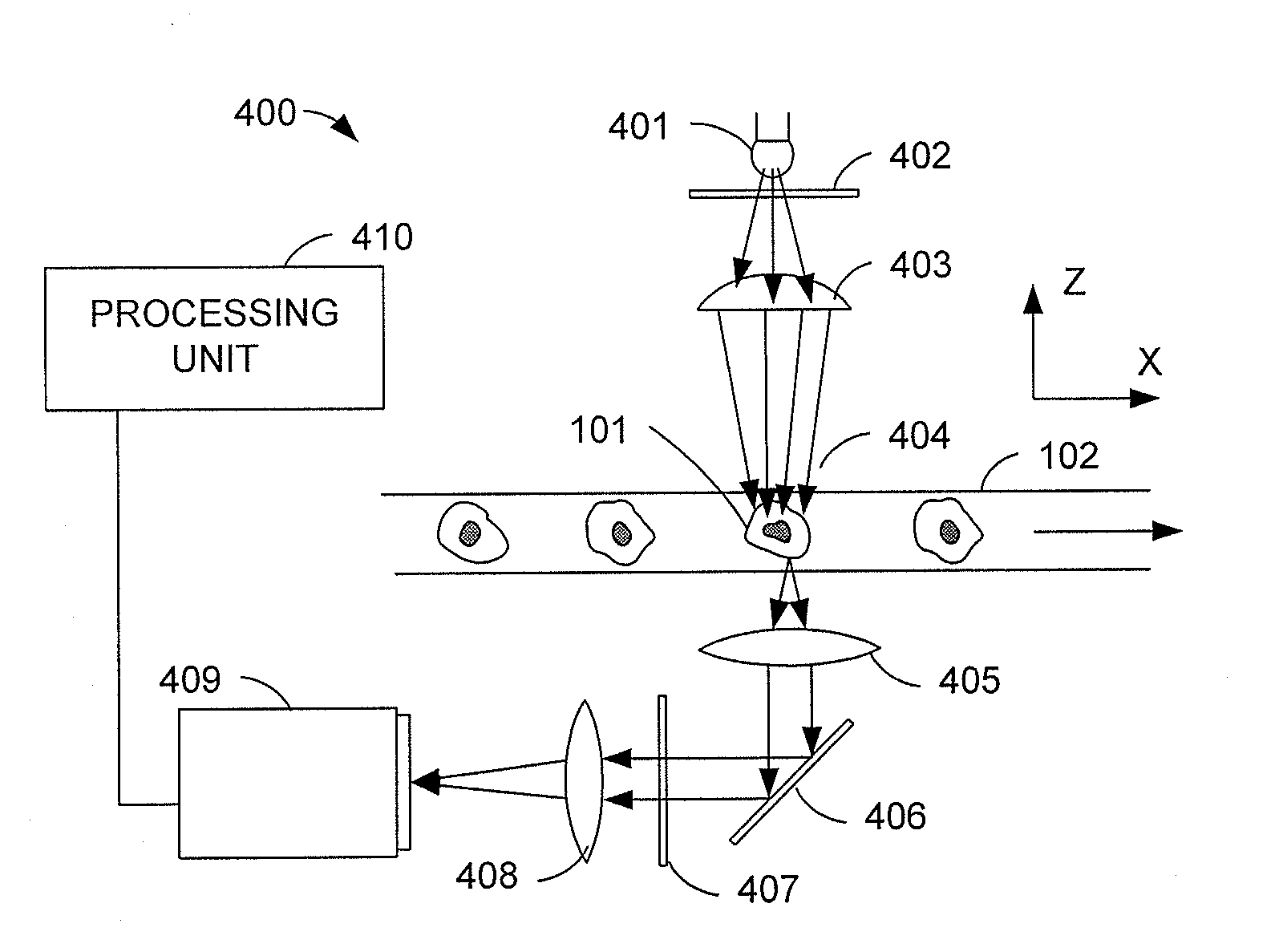
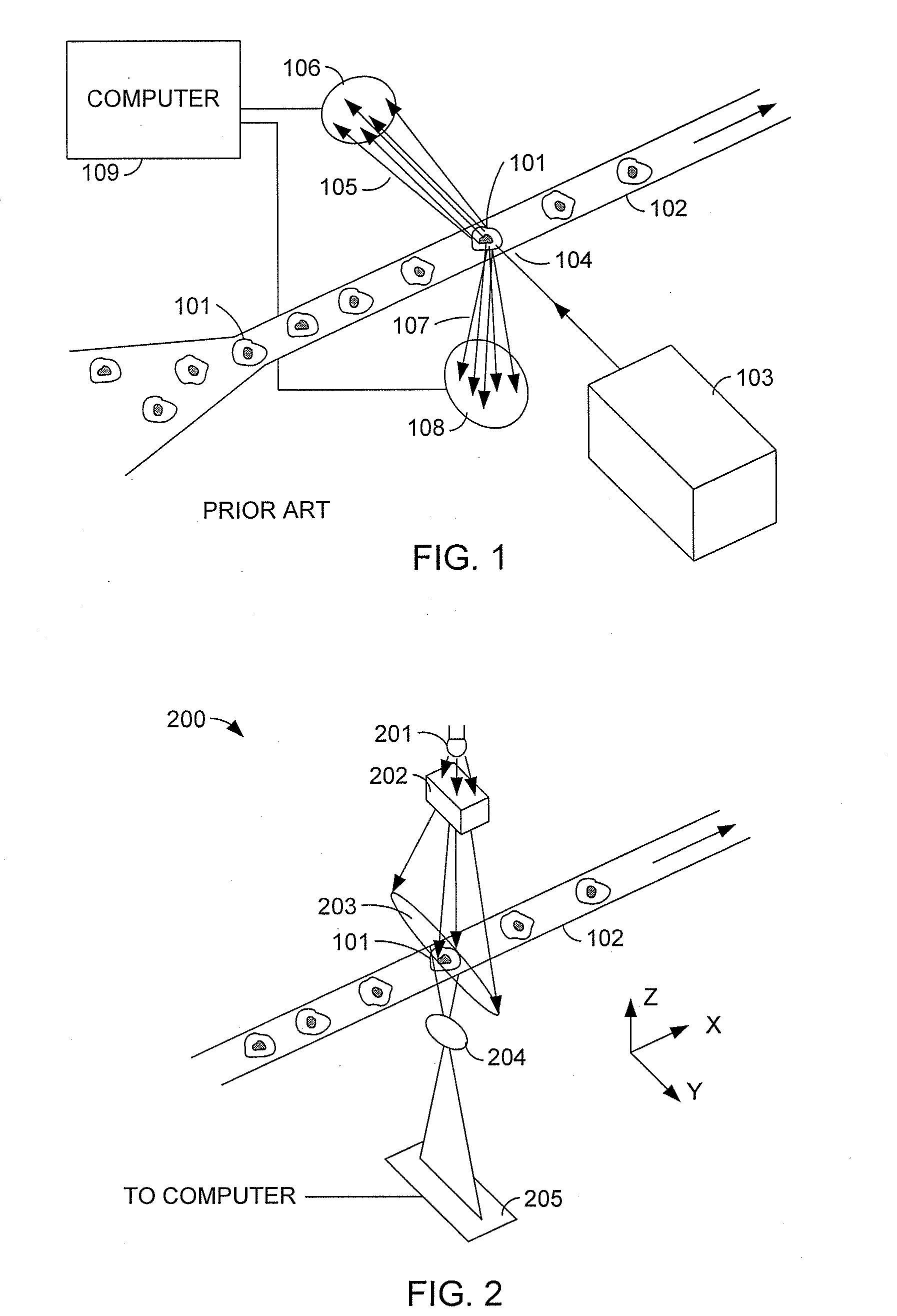
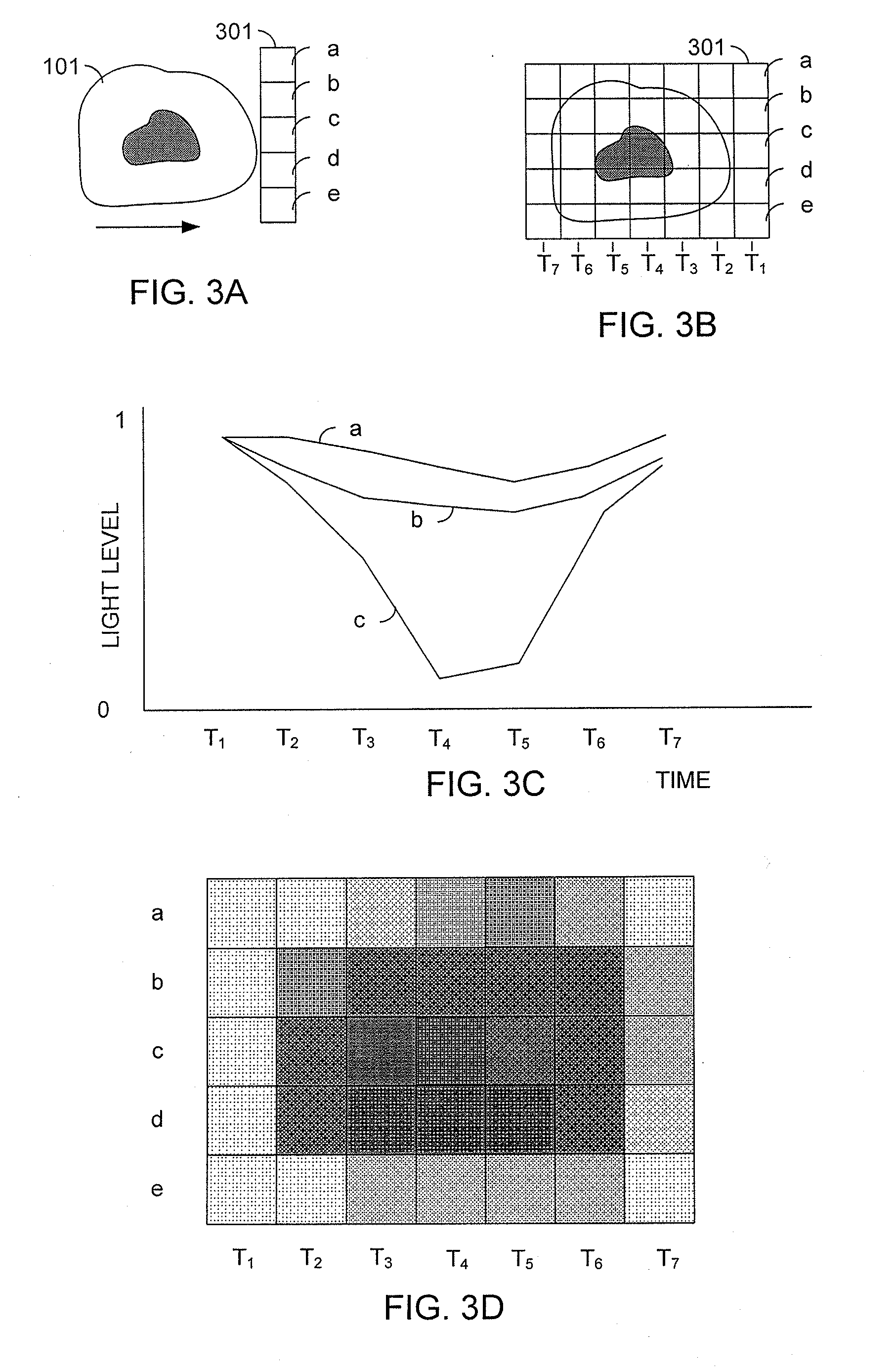
Patents
Literature
1763 results about "Fluorescent imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorescence imaging (FLI) relies on light emission from a fluorophore or fluorescent protein after excitation by a light source at the appropriate wavelength. FLI can be applied to cell lines or transgenics expressing fluorescent proteins or by the use of exogenous probes labeled with fluorophores.
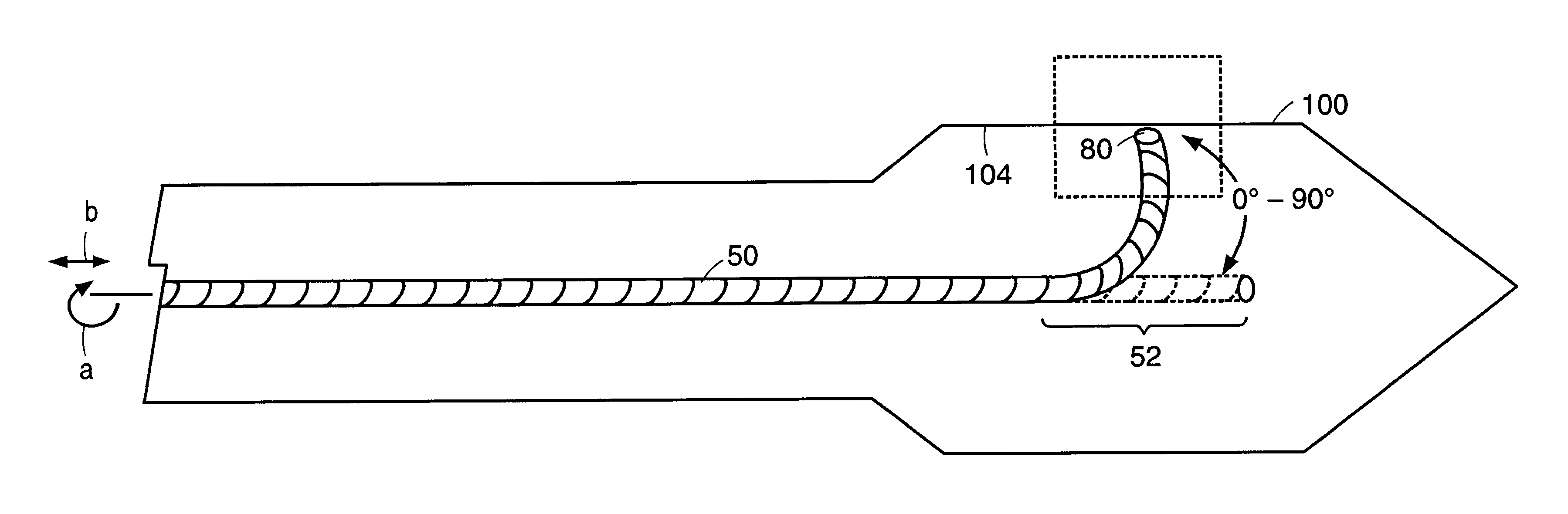
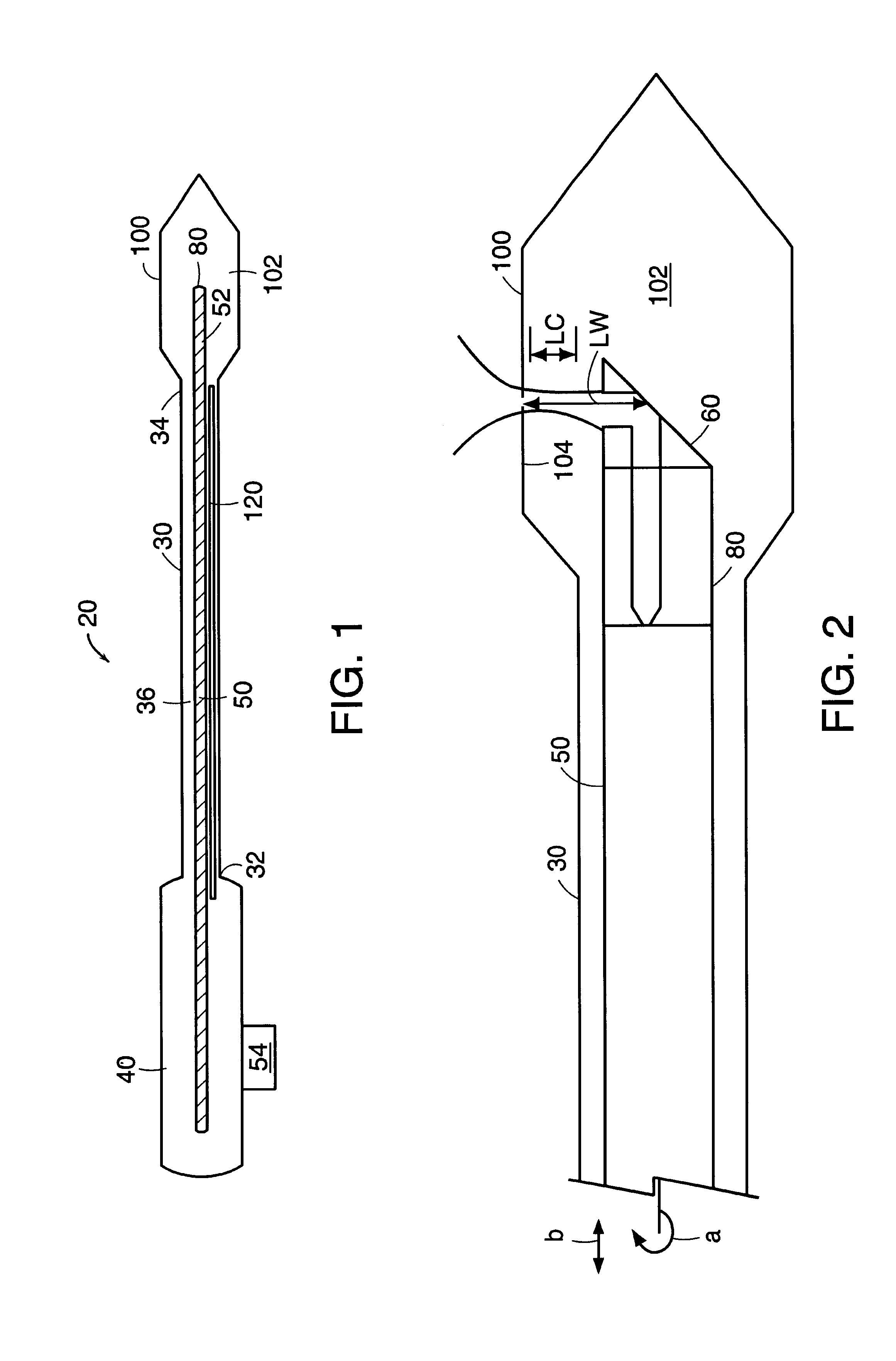
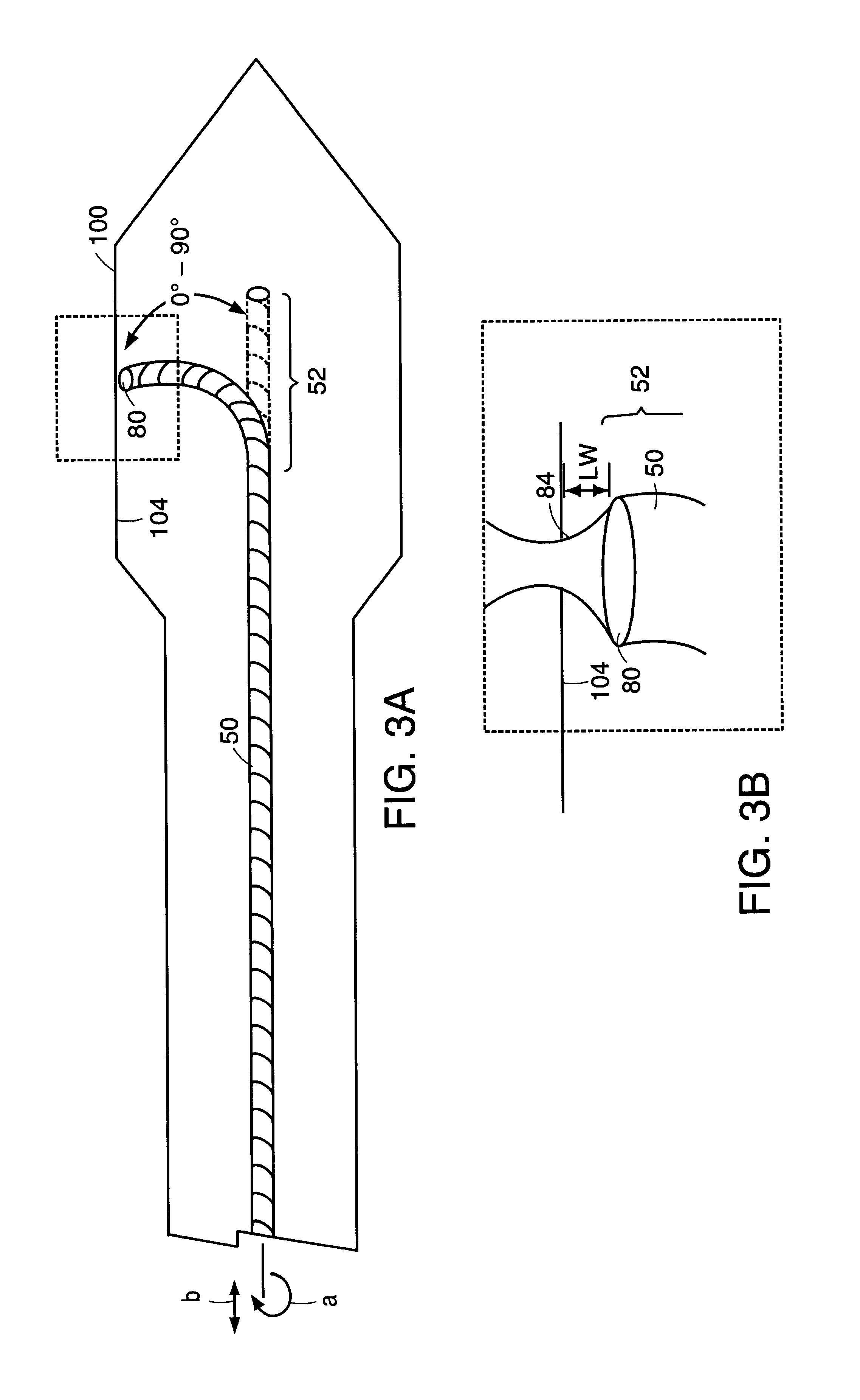
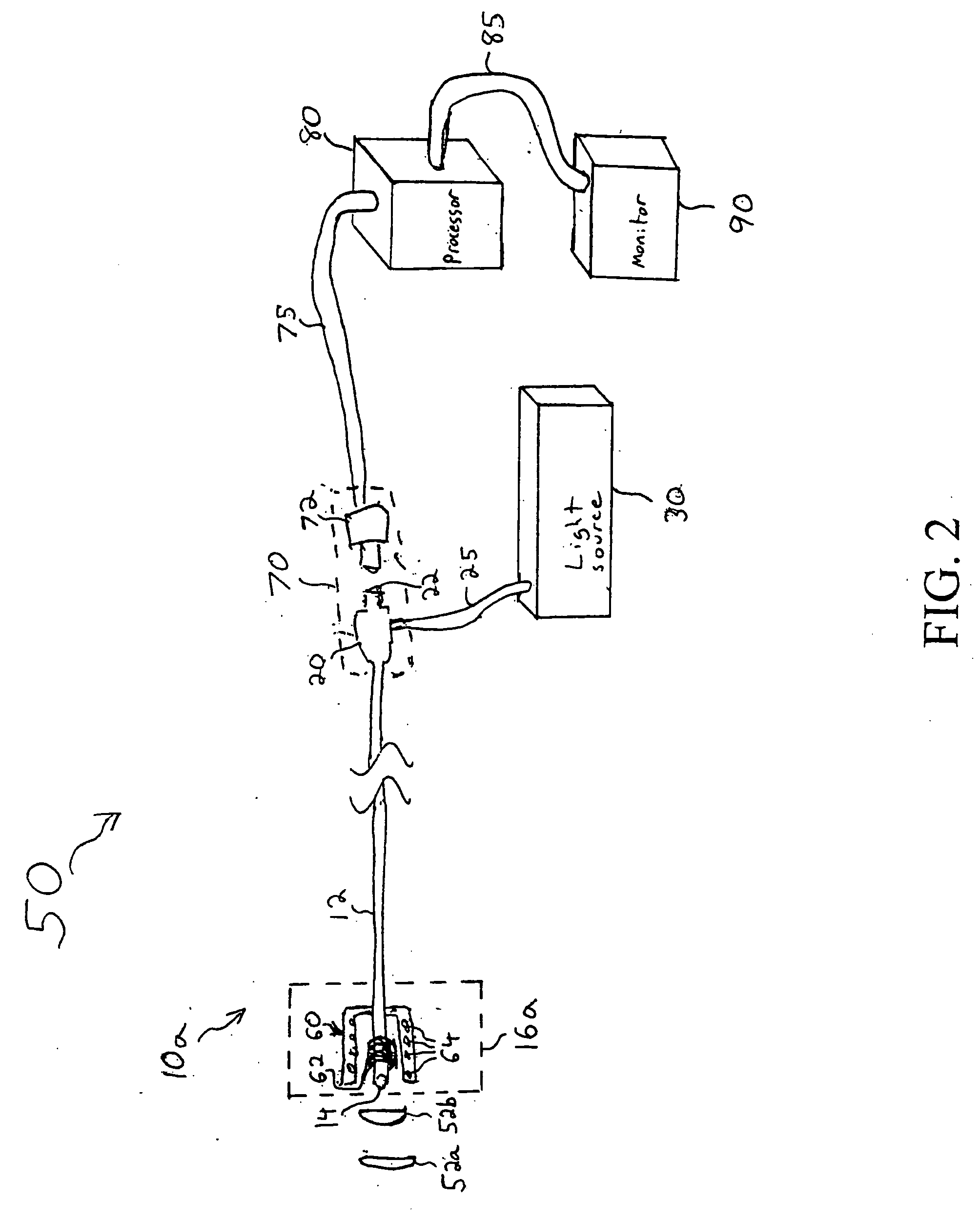
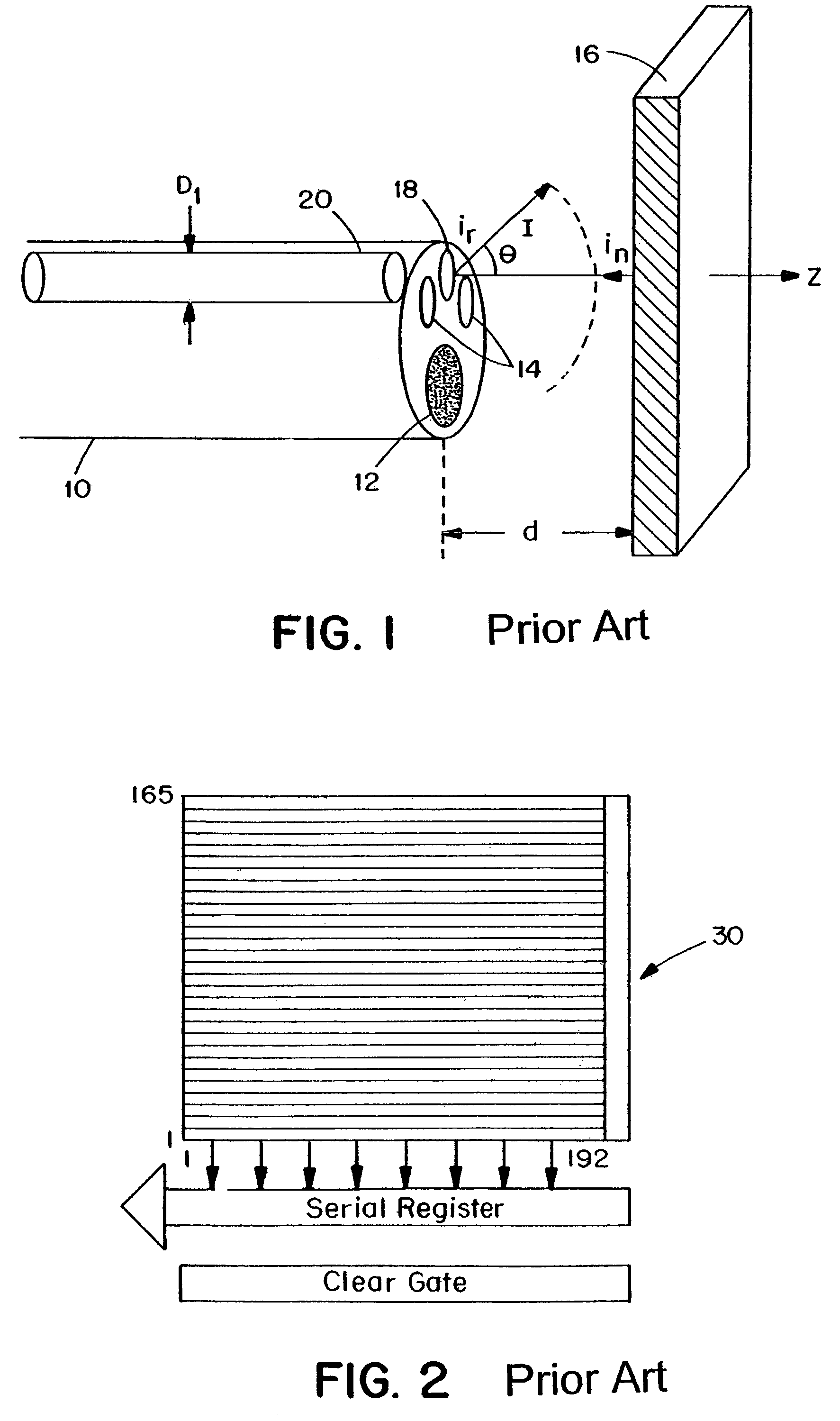
Fiber optic endoscopic gastrointestinal probe
A fiber optic probe and a balloon catheter used in conjunction with optical imaging systems, in particular with systems which deliver and collect a single spatial mode beam, such as a single photon, a multiphoton, confocal imaging and ranging systems, such as fluorescence imaging systems.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
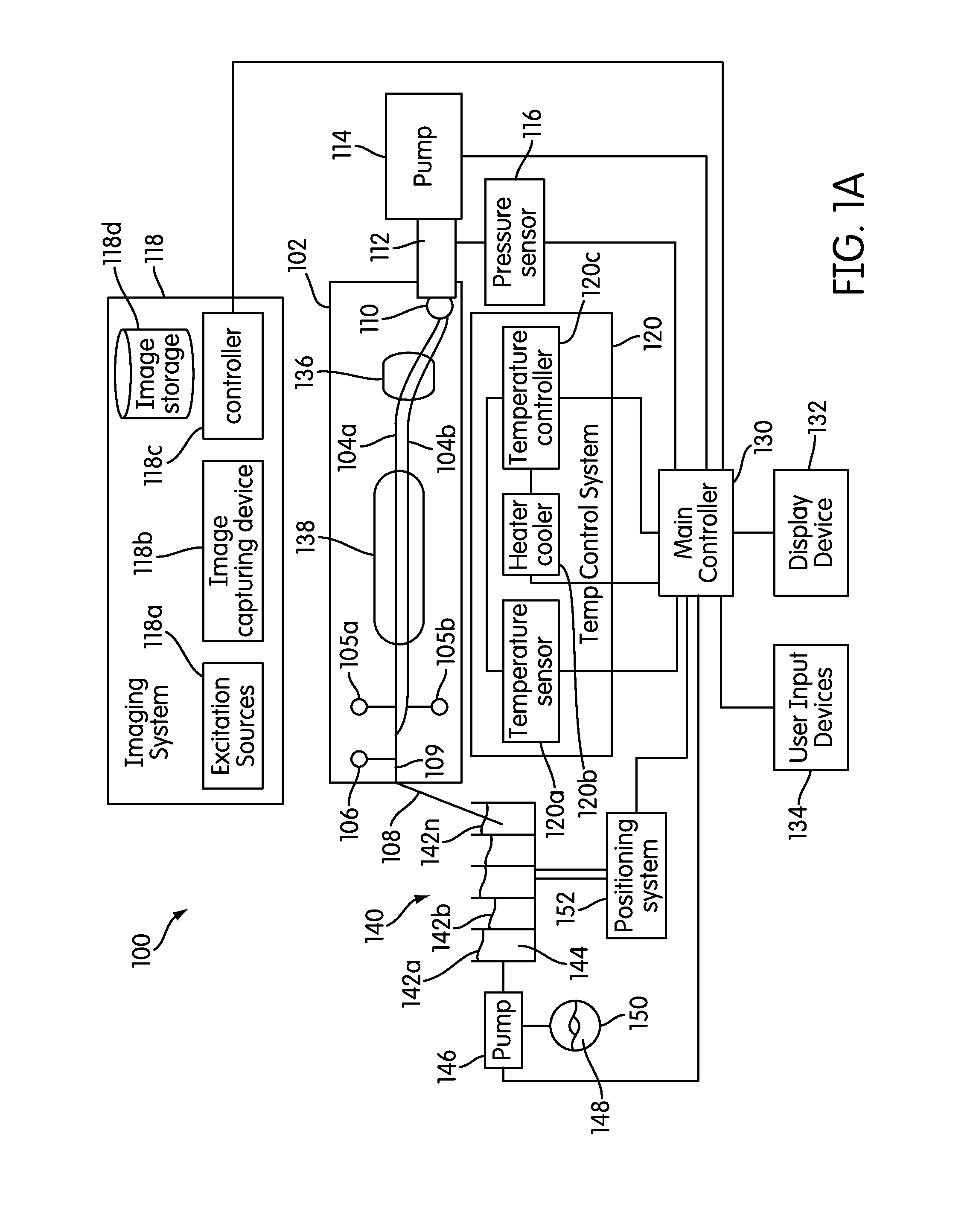
Microfluidic devices and methods
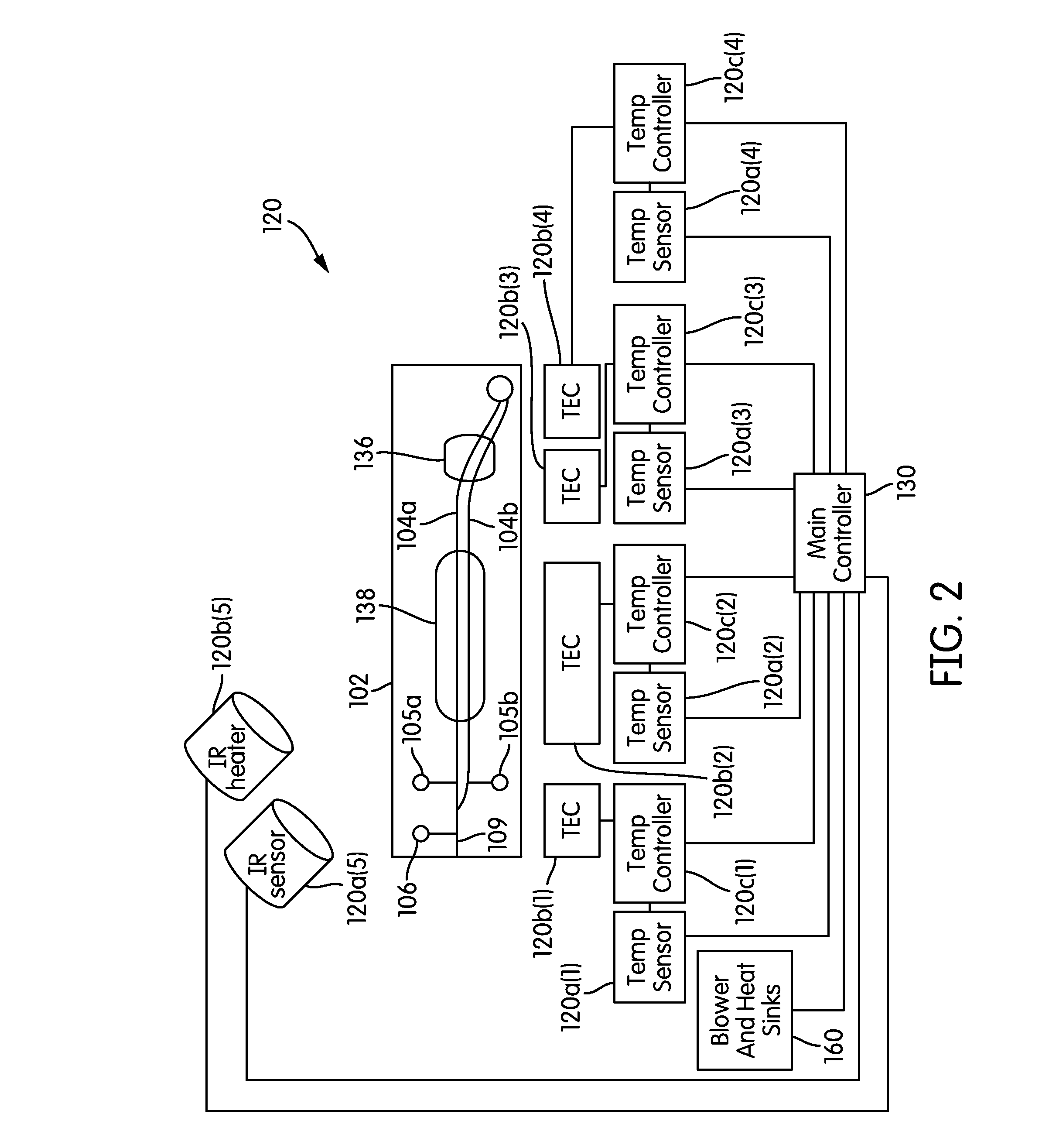
ActiveUS20100230613A1Shorten mixing timeManufacturing yield rate is increasedOptical radiation measurementHeating or cooling apparatusTemperature controlFluorescent imaging
Embodiments of the present invention provide improved microfluidic devices and related apparatus, systems, and methods. Methods are provided for reducing mixing times during use of microfluidic devices. Microfluidic devices and related methods of manufacturing are provided with increased manufacturing yield rates. Improved apparatus and related systems are provided for supplying controlled pressure to microfluidic devices. Methods and related microfluidic devices are provided for reducing dehydration of microfluidic devices during use. Microfluidic devices and related methods are provided with improved sample to reagent mixture ratio control. Microfluidic devices and systems are provided with improved resistance to compression fixture pressure induced failures. Methods and systems for conducting temperature controlled reactions using microfluidic devices are provided that reduce condensation levels within the microfluidic device. Methods and systems are provided for improved fluorescent imaging of microfluidic devices.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Methods and apparatus for imaging with multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS20150015879A1Radiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLight dispersionImage resolution
A multimode waveguide illuminator and imager relies on a wave front shaping system that acts to compensate for modal scrambling and light dispersion by the multimode waveguide. A first step consists of calibrating the multimode waveguide and a second step consists in projecting a specific pattern on the waveguide proximal end in order to produce the desire light pattern at its distal end. The illumination pattern can be scanned or changed dynamically only by changing the phase pattern projected at the proximal end of the waveguide. The third and last step consists in collecting the optical information, generated by the sample, through the same waveguide in order to form an image. Known free space microscopy technique can be adapted to endoscopy with multimode waveguide, such as, but not limited to, fluorescence imaging or Raman spectroscopy or imaging, 3D linear scattering imaging or two-photon imaging. Super-resolution, i.e., resolution below the diffraction limit, is achieved for example but not limited to, using the STimulated Emission Depletion microscopy (STED) technique or the Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) technique or a stochastic illumination based method (PALM, STORM) in combination with the multimode waveguide imaging method.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
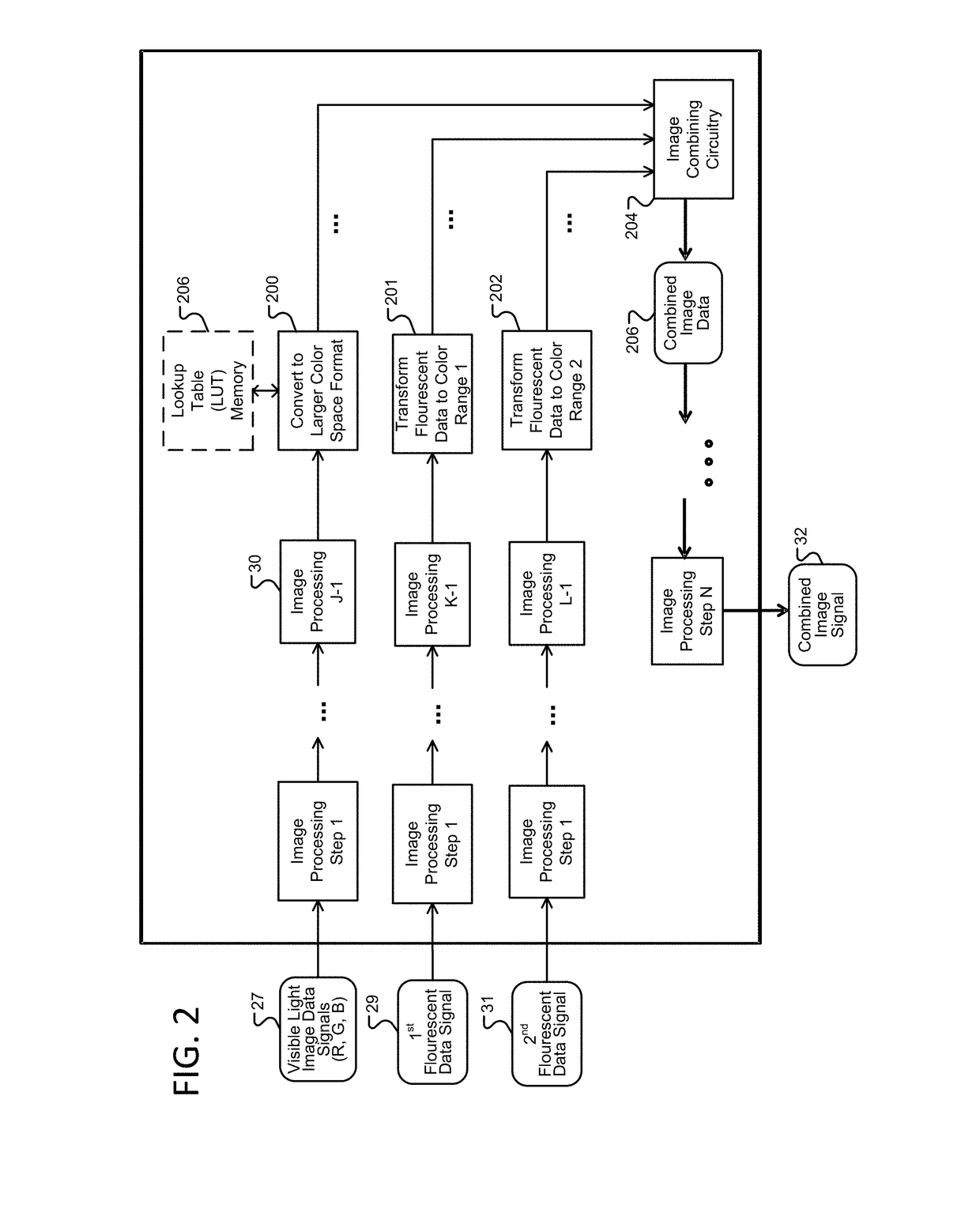
Autofluorescence imaging system for endoscopy
InactiveUS20110213252A1Improve featuresQuantitative precisionSurgeryEndoscopesColor imageUltraviolet lights
A system and method for imaging tissue autofluorescence through a video endoscope is described, comprising a light source capable of providing both ultraviolet light capable of inducing tissue autofluorescence and visible light which induces little or no autofluorescence, an optical system to deliver both wavelength bands to the tissue with the same apparent spatial and angular intensity distribution, a means for digitally acquiring the resulting, visible fluorescence and visible reflectance images using a single imaging detector at the distal tip of the endoscope and a means for digitally processing said images to generate a final, false-color image for display which indicates regions of tissue dysplasia. This system can either be added on to an existing video endoscope or integrated into its structure. The combined system can be electronically switched between normal white light imaging and fluorescence imaging.
Owner:HOYA CORP
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR WIDEFIELD FUNCTIONAL IMAGING (WiFI) USING INTEGRATED STRUCTURED ILLUMINATION AND LASER SPECKLE IMAGING
ActiveUS20090118622A1Minimal artifactHigh degree of fidelity and spatial localizationMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterWide fieldFunctional imaging
An apparatus for wide-field functional imaging (WIFI) of tissue includes a spatially modulated reflectance / fluorescence imaging (SI) device capable of quantitative subsurface imaging across spatial scales, and a laser speckle imaging (LSI) device capable of quantitative subsurface imaging across spatial scales using integrated with the (SI) device. The SI device and LSI device are capable of independently providing quantitative measurement of tissue functional status.
Owner:MODULATED IMAGING
Surface plasmon resonance imaging of micro-arrays
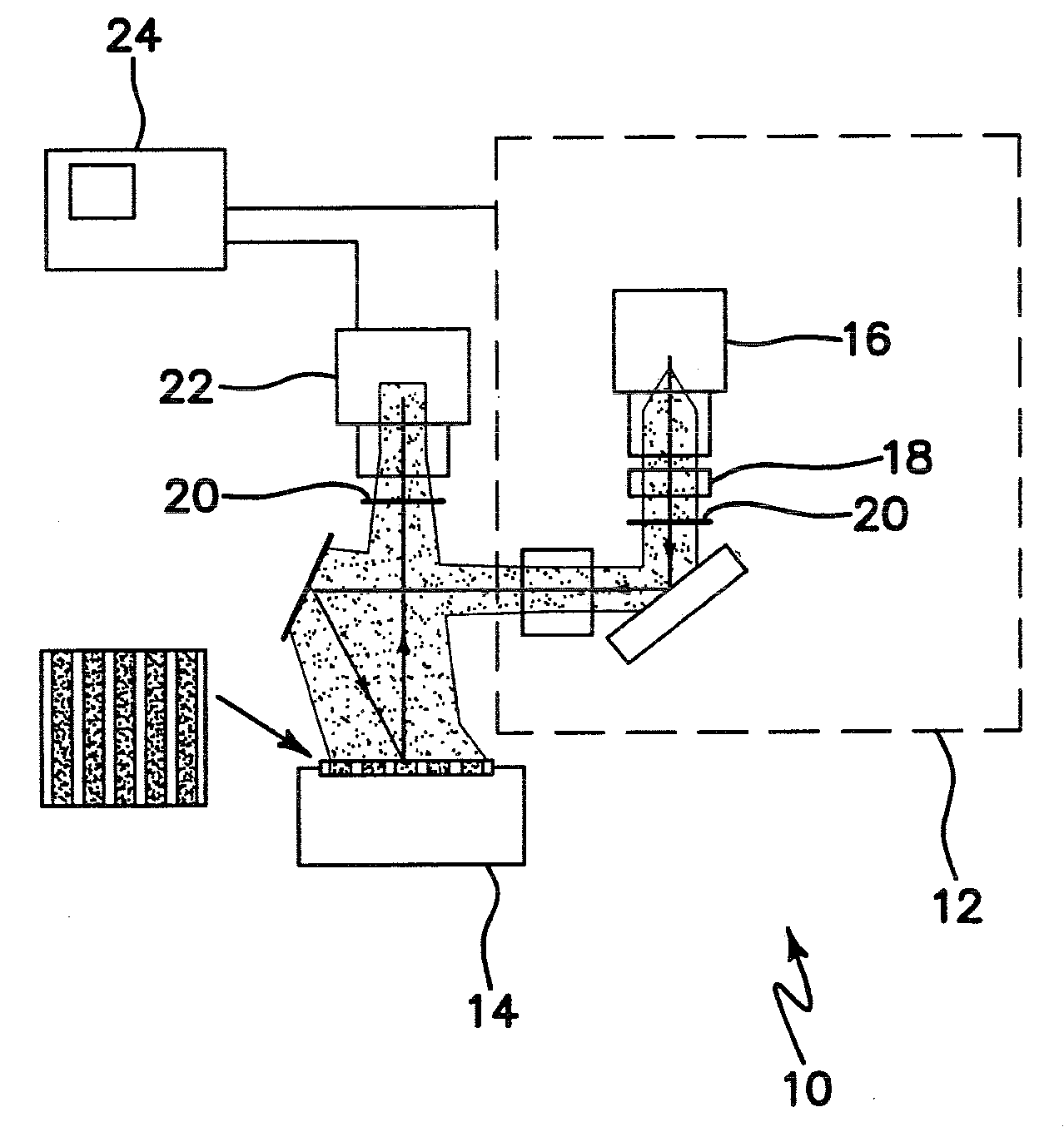
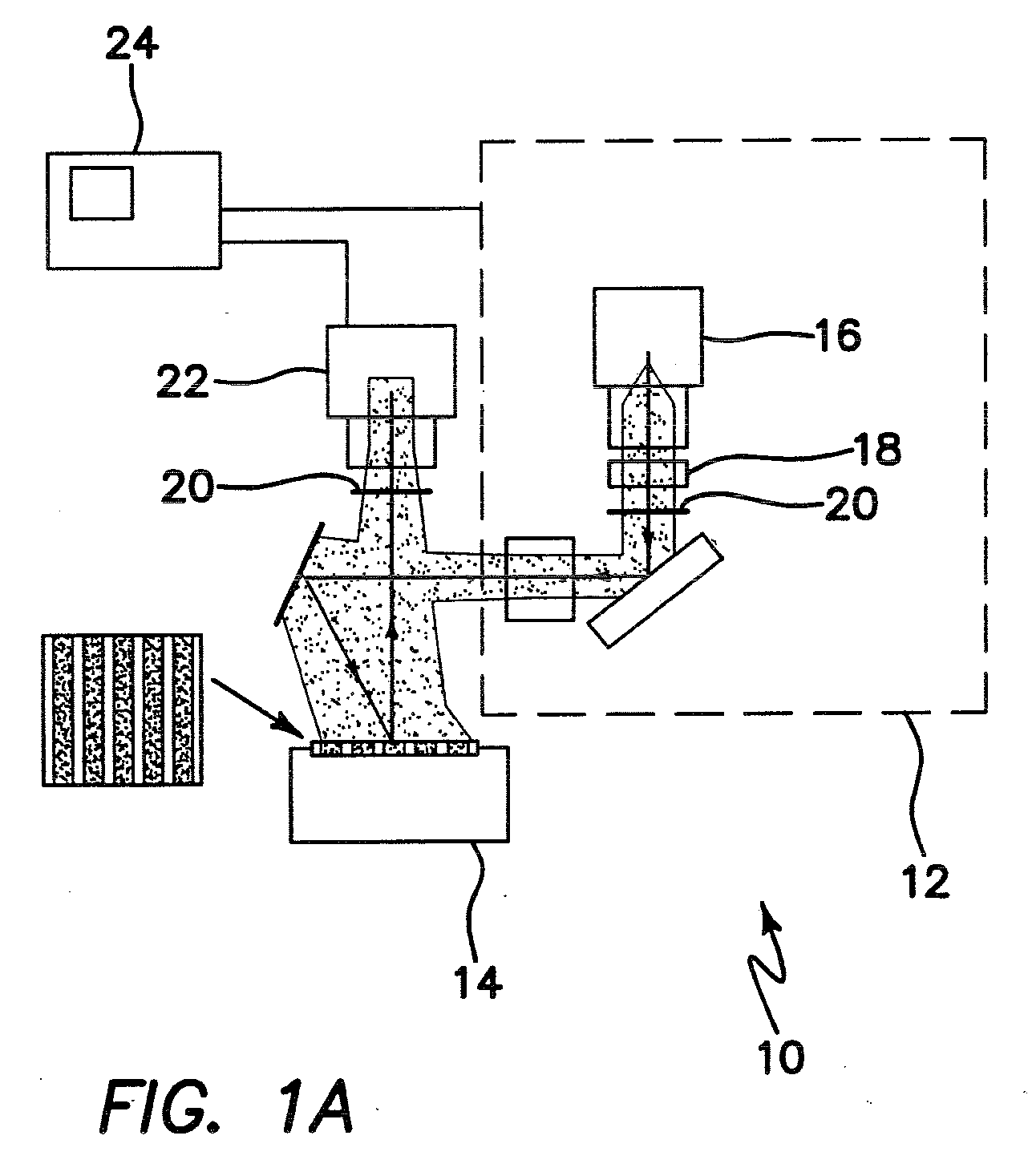
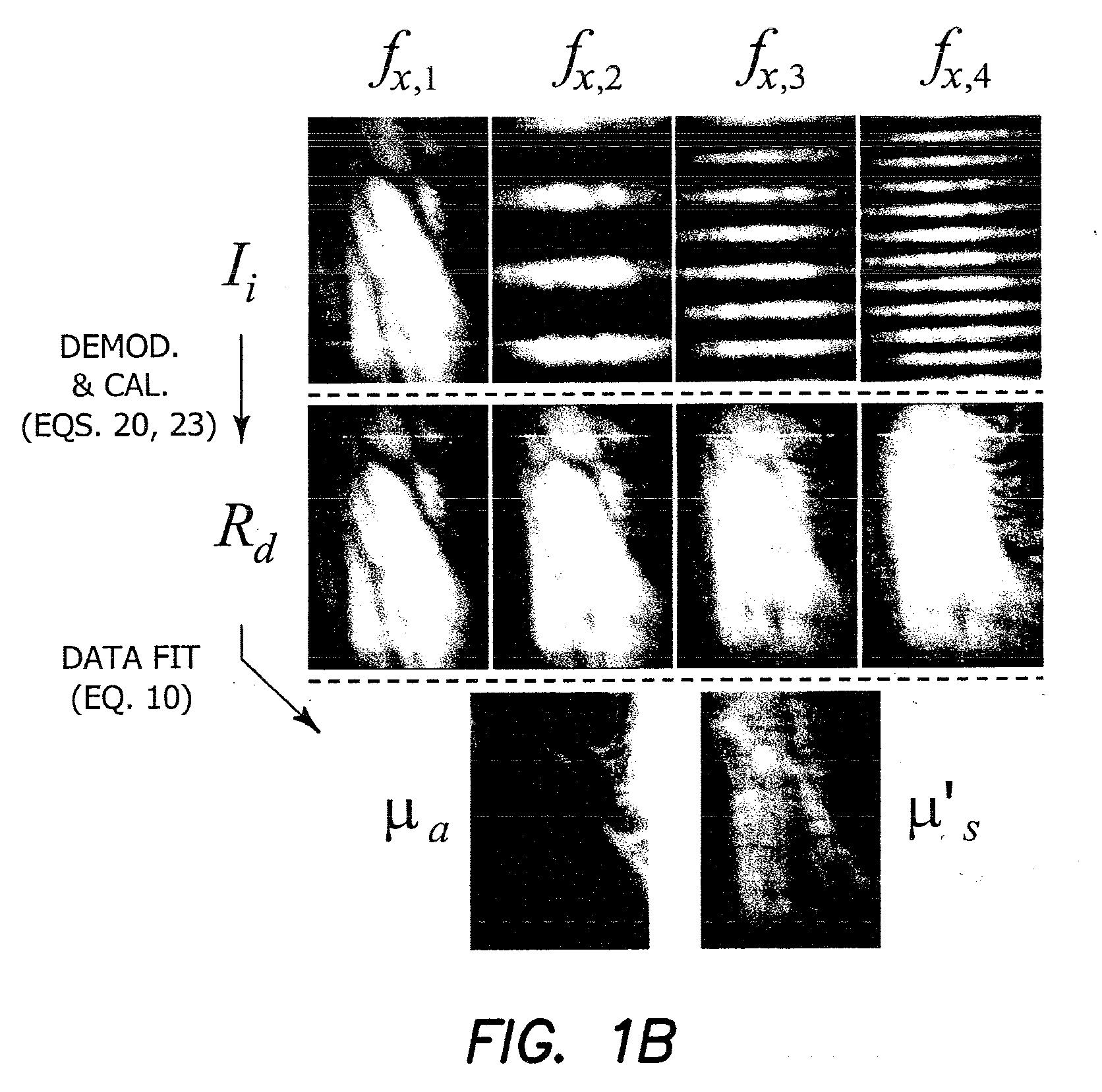
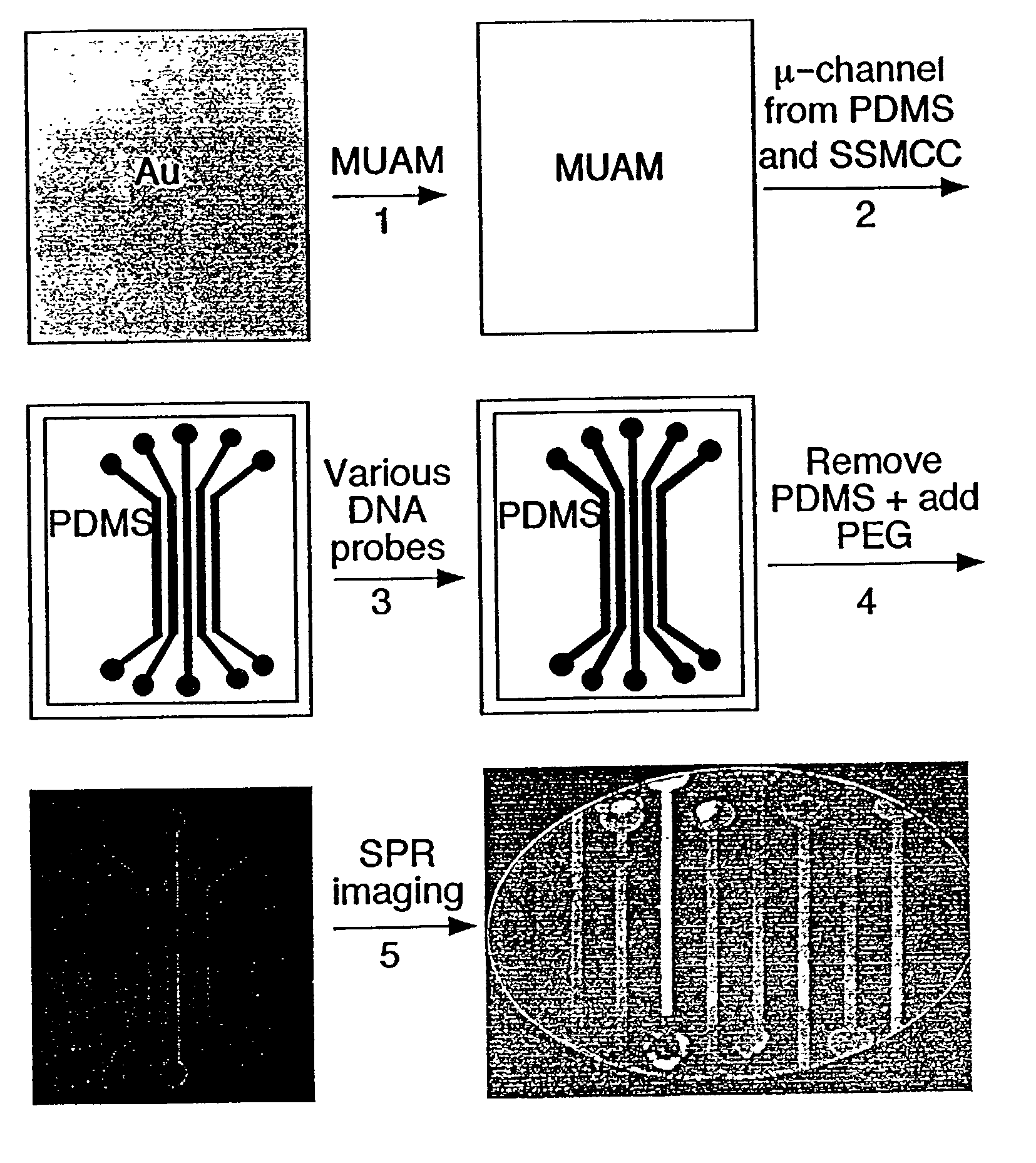
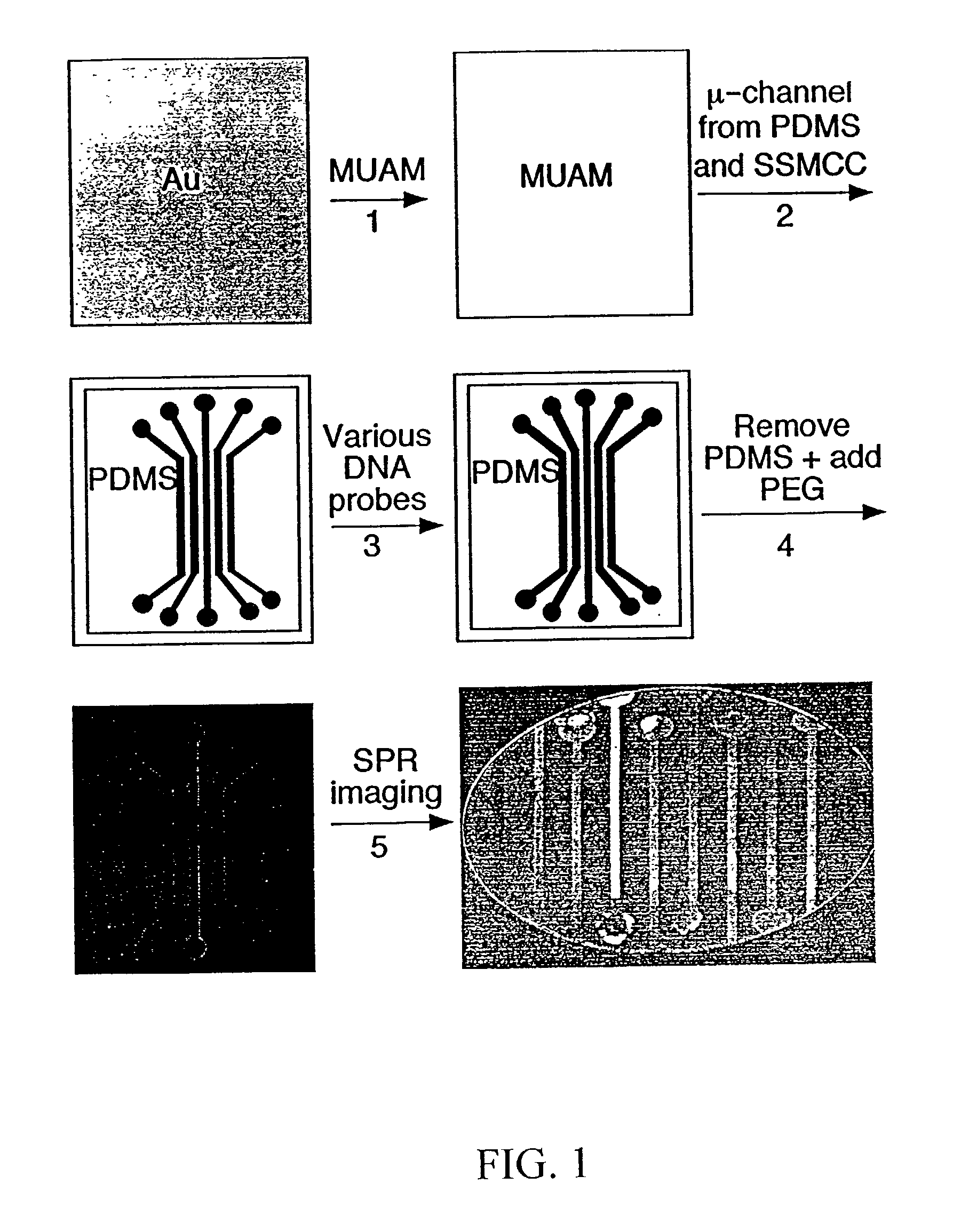
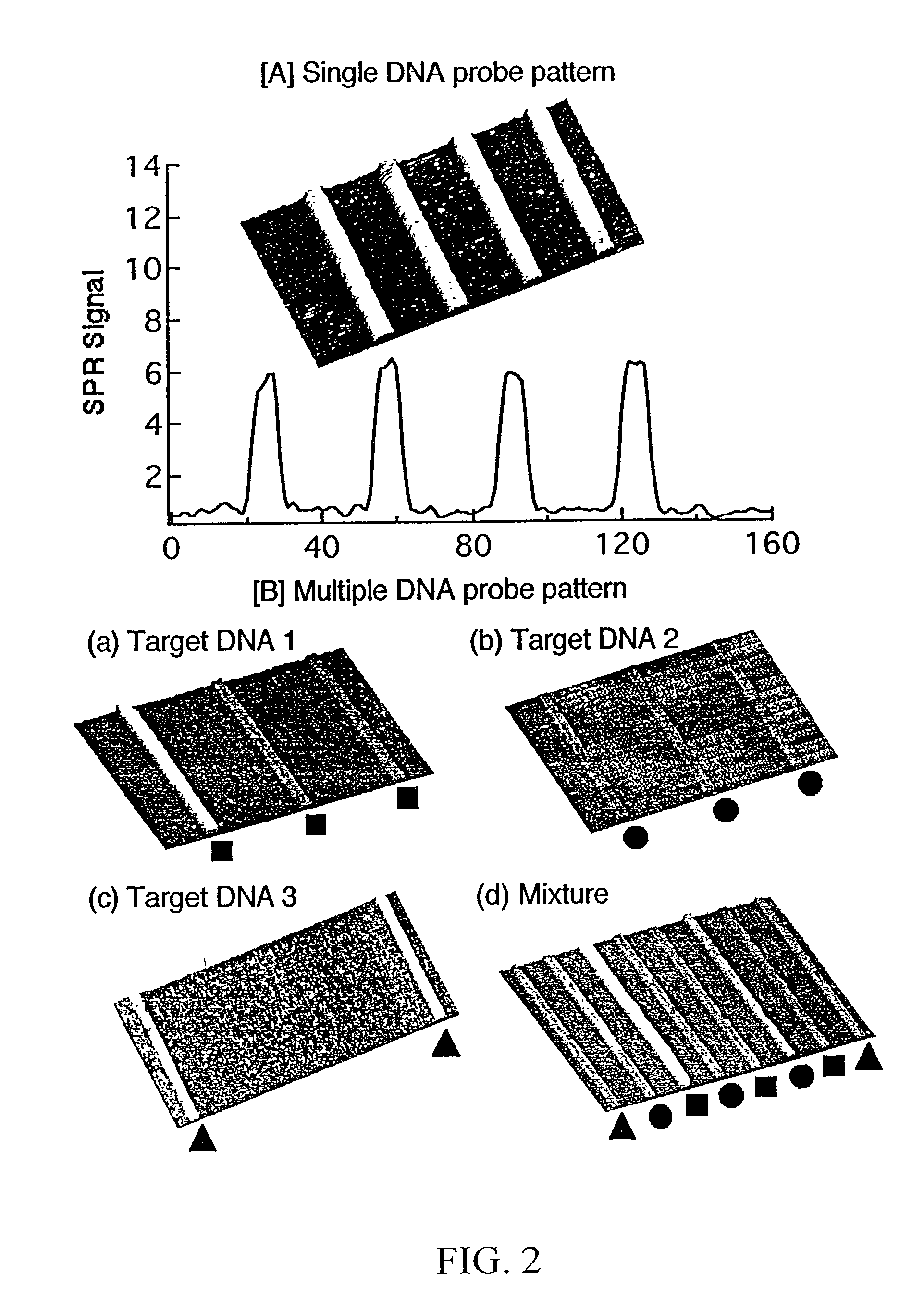
InactiveUS20030017579A1Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSpr imagingMicrofluidic channel
Disclosed is a method for fabricating 1-dimensional micro-arrays using parallel micro-fluidic channels on chemically-modified metal, carbon, silicon, and / or germanium surfaces; a muL detection volume method that uses 2-dimensional nucleic acid micro-arrays formed by employing the 1-dimensional DNA micro-arrays in conjunction with a second set of parallel micro-fluidic channels for solution delivery, and the 1-dimensional and 2-dimensional arrays used in the methods. The methodology allows the rapid creation of 1- and 2-dimensional arrays for SPR imaging and fluorescence imaging of DNA-DNA, DNA-RNA, DNA-protein, and protein-protein binding events. The invention enables very small volumes necessary for a variety of bioassay applications to be analyzed by SPR. Target solution volumes as small as 200 pL can be analyzed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
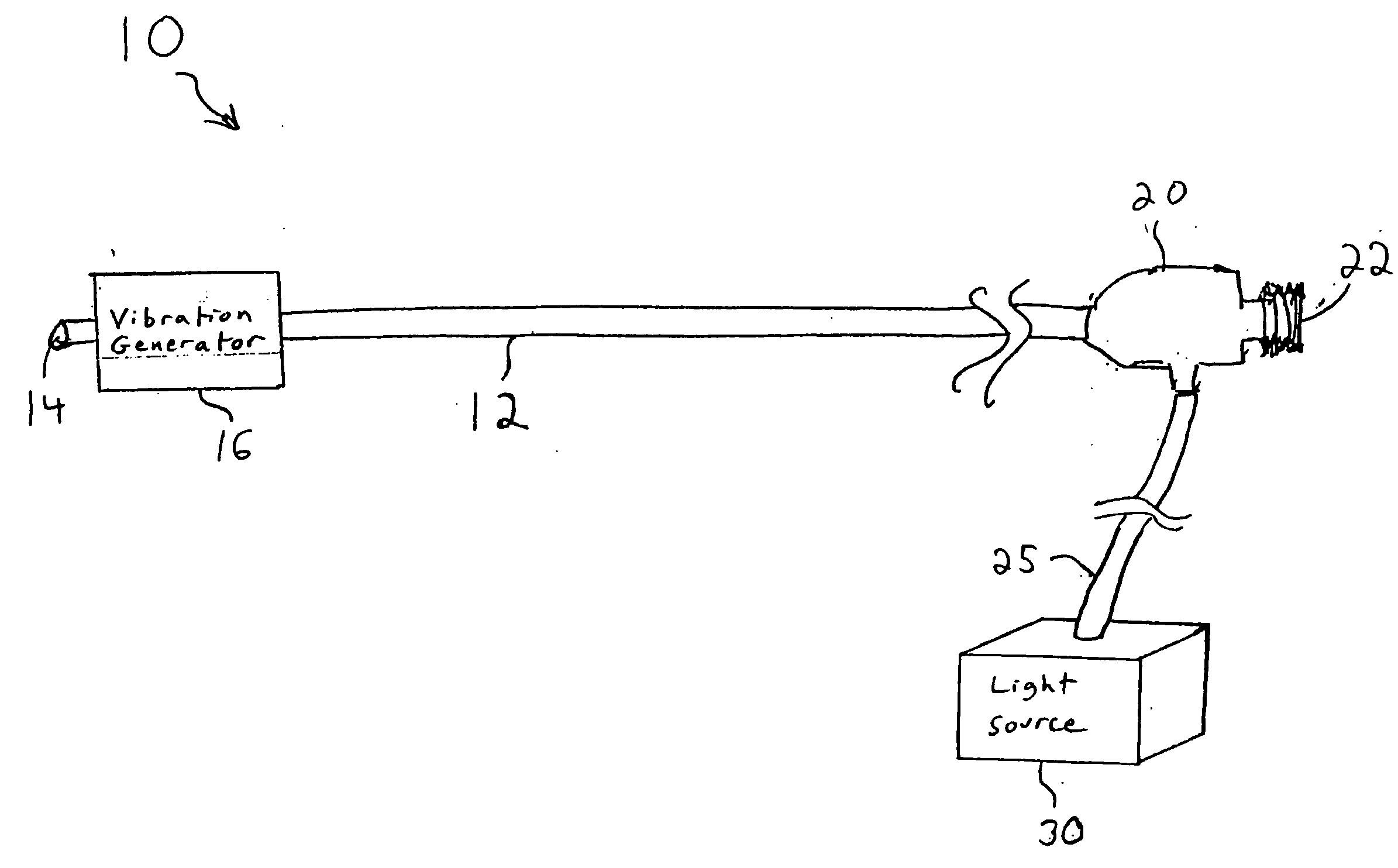
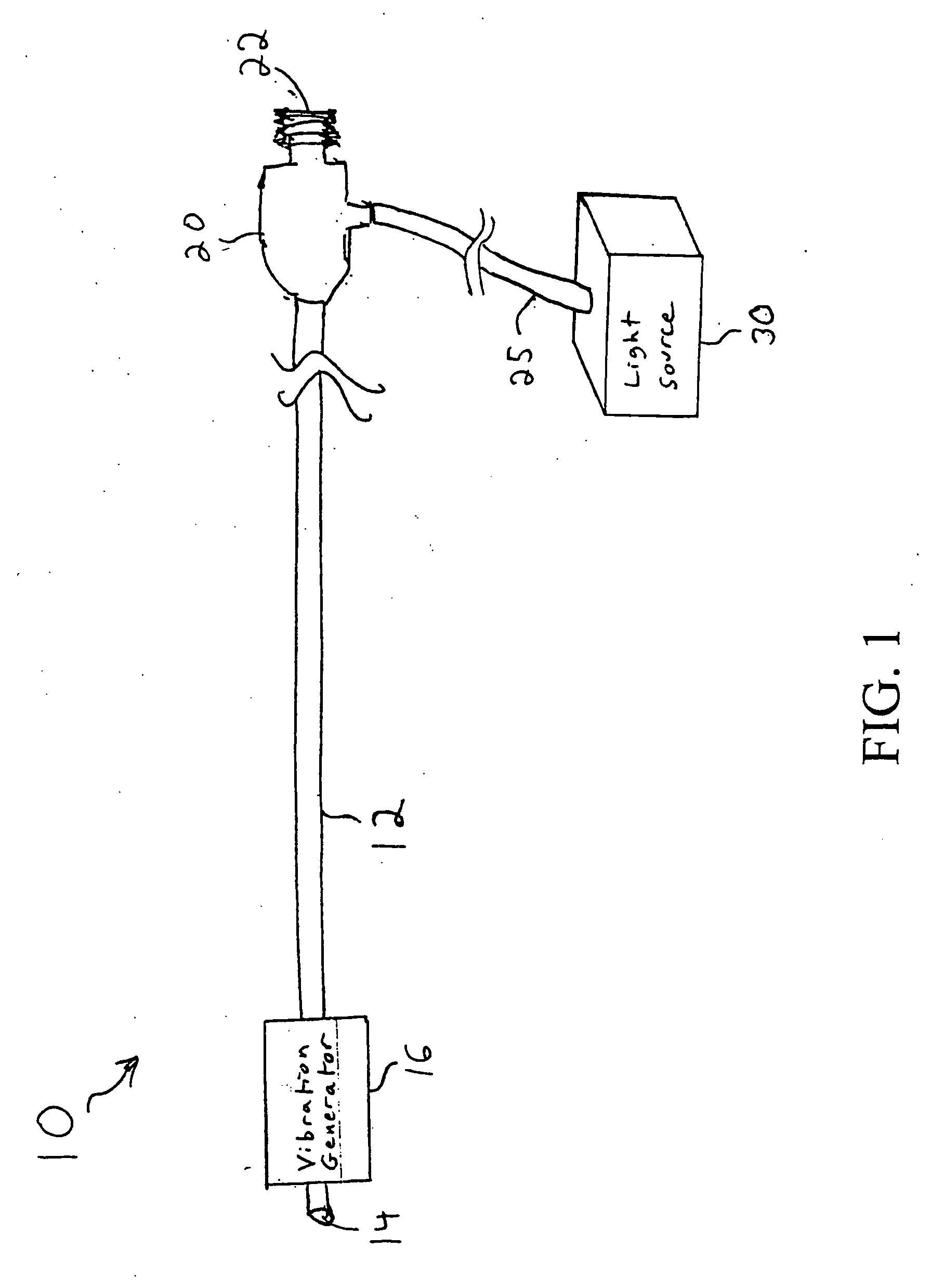
Vision catheter
A catheter with a small optical fiber or bundle of fibers includes a scanning mechanism constructed with the use of any vibration capable component. Magnetic, piezoelectric or other mechanisms are used to vibrate the end of the fiber and thus create a scanning effect which extends the field of view. One or more lenses may be utilized, including a lens attached to the distal tip of the image fiber, or a lens attached to the distal tip of the catheter for creating an image plane which can be scanned by the fiber. In one embodiment, multiple light sources may be connected to the fiber for enabling the use of field sequential color techniques for real-time imaging, as well as real-time fluorescent imaging for disease detection. A photodetector assembly connected to the proximal end may contain both filtered and unfiltered detectors for use with both standard imaging and fluorescent imaging. The resulting vision catheter is relatively inexpensive and disposable.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS7335898B2Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Image transformation and display for fluorescent and visible imaging
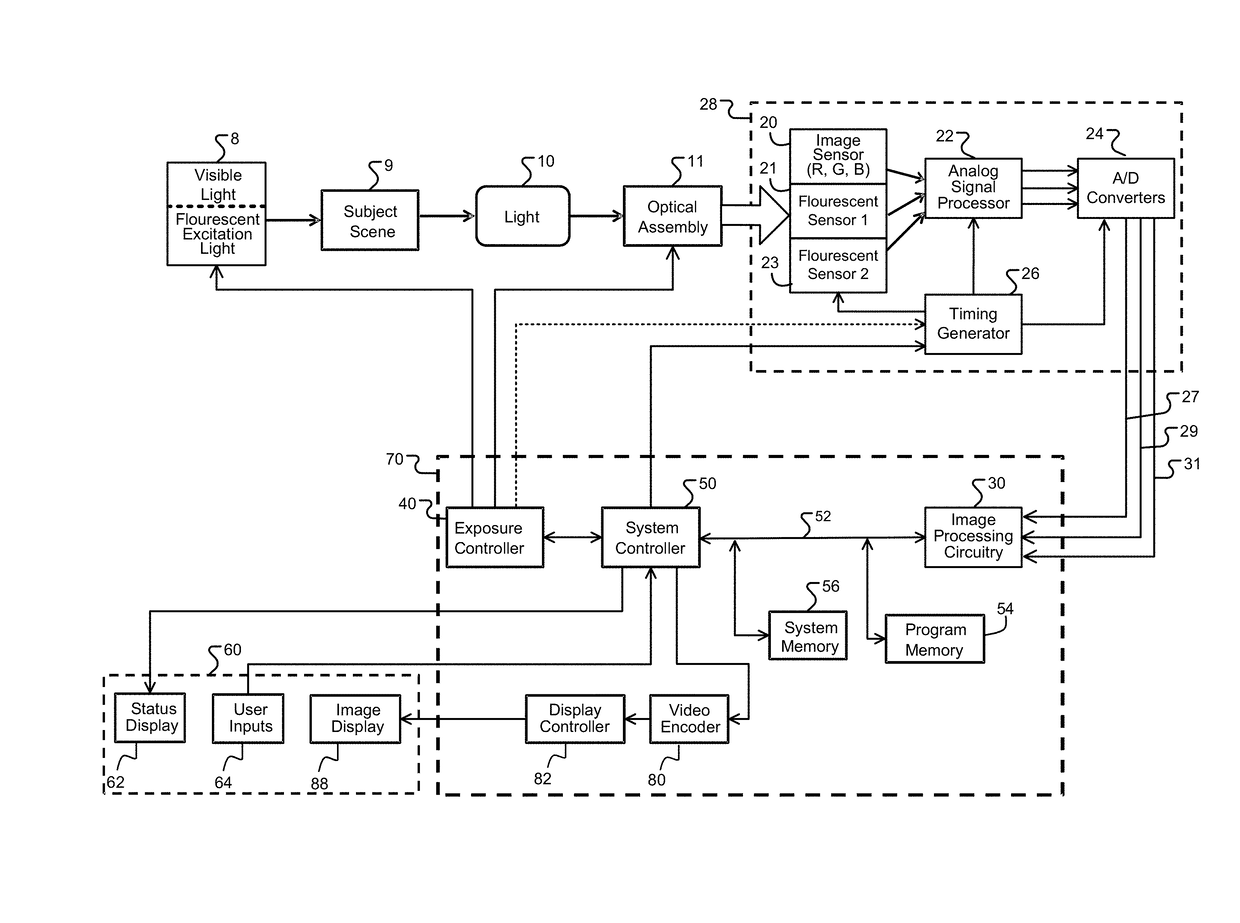
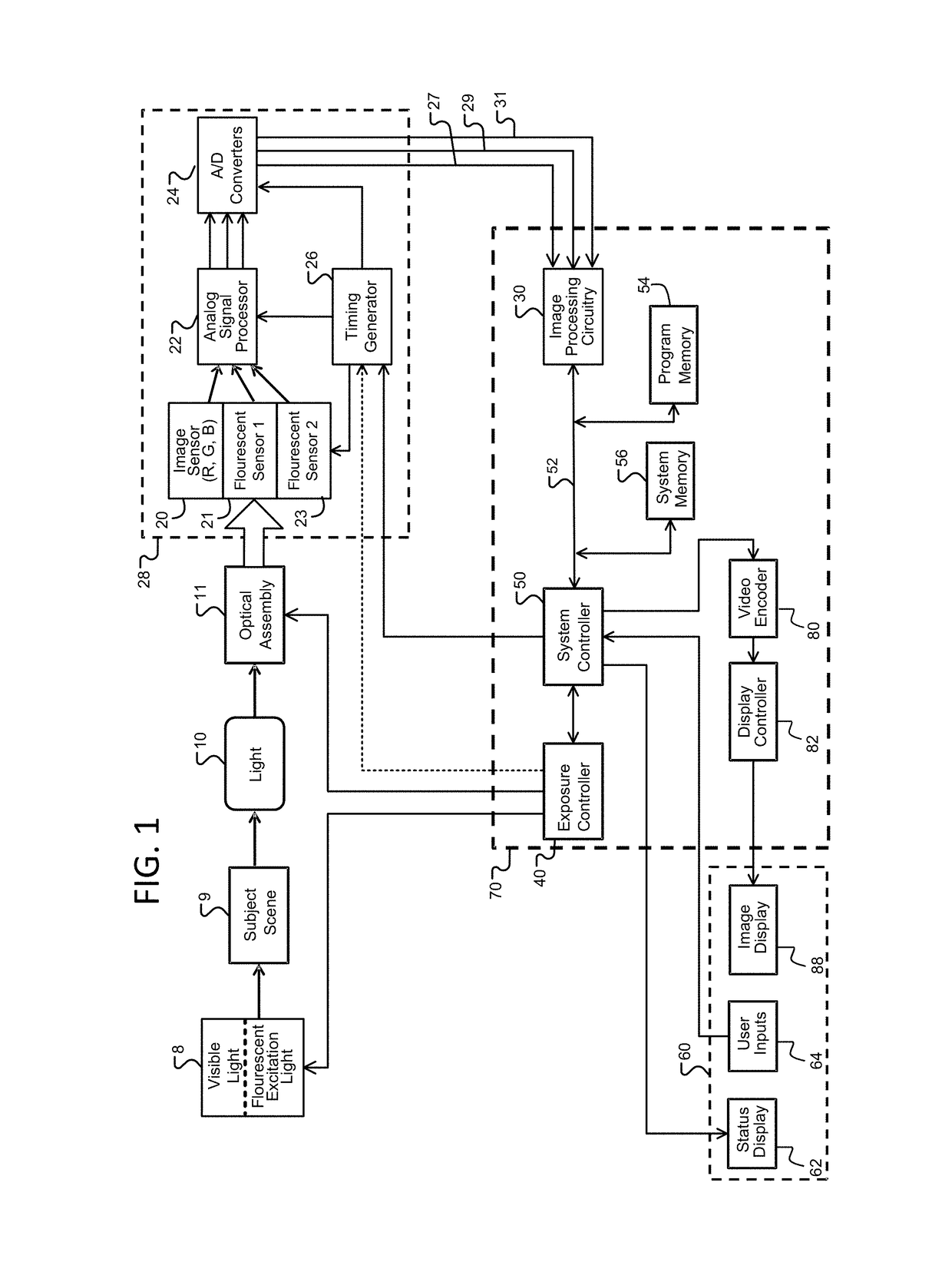
ActiveUS20170280029A1Improve the display effectImprove discriminationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementFluorescent imagingTime processing
Improved fluoresced imaging (FI) and other sensor data imaging processes, devices, and systems are provided to enhance display of different secondary types of images and reflected light images together. Reflected light images are converted to a larger color space in a manner that preserves the color information of the reflected light image. FI or secondary images are transformed to a color range within the larger color space, but outside the color area of the reflected light images, allowing the FI or secondary images to be combined with them in a manner with improved distinguishability of color. Hardware designs are provide to enable real-time processing of image streams from medical scopes. The combined images are encoded for an electronic display capable of displaying the larger color space.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Fluorescence imaging endoscope
InactiveUS7235045B2Simplify System DesignConvenient registrationRaman/scattering spectroscopySurgeryLaser lightReflectivity
An endoscope having an optical guide that is optically coupled to a first broadband light source and a second laser light source that emits light at a wavelength in a range of 350 nm to 420 nm. The endoscope has an image sensor at a distal end and collects a reflectance image including red, green and blue components with the image sensor in response to illumination by said broadband light source. The image sensor also collects an autofluorescence image having a blue component, a green component and a red component. A processor processes the fluorescence image by determining a ratio of the fluorescence image and the reflectance image to provide a processed fluorescence image.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
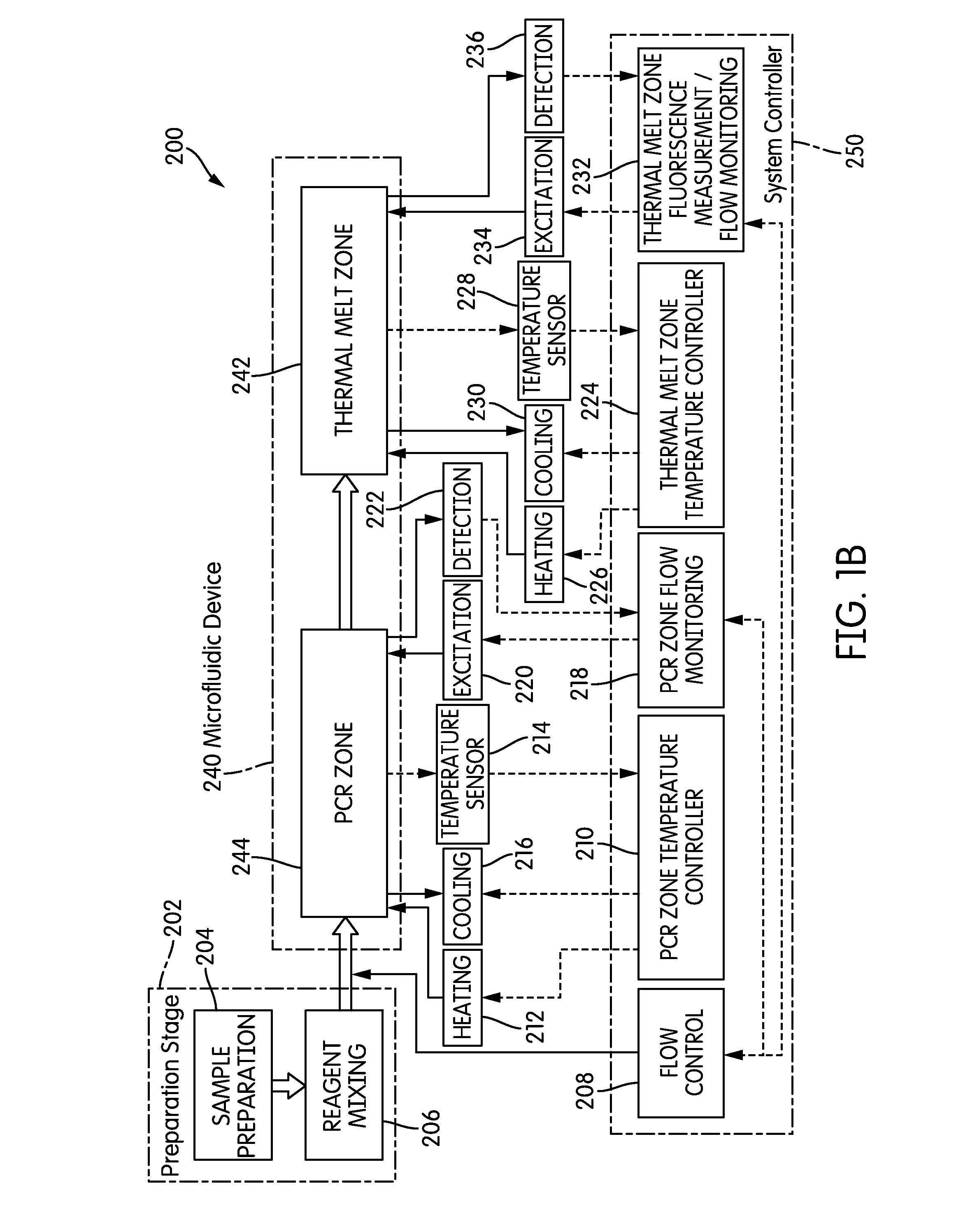
System and method for serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20120052560A1Rapid serial processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHandling systemData store
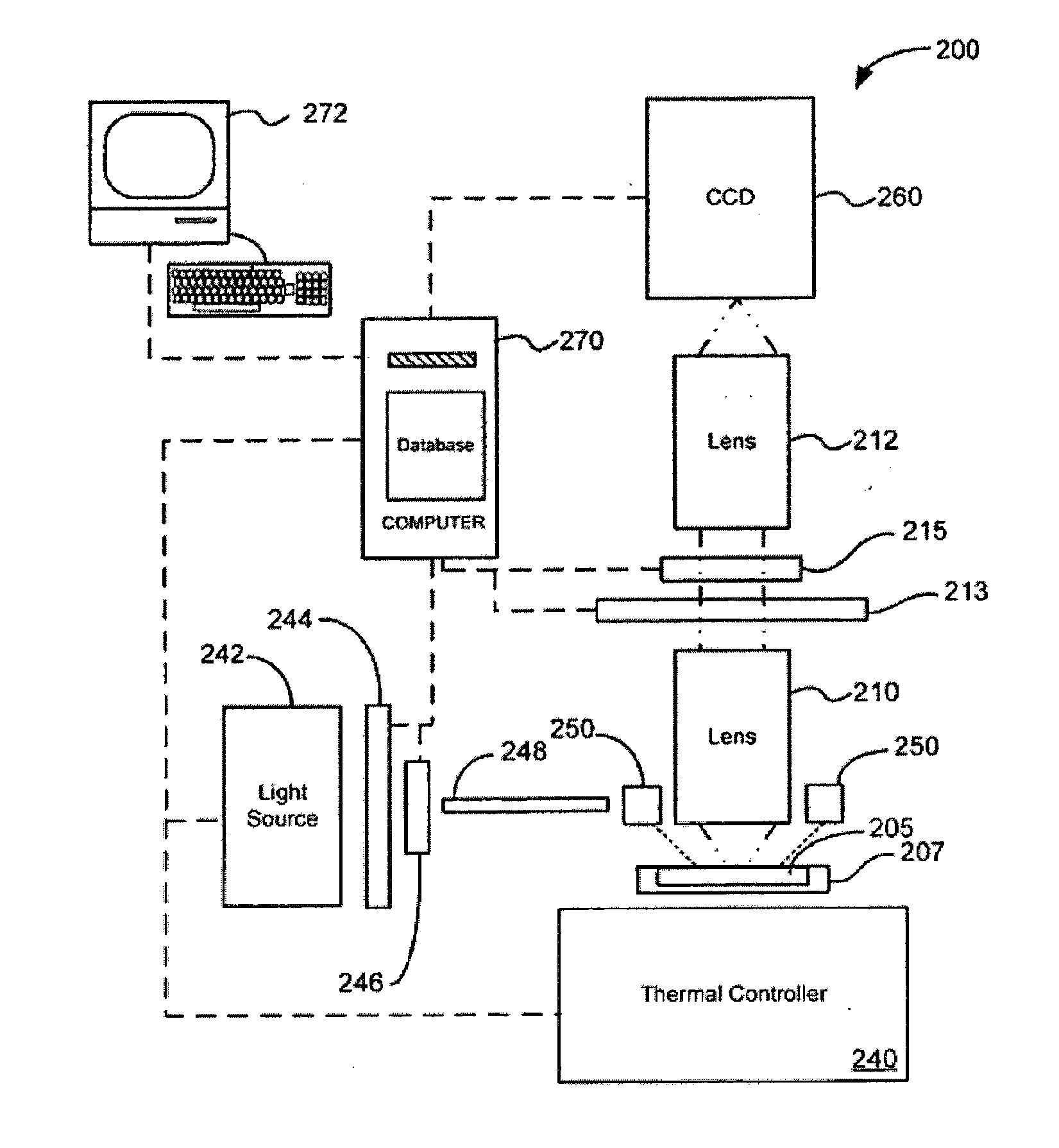
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays. More particularly, the present invention provides for the real time processing of nucleic acid during polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and thermal melt applications. According to an aspect of the invention, a system for the rapid serial processing of multiple nucleic acid assays is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes, but is not limited to: a microfluidic cartridge having microfluidic (flow-through) channels, a fluorescence imaging system, a temperature measurement and control system; a pressure measurement and control system for applying variable pneumatic pressures to the microfluidic cartridge; a storage device for holding multiple reagents (e.g., a well-plate); a liquid handling system comprising at least one robotic pipettor for aspirating, mixing, and dispensing reagent mixtures to the microfluidic cartridge; systems for data storage, processing, and output; and a system controller to coordinate the various devices and functions.
Owner:CANON USA
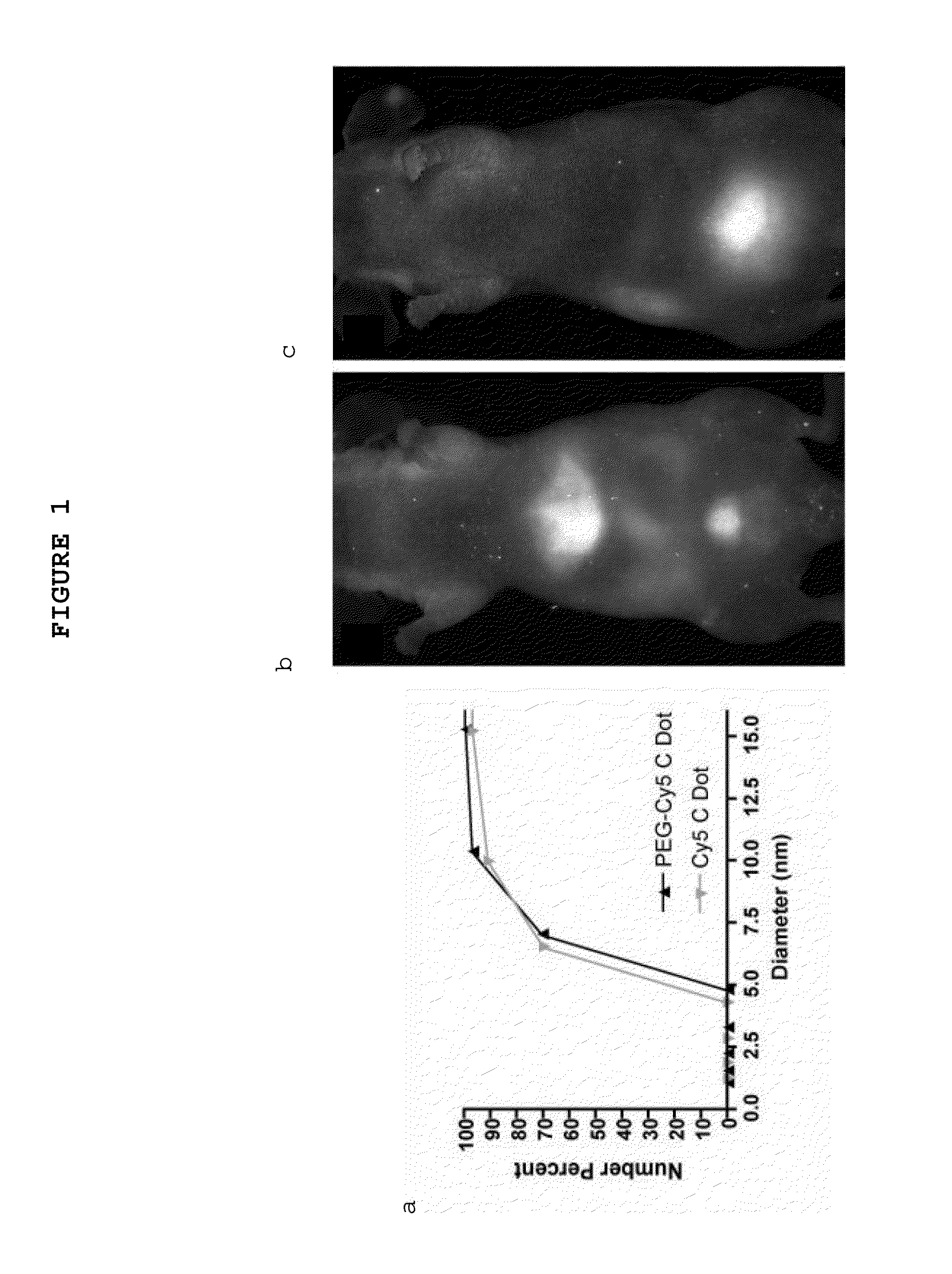
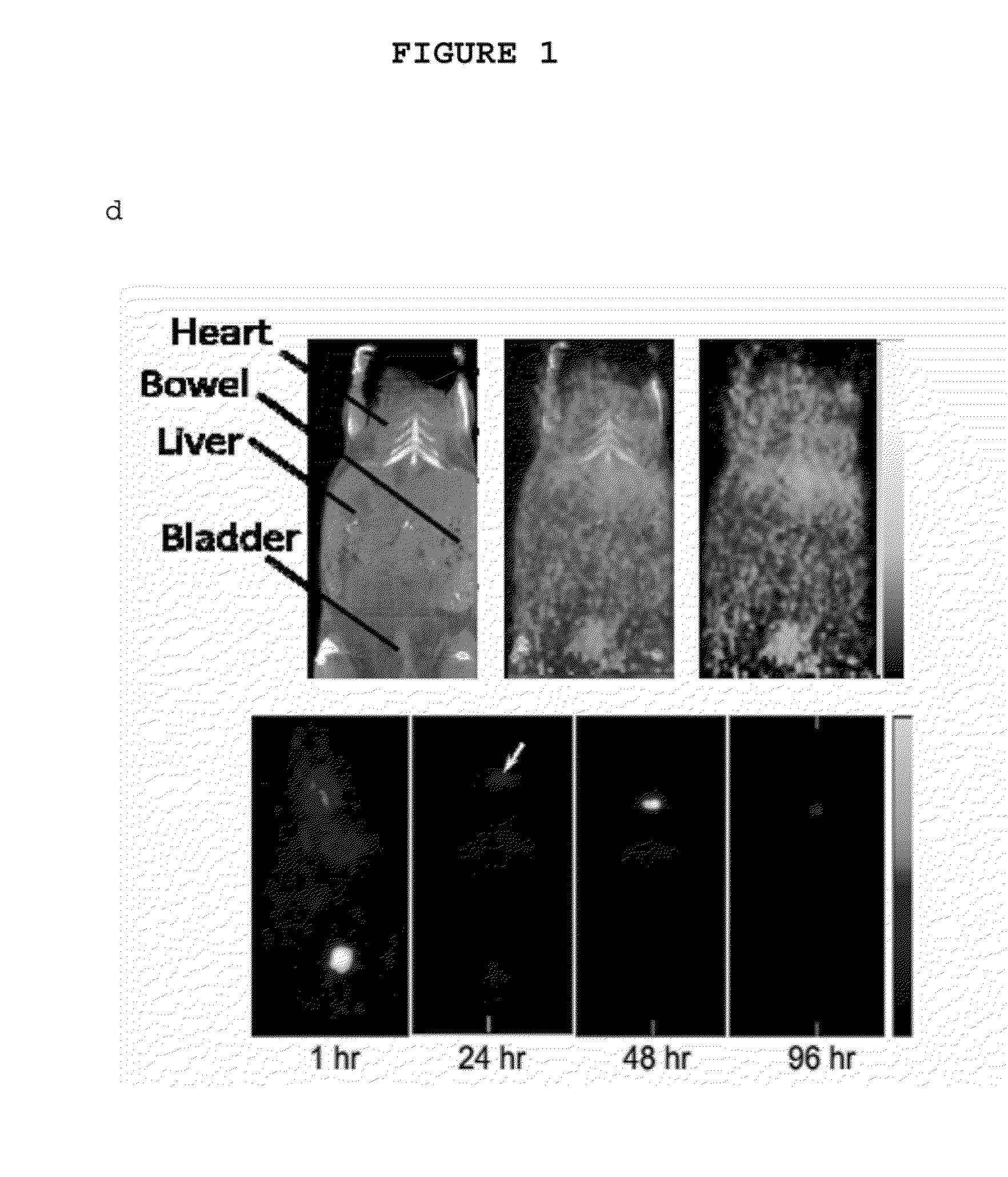
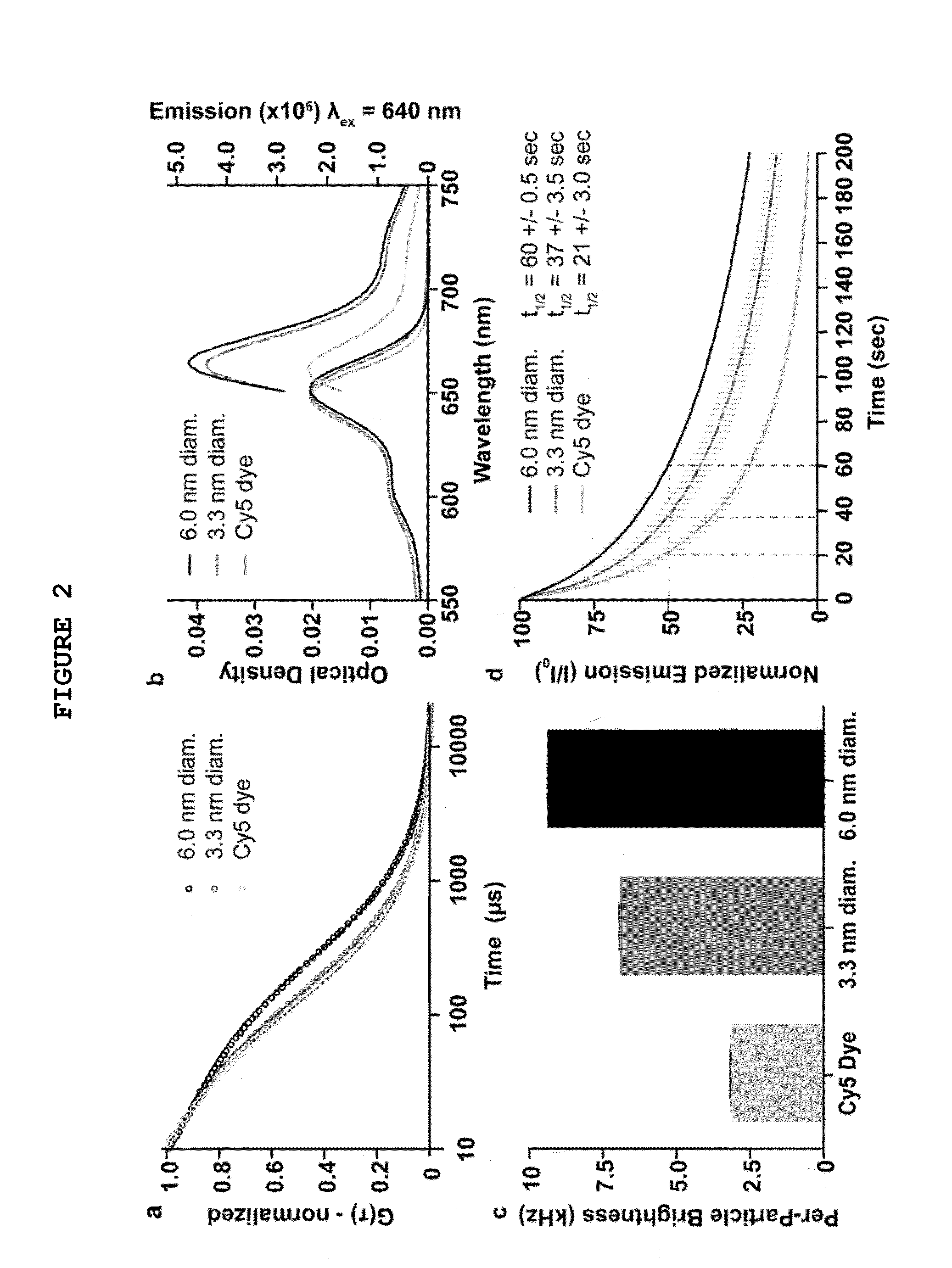
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Laser scanning digital camera with simplified optics and potential for multiply scattered light imaging
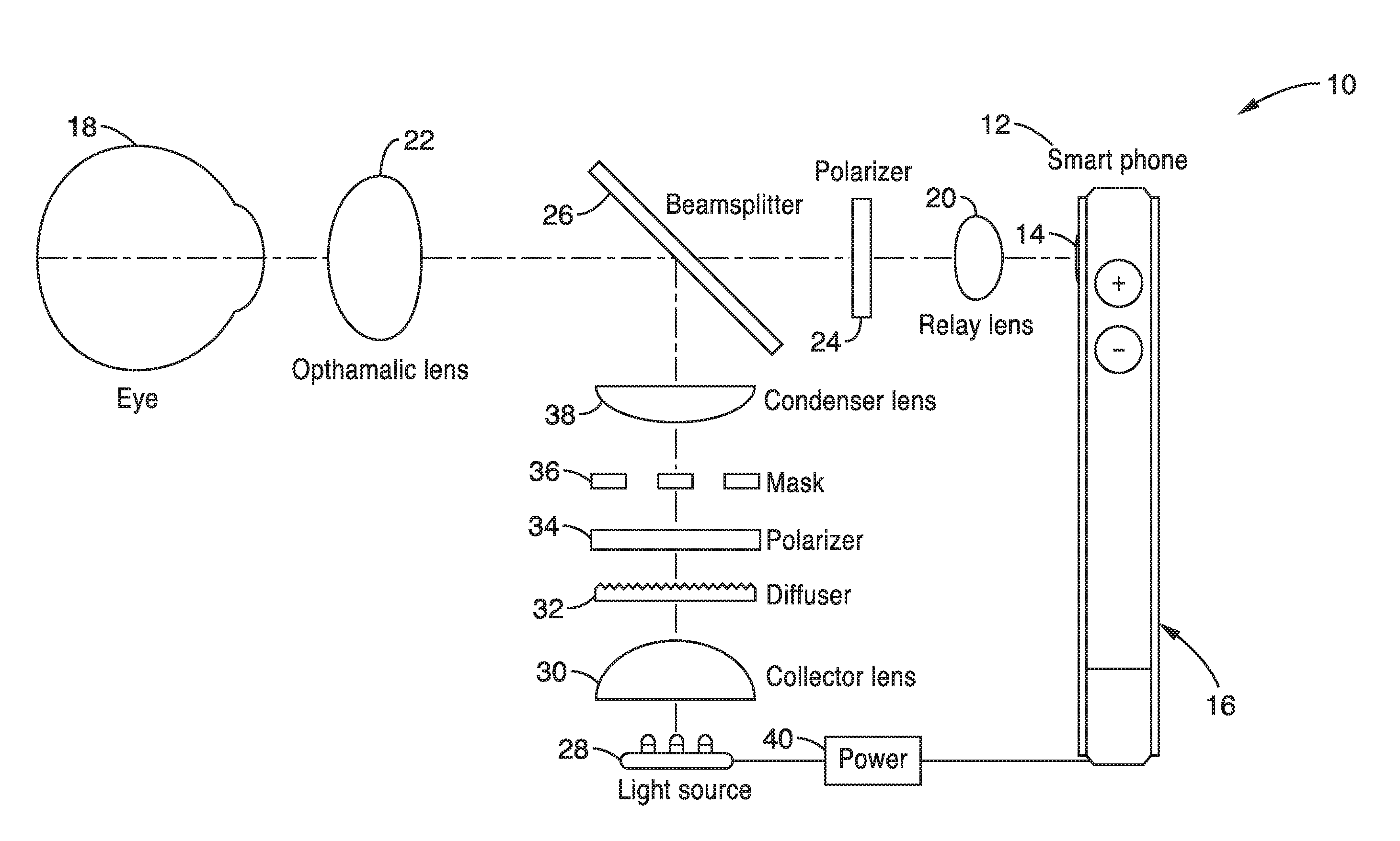
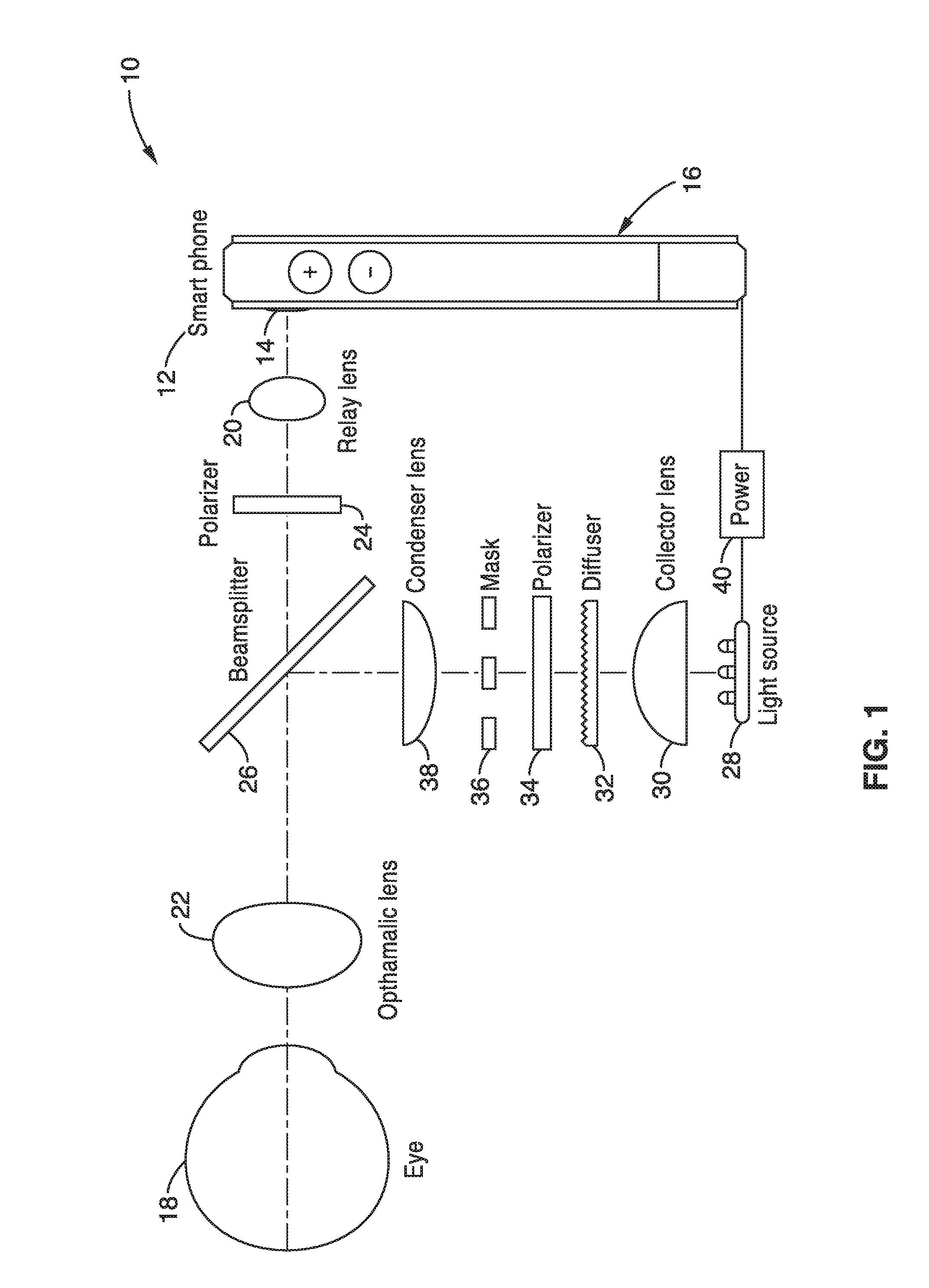
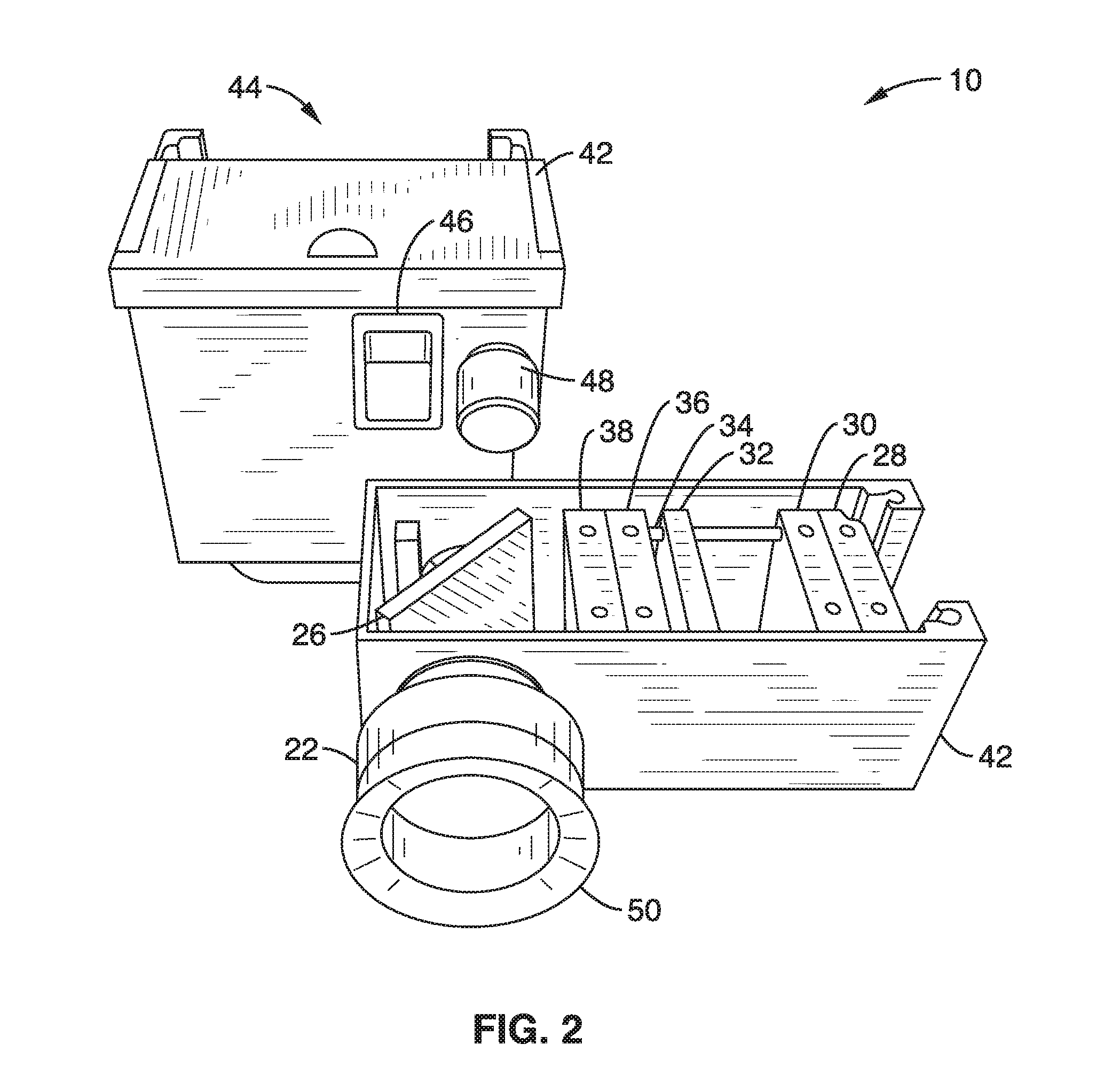
ActiveUS7831106B2Increase illuminationConvenient lightingCharacter and pattern recognitionEye diagnosticsGeneral practionerDigital imaging
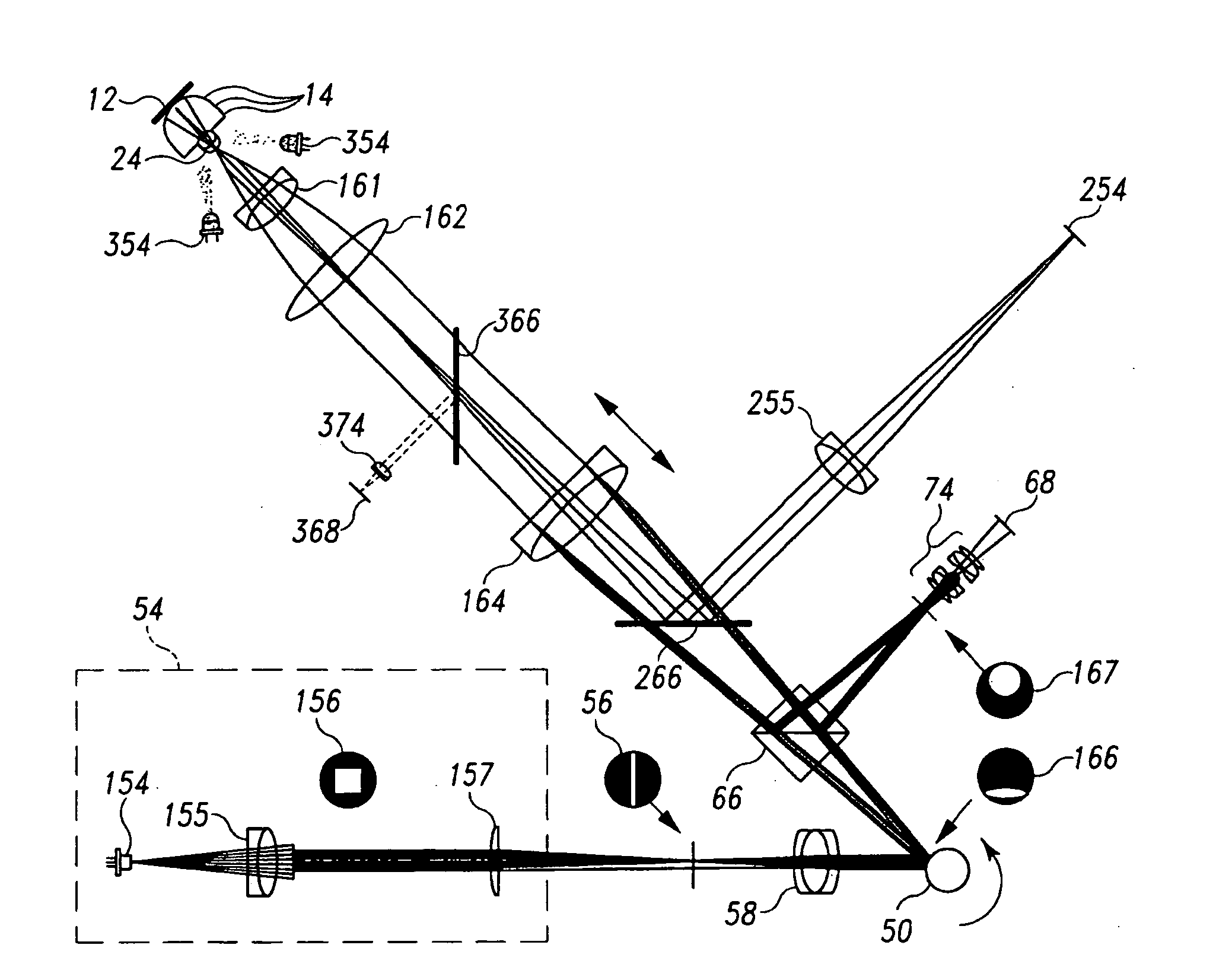
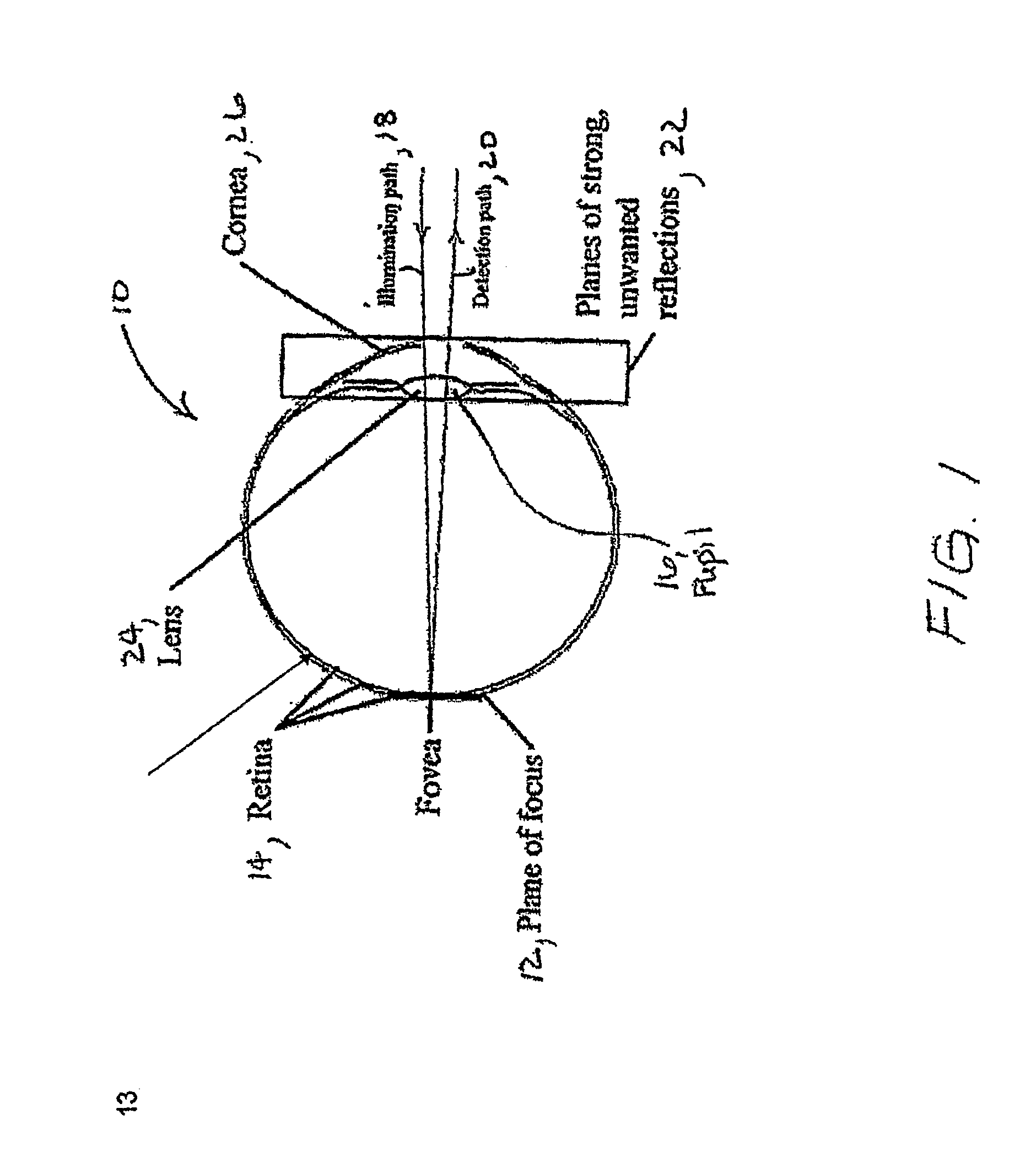
A portable, lightweight digital imaging device uses a slit scanning arrangement to obtain an image of the eye, in particular the retina. The scanning arrangement reduces the amount of target area illuminated at a time, thereby reducing the amount of unwanted light scatter and providing a higher contrast image. A detection arrangement receives the light remitted from the retinal plane and produces an image. The device is operable under battery power and ambient light conditions, such as outdoor or room lighting. The device is noncontact and does not require that the pupil of the eye be dilated with drops. The device can be used by personnel who do not have specialized training in the eye, such as emergency personnel, pediatricians, general practitioners, or volunteer or otherwise unskilled screening personnel. Images can be viewed in the device or transmitted to a remote location. The device can also be used to provide images of the anterior segment of the eye, or other small structures. Visible wavelength light is not required to produce images of most important structures in the retina, thereby increasing the comfort and safety of the device. Flexible and moderate cost confocal and fluorescent imaging, multiply scattered light images, and image sharpening are further functionalities possible with the device.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Systems, devices, methods, apparatus and computer-accessible media for providing optical imaging of structures and compositions
ActiveUS20120101374A1Enhance the imageRaman scatteringDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionFiberAnatomical structures
Exemplary systems, devices, methods, apparatus and computer-accessible media for providing and / or utilizing optical frequency domain imaging (OFDI) and fluorescence of structures and, e.g., multimodality imaging using OFDI techniques and fluorescence imaging techniques are described. For example, an arrangement can provide at least one electro-magnetic radiation to an anatomical structure. Such exemplary arrangement can include at least one optical core and at least one cladding at least partially surrounding the fiber(s). A region between the optical core(s) and the cladding(s) can have an index that is different from indexes of the optical core(s) and the cladding(s). The arrangement can also include at least one apparatus which is configured to transmit the radiation(s) via the optical core(s) and the cladding(s) to the anatomical structure.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
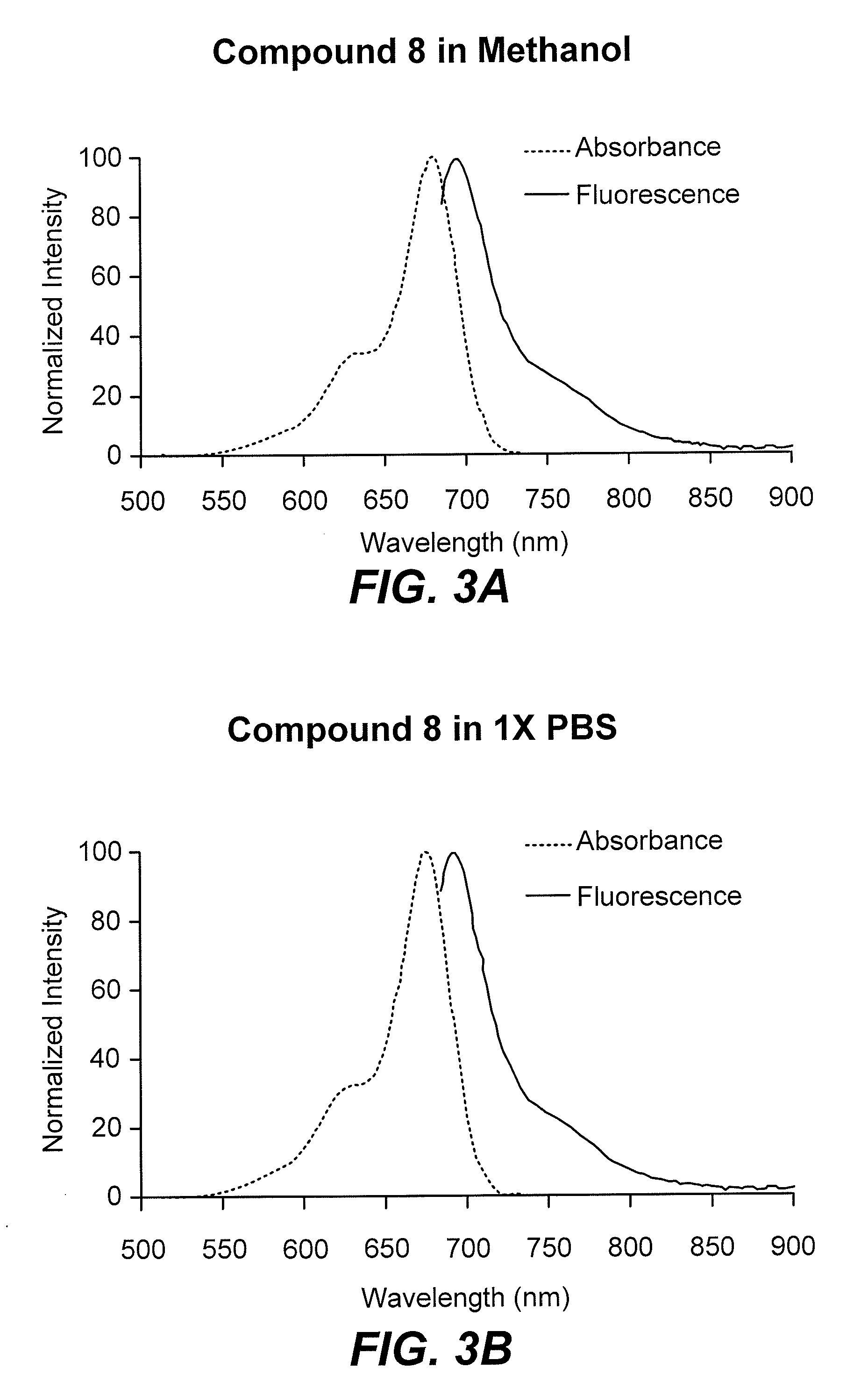
Near infrared fluorescent contrast agent and fluorescence imaging
InactiveUS7488468B1Low toxicGood water solubilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityConfocal
A near infrared fluorescent contrast agent comprising a compound having three or more sulfonic acid groups in a molecule, and a method of fluorescence imaging comprising introducing the near infrared fluorescent contrast agent of the present invention into a living body, exposing the body to an excitation light, and detecting near infrared fluorescence from the contrast agent. The near infrared fluorescent contrast agent of the present invention is excited by an excitation light and emits near infrared fluorescence. This infrared fluorescence is superior in transmission through biological tissues. Thus, detection of lesions in the deep part of a living body has been made possible. In addition, the inventive contrast agent is superior in water solubility and low toxic, and therefore, it can be used safely.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells
InactiveUS20150225801A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular pathwaysFluorescent imaging
Methods and systems for recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells are provided. Molecular changes, which may result from random or specific molecular events, are introduced to defined regions in cells over multiple cell cycle generations. Techniques such as fluorescent imaging are applied to track and identify the molecular changes before such information is used for lineage analysis or for identifying key processes and key players in cellular pathways.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Laser scanning digital camera with simplified optics and potential for multiply scattered light imaging
ActiveUS20090244482A1Increase illuminationLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionEye diagnosticsGeneral practionerContrast level
A portable, lightweight digital imaging device uses a slit scanning arrangement to obtain an image of the eye, in particular the retina. The scanning arrangement reduces the amount of target area illuminated at a time, thereby reducing the amount of unwanted light scatter and providing a higher contrast image. A detection arrangement receives the light remitted from the retinal plane and produces an image. The device is operable under battery power and ambient light conditions, such as outdoor or room lighting. The device is noncontact and does not require that the pupil of the eye be dilated with drops. The device can be used by personnel who do not have specialized training in the eye, such as emergency personnel, pediatricians, general practitioners, or volunteer or otherwise unskilled screening personnel. Images can be viewed in the device or transmitted to a remote location. The device can also be used to provide images of the anterior segment of the eye, or other small structures. Visible wavelength light is not required to produce images of most important structures in the retina, thereby increasing the comfort and safety of the device. Flexible and moderate cost confocal and fluorescent imaging, multiply scattered light images, and image sharpening are further functionalities possible with the device.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
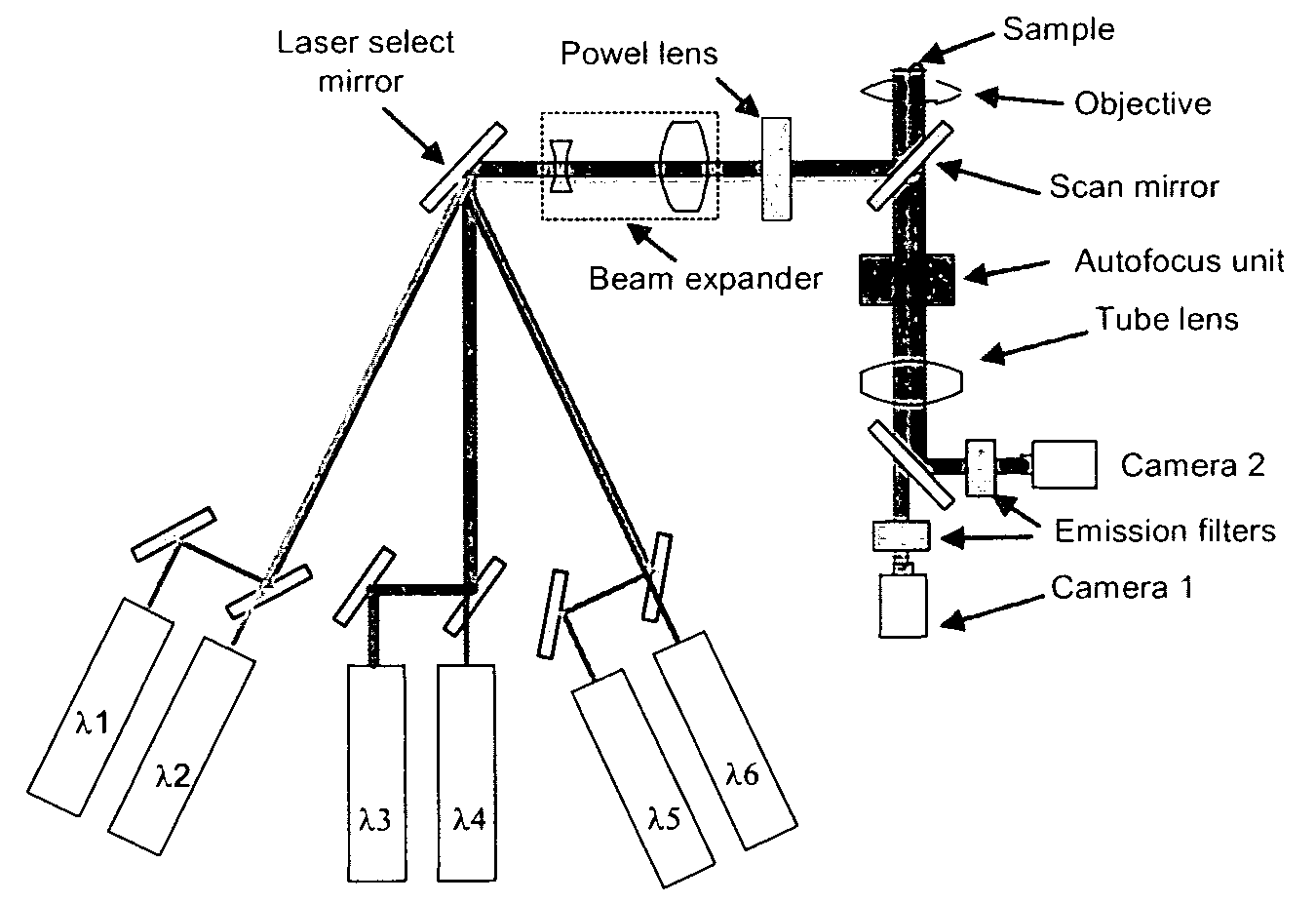
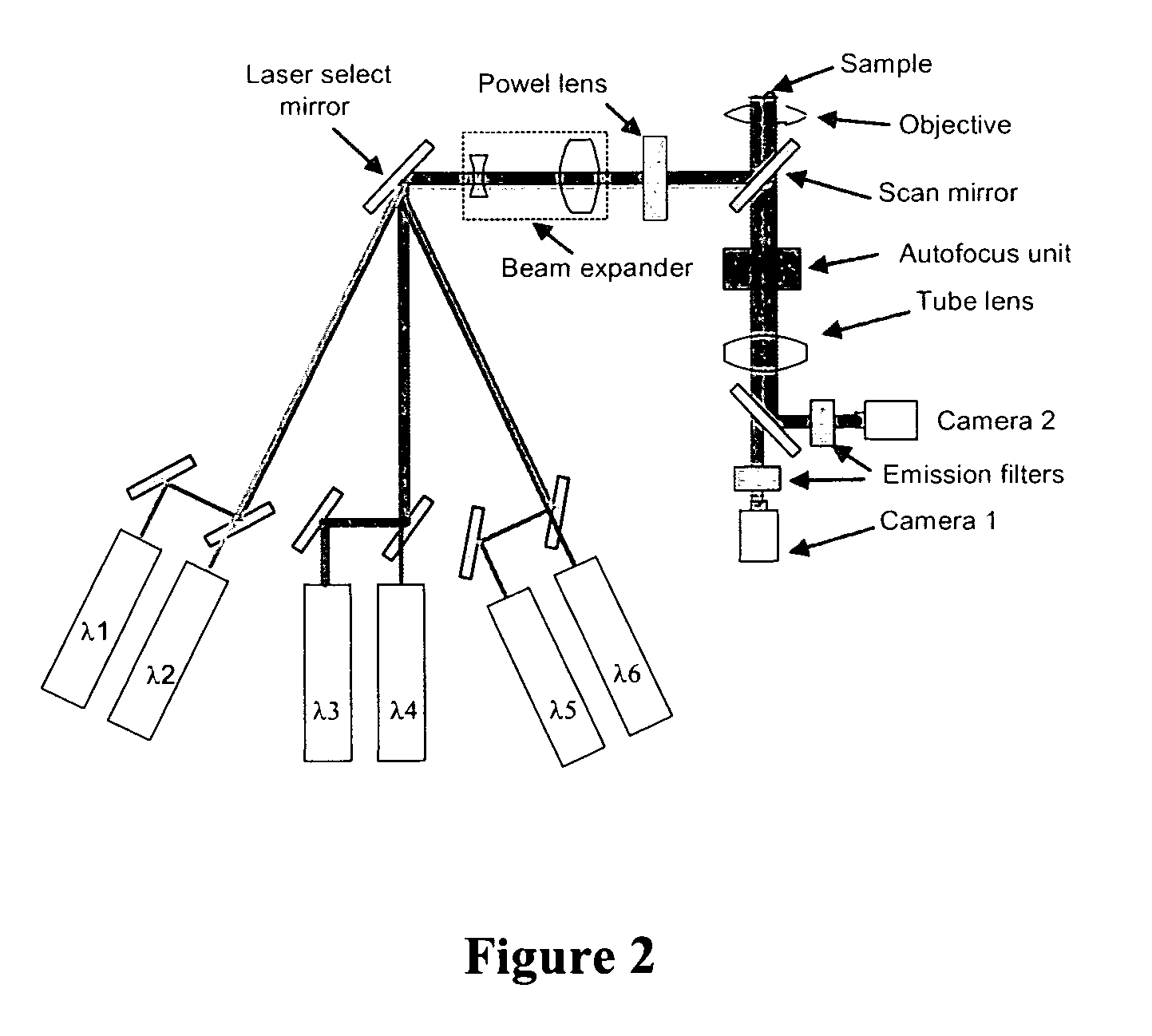
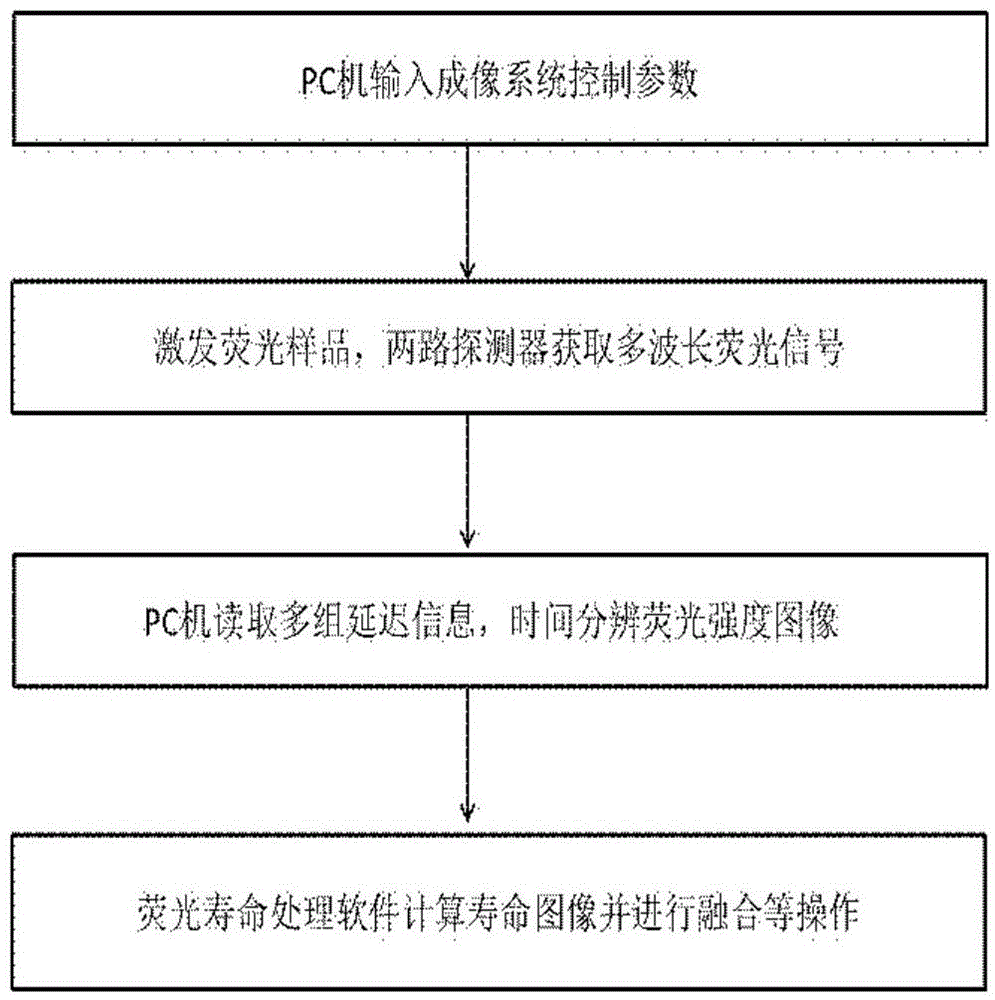
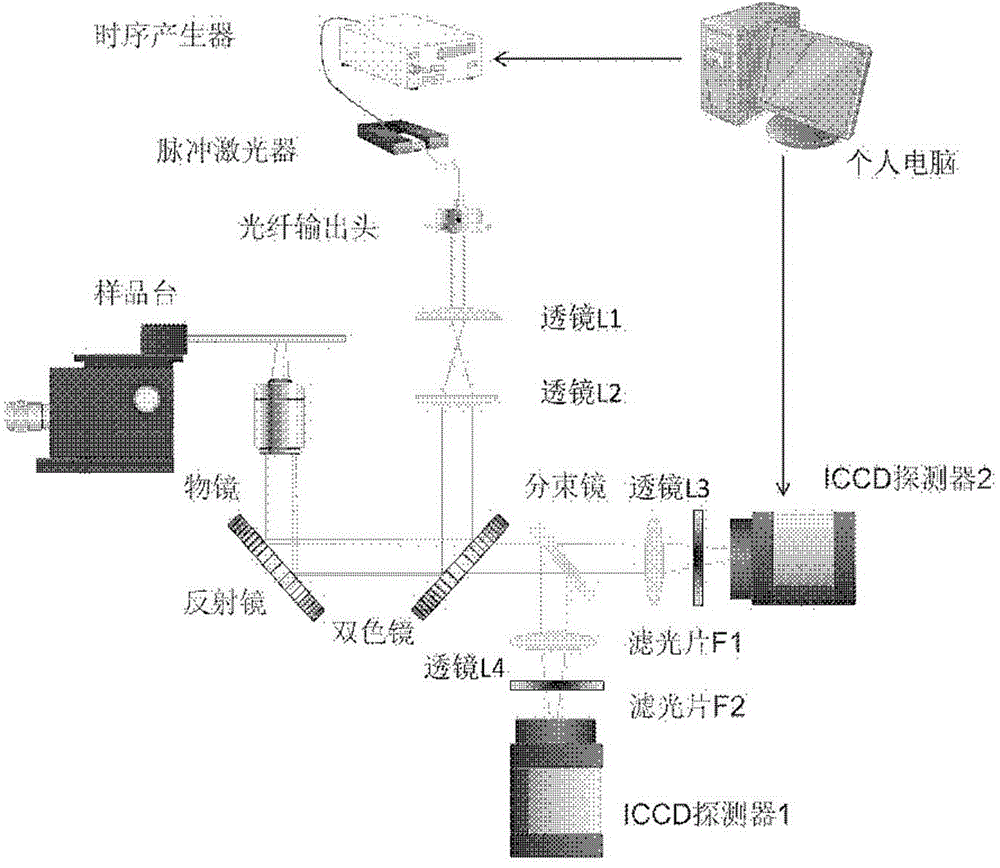
Two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method
ActiveCN104614353AFluorescence Imaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond pulsed laserFluorescence microscope
The invention is applicable to the field of optics, biomedicine, life science and the like, and provides a two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, wherein the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system comprises a picosecond pulse laser device, a fluorescent excitation and collection light path, a microscopic objective lens, a light beam lens, a double-ICCD detector, and a control and processing module. The invention further discloses a method for performing multi-spectrum imaging by utilizing the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system. According to the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, the limitation of the existing fluorescent microscope and a fluorescent life imaging microscopic system only can acquire single wavelength fluorescent signal with one-time detection can be effectively solved, the simultaneous acquisition of the multi-spectrum fluorescent strength and fluorescent light image aiming at the dynamic process of fluorescent intensity-related detection limited in biomedicine and life science can be performed, so that the research and application ranges of biophotonics can be extended.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
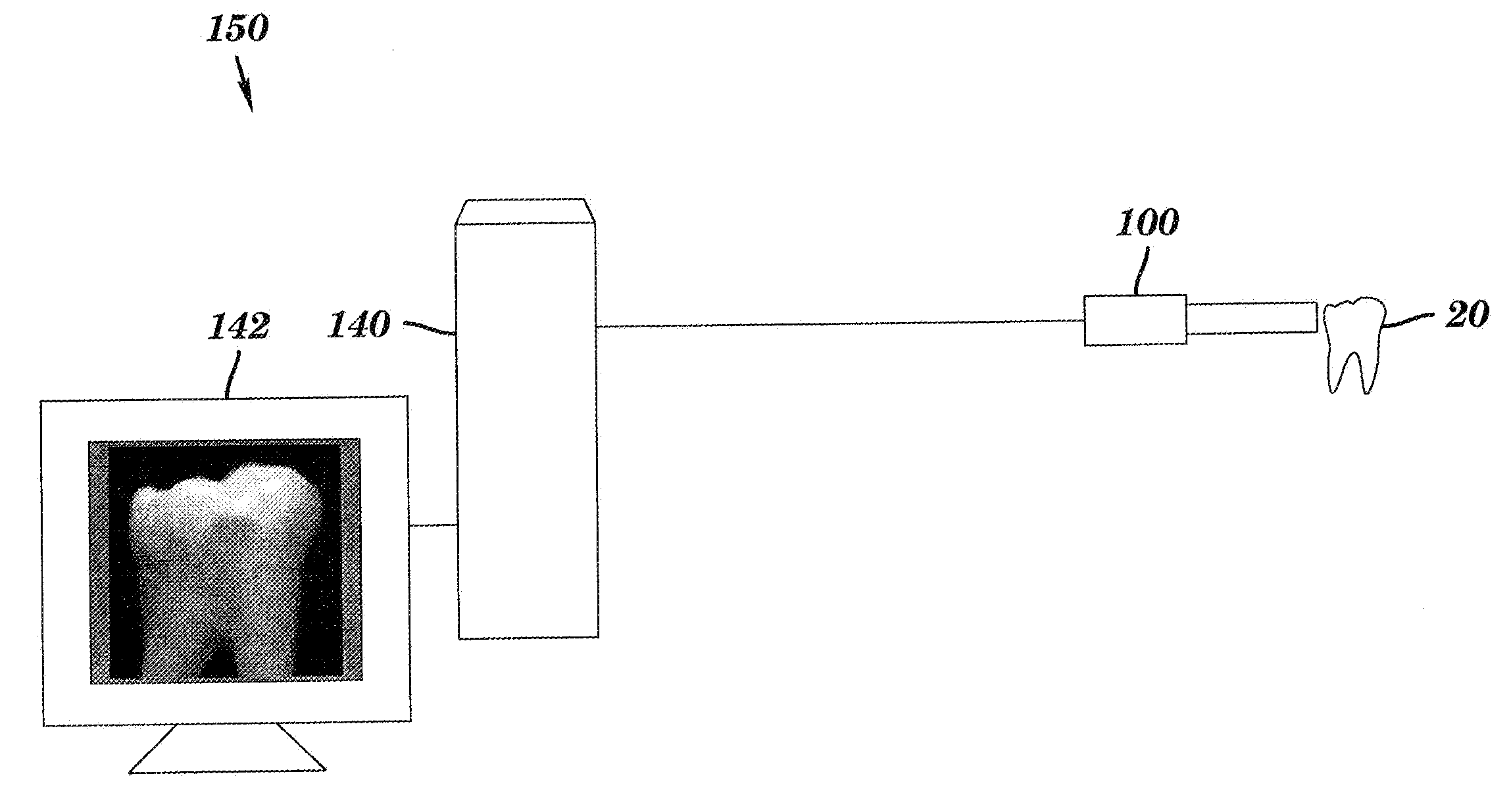
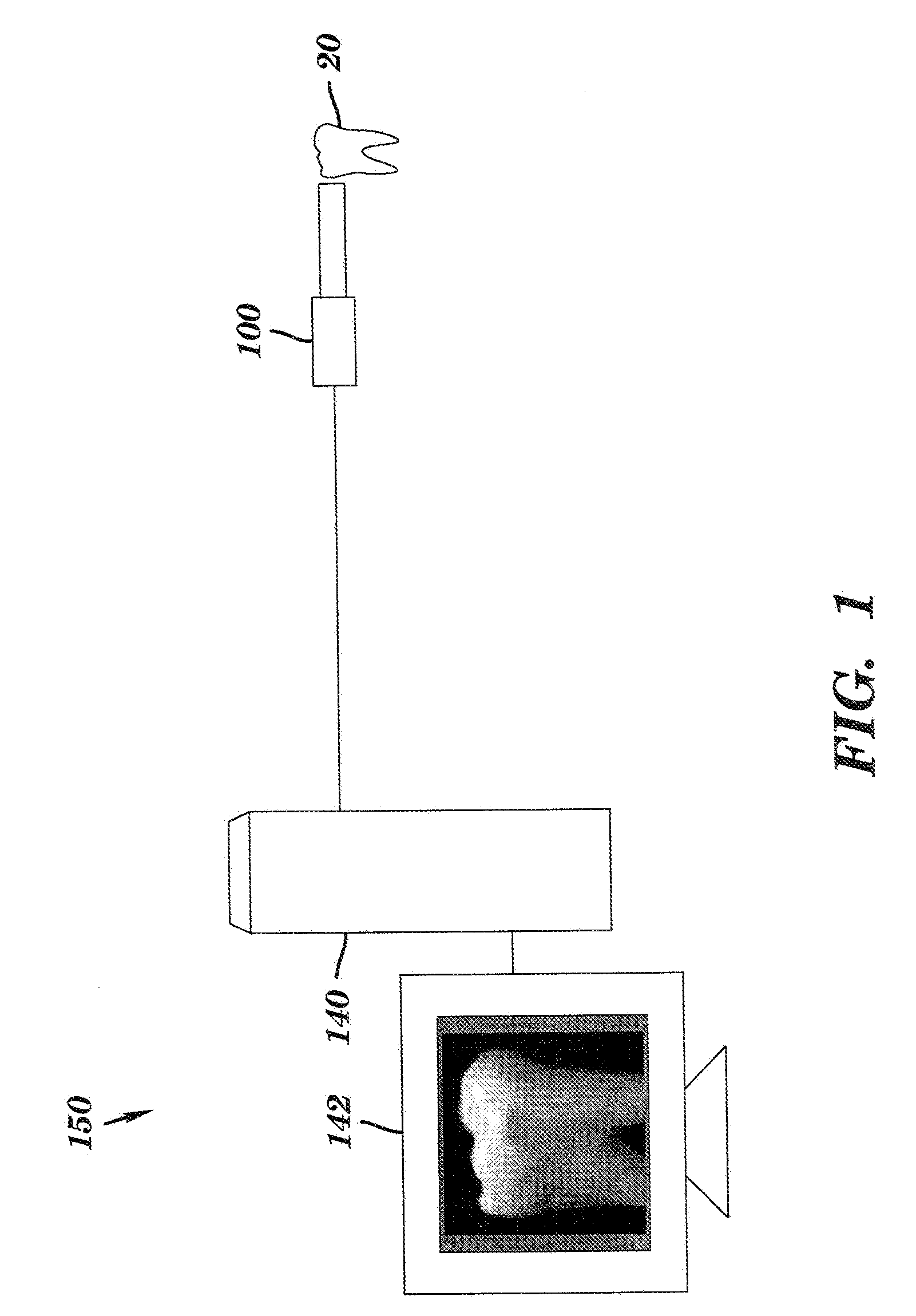
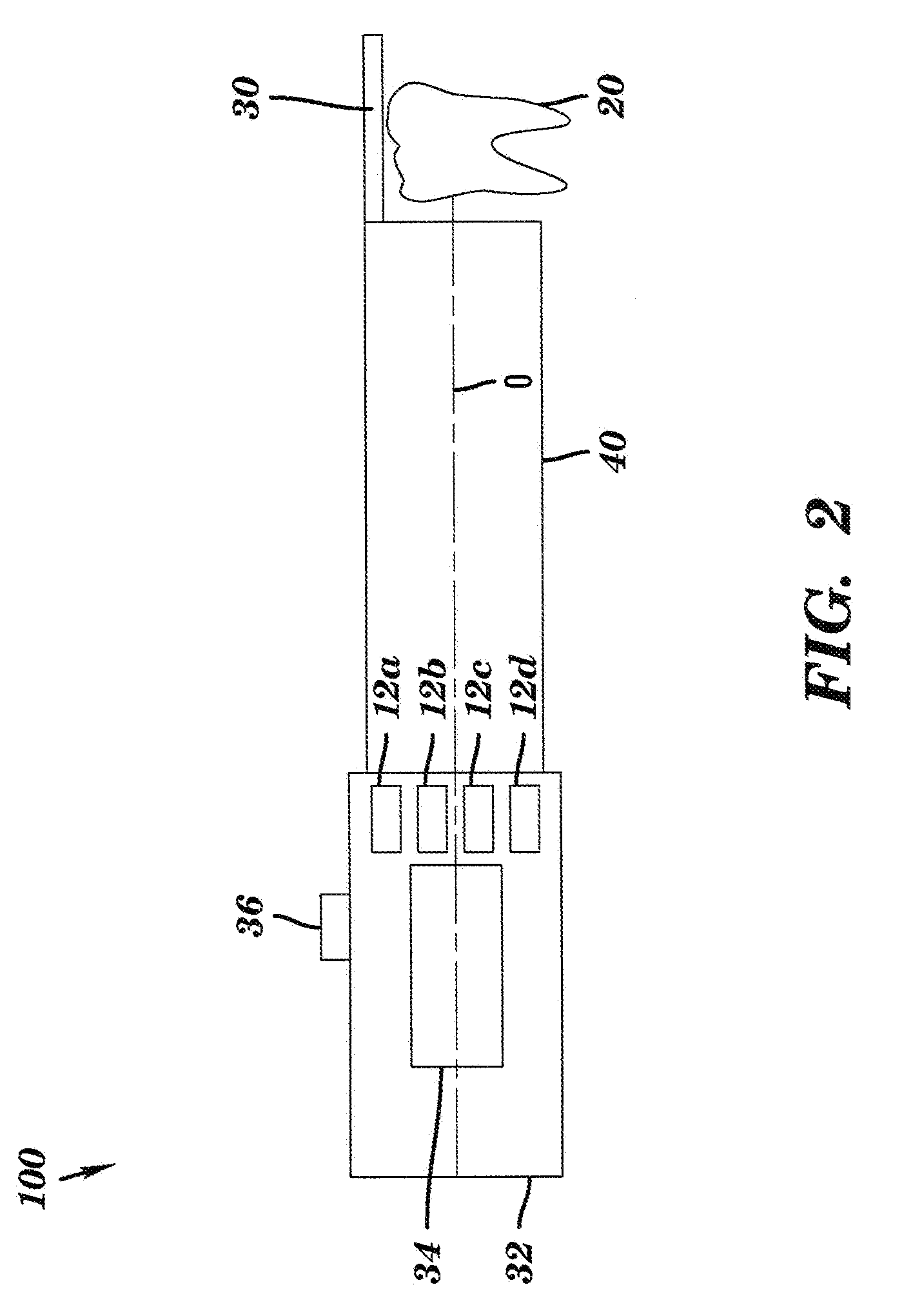
Intra-oral camera for diagnostic and cosmetic imaging
An apparatus for obtaining images of a tooth comprises at least one image sensor disposed along an optical axis to take polarized reflectance image and fluorescence image, at least one broadband illumination apparatus for reflectance imaging, and a narrow-band ultraviolet illumination apparatus for fluorescence imaging. In order to remove the specular reflection, one or more polarization elements are disposed along the optical axis. A filter is disposed along the optical axis to block narrow-band ultraviolet light, and a switch for selecting one of the operation modes.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Serial-line-scan-encoded multi-color fluorescence microscopy and imaging flow cytometry
InactiveUS20100238442A1Improved signal-to-noise ratioRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryHigh resolution imagingSerial line
A system for performing high-speed, high-resolution imaging cytometry utilizes a line-scan sensor. A cell to be characterized is transported past a scan region. An optical system focuses an image of a portion of the scan region onto at least one linear light sensor, and repeated readings of light falling on the sensor are taken while a cell is transported though the scan region. The system may image cells directly, or may excite fluorescence in the cells and image the resulting light emitted from the cell by fluorescence. The system may provide a narrow band of illumination at the scan region. The system may include various filters and imaging optics that enable simultaneous multicolor fluorescence imaging cytometry. Multiple linear sensors may be provided, and images gathered by the individual sensors may be combined to construct an image having improved signal-to-noise characteristics.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
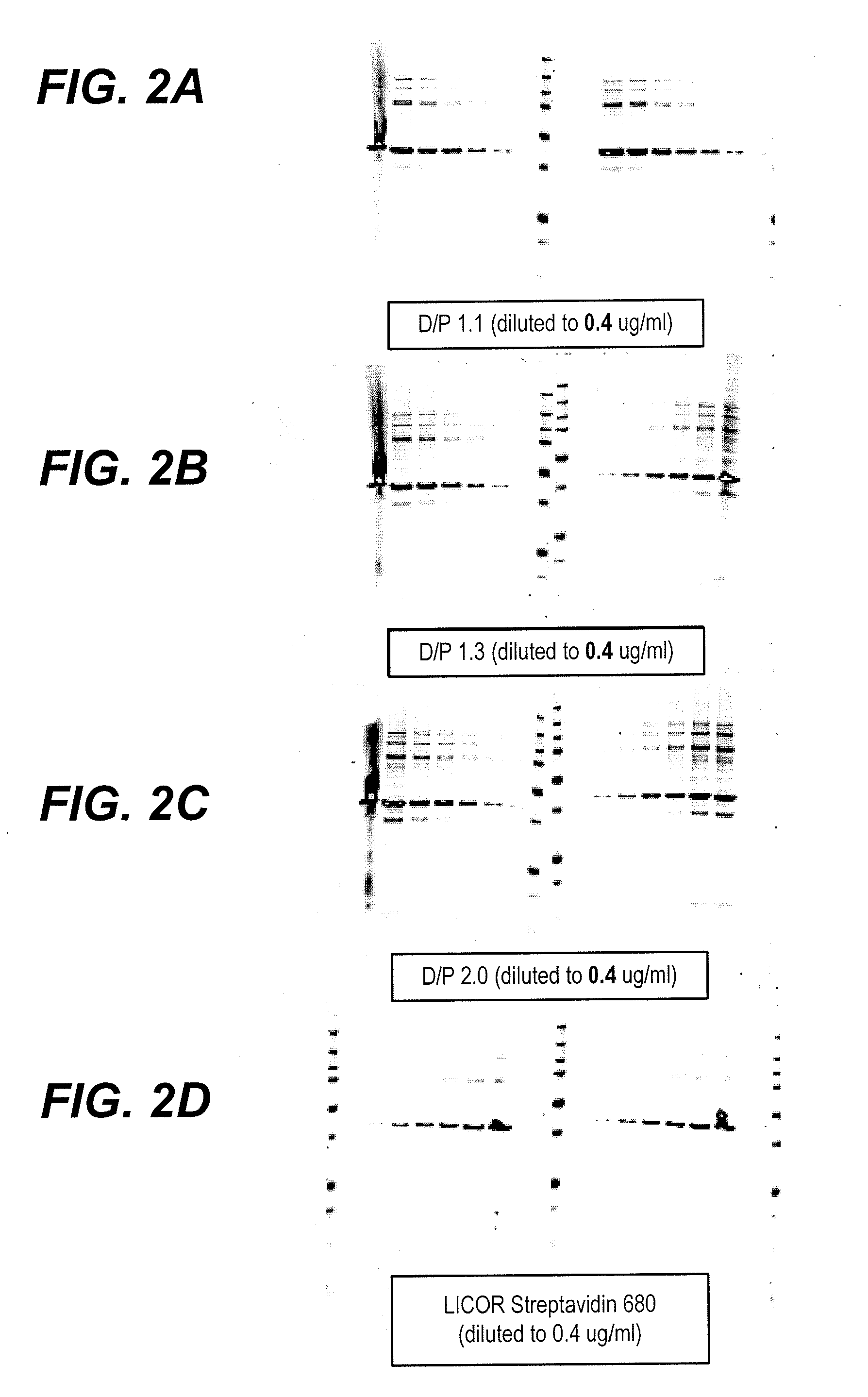
Fluorescent imaging with substituted cyanine dyes
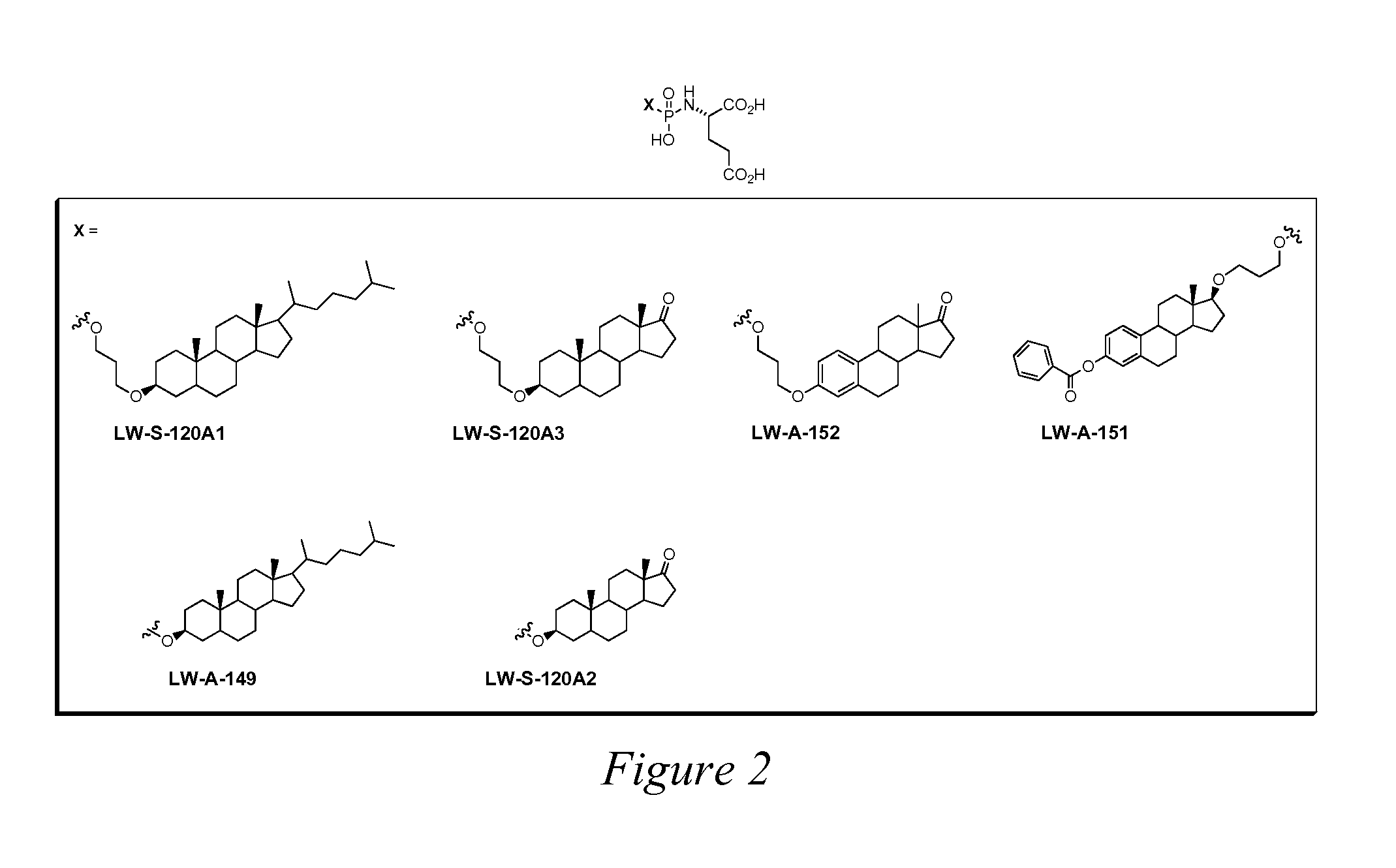
Compounds and methods are disclosed that are useful for noninvasive imaging in the near-infrared spectral range. The cyanine compounds of Formula I are presented:wherein Q is a portion of a polymethine bridge selected from the group consisting of:Also included are bioconjugates of the compounds of Formula I, methods of labeling biomolecules with the compounds, and methods of imaging.
Owner:LI COR
Cultured cell and method and apparatus for cell culture
InactiveUS20070161106A1Improve image qualityEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCultured cellFluorescent imaging
One or more cells can be cultured when confined in space by barriers. The distance between barriers can be comparable to the size of a cell to be cultured. The space between barriers can also be sufficiently small to allow control of cell properties or monitoring of the cell(s) cultured therein. The cell(s) may be confined completely or may be mobile between two opposing barrier surfaces. The gap between two opposing barriers may be sufficiently narrow to allow only a monolayer of cells to be cultured. A barrier can be transparent. The surfaces of the barriers may have one or more pre-selected characteristics that mimic the characteristics of a biological niche of the cells(s). The number of cells in a cell culture may be limited to permit control of properties of individual cells. The cultured cell(s) may be monitored, such as imaged, over a long period of time, using standard bright field or fluorescent imaging techniques.
Owner:WATERLOO UNIV OF
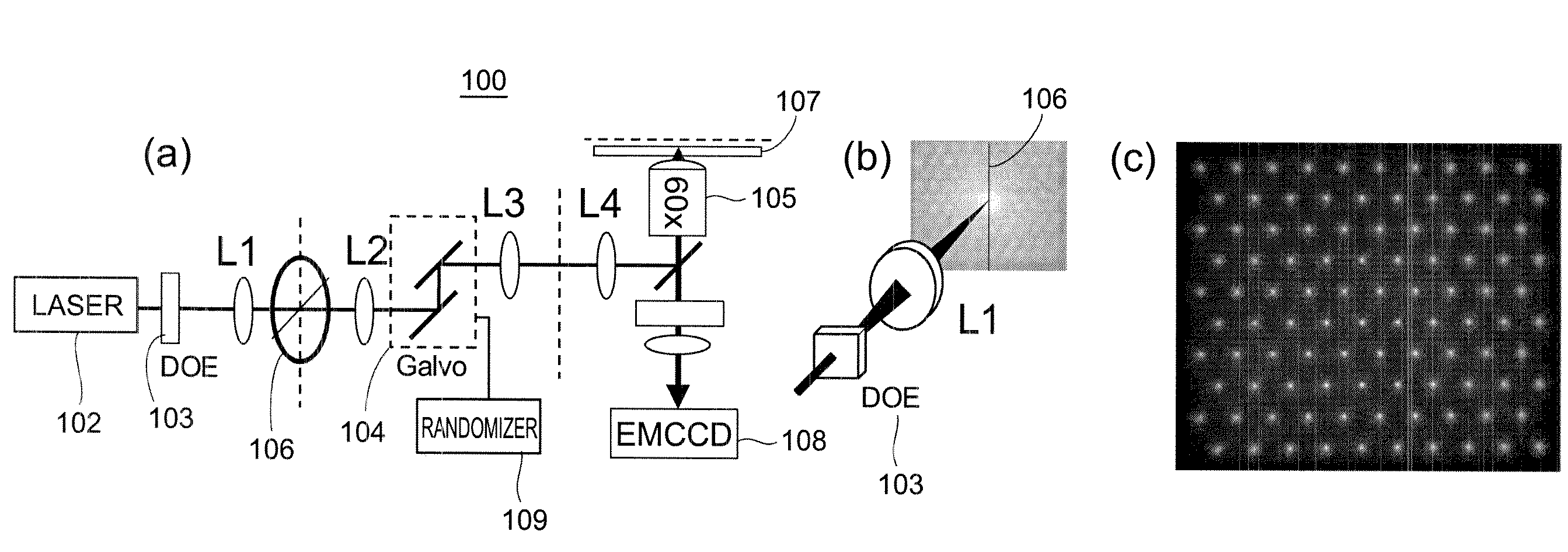
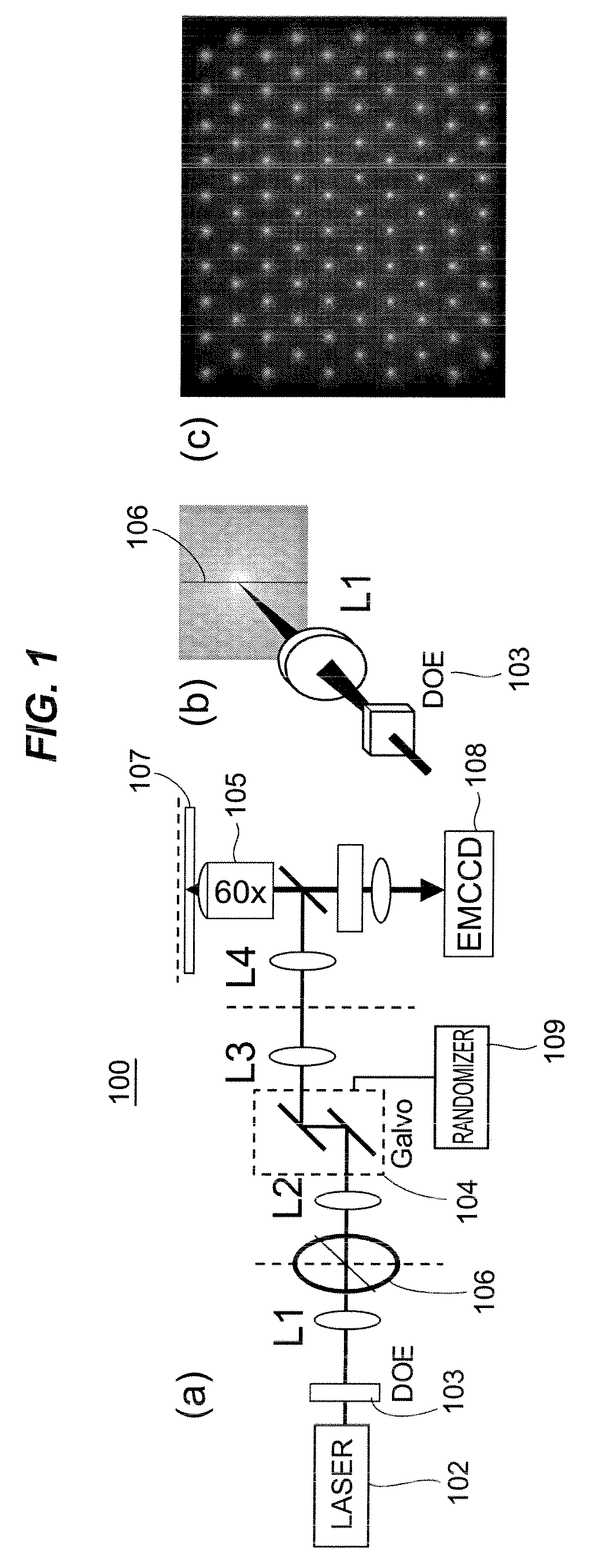
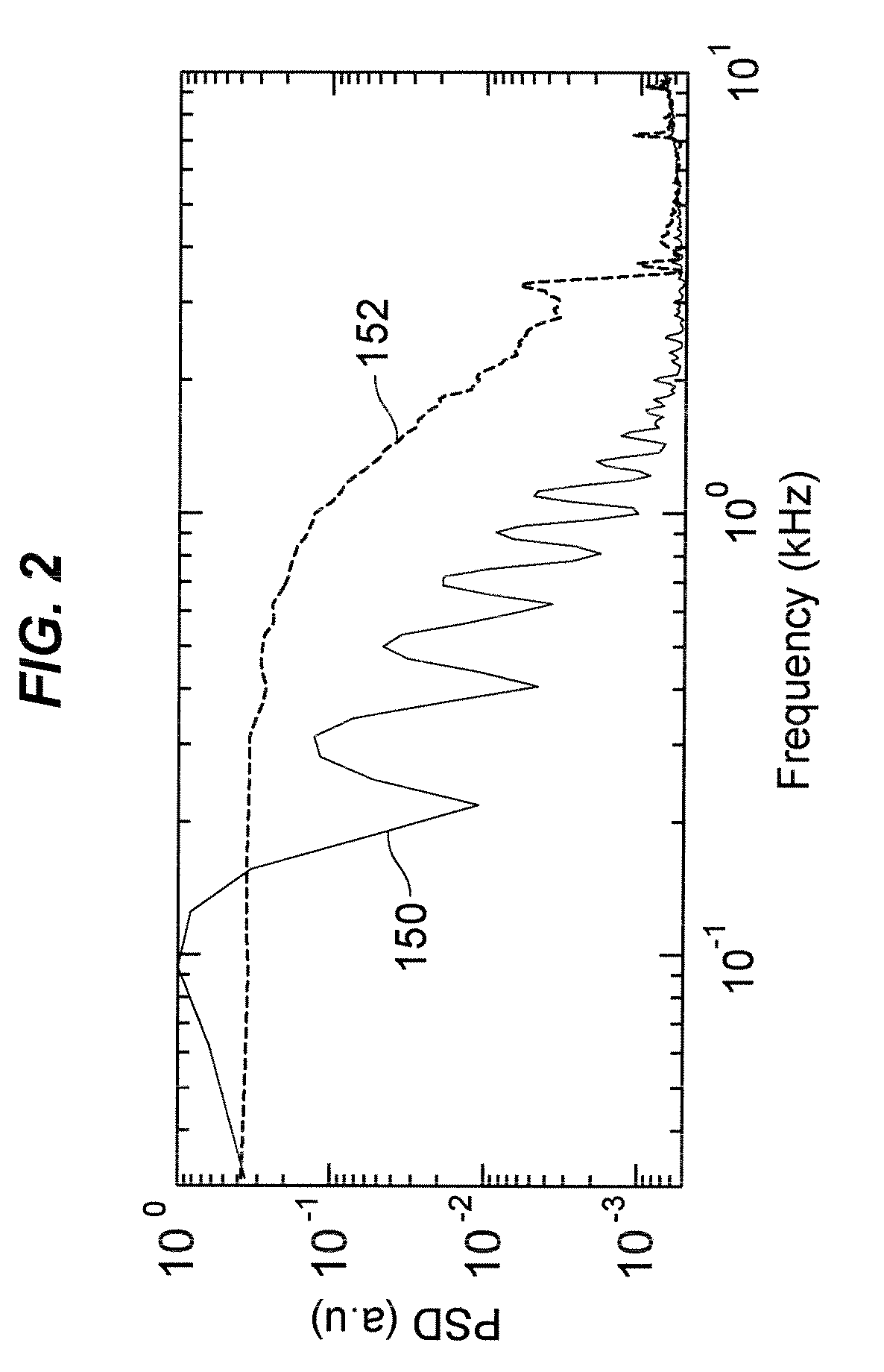
Stochastic Scanning Apparatus Using Multiphoton Multifocal Source
A rapid-sampling stochastic scanning multiphoton multifocal microscopy (SS-MMM) fluorescence imaging technique enables multiparticle tracking at rates upwards of 1,000 times greater than conventional single point raster scanning. Stochastic scanning of a diffractive optical element may generate a 10×10 hexagonal array of foci with a white noise driven galvanometer to yield a scan pattern that is random yet space-filling. SS-MMM may create a more uniformly sampled image with fewer spatio-temporal artifacts than obtained by conventional or multibeam raster scanning.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Retinal cellscope apparatus
A handheld, ocular imaging device and system that employs the camera, processor and programming of a mobile phone, tablet or other smart device coupled to optical elements and illumination elements that can be used to image the structures of the eye in home-based, ambulatory-care, hospital-based, or emergency-care settings, is presented. The modular device provides multi-functionality (fluorescein imaging, fluorescence, brightfield, infrared (IR) imaging, near-infrared (NIR) imaging) and multi-region imaging (retinal, corneal, external, etc.) of the eye along with the added features of image processing, storage and wireless data transmission for remote storage and evaluation. Acquired ocular images can also be transmitted directly from the device to the electronic medical records of a patient without the need for an intermediate computer system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
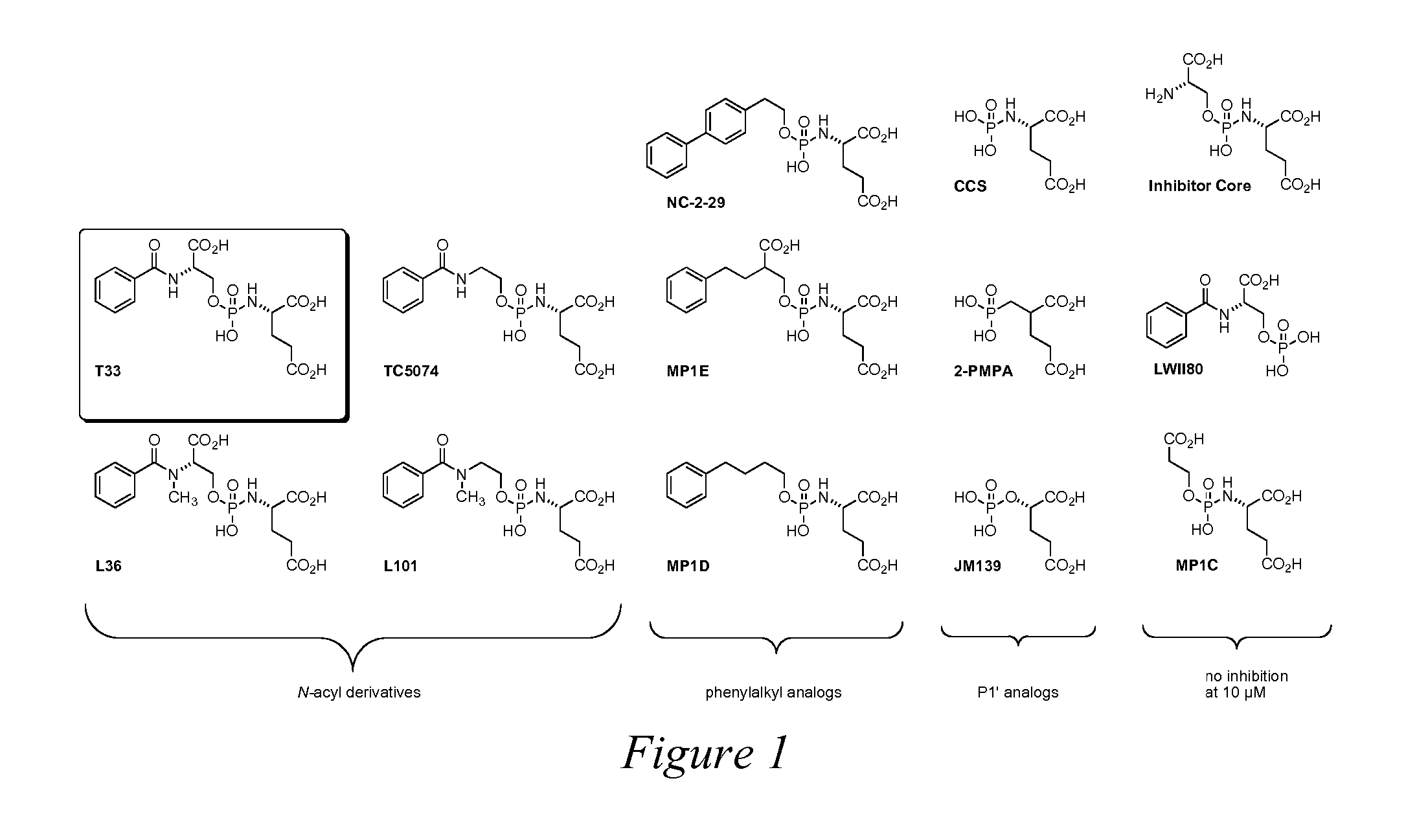
Peptidomimetic inhibitors of PSMA, compounds comprising them, and methods of use
ActiveUS7696185B2More cost-effectivelyBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsAntigenProstate cancer cell
Compounds of the formula, A—L—B, wherein A is glutamate or a glutamate analog; L is a phosphoramidate or a phosphoramidate analog; and B is serine or a serine analog are described which are potent inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PMSA). Such compounds are useful in treatment of prostate cancer; and when chemically attached to a fluorescent dye, can efficiently and selectively label prostate cancer cells for fluorescent imaging.
Owner:CANCER TARGETED TECH
System and Method for Multi-Color Laser Imaging and Ablation of Cancer Cells Using Fluorescence
ActiveUS20140187967A1Reduce deficiencyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionSurgical instrument detailsCancer cellWound care
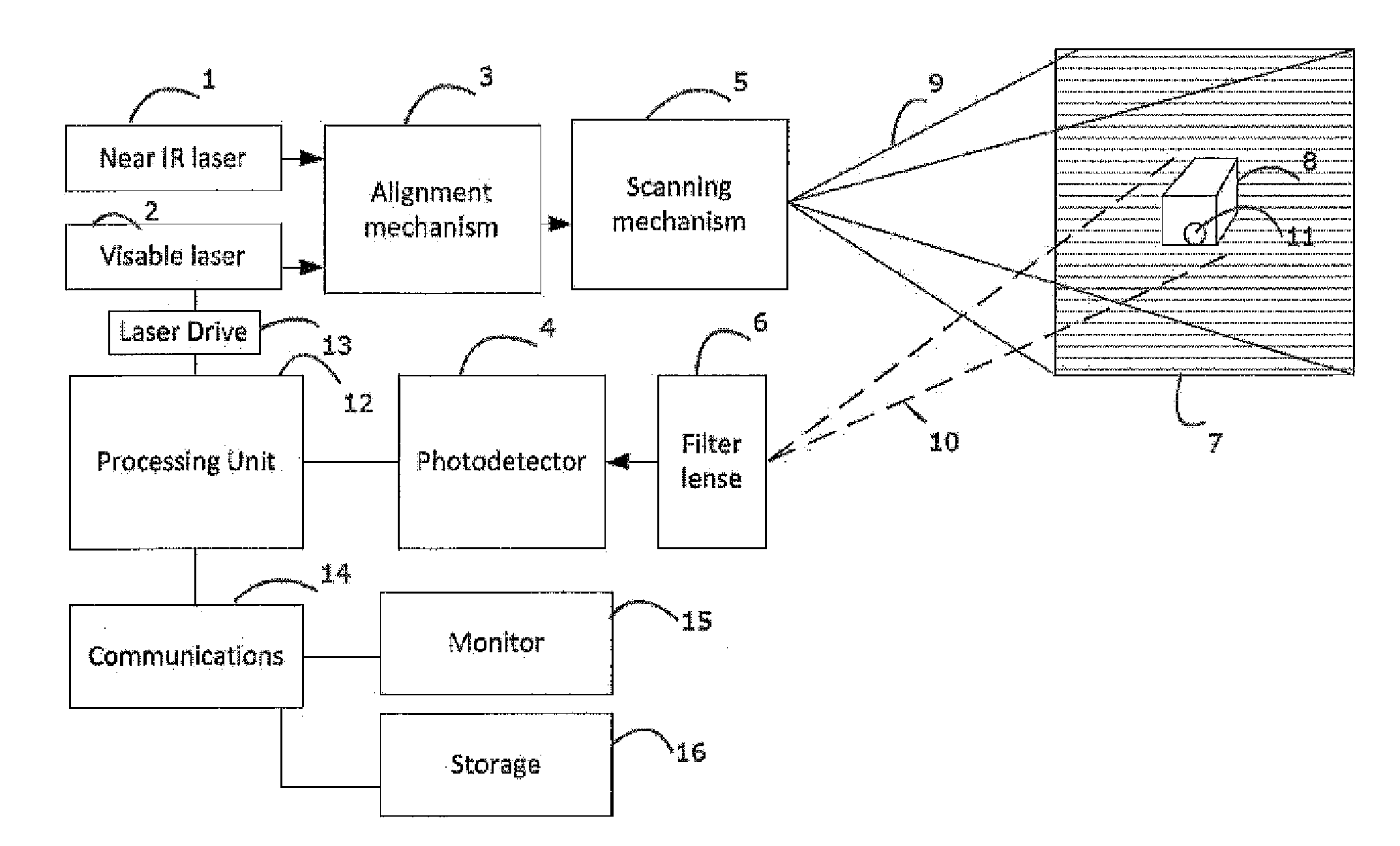
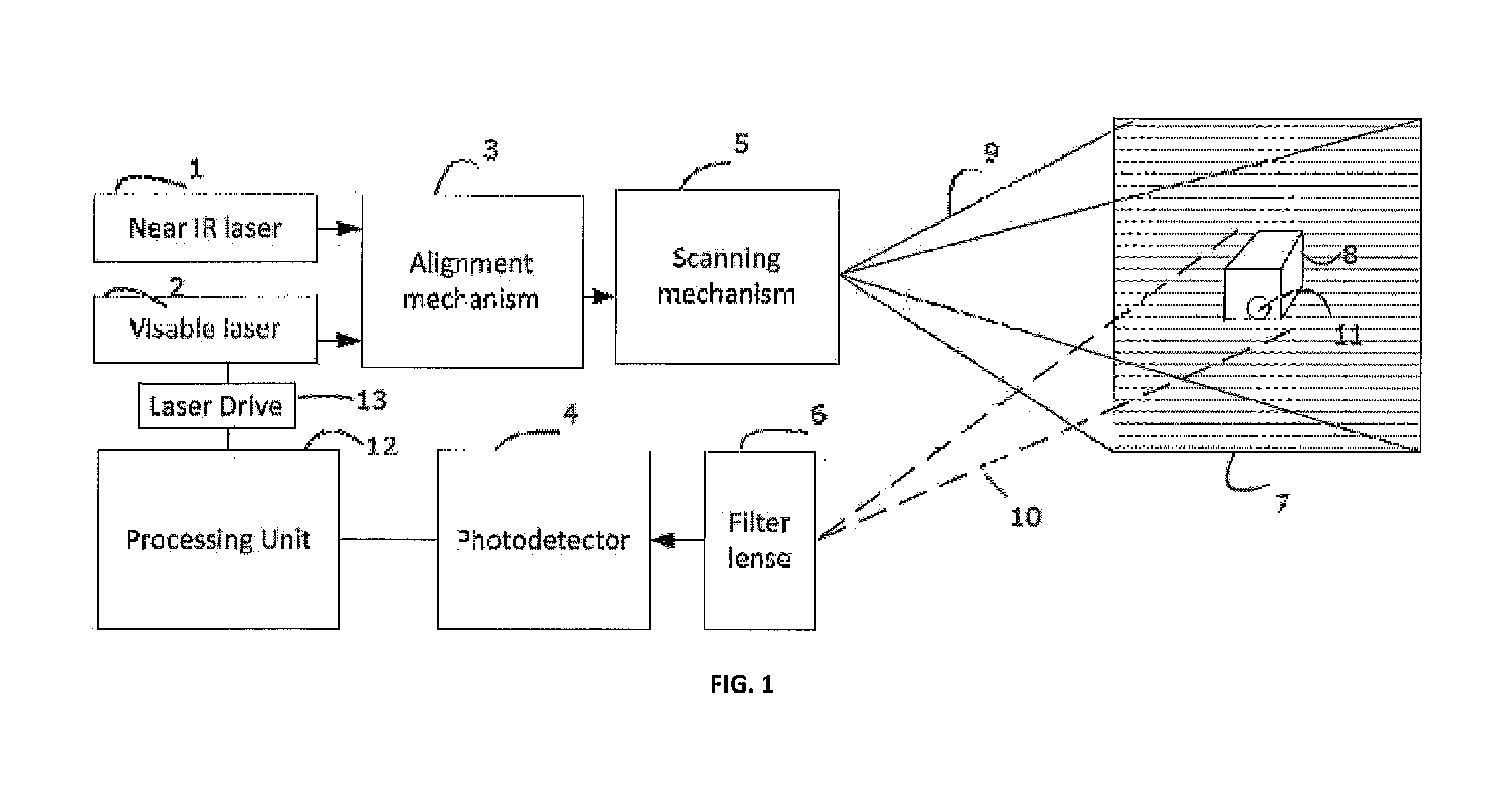
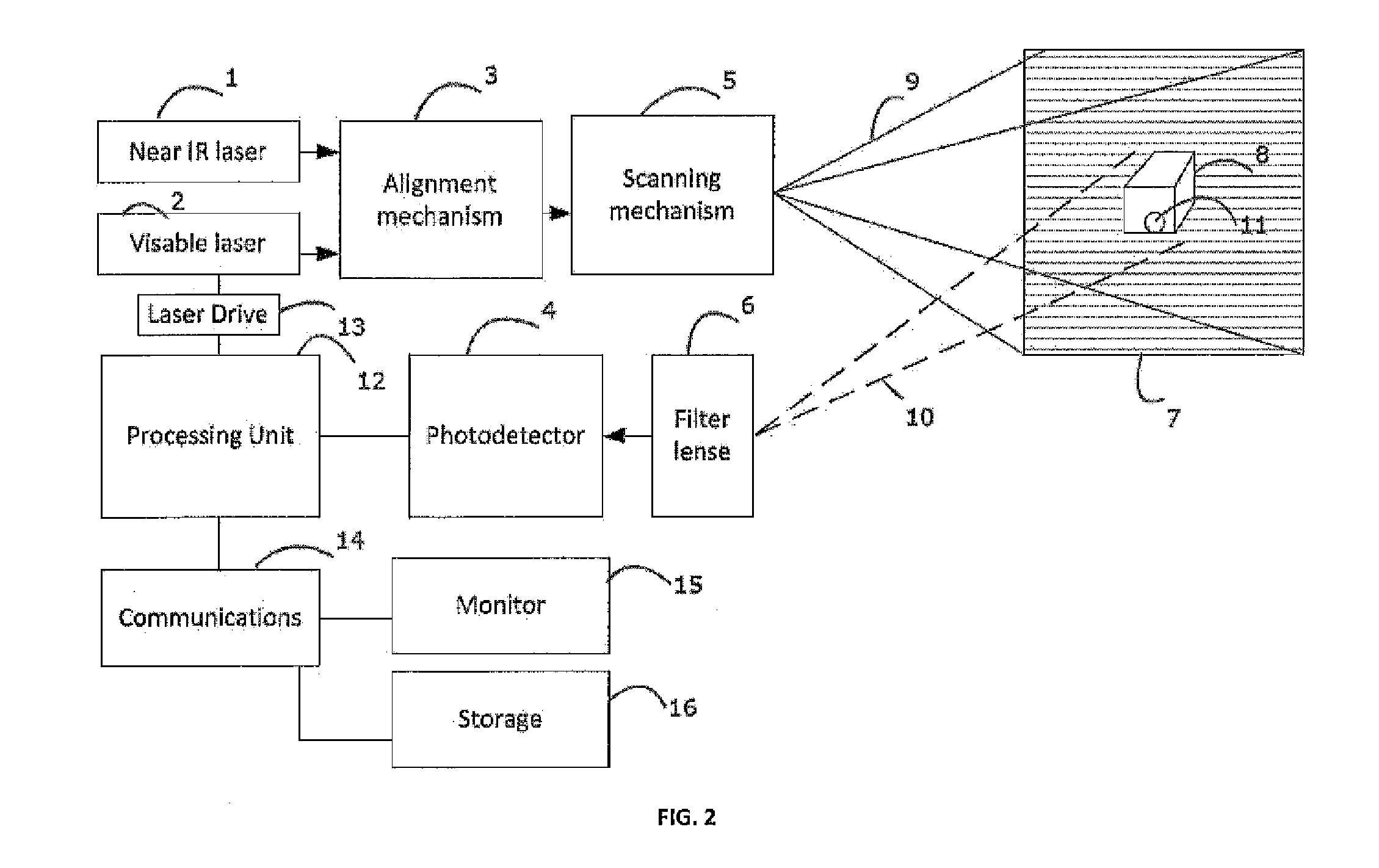
A fluorescence imaging device detects fluorescence in parts of the visible and invisible spectrum, and projects the fluorescence image directly on the human body, as well as on a monitor, with improved sensitivity, video frame rate and depth of focus, and enhanced capabilities of detecting distribution and properties of multiple fluorophores. Direct projection of three-dimensional visible representations of florescence on three-dimensional body areas advantageously permits view of it during surgical procedures, including during cancer removal, reconstructive surgery and wound care, etc. A NIR laser and a human visible laser (HVL) are aligned coaxially and scanned over the operating field of view. When the NIR laser passes over the area where the florescent dye is present, it energizes the dye which emits at a shifted NIR frequency detected by a photo diode. The HVL is turned on when emission is detected, providing visual indication of those positions.
Owner:ACCUVEIN
Cultured cell and method and apparatus for cell culture
InactiveUS7919319B2Facilitate direct observation of cell growthImprove image qualityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCultured cellFluorescent imaging
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
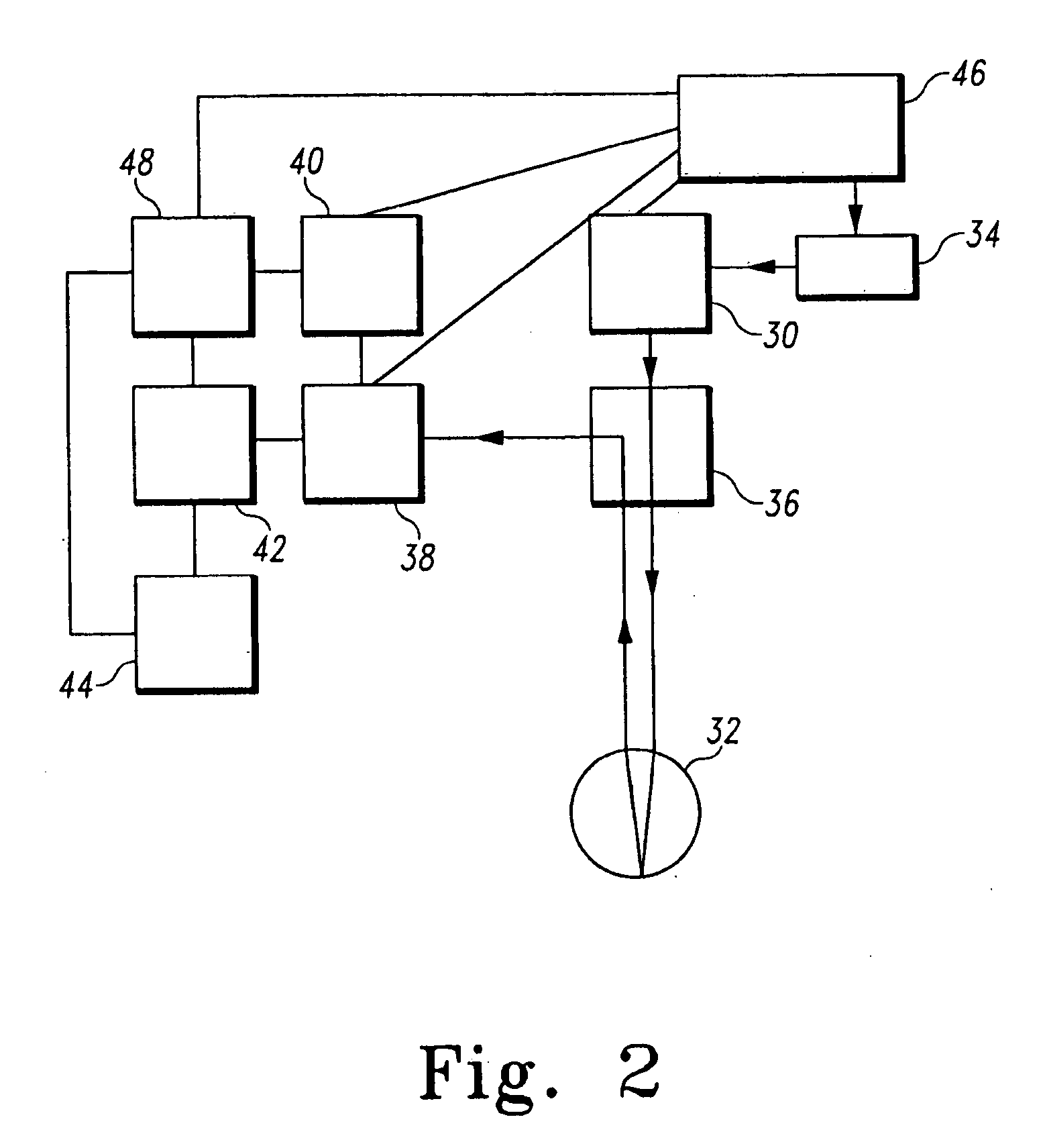
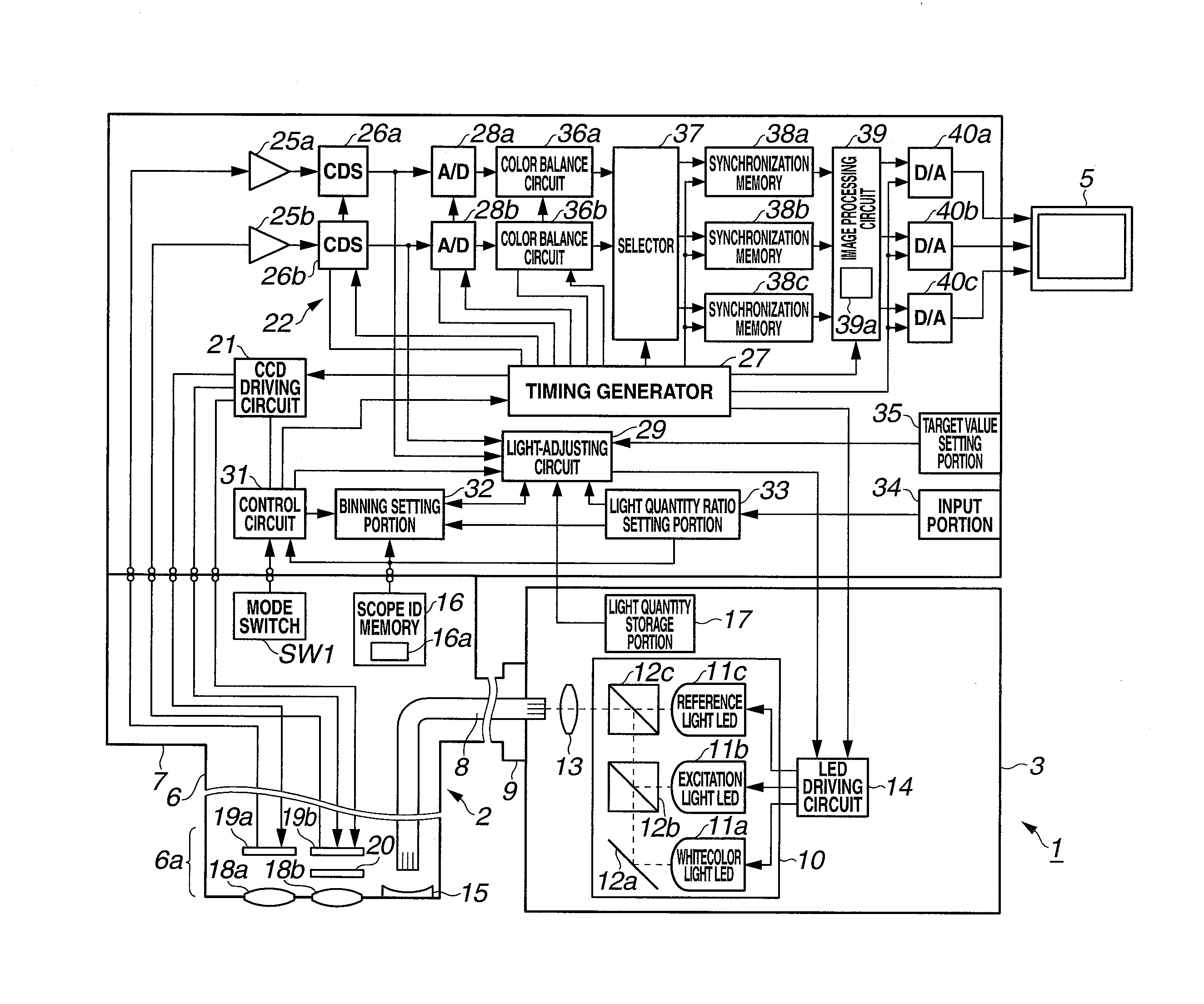
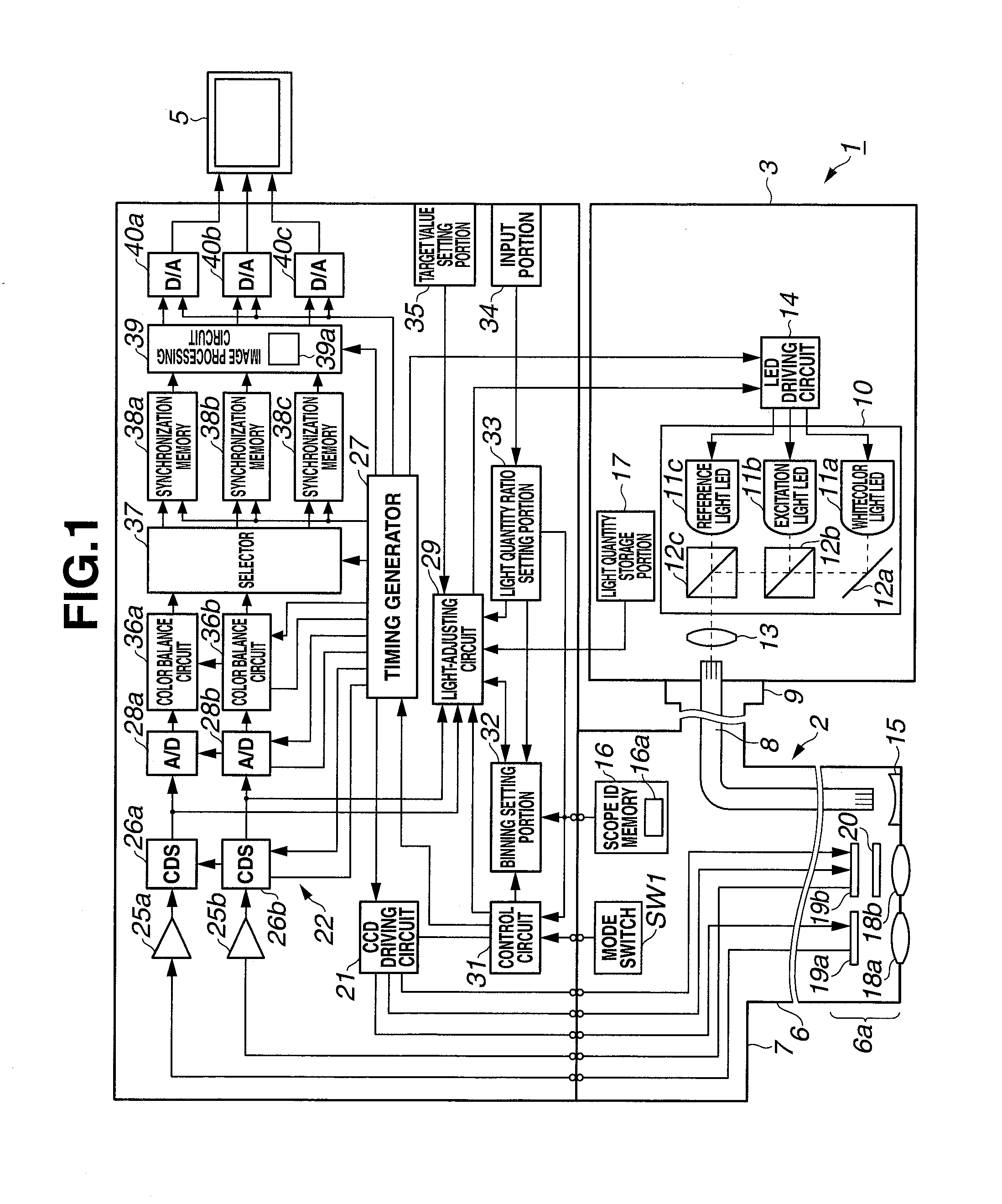
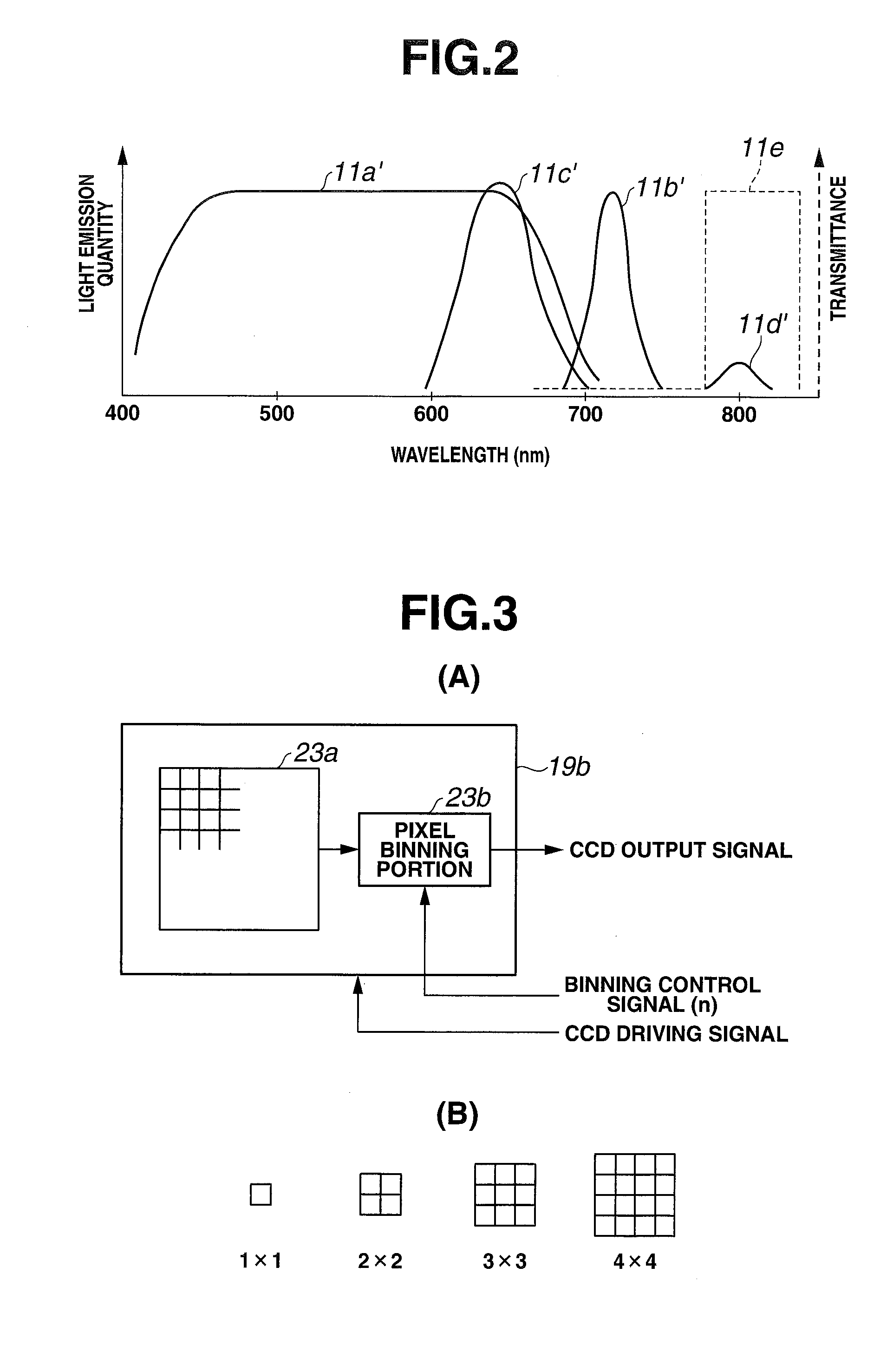
Endoscope apparatus and method for controlling fluorescence imaging apparatus
An endoscope apparatus includes: a light source portion that irradiates an excitation light and a reference light alternately; an image pickup portion that picks up images of the fluorescence from the living tissue and the reflected light; a signal processing portion that generates image signals from picked up signals; an addition processing portion that generates, from image signals of fluorescence, addition processed signals of fluorescence in which pixels are added; a light quantity control portion that controls the quantity of light so as to maintain a predetermined light quantity ratio between the quantities of the excitation light and the reference light from the addition processed signals of fluorescence and image signals of the reflected light; and a superimposition processing portion that superimposes the addition processed signals and the image signals of the reflected light, with the predetermined light quantity ratio being maintained.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
One-dimensional biological chip and application in gene, protein expression analysis
Disclosed is an one-dimensional biochip belonging to a serial analytic technique for micro-total analysis systems. The one-dimensional biochip is provided with a plurality of cellules on the micro-separation channel of micro flow control chip, microparticles modified by different biomolecules on surface are arranged in different cellules; in the gene or protein analysis, when the sample flows through the microchannel with a plurality of cellules, the microparticles can specifically identify and capture multiple target molecules, then a reagent with fluorescence labels can be introduced, and finally the microparticles will specifically combine with the fluorescence labels on surface to be detected by fluorescent imaging. The one-dimensional biochip provided by the invention not only has advantages of micro flow control technology and array analysis, but also improves the detection sensitivity and identification capability of target molecules, and provides an effective research measure for the gene and protein expression analysis at single cell level, and tumor research and drug screening.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Optical fluorescent imaging
InactiveUS20060280688A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMethine/polymethine dyesAbnormal tissue growthNoninvasive imaging
Compounds and methods are disclosed that are useful for noninvasive imaging in the near-infrared (NIR) spectral range. The NIR is highly sensitive for tumor detection and tracking. The application discloses targeting a tumor-enriched cell surface receptor with a ligand-conjugated fluorescent probe, which specifically allows detection of the tumor relative to the negligible animal autofluorescence.
Owner:LI COR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com