Patents
Literature
114 results about "Optical bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
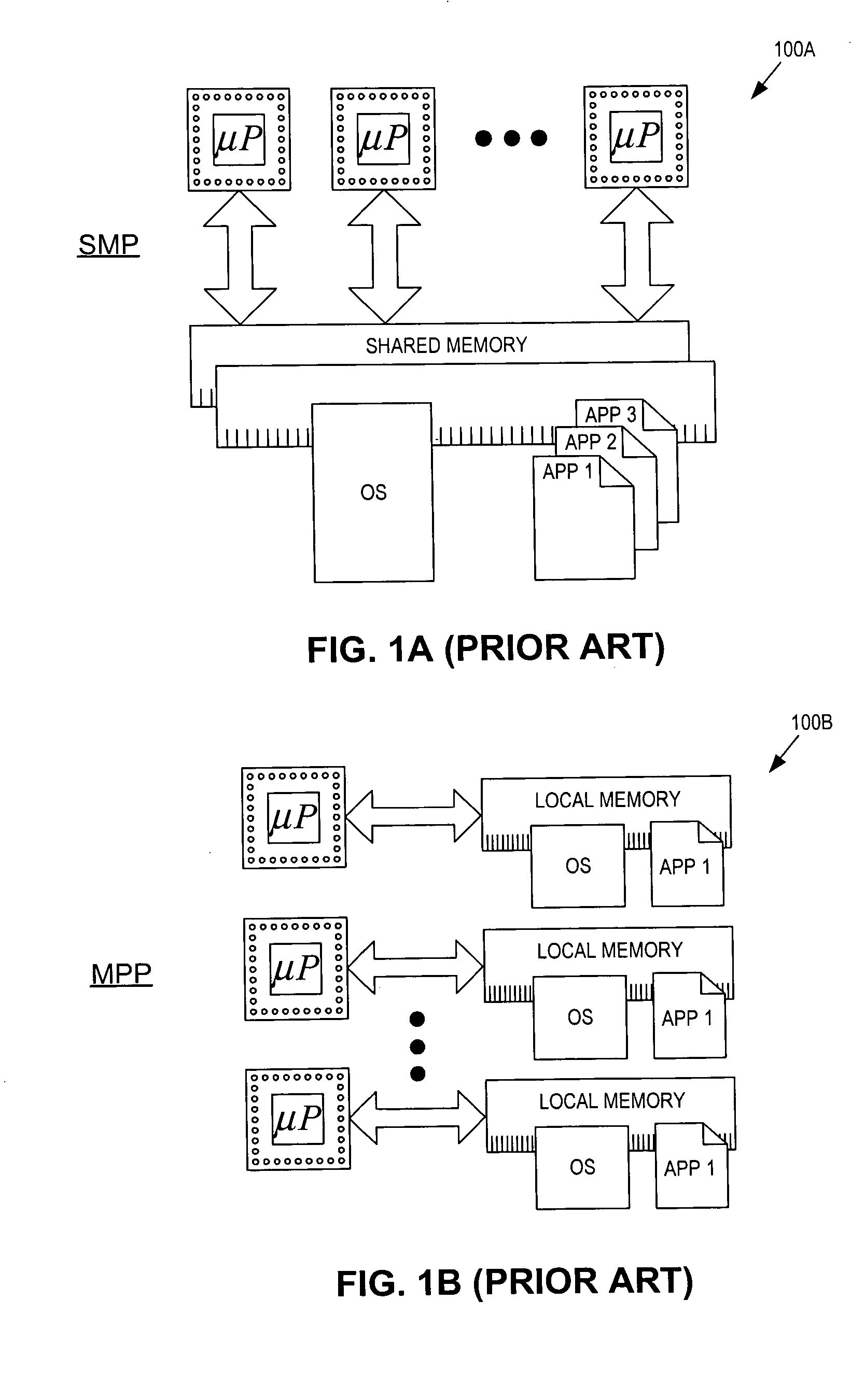
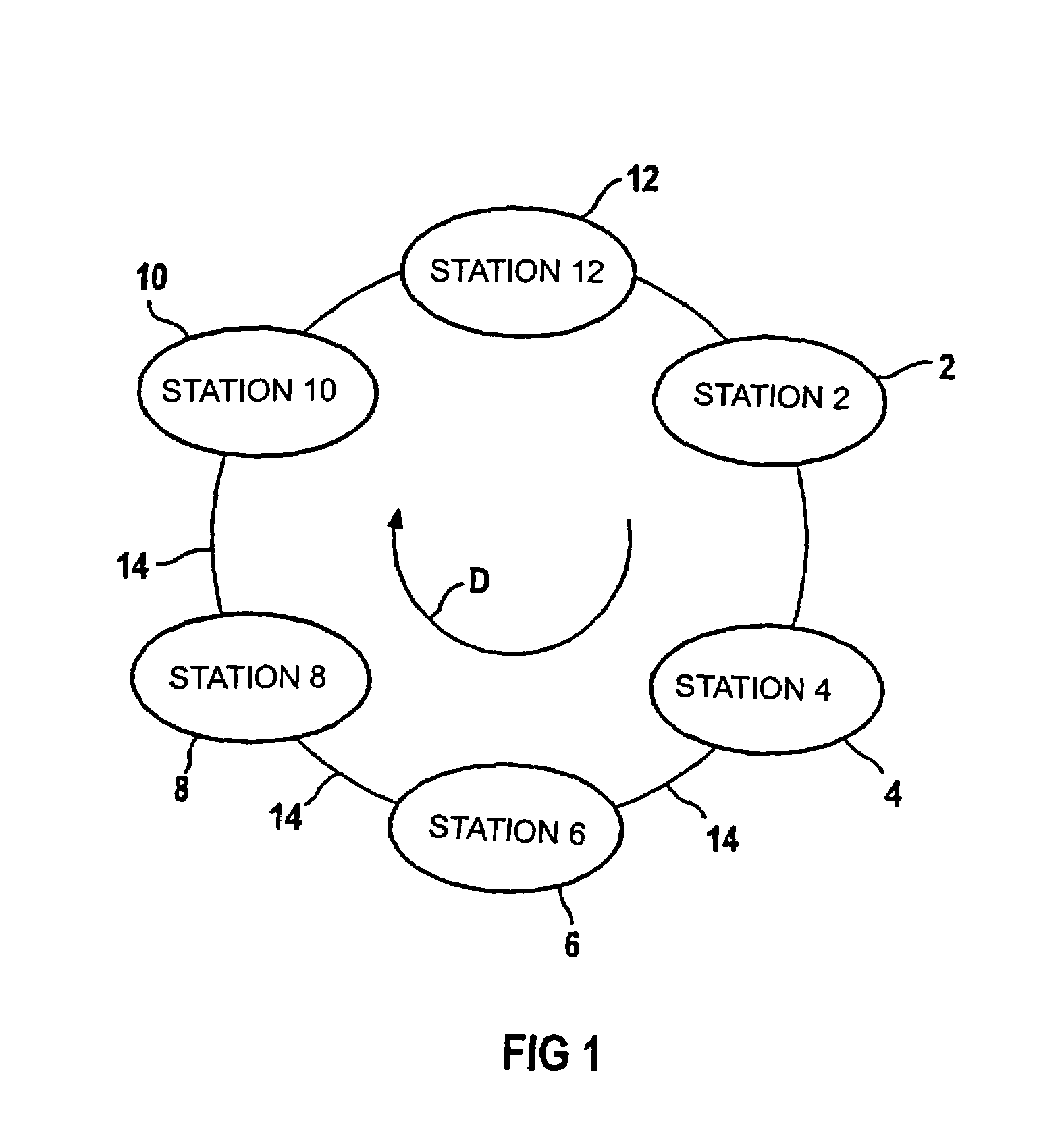
Ring architecture for an optical satellite communication network with passive optical routing
InactiveUS6912075B1Reduce power consumptionReduce weightSatellite communication transmissionOptical multiplexFiberLength wave
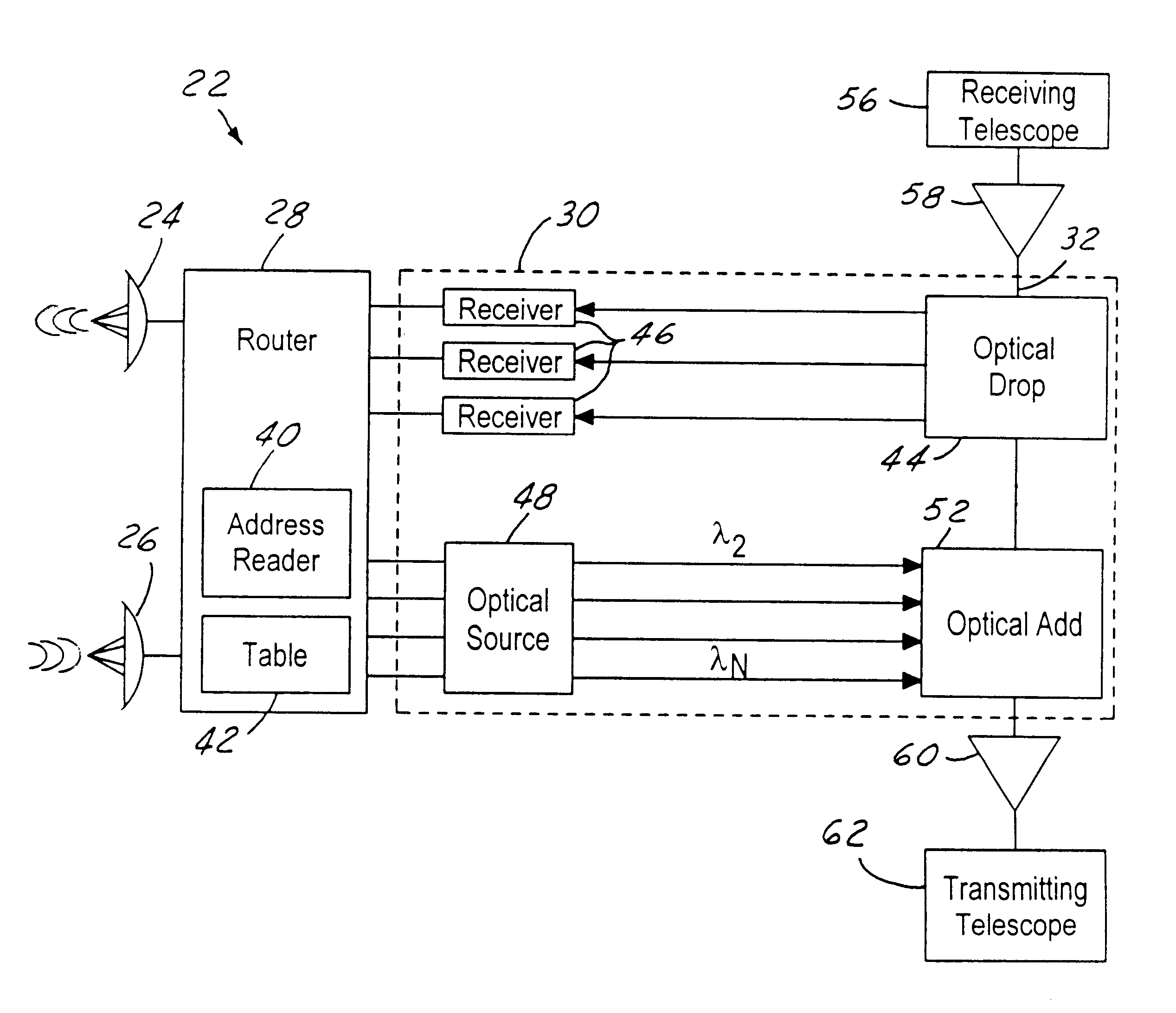
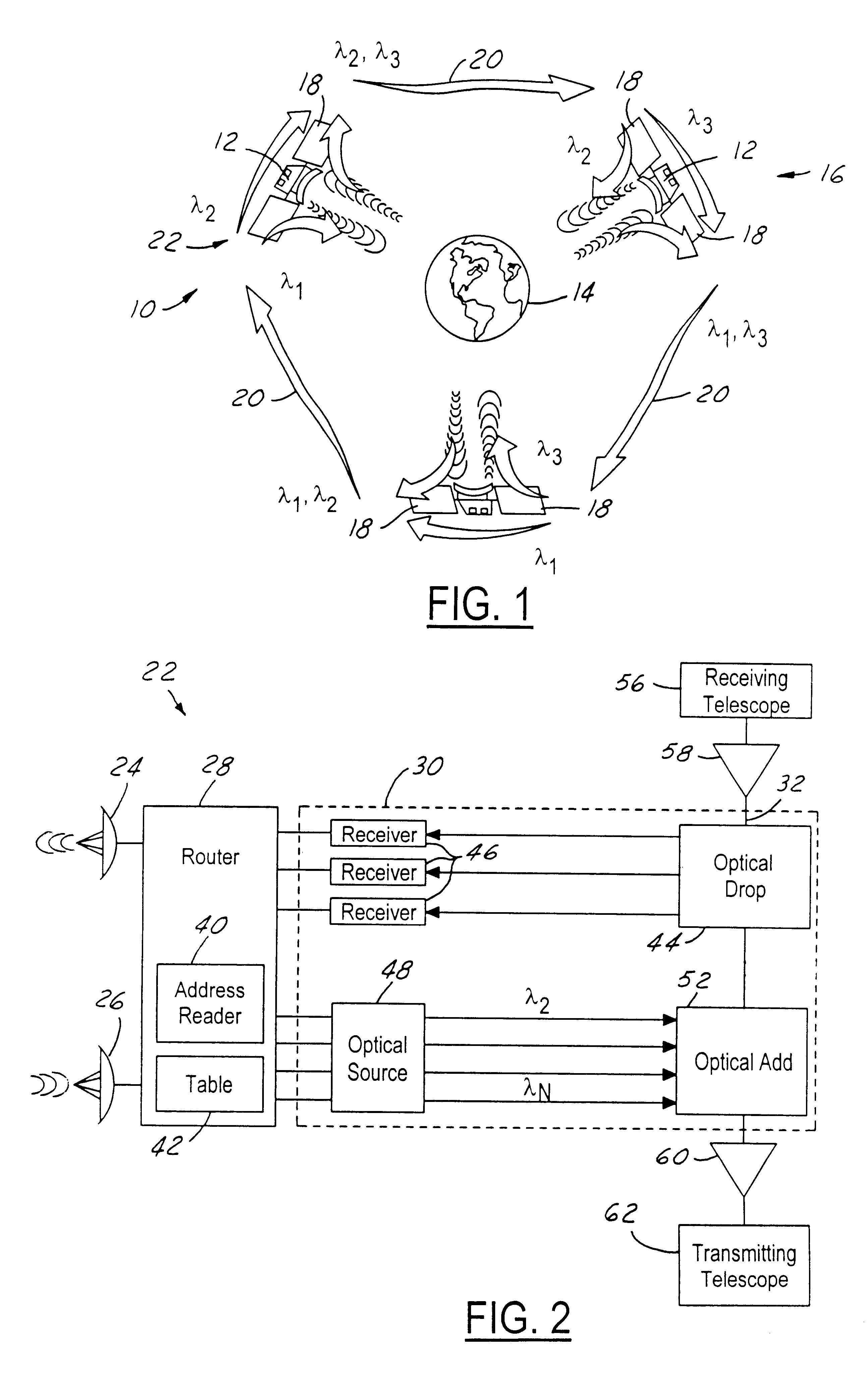
A node for satellite system communications between a ground station and a satellite includes a fiber optic bus on the satellite. An optical drop is coupled to the bus. The optical drop resolves an optical signal destined to the given satellite from the optical bus. An uplink and downlink receive and transmit communications from a ground terminal. A router is coupled to the optical drop and the uplink and downlink. An address reader and a table are used by the router to determine the destination of the received RF signals. The received RF signals are converted to optical signals by an optical source. The optical source has a wavelength that corresponds with the destination satellite. The optical signals are transmitted to an adjacent satellite by an optical transmitter such as a transmitting telescope.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Scalable reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer
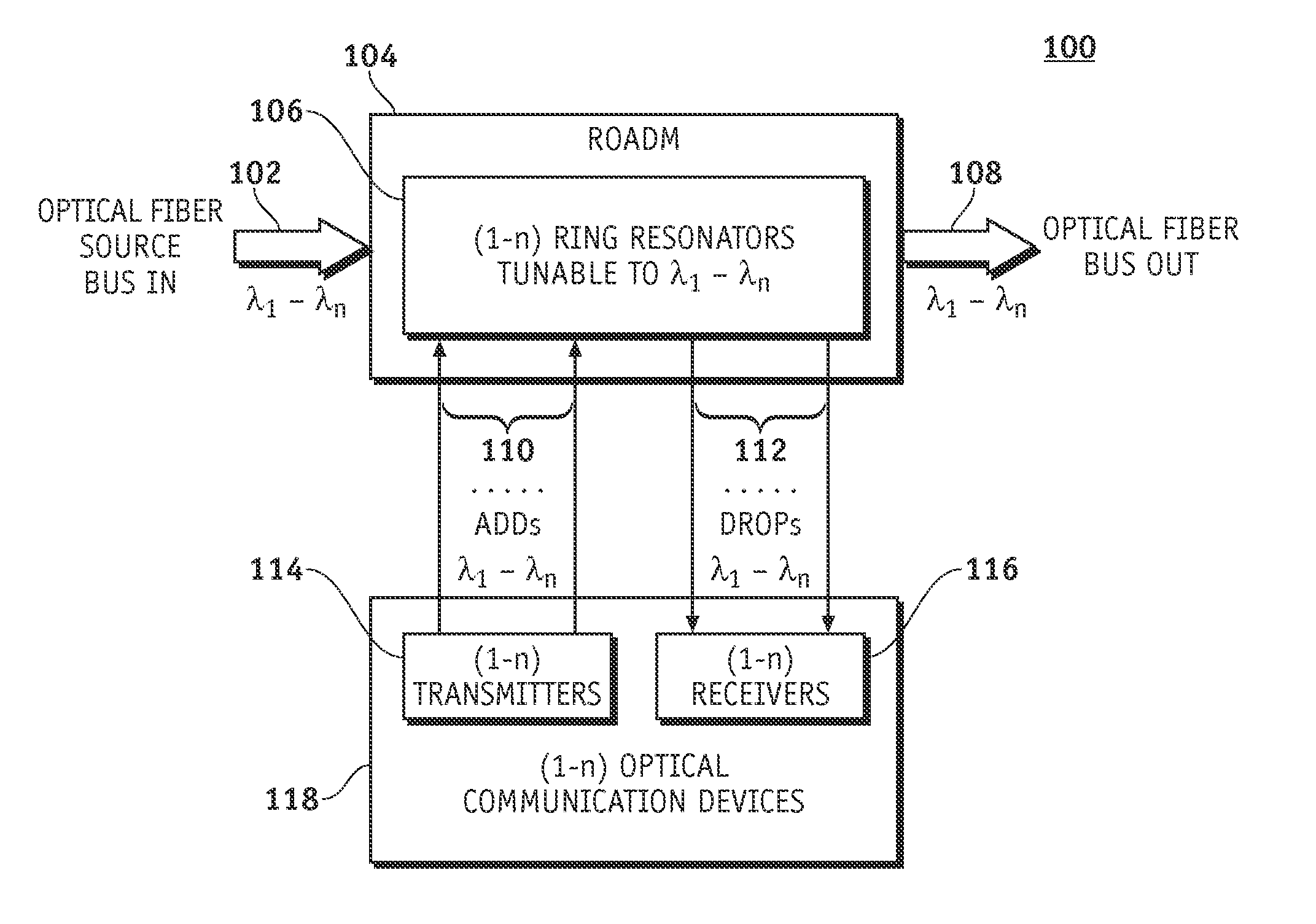
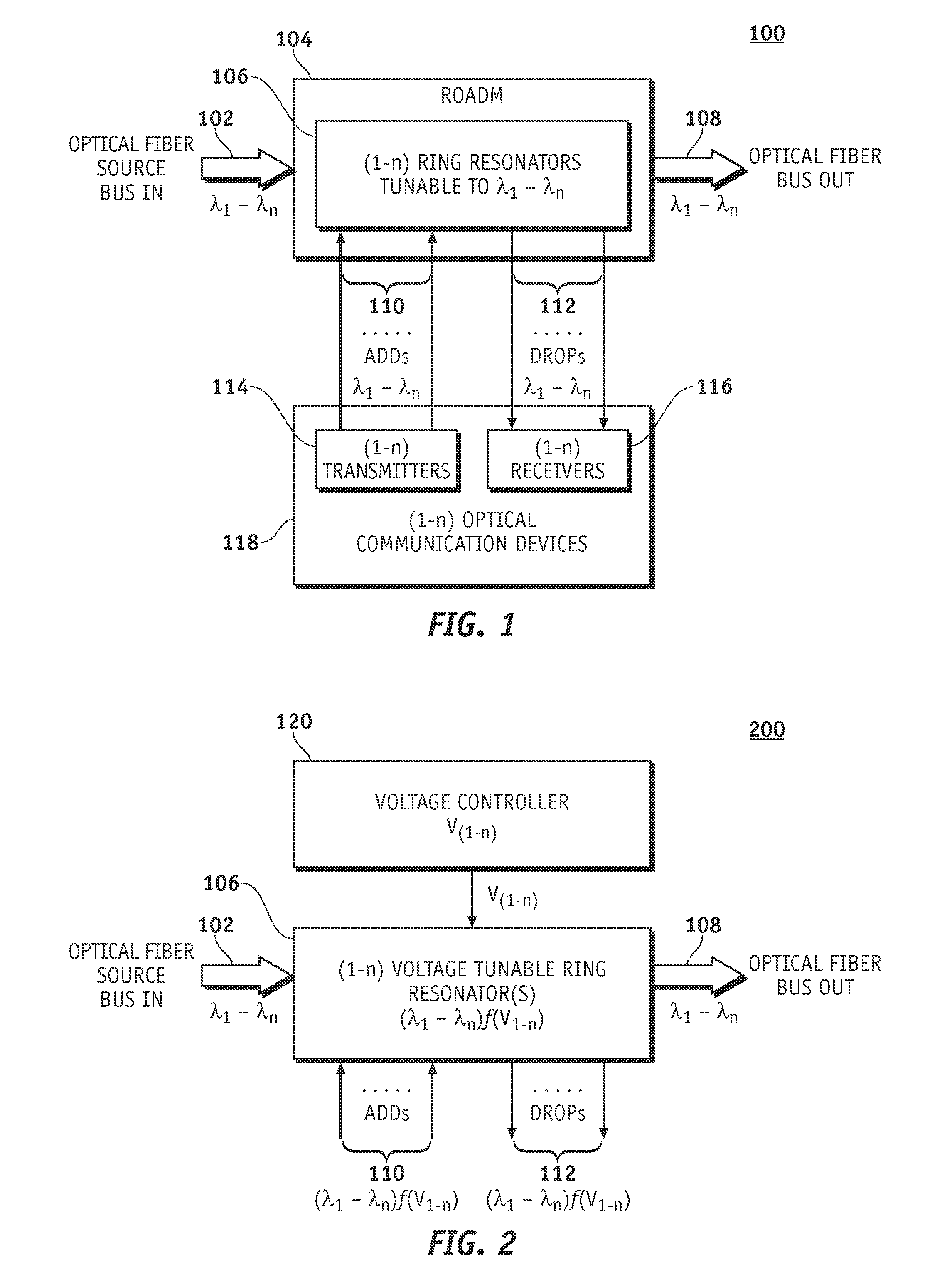
ActiveUS20080193133A1High index contrastGood wavelength selectivityWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesLength waveOptical bus
A system and methods are disclosed for a hybrid silicon-organic scalable reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer. An embodiment of a scalable reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) includes an optical bus for optical signals of different wavelengths, a plurality of add / drop optical waveguides, and a plurality of ring resonators, each being optically coupled to the optical bus and to one of the add / drop optical waveguides. The ring resonators are coated with an organic electro-optic cladding layer and are configured to switch wavelength selected optical signals between the optical bus and the add / drop optical waveguides in response to control voltages applied to the organic electro-optic cladding layer. The individual ring resonators of the ROADM can be independently modulated and tuned to filter specific wavelengths.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +2
Improved free space optical bus
InactiveUS20060251421A1Quality improvementImprove transmission qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementPolarisation/directional diversityCross-linkAntenna gain
A method and apparatus for improving the transmission quality of a free space optical bus between circuitry elements in high speed computing, communication and signal processing systems. Use is made of an adaptive algorithm that learns the transmission properties of the bus, and selects or adjusts transmission paths or characteristics to provide optimum bus performance. Each transmitter on the bus transmits a signal which is generally measured by all of the receivers on the bus, and the measured signals are used to generate a matrix which maps desired transmission along information links, and cross-link interference. Transmission quality is optimized by adjusting one or more characteristics associated with transmission along the bus, including emitted power, beam divergence, wavelength, beam polarization, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the transmitters, and power sensitivity, gain, equalizer coefficients, field of view, polarization sensitivity, antenna gain and antenna polar diagram of the receivers. Novel bus configurations are described, including use of different wavelengths for different bus functions.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Optical add/drop interconnect bus for multiprocessor architecture
InactiveUS7366368B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMulti processorEngineering
Owner:INTEL CORP
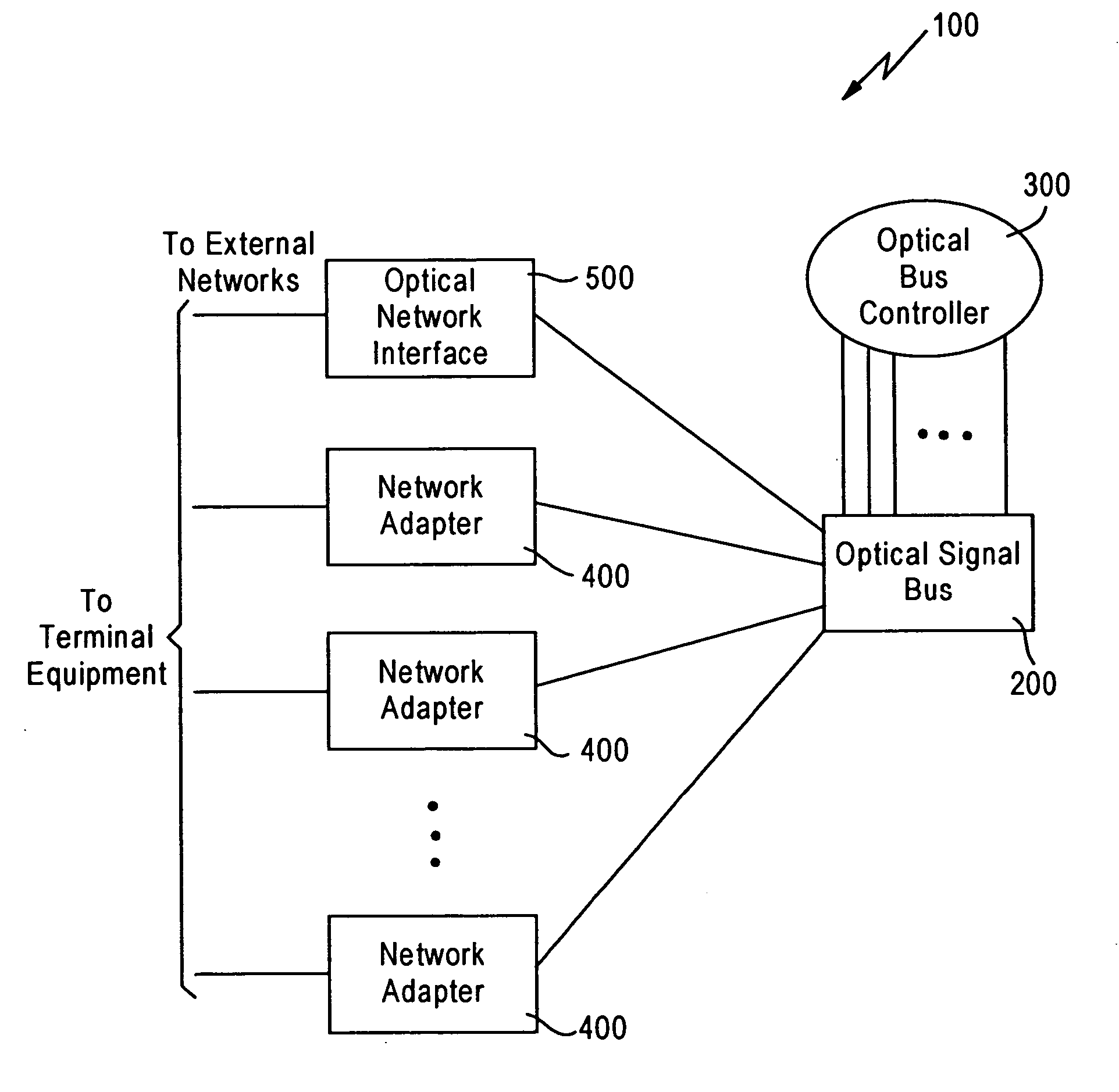
Optical burst switch network system and method with just-in-time signaling
InactiveUS20050013613A1Lower latencyRich varietyMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionNetwork terminationOptical burst switching
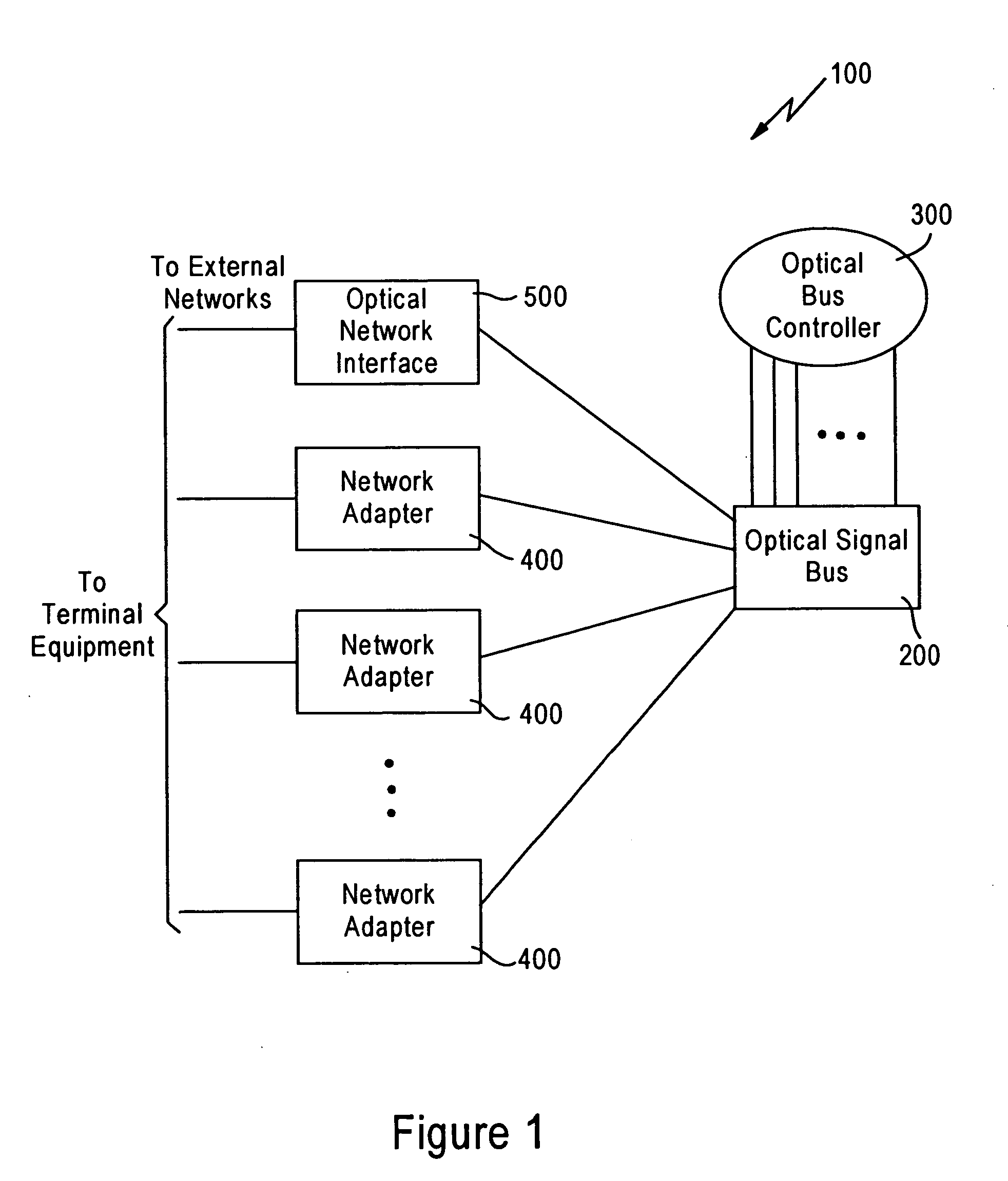
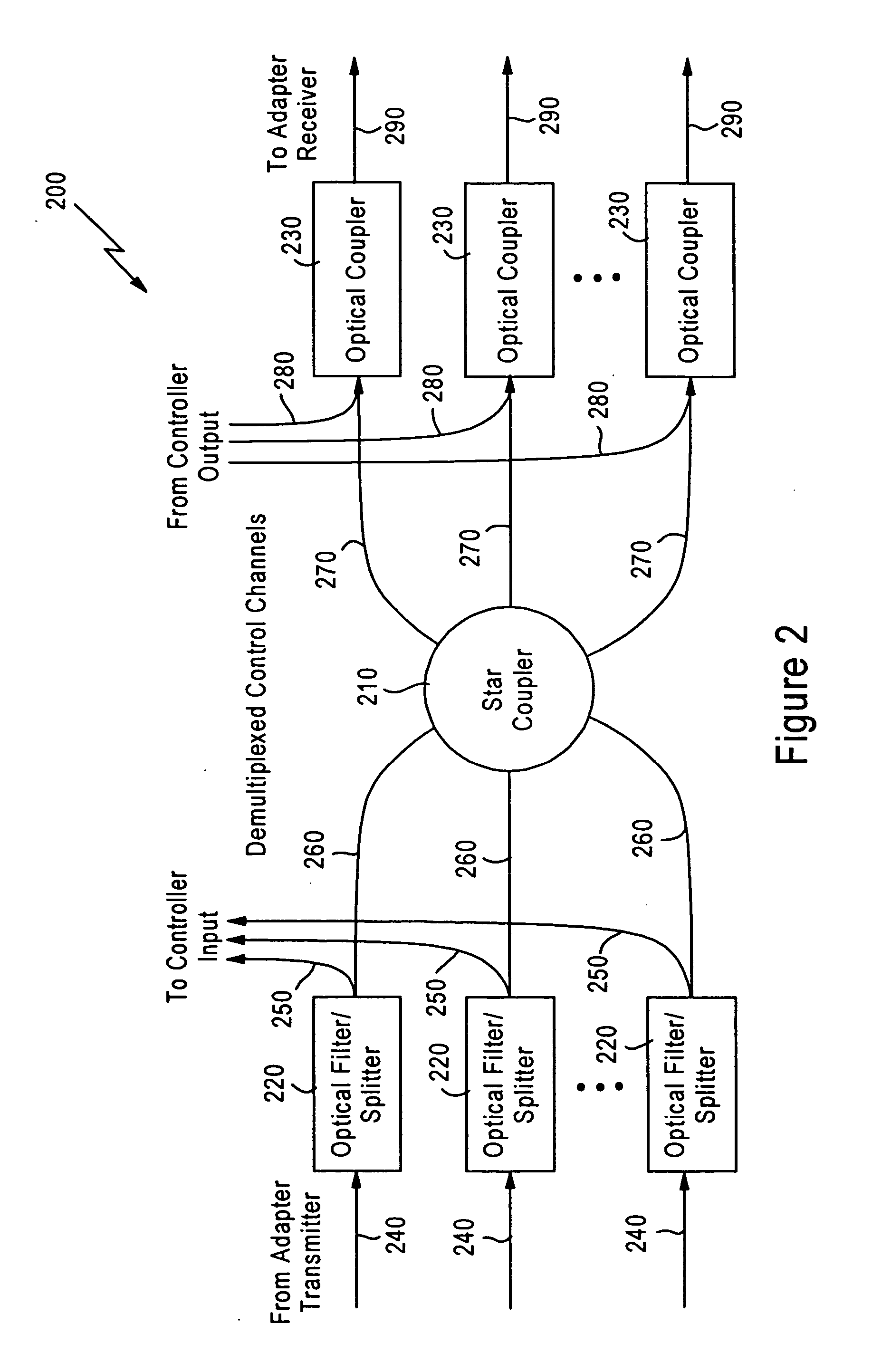
Optical burst switch network system and method with Just-in-Time (JIT) signaling and advanced data transmission and memory access and management. The system and method allow concurrent data transmission having arbitrary signal types, such as analog and digital signal types, in which the JIT signaling allows for subsequent simultaneous transmission of optical signals that do not require electro-optical conversion. The system includes an optical signal bus having a passive star coupler. A plurality of network adapters that are in optical communication with the optical signal bus and in network communication with network terminal devices are provided. The network adapters include receivers, transmitters and control logic that allows for bi-directional movement of data signals as bursts between the terminal equipment and the network system. The transmitter and receiver may be fixed or tunable. The system further includes an optical bus controller in optical communication with the optical signal bus that processes signals from the optical signal bus to connect a requested network adapter to a requesting network adapter in accordance with the user-to-network protocol. The network system implements a just-in-time signaling protocol to signal nodes in the network that burst communications are forthcoming. Optionally, the system allows comprehensive memory access in a Local Area Network (LAN). The nodes in the network are capable of seamlessly addressing memories of all other nodes that comprise the network.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
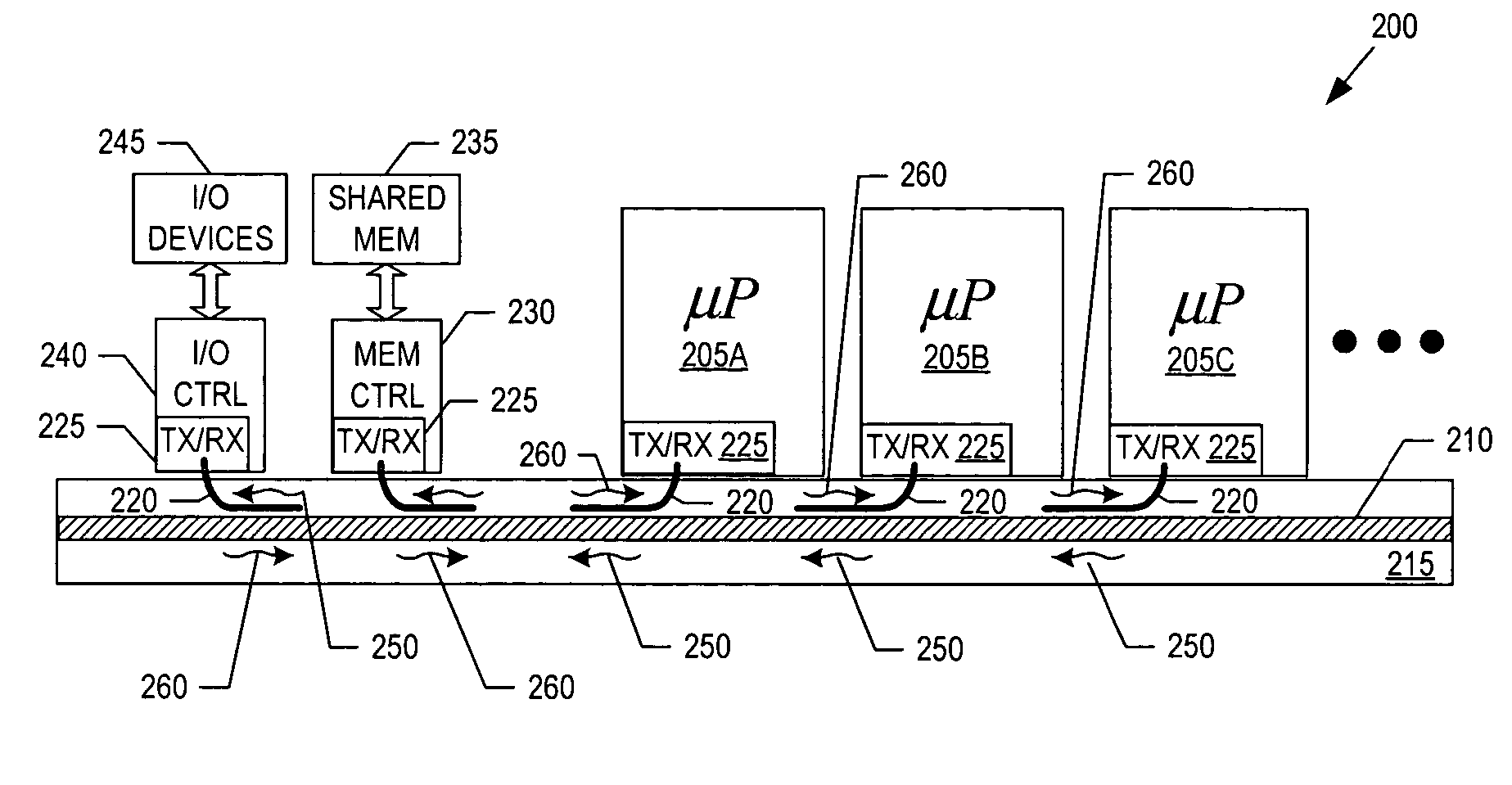
Optical bus system and method
InactiveUS6628441B1Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsTransfer systemOptical data transmission
The invention relates to a bi-directional optical data transfer system. The data is transferred by a diffuse light between several electronic components with several transmission links, wherein each transmission link is provided with a covering to prevent the transmission links from interfering with each other.
Owner:IBM CORP
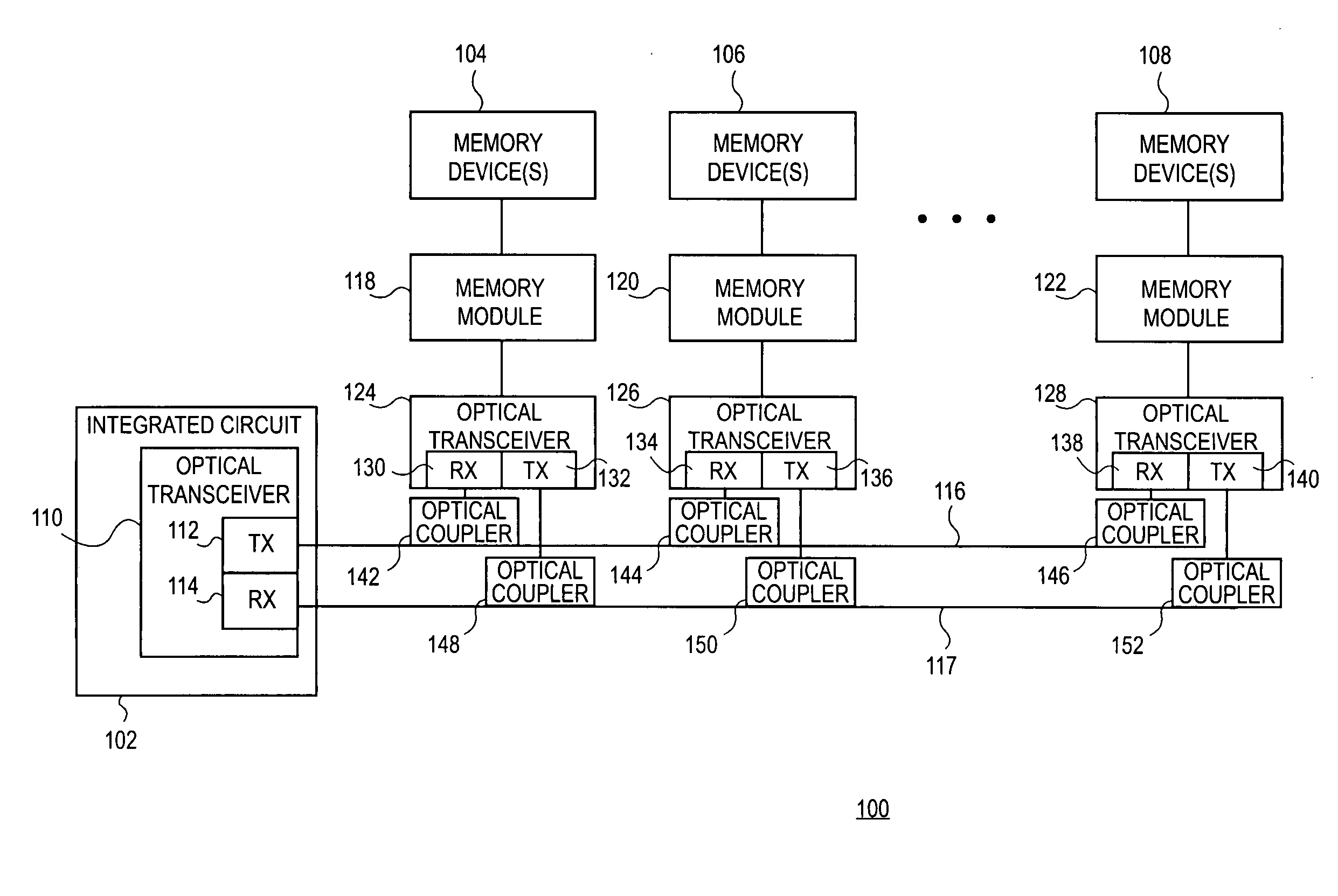
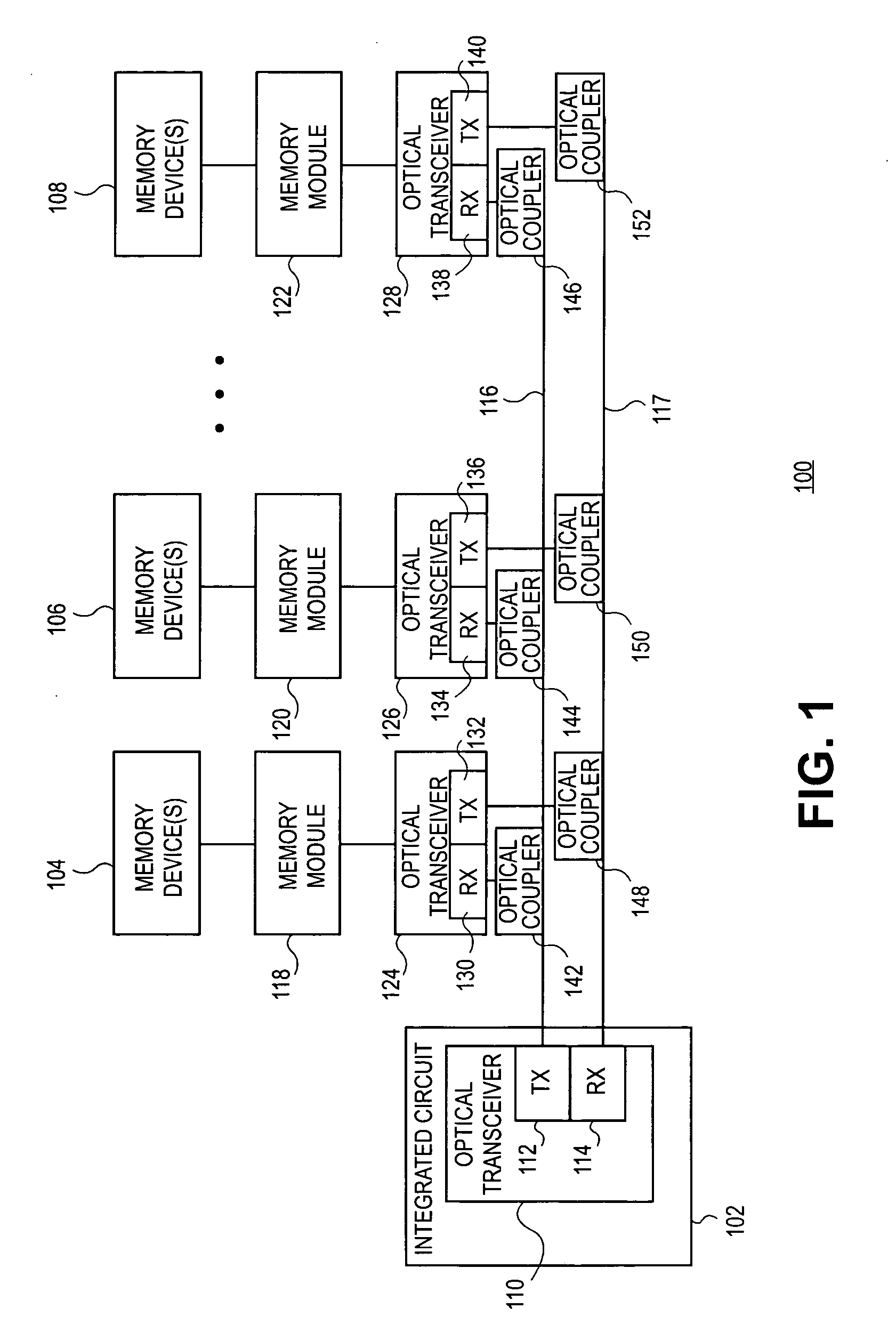
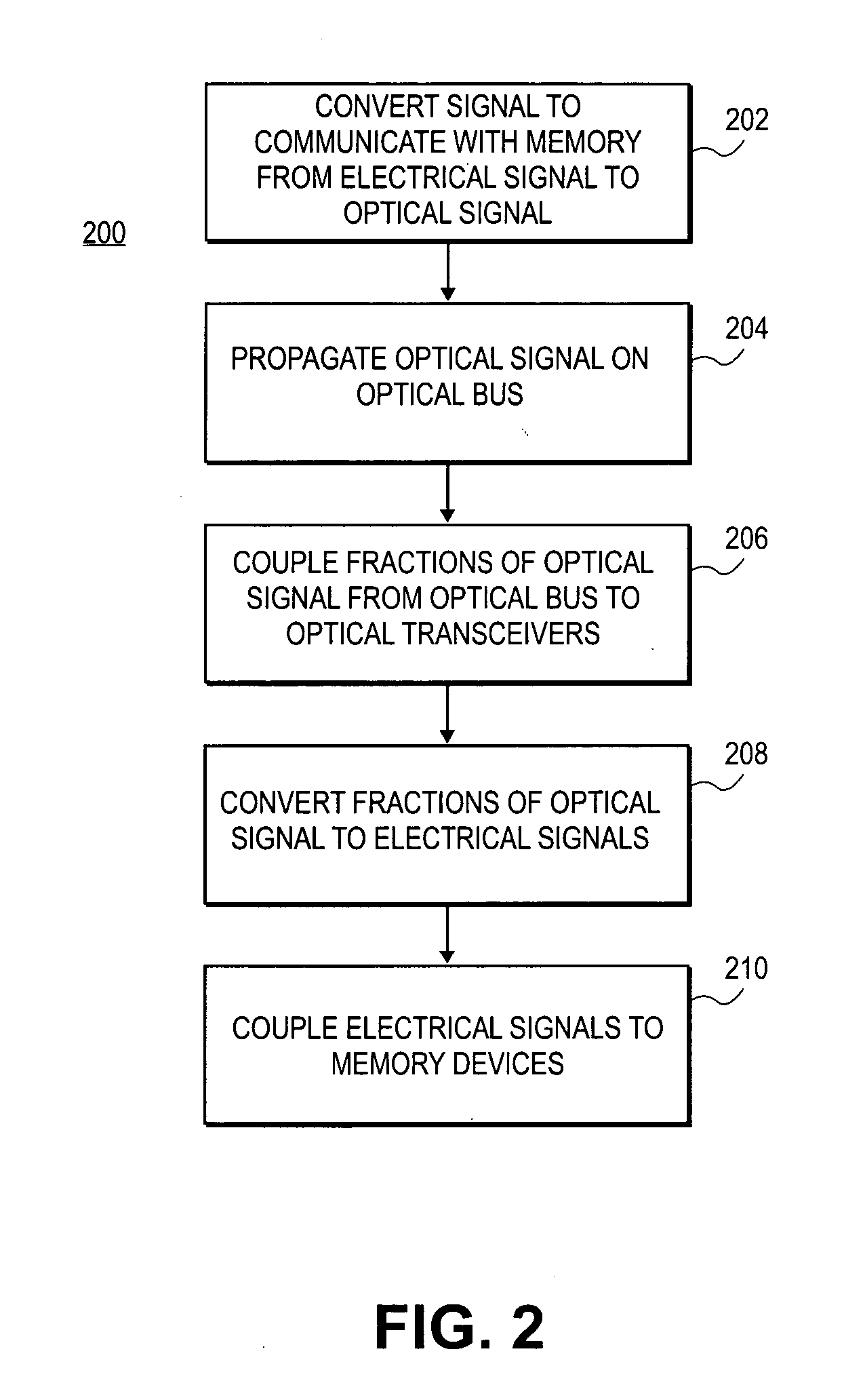
Low latency optical memory bus
Embodiments of the present invention include an integrated circuit to communicate with a memory device. The integrated circuit includes an optical transmitter and an optical bus coupled to the integrated circuit's optical transmitter. N optical receivers are coupled to the optical bus via N optical couplers. N memory modules are coupled to the N optical receivers. M memory devices are coupled to the N memory modules. The optical transmitter converts a signal to communicate with the N memory modules from an electrical signal to an optical signal. The optical bus propagates the optical signal. Each of the N optical couplers to couple a one-Nth of the optical signal from the optical bus to each one of the N optical receivers, each of the N optical receivers converts its one-Nth of the optical signal to an electrical signal for its associated memory device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Bus line inquiry method
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Optical add/drop interconnect bus for multiprocessor architecture
InactiveUS20050276604A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMulti processorOptical coupler
An optical bus interconnects two or more processors in a multiprocessor system. One or more electrical-to-optical (“E-O”) transmitters are optically coupled to the optical bus using optical couplers. The E-O transmitters receive electrical signals from the processors and convert the electrical signals to optical signals to be guided onto the optical bus. Optical-to-electrical (“O-E”) receivers are also coupled to the optical bus using the optical couplers. The O-E receivers receive optical signals from the optical bus and convert the optical signals to electrical signals for the processors.
Owner:INTEL CORP
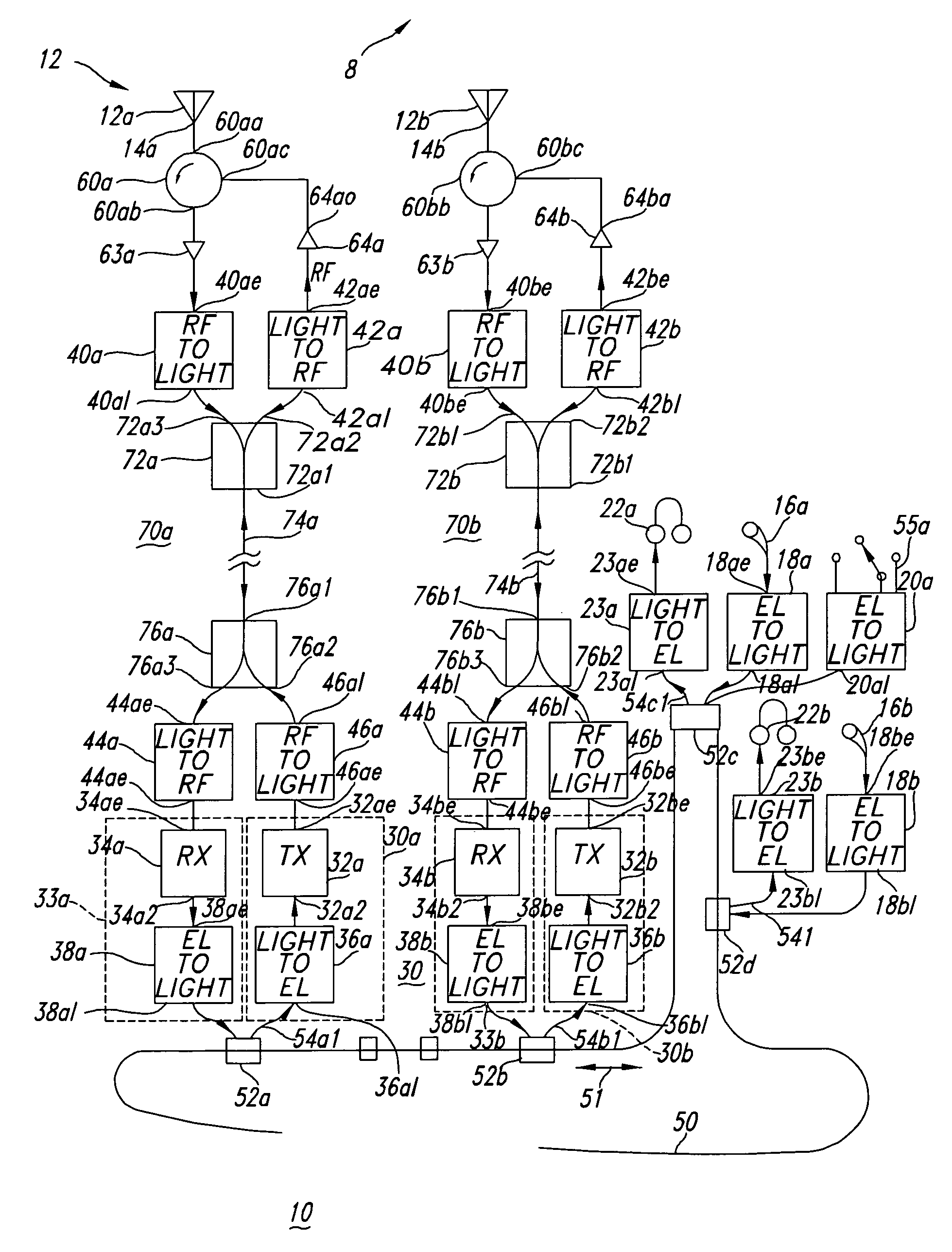
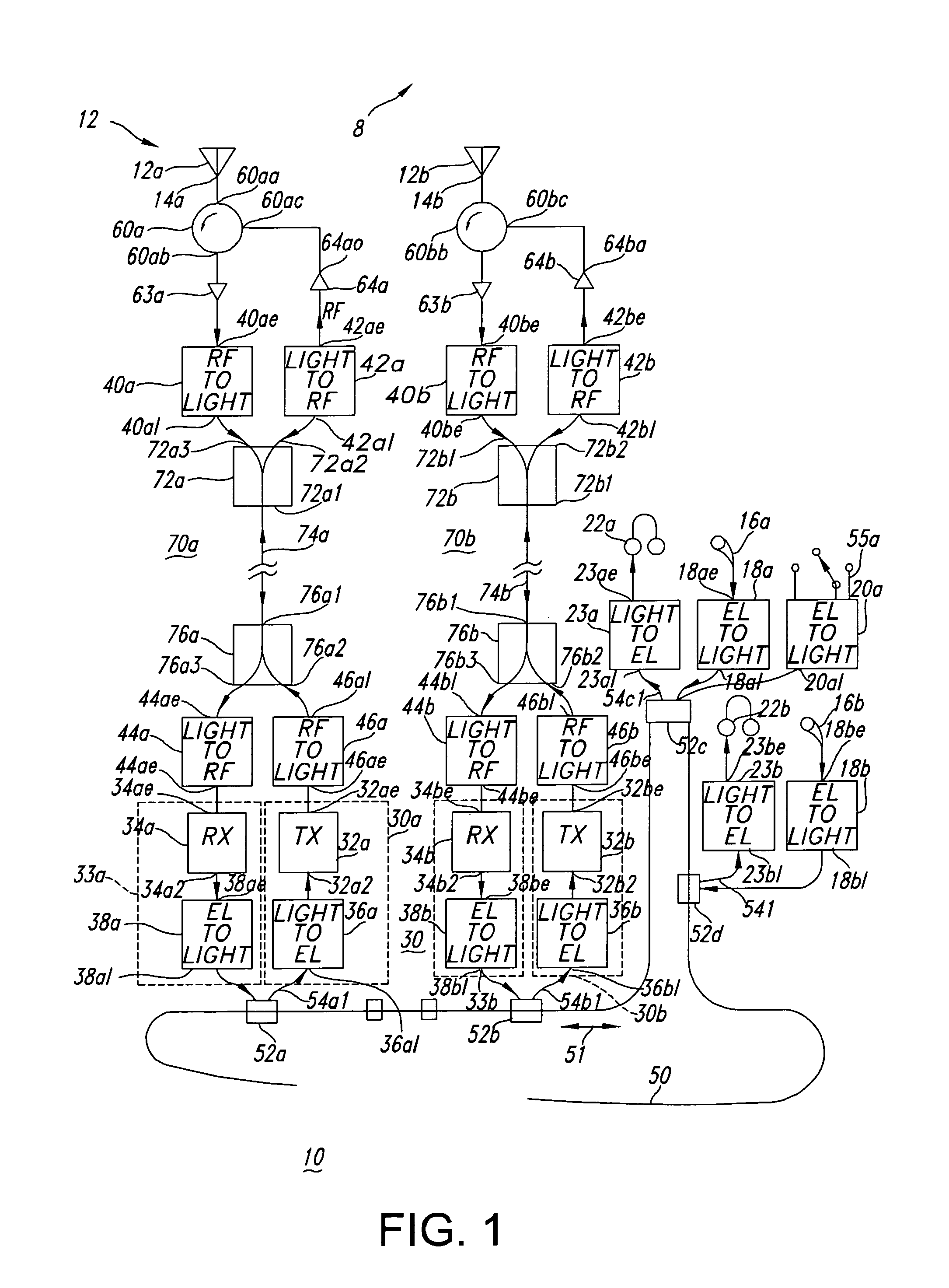
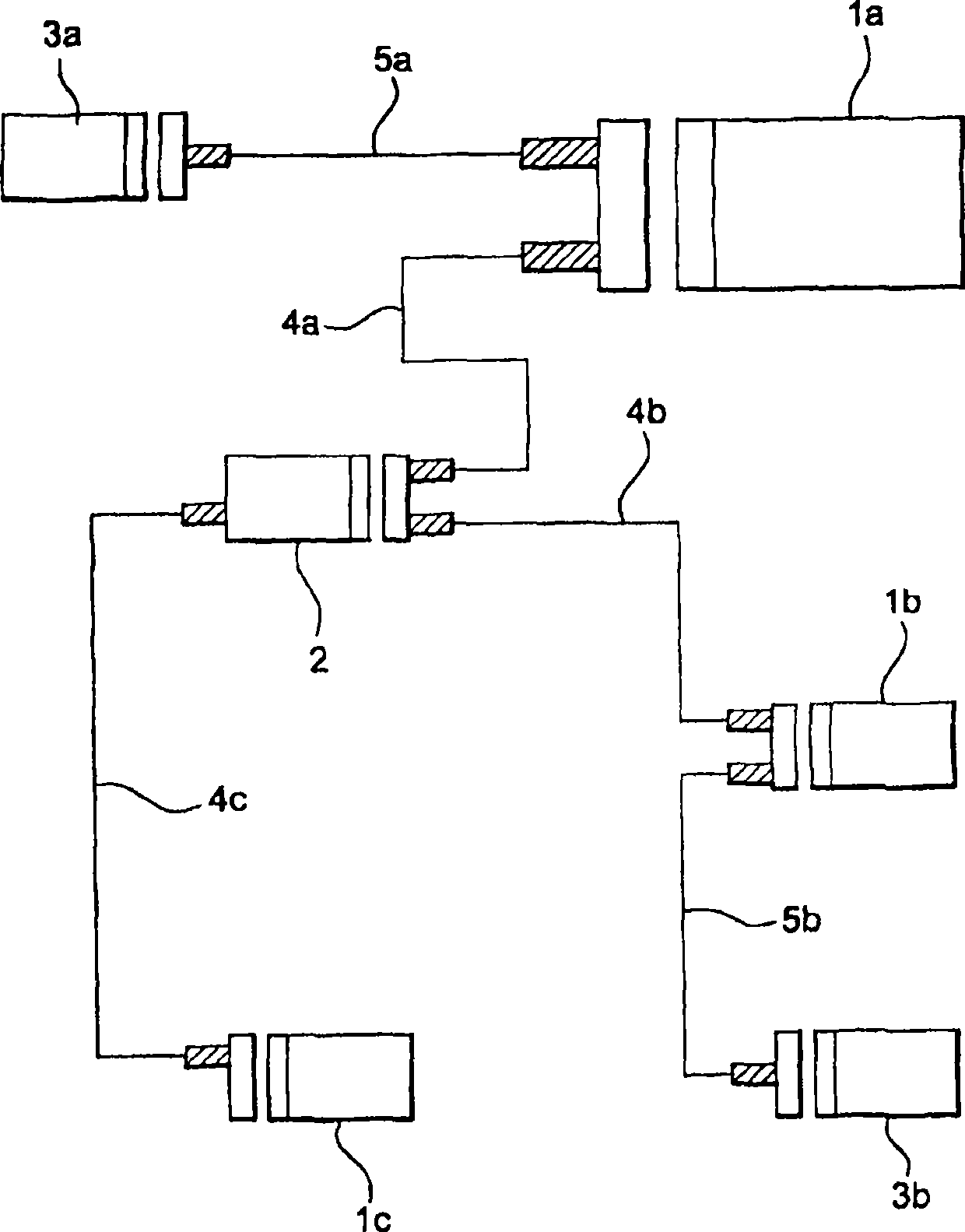
Vehicular communication system
ActiveUS7085497B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemLight signal
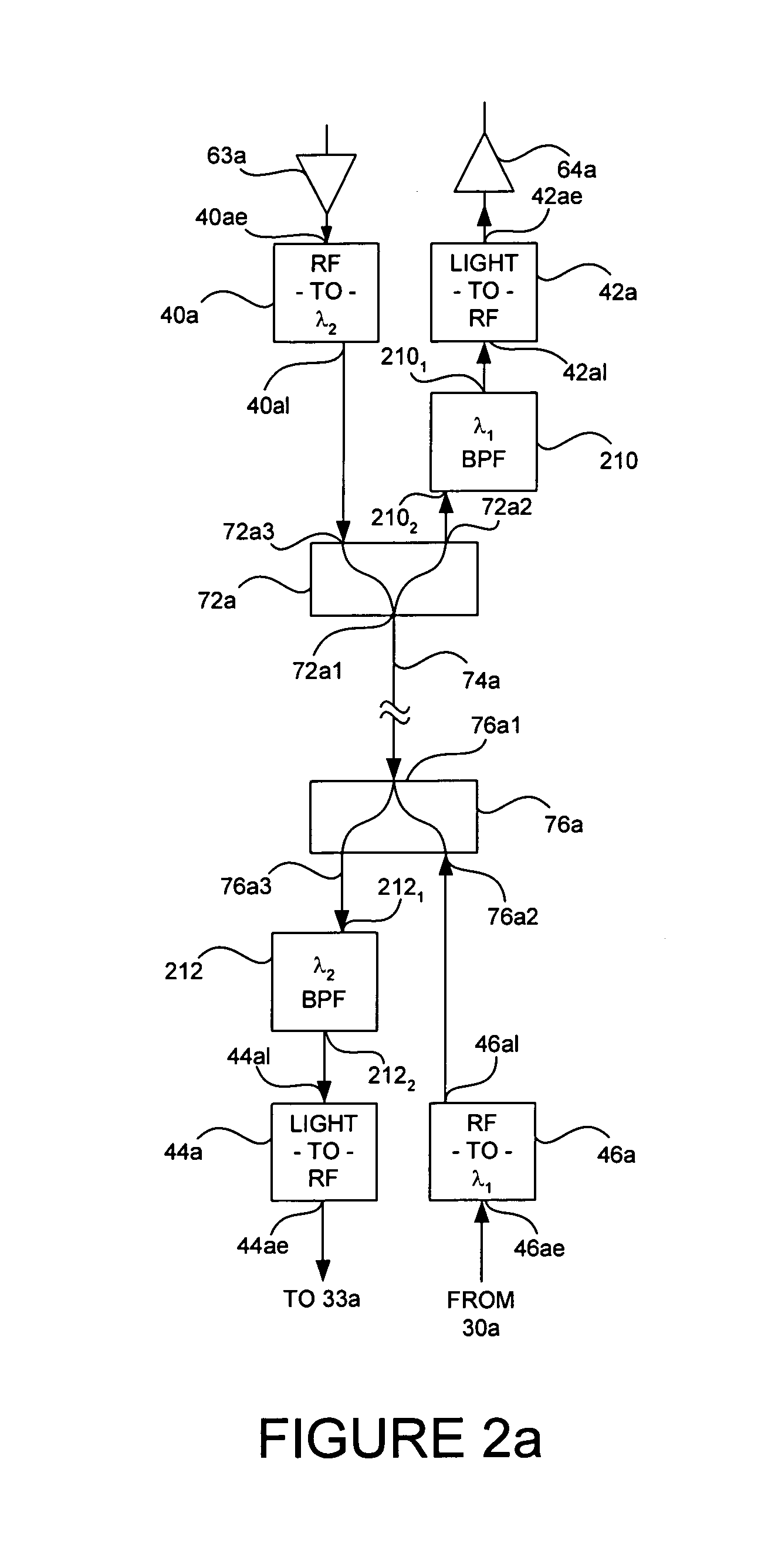
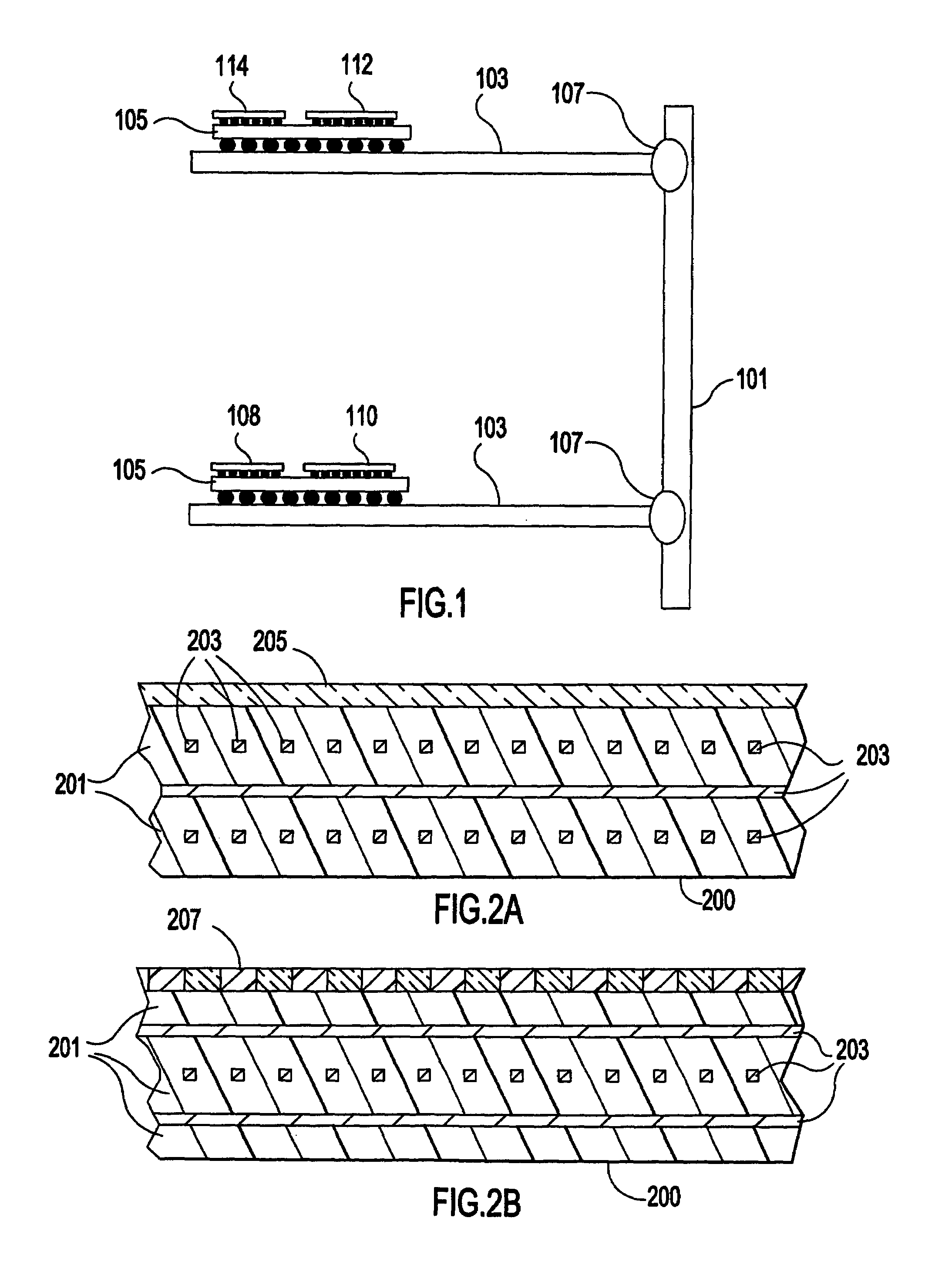
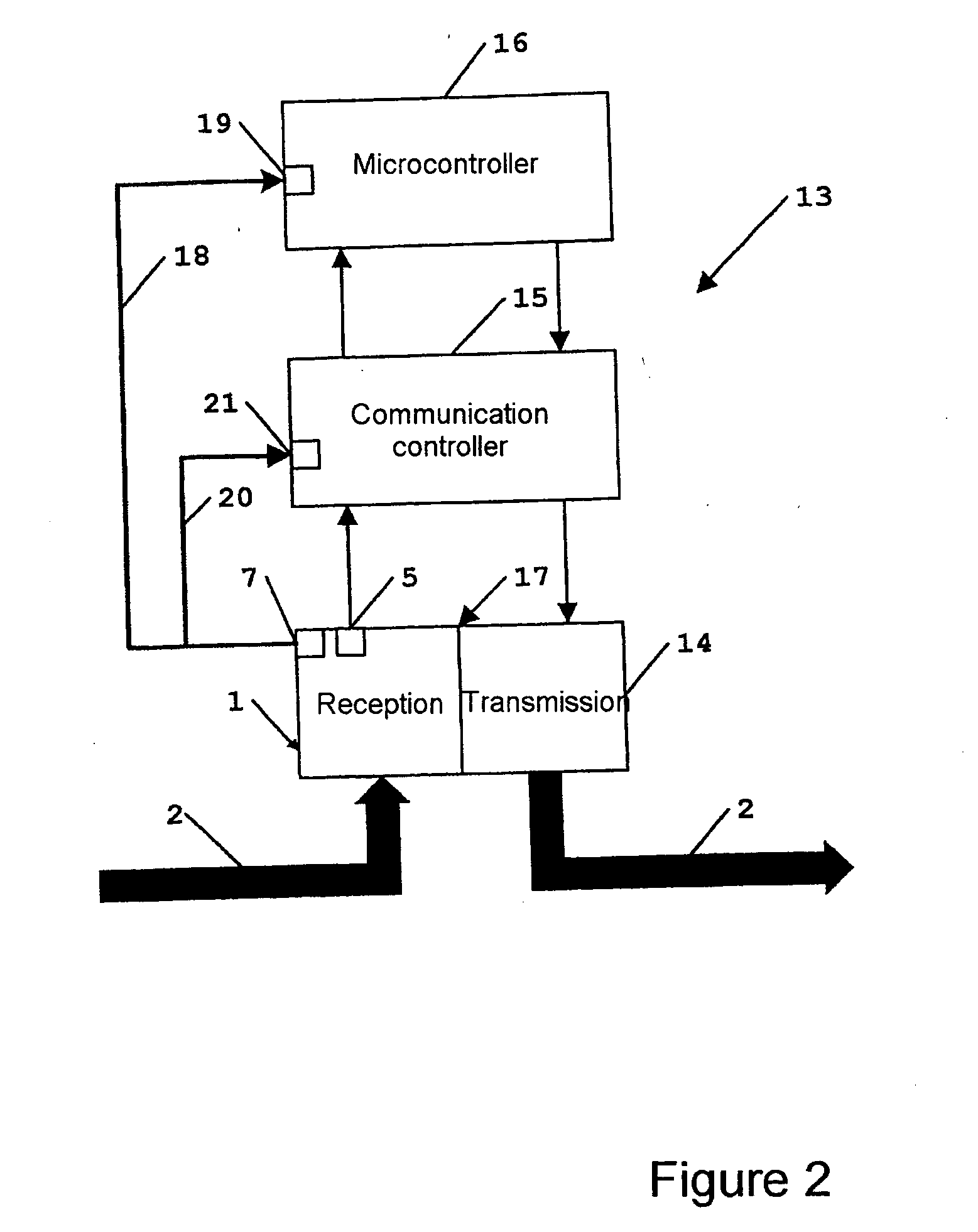
A communication system includes an optical “LAN” (50) interconnecting a plurality of information sources (16a) and sinks (22a) with a light-to-electrical converter (36a) associated with an electrical RF transmitters (32a) and an RF-to-light converter (38a) to a receiver (34a). The transmitter is coupled by way of electrical-to-light converter (46a), and the receiver is coupled by way of light-to-electrical converter (44a), and by way of a directional coupler (76a), to an end of an optical bus (74a), so that light signals representing signals to be transmitted flow in one direction, and light signals representing received signals flow in the other direction through the bus. A directional coupler (72a) at the other end of the optical bus routes the transmit light signals to a light-to-RF converter (47a) which feeds a sink or antenna (12a), and received signals from a source or antenna are routed by way of an RF-to-light converter (40a) and the directional coupler (72a) onto the optical bus (74a).
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
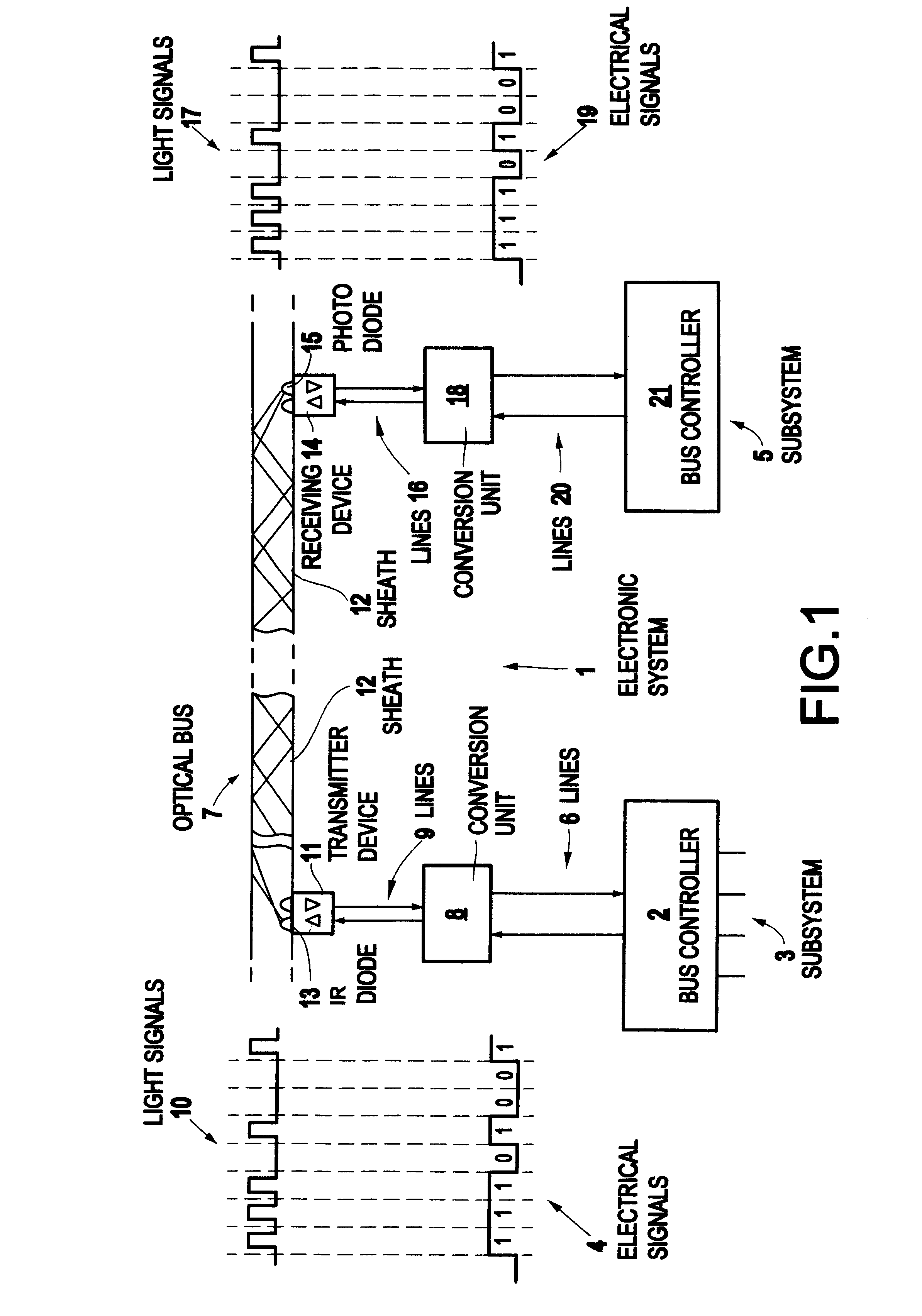
Method and a device for communication among equal-access stations of a ring-shaped serial fiber-optic bus
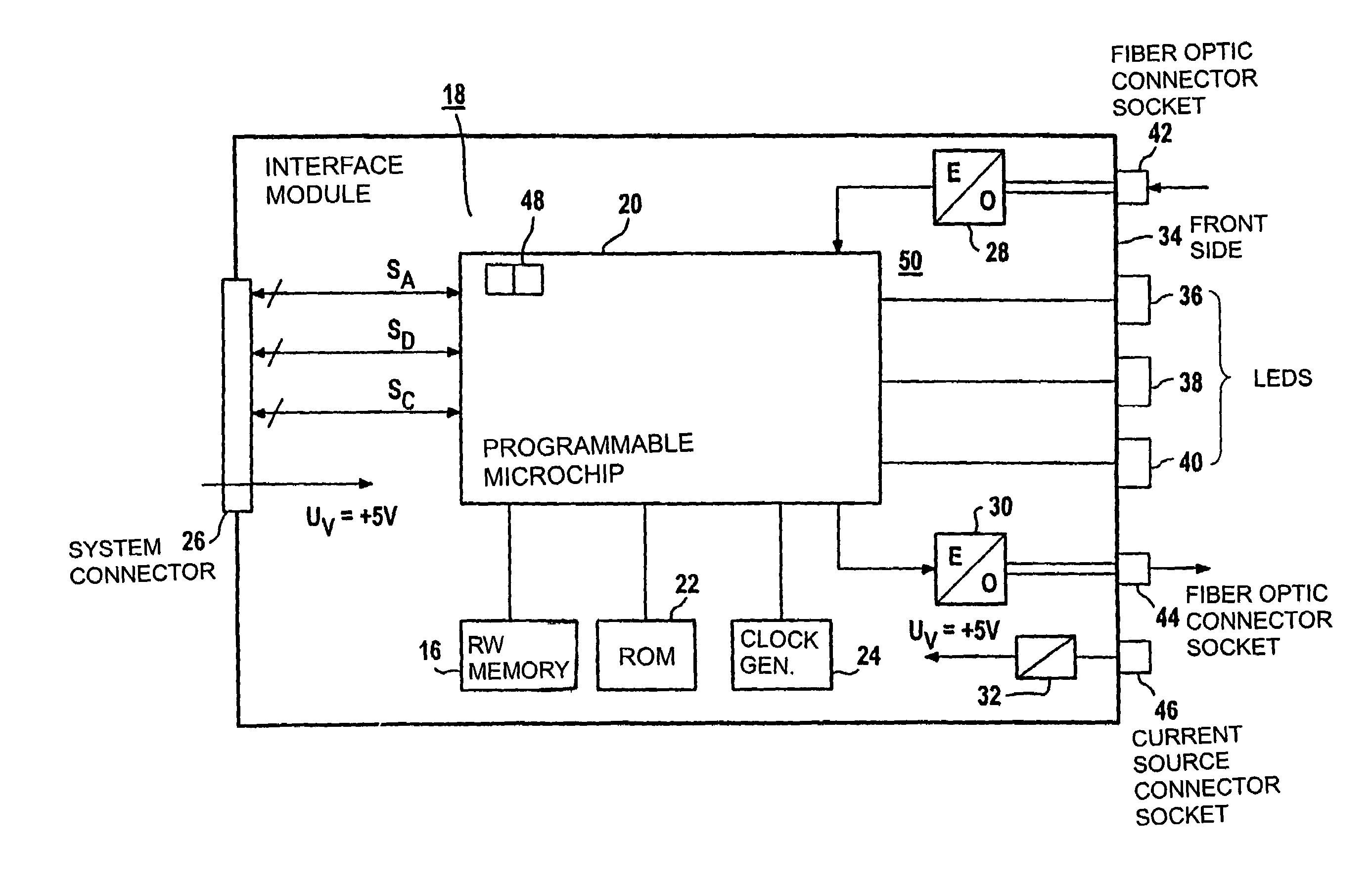
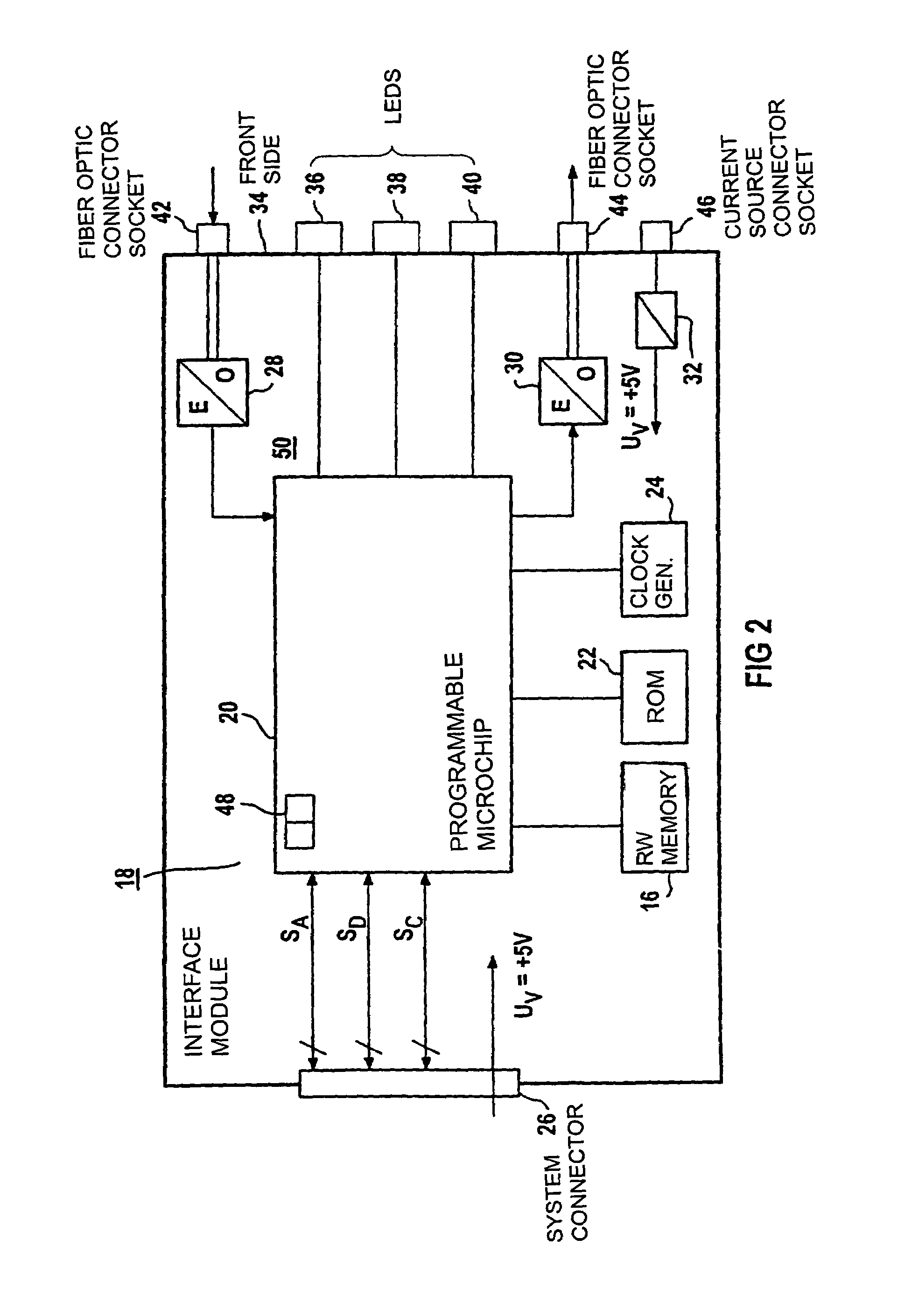
A method is described for communication among equal-access stations of a ring-shaped, serial fiber-optic bus and to a device for carrying out this communications method. One station, during a bus cycle, generates container messages in a strictly time-cyclical manner, addresses them, and provides them to the serial bus, and it transmits a synchronization message at the end of the bus cycle time, each station writing its data into container messages that are addressed to it, and each station, depending on its read authorization, reading the container messages of the serial bus, all the data that have been read in the stations being imported with the assistance of the synchronization message. Thus, equal-access stations of a ring-shaped, serial fiber-optic bus can exchange data, in direct-access, extremely quickly and in a strictly time-cyclical manner.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
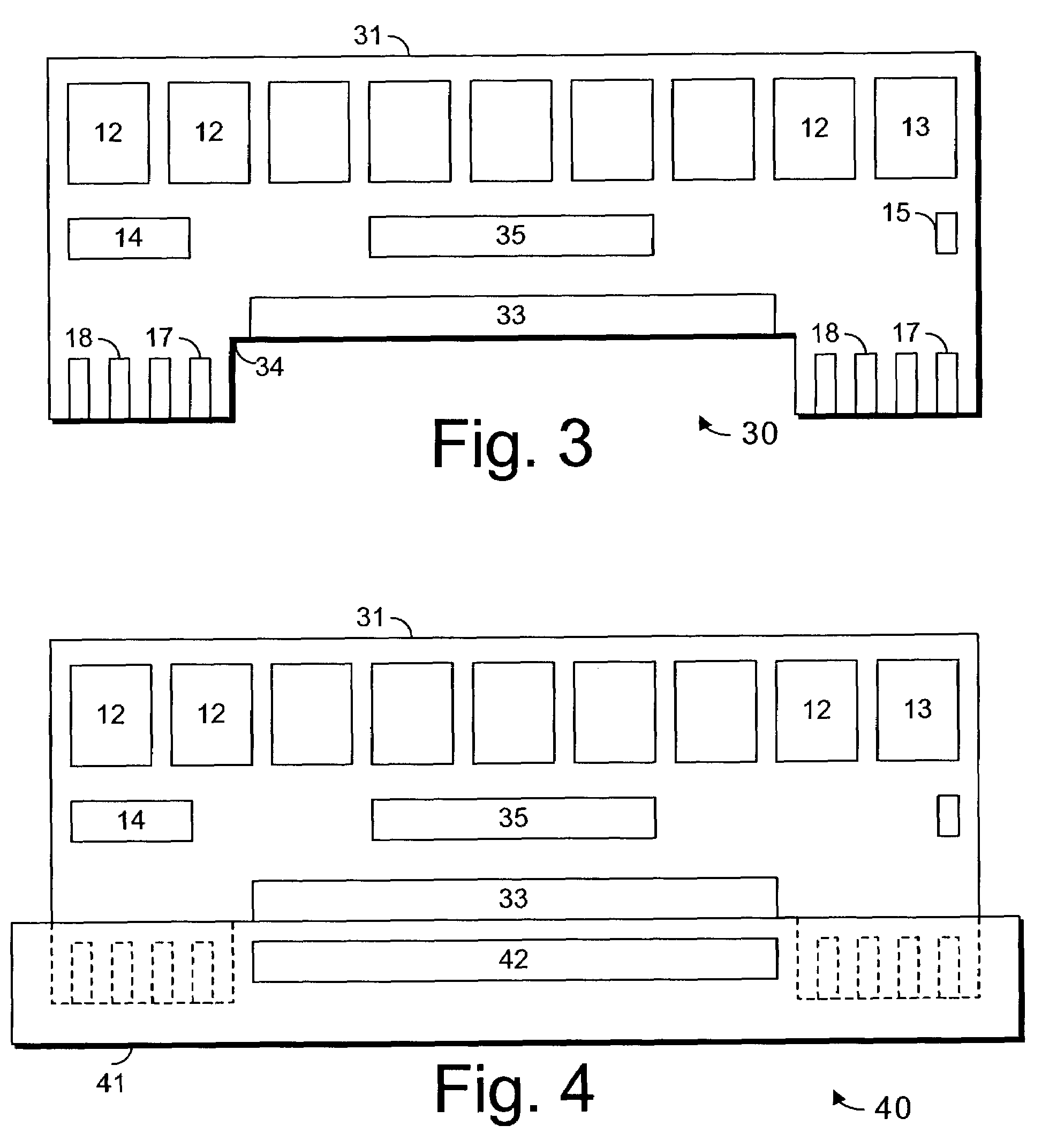
Printer circuit board for an optoelectric computer system
InactiveUS6185648B1Circuit optical detailsTransmission monitoringElectrical devicesComputerized system
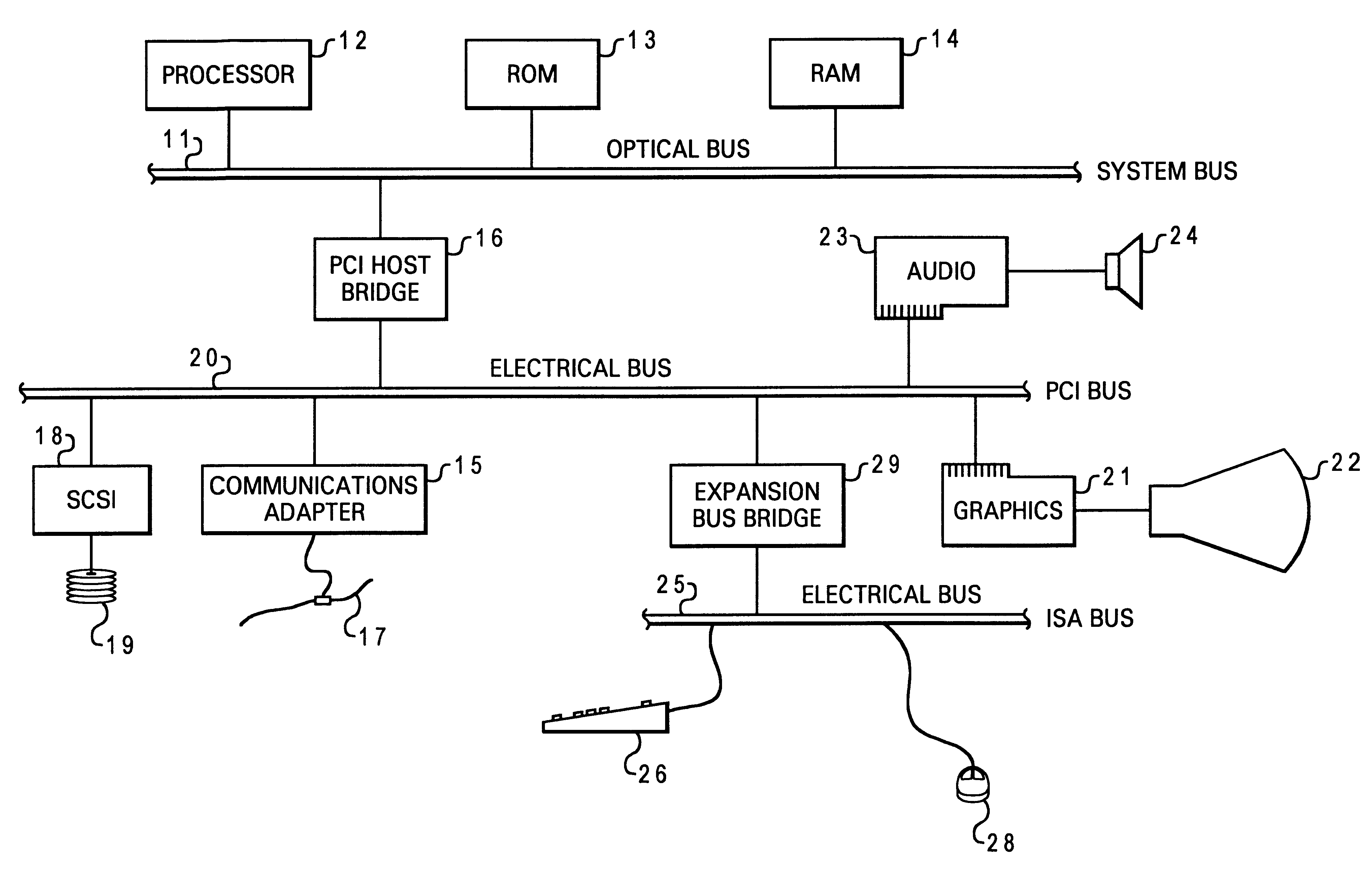
An improved architecture for an optoelectric computer system is disclosed. The computer system includes an optical bus and an electrical bus. With this computer system, electrical devices are connected to the electrical bus and optoelectric devices are connected to the optical bus. Furthermore, a few optoelectric devices are utilized to provide communications between the optical bus and the electrical bus.
Owner:IBM CORP
Free space optical bus
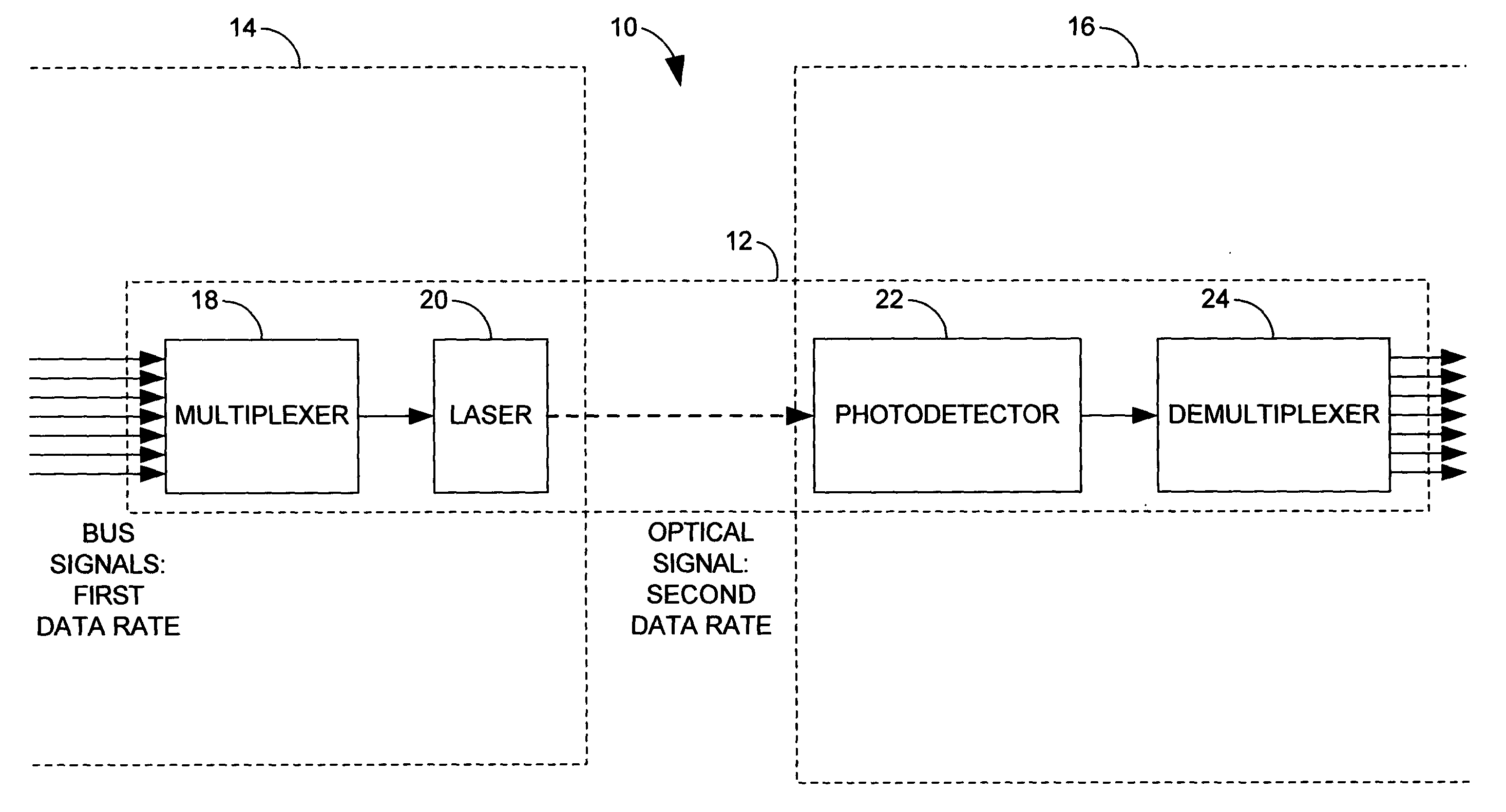
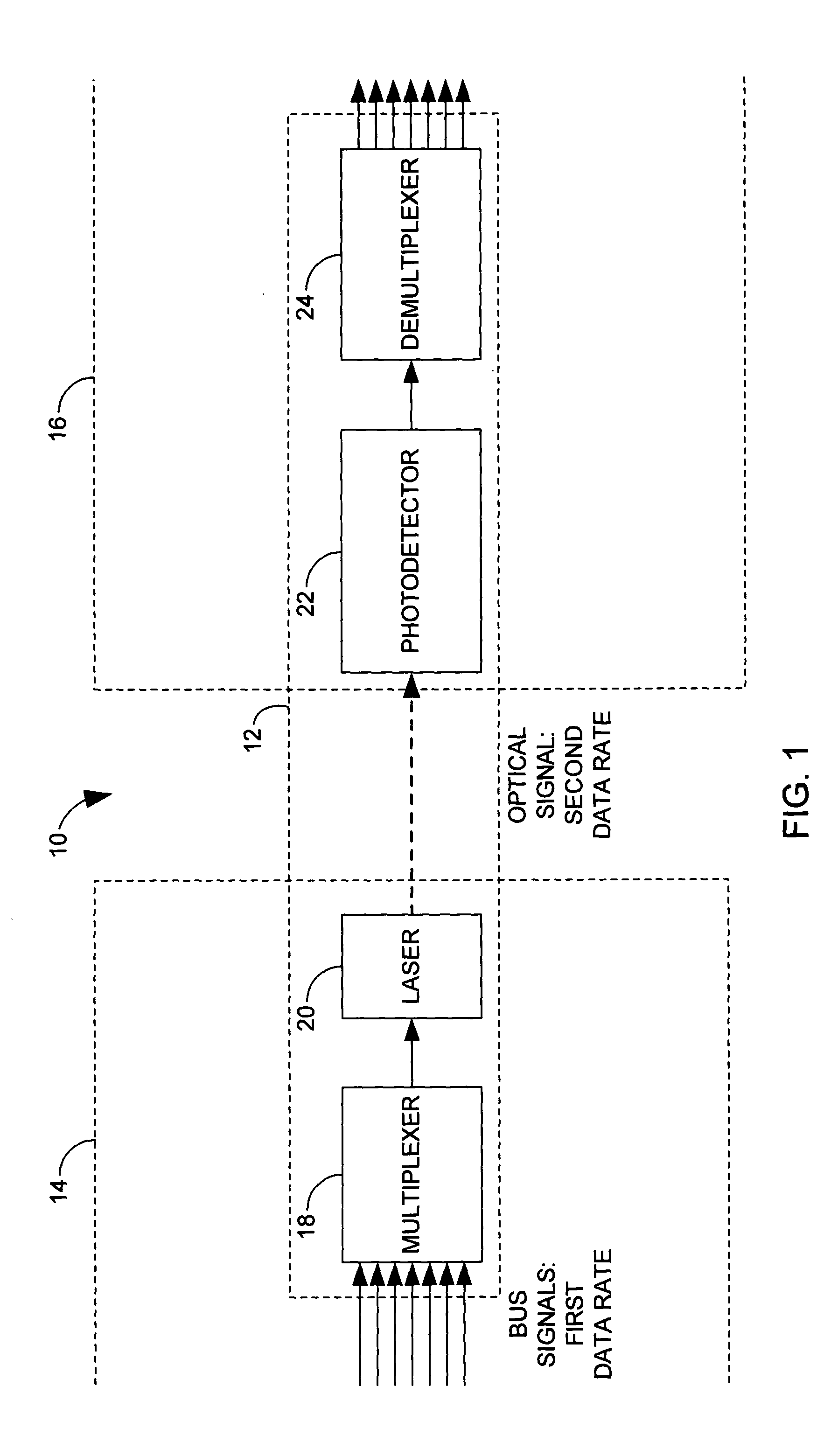
ActiveUS20050036789A1Cosmonautic vehiclesTime-division optical multiplex systemsPhotodetectorMultiplexer
A free space optical bus system and method are provided for connecting two units of circuitry across a free space gap. A first unit of circuitry includes a multiplexer that combines a plurality of bus signals to obtain an electronic combined signal and a laser that is driven by the electronic combined signal to transmit an optical signal. A second unit of circuitry is separated from the first unit of circuitry by a free space gap. The second unit of circuitry includes a photodetector that receives the optical signal and transforms it into an electronic composite signal and a demultiplexer that divides the composite signal into a plurality of constituent signals.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
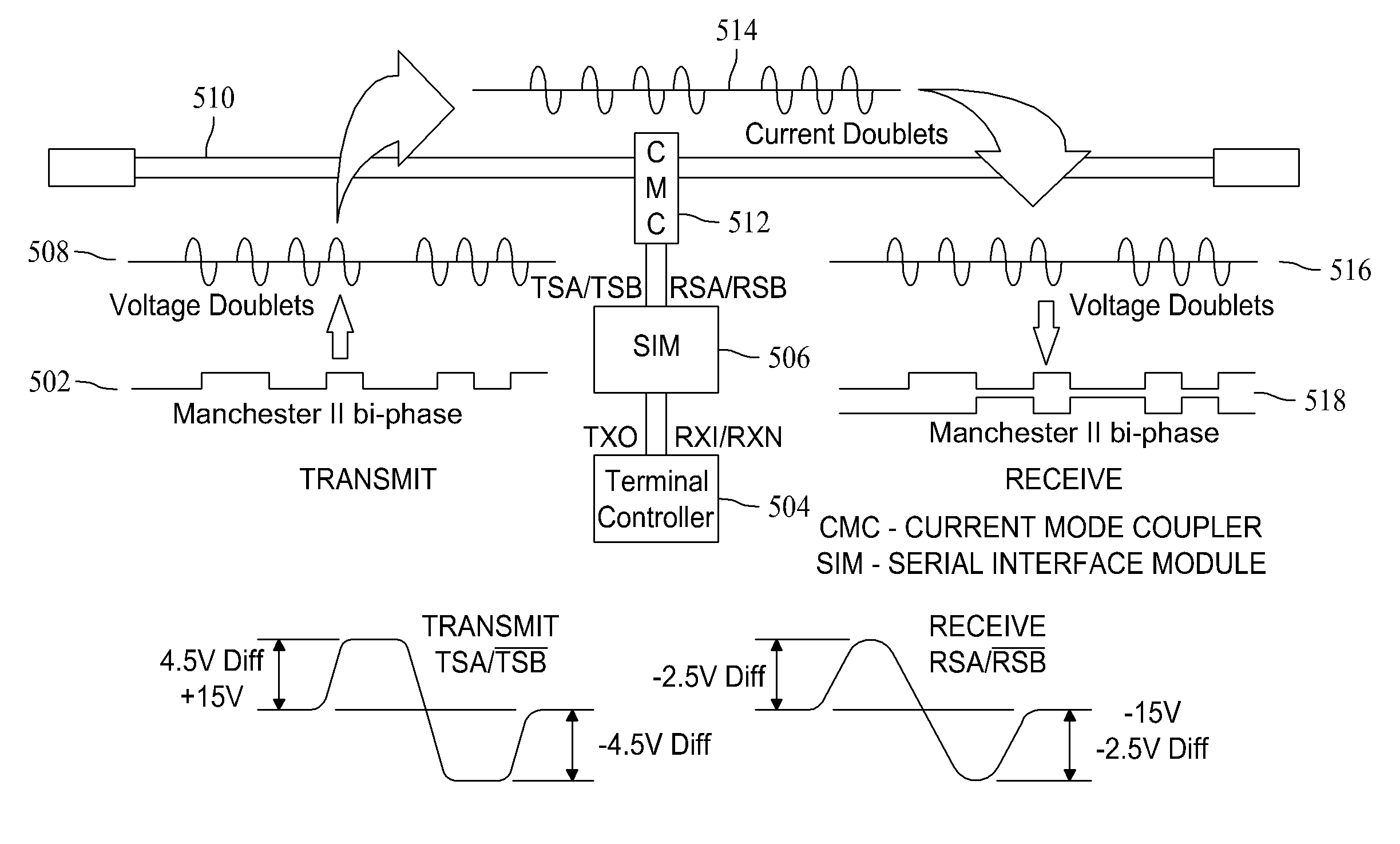
Burst mode optical media converter with fast analog conversion
A media converter for interfacing an optical fiber bus to an electrical interface of an electronic device is described. The media converter includes an interface circuit configured to convert electrical signals received from a transmitting channel of the electrical device in a voltage doublet format to positive logic electrical pulses and convert received electrical signals for application to a receiving channel of the electrical device from positive logic electrical pulses to a voltage doublet format, a DC coupled receiver comprising an optical interface operable for receiving optical signals from the optical fiber data bus, the receiver operable for converting the optical signals to positive logic electrical pulses for application to the interface circuit, a laser diode operable to transmit optical signals onto the optical bus, and a laser diode driver operable for receiving the positive logic electrical pulses from the interface circuit and converting the electrical signals to signals compatible for operating the laser diode.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
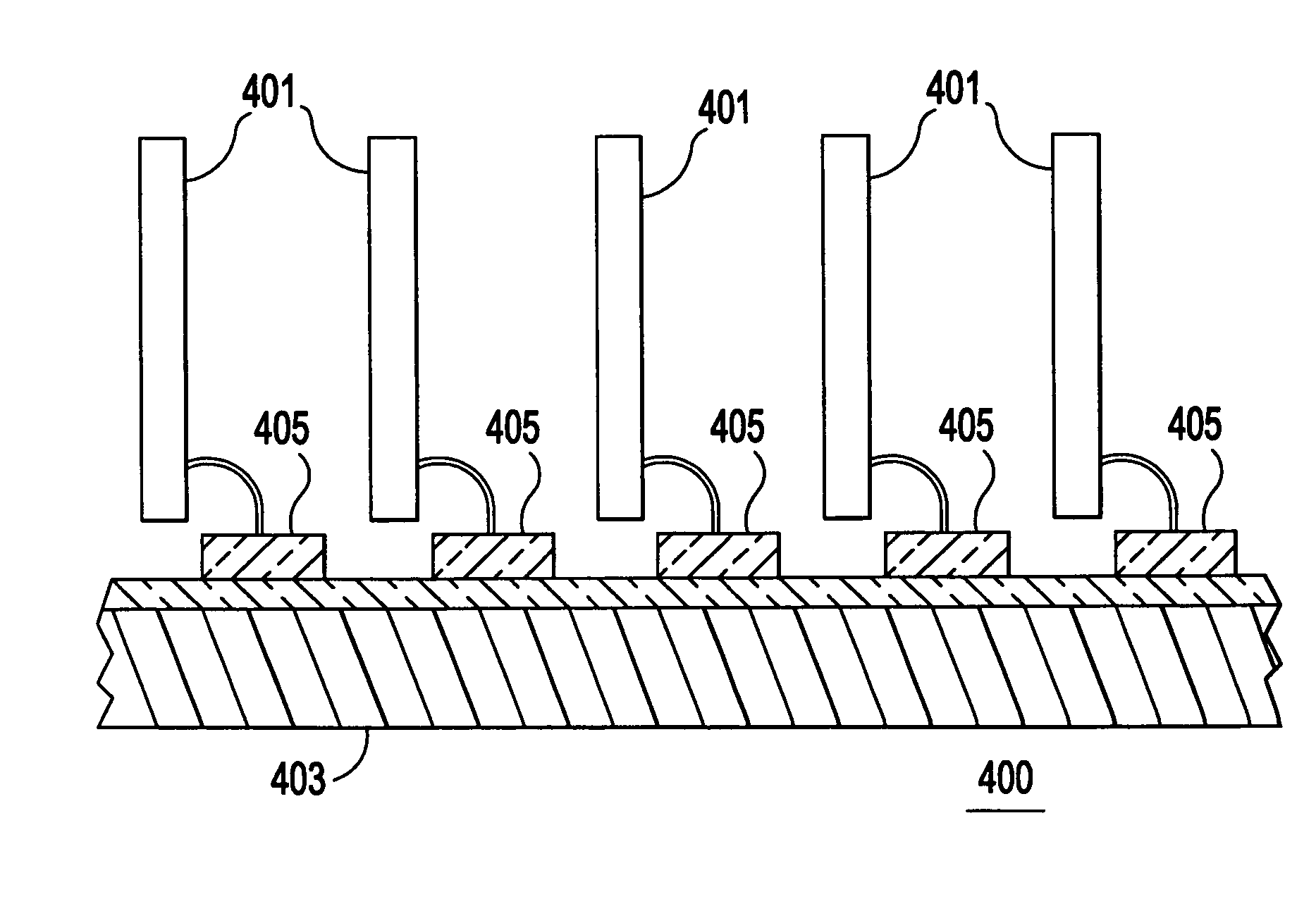
Optical bus extension device
The present invention comprises a computer communication device that includes an interface circuit mounted with a computer. The interface circuit is connected between a computer bus and fiber optic transceiver. Another interface circuit is mounted remotely from the computer. The other interface circuit is connected between a peripheral device bus and another fiber optic transceiver. Both fiber optic transceivers can be connected to opposite ends of a fiber optic cable. The computer communication device allows a peripheral device to be located remote from the computer.
Owner:CUBIX CORP
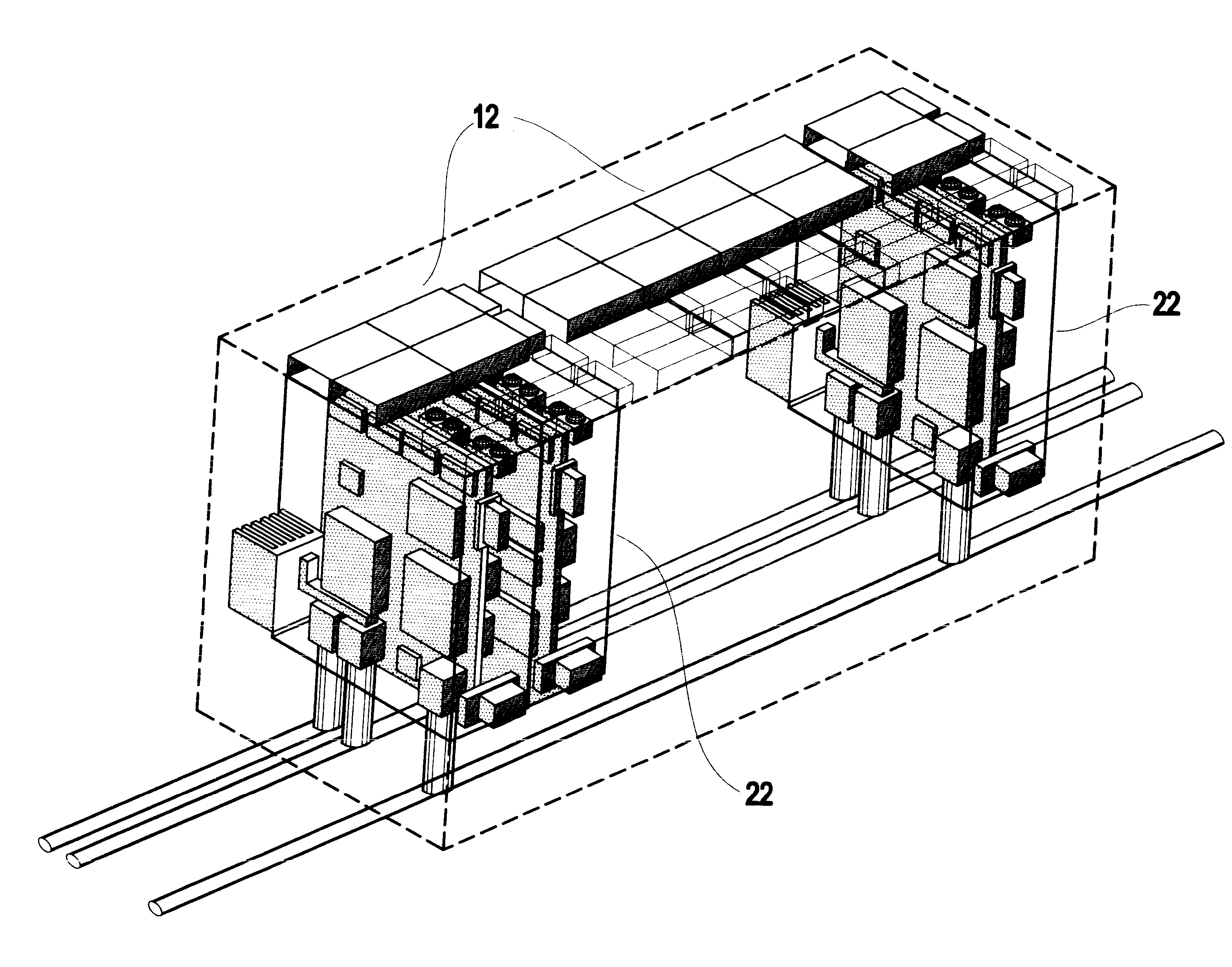
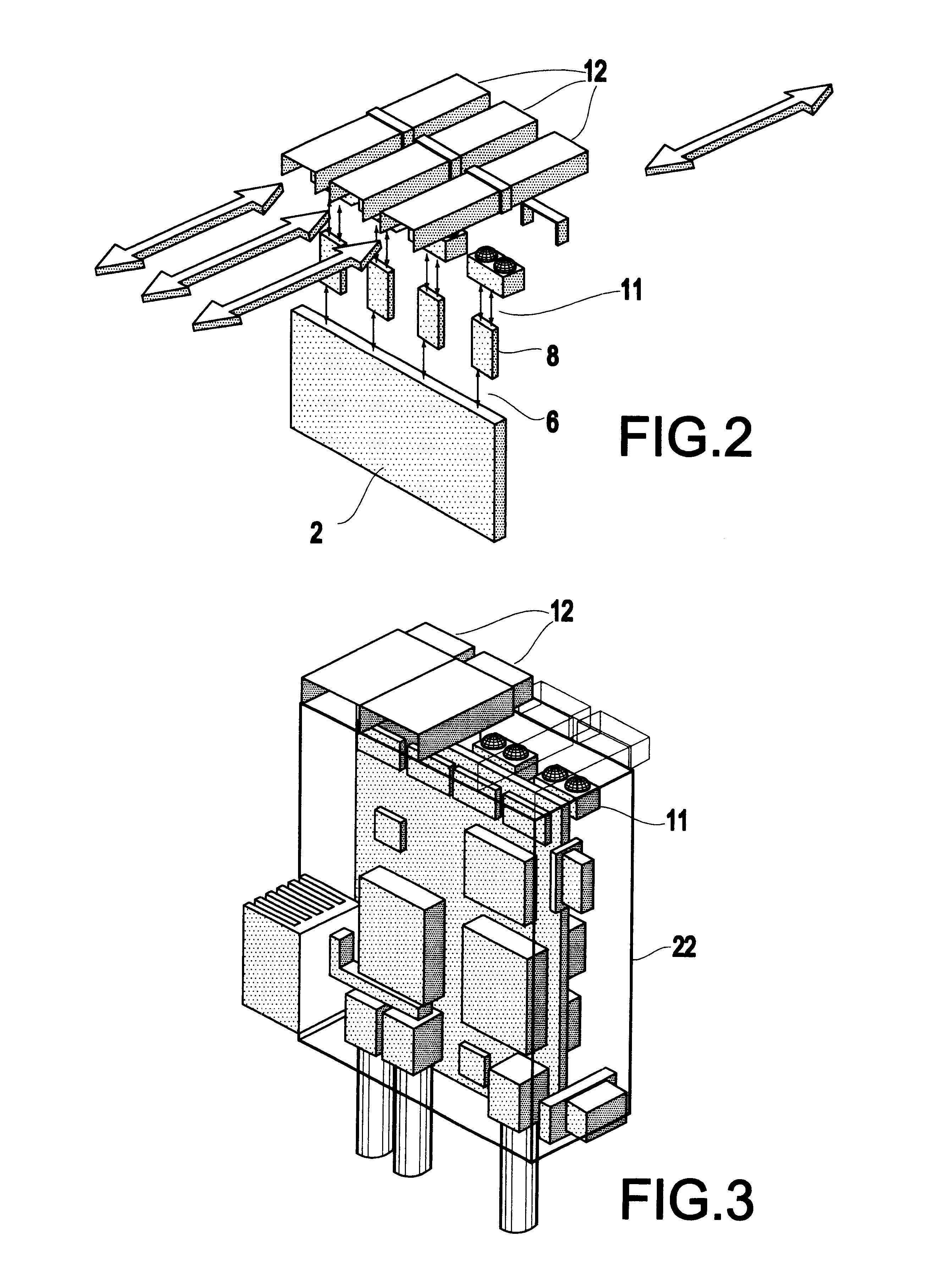
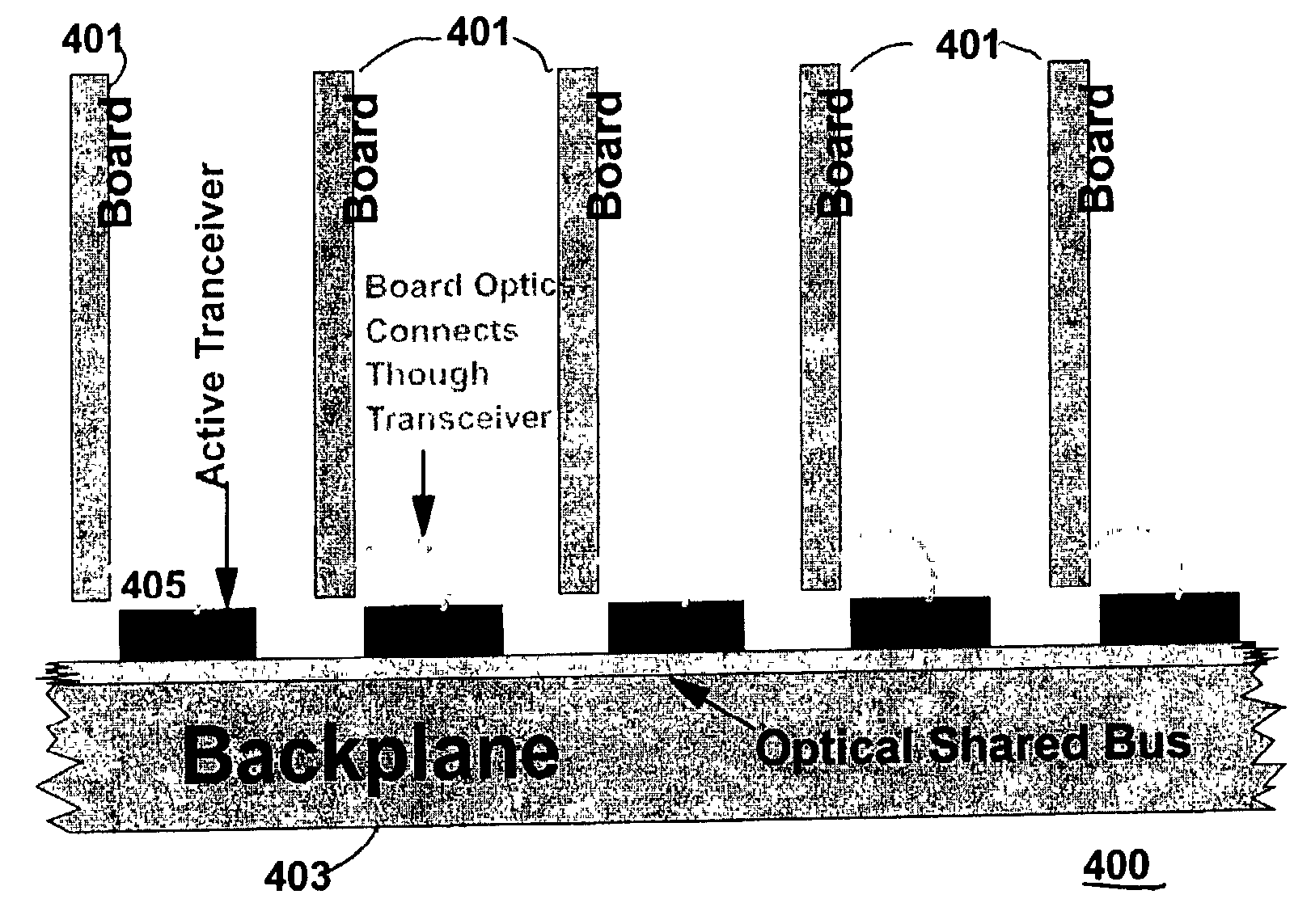
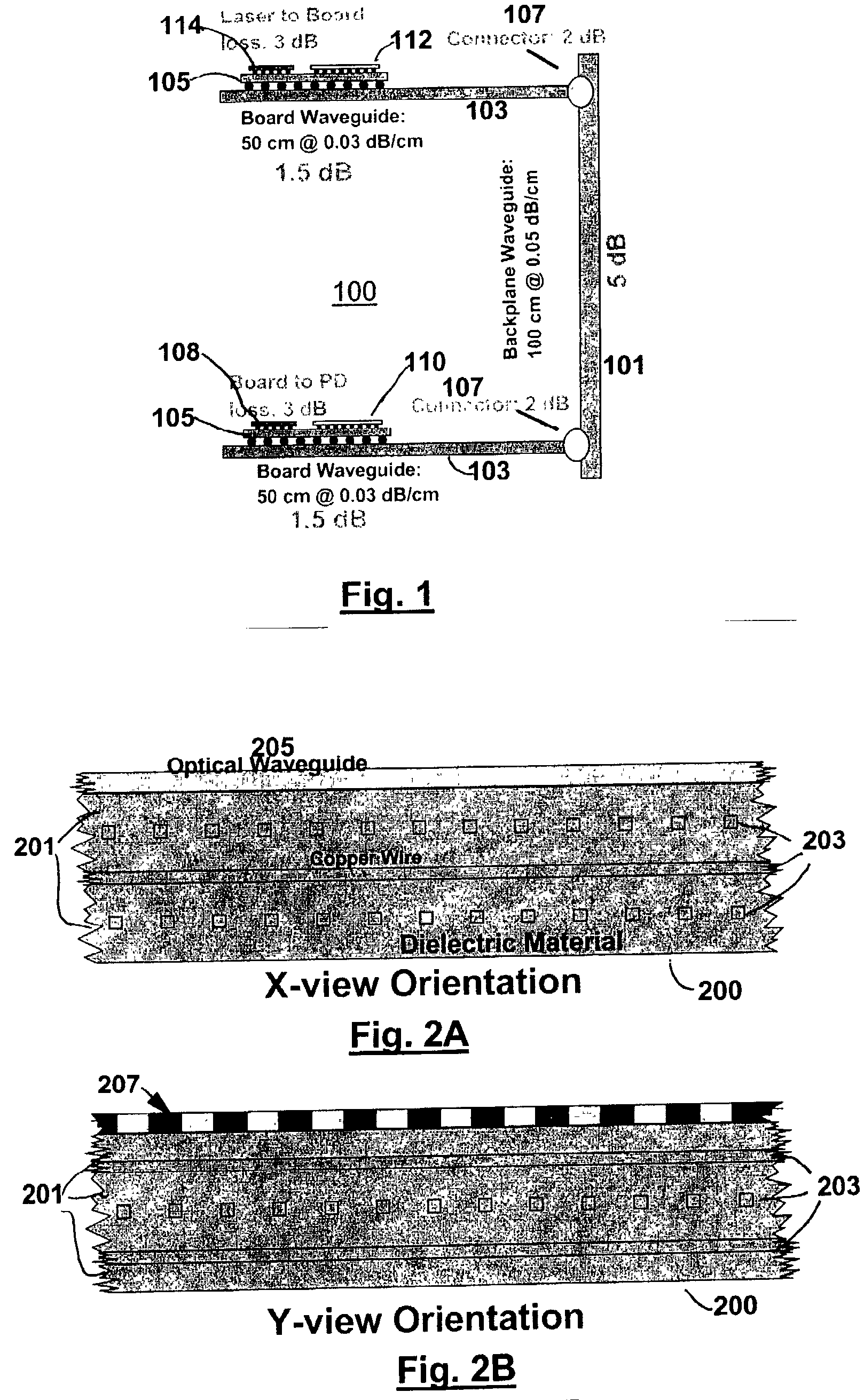
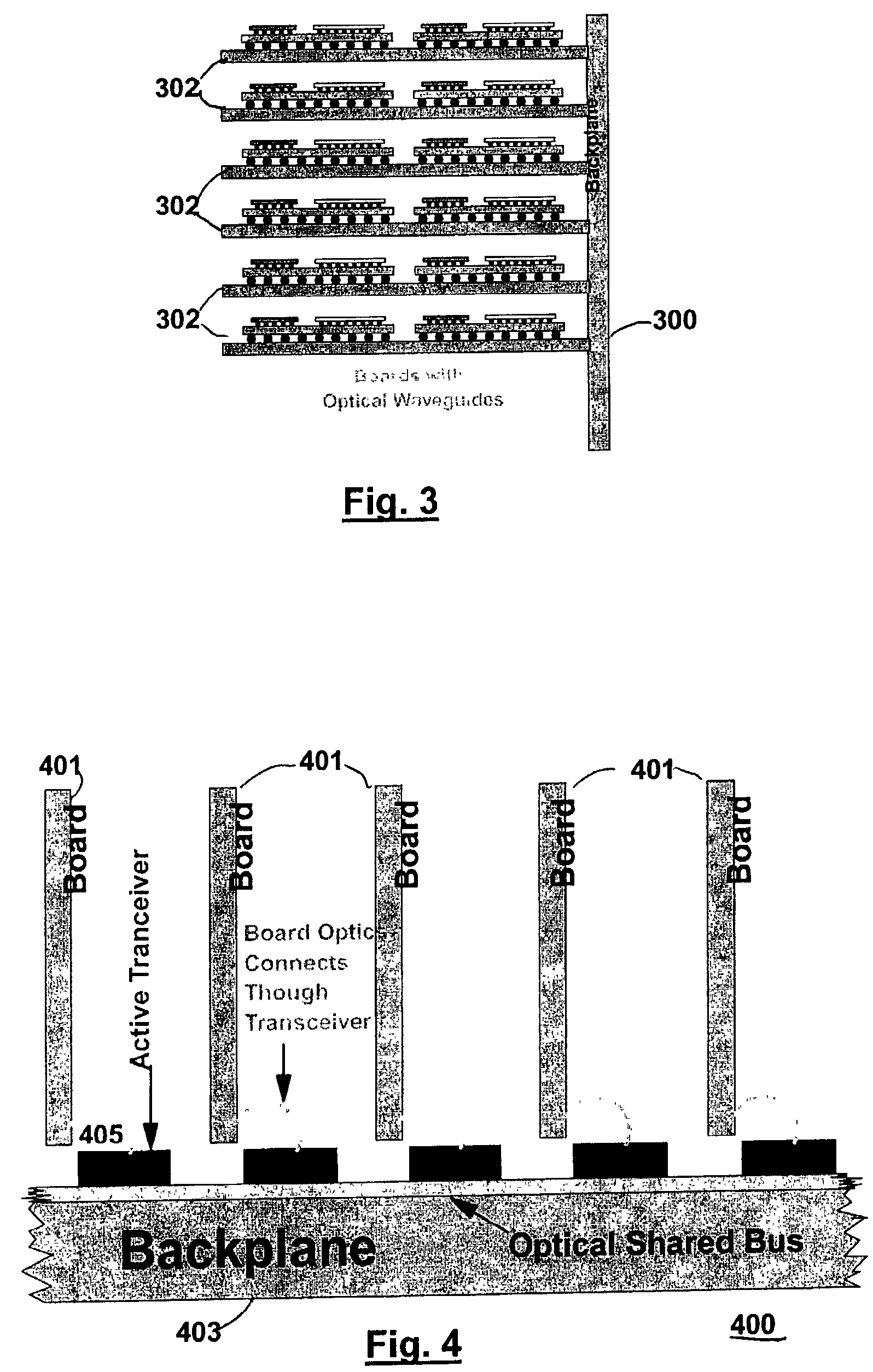
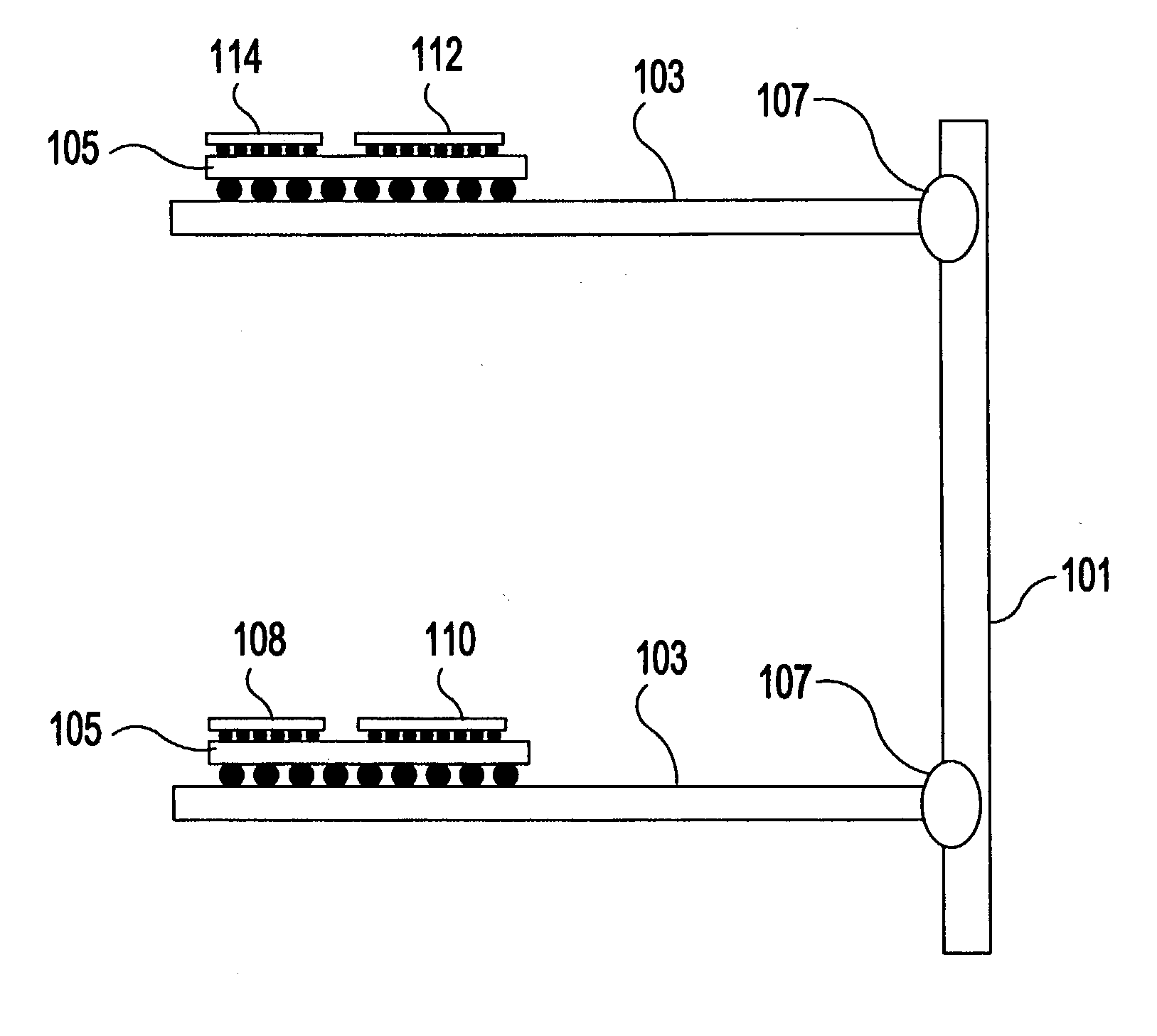
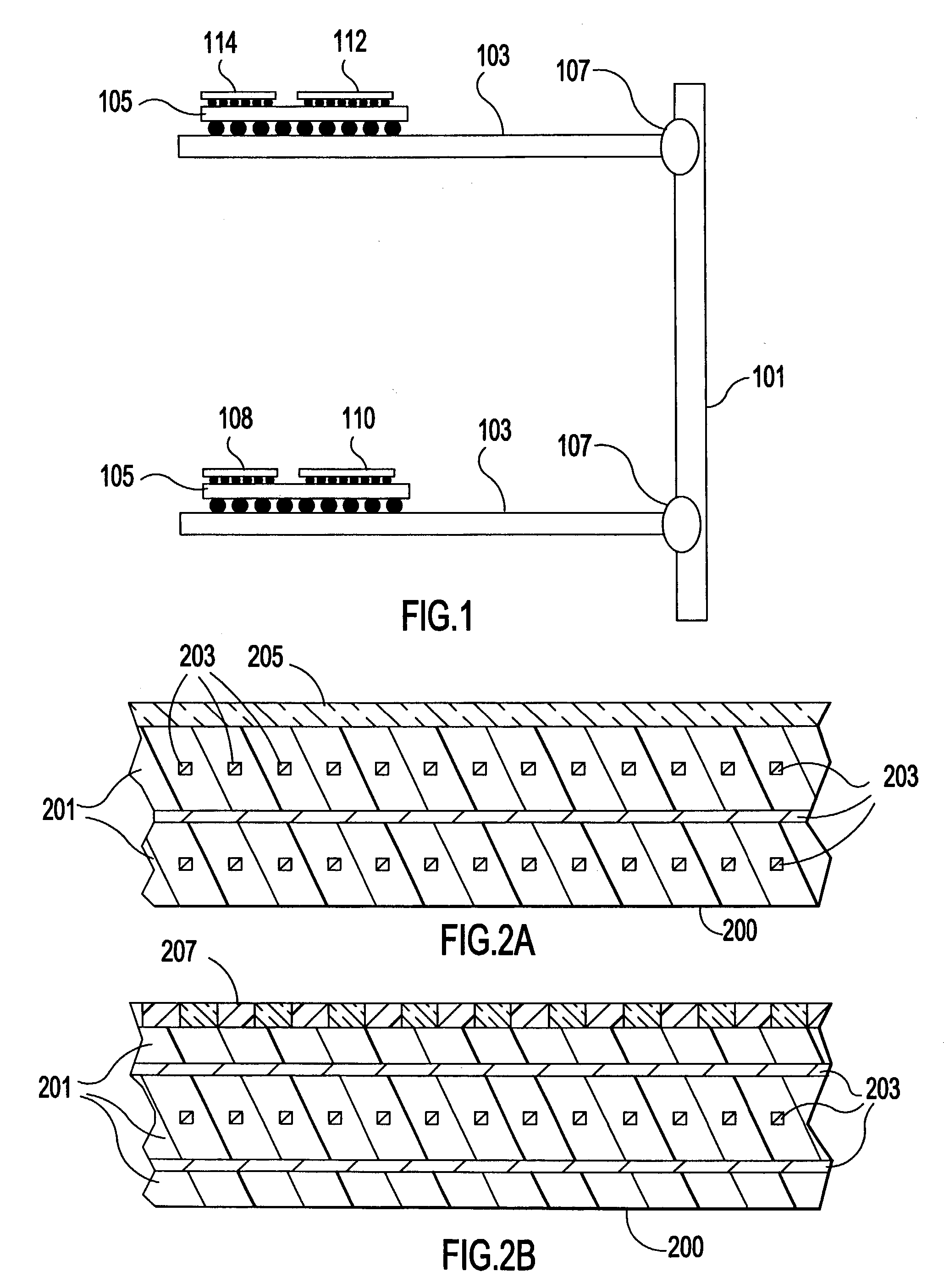
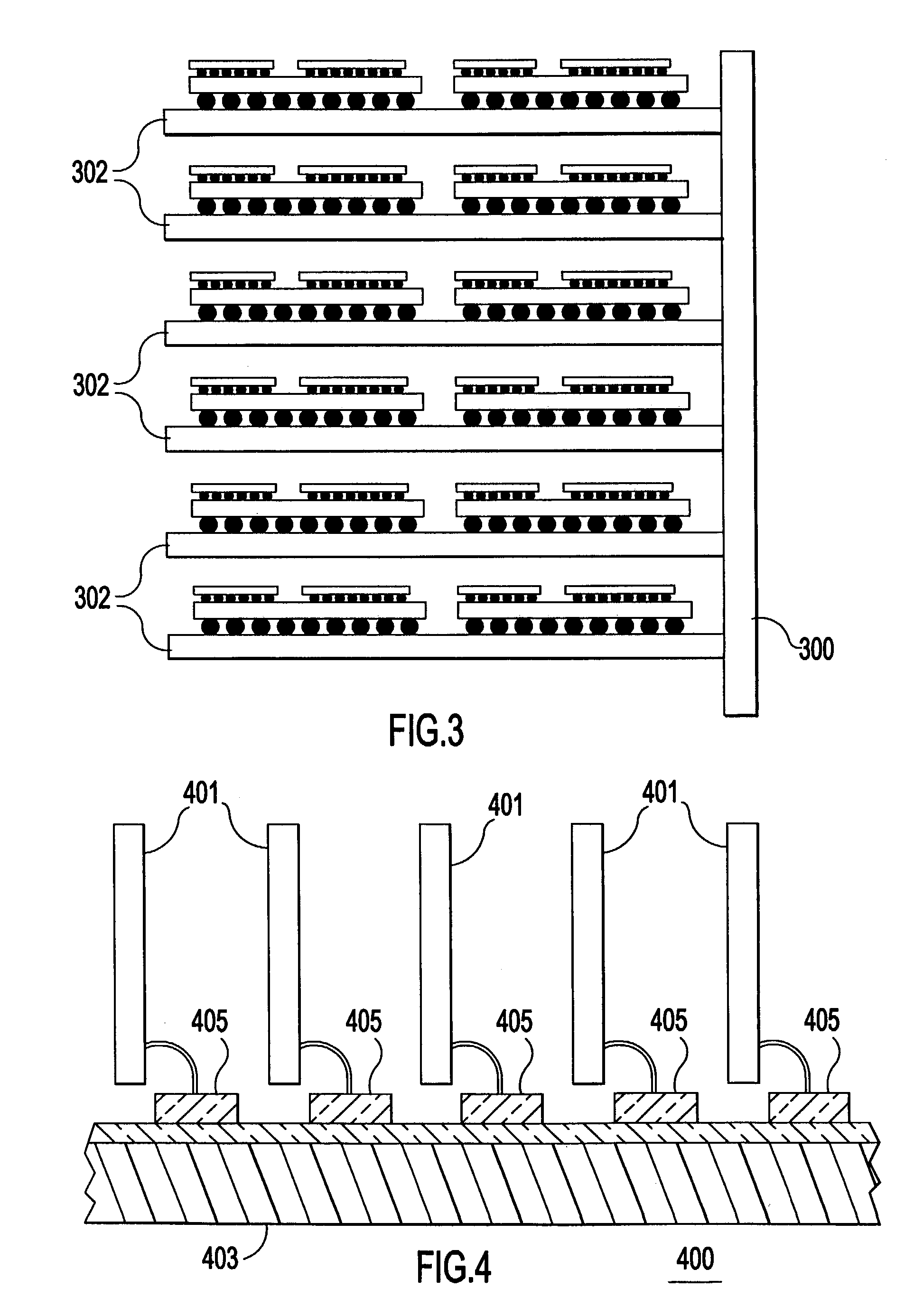
Backplane assembly with board to board optical interconnections
An electronic system with components communicating over optical channels, a board initialization and continuity check and a method of transferring data over the optical channels. The system include a backplane with board to board signal wiring and a shared optical bus. Optical gratings are attached to the backplane and to circuit boards to pass optical energy between an optical transceiver and board / backplane. An optical transceiver at each end of each optical jumper relays optical signals between the optical jumpers and the connected circuit board or the backplane. Optical jumpers optically connect the circuit boards to the backplane.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
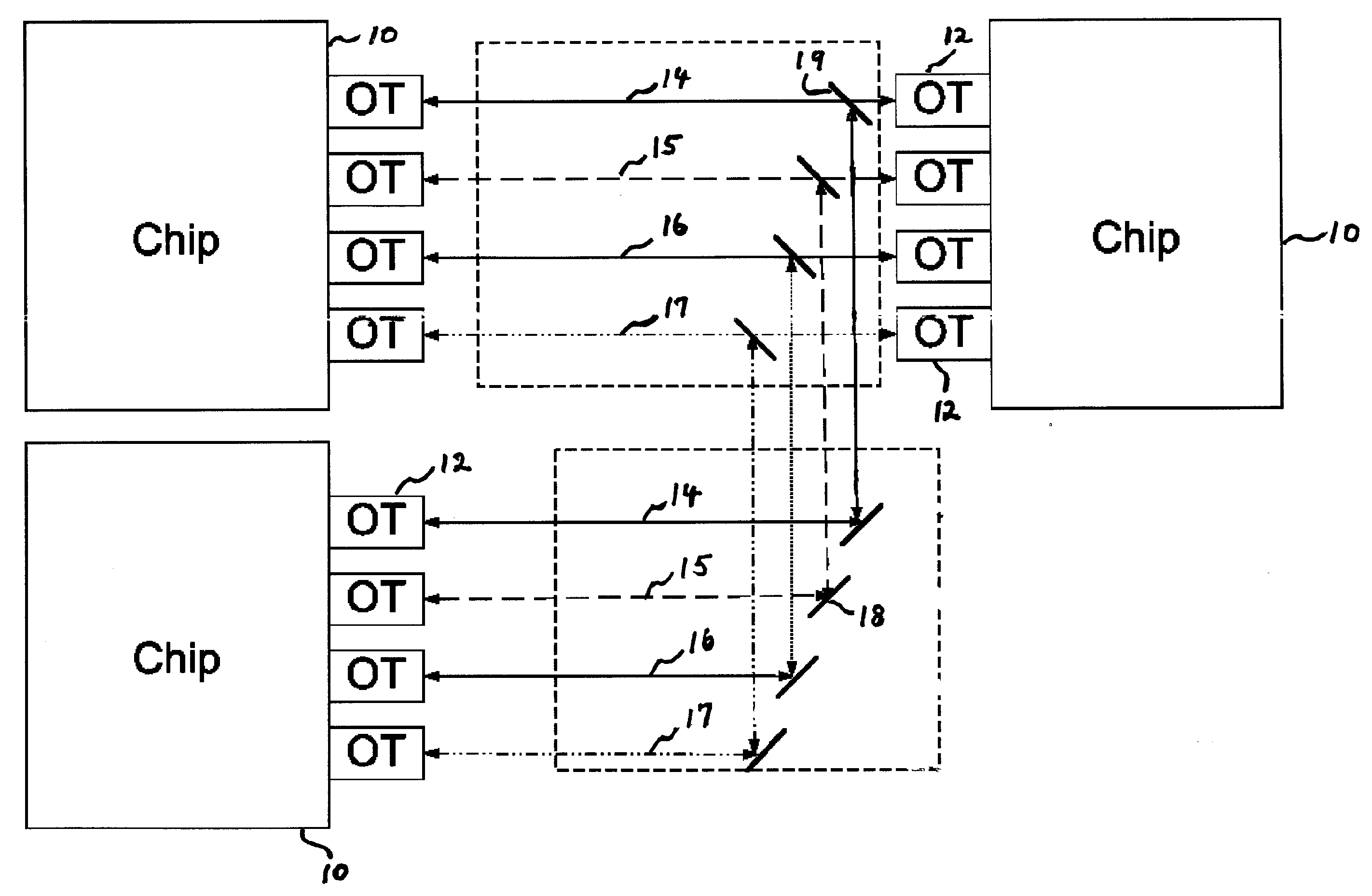
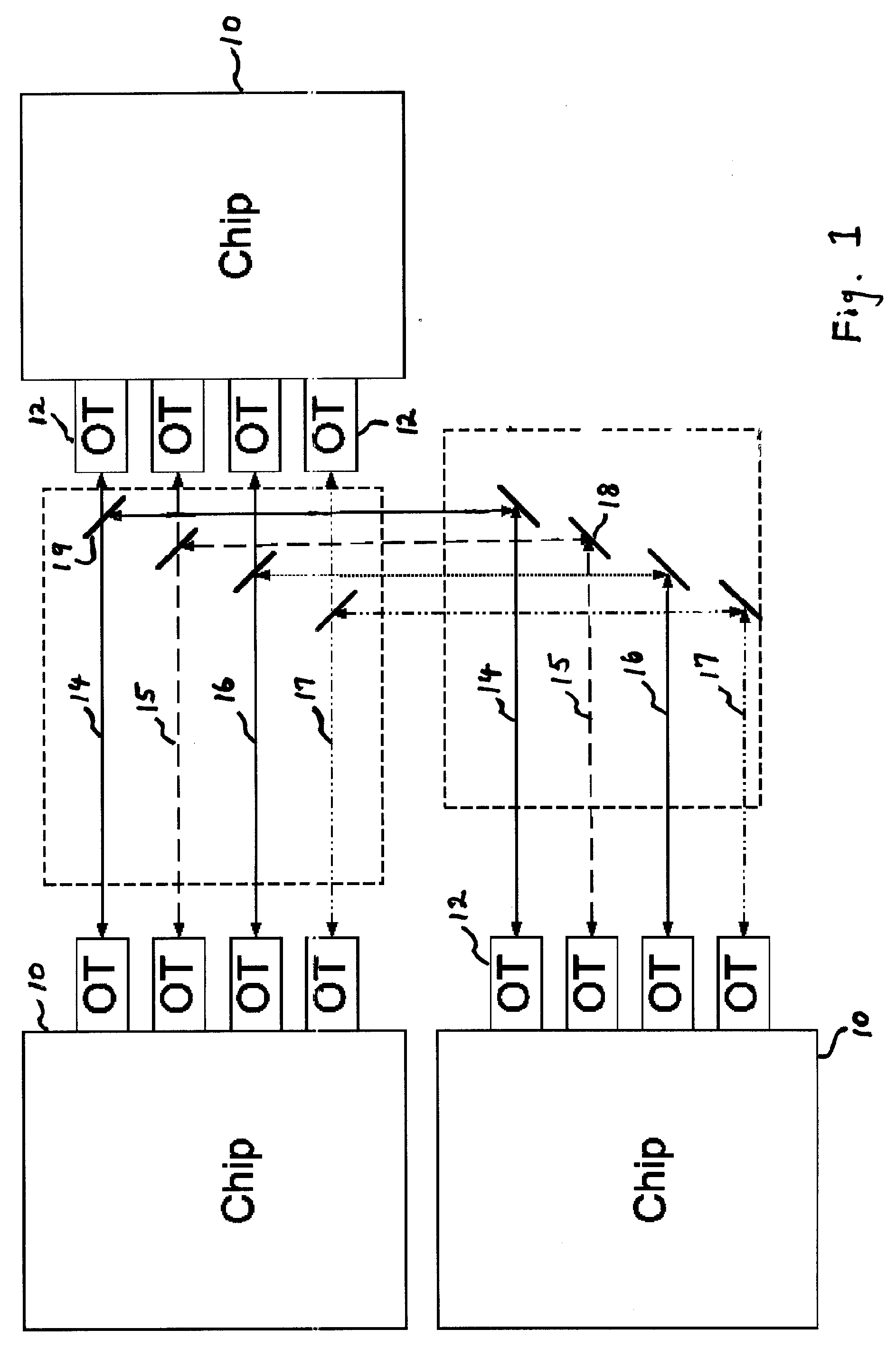
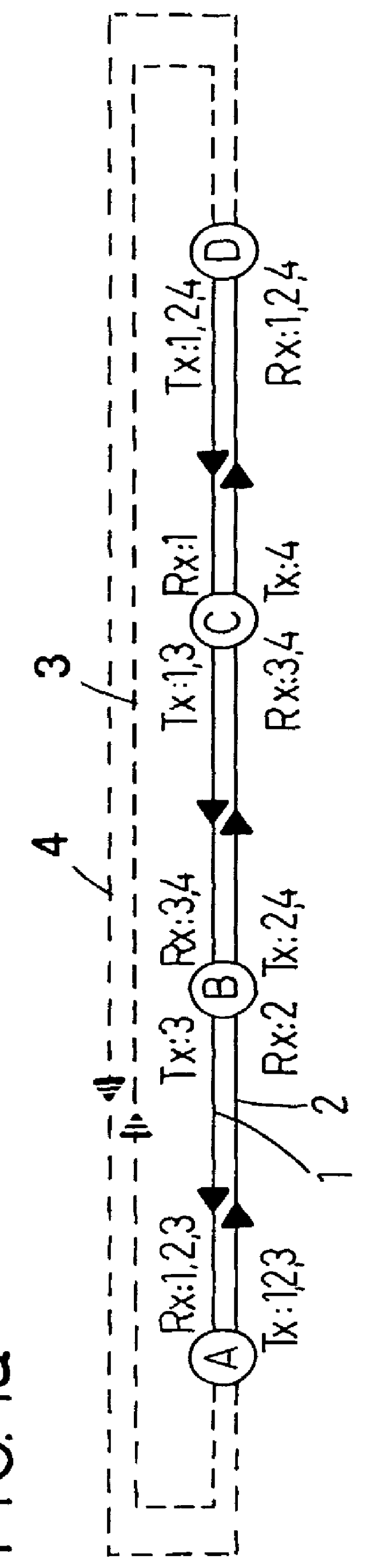
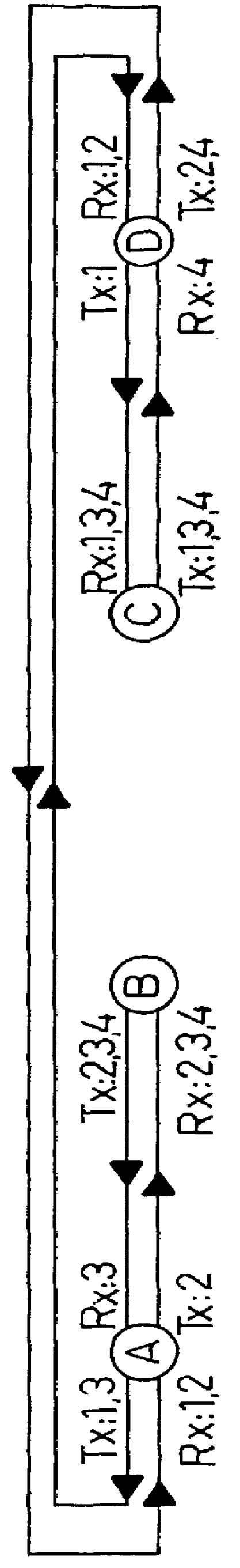
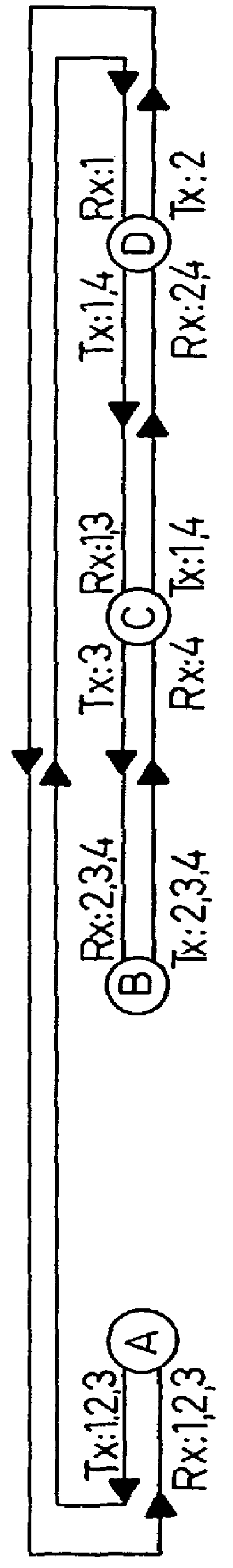
Optical node in an optical bus network
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00323 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 20, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 20, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 13, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 31025 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 3, 1996An optical node in an optical network includes transmitters (Tx:1-3) and receivers (Rx:1-3) adapted to particular wavelength channels and arranged to communicate via the optical bus network, with receivers and transmitters for corresponding wavelength channels in other nodes. The node includes optical safety switching devices (S1-S5) in connection with the transmitters (Tx:1-3) and receivers (Rx:1-3) of the node, so that the transmitters (Tx:1-3) and receivers (Rx:1-3) can be switched from a first optical fiber (1,2) to a second optical fiber (1,2).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
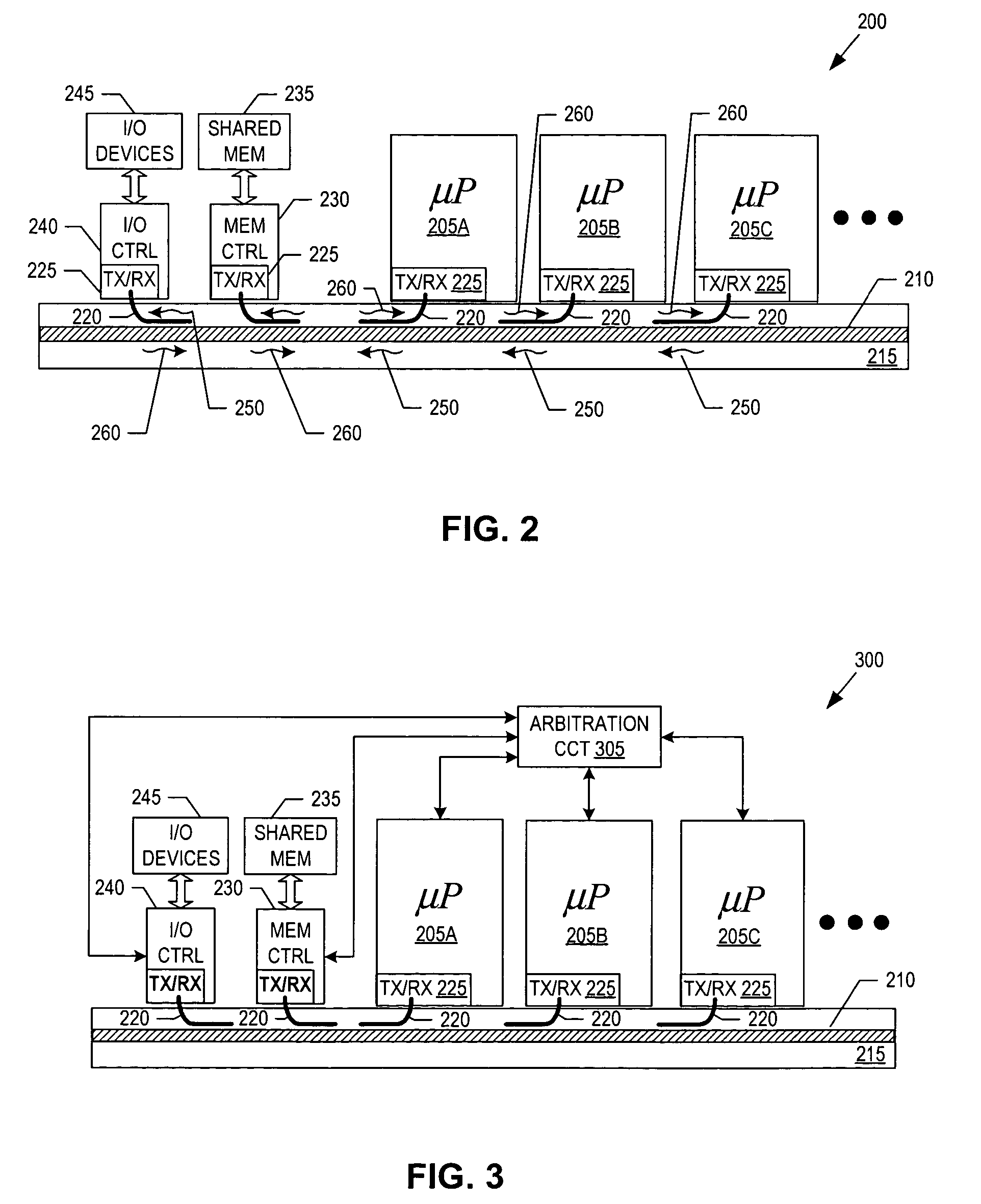
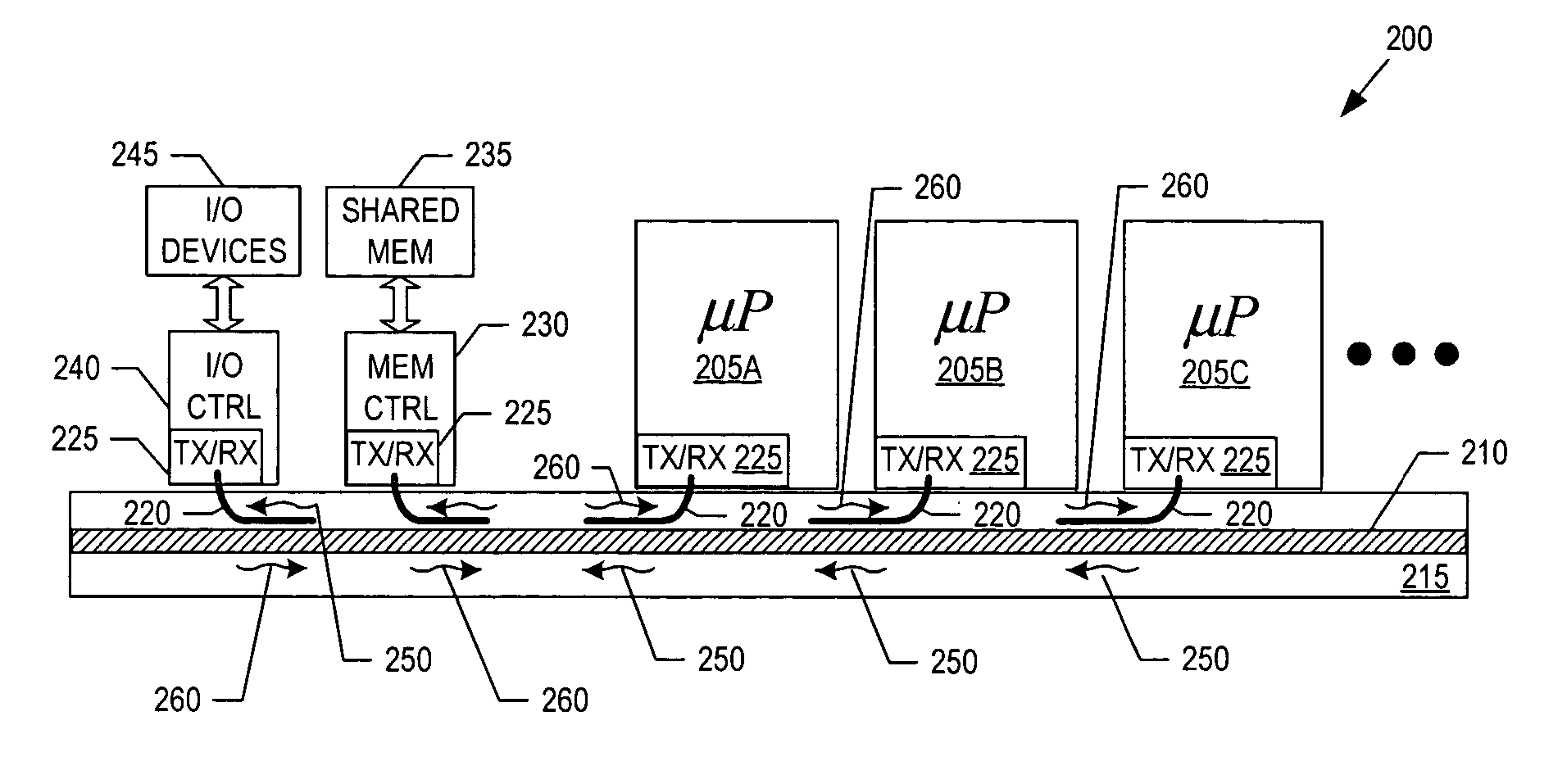
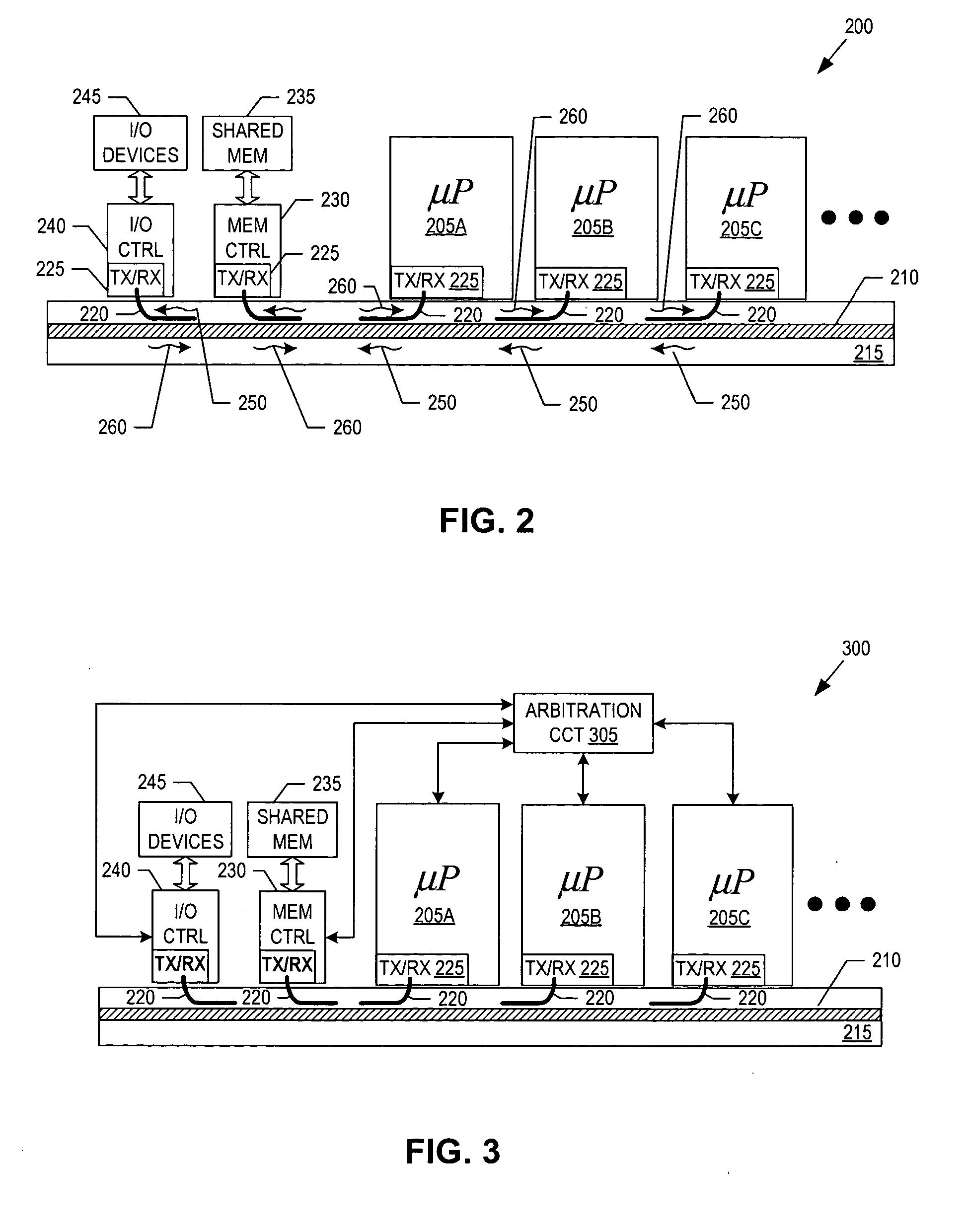
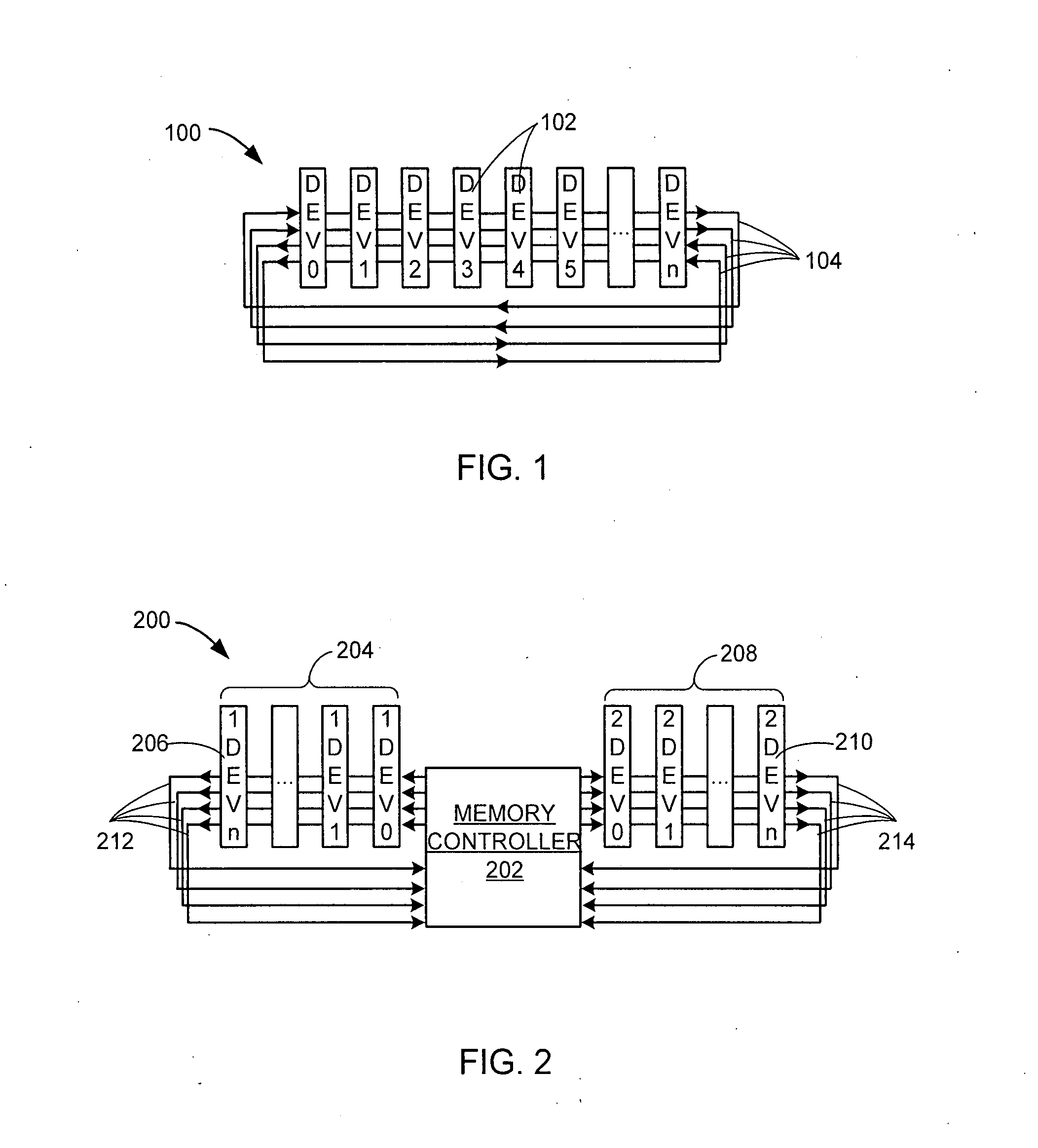
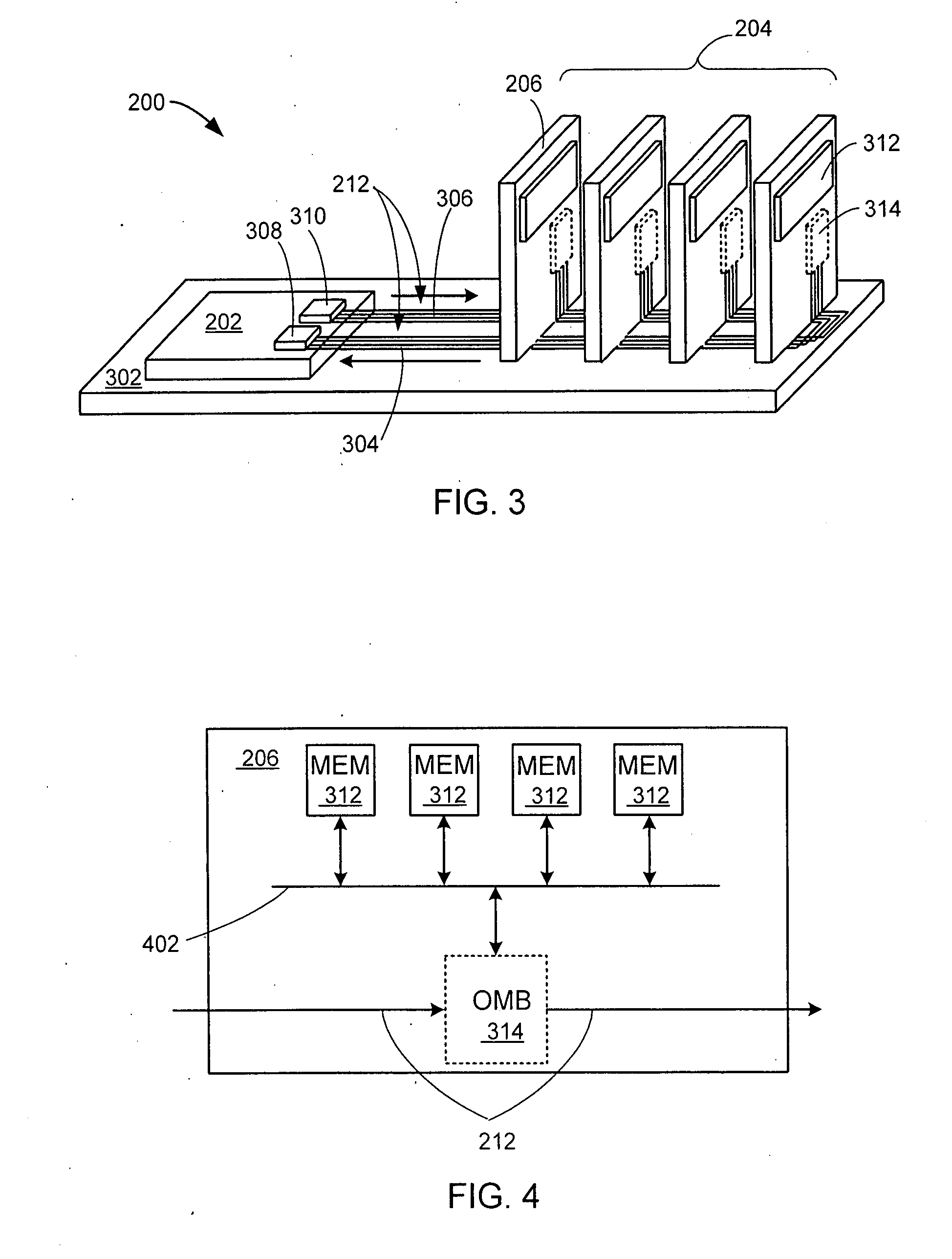
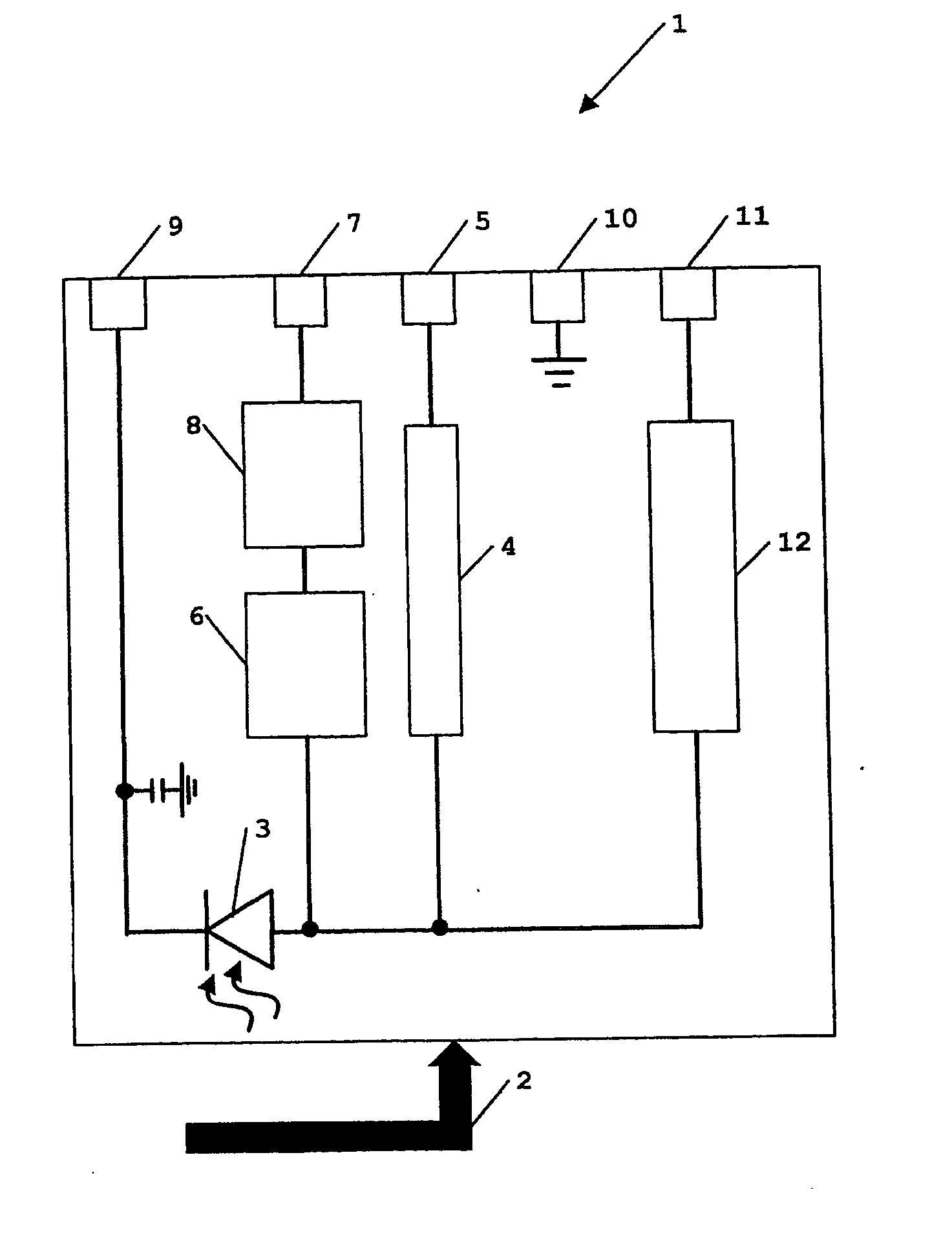
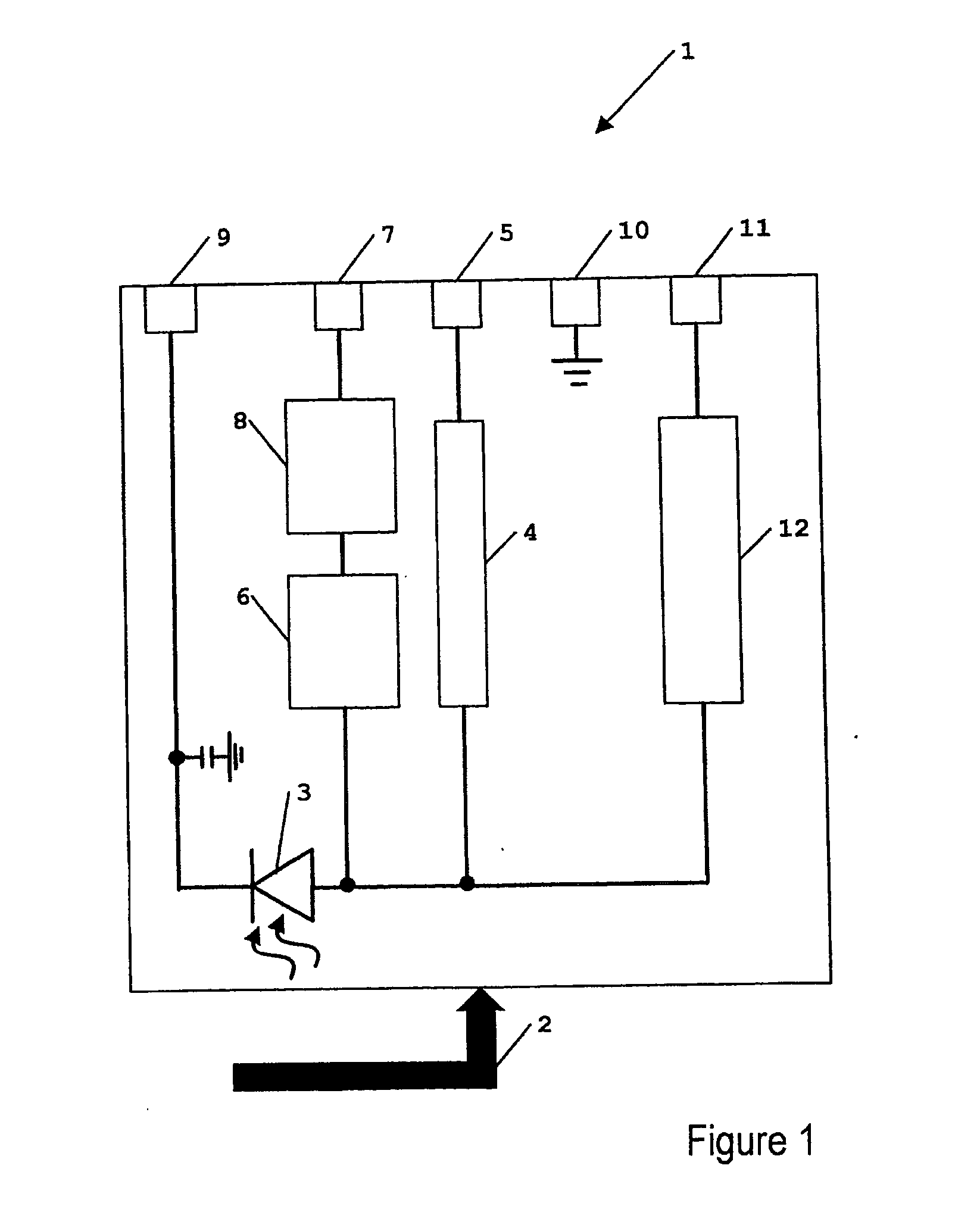
System having multiple agents on optical and electrical bus
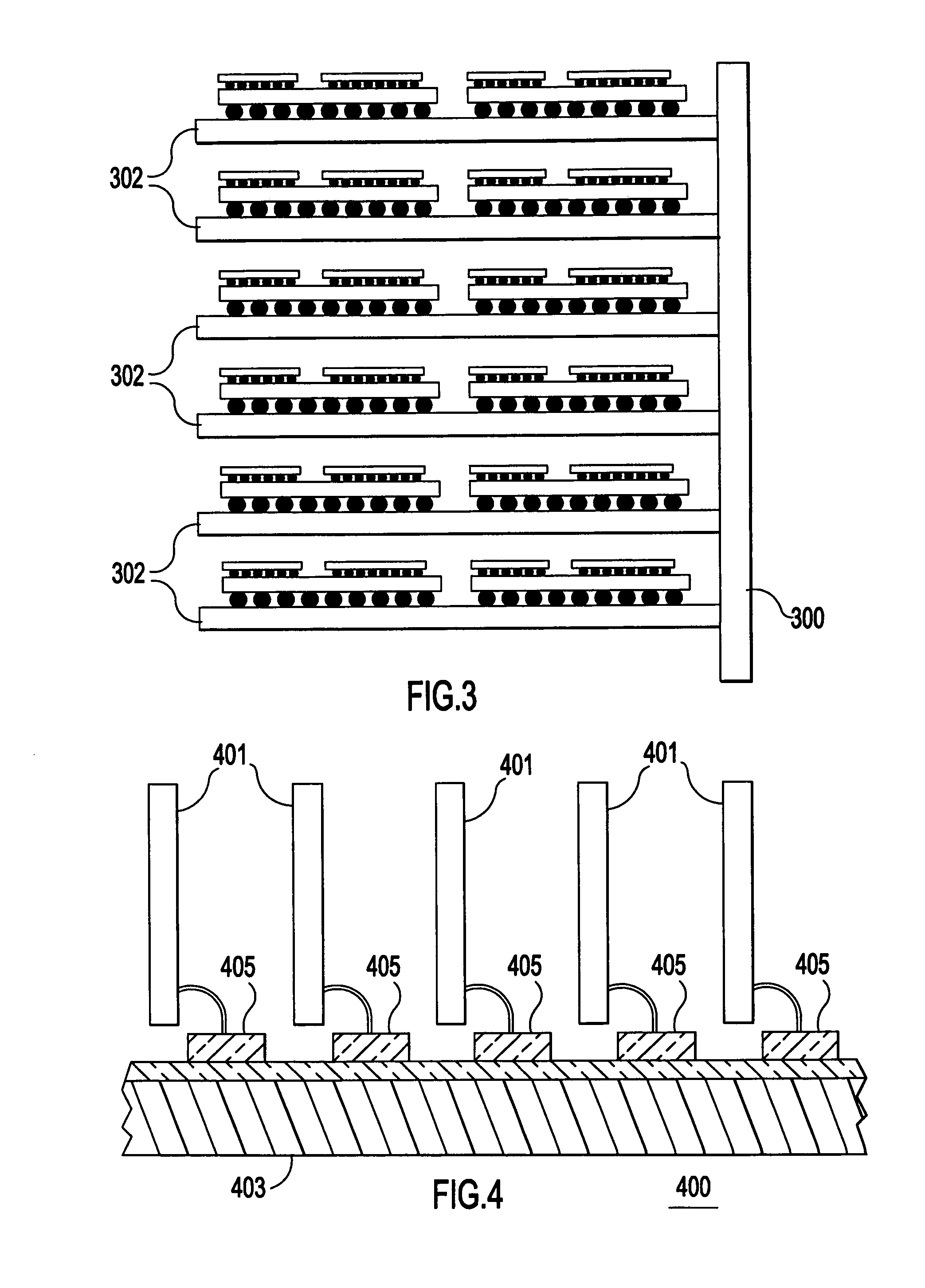
A system includes multiple agents coupled to an optical bus for transmission of high speed signals and to an electrical bus for transmission of low speed signals. The agents can be memory modules, such as DIMMs. An optical connector housing for coupling the agent to the optical bus can include a reflective device such a mirror, a semi reflective mirror, a pellicle beamsplitter, or the like. The low speed signals can be, for example, power, ground, and supervisory signals. The high speed signals can be, for example, data, address, control, and clock signals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
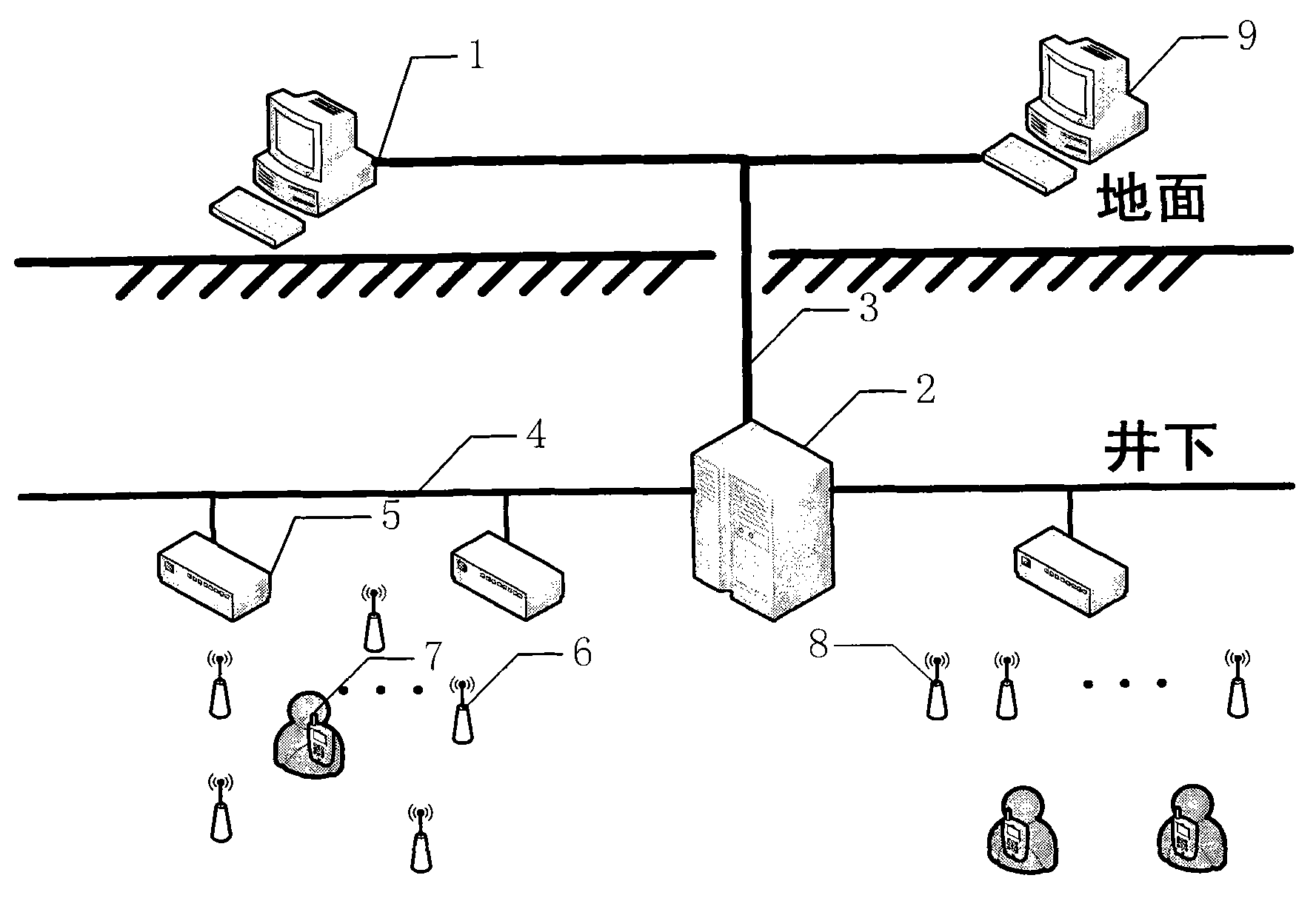
Underground coal mine personnel positioning system and positioning method
InactiveCN103228041ASmall amount of calculationDensity Requirements ReducedMining devicesWireless communicationSystem testingTriangulation
The invention discloses an underground coal mine personnel positioning system and an underground coal mine personnel positioning method. The underground coal mine personnel positioning system comprises a ground control center which is arranged aboveground, and a transmitting base station, multiple gateway nodes, an optical fiber, a bus, multiple beacon nodes and multiple mobile nodes which are arranged underground, wherein all the underground equipment is intrinsically safe. The underground coal mine personnel positioning method is a BP (Back Propagation) neural network-based and non-ranging APIT (Approximate Point-in-triangulation Test) underground personnel positioning method. The underground coal mine personnel positioning method comprises the following steps: according to the structure of an underground laneway, deploying the beacon nodes; in a training state, generating coordinates of intersection points of every two circumcircles of three intersected triangles which are formed by the beacon nodes through training, and storing the coordinates in a database; in a positioning stage, testing according to a PIT (Power Interruption Test) test system to obtain rough positions of unknown nodes; comparing the rough positions with information in the database, and deploying mobile nodes at corresponding coordinate positions; and testing by using the PIT test system for precise positioning. The underground coal mine personnel positioning method has the advantages of high positioning accuracy, small calculating amount and small influence from the density of the beacon nodes.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
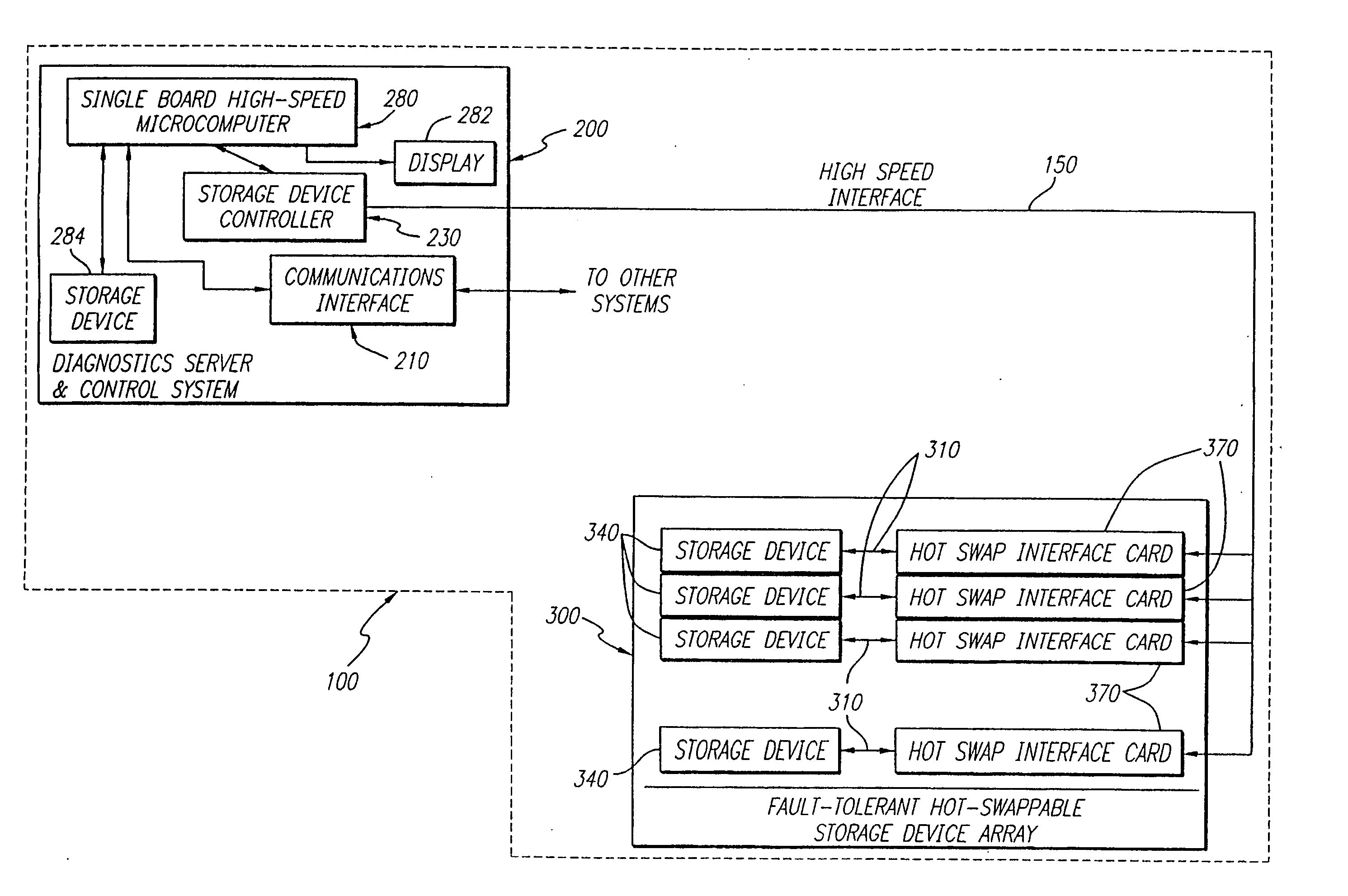
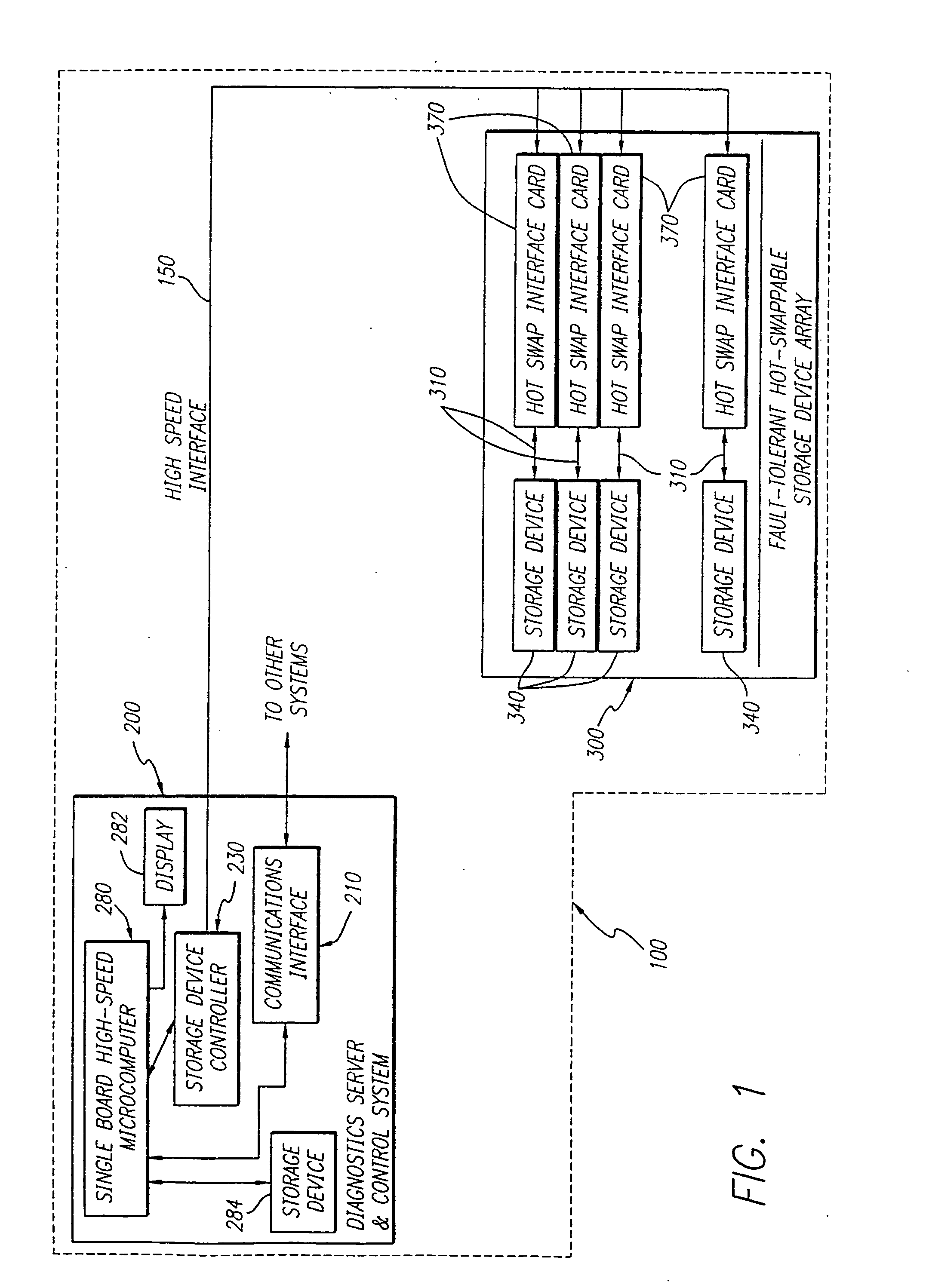
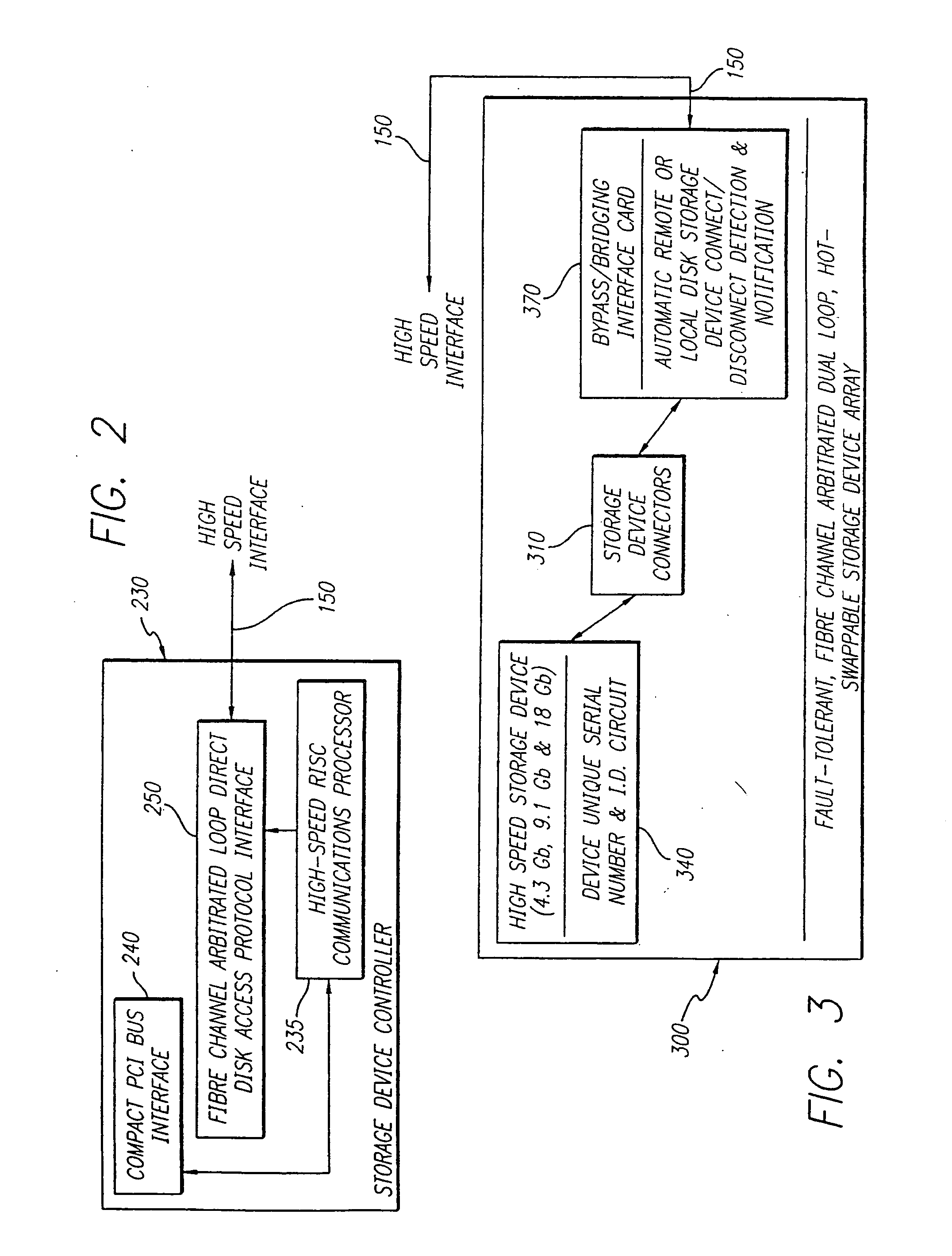
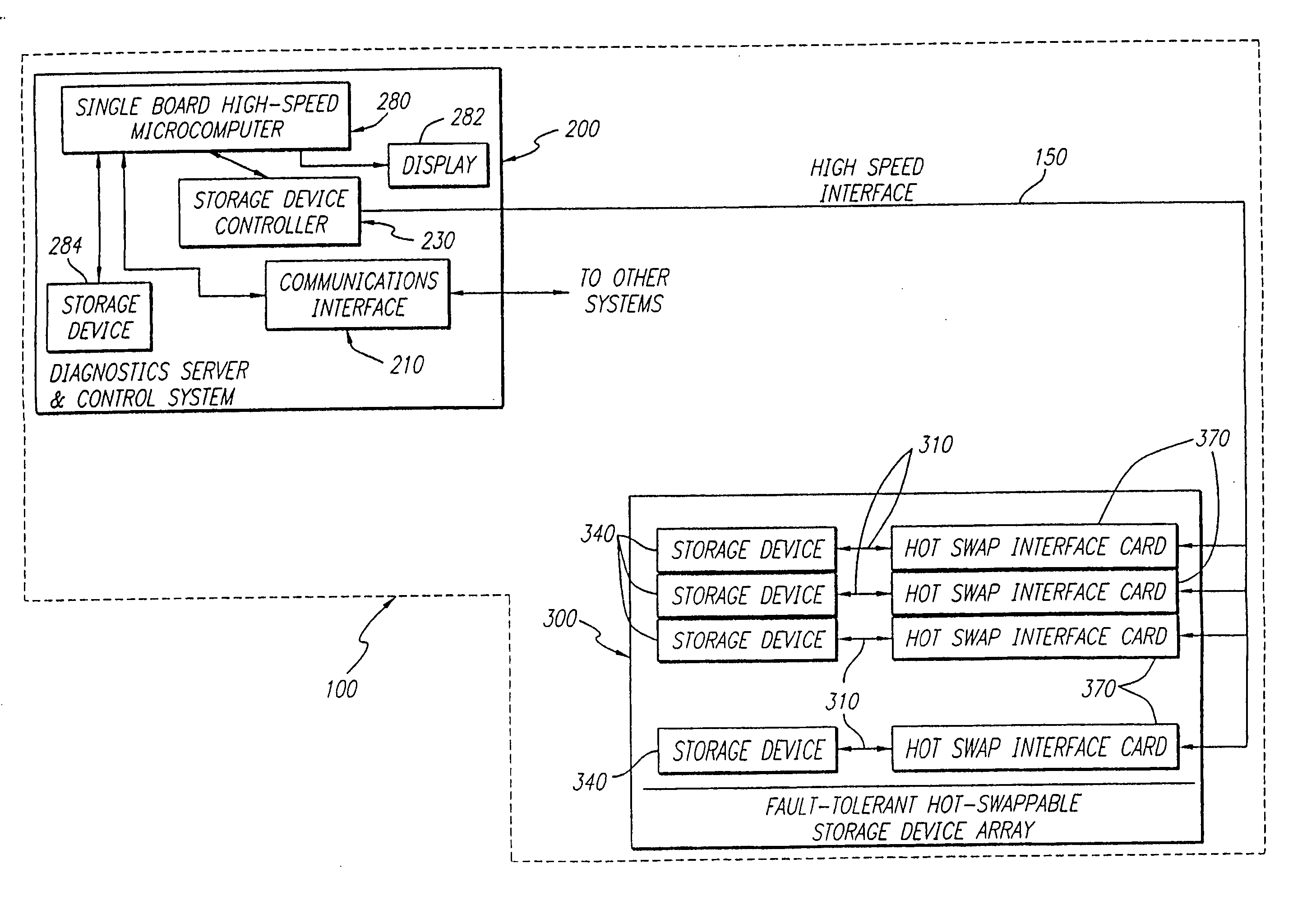
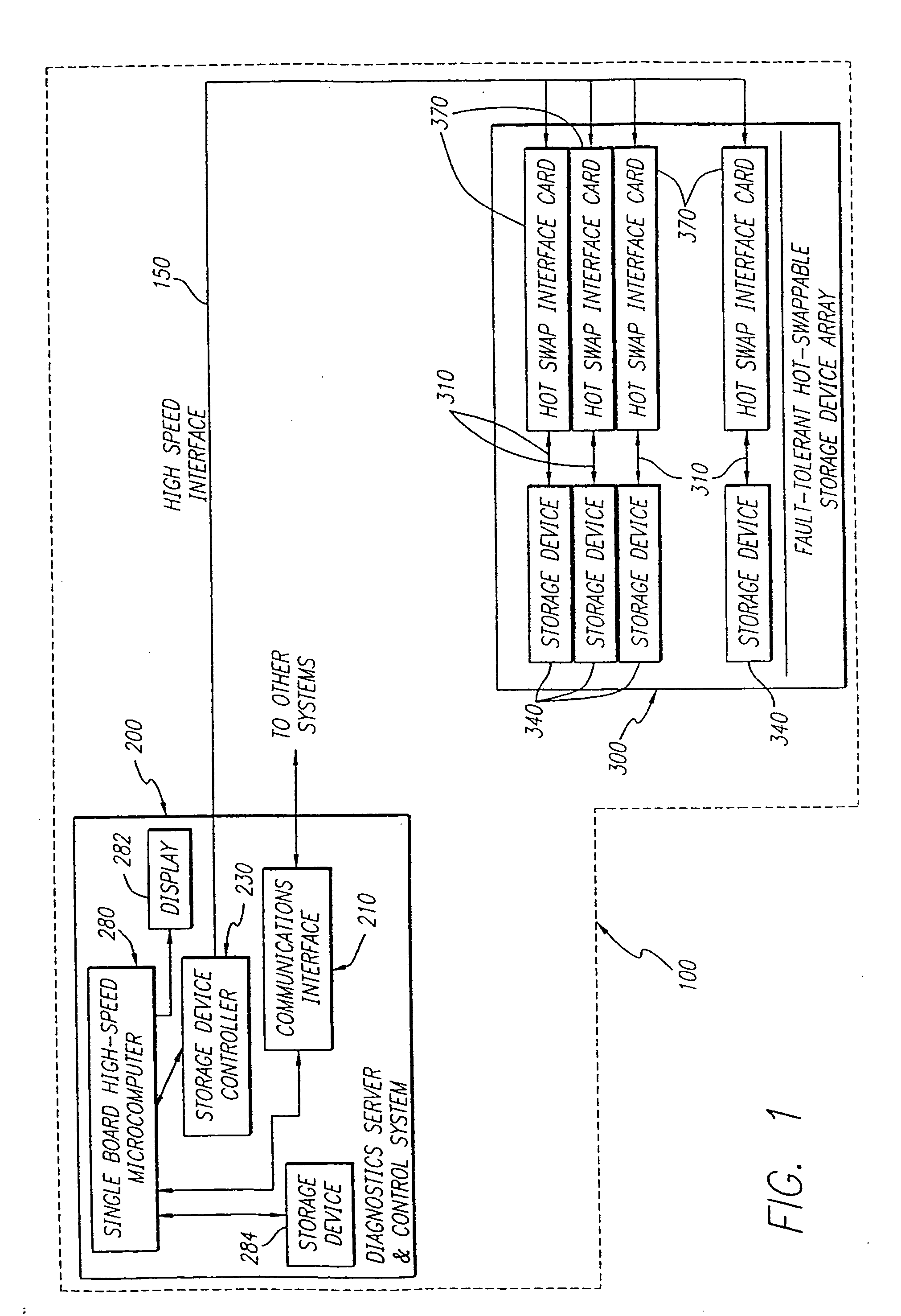
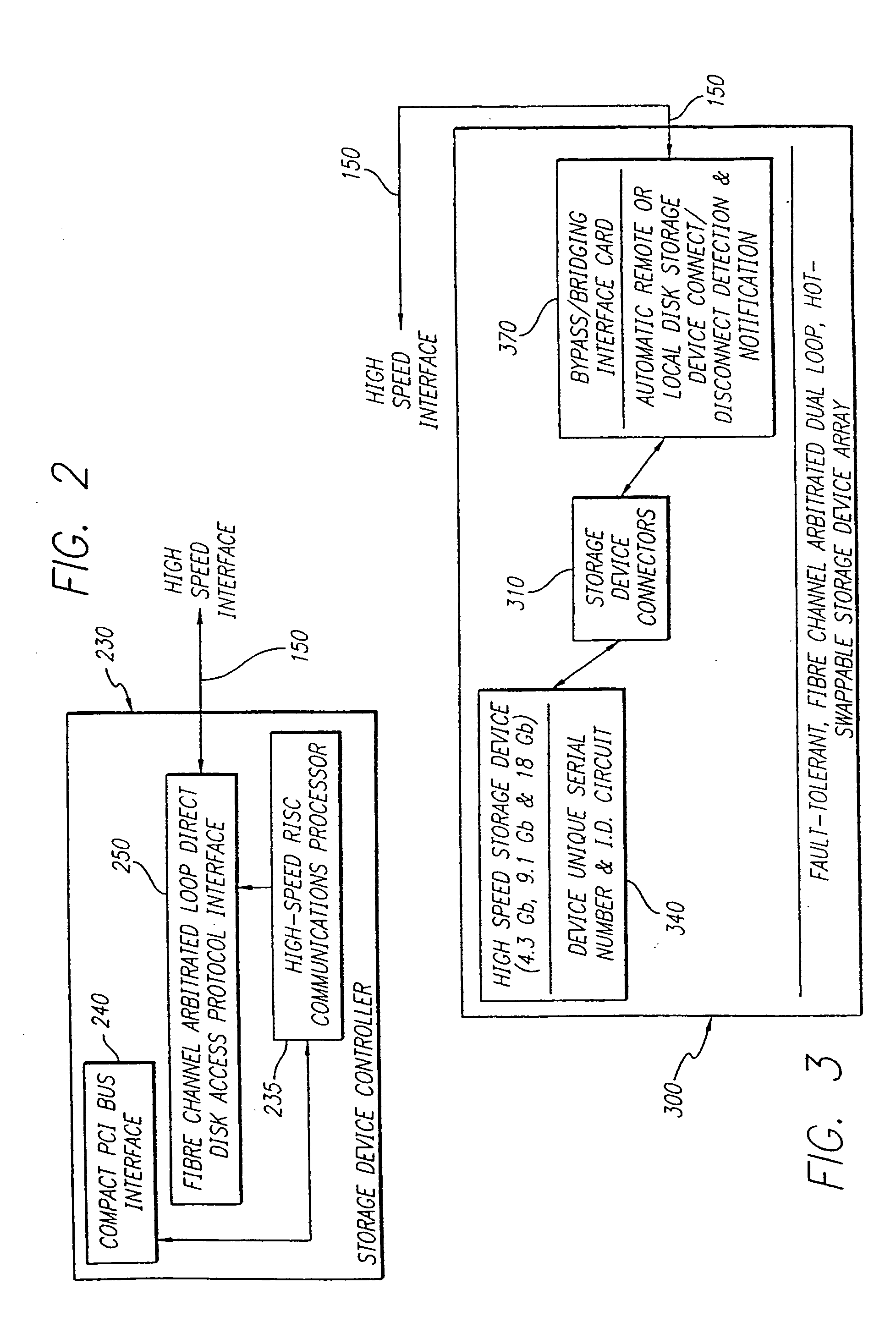
High speed fault tolerant mass storage network information server
InactiveUS20050033916A1Avoid writingEliminate requirementsInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsMass storageFiber
The information server system incorporates a high speed, microcomputer based server running industry standard operating system software enhanced to include functionality directed to operation of a new disk array controller, which controls the physically independent or integral disk storage device array, and communications interface. The disk array controller subsystem controls and communicates with the disk storage device array with a Fibre Channel protocol. The disk storage device array incorporates a plurality of disk storage devices with a corresponding number of bypass interface cards configured to facilitate the on-line addition, removal and replacement of disk storage devices. In additional to incorporating the above described buses and Fibre Channel capability, the disk array further incorporates a physically independent Fibre Channel compatible optical bus for high speed, communication between disk storage device array subsystem components, including the internal disk storage devices, independent from the information server. A wide array of user reconfigurable options are available as well as a scalable expansion capability.
Owner:DELLACONA RICHARD
High speed fault tolerant mass storage network information server
InactiveUS20050193059A1Eliminate requirementsFacilitate on-line addition and removal and replacementInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsMass storageFiber
The information server system incorporates a high speed, microcomputer based server running industry standard operating system software enhanced to include functionality directed to operation of a new disk array controller, which controls the physically independent or integral disk storage device array, and communications interface. The disk array controller subsystem controls and communicates with the disk storage device array with a Fibre Channel protocol. The disk storage device array incorporates a plurality of disk storage devices with a corresponding number of bypass interface cards configured to facilitate the on-line addition, removal and replacement of disk storage devices. In additional to incorporating the above described buses and Fibre Channel capability, the disk array further incorporates a physically independent Fibre Channel compatible optical bus for high speed, communication between disk storage device array subsystem components, including the internal disk storage devices, independent from the information server. A wide array of user reconfigurable options are available as well as a scalable expansion capability.
Owner:DELLACONA RICHARD
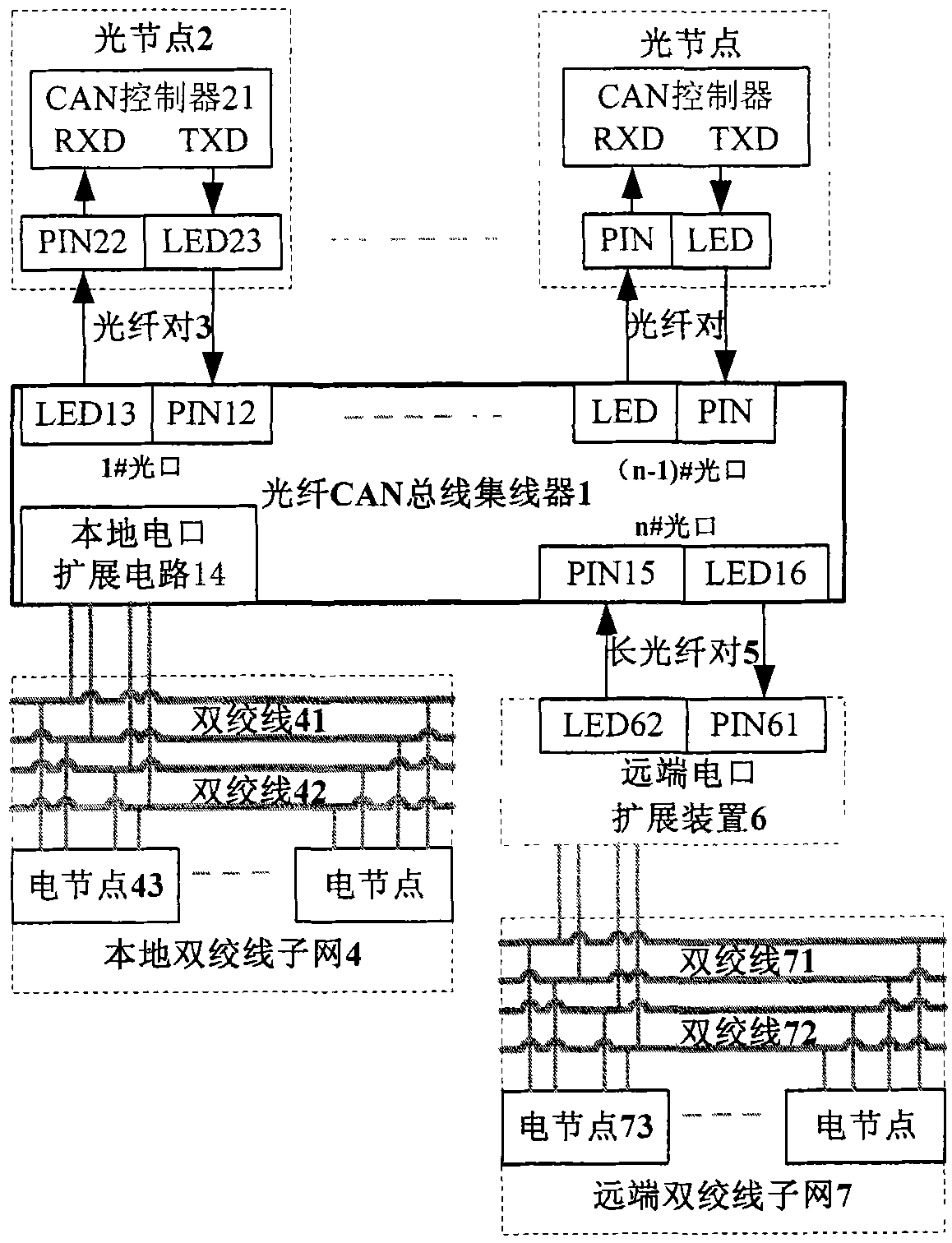
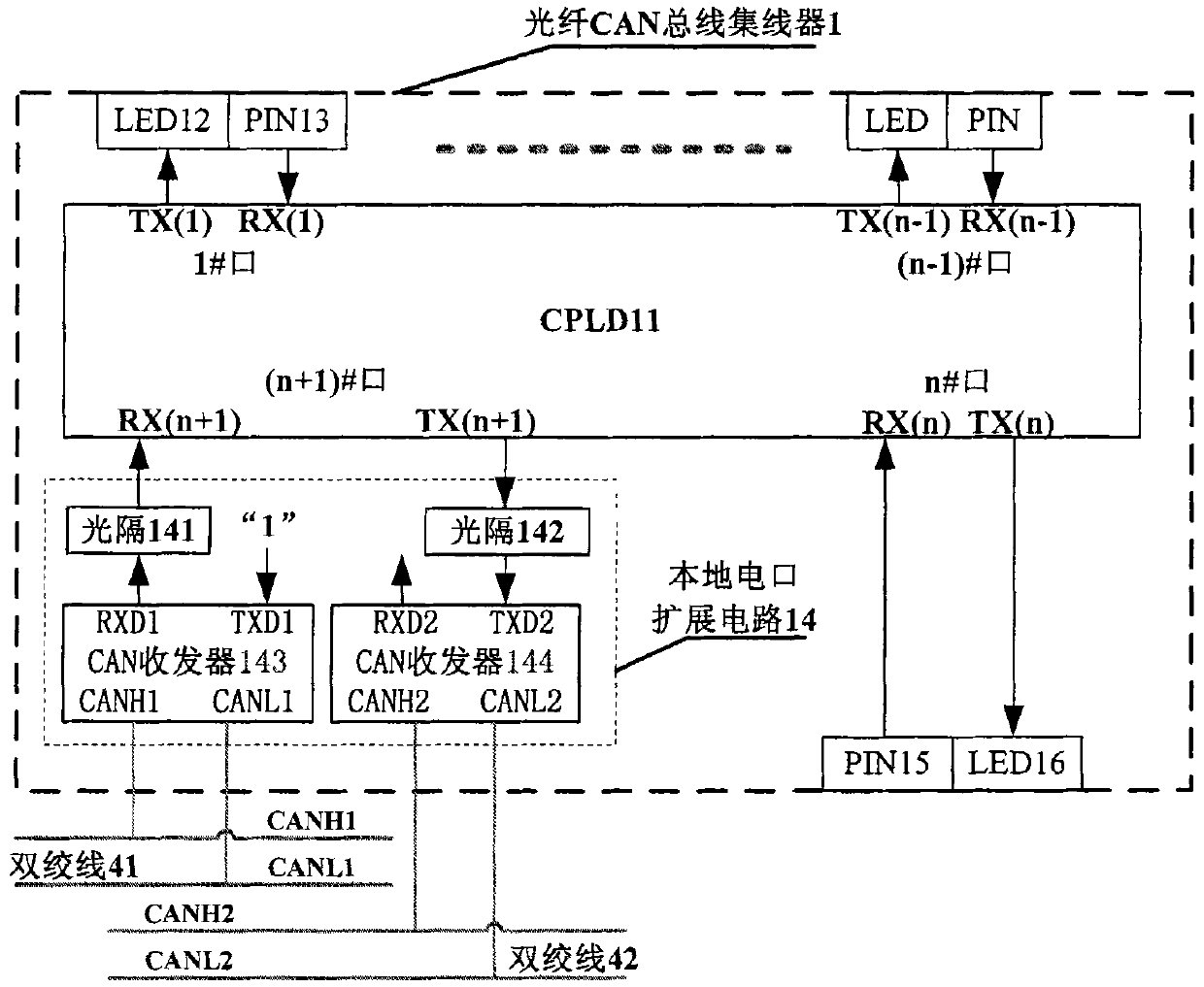
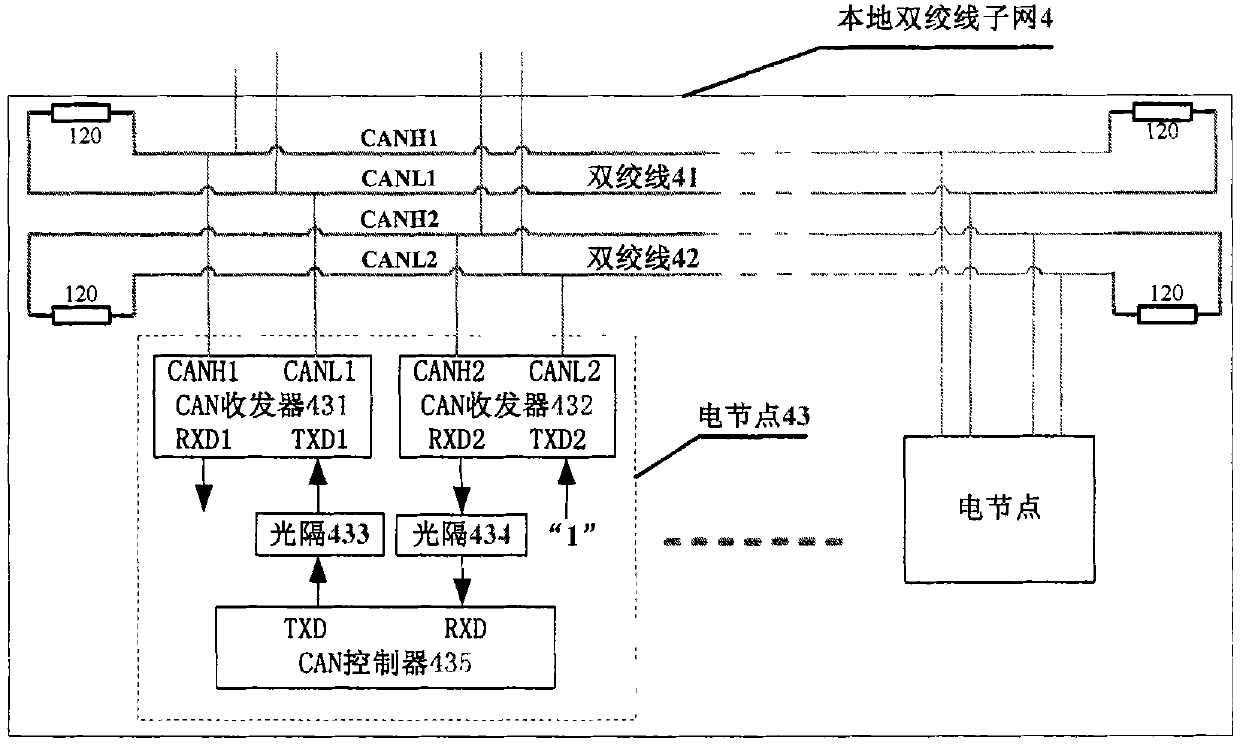
Optical fiber CAN bus hub and networking method thereof
InactiveCN102026050AMultiplex system selection arrangementsBus-type electromagnetic networksTransceiverComplex programmable logic device
The invention discloses a networking method of an optical fiber control area network (CAN) bus hub. A main hub of an optical fiber CAN bus with n optical fiber interfaces and a local twisted pair electrical interface extension circuit and n twisted pair CAN sub-networks for connecting the main hub with n optical nodes, n secondary hubs or n remote electric interface extension devices are connected with a local twisted pair CAN sub-network to form a network; signals are transmitted, received and separated by using the optical fiber CAN bus hub which realizes a wired and function through a complex programmable logic device (CPLD) and is provided with a plurality of optical interfaces and a twisted pair electric interface extension circuit, double CAN transceivers and two twisted pairs, so self-excitation blocking communication caused by a signal transmission loop is avoided; and the optical nodes, the local twisted pair CAN bus sub-network and the remote twisted pair CAN bus sub-network are connected by using the optical fiber CAN bus hub, the optical fiber pair and the remote electric interface extension device to form a high-network-speed wide area networking scheme.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Burst mode optical media converter with fast analog conversion
A media converter for interfacing an optical fiber bus to an electrical interface of an electronic device is described. The media converter includes an interface circuit configured to convert electrical signals received from a transmitting channel of the electrical device in a voltage doublet format to positive logic electrical pulses and convert received electrical signals for application to a receiving channel of the electrical device from positive logic electrical pulses to a voltage doublet format, a DC coupled receiver comprising an optical interface operable for receiving optical signals from the optical fiber data bus, the receiver operable for converting the optical signals to positive logic electrical pulses for application to the interface circuit, a laser diode operable to transmit optical signals onto the optical bus, and a laser diode driver operable for receiving the positive logic electrical pulses from the interface circuit and converting the electrical signals to signals compatible for operating the laser diode.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
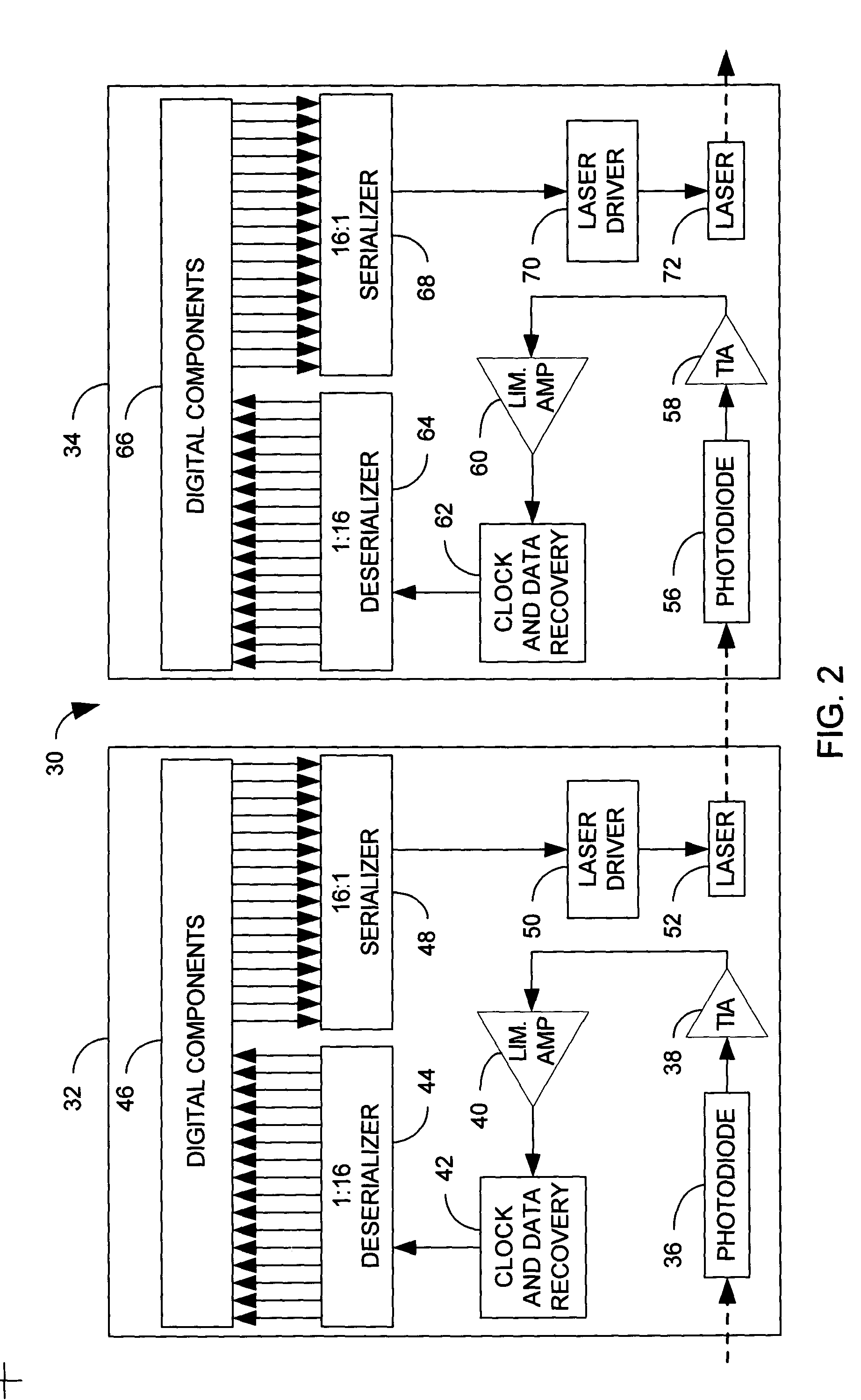
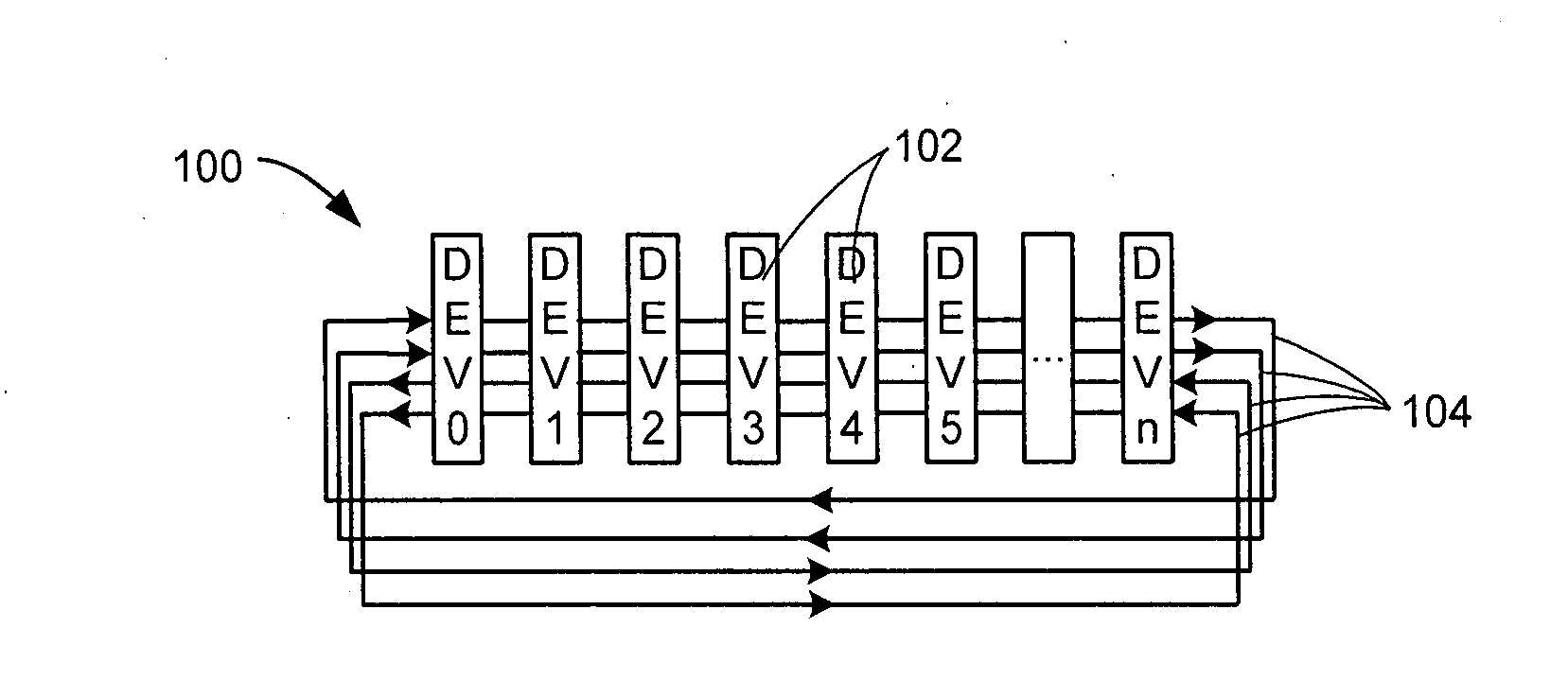
Synchronous optical bus providing communication between computer system components
A synchronous optical bus system for communication between computer system components is described. In one example, the optical bus system is used for communication between a memory controller and memory devices optically coupled to an optical interconnect. Optical bus interface units couple the components to the optical interconnect and are arranged on the optical interconnect in order that a sum of an optical path length from a controller component to each computer system component and from each computer system component to the controller component is the same for all the coupled computer system components. A synchronous protocol is used for communication between the components.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Backplane assembly with board to board optical interconnections and a method of continuity checking board connections
An electronic system with components communicating over optical channels, a board initialization and continuity check and a method of transferring data over the optical channels. The system include a backplane with board to board signal wiring and a shared optical bus. Optical gratings are attached to the backplane and to circuit boards to pass optical energy between an optical transceiver and board / backplane. An optical transceiver at each end of each optical jumper relays optical signals between the optical jumpers and the connected circuit board or the backplane. Optical jumpers optically connect the circuit boards to the backplane.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
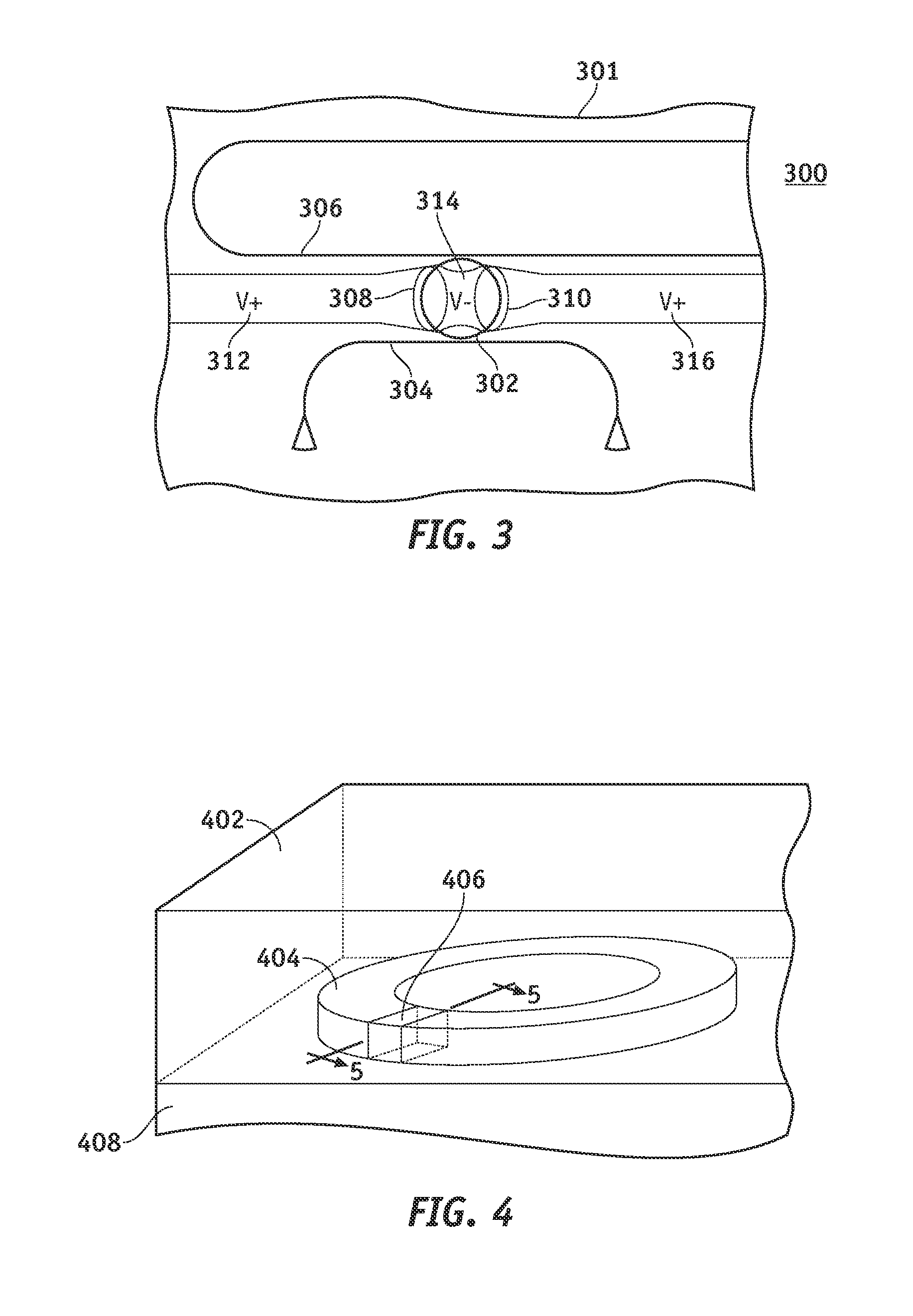
Detection of optical light power
ActiveUS20050019041A1Length minimizationReduce decreaseLoop networksElectromagnetic receiversOptical powerOptical bus
A receiving unit for a controller for reception of input data is disclosed. The input data is transmitted as optical signals in an optical bus system in a vehicle. The receiving unit is coupled to an optical bus system and has a means for conversion of optical signals to electrical signals. A measurement arrangement is provided which measures a characteristic variable for the optical received power. The receiving unit optimizes the dynamic control of the optical level. The measurement arrangement is in the form of a digital circuit. Furthermore, an output port is provided for passing on the digitized measurement data.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Optical wiring board, optical bus system, and method of manufacturing optical wiring board
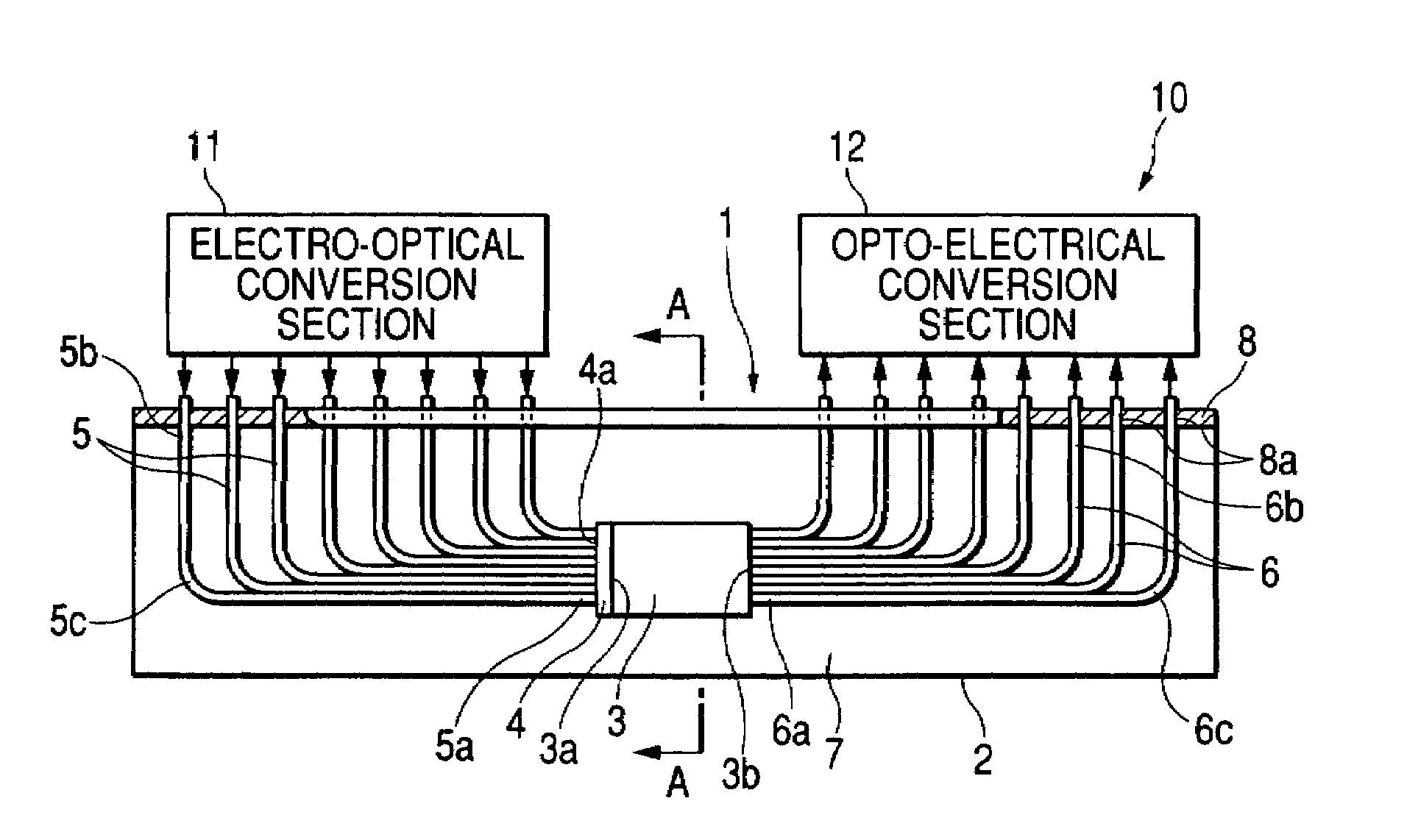
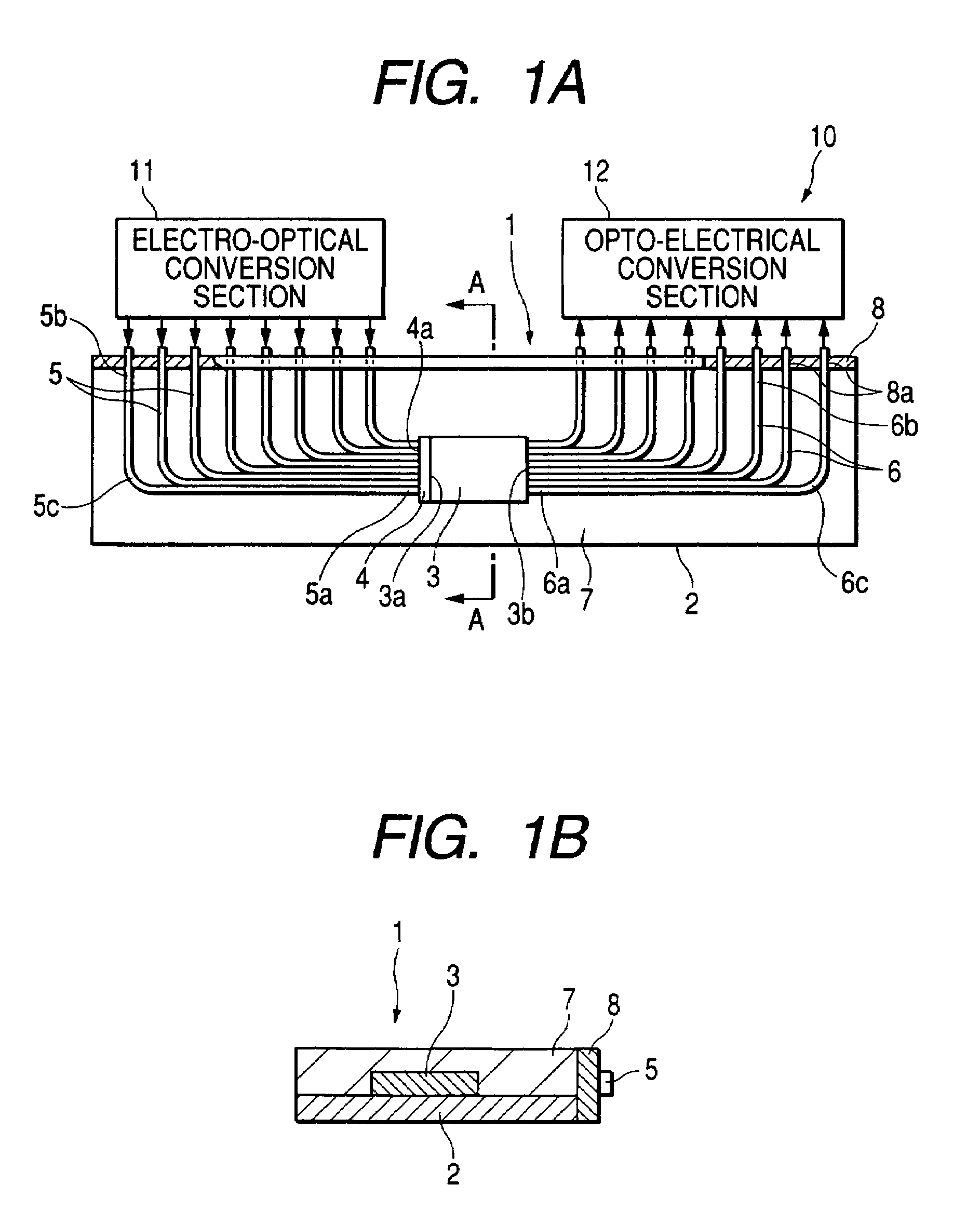
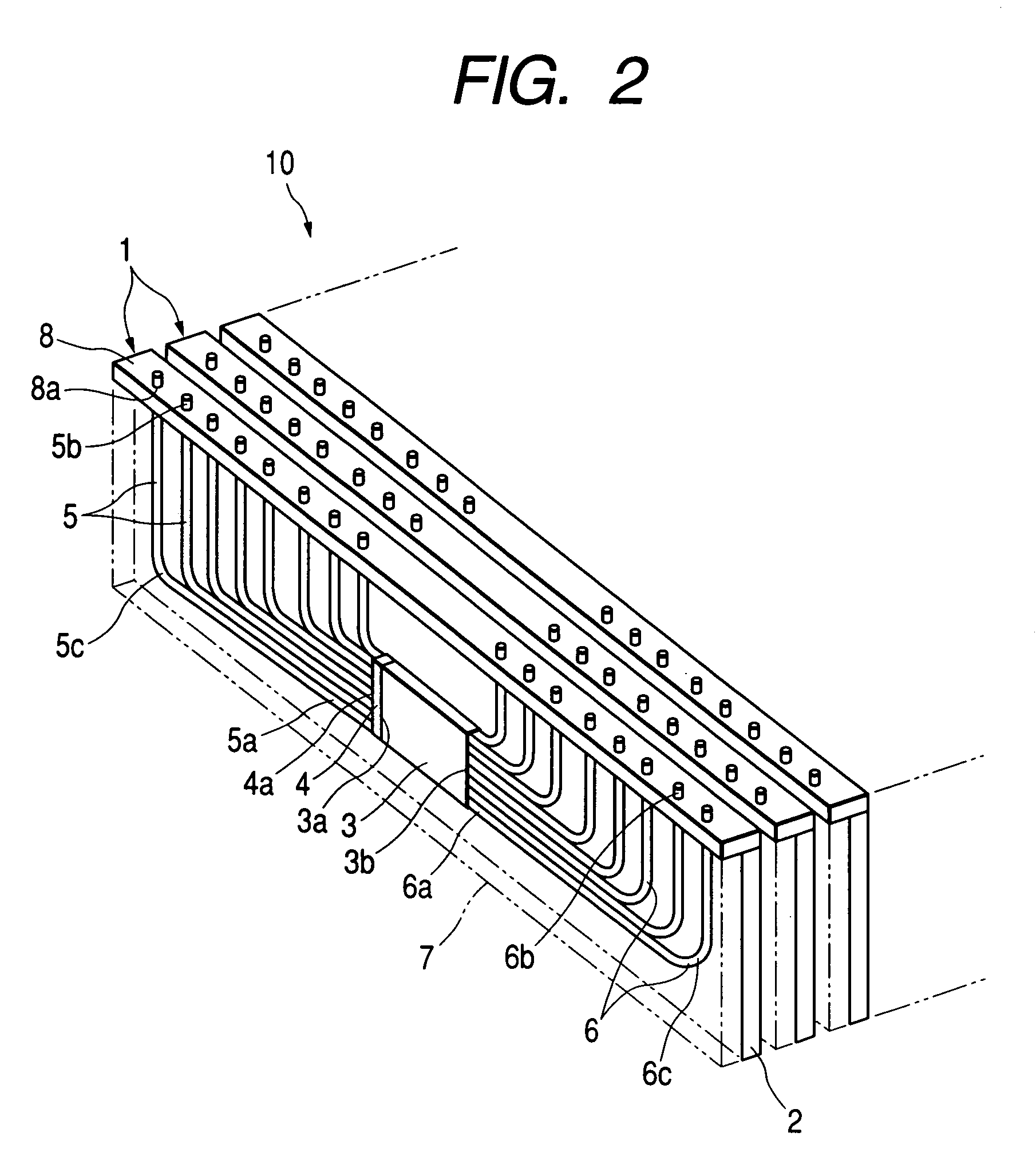
InactiveUS7146065B2Easy to manufactureIncrease freedomCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringOptical bus
In an optical wiring board, an optical components including a planar optical waveguide, a plurality of first optical fibers optically connected via a transmissive diffusion plate to a light incident face of the waveguide, and a plurality of second optical fibers optically connected to a light emitting face of the waveguide is placed on a support board. The optical component is sealed by a sealing member made of a resin.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Method for in-situ continuity check on an optical bus
InactiveUS20040102084A1Material analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesOptical busLight source
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
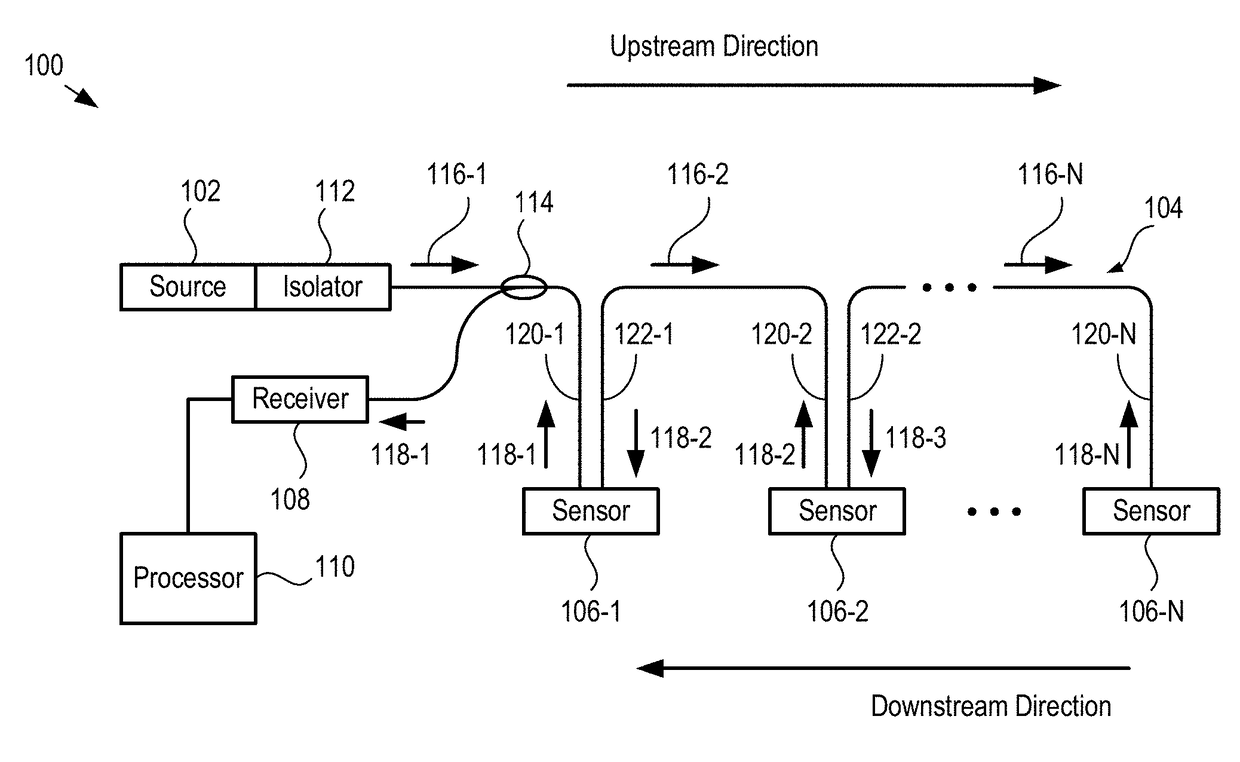
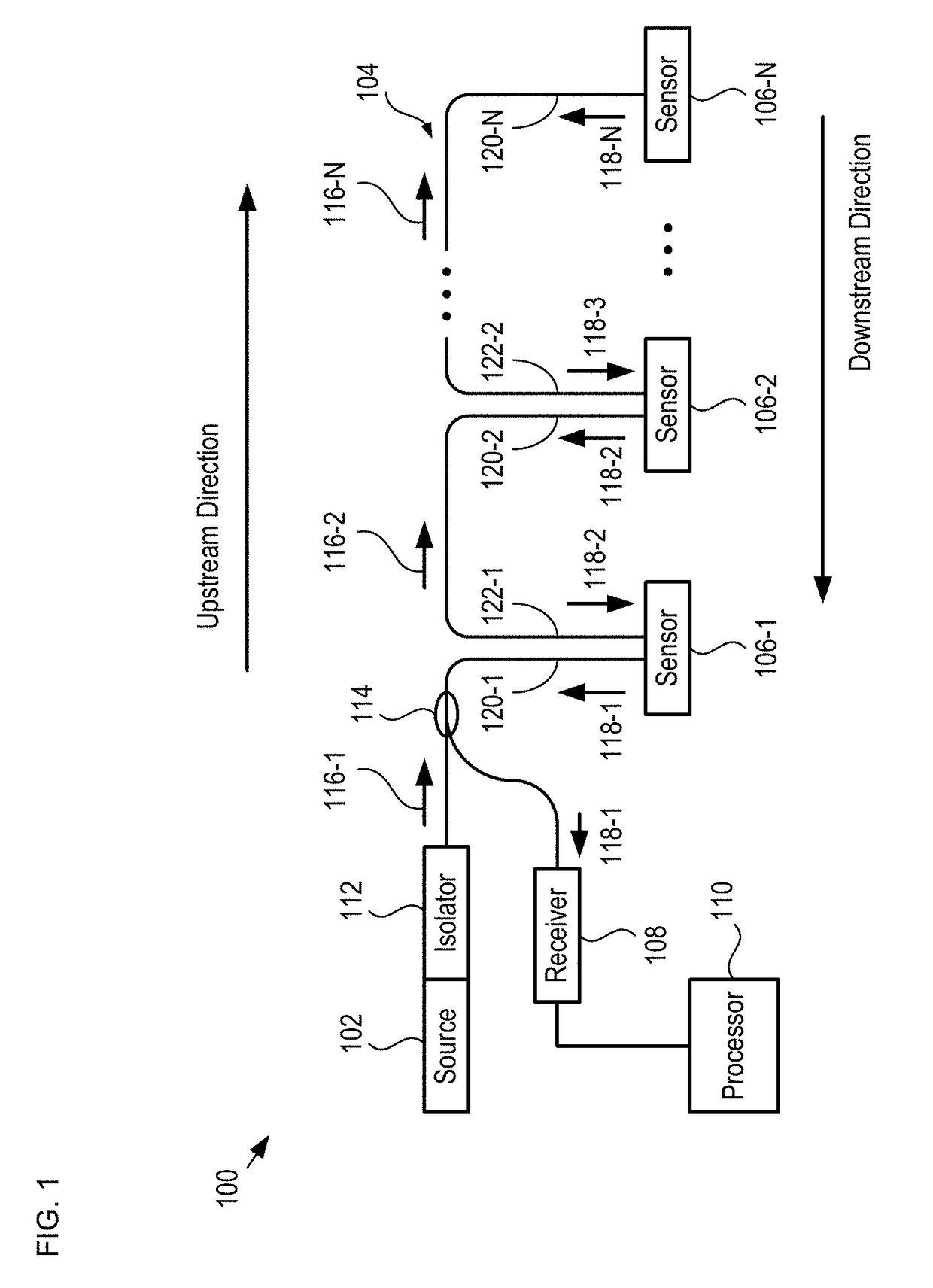
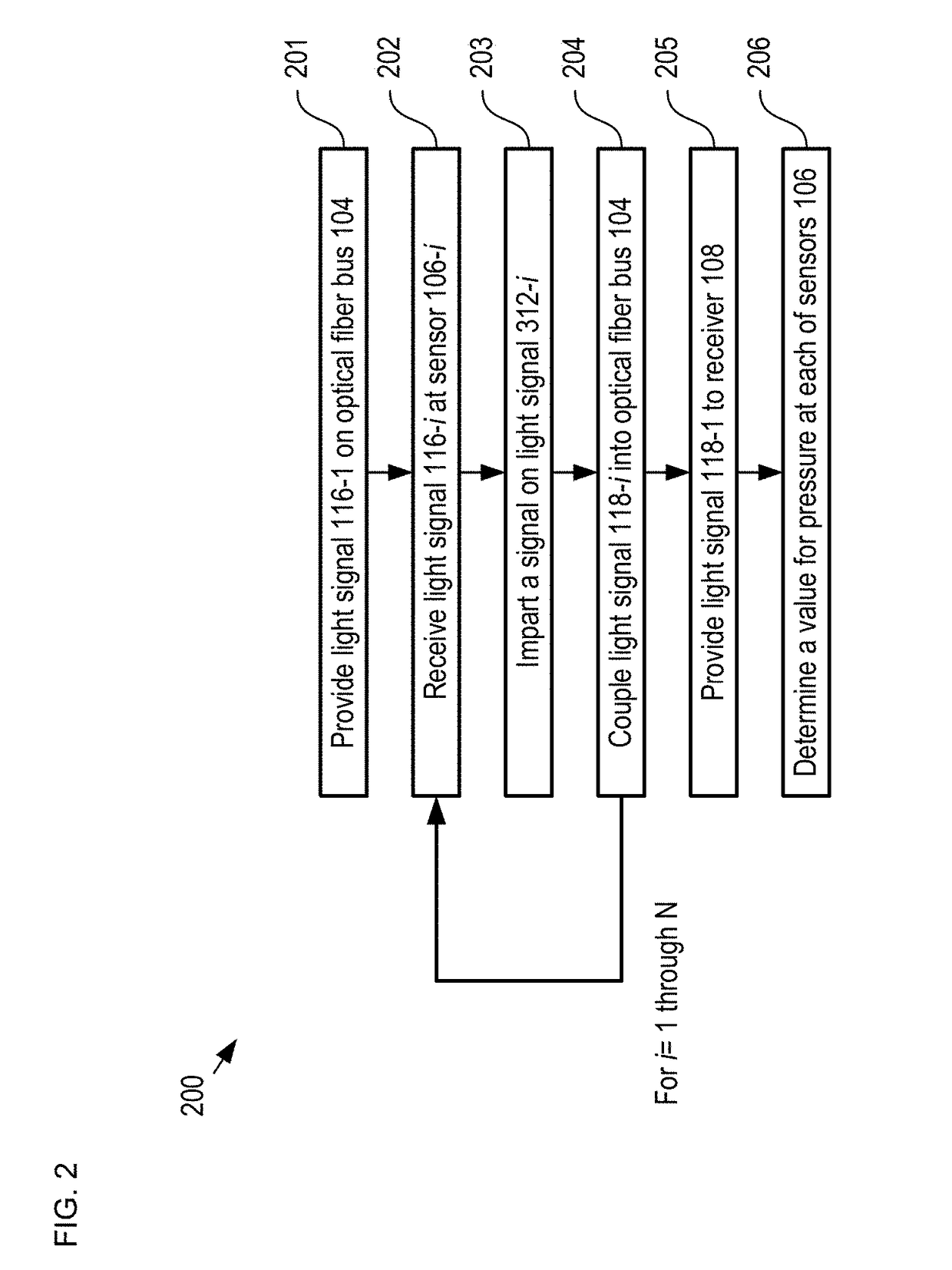
Multiplexed Fiber-Coupled Fabry-Perot Sensors and Method Therefor
ActiveUS20170356767A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsMultiplexingWavelength filter
A sensor network having a series arrangement of fiber-coupled, reflective sensors is disclosed. In operation, a first light signal having multiple wavelength bands is launched in an upstream direction on a fiber bus. Each sensor includes a wavelength filter and an FP sensor that is sensitive to a parameter. Each wavelength filter (1) selectively passes a different one of the wavelength bands to its FP sensor and (2) reflects the remaining wavelength bands back into the fiber bus to continue upstream. The FP sensor imprints a signal based on the parameter onto its received light and reflects it as a second light signal. The collimator, wavelength filter, and FP sensor of each sensor are arranged such that each second light signal is returned to the fiber bus, which conveys them in a downstream direction to a processor that measures them and estimates the parameter at each sensor.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
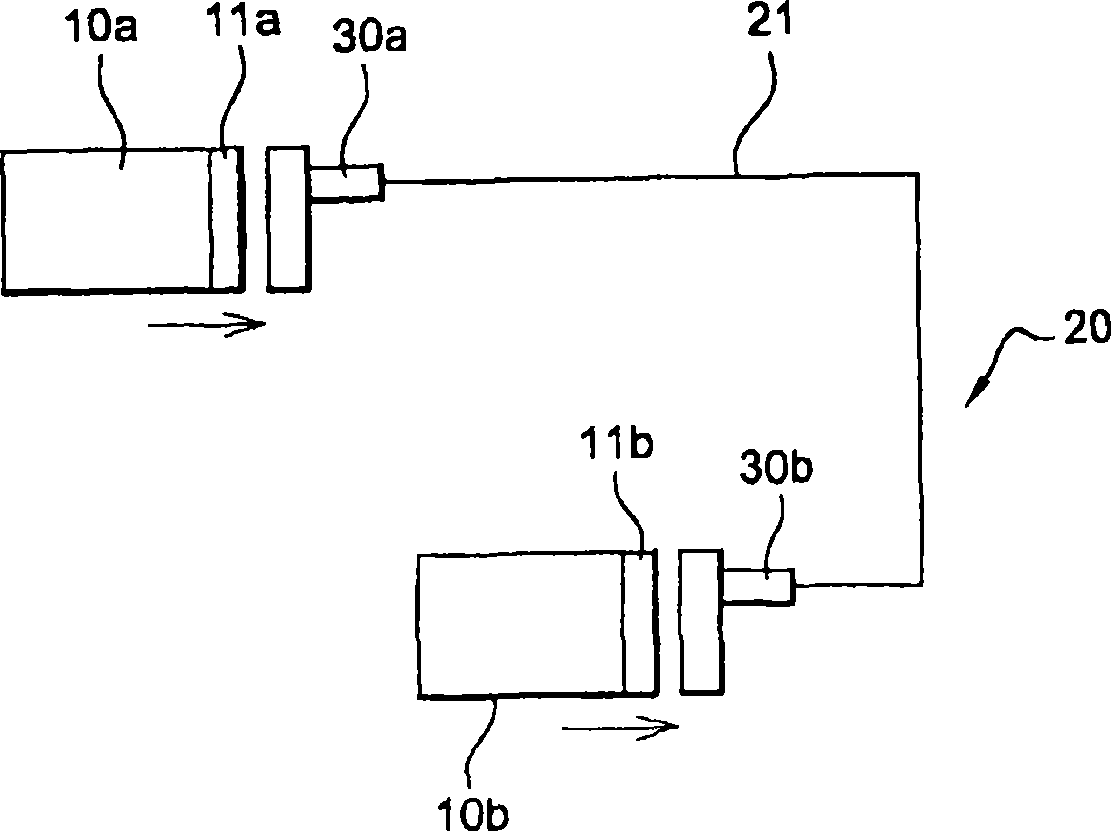
Optical communication bus network for avionic equipment
InactiveCN101375193ACoupling light guidesMultimode transmissionElectricityCommunications-electronics
The invention relates to an avionic system for an aircraft comprising at least two pieces of equipment (10a, 10b) which can exchange information by means of at least one electrical bus for simultaneous bidirectional communication, in which the information can be exchanged between pieces of equipment (10a, 10b) via an optical bus (20) that can be connected to the electrical interfaces (11a, 11b) of said equipment. The optical bus (20) of the avionic system comprises at least one optical cable (21) consisting of at least one optical fibre (22) and, at each end, a connector (30) comprising means(41, 42, 45, 46) for converting electrical signals into optical signals and means for converting optical signals into electrical signals. The optical bus (20) is connected to the electrical outlets of existing equipment.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com