Patents
Literature
132 results about "Reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
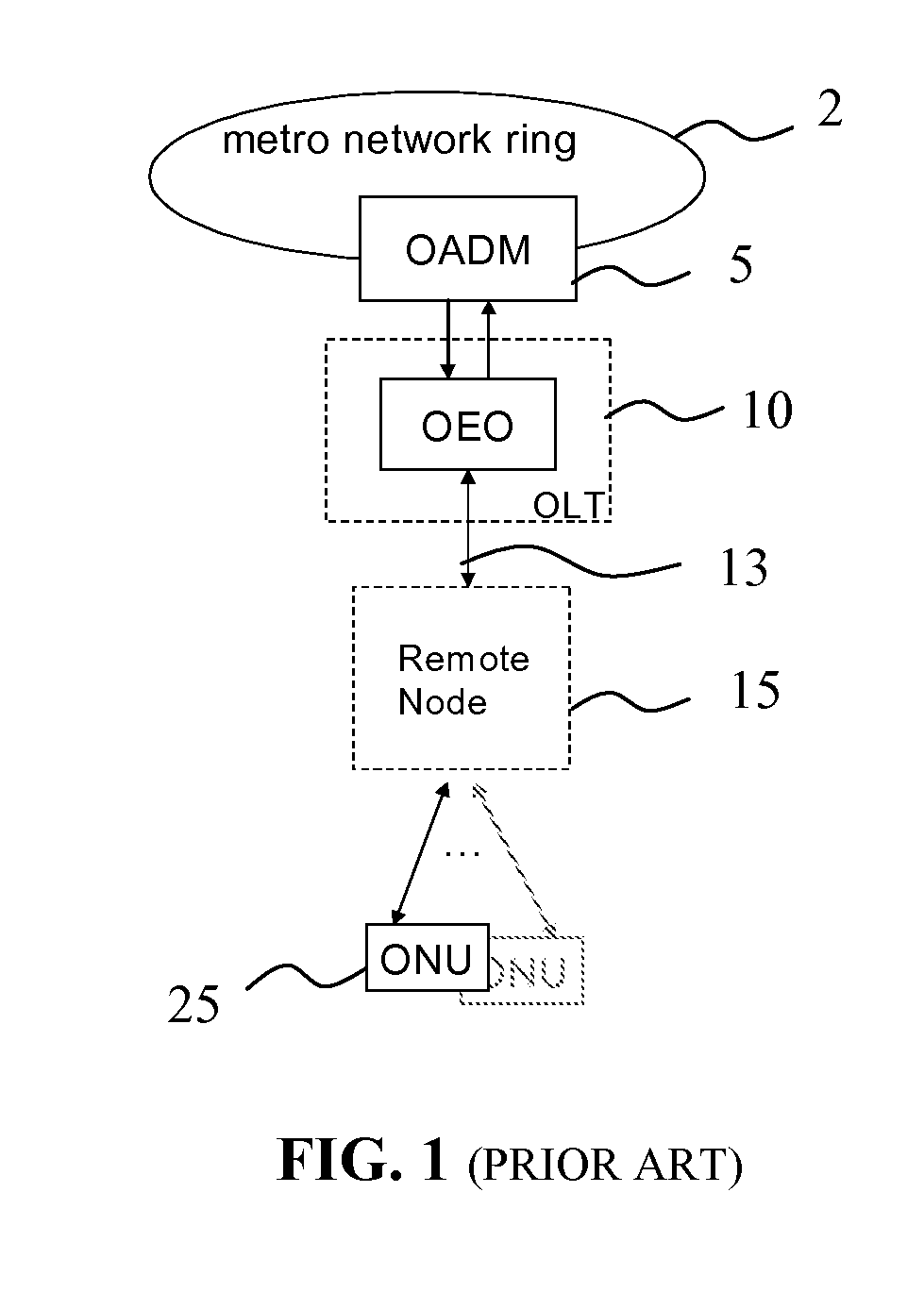
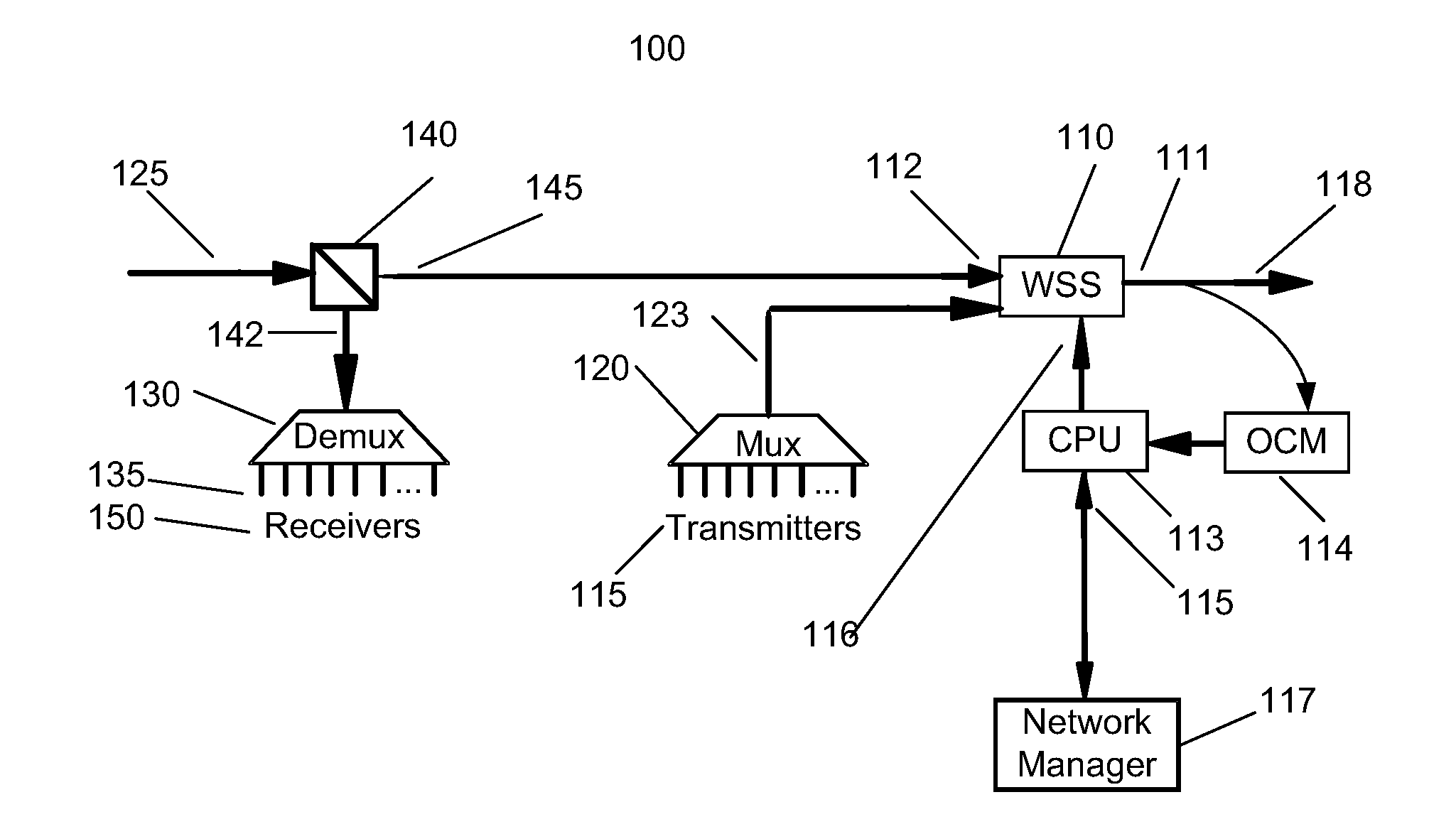
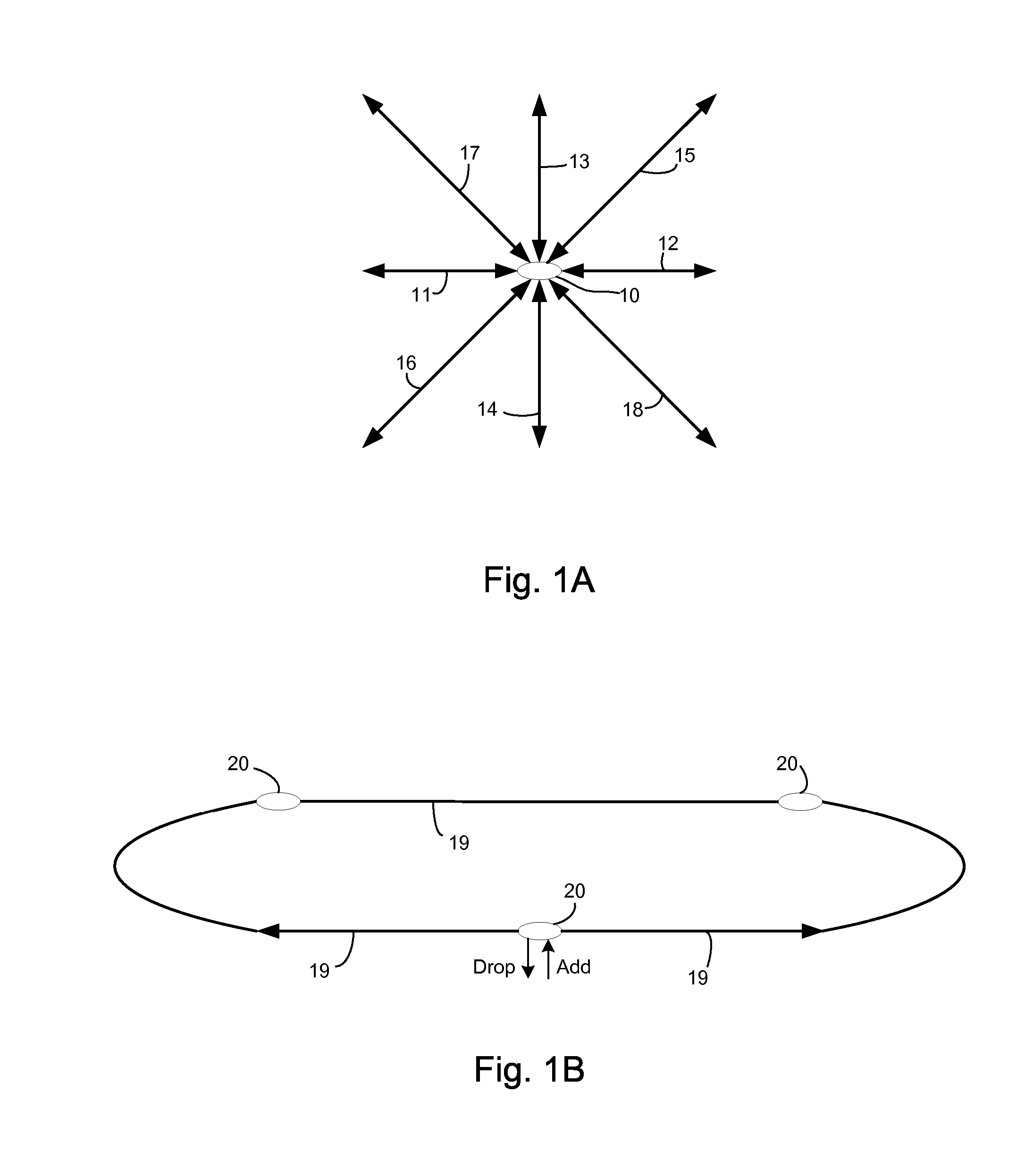
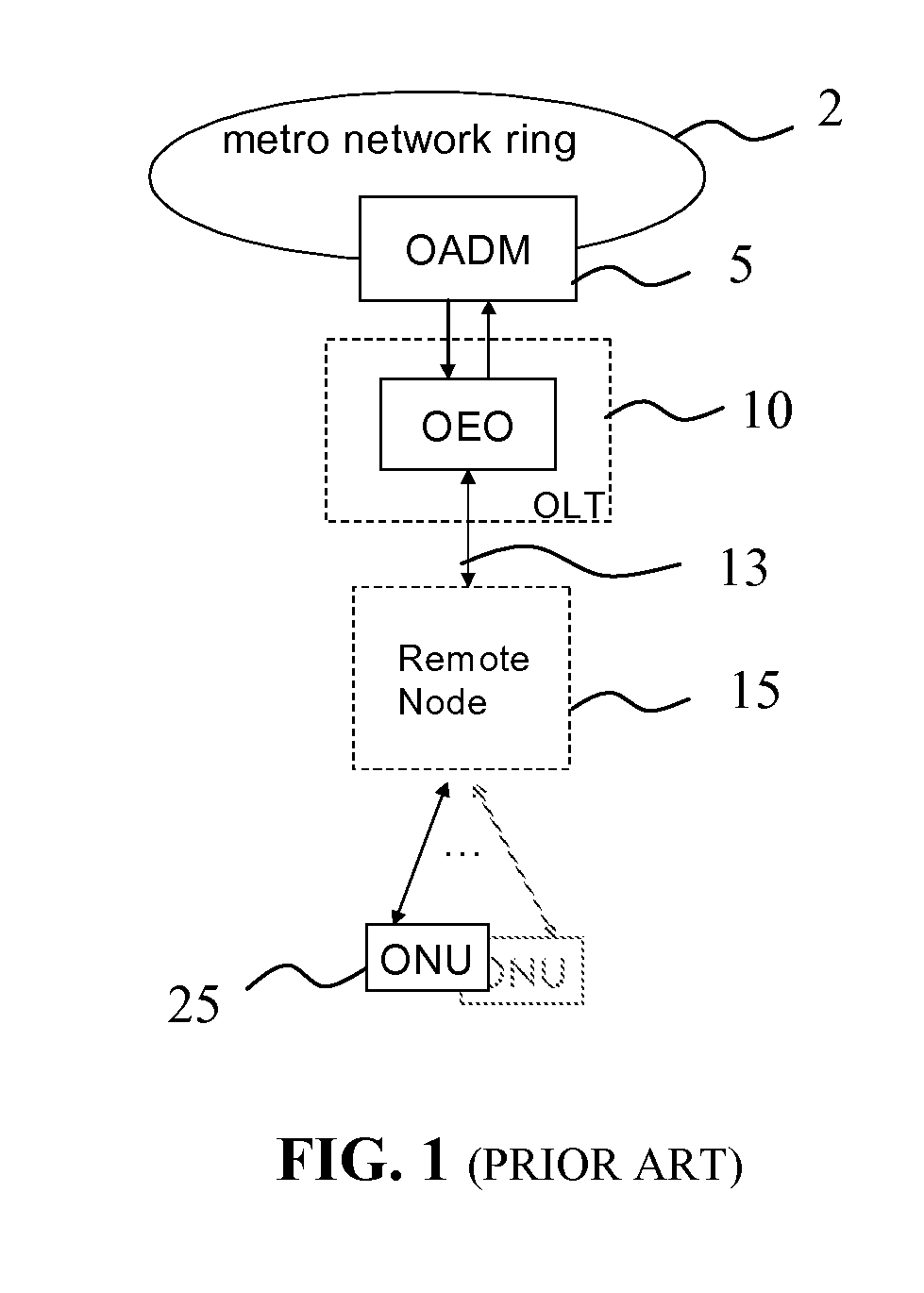
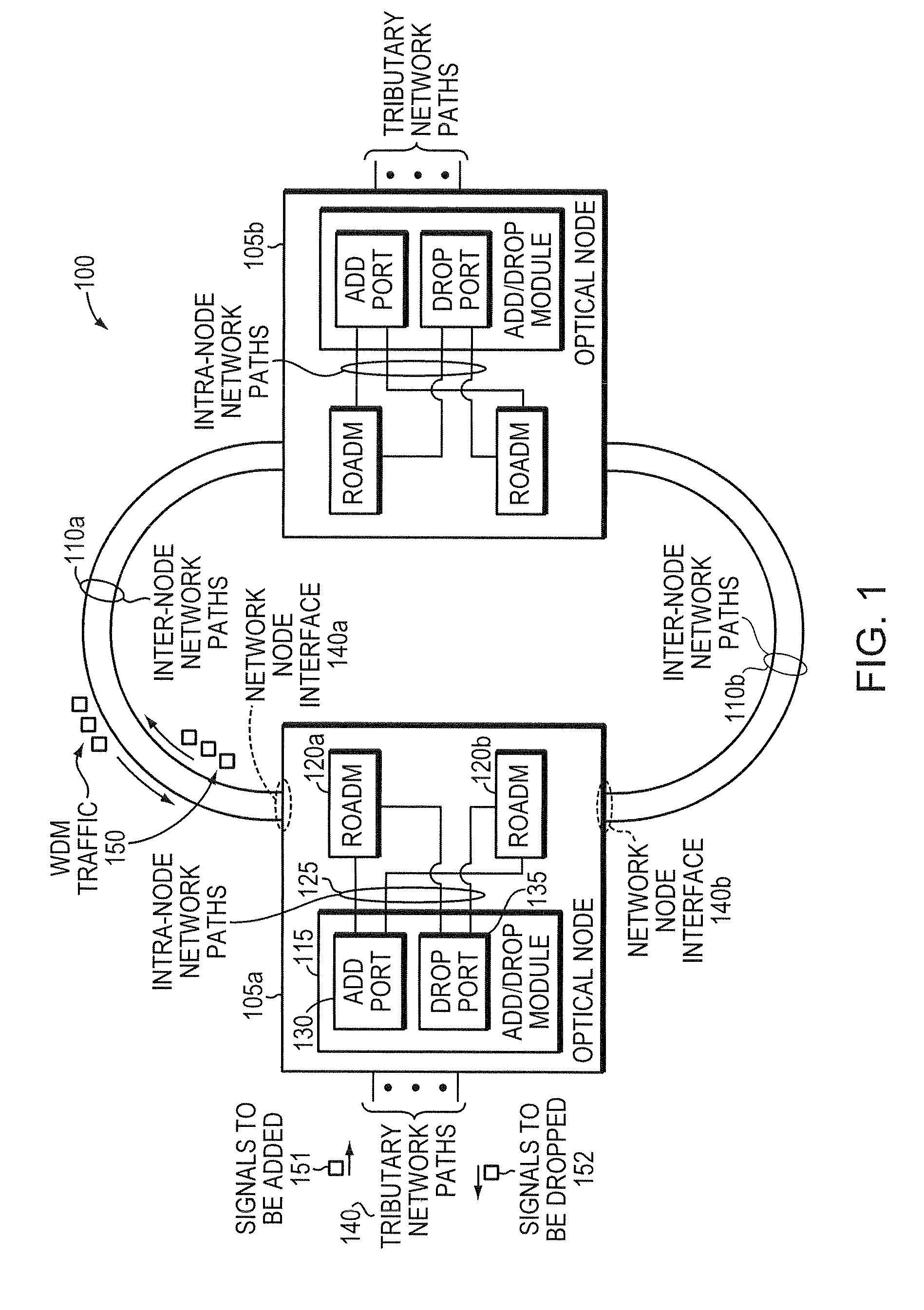
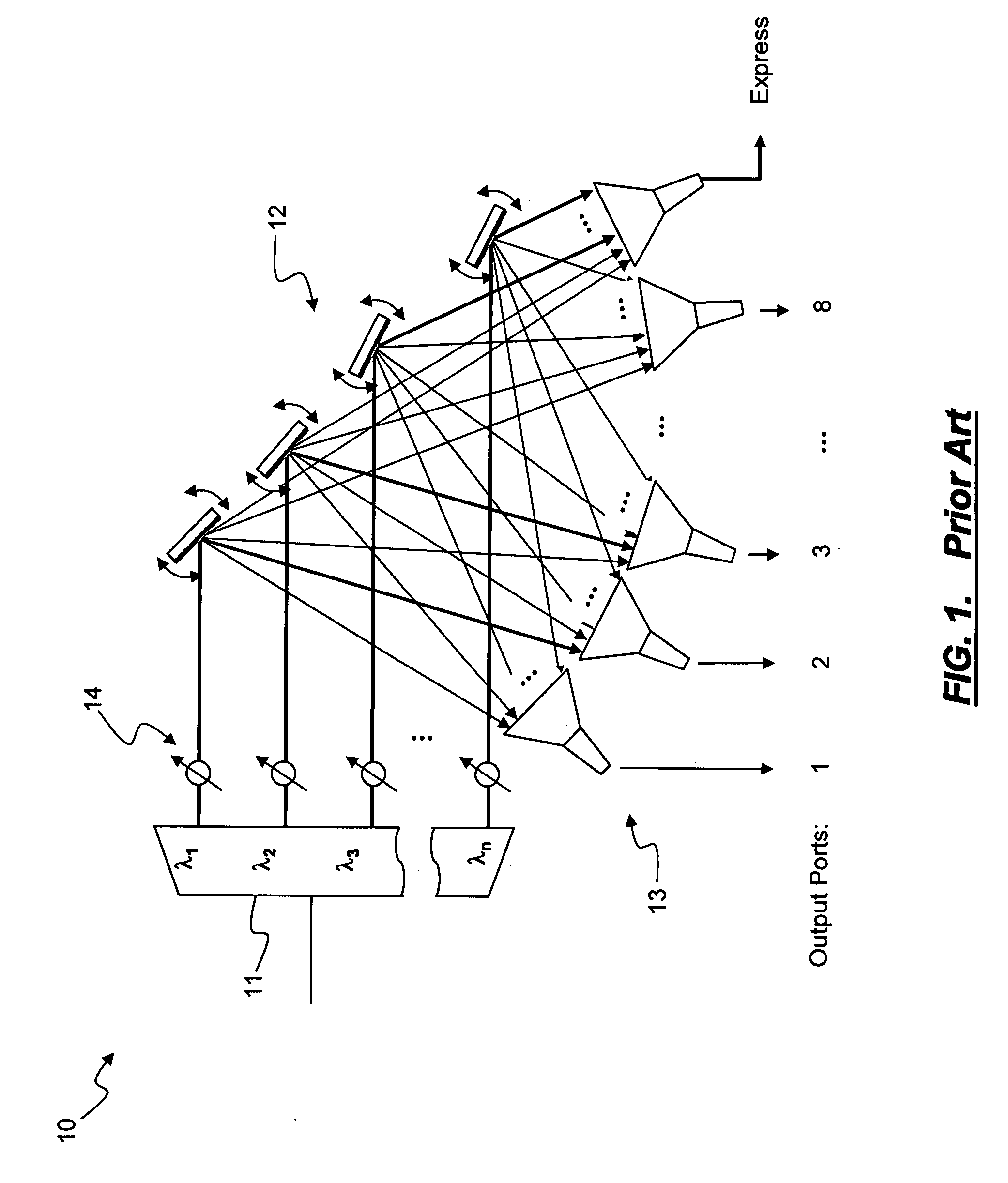
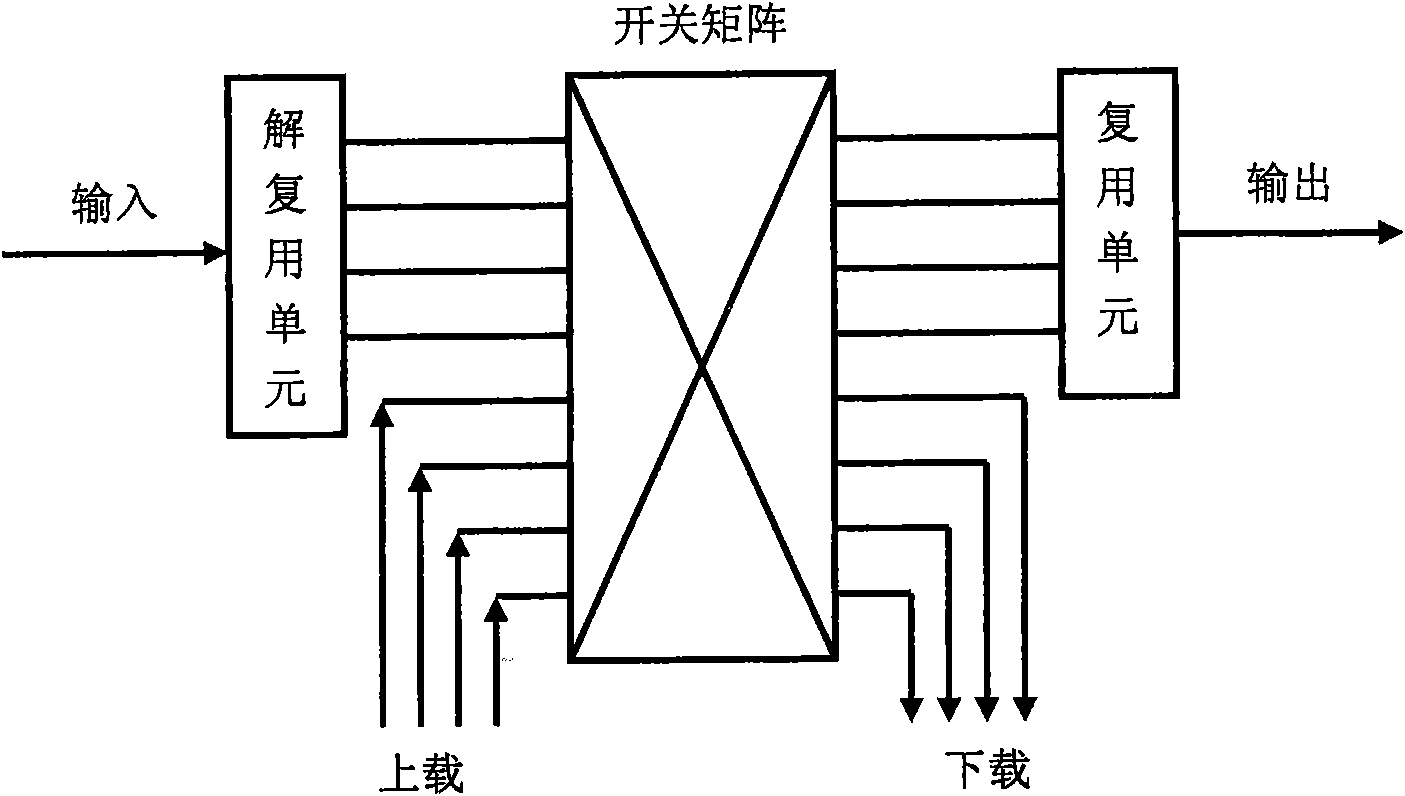
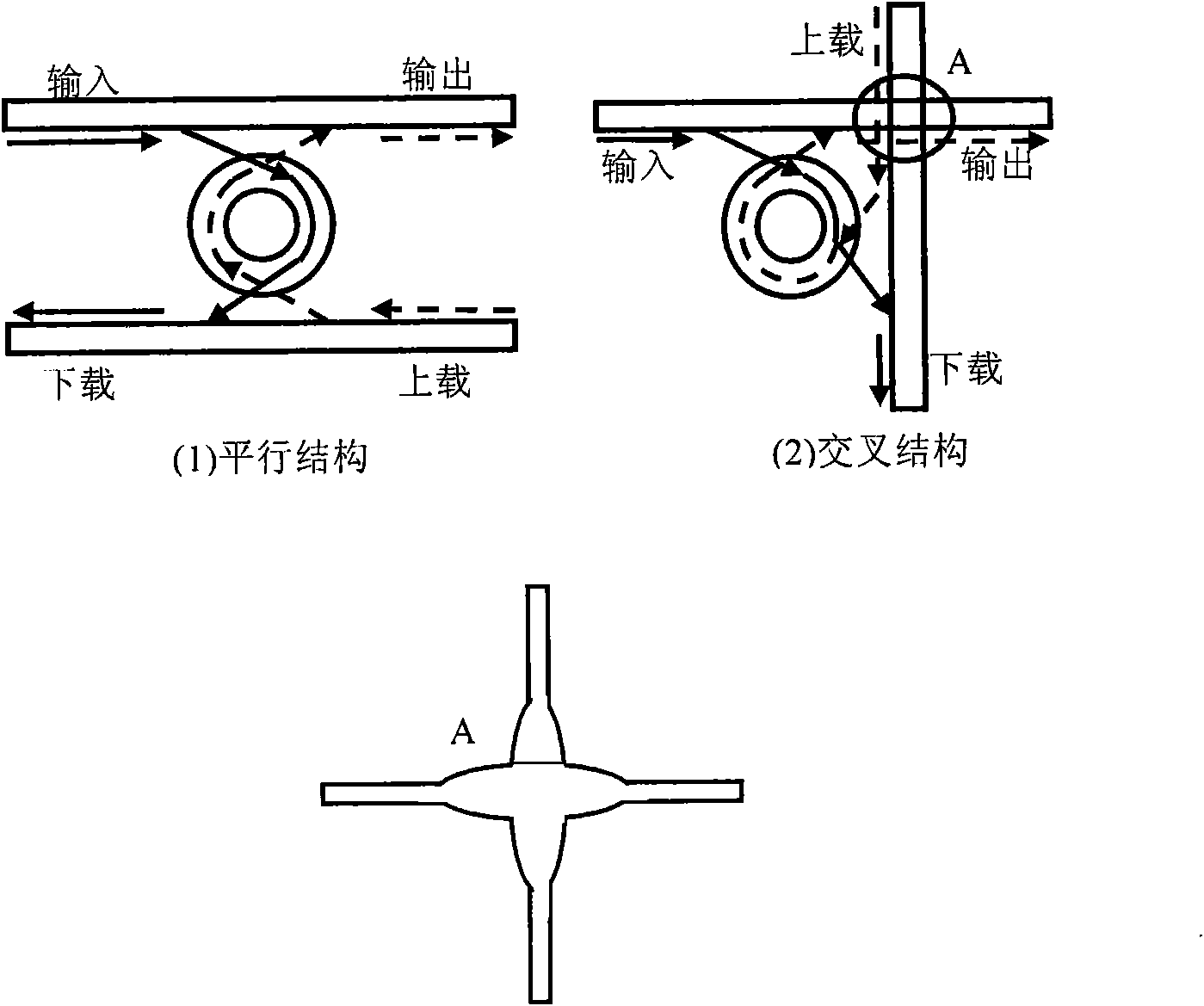
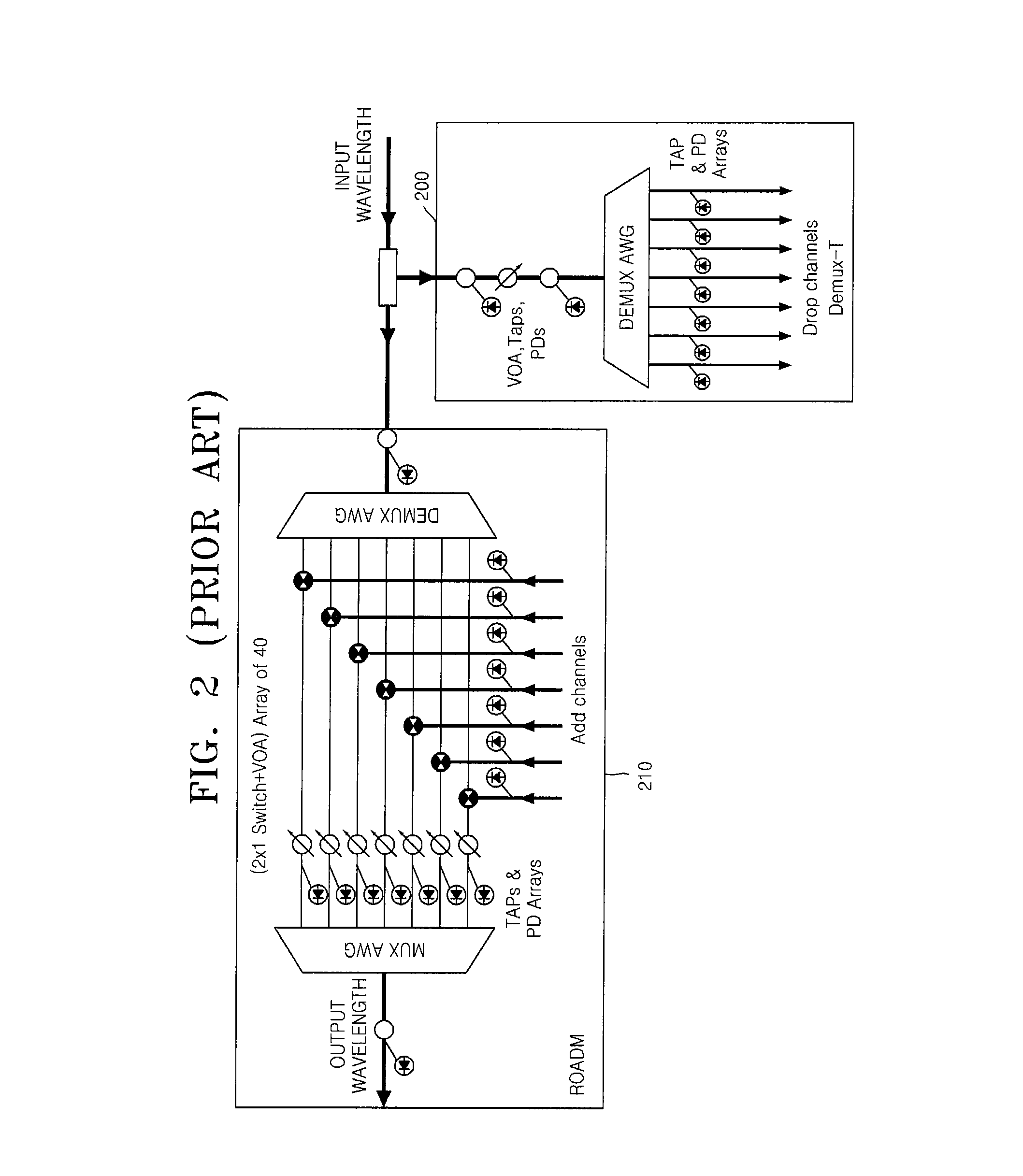
In fiber optics, a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) is a form of optical add-drop multiplexer that adds the ability to remotely switch traffic from a wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) system at the wavelength layer. This is achieved through the use of a wavelength selective switching module. This allows individual or multiple wavelengths carrying data channels to be added and/or dropped from a transport fiber without the need to convert the signals on all of the WDM channels to electronic signals and back again to optical signals.
Reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer
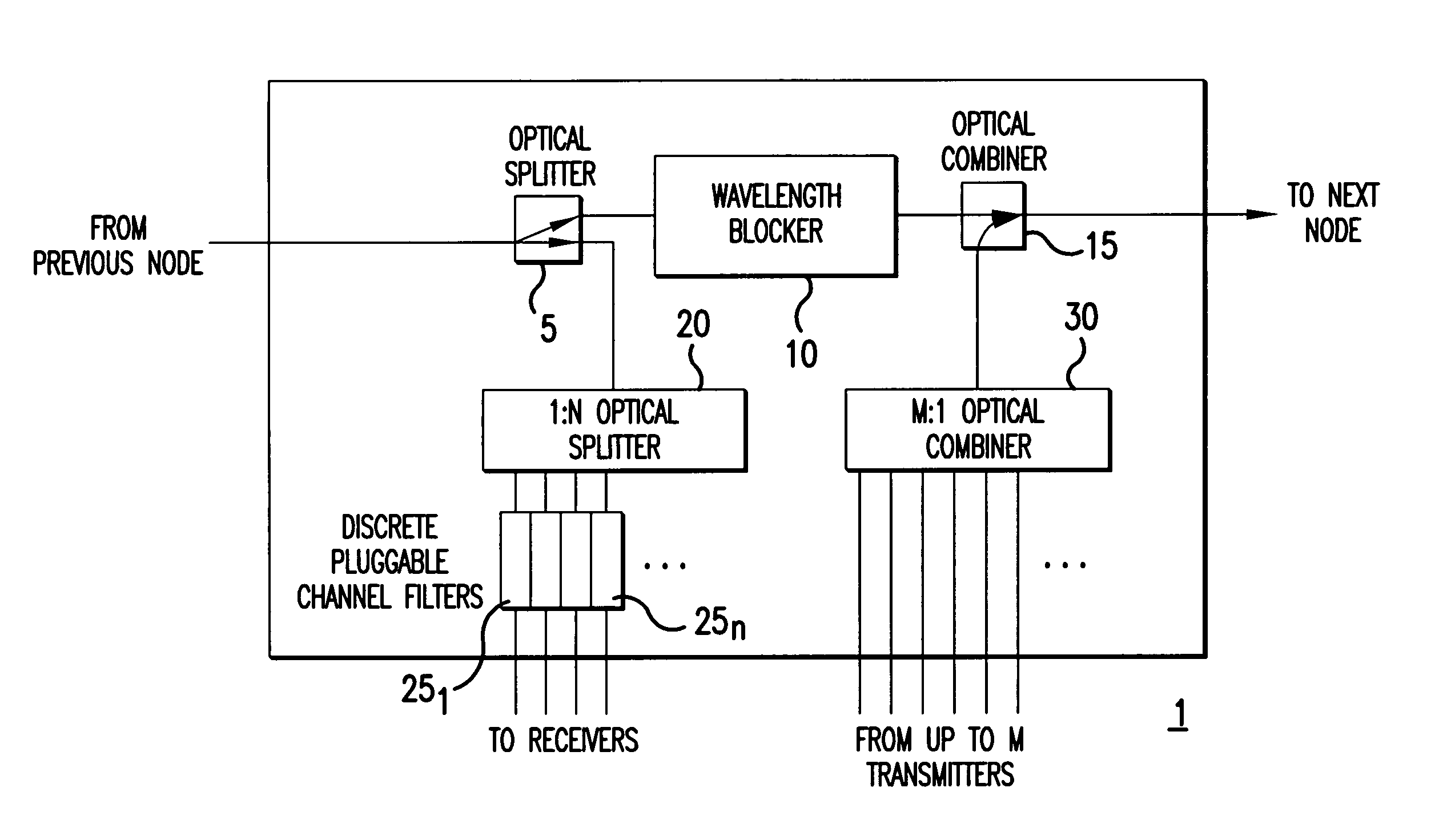
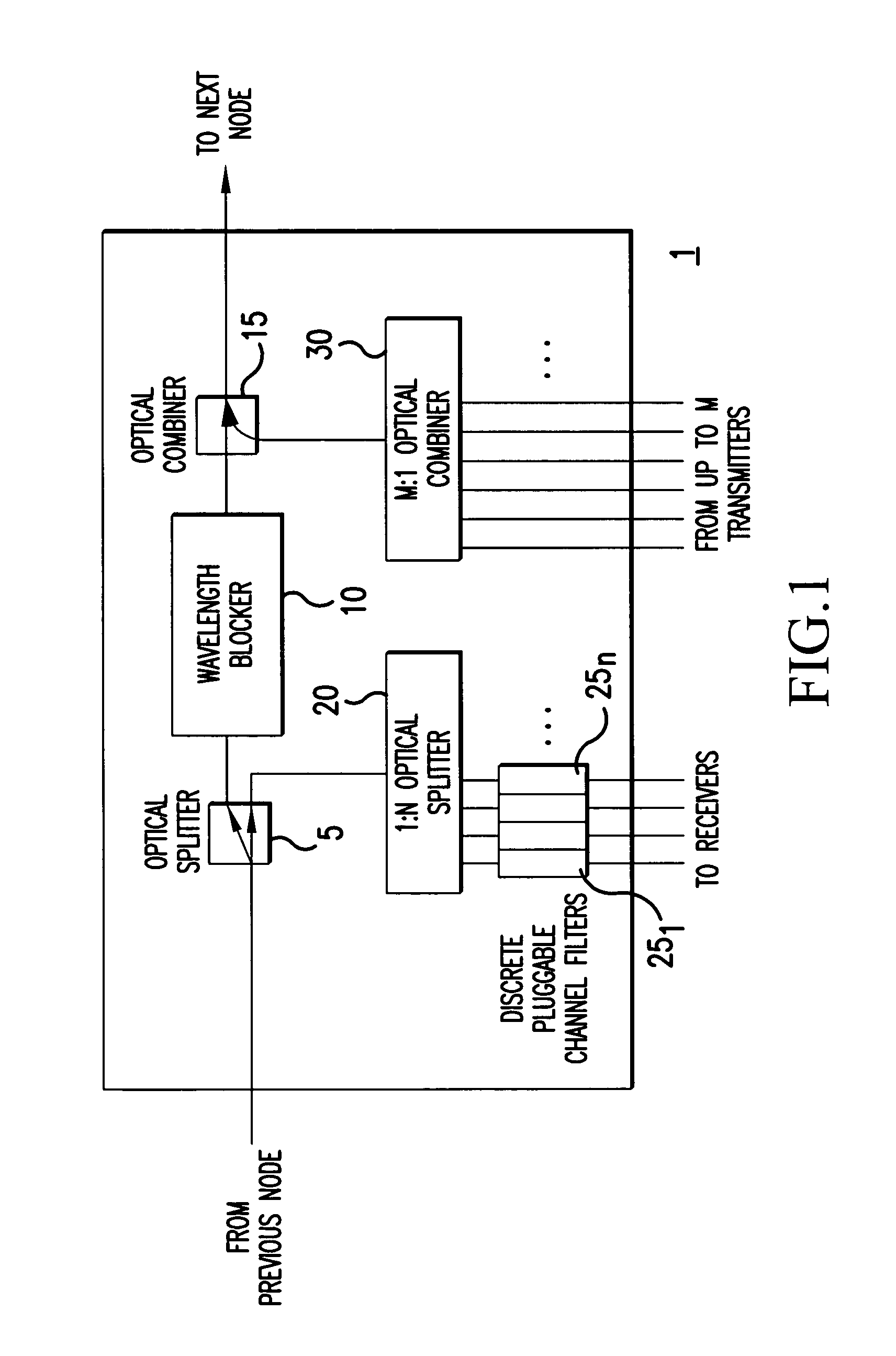
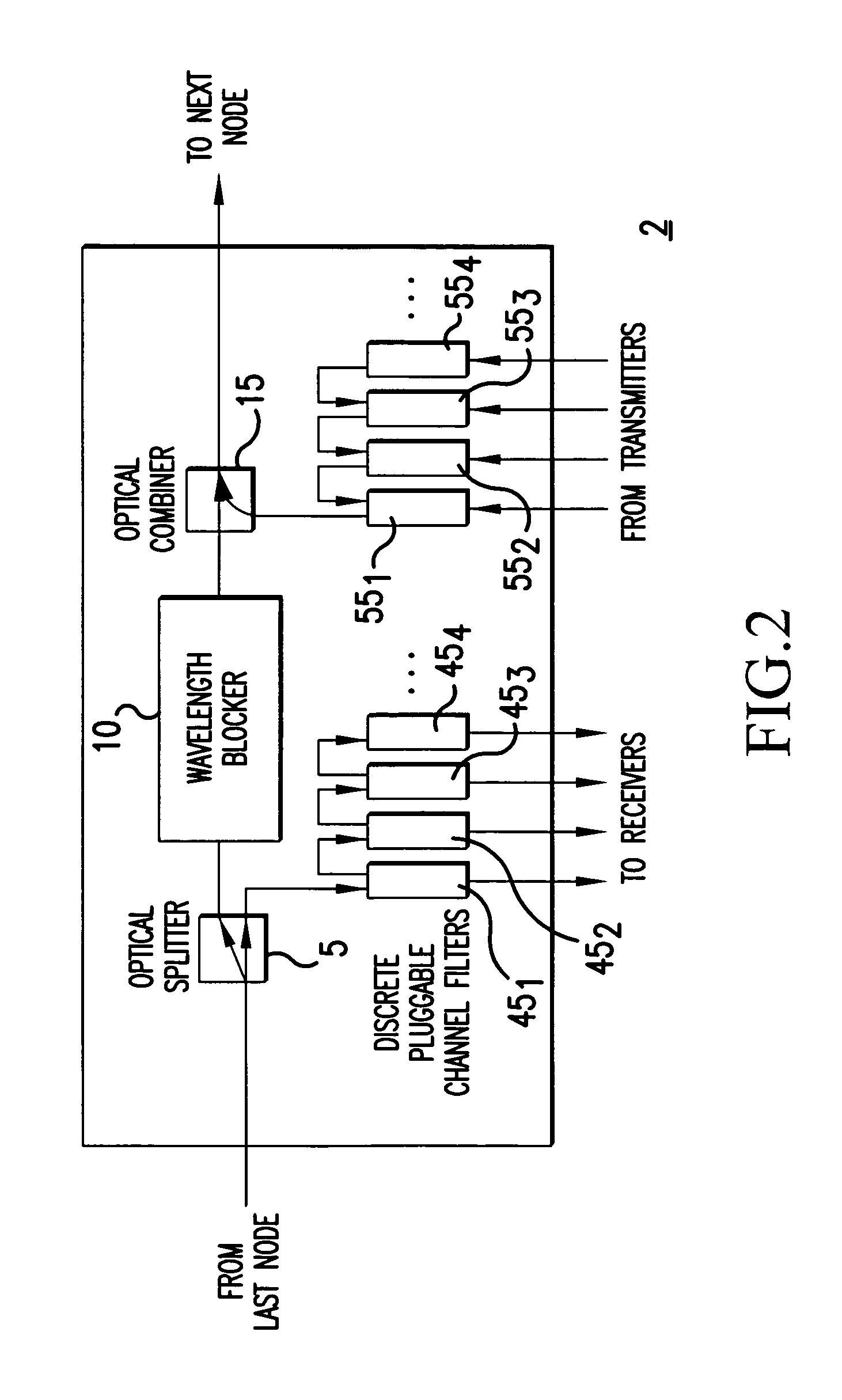
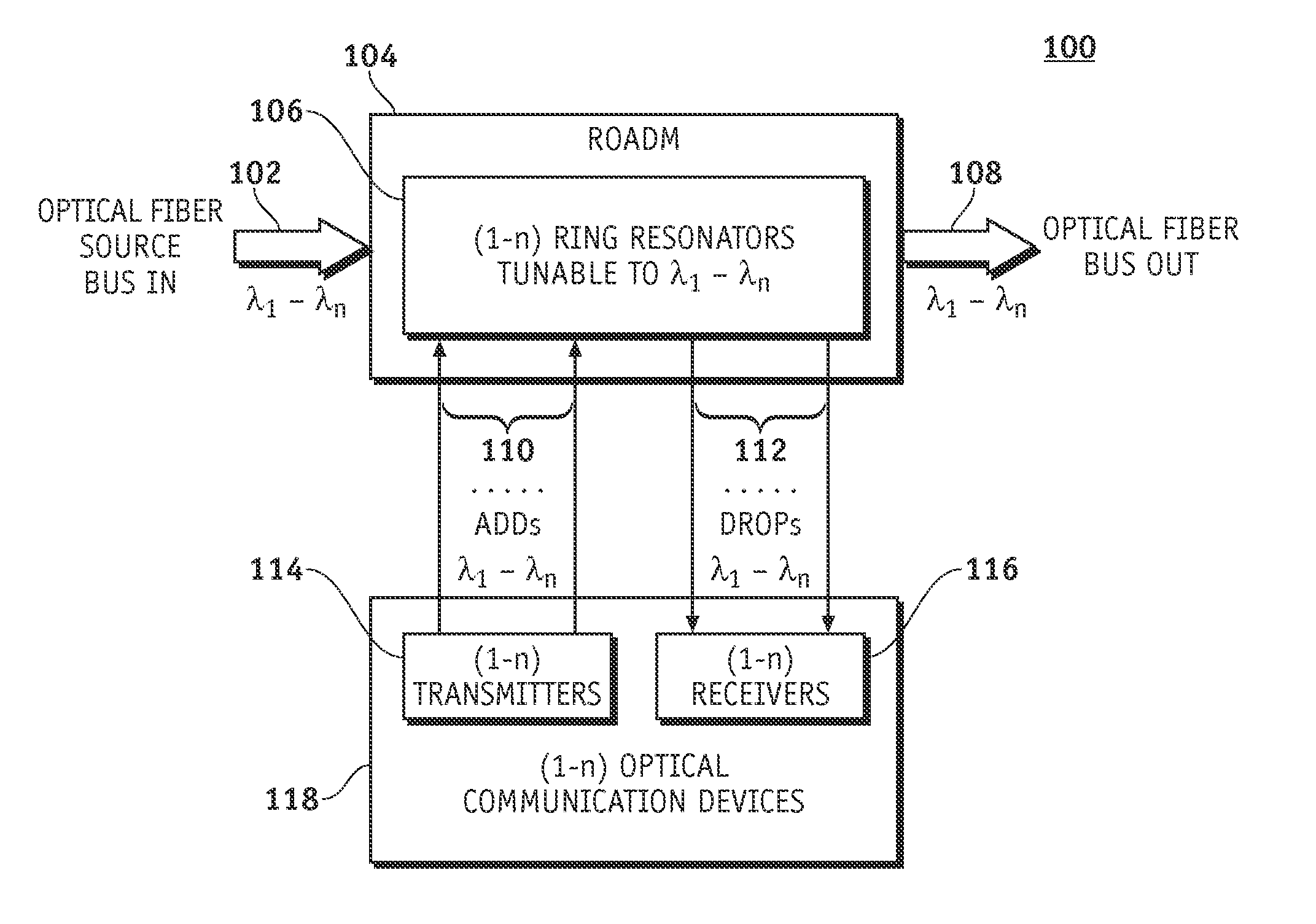
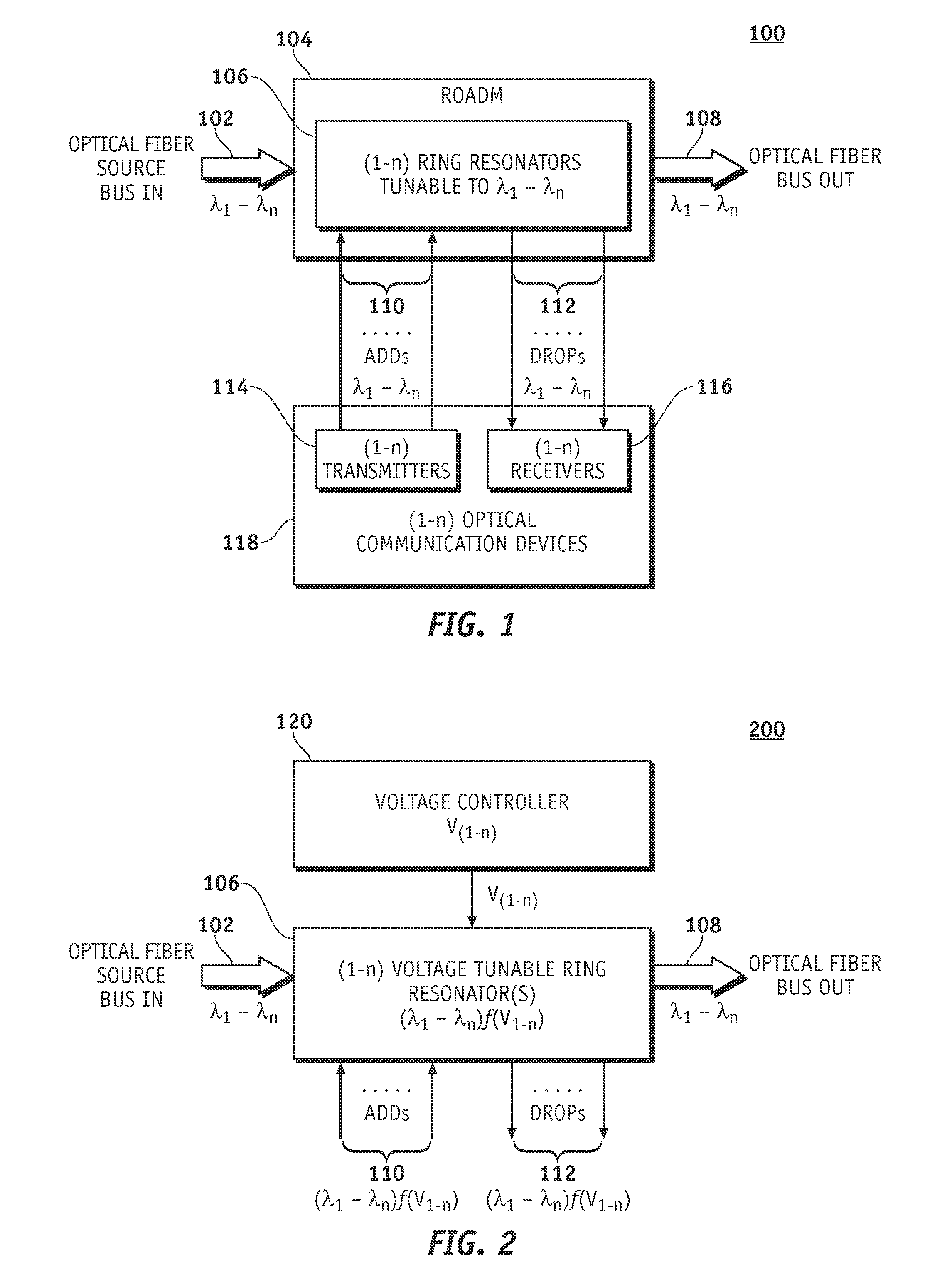
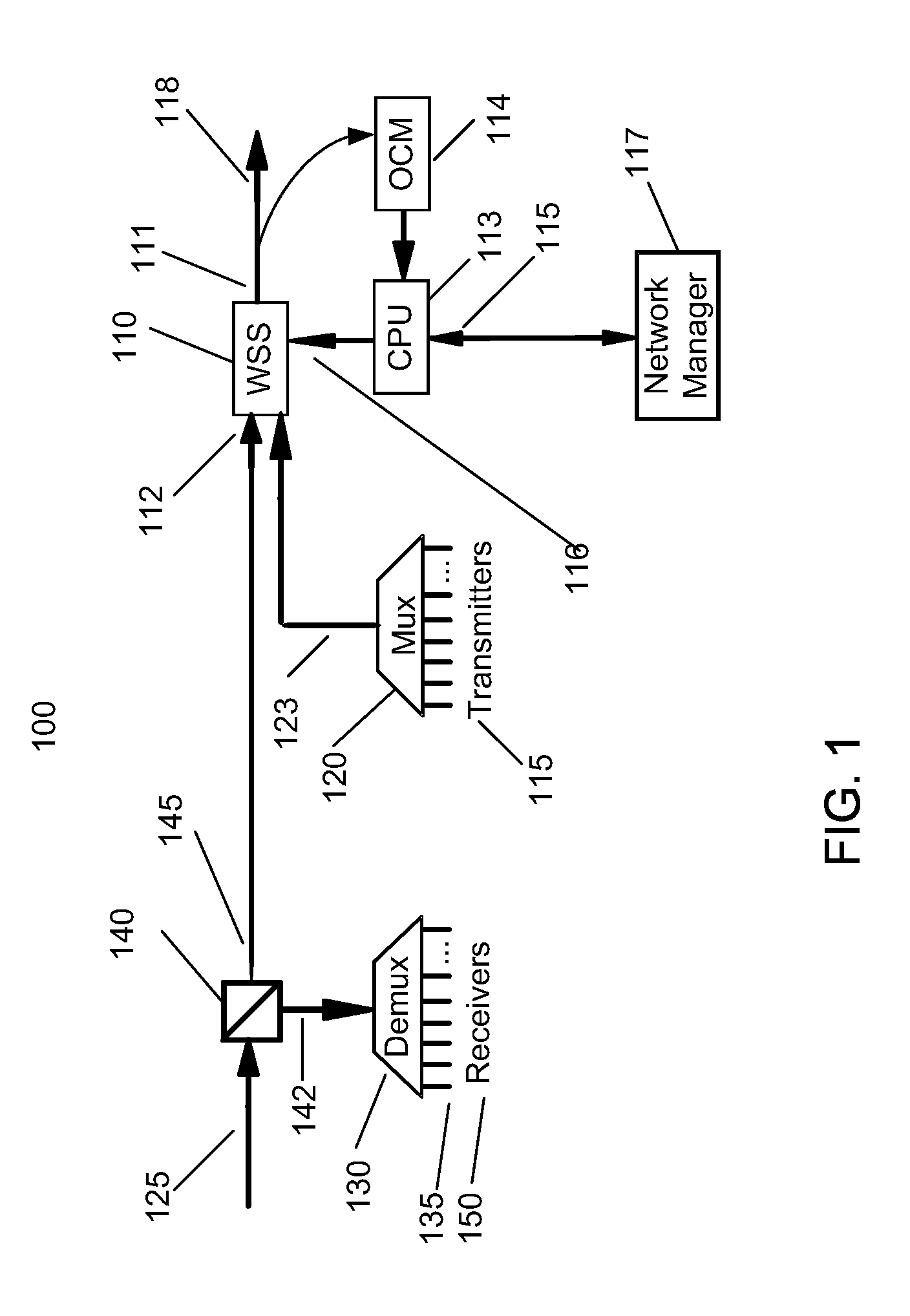
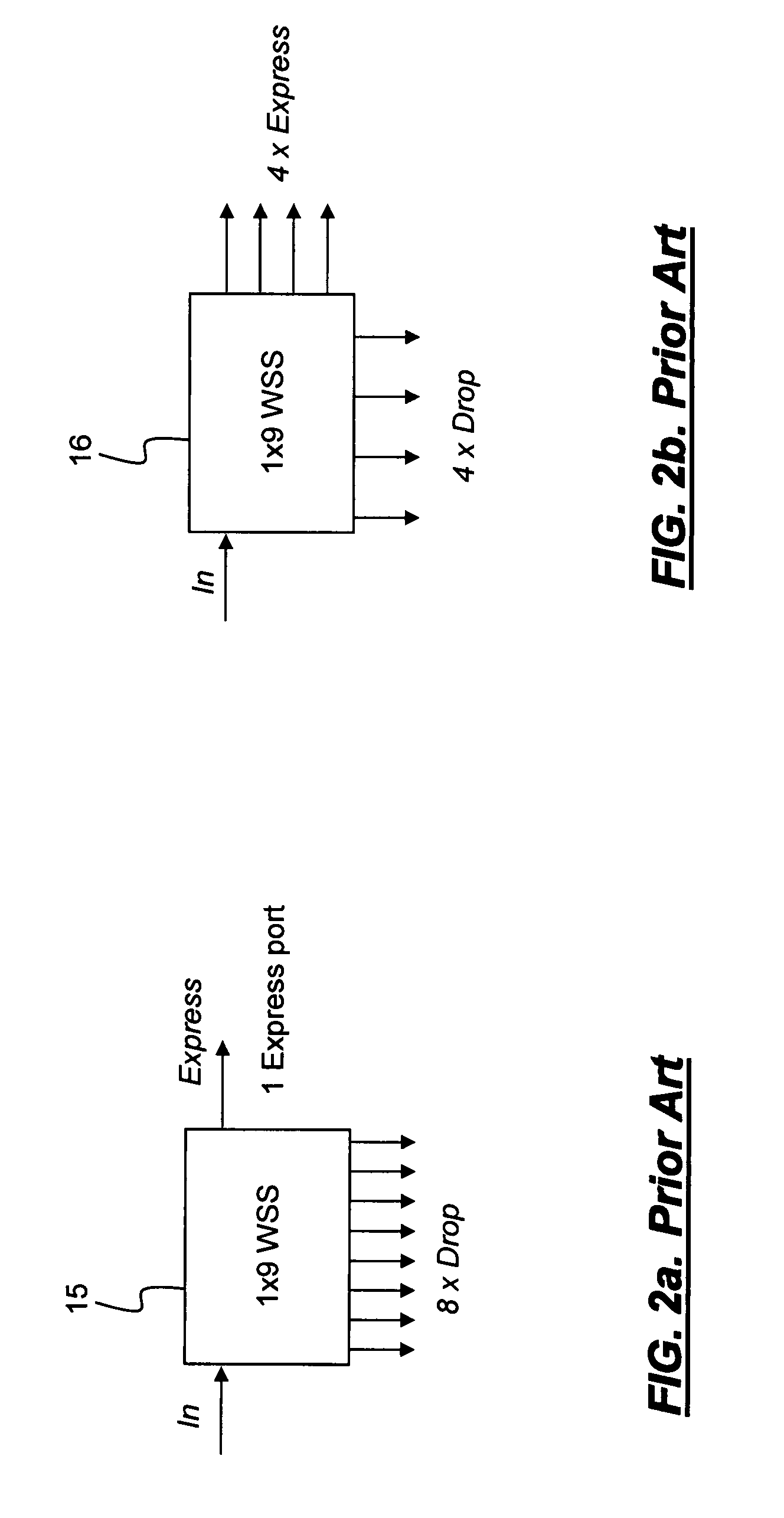
A reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer is disclosed including an optical splitter receiving an input optical signal and splitting the input optical signal into a dropped optical signal and an express optical signal; a wavelength blocker optically coupled to the optical splitter, the wavelength blocker blocking particular wavelengths in the express optical signal; a cassette having a plurality of slots capable of accepting a plurality of pluggable optical filters; at least one pluggable optical filter optically coupled to the optical splitter, the pluggable optical filter filtering wavelengths so as to output a particular wavelength channel from the dropped optical signal; and an optical combiner optically coupled to the wavelength blocker and to an optical add path on which an optical add signal may be carried, the optical combiner combining the express optical signal having particular wavelengths expressed by the wavelength blocker and the optical add signal.
Owner:CIENA
Wavelength reconfigurable optical network
ActiveUS20080013950A1Selectively changeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionMultiplexerNetwork architecture
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Scalable reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer
ActiveUS20080193133A1High index contrastGood wavelength selectivityWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesLength waveOptical bus
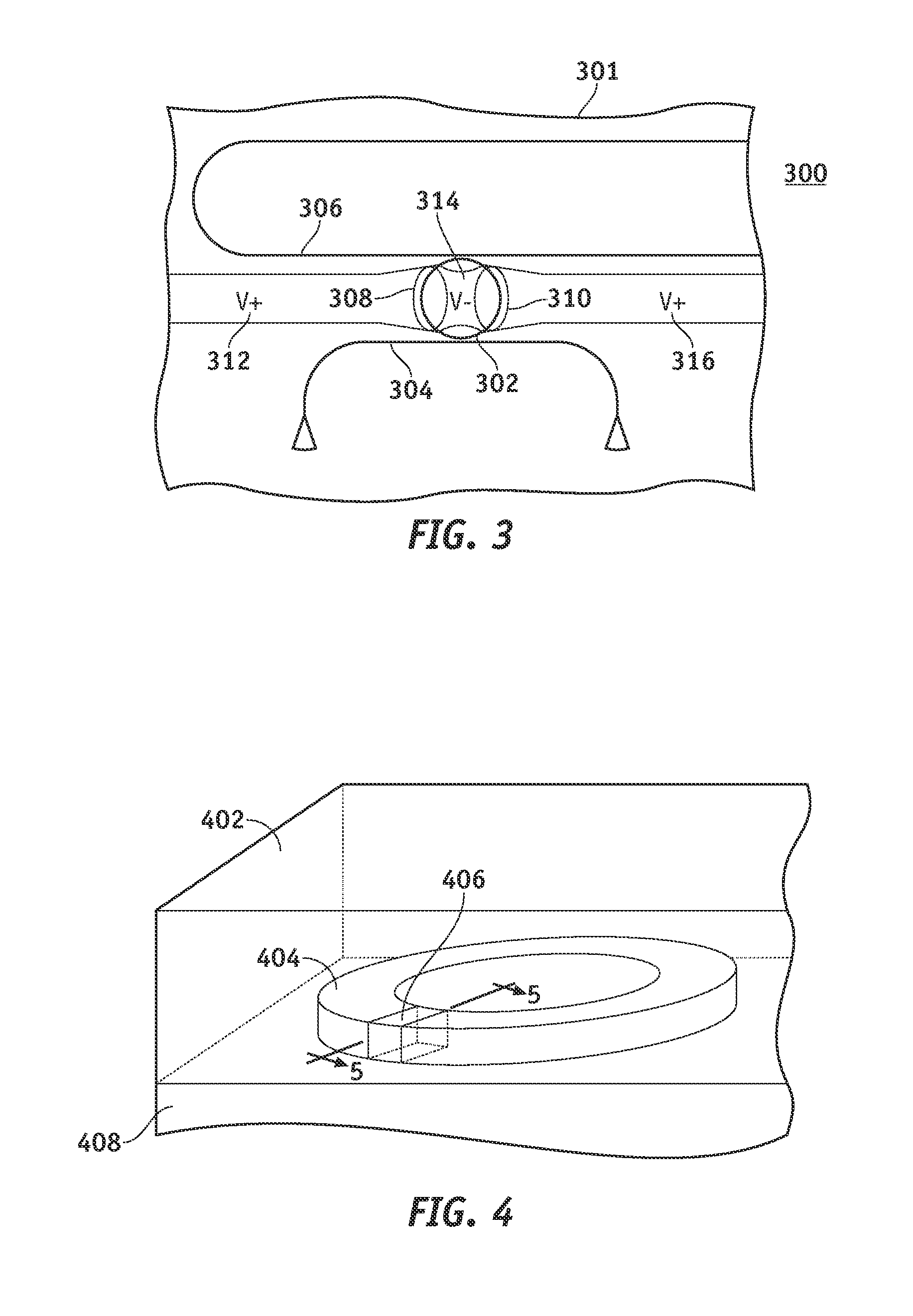
A system and methods are disclosed for a hybrid silicon-organic scalable reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer. An embodiment of a scalable reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) includes an optical bus for optical signals of different wavelengths, a plurality of add / drop optical waveguides, and a plurality of ring resonators, each being optically coupled to the optical bus and to one of the add / drop optical waveguides. The ring resonators are coated with an organic electro-optic cladding layer and are configured to switch wavelength selected optical signals between the optical bus and the add / drop optical waveguides in response to control voltages applied to the organic electro-optic cladding layer. The individual ring resonators of the ROADM can be independently modulated and tuned to filter specific wavelengths.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +2
Directionless optical architecture and highly available network and photonic resilience methods
ActiveUS20090232492A1Lightweight deploymentIncrease elasticityMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsTransceiverRoute diversity
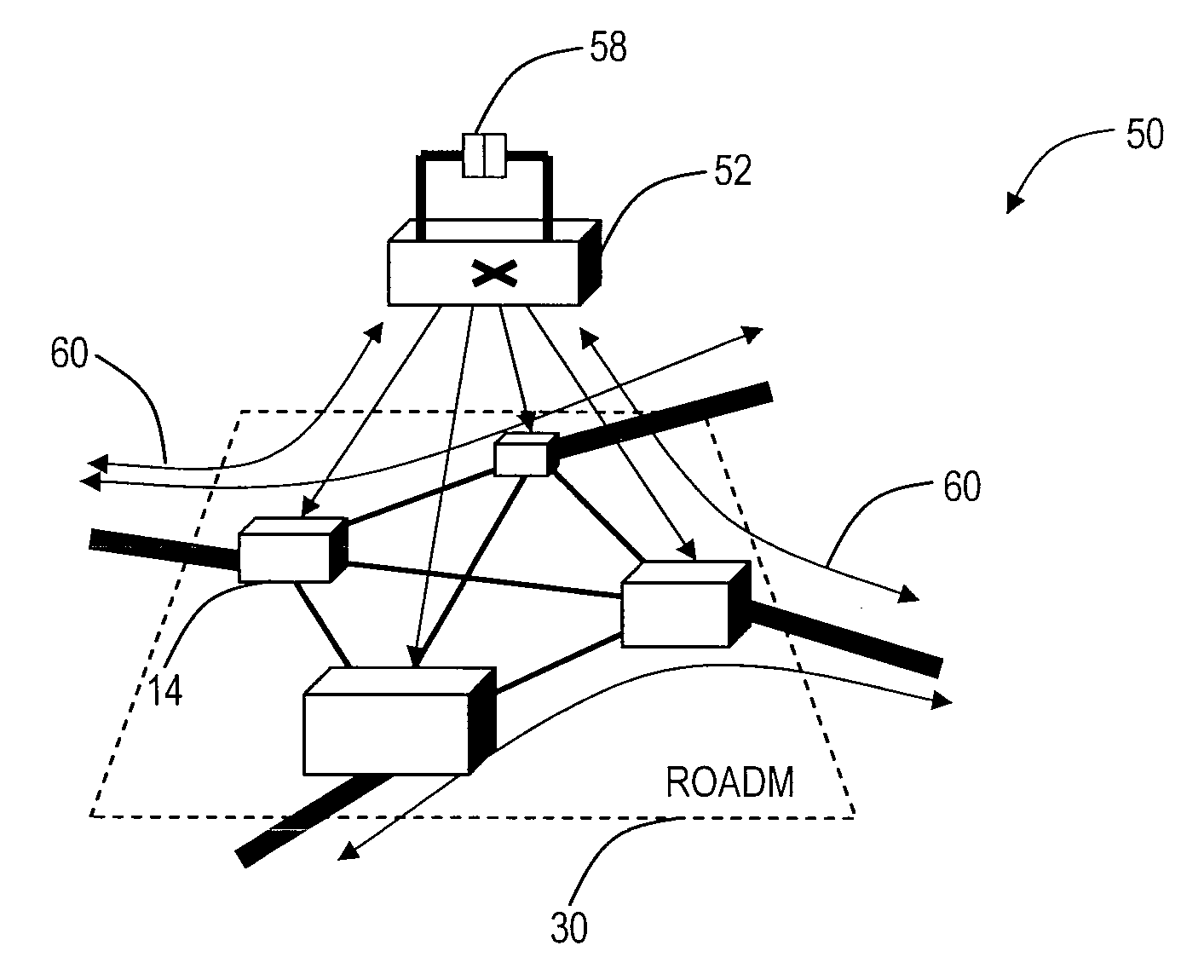
The present invention provides a directionless optical architecture for reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexers (ROADMs) and wavelength selective switches (WSSs). The directionless architecture utilizes a directionless wavelength switch coupled between client devices and ROADMs / WSSs to eliminate the need to hard-wire client devices to a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) network. Accordingly, client device connections can be automatically routed without manual intervention to provide a highly resilient network design which can recover route diversity during failure scenarios. Additionally, the present invention minimizes deployments of costly optical transceivers while providing superior resiliency. Further, the present invention couples the directionless optical architecture and associated optical protection mechanisms with existing mesh restoration schemes to provide additional resiliency.
Owner:CIENA
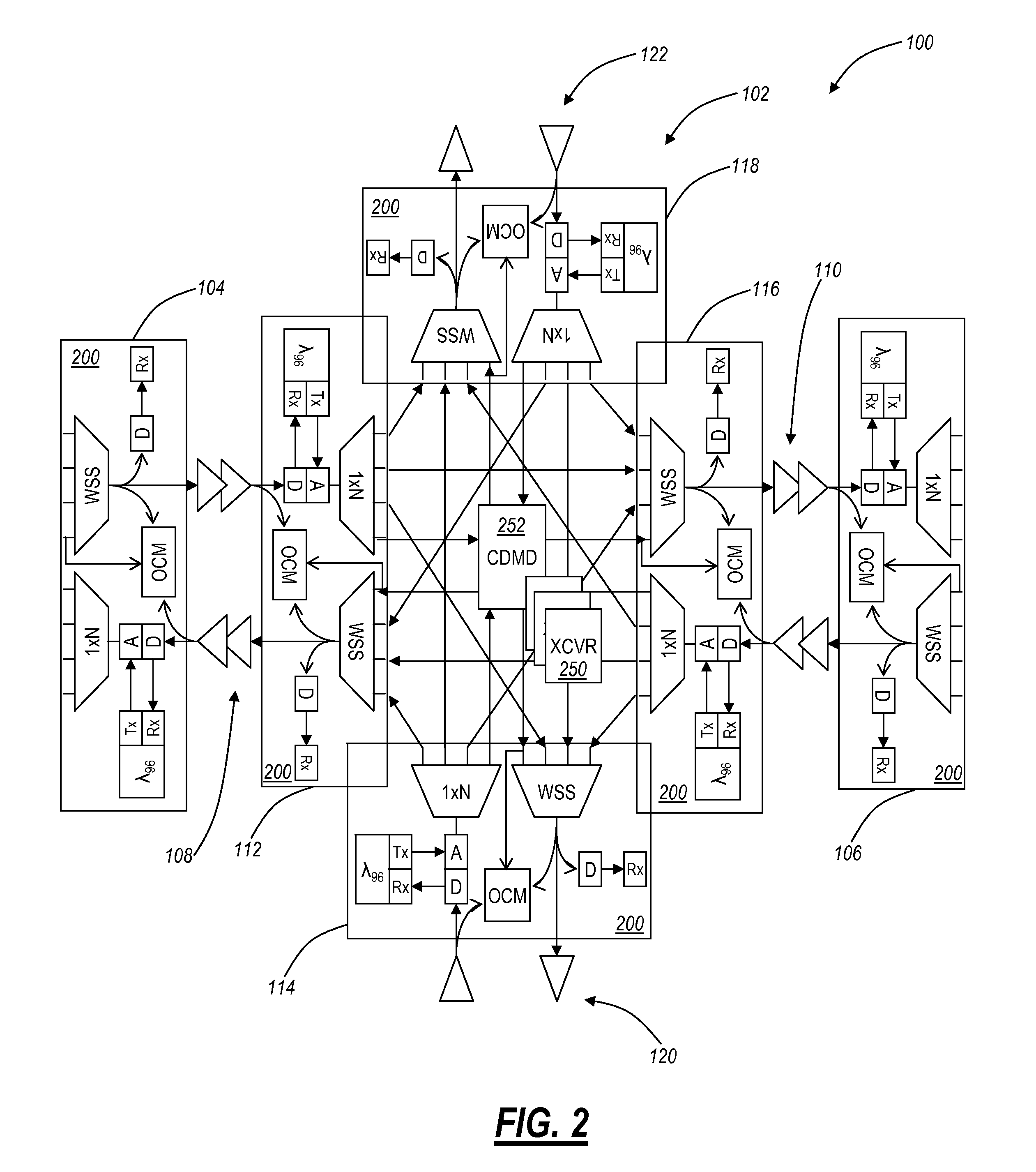
Reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer node automated topology discovery systems and methods
The present disclosure provides reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) node automatic topology discovery systems and methods providing a mapping of optical connections within a mesh optical network that includes tunable lasers and multi-degree ROADM's with colorless / directionless add / drop. The present disclosure may include additional transceiver, receiver, and add / drop filter equipment integrated in or disposed at a ROADM degree. This equipment supports a so-called topology wavelength which is one of a plurality of wavelengths supported by a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) system that is dedicated and used solely for topology discovery. The topology wavelength may be utilized by the system to detect interconnects between ROADM degrees and between XCVRs / CDMDs. Further, the automated topology discovery may be integrated within a management system and / or control plane.
Owner:CIENA
Multifunctional and reconfigurable optical node and optical network
ActiveUS20080013954A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringLength wave
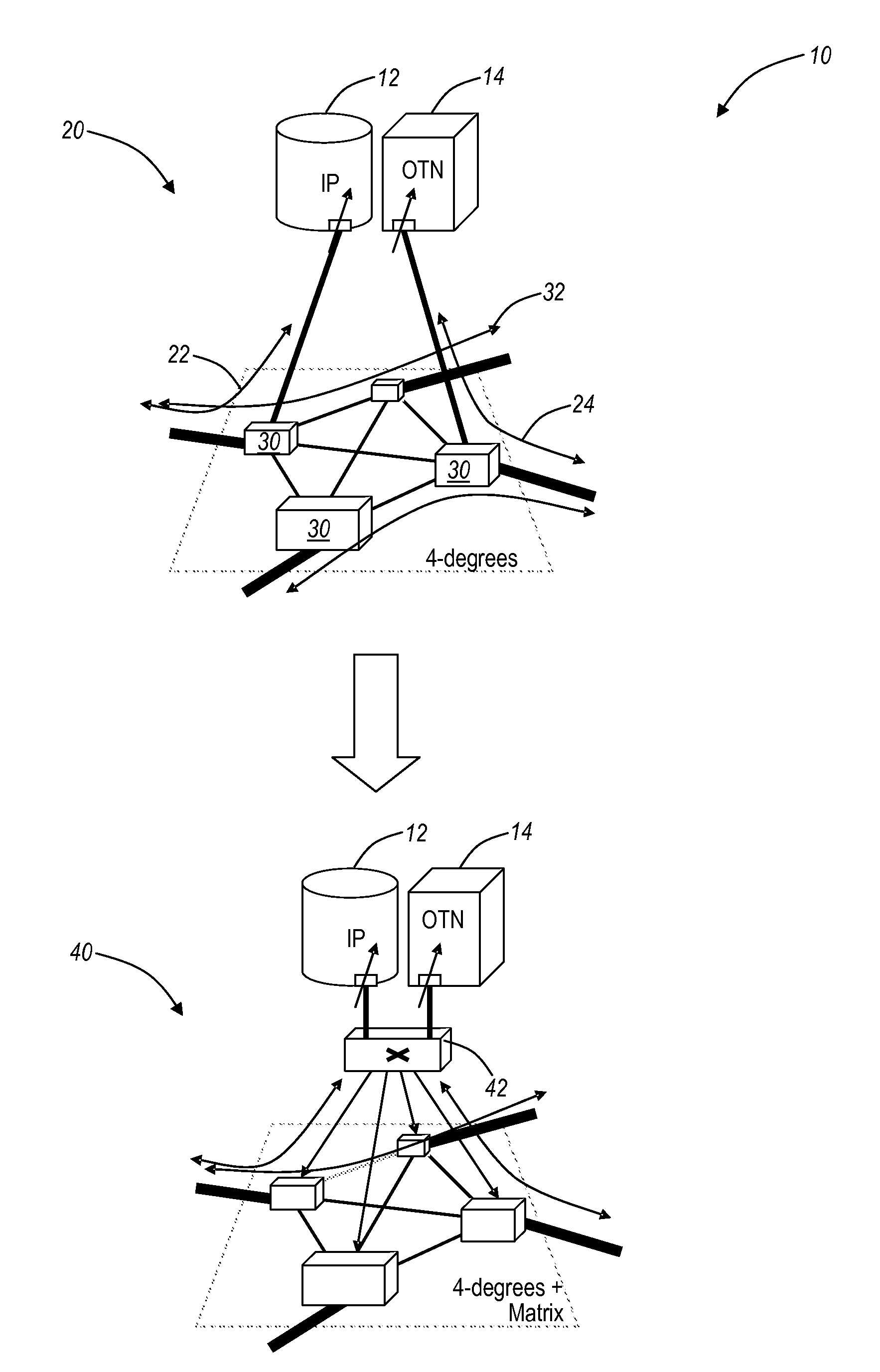
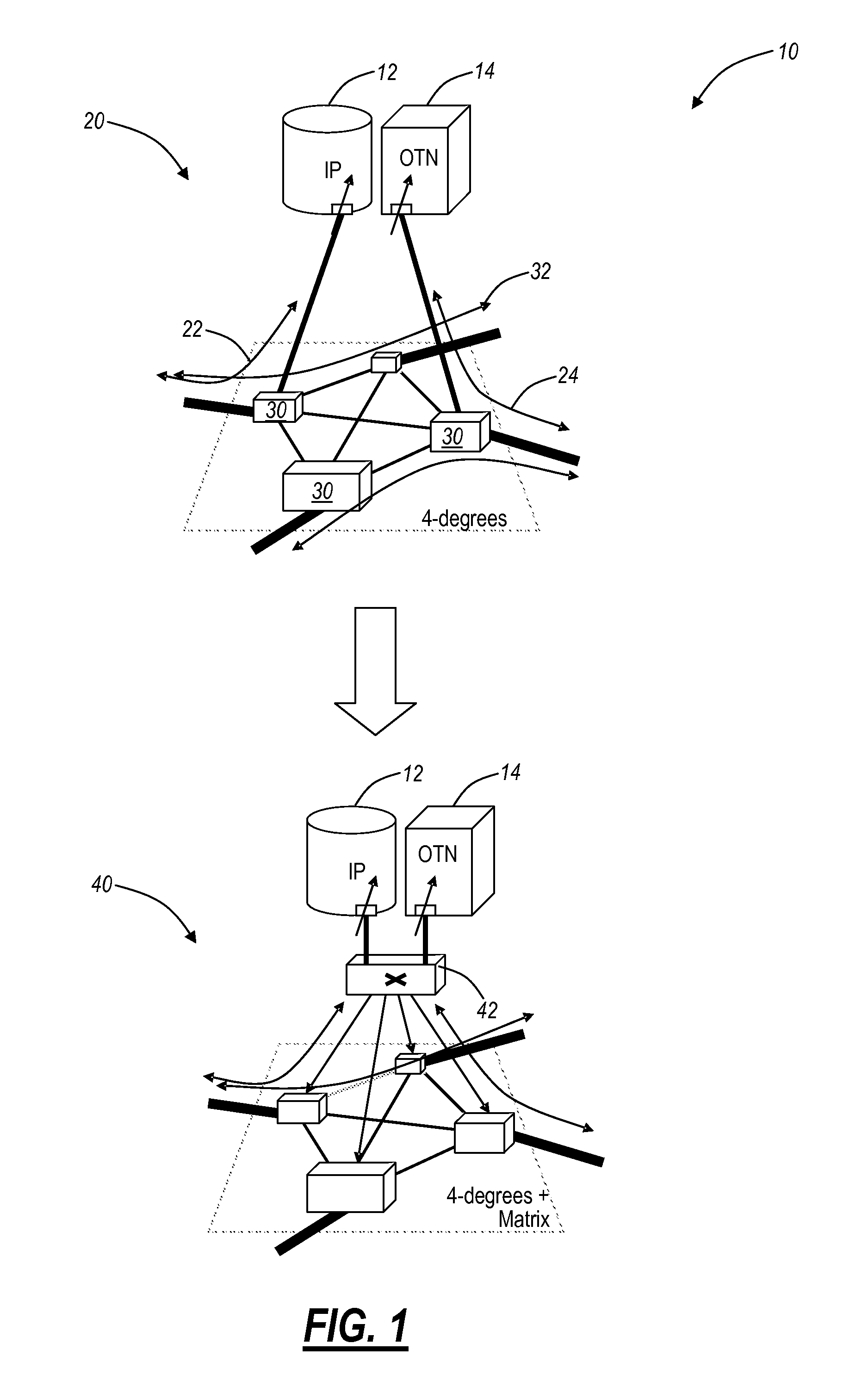
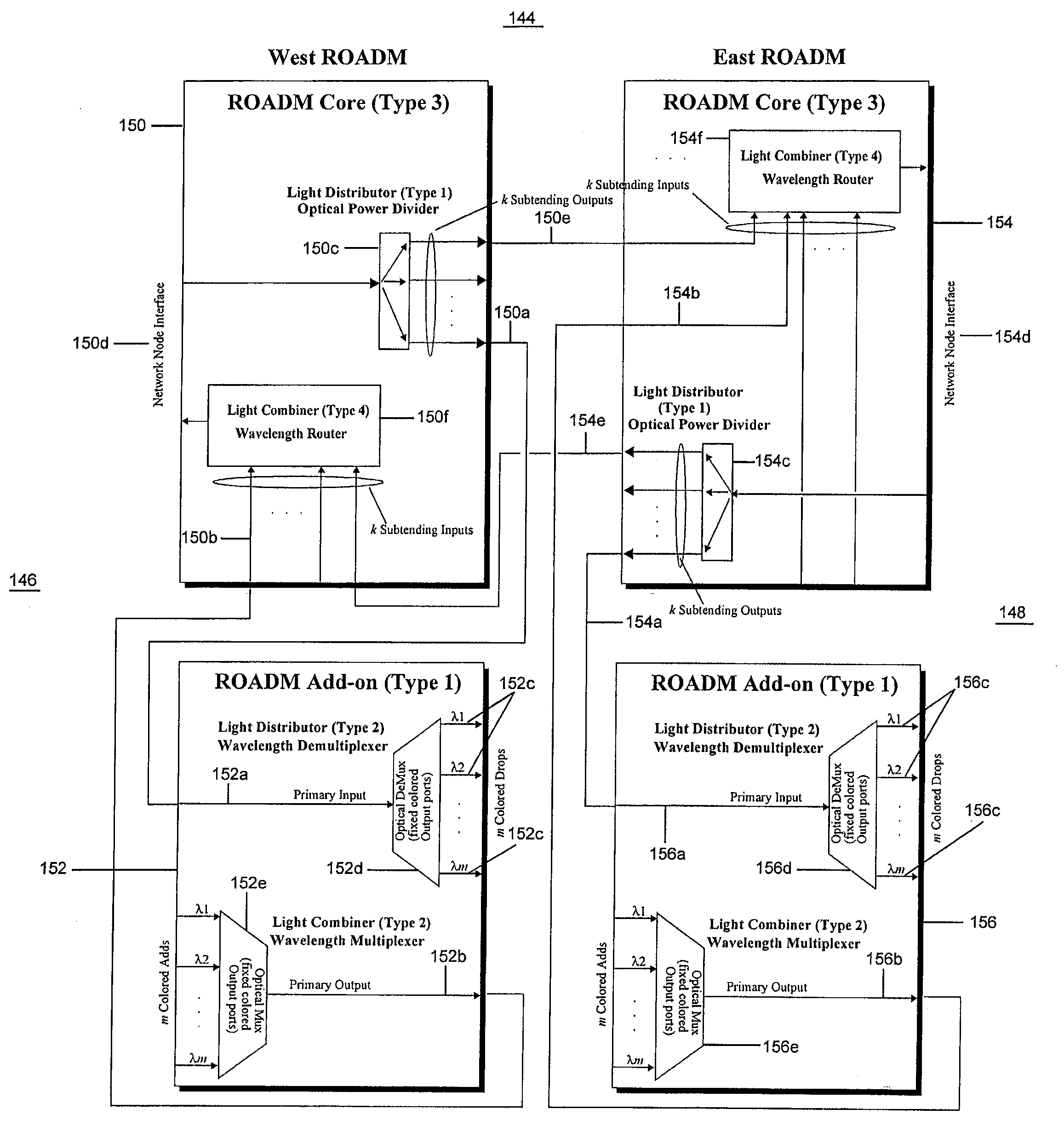
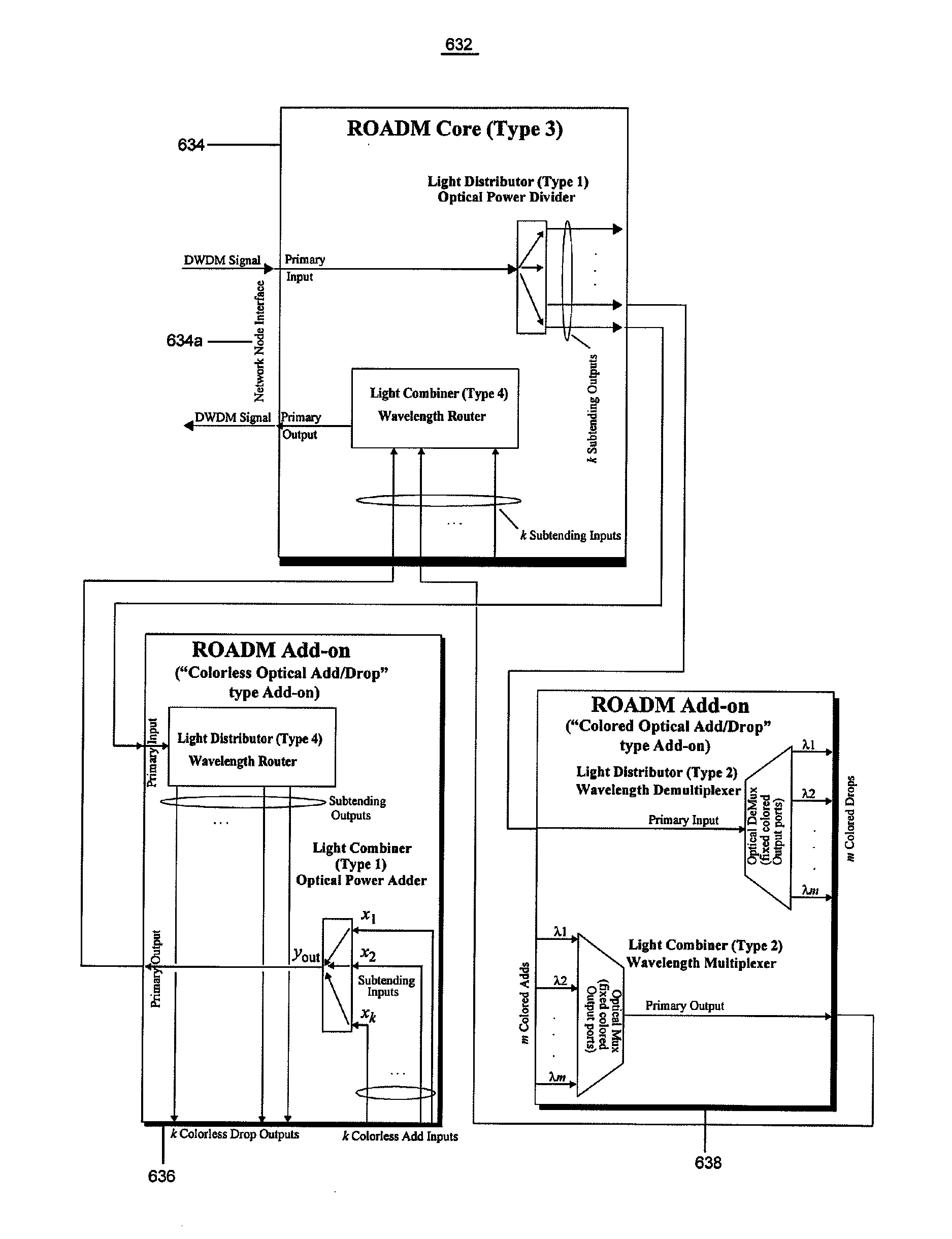
An optical node includes a reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) core configured to transmit optical signals of multiple wavelengths to and receive optical signals of multiple wavelengths from another optical node. The ROADM core is also configured to add optical signals thereto and to drop optical signals therefrom. The node also includes two different types of add-on devices, each connected to the ROADM core device and configured to process optical signals of multiple wavelengths. As a result, a multifunctional and reconfigurable optical node can be provided.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
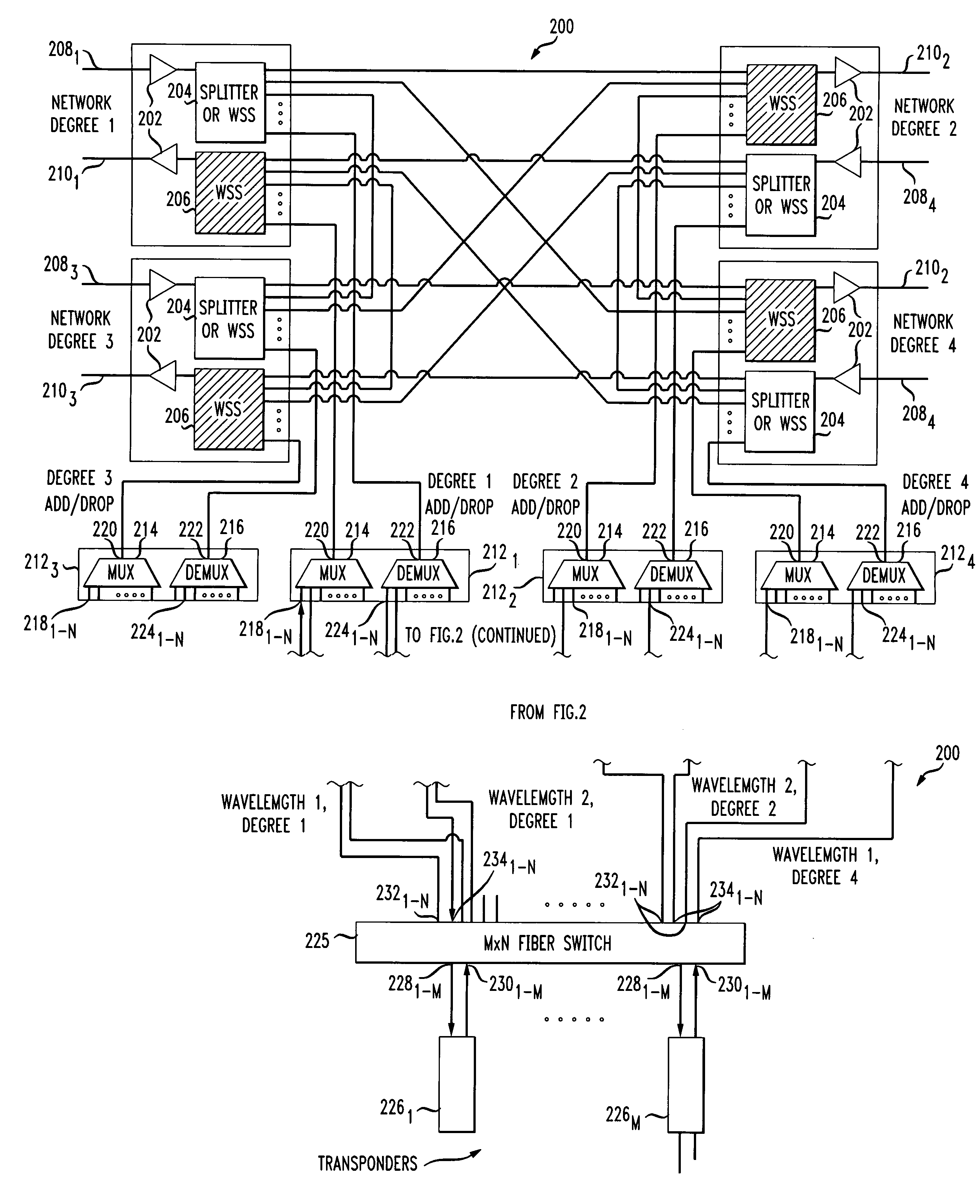
Methods for dynamic wavelength add/drop in a ROADM optical network
ActiveUS20100142961A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberMultiplexer
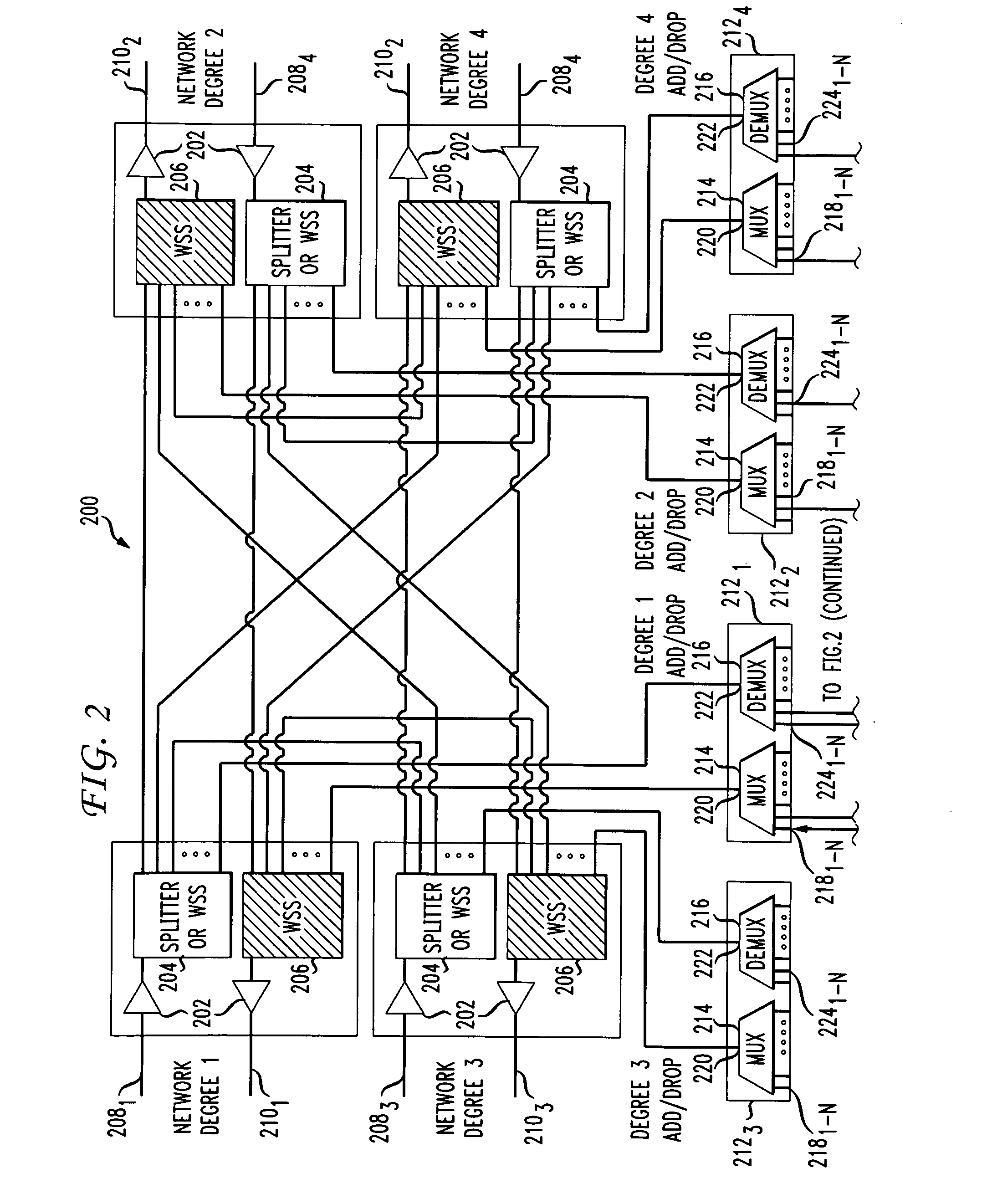
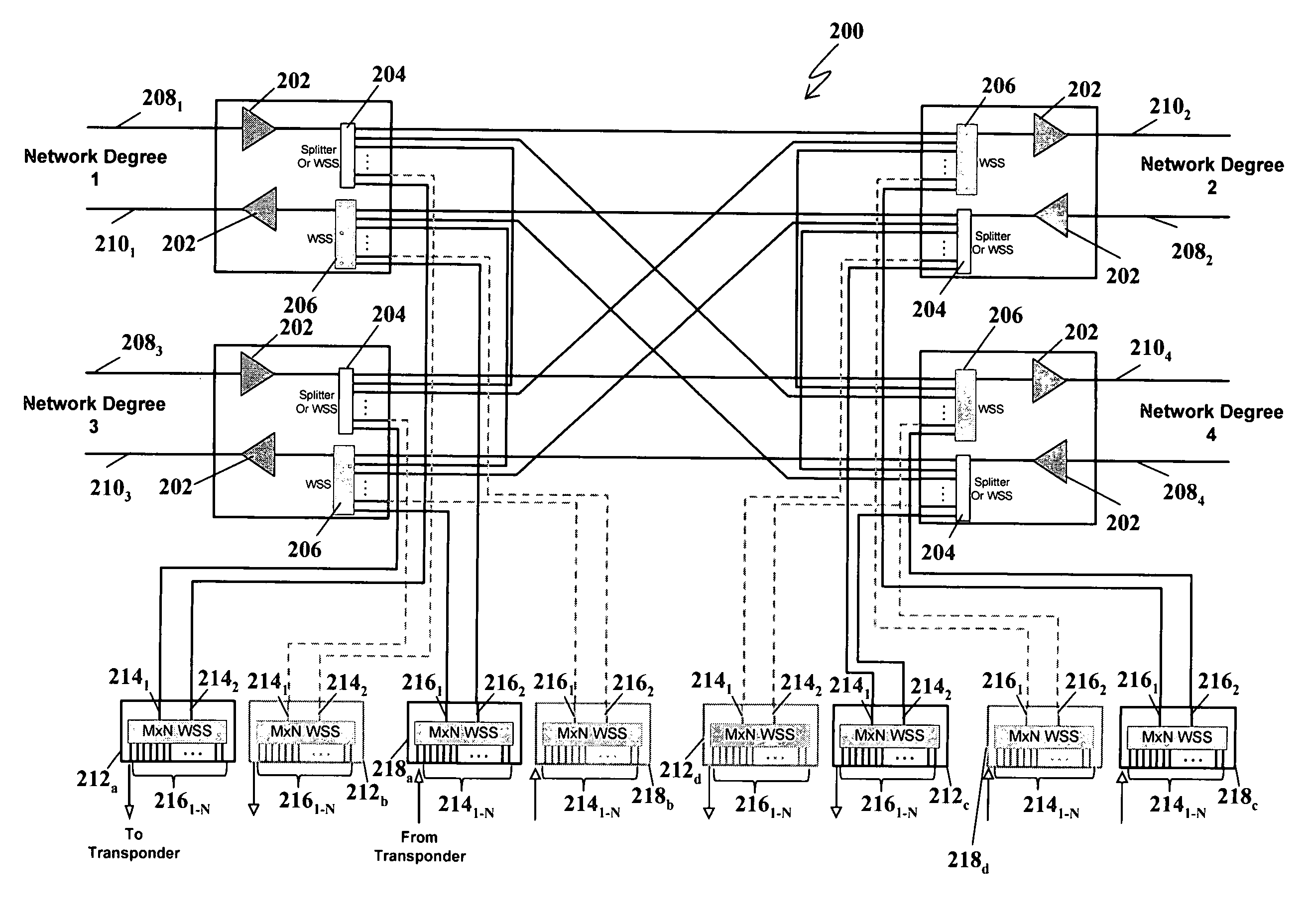
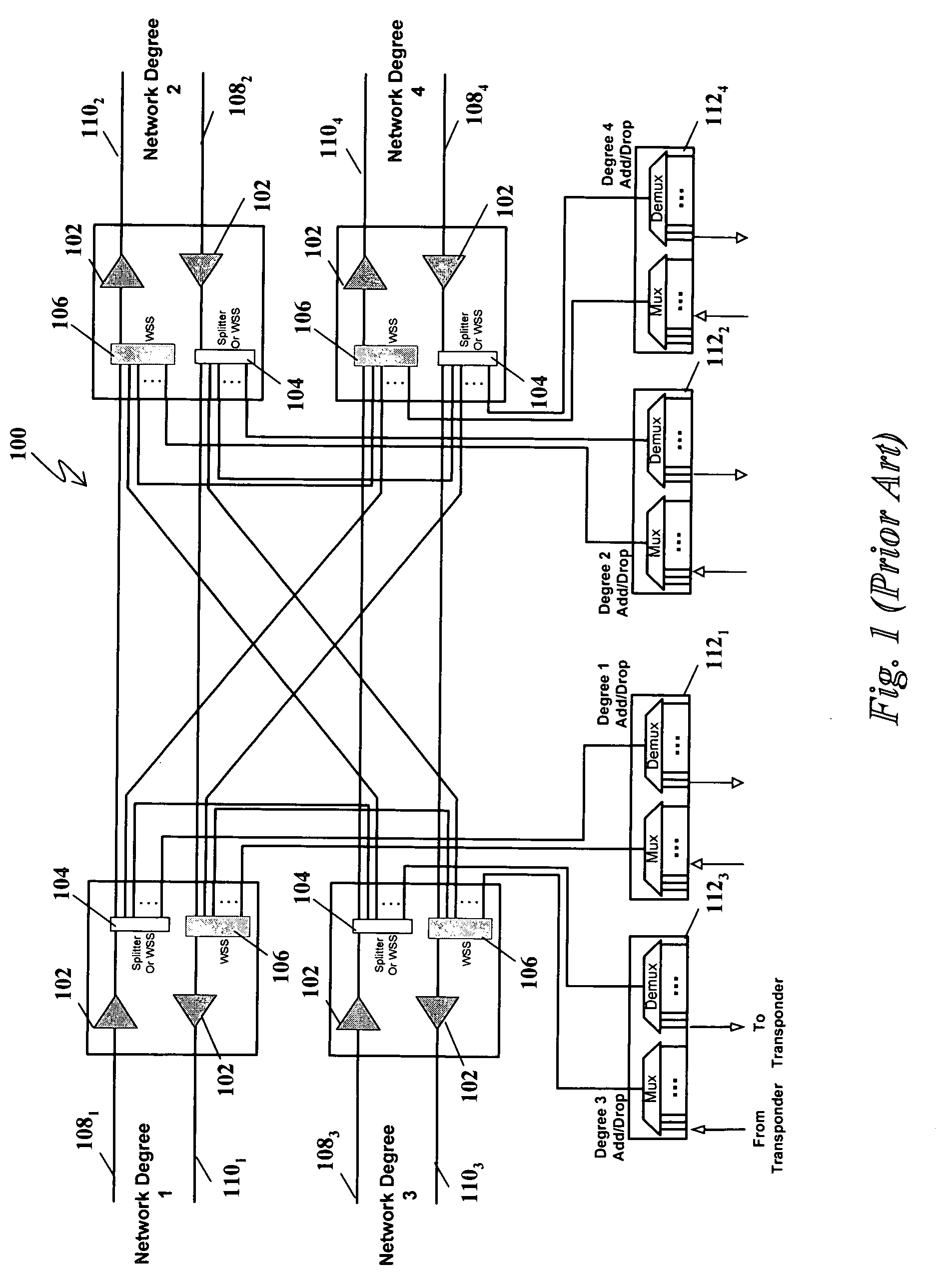
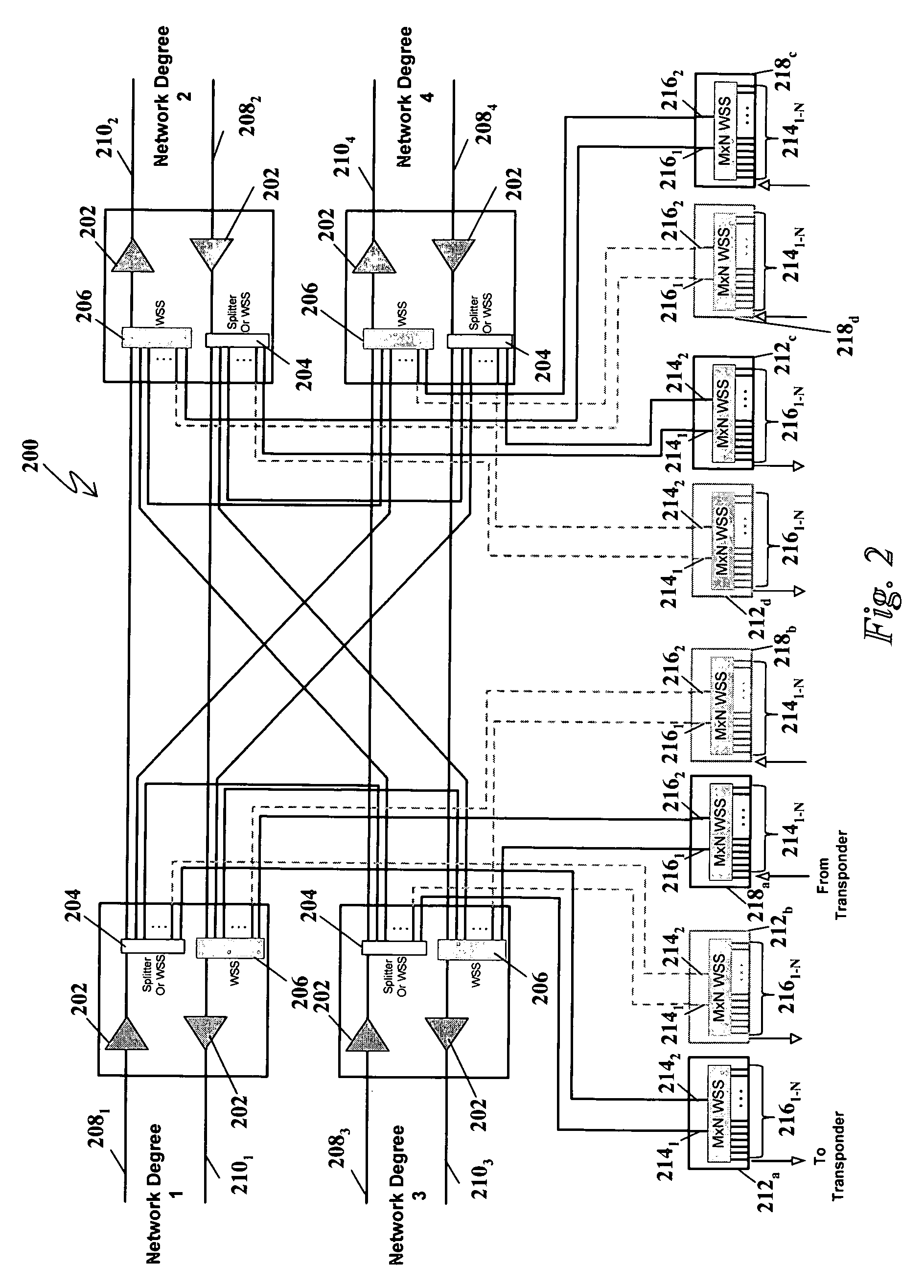
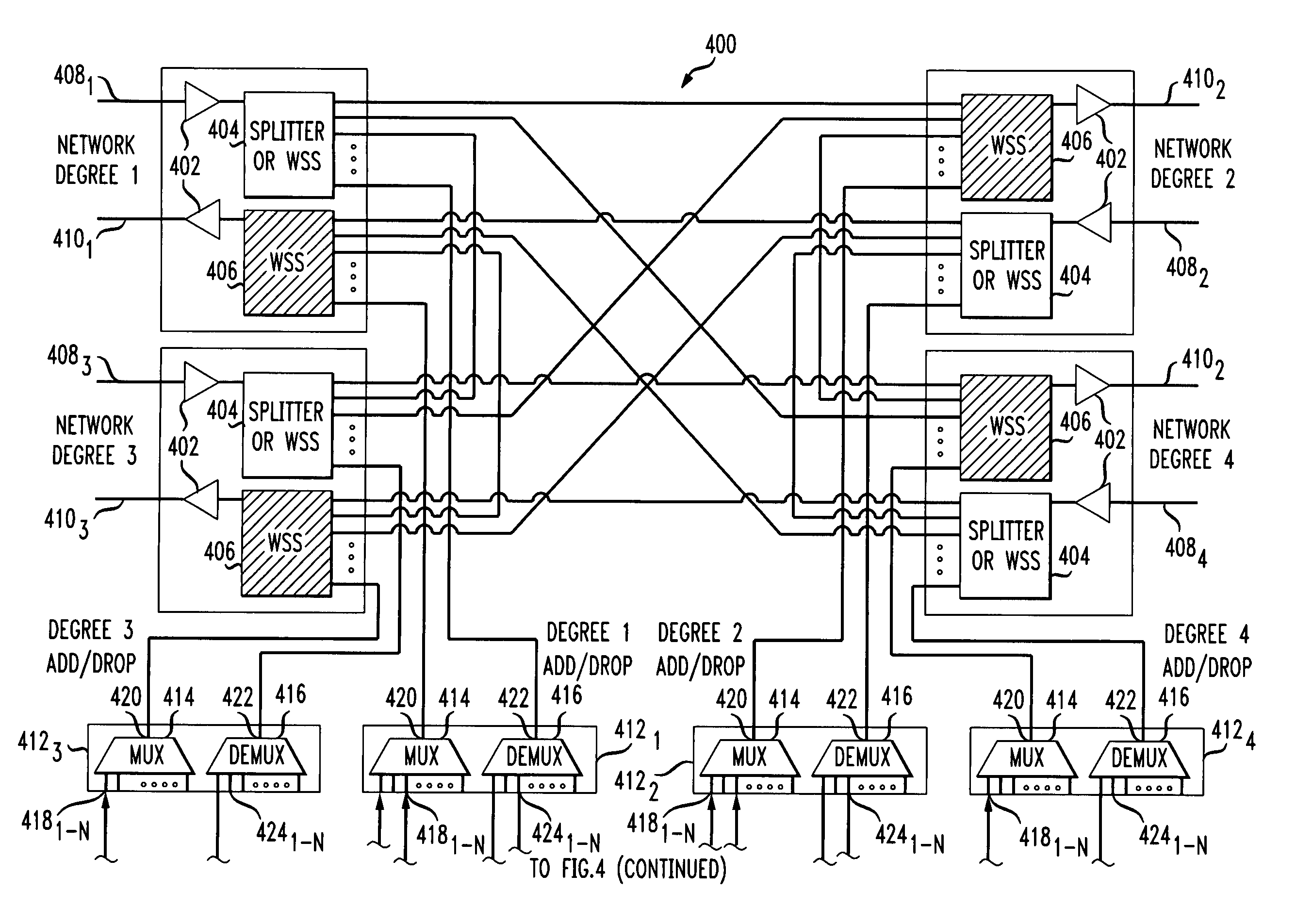
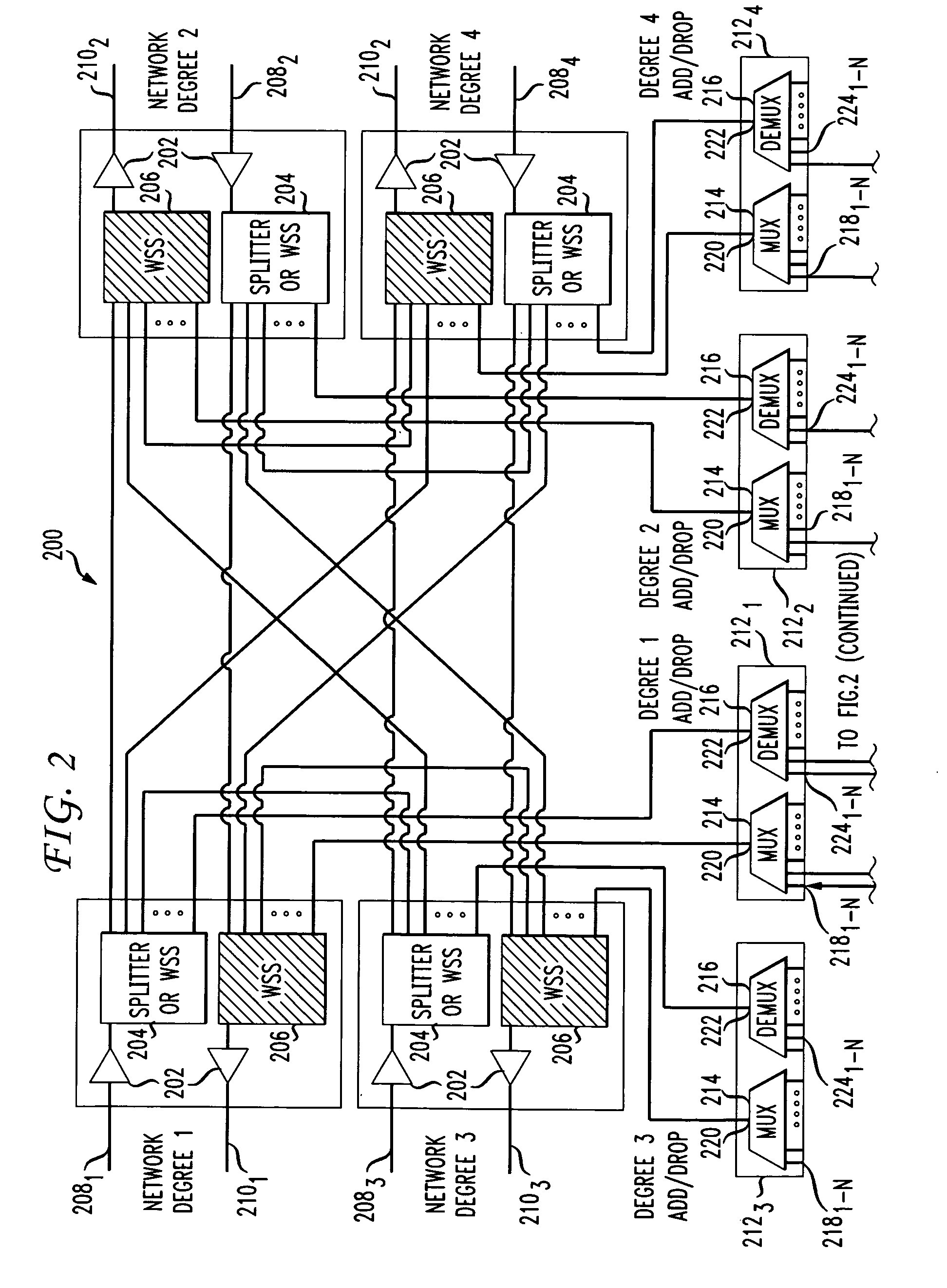
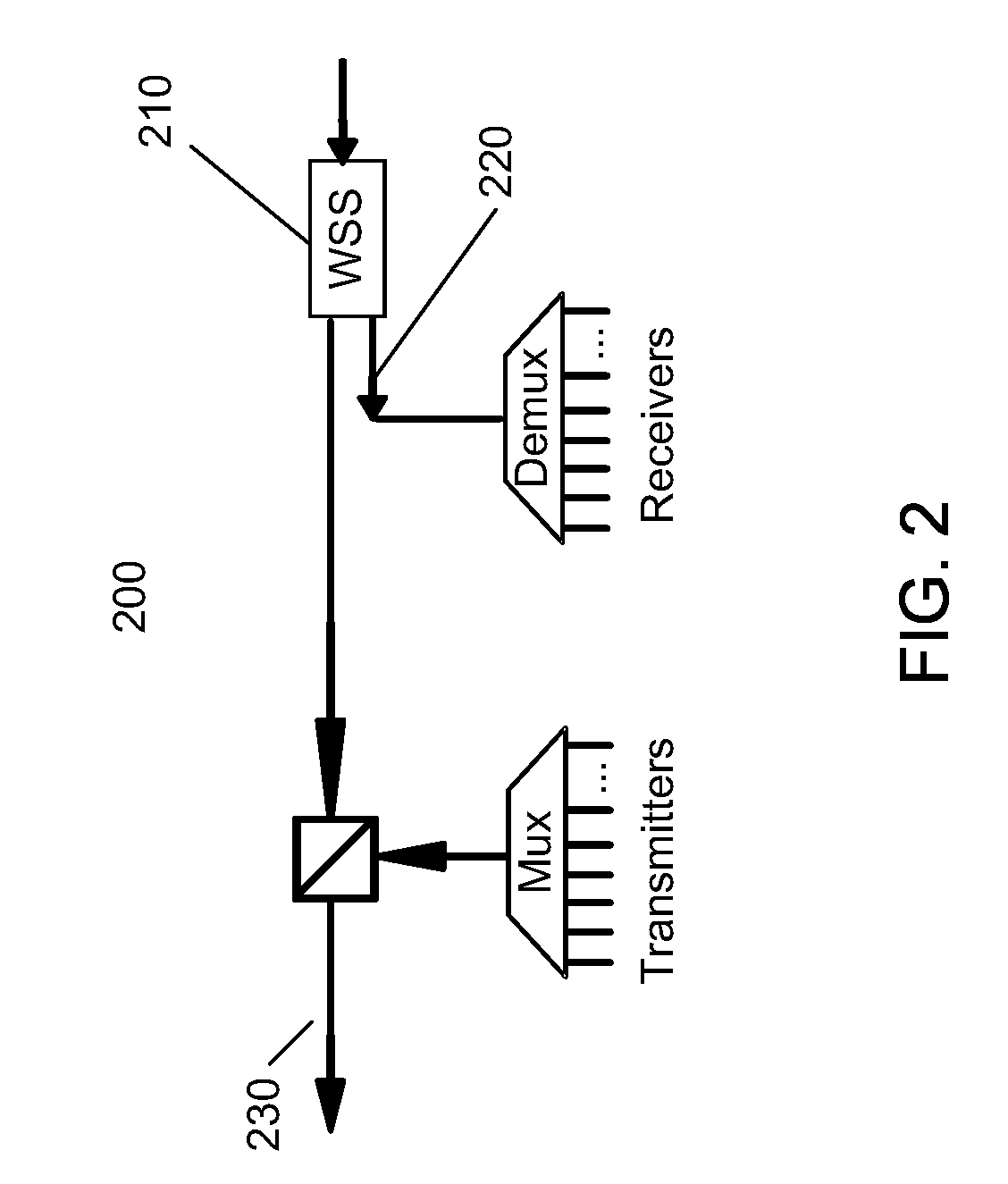
A system and method for dynamically adding / dropping wavelengths in a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) transport network is disclosed. The system includes at least one optical transponder, a plurality of optical fan-out devices, each arranged to receive an input signal from a network degree and coupled to at least one of a plurality of optical fan-in devices, each optical fan-in device arranged to output a signal to a network degree, the optical fan-out devices comprising at least one wavelength selective switch and the optical fan-in devices comprising at least one wavelength selective switch, the optical fan-out devices and optical fan-in devices being connected so as to enable signals input from each of the plurality of network degrees to be switched to another network degree of the plurality of network degrees; a plurality of demultiplexers for locally dropping selected wavelengths; a plurality of multiplexers for locally adding selected wavelengths; and at least one fiber switch interposed between the at least one optical transponder and the plurality of demultiplexers and multiplexers. The fiber switch is coupled to wavelengths and degrees that are allocated for a bandwidth-on-demand application. Other configurations include additional fan-in and fan-out devices interposed between a mux / demux assembly and the optical transponders to support wavelength redistribution applications.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
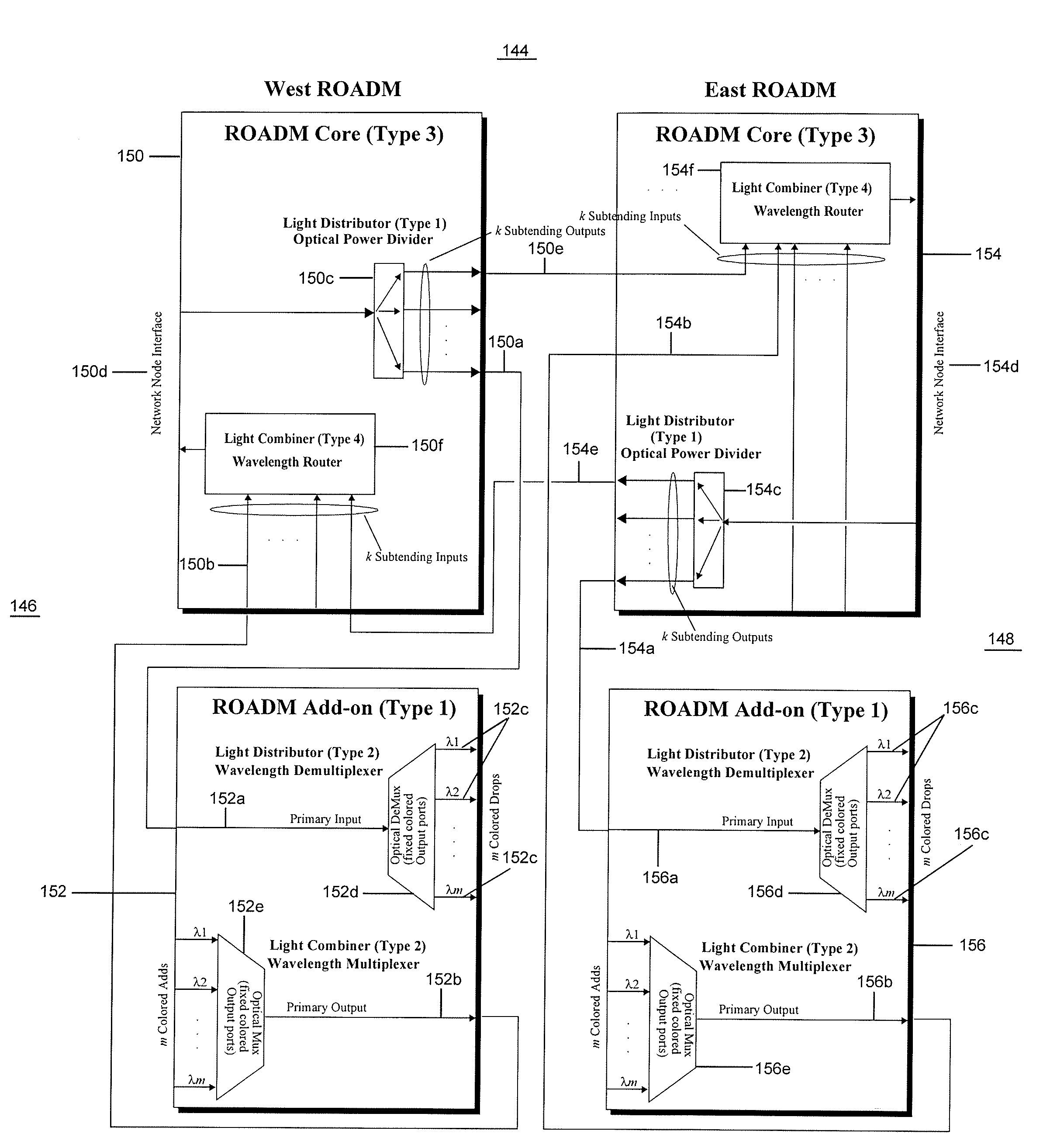
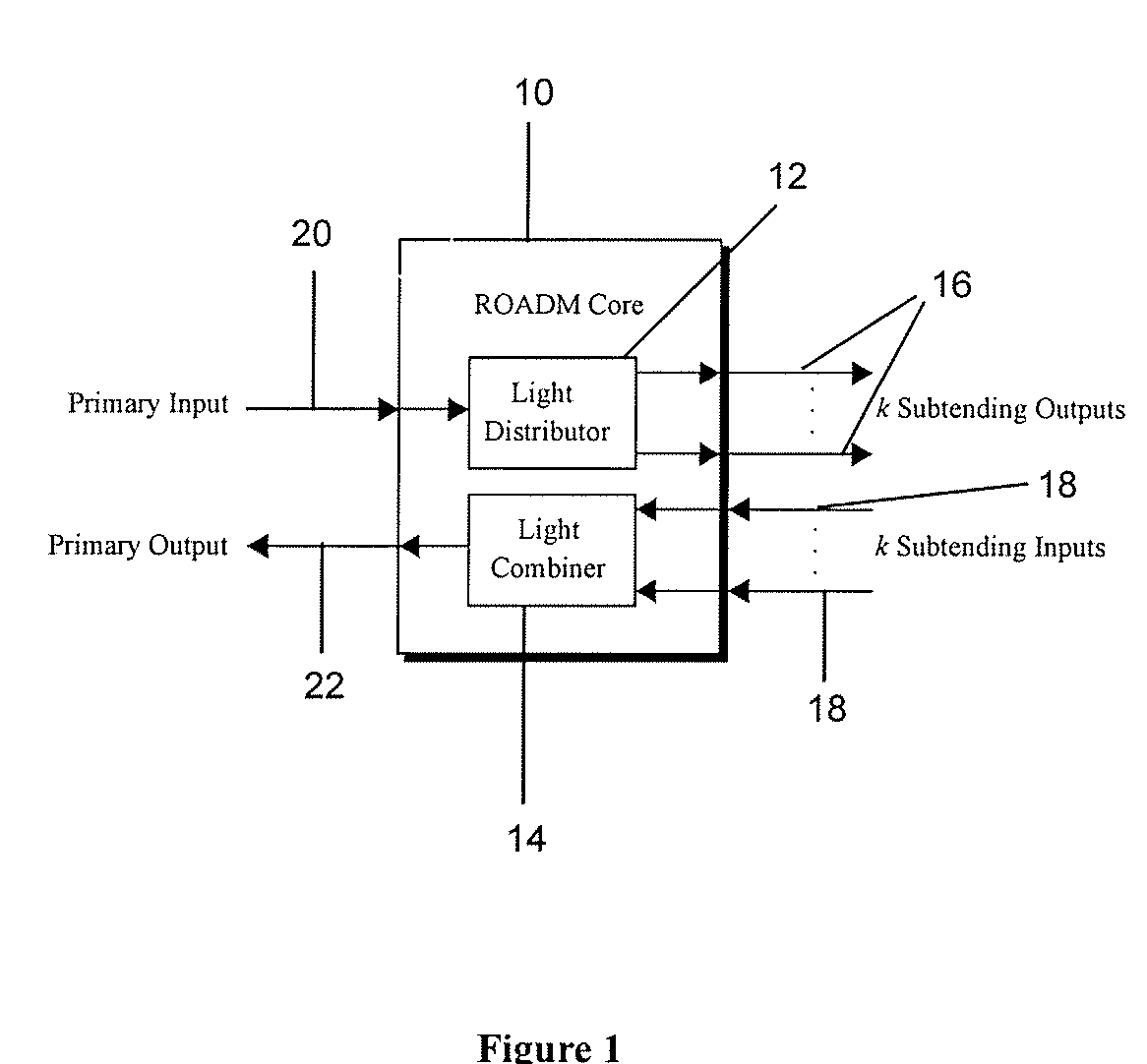
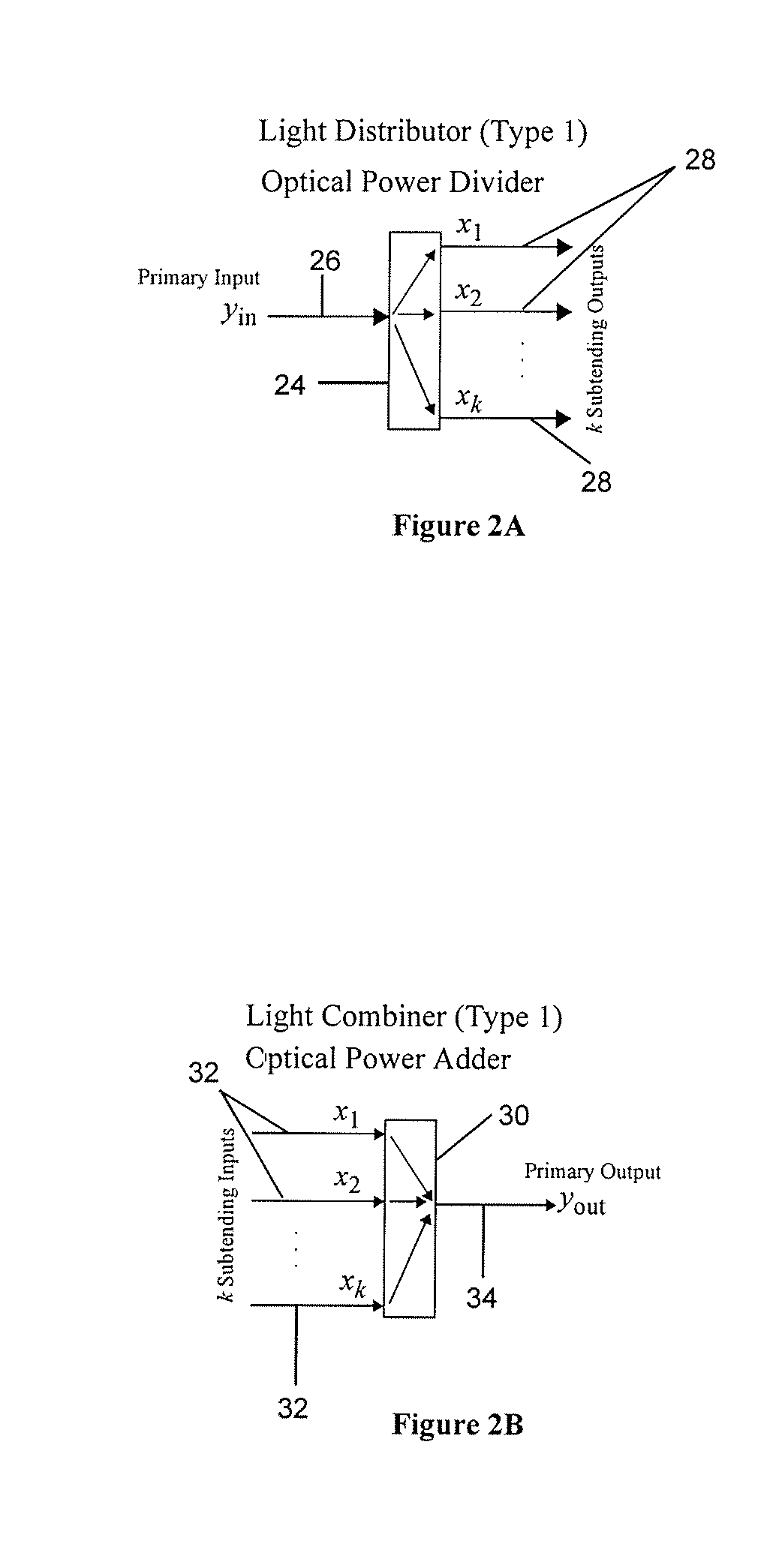
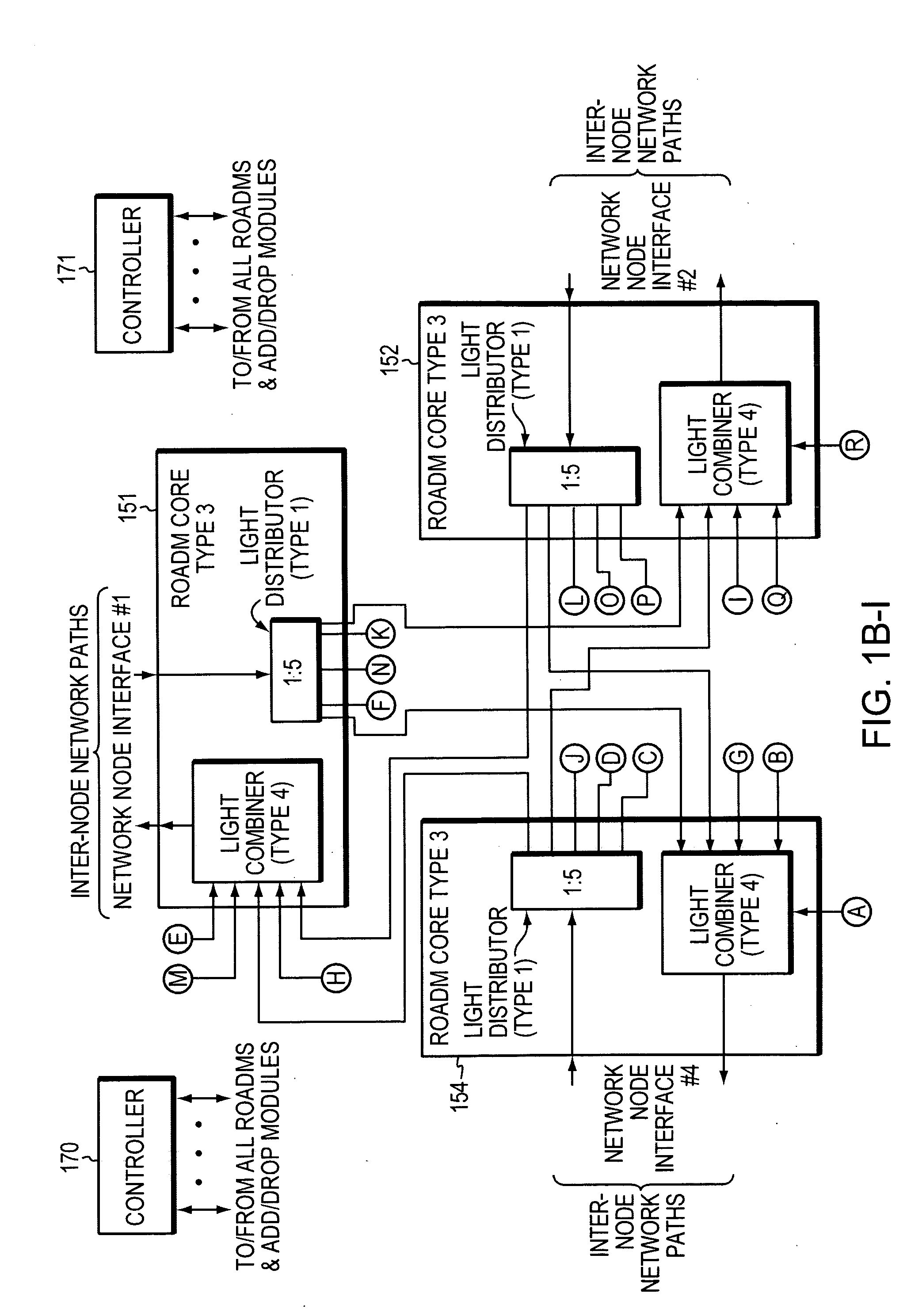
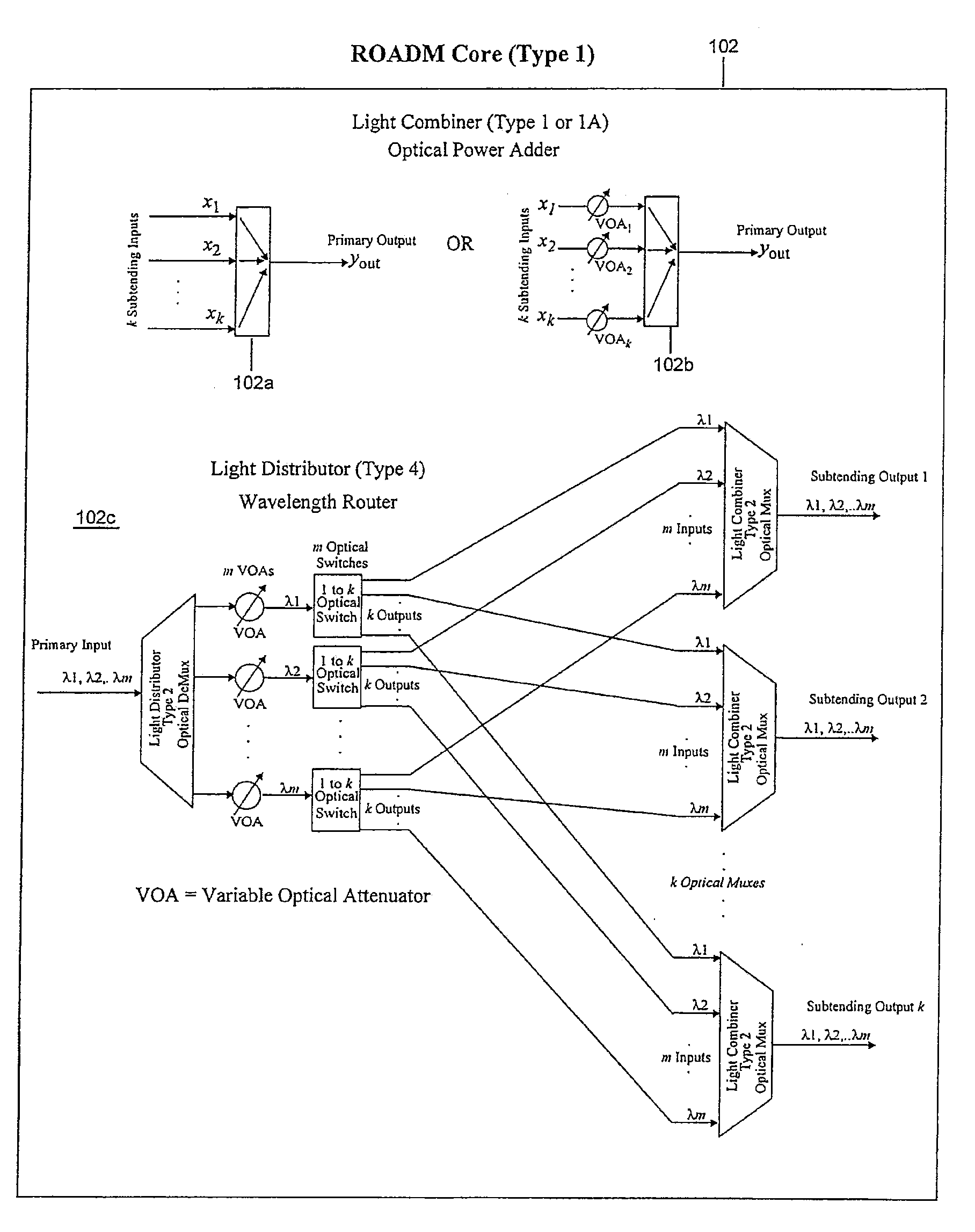
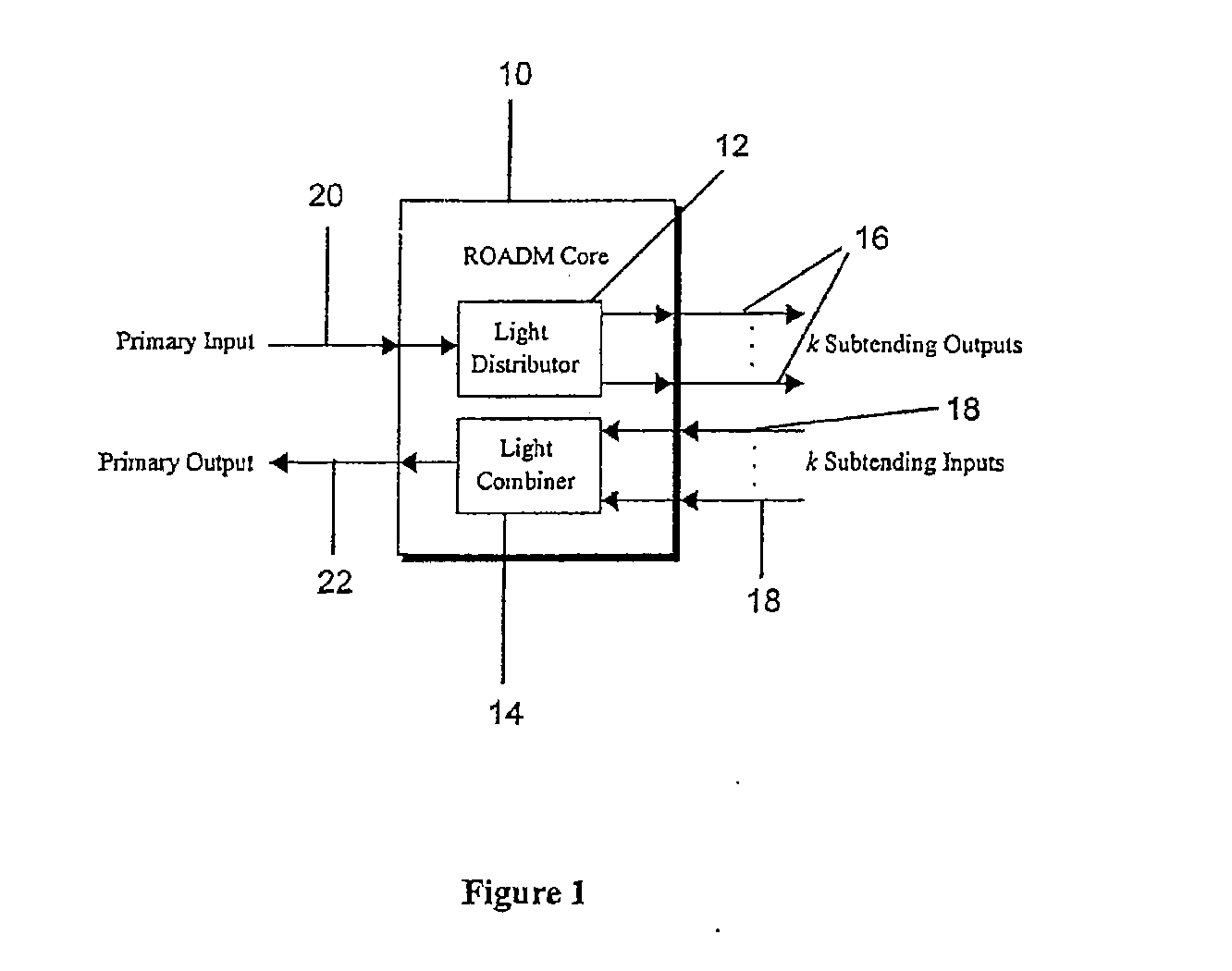
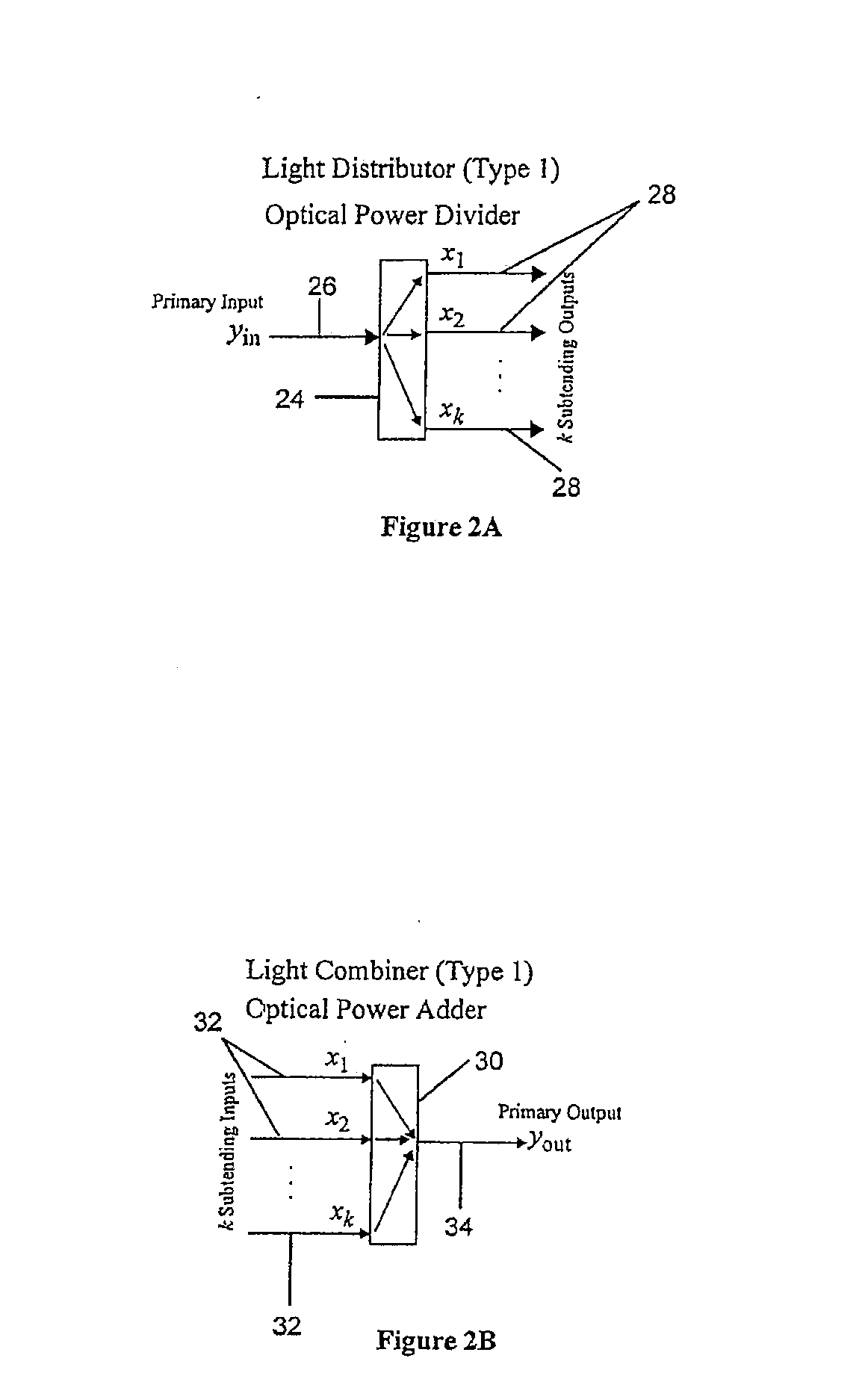
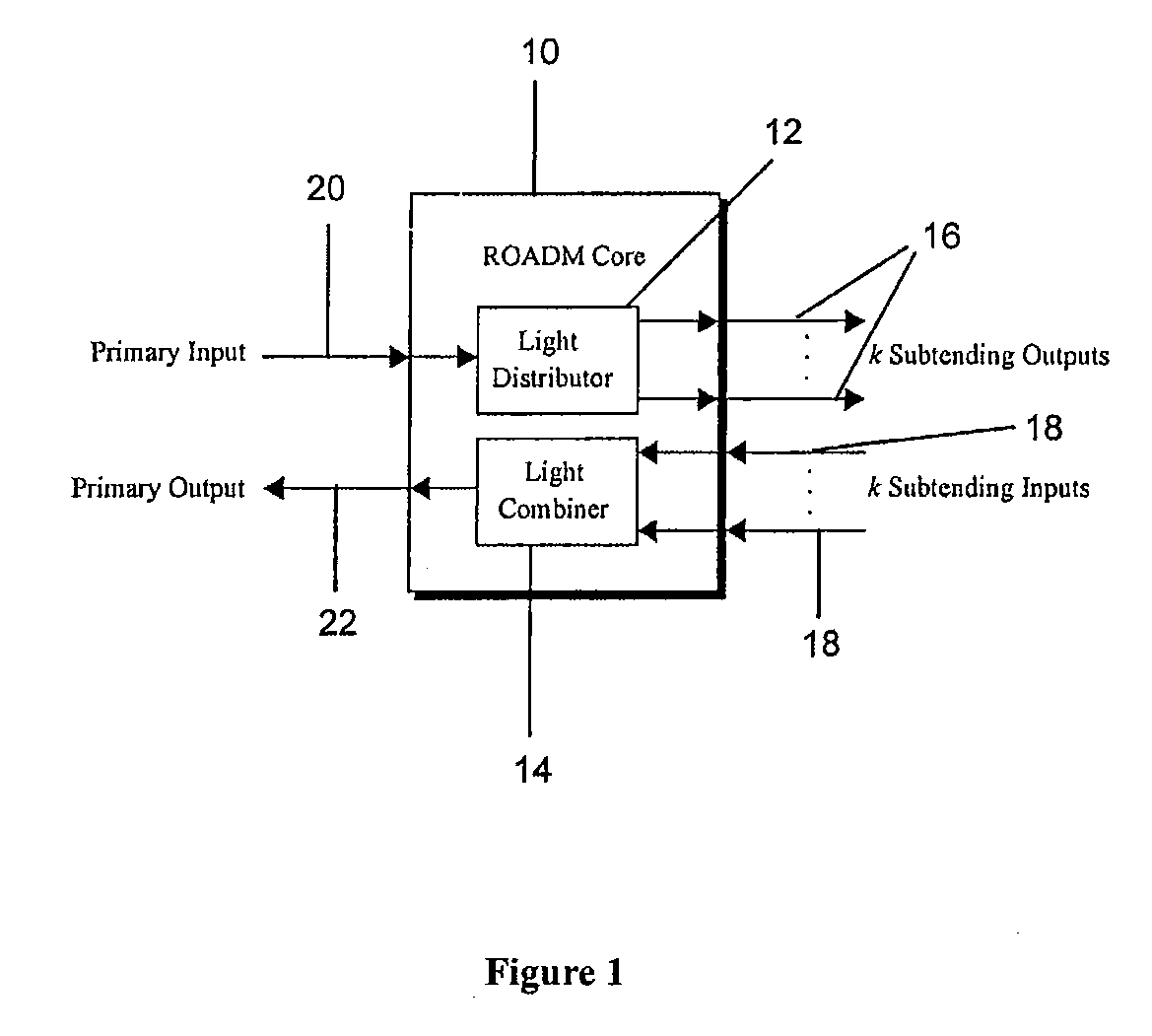
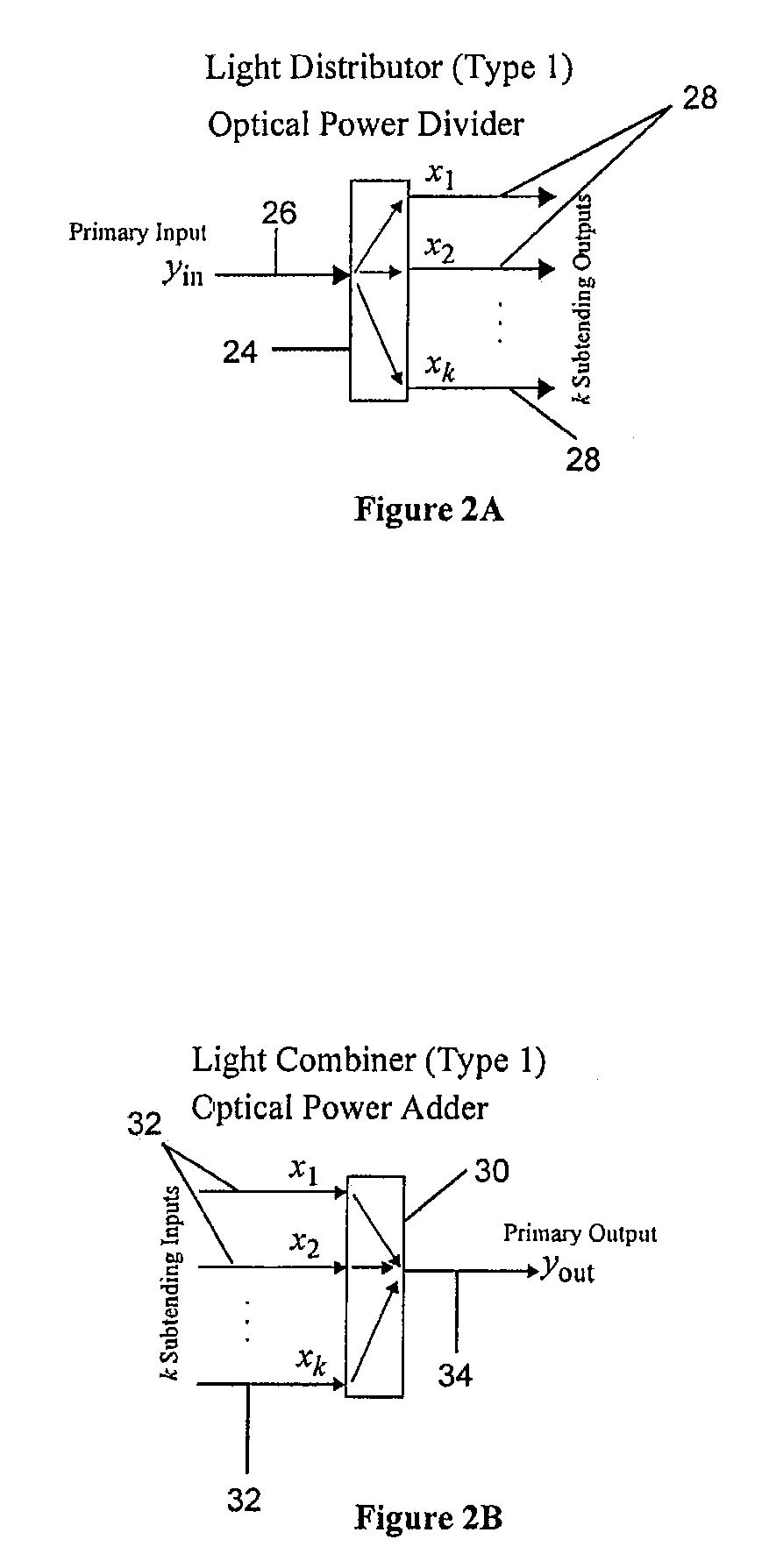
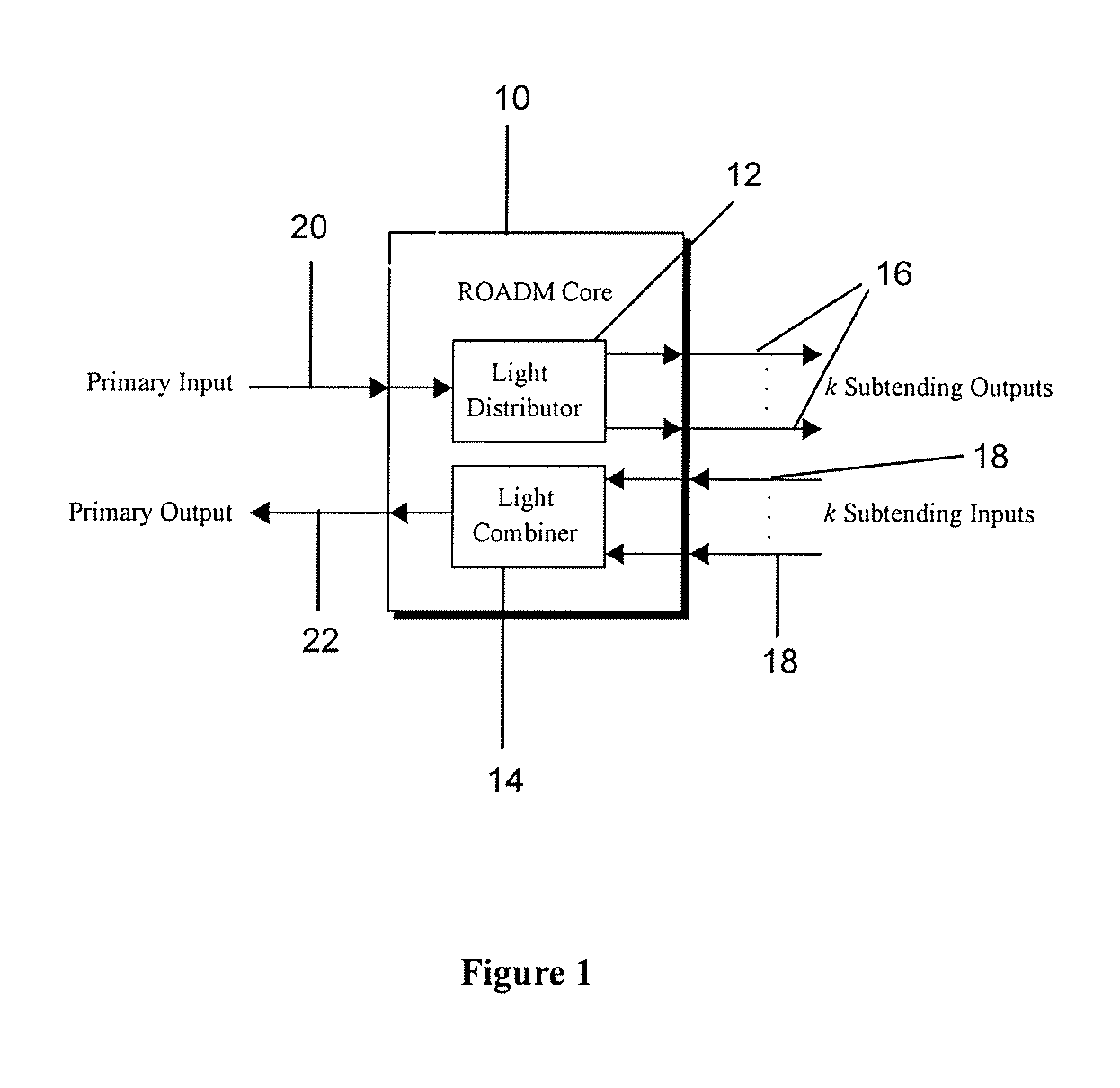
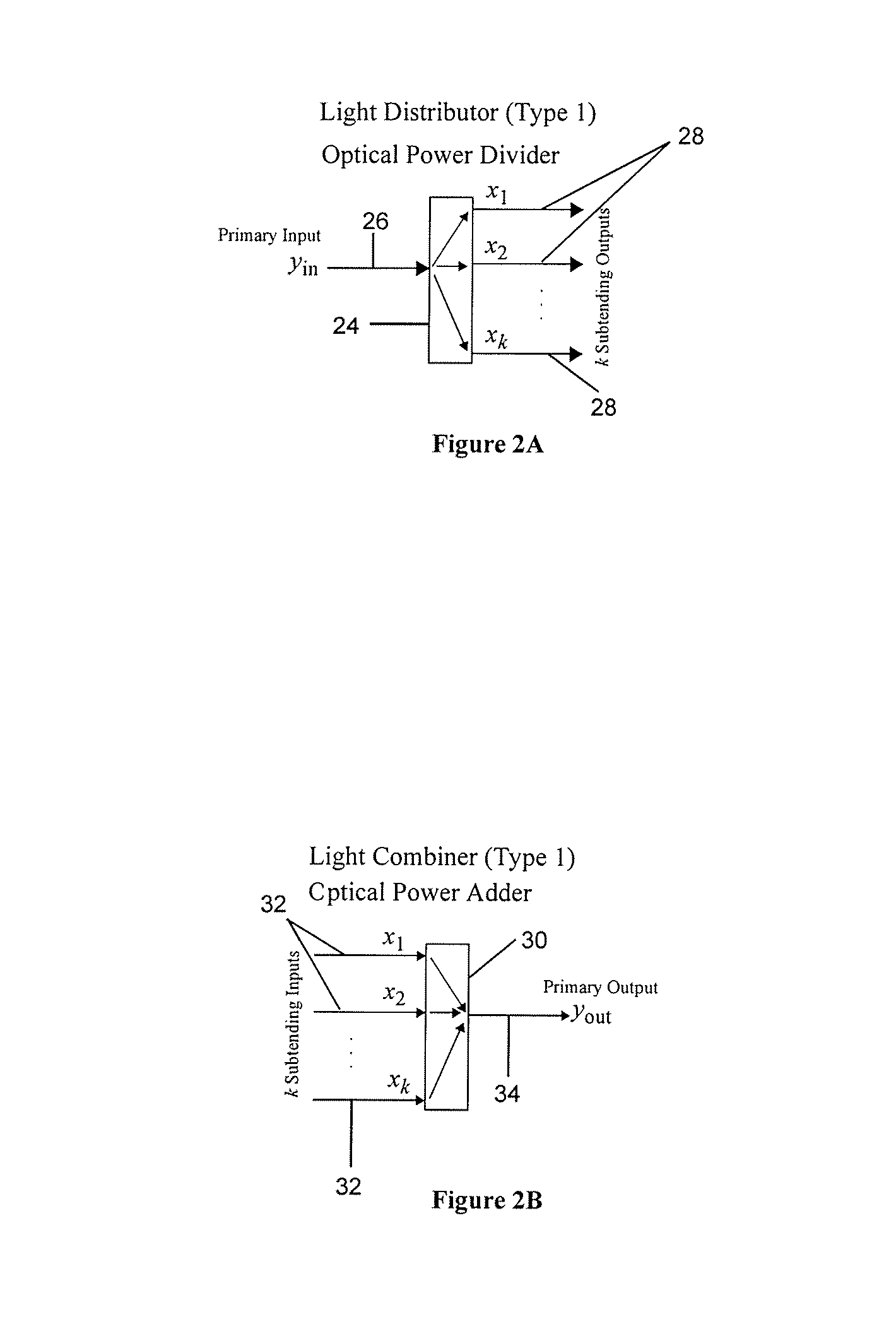
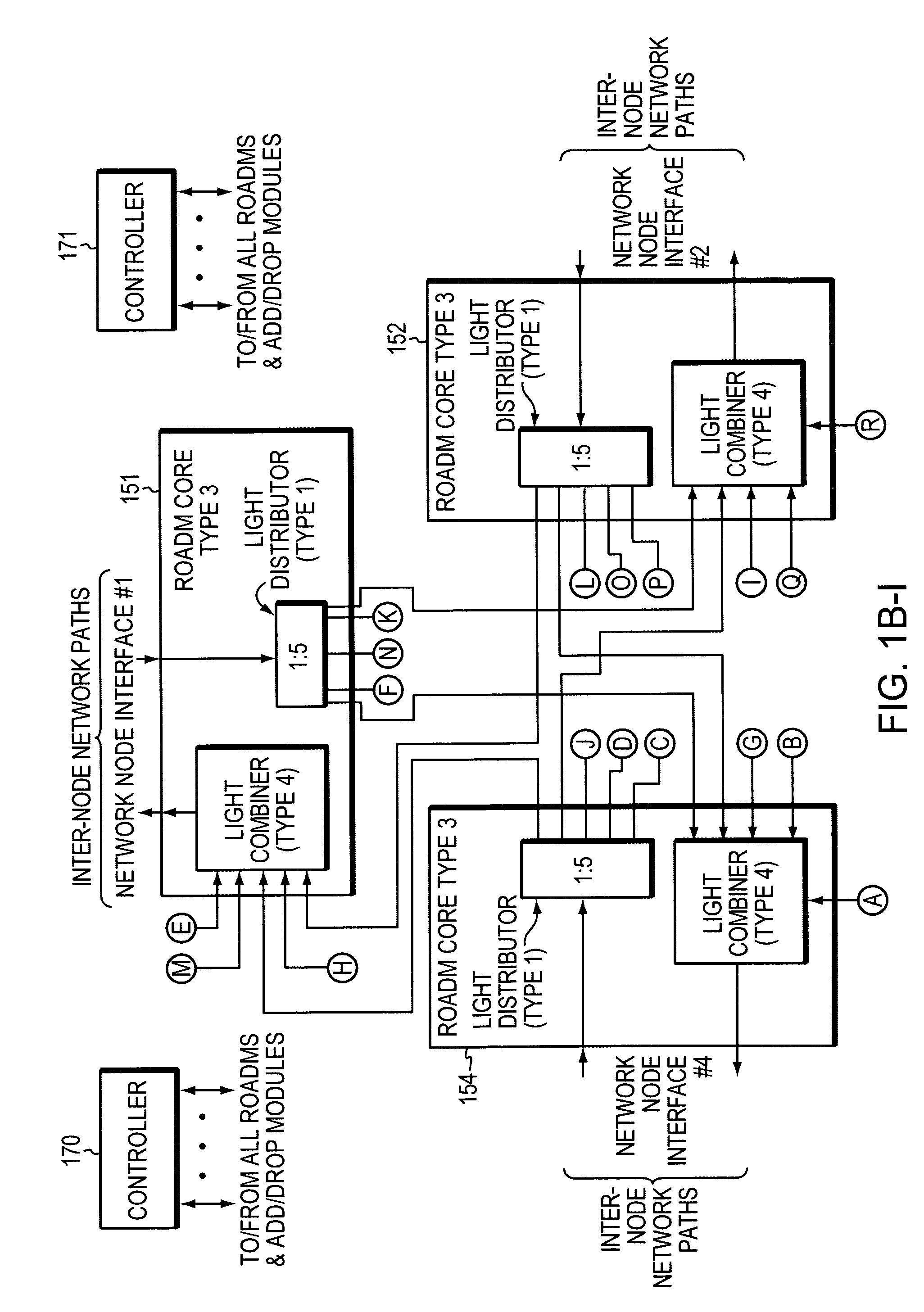
Reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device, procedure and system using such device, optical light distributor, and coupling-ratio assigning procedure
ActiveUS20080260386A1Maximize power levelPower maximizationWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical add-drop multiplexerCoupling ratio
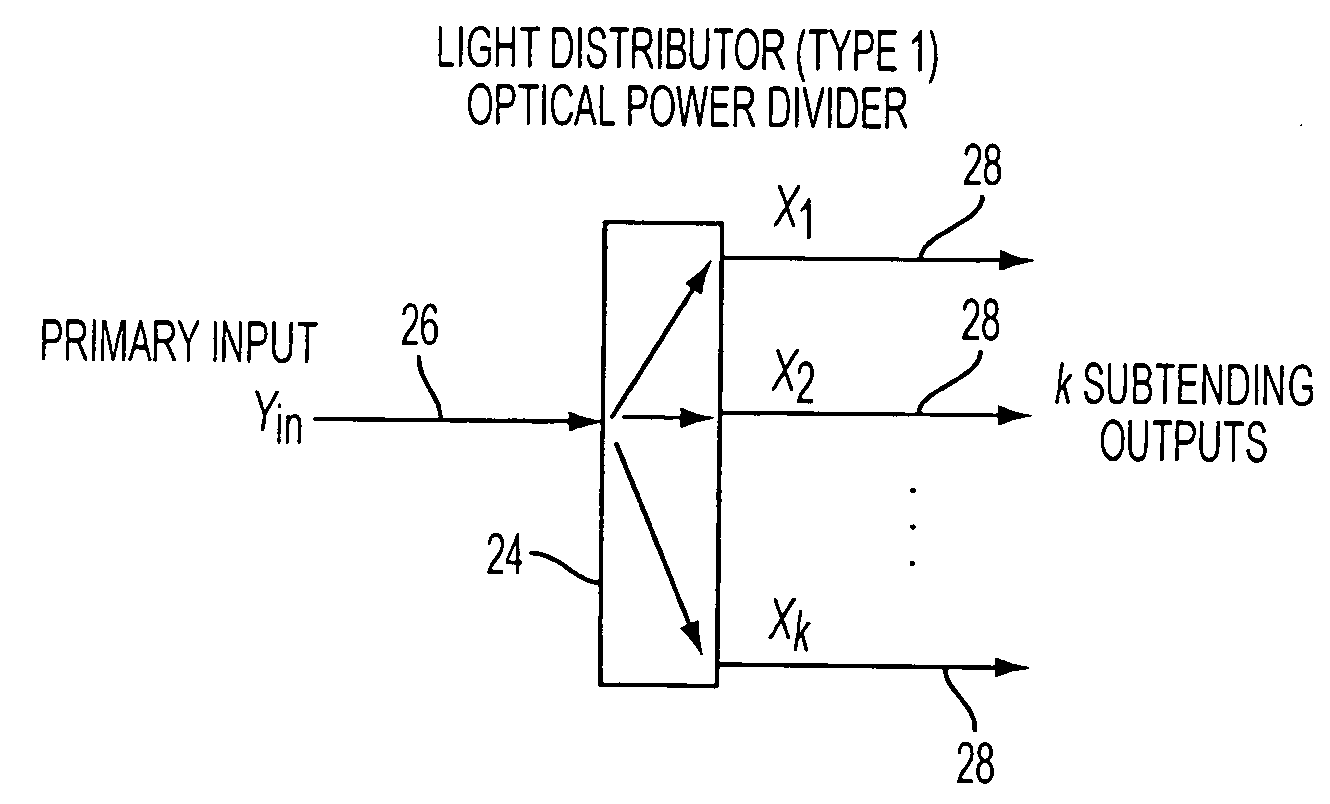
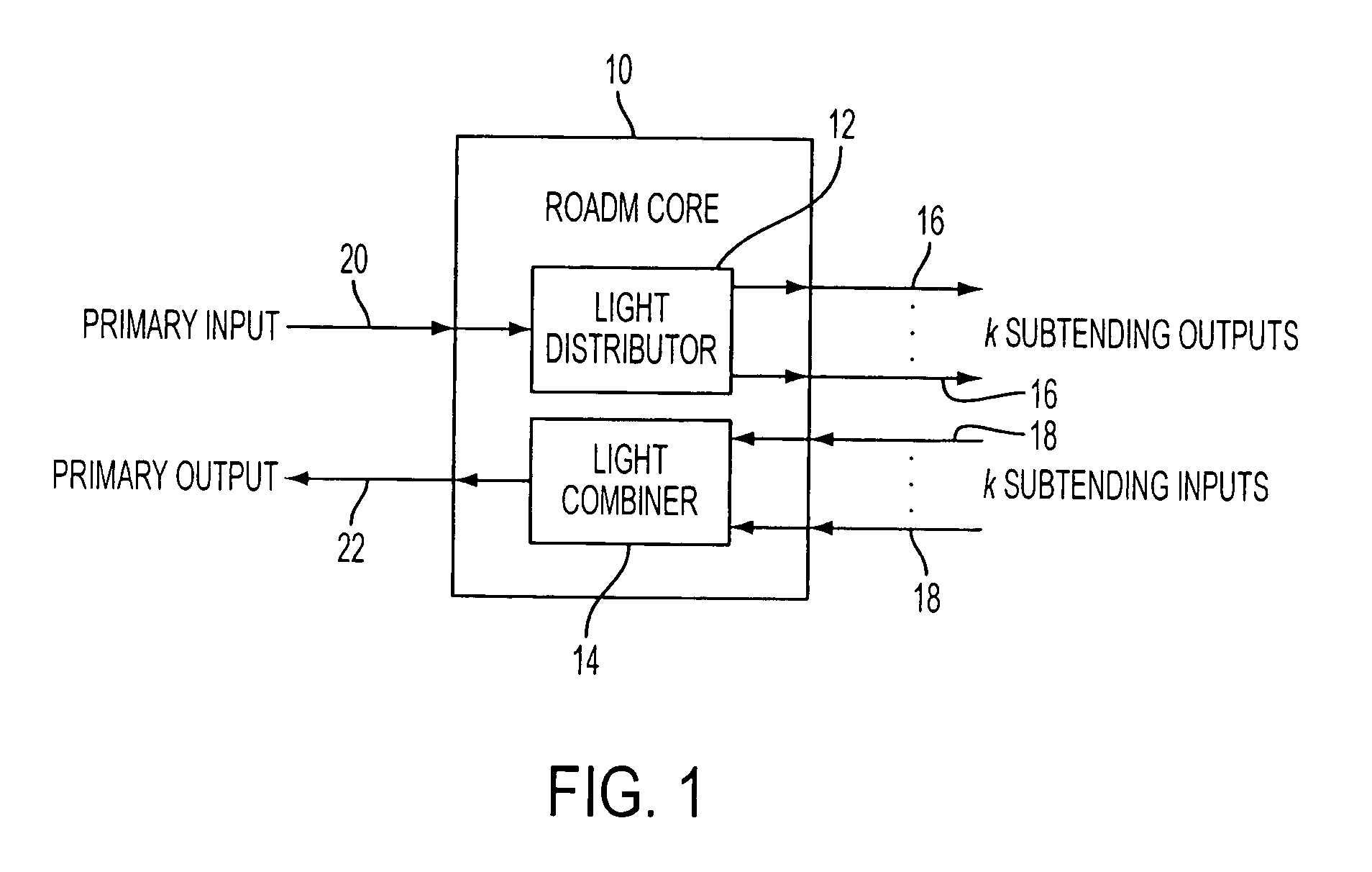
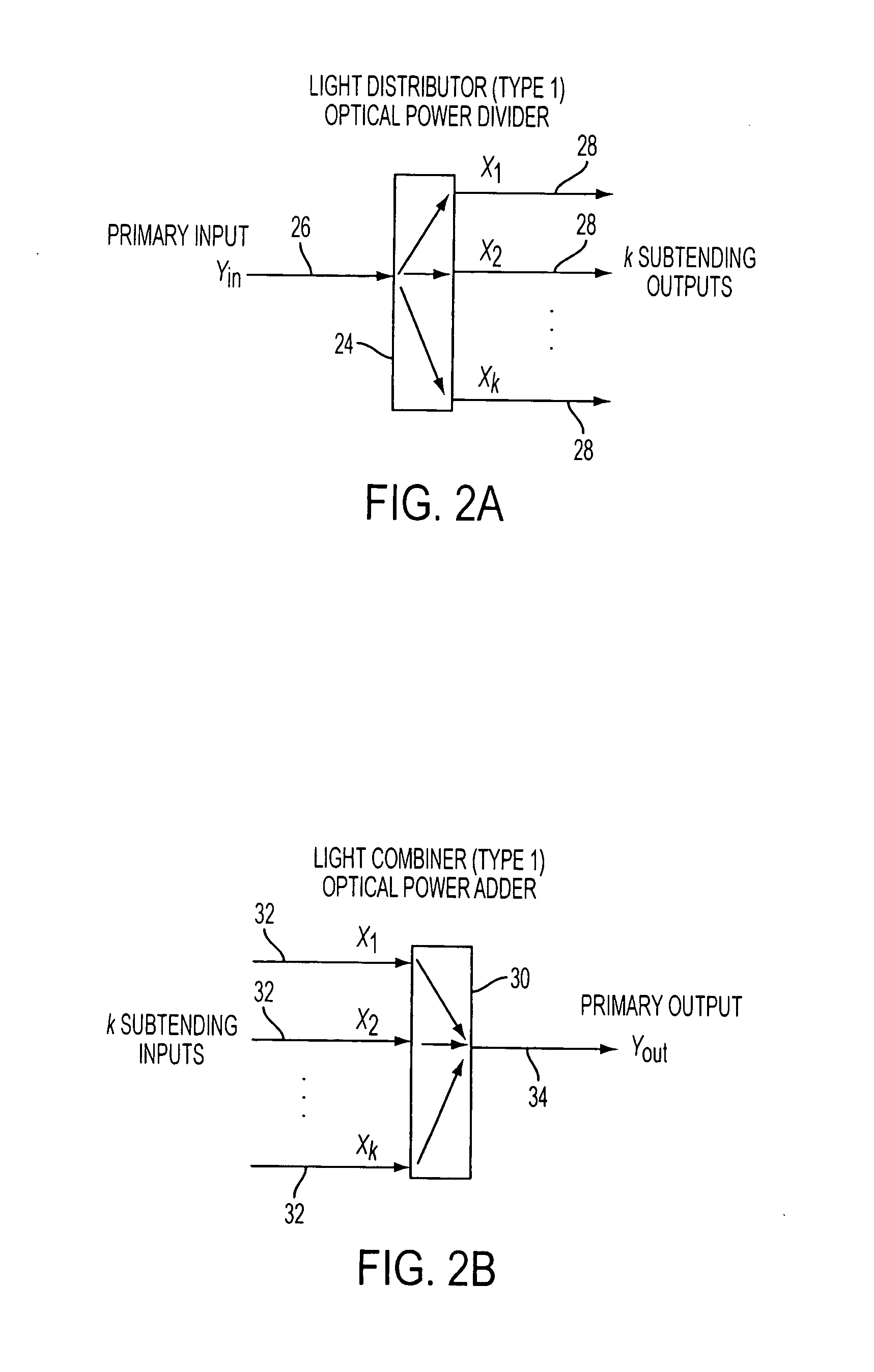
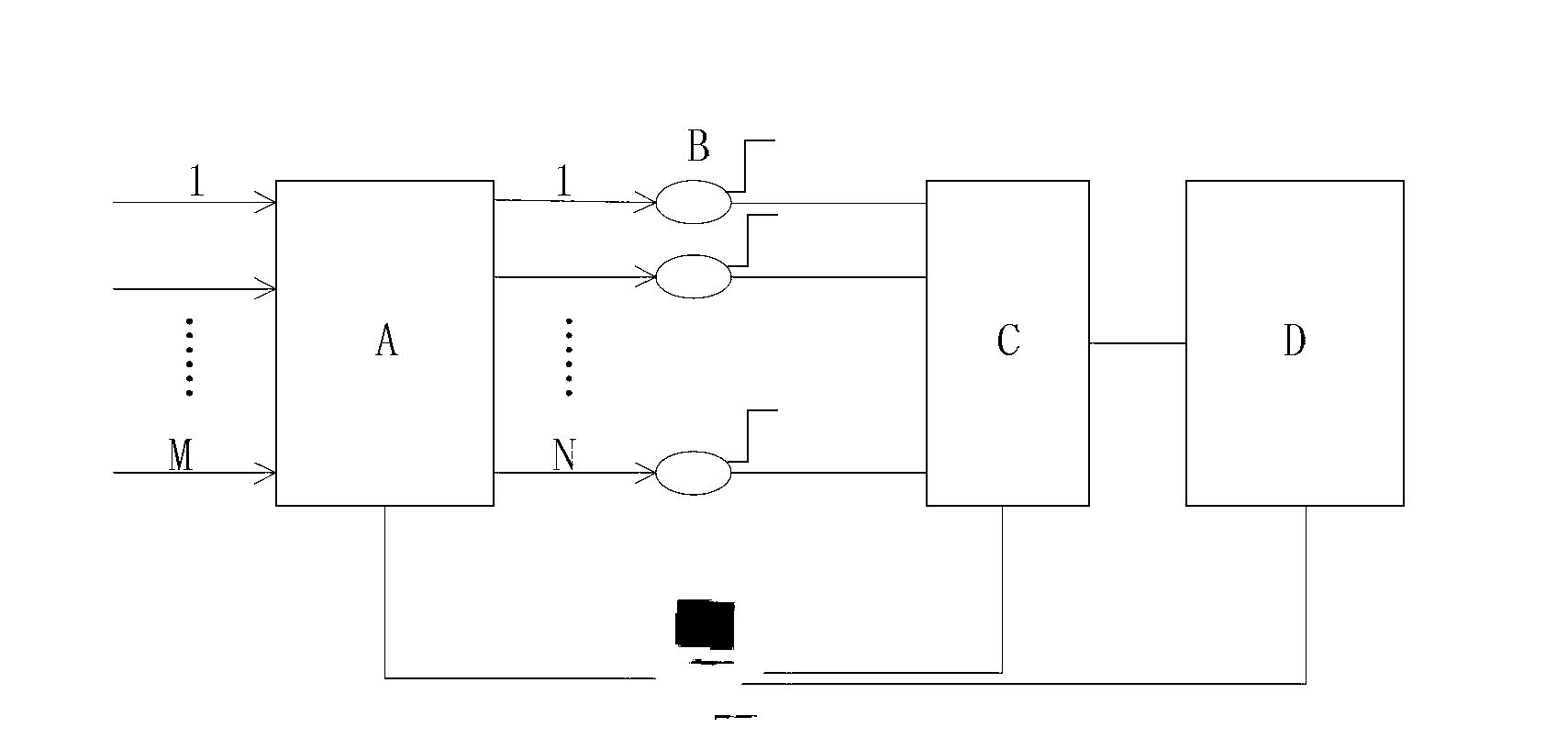
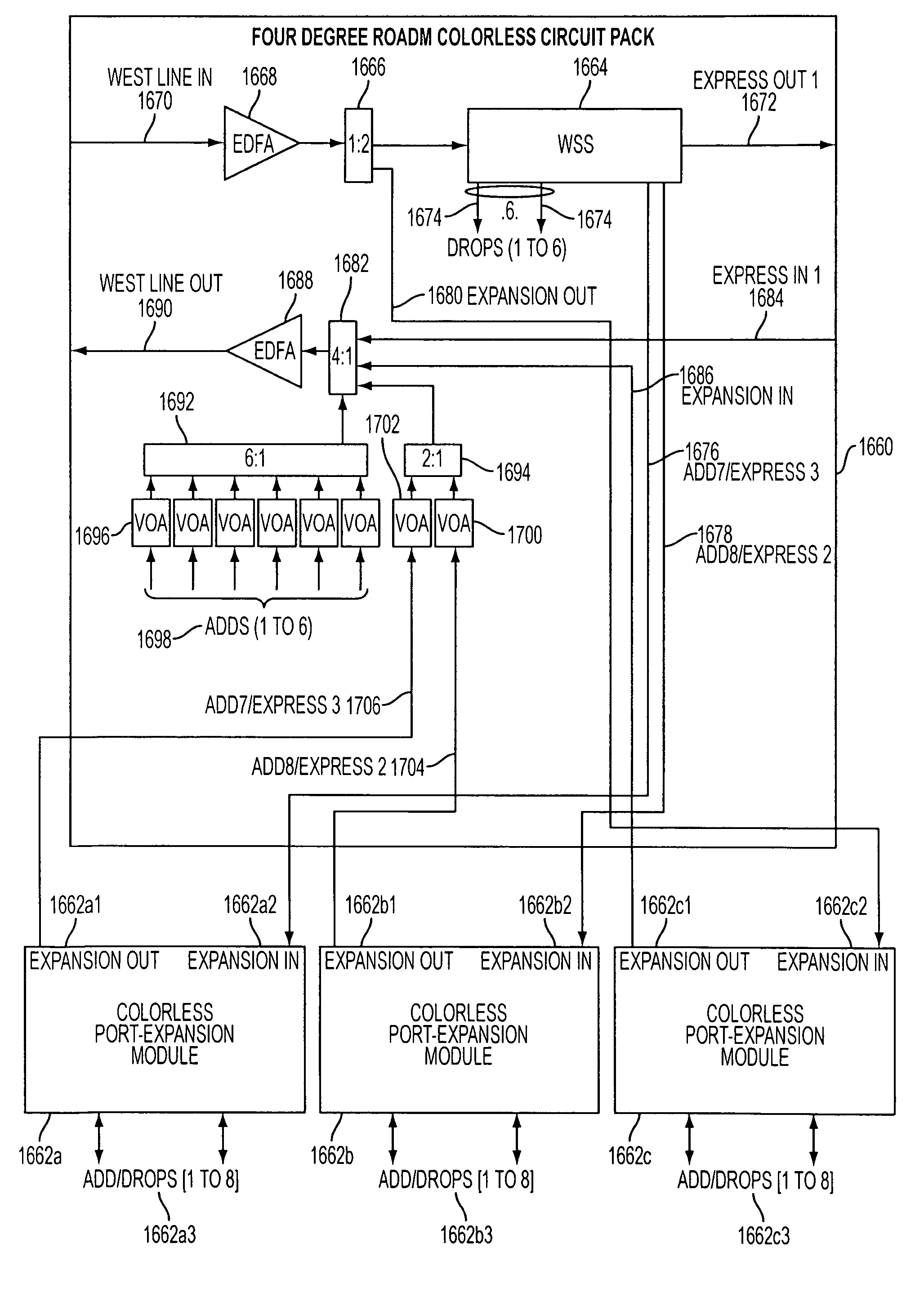
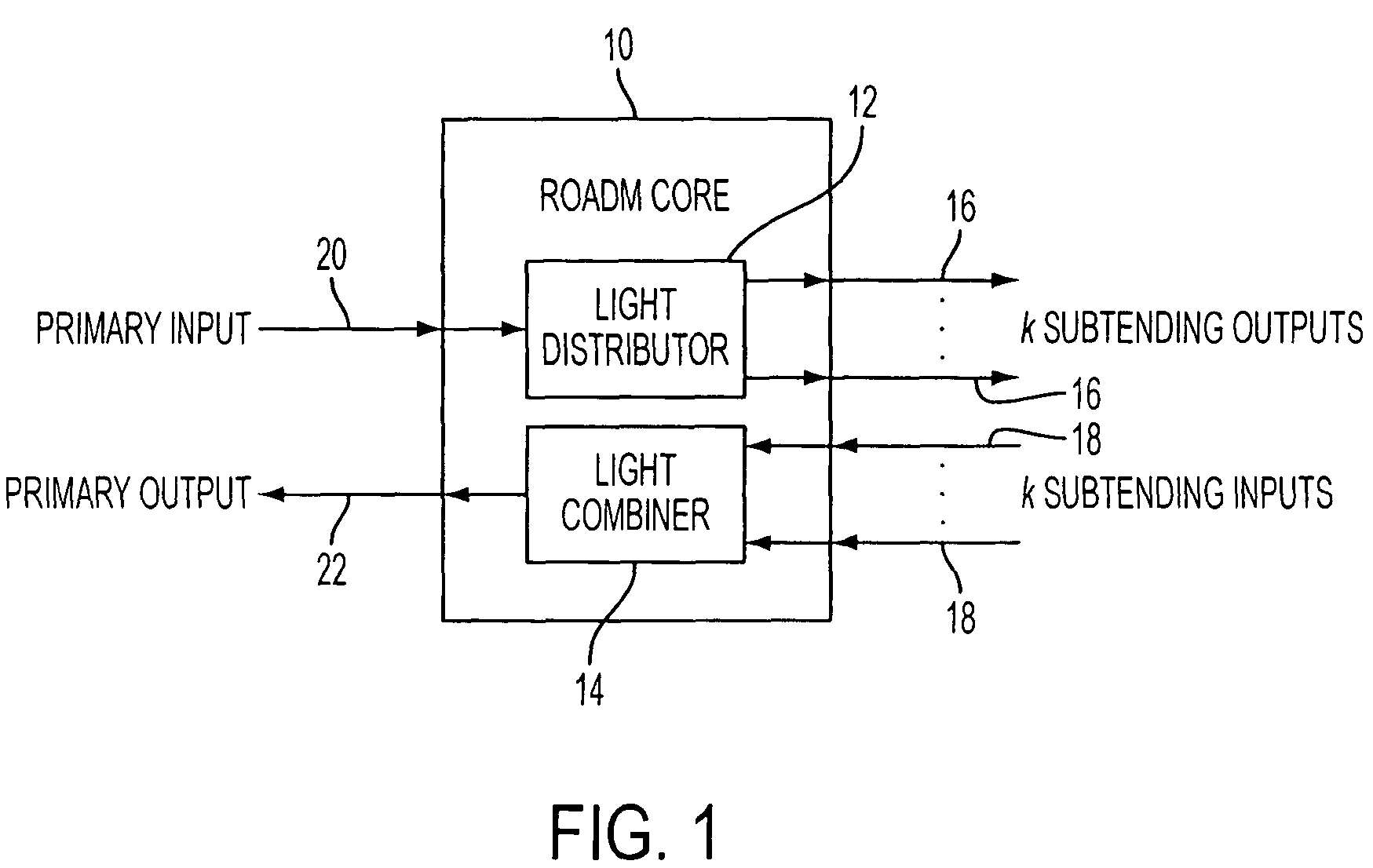
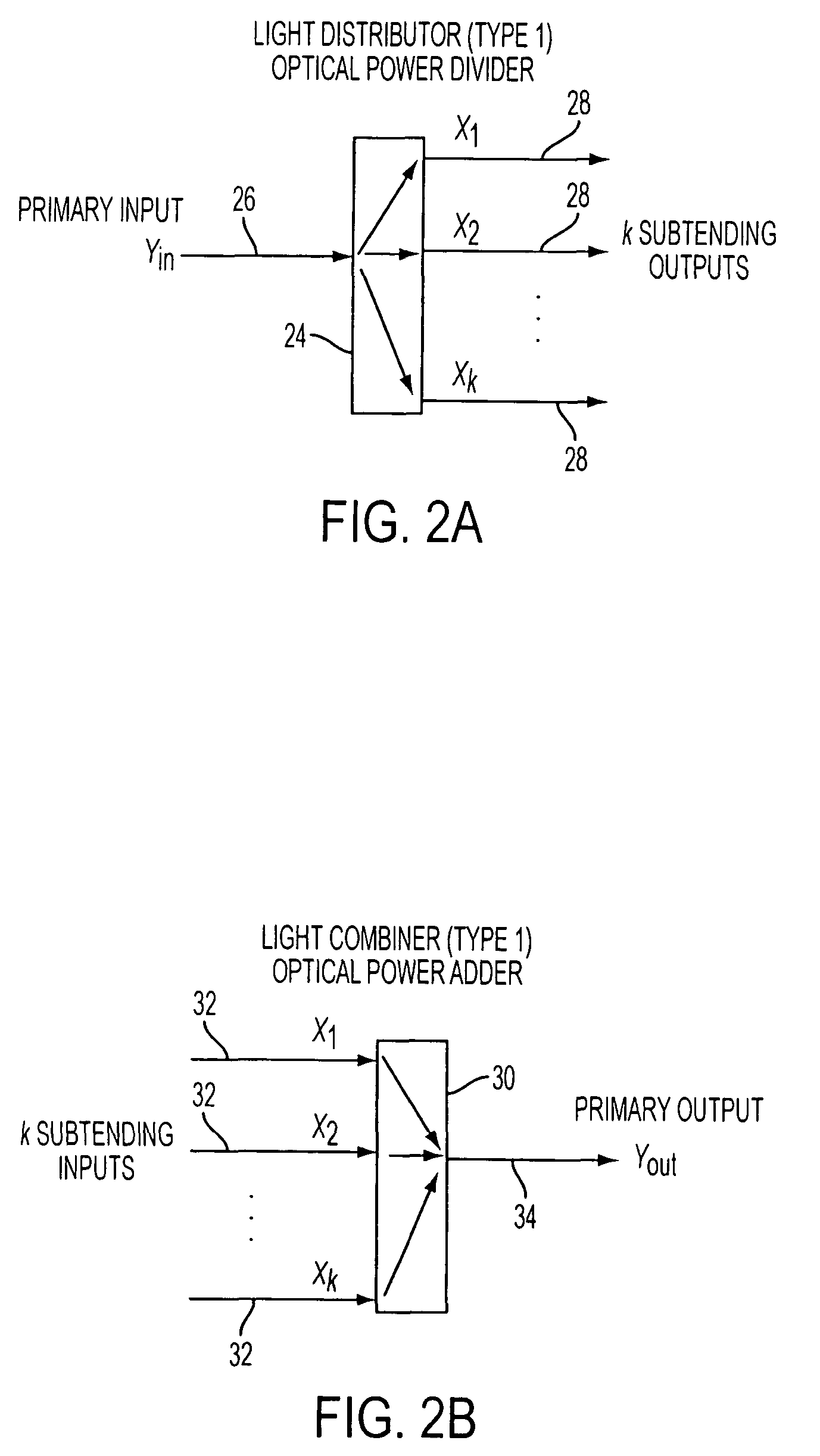
A reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device includes a light distributor, a light combiner, and first and second sets of add and drop ports. The light distributor is configured to receive an optical signal along a primary input of the reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device and to distribute the received optical signal along a plurality of subtending outputs. The light combiner is configured to receive optical signals along a plurality of subtending inputs, to combine the received optical signals into a combined signal, and to output the combined signal. The add and drop ports in the first set function as add and drop ports, respectively, and the add and drop ports in the second set function as both add and drop ports, respectively, and as express ports connectable to another reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Shared, Colorless Add/Drop Configuration for a ROADM Network using MxN Wavelength Swithches
InactiveUS20100202778A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesLength waveTransmission network
A system and method for dynamically adding / dropping wavelengths in a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) transport network is disclosed. The system includes a plurality of M×N wavelength selective switches (WSS) for locally dropping selected wavelengths at a node, where each M×N WSS has M inputs connected to optical fan-out devices in each of M network degrees, and a plurality of M×N wavelength selective switches for locally adding selected wavelengths to a node, where each M×N WSS has M outputs connected to optical fan-in devices in each of M network degrees. Several expedients of M×N wavelength selective switches comprising M switching elements for use in the system are also disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
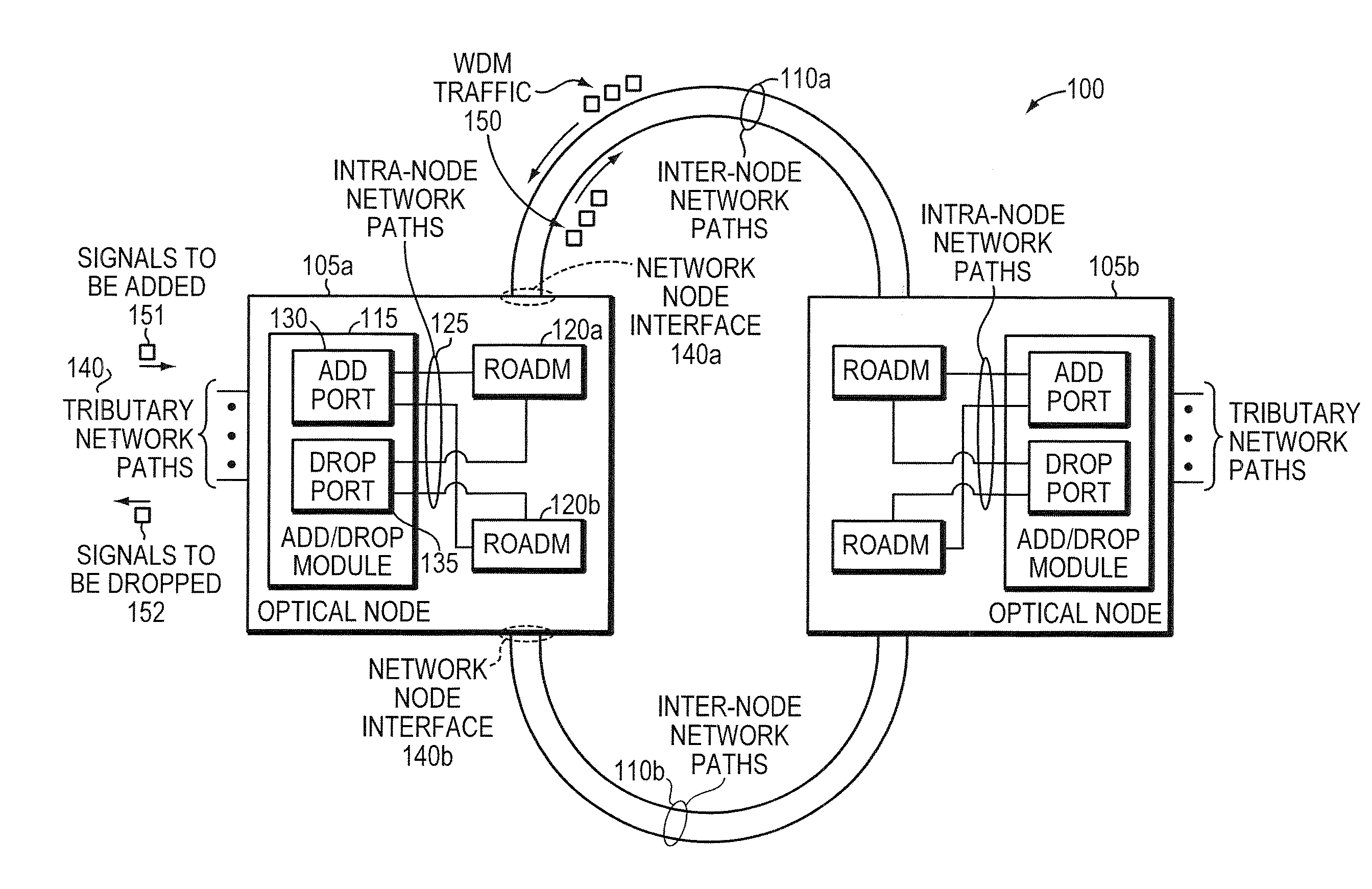
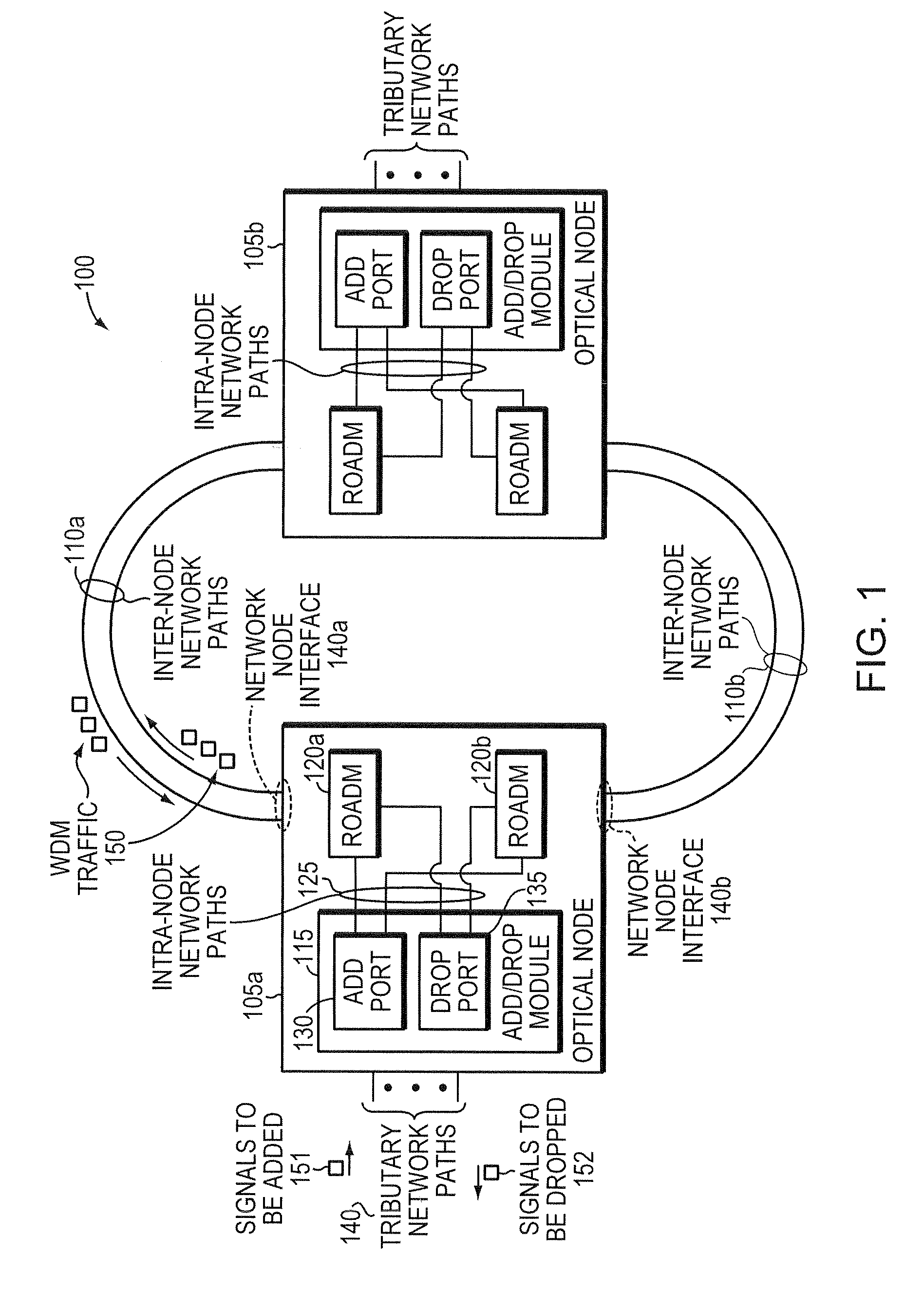
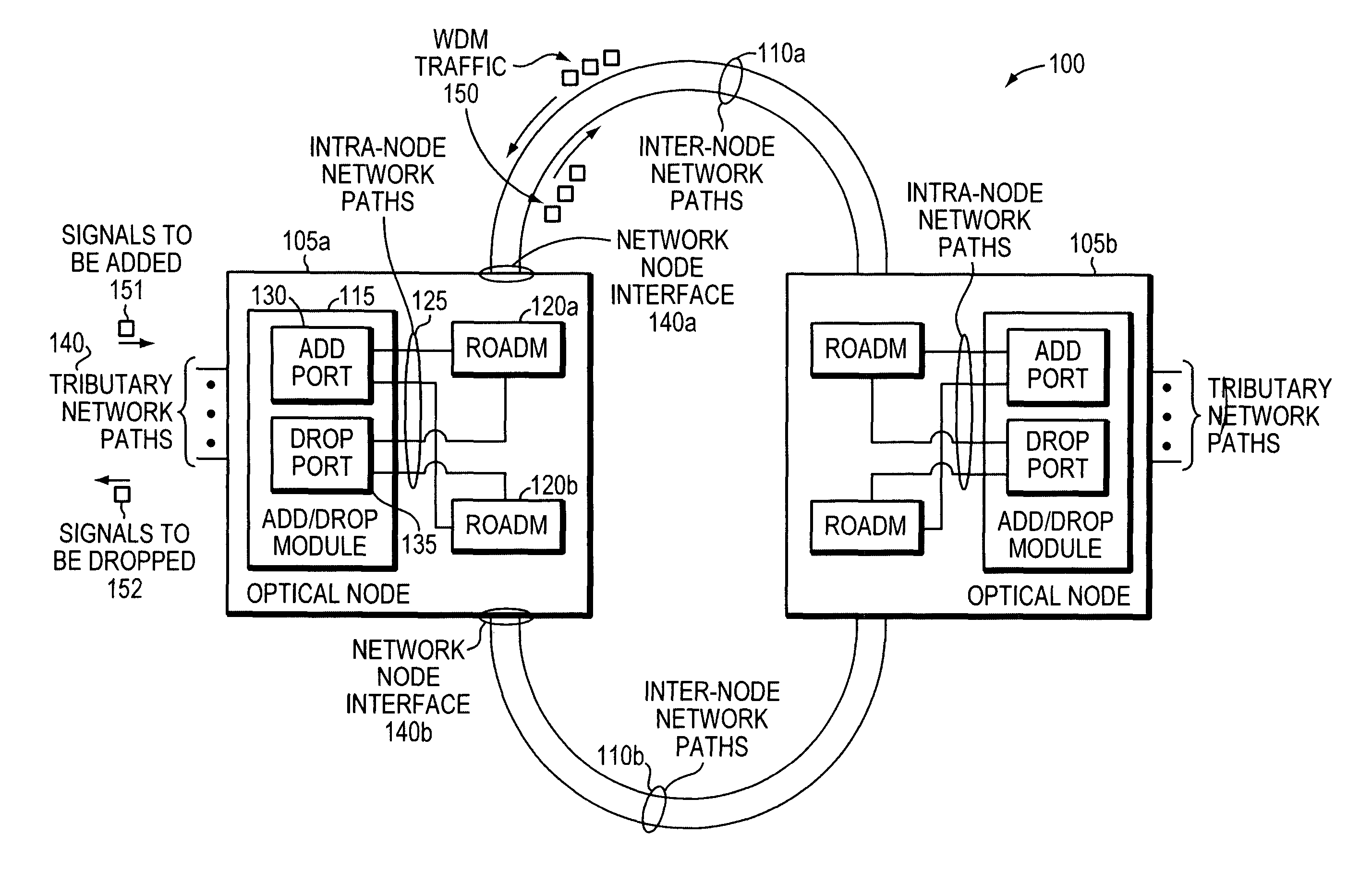
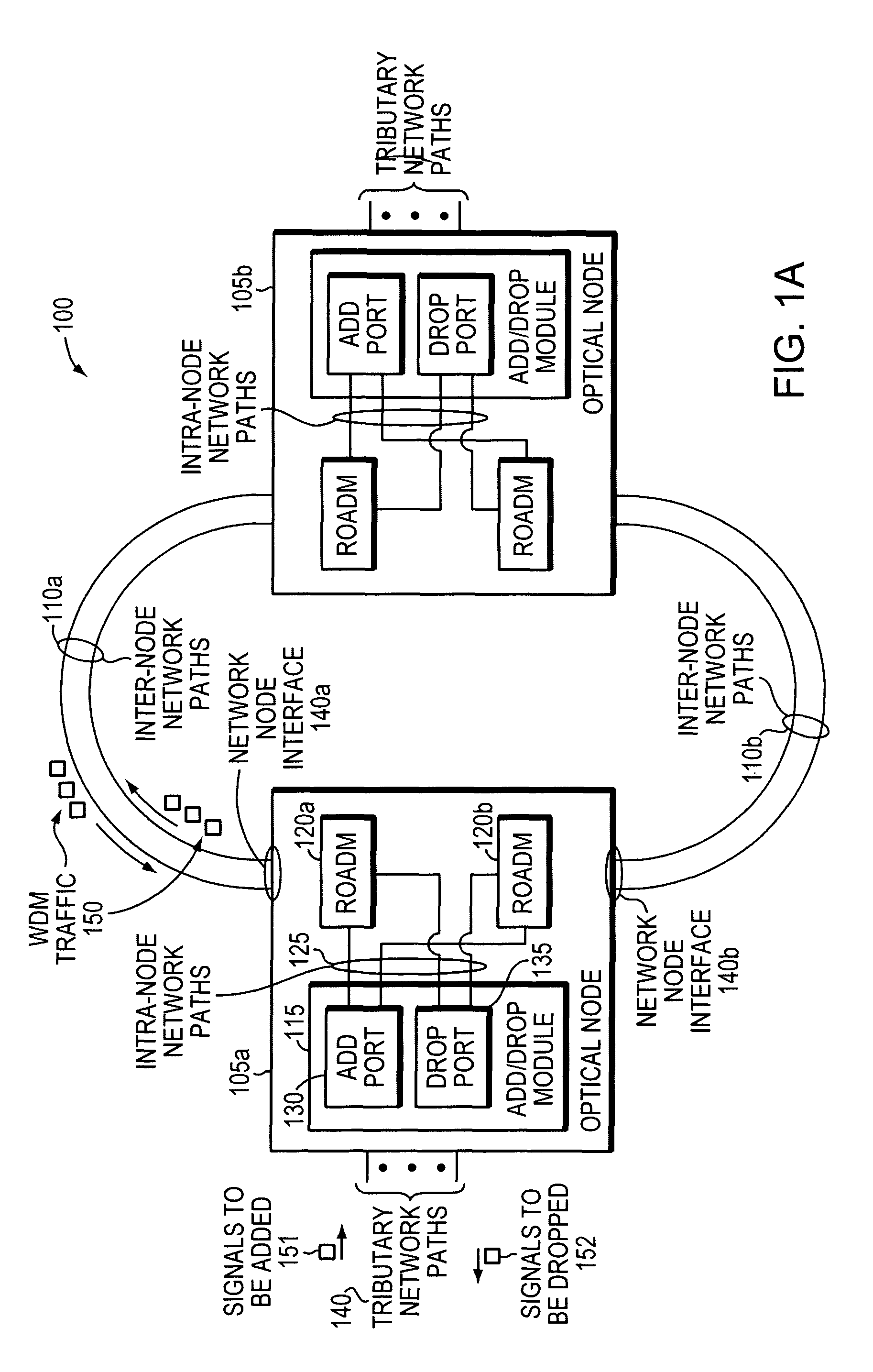
Methods and apparatus for performing directionless wavelength addition and subtraction within a ROADM based optical node
ActiveUS20090180779A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationComputer networkMultiplexer
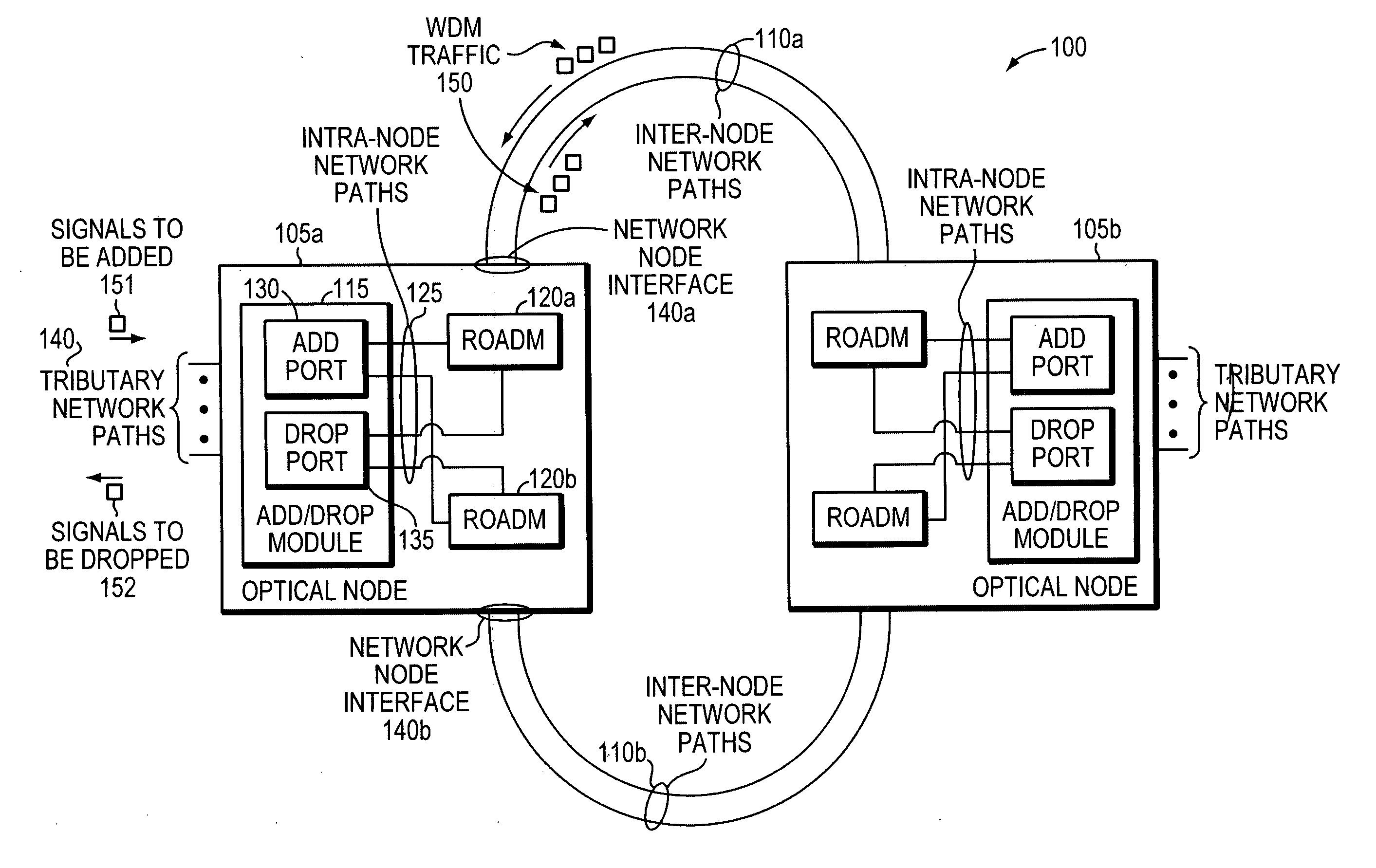
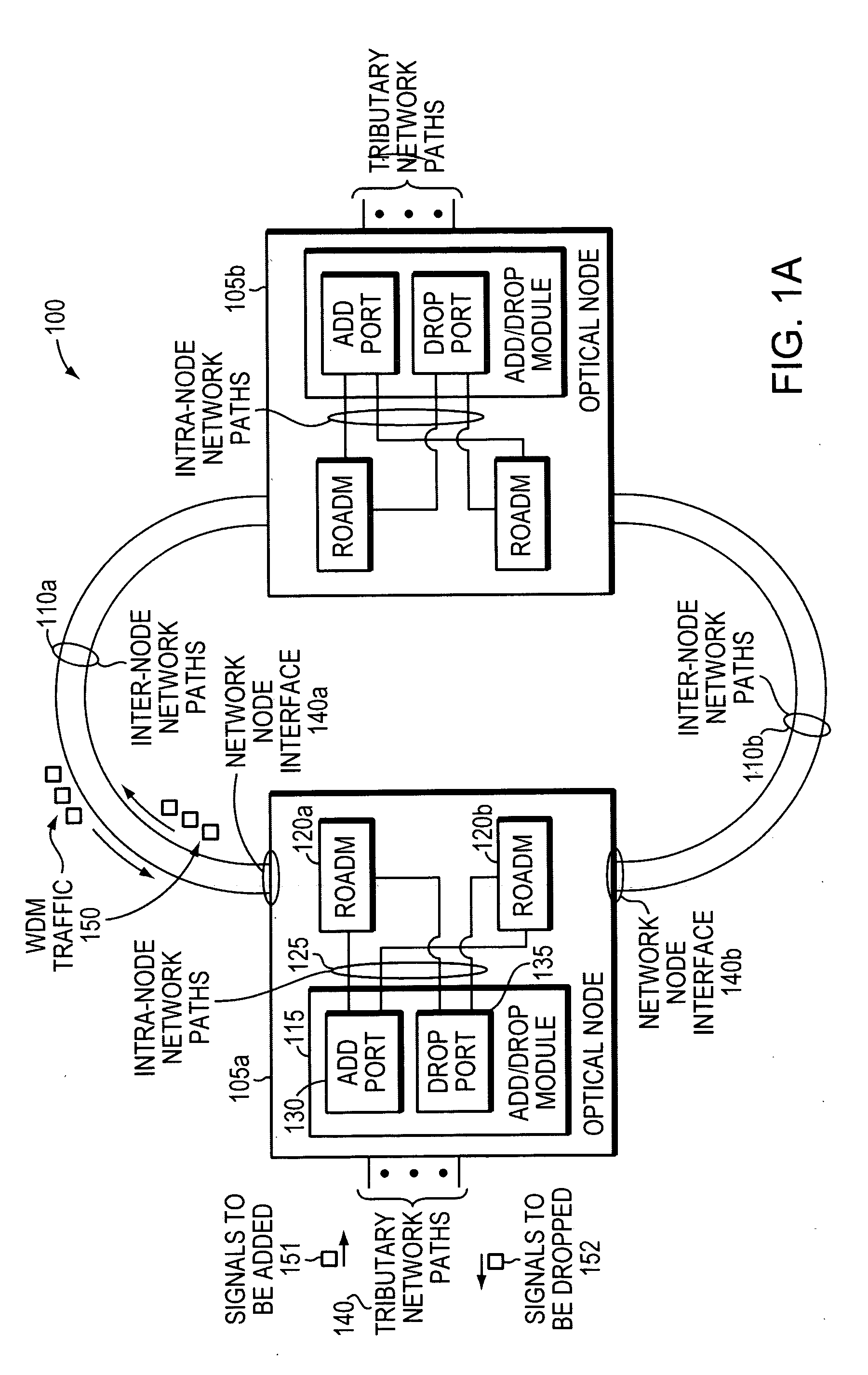
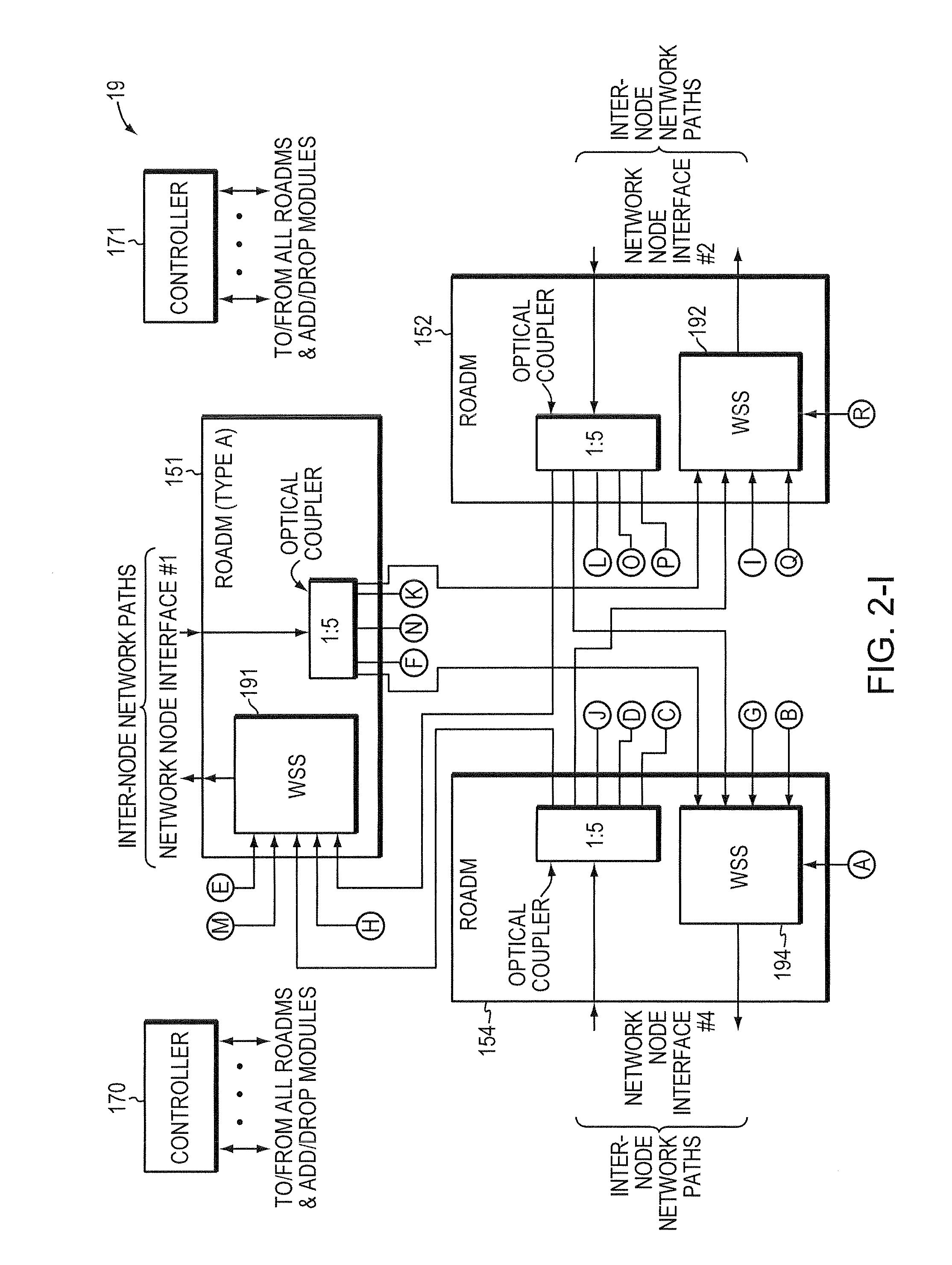
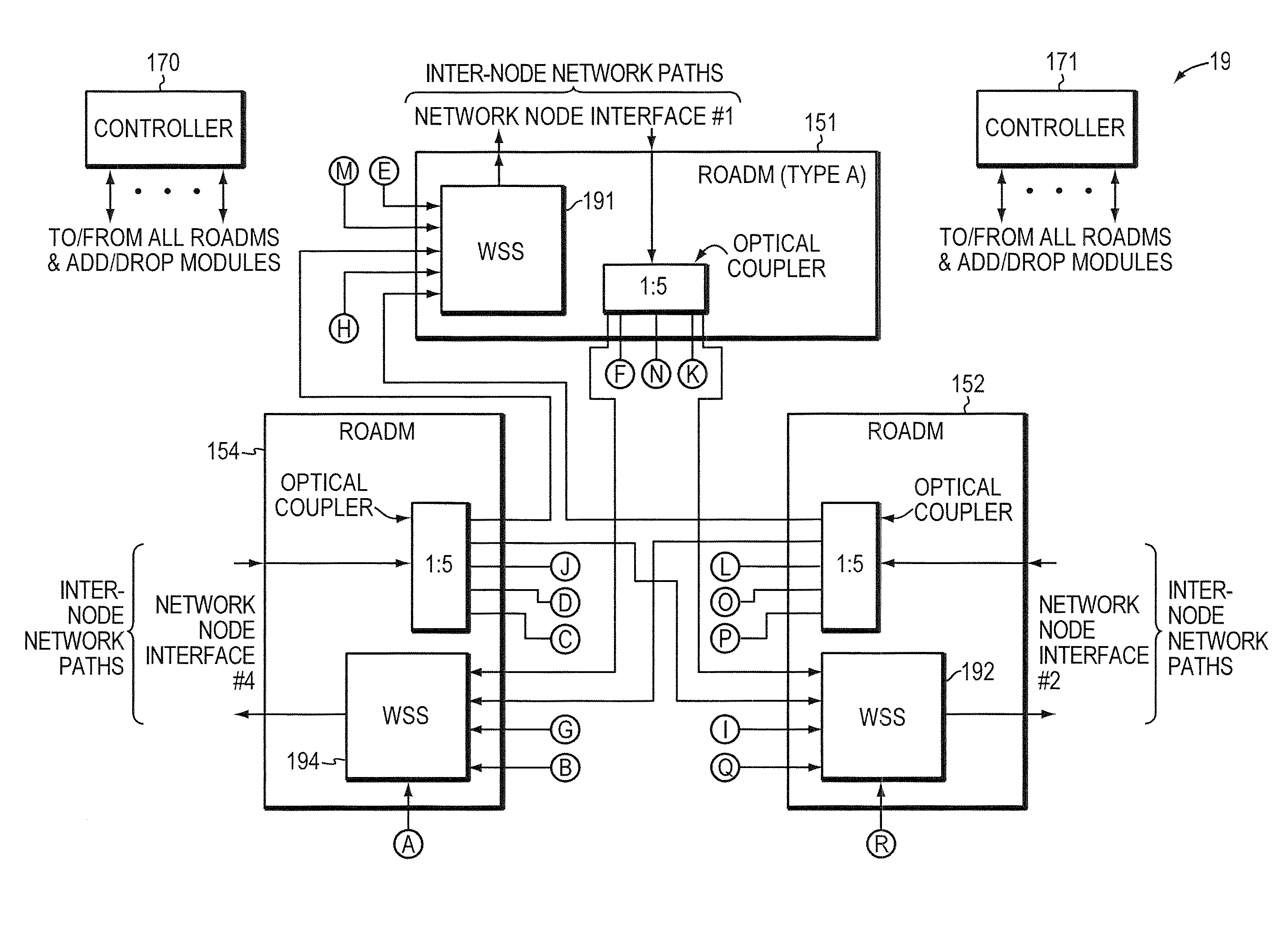
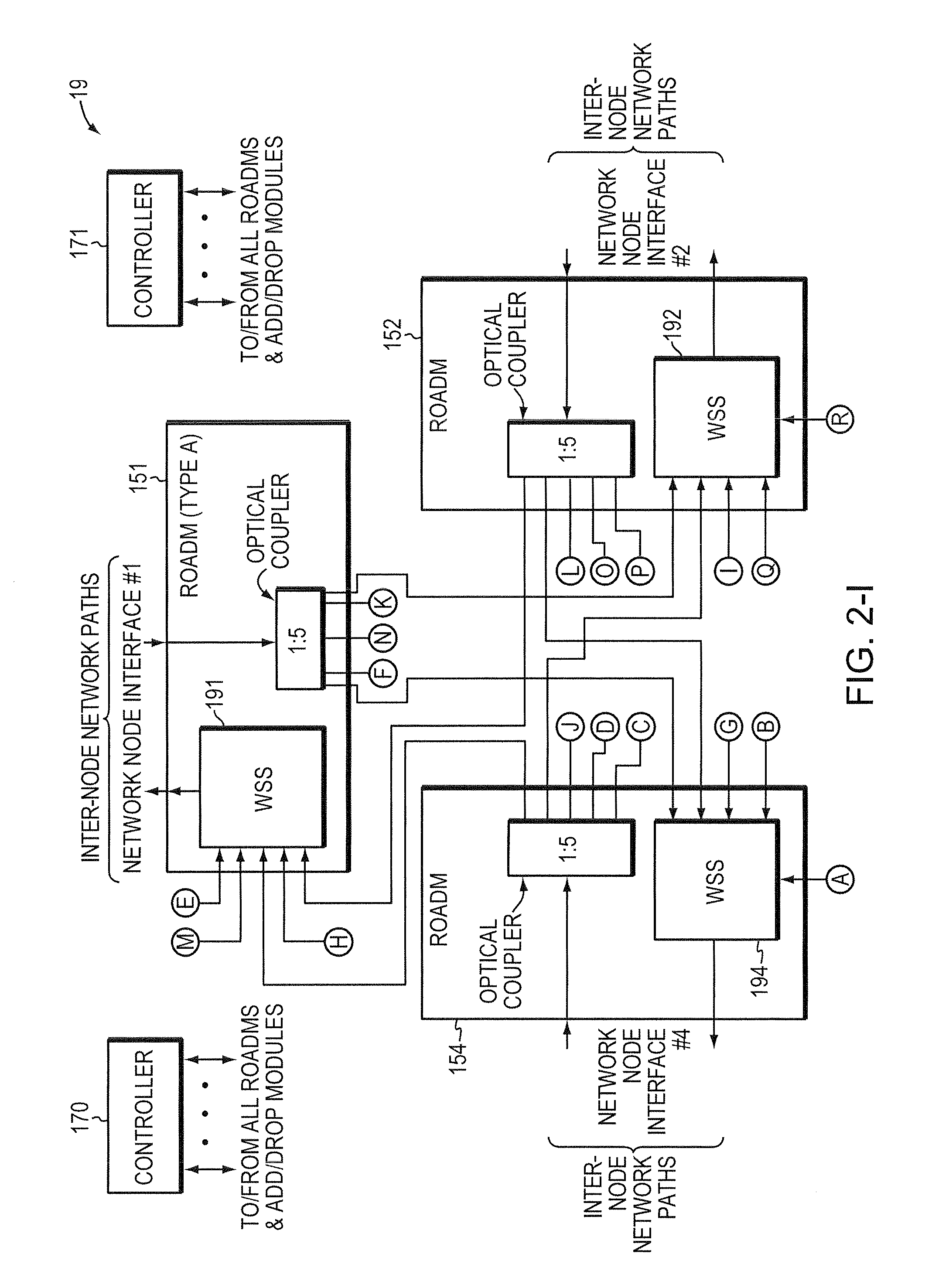
In today's reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexer (ROADM) based optical node, transponders associated with the ROADMs' add / drop ports are dedicated to a given network node interface. Dedicated transponders reduce the flexibility to route around network failures. Example embodiments of the invention includes an optical node and corresponding method for routing optical signals within an optical node. The optical node may include at least two ROADMs to transmit respective wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) signals onto at least two inter-node network paths and at least one add / drop module including add ports to direct add wavelengths received from tributary network paths to each of the ROADMs via intra-node network paths to allow the wavelengths to be available to be added to the inter-node network paths. Advantageously, a transponder may transmit and receive to and from different network node interfaces within the optical node, thereby improving the optical node's ability to route around network failures.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
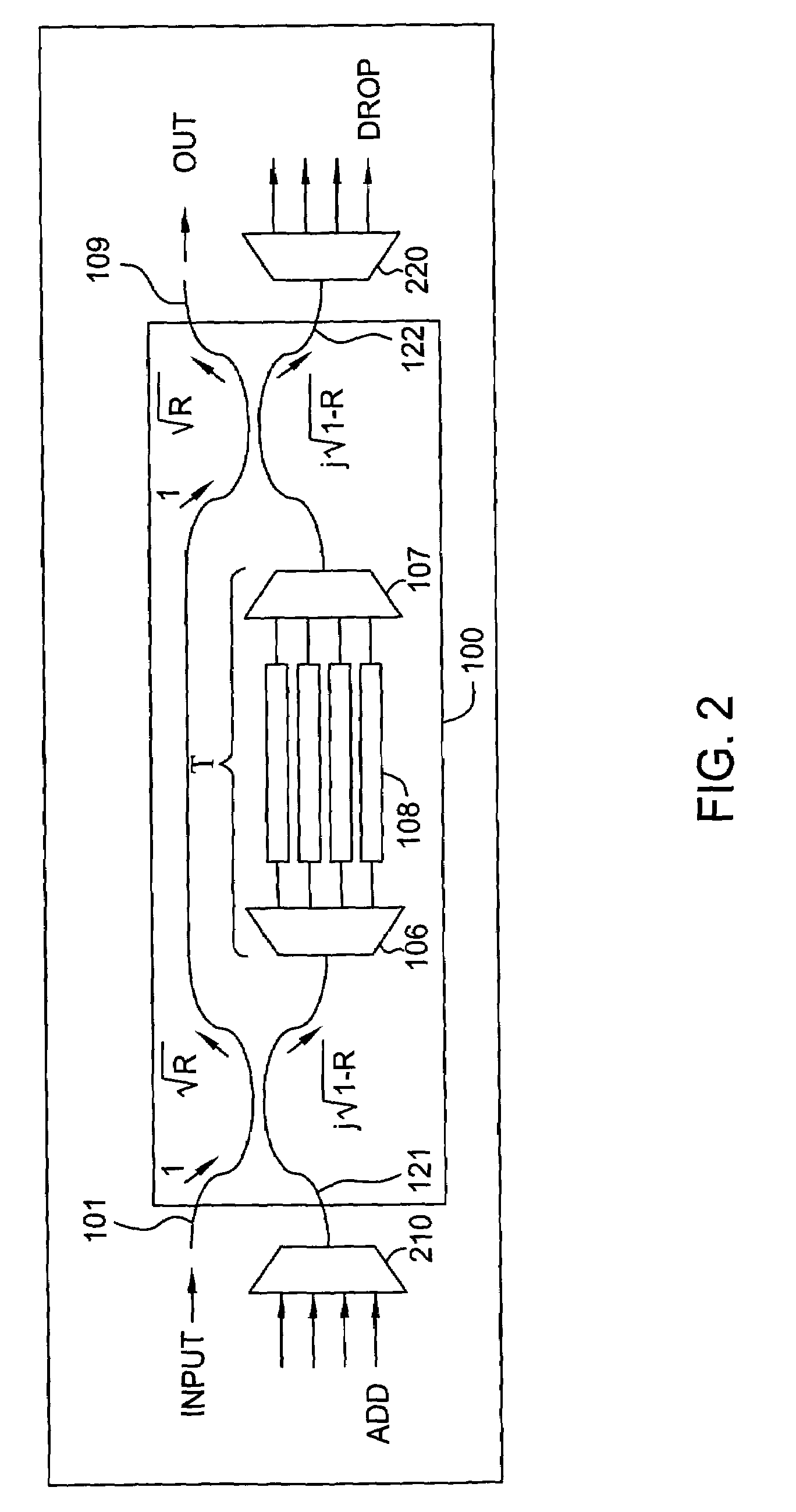
Reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer
InactiveUS7343066B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesPhase shiftedMultiplexer
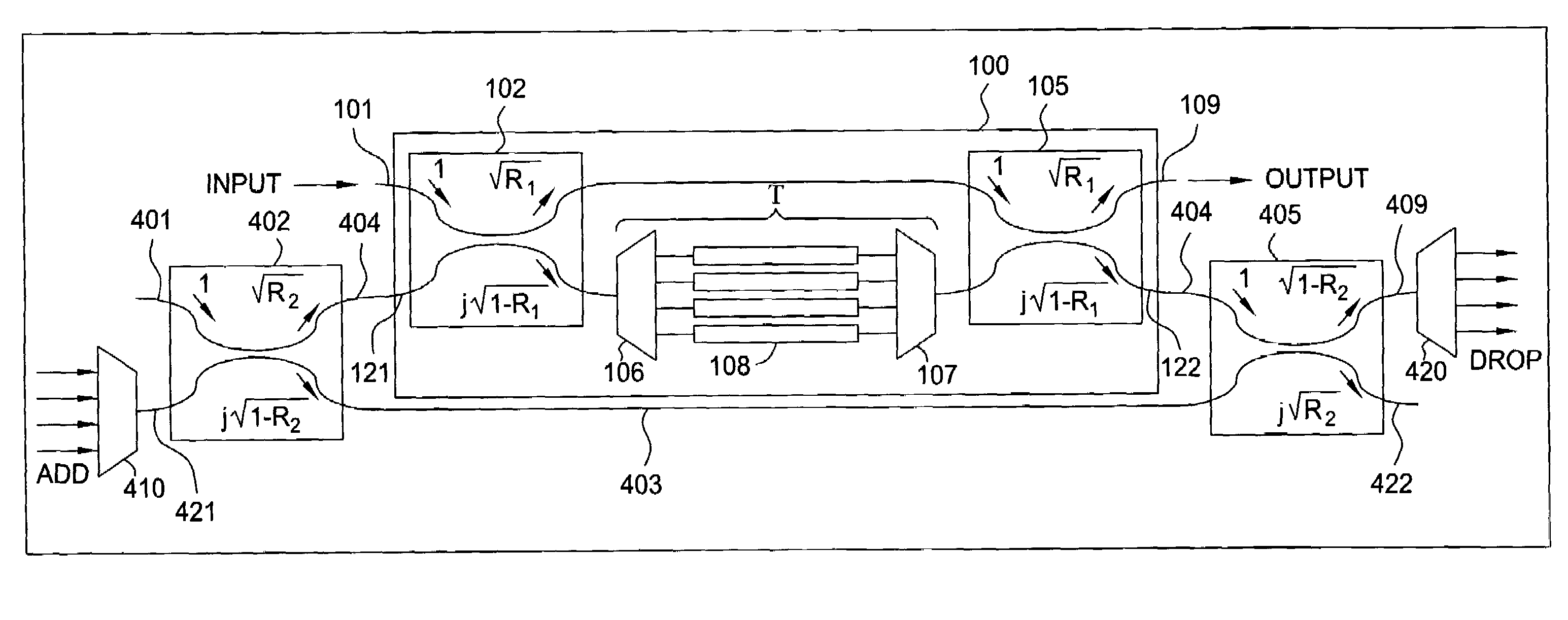
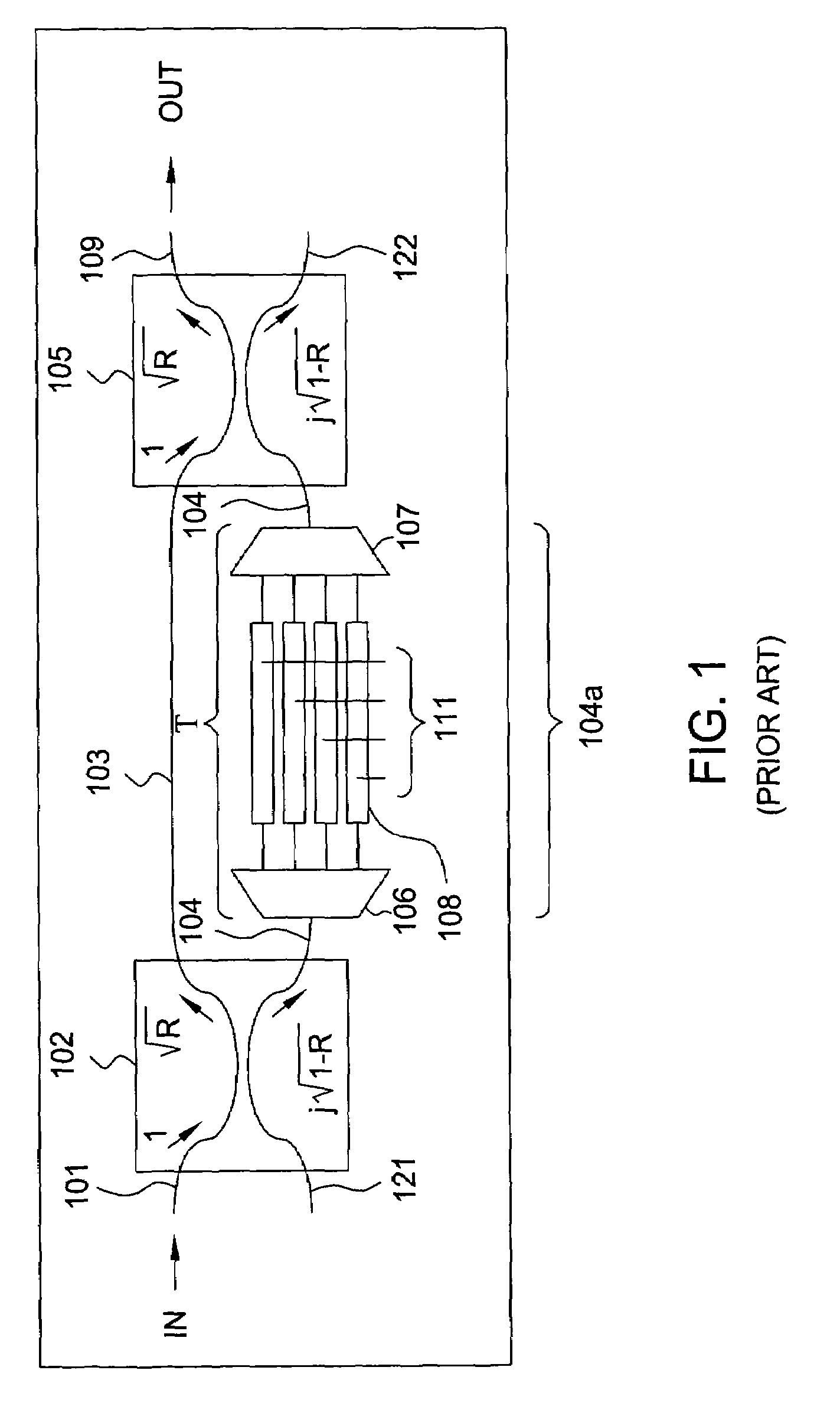
A reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexer (ROADM) includes a first optical dynamic gain equalization filter (DGEF) having a first input for receiving an initial wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) signal, a first output for sending a phase shifted WDM signal, and a second output connected to a demultiplexer for demultiplexing a WDM drop signal thereby producing a plurality of drop channels. A second DGEF having a first input for receiving the phase shifted WDM signal, a second input connected to a multiplexer, for multiplexing a plurality of add channels to produce thereby a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) add signal, and an output for sending a second adjusted WDM signal. The ROADM allows for the channels from the initial WDM signal to be dropped, added and equalized.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Dynamic wavelength service over a ROADM optical network
A system and method for dynamically adding / dropping wavelengths in a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) transport network to form a wave division multiplexing virtual private network is disclosed. The system includes at least one optical transponder, a plurality of optical fan-out devices, each arranged to receive an input signal from a network degree and coupled to at least one of a plurality of optical fan-in devices, each optical fan-in device arranged to output a signal to a network degree, the optical fan-out devices comprising at least one wavelength selective switch and the optical fan-in devices comprising at least one wavelength selective switch, the optical fan-out devices and optical fan-in devices being connected so as to enable signals input from each of the plurality of network degrees to be switched to another network degree of the plurality of network degrees; a plurality of demultiplexers for locally dropping selected wavelengths; a plurality of multiplexers for locally adding selected wavelengths; and at least one customer-dedicated fiber switch interposed between the at least one optical transponder and the plurality of demultiplexers and multiplexers. The fiber switch is coupled to wavelengths and degrees that are allocated for a bandwidth-on-demand application. Other configurations include additional fan-in and fan-out devices interposed between a mux / demux assembly and the optical transponders to support wavelength redistribution applications.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Optimized reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer architecture with MEMS-based attenuation or power management
ActiveUS20060228072A1Improve featuresAccurate and stable alignmentElectromagnetic network arrangementsCoupling light guidesFrequency spectrumElectronic feedback
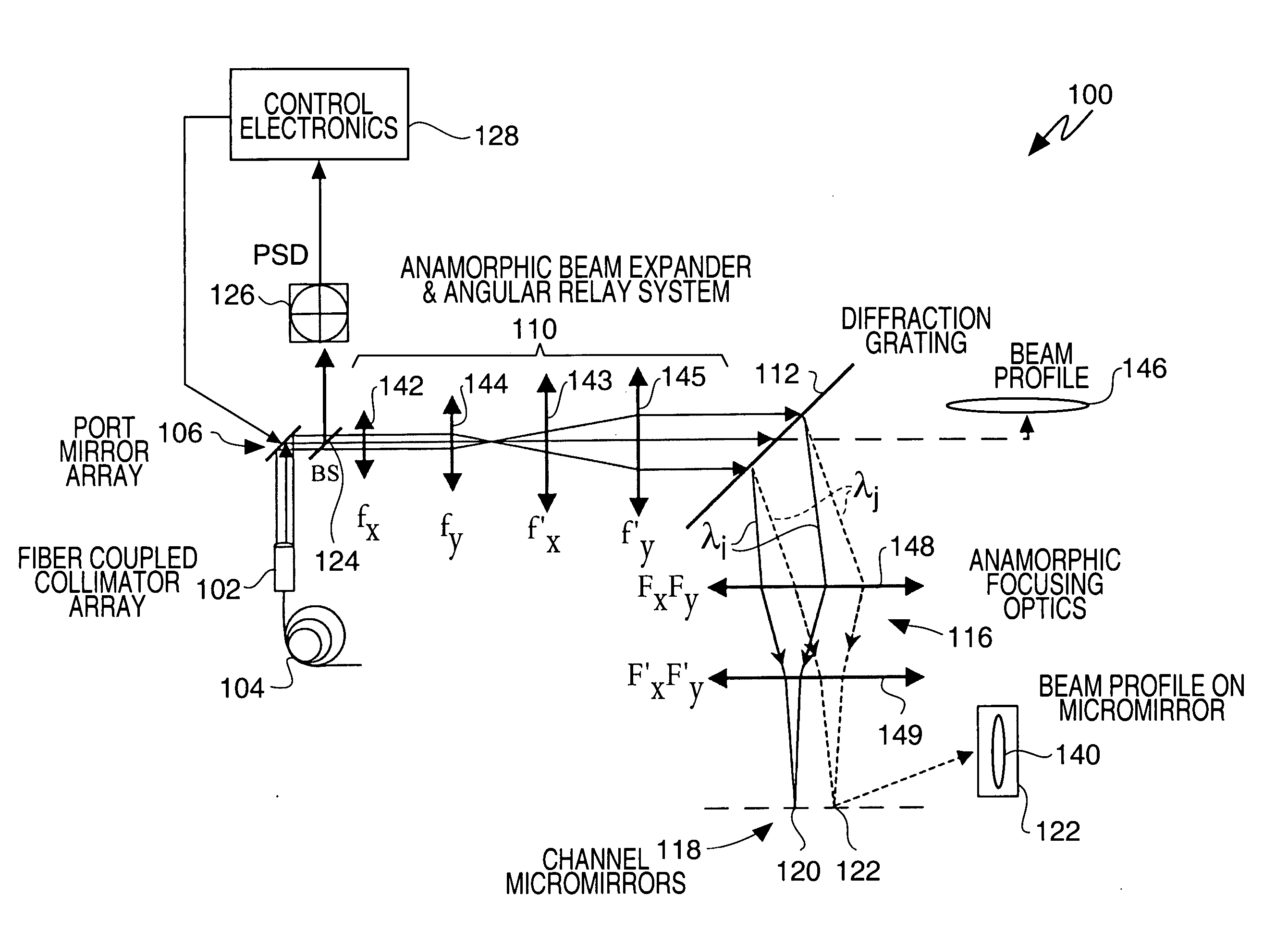
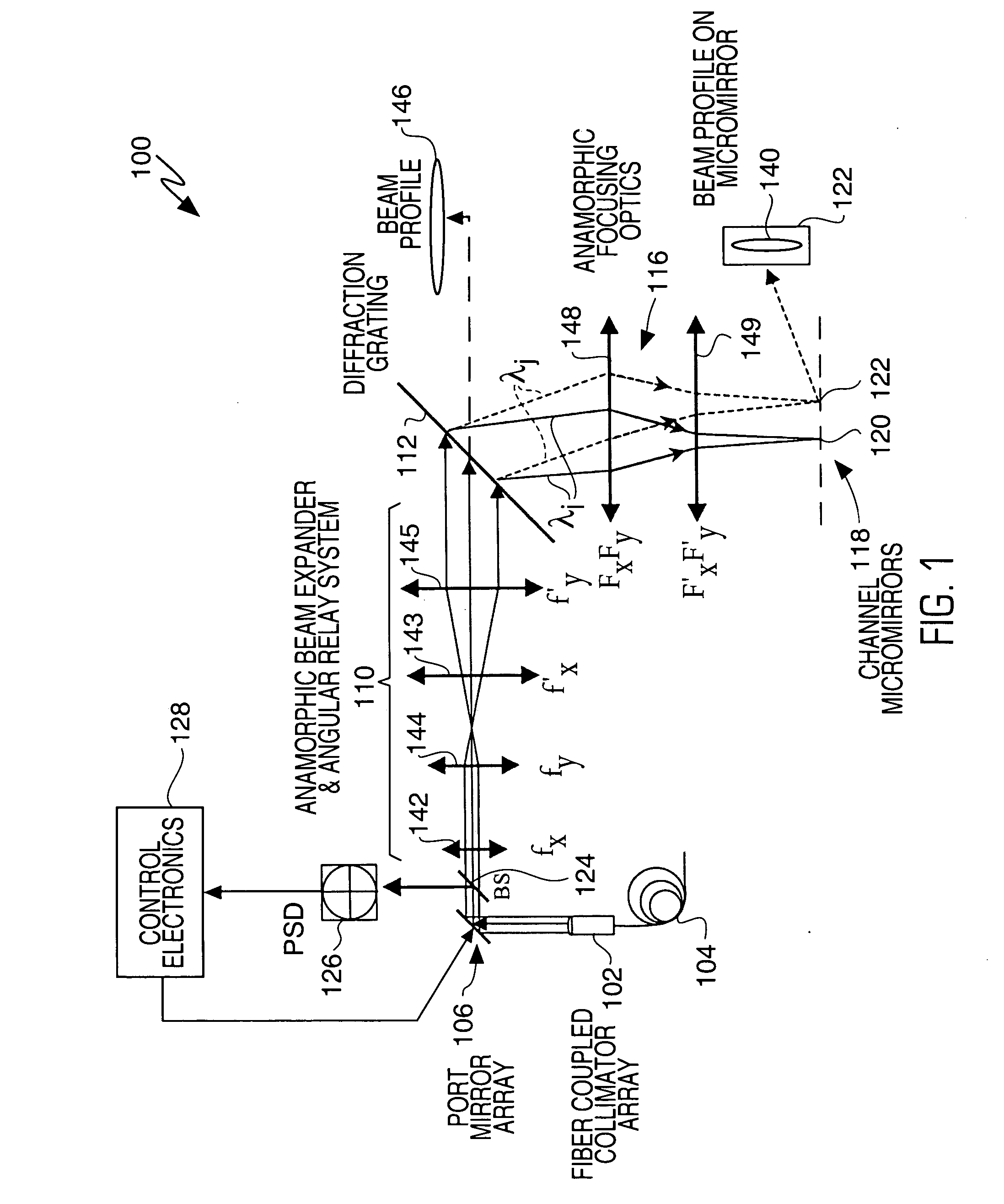
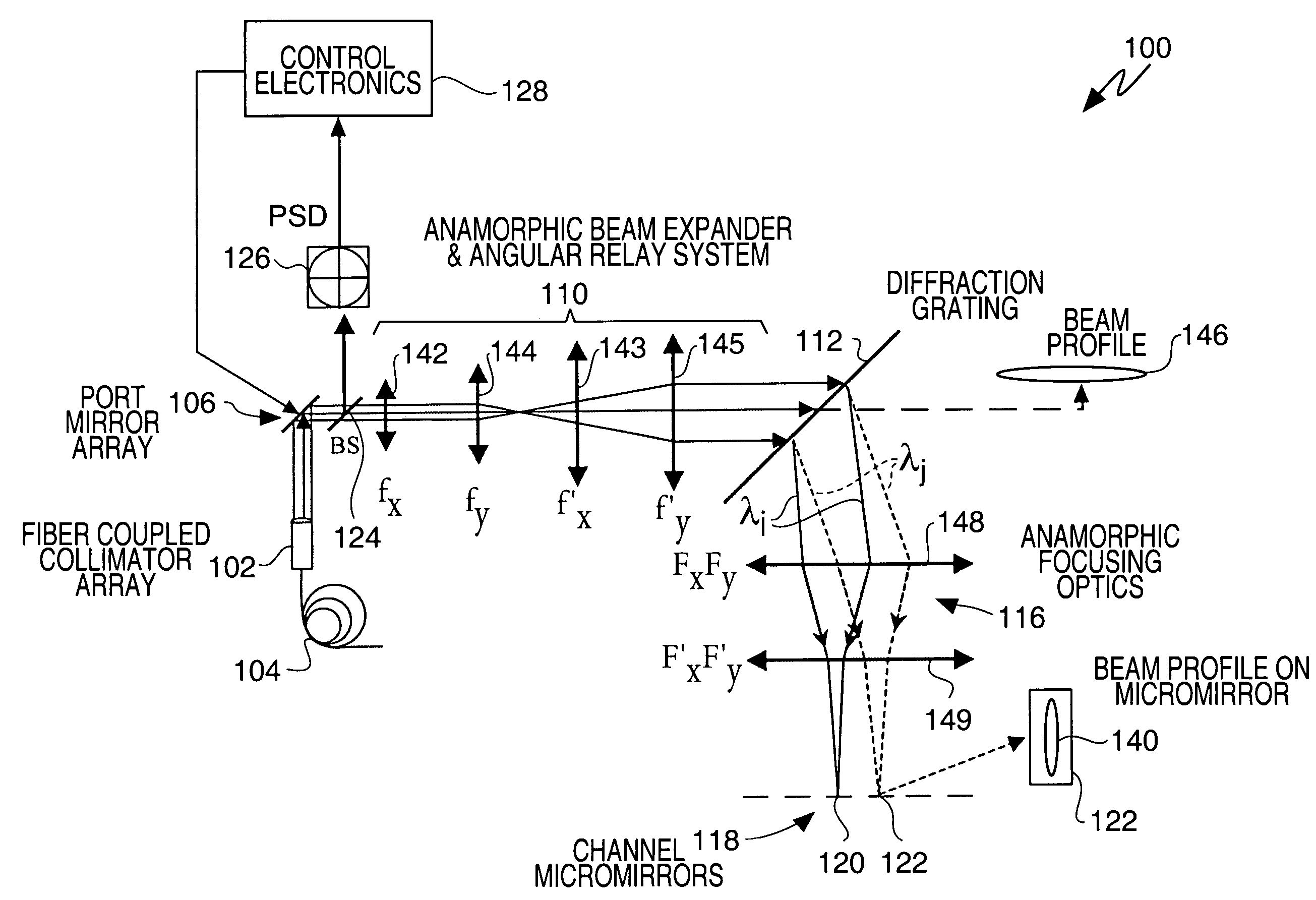
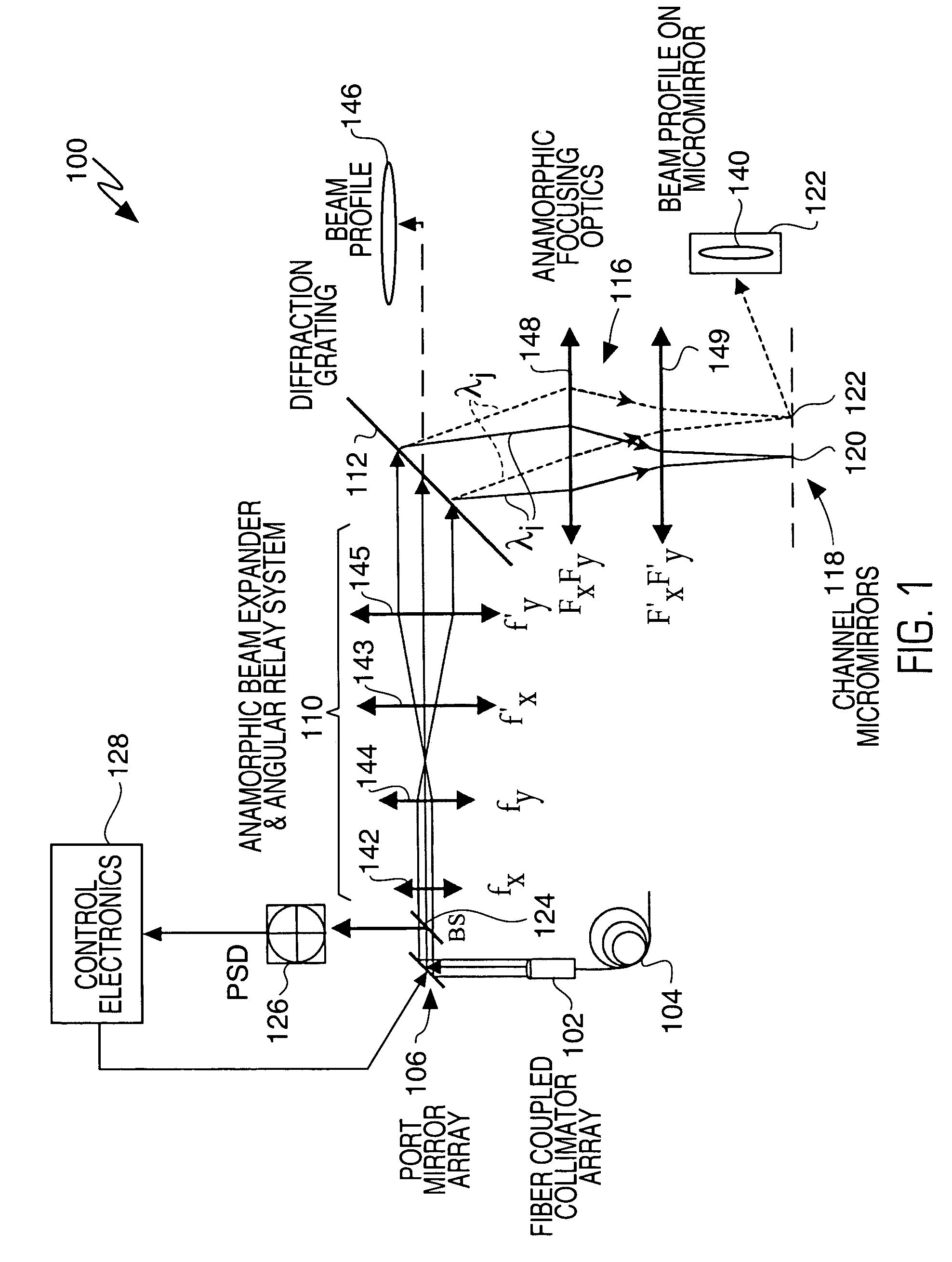
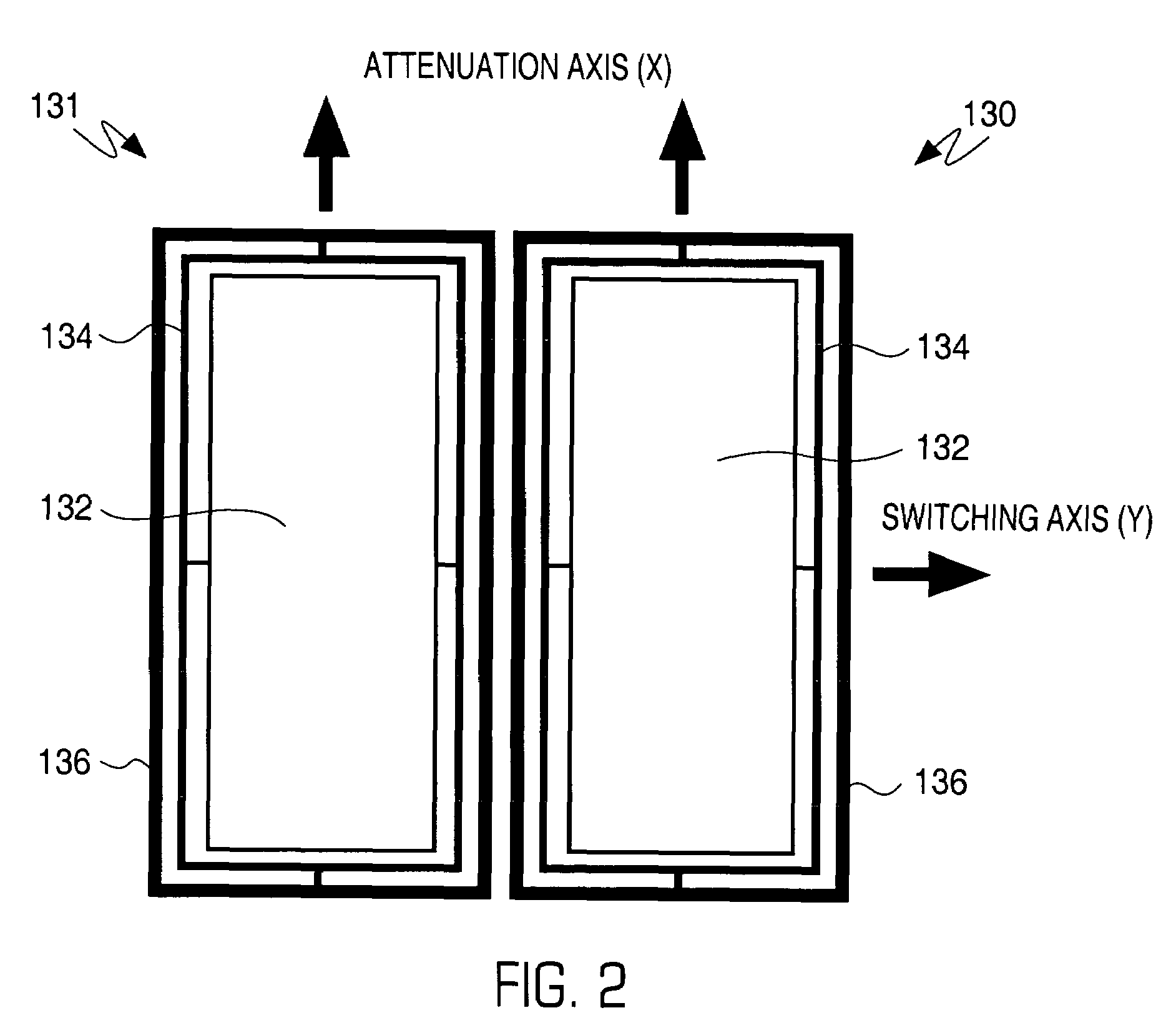
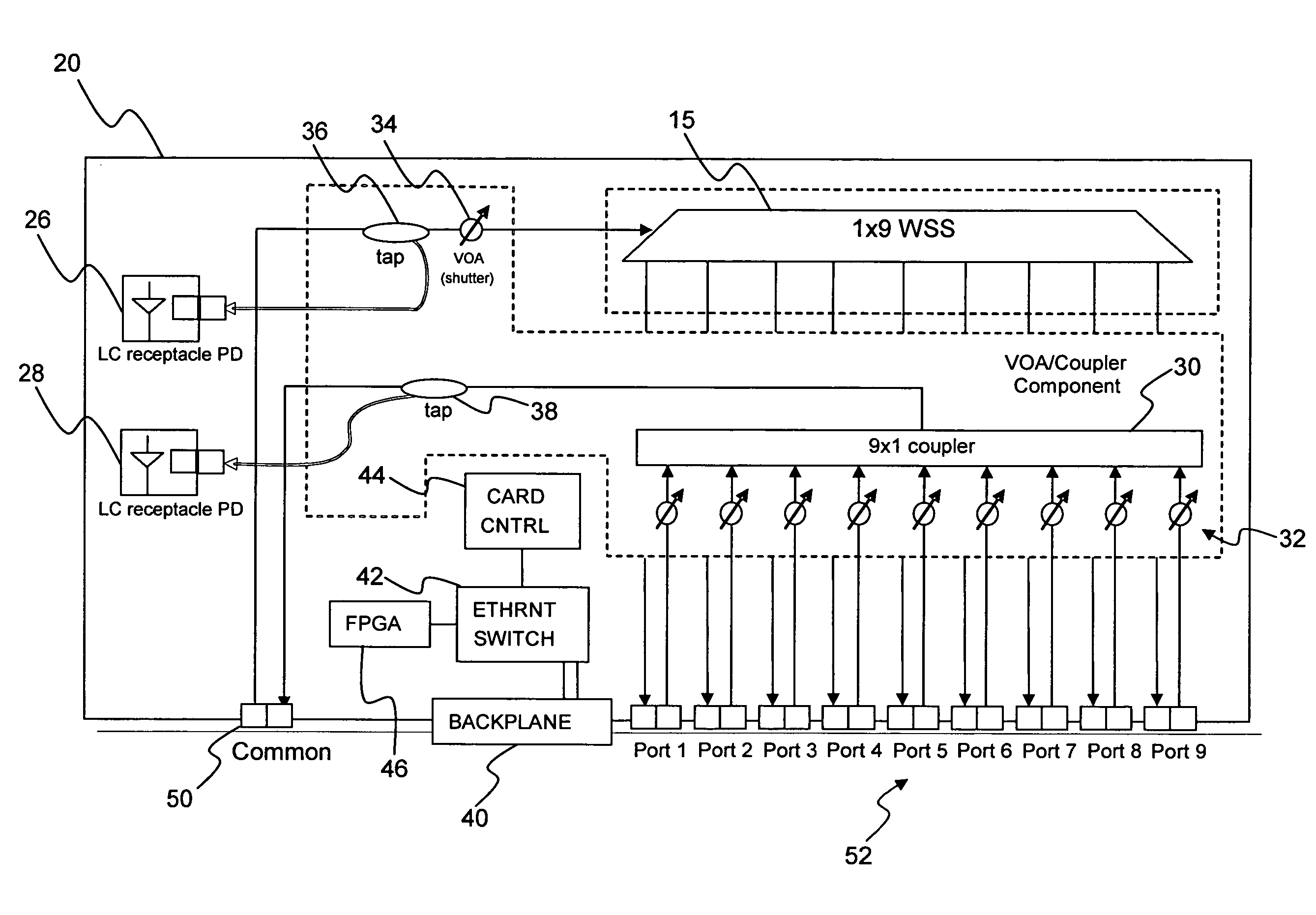
A wavelength selective switch architecture for ROADMs for switching the spectral channels of a multi-channel, multi-wavelength optical signal between input and output ports employs a biaxial MEMS port mirror array for optimal coupling efficiency and ITU grid alignment, an anamorphic beam expander for expanding input optical signals to create an elongated beam profile, a diffraction grating for spatially separating the spectral channels, an anamorphic focusing lens system, an array of biaxial elongated channel MEMS micromirrors, a built-in Optical Channel Monitor, and an electronic feedback control system. The bi-axial channel micromirrors are rotatable about one axis to switch spectral channels between ports, and are rotatable about an orthogonal axis to vary the coupling of the spectral channel to an output port and control attenuation of the spectral signal for complete blocking or for a predetermined power level. The architecture affords hitless switching, near notchless operation, ITU channel alignment, high passband, stability over a broad temperature range, and minimum insertion loss through the optimal optical coupling efficiency enabled by the feedback control system.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
Reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer and procedure for outputting optical signals from such multiplexer
A reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) includes local interfaces at which optical signals of different wavelengths are locally input into the ROADM, and a network interface configured to connect the ROADM to a network from which multiplexed optical signals of different wavelengths are transmitted to the network. In a first configuration, the ROADM is configured to transmit from the network interface to the network multiplexed signals of different wavelengths having a first minimum frequency difference. In a second configuration, the ROADM is configured to transmit from the network interface to the network multiplexed signals of different wavelengths having a second minimum frequency difference. The second minimum frequency difference is greater than the first minimum frequency difference. This arrangement reduces the power of four wave mixing cross products produced when optical signals of three wavelengths are multiplexed and transmitted from the ROADM to NZDSF or DSF fiber types.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Methods and apparatus for performing directionless and contentionless wavelength addition and subtraction
ActiveUS20100272441A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerEngineering
In today's reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexer (ROADM) based optical node, ROADMs multiplex (and demultiplex) colored optical signals to form wavelength-division multiplexed (WDM) signals. Transponders connected to the ROADMs' add / drop ports convert noncolored optical signals to colored optical signals (and vice versa). Dedicating transponders to given ports degrades the node's ability to route around network failures. Example embodiments of the invention include an optical node and corresponding method for routing optical signals within an optical node that compensate for this inflexibility. The optical node may include two ROADMs to transmit respective WDM signals onto at least two internode network paths and a routing module that can direct channels of the same wavelength along different internode network paths. Advantageously, a transponder may transmit (receive) different signals at the same wavelength to (from) different network node interfaces within the optical node, thereby improving the optical node's ability to route around network failures.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer based on M*N ports of silicon substrate liquid crystal
InactiveCN103281153AIngenious structureFunctionalWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesWavelengthVlsi chip
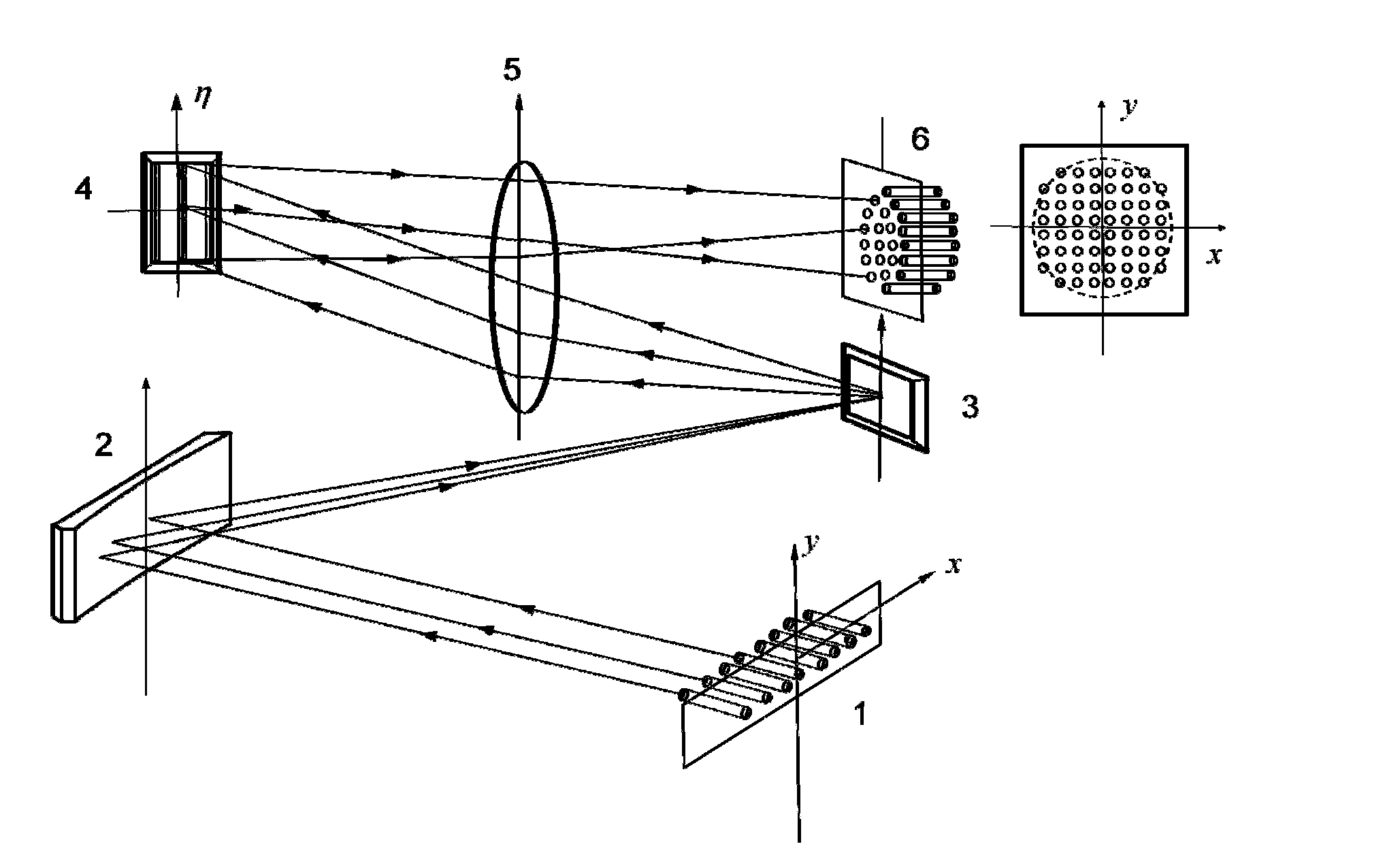
The invention discloses a reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) based on M*N ports of silicon substrate liquid crystal. The ROADM comprises an optical fiber collimator input array with M ports, a spherical reflector, a body optical grating, an LCoS Opto-VLSI chip, a lens and an optical fiber collimator output array with N ports. The ROADM based on M*N ports of LCoS is realized. An optical system inside the equipment is unique in design, exquisite in structure, and good in function, uses the high-density scoring body grating as a dispersion element, adopts a method that phase gratings of different two-dimension orientations are loaded on an LCoS chip, and realizes efficient and flexible assignments of a large scale optical integrated chip on an incident wave length passage through changing the period of the grating and grating orientation modulation light beam phases. The ROADM has a high port number and optimized spectrum flexibility, has the functions of dispersion adjustments, pulse shaping and the like, and can conduct remote control and upgrade conveniently through software.
Owner:MINZU UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device, procedure and system using such device, optical light distributor, and coupling-ratio assigning procedure
ActiveUS8116629B2Power maximizationWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical add-drop multiplexerCoupling ratio
A reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device includes a light distributor, a light combiner, and first and second sets of add and drop ports. The light distributor is configured to receive an optical signal along a primary input of the reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device and to distribute the received optical signal along a plurality of subtending outputs. The light combiner is configured to receive optical signals along a plurality of subtending inputs, to combine the received optical signals into a combined signal, and to output the combined signal. The add and drop ports in the first set function as add and drop ports, respectively, and the add and drop ports in the second set function as both add and drop ports, respectively, and as express ports connectable to another reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer core device.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Minimizing Bandwidth Narrowing Penalties in a Wavelength Selective Switch Optical Network
ActiveUS20120195592A1Minimize bandwidth narrowing penaltyReduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringWavelength
This invention relates to provisioning wavelength-selective switches and reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexers to minimize the bandwidth narrowing effect from the optical filters. Novel architectures and methods are disclosed that can significantly reduce bandwidth-narrowing on channels in a reconfigurable WDM network where a large number of optical filter elements are cascaded. Instead of blocking unused channels as in the prior art, unused channels are selectively provisioned depending on the state of their adjacent channels. Unused adjacent channels of an active channel are provisioned to follow the same path as the active channels. As each channels is deployed, the channel frequency is selected so as to minimize bandwidth narrowing.
Owner:SNELL HLDG LLC +1
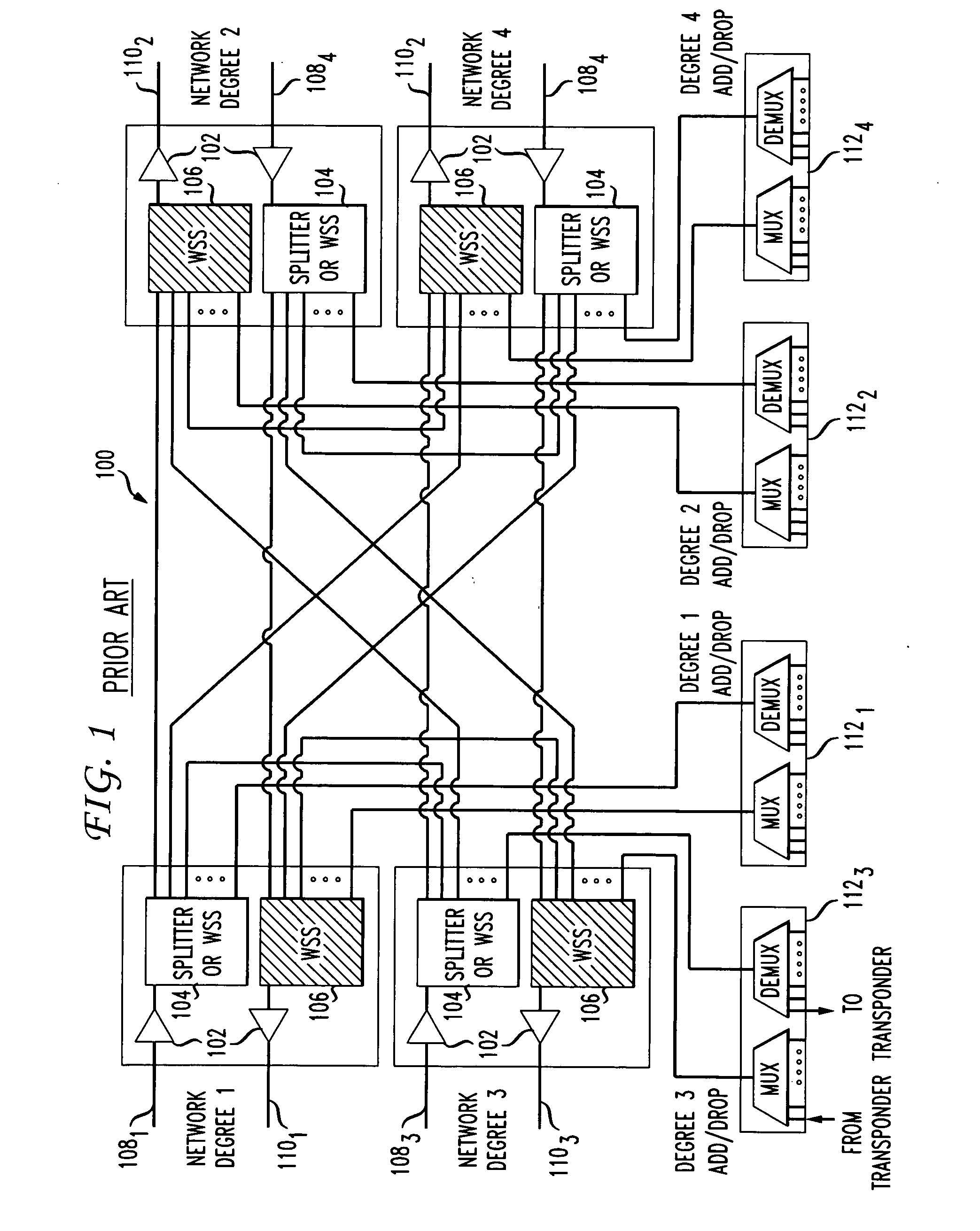
Optical Switching Architectures for Nodes in WDM Mesh and Ring Networks
ActiveUS20070237524A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerProtection mechanism
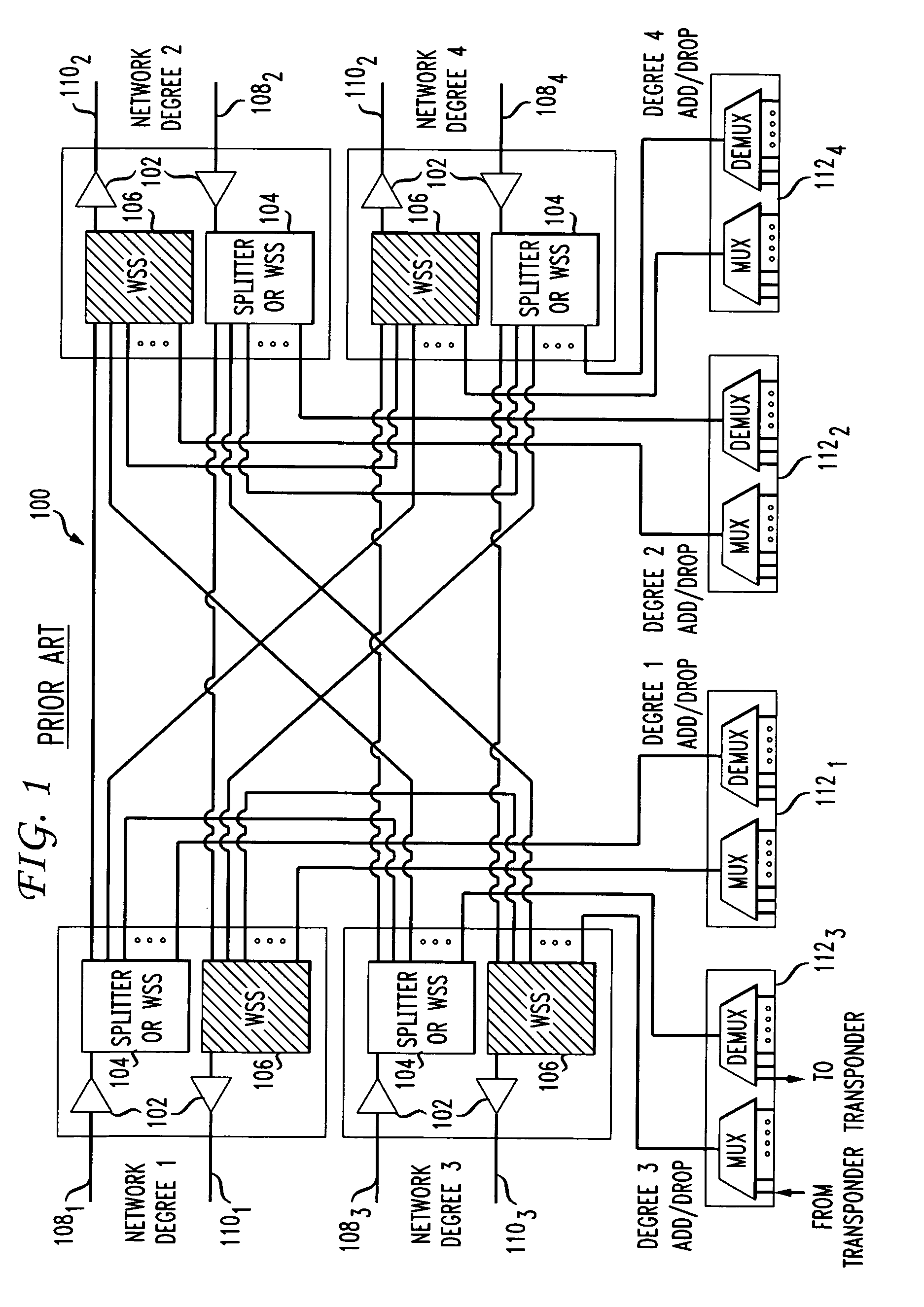
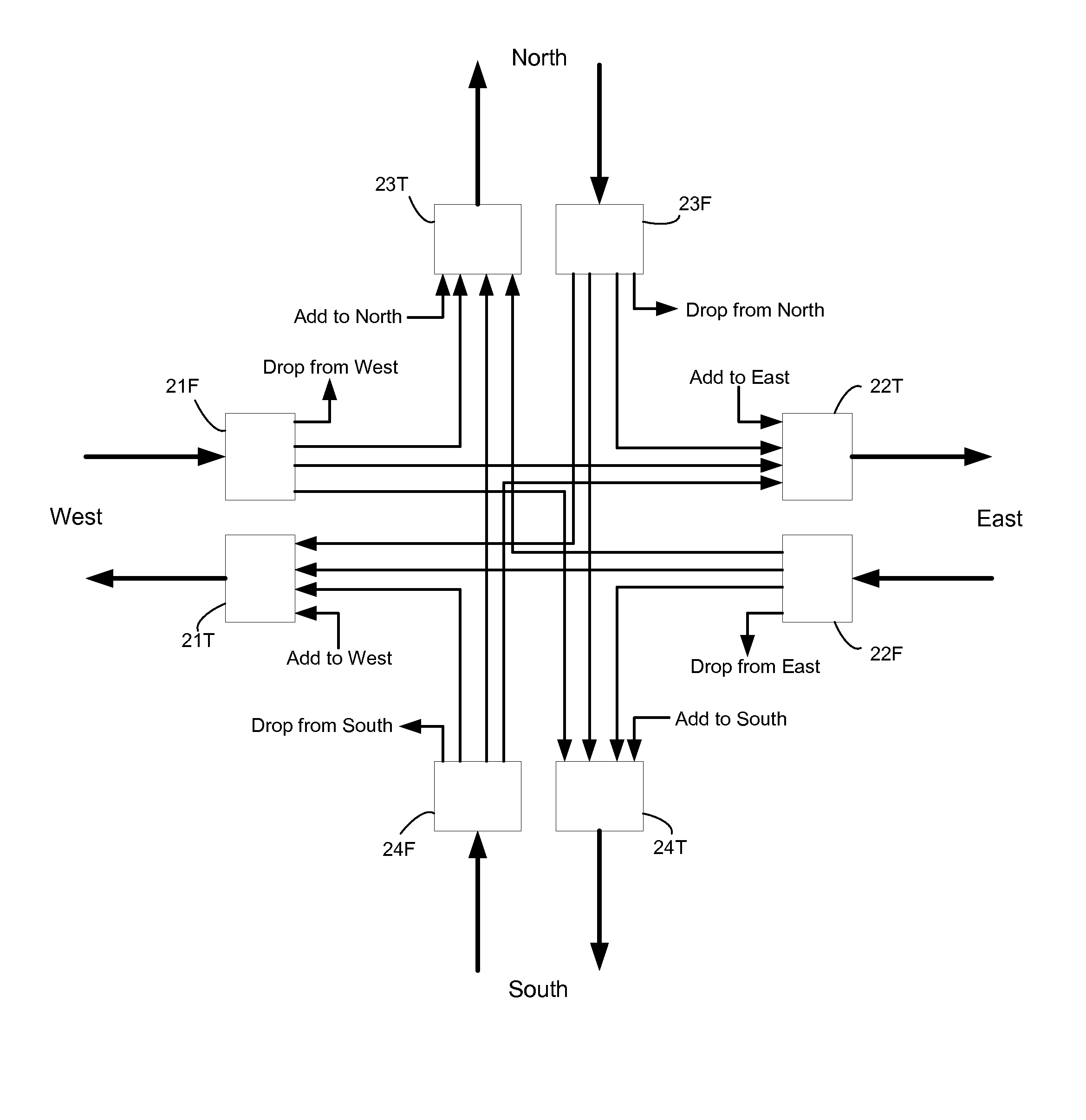
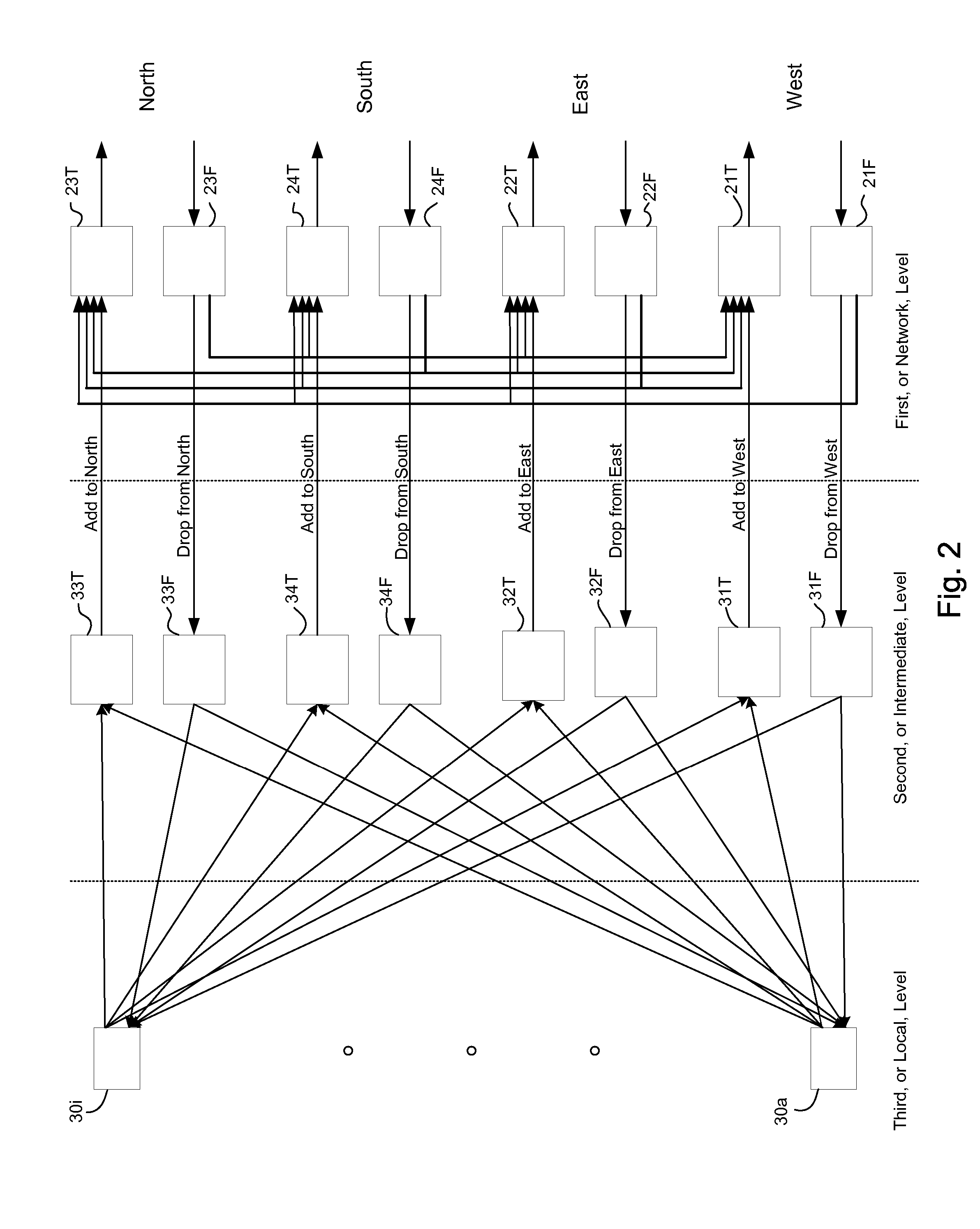
Switching architectures for WDM mesh and ring network nodes are presented. In mesh networks, the switching architectures have multiple levels - a network level having wavelength routers for add, drop and pass-through functions, an intermediate level having device units which handle add and drop signals, and a local level having port units for receiving signals dropped from the network and transmitting signals to be added to the network. The intermediate level device units are selected and arranged for performance and cost considerations. The multilevel architecture also permits the design of reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexers for ring network nodes, the easy expansion of ring networks into mesh networks, and the accommodation of protection mechanisms in ring networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optimized reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer architecture with MEMS-based attenuation or power management
ActiveUS7263253B2Improve featuresAccurate and stable alignmentCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic network arrangementsElectronic feedbackFeedback control
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
Multifunctional and reconfigurable opticalnode and optical network
InactiveUS20080013953A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveReconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer
An optical node includes a reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM) core configured to transmit optical signals of multiple-wavelengths to and receive optical signals of multiple-wavelengths from another optical node via a network interface, and to add optical signals thereto and to drop optical signals therefrom. The node also includes two of a colorless optical add / drop device, a colored optical add / drop device, and a spur optical device configured to receive signals from the network interface and output the received signals from a spur interface, to add signals that are output from the spur interface without passing through the network interface, to receive signals from the spur interface and transmit the received signals to the ROADM core and the network interface, and to receive signals from the spur interface and drop the received signals without passing through the network interface.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
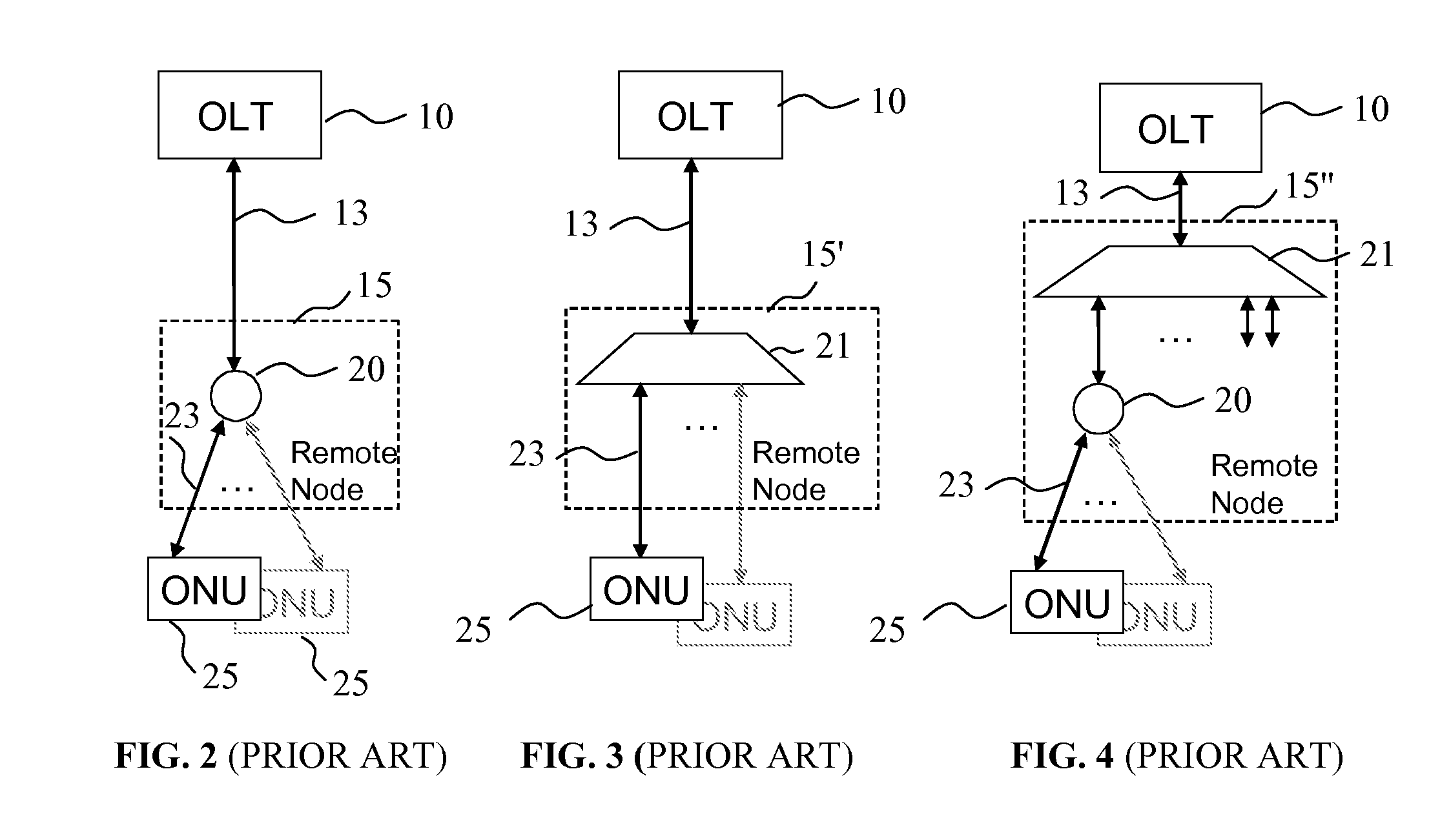
Wavelength reconfigurable optical network
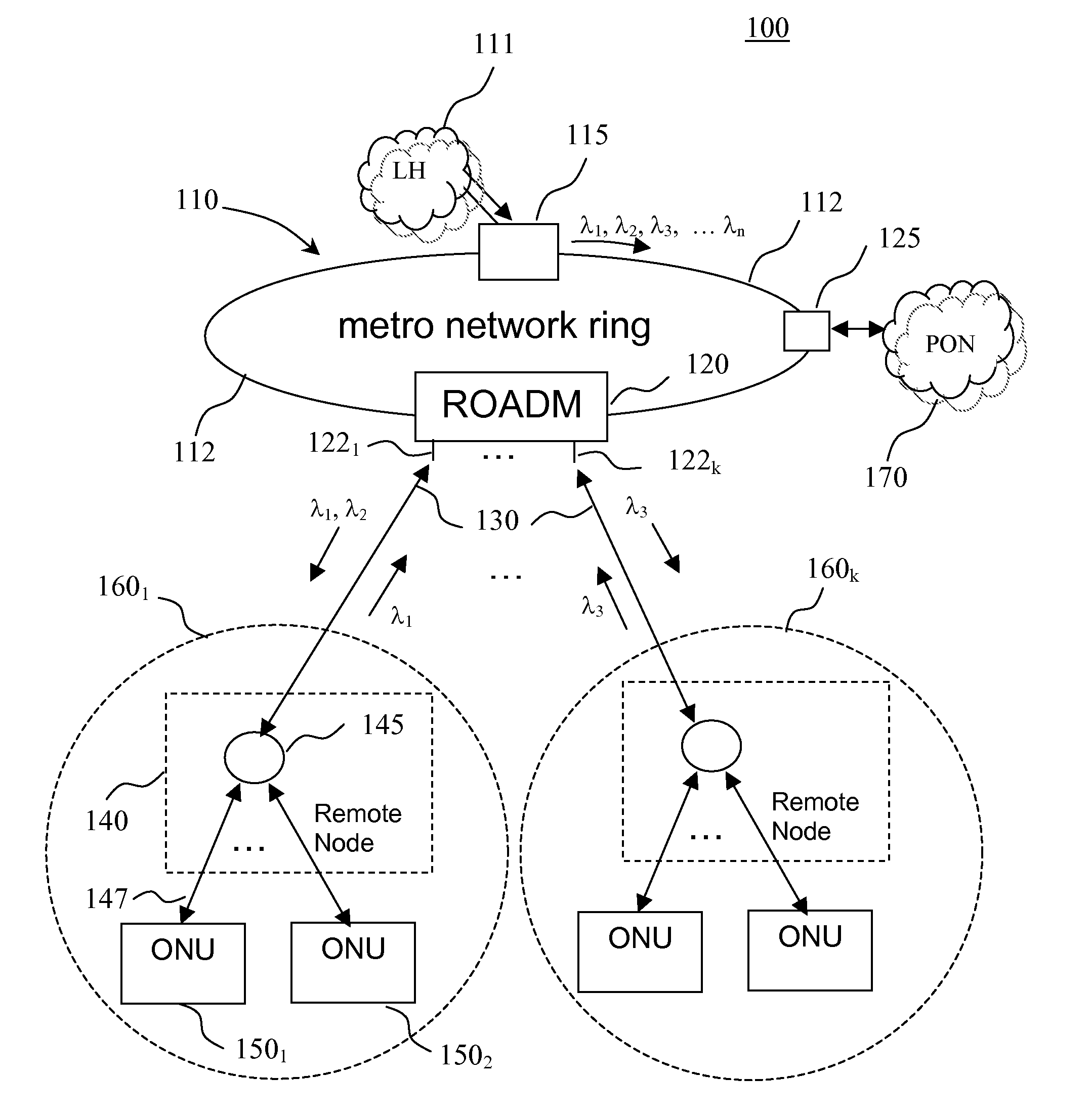
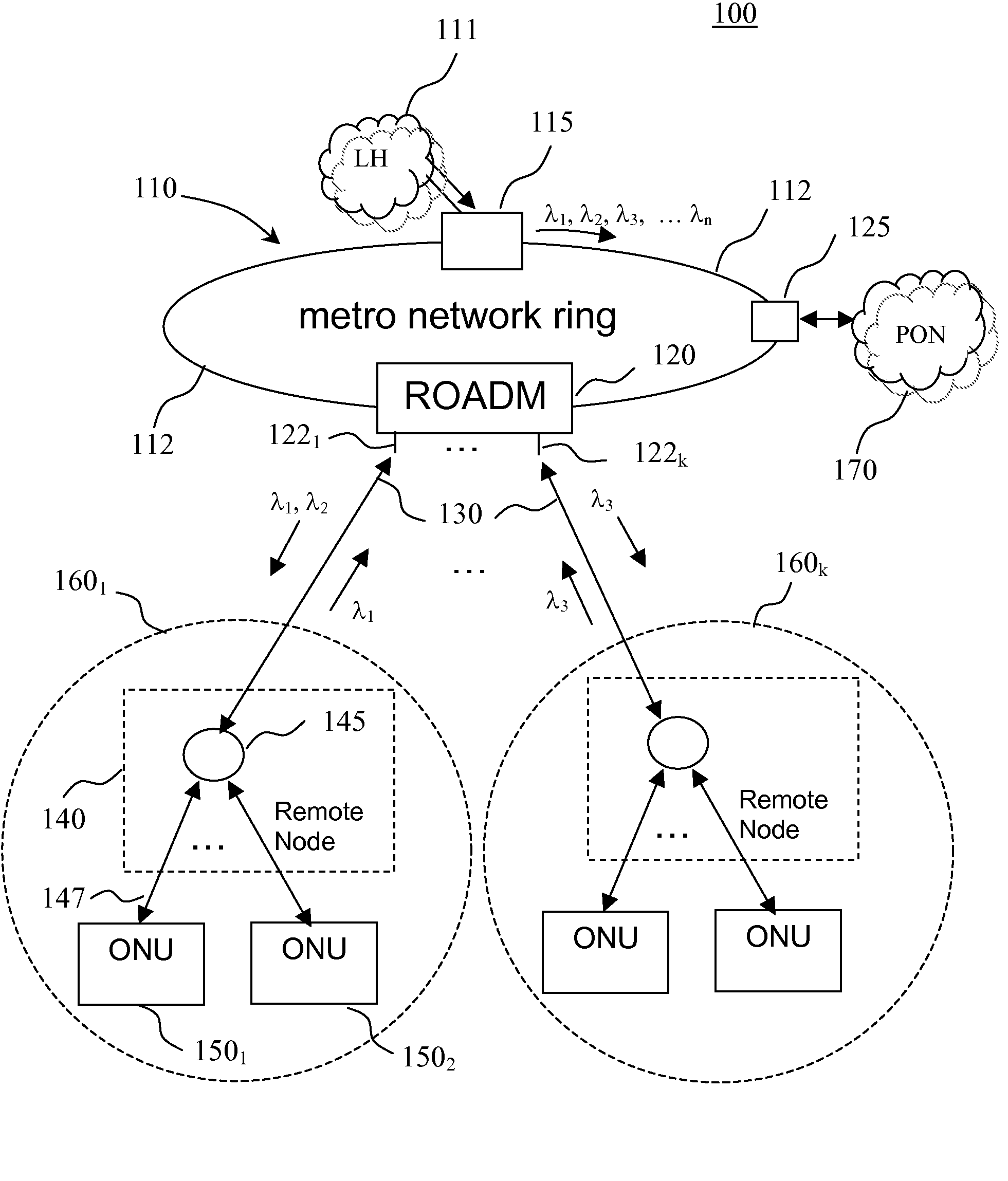
The invention provides a unified optical network architecture for metro and access communication networks, wherein a metro ring network interfaces access PONs through one or more reconfigurable Optical Add / Drop Multiplexers to provide wavelength-reconfigurable all-optical transmission of communication signals from the metro ring network to designated optical network units associated with the end-users, and wherein one metro hub located in the metro ring network is utilized to set transmission wavelengths and timing for both downstream and upstream signal transmission for multiple access PONs.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Multifunctional and reconfigurable optical node and optical network
ActiveUS8190027B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringLight signal
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Methods and apparatus for performing directionless wavelength addition and subtraction within a ROADM based optical node
ActiveUS8165468B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching by path configurationComputer networkMultiplexer
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Methods and apparatus for performing directionless and contentionless wavelength addition and subtraction
ActiveUS8447183B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerComputer module
In today's reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexer (ROADM) based optical node, ROADMs multiplex (and demultiplex) colored optical signals to form wavelength-division multiplexed (WDM) signals. Transponders connected to the ROADMs' add / drop ports convert noncolored optical signals to colored optical signals (and vice versa). Dedicating transponders to given ports degrades the node's ability to route around network failures. Example embodiments of the invention include an optical node and corresponding method for routing optical signals within an optical node that compensate for this inflexibility. The optical node may include two ROADMs to transmit respective WDM signals onto at least two internode network paths and a routing module that can direct channels of the same wavelength along different internode network paths. Advantageously, a transponder may transmit (receive) different signals at the same wavelength to (from) different network node interfaces within the optical node, thereby improving the optical node's ability to route around network failures.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Systems and methods for adaptive gain control to compensate OSNR penalty caused by side-lobe of MEMS-based reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexers
ActiveUS7826748B2Solves OSNR penaltyThe right amountWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
Owner:CIENA
Reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer structure for realizing 16 channels with multiple orders
InactiveCN101552648AImprove response rateReduce the difficulty of temperature controlWavelength-division multiplex systemsTemperature controlFrequency spectrum
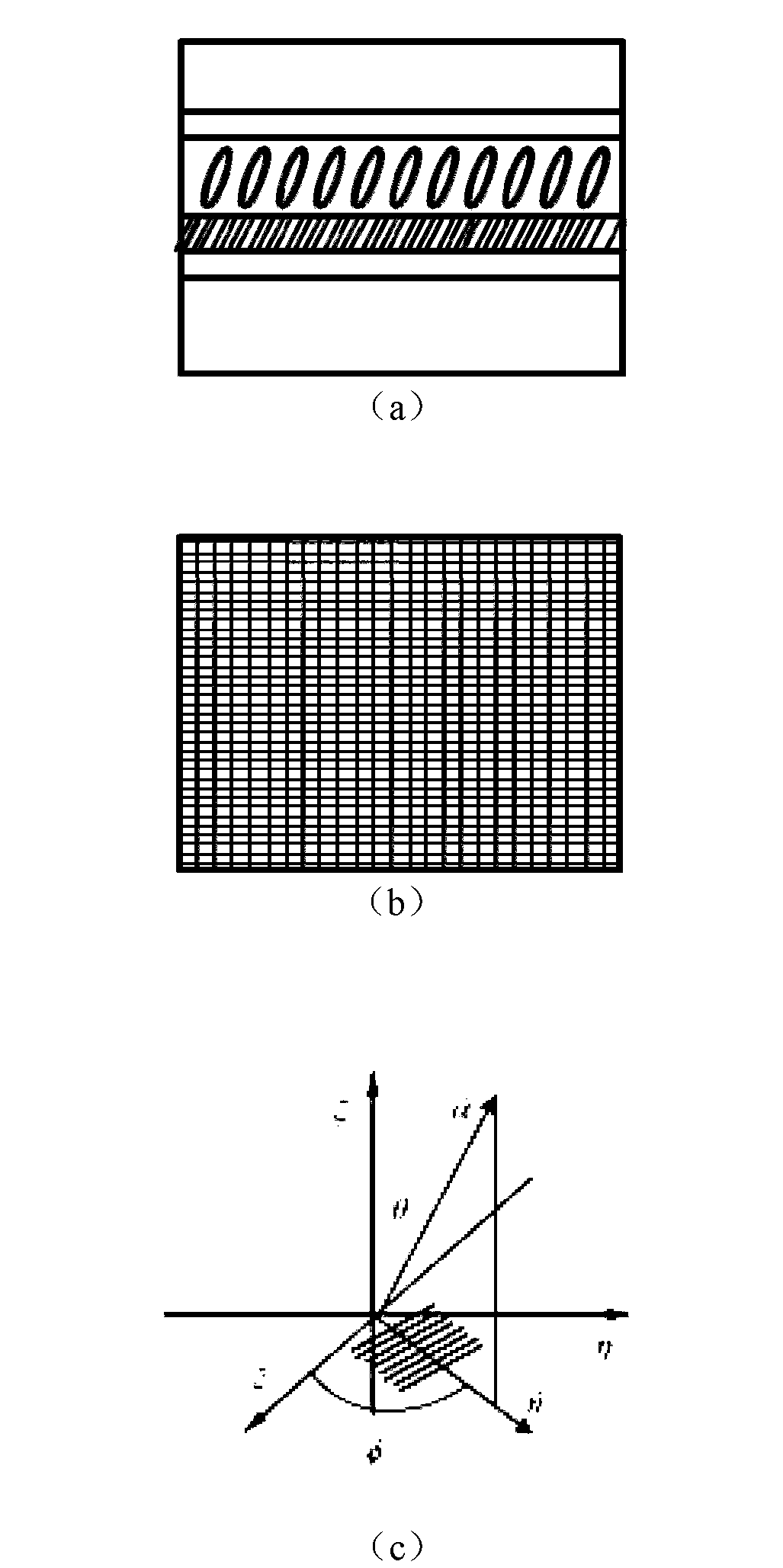
The invention discloses a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (an ROADM structure) for realizing 16 channels with multiple orders. The ROADM structure comprises an input part, a first-order filtration area, a second-order filtration area, a local download area, a combiner and an output part which are connected through nanometer wire waveguides. The ROADM structure has a certain width by utilizing the free spectral width of a micro-ring resonator and filters a plurality of paths of incident wavelengths with respective orders so as to ensure that the wavelength number in each download waveguide is reduced progressively and finally realize the single wavelength download in each output port, thereby reducing the temperature control difficulty and improving the response speed of devices.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Realization method and system of optical label
InactiveCN102195739ALower requirementEasy extractionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsLength waveComputer science
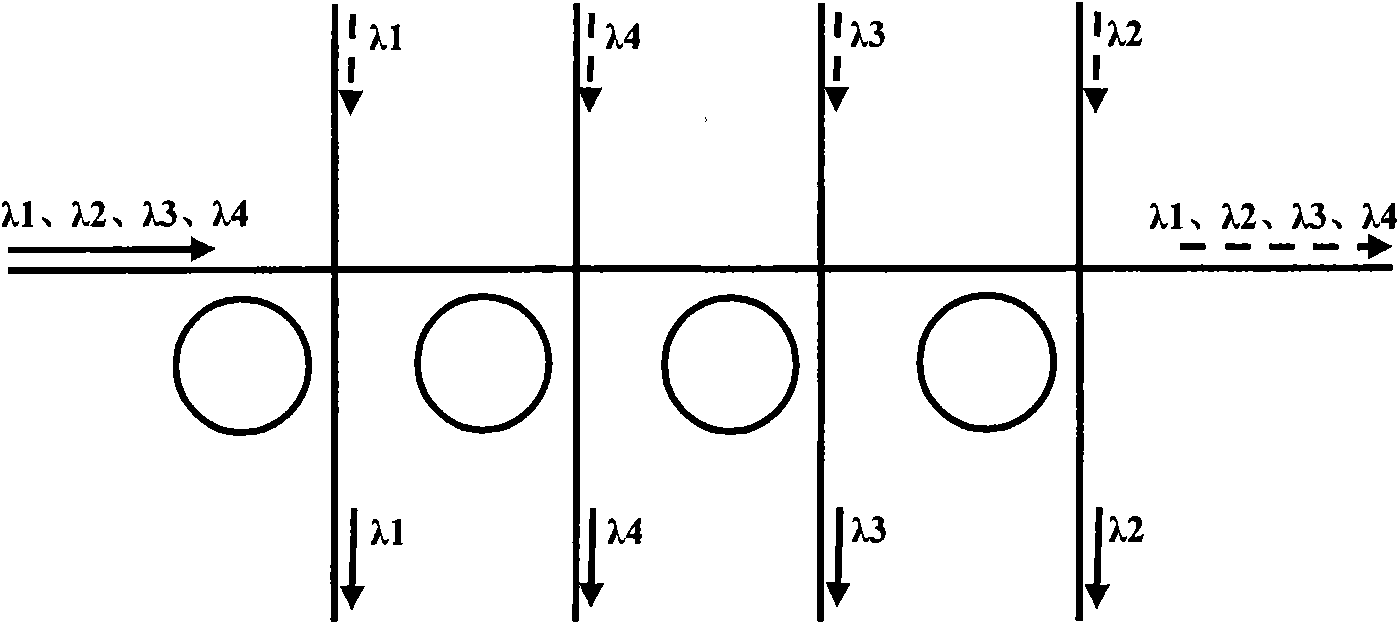
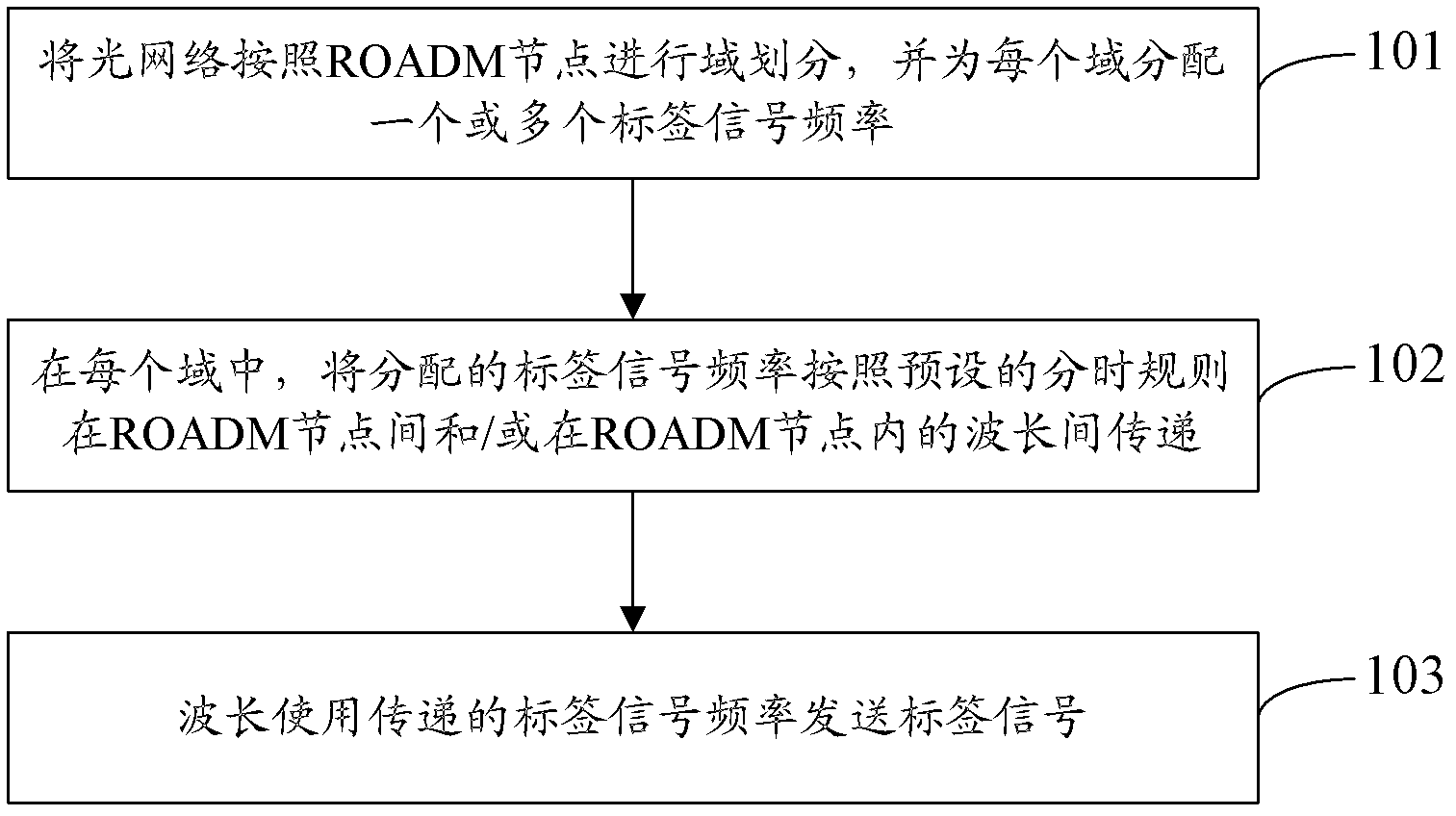
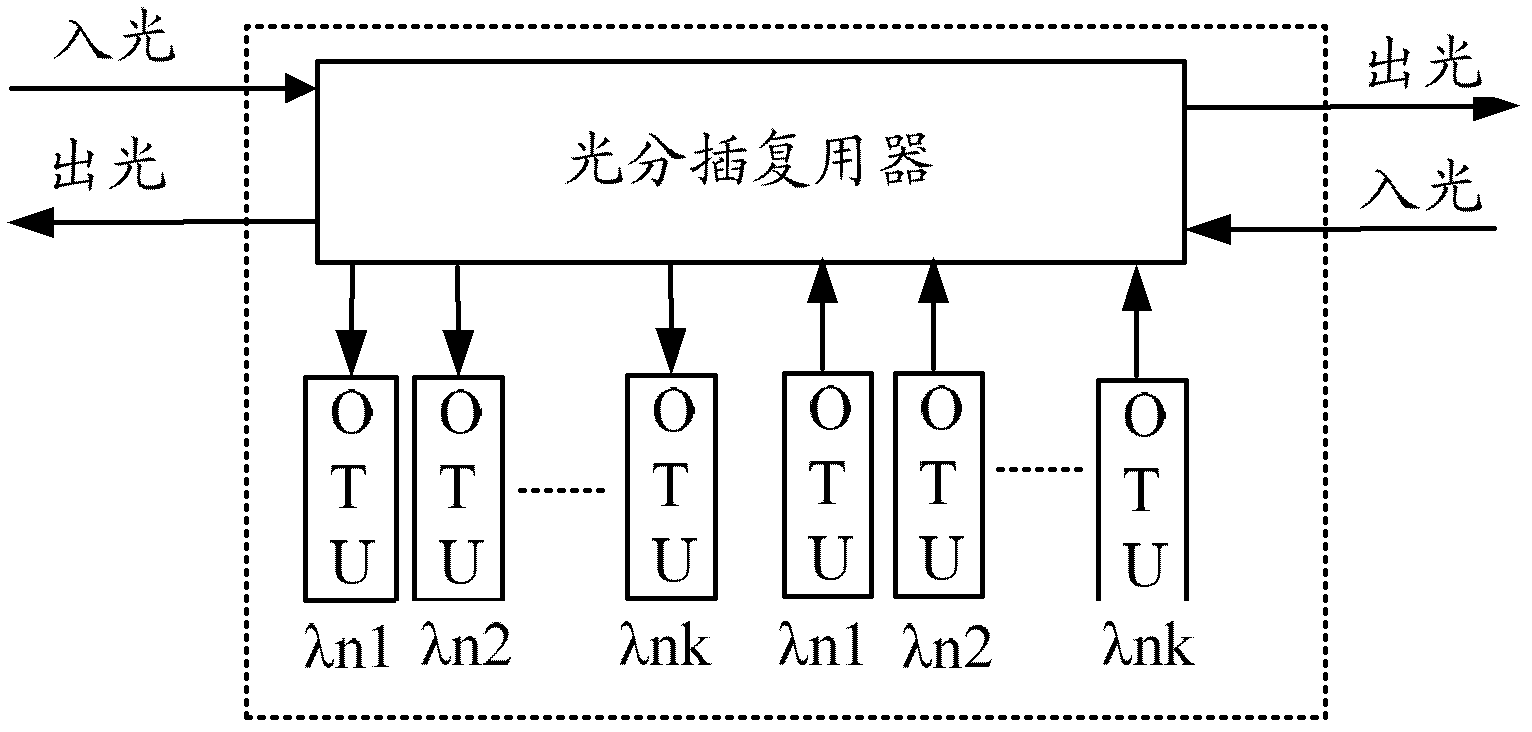
The invention discloses a realization method of an optical label, and the realization method comprises the following steps: carrying out the domain division of an optical network according to the nodes of an ROADM (reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer) and distributing one or multiple label signal frequencies for each domain; transferring the distributed label signal frequencies among the nodes of the ROADM and / or among the wavelengths in the nodes of the ROADM according to the preset time division rule in each domain; and transmitting label signals according to the label signal frequencies used by the wavelengths to transfer. The invention also discloses a realization system of the optical label. The scheme in the invention realizes the purpose of transmitting the label signals which have the multiple numbers of the wavelengths, reduces the requirements of the system on the label frequencies and is beneficial to the extraction of the label signals through fewer label signal frequencies.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Directionless reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer systems and methods
ActiveUS8625994B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerEngineering
The present invention provides a directionless reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexer (ROADM) system. The present invention provides a scalable all-optical switching element that includes a combination of 1×N wavelength selective switches (WSS), 1×N splitters / combiners, optical amplifiers, and tunable filters to provide a fully non-blocking solution which can be deployed in a scalable manner. The 1×N splitters are configured to split multiples copies of a plurality of drop wavelengths which can be amplified and sent to a tunable filter which selects out a particular wavelength for drop. The 1×N combiners are configured to combine multiple add wavelengths for egress transmission.
Owner:CIENA
Optical network node device
InactiveUS20080131130A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionWavelength
Provided is an optical network node device. According to the optical network node device, a planar lightwave circuit (PLC) based or a blocker based 4-terminals ROADM can be used in a node of at least degree 3, a proceeding direction of a wavelength channel can be changed in an electrical cross connect switch, and transmission in a unit smaller than a wavelength channel can be cross connected, dropped, and added, or transmission capacity can be redistributed in the electrical cross connect switch. Accordingly, efficient transmission in a small capacity and large capacity transmission of a wavelength channel can be performed simultaneously, and thus an optical network can be effectively managed. Also, since the node of at least degree 3 uses the PLC based or a blocker based reconfigurable optical add drop multiplexer (ROADM), the node of at least degree 3 can use the same ROADM module as a node of degree 2. Accordingly, the optical network node device has an advantage in manufacturing and managing a node.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com