Patents
Literature
3932 results about "Dynamic control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
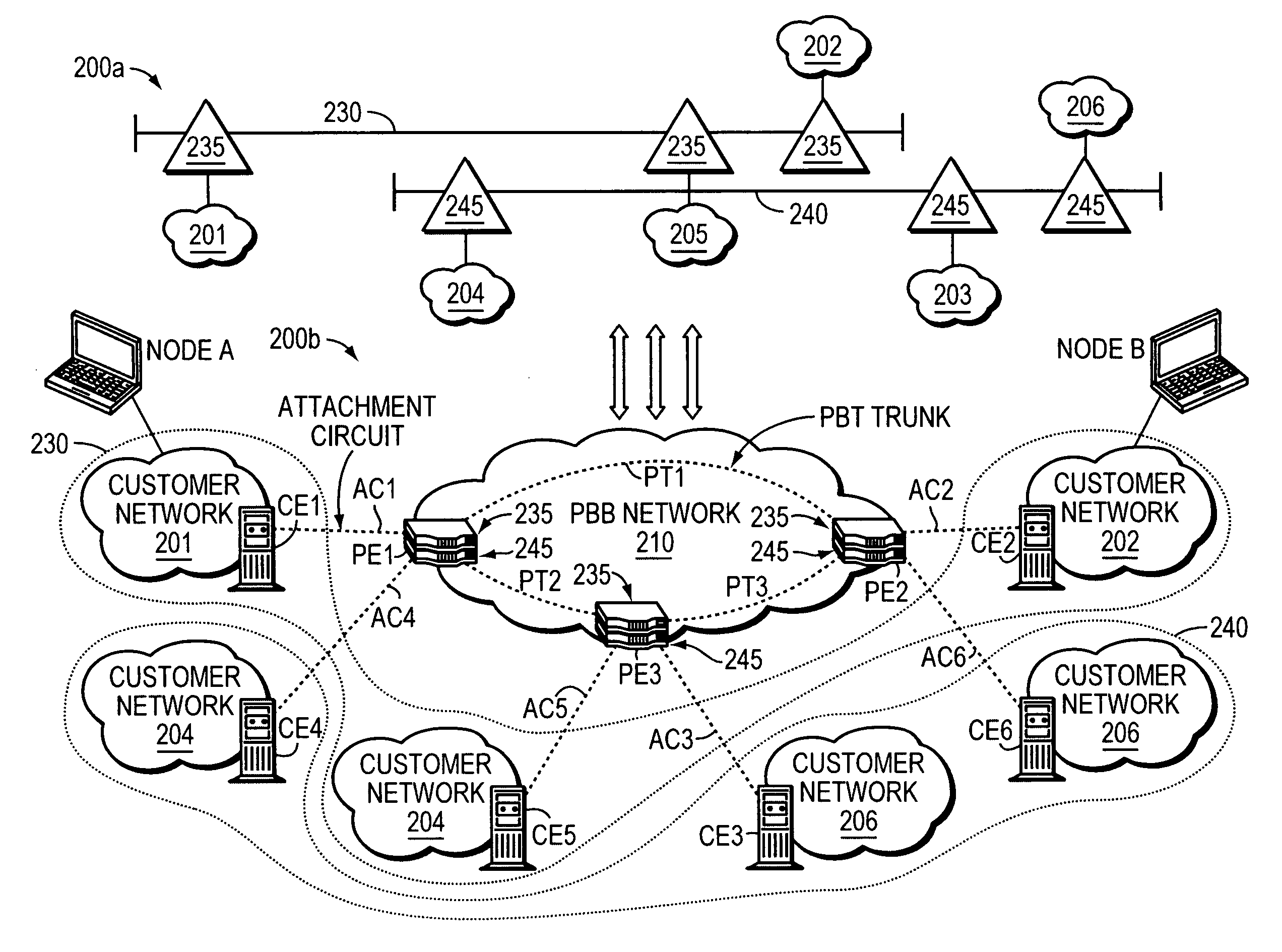
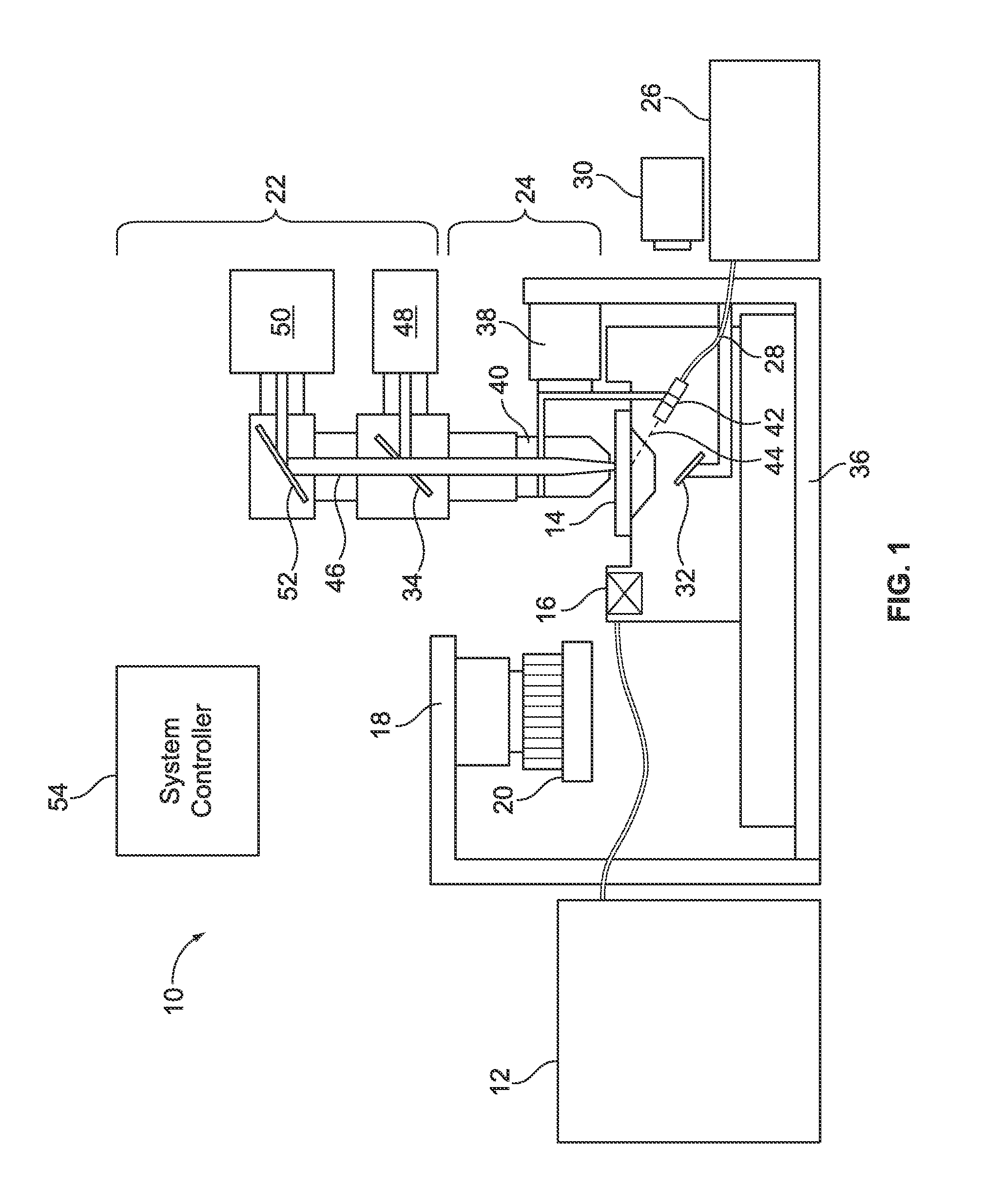
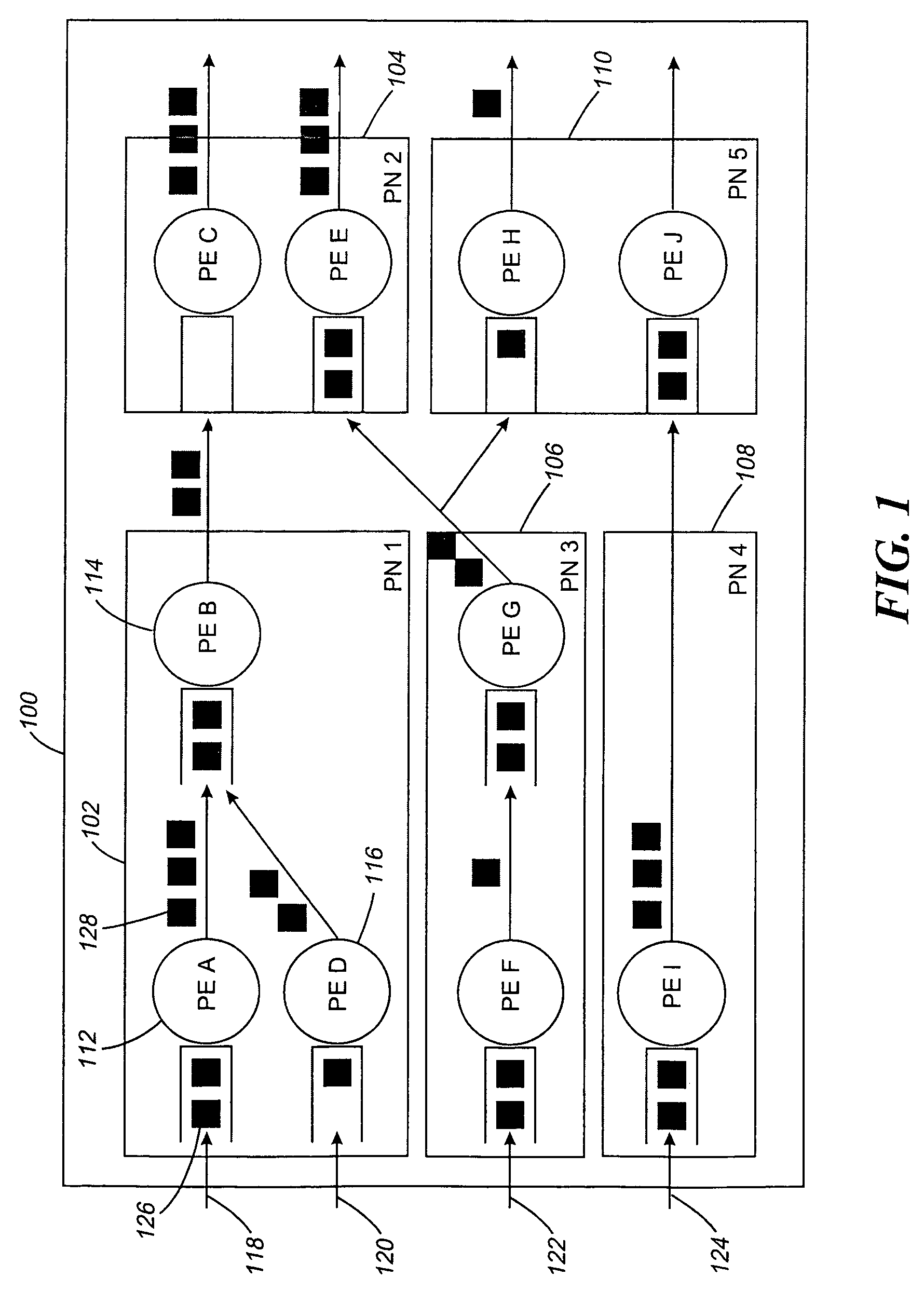
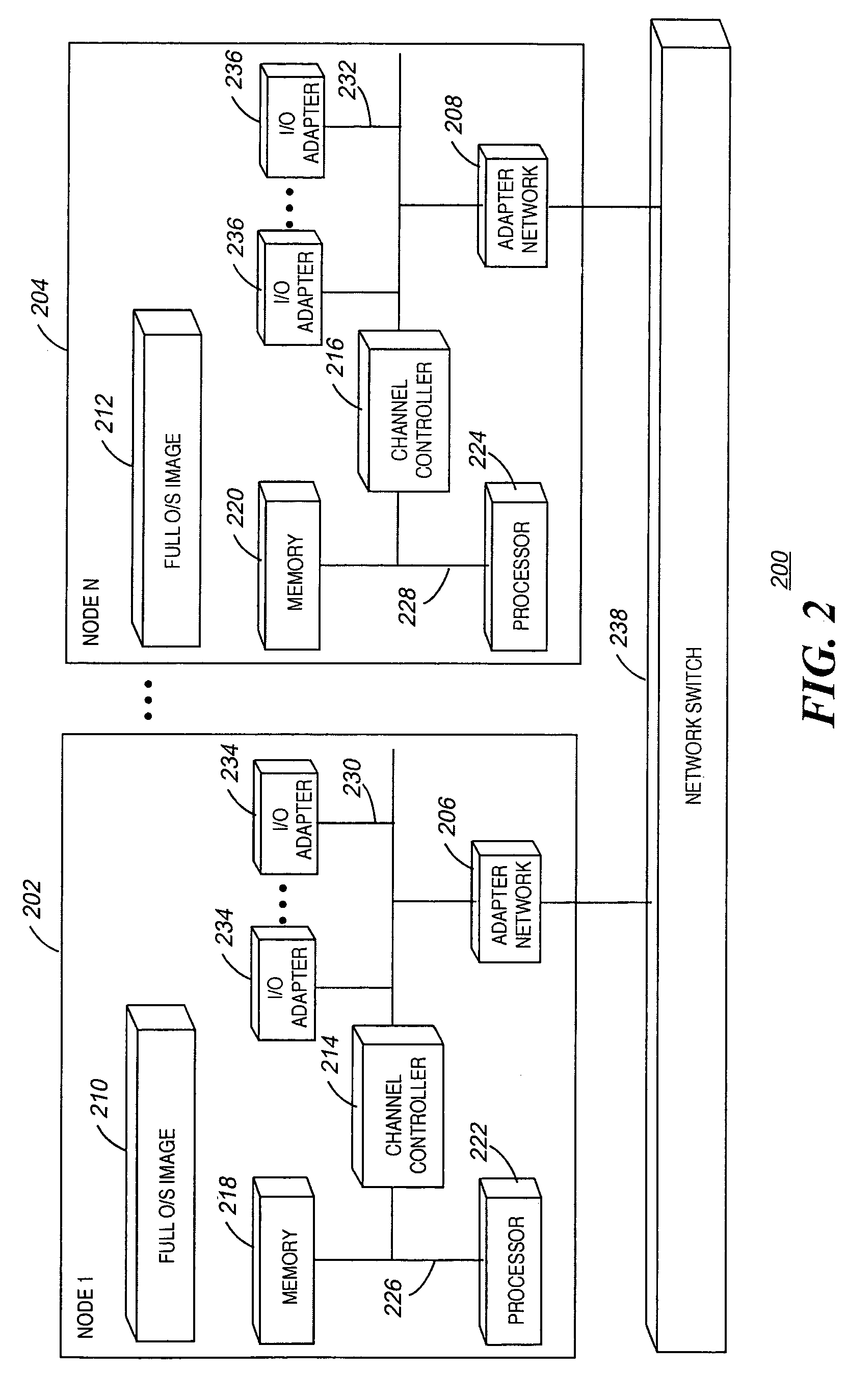
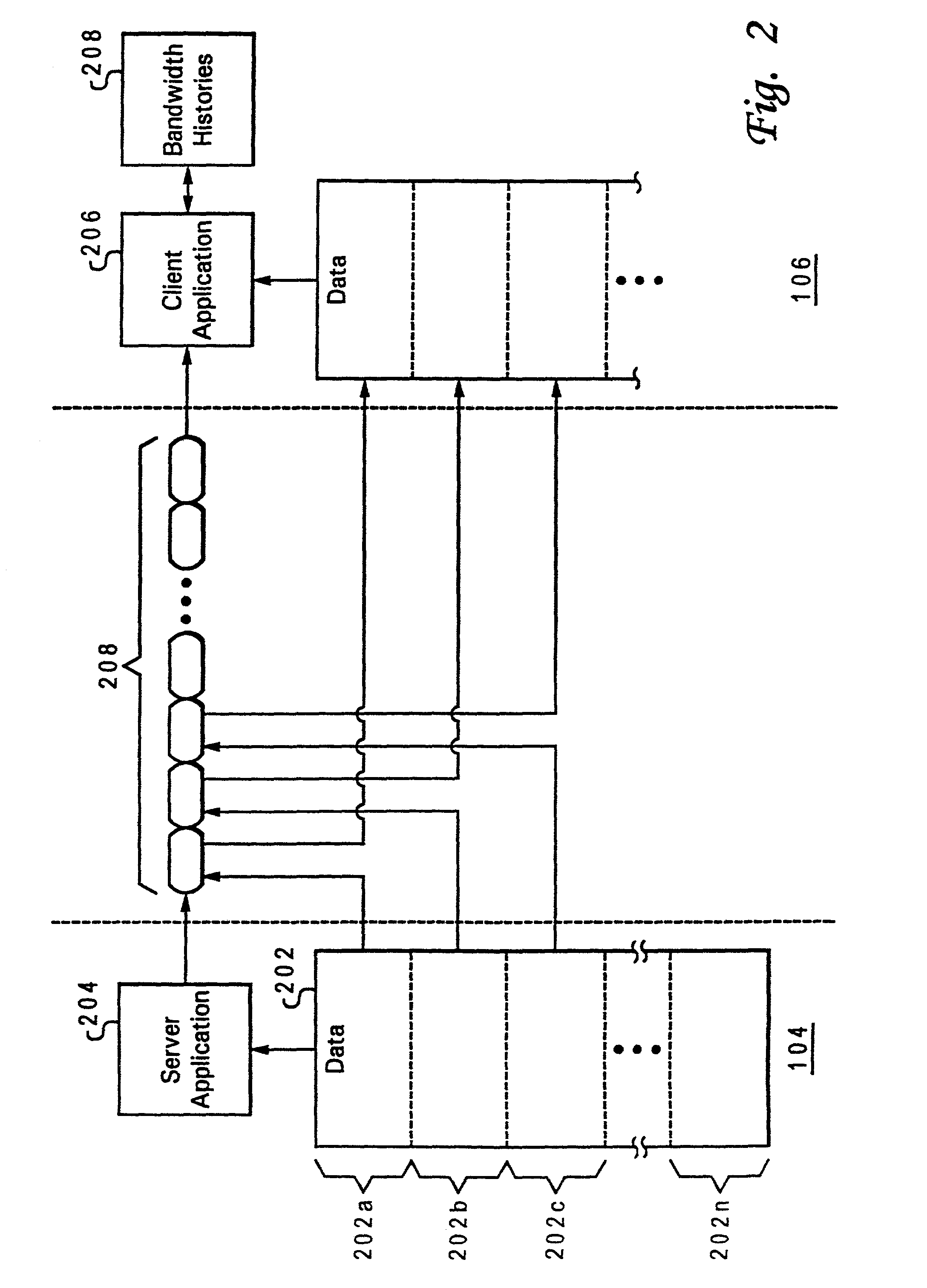
Software control plane for switches and routers
ActiveUS20080219268A1Bridging the gapImprove convenienceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceAbstraction layer
A Provider Network Controller (PNC) addresses the challenges in building services across Next Generation Network (NGN) architectures and creates an abstraction layer as a bridge, or glue, between the network transport and applications running over it. The PNC is a multi-layer, multi-vendor dynamic control plane that implements service activation and Layer 0-2 management tools for multiple transport technologies including Carrier Ethernet, Provider Backbone Transport (PBT), Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS), Transport MPLS (T-MPLS), optical and integrated networking platforms. Decoupling transport controls and services from the network equipment simplifies service creation and provides options for carriers to choose best-in-class equipment that leverages the PNC to enable rapid creation and management of transports and services. The PNC provides Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) interfaces to abstract transport objects expressly designed to support both wholesale and retail services, and supports service offerings with varied bandwidth and Quality of Service (QoS) requirements, thus achieving enterprise Ethernet economics.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
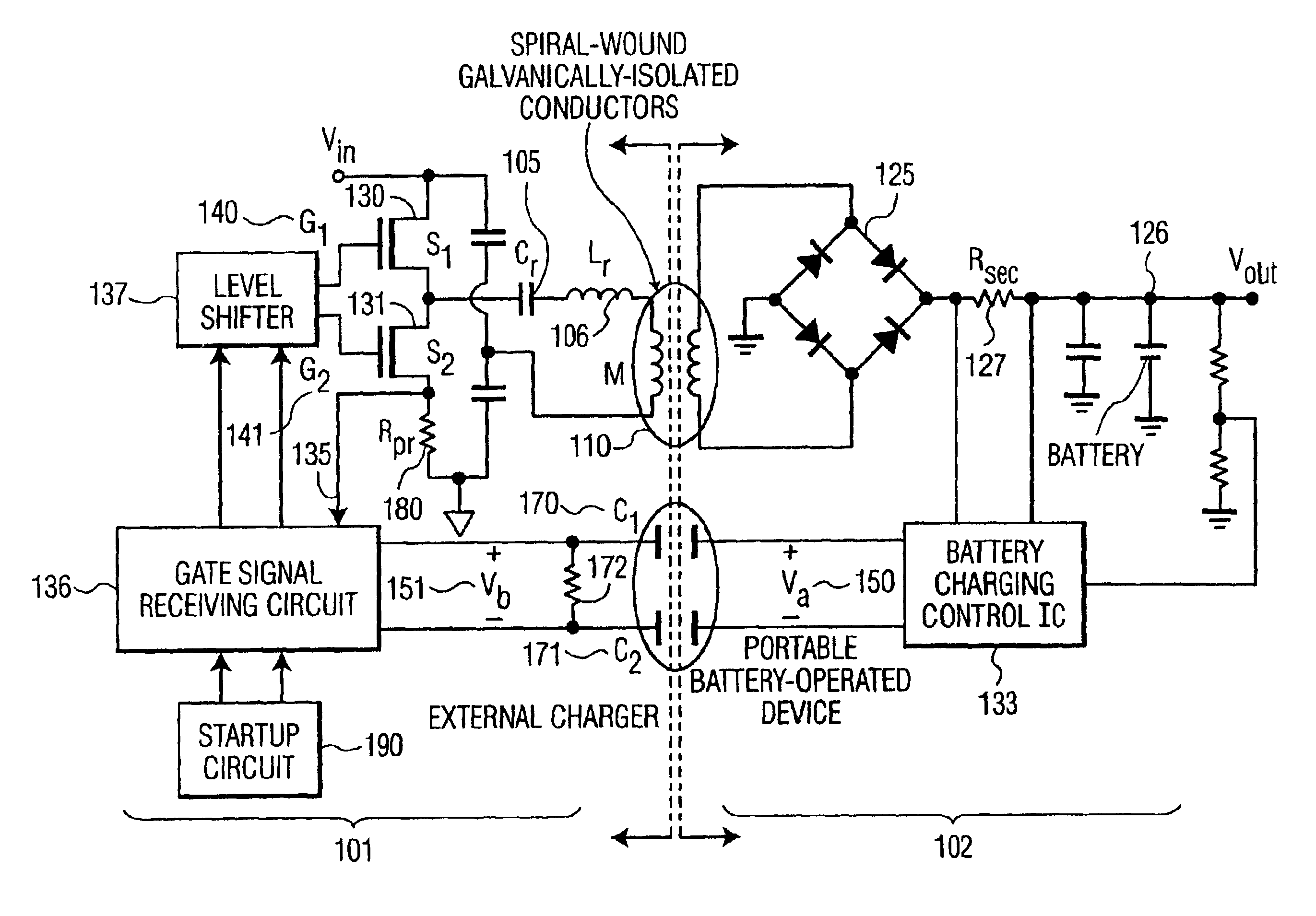
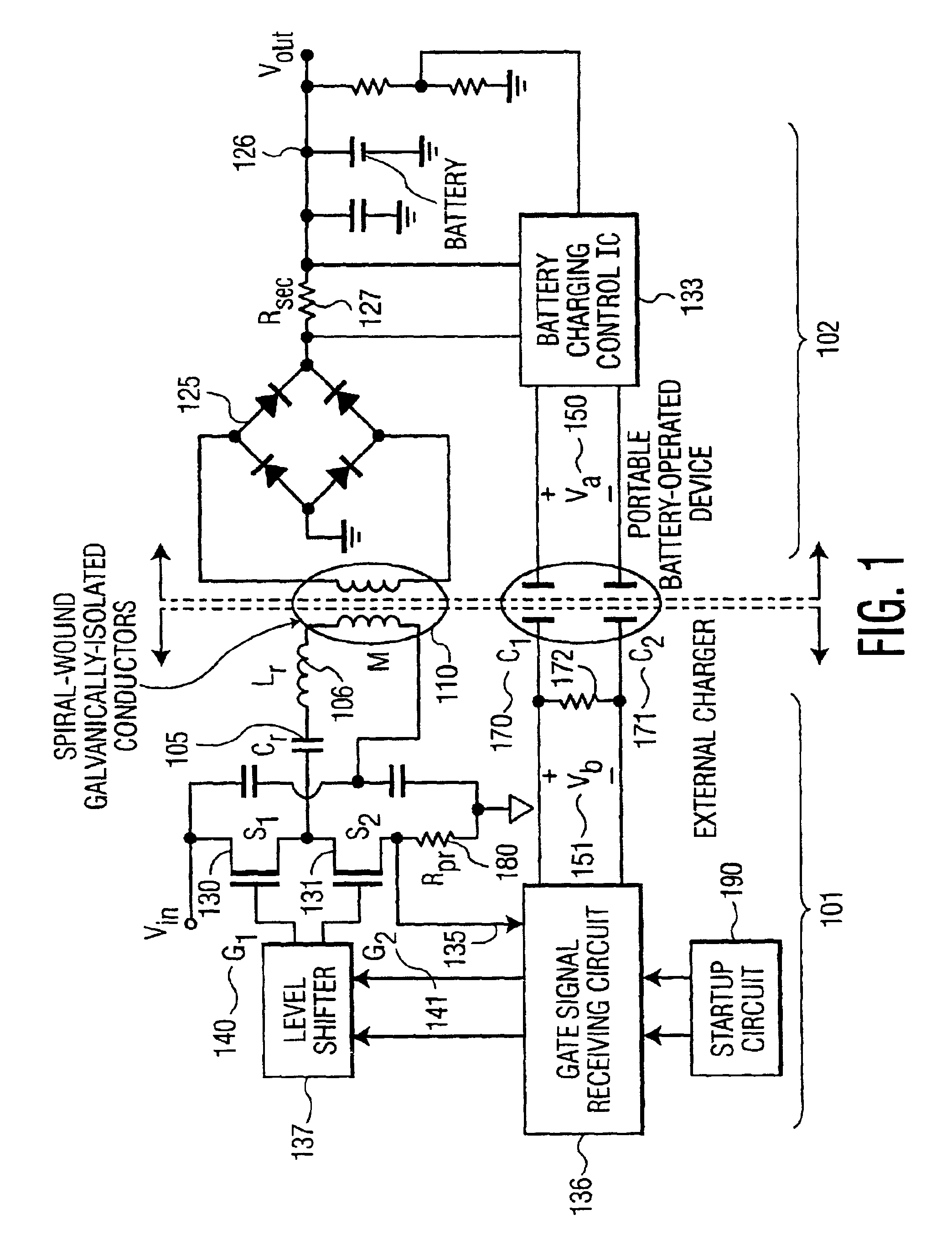
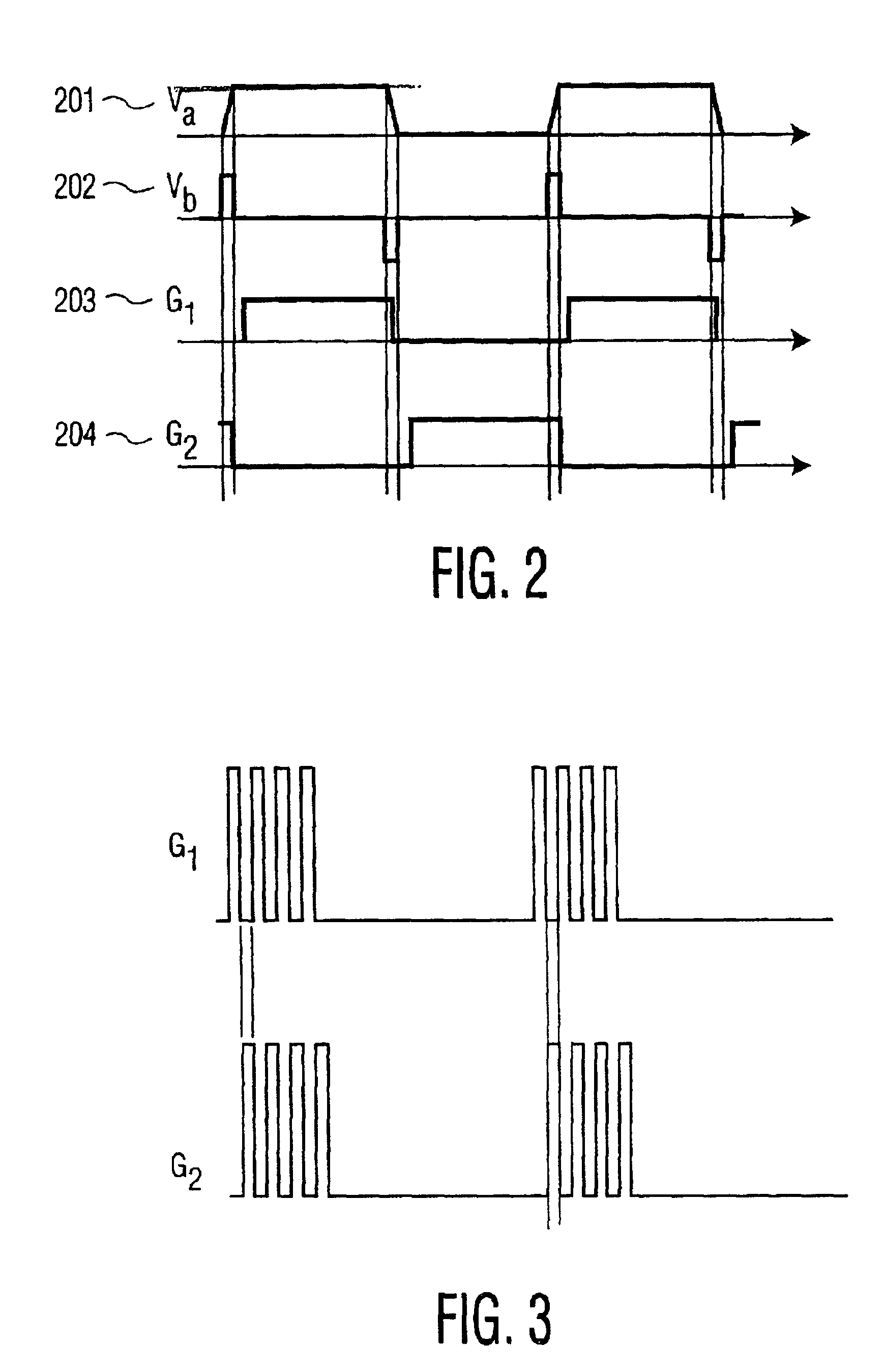
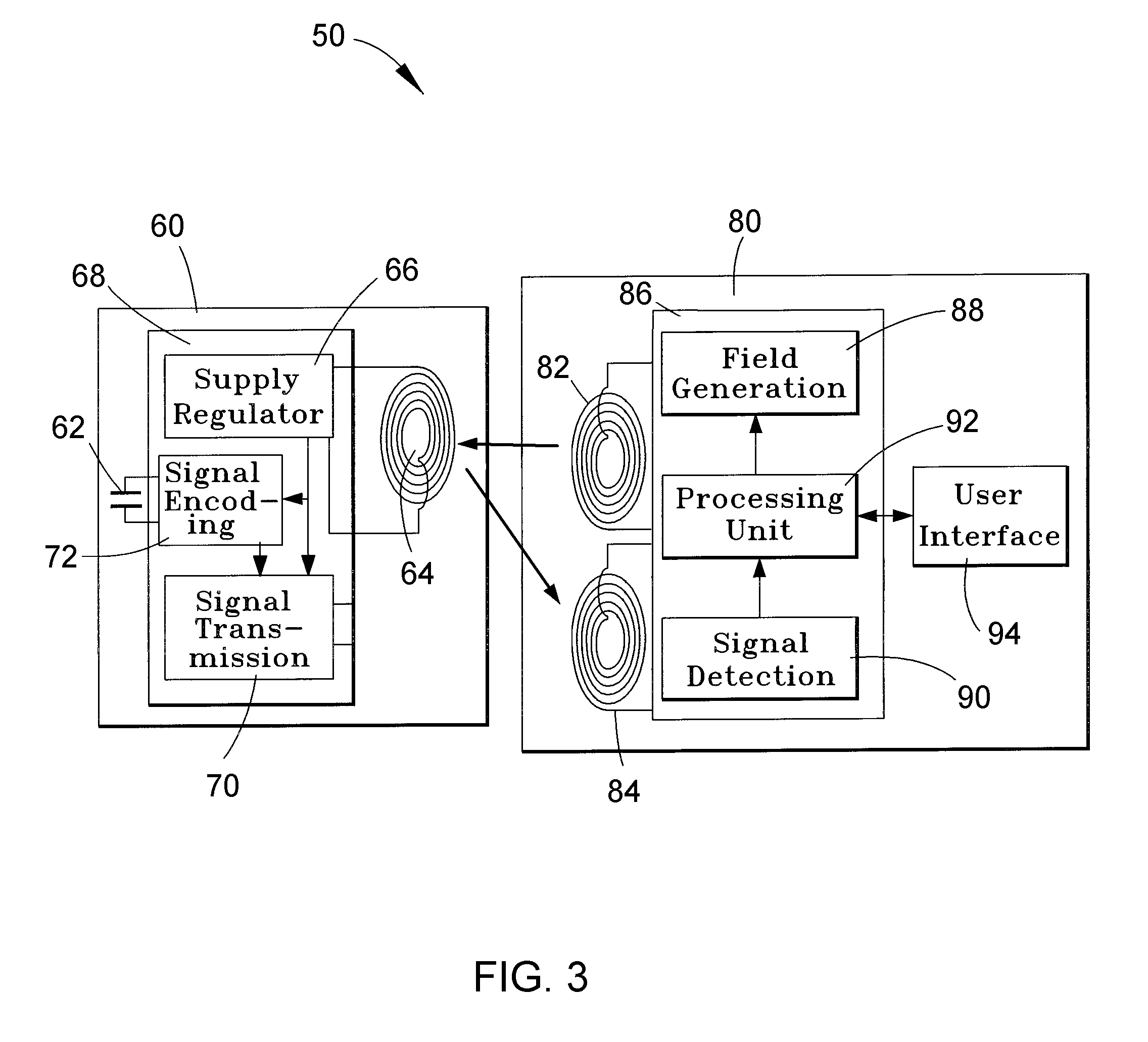
System, method and apparatus for contact-less battery charging with dynamic control
InactiveUS6844702B2Reduce complexityImprove efficiencyNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemBattery chargeEngineering
A system, method and apparatus for contact-less charging of battery operated devices, including a host charger with a power converter and resonant tank circuit and a portable device where the battery is located, with a battery charging control IC, wherein the method obviates the need for a voltage controller in each of both the host and the portable stages. The charging of the battery in the portable device is controlled by a charging controller therein, which is in continual electric communication with the host, whose output power the control IC dynamically monitors and controls. In one embodiment, component count is minimized but battery charging is not optimized when the battery voltage is very low. In the other embodiment, charging efficiency is maximized regardless of the output voltage of the battery.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
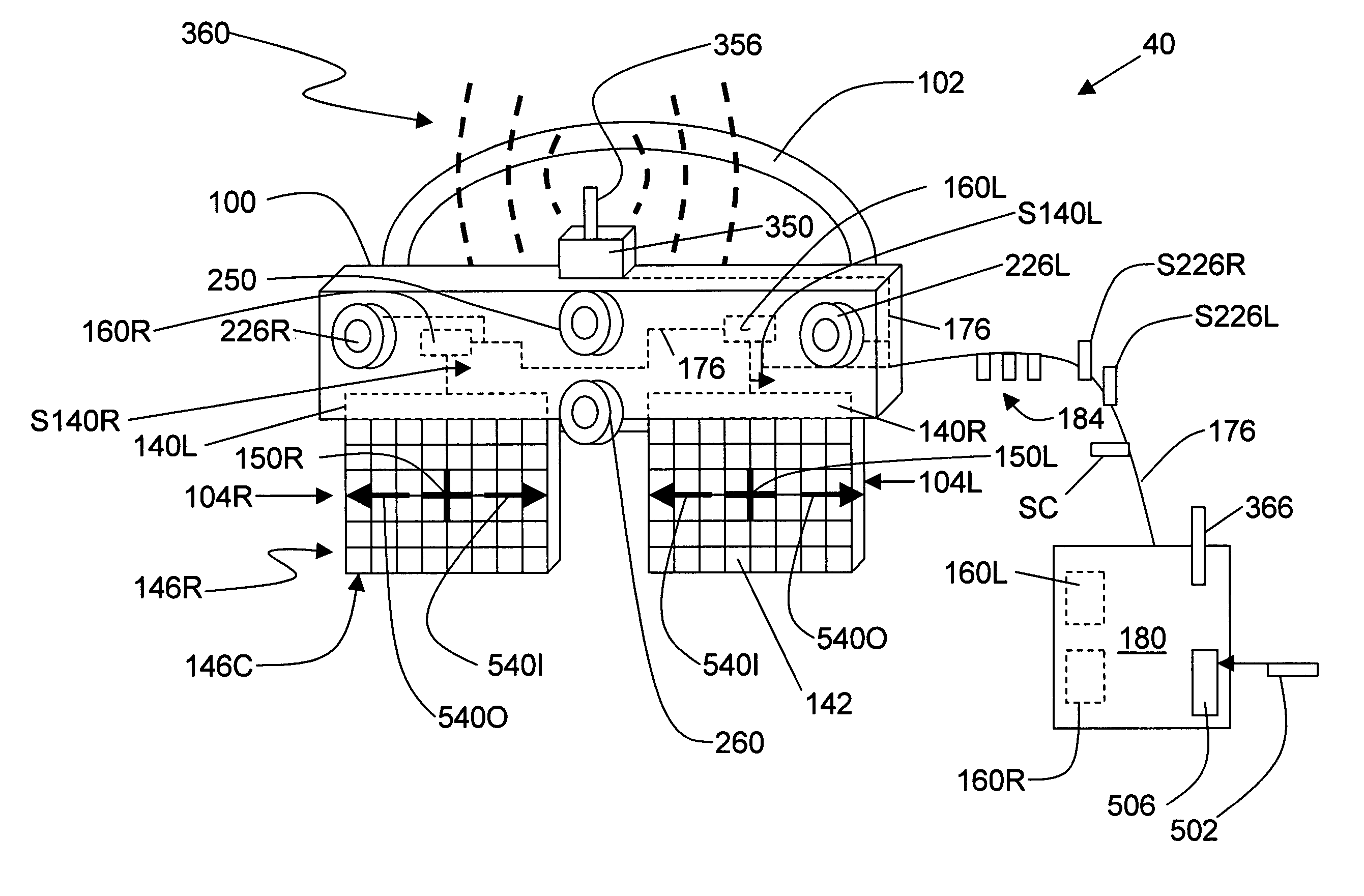
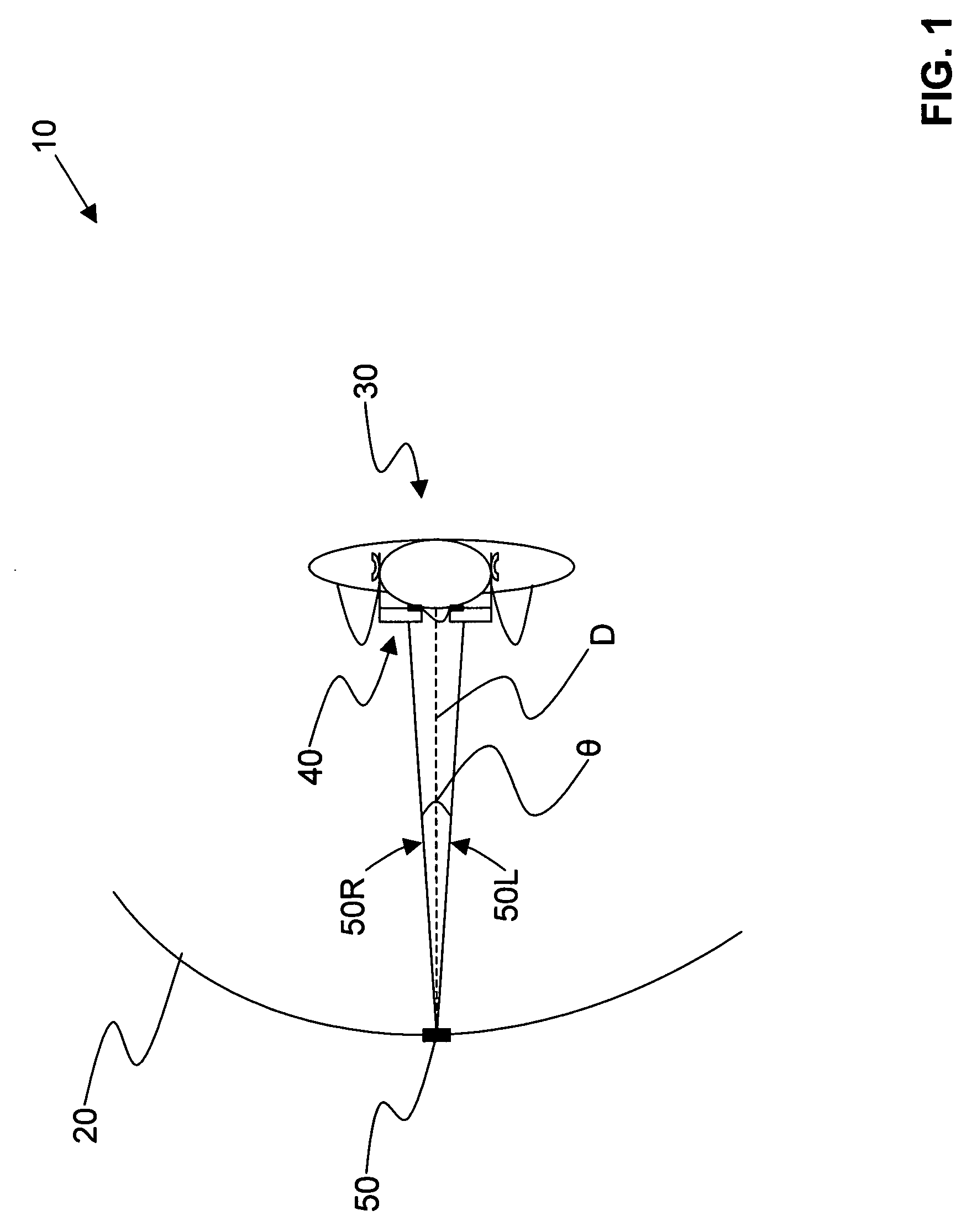
Dynamic vergence and focus control for head-mounted displays
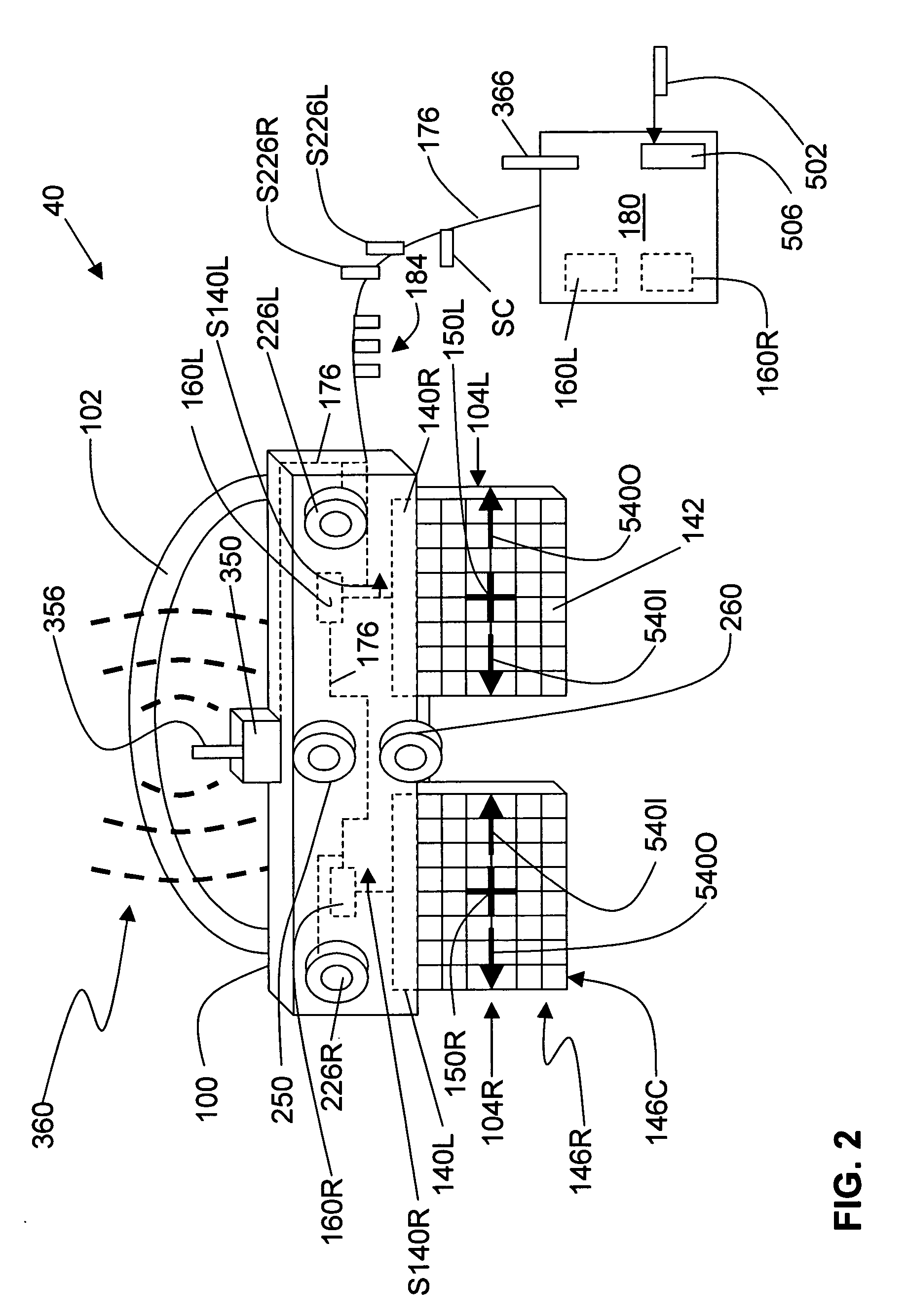
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling vergence and focus for a see-through head-mounted display (ST-HMD) used as part of an augmented reality (AR) system are disclosed. The ST-HMD (40) allows a user (30) to view left and right images (150L, 150R) through corresponding left and right eyepieces (104L, 104R) so that a single virtual object (150V) based on the right and left images as seen at a real object such as a screen (20). When the user moves relative to the real object, however, the vergence changes and the virtual object does not appear in focus at the real object. Changes in the vergence are compensated by tracking the user's head position with a tracking unit (350) and providing the tracking data to a controller (180). Based on the tracking data and the interpupilary distance (IPD) of the user, the controller calculates the offset (H) needed to be imparted to the images formed in the eyepieces to maintain the vergence of the virtual object at the real object even when the user's position changes relative to the real object.
Owner:OPTICS 1
Method and apparatus for dynamically controlling scroller speed employed for a user interface of a wearable appliance
InactiveUS7081905B1Amount of user manipulation of the scroller to get to a particular positionElectric indicationFrequency stabilisation mechanismDisplay deviceHuman–computer interaction
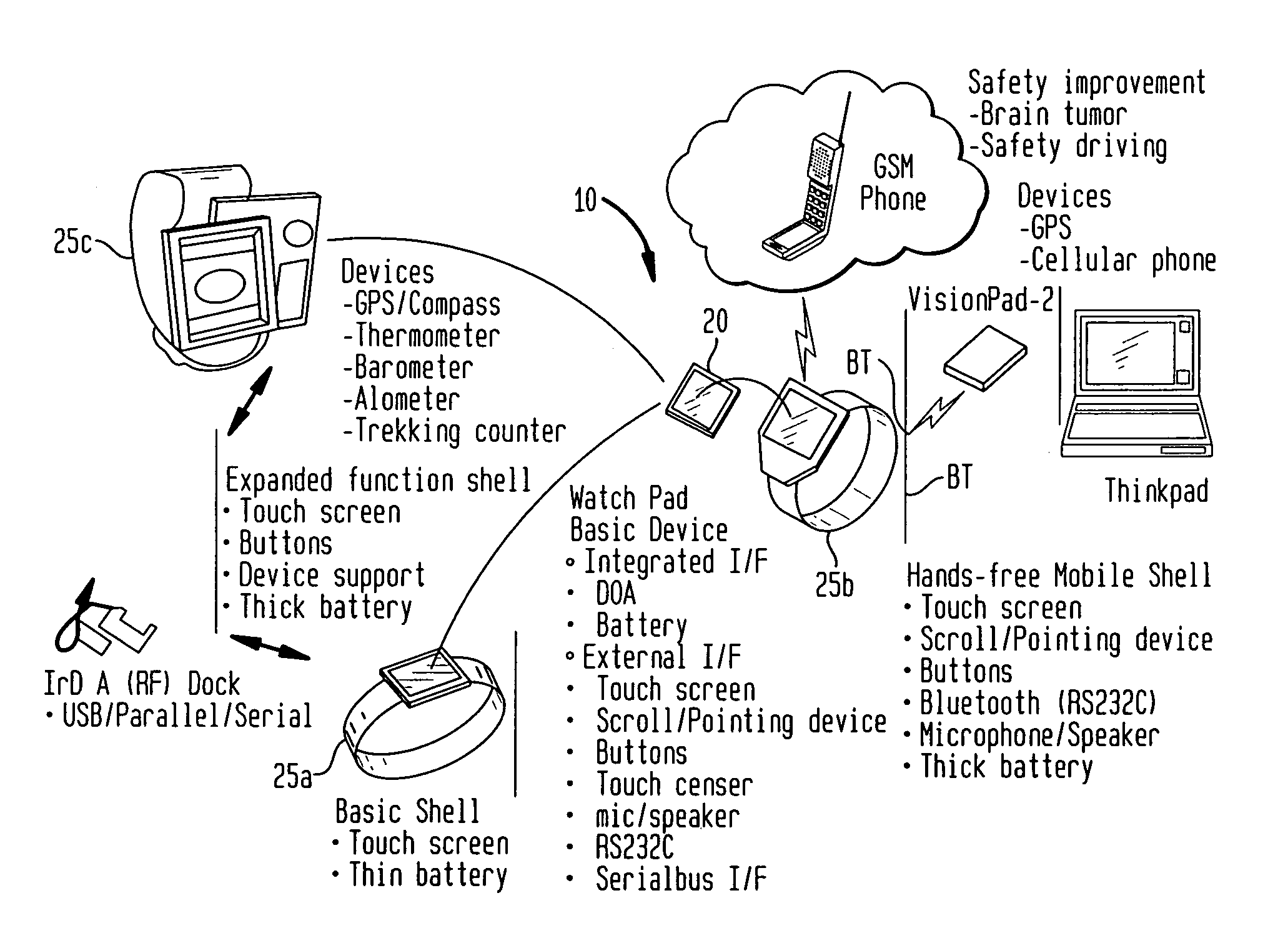
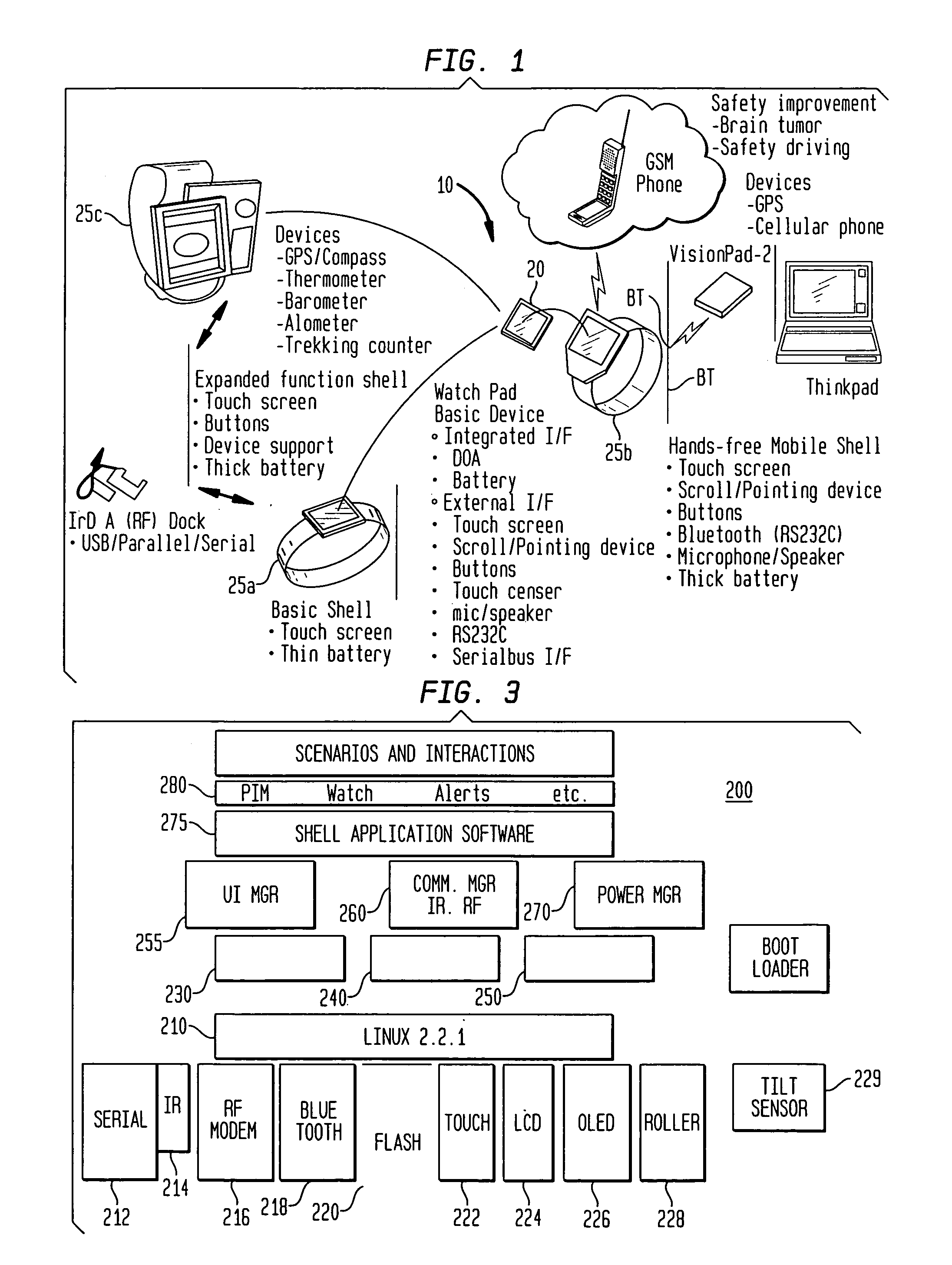
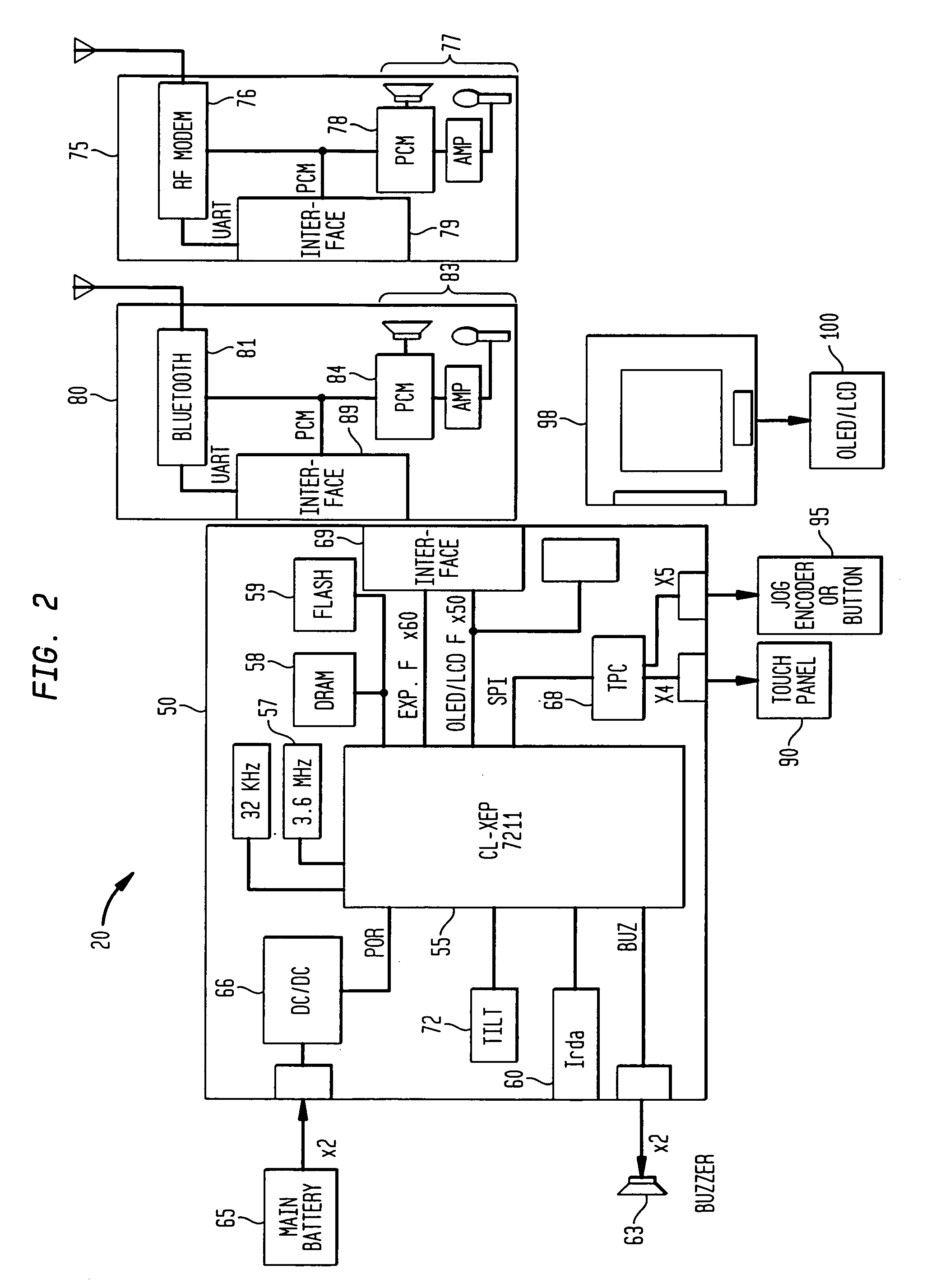
A wearable mobile computing device / appliance (e.g., a wrist watch) with a high resolution display that is capable of wirelessly accessing information from the network and a variety of other devices. The Wrist Watch device / appliance includes a user interface that is used to efficiently interact with alarms, time keeping functions and notifications on the watch via use of a scroll device implementing dynamic scroll speed controller capability which enables seamless fine-grain and coarse-grain scroll and / or cursor movement through displayed content without notice to the user of the scroll device.
Owner:IBM CORP
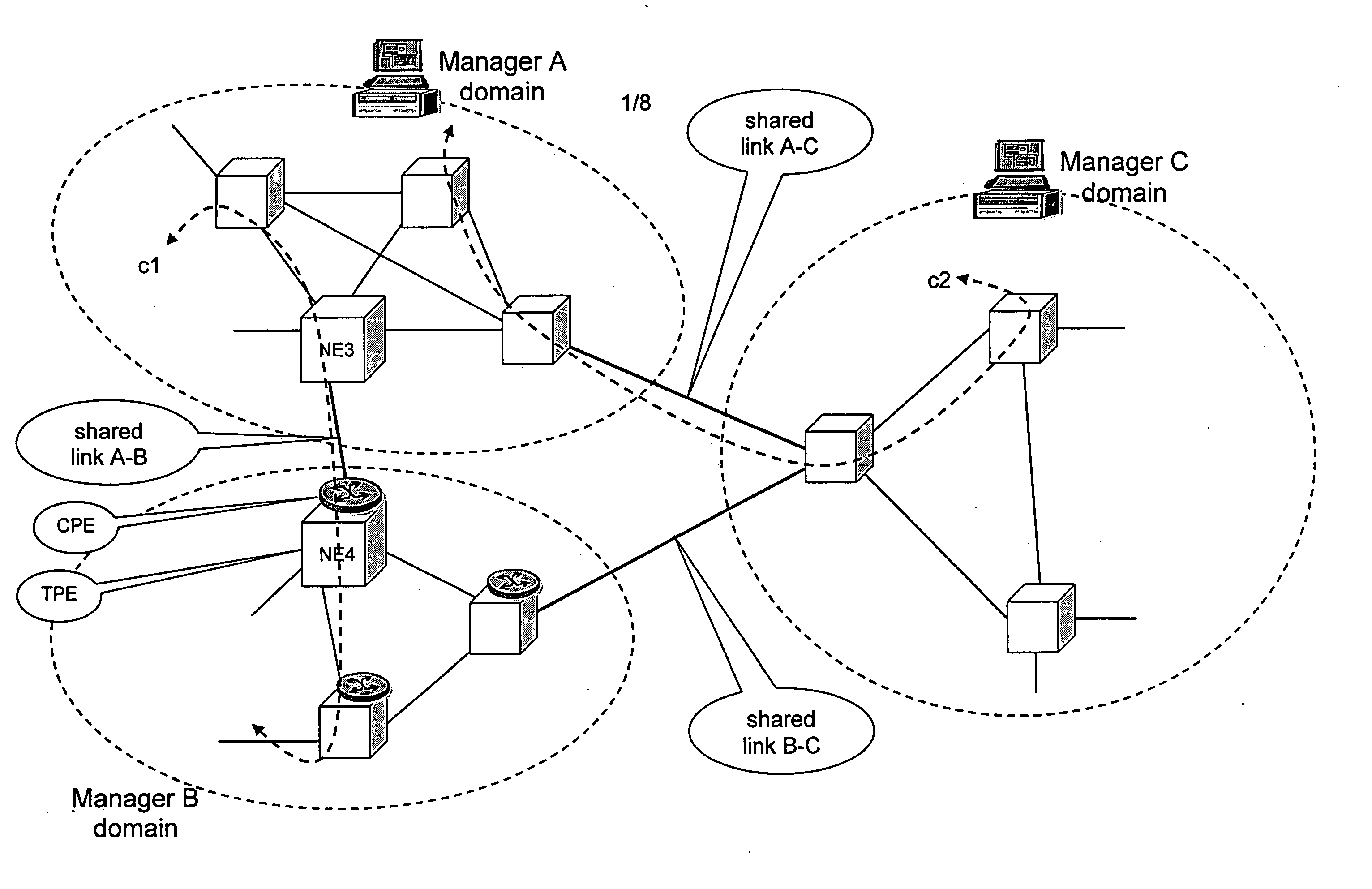
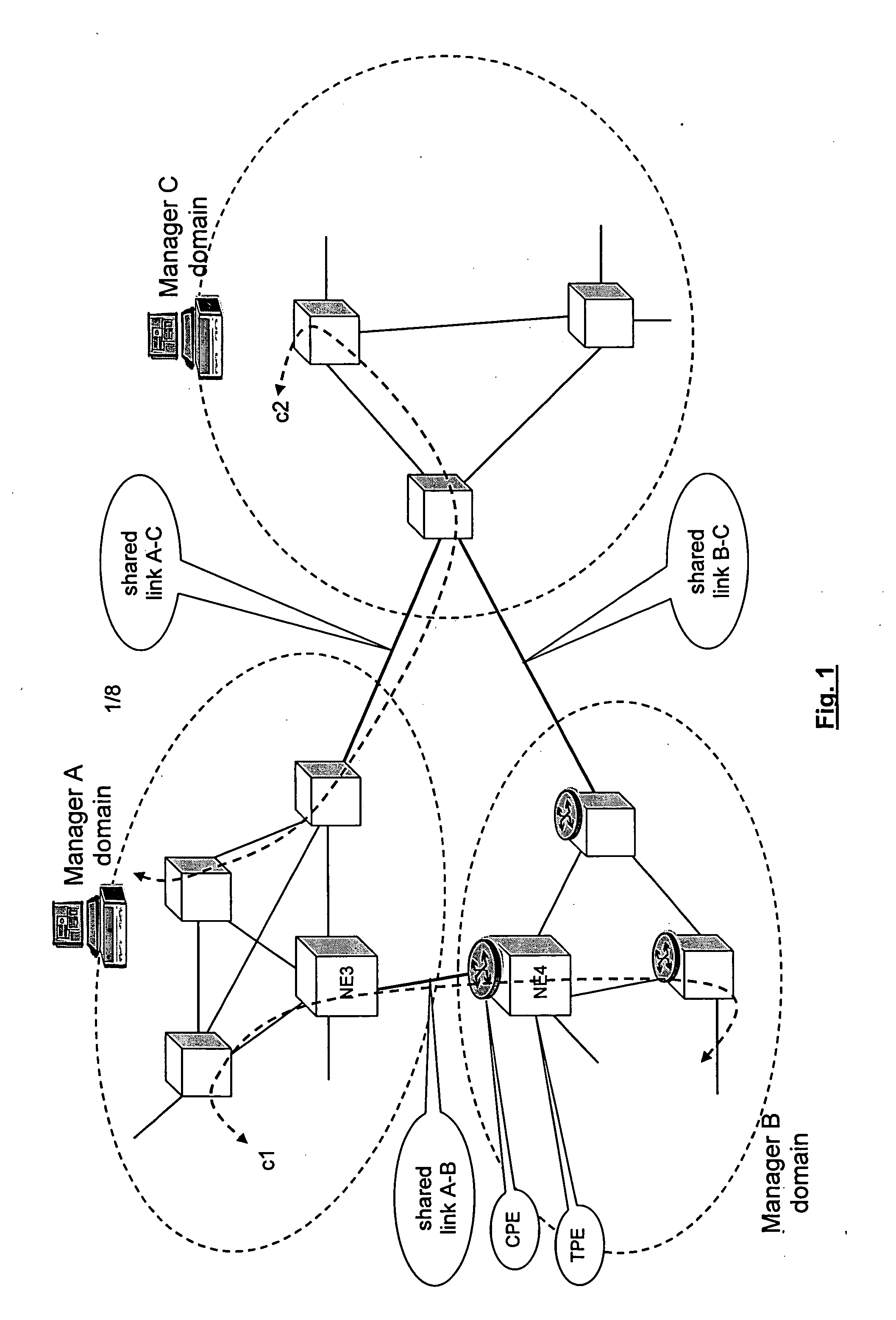
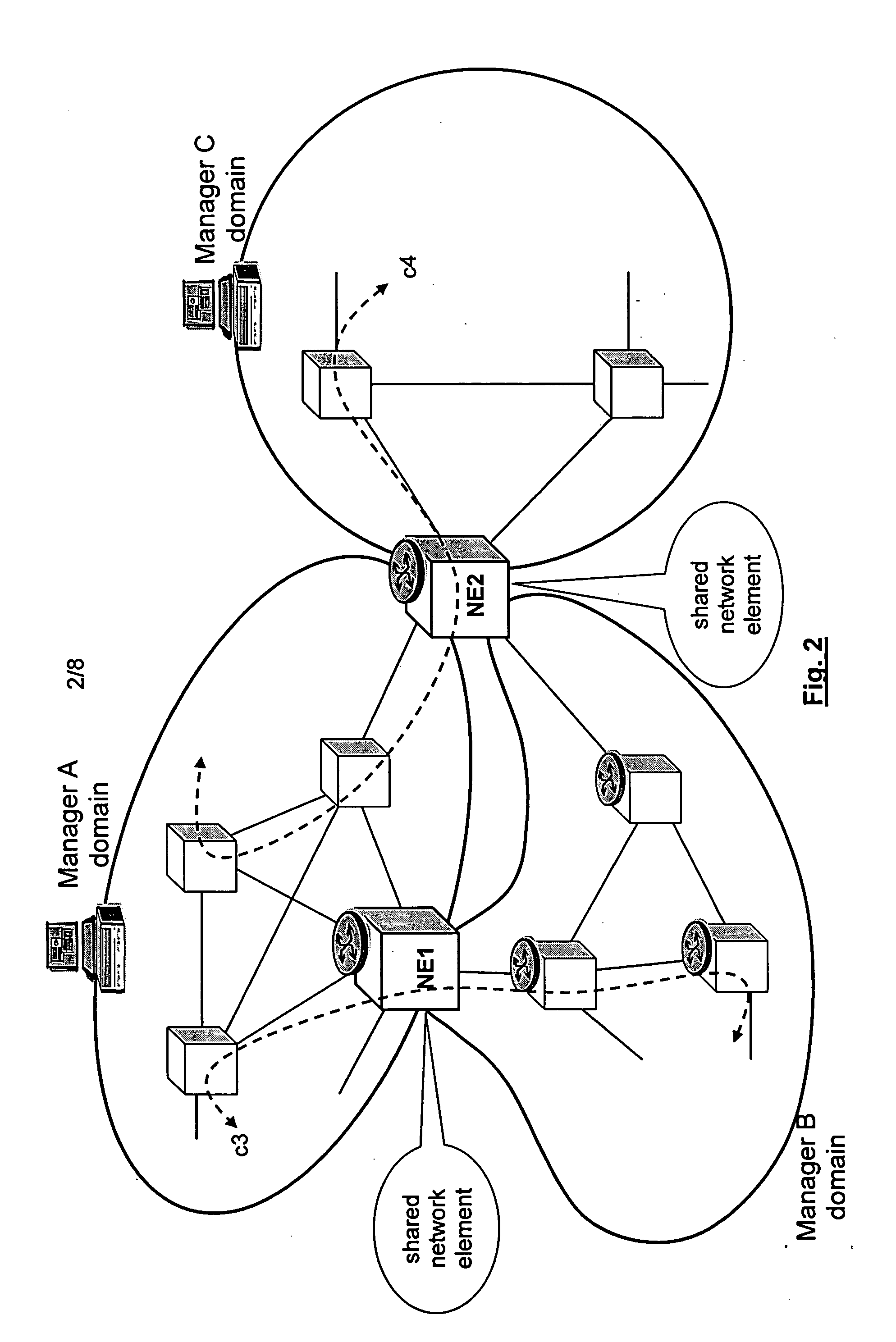
Shared resources in a multi manager environment
ActiveUS20060026225A1Reduce network element performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInformation repositoryManagement information base
A method is described for controlling a shared resource for interconnecting two or more network domains being controlled by different Managers. Multiple Managers control the shared resource for the configuration of a segment of a connection between two different domains and the Managers cooperate in order to control dynamically the shared resource. Different network domains can be connected by a network element or by a link between different network elements belonging to the different network domains. In the first case the shared resource is a connection matrix of the network element, in the second case the shared resource includes the connection matrixes of the different network elements and the link between the network elements. A shared connection matrix includes some connection points for performing the cross-connections within the matrix: some connection points are controlled by one Manager, other connection points are controlled by another Manager and some shared connection points are controlled by both Managers. Multiple Managers control the shared resource by reading and writing information stored into a management information base, according to an explicit or implicit mode, or alternatevely by transmitting messages in the network directly between the Managers, according to a signalling protocol.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
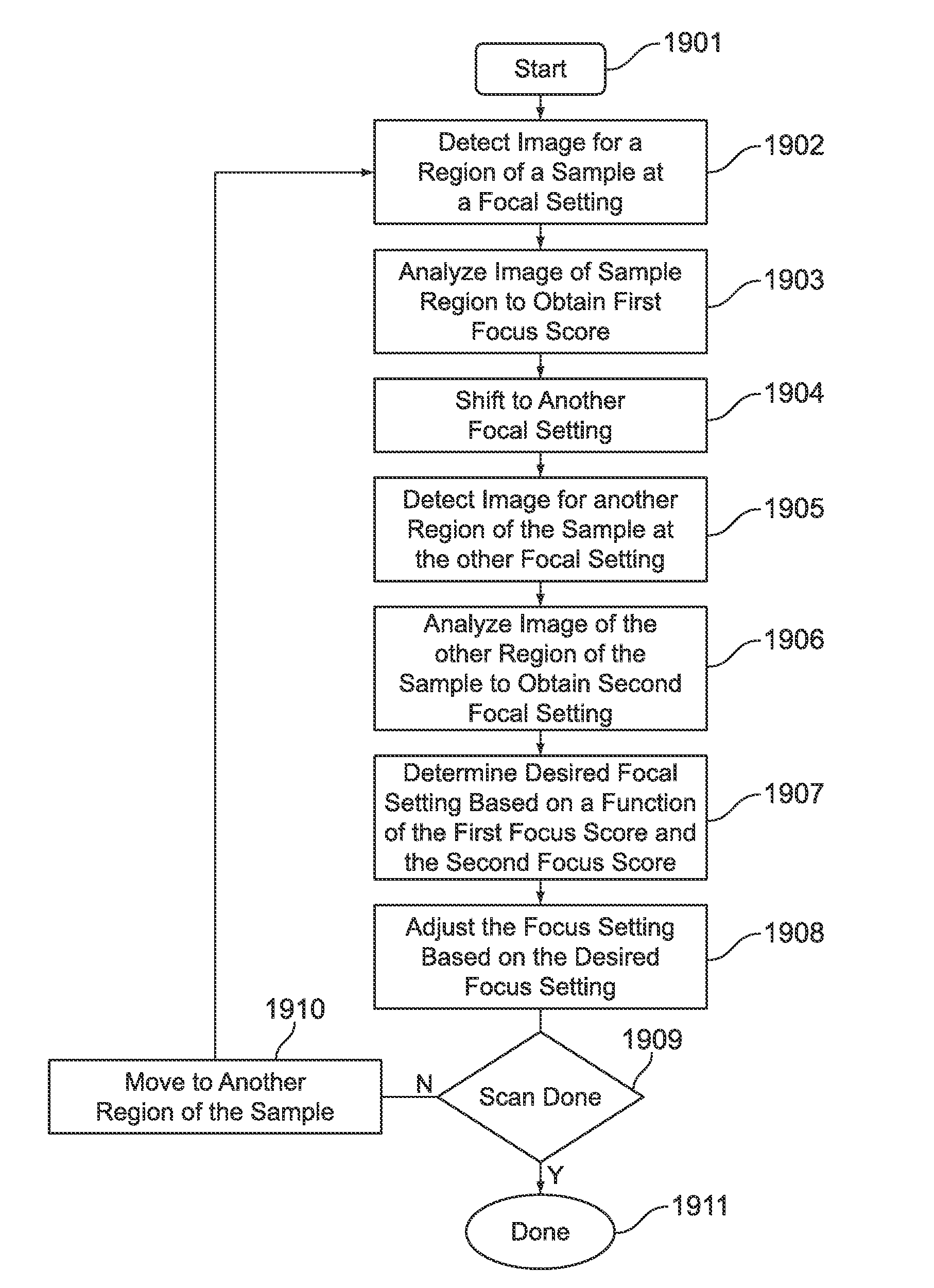
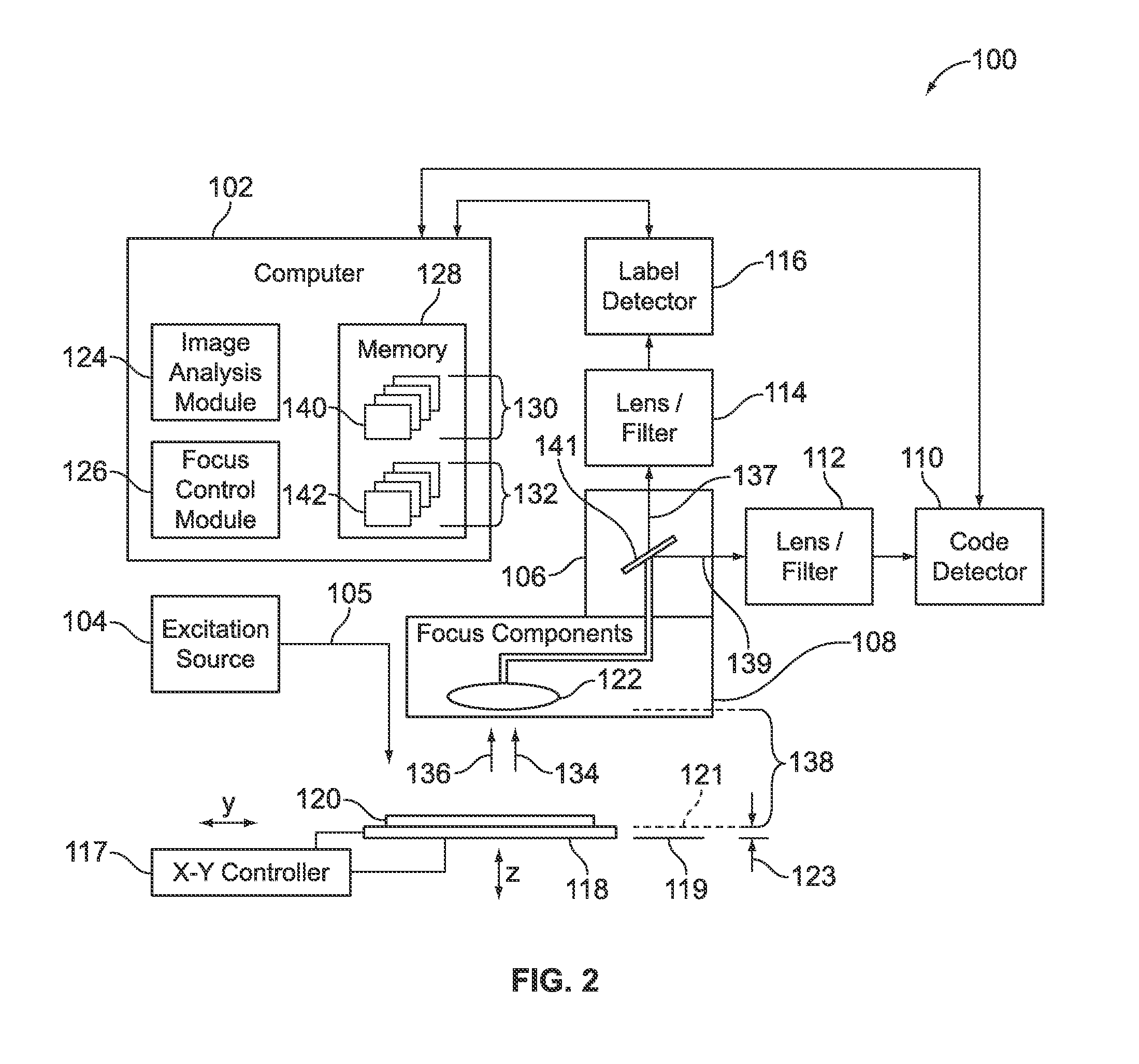
Dynamic autofocus method and system for assay imager
InactiveUS20100157086A1Television system detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayAssociate degree
A method and system are provided for controlling focus dynamically of a sample imager. The method comprises scanning a sample with an optical assembly that apportions the sample into regions based on a scan pattern. The optical assembly has a focal setting with respect to the sample. The method further comprises shifting the focal setting of the optical assembly during scanning of the sample, and detecting one or more images representative of one of the regions from the sample. The one or more images have associated degrees of focus corresponding to the focal setting of the optical assembly. The method analyzes the image(s) to obtain a focus score or scores corresponding thereto, where the focus scores represent a degree to which the optical assembly was in focus when detecting the images. The method adjusts the focus setting based on the focus score(s).
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Enhanced viewing experience of a display through localised dynamic control of background lighting level
ActiveUS20060125745A1Improve video viewing experienceEnhanced and modified visual experienceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceEffect light
A method of controlling brightness, colour, hue, colour temperature, gamma response or contrast of at least one image for display on a multi-layer display device characterized by carrying out the steps of: receiving said at least one image(s) to be displayed, detecting the brightness, colour, hue, colour temperature, gamma response or contrast of said image(s) to be displayed, determining the transmissivity of each layer of the multi layer display device in the localized area of said image(s) to achieve the brightness, colour, hue, colour temperature, gamma response and / or contrast detected or received, communicating the determined transmissivity of each layer of the multi layer display device in the localized area of said image(s) to a display device or storage device. A software device designed to do the same and a display device which can be utilized to controlling brightness, colour, hue, colour temperature, gamma response or contrast of at least one image.
Owner:PUREDEPTH
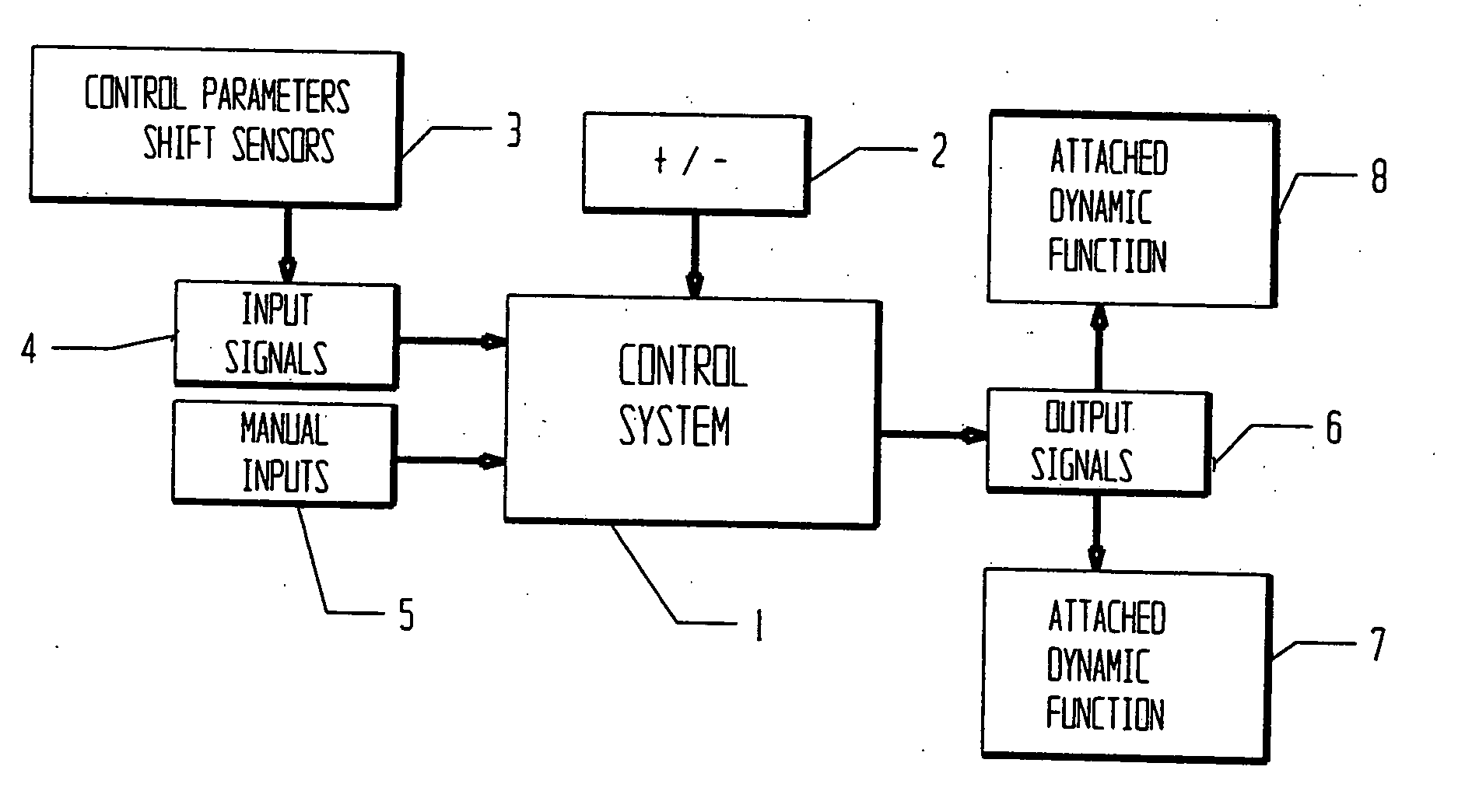
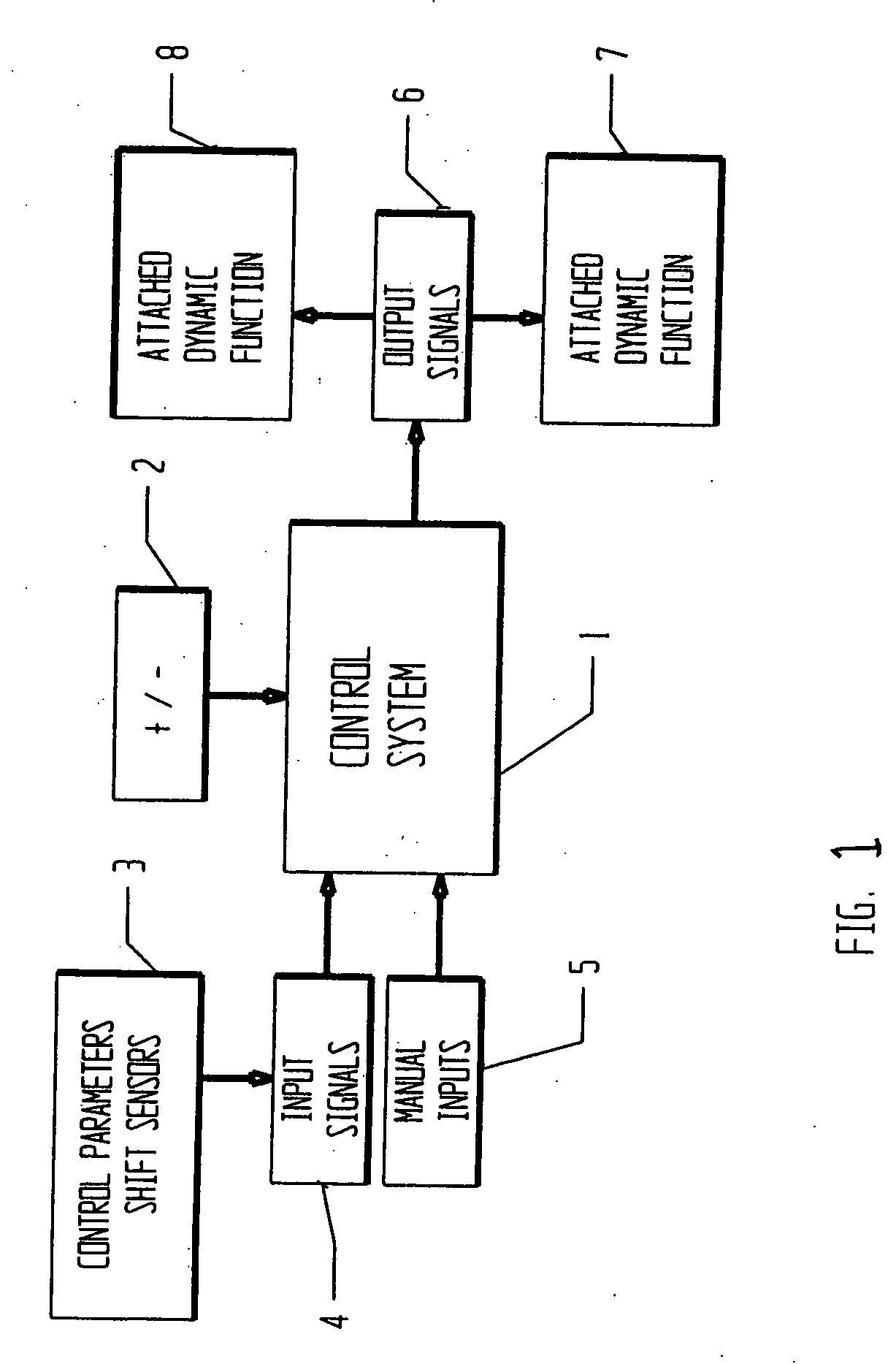
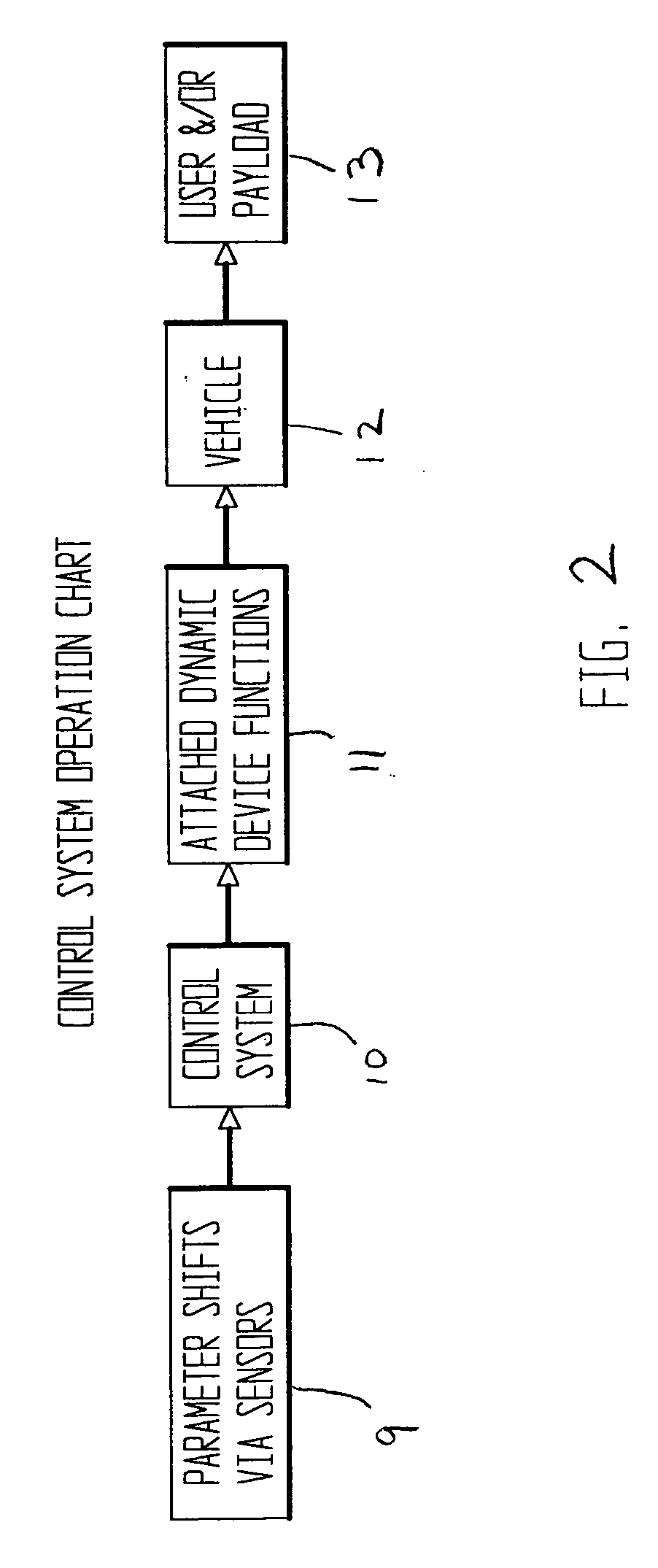
Vehicle systems and method
InactiveUS20060064223A1Improvement in vehicle ride characteristicEnhance ride characteristicDigital data processing detailsAxle suspensionsControl systemParameter control
A multiple parameter control system for a vehicle includes sensors to measure the control parameter shifts in relation to the vehicle, a controller to determine outputs, a dynamically adjustable vehicle system with controllable functions, and a power supply. The sensors measure the control parameter shifts and create representative input signals that are sent to the controller. The controller determines the appropriate outputs in response to the relative control parameter shift input signals received. The dynamically adjustable vehicle system with controllable functions receives the controller output and performs a dynamic control function adjustment to improve a vehicle ride characteristic.
Owner:VOSS
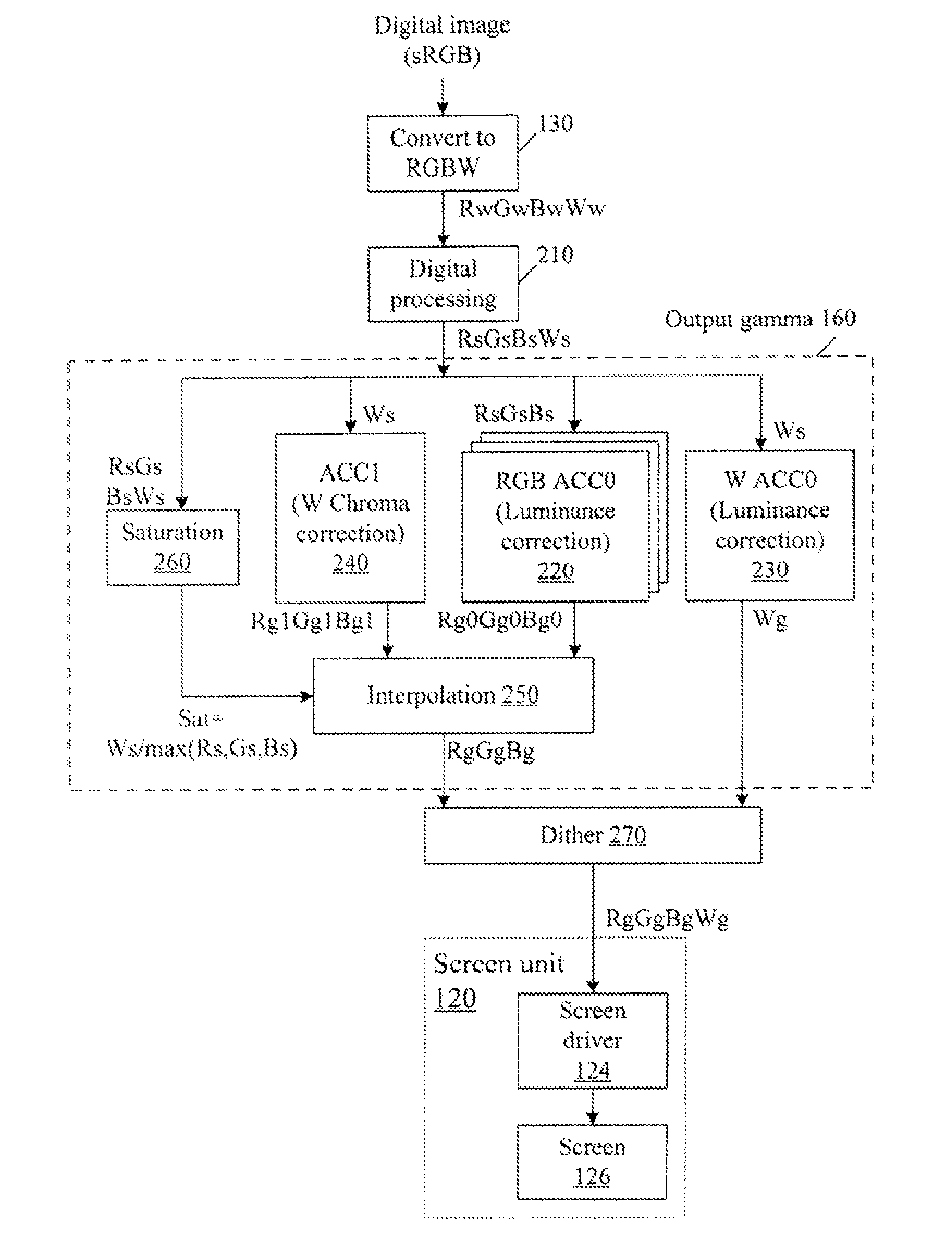
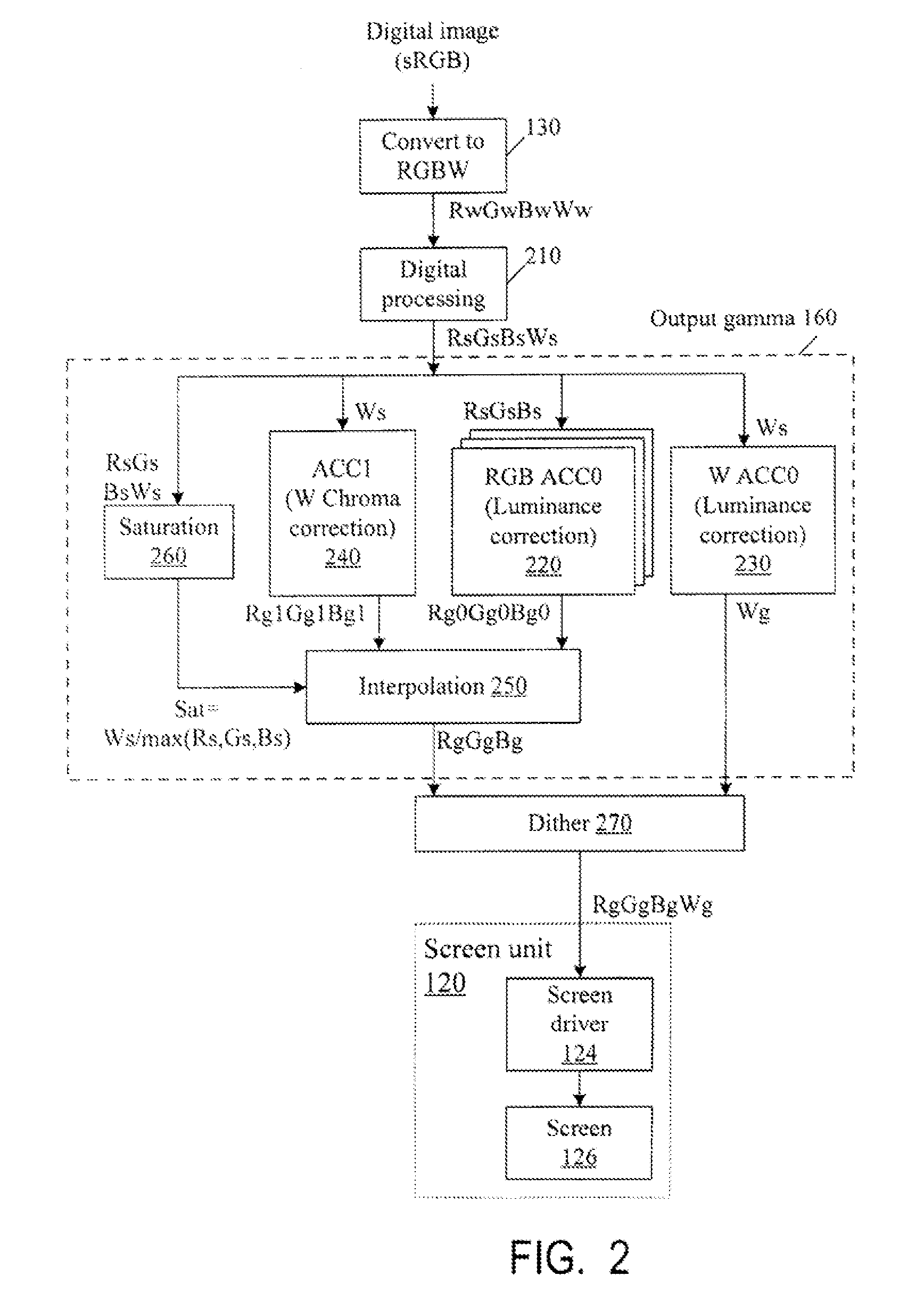
Color correction to compensate for displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics
ActiveUS20110149166A1Image degradation can be highIncrease brightnessTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor correctionDisplay device
Displays are provided with circuitry performing color correction to compensate for the displays' luminance and chrominance transfer characteristics. Some techniques are suitable for RGBW displays and for subpixel-rendered displays. Some displays include an external light source (e.g. a backlight unit in LCDs), and the color correction is coordinated with dynamic control of the light source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Dynamic stabilization for a stream processing system
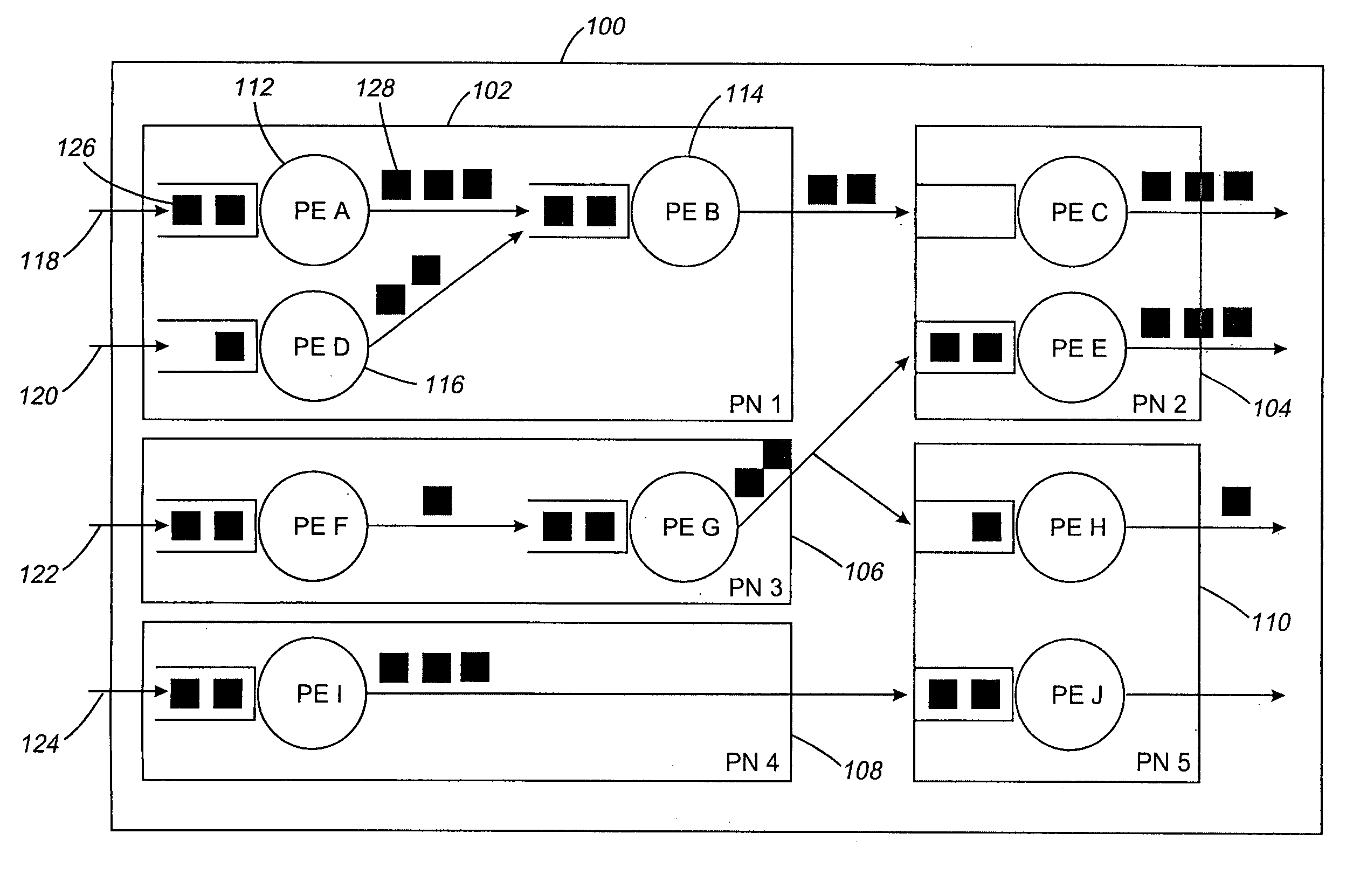
InactiveUS7613848B2Function maximizationMaintain stabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDownstream processingProcessing element
Disclosed are a method, upstream processing node, and computer readable medium for dynamically stabilizing a stream processing system. The method includes receiving at least one computing resource allocation target. The method further includes determining that an input data flow rate of at least one upstream processing element varies. The computing resource is dynamically allocated to the upstream processing element in response to the input rate of the upstream processing element varying. Data flow is dynamically controlled between the upstream processing element and at least one downstream processing element.
Owner:IBM CORP
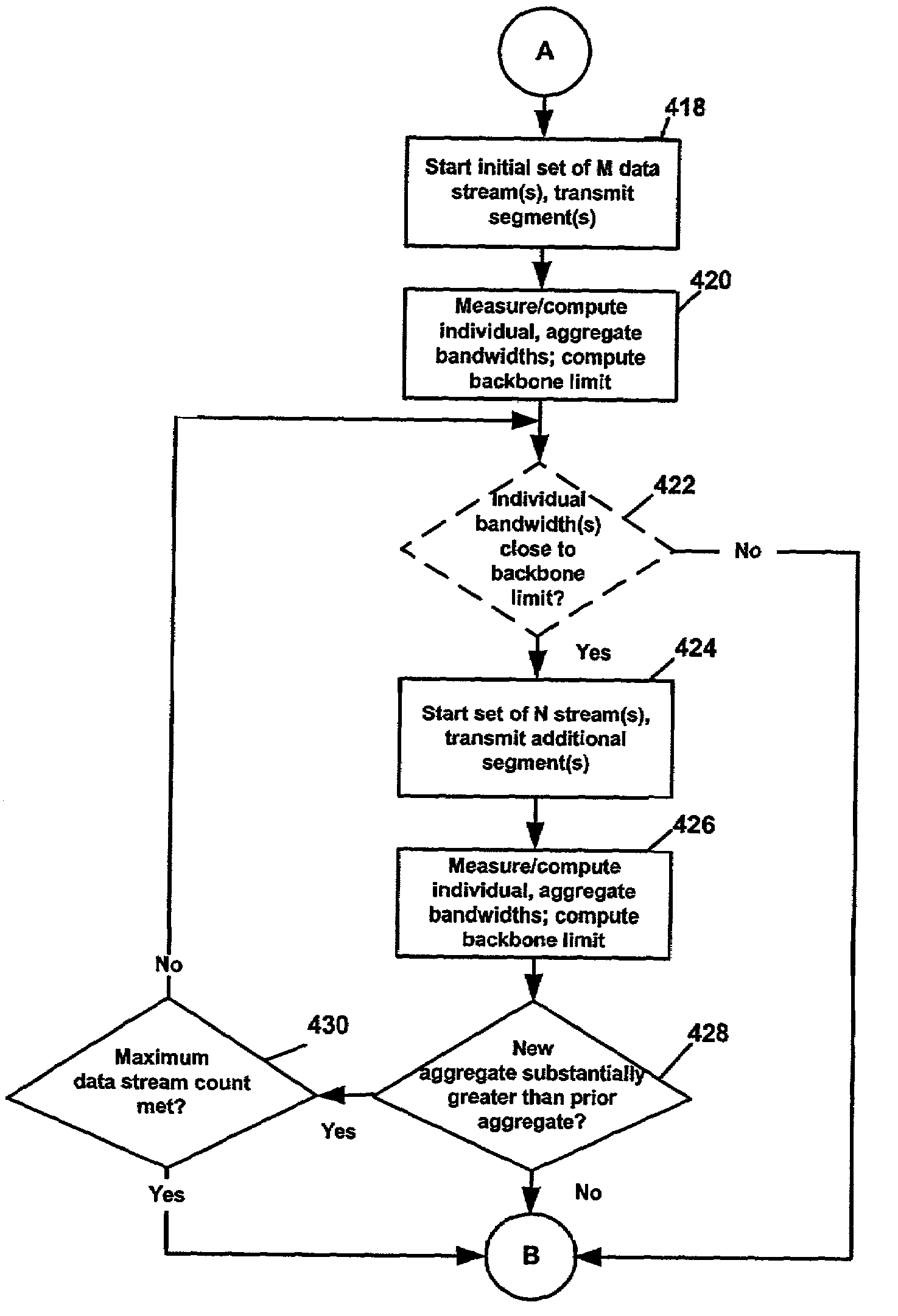
Load balancing and dynamic control of multiple data streams in a network
InactiveUS7047309B2Increase transfer rateHigh bandwidthTelephonic communicationData switching by path configurationLoad SheddingData stream
Available bandwidth utilization during transfer of large files over a TCP / IP network is improved by load balancing data streams and dynamically controlling the number of data streams utilized. A determination is made of the optimum number of data streams for a particular data file transfer in the early stage of transmission. An initial number of data streams, which is one unless otherwise specified or determined, is used to transmit one or more file segments, each on a different data stream, immediately followed by a second initial number of data streams, which is at least two greater than the initial number of data streams, is used to transmit another portion of the large data file. During each transmission, individual and aggregate transmission bandwidths are determined. Responsive to a determination that the latest aggregate transmission bandwidth is significantly different from the previous aggregate transmission bandwidth, the number of data streams is modified.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
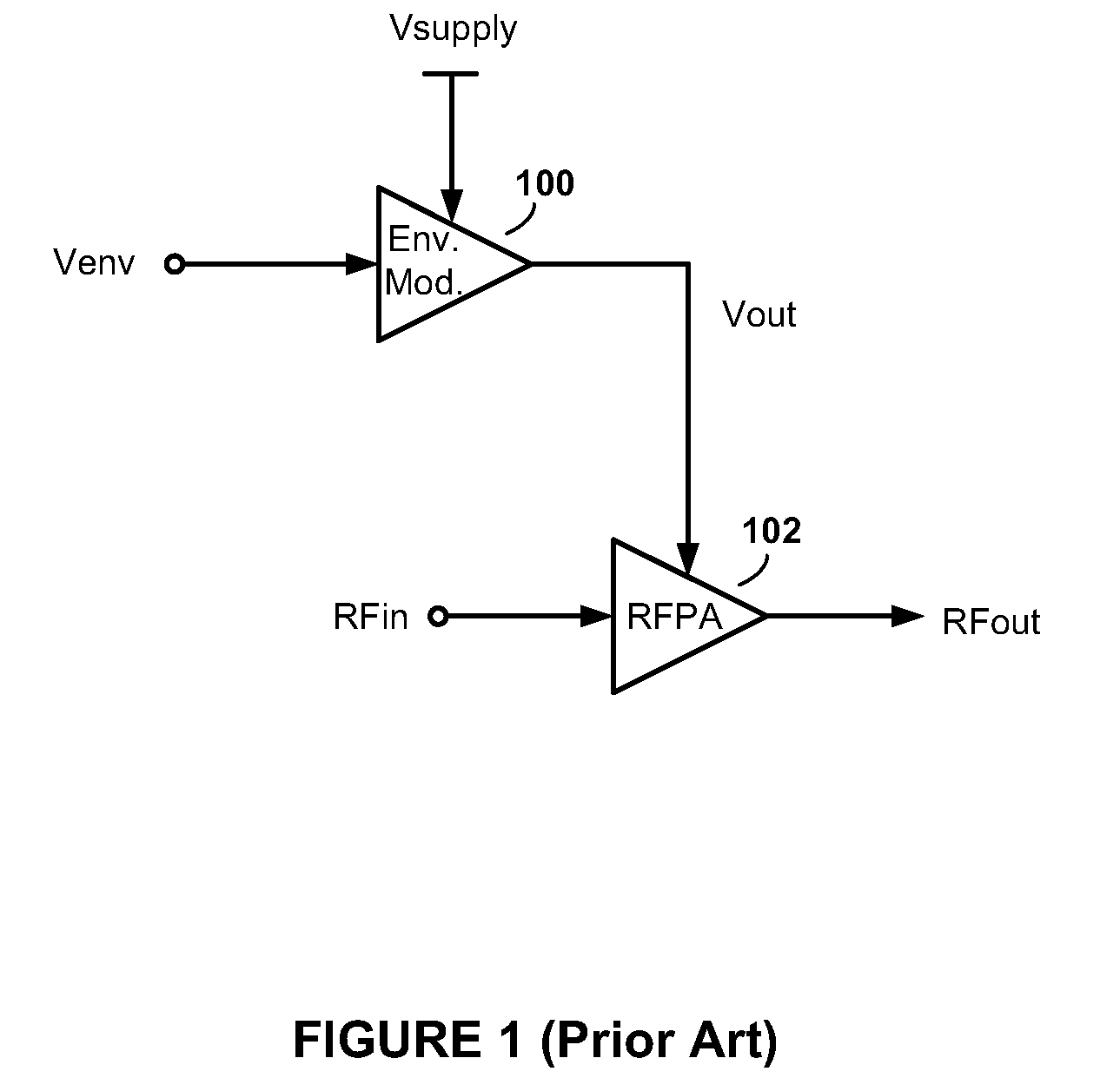
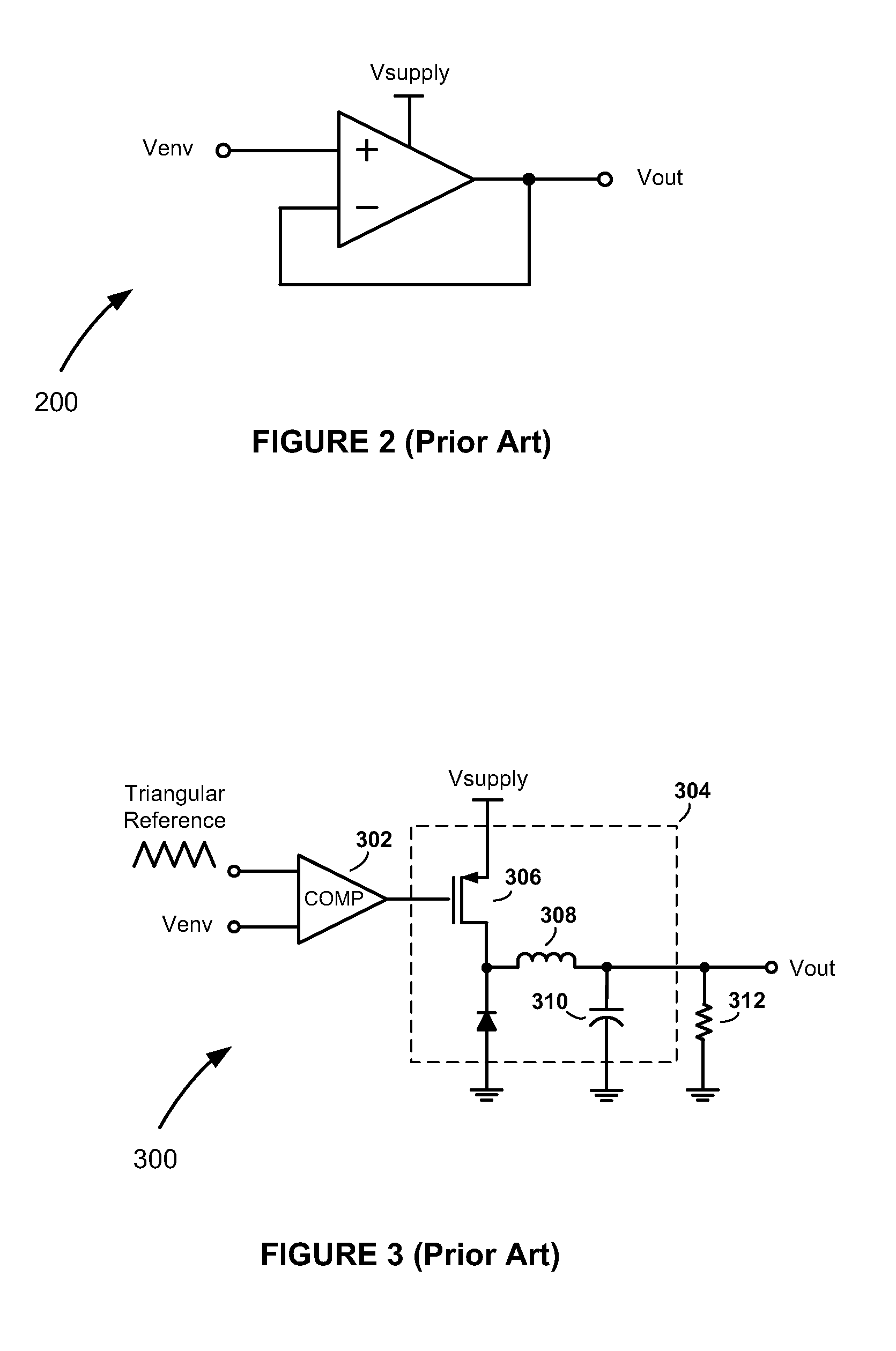
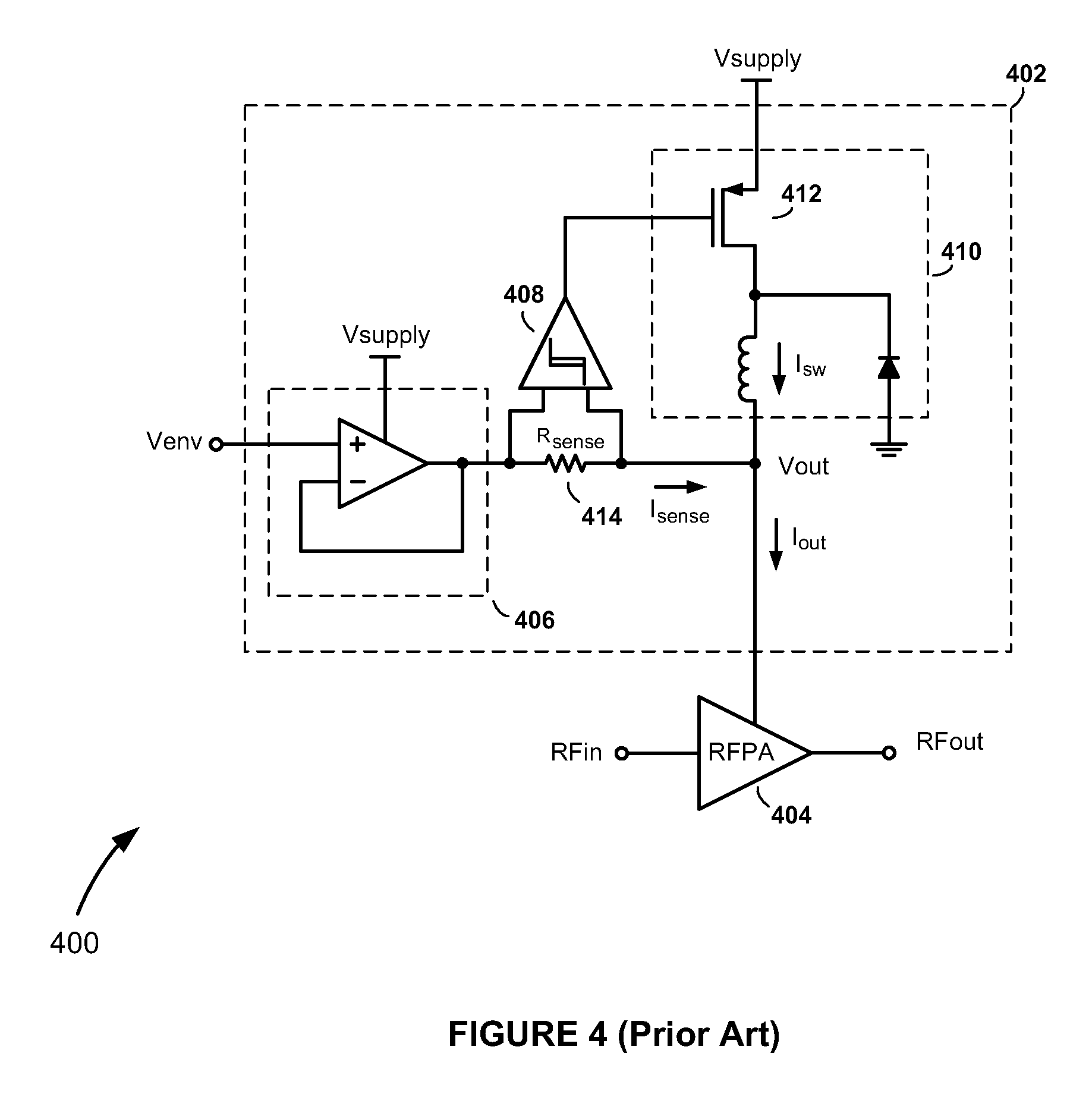
High-Efficiency Envelope Tracking Systems and Methods for Radio Frequency Power Amplifiers
ActiveUS20090289720A1Efficiency penaltyDc network circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersLinear regulatorControl power
High-efficiency envelope tracking (ET) methods and apparatus for dynamically controlling power supplied to radio frequency power amplifiers (RFPAs). An exemplary ET circuit includes a switch-mode converter coupled in parallel with a split-path linear regulator. The switch-mode converter is configured to generally track an input envelope signal Venv and supply the current needs of a load (e.g., an RFPA). The split-path linear regulator compensates for inaccurate envelope tracking by sourcing or sinking current to the load via a main current path. A current sense path connected in parallel with the main current path includes a current sense resistor used by a hysteresis comparator to control the switching of the switch-mode converter. The split-path linear regulator is configured so that current flowing in the current sense path is a lower, scaled version of the current flowing in the main current path.
Owner:INTEL CORP
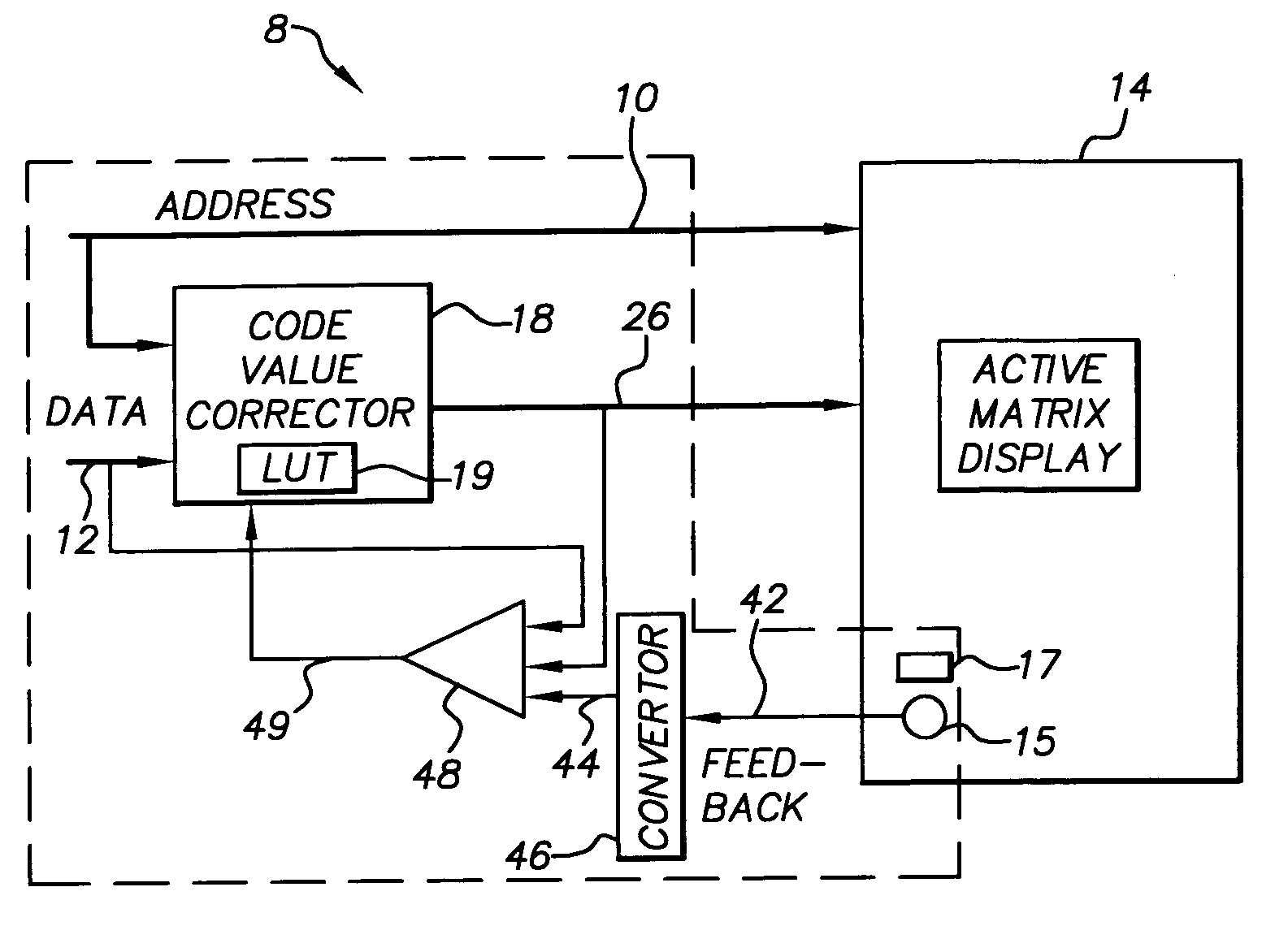
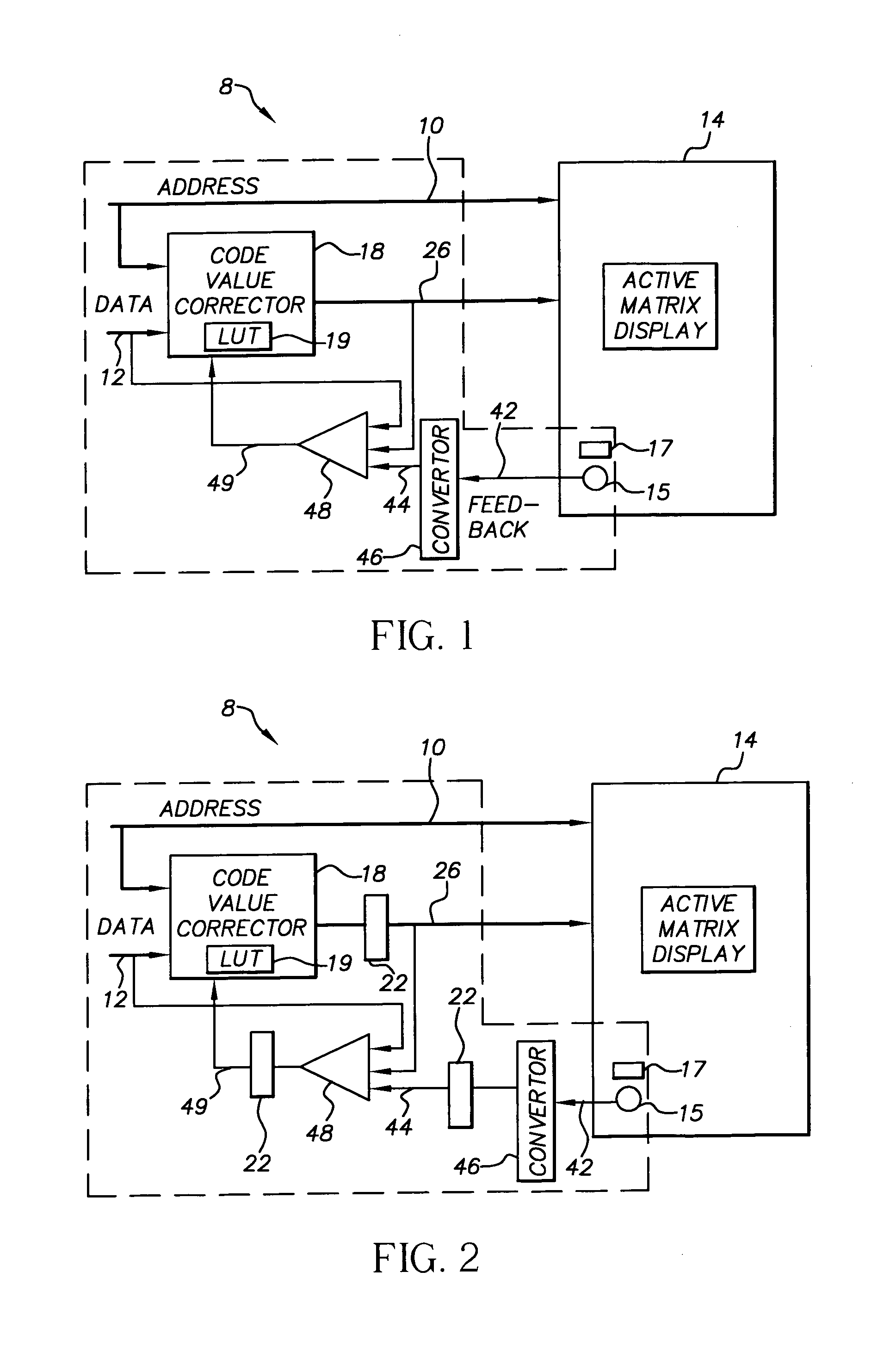
Dynamic controller for active-matrix displays
A dynamic controller for a light emitting active-matrix display, the display being responsive to code values for producing a light output, including: photosensor located on the display for sensing the light output from the display and generating a feedback signal representative thereof; a feedback signal converter for converting the feedback signal to a converted feedback signal having the same form as the code value; a code-value corrector including a memory responsive to a code value for producing a corrected code value; and an update calculator responsive to the converted feedback signal, the code value and the corrected code value to update the memory to minimize the difference between the converted feedback signal and the code value.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
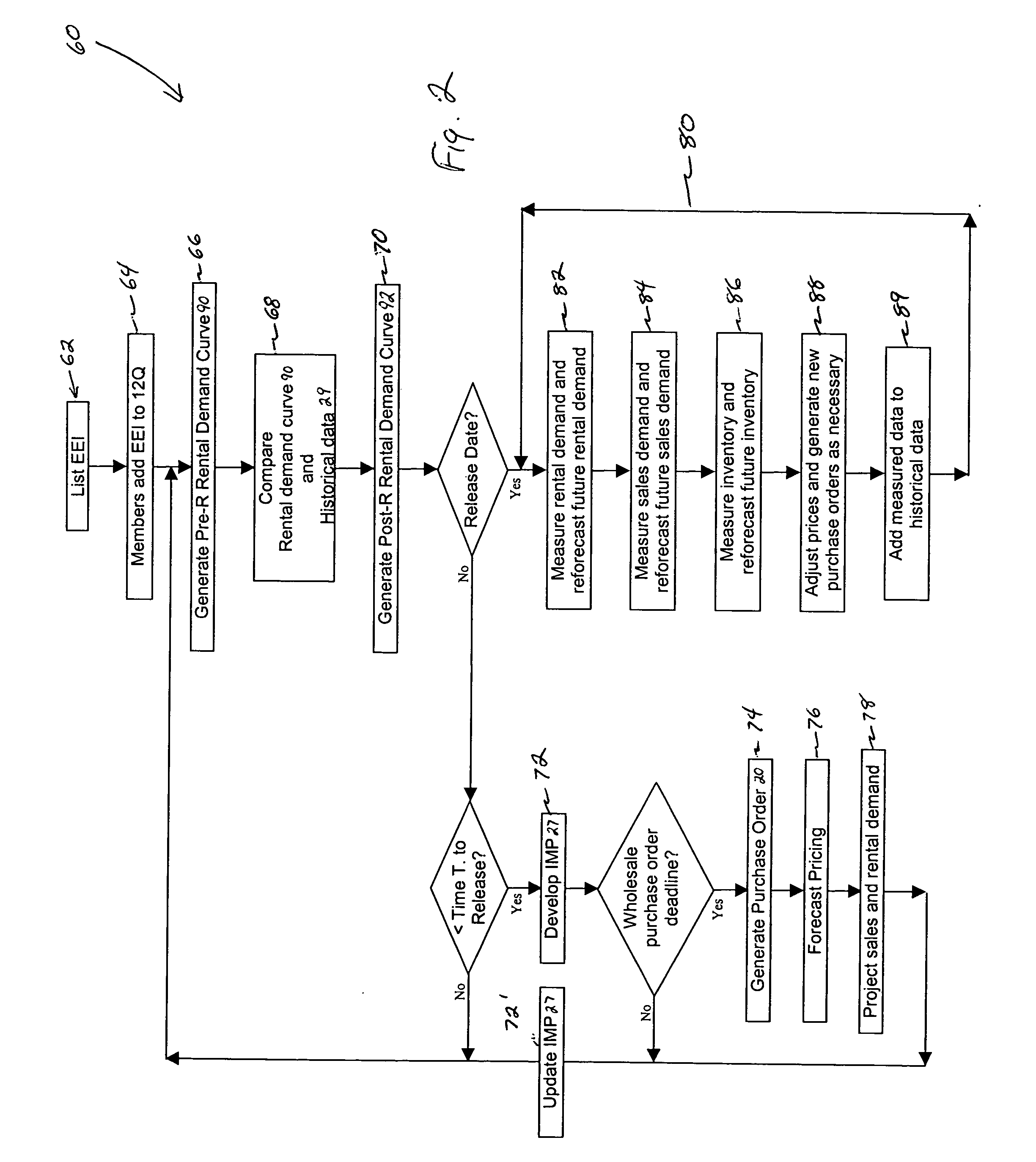
Method and apparatus for managing demand and inventory
InactiveUS20040068451A1Increase salesDecrease stockSpecial data processing applicationsMarketingComputer scienceInventory level
The present invention is directed to a method and system for managing the inventory level of, and the distribution of, electronic media rental units, including but not limited to videogame discs, musical compact disks, or movie VCD / DVDs. More specifically, preferred embodiments of the present invention forecasts future rental and sales demand for a given electronic media, such as a videogame, prior to the release of that electronic media to the general public. The forecast is based on the pre-release demand of the electronic media in that the future rental and sales demand is estimated from the rental and sales demand of previously released electronic media having similar pre-release demand. Furthermore, the preferred embodiments of the present invention allows registered members of a rental user group to keep rented units of the electronic media for a purchase price, which is dynamically controlled to minimize rental shortage and maximize profits.
Owner:GAMEFLY
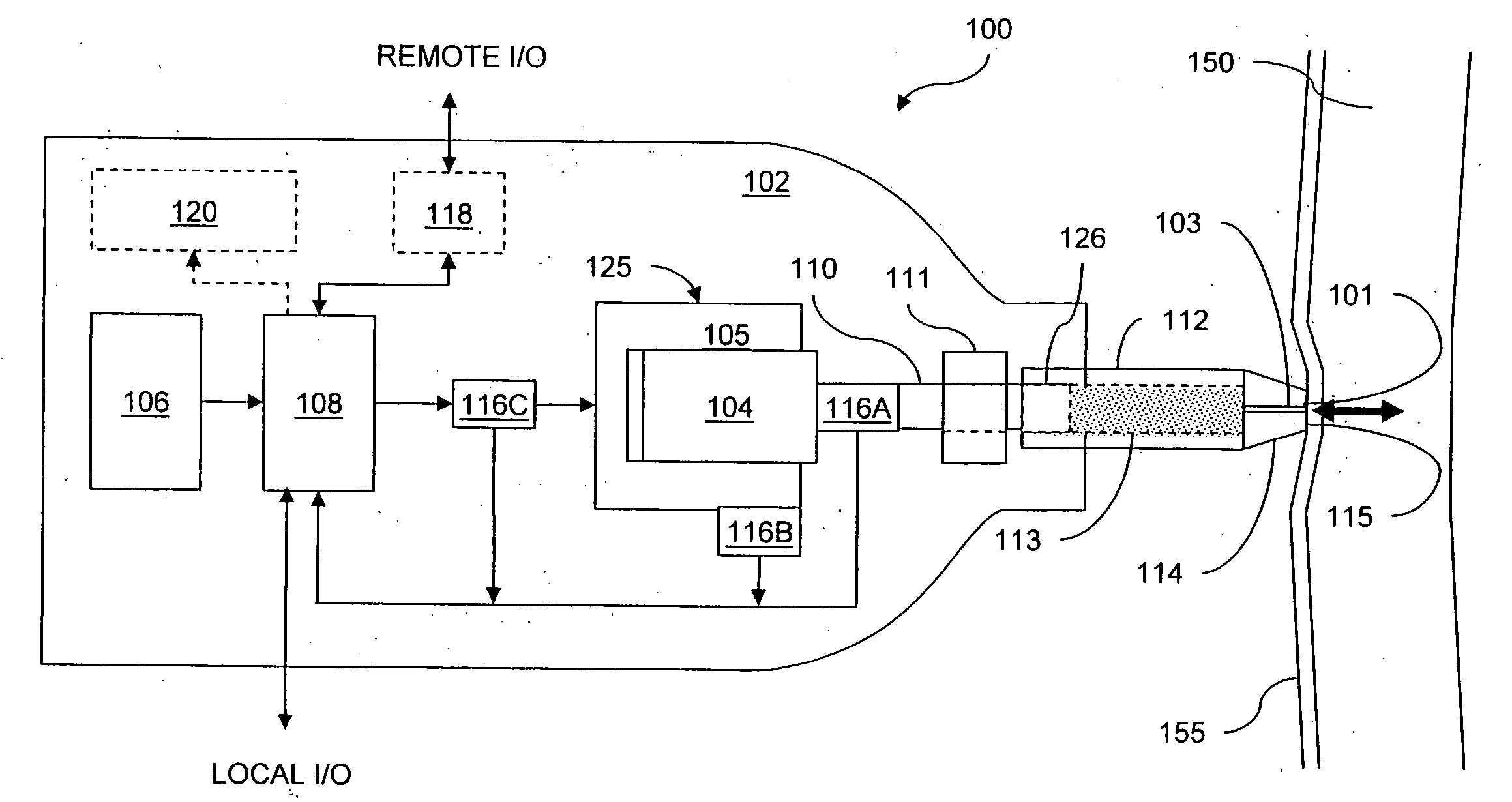
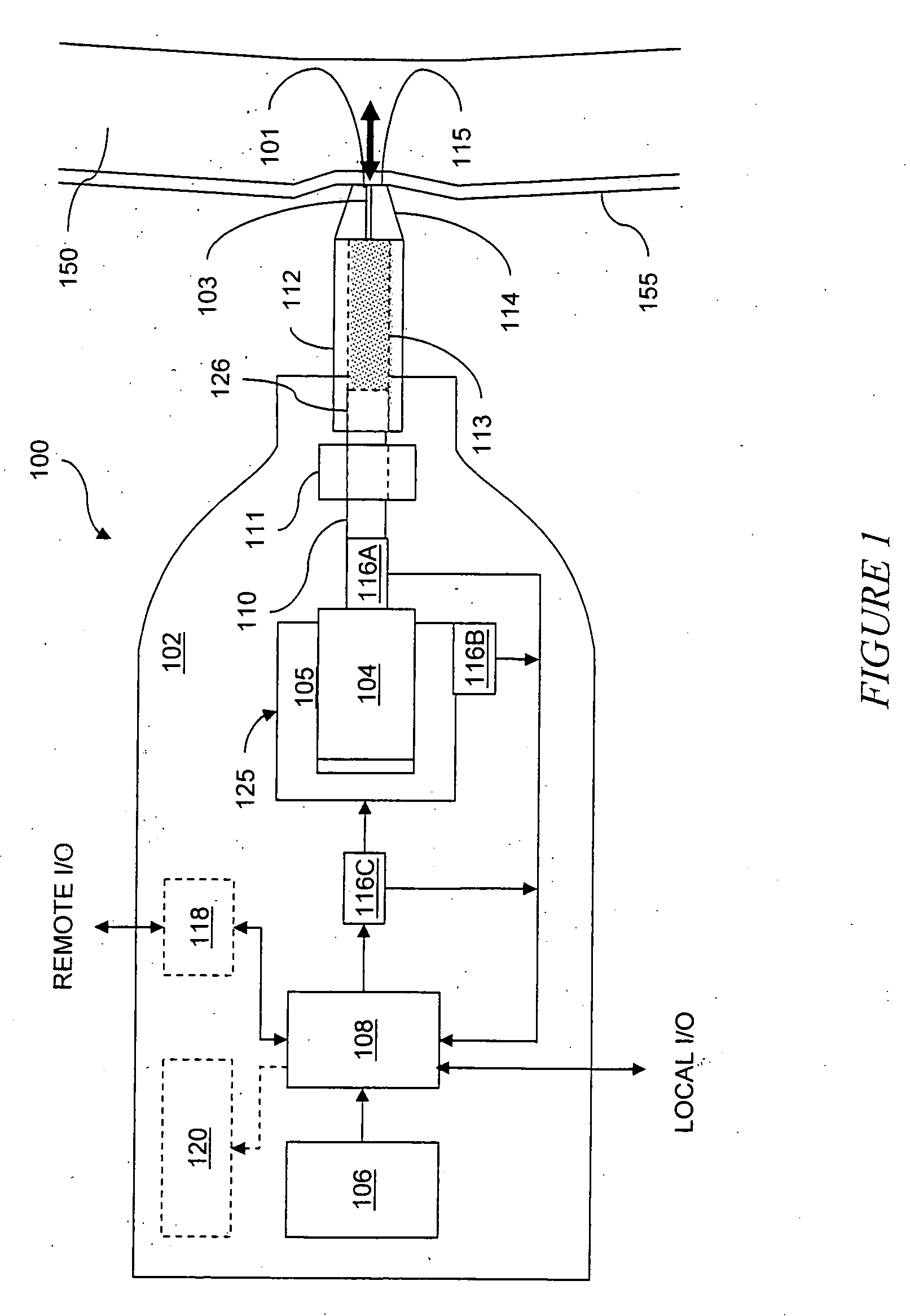
Controlled needle-free transport
InactiveUS20060258986A1Easy to controlJet injection syringesAutomatic syringesNeedle freeBiological body
A needle-free transdermal transport device for transferring a substance across a surface of a biological body includes a reservoir for storing the substance, a nozzle in fluid communication with the reservoir and a controllable electromagnetic actuator in communication with the reservoir. The actuator, referred to as a Lorentz force actuator, includes a stationary magnet assembly and a moving coil assembly. The coil assembly moves a piston having an end portion positioned within the reservoir. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a corresponding force acting on the piston and causing a needle-free transfer of the substance between the reservoir and the biological body. The magnitude, direction and duration of the force are dynamically controlled (e.g., servo-controlled) by the electrical input and can be altered during the course of an actuation cycle. Beneficially, the actuator can be moved in different directions according to the electrical input.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
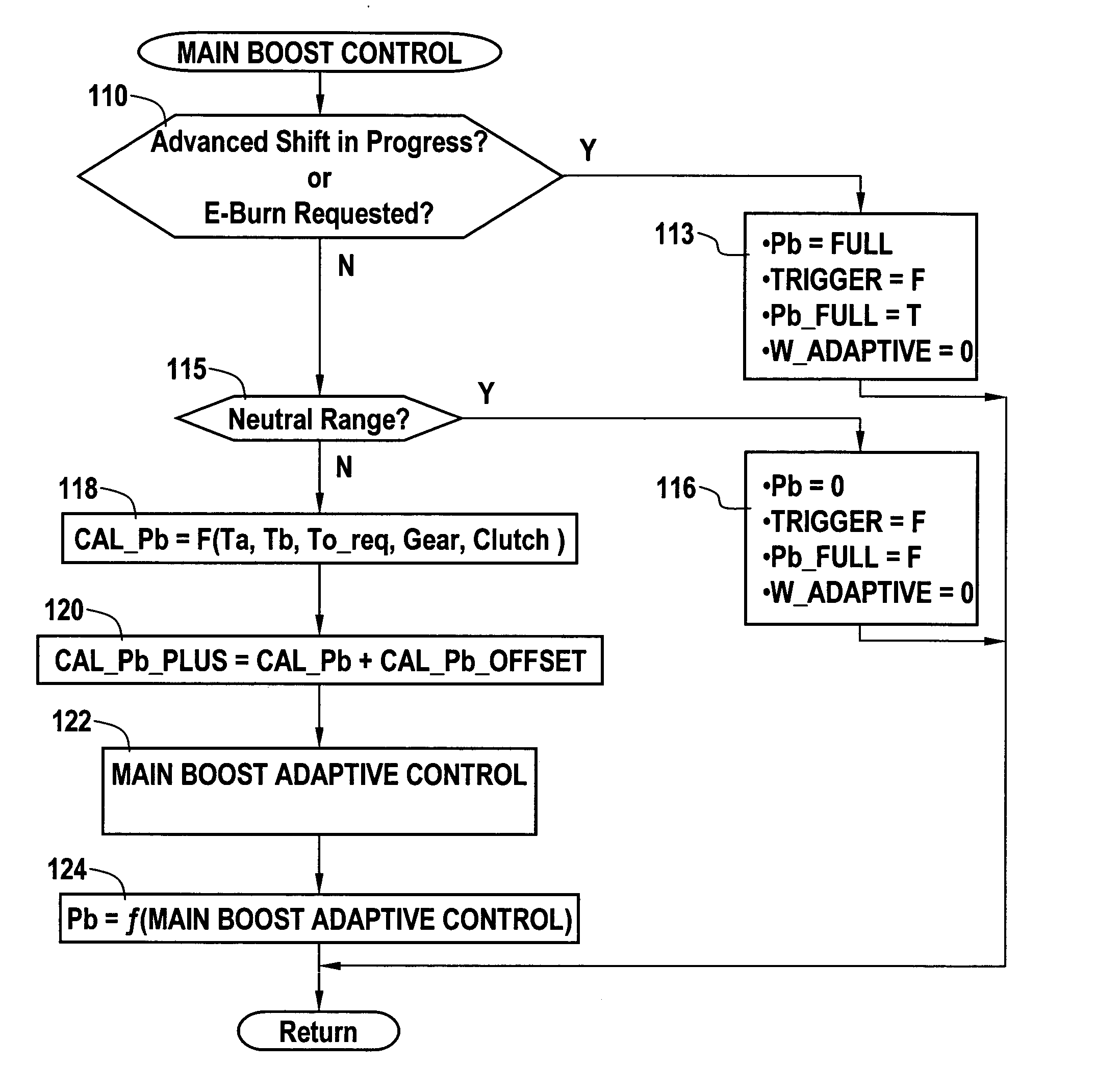
Method and apparatus to control hydraulic pressure in an electrically variable transmission
A method and apparatus to control an electrically variable transmission, by dynamically controlling system main hydraulic clutch pressures, based upon required clutch capacity, as determined by output load of the transmission. Included is a method to regulate hydraulic clutch pressure in an electrically variable transmission equipped with at least one clutch. This comprises monitoring magnitude of slippage of the clutches and controlling hydraulic boost pressure based upon the magnitude of clutch slippage. Controlling hydraulic boost pressure based upon the magnitude of clutch slippage comprises monitoring operator inputs, determining a requested operator torque command, and determining a required main boost pressure. The main boost pressure is based upon the requested operator torque command, the monitored operator inputs, parameters of the EVT and clutches. Commanded main boost pressure is then determined based upon the determined required main boost pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
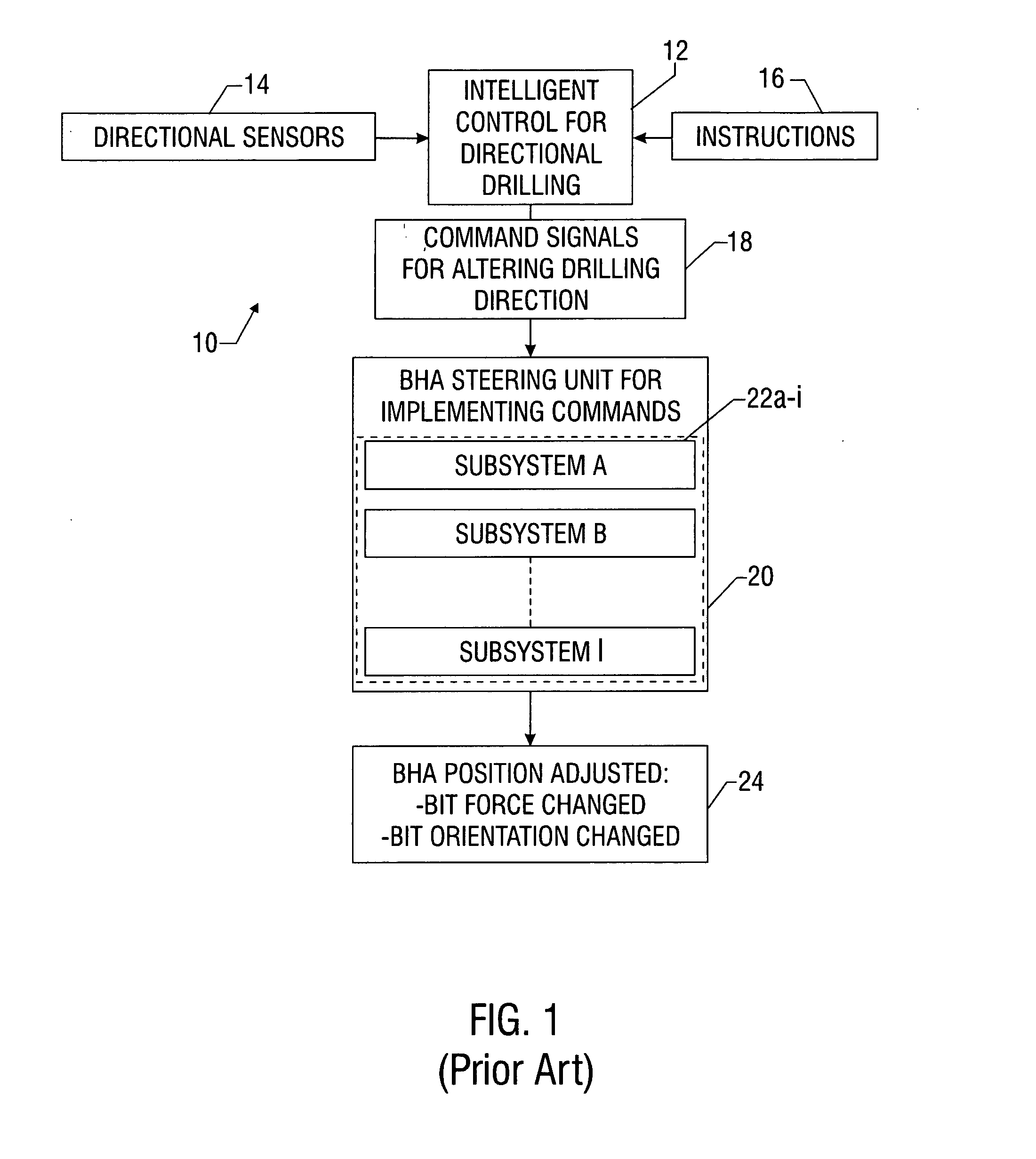
Steerable bit assembly and methods
ActiveUS20050056463A1Efficient and cost-effectiveFaster and less mechanically complexDrill bitsDrilling rodsShape changeExternal reference
A drilling system includes a steerable bottomhole assembly (BHA) having a steering unit and a control unit that provide dynamic control of drill bit orientation or tilt. Exemplary steering units can adjust bit orientation at a rate that approaches or exceeds the rotational speed of the drill string or drill bit, can include a dynamically adjustable articulated joint having a plurality of elements that deform in response to an excitation signal, can include adjustable independently rotatable rings for selectively tilting the bit, and / or can include a plurality of selectively extensible force pads. The force pads are actuated by a shape change material that deforms in response to an excitation signal. A method of directional drilling includes continuously cycling the position of the steering unit based upon the rotational speed of the drill string and / or drill bit and with reference to an external reference point.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
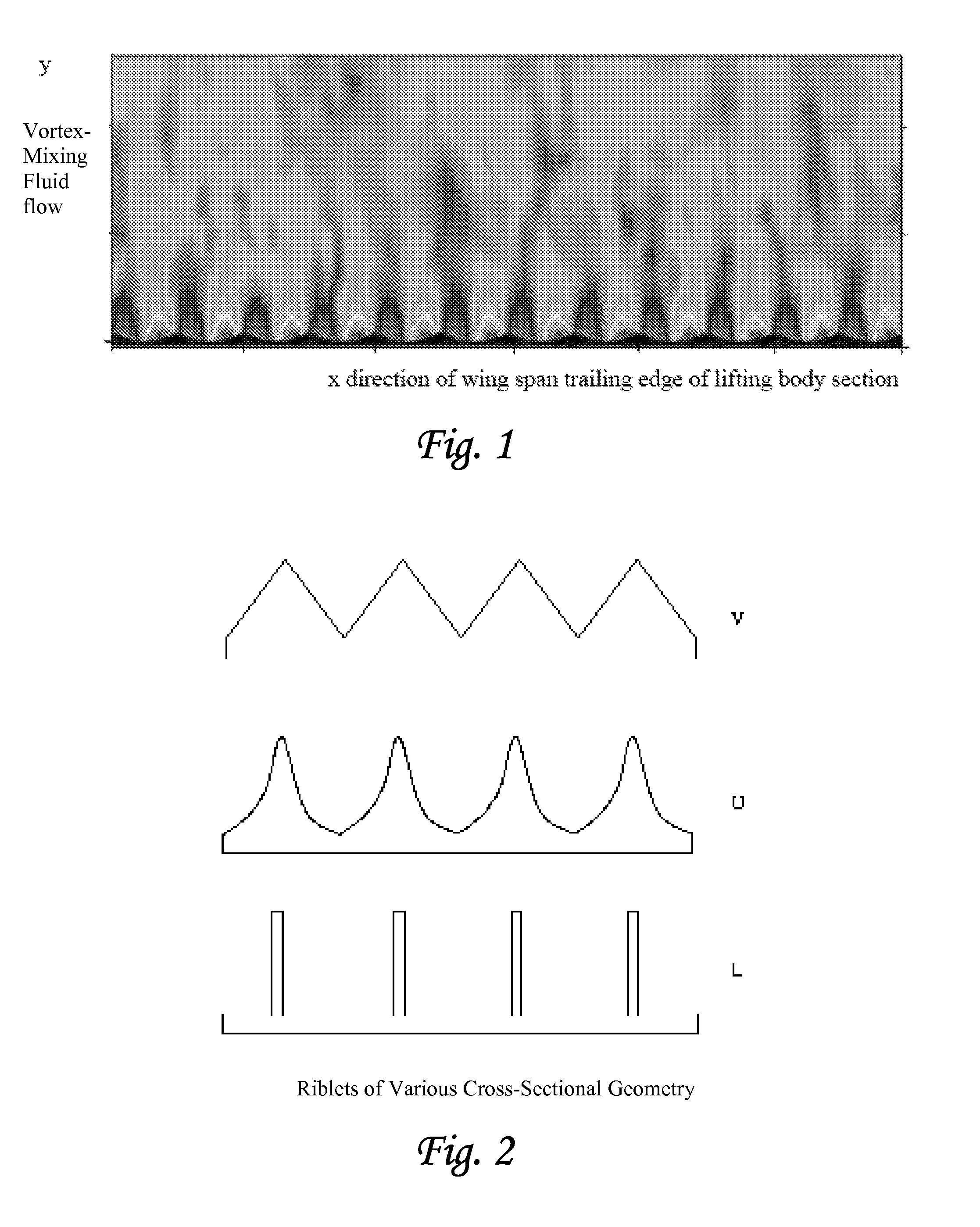
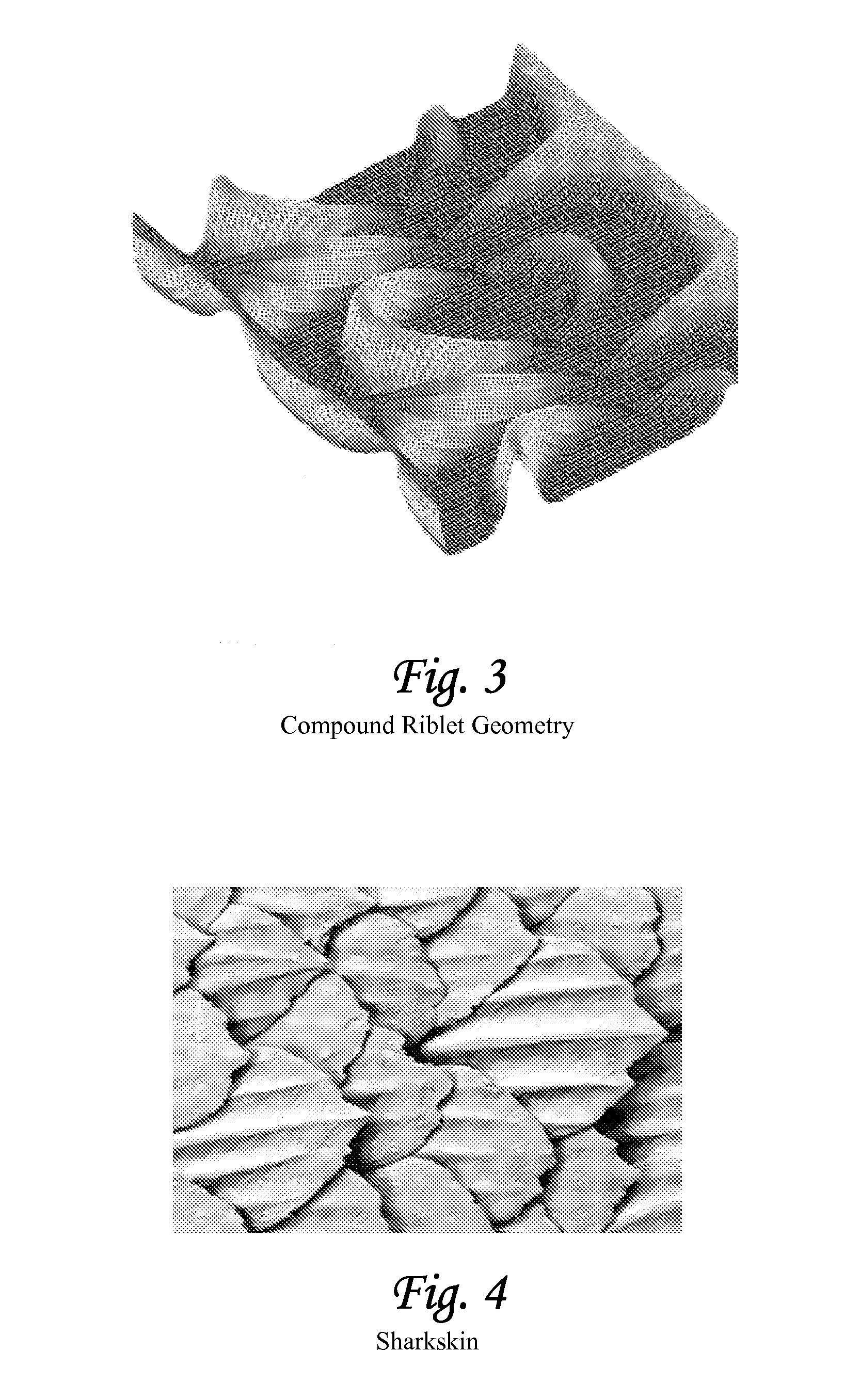
Method and apparatus for mitigating trailing vortex wakes of lifting or thrust generating bodies
ActiveUS20080061192A1Easy to controlReduce resistanceWind motor controlAircraft stabilisationDynamic controlFluid power
This patent provides for a method and apparatus for mitigating the formation of concentrated wake vortex structures generated from lifting or thrust-generating bodies and maneuvering control surfaces wherein the use of contour surface geometries promotes vortex-mixing of high and low flow fluids. The method and apparatus can be combined with various drag reduction techniques, such as the use of riblets of various types and / or compliant surfaces (passive and active). Such combinations form unique structures for various fluid dynamic control applications to suppress transiently growing forms of boundary layer disturbances in a manner that significantly improves performance and has improved control dynamics.
Owner:DELOS AEROSPACE
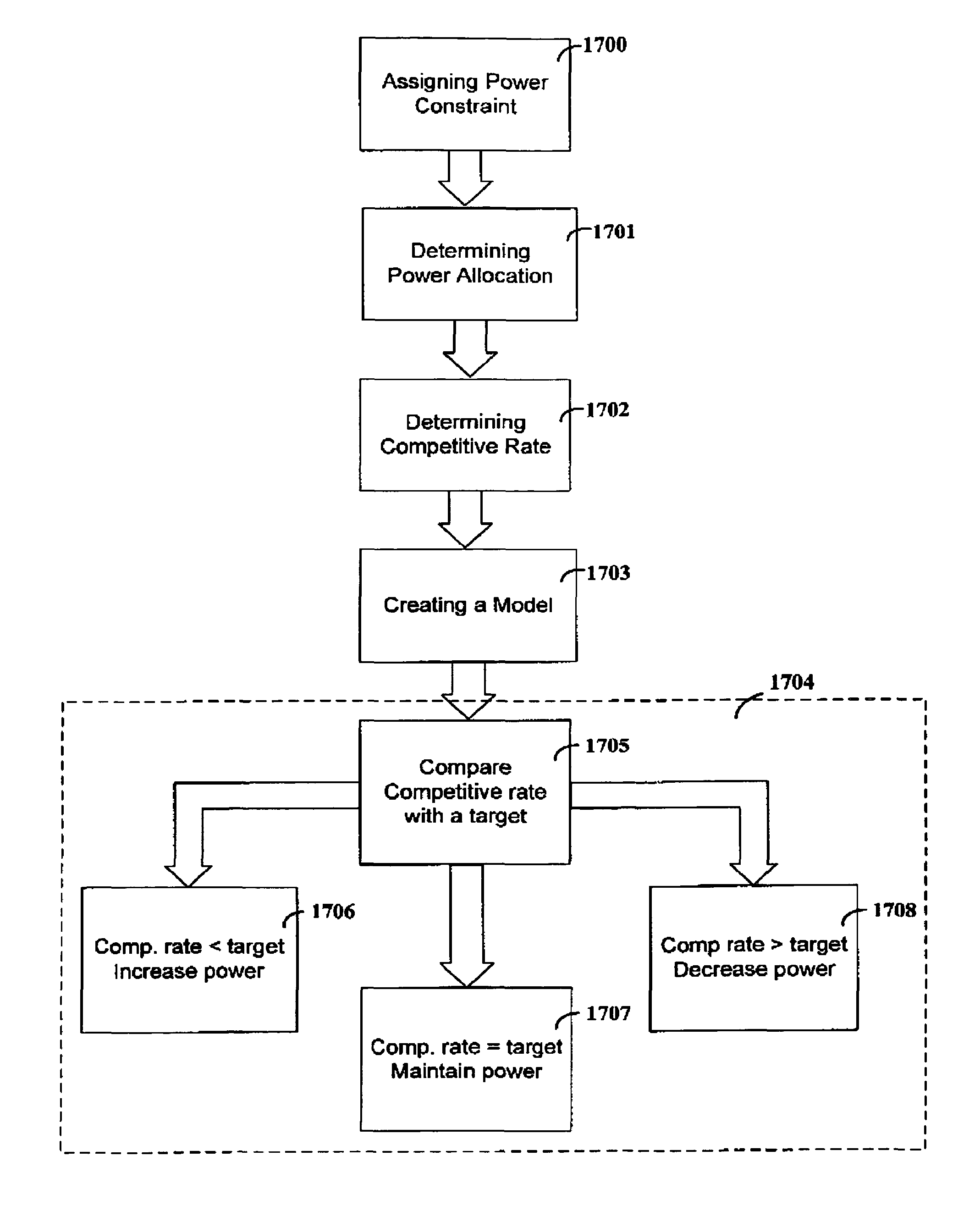
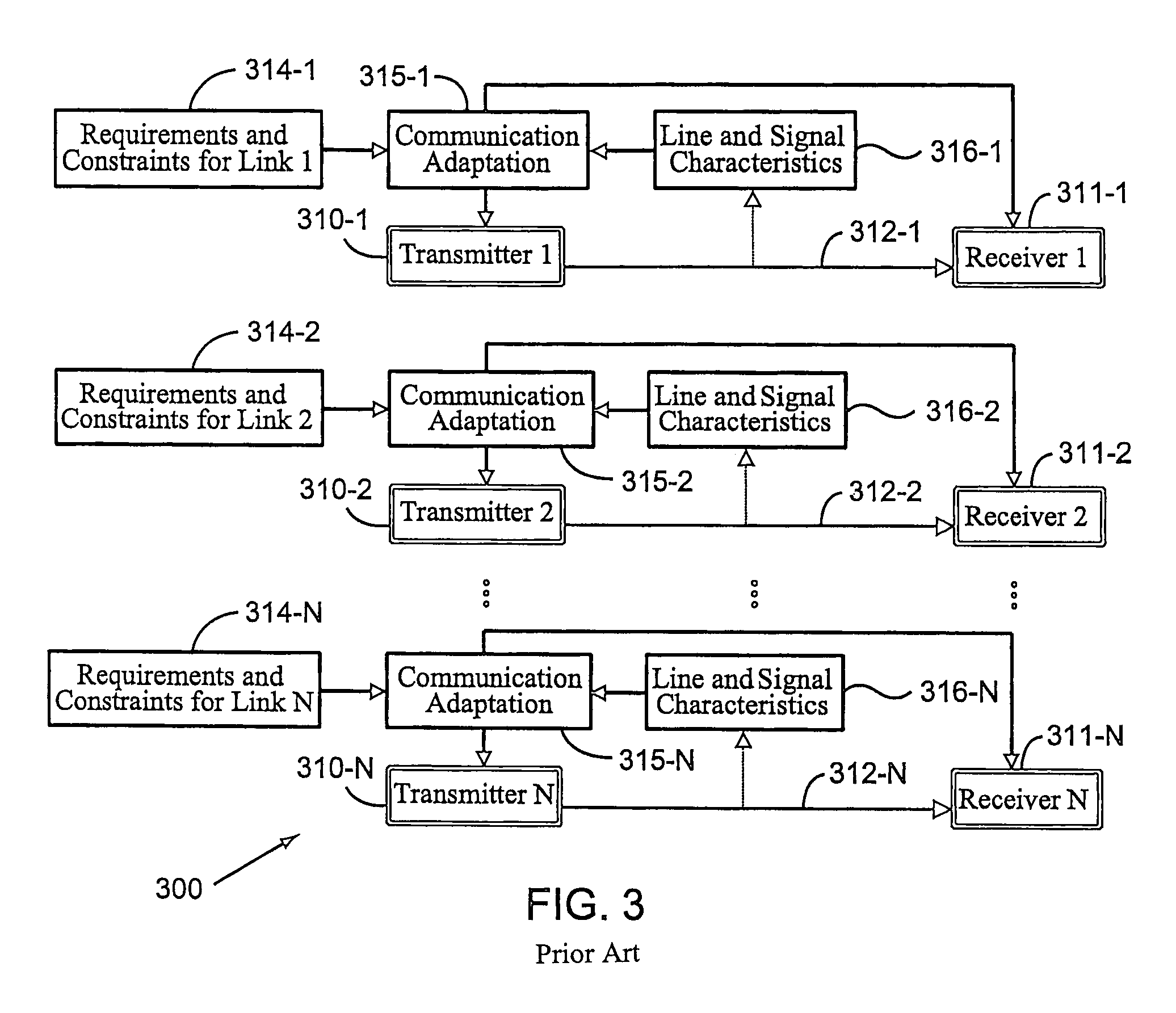
Dynamic digital communication system control
InactiveUS7158563B2Improve performanceMinimize impactError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemControl system
Methods, apparatus and systems for dynamically controlling a digital communication system, such as a DSL system, collect information about digital communication lines in the system and adaptively and / or dynamically determine line and signal characteristics of the digital communication lines, including interference effects. Based on the determined characteristics and the desired performance parameters, operation of the digital communication lines is adjusted to improve or otherwise control the performance of the system. The collection and processing of information may be performed by a party that is not a user in the system. This independent party also may control operational characteristics and parameters of the system. The invention can be used to eliminate or reduce signal interference such as crosstalk that can be induced on communication lines in systems such as DSL systems. Specific iterative power allocation and vectored transmission techniques and apparatus are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
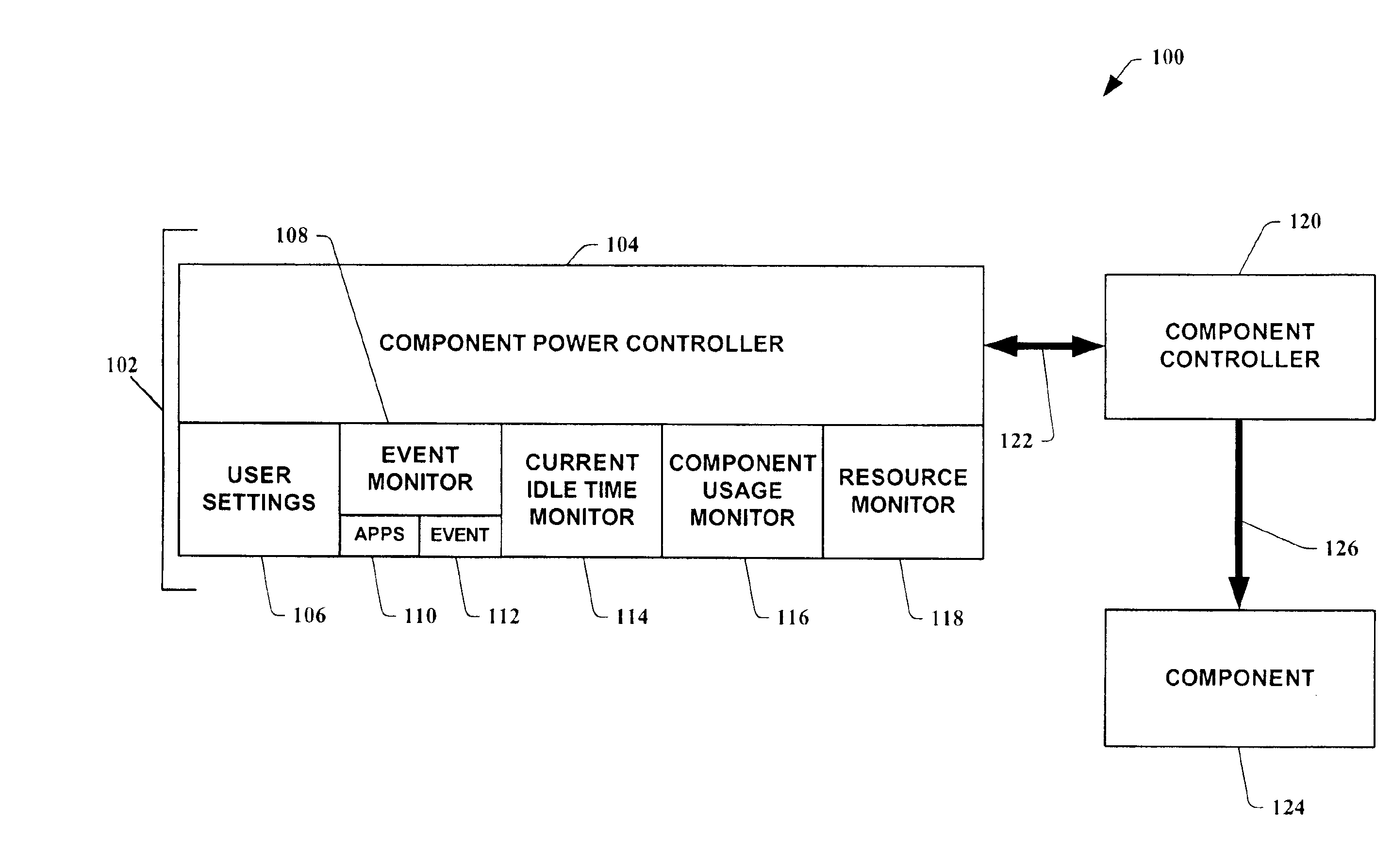
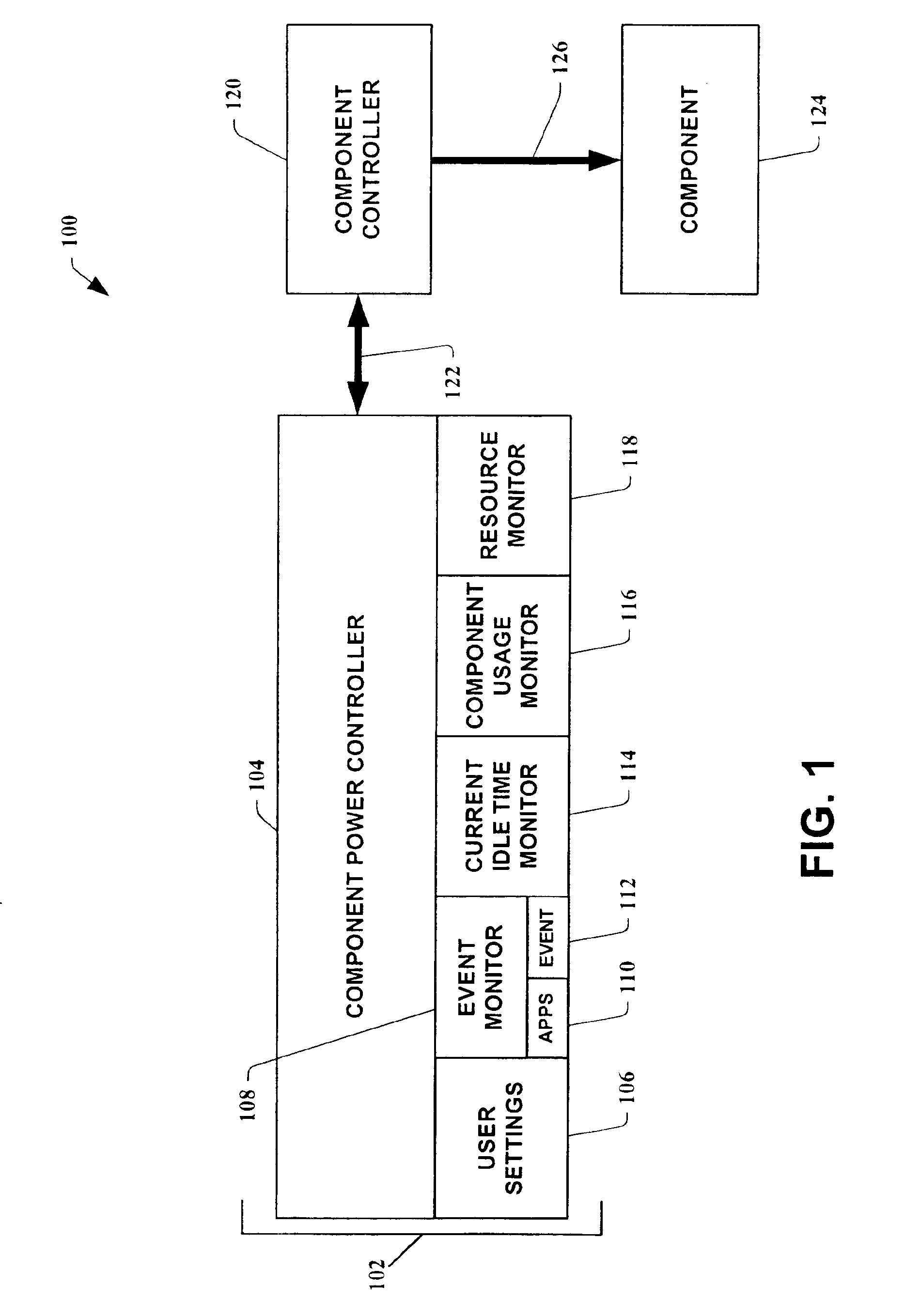
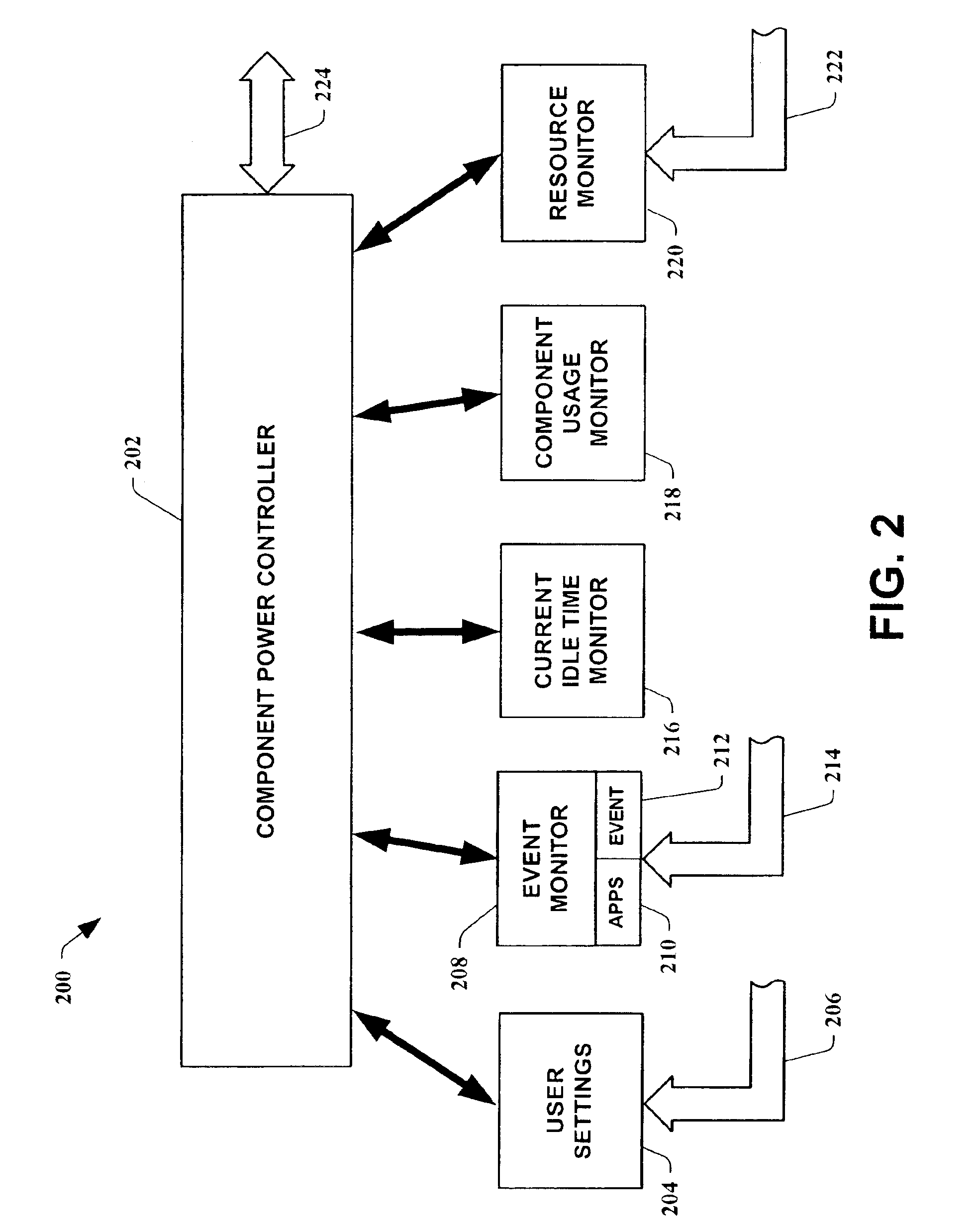
Dynamic power control apparatus, systems and methods
InactiveUS6885974B2Reduce dependenceImprove practicalityEnergy efficient ICTElectric devicesPower controllerIdle time
Dynamic power controller apparatus, systems and methods are provided which utilize system and user data to control power to components. The present invention employs dynamically controlled idle timeout values which are based, in part, on the historical use of the component. It can also employ user settings, event occurrences and available resources of a system to dynamically control the power to one of the system's components or a remote component. In an instance of the present invention related to hard disk power control, it is employed in an operating system's kernel where disk idleness is monitored. When the hard disk's idle time meets a dynamically computed power control idle timeout, the disk driver is commanded to power down the device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
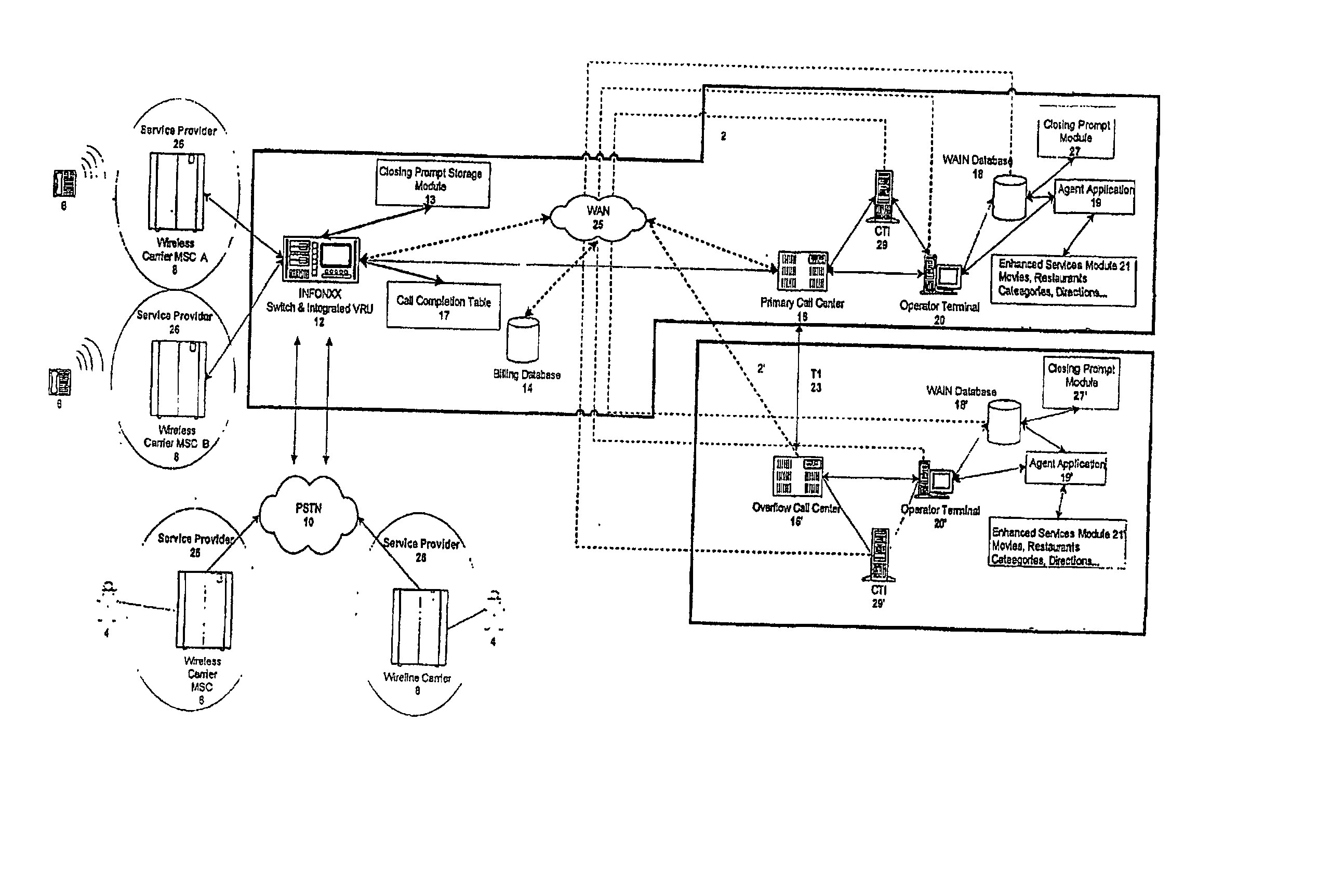
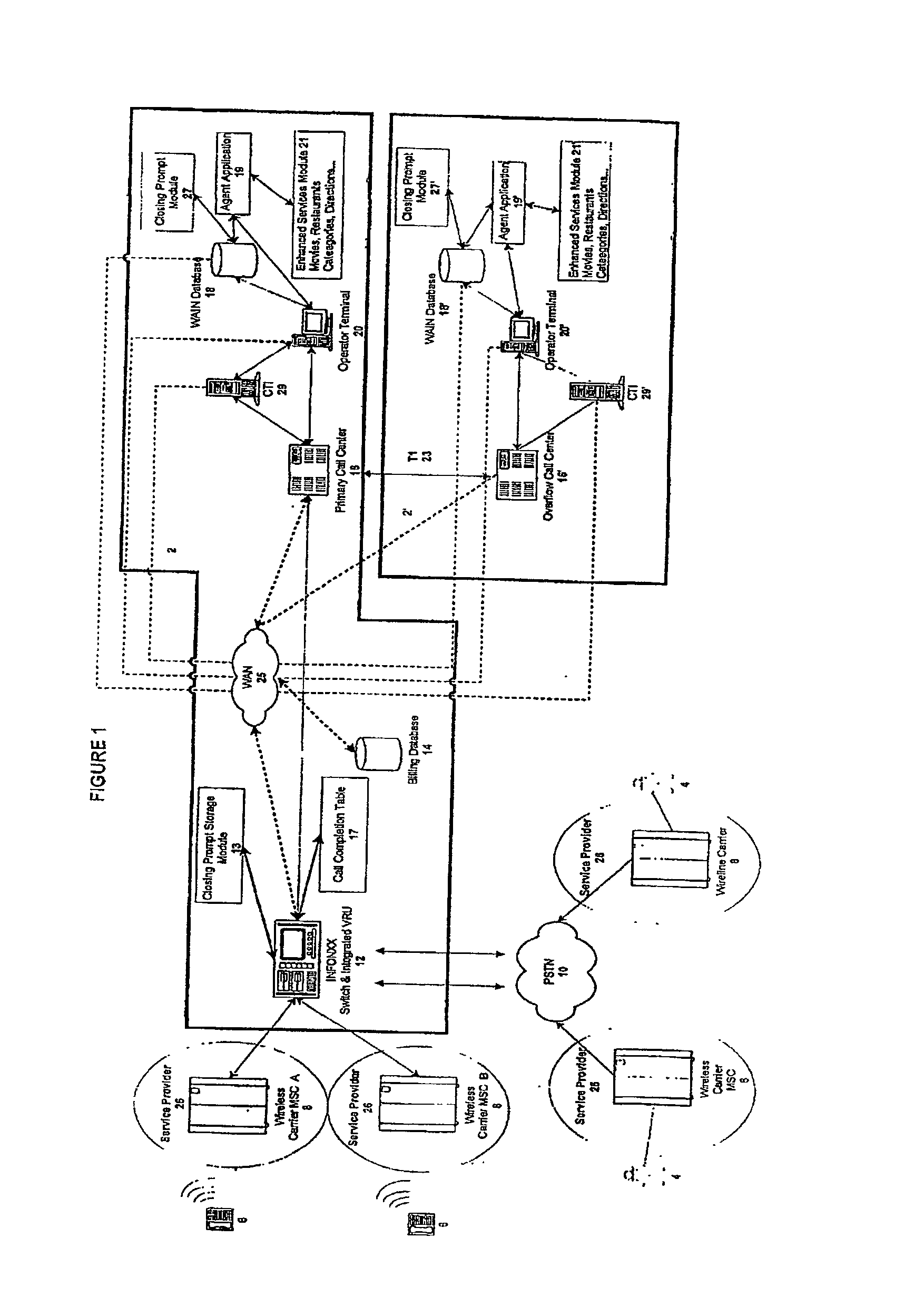
Communication assistance system and method
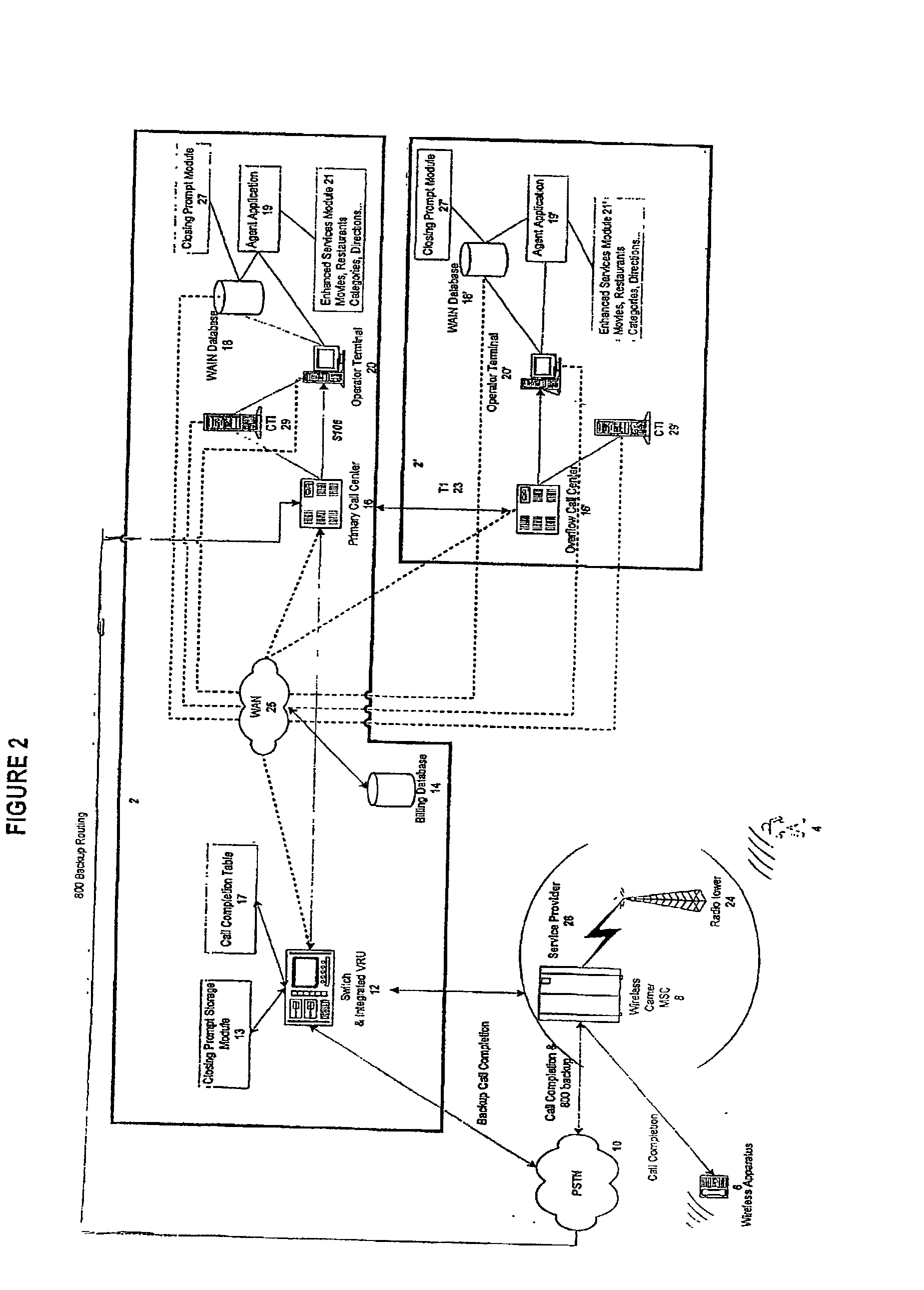
InactiveUS20030007625A1Convenient and efficient accessImprove securitySynchronisation arrangementInterconnection arrangementsMobile Telephone NumberAuxiliary system
A communication assistance system (2) is provided for accessing information corresponding to a plurality of subscribers (6). This system is comprised of a telephone switch (12) for receiving calls from a plurality of requesters (4), a call center (16) for routing each of said received calls to an operator terminal (20), and a first database (18) configured to store said information corresponding to each of said subscribers (6). The system (2) provides: a dynamically controlled closing prompt; an interface feature allowing subscribers (6) to update their own information; a dial string translator for identifying service provider of the requester (4); a billing database (14) for transferring call charges of the subscriber (6) to the requester (4); a processor to notify subscribers (6) to update their information; the ability to store license plate numbers of the subscribers (6); a masking feature that allows system (32) to connect requester (4) to subscriber (6) without revealing subscriber's (6) mobile telephone number, a searchable database of subscriber (6) information based on particular information found in the subscriber (6) listing.
Owner:GRAPE TECH GROUP
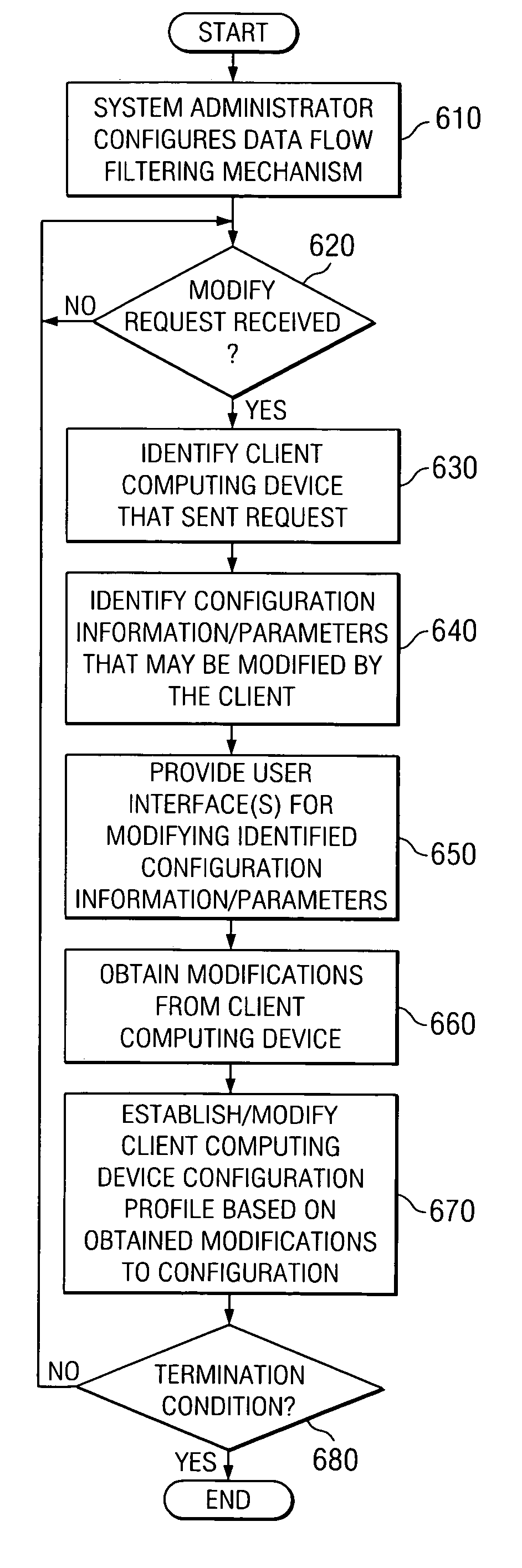
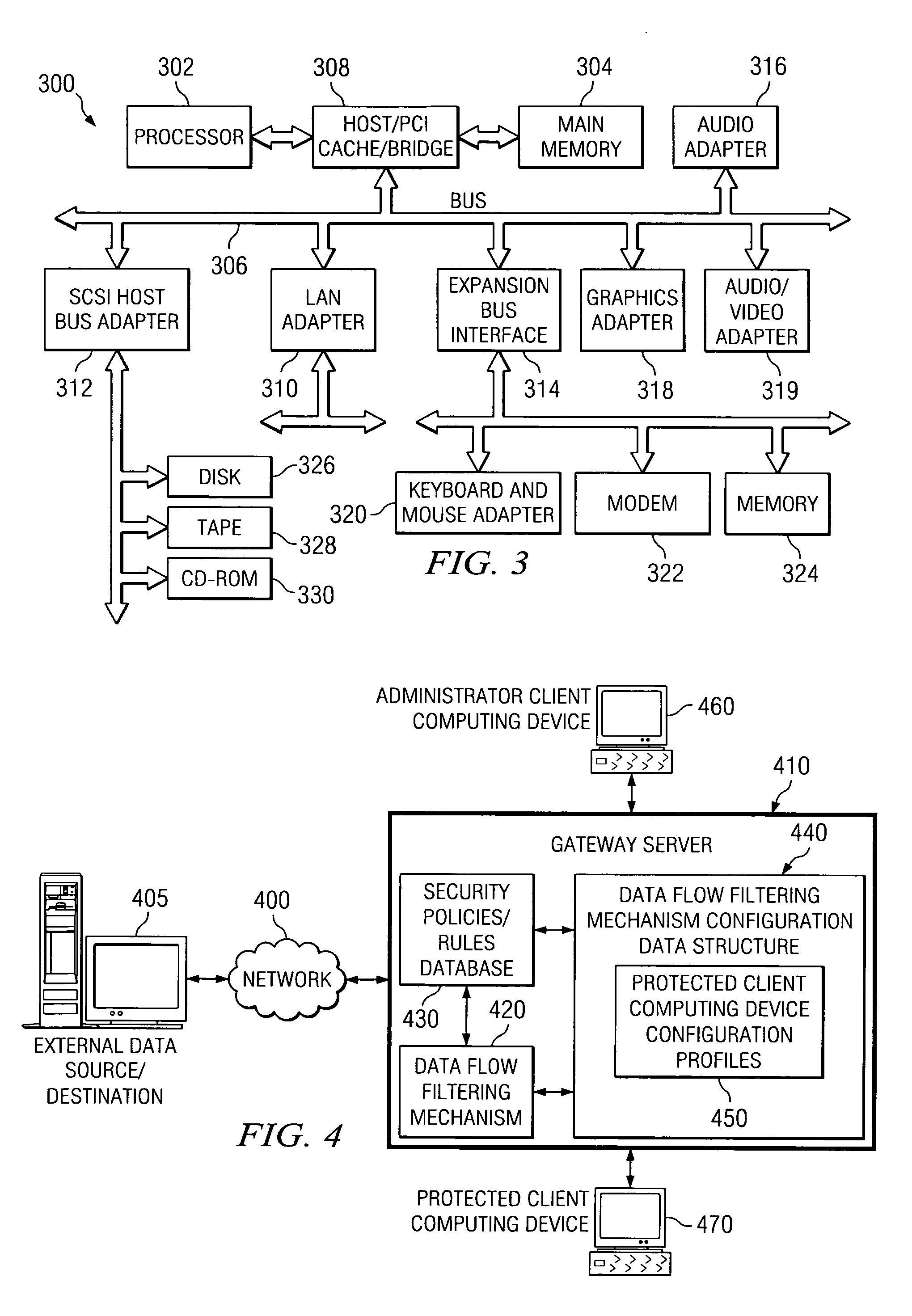
System and method for on-demand dynamic control of security policies/rules by a client computing device
A system and method for an end user to change the operation of a data flow filter mechanism, such as a firewall, that operates to control data flows between a plurality of protected computing devices and one or more non-protected computing devices. With the system and method, an administrator of a sub-network of computing devices may set a client computing device's scope of rules / policies that may be changed by a user of the client computing device, with regard to a data flow filter mechanism. The user of the client computing device, or the client computing device itself, may then log onto the data flow filter mechanism and modify the operation of the data flow filter mechanism within the limits established by the administrator.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
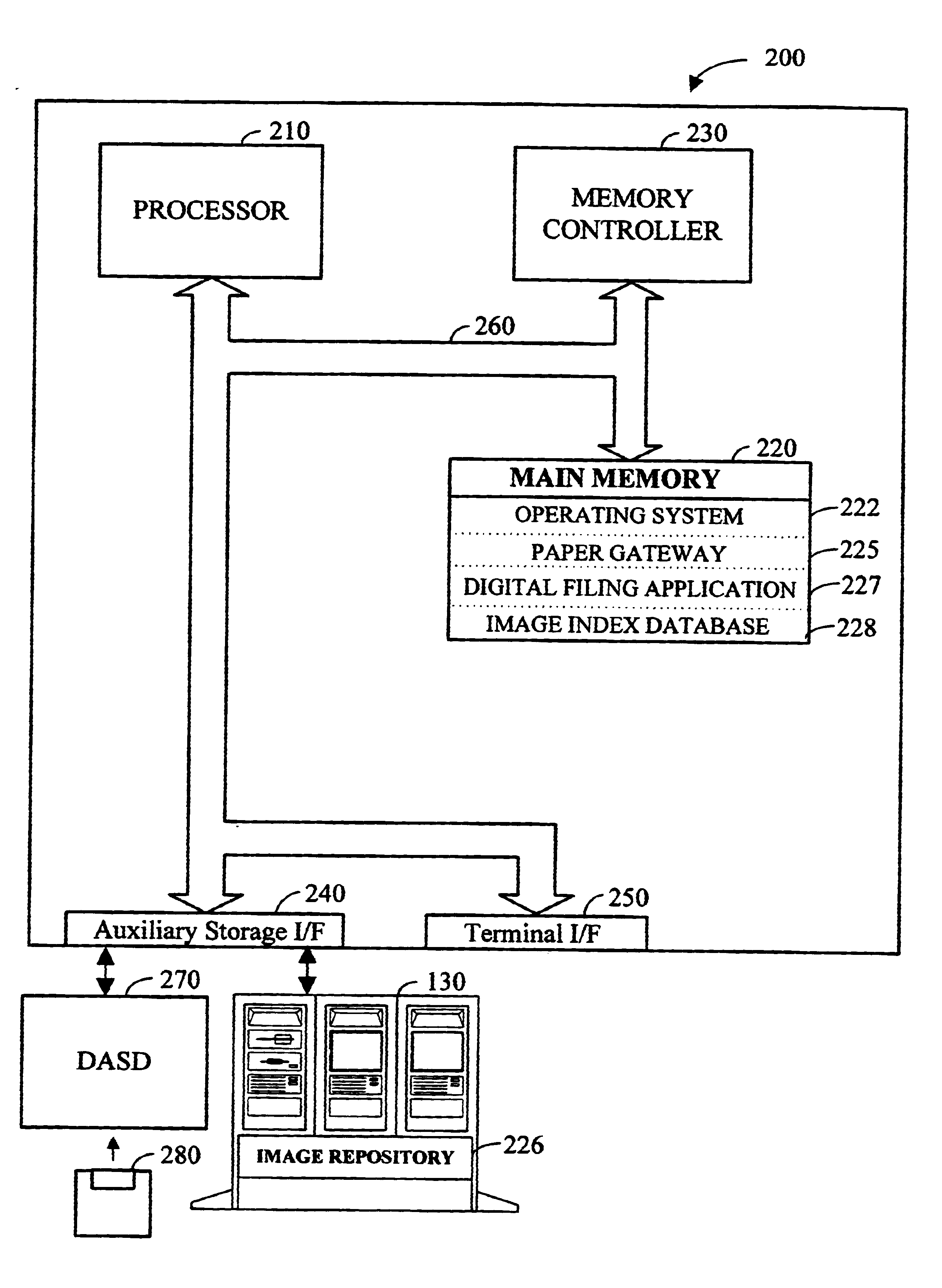
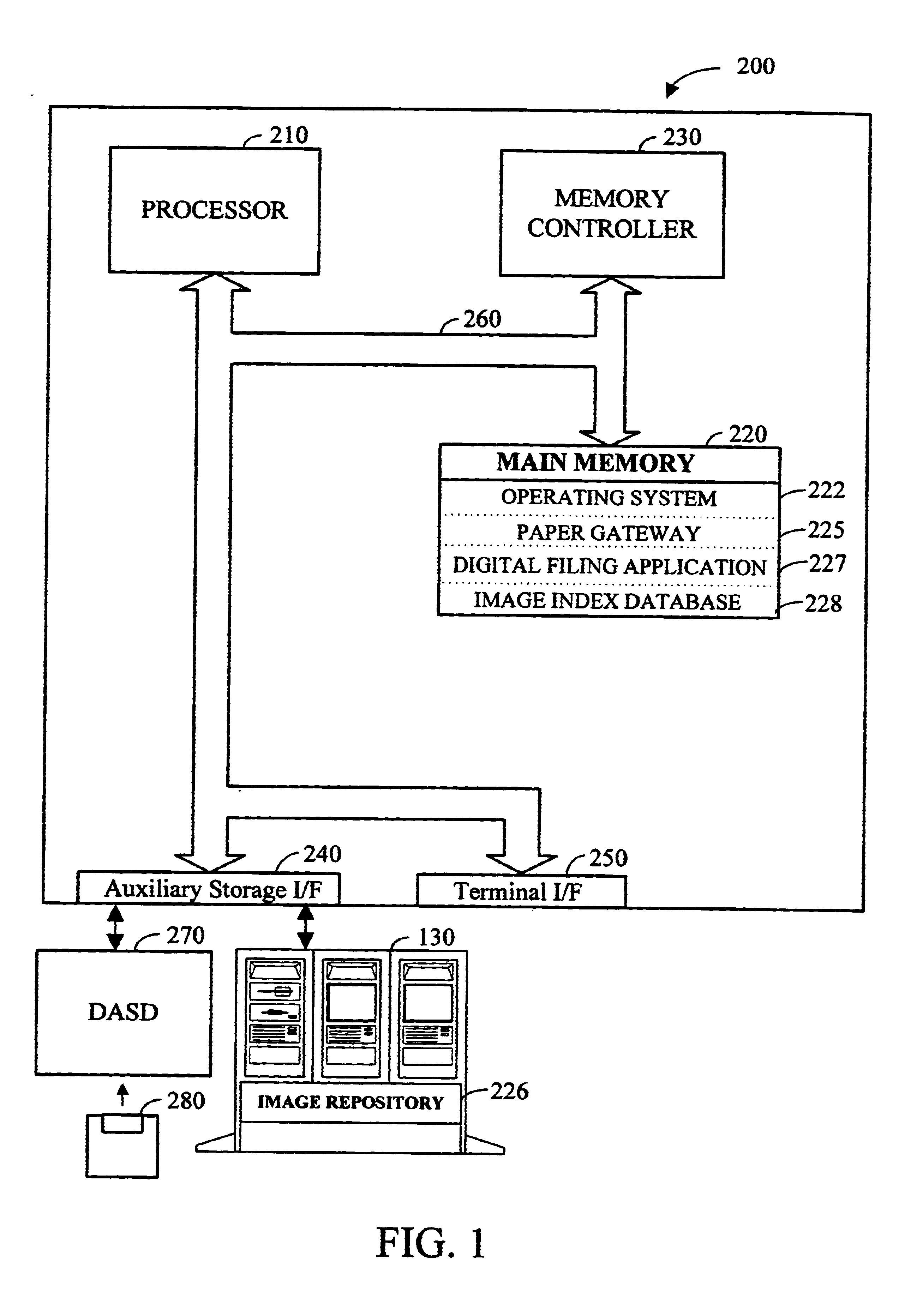
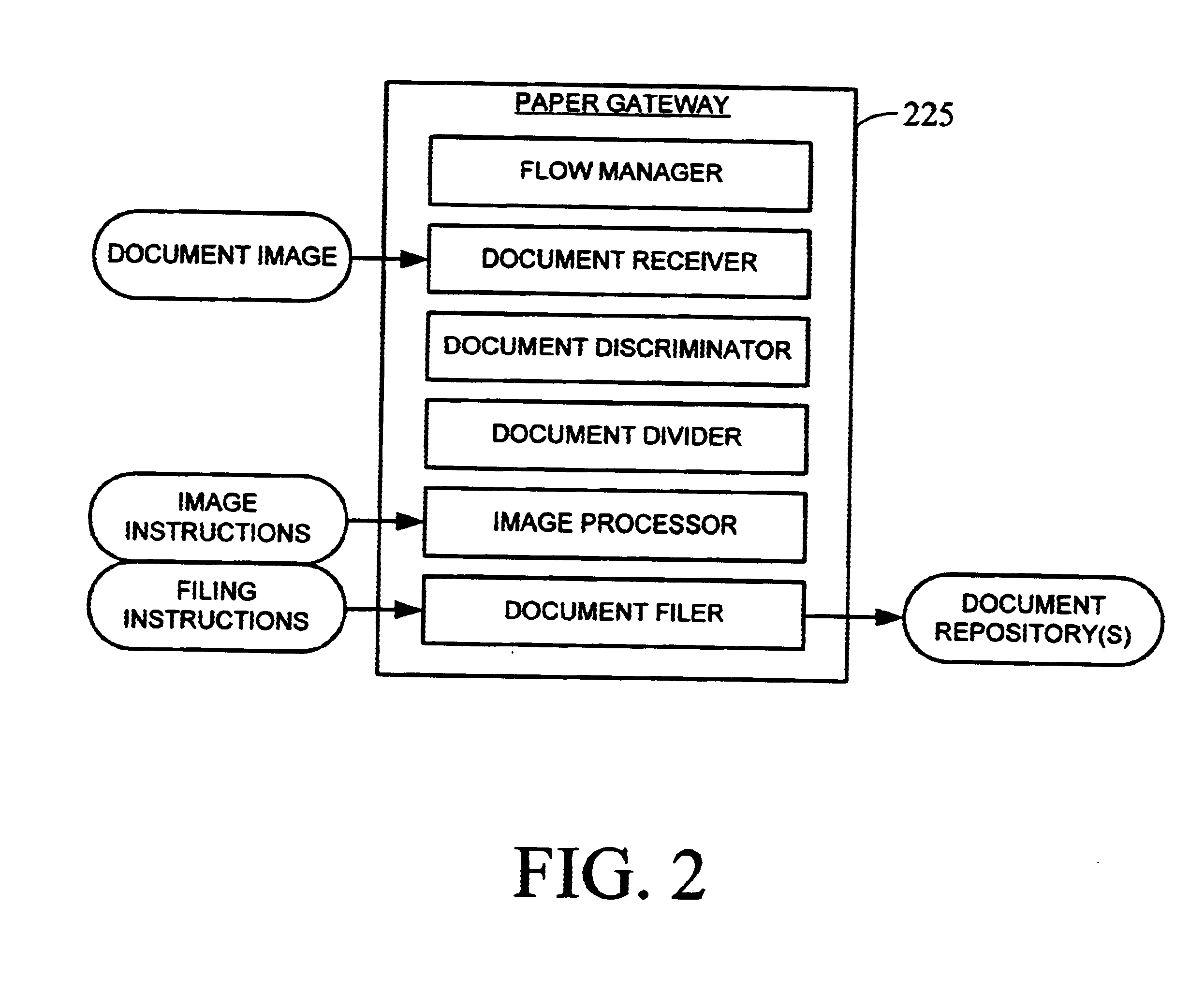
Apparatus and method for dynamically routing documents using dynamic control documents and data streams
InactiveUS6674924B2Easy to operateEasy to createData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsData streamPaper based
According to the preferred embodiments, an apparatus and method for dynamic routing using dynamic data streams is disclosed. Dynamic routing using dynamic data streams facilitates the creation of a flexible paper gateway in a digital filing system that provides for receiving, processing and storing document images from a wide variety of sources. When thus implemented, dynamic routing allows the digital filing system to efficiently operate while providing digital filing services to a wide variety of users with different needs. Thus, the preferred embodiments provide for the efficient digital filing and efficient management of paper-based information from its receipt at the desktop through an indexing, scanning, image storage and image retrieval process.
Owner:WRIGHT STEVEN F +2
Dynamic stabilization for a stream processing system
InactiveUS20080005392A1Maximize objective functionMaintain stabilityTransmissionInput/output processes for data processingDownstream processingProcessing element
Disclosed are a method, upstream processing node, and computer readable medium for dynamically stabilizing a stream processing system. The method includes receiving at least one computing resource allocation target. The further includes determining that an input data flow rate of at least one upstream processing element varies. The computing resource is dynamically allocated to the upstream processing element in response to the input rate of the upstream processing element varying. Data flow is dynamically controlled between the upstream processing element and at least one downstream processing element.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wireless dynamic power control of an implantable sensing device and methods therefor
InactiveUS20100161004A1Improve functionalityEnhanced data rate transferElectrotherapyDiseaseCommunications system
Communication systems and methods for dynamically controlling the power wirelessly delivered by a remote reader unit to separate sensing device, such as a device adapted to monitor a physiological parameter within a living body, including but not limited to intraocular pressure, intracranial pressure (ICP), and cardiovascular pressures that can be measured to assist in diagnosing and monitoring various diseases. The communication method entails electromagnetically delivering power from at least one telemetry antenna within the reader unit to at least one telemetry antenna within the sensing device, and controlling the power supplied to the sensing device within a predetermined operating power level range of the sensing device.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSING SYST INC
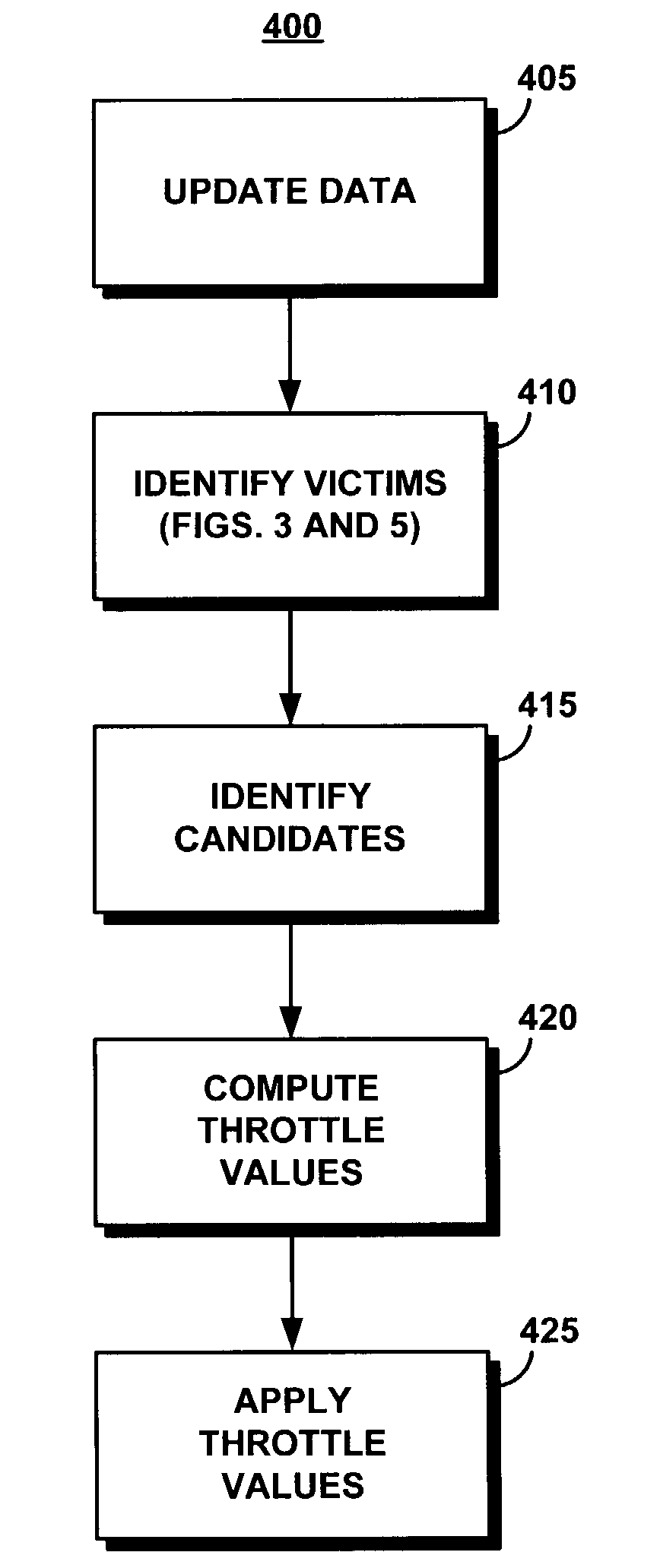
System and method for utilizing informed throttling to guarantee quality of service to I/O streams
InactiveUS7519725B2Good decisionAccurate I/O throttling decisionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceWorkload
The present system and associated method resolve the problem of providing statistical performance guarantees for applications generating streams of read / write accesses (I / Os) on a shared, potentially distributed storage system of finite resources, by initiating throttling whenever an I / O stream is receiving insufficient resources. The severity of throttling is determined in a dynamic, adaptive way at the storage subsystem level. Global, real-time knowledge about I / O streams is used to apply controls to guarantee quality of service to all I / O streams, providing dynamic control rather than reservation of bandwidth or other resources when an I / O stream is created that will always be applied to that I / O stream. The present system throttles at control points to distribute resources that are not co-located with the control point. A competition model is used with service time estimators in addition to estimated workload characteristics to determine which I / O needs to be throttled and the level of throttling required. A decision point issues throttling commands to enforcement points and selects which streams, and to what extent, need to be throttled.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method of reproducing virtual sound
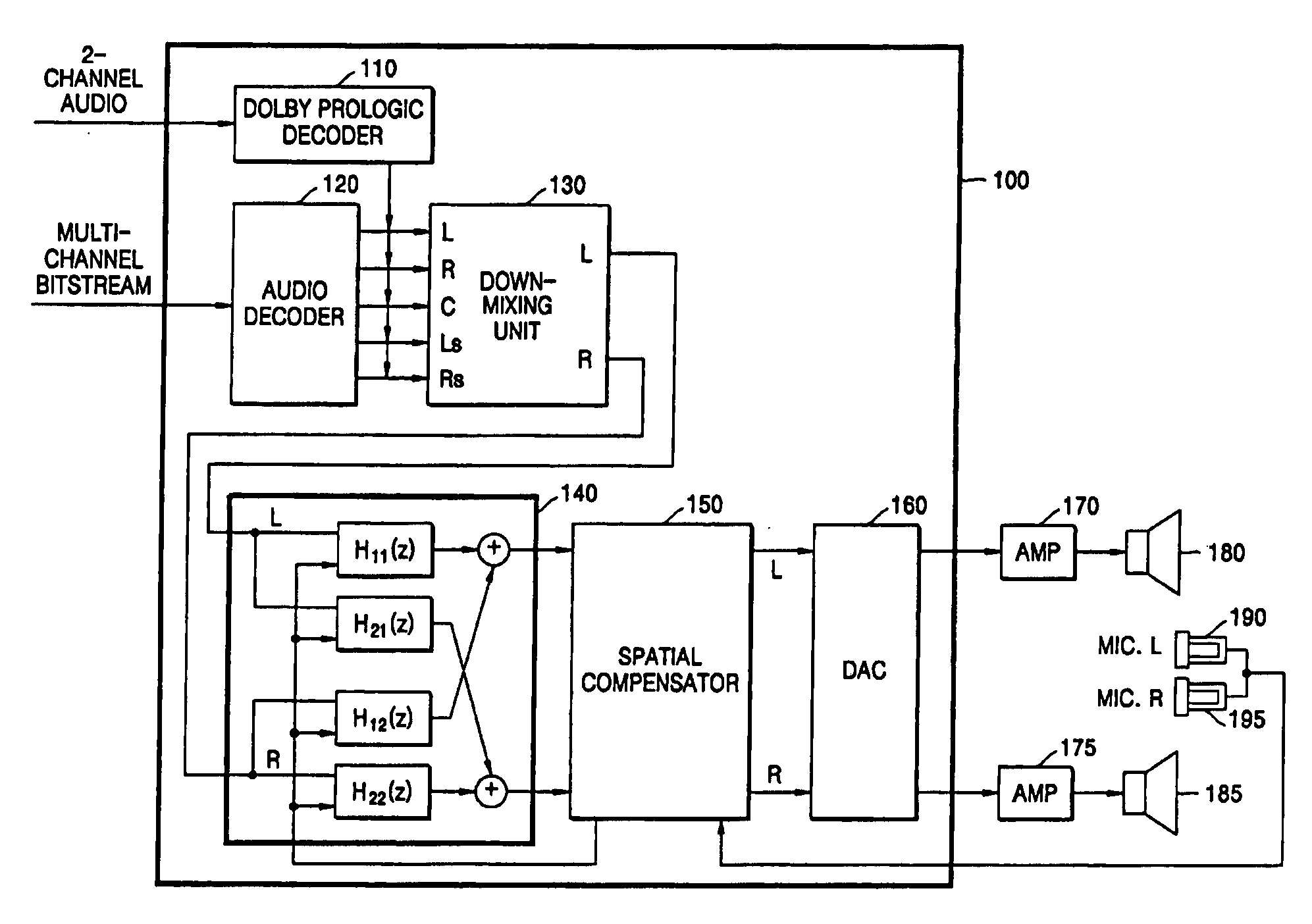
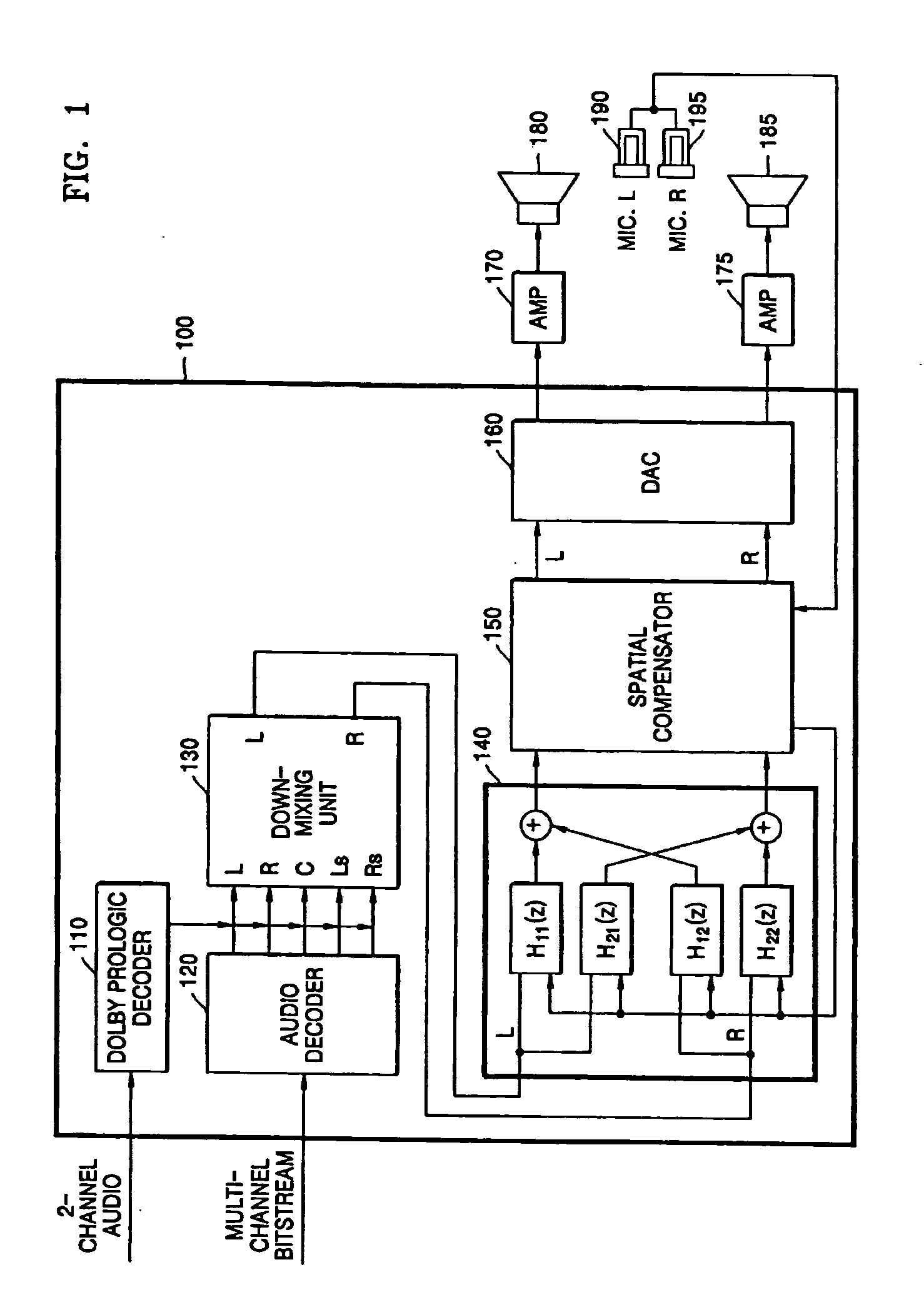
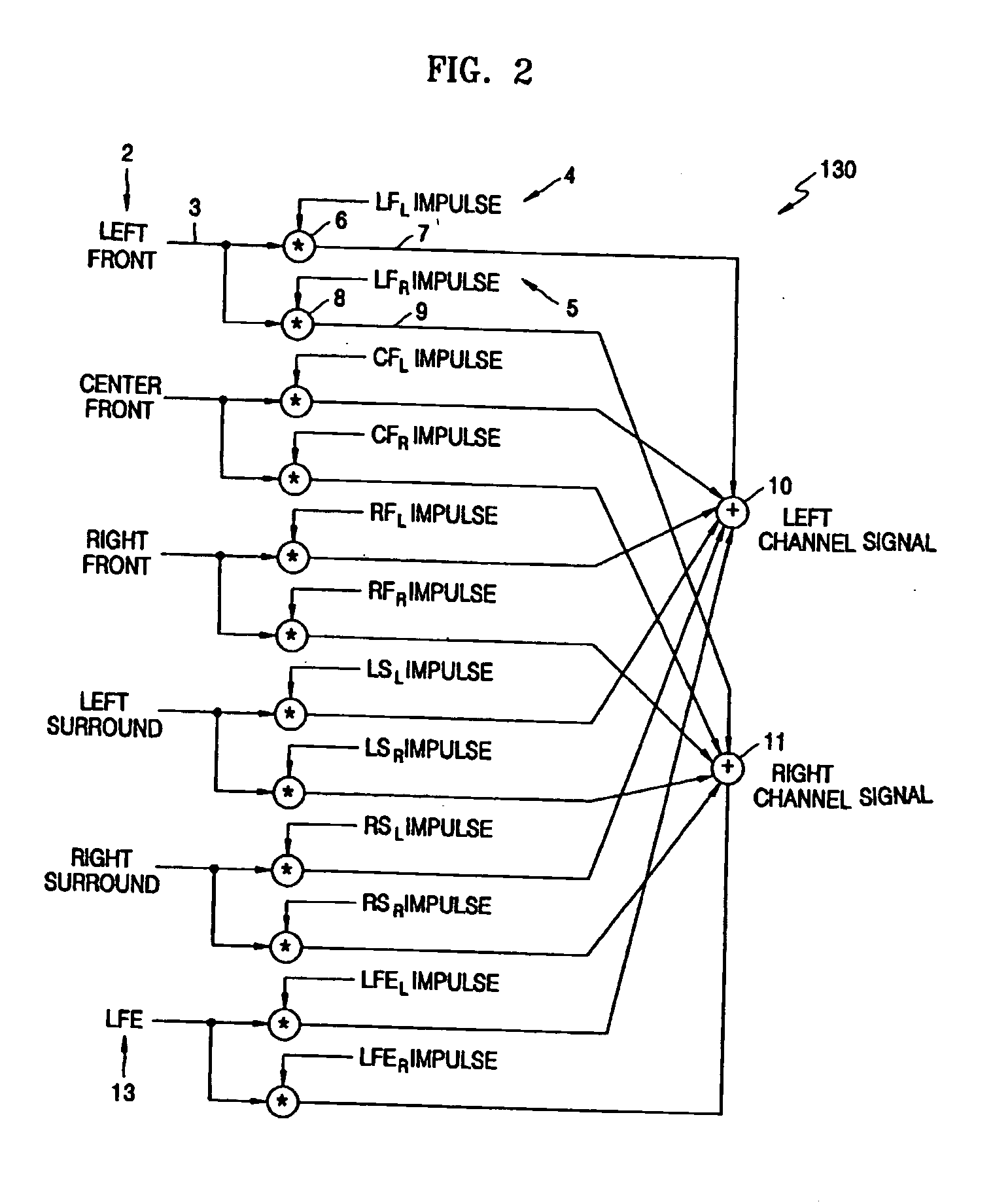
InactiveUS20050135643A1Pseudo-stereo systemsTwo-channel systemsCrosstalk cancellationFrequency spectrum
An apparatus and method of reproducing a 2-channel virtual sound while dynamically controlling a sweet spot and crosstalk cancellation are disclosed. The method includes: receiving broadband signals, setting compensation filter coefficients according to response characteristics of bands and setting stereophonic transfer functions according to spectrum analysis; down mixing an input multi-channel signal into two channel signals by adding head related transfer functions (HRTFs) measured in a near-field and a far-field to the input multi-channel signal, canceling crosstalk of the down mixed signals on the basis of compensation filter coefficients calculated using the set stereophonic transfer functions, and compensating levels and phases of the crosstalk cancelled signals on the basis of the set compensation filter coefficients for each of the bands.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
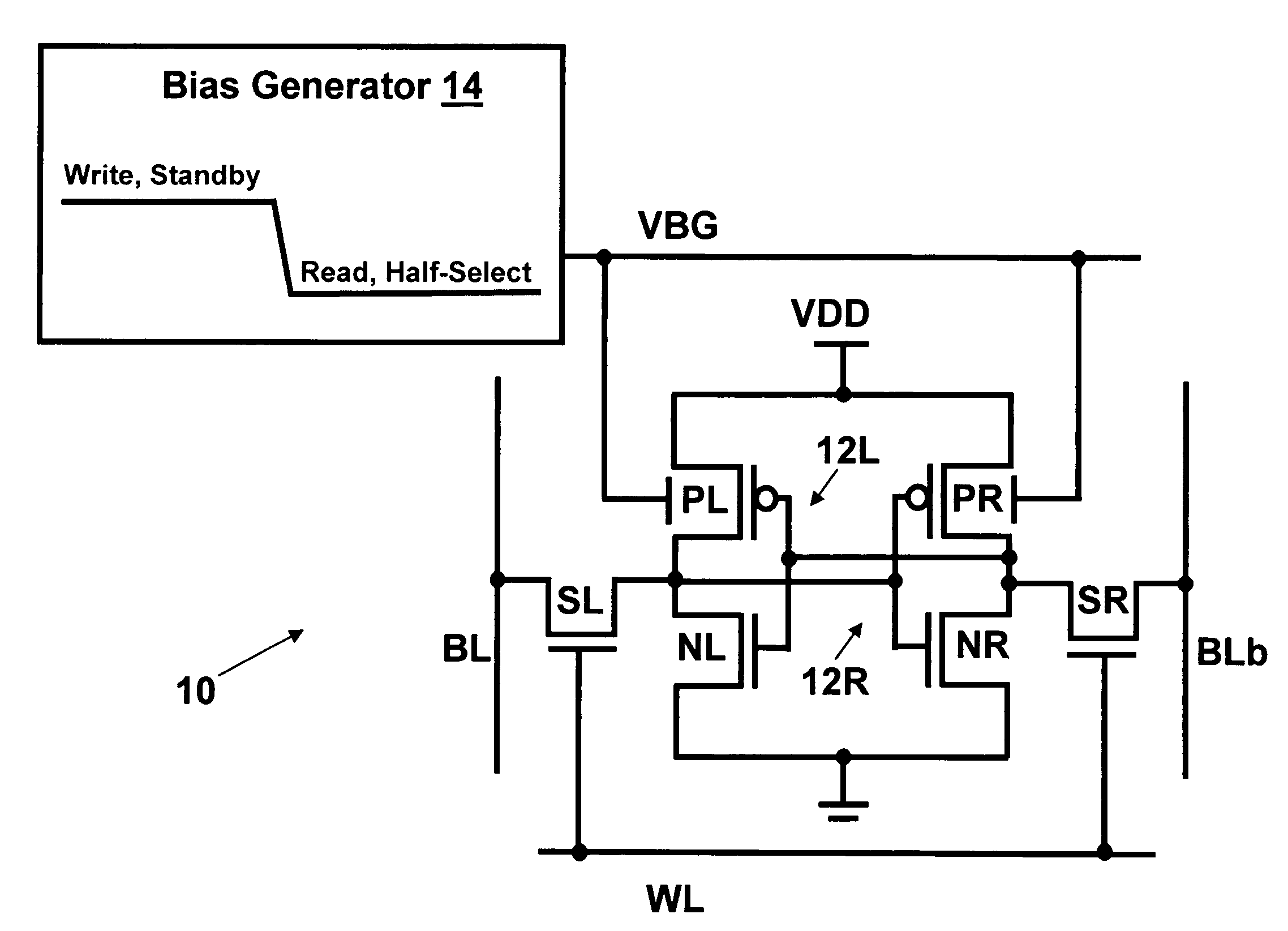
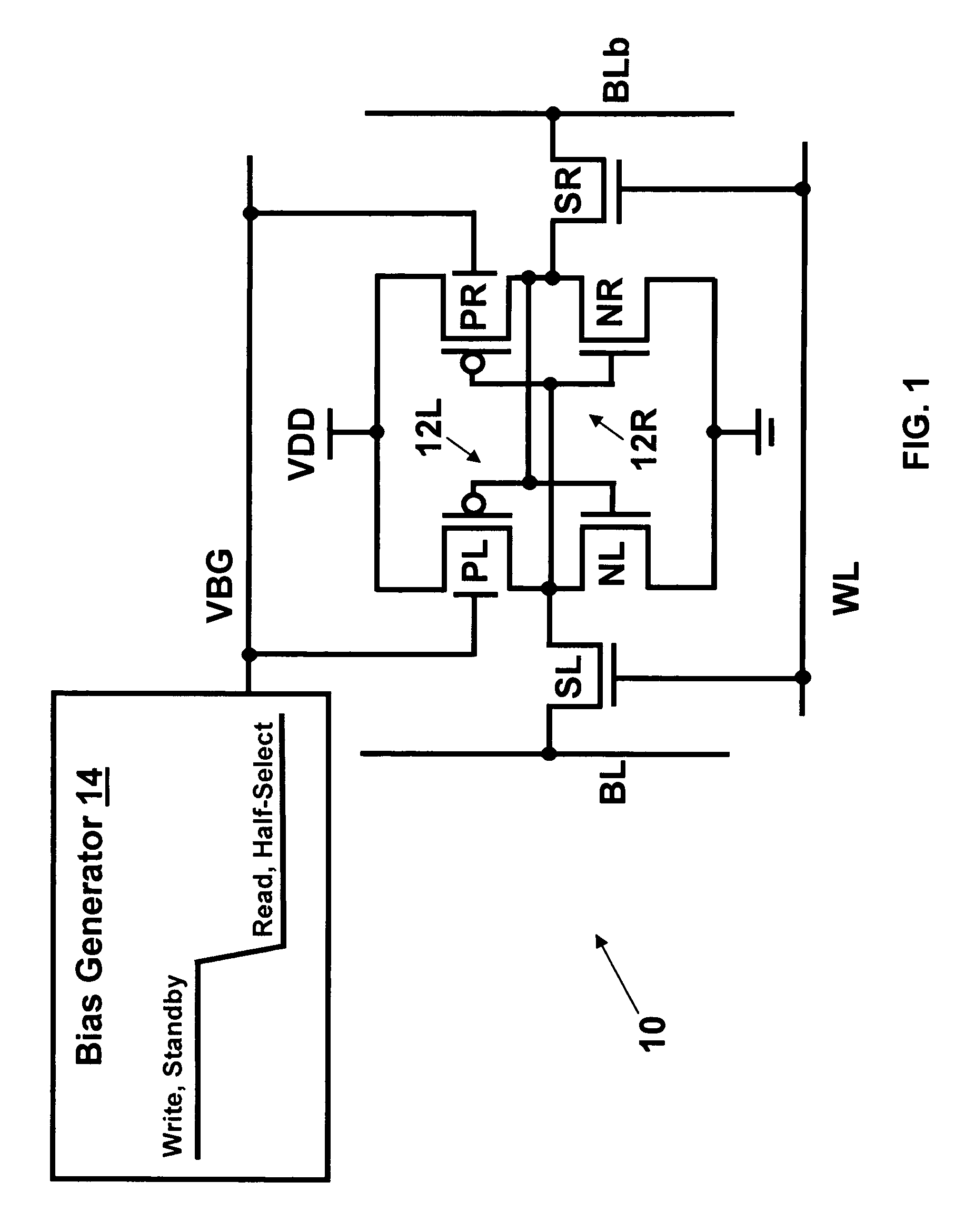
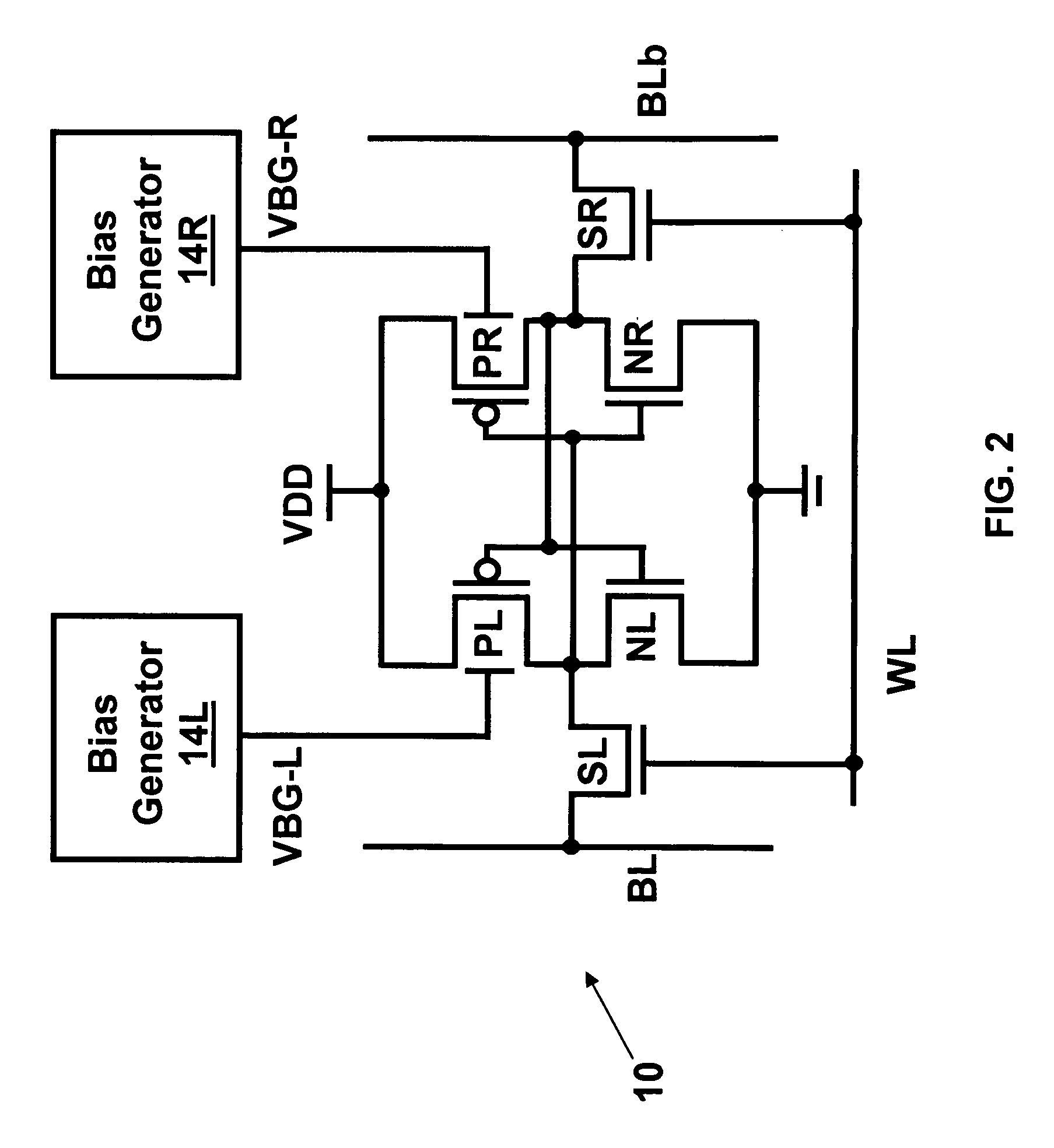
Dynamic control of back gate bias in a FinFET SRAM cell
The present invention provides dynamic control of back gate bias on pull-up pFETs in a FinFET SRAM cell. A method according to the present invention includes providing a bias voltage to a back gate of at least one transistor in the SRAM cell, and dynamically controlling the bias voltage based on an operational mode (e.g., Read, Half-Select, Write, Standby) of the SRAM cell.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dynamic control containment unit
InactiveUS20030117281A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageEngineeringDynamic control
The present invention is a dynamic control containment unit for holding a plurality of discrete items, including a signal emitting mechanism associated with each of the plurality of discrete items, an enclosed housing having at least one receptacle accessible by a user and having at least one of the plurality of items contained therein, a passive signal receiving mechanism in communication with the receptacle for receiving signals emanating from the signal emitting mechanism and a securement system configured to prevent unauthorized access to the dynamic control containment unit. A controller is in communication with the signal receiving mechanism and initiates actions based upon the signal content.
Owner:MOBILE ASPECTS INC
Method and apparatus for dynamically controlling traffic in wireless station
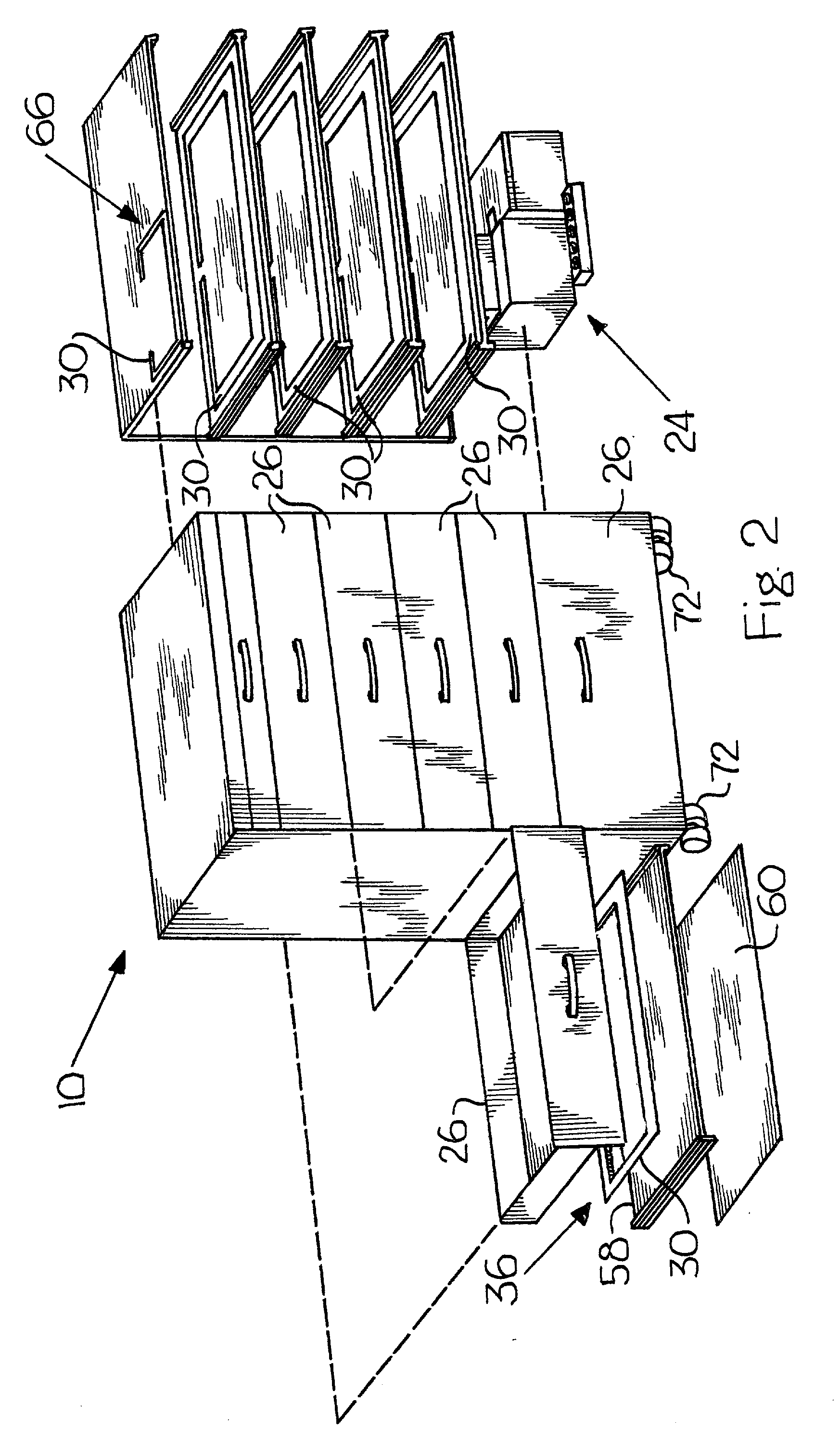
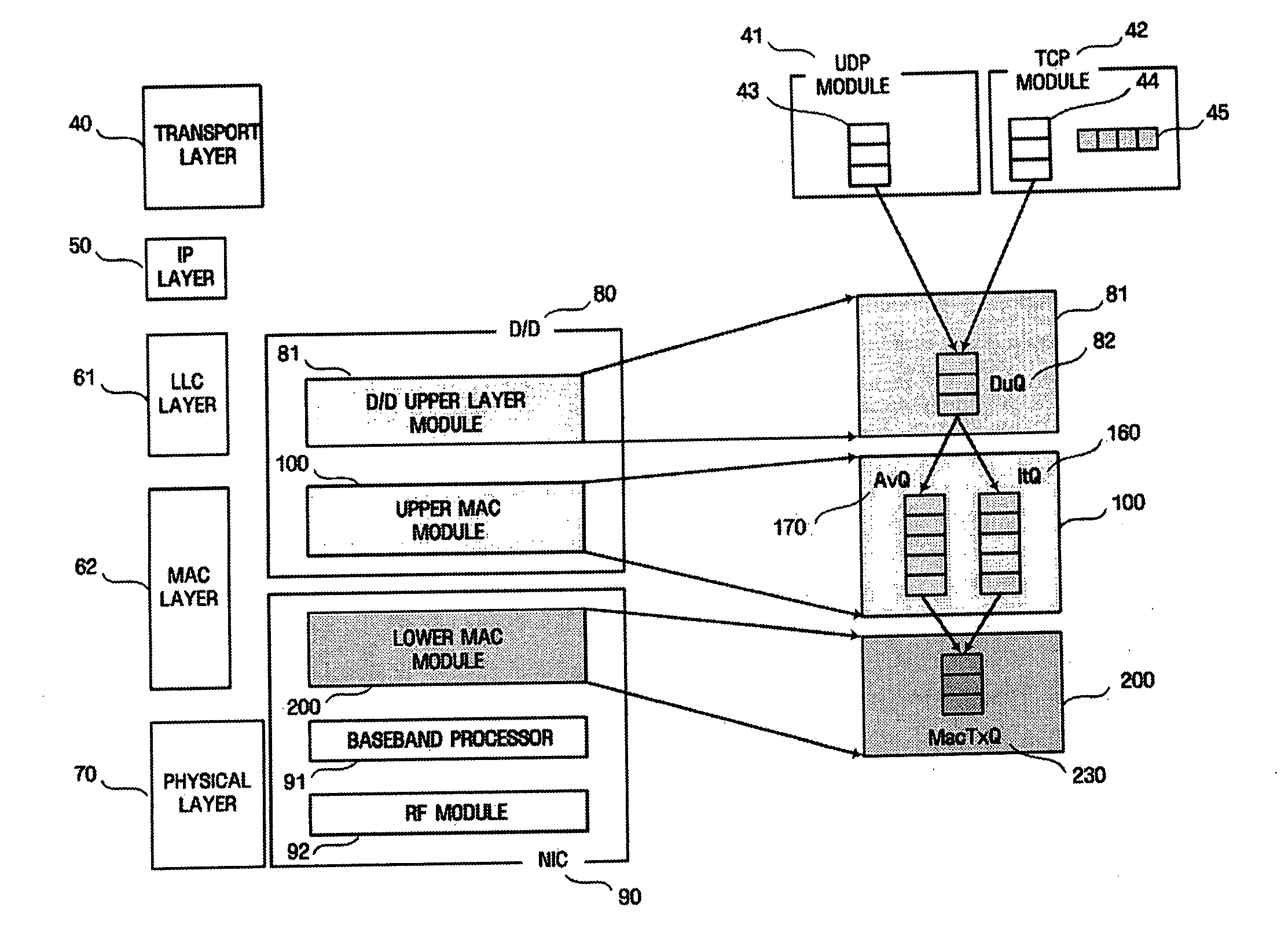
InactiveUS20050195821A1Reduce window sizeGuaranteed normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationMultimedia streamsControl data
A method and apparatus dynamically control data traffic, such as multimedia streams, needing a guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS) and normal data traffic, according to a variable communication environment. The method of dynamically controlling traffic in a wireless station includes reading header information of a packet received from an upper layer and determining a type of the packet, setting a priority according to the type of the packet, adjusting a size of a variable buffer by performing appropriate dynamic buffering according to the type of the packet, enqueuing the packet in a fixed buffer if the priority is high and enqueuing the packet in the variable buffer if the priority is low, and transmitting the packet enqueued in the fixed buffer to a destination station prior to the packet enqueued in the variable buffer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com