Patents
Literature
2980results about "Vehicle route interaction devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of hydrophilizing materials
InactiveUS6863933B2Easy to controlGood removal effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsRadiation applicationsPolymer scienceNanoparticle
Coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture comprising a nanoparticle system employing same to impart surface modifying benefits for all types of soft surfaces, and in some cases, hard surfaces, are disclosed. In some embodiments, dispersement of nanoparticles in a suitable carrier medium allows for the creation of coating compositions, methods and articles of manufacture that create multi-use benefits to the modified surfaces. These surface modifications can produce long lasting or semi-permanent multi-use benefits that, in some embodiments, may include at least one of the following improved surface properties: cleaning, wettability, liquid strike-through, comfort, stain resistance, soil removal, malodor control, modification of surface friction, reduced damage to abrasion and color enhancement, relative to the surfaces unmodified with such nanoparticle systems.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Sequential method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6428859B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSequential methodHigh density
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods of forming a coating for a prosthesis
InactiveUS6503556B2Increase the amount addedIncrease the number ofRadiation applicationsGlovesProsthesisImplanted device
Methods of forming a coating onto an implantable device or endoluminal prosthesis, such as a stent, are provided. The coating may be used for the delivery of an active ingredient. The coating may have a selected pattern of interstices for allowing a fluid to seep through the coating in the direction of the pattern created.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Multilayered material and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20120107607A1Reduce the impactIncrease production capacityRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesWater vaporPolysilazane
A multilayered material is provided which includes a substrate and a silicon-containing film formed on the substrate, wherein the silicon-containing film has a nitrogen-rich area including silicon atoms and nitrogen atoms, or silicon atoms, nitrogen atoms, and an oxygen atoms and the nitrogen-rich area is formed by irradiating a polysilazane film formed on the substrate with an energy beam in an atmosphere not substantially including oxygen or water vapor and denaturing at least a part of the polysilazane film. A method of producing the multilayered material is also provided.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Sequential UV induced chemical vapor deposition
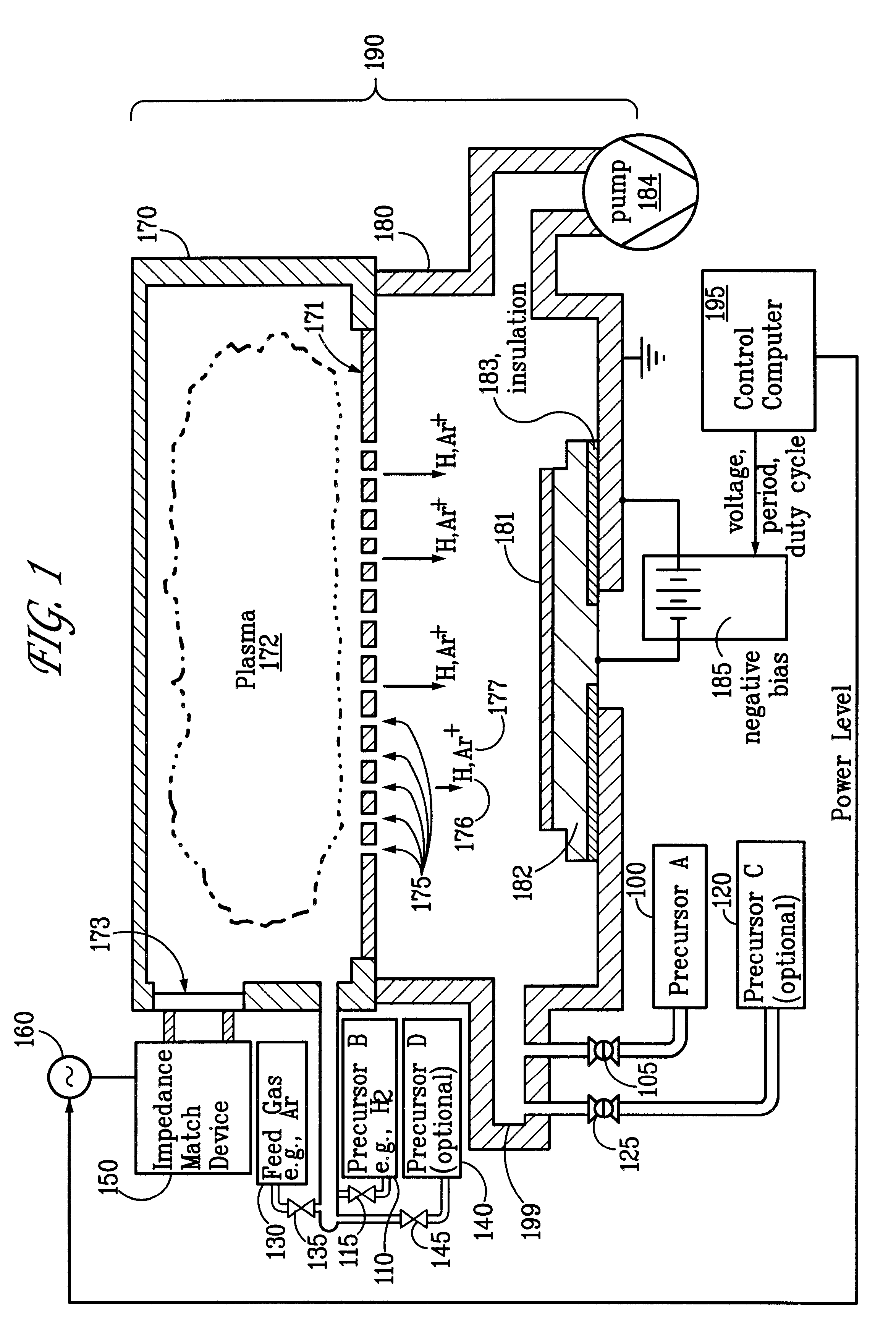
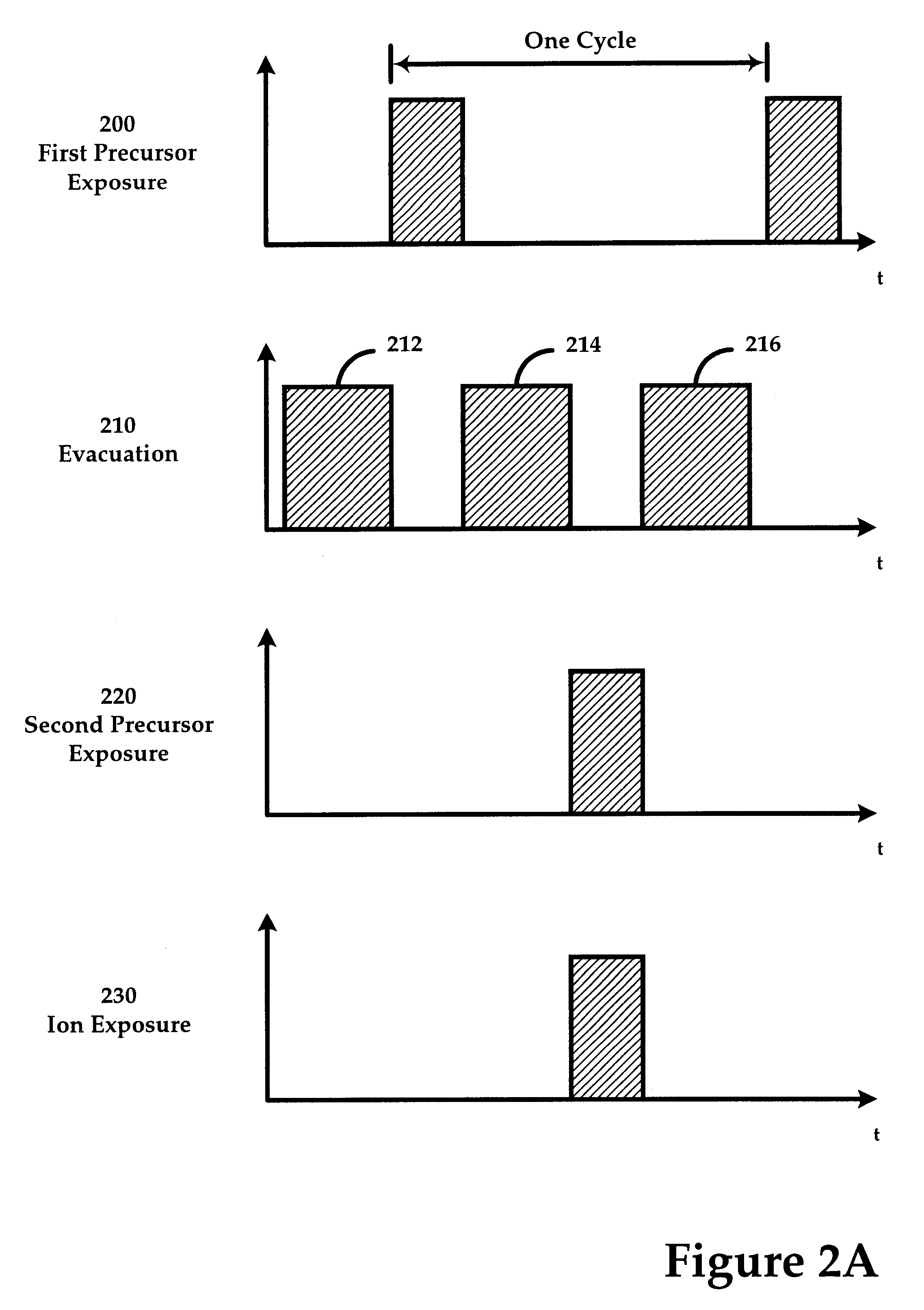
Ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes are disclosed where an ion flux, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or an electron flux, respectively, is used to induce the chemical reaction in the process. The process for depositing a thin film on a substrate includes introducing a flow of a first reactant gas in vapor phase into a process chamber where the gas forms an adsorbed saturated layer on the substrate and exposing the substrate to a flux of ions, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or a flux of electrons for inducing a chemical reaction of the adsorbed layer of the first reactant gas to form the thin film. A second reactant gas can be used to form a compound thin film. The ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential CVD process of the present invention can be repeated to form a thin film of the desired thickness.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
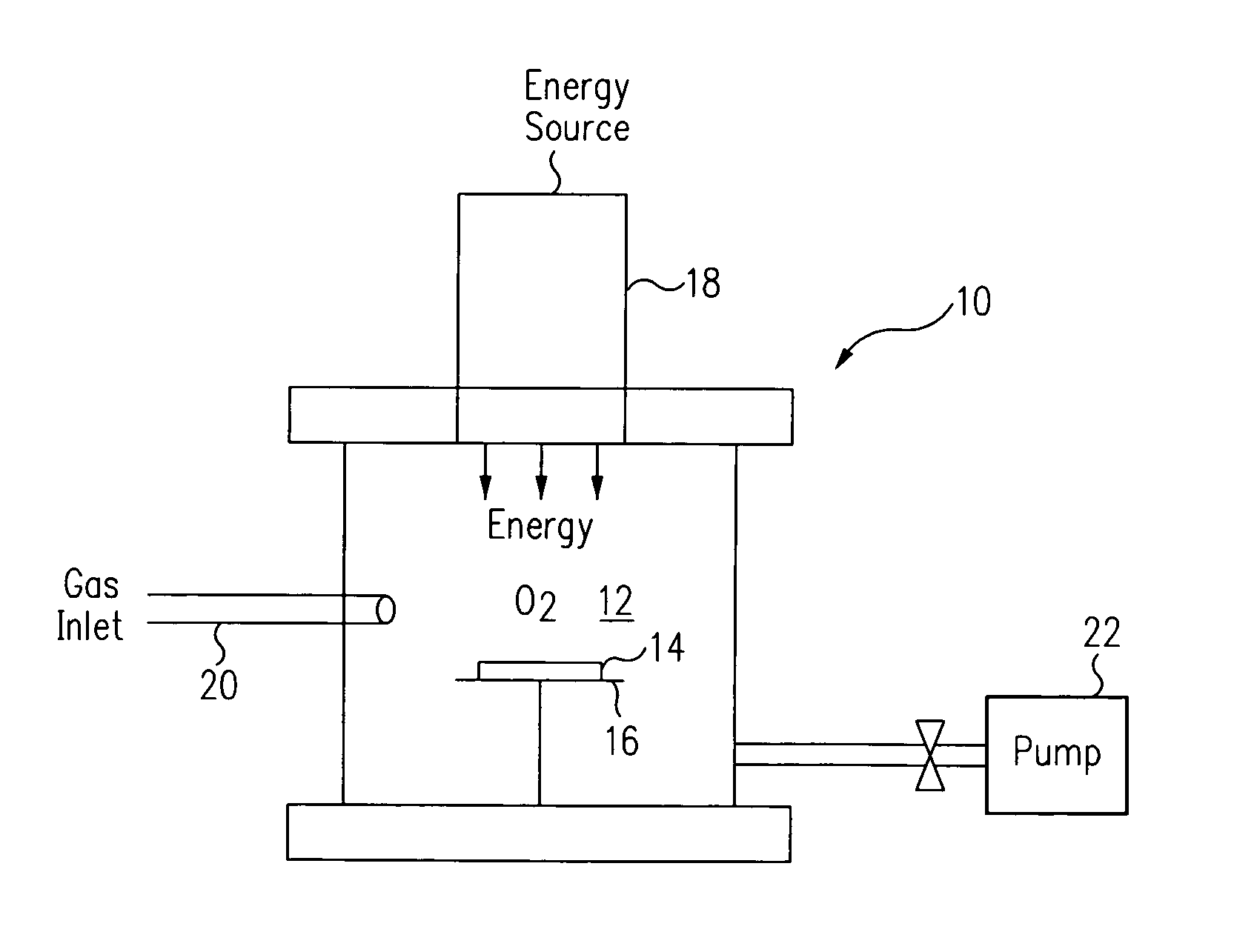
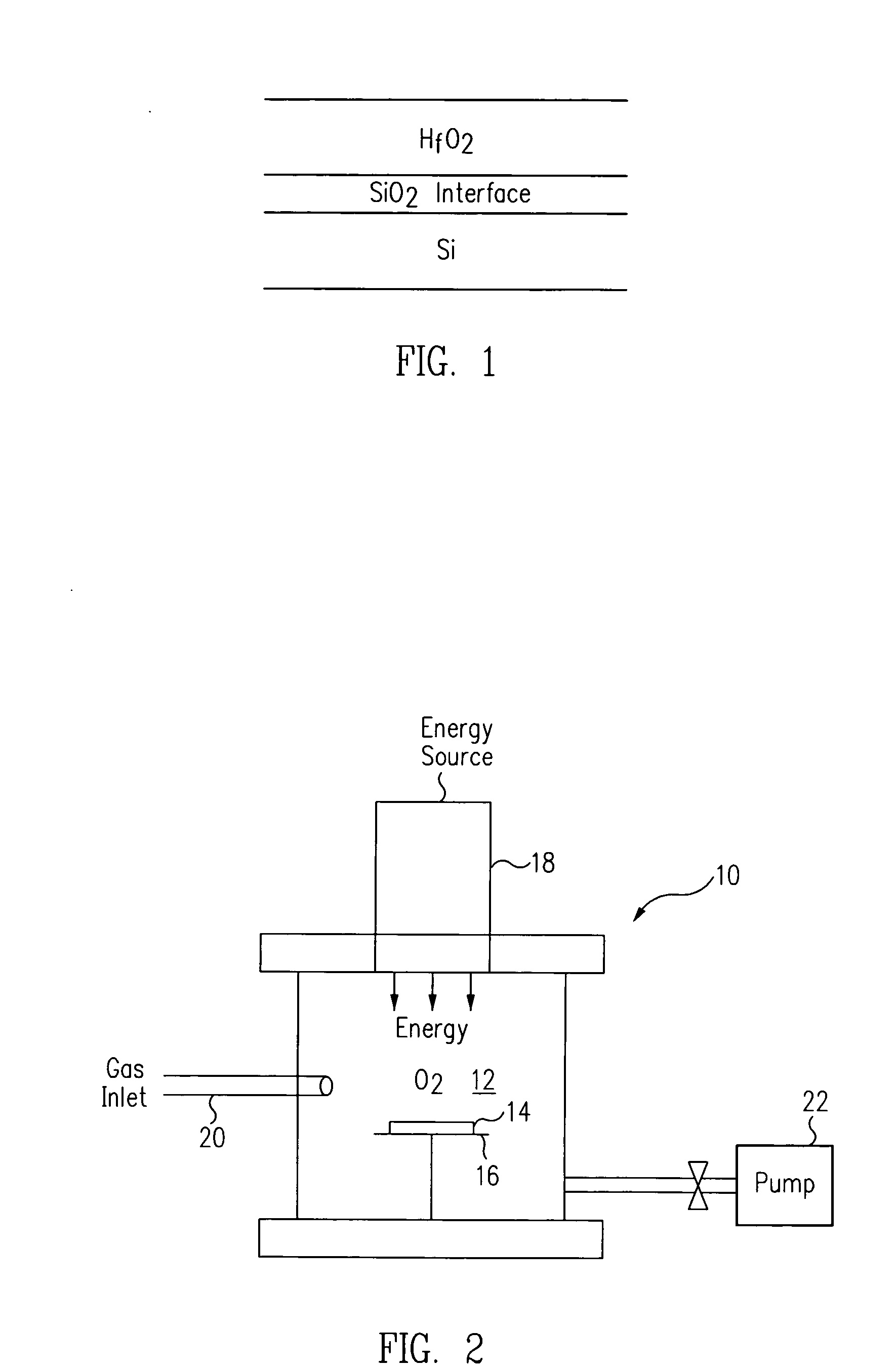
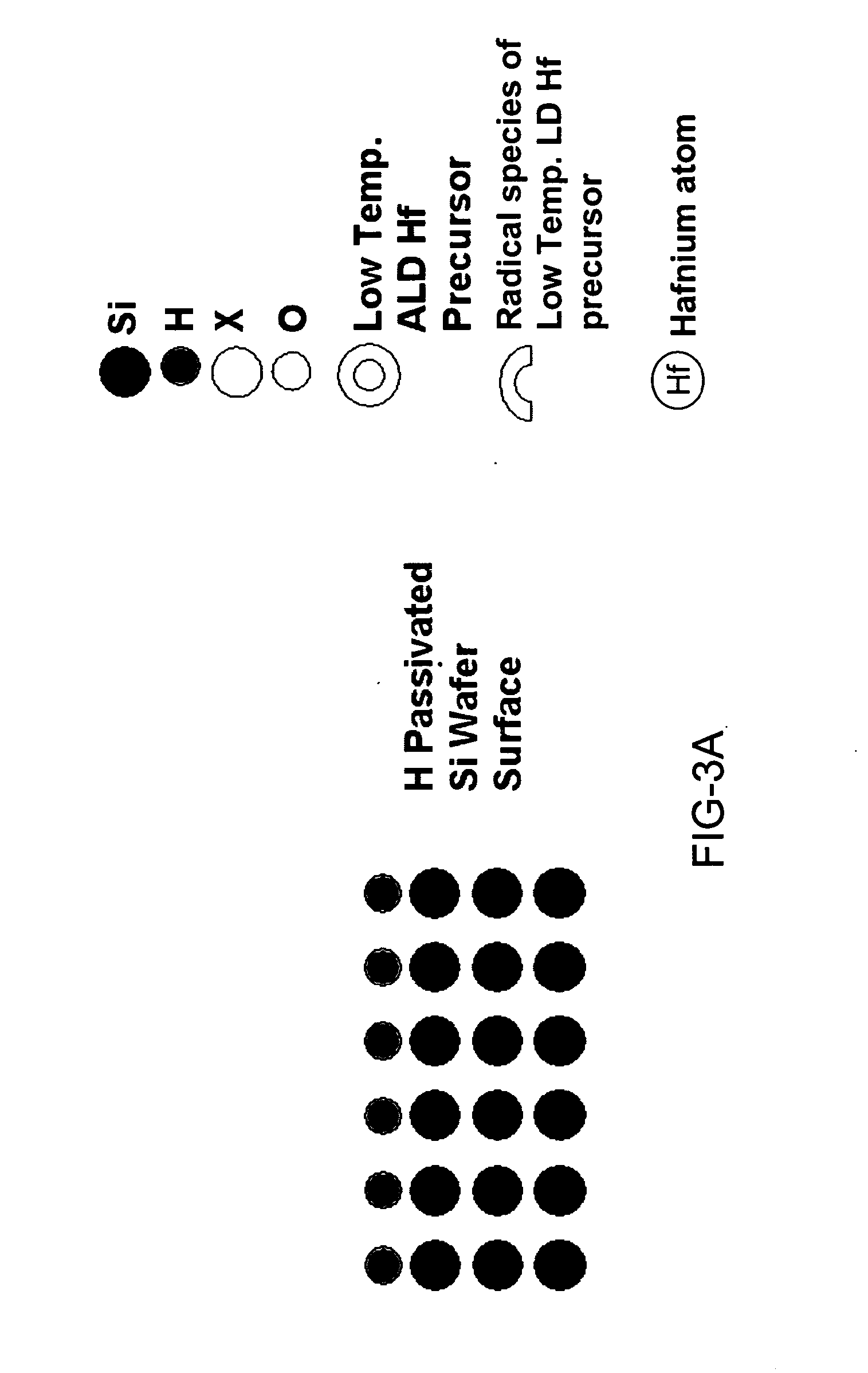
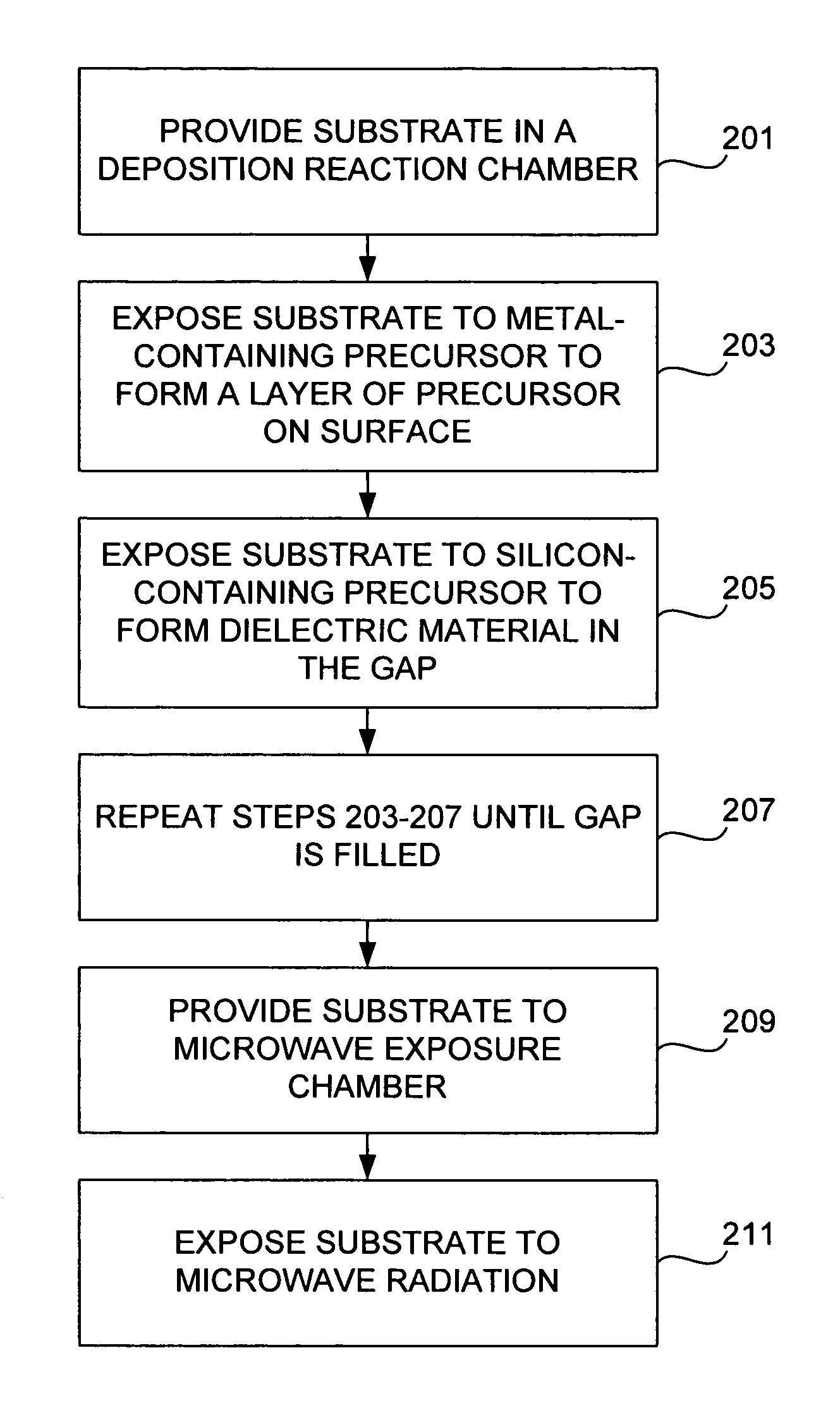
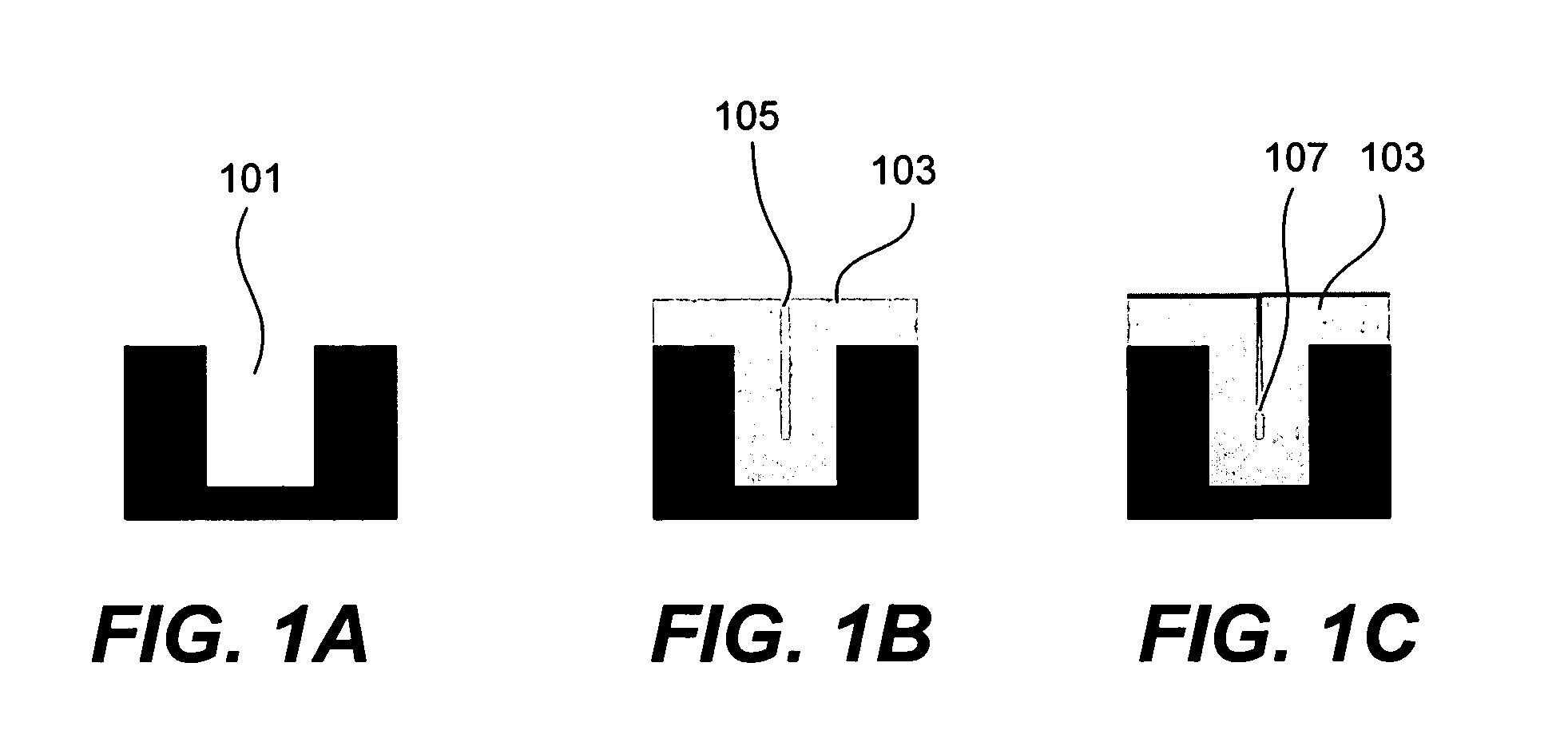
Method for energy-assisted atomic layer deposition and removal
InactiveUS20050175789A1High energyGood initiativeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesProduct gasElectromagnetic radiation
A method for energy-assisted atomic layer deposition and removal of a dielectric film are provided. In one embodiment a substrate is placed into a reaction chamber and a gaseous precursor is introduced into the reaction chamber. Energy is provide by a pulse of electromagnetic radiation which forms radical species of the gaseous precursor. The radical species react with the surface of the substrate to form a radical terminated surface on the substrate. The reaction chamber is purged and a second gaseous precursor is introduced. A second electromagnetic radiation pulse is initiated and forms second radical species. The second radical species of the second gas react with the surface to form a film on the substrate. Alternately, the gaseous species can be chosen to produce radicals that result in the removal of material from the surface of the substrate.
Owner:HELMS JR AUBREY L +3
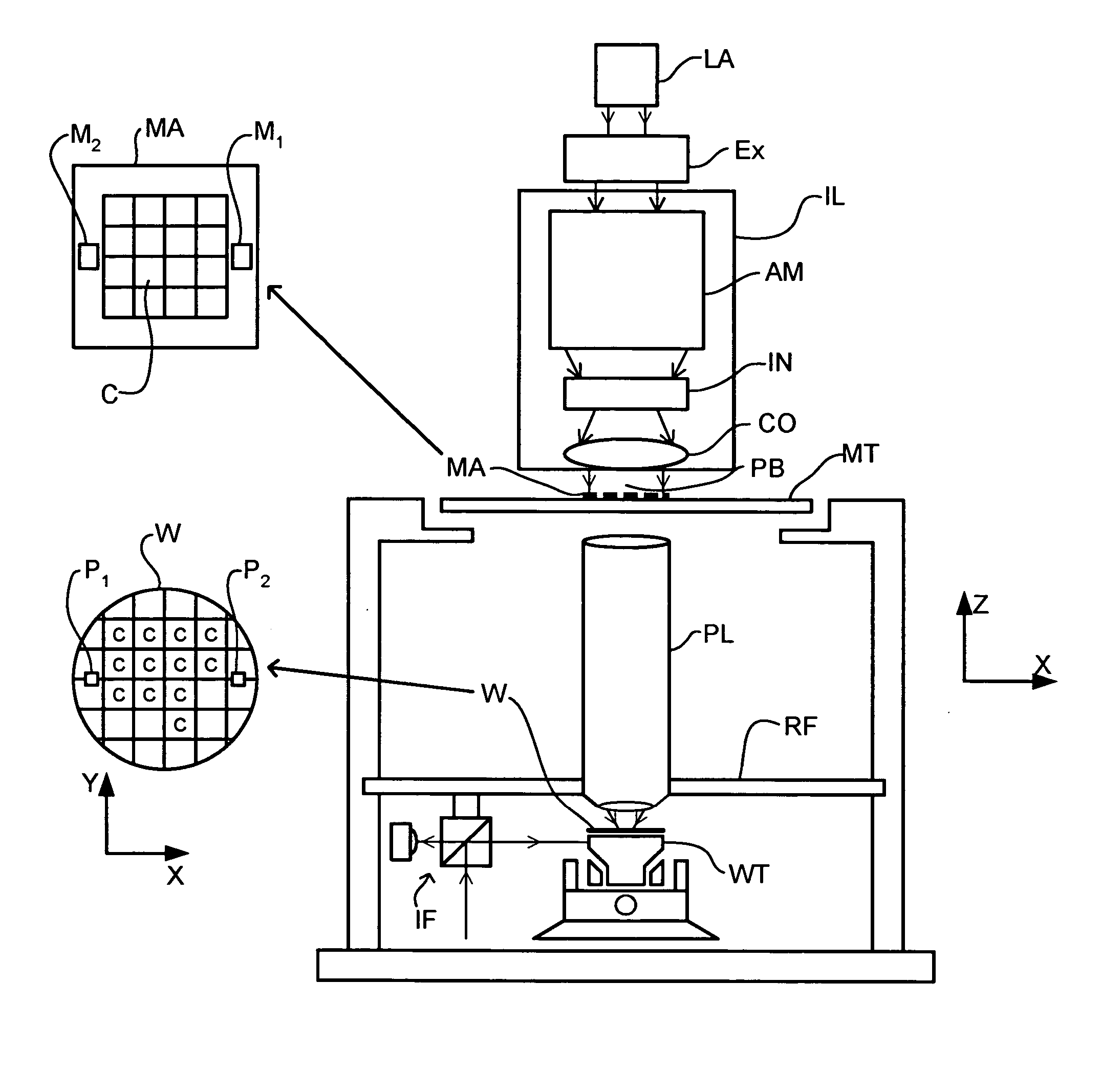
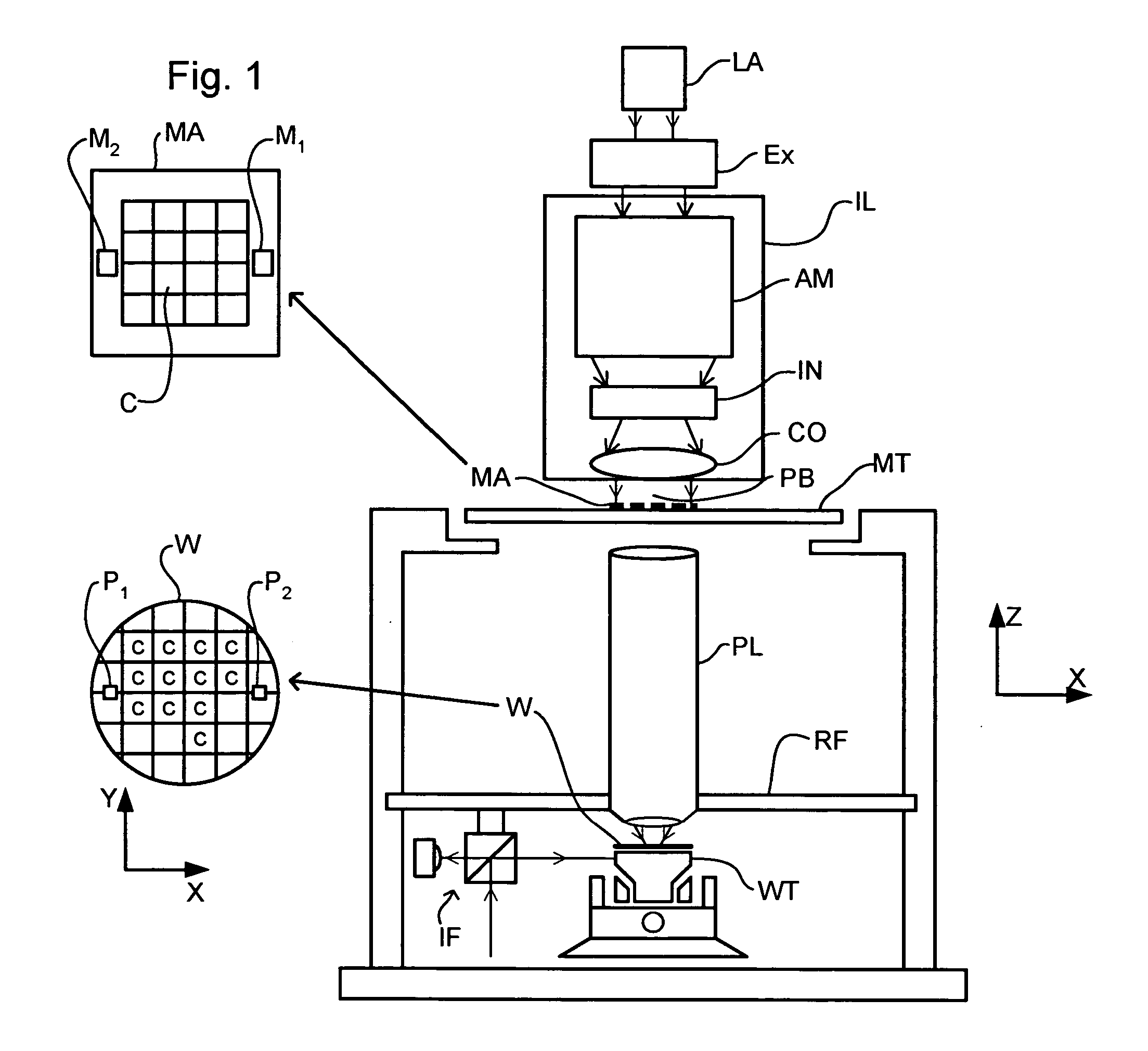
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050048220A1ConstantAvoid pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesEngineeringImmersion lithography
In an immersion lithography apparatus, the immersion liquid is supplied from a tank via a flow restrictor. The liquid held in the tank is maintained at a substantially constant height above the flow restrictor to ensure a constant flow of liquid.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
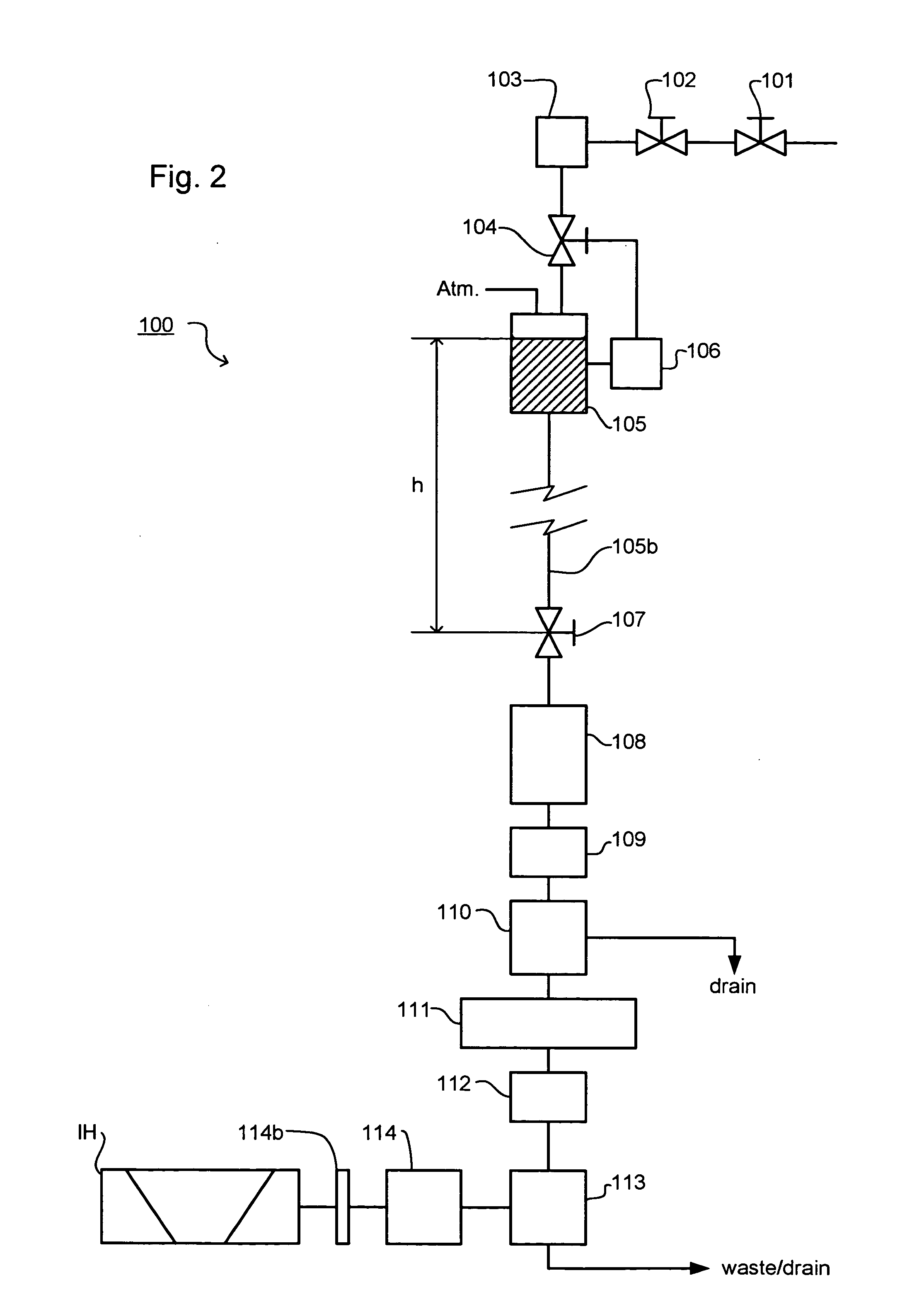
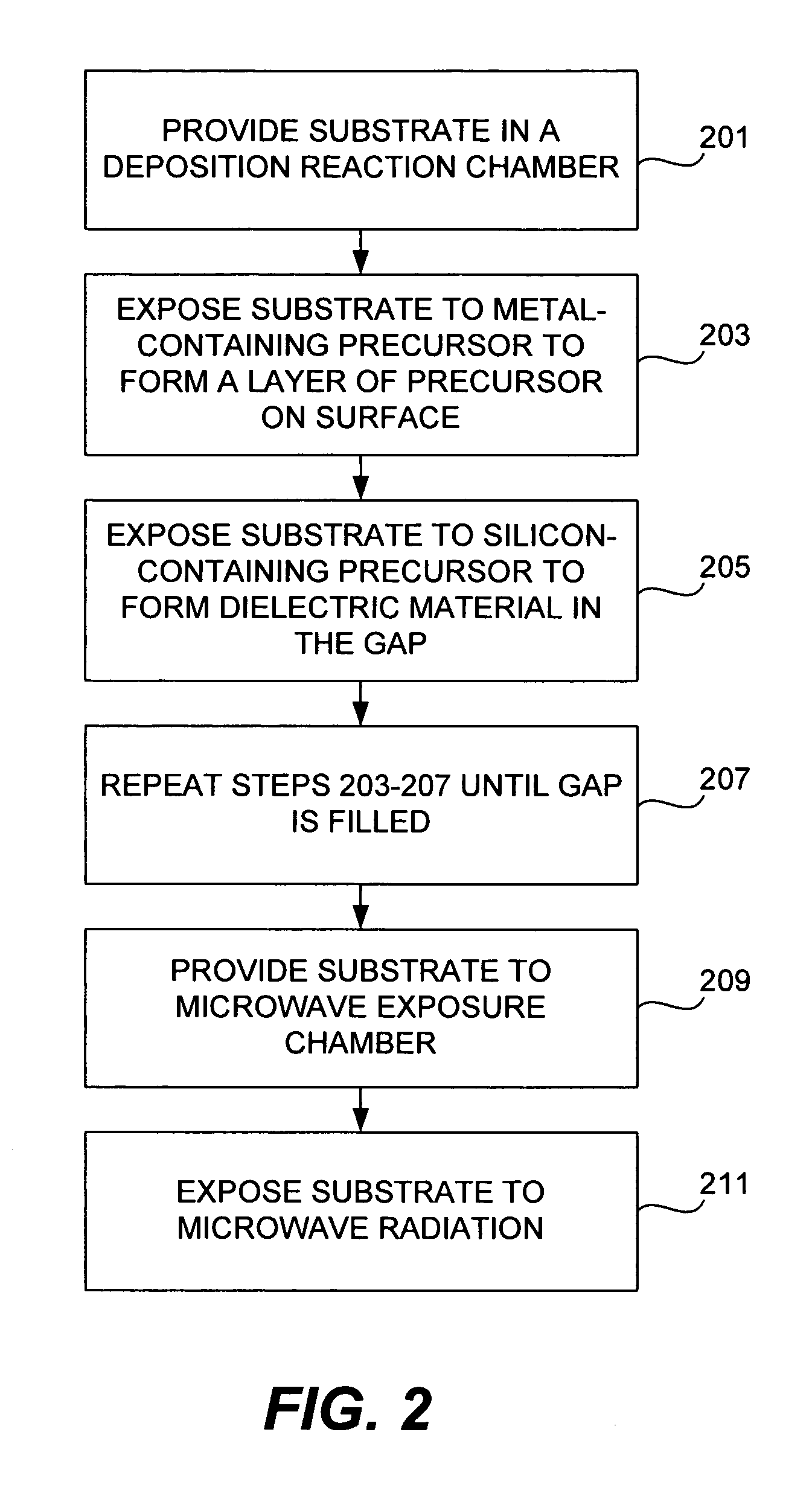
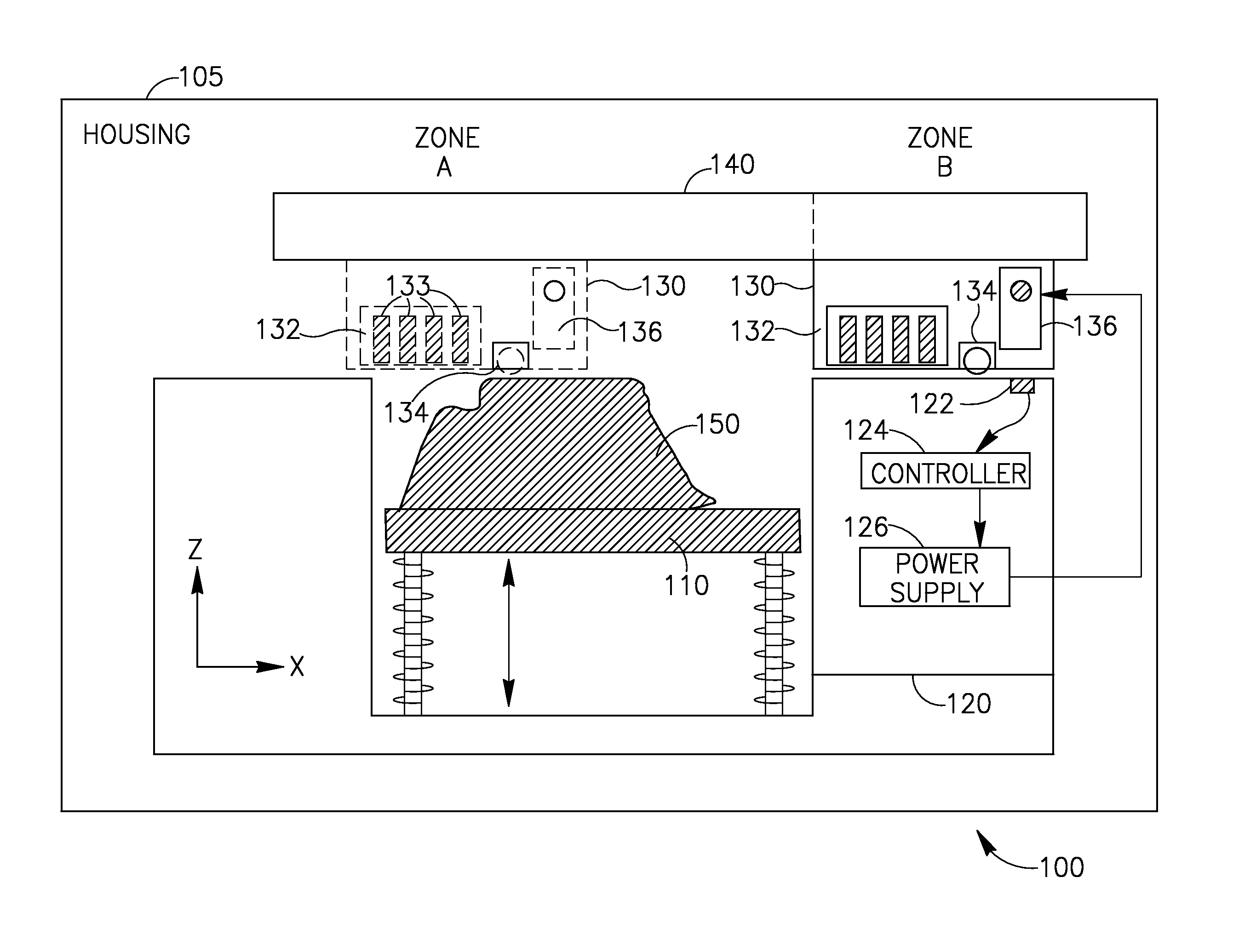
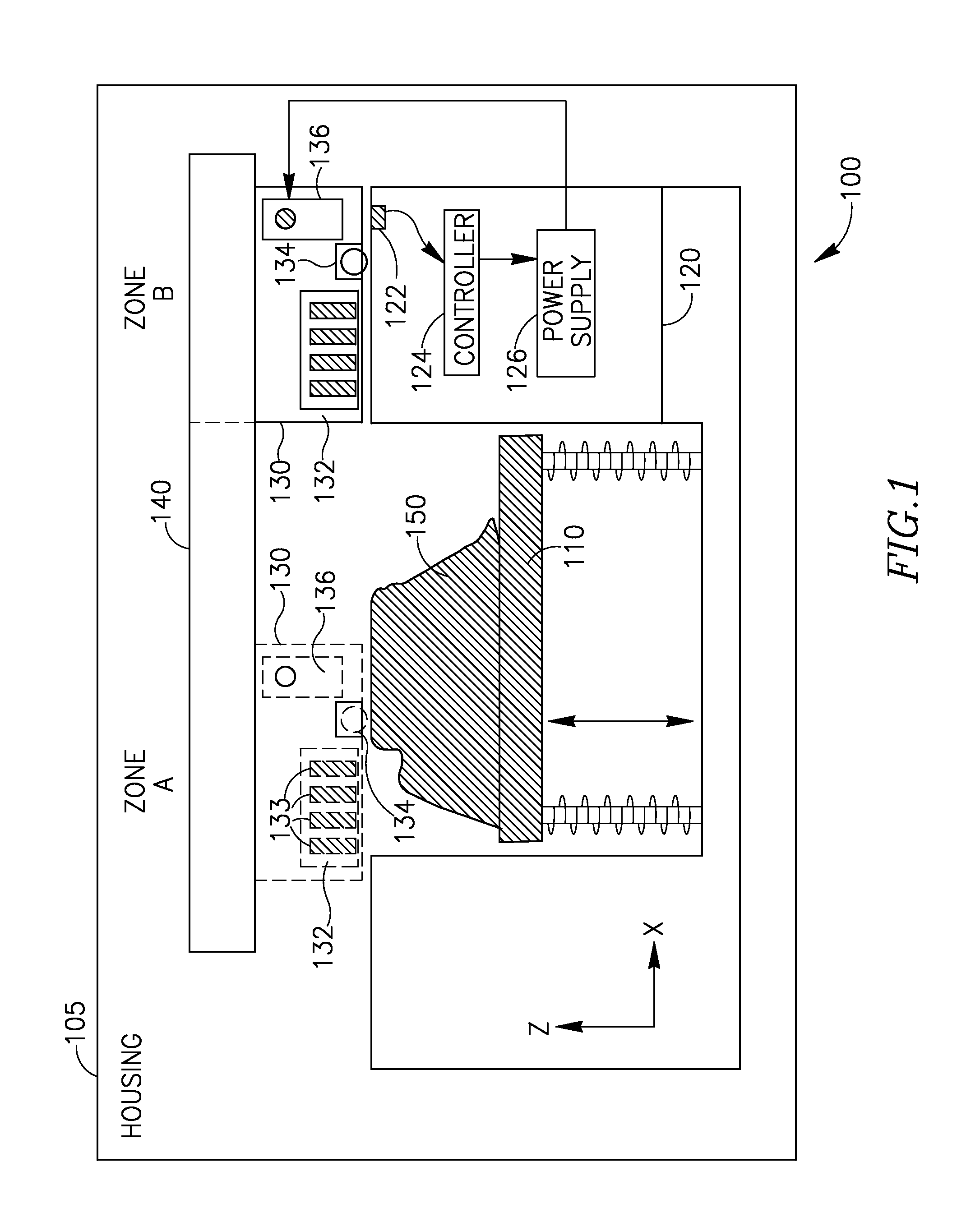
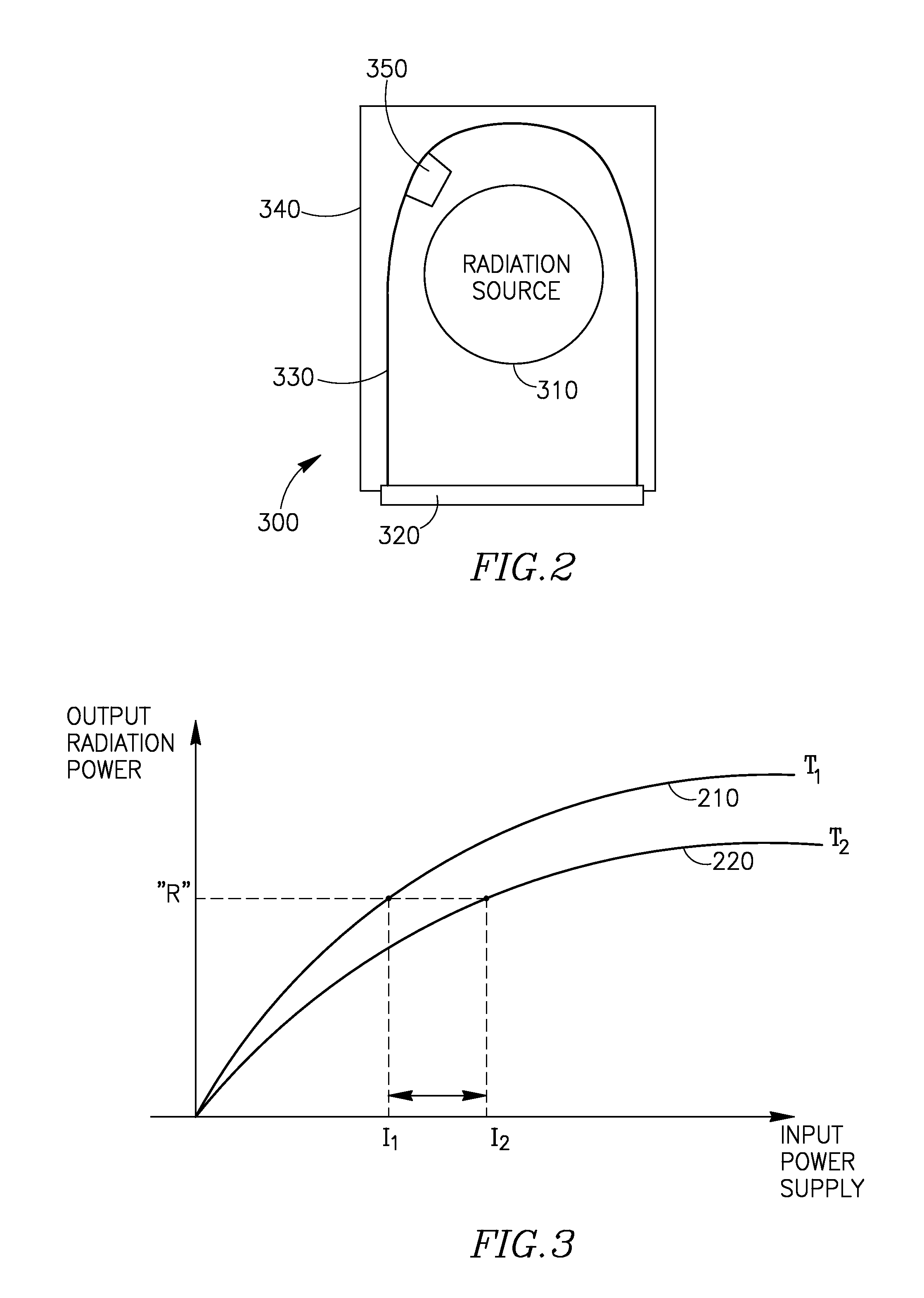
Hydroxyl bond removal and film densification method for oxide films using microwave post treatment
ActiveUS7589028B1High densityImprove film propertiesRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMicrowave
Methods of forming dielectric films with increased density and improved film properties are provided. The methods involve exposing dielectric films to microwave radiation. According to various embodiments, the methods may be used to remove hydroxyl bonds, increase film density, reduce or eliminate seams and voids, and optimize film properties such as dielectric constant, refractive index and stress for particular applications. In certain embodiments, the methods are used to form conformal films deposited by a technique such as PDL. The methods may be used in applications requiring low thermal budgets.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for monitoring electro-magnetic radiation power in solid freeform fabrication systems
Owner:STRATASYS LTD
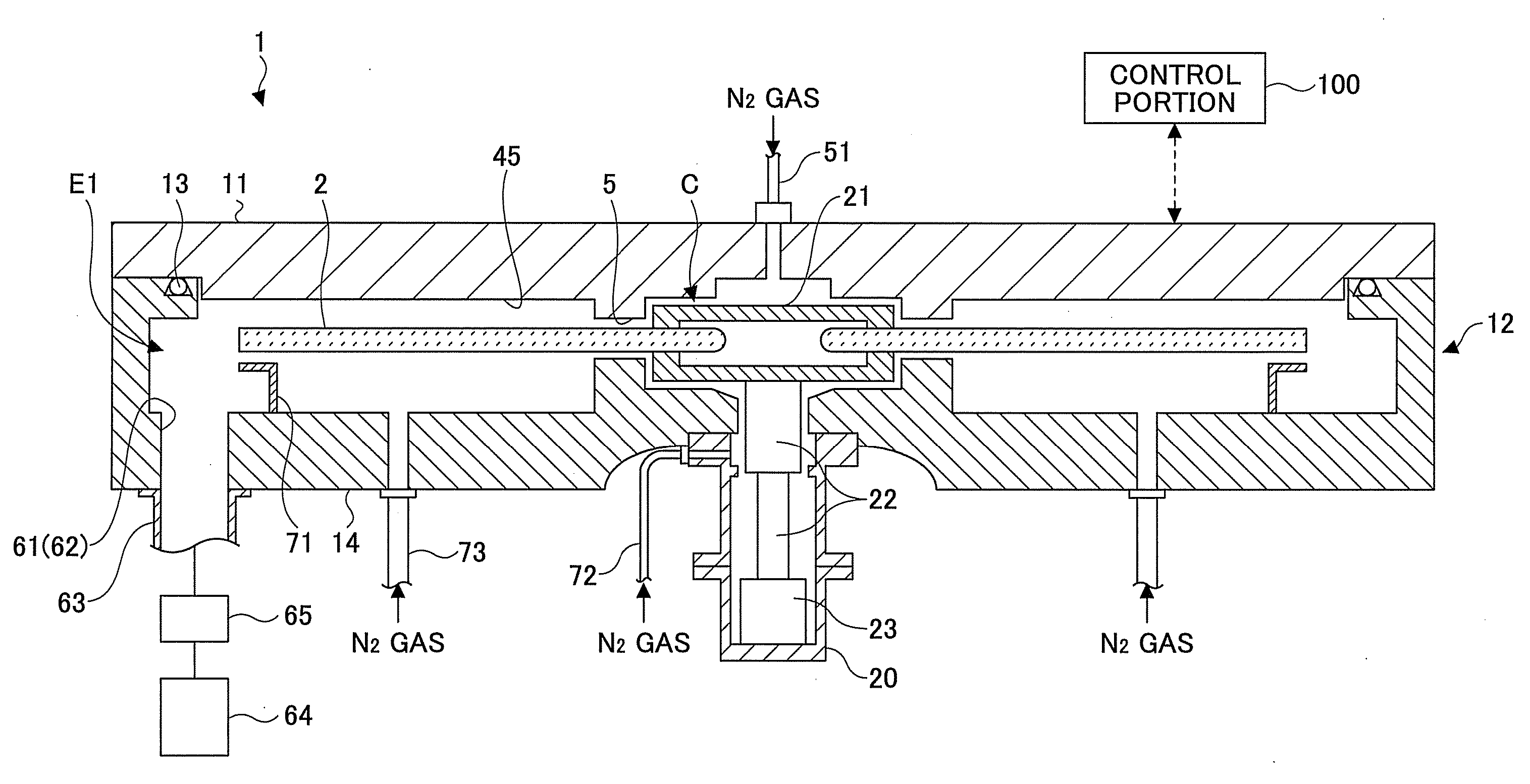
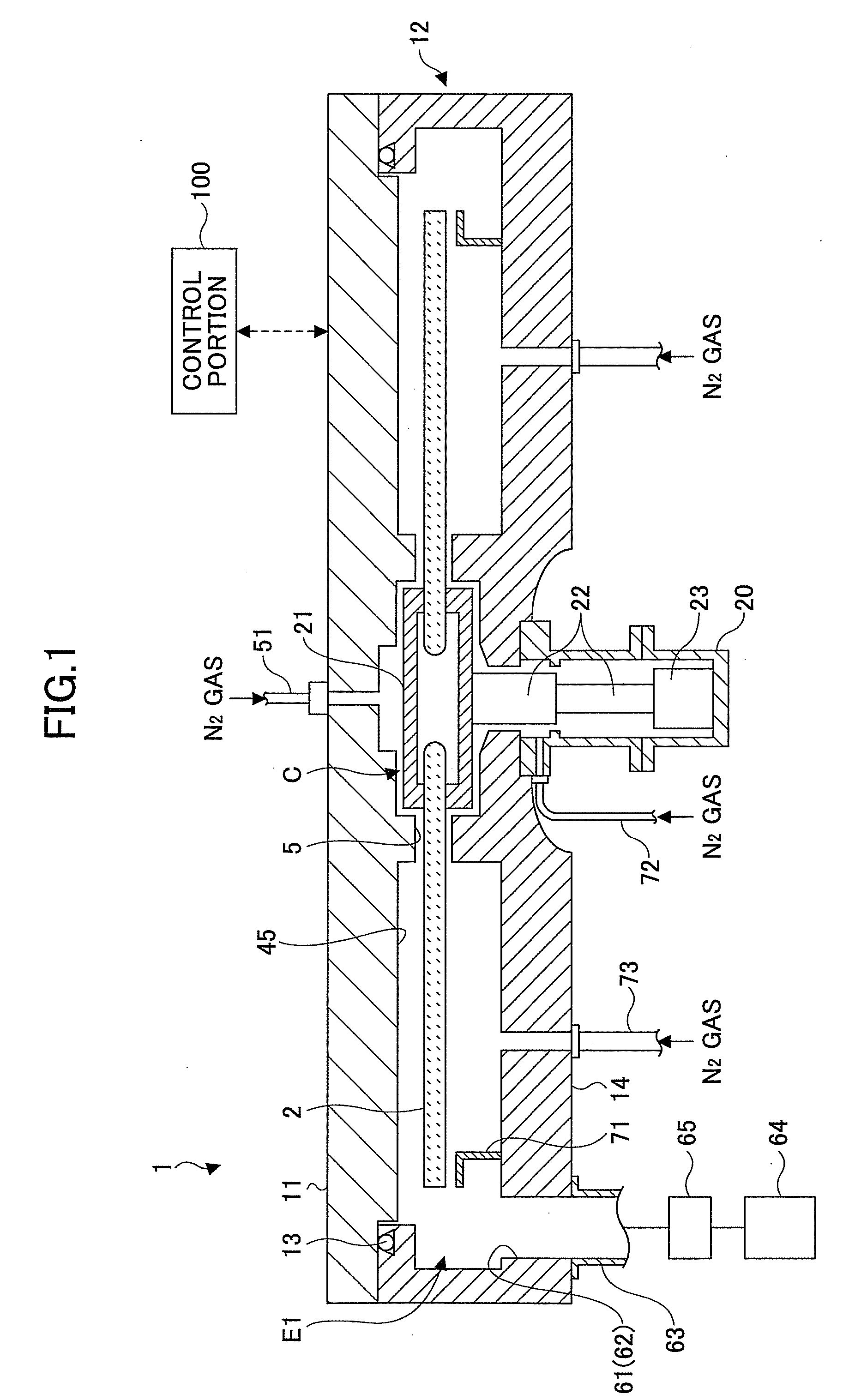
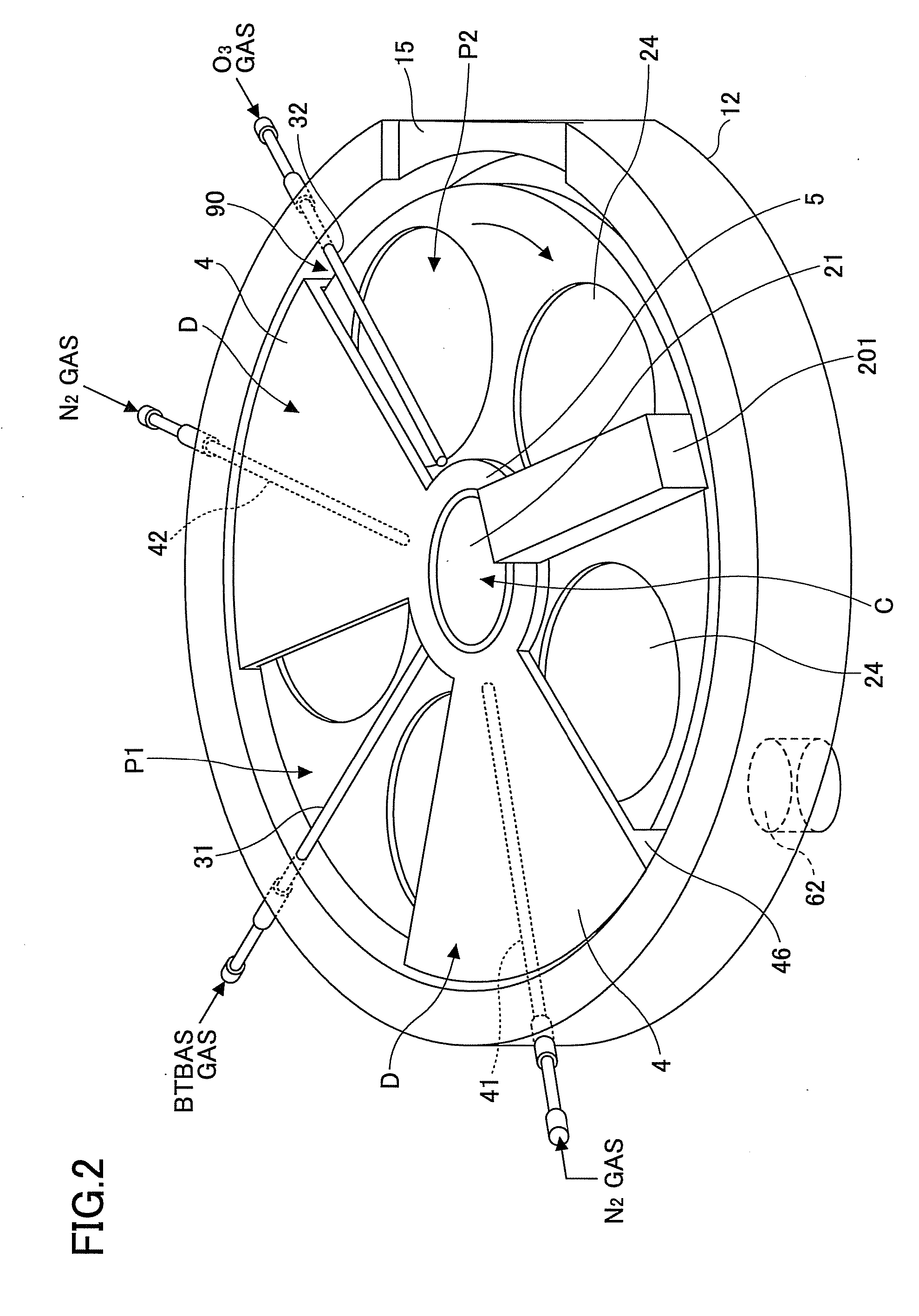
Film deposition apparatus, film deposition method, and storage medium
In a film deposition apparatus where bis (tertiary-butylamino) silane (BTBAS) gas is adsorbed on a wafer and then O3 gas is adsorbed on the wafer so that the BTBAS gas is oxidized by the O3 gas thereby depositing a silicon oxide film by rotating a turntable on which the wafer is placed, a laser beam irradiation portion is provided that is capable of irradiating a laser beam to an area spanning from one edge to another edge of a substrate receiving area of the turntable along a direction from an inner side to an outer side of the table.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Systems and methods for synthesis of extended length nanostructures
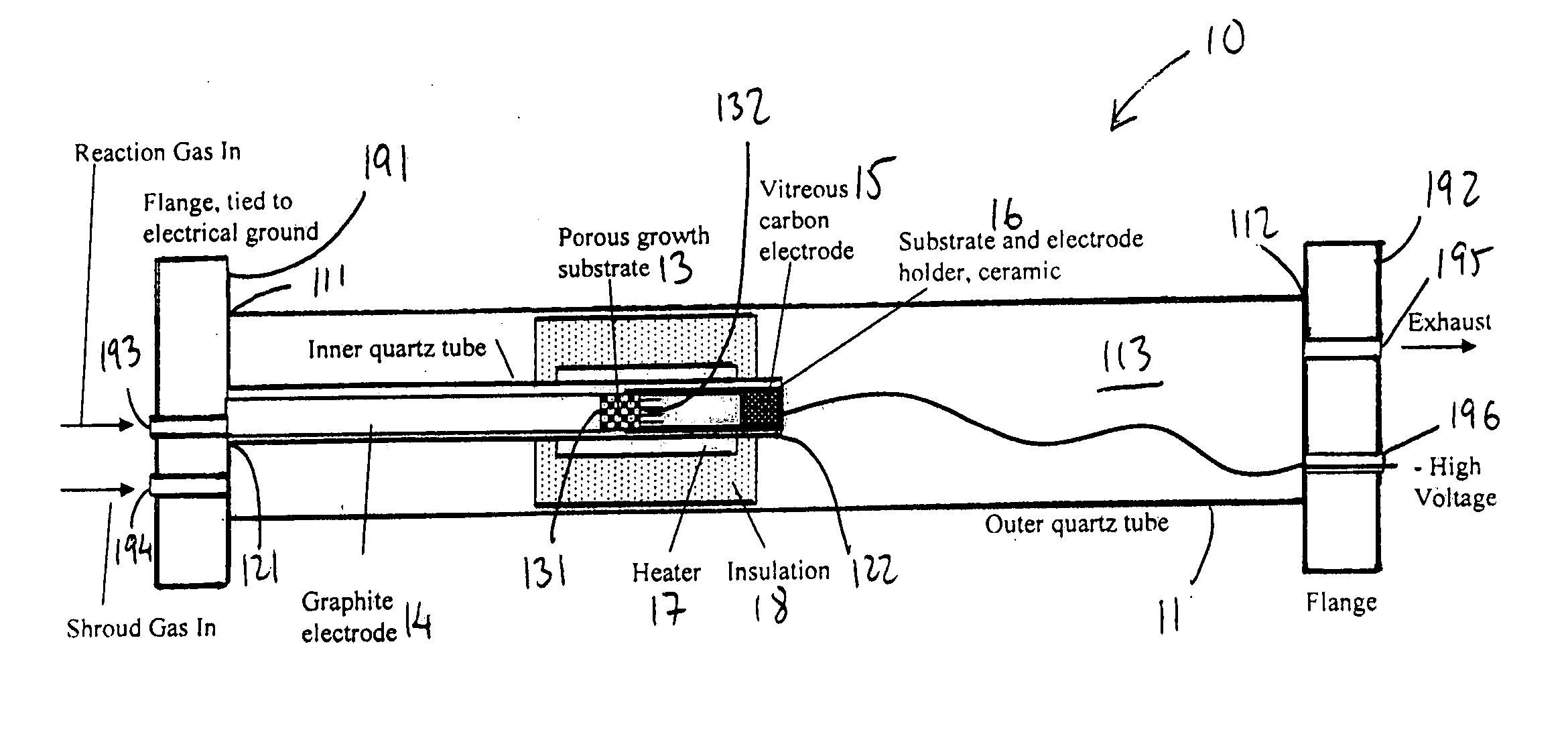
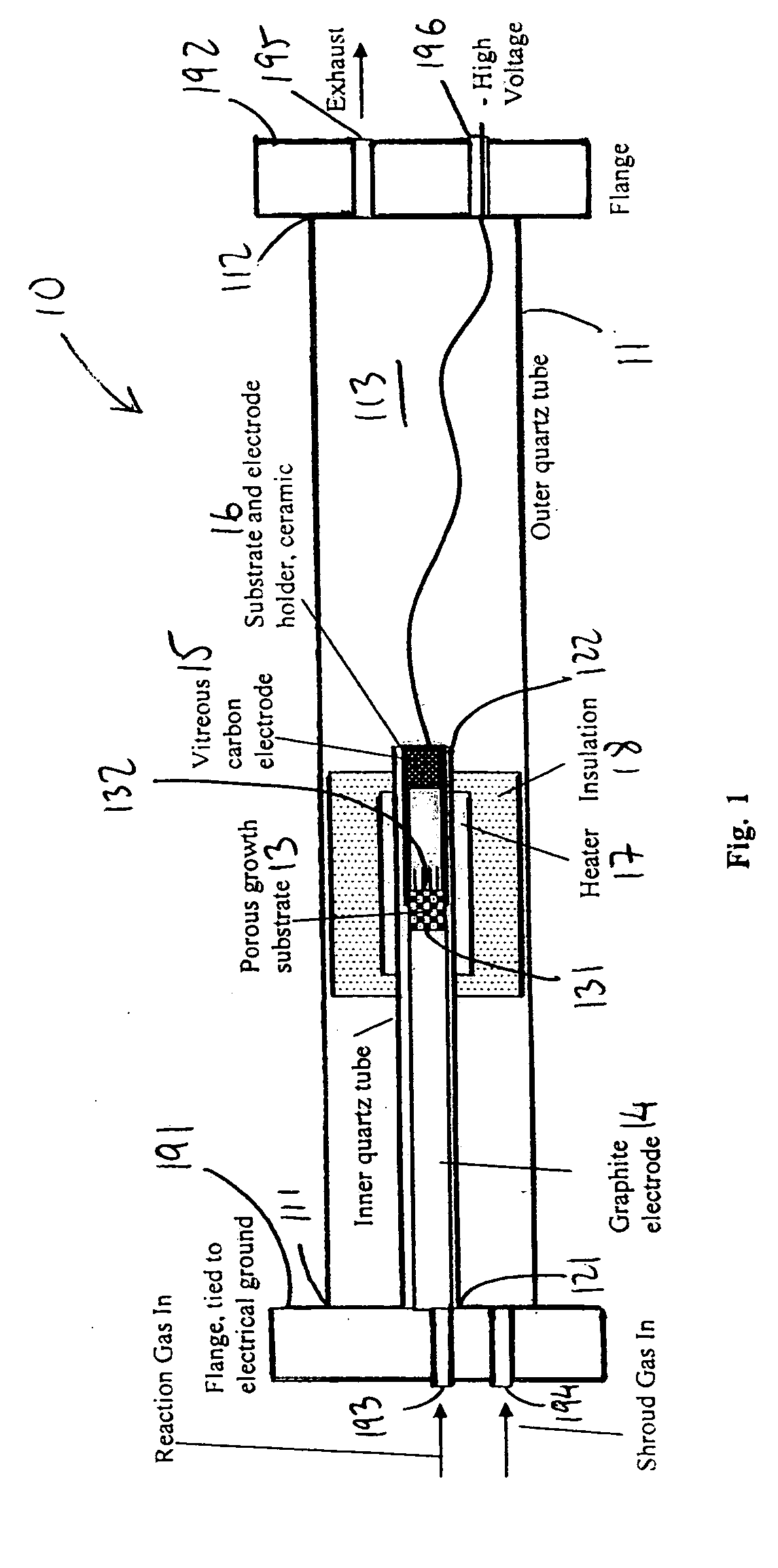
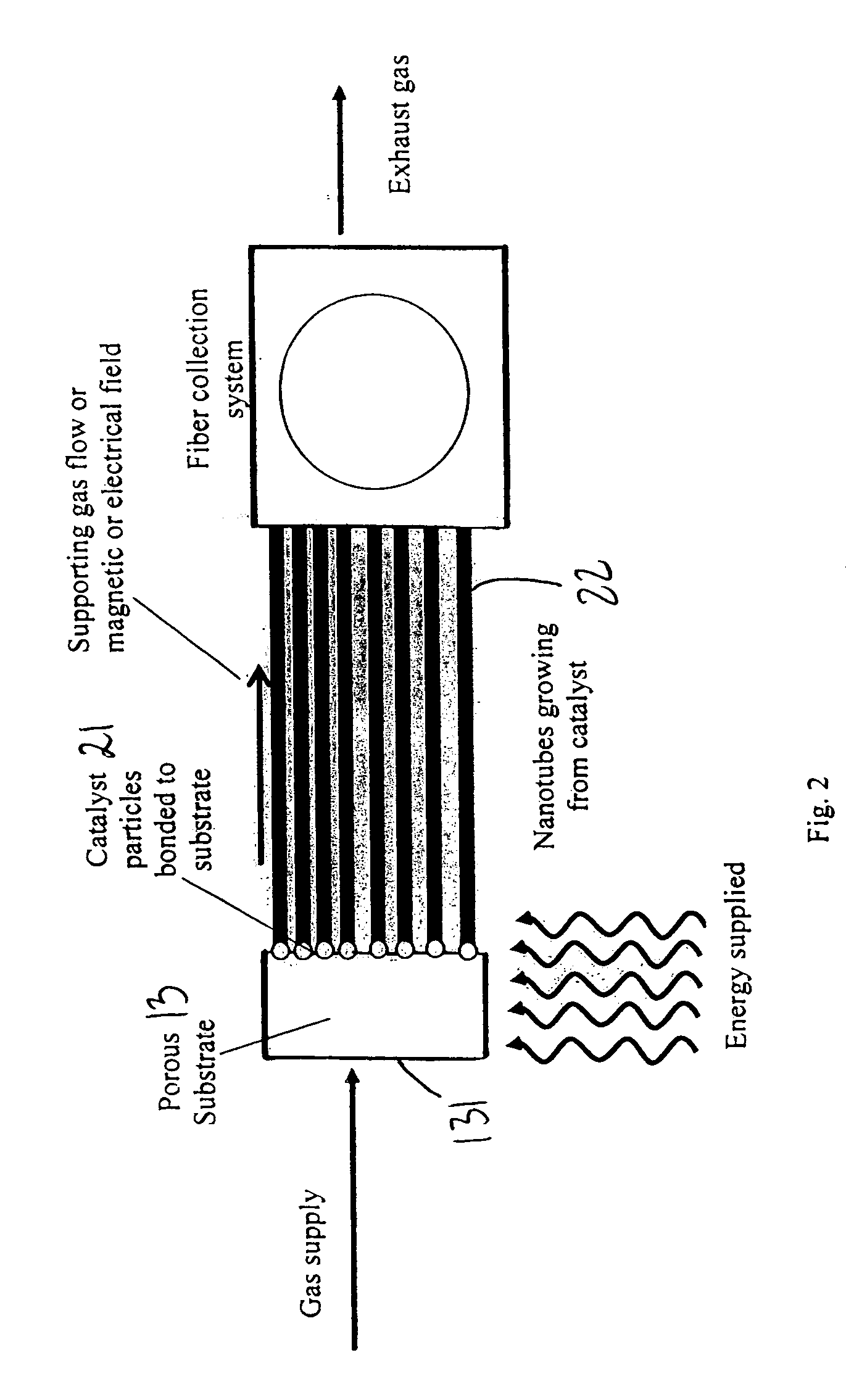
ActiveUS20050170089A1Equally distributedMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsPorous substrateGas phase
A system for synthesizing nanostructures using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is provided. The system includes a housing, a porous substrate within the housing, and on a downstream surface of the substrate, a plurality of catalyst particles from which nanostructures can be synthesized upon interaction with a reaction gas moving through the porous substrate. Electrodes may be provided to generate an electric field to support the nanostructures during growth. A method for synthesizing extended length nanostructures is also provided. The nanostructures are useful as heat conductors, heat sinks, windings for electric motors, solenoid, transformers, for making fabric, protective armor, as well as other applications.
Owner:NANCOMP TECHNOLOGIES INC
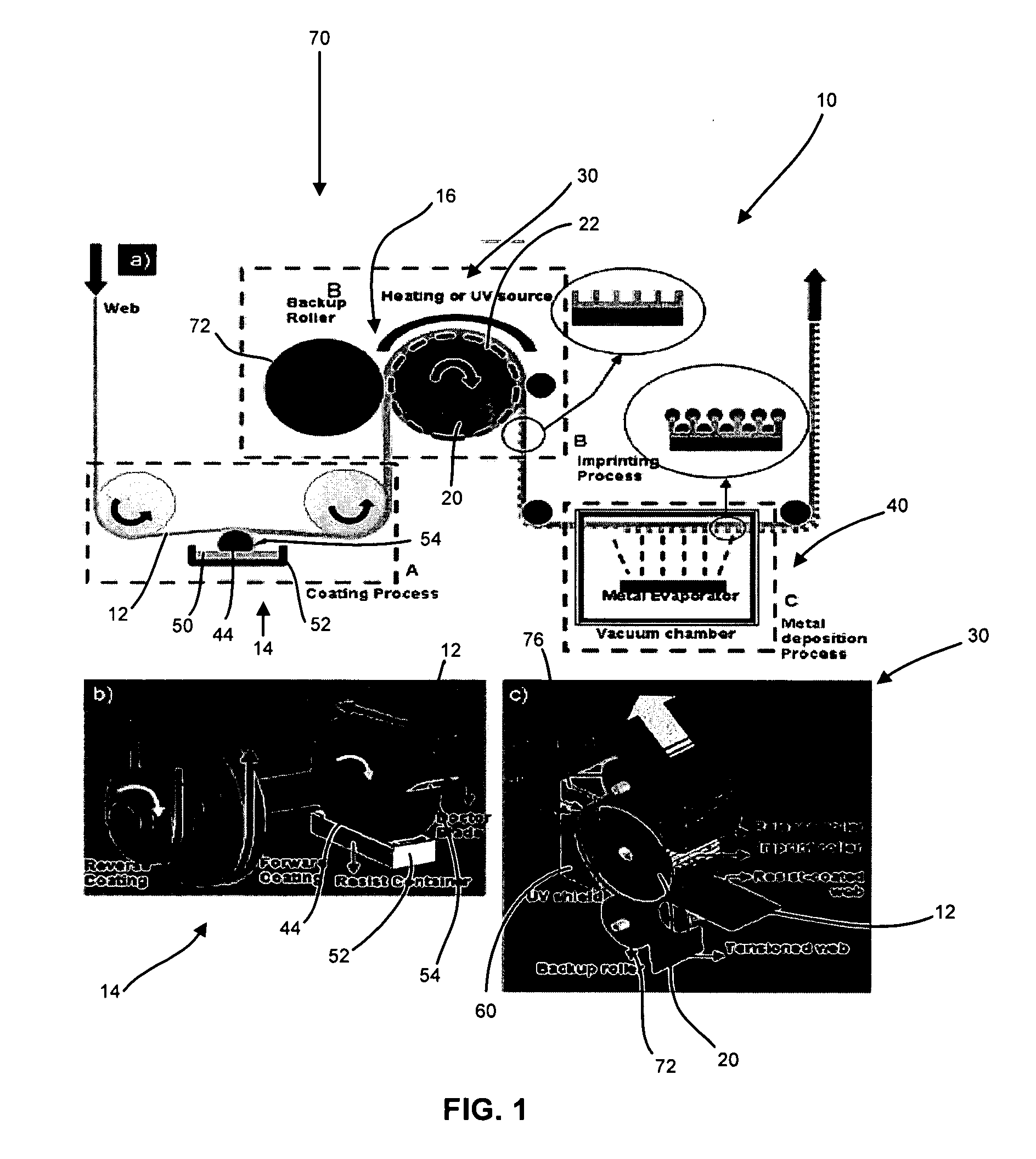
Roll to roll nanoimprint lithography
Apparatus and methods for a nano-patterning process to fabricate nanostructures. A roller type mold is used to continuously imprint nanostructures onto a flexible web or a rigid substrate. The process includes a coating and an imprinting module, which rotate the web synchronously. Liquid resist materials are used for imprinting and the patterns are set by thermal or UV curing. The process is used to produce bilayer metal wire-grid polarizers, organic solar cells, and organic light emitting diodes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Selective laser melting / sintering using powdered flux
InactiveUS20130136868A1TurbinesRadiation applicationsSelective laser meltingSelective laser sintering
An additive manufacturing process (110) wherein a powder (116) including a superalloy material and flux is selectively melted in layers with a laser beam (124) to form a superalloy component (126). The flux performs a cleaning function to react with contaminants to float them to the surface of the melt to form a slag. The flux also provides a shielding function, thereby eliminating the need for an inert cover gas. The powder may be a mixture of alloy and flux particles, or it may be formed of composite alloy / flux particles.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
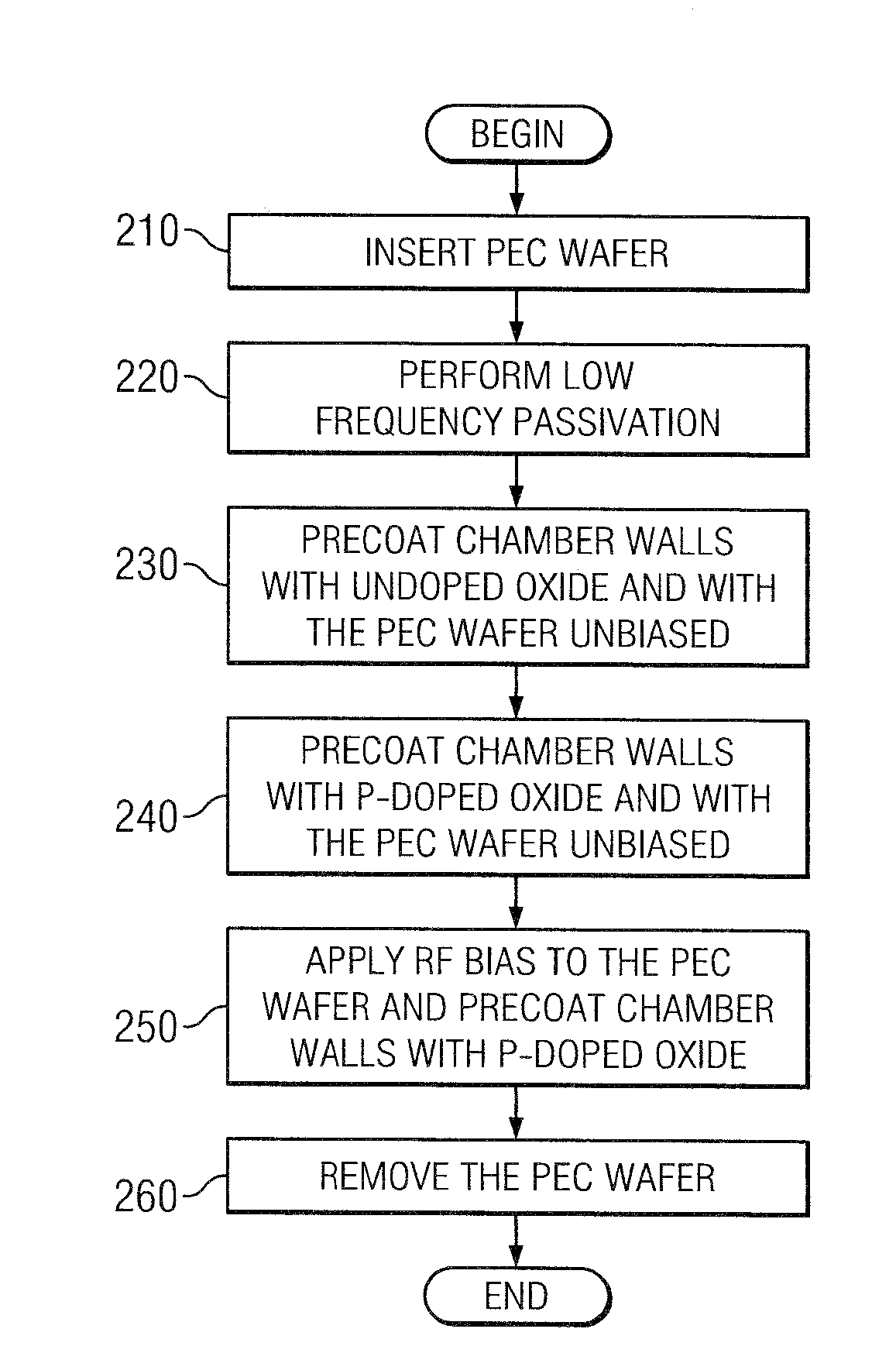
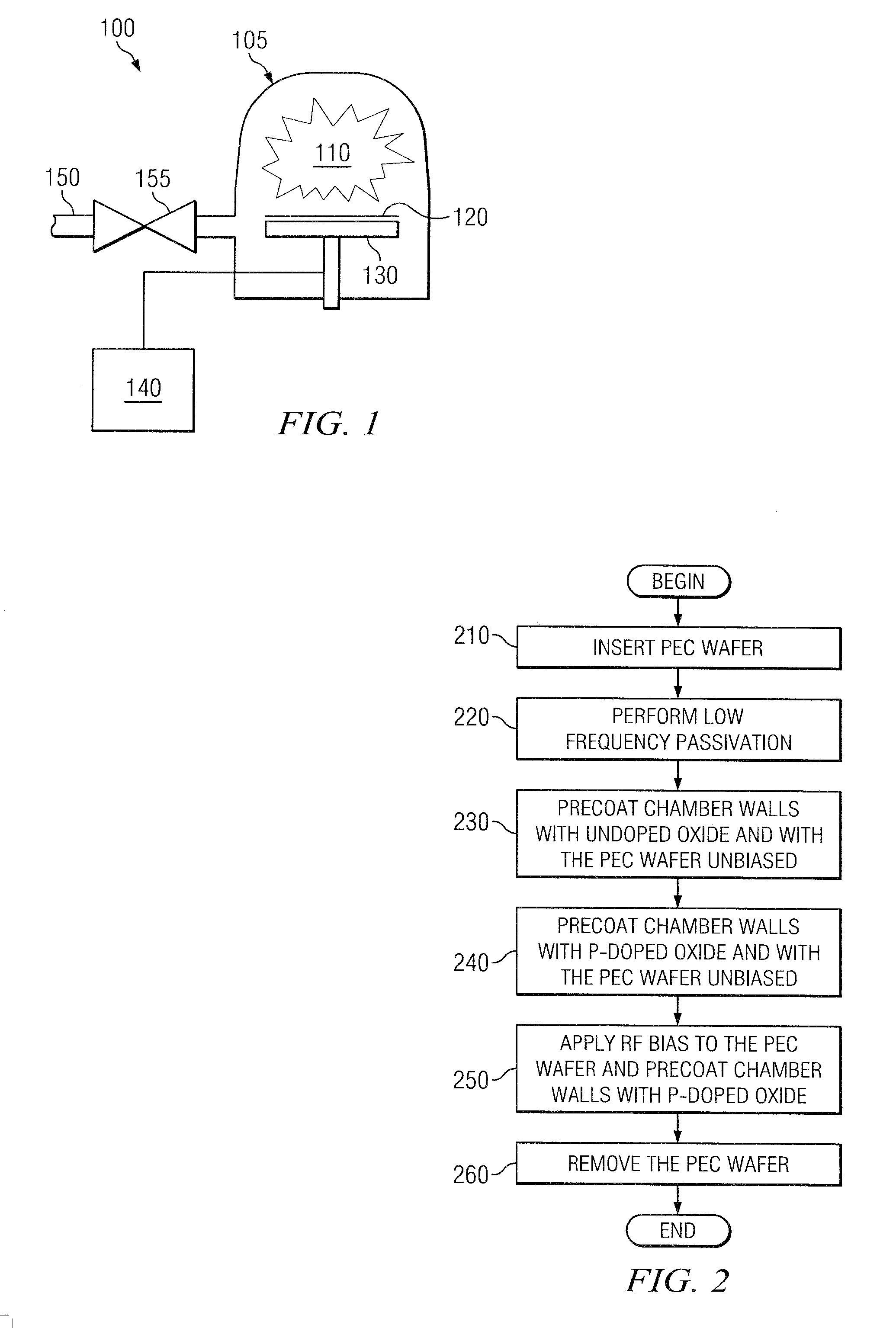
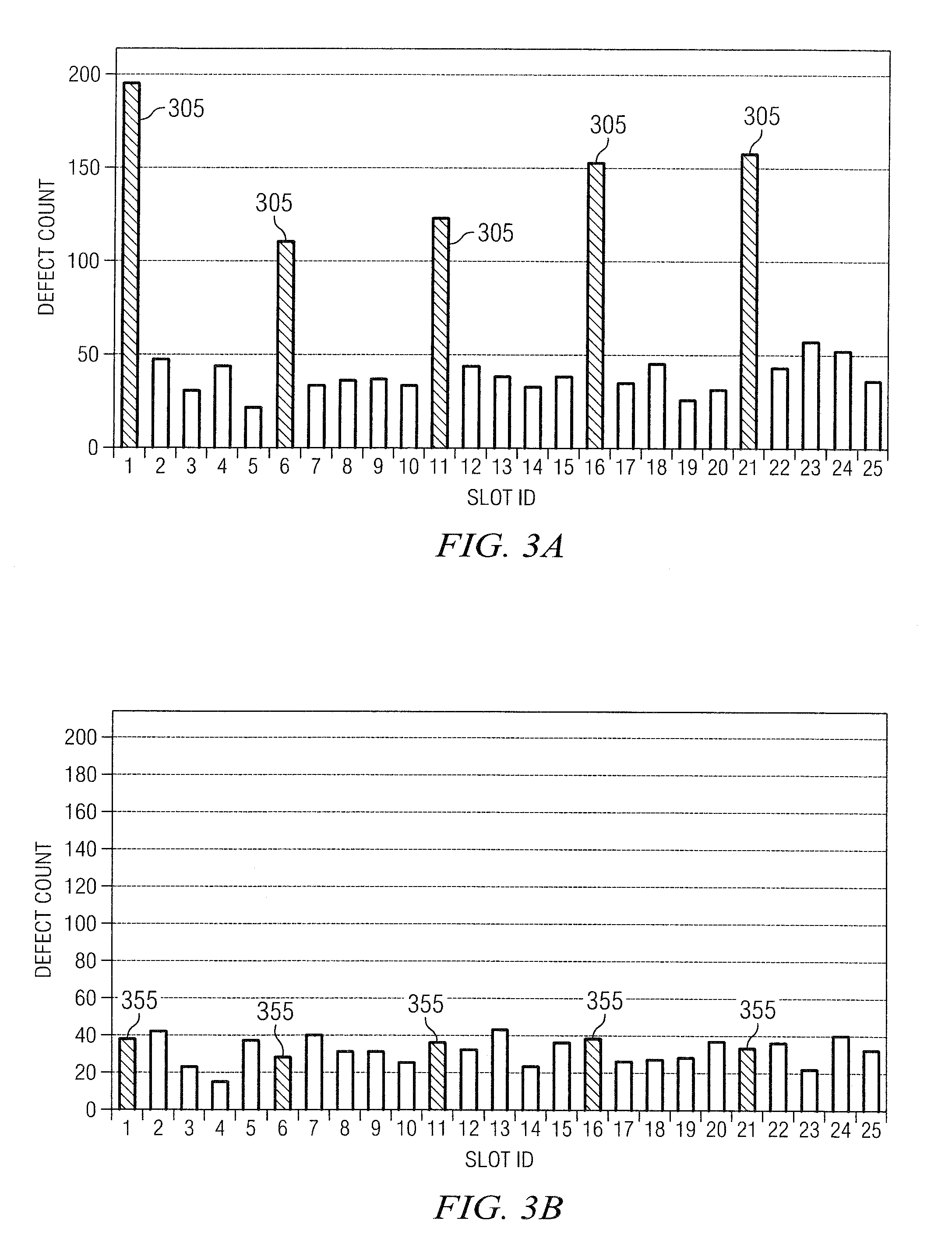
Use of a biased precoat for reduced first wafer defects in high-density plasma process
ActiveUS20100190352A1Minimizing yield lossReducing first wafer defectRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesHigh densityGas phase
According to various embodiments, the present teachings include methods for reducing first wafer defects in a high-density plasma chemical vapor deposition process. In an exemplary embodiment, the method can include running a deposition chamber for deposition of film on a first batch of silicon wafers and then cleaning interior surfaces of the deposition chamber. The method can further include inserting a protective electrostatic chuck cover (PEC) wafer on an electrostatic chuck in the deposition chamber and applying power to bias the PEC wafer while simultaneously precoating the deposition chamber with an oxide. The exemplary method can also include re-starting the deposition chamber for deposition of film on a second batch of silicon wafers.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Raman-active taggants and their recognition
InactiveUS6610351B2Easy to useQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsMaximum dimensionActive component
An organic or organoelement, linear or branched, monomeric or polymeric composition of matter having a Raman-active component in the form of particles. The particles having a maximum dimension of 50 mum. The Raman-active compound is applied to a substrate. When the Raman-active compound is exposed to a laser light wavelength which is batochromically well beyond a spectral region of maximum absorbance of said Raman-active compound, Raman scattering can be detected.
Owner:QUANTAG SYST
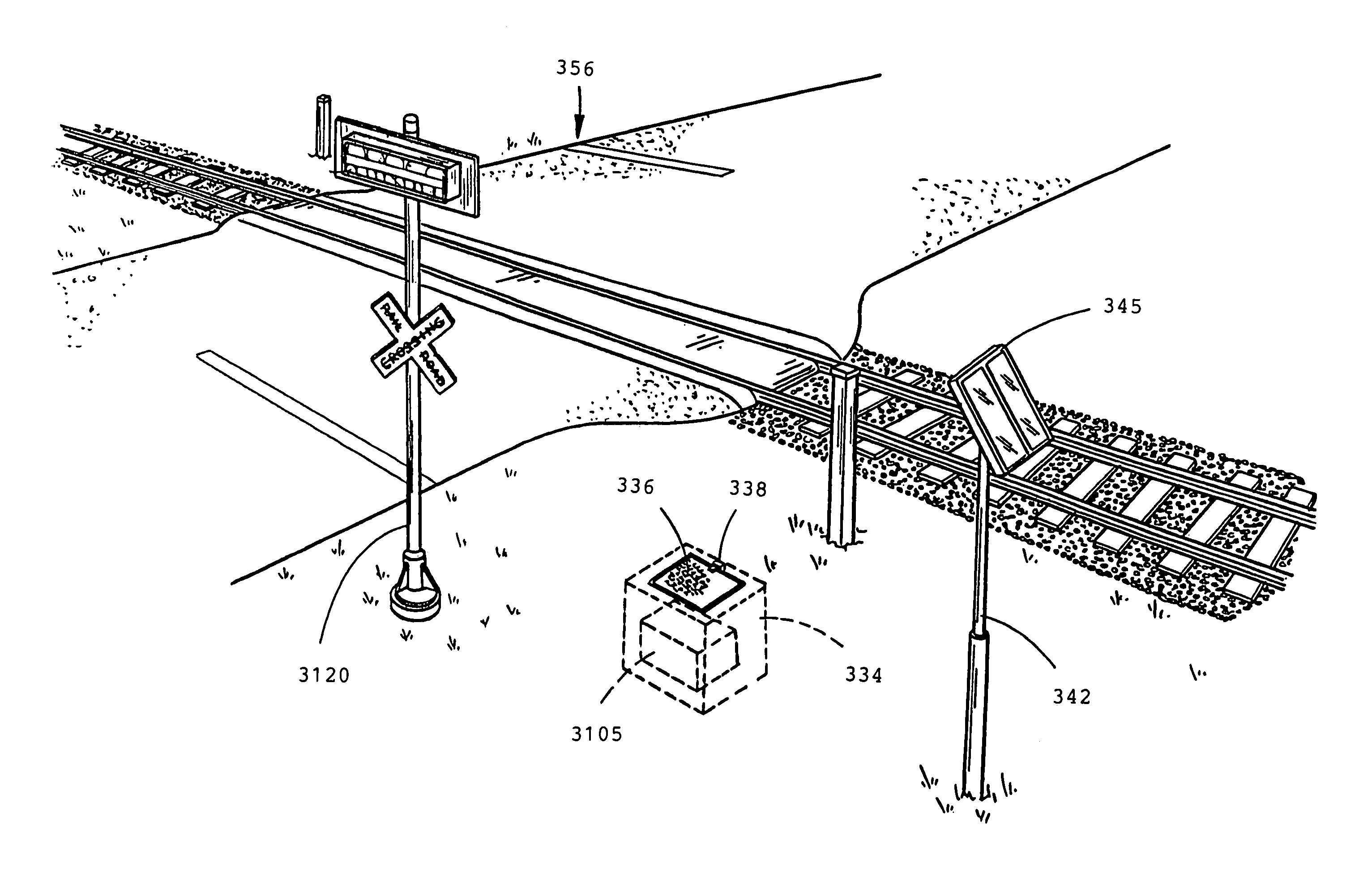
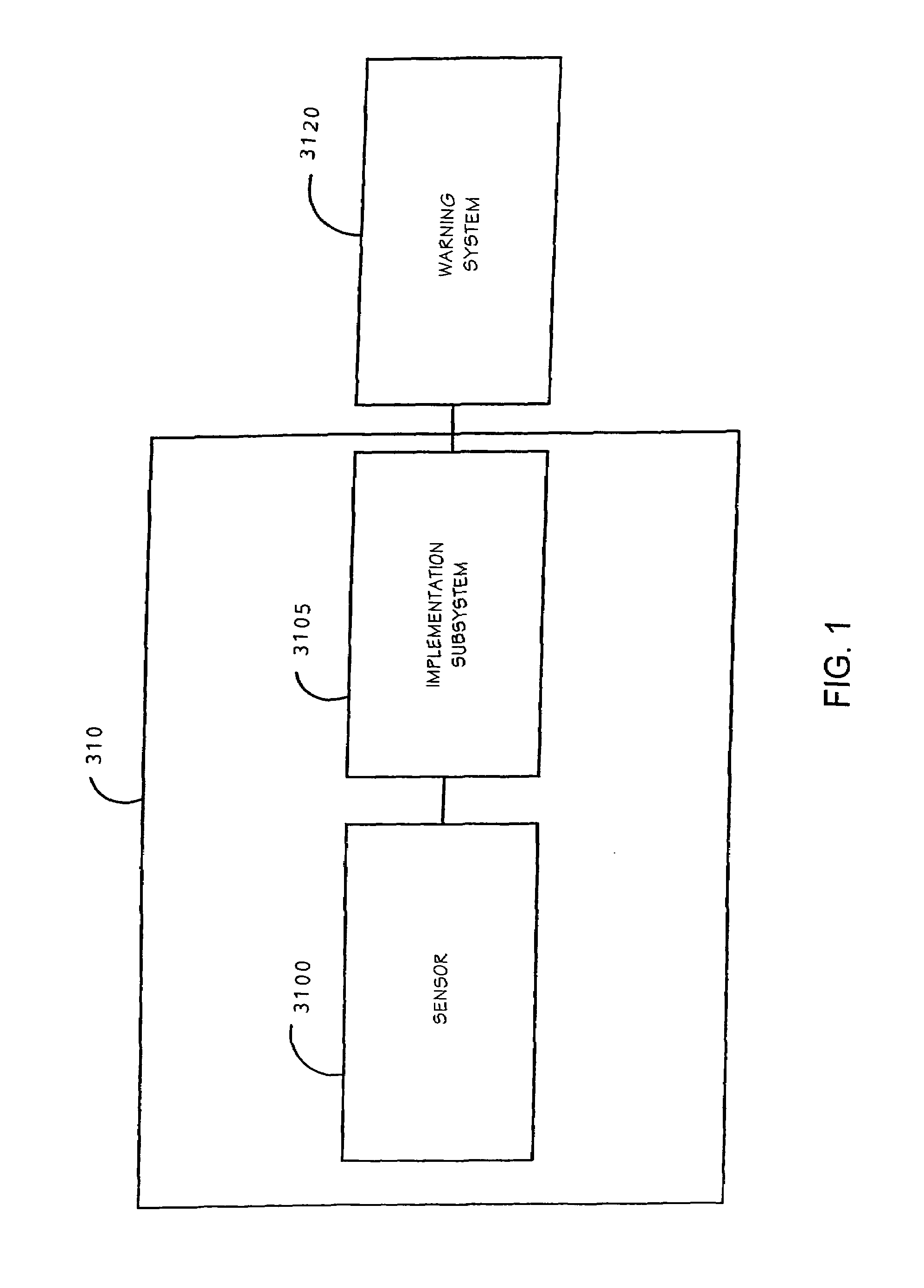
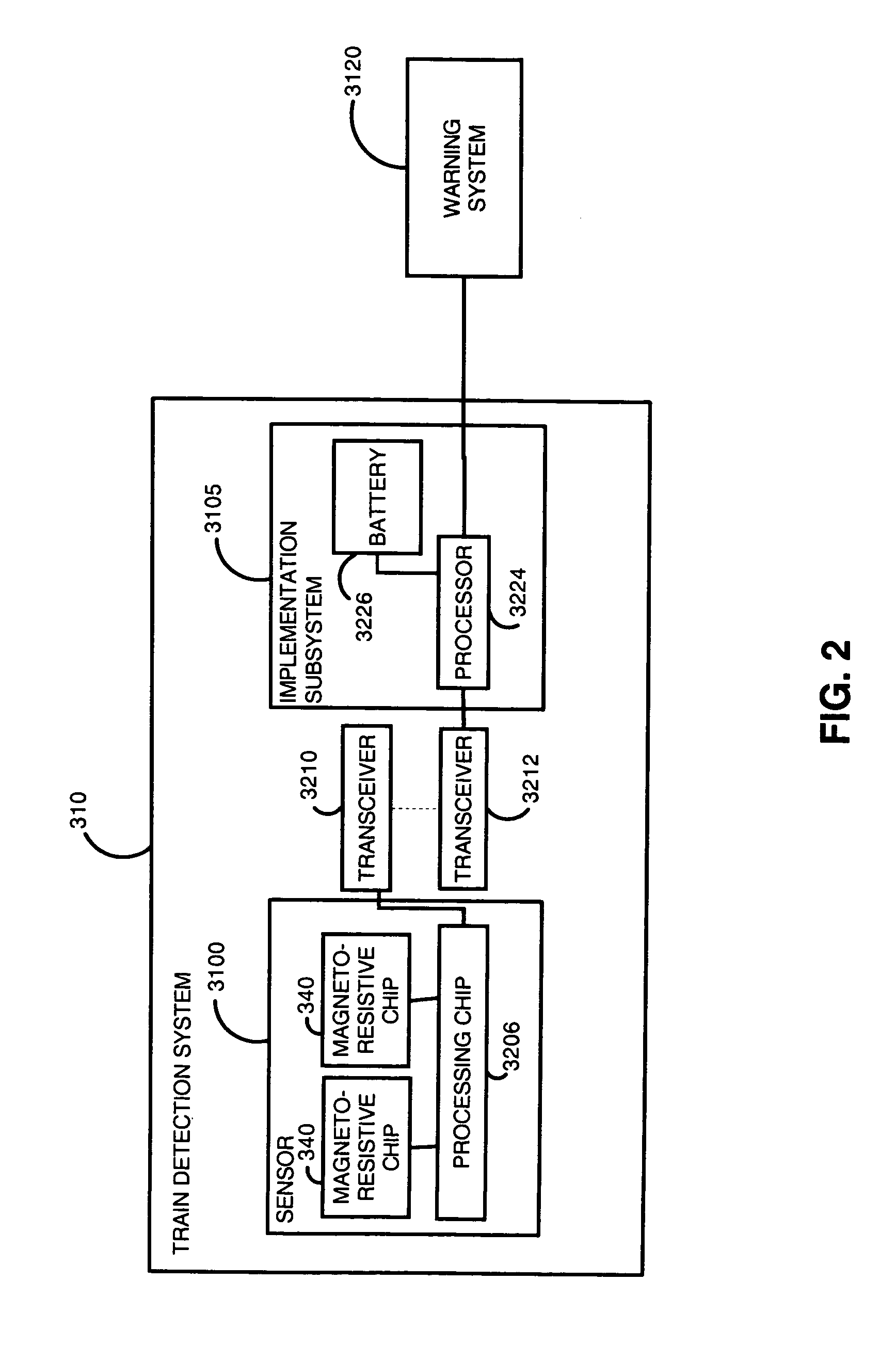
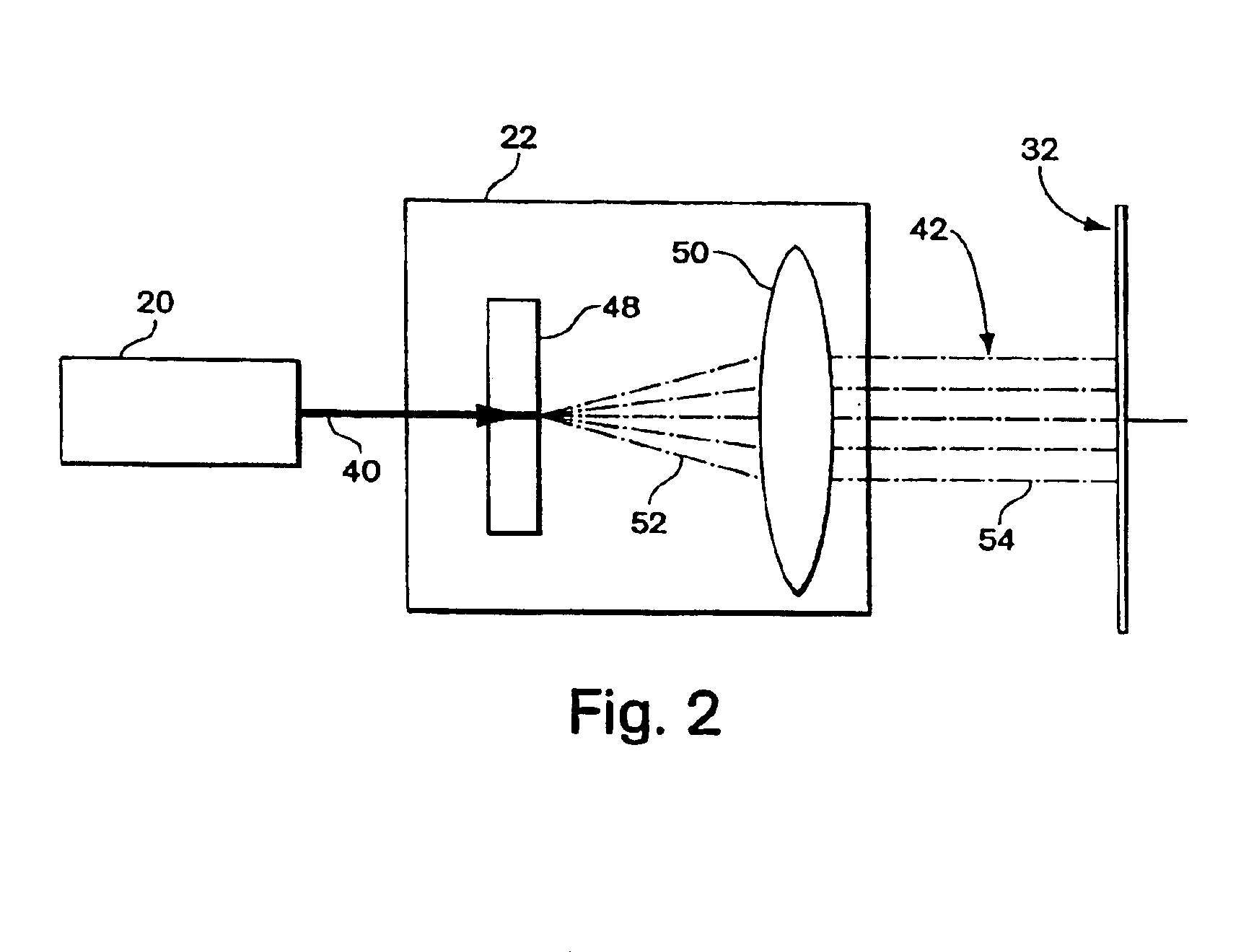
Traffic warning system
InactiveUS7075427B1Increase awarenessProvide informationDetection of traffic movementAnti-collision systemsSecure stateLevel crossing
The present invention is directed to a train detection system for detecting the velocity, presence, and direction of a railroad car which may be utilized in existing railroad crossing installations. The train detection system is suitable for self-testing of its components and if an anomaly has been detected, the train detection system is capable of placing the system in a fail-safe state. The train detection system of the present invention is also capable of constant communication between the sensor of said system and the implementing device of the train detection system via a wireless link.
Owner:EVA SIGNAL CORP
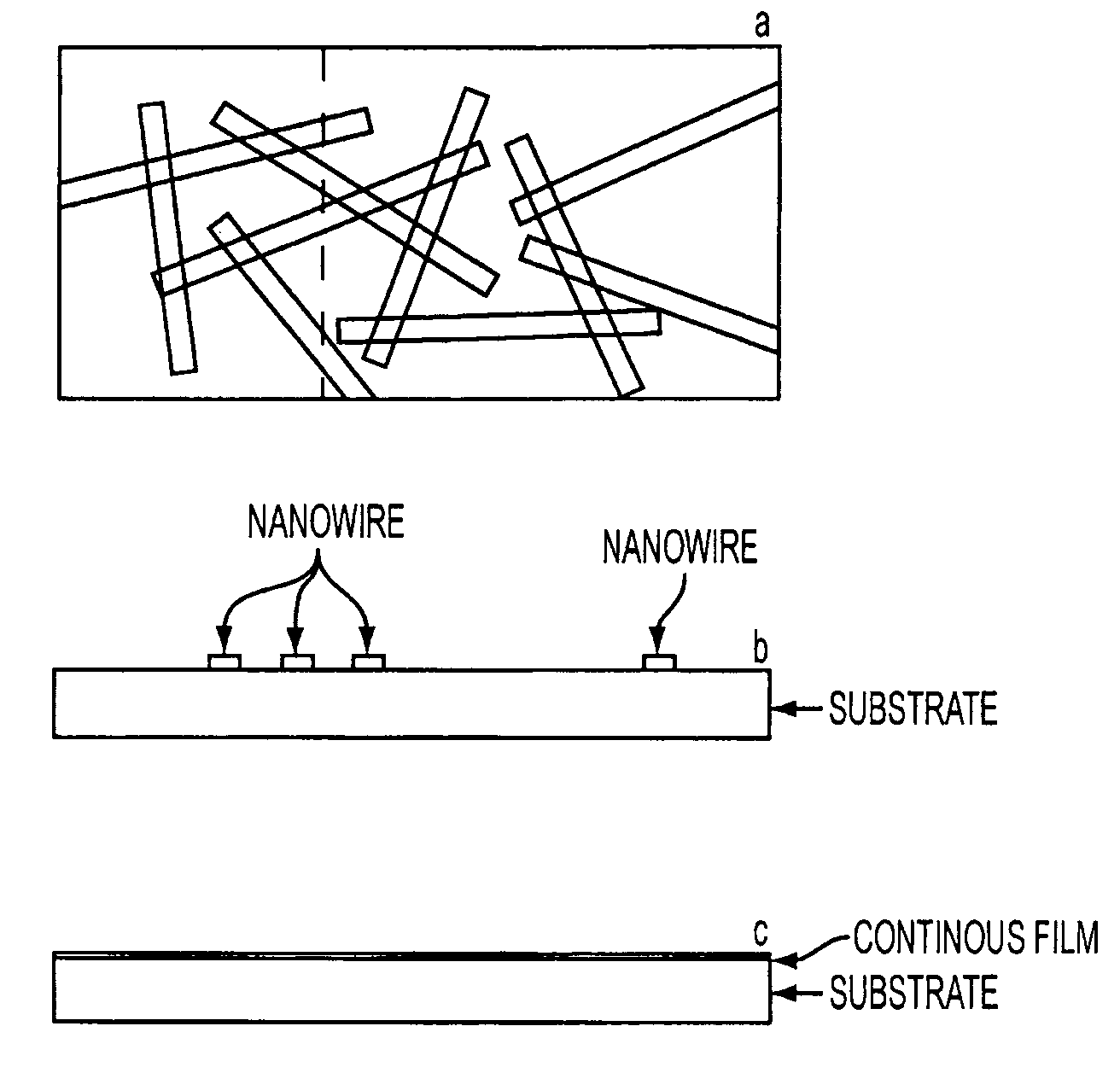
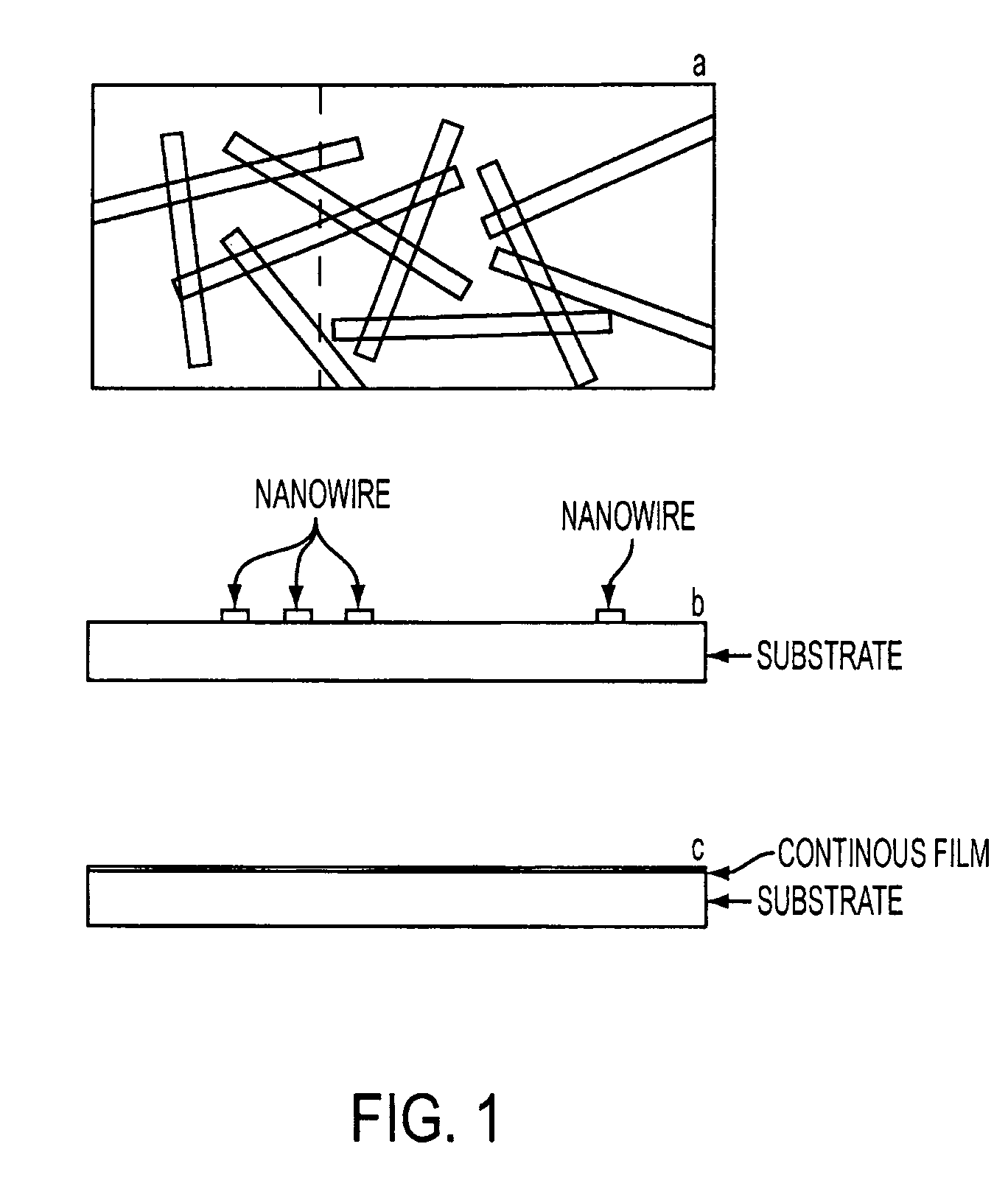
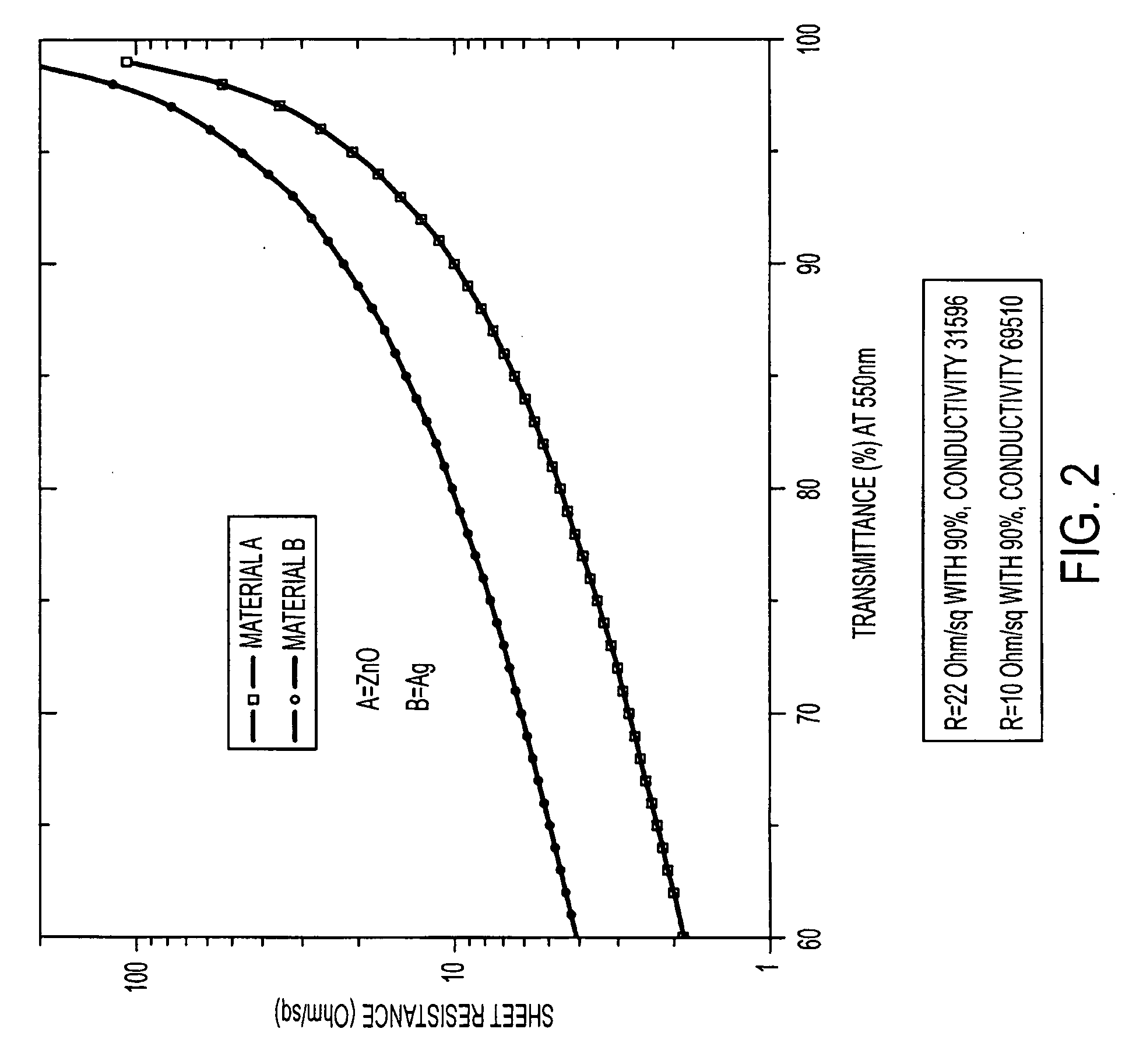
Electrically conducting and optically transparent nanowire networks
A network of nanowires has a plurality of interconnected nanowires. Each interconnected nanowire includes a metal in its composition. The network of nanowires is electrically conducting and substantially transparent to visible light. An electronic or electro-optic device has a network of nanowires. The network of nanowires has a plurality of interconnected nanowires, each interconnected nanowire including a metal in its composition. The network of nanowires is electrically conducting and substantially transparent to visible light. A metal-oxide nanowire has a metal oxide doped with a second metal in a composition thereof. The metal-oxide nanowire is electrically conducting and substantially transparent to visible light.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
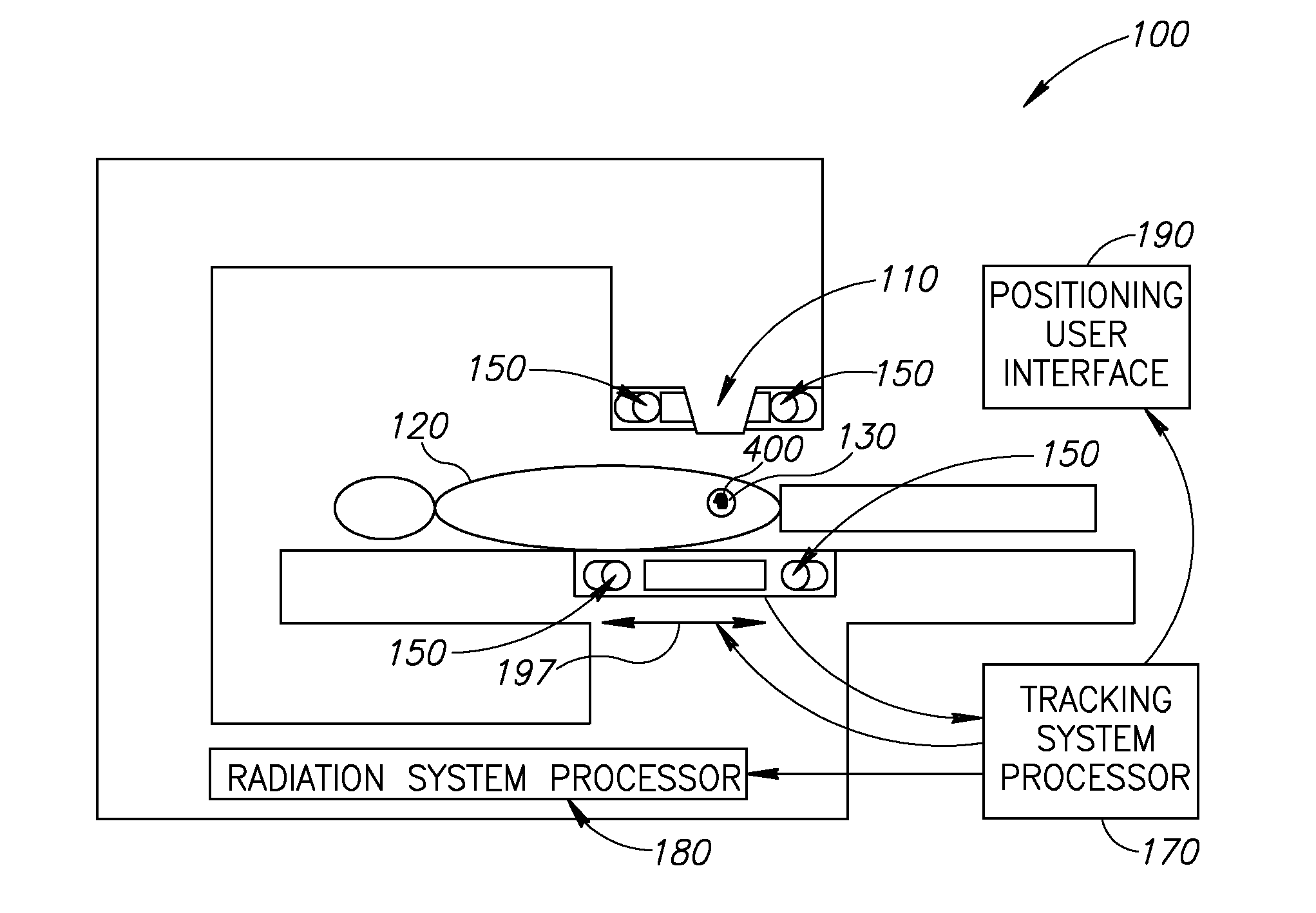
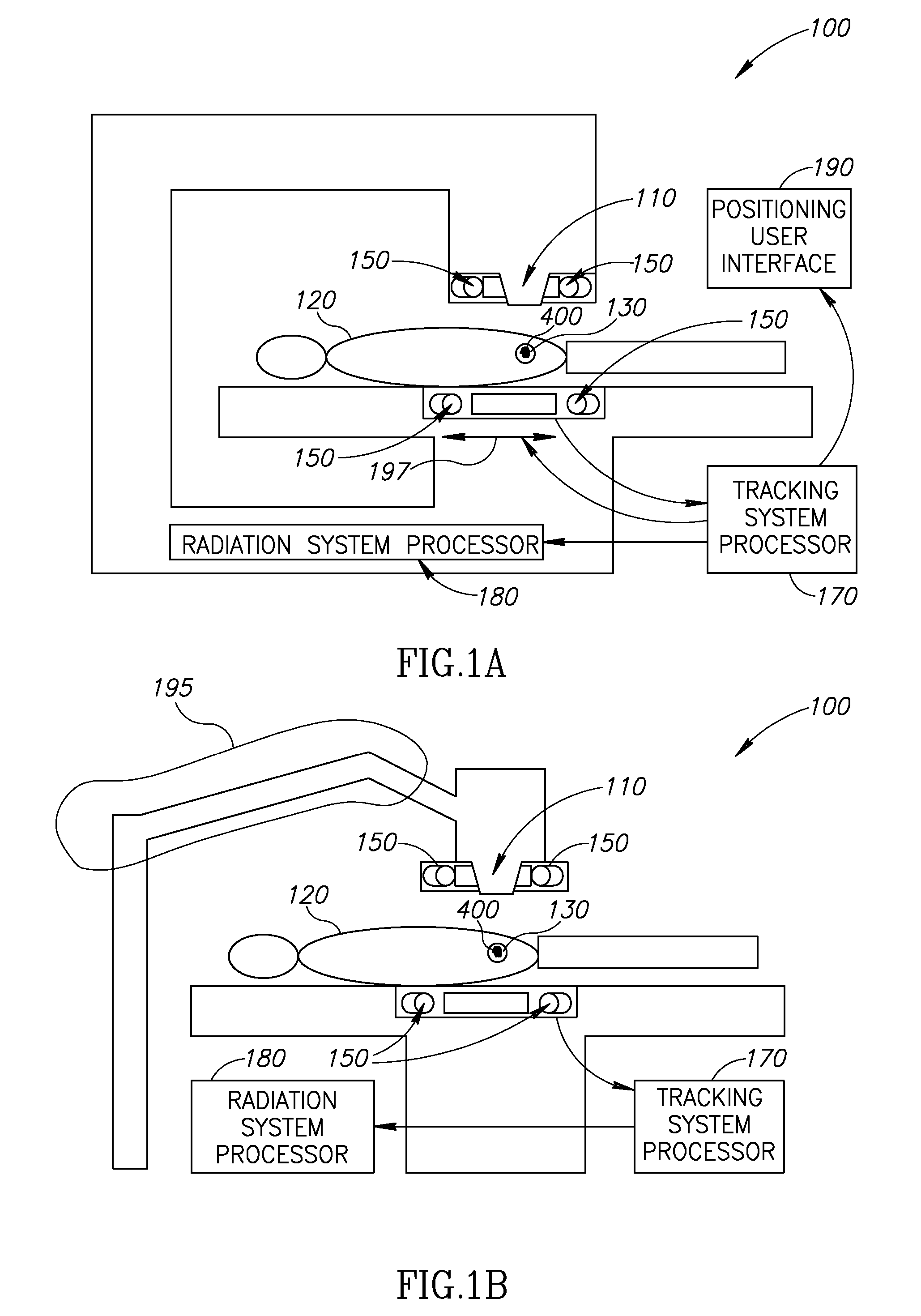
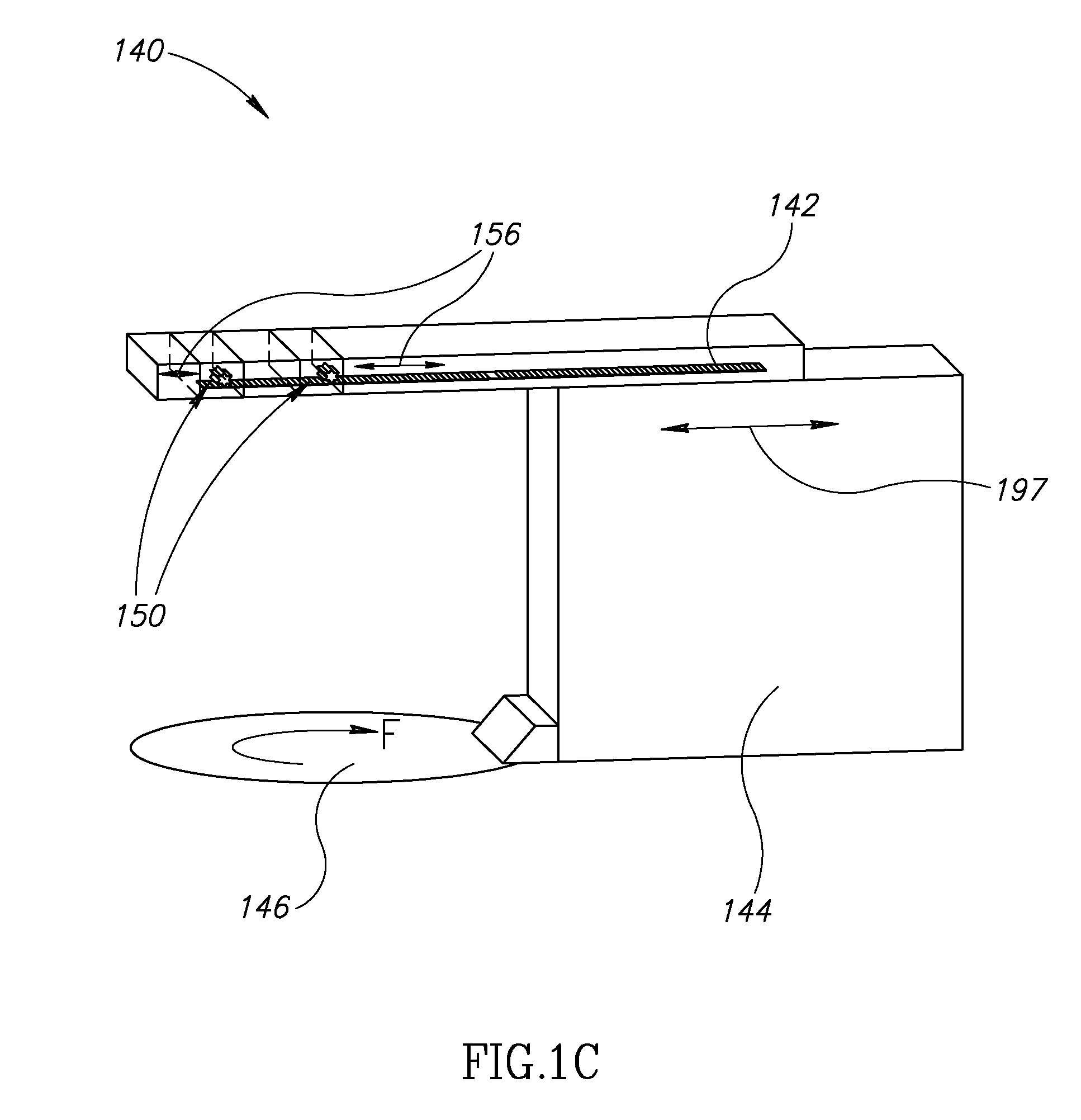
Medical Treatment System and Method
InactiveUS20070055144A1Inhibit migrationRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesTarget tissuePosition sensor
A method of guiding a tool, the method comprising: (a) implanting a source of radioactivity at a position having a geometric relationship to a target tissue; (b) determining at least an indication of a location of said source using at least one radioactivity detecting position sensor; and (c) positioning a tool at a desired relative location with respect to said target tissue based on said determined location.
Owner:NAVOTEK MEDICAL
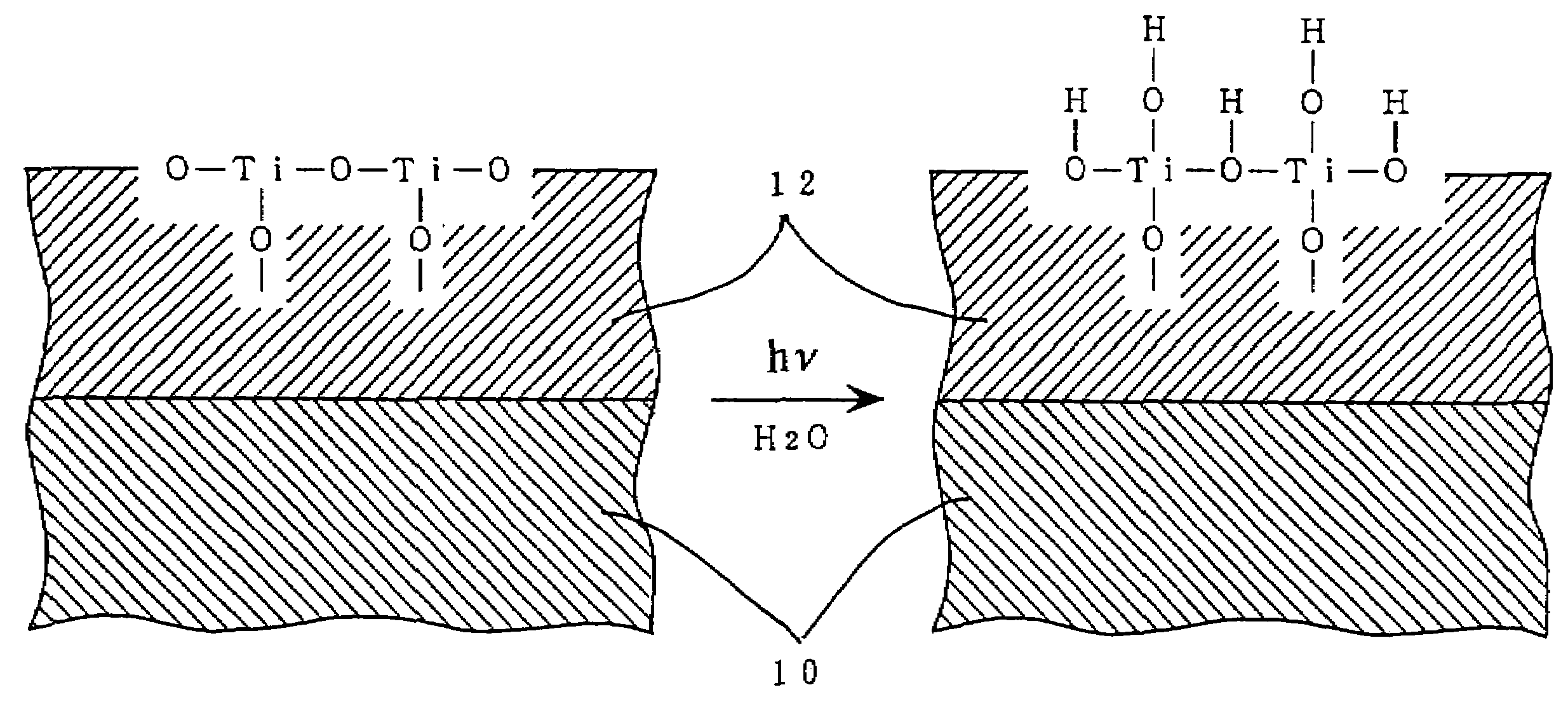
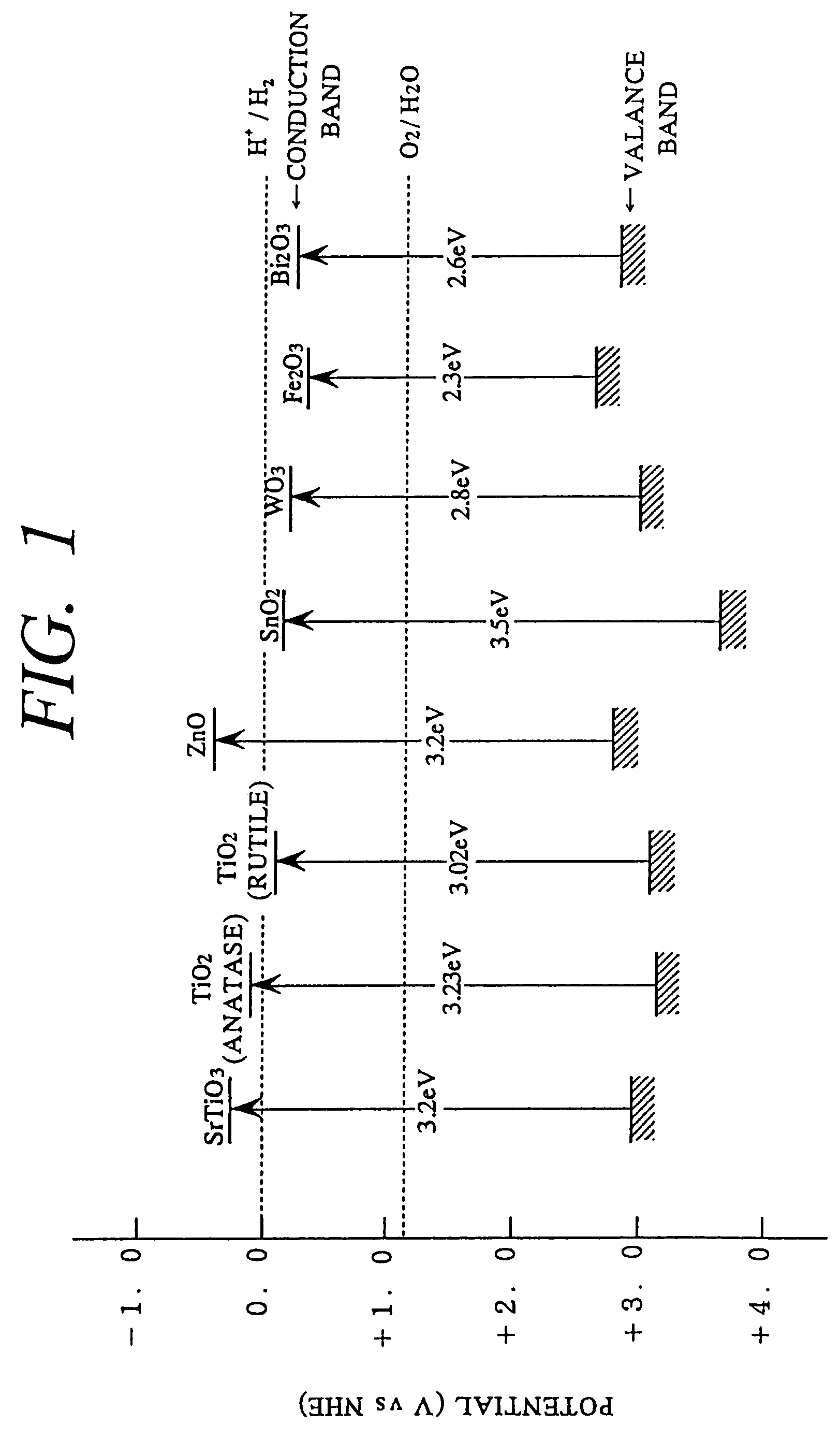
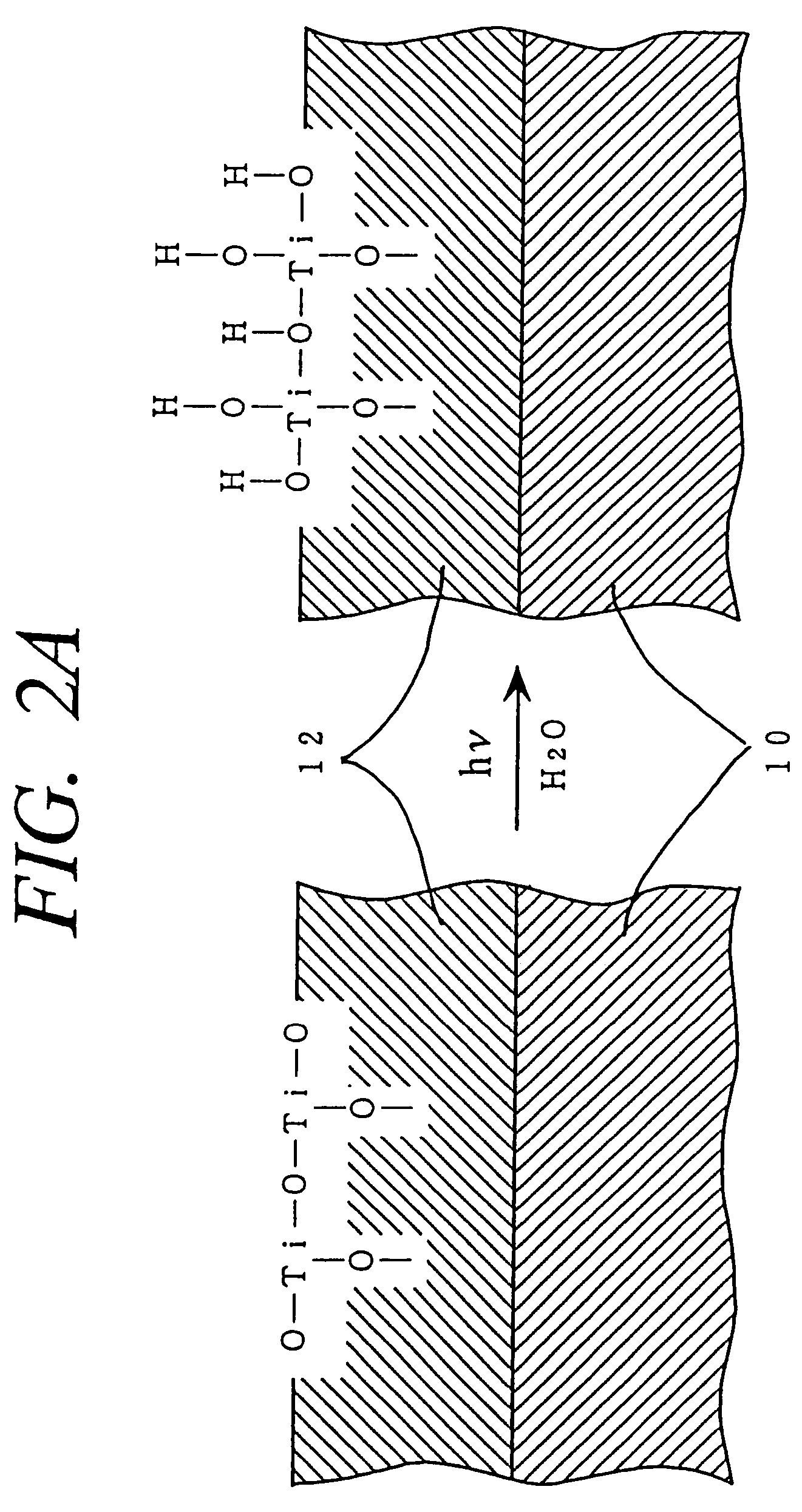
Method for photocatalytically rendering a surface of a substrate superhydrophilic, a substrate with superhydrophilic photocatalytic surface, and method of making thereof
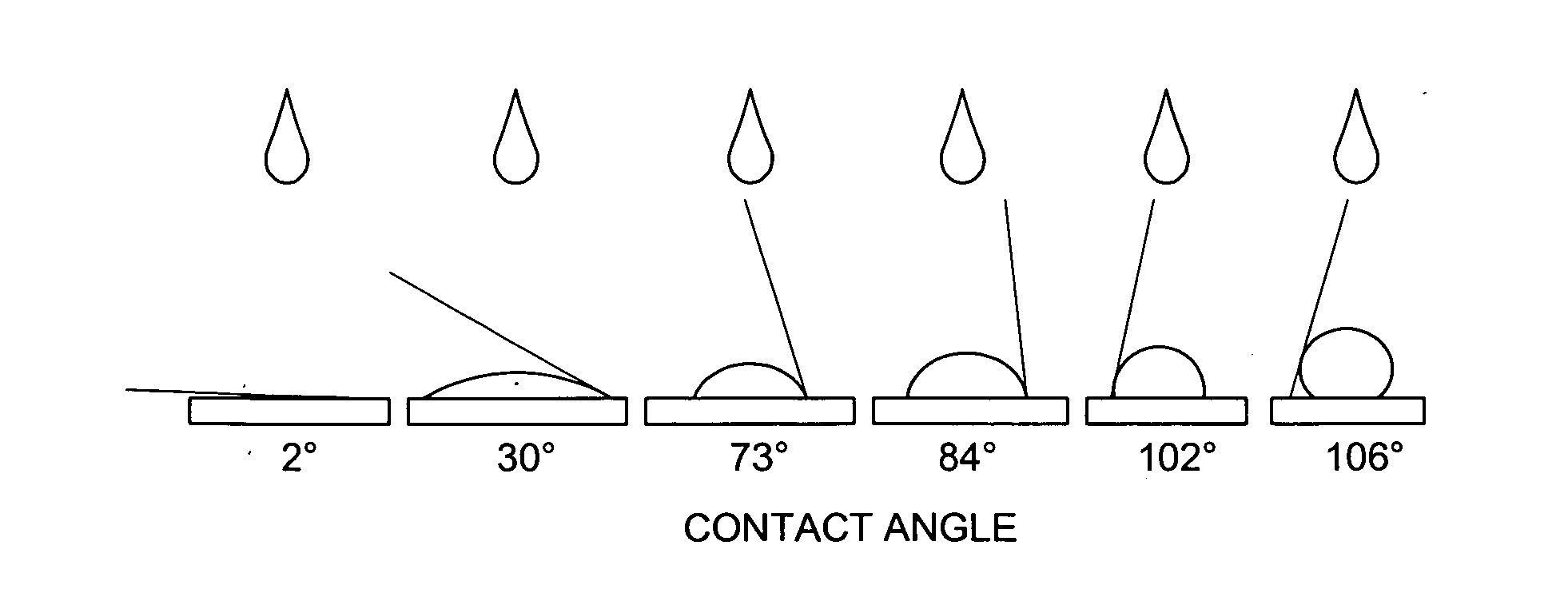
A method of preventing or reducing fogging of a surface of a composite when subjected to humid conditions includes providing a composite with a surface. The composite includes a substrate and a photocatalytic surface layer. The photocatalytic surface layer includes a photocatalyst. The method further includes subjecting the photocatalyst to photoexcitation to render the surface of the composite hydrophilic, wherein, after the photoexcitation, the surface of the composite has a water wettability of less than 10° in terms of the contact angle with water. The method further includes subjecting the composite to humidity that is sufficient to induce fogging of the substrate if the photocatalytic surface layer were absent.
Owner:TOTO LTD
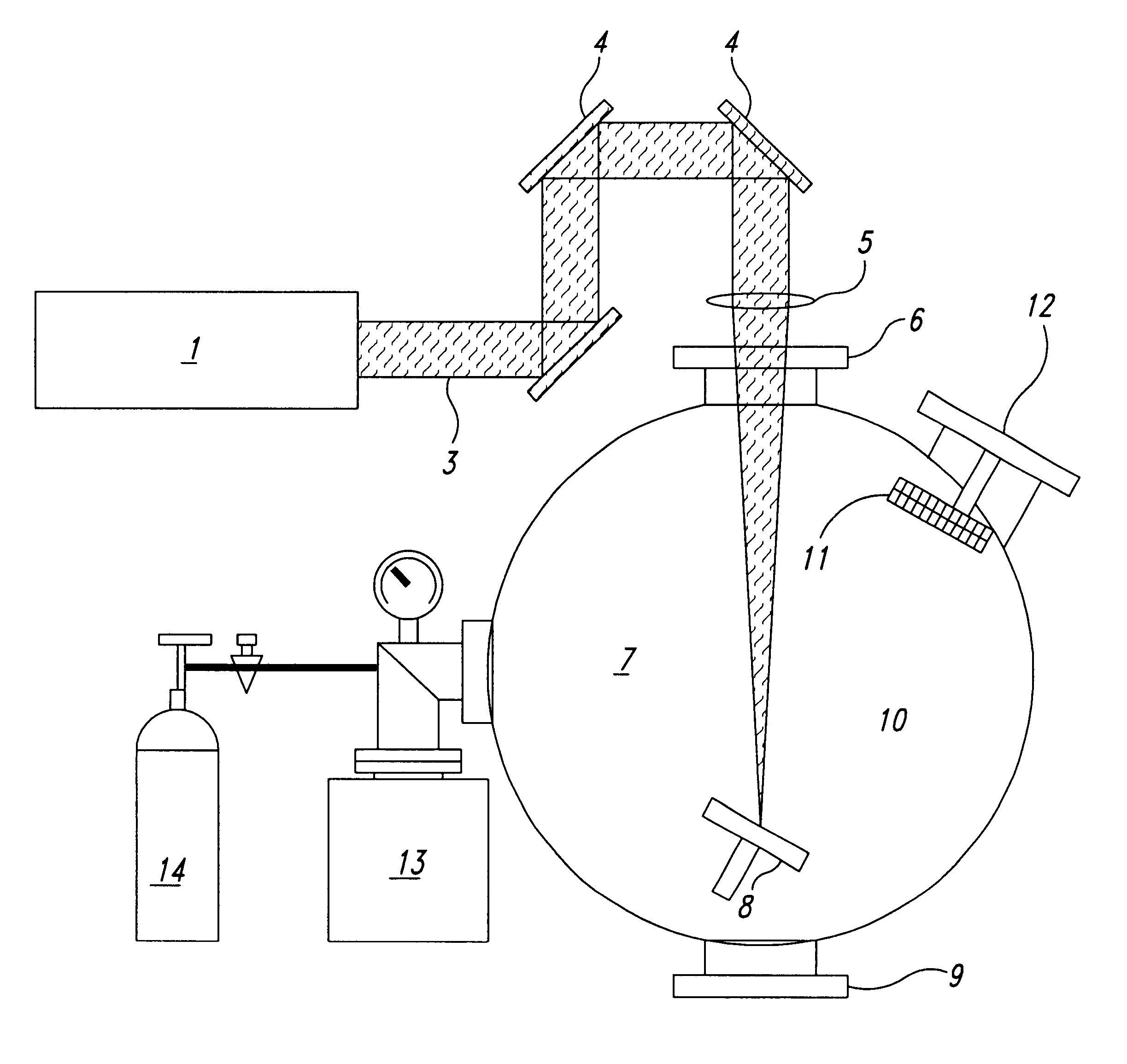
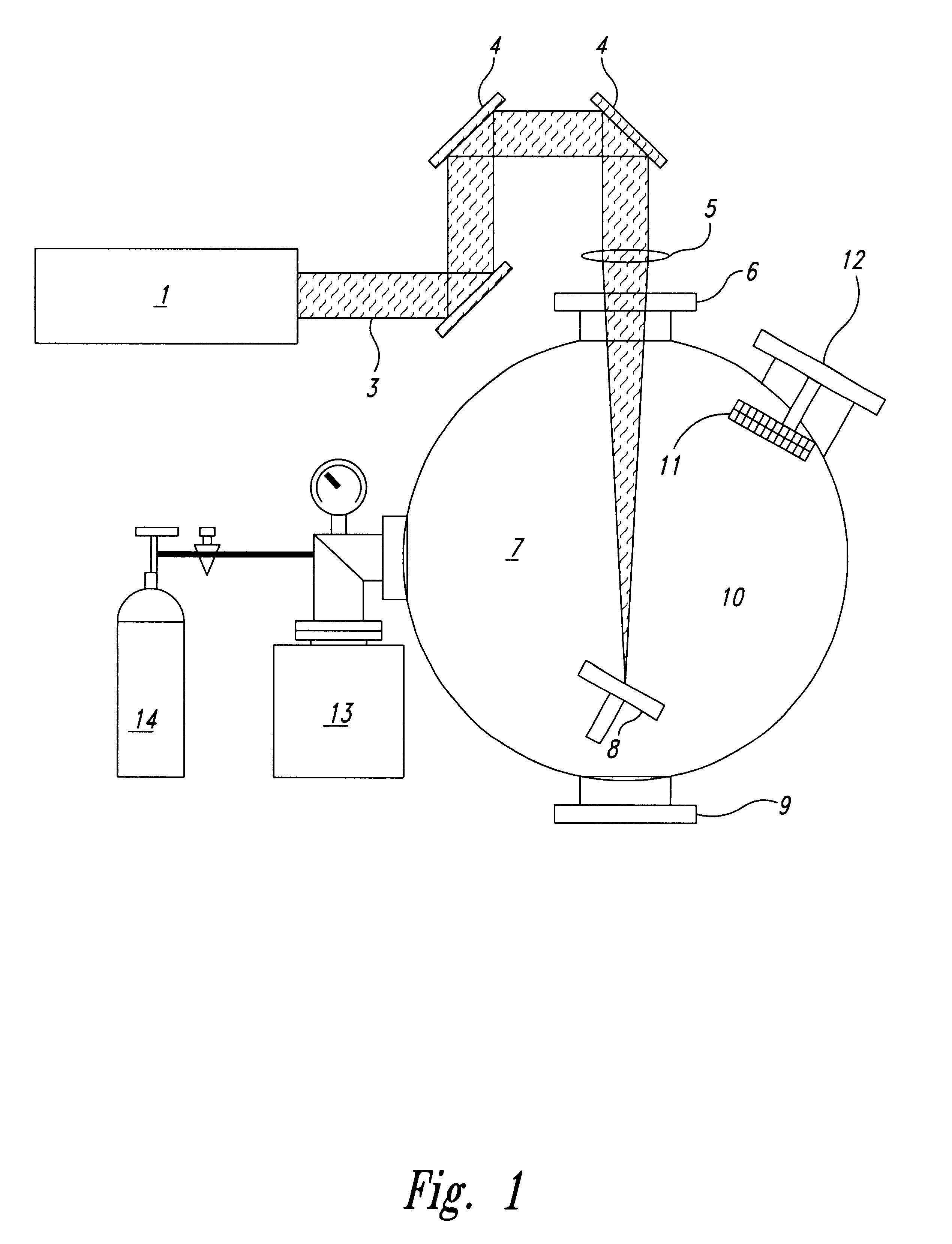
Method of deposition of thin films of amorphous and crystalline microstructures based on ultrafast pulsed laser deposition
InactiveUS6312768B1Improve surface qualityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingMacroscopic scaleCarbon nanotube
Powerful nanosecond-range lasers using low repetition rate pulsed laser deposition produce numerous macroscopic size particles and droplets, which embed in thin film coatings. This problem has been addressed by lowering the pulse energy, keeping the laser intensity optional for evaporation, so that significant numbers of the macroscopic particles and droplets are no longer present in the evaporated plume. The result is deposition of evaporated plume on a substrate to form thin film of very high surface quality. Preferably, the laser pulses have a repetition rate to produce a continuous flow of evaporated material at the substrate. Pulse-range is typically picosecond and femtosecond and repetition rate kilohertz to hundreds of megahertz. The process may be carried out in the presence of a buffer gas, which may be inert or reactive, and the increased vapour density and therefore the collision frequency between evaporated atoms leads to the formation of nanostructured materials of increasing interest, because of their peculiar structural, electronic and mechanical properties. One of these is carbon nanotubes, which is a new form of carbon belonging to the fullerene (C60) family. Carbon nanotubes are seamless, single or multishell co-axial cylindrical tubules with or without dome caps at the extremities. Typically diameters range from 1 nm to 50 nm with a length >1 mum. The electronic structure may be either metallic or semiconducting without any change in the chemical bonding or adding of dopant. In addition, the materials have application to a wide range of established thin film applications.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Non-fouling, Anti-microbial, Anti-thrombogenic graft-from compositions
InactiveUS20100152708A1Reduce penetrationRadiation applicationsSurgeryMicroorganismPolymer substrate
Substrates, optionally coated with an undercoating layer, having grafted there from one or more non-fouling materials are described herein. The non-fouling, polymeric material can be grafted from a variety of substrate materials, particularly polymeric substrates and / or polymeric undercoating layers. The graft-from techniques described herein can result in higher surface densities of the non-fouling material relative to graft-to formulations. Graft-from methods can be used to produce covalently tethered polymers. The compositions described herein are highly resistant protein absorption, particularly in complex media and retain a high degree of non-fouling activity over long periods of time. The compositions described herein may also demonstrate antimicrobial and / or anti-thrombogenic activity. The non-fouling material can be grafted from the substrate, or optionally from an undercoating layer on the substrate, preferably without significantly affecting the mechanical and / or physical properties of the substrate material.
Owner:ARROW INT INC
Prosthetic knee joint having at least one diamond articulation surface
InactiveUS7077867B1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesKnee Joint
Owner:DIAMICRON
Controlled vapor deposition of biocompatible coatings over surface-treated substrates
ActiveUS20060088666A1Improve bindingThe surface is moreMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation applicationsGas phaseBiocompatible coating
We have developed an improved vapor-phase deposition method and apparatus for the application of layers and coatings on various substrates. The method and apparatus are useful in the fabrication of biofunctional devices, Bio-MEMS devices, and in the fabrication of microfluidic devices for biological applications. In one important embodiment, a siloxane substrate surface is treated using a combination of ozone and UV radiation to render the siloxane surface more hydrophilic, and subsequently a functional coating is applied in-situ over the treated surface of the siloxane substrate.
Owner:SPTS TECH LTD
Detector for sensing motion and direction of a railway device
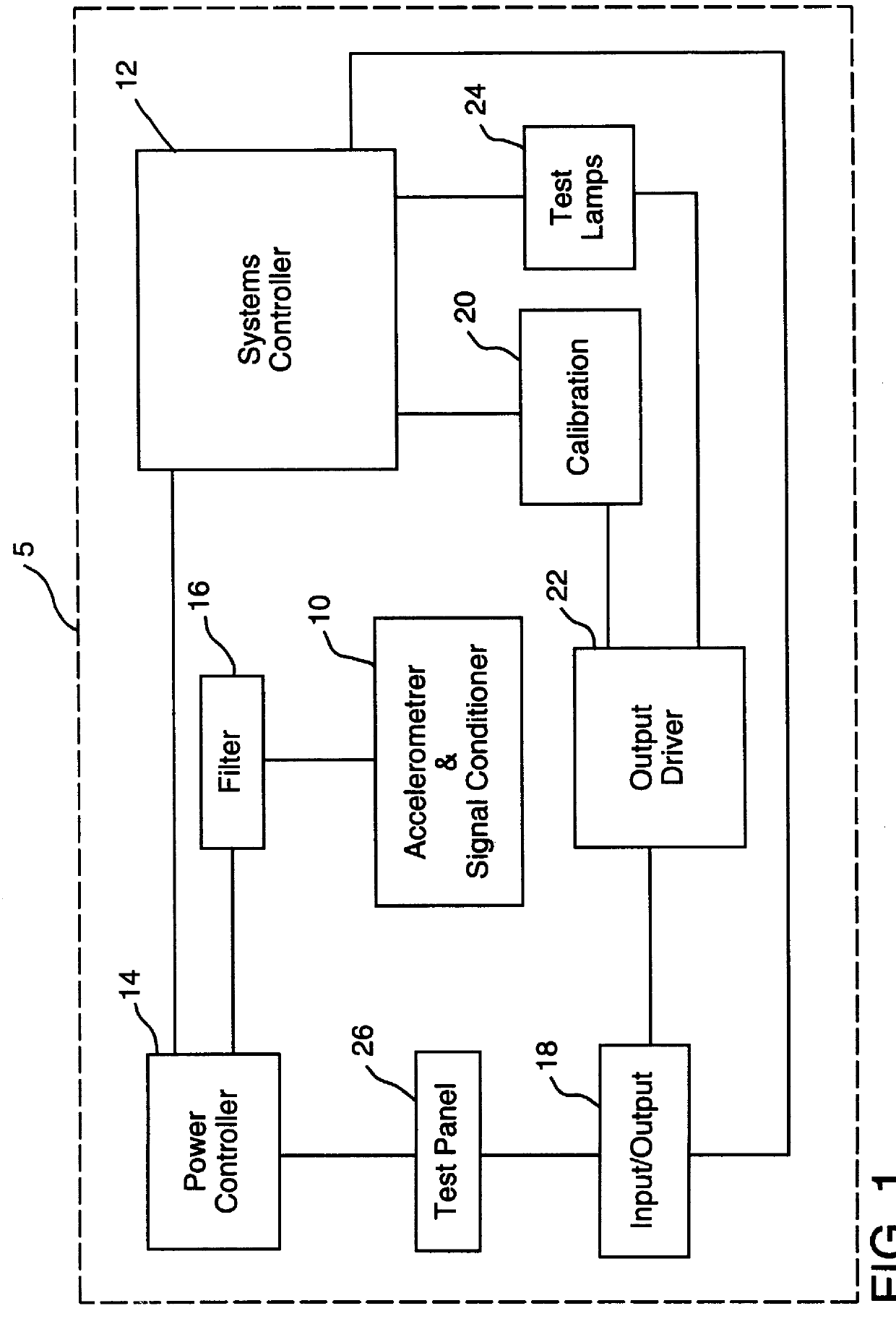
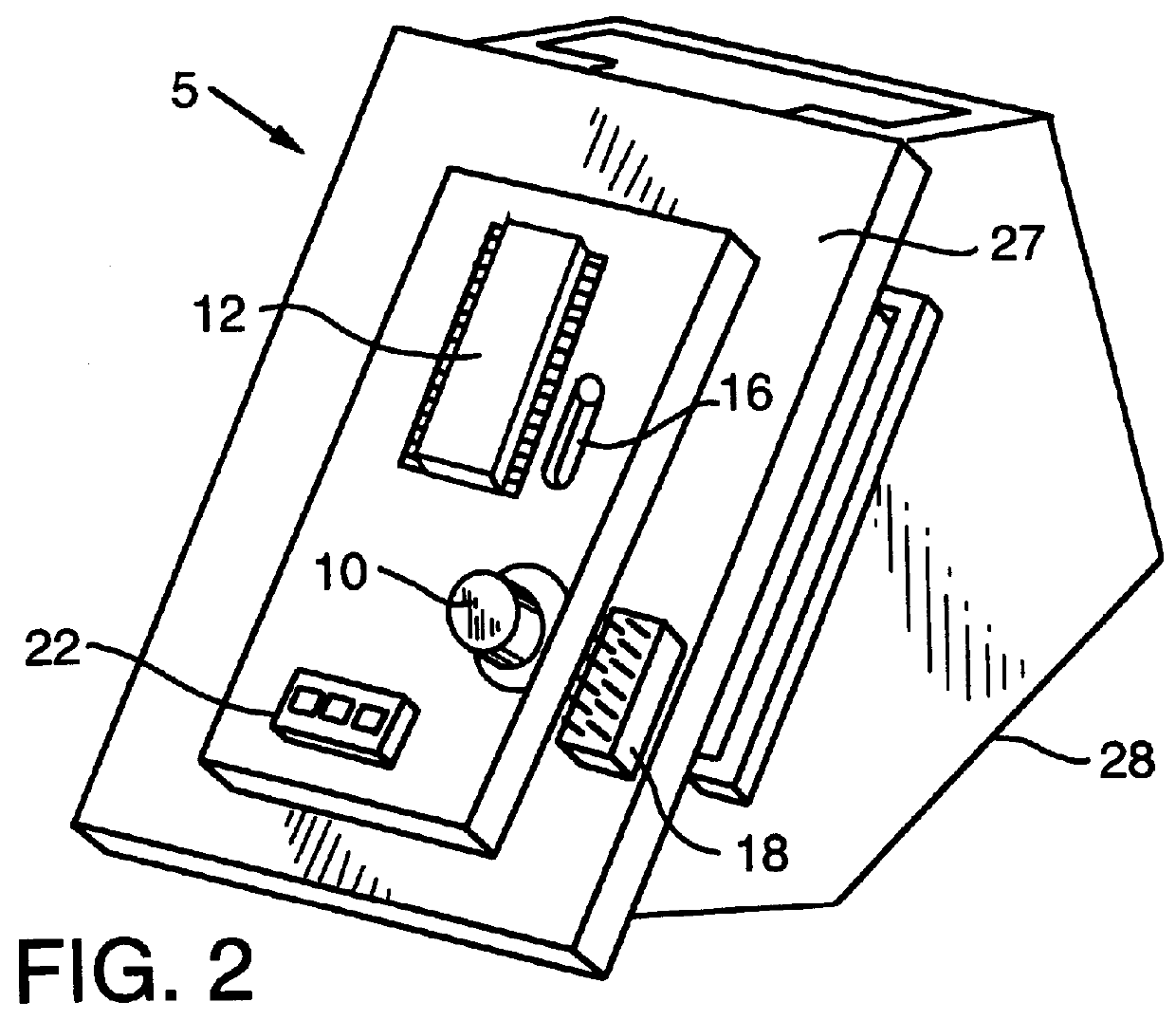
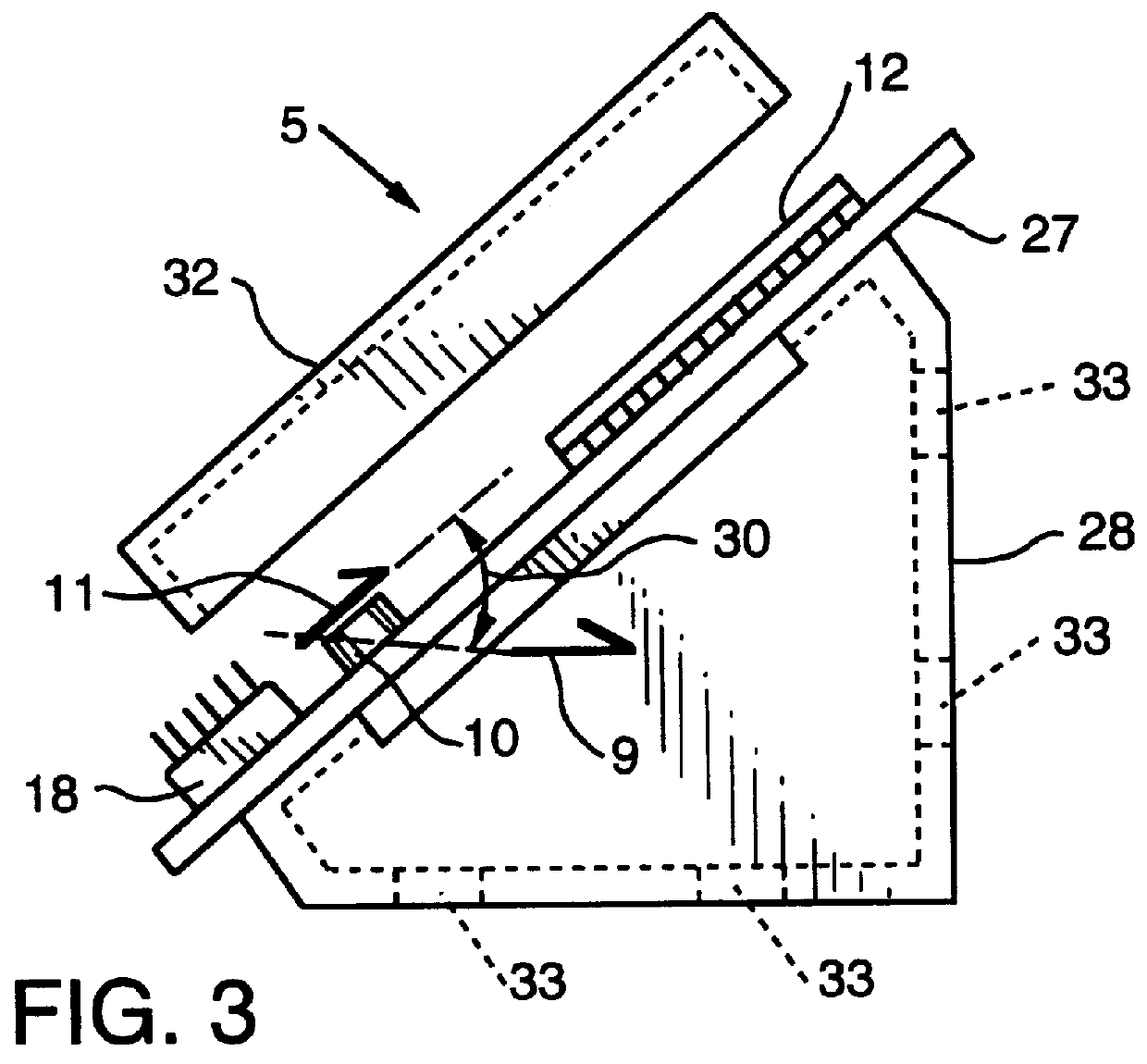
InactiveUS6087950AElectric signal transmission systemsMeasurement devicesPower controllerMotion detector
A motion detector for detecting movement of a rail based vehicle and the direction of that movement is provided. The motion detector can be integral with or attachable to an end-of-train unit and can include a single axis accelerometer mounted at an angle from the rails for detecting acceleration in both the lateral and vertical directions. A systems controller, which can include an analyzer, can be provided to receive and analyze output from the accelerometer to determine a motion state and a direction. A power controller can be provided for supplying power to the accelerometer on an intermittent basis to conserve power. A calibration unit can be provided to both initially calibrate and to subsequently recalibrate the accelerometer after a stopped motion state is detected. Additionally, an input / output port and an output driver for conditioning the signal for output to the end-of-train unit can be provided.
Owner:THE UNION SWITCH & SIGNAL
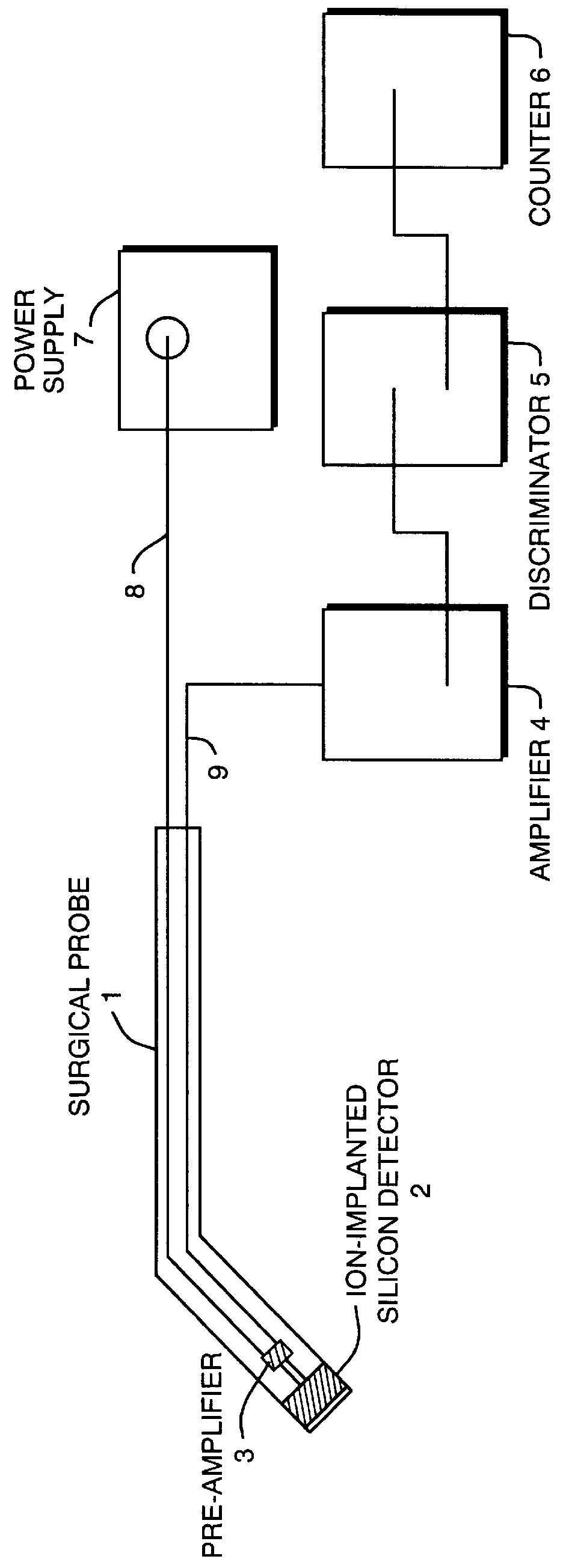
Solid state beta-sensitive surgical probe
InactiveUS6076009ASensitive highMinimizing requisite sizeRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesInfraredAudio power amplifier
An intraoperative probe system for preferentially detecting beta radiation over gamma radiation emitted from a radiopharmaceutical is described. In one embodiment, the probe system of the present invention is a probe having an ion-implanted silicon charged-particle detector for generating an electrical signal in response to received beta particles. In such an embodiment, a preamplifier may be located in close proximity to the detector filters and amplifies the electrical signal. Furthermore, a wire may be used to couple the probe to a processing unit for amplifying and filtering the electrical signal, and a counter may be utilized to analyze the resulting electrical signal to determine the number of beta particles being received by the detector. Alternatively, the wire can be replaced with an infrared or radio transmitter and receiver for wireless operation of the probe.
Owner:MICHIGAN THE UNIV OF RGT
Method for forming a servo pattern on a magnetic tape
InactiveUS7029726B1Maintain alignmentTrack finding/aligningRadiation applicationsMagnetic tapeControl theory
The systems, methods and products of the invention include systems and methods for manufacturing servo tracks on a magnetic tape. In one aspect, the invention includes systems for manufacturing magnetic tapes having servo tracks thereon wherein the servo tracks are optically detectable and are capable of being processed by a servo control system for maintaining alignment of a magnetic recording head with the data tracks on the recording side of the magnetic tape. In one practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the non-recording side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the non-recording side of the magnetic tape. In another practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the magnetic side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the magnetic side of the magnetic tape. Such engraved patterns can act as optical servo tracks for maintaining alignment of the recording head with the data tracks on the magnetic tape.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
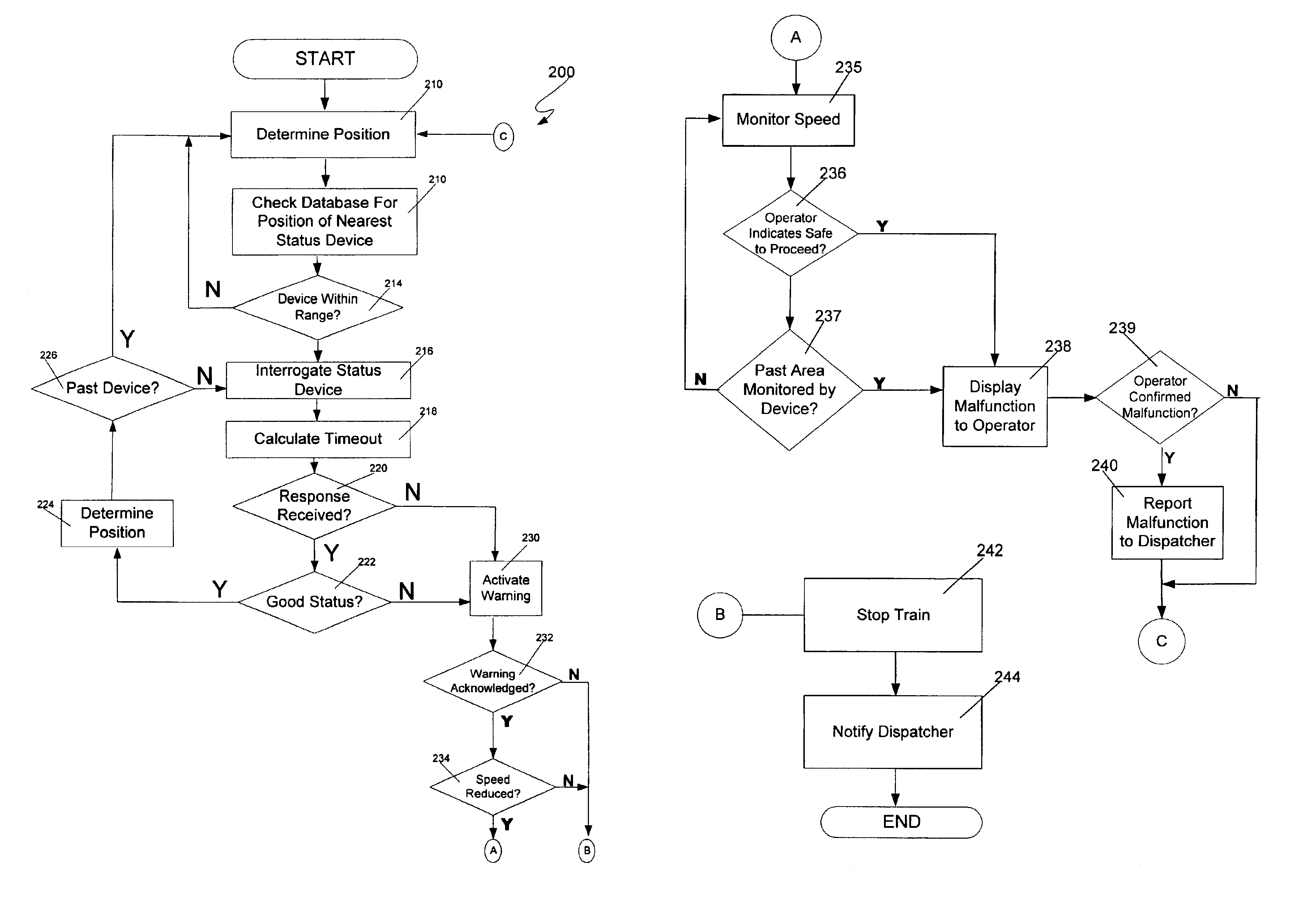
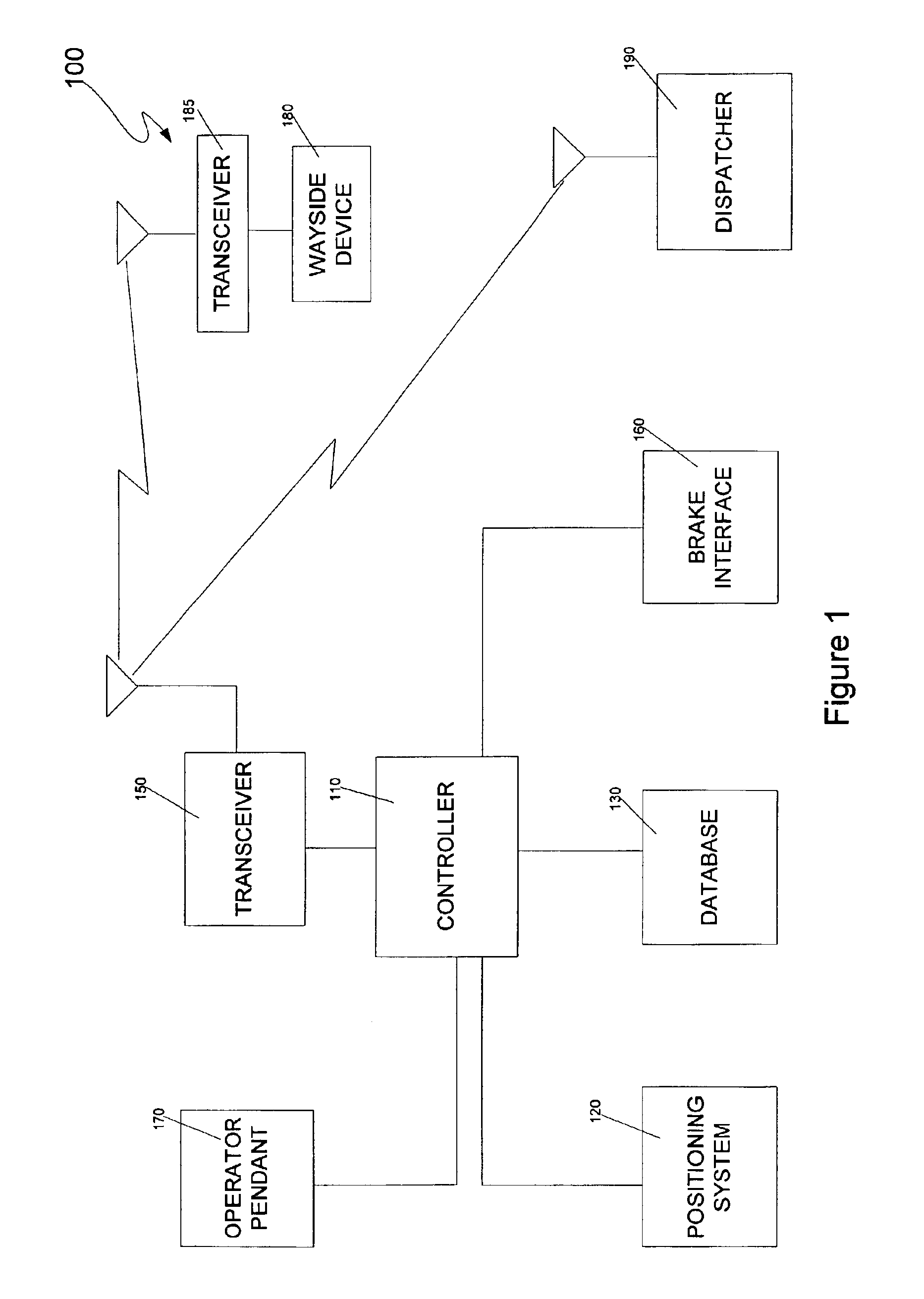
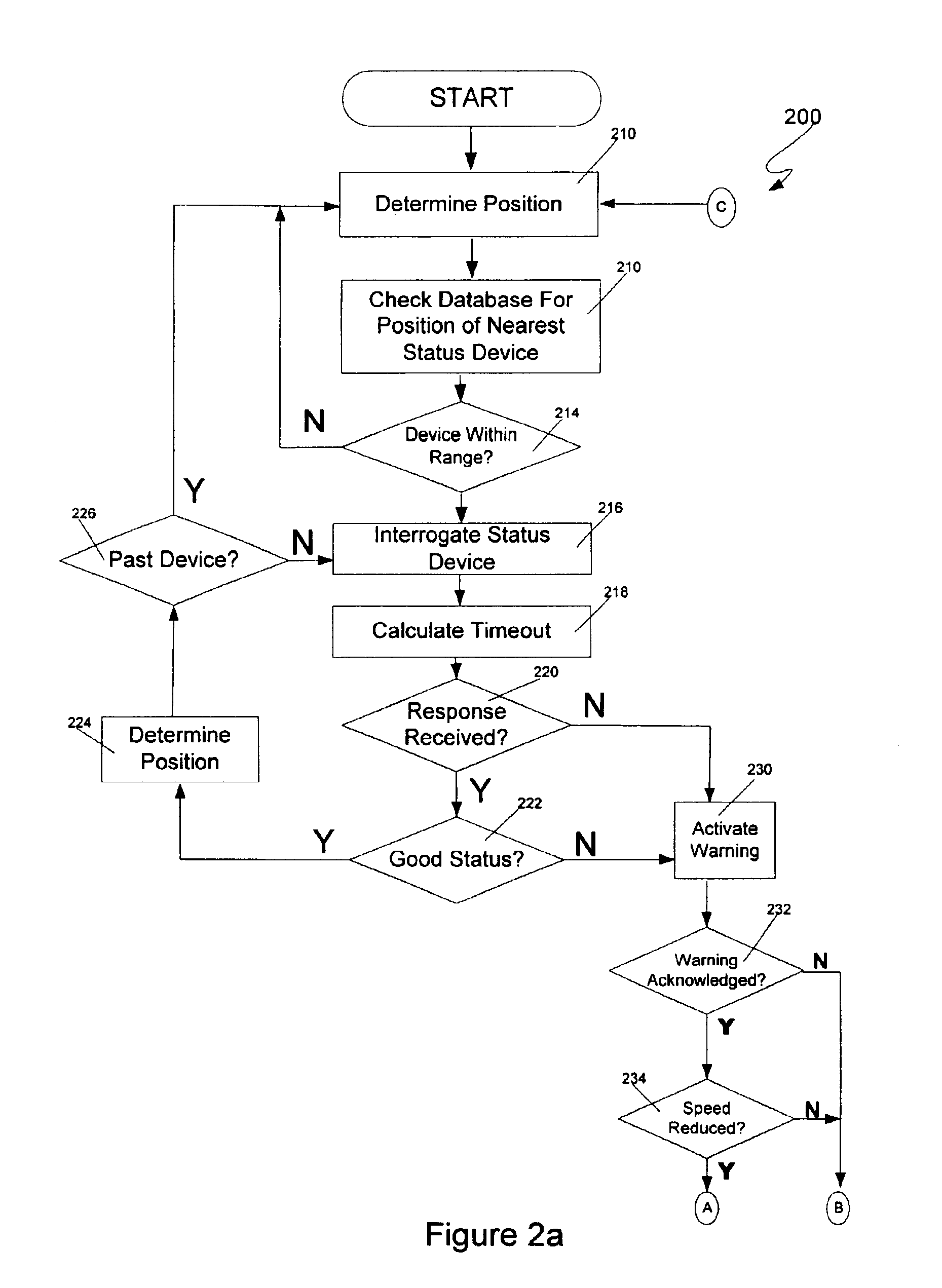
Method and system for automated fault reporting
InactiveUS6863246B2Shorten speedDigital data processing detailsTrack side maintainanceEngineeringVisual perception
An automated fault reporting system for a train includes a controller that gathers information concerning malfunctioning wayside status devices and automatically reports the information to an appropriate party. In one embodiment, the control module uses a positioning system and a database including device locations in order to determine when the train is near a device. If no status information is received from the device as the train approaches, or the status information indicates a problem, the train is allowed to continue at a reduced speed to allow the operator to visually confirm that it is safe to proceed. If an area monitored by the device has been passed, or if the operator indicates that there is no problem, or the device fails to respond, the controller records and reports the malfunction.
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY INC
Communication-based interconnected and intercommunicated I-CBIT train operation control system
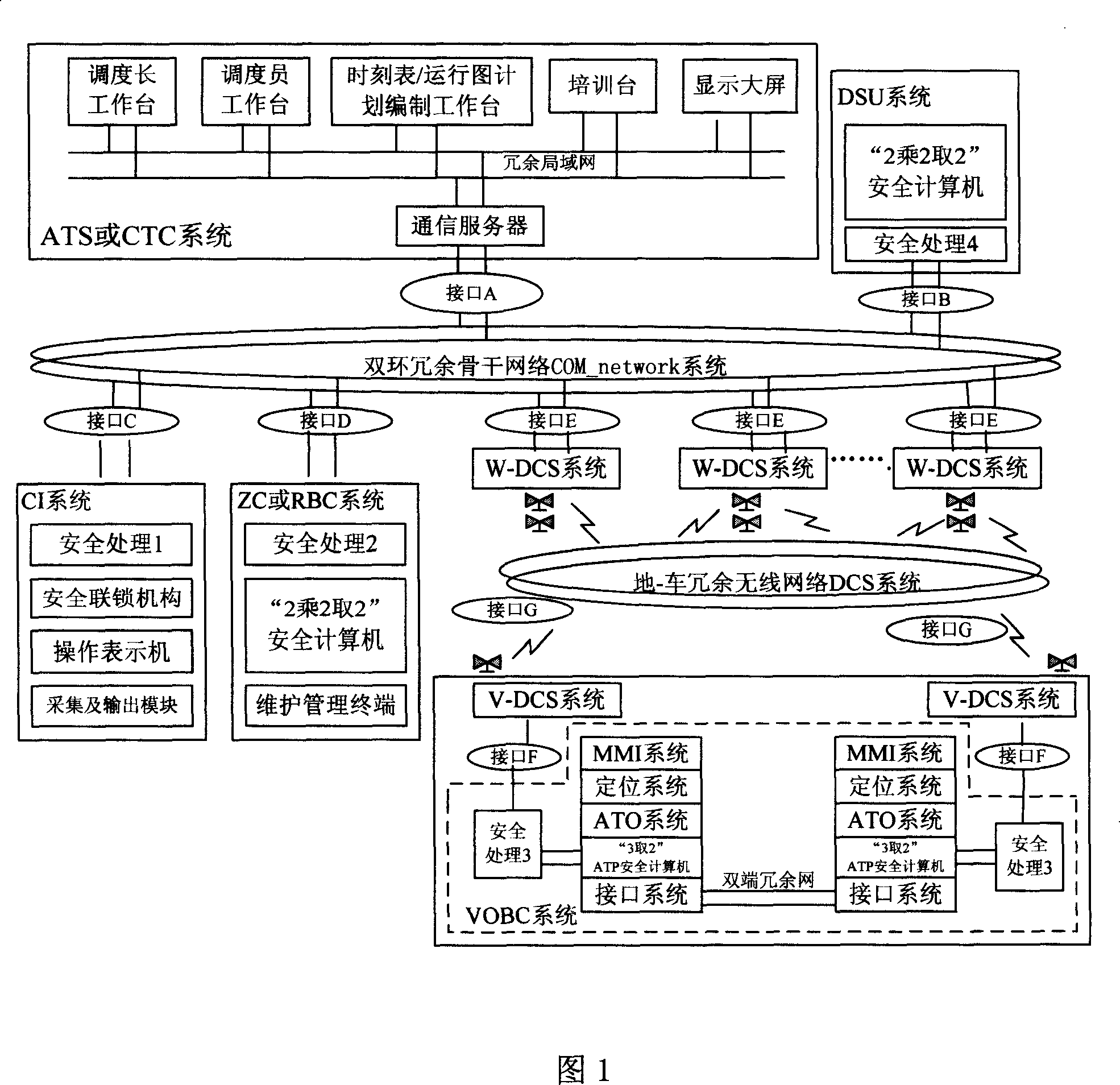
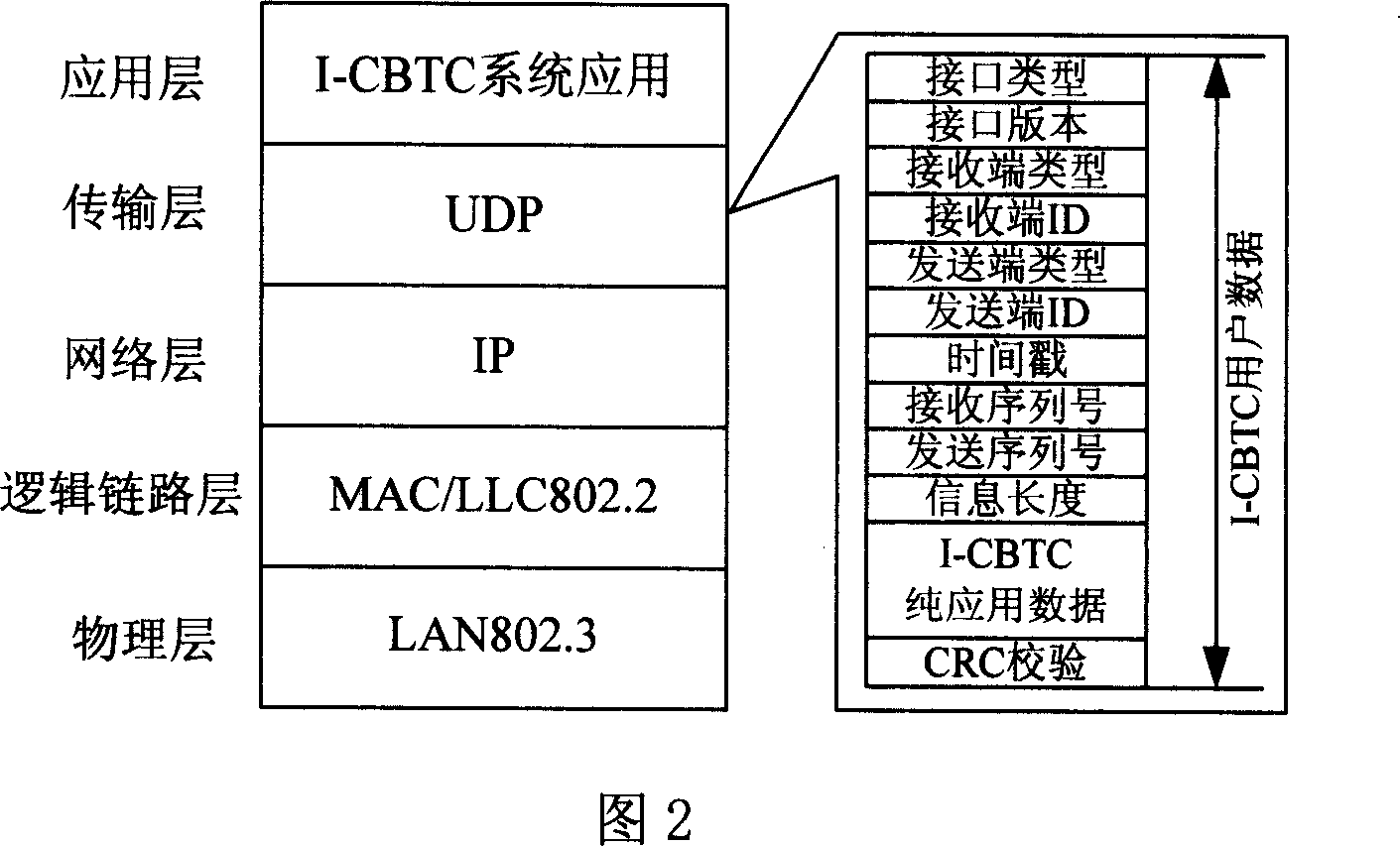
ActiveCN101009679AFacilitate resource sharingMaintain "transparencyVehicle route interaction devicesTransmissionOperational costsControl system
The disclosed I-CBTC mobile closed train operation control system applies wireless communication way to transmit information between ground control center and train, and comprises an ATS or CTC system, a DSU system, a CI system, a ZC or RBC system, a VOBC system, a dual-ring redundant backbone network COM_network system, a ground-train redundant wireless network DCS system, and interfaces among nodes. This invention normalizes and standardizes former function, performance index and interfaces, and reduces cost greatly.
Owner:TRAFFIC CONTROL TECH CO LTD
Apparatus for producing metal coated polymers
InactiveUS6106627AHigh breakdown strengthAvoid depositionRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingCross-linkBreakdown strength
A method of improving the breakdown strength of polymer multi-layer (PML) capacitors is provided and of providing a window in food packaging is provided. The method comprises patterning the aluminum coating, either by selective removal of deposited aluminum or by preventing deposition of the aluminum on selected areas of the underlying polymer film. Apparatus is also provided for patterning metal deposition on polymer films comprising masking for defining regions in which metal is deposited. The apparatus comprises: (a) a rotating drum; (b) a monomer evaporator for depositing a monomer film on the rotating drum; (c) a radiation curing element for curing the monomer film to form a cross-linked polymer film; and (d) a resistive evaporator for depositing a metal film on the cross-linked polymer film. The foregoing elements are enclosed in a vacuum chamber. The masking comprising one of the following: (e1) a web mask provided with openings for depositing the metal film therethrough, the web mask including a portion adapted for positioning between the resistive evaporator for depositing the metal film on the cross-linked polymer film and the rotating drum; or (e2) a rotating element for transferring liquid from a source to the rotating drum, the rotating element adapted to transfer the liquid to the rotating drum after the monomer evaporator for depositing the polymer film and before the resistive evaporator for depositing the metal film.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONE
Laser direct structuring materials with all color capability
InactiveUS20120276390A13D rigid printed circuitsRadiation applicationsPersonal computerMechanical property
Thermoplastic compositions that are capable of being used in a laser direct structuring process to provide enhanced plating performance and good mechanical properties. The compositions include a thermoplastic base resin, a laser direct structuring additive, and a mineral filler. The compositions can be used in a variety of applications such as personal computers, notebook and portable computers, cell phone antennas and other such communications equipment, medical applications, RFID applications, and automotive applications.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com