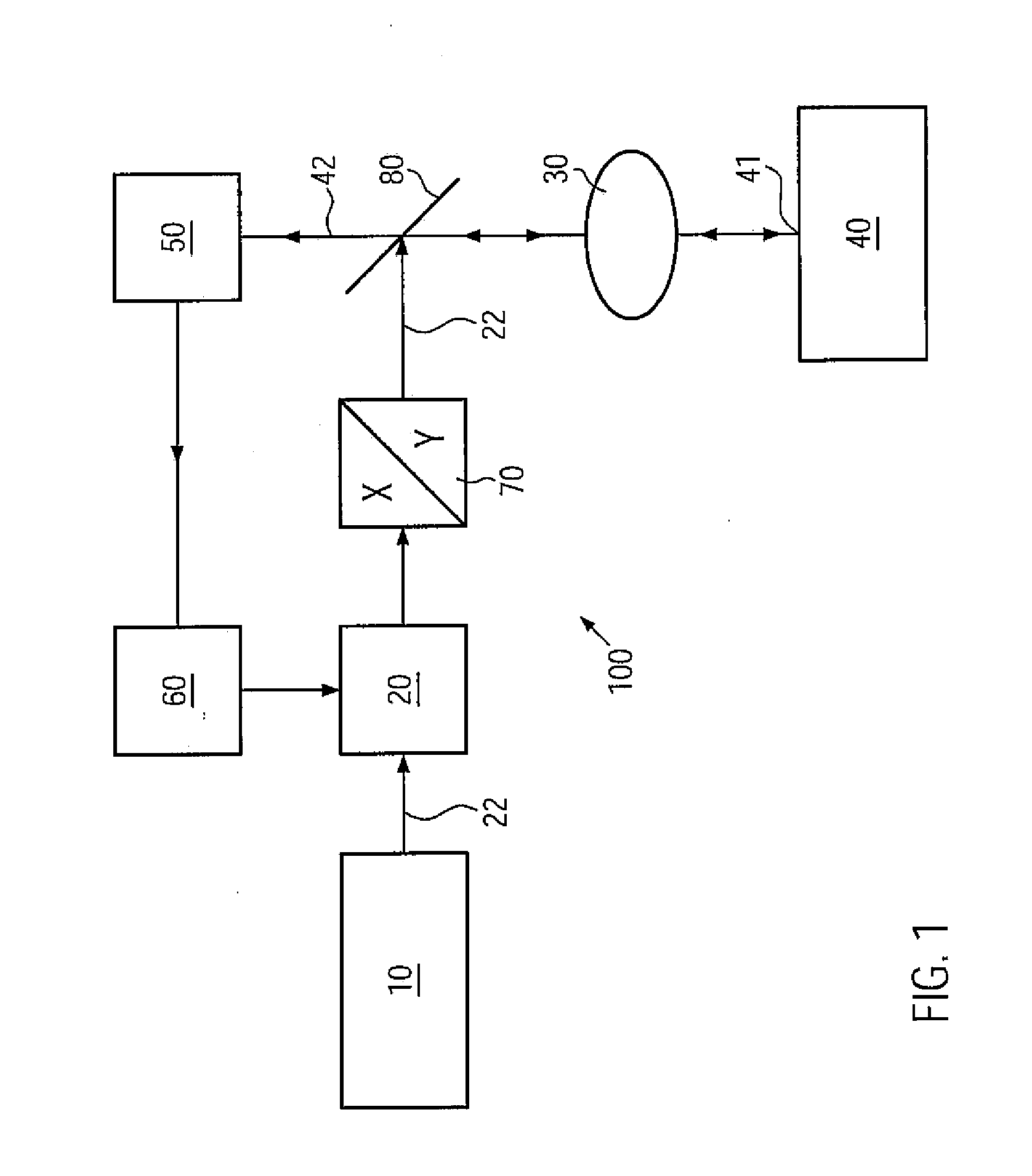
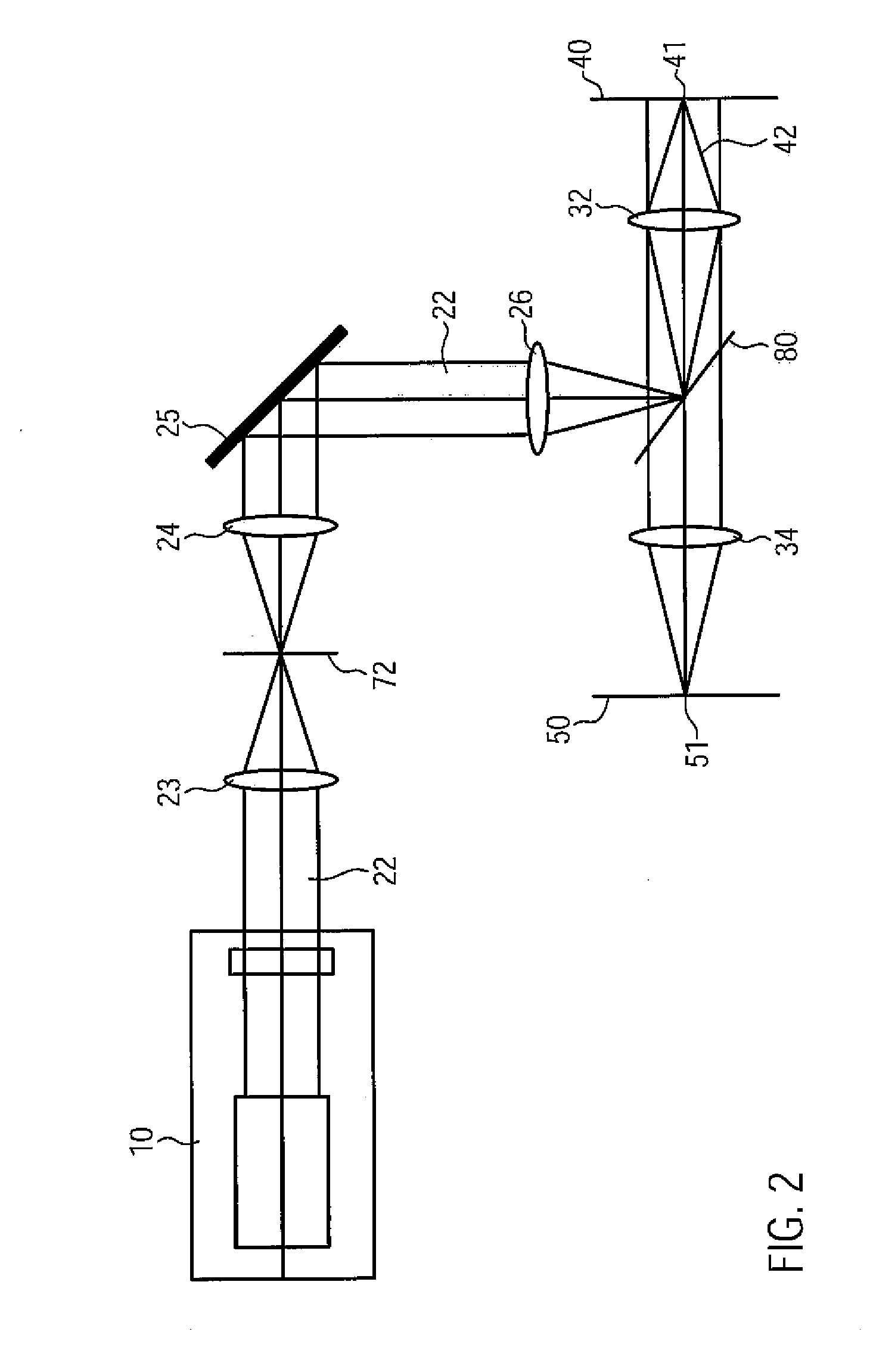
Patents
Literature
130 results about "Spectral composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
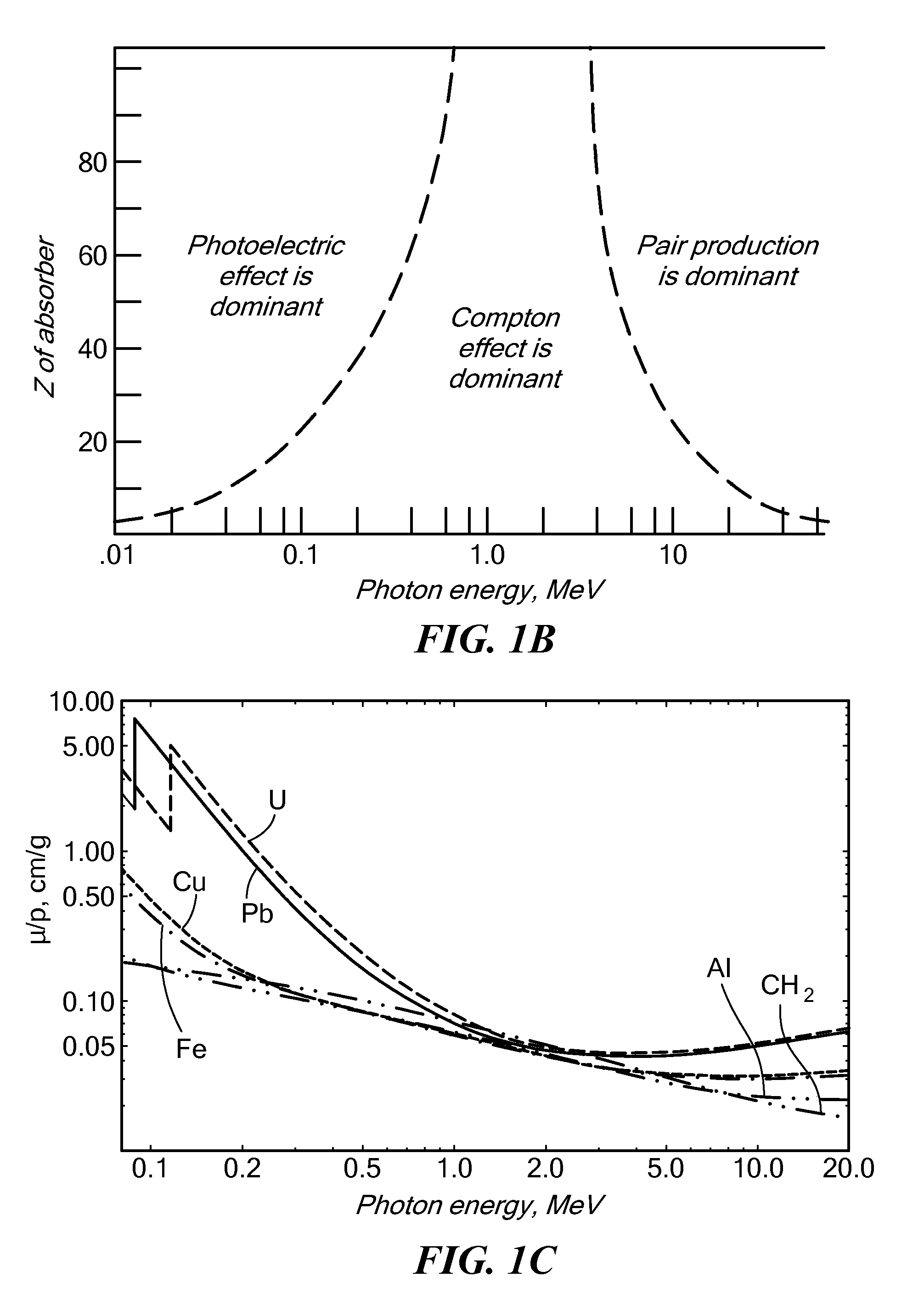
Spectral composition. The distribution of radiative power among the various frequencies, i.e., wavelengths, contained in electromagnetic radiation, particularly radiation in the optical spectrum, at a point in free space or in a material medium.
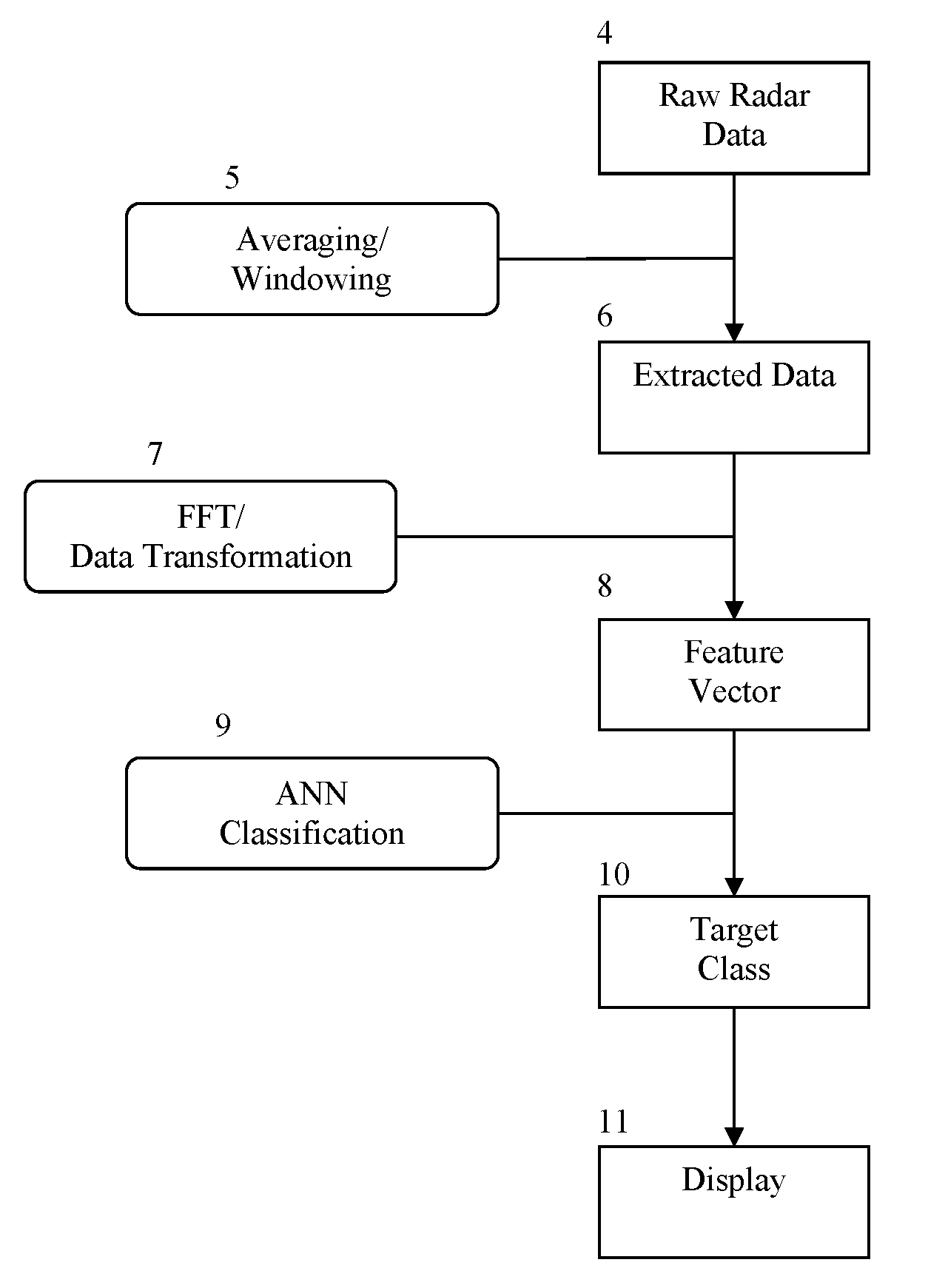
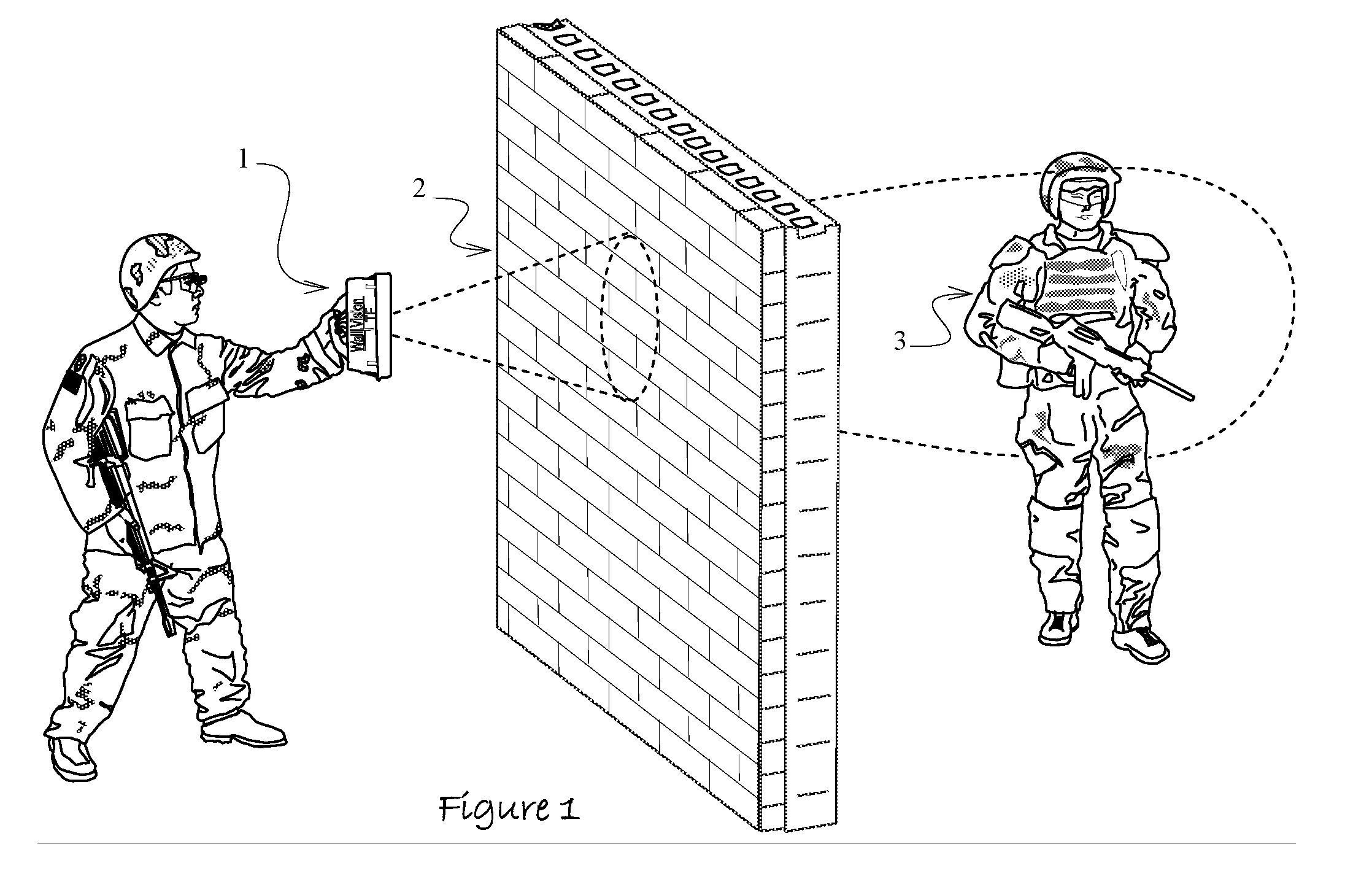
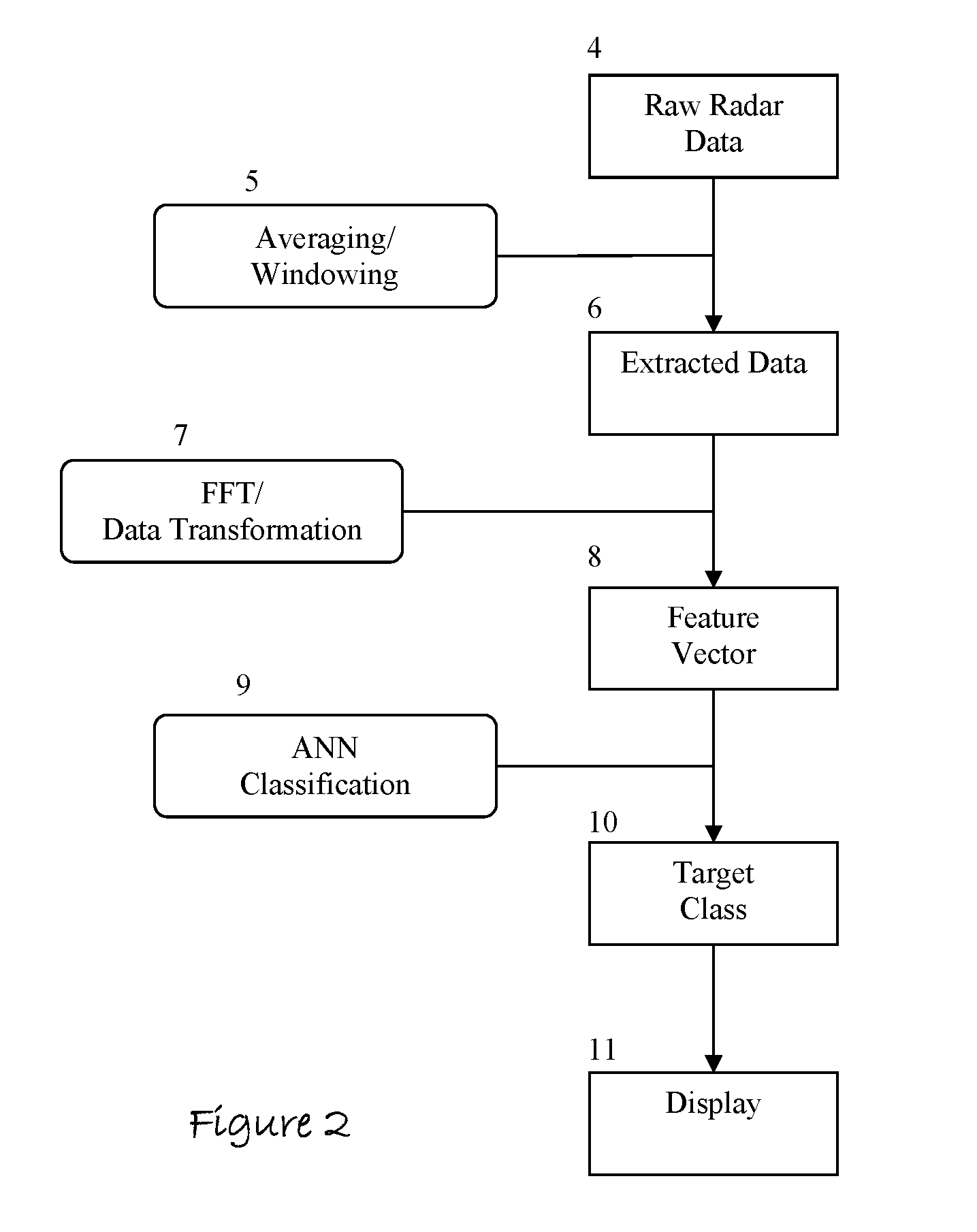
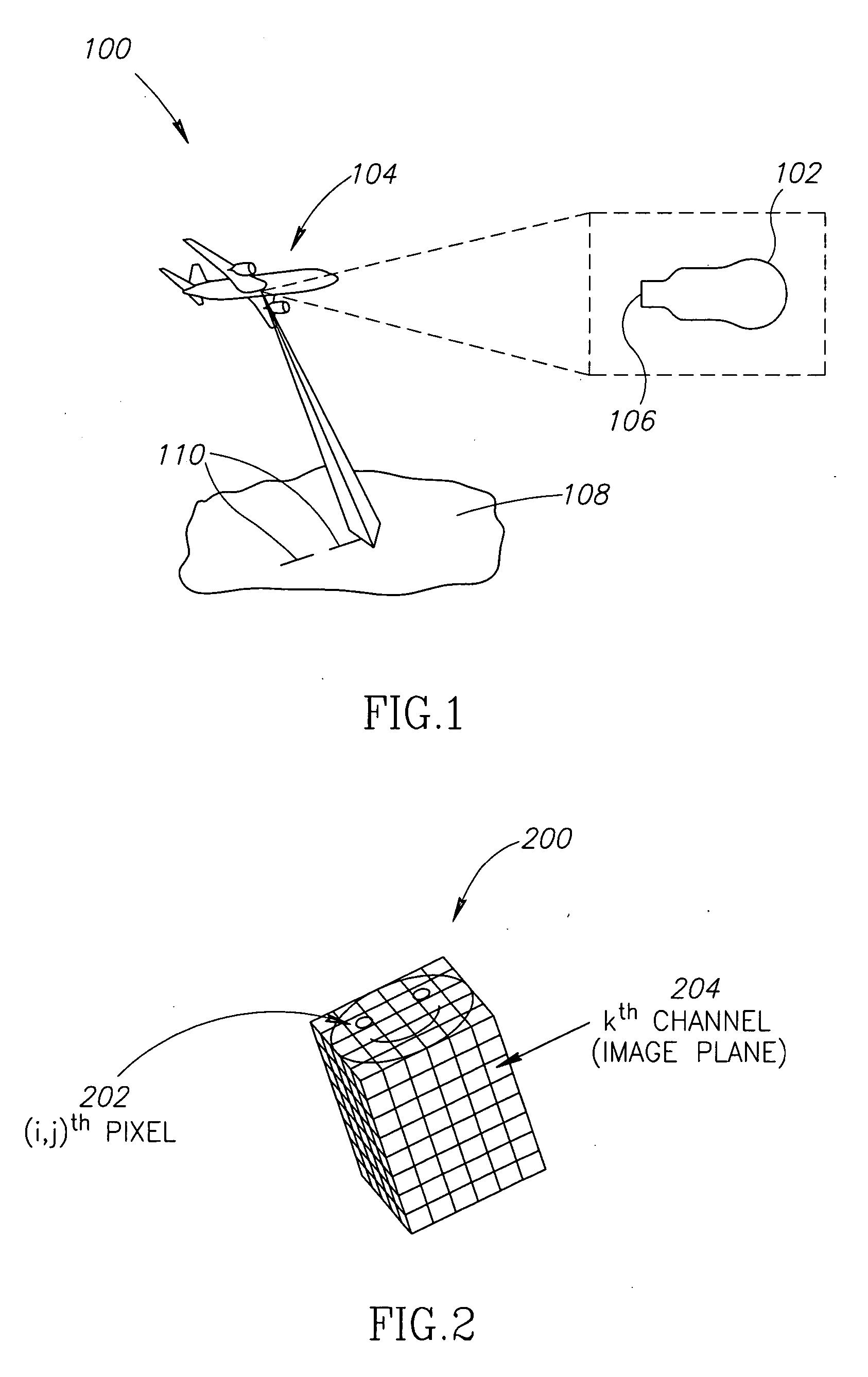
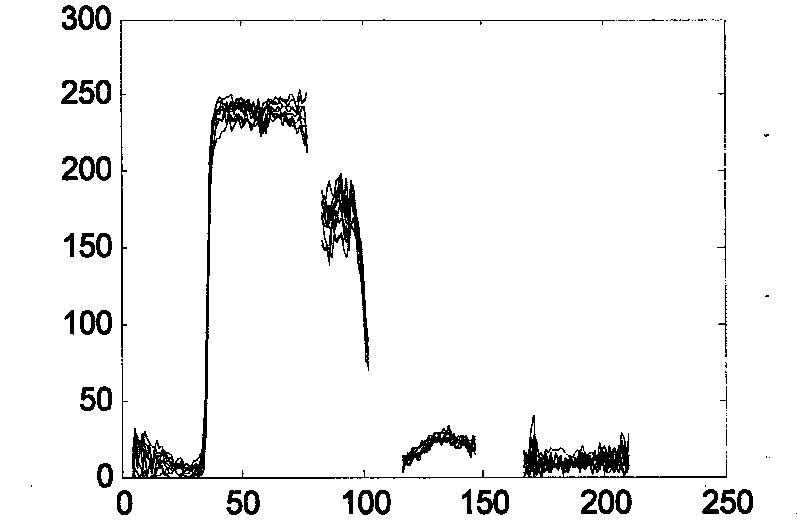
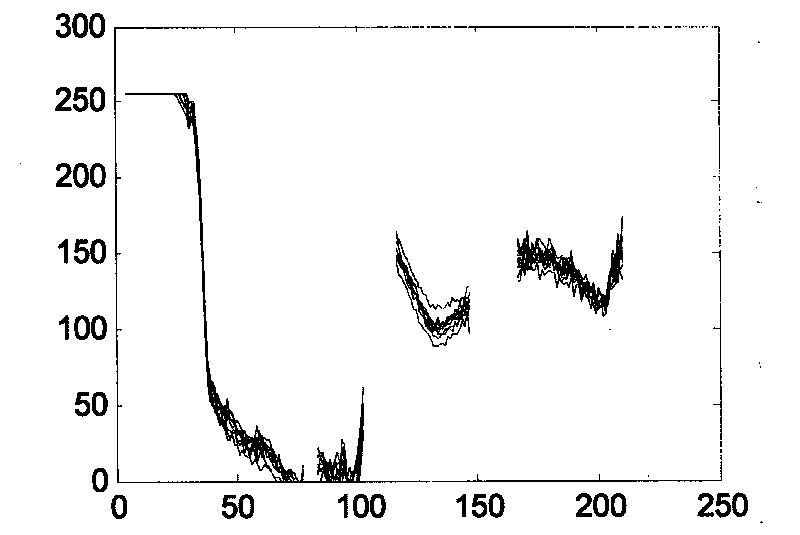
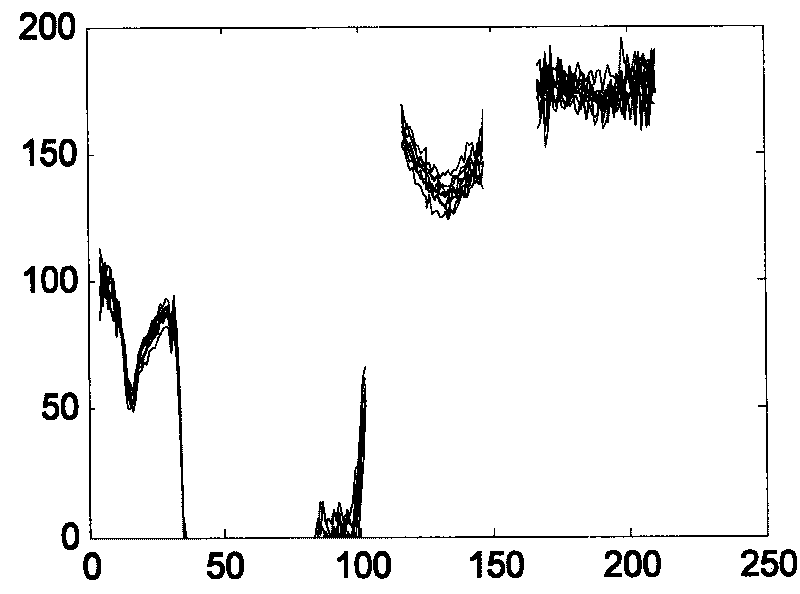
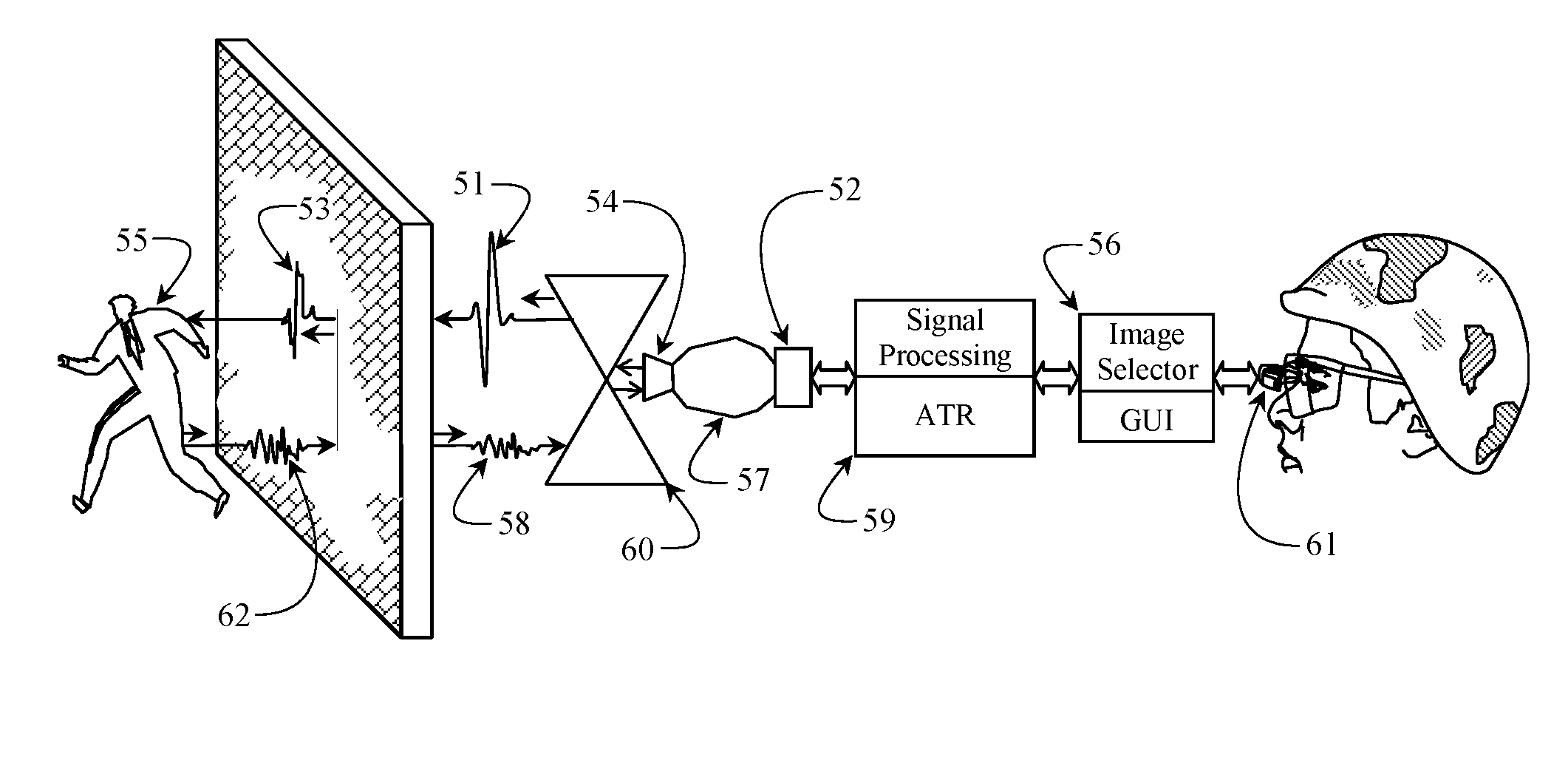
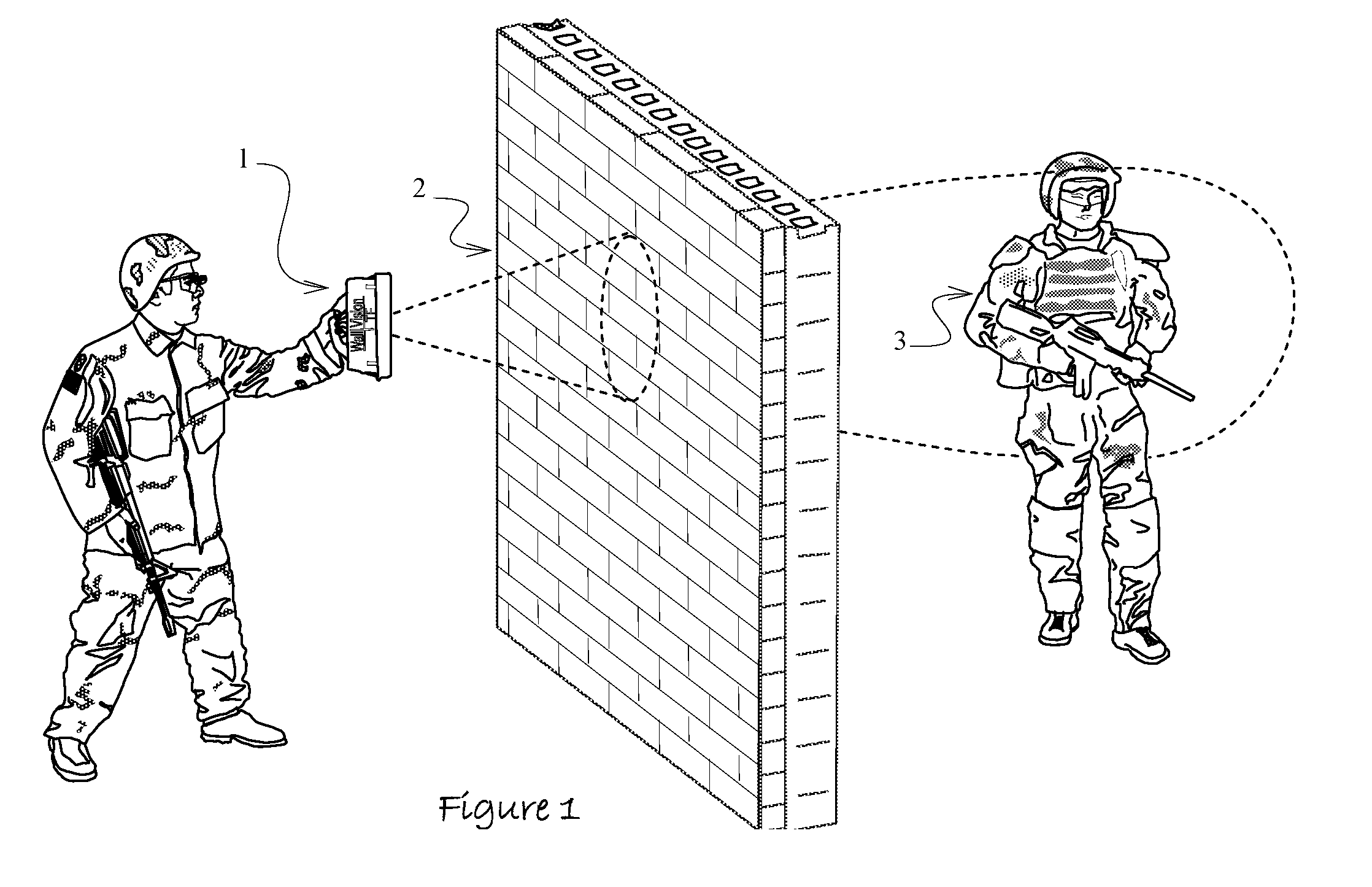
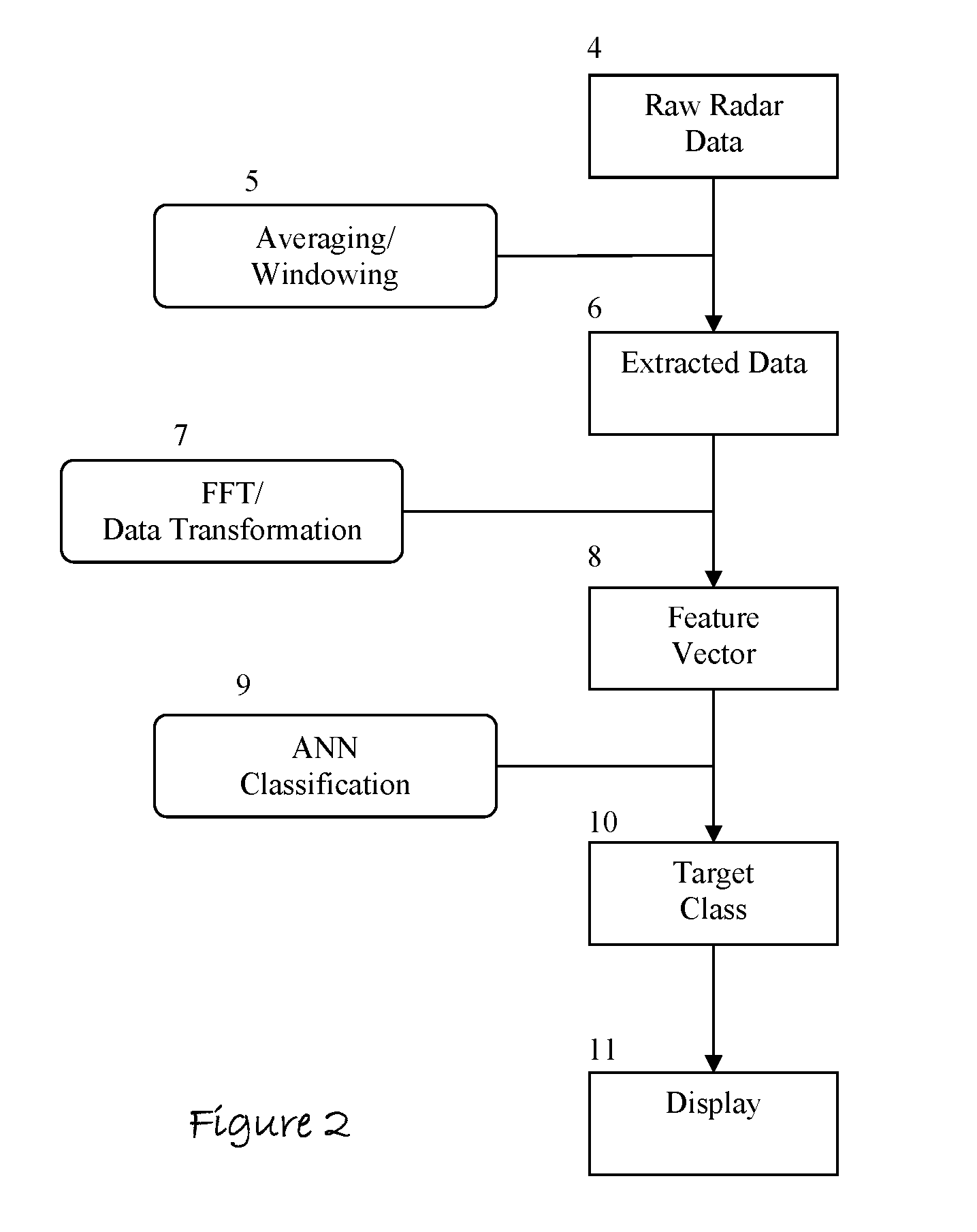
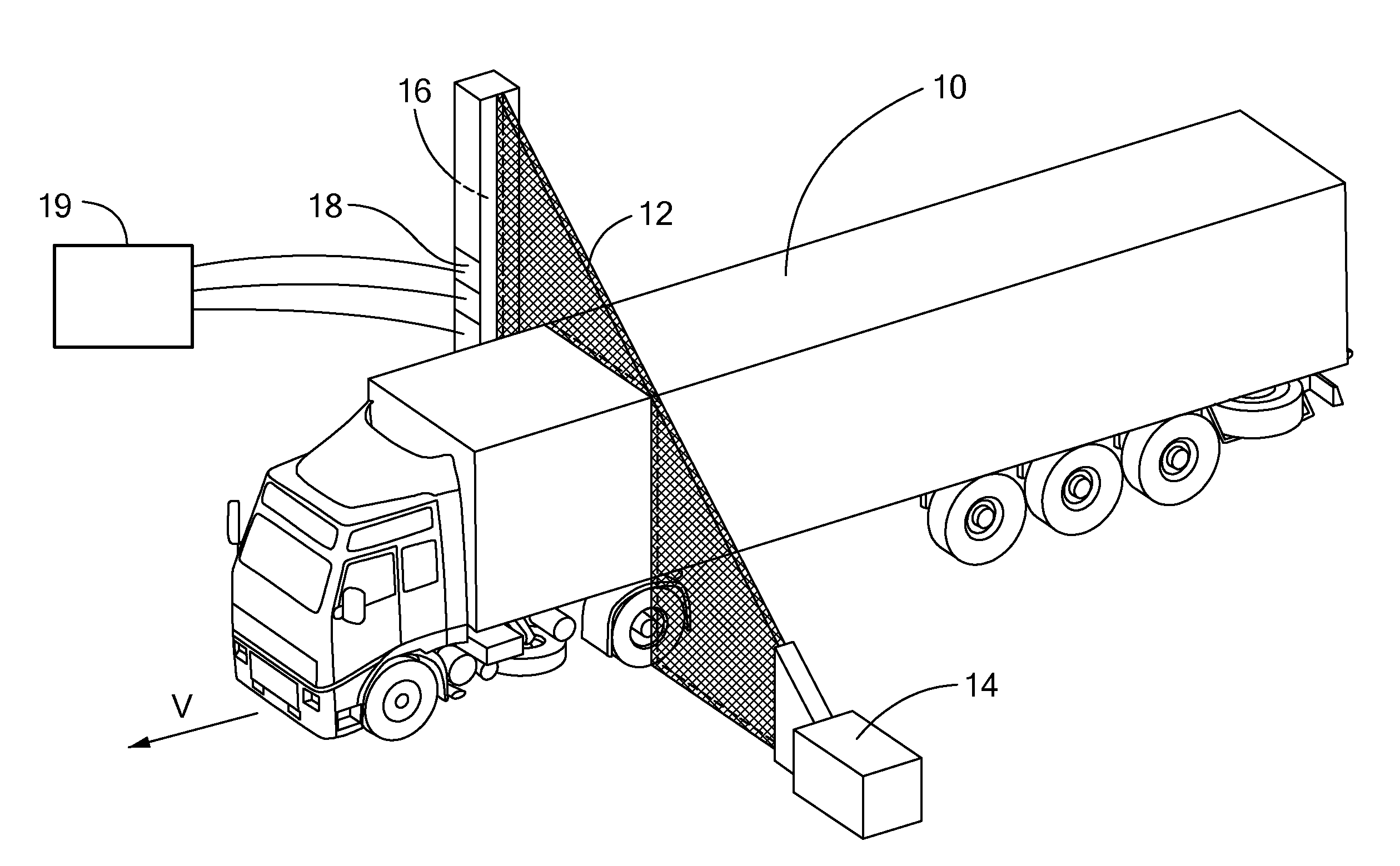
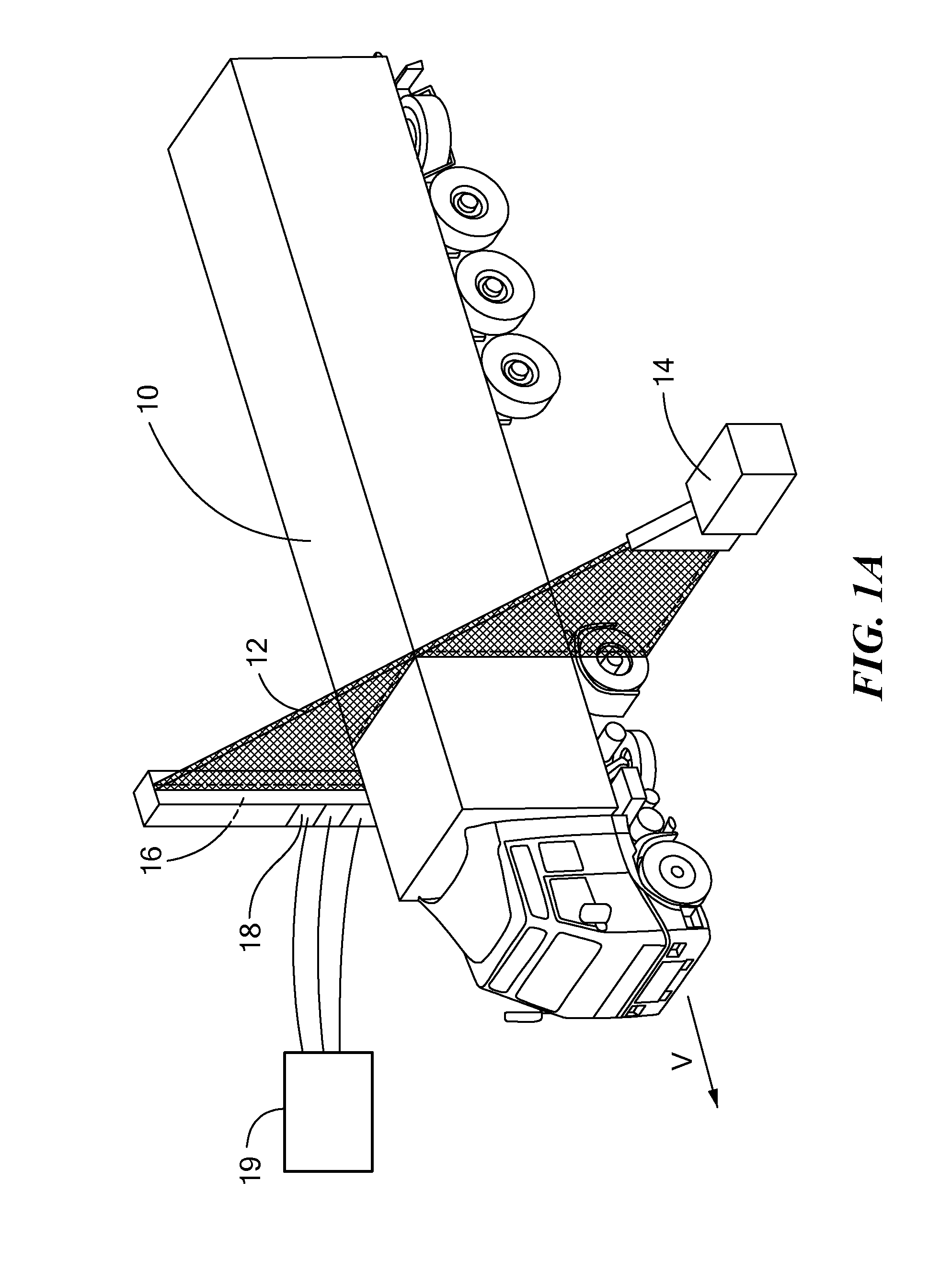
Apparatus and Method to Identify Targets Through Opaque Barriers
InactiveUS20070205937A1Well representedMitigation extensionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandFrequency spectrum
The present invention is a method and apparatus that provides detection, characterization, and intuitive dissemination of targets. This disclosure combines improvements to ultra-wideband (UWB) sensing and machine target characterization with a means to convey data in a format that is quickly and readily understood by practitioners of the technology. The invention is well suited for Situational Awareness (SA) support in areas that are occluded by rain, fog, dust, darkness, distance, foliage, building walls, and any material that can be penetrated by ultra-wideband RF signals. Sense Through The Wall (STTW) performance parameters including target range, stand-off distance, and probability of detection are improved herein by combining a dynamically positioned sliding windowing function with orthogonal feature vectors that include but are not limited to time amplitude decay, spectral composition, and propagation time position in the return signal data. This invention is particularly useful for STTW and SA applications including urban combat, law enforcement, fire protection, transportation security, and homeland security. The invention can also be used to detect objects that are concealed by clothing, debris, and other non-metallic materials.
Owner:REALTRONICS CORP
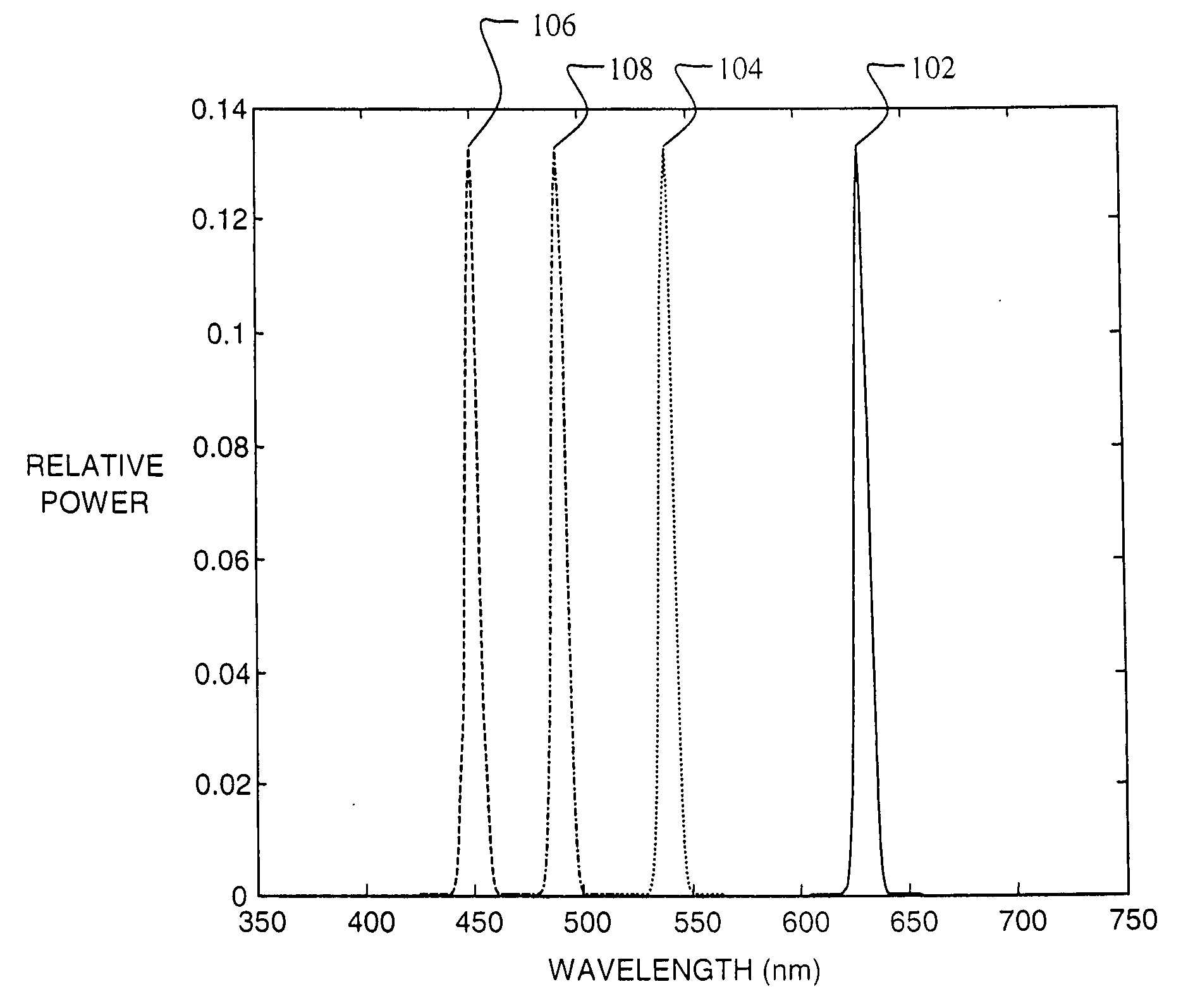
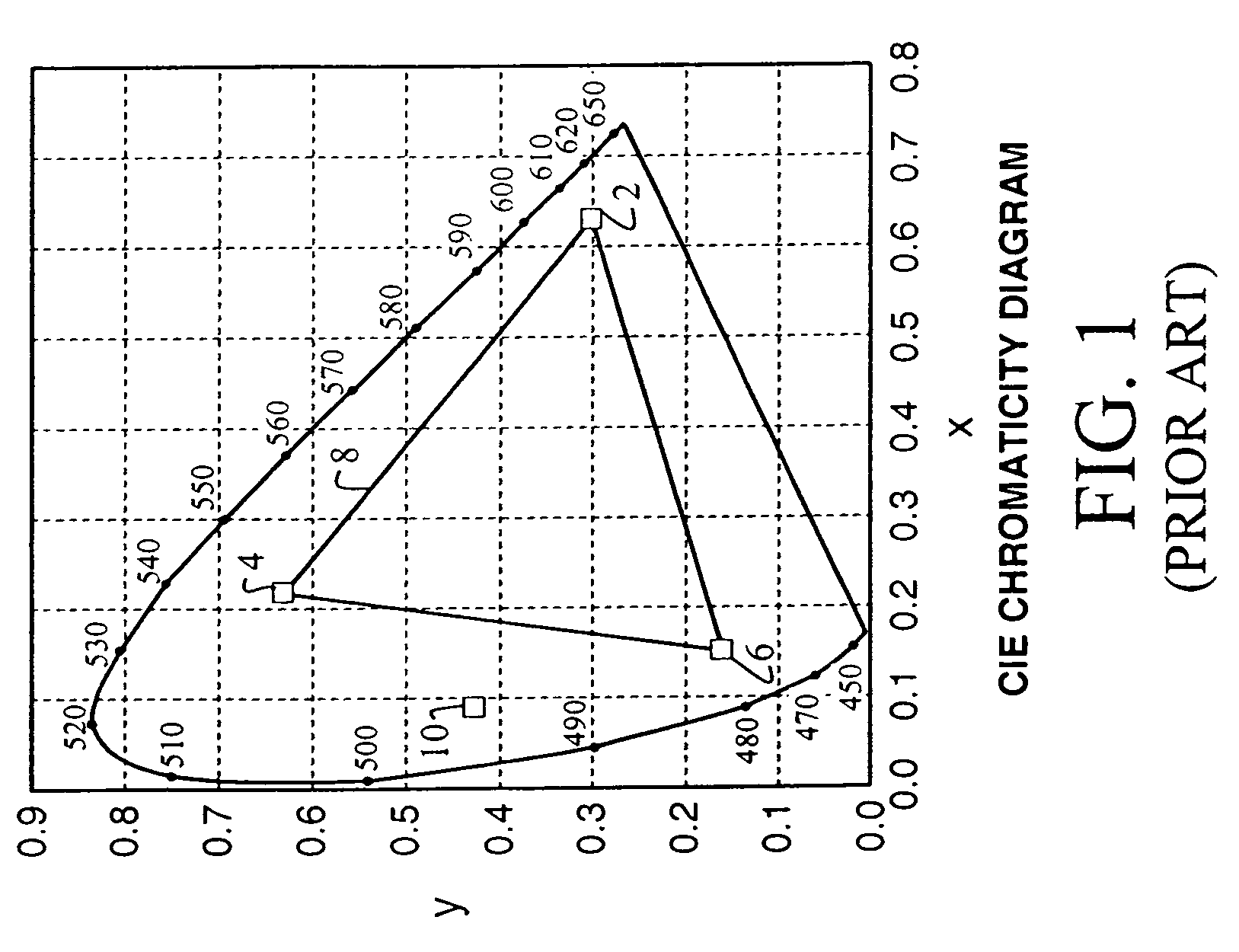
Four color digital cinema system with extended color gamut and copy protection
A color display system including a display device for four or more visible color primaries and a processor for controlling the four or more color primaries to selectively render portions of an image or image sequence such that visually equivalent colors displayed in two or more image portions differ in their spectral composition.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Raman spectroscopic system with integrating cavity
InactiveUS6975891B2Efficient collectionImprove power densityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSpectral widthSpectrum analyzer
The present invention provides an apparatus for measurement of Raman scattered radiation comprising. The apparatus comprises at least one source of electromagnetic radiation for producing an electromagnetic radiation beam characterized by a narrow spectral width, an integrating cavity having an interior and an exterior, wherein a sample is placed in said interior. The integrating cavity further having at least one port for insertion of the sample in the interior and for transmission of the electromagnetic radiation into and out from the interior, the at least one port extending from the exterior to said interior of said integrating cavity. The integrating cavity also comprises a first optical element for transmitting the electromagnetic radiation into the interior of the integrating cavity through the at least one port, and a second optical element for collecting Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation from the sample through the at least one port. The apparatus also comprises a spectrum analyzer for determining spectral composition of the Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation, a detector for measuring the Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation; and a system for determining concentration of at least one chemical compound from the measured Raman scattered electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus may also comprise a radiation expanding element. A method for measuring the concentration of one or more chemical compounds in a sample using Raman scattering is also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
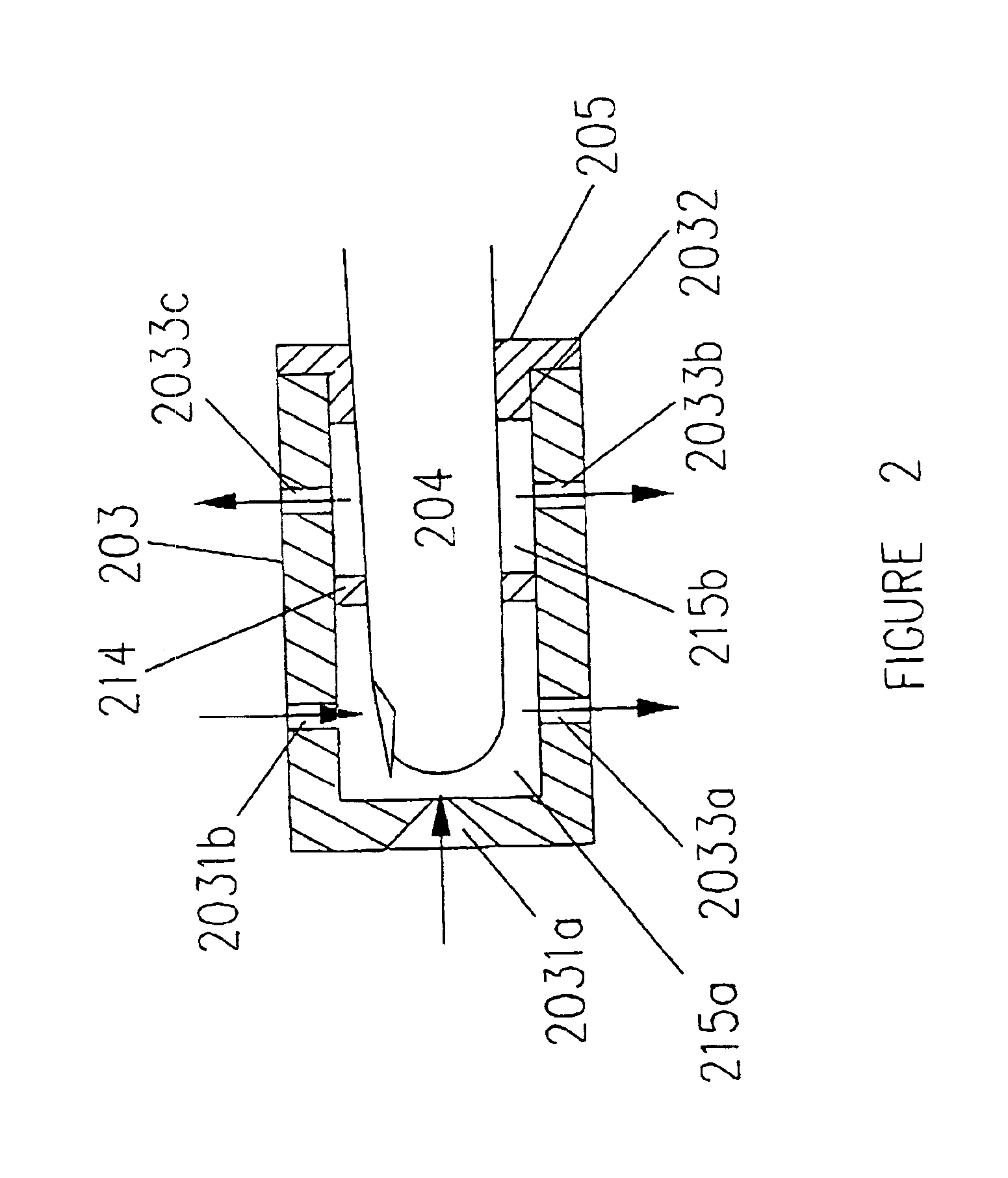
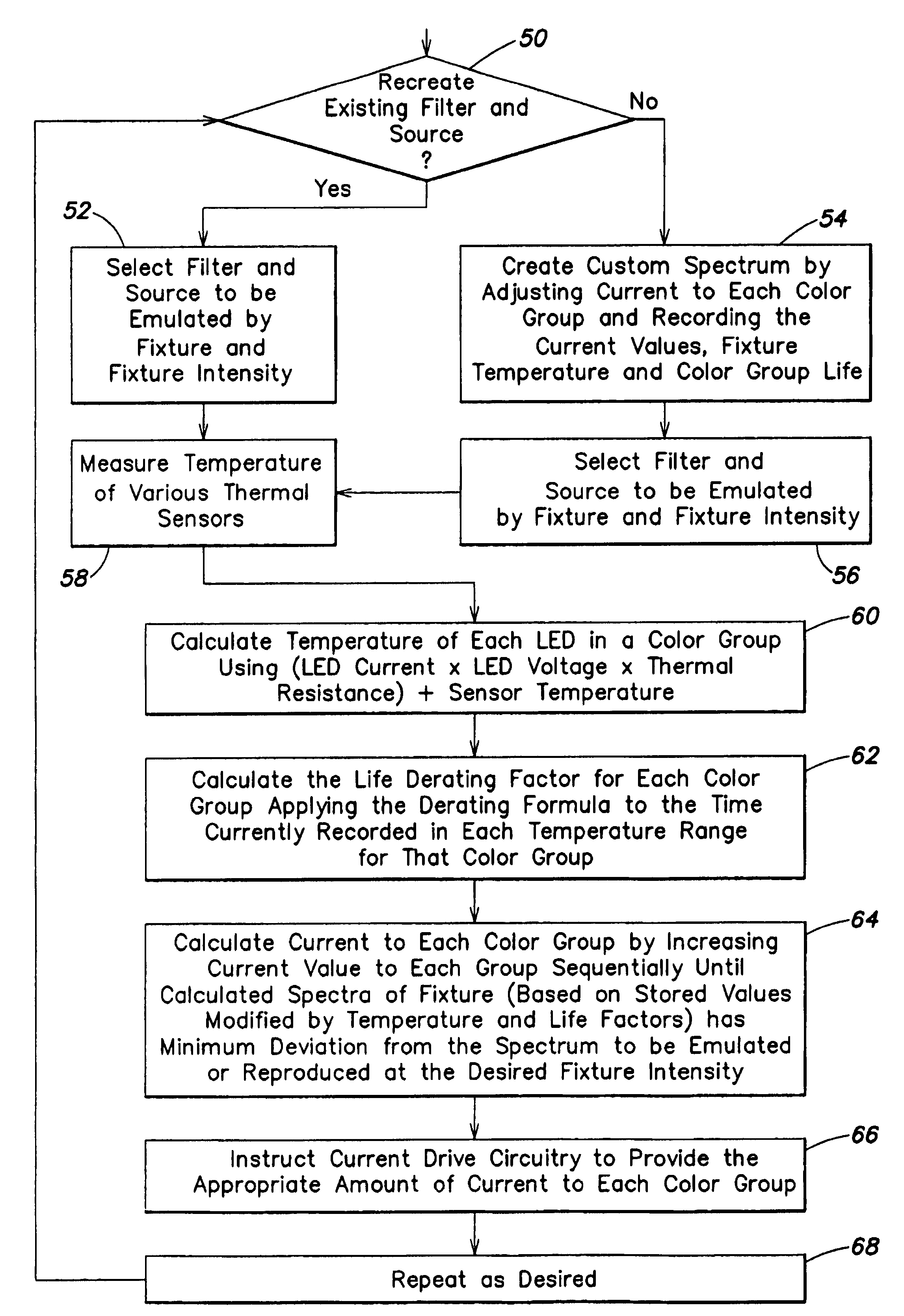
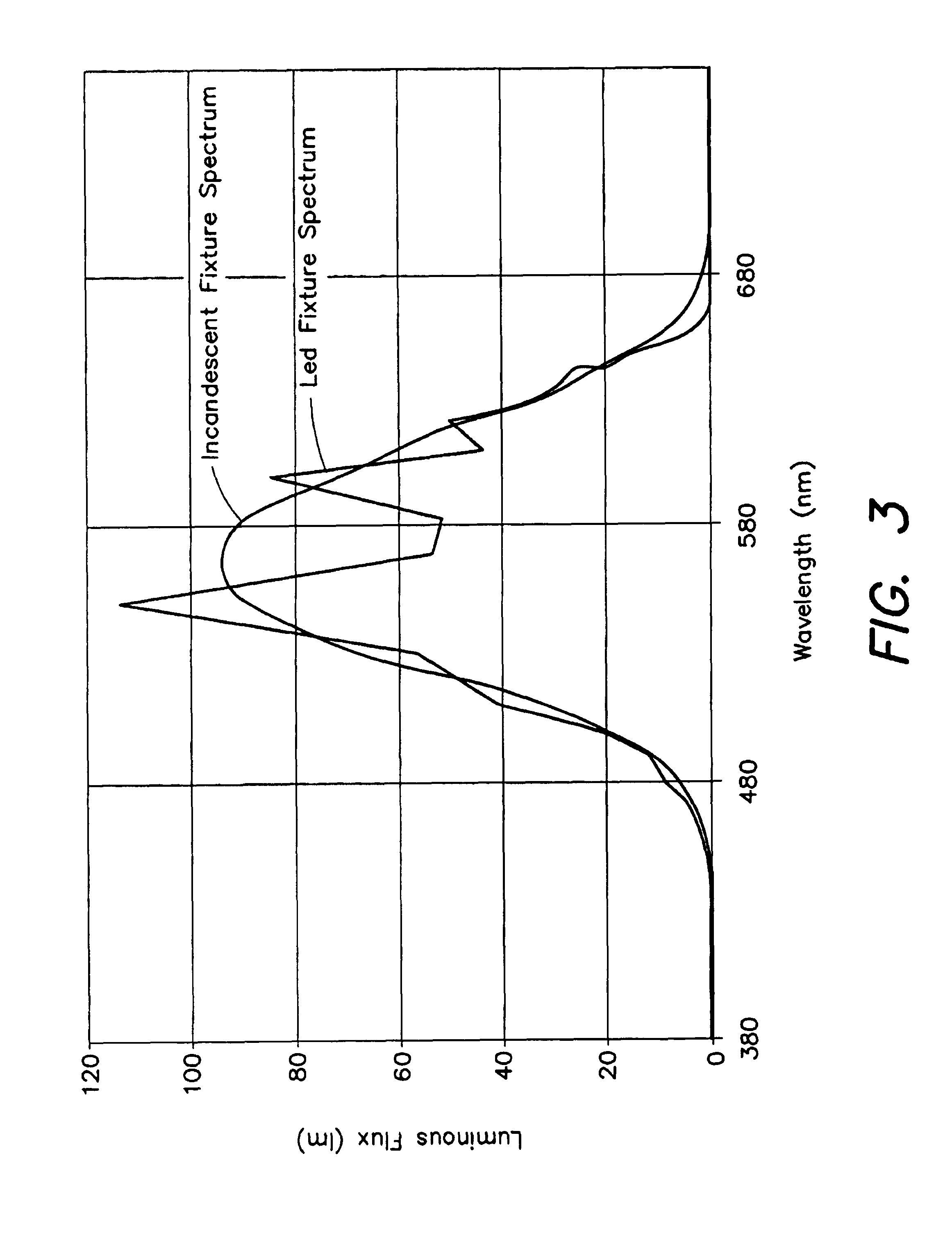
Method for controlling the luminous flux spectrum of a lighting fixture
A method is disclosed for controlling a lighting fixture of a kind having individually colored light sources, e.g., LEDs, that emit light having a distinct luminous flux spectrum that varies in its initial spectral composition, that varies with temperature, and that degrades over time. The method controls such fixture so that it projects light having a predetermined desired flux spectrum despite variations in initial spectral characteristics, despite variations in temperature, and despite flux degradations over time.
Owner:CUNNINGHAM DAVID W
Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system
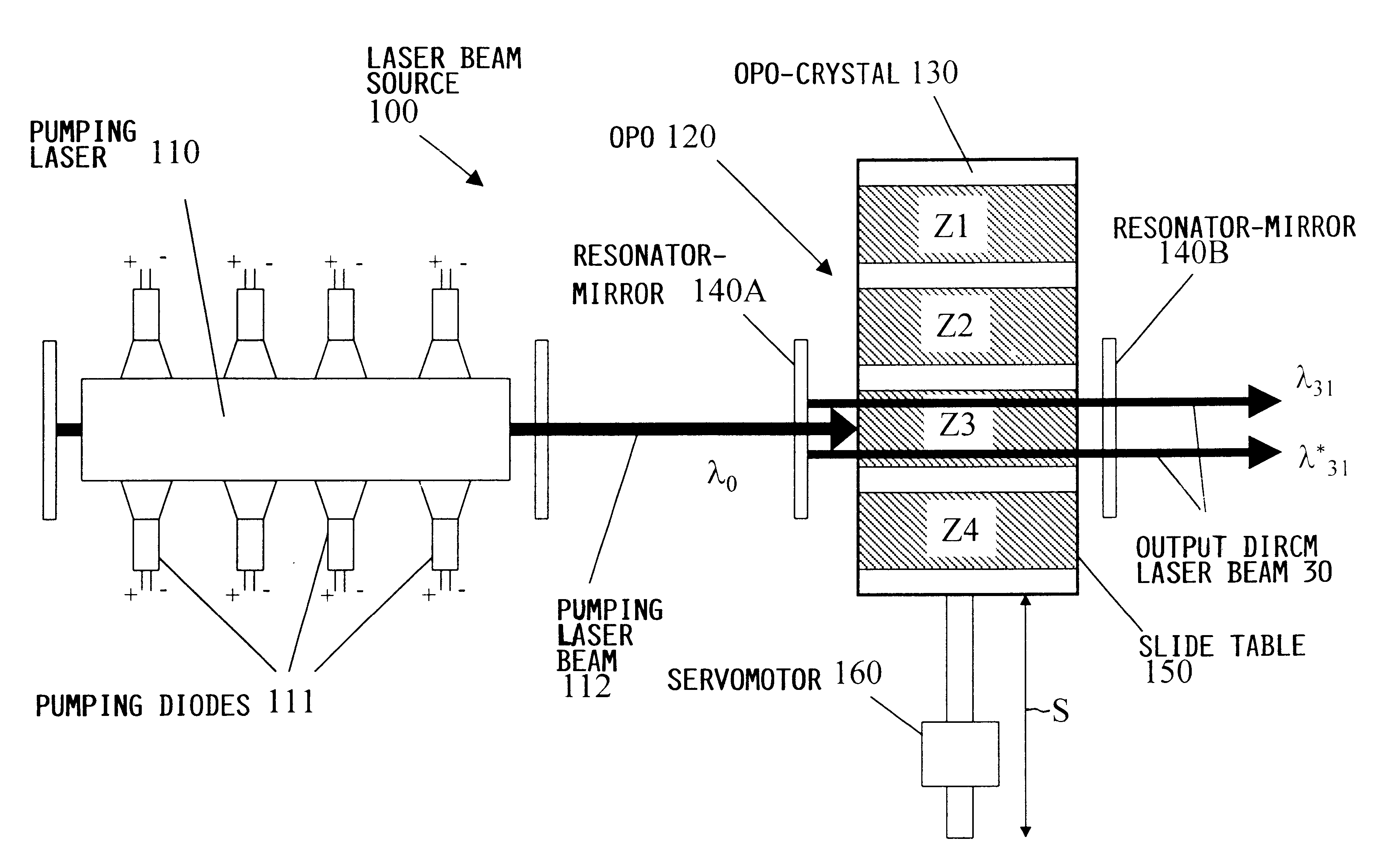
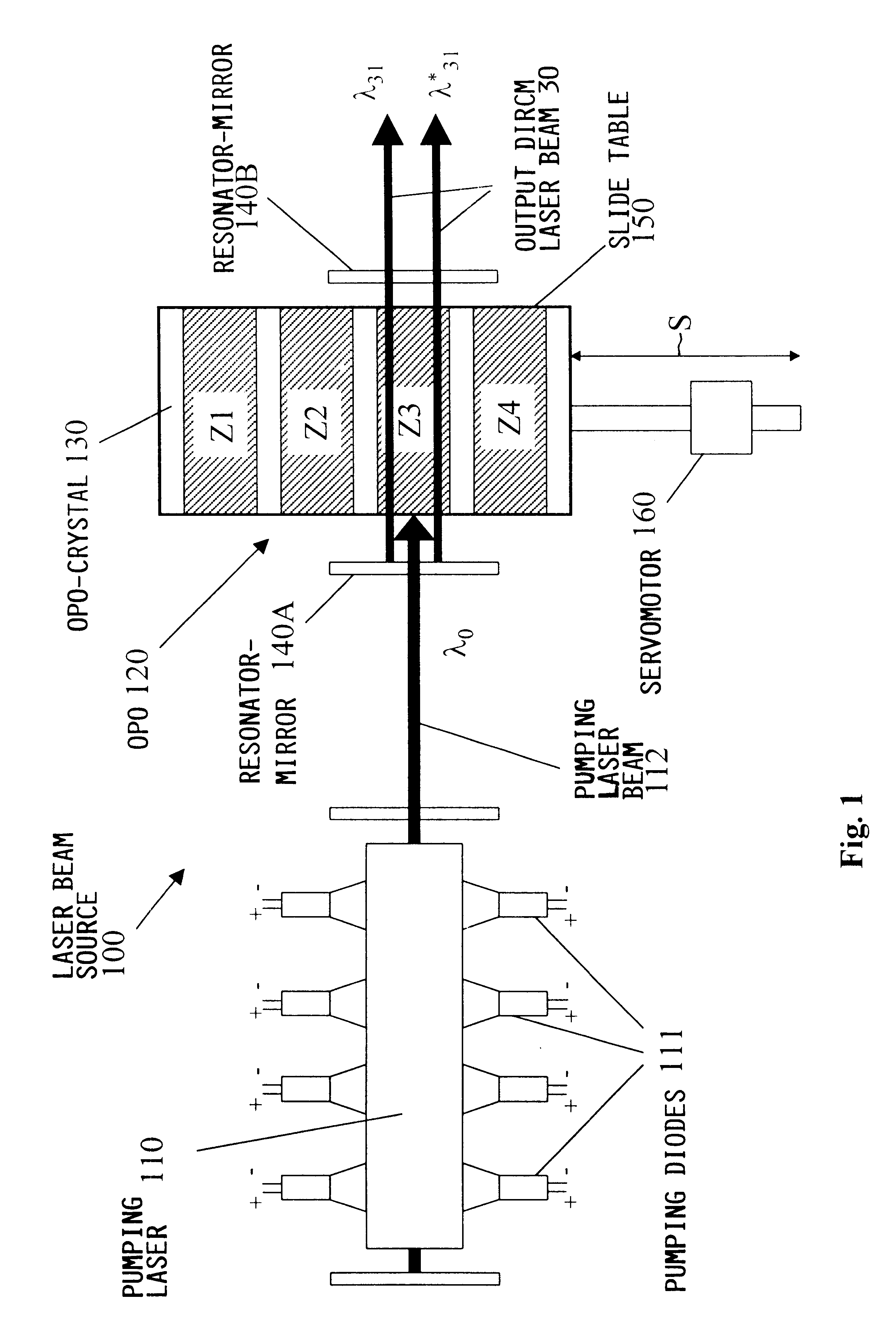
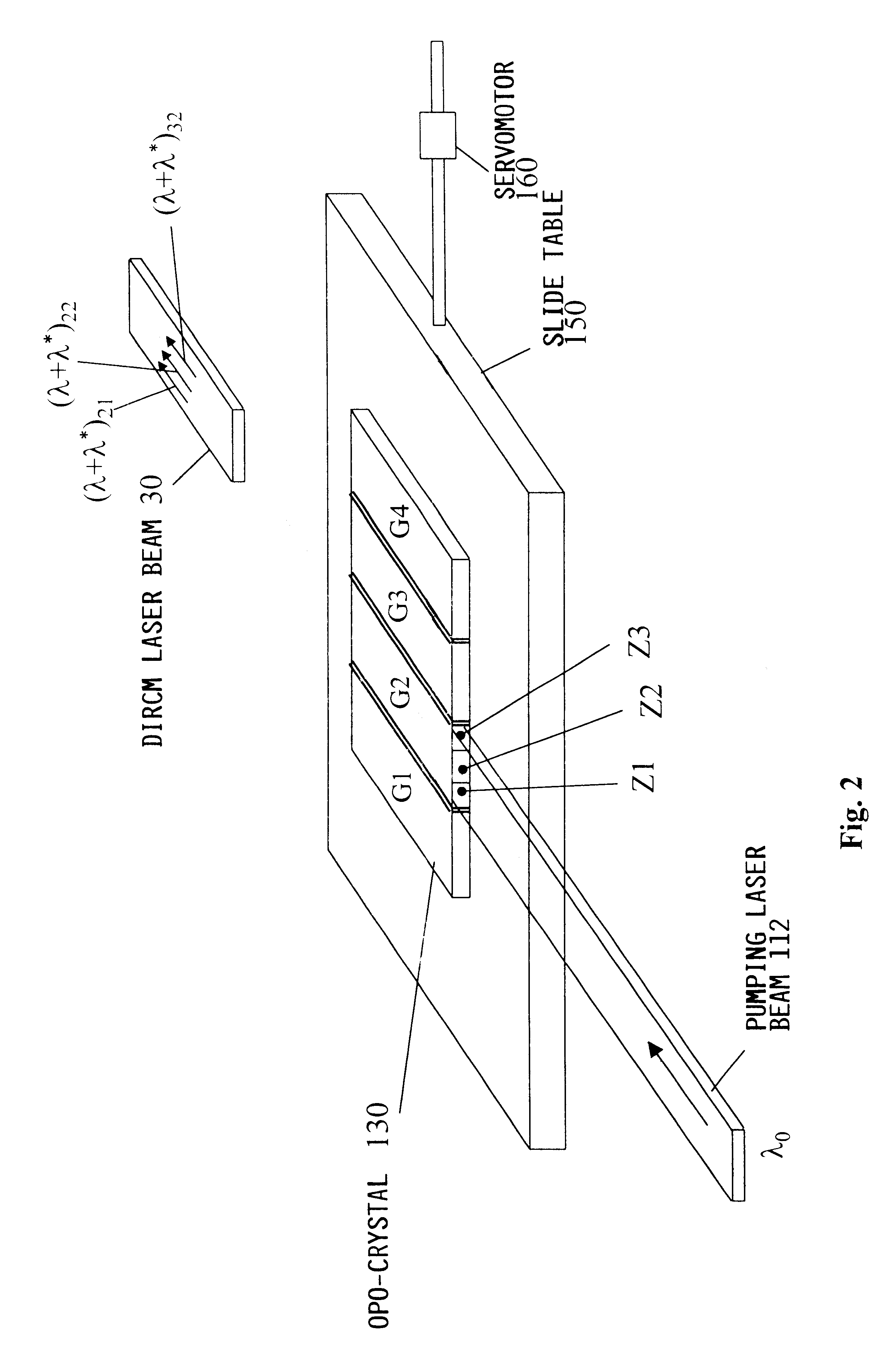
A laser beam source and an operating method thereof is provided for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system for defensively countering guided missiles having infrared seeking heads, by directing an infrared laser beam at the guided missile so as to disorient, saturate, or irreversibly destroy the IR detectors and circuitry arranged in the target seeking head. The power, pulse frequency and spectral composition of the laser beam is adjustable and selectable as required to adapt to any particular defensive engagement. To achieve this, the laser beam source comprises an Nd:YAG pumping laser and an optical parametric oscillator including an oscillator crystal arranged in a resonator cavity. The crystal includes a plurality of different periodically polarized crystal zones having different lattice constants. The adjacent zones can be grouped together into selectable crystal zone groups. The beam cross-section of the pumping laser beam corresponds to the cross-section of a single crystal zone or of a crystal zone group encompassing plural zones. The crystal is arranged on a slide table that is slidably displaceable by a servomotor, to move a selected crystal zone or group into the path of the pumping laser beam. Thereby the wavelength components and the relative intensities thereof of the output laser beam can easily be selectively adjusted.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Methods and apparatus for adaptive foreground background analysis
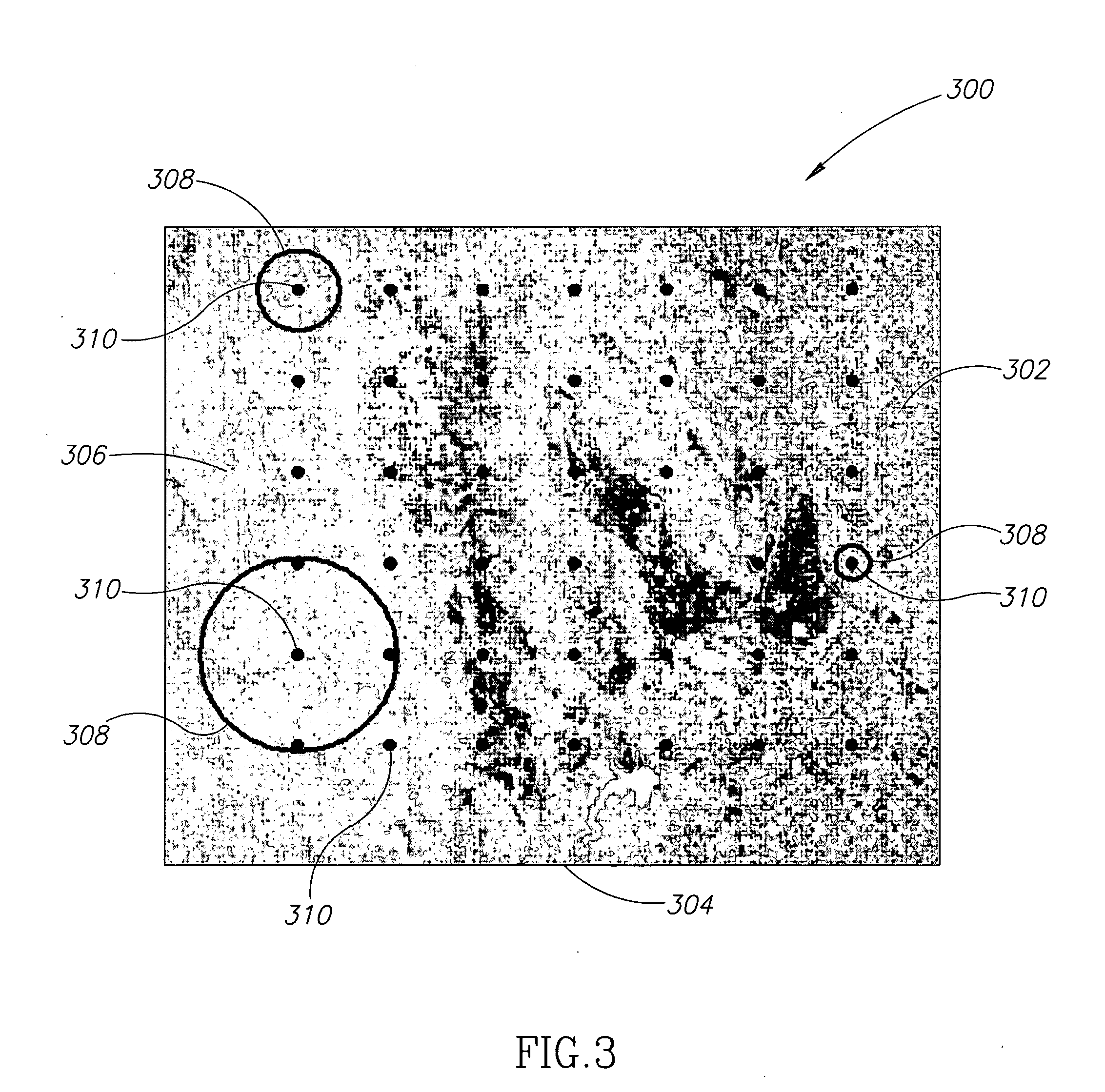
ActiveUS20060233421A1Easy to detectReduce data volumeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPosition dependent
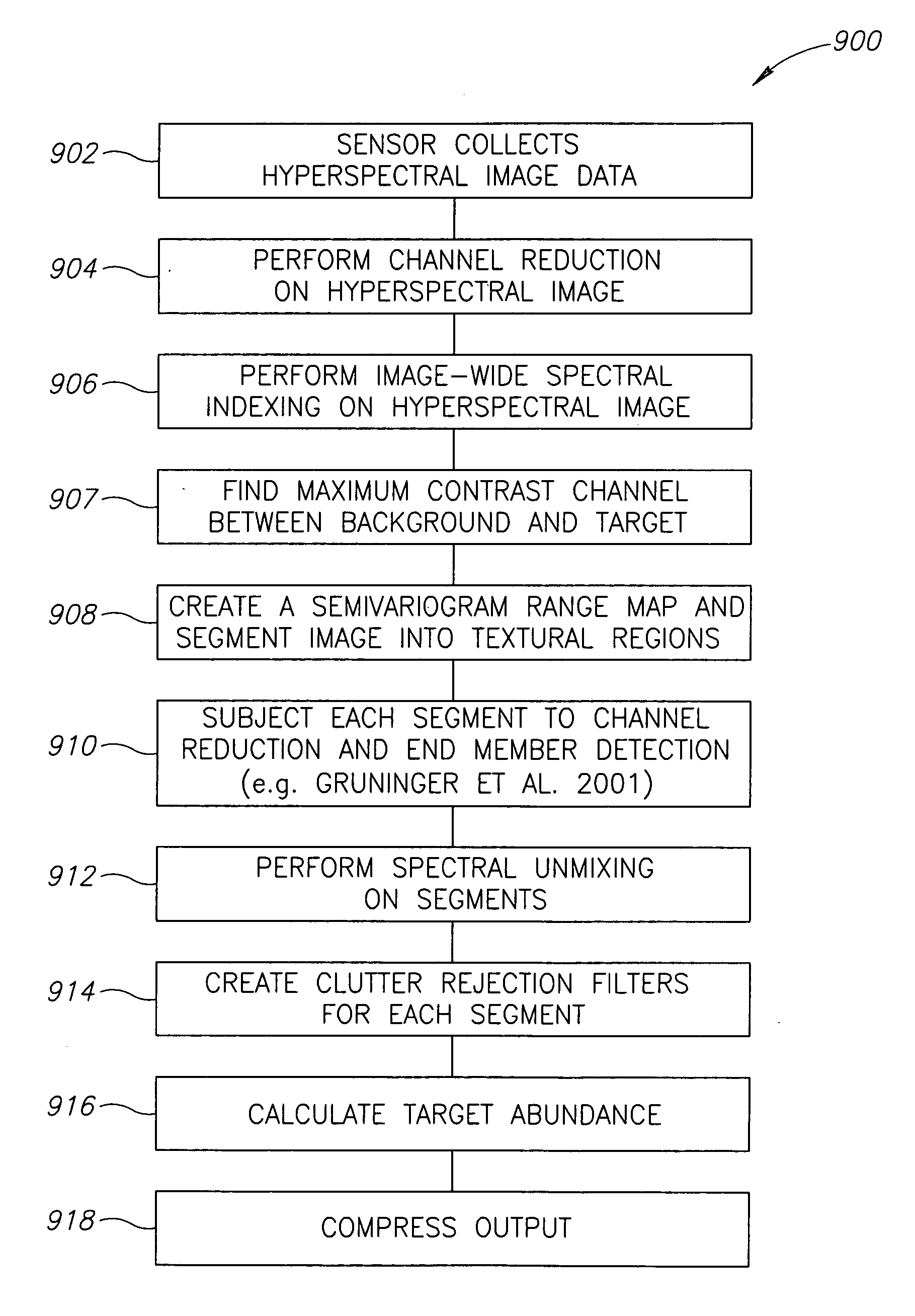
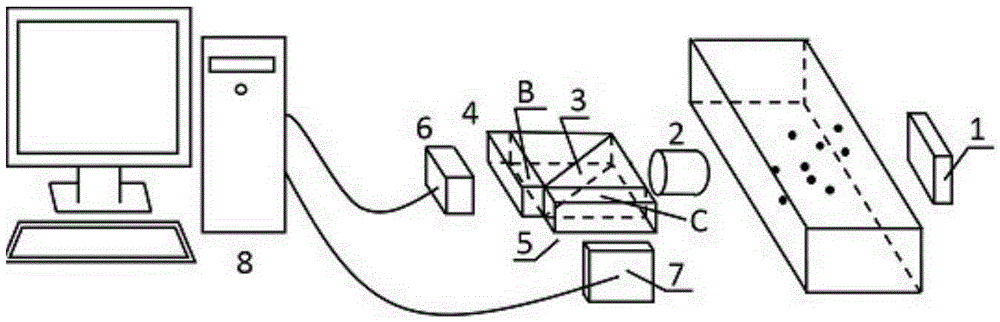
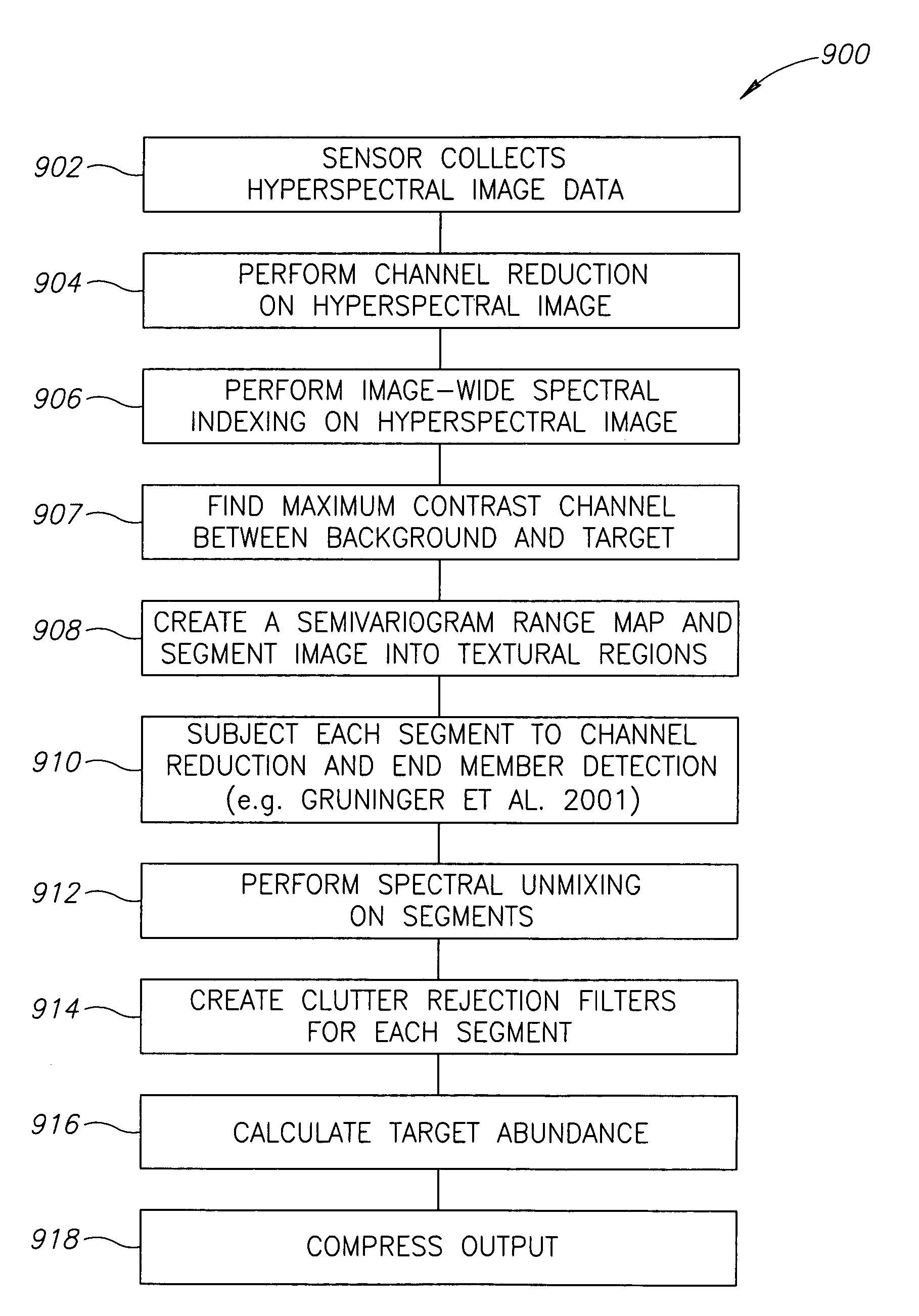
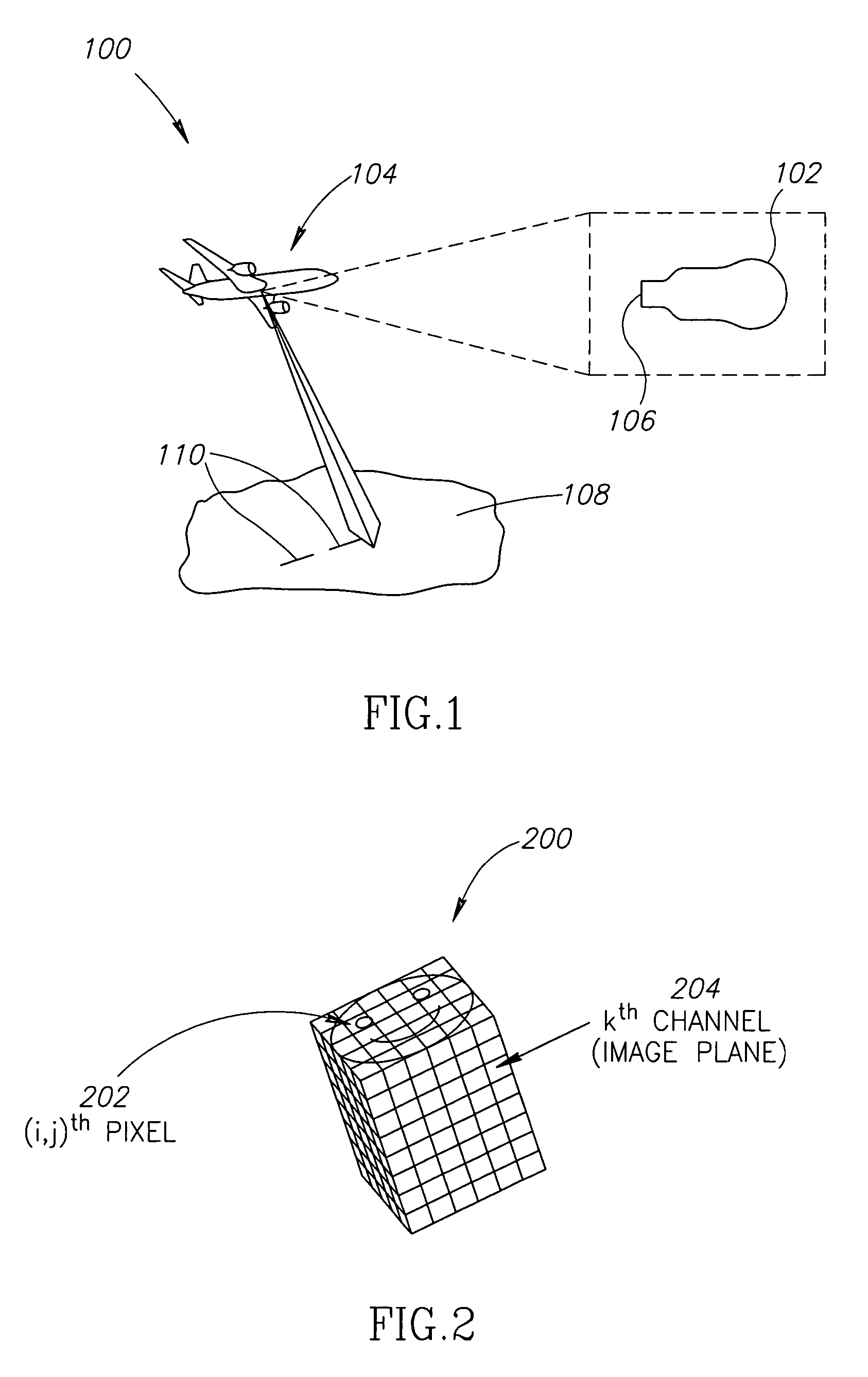
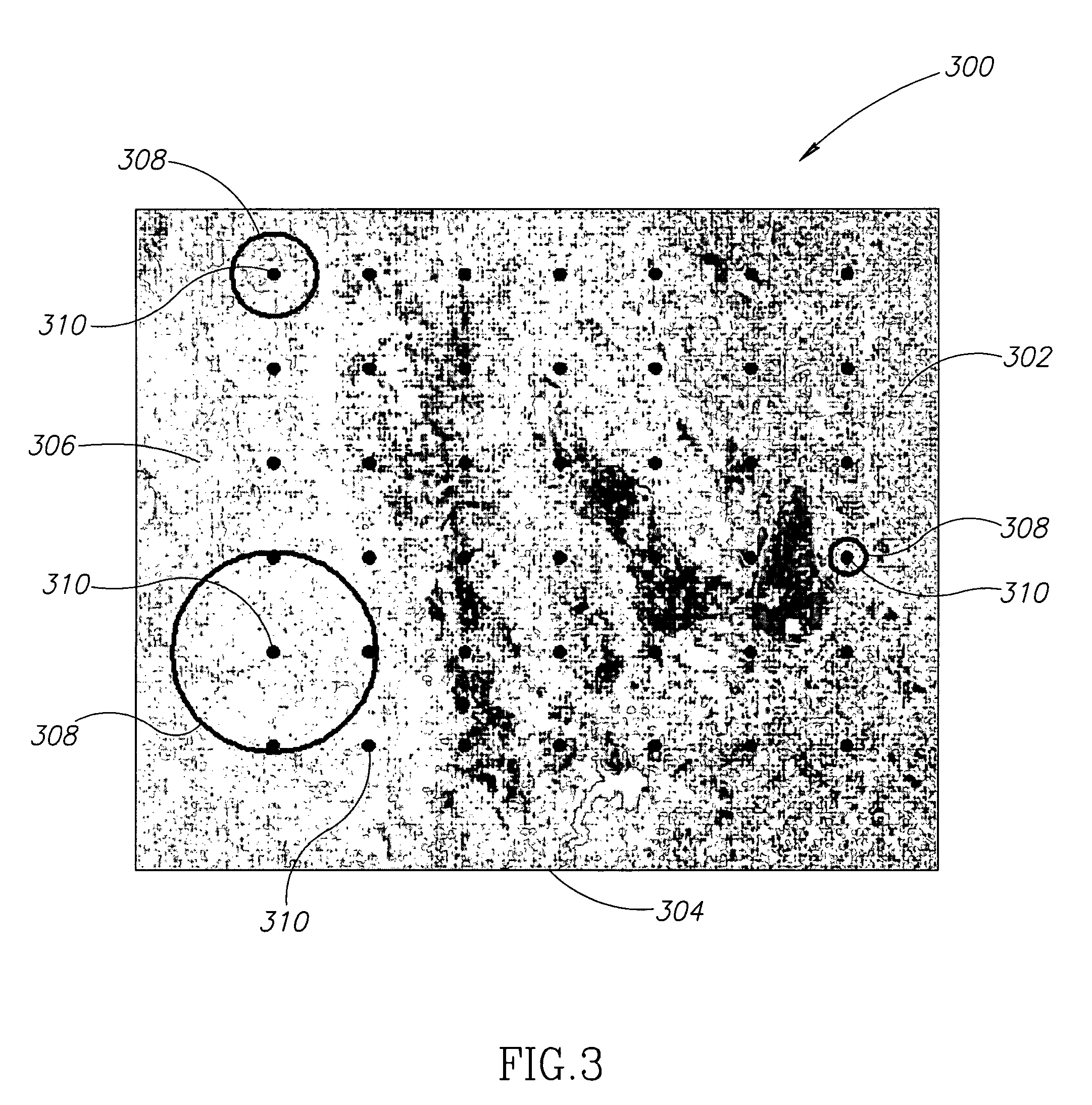
Apparatus and methods for target detection in hyperspectral images are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of detecting a target in a hyperspectral image includes spectrally unmixing the hyperspectral image into segments, each segment having at least one of similar spectral composition, similar textural composition, and similar variation, and spectrally unmixing at least one of the segments. The method further includes creating a clutter rejection filter for at least one segment, filtering at least one segment, and calculating target abundances in at least one segment. In alternate embodiments, channel reduction can be performed on the hyperspectral image and also on at least one segment. In further embodiments, data associated with the location of possible targets in the segments may be compiled. In yet another embodiment, this data may be compressed by cross referencing data from all segments and eliminating redundancies.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Four color digital cinema system with extended color gamut and copy protection
A color display system including a display device for four or more visible color primaries and a processor for controlling the four or more color primaries to selectively render portions of an image or image sequence such that visually equivalent colors displayed in two or more image portions differ in their spectral composition.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
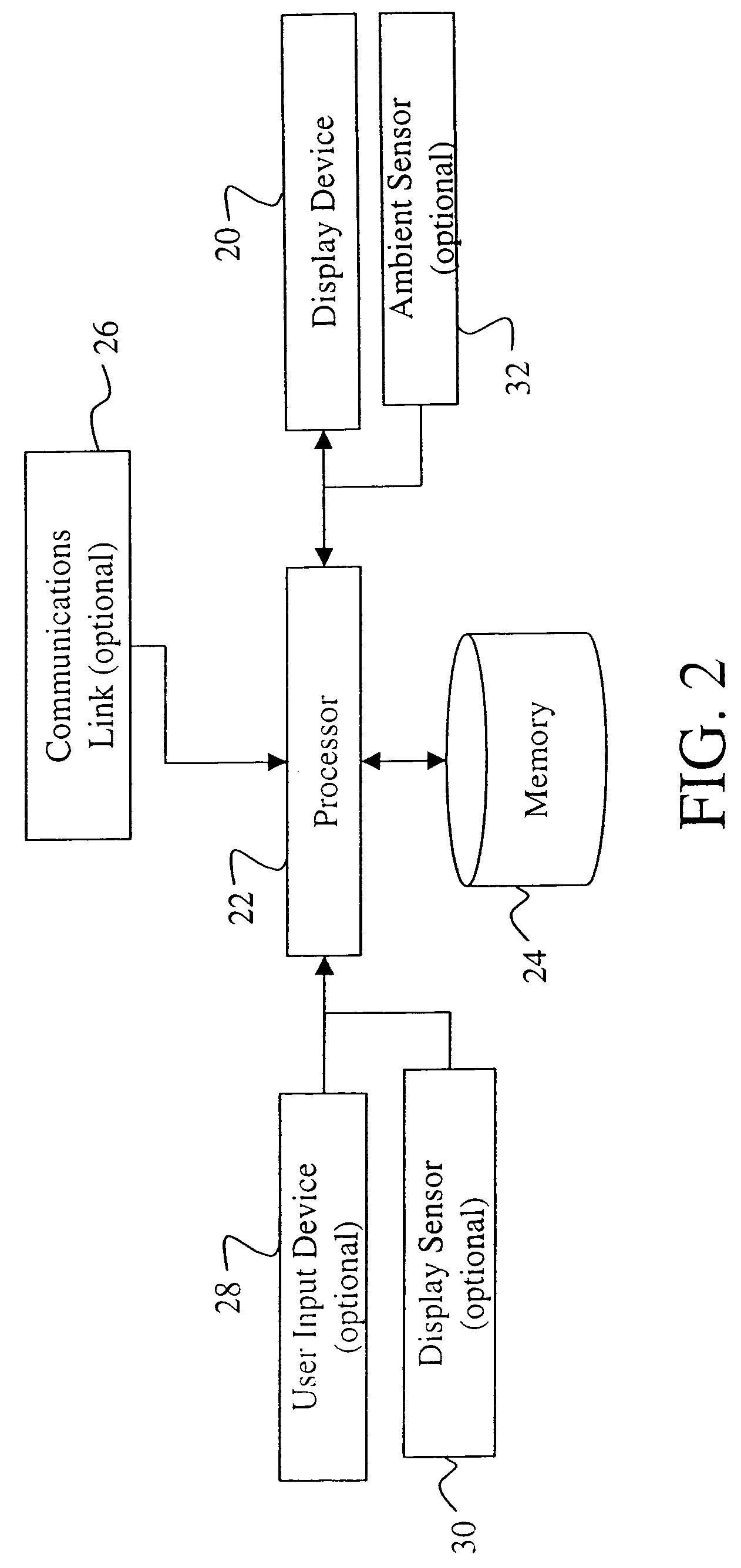
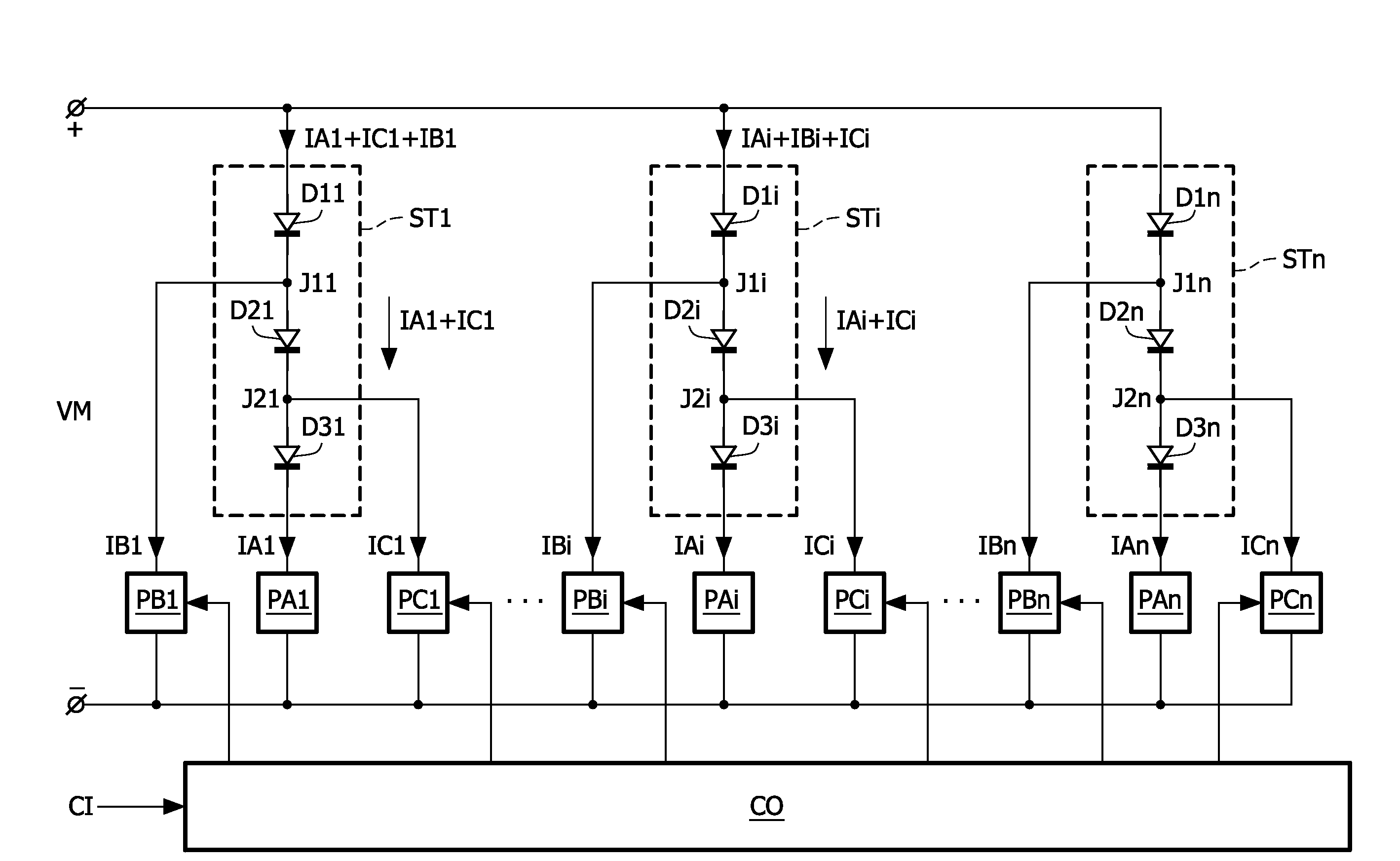
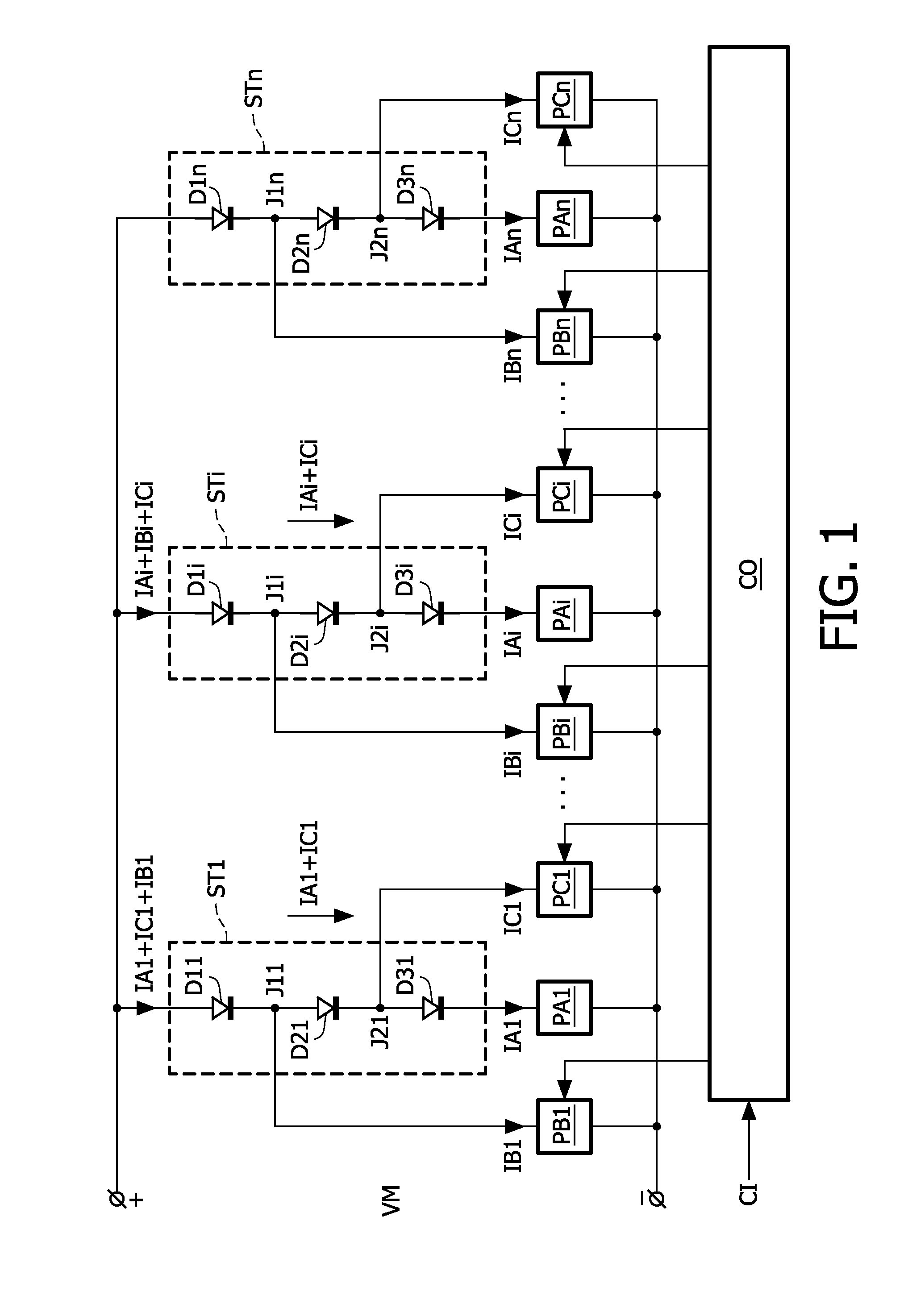
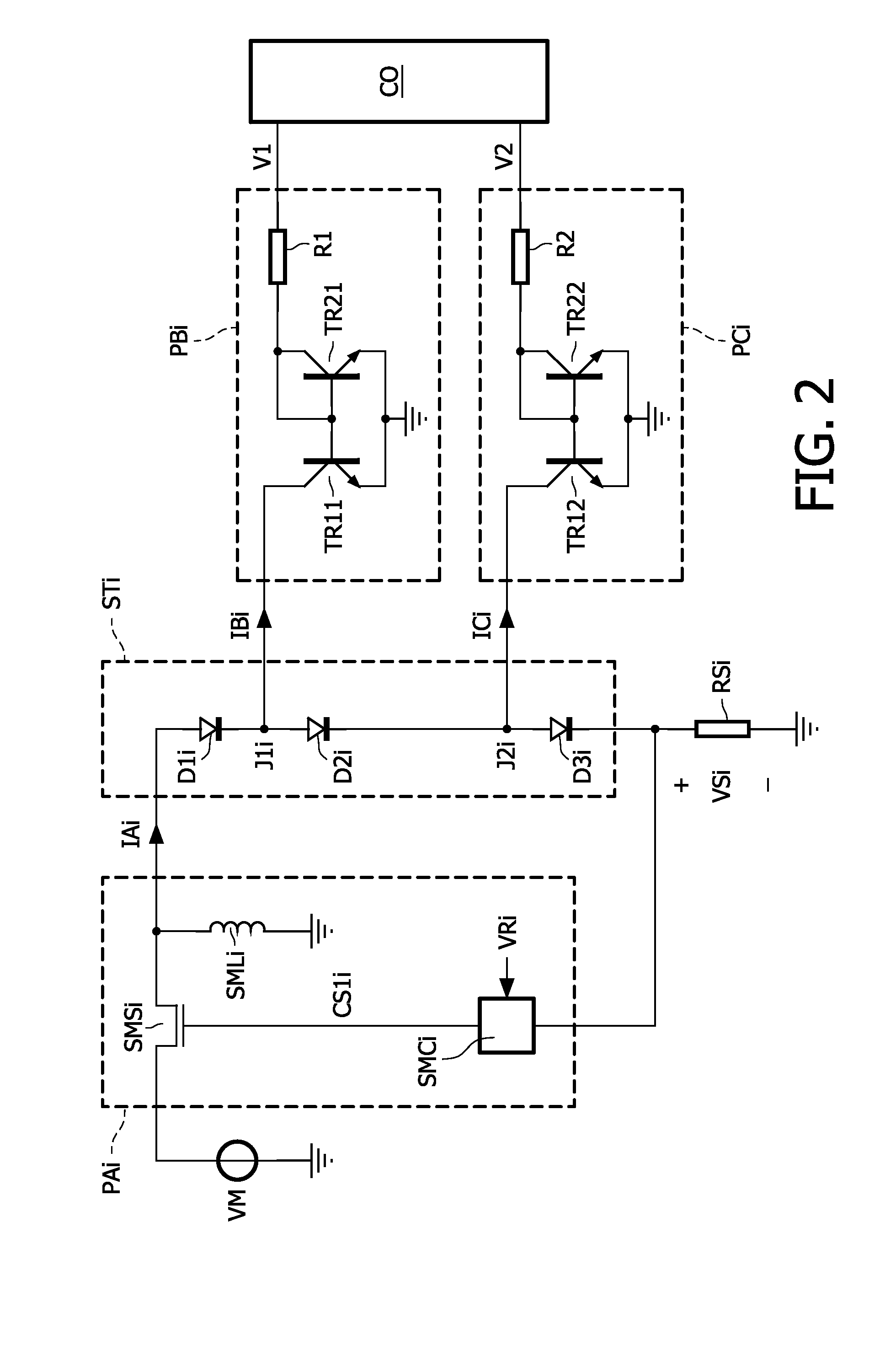
Driving light emitting diodes
ActiveUS20100102732A1Minimize the numberLittle powerElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
The present invention relates to a driver for a string (STi) of series arranged light emitting diodes (D1i, D2i, D3i) of which at least two emit light having different spectra. The driver comprises a main power supply (PAi) which has outputs coupled across the string (STi) to supply a main current (IAi) to the string (STi). A secondary power supply (PBi) is coupled to at least one of junctions (J1i) between successive light emitting diodes (D1i, D2i) in the string (STi) to supply or withdraw a delta current (IBi) from the junction (J1i). The delta current (IBi) is at least a factor 5 smaller than the main current (IAi). A controller (CO) controls the secondary power supply (PBi) to generate the delta current (IBi) to obtain a desired spectral composition of the mixed light emitted by the string (STi).
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Fisher judged null space based method for decomposing mixed pixels of high-spectrum remote sensing image
InactiveCN101692125ASmall spectral differenceReduce the impactWave based measurement systemsImage analysisDecompositionComputer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing, and particularly discloses a Fisher judged null space based method for decomposing mixed pixels of a high-spectrum remote sensing image. A Fisher judged null space method is provided aiming at the problem that the decomposition precision is reduced due to the phenomenon of same objects and different spectrums generally existing in the mixed pixel decomposition. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing a training sample consisting of pure pixel spectrums of an end member, constructing an intra-class scattering matrix null space of the training sample, making the spectrum difference in the end member become null, searching a judgment vector causing the scattering degree of the intra-class scattering matrix to be maximum in the null space, and making the separation degree of end member spectrums of different classes maximum so as to furthest reduce the decomposition error caused by the same objects and different spectrums. The method of the invention has particularly important application values in the aspects of high-precision surface feature decomposition of the high-spectrum remote sensing image and detection and identification of ground targets.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Apparatus and method to identify targets through opaque barriers
InactiveUS7920088B2Well representedMitigation extensionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandFrequency spectrum
The present invention is a method and apparatus that provides detection, characterization, and intuitive dissemination of targets. This disclosure combines improvements to ultra-wideband (UWB) sensing and machine target characterization with a means to convey data in a format that is quickly and readily understood by practitioners of the technology. The invention is well suited for Situational Awareness (SA) support in areas that are occluded by rain, fog, dust, darkness, distance, foliage, building walls, and any material that can be penetrated by ultra-wideband RF signals. Sense Through The Wall (STTW) performance parameters including target range, stand-off distance, and probability of detection are improved herein by combining a dynamically positioned sliding windowing function with orthogonal feature vectors that include but are not limited to time amplitude decay, spectral composition, and propagation time position in the return signal data. This invention is particularly useful for STTW and SA applications including urban combat, law enforcement, fire protection, transportation security, and homeland security. The invention can also be used to detect objects that are concealed by clothing, debris, and other non-metallic materials.
Owner:REALTRONICS CORP
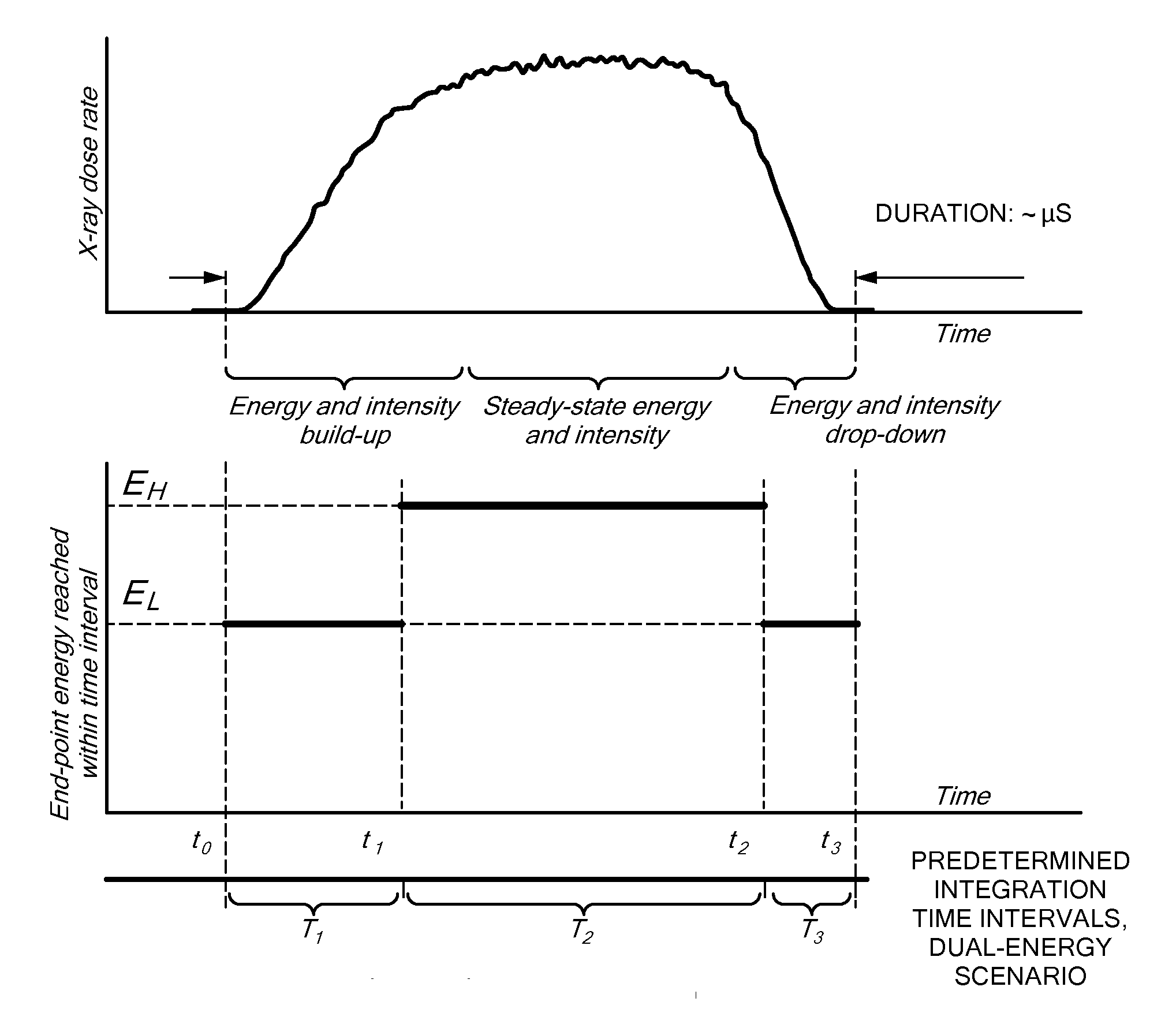
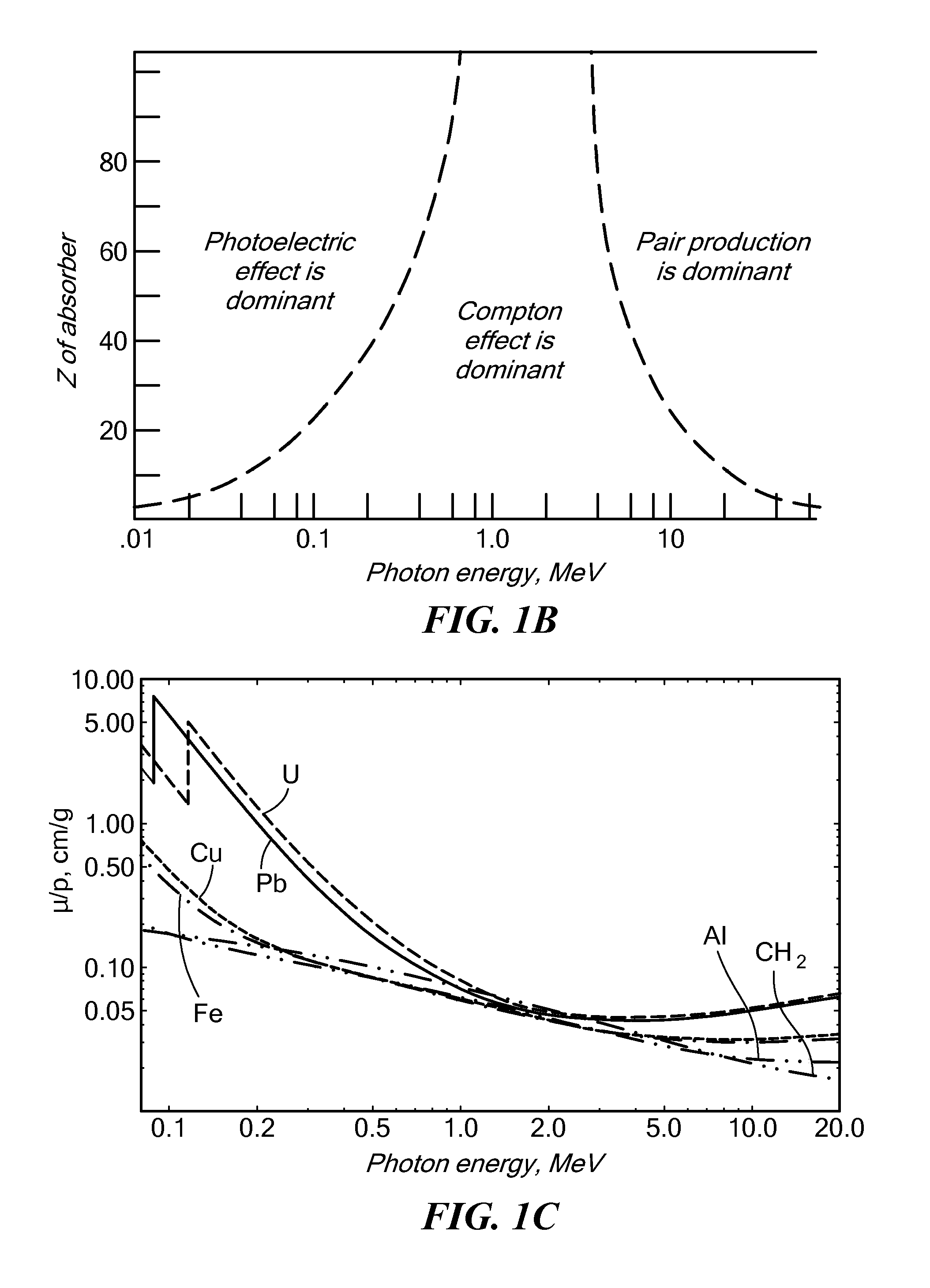
System and methods for intrapulse multi-energy and adaptive multi-energy X-ray cargo inspection
Methods and systems for x-ray inspection of an object using pulses whose spectral composition varies during the course of each pulse. A temporal sequence of pulses of penetrating radiation is generated such that the spectral content of each pulse evolves with time. The pulses are formed into a beam that is scanned across the object and detected after traversing the object. The detector signal is processed to derive at least one material characteristic of the object, such as effective atomic number, on the basis of temporal evolution of the detector signal during the course each pulse of the sequence of pulses. The time intervals may be predetermined, or else adapted based on features of the detected signal.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
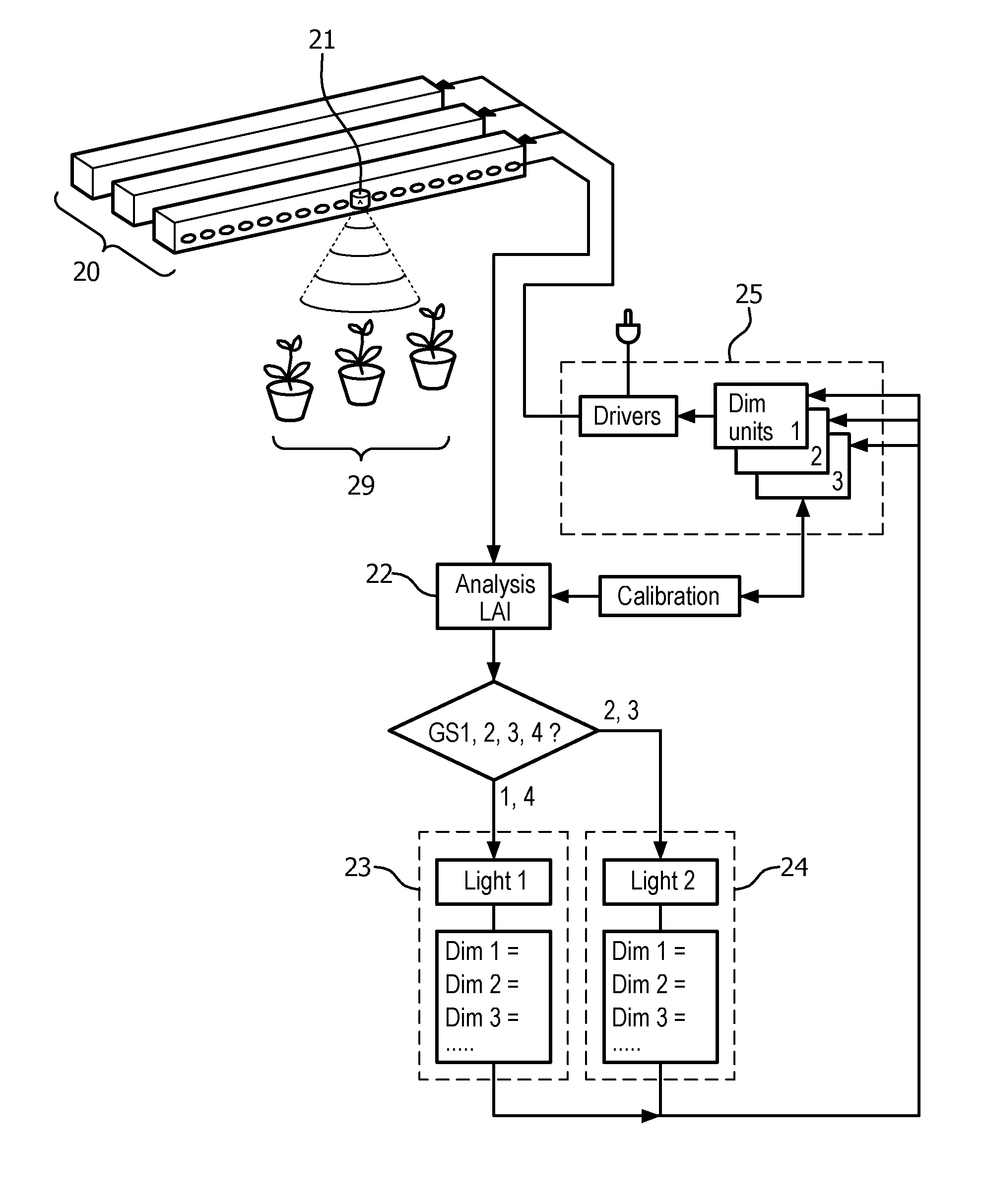
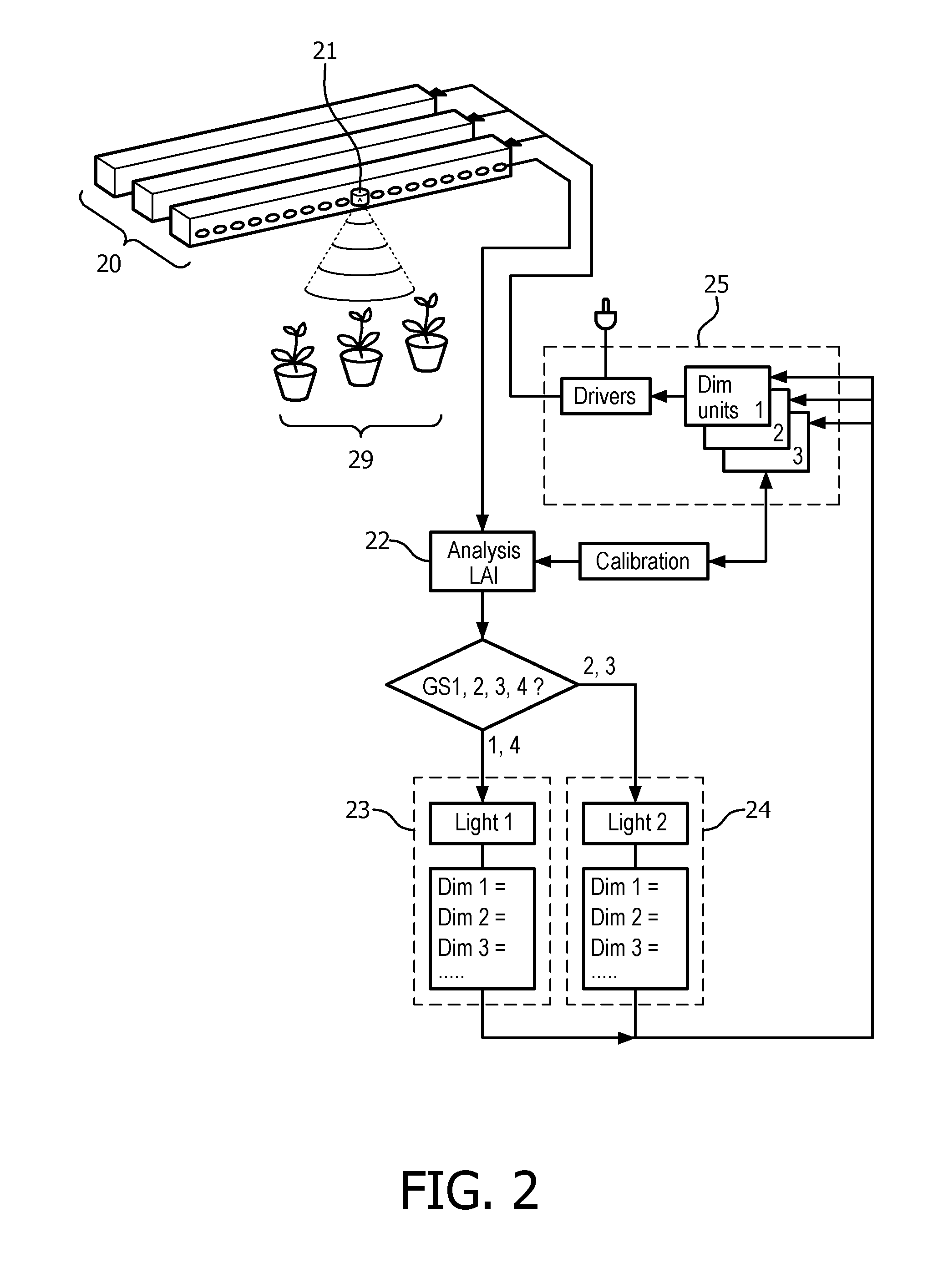
Dynamic light recipe for horticulture
InactiveUS20160088802A1Improve controlImprove fine tune morphologyRoot feedersElectrical apparatusDaylightGrow light
A lighting system and method for the growing of a plant seedling is disclosed, including at least one light source (30) for illuminating the plant seedling (39) with grow light during growth stages of the plant seedling growth process, and a controller for the controlling the spectral power distribution of the grow light emitted from the light source (30) such that the grow light in at least some growth stages of the plant seedling growth process comprises more energy in the blue wavelength range than in other growth stages of the plant seedling growth process. In use cases where the grow light is supplementing available daylight, an additional sensor (33) may be used to measure the amount and spectral composition of daylight and control the grow light such that spectral power distribution of total light received by the plant seedling is controlled accordingly.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
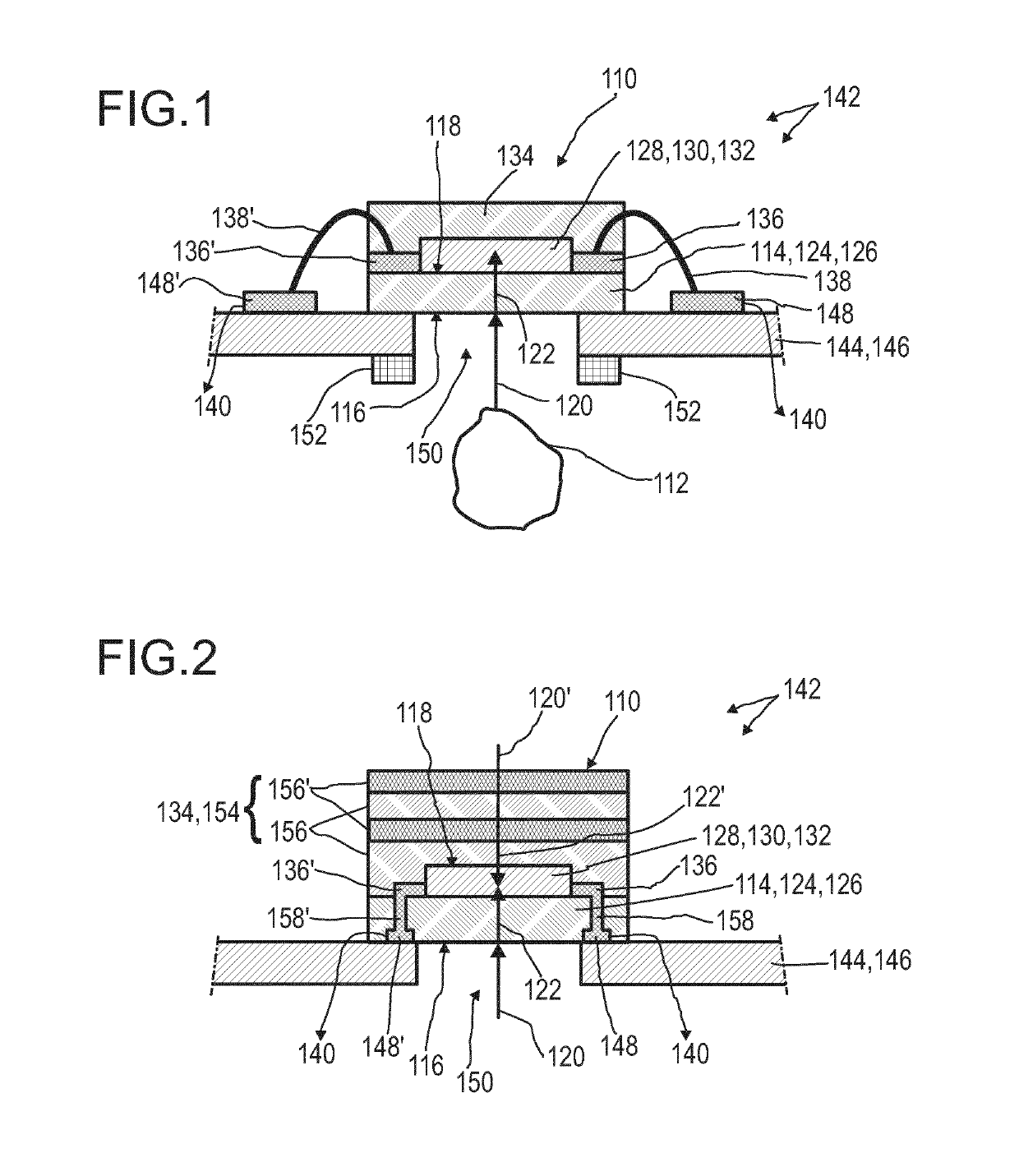
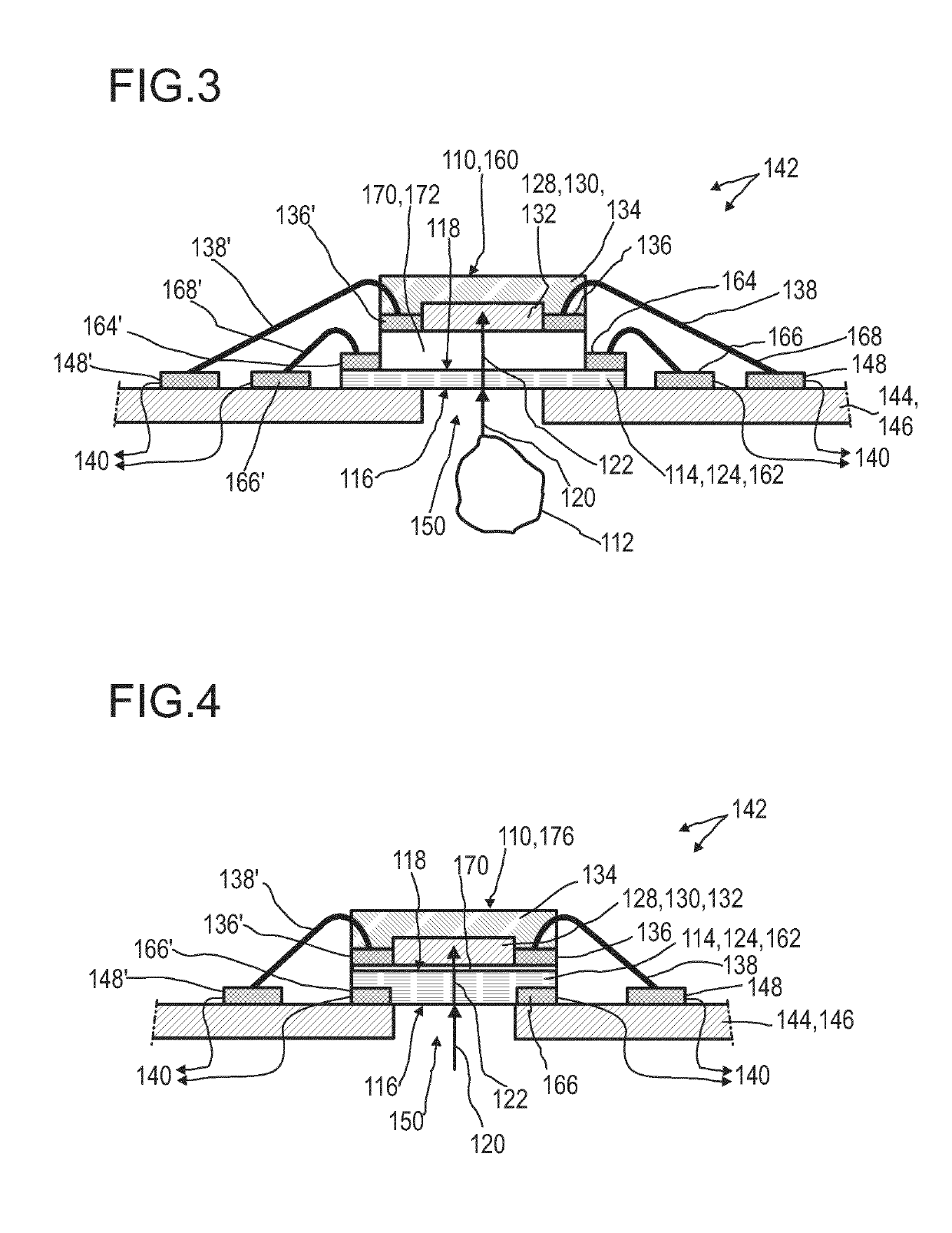
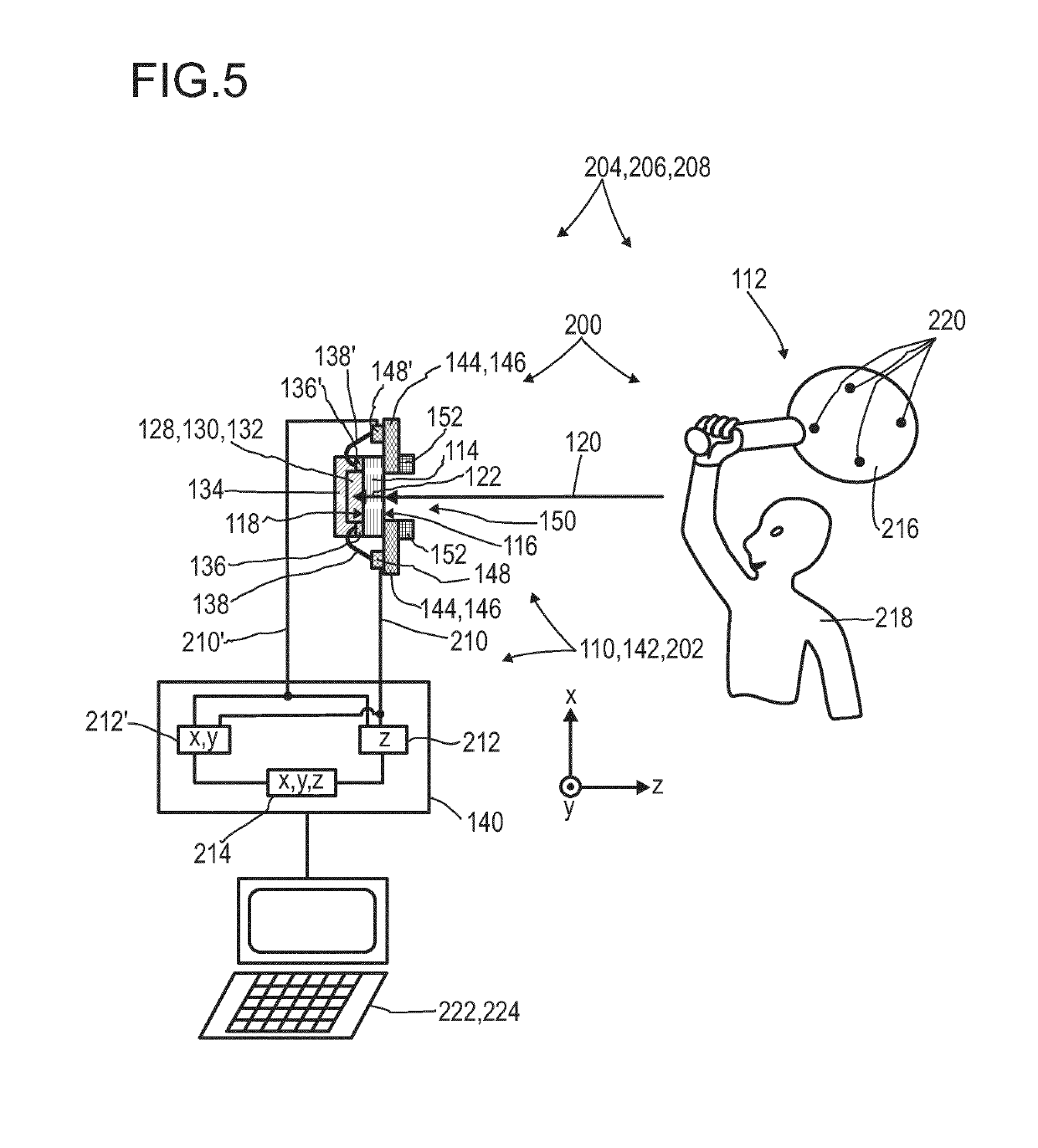
Optical detector for an optical detection
ActiveUS20190277703A1Improve purposeEnhance layeringLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureOptical radiationTransmittance
The invention relates to an optical detector (110) for an optical detection, in particular, of radiation within the infrared spectral range, specifically, with regard to sensing at least one optically conceivable property of an object (112). More particular, the optical detector (110) may be used for determining transmissivity, absorption, emission, reflectance, and / or a position of at least one object (112). Further, the invention relates to a method for manufacturing the optical detector (110) and to various uses of the optical detector (110). The optical detector (110) comprises —an optical filter (114) having at least a first surface (116) and a second surface (118), the second surface (118) being located oppositely with respect to the first surface (116), wherein the optical filter (114) is designed for allowing an incident light beam (120) received by the first surface (116) to pass through the optical filter (114) to the second surface (118), thereby generating a modified light beam (122) by modifying a spectral composition of the incident light beam (120); —a sensor layer (128) comprising a photosensitive material (130) being deposited on the second surface (118) of the optical filter (114), wherein the sensor layer (128) is designed to generate at least one sensor signal in a manner dependent on an illumination of the sensor layer (128) by the modified light beam (122); and —an evaluation device (140) designed to generate at least one item of information provided by the incident light beam (120) by evaluating the sensor signal. The optical detector (110) constitutes an improved simple, cost-efficient and, still, reliable detector for detecting optical radiation, especially within the infrared spectral range, specifically with regard to sensing at least one of transmissivity, absorption, emission and reflectance. Hereby, the optical detector (110) is capable of effectively removing stray light as far as possible.
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
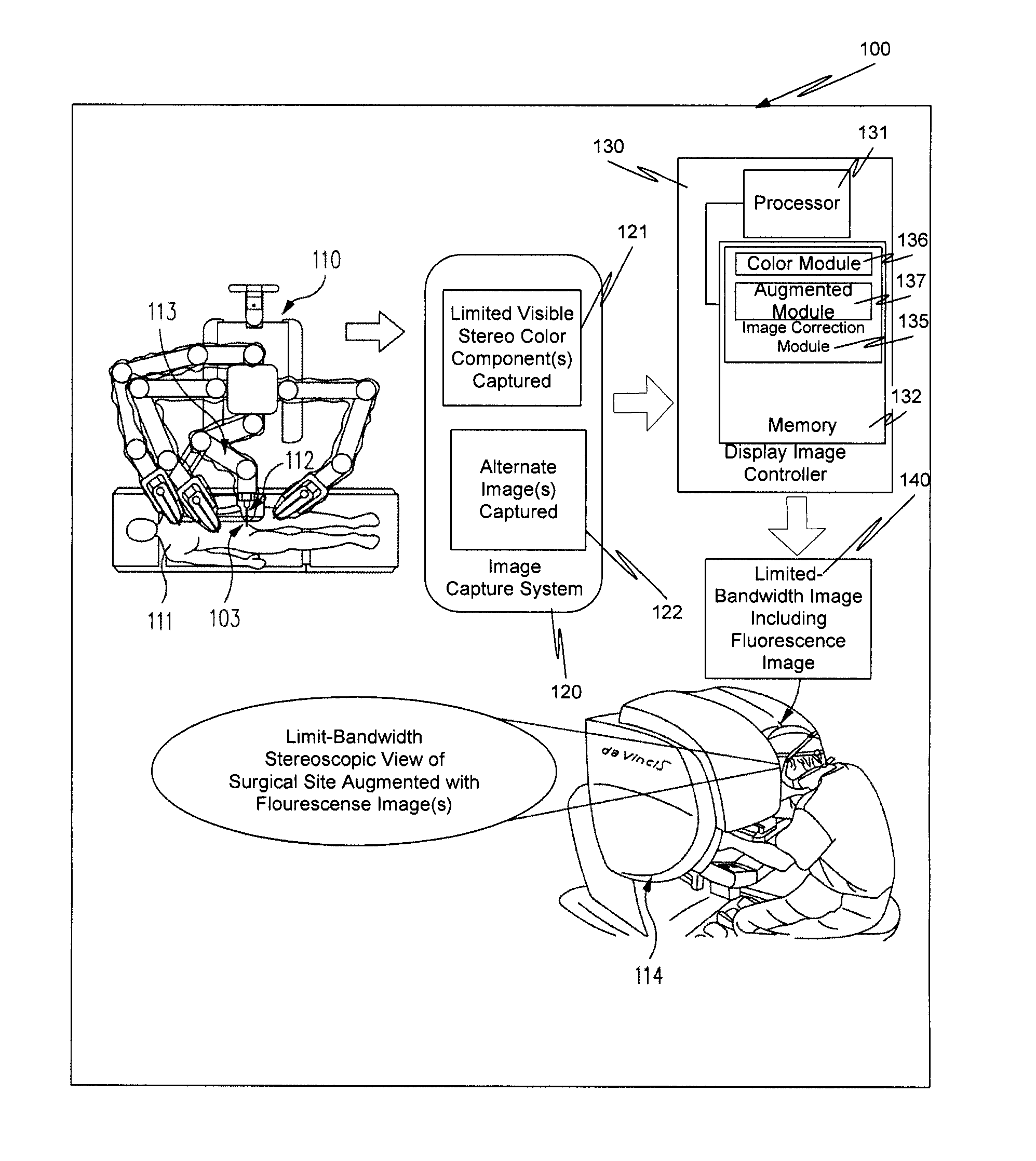
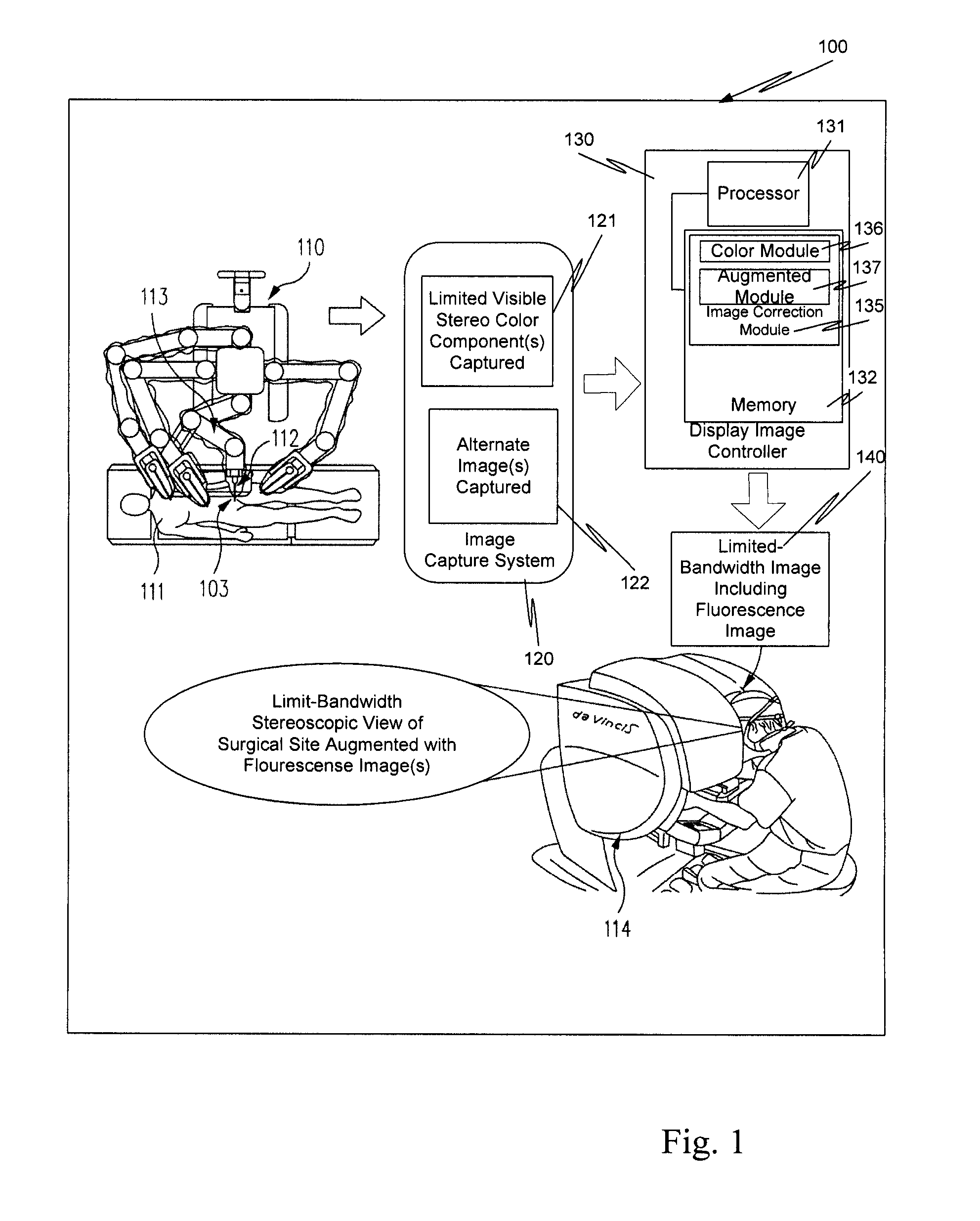
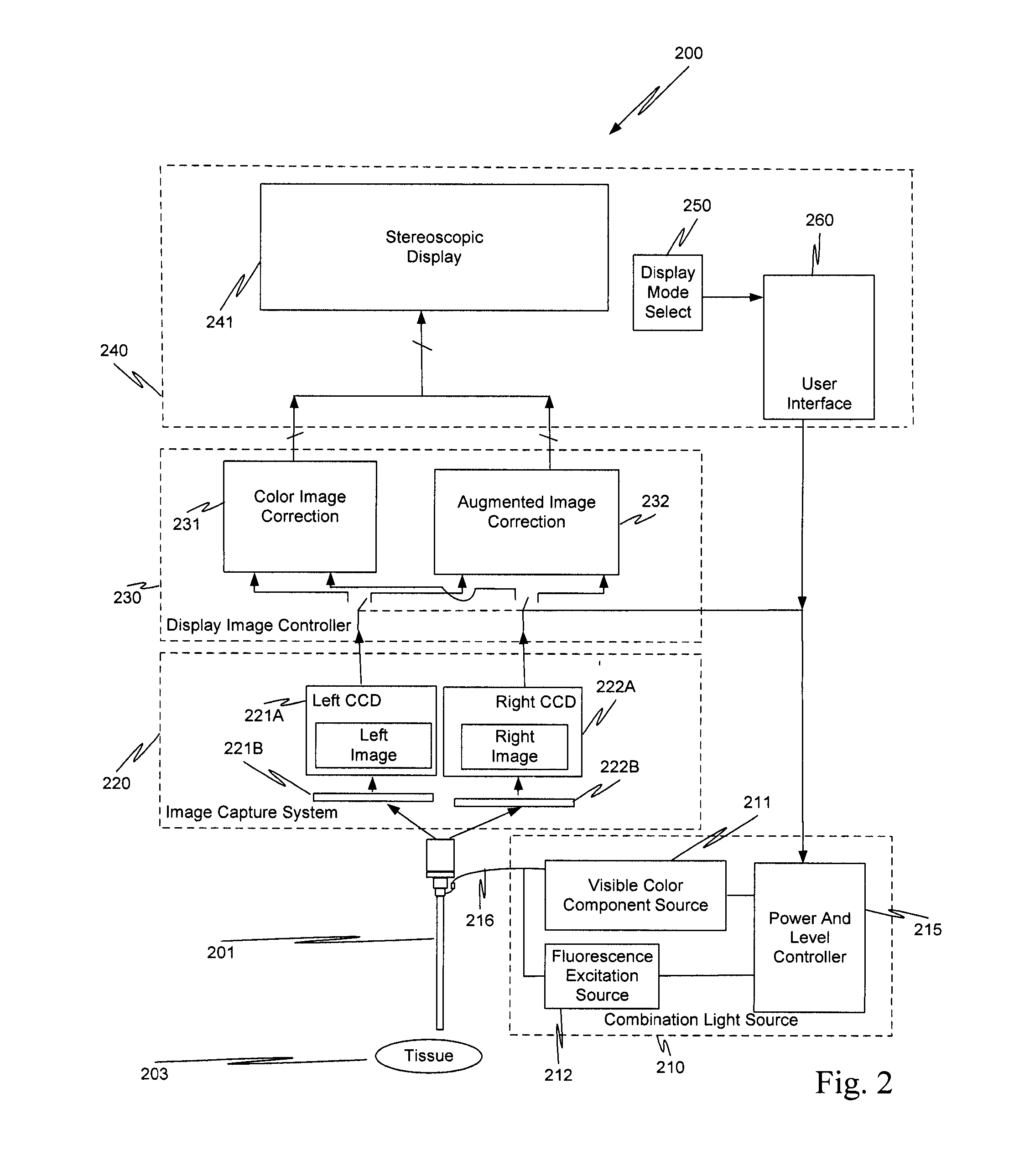
Method and system for fluorescent imaging with background surgical image composed of selective illumination spectra
ActiveUS20120004557A1Low system requirementsLower requirementSurgeryEndoscopesSurgical siteFluorescent imaging
A surgical site is simultaneously illuminated by less than all the visible color components that make up visible white light, and a fluorescence excitation illumination component by an illuminator in a minimally invasive surgical system. An image capture system acquires an image for each of the visible color components illuminating the surgical site and a fluorescence image, which is excited by the fluorescence excitation component from the illuminator. The minimally invasive surgical system uses the acquired images to generate a background black and white image of the surgical site. The acquired fluorescence image is superimposed on the background black and white image, and is highlighted in a selected color, e.g., green. The background black and white image with the superimposed highlighted fluorescence image is displayed for a user of the system. The highlighted fluorescence image identifies tissue of clinical interest.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
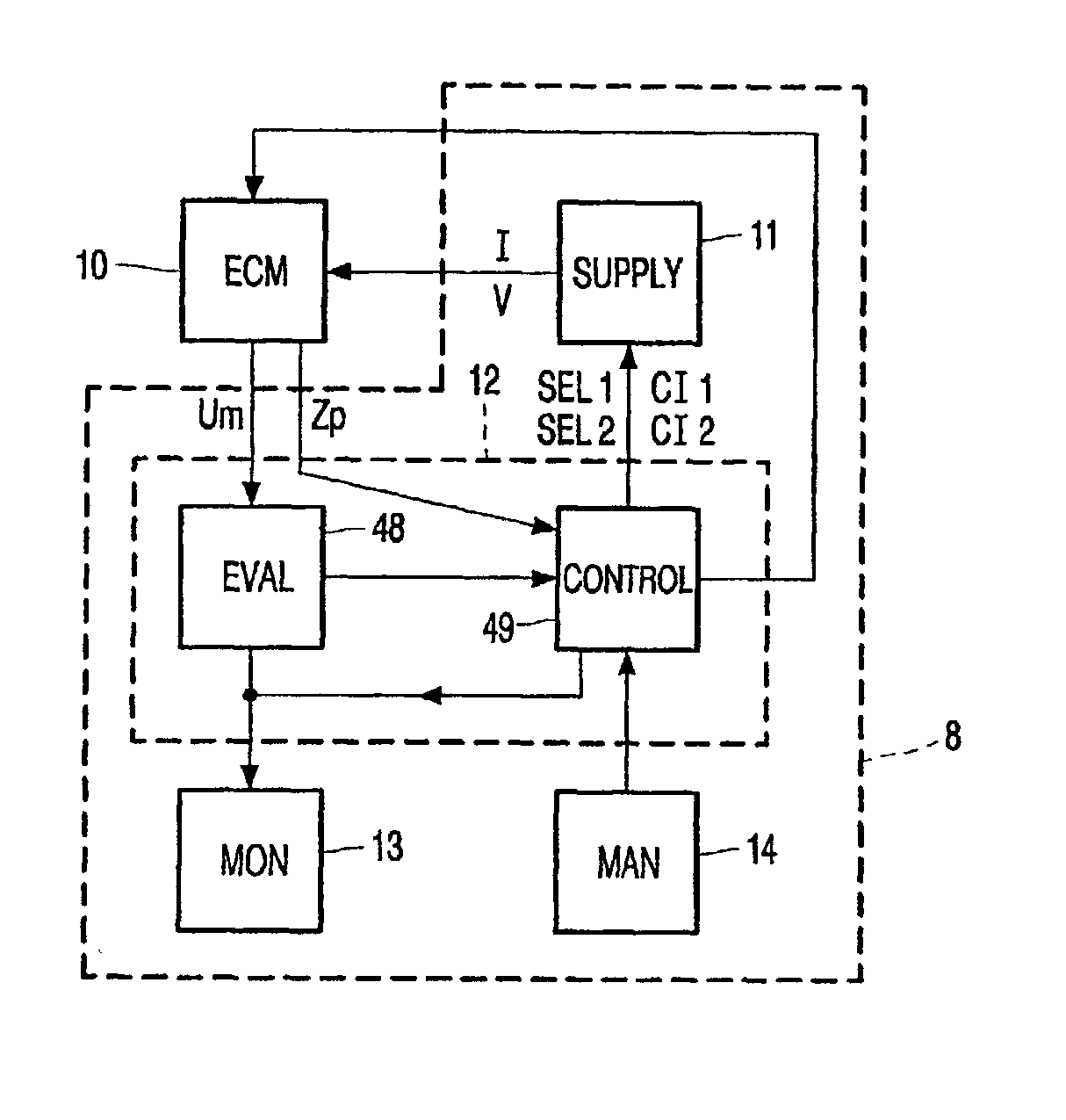
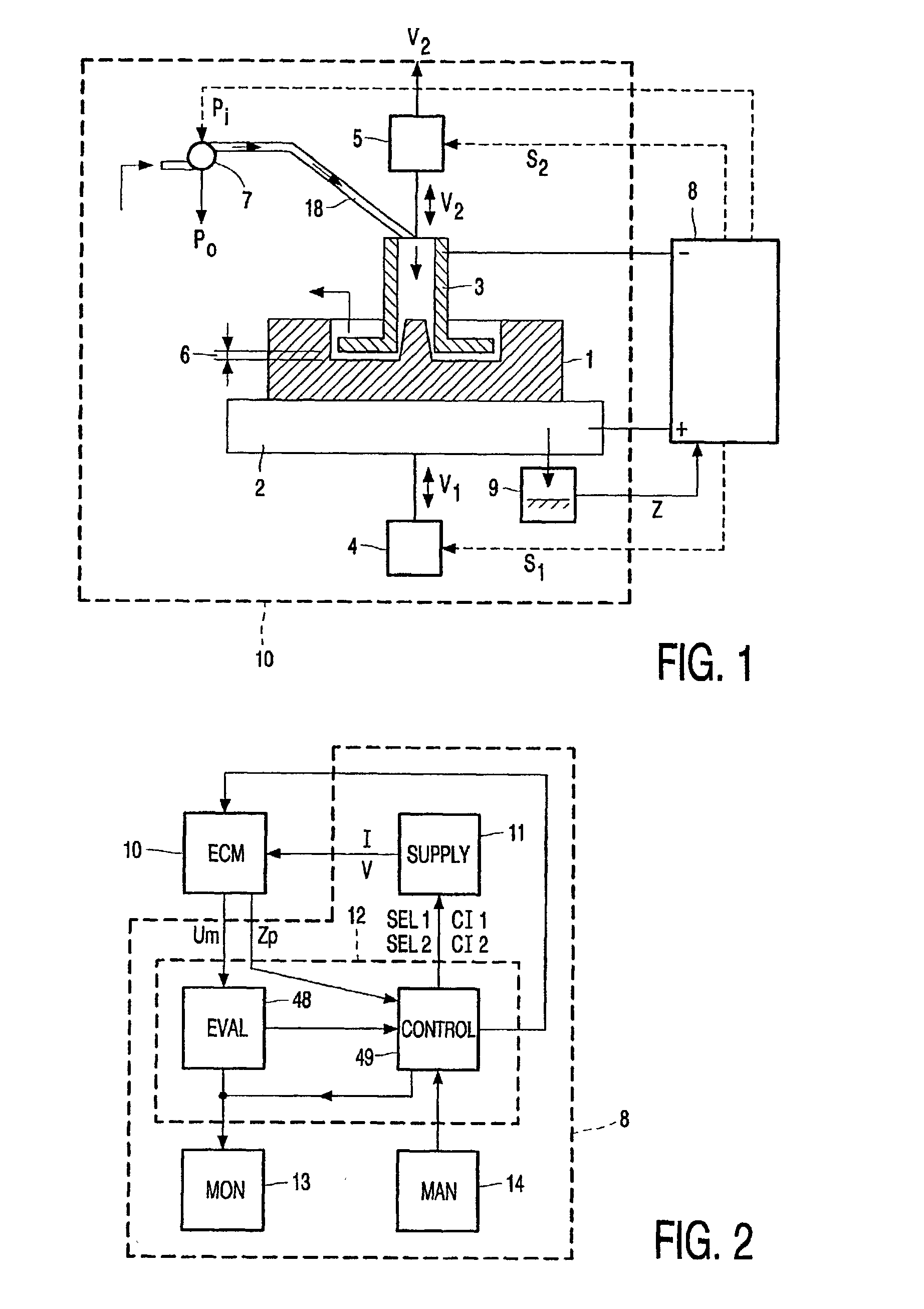
Method of controlling an electrochemical machining process
InactiveUS20020169516A1Improve machining accuracyAvoid large gapsMachining electric circuitsElectric circuitsElectrochemistryElectrochemical machining
A method of controlling a process of electrochemically machining an electrically conductive workpiece employing the spectral composition of the measured voltage within a predetermined measuring period such as induced by an applied current between the electrically conductive workpiece and an electrode tool. A process of electrochemically machining employing a material removing step with electric current supplied continuously and an a workpiece shaping step with electric current supplied intermittently. An advantageous embodiment employs extreme short pulses.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Radiation Generation Device for Generating Electromagnetic Radiation Having an Adjustable Spectral Composition, and Method of Producing Same
ActiveUS20110128541A1Limited spectral rangeFlexible choiceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
A radiation generation device for generating resulting electromagnetic radiation having an adjustable spectral composition includes: a multitude of radiation elements (configured to generate a radiation element specific electromagnetic radiation, respectively, upon being activated, a first radiation element of the multitude of radiation elements being activatable independently of a second radiation element of the multitude of radiation elements; a dispersive optical element; and an optical opening; the dispersive optical element being configured to deflect the radiation element specific electromagnetic radiations, in dependence on their wavelength and on a position of the radiation element generating the respective radiation element specific electromagnetic radiation, such that a particular spectral range of each of the radiation element specific electromagnetic radiations may exit through the optical opening, so that the spectral composition of the resulting electromagnetic radiation exiting through the optical opening is adjustable by selectively activating the multitude of radiation elements.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
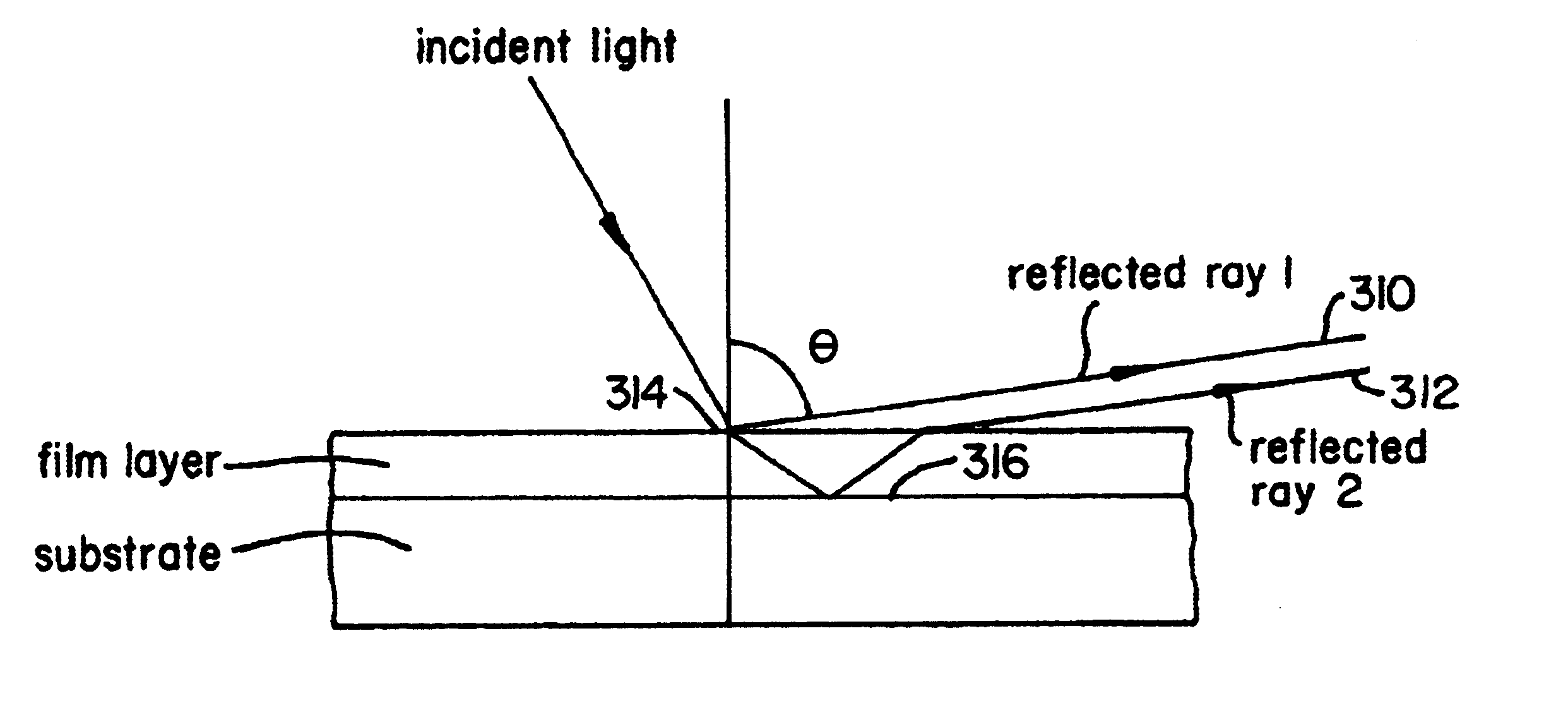
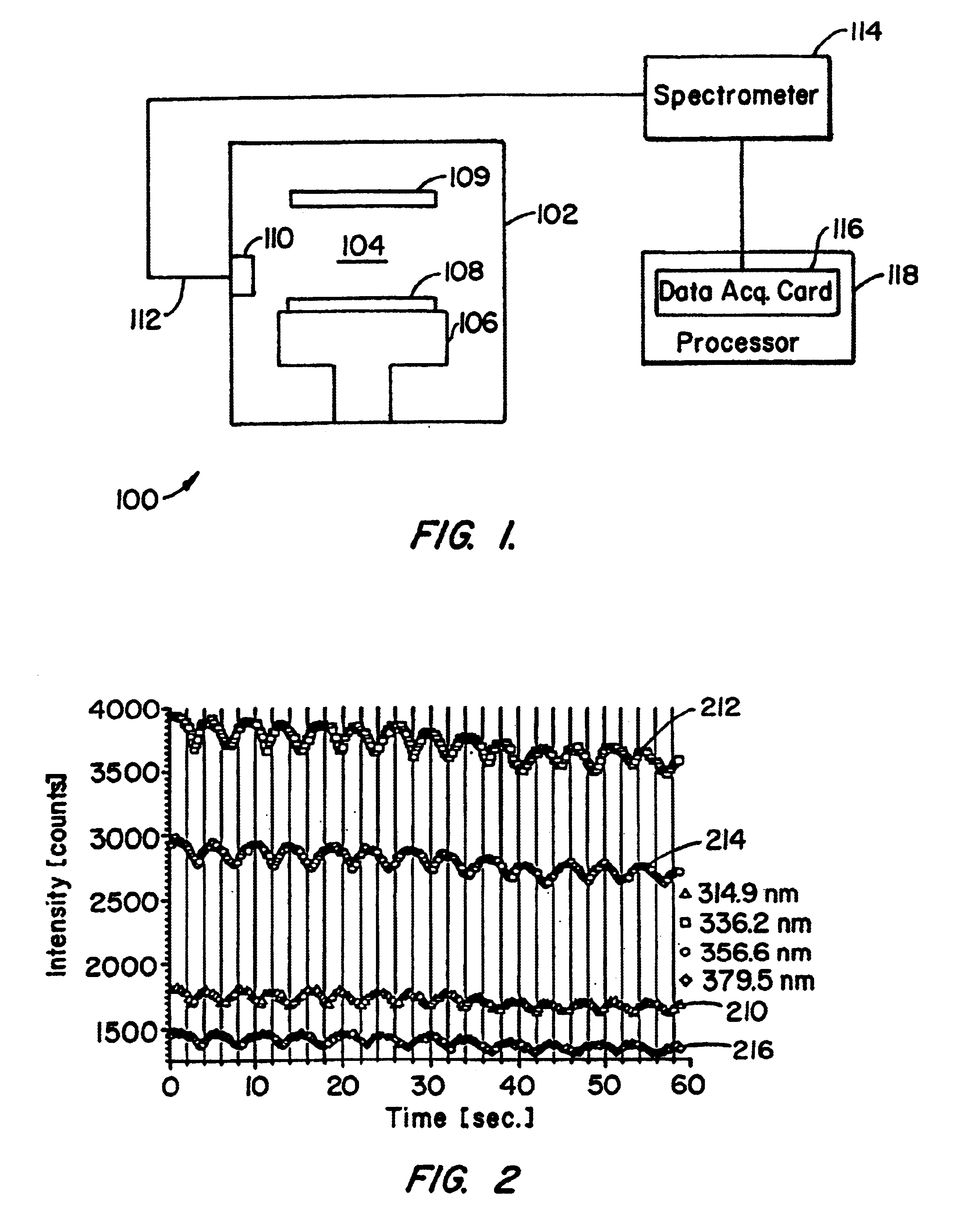
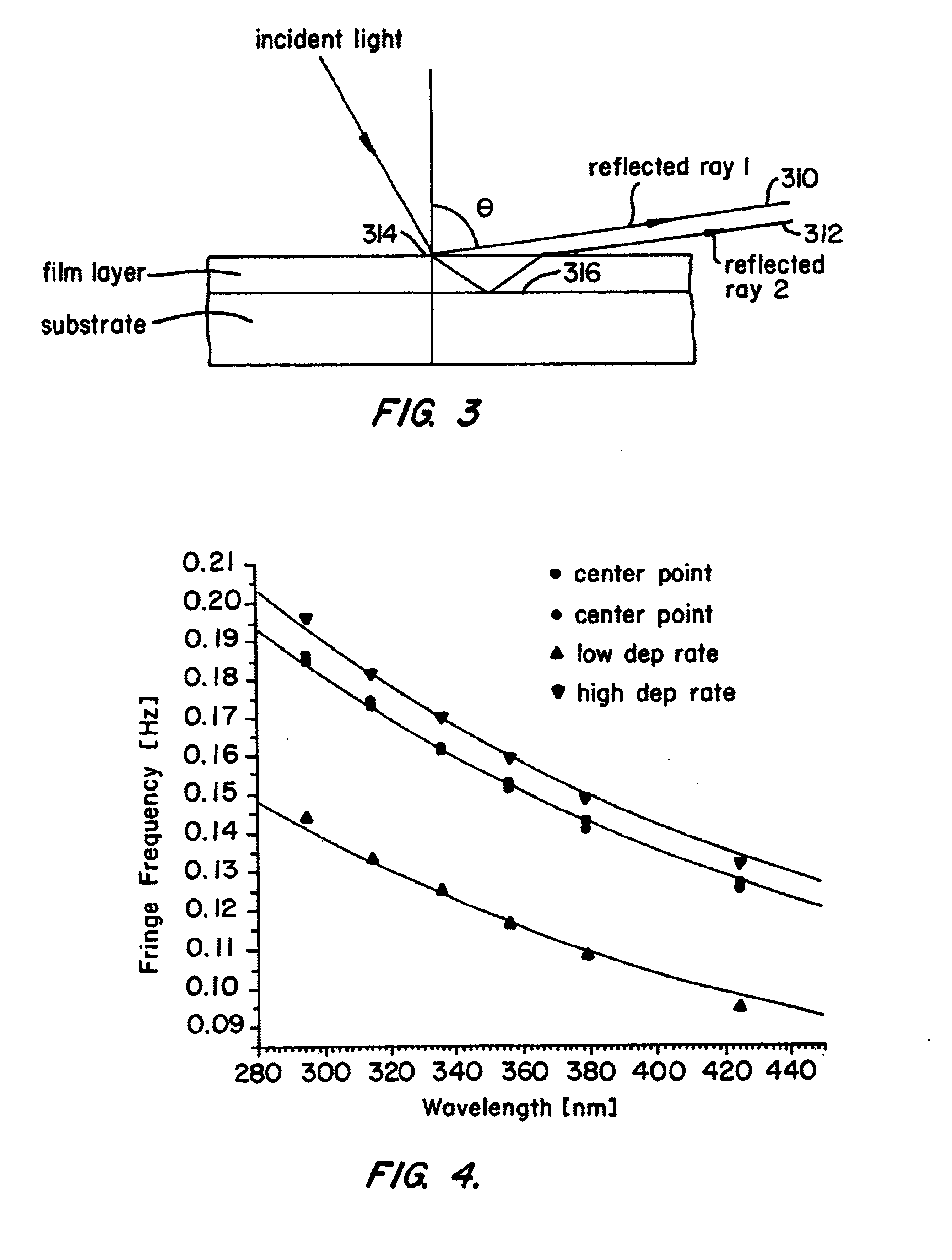
In-situ film thickness measurement using spectral interference at grazing incidence
InactiveUS6888639B2Low costImprove signal-to-noise ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPlasma depositionLength wave
A method and system using spectral interference of light from plasma emissions collected at near grazing incidence to in-situ monitor and control the film thickness of a non-opaque film. Embodiments of this invention are particularly useful to all substrate processing chambers equipped to form an in-situ plasma within the chamber and which are used to deposit or etch non-opaque films. One embodiment of the method of the present invention forms a plasma within a substrate processing chamber to deposit a non-opaque film on a wafer substrate within the chamber. During the plasma deposition process, a plurality of wavelengths of radiation including those reflected from the top and bottom layer of the film being deposited upon a wafer surface are collected through an existing viewport, and conveyed to a spectrometer for measurements via an optical fiber attached near this viewport. These measurements are analyzed to determine the film's thickness. An alternate embodiment of the method of the present invention uses an interference filter to confine the spectral composition of the plasma emissions to an emission at a narrow wavelength interval and a photodiode to detect the intensity of the emission.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Light spectrum reshaping modulating method for chirp pulse amplification
InactiveCN101231385AFix what doesn't applyImprove general performanceOptical measurementsSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsChirped pulse amplificationLighting spectrum
The invention relates to a spectral reshaping / modulation method used for a chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system. During the spectral reshaping / modulation process, the method employs a CTSI system consisting of a CTSI spectral decomposition system and a CTSI spectral composition system, wherein, the two systems are symmetrical to each other, and employs a spectral modulation system. The CTSI spectral decomposition subsystem realizes the complete and actual development of laser chirped pulses onto a spectral plane; the spectral modulation subsystem performs the spectral modulation on an image plane; then the CTSI spectral composition subsystem restores the modulated spectra to modulated chirped pulses without distortions, thereby realizing the spectral modulation and reshaping of chirped pulses. The inventive method can realize the spectral modulation and reshaping of common laser pulses, and is particularly suitable for the spectral modulation and reshaping of large-aperture high-power CPA system with band width of several nanometers.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
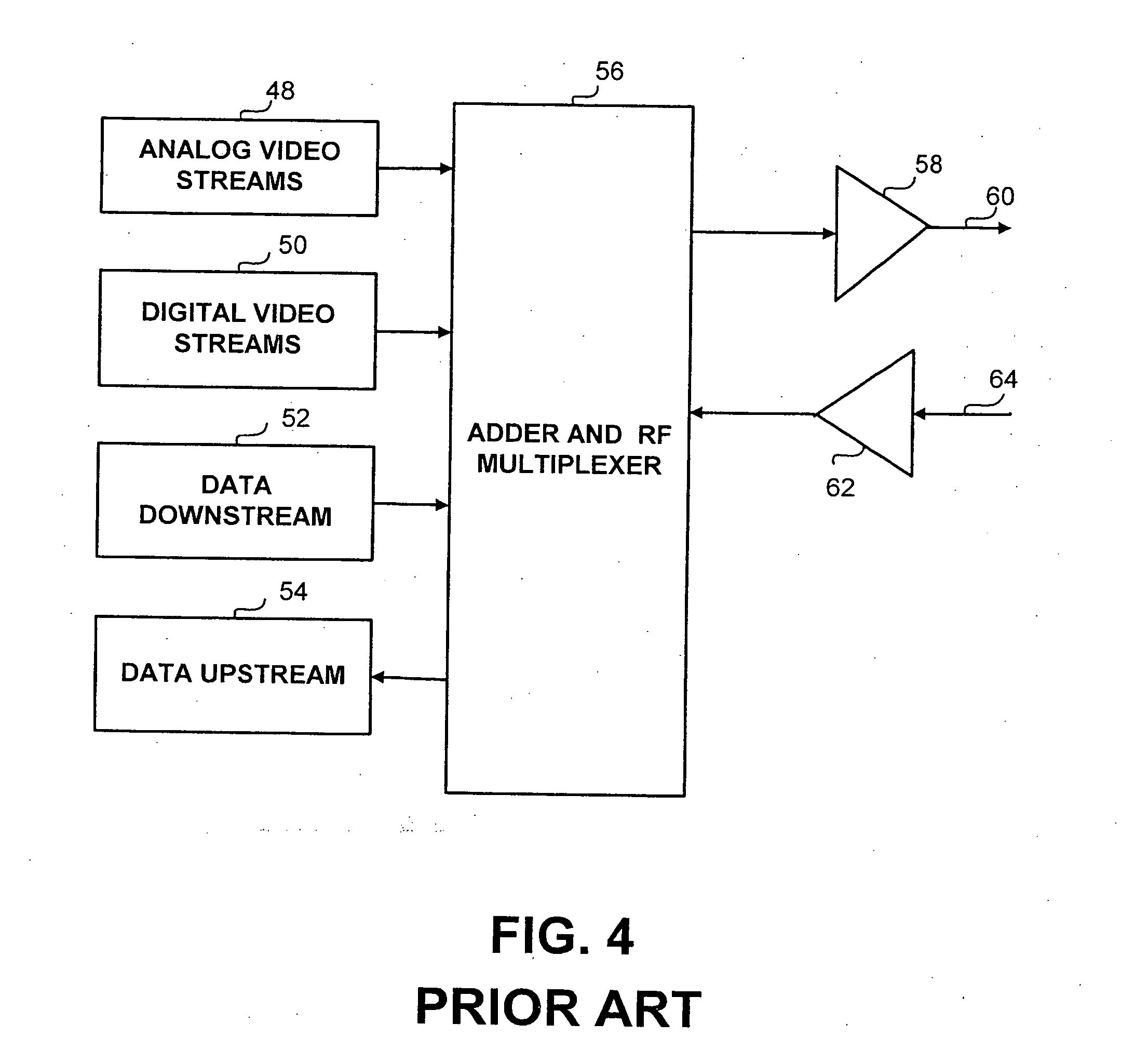
System and method to expand catv transmission spectrum using high frequency spectrum overlays
InactiveUS20060053462A1Two-way working systemsSelective content distributionFrequency spectrumDistribution system
A system and method for the expansion of the spectrum by the generation and introduction of high frequency spectrum overlays is disclosed. In an electronic content distribution system a plurality of input stream are combined at a head end into two combined signals having separate frequency band ranges. The signals are transmitted to the network and are dynamically combined into a single signal where the spectral composition of the signal is controlled by pre-defined parameters. The first signal carries a plurality of existing channels while the second signal could carry an additional set of channels. The second signal could carry spectral overlays generated from specific input streams the in accordance with pre-defined system parameters. The spectral overlays are selectively extracted from the second signal and introduced into the combined signal in the network in accordance with pre-defined subscriber-specific information.
Owner:XTEND NETWORKS
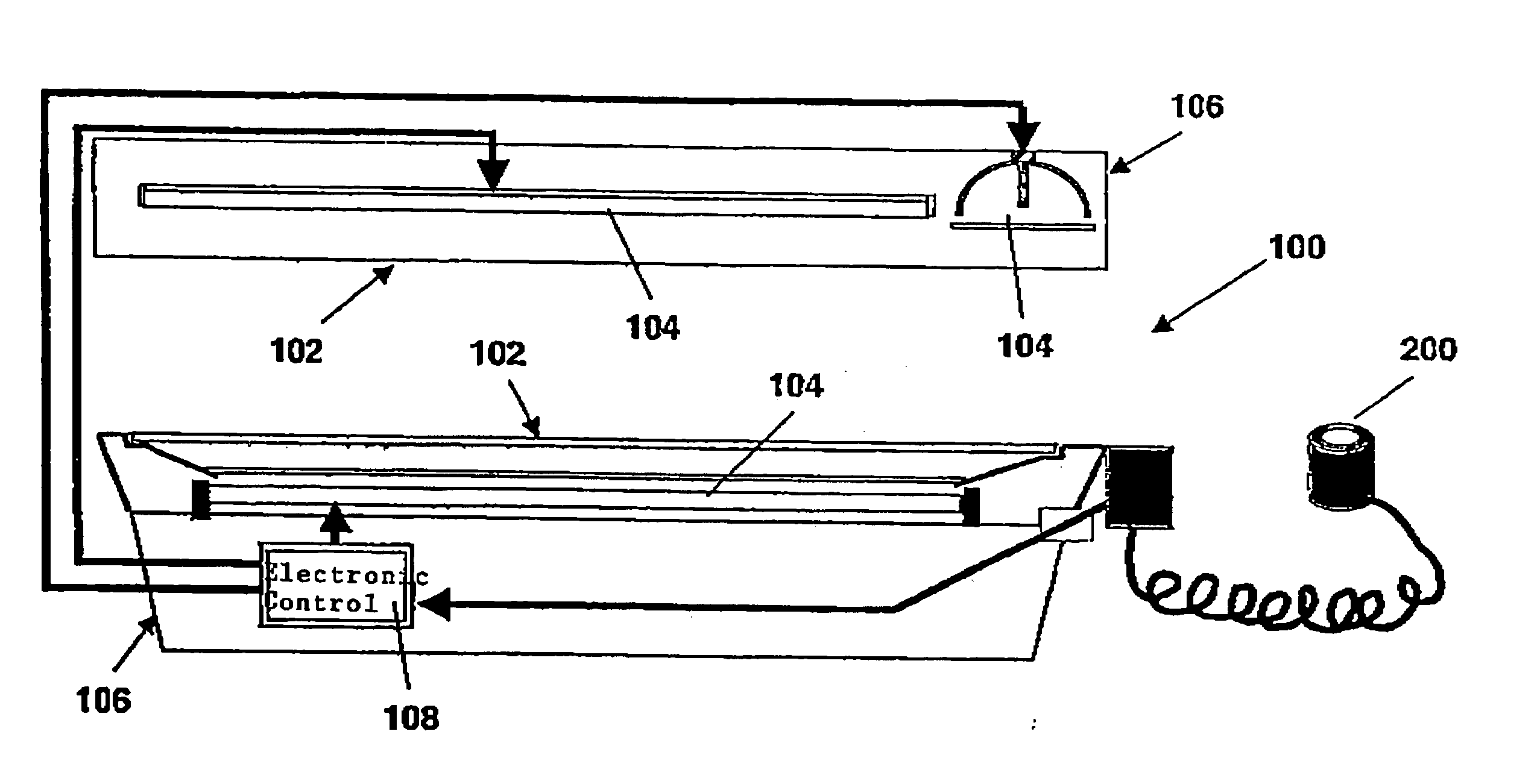
Device and process for a controlled irradiation of the human body
InactiveUS20050085877A1Avoid overexposureEasy to useDiagnostics using lightSensorsHuman bodyIrradiation
The invention relates to a device (200) for a measurement of the status, as far as relevant for determining the UV irradiation dose, of the skin of a person on his / her skin (cutis), comprising (a) a means (201) for emitting radiation having a defined spectral composition onto the skin (cutis); (b) optionally a means (211) for advancing the radiation of a defined composition to the emission means (201); (a) a sensor (202) for measuring the portion of the radiation irradiated by the emission means (201) which is reflected or absorbed by the skin (cutis); and (d) means (212) for providing energy to the means (201) and / or to the sensor (202) and for transmitting measured data to a data analyzing means (203). The invention also relates to an apparatus (100) and a process for irradiating the body of a user for cosmetic and medical purposes.
Owner:JK HLDG
System and Methods for Intrapulse Multi-energy and Adaptive Multi-energy X-ray Cargo Inspection
Methods and systems for x-ray inspection of an object using pulses whose spectral composition varies during the course of each pulse. A temporal sequence of pulses of penetrating radiation is generated, each pulse characterized by an onset and by a spectral content that evolves with time subsequent to the onset. The pulses are formed into a beam that is scanned across the object. The penetrating radiation from the beam that has traversed the object is detected, generating a detector signal. The detector signal is processed to derive at least one material characteristic of the object, such as effective atomic number, on the basis of temporal evolution of the detector signal during the course each pulse of the sequence of pulses. The detector signal is separately acquired for multiple time intervals relative to the pulse onset, and processed to obtain values corresponding to multiple-energy analysis of the transmitted radiation. The time intervals may be predetermined, or else adapted based on features of the detected signal.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
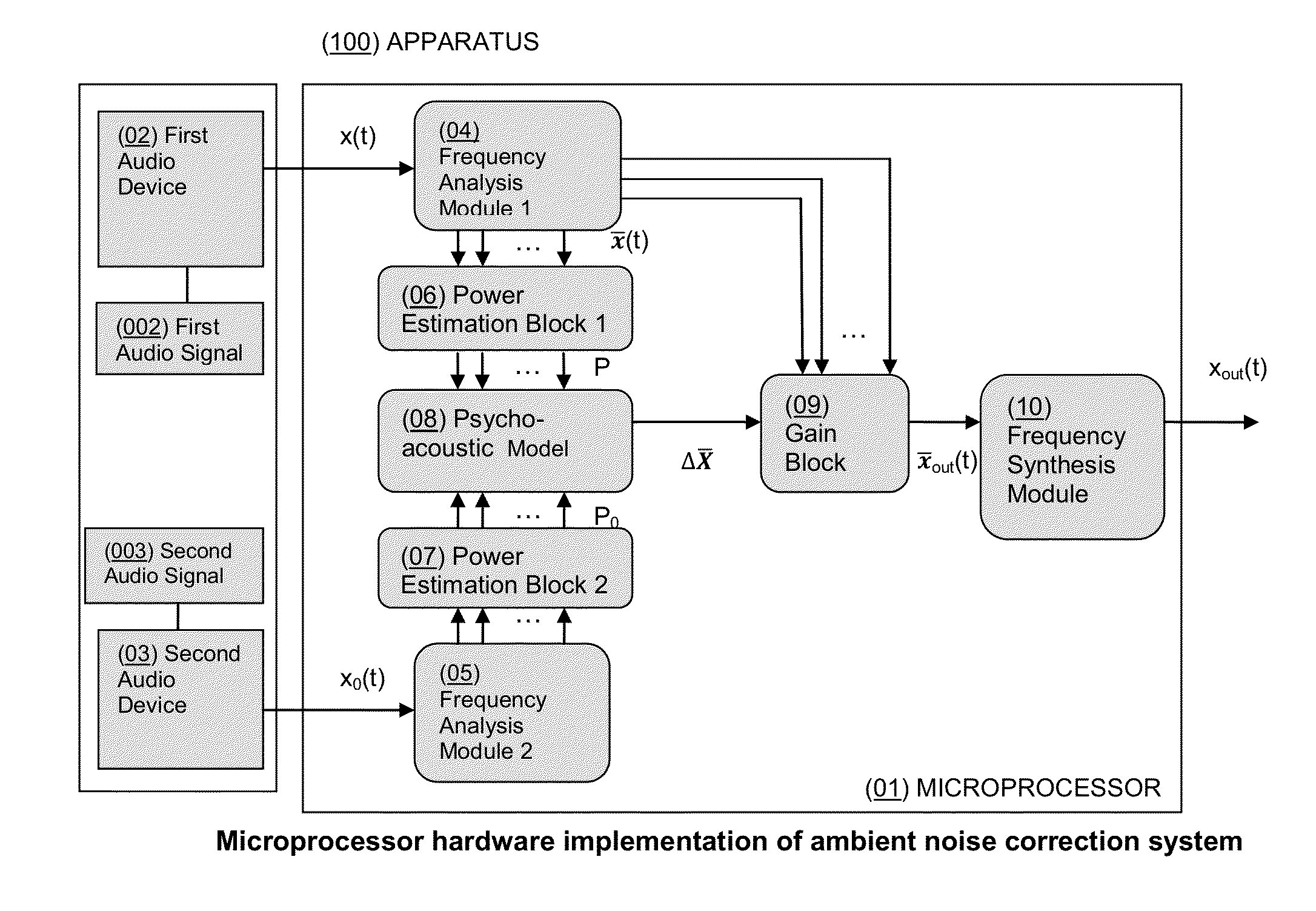
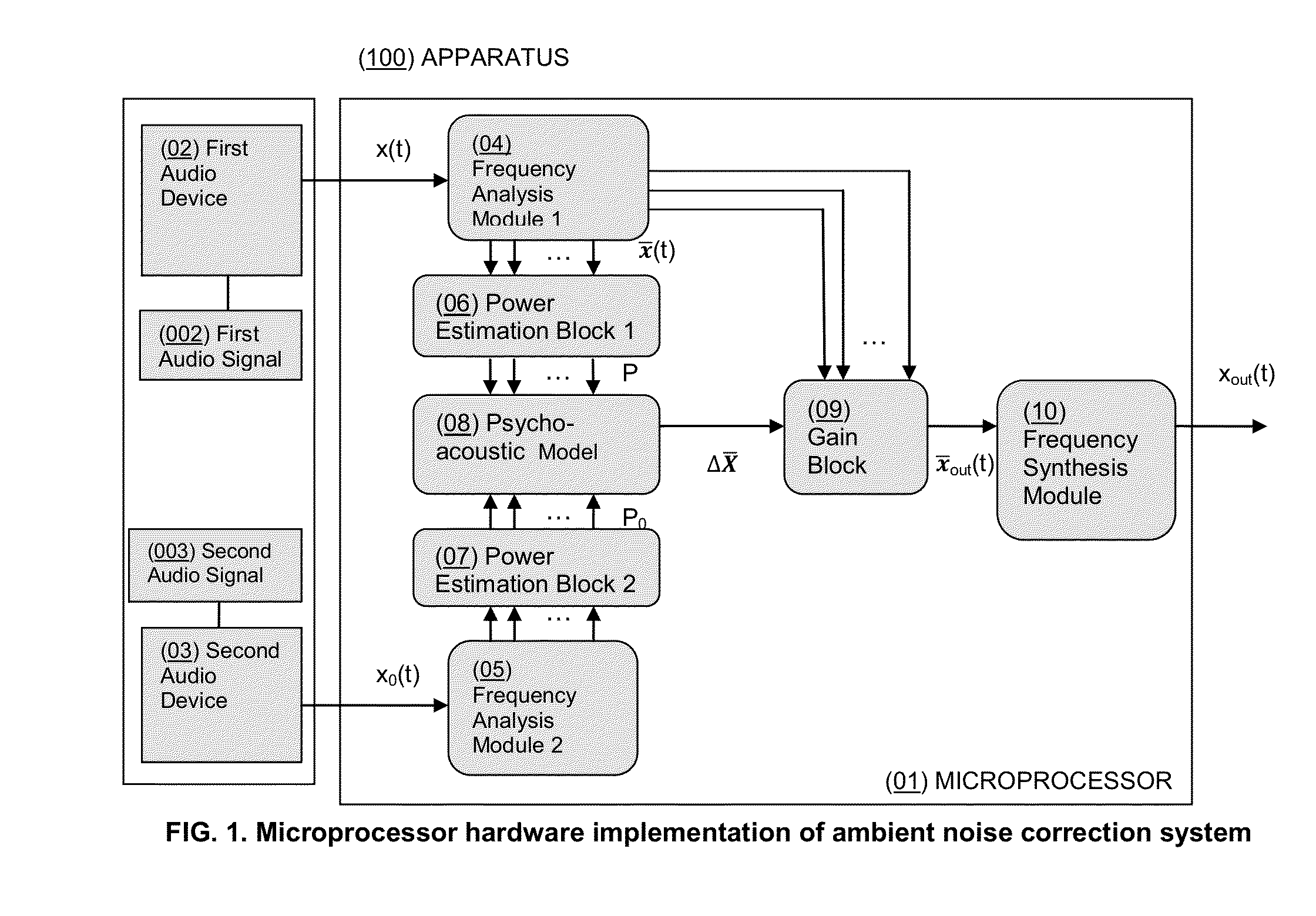
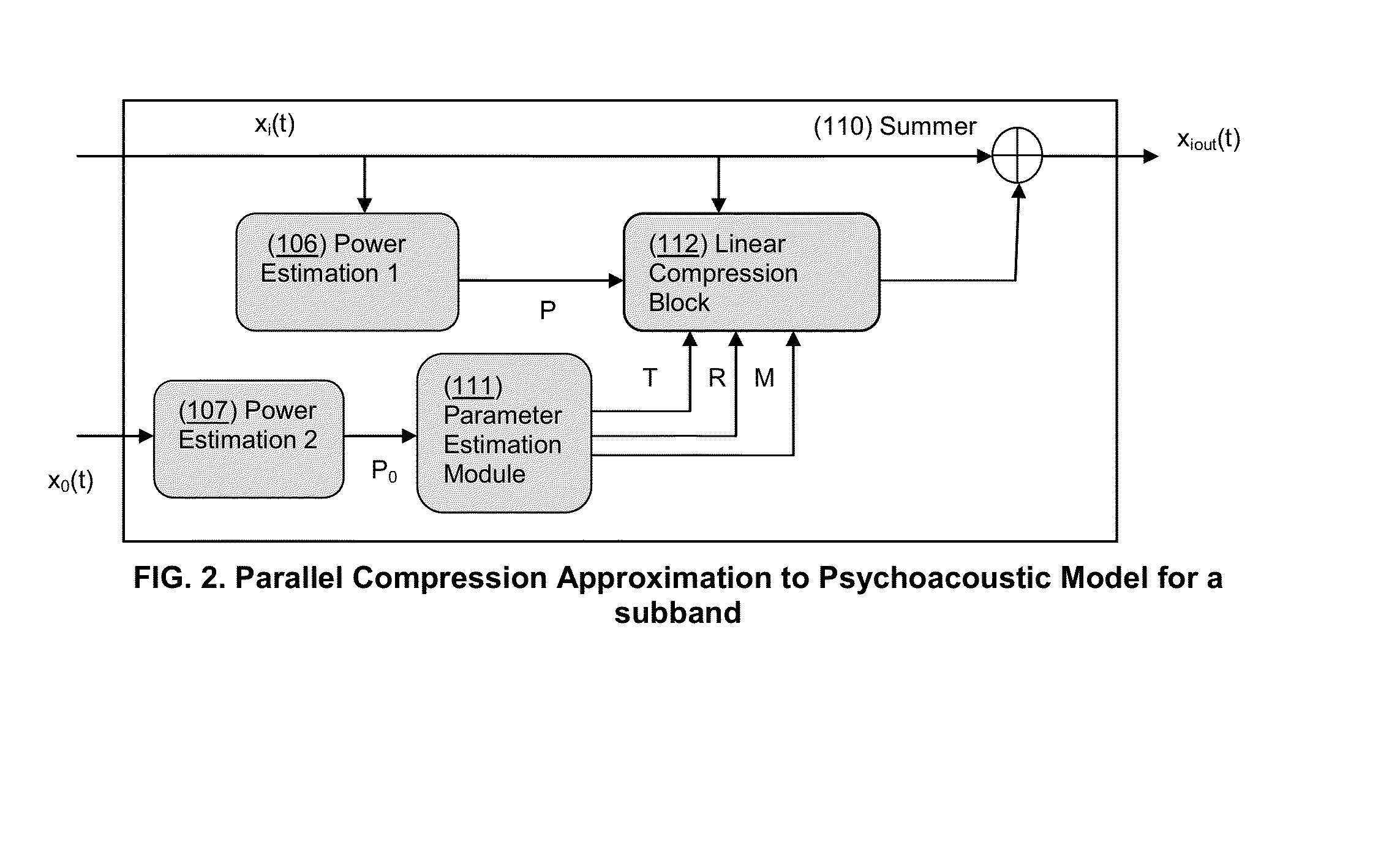
System for Dynamic Spectral Correction of Audio Signals to Compensate for Ambient Noise
The present invention features systems for adjusting audio signals by applying a gain to the signal in a spectrally varying manner to compensate for ambient noise in the environment of the listener. The system allows a listener to hear what ought to be heard, over the ambient noise, by applying a gain to the source that varies according to the spectral composition of the noise, rather than cancelling or filtering the noise. The spectral composition of the source is thus preserved in the listener's awareness without the removal of the noise signal. After application of these corrective gains to the source, the listener's perception of the source sound is as if the noise was not present. Systems may be incorporated into apparatuses including but not limited to mobile phones and music players.
Owner:SOUND ENHANCEMENT TECH
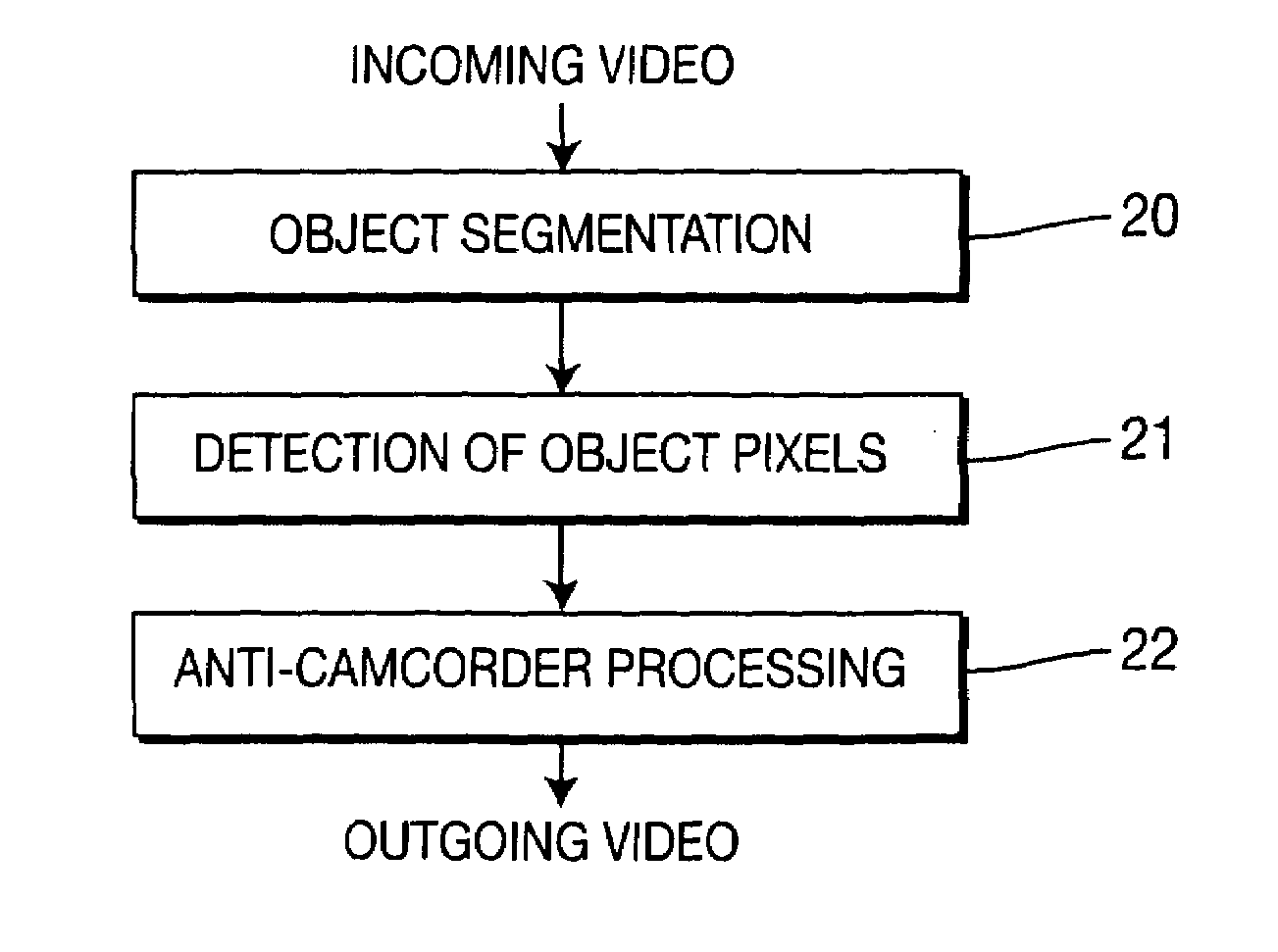
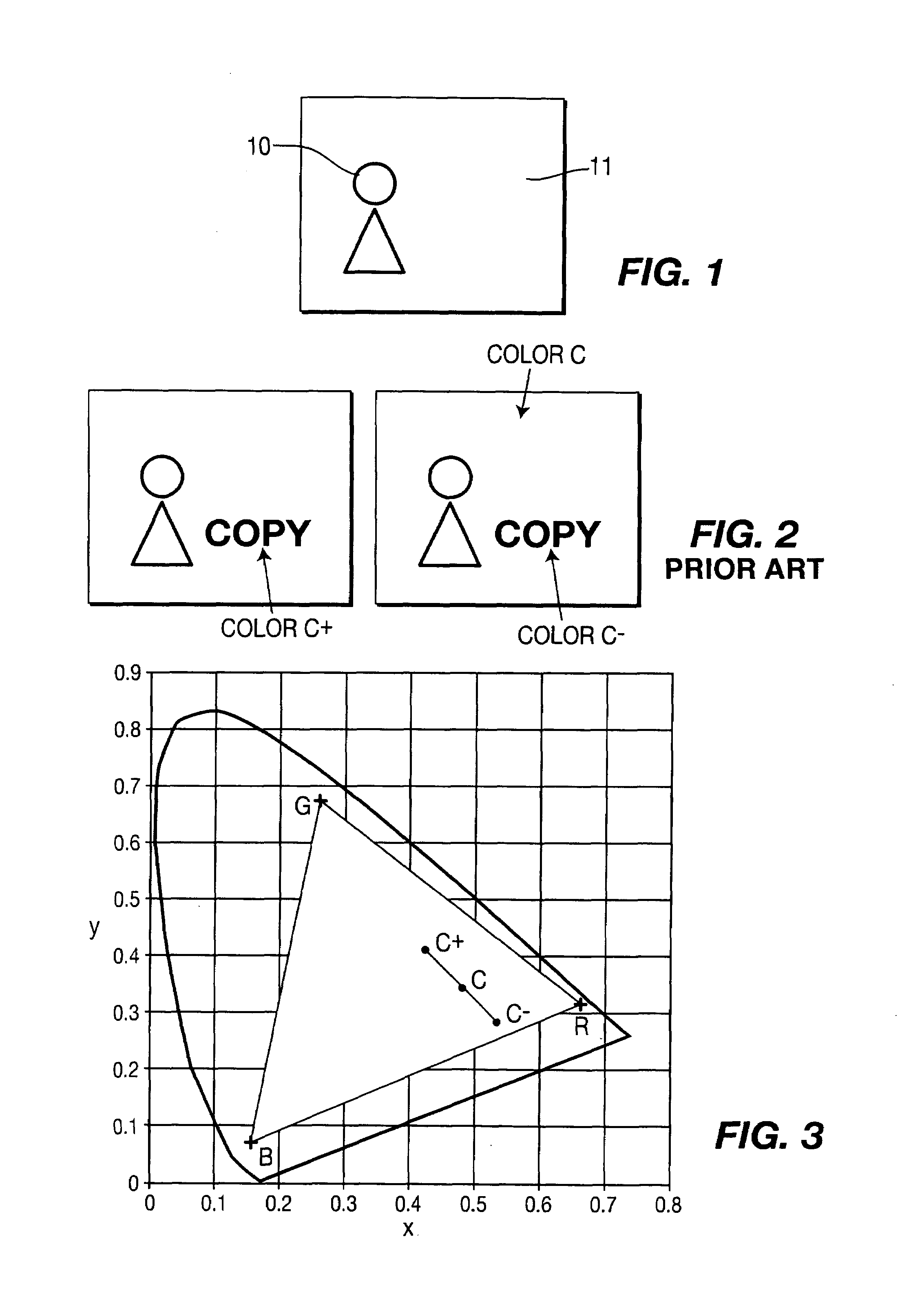
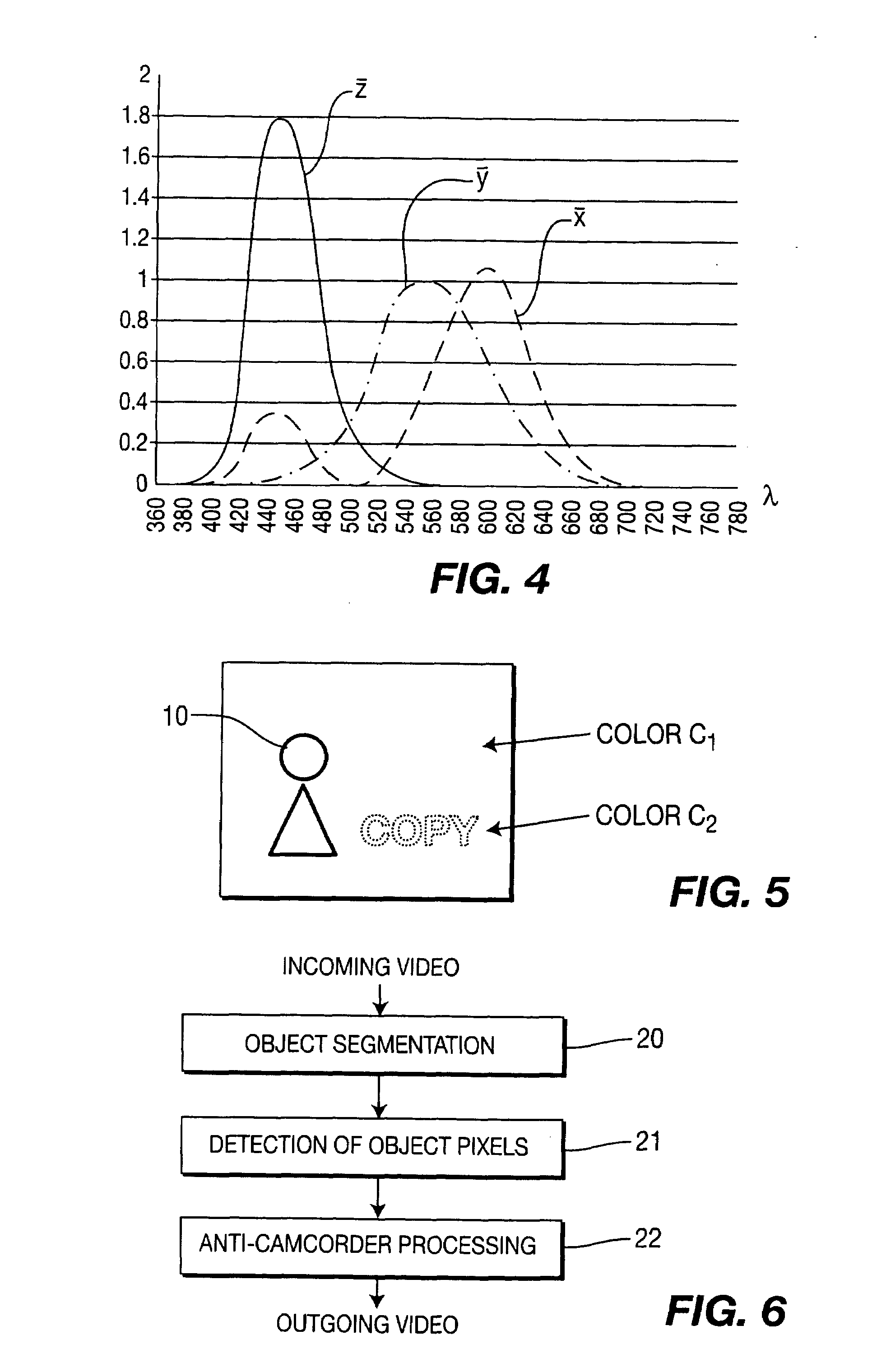
Method of processing images to combat copying
The invention relates to a method of processing source images which is intended to combat their copying by a camcorder or a camera during their display, for example in a cinema hall. The source image sequence represents a scene. According to the invention, the method comprises the following steps:detection, in the said scene, of at least one zone corresponding to an object of the scene,selection of the entirety of the pixels of the said at least one zone in at least one source image of the sequence; andprocessing of the said at least one source image to modify the colour of the selected pixels or the spectral composition of the light emitted by the selected pixels so that the perceived colour of the selected pixels is unchanged in the processed source image with respect to the source image.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method and apparatus for thin film quality control
InactiveUS20100006785A1Investigating moving sheetsColor/spectral properties measurementsQuality controlOptical switch
Photovoltaic thin film quality control is obtained where the thin film is supported by a support and a section of the film is illuminated by a polychromatic illumination source. The source forms on the thin film a continuous illuminated line. Discrete sampled points located on the illuminated line are imaged onto a two dimensional optical switch. A concordance look-up-table between the coordinates of the above sampled points on the thin film and their coordinates on the two dimensional optical switch are generated. The spectral composition of the illumination reflected by the sampled points is determined and photovoltaic thin film parameters applicable to the quality control are derived from the spectral composition of reflected or transmitted by the photovoltaic thin film illumination.
Owner:BRIGHTVIEW SYST LTD
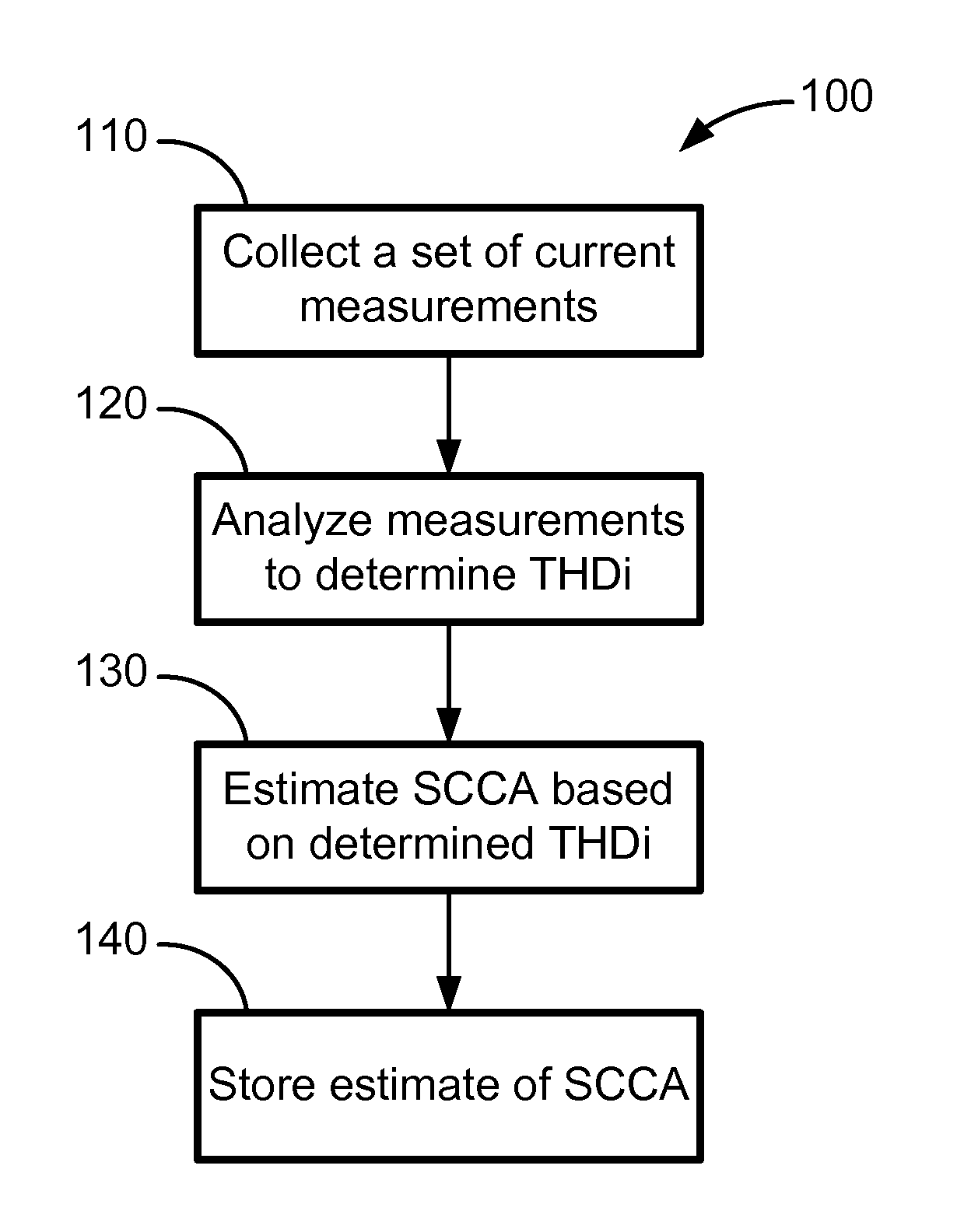
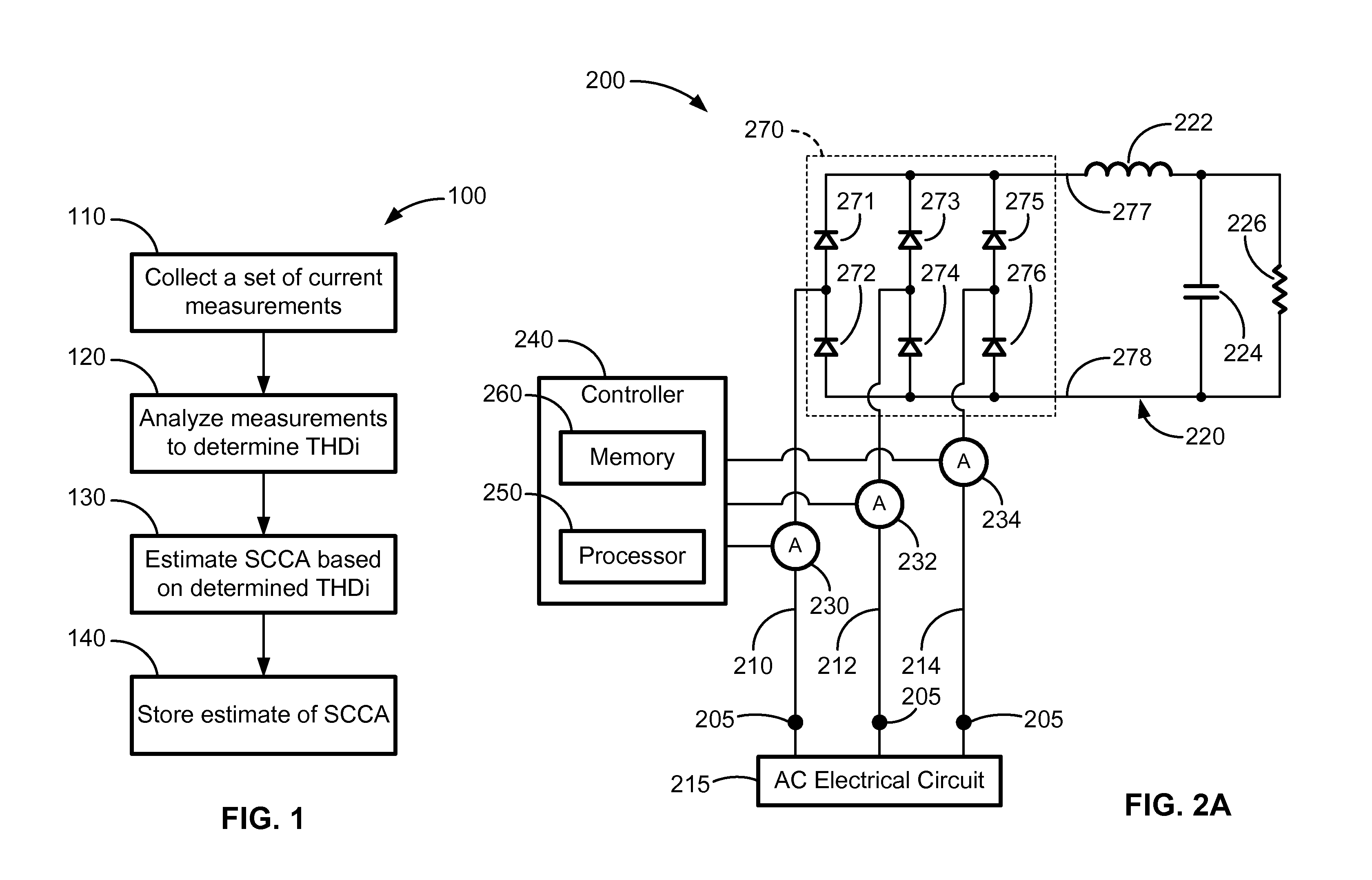
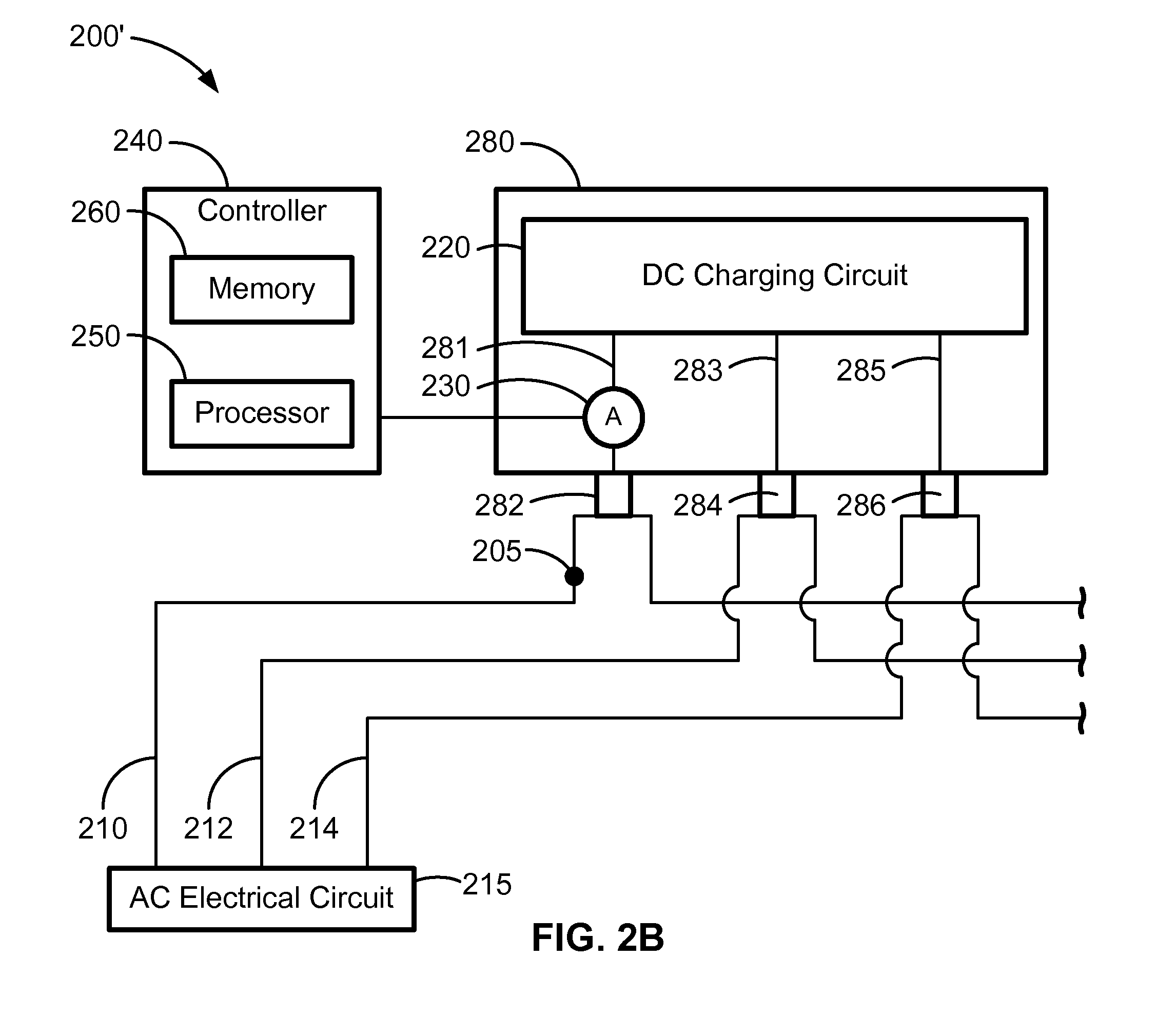
Method of Estimating Short Circuit Current Available by Analysis of DC Charging Circuit
ActiveUS20120095709A1Accurate modelingTesting dielectric strengthCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceFrequency spectrum
A system and method of dynamically estimating the short circuit current availability (SCCA) at a node in an alternating current electrical distribution system by examining the spectral composition of current drawn by a direct current charging circuit connected to the node. A correlative relationship between the total harmonic current distortion (THDi) in the current drawn by the charging circuit and the SCCA at the node is established for a particular charging circuit. An estimation of the SCCA at the node is accomplished by taking current measurements of current drawn by the charging circuit, analyzing those current measurements to determine the THDi, and estimating a corresponding value of SCCA based on the determined THDi. A method is also provided for calibrating a particular charging circuit to have a reactance and resistance suitable for use in estimating SCCA.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC USA INC
Method and device for changing light in an adjustable manner
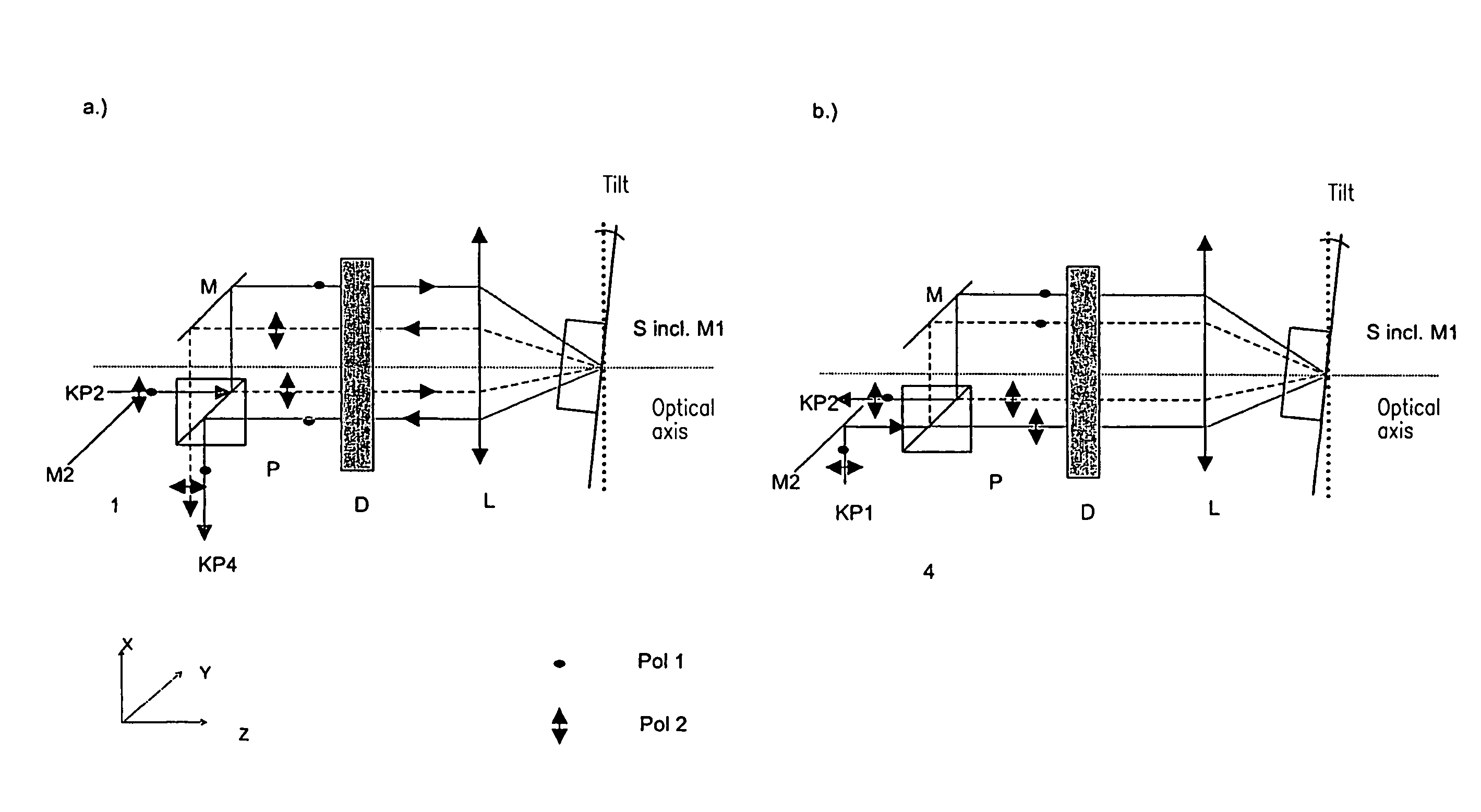
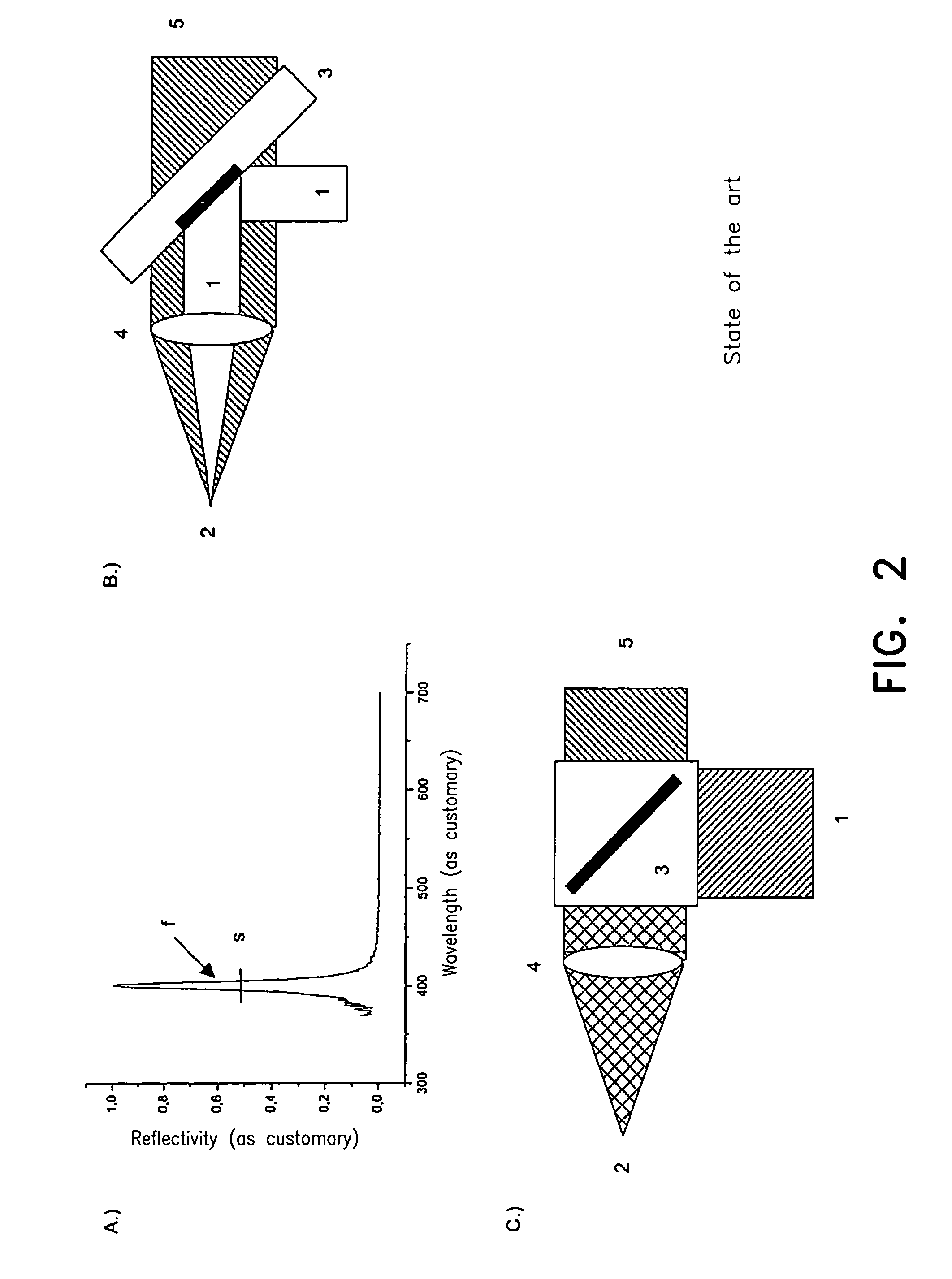
InactiveUS7605976B1Raman/scattering spectroscopyPolarisation-affecting propertiesUltimate tensile strengthOptical polarization
Method and device for changing the illumination light and / or specimen light with respect to its spectral composition and / or intensity in an adjustable manner, wherein a spatial separation into the radiation components of different polarization is carried out with the first polarization means (Pol 1), a spectral spatial splitting of at least one radiation component is carried out with the first dispersion means (Disp1), and the polarization state of at least one part of the spectrally spatially split radiation component is changed, wherein a reflection of the illumination light and / or the detection light is carried out.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
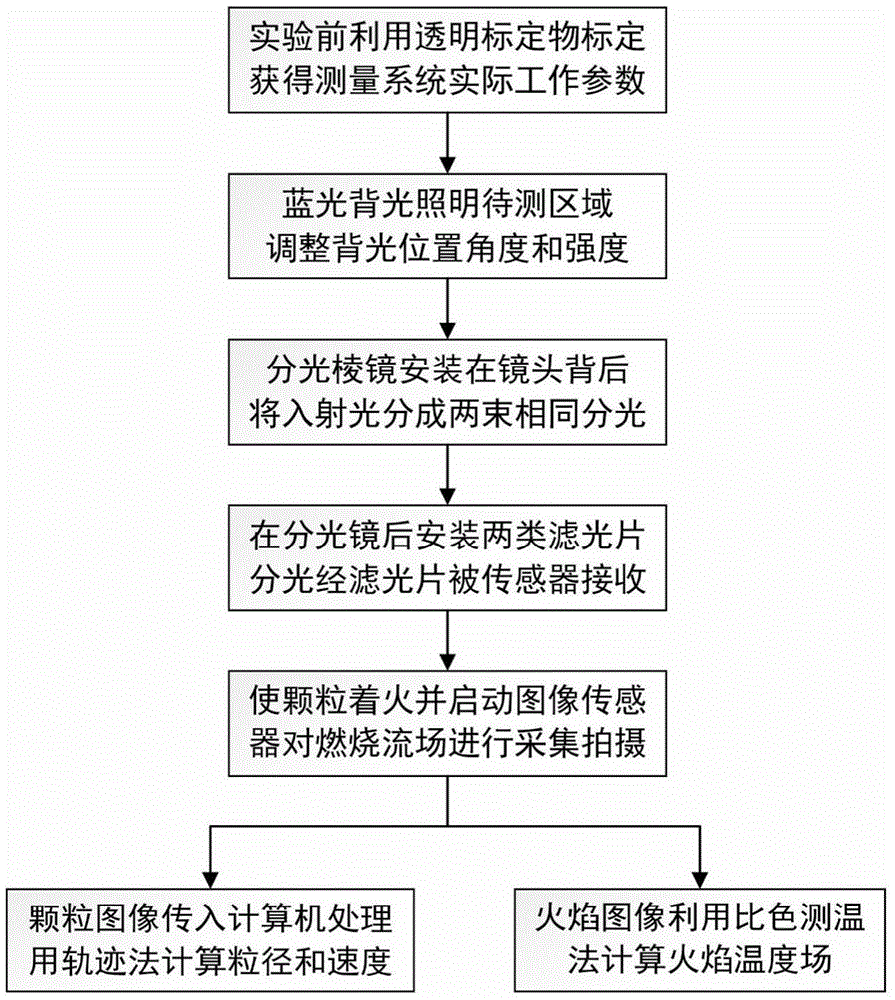
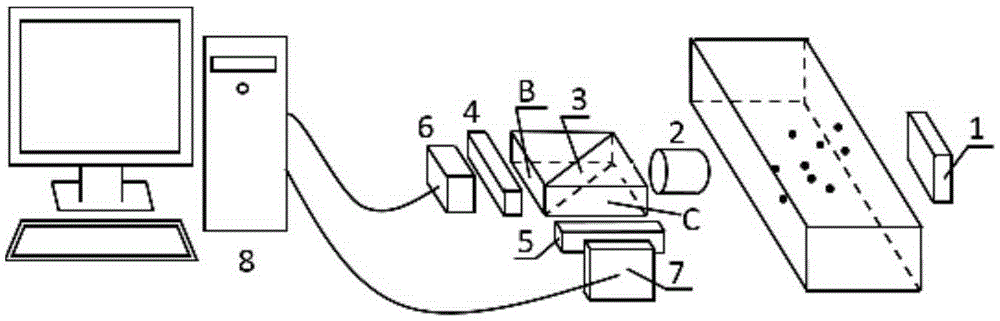
Combustion particle multi-parameter measurement device and method adopting blue-ray back lighting
ActiveCN105424558ASame field of viewAvoid the effects of glowScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisBeam splitterMeasurement device
The invention discloses a combustion particle multi-parameter measurement device and method adopting blue-ray back lighting. The device comprises a blue-ray light source, a camera and a computer, wherein the camera consists of a lens, a beam splitter, a blue-ray band-pass filter, a blue-ray cut-off filter, a first image sensor and a second image sensor. The blue-ray light source illuminates a region to be measured in a back lighting mode, the beam splitter is installed behind the lens, the lens receives light beams emitted by the blue-ray light source and light beams scattered by measured particles in the region to be measured, the beam splitter divides light entering the lens into two split light beams identical in spectral composition and intensity, one split light beam is filtered by the blue-ray band-pass filter and then is received by the first image sensor, the other split light beam is filtered by the blue-ray cut-off filter and then is received by the second image sensor, and the first image sensor and the second image sensor convert optical signals into television signals to be transmitted to the computer so as to perform image processing for characteristic information obtaining. The technical problem that flame self-emitted light and backlight for illumination are mutually interfered in the image acquisition process is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Methods and apparatus for adaptive foreground background analysis
ActiveUS7505608B2Easy to detectReduce data volumeTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionPosition dependent
Apparatus and methods for target detection in hyperspectral images are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of detecting a target in a hyperspectral image includes spectrally unmixing the hyperspectral image into segments, each segment having at least one of similar spectral composition, similar textural composition, and similar variation, and spectrally unmixing at least one of the segments. The method further includes creating a clutter rejection filter for at least one segment, filtering at least one segment, and calculating target abundances in at least one segment. In alternate embodiments, channel reduction can be performed on the hyperspectral image and also on at least one segment. In further embodiments, data associated with the location of possible targets in the segments may be compiled. In yet another embodiment, this data may be compressed by cross referencing data from all segments and eliminating redundancies.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Radiation generation device for generating electromagnetic radiation having an adjustable spectral composition, and method of producing same
ActiveUS8351032B2Flexible choiceHigh strengthRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationElectromagnetic radiationWavelength
A radiation generation device for generating resulting electromagnetic radiation having an adjustable spectral composition includes: a multitude of radiation elements (configured to generate a radiation element specific electromagnetic radiation, respectively, upon being activated, a first radiation element of the multitude of radiation elements being activatable independently of a second radiation element of the multitude of radiation elements; a dispersive optical element; and an optical opening; the dispersive optical element being configured to deflect the radiation element specific electromagnetic radiations, in dependence on their wavelength and on a position of the radiation element generating the respective radiation element specific electromagnetic radiation, such that a particular spectral range of each of the radiation element specific electromagnetic radiations may exit through the optical opening, so that the spectral composition of the resulting electromagnetic radiation exiting through the optical opening is adjustable by selectively activating the multitude of radiation elements.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
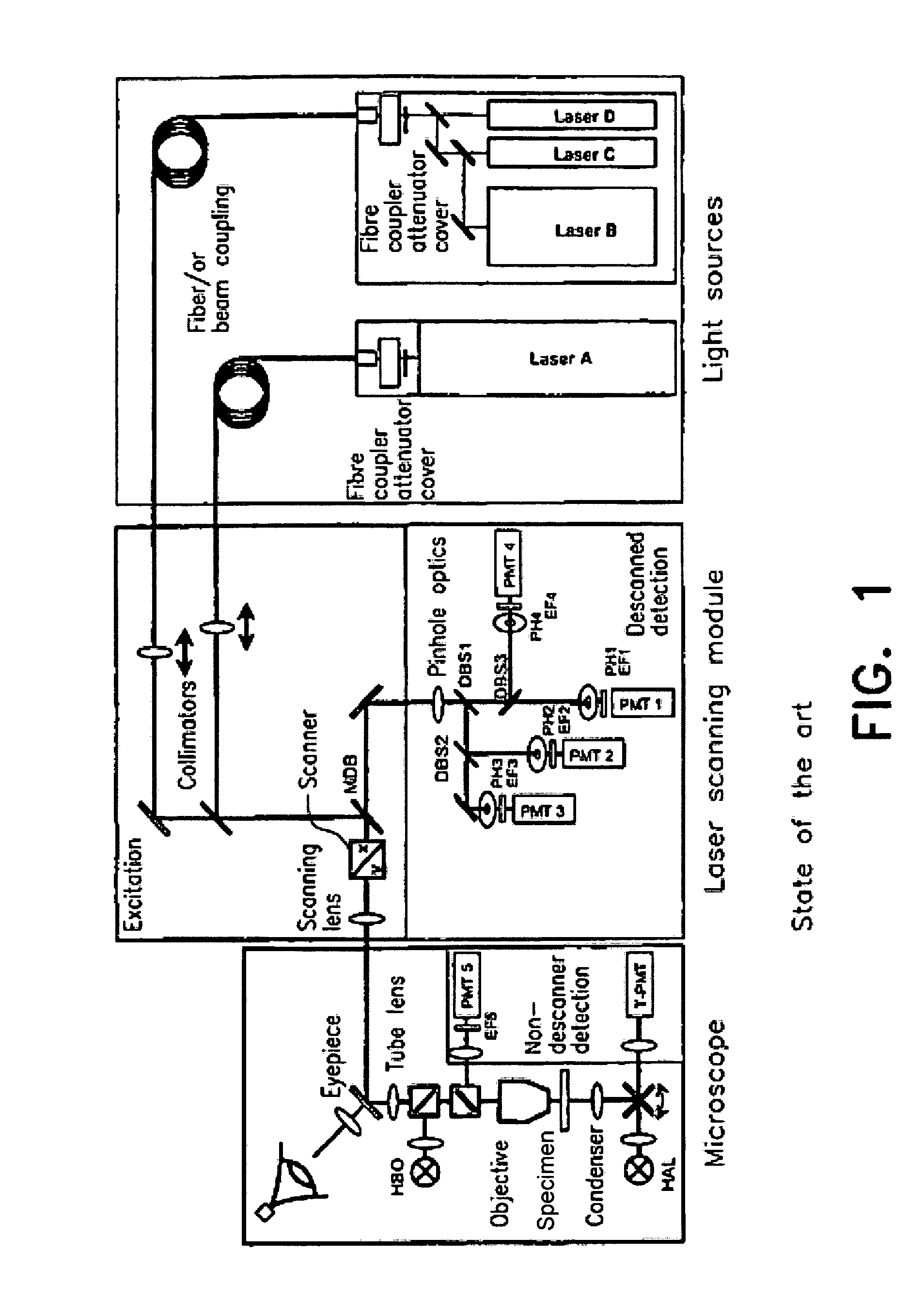
Microscope and method for operating a microscope
The invention relates to a method for operating a microscope in which excitation light is focused on, or beamed to, different points of a specimen, in which an intensity of the excitation light is point-specifically varied and in which an intensity of the light reflected by said specimen in at least one spectral range is measured point-specifically and quantitatively. The method according to the invention is characterized in that the intensity and / or a spectral composition of the excitation light beamed to a specific point of said specimen is automatically adjusted by a regulating device on the basis of information previously gained from measured data of said specimen concerning an estimated or actual intensity of the light reflected in the spectral range by said point such that an integral of the intensity of the light reflected in the spectral range by this point during a pixel dwell time is within a predefined value interval. The invention also relates to a microscope.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com