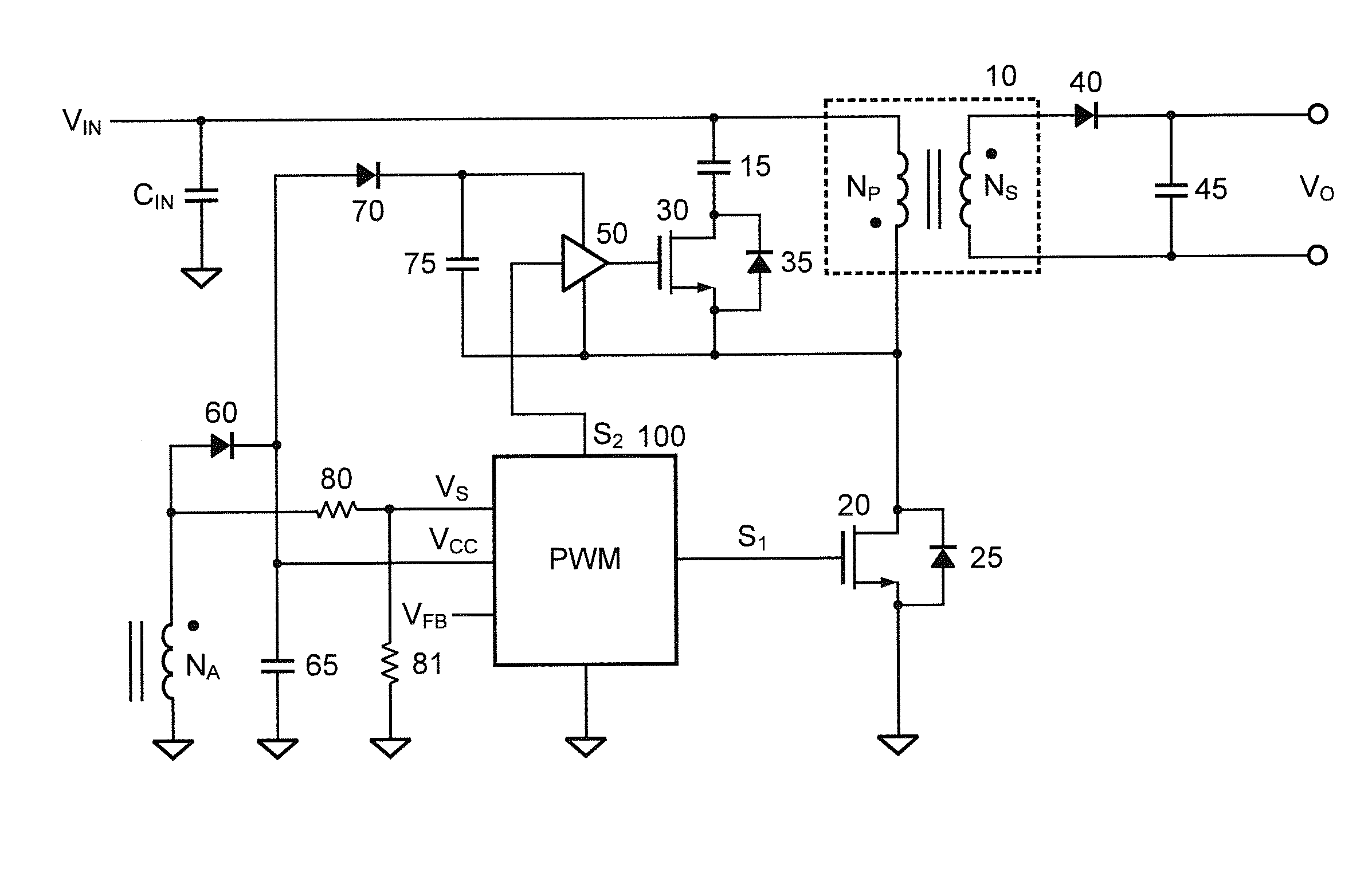
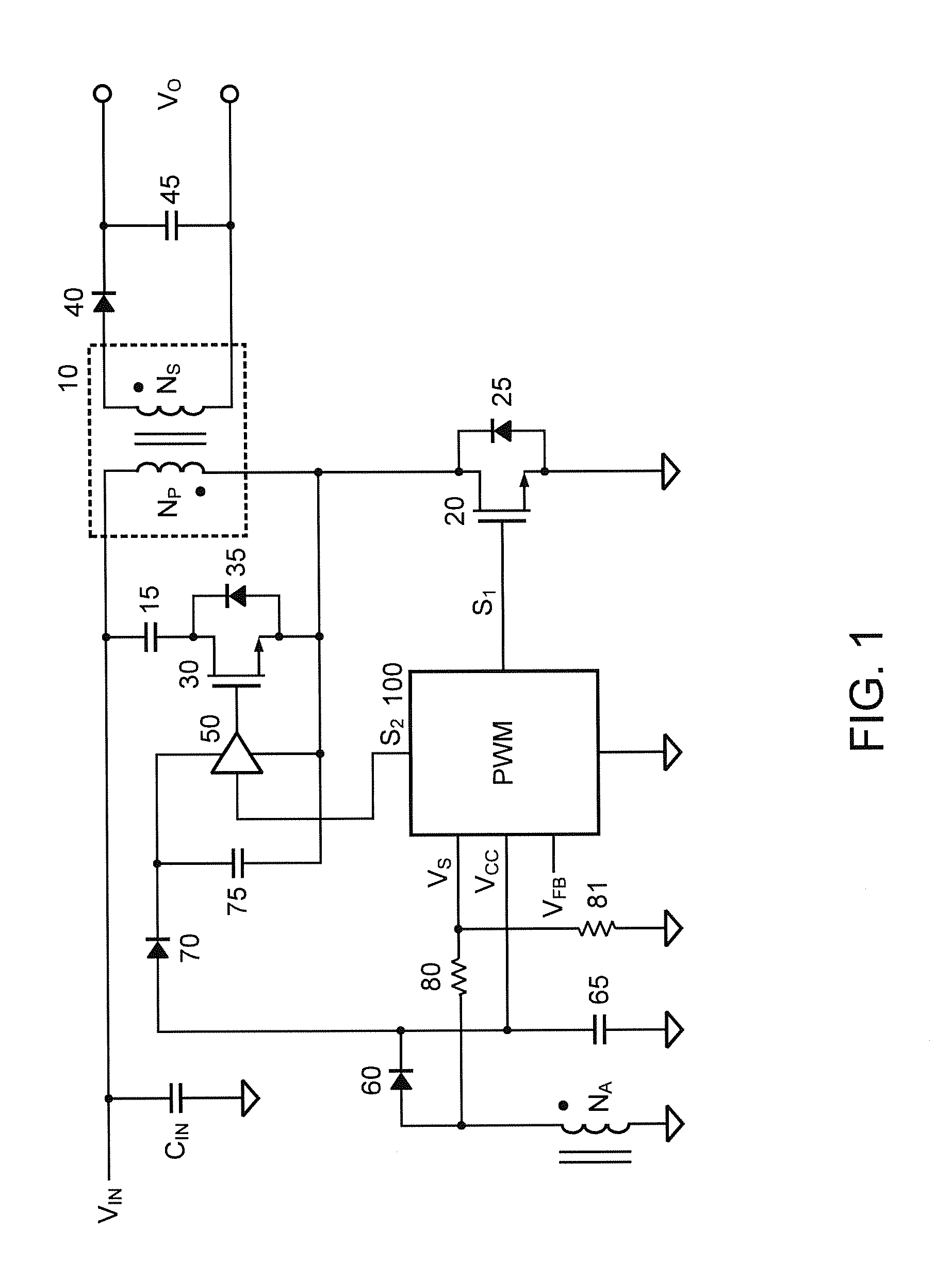
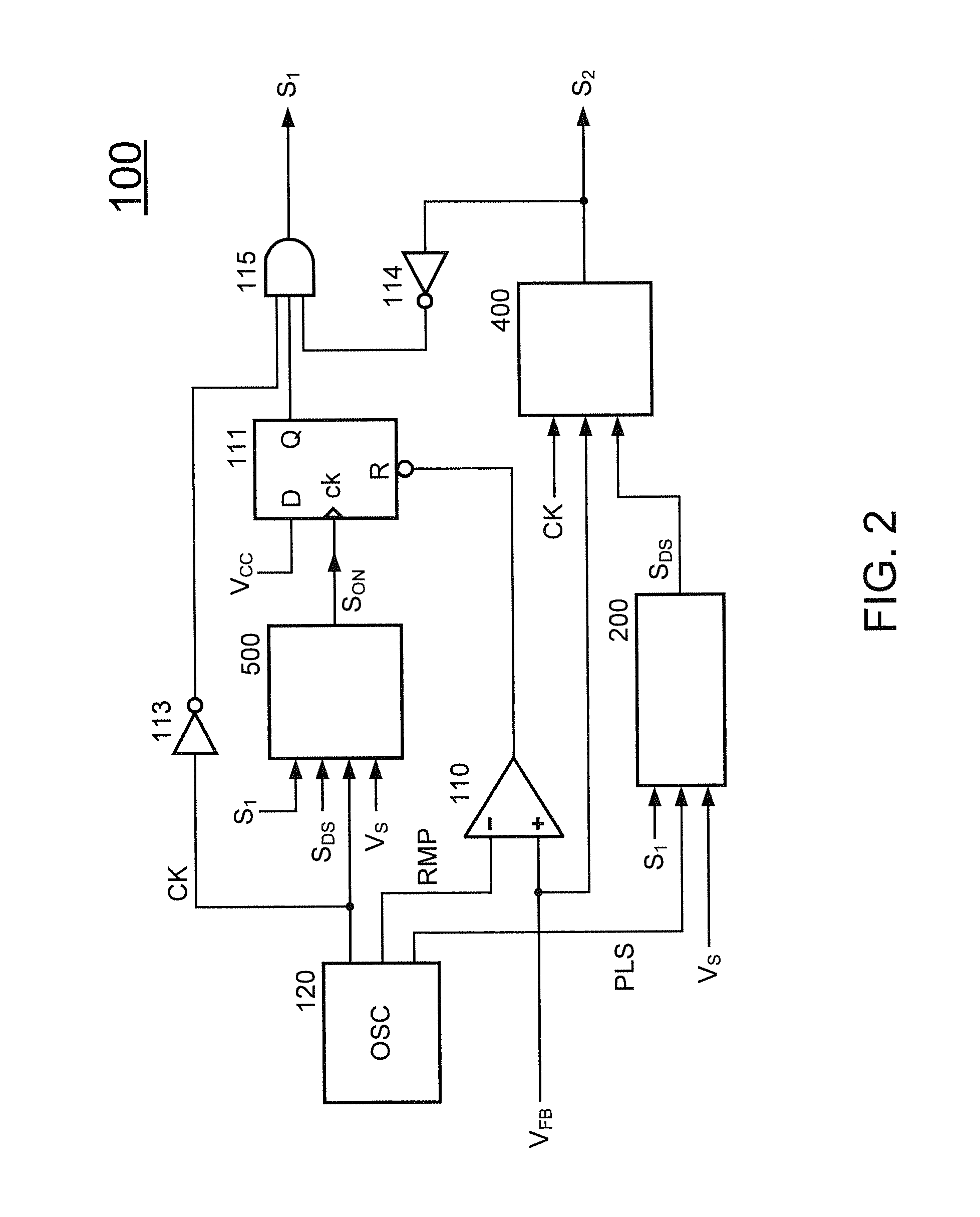
Adaptive active clamp of flyback power converter with high efficiency for heavy load and light load
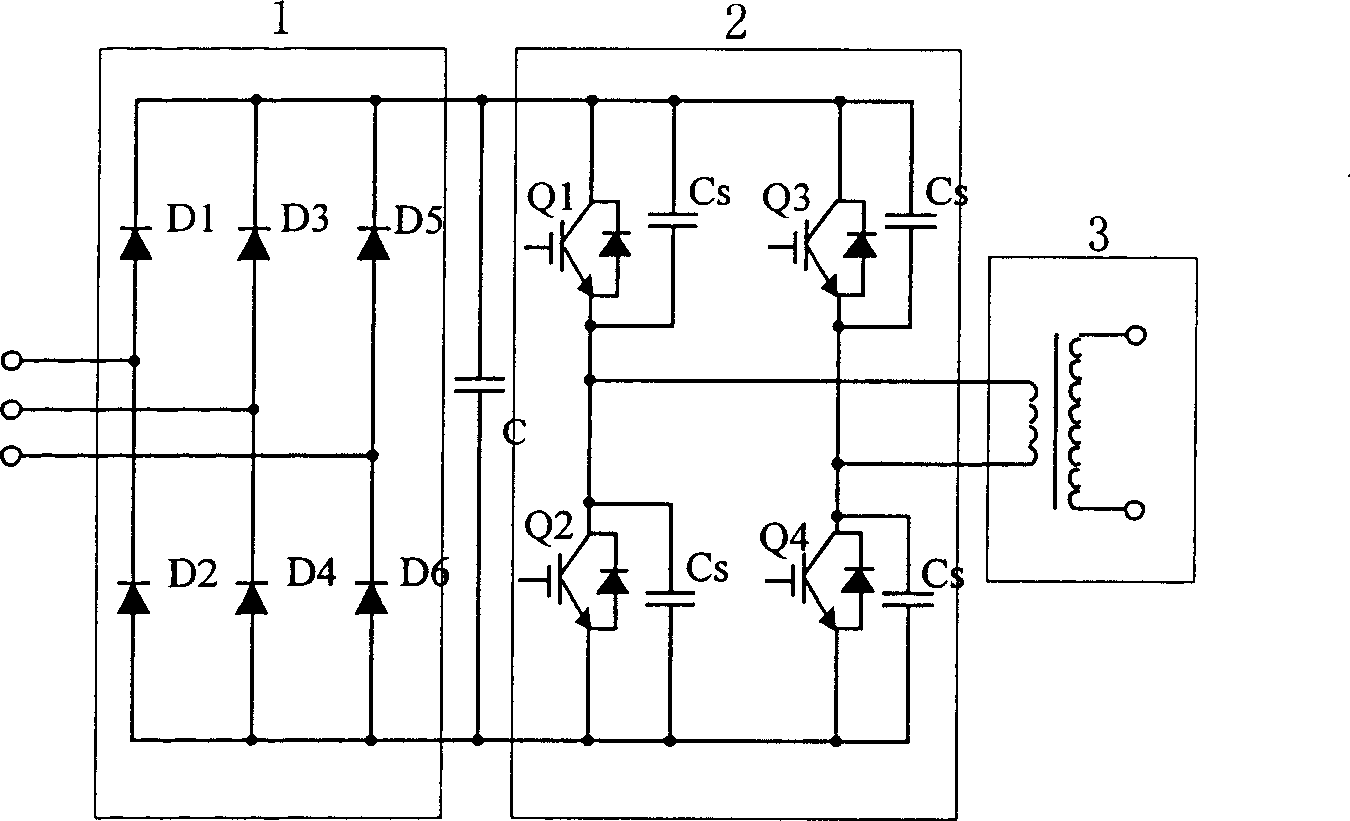
ActiveUS20140233275A1Improve efficiencyIncrease the switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionActive clampTransformer
A control circuit of a flyback power converter according to the present invention comprises a low-side transistor, an active-damper, a high-side drive circuit, and a controller. The low-side transistor is coupled to switch a transformer. The active-damper is coupled in parallel with the transformer. The high-side drive circuit is coupled to drive the active-clamper. The controller generates a switching signal and an active-clamp signal. The switching signal is coupled to drive the low-side transistor. The switching signal is generated in accordance with a feedback signal for regulating an output of the flyback power converter. The active-clamp signal is coupled to control the high-side drive circuit and the active-damper. The active-clamp signal is generated in response to a demagnetizing time of the transformer. The pulse number of the active-clamp signal is less than the pulse number of the switching signal in a light load condition.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
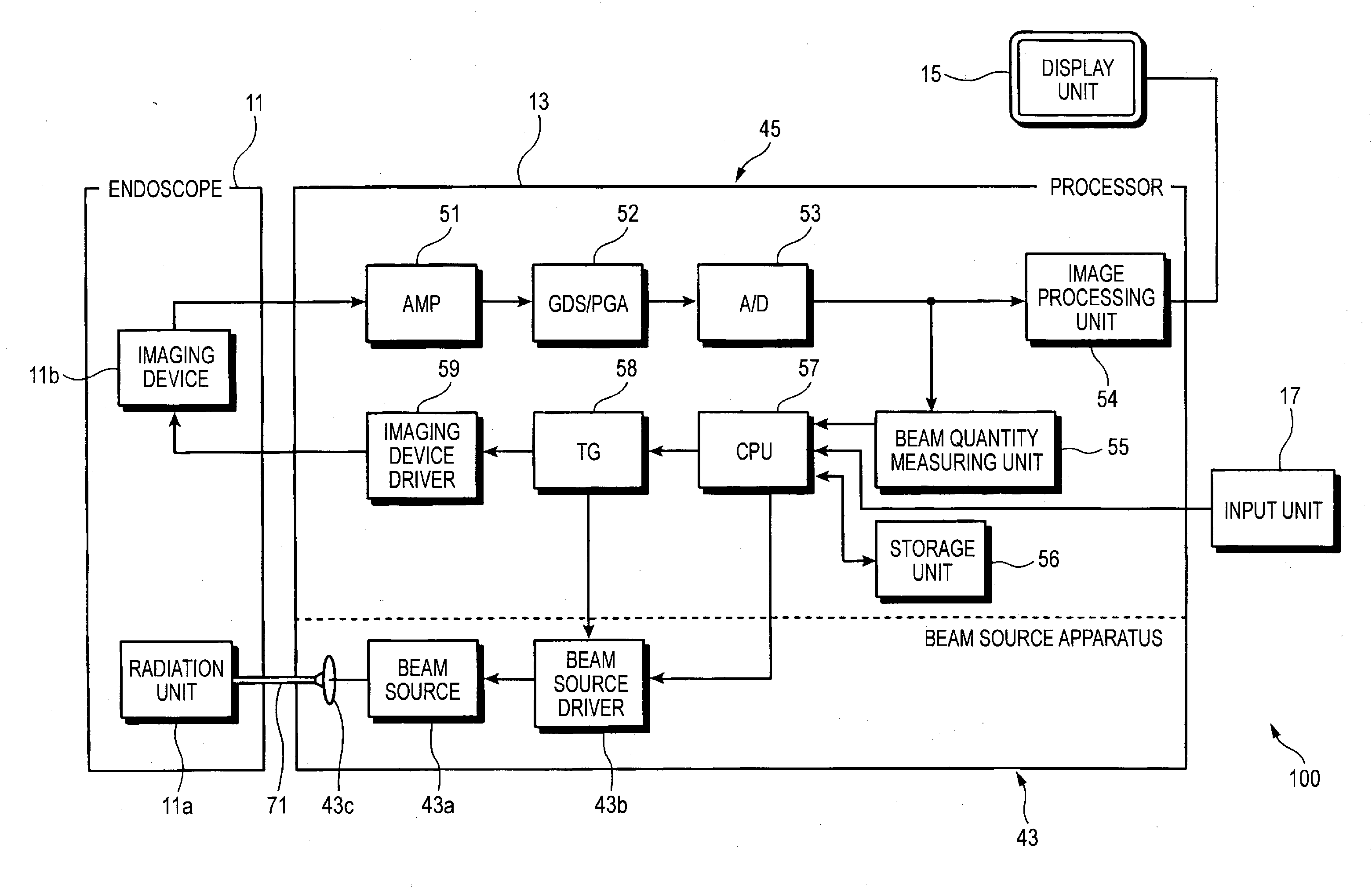
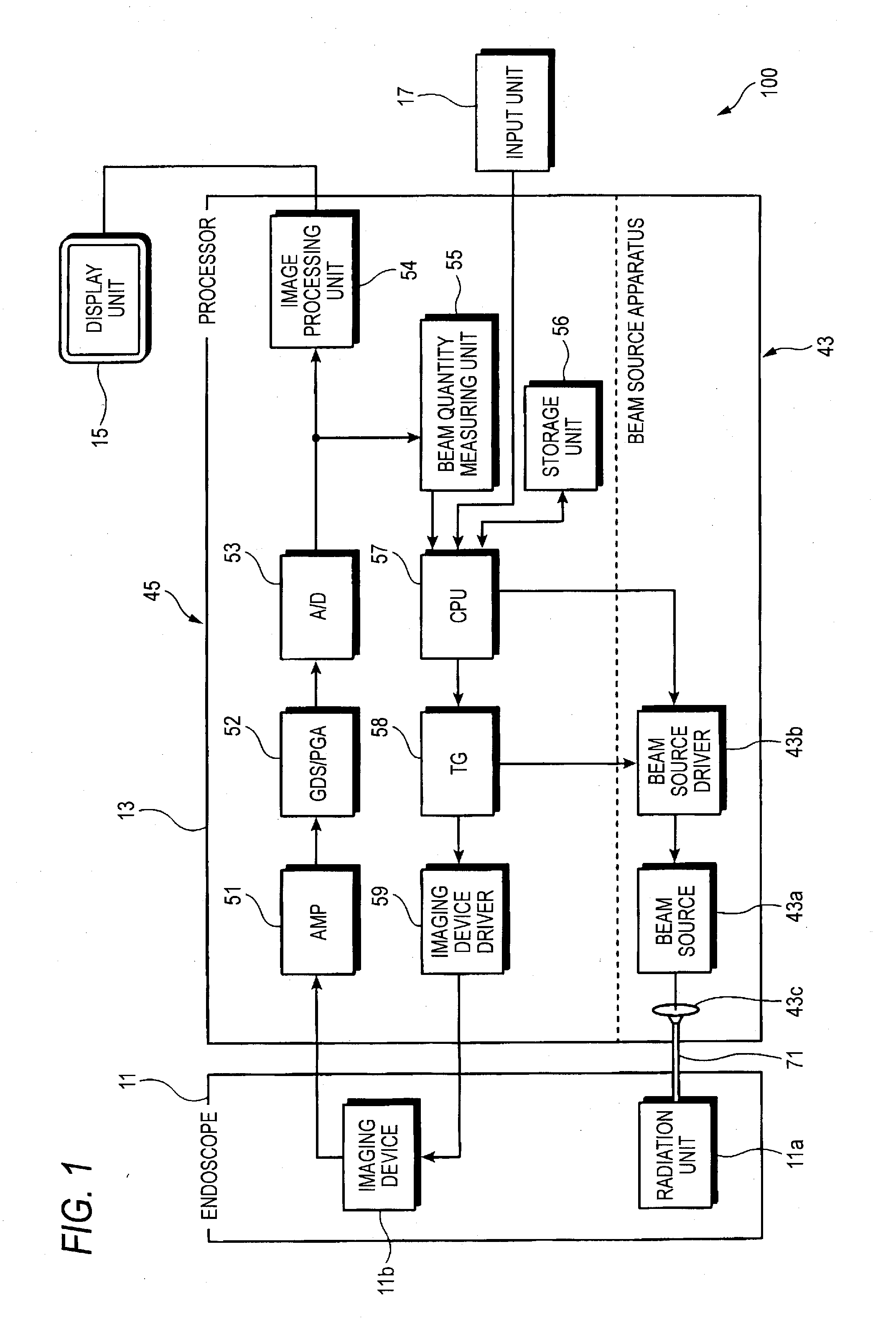
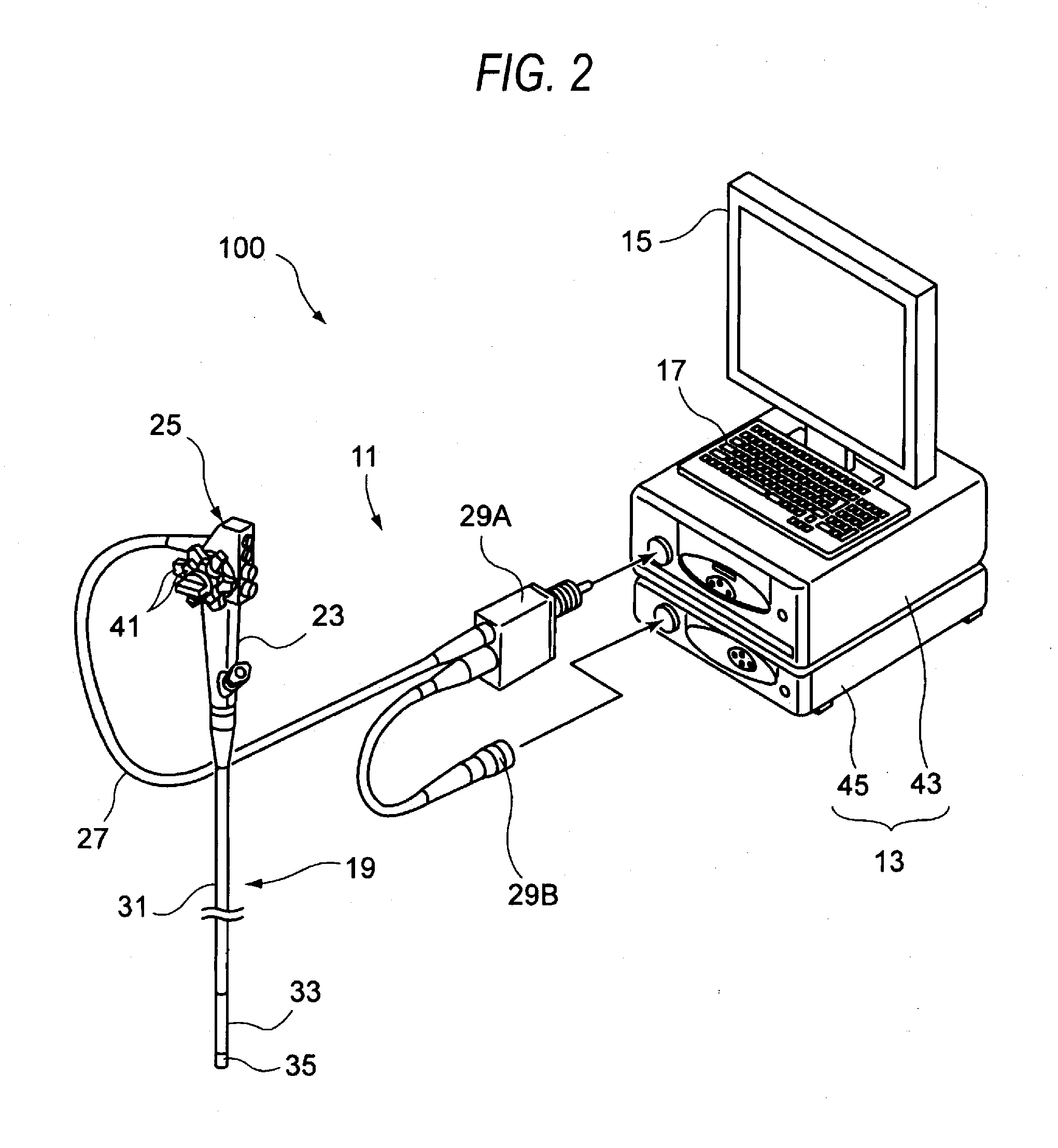
Endoscope beam source apparatus and endoscope system
The endoscope beam source apparatus includes a beam source for emitting a radiation beam to be supplied to the endoscope, and a beam source control unit for controlling the emission beam intensity of the beam source according to a beam quantity specified value input therein. The beam source control unit specifies the emission beam intensity corresponding to the beam quantity specified value based on at least three of control amounts. The control amounts include a control amount corresponding to pulse number modulation (PNM) control for changing lighting time of the beam source, a control amount corresponding to pulse width modulation (PWM) control for changing a plus width which indicates the lighting or lighting-out time within a control cycle, a control amount corresponding to pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) control for changing the lighting intensity, and a control amount corresponding to pulse density modulation (PDM) control for changing a lighting interval.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for calculating average fuel consumption, remaining fuel and driving range
ActiveCN101738233AAccurate Average Fuel ConsumptionReduce consumptionRelative volume flow measurementsSprayerFuel tank
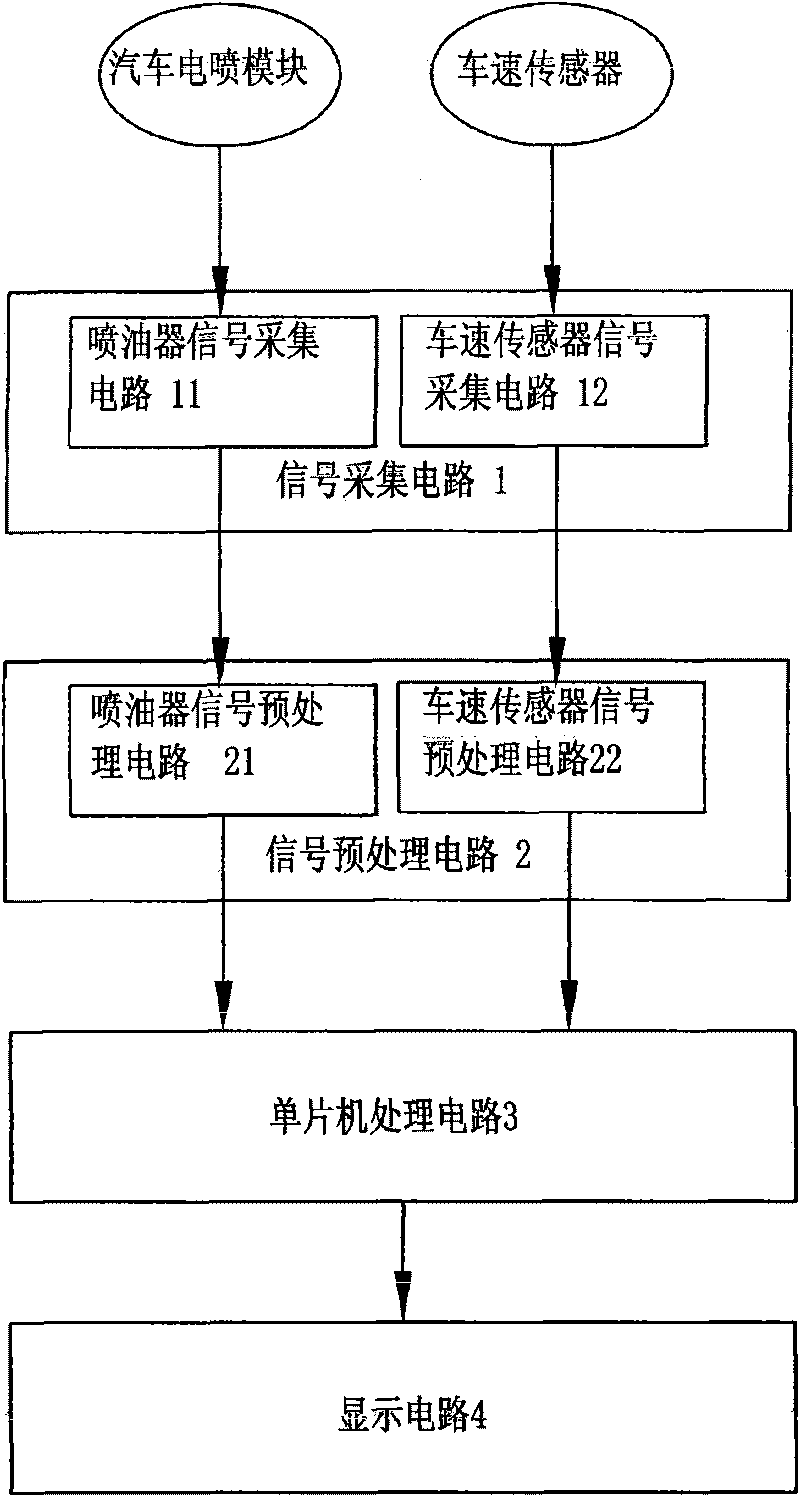
The invention mainly discloses a method and a device for calculating average fuel consumption, remaining fuel and driving range. The average fuel consumption S can be worked out according to both the acquired drop number N of the fuel sprayed by a fuel spray nozzle, pulse number P of a vehicle speed signal and pulse number ppk of per kilometer vehicle speed signal and the volume SN represented by each drop of fuel. The remaining fuel deltaS can be worked out by subtracting the total amount NXSN of consumed fuel sprayed by a fuel sprayer from the total amount S of oil in an oil tank after ignition. The driving range can be worked out by dividing the remaining fuel deltaS by the average fuel consumption S. The method can help a driver to obtain accurate information on the average fuel consumption, remaining fuel and driving range of an automobile, get an idea of the running condition of the automobile and the consumption condition of the fuel and select a driving mode consuming the lest fuel, thereby saving fuel consumption and protecting environment.
Owner:延锋伟世通怡东汽车仪表有限公司
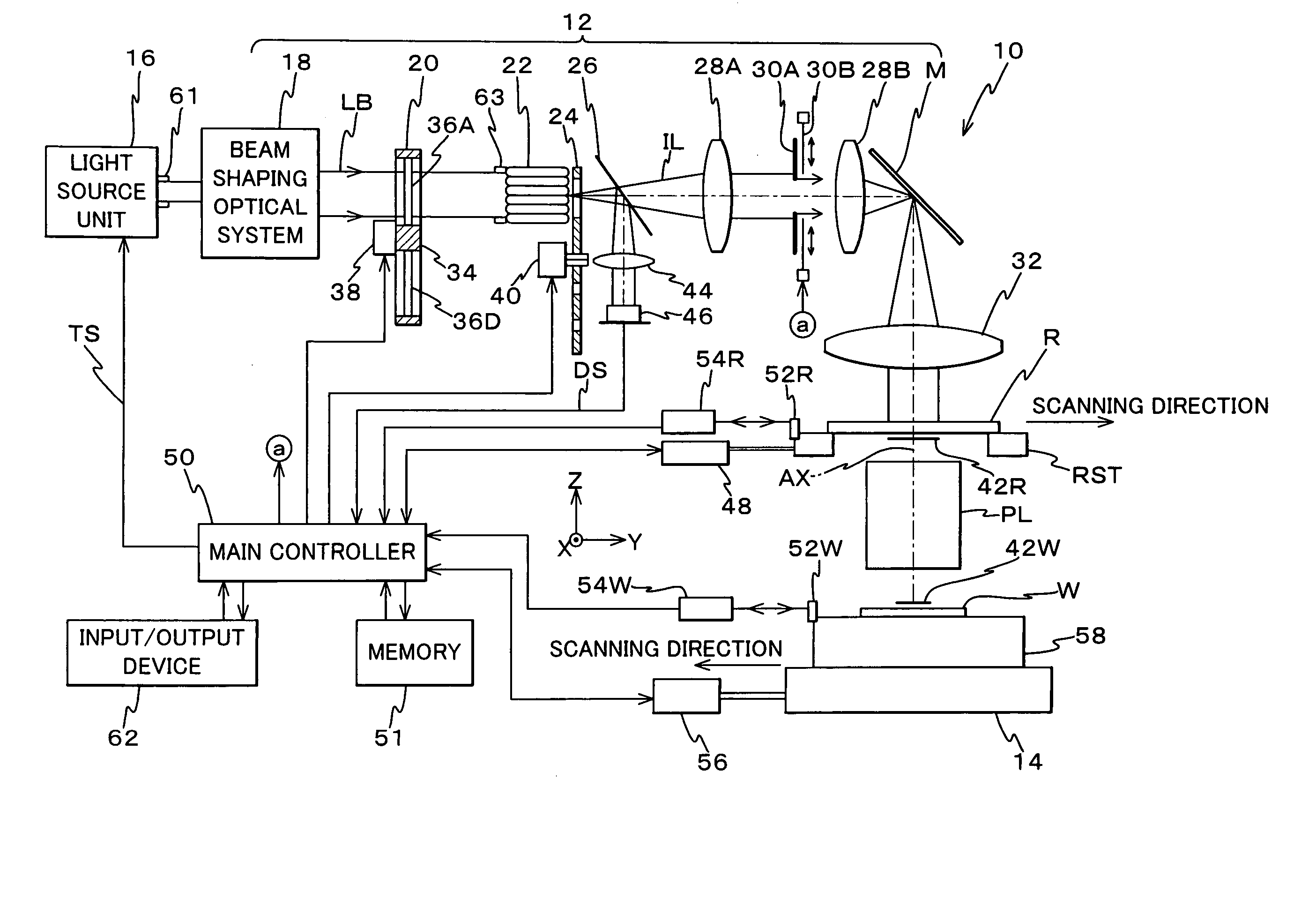
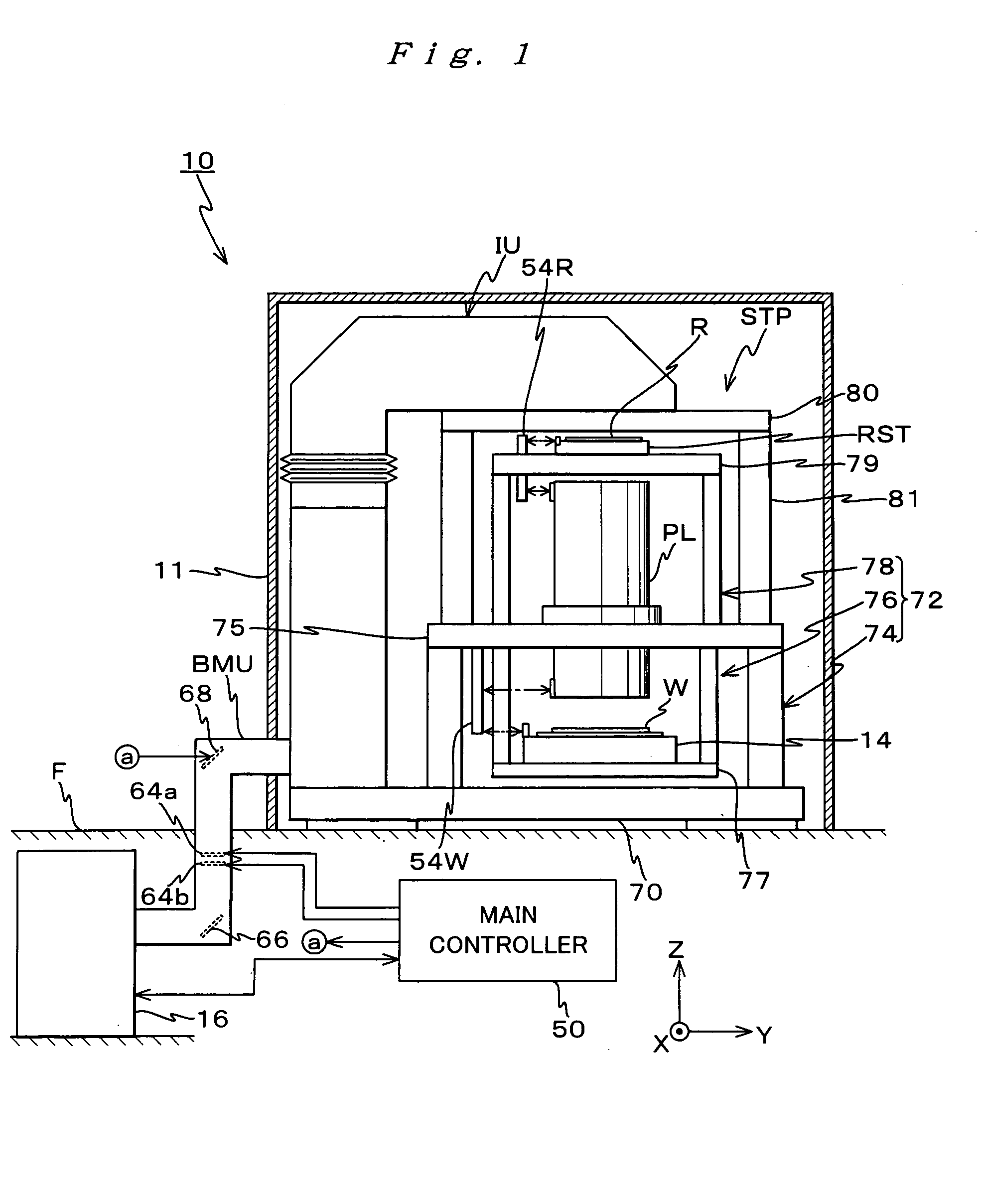
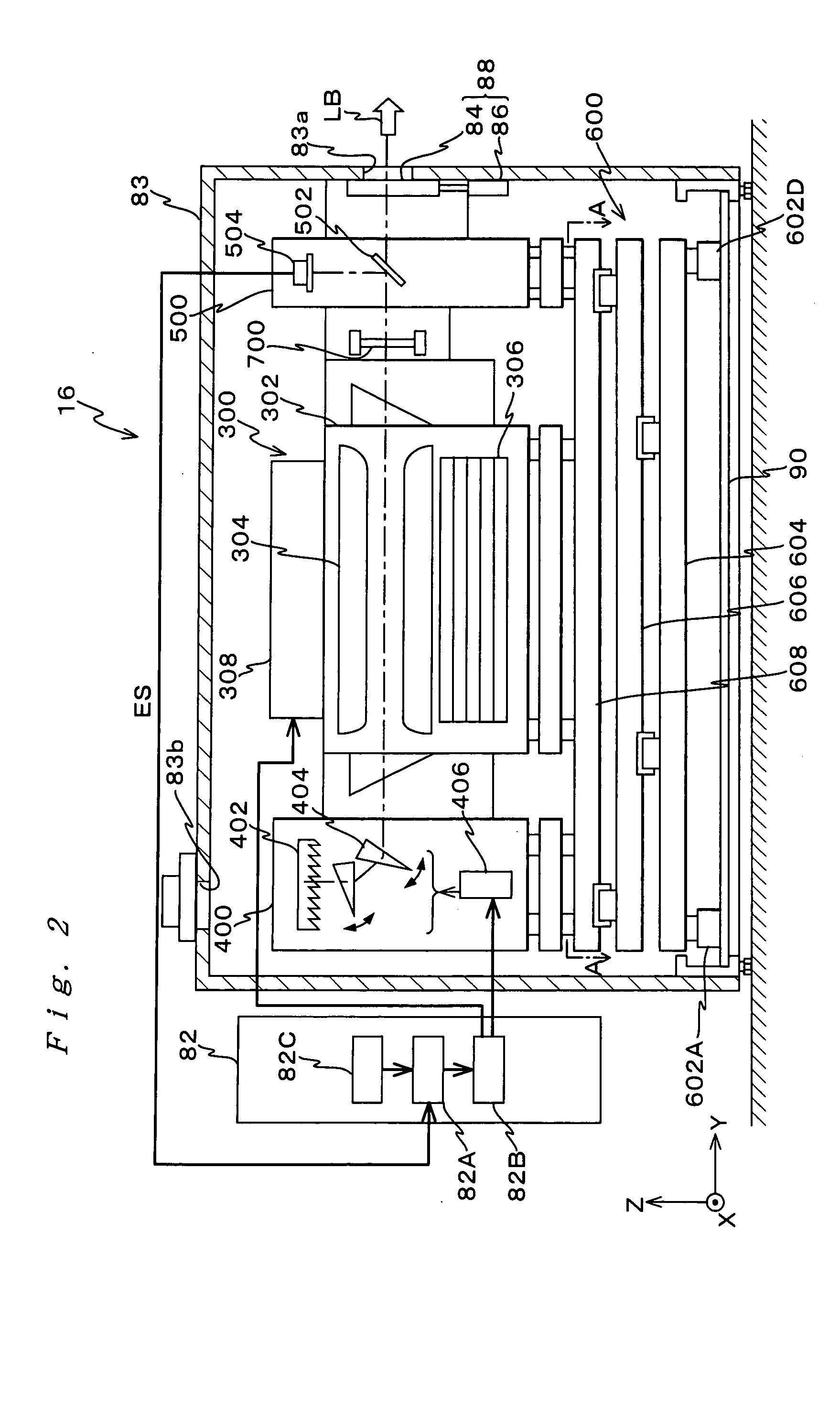
Exposure method and exposure apparatus, light source unit and adjustment method of light source unit, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050094122A1Small workloadImprove Exposure AccuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPulse numberPulse energy
When scanning exposure is performed by illuminating an illumination area on a mask with a pulse light from a pulse light source, synchronously moving the mask and a photosensitive object, and transferring a pattern of the mask onto the photosensitive object, a main controller performs dose control on a high sensitivity range where scanning velocity of the mask and the photosensitive object is set at a maximum so as to maintain an exposure pulse number at a minimum exposure pulse number. A pulse light source, which pulse energy is variable within a predetermined range, maintains the exposure pulse number at the minimum exposure pulse number within the variable range. The pulse light source comprises a housing in which an outgoing opening that emits a light is formed, a plurality of units housed in the housing, and a drive unit that moves the plurality of units, partially or in total inside the housing.
Owner:NIKON CORP
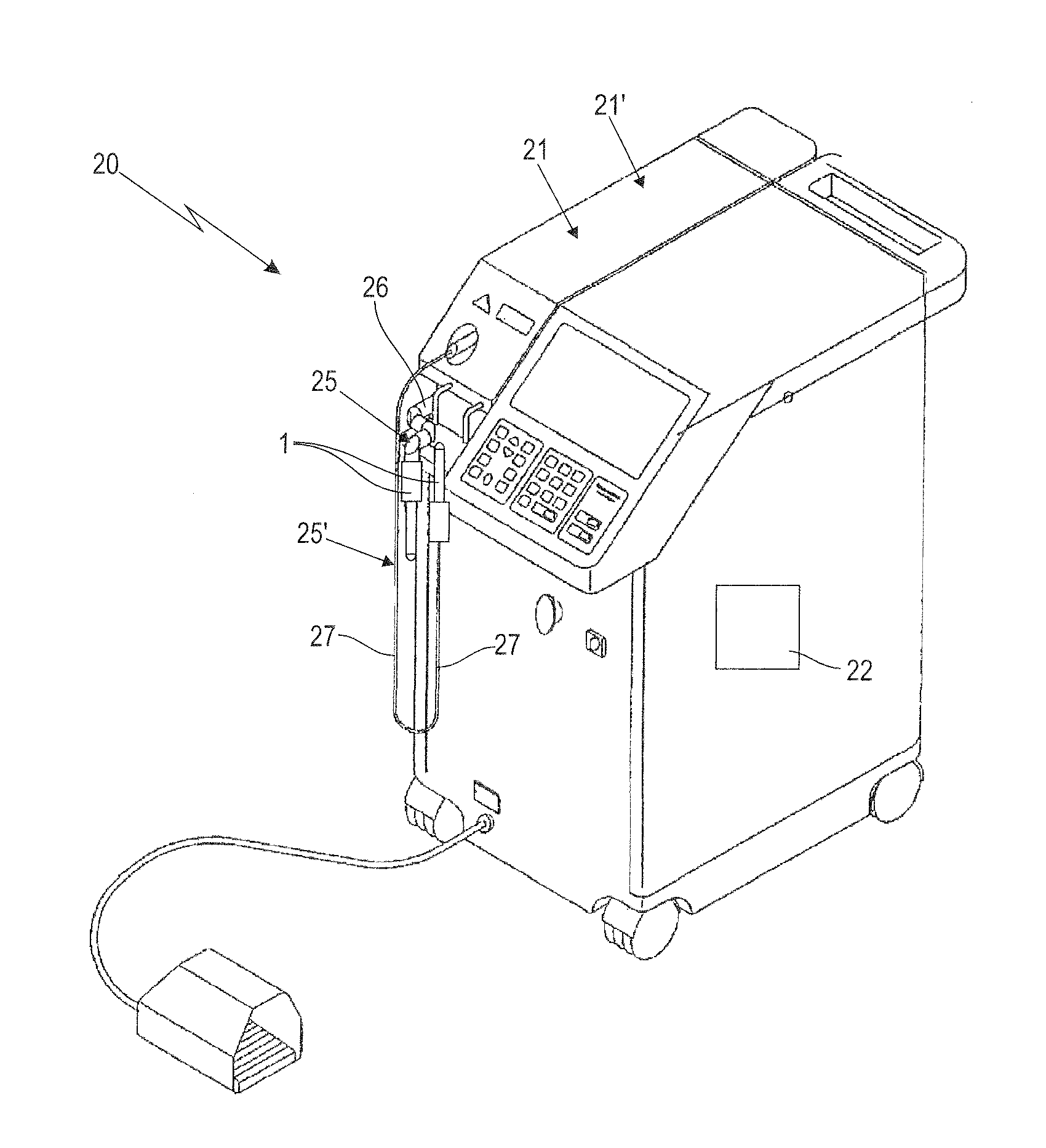
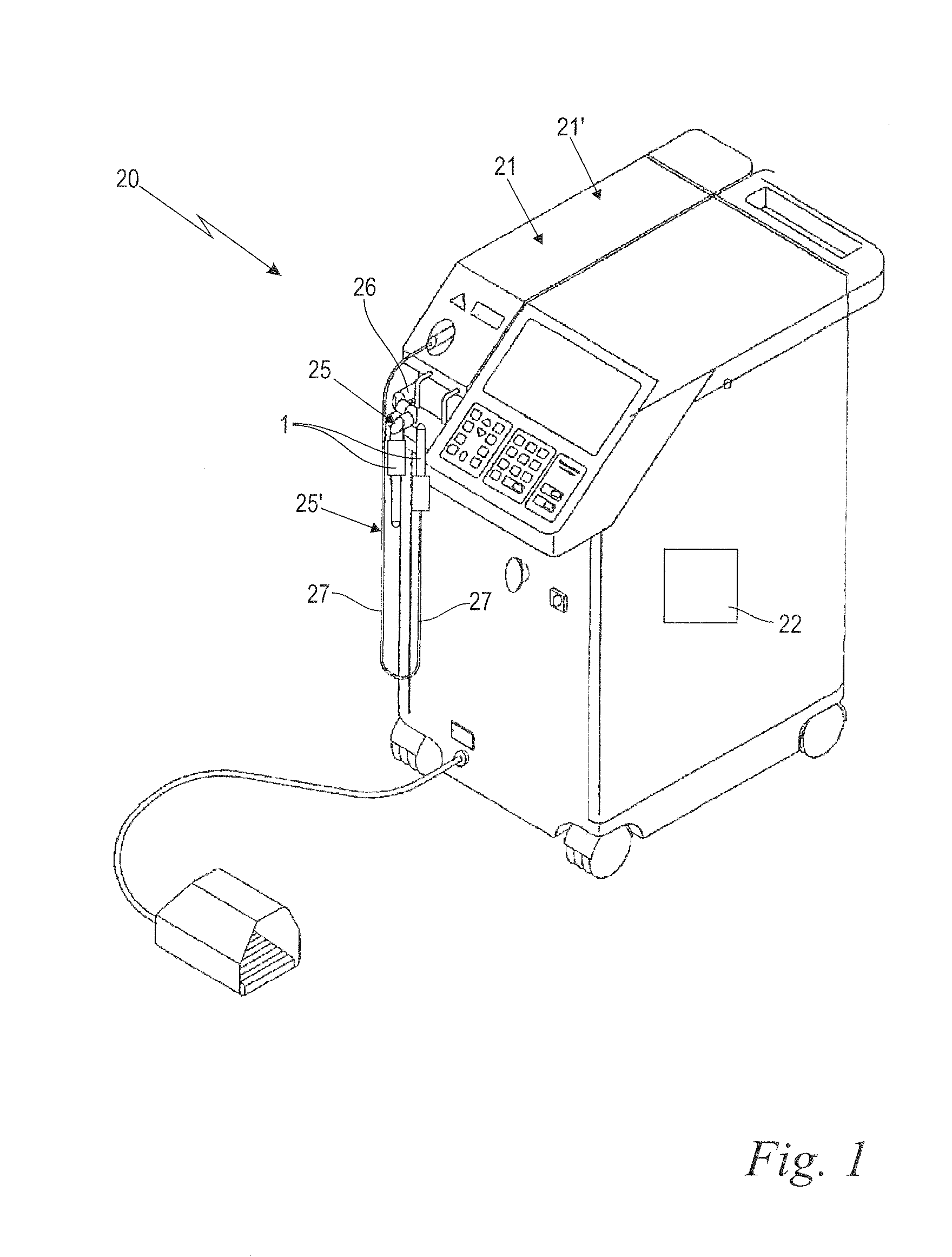
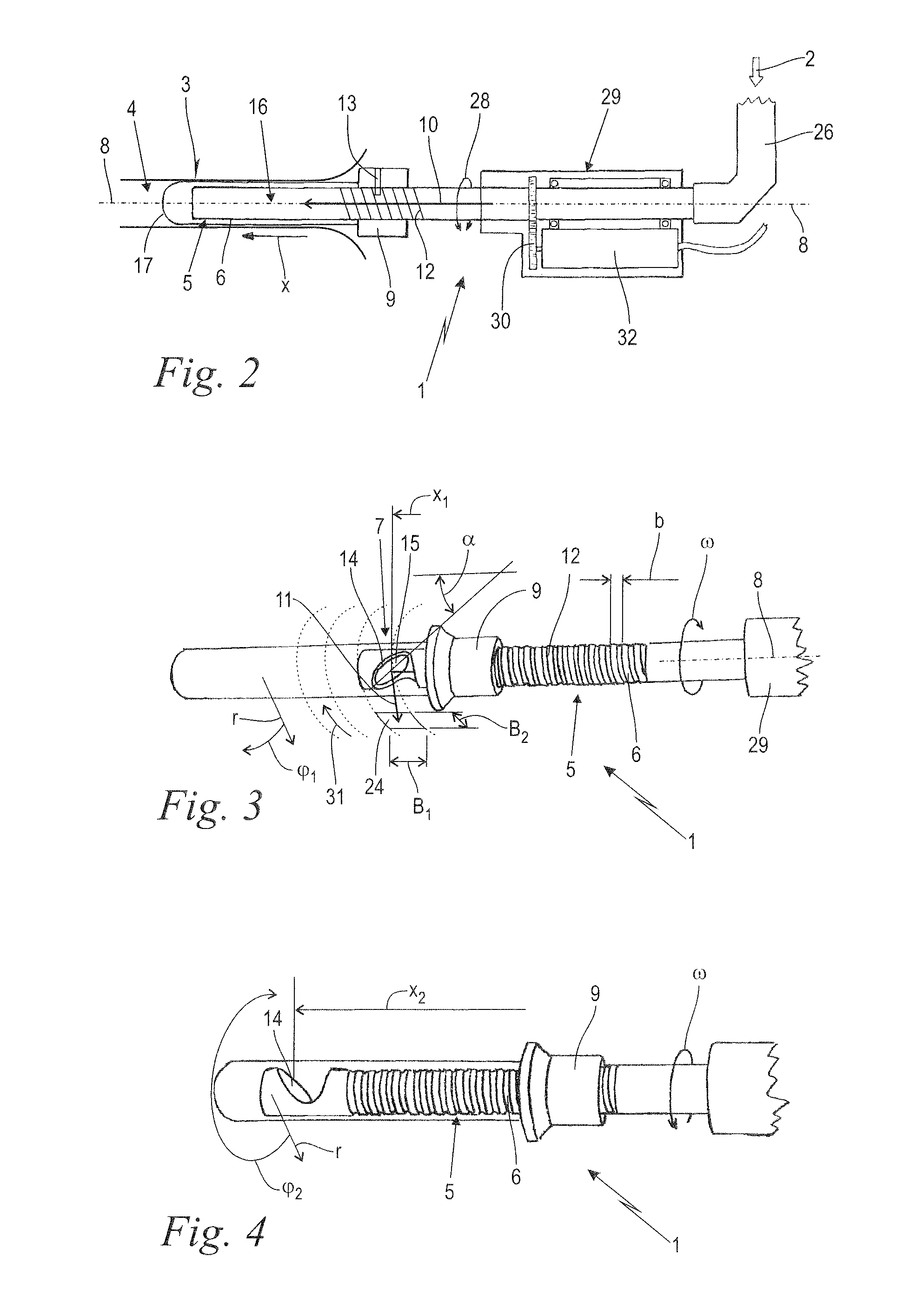
Laser system and laser treatment head therefor
ActiveUS20150367142A1Simple and reliable meanAvoiding and minimizing ablationSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyPulse numberIrradiation
A laser treatment head guides a laser beam to a target area within a body cavity and includes a laser output element having a deflection element. The laser output element with deflection element is rotatable relative to a guide element about an axis. First and second thread elements mutually engage to cause the deflection element to perform a combined axial and rotational movement relative to the guide element. A control unit and the laser treatment head are configured such that the target area is irradiated by individual pulses (p) in a helical pattern of irradiation spots over a section of the circumference of the body cavity. The control unit is further configured such that reference locations (X) on the target area are irradiated by an individual pulse number (N) of subsequent pulses (p), thereby heating the mucosa tissue within the target area to a predetermined temperature.
Owner:FOTONA D O O
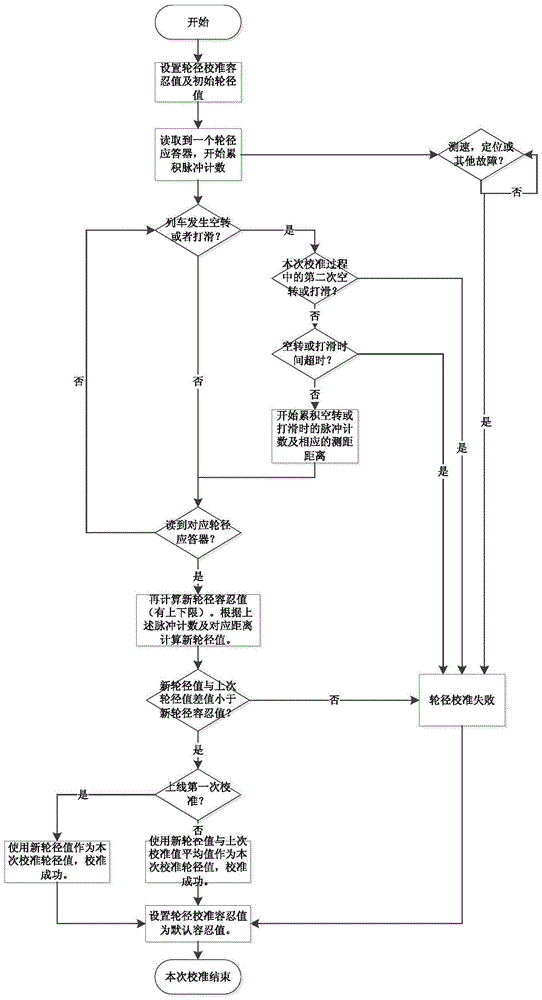
Rail transit train wheel diameter calibrating method
ActiveCN105667542AWide coverageWide rangeVehicle route interaction devicesPulse numberError tolerance
The invention discloses a rail transit train wheel diameter calibrating method. The method comprises the steps that if the rail transit train wheel diameter calibrating conditions are met, the increase amplitude of rail transit train wheel diameter error tolerance values during slipping and idling are obtained correspondingly; the actual running distance of a train of which train wheels slip and the corresponding number of accumulated pulses thereof are obtained; the number of actual running accumulated pulses of the train of which the train wheels idle and the corresponding actual distance of a transponder in pair are obtained; a train wheel diameter value is calculated according to each cycle of the fixed pulse number of a speed sensor and the actual distance of the transponder, if an absolute value of the difference between the train wheel diameter value obtained through calculation of the round and a calibrated train wheel diameter value of the last round is smaller than the wheel diameter error tolerance value, the wheel diameter calibrating succeeds, and otherwise the wheel diameter calibrating fails; if calibrating succeeds, the train wheel diameter value is the arithmetic average of the train wheel diameter value obtained through calculation of the round and the calibrated train wheel diameter value of the last round; and if calibrating fails, the steps are repeated to calibrate the wheel diameter again.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUXIN INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com