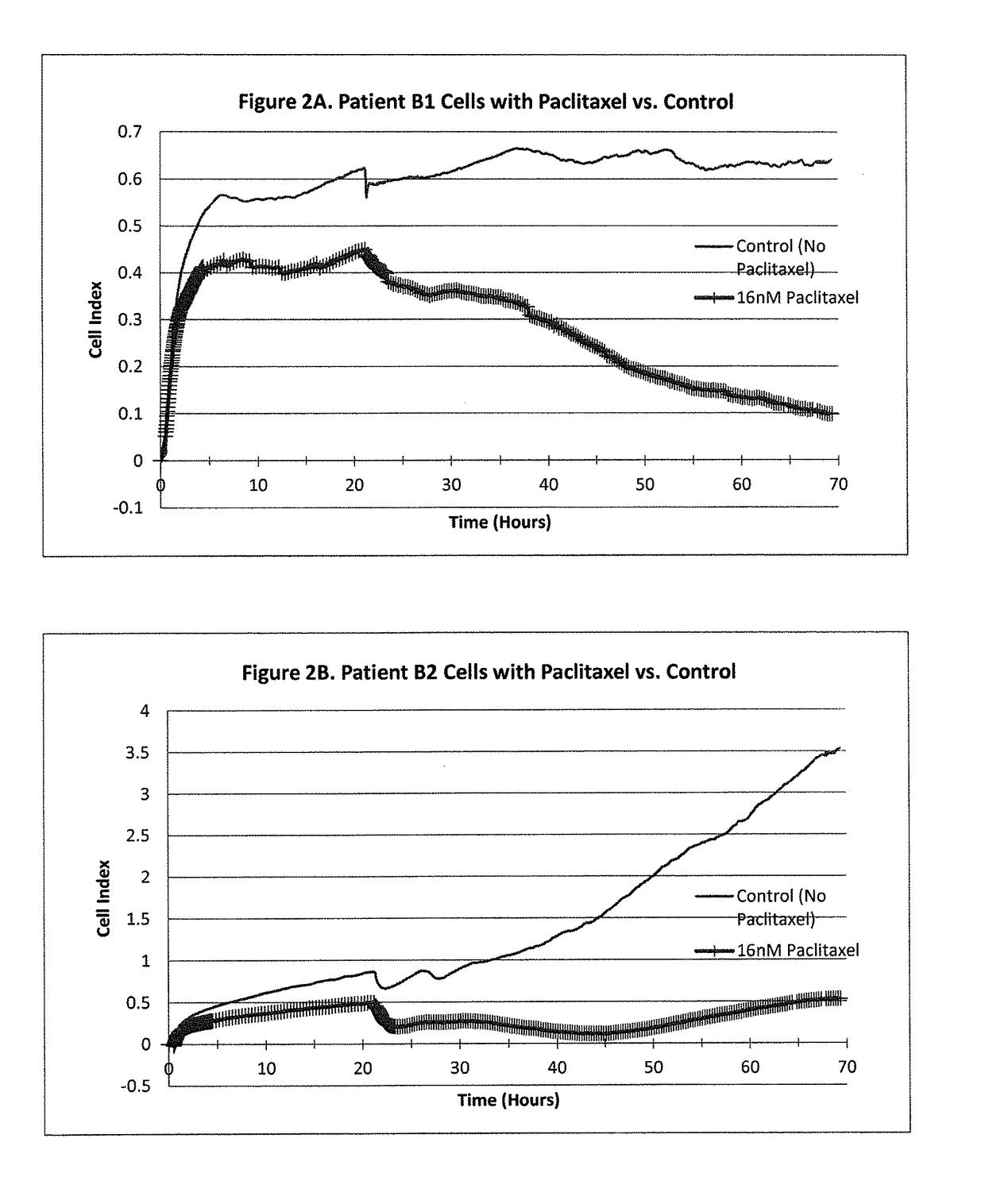
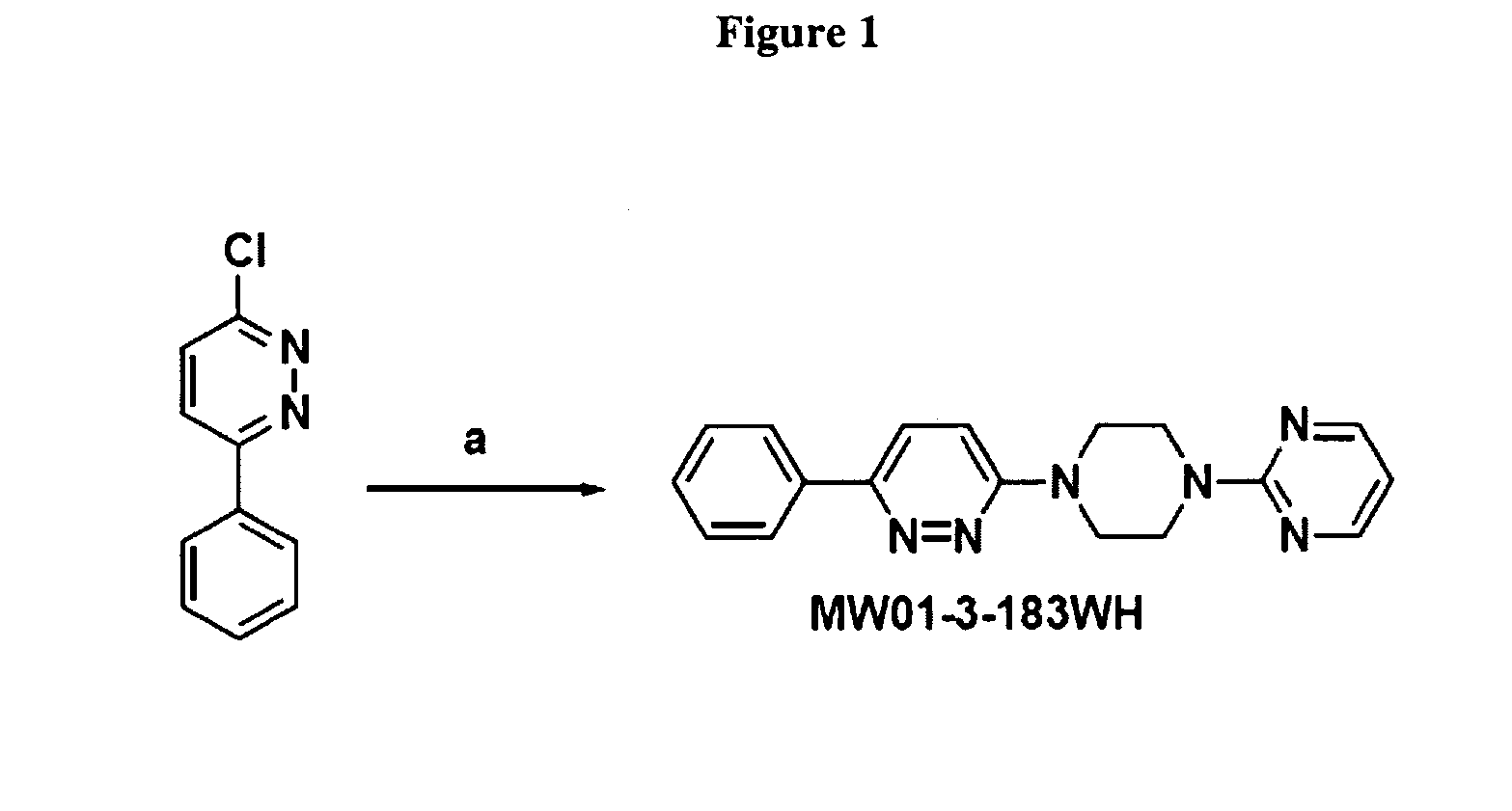
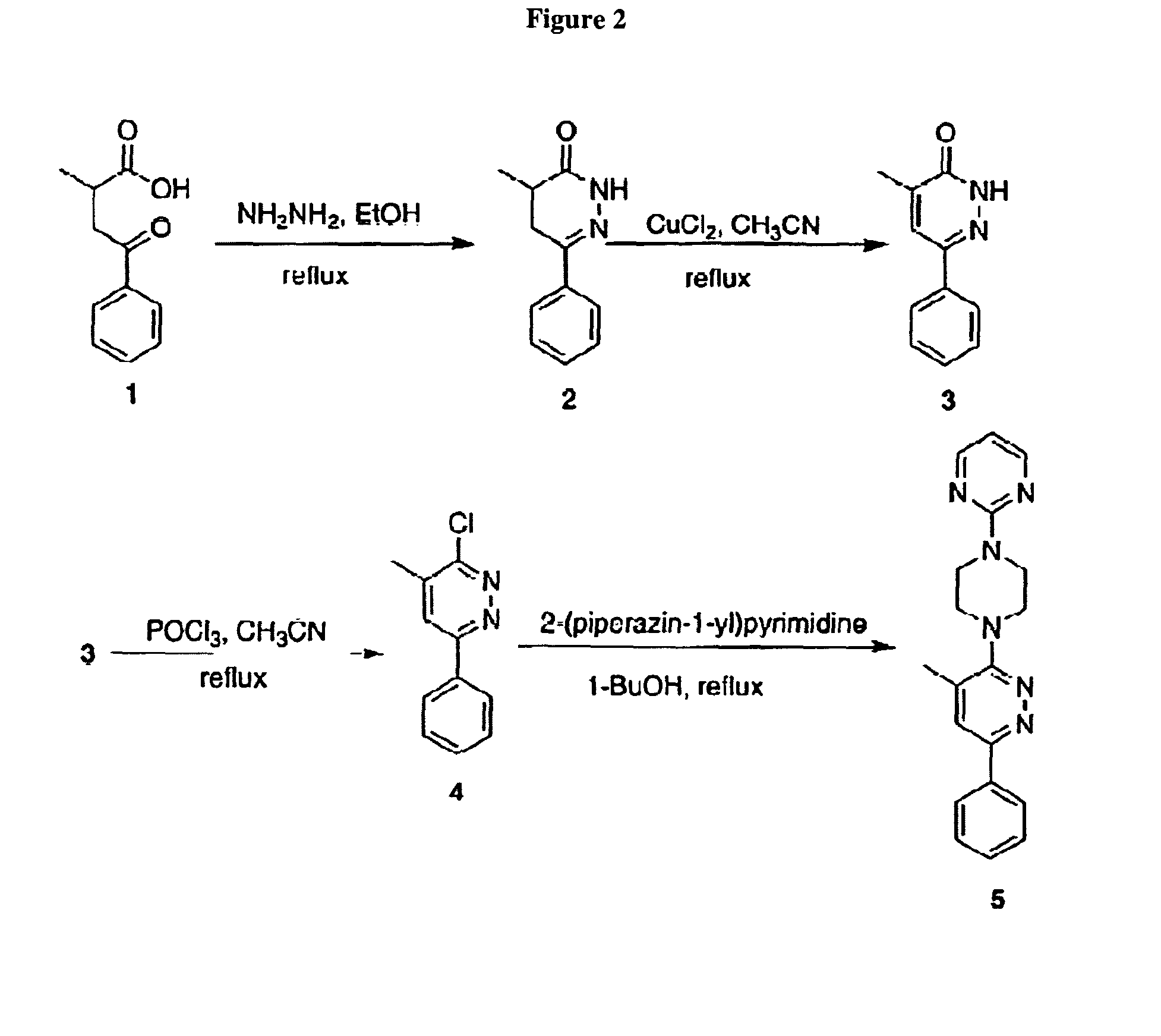
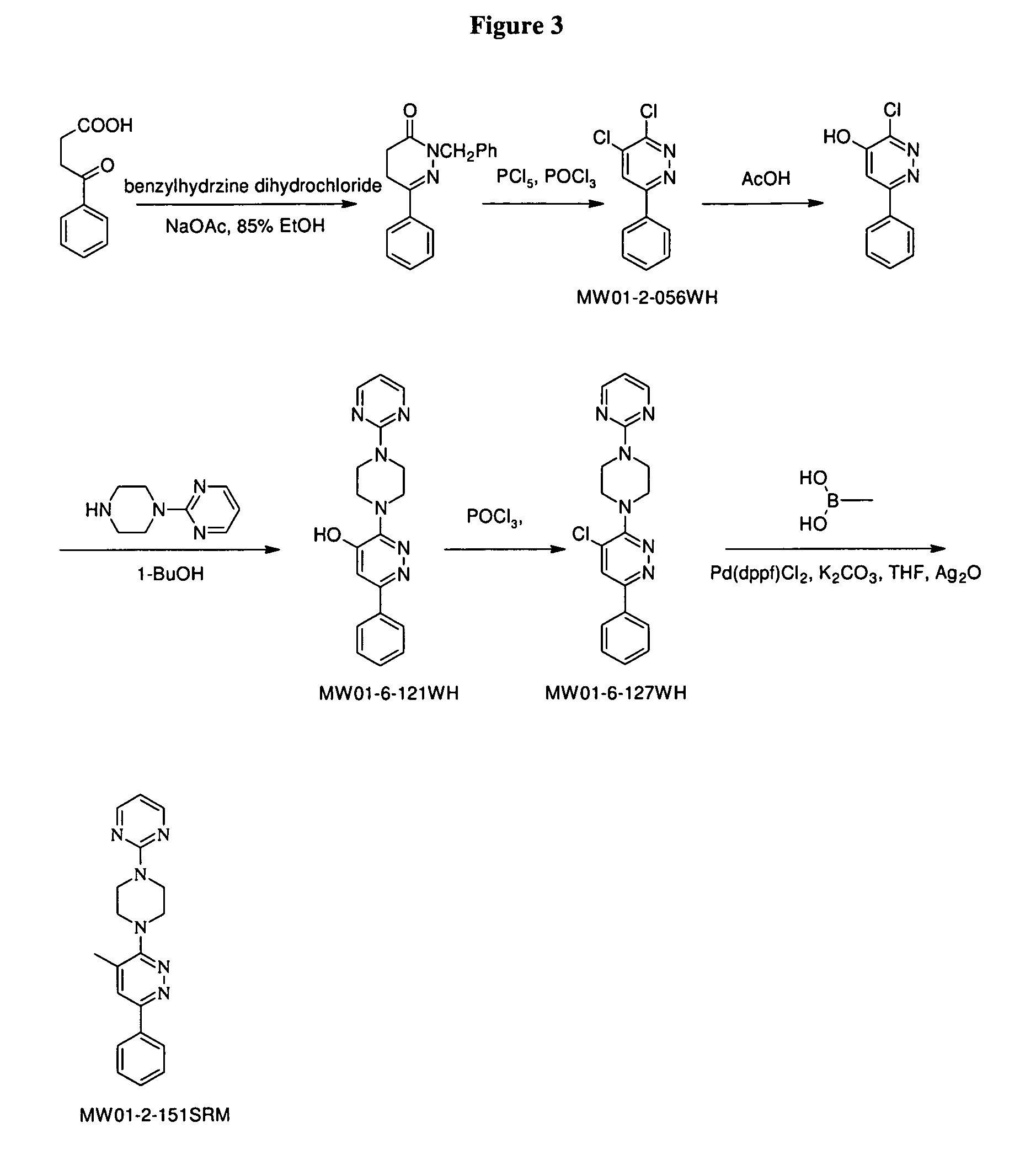
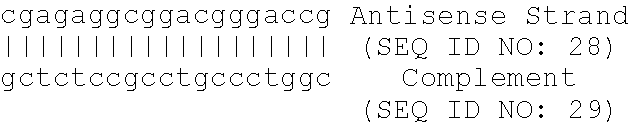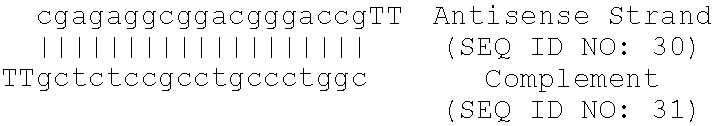Patents
Literature
62 results about "Cellular pathways" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
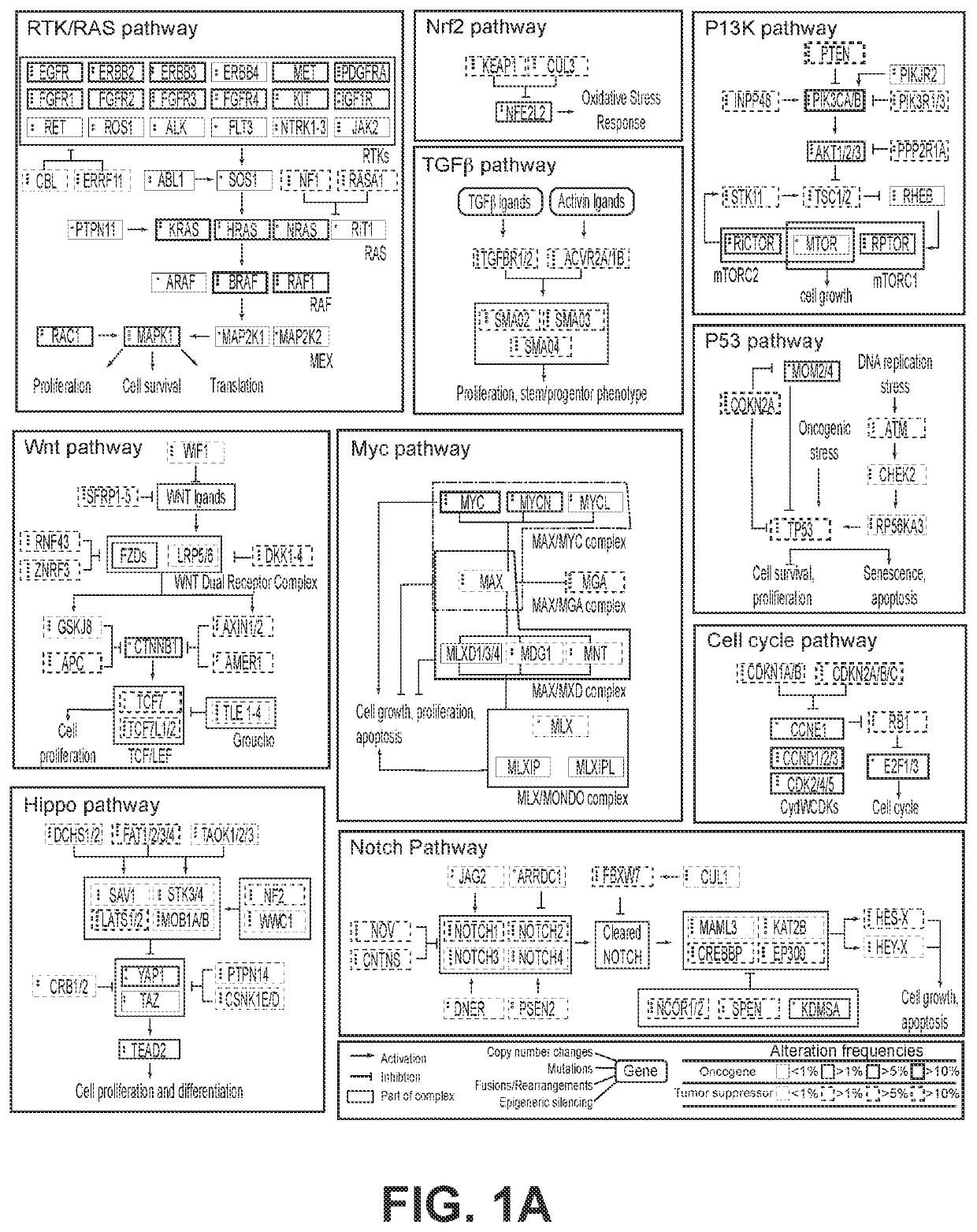
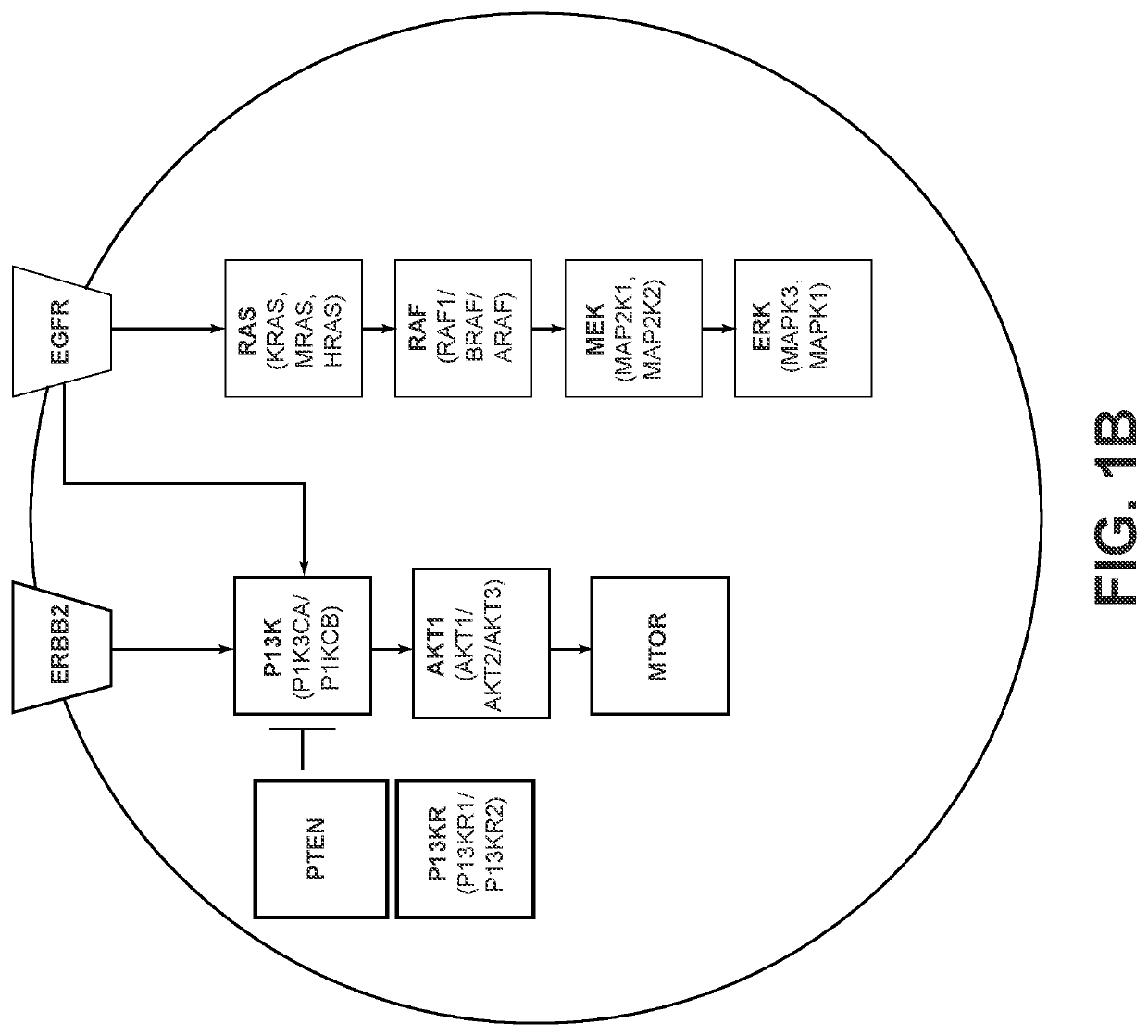
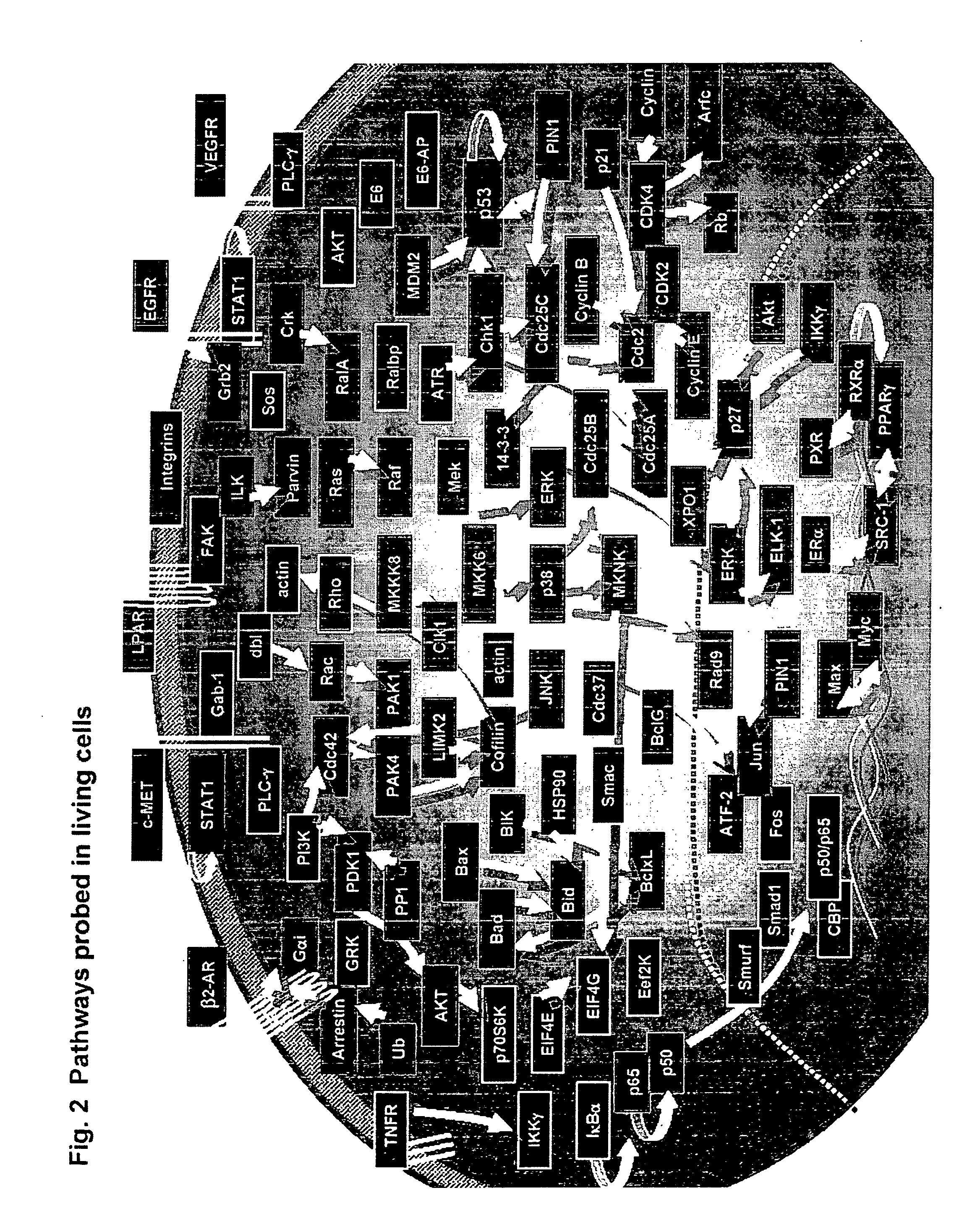
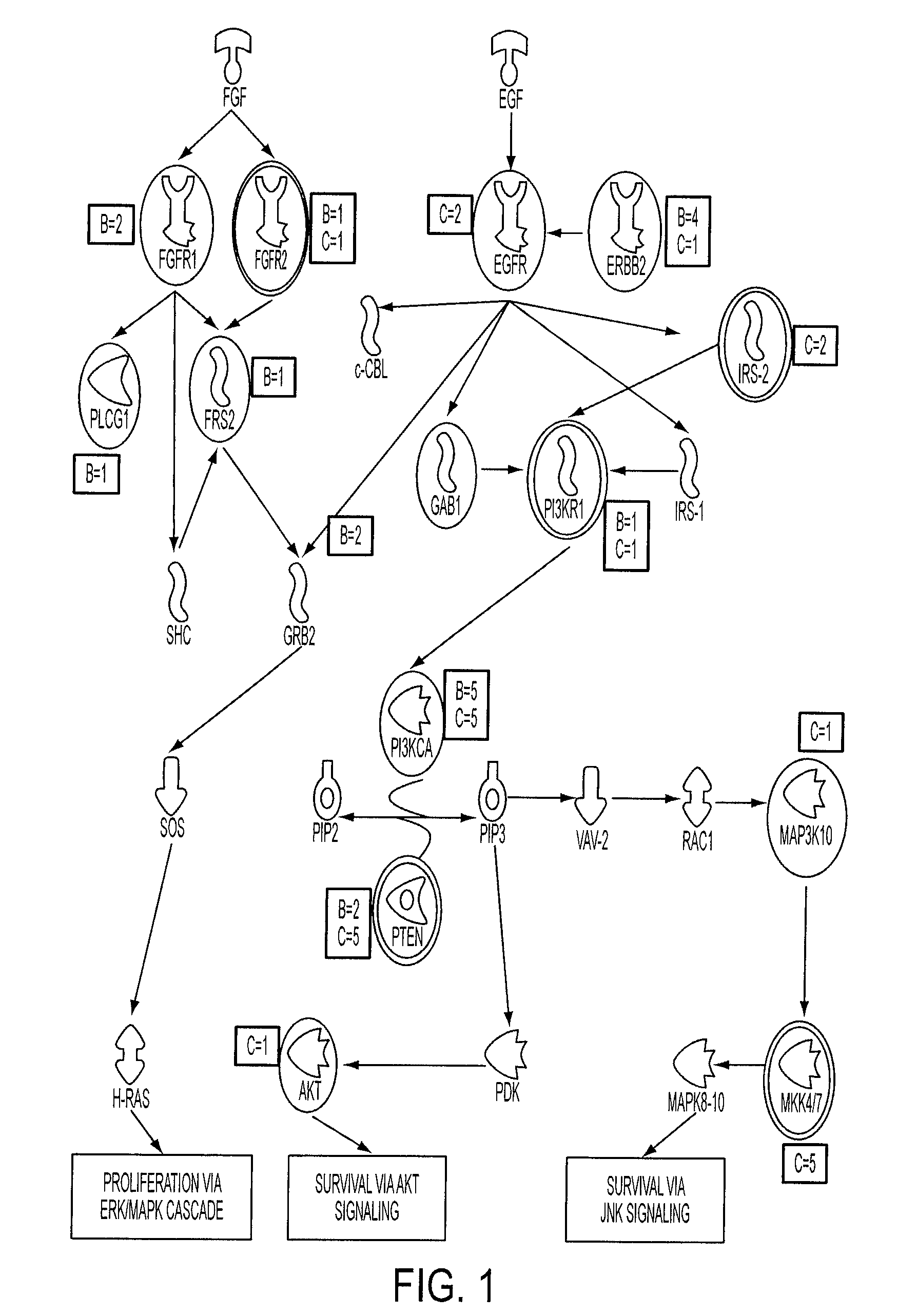
Cell signaling pathways can be generally categorized into groups based on area of biology. Here, you can explore all available pathways, including those that fall under a variety of areas of biology—from angiogenesis and apoptosis to bone biology, metabolism, transcription factors, and others. View pathways by area of biology.
Effects of apolipoprotein B inhibition on gene expression profiles in animals
InactiveUS20060009410A1Inhibition of secretionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCellular pathwaysSerum ige
Methods are provided for modulating the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism, useful in the treatment of conditions associated with cardiovascular risk. Antisense oligonucleotides targeted to apolipoprotein B reduce the level of apolipoprotein B mRNA, lower serum cholesterol and shift liver gene expression profiles from those of an obese animal towards those of a lean animal. Further provided are methods for improving the cardiovascular risk of a subject through antisense inhibition of apolipoprotein B. Also provided are methods for employing antisense oligonucleotides targeted to apolipoprotein B to modulate a cellular pathway or metabolic process.
Owner:KASTLE THERAPEUTICS LLC
Analysis of nodes in cellular pathways
InactiveUS20100215644A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular pathwaysCell Cycle Pathway
An embodiment of the present invention is a method for measuring activity of cell pathways, such as the cell cycle pathway and correlating the resulting profile to phenotypes. The resulting correlations are useful in diagnosis, prognosis, selection and development of drug treatment regimens, and drug screening applications.
Owner:NODALITY
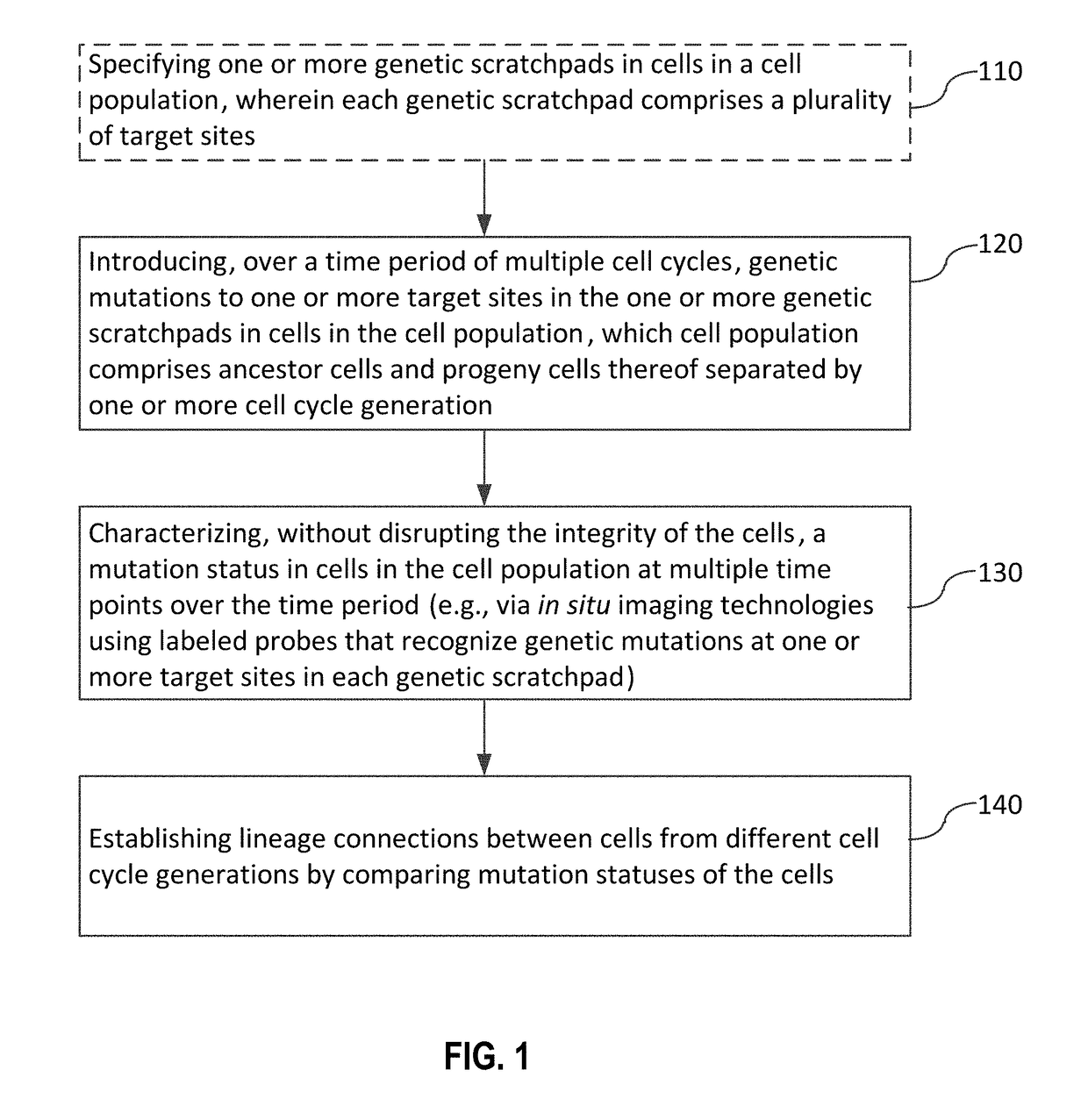
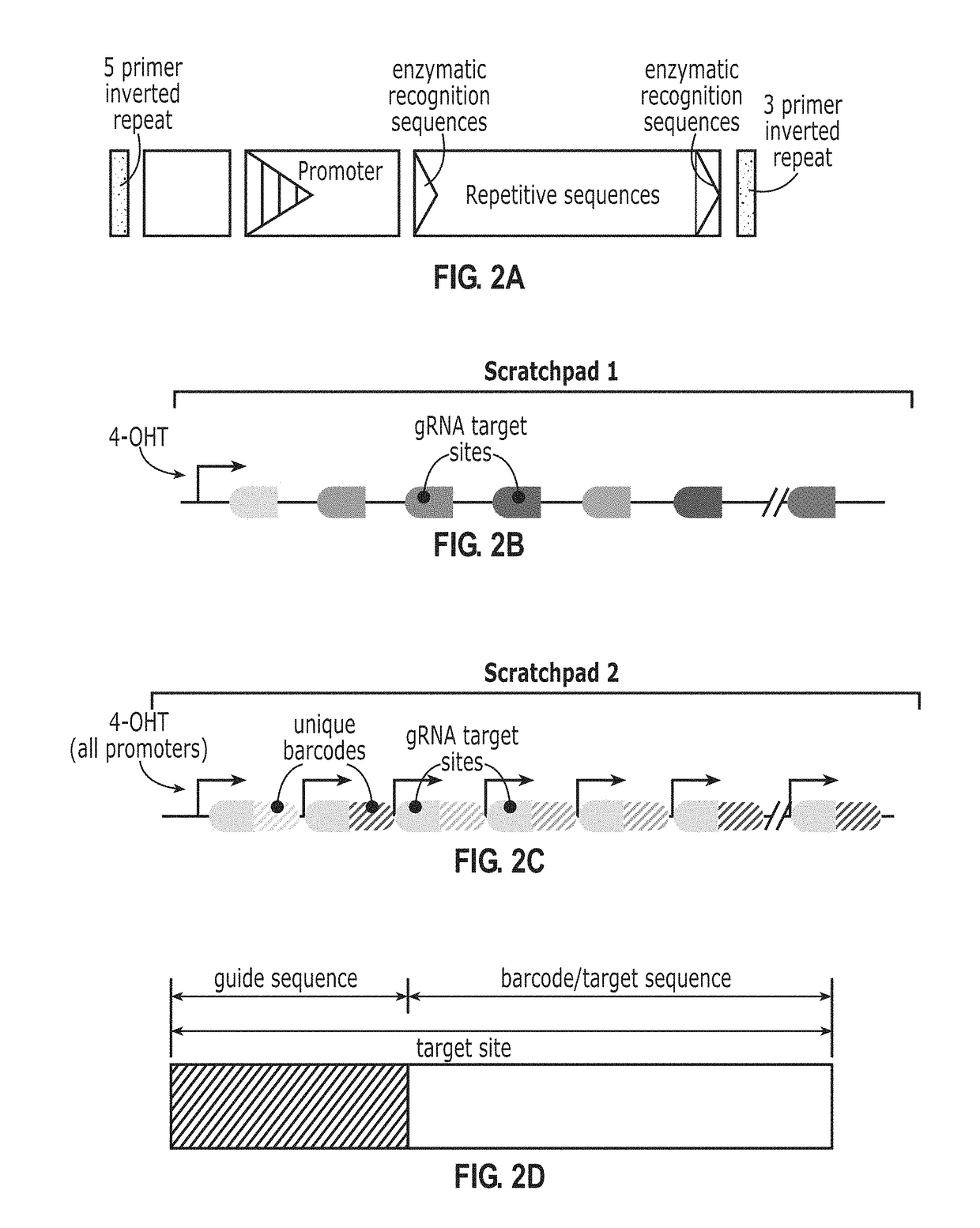
Recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells
InactiveUS20150225801A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular pathwaysFluorescent imaging
Methods and systems for recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells are provided. Molecular changes, which may result from random or specific molecular events, are introduced to defined regions in cells over multiple cell cycle generations. Techniques such as fluorescent imaging are applied to track and identify the molecular changes before such information is used for lineage analysis or for identifying key processes and key players in cellular pathways.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Gene expression profile biomarkers and therapeutic targets for brain aging and age-related cognitive impairment
InactiveUS20050071088A1Increase neuronal vulnerabilityImprove lipid metabolismMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAntigenDisease cause
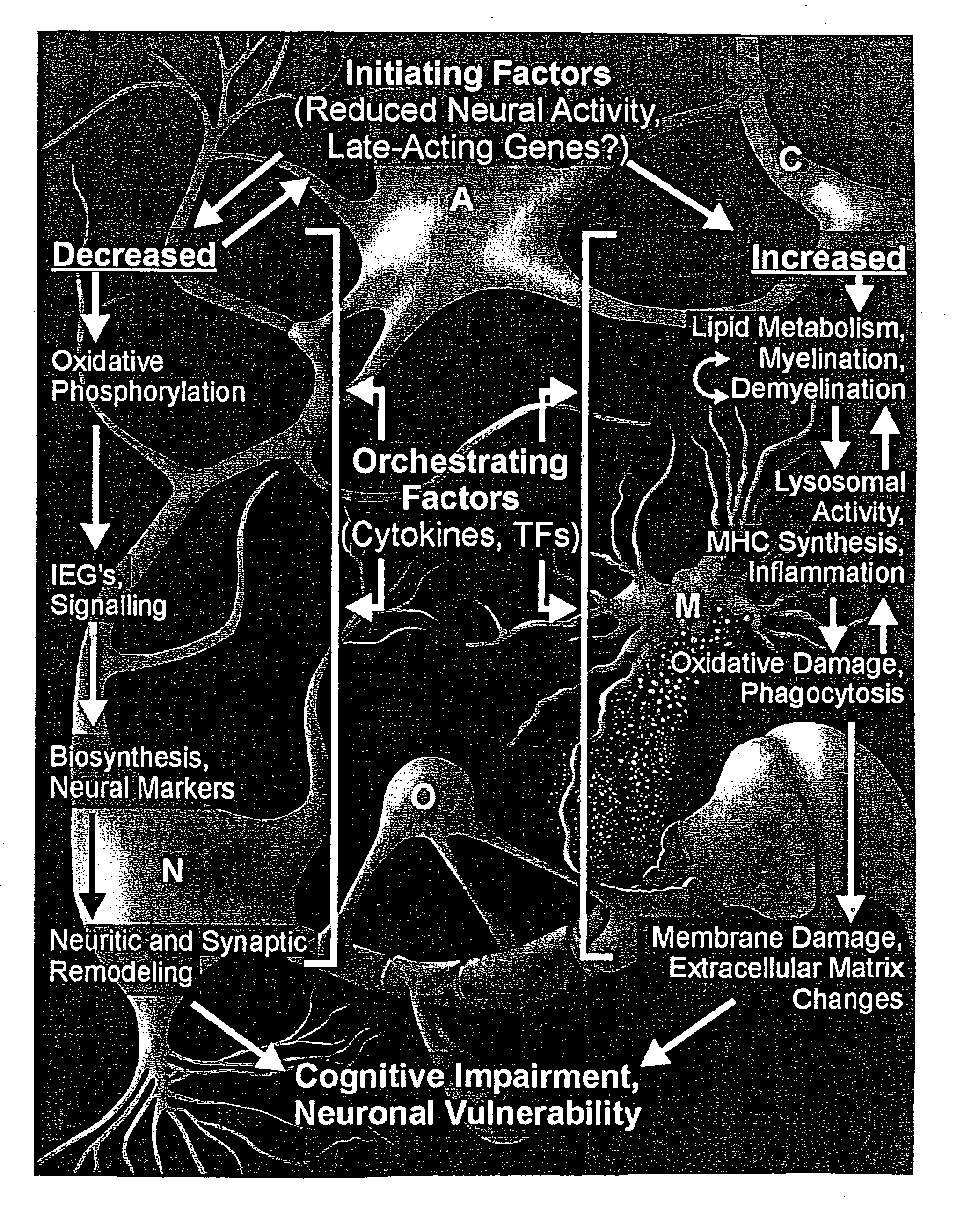
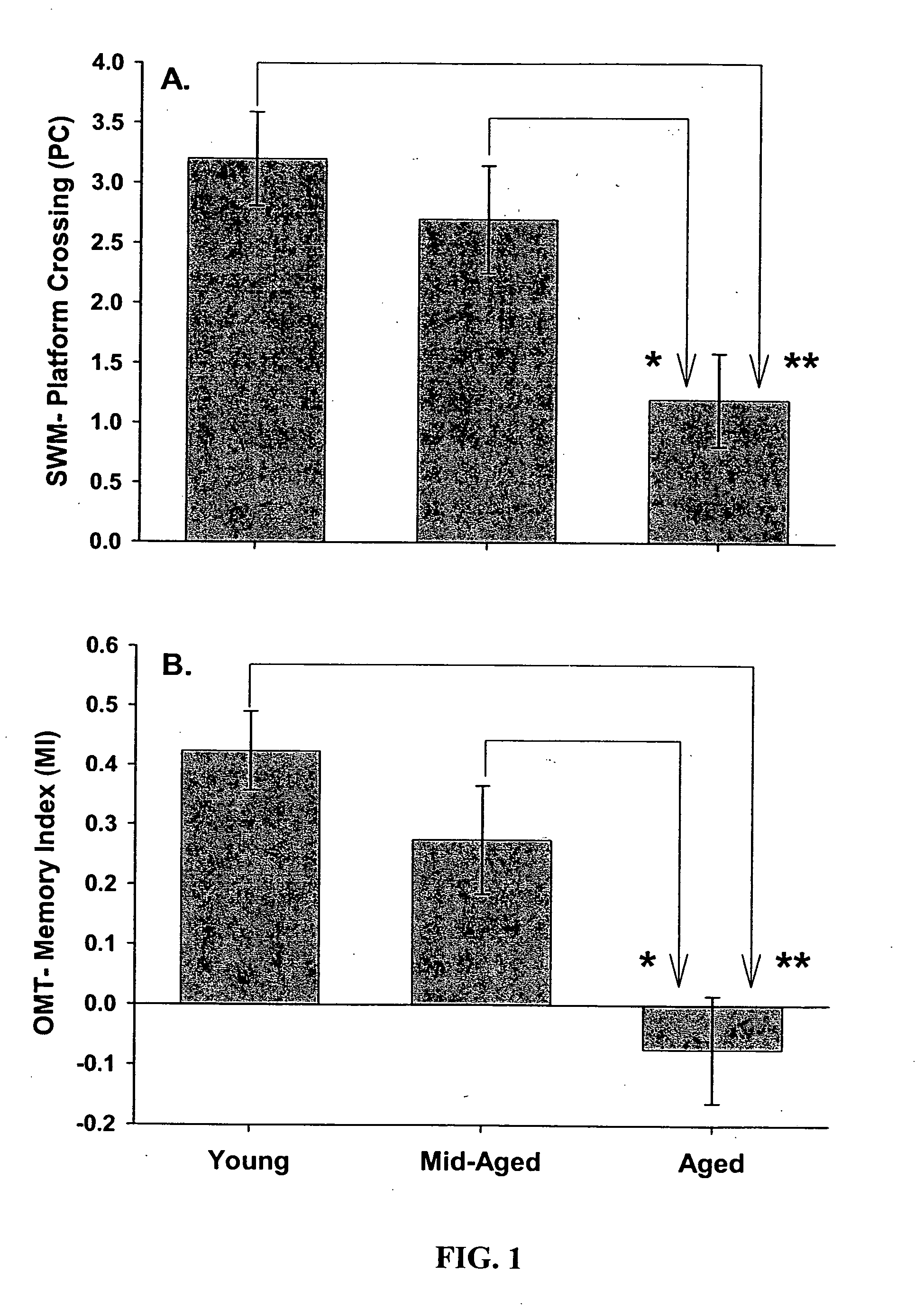
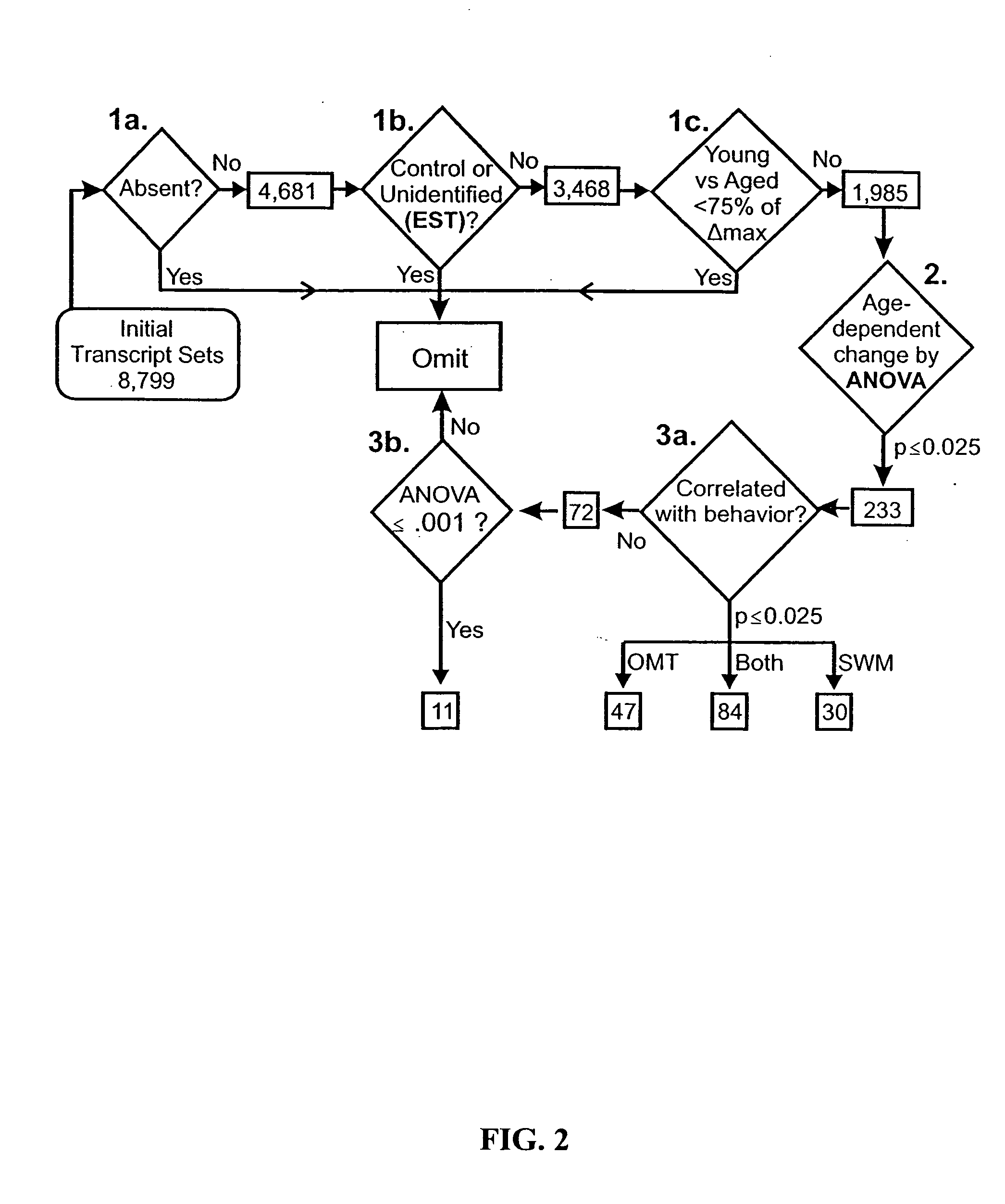
A statistical and functional correlation strategy to identify changes in cellular pathways specifically linked to impaired cognitive function with aging. Analyses using the strategy identified multiple groups of genes expressed in the hippocampi of mammals, where the genes were expressed at different levels for several ages. The aging changes in expression began before mid-life. Many of the genes were involved in specific neuronal and glial pathways with previously unrecognized relationships to aging and / or cognitive decline. The processes identified by the strategy suggest a new hypothesis of brain aging in which initially decreased neuronal activity and / or oxidative metabolism trigger separate but parallel genomic cascades in neurons and glia. In neurons, the cascade results in elevations in calcium signaling and reductions of immediate early gene signaling, biosynthesis, synaptogenesis and neurite remodeling. In contrast, glia undergo increased lipid metabolism and mediate a cycle of demyelination and remyelination that induces antigen presentation, inflammation, oxidative stress and extracellular restructuring. These identified genes and the proteins they encode can be used as novel biomarkers of brain aging and as targets for developing treatment methods against age-related cognitive decline, Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Effects of apolipoprotein b inhibition on gene expression profiles in animals
Methods are provided for modulating the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism, useful in the treatment of conditions associated with cardiovascular risk. Antisense oligonucleotides targeted to apolipoprotein B reduce the level of apolipoprotein B mRNA, lower serum cholesterol and shift liver gene expression profiles from those of an obese animal towards those of a lean animal. Further provided are methods for improving the cardiovascular risk of a subject through antisense inhibition of apolipoprotein B. Also provided are methods for employing antisense oligonucleotides targeted to apolipoprotein B to modulate a cellular pathway or metabolic process.
Owner:KASTLE THERAPEUTICS LLC
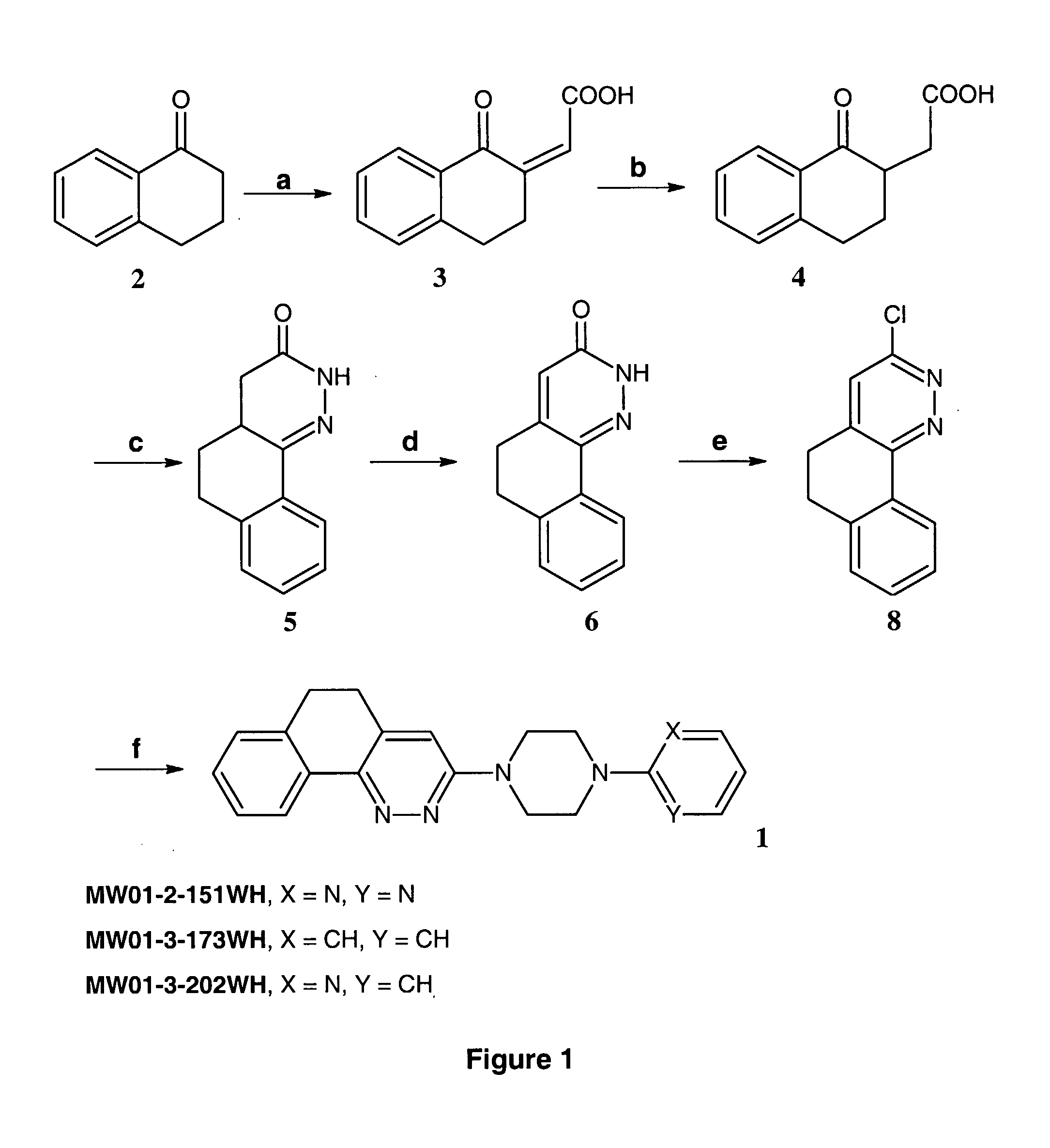
Pyridazine Compounds, Compositions and Methods
ActiveUS20080318899A1Prevent and inhibit activationReduce and inhibit and activationBiocideNervous disorderCellular pathwaysDisease
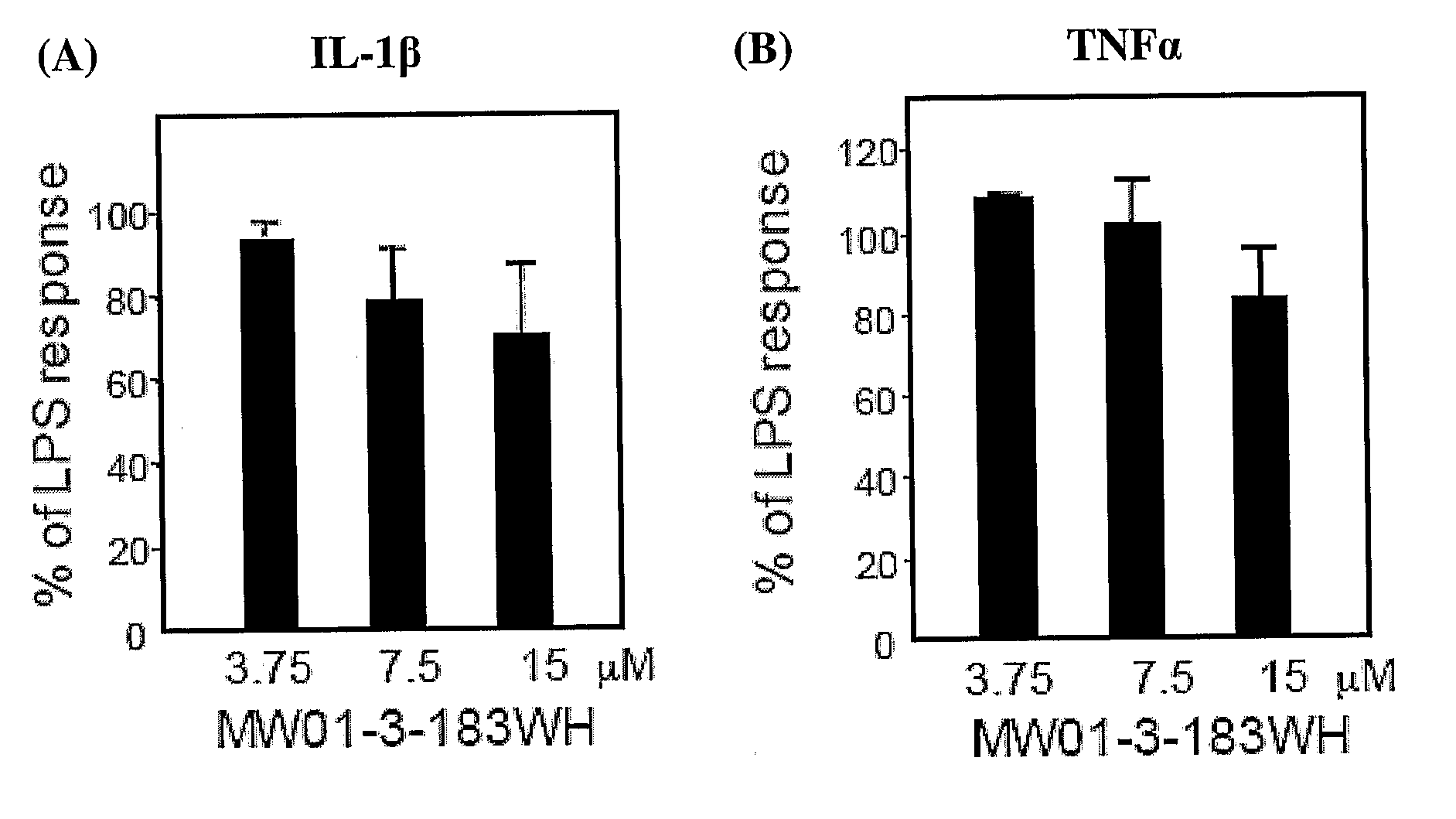
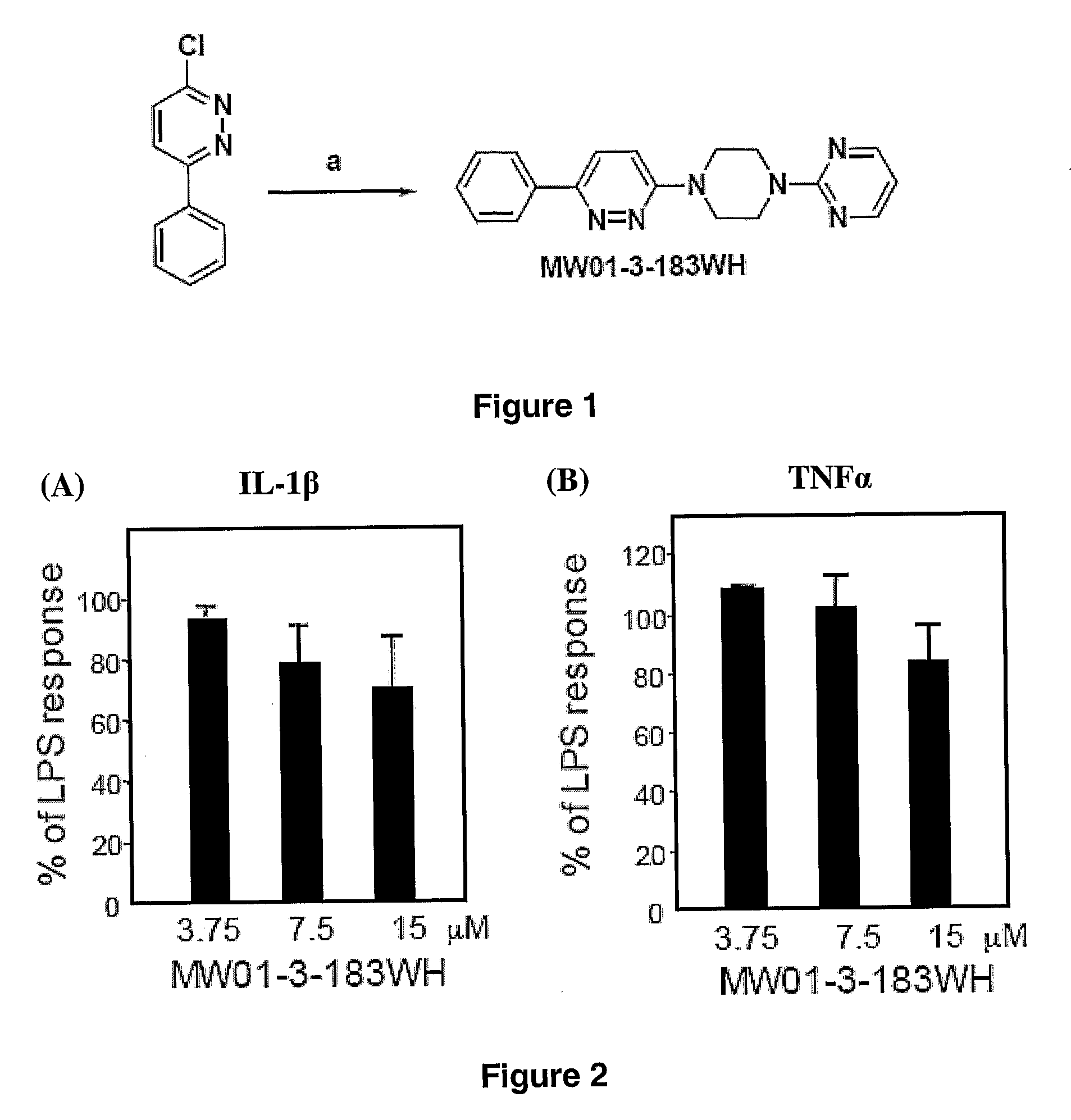
The invention relates to novel chemical compounds and methods of making and using the same. In particular, the invention provides pyridazine compounds and / or related heterocyclic derivatives, compositions comprising the same, and methods of using pyridazine compounds and / or related heterocyclic derivatives and compositions comprising the same, for modulation of cellular pathways (e.g., signal transduction pathways), for treatment or prevention of inflammatory diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's disease), for research, drug screening, and therapeutic applications.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +2
Pathways characterization of cells
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the characterization of cellular pathways in cells containing genetic alterations.
Owner:NODALITY
Multi-functional small molecules as anti-proliferative agents
The present invention relates to the compositions, methods, and applications of a novel approach to selective inhibition of several cellular or molecular targets with a single small molecule. More specifically, the present invention relates to multi-functional small molecules wherein one functionality is capable of inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDAC) and the other functionality is capable of inhibiting a different cellular or molecular pathway involved in aberrant cell proliferation, differentiation or survival.
Owner:CURIS INC
Cells exhibiting neuronal cell progenitor characteristics and methods of making them
Disclosed are cells exhibiting neuronal progenitor cell characteristics, and methods of making them from marrow adherent stem cells by regulating cellular pathways in the marrow adherent stem cells that are associated with glial transdifferentiation of the marrow adherent stem cells.
Owner:SANBIO
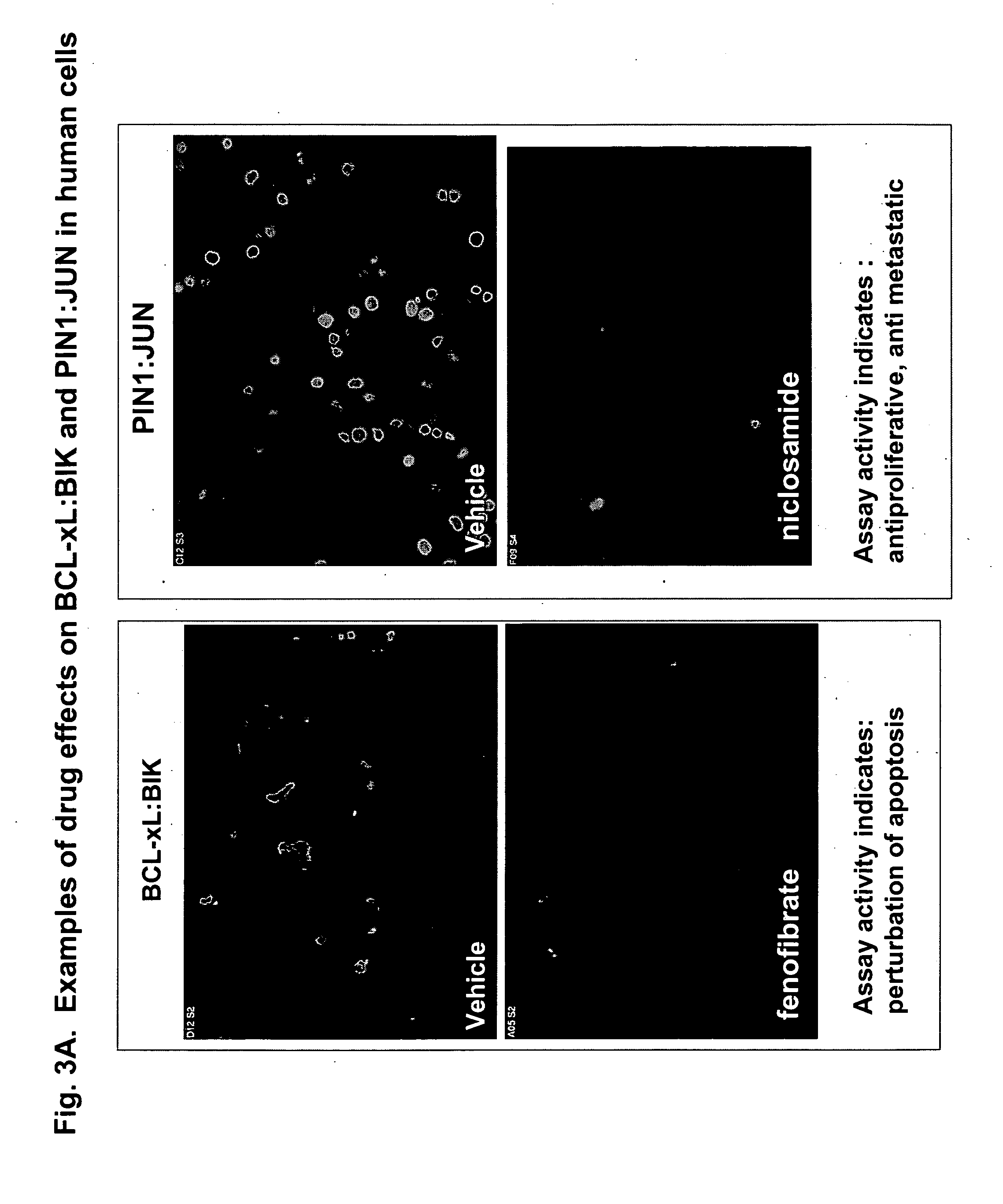
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
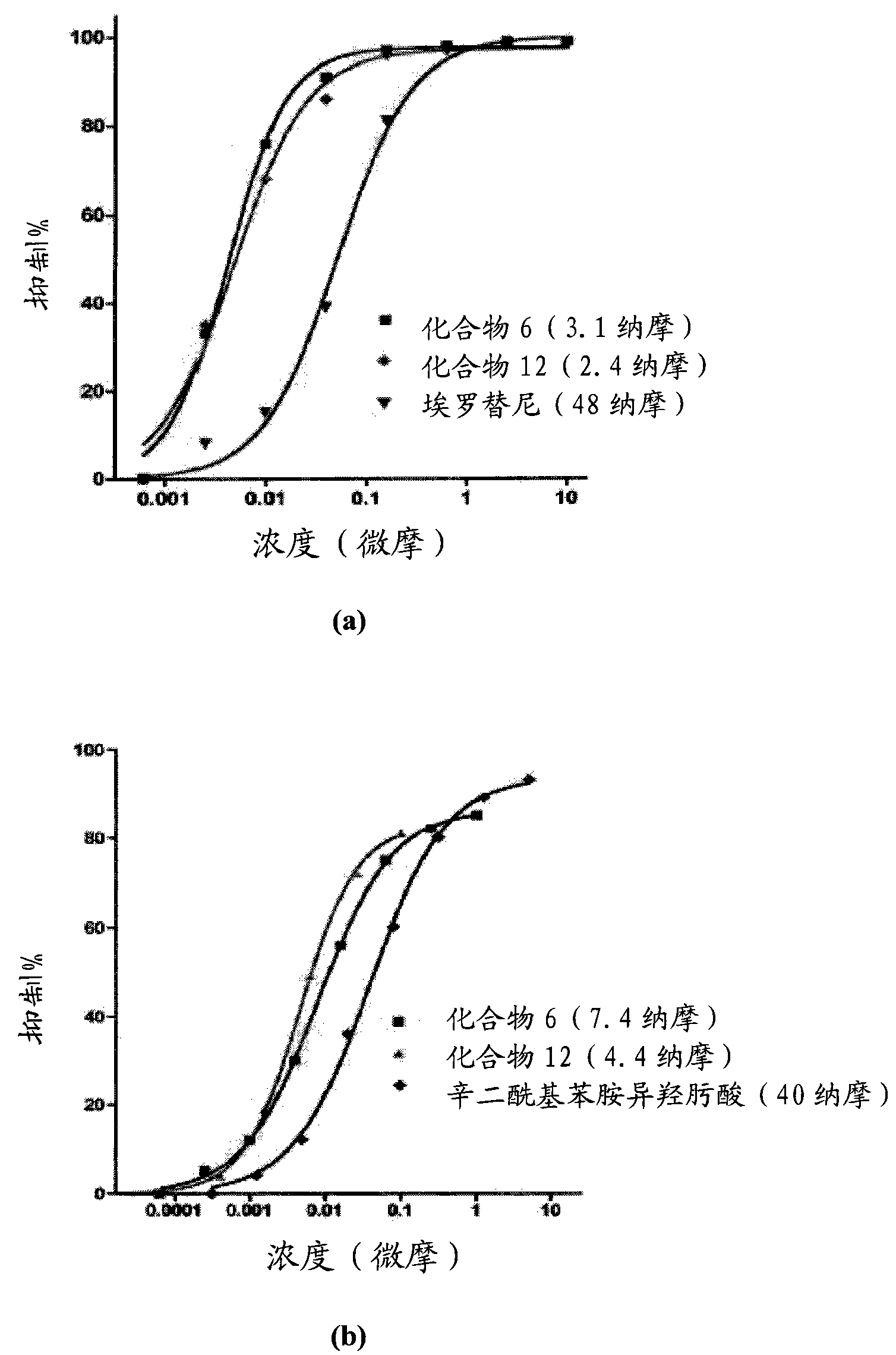
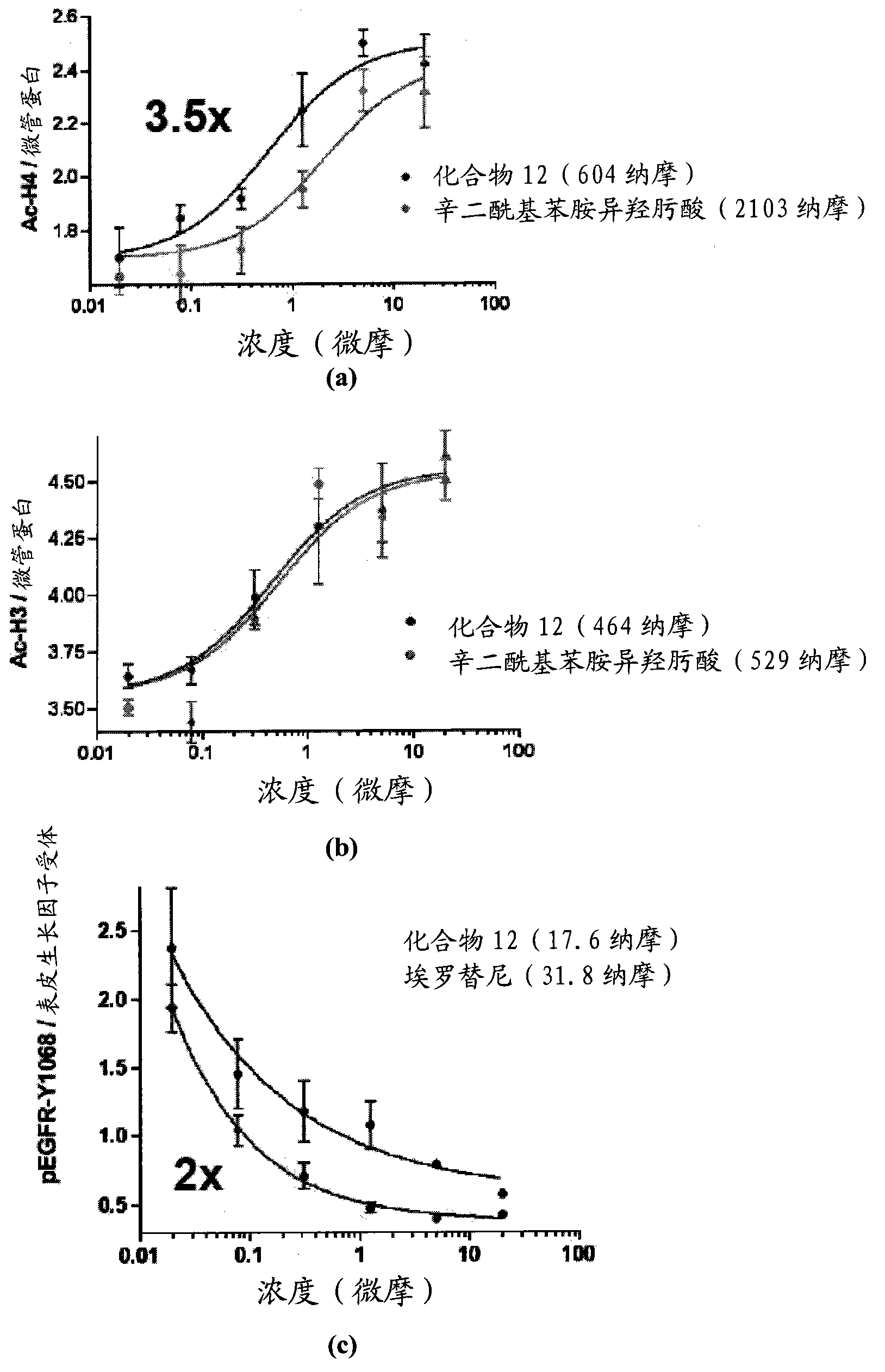
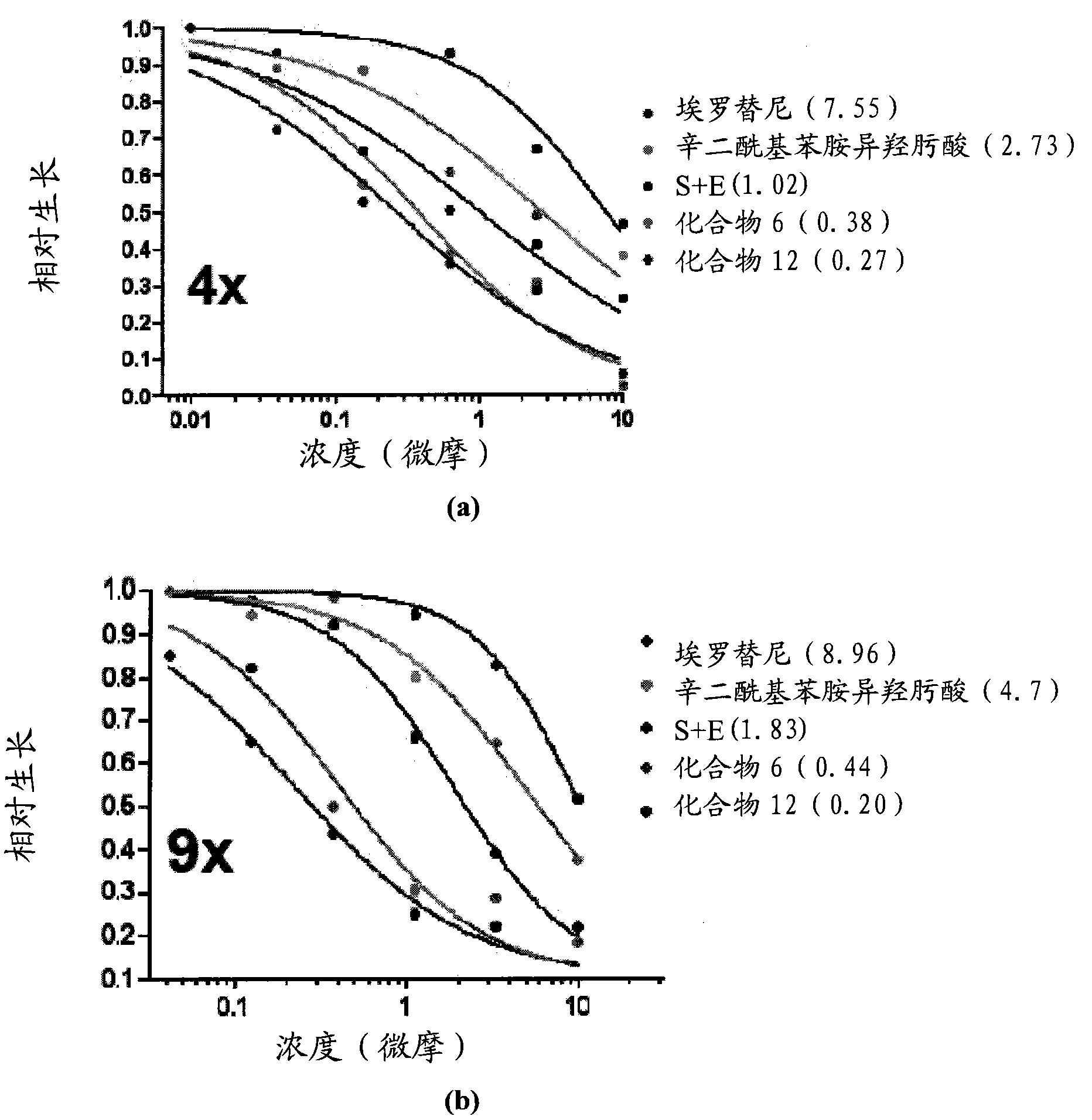
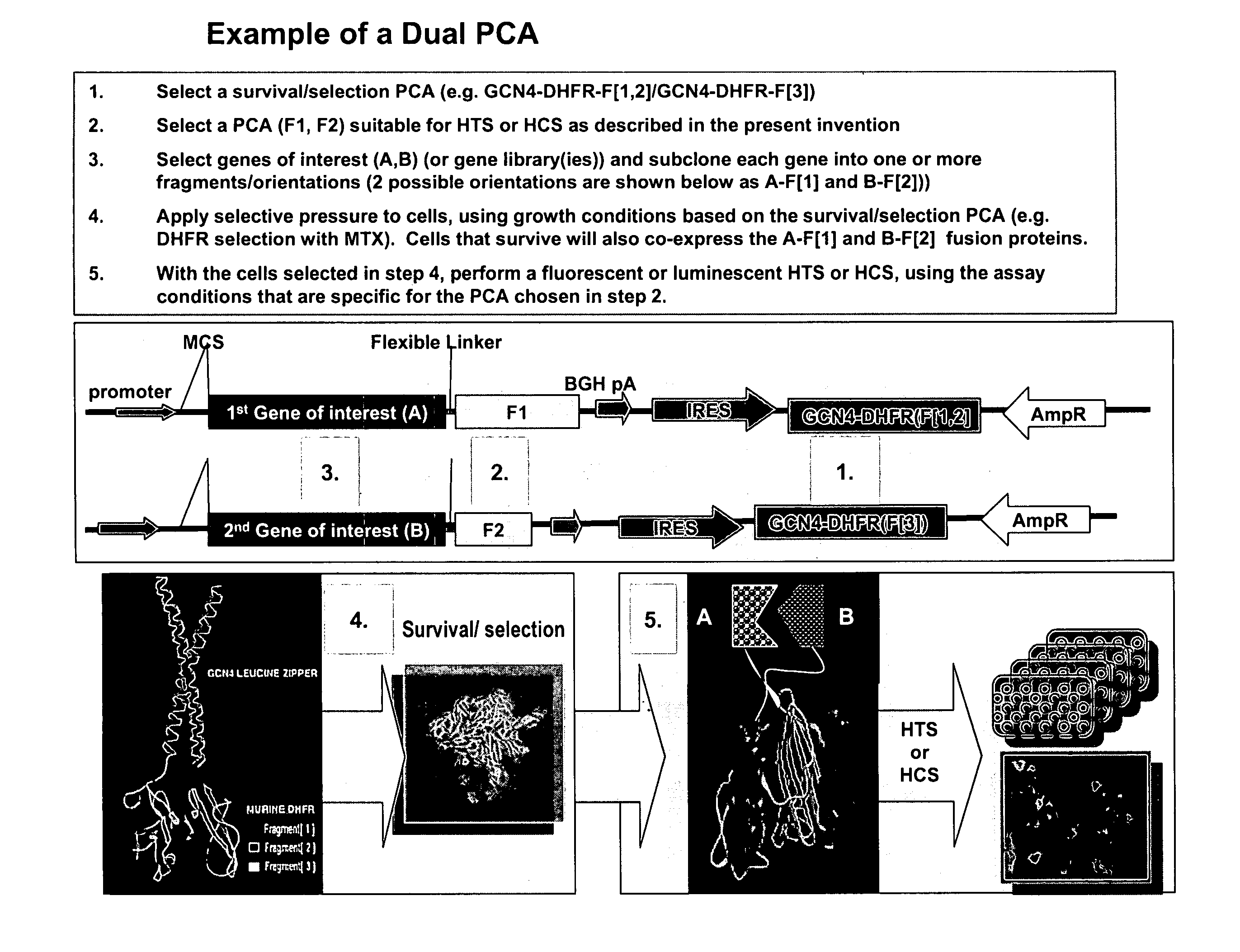
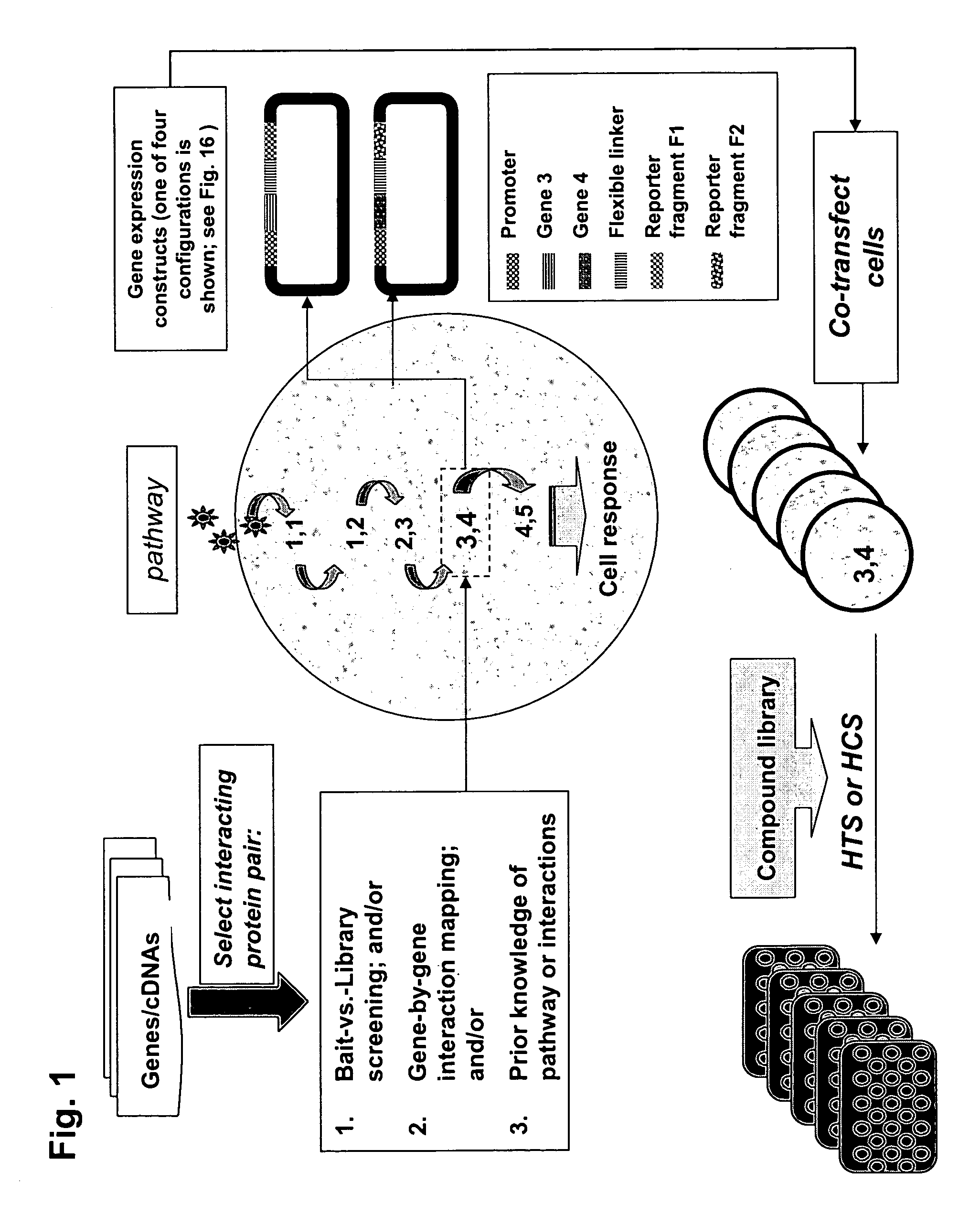
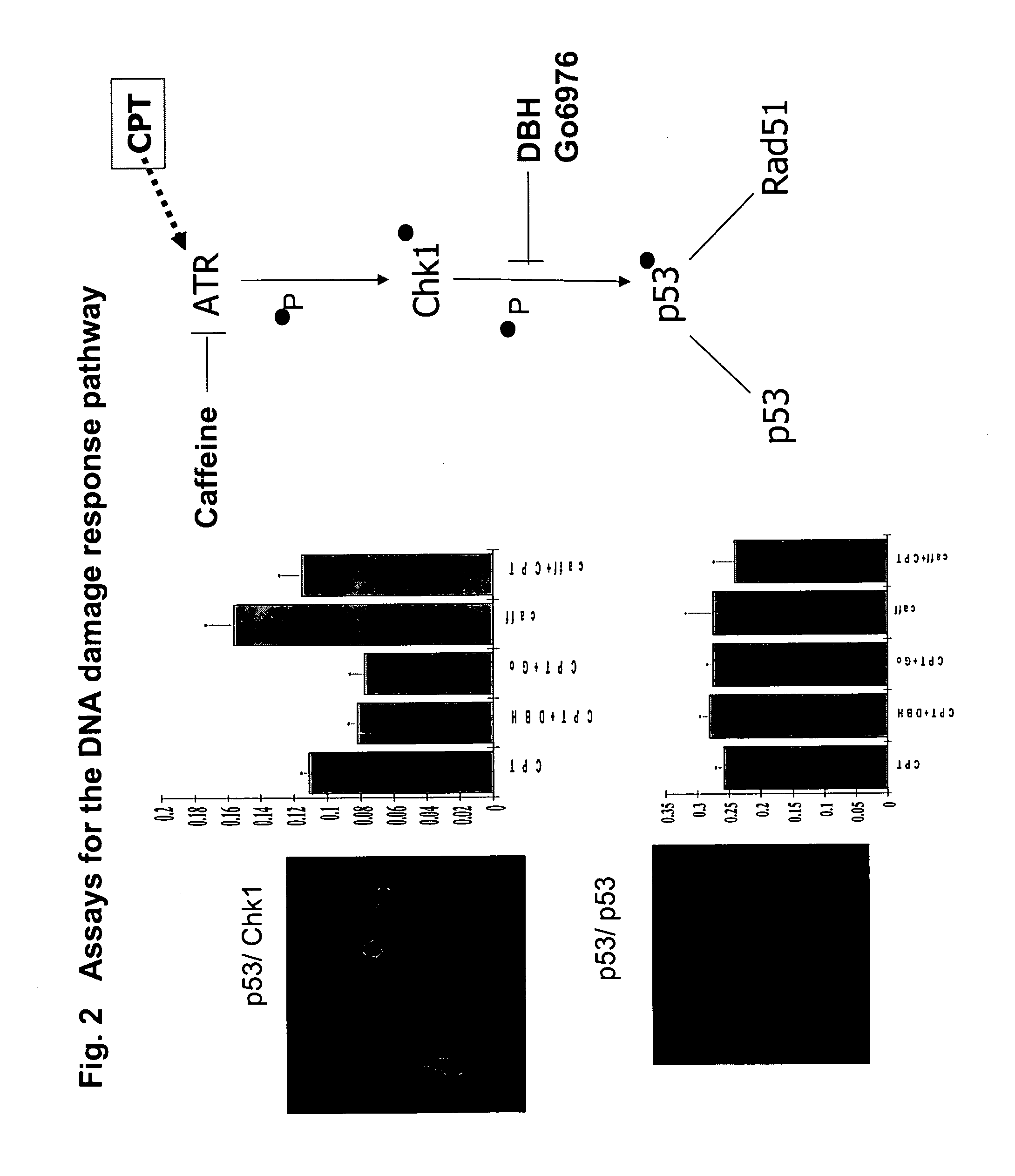
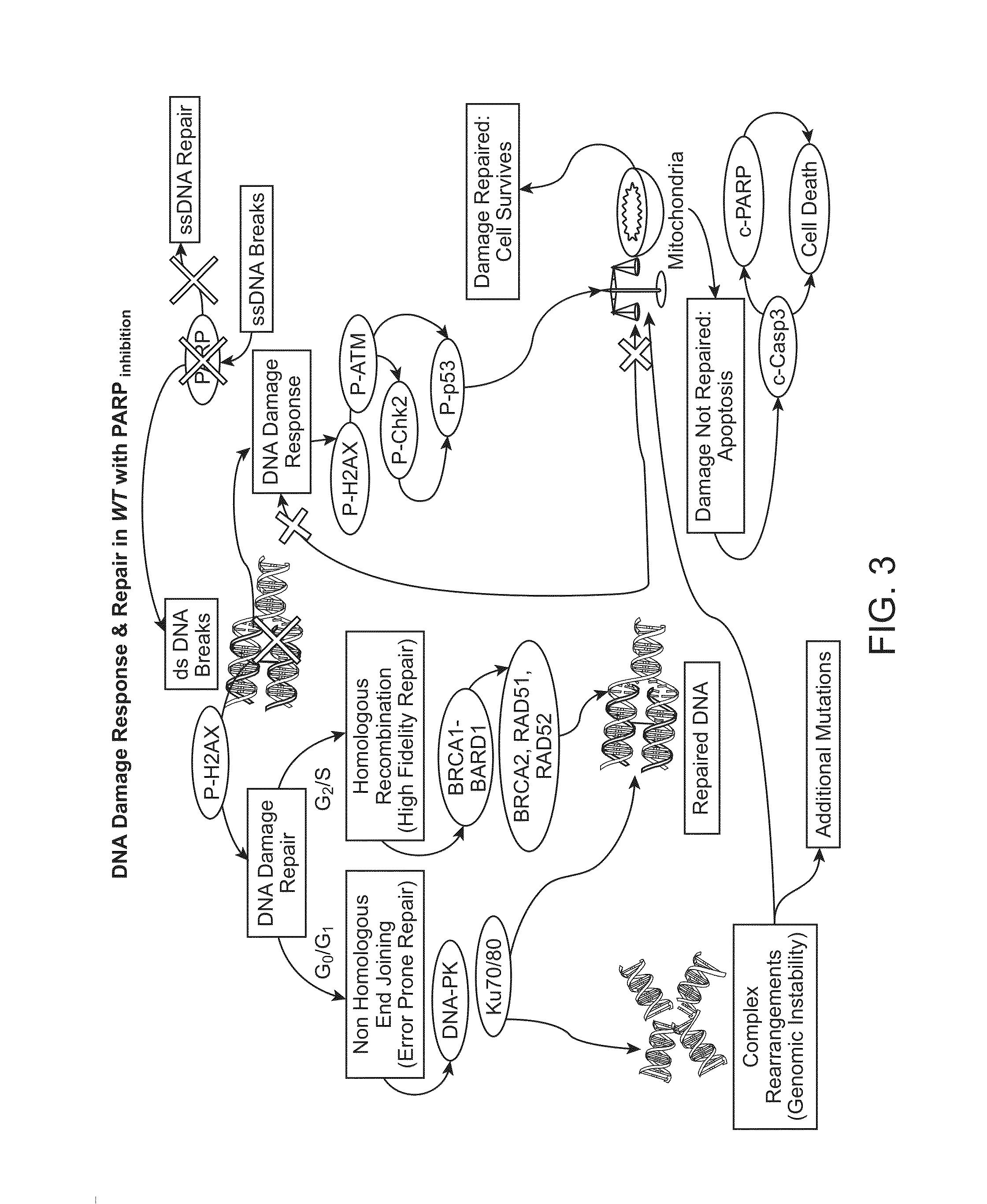
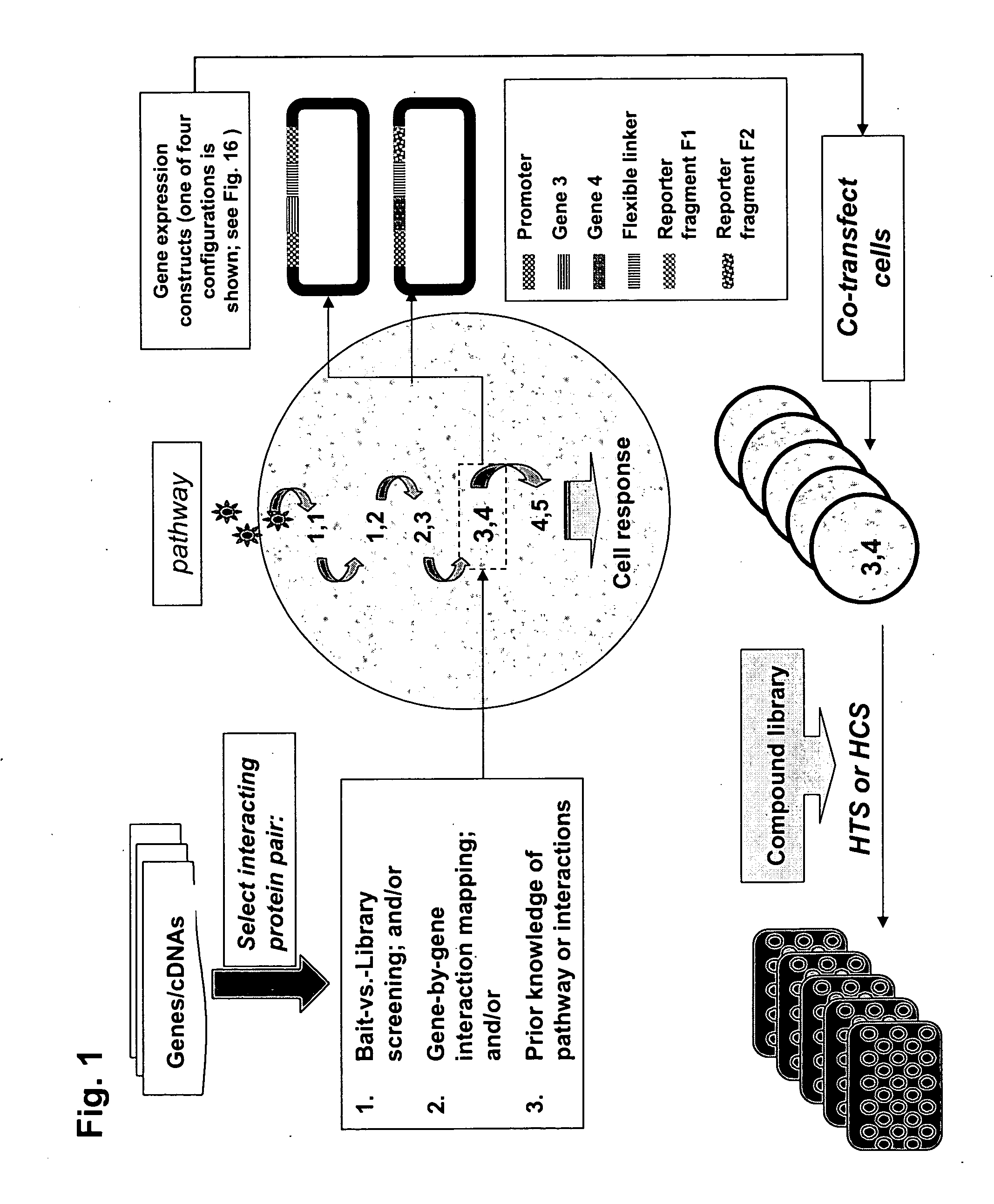
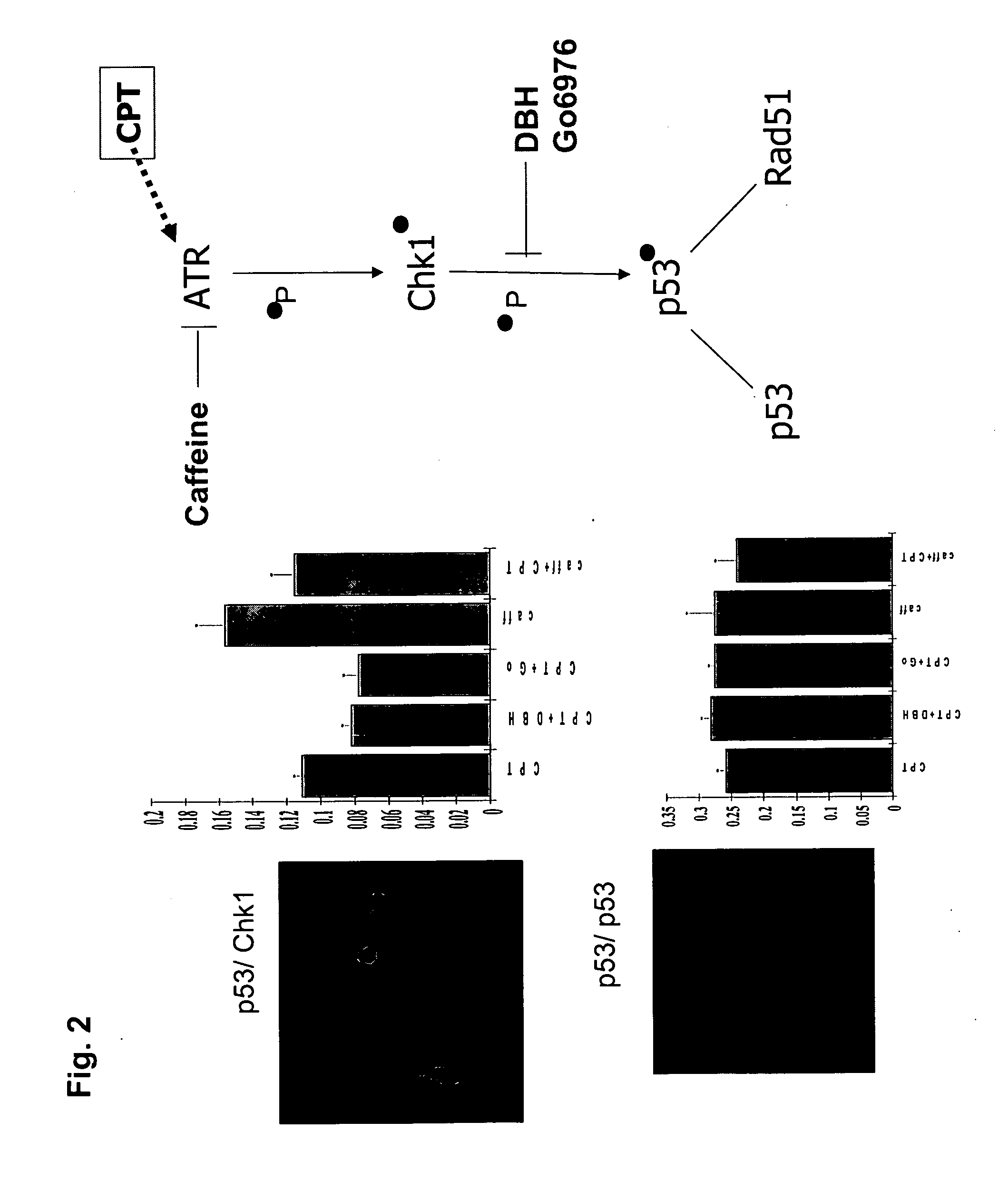
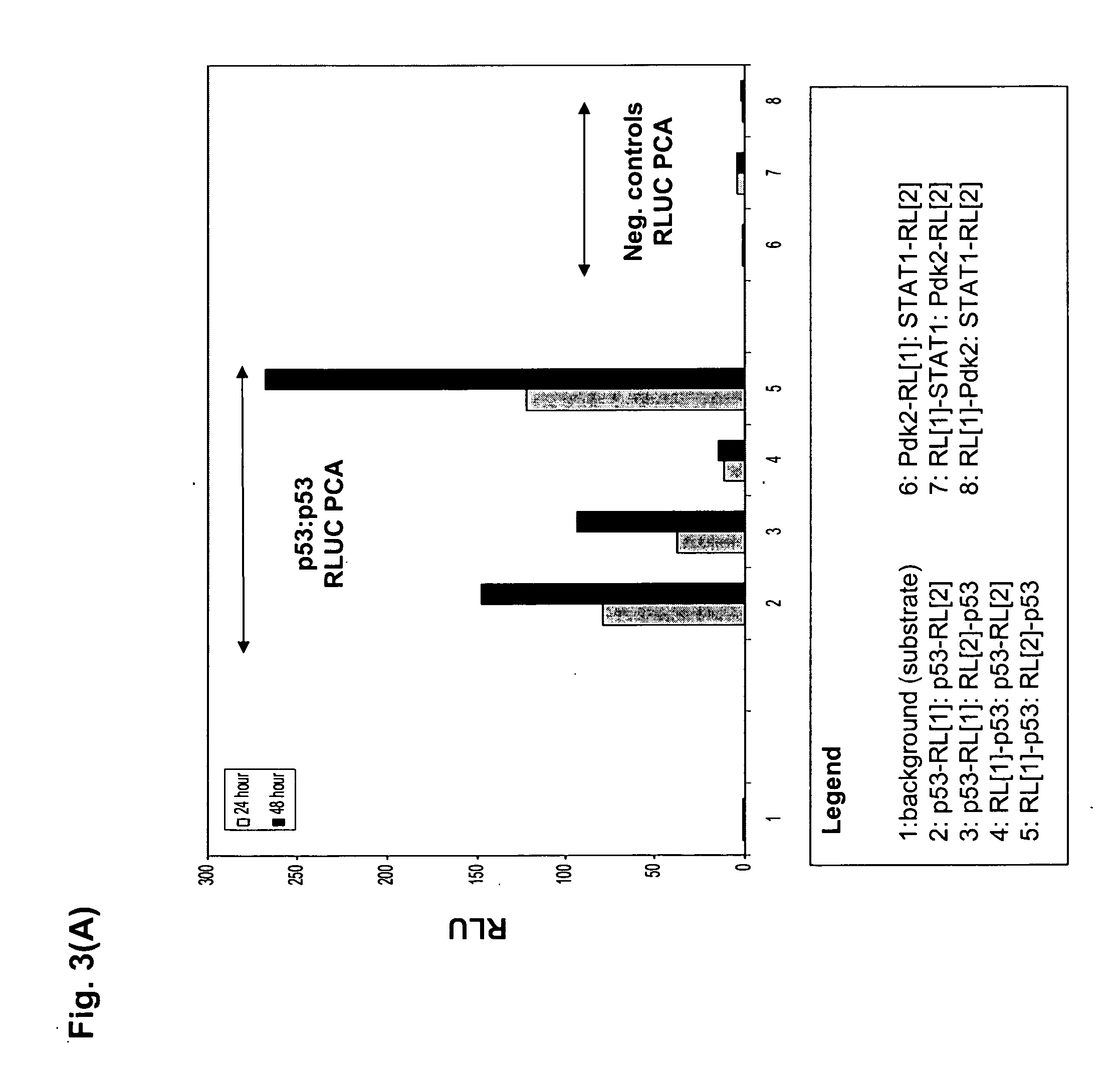
The present invention provides protein fragment complementation assays for drug discovery, in particular to identify compounds that activate or inhibit cellular pathways. Based on the selection of an interacting protein pair combined with an appropriate PCA reporter, the assays may be run in high-throughput or high-content mode and may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds. The interacting pair may be selected by cDNA library screening; by gene-by-gene interaction mapping; or by prior knowledge of a pathway. Fluorescent and luminescent assays can be constructed using the methods provided herein. The selection of suitable PCA reporters for high-throughput or high-content (high-context) assay formats is described for a diversity of reporters, with particular detail provided for examples of monomeric enzymes and fluorescent proteins. Methods are described for constructing such assays for one or more steps in a biochemical pathway; testing the effects of compounds from combinatorial, natural product, peptide, antibody, nucleic acid or other diverse libraries on the protein or pathway(s) of interest; and using the results of the screening to identify specific compounds that activate or inhibit the protein or pathway(s) of interest. Single-color and multi-color assays are disclosed. Further disclosed are universal expression vectors with cassettes that allow the rapid construction of assays for a large and diverse number of gene / reporter combinations. The development of such assays is shown to be straightforward, providing for a broad, flexible and biologically relevant platform for drug discovery.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Pathway characterization of cells
InactiveUS20140017678A1Reduce the impactHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular pathwaysGenetic Alteration
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the characterization of cellular pathways in cells containing genetic alterations.
Owner:NODALITY
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Systems and methods for detecting cellular pathway dysregulation in cancer specimens
Disclosed herein are systems, methods, and compositions useful for determining cellular pathway disruption comprising the use of RNA expression level information. This determined level of disruption can assist in the identification of genetic variants that alter pathway activity, to correlate these variants with disease state and disease progression, and to identify those therapeutics most likely to be effective and which should be avoided.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS
Pyridazine compounds and methods
ActiveUS20090029985A1Prevent and inhibit activationPromote progressBiocideNervous disorderCellular pathwaysPyridazine
The invention relates to novel chemical compounds, compositions and methods of making and using the same. In particular, the invention provides pyridazine compounds and / or related heterocyclic derivatives, compositions comprising the same, and methods of using pyridazine compounds and / or related heterocyclic derivatives and compositions comprising the same, for modulation of cellular pathways (e.g., signal transduction pathways), for treatment or prevention of inflammatory diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's disease), for research, drug screening, and therapeutic applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG
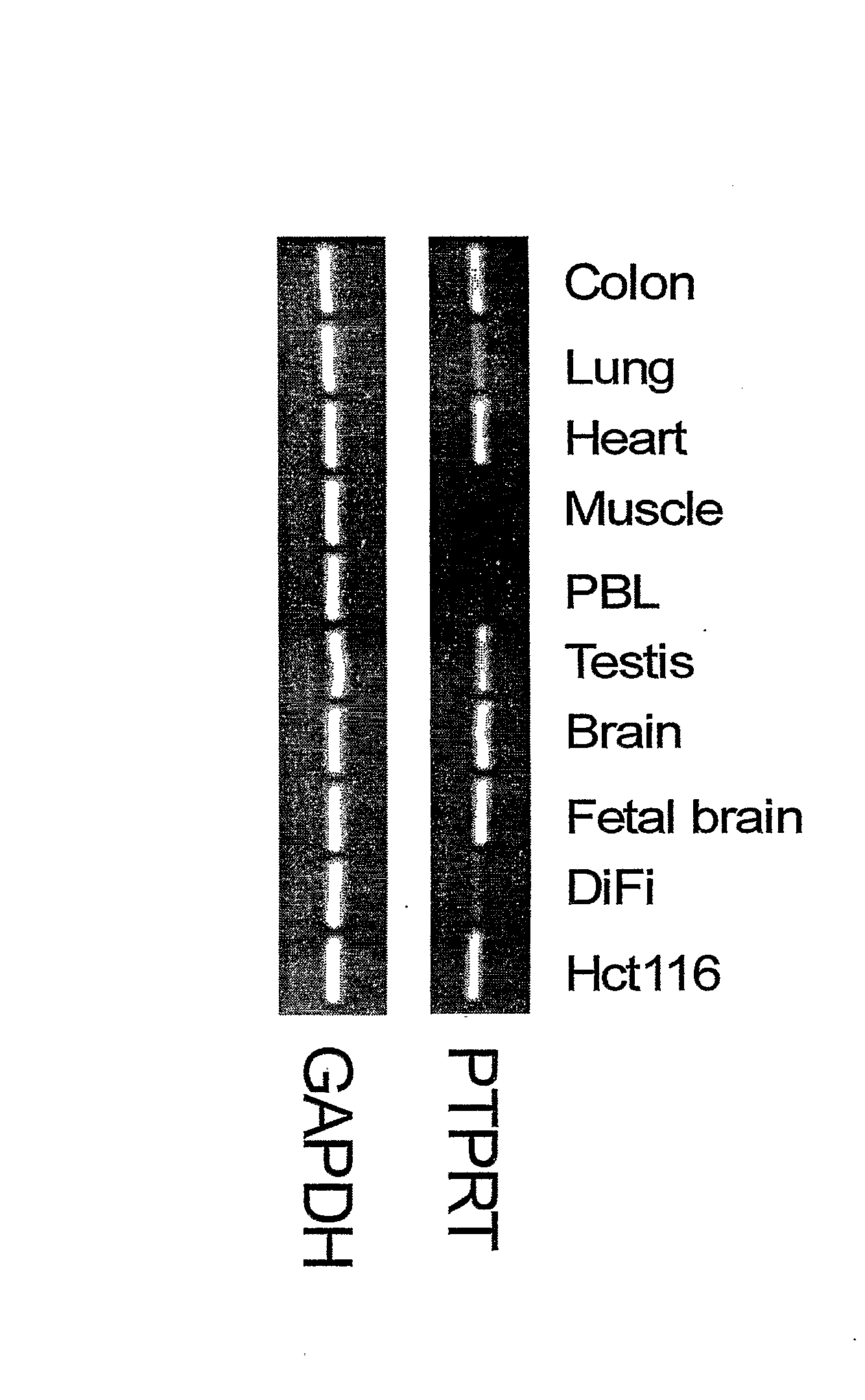
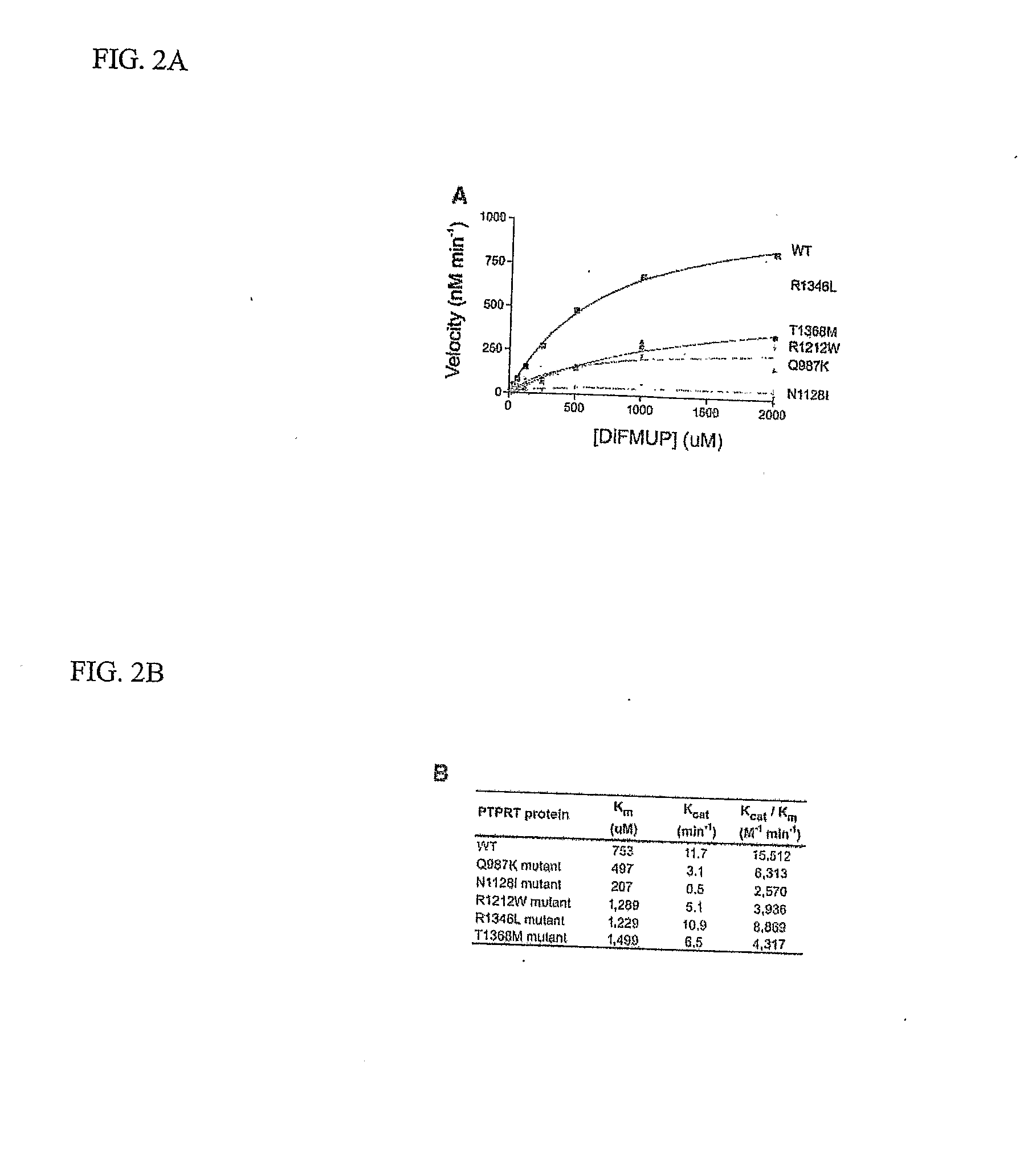
Protein Tyrosine Phosphate Mutations in Cancers
ActiveUS20080039417A1Growth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthCellular pathways
Tyrosine phosphorylation, regulated by protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) and kinases (PTKs), is important in signaling pathways underlying tumorigenesis. A mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatase gene superfamily in human cancers identified 83 somatic mutations in six PTPs (PTPRF, PTPRG, PTPRT, PTPN3, PTPN13, PTPN14) affecting 26% of colorectal cancers and a smaller fraction of lung, breast and gastric cancers. Fifteen mutations were nonsense, frameshift or splice site alterations predicted to result in truncated proteins lacking phosphatase activity. Five missense mutations in the most commonly altered PTP (PTPRP) were biochemically examined and found to reduce phosphatase activity. Expression of wild-type but not a mutant PTPRT in human cancer cells inhibited cell growth. These observations suggest that the tyrosine phosphatase genes are tumor suppressor genes, regulating cellular pathways that may be amenable to therapeutic intervention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Proteins comprising amino-terminal proximal shiga toxin a subunit effector regions and cell-targeting immunoglobulin-type binding regions
InactiveUS20160376328A1Reduces and eliminates cytotoxicityFacilitates cellular internalizationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular pathwaysCytotoxicity
The present invention provides proteins comprising immunoglobulin-type binding regions for cell-type specific targeting and Shiga toxin A Subunit effector regions for Shiga toxin effector functions (e.g. cellular internalization, directing subcellular routing, and / or cytotoxicity), wherein the binding regions and Shiga toxin effector regions are combined such that the Shiga toxin effector regions are proximal to the amino-terminals of the proteins. The presently disclosed proteins can comprise additional exogenous materials, such as, e.g., antigens, cytotoxic agents, and detection-promoting agents, and are capable of targeted delivery of these additional exogenous materials into the interiors of target cells. The proteins of the present invention have uses in methods such as, e.g., methods involving targeted killing of target cells, delivering exogenous materials into target cells, labeling subcellular compartments of target cells, and diagnosing and / or treating a variety of conditions including cancers, tumors, other growth abnormalities, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Compositions and methods for reducing the signs of aging of the skin
InactiveUS20110301091A1Reducing sign of agingReduce probabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCellular pathwaysHuman skin
Compositions and methods used to reduce the visible signs of aging of the skin by recalibrating the expression of genes, genetic networks, and cellular pathways in the human skin, particularly using combinations of natural compounds that produce synergistic effects on the expression of genes and genetic networks.
Owner:DERMACHIP
Methods for identifying new drug leads and new therapeutic uses for known drugs
InactiveUS20060094059A1Large scaleWide applicabilityPeptide librariesLibrary screeningCellular pathwaysHuman tumor
The screening system utilizes dynamic measurements of pathway activity to detect the activities of drugs within cellular pathways. The methods of the invention can be used to identify previously unknown drug activities and therapeutic uses, even for drugs that have been well characterized with standard biochemical assays. We demonstrated the utility of the invention by screening a portion of the known pharmacopeia. We identified dozens of drugs, previously or currently marked for a variety of indications, with surprising and previously-unsuspected activity against ‘hallmark’ cancer pathways. We also showed that over 20 of these drugs indeed have anti-proliferative activity in human tumor cells, underscoring the utility and predictability of the screening system. The methodology will extend the utility of the current pharmacopeia and provide the basis for de novo discovery of drugs with a broad range of therapeutic indications.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Integrated Analyses of Breast and Colorectal Cancers
InactiveUS20100136560A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCellular pathwaysIntracellular signalling
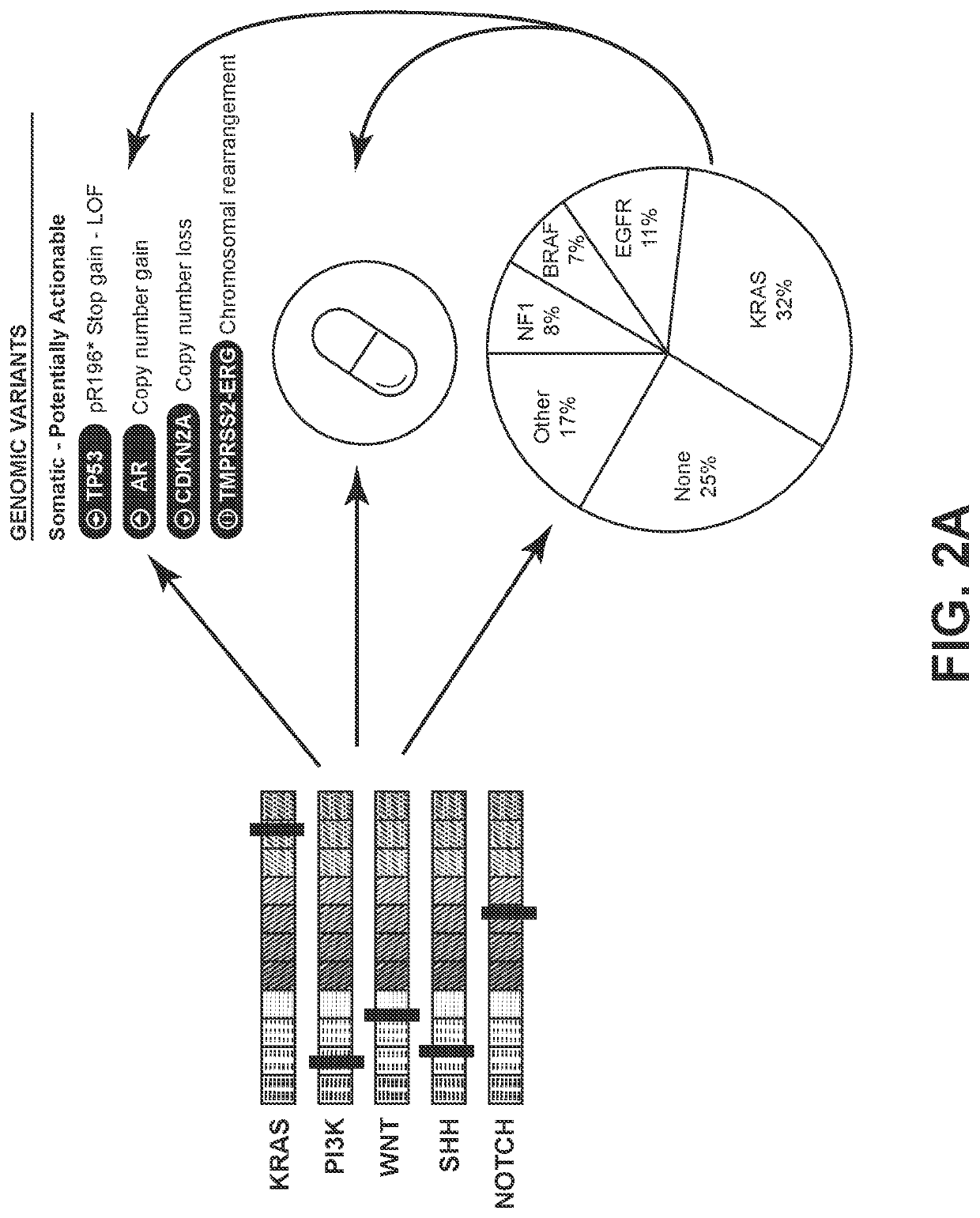
Genome-wide analysis of copy number changes in breast and colorectal tumors used approaches that can reliably detect homozygous deletions and amplifications. The number of genes altered by major copy number changes—deletion of all copies or amplification of at least twelve copies per cell—averaged thirteen per tumor. These data were integrated with previous mutation analyses of the Reference Sequence genes in these same tumor types to identify genes and cellular pathways affected by both copy number changes and point alterations. Pathways enriched for genetic alterations include those controlling cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, DNA topological change, and cell cycle control. These analyses provide an integrated view of copy number and sequencing alterations on a genome-wide scale and identify genes and pathways that are useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Peptide combination for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20030050233A1Broad spectrumInhibit growthPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesCellular pathwaysMedicine
The present invention relates to a combination of peptides that may be used for treatment of cancer. The combination of peptides modulates multiple cellular pathways implicated in cell proliferation by altering the levels of key intracellular molecules thereby showing a broad spectrum of anticancer activity. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing a combination of such peptide analogs.
Owner:DABUR PHARM LTD
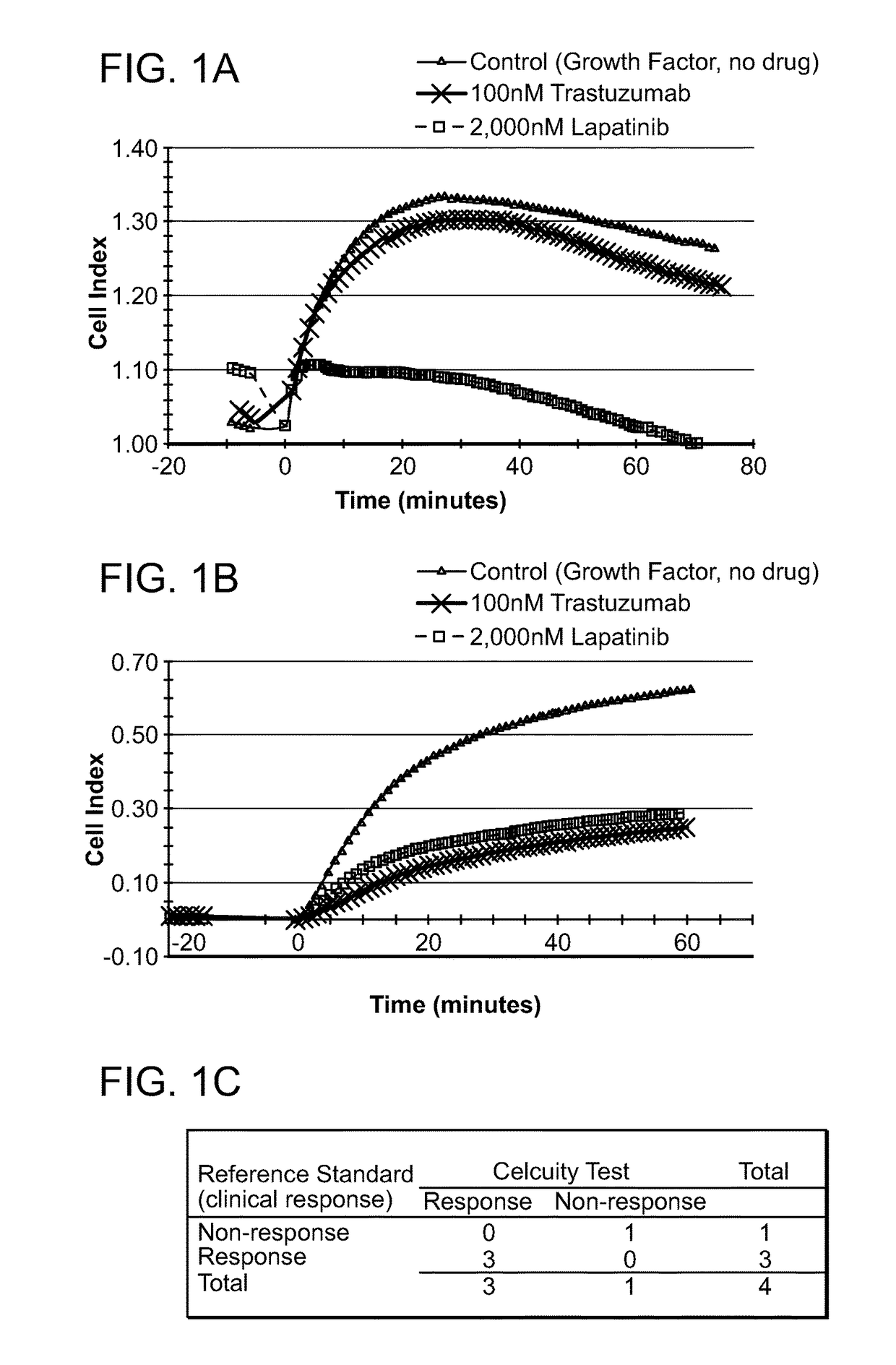
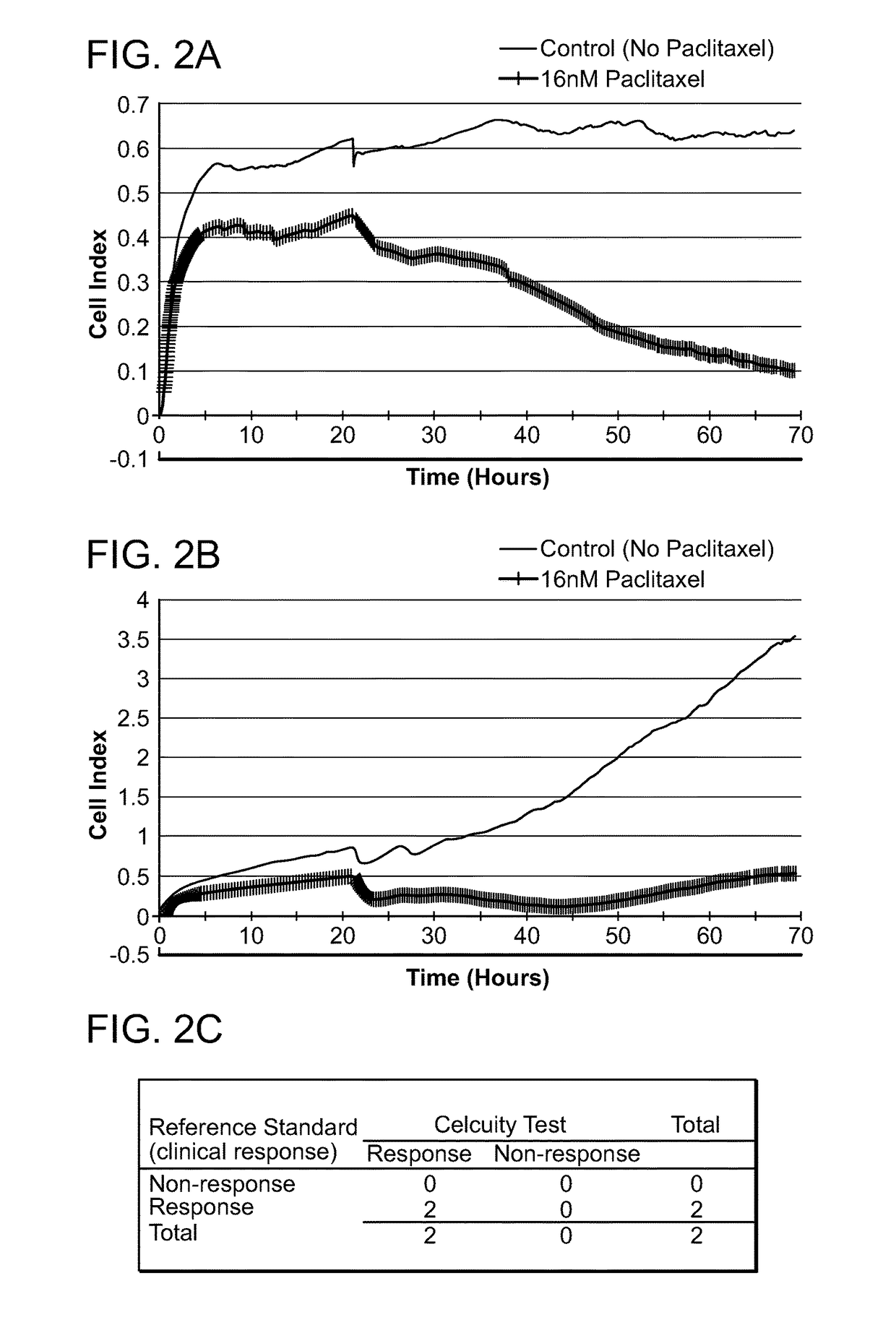
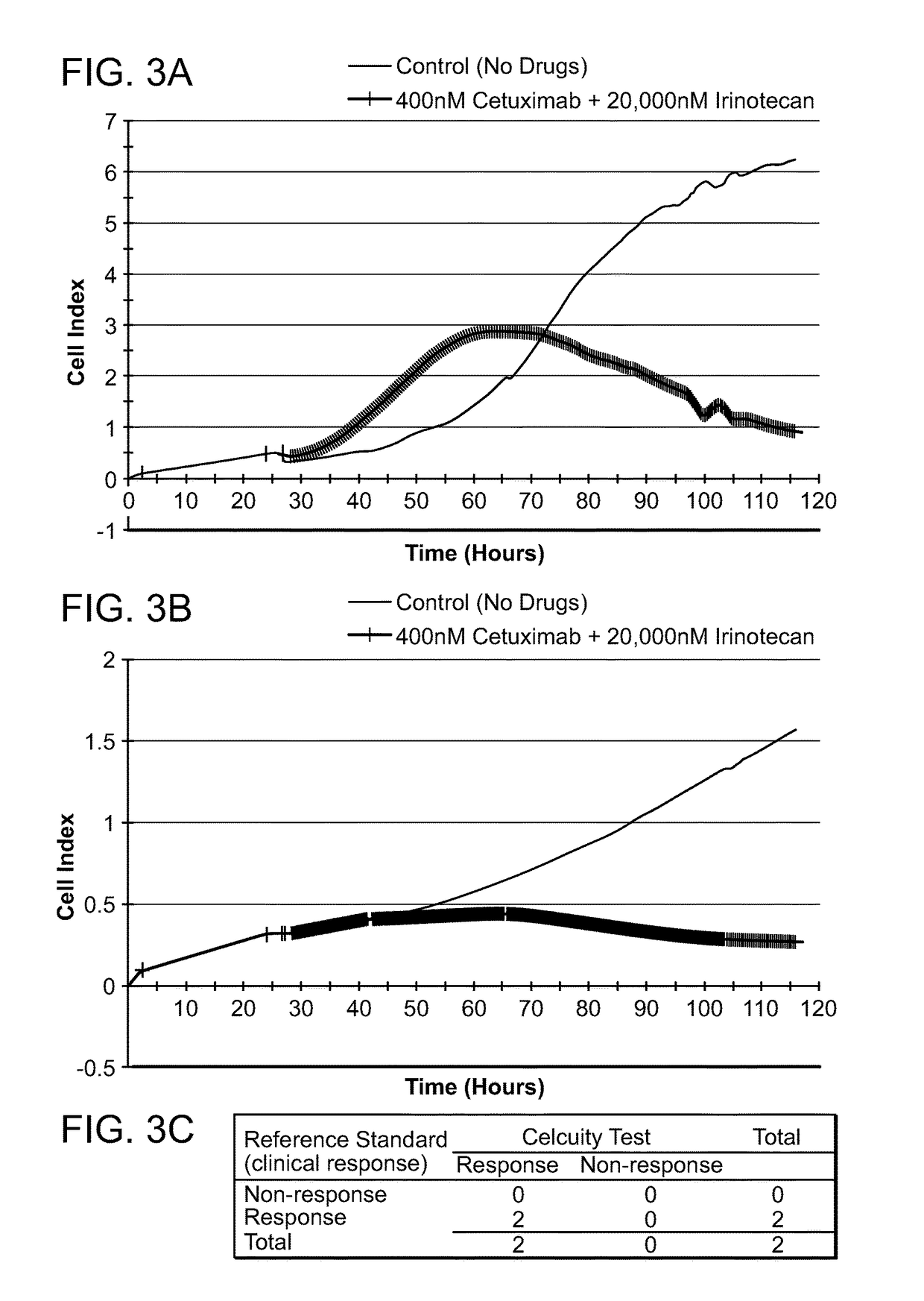
Assays and methods for determining the responsiveness of an individual subject to a therapeutic agent
ActiveUS20170067875A1Guaranteed monitoring effectOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsCellular pathwaysVariation of parameters
Provided herein are methods for determining the functional status of a cellular pathway in a diseased cell sample obtained from an individual subject. These methods involve contacting a diseased cell sample obtained from the subject with a perturbing agent (e.g., an activating agent) known to perturb a specific cellular pathway when the pathway is functioning normally. A change in one or more physiological response parameters in the presence of the perturbing agent indicates that the cellular pathway targeted by the perturbing agent is functional in the individual subject. Methods of selecting a targeted therapeutic agent for an individual subject are also provided.
Owner:CELCUITY INC
Compositions and treatments using pyridazine compounds and cholinesterase inhibitors
ActiveUS8158627B2Improve toleranceReduce adverse effectsNervous disorderAntipyreticDiseaseCellular pathways
The invention relates to compositions, conjugates and methods comprising pyridazine compounds and cholinesterase inhibitors for modulation of cellular pathways (e.g., signal transduction pathways), for treatment or prevention of inflammatory diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's disease), for research, drug screening, and therapeutic applications.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Analysis of nodes in cellular pathways
Owner:NODALITY
Pyridazine compounds and methods
ActiveUS8063047B2Prevent and inhibit activationPromote progressBiocideNervous disorderCellular pathwaysChemical compound
The invention relates to novel chemical compounds of Formula Icompositions and methods of using the same. In particular, the invention provides pyridazine compounds and / or related heterocyclic derivatives, compositions comprising the same, and methods of using pyridazine compounds and / or related heterocyclic derivatives and compositions comprising the same, for modulation of cellular pathways (e.g., signal transduction pathways), for treatment or prevention of inflammatory diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's disease), for research, drug screening, and therapeutic applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG
Immortalized rabbit small intestine epithelium cell line and construction method thereof
PendingCN107217040ACytology tools are goodGastrointestinal cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsEnzymatic digestionCellular pathways
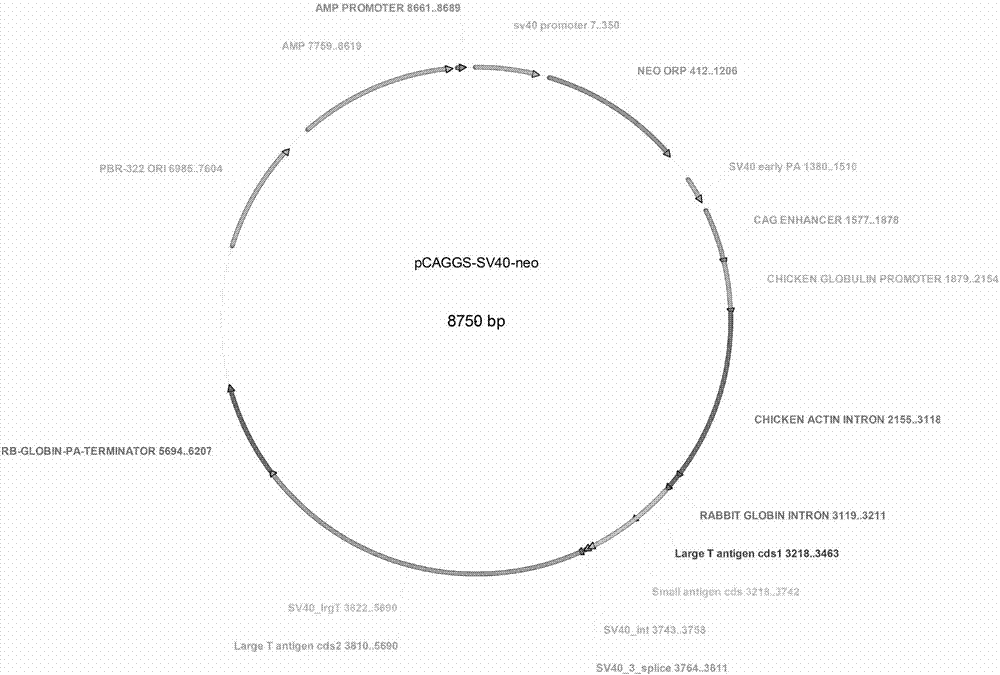
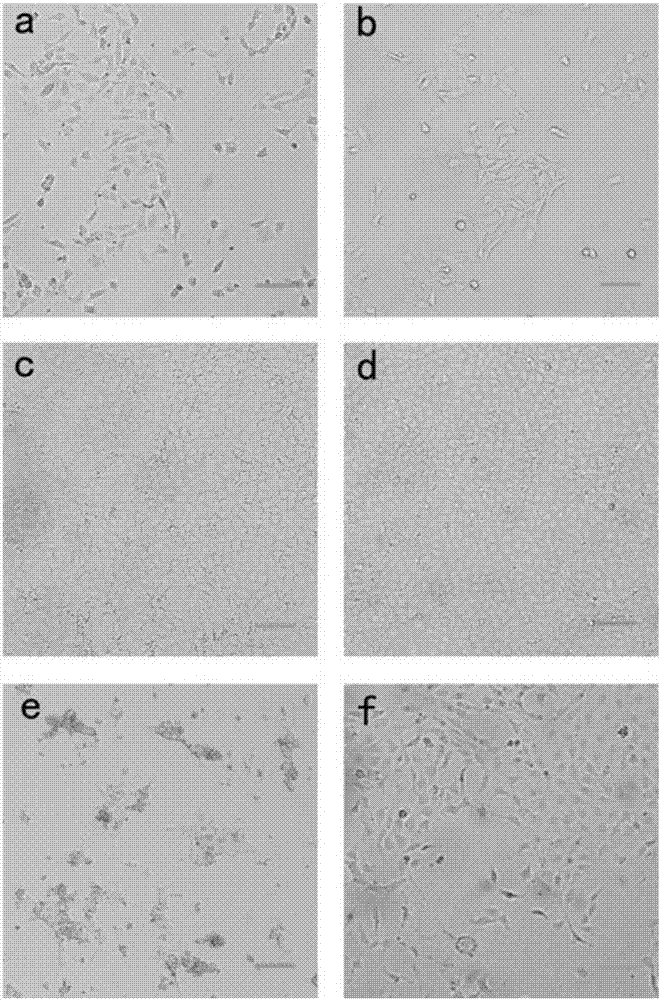
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and specifically discloses an immortalized rabbit small intestine epithelium cell line and a construction method thereof. The small intestines of a newly born rabbit are collected, the enzymatic digestion juice containing collagenase and neutral protease is utilized to digest, and after the digestion, a method for re-suspending centrifuging and differential adherence is adopted for purifying the pit cell cluster, so that high-purity primary pit epithelium cells can be obtained. The pit epithelium cells can participate in culture and passage. The obtained pit epithelium cells are used for performing liposome transfection expression on the SV40 big T antigenic plasmid, the passage is continued, and the immortalized rabbit small intestine epithelium cell line is finally screened. The immortalized rabbit small intestine epithelium cell line can simultaneously express intestine epithelium surface marker molecules and pit basic stem cell surface molecules. The intestine epithelium surface marker molecules include but not limited to keratin 8, E-calcitonin and ki67; and the pit basic stem cell surface molecules include but not limited to Lgr5 and sox9. The immortalized rabbit small intestine epithelium cell line can be used for establishing a rabbit small intestine epithelium in vitro model and can be used for researching a nutrition absorbing mechanism, cellular pathway excavation and pathogen in vitro culture.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Conditional allele system
InactiveUS20050214738A1Unable to regulateLack of expressionFusion with degradation motifTissue cultureCellular pathwaysProtein target
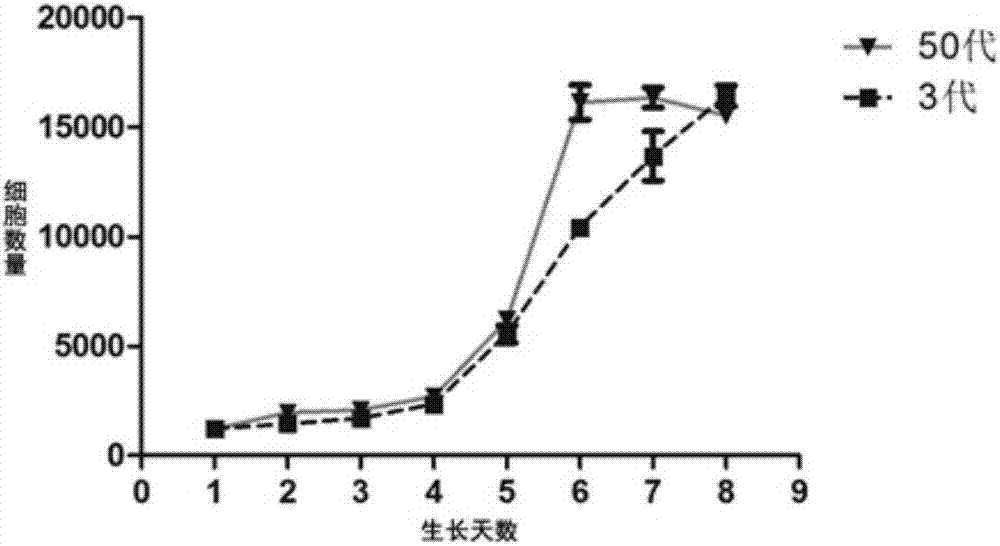
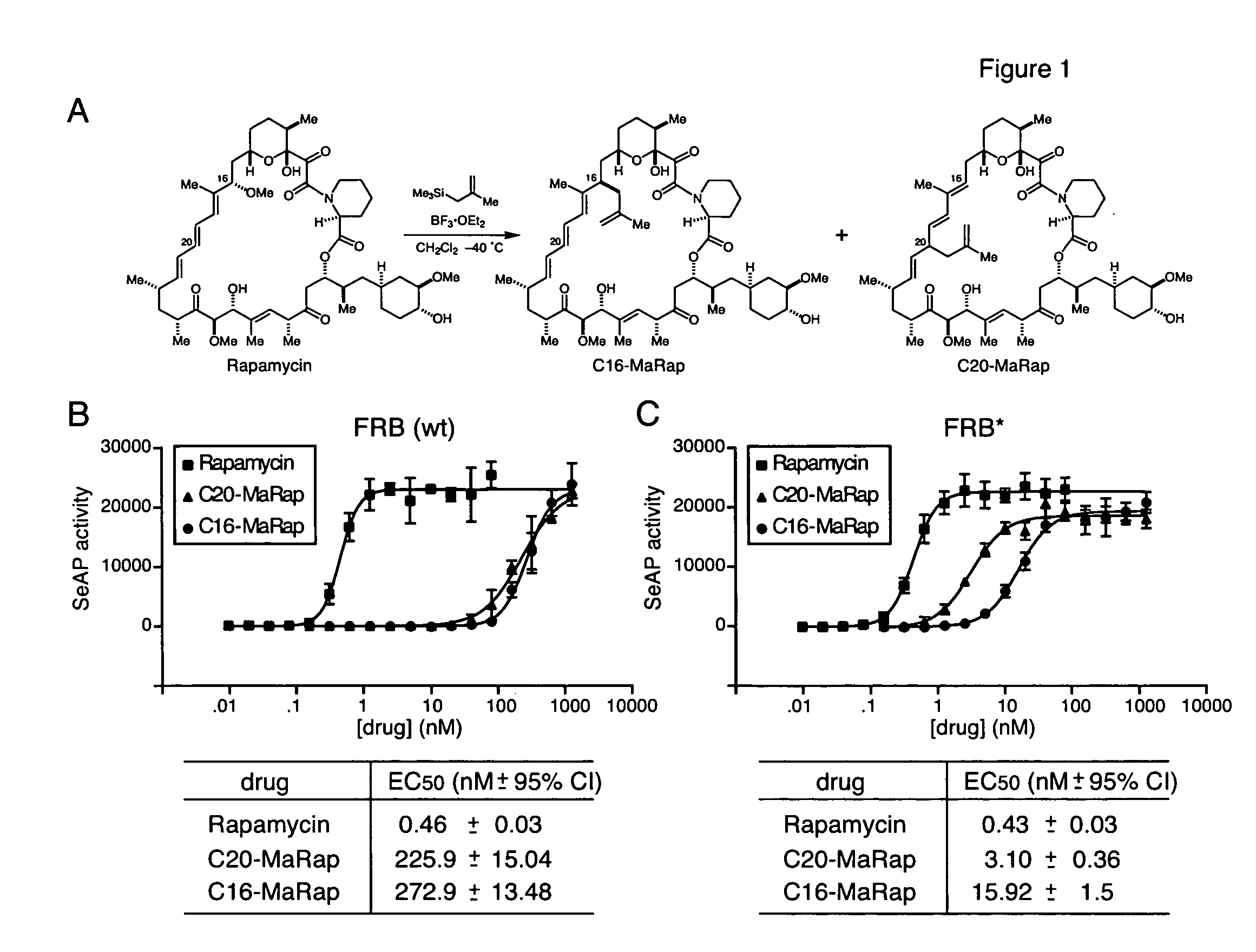
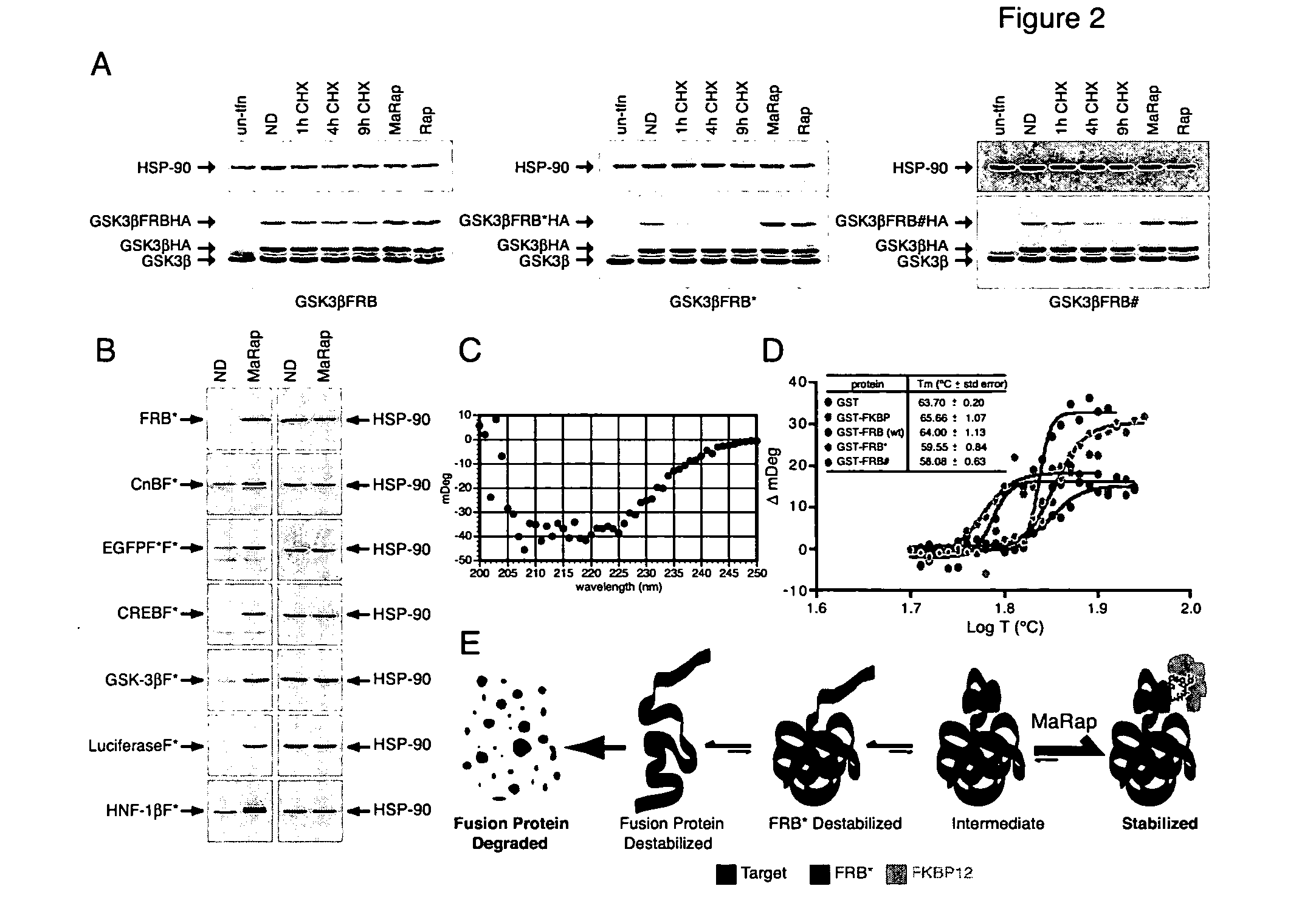
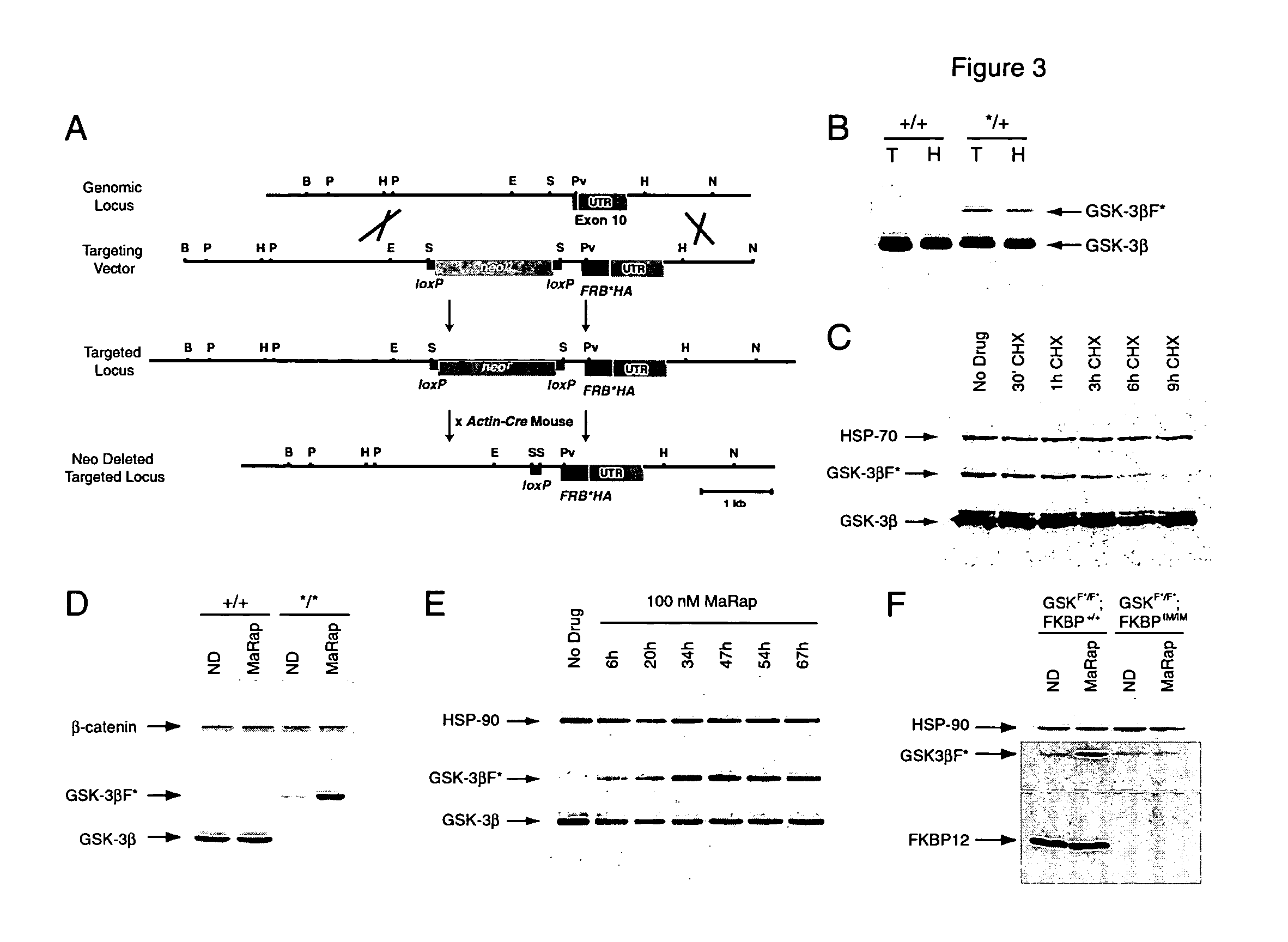
A conditional allelic system is provided where recombinant cells express a fusion protein, where the fusion protein comprises at least a functional portion of a target protein and a destabilizing peptide. The destabilizing peptide binds to a small stabilizing molecule that results in the stabilization of the fusion protein in a functional form, while in the absence of the small stabilizing molecule, the protein function is substantially reduced. The system finds use in studying cellular pathways, preparing transgenic animals that can develop in the presence of the small stabilizing molecule and can then be studied in the presence and absence of the fusion protein to determine the functions and / or effects of target protein function in and / or on various environments. Specifically, a mutated peptide from mTOR is employed as the destabilizing peptide and a modified rapamycin is employed as the small stabilizing molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Methods of measuring erbb signaling pathway activity to diagnose and treat cancer patients
InactiveUS20170343554A1Increase heightExpand the populationHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCellular pathwaysSignalling pathways
Provided herein are methods for determining the functional status of a cellular pathway in a diseased cell sample obtained from an individual subject. These methods involve contacting a diseased cell sample obtained from the subject with a perturbing agent (e.g., an activating agent) known to perturb a specific cellular pathway when the pathway is functioning normally. A change in one or more physiological response parameters in the presence of the perturbing agent indicates that the cellular pathway targeted by the perturbing agent is functional in the individual subject. Methods of selecting a targeted therapeutic agent for an individual subject are also provided.
Owner:CELCUITY INC
Hair growth inducer
InactiveCN106138058AReduces symptoms associated with shedding diseaseImprove regenerative abilityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsDiseaseTofacitinib
The invention discloses a hair growth inducer, which comprises an active ingredient composed of tofacitinib and minoxidil with a mass percentage of 0.1:99.9-99.9:0.1. The hair growth inducing agent provided by the invention, its active ingredient comprises tofacitinib and minoxidil, wherein tofacitinib is a kind of JAK inhibitor, can interact with target cells (such as dermis, epidermis, dermal papilla cells or hair follicles) Cell) specific protein active site selectively binds, inhibits the transmission of cell pathway signals and the synthesis of characteristic cytokines, thereby reducing the symptoms associated with hair loss diseases; Minoxidil is a potassium ion channel opener that can directly relax Vascular smooth muscle has a powerful dilation effect on small arteries, reduces peripheral resistance, promotes the growth of hair follicle cells, and thus regenerates hair; the combination of these two substances synergistically acts on the target protein of target cells and vascular smooth muscle, and inhibits cytokines Synthesis and accelerated blood circulation, in order to achieve a significant effect of promoting hair regeneration.
Owner:颜晓丽
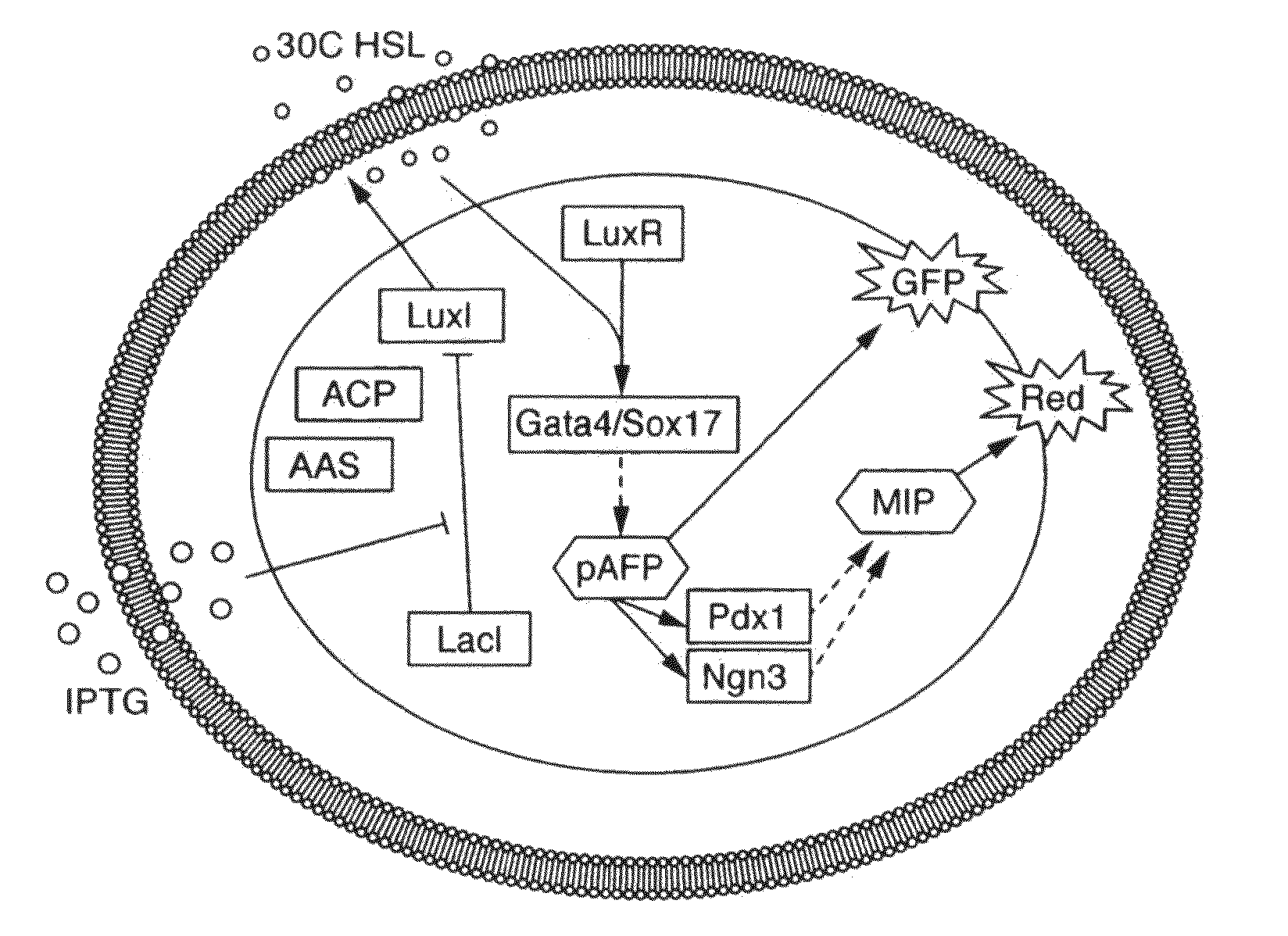
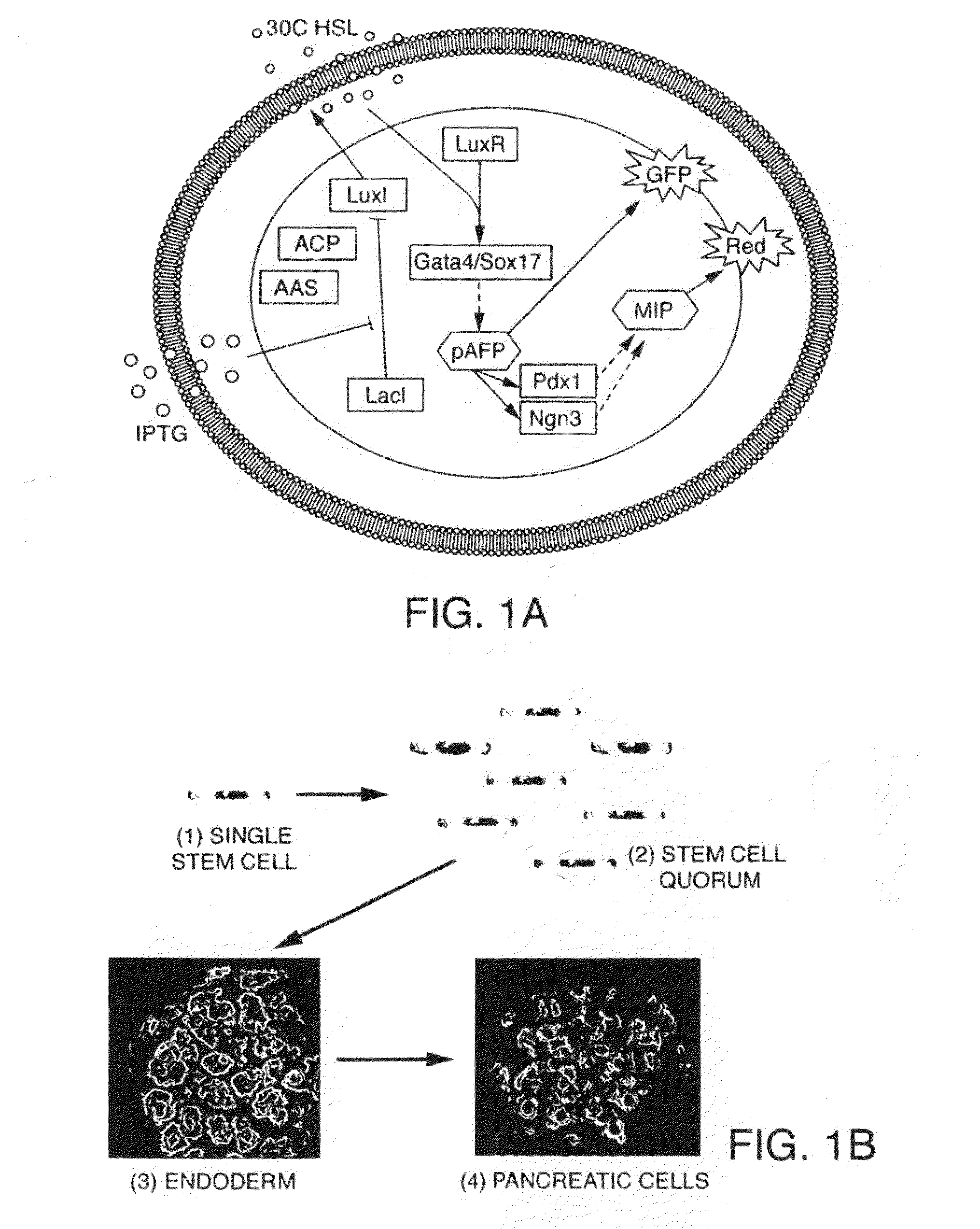
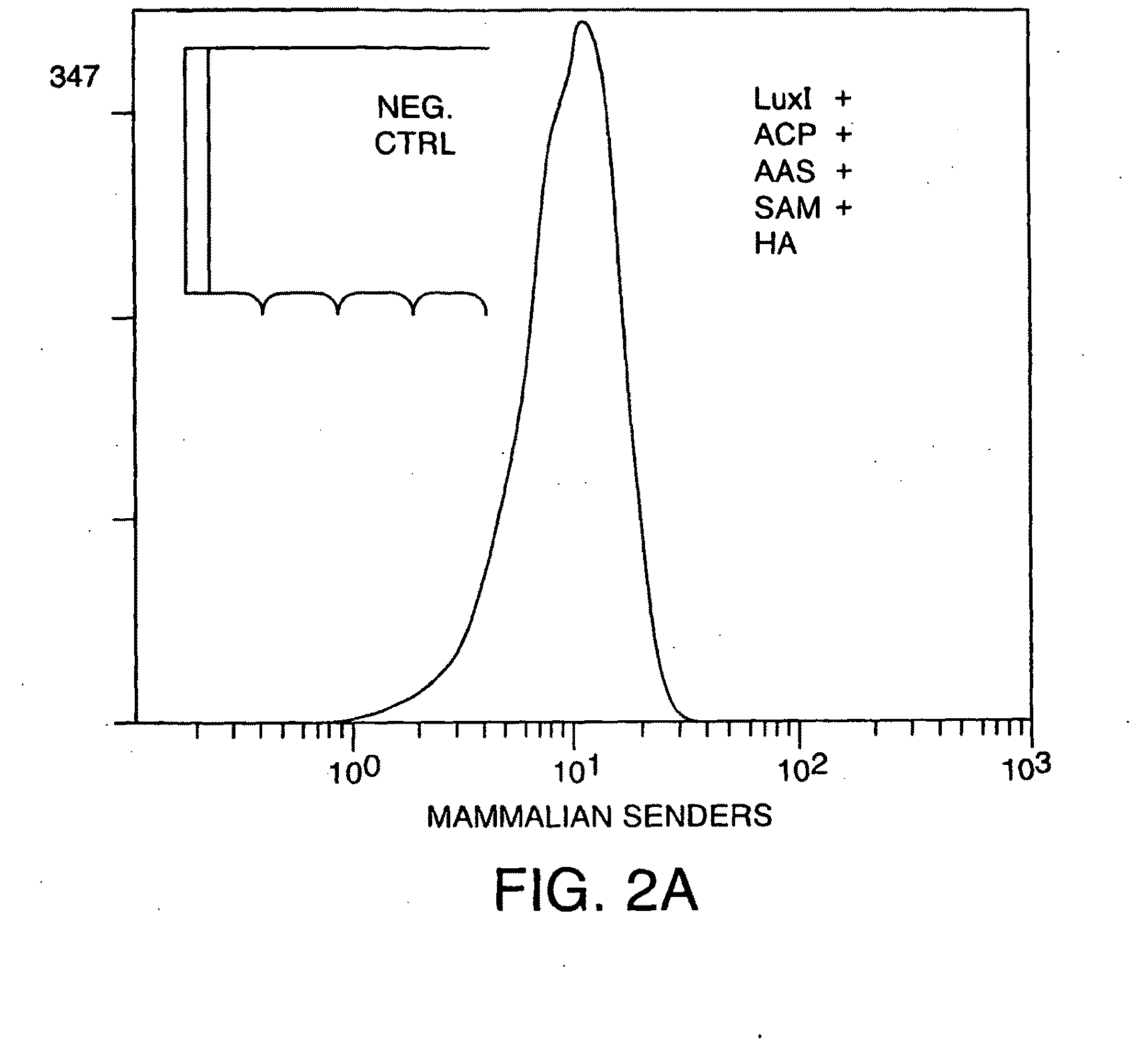
Engineered cellular pathways for programmed autoregulation of differentiation
ActiveUS20100285584A1Growth inhibitionPrevent proliferationArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCellular pathwaysCell type
The present invention provides compositions and methods for programming mammalian cells to perform desired functions. In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods for programming stem cells to differentiate into a desired cell type. A quorum sensing systems that regulates the expression of cell fate regulators is introduced into mammalian host cells, such as stem cells. The quorum sensing systems generally comprises vectors that express the components of a bacterial quorum sensing pathway, including proteins which catalyze the synthesis of an autoinducer and a gene encoding a regulatory partner of the autoinducer, and vectors in which genes encoding cell fate regulators are operably linked to a promoter induced by the autoinducer / regulatory partner complex. The system can also comprise vectors in which genes encoding additional cell fate regulators are operably linked to a promoter that is induced by a factor synthesized in response to a first stage of differentiation, so that a second stage of differentiation is triggered.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells
PendingUS20180142307A1Microbiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsCellular pathwaysFluorescent imaging
Methods and systems for recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells are provided. Molecular changes, which may result from random or specific molecular events, are introduced to defined regions in cells over multiple cell cycle generations. Techniques such as fluorescent imaging are applied to track and identify the molecular changes before such information is used for lineage analysis or for identifying key processes and key players in cellular pathways.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com