Patents
Literature
2015 results about "Photomultiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
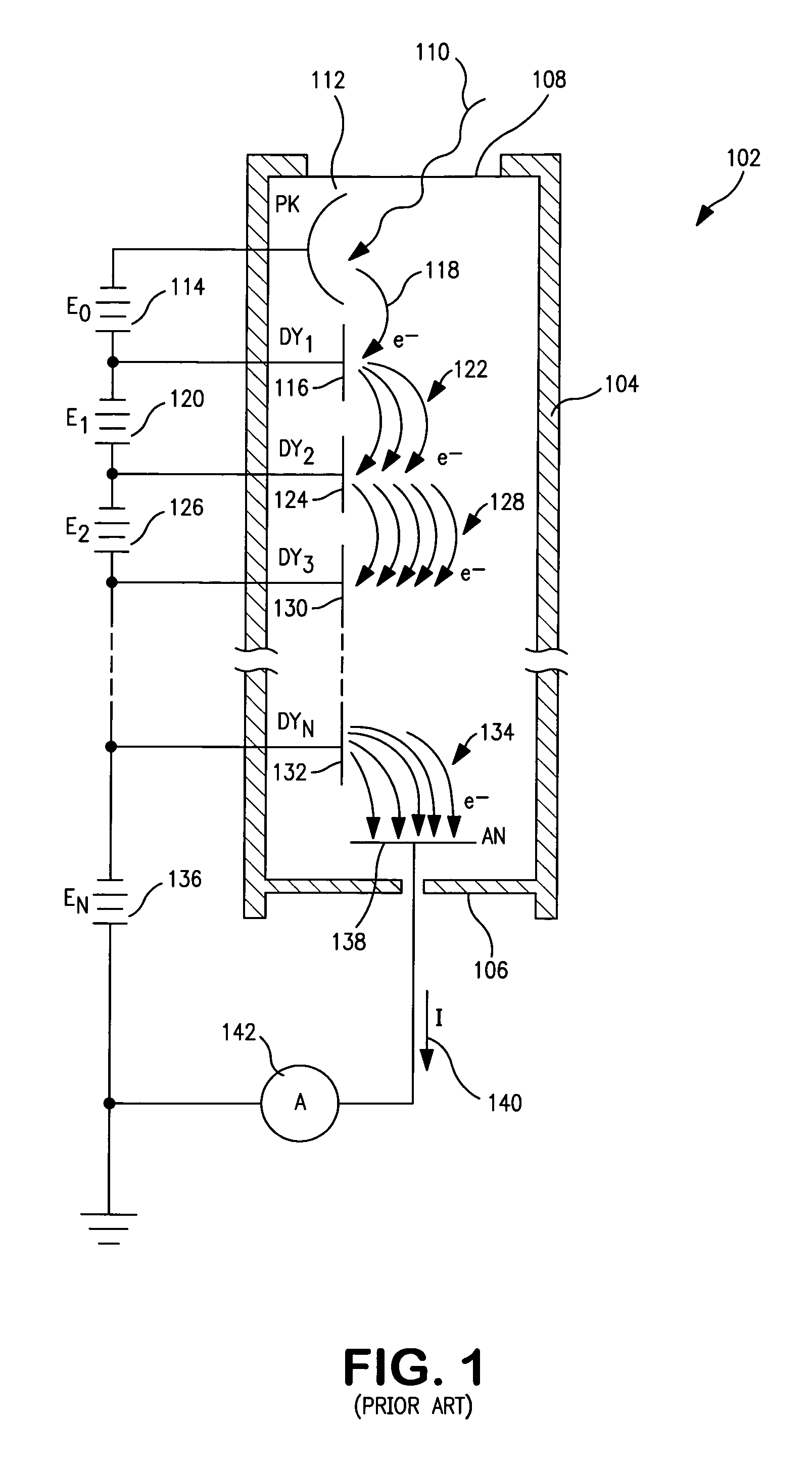
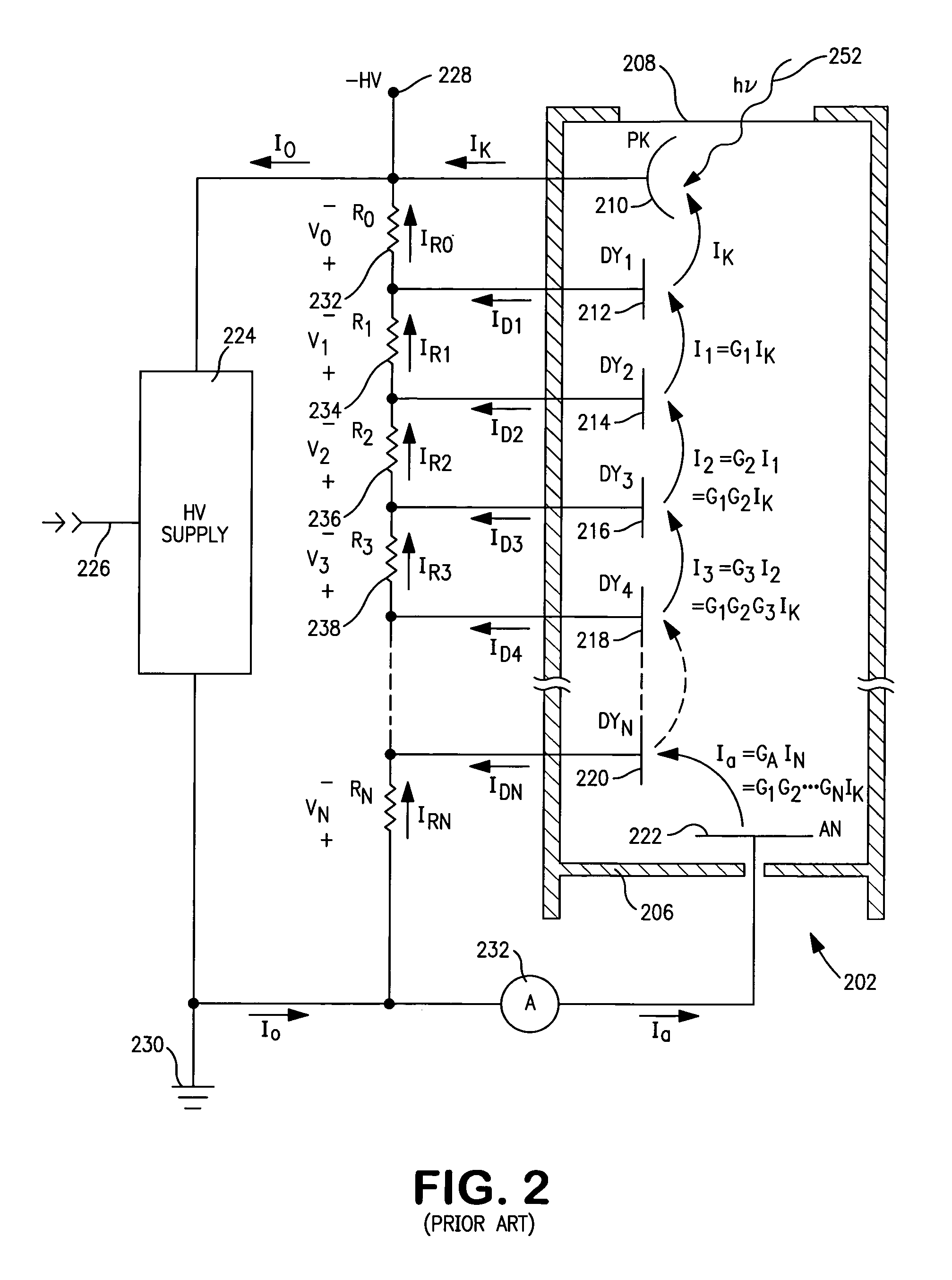
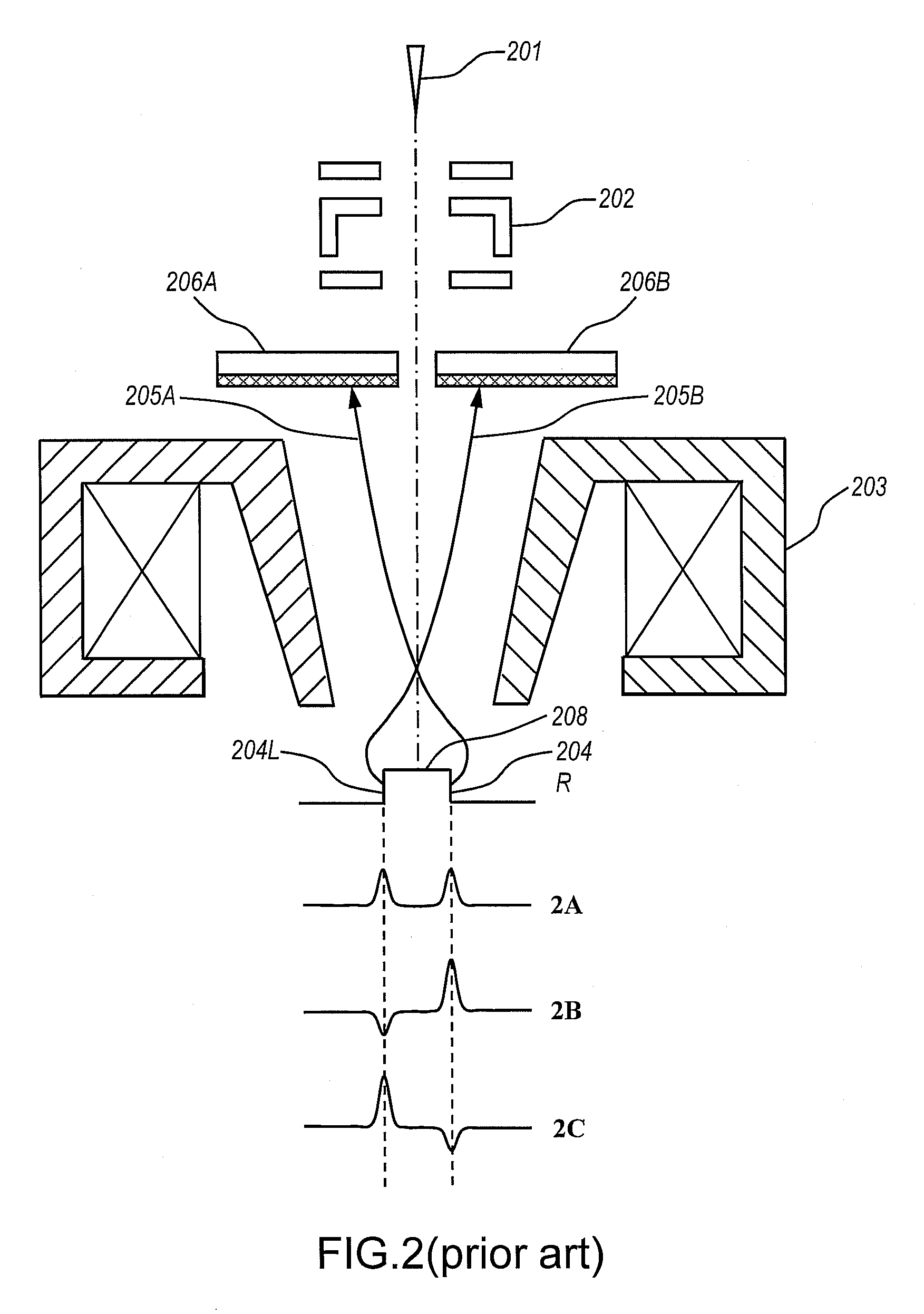
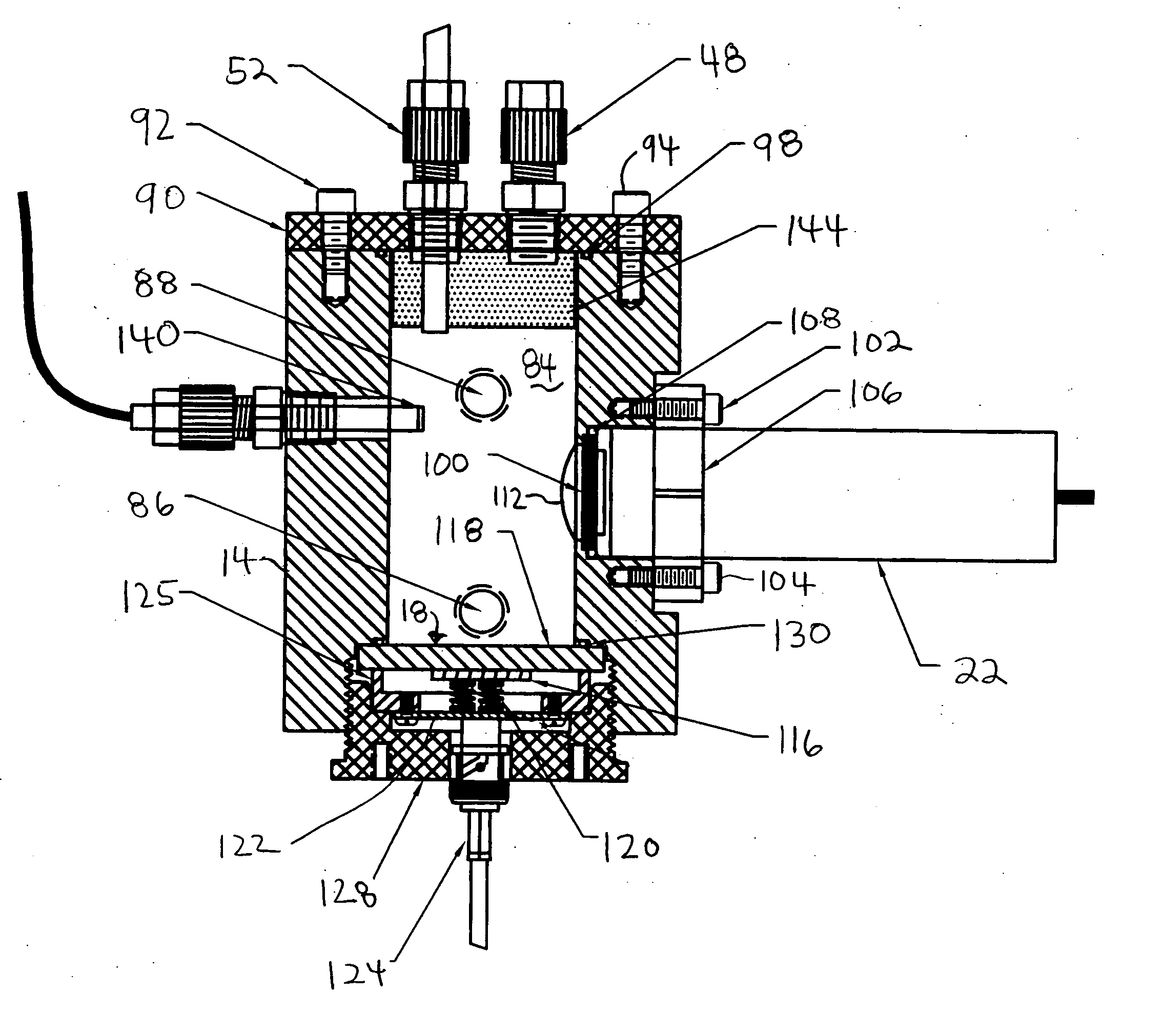
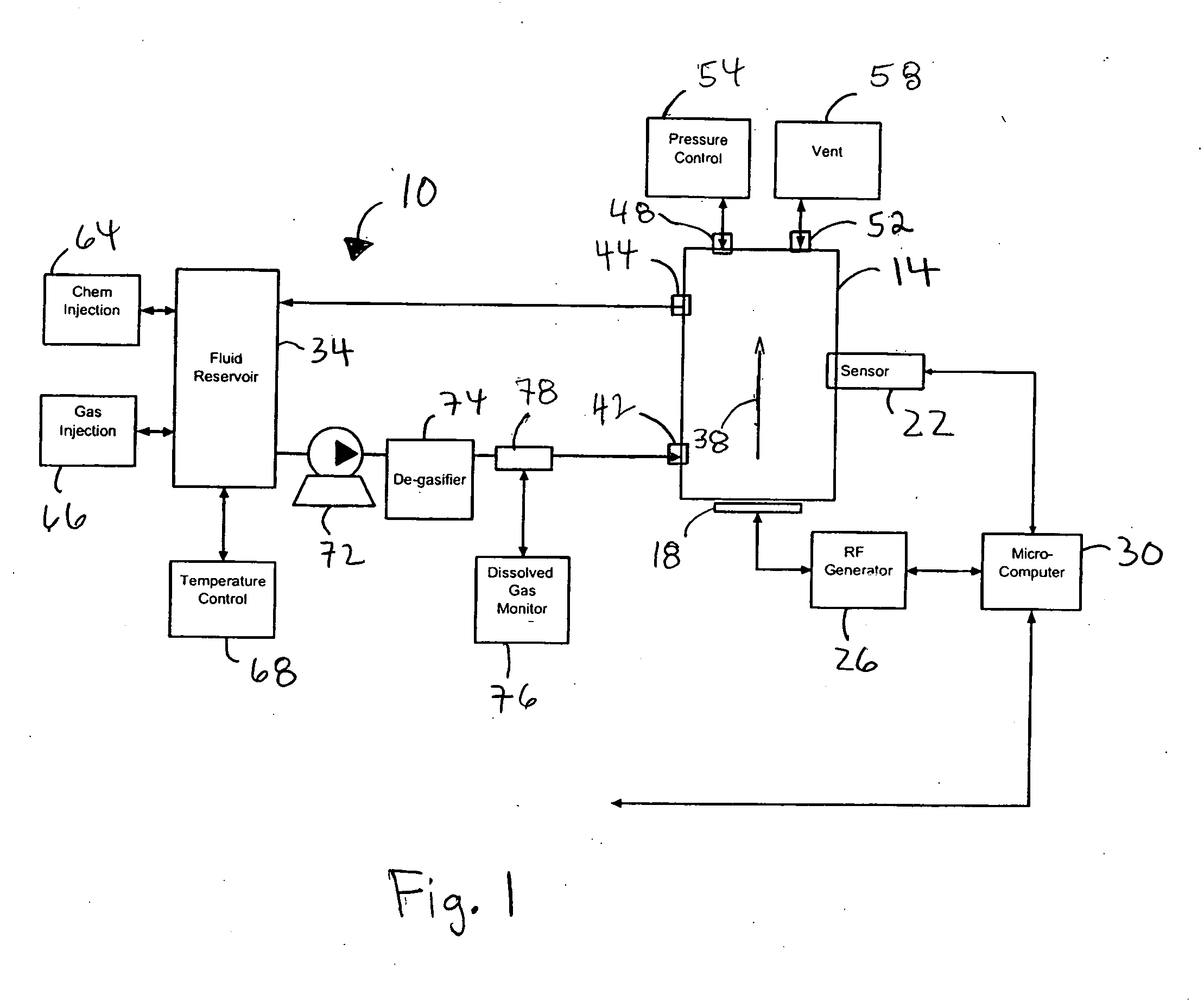
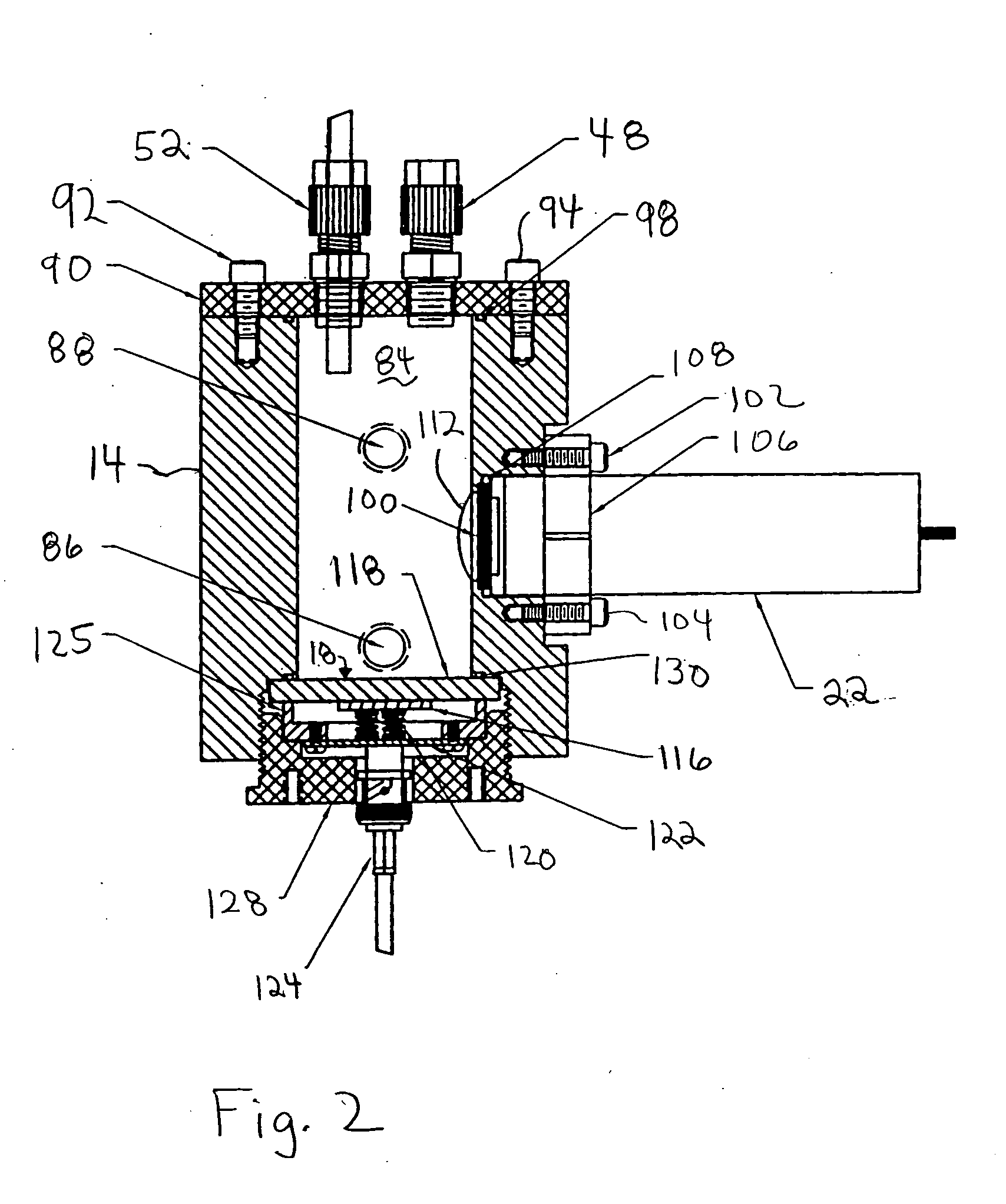
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short), members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times or 10⁸ (i.e., 160 dB), in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low.
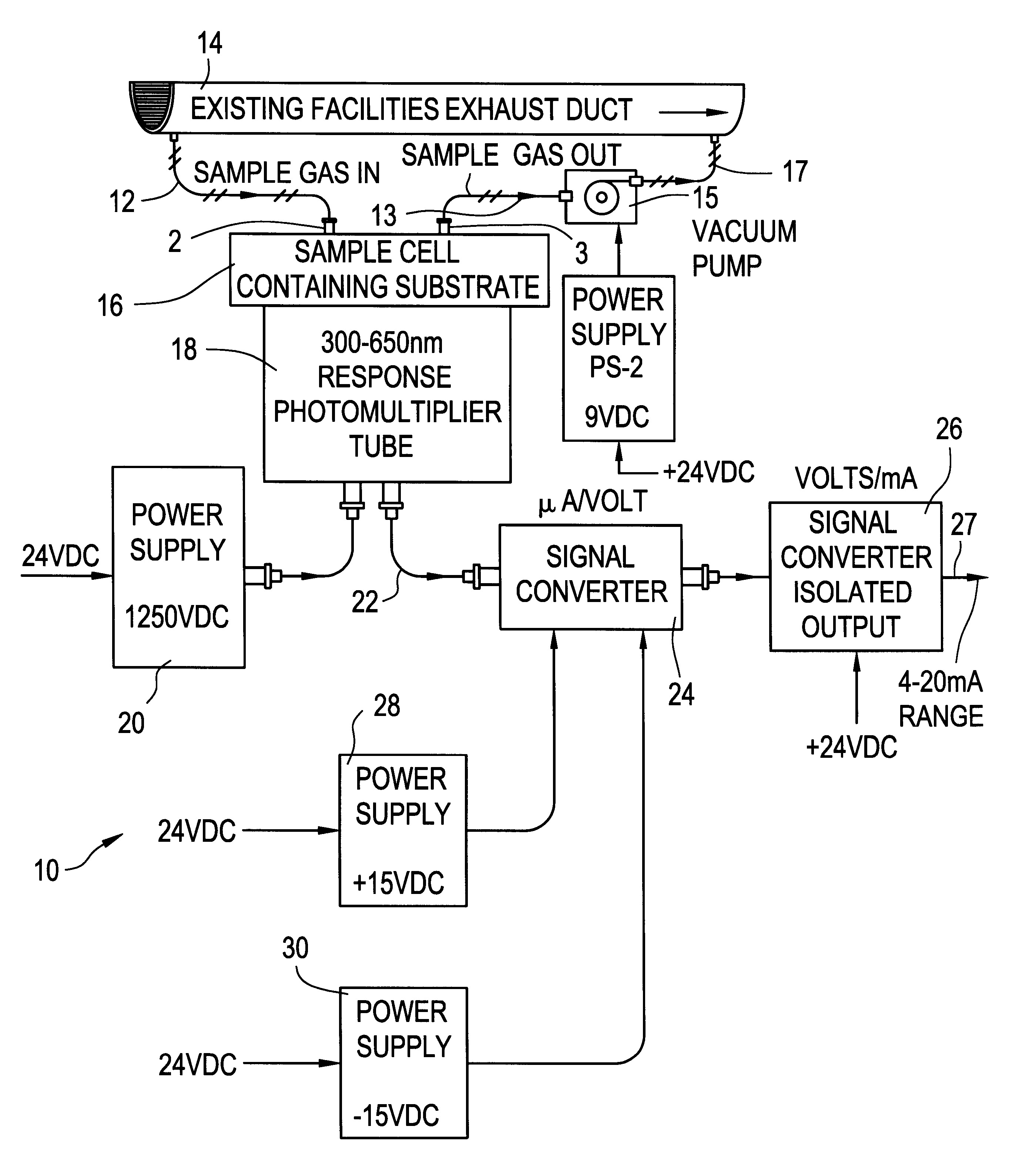
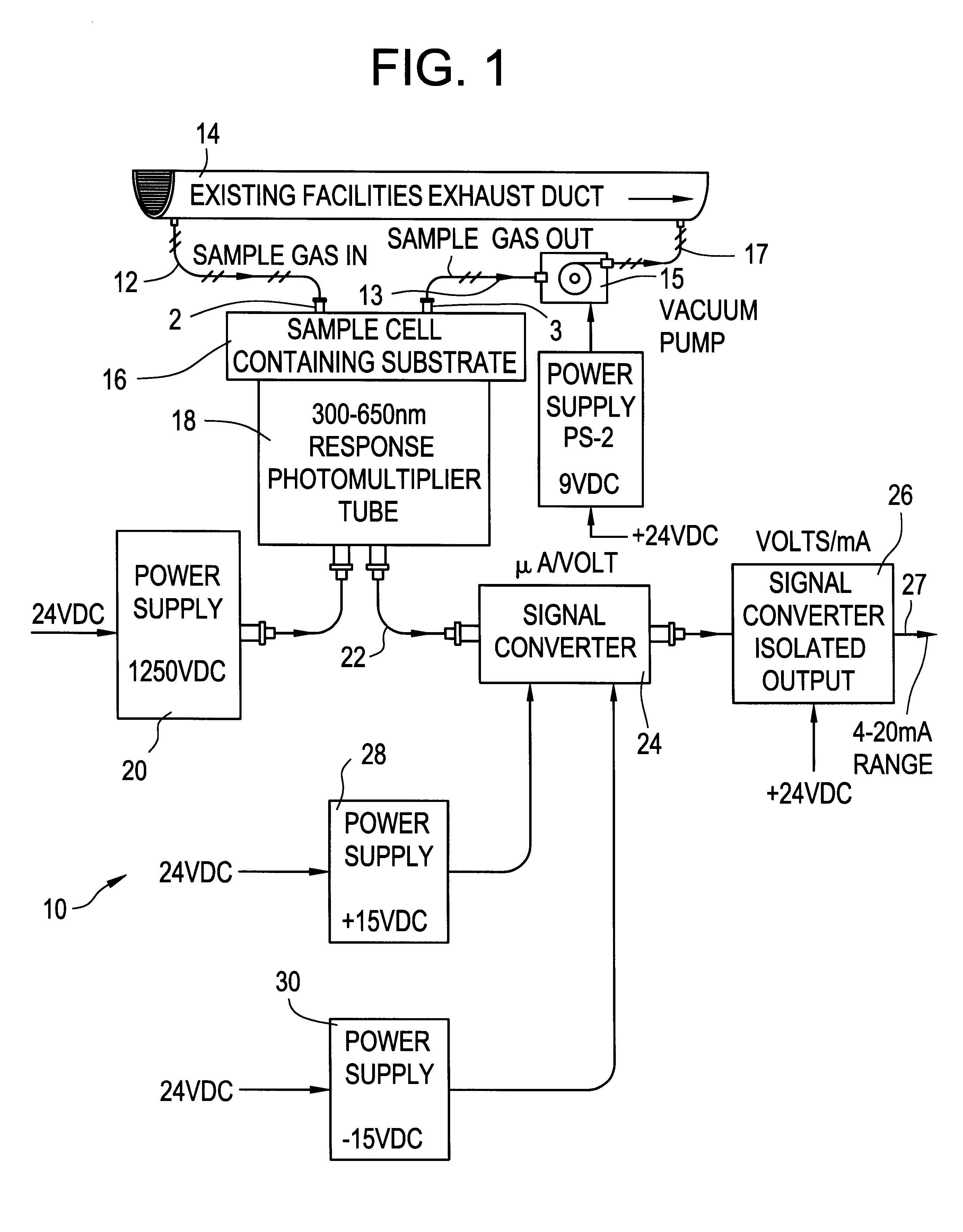
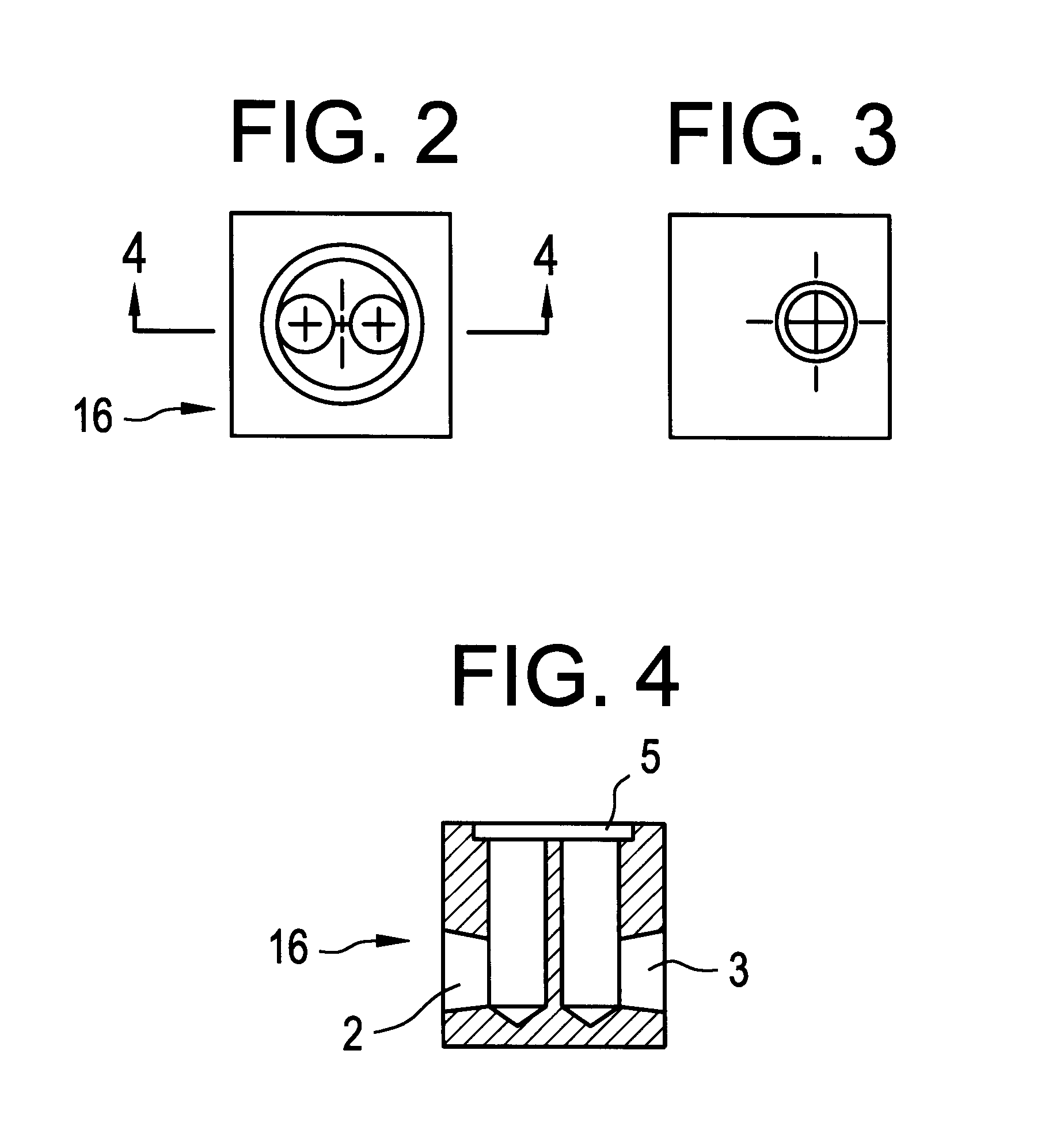
Solid state fluorine sensor system and method
InactiveUS6321587B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElectricityElectrical battery
A gaseous fluorine detection system is provided which includes a generally enclosed sample cell containing a substrate comprising a material which interacts with fluorine gas to generate radiant energy. A gas sample of fluorine, the concentration levels of which are to be evaluated is flowed through the cell. A photomultiplier tube is positioned to receive the resulting radiant energy and generate an electrical output signal related to the level of said radiant energy. Means are provided for measuring the said photomultiplier output signal and relating same to the fluorine concentration of the gas sample provided to the cell.
Owner:RADIAN INT
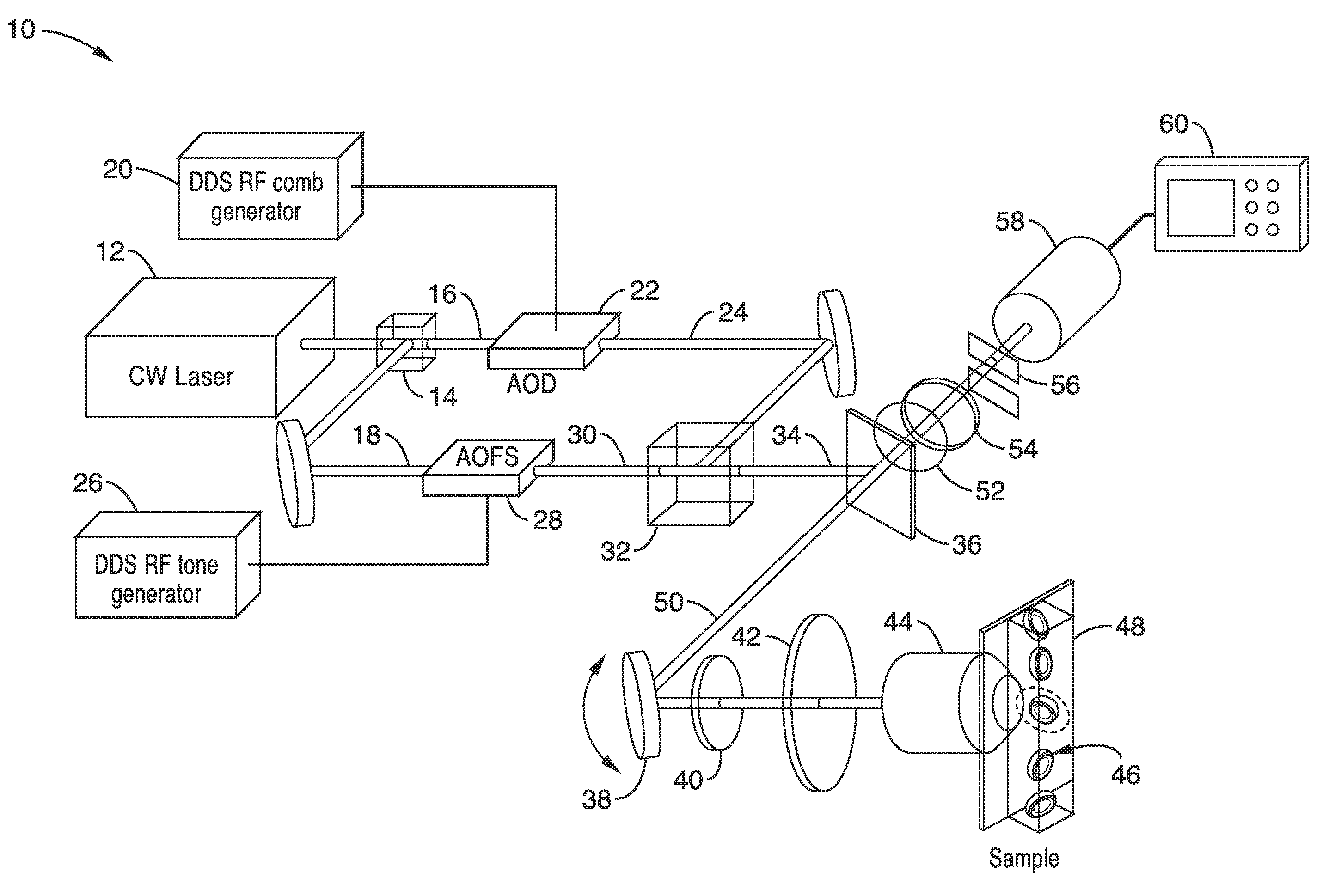
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
ActiveUS9423353B2Reduce image noiseScalable approachMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
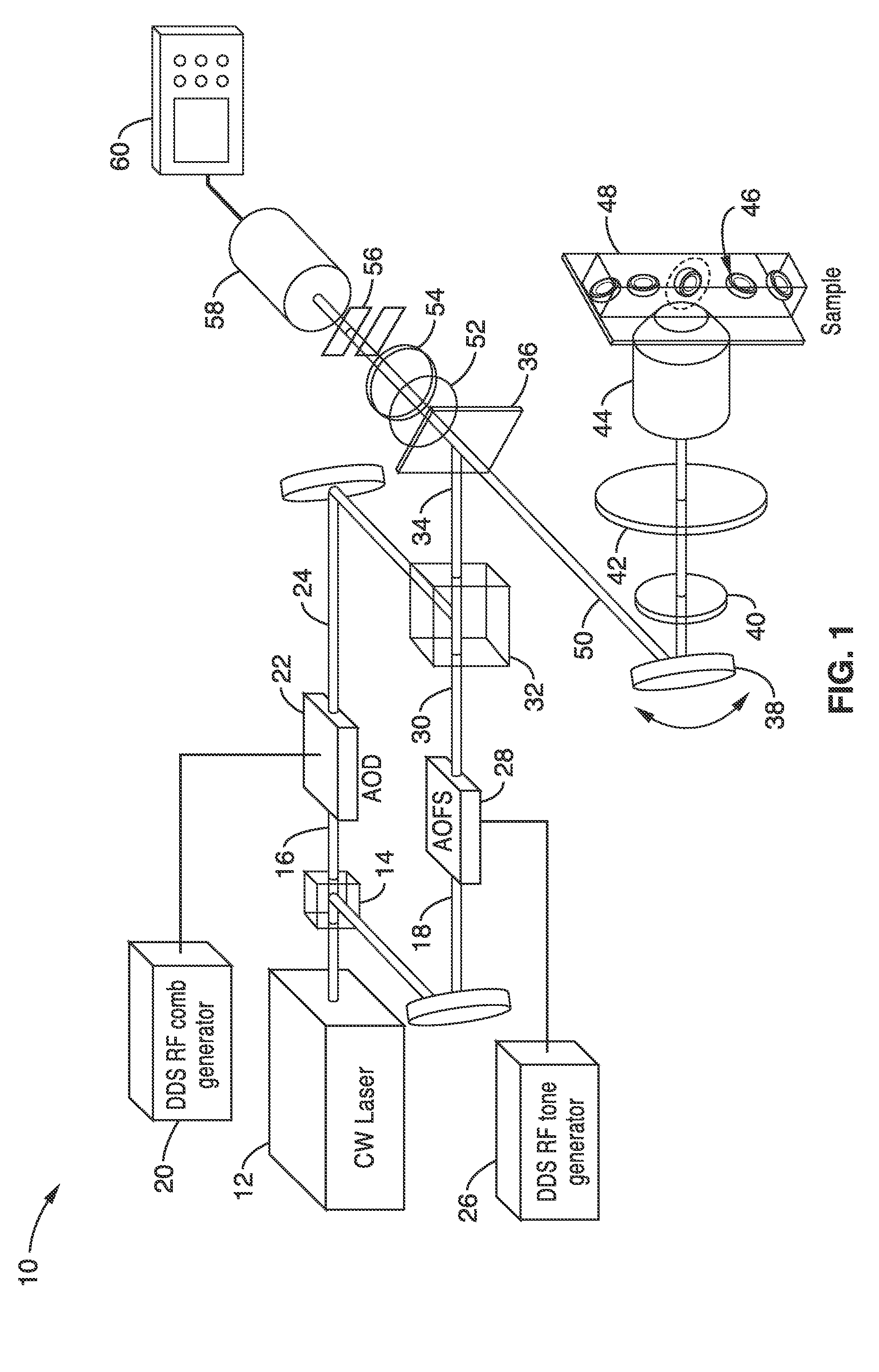
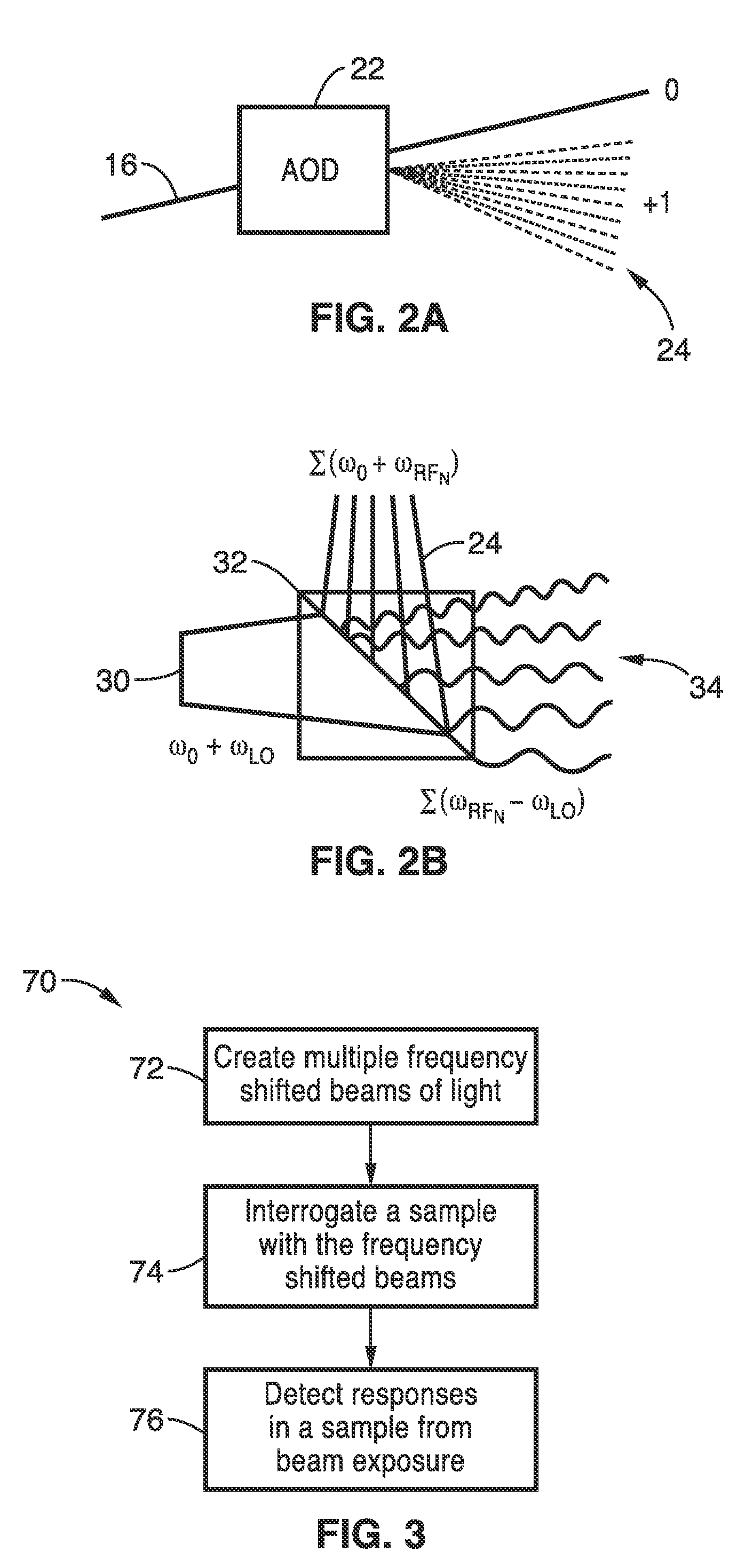
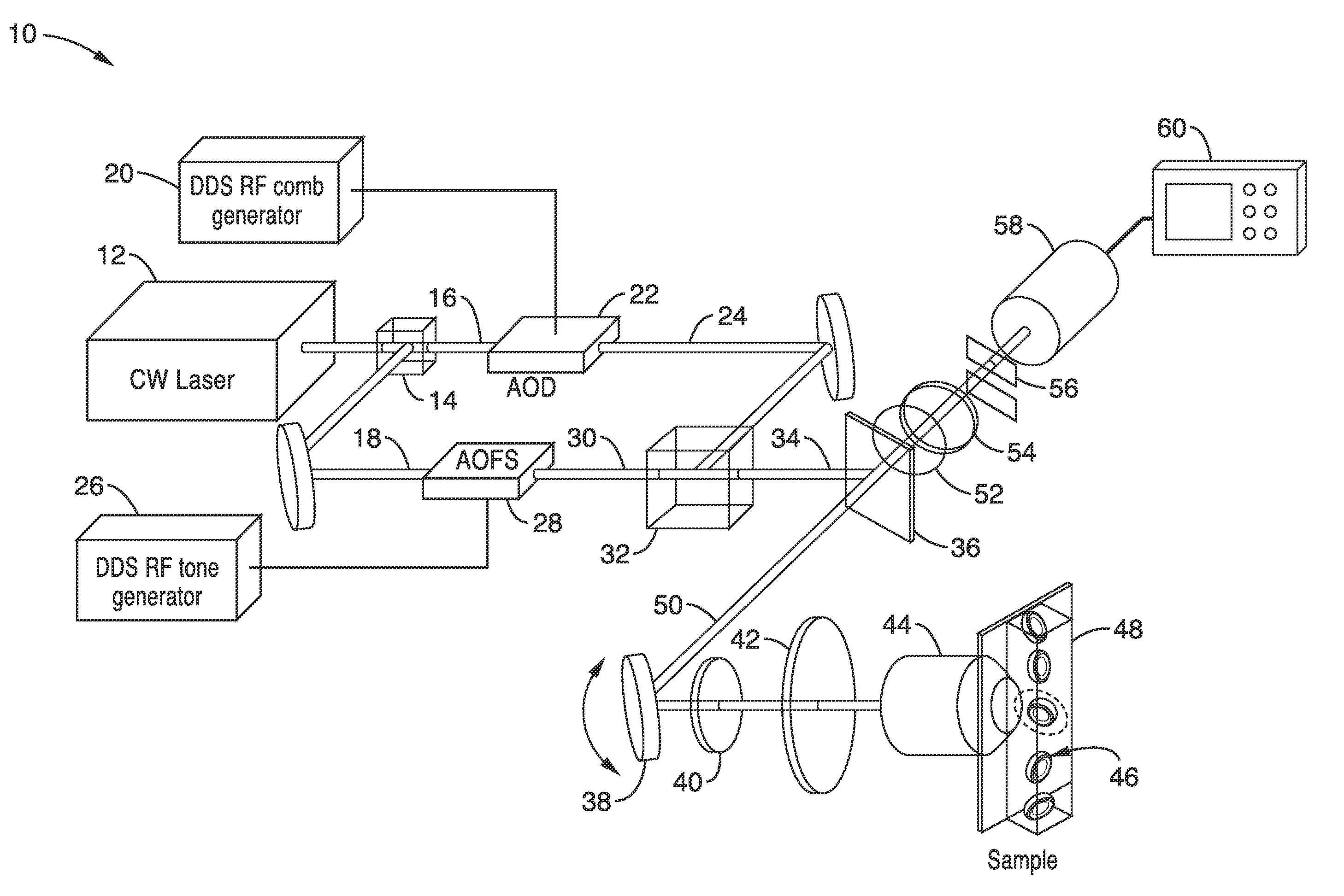
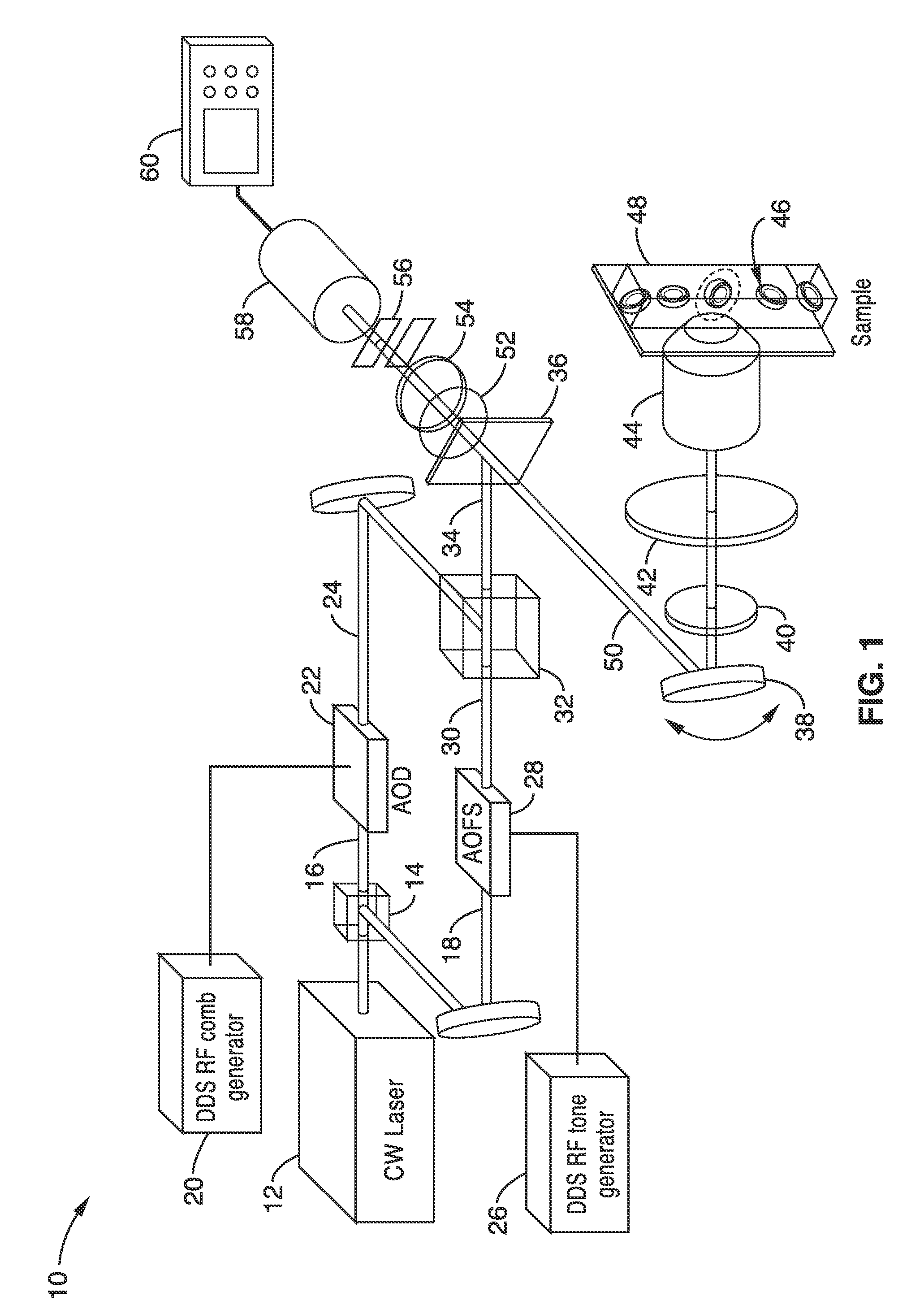
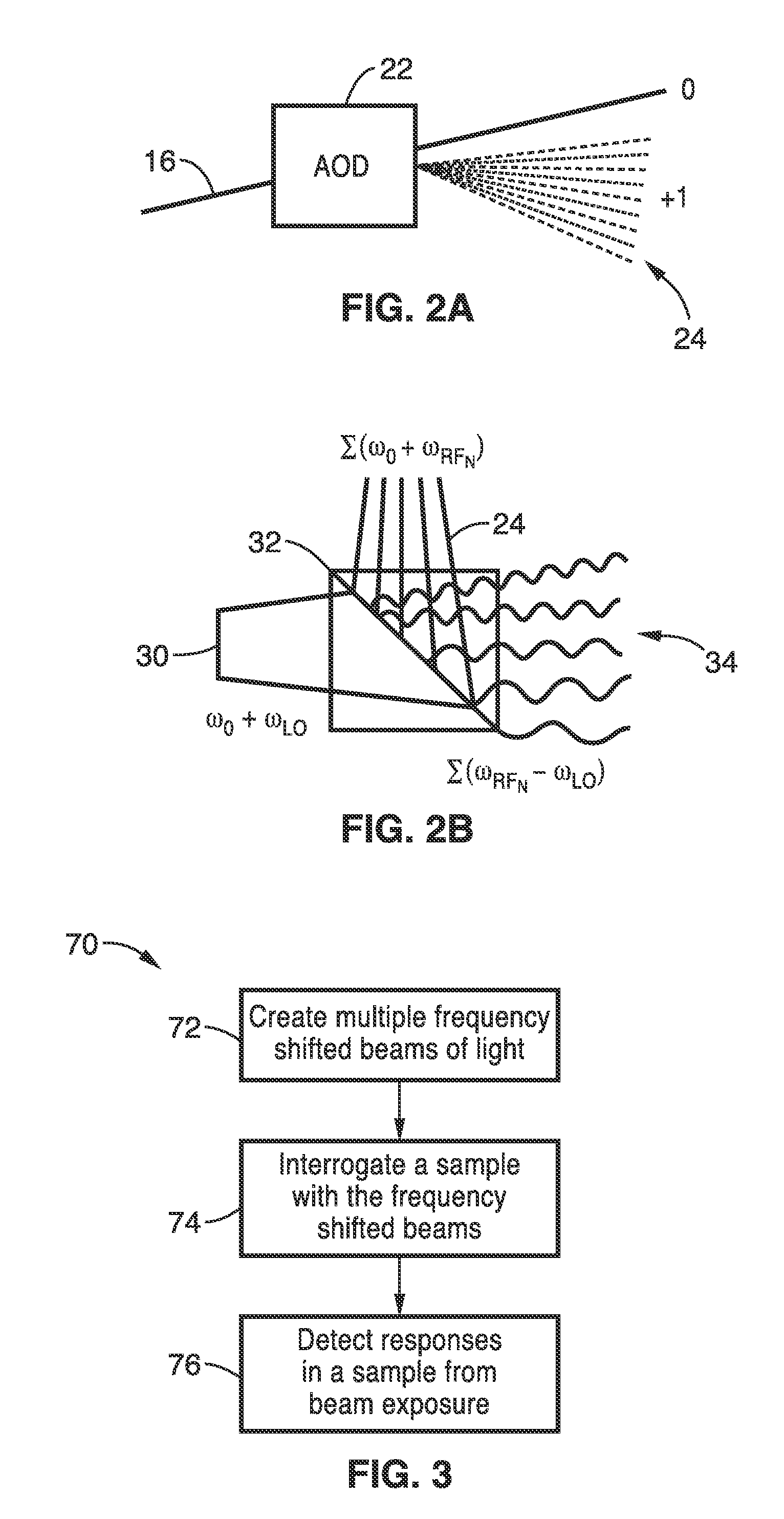
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
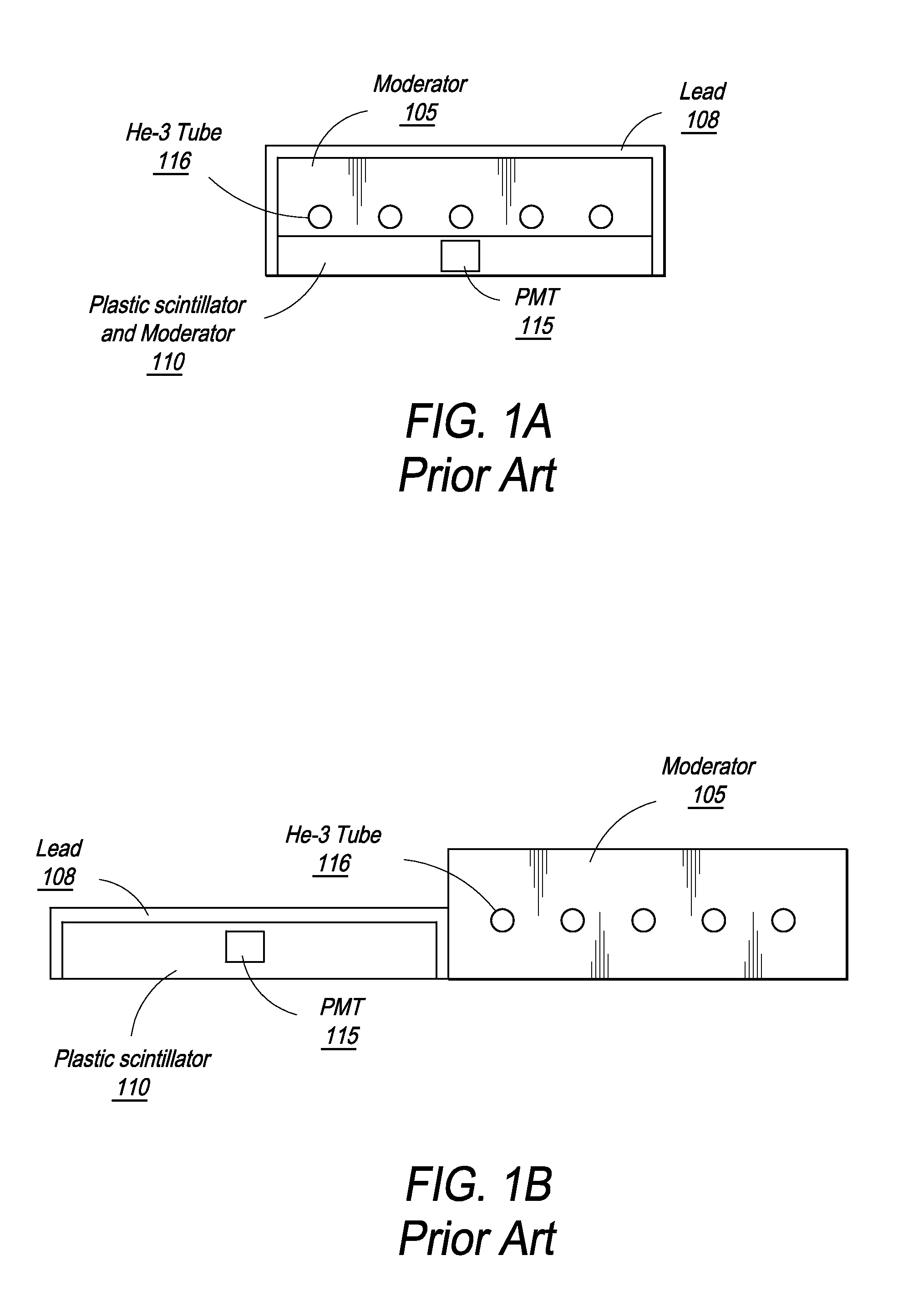
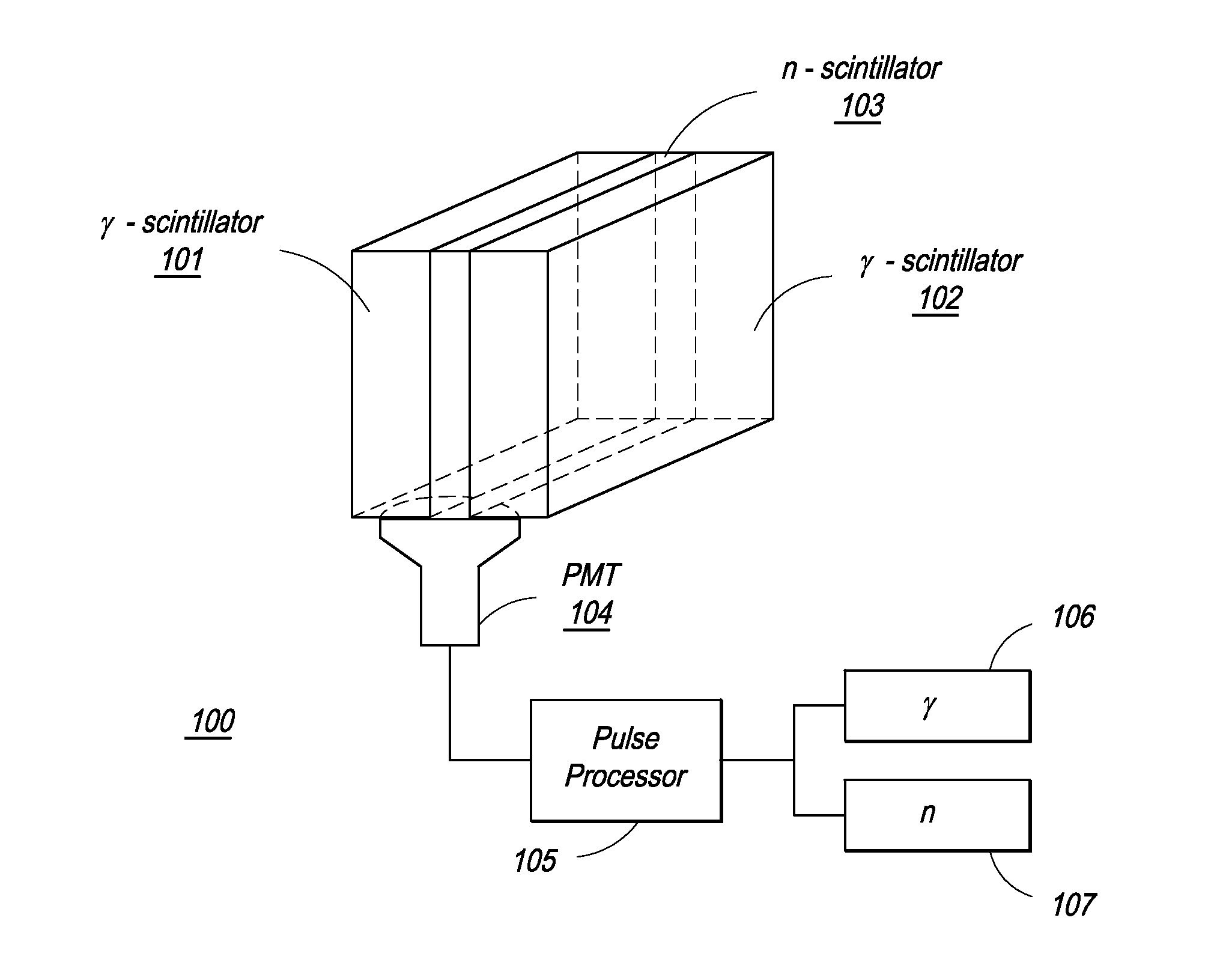
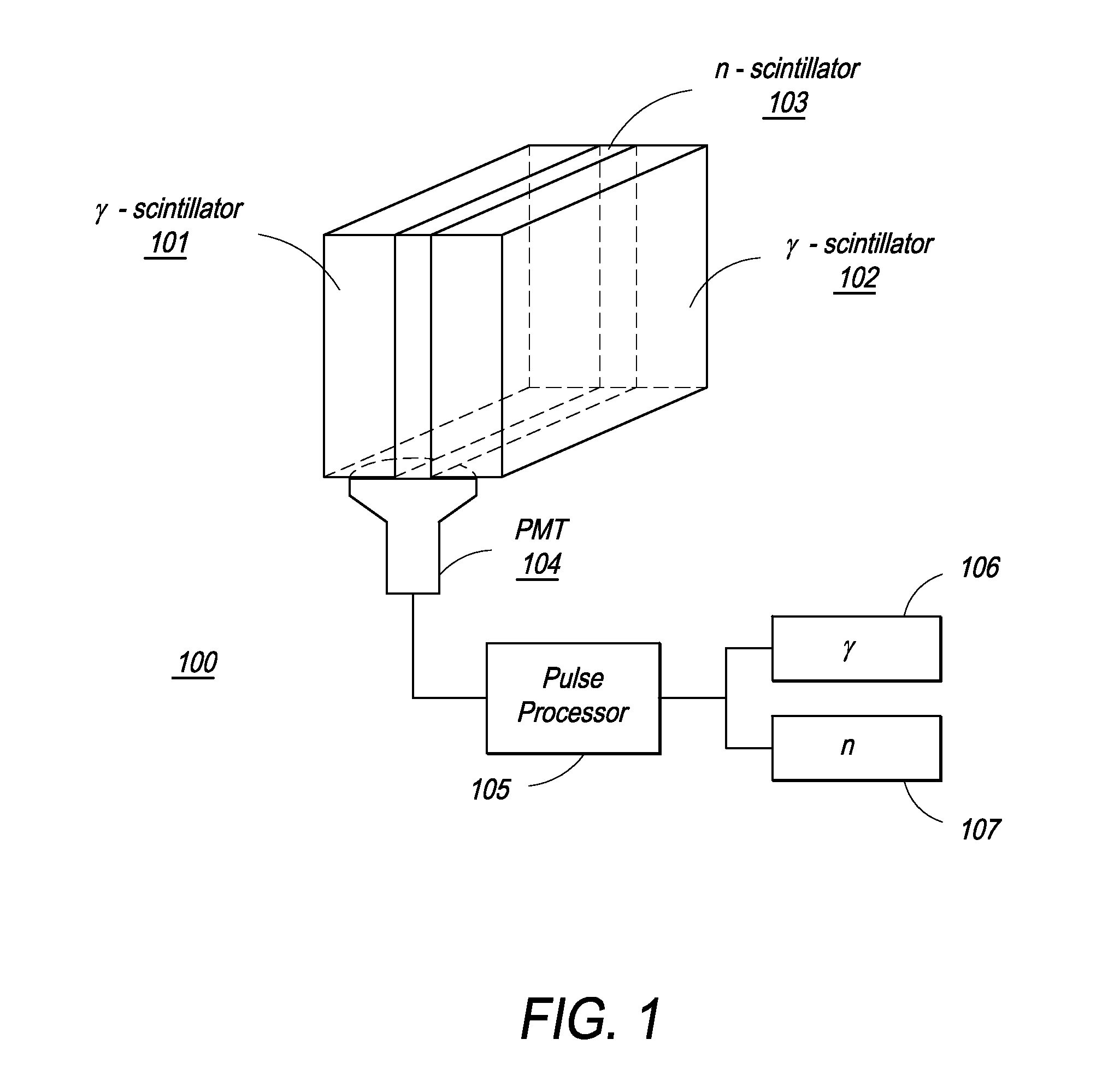
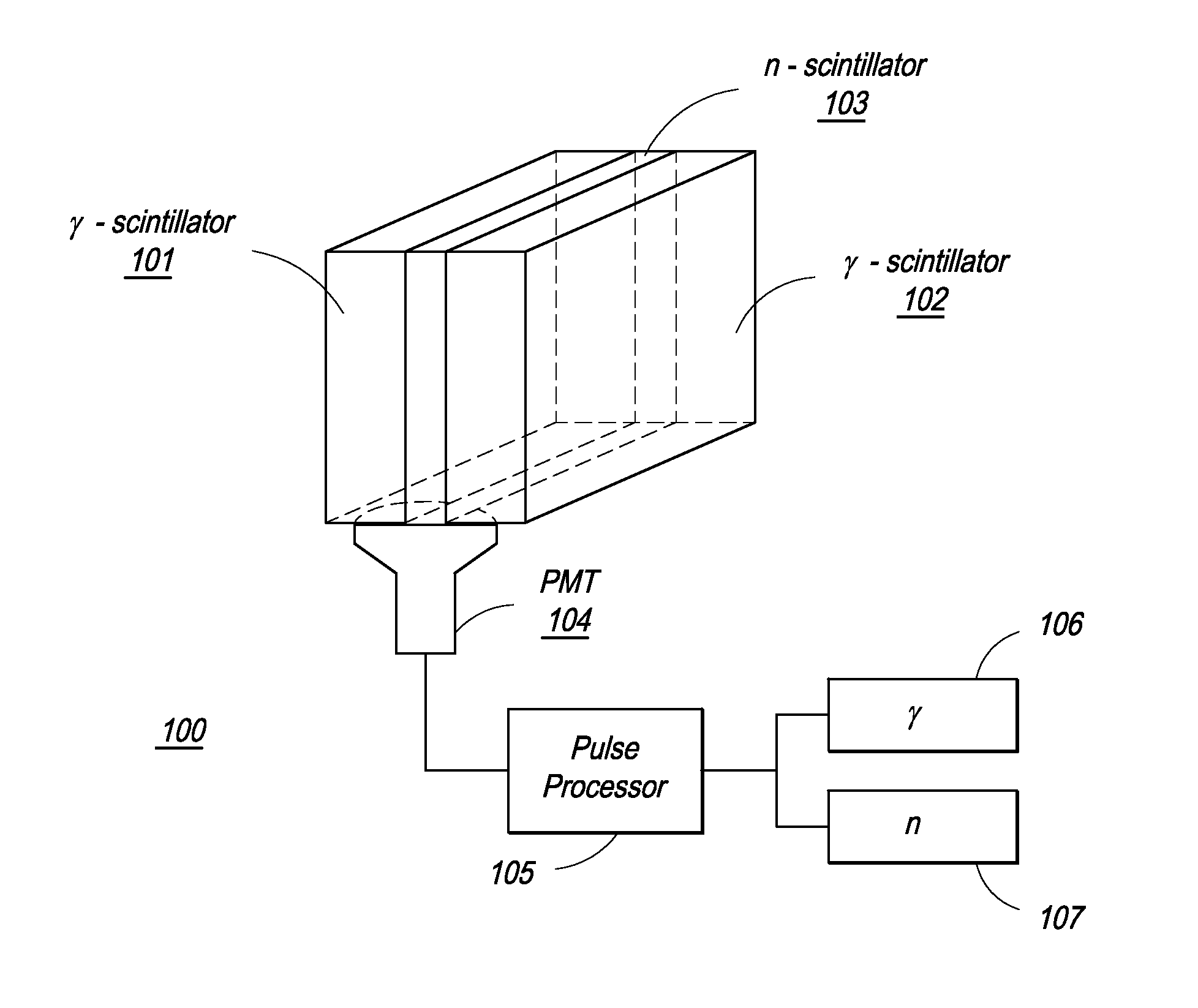
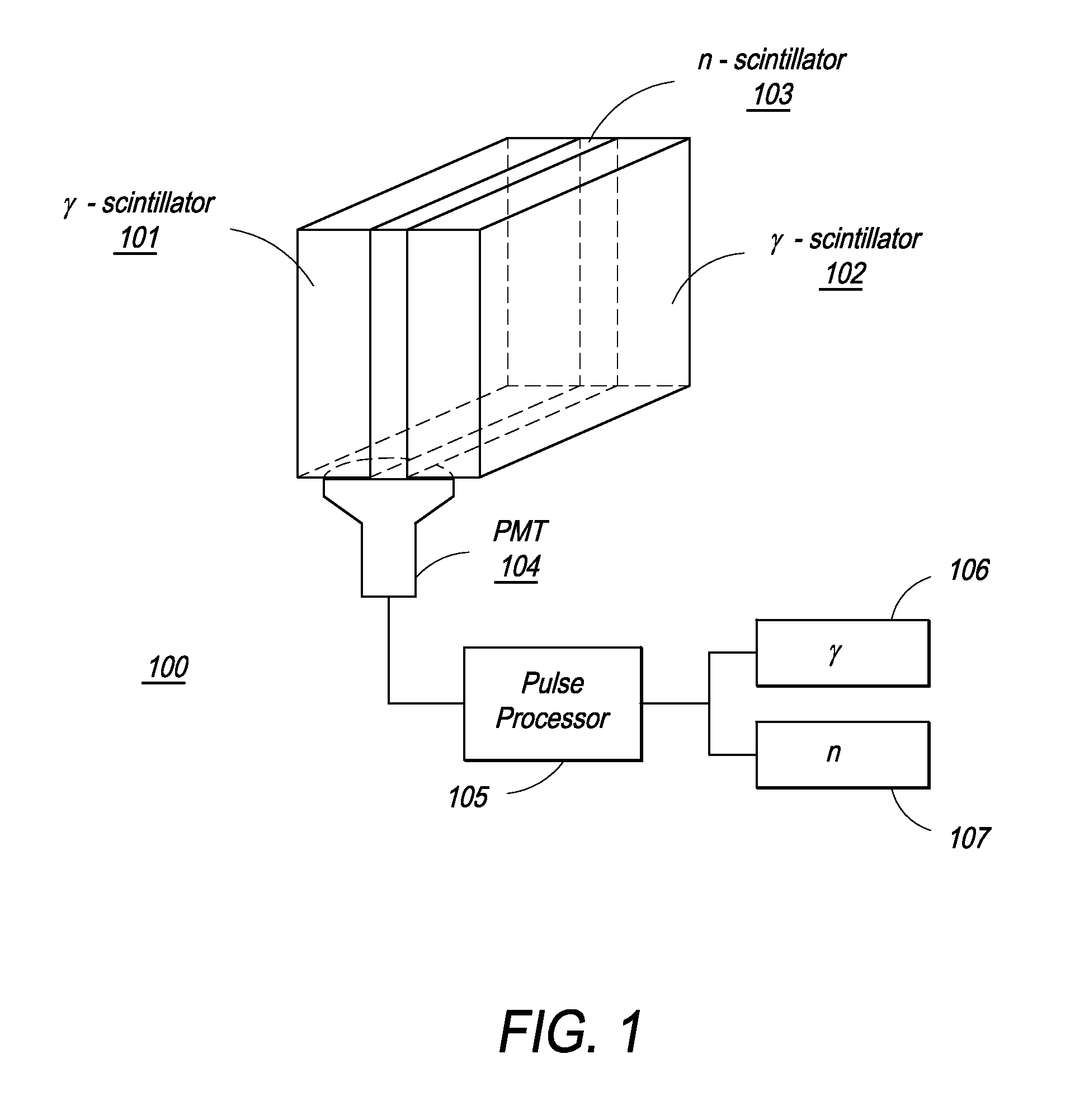
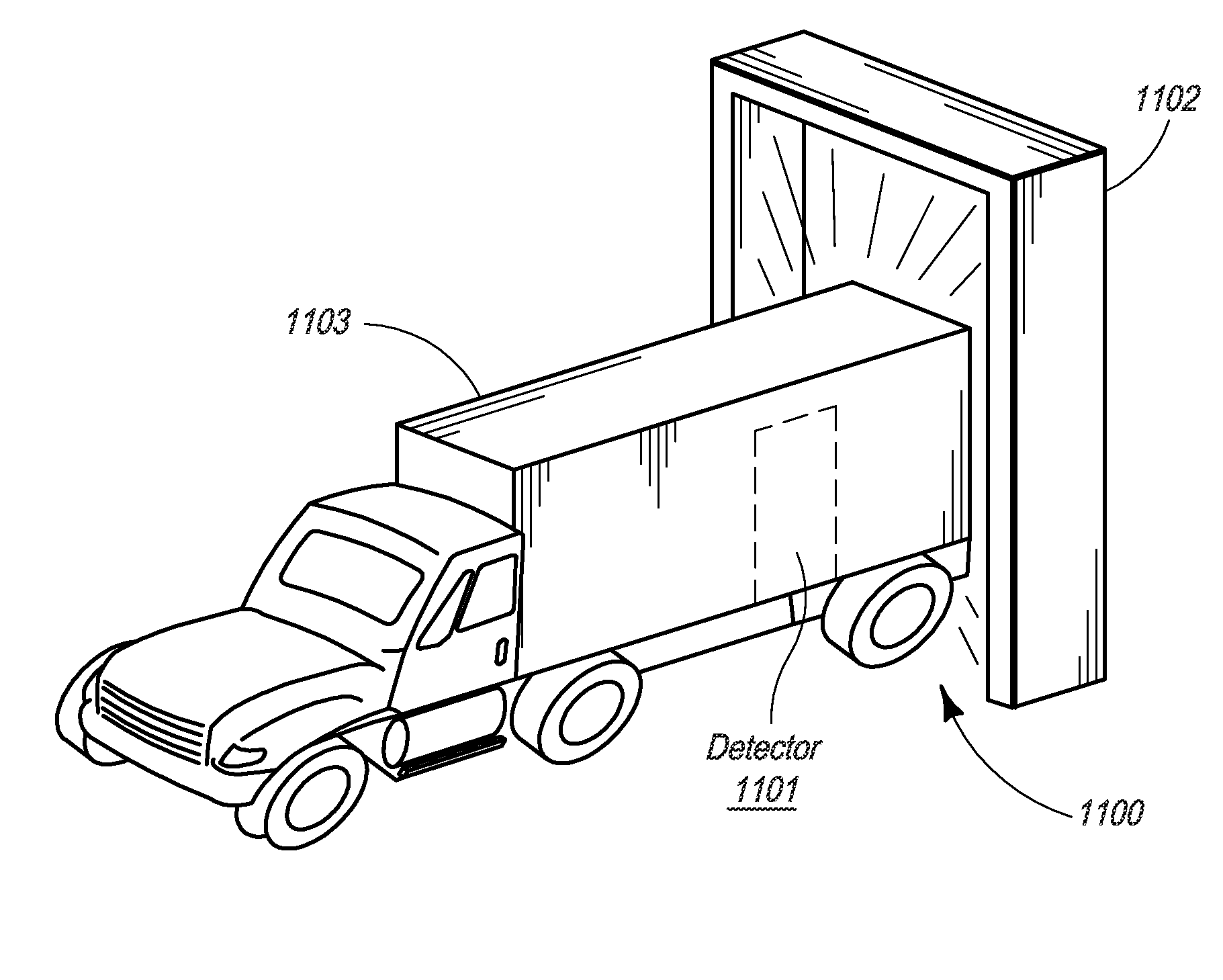
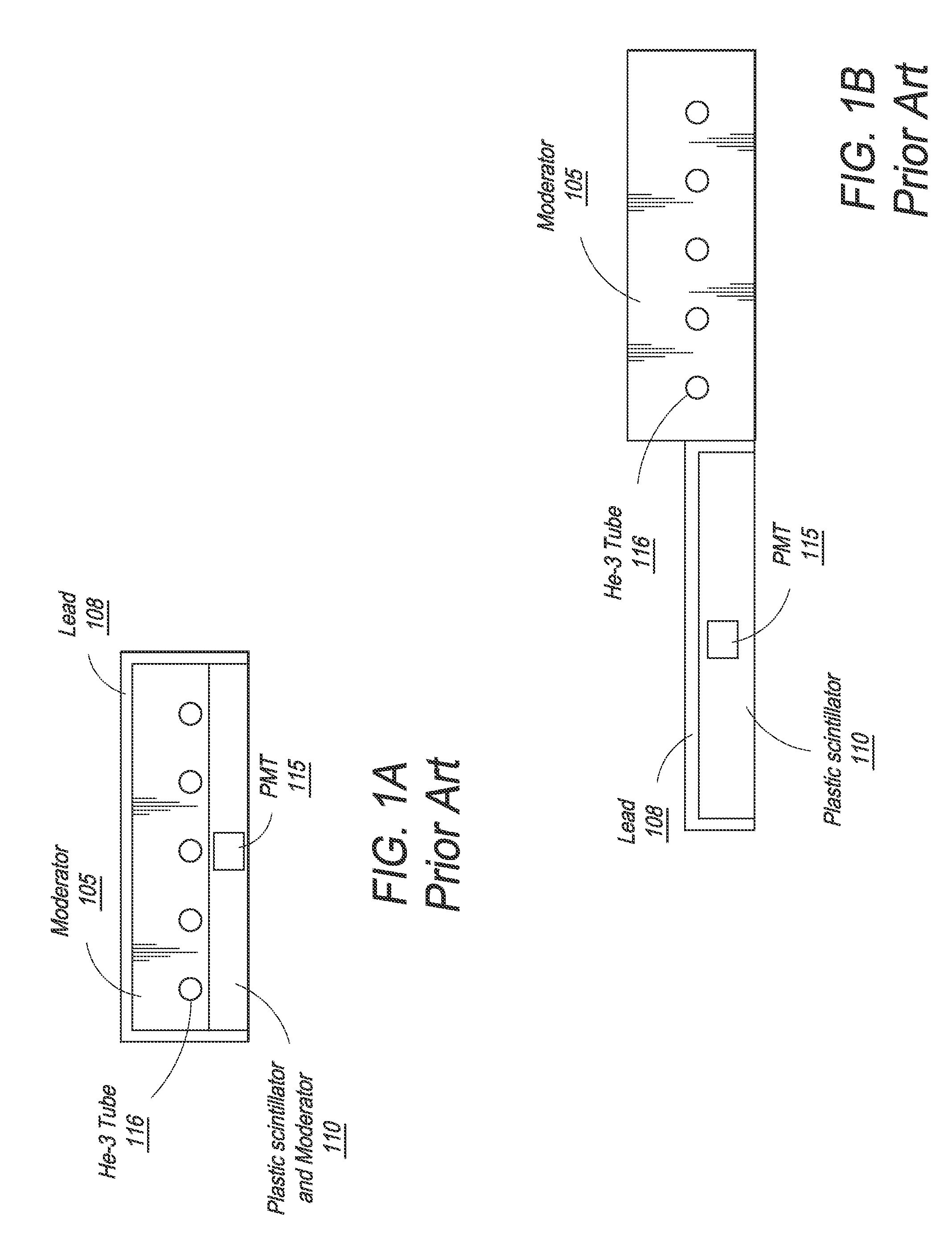
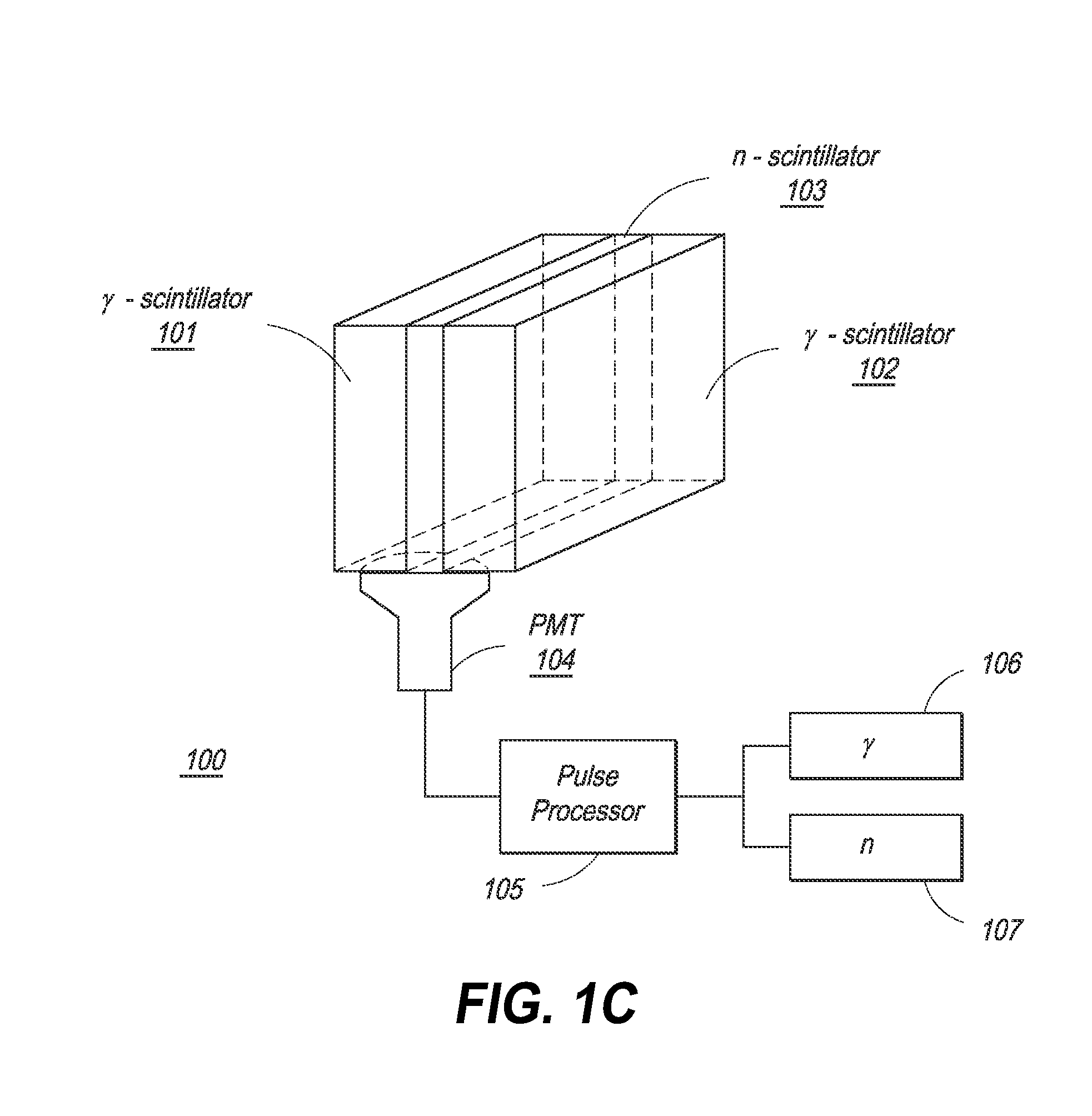
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20110204243A1Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
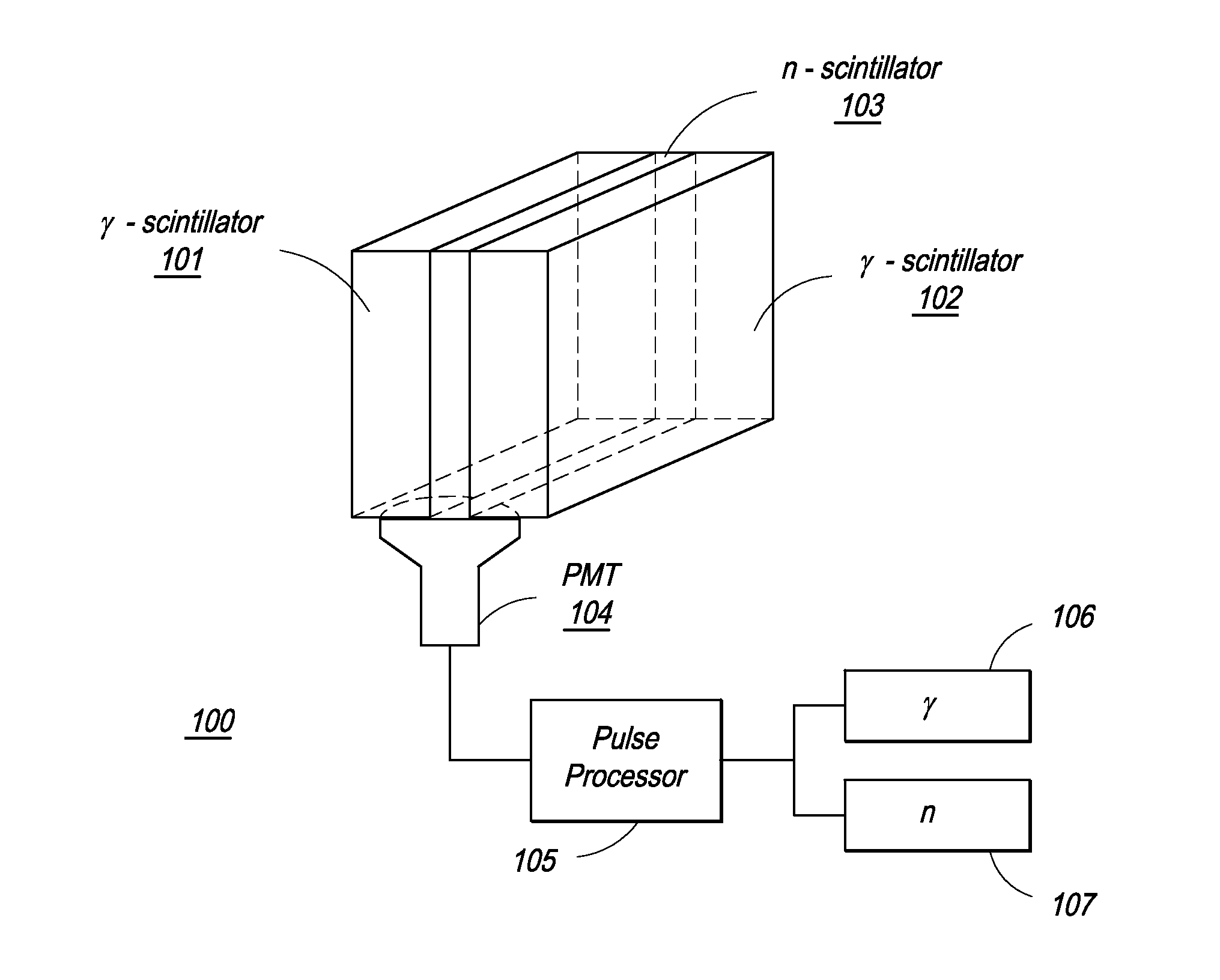
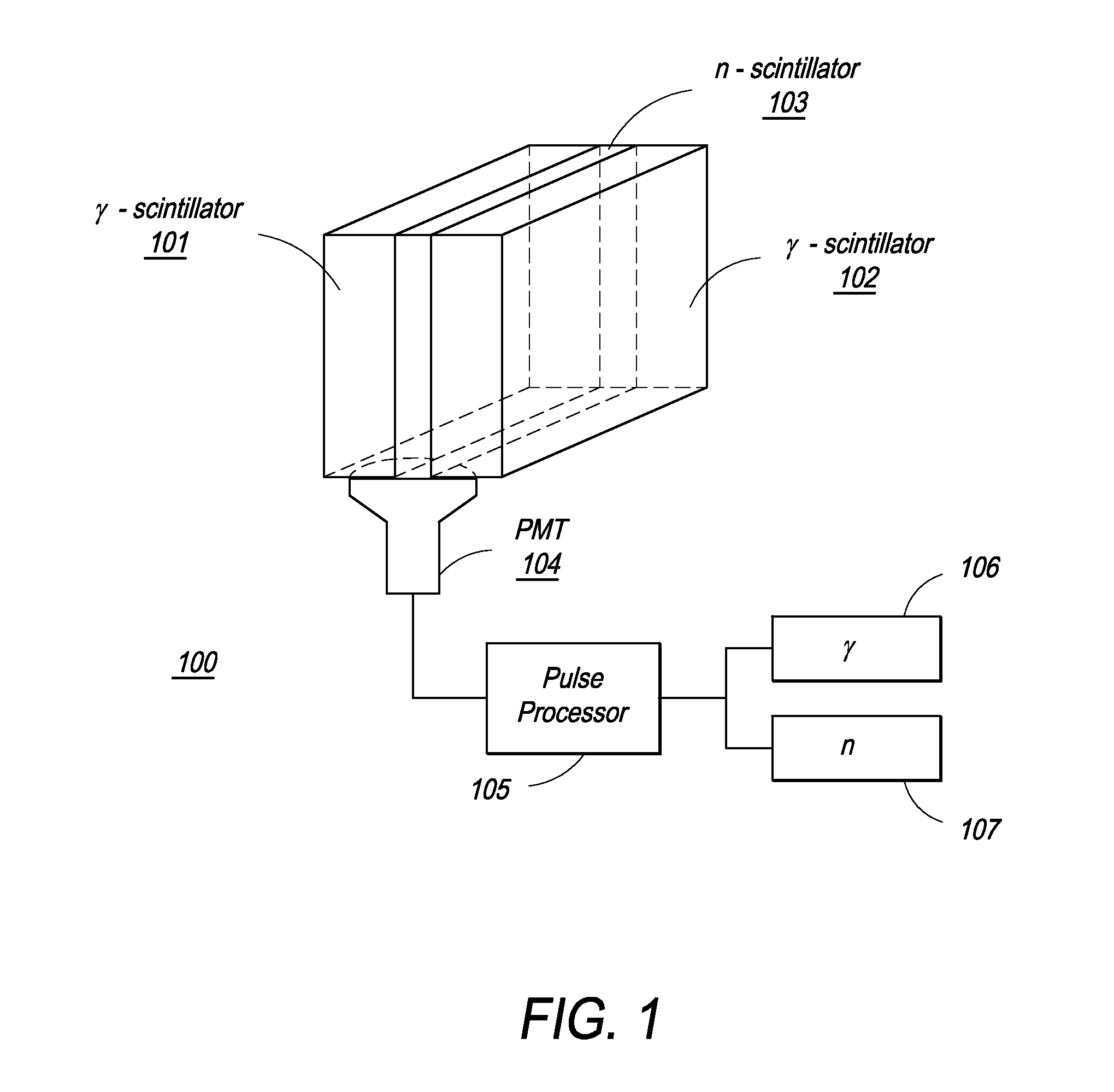
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Automated sample analysis
ActiveUS7595197B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotomultiplierAnalysis sample
Samples of materials used in industrial processes are analyzed to determine the concentration of certain materials of interest. The quantitative analysis of samples for these materials is provided without the need for manual methods such as titration. Indicators such as fluorescent dyes for which the intensity of fluorescence is indicative of the concentration of a material of interest are used. The dyes are made to fluoresce by means of a light source, and a photomultiplier or other detector capable of measuring light intensity detects the resulting fluorescence. The intensity of fluorescence in the sample is compared to the intensities of fluorescence produced by samples with known concentrations of the material of interest to determine the concentration of the material of interest of the sample.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Magnetic particle based electrochemiluminescent detection apparatus and method
InactiveUS6133043AHigh sensitivityFaster assay timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMagnetic field gradientElectrochemiluminescence
A method and apparatus for measuring electrochemiluminescence from a sample composition are described wherein magnetically responsive electrochemiluminescent active species are captured on the electrode with the aid of a capture magnet having a configuration such that the magnetic flux lines (or the magnetic field gradient) of at least one magnetic field source therein are compressed and / or dispersed. This capture magnet improves the distribution of the magnetically responsive electrochemiluminescent active species on the electrode surface and reduces interference with the photomultiplier tube, thereby enhancing the ECL signal and improving sensitivity. The improved capture and distribution also allows for shorter assay times.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
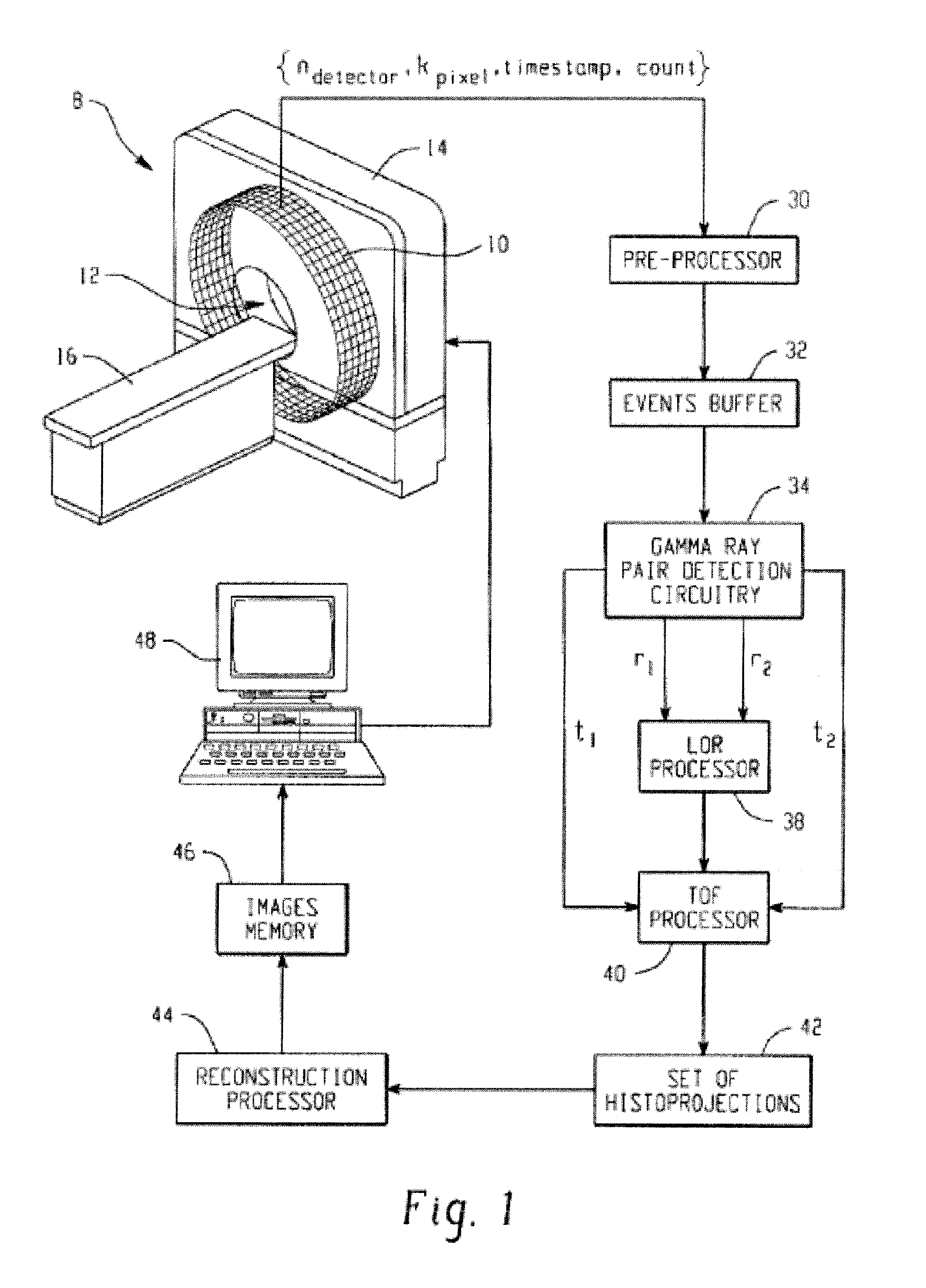
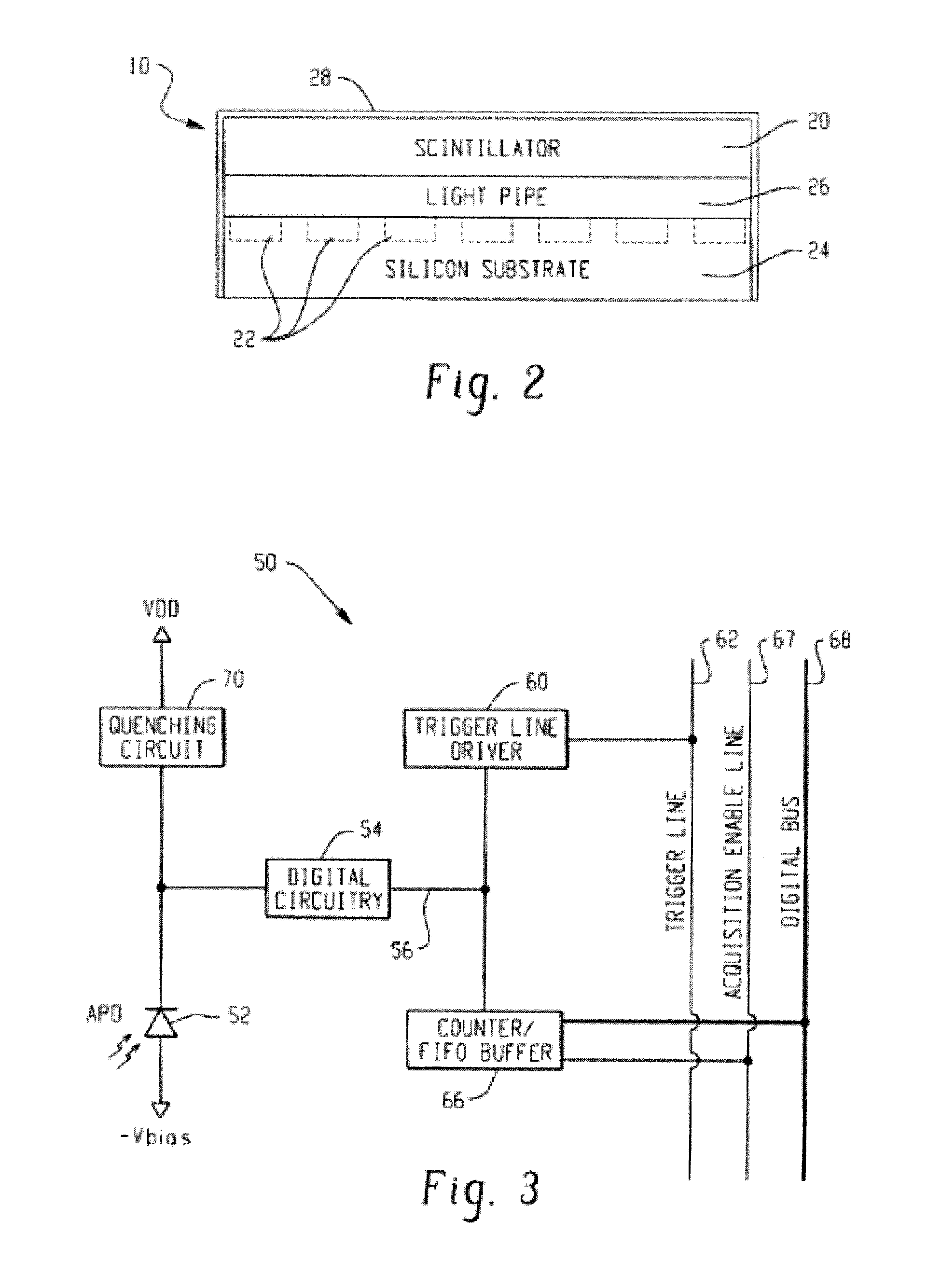
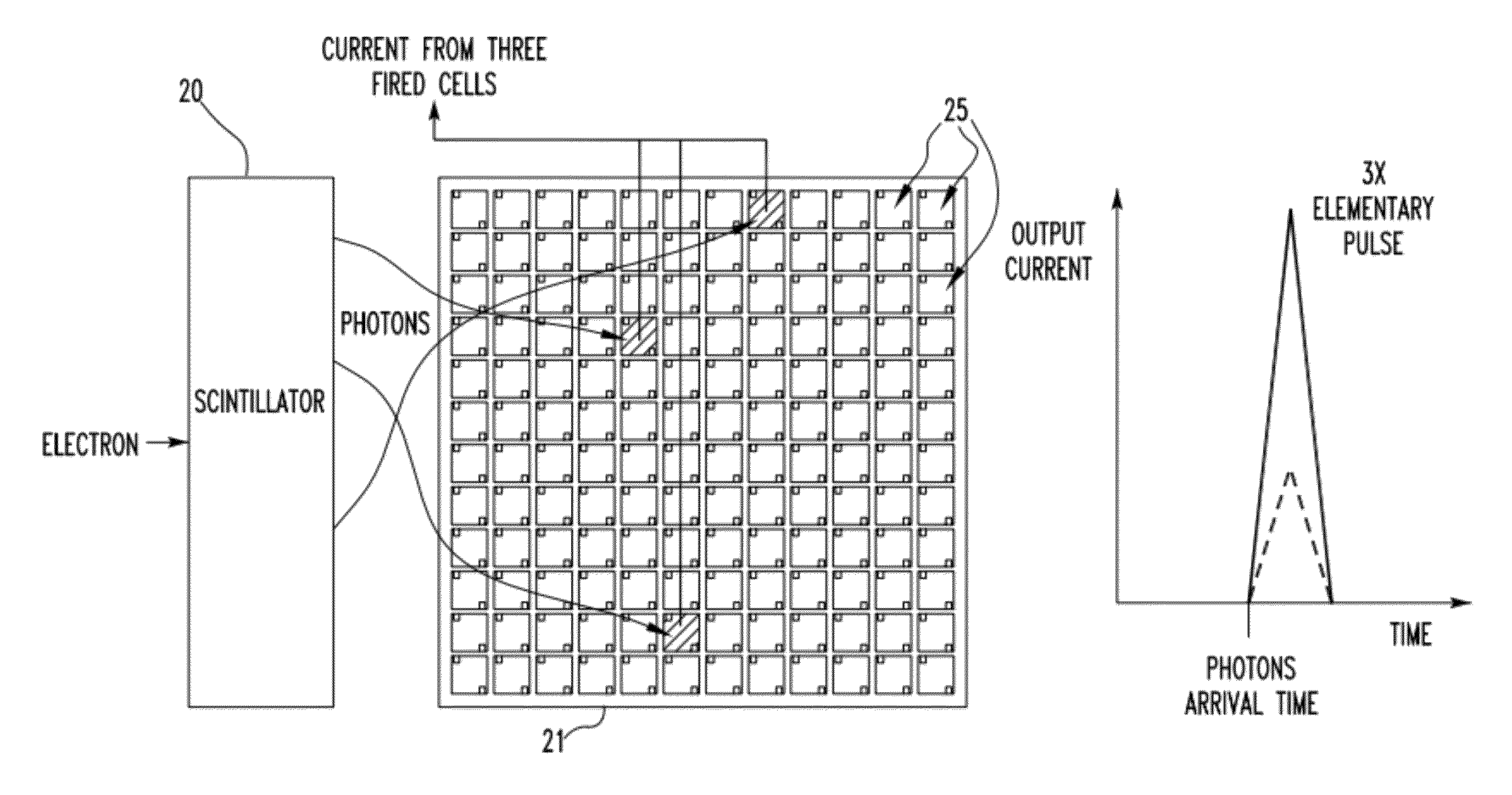
Digital silicon photomultiplier for TOF PET
ActiveUS8395127B1High data-rate radiation detectionImproved spatial detector resolutionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansQuiescent stateSilicon photomultiplier
A radiation detector includes an array of detector pixels each including an array of detector cells. Each detector cell includes a photodiode biased in a breakdown region and digital circuitry coupled with the photodiode and configured to output a first digital value in a quiescent state and a second digital value responsive to photon detection by the photodiode. Digital triggering circuitry is configured to output a trigger signal indicative of a start of an integration time period responsive to a selected number of one or more of the detector cells transitioning from the first digital value to the second digital value. Readout digital circuitry accumulates a count of a number of transitions of detector cells of the array of detector cells from the first digital state to the second digital state over the integration time period.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Electron detector including an intimately-coupled scintillator-photomultiplier combination, and electron microscope and x-ray detector employing same
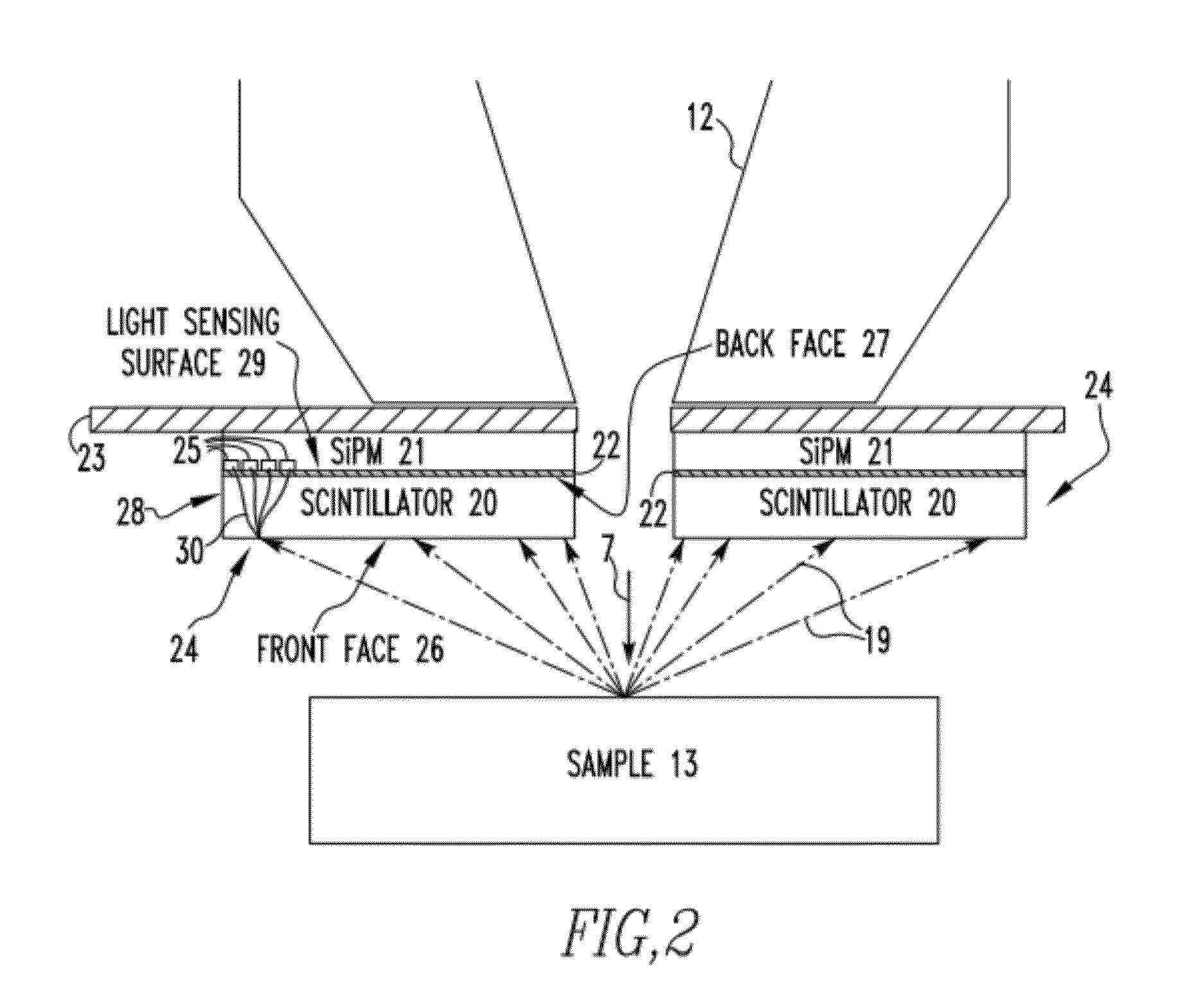
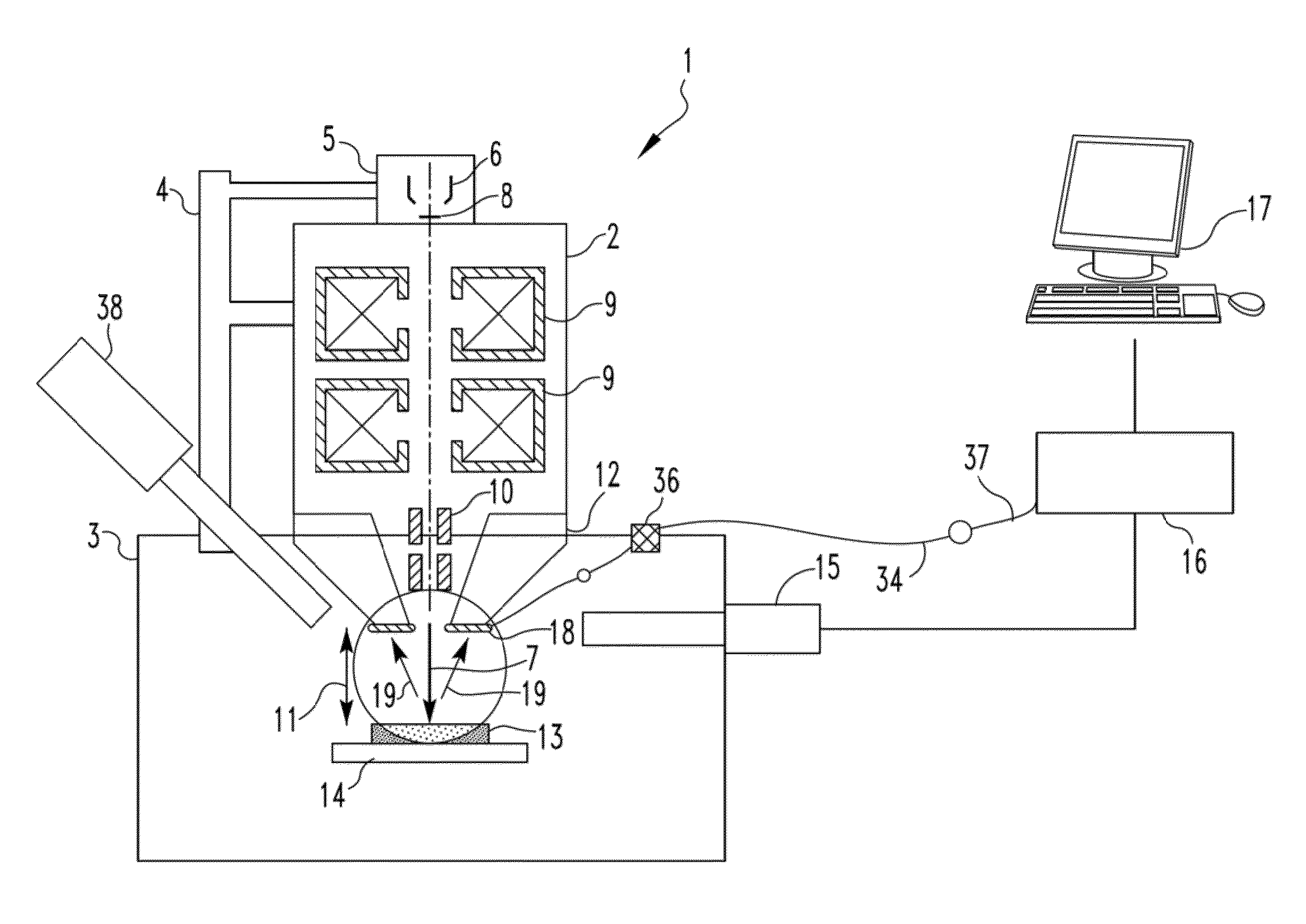
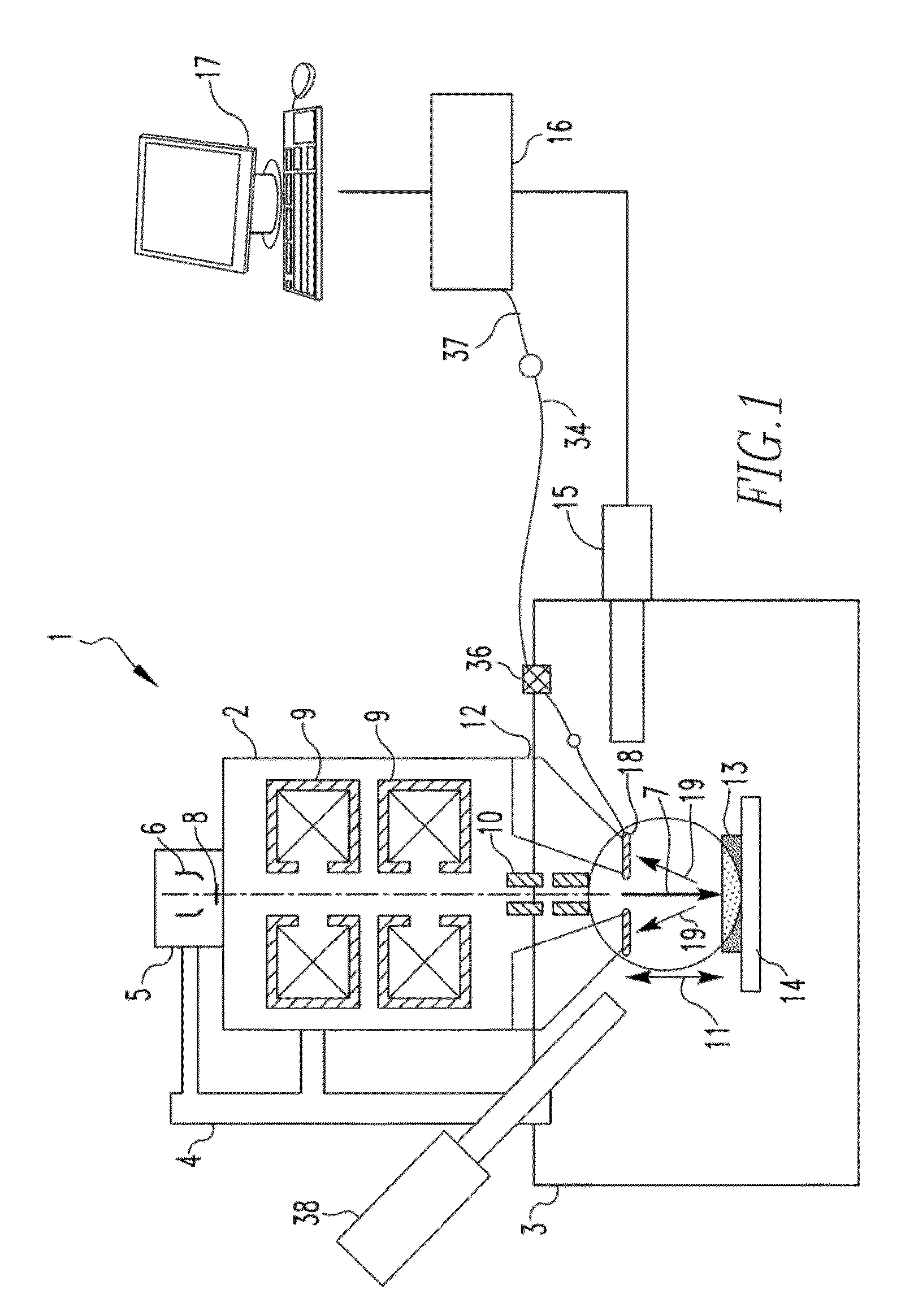
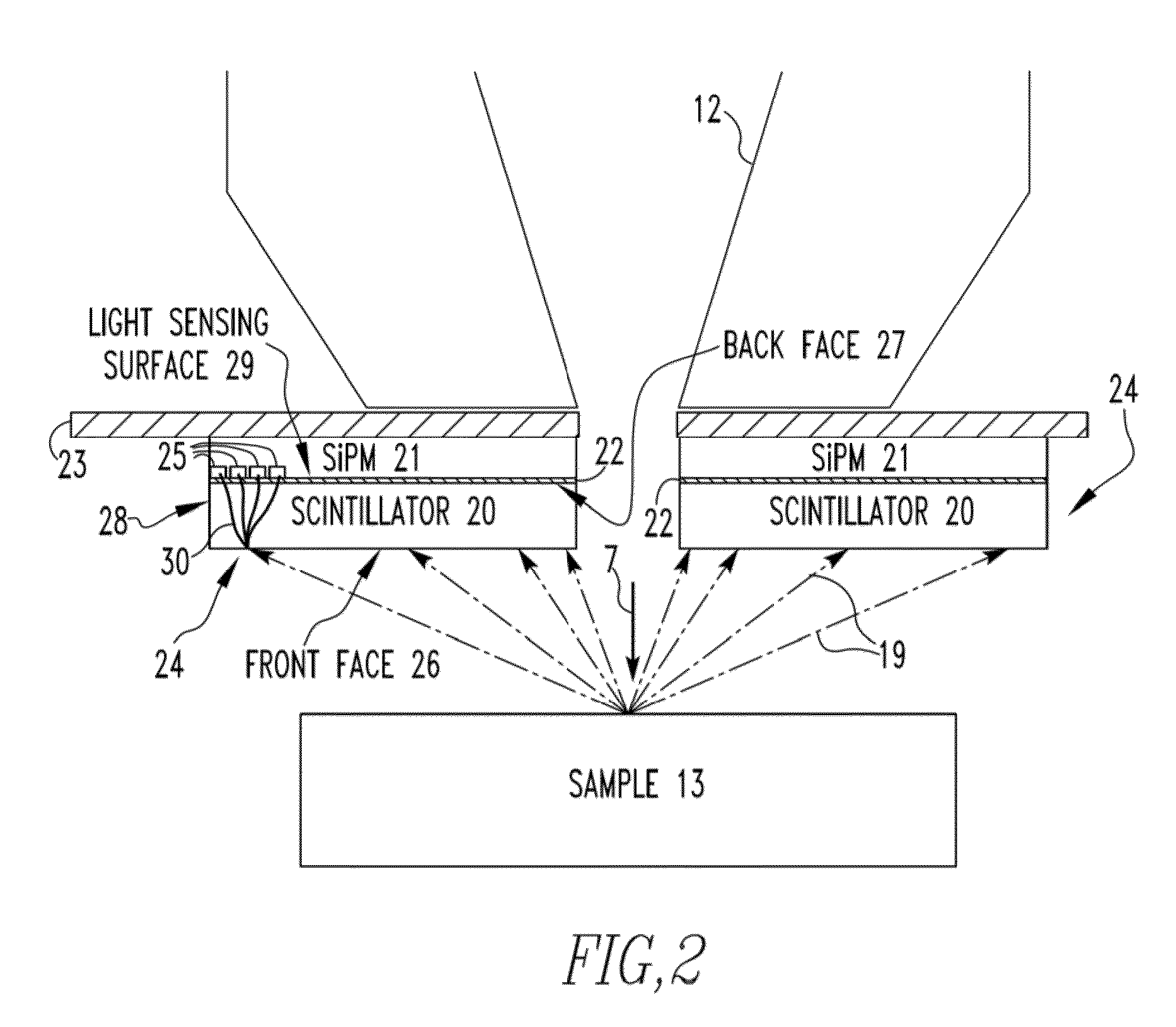
ActiveUS20120025074A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
A charged particle beam device includes an electron source structured to generate an electron beam, the electron source being coupled to an electron column that at least partially houses a system structured to direct the electron beam toward a specimen positioned in a sample chamber to which the electron column is coupled, and an electron detector. The electron detector includes one or more assemblies positioned within the electron column or the sample chamber, each of the assemblies including an SiPM and a scintillator directly connected face-to-face to an active light sensing surface of the SiPM without a light transporting device being positioned in between the scintillator and the SiPM.
Owner:FEI CO
Electron detector including one or more intimately-coupled scintillator-photomultiplier combinations, and electron microscope employing same
ActiveUS20130032713A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesClose couplingLight sensing
An electron detector includes a plurality of assemblies, the plurality of assemblies including a first assembly having a first SiPM and a first scintillator made of a first scintillator material directly connected to an active light sensing surface of the first SiPM, and a second assembly having a second SiPM and a second scintillator made of a second scintillator material directly connected to an active light sensing surface of the second SiPM, wherein the first scintillator material and the second scintillator material are different than one another. Alternatively, an electron detector includes an assembly including an SiPM and a scintillator member having a front surface and a back surface, the scintillator member being a film of a scintillator material directly deposited on to an active light sensing surface of the SiPM.
Owner:FEI CO
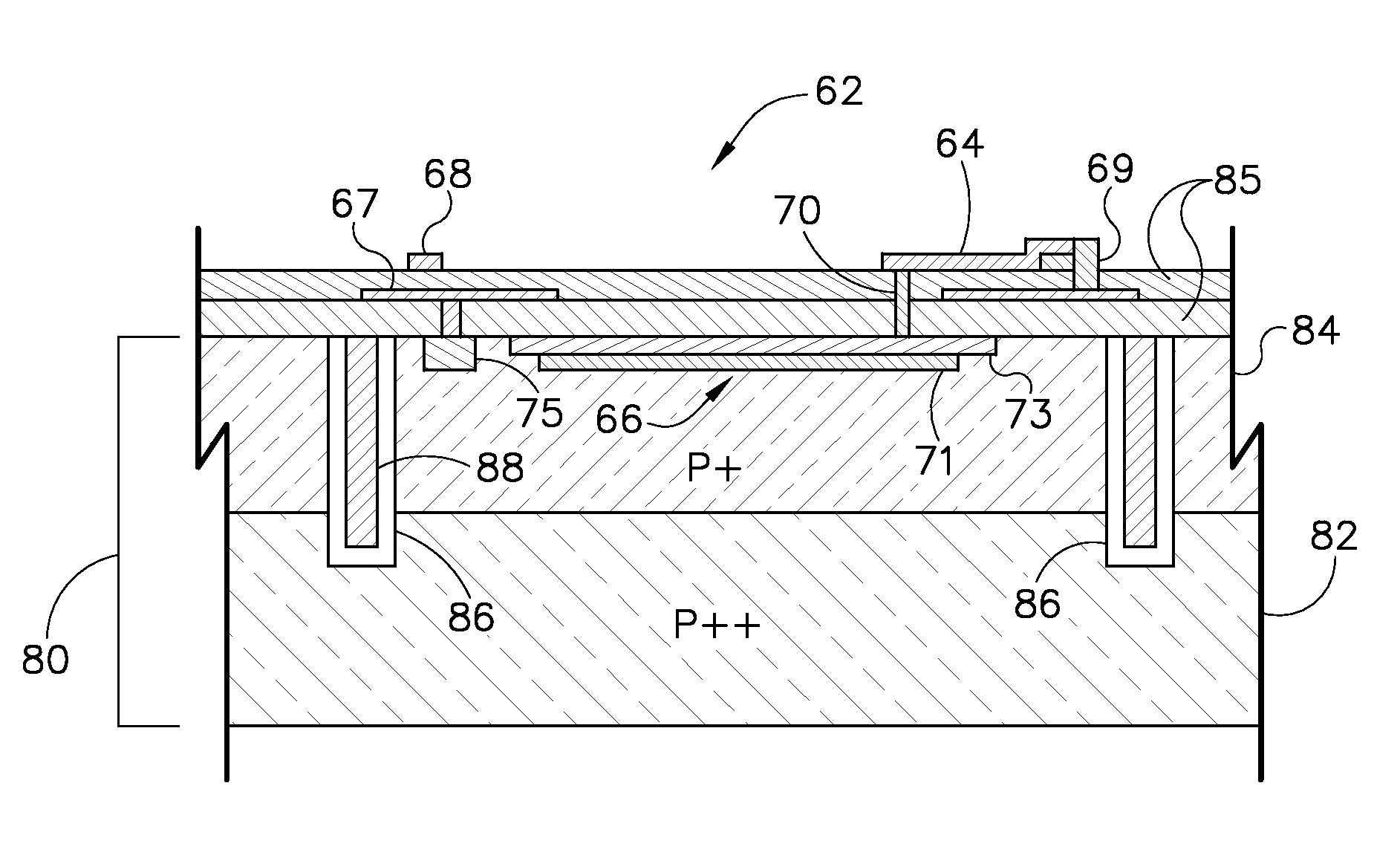
Structure of a solid state photomultiplier
ActiveUS20080308738A1Dark count rate also increasesIncrease ratingsSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDark count ratePhotomultiplier
A solid-state photomultiplier (SSPM) includes an optical isolation structure therein. The SSPM includes a substrate and an epitaxial diode layer positioned on the substrate. A plurality of avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are fabricated on the epitaxial diode layer and the optical isolation structure is positioned about the plurality of APDs to separate each of the plurality of APDs from adjacent APDs. The optical isolation structure contains at least one of a light absorbing material and a light reflecting material deposited therein to reduce optical crosstalk and dark count rate in the SSPM.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Parallel detection chromatography systems
High throughput liquid chromatography systems include multiple separation columns and multiple flow-through detection regions in sensory communication with a common radiation source and a multi-channel detector. Preferred detector types include a multi-anode photomultiplier tube, a charge-coupled device detector, a diode array, and a photodiode array. In certain embodiments, separation columns are microfluidic and integrated into a unitary microfluidic device. The optical path through a detection region is preferably coaxial with the path of eluate flow along a flow axis through a detection region. On-board or off-board detection regions may be provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Photomultiplier tube gain stabilization for radiation dosimetry system
InactiveUS7157681B1Low costSmall sizePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimetry radiationDosimeter
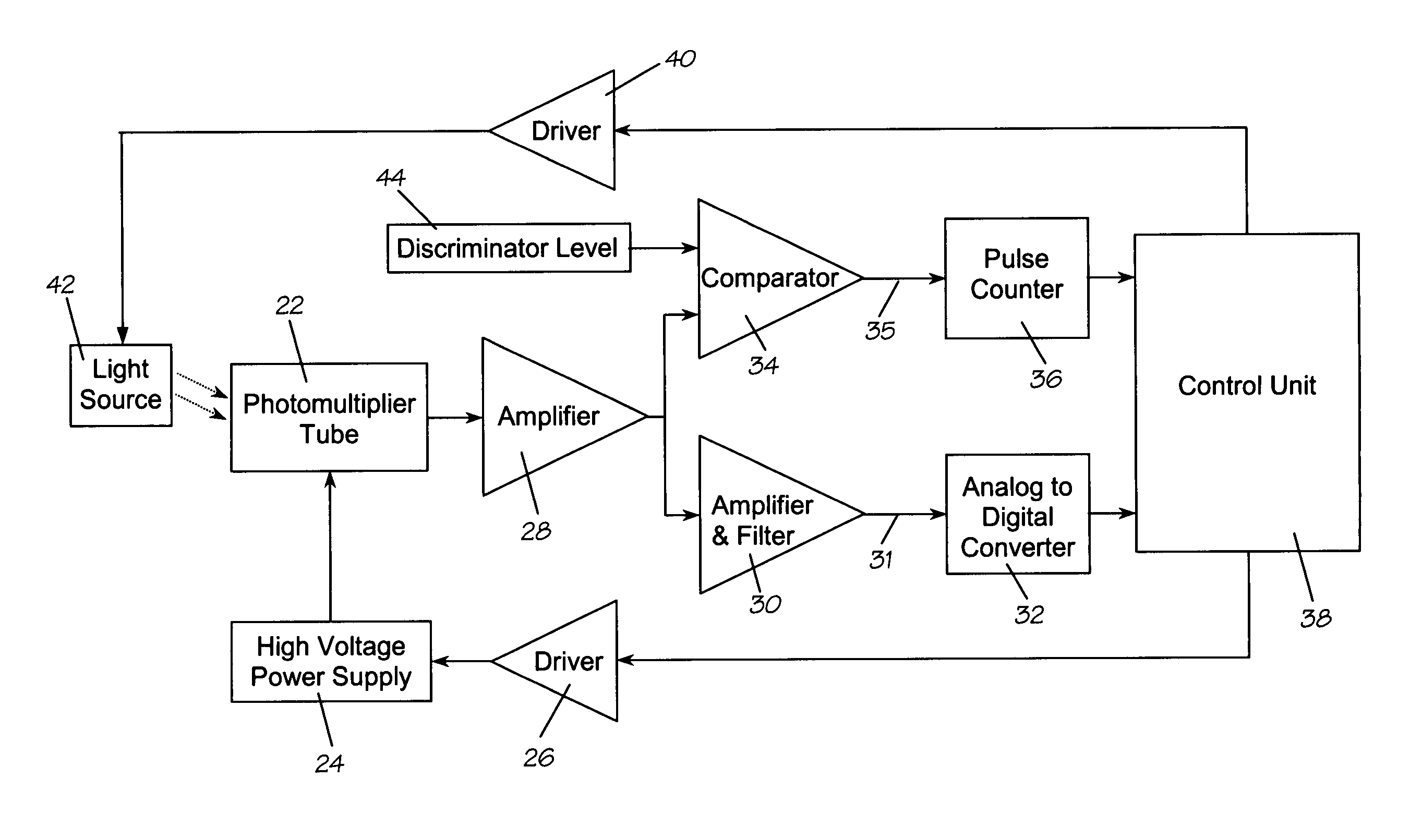
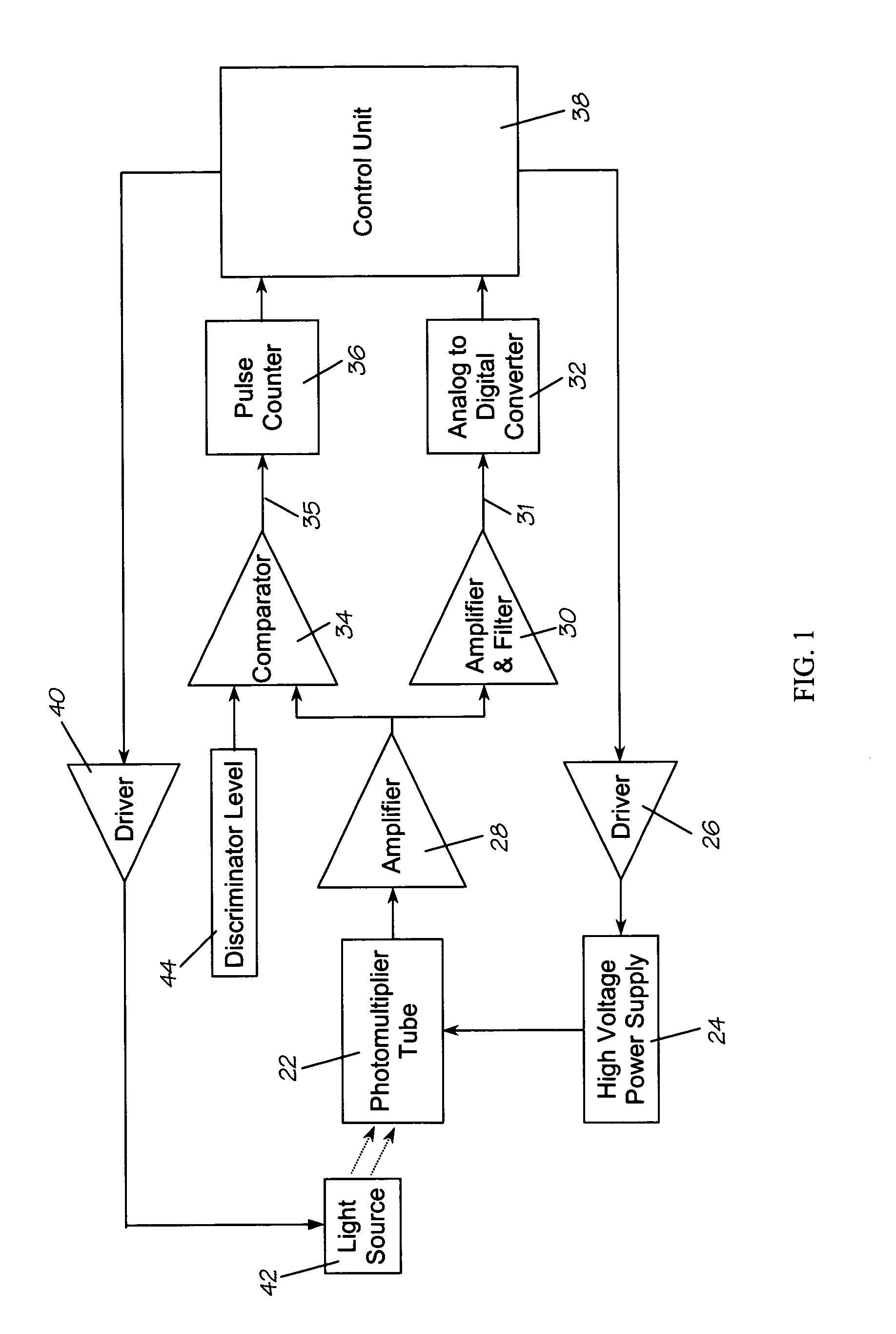
Methods and means for measuring and adjusting the gain of a photomultiplier tube (PMT), or other photo-detector with electron multiplication gain, for the purpose of achieving accurate light measurement, such as in a luminescent radiation dosimeter reader. With a PMT illuminated by a light emitting diode or other light source, the PMT output signal is measured in two modes, signal integration and photon pulse counting. The measured PMT gain is calculated as the ratio of the integrated signal to the photon pulse count. The PMT high voltage may be adjusted to cause the measured PMT gain to correspond to an established calibration gain value, or the data from the PMT may be adjusted to compensate the deviation of the measured PMT gain from the calibration gain value. The light source may be a controllable light source that can be adjusted to provide a specific photon count rate output as measured by the PMT. This invention provides for maintaining light measurement calibration without requiring temperature stabilization or a fixed light source.
Owner:TETZLAFF WOLFGANG
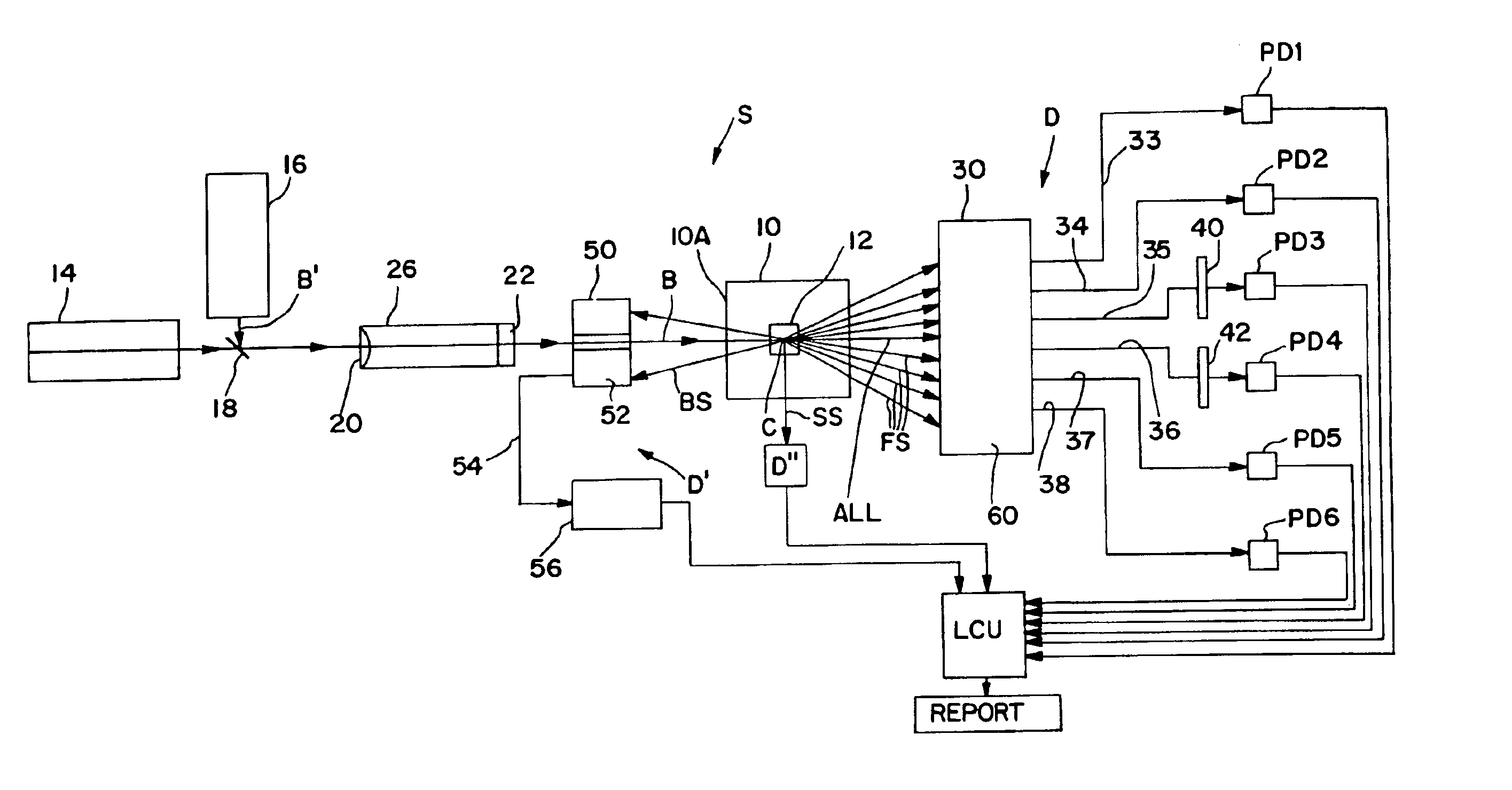
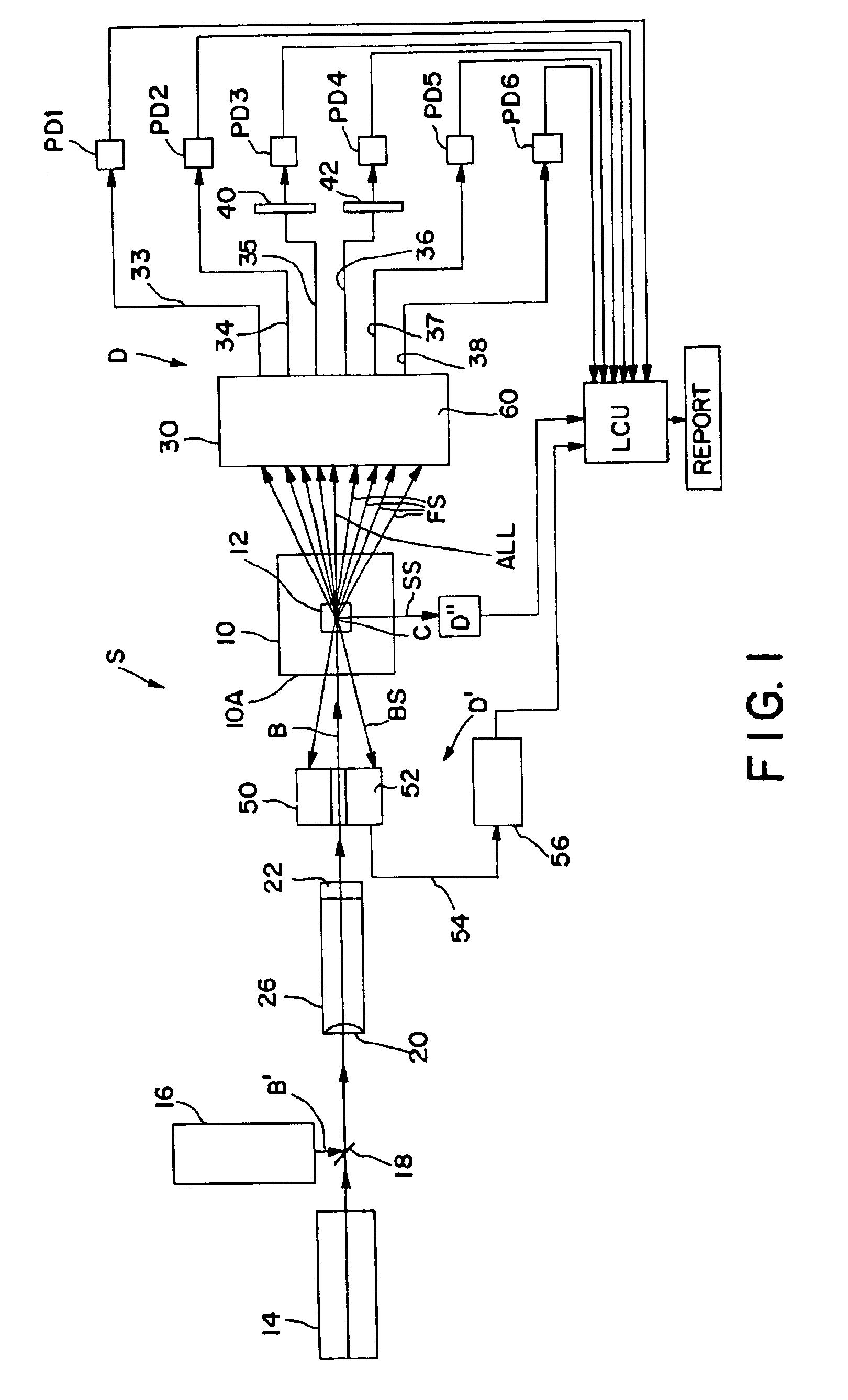
Method and apparatus for gas discharge laser output light coherency reduction
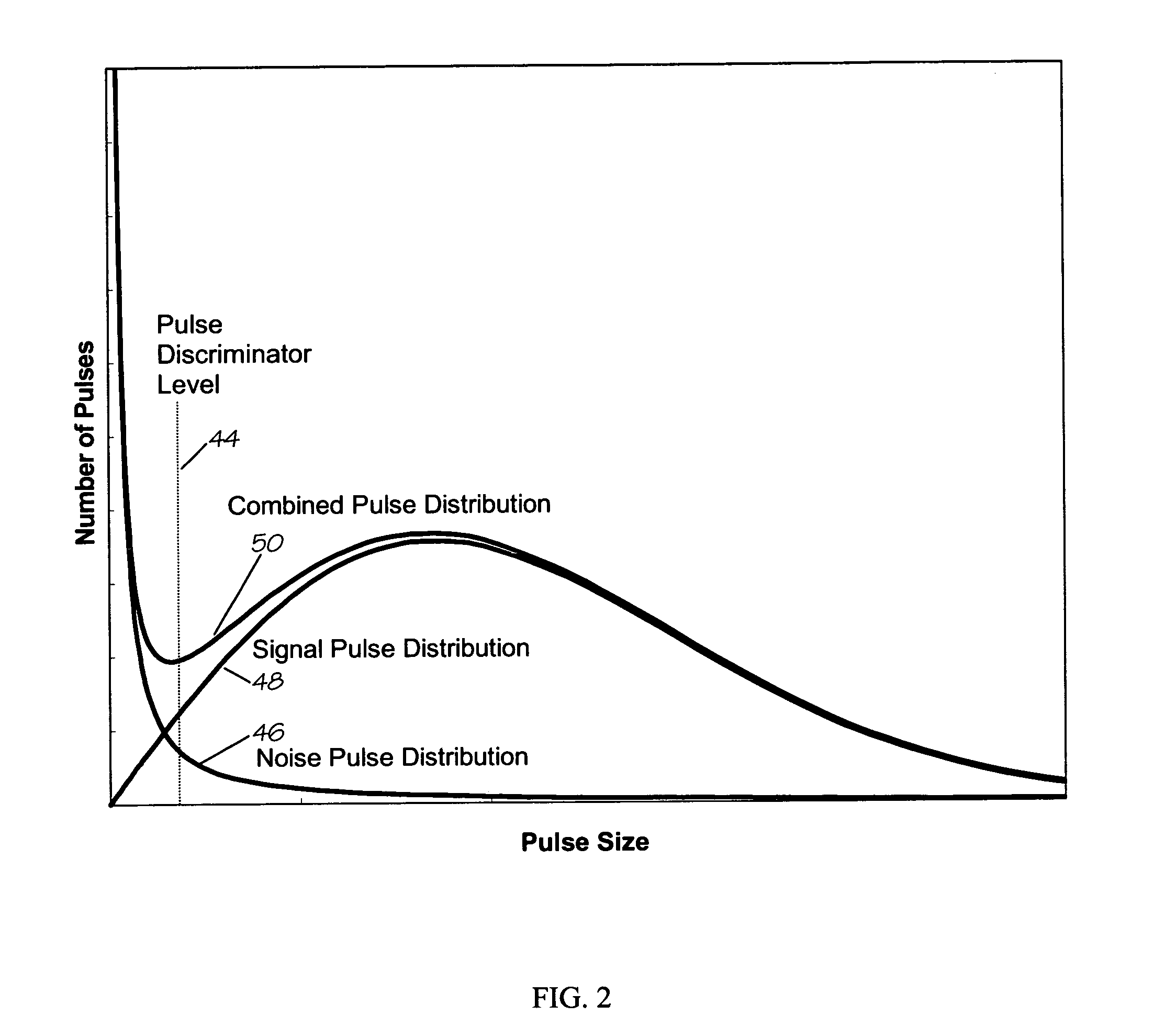
A method and apparatus for producing with a gas discharge laser an output laser beam comprising output laser light pulses, for delivery as a light source to a utilizing tool is disclosed which may comprise a beam path and a beam homogenizer in the beam path. The beam homogenizer may comprise at least one beam image inverter or spatial rotator, which may comprise a spatial coherency cell position shifter. The homogenizer may comprise a delay path which is longer than, but approximately the same delay as the temporal coherence length of the source beam. The homogenizer may comprise a pair of conjoined dove prisms having a partially reflective coating at the conjoined surfaces of each, a right triangle prism comprising a hypotenuse face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or an isosceles triangle prism having a face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or combinations of these, which may serve as a source beam multiple alternating inverted image creating mechanism. The beam path may be part of a bandwidth measuring the bandwidths of an output laser beam comprising output laser light in the range of below 500 femtometers at accuracies within tens of femtometers. The homogenizer may comprise a rotating diffuser which may be a ground glass diffuser which may also be etched. The wavemeter may also comprise a collimator in the beam path collimating the diffused light; a confocal etalon creating an output based upon the collimated light entering the confocal etalon; and a detector detecting the output of the confocal etalon and may also comprise a scanning mechanism scanning the angle of incidence of the collimated light entering the confocal etalon which may scan the collimated light across the confocal etalon or scan the etalon across the collimated light, and may comprise an acousto-optical scanner. The confocal etalon may have a free spectral range approximately equal to the E95 width of the beam being measured. The detector may comprise a photomultiplier detecting an intensity pattern of the output of the confocal etalon.
Owner:CYMER INC
Photon counting CT detector using solid-state photomultiplier and scintillator
ActiveUS7403589B1Improved saturation characteristicHigh gainMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorX-ray
A detector module for a CT imaging system includes a scintillator to convert x-rays to optical photons. The scintillator is optically coupled to a solid-state photomultiplier with internal gain to receive the optical photons and convert them into a corresponding electrical signal output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
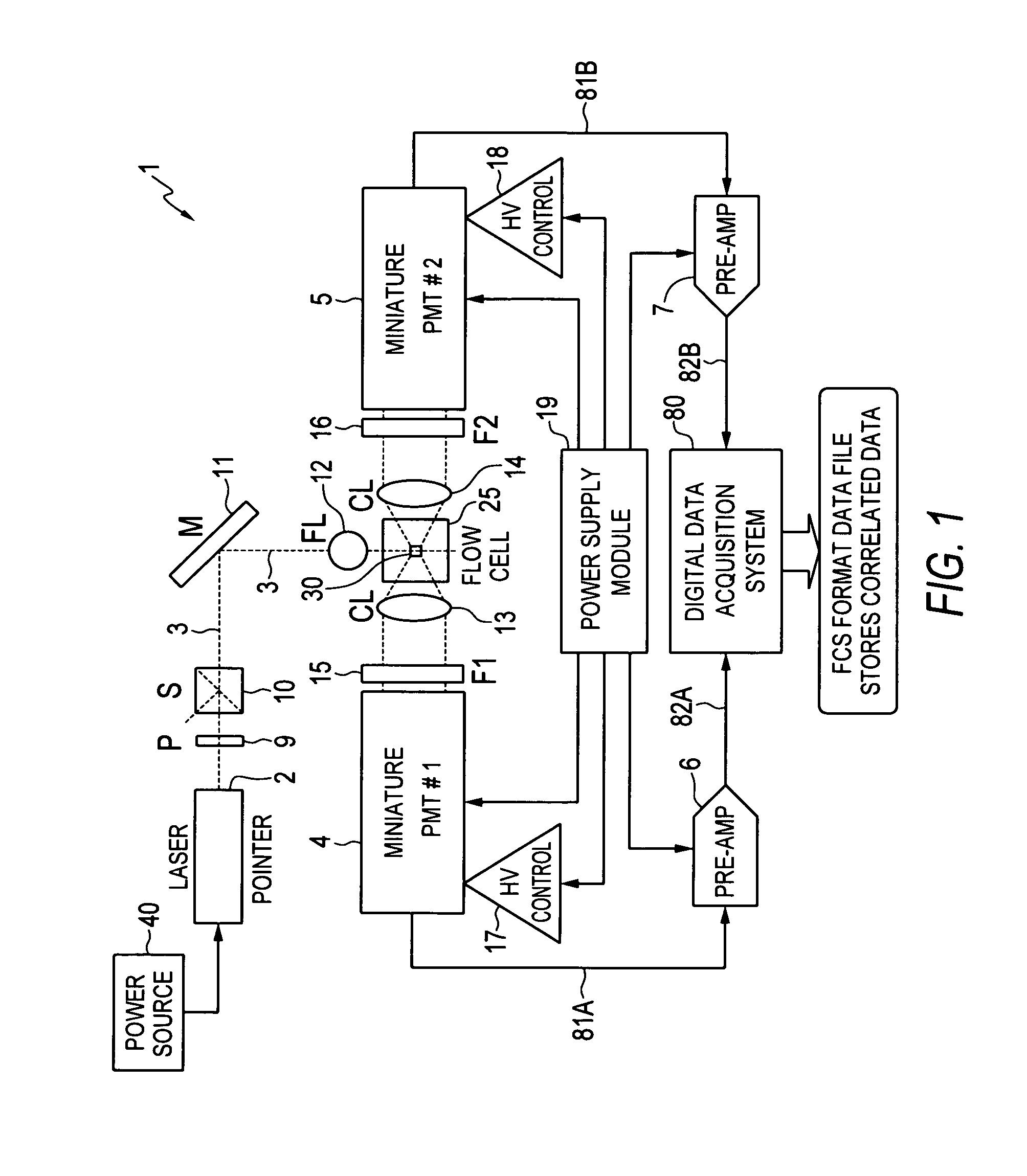
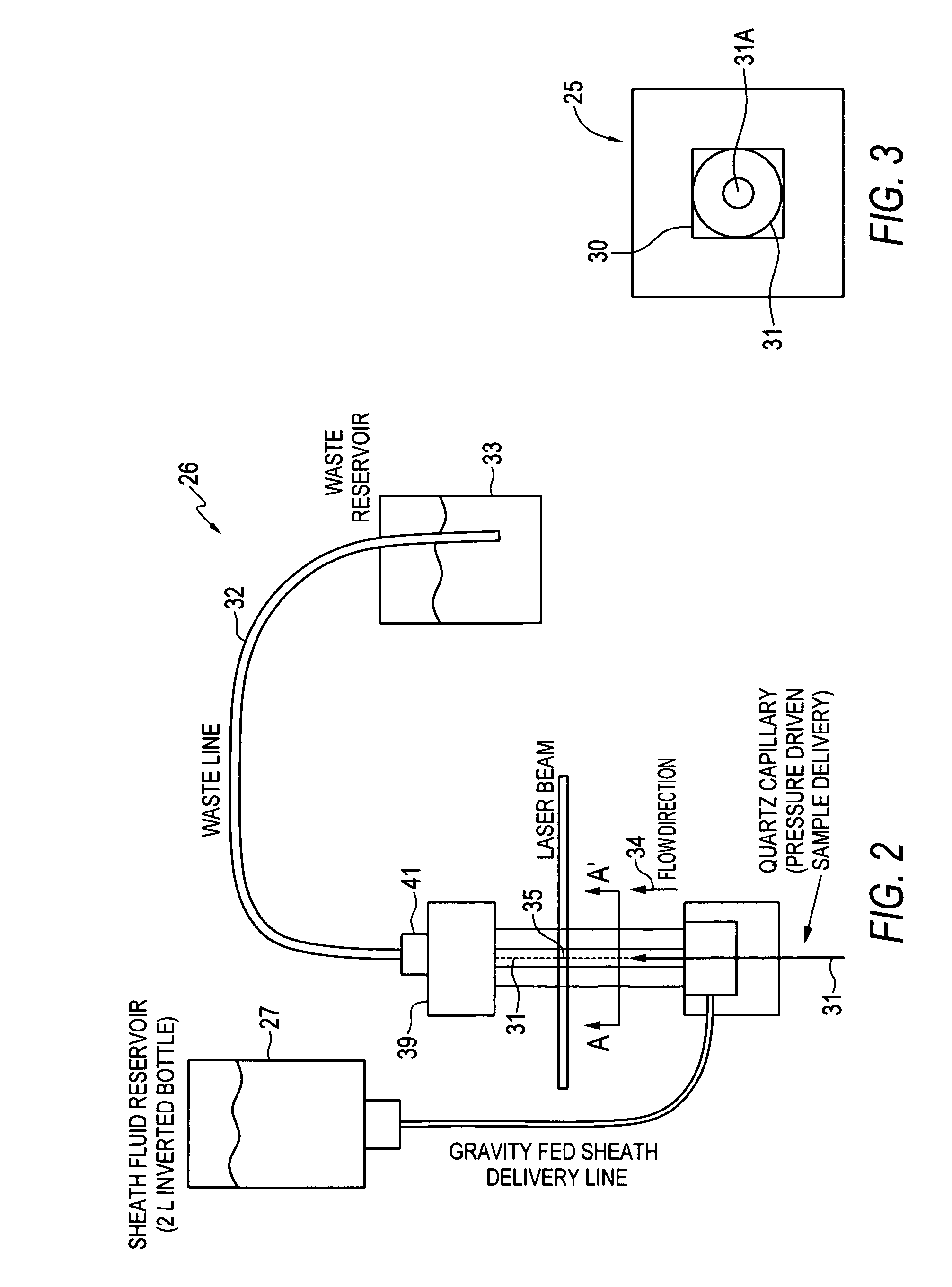
System and method for measuring particles in a sample stream of a flow cytometer or the like
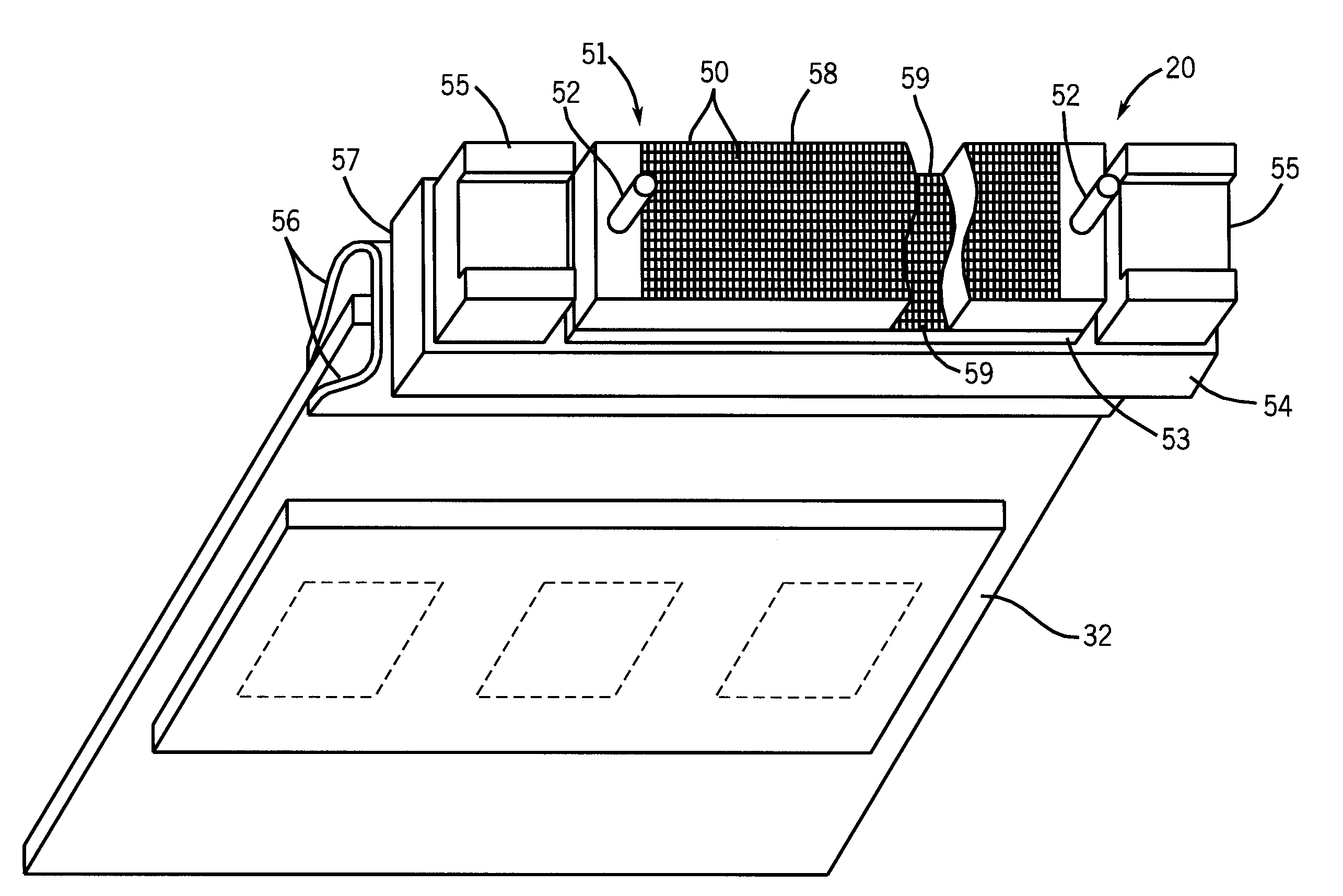
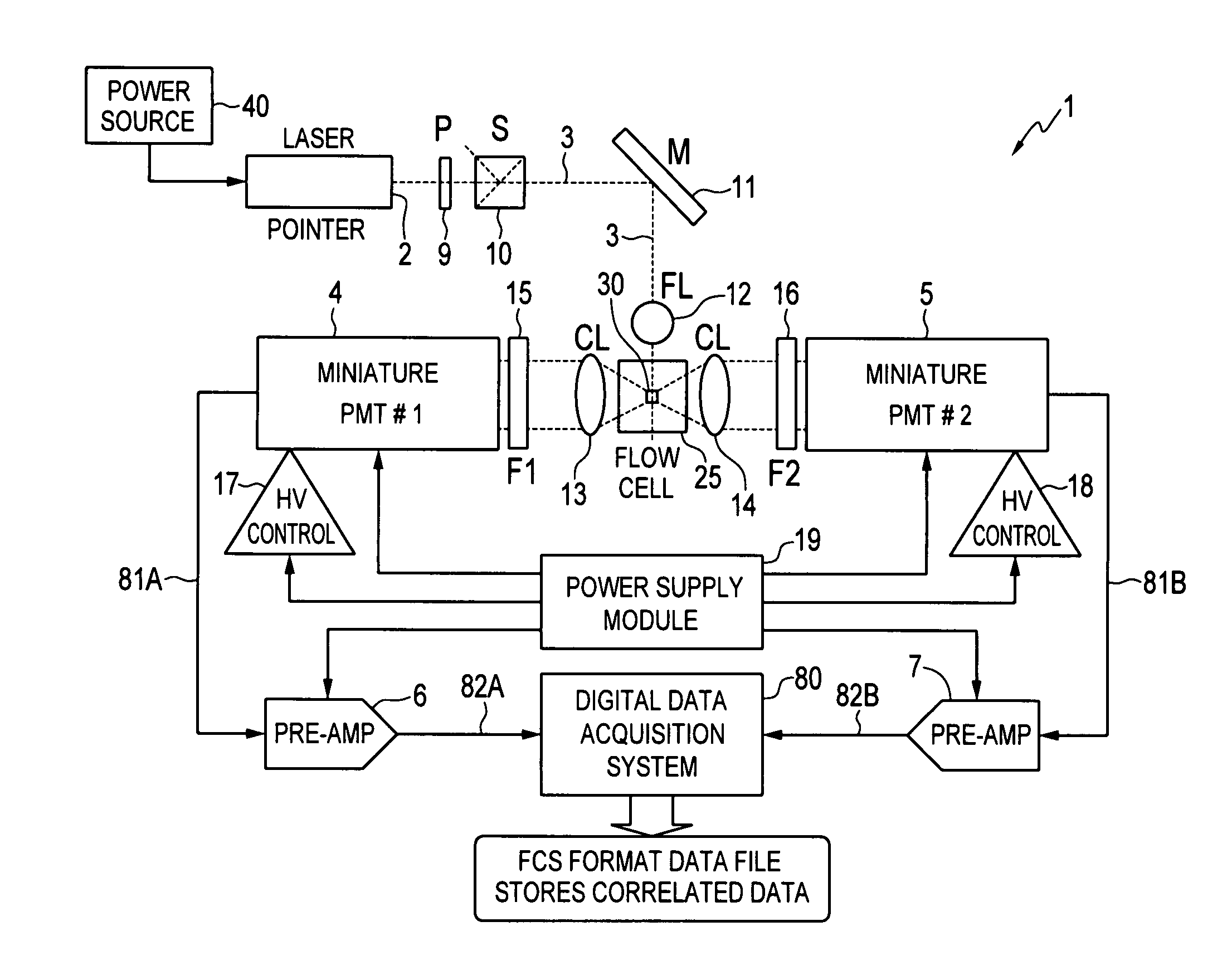
ActiveUS20080106736A1Low costExtended shipping timeScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluidicsSignal conditioning
A system and method for analyzing a particle in a sample stream of a flow cytometer or the like. The system has a light source, such as a laser pointer module, for generating a low powered light beam and a fluidics apparatus which is configured to transport particles in the sample stream at substantially low velocity through the light beam for interrogation. Detectors, such as photomultiplier tubes, are configured to detect optical signals generated in response to the light beam impinging the particles. Signal conditioning circuitry is connected to each of the detectors to condition each detector output into electronic signals for processing and is designed to have a limited frequency response to filter high frequency noise from the detector output signals.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Apparatus for differentiating blood cells using back-scatter
InactiveUS6869569B2Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotodetectorRed blood cell
Blood cells of interest are readily distinguishable from other blood cells and look-a-like particles found in a blood sample by their back-scatter signature. A preferred method for differentiating platelets in a blood sample is to irradiate the cells and particles, one at a time, with a beam of radiation, and to detect back-scattered (reflected) radiation using a plurality of optical fibers to transmit the back-scattered radiation to a high-gain photodetector, e.g. a photomultiplier tube. Preferably, the back-scatter signal so obtained is combined with a second signal representing, for example, either the level of forward-scatter within a prescribed, relatively narrow angular range, or the level of side-scattered radiation, or the level of attenuation of the cell-irradiating beam caused by the presence of the irradiated cell or particle in the beam, or the electrical impedance of the irradiated cell or particle, to differentiate the cells of interest. The method and apparatus of the invention are particularly useful in differentiating platelets and basophils in a blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
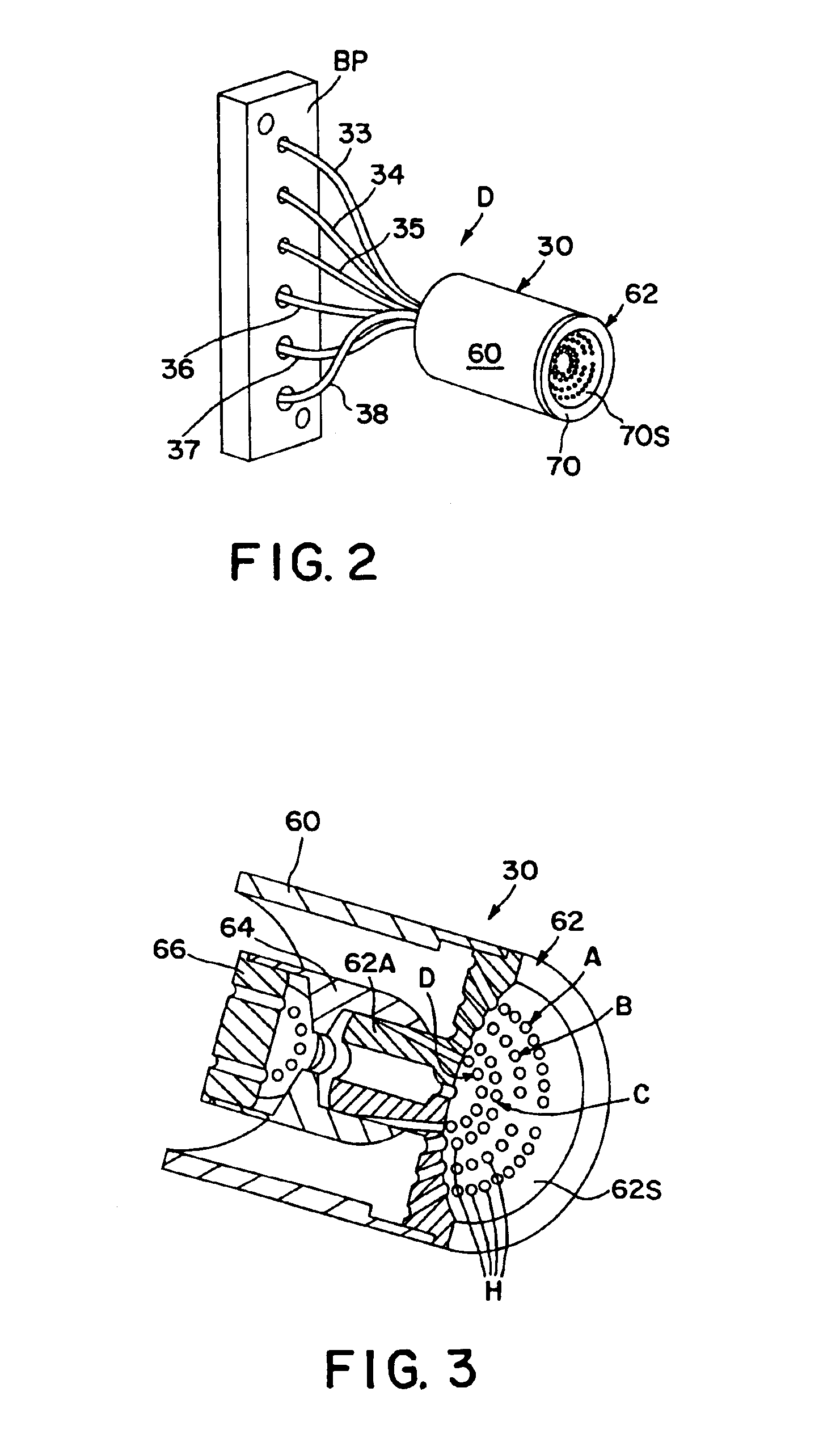
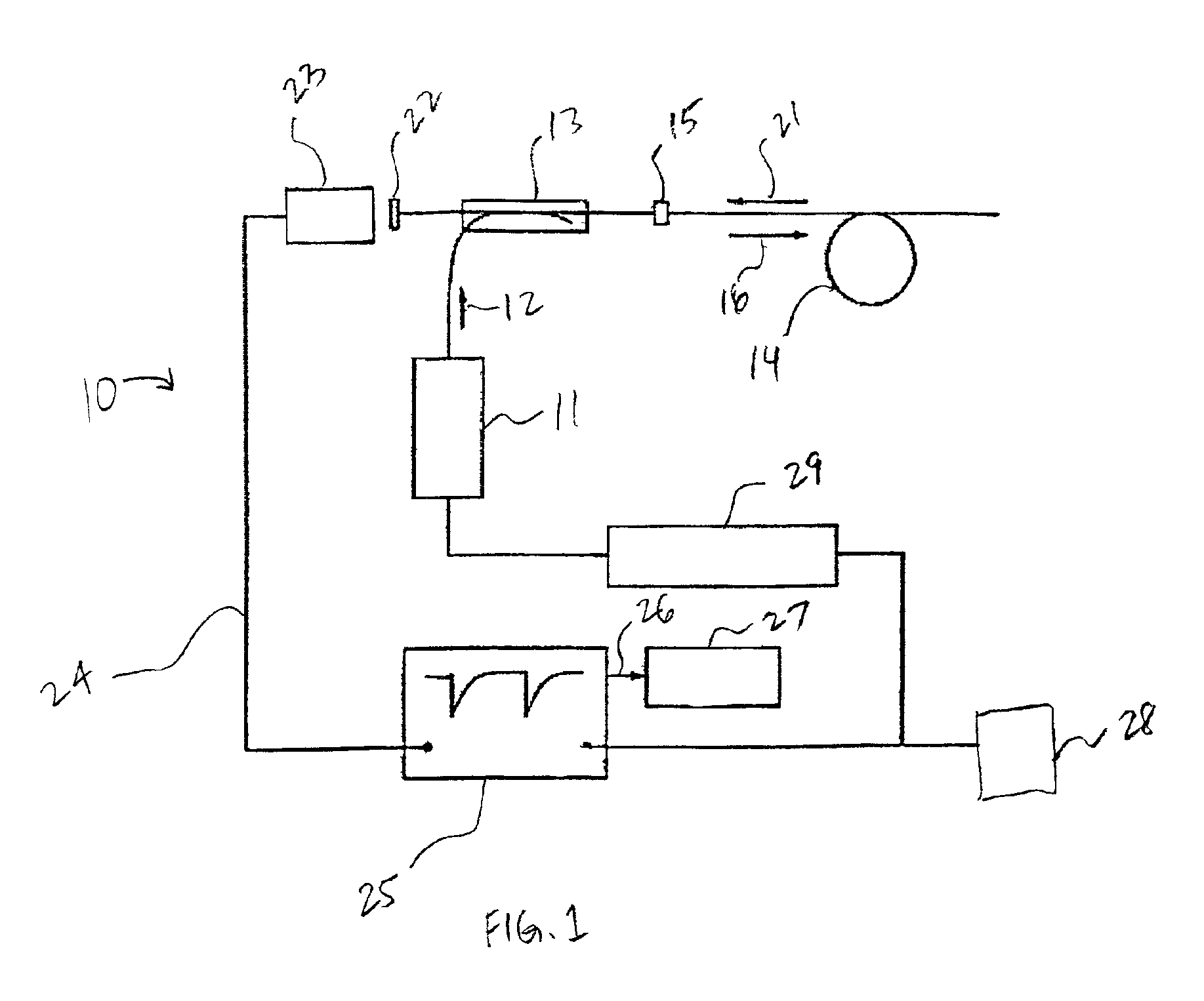
Catheters with fluorescent temperature sensors
A catheter with a fluorescent temperature sensor is shown and described. The catheter includes a lumen, a fiber-optic cable that extends through the lumen. A distal end of the fiber-optic cable is coated with a fluorescent material and a proximal end of the fiber-optic cable is connected to a console. The console includes a light source for transmitting light through the fiber-optic cable for exciting the fluorescent material. The console further includes a photo multiplier tube for converting light emitted by the excited fluorescent material to a plurality of analog voltage signals. The console further includes a digital oscilloscope linked to the photo multiplier tube for converting the plurality of analog voltage signals to at least one digital signal. The console further includes a processor linked to the digital oscilloscope for converting the at least one digital signal to a temperature value for the distal end of the fiber-optic cable.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
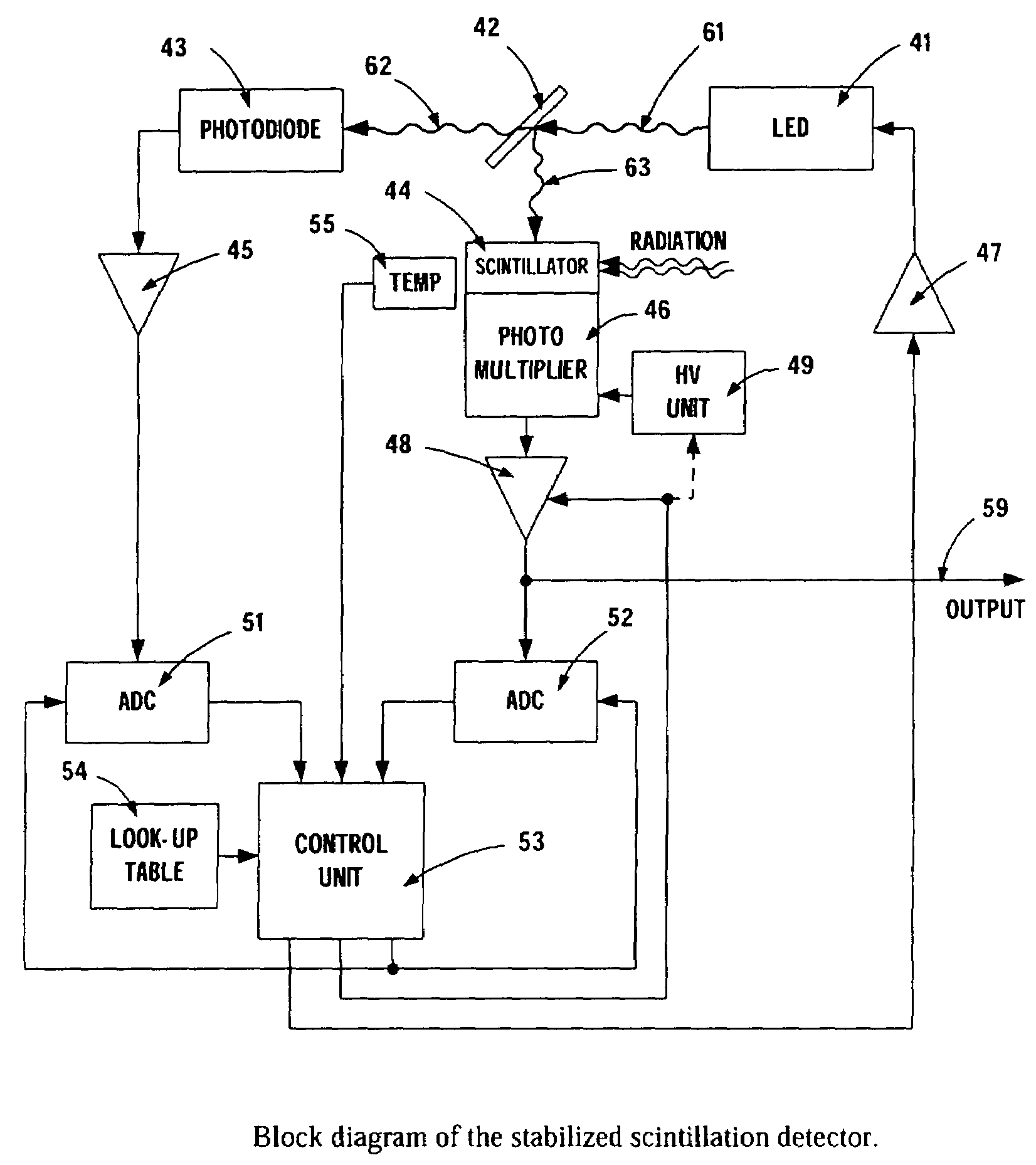
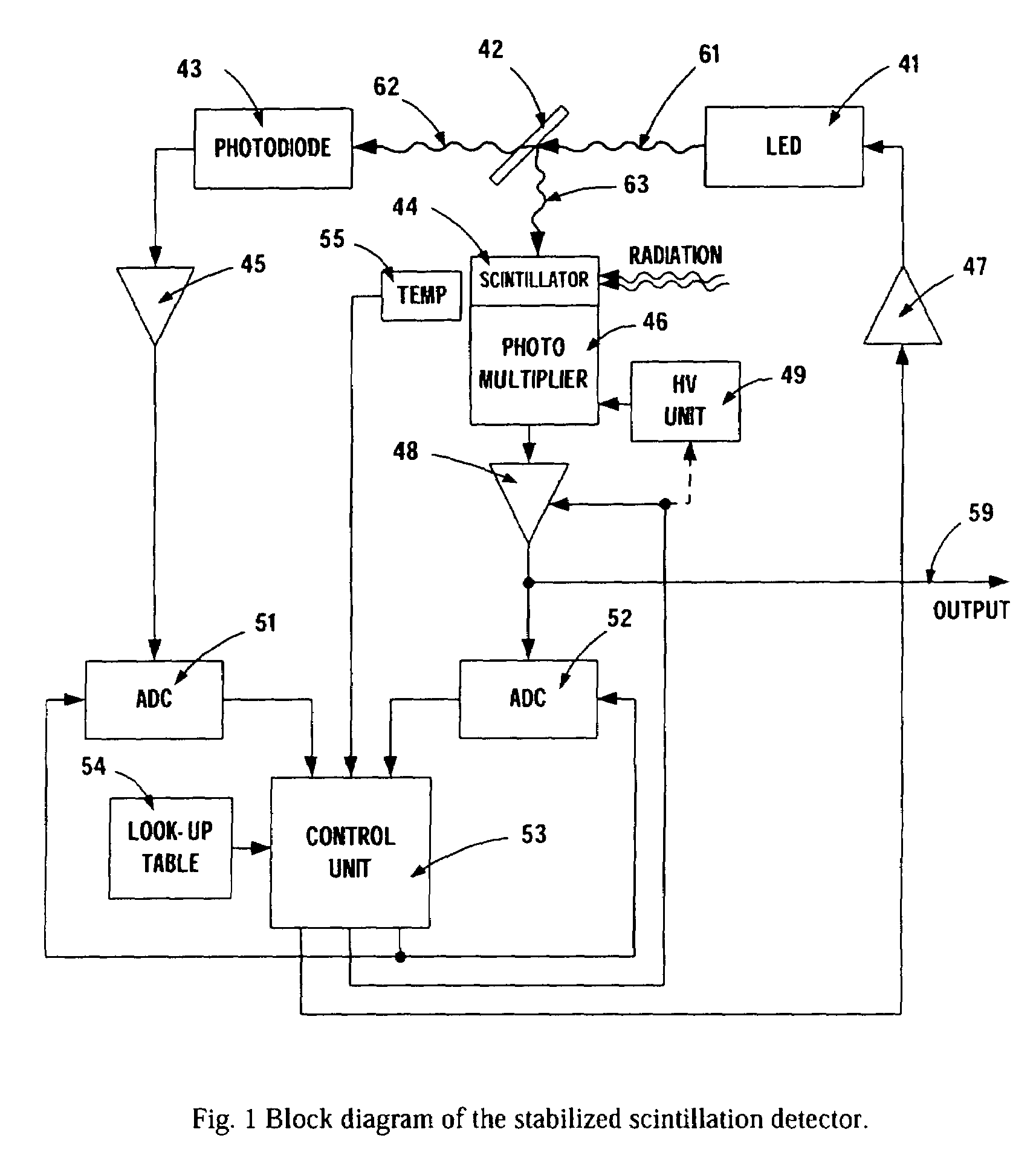
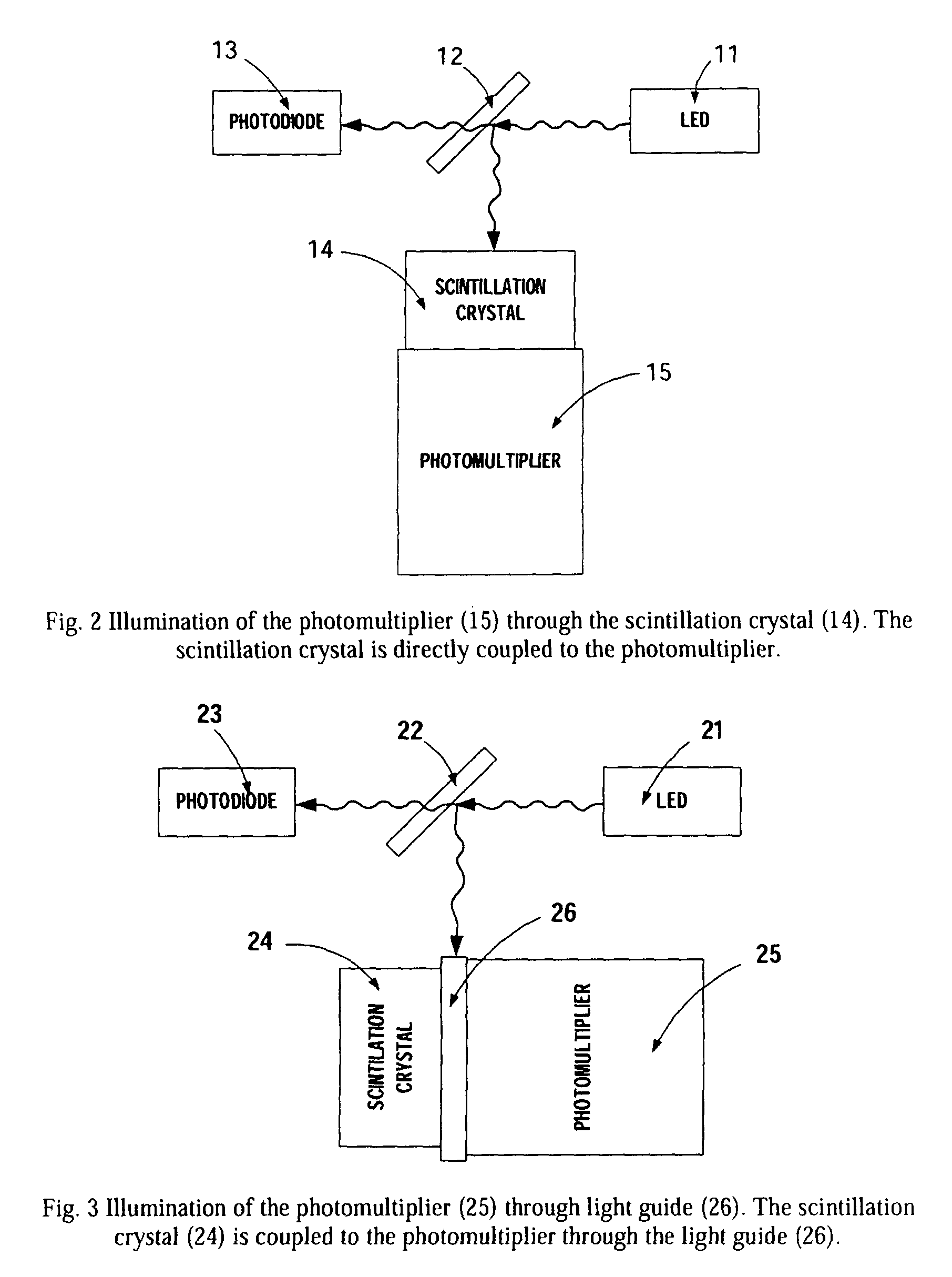
Stabilized scintillation detector for radiation spectroscopy and method
ActiveUS7005646B1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsBeam splitter
In a preferred embodiment, a stabilized scintillation detector, including: an LED that periodically produces a light pulse; a beam splitter that impinges some of the light pulse on a photodetector and on a photomultiplier; a scintillator that receives radiation and is coupled to the photomultiplier; and a control unit that receives signals from the photodetector and the photomultiplier representative of the light pulse received by the photodetector and the photomultiplier and receives a signal representative of temperature of the scintillator and outputs, in part, a signal to the photomultiplier to stabilize the photomultiplier. A method of using the scintillator is also provided.
Owner:CANBERRA IND INC
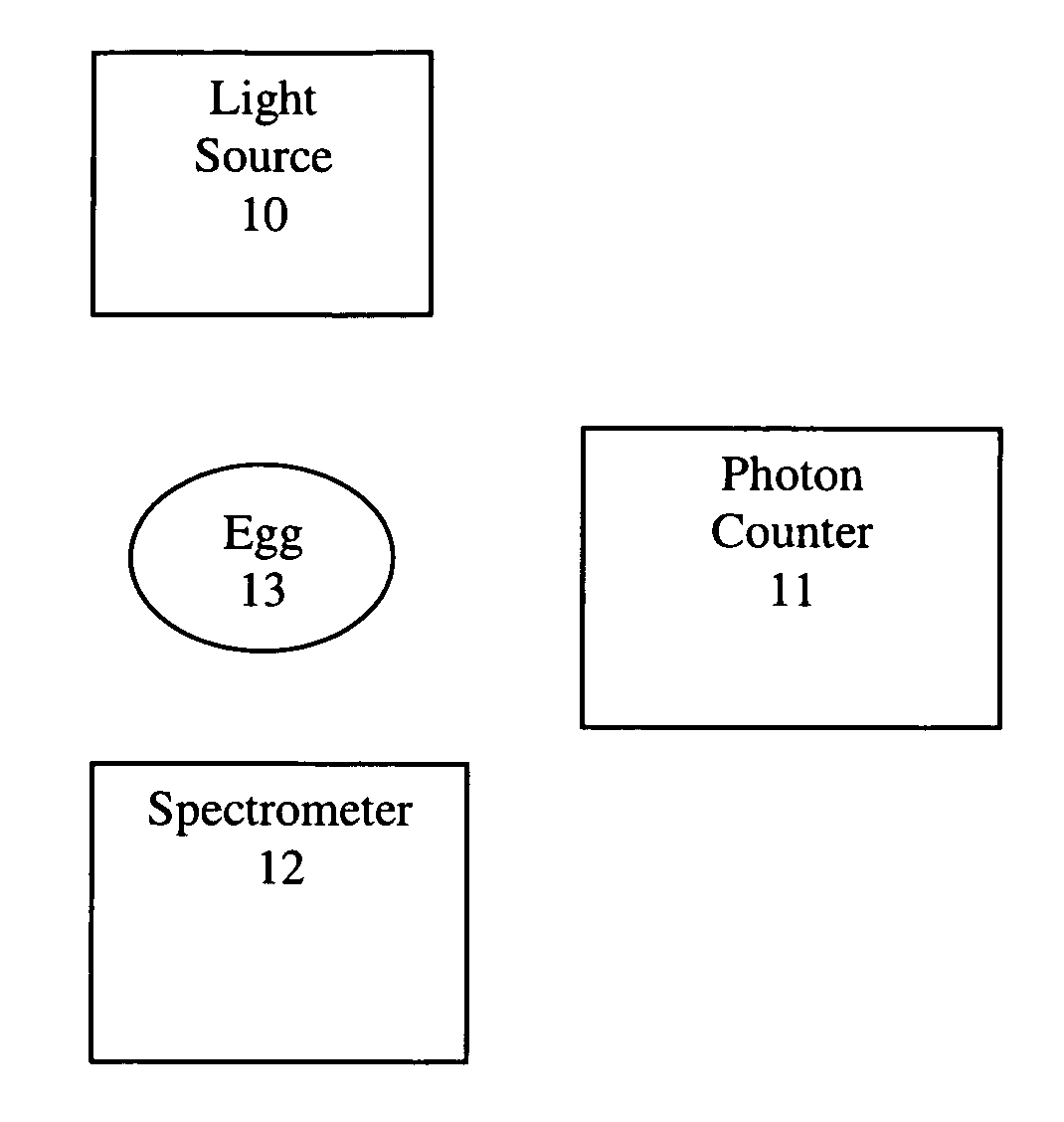
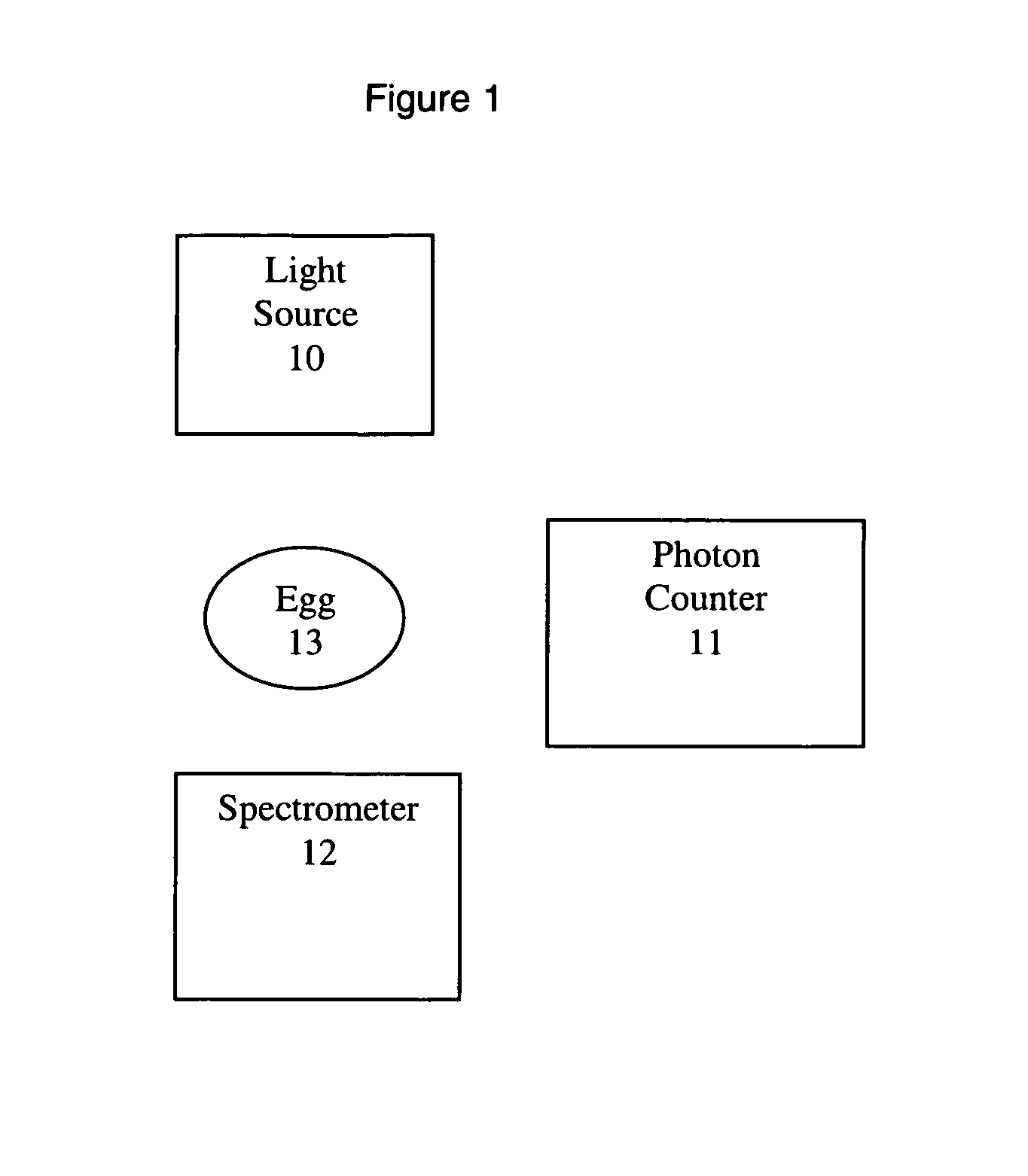
Avian egg fertility and gender detection
Following exposure to an external light source, determining: 1) the fertility of an avian egg by measuring the photon intensity (photons per second) of the egg's biophoton and luminescence; and 2) the gender of an avian egg by measuring the photon spectrum of the egg's biophoton emission and luminescence. The external light source is either an incandescent, fluorescent, LED, (pulsed or continuous wave) monochromatic or dichromatic laser light source. The detector of the photon intensity is either a low light sensing photomultiplier tube (PMT), silicon based photon counting sensor, or Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode detector. The detector of the photon spectrum is a spectrometer. Following exposure to the referenced light sources, fertile avian eggs will exhibit a higher intensity of photons than that of unfertilized avian eggs, and avian eggs of the female gender will emit a different spectrum of photons than will avian eggs of the male gender.
Owner:ROLLINS JACK DEAN
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
ActiveUS20160003741A1Reduce image noiseScalable approachPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
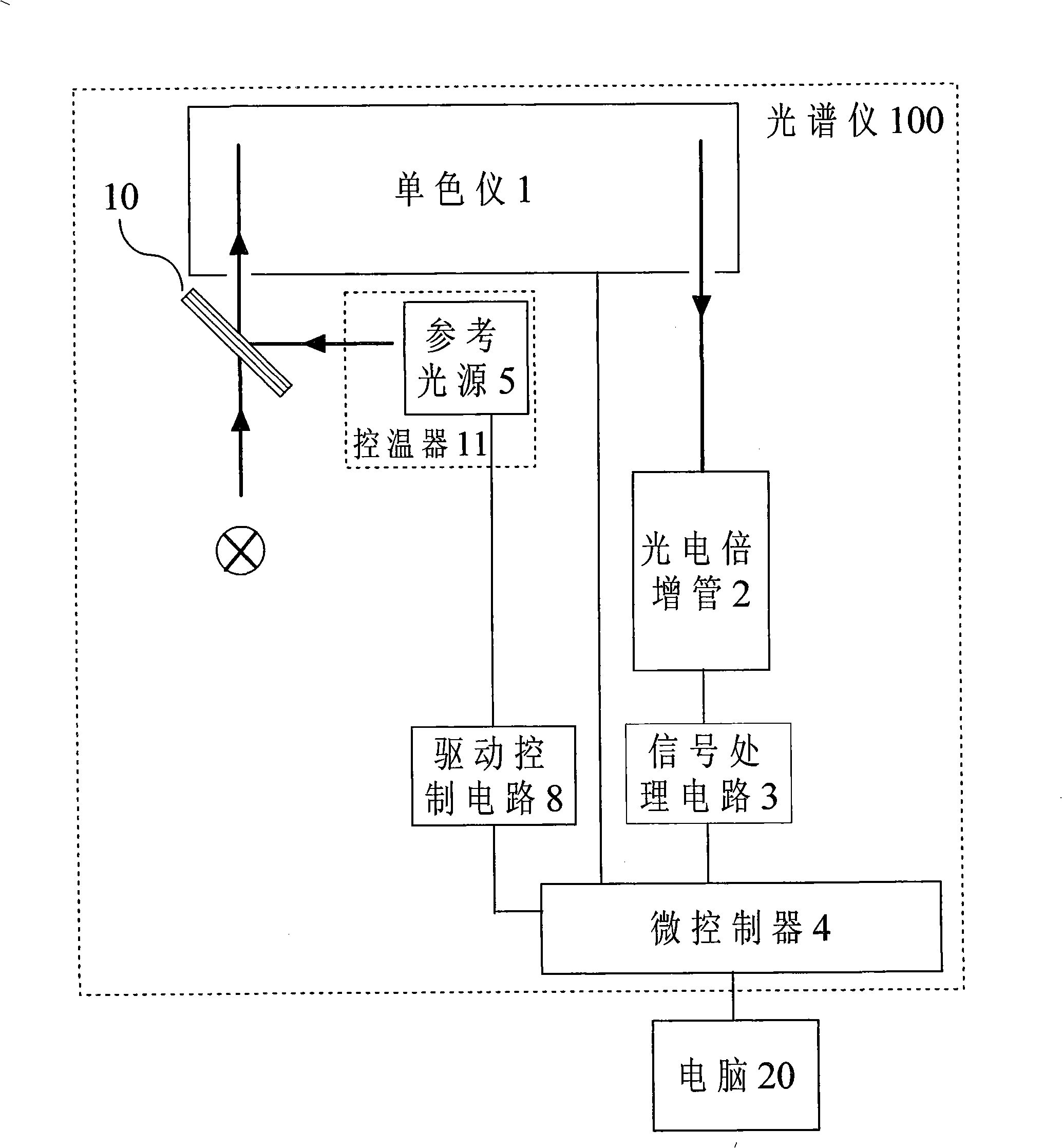
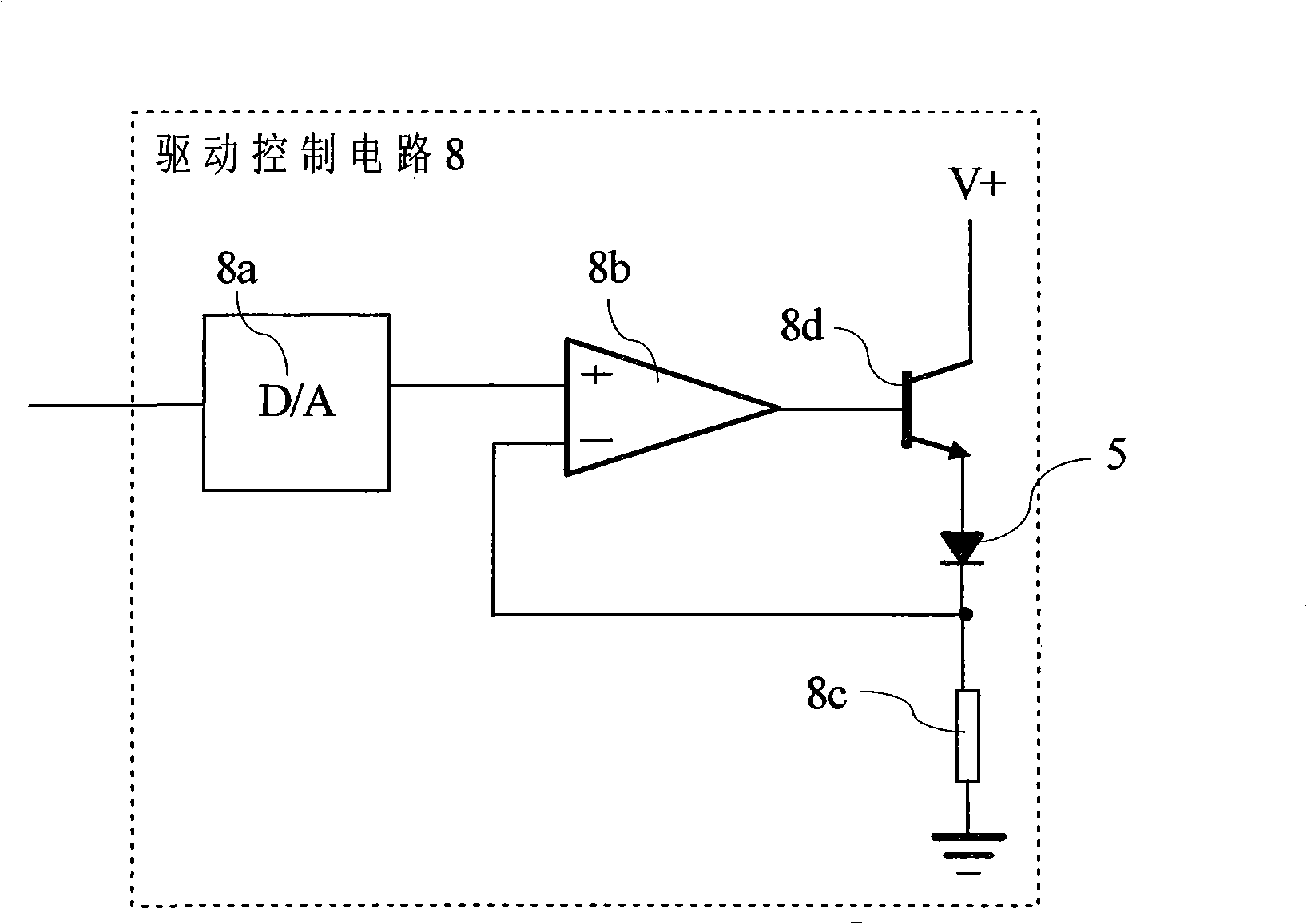
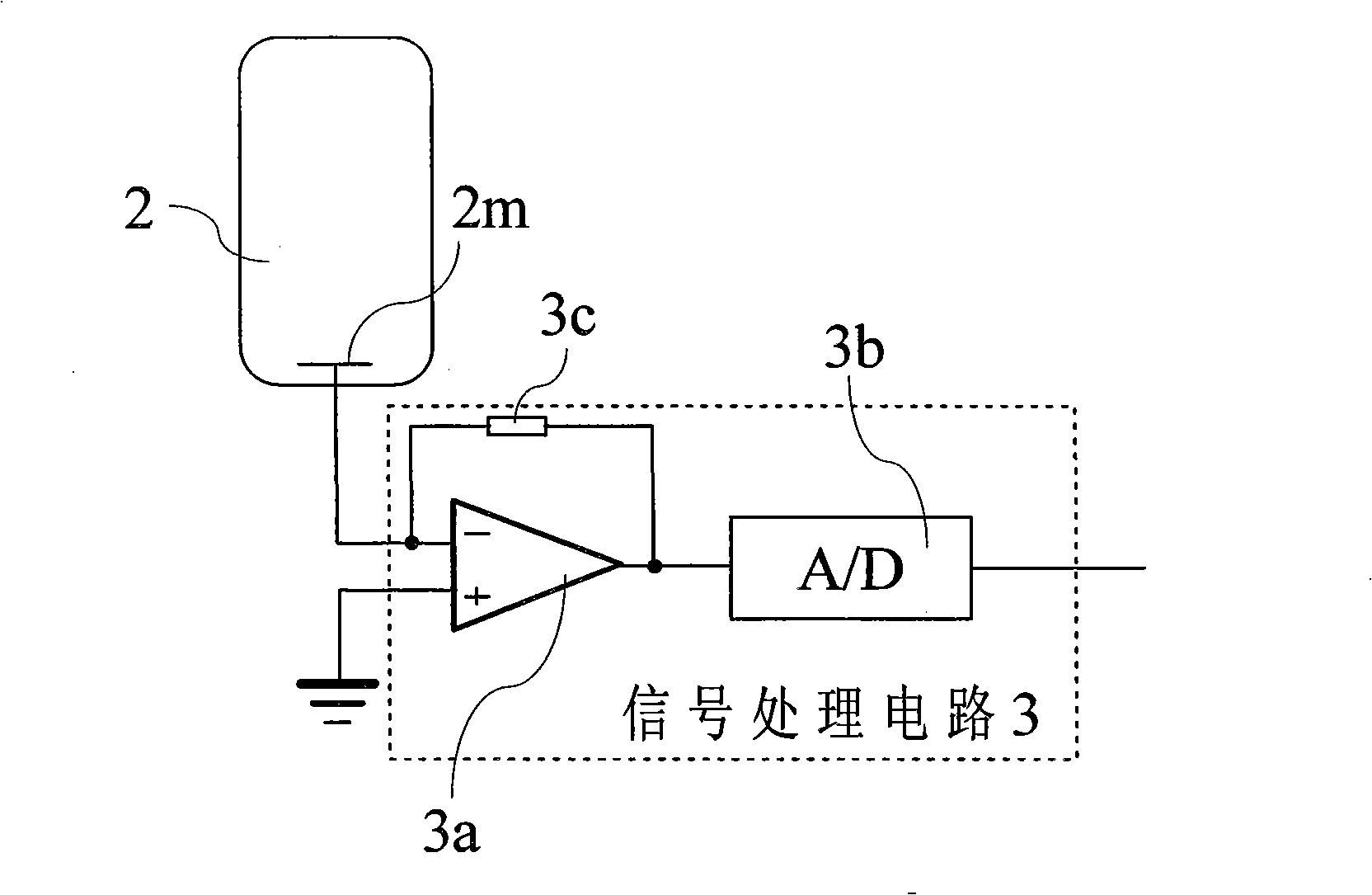
Spectrometer and method for correcting the same
InactiveCN101354287AImprove performanceGood response linearityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicrocontrollerSignal processing circuits
The invention relates to an optical spectrometer and a calibration method thereof. The optical spectrometer comprises a monochromator used for dividing the measured light into monochromatic lights, a photomultiplier used for receiving the monochromatic lights; the monochromator and the photomultiplier are optically connected. The photomultiplier is electrically connected with a microcontroller by a signal processing circuit. The optical spectrometer is characterized by further comprising a reference light source used for creating reference light; the reference light source which is alight-emitting diode is connected with the micro-controller. Compared with the prior art, the optical spectrometer and the calibration method thereof have the advantages as follows: 1. reasonable design, simple structure and large measuring dynamic range are ensured; 2. the absolute sensitivity of the photomultiplier is reasonably calibrated, therefore, the response linearity of the optical spectrometer is good; 3. thermostatic control is carried out to a reference detector, the reference light source and the photomultiplier, thus effectively enhancing the work stability of the optical spectrometer; and 4. the performance of the optical spectrometer is substantially enhanced under the condition that a small amount of cost is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU EVERFINE PHOTO E INFO
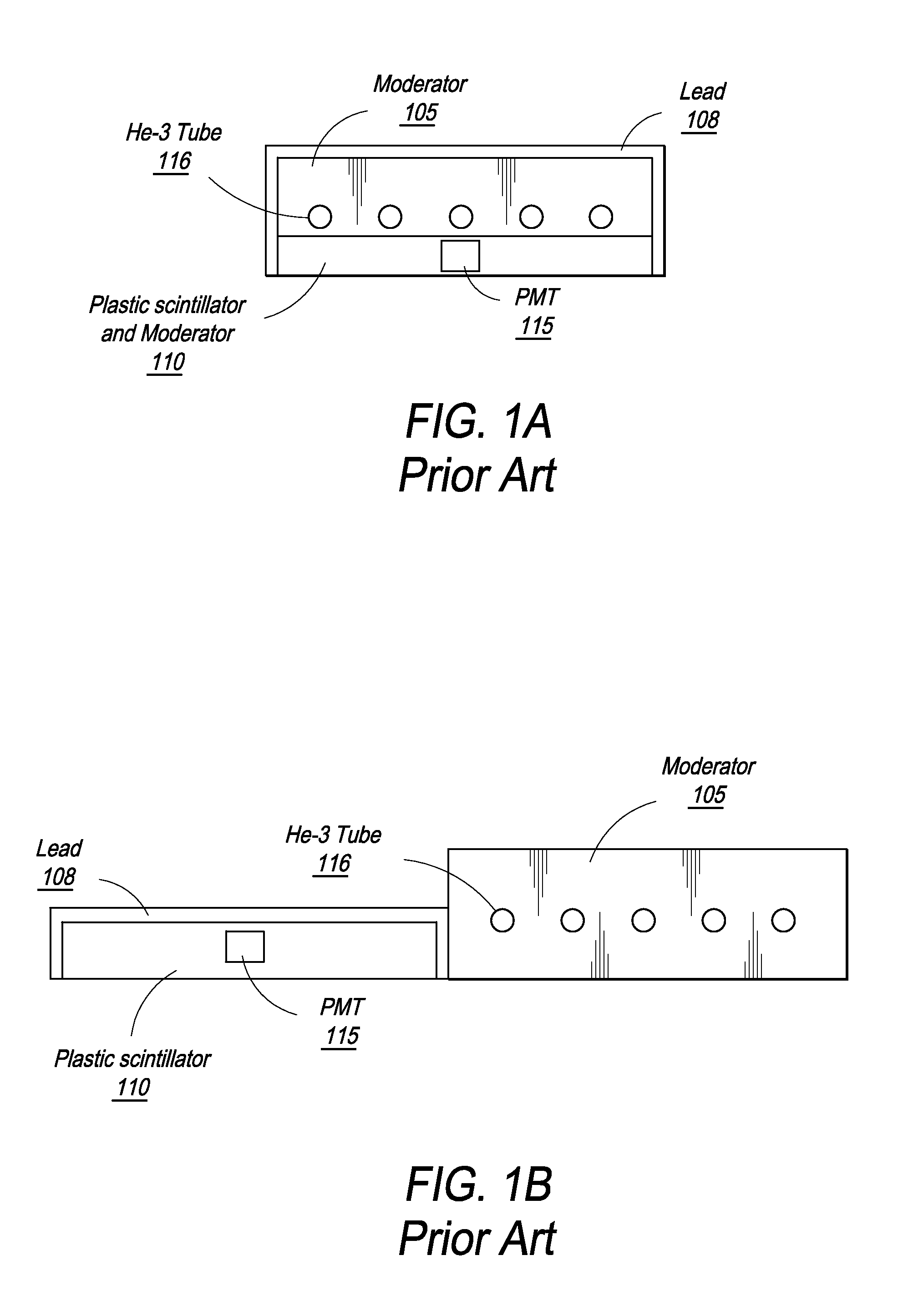
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
ActiveUS8389941B2Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
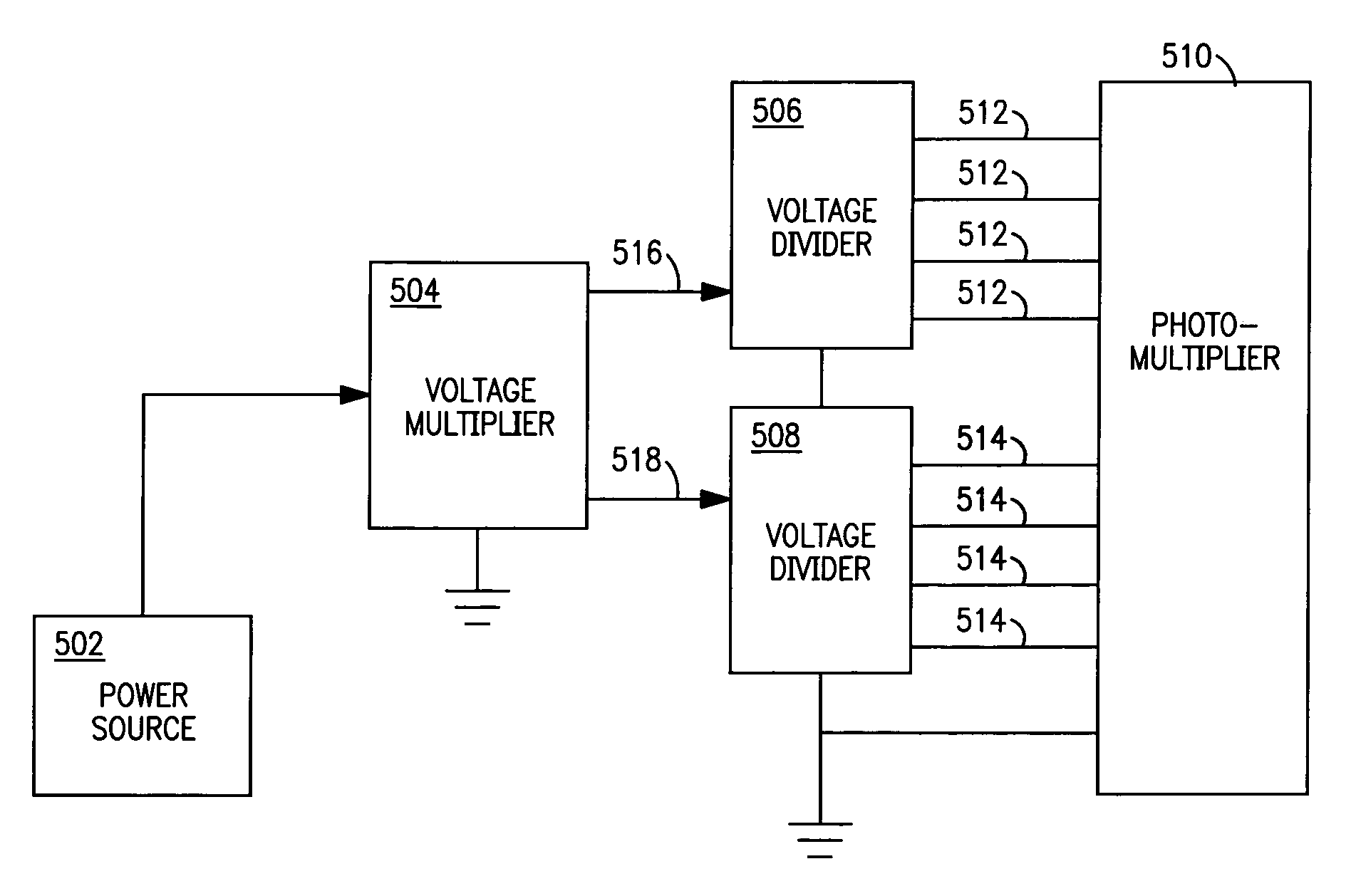
Low power stabilized voltage divider network
InactiveUS7005625B1Reduce the required powerReduce power consumptionMultiplier circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansVoltage multiplierPhotomultiplier
A voltage divider network in combination with a voltage multiplier circuit voltage biases the electrodes of a photomultiplier tubes or related device. The circuit exploits the several voltage levels produced at successive stages of a voltage multiplier circuit in order to optimize the voltage divider network with respect to power consumption, current draw from the power supply, operating stability, and linear operation of the photomultiplier tube.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
InactiveUS20140197321A1Avoid cross contaminationMeasurement with scintillation detectorsPhotometryHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:BENDAHAN JOSEPH +1
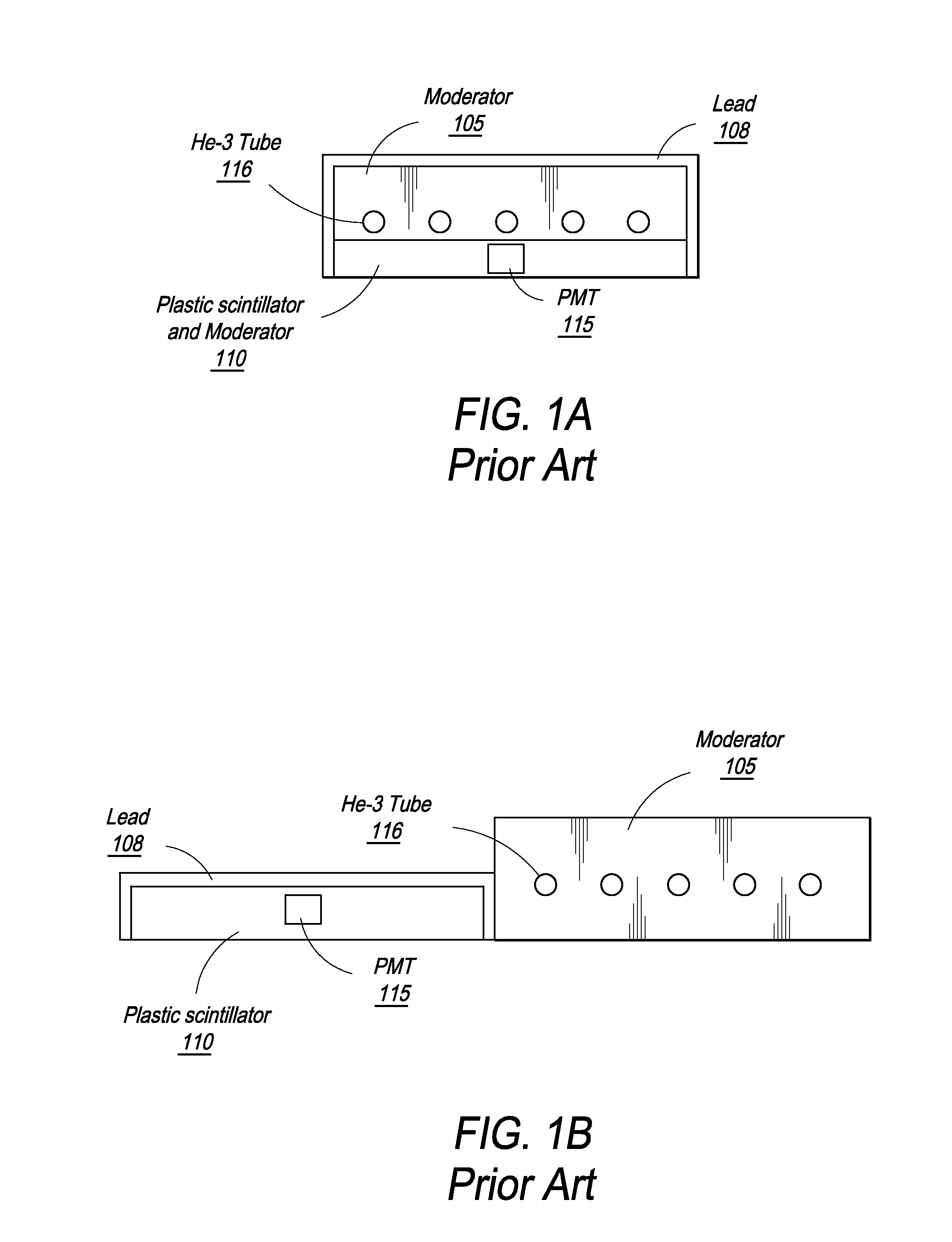
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20140042330A1Improve efficiencyEasy constructionMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particlePhotomultiplier
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. In one configuration, B-10 based detector is used in a parallel electrode plate geometry that integrates neutron moderating sheets, such as polyethylene, on the back of the electrode plates to thermalize the neutrons and then detect them with high efficiency. The moderator can also be replaced with plastic scintillator sheets viewed with a large area photomultiplier tube to detect gamma-rays as well. The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
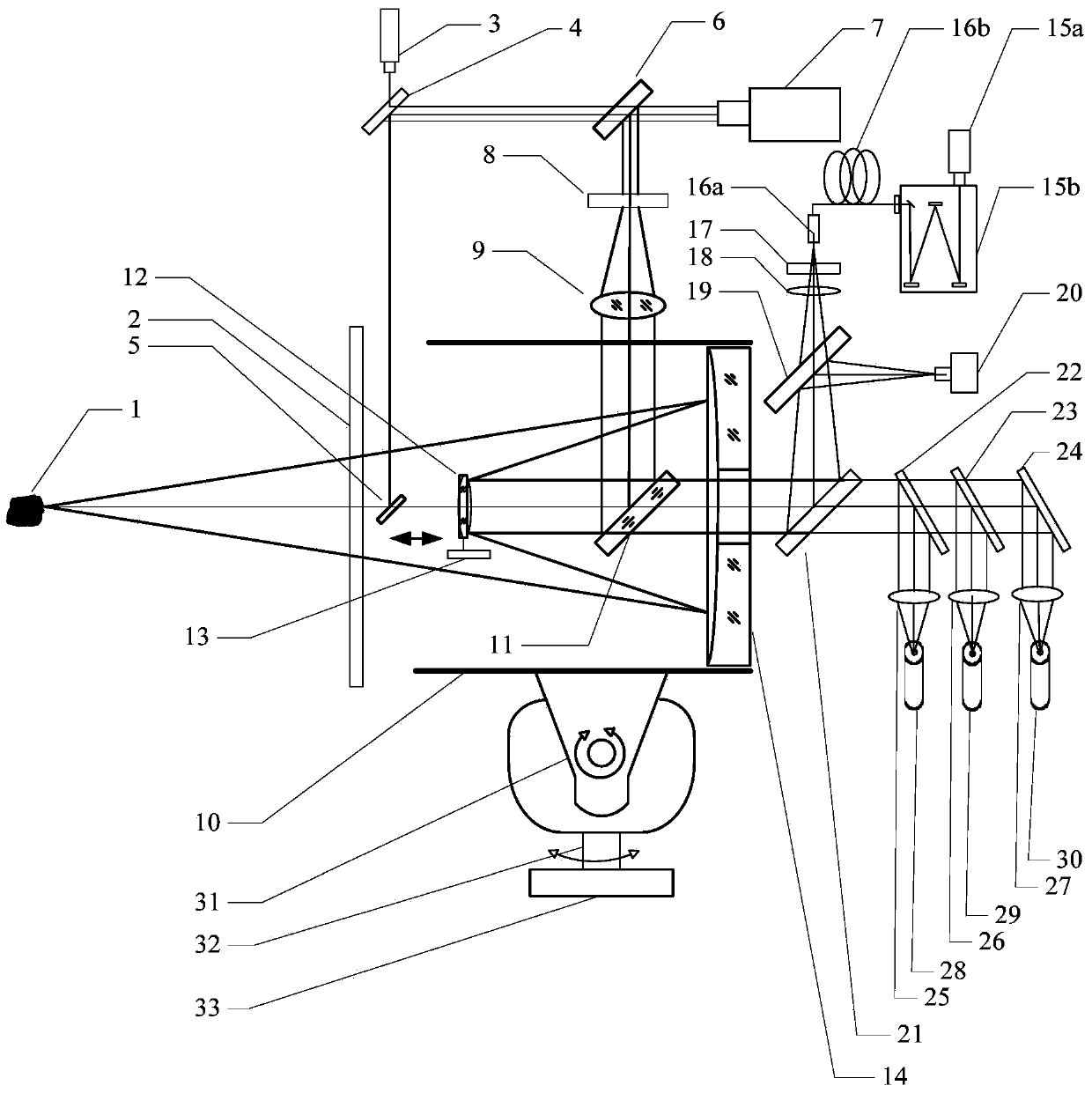
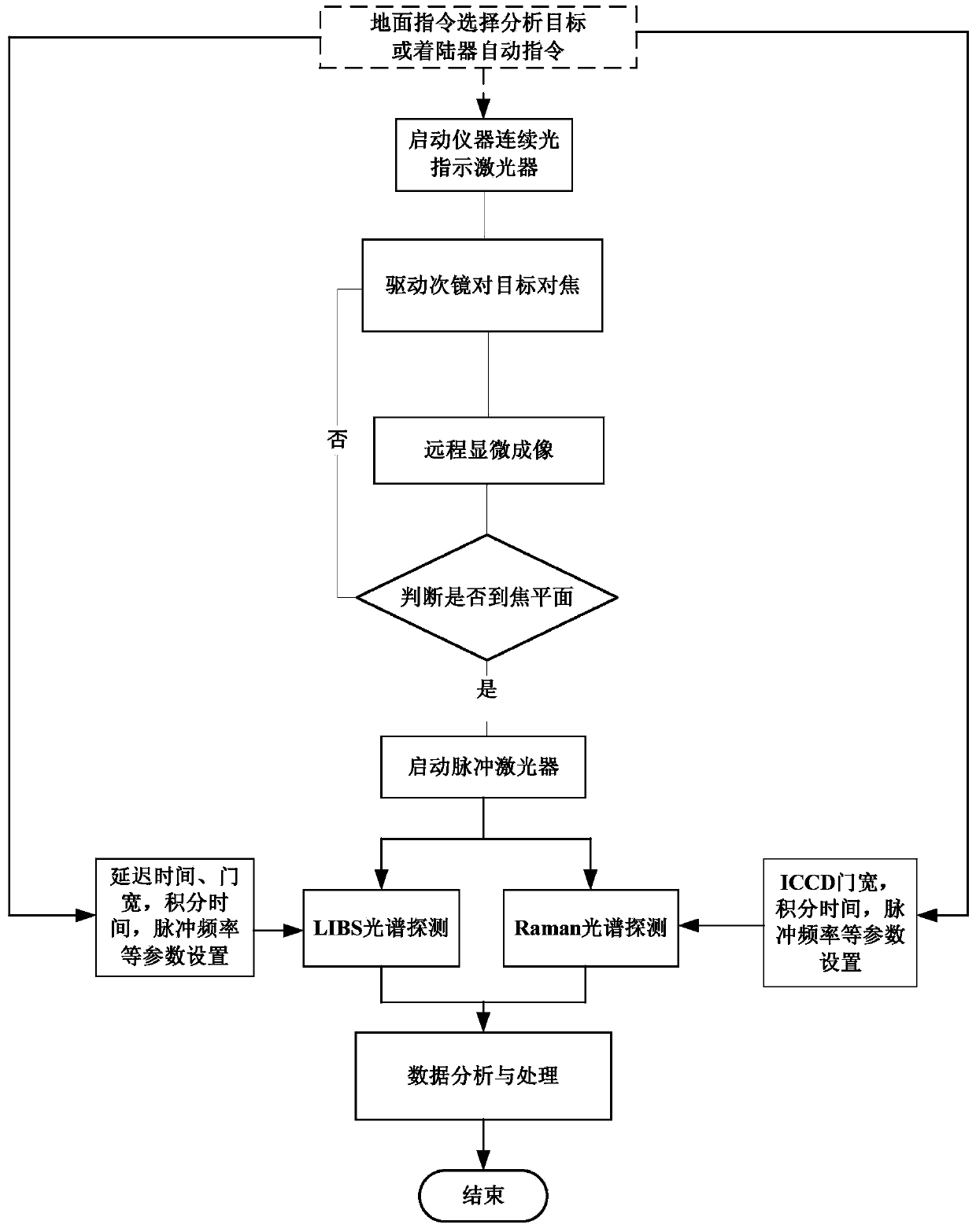
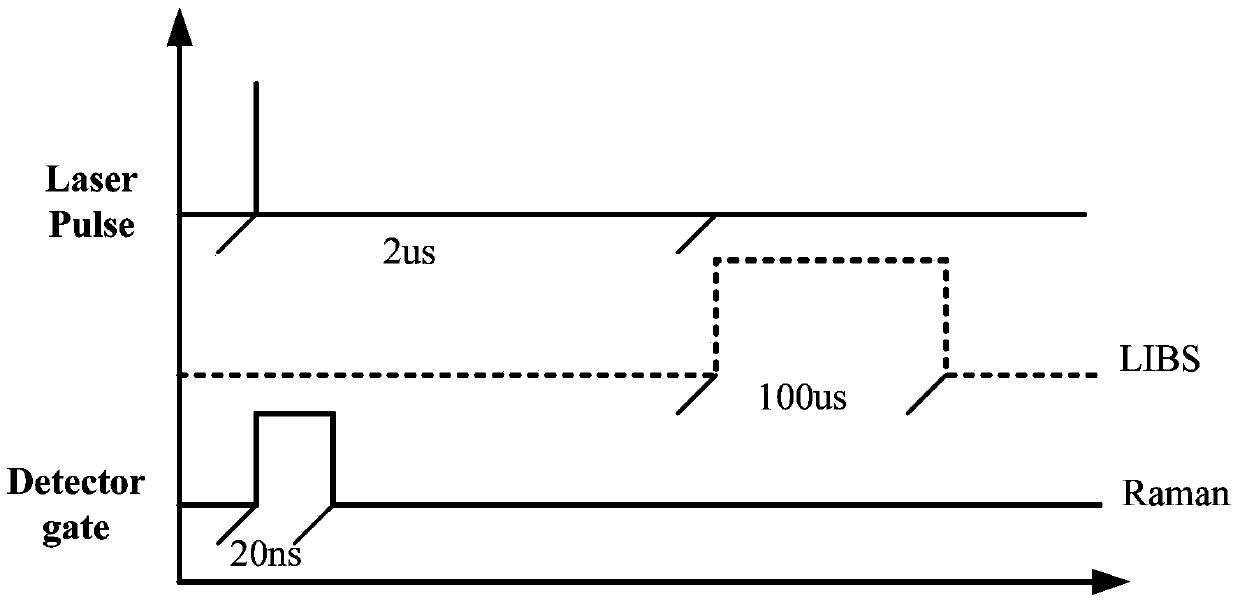
Remote in-situ integrated test system for planet surface substances and atmosphere
ActiveCN103743719ARapid positioningReduce volumeRaman scatteringElectromagnetic wave reradiationContinuous lightElement analysis
The invention discloses a remote in-situ integrated test system for planet surface substances and atmosphere. The whole system comprises: a miniature pulse solid state laser, a Cassegrain telescope system, a one-dimensional precise mobile platform, a continuous light indicating positioning laser, various optical elements and echelle spectrographs, ICCD, a high-resolution camera and a photomultiplier. According to the system and method of the invention, the combination of technologies of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Raman spectroscopy (Raman), and laser radar is realized in the same system; the system of the invention adopts modular design, is high in integration level, small in size, and light in weight, and can realize long-distance surface microimaging, long-distance substance element analysis, long-distance substance composition analysis, and planet boundary layer atmosphere detection.
Owner:东莞市中科原子精密制造科技有限公司
Charged particle detection devices
ActiveUS20080315094A1Thermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLight guideCharged particle detectors
A charged particle detector consists of a plurality independent light guide modules assembled together to form a segmented in-lens on-axis annular detector, with a center hole for allowing the primary charged particle beam to pass through. One side of the assembly facing the specimen is coated with or bonded to scintillator material as the charged particle detection surface. Each light guide module is coupled to a photomultiplier tube to allow light signals transmitted through each light guide module to be amplified and processed separately. A charged particle detector is made from a single block of light guide material processed to have a cone shaped circular cutout from one face, terminating on the opposite face to an opening to allow the primary charged particle beam to pass through. The opposite face is coated with or bonded to scintillator material as the charged particle detection surface. The outer region of the light guide block is shaped into four separate light guide output channels and each light guide output channel is coupled to a photomultiplier tube to allow light signal output from each channel to be amplified and processed separately.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for cavitation threshold characterization and control
ActiveUS20060061225A1Reduce chemical consumptionAvoid damaging effectsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidAcoustic energySonoluminescence
An apparatus and method for characterizing cavitation that occurs in a fluid exposed to acoustic energy. The apparatus comprises a vessel for holding the fluid; an acoustic energy generating means for generating acoustic energy, the acoustic energy generating means being positioned to transmit the acoustic energy into the fluid while the fluid is held in the vessel; and a cavitation detection means for detecting cavitation in the fluid held in the vessel. In a preferred embodiment, the cavitation detection means comprises a light detection means, such as a photomultiplier tube, that detects sonoluminescent emission from the fluid. The method comprises the steps of exposing a volume of process fluid to acoustic energy at a specified power level; measuring the photon output from the fluid over a period of time; and when the photon output deviates from a desired level, initiating a remedial step to bring the photon output back to approximately the desired level.
Owner:PROD SYST
Optical detection device for corona discharge
InactiveCN101706548AEasy for quantitative analysisLow visible light transmittance requirementTesting dielectric strengthFault locationCamera lensSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses an optical detection device for corona discharge. An atmospheric ultraviolet window band imaging detection optical path thereof comprises a stray light shield, an atmospheric ultraviolet window band ultraviolet lens, an atmospheric ultraviolet window band band-pass ultraviolet filter, an ultraviolet image intensifier, a light cone, a CCD or CMOS area array image sensor, an image processing circuit and a first liquid crystal display which are arranged in sequence. A solar blind ultraviolet band non-imaging detection optical path thereof comprises a total emission mirror, a spectroscope, a solar blind ultraviolet band-pass filter, a solar blind ultraviolet lens, a multiplier phototube, a signal processing circuit module and a second liquid crystal display. The device has the main advantages that the corona detection data is more complete and reliable, and the failure level of corona discharge and discharge degree are convenient to be analyzed.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
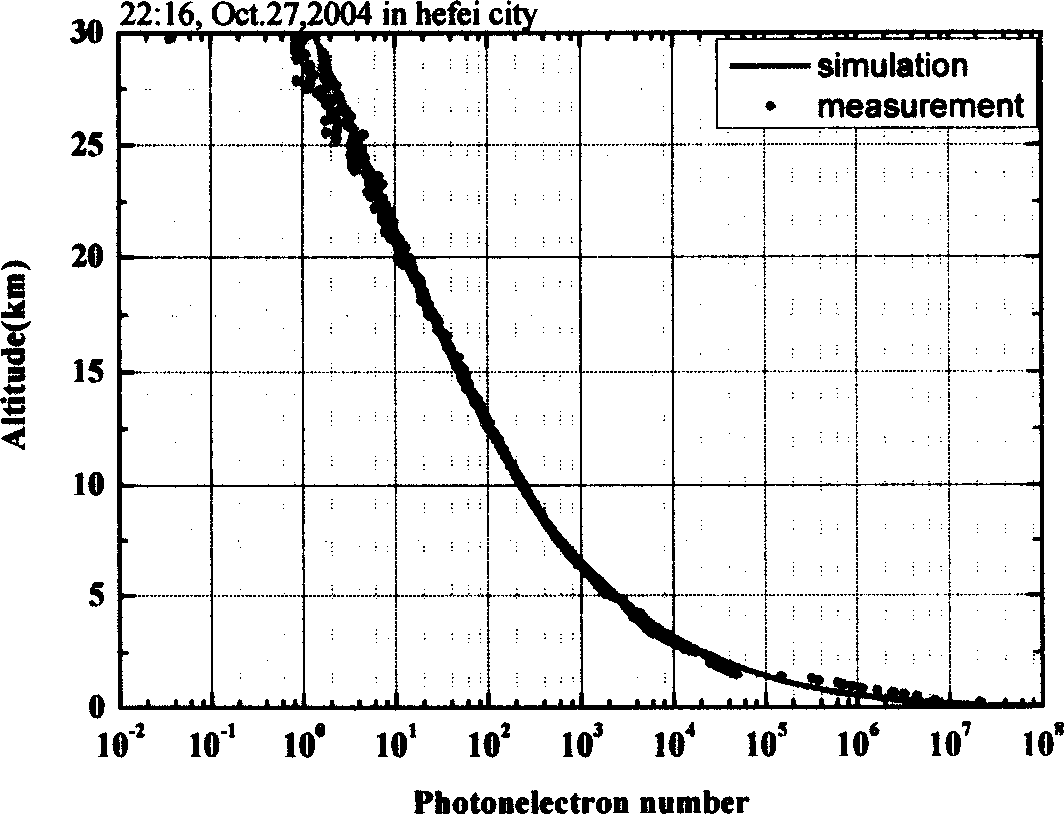
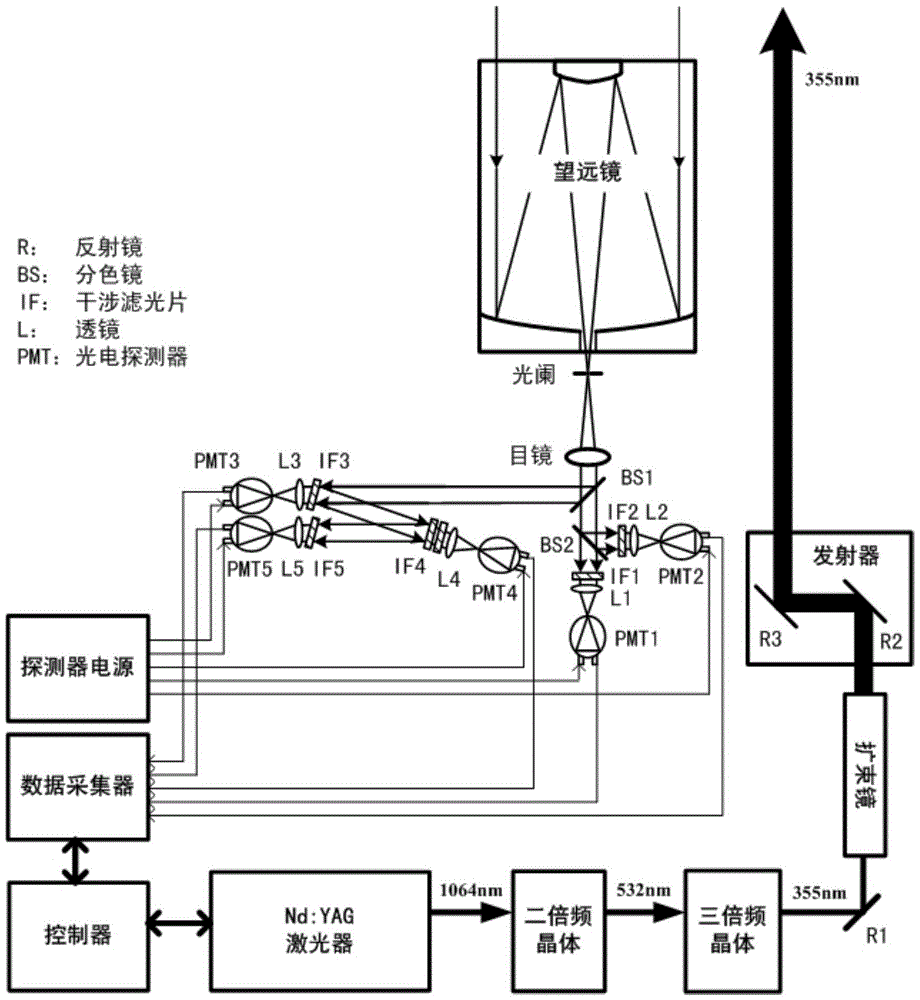
Detection method and laser radar of Raman-Mie scattering laser atmospheric signal
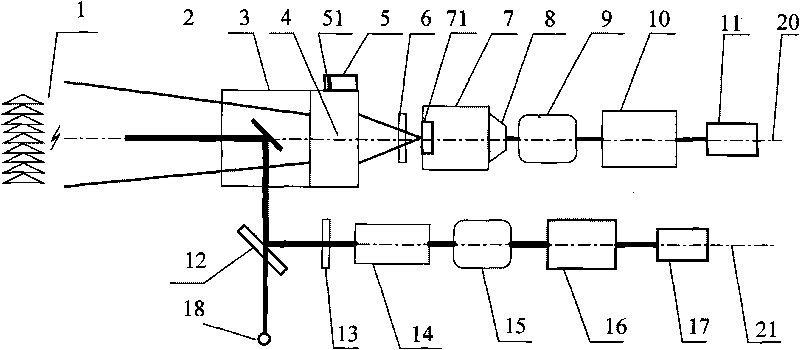
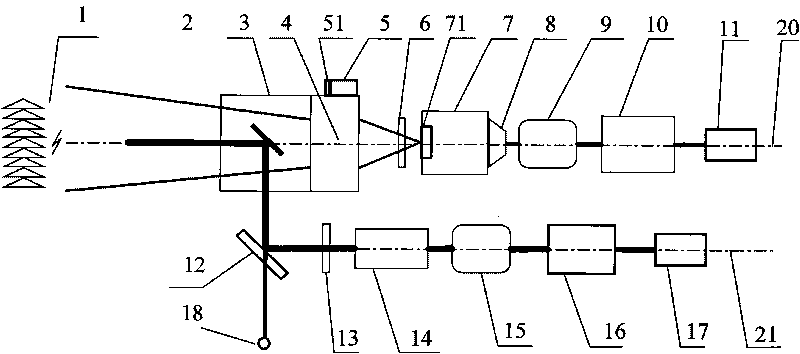
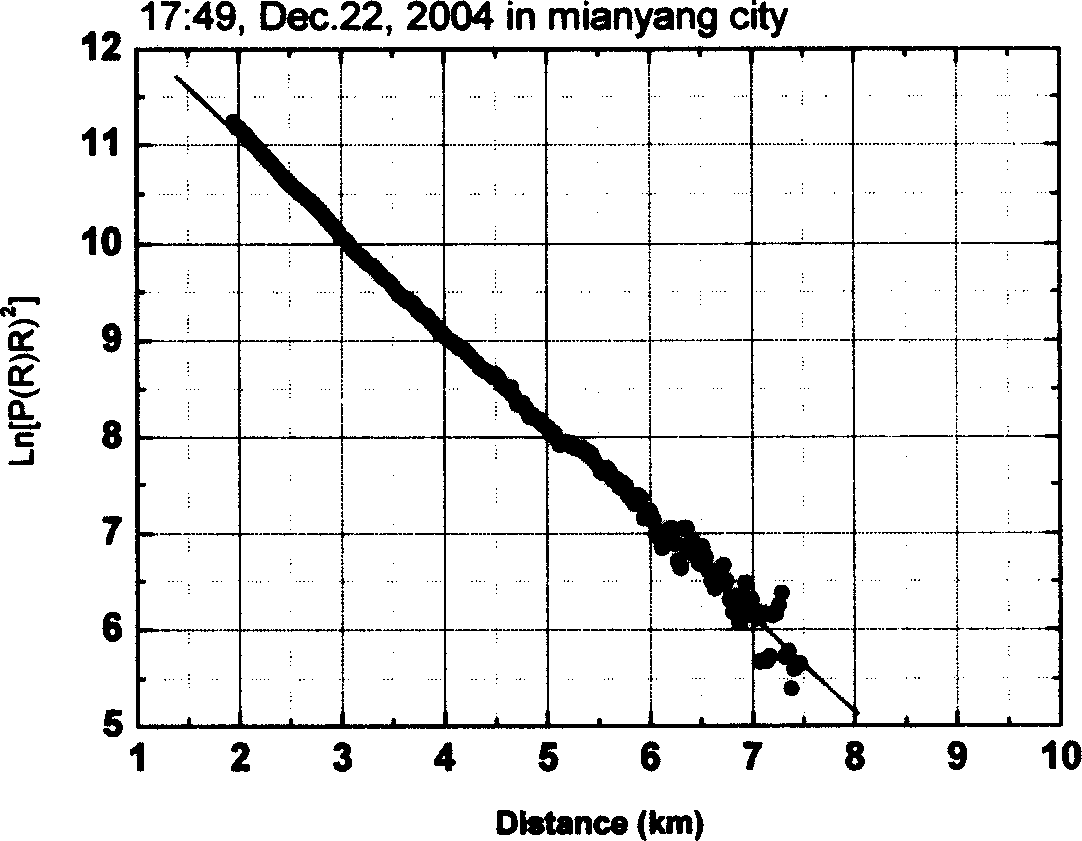
InactiveCN1657972ARealize continuous observationRealize measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationEyepieceTropospheric aerosol
This invention is a detecting of Roman-Mie dispersion laser atmosphere signal and laser radar. It sets up the radar with the output of double-frequency 532nm and triple-frequency 355nm, launches the 532nm, 15% of the 35nm to the sky and 85% of the 355nm after diffusion, and the two optical paths parallel with the optical path of the receiving telescope, and simultaneously carry out the pitching motion with the receiving telescope; the receiving telescope backward dispersing light, the backward light gets into the telescope, then passes the glare tube, the adjusting field view stop and ocular glass, and the dichroic mirror process, and divides the 407nm, the 386nm and the 532nm scattered light into three beams, and the 532nm scattered light is divided into 15% and 85% beams, and the four beams are respectively received by the multiplier phototube, magnified by the magnifier and collect and process the data. It can detect the level visibility of the atmosphere, the aerosol of the whole troposphere and the vertical outline of winding cloud light eliminating system and the water and air mixture ratio from the ground to the lower part of the troposphere. The detecting error of the level visibility is 15%, the errors of the aerosol light eliminating modulus and the vertical outline of the water and air mixture are 20%.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
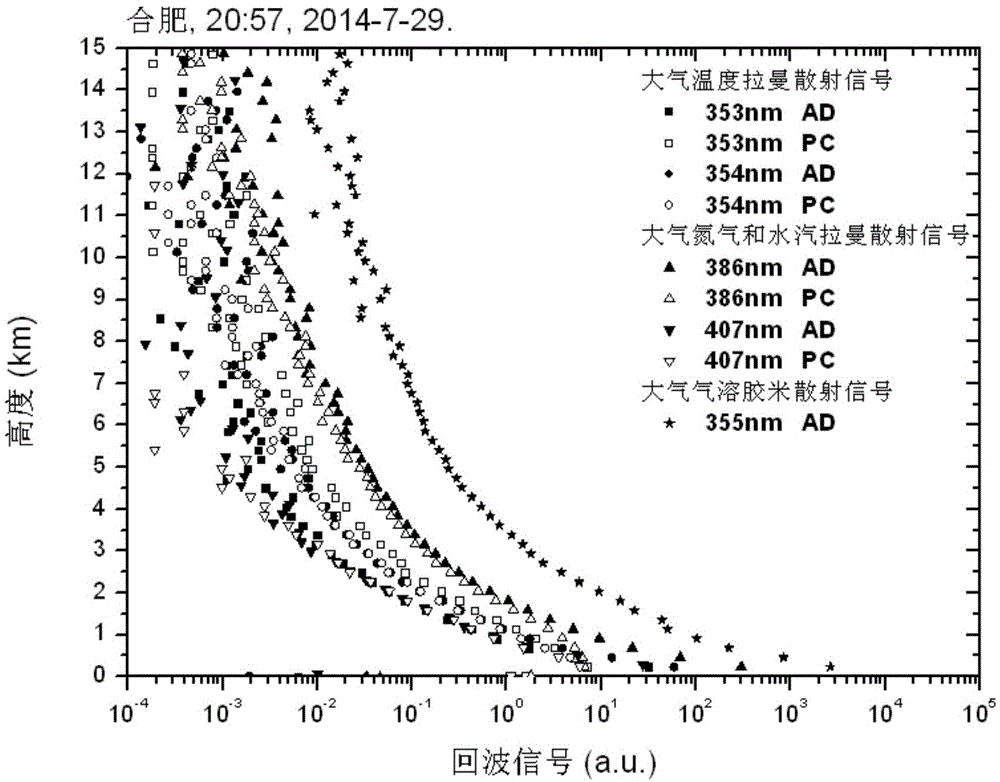
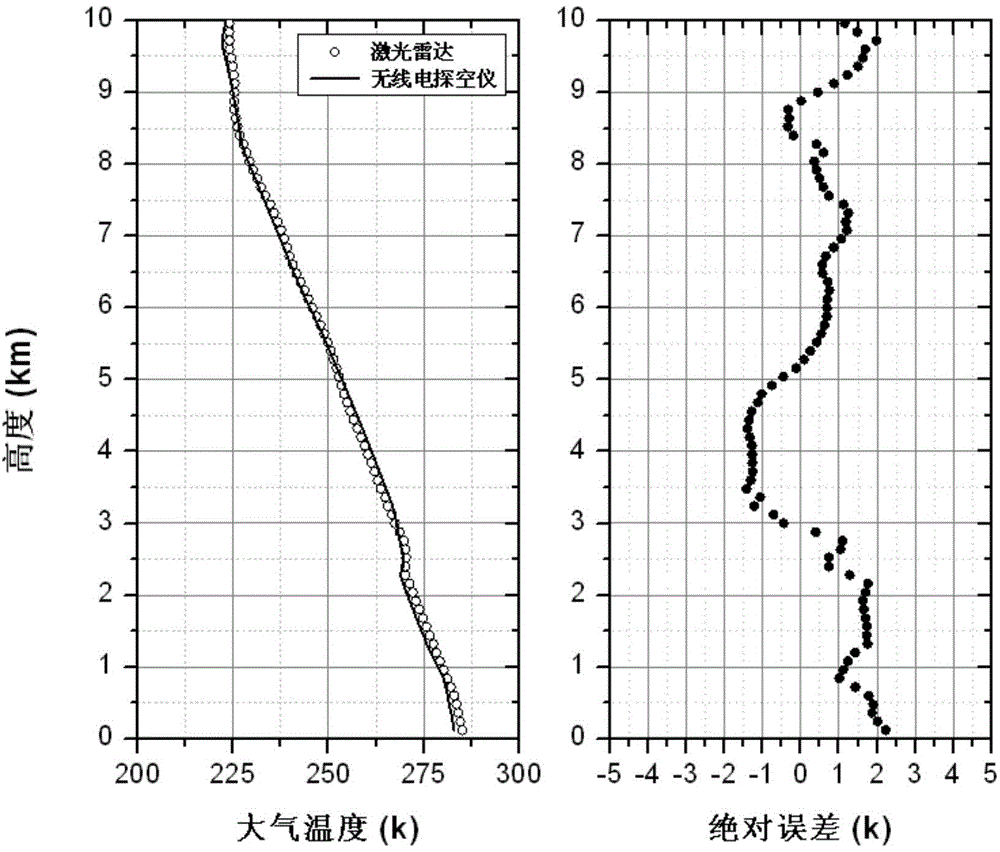
Single-wavelength four-Raman laser radar detection system and detection method
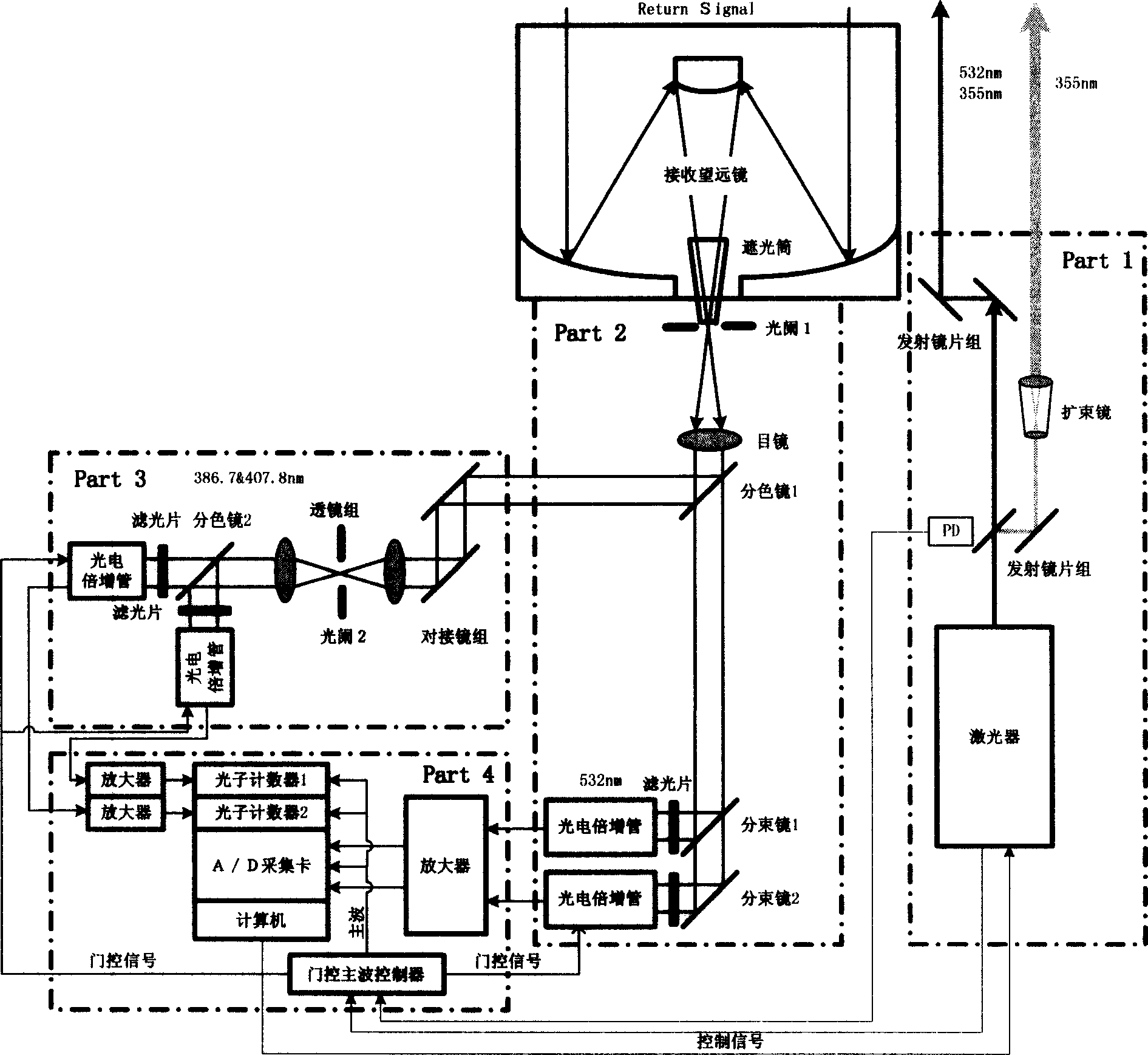
ActiveCN104880711AEfficient collectionEliminate the effects ofElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRadar systemsData acquisition
The invention discloses a single-wavelength four-Raman laser radar detection system and a detection method. The system combines three laser radar technologies of atmospheric temperature measurement via pure-rotation Raman scattering, vapor measurement via vibration Raman scattering, and measurement of atmosphere aerosol optical characteristics via Raman Mie scattering and an inversion method. The laser radar system employs 355 nm single-wavelength pulse laser as a detection light source and a large-diameter optical reception telescope with high transmittance for measuring the wavelength to collect atmospheric back scattering light signals, four wavelength atmospheric Raman scattering light signals and Mie scattering echo light signals of 353 nm, 354 nm, 355 nm, 386 nm, and 407 nm are mutually separated via an angle separation method of color separation filters and interference filters by a following optical path, the above five-wavelength scattering light signals are gated via narrowband interference filters, photoelectric conversion of photomultipliers of the same type is accomplished, and data acquisition is accomplished by a five-channel data collector.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com