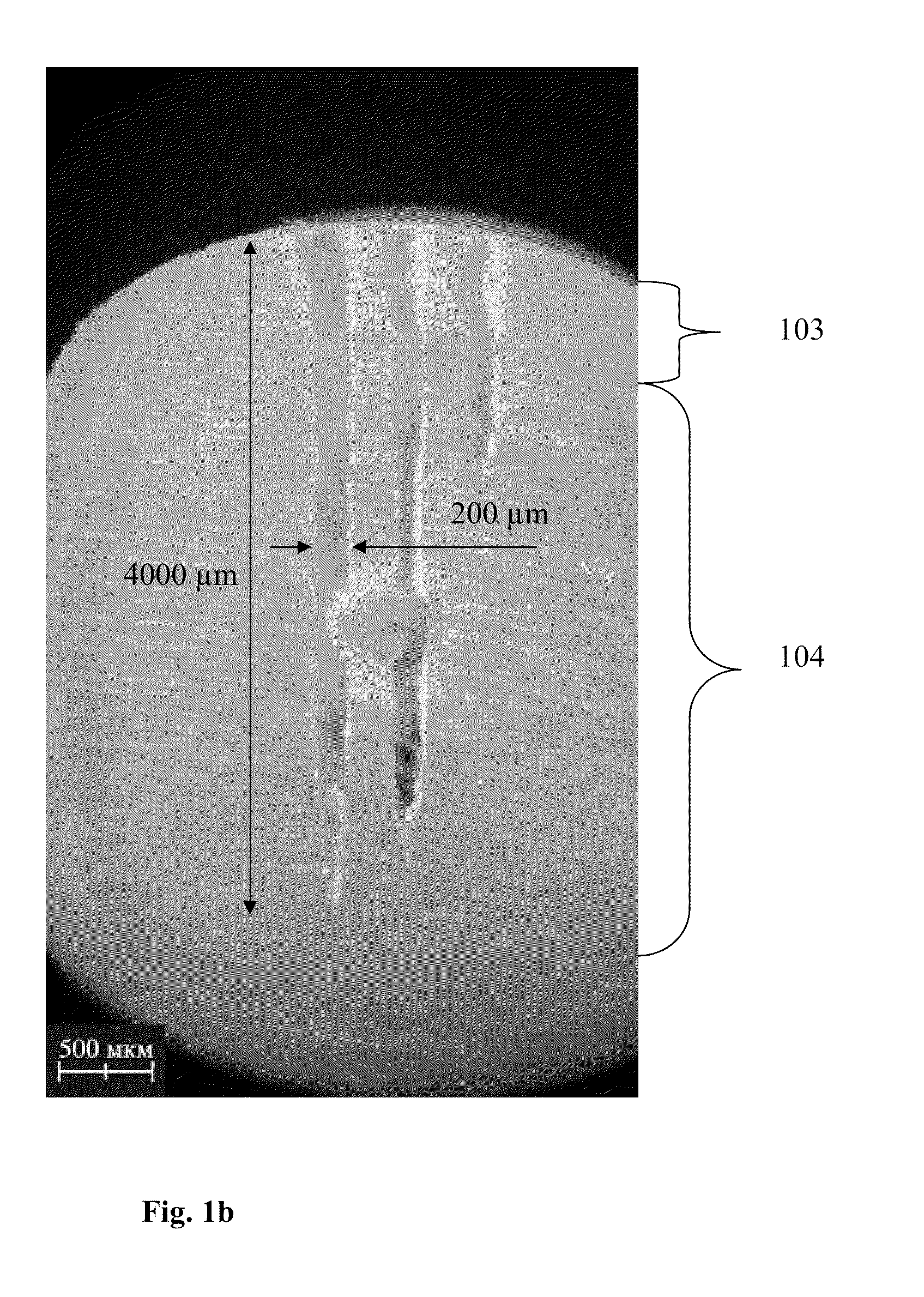
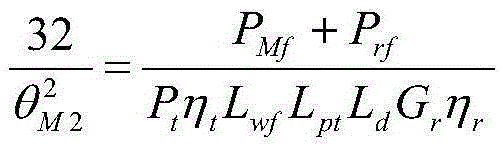Patents
Literature
281 results about "Beam divergence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
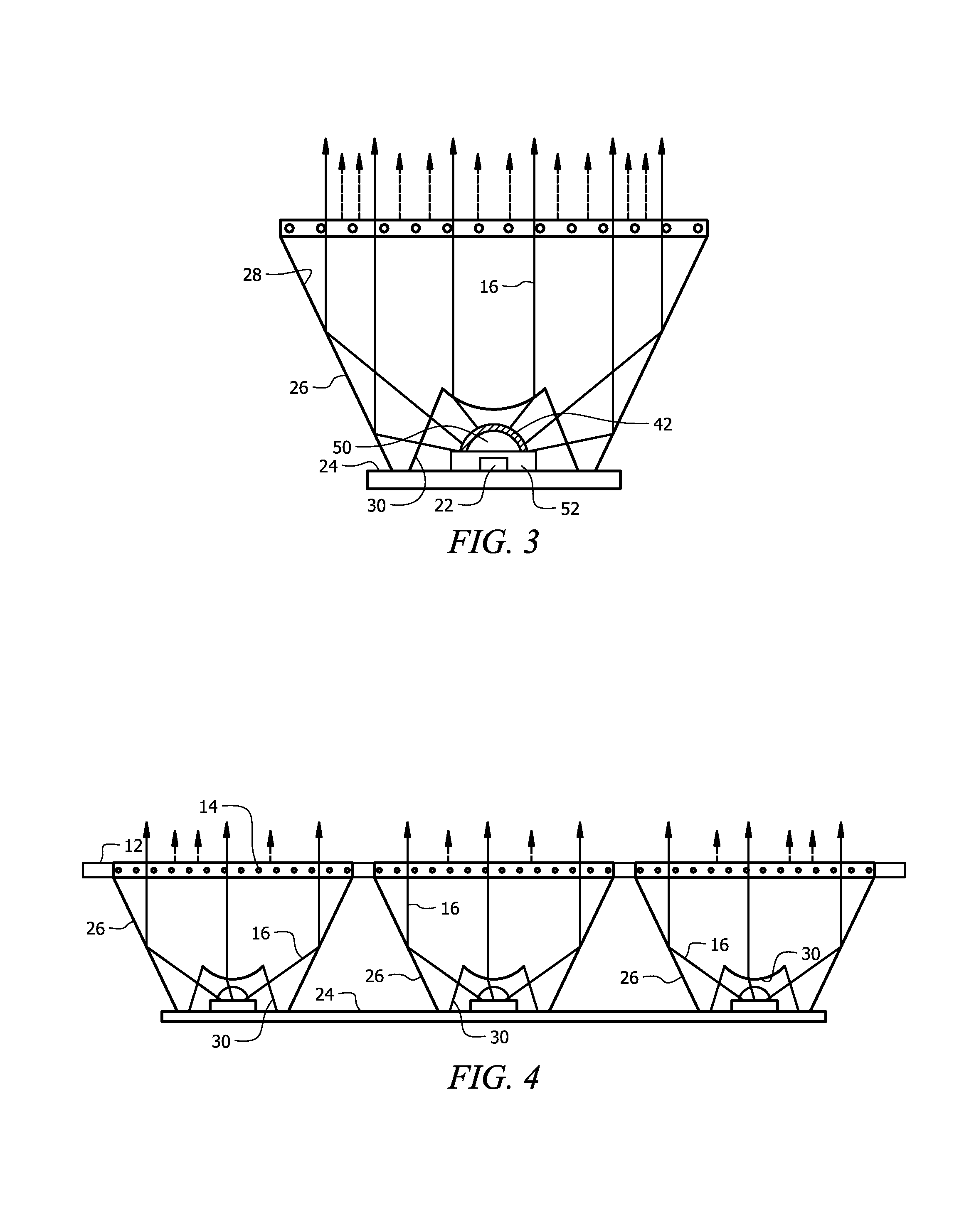
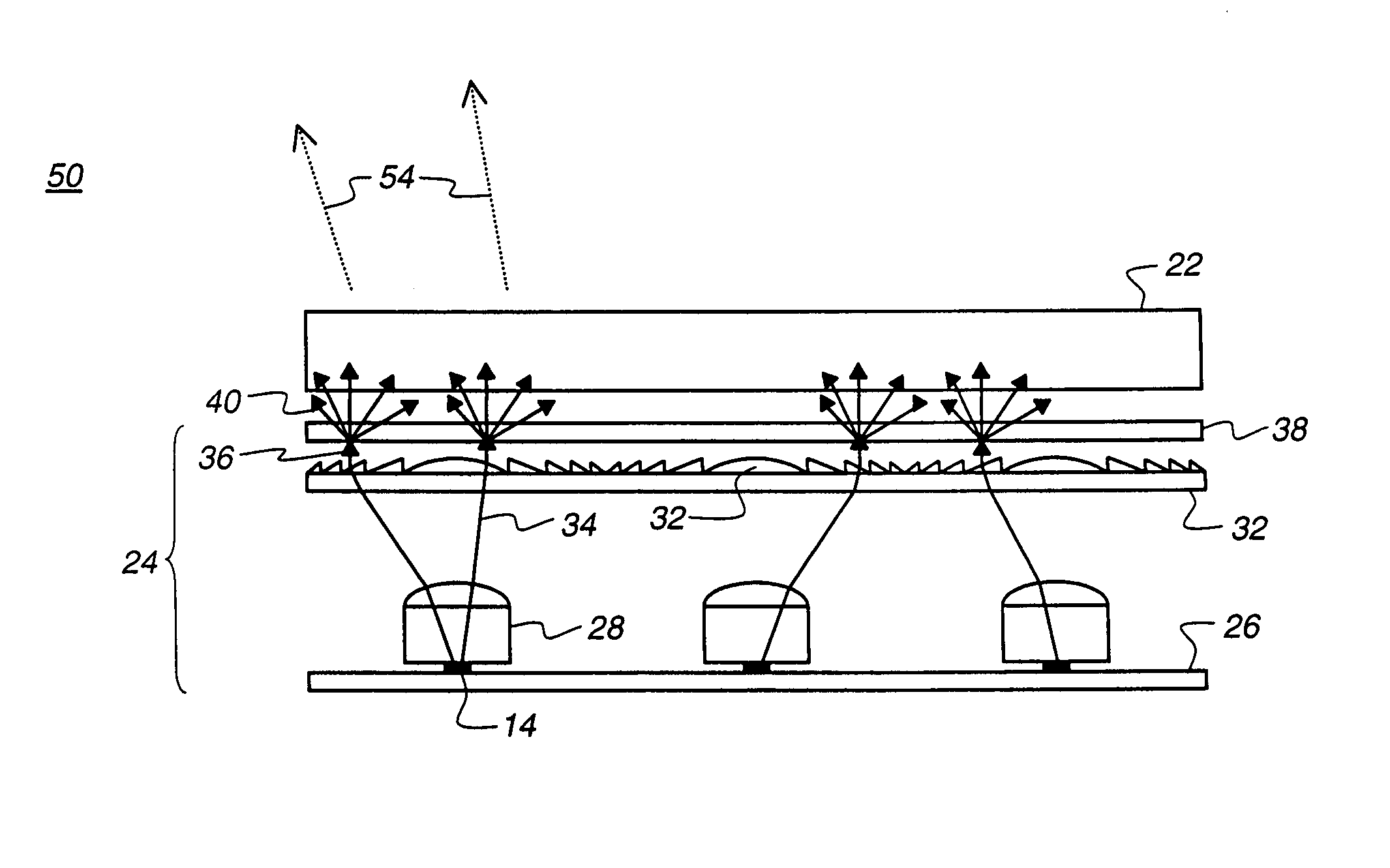
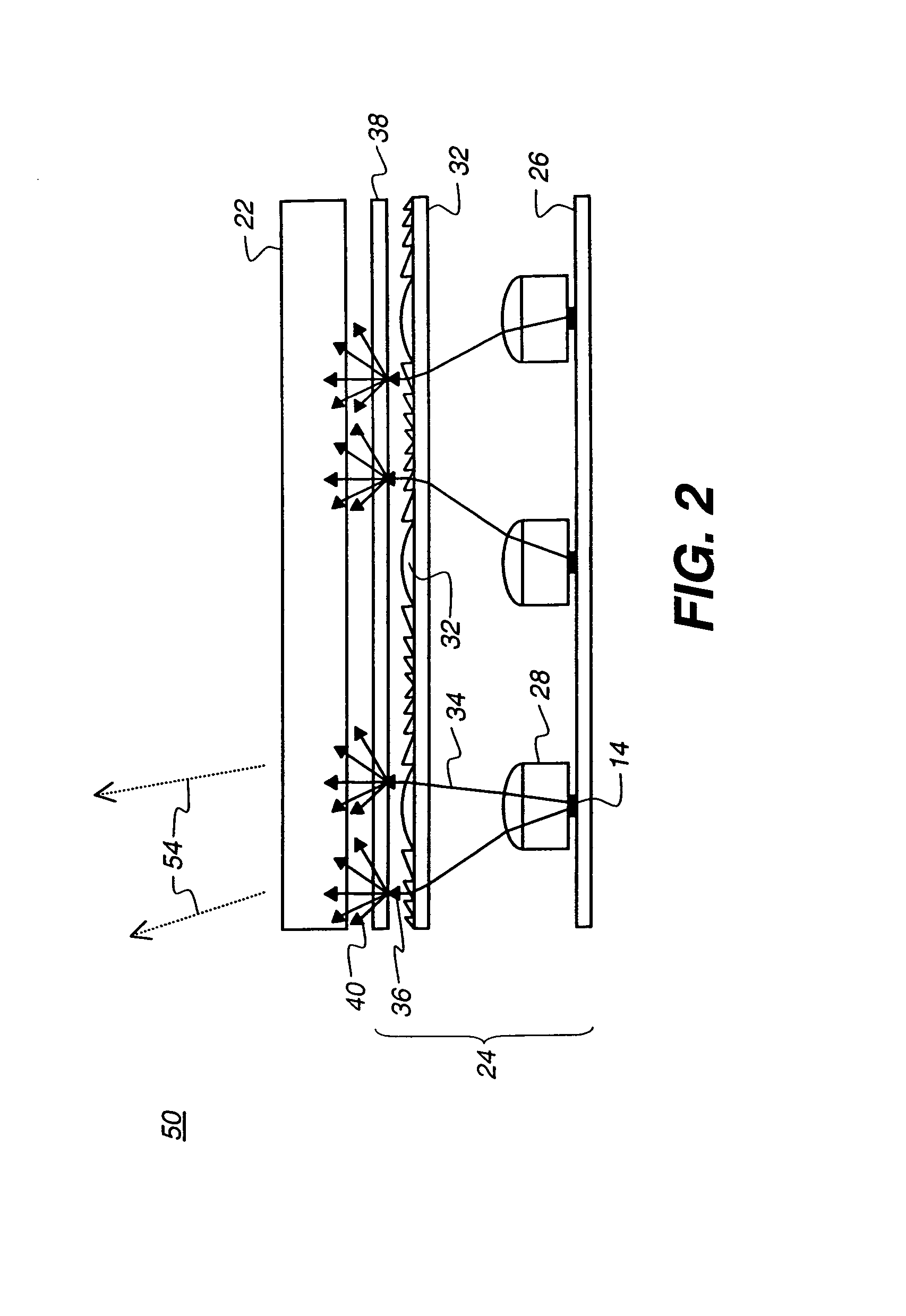
In electromagnetics, especially in optics, beam divergence is an angular measure of the increase in beam diameter or radius with distance from the optical aperture or antenna aperture from which the beam emerges. The term is relevant only in the "far field", away from any focus of the beam. Practically speaking, however, the far field can commence physically close to the radiating aperture, depending on aperture diameter and the operating wavelength.
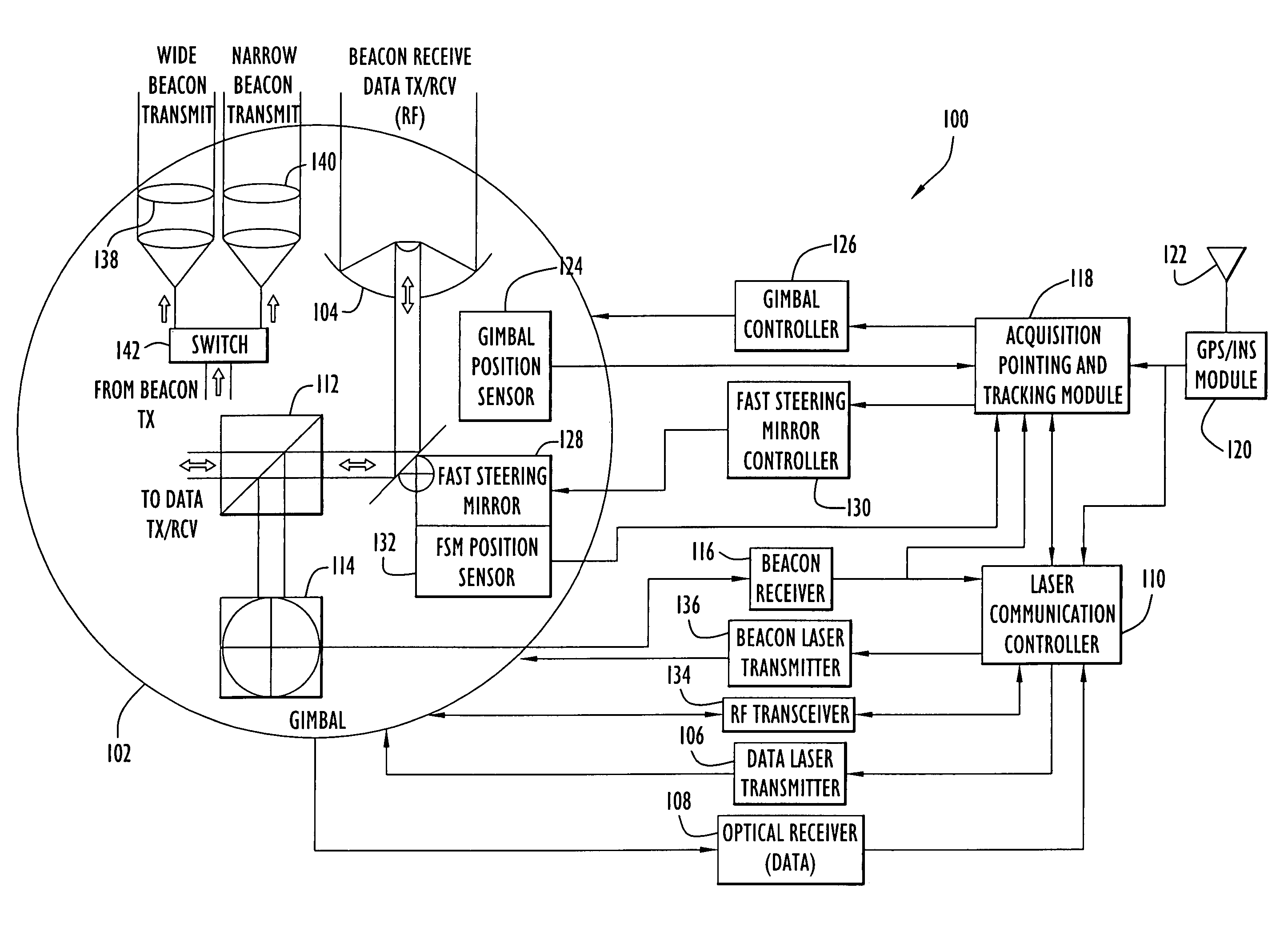
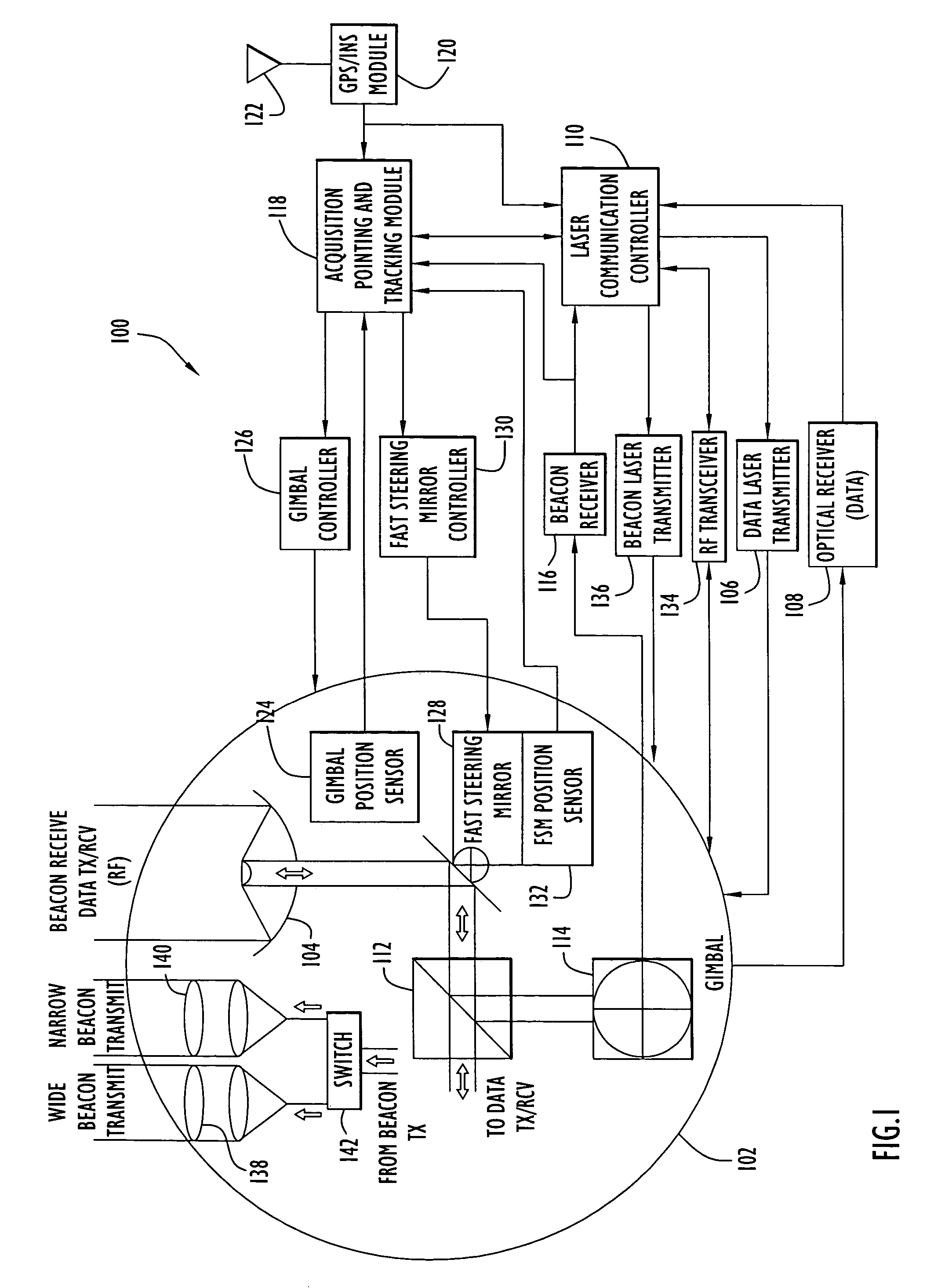
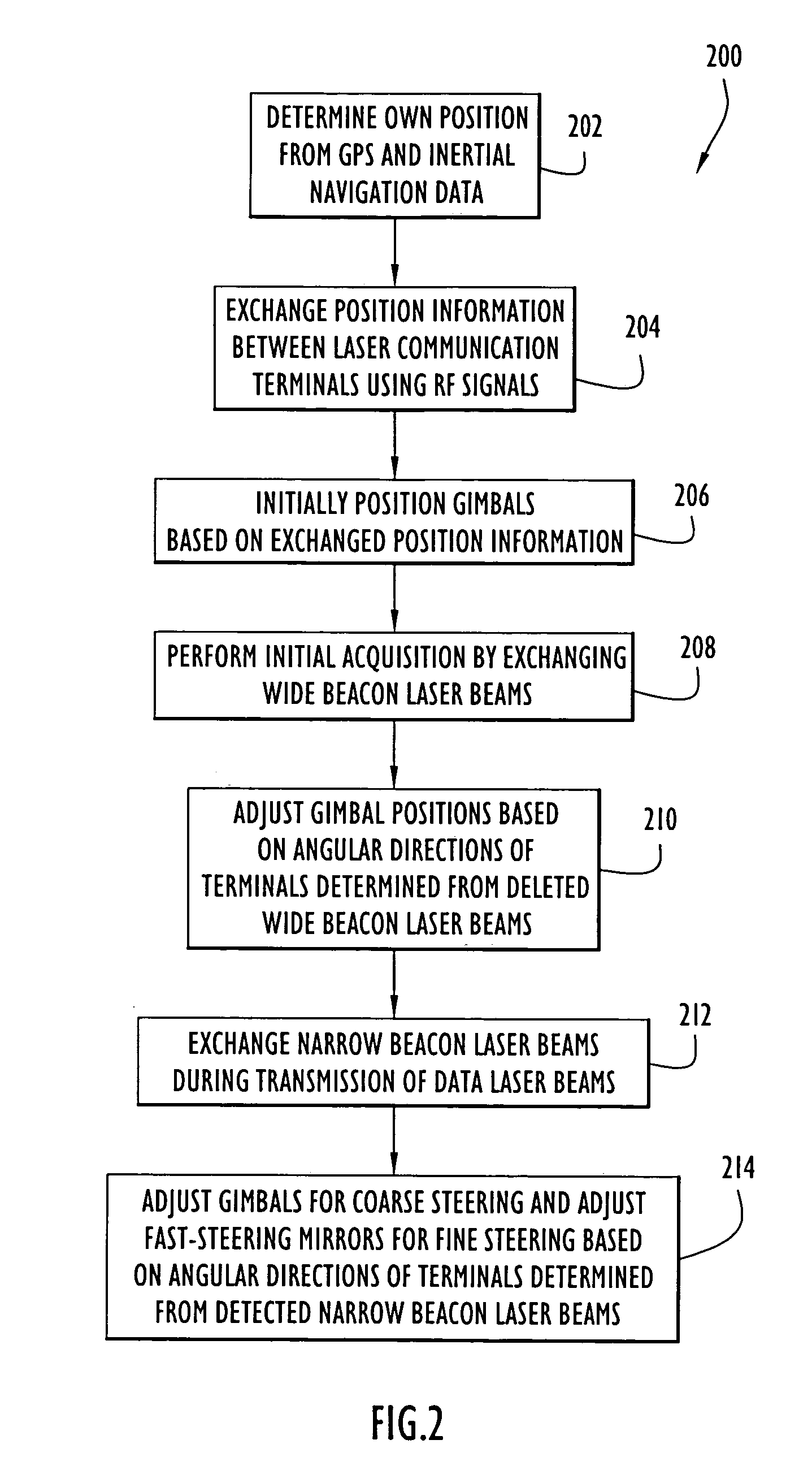
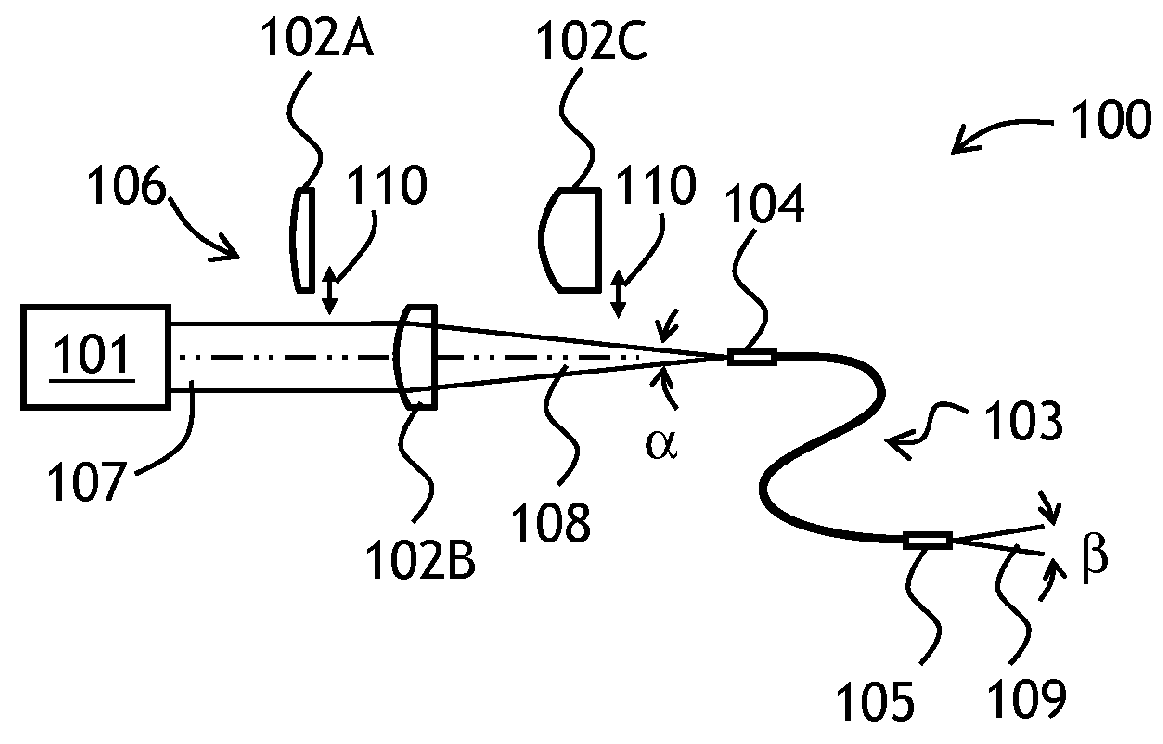
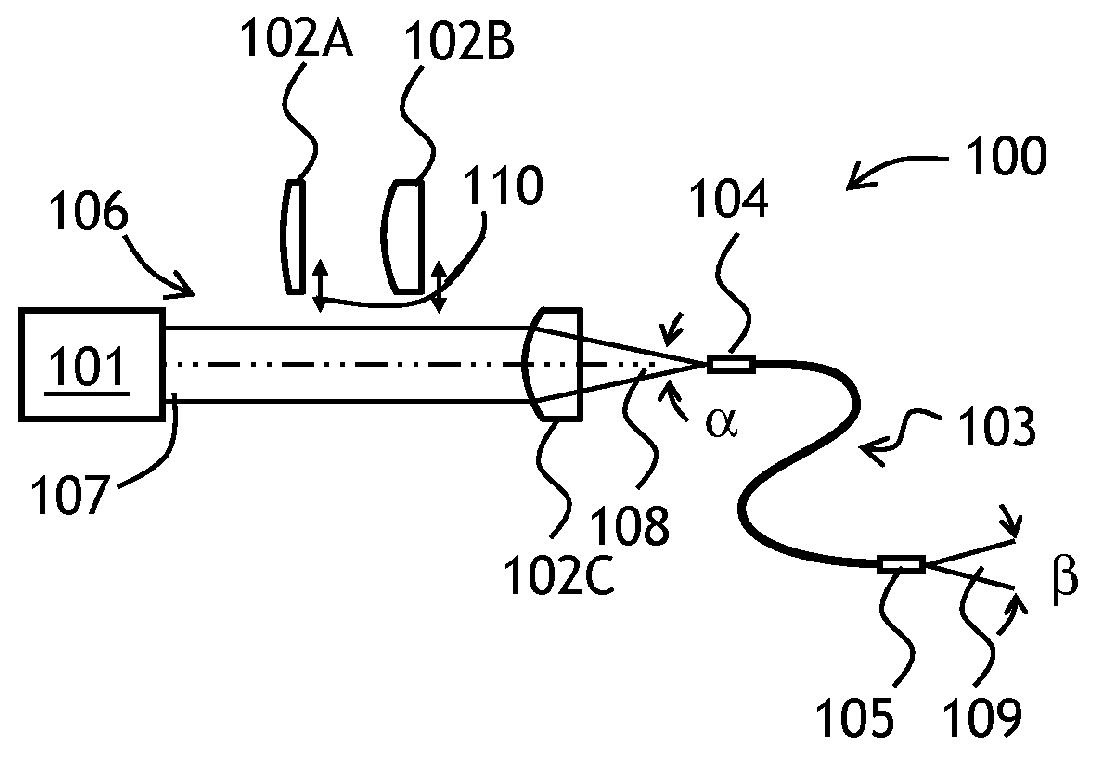
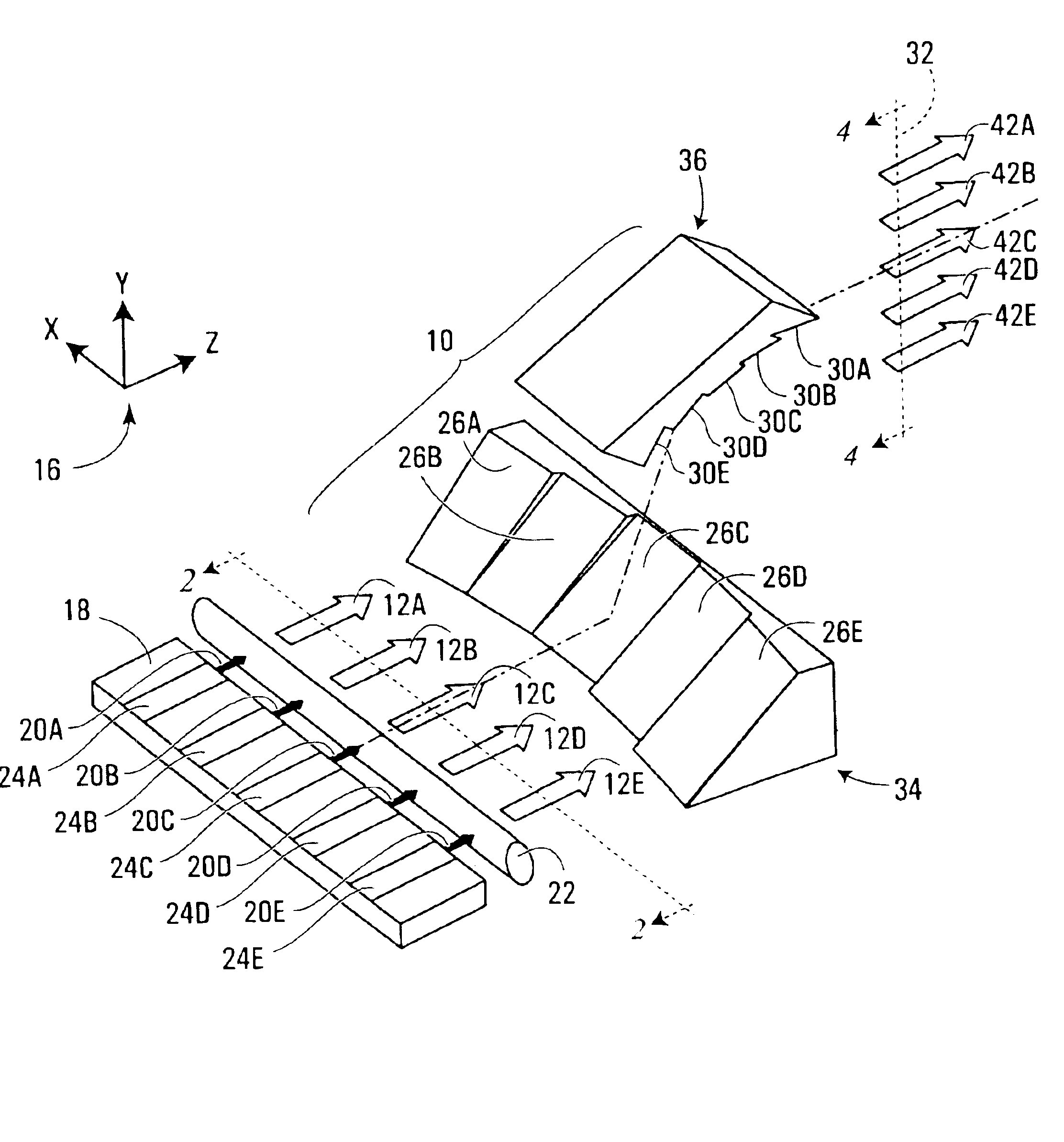
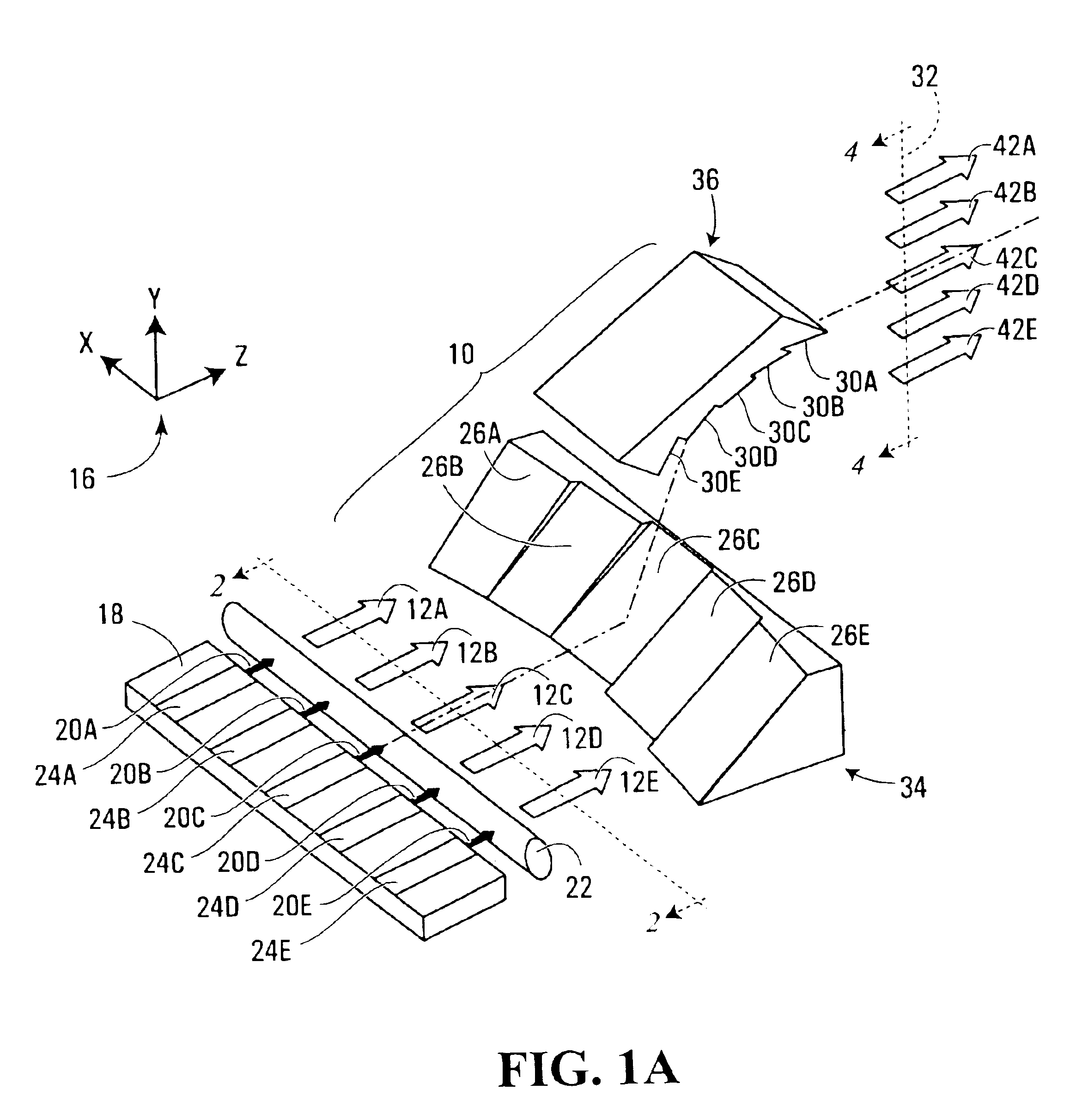
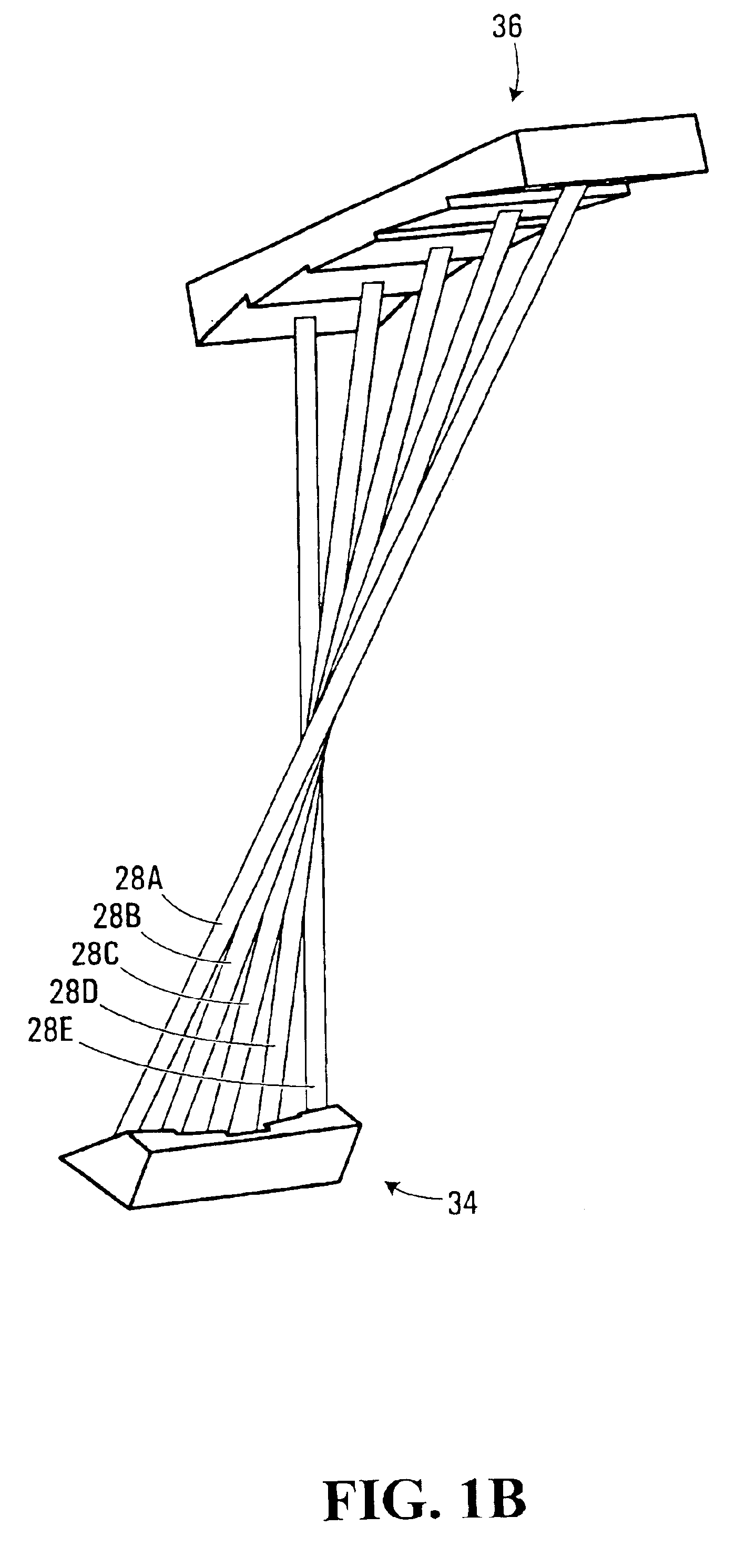
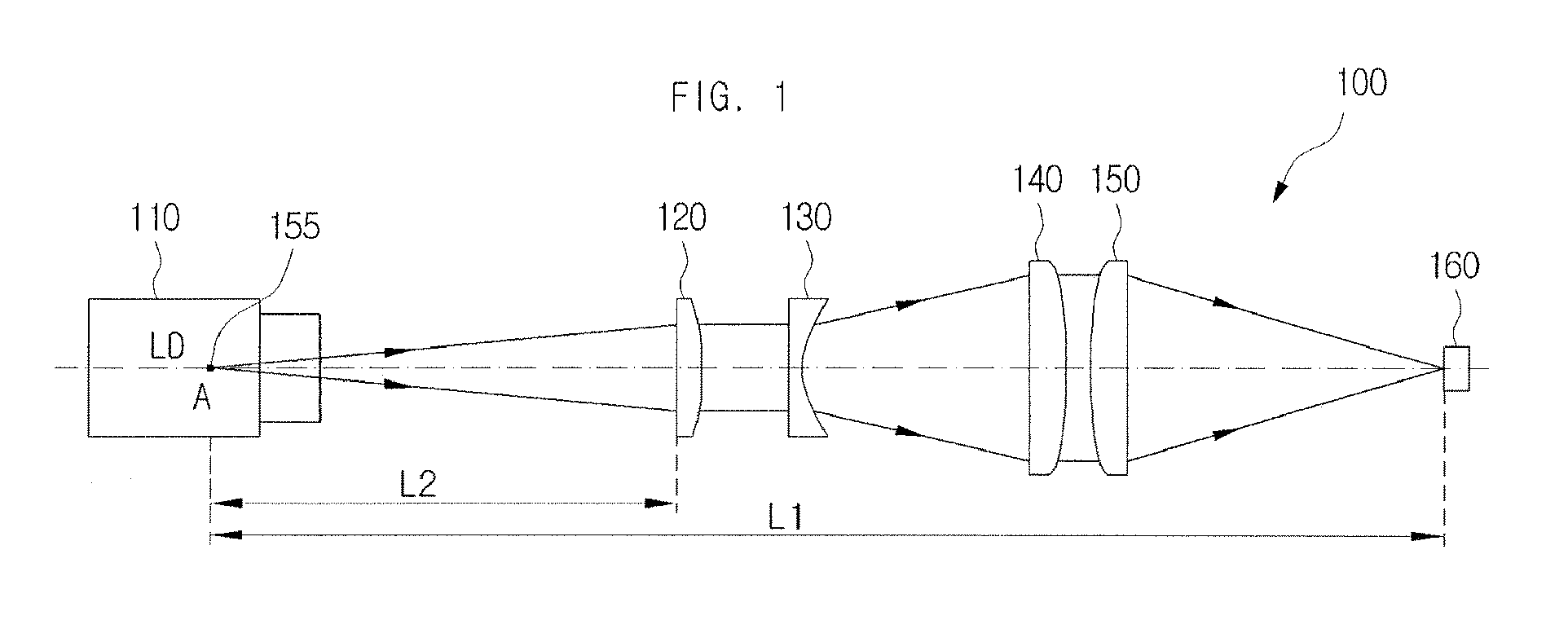
Acquisition, pointing, and tracking architecture for laser communication
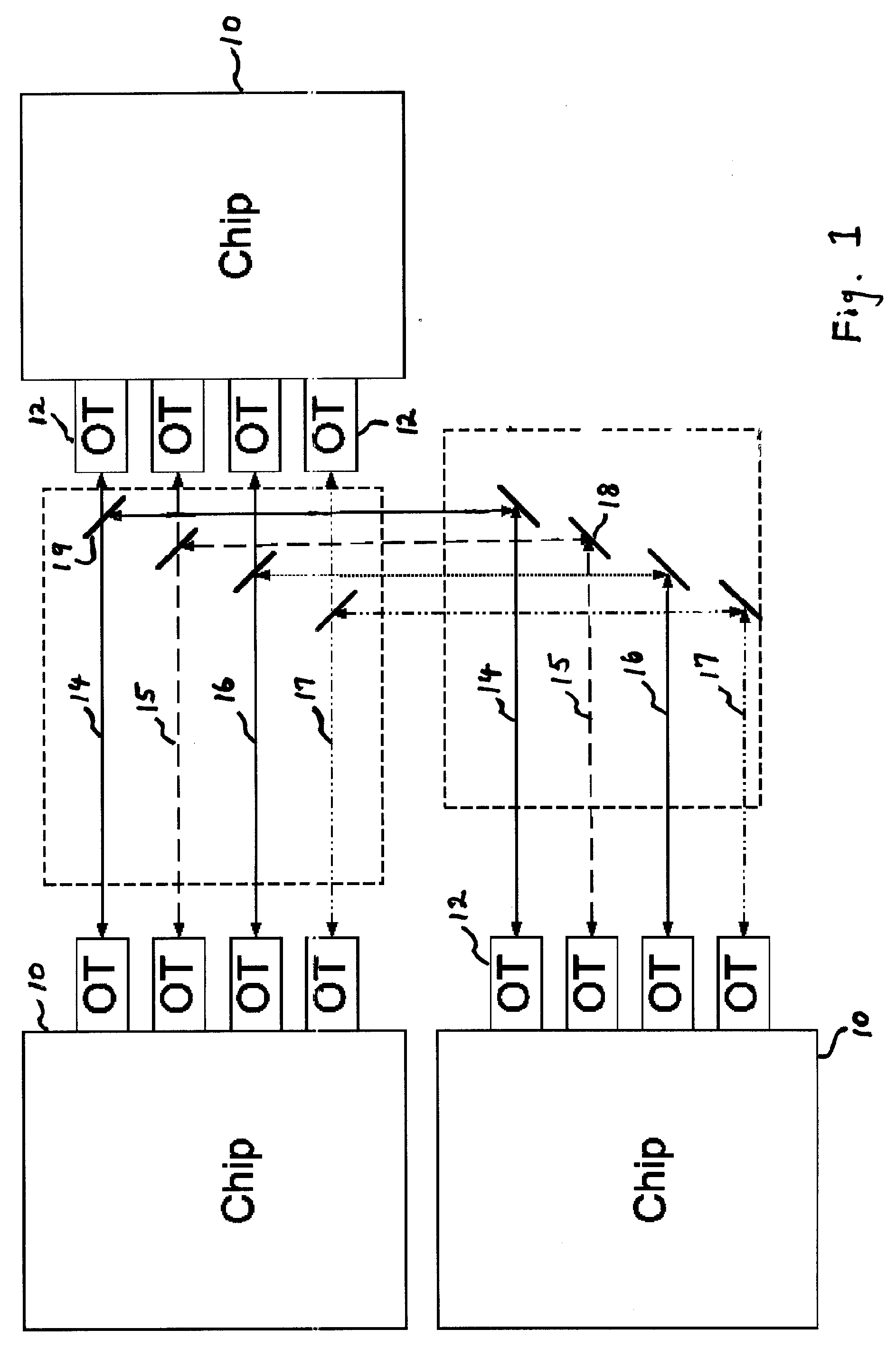
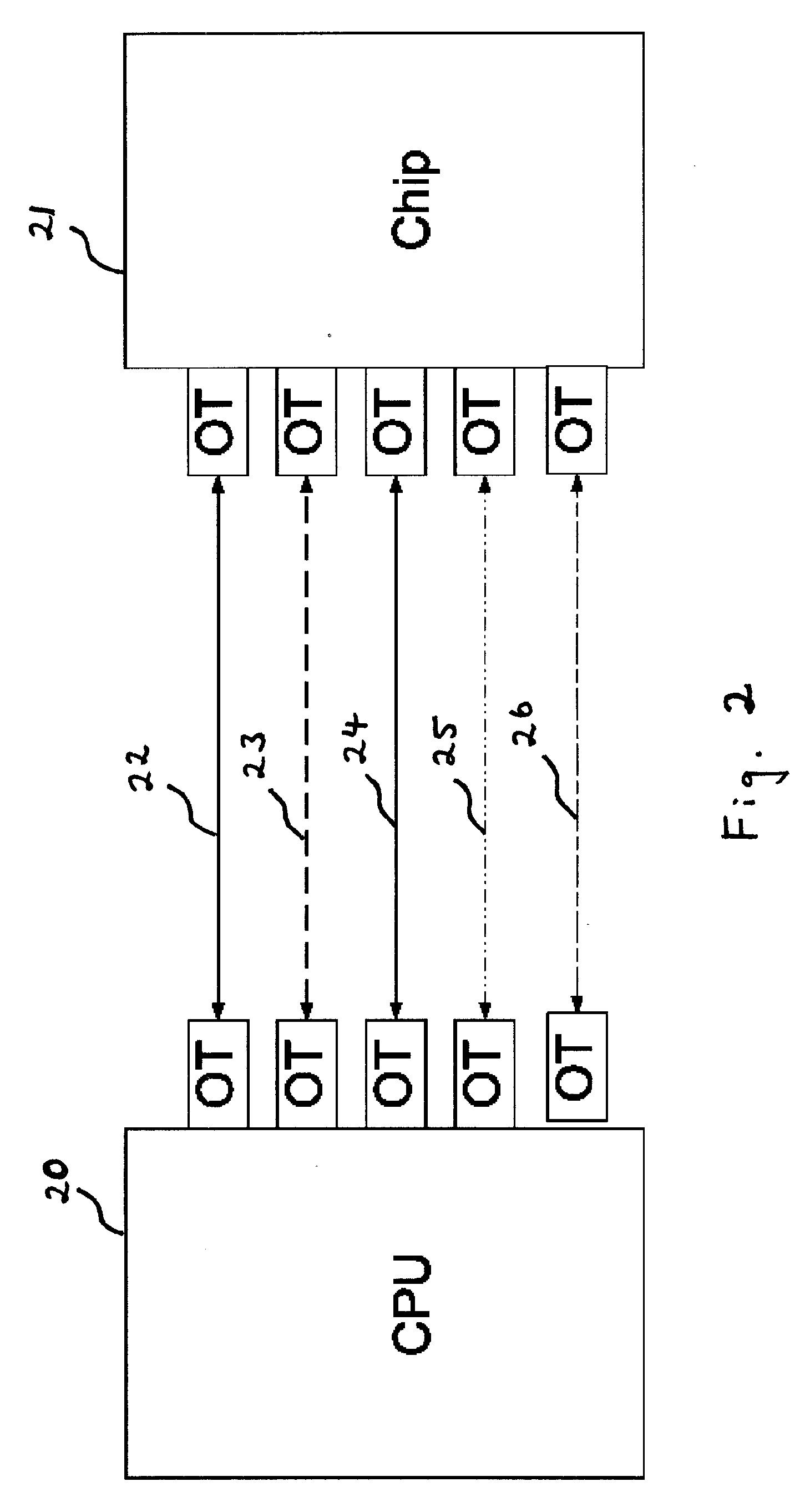
ActiveUS20070031151A1Reduce sensitivitySatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionCommunications systemLight beam
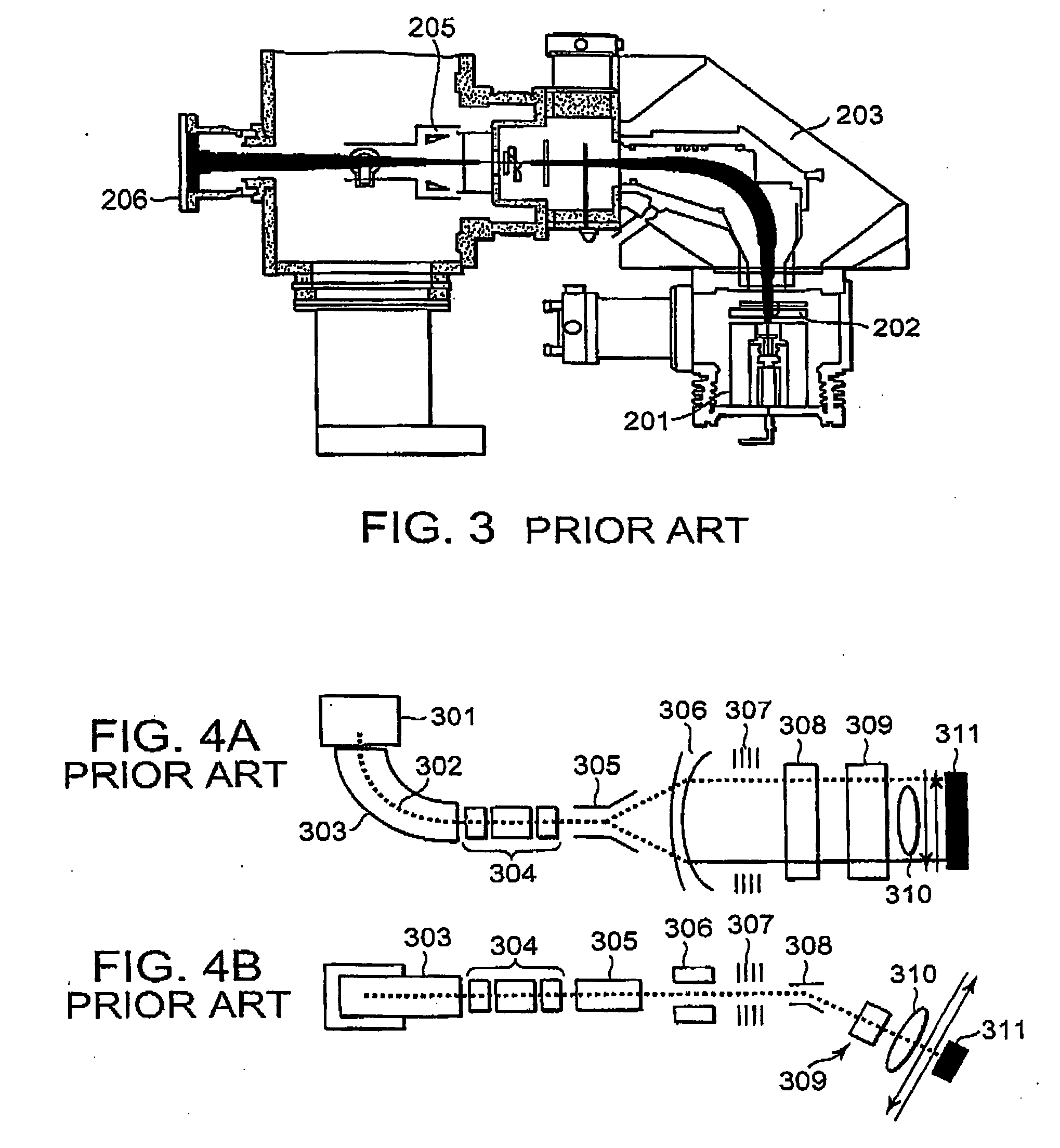
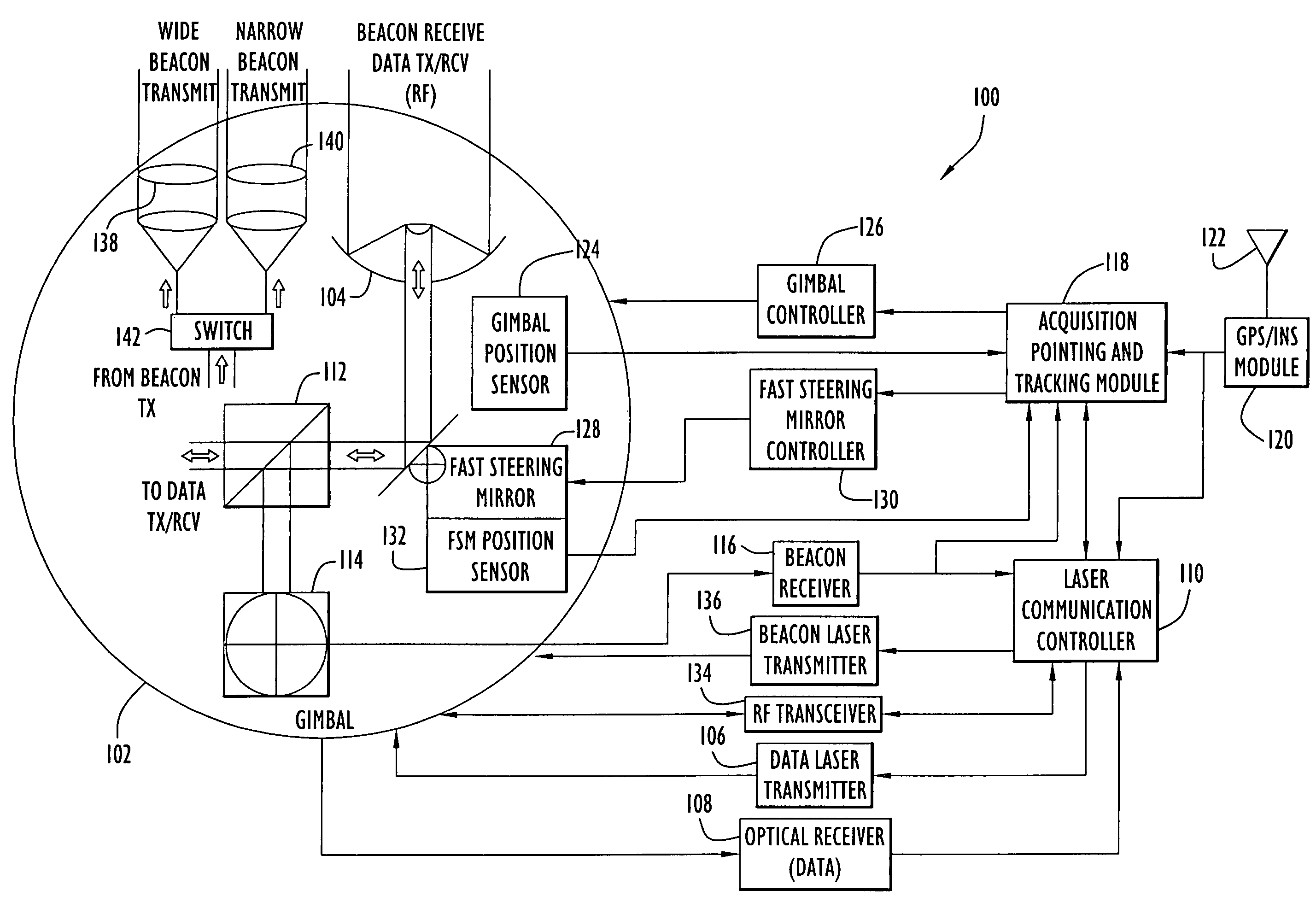
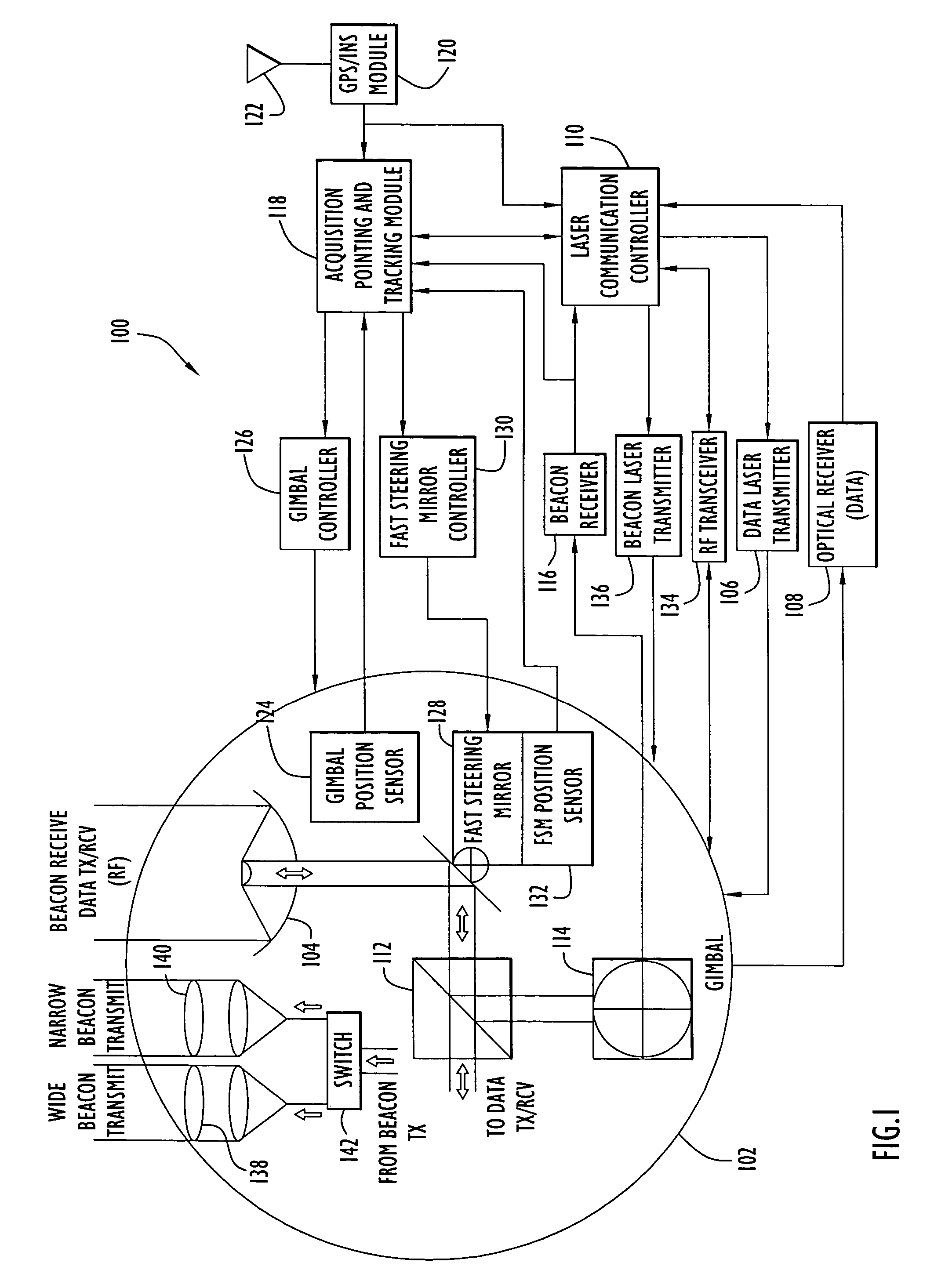
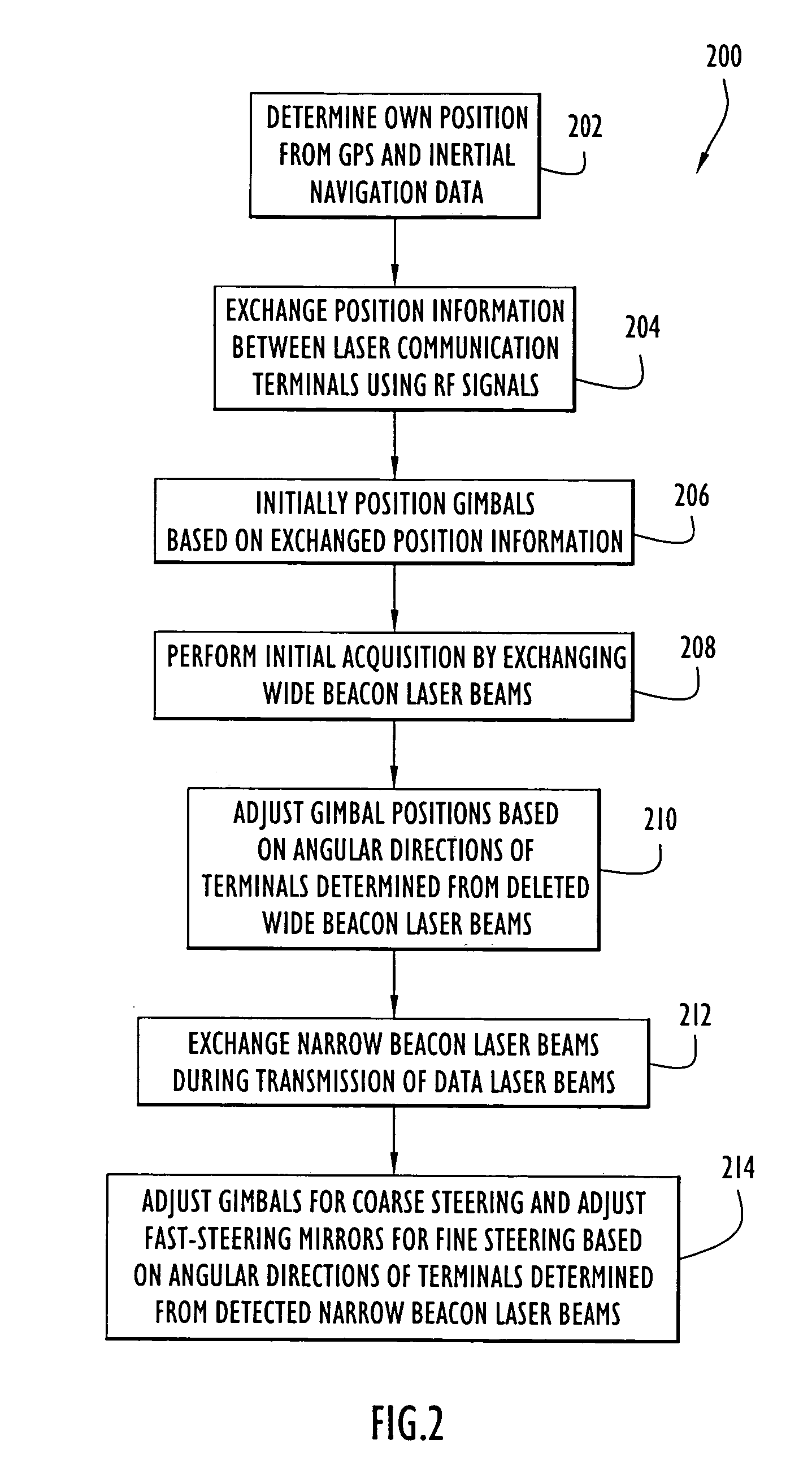
A technique for acquiring and tracking terminals in a free-space laser communication system involves exchanging beacon laser beams between the terminals to acquire and then track the terminals such that data laser beams exchanged by the terminals for communication are steered based on feedback from detection of the beacon laser beams. The beacon laser beams used for acquisition have a greater beam divergence than those used for tracking. Gimbals provide coarse steering of the data laser beams, and steering mirrors provide fine steering. GPS position data exchanged via an RF link can be used for initial pointing of the beacon laser beams for acquisition. The beacon laser beams can be chopped such that all terminals can use the same beacon wavelength and are distinguished by using different chopping frequencies. By detecting a chopped signal, the position sensor detector can be AC coupled to reduce sensitivity to solar radiation and glint.
Owner:PERATON INC
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
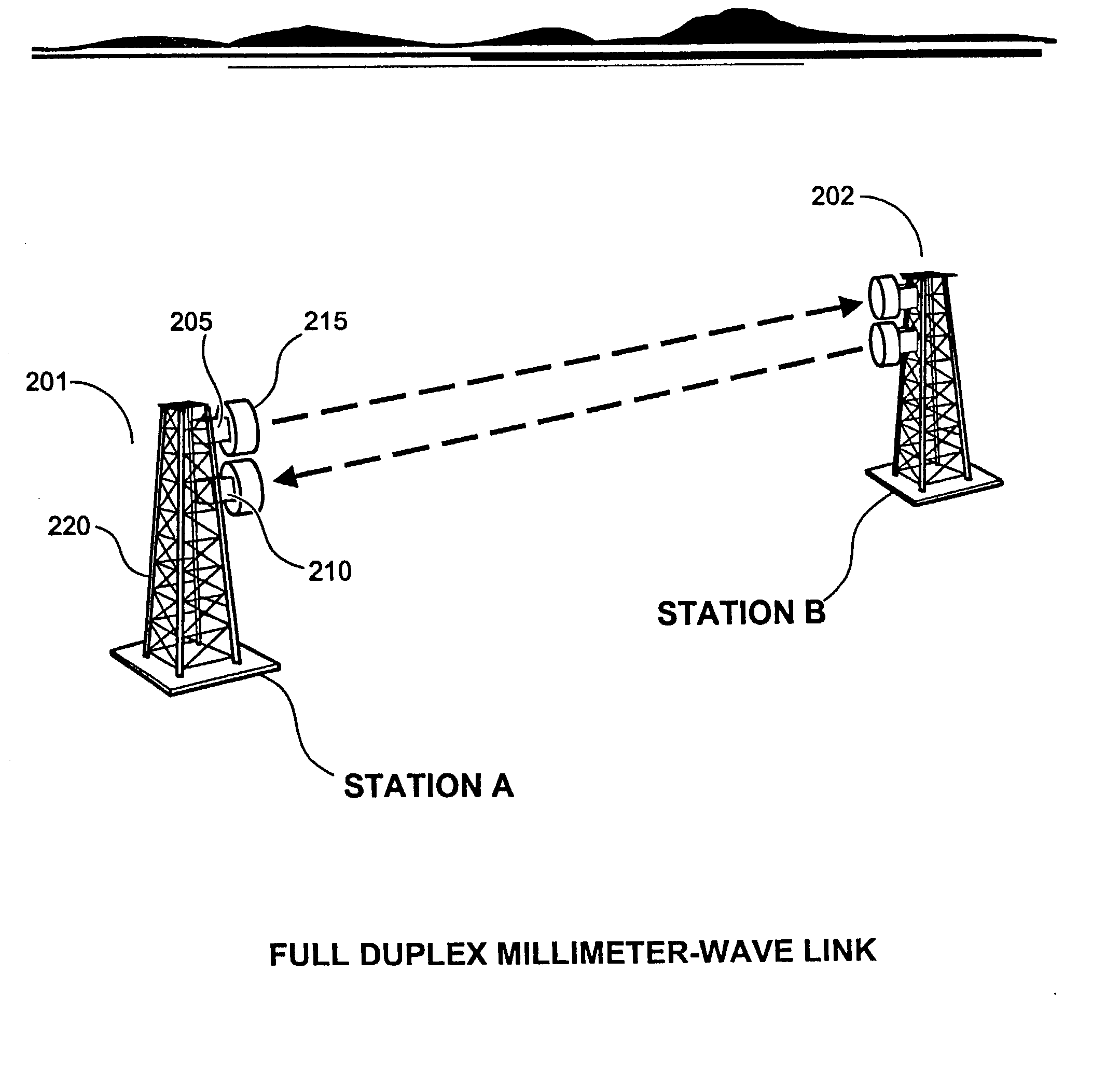
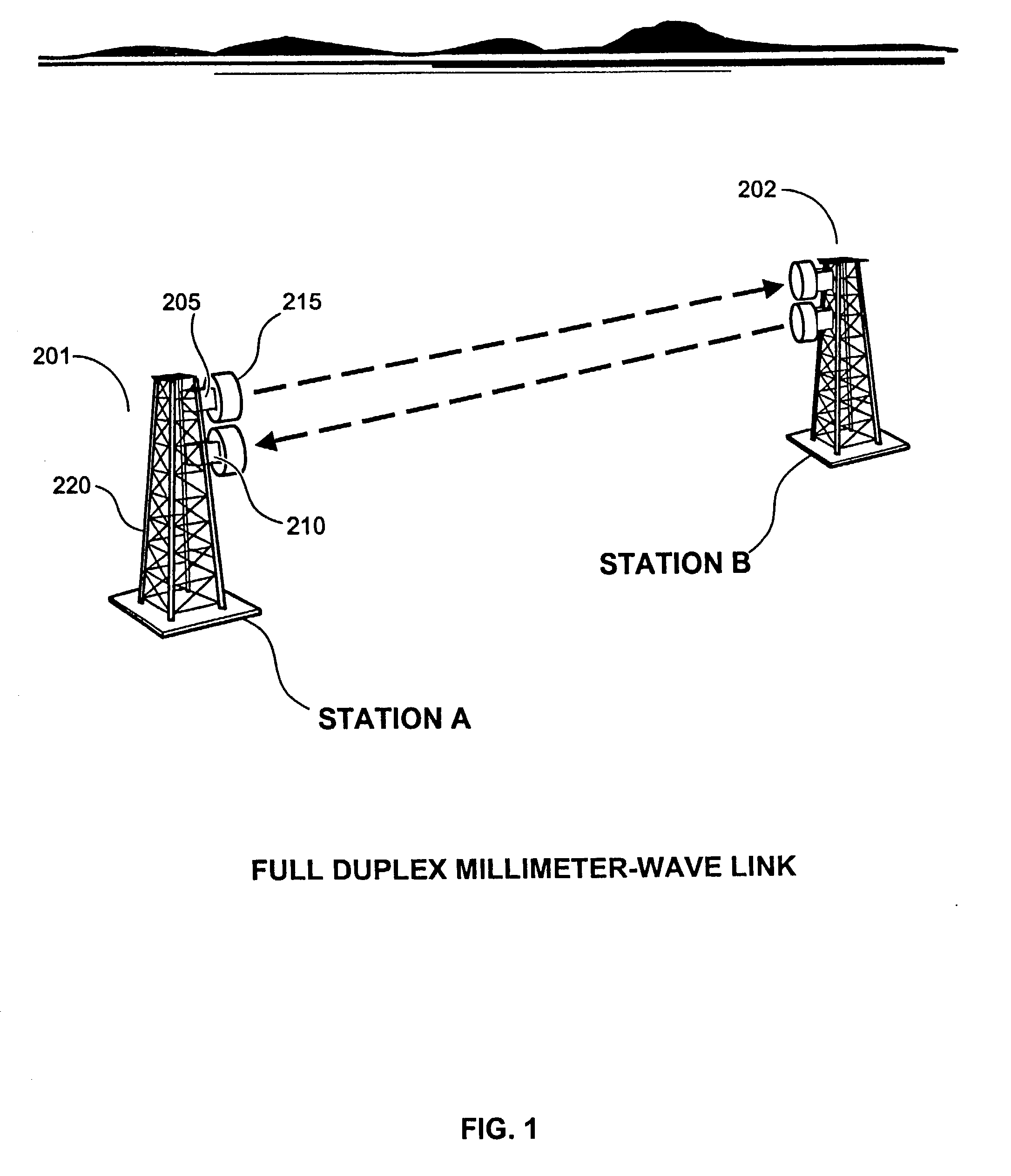
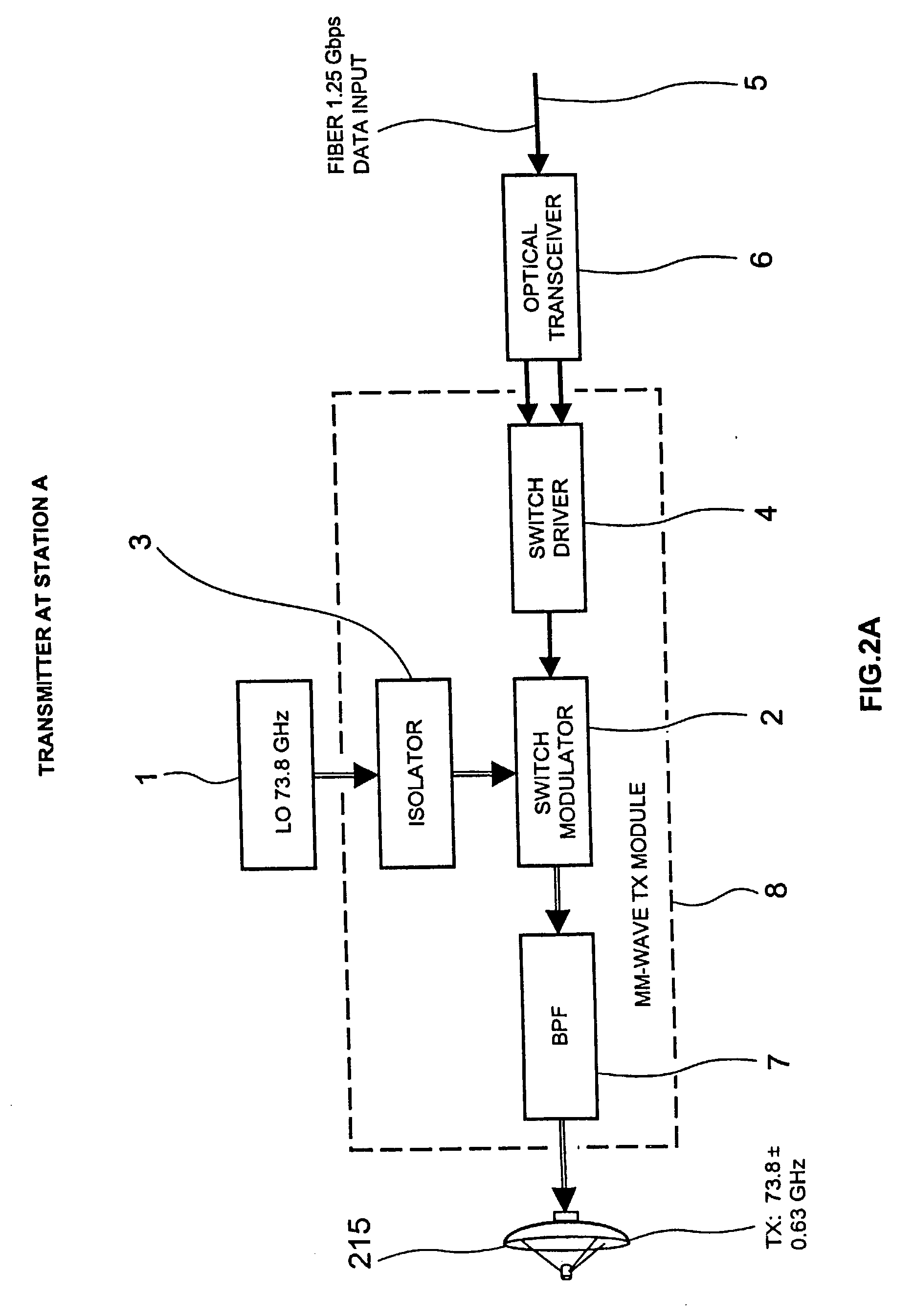
High data rate wireless communication system
InactiveUS20030224801A1Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverTelecommunications link
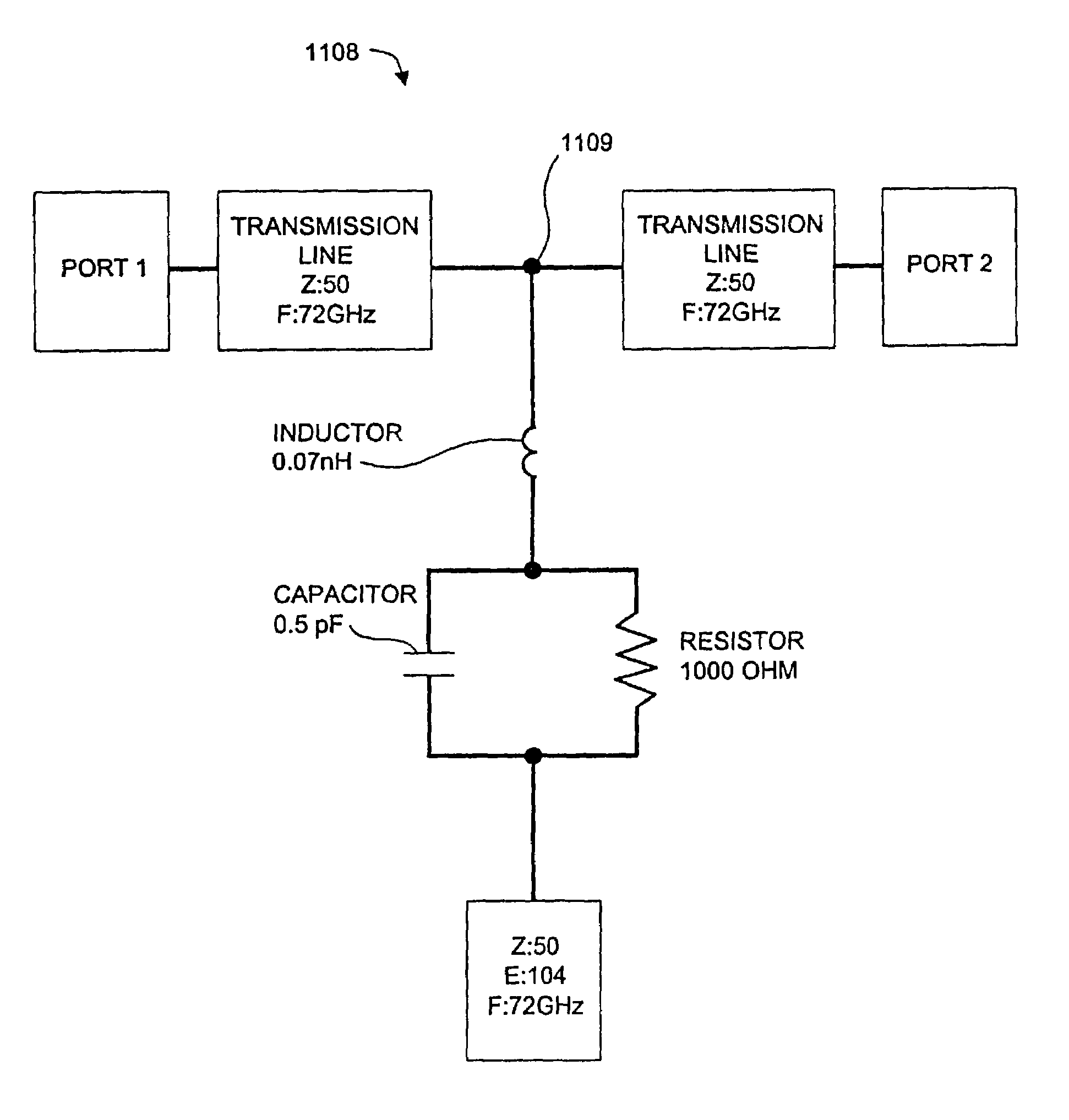
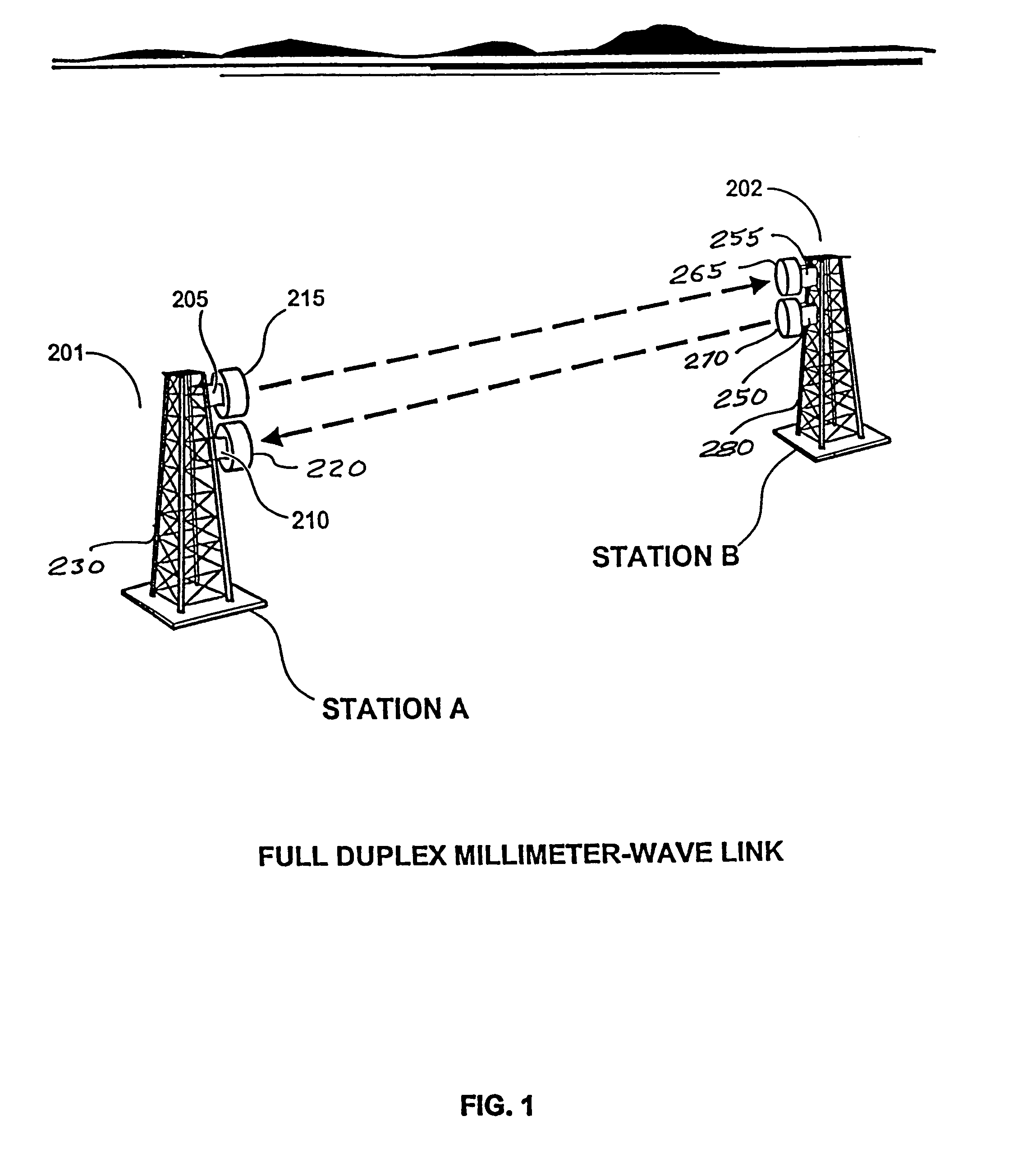
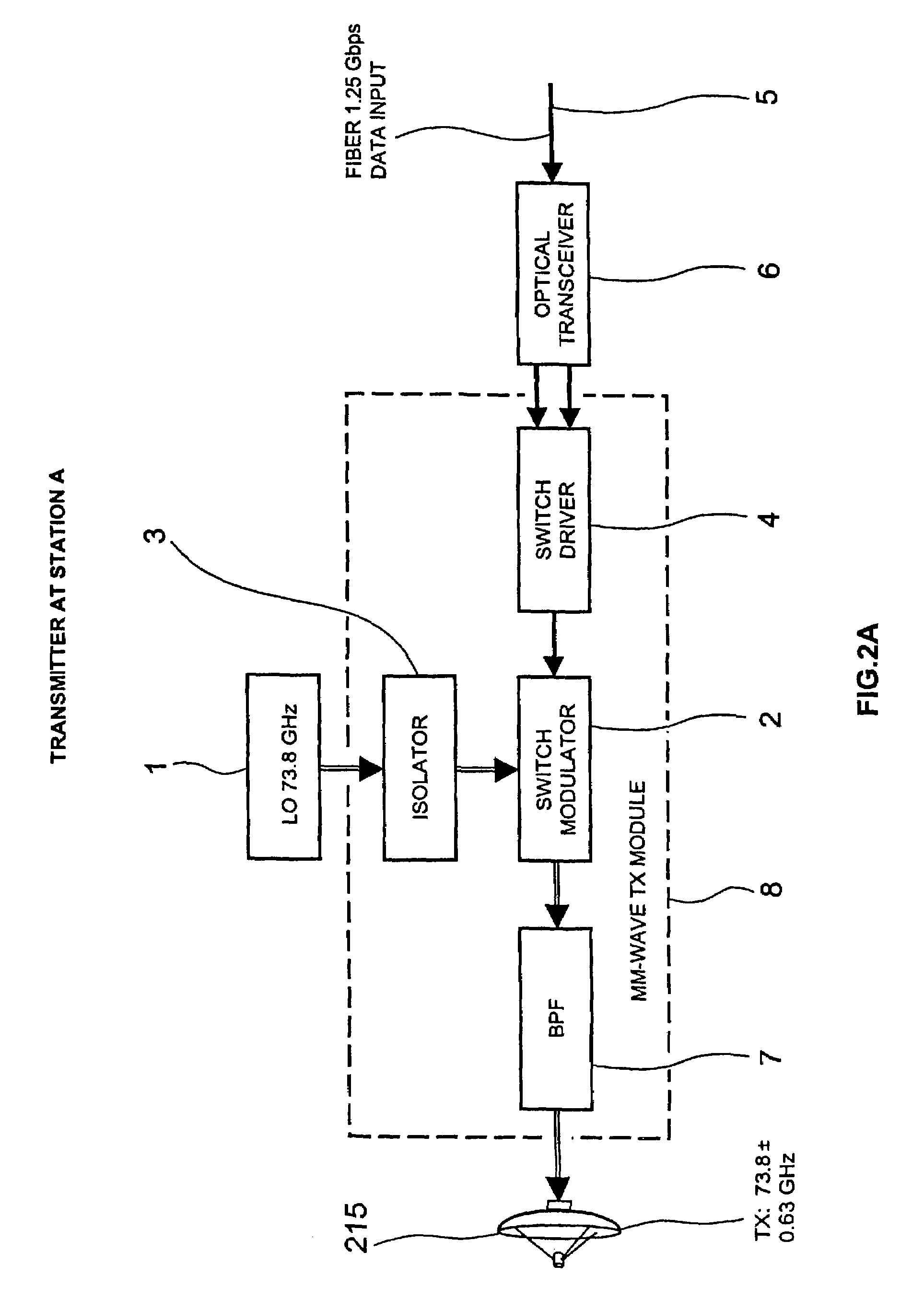
A high data rate communication system operating at frequencies greater than 70 MHz and at data rates of about 1.25 Gbps or greater. Preferred embodiments include modulators with a resonant LC circuit including a diode which is back-biased for "off" (i.e., no transmit) and forward biased for "on" (or transmit). The modulator is a part of high performance transceivers for wireless, millimeter wave communications links. A preferred embodiment provides a communication link of more than eight miles which operates within the 71 to 76 GHz portion of the millimeter spectrum and provides data transmission rates of 1.25 Gbps with bit error rates of less than 10<-10 >. A first transceiver transmits at a first bandwidth and receives at a second bandwidth both within the above spectral range. A second transceiver transmits at the second bandwidth and receives at the first bandwidth. The transceivers are equipped with antennas providing beam divergence small enough to ensure efficient spatial and directional partitioning of the data channels so that an almost unlimited number of transceivers will be able to simultaneously use the same spectrum. In a preferred embodiment the first and second spectral ranges are 71.8+ / -0.63 GHz and 73.8+ / -0.63 GHz and the half power beam width is about 0.2 degrees or less. Preferably, a backup transceiver set is provided which would take over the link in the event of very bad weather conditions. In other embodiments especially useful for mobile applications at least one of the transceivers include a GPS locator.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Optical system
ActiveUS8203702B1Reduce frictionEnormous difference potential speedAngle measurementAdditive manufacturing apparatusBeam divergencePiston
Method / system locate external articles using source, detector (PSD), entrance aperture, and magnifying / reducing afocal element—expanding FOR>90°, or refining precision. Between (1) source or detector and (2) aperture, at least one plural-axis-rotatable mirror addresses source / detector throughout FOR. ½- to 15-centimeter mirror enables ˜25 to ˜45 μradian beam divergence. Aperture, afocal element, and mirror(s) define source-detector path. Mirror(s) rotate in refractory- (or air / magnetic-) bearing mount; or mirror array. Auxiliary optics illuminate mirror back, monitoring return to measure (null-balance feedback) angle. To optimize imaging, auxiliary radiation propagates via splitters toward array (paralleling measurement paths), then focusing on imaging detector. Focal quality is developed as a PSF, optimized vs. angle; stored results later recover optima. Mirror drive uses magnet(s) on mirror(s). “Piston” motion yields in-phase wavefronts, so array dimensions set diffraction limit. Also: destructive reply; scaling optimizes acceleration vs. thickness; passive systems.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Millimeter wave communications system with a high performance modulator circuit
InactiveUS7065326B2Spatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsMillimeter wave communication systemsFrequency spectrum
A high data rate communication system operating at frequencies greater than 70 MHz and at data rates of about 1.25 Gbps or greater. Preferred embodiments include modulators with a resonant LC circuit including a diode which is back-biased for “off” (i.e., no transmit) and forward biased for “on” (or transmit). The modulator is a part of high performance transceivers for wireless, millimeter wave communications links. A preferred embodiment provides a communication link of more than eight miles which operates within the 71 to 76 GHz portion of the millimeter spectrum and provides data transmission rates of 1.25 Gbps with bit error rates of less than 10−10 . A first transceiver transmits at a first bandwidth and receives at a second bandwidth both within the above spectral range. A second transceiver transmits at the second bandwidth and receives at the first bandwidth. The transceivers are equipped with antennas providing beam divergence small enough to ensure efficient spatial and directional partitioning of the data channels so that an almost unlimited number of transceivers will be able to simultaneously use the same spectrum. In a preferred embodiment the first and second spectral ranges are 71.8+ / −0.63 GHz and 73.8+ / −0.63 GHz and the half power beam width is about 0.2 degrees or less. Preferably, a backup transceiver set is provided which would take over the link in the event of very bad weather conditions. In other embodiments especially useful for mobile applications at least one of the transceivers include a GPS locator.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
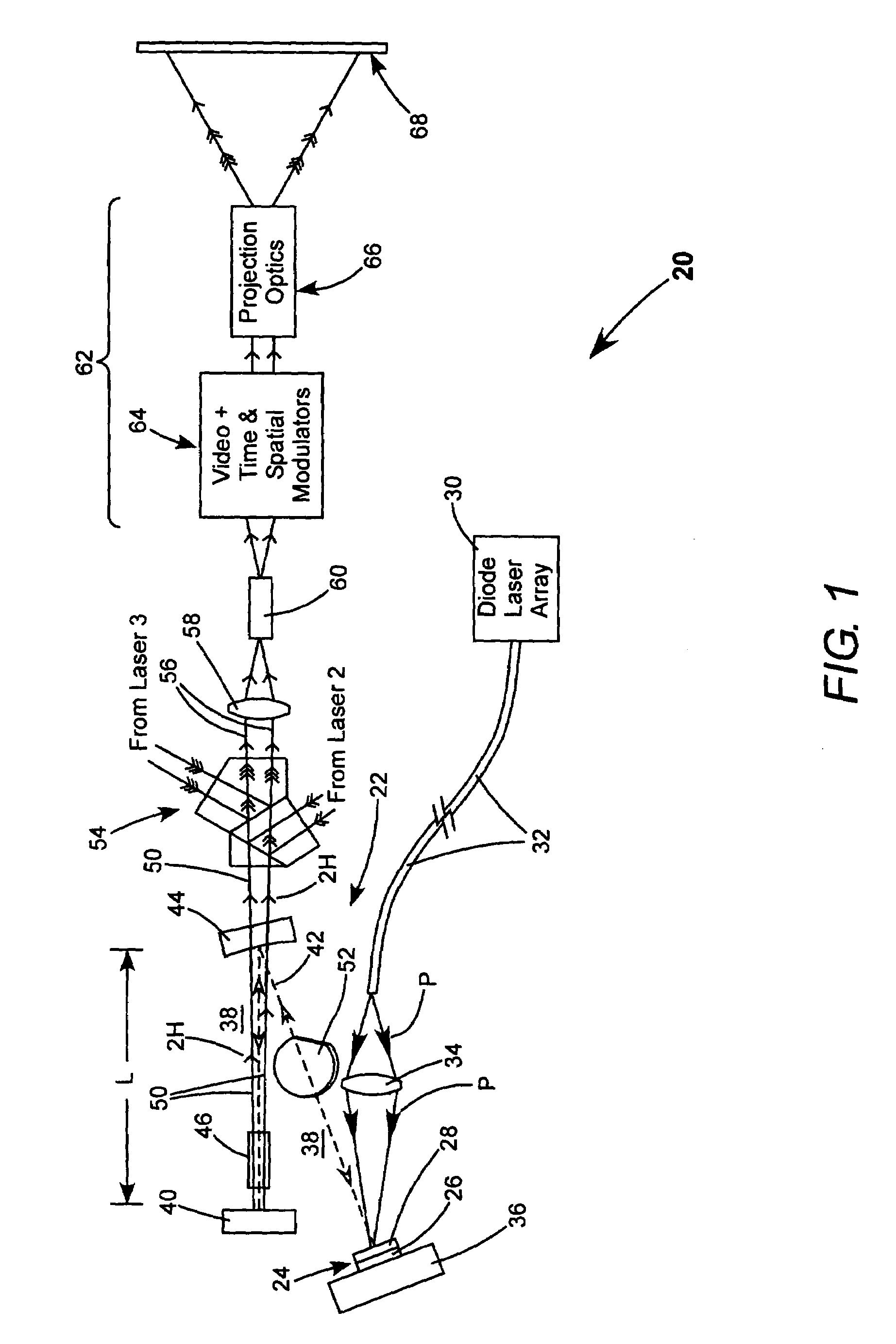
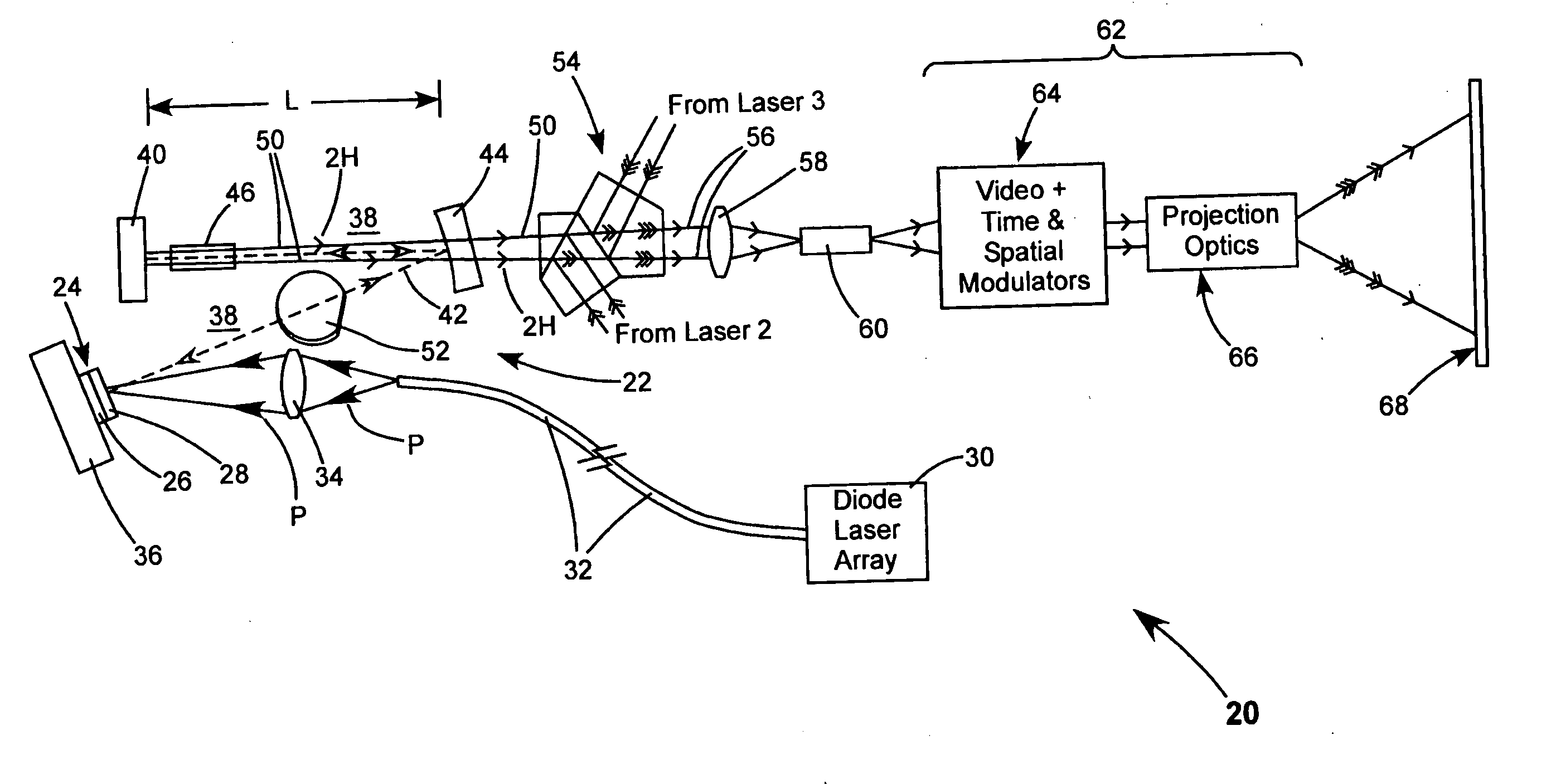
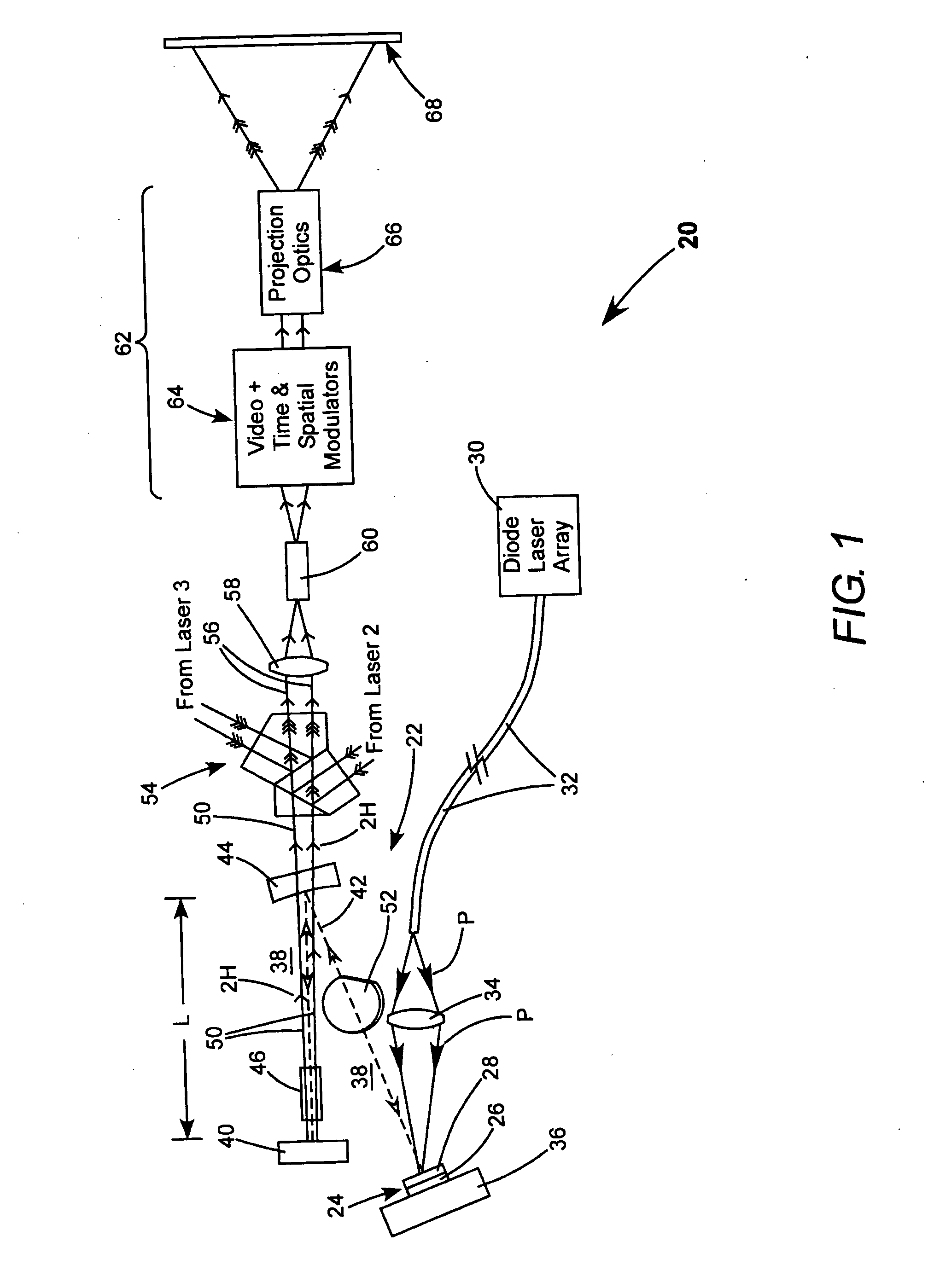
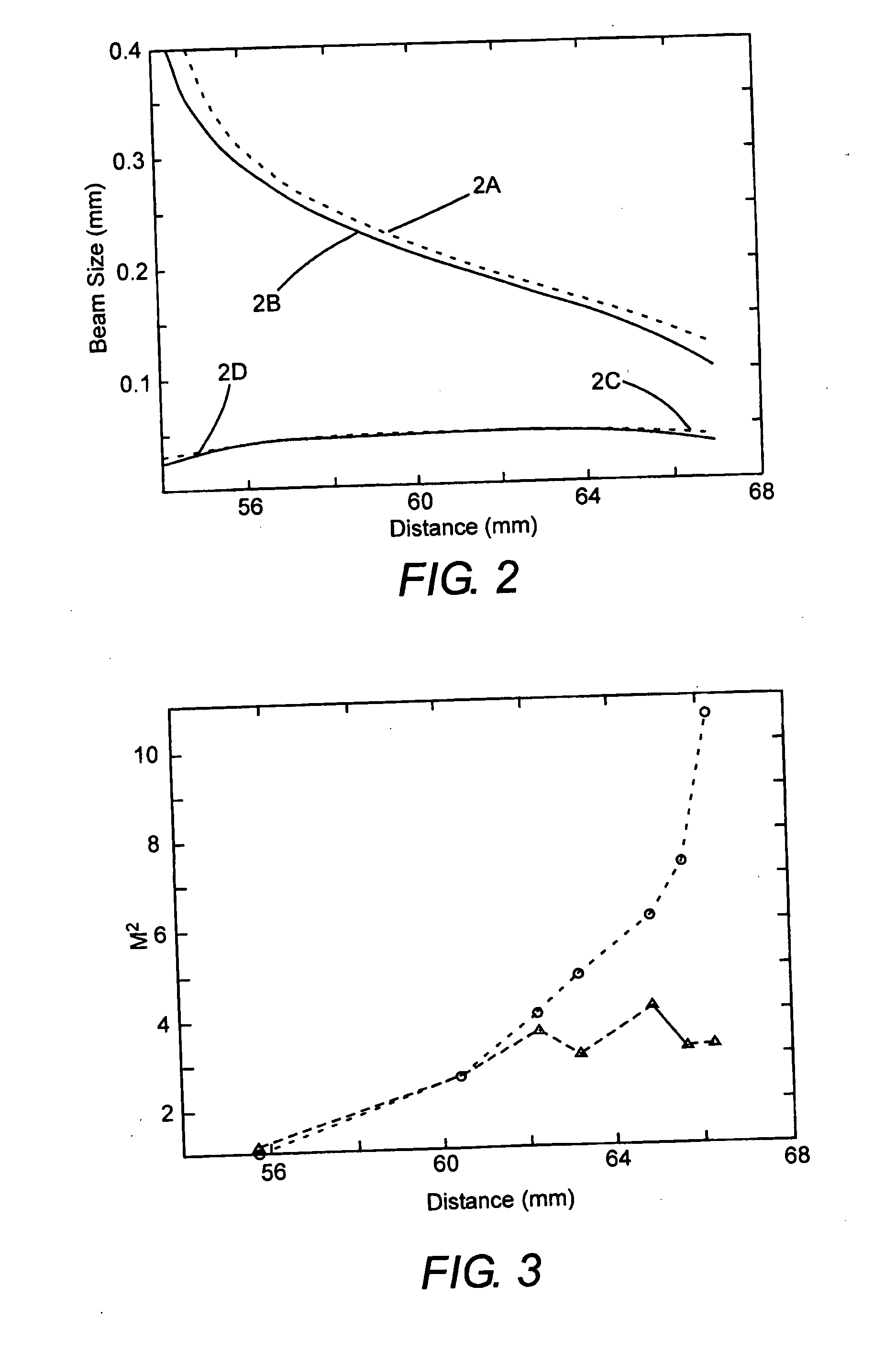
Laser illuminated projection displays
InactiveUS7244028B2Reduced coherence radiusMinimizing speckle contrastBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A projection video display includes at least one laser for delivering a light beam. The display includes a beam homogenizer and a condenser lens. A scanning arrangement is provided for scanning the light in beam in a particular pattern over the condenser lens in a manner that effectively increases the beam divergence. The scanned beam is homogenized by a beam homogenizer and a spatial light modulator is arranged to receive the homogenized scanned light beam and spatially modulate the beam in accordance with a component of an image to be displayed. Projection optics are projecting the homogenized scanned light beam onto a screen. The scanning provides that the homogenized scanned light beam at the screen has a coherence radius less than the original coherence radius of the beam. The reduced coherence radius contributes to minimizing speckle contrast in the image displayed on the screen. The screen includes one or more features providing a further contribution to minimizing speckle contrast in the displayed image. In one example, the screen includes a transparent cell containing a liquid having light scattering particles in suspension.
Owner:COHERENT INC
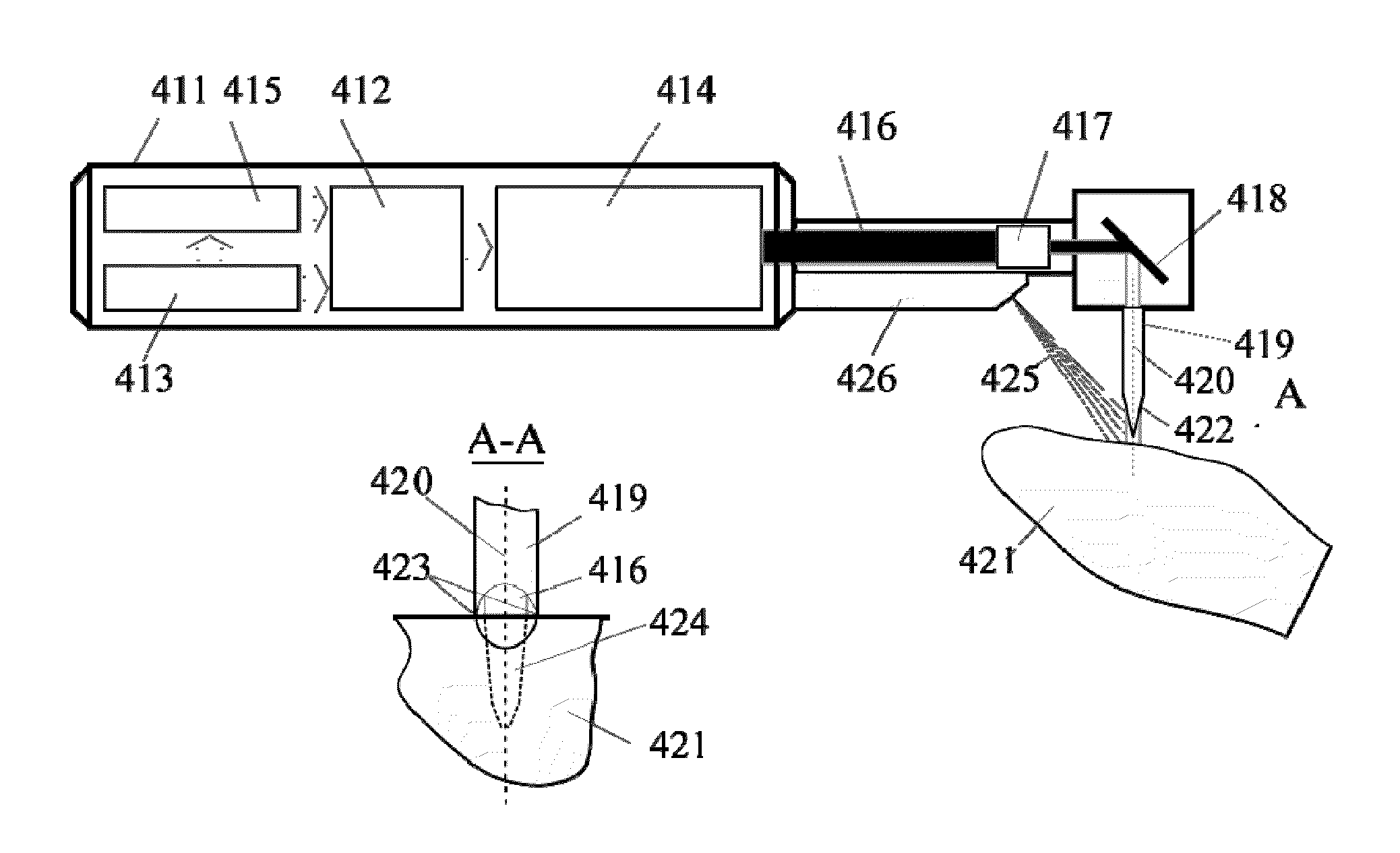
Method and apparatus for diagnostic and treatment using hard tissue or material microperforation
InactiveUS20100015576A1Reliable and minimally invasive fasteningControlled diffusionTeeth fillingDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse energyLight beam
A method of modifying or treating biological tissue by microperforating hard tissue is disclosed. The method comprises identifying a target area associated with the hard tissue, using a laser beam to perforate at least one incision in the hard tissue, wherein at least one incision has a diameter from a range of 0.001 mm to 0.5 mm and an aspect ratio from a range of 1 to 100 times, introducing a treatment substance into the incision, and causing the treatment substance to interact with the target area. Also a device for microperforating hard biological tissue is disclosed, comprising a laser pump system and a laser head coupled to the laser pump system for generating a pulsed laser having ranges of wavelengths, a pulse duration, pulse energy from a selected range, a beam divergence factor less than 5, a repetition rate higher than 50 Hz; and a beam delivery system comprised of a focusing system for creating a beam having a diameter from a range of 0.001 mm to 0.5 mm.
Owner:REJUVEDENT
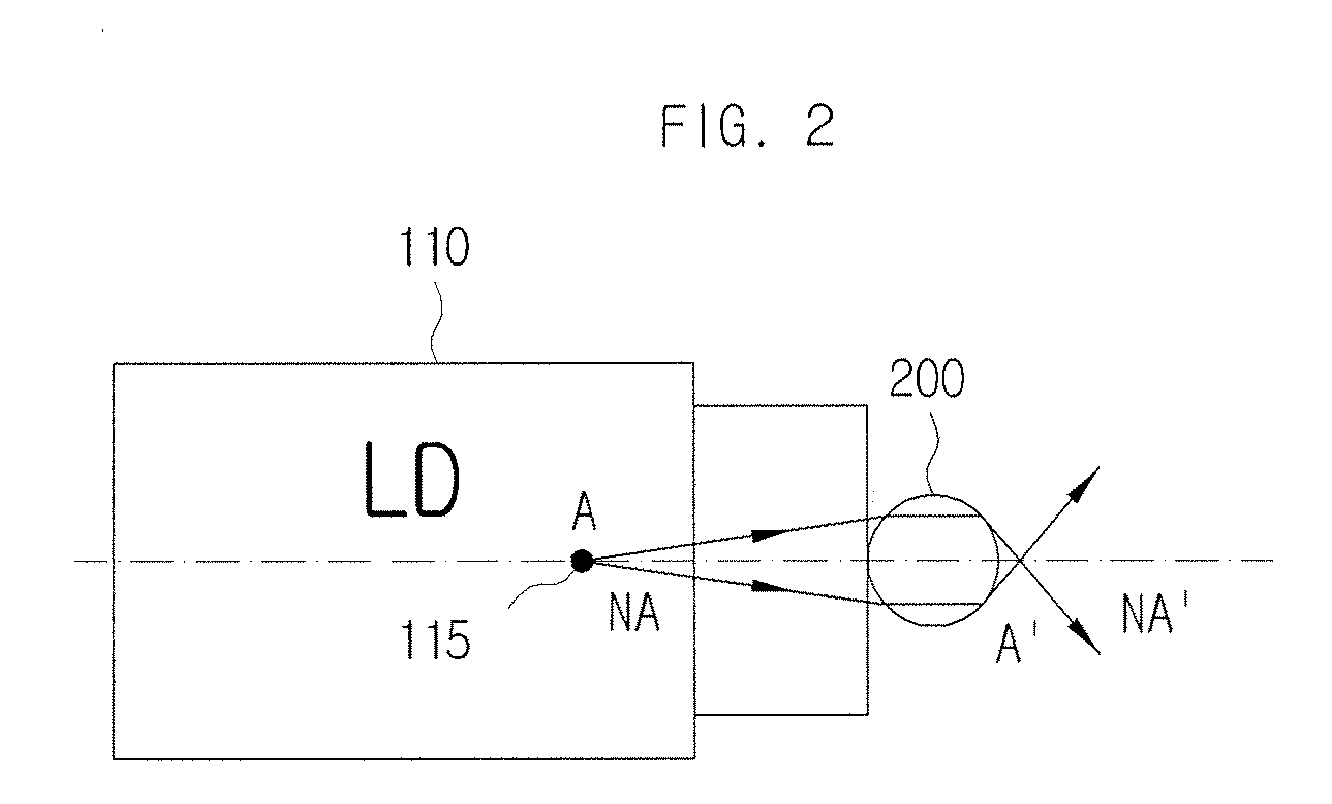
LED module
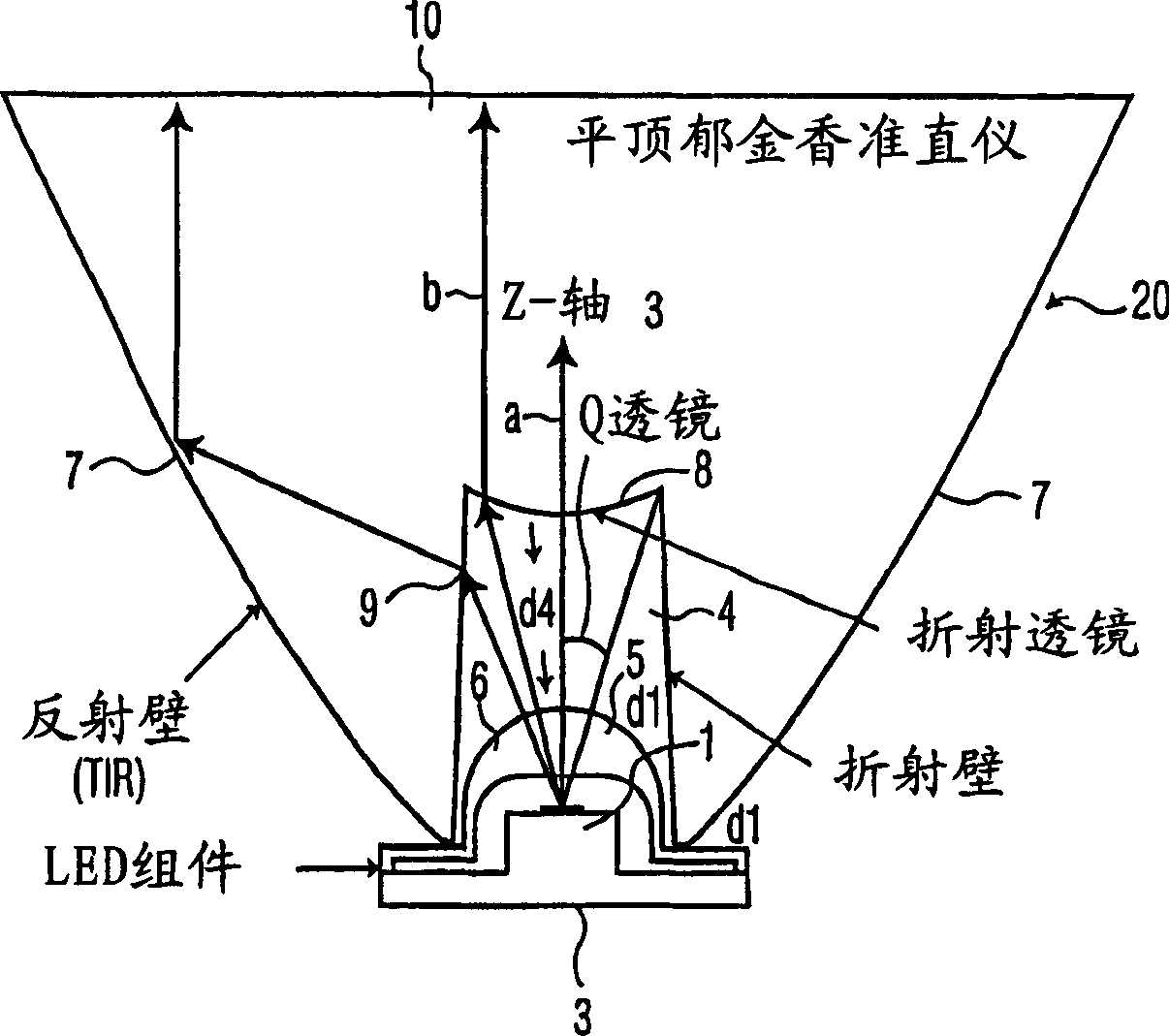
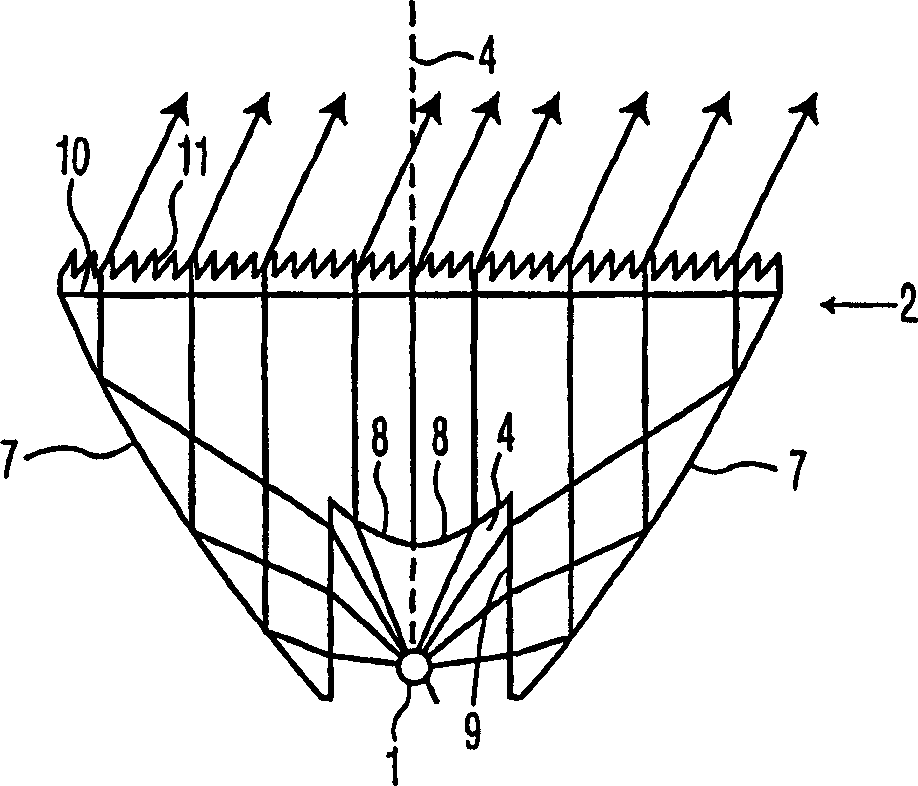
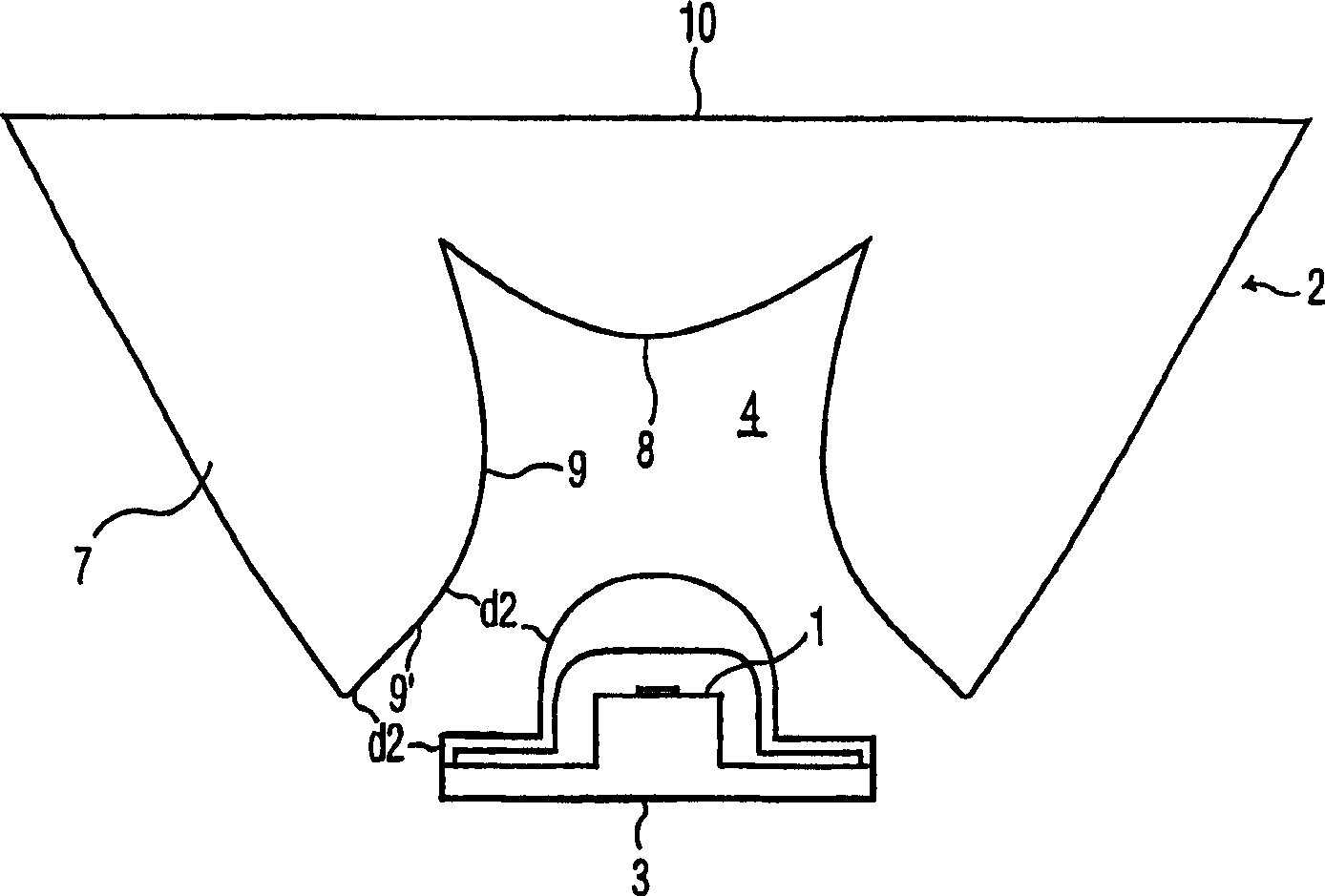
An LED module that includes an LED (light-emitting diode) (1) and a rotationally symmetrical, bowl-shaped collimator lens (2) is provided. The collimator lens has an inner refractive wall (9), an outer reflective wall (7), a first surface (8) having an entrance aperture (3) with a recess (4) in which the LED is situated and which collimator lens is also provided with a second surface (10) from which light generated by the LED emerges, the normal to the surface extending substantially parallel to the axis of symmetry of the lens, and the LED module also includes one or more of the following structures : (1) a conic wall portion of the recess (4) of the inner refractive wall (9) at the entrance aperture (3) that includes a curved portion (9'), and an outer reflective wall (7) so configured in accordance with the structure of the inner refractive wall (9) to achieve substantial collimation of a source of light (1) at the entrance aperture; and / or (2) a first surface (8) of the lens (2) that is recessed away from the LED source (1); and / or (3) two surfaces (8), (11) of said refractive wall (9) between which the refractive function of said refractive wall (9) is divided. The LED module offers an improvement in the performance of the Flat top Tulip Collimator known in terms of reduced size, beam divergence, beam uniformity, and to some degree efficiency. Moreover, it allows a wider variety of choices in optimizing various performance characteristics, and this in turn allows more flexibility in the structure design.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam generation apparatus and method
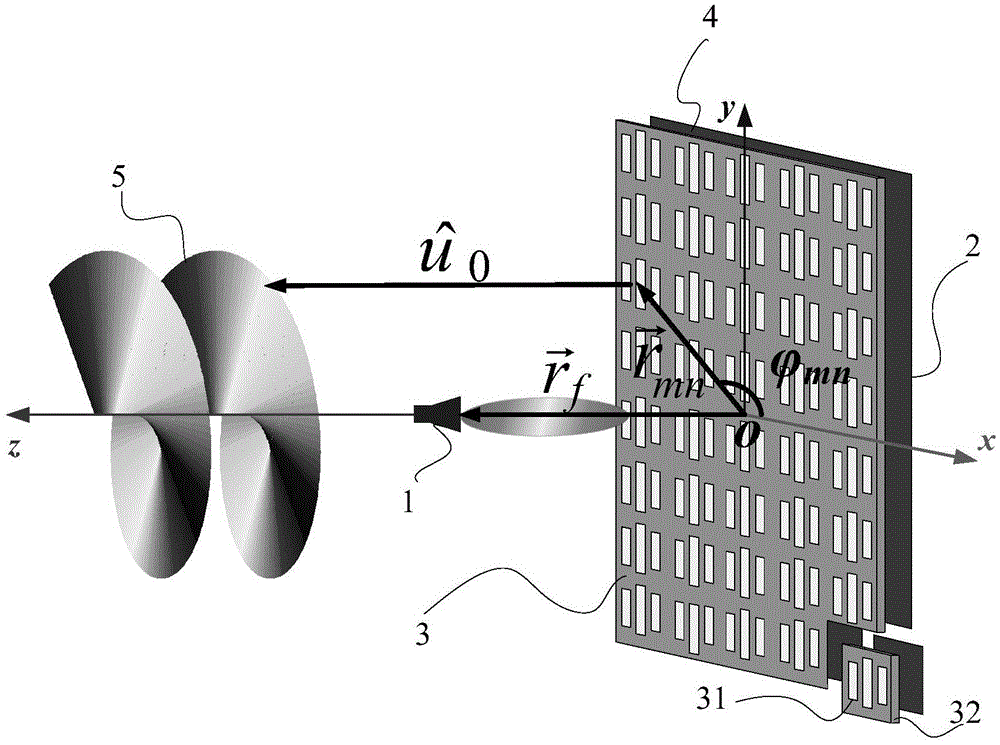
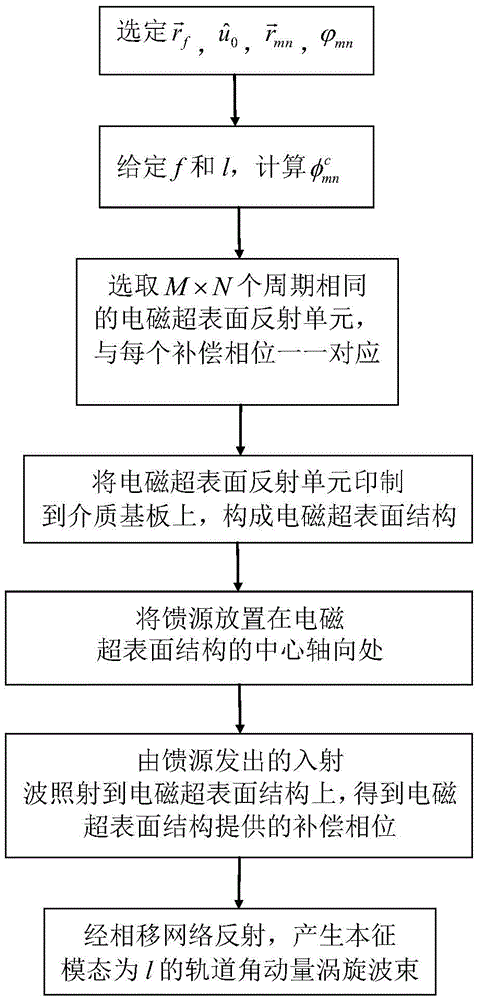
The invention discloses an orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam generation apparatus and method. According to the technical scheme, an electromagnetic super-surface structure (3) is formed by M lines and N columns of electromagnetic super-surface reflection units (31) and dielectric substrates (32); a phase-shifting network (4) is formed by the electromagnetic super-surface structure (3) and a metal back plate (2); the metal back plate (2) is positioned on the back surface of the electromagnetic super-surface structure (3), and the metal back plate is also used as an earth plate; a feed source (1) is put in the central axial position of the electromagnetic super-surface structure (3); incident wave from the feed source (1) irradiates on the electromagnetic super-surface structure; and after the incident wave obtains compensated phase position from the electromagnetic super-surface structure, the incident wave is reflected by the phase-shifting network (4) to generate the orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam(5) with an intrinsic mode 1. According to the orbital angular momentum vortex wave beam generation apparatus and method, the problems of complex technical structure, high cost, beam divergence and low efficiency in the prior art are solved; and the apparatus and method can be used for information transmitting and receiving in the communication technology, and the communication capacity can be increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Improved free space optical bus
InactiveUS20060251421A1Quality improvementImprove transmission qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementPolarisation/directional diversityCross-linkAntenna gain
A method and apparatus for improving the transmission quality of a free space optical bus between circuitry elements in high speed computing, communication and signal processing systems. Use is made of an adaptive algorithm that learns the transmission properties of the bus, and selects or adjusts transmission paths or characteristics to provide optimum bus performance. Each transmitter on the bus transmits a signal which is generally measured by all of the receivers on the bus, and the measured signals are used to generate a matrix which maps desired transmission along information links, and cross-link interference. Transmission quality is optimized by adjusting one or more characteristics associated with transmission along the bus, including emitted power, beam divergence, wavelength, beam polarization, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the transmitters, and power sensitivity, gain, equalizer coefficients, field of view, polarization sensitivity, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the receivers. Novel bus configurations are described, including use of different wavelengths for different bus functions.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
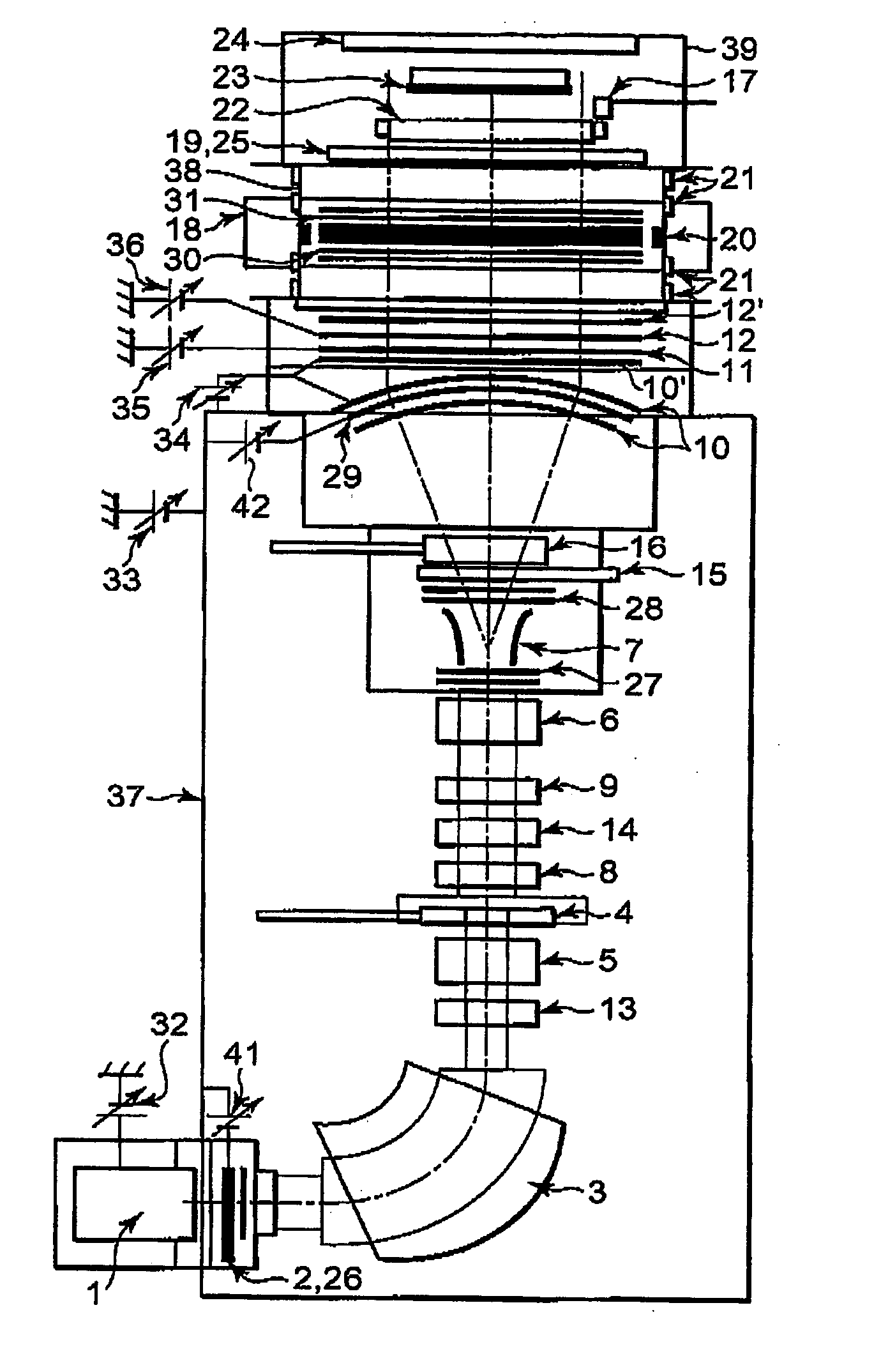
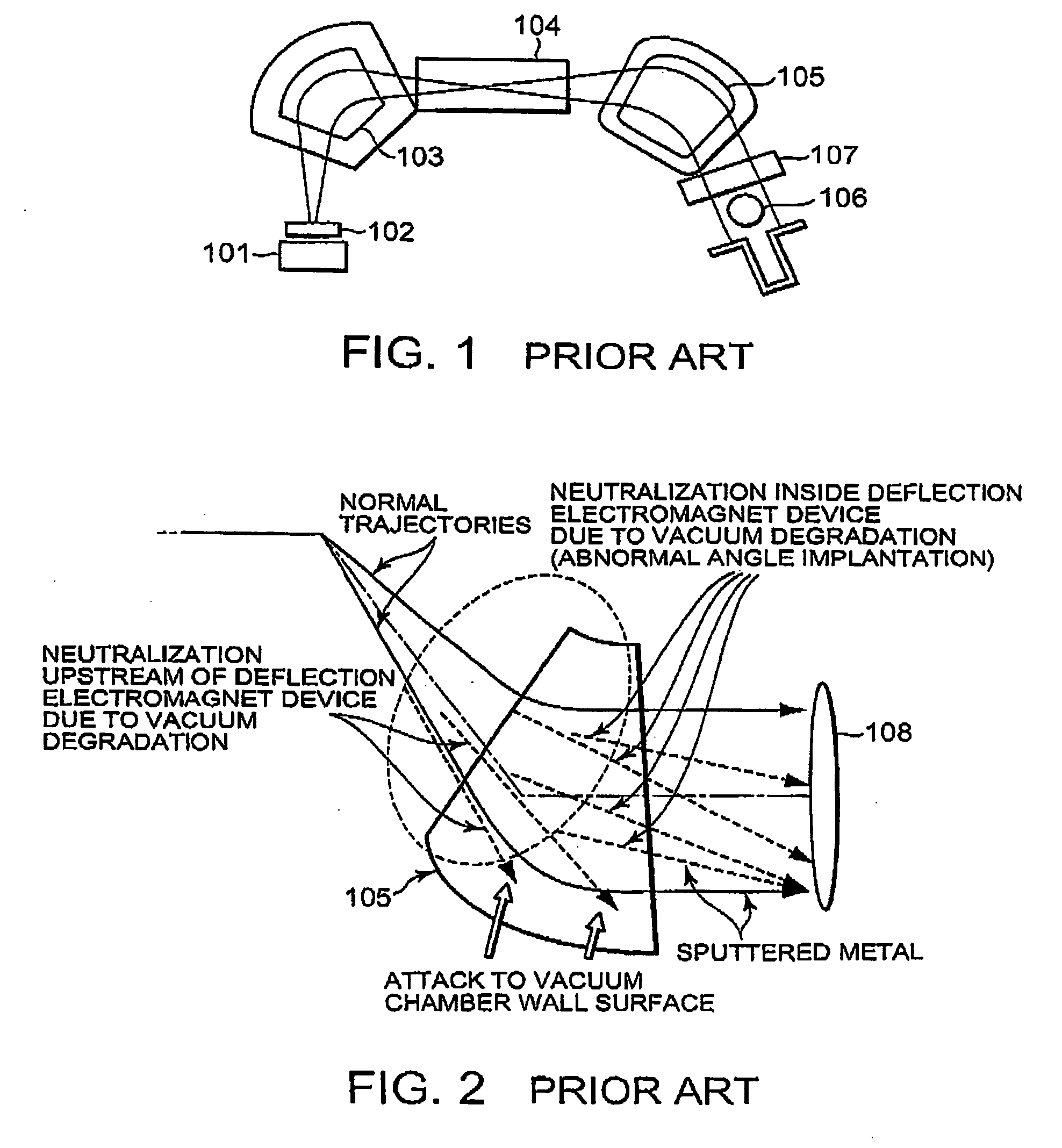
Irradiation system ion beam and method to enhance accuracy of irradiation
ActiveUS20060113493A1Improve beam irradiation accuracyImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon beam tubesTransformerLight beam
The present invention is a method to enhance accuracy of irradiation with beam for an irradiation system with a beam. The irradiation system comprises a beam generation source, a mass analysis device, a beam transformer, a scanner which swings the beam reciprocally with high speed, a beam parallelizing device, an acceleration / deceleration device, an energy filtering device, and beam monitors. The beam transformer comprises a vertically focusing synchronized quadrupole electromagnet syQD and a horizontally focusing synchronized quadrupole electromagnet syQF. Consequently, it is possible to correct at least one of a deviation in beam divergence angle and a deviation in beam size within a range between a center trajectory and an outer trajectory after swinging of the beam by the scanner.
Owner:SENCORP
Acquisition, pointing, and tracking architecture for laser communication
ActiveUS7609972B2Reduce sensitivitySatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionCommunications systemLight beam
A technique for acquiring and tracking terminals in a free-space laser communication system involves exchanging beacon laser beams between the terminals to acquire and then track the terminals such that data laser beams exchanged by the terminals for communication are steered based on feedback from detection of the beacon laser beams. The beacon laser beams used for acquisition have a greater beam divergence than those used for tracking. Gimbals provide coarse steering of the data laser beams, and steering mirrors provide fine steering. GPS position data exchanged via an RF link can be used for initial pointing of the beacon laser beams for acquisition. The beacon laser beams can be chopped such that all terminals can use the same beacon wavelength and are distinguished by using different chopping frequencies. By detecting a chopped signal, the position sensor detector can be AC coupled to reduce sensitivity to solar radiation and glint.
Owner:PERATON INC
Laser illuminated projection displays
InactiveUS20060126022A1Reduced coherence radiusMinimizing speckle contrastBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A projection video display includes at least one laser for delivering a light beam. The display includes a beam homogenizer and a condenser lens. A scanning arrangement is provided for scanning the light in beam in a particular pattern over the condenser lens in a manner that effectively increases the beam divergence. The scanned beam is homogenized by a beam homogenizer and a spatial light modulator is arranged to receive the homogenized scanned light beam and spatially modulate the beam in accordance with a component of an image to be displayed. Projection optics are projecting the homogenized scanned light beam onto a screen. The scanning provides that the homogenized scanned light beam at the screen has a coherence radius less than the original coherence radius of the beam. The reduced coherence radius contributes to minimizing speckle contrast in the image displayed on the screen. The screen includes one or more features providing a further contribution to minimizing speckle contrast in the displayed image. In one example, the screen includes a transparent cell containing a liquid having light scattering particles in suspension.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser delivery system for eye surgery
ActiveUS20120316544A1Increases dimensional scanning abilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsSurgical microscopeLight beam
A photodisruptive laser delivery system and method for use in eye surgery. The photo disruptive laser delivered in pulses in the range of <10000 femtoseconds, used to create incisions in eye tissue is delivered by novel means to minimize optical aberrations without the use of a complex system of multiply precisely arranged lenses. This novel means include a scanning design that allows the focusing lens to always remain under normal incidence to the photodisruptive laser beam, negating the need for overly complex aberration correction set up. The focusing lens is configured to move within a surrounding beam to facilitate two dimensional controls over the treatment space. Controlling beam divergence prior to focusing allows for 3D incisions. The system and methods of use accomplish precise treatment without the need to contact the patient and can be integrated into standard surgical microscopes to improve operational efficiency and hospital workflow.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
Apparatus for reshaping an optical beam bundle
Apparatus for shaping an optical beam bundle carrying a plurality of substantially parallel optical beams disposed in a common plane of travel. First reflective facets and second reflective facets are provided, the first reflective facets being oriented so as to deflect the optical beams of the bundle into a plurality of intermediate, substantially non-parallel optical beams. Each of the second reflective facets is spatially disposed so as to receive a respective one of the intermediate optical beams at a different respective distance from the plane of travel of the optical beam bundle. Also, the second reflective facets are oriented so as to deflect the intermediate optical beams into a bundle of substantially parallel output optical beams. In this way, the output beam can be more adapted for a particular application. In certain cases, this also achieves increased brightness of a laser beam through reduced output beam divergence and / or total cross-sectional area.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
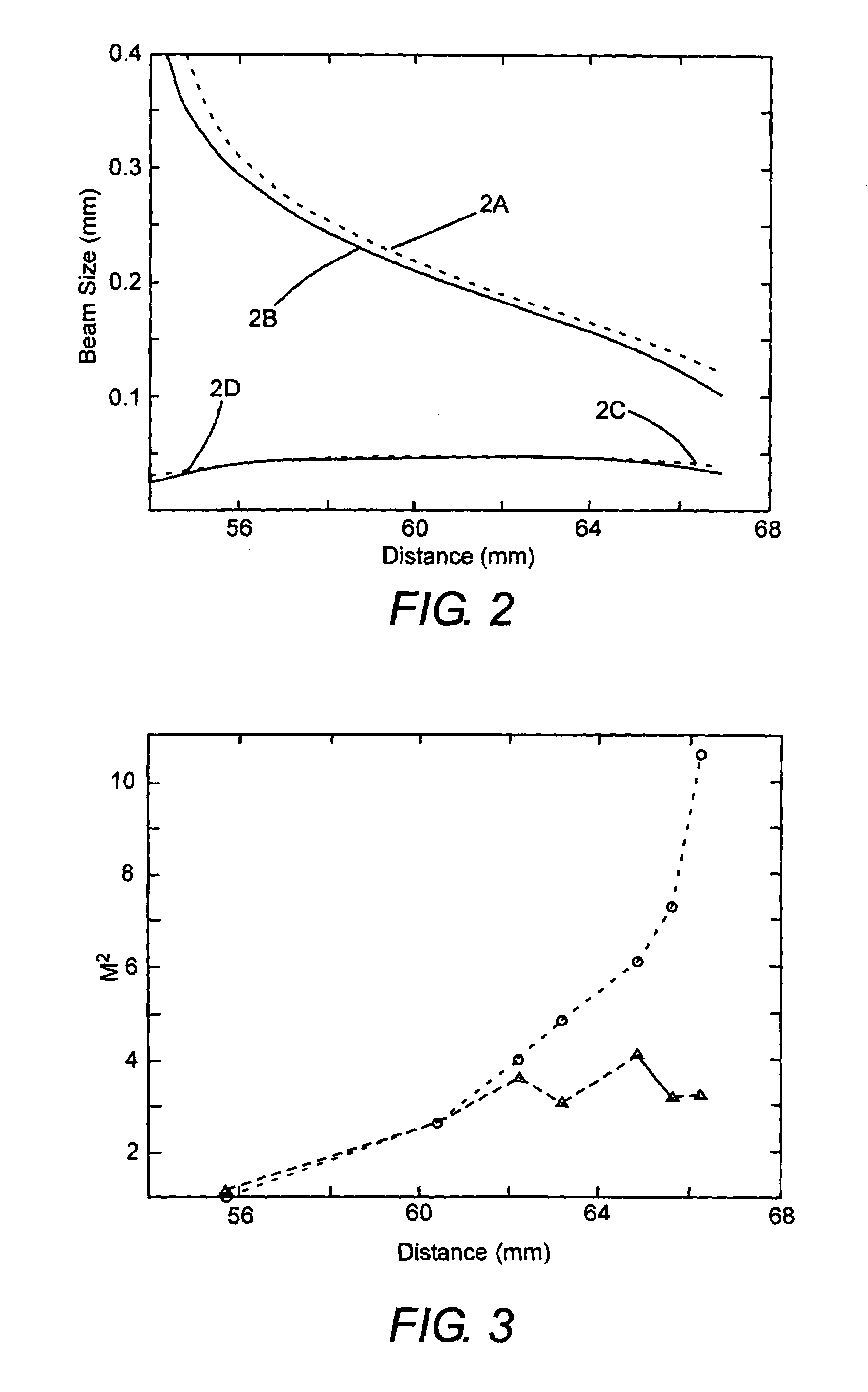
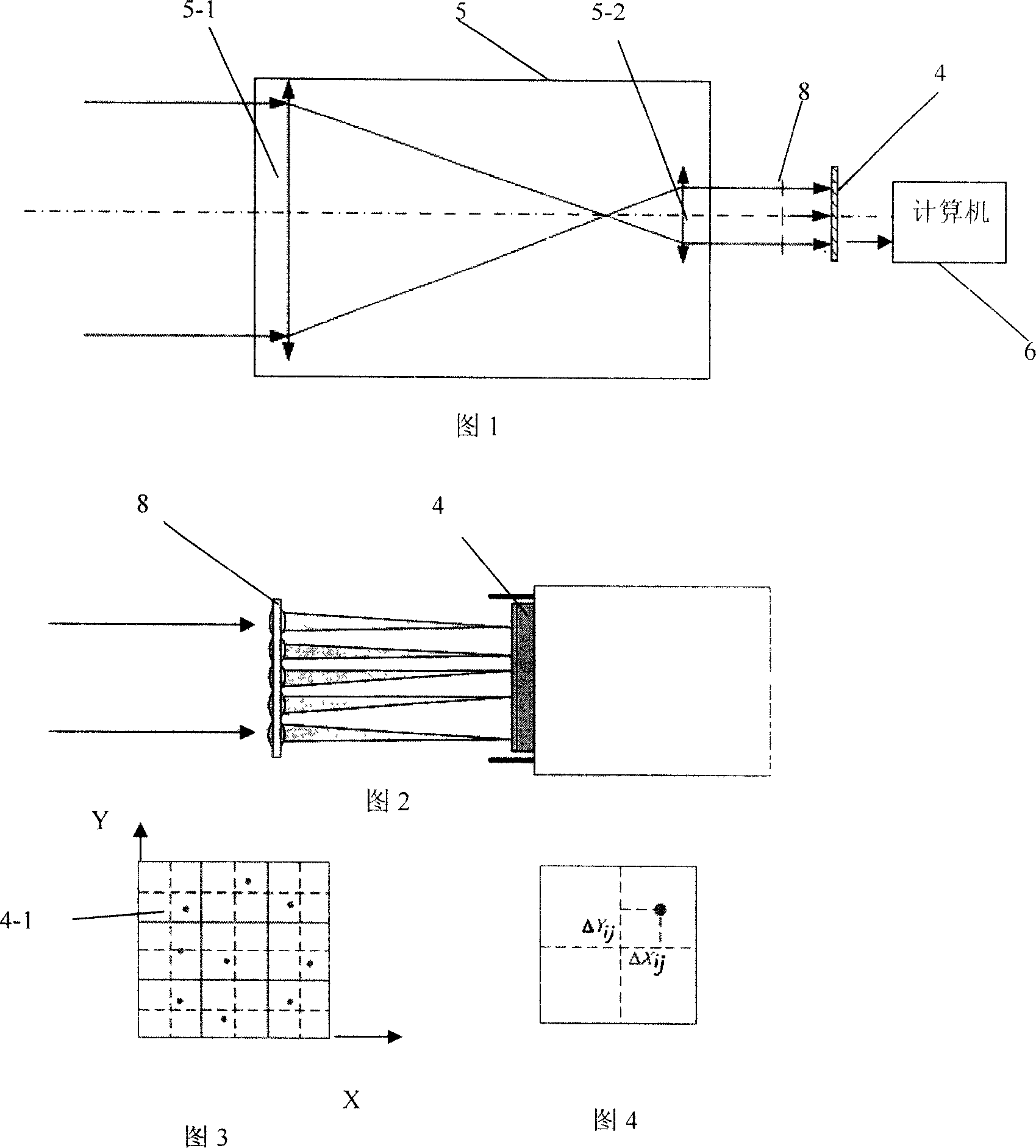
Embedded type laser beam quality measuring device
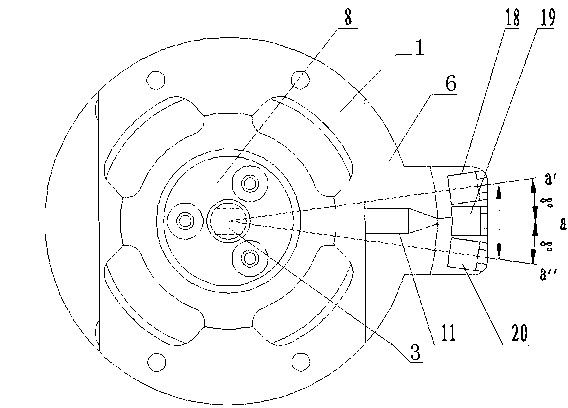
InactiveCN101644600AReduce volumeEasy to usePhotometryUsing optical meansDigital signal processingOptoelectronics
The invention provides an embedded type laser beam quality measuring device, which comprises an optical unit (1), a mechanical unit (2) and an electronics unit (3). The embedded type laser beam quality measuring device images laser faculae by using a camera 45, controls and samples laser faculae information of a plurality of positions by a digital signal processor 42; an embedded process ARM 11 41runs software 69 of the embedded type laser beam quality measuring device to perform laser faculae image processing and calculate a beam quality factor M<2>, a beam-width product, a beam-waist radiusW and an far-field beam divergence angle theta; and the measurement accuracy of the laser beam quality reaches + / - 6 percent. The embedded type laser beam quality measuring device has the advantagesof having small volume and convenient use, and avoiding a personal computer in work.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Beam alignment chamber providing divergence correction
A beam alignment chamber comprising: a base, first and second side walls connected to the base, and a front wall located at the front edge of the base having an output opening. The beam alignment chamber further including a plurality of light sources disposed to direct light beams through the first or second side walls, a plurality of reflectors mounted on the base, each having independent yaw and pitch adjustments, each being disposed to direct the light beams from a corresponding light sources along the length of the beam alignment chamber through the output opening forming an aligned array of parallel light beams, and one or more optical elements positioned in the optical path of the aligned array of light beams disposed to correct the beam divergence with respect to at least one axis.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Achromatic and uncoupled medical gantry
ActiveUS8063381B2Reduced apertureStability-of-path spectrometersElectrode and associated part arrangementsLight beamIrradiation
A medical gantry that focus the beam from the beginning of the gantry to the exit of the gantry independent of the rotation angle of the gantry by keeping the beam achromatic and uncoupled, thus, avoiding the use of collimators or rotators, or additional equipment to control the beam divergence, which may cause beam intensity loss or additional time in irradiation of the patient, or disadvantageously increase the overall gantry size inapplicable for the use in the medical treatment facility.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Microlen array based laser beam divegence angle testing method
InactiveCN101013030AAvoid the difficult problem of not easy to measure accuratelyConveniently Realize Real-Time MeasurementsLaser detailsUsing optical meansObservational errorLight spot
The invention is a laser beam divergence angle testing method based on the micro-lens array, and the invention belongs to the optical field, specifically relating to the laser beam divergence angle testing method. It overcomes the existing deficiencies of the existing beam scattered angle method with larger measurement error and less measurement real-time feature. It includes the following steps: the measured beam is incidence to the telescope system, matching the output beam diameter and the micro-lens array shape, and the micro-lens array contains mXn matrix sub-lens; using micro-lens array to divide the measured beam into the sub-beams, and through CCD to detect the launch angle of each sub-beam, and through statistical method to calculate the measured beam divergence angle, the measurement accuracy reaching 0.1mu rad. Because this method does not require the measurement light spot diameter, it avoids the problem that the light spot diameter is difficult to be accurately measured. This method in the invention is only measuring in the one position of the optical path; therefore the method can facilitate to realize the real-time measurement of the beam divergence angle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
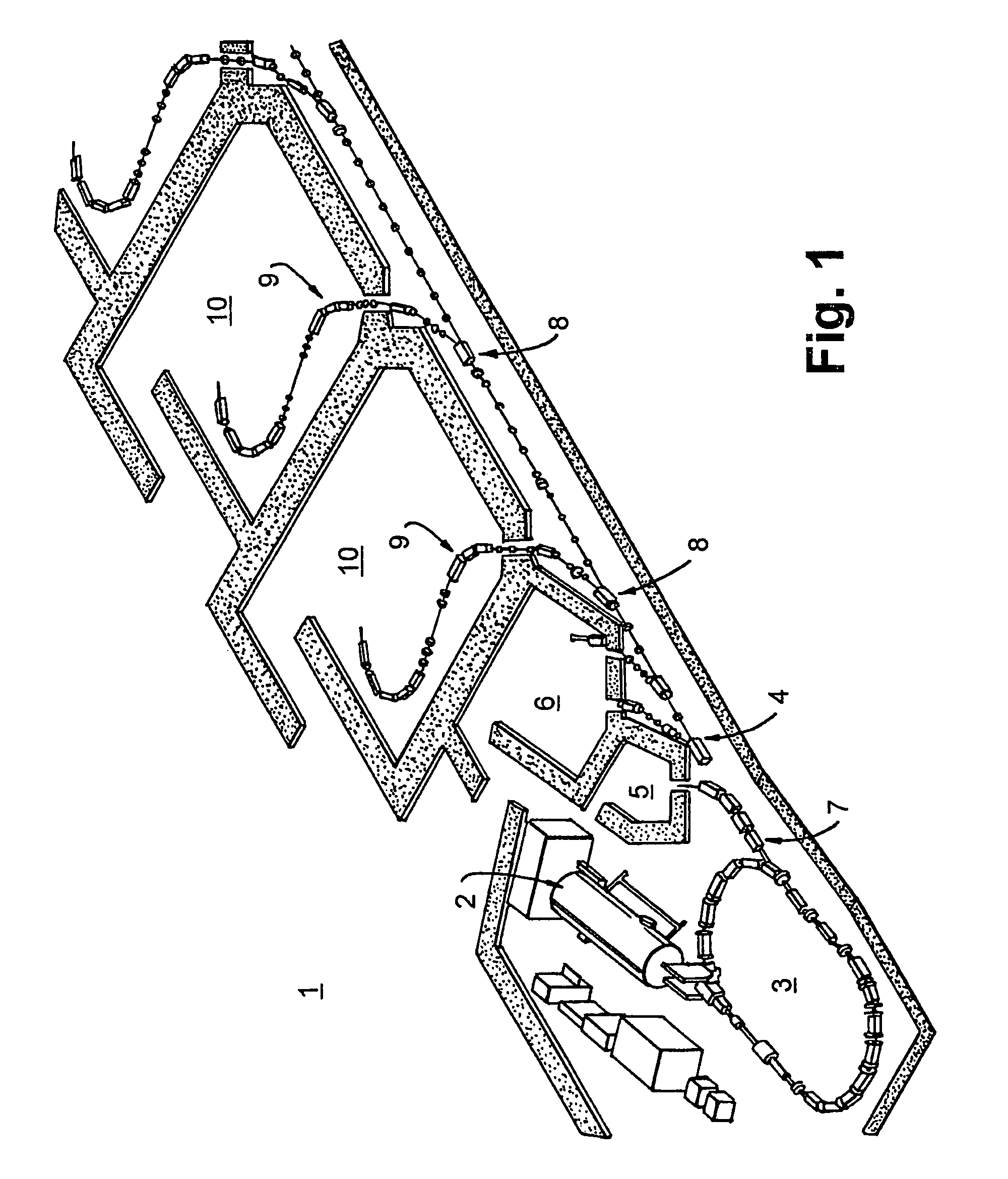
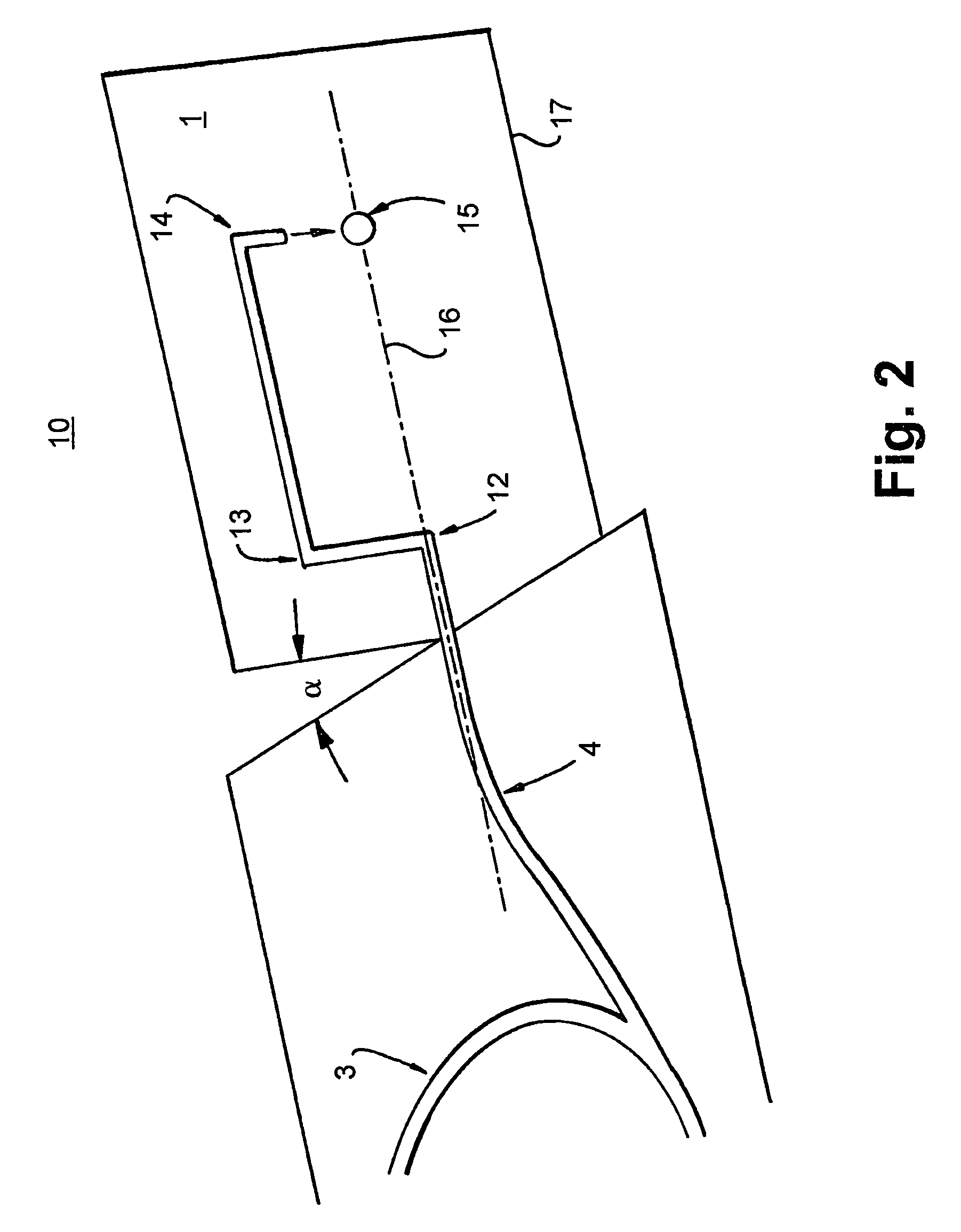
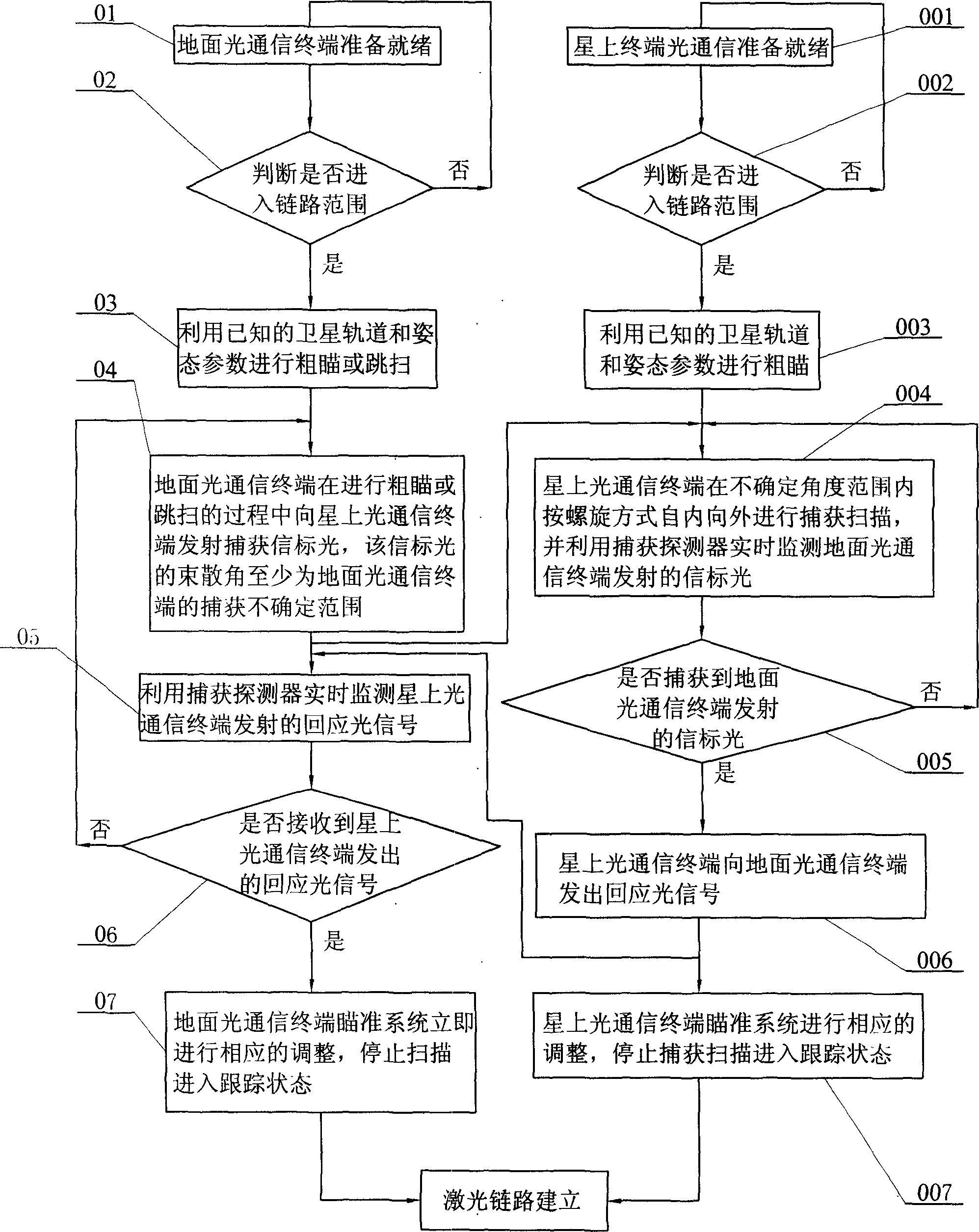
Method for establishing laser link between low orbit safellite and ground station
InactiveCN1825787AQuick buildQuick follow-upSatellite communication transmissionGround stationLight signal
This invention relates to a method for setting up laser links between a low orbit satellite and the ground station, after the satellite and ground terminals enter into the link sphere, they aim roughly first, the ground terminal emits a capture beacon light and its beam divergence angle is at least in the uncertainty sphere of its communication terminal, the satellite terminal carries out capture and scan from inside to outside in the mode of screw in the uncertainty sphere and sends back a response signal to the ground and enters into the track state when it captures the beacon light and the ground terminal captures the response light signals and enters into the track state to set up the laser link, which applies a single-way scanning to replace the ordinary two-way.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Laser communication capturing and tracking system and method thereof
ActiveCN105356943AGuaranteed Tracking AccuracyExtended capture timeSatellite communication transmissionNon-linear opticsCommunications systemComputer module
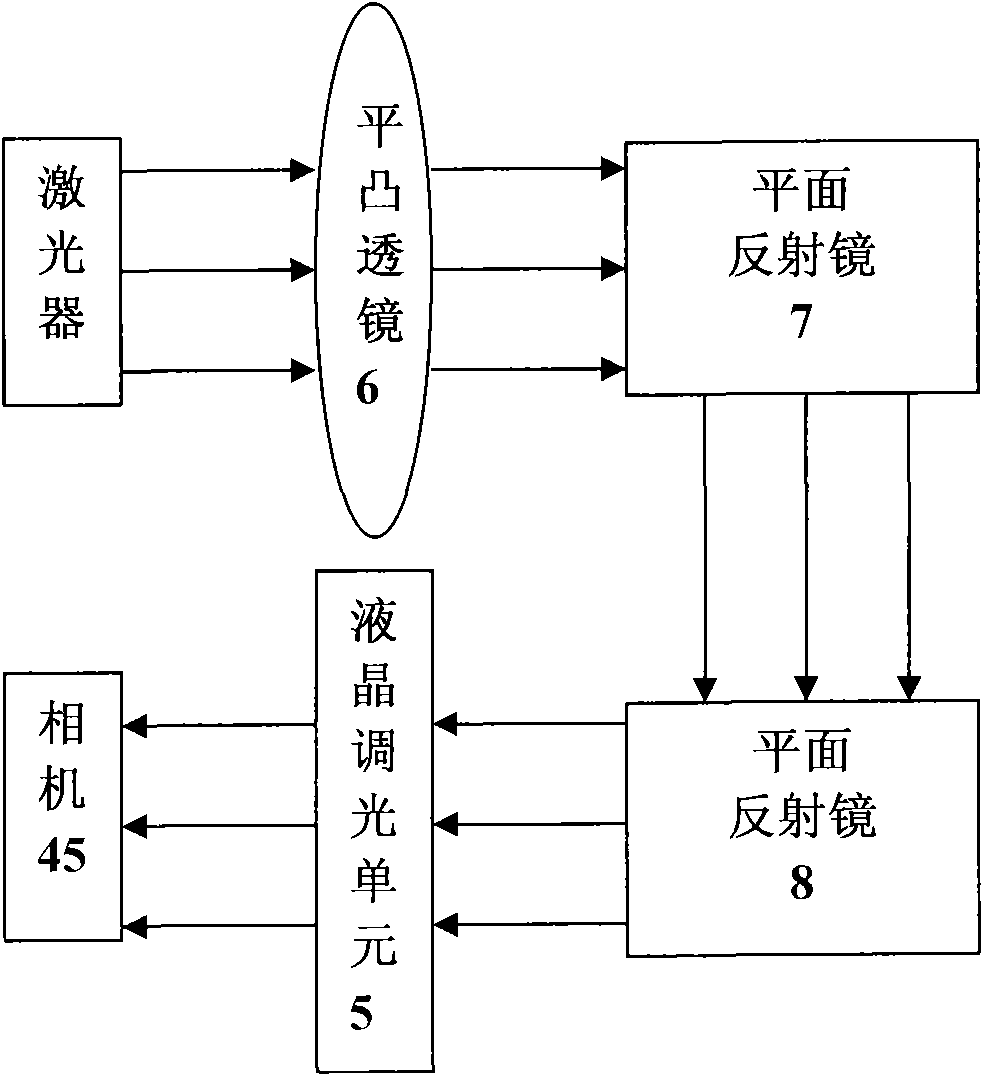
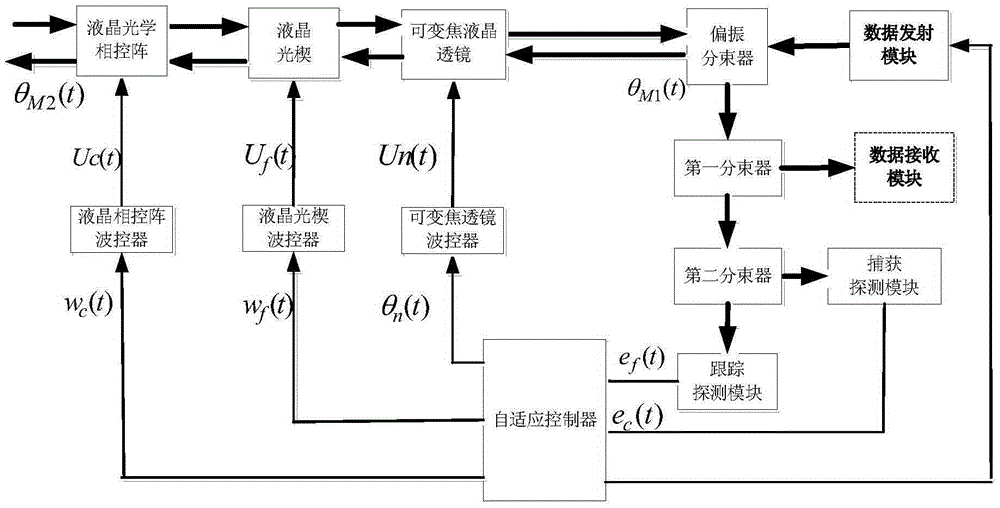
The invention discloses a laser communication capturing and tracking system. A variable-focus liquid crystal lens is combined with a liquid crystal optical phased array and a liquid crystal optical wedge; the receiving powers of a coarse capturing detection module and a fine tracking detection module are detected in real time in a process of capturing and tracking space laser communication; according to change of the optical receiving power, the variable-focus liquid crystal lens dynamically controls the beam-divergence angle of a laser communication system; the beam-divergence angle is self-adaptively controlled in the capturing and tracking process; and the capturing time can be effectively increased while the tracking precision is ensured. Based on the laser communication capturing and tracking system disclosed by the invention, the invention further provides a capturing and tracking method for self-adaptively controlling the beam-divergence angle of the liquid crystal optical phased array; and a laser communication link is established through respective laser communication capturing and tracking systems of two communication sides.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Optical sensor
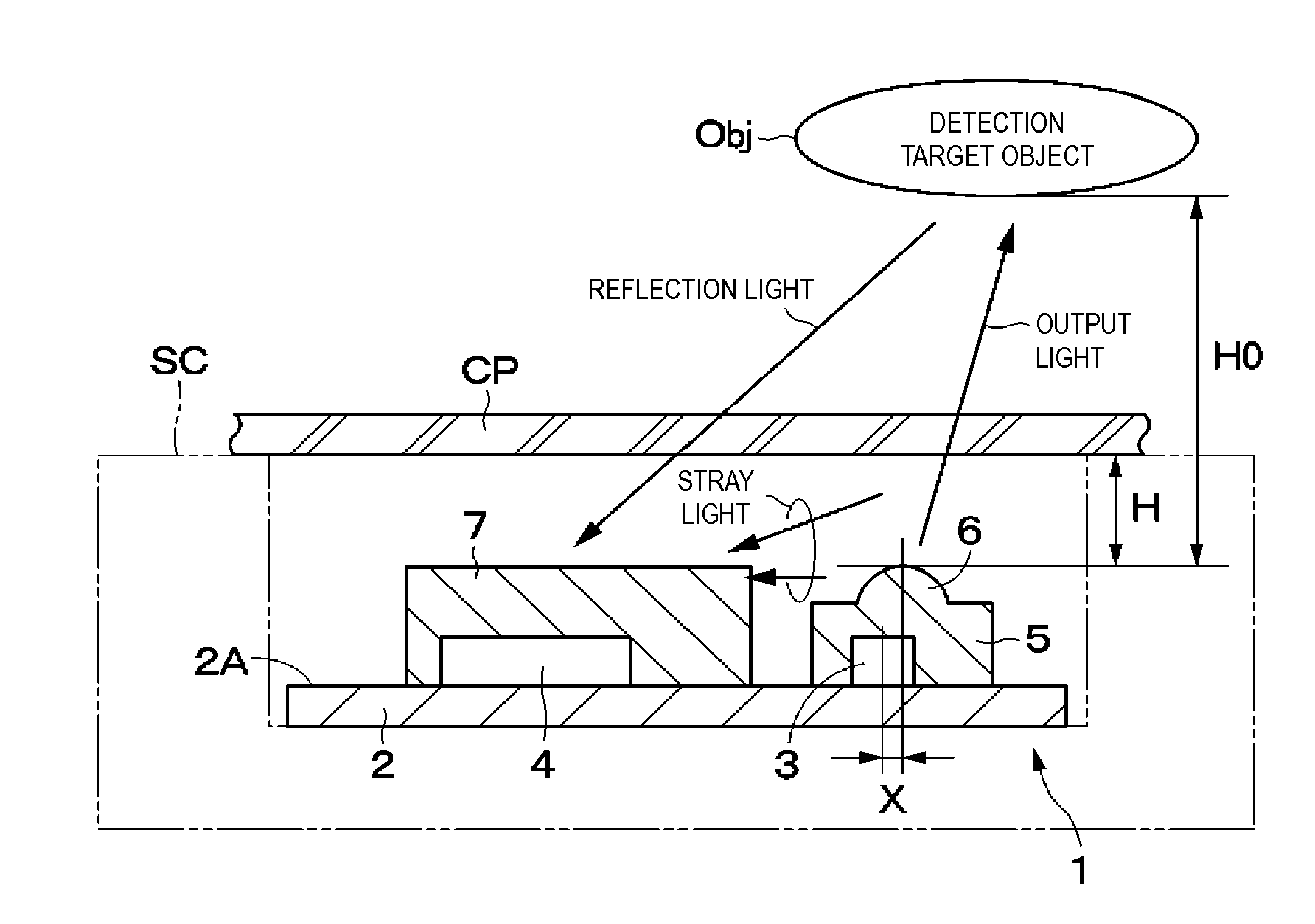
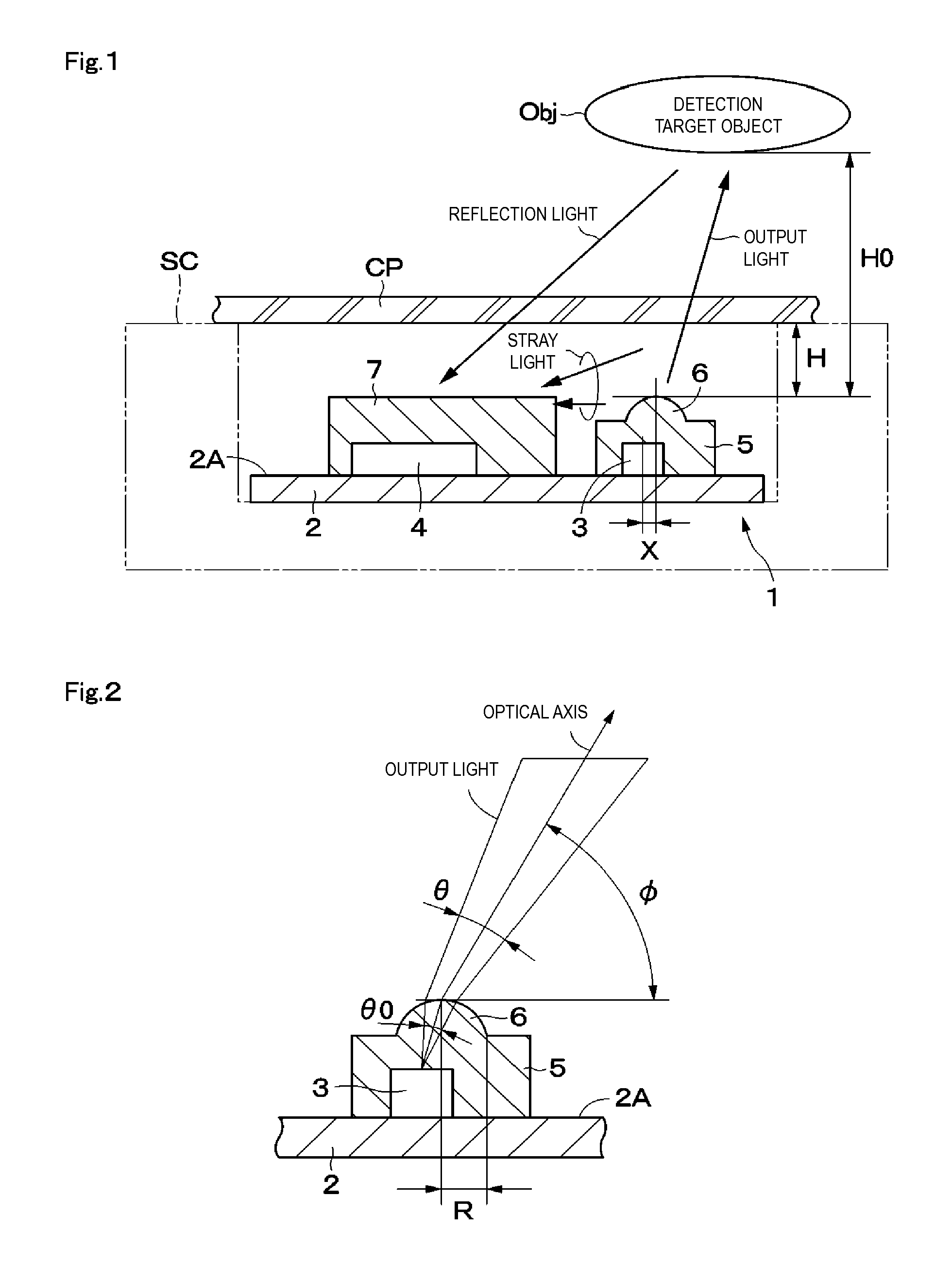
ActiveUS20150212208A1Reduce stray lightLower Level RequirementsSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCamera lensElevation angle
A light-emitting element and a light-receiving element are provided on a surface of a substrate. The light-emitting element and the light-receiving element are sealed by transparent resin members and, respectively. A lens is provided at the transparent resin member at a position above the light-emitting element. The center of the lens and a mounting position of the light-emitting element are disposed being shifted from each other. With this, an optical axis of light outputted via the lens is slanted toward an opposite direction side with respect to the light-receiving element at a predetermined elevation angle. In this case, a beam divergence angle of light outputted from the lens is set to a predetermined value.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
High efficiency solid state directional lighting including luminescent nanocrystal particles
InactiveUS8508126B1Reduce heat transferPoint-like light sourceDischarge tube main electrodesBeam divergencePhysics
A solid state directional lighting device includes a semiconductor light source emitting a primary short wavelength light and a light collimation component disposed in light-reflecting relation to the light source to generate a collimated light with beam divergence angle less than forty degrees (40°). A luminescent nanocrystal conversion layer is disposed in the path of the collimated light and includes a luminescent nanocrystal conversion layer including luminescent nanocrystal particles with nano-particles sizes less than fifteen nanometers (15 nm). The luminescent nanocrystal particles absorb at least a portion of the collimated short wavelength light and convert the absorbed light into at least one long wavelength spectral light. A mixture of leakage primary short wavelength light and long wavelength light converted by the luminescent nano-particles produces a directional white light with luminous efficacy of at least one hundred lumens per Watt (100 lm / W). Light scattering is reduced due to the nano-particle size.
Owner:LEDNOVATION
Backlight using surface-emitting light sources
InactiveUS7229199B2Reduce divergenceImprove uniformityShow cabinetsNon-electric lightingBeam angleLuminous intensity
A lighting apparatus for providing illumination, comprising:a) an array of surface-emitting light sources, wherein each surface-emitting light source directs a source illumination beam, over a beam angle θ, toward an illumination plane;b) an array of beam spreading optical elements corresponding with the array of surface-emitting light sources, wherein refraction of the source illumination beam by each beam spreading optical element substantially satisfies a distribution function:dy / dθ=f(θ)wherein y is a radial distance along the illumination plane from the optical axis of the beam-spreading optical element,dy is an arbitrarily small increment of the radial distance,dθ is the angular increment of the beam angle corresponding to dy, andƒ(θ) is the distribution function for the angular distribution of the light source, such that each beam spreading optical element adjusts the luminous intensity of the source illumination beam from the corresponding surface-emitting light source to provide a uniformized illumination beam directed toward the illumination plane;and,c) an array of beam-divergence reducing lens elements, wherein each beam-divergence reducing lens element reduces the angular divergence of a corresponding uniformized illumination beam,providing illumination having improved uniformity and reduced beam divergence thereby.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
Apparatus for reshaping an optical beam bundle
InactiveUS6870682B1Increase brightnessReduced output beam divergenceGlobesCondensersLight beamLaser beams
Apparatus for shaping an optical beam bundle carrying a plurality of substantially parallel optical beams disposed in a common plane of travel. First reflective facets and second reflective facets are provided, the first reflective facets being oriented so as to deflect the optical beams of the bundle into a plurality of intermediate, substantially non-parallel optical beams. Each of the second reflective facets is spatially disposed so as to receive a respective one of the intermediate optical beams at a different respective distance from the plane of travel of the optical beam bundle. Also, the second reflective facets are oriented so as to deflect the intermediate optical beams into a bundle of substantially parallel output optical beams. In this way, the output beam can be more adapted for a particular application. In certain cases, this also achieves increased brightness of a laser beam through reduced output beam divergence and / or total cross-sectional area.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Illumination optical apparatus
InactiveUS20080266862A1Small sizeReduce volumeColor television detailsRefractorsLight beamOptoelectronics
Disclosed is an illumination optical apparatus that can enlarge a beam divergence angle. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the illumination optical apparatus can include a light source, emitting a beam of light in a predetermined direction at a beam output point; a ball lens, arranged in a forward direction of the beam of light emitted from the light source; and a condensing lens group, condensing the beam of light which has passed through the ball lens on a predetermined point. With the present invention, the size and the volume of the illumination optical apparatus can be reduced by enlarging the beam divergence angle by further including a ball lens.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Vehicle-borne scanning semiconductor laser early-warning radar and method for detecting obstacles thereby
InactiveCN102998677ASimplify the calibration processSmall attenuationElectromagnetic wave reradiationUltrasound attenuationRadar
The invention relates to vehicle-borne scanning semiconductor laser early-warning radar used on a vehicle to detect and calculate the distance and angle of an obstacle ahead and to perform related data processing and warning, and a method for detecting obstacles by the vehicle-borne scanning semiconductor laser early-warning radar. A central line of a receiving optical axis is parallel with a central line of a transmitting optical axis of a laser transmitting antenna sleeve, laser receiving field angle is guaranteed to be approximate to laser transmitting beam divergence angle in design, objective diameter of an laser transmitting antenna is approximate to that of a laser receiving antenna, and accordingly signal attenuation is relieved, the size and weight of equipment is reduced, operational noise of the equipment is lowered, optical axis calibrating process is simpler, product reliability is better, production cost is lower and batch production is facilitated. By the use of the method for detecting obstacles by the vehicle-borne scanning semiconductor laser early-warning radar, information data processing is faster and more accurate and warning is timely.
Owner:孝感华中精密仪器有限公司
Laser pulse distance measuring method for correcting measurement error by utilizing received signal width
InactiveCN109633670ALow costSimple technologyElectromagnetic wave reradiationObservational errorTime delays
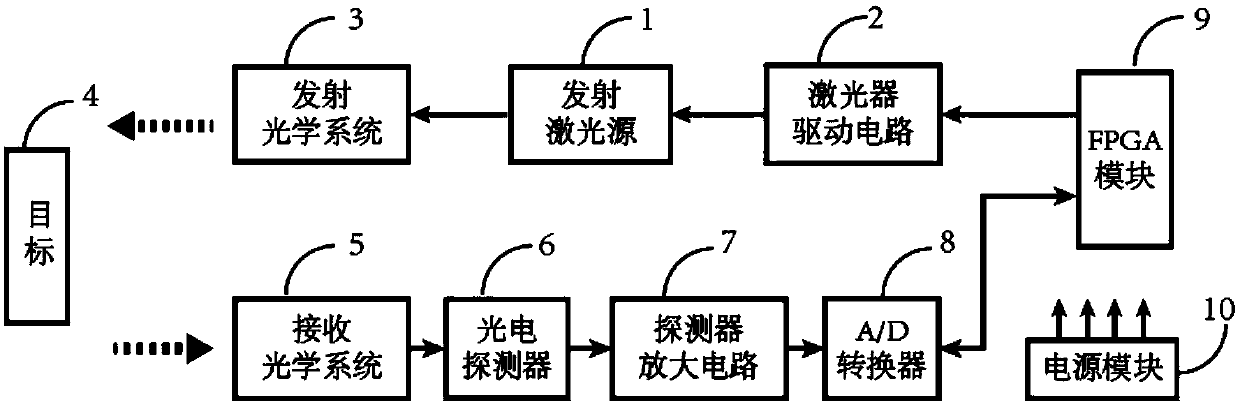
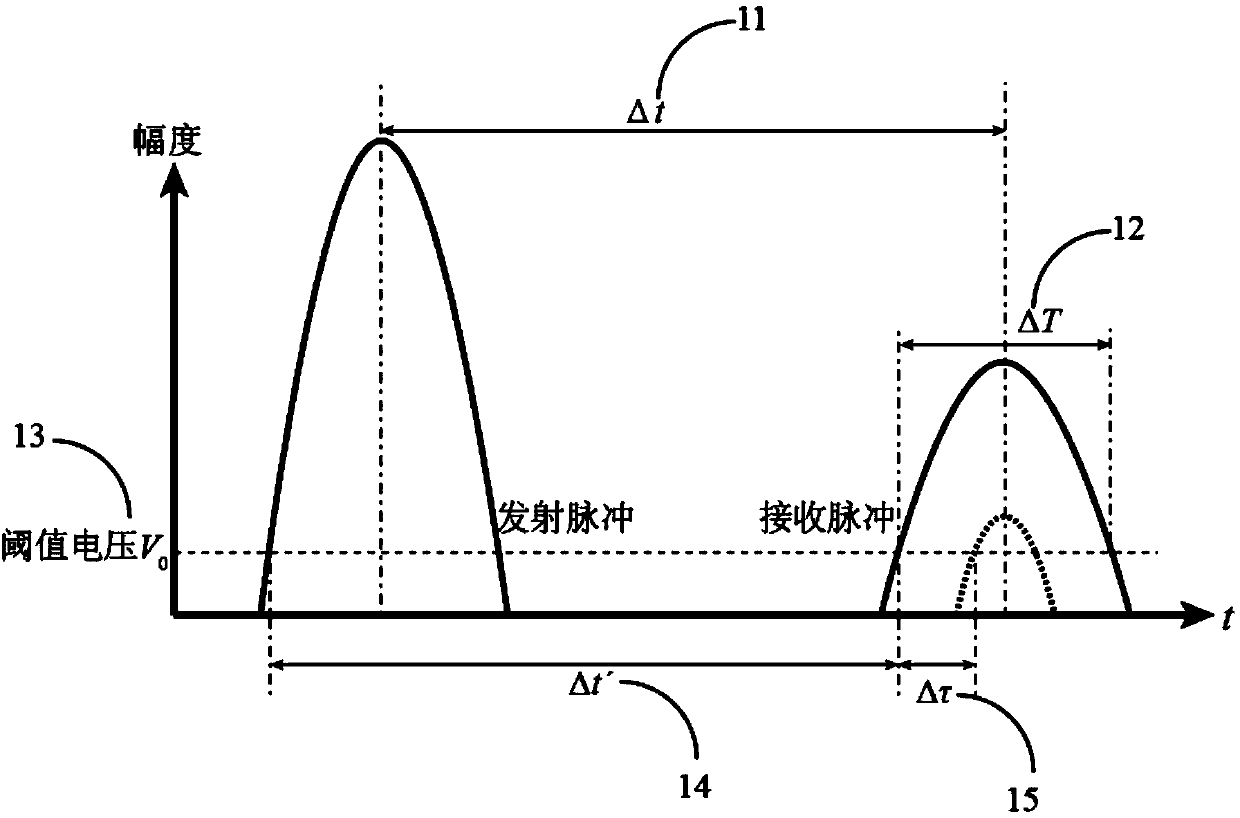
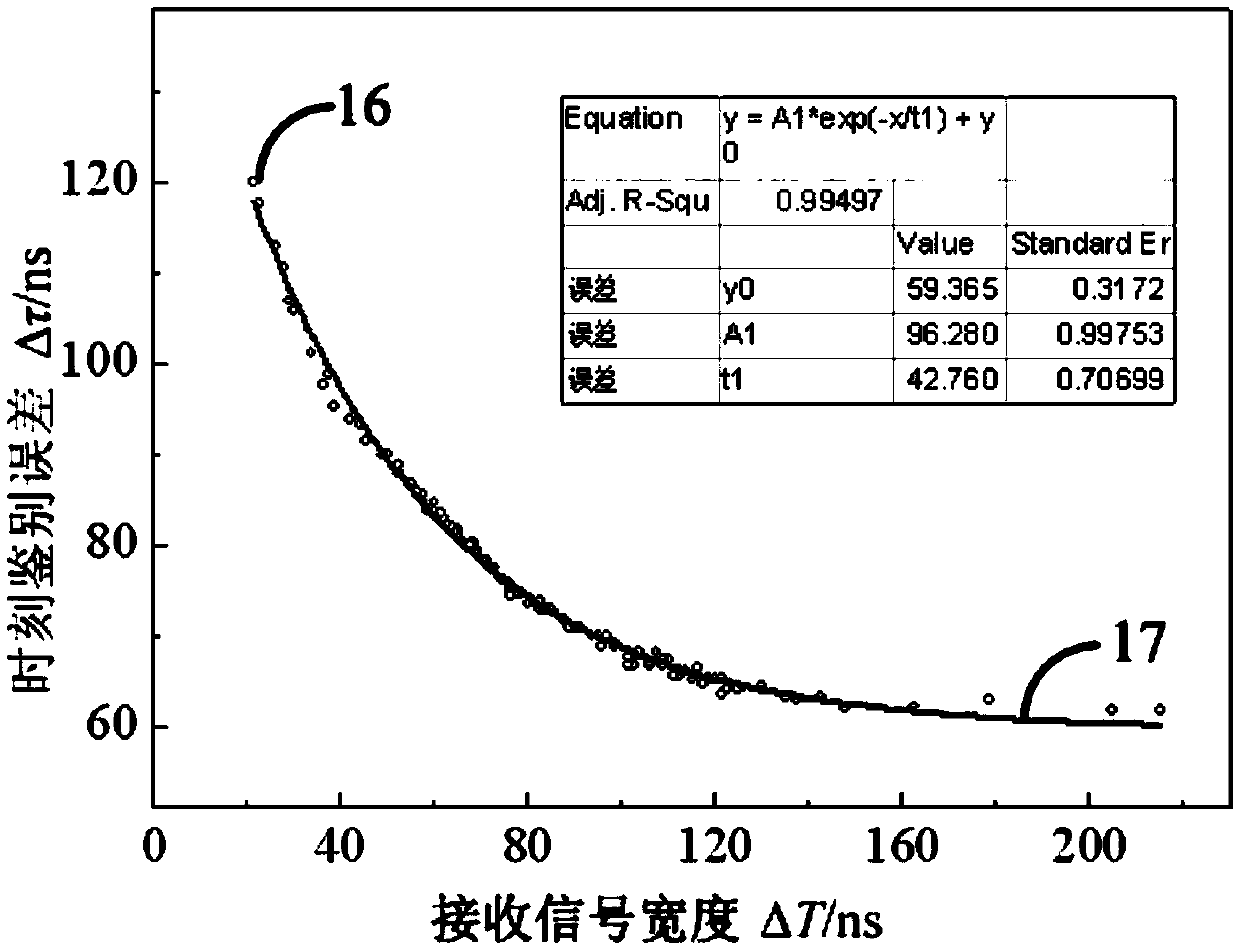
The invention discloses a laser pulse distance measuring method for correcting a measurement error by utilizing received signal width. The method comprises the following steps that a pulse laser is adopted for a light source, a driving circuit drives the laser to emit narrow-pulse-width laser pulses, and the laser pulses are emitted at a certain beam-divergence angle after being shaped by a transmitting optical system. Target echo signals are converged on the photosensitive surface of a photoelectric detector through a receiving optical system to achieve photoelectric conversion. Electric signals are converted into digital signals after being preprocessed. An FPGA phase-shifting clock is used for carrying out high-speed sampling on echoes, and the time delay and the receiving signal widthof the reflected echoes are measured. A data table is made according to the relation curve of actually measured received signal width and the delay compensation amount. A distance measuring machine isused for obtaining time identification errors so as to correct a distance measuring result through a table look-up mode according to the leading edge time and the received signal width measured by the FPGA. According to the invention, higher distance measuring precision can be realized, and the method has a good application prospect in the relevant field of laser distance measuring.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
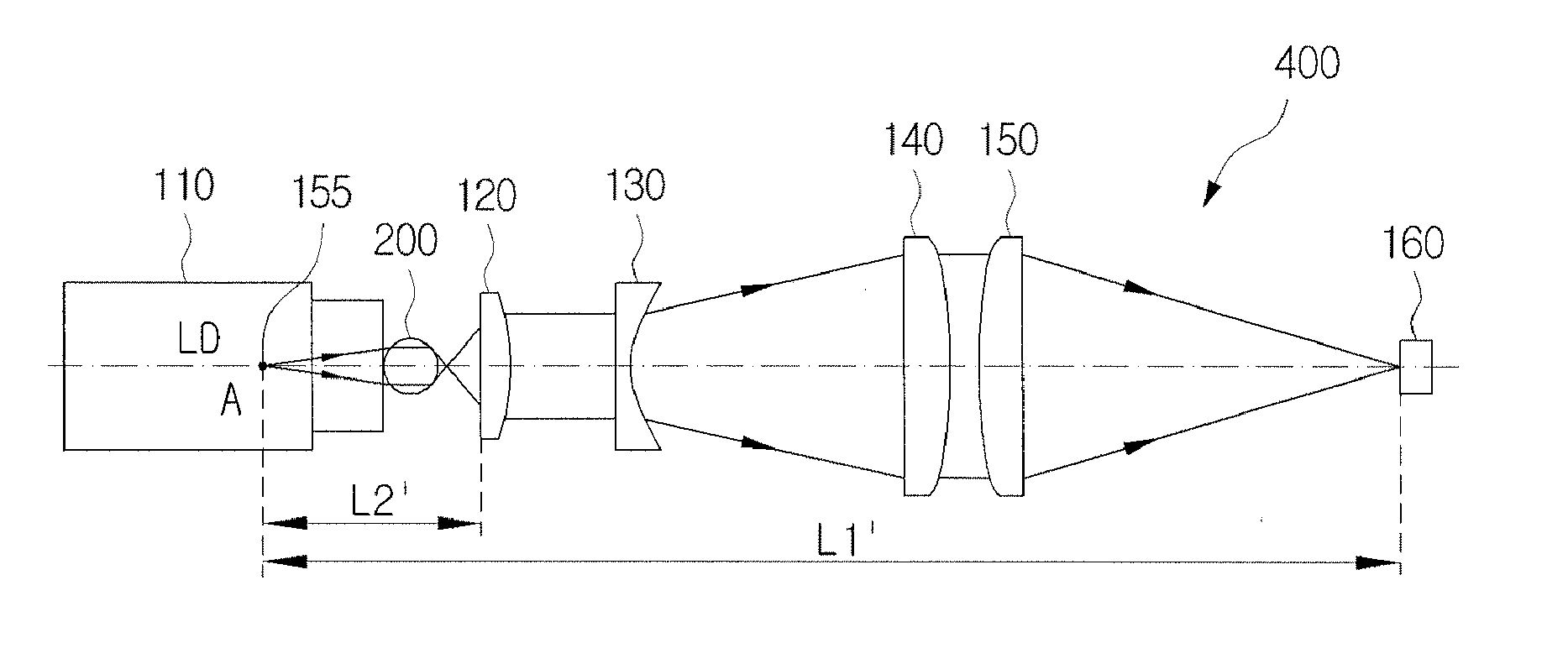
Apparatus for and method of frequency conversion
InactiveUS6928099B2Laser optical resonator constructionNanoinformaticsNonlinear optical crystalFrequency conversion
Apparatus for frequency conversion of light, the apparatus comprises: a light-emitting device for emitting a light having a first frequency, the light-emitting device being an edge-emitting semiconductor light-emitting diode having an extended waveguide selected such that a fundamental transverse mode of the extended waveguide is characterized by a low beam divergence. The apparatus further comprises a light-reflector, constructed and designed so that the light passes a plurality of times through an external cavity, defined between the light-emitting device and the light-reflector, and provides a feedback for generating a laser light having the first frequency. The apparatus further comprises a non-linear optical crystal positioned in the external cavity and selected so that when the laser light having the first frequency passes a plurality of times through the non-linear optical crystal, the first frequency is converted to a second frequency being different from the first frequency.
Owner:PBC LASERS LTD
Laser emission axis and mechanical base level coaxiality measuring method based on secondary light source
InactiveCN101210806ANot limited by the minimum measuring rangeHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansOptical testLight spot
A method is provided to measure the coaxiality between a laser emission shaft and a mechanical reference surface based on a secondary light source. The invention relates to the measurement field and solves the problem that no method is available for accurately measuring the included angle between the laser emission shaft and the mechanical reference surface in an optical test system with small beam divergence angle and strict requirement for pointing control accuracy. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly detecting emergent light spots of a laser emission system to be measured; then installing a porous light diaphragm; installing the secondary light source for the detection of reflected light spots; and finally calculating the directional angular deviation and the pitch angle deviation. Based on the secondary light source and a beam splitting system, the invention can increase the measurement accuracy up to 0.1 Mu rad by focal plane imaging method, and also can prevent the minimal measurement range being limited by the size of light spots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com