Patents
Literature
138 results about "Photoexcitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
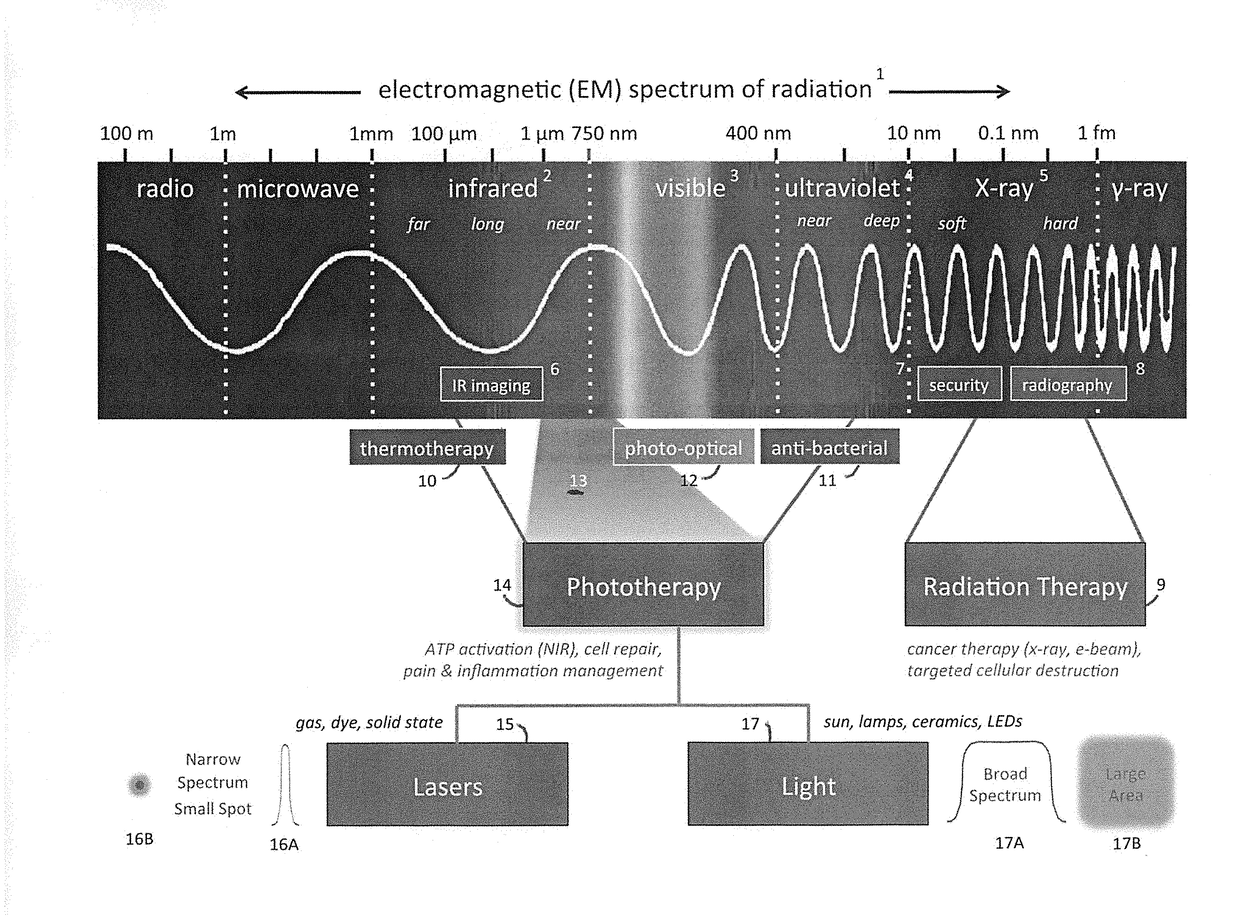
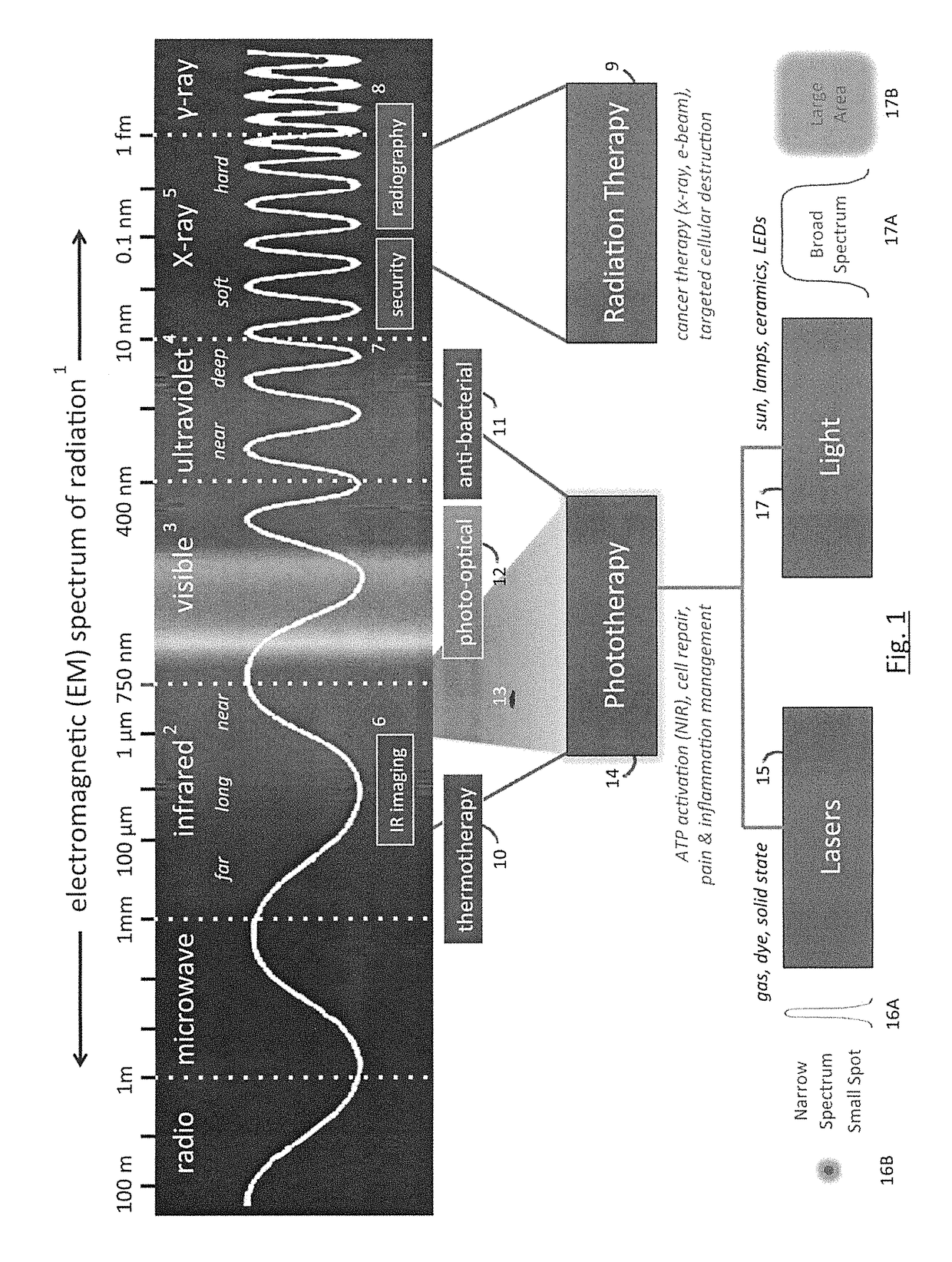
Photoexcitation is the production of an excited state of a quantum system by photon absorption. On the atomic and molecular scale photoexcitation is the photoelectrochemical process of electron excitation by photon absorption, when the energy of the photon is too low to cause photoionization. The absorption of the photon takes place in accordance with Planck's quantum theory.
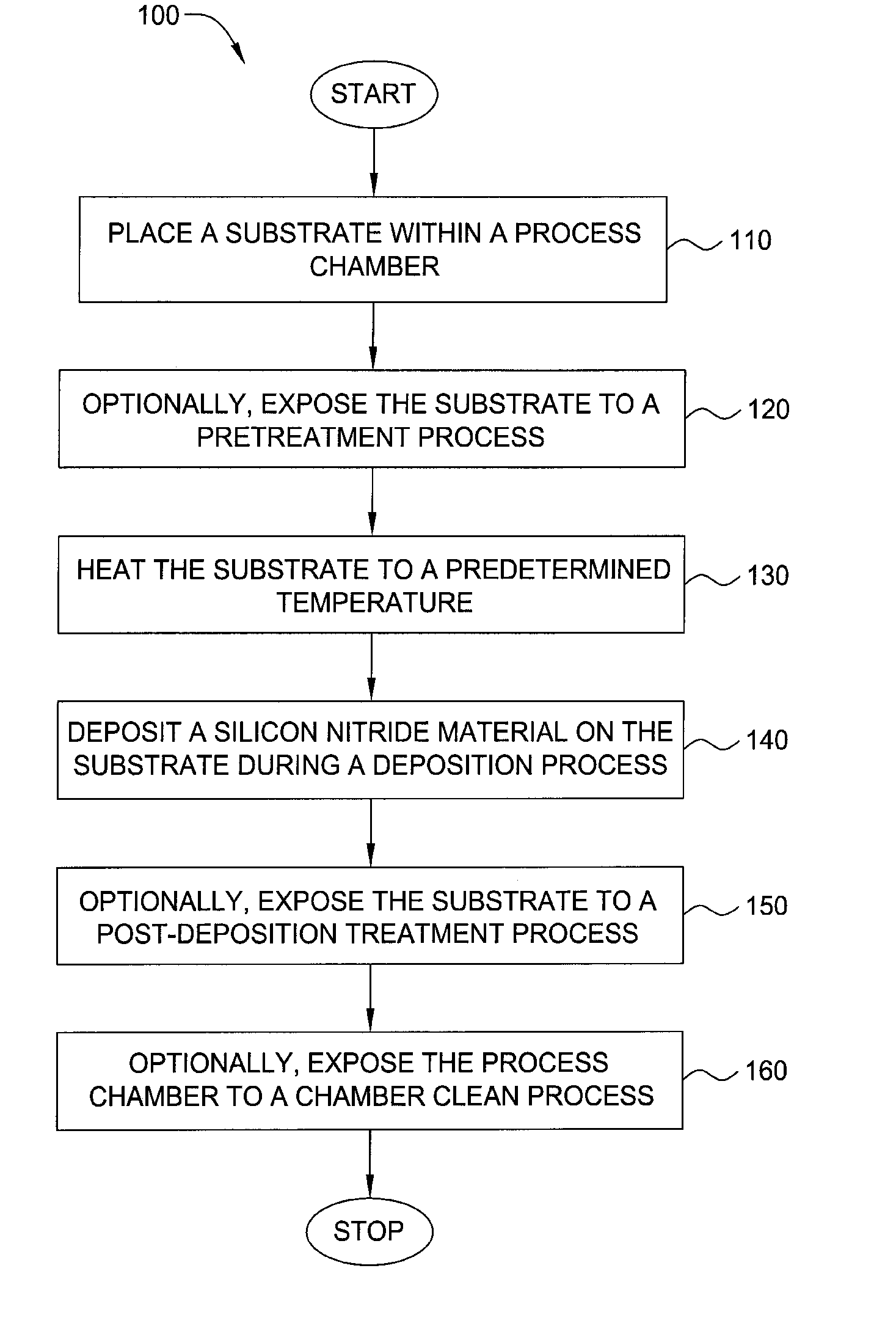
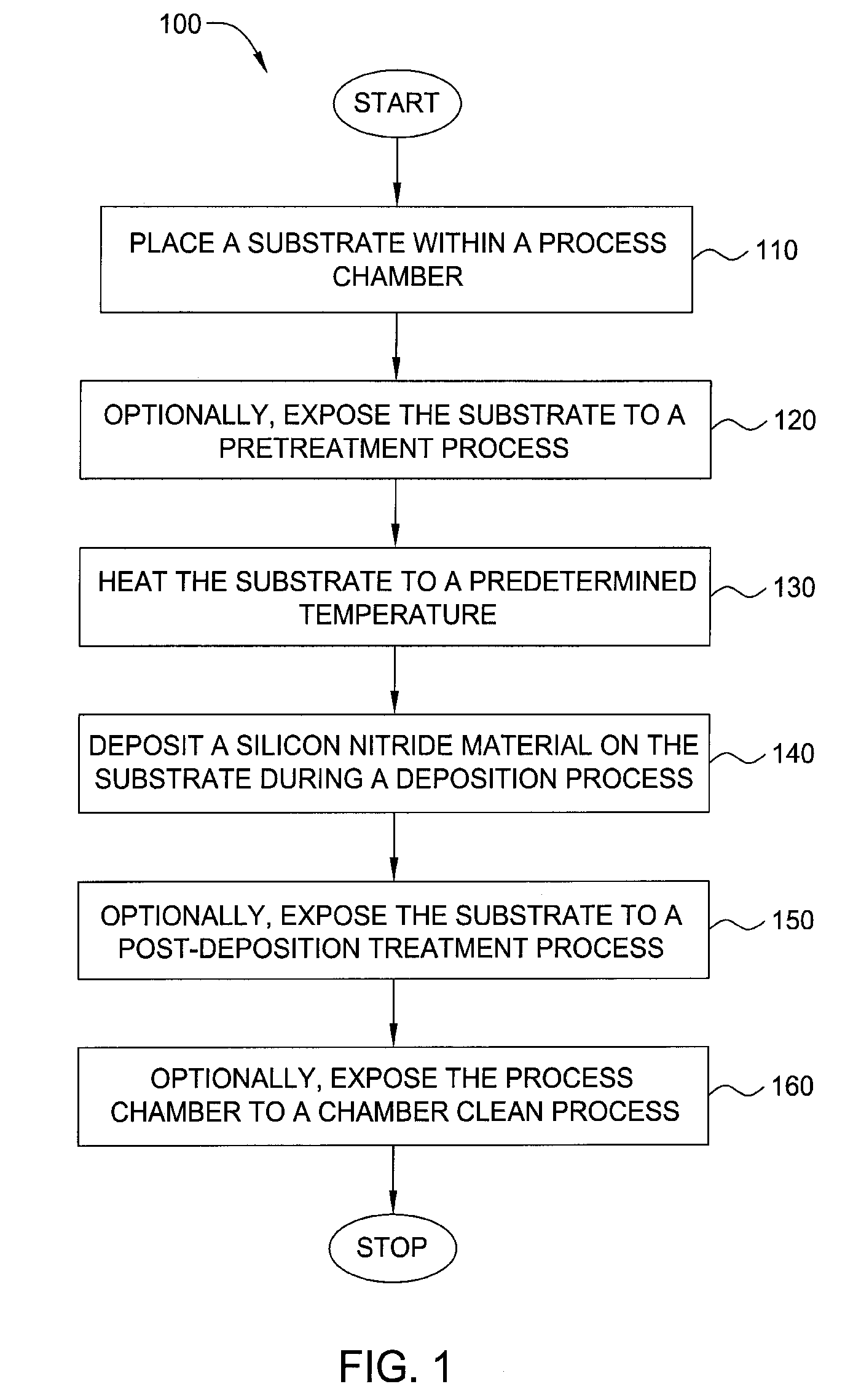
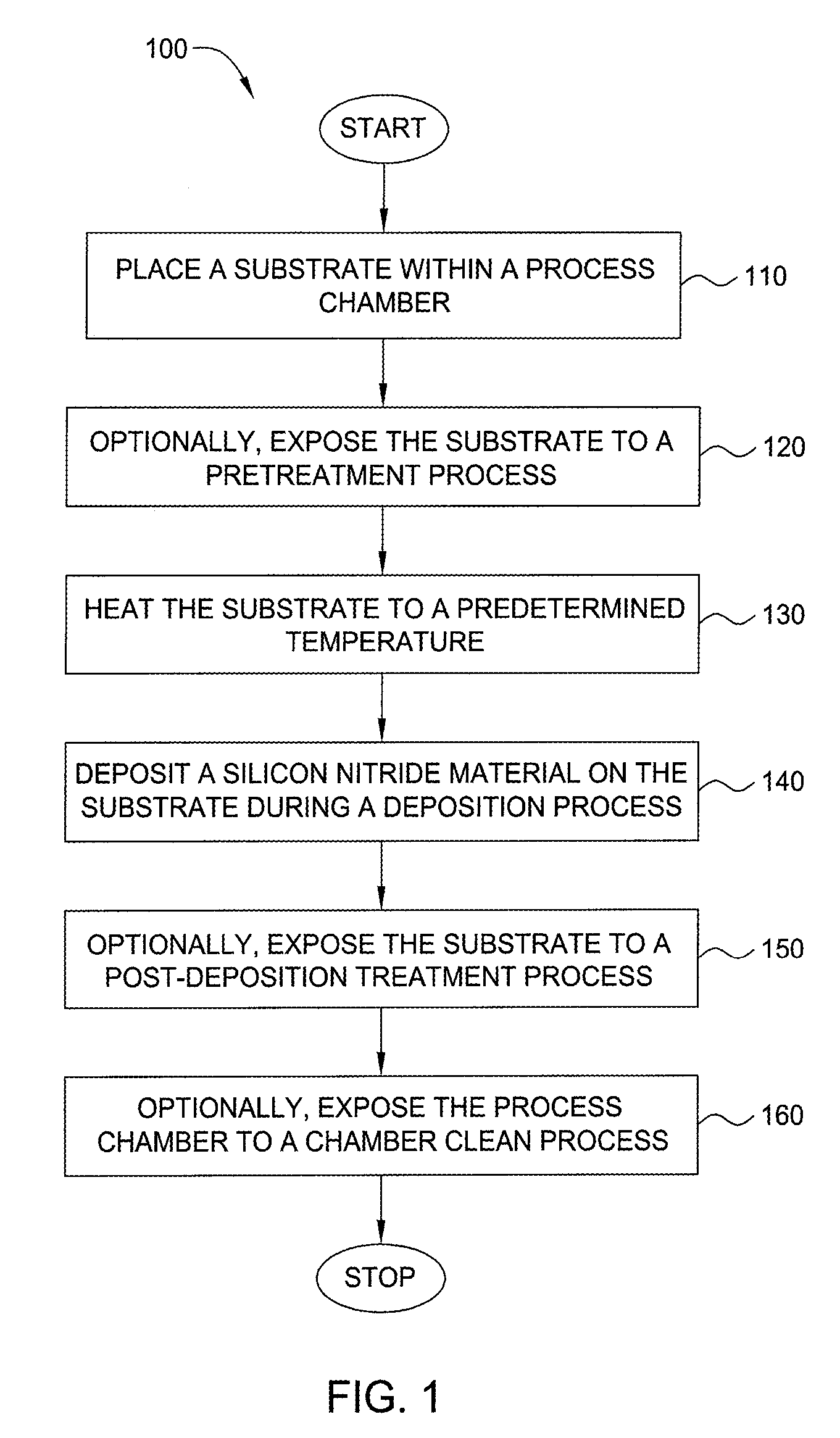
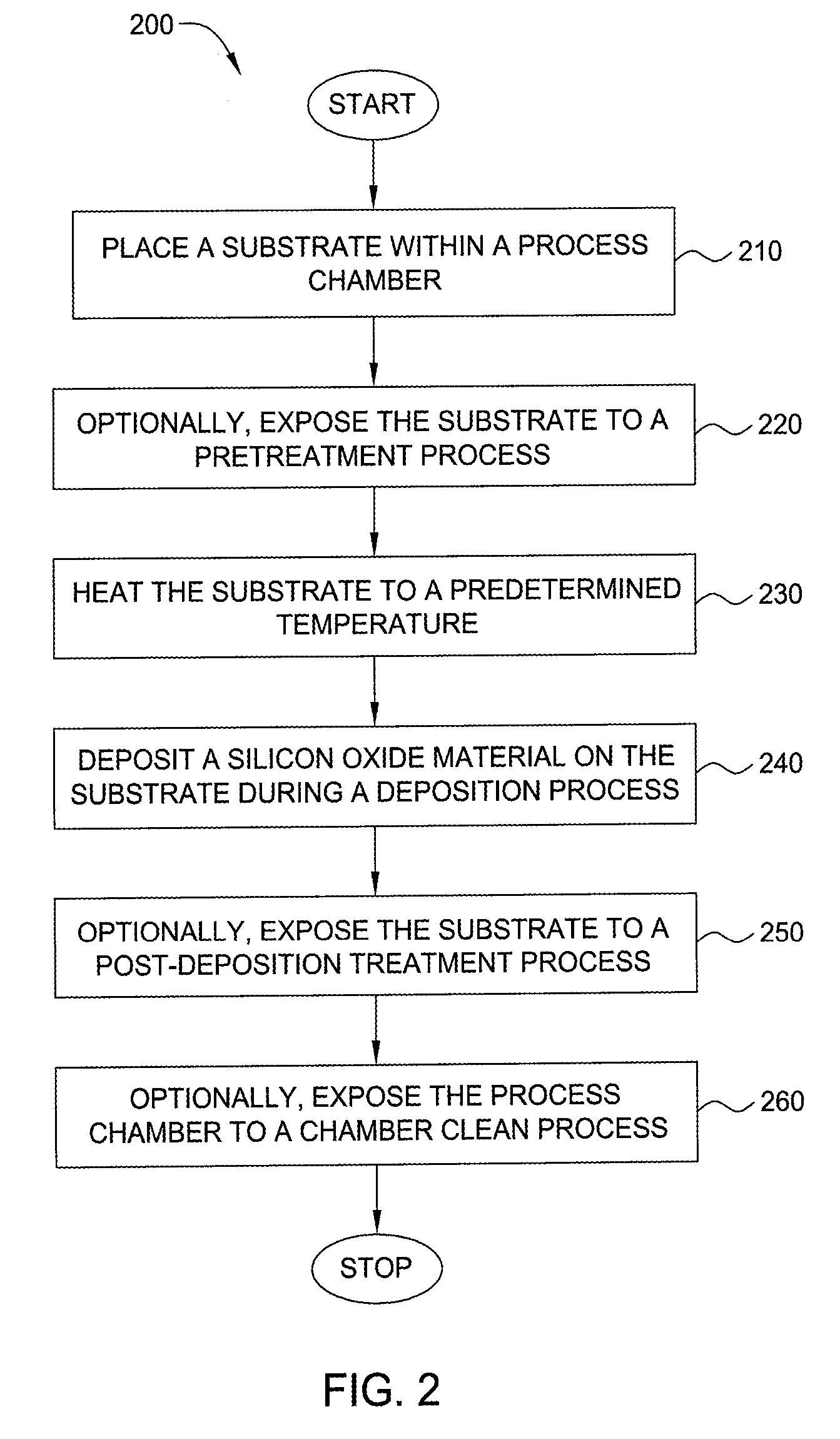
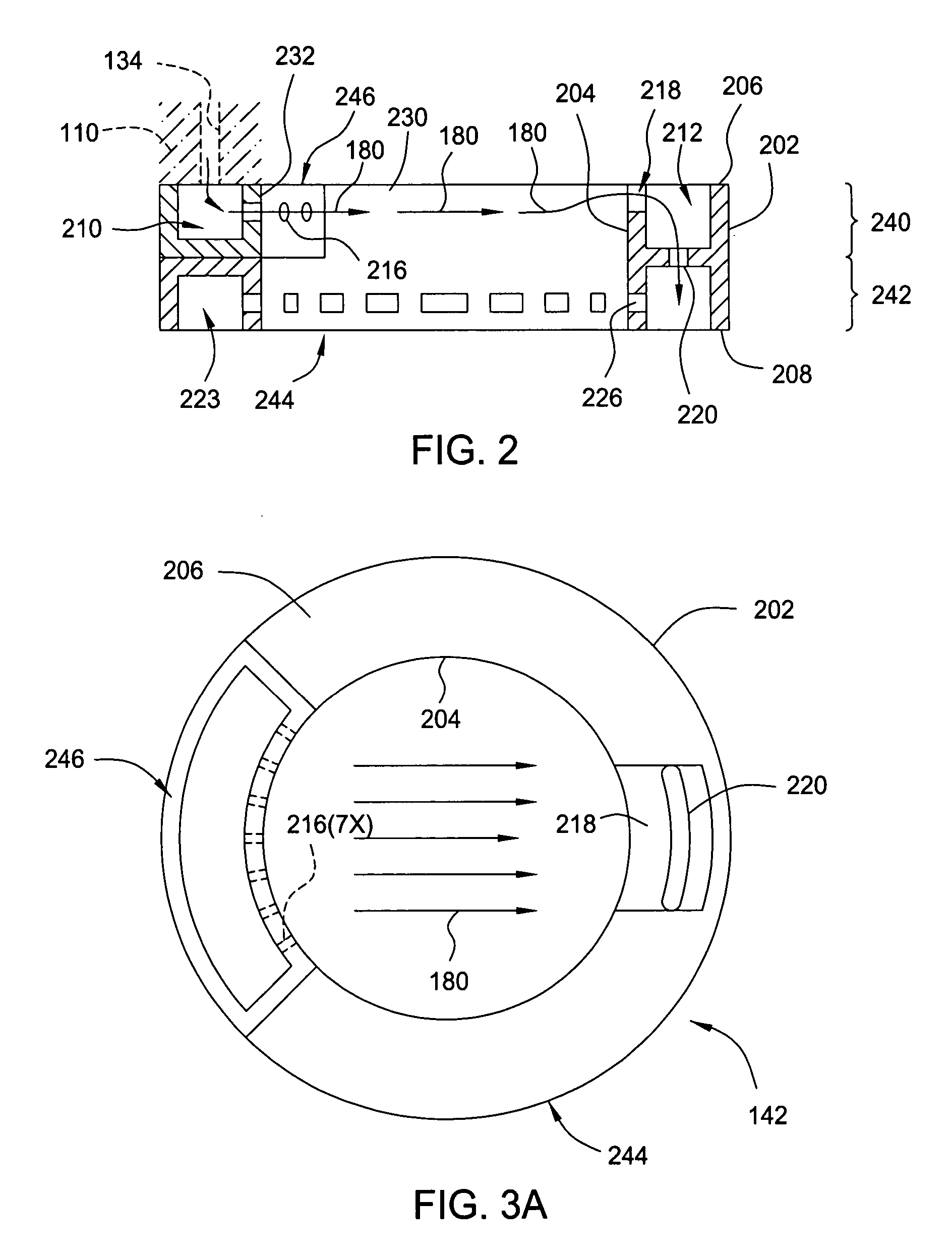
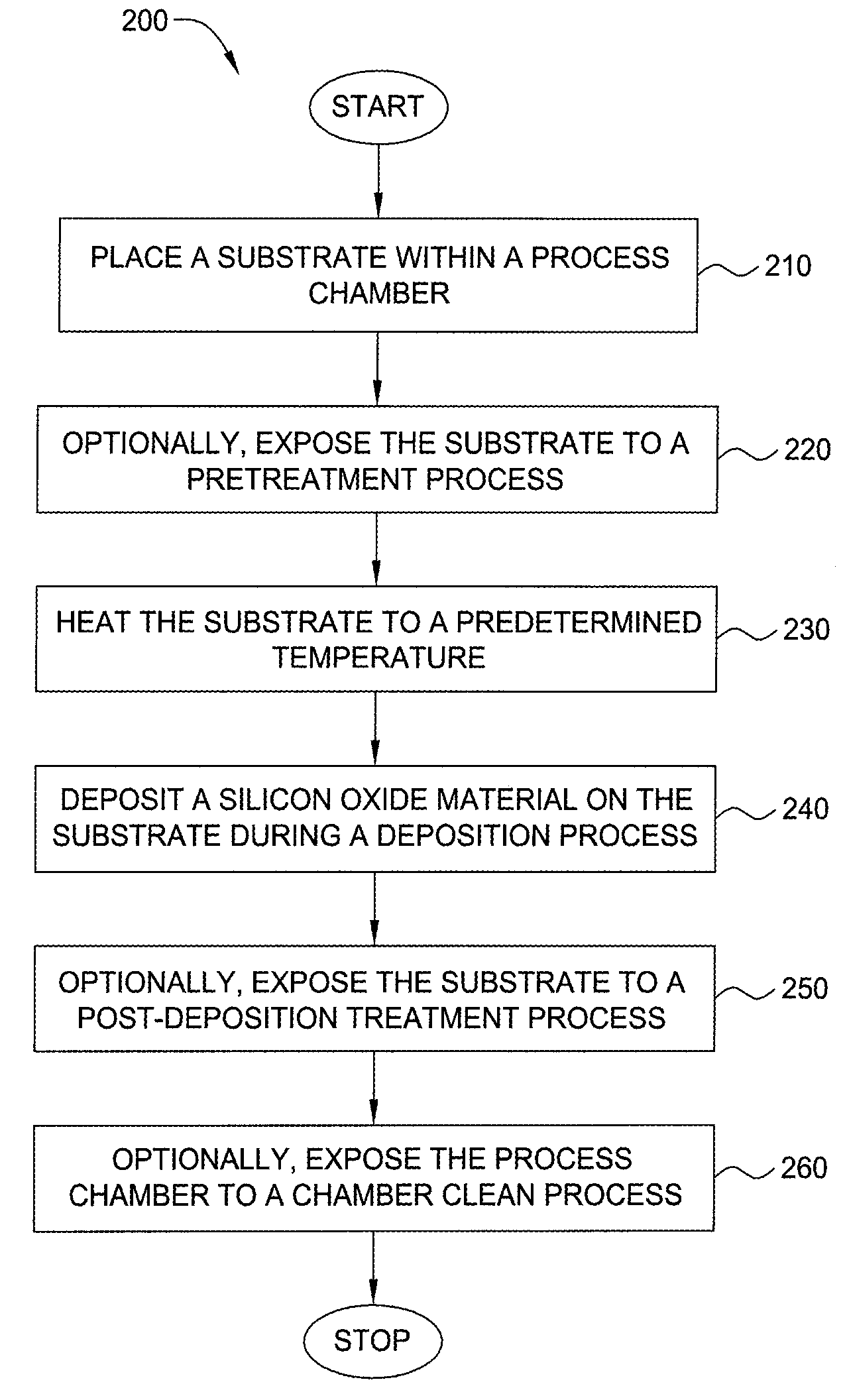
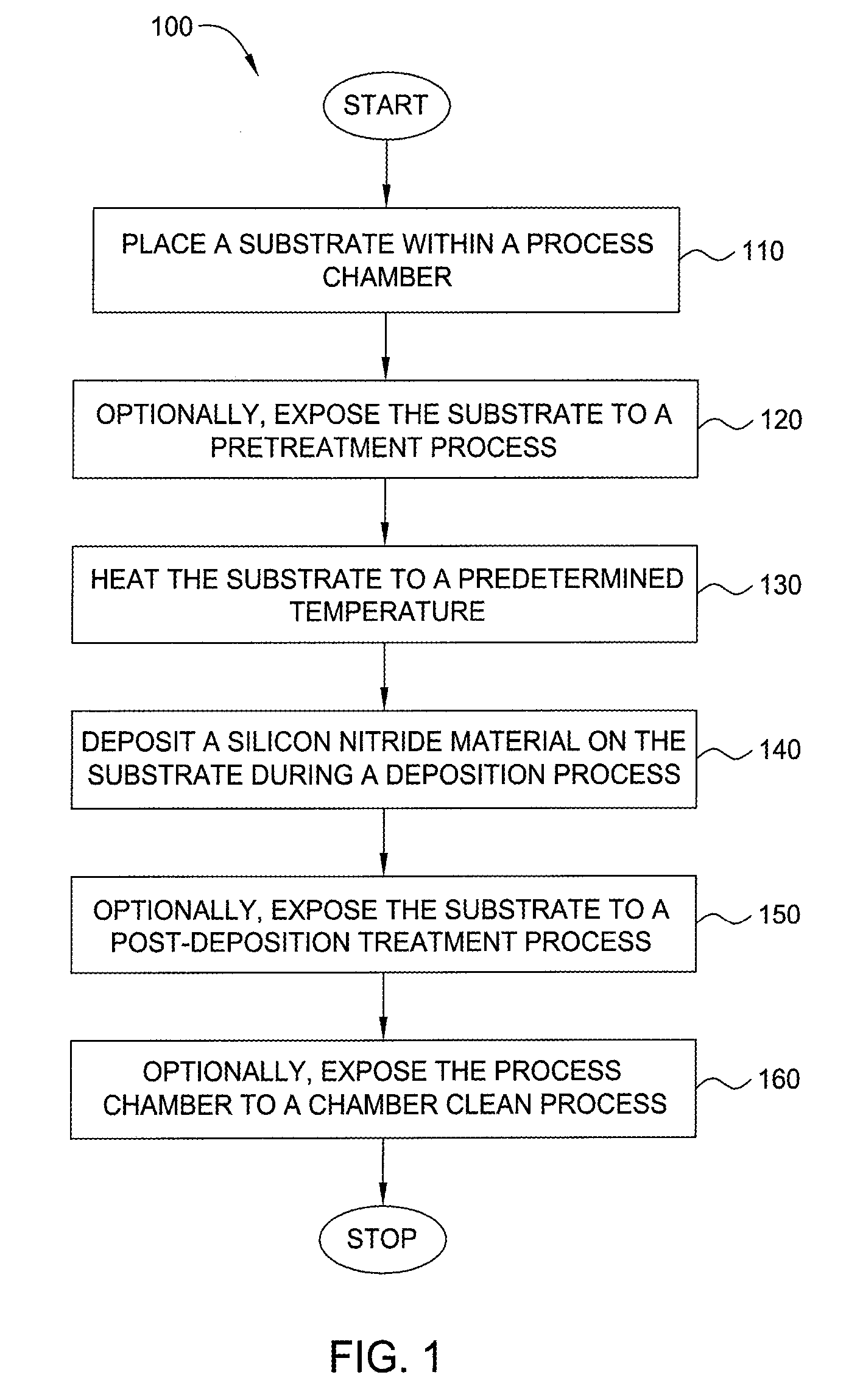
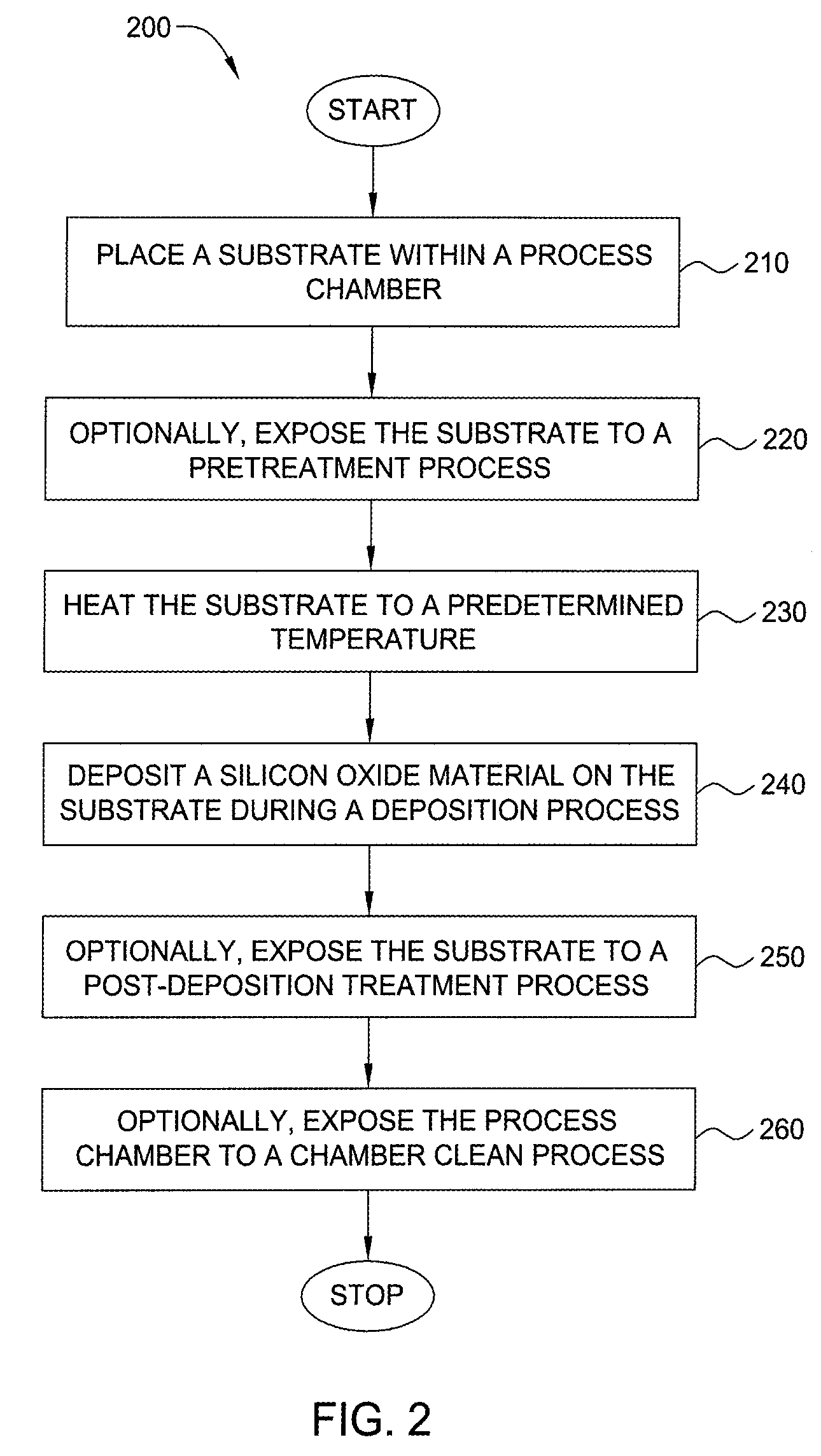
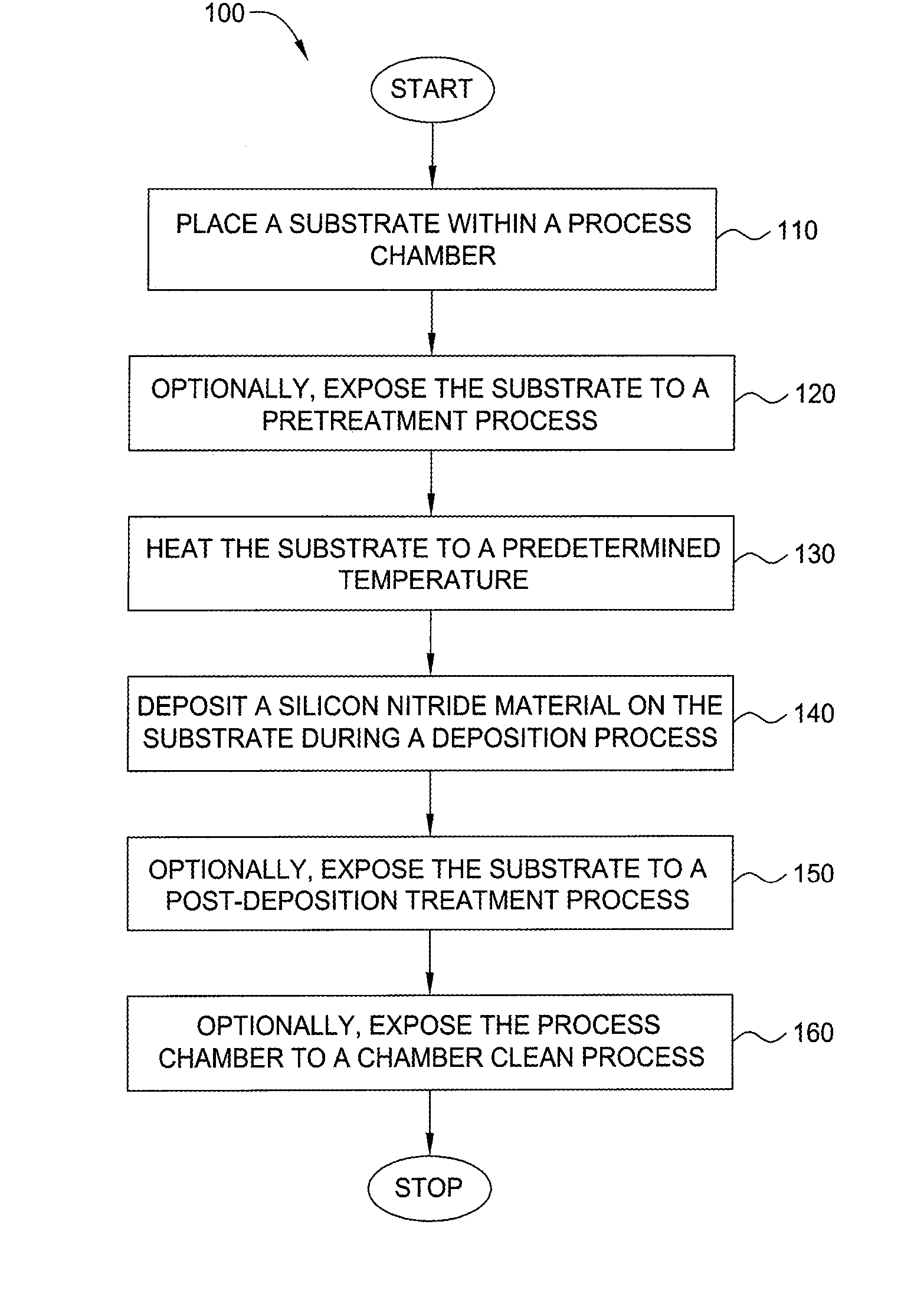
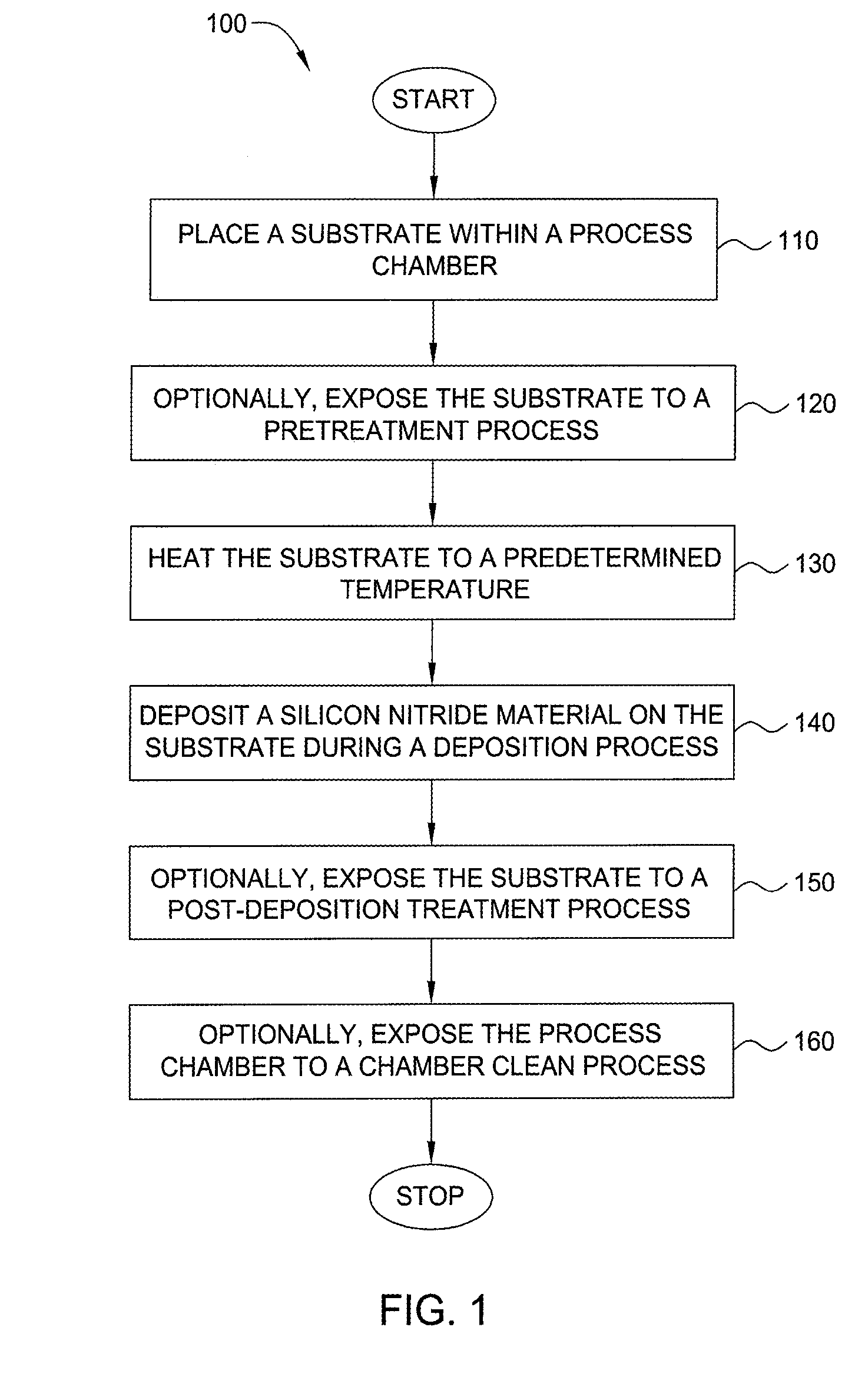
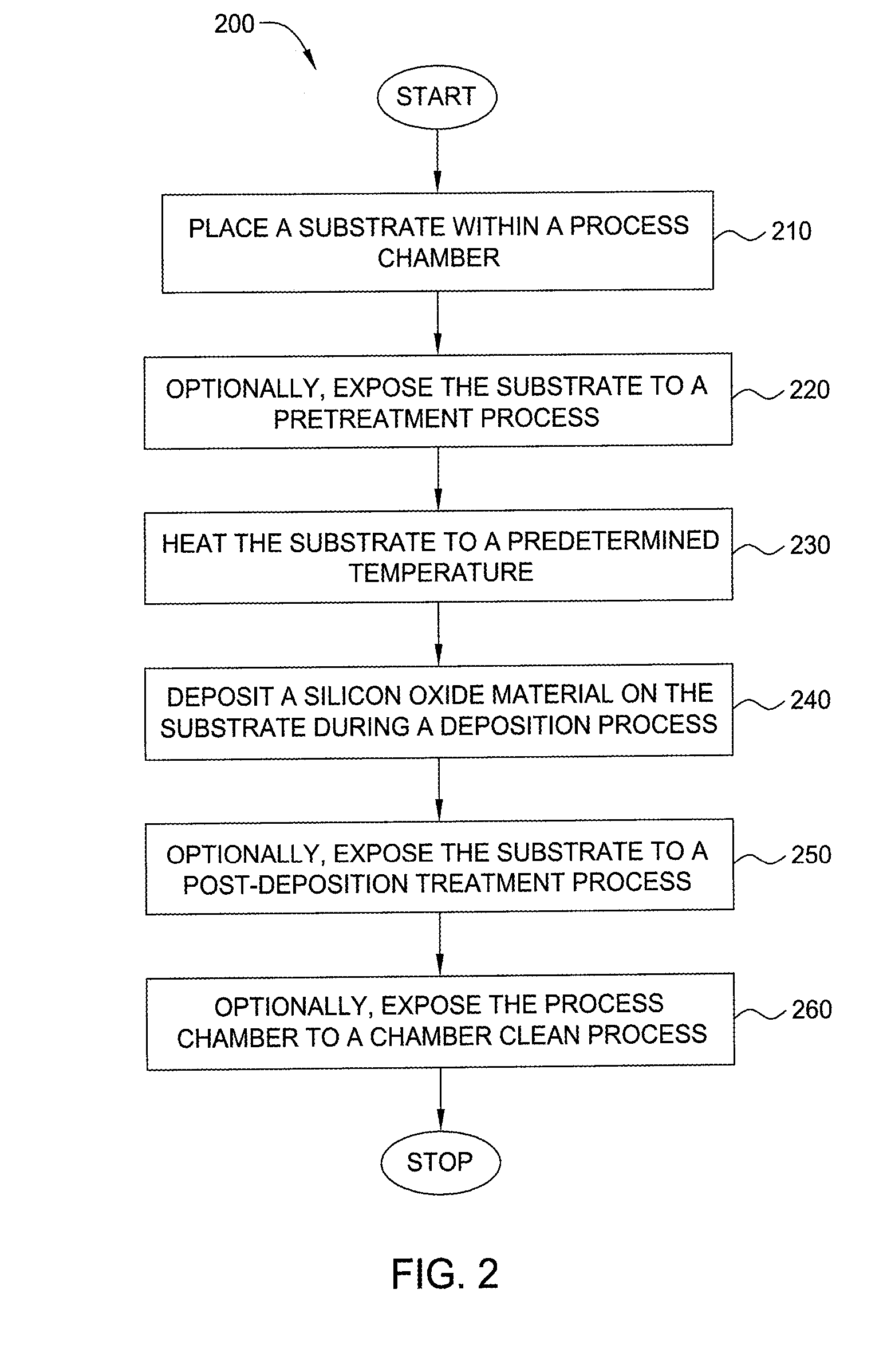
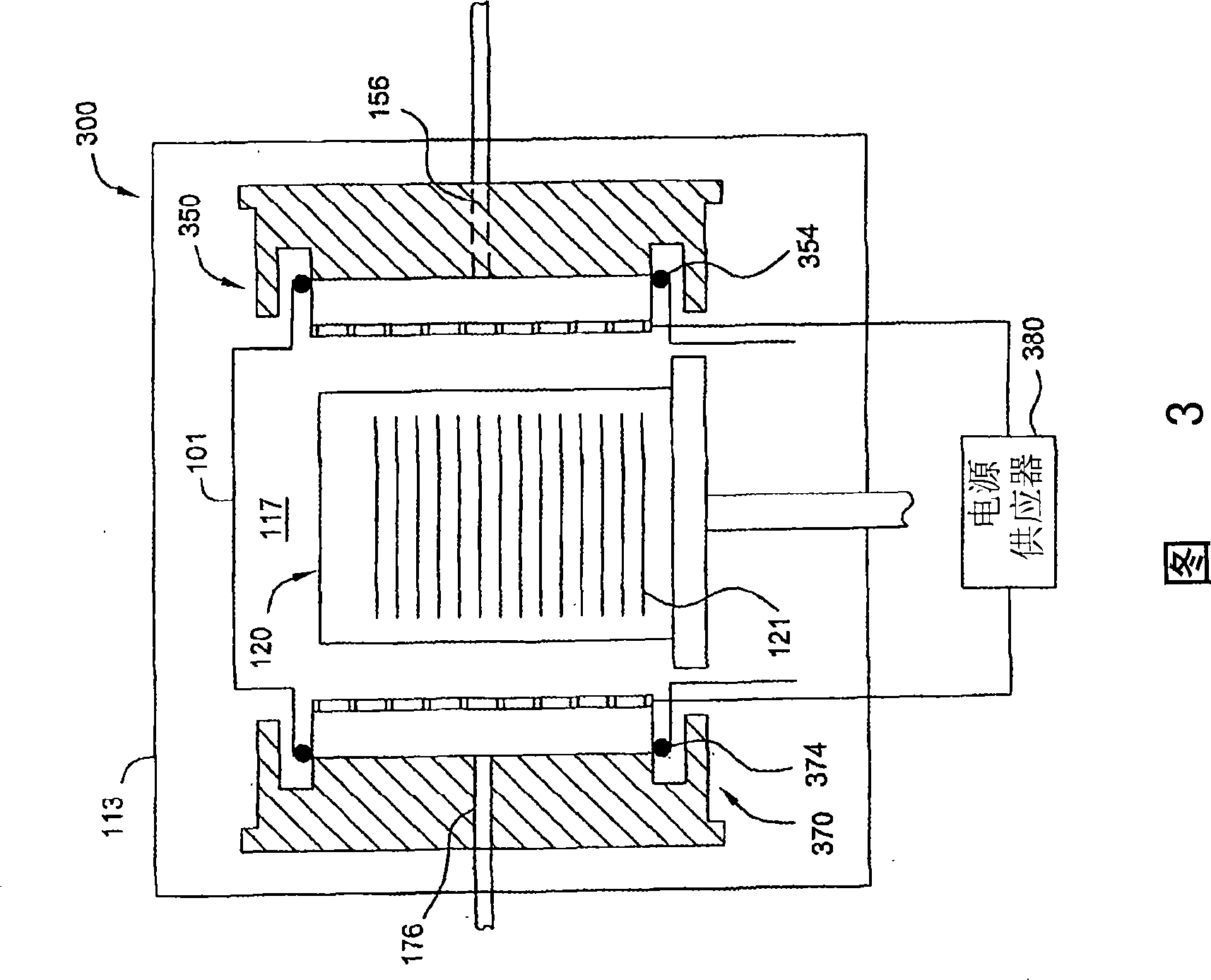
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286774A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
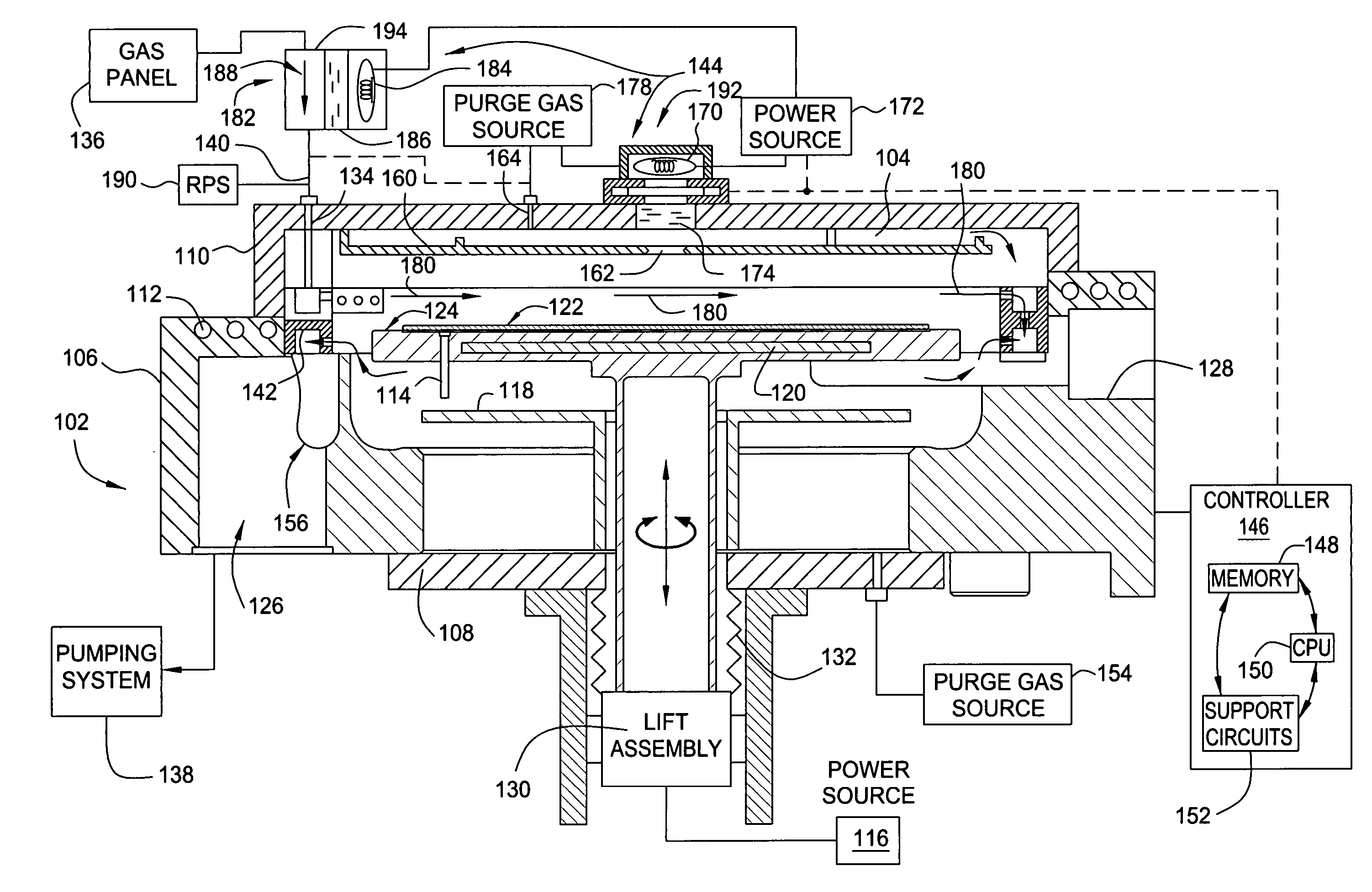
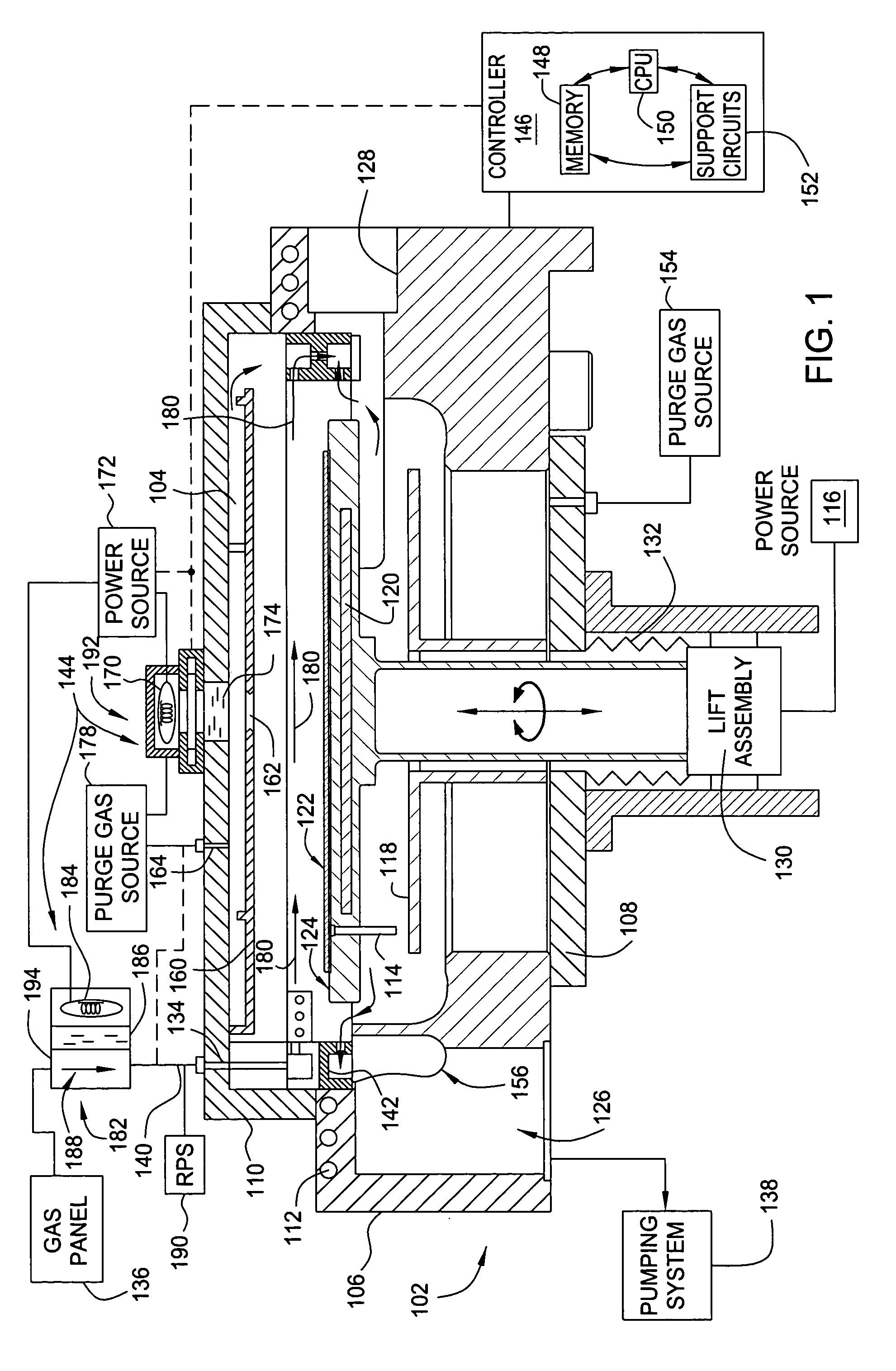
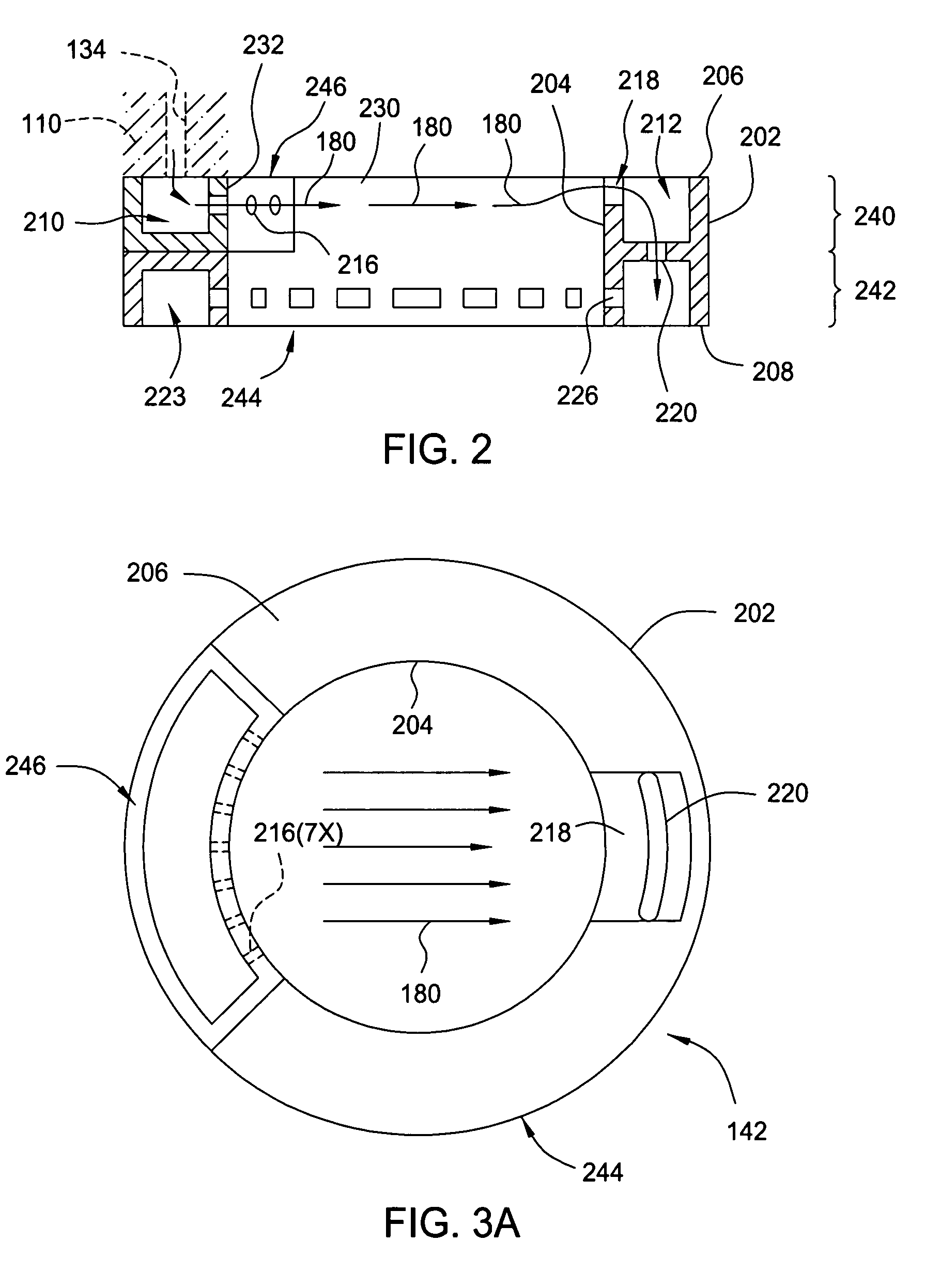
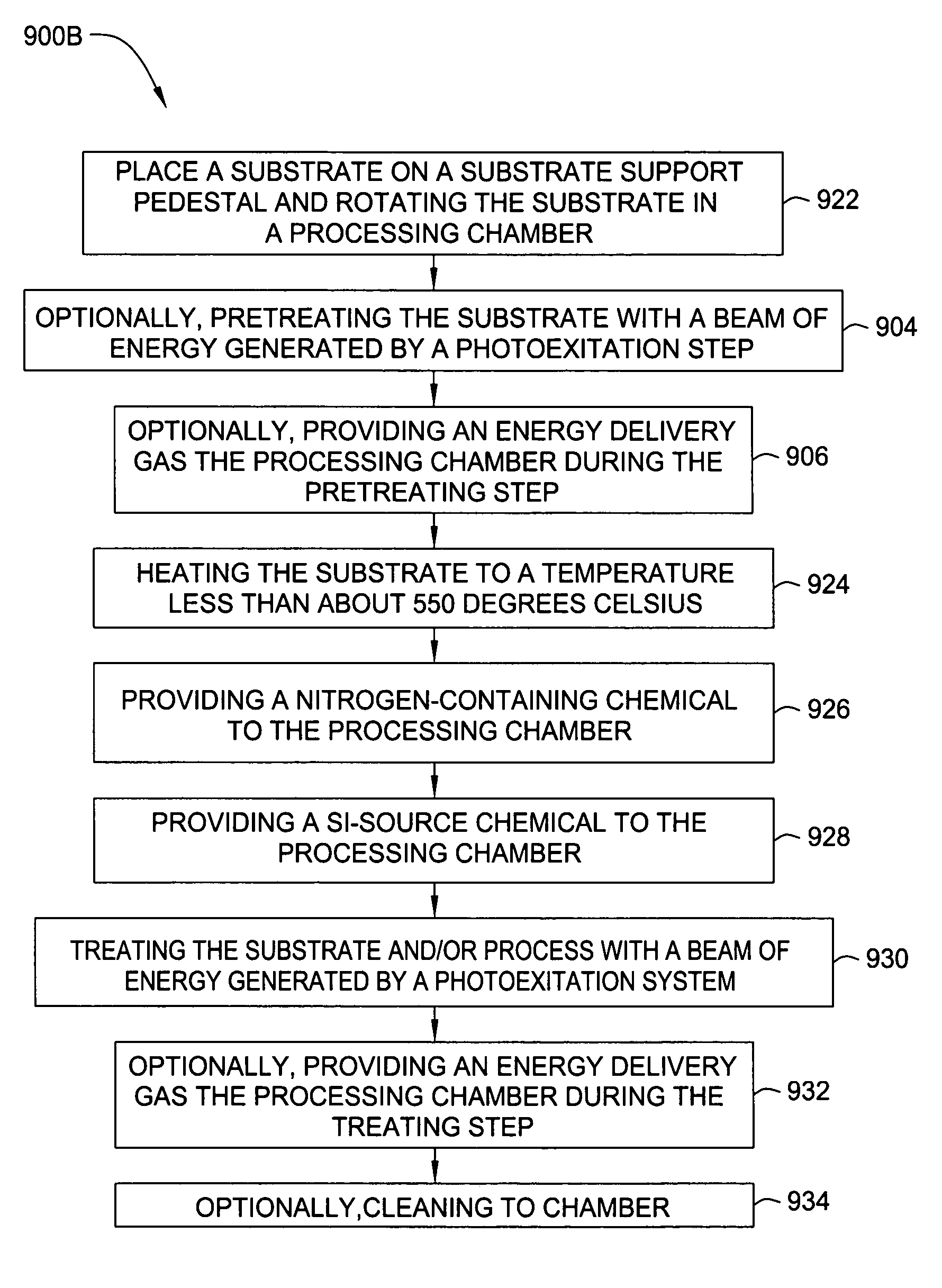
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7651955B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
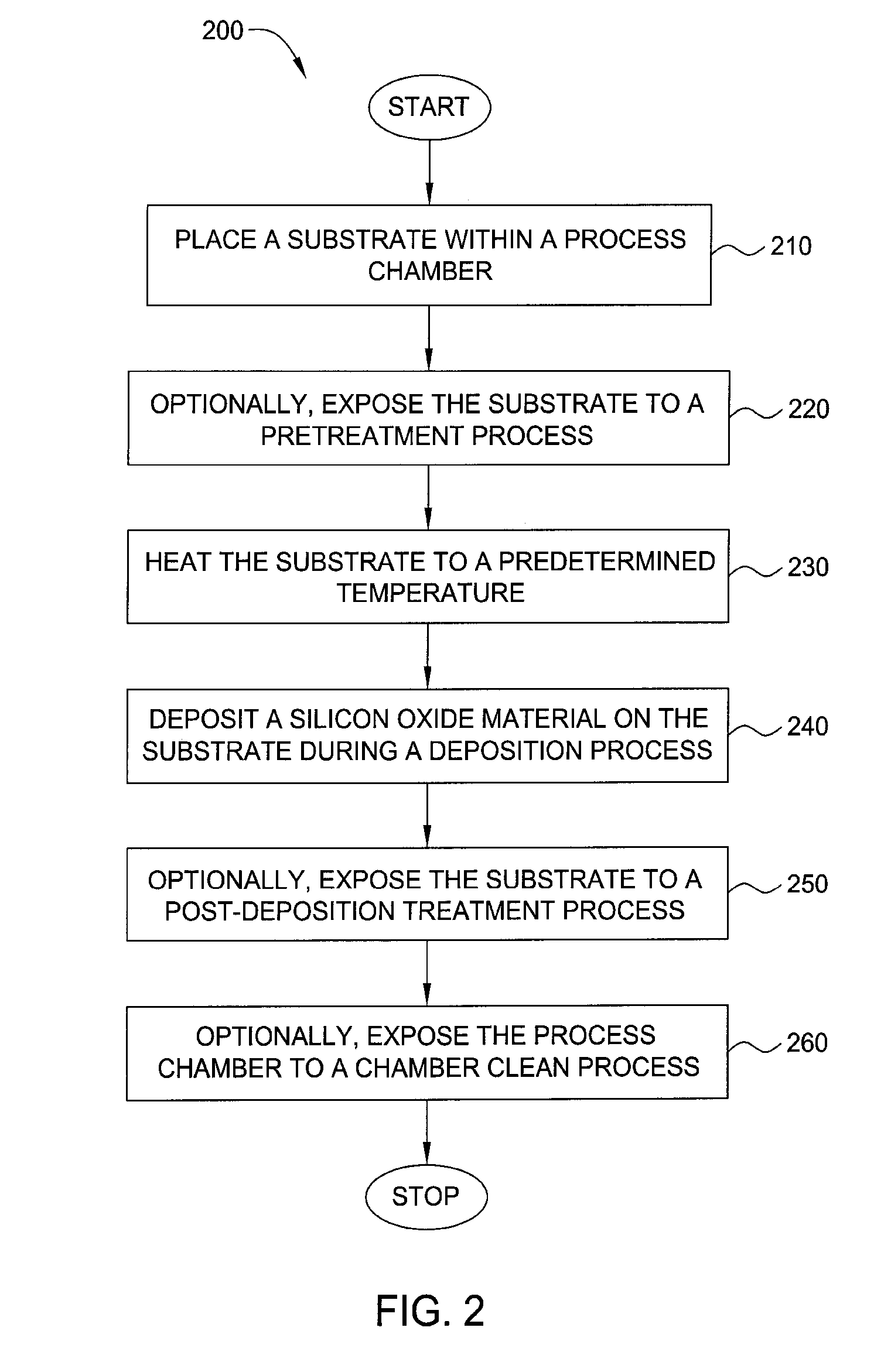
Method for silicon based dielectric deposition and clean with photoexcitation
InactiveUS20060286819A1Enhancing chamber cleaningSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricCompound (substance)
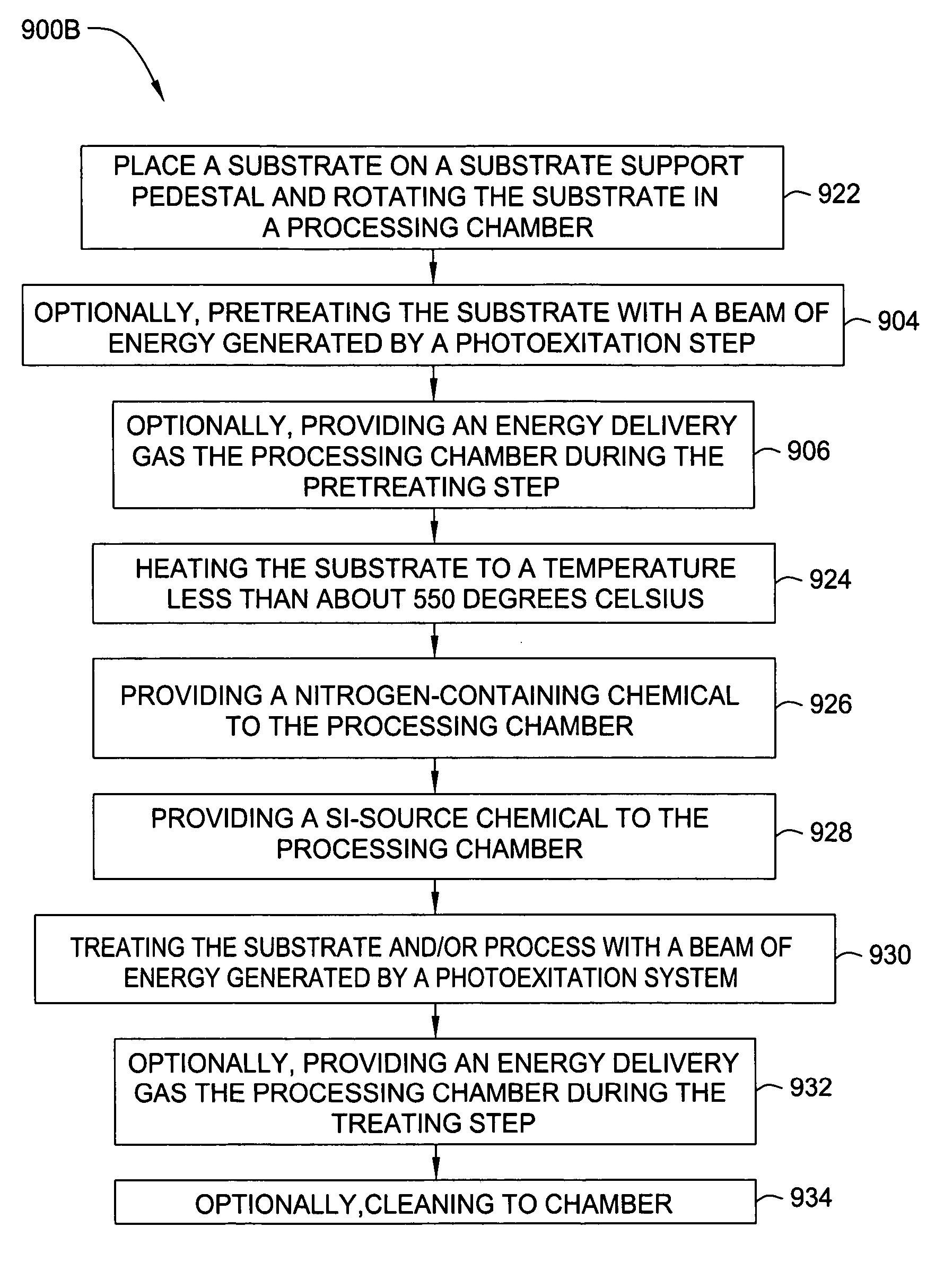
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7648927B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for treating substrates and films with photoexcitation
InactiveUS7601652B2Easy to cleanSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
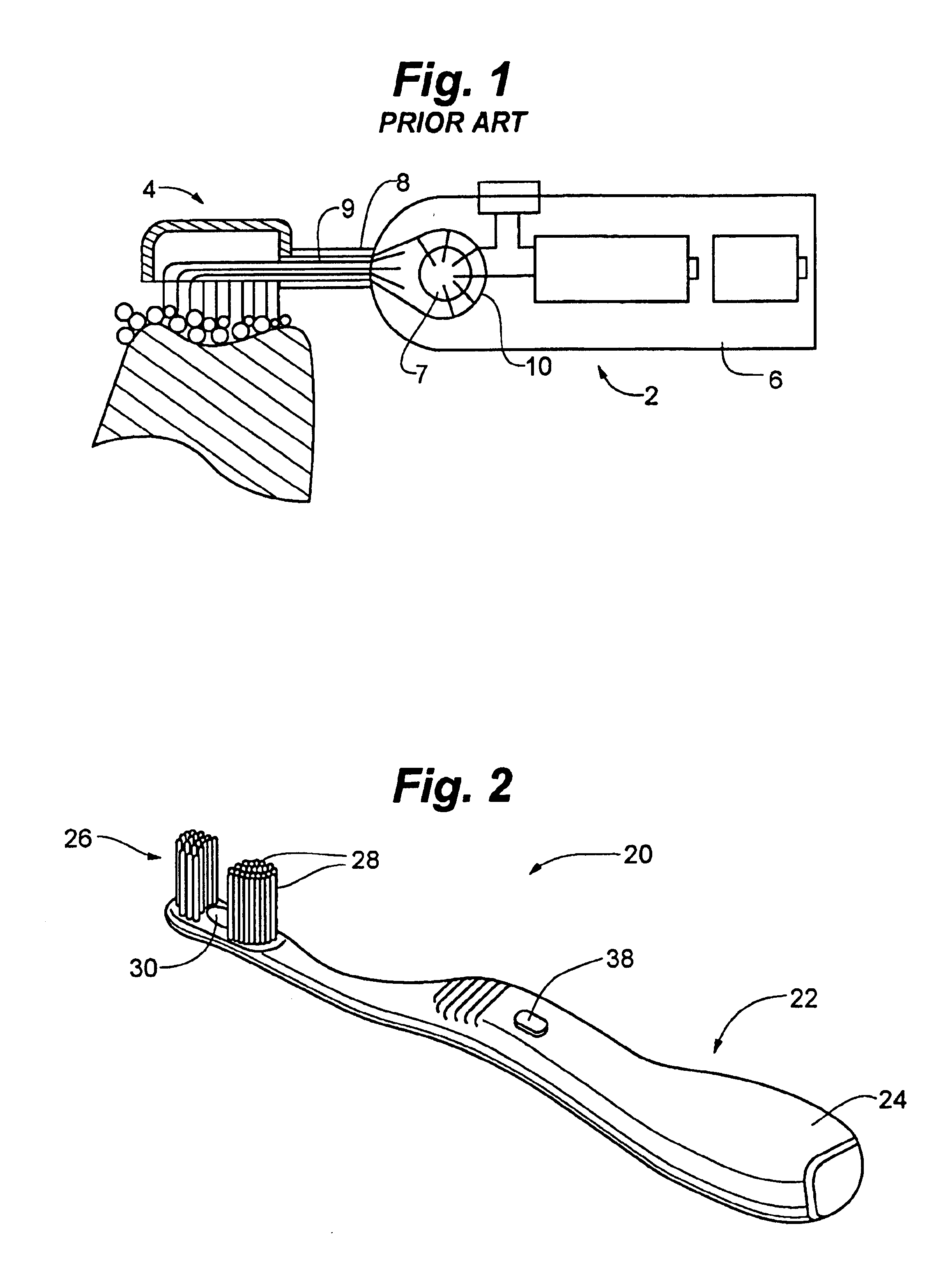
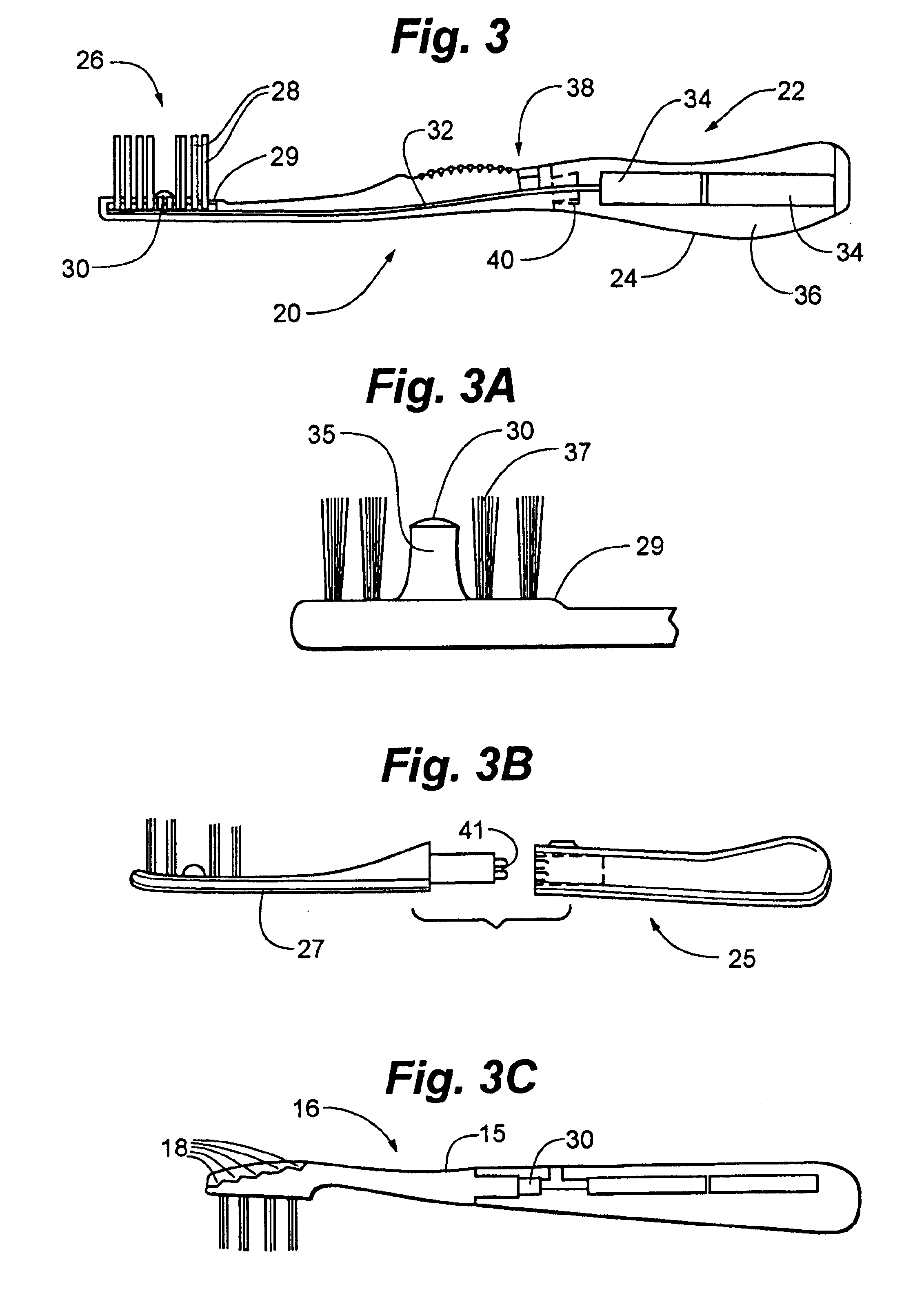
Enhanced dental hygiene system with direct UVA photoexcitation
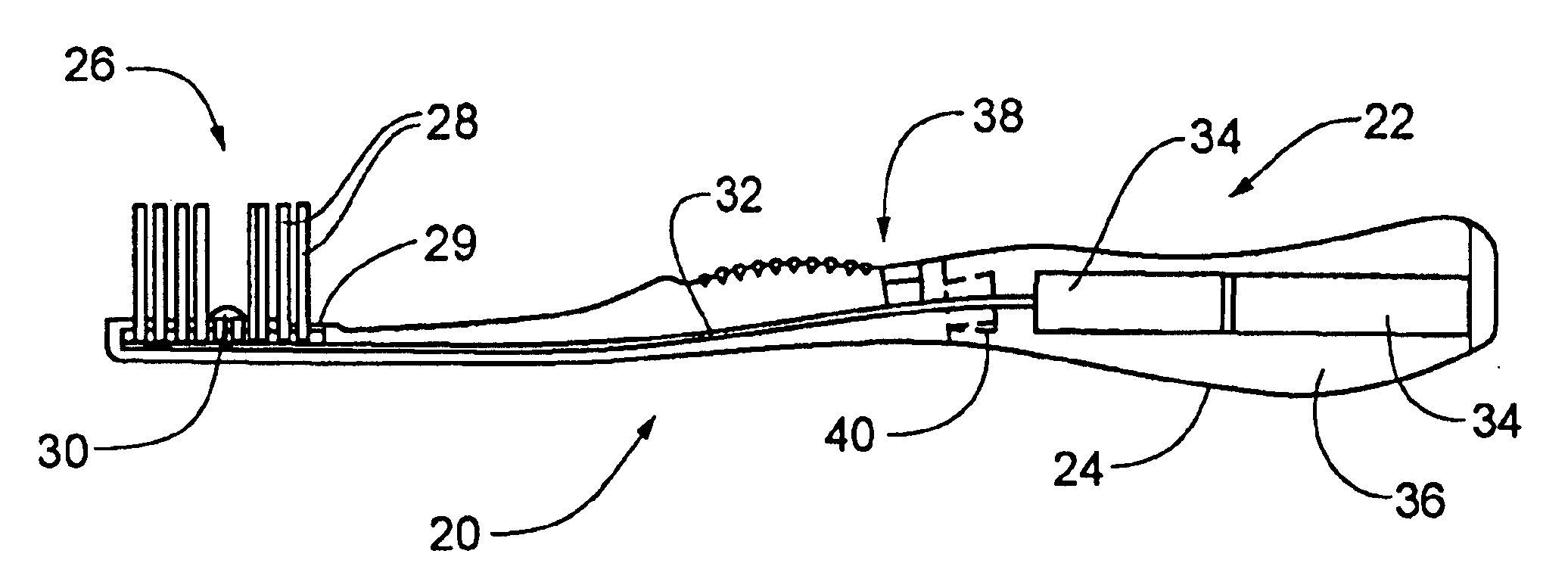
A device and a method for delivering UVA light to the mouth in which a photocatalytic agent is distributed in the mouth and a UVA light source is located contiguously to the head of the device so that the photocatalytic agent distributed in the mouth is efficiently activated by UVA light produced by the device. The UVA light delivery device of the invention may be, inter alia, a toothbrush, a tongue scraper, an interdental toothbrush, a denture brush, a flossing device, a dental hand tool, or a wand adapted exclusively to applying UVA light to photocatalyst coated surfaces.
Owner:SUSR AMERICAS
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286776A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for photocatalytically hydrophilifying surface and composite material with photocatalytically hydrophilifiable surface
InactiveUS6090489AImproved oil repellencyEasy to disassembleOther chemical processesPretreated surfacesAtmospheric airSolid acid
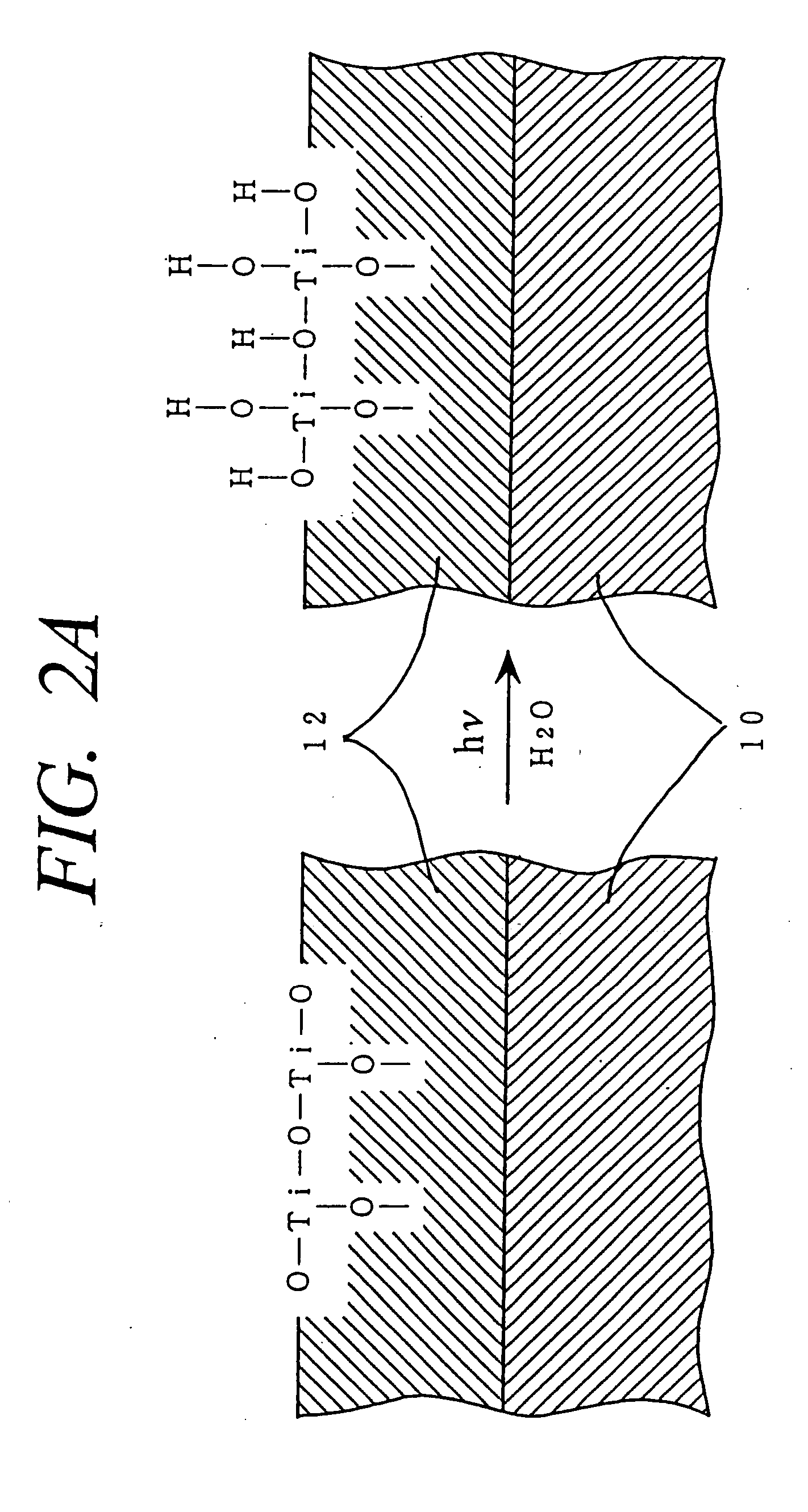
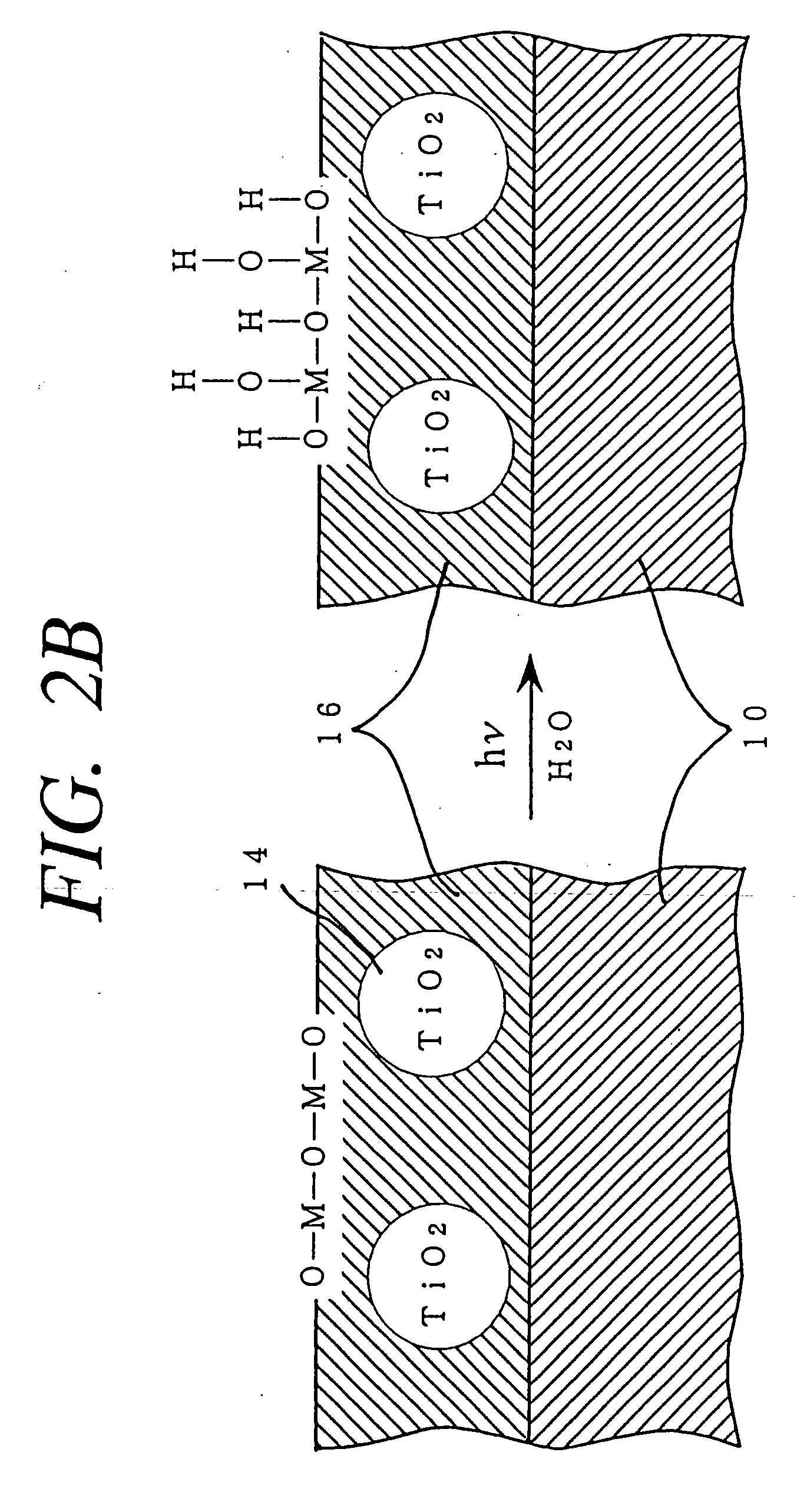
A method for hydrophilifying the surface of a substrate by taking advantage of photocatalytic action. The substrate has a photocatalytic titania coating (10). The surface of the photocatalytic coating (10) bears the solid acid that increases a hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy in the solid / gas interface of the coating. Photoexcitation of the photocatalyst enhances the hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy of the photocatalytic coating (10), accelerating the physical adsorption of molecules of water in the atmosphere through a hydrogen bond (16) onto hydrogen atoms in a terminal OH group (12), bonded to a titanium atom, and a bridge OH group (14) on the surface of the coating. This results in the formation of a high density, physically adsorbed water layer (18) on the surface of the photocatalytic coating (10), thus permitting the surface of the substrate to be easily hydrophilified. The method is applicable to antifogging, antifouling, selfcleaning and cleaning of articles.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Method for photocatalytically rendering a surface of a substrate superhydrophilic, a substrate with superhydrophilic photocatalytic surface, and method of making thereof
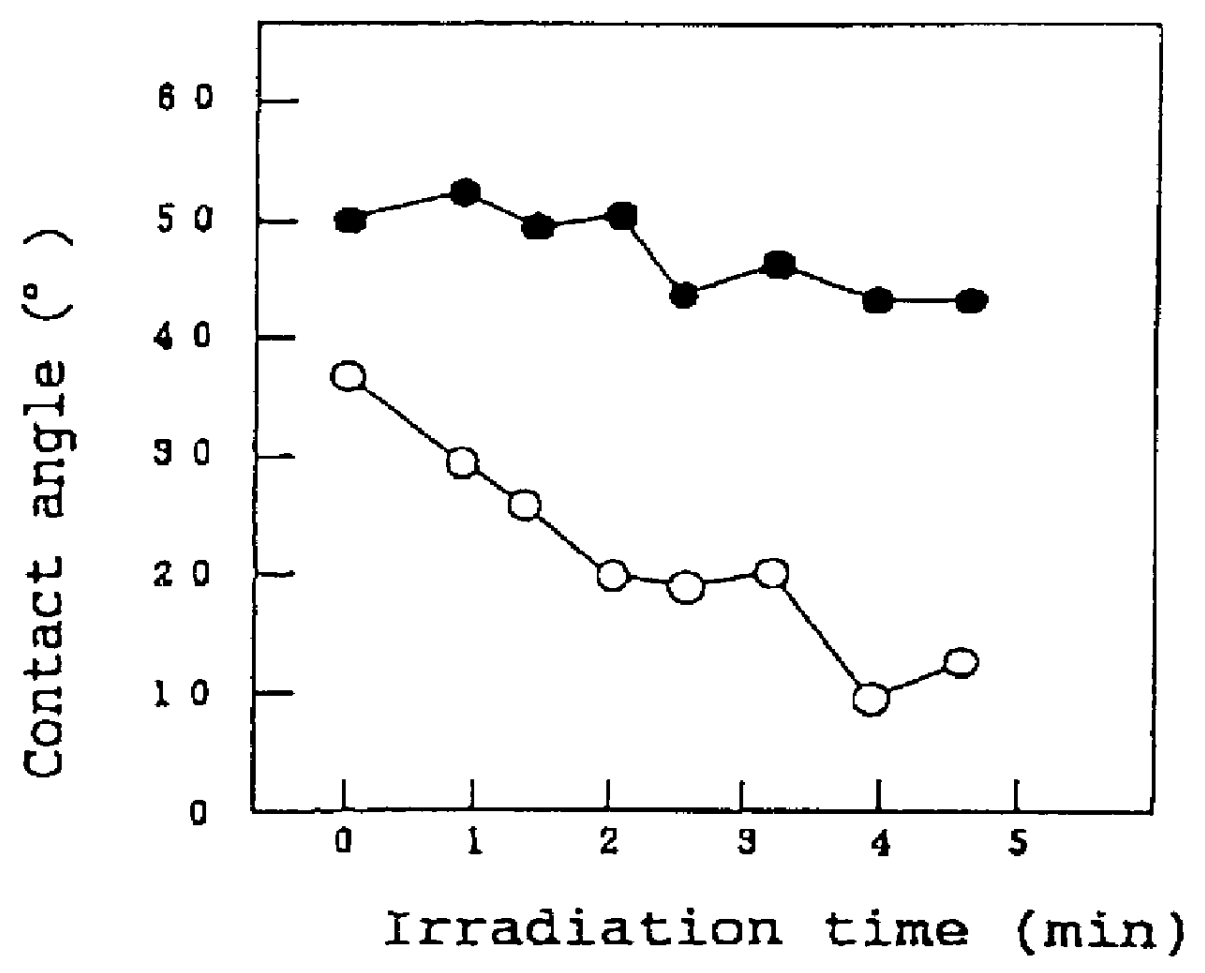
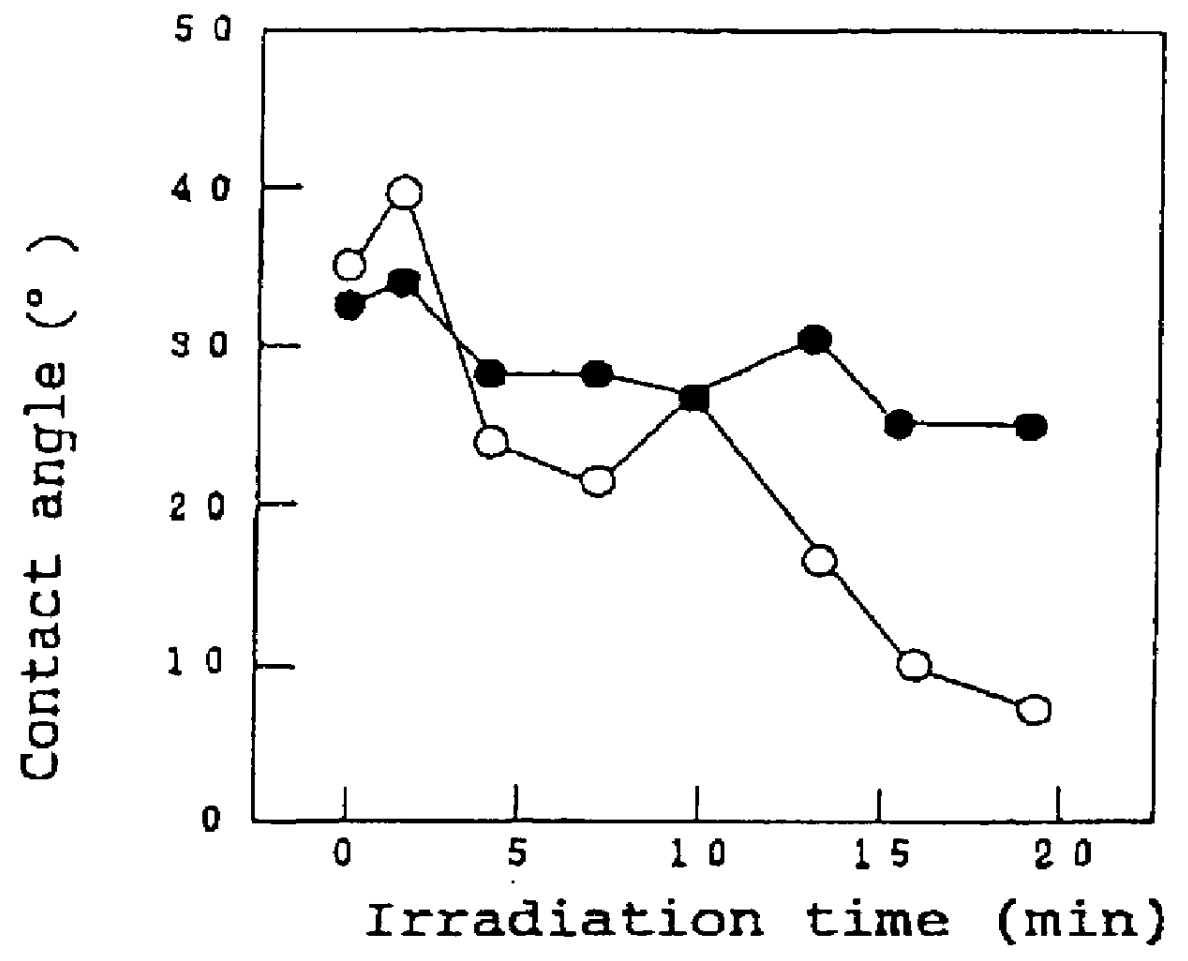
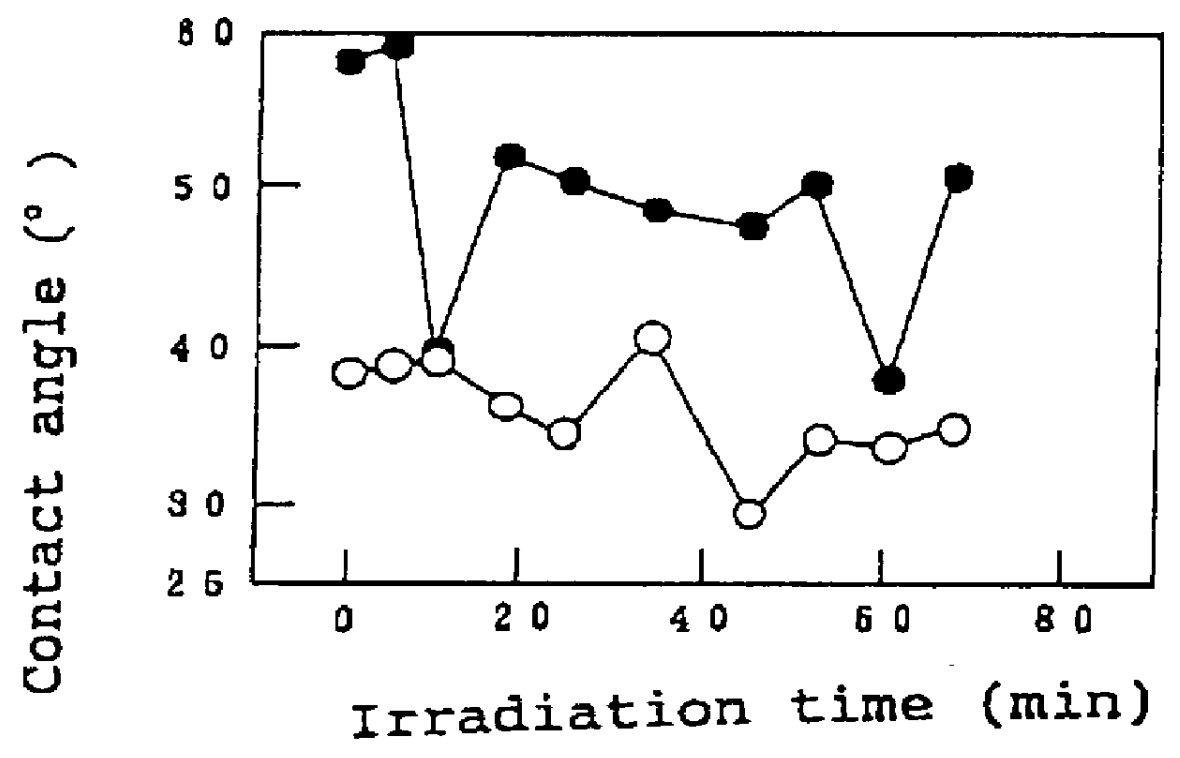
A method of preventing or reducing fogging of a surface of a composite when subjected to humid conditions includes providing a composite with a surface. The composite includes a substrate and a photocatalytic surface layer. The photocatalytic surface layer includes a photocatalyst. The method further includes subjecting the photocatalyst to photoexcitation to render the surface of the composite hydrophilic, wherein, after the photoexcitation, the surface of the composite has a water wettability of less than 10° in terms of the contact angle with water. The method further includes subjecting the composite to humidity that is sufficient to induce fogging of the substrate if the photocatalytic surface layer were absent.
Owner:TOTO LTD
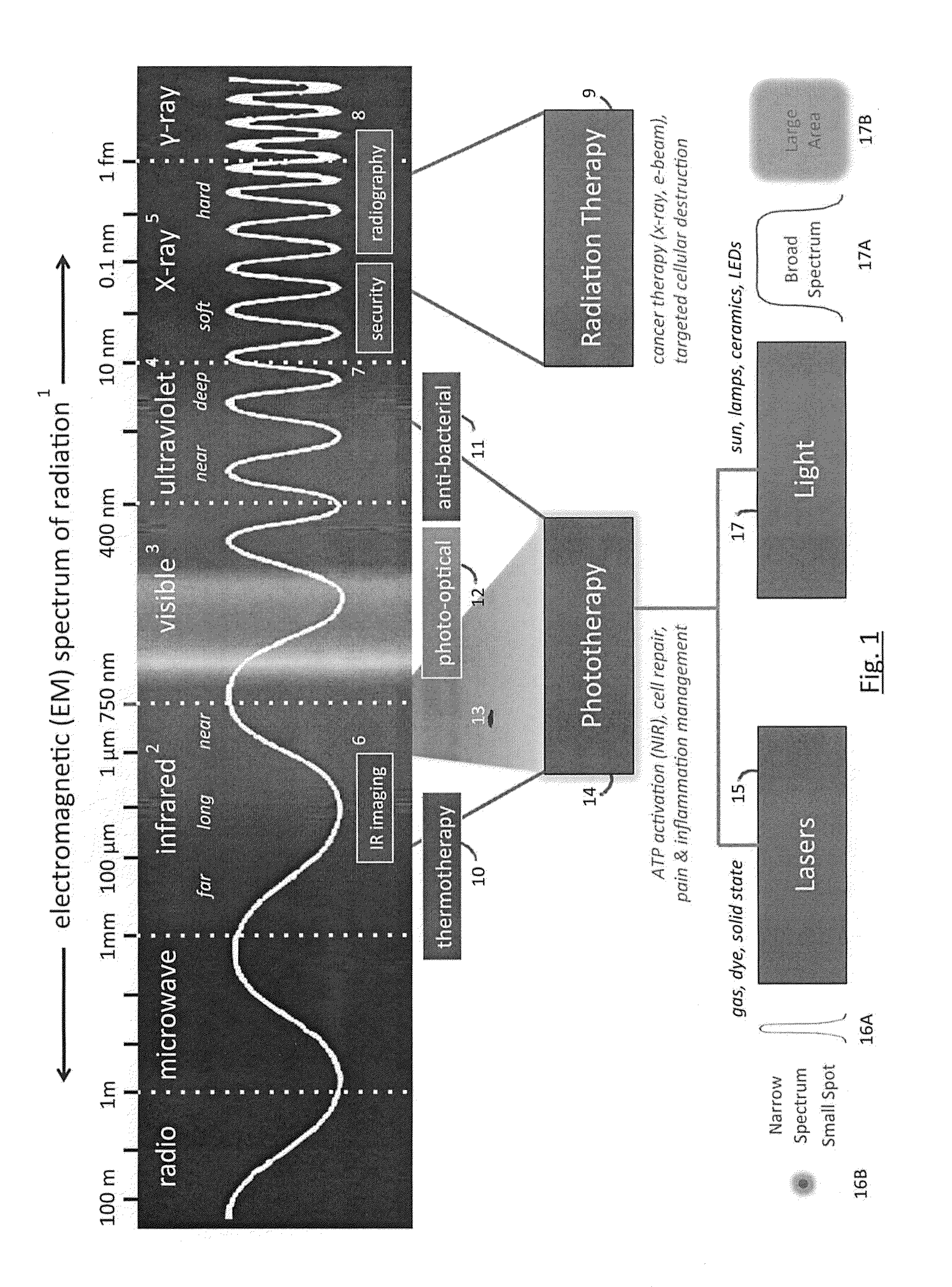
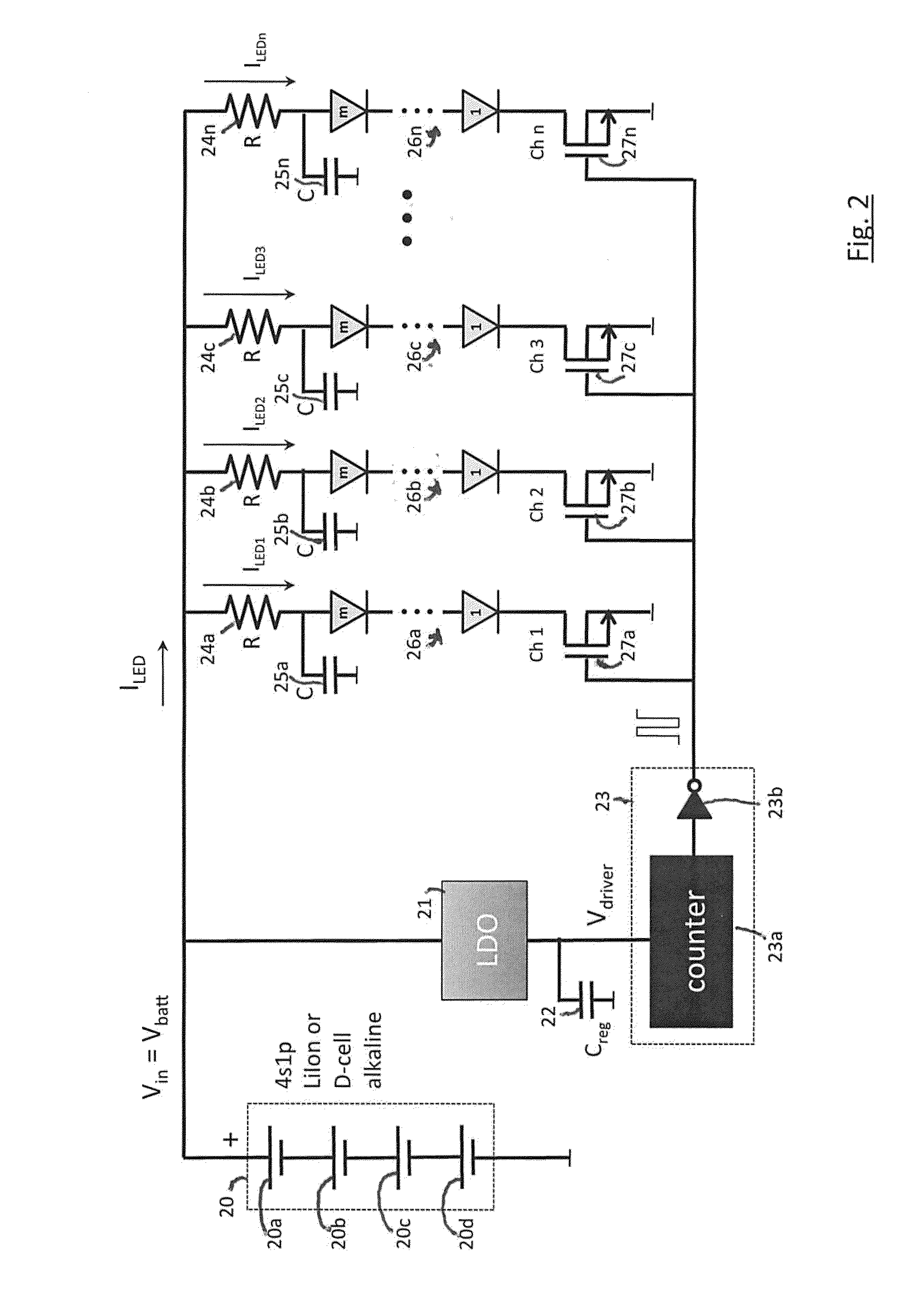
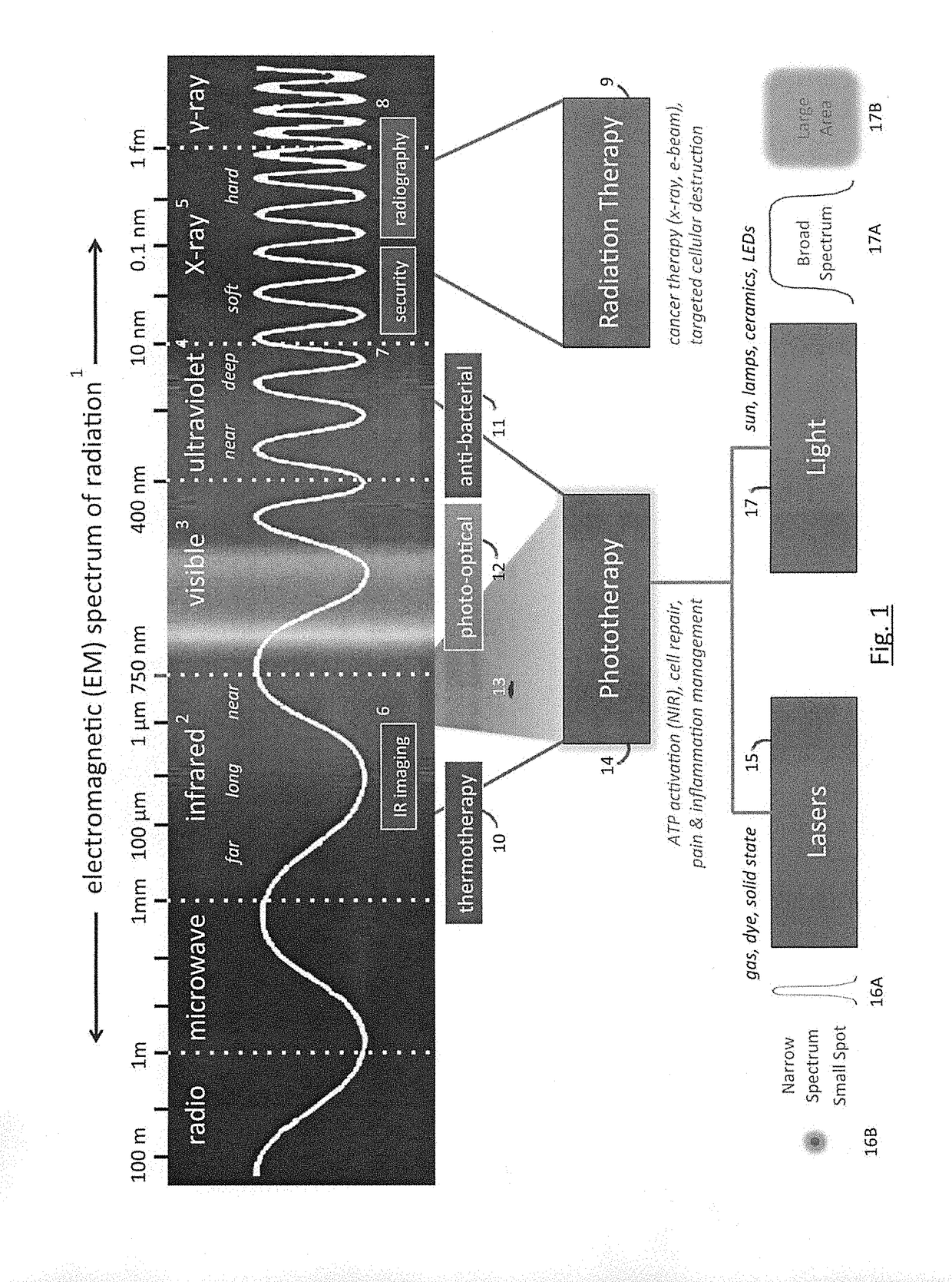
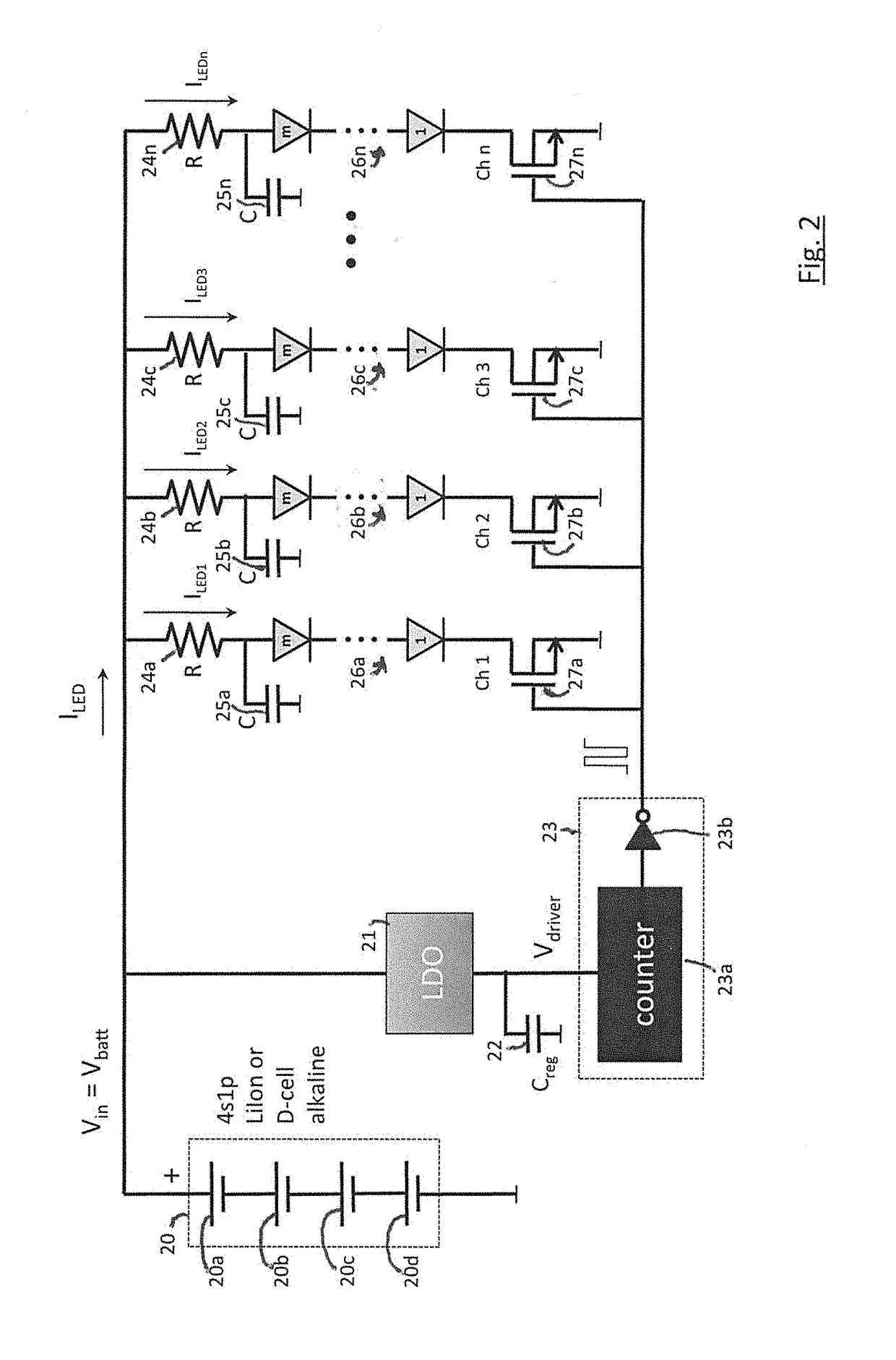
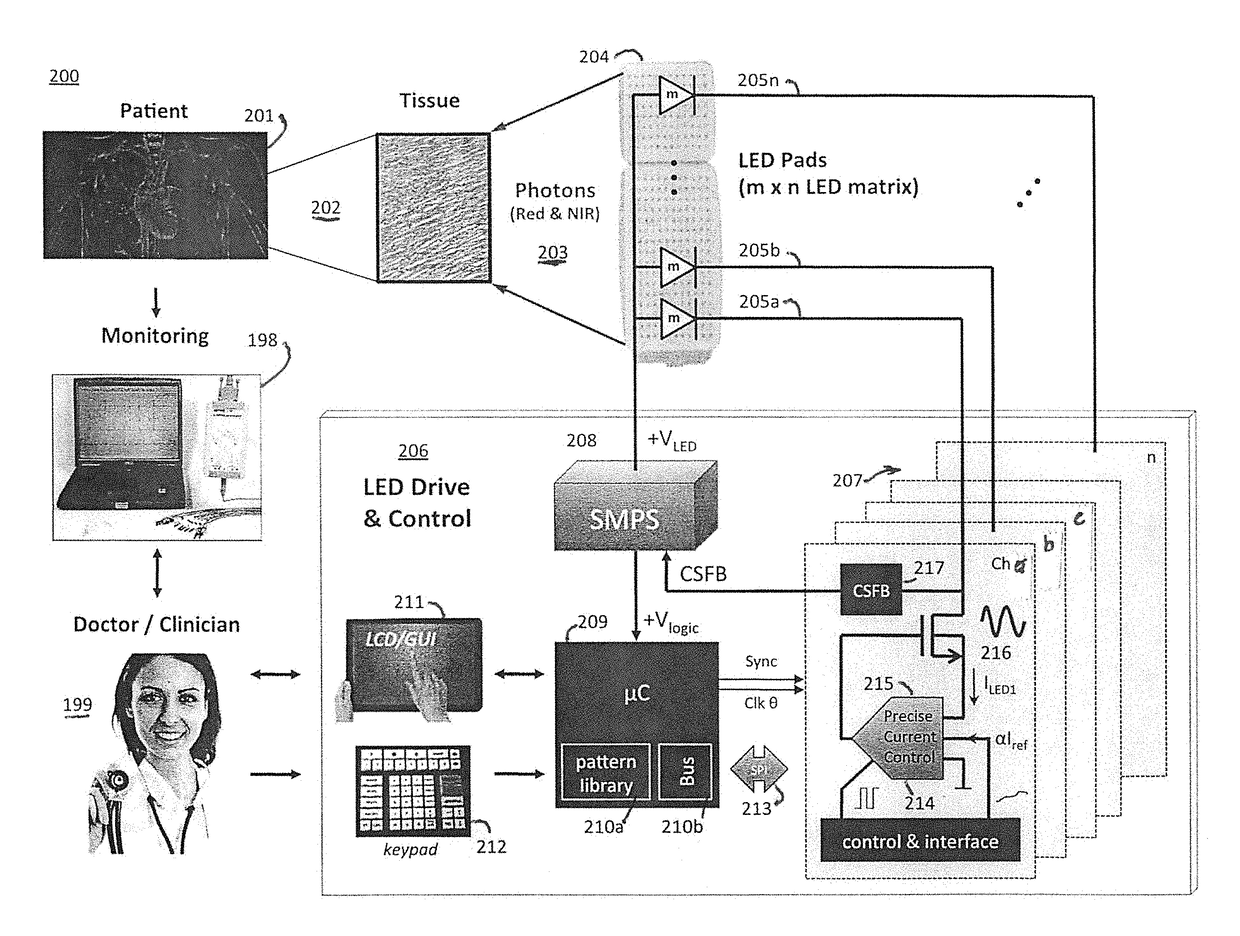
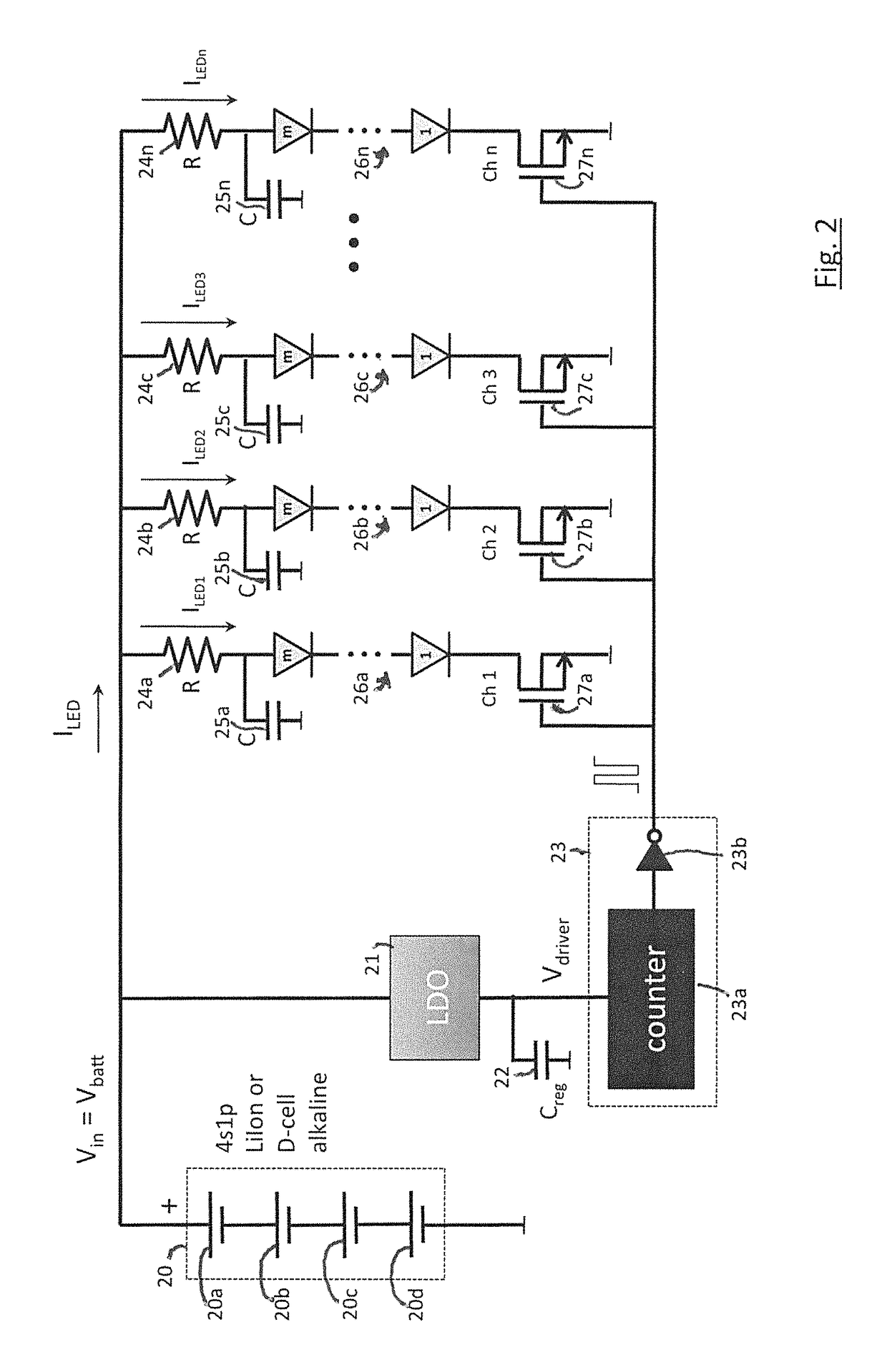
Phototherapy System And Process Including Dynamic LED Driver With Programmable Waveform
ActiveUS20140128941A1Extensive program flexibilityExtended durationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMicrocontrollerBiological body
A phototherapy or photobiomodulation process employing the application of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) to a living organism, typically a human being. The EMR is generated by one or more strings of LEDs and is programmed to emit one or more wavelengths, typically in the visible and infrared portions of the spectrum, the EMR in each wavelength being delivered in pulses having specified on-times, off-times, photoexcitation frequencies, duty factors, phase delays, and power amplitudes. A system for providing such EMR includes a microcontroller having a pattern library of algorithms, each of which defines a particular sequence of synthesized pulses, and an application pad, preferably flexible, containing the LED strings.
Owner:APPLIED BIOPHOTONICS
Quantum dot color filter, liquid crystal panel and display device
The invention relates to the technical field of display, which discloses a quantum dot color filter, a liquid crystal panel and a display device. The quantum dot color filter is used for the liquid crystal panel. The liquid crystal panel is provided with a plurality of pixels, wherein each pixel is provided with a plurality of sub-pixels. Each sub-pixel corresponds to a color. The color filter comprises sub-areas in one-to-one correspondence to the sub-pixels. At least one sub-area is formed by quantum dot materials. Light generated by the quantum dot materials activated is as same as the corresponding sub-pixel in color. According to the invention, the color filter of a display is formed by the quantum dot materials, and a red, or green, or blue filter is made of quantum dot materials which generate red, or green, or blue light through photoexcitation, so that the utilization ratio of a backlight source is improved, and meanwhile, colored light with higher purity can be obtained. Therefore, the quantum dot display can realize high color gamut and low power consumption of color display.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
White and color photoexcitation light emitting sheet and method for the fabrication thereof
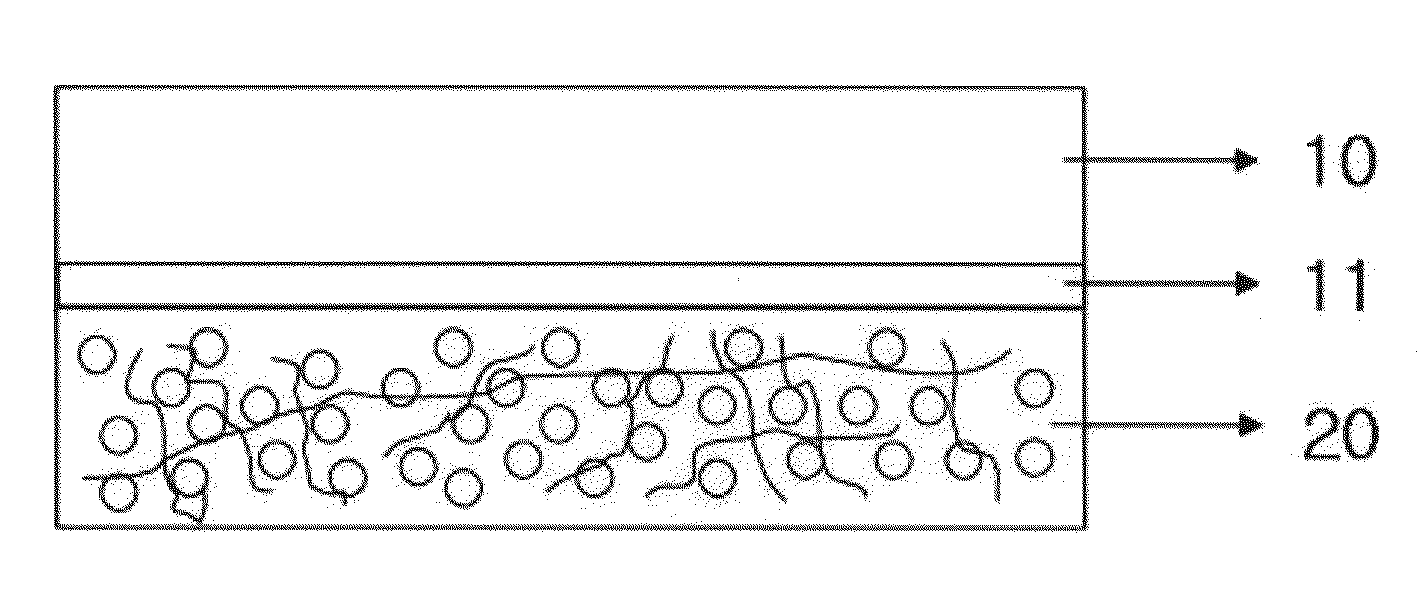
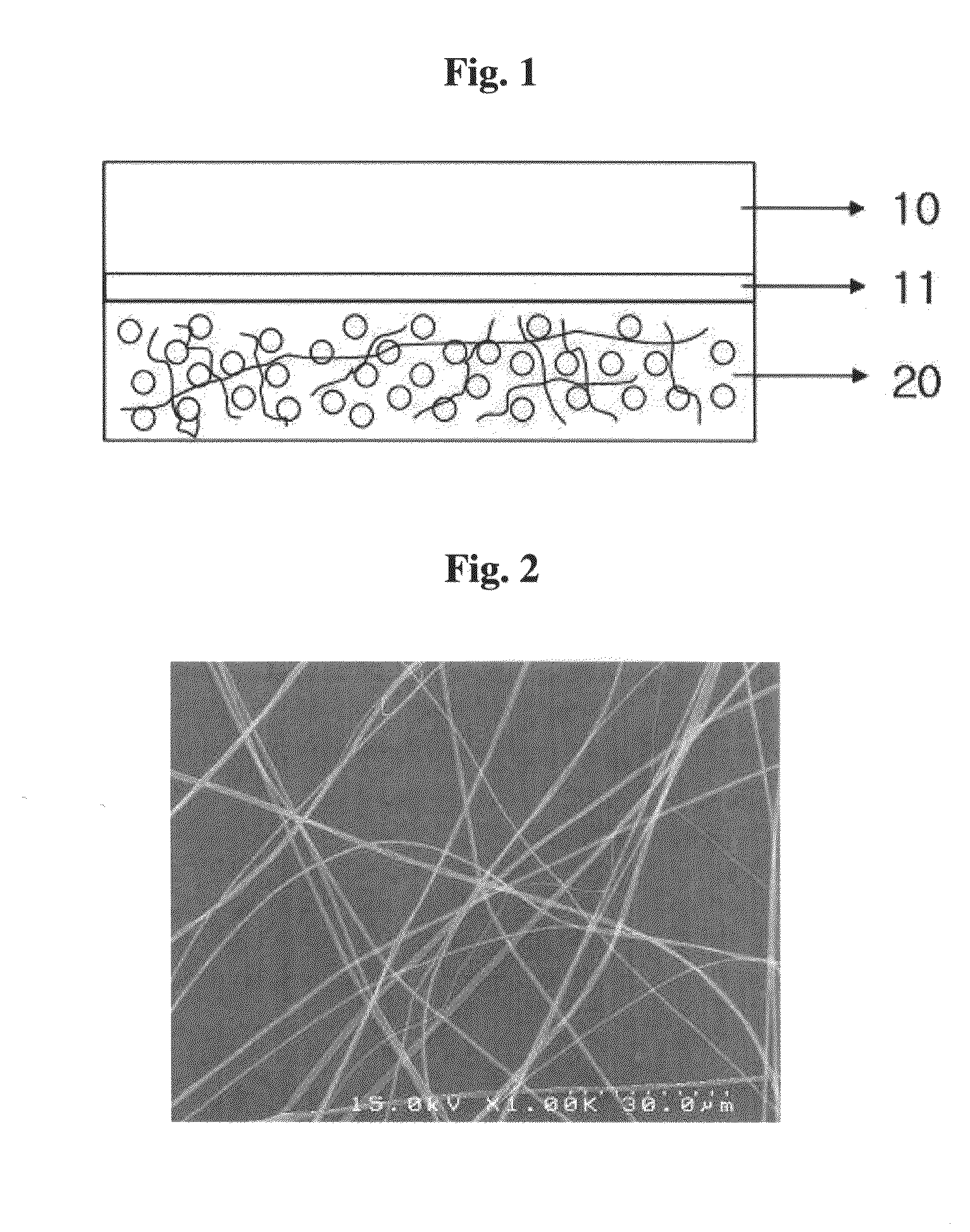
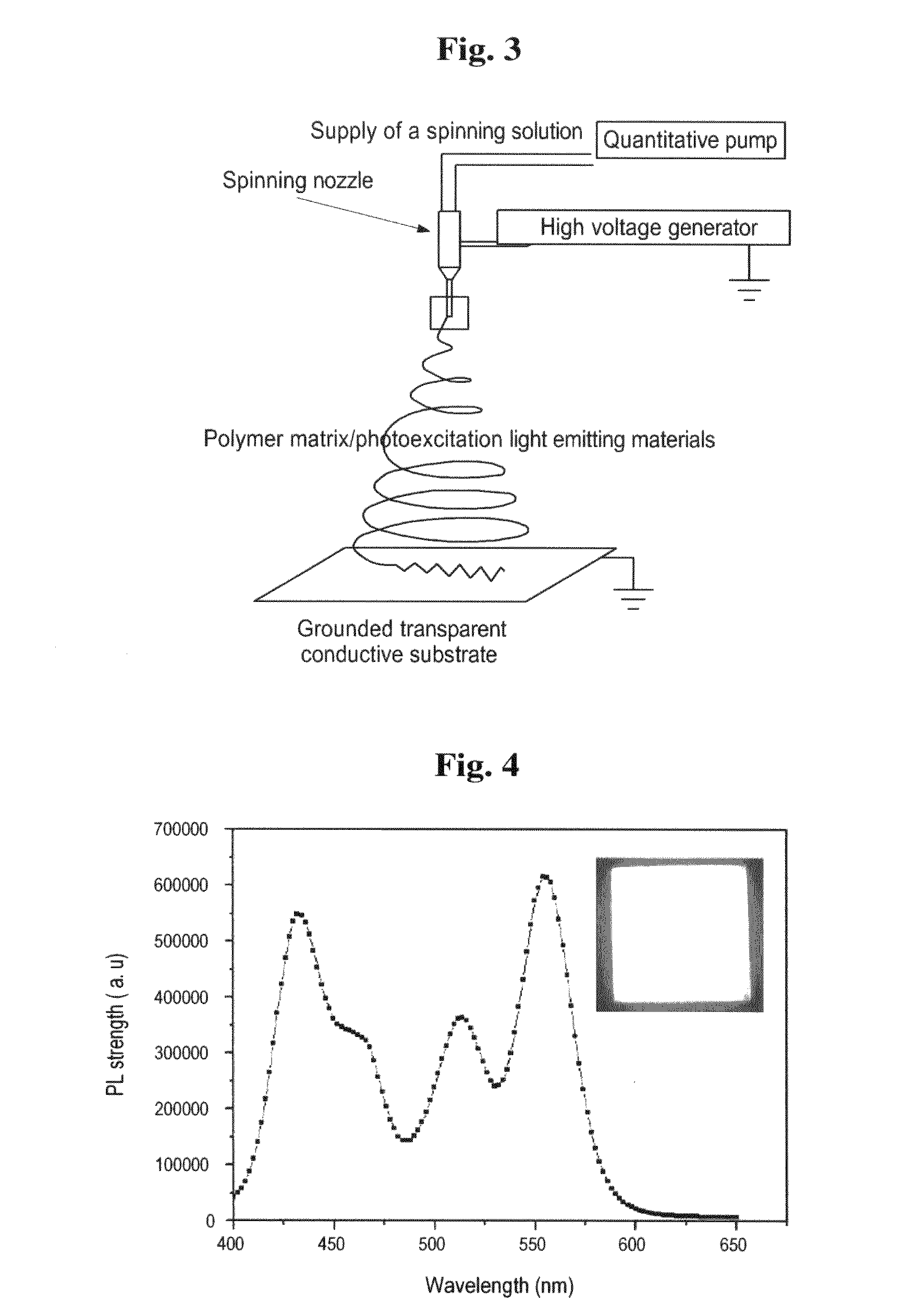
The present invention relates to a white and color photoexcitation light emitting sheet comprising a substrate, a light source formed on the substrate, and a white and color photoexcitation light emitting layer capable of converting a light emitted from the light source into a light having a different wavelength, where the white and color photoexcitation light emitting layer is fabricated by mixing a matrix polymer, white and color photoexcitation light emitting materials and a solvent, spinning the resulting mixture to prepare an ultrafine composite fiber layer of the matrix polymer / photoexcitation light emitting materials, and thermocompressing the ultrafine composite fiber layer; and a method for fabrication thereof. The white and color photoexcitation light emitting sheet according to the present invention has uniform brightness and color coordinates and exhibits high color reproducibility.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
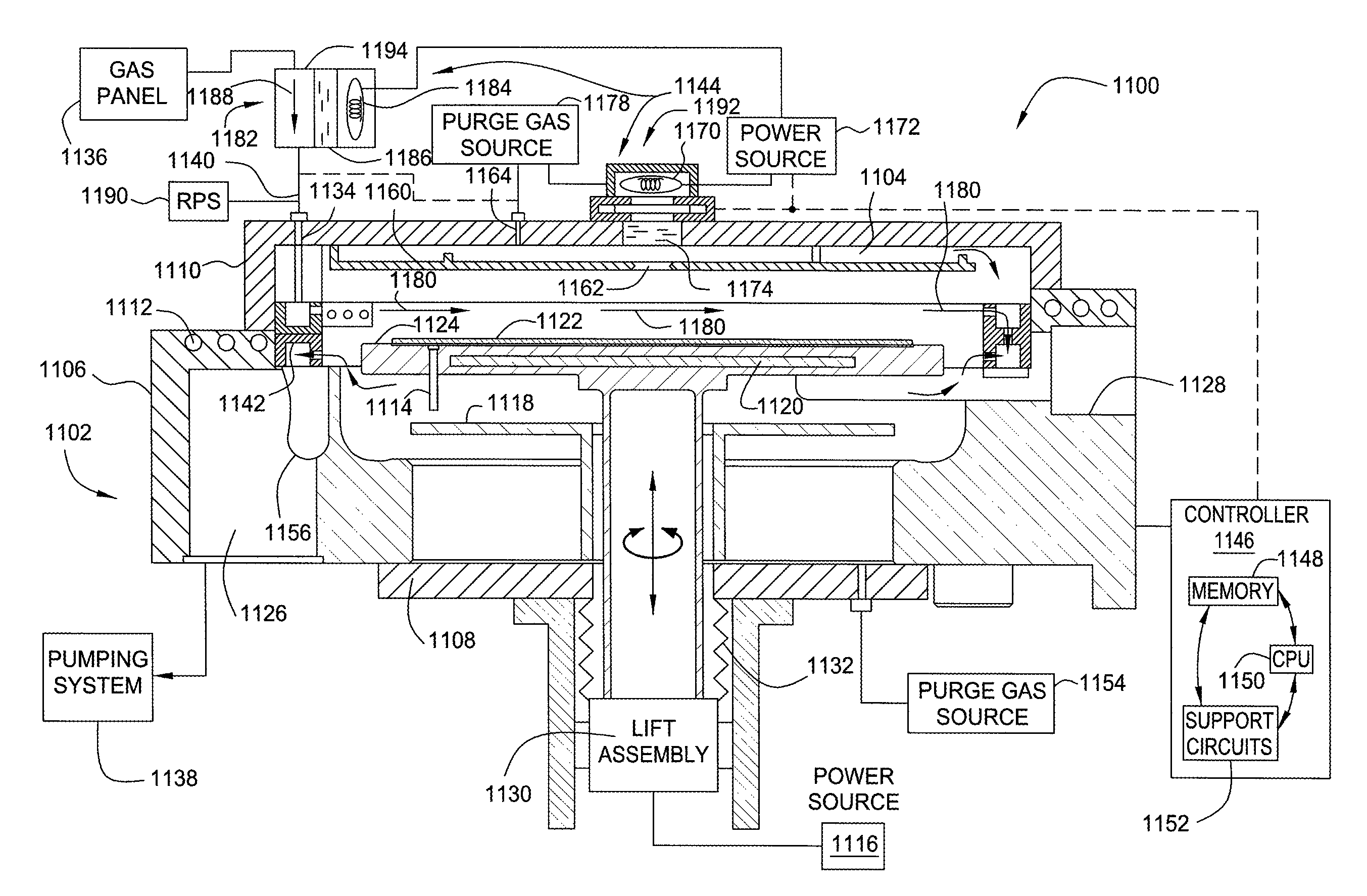
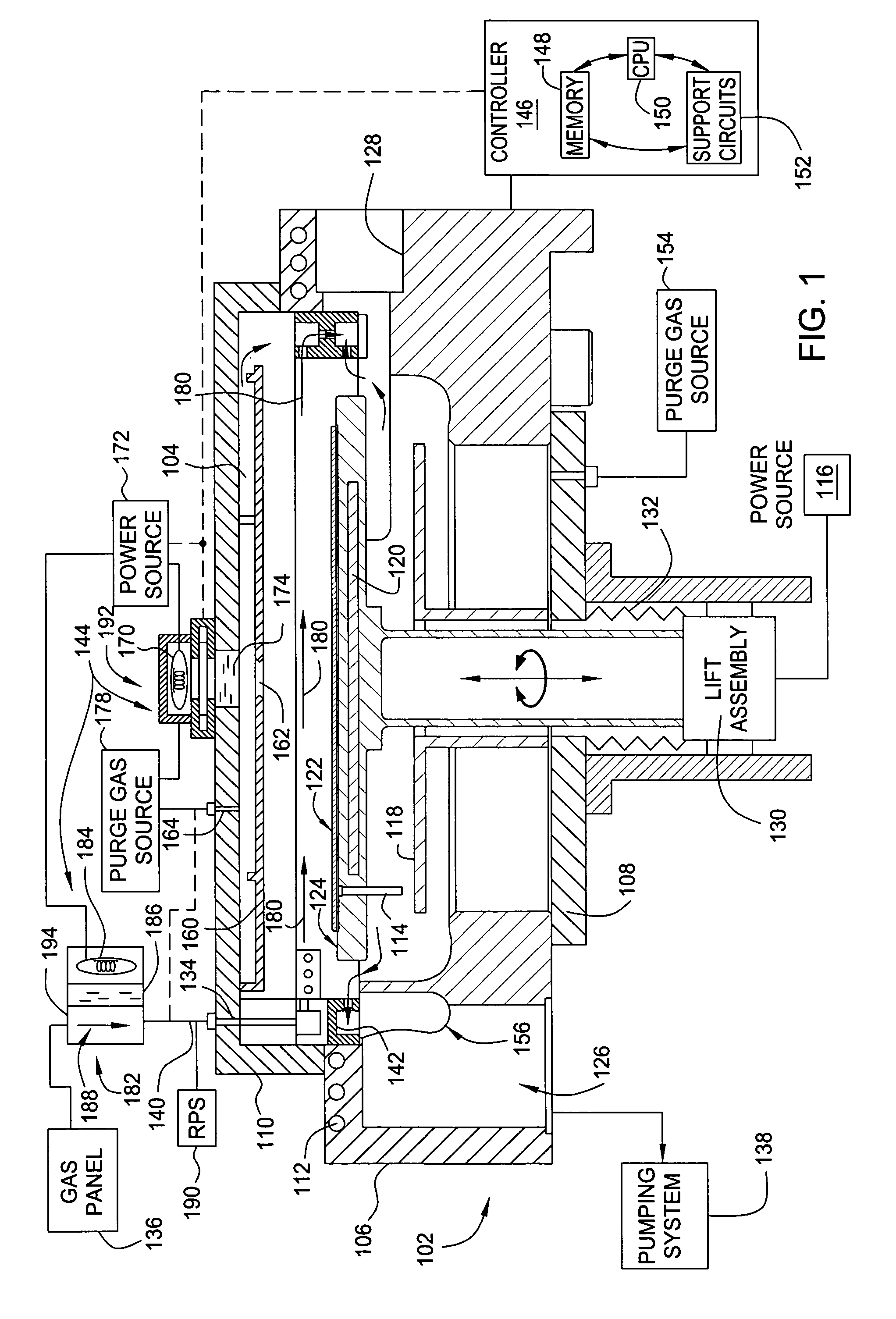
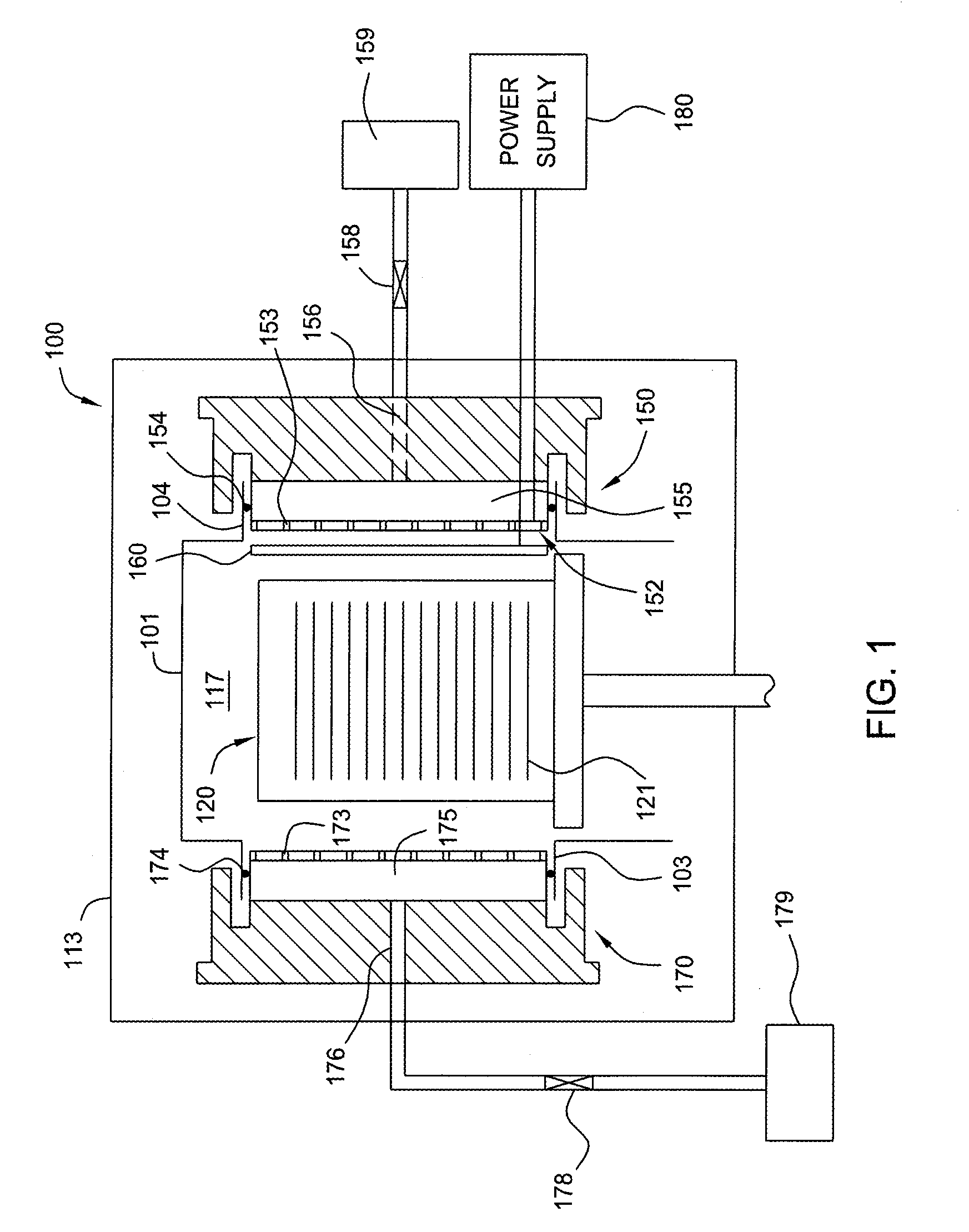
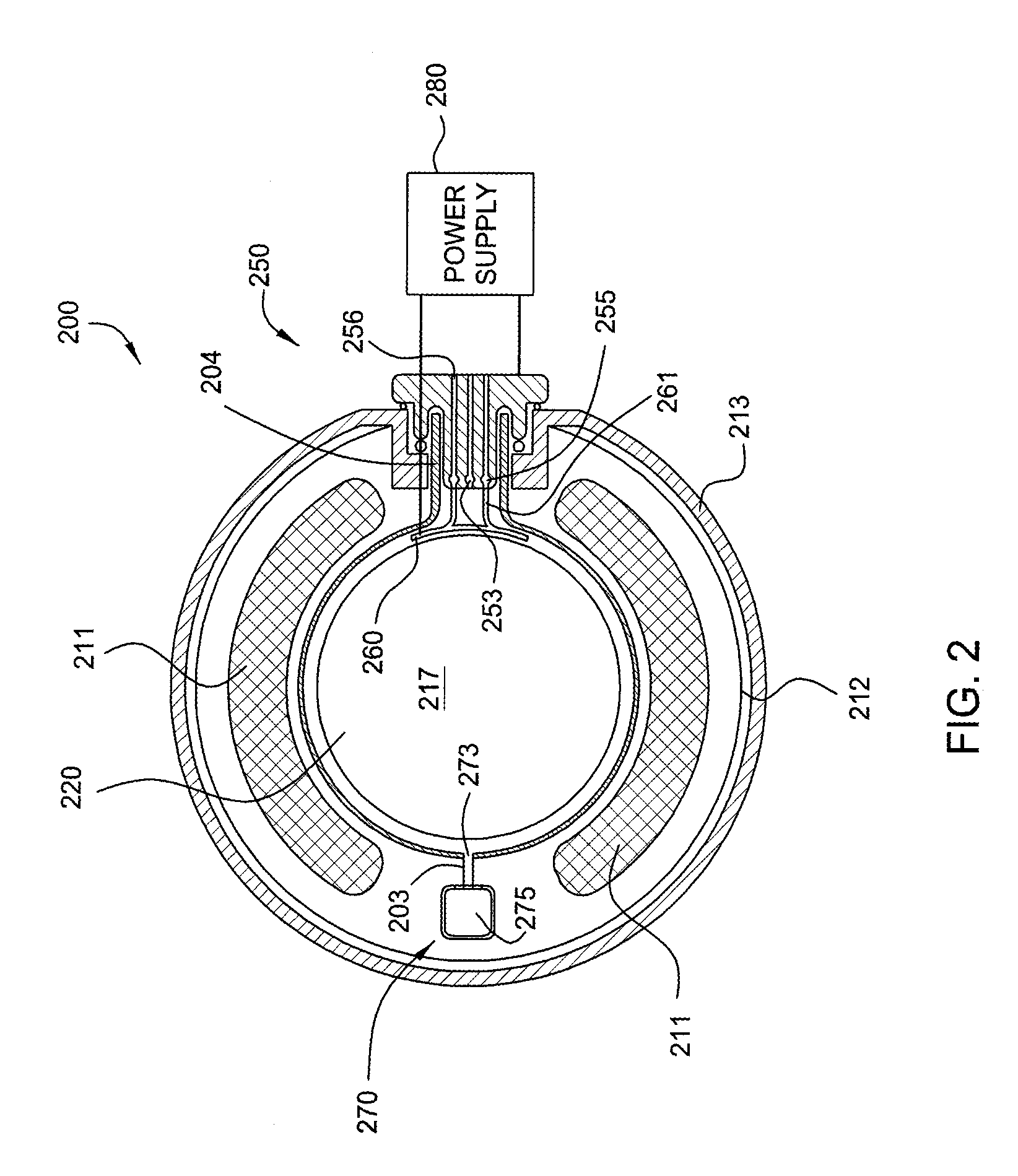
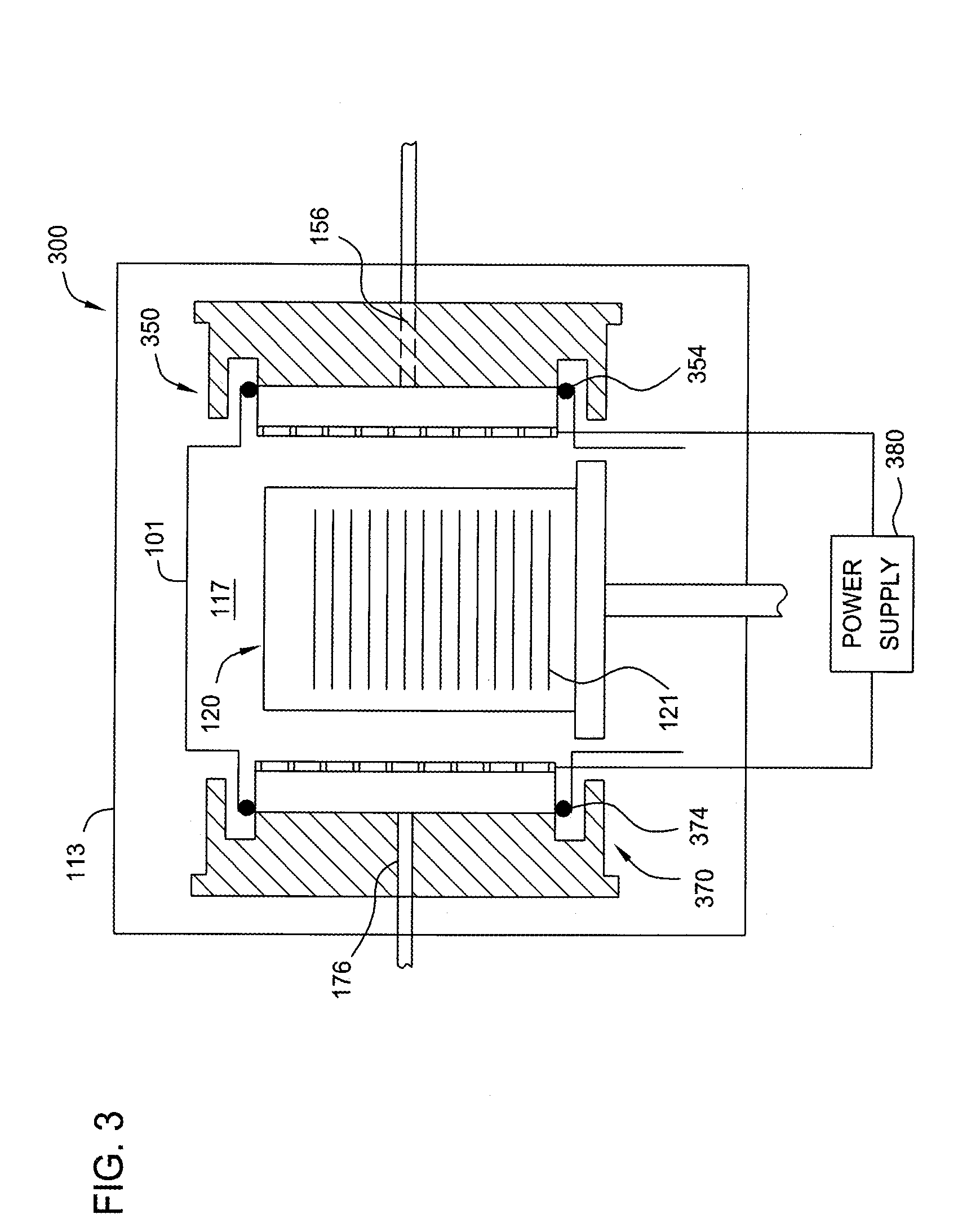
Method and apparatus for photo-excitation of chemicals for atomic layer deposition of dielectric film
InactiveUS20070259111A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMetallurgy
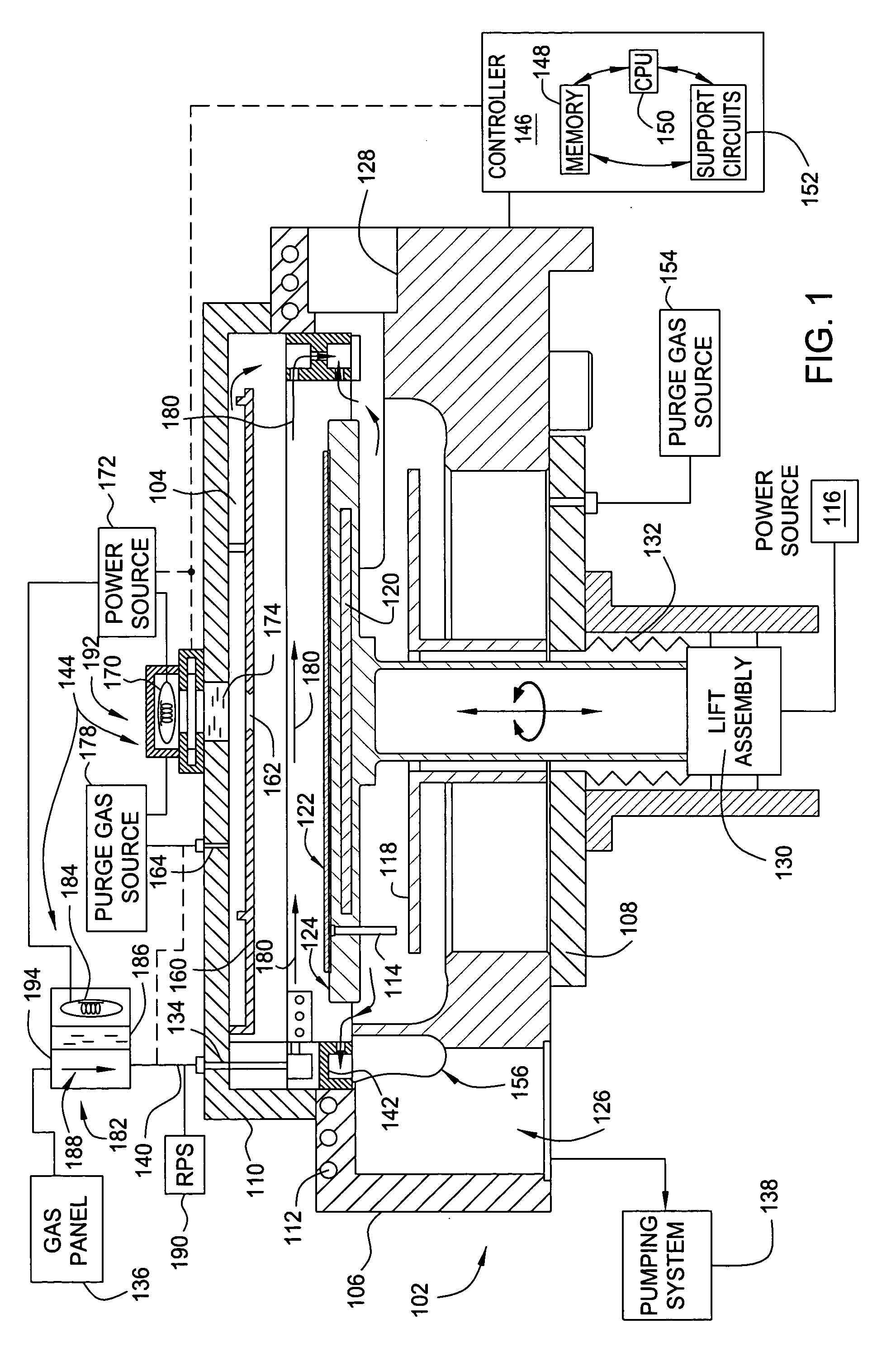
The invention generally provides a method for depositing materials, and more particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to chemical vapor deposition processes and atomic layer deposition processes utilizing photoexcitation techniques to deposit barrier layers, seed layers, conductive materials, and dielectric materials. Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods of the assisted processes and apparatuses, in which the assisted processes may be conducted for providing uniformly deposited material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
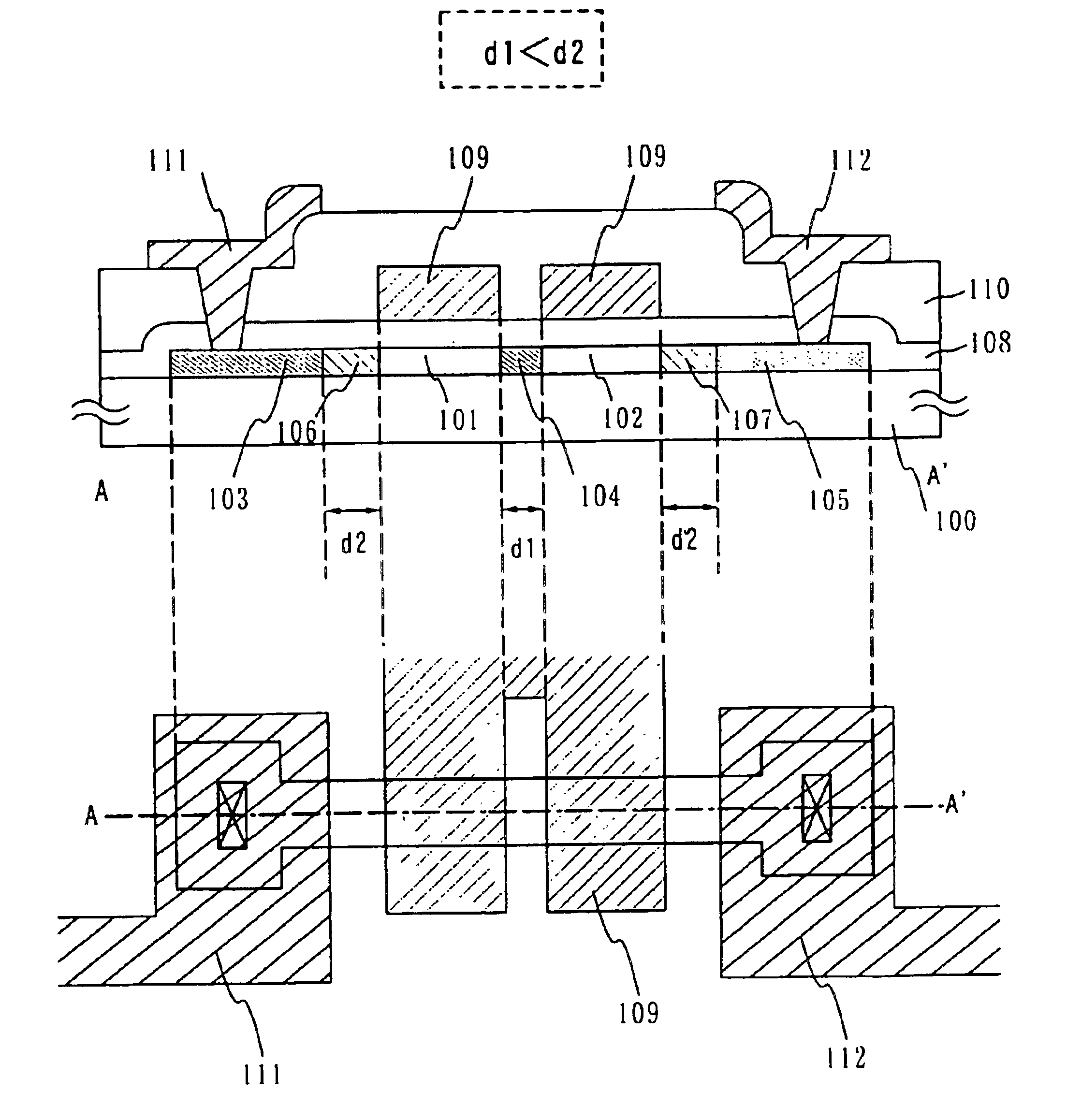
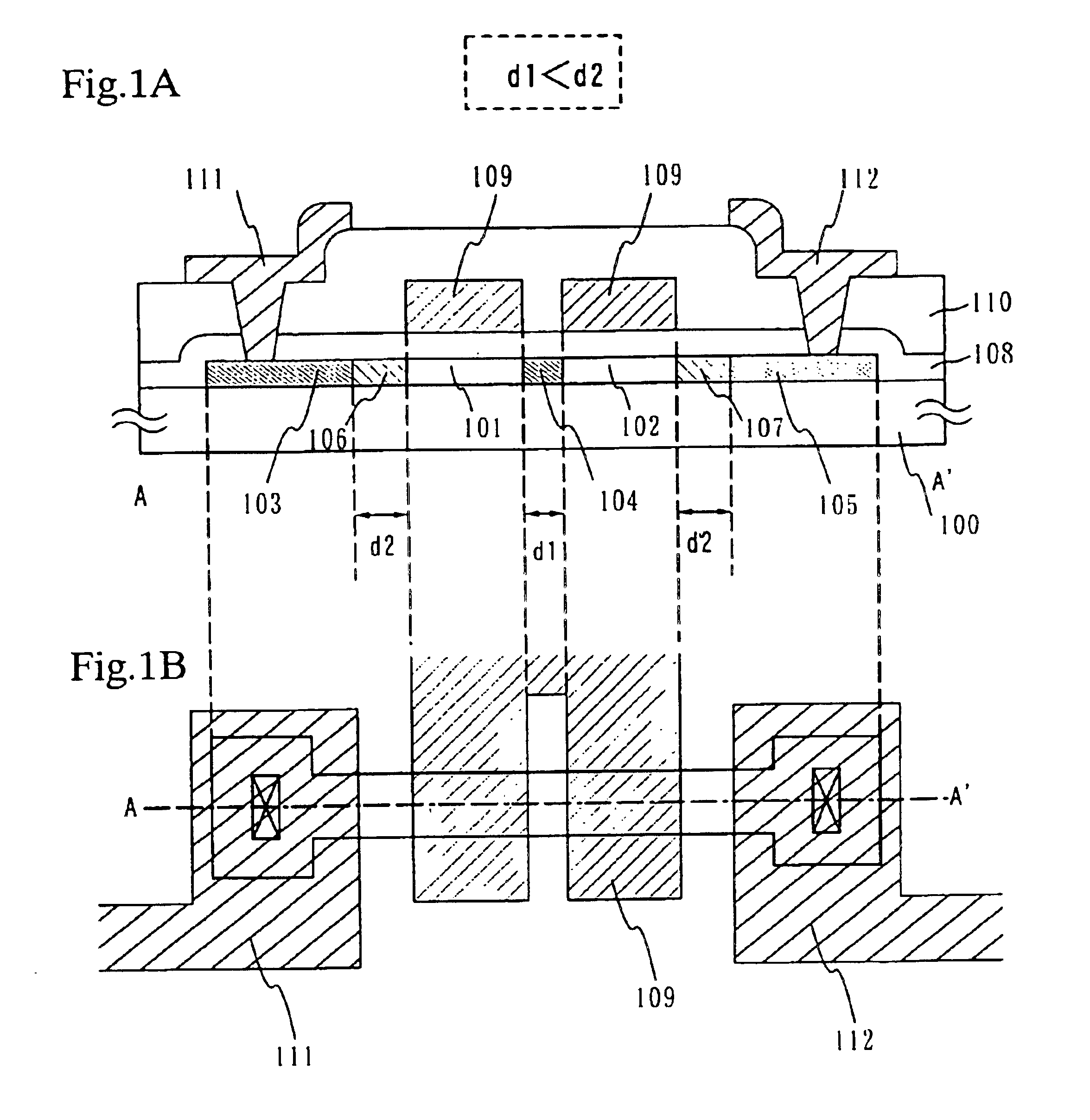
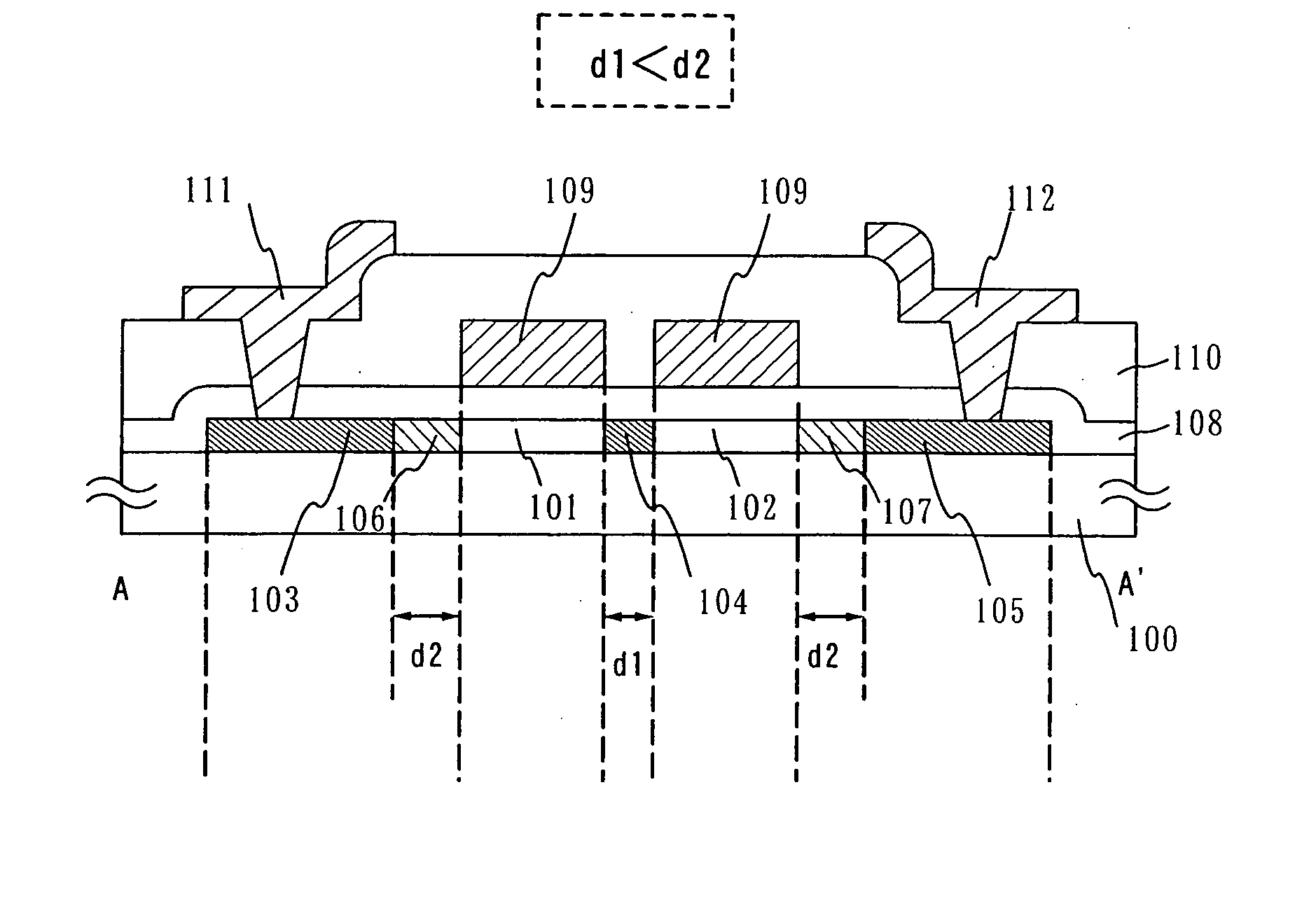
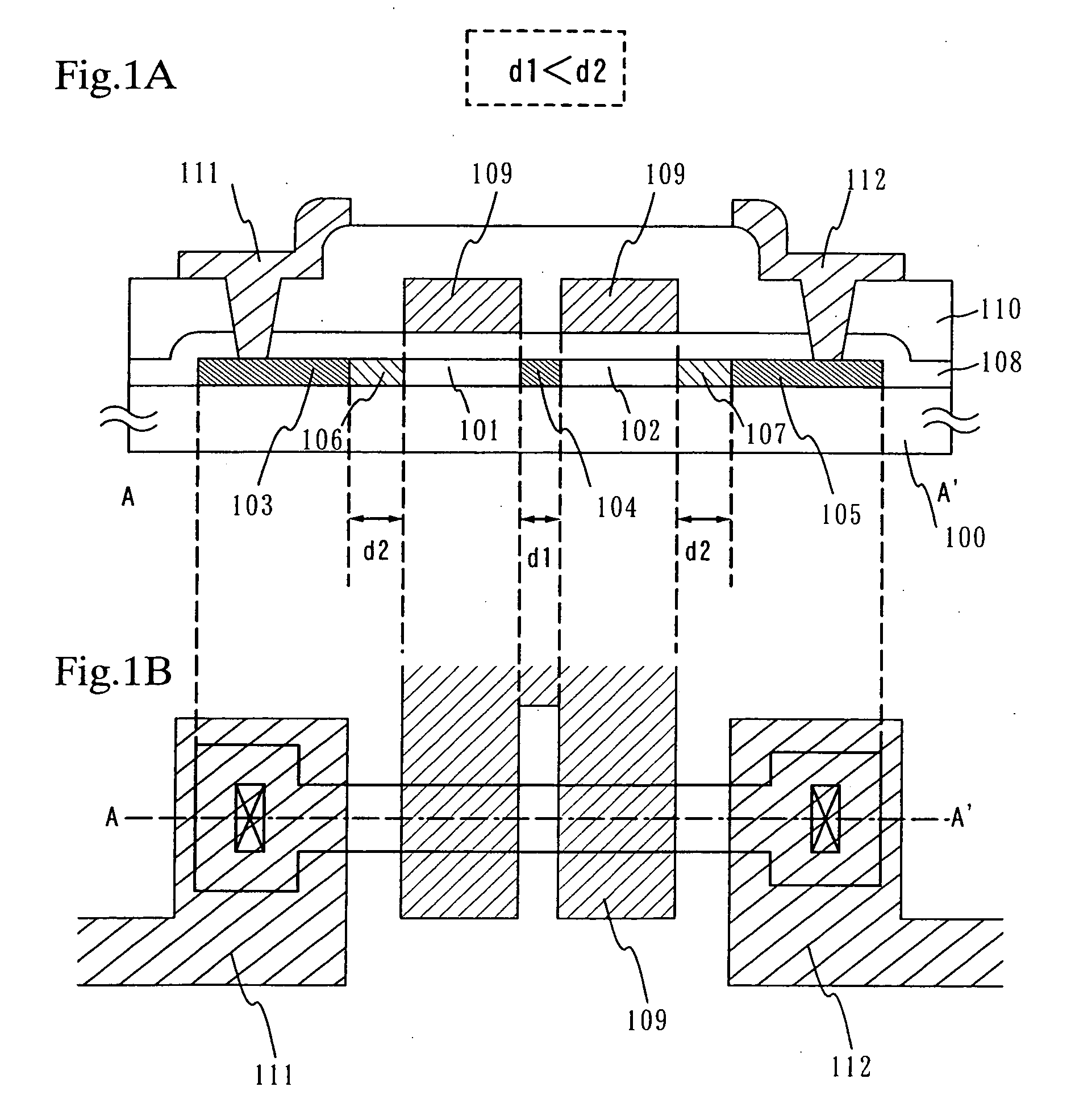
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, and display device
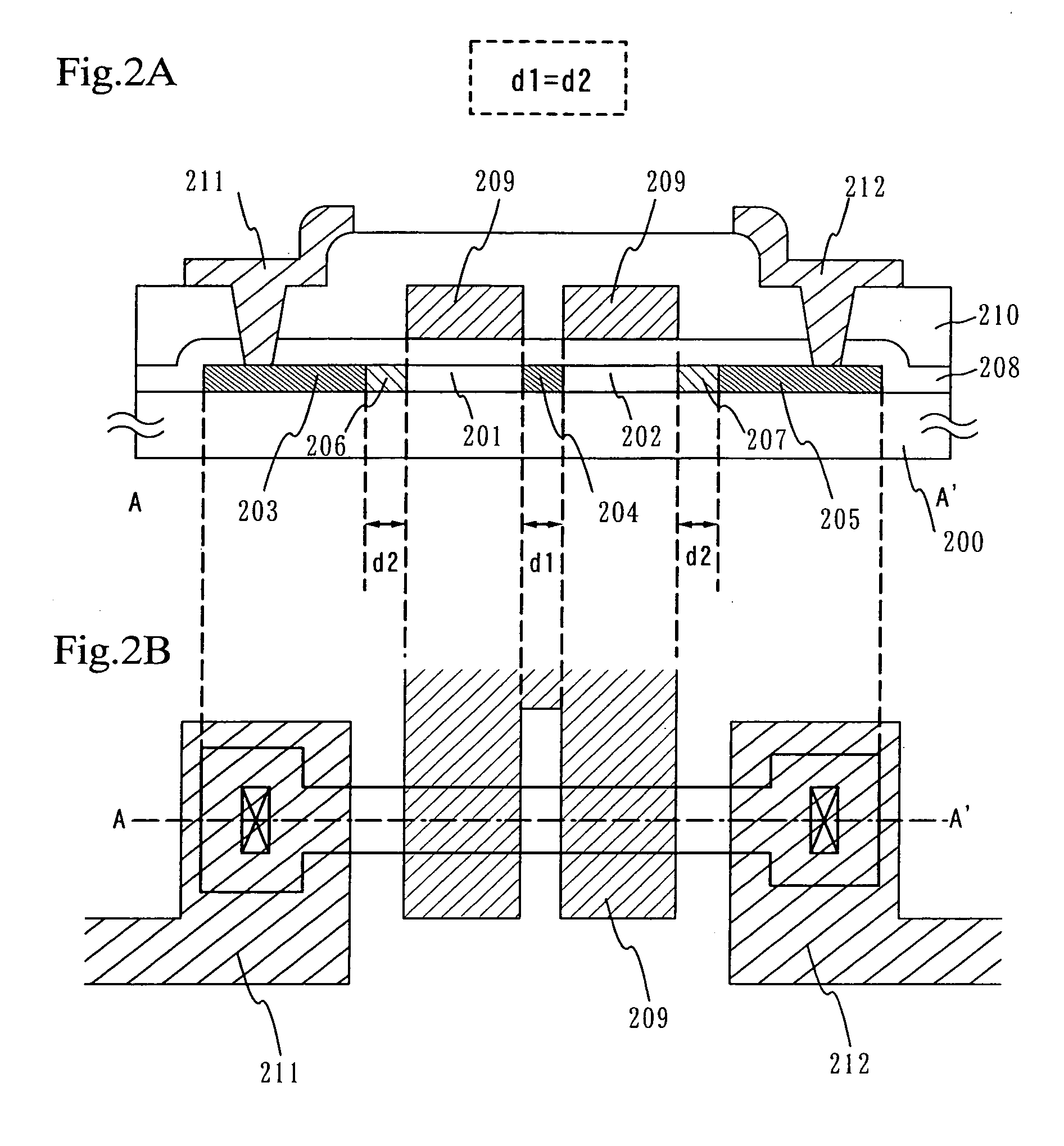
InactiveUS6897477B2Suppress mutationAvoid alternationTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationCharge carrier
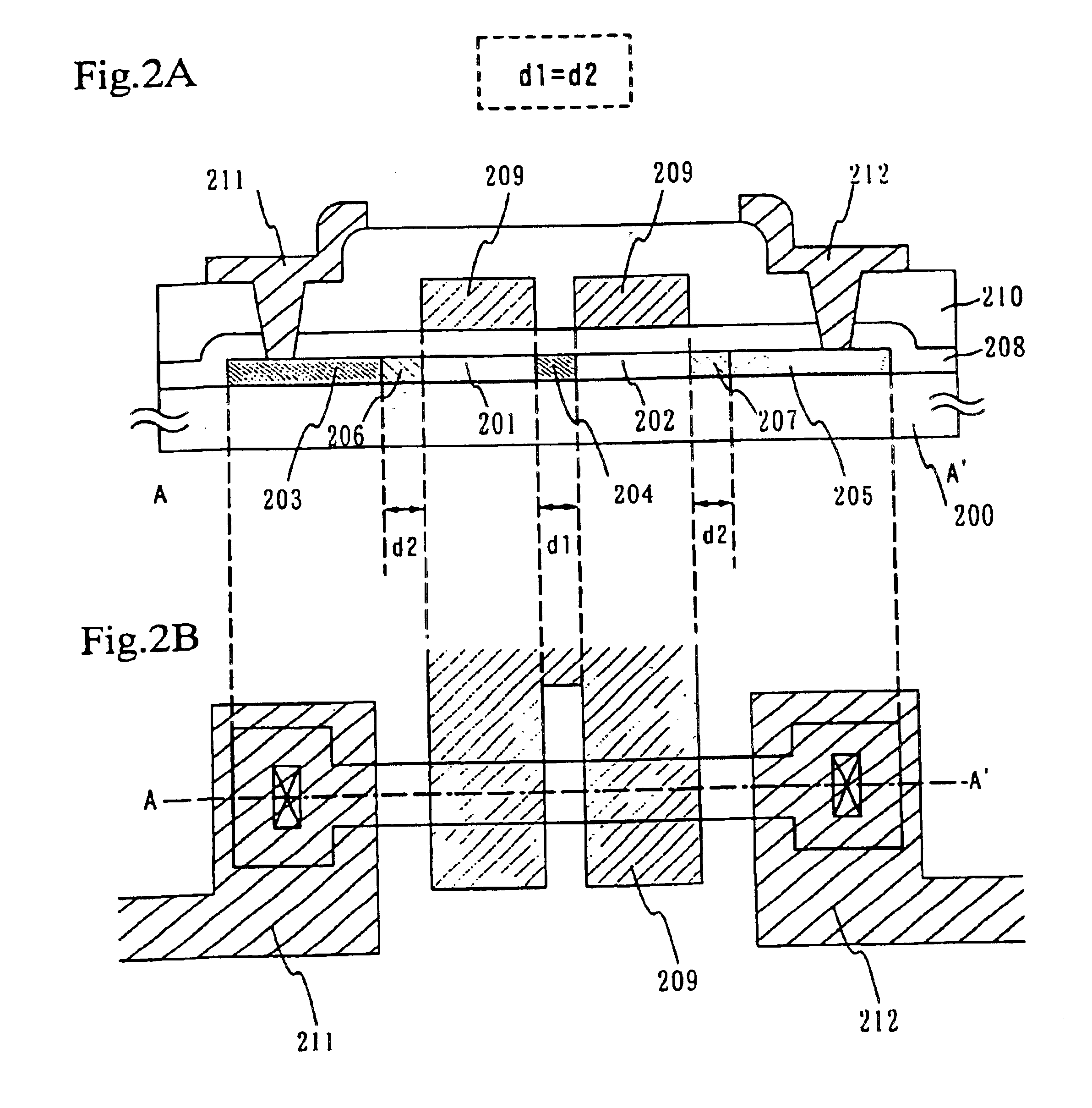
A multi-gate structure is used and a width (d1) of a high concentration impurity region sandwiched by two channel forming regions in a channel length direction is set to be shorter than a width (d2) of low concentration impurity regions in the channel length direction. Thus, a resistance of the entire semiconductor layer of a TFT which is in an on state is reduced to increase an on current. In addition, a carrier life time due to photoexcitation produced in the high concentration impurity region can be shortened to reduce light sensitivity.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for treating substrates and films with photoexcitation
InactiveUS20060286820A1Enhancing chamber cleaningSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films using photoexcitation. The photoexcitation may be utilized for at least one of treating the substrate prior to deposition, treating substrate and / or gases during deposition, treating a deposited film, or for enhancing chamber cleaning. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon and nitrogen-containing film on a substrate includes heating a substrate disposed in a processing chamber, generating a beam of energy of between about 1 to about 10 eV, transferring the energy to a surface of the substrate; flowing a nitrogen-containing chemical into the processing chamber, flowing a silicon-containing chemical with silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and depositing a silicon and nitrogen-containing film on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
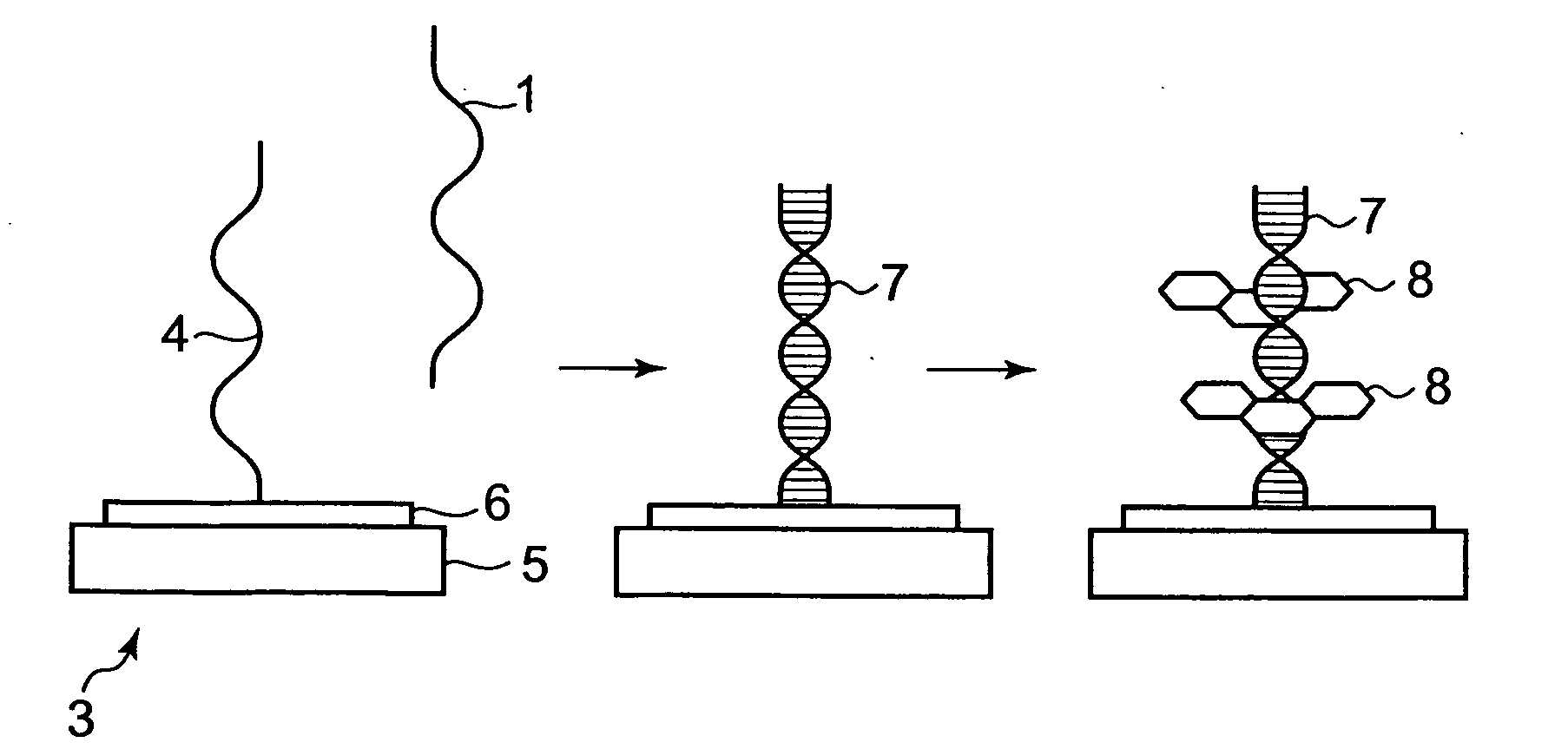
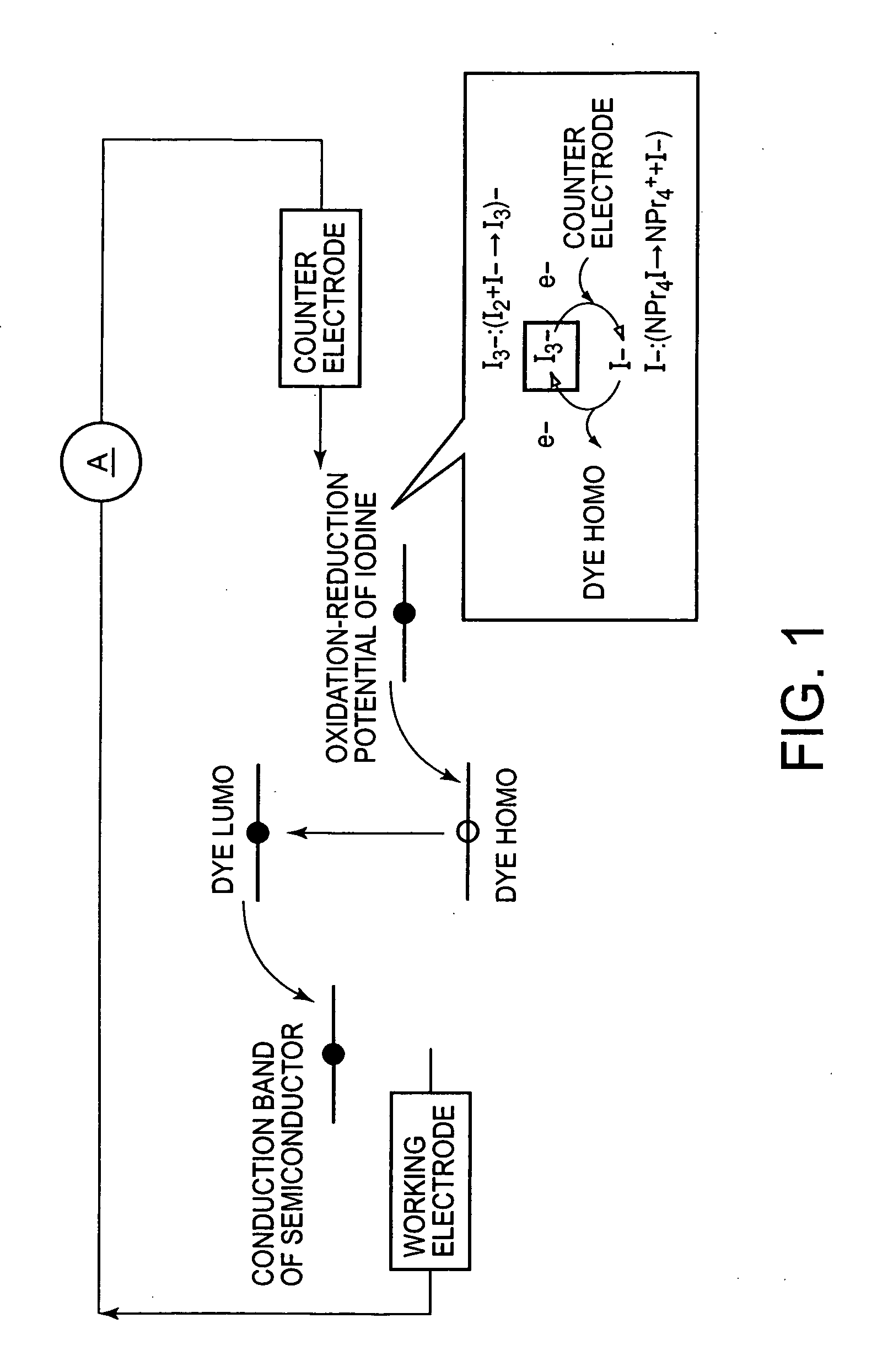
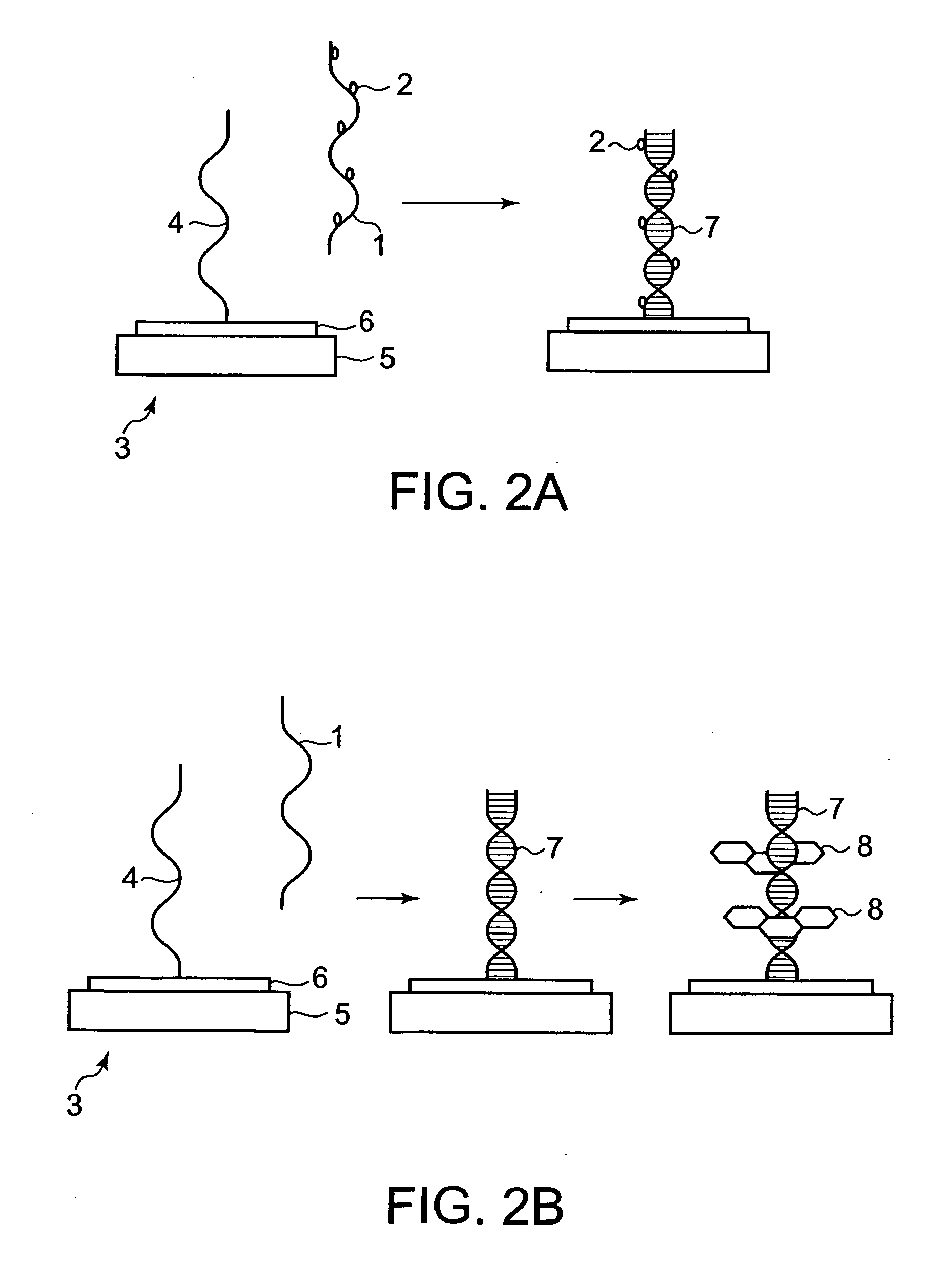
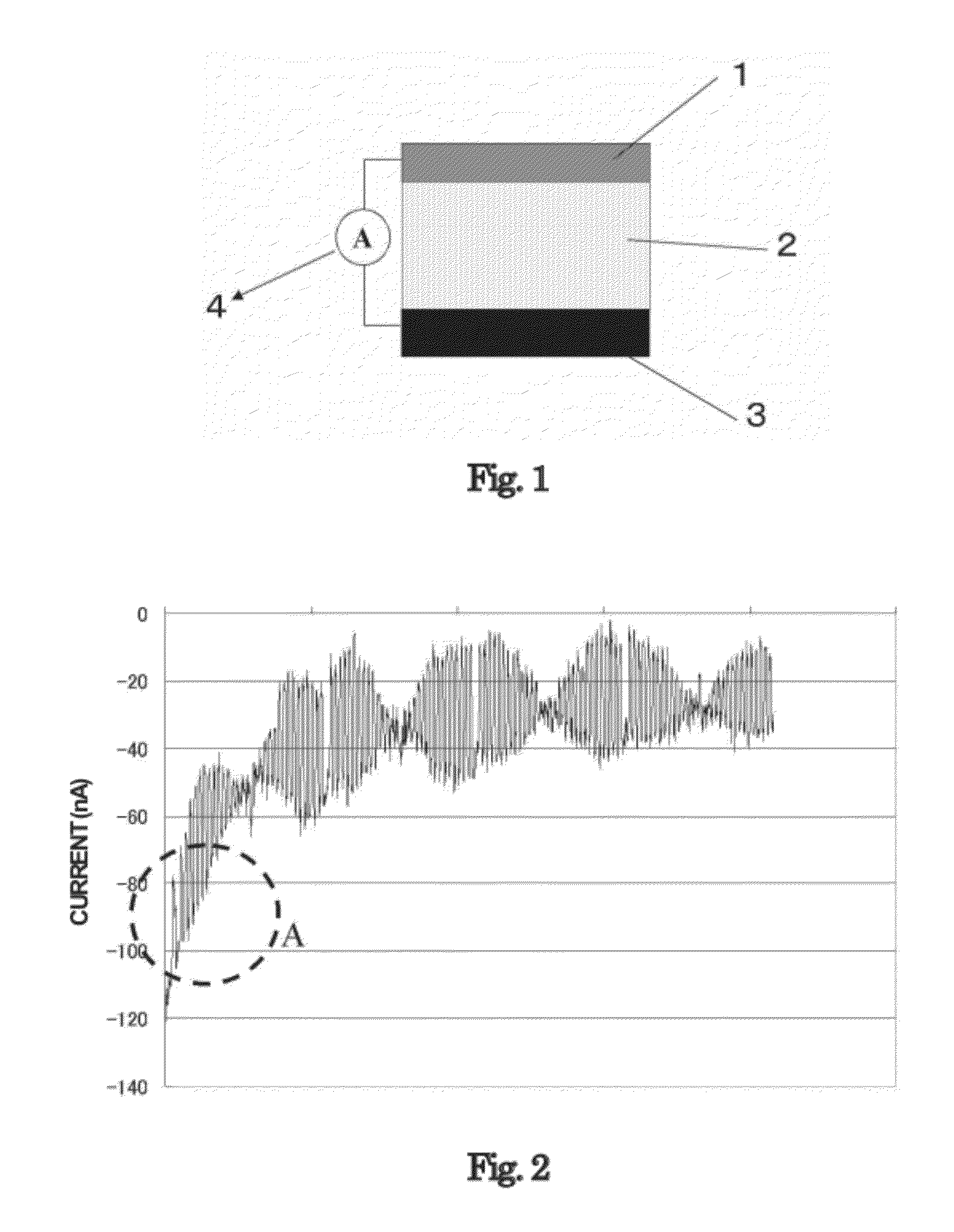
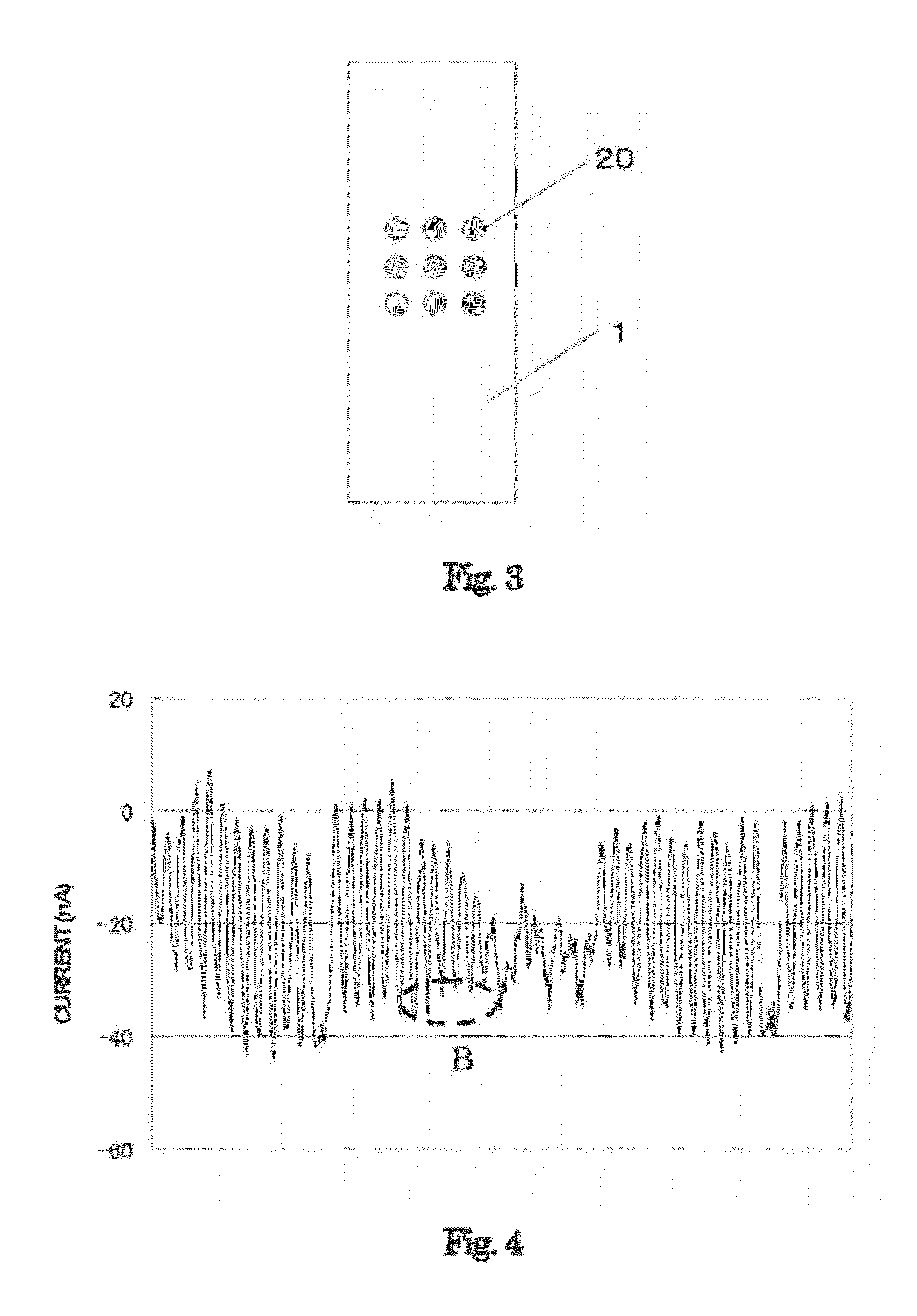
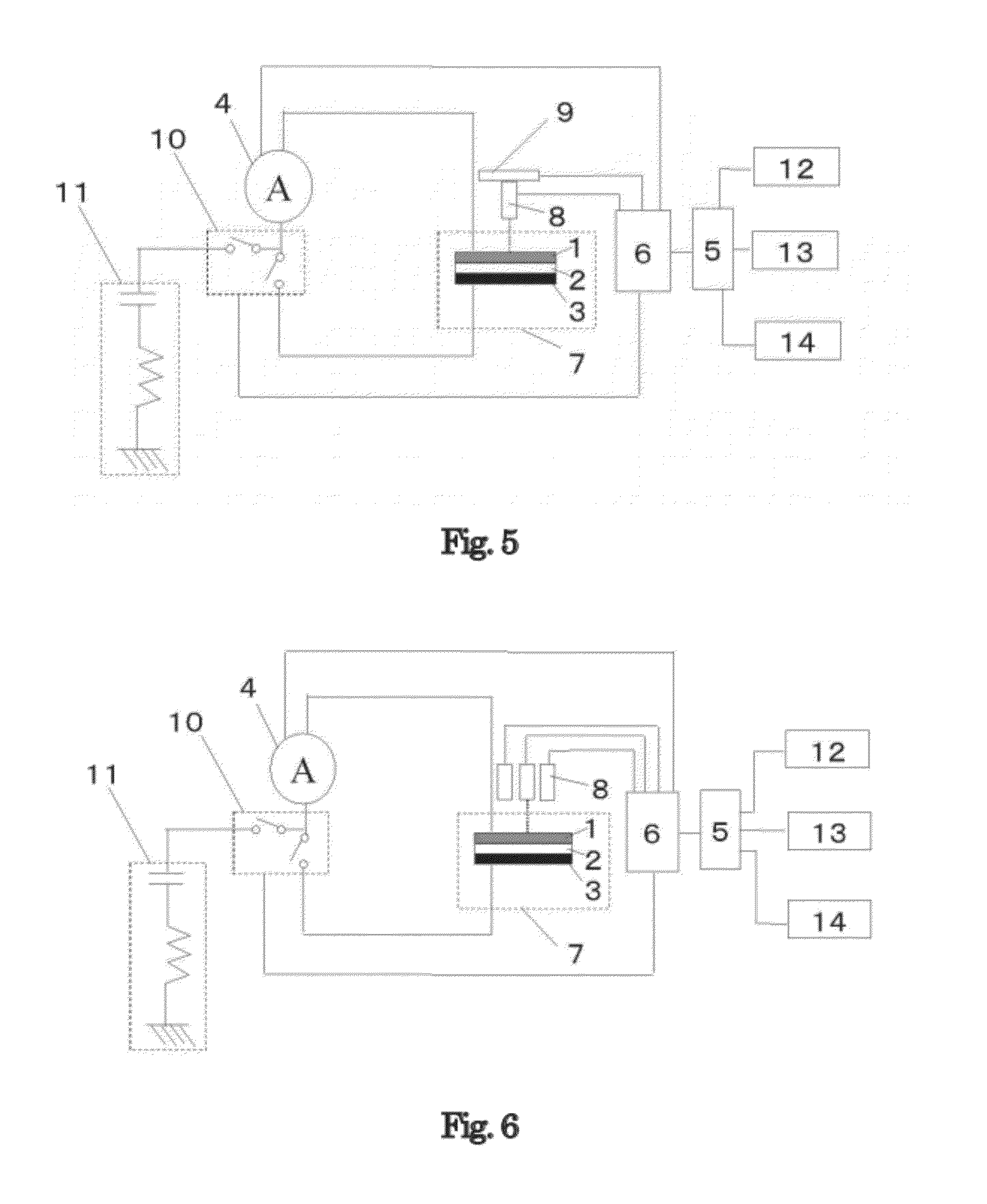
Method for Specifically Detecting Analyte Using Photocurrent, and Electrode, Measuring Cell and Measuring Device for Use Therein
InactiveUS20090294305A1Sensitive and simple and accurate mannerWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMeasurement devicePhotocurrent
A method, an electrode, a measuring cell, and a measuring device are disclosed which can detect and quantitatively determine an analyte having specific bonding properties, in a highly sensitive, simple and accurate manner using photocurrent. This method comprises contacting a working electrode and a counter electrode with an electrolyte medium, wherein the working electrode has an analyte immobilized thereon through a probe substance and wherein the analyte is bonded to a sensitizing dye; irradiating the working electrode with light to photoexcite the sensitizing dye; and detecting photocurrent flowing between the working electrode and the counter electrode, wherein the photocurrent is generated by transfer of electrons from the photoexcited sensitizing dye to the working electrode. The working electrode comprises an electron accepting layer comprising an electron accepting substance capable of accepting electrons released from the sensitizing dye in response to photoexcitation, wherein the probe substance is supported on a surface of the electron accepting layer. The electron accepting substance is an oxide semiconductor having an energy level lower than that of a lowest unoccupied molecular orbit (LUMO) of the sensitizing dye. The electrolyte medium comprises an electrolyte and at least one solvent selected from an aprotic solvent and a protic solvent, wherein the electrolyte comprises a salt capable of providing an oxidized sensitizing dye with electrons.
Owner:TOTO LTD
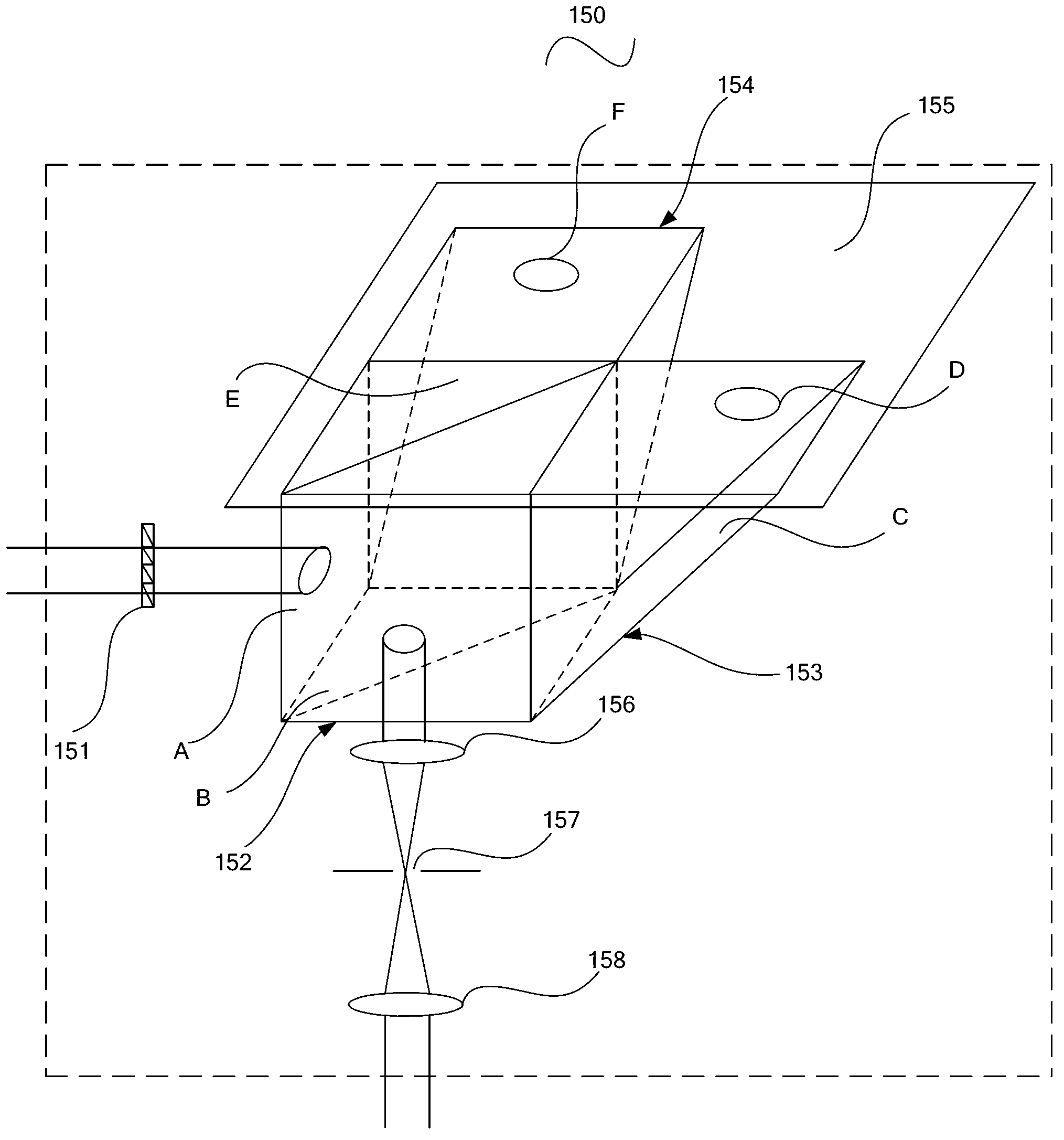
Stimulated radiation loss micro imaging system
ActiveCN103257130AImprove optical resolutionDistribution exact matchFluorescence/phosphorescenceRadiation lossFluorescence
The invention provides a stimulated radiation loss micro imaging system which comprises an exciting light laser, a first dichroscope, a fluorescent light activating and imaging unit, a loss photoexcitation light, a vector beam modulation unit and a control unit, wherein the fluorescent light activating and imaging unit comprises a second dichroscope, an XY vibrating mirror scanning part, a scanning lens, a cylinder mirror, an objective lens, a probe hole and a photomultiplier tube. The stimulated radiation loss micro imaging system provided by the invention adopts the vector beam modulation unit to modulate the incident loss light laser beam amplitude, a phase and a polarization state, the loss light wave amplitude, the phase and the polarization state of the pupil of an objective lens are utilized to form loss light focal spots, and meanwhile, the loss light focal spots are reshaped in a fine and complicated manner under the action of the multiple physical quantities, so that the generated loss light focal spots are exactly matched with the exciting light focal spot distribution, meanwhile, the diameter of a centre dark region of the loss light focal spots is minimal under the condition of a certain signal-to-noise ratio, and the stimulated radiation loss micro imaging system has high optical resolution.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, and display device
InactiveUS20050247940A1Deterioration of image qualitySmall off current valueTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationDevice material
A multi-gate structure is used and a width (d1) of a high concentration impurity region sandwiched by two channel forming regions in a channel length direction is set to be shorter than a width (d2) of low concentration impurity regions in the channel length direction. Thus, a resistance of the entire semiconductor layer of a TFT which is in an on state is reduced to increase an on current. In addition, a carrier life time due to photoexcitation produced in the high concentration impurity region can be shortened to reduce light sensitivity.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for photocatalytically rendering a surface of a substrate superhydrophilic, a substrate with superhydrophilic photocatalytic surface, and method of making thereof
InactiveUS20050019700A1Radiation applicationsPhotomechanical apparatusSurface layerMaterials science
A method of preventing or reducing fogging of a surface of a composite when subjected to humid conditions includes providing a composite with a surface. The composite includes a substrate and a photocatalytic surface layer. The photocatalytic surface layer includes a photocatalyst. The method further includes subjecting the photocatalyst to photoexcitation to render the surface of the composite hydrophilic, wherein, after the photoexcitation, the surface of the composite has a water wettability of less than 10° in terms of the contact angle with water. The method further includes subjecting the composite to humidity that is sufficient to induce fogging of the substrate if the photocatalytic surface layer were absent.
Owner:TOTO LTD
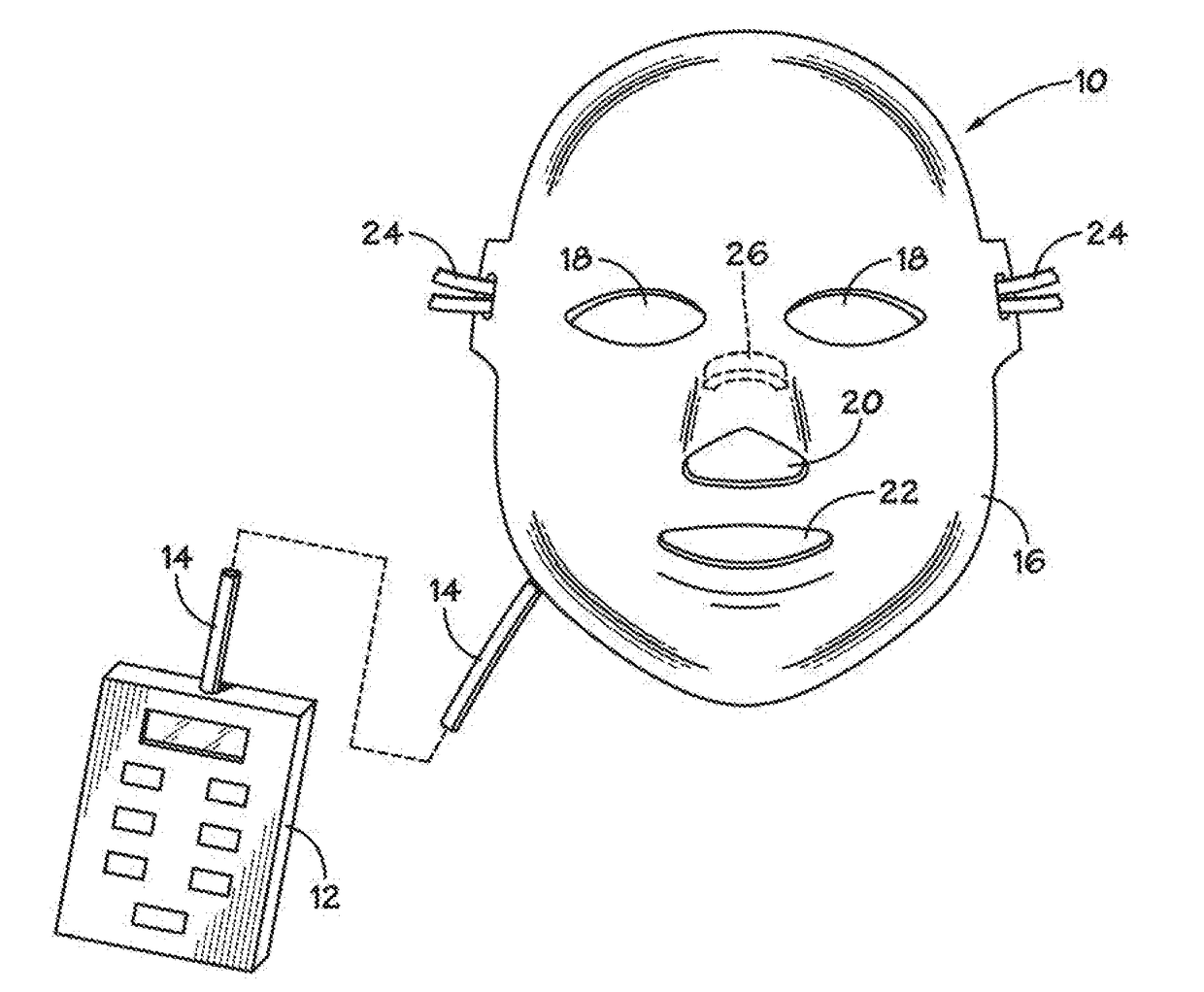
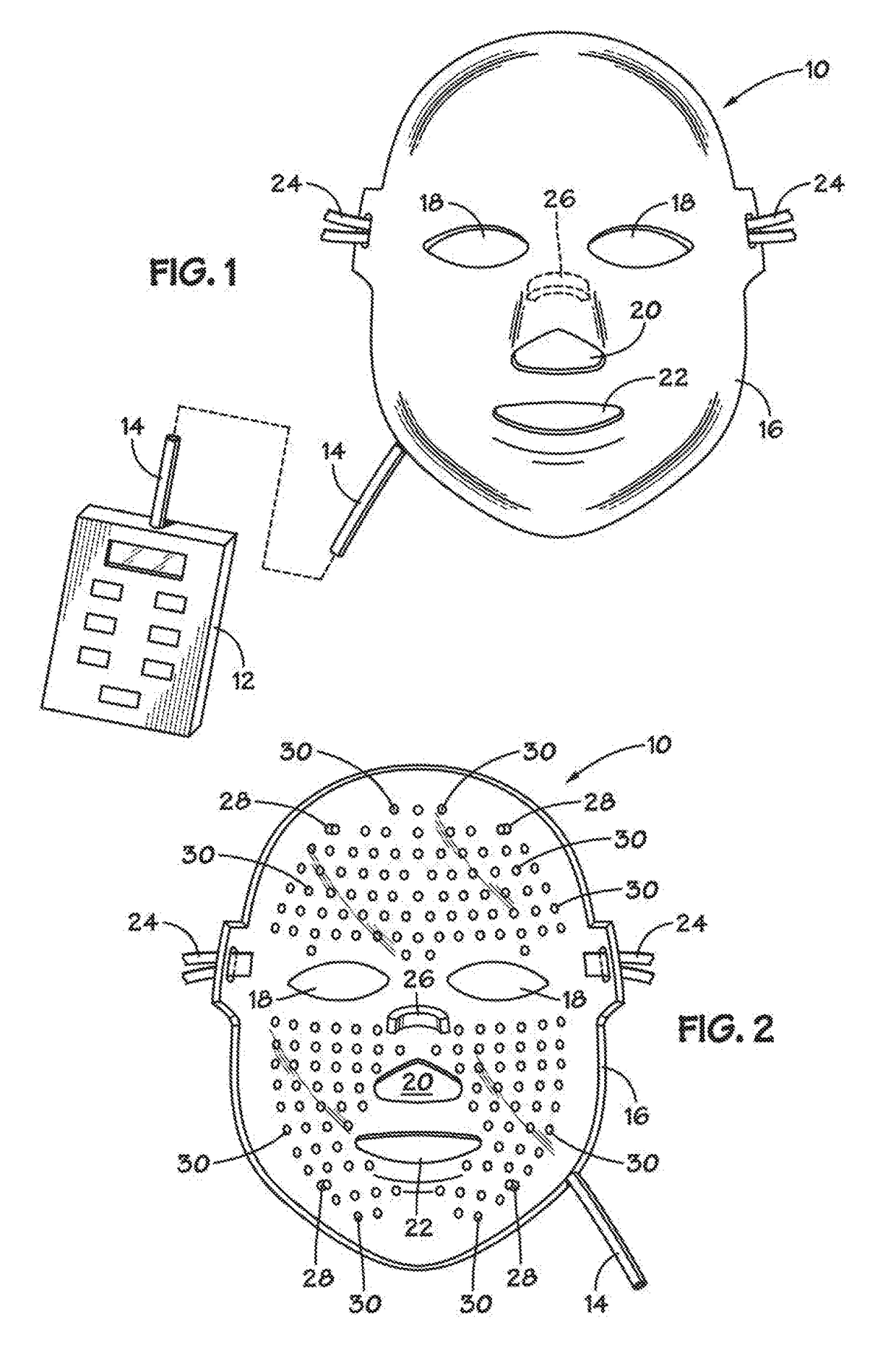
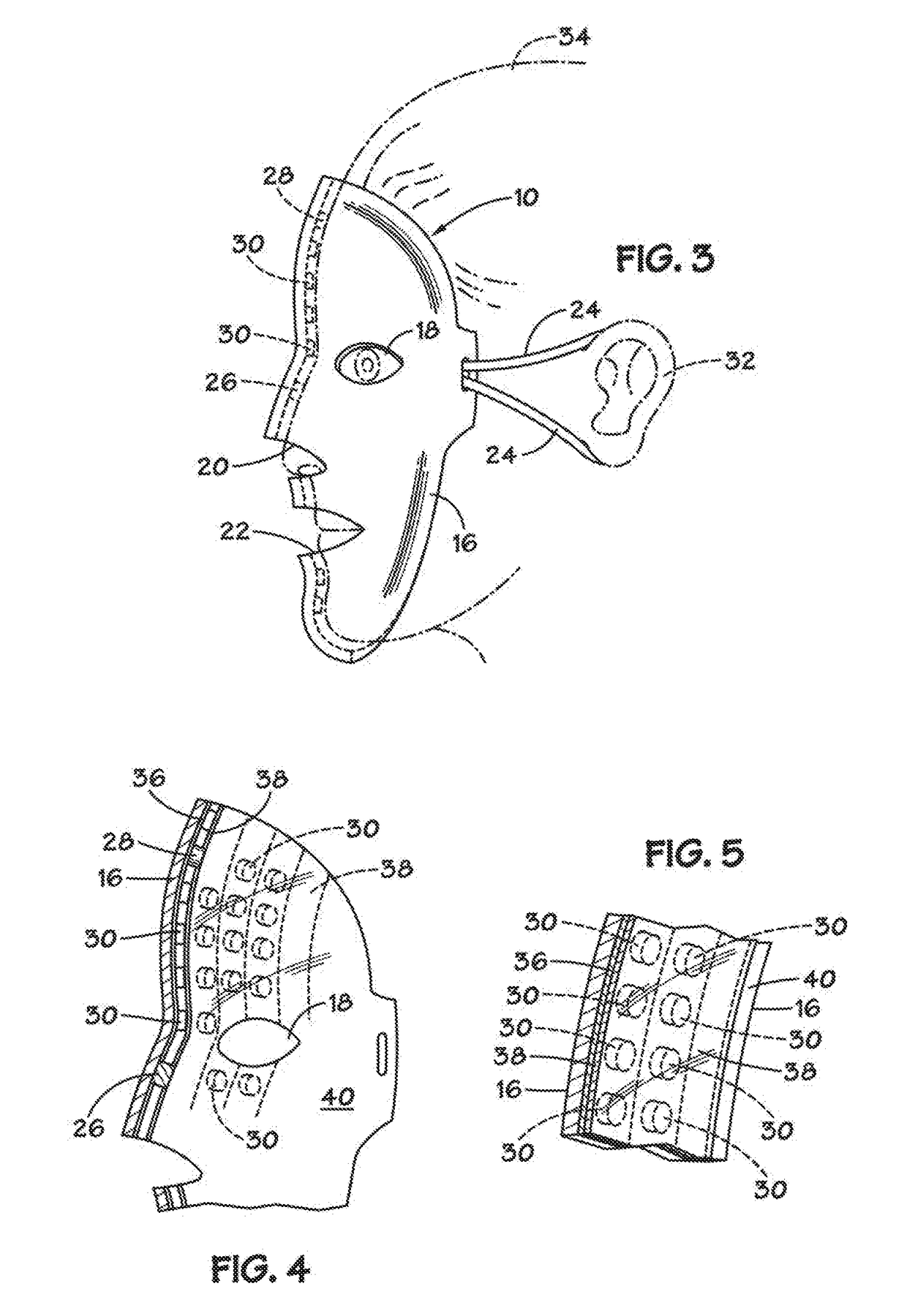
Phototherapy Mask With Quantum Dot Phosphors
A phototherapy device comprises a face mask having a rigid (or semi-rigid) shell contoured to the human face. A flexible array of LEDs is affixed to the inner surface of the mask. A flexible, quantum dot-containing film is situated over the flexible array of LEDs. The quantum dots in the QD-containing film are selected to photo-luminesce at one or more particular wavelengths in response to photoexcitation by the light emitted from the LEDs. The LEDs emit “primary light” and the quantum dots down-convert at least a portion of the primary light to “secondary light.” The flexible, quantum dot-containing film may be interchangeable such that the wavelength(s) of the secondary light may be tailored to various phototherapy treatment regimes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Phototherapy Process Including Dynamic LED Driver With Programmable Waveform
ActiveUS20180146520A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMicrocontrollerLight treatment
A phototherapy or photobiomodulation process employing the application of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) to a living organism, typically a human being. The EMR is generated by one or more strings of LEDs and is programmed to emit one or more wavelengths, typically in the visible and infrared portions of the spectrum, the EMR in each wavelength being delivered in pulses having specified on-times, off-times, photoexcitation frequencies, duty factors, phase delays, and power amplitudes. A system for providing such EMR includes a microcontroller having a pattern library of algorithms, each of which defines a particular sequence of synthesized pulses, and an application pad, preferably flexible, containing the LED strings.
Owner:APPLIED BIOPHOTONICS
Method and apparatus for photo-excitation of chemicals for atomic layer deposition of dielectric film
InactiveCN101438391AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricMetallurgy
The invention generally provides a method for depositing materials, and more particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to chemical vapor deposition processes and atomic layer deposition processes utilizing photoexcitation techniques to deposit barrier layers, seed layers, conductive materials, and dielectric materials. Embodiments of the invention generally provide methods of the assisted processes and apparatuses, in which the assisted processes may be conducted for providing uniformly deposited material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Phototherapy system and process including dynamic LED driver with programmable waveform
A phototherapy or photobiomodulation process employing the application of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) to a living organism, typically a human being. The EMR is generated by one or more strings of LEDs and is programmed to emit one or more wavelengths, typically in the visible and infrared portions of the spectrum, the EMR in each wavelength being delivered in pulses having specified on-times, off-times, photoexcitation frequencies, duty factors, phase delays, and power amplitudes. A system for providing such EMR includes a microcontroller having a pattern library of algorithms, each of which defines a particular sequence of synthesized pulses, and an application pad, preferably flexible, containing the LED strings.
Owner:APPLIED BIOPHOTONICS
Metal oxide composite sol, coating composition, and optical member
InactiveCN101815675AGood weather resistanceGood light fastnessMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentRefractive indexOxide composite
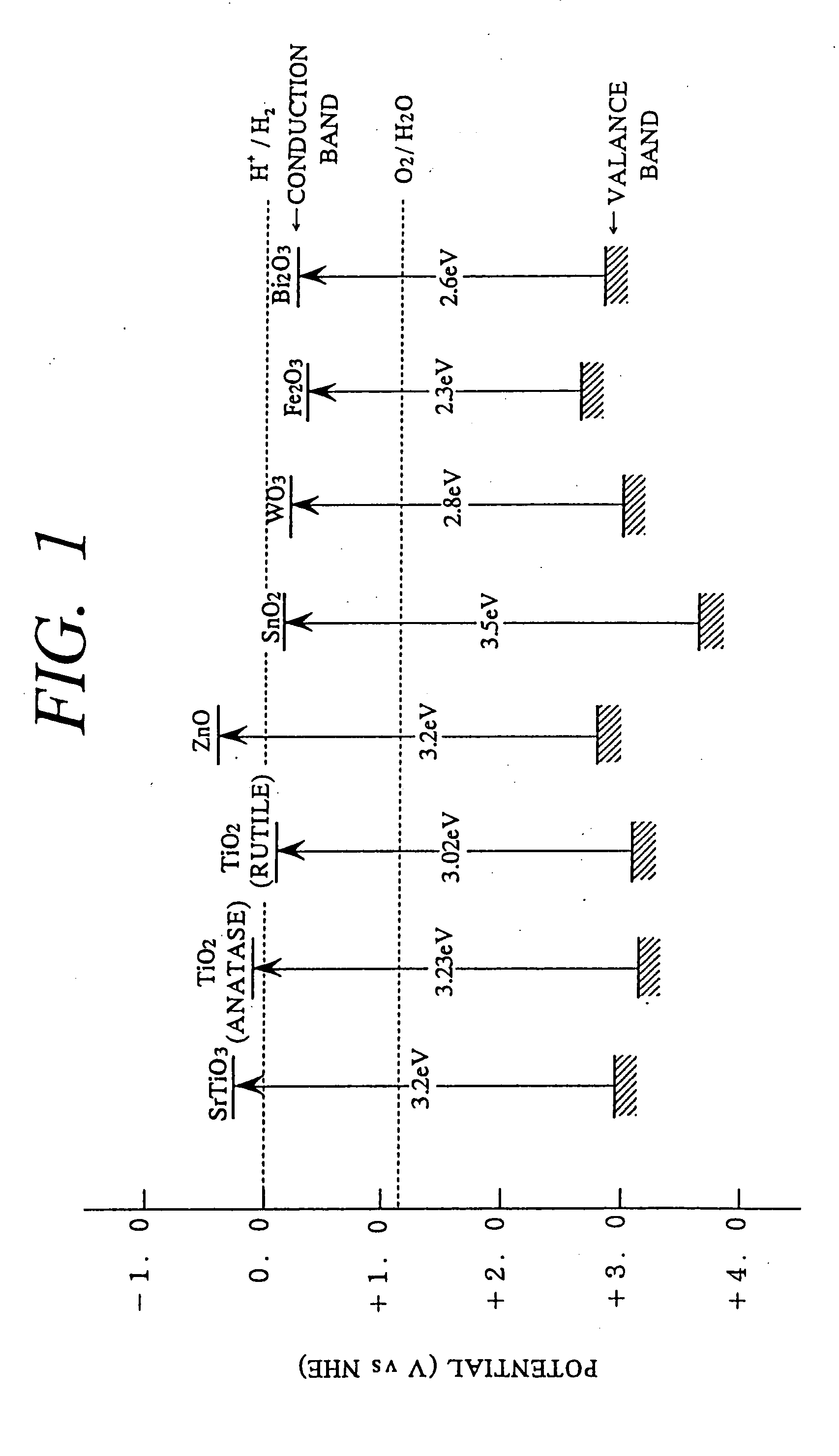
To provide a sol of metal oxide composite colloidal particles which are almost completely inhibited from being discolored by photoexcitation, contain titanium oxide excellent in light resistance and weatherability, and have a high refractive index. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] The metal oxide composite colloidal particles comprise titanium oxide / tin oxide / zirconium oxide / tungsten oxide composite colloidal particles which have a primary-particle diameter of 2-50 nm and have an SnO2 / TiO2 molar ratio of 0.1-1.0, ZrO2 / TiO2 molar ratio of 0.1-0.4, and WO3 / TiO2 molar ratio of 0.03-0.15.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM CORP
Test chip, detection apparatus, and method for detecting analyte
InactiveUS20100112578A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSemiconductor electrodeAnalyte
A test chip for detecting an analyte modified with a modulator releasing electrons upon photoexcitation, comprising: semiconductor electrode part including a metal layer formed on a semiconductor layer; a probe immobilized on the metal layer, the probe trapping the analyte; and a counter electrode part including a conductive layer. A detection apparatus and a method for detecting an analyte are also disclosed.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Modified metal-oxide composite sol, coating composition, and optical member
InactiveCN101815676AGood weather resistanceGood light fastnessPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyRefractive indexOxide composite
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
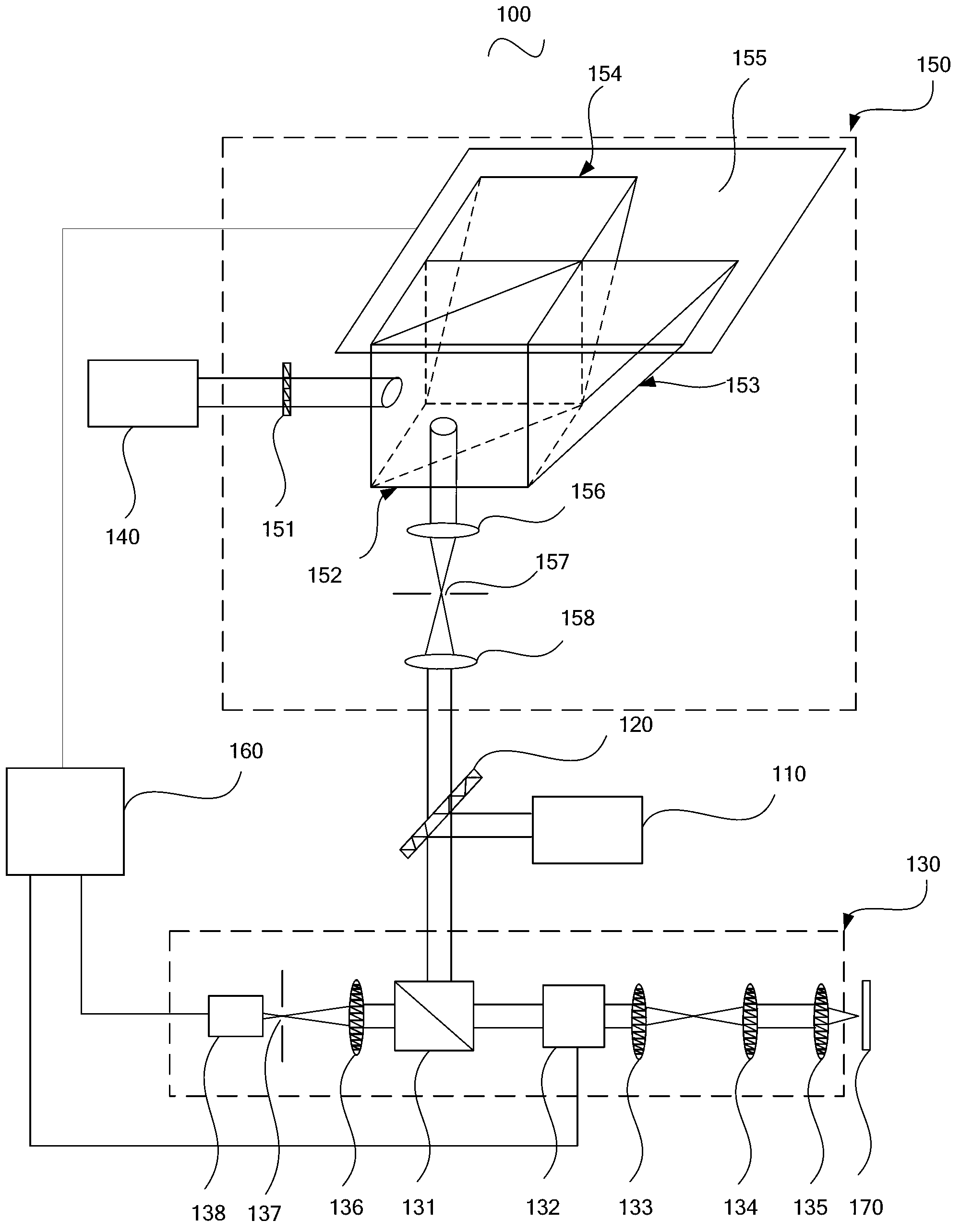
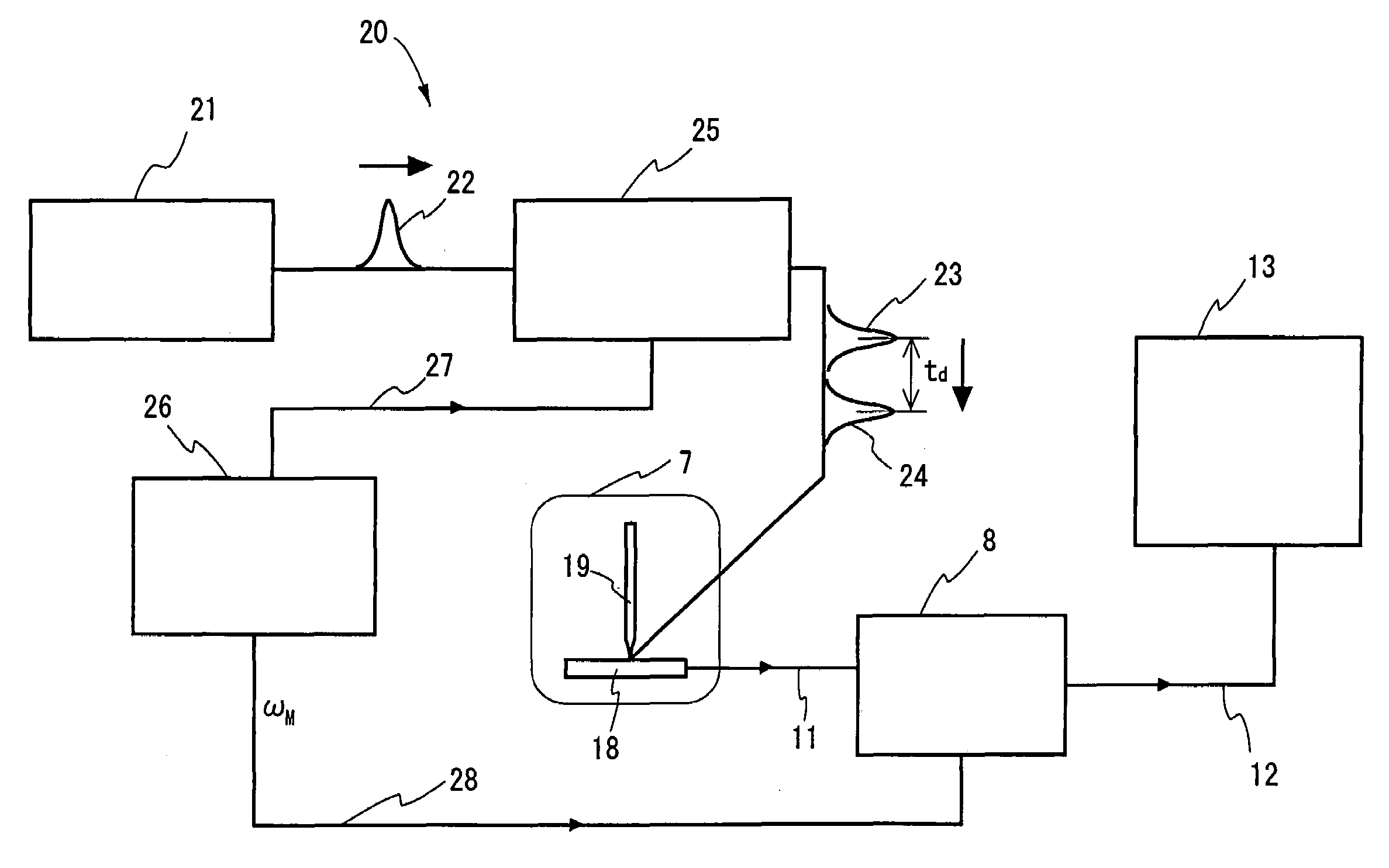
Delay time modulation femtosecond time-resolved scanning probe microscope apparatus
InactiveUS7002149B2Prevent surfaceAvoid probabilityNanotechRadiation pyrometryDifferential coefficientTemporal resolution
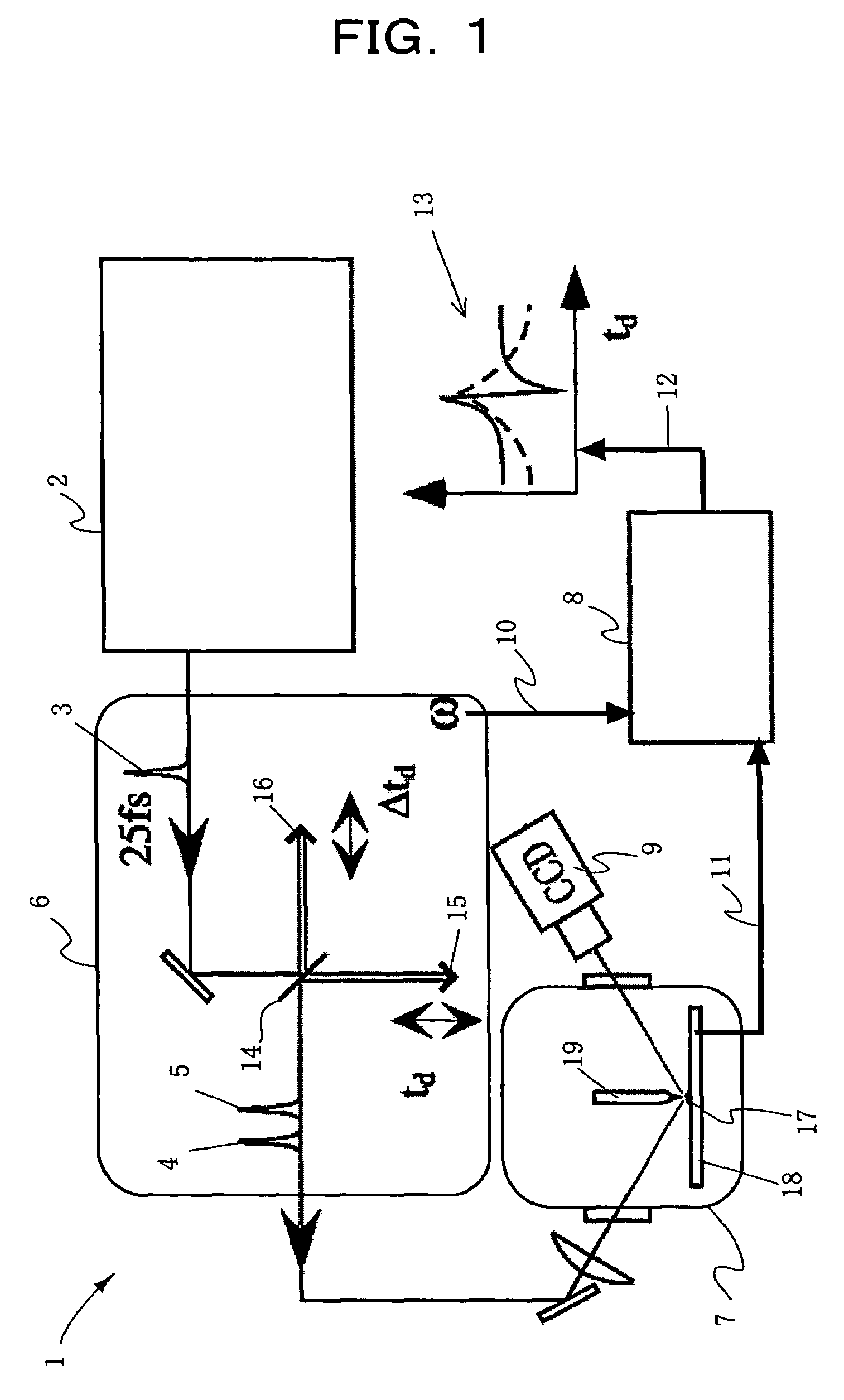
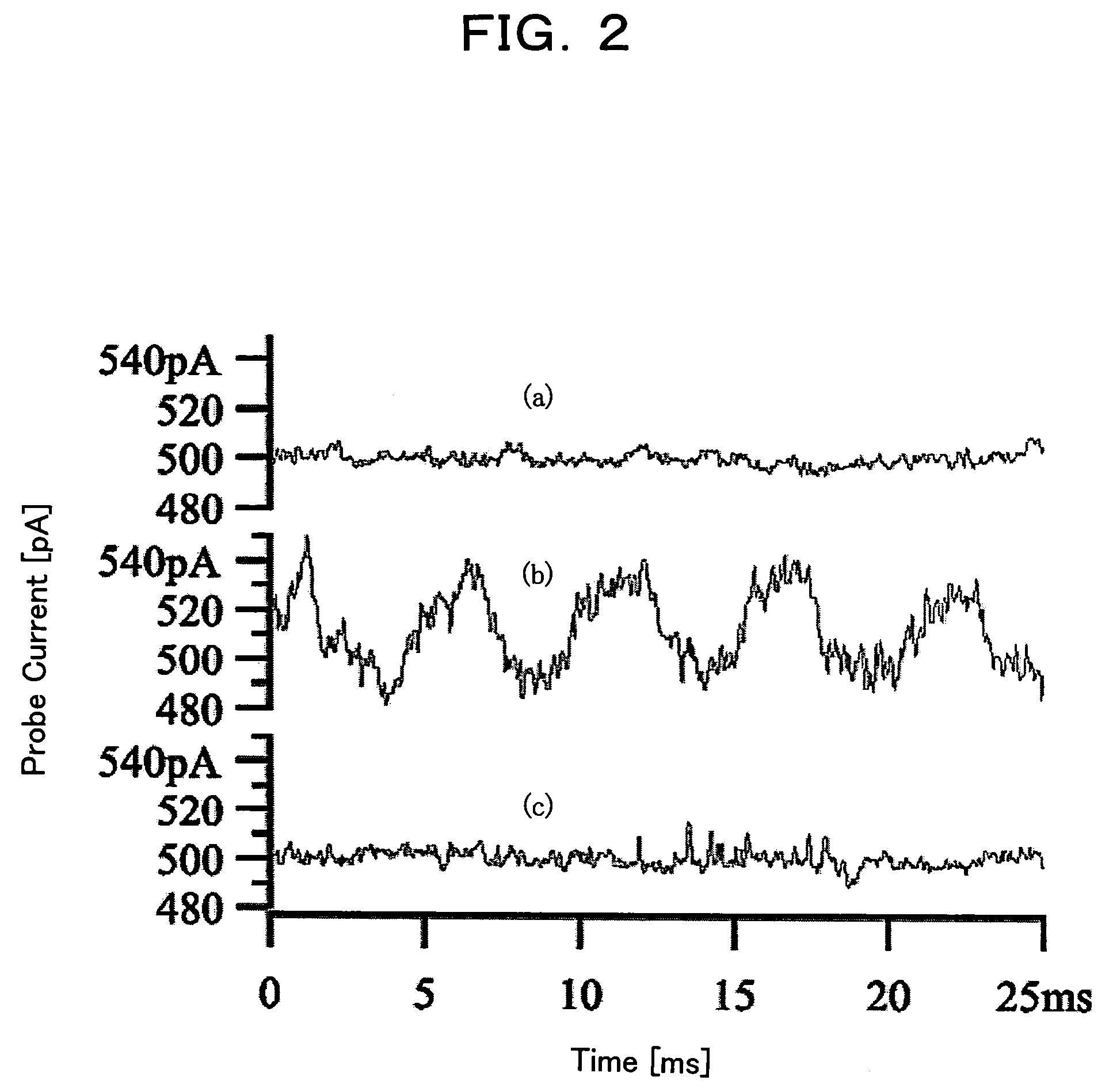
Disclosed is a measuring apparatus for a physical phenomenon by photoexcitation, in particular a delay time modulated and time-resolved, scanning probe microscope apparatus providing an ultimate resolution both temporal and spatial. The apparatus comprises an ultrashort laser pulse generator (2); a delay time modulating circuit (6) which splits an ultrashort laser pulse (3) produced by the ultrashort laser pulse generator (2) into two and which also modulates a delay time td between the two ultrashort laser pulses (4 and 5) with a frequency (ω); a scanning probe microscope (7); and a lock-in detection unit (8) which performs lock-in detection with the delay time modulation frequency (ω) of a probe signal (11) from the scanning probe microscope (7). It can detect the delay time dependency of the probe signal (11) as its differential coefficient to the delay time, with no substantial influence from fluctuations in the intensity of ultrashort laser pulses (3) while preventing the probe apex (19) from thermal expansion and shrinkage by repeated irradiation with ultrashort laser pulses (3). A photoexcited physical phenomenon dependent on a delay time between ultrashort laser pulses can thus be measured at a temporal resolution in the order of femtoseconds and at a spatial resolution in the order of angstroms.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Modified metal-oxide composite sol, coating composition, and optical member
InactiveUS20100221556A1High refractive indexGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentWeather resistanceOxide composite
There is provided a sol of modified metal oxide composite colloidal particles including titanium oxide having a high refractive index and excellent light resistance and weather resistance that discoloration of the colloidal particles by photoexcitation is almost completely inhibited. A modified metal oxide composite colloidal particle comprises; a titanium oxide-tin oxide-zirconium oxide-tungsten oxide composite colloidal particle (A) having a primary particle diameter of 2 to 50 nm and having a SnO2 / TiO2 molar ratio of 0.1 to 1.0, a ZrO2 / TiO2 molar ratio of 0.1 to 0.4, and a WO3 / TiO2 molar ratio of 0.03 to 0.15, as a core; and a tungsten oxide-tin oxide-silicon dioxide composite colloidal particle (B) having a primary particle diameter of 1 to 7 nm with which a surface of the core is coated.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Device and method for treating high-concentration and degradation-resistant organic waste water
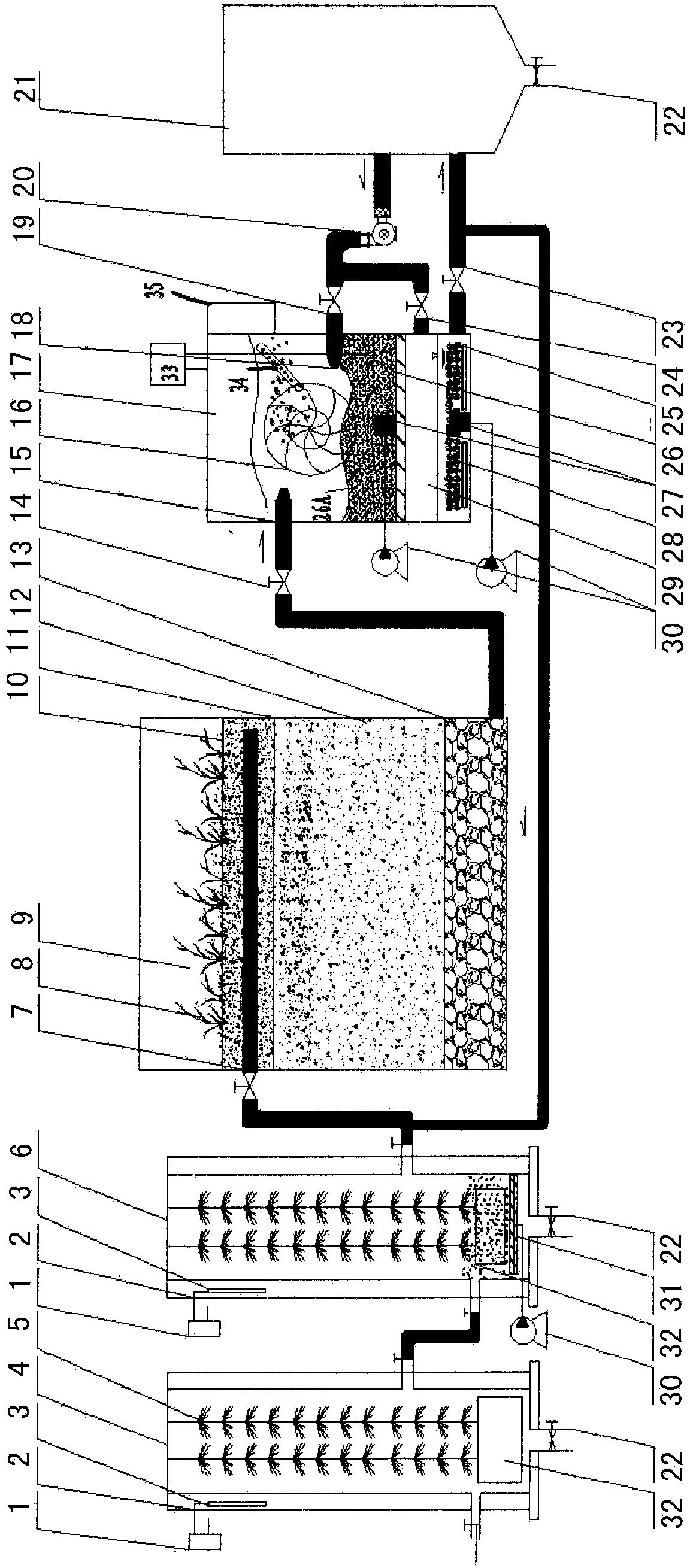
ActiveCN104193074AIncrease incidenceImprove the effect of advanced oxidationMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationConstructed wetland
The invention relates to a device for treating high-concentration and degradation-resistant organic waste water. The device for treating the high-concentration and degradation-resistant organic waste water mainly comprises an anaerobic bio-membrane reactor, an aerobic bio-membrane reactor, an artificial wetland system, a turbine sieve filter and a sand setting tank. The invention also discloses a method for removing high-concentration organic pollutants in sewage by utilizing the device provided by the invention. The device and method for treating the high-concentration and degradation-resistant organic waste water have the advantages that a nano aeration technology is adopted, two methods, namely photoexcitation and photocatalysis, are combined, hydroxyl free radicals are produced at high efficiency, biologically treated sewage effluent is subjected to deep treatment in a lasting and effective manner by utilizing strong oxidizing property of the hydroxyl free radicals, the pollutants with poor biodegradability and relative high molecular weight can be completely oxidized and degraded, and bacteria and pathogenic bacteria in sewage are killed, so that the sterilization and disinfection effects are realized.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
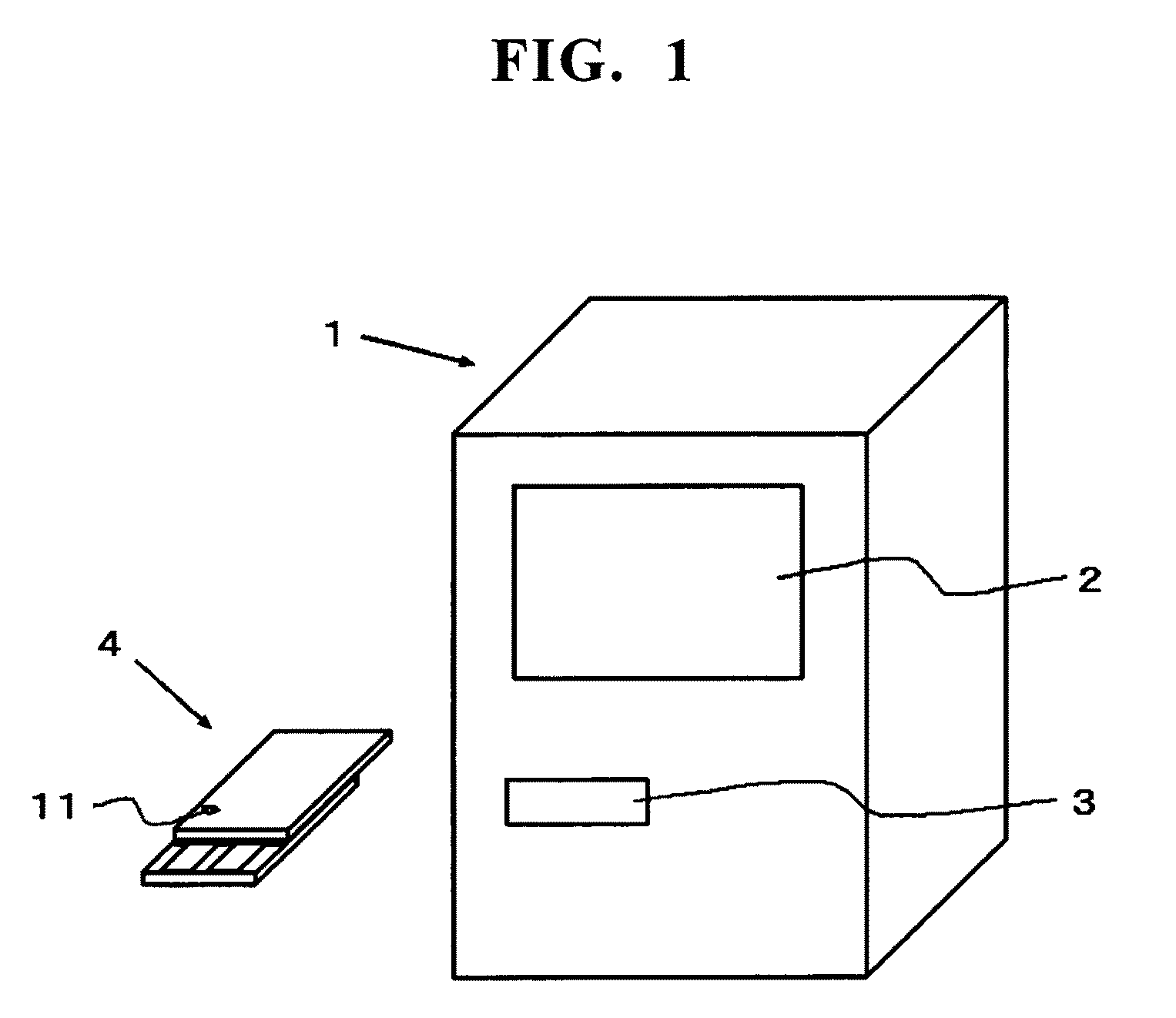
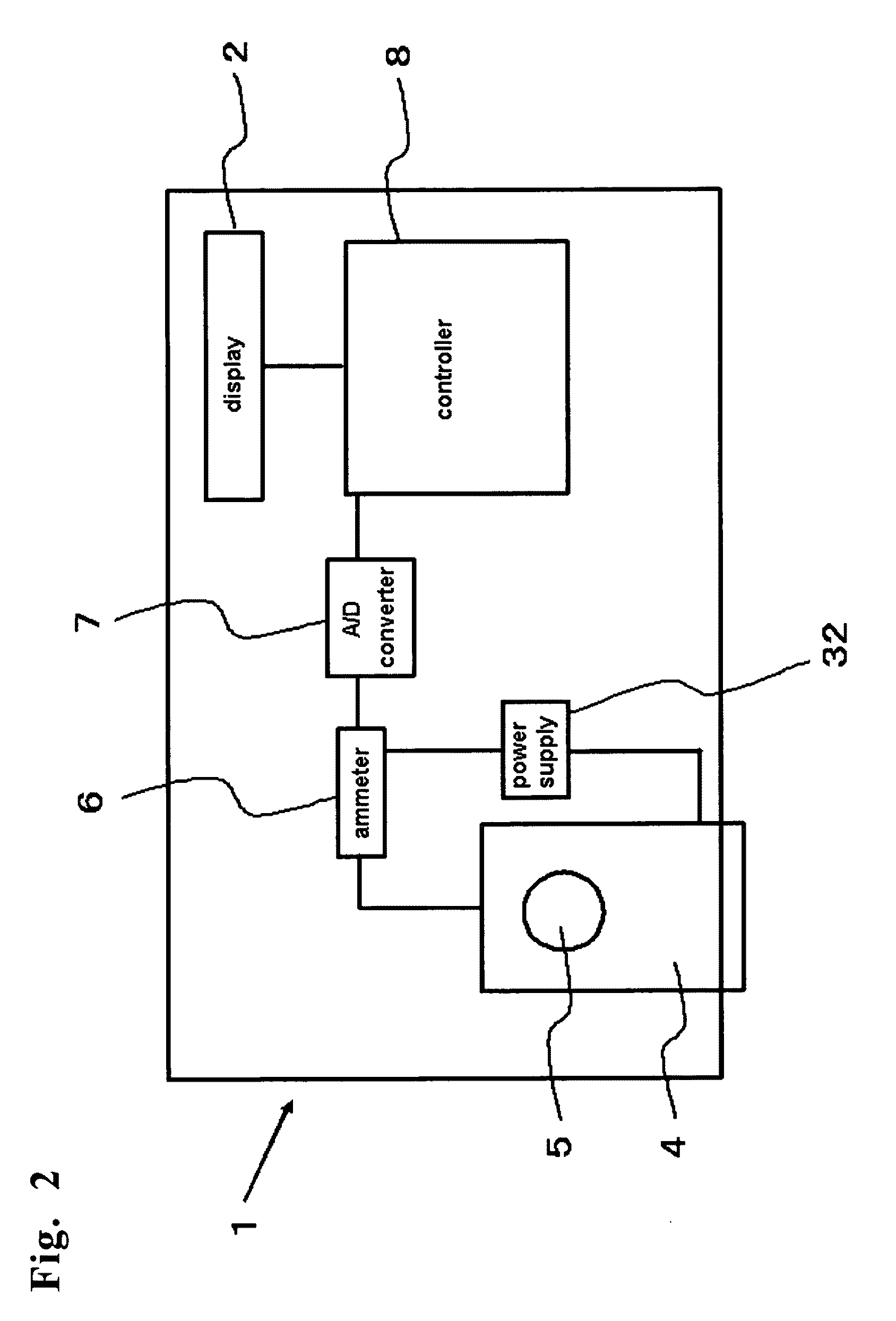
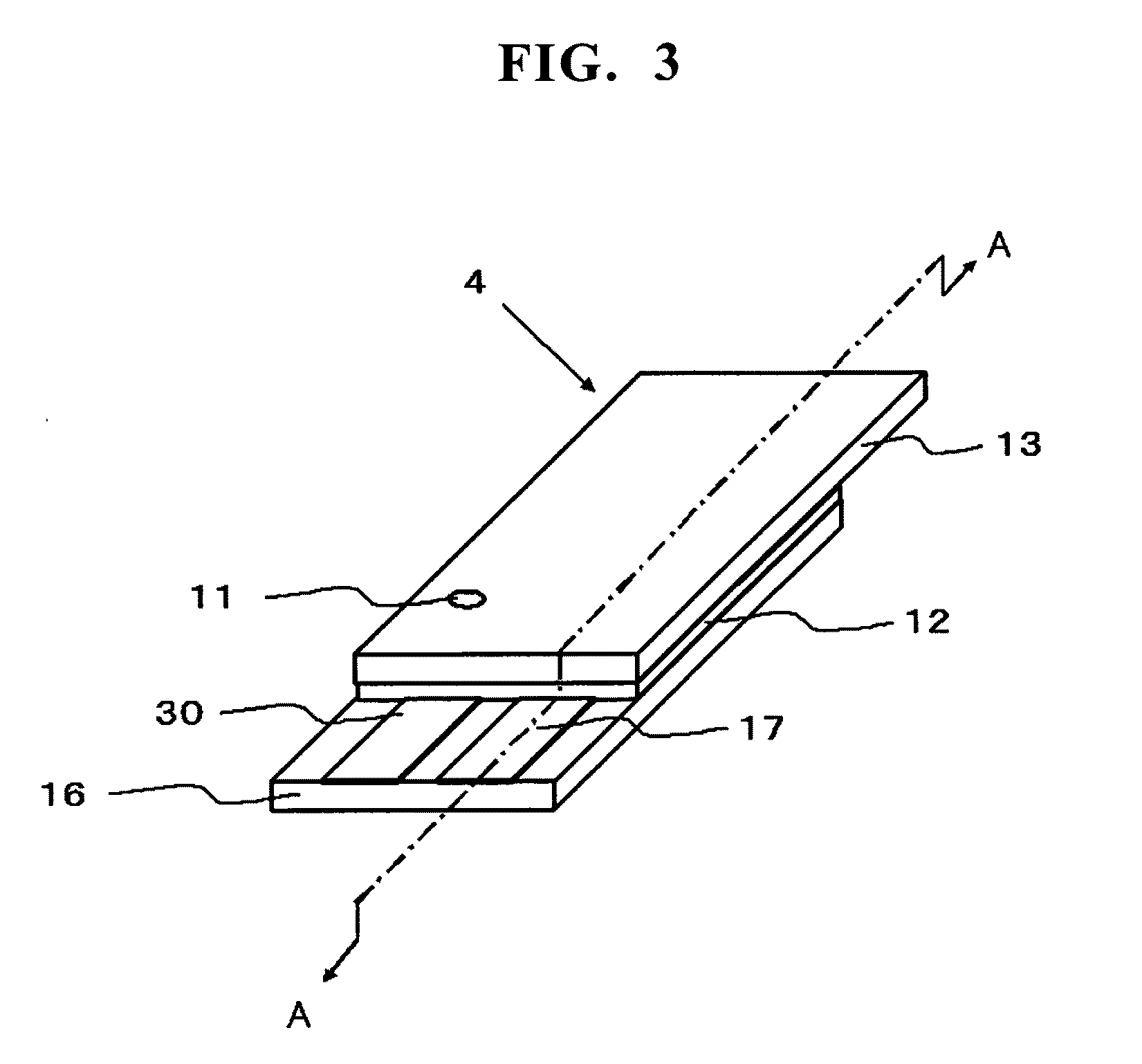
Measurement device used for specifically detecting substance to be examined using photocurrent, sensor unit used for same, and method for specifically detecting substance to be examined using photocurrent
InactiveUS20120100627A1Improve detection accuracyShorten detection timeMaterial thermal conductivityComponent separationMeasurement devicePhotocurrent
In utilizing photocurrent generated in the photoexcitation of a dye in specific detection of an analyte, highly accurate detection can be realized by discharging charged current generated in the formation of a sensor unit and, in the detection of photocurrent of a plurality of detection spots provided on a working electrode, discharging photocurrent which is derived from a detection spot subjected to the latest photocurrent measurement and becomes noise current. The present invention provides a measuring apparatus comprising a sensor unit comprising a working electrode, a counter electrode, and an electrolyte-containing substance, a single or plurality of light sources that apply light to the working electrode, an XY moving device provided when the light source is moved relatively in an XY direction relative to the working electrode, an ammeter that measures current which flows across the working electrode and the counter electrode, and a discharge device that discharges charged current and photocurrent derived from a detection spot subjected to the latest photocurrent measurement. The specific detection method using the measuring apparatus is carried out by controlling the timing of light irradiation and the timing of connection to the ammeter and the discharge device.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com