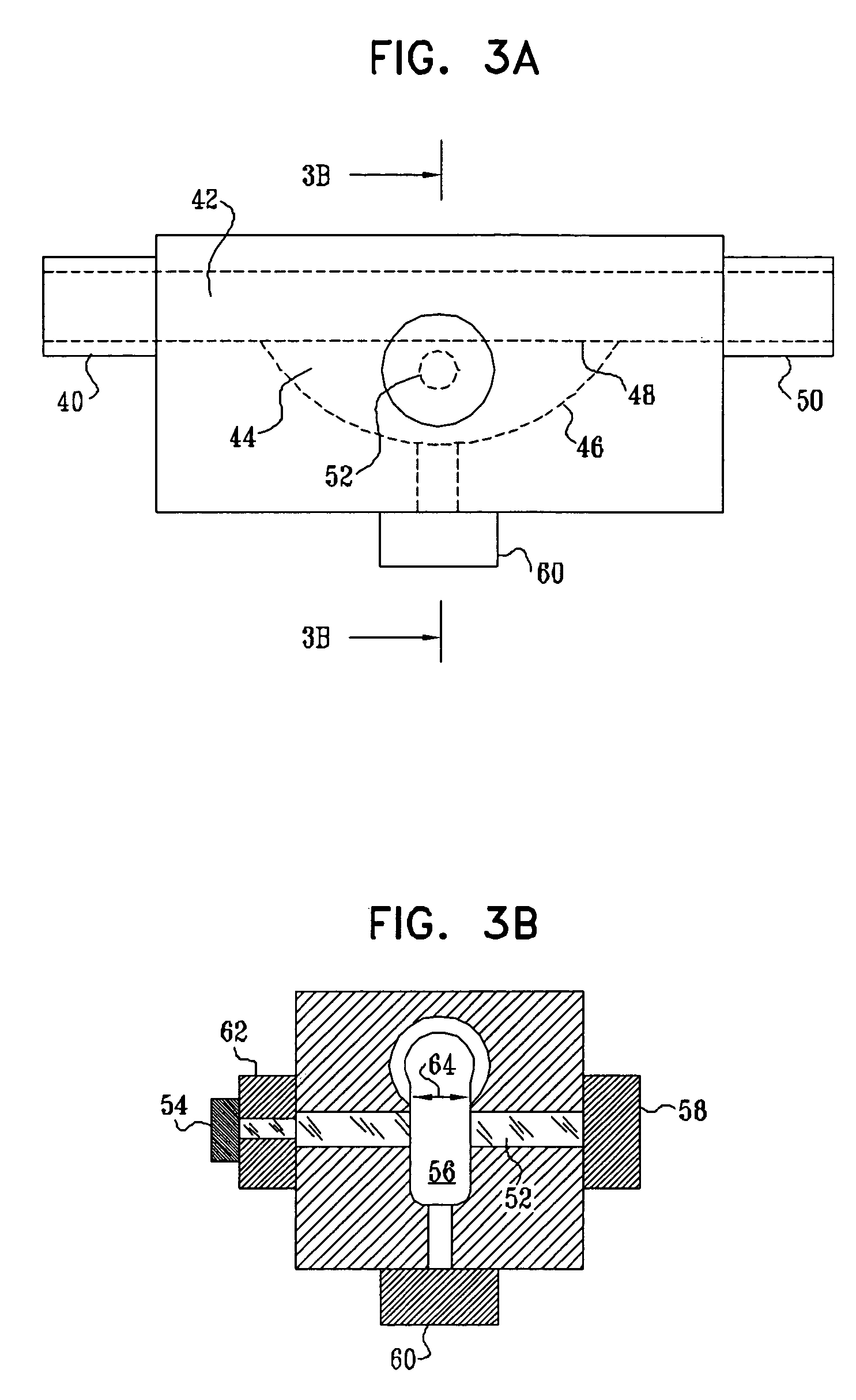
Patents
Literature
446 results about "Spectral width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
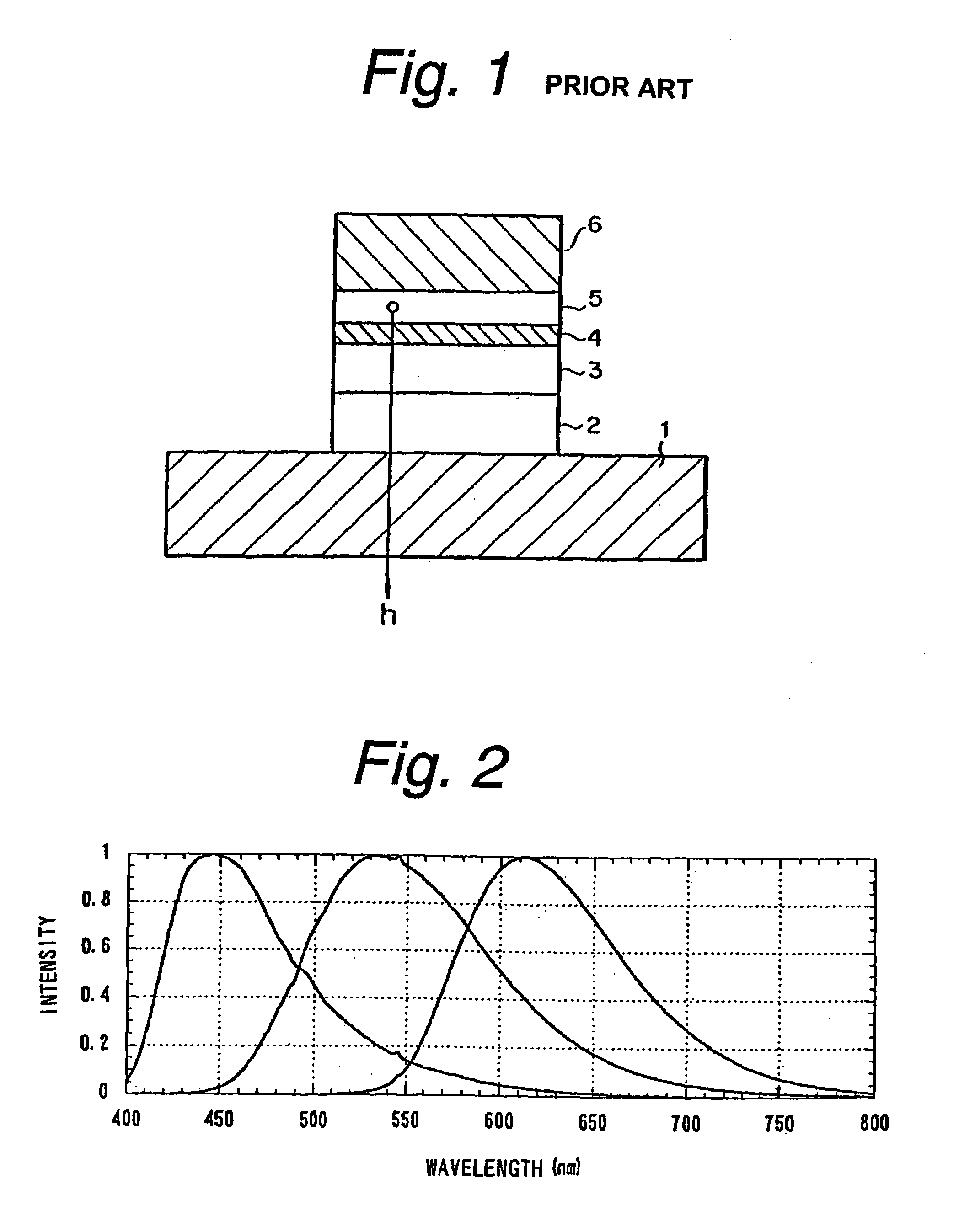
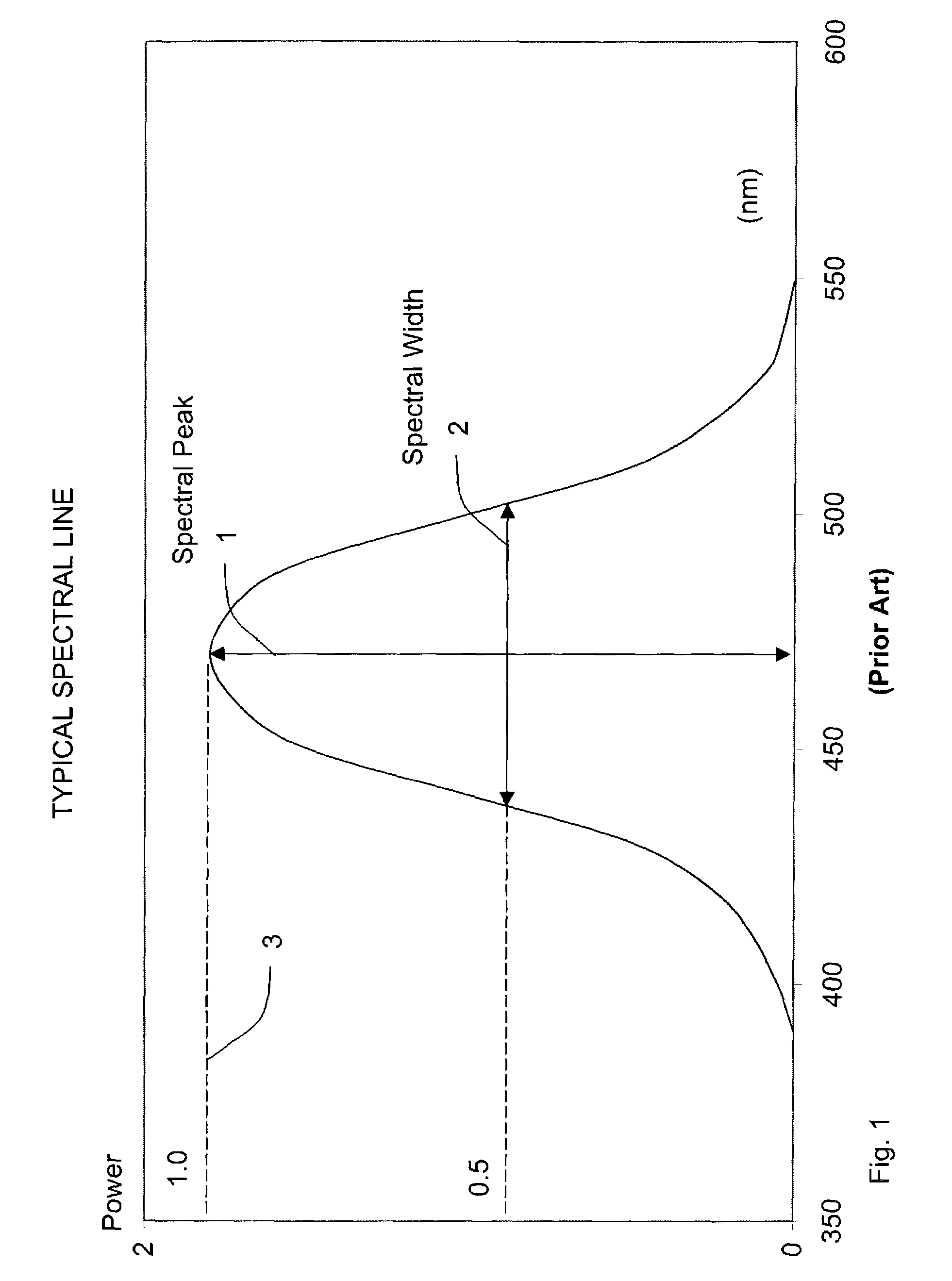
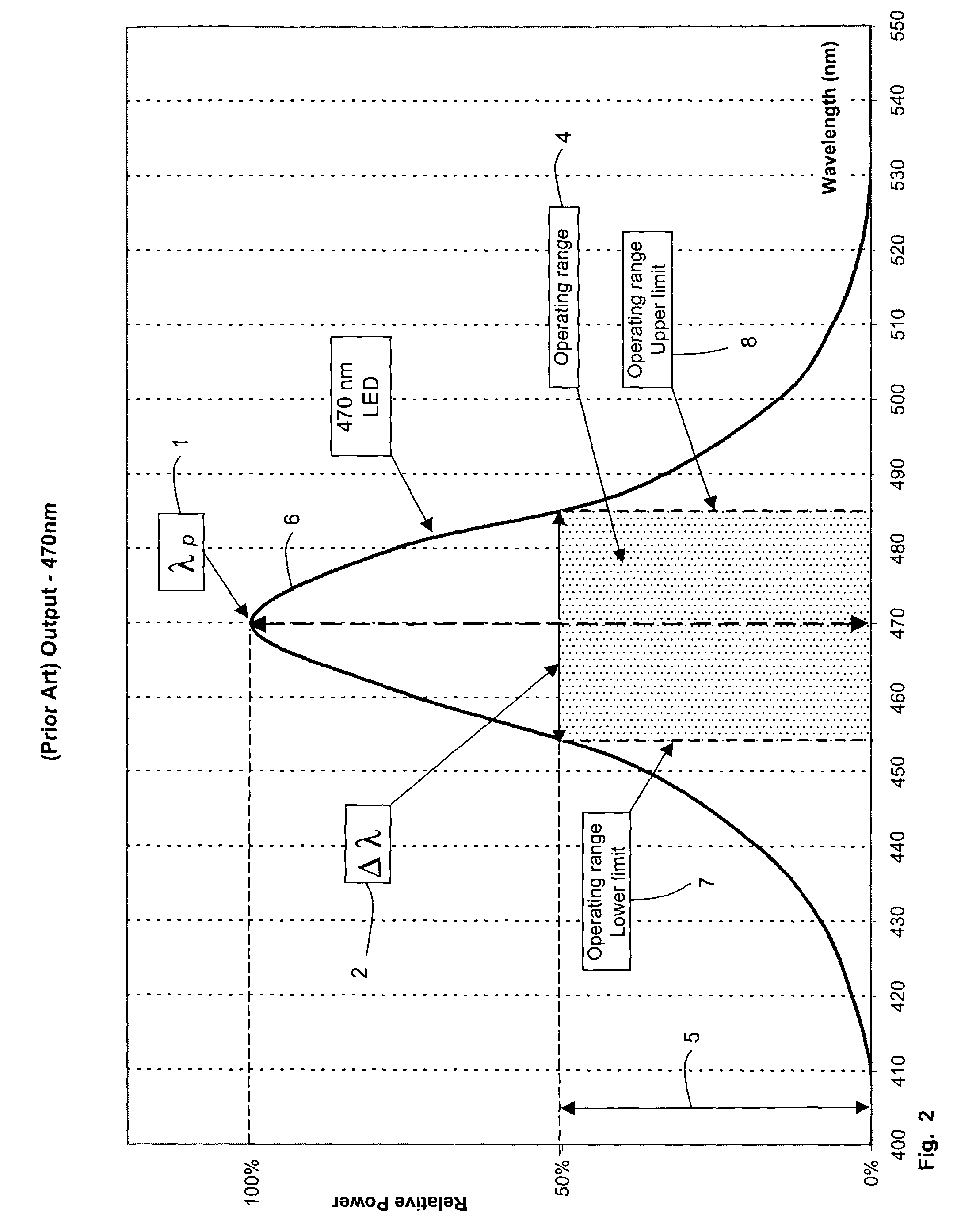
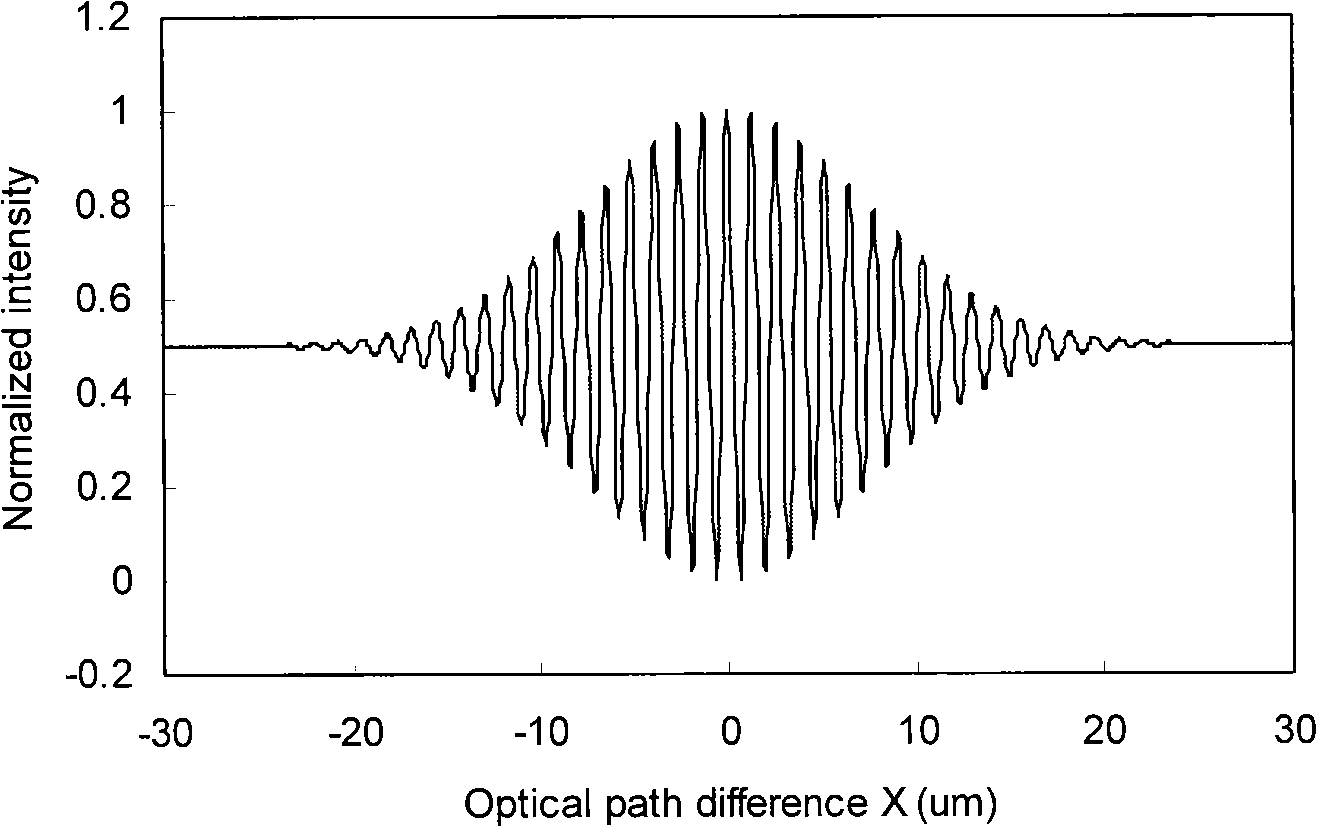
In telecommunications, spectral width is the wavelength interval over which the magnitude of all spectral components is equal to or greater than a specified fraction of the magnitude of the component having the maximum value.
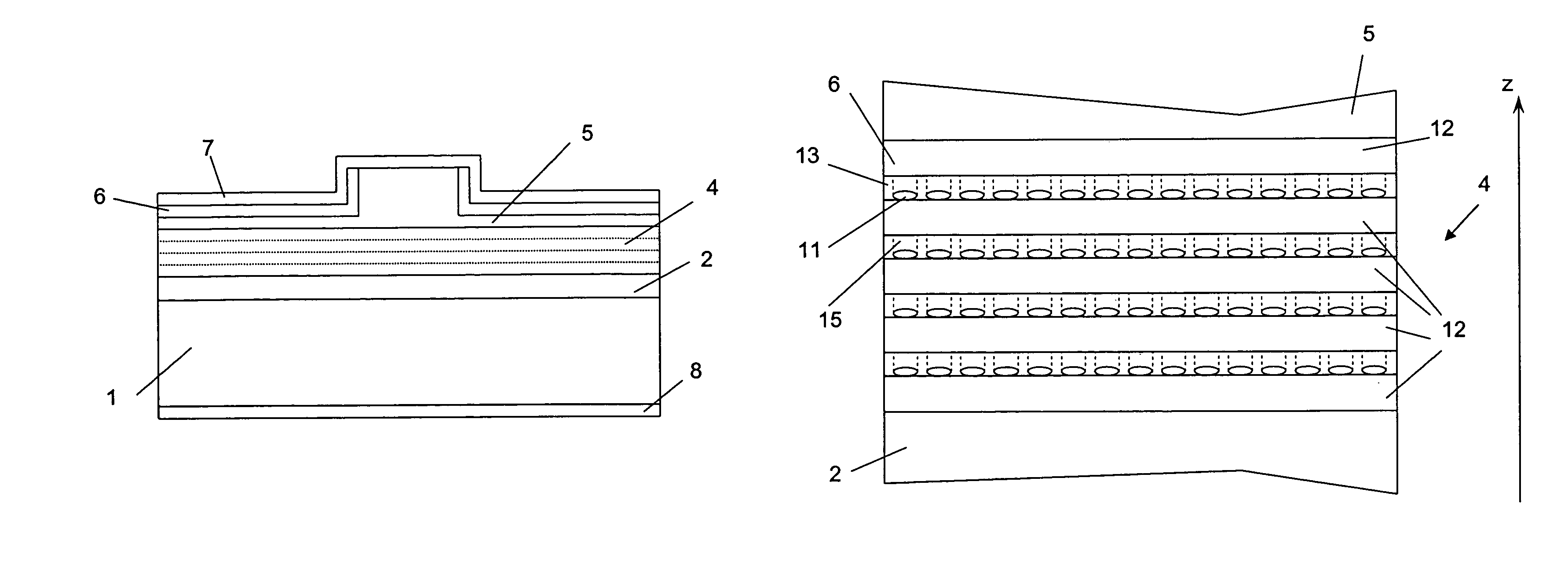
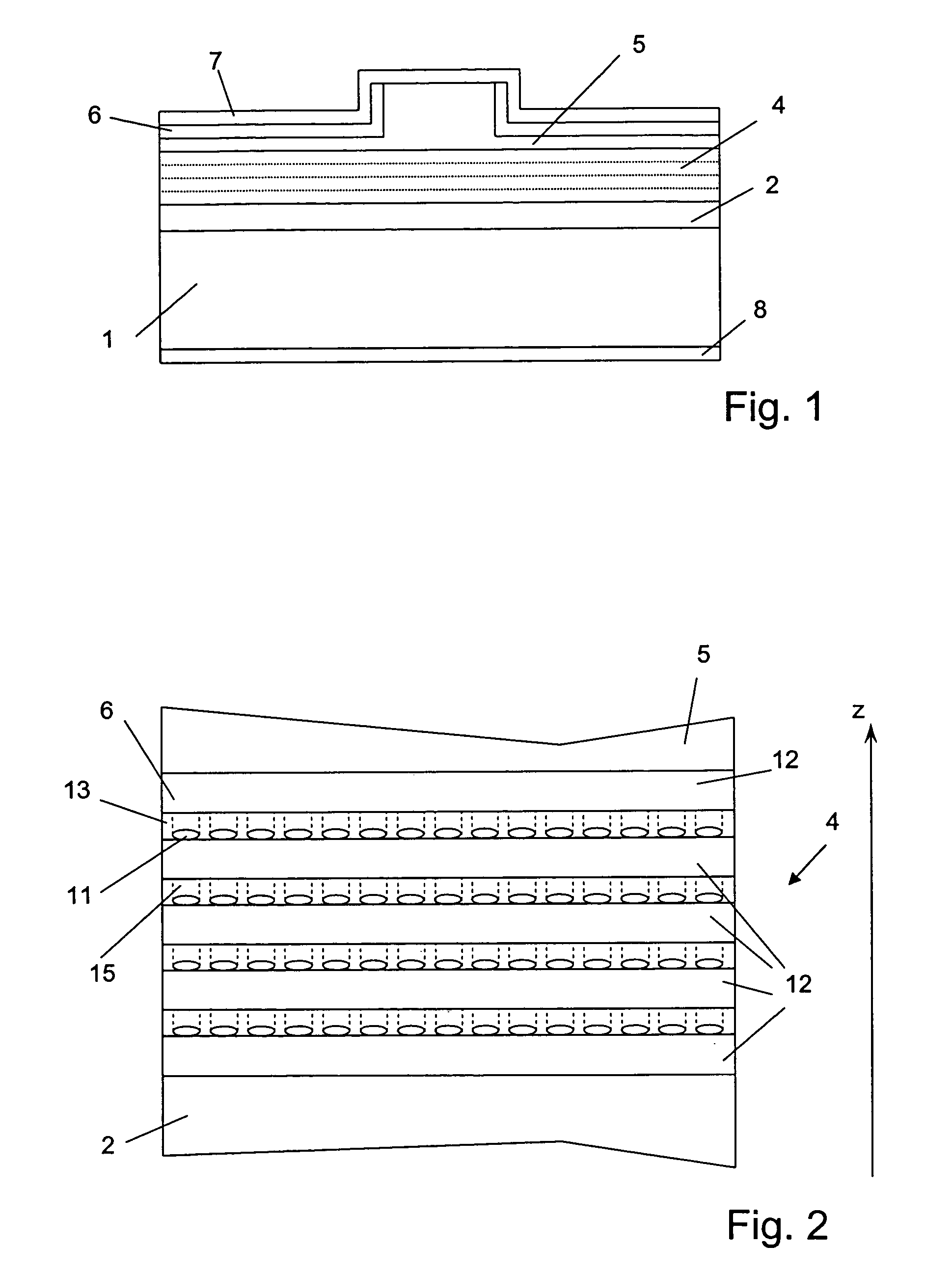
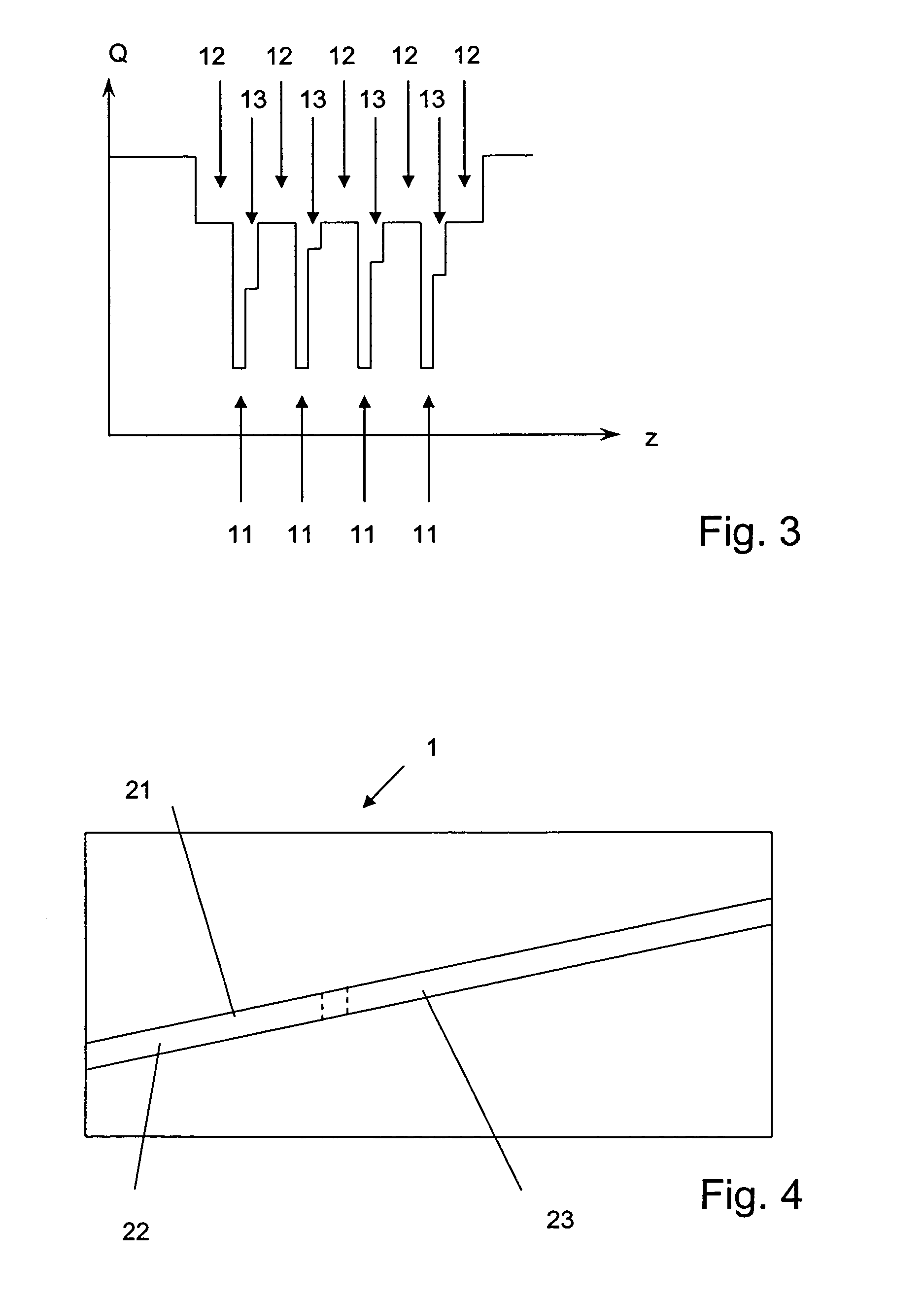
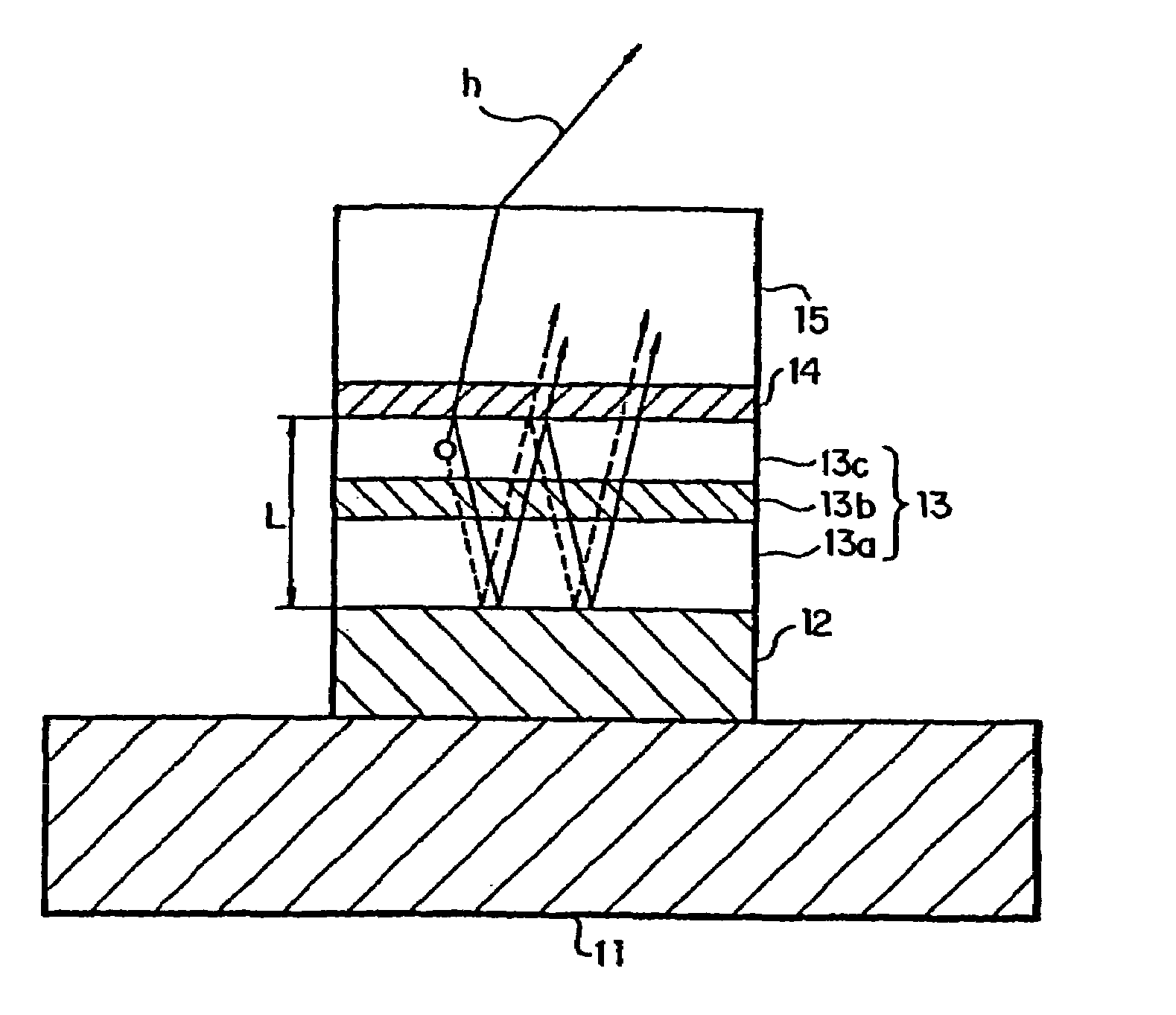
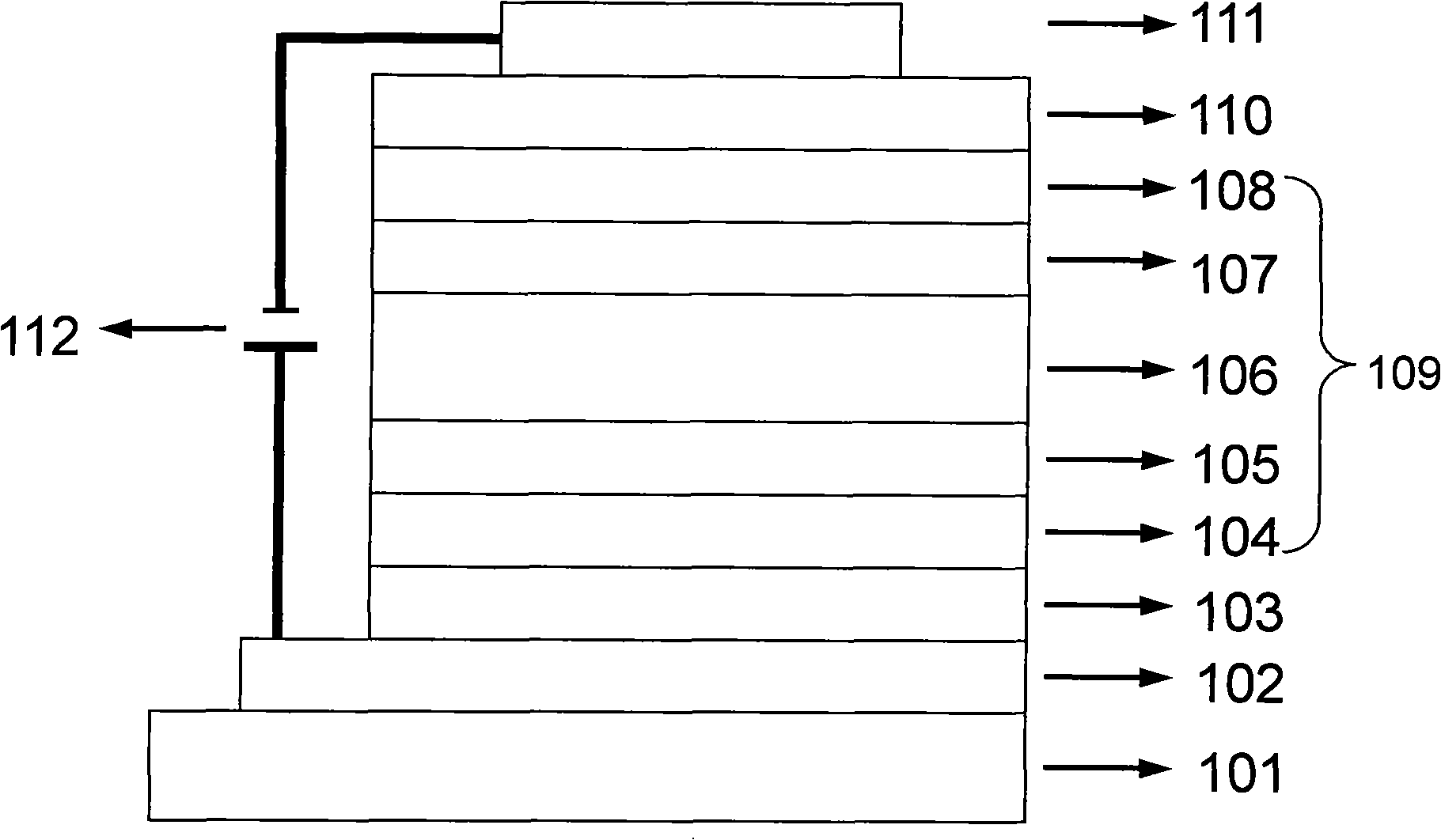
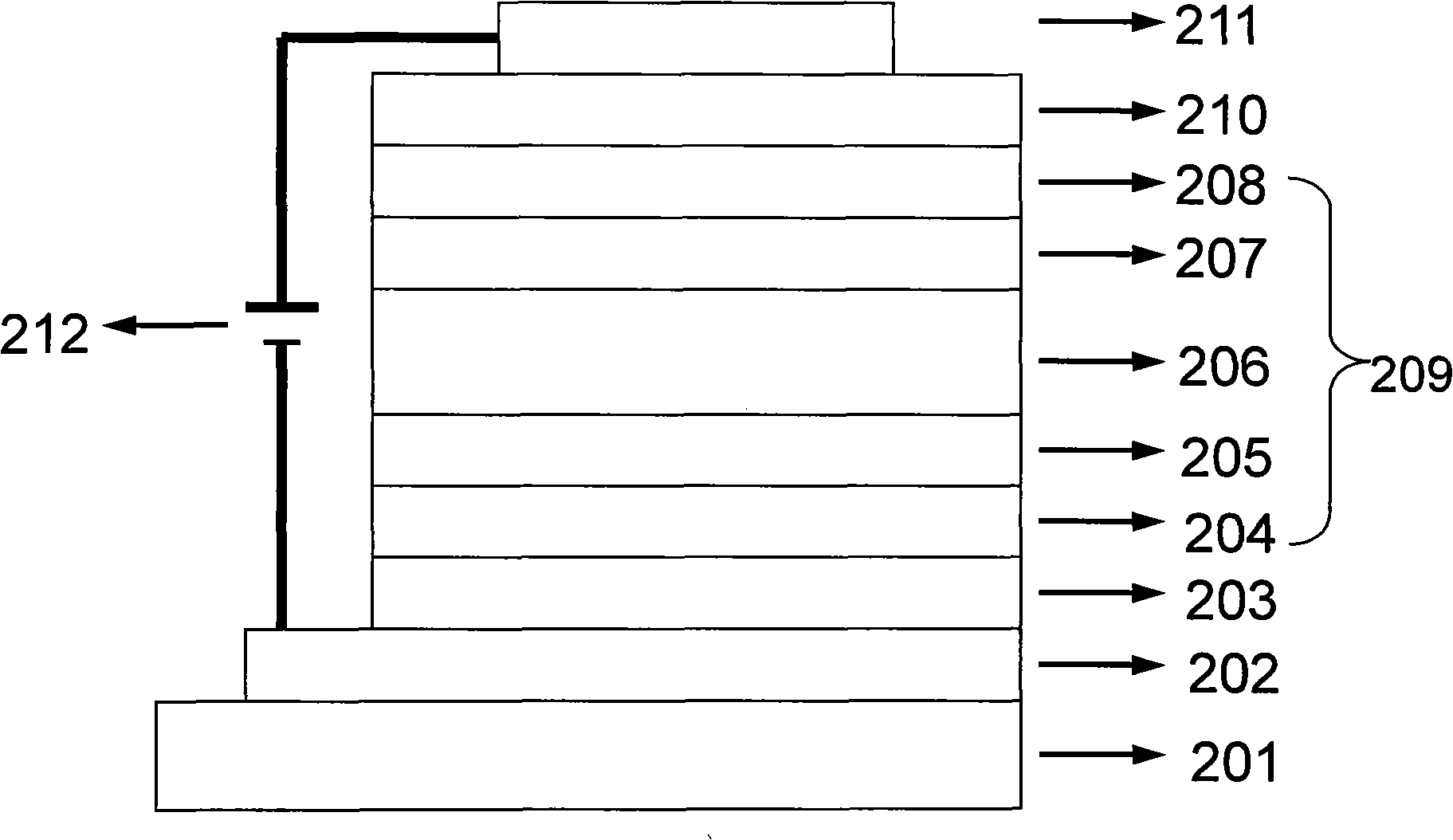
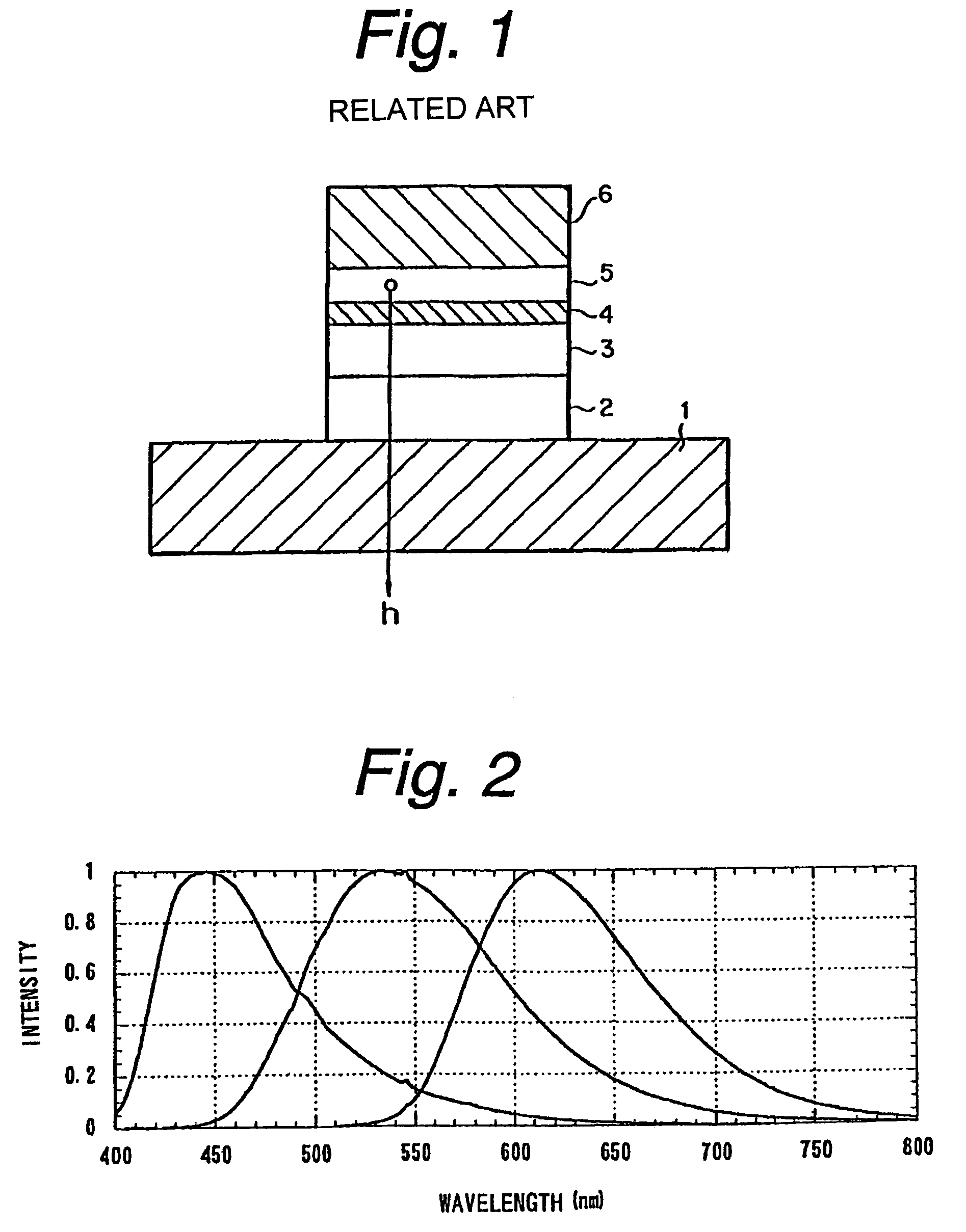
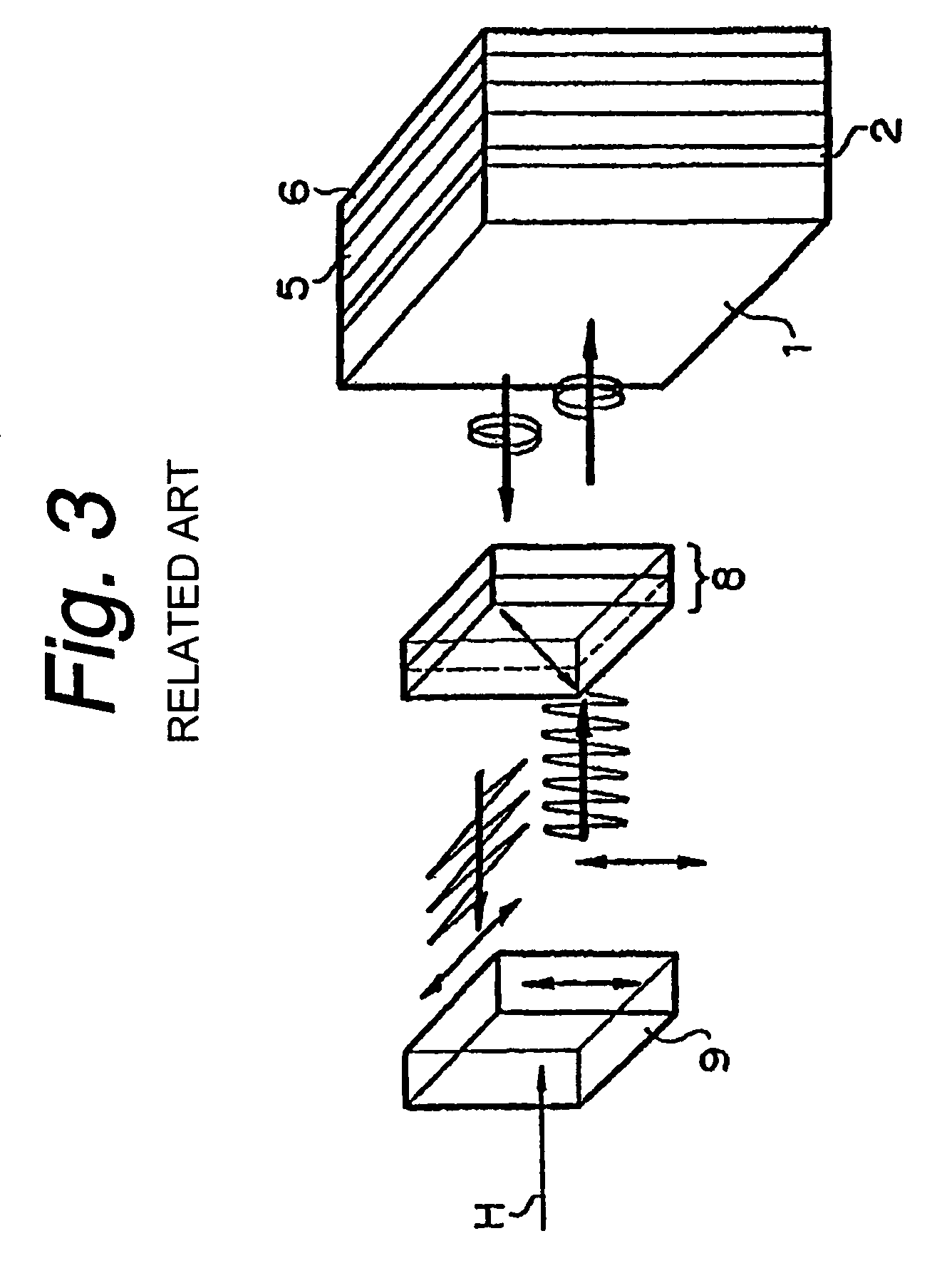
Broadband light emitting device
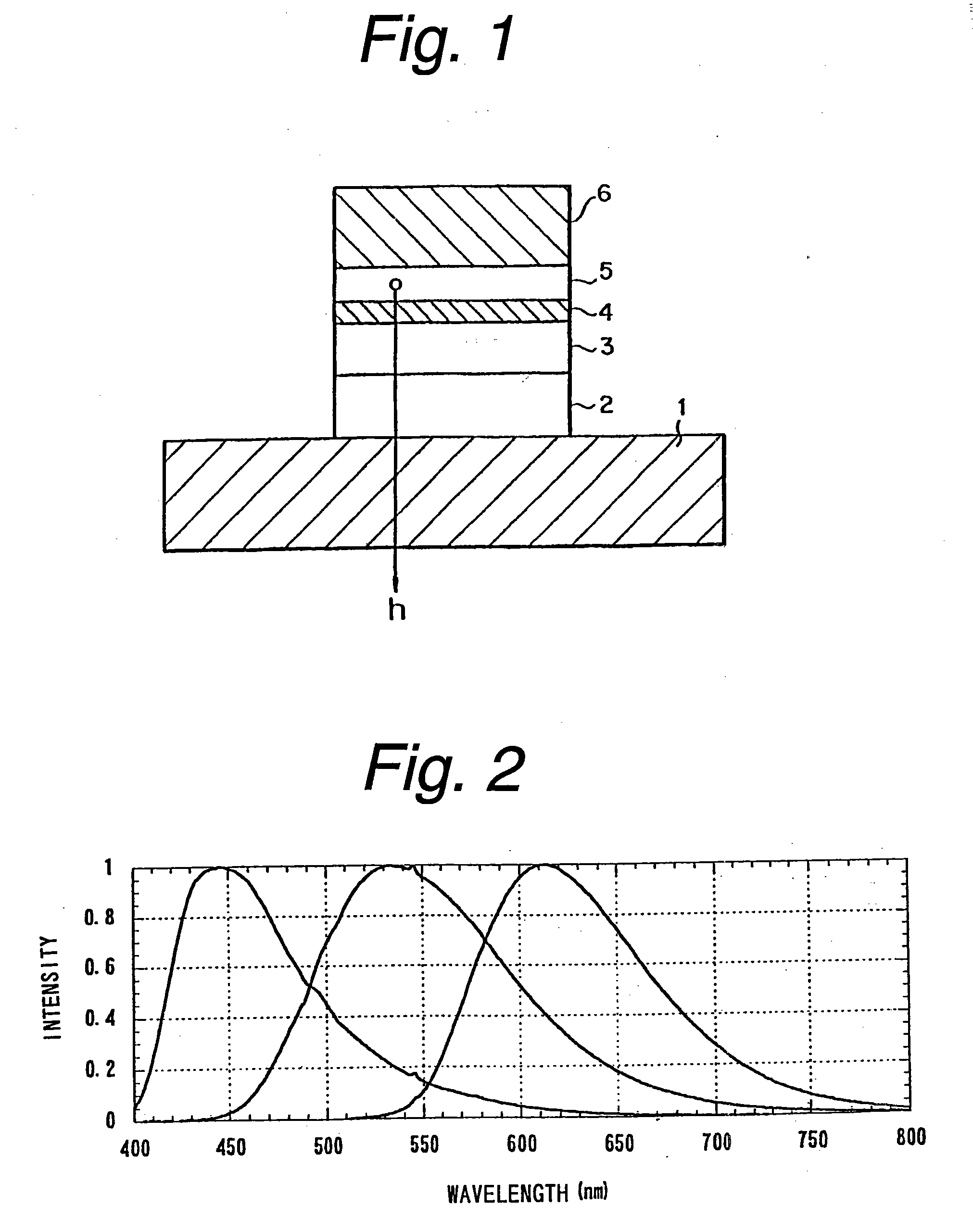
ActiveUS7019325B2Increase heightBroad emission spectrumLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionStimulated emissionP–n junction
The invention concerns a superluminescent light emitting diode (SLED) comprising a semiconductor heterostructure forming a PN junction and a waveguide. The semiconductor heterostructure includes a gain region with a contact means for biasing the PN junction so as to produce light emission including stimulated emission from an active zone of the gain region, and in the active zone a plurality of quantum dot layers, each quantum dot layer made up of a plurality of quantum dots and a plurality of adjoining layers, each adjoining layer adjacent to one of said quantum dot layers. The material composition or a deposition parameter of at least two adjoining layers is different. This ensures an enhanced emission spectral width.
Owner:EXALOS
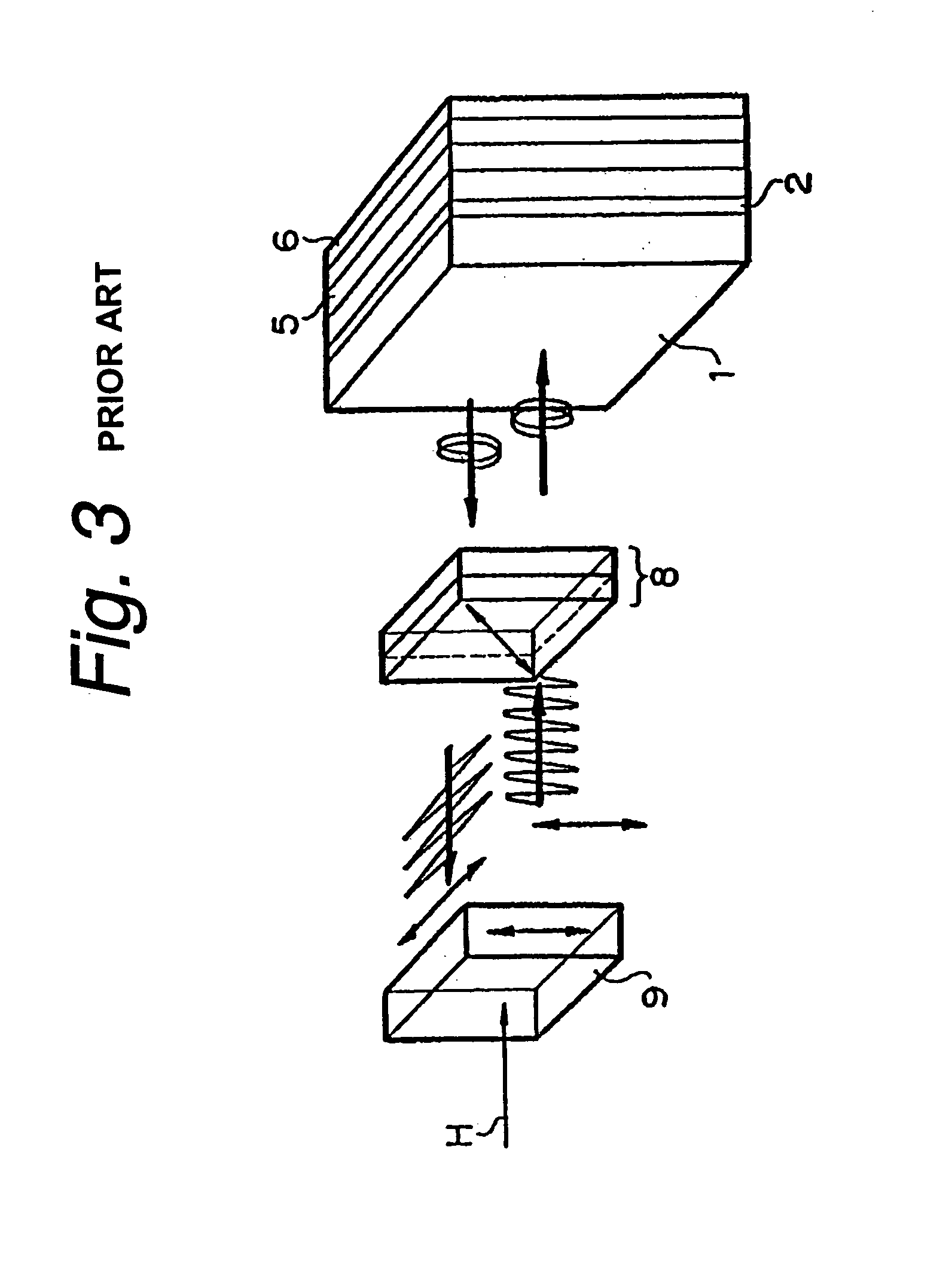
Display device with a cavity structure for resonating light
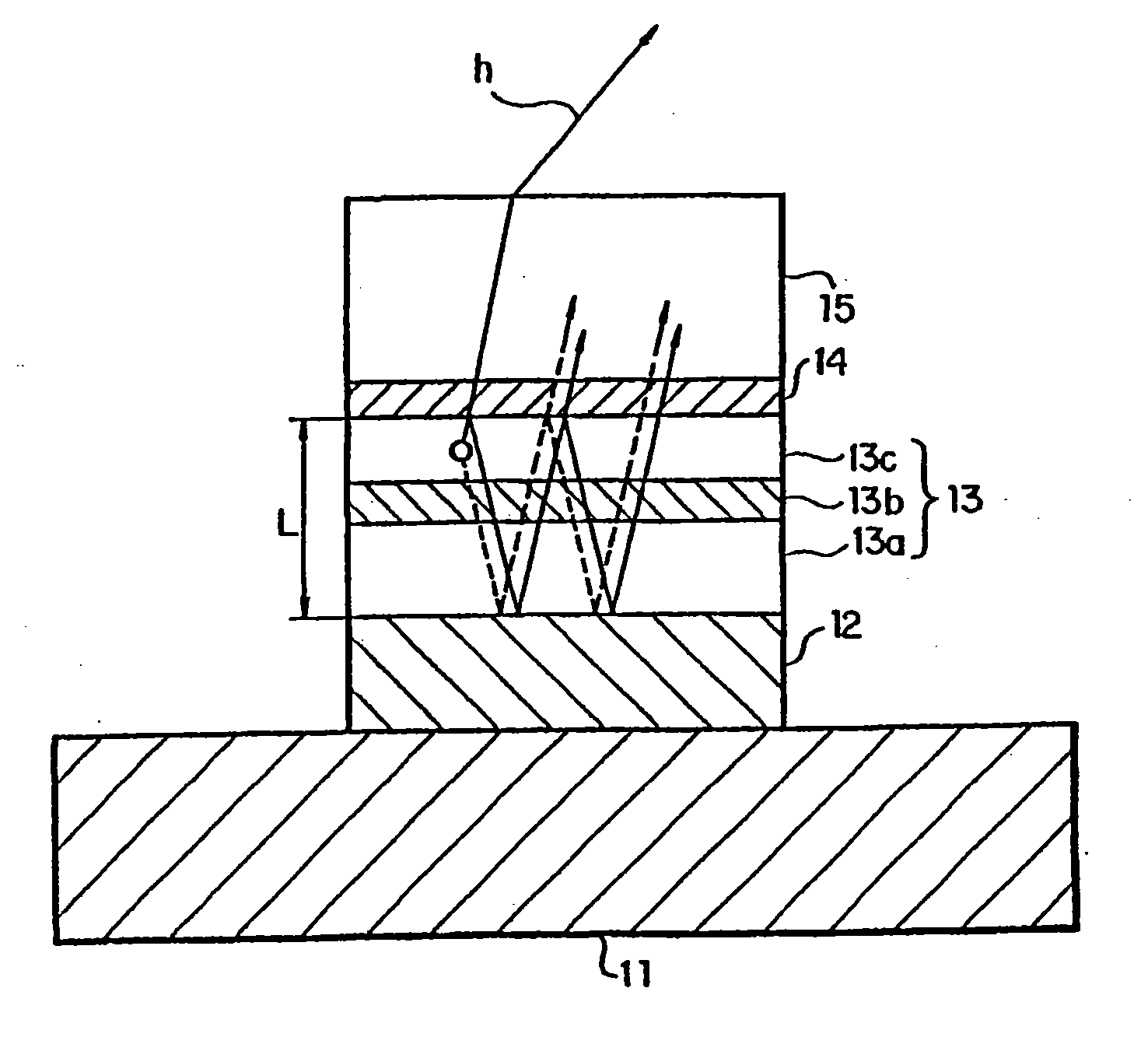
InactiveUS7102282B1Shifting amount is very smallIncreased peak intensityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSpectral widthPhase shifted
In an organic EL device having a first electrode of a light reflective material, organic layer including an organic light emitting layer, semitransparent reflection layer, and second electrode of a transparent material that are stacked sequentially, and so configured that the organic layer functions as a cavity portion of a cavity structure, light that resonates in a certain spectral width (wavelength λ) is extracted by so configuring that optical path length L becomes minimum in a range satisfying (2L) / λ+Φ(2Π)=m (m is an integer) where the phase shift produced in light generated in the organic light emitting layer when reflected by opposite ends of the cavity portion is Φ radians, L is optical path length of the cavity portion, and λ is the peak wavelength of the spectrum of part of light to be extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
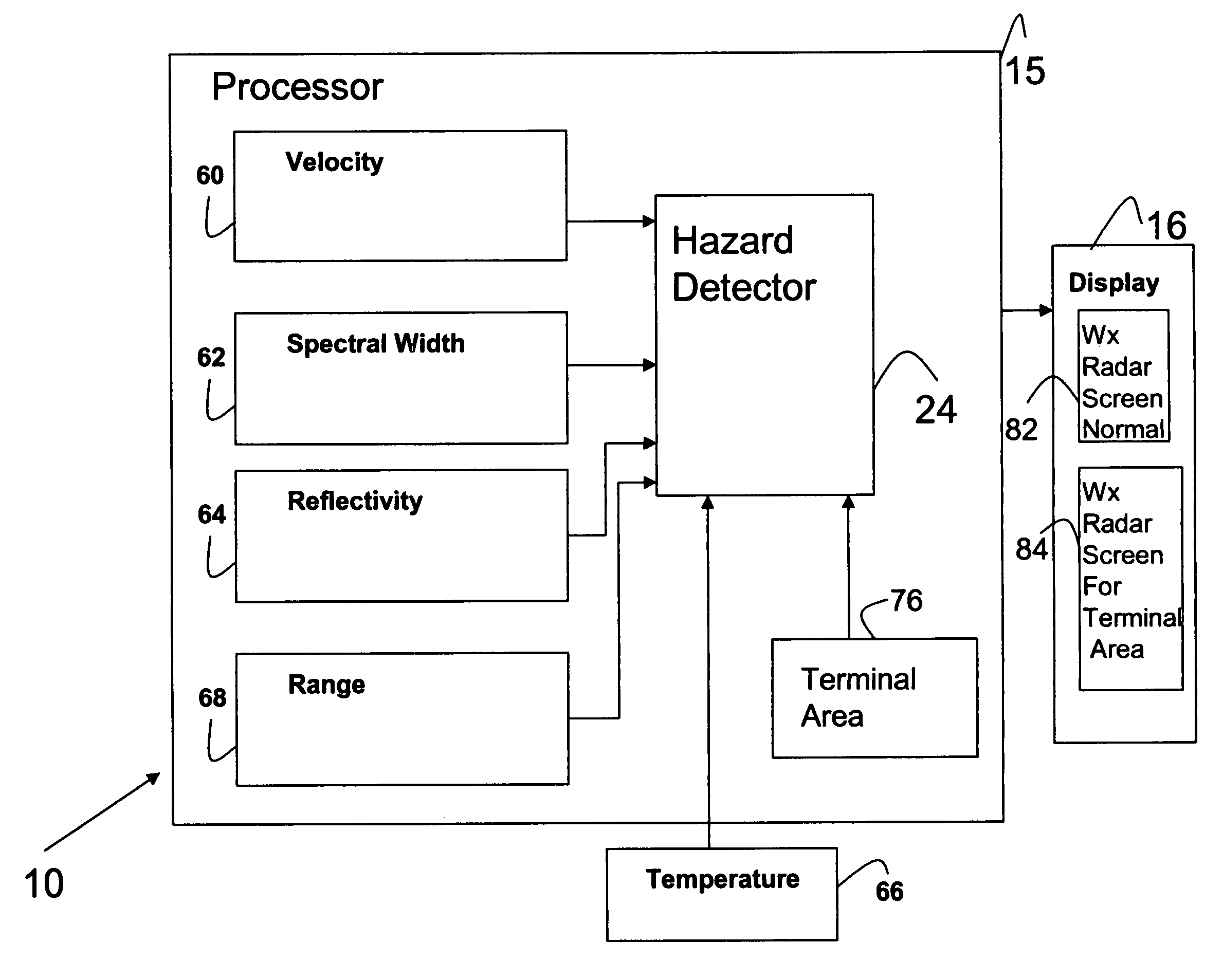
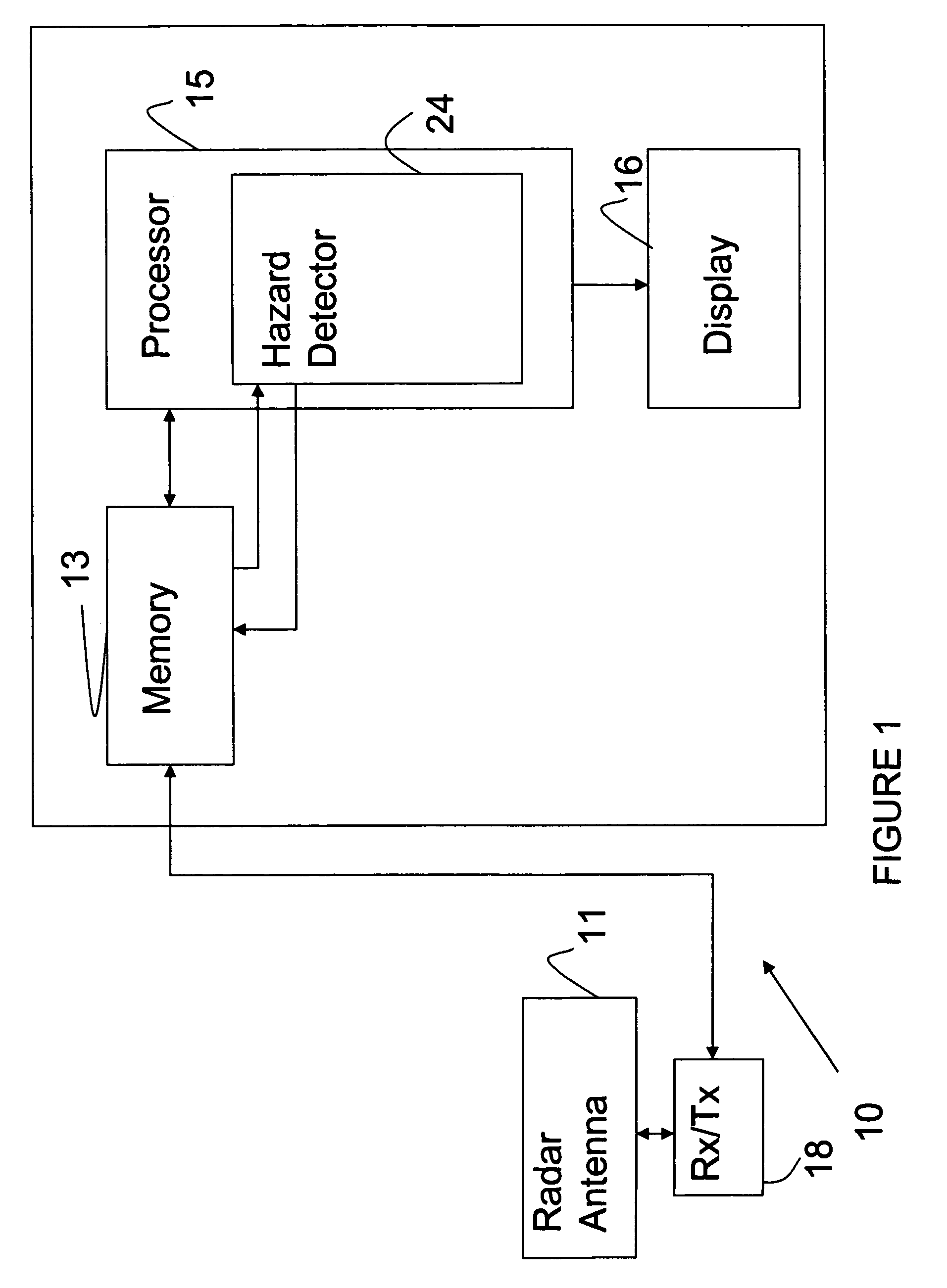
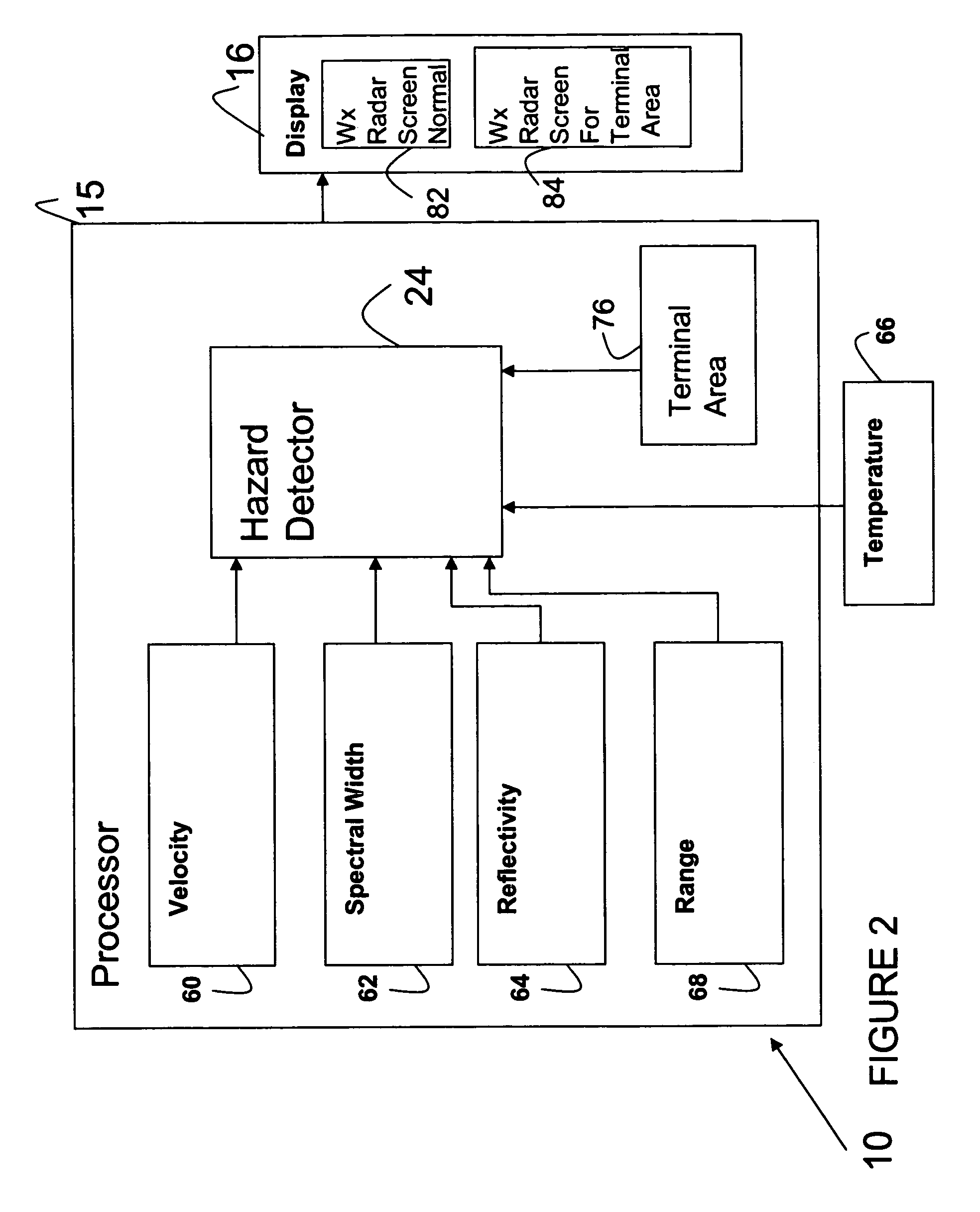
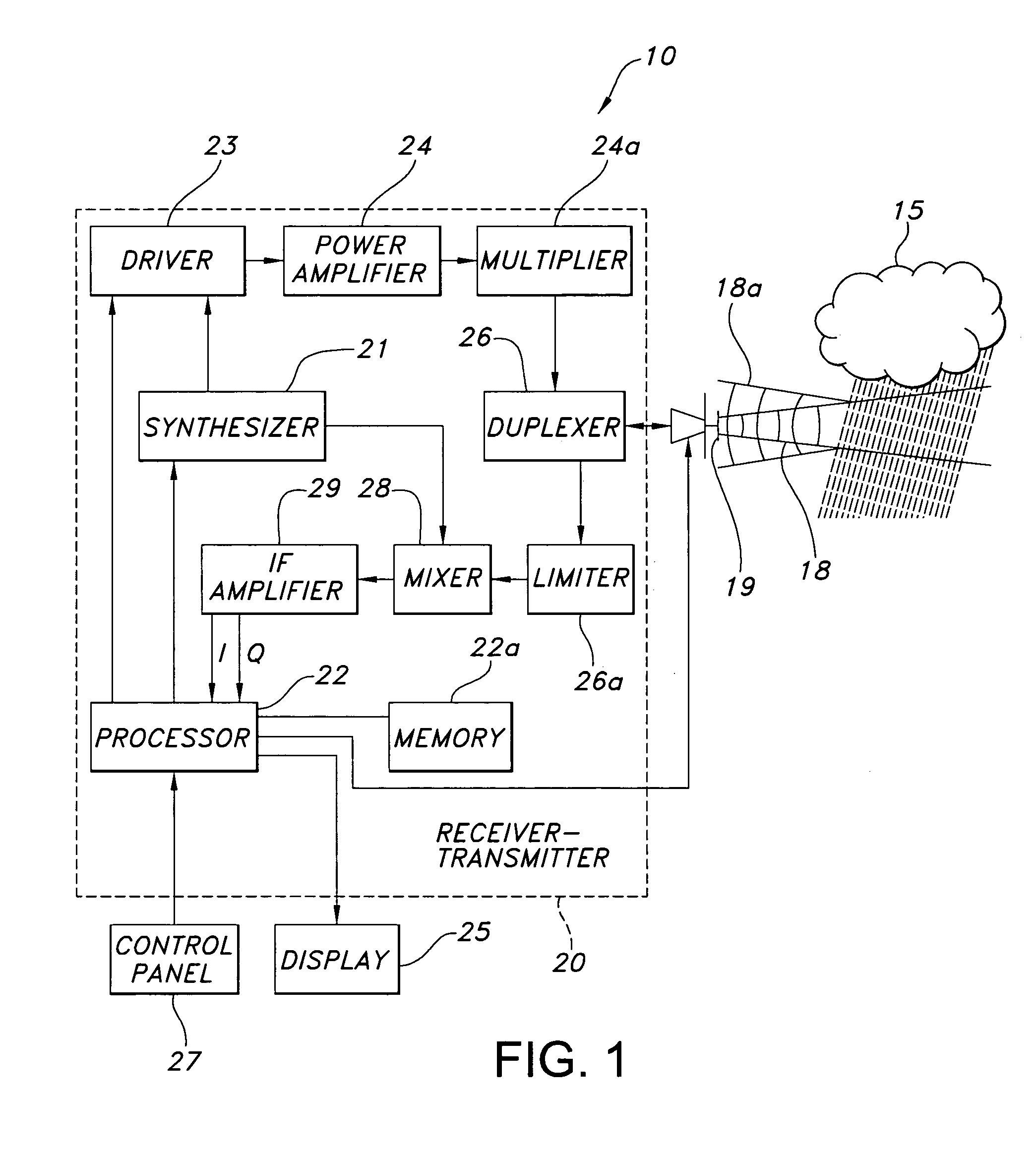
Aircraft hazard detection and alerting in terminal areas
A weather radar system or method can be utilized to determine potential weather hazard for an aircraft in a terminal area. The weather radar system can utilize processing electronics coupled to an antenna. The processing electronics can determine presence of the potential in response to data related to returns received by the weather radar antenna. The data can include a mean velocity parameter or a spectral width parameter or reflectivity.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
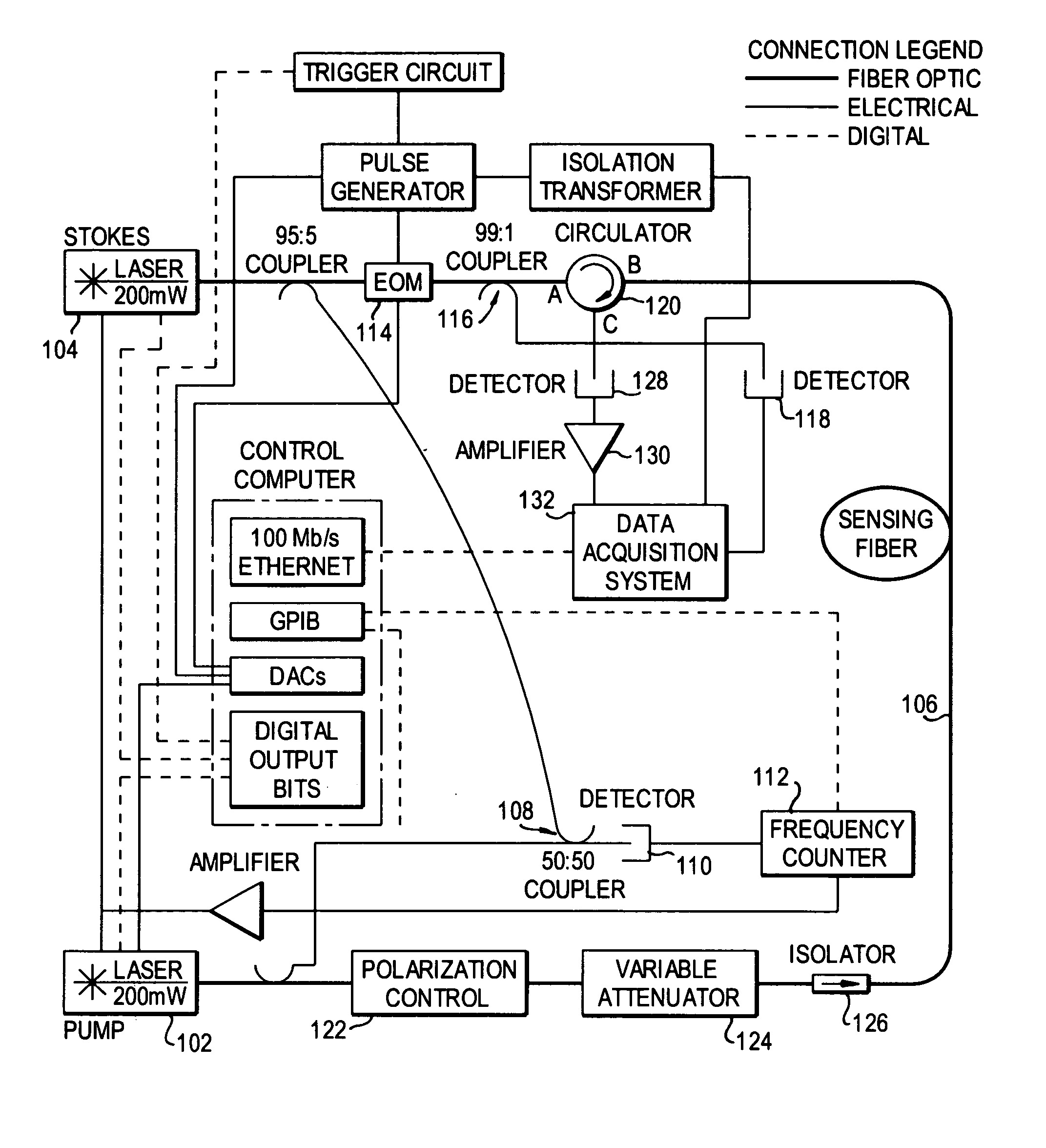
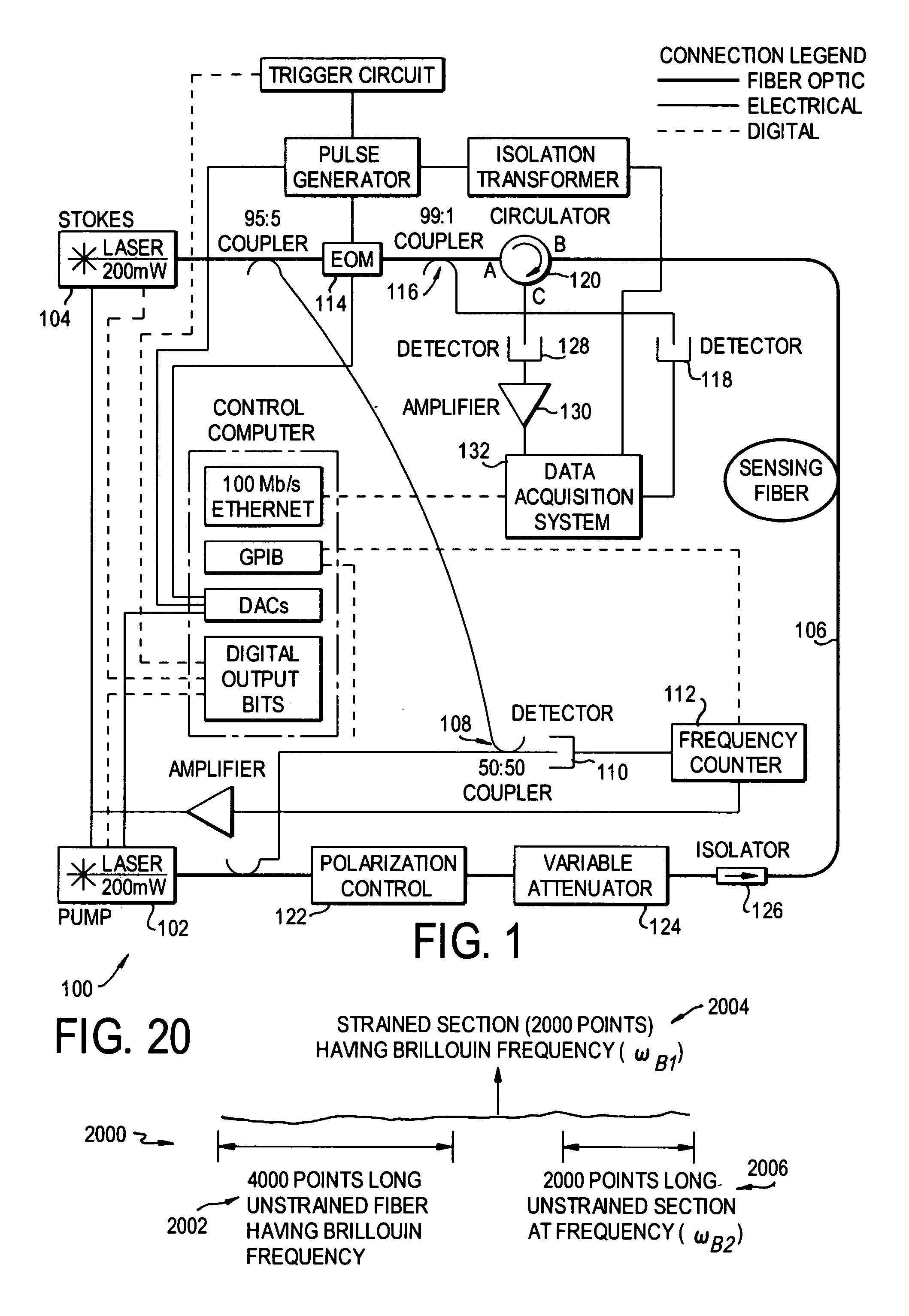
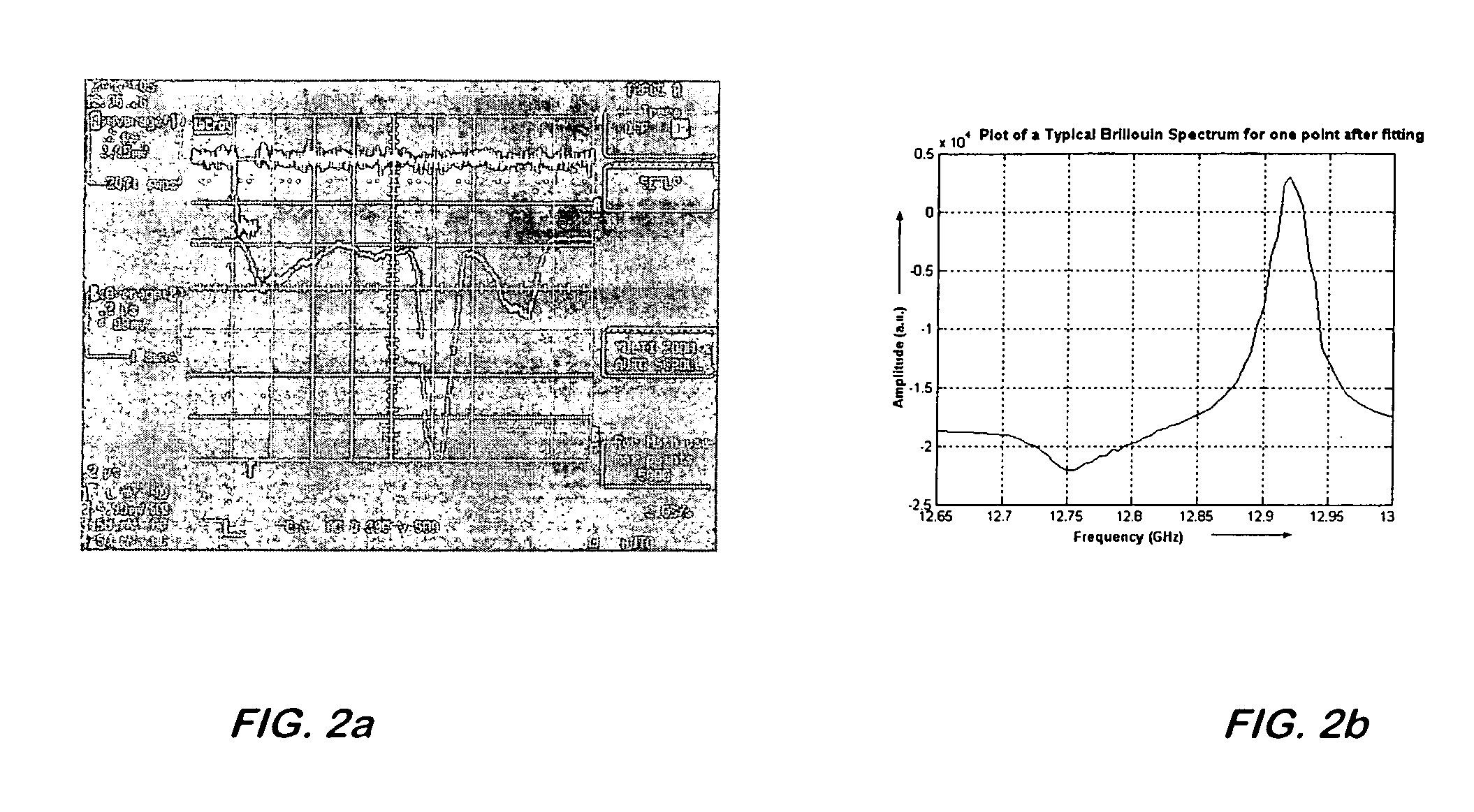
Dynamic strain distributed fiber optic sensor
InactiveUS20060285850A1Short measurement timeQuick measurementRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansConstant frequencySpectral width
A distributed fiber optic sensor simultaneously interrogates the sensing fiber with two counter propagating light beams. One beam is set to a constant frequency. The second beam is modified to contain a “comb” of frequencies, with each frequency component in the comb offset by a predetermined amount. Each of the frequency components in the comb, herein referred to as teeth, is able to interact with the counter-propagating beam through the Brillouin scattering process. With proper selection of the comb characteristics such as the number of teeth, the frequency spacing of teeth, the spectral width of teeth, and the relative amplitude of the teeth, a representation of the Brillouin spectrum at each point in the fiber can be obtained simultaneously with a single pass through the fiber.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Raman spectroscopic system with integrating cavity
InactiveUS6975891B2Efficient collectionImprove power densityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSpectral widthSpectrum analyzer
The present invention provides an apparatus for measurement of Raman scattered radiation comprising. The apparatus comprises at least one source of electromagnetic radiation for producing an electromagnetic radiation beam characterized by a narrow spectral width, an integrating cavity having an interior and an exterior, wherein a sample is placed in said interior. The integrating cavity further having at least one port for insertion of the sample in the interior and for transmission of the electromagnetic radiation into and out from the interior, the at least one port extending from the exterior to said interior of said integrating cavity. The integrating cavity also comprises a first optical element for transmitting the electromagnetic radiation into the interior of the integrating cavity through the at least one port, and a second optical element for collecting Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation from the sample through the at least one port. The apparatus also comprises a spectrum analyzer for determining spectral composition of the Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation, a detector for measuring the Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation; and a system for determining concentration of at least one chemical compound from the measured Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus may also comprise a radiation expanding element. A method for measuring the concentration of one or more chemical compounds in a sample using Raman scattering is also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Luminescent materials that emit light in the visible range or the near infrared range
InactiveUS20080014463A1Narrow spectral widthEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhotoluminescenceElectron donor
Luminescent materials and the use of such materials in anti-counterfeiting, inventory, photovoltaic, and other applications are described herein. In one embodiment, a luminescent material has the formula: [AaBbXxX′x′X″x″][dopants], wherein A is selected from at least one of elements of Group IA; B is selected from at least one of elements of Group VA, elements of Group IB, elements of Group IIB, elements of Group IIIB, elements of Group IVB, and elements of Group VB; X, X′, and X″ are independently selected from at least one of elements of Group VIIB; the dopants include electron acceptors and electron donors; a is in the range of 1 to 9; b is in the range of 1 to 5; and x, x′, and x″ have a sum in the range of 1 to 9. The luminescent material exhibits photoluminescence having: (a) a quantum efficiency of at least 20 percent; (b) a spectral width no greater than 100 nm at Full Width at Half Maximum; and (c) a peak emission wavelength in the near infrared range.
Owner:OMNIPV
Spectroscopic fluid analyzer
InactiveUS7236237B2Readily availableEasy to applyRadiation pyrometryWithdrawing sample devicesPhotodetectorStatistical analysis
An NIR spectroscopy fluid analyzing system using a series of LED's, each having its own preselected center wavelength, as illumination sources. These wavelengths have overlapping spectral widths, such that the measurement covers a broad spectrum. The LED's illuminate the fluid sample sequentially, and subsequently the transmission absorbance through the sample and the reflectance or scattering from the sample is measured for the wavelength range of each LED. The measurements are performed using photodetectors. The concentrations of component parts of the fluid are expressed in the form of a polynomial, which is a function of the measured transmitted and / or reflected intensities, and of empirical coefficients, which are extracted by prior statistical analysis on measured intensities obtained from a large number of test samples having known concentrations of the component. A novel sample chamber, capable of performing optical absorption measurements on a flowing sample of fluid, is described.
Owner:AFIMILK AGRI COOP
Luminescent materials that emit light in the visible range or the near infrared range
InactiveUS7641815B2Narrow spectral widthEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPhotoluminescenceElectron donor
Luminescent materials and the use of such materials in anti-counterfeiting, inventory, photovoltaic, and other applications are described herein. In one embodiment, a luminescent material has the formula: [AaBbXxX′x′X″x″][dopants], wherein A is selected from at least one of elements of Group IA; B is selected from at least one of elements of Group VA, elements of Group IB, elements of Group IIB, elements of Group IIIB, elements of Group IVB, and elements of Group VB; X, X′, and X″ are independently selected from at least one of elements of Group VIIB; the dopants include electron acceptors and electron donors; a is in the range of 1 to 9; b is in the range of 1 to 5; and x, x′, and x″ have a sum in the range of 1 to 9. The luminescent material exhibits photoluminescence having: (a) a quantum efficiency of at least 20 percent; (b) a spectral width no greater than 100 nm at Full Width at Half Maximum; and (c) a peak emission wavelength in the near infrared range.
Owner:OMNIPV
Display device
InactiveUS20060175966A1Reducing reflection of external lightIncrease contrastIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensSpectral widthPhase shifted
In an organic EL device having a first electrode of a light reflective material, organic layer including an organic light emitting layer, semitransparent reflection layer, and second electrode of a transparent material that are stacked sequentially, and so configured that the organic layer functions as a cavity portion of a cavity structure, light that resonates in a certain spectral width (wavelength λ) is extracted by so configuring that optical path length L becomes minimum in a range satisfying (2L) / λ+Φ((2π)=m (m is an integer) where the phase shift produced in light generated in the organic light emitting layer when reflected by opposite ends of the cavity portion is Φ radians, L is optical path length of the cavity portion, and λ is the peak wavelength of the spectrum of part of light to be extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Removal of spurious aircraft detections on weather radar
ActiveUS7417578B1Improve performanceAvoid confusionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocitySpectral width
A weather radar detects and removes spurious aircraft from a weather radar display by using one of the methods of differentiating radar return length, estimating a vertical gradient of reflectivity, tracking radar returns into regions that are eliminated from the weather display to provide differentiation, tracking areas of radar returns that allow detection and removal of the spurious aircraft in relative geometries, differentiating Doppler velocity, and differentiating spectral width. The methods may be used individually or in combination to improve performance.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
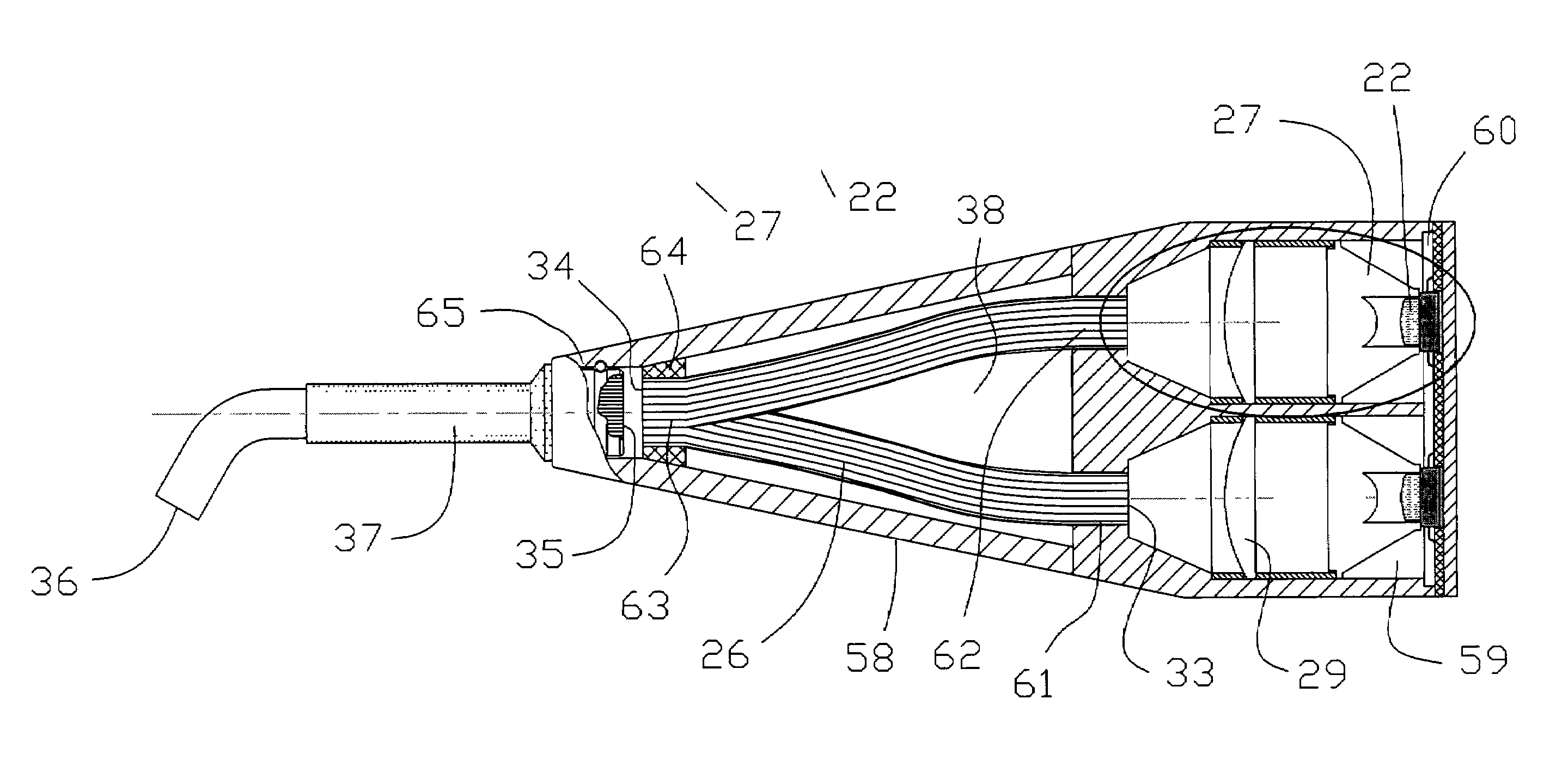
Curing light with engineered spectrum and power compressor guide
A light for a curing instrument includes a plurality of light sources, each producing an incident light beam. The incident light beams are combined to produce a single output beam, which exhibits a broader spectral width than any of the incident light beams. In one embodiment of the invention, the output beam exhibits an intensity over a spectral range defined by a first characteristic wavelength of a first of the plurality of light sources and a second characteristic wavelength of a second of the plurality of lights sources such that the intensity varies by no more than 25 percent over the range. In another embodiment of the invention including a one or more blue LED light sources among the plurality of light sources, at least one white LED is included in the plurality of light sources in order to generate an output light beam having a component portion that is characterized as green. In a third embodiment of the invention, a plurality of fiber optic bundles receive the incident light beams, and are arranged at a transmitting end so that individual fibers from the plurality of bundles are randomly combined to form a single output surface for transmitting the output beam.
Owner:COLTENE WHALEDENT INC
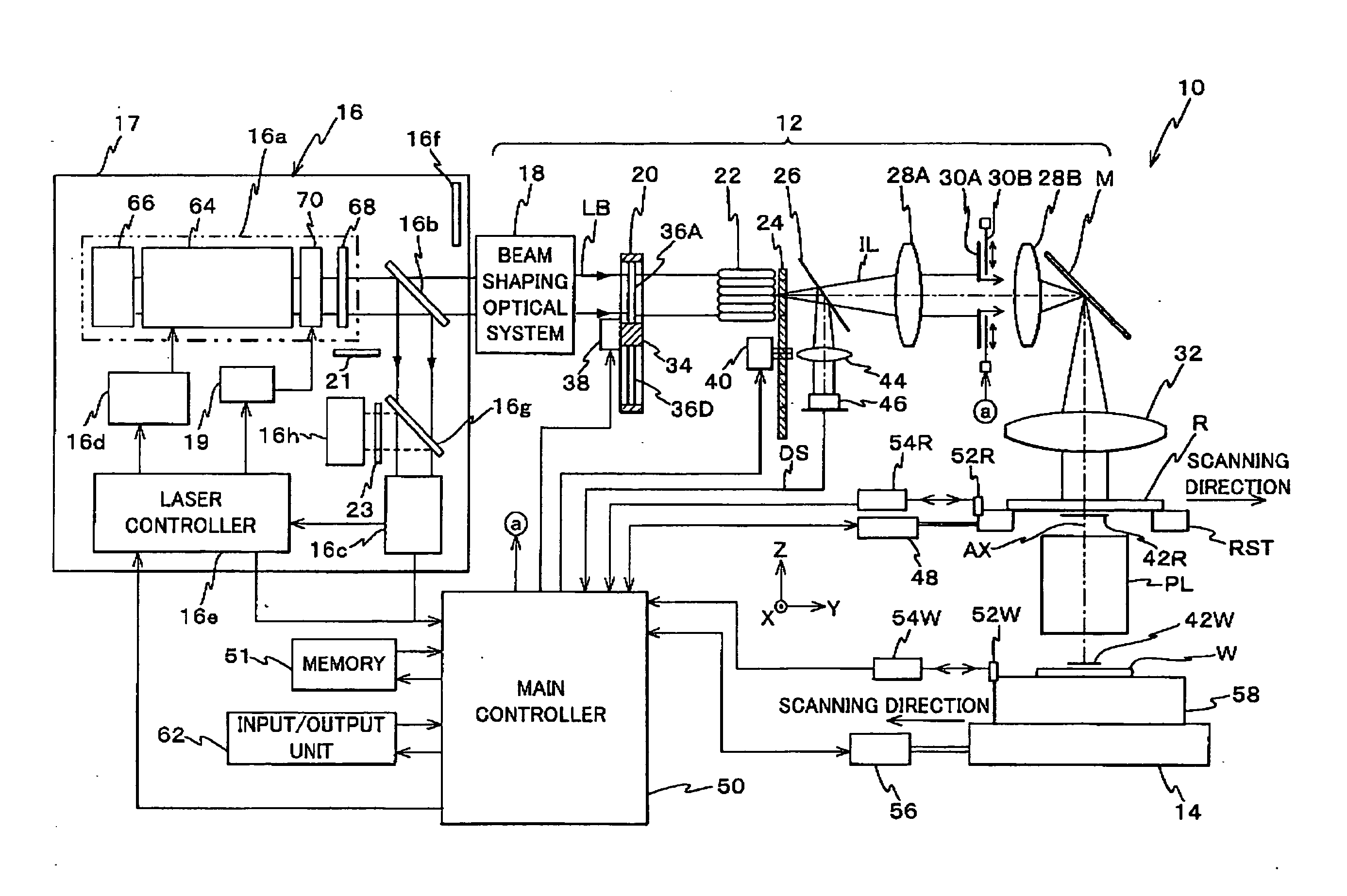
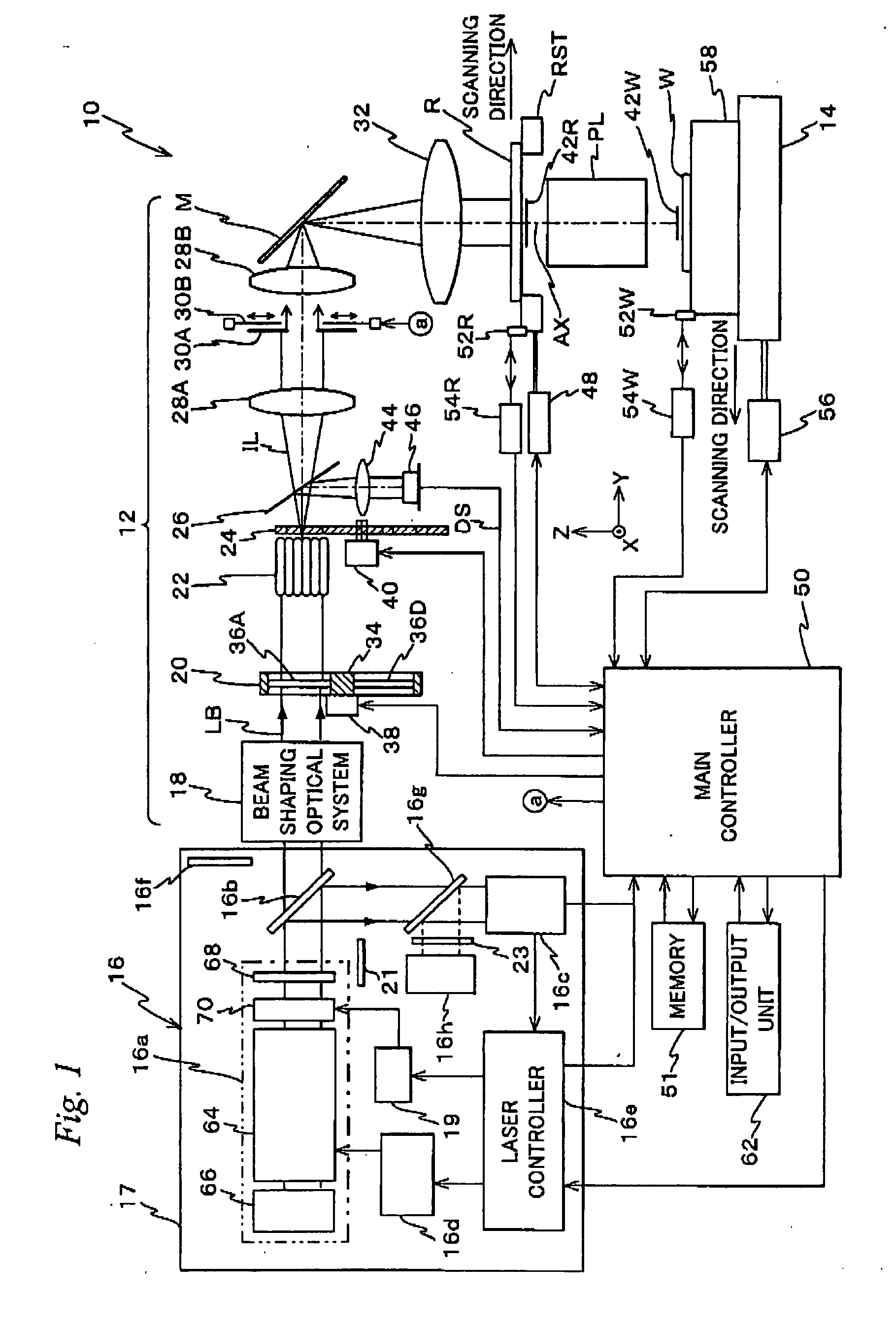
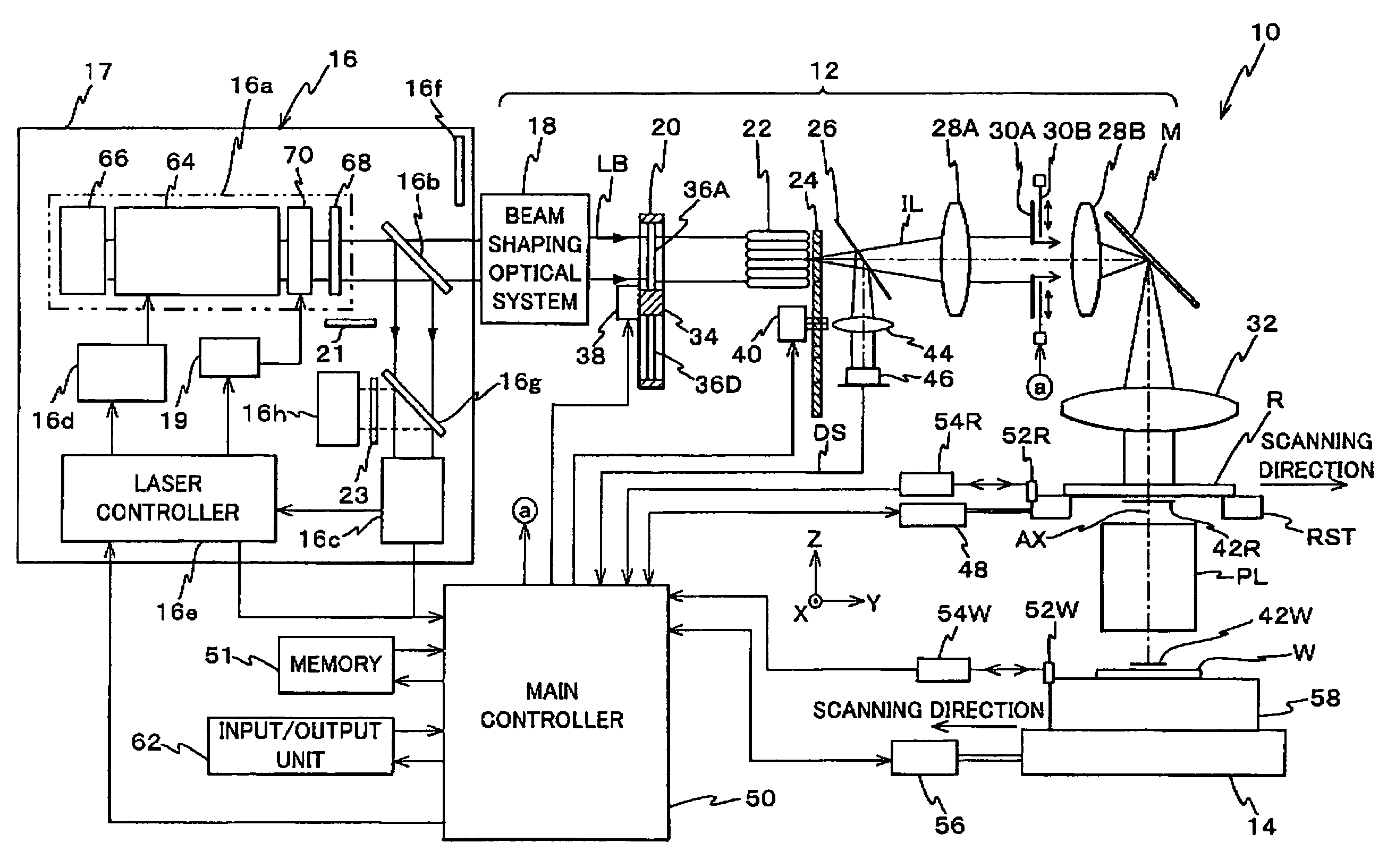
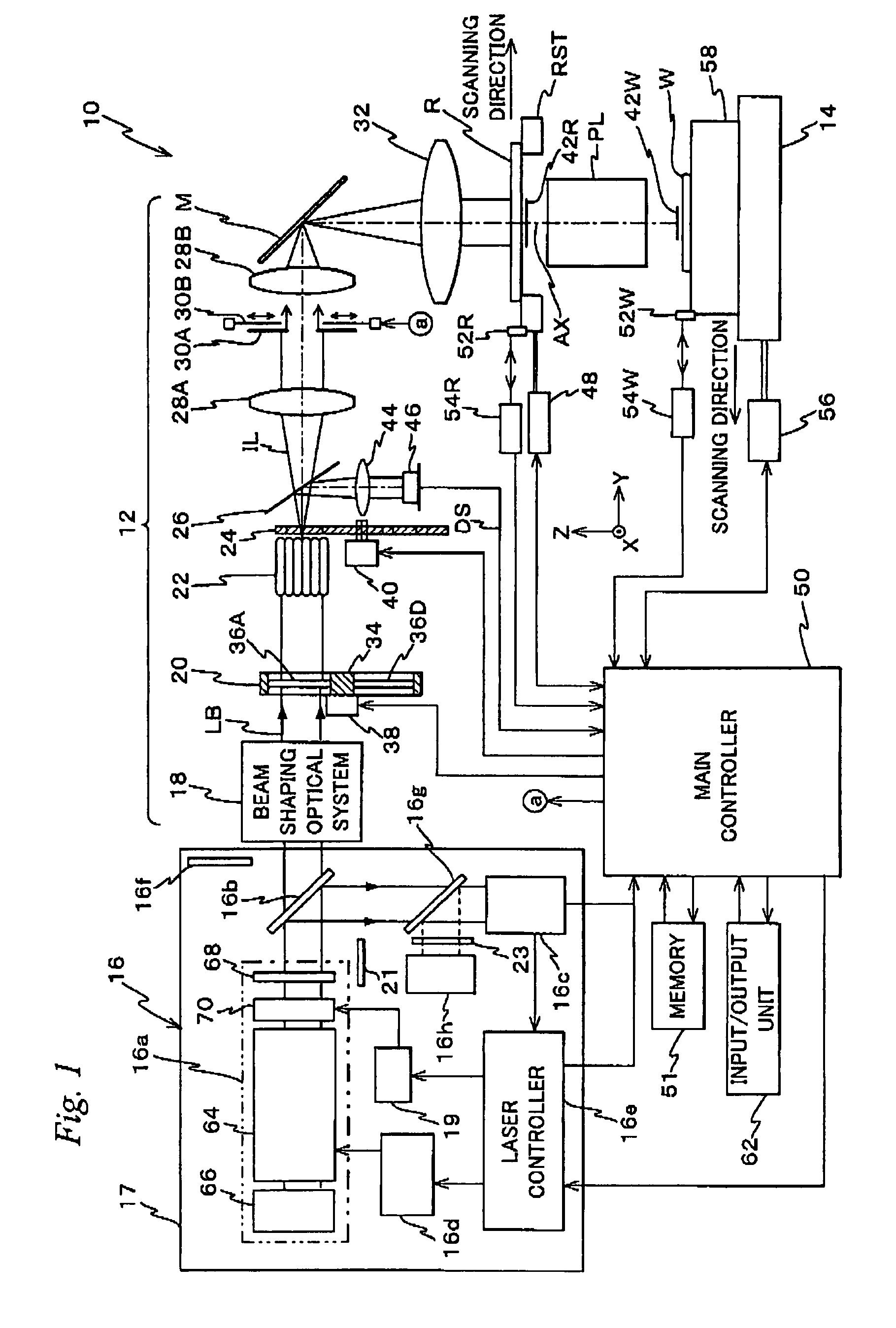
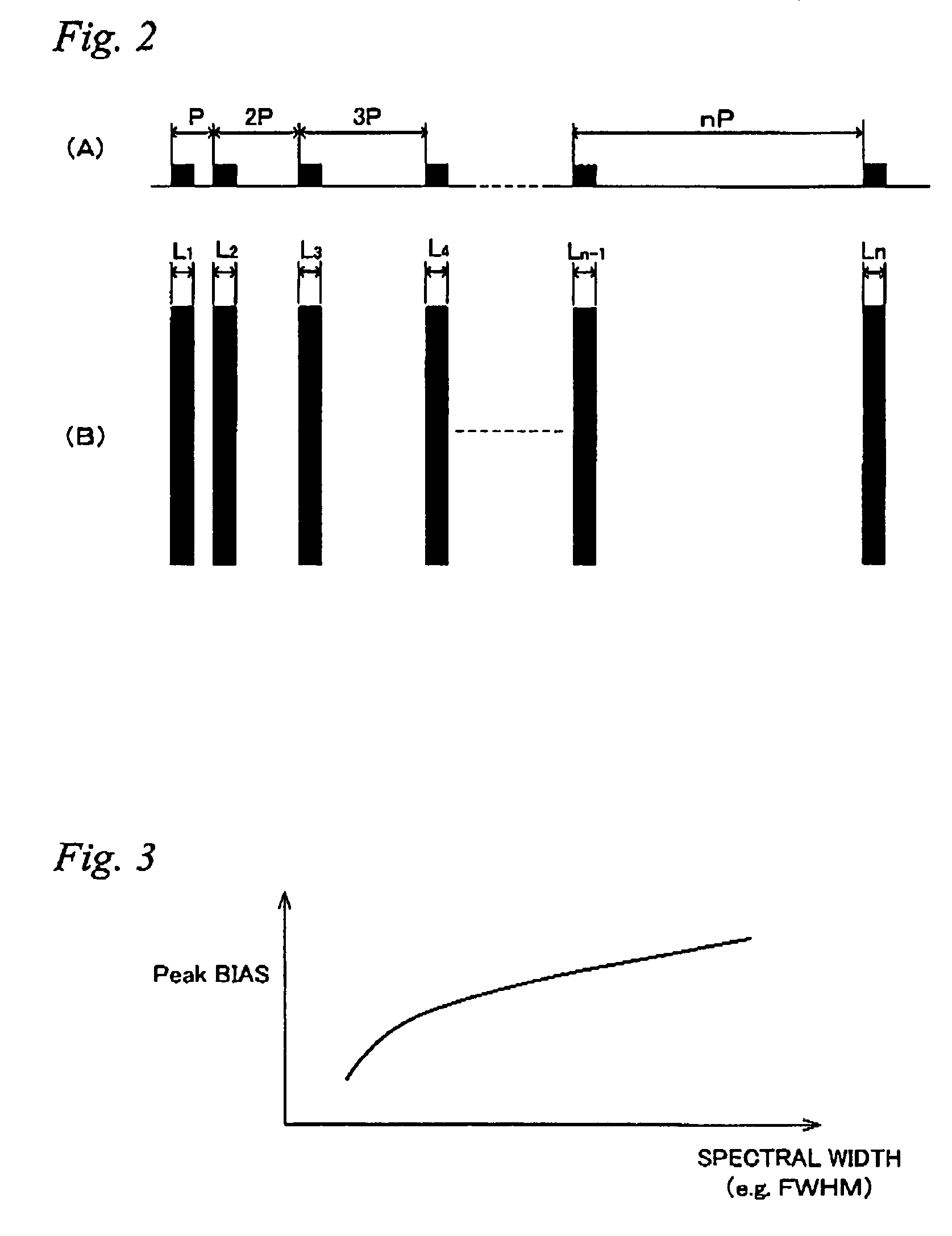
Exposure Apparatus, Exposure Method, Device Manufacturing Method, and System
ActiveUS20070273852A1Good precisionEasy to monitorLaser detailsPhotomechanical apparatusSpectral widthLine width
Owner:NIKON CORP
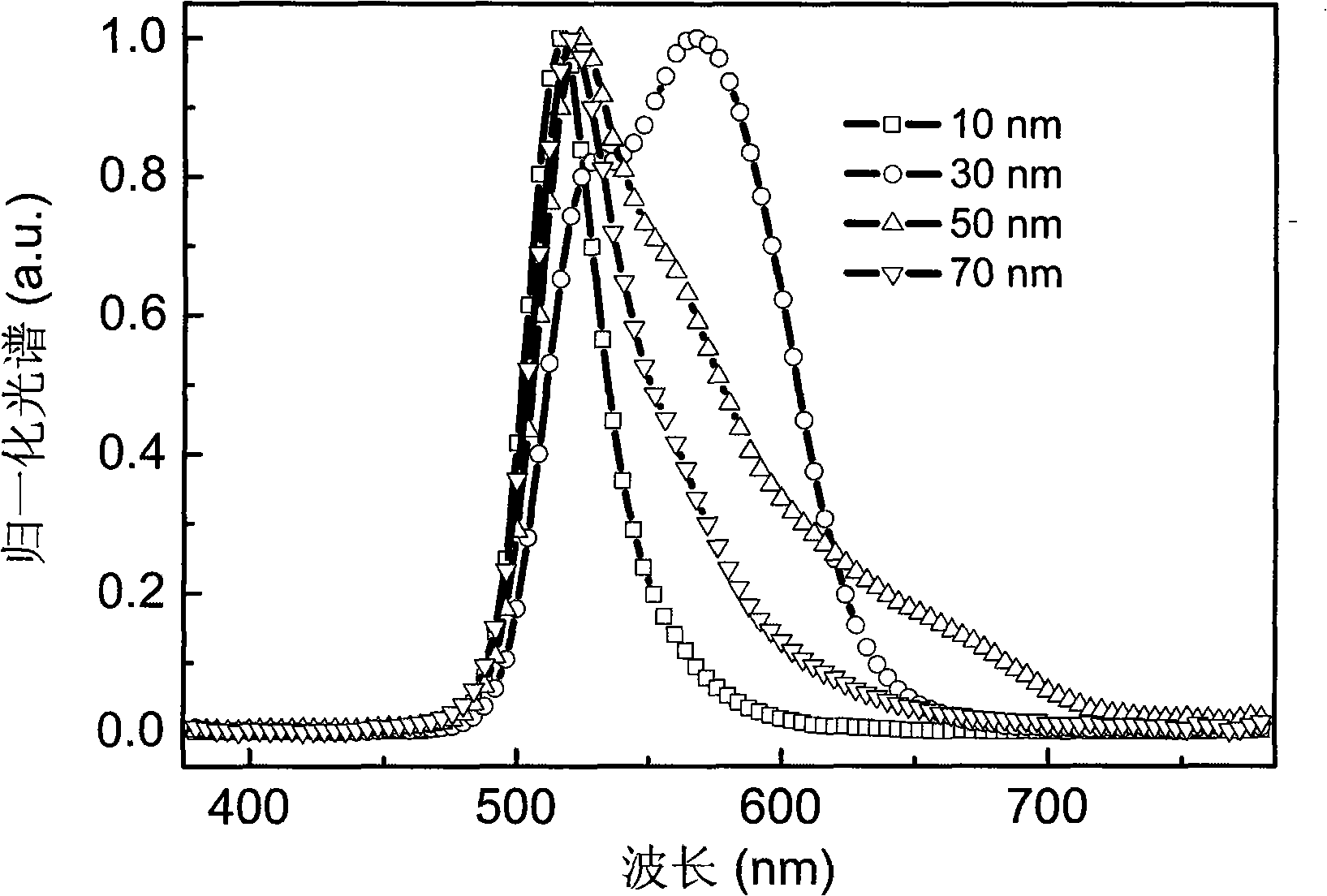
Top radiation organic EL part with optical spectrum adjustable
InactiveCN101359721ATuning the resonance wavelengthSimple processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectral widthPeak value
The invention belongs to the organic electroluminescence field, in particular to a top-emitting organic electroluminescent device having two structures and being capable of adjusting luminescent spectrums. The top-emitting device adopting an upright structure sequentially comprises a substrate, a metal anode, an organic function layer and a metal cathode, and a spectrum adjustment layer structure is introduced between the metal cathode and the organic function layer; and the top-emitting device adopting an inverted structure sequentially includes a substrate, a metal cathode, an organic function layer and a metal anode in structure, and a spectrum adjustment layer structure is introduced between the metal anode and the organic function layer. The introduction of the spectrum adjustment layer can adjust the spectral width of luminescent spectrum and the emission spectrum peak value of the top-emitting organic electroluminescent device, thereby changing the luminescent color of the device and finally realizing the top-emitting white light organic electroluminescent device with high brightness and high color-rendering indexes. The prepared top-emitting organic electroluminescent device with multiple photo-peaks and adjustable spectrums has the advantages of high brightness, high efficiency, less working procedure and simple process.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
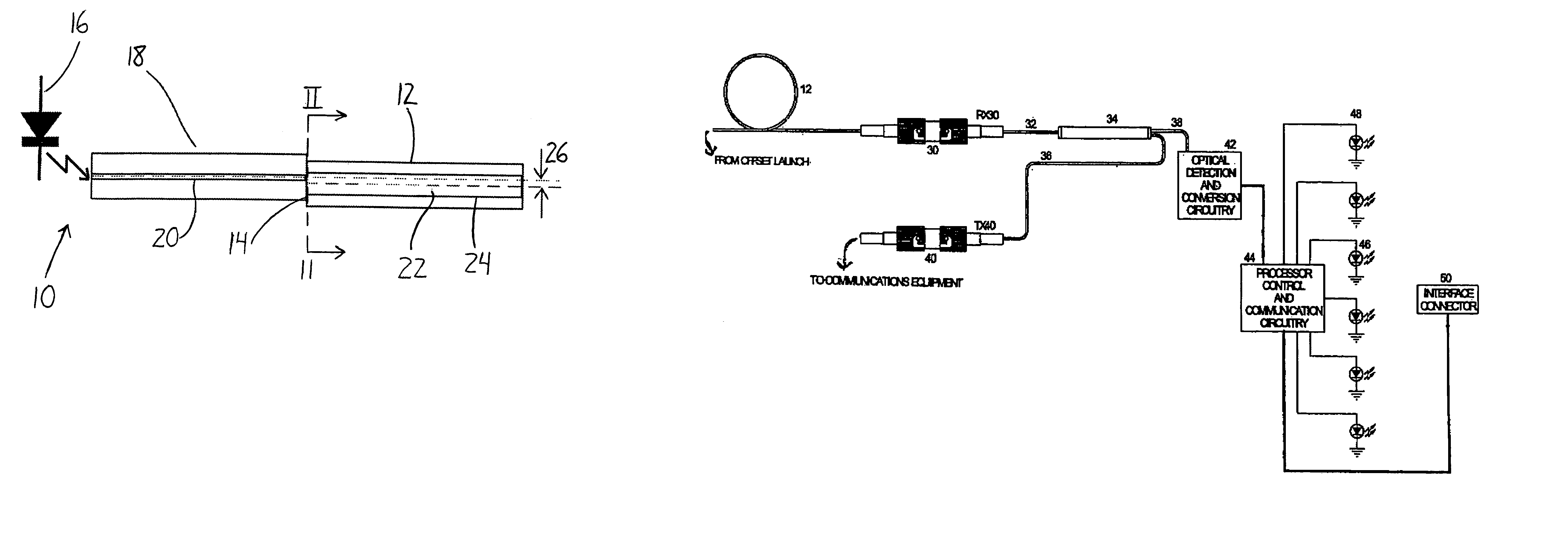
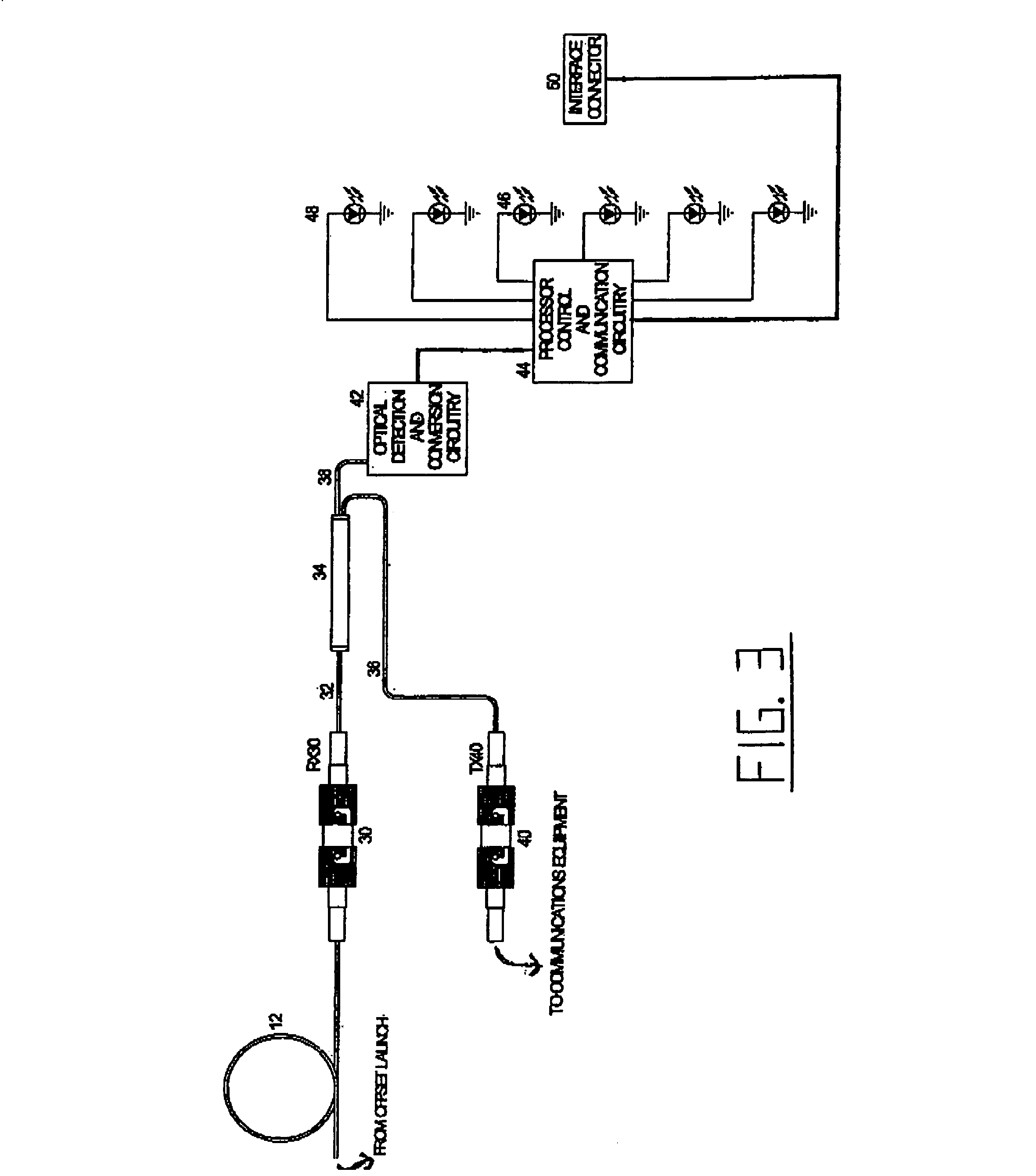
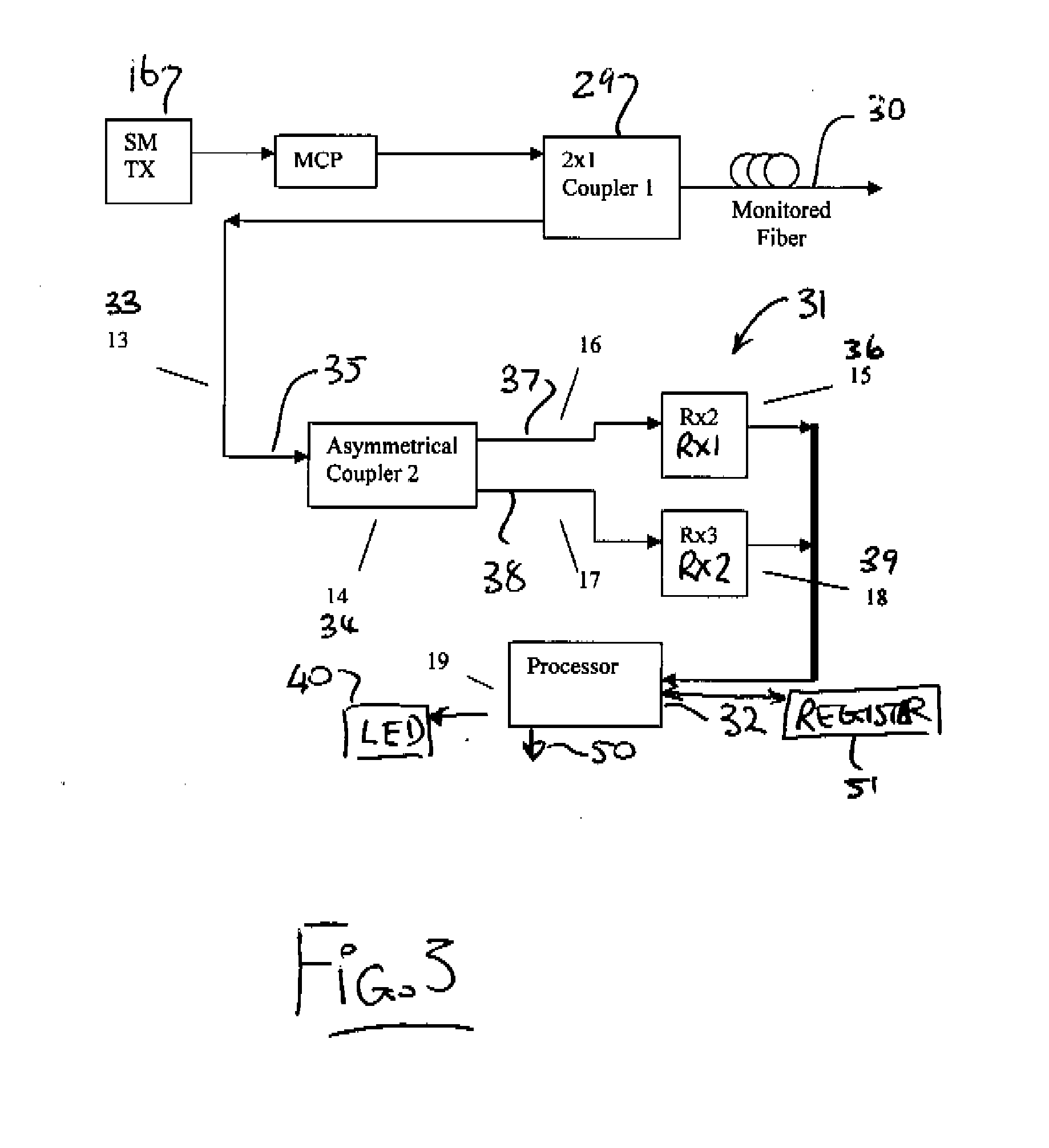
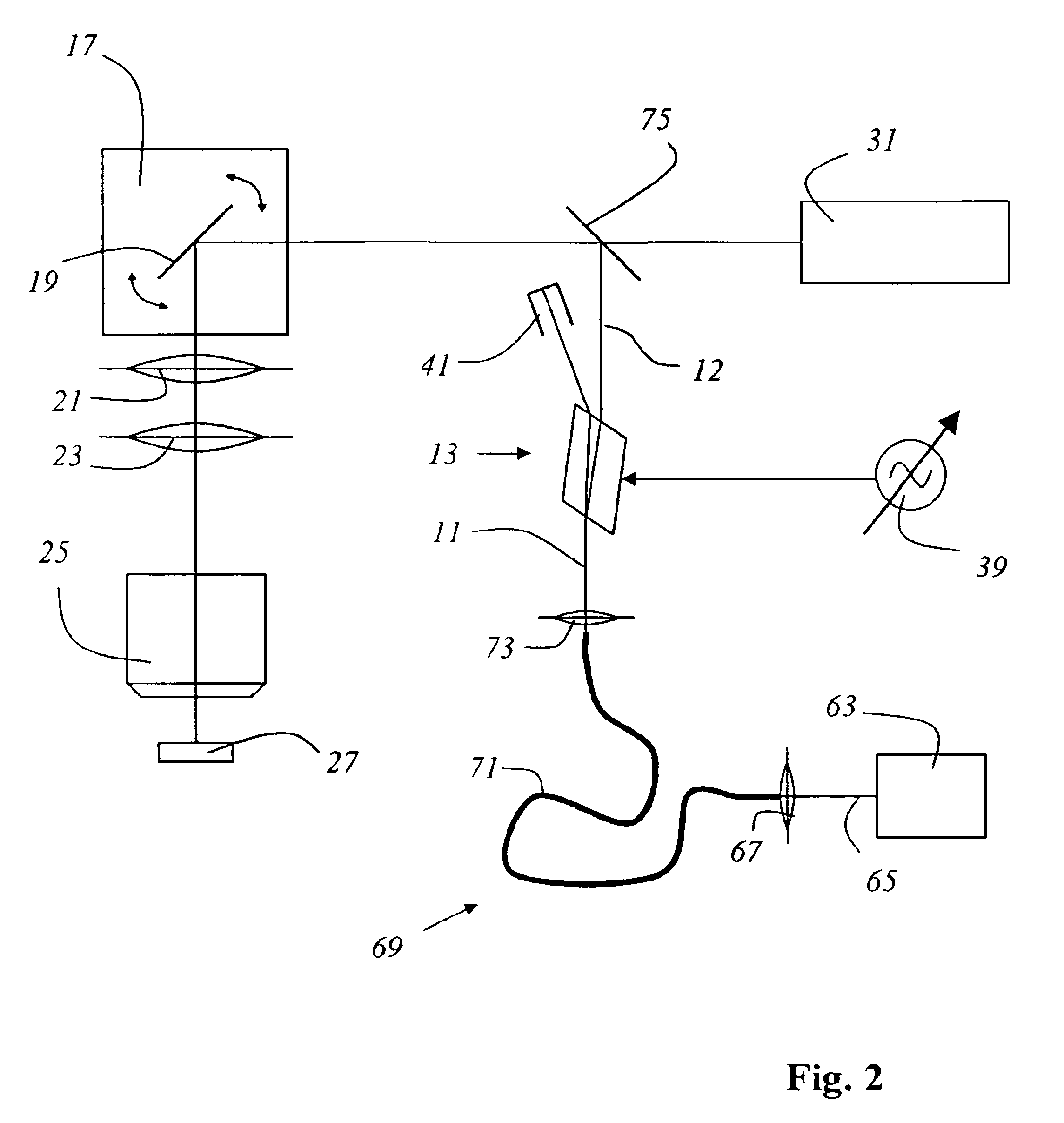
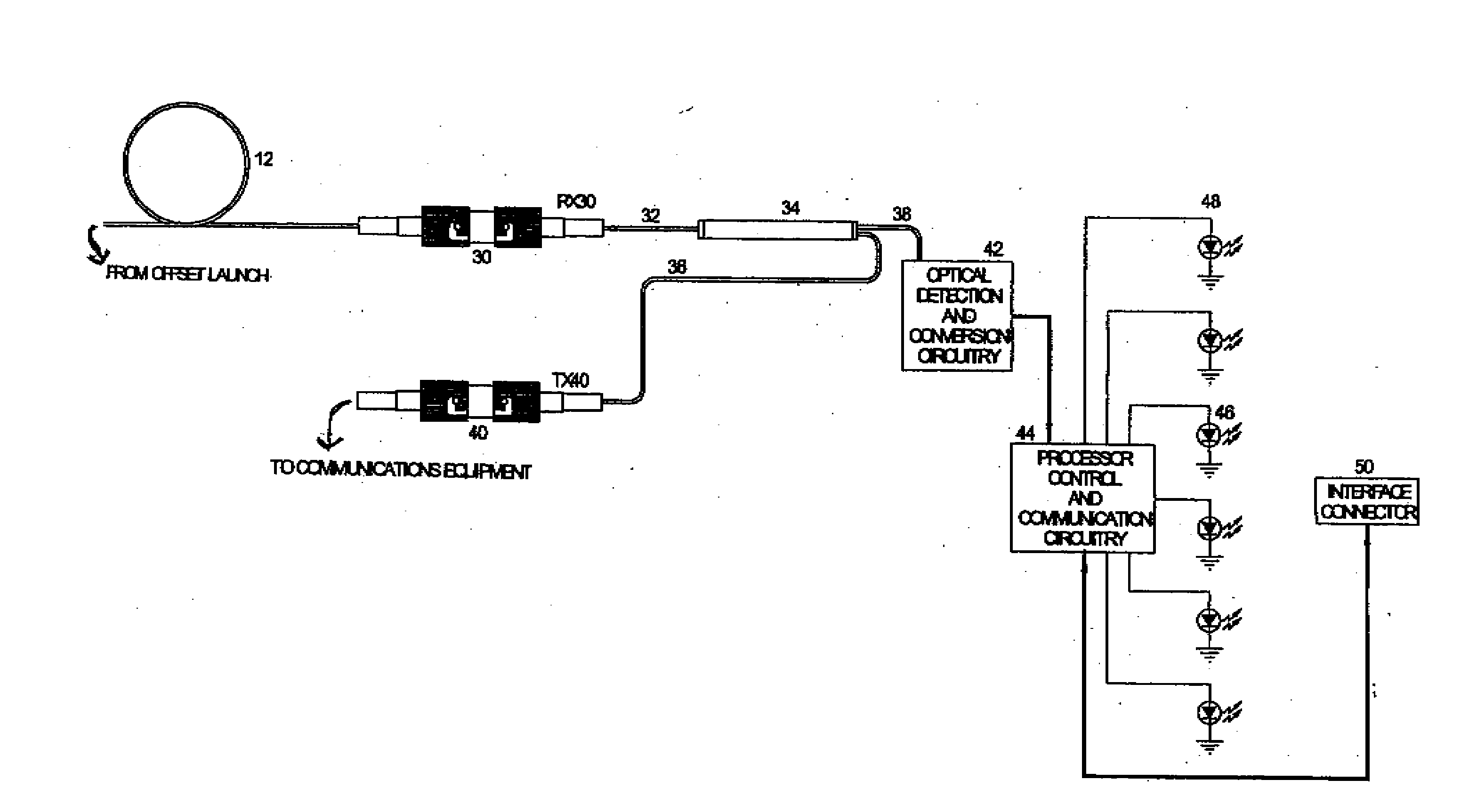
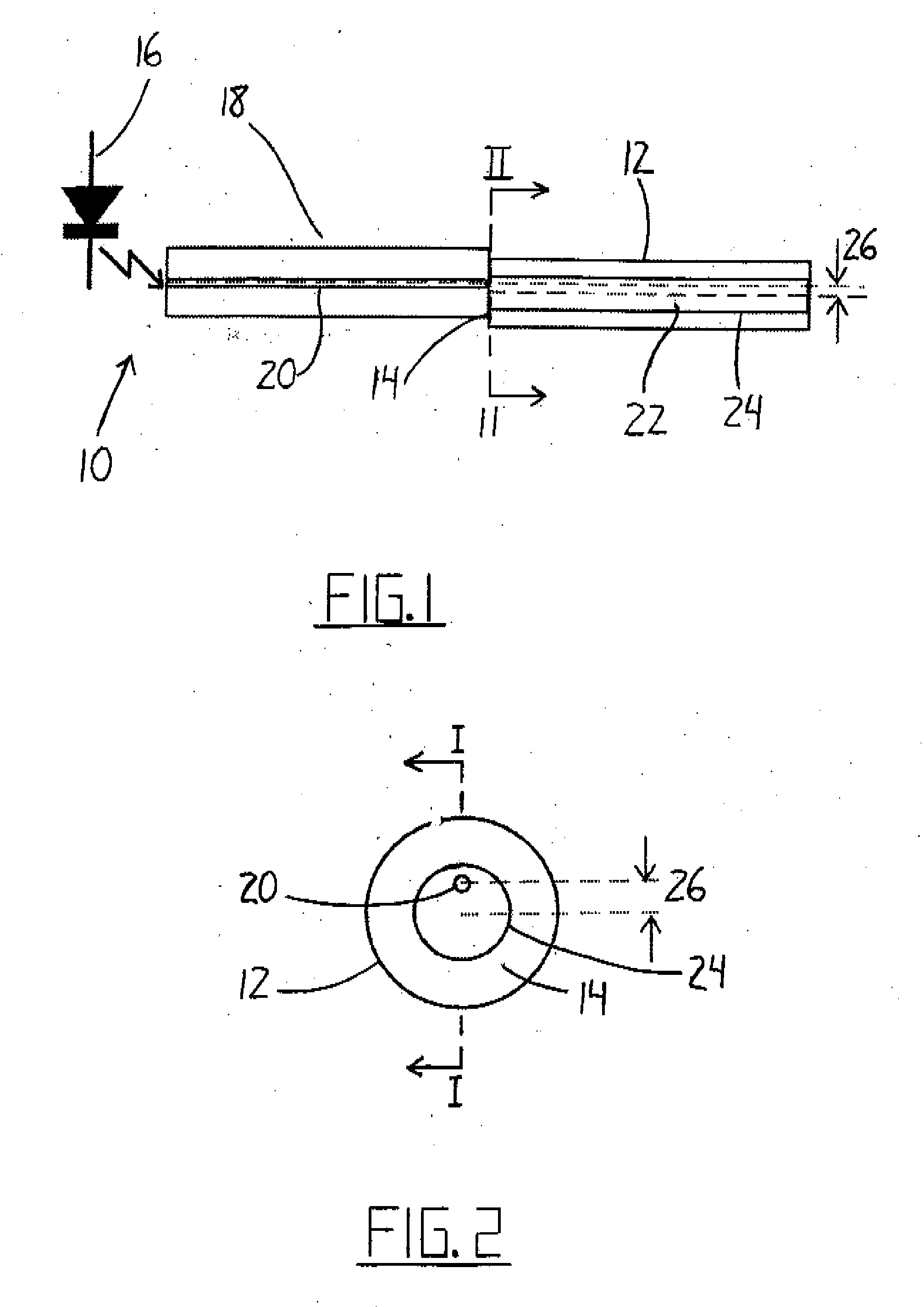
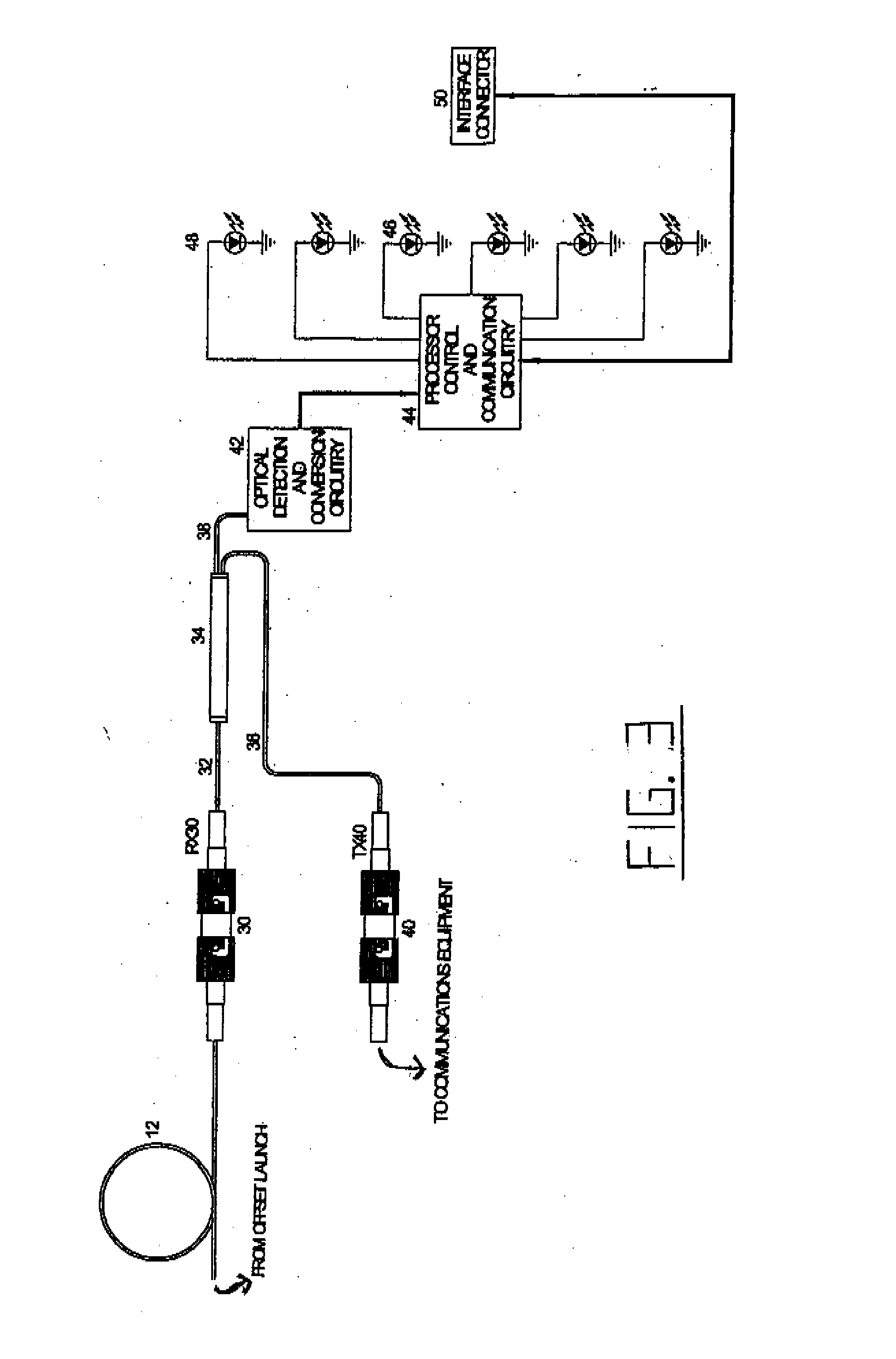
Intrusion detection system for use on an optical fiber using a translator of transmitted data for optimum monitoring conditions
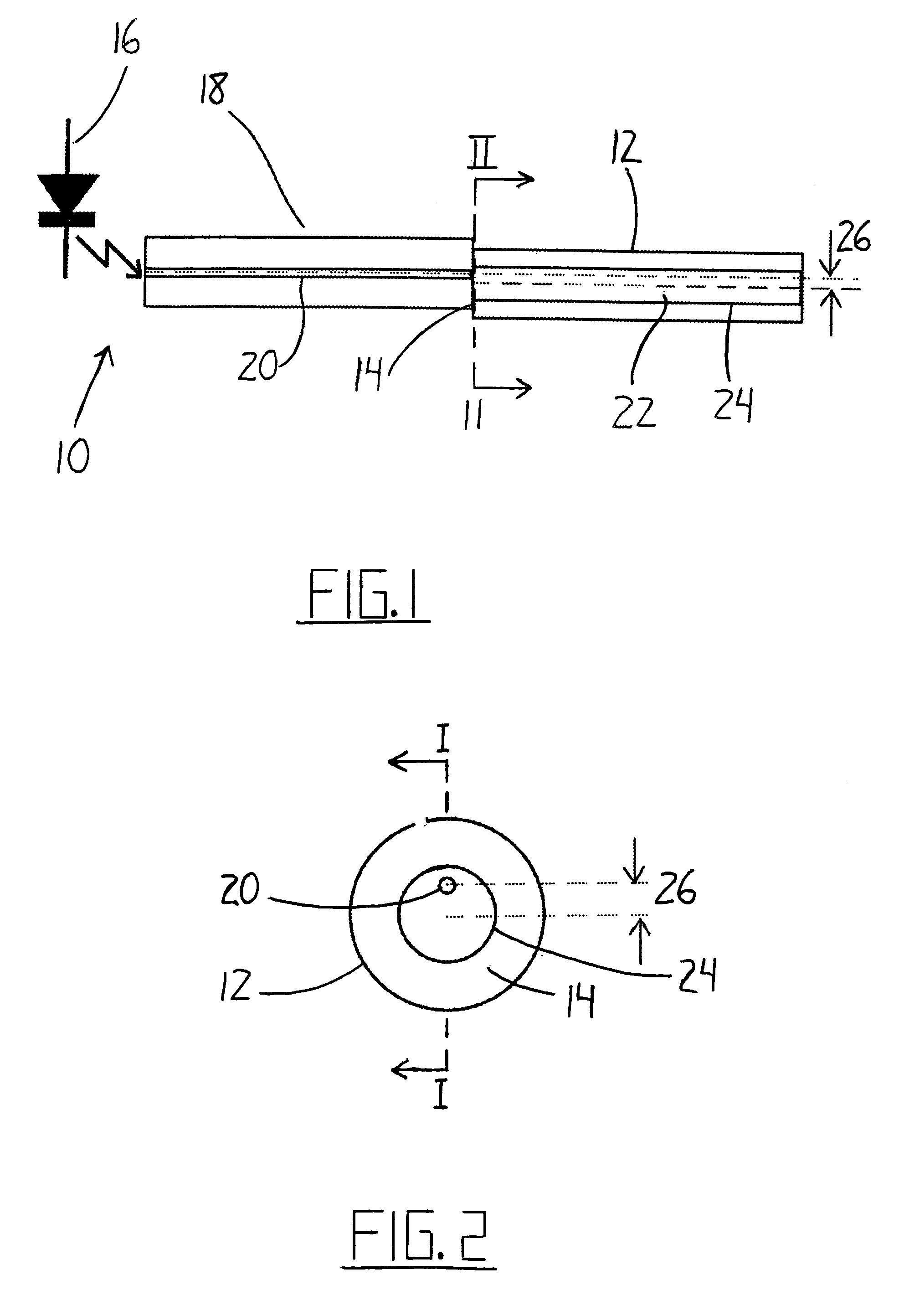
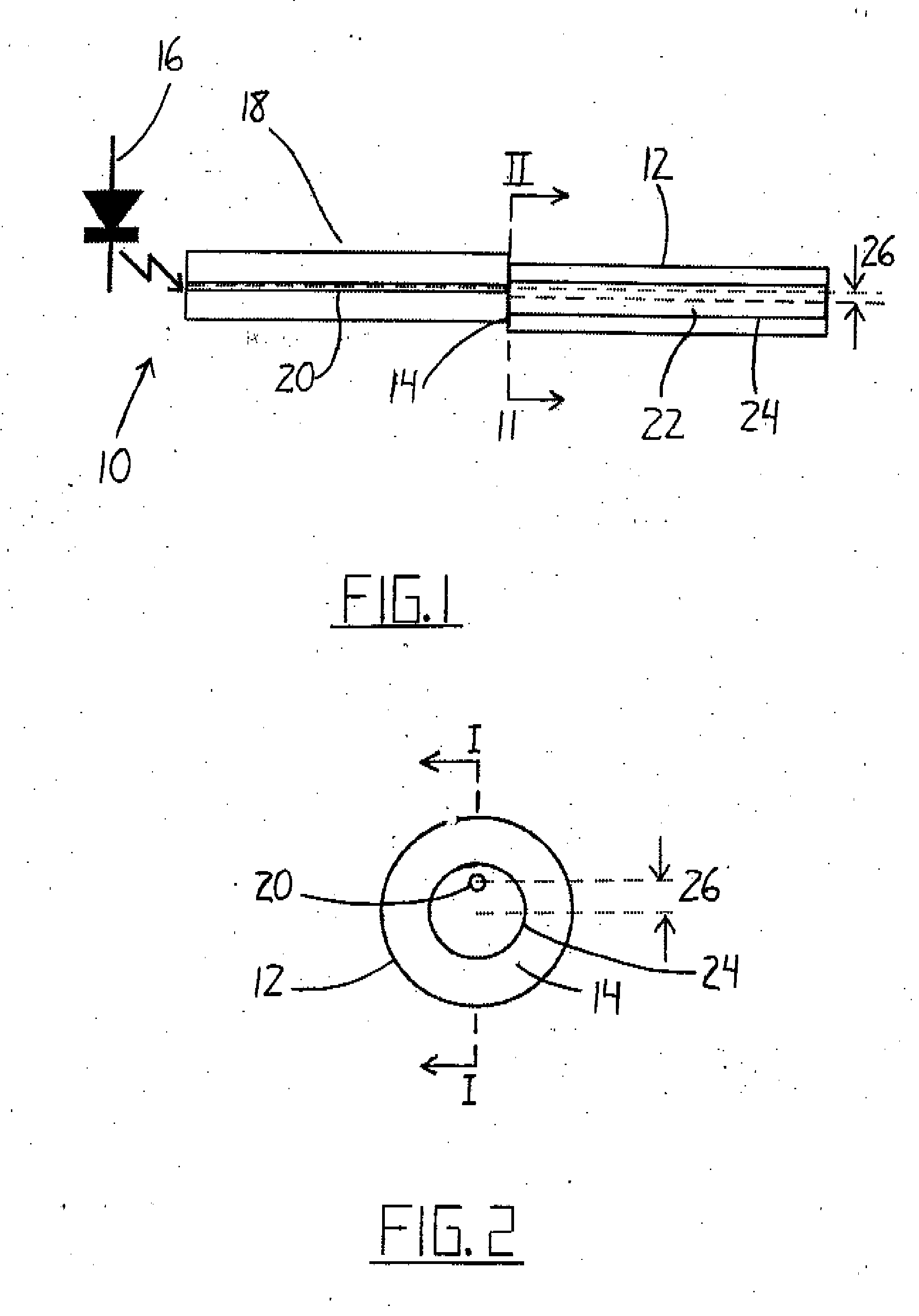
ActiveUS7092586B2Maximum sensitivityRapid location and interceptionCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresFiberSpectral width
A method and system of intrusion detection system for a multimode fiber optic cable. A light signal is launched into the cable fiber to establish a narrow spectral width, under-filled non-uniform mode field power distribution in the cable. A small portion of the higher order signal modes arriving at the remote end of the cable is sampled by use of a coupler and monitored for transient changes in the mode field power distribution. The power distribution changes with physical disturbance of the cable. When those changes are detected as being characteristic of fiber intrusion, the system activates an alarm. This method can sense and alarm any attempt to access the optical fibers in a fiber optic communication cable. In preferred embodiments, the active signal of a multimode optical fiber is monitored for both signal degradation and transient power disturbance patterns that could indicate fiber damage or physical intrusion. A translator can be provided in an existing optical fiber system in which the data signals are translated in wavelength and / or launch conditions to optimize the monitoring signals in an otherwise non-optimized system.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
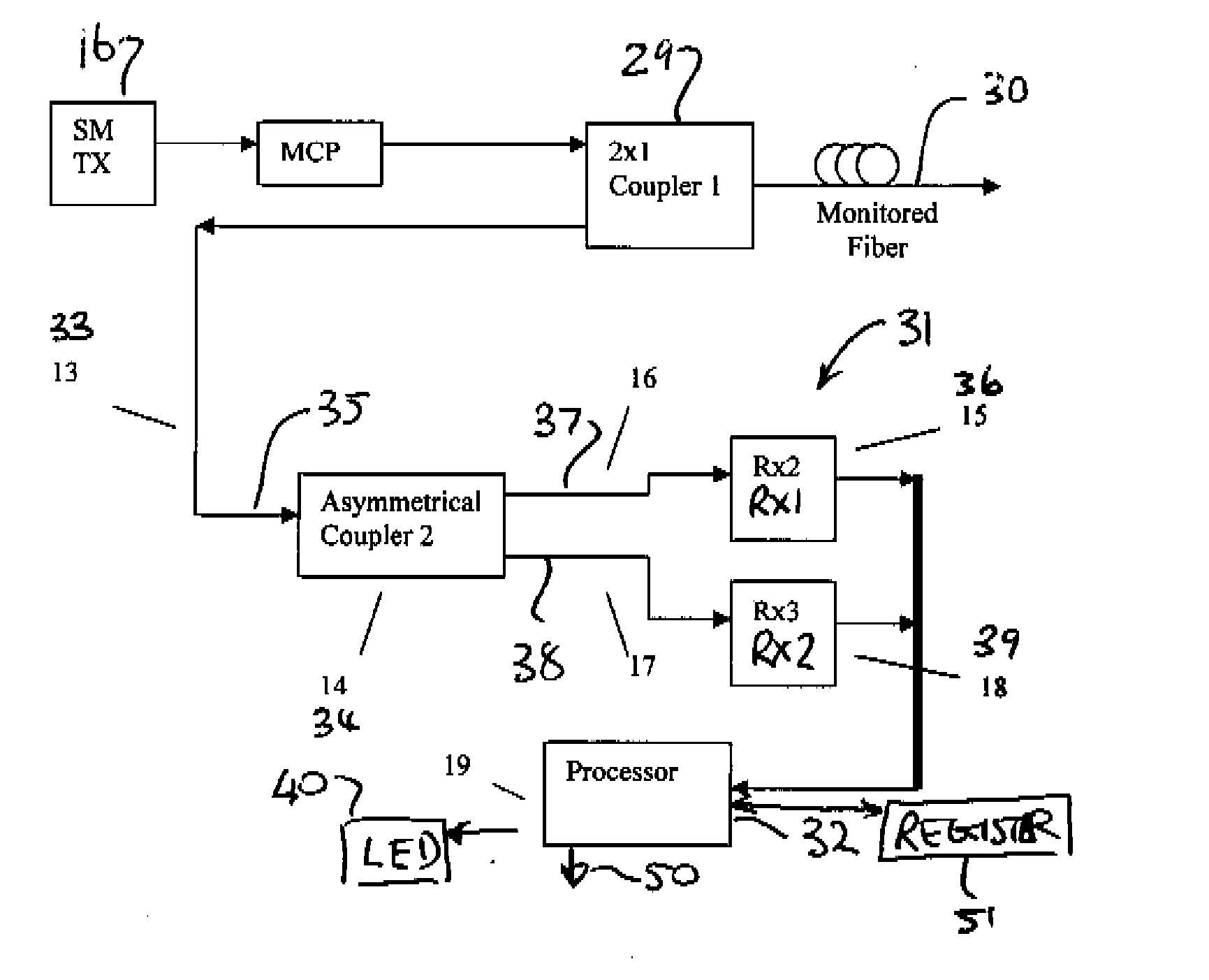
Intrusion detection and location system for use on multimode fiber optic cable
ActiveUS20070133922A1Overcome limitationsMaximum sensitivityCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionFiberSpectral width
A telecommunications multimode optical fiber is secured against intrusion by detecting manipulation of the optical fiber prior to an intrusion event. Pulses are injected using a launch arrangement which generates a narrow spectral width, under-filled, non-uniform mode field power distribution in the multimode optical fiber and Fresnel reflections and Rayleigh backscattering from the pulse are detected at the transmit end to monitor the modal power distribution in the fiber which changes on manipulation of the fiber. The Rayleigh backscattering time sliced data can be stored in a register until an intrusion event is detected. The detection is carried out by a modal power distribution detection system which includes an optical coupler to tap off a portion of the light which contains the higher order signal modes.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
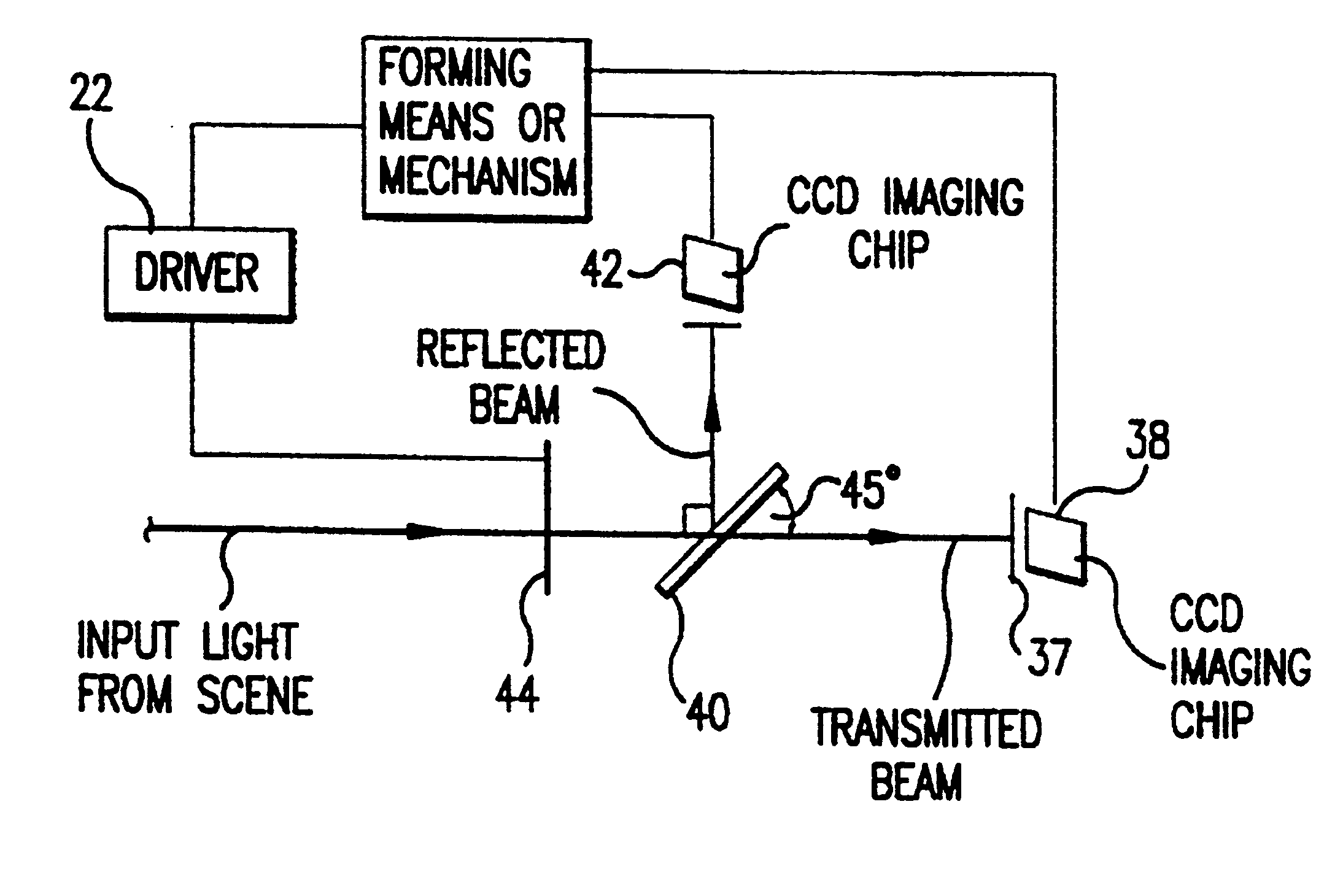
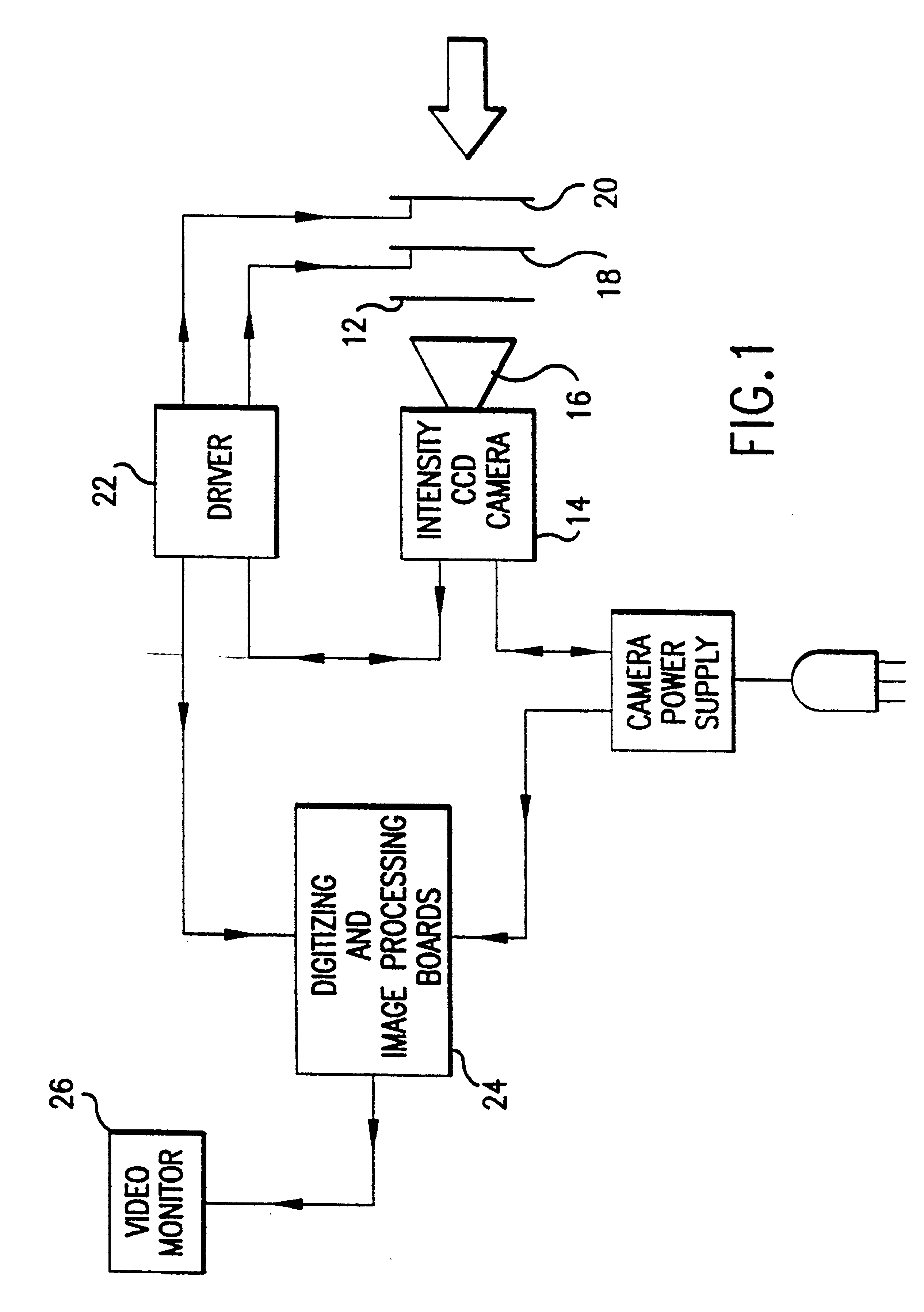
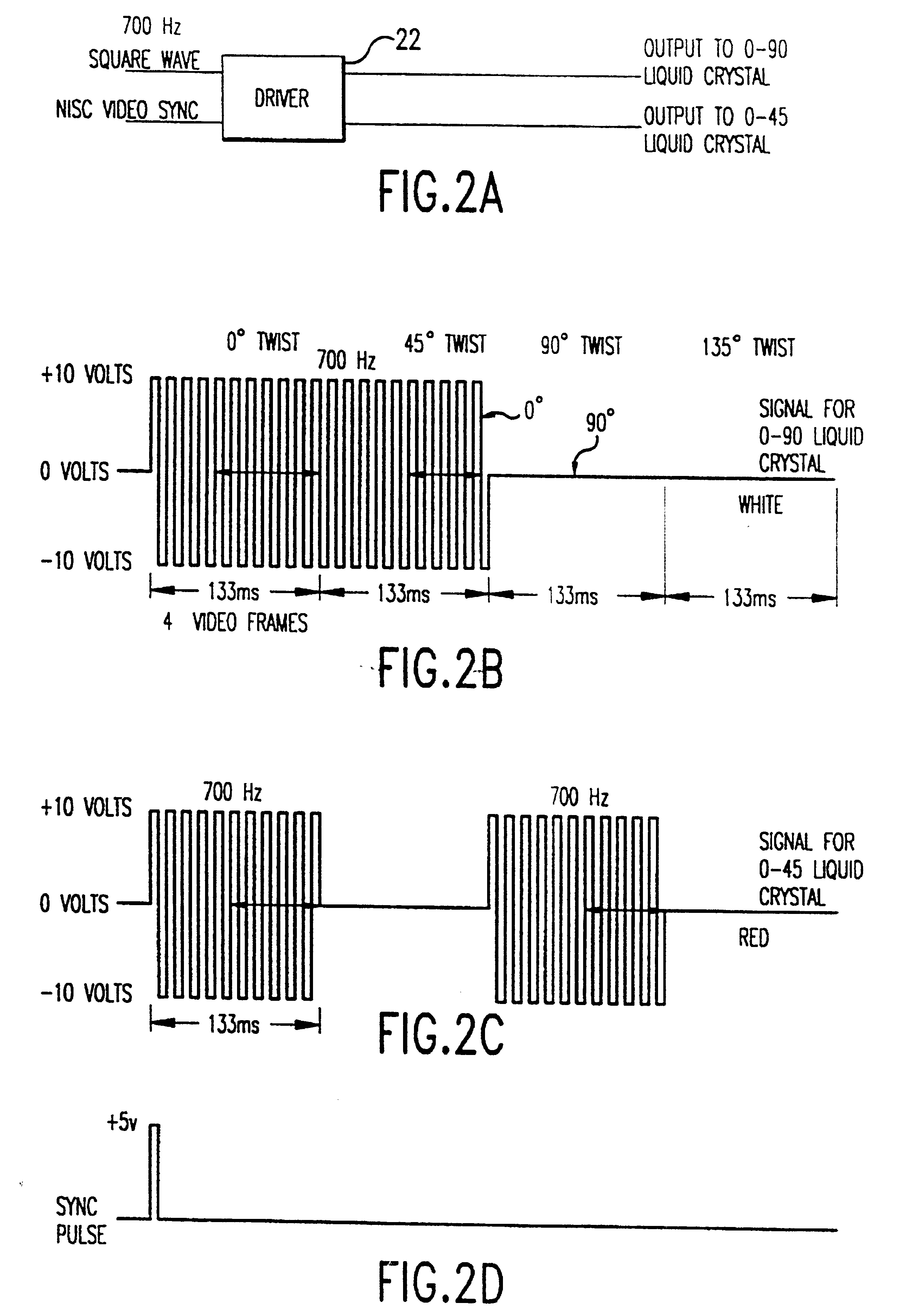
Polarization viewer
A polarization viewer comprising a mechanism for forming a broadview image having a spectral width greater than 2 angstroms and 0.50° based on polarization information of a scene. The polarization viewer is also comprised of a mechanism for providing polarization information to the forming mechanism. The providing mechanism is in communication with the forming mechanism. In a first embodiment, the providing mechanism includes a camera mechanism in communication with the forming mechanism. The camera mechanism includes a fixed polarizer analyzer disposed such that electromagnetic radiation entering the camera mechanism passes through the polarizer analyzer. The providing mechanism can also include a mechanism for steering a polarization plane of the radiation. The steering mechanism is disposed such that radiation passing through the polarizer analyzer first passes through the steering mechanism. The steering mechanism preferably includes a first twist crystal and at least a second twist crystal aligned with the first twist crystal such that radiation passing through the first crystal then passes through the second crystal. Each crystal has a first state and a second state. The first state does not effect the polarization plane of the radiation as the radiation passes through the crystal. The second state rotates the polarization plane of the radiation as the radiation passes through the crystal.
Owner:EQUINOX CORP
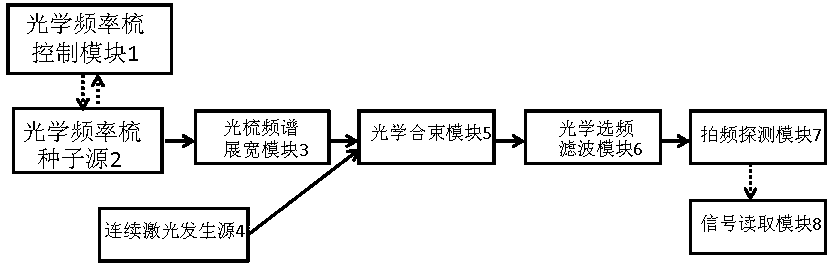
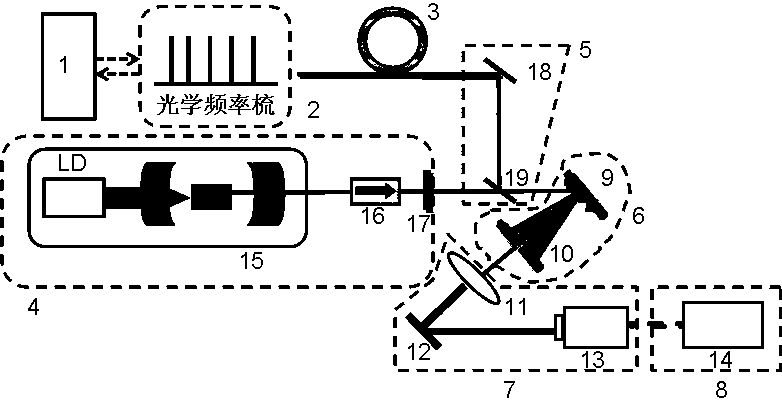
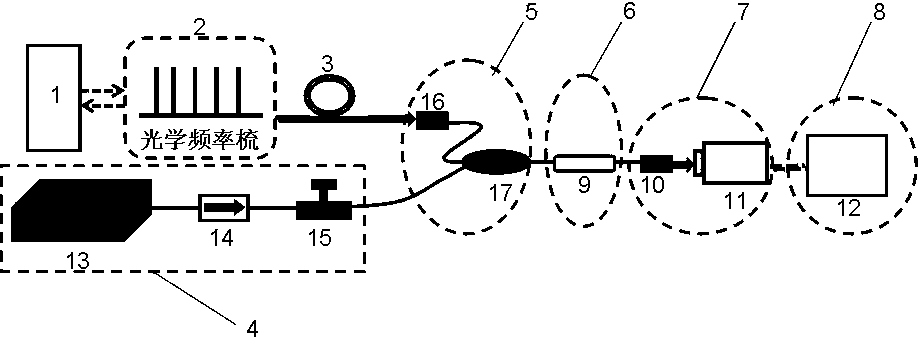
Continuous laser device spectral line width measurement device based on optical frequency comb
ActiveCN103712689AWide range of availableRealize measurementSpectrum investigationMeasurement deviceSpectral width
The invention discloses a continuous laser device spectral line width measurement device based on an optical frequency comb. The continuous laser device spectral line width measurement device is characterized by comprising an optical frequency comb control module, an optical frequency comb seed source, an optical frequency comb spectrum broadening module, a continuous laser generating source, an optical beam combining module, an optical frequency selecting filtering module, a beat frequency detecting module and a signal reading module. The spectrum of the precisely-controlled optical frequency comb is broadened, output light of the precisely-controlled optical frequency comb and output light of the continuous laser generating source together enter the optical beam combining module, the light spots of two outgoing laser beams coincide, and then the two laser beams together enter the optical frequency selecting filtering module, two laser beams obtained through filtering pass through the beat frequency detecting module, the sizes of light spots are changed through shaping, and the light spots are concentrated on a detector, beat frequency signals are obtained through coherent combination, and the output spectral width of the continuous lasers to be measured can be contained through the signal reading module. The continuous laser device spectral line width measurement device is stable in structure and high in practicability, the measurement process is rapid and simple, and the output spectral width of one or more wave length continuous lasers can be obtained in real time.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANGYAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Display device
InactiveUS7218049B2Shifting amount is very smallIncreased peak intensityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSpectral widthPhase shifted
In an organic EL device having a first electrode of a light reflective material, organic layer including an organic light emitting layer, semitransparent reflection layer, and second electrode of a transparent material that are stacked sequentially, and so configured that the organic layer functions as a cavity portion of a cavity structure, light that resonates in a certain spectral width (wavelength λ) is extracted by so configuring that optical path length L becomes minimum in a range satisfying (2L) / λ+Φ((2π)=m (m is an integer) where the phase shift produced in light generated in the organic light emitting layer when reflected by opposite ends of the cavity portion is Φ radians, L is optical path length of the cavity portion, and λ is the peak wavelength of the spectrum of part of light to be extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and methods for surface contour measurement
InactiveUS20060012802A1Reduce impactReduce measurementUsing optical meansSpectral widthControl system
Apparatus and methods of measuring three-dimensional position information of a point on the surface of an object. The invention also relates to an apparatus for projecting fringes onto a surface of an object including two sources of radiation separated by a distance, each source having a spectral distribution, and being coherent with respect to the other of the sources, a control system moving each of the sources relative to the other of the sources, and a detector positioned to receive radiation scattered from the point on the surface of the object. In another embodiment, the two sources of radiation include, an initial source of a beam of radiation having a spectral width, a beam separator in optical communication with the initial source of a beam of radiation generating a first optical beam and a second optical beam, and an imaging system optically connected to the beam separator.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
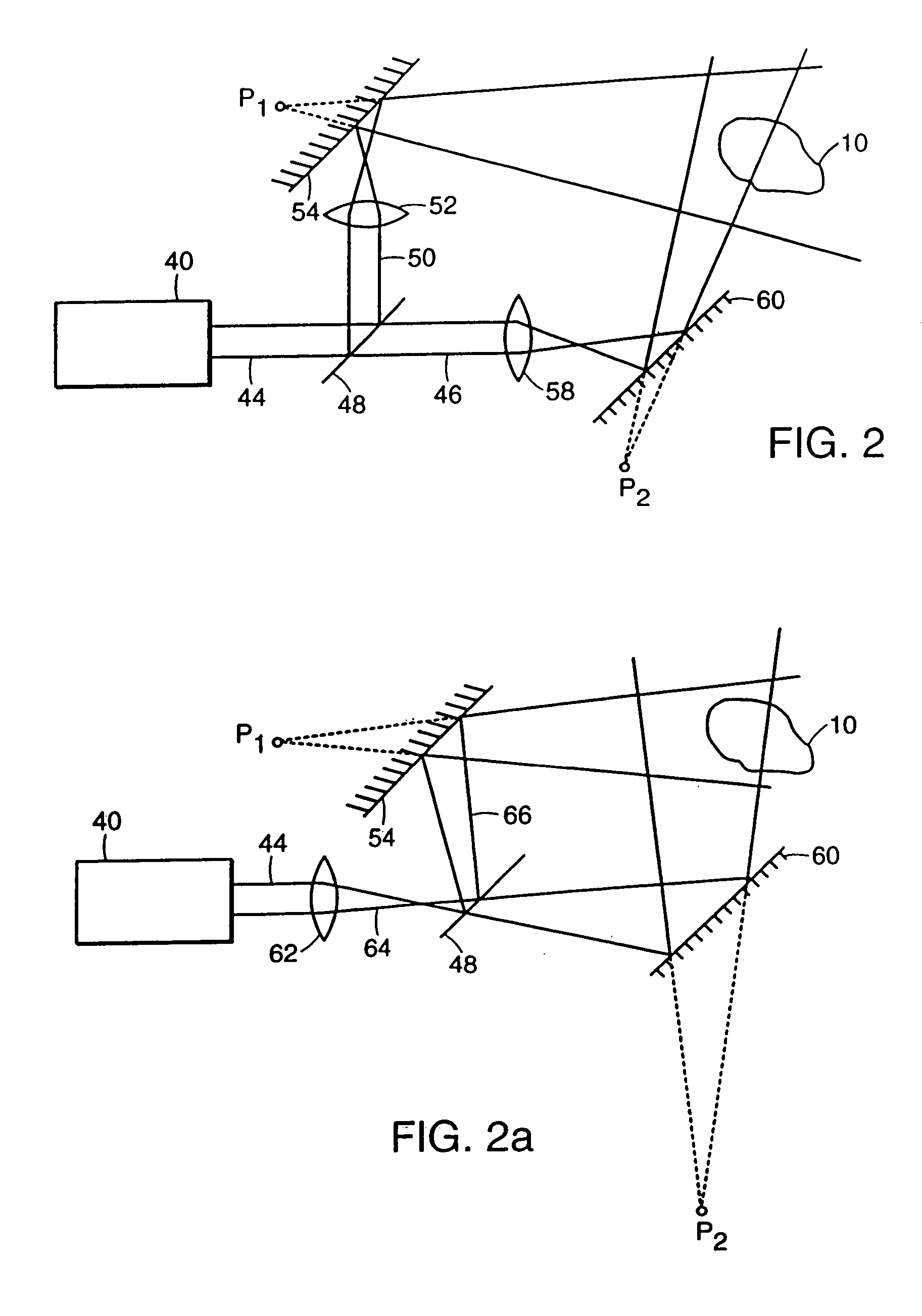
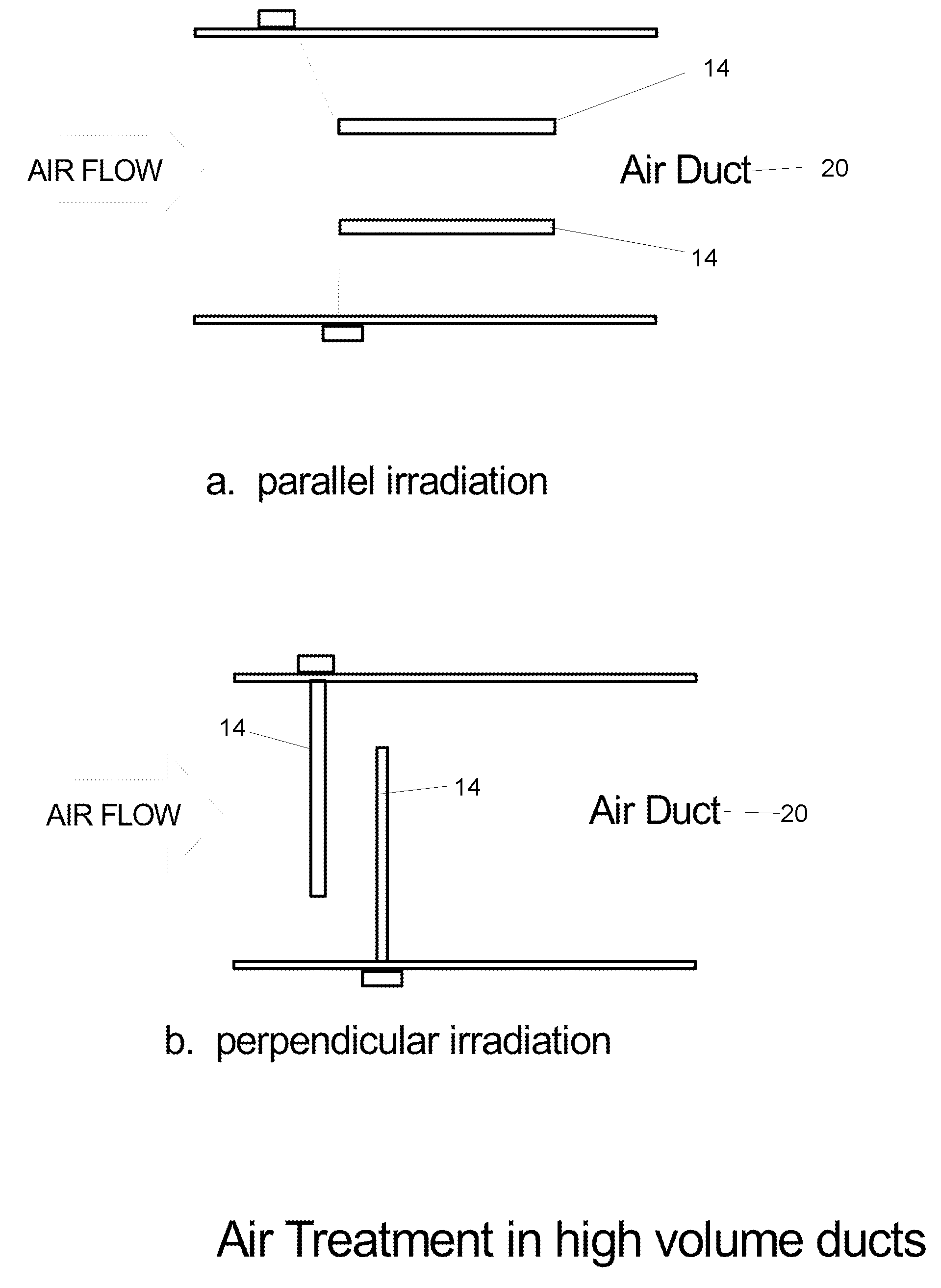
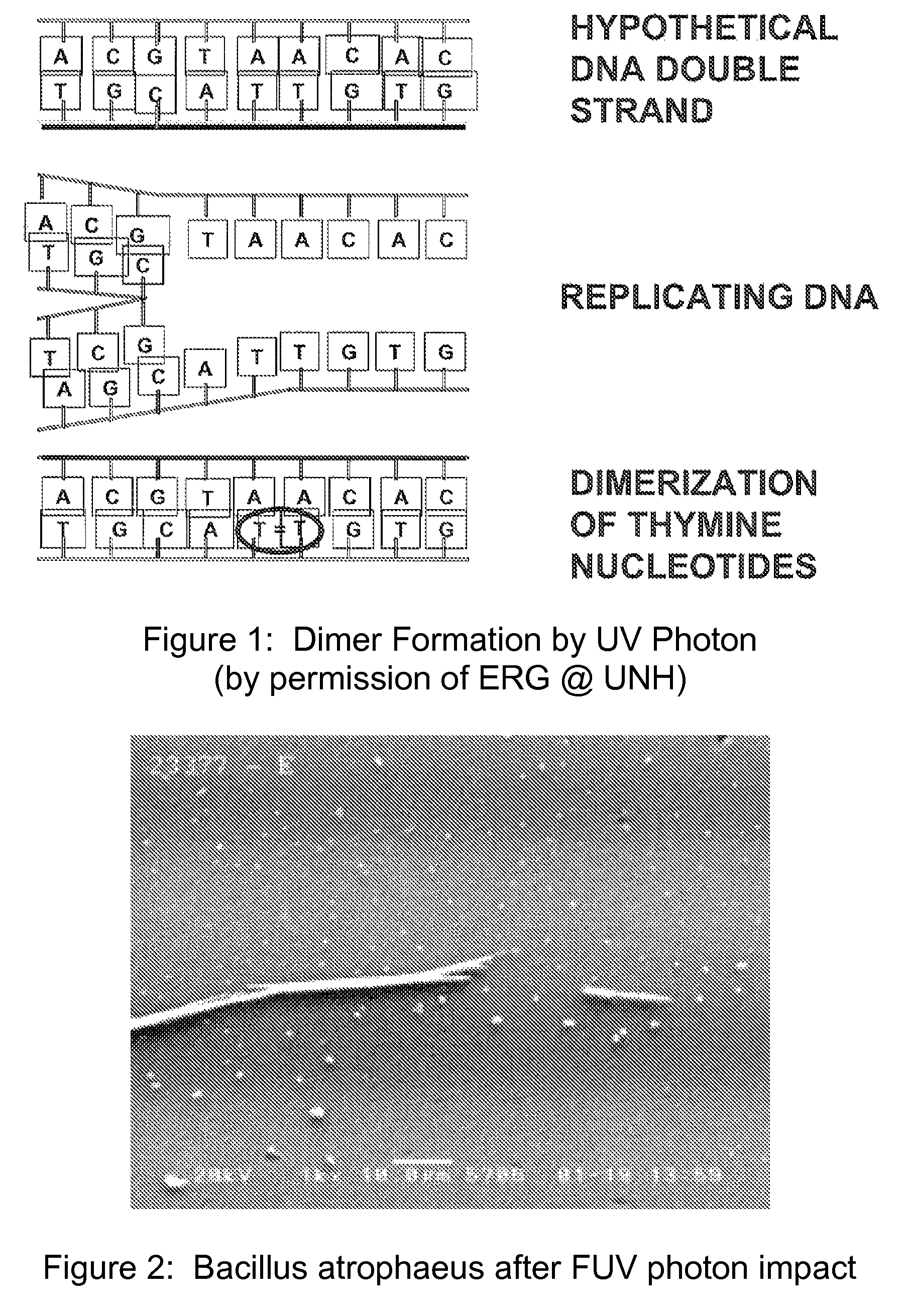
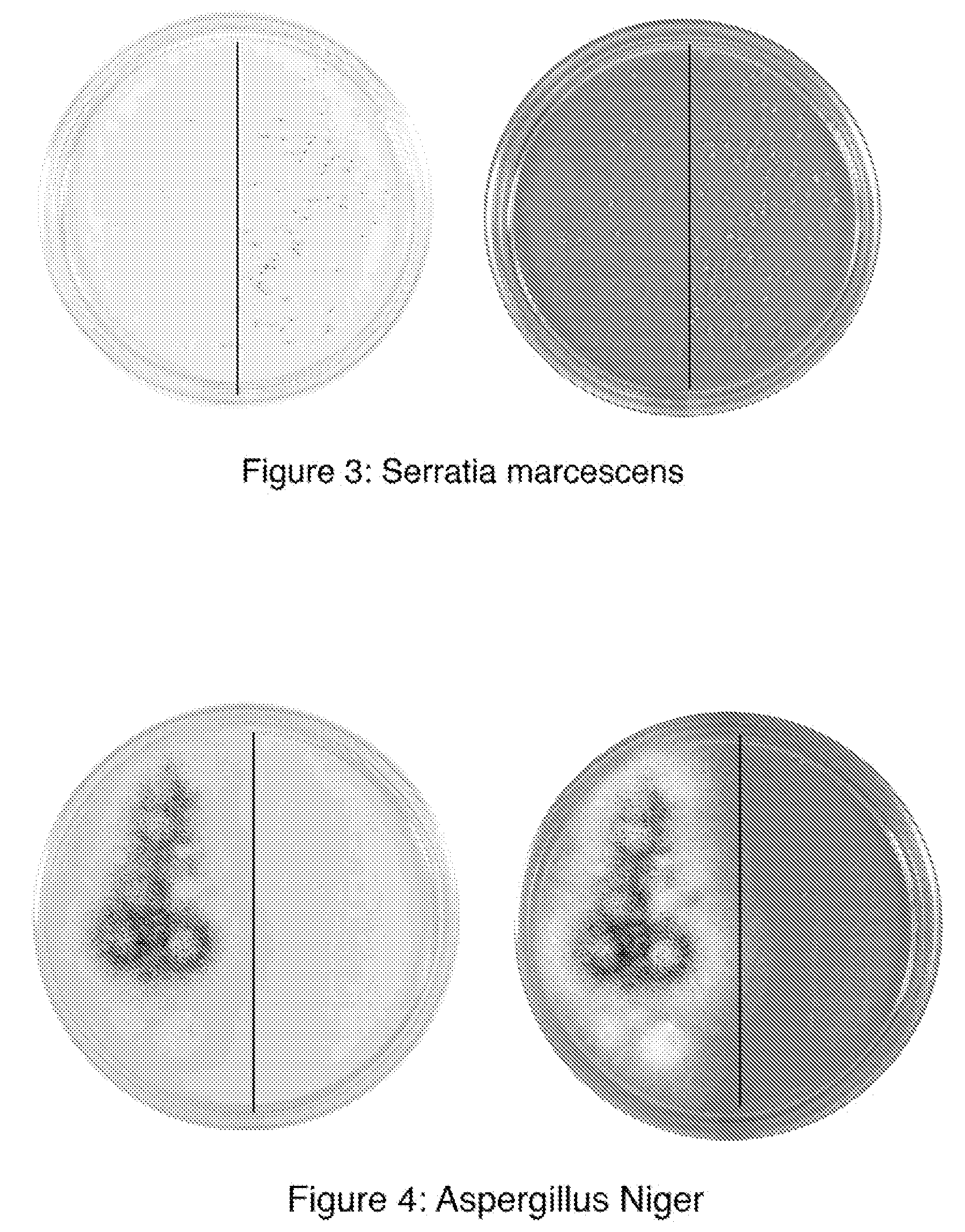
Method and apparatus for producing a high level of disinfection in air and surfaces
ActiveUS8481985B2Significantly effectiveOptical radiation measurementWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSporeSpectral width
This specification relates to an improved method, process and apparatus for disinfecting and sterilizing all types of surfaces and indoor air and room air contaminated with microorganisms. The improved apparatus consists of a multi-wavelength narrow spectral width UV source that is more effective than mercury based 254 nm germicidal lamps for destroying the DNA and outer shell or membrane of virus, bacteria, spores and cists.
Owner:CASALE RICHARD
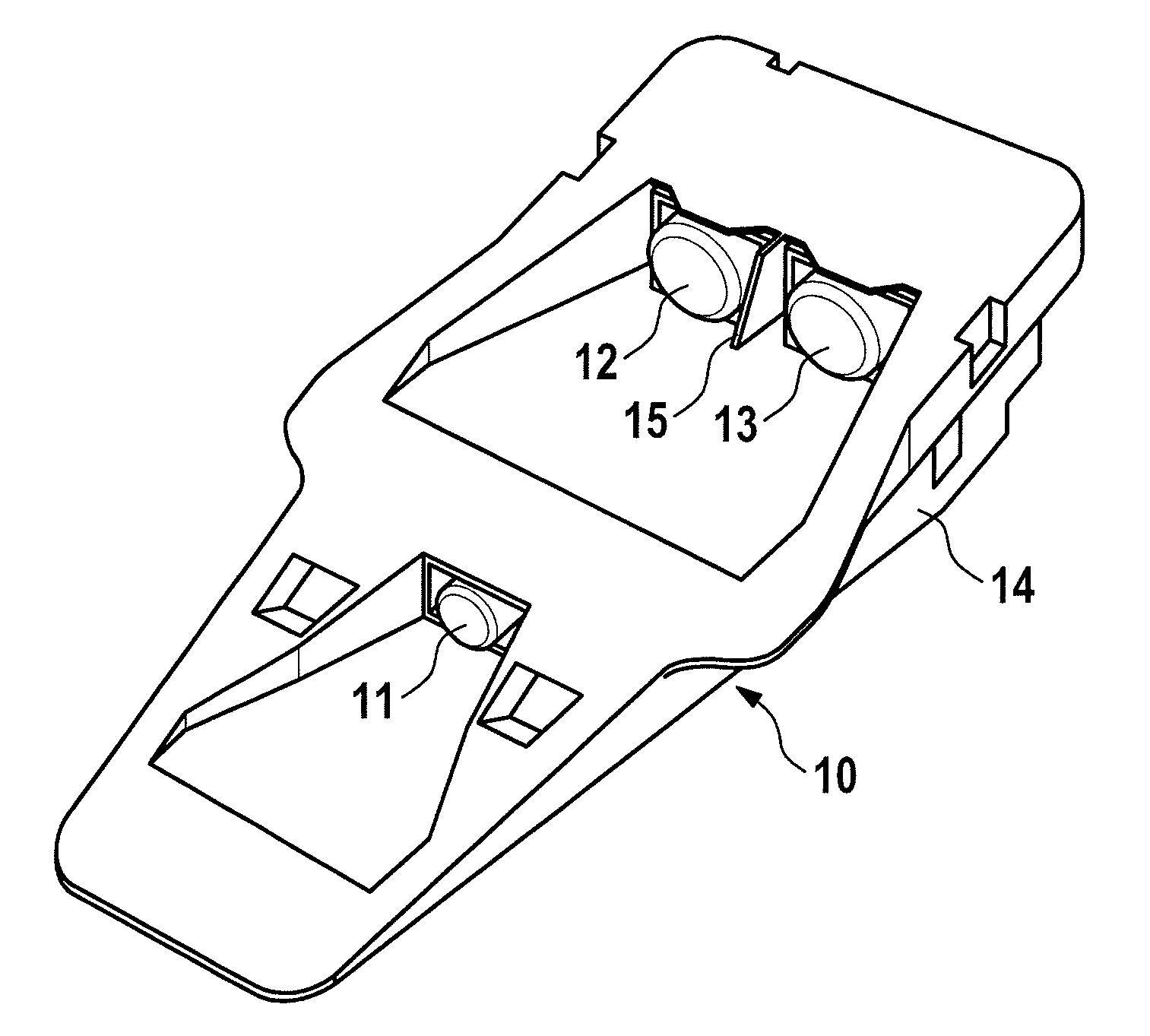
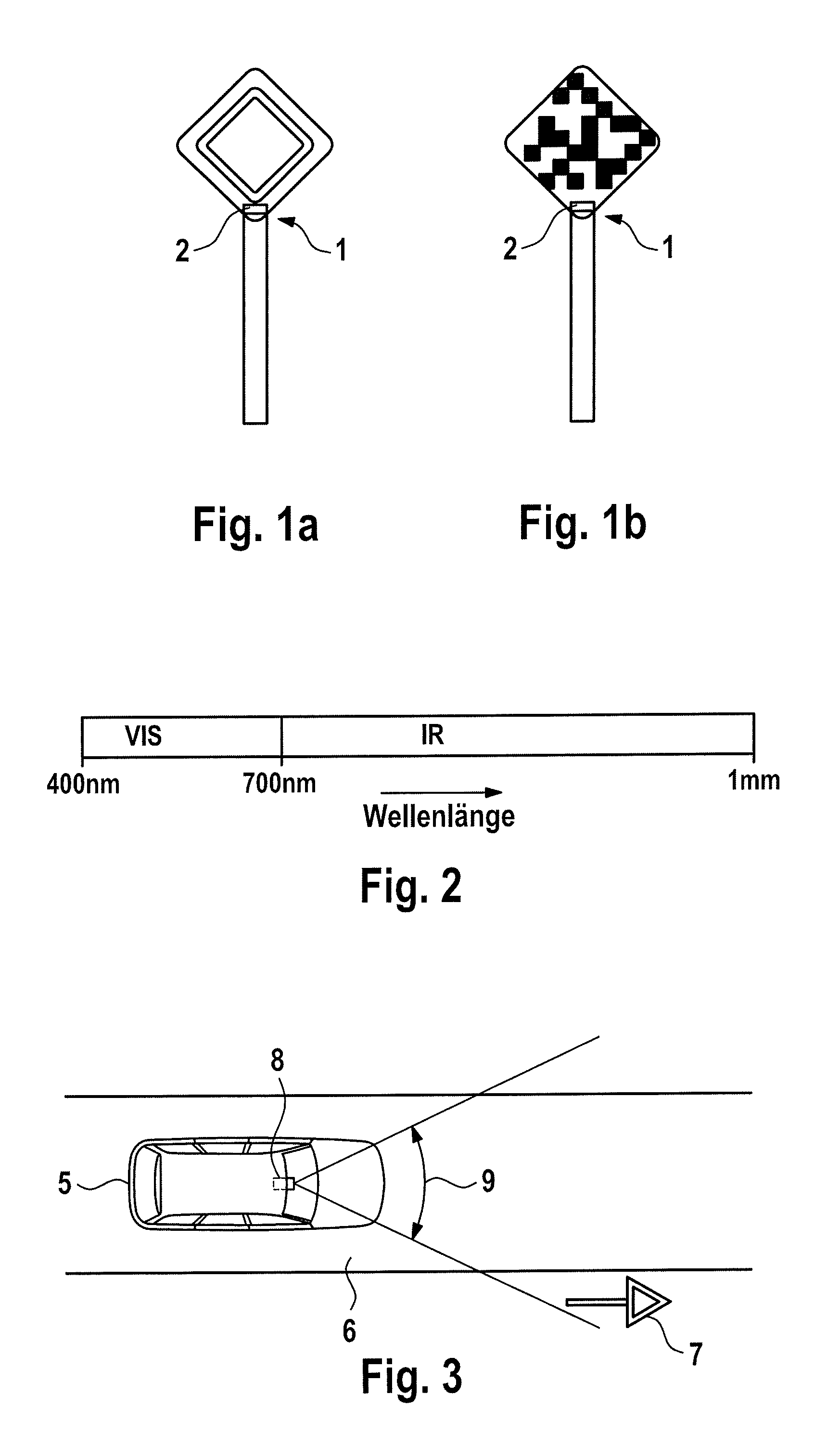
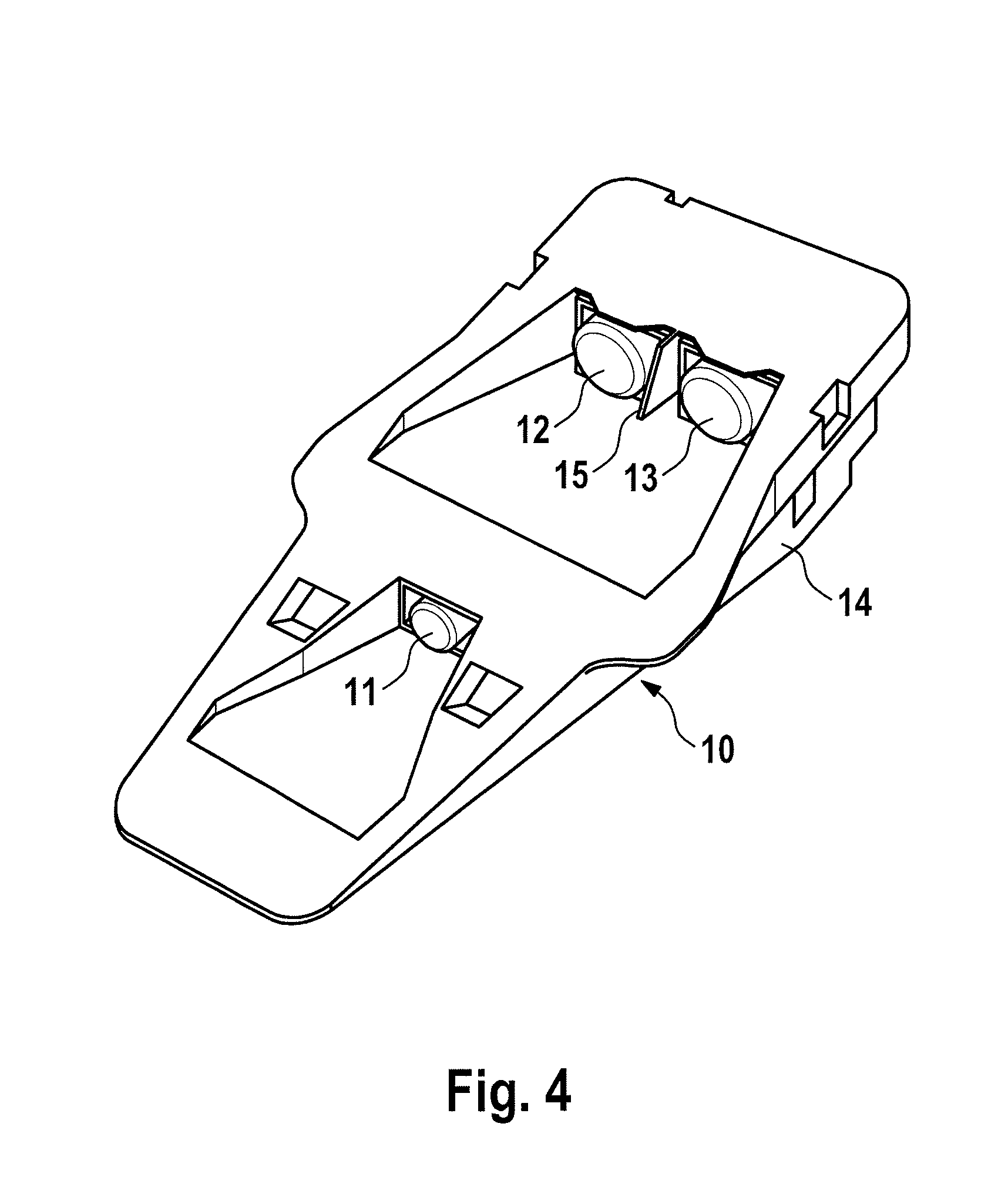
Signal transmitter, system and method for highlighting objects in road traffic, use of the system, and use of the signal transmitter
InactiveUS20150019098A1Improve securityIncrease costAnalogue computers for trafficRoad vehicles traffic controlSpectral widthNanoparticle
A signal generator for highlighting objects in road traffic, including a marker and a carrier material. The marker is arranged on the carrier material in such a manner that the marker covers one surface side of the carrier material and / or is added to a substance of the carrier material. The signal transmitter reflects incident electromagnetic radiation of at least one predeterminable wavelength band by the marker. A spectral width and a spectral position of the at least one predeterminable wavelength band are distinguished by a size and / or a size distribution and / or a shape of nanoparticles contained in the marker and / or by a surface nanostructuring of the marker. The spectral position of the at least one predeterminable wavelength band is located in an infrared spectral range. The invention further relates to a corresponding system, a corresponding method, the use of the signal generator, and the use of the system.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
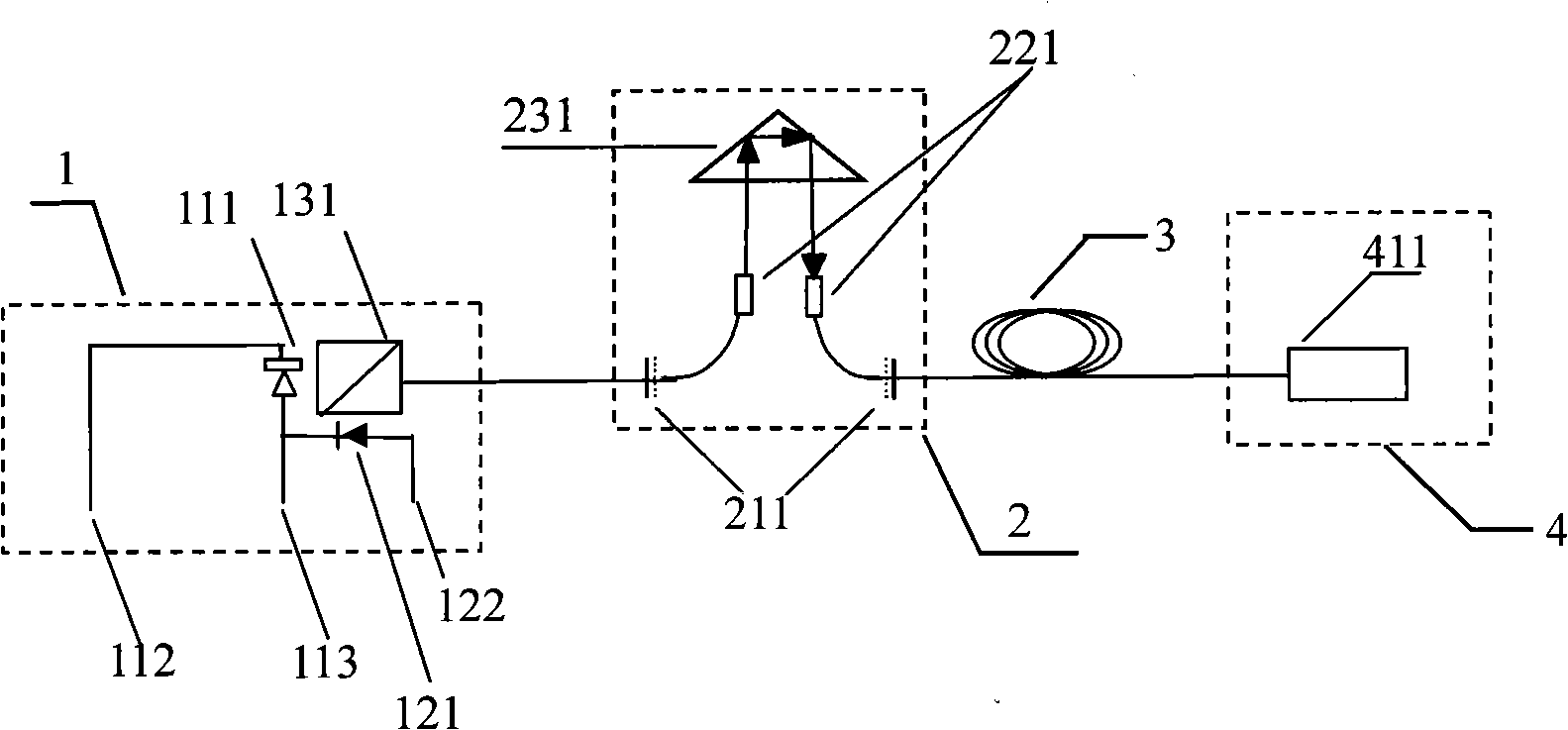
Distributed optical fiber white light interference sensor array based on adjustable Fabry-Perot resonant cavity
InactiveCN101324445AWith common light path structureImprove temperature stabilityCoupling light guidesConverting sensor output opticallySensor arrayBeam splitter
The invention provides a distributed fiber white-light interference sensor array based on tunable Fabry-Perot resonant cavity, which is composed of a duplex photoelectric device, a tunable Fabry-Perot resonant cavity, a single-mode connection fiber and a sensor, wherein the tunable Fabry-Perot resonant cavity is composed of a scanning prism, a self-focusing lens, and a single-mode optical fiber with partial reflection surface; the duplex photoelectric device is composed of a wide-spectrum light source with a common base, an emitter and a collector, a photodetector, and a beam splitter prism; the beam with a certain spectral width is emitted by the light source to the resonant cavity directly through the beam splitter prism and is reflected multiple times by the left and the right surfaces of the resonant cavity to obtain a signal light; and the signal light outputted from the right cavity surface enters the sensor through the single-mode connection fiber, reflected by the left and the right end faces of the sensor, returns along the original path to the resonant, and is outputted from the left cavity surface to the photodetector. The distributed fiber white-light interference sensor array has a common light path structure and has the advantages of good temperature stability, simplest optical fiber path structure, low cost and high practicality.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
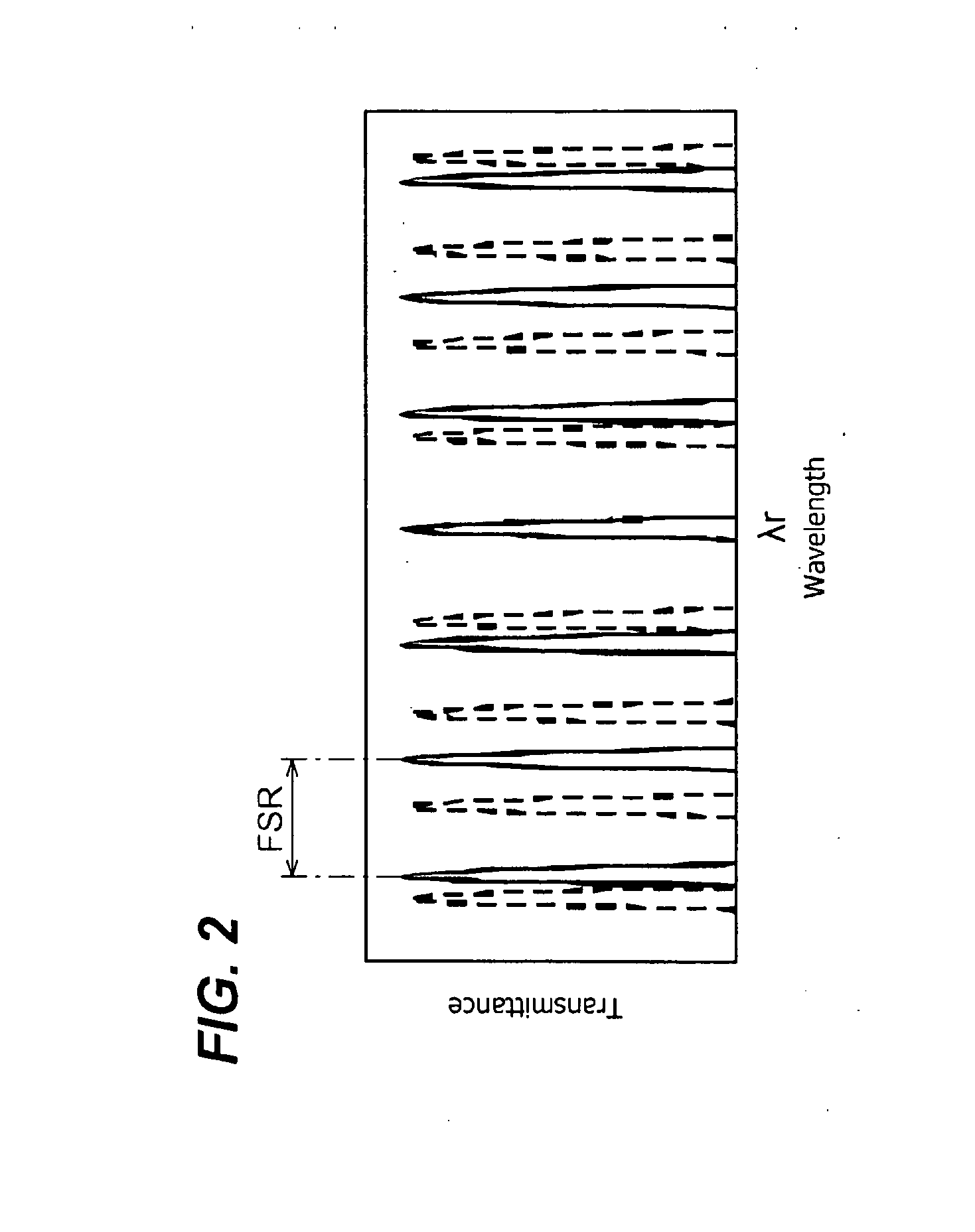
Light-emitting device with precisely tuned and narrowed spectral width of optical output and an optical signal source providing the same
InactiveUS20090046748A1Narrow widthLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionWavelength filterSpectral width
A light-emitting device whose output wavelength is easily variable is disclosed. The device provides a light-generating portion that emits light by the carrier injection and a variable wavelength filter that sets a specific wavelength λr. The variable wavelength filter includes two ring waveguide optical coupled with each other and having optical paths different from each other and at least an electrode to apply an electrical signal to the corresponding ring waveguide. By tuning the specific wavelength λr to the wavelength emitted from the light-generating portion, the output wavelength from the light-emitting device may be narrowed.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Broadband light emitting device
ActiveUS20050279989A1Increase heightBroad emission spectrumLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionStimulated emissionP–n junction
The invention concerns a superluminescent light emitting diode (SLED) comprising a semiconductor heterostructure forming a PN junction and a waveguide. The semiconductor heterostructure includes a gain region with a contact means for biasing the PN junction so as to produce light emission including stimulated emission from an active zone of the gain region, and in the active zone a plurality of quantum dot layers, each quantum dot layer made up of a plurality of quantum dots and a plurality of adjoining layers, each adjoining layer adjacent to one of said quantum dot layers. The material composition or a deposition parameter of at least two adjoining layers is different. This ensures an enhanced emission spectral width.
Owner:EXALOS
Exposure apparatus, exposure method, device manufacturing method, and system
ActiveUS7701555B2Reduce sizeGood precisionLaser detailsPhotomechanical apparatusSpectral widthLine width
An exposure apparatus is equipped with a laser unit that emits a laser beam, a memory that stores a first information which shows a first relation indicating a relation between a linewidth error of a pattern formed on a wafer and a spectral characteristic of the laser beam emitted from the laser unit, and a main controller that controls the spectral width of the laser beam via a laser controller, based on the first information and on information related to a reticle that is to be used. Main controller performs spectral width control of the laser beam so as to suppress linewidth error, based on the first information and on the information related to the reticle that is to be used.
Owner:NIKON CORP
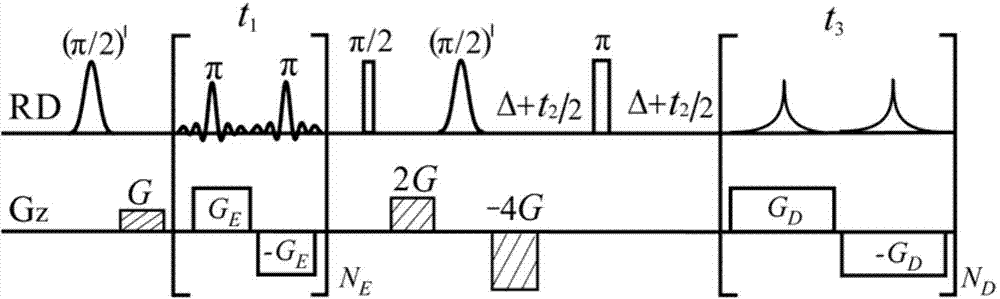
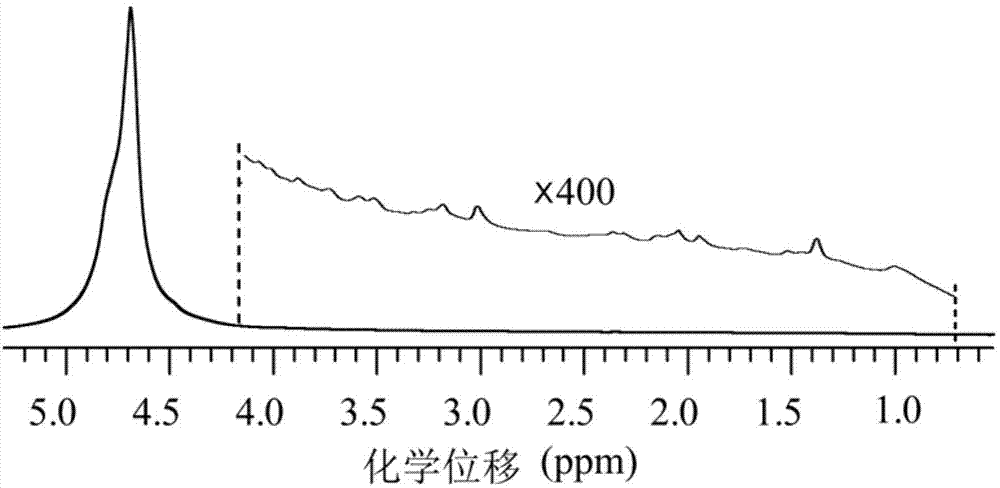
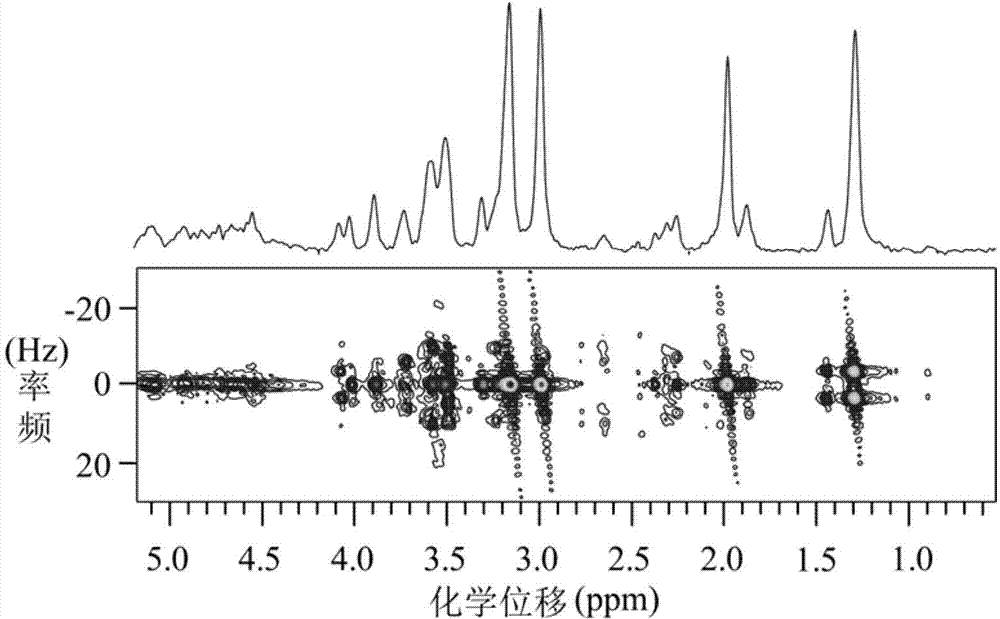
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy in non-uniform magnetic field
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for scanning microscopy; and scanning microscope
A method for scanning microscopy is disclosed. It contains the step of generating an illuminating light beam that exhibits at least a first substantially continuous wavelength spectrum whose spectral width is greater than 5 nm; the choosing of a second wavelength spectrum that is arranged spectrally within the first wavelength spectrum; the step of selecting the light of the second wavelength spectrum out of the illuminating light beam using an acoustooptical component; and the step of illuminating a specimen with the illuminating light beam. A scanning microscope is also disclosed.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Remote location of active section of fiber in a multimode intrusion detection system
ActiveUS20070092176A1Maximum sensitivityFast locationWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesSpectral widthData signal
Intrusion detection of one section only of a multimode fiber uses a light signal launched into the fiber at a location spaced from the source through a single mode fiber to establish a narrow spectral width, under-filled non-uniform mode field power distribution in the fiber. A small portion of the higher order signal modes at the a second location also spaced from the destination is sampled by a tap coupler and monitored for transient changes in the mode field power distribution which are characteristic of intrusion to activate an alarm. The active signal of a multimode optical fiber is monitored for both signal degradation and transient power disturbance patterns that could indicate fiber damage or physical intrusion. A translator can be provided in an existing optical fiber system in which the data signals are translated in wavelength and / or launch conditions to optimize the monitoring signals in an otherwise non-optimized system.
Owner:NETWORK INTEGRITY SYST
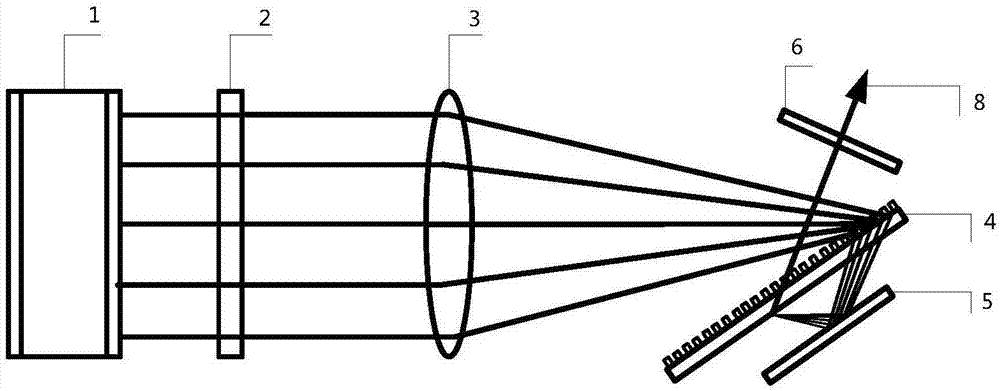
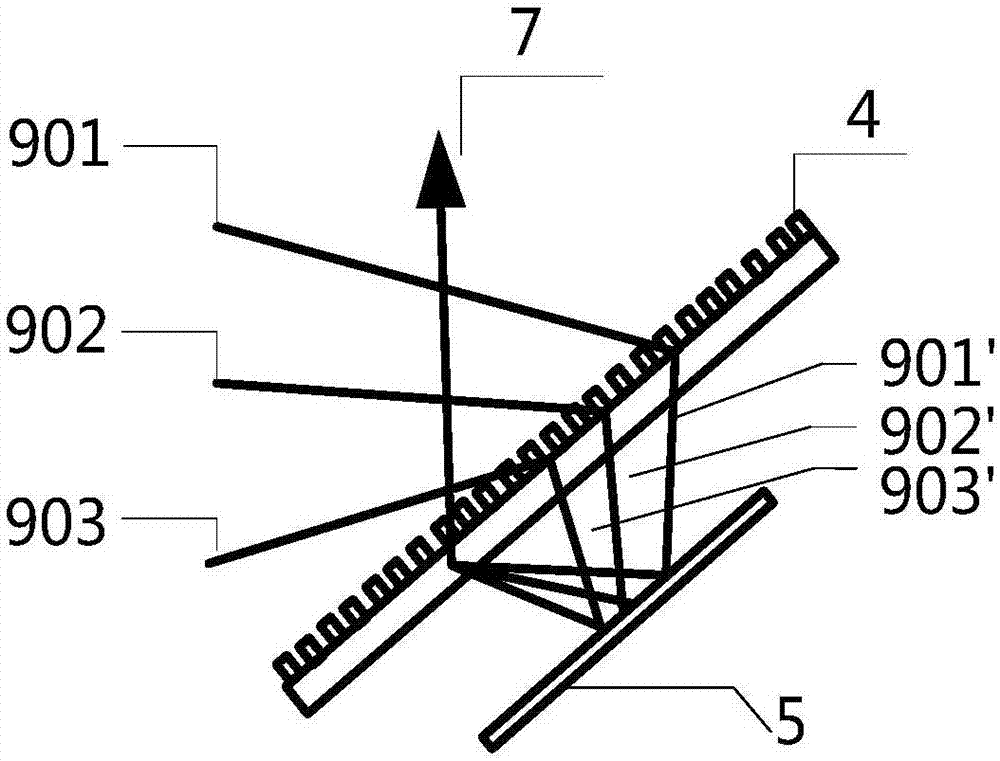
Spectral beam combining device for realizing spectral width compression through two-time diffraction by using grating and reflecting element
ActiveCN107272214AImprove dispersionAchieving secondary dispersionOptical elementsGratingLaser array
Disclosed is a semiconductor laser spectral beam combining device for for realizing spectral width compression through two-time diffraction by using a grating and a reflecting element. The device comprises a semiconductor laser light source, a slow axis collimating cylindrical lens, a transforming lens, a grating, a reflecting element and an output coupling mirror. In the invention, the single grating is used as a diffraction element, the reflecting element reflects the beam which is diffracted by the grating for the first time, the beam is secondarily dispersed when passing through the grating again, and the dispersive power is doubled. Through the feedback of the output coupling mirror, the laser of each unit of a semiconductor laser array is locked at a different wavelength to obtain a laser output of high power and high brightness. The device of the invention overcomes the limitation of the gain line width of a gain material in the traditional spectral beam combination to the number of beam combining units, can increase the number of beam combining units within the gain line width and the high-efficiency diffraction wavelength range of the grating, increases the output power significantly, reduces the resonant cavity length with a certain spectral width, makes the laser structure compact and improves laser mode stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Projection System Using High-Frequency Drive Modulation to Reduce Perceived Speckle
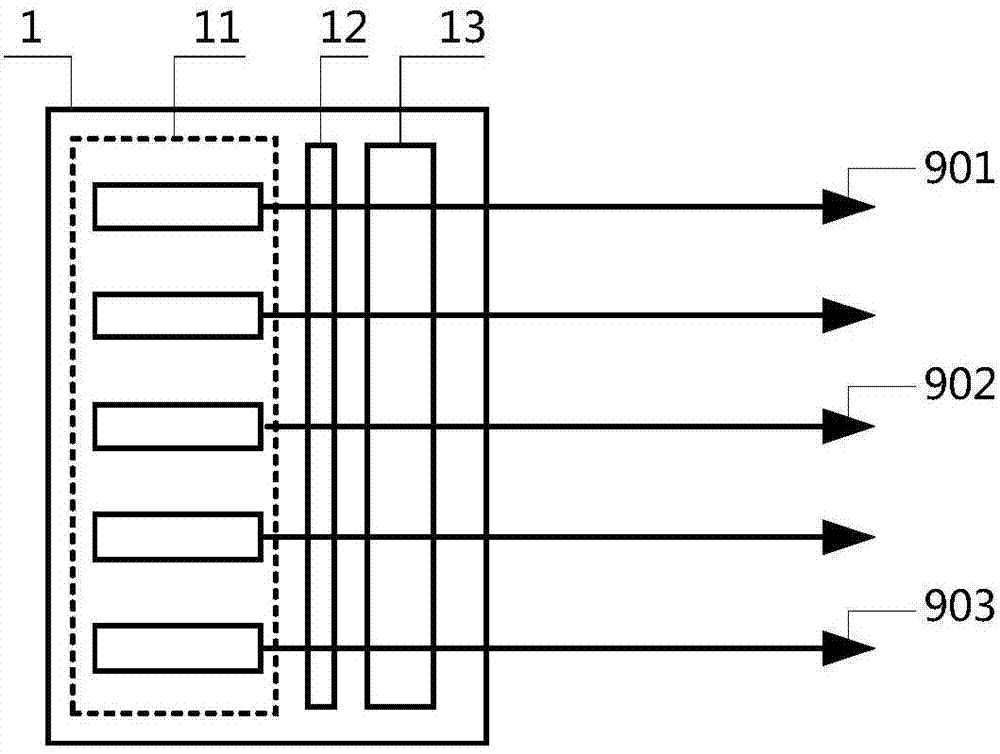
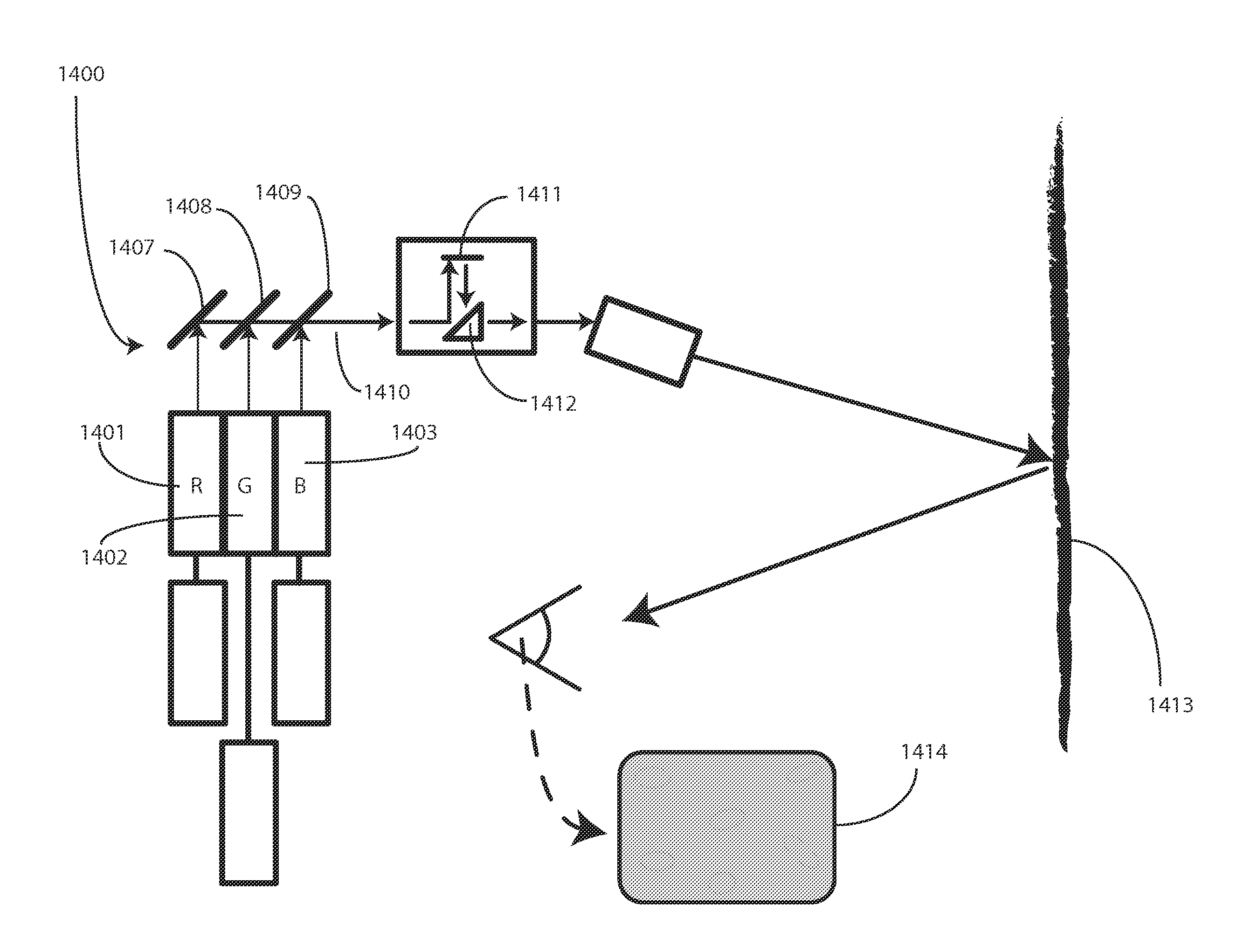
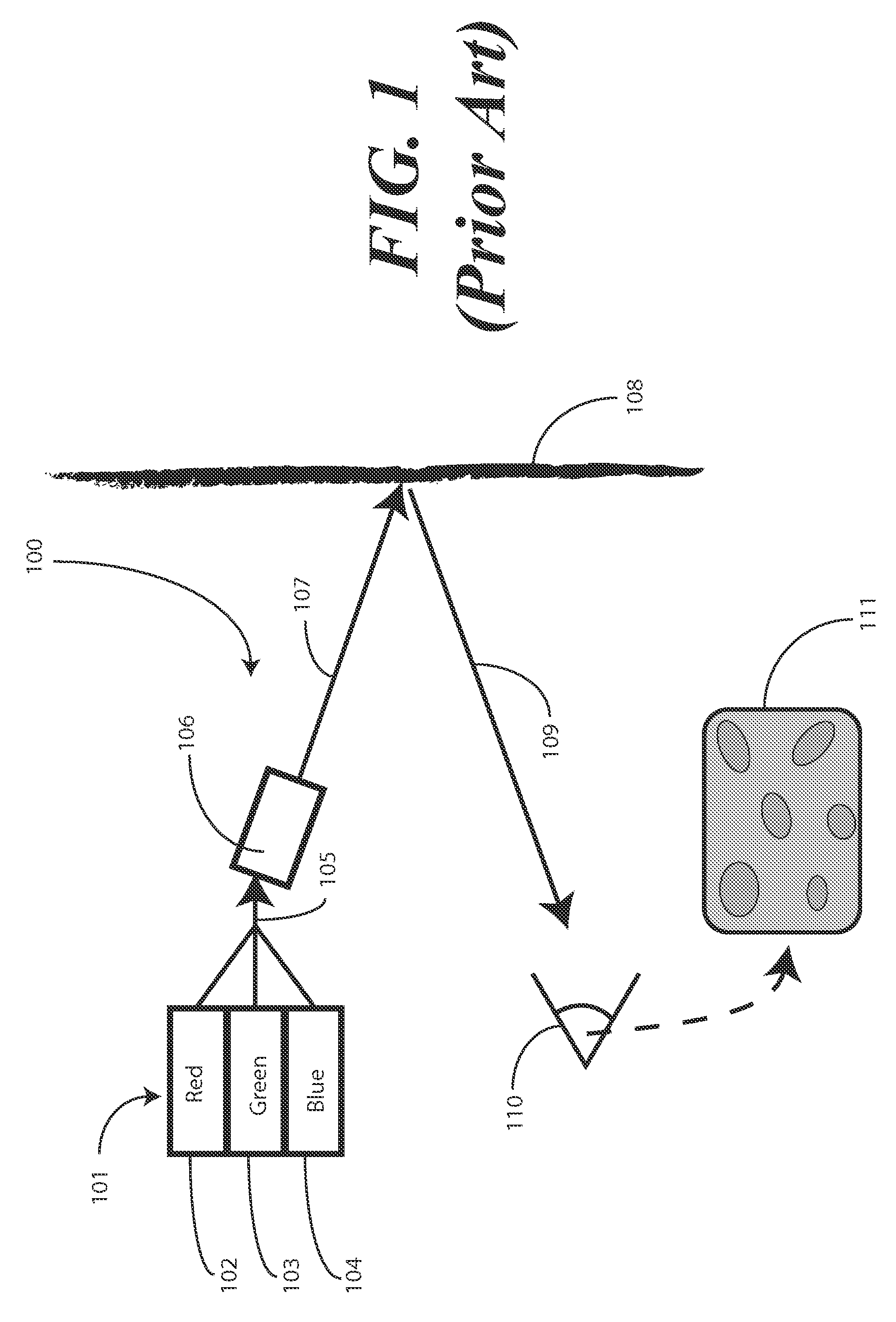
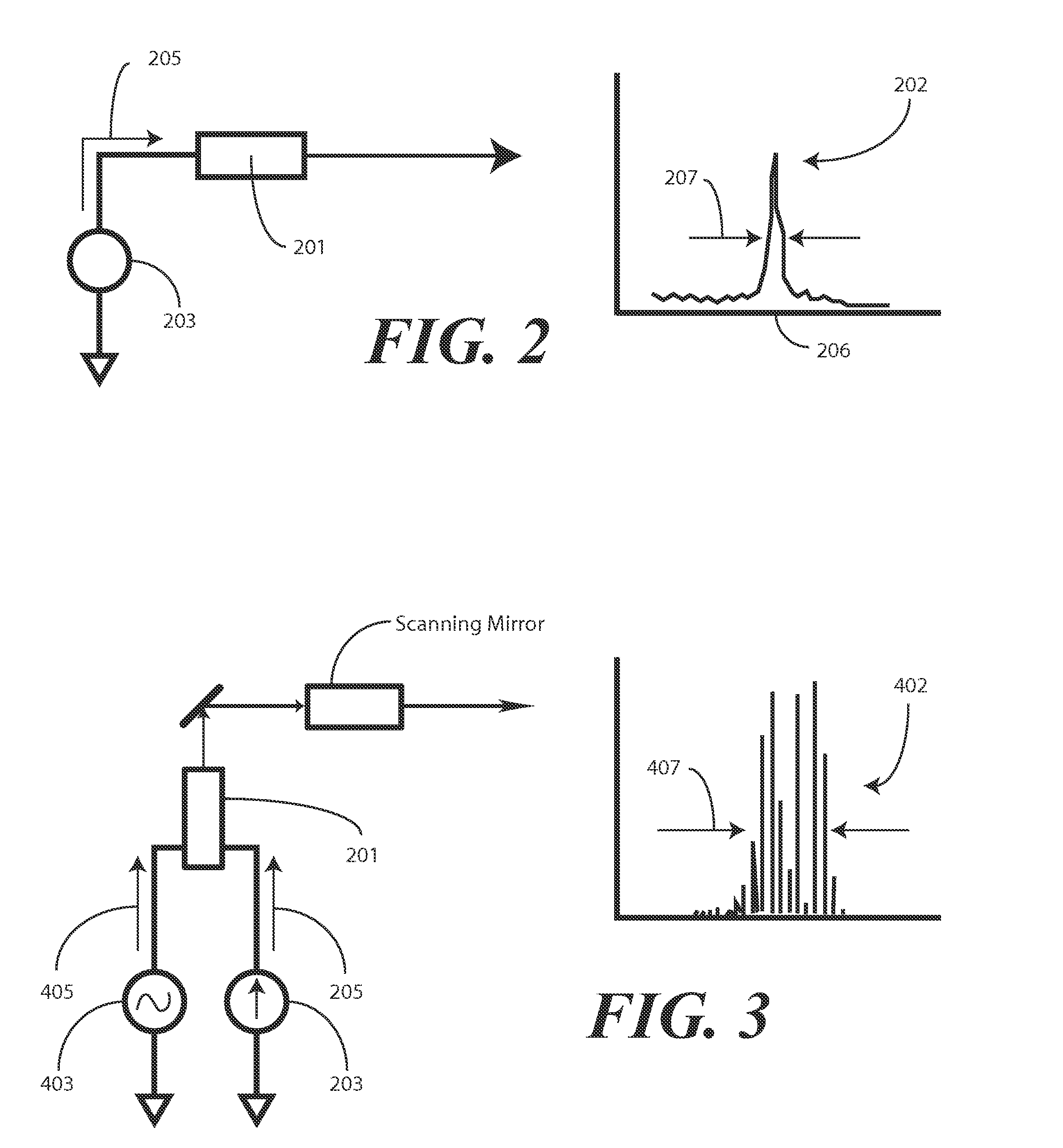
InactiveUS20100097534A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionEngineeringAlternating current
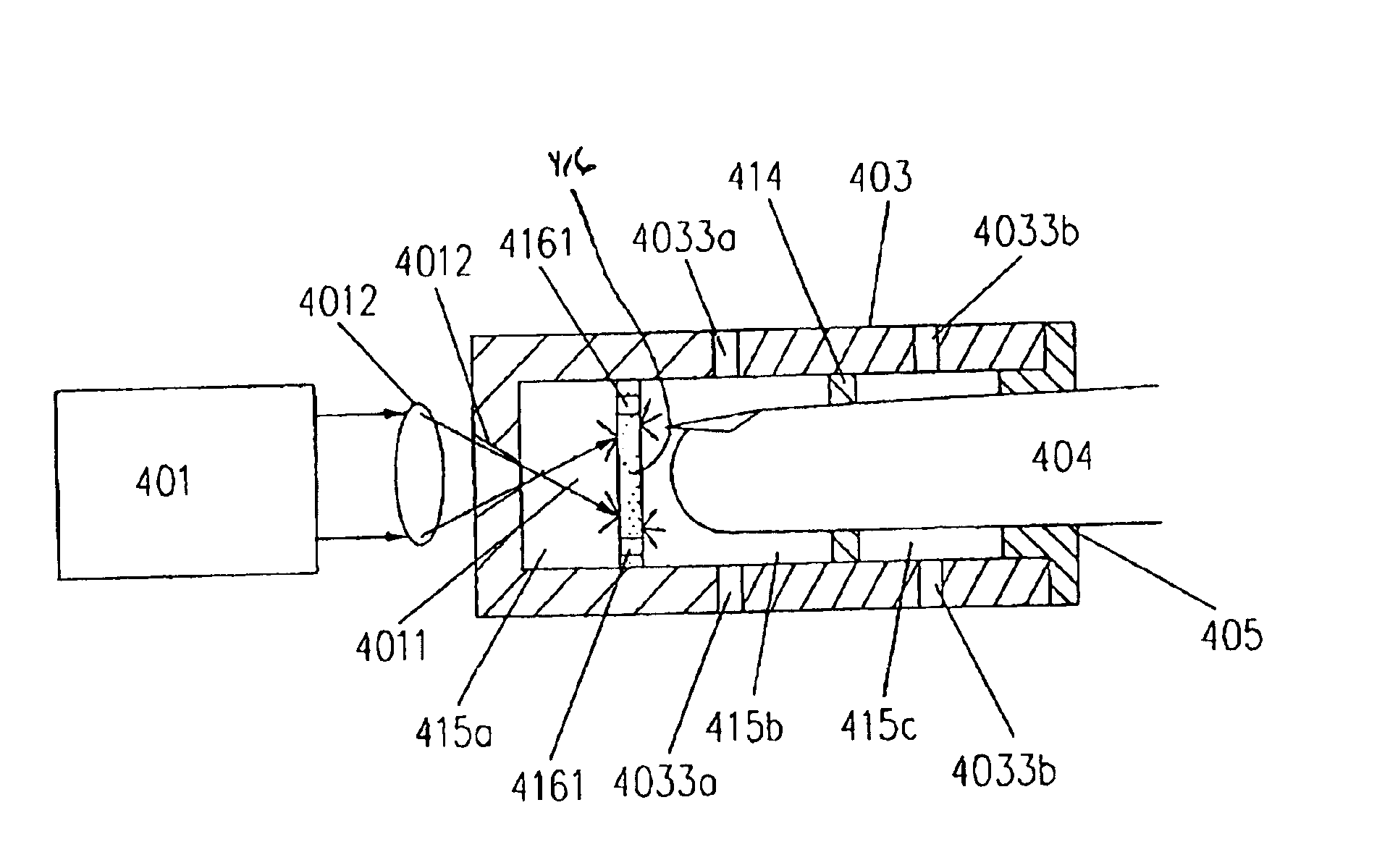
An image producing system (1400) delivers images (1414) having reduced speckle by employing one or more drive circuits (1404, 1405, 1406) that deliver both a direct current drive signal (205) and an alternating current drive signal (405) to one or more lasers (1401, 1402, 1403). Specifically, an alternating current drive circuit (403) is used in conjunction with a direct current drive circuit (203) to modulate a drive signal. The modulation can be at a frequency of between 400 MHz and 600 MHz. When lasers, such as the red laser (1401) or the blue laser (1403) of a multi-laser system are modulated in such a fashion, their emitted spectral widths (407) greatly expand, thereby reducing speckle in projected images (1414).
Owner:MICROVISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com