Polarization viewer
a viewer and component technology, applied in the field of polarization viewers, can solve the problems of inability to obtain polarization component images, complicated or possibly infeasible,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
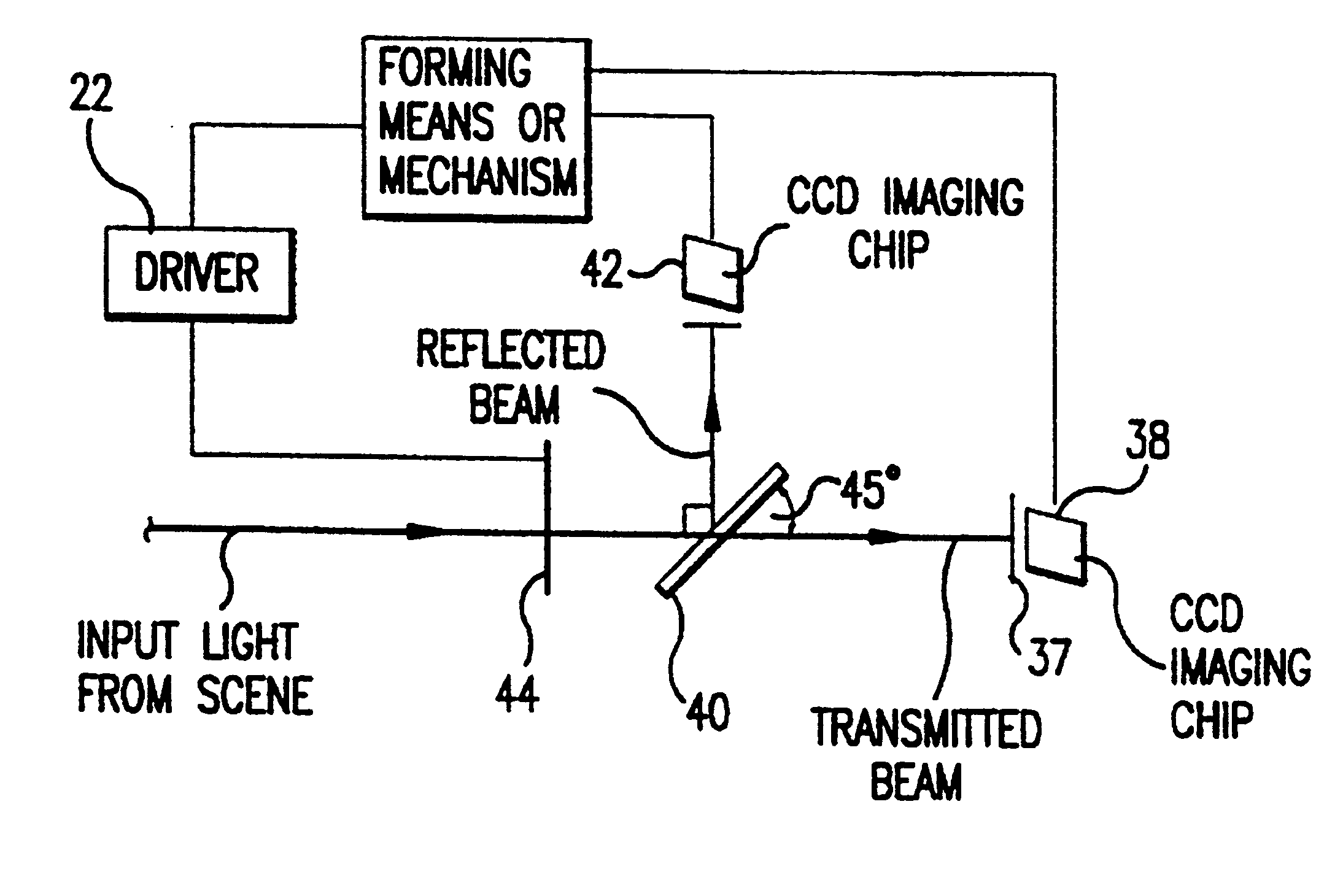
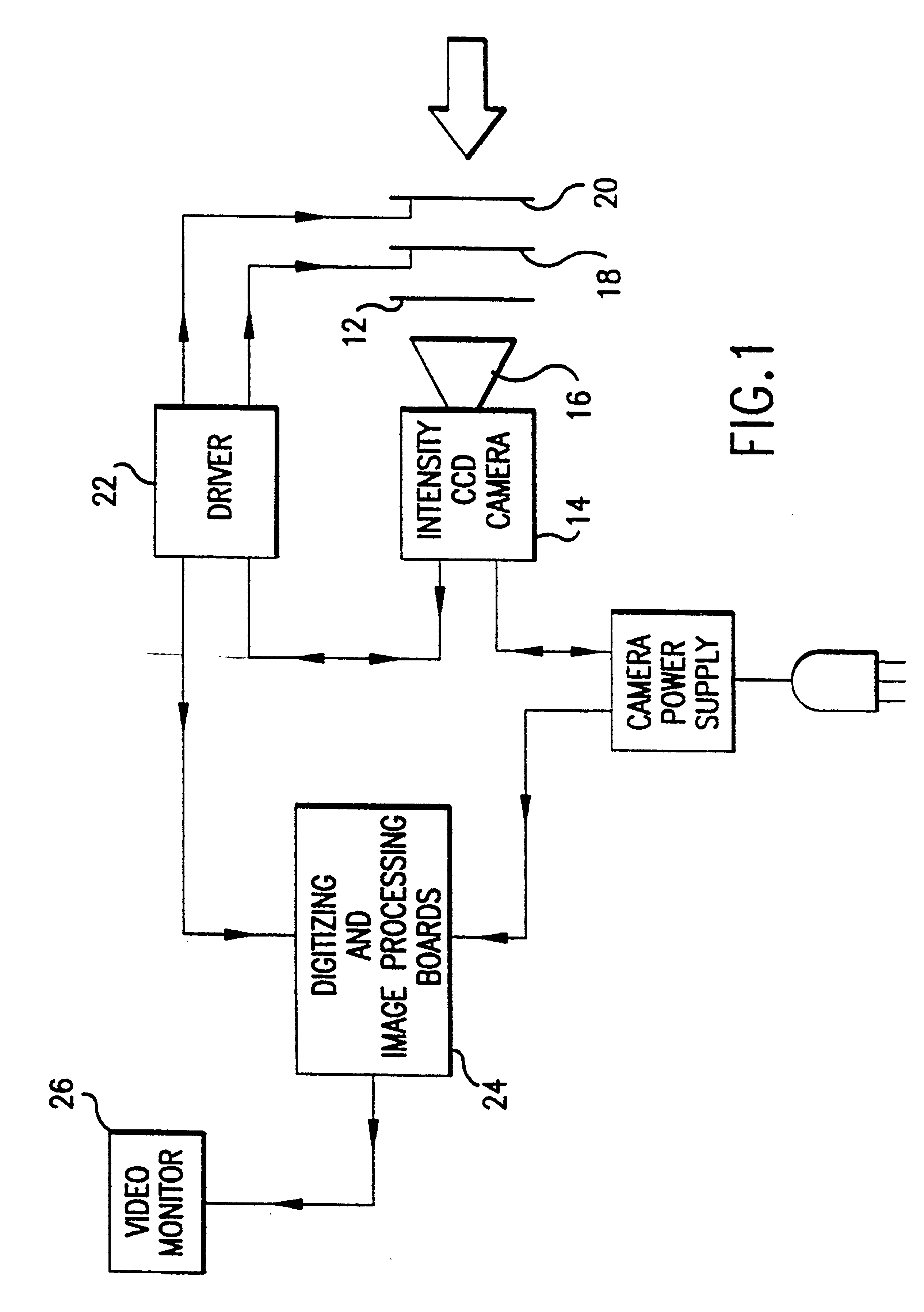
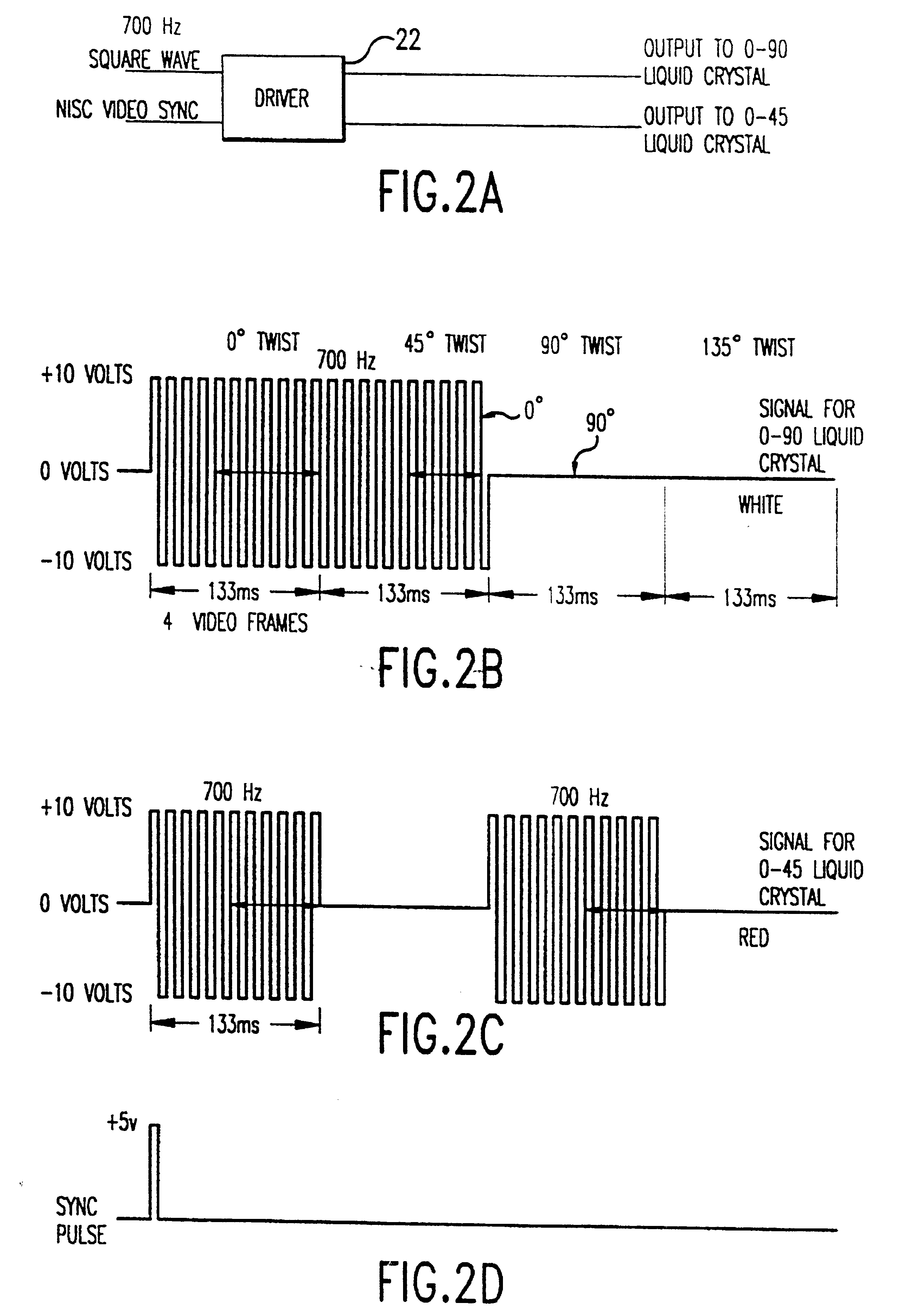
Referring now to the drawings wherein like reference numerals refer to similar or identical parts throughout the several views, and more specifically to FIG. 1 thereof, there is shown a polarization viewer 10. The polarization viewer 10 is comprised of a mechanism or means for forming a broadview image having a spectral width preferably greater than 2 angstroms and 0.50.degree. based on polarization information of a scene, although it can be used within this range. Preferably, the spectral width is between 100-11,000 nanometers and at least 380-800 nanometers, while the angle can be .+-.20.degree.. The viewer 10 is also comprised of a mechanism or means for providing polarization information to the forming mechanism or means. The providing mechanism or means preferably includes a camera mechanism or camera means in communication with the forming mechanism or means. The camera mechanism or camera means preferably includes a fixed polarizer analyzer 12 disposed such that electromagnet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com