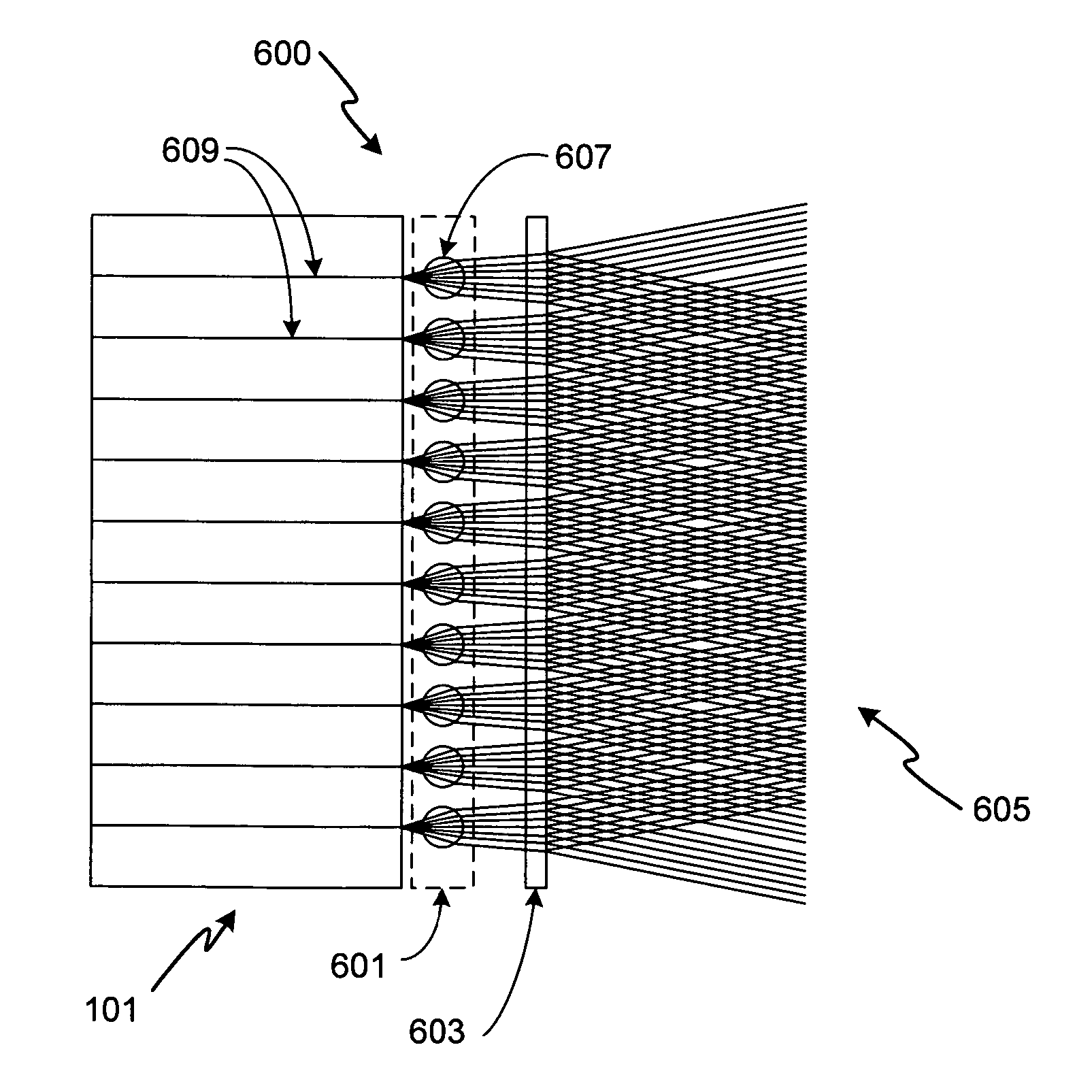
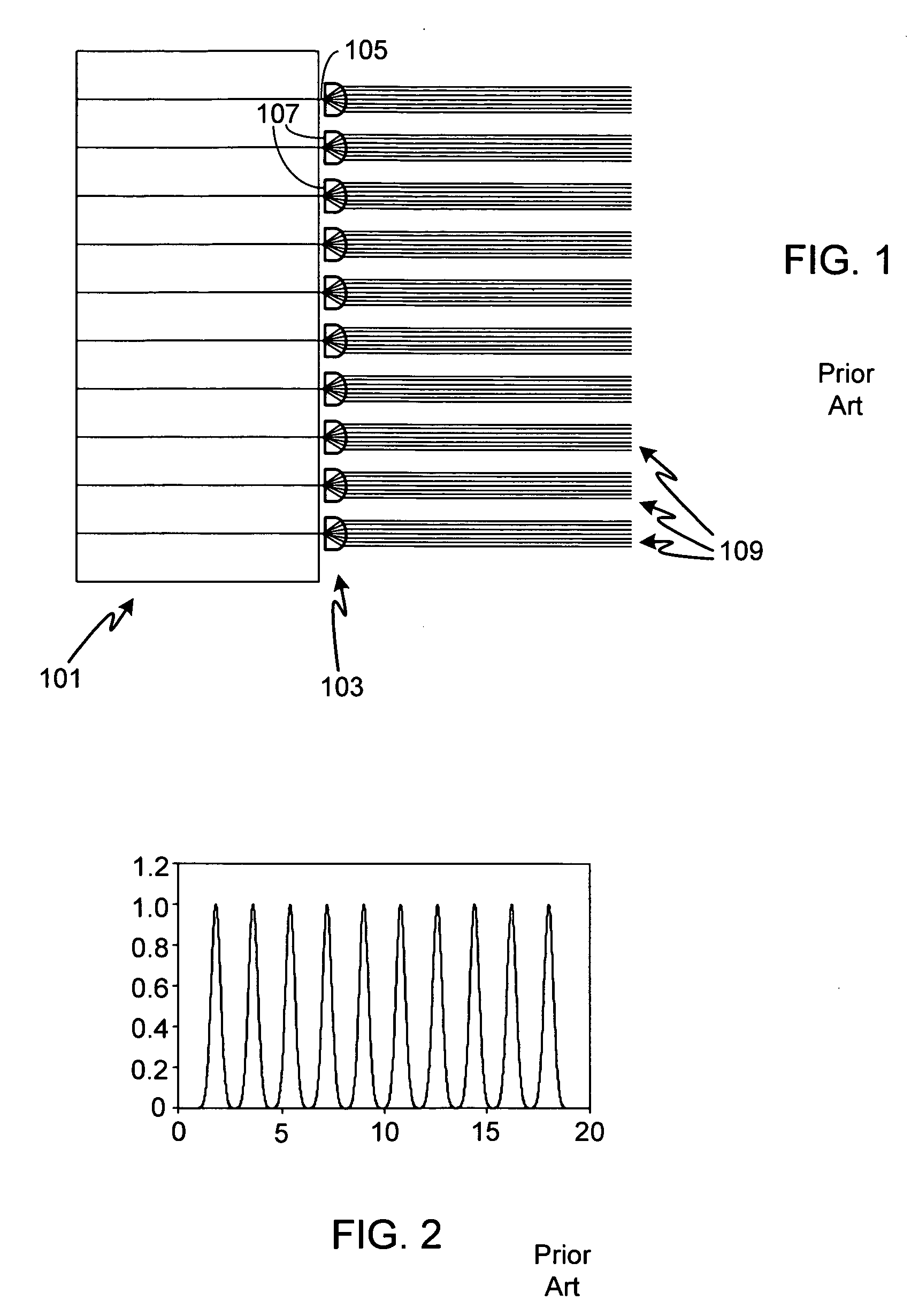
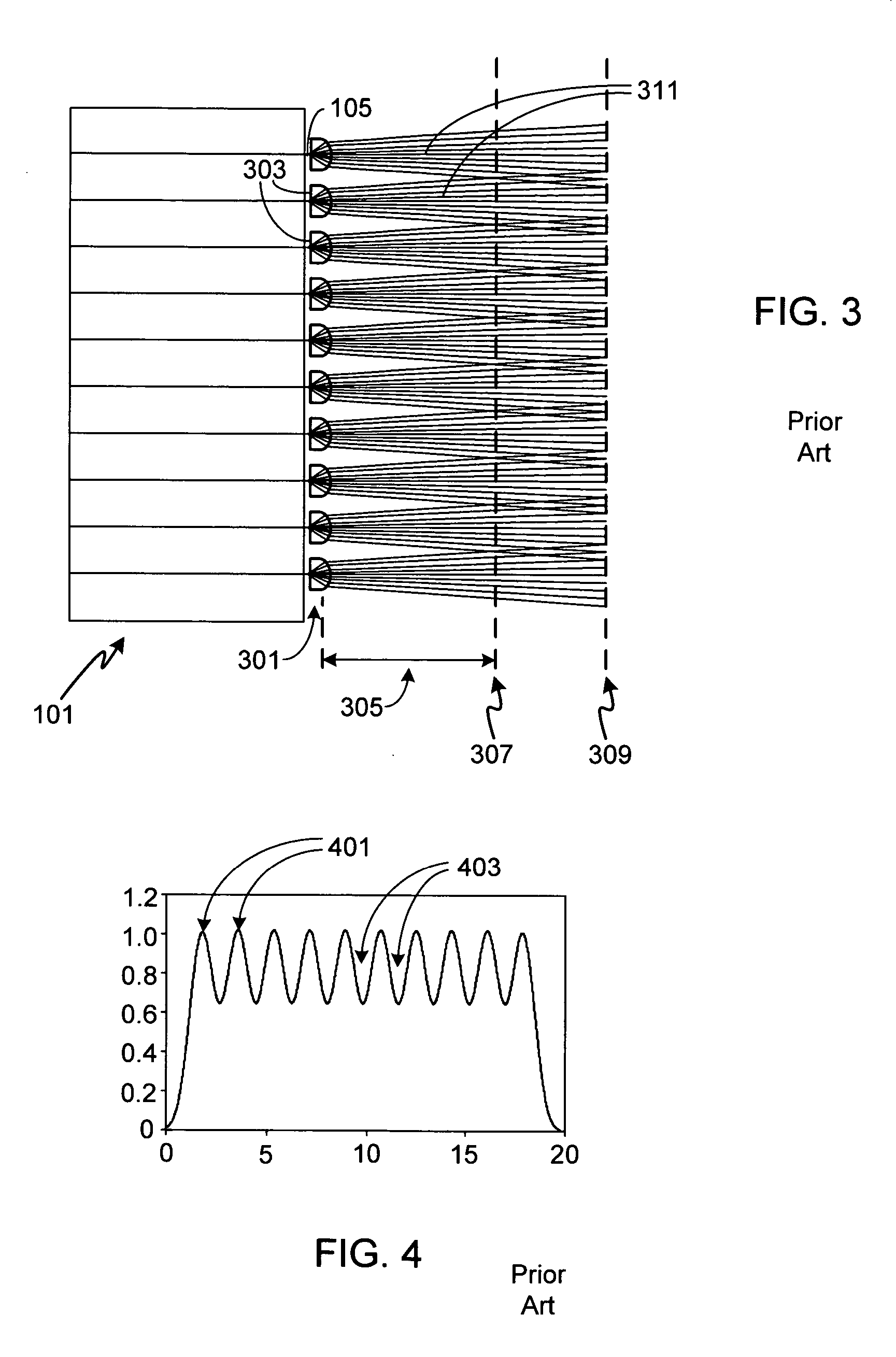
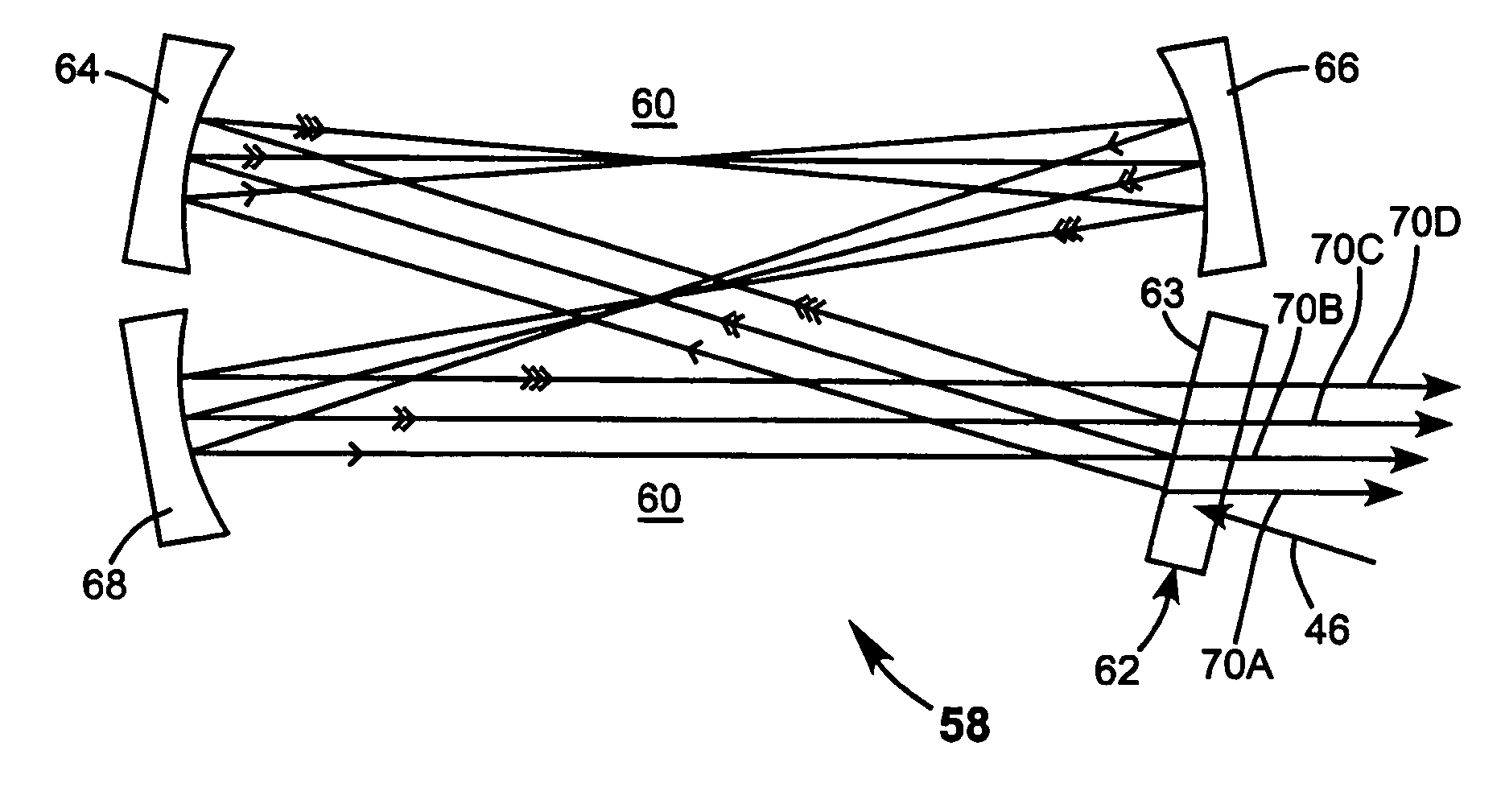
Patents
Literature
71 results about "Beam homogenizer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
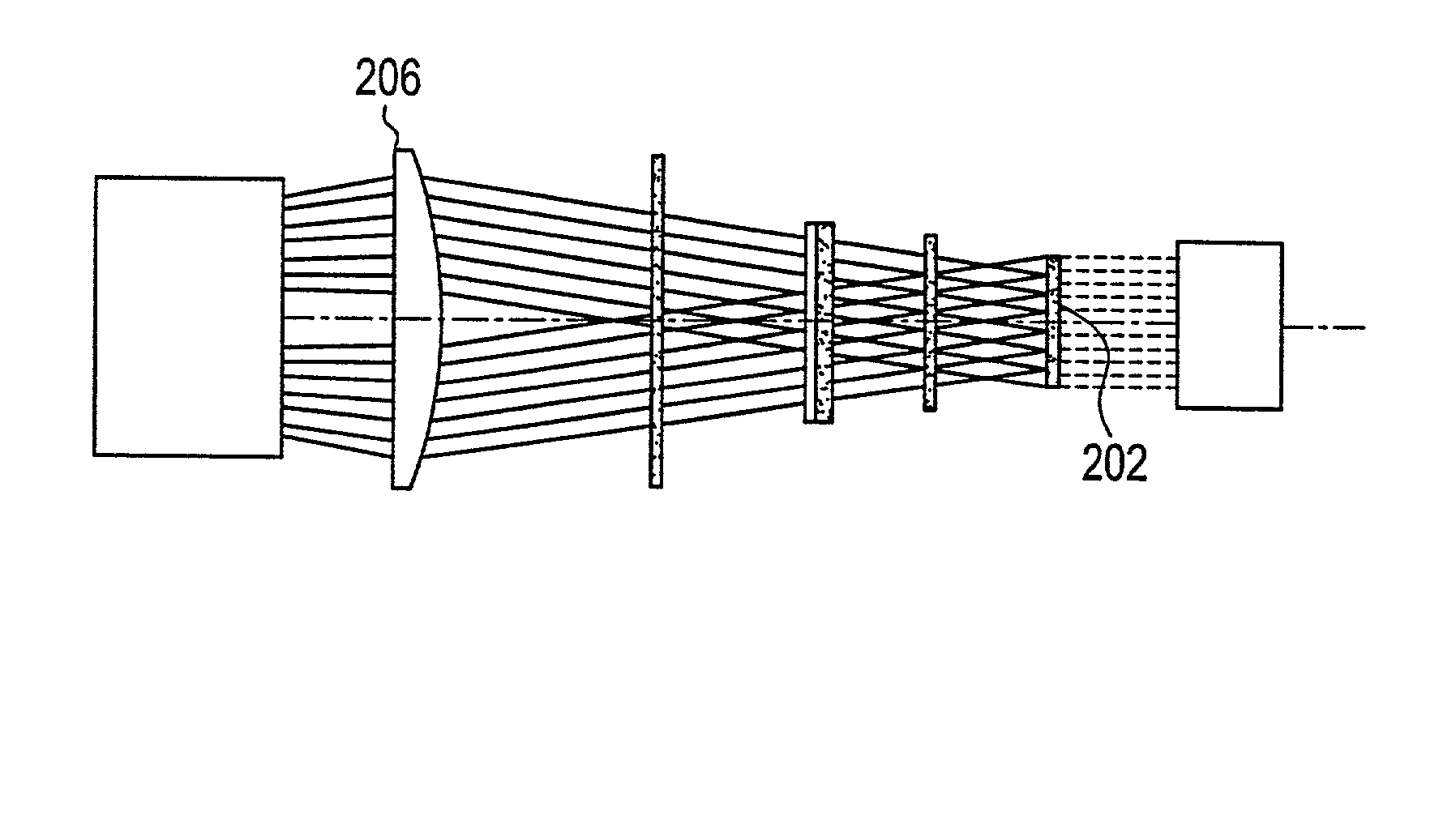
A beam homogenizer is a device that smooths out the irregularities in a laser beam profile and creates a more uniform one. Most beam homogenizers use a multifaceted mirror with square facets. The mirror reflects light at different angles to create a beam with uniform power across the whole beam profile (a "top hat" profile). Some applications of beam homogenizers include their use with excimer lasers for making computer processing chips and with CO₂ lasers for heat treating.
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS6393042B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamOptoelectronics
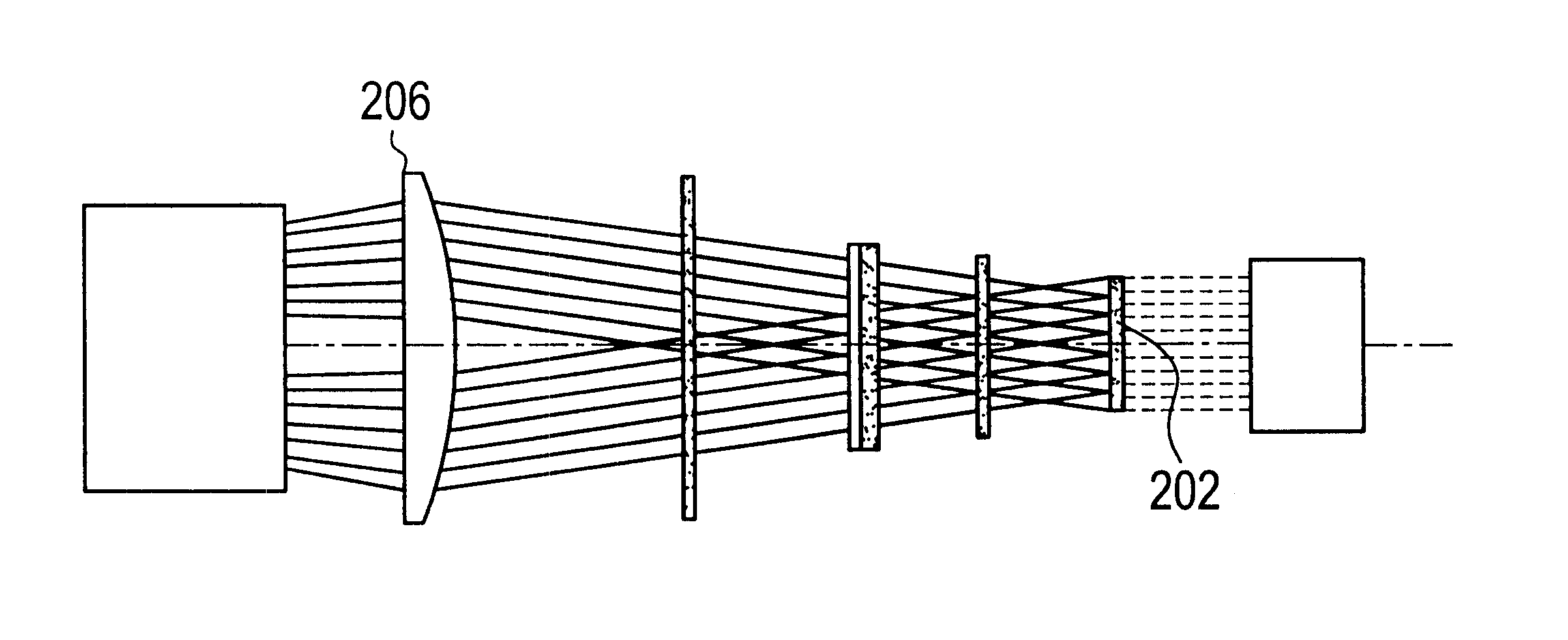
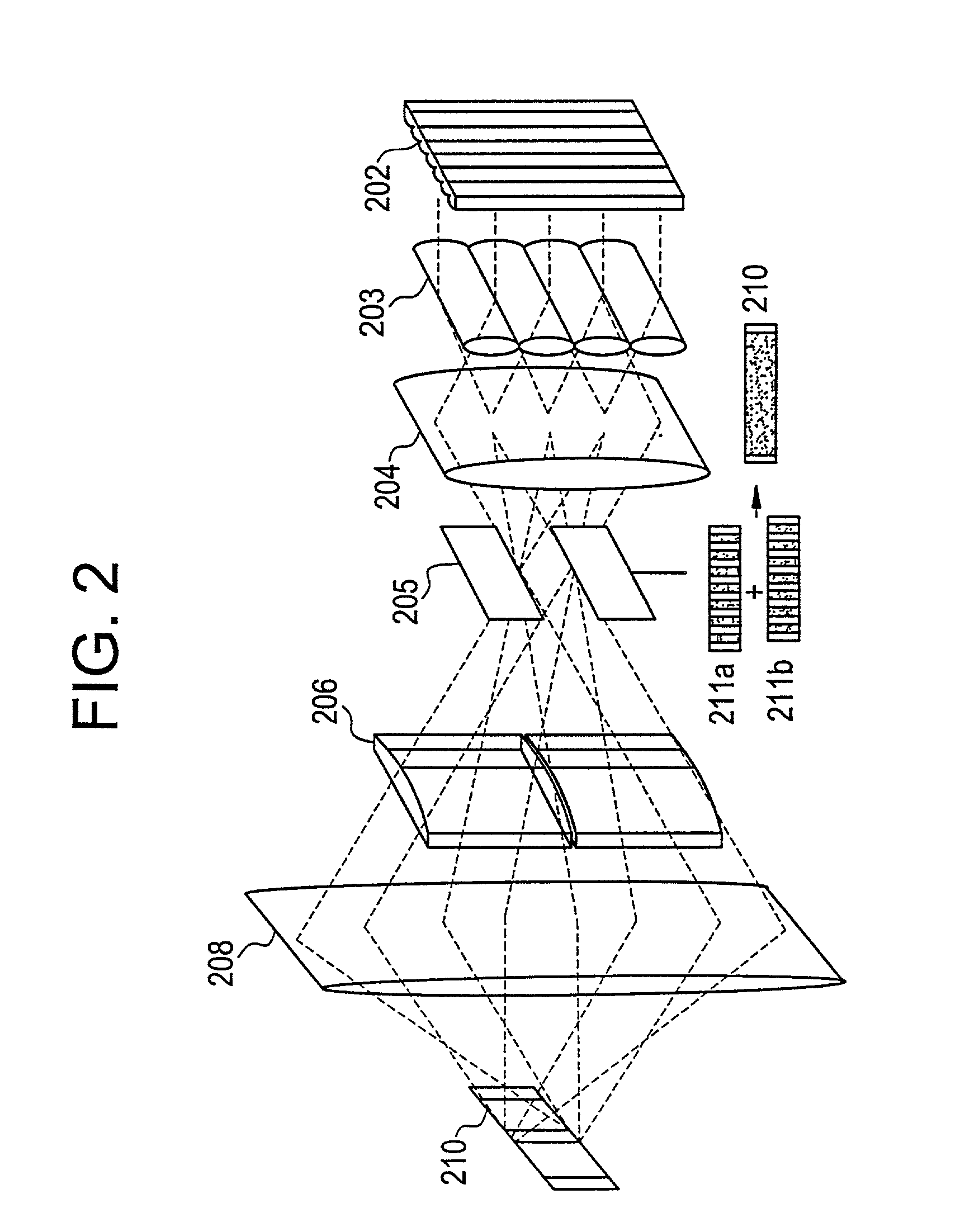
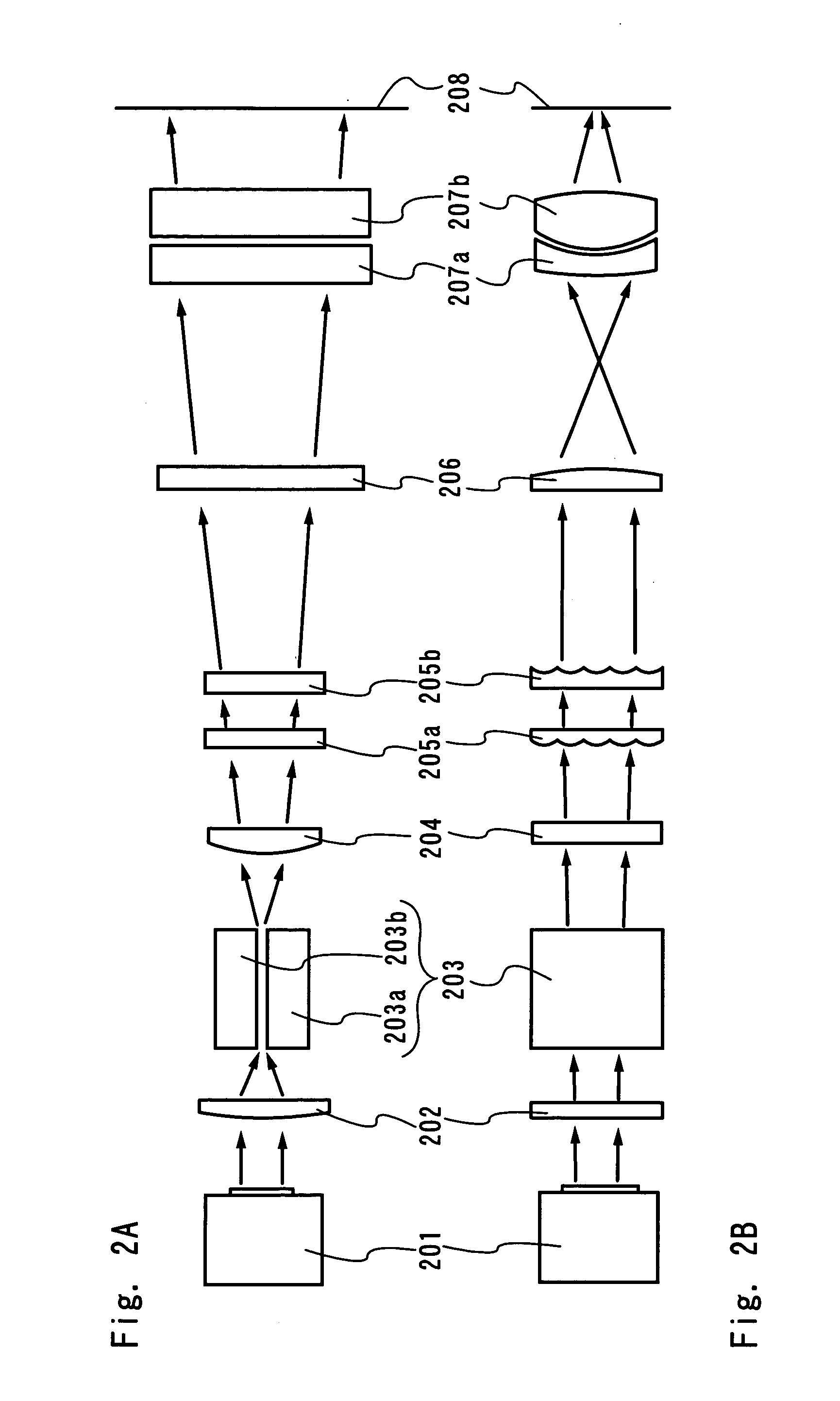
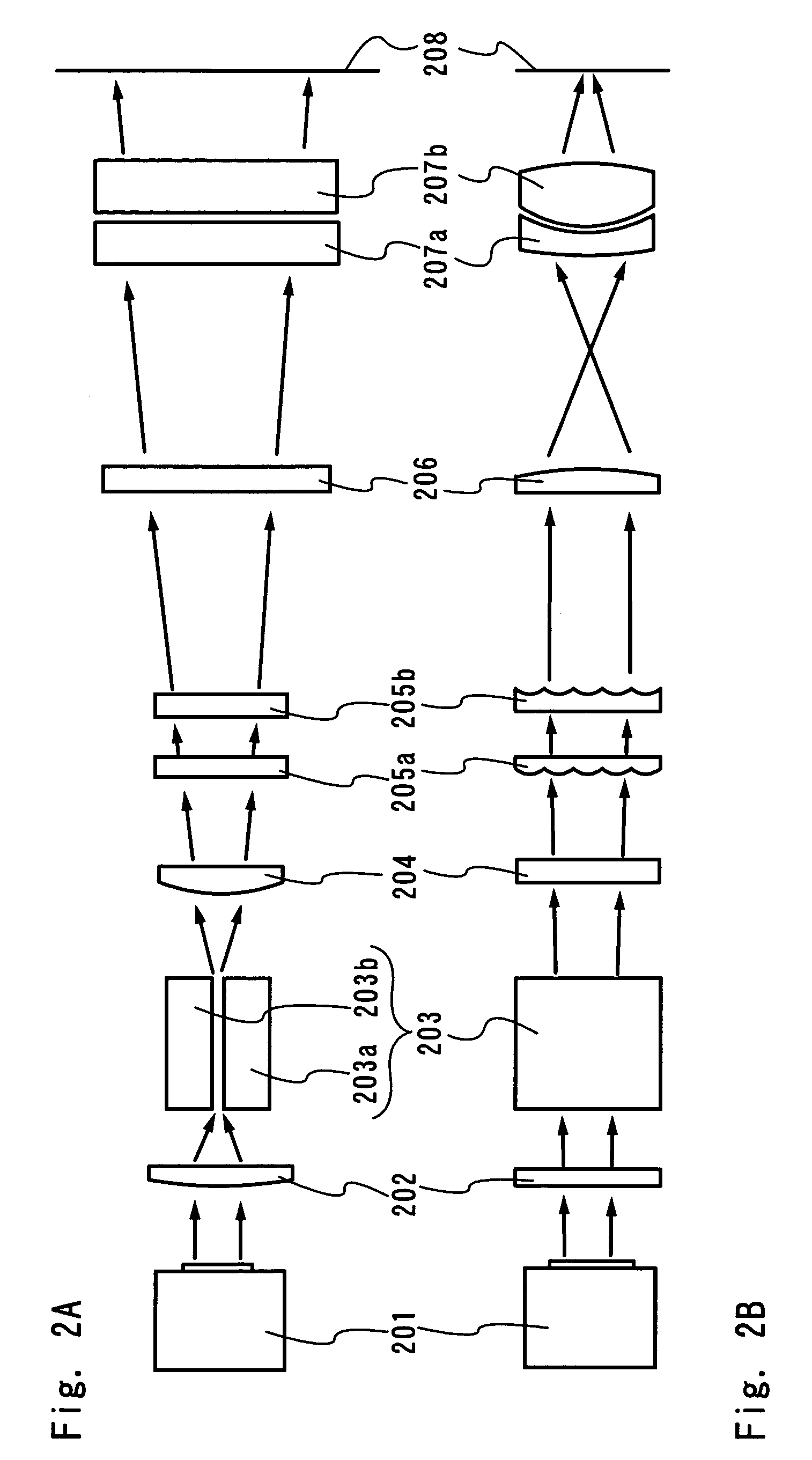
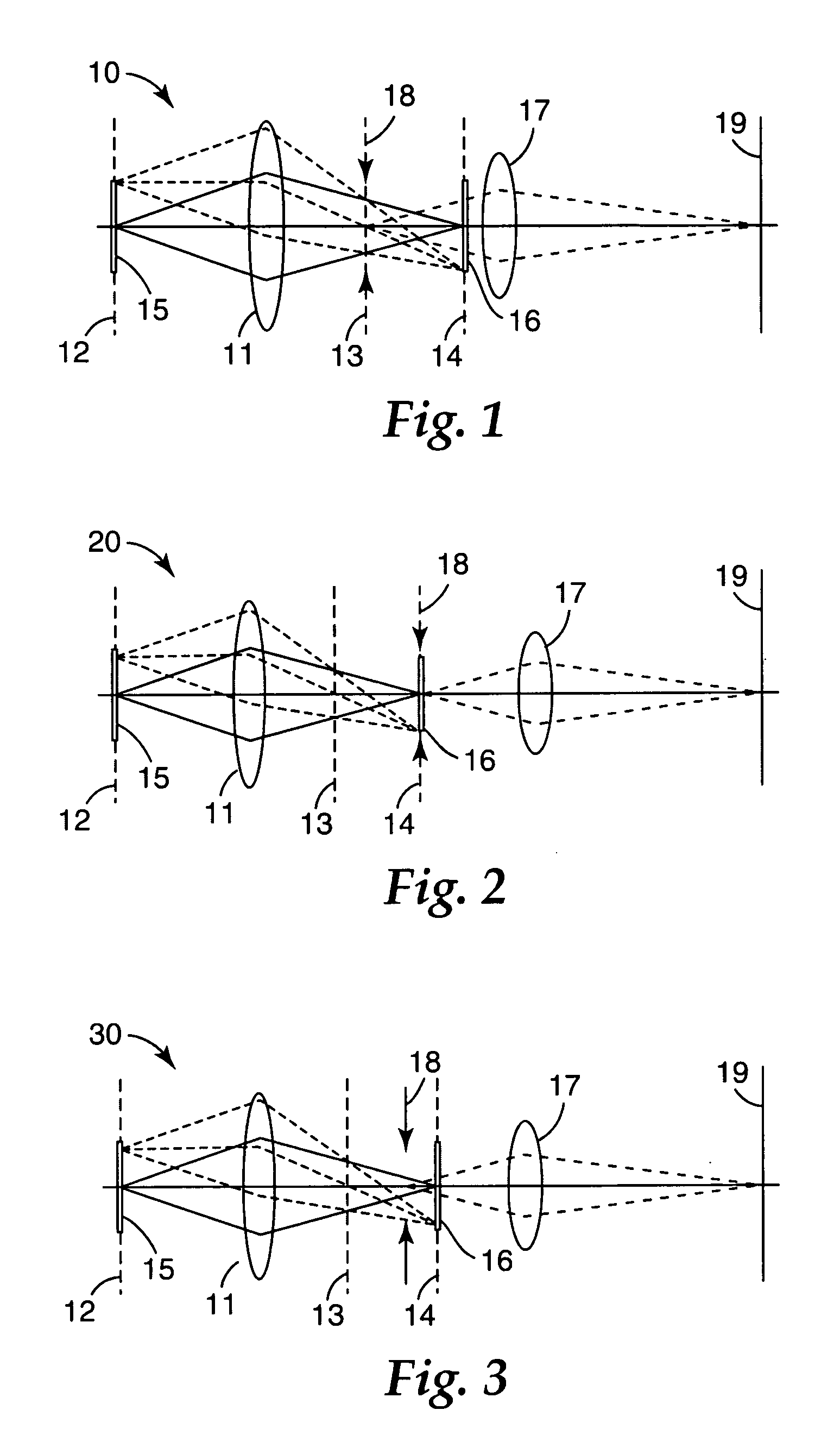
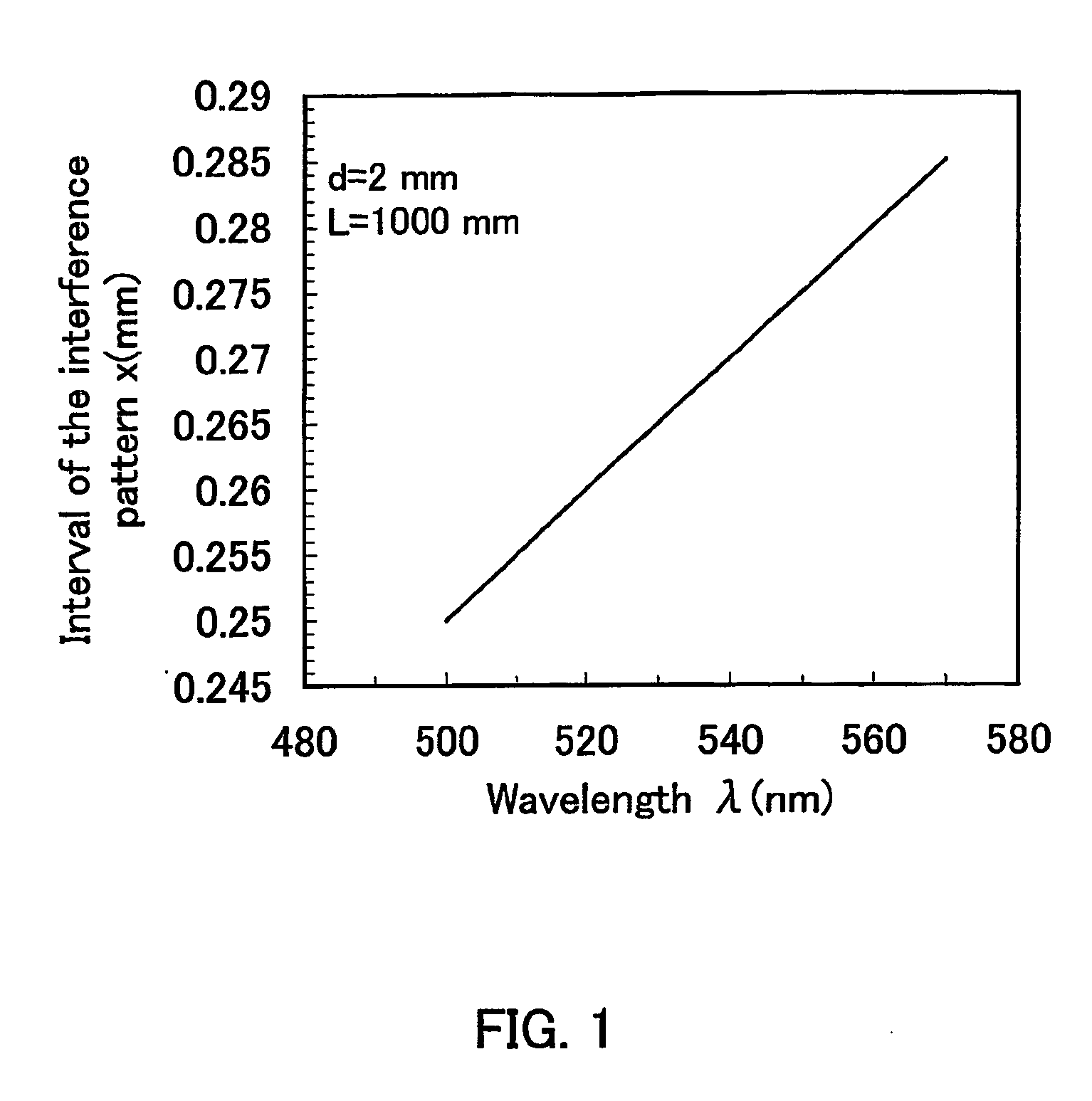
There is provided a beam homogenizer which can unify the energy distribution of a linear laser beam in a longitudinal direction. In the beam homogenizer including cylindrical lens groups for dividing a beam, and a cylindrical lens and a cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams, the phases, in the longitudinal direction, of linear beams passing through individual cylindrical lenses of the cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams are shifted, and then, the beams are synthesized, so that the intensity of interference fringes of the linear beam on a surface to be irradiated is made uniform.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Systems and methods using sequential lateral solidification for producing single or polycrystalline silicon thin films at low temperatures
System and methods for processing an amorphous silicon thin film sample into a single or polycrystalline silicon thin film are disclosed. The system includes an excimer laser for generating a plurality of excimer laser pulses of a predetermined fluence, an energy density modulator for controllably modulating fluence of the excimer laser pulses, a beam homoginizer for homoginizing modulated laser pulses in a predetermined plane, a mask for masking portions of the homoginized modulated laser pulses into patterned beamlets, a sample stage for receivingthe patterned beamlets to effect melting of portions of any amorphous silicon thin film sample placed thereon corresponding to the beamlets, translating means for controllably translating a relative position of the sample stage with respect to a position of the mask and a computer for controlling the controllable fluence modulation of the excimer laser pulses and the controllable relative positions of the sample stage and mask, and for coordinating excimer pulse generation and fluence modulation with the relative positions of the sample stage and mask, to thereby process amorphous silicon thin film sample into a single or polycrystalline silicon thin film by sequential translation of the sample stage relative to the mask and irradiation of the sample by patterned beamlets of varying fluence at corresponding sequential locations thereon.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Laser annealing apparatus, TFT device and annealing method of the same
InactiveUS6943086B2Reducing and eliminating influenceTransistorSolid-state devicesEnergy variationSingle crystal
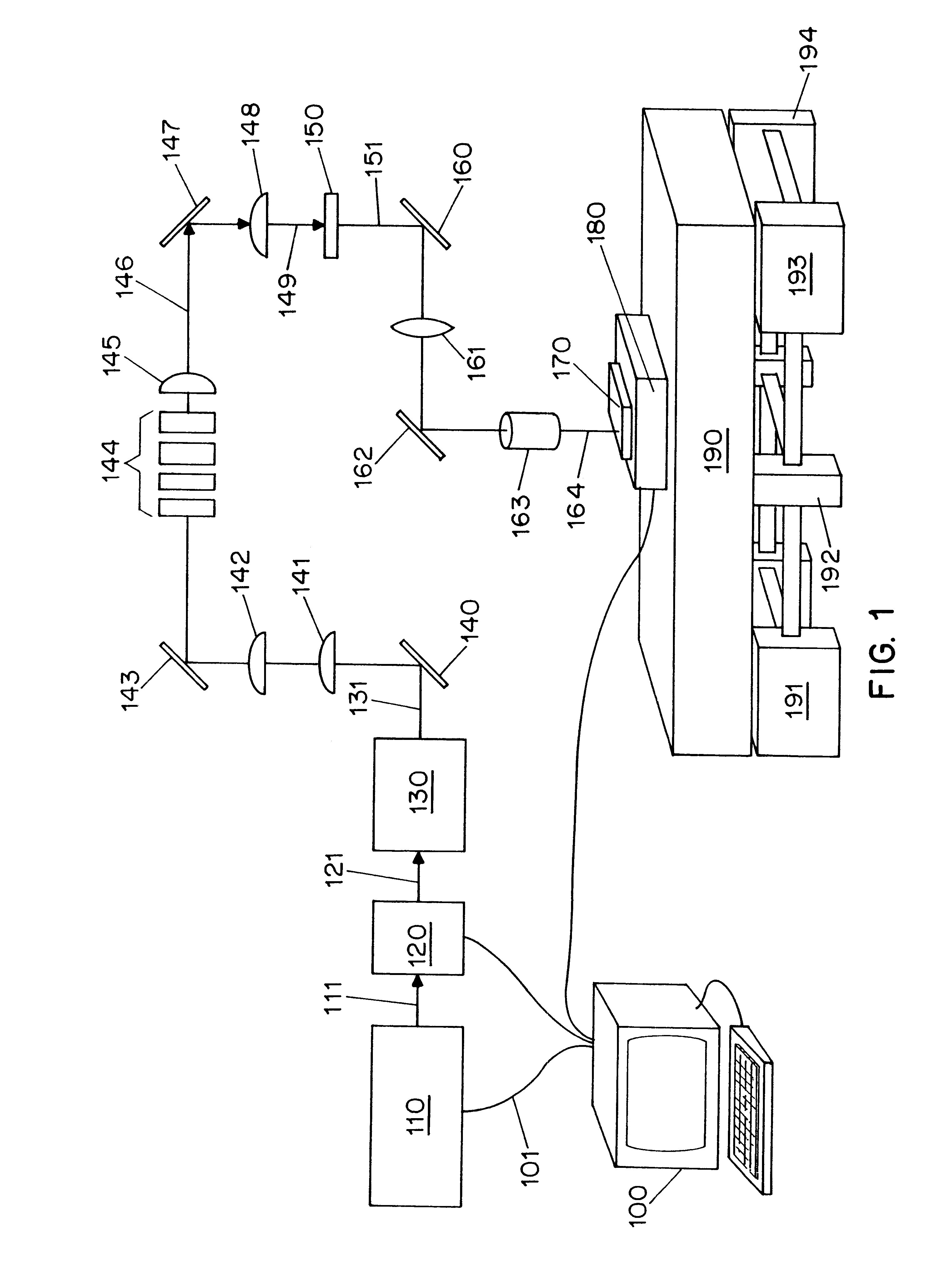
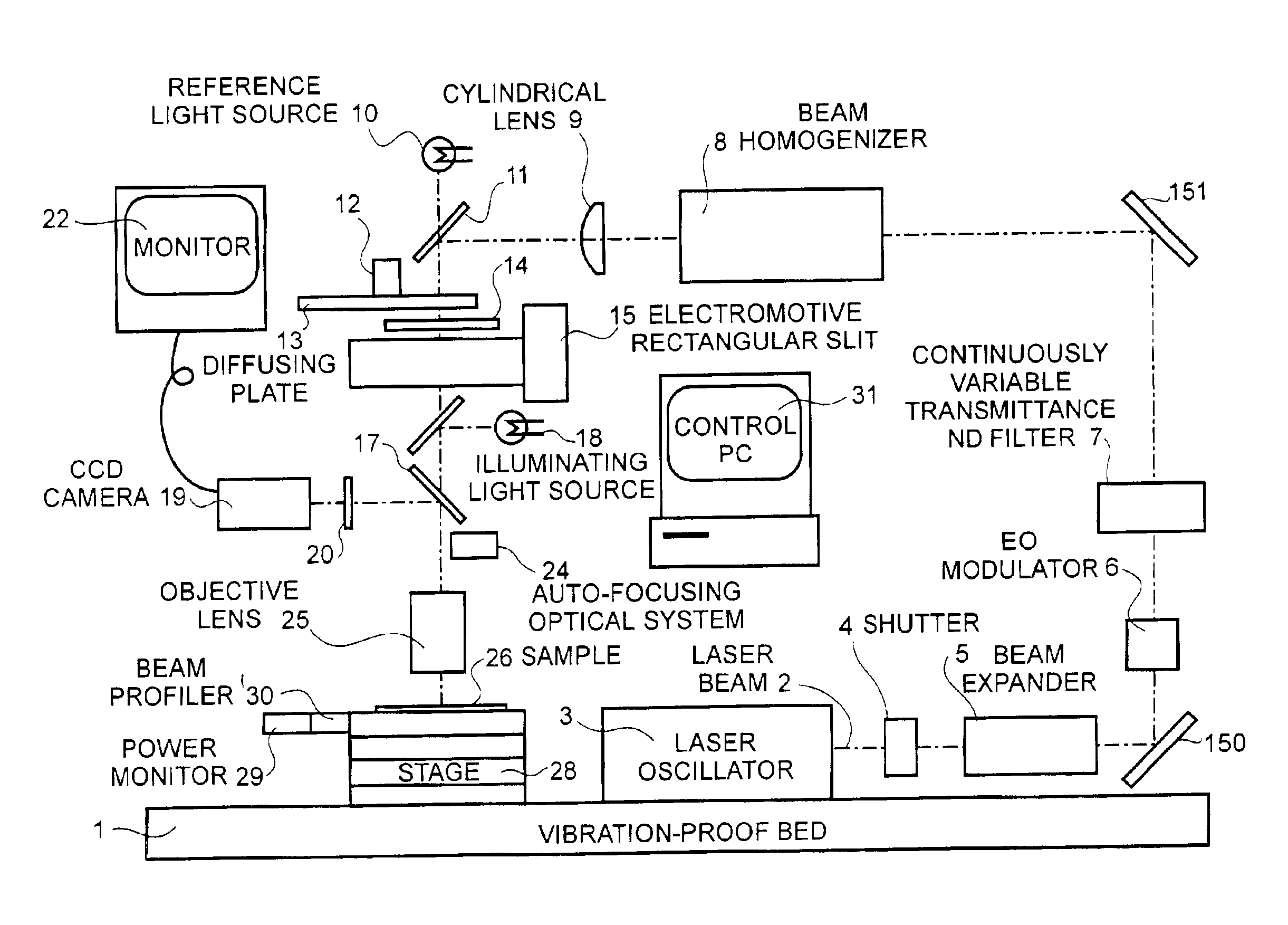
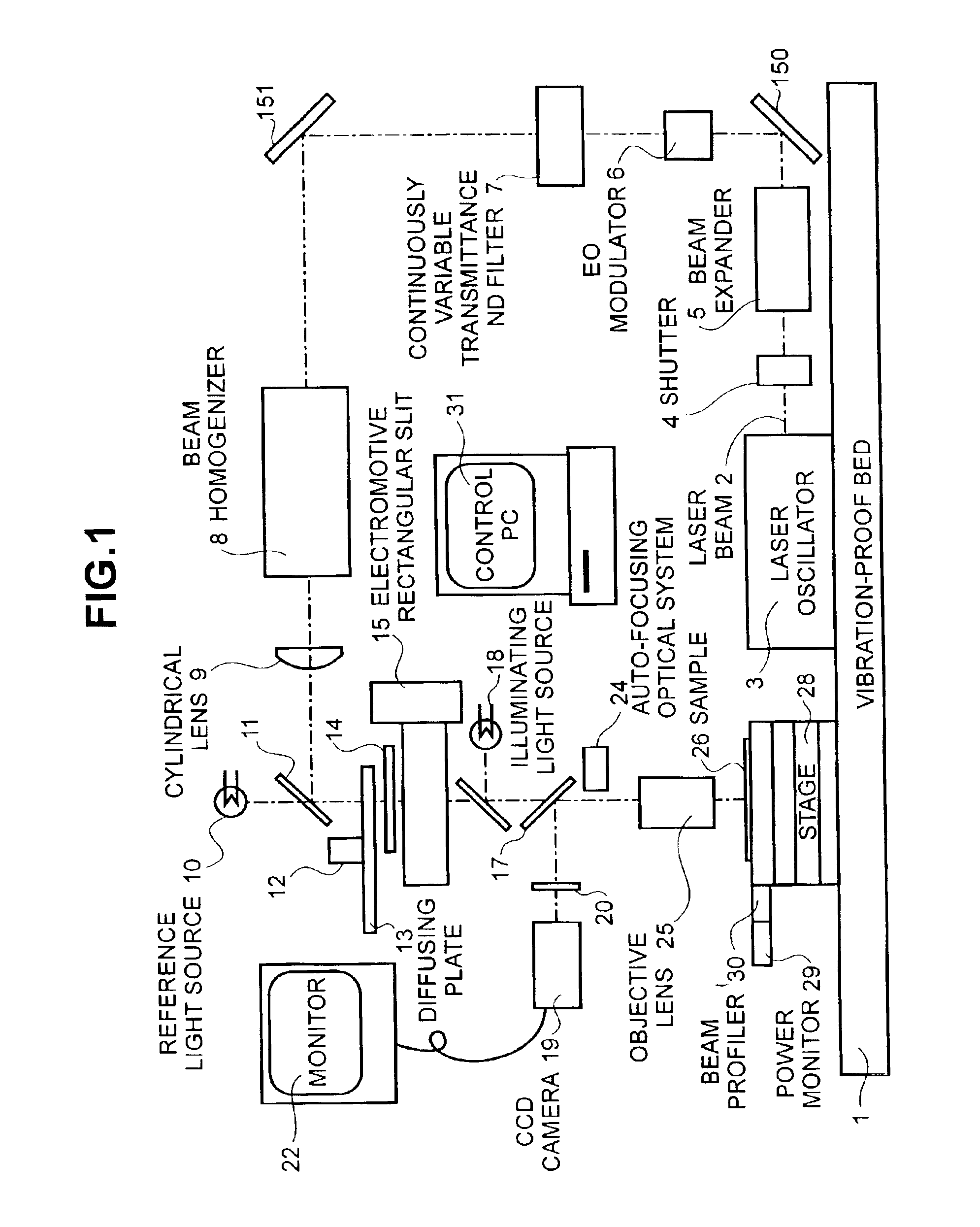
A laser beam is concentrated using an objective lens and radiated on a amorphous silicon film or polycrystalline silicon film having a grain size of one micron or less, the laser beam being processed from a continuous wave laser beam (1) to be pulsed using an EO modulator and to have arbitrary temporal energy change while pulsing ; (2) to have an arbitrary spatial energy distribution using a beam-homogenizer, filter having an arbitrary transmittance distribution, and rectangular slit; and (3) to eliminate coherency thereof using a high-speed rotating diffuser. In this manner, it is possible to realize a liquid crystal display device in which a driving circuit comprising a polycrystalline silicon film having substantially the same properties as a single crystal is incorporated in a TFT panel device.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Laser illuminated projection displays
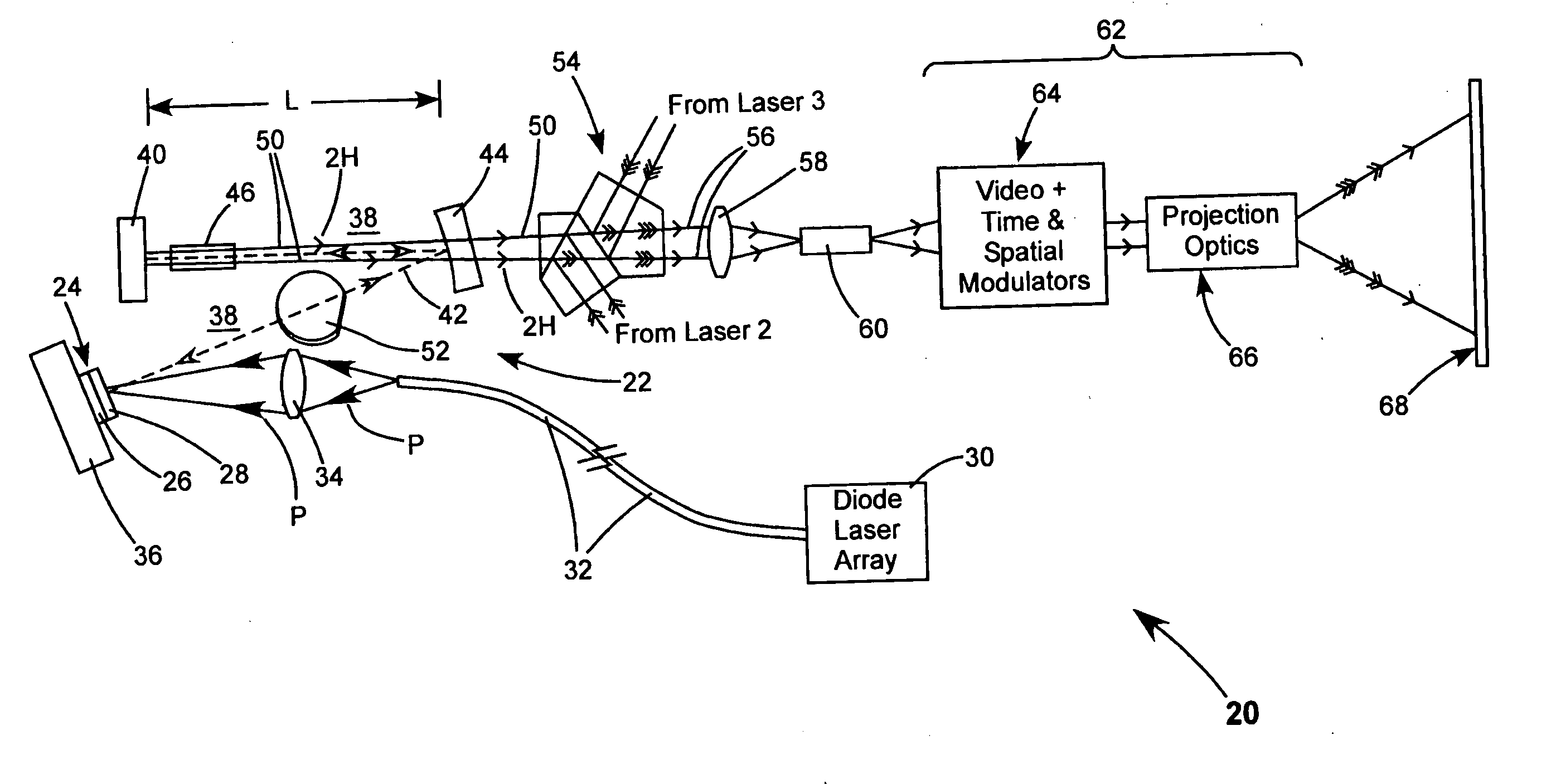
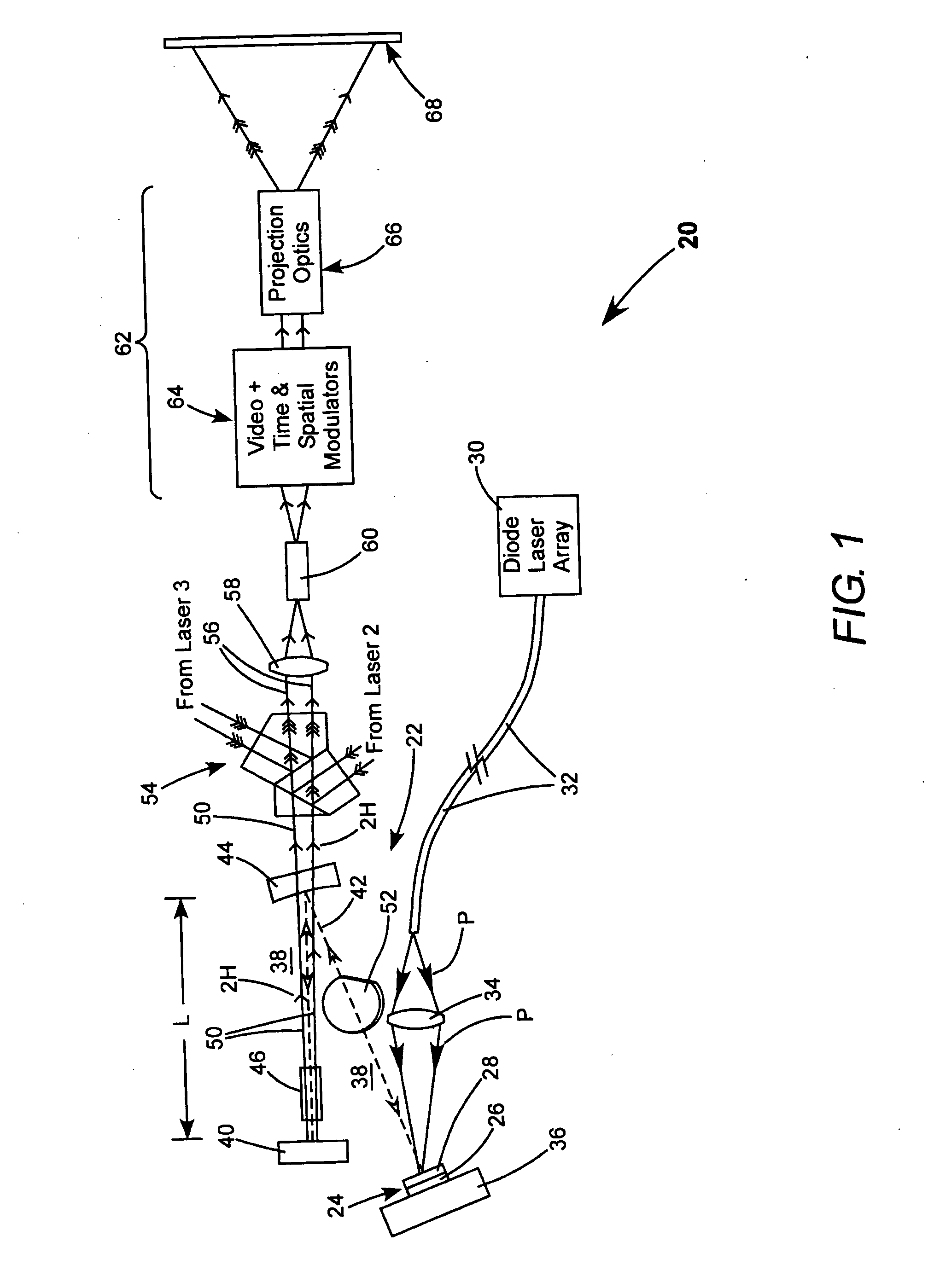
InactiveUS7244028B2Reduced coherence radiusMinimizing speckle contrastBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
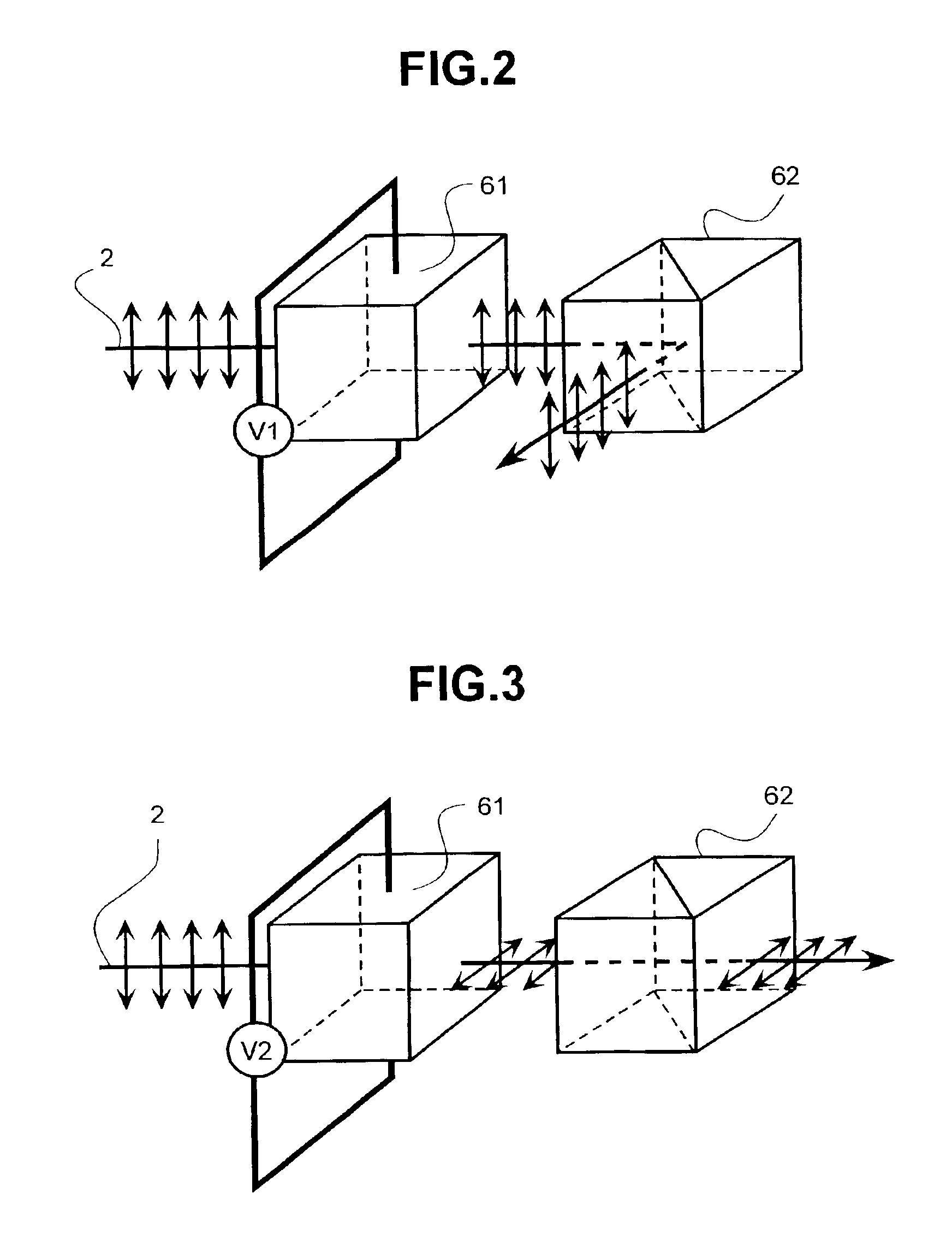
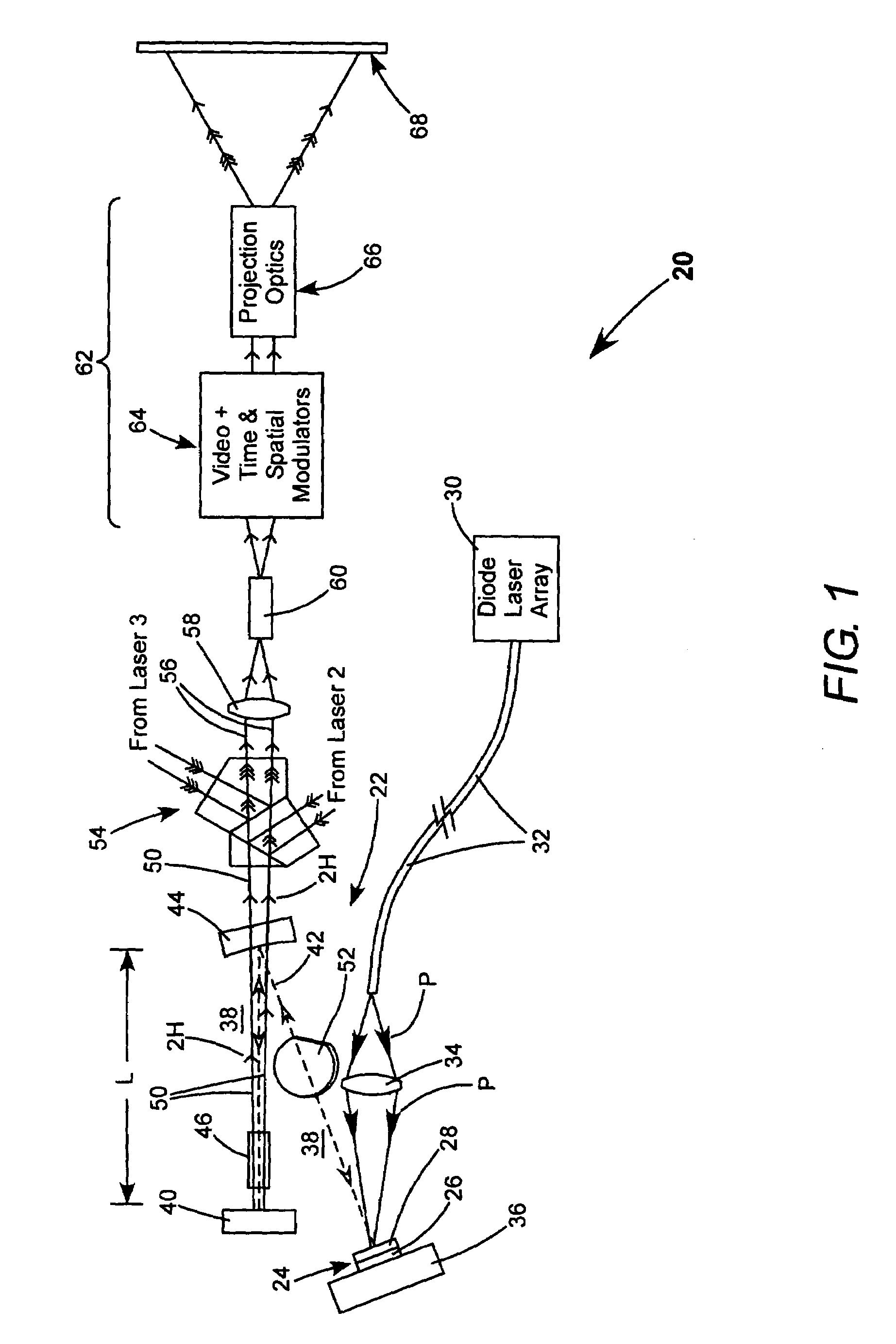
A projection video display includes at least one laser for delivering a light beam. The display includes a beam homogenizer and a condenser lens. A scanning arrangement is provided for scanning the light in beam in a particular pattern over the condenser lens in a manner that effectively increases the beam divergence. The scanned beam is homogenized by a beam homogenizer and a spatial light modulator is arranged to receive the homogenized scanned light beam and spatially modulate the beam in accordance with a component of an image to be displayed. Projection optics are projecting the homogenized scanned light beam onto a screen. The scanning provides that the homogenized scanned light beam at the screen has a coherence radius less than the original coherence radius of the beam. The reduced coherence radius contributes to minimizing speckle contrast in the image displayed on the screen. The screen includes one or more features providing a further contribution to minimizing speckle contrast in the displayed image. In one example, the screen includes a transparent cell containing a liquid having light scattering particles in suspension.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Beam Homogenizer
InactiveUS20120168411A1Increase beam numerical apertureIncrease the number ofCosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical apparatusLight pipeLight beam
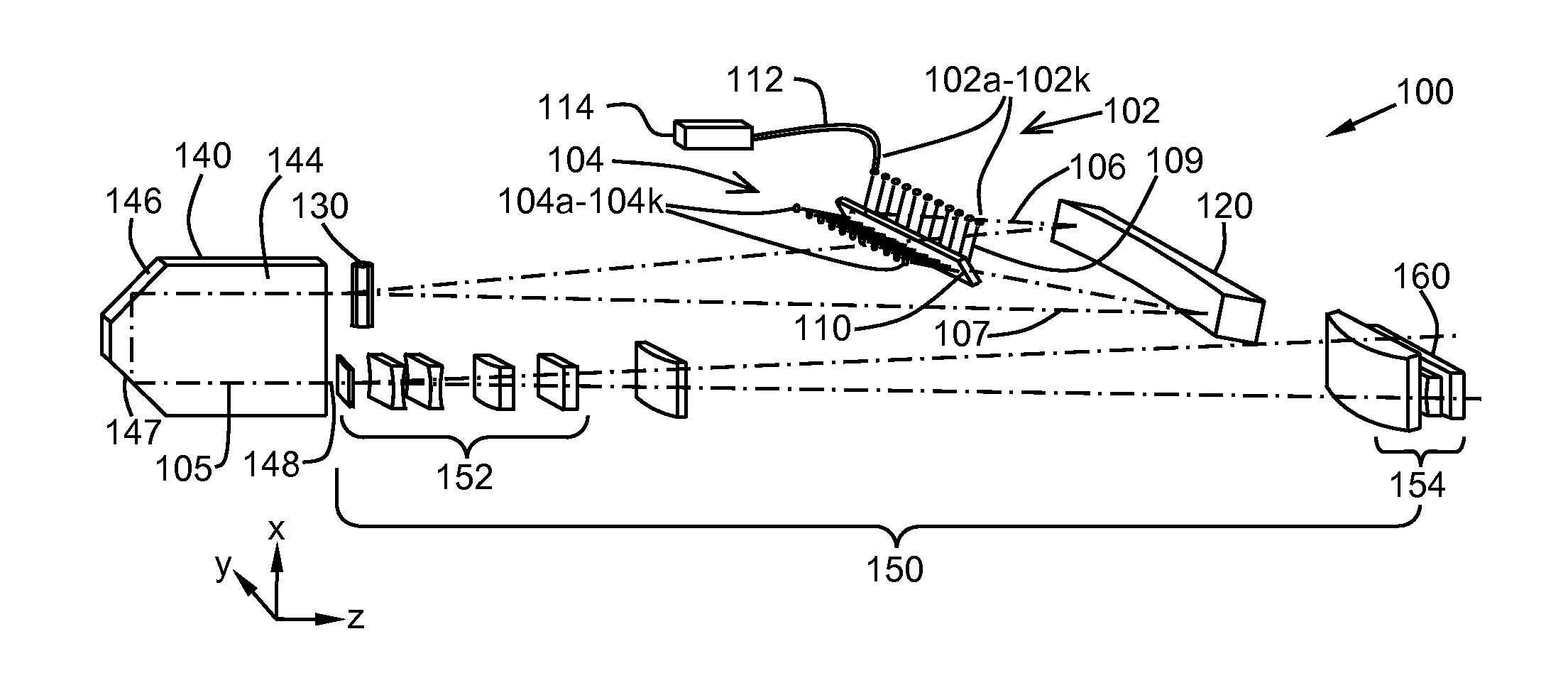
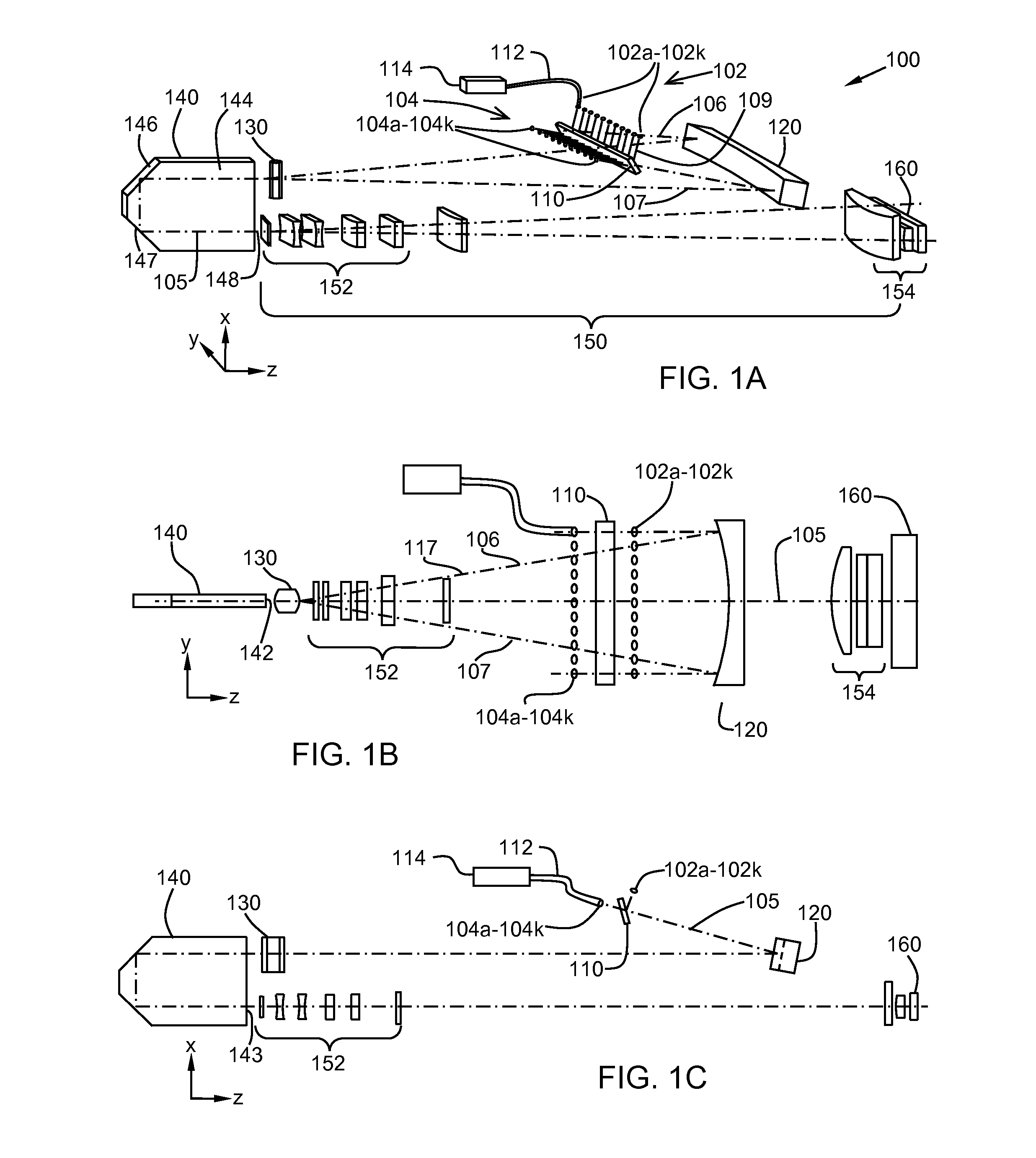
A system for homogenizing the intensity profile of light includes a plurality of fiber coupled light sources for emitting fiber output beams from fiber output ends, and a light pipe optically coupled to the fiber output beams for producing a uniform light pipe output beam, an interleaver that transmits a first set of fiber output beams and reflects a second set of fiber output beams so that the principal rays of the fiber output beams propagate in a common plane, a first optical element for converging the principal rays, and a second optical element for telecentrically imaging the beams into the light pipe such that the principal rays of the beams propagate parallel to each other and the beams are focused in the light pipe in a focal plane transverse to the direction of propagation.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS20020146873A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsLight beamOptoelectronics
There is provided a beam homogenizer which can unify the energy distribution of a linear laser beam in a longitudinal direction. In the beam homogenizer including cylindrical lens groups for dividing a beam, and a cylindrical lens and a cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams, the phases, in the longitudinal direction, of linear beams passing through individual cylindrical lenses of the cylindrical lens group for condensing the divided beams are shifted, and then, the beams are synthesized, so that the intensity of interference fringes of the linear beam on a surface to be irradiated is made uniform.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, semiconductor device, and method of fabricating the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20010010702A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamIrradiation
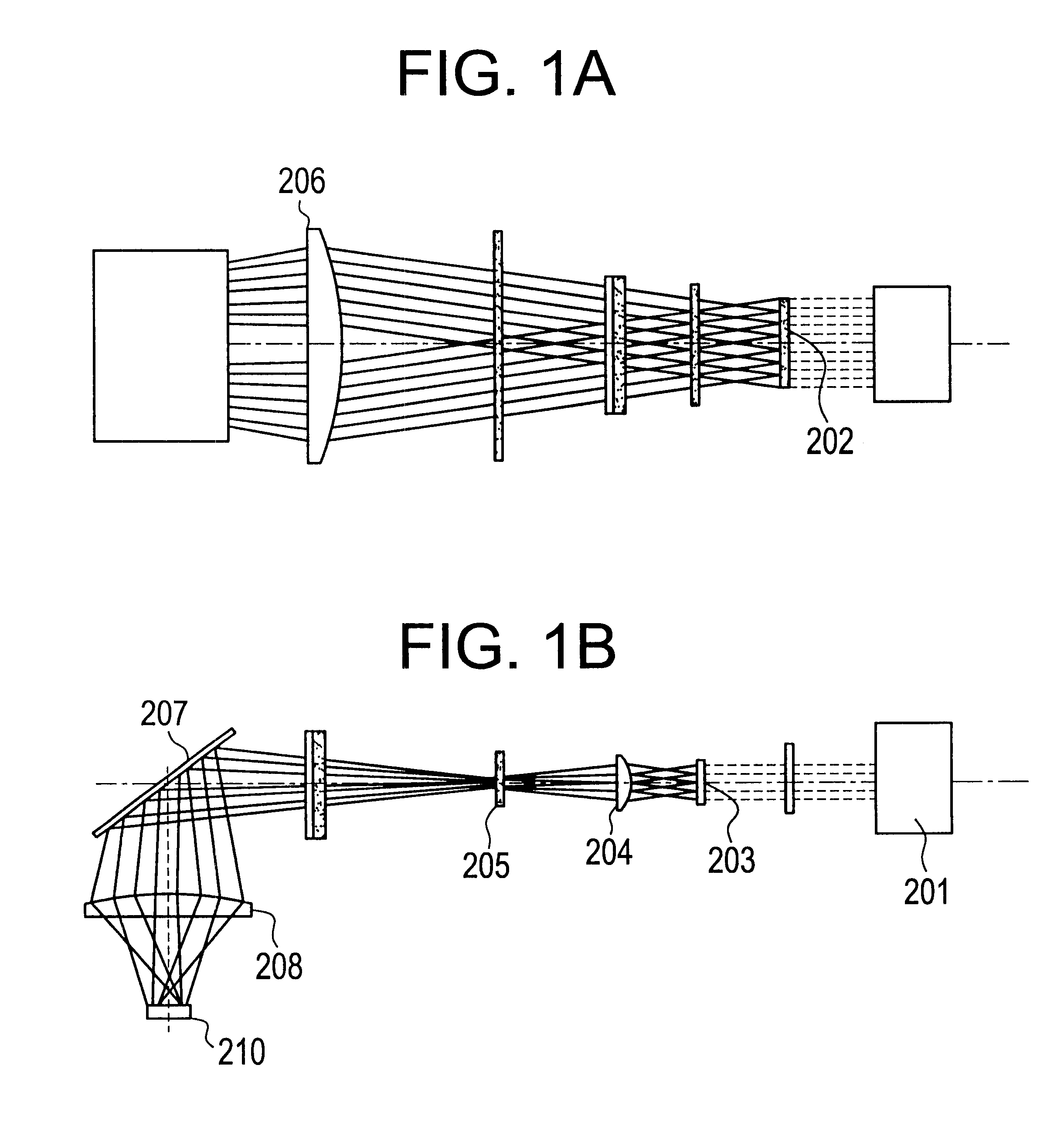
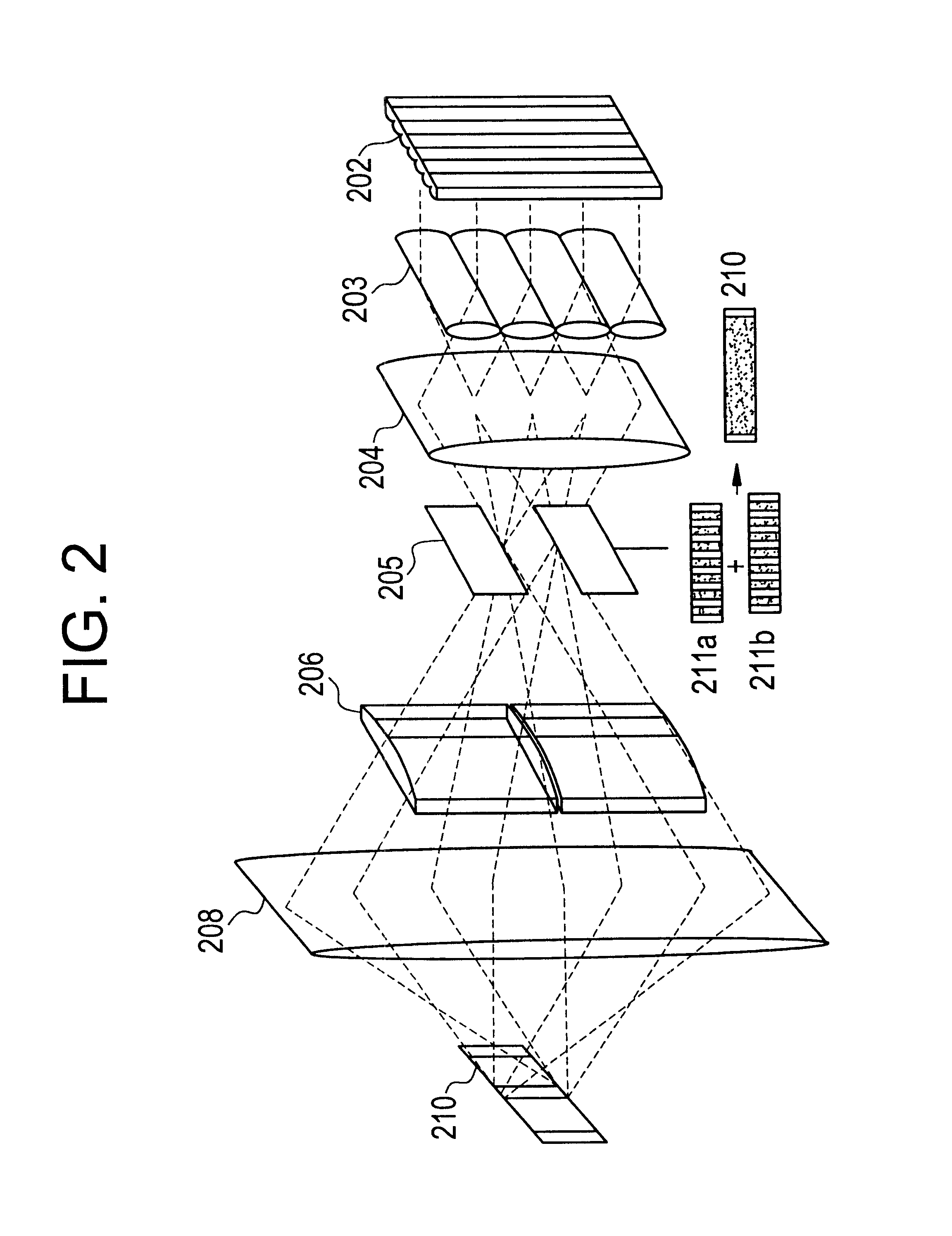
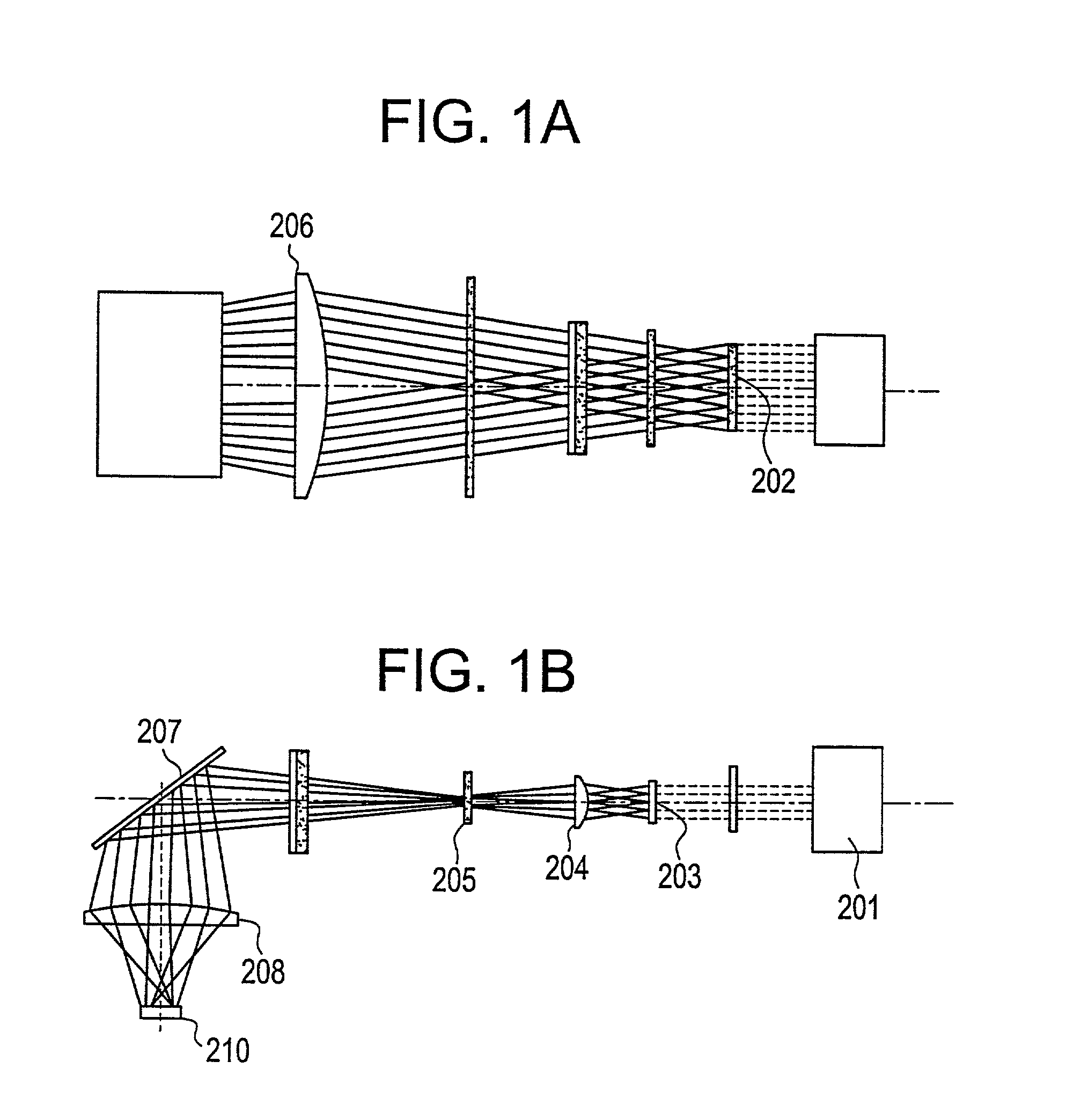
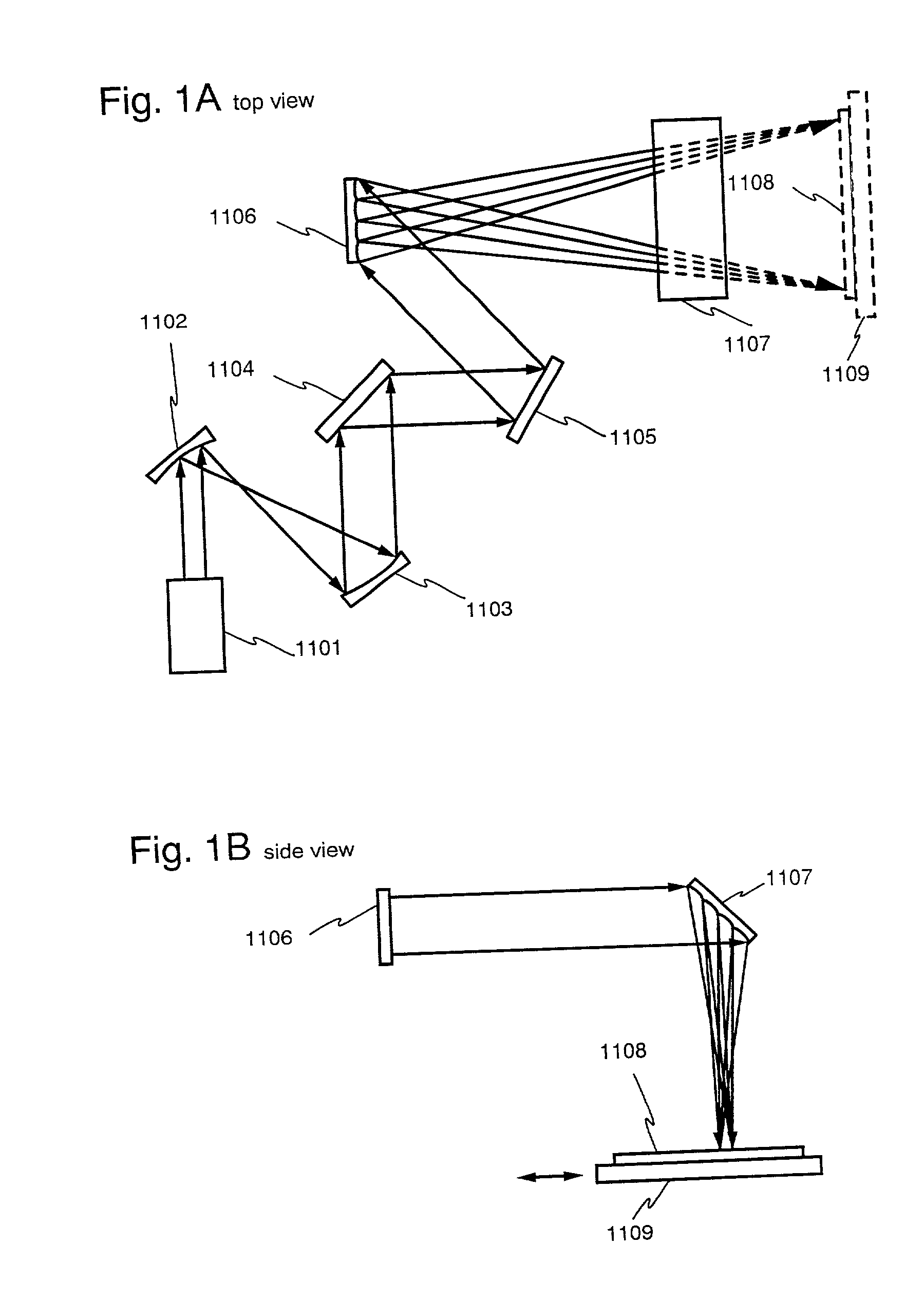
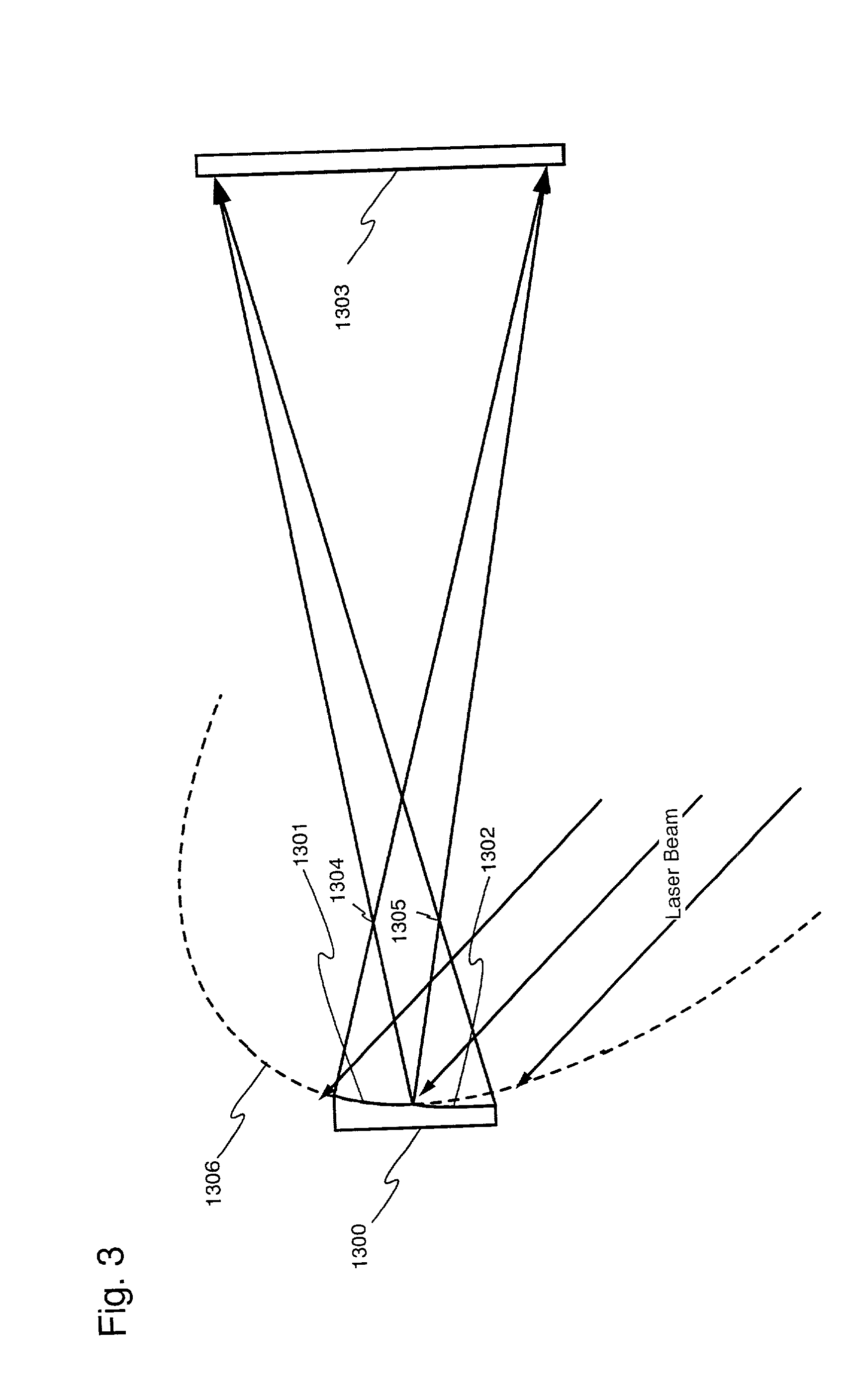
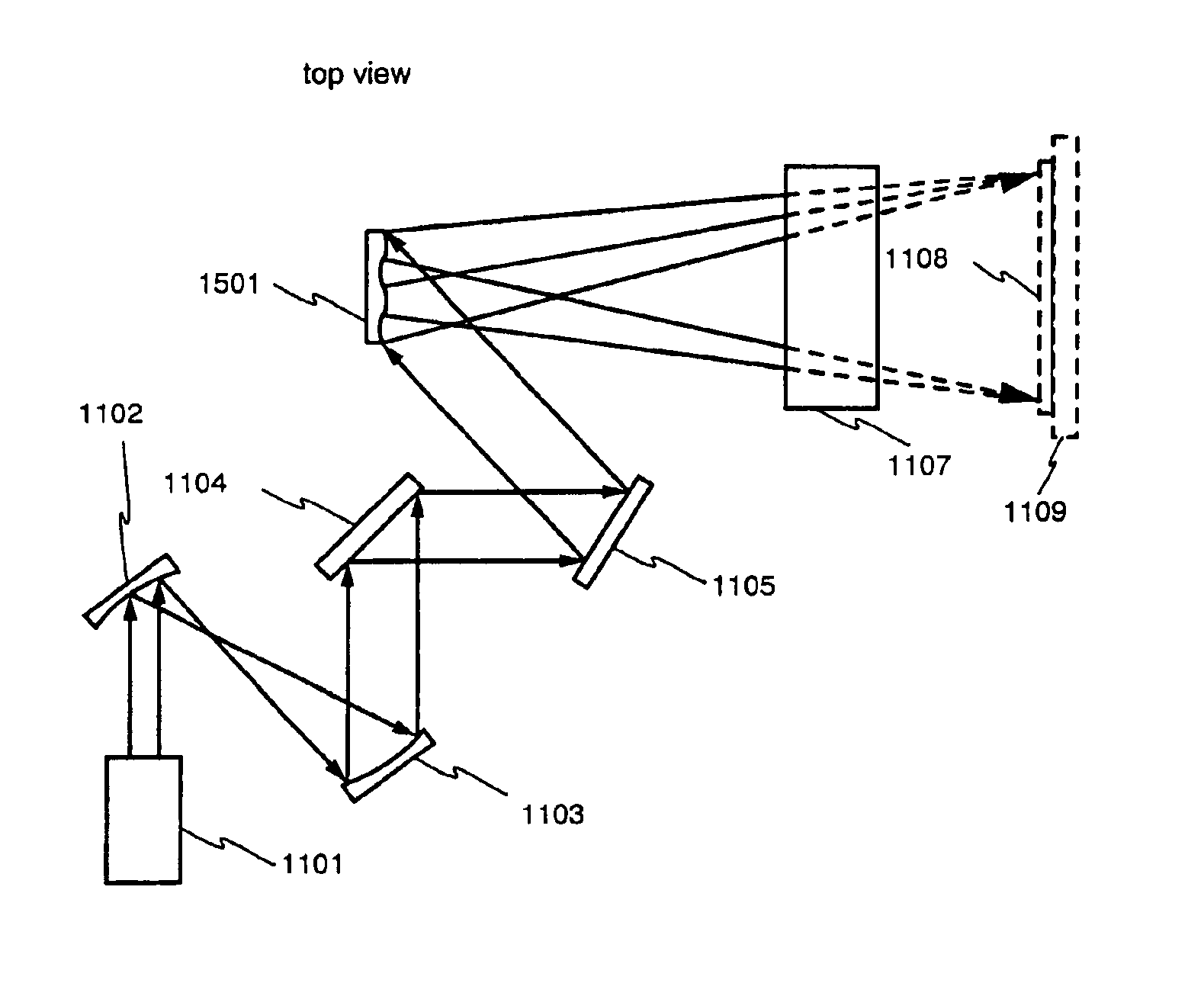
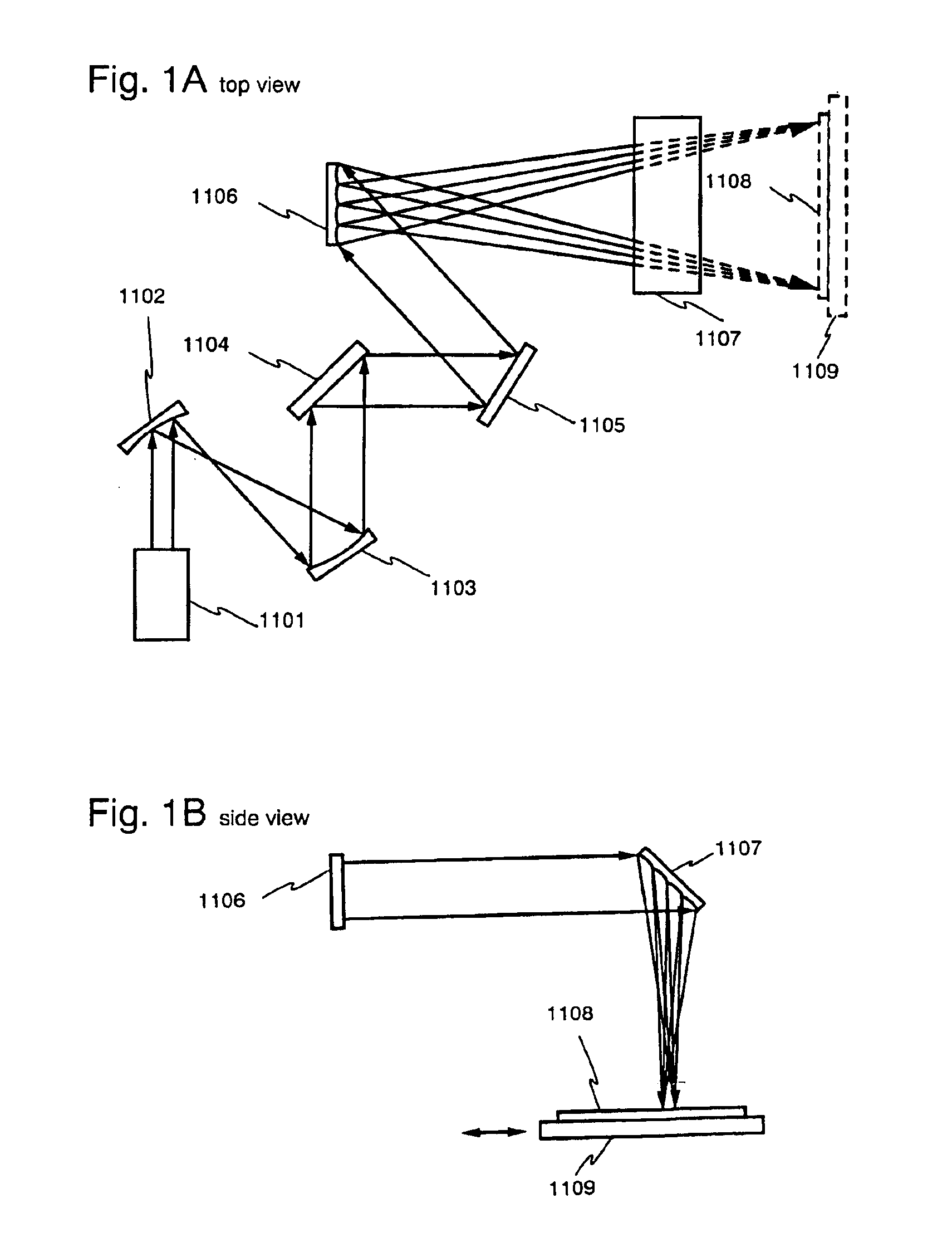
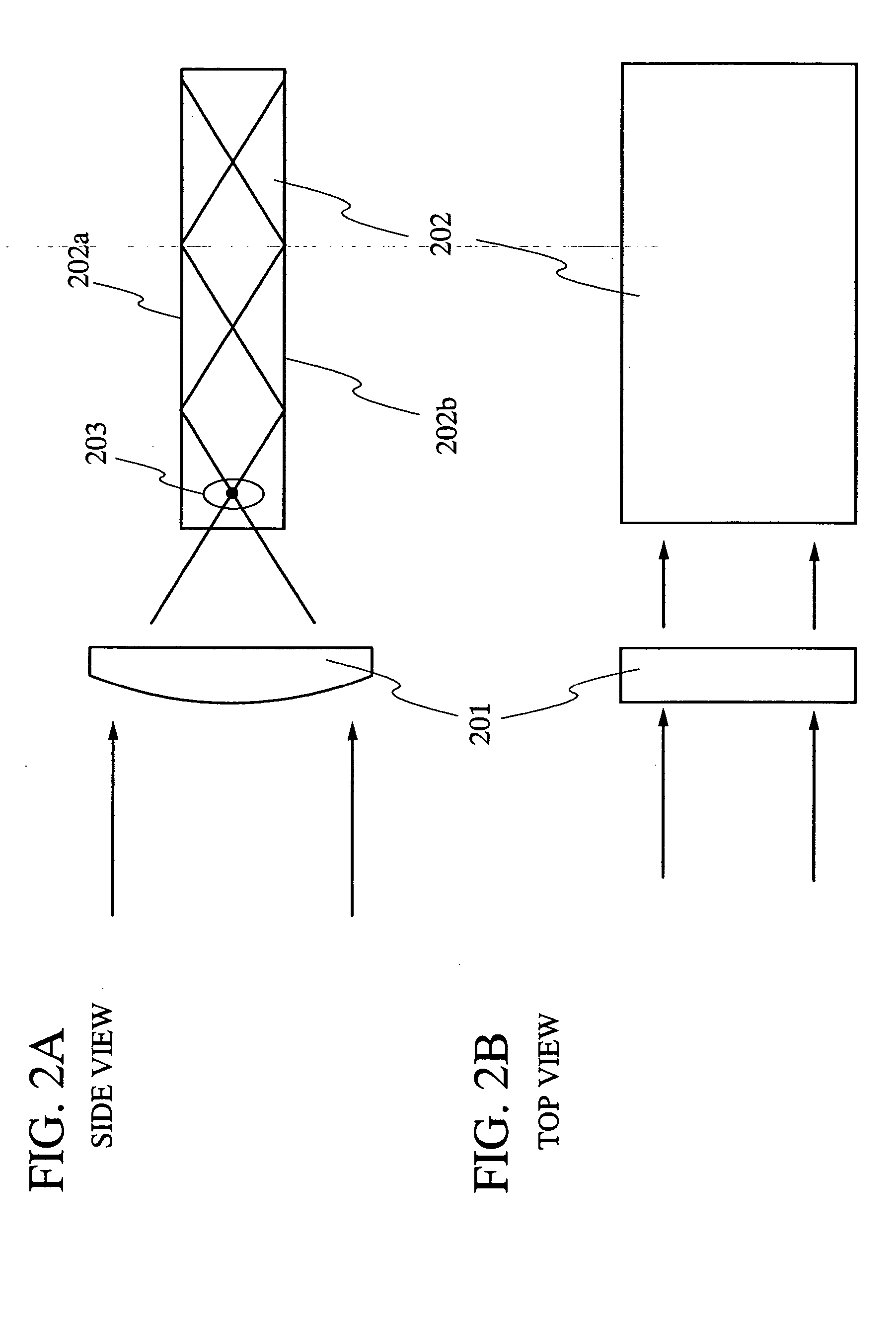
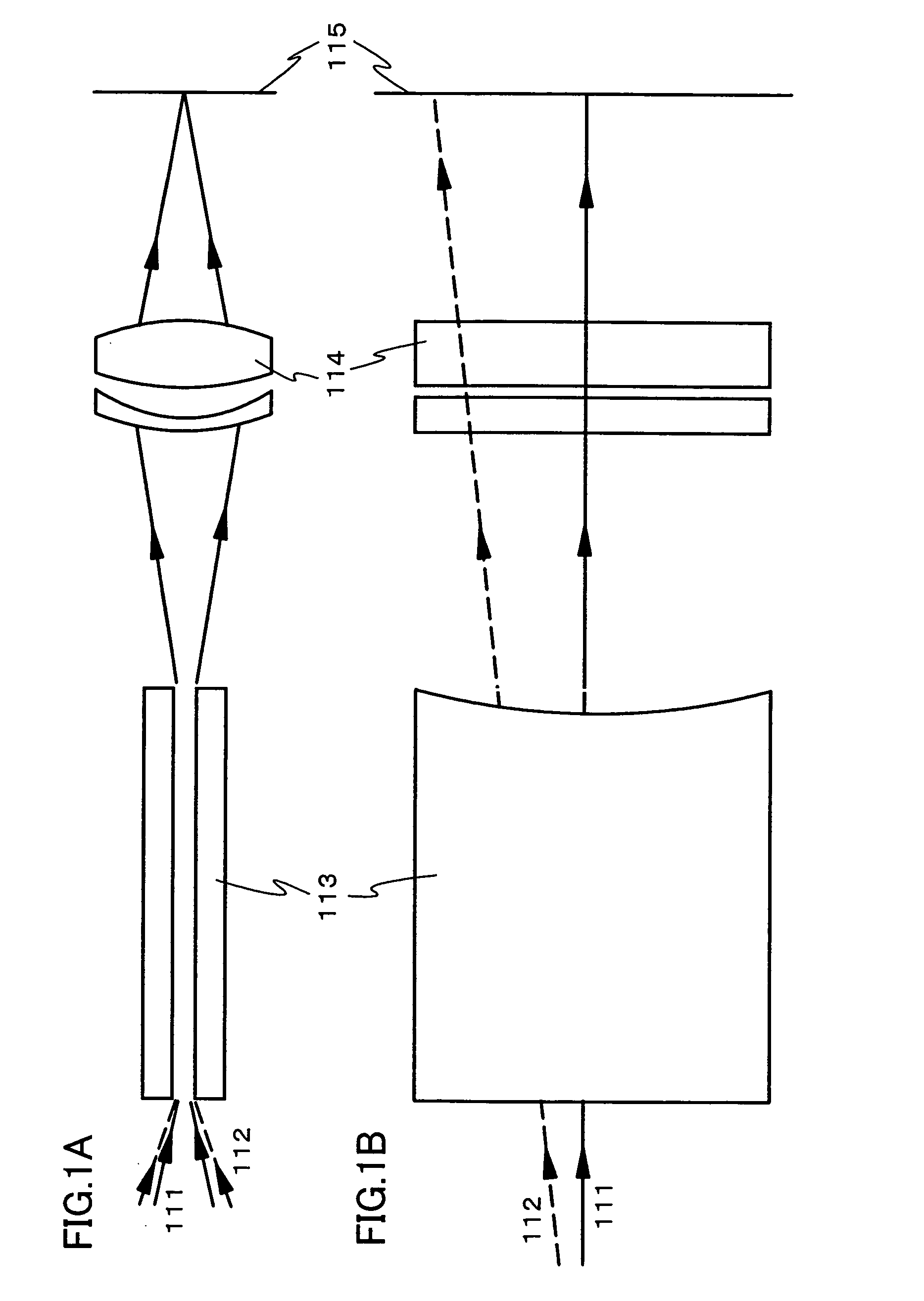
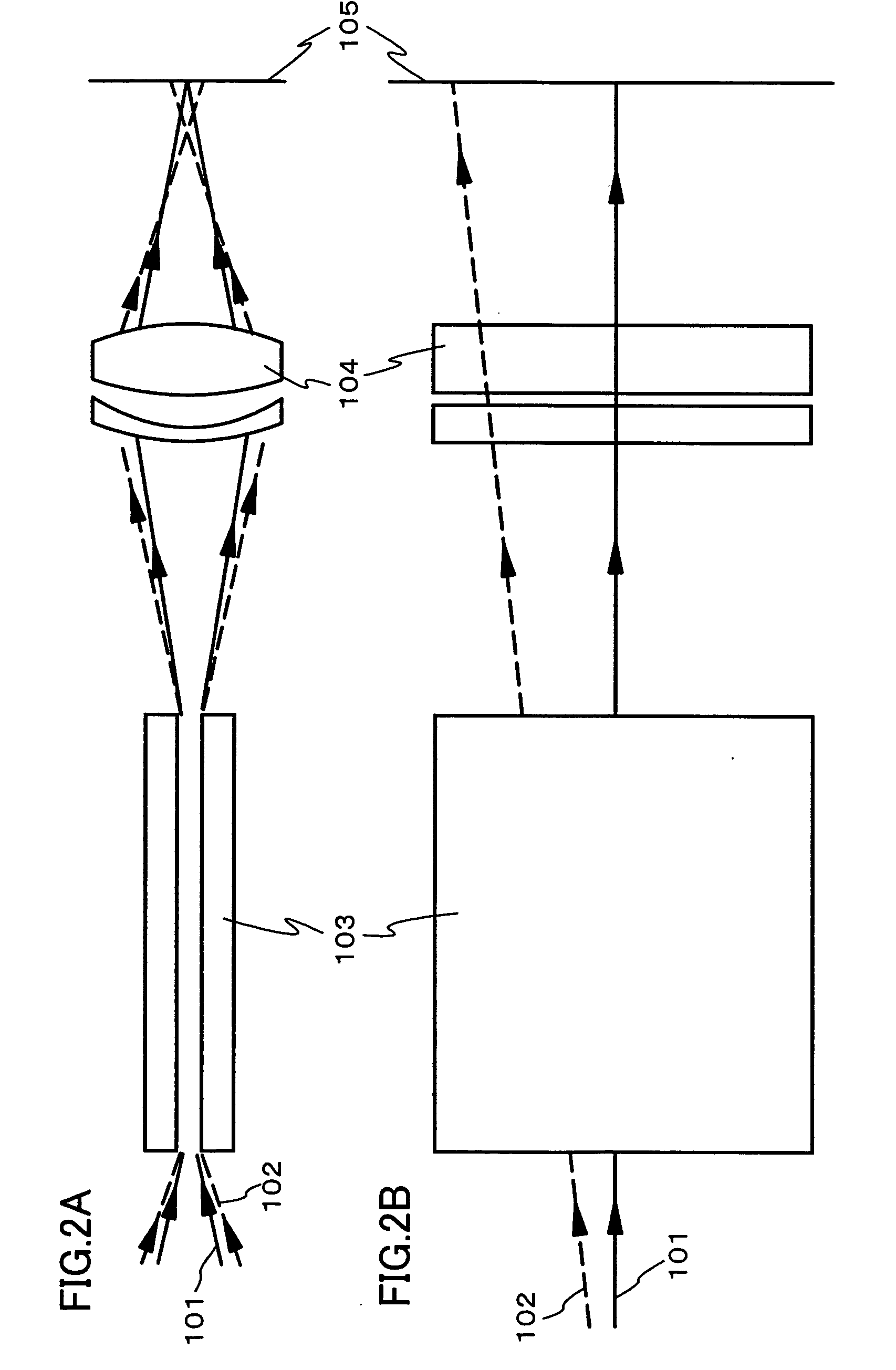
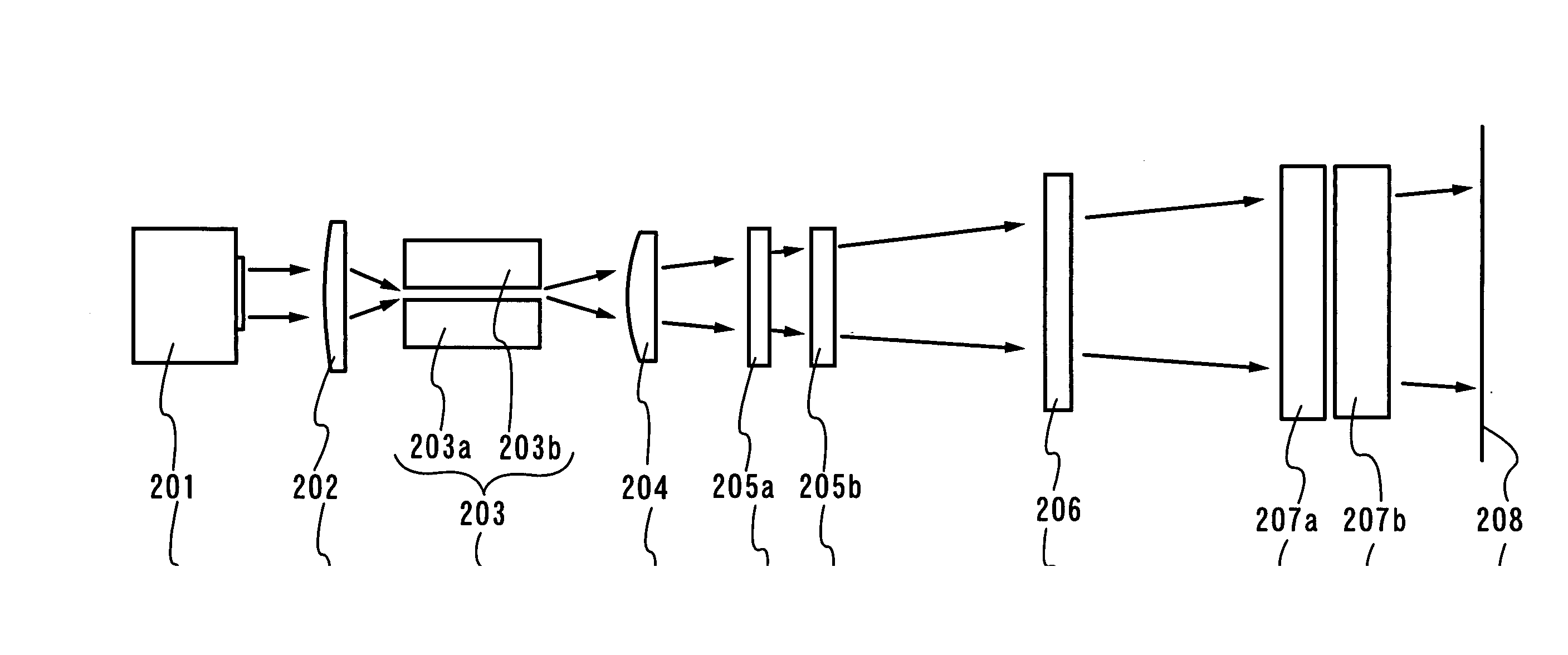
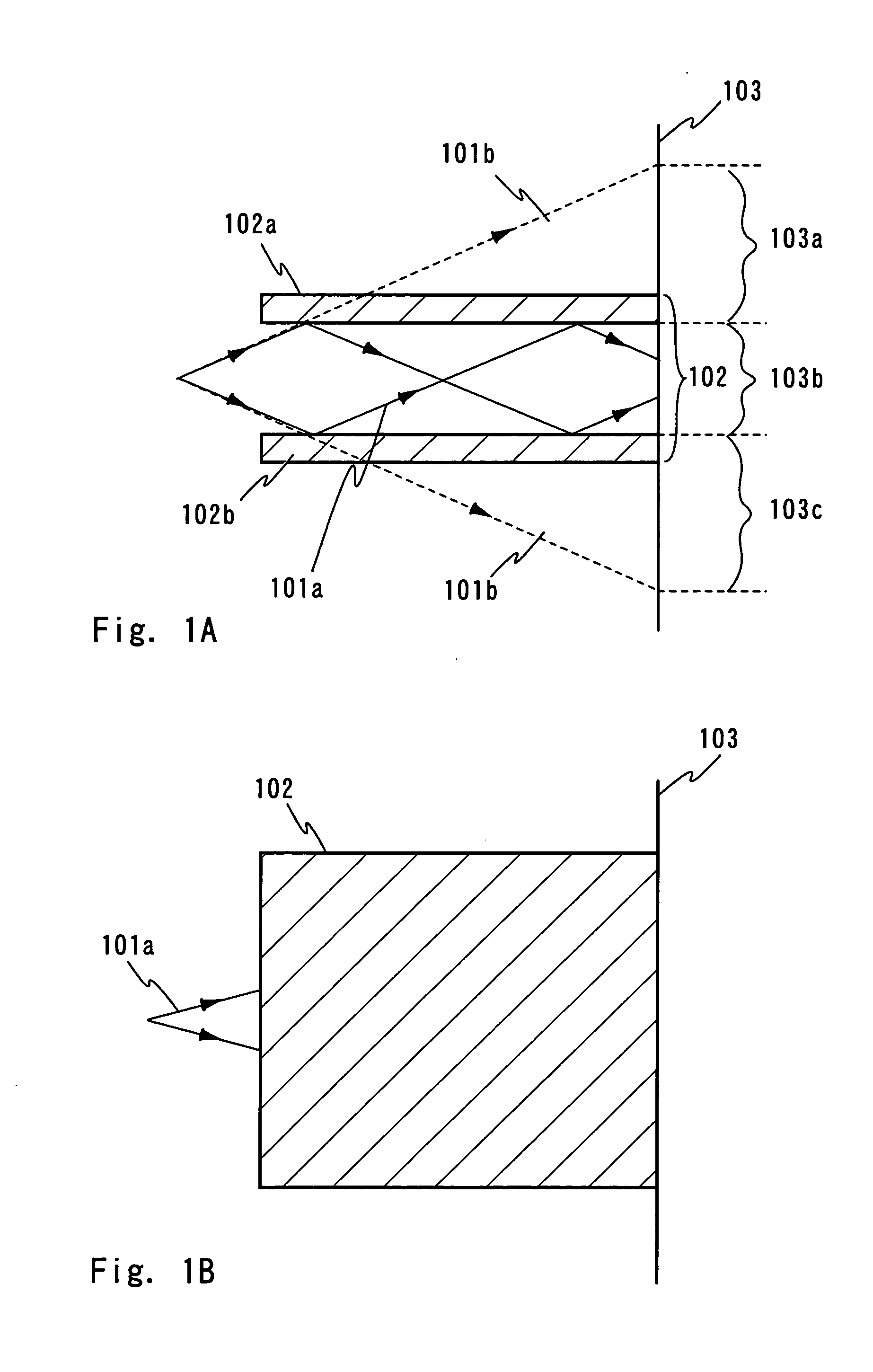
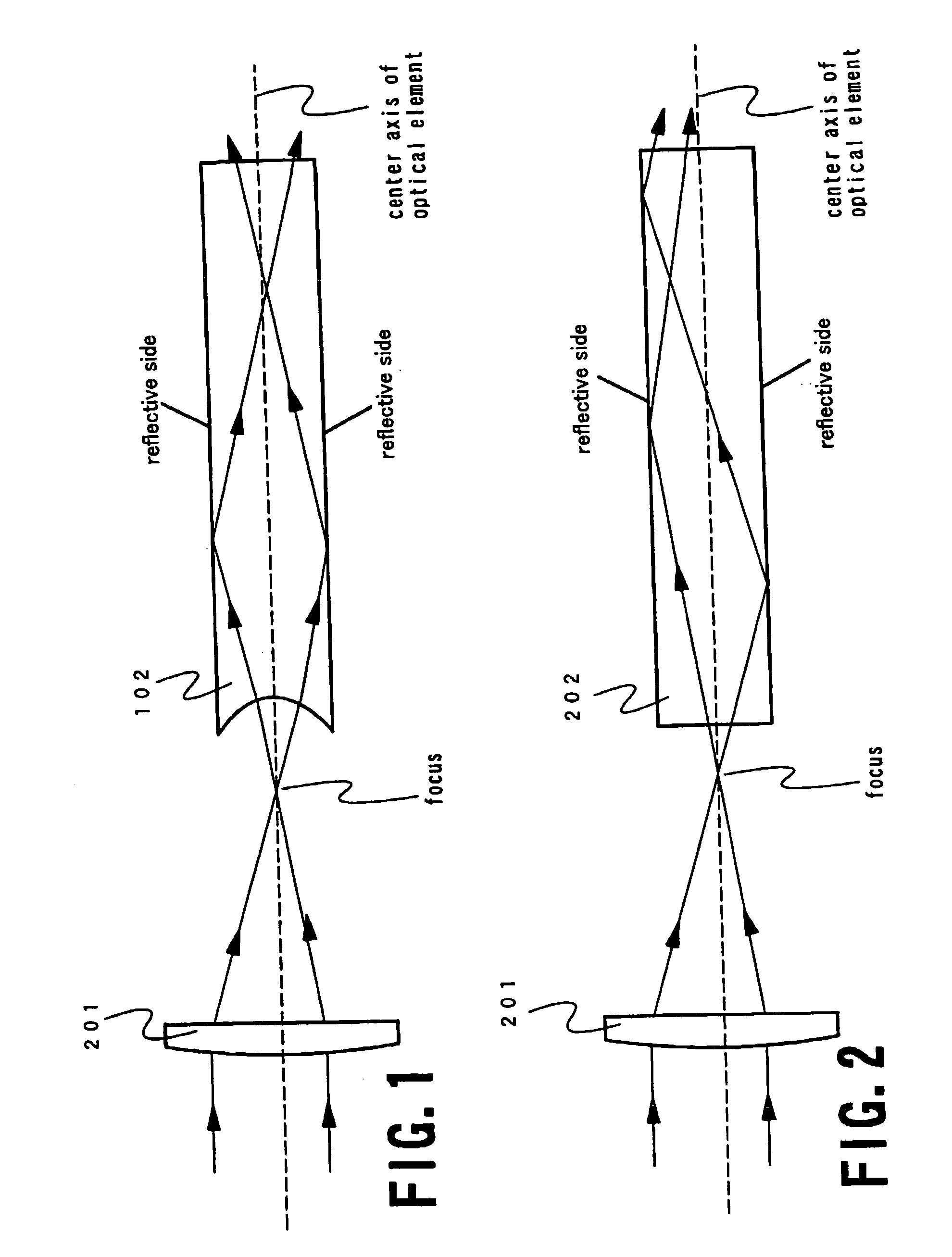
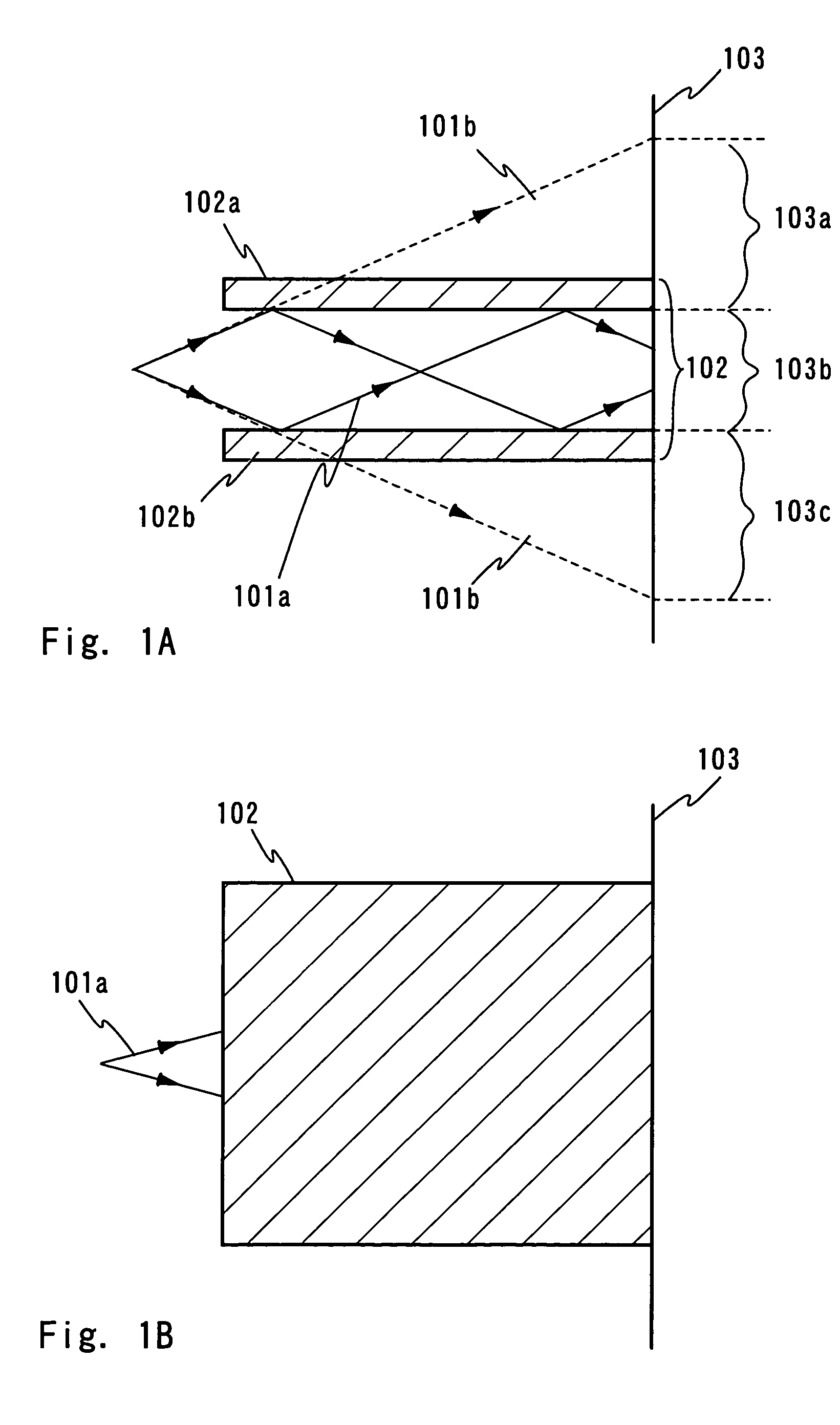
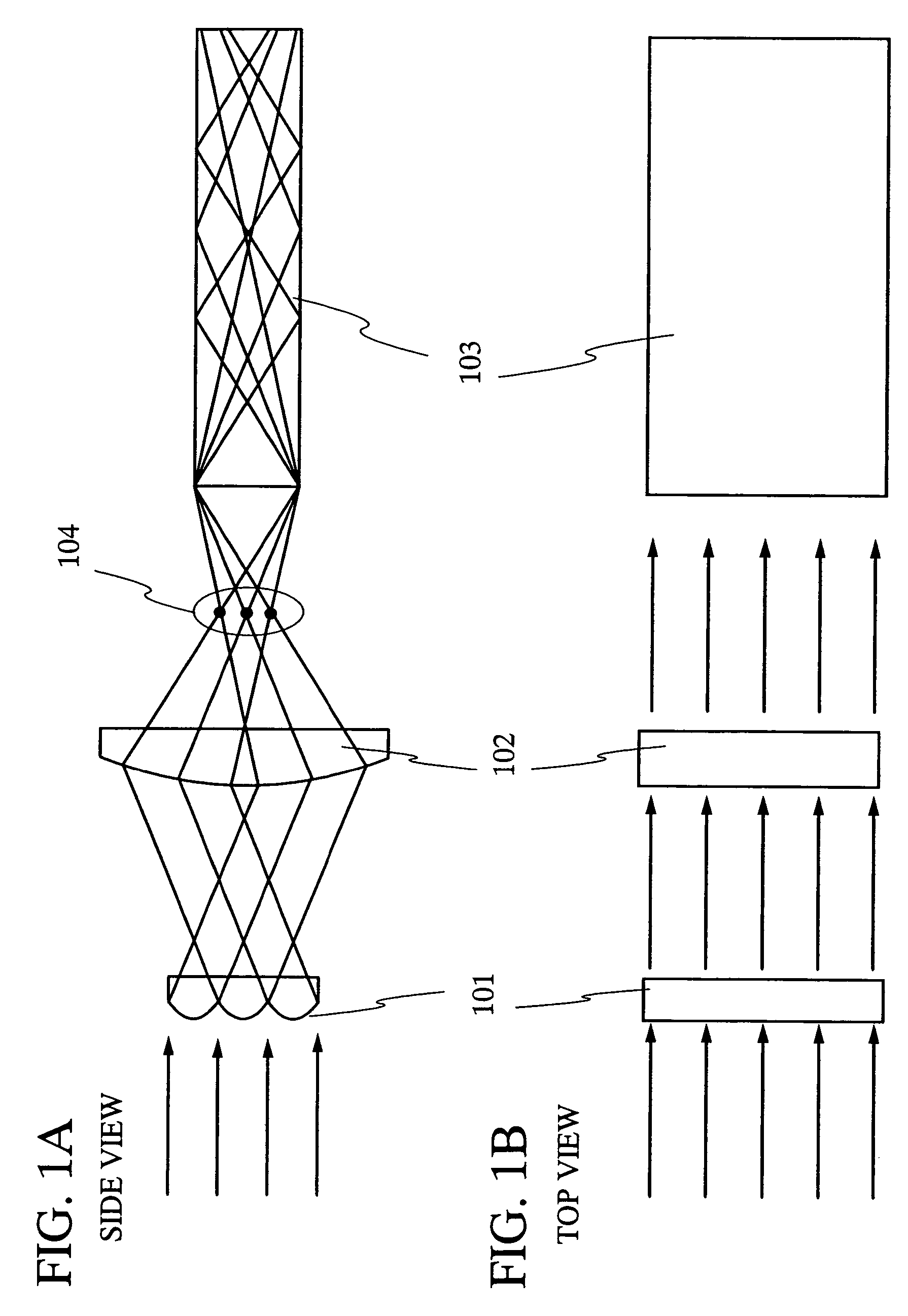
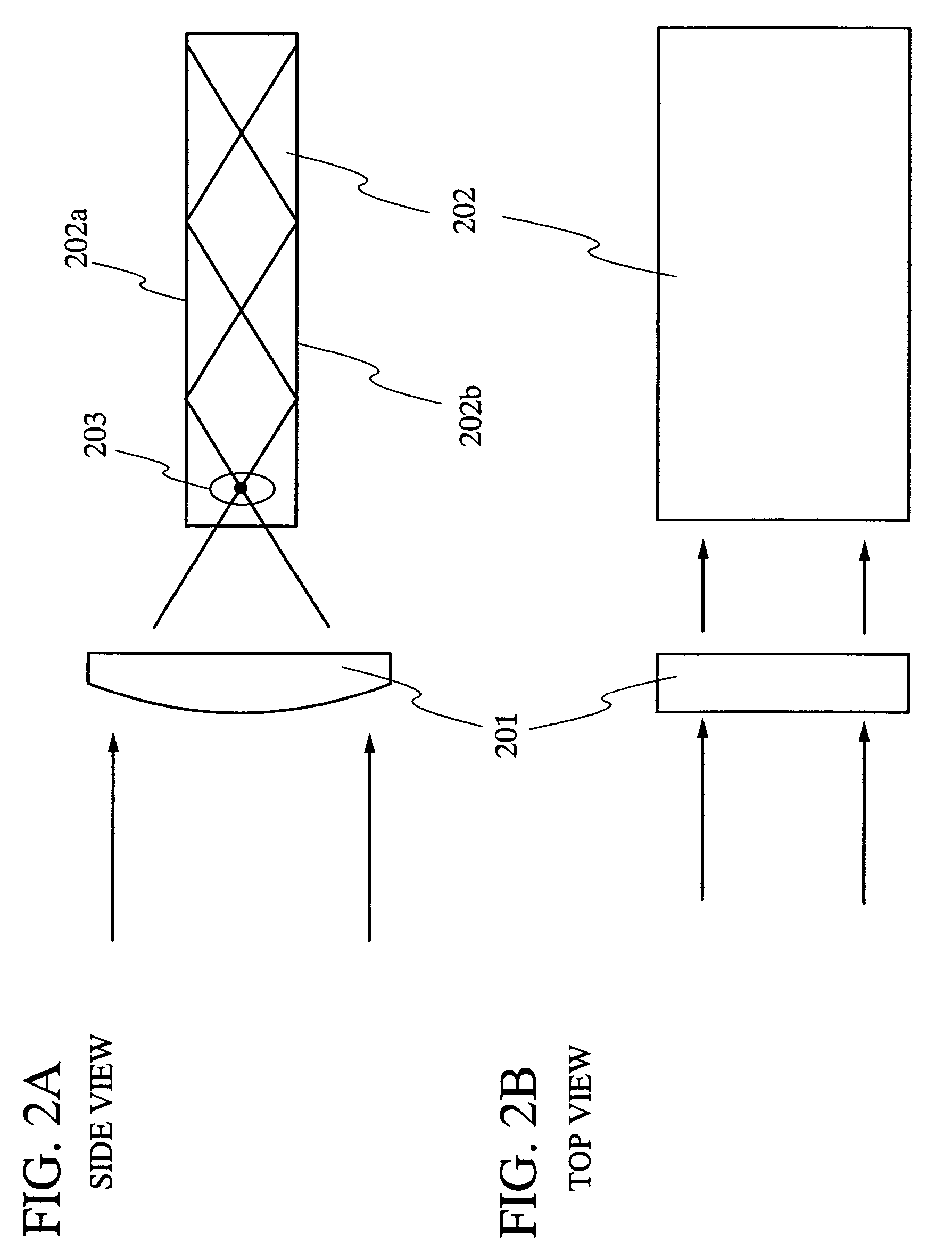
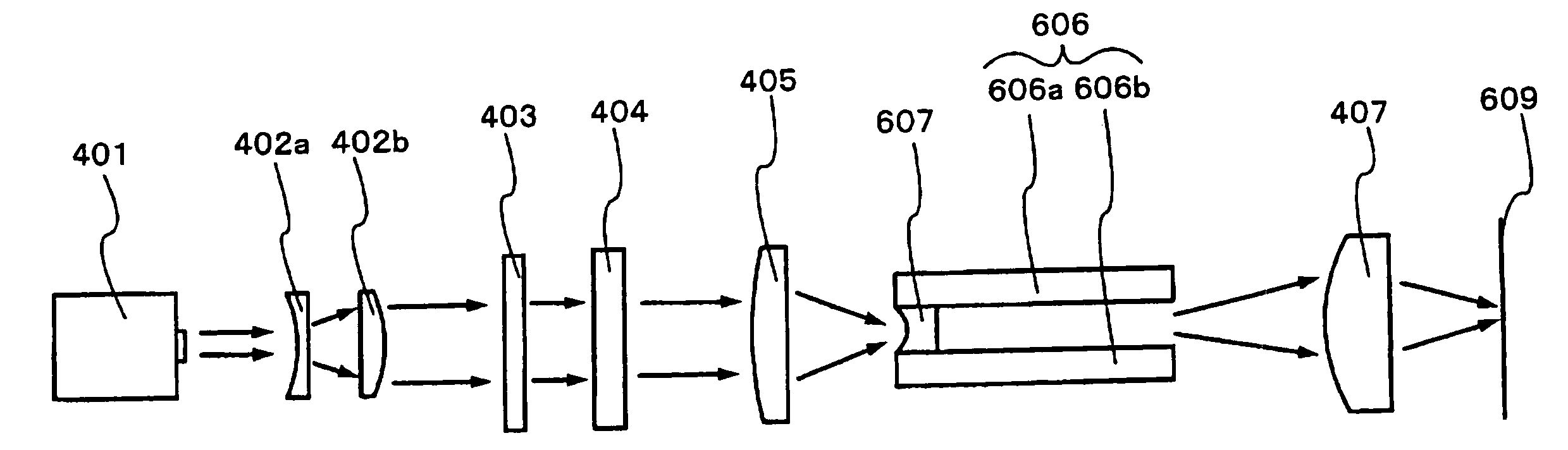
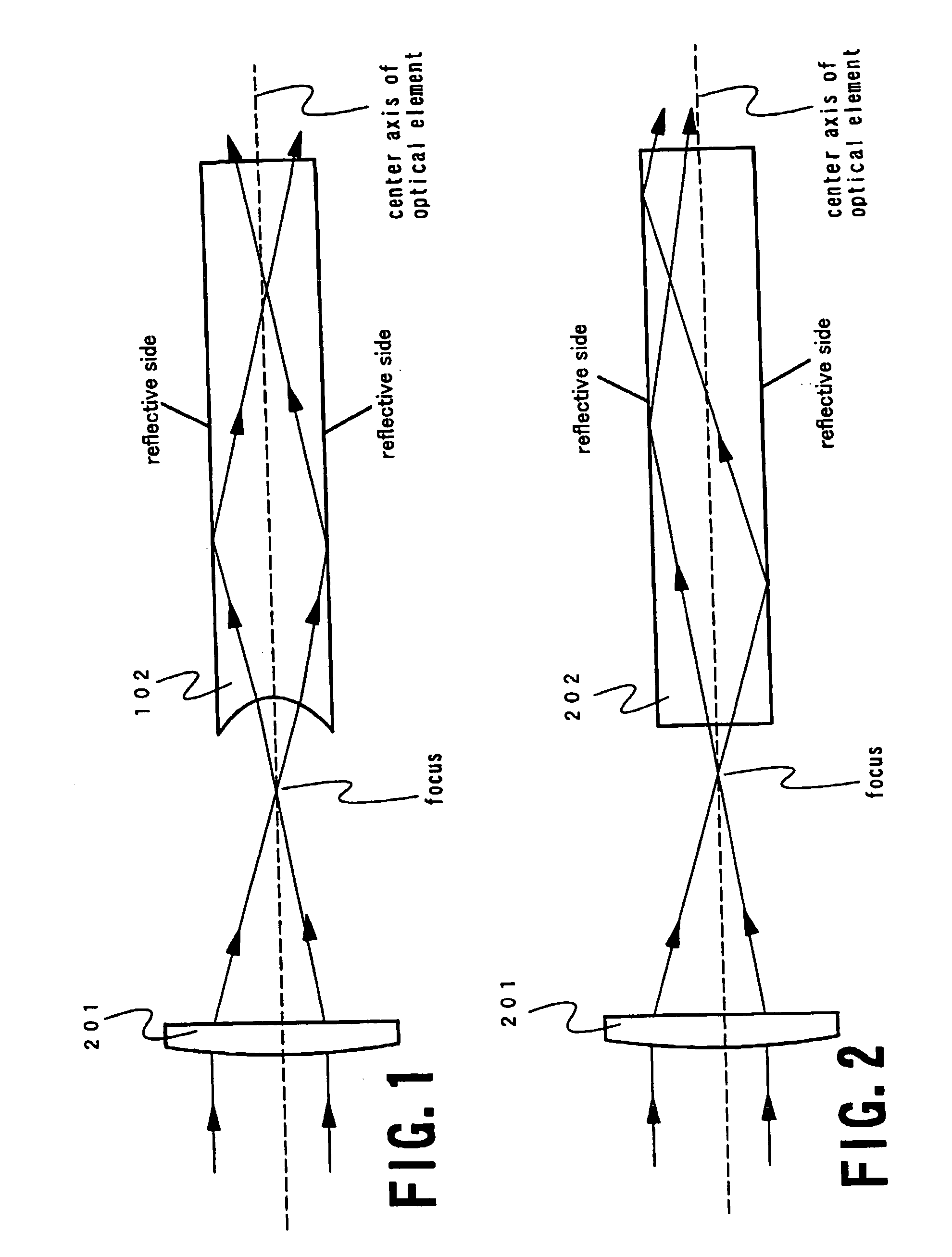
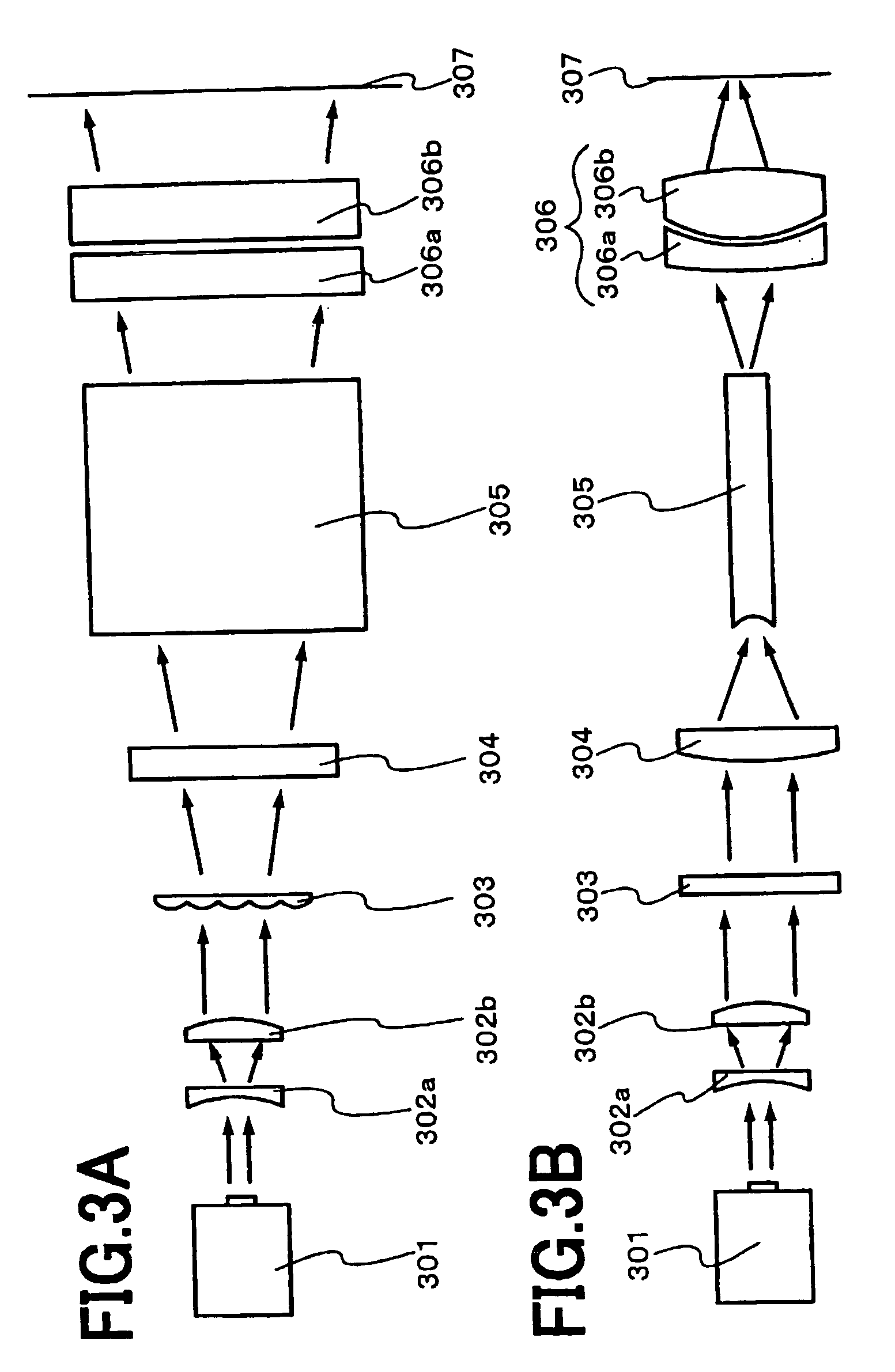
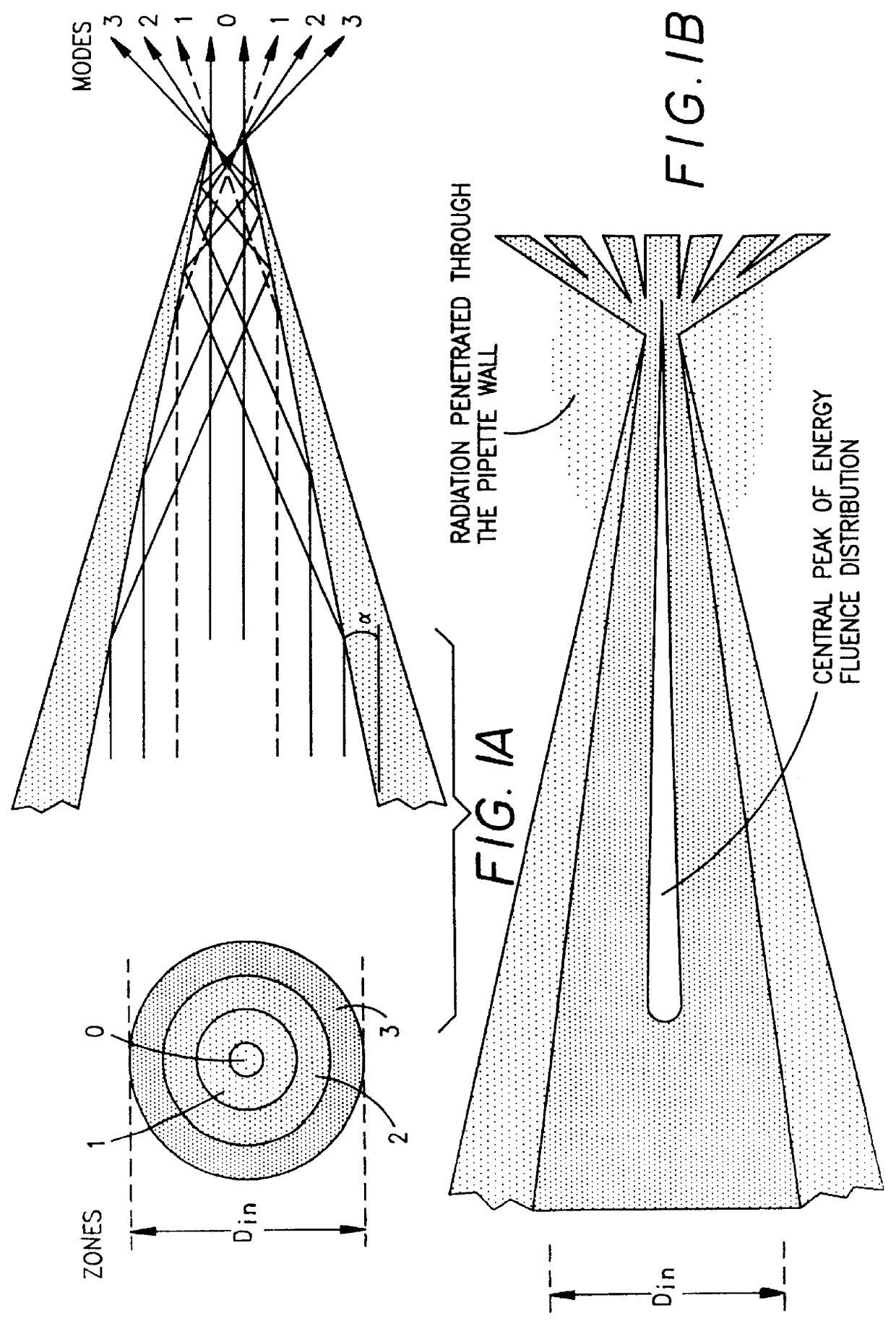
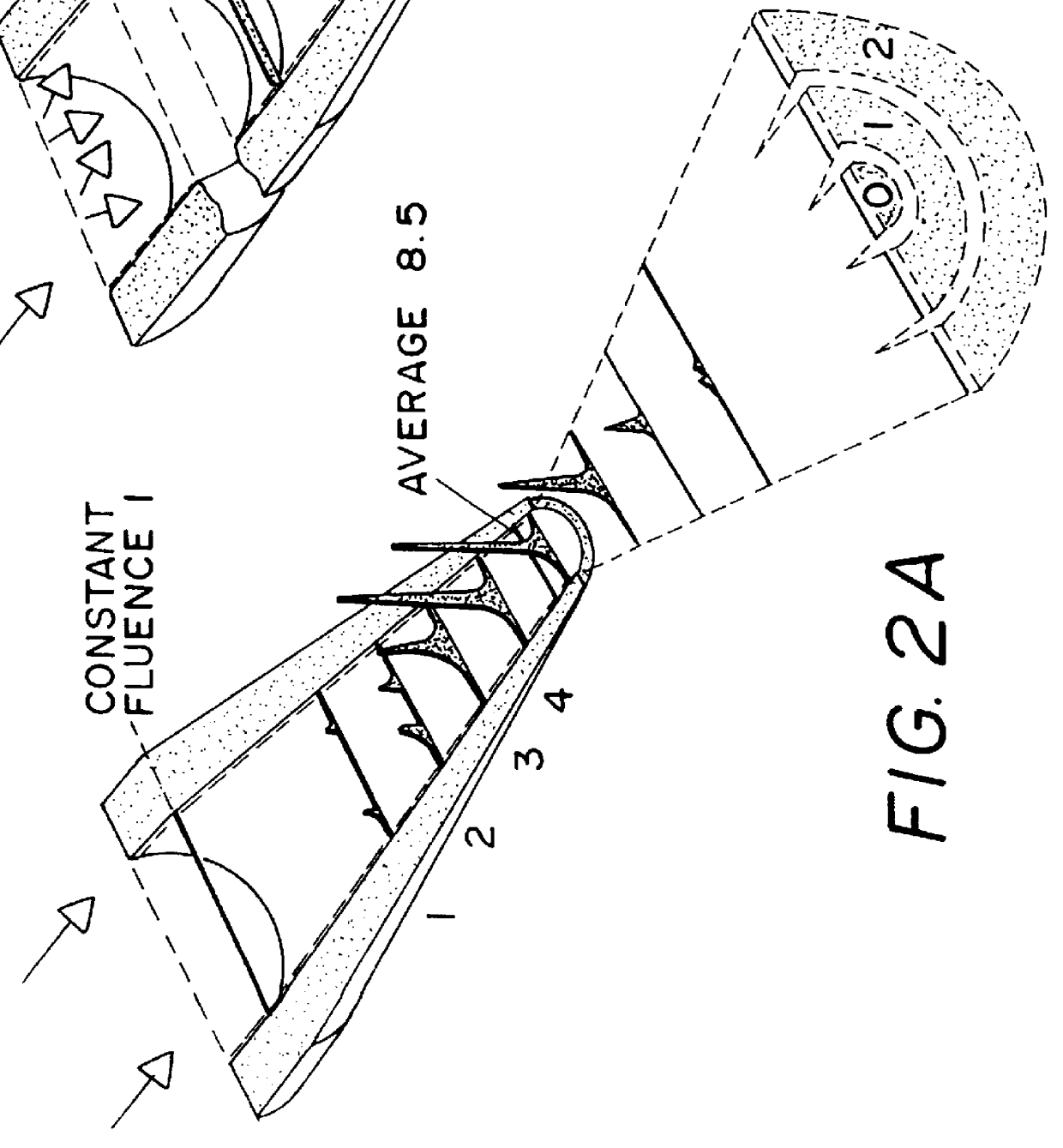
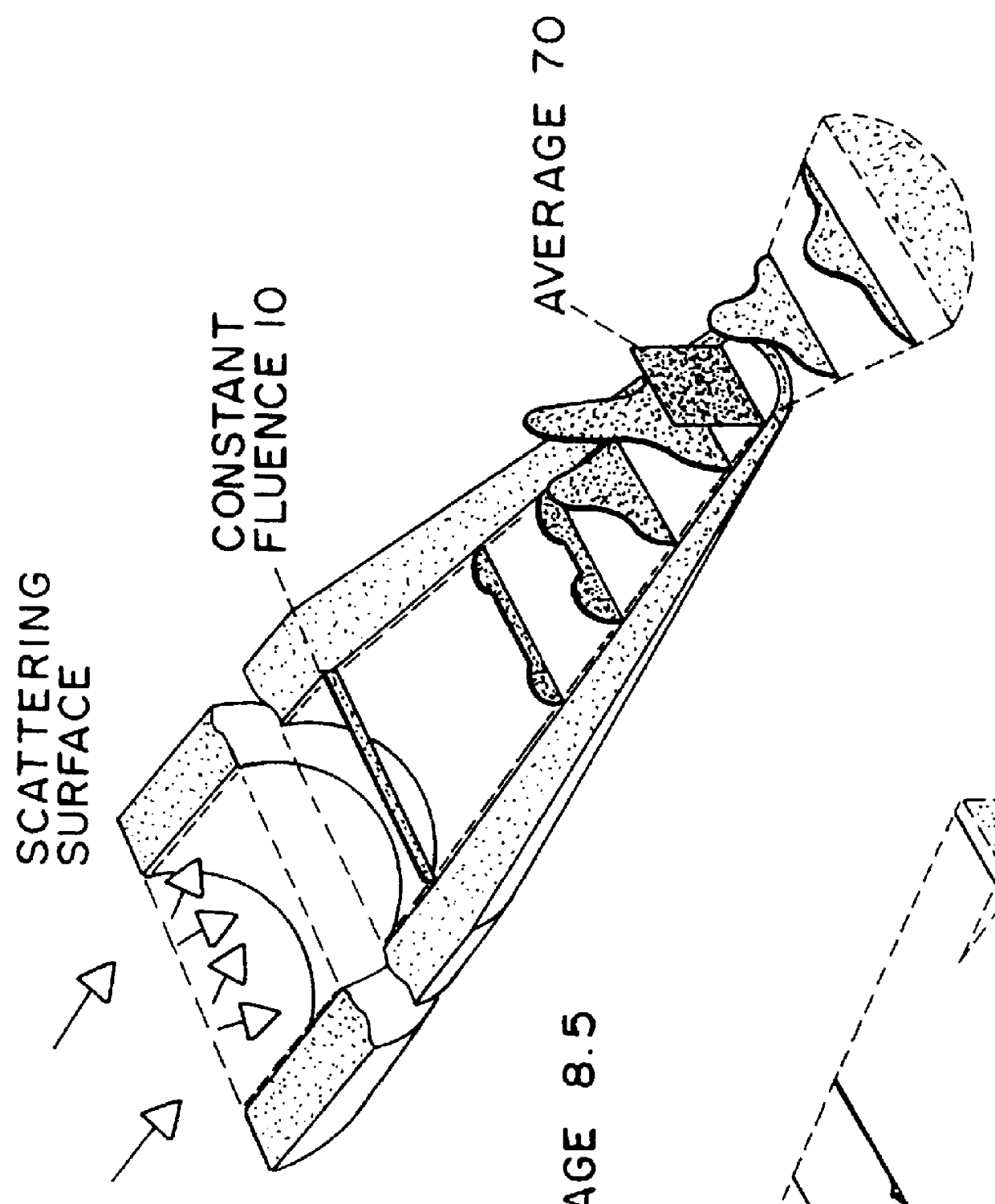
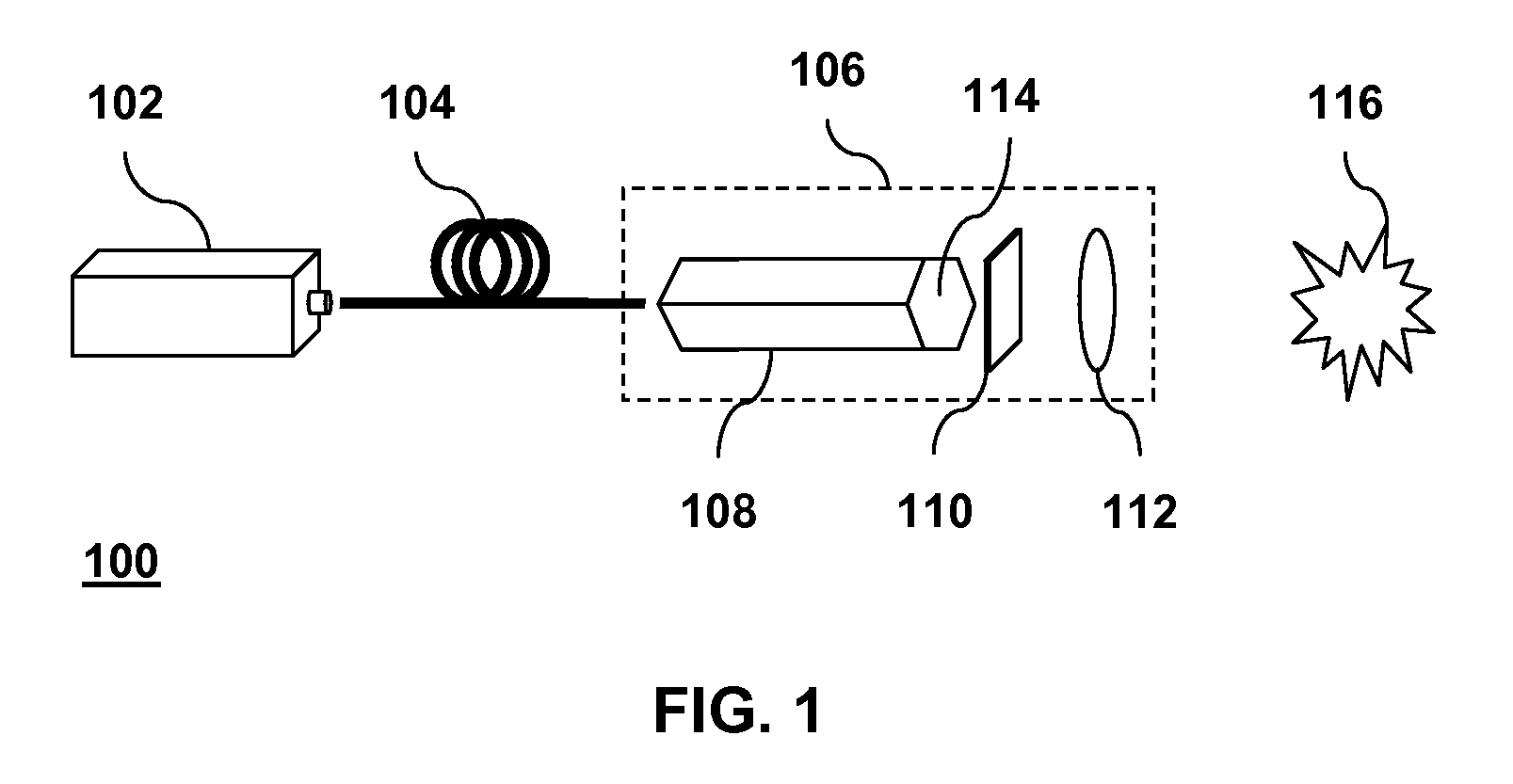
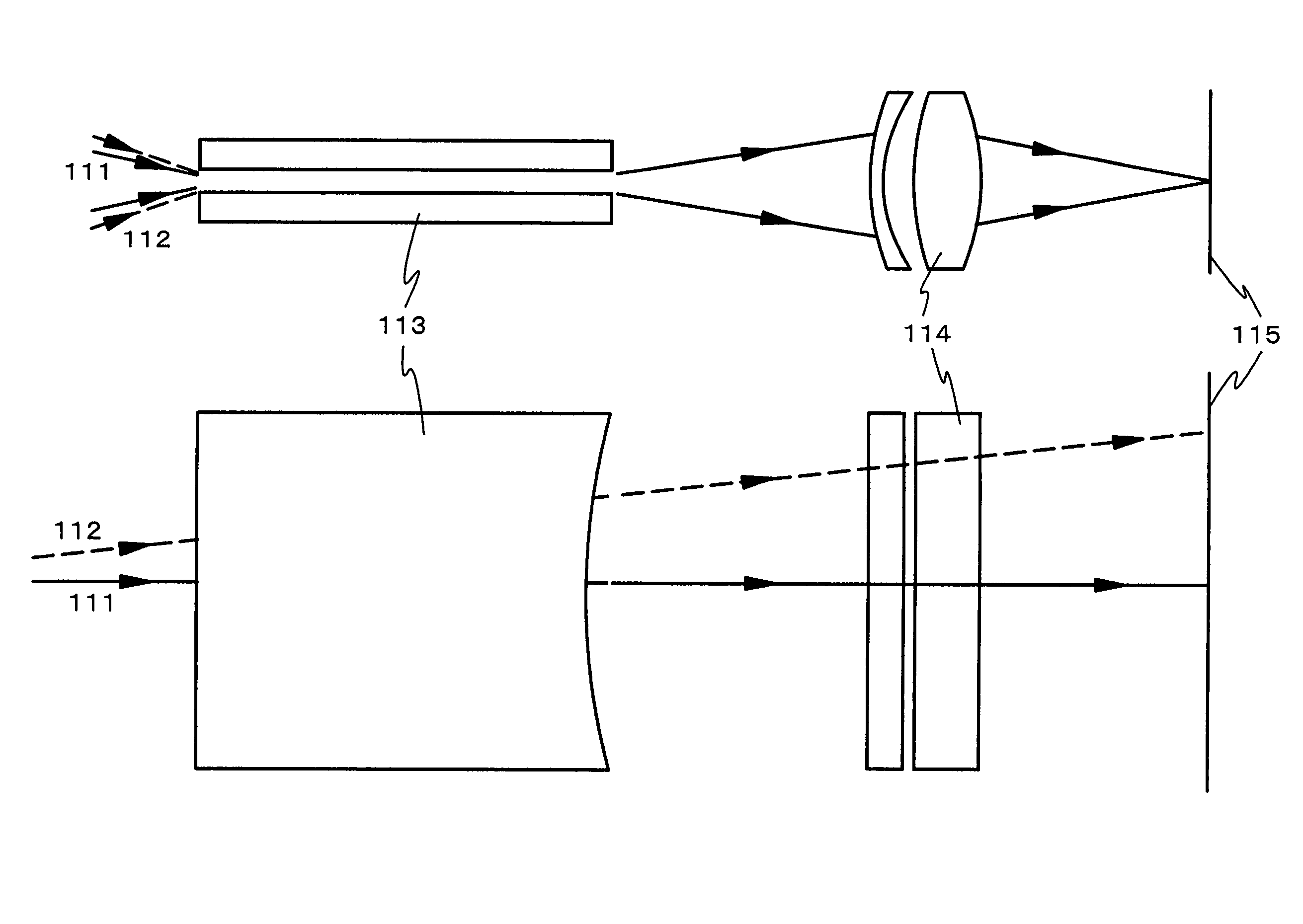
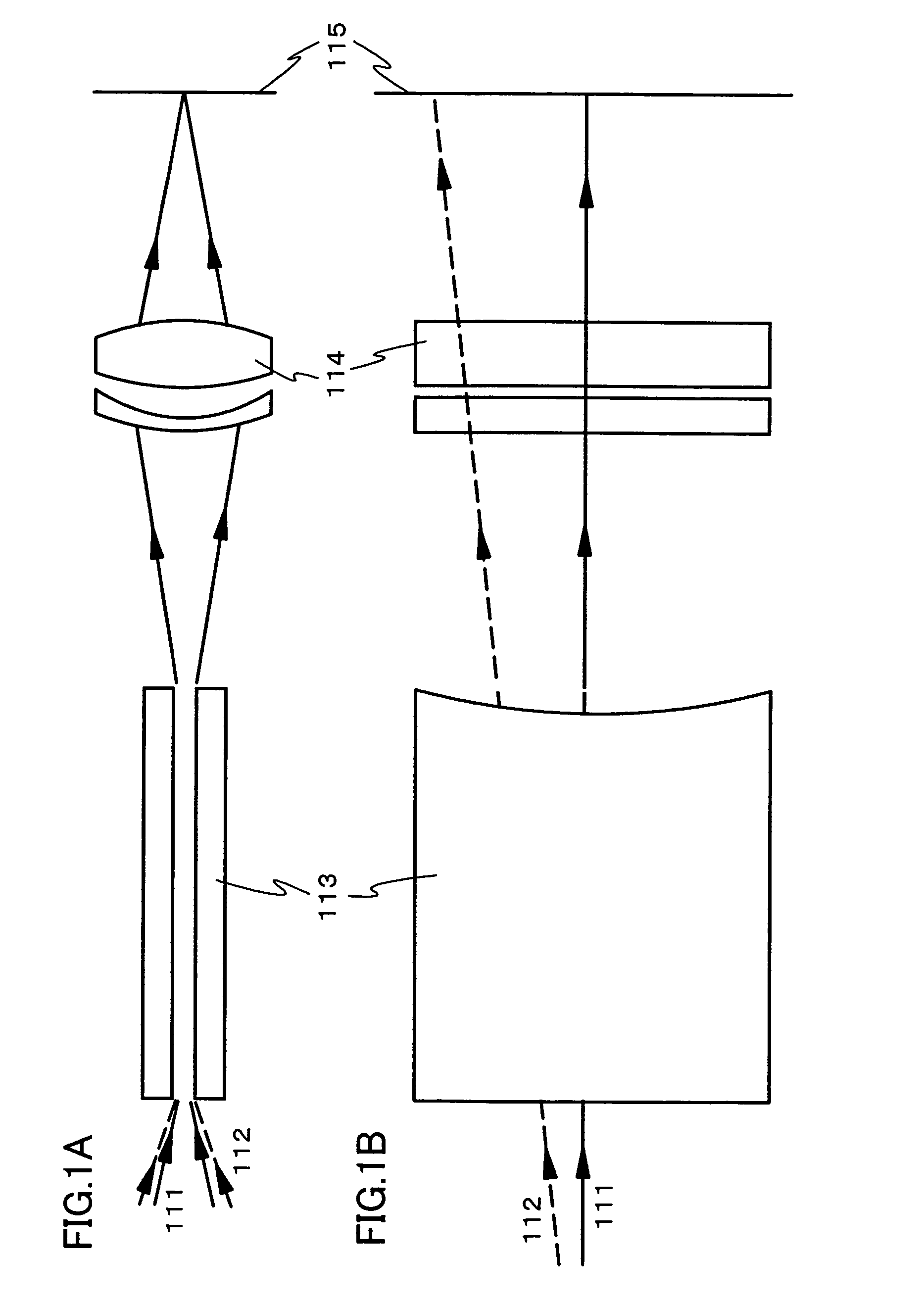
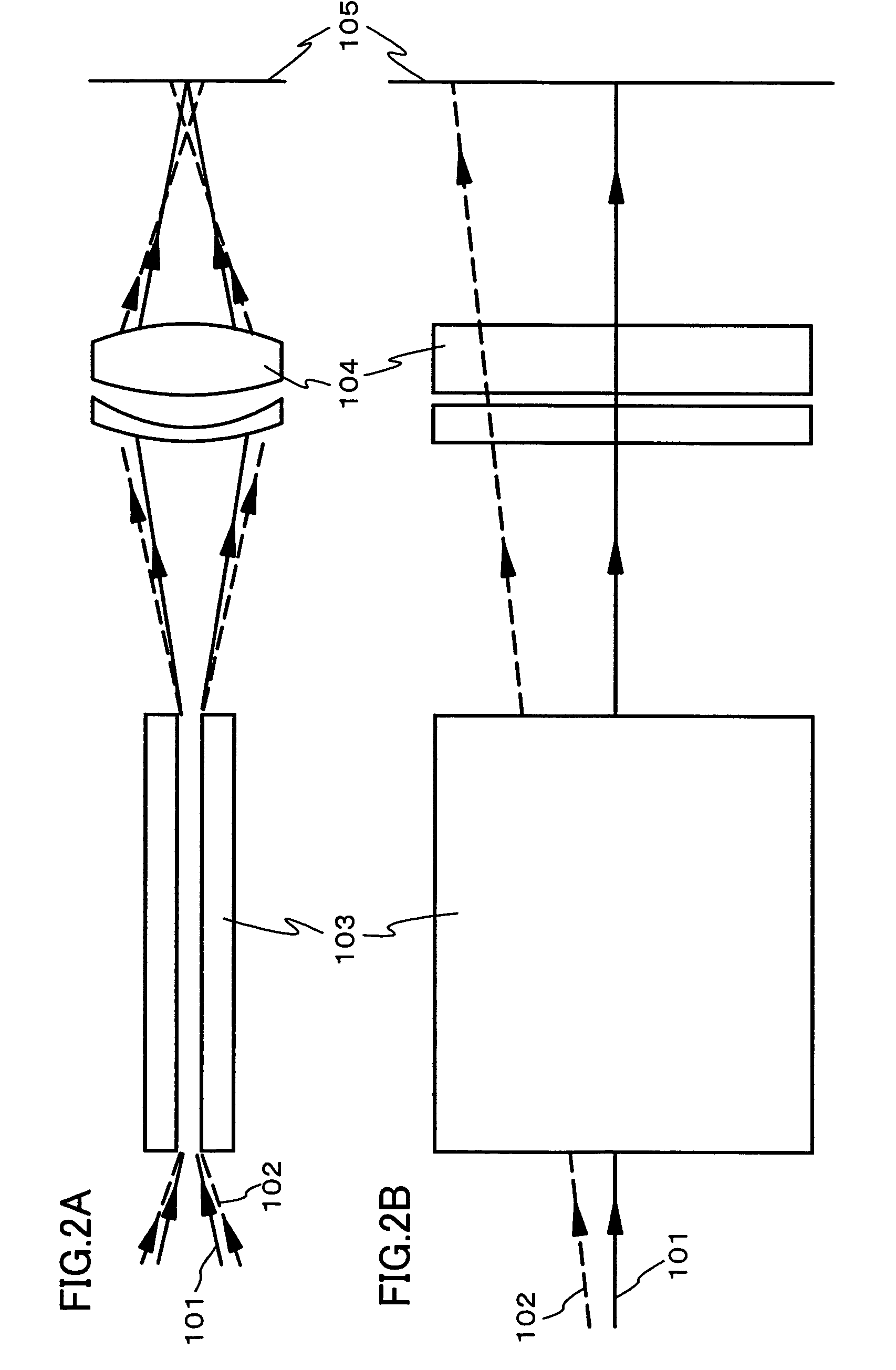
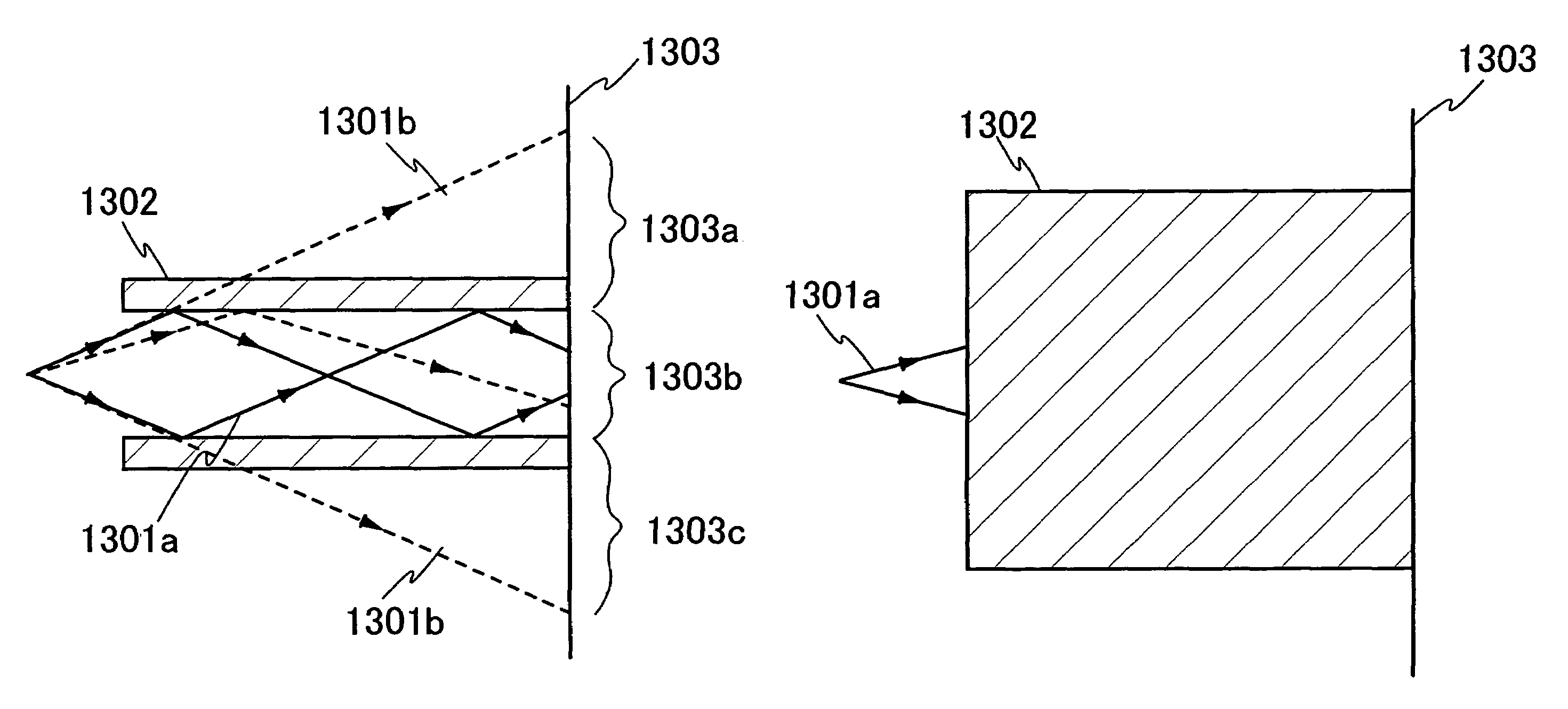
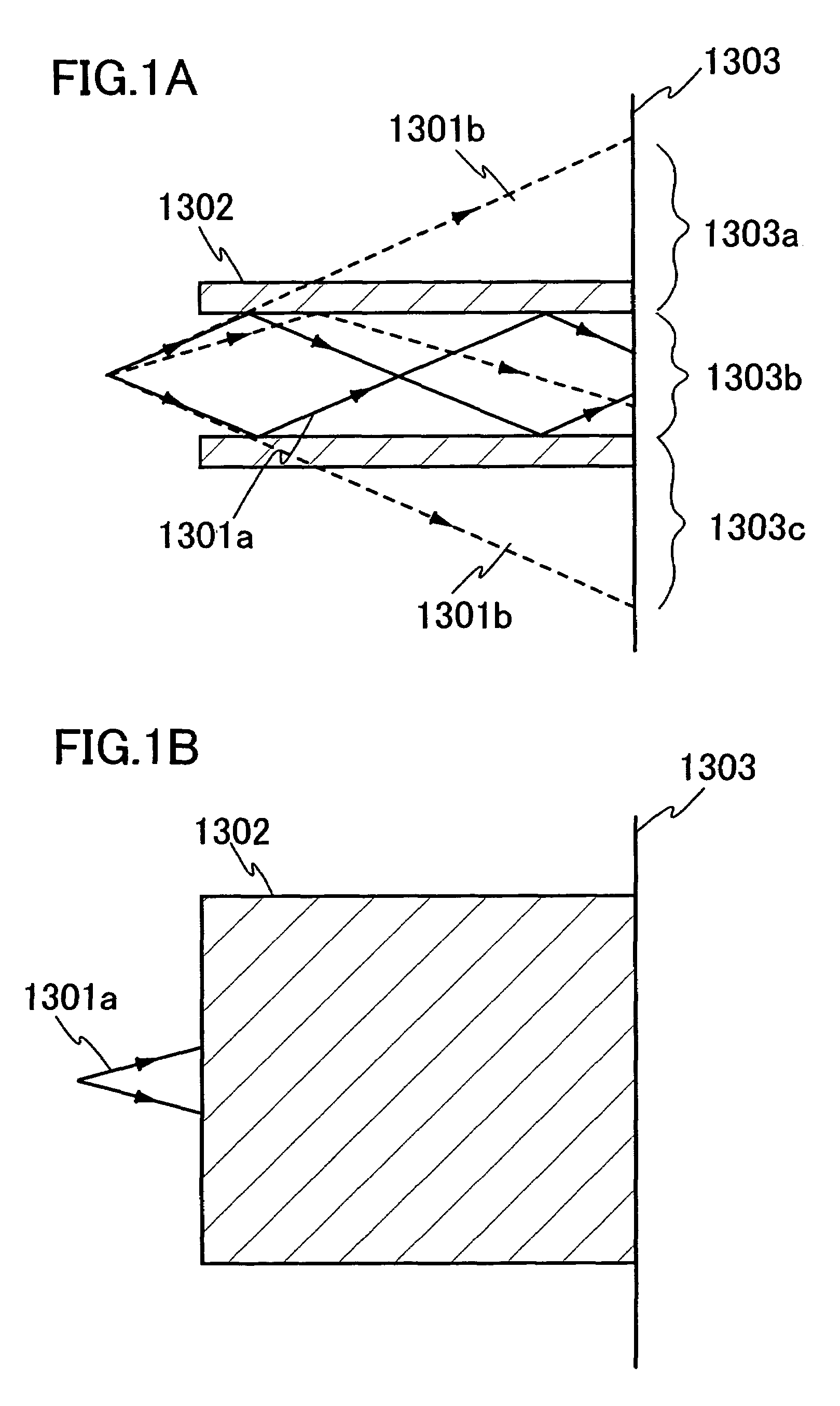
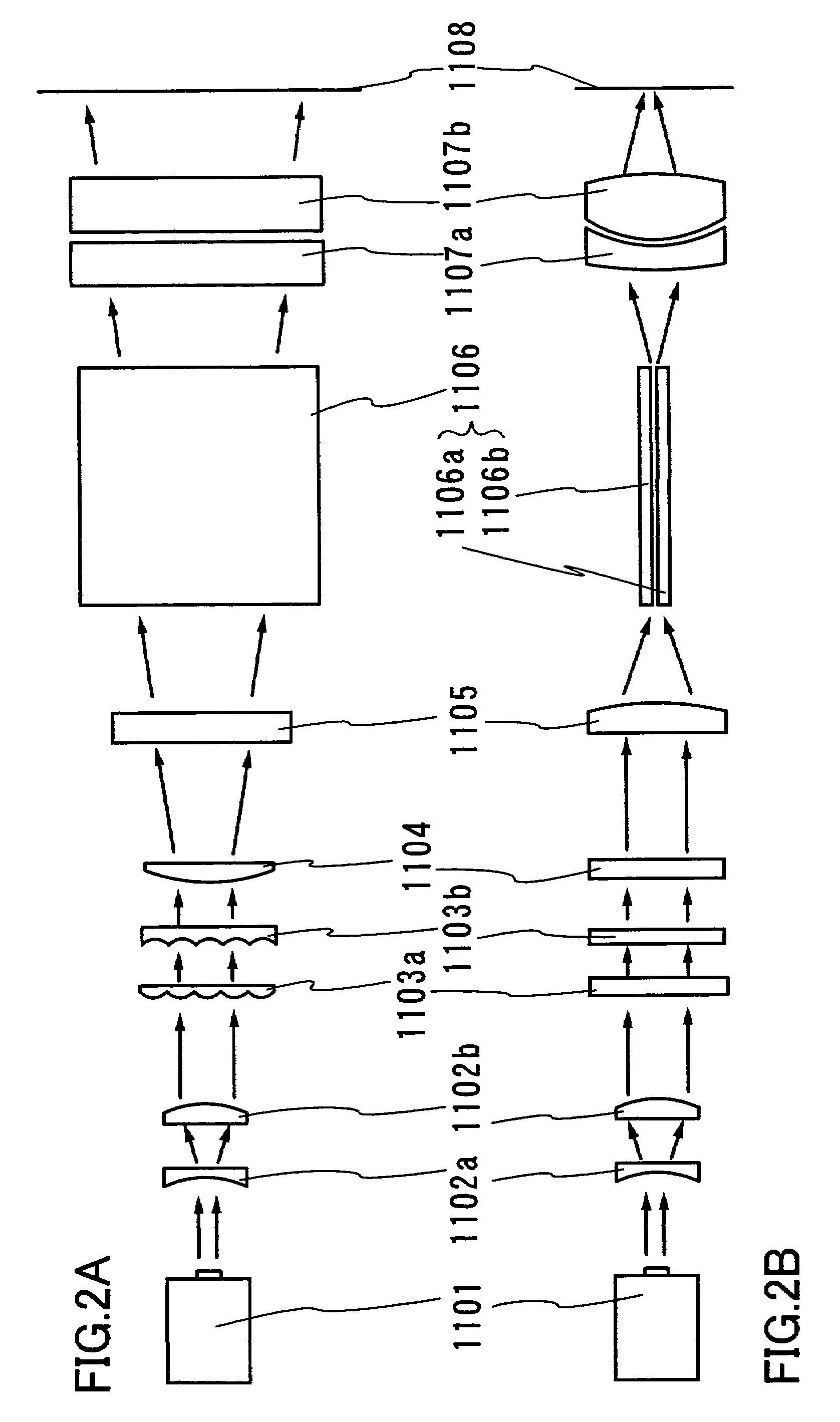
An optical system (in FIGS. 1A and 1B) wherein a rectilinear laser beam of homogeneous energy distribution is defined for annealing a non-single crystalline semiconductor film (a surface to-be-irradiated 1108), is constructed of reflectors (1106, 1107 etc.) easily and inexpensively without including lenses of transmission type. The rectilinear laser beam can be defined having a length of at least 600 (mm) which corresponds to the shorter latus of a large-sized substrate for mass production.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus
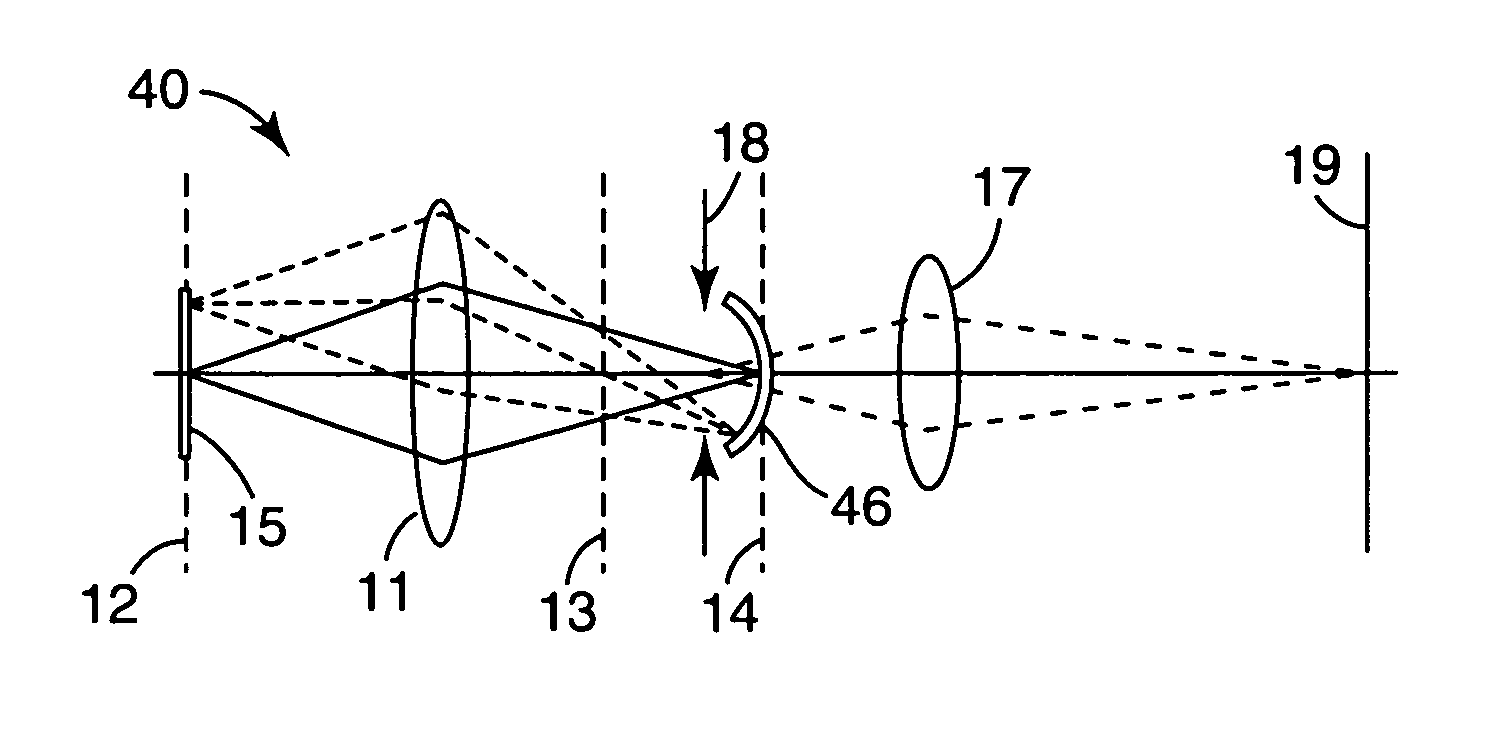
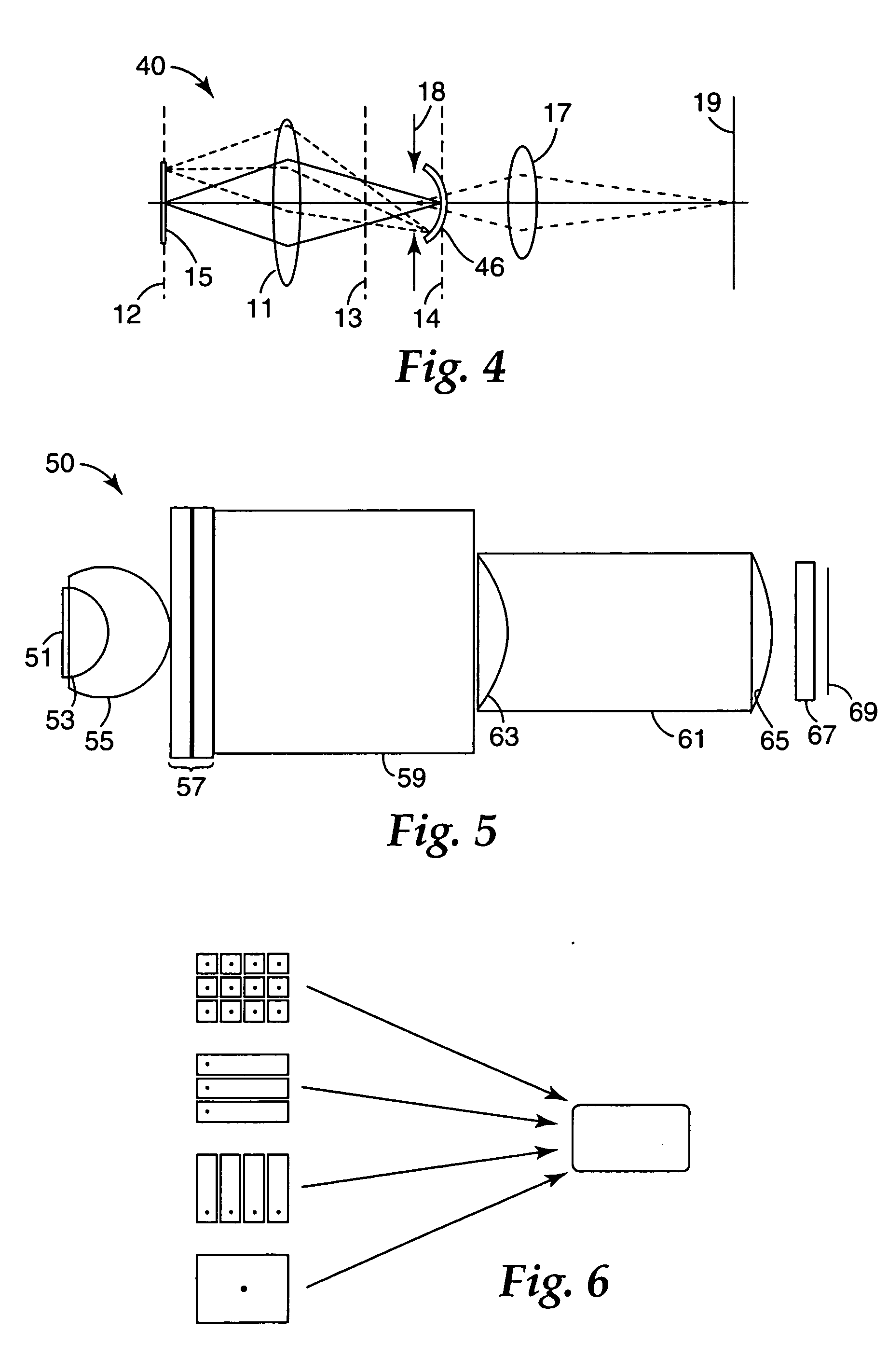
ActiveUS20060222041A1Shorten the optical path lengthSmall foot printOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
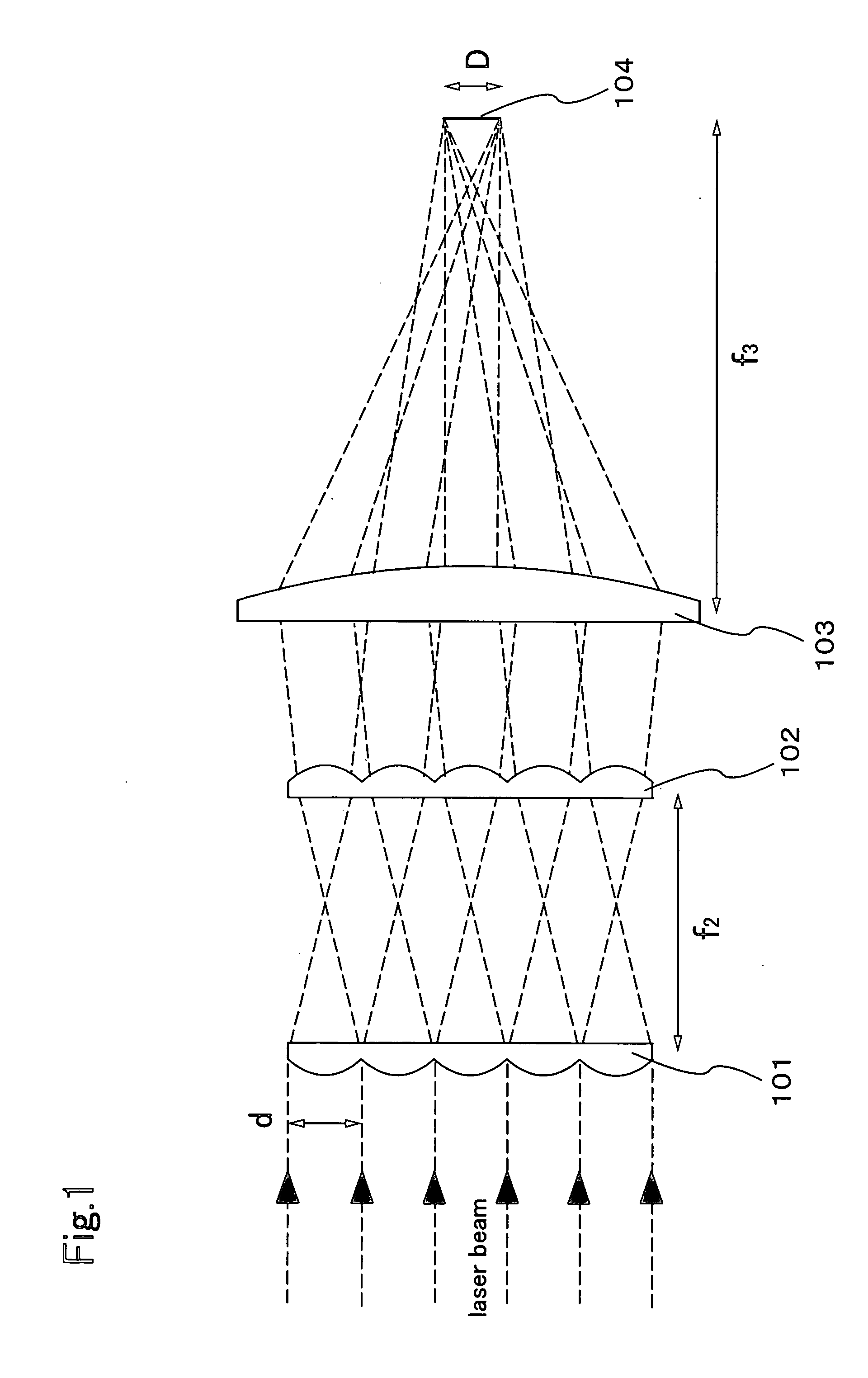
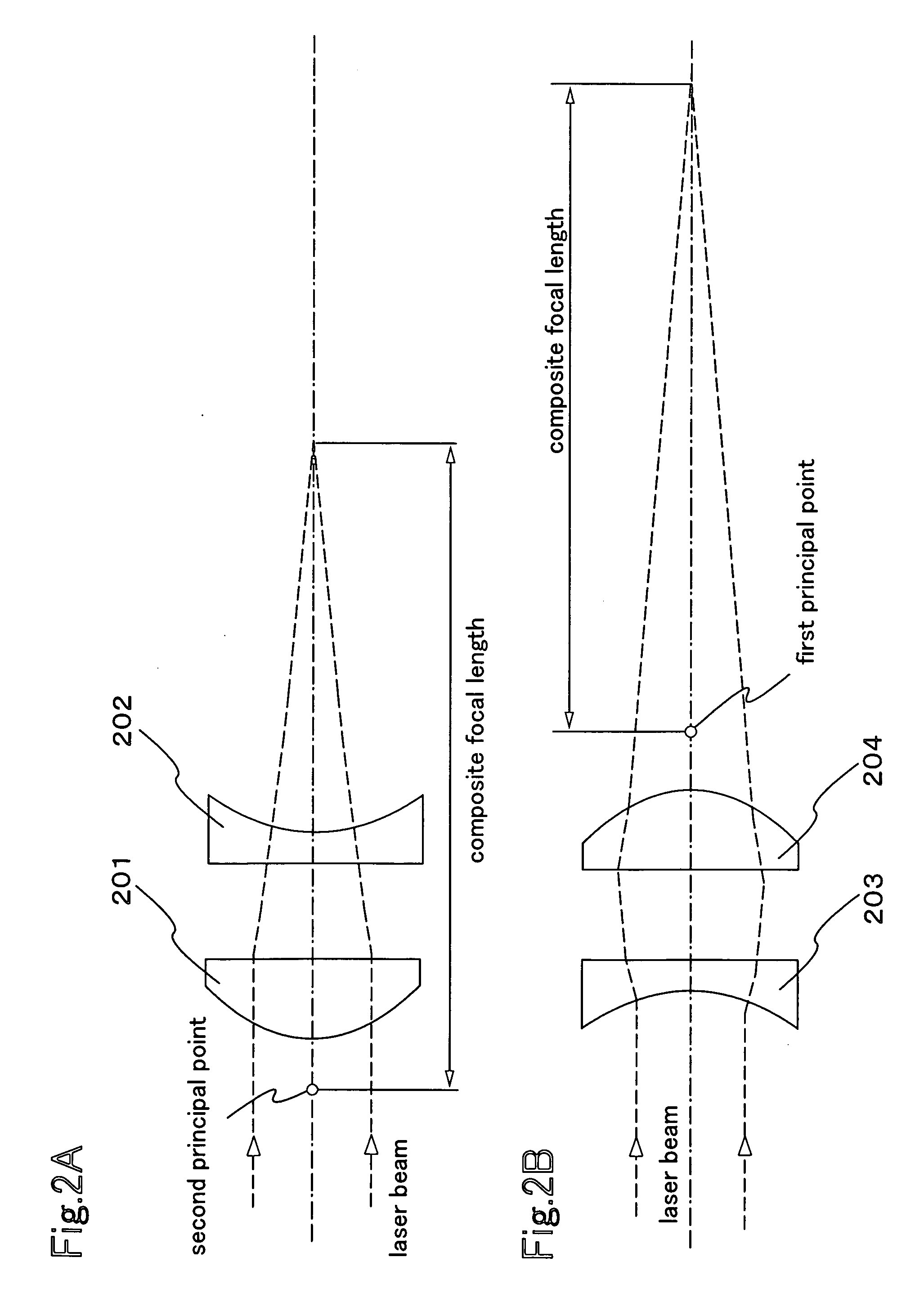
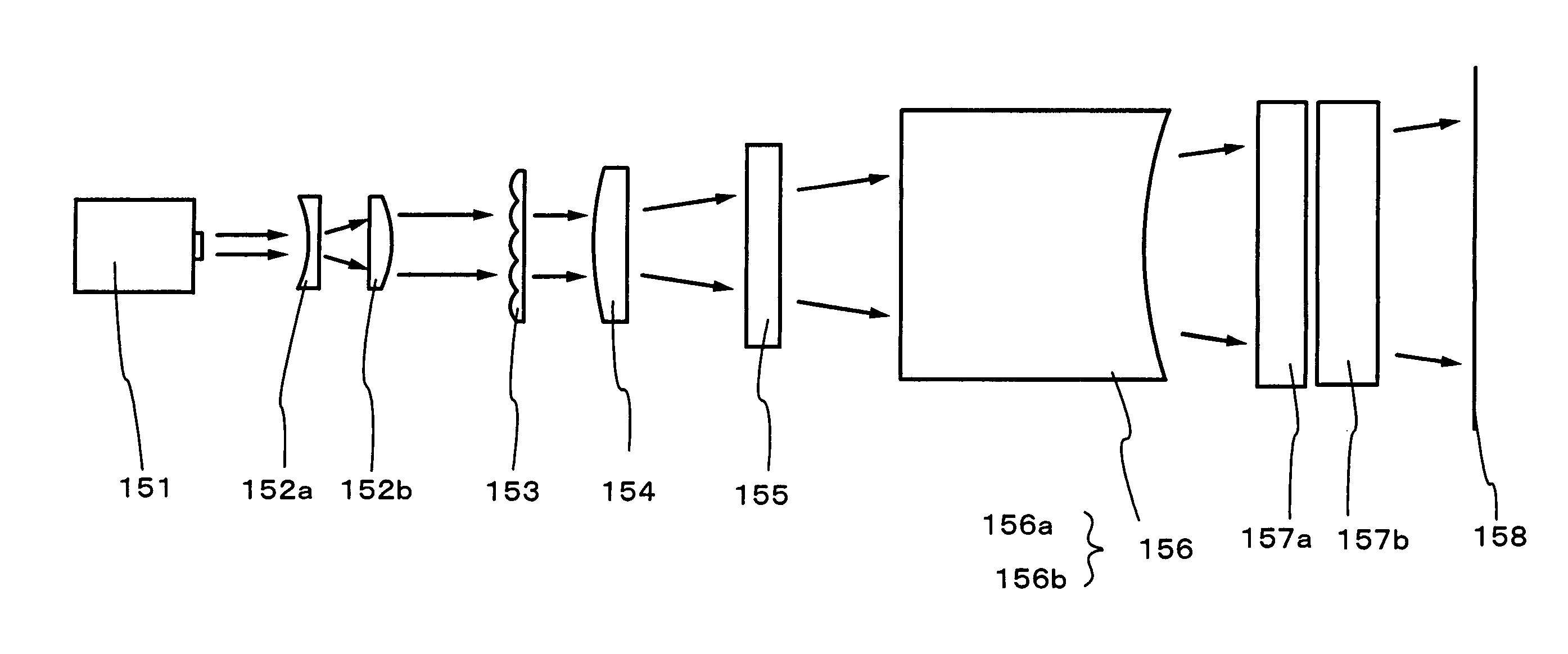
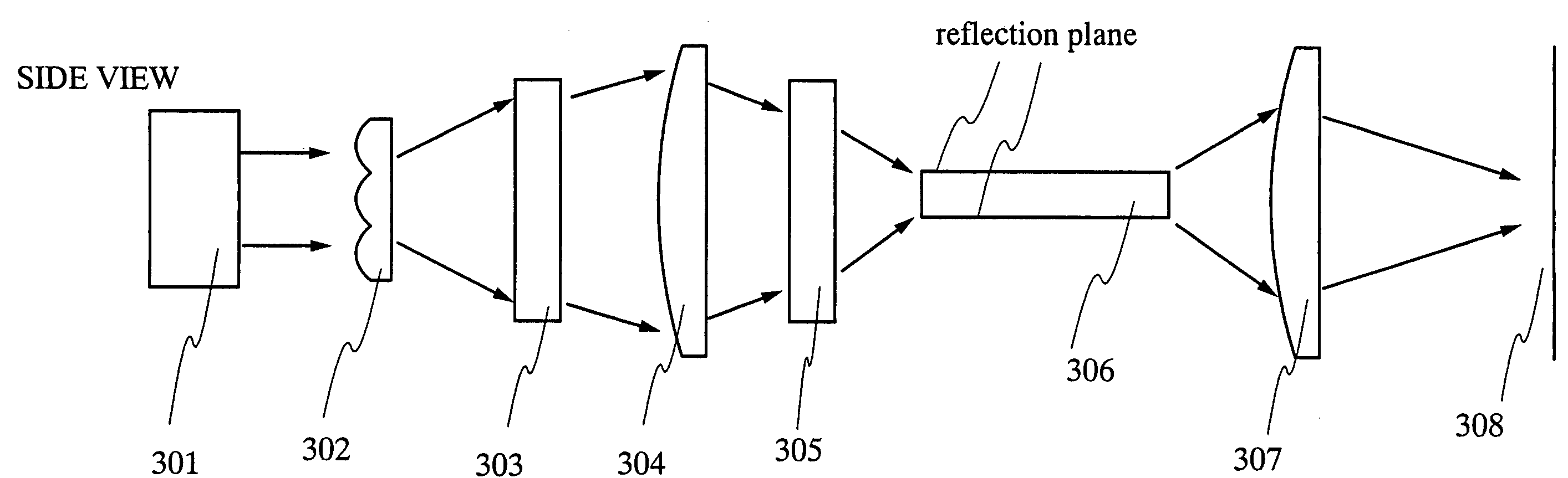
The present invention provides a beam homogenizer for homogenizing energy distribution by making the distance between lenses small to shorten the optical path length with the use of an array lens of an optical path shortened type, and a laser irradiation apparatus using the beam homogenizer. The beam homogenizer is equipped with a front side array lens of an optical path shortened type whose second principal point is positioned ahead on a beam incidence side, a back side array lens of an optical path shortened type whose first principal point is positioned behind on a beam emission side, and a condensing lens, wherein the distance between the second principal point of the front side array lens and the first principal point of the back side array lens is equal to the focal length of the back side array lens.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
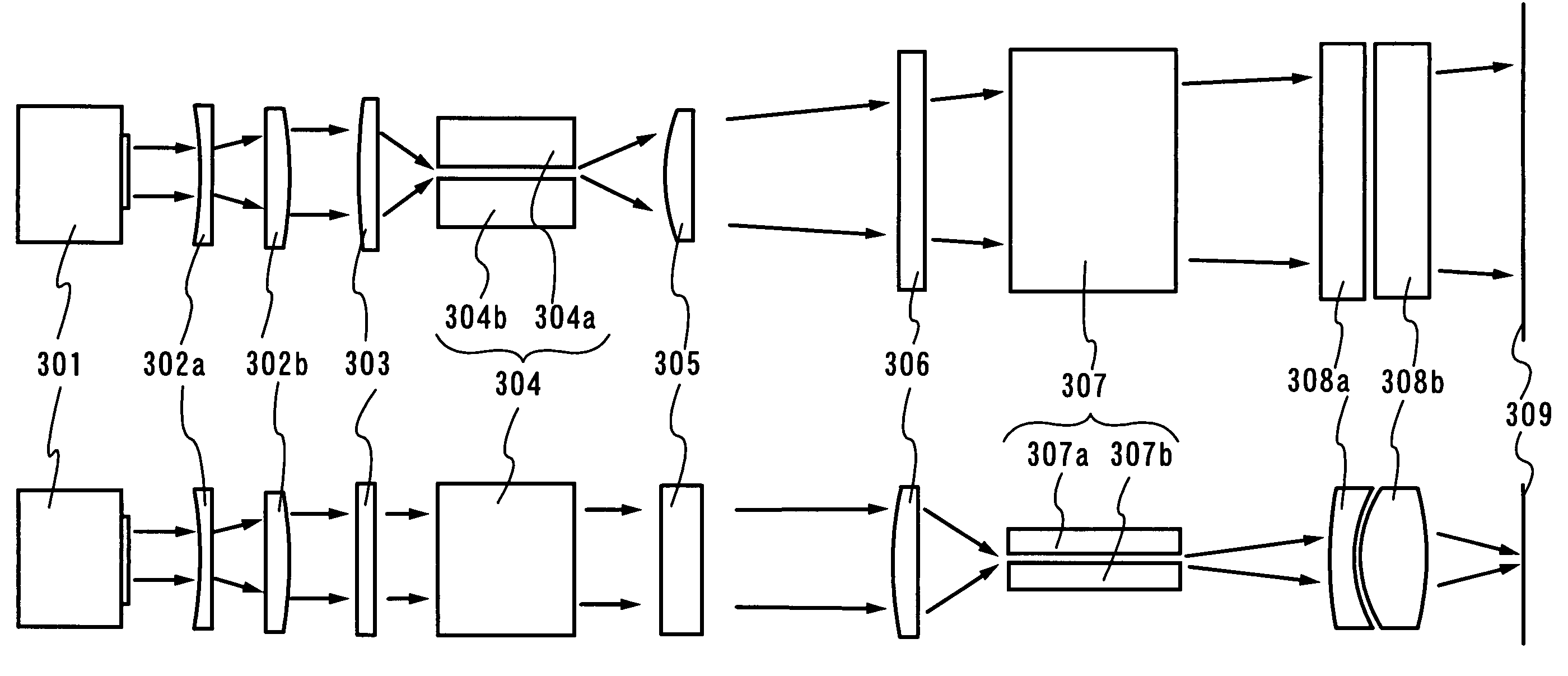
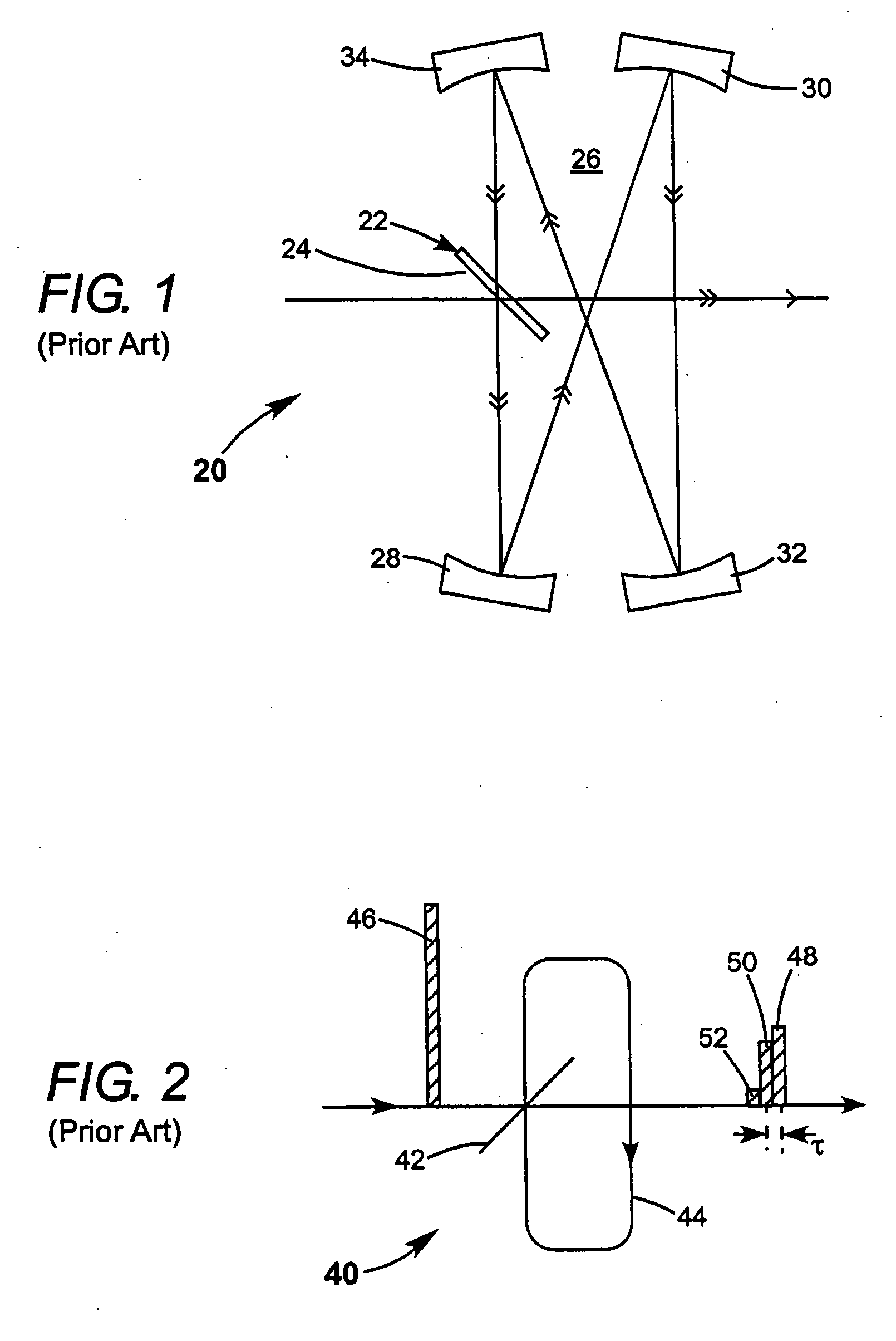
Method and apparatus for gas discharge laser output light coherency reduction
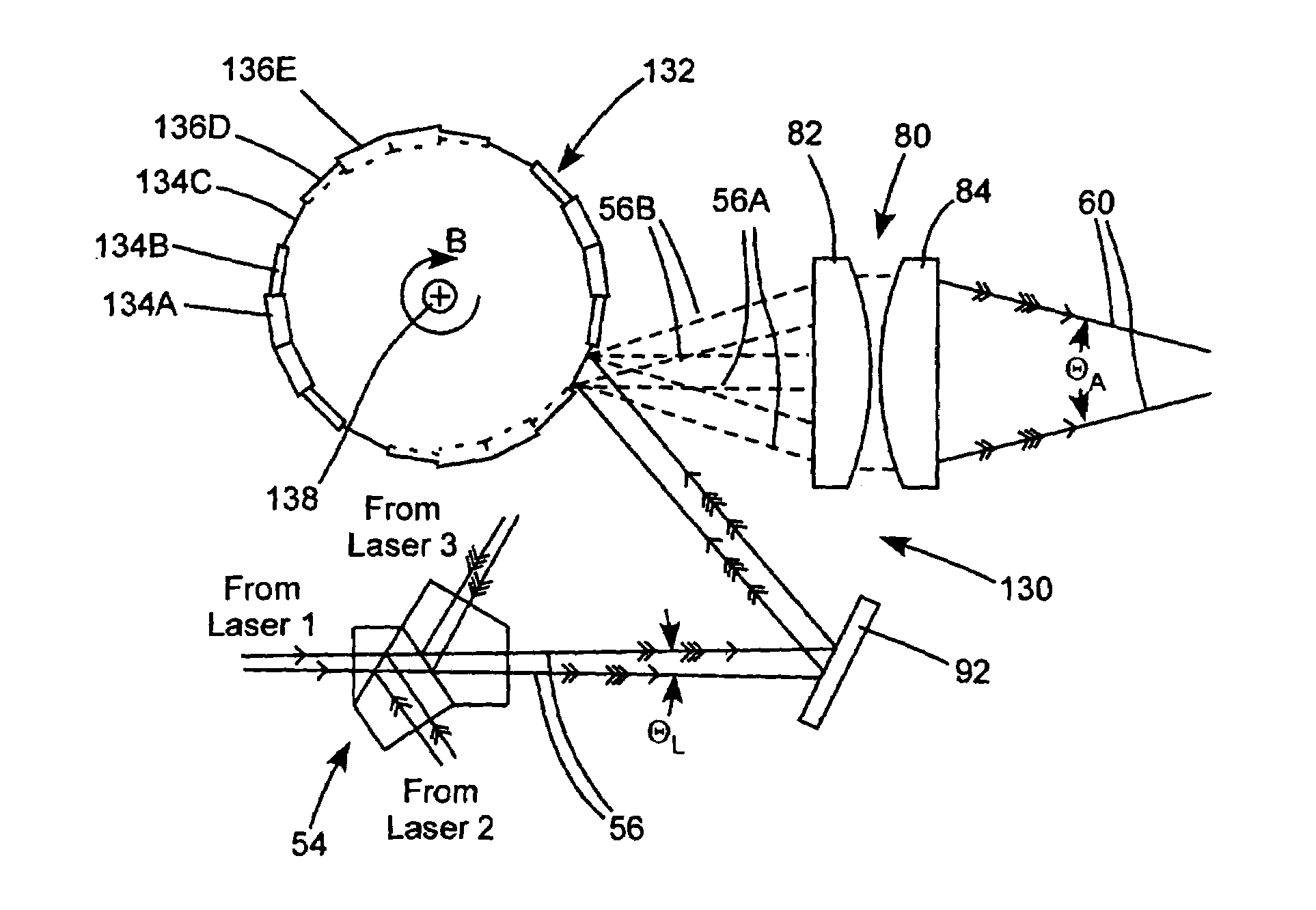
A method and apparatus for producing with a gas discharge laser an output laser beam comprising output laser light pulses, for delivery as a light source to a utilizing tool is disclosed which may comprise a beam path and a beam homogenizer in the beam path. The beam homogenizer may comprise at least one beam image inverter or spatial rotator, which may comprise a spatial coherency cell position shifter. The homogenizer may comprise a delay path which is longer than, but approximately the same delay as the temporal coherence length of the source beam. The homogenizer may comprise a pair of conjoined dove prisms having a partially reflective coating at the conjoined surfaces of each, a right triangle prism comprising a hypotenuse face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or an isosceles triangle prism having a face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or combinations of these, which may serve as a source beam multiple alternating inverted image creating mechanism. The beam path may be part of a bandwidth measuring the bandwidths of an output laser beam comprising output laser light in the range of below 500 femtometers at accuracies within tens of femtometers. The homogenizer may comprise a rotating diffuser which may be a ground glass diffuser which may also be etched. The wavemeter may also comprise a collimator in the beam path collimating the diffused light; a confocal etalon creating an output based upon the collimated light entering the confocal etalon; and a detector detecting the output of the confocal etalon and may also comprise a scanning mechanism scanning the angle of incidence of the collimated light entering the confocal etalon which may scan the collimated light across the confocal etalon or scan the etalon across the collimated light, and may comprise an acousto-optical scanner. The confocal etalon may have a free spectral range approximately equal to the E95 width of the beam being measured. The detector may comprise a photomultiplier detecting an intensity pattern of the output of the confocal etalon.
Owner:CYMER INC
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, semiconductor device, and method of fabricating the semiconductor device
An optical system (in FIGS. 1A and 1B) wherein a rectilinear laser beam of homogeneous energy distribution is defined for annealing a non-single crystalline semiconductor film (a surface to-be-irradiated 1108), is constructed of reflectors (1106, 1107 etc.) easily and inexpensively without including lenses of transmission type. The rectilinear laser beam can be defined having a length of at least 600 (mm) which corresponds to the shorter latus of a large-sized substrate for mass production.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050031261A1High strengthReduce lossesLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialWaveguide
A cylindrical lens array cannot be manufactured so that each cylindrical lens has the same radius of curvature and the same accuracy in the surface. Therefore, when the laser annealing is performed using the cylindrical lens array, the beam spots divided by the cylindrical lens array cannot be superposed completely in the same surface. As a result, there is a region where the energy is attenuated in the edge portion of the rectangular beam to be formed, and therefore the intensity distribution of the laser beam becomes inhomogeneous. In the present invention, the cylindrical lens array is used in combination with the optical waveguide. After dividing the laser beam in a predetermined direction by the cylindrical lens array, the divided beams are combined, and then the laser beam is incident into the optical waveguide that acts upon the same direction as the predetermined direction. This can correct the variation in the intensity of the laser beam due to the processing inaccuracy of the cylindrical lens array.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam Homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
The present invention provides a beam homogenizer being equipped with an optical waveguide having a pair of reflection planes provided oppositely, having one end surface into which the laser beam is incident, and having the other end surface from which the laser beam is emitted in the optical system for forming the beam spot. The optical waveguide is a circuit being able to keep radiation light in a certain region and to transmit the radiation light in such a way that the energy flow thereof is guided in parallel with an axis of the channel.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20040213514A1Uniform high operating characteristicReduce display unevennessCoupling light guidesOptical devices for laserLight beamCrystallinity
The present invention provides a beam homogenizer being able to form a rectangular beam spot having homogeneous energy distribution in a direction of its major axis without using the optical lens requiring to be manufactured with high accuracy. In addition, the present invention provides a laser irradiation apparatus being able to irradiate the laser beam having homogeneous energy distribution in a direction of its major axis. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device being able to enhance crystallinity in the surface of the substrate and to manufacture TFT with a high operating characteristic. The beam homogenizer, one of the present invention, is to shape the beam spot on the surface to be irradiated into a rectangular spot having an aspect ratio of 10 or more, preferably 100 or more, and comprises an optical waveguide for homogenizing the energy distribution of the rectangular beam spot in the direction of its major axis.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
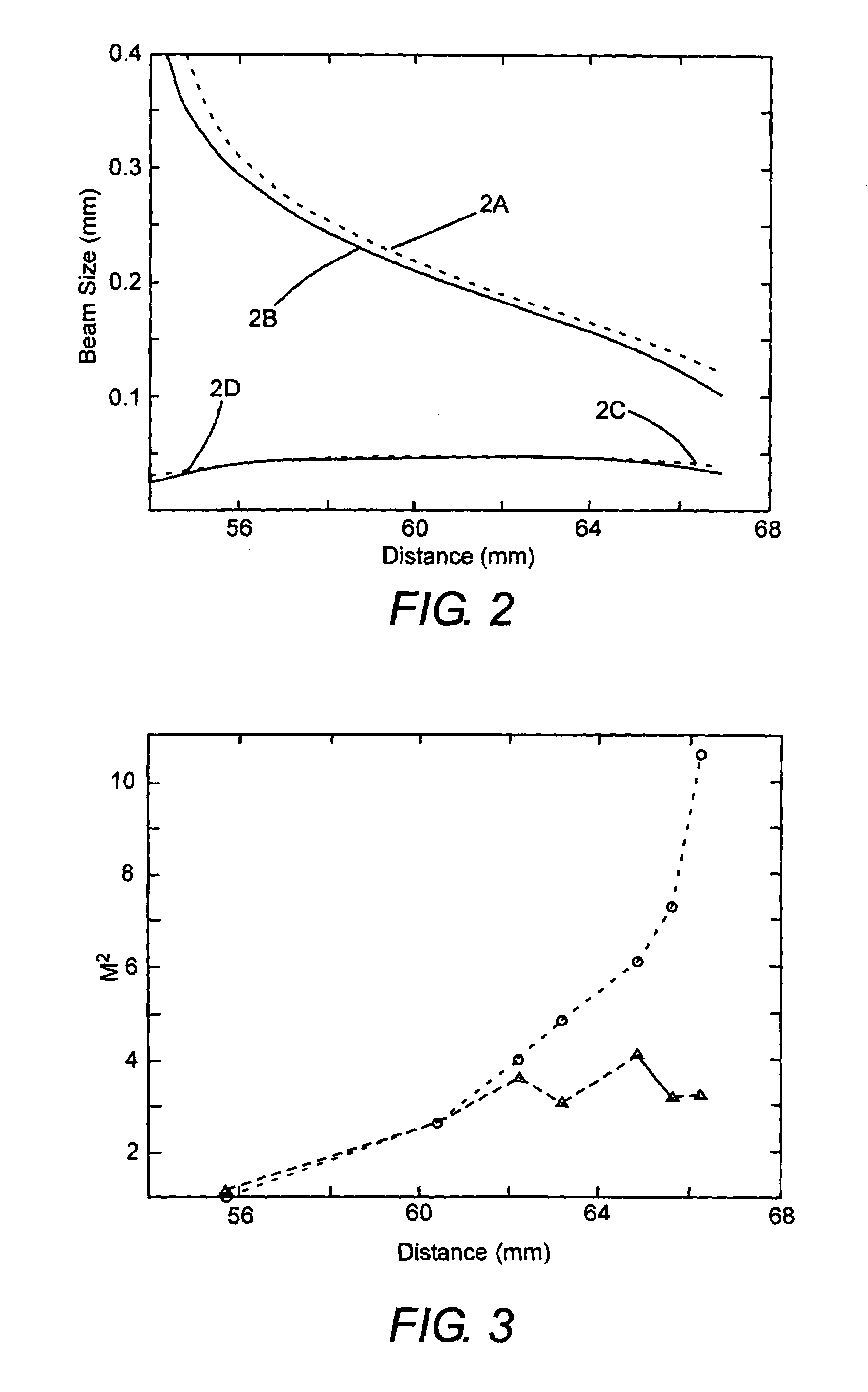
ActiveUS20050079645A1Suppress inhomogeneous crystallinityImprove homogeneityCombination recordingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCurve shapeLight beam
The energy distribution of the beam spot on the irradiated surface changes due to the change in the oscillation condition of the laser or before and after the maintenance. The present invention provides an optical system for forming a rectangular beam spot on an irradiated surface including a beam homogenizer for homogenizing the energy distribution of the rectangular beam spot on the irradiated surface in a direction of its long or short side. The beam homogenizer includes an optical element having a pair of reflection planes provided oppositely for reflecting the laser beam in the direction where the energy distribution is homogenized and having a curved shape in its entrance surface. The entrance surface of the optical element means a surface of the optical element where the laser beam is incident first.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Laser illuminated projection displays
InactiveUS20060126022A1Reduced coherence radiusMinimizing speckle contrastBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A projection video display includes at least one laser for delivering a light beam. The display includes a beam homogenizer and a condenser lens. A scanning arrangement is provided for scanning the light in beam in a particular pattern over the condenser lens in a manner that effectively increases the beam divergence. The scanned beam is homogenized by a beam homogenizer and a spatial light modulator is arranged to receive the homogenized scanned light beam and spatially modulate the beam in accordance with a component of an image to be displayed. Projection optics are projecting the homogenized scanned light beam onto a screen. The scanning provides that the homogenized scanned light beam at the screen has a coherence radius less than the original coherence radius of the beam. The reduced coherence radius contributes to minimizing speckle contrast in the image displayed on the screen. The screen includes one or more features providing a further contribution to minimizing speckle contrast in the displayed image. In one example, the screen includes a transparent cell containing a liquid having light scattering particles in suspension.
Owner:COHERENT INC
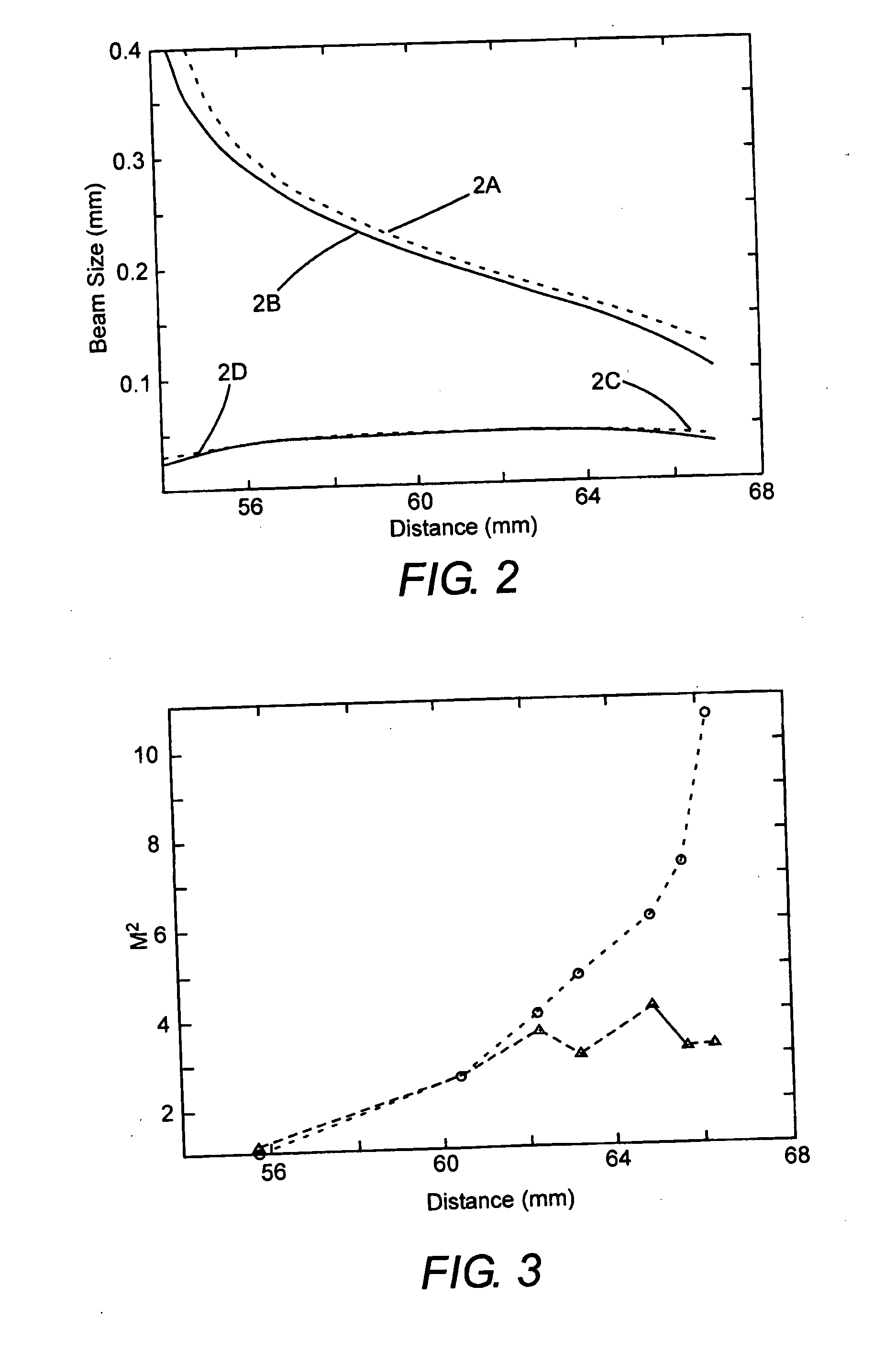
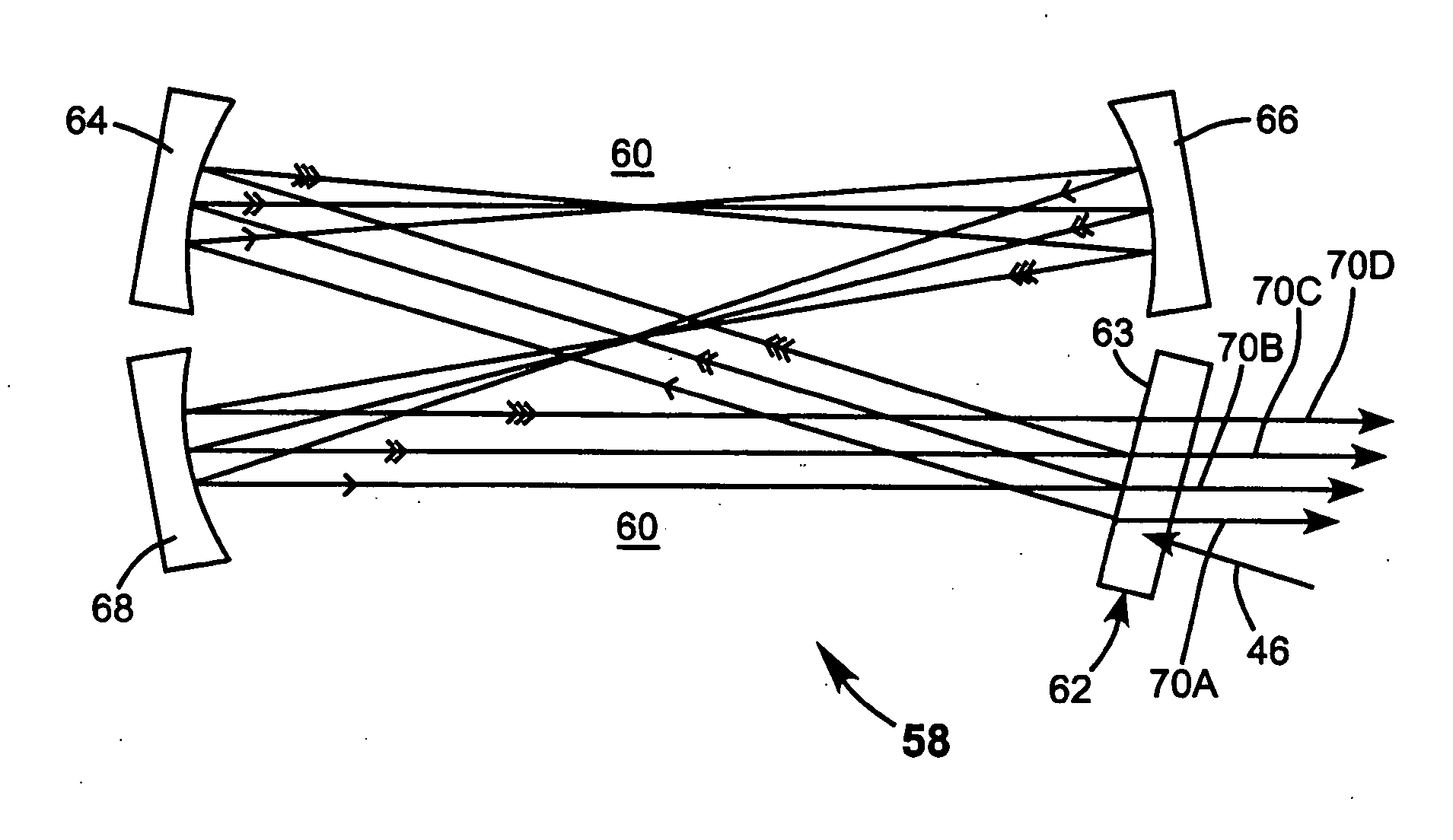
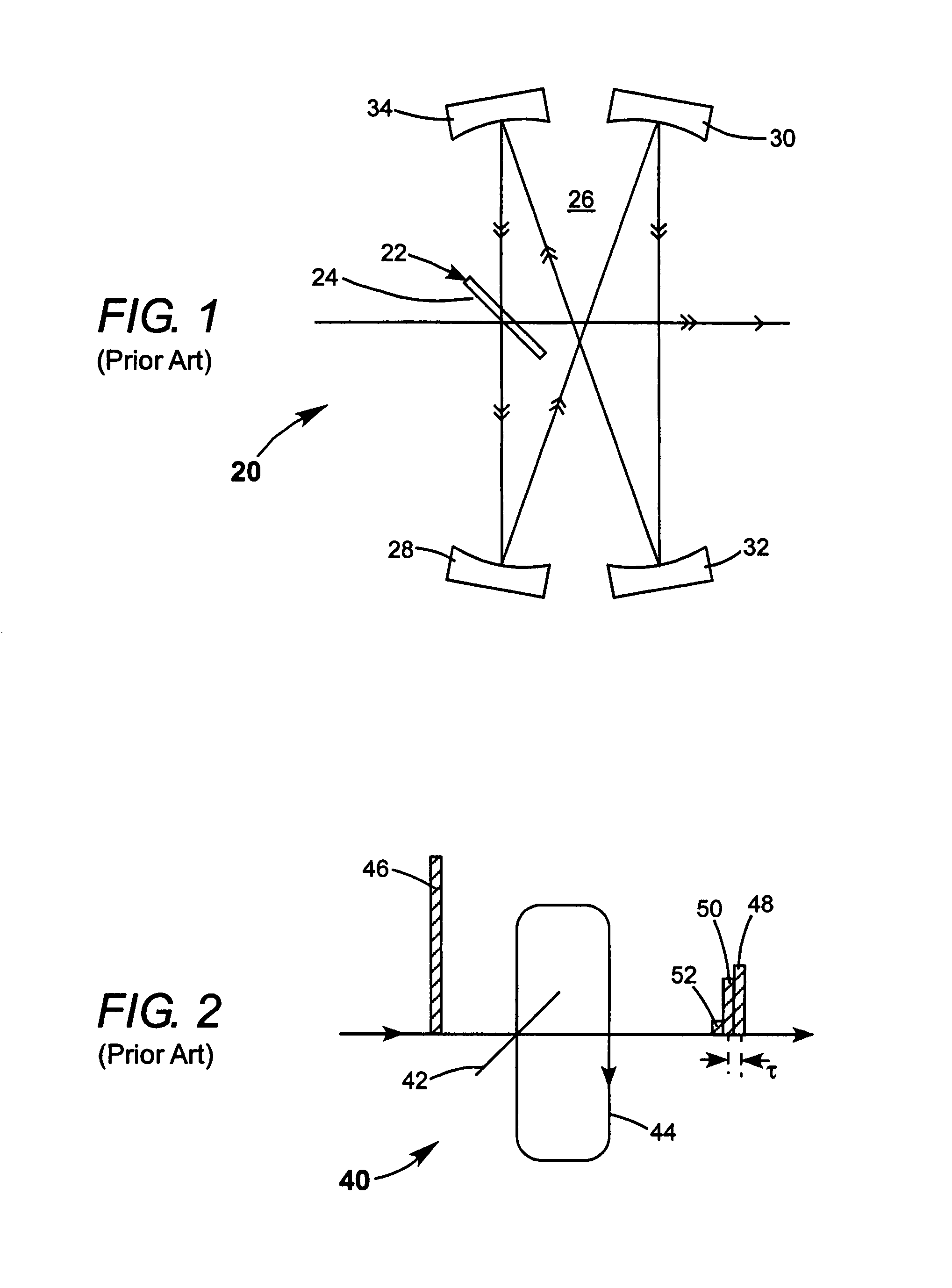
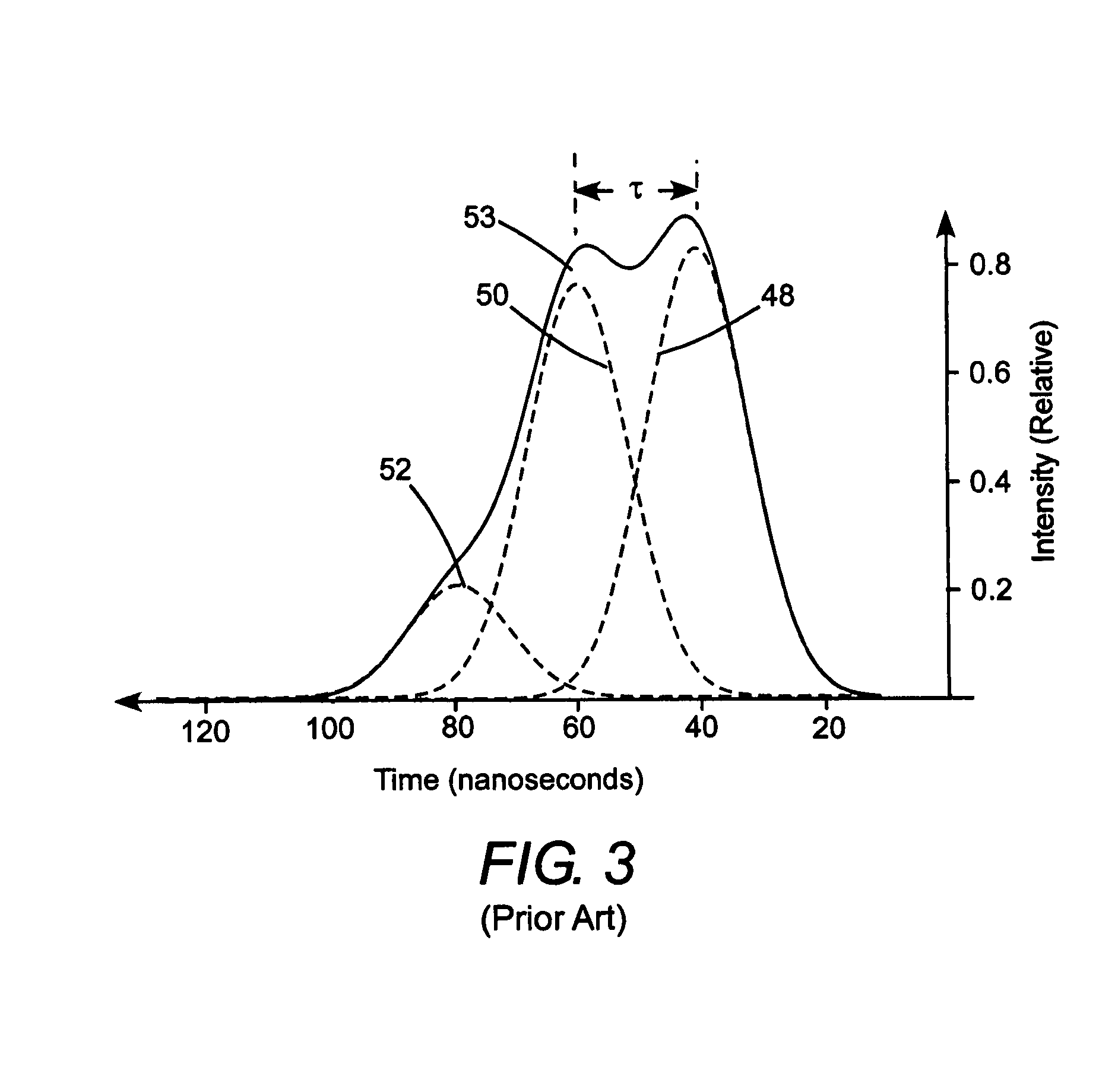
Optical pulse duration extender
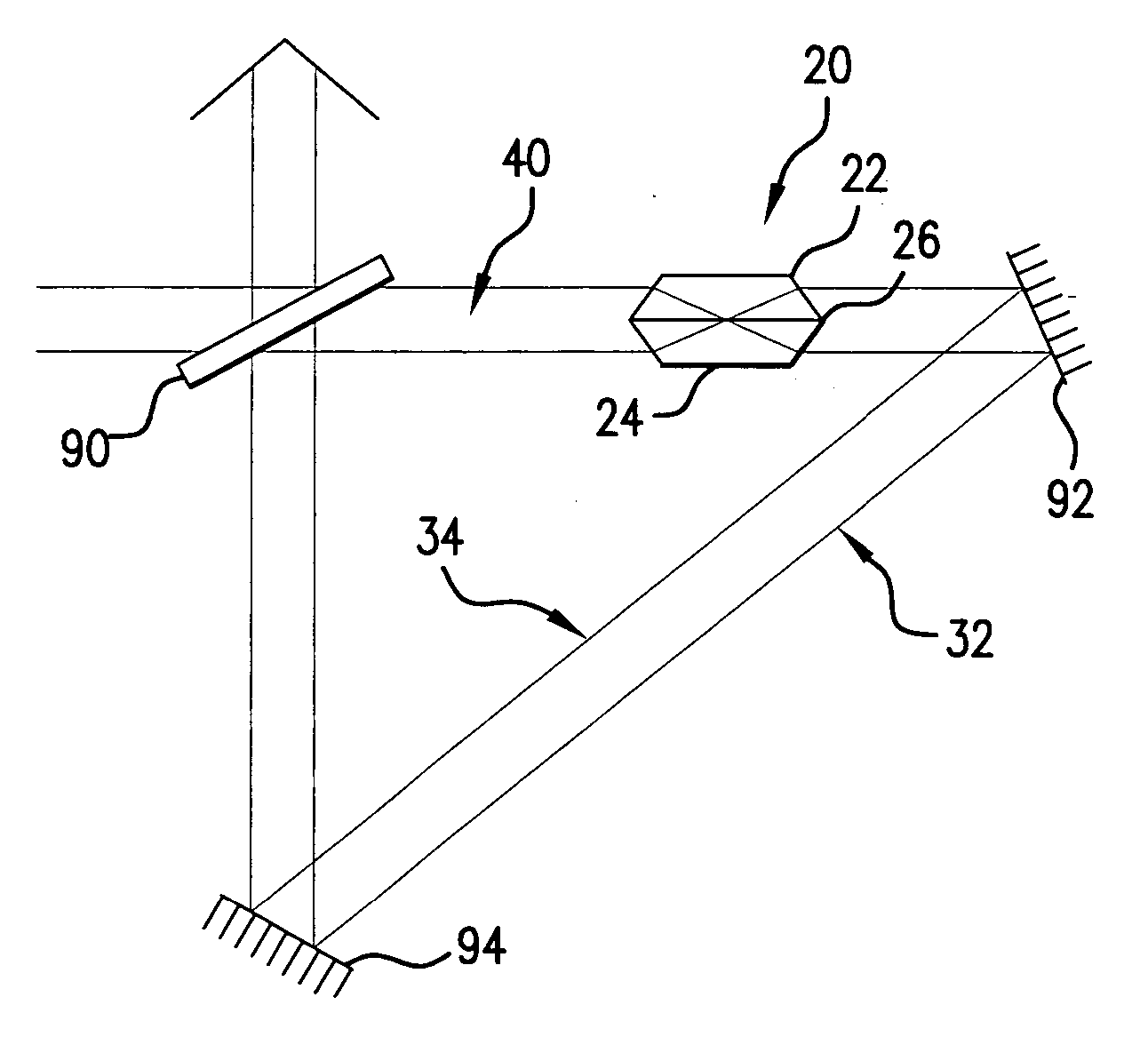
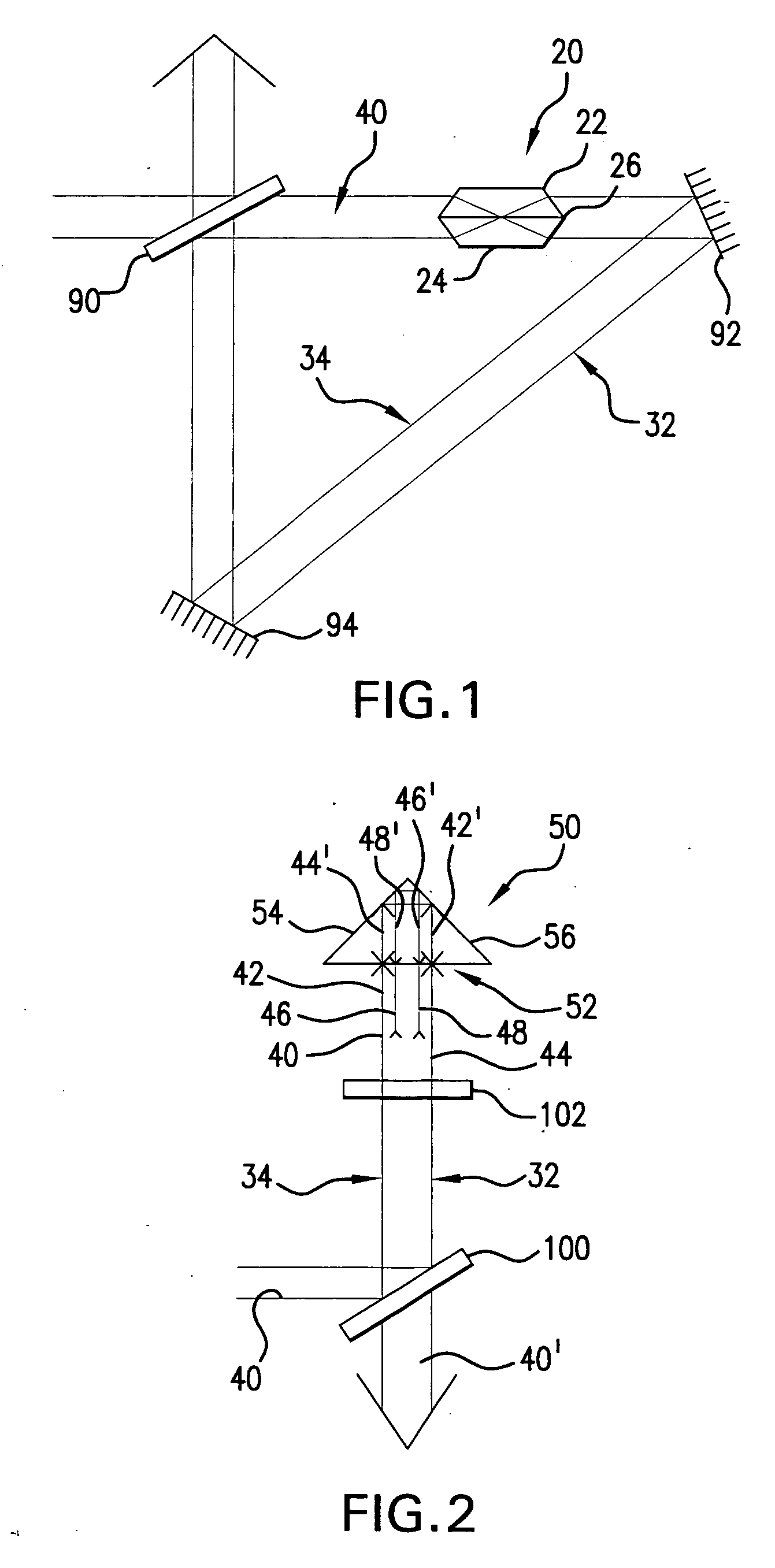
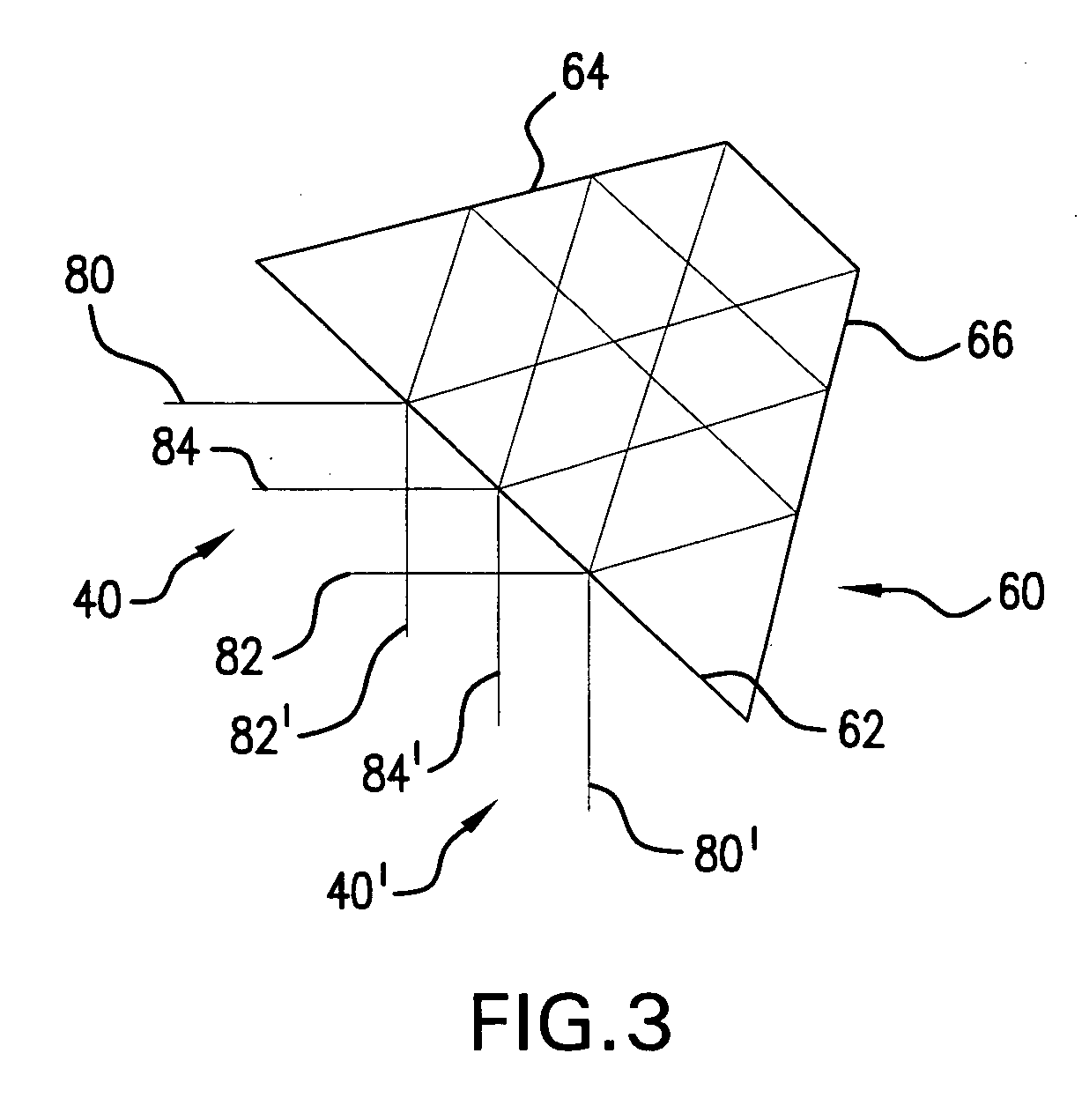
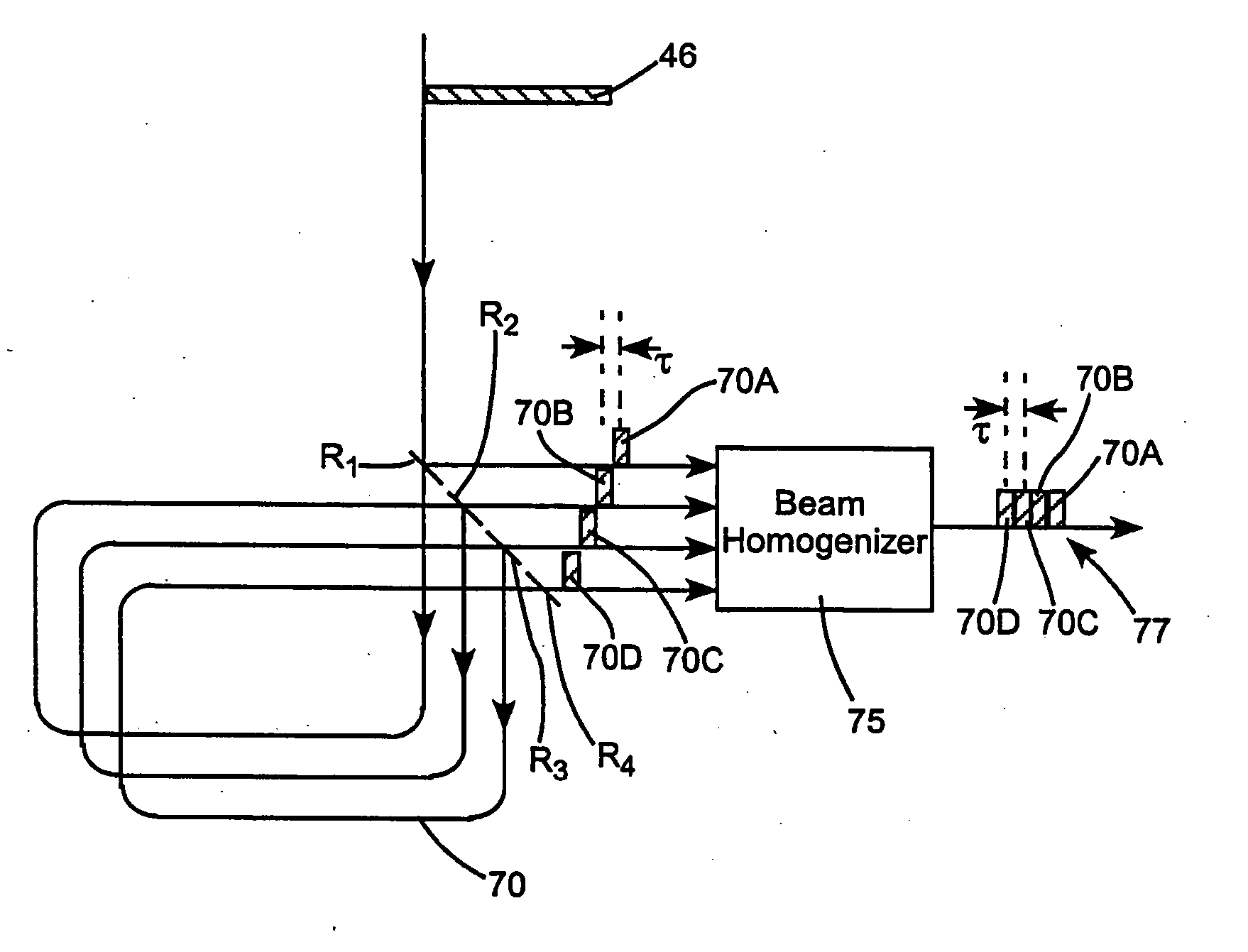
ActiveUS20050190452A1Increase the number ofReduce in quantityOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialLight beamPulse duration
An optical pulse extender includes a delay loop formed by a plurality of mirrors and a graded reflectivity beamsplitter. The mirrors and the beamsplitter are configured and aligned such that a pulse to be broadened makes a predetermined number of round trips in the delay loop and is incident on a different zone of the beamsplitter after each round trip. The different zones of the beamsplitter have different reflection values and different transmission values. These values are selected such that the pulse extender delivers a plurality of temporally and spatially separated replica pulses each thereof having about the same energy. The delivered replica pulses together provide an extended pulse having a longer duration than the input pulse. The replica pulses may be passed through a beam homogenizer to spatially homogenize the temporal characteristics of the extended pulse.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Diode laser array beam homogenizer
InactiveUS20060045144A1Minimal design complexityReduce disagreementOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser arrayLight beam
A means of achieving a spatially uniform output beam from a laser diode array with minimal design complexity is provided. The means is comprised of one or more optical elements located adjacent to the output of the diode array, the optical element(s) reducing the divergence of the output of the individual emitters of the diode array in at least one axis to within an acceptable range, preferably within the range of 0.1 to 10 degrees. The means is further comprised of a diffusing element, the output of the emitters passing through the optical element(s) prior to passing through the diffusing element. The diffusing element, preferably either a holographic diffuser or an engineered diffuser™ which provides control over the light diffusion angles, smoothes out the ripples formed by the overlapping output beams of the emitters in order to achieve the desired spatially uniform beam.
Owner:NLIGHT PHOTONICS
Optical pulse duration extender
ActiveUS7035012B2Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialLight beamPulse duration
An optical pulse extender includes a delay loop formed by a plurality of mirrors and a graded reflectivity beamsplitter. The mirrors and the beamsplitter are configured and aligned such that a pulse to be broadened makes a predetermined number of round trips in the delay loop and is incident on a different zone of the beamsplitter after each round trip. The different zones of the beamsplitter have different reflection values and different transmission values. These values are selected such that the pulse extender delivers a plurality of temporally and spatially separated replica pulses each thereof having about the same energy. The delivered replica pulses together provide an extended pulse having a longer duration than the input pulse. The replica pulses may be passed through a beam homogenizer to spatially homogenize the temporal characteristics of the extended pulse.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7418172B2Uniform high operating characteristicReduce display unevennessCoupling light guidesOptical devices for laserLight beamCrystallinity
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7245802B2Loss in the photoconduction can be decreasedReduce lossesLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamWaveguide
A cylindrical lens array cannot be manufactured so that each cylindrical lens has the same radius of curvature and the same accuracy in the surface. Therefore, when the laser annealing is performed using the cylindrical lens array, the beam spots divided by the cylindrical lens array cannot be superposed completely in the same surface. As a result, there is a region where the energy is attenuated in the edge portion of the rectangular beam to be formed, and therefore the intensity distribution of the laser beam becomes inhomogeneous. In the present invention, the cylindrical lens array is used in combination with the optical waveguide. After dividing the laser beam in a predetermined direction by the cylindrical lens array, the divided beams are combined, and then the laser beam is incident into the optical waveguide that acts upon the same direction as the predetermined direction. This can correct the variation in the intensity of the laser beam due to the processing inaccuracy of the cylindrical lens array.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Projection system with beam homogenizer
A projection system having a prescribed relationship between the condenser and the projection lens is disclosed, where an imager gate normally coinciding with a projection object plane is between and spaced away from a condenser back focal plane and a condenser image plane. The condenser images an extended source onto the condenser image plane. A pixilated panel or film defining a graphic image is located at the imager gate. The magnification of the condenser is chosen so the image of the source is essentially the same size as the pixilated panel. Positioning the imager gate away from the condenser image plane provides blurring of any brightness non-uniformities across the area of the source, providing a relatively uniform illumination pattern whose outer shape matches the shape of the imager gate.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Laser irradiation apparatus and laser irradiation method
InactiveUS20070063226A1Reduced areaLow optical transmissivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamIrradiation
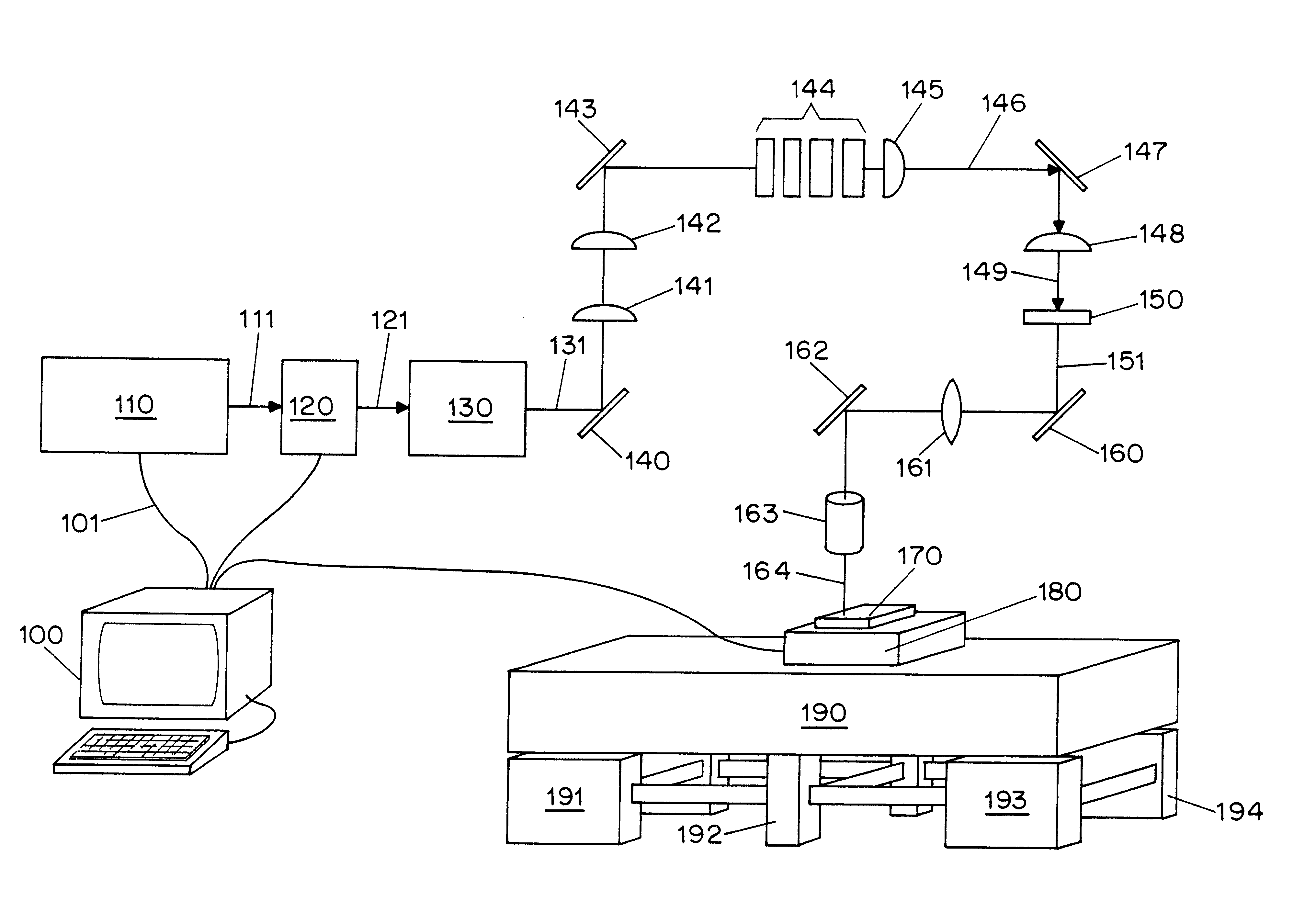
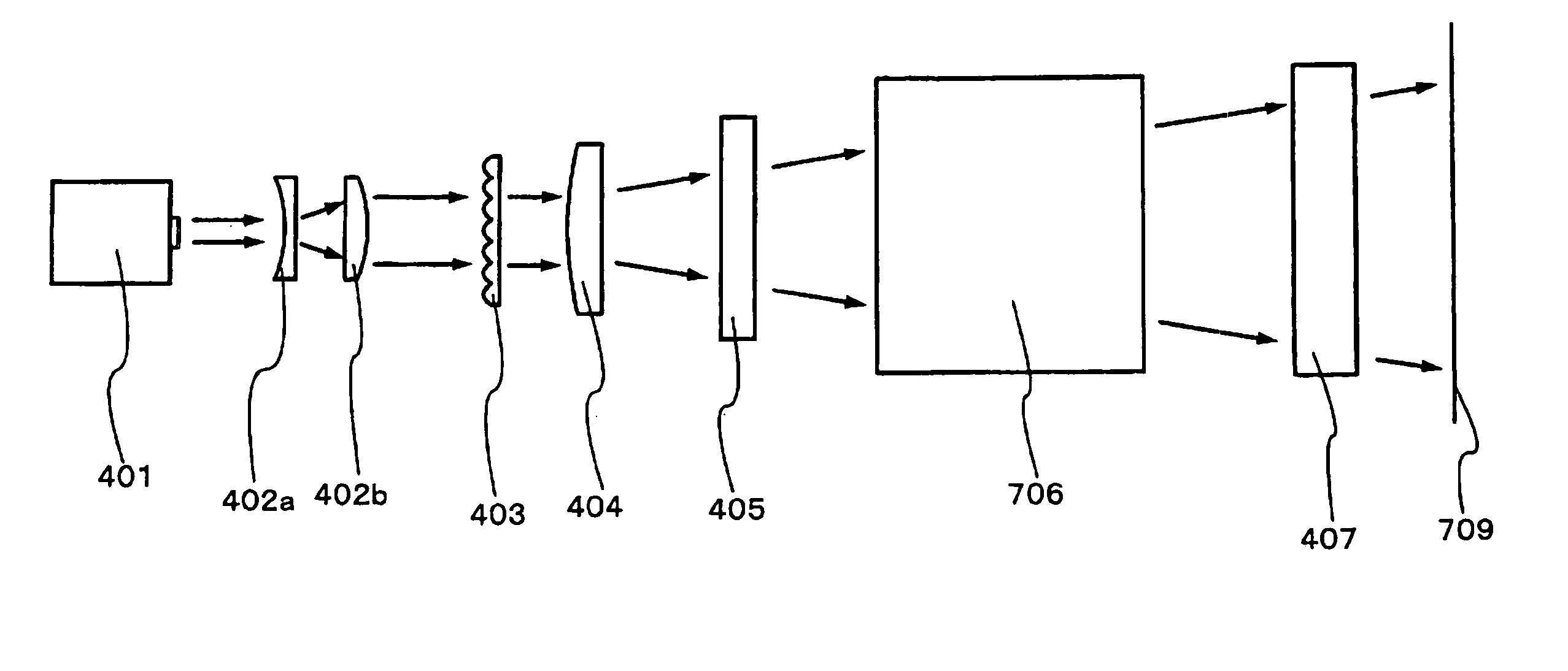
It is an object of the present invention to provide a laser irradiation apparatus and a laser irradiation method which can conduct a laser process homogeneously to the whole surface of a semiconductor film. A laser beam oscillated from a laser crystal having a wide wavelength range and a beam homogenizer are used. Since the laser beam having a wide wavelength range has low coherency, an interference pattern does riot appear on a semiconductor film. Moreover, a linear beam having a length of several meters or more in its major axis can be formed, which increases throughput of a laser anneal process.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer
InactiveUS8835804B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsLight pipeLight beam
A system for homogenizing the intensity profile of light includes a plurality of fiber coupled light sources for emitting fiber output beams from fiber output ends, and a light pipe optically coupled to the fiber output beams for producing a uniform light pipe output beam, an interleaver that transmits a first set of fiber output beams and reflects a second set of fiber output beams so that the principal rays of the fiber output beams propagate in a common plane, a first optical element for converging the principal rays, and a second optical element for telecentrically imaging the beams into the light pipe such that the principal rays of the beams propagate parallel to each other and the beams are focused in the light pipe in a focal plane transverse to the direction of propagation.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
Beam homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS7169630B2Keep shapeImprove homogeneityCombination recordingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCurve shapeLight beam
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and apparatus for concentrating laser beams
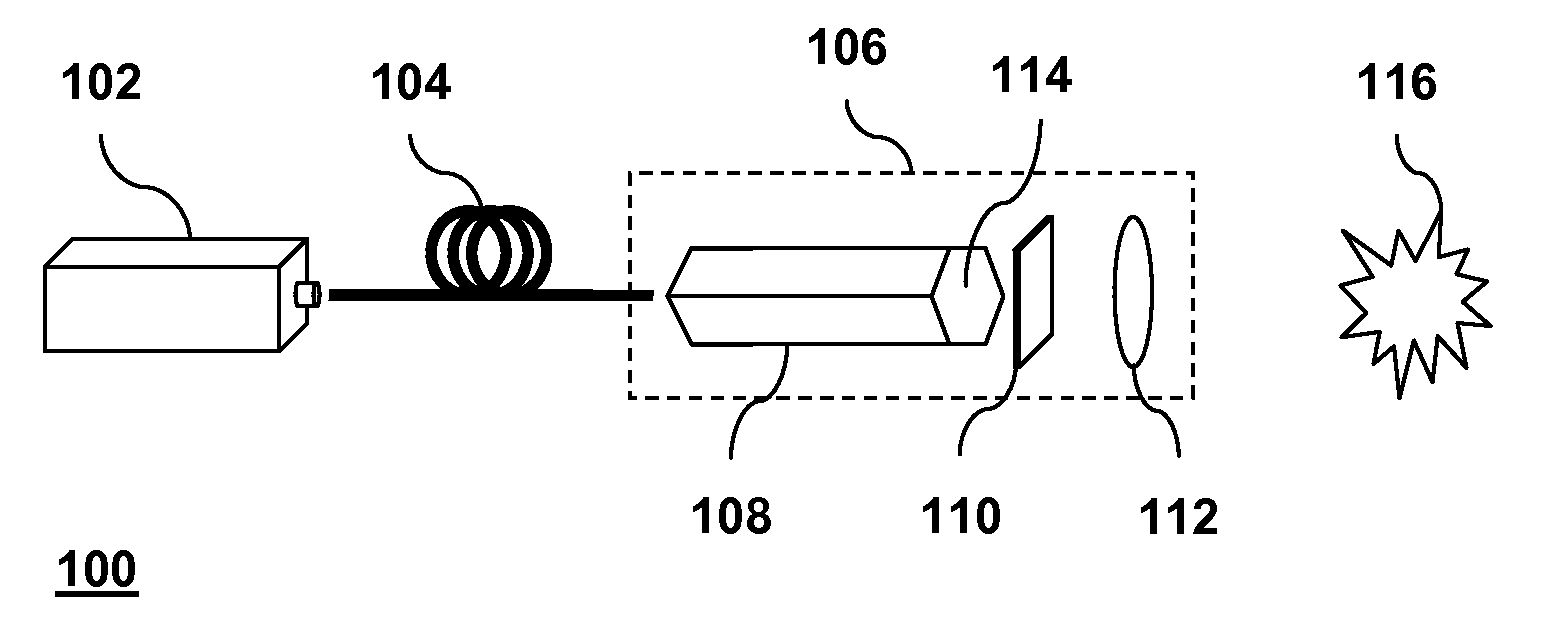
PCT No. PCT / US95 / 00540 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 15, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 15, 1996 PCT Filed Jan. 23, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 19811 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 27, 1995The invention includes the use of a beam homogenizer (scattering surface) at the input aperture of a tapered optical fiber to avoid hot spots (2) in the tapered section which would otherwise destroy the fiber (10).
Owner:NANOPTICS
Medical Laser Apparatus with Output Beam Homogenizer
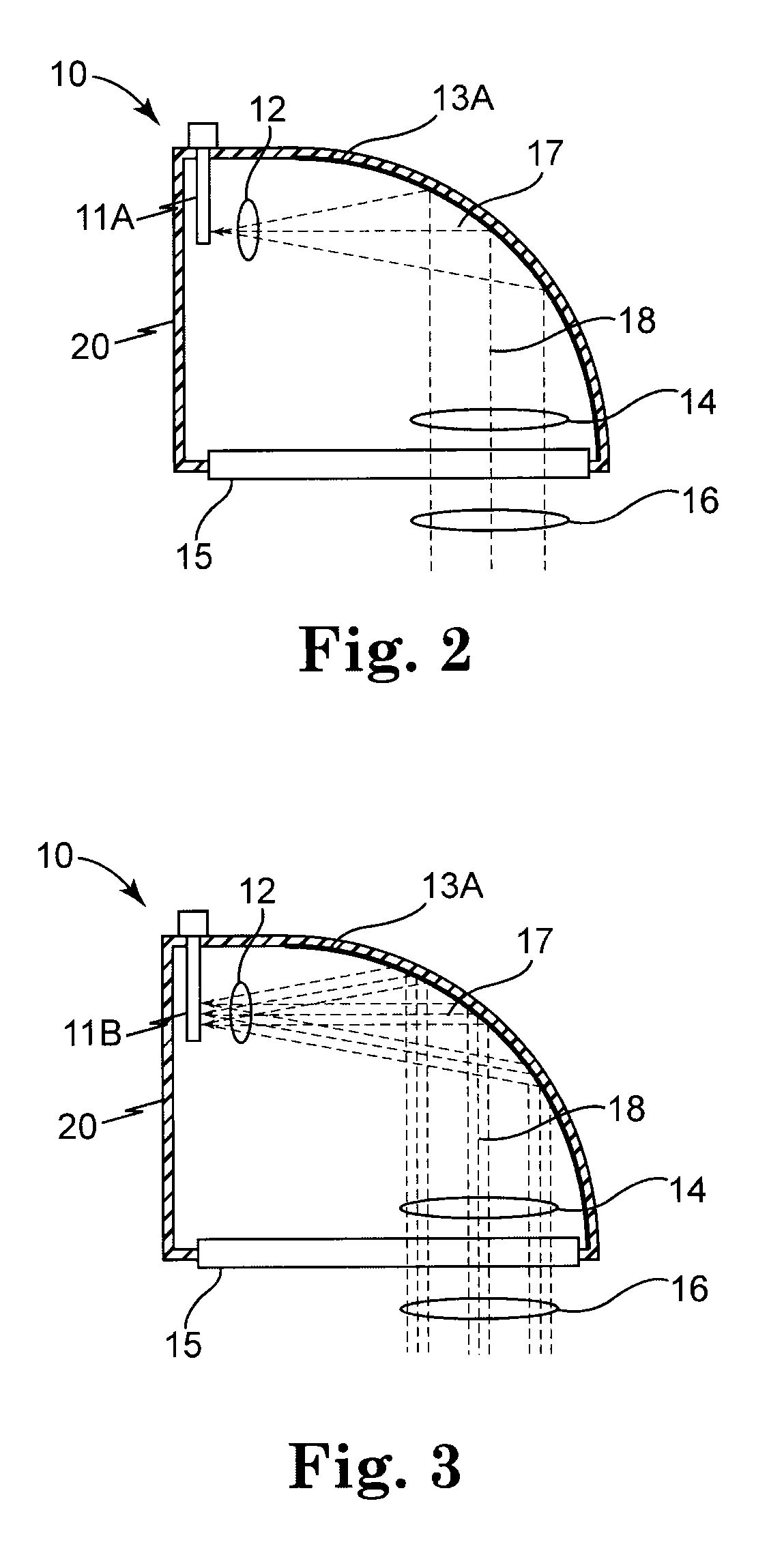
InactiveUS20110034973A1Uniform outputSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyTotal internal reflectionLight pipe
A medical laser apparatus with a beam homogenizer for producing a uniform output beam profile. The beam homogenizer comprises a light pipe which expands the laser beam and mixes the laser light through total internal reflection as well as an optical diffuser to provide further control of the intensity distribution of the laser beam.
Owner:BWT PROPERTY
Beam Homogenizer, laser irradiation apparatus, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS7327916B2Avoid changeHomogenize the energy distributionLaser optical resonator constructionSolid-state devicesLight beamWaveguide
The present invention provides a beam homogenizer being equipped with an optical waveguide having a pair of reflection planes provided oppositely, having one end surface into which the laser beam is incident, and having the other end surface from which the laser beam is emitted in the optical system for forming the beam spot. The optical waveguide is a circuit being able to keep radiation light in a certain region and to transmit the radiation light in such a way that the energy flow thereof is guided in parallel with an axis of the channel.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Beam homogenizer and laser irradiation apparatus and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7594965B2High evennessIncrease the number ofFrom gel stateFrom solid stateStructural ProblemLight guide
The inhomogeneous energy distribution at the beam spot on the irradiated surface is caused by a structural problem and processing accuracy of the cylindrical lens array forming an optical system.According to the present invention, in the optical system for forming a rectangular beam spot, an optical system for homogenizing the energy distribution of the shorter side direction of a rectangular beam spot of a laser light on an irradiated surface is replaced with a light guide. The light guide is a circuit that can confine emitted beams in a certain region and guide and transmit its energy flow in parallel with the axis of a path thereof.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
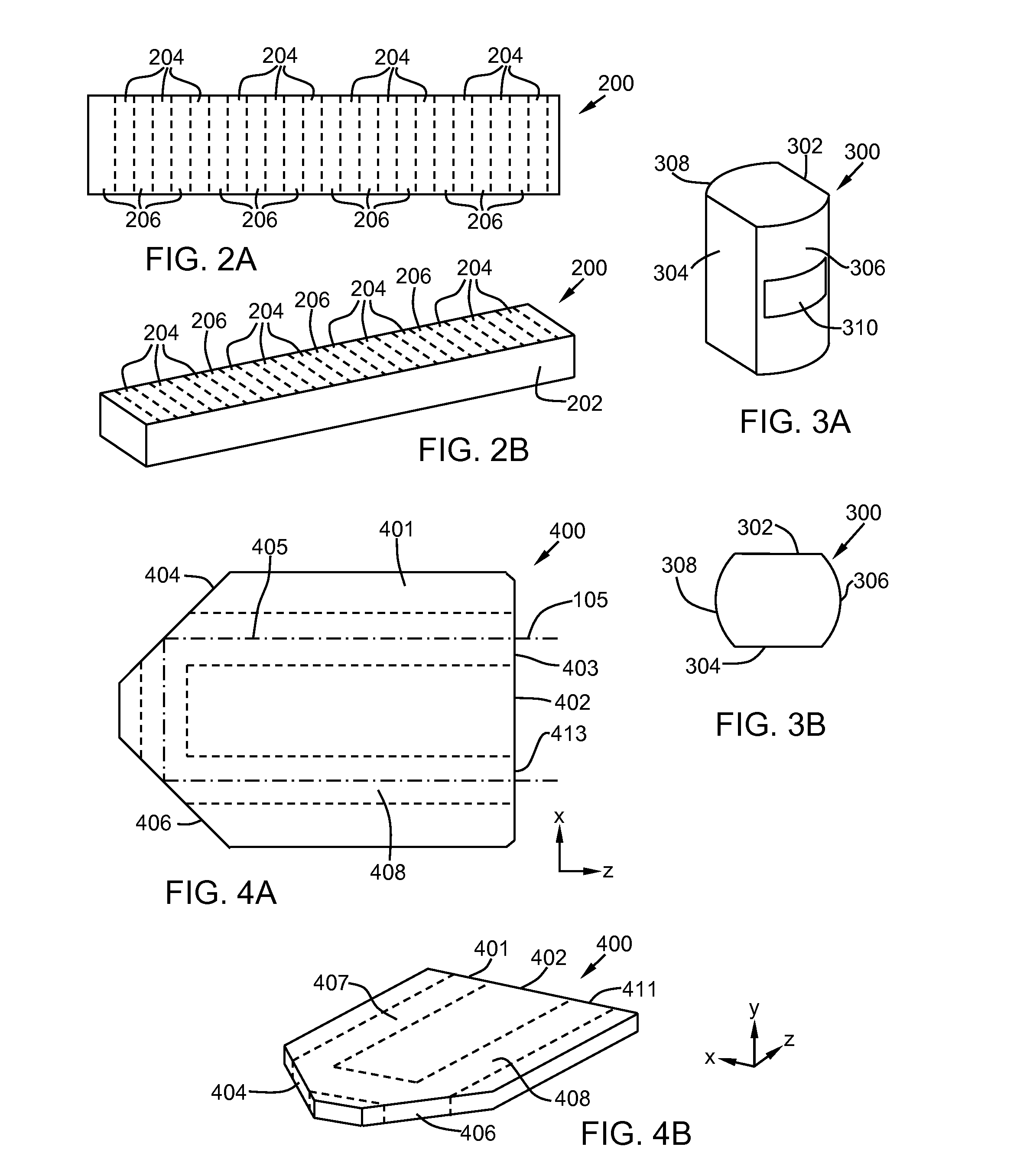
Rear-loaded light emitting diode module for automotive rear combination lamps
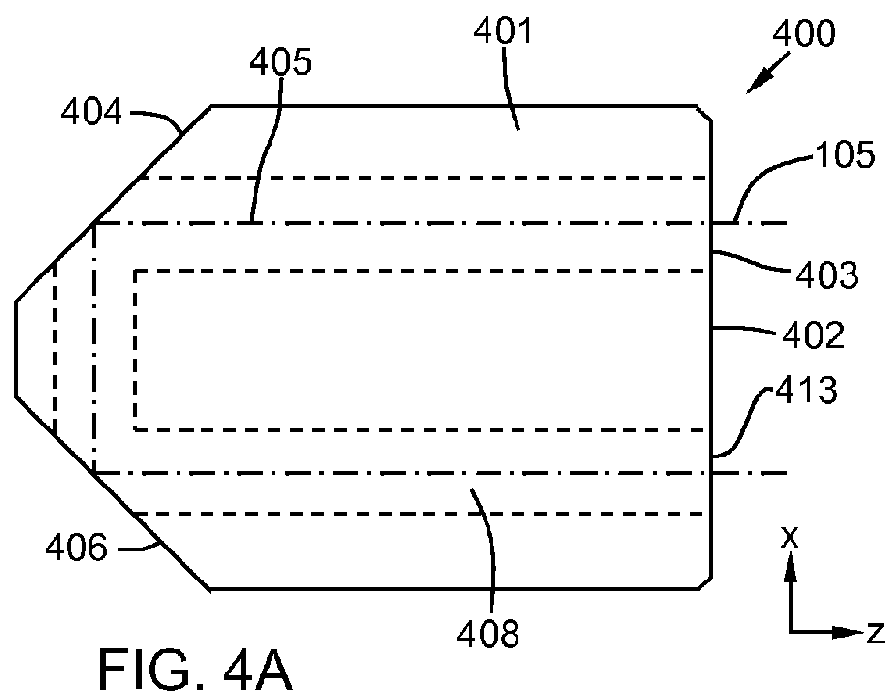
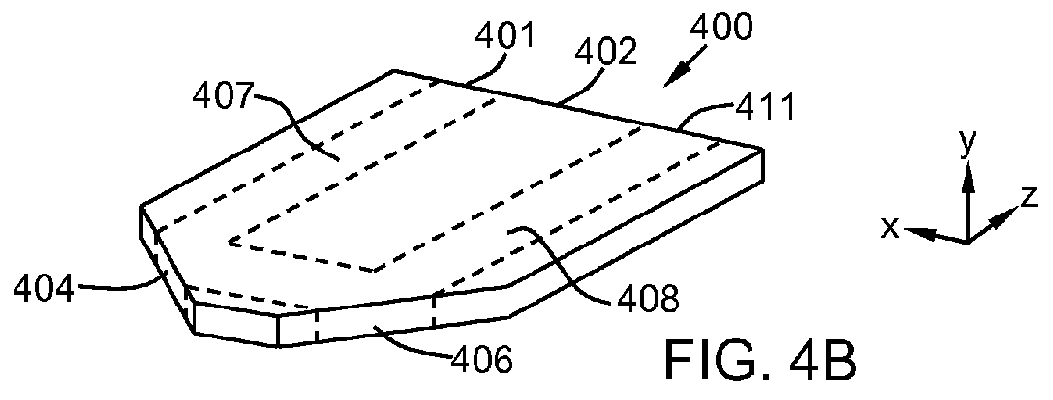
A rear-loading LED module for a rear combination lamp is disclosed. One or more LEDs are mounted on a printed circuit board that electrically powers and mechanically holds them outside a faceted, parabolic reflector. Light emitted from the LEDs enters a light propagation region, formed between the reflective adjacent faces of two nested cylinders. The cylinders extend from the LEDs, outside the reflector, longitudinally through a hole at the vertex of the reflector, to the focus of the reflector. In some applications, the light propagation region may act as a beam homogenizer, so that light exiting the light propagation region may have roughly uniform intensity. Light from the light propagation region strikes an outwardly-flared reflector that directs it largely transversely onto the parabolic reflector. The parabolic reflector collimates the light and directs it longitudinally, through a transparent cover and out of the lamp. The parabolic reflector may have facets that angularly divert portions of the reflected light to form a desired two-dimensional angular distribution for the exiting beam.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Optical pulse duration extender
An optical pulse extender includes a delay loop formed by a plurality of mirrors and a graded reflectivity beamsplitter. The mirrors and the beamsplitter are configured and aligned such that a pulse to be broadened makes a predetermined number of round trips in the delay loop and is incident on a different zone of the beamsplitter after each round trip. The different zones of the beamsplitter have different reflection values and different transmission values. These values are selected such that the pulse extender delivers a plurality of temporally and spatially separated replica pulses each thereof having about the same energy. The delivered replica pulses together provide an extended pulse having a longer duration than the input pulse. The replica pulses may be passed through a beam homogenizer to spatially homogenize the temporal characteristics of the extended pulse.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com