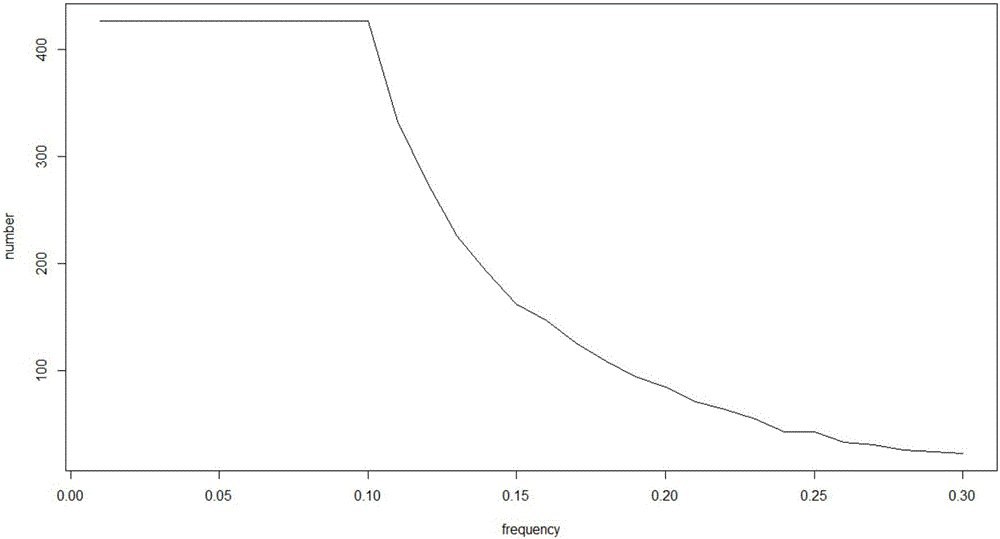
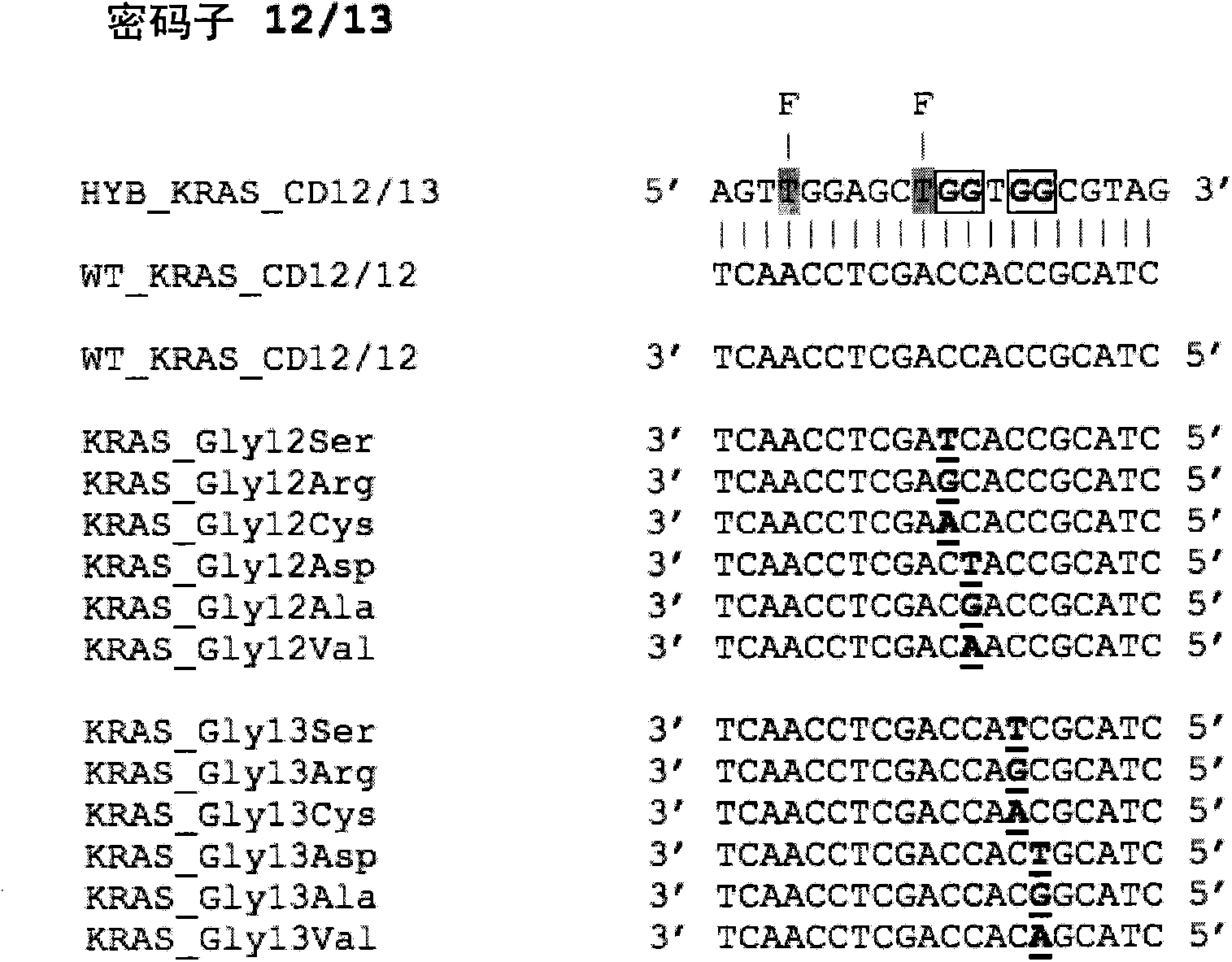
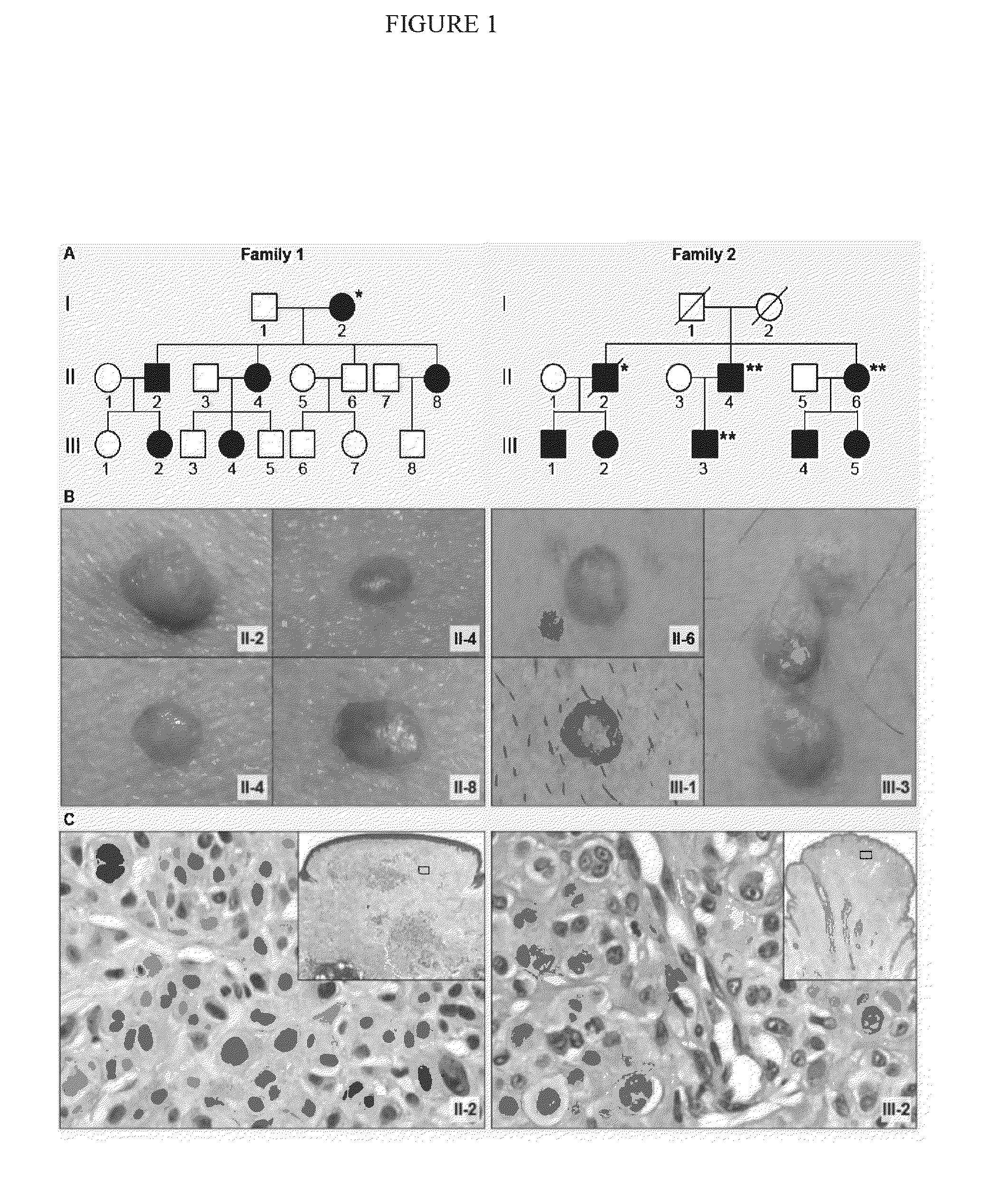
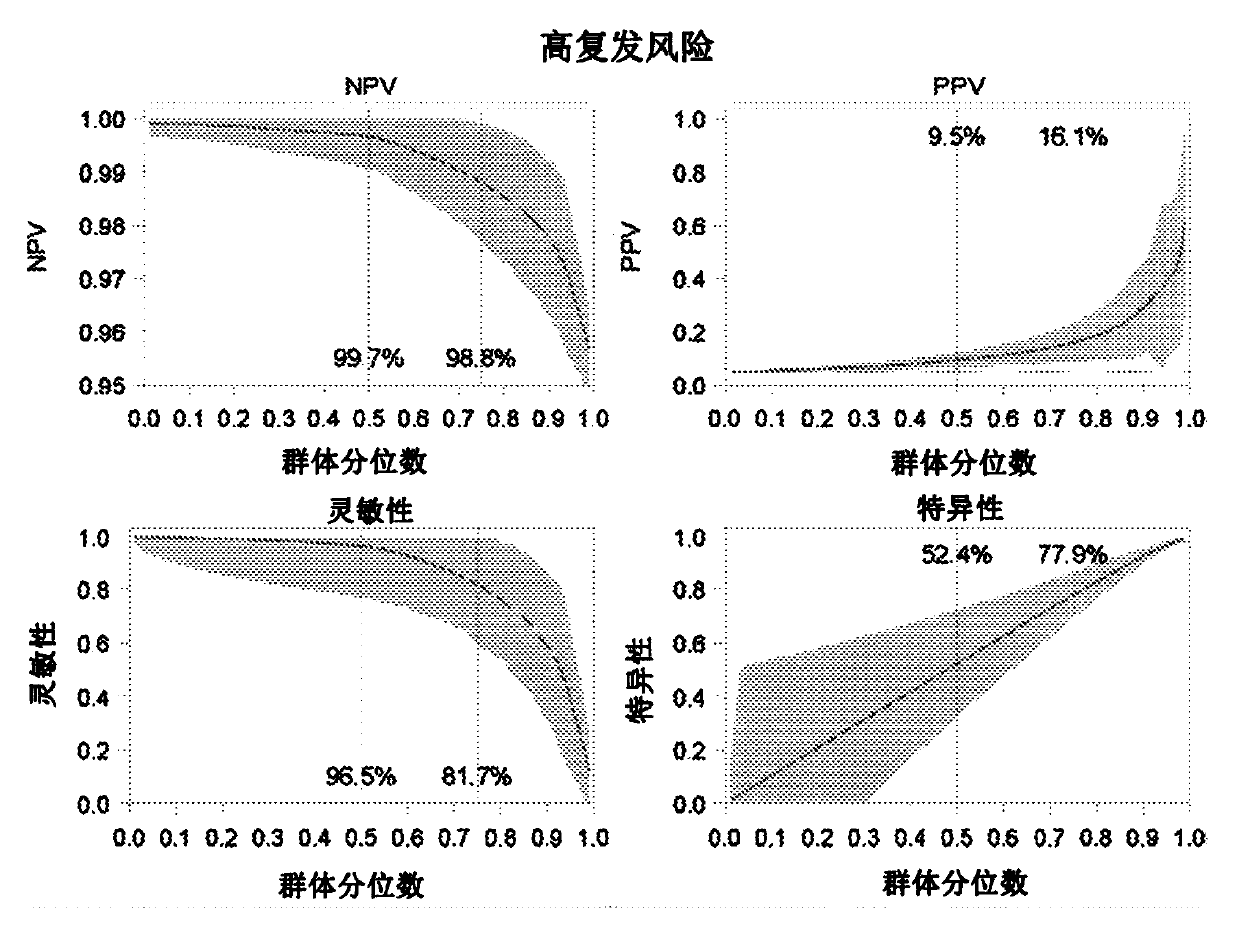
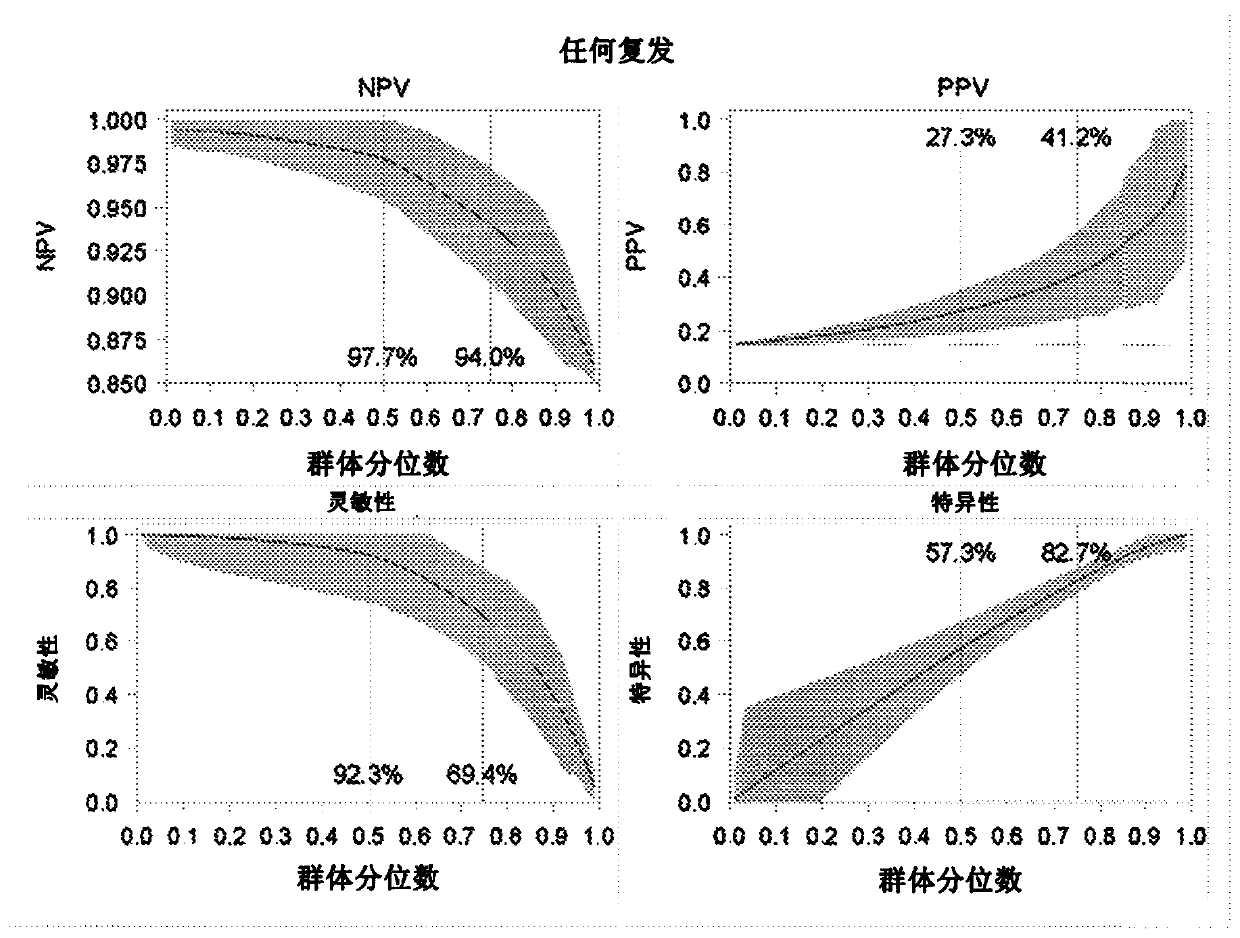
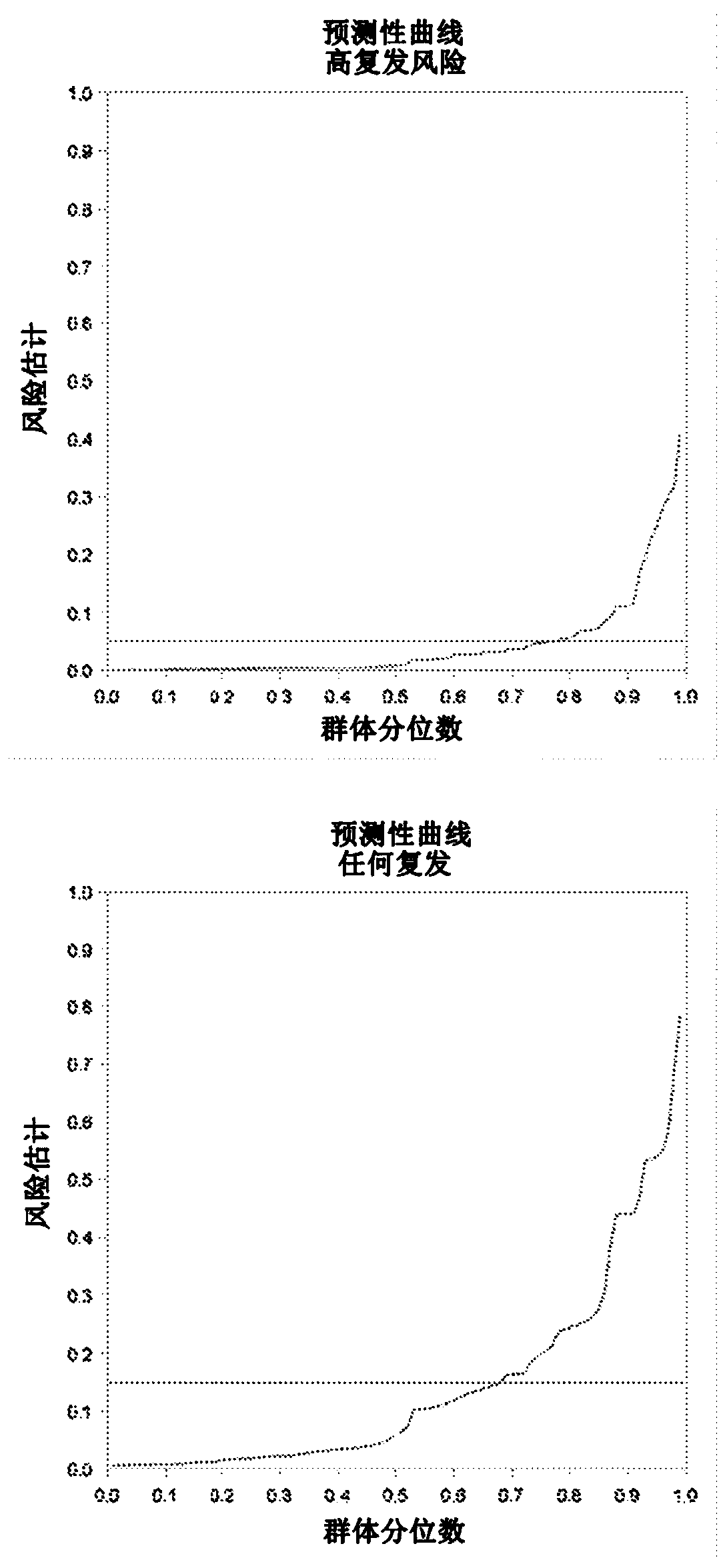
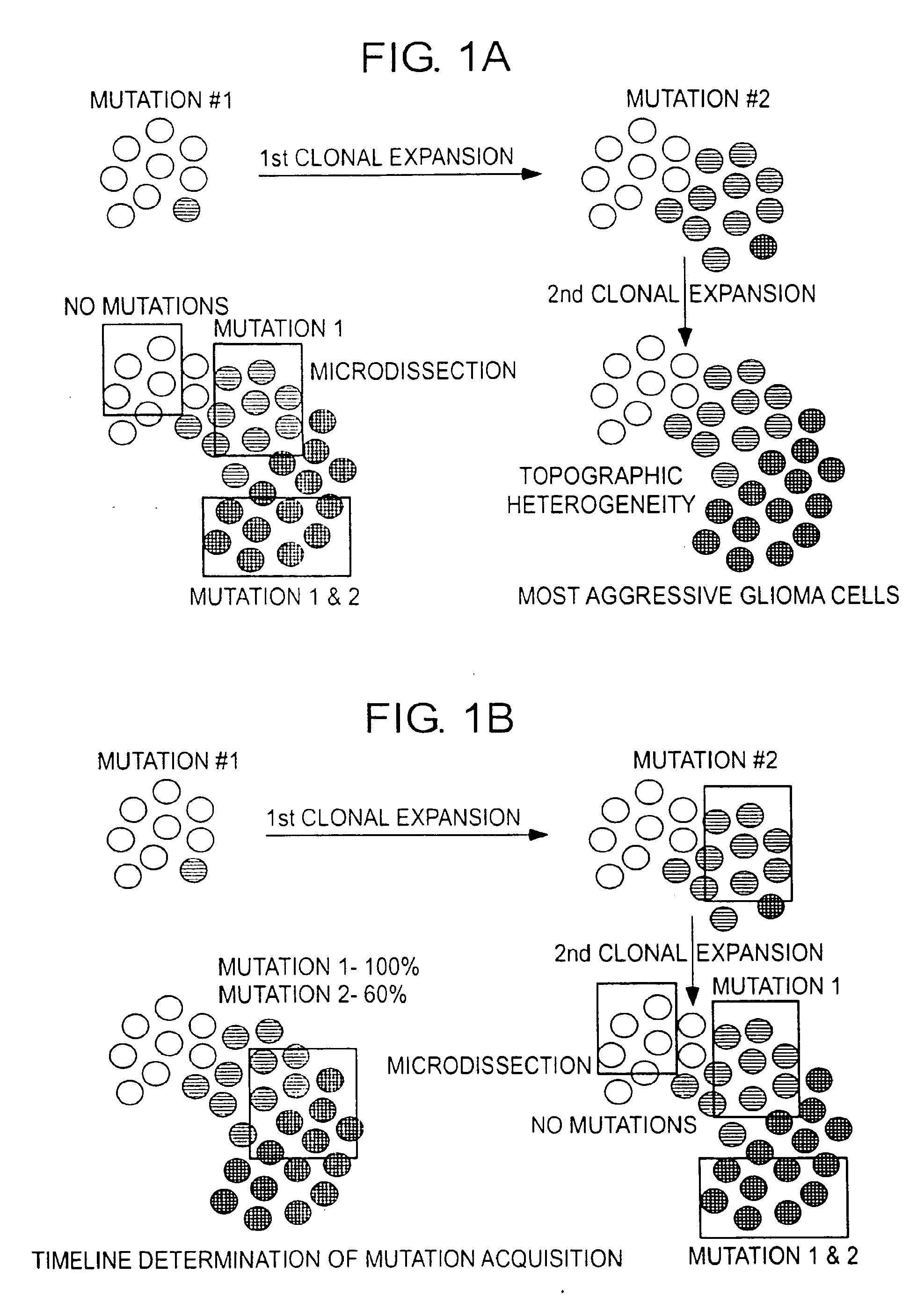
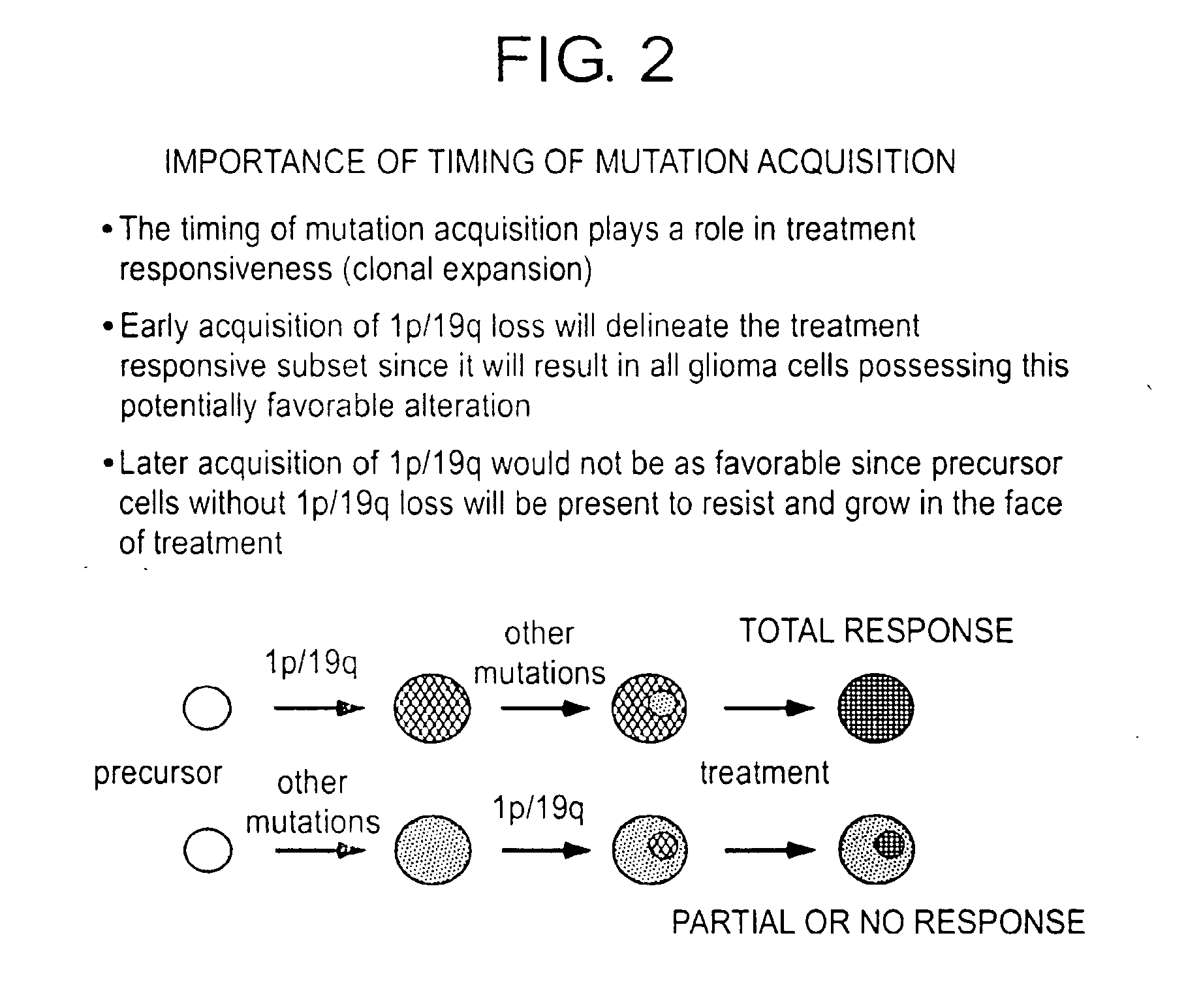
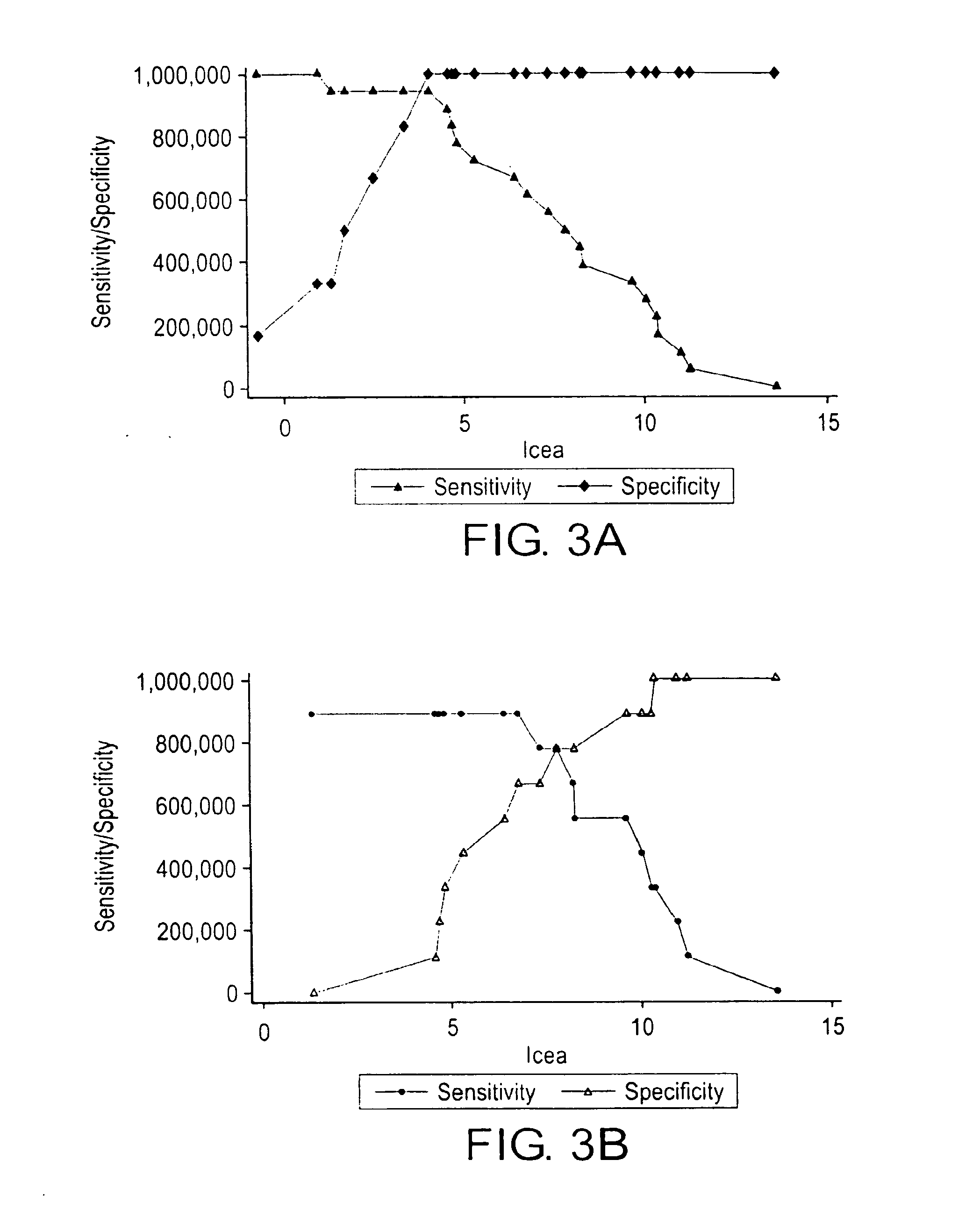
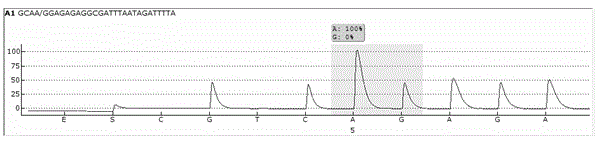
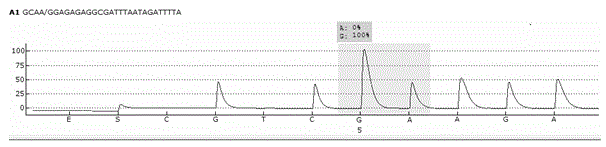
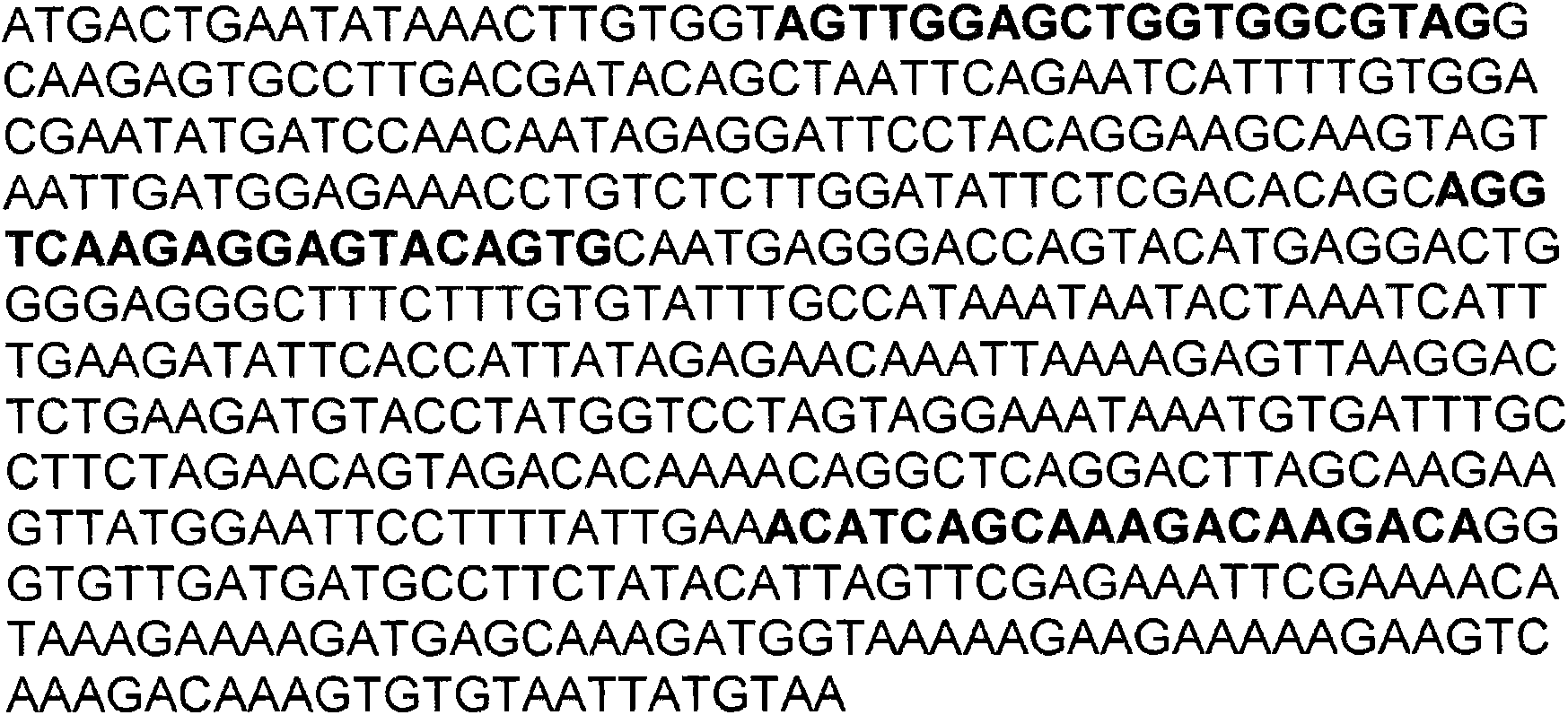Patents
Literature
56 results about "Mutational analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mutational analysis is especially important in GIST because most GISTs are defined by activating mutations in the KIT or PDGFRA genes. Moreover, the response of GISTs to certain drug treatments varies according to the mutation status of the tumors.
System, array and non-porous solid support comprising fixed or immobilized nucleic acids
InactiveUS7064197B1Easy to quantifyPromote repairSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementImmobilized Nucleic AcidsDouble strand
Nucleic acids are fixed or immobilized to non-porous solid supports (substrates), and include systems containing such supports and arrays with fixed or immobilized nucleic acids. These compositions are useful for nucleic acid analyses and a host of applications, including, for example, detection, mutational analysis and quantification. The non-porous solid supports can be transparent or translucent, and the surfaces can be treated with agents to fix or immobilize the nucleic acids. Such agents include, for example, amine providing compounds, epoxy compounds and acid solutions. The fixed or immobilized nucleic acids can be unlabeled, or labeled with at least one non-radioactive signaling moiety, such as the case when the nucleic acids are double-stranded.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
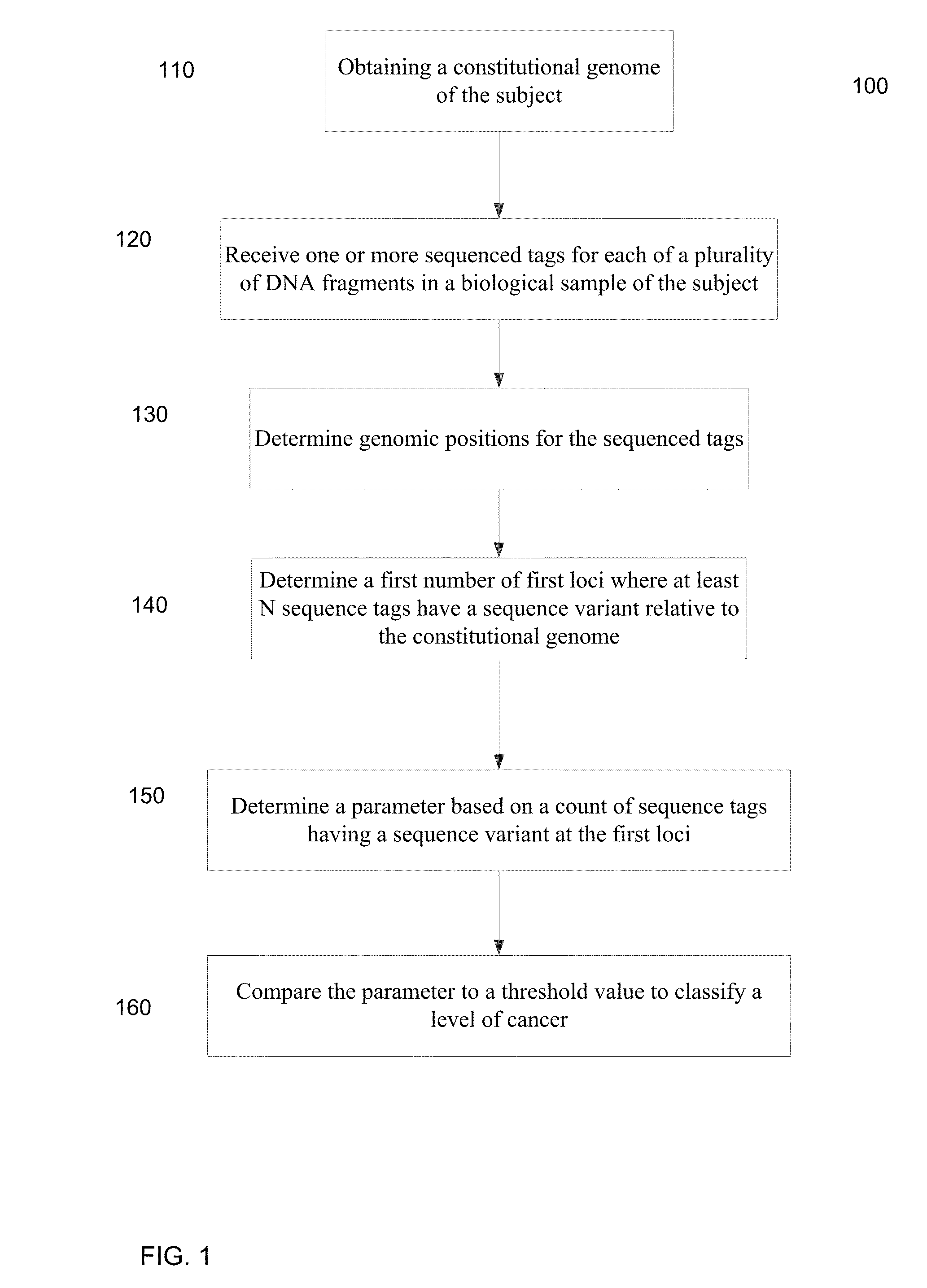
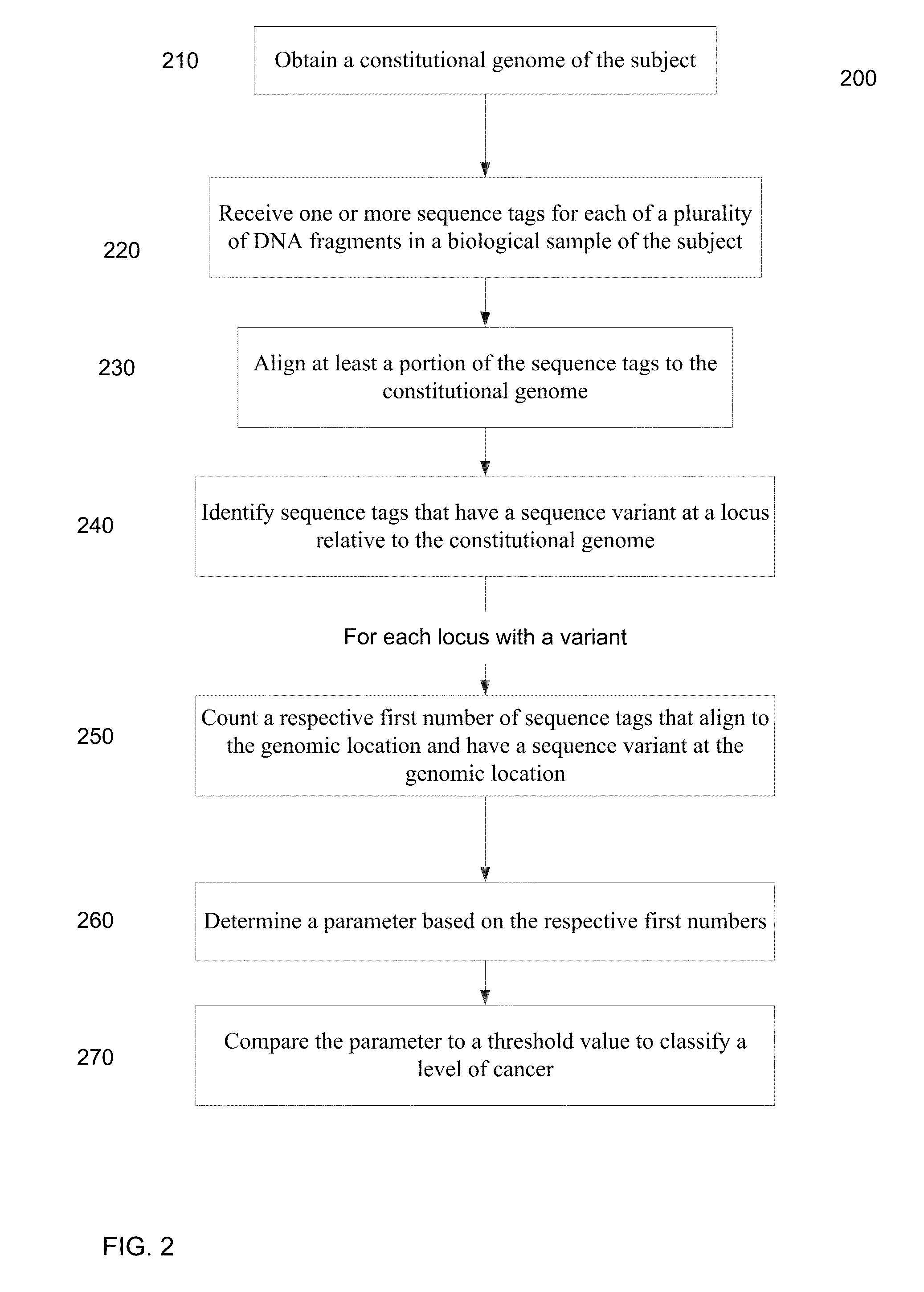
Mutational analysis of plasma DNA for cancer detection
ActiveUS20140100121A1Accurate parameterLevel of heterogeneity of tumorsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation frequencyBlood plasma
A frequency of somatic mutations in a biological sample (e.g., plasma or serum) of a subject undergoing screening or monitoring for cancer, can be compared with that in the constitutional DNA of the same subject. A parameter can derived from these frequencies and used to determine a classification of a level of cancer. False positives can be filtered out by requiring any variant locus to have at least a specified number of variant sequence reads (tags), thereby providing a more accurate parameter. The relative frequencies for different variant loci can be analyzed to determine a level of heterogeneity of tumors in a patient.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Mutation analysis using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6503710B2Rapid and economic sample preparationAccurate massSamplingSugar derivativesChemical treatmentFree form
The invention presents a method for examining genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) to detect the presence of pre-known mutations, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), using mass spectrometry with ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). The invention uses nucleoside triphosphates with modified sites for the method of primer extension in a duplicating, enzymatic reaction and at least partially removal of primers from the extension product, in combination with product neutralization by chemical treatment of the modified sites, so that the resulting DNA products can be, by using special matrix materials, preferredly ionized in an adduct-free form over other constituents in the reaction solution without any further cleaning. The method is particularly suitable for simultaneous identification of several mutations by multiplexing.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Topographic genotyping for determining the diagnosis, malignant potential, and biologic behavior of pancreatic cysts and related conditions
InactiveUS20060088870A1Easy to analyzeEnhancing definitive diagnosisHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular analysisMicrosatellite
The application relates to a method of a predicting the presence of invasive pancreatic cancer or high grade dysplasia, pre-cancerous pancreatic states and non-neoplastic conditions comprising detailed molecular analysis incorporating DNA quality and quantity, K-ras mutational analysis and a broad spectrum of tumor suppressor gene linked microsatellite LOH. Methods of diagnosing, determining prognosis of and determining a course of treatment for pancreatic cancer or high grade dysplasia, pre-cancerous pancreatic states and non-neoplastic conditions are also provided.
Owner:REDPATH INTEGRATED PATHOLOGY INC
Light addressable electrochemical detection of duplex structures
InactiveUS7829275B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideMessenger RNA
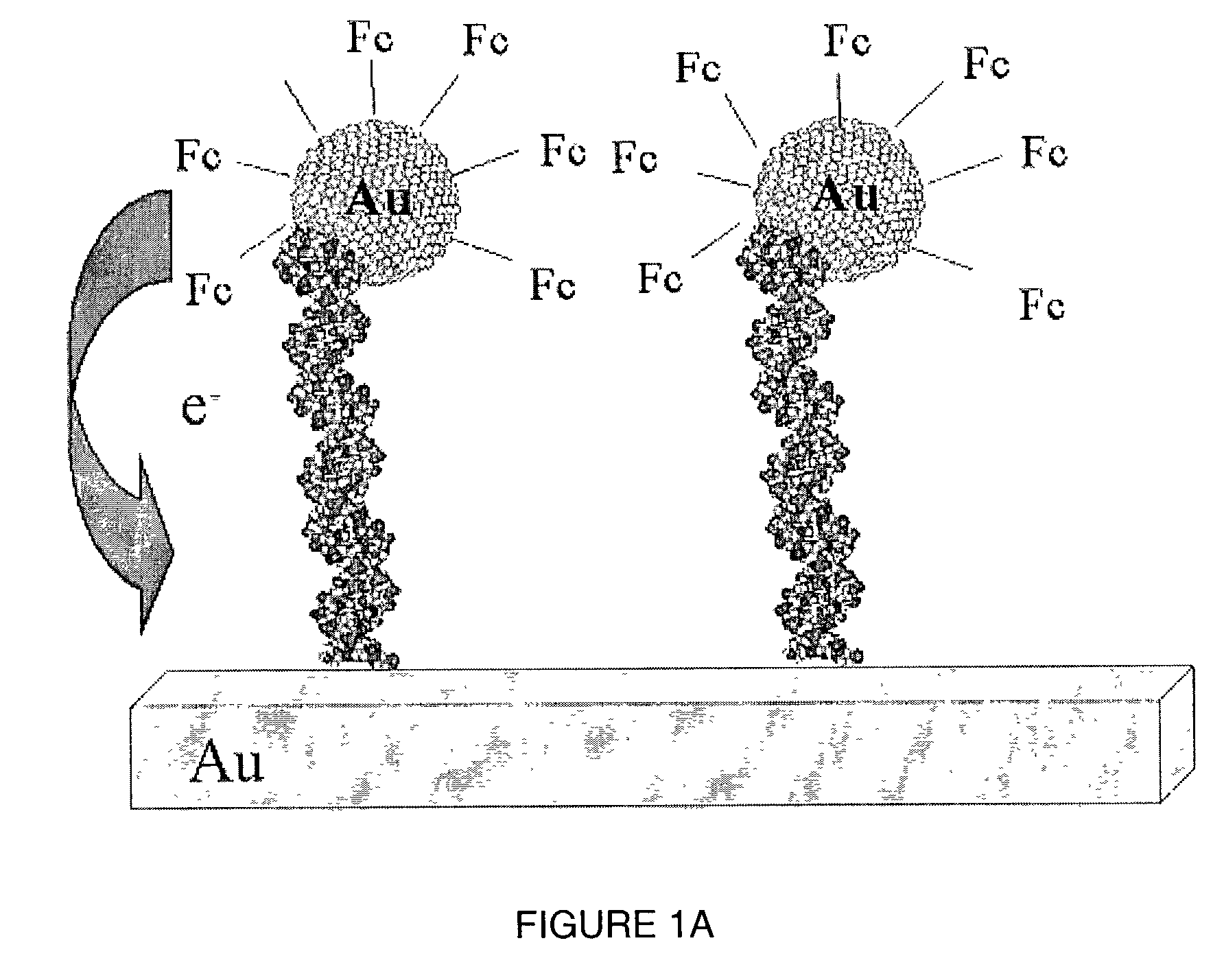
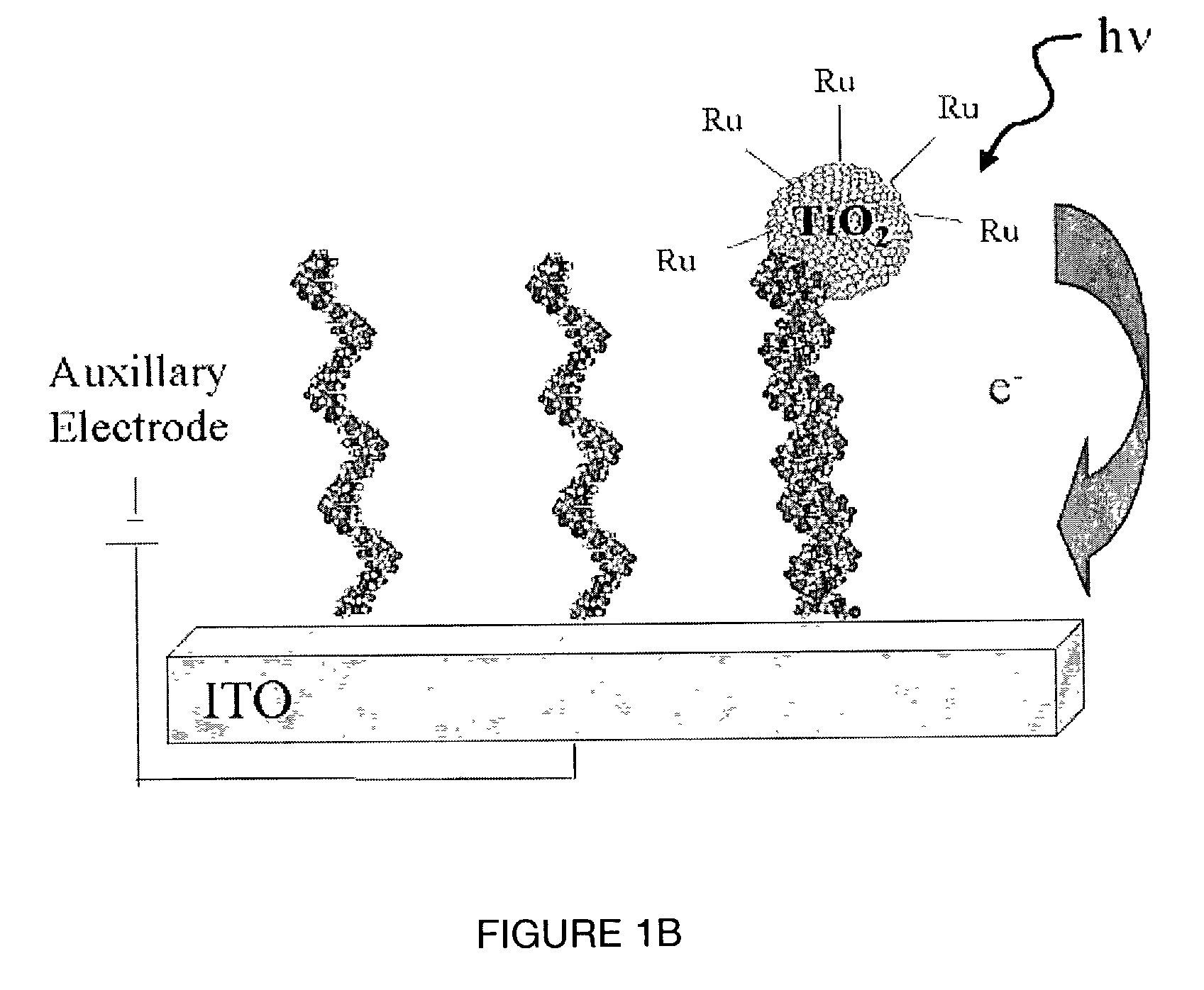
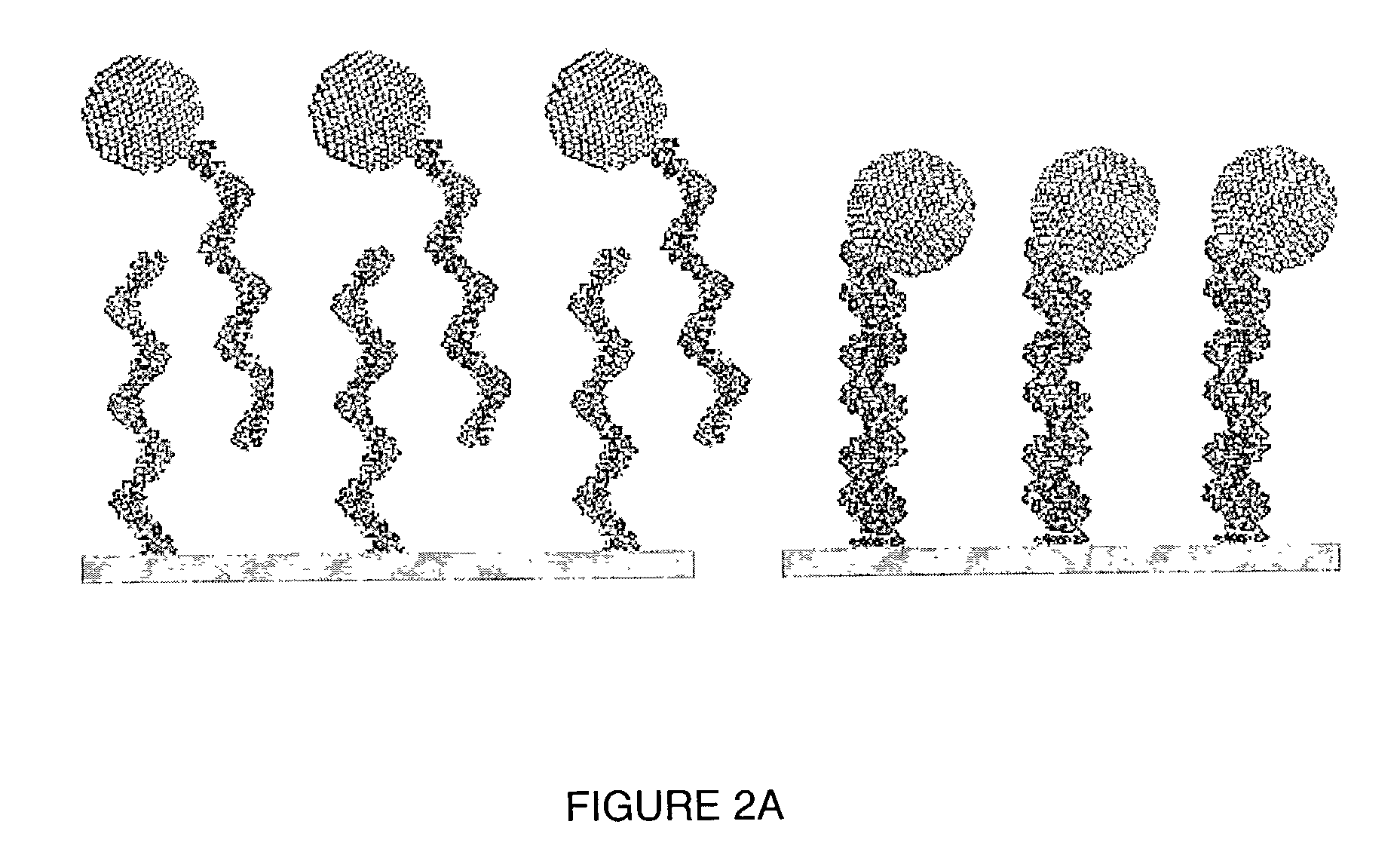
A method of detecting the presence of an analyte, such as a target nucleic acid sequence, protein sequence or small molecule, which can also be employed to detect the formation of duplex structures, is disclosed. The method can comprise nucleic acids, proteins and small molecules, employing photoelectrochemically active nanoparticles, branched polymers or other structures that carry photoelectrochemically active molecules capable of generating a photocurrent when excited by light in the presence of an electric field is disclosed. The method can be employed to detect hybridization on an array and can be employed in sequencing, mutational analysis (for example, single nucleotide polymorphisms and other variations in a population) and for monitoring gene expression by analysis of the level of expression of messenger RNA extracted from a cell. The method is applicable to the detection of antibody binding or other protein binding for analyte detection in an array format. The creation of an array addressable by light is disclosed.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Protein Tyrosine Phosphate Mutations in Cancers
ActiveUS20080039417A1Growth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthCellular pathways
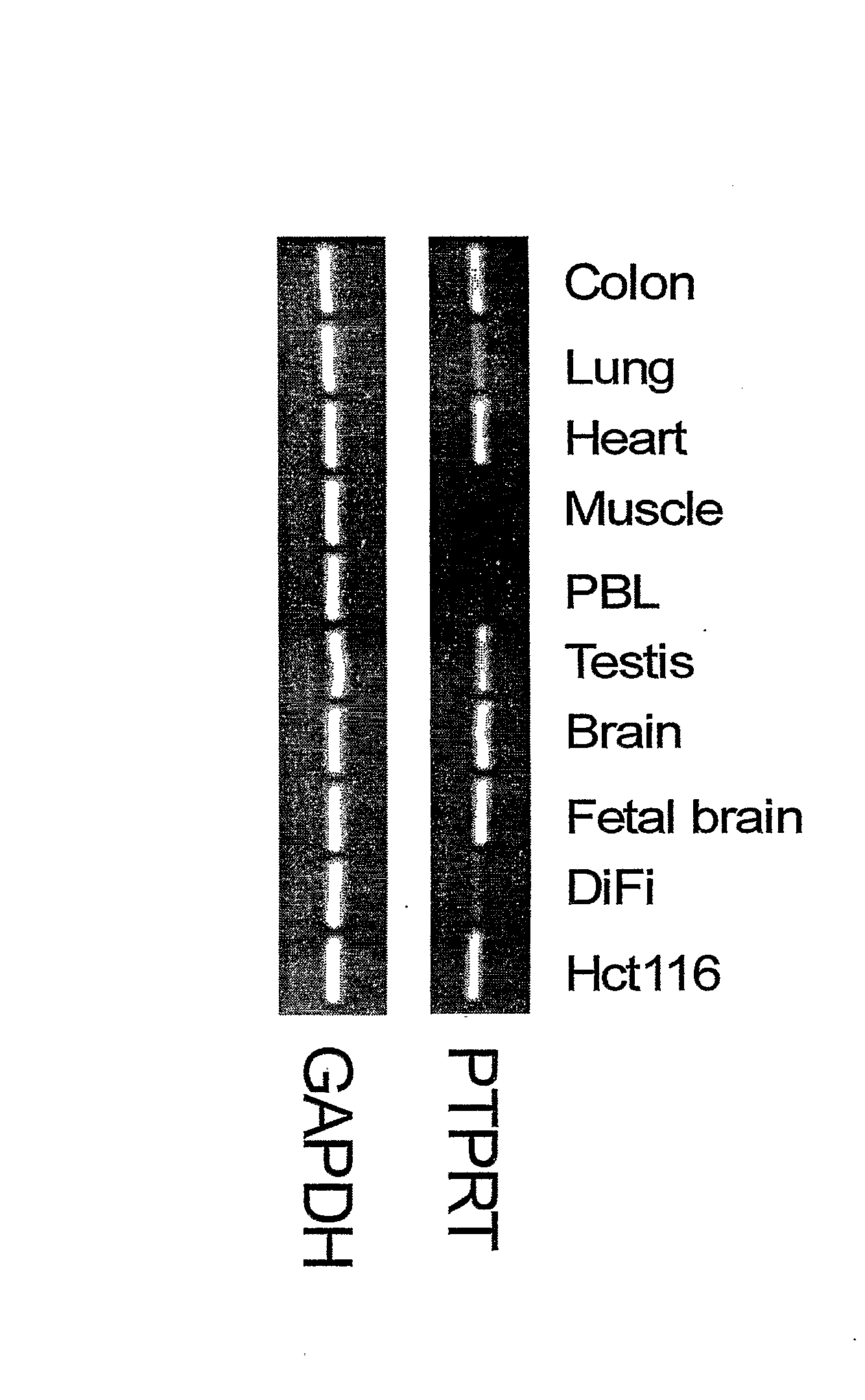
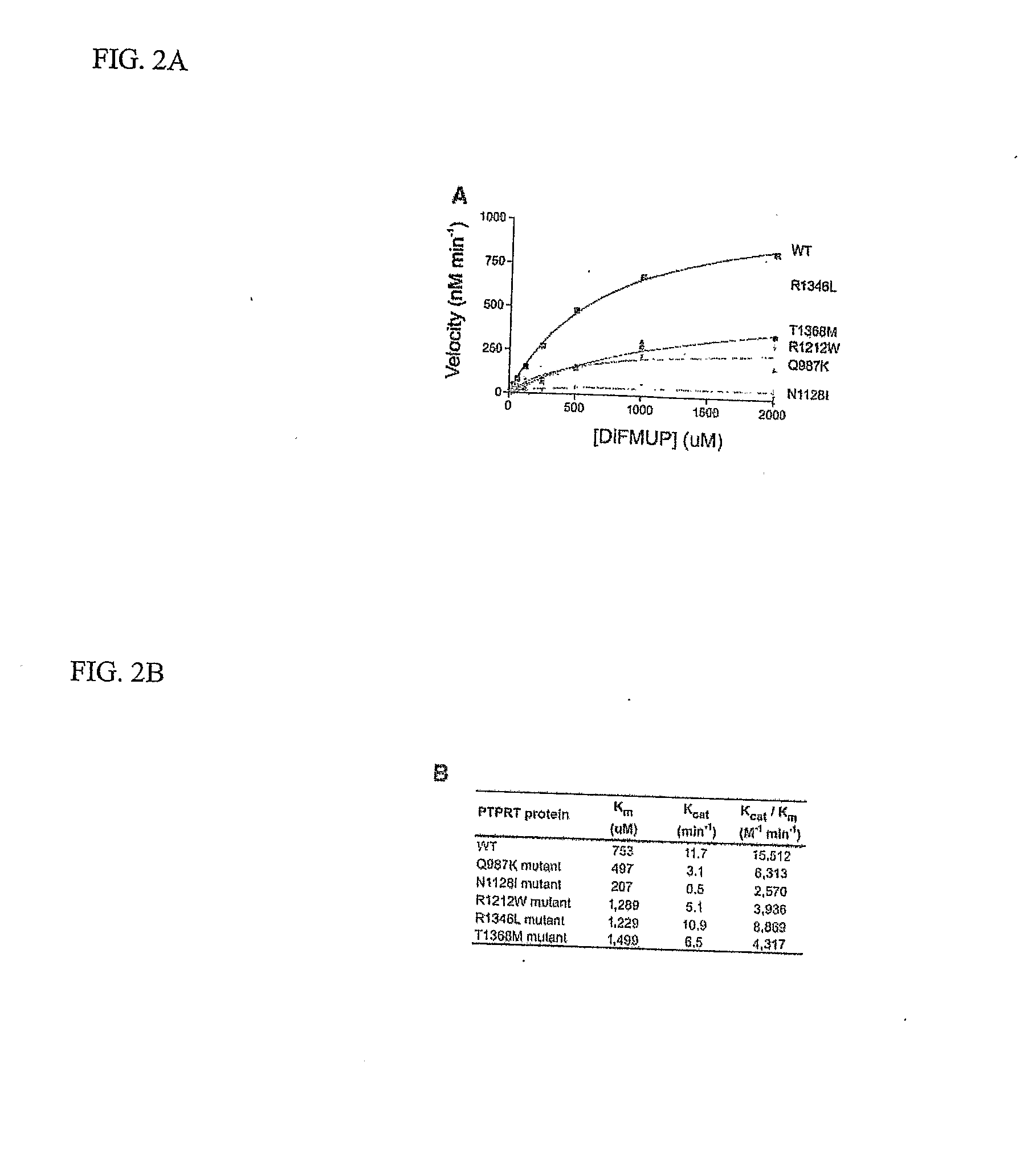
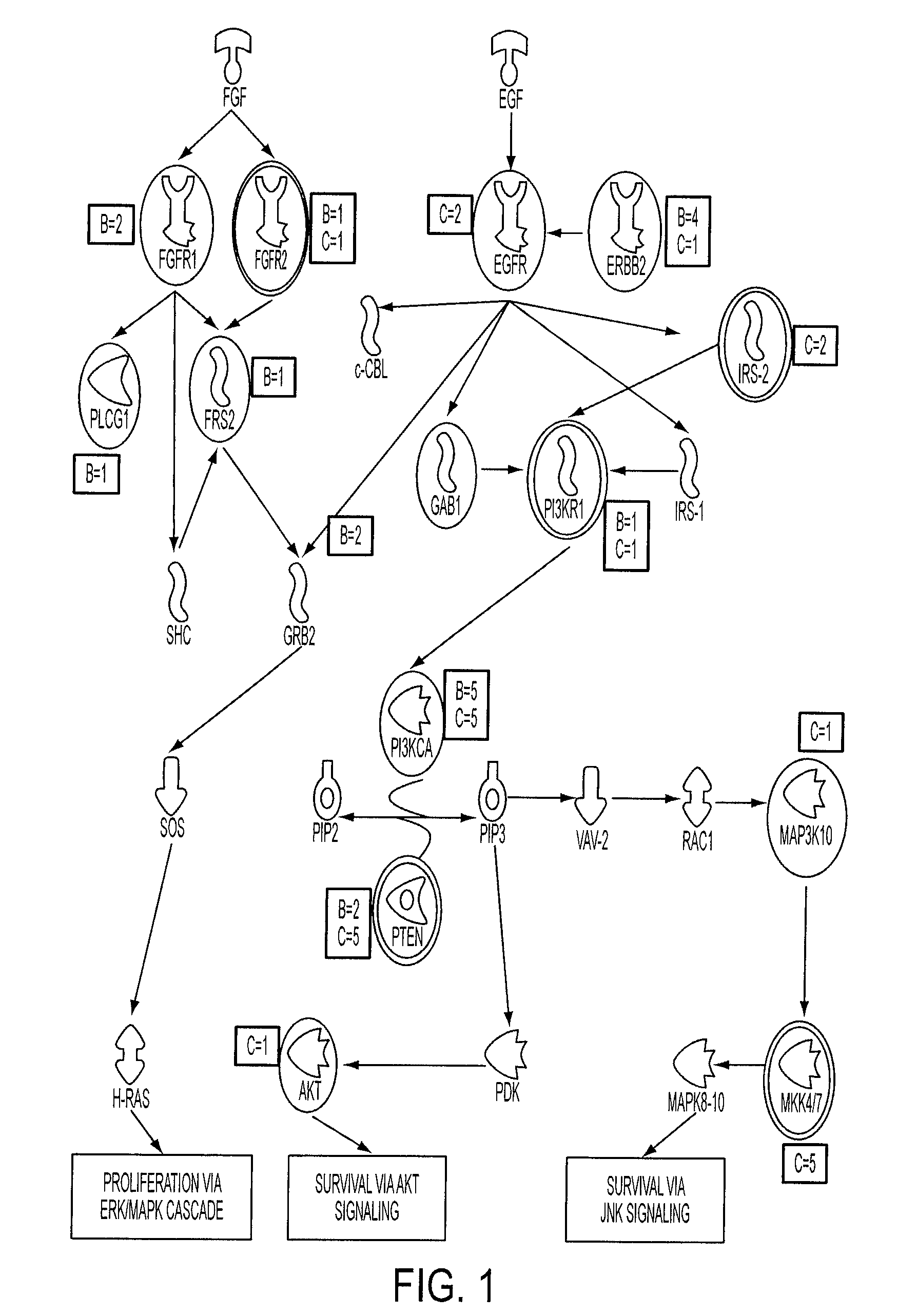
Tyrosine phosphorylation, regulated by protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) and kinases (PTKs), is important in signaling pathways underlying tumorigenesis. A mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatase gene superfamily in human cancers identified 83 somatic mutations in six PTPs (PTPRF, PTPRG, PTPRT, PTPN3, PTPN13, PTPN14) affecting 26% of colorectal cancers and a smaller fraction of lung, breast and gastric cancers. Fifteen mutations were nonsense, frameshift or splice site alterations predicted to result in truncated proteins lacking phosphatase activity. Five missense mutations in the most commonly altered PTP (PTPRP) were biochemically examined and found to reduce phosphatase activity. Expression of wild-type but not a mutant PTPRT in human cancer cells inhibited cell growth. These observations suggest that the tyrosine phosphatase genes are tumor suppressor genes, regulating cellular pathways that may be amenable to therapeutic intervention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Mutation analysis method and device for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) sequencing data
InactiveCN112111565AHigh mutation sensitivityImprove verification accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsRepetitive SequencesSomatic cell
The invention relates to a mutation analysis method and device for cell-free DNA (cfDNA) sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing original sequencing data; 2, comparing the sequencing data with a reference standard genome, identifying and eliminating PCR repetitive sequences, and correcting comparison errors of sequences to obtain an accurate sequence comparisonfile; 3, identifying tumor-related somatic cell variation sites, adopting a Sentieon software TNScope tool, setting parameters to ensure that cfDNA variation sites higher than 5 / 10000 variation abundance can be detected, and obtaining a potential tumor-related somatic cell variation site table; and 4, analyzing and identifying the highly credible low-frequency variation, and finally obtaining an expected positive variation analysis result. The method can achieve ultrahigh mutation sensitivity detection and high verification accuracy.
Owner:上海其明信息技术有限公司
Integrated Analyses of Breast and Colorectal Cancers
InactiveUS20100136560A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsCellular pathwaysIntracellular signalling
Genome-wide analysis of copy number changes in breast and colorectal tumors used approaches that can reliably detect homozygous deletions and amplifications. The number of genes altered by major copy number changes—deletion of all copies or amplification of at least twelve copies per cell—averaged thirteen per tumor. These data were integrated with previous mutation analyses of the Reference Sequence genes in these same tumor types to identify genes and cellular pathways affected by both copy number changes and point alterations. Pathways enriched for genetic alterations include those controlling cell adhesion, intracellular signaling, DNA topological change, and cell cycle control. These analyses provide an integrated view of copy number and sequencing alterations on a genome-wide scale and identify genes and pathways that are useful for cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Second-generation sequencing method for dimolecular self-checking library preparation and hybrid capture used for trace DNA ultralow frequency mutation detection
ActiveCN107604046AIncrease profitHigh yieldNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary preparationData error
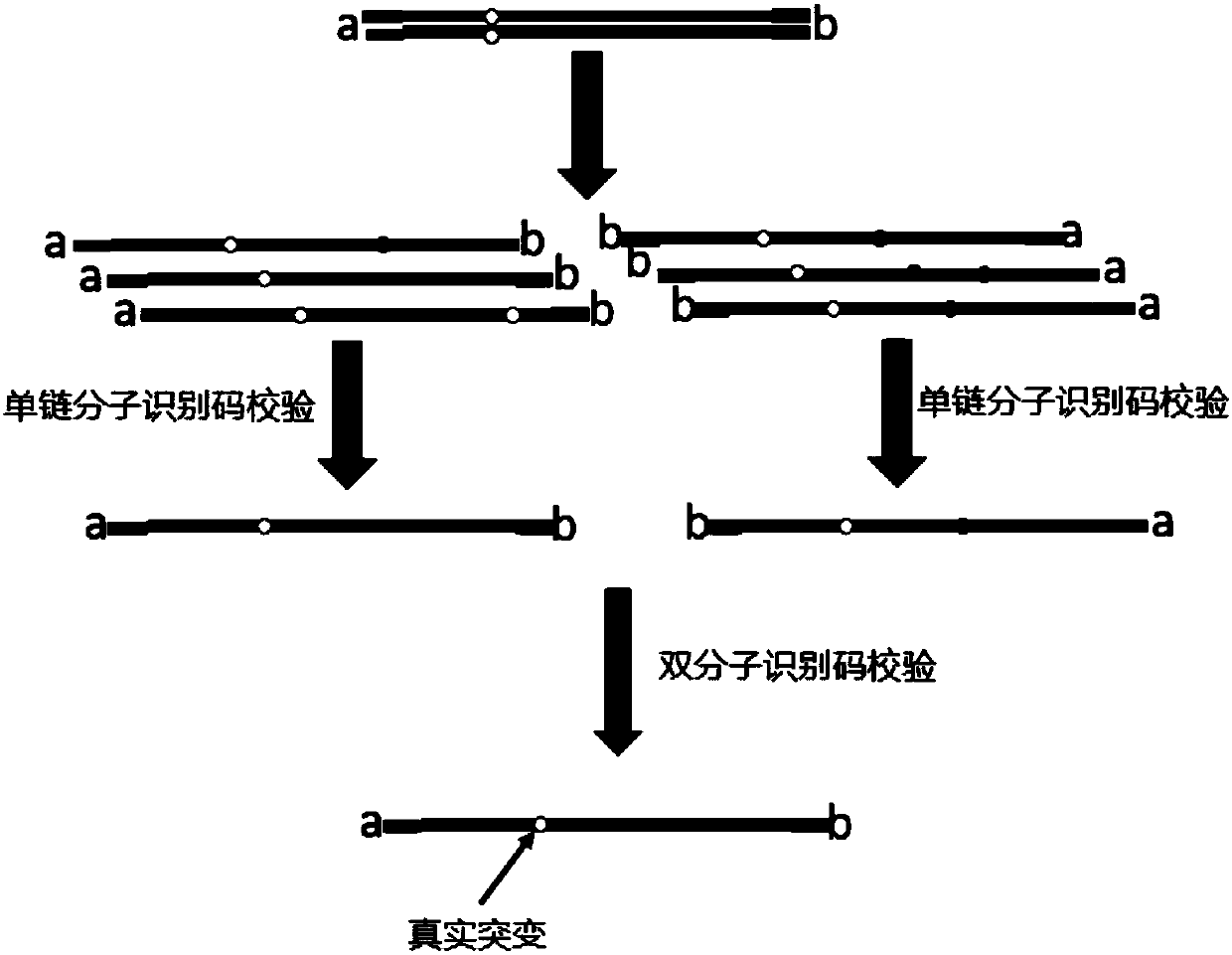
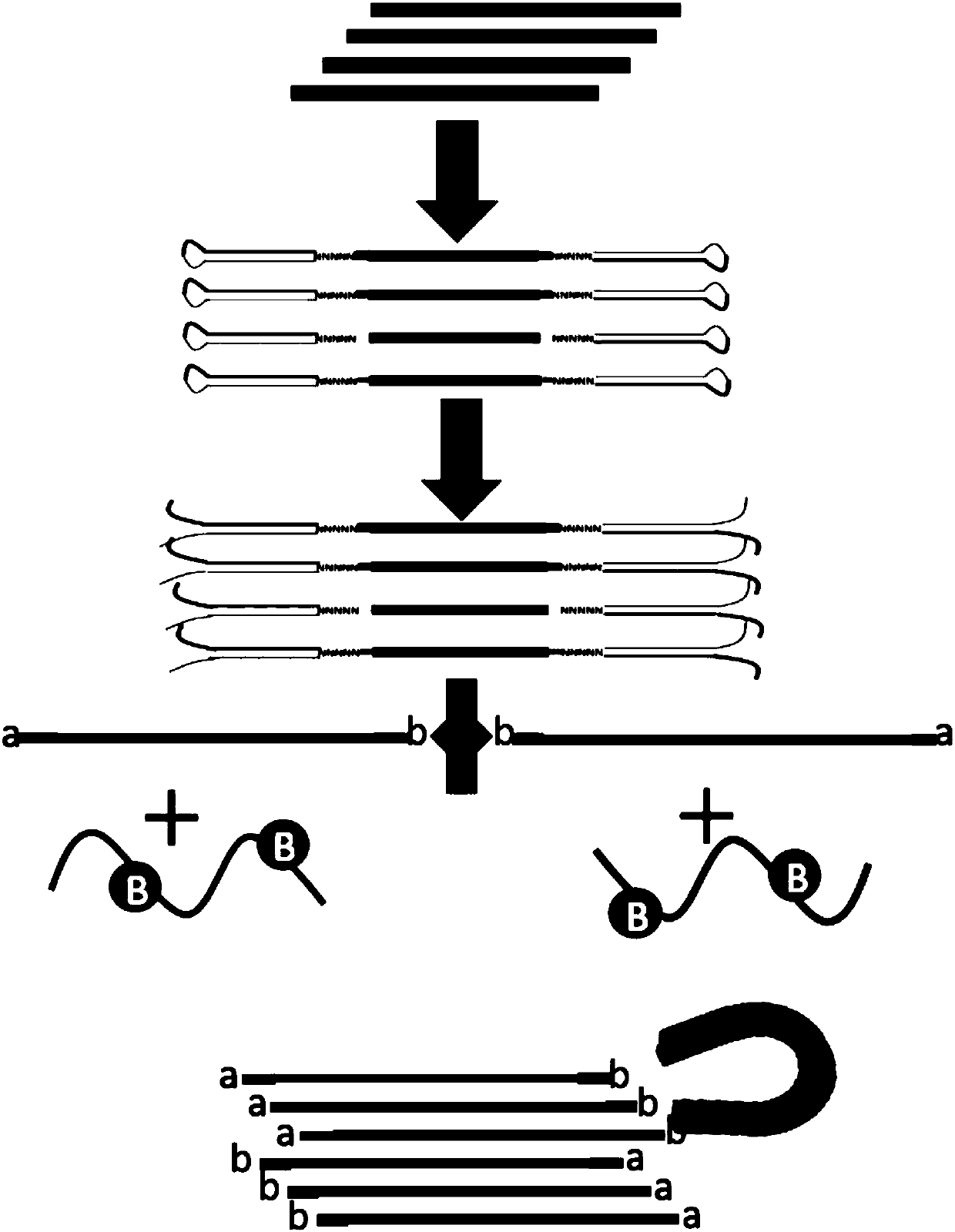
The invention discloses a second-generation sequencing method for dimolecular self-checking library preparation and hybrid capture used for trace DNA ultralow frequency mutation detection. The methodcomprises the following steps: extracting plasma free DNA, performing DNA chemical error repair, preparing a self-checking dimolecular identification code hairpin type joint, repairing plasma free DNA, connecting DNA with the joint, and performing Pre-PCR amplification, excessive hybrid capture, Post-PCR amplification, computer sequencing, data error correction, and mutation analysis and annotation. The method disclosed by the invention can efficiently realize low frequency mutation detection of plasma free DNA. DNA error repair and dual redundancy checking technology can enable the method tohave ultralow false positive rate and high sensitity while detecting trace samples, thus avoiding defects of existing plasma circulating free DNA detection methods, not only realizing cancer mutationdetection and targeted medication guidance, but also realizing early screening of genetic and birth defects of fetus.
Owner:SHANGHAI DYNASTYGENE CO
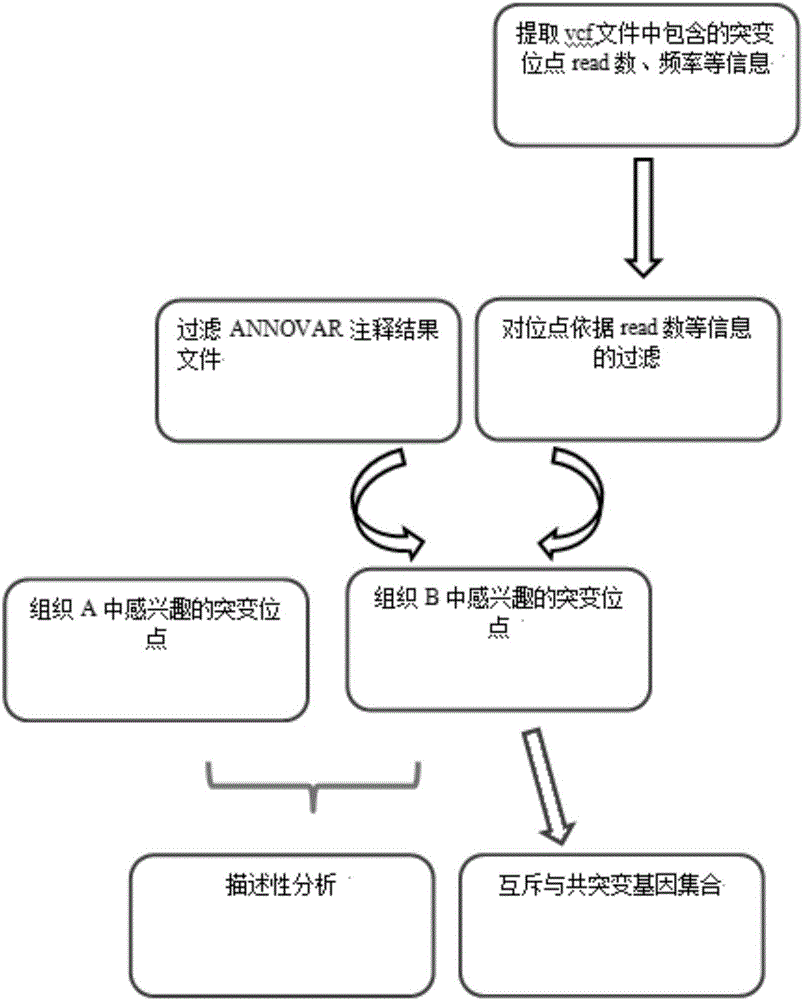
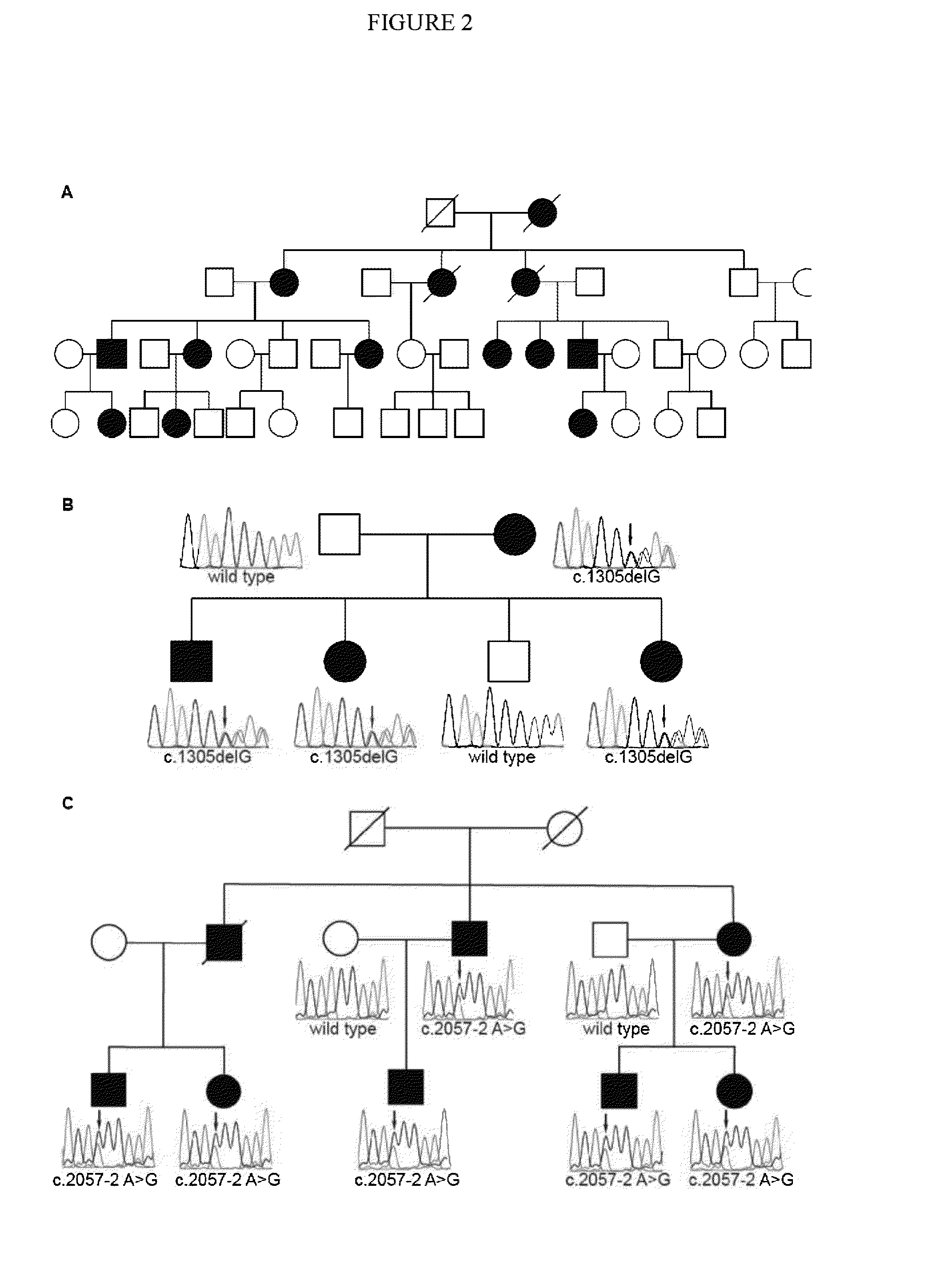
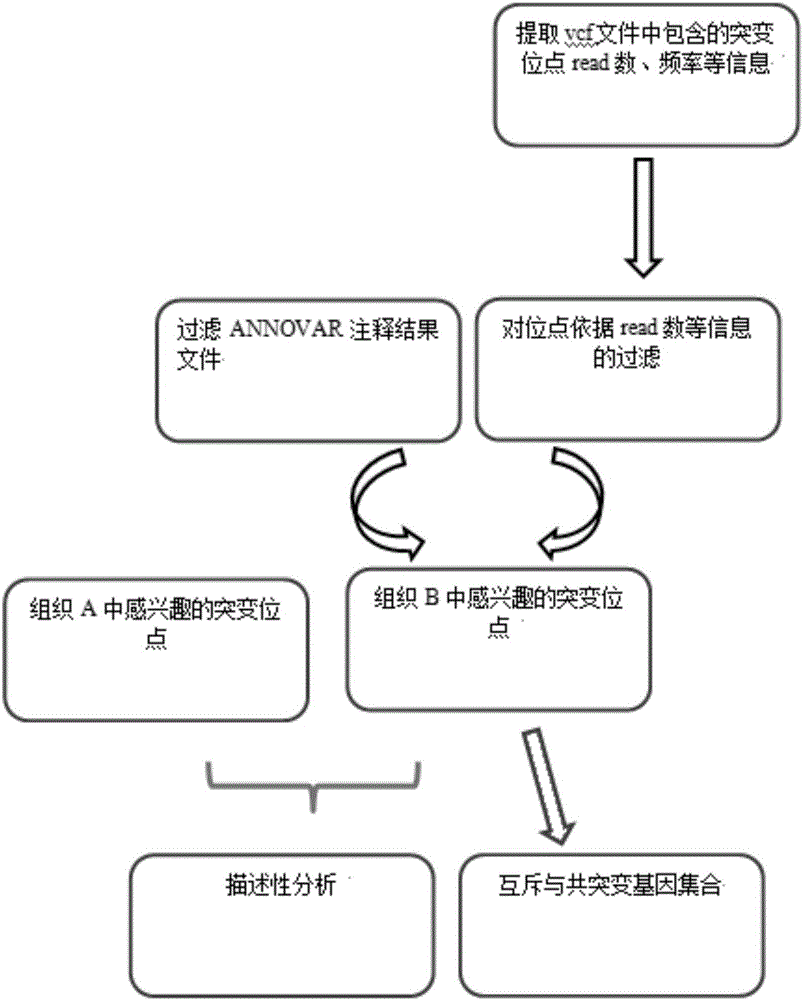
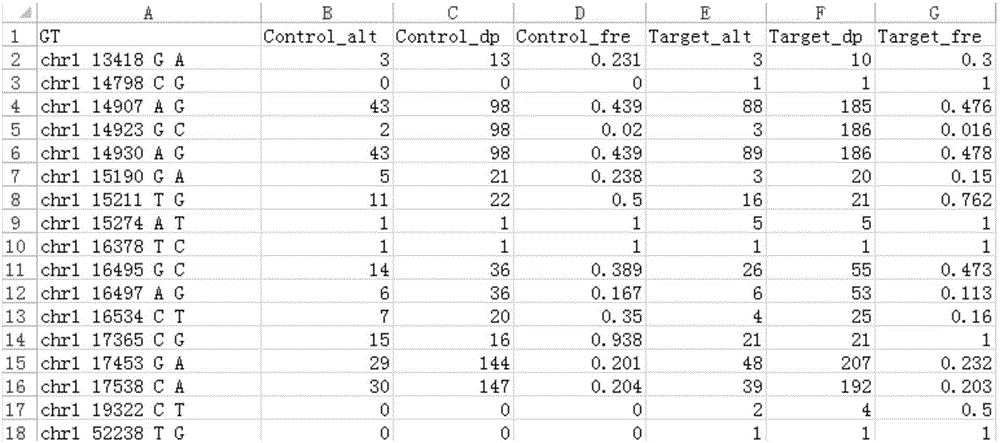
Tumor mutation site screening and mutual exclusion gene mining method
InactiveCN106021994AFacilitate biological interpretationHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsWilms' tumorAnnotation
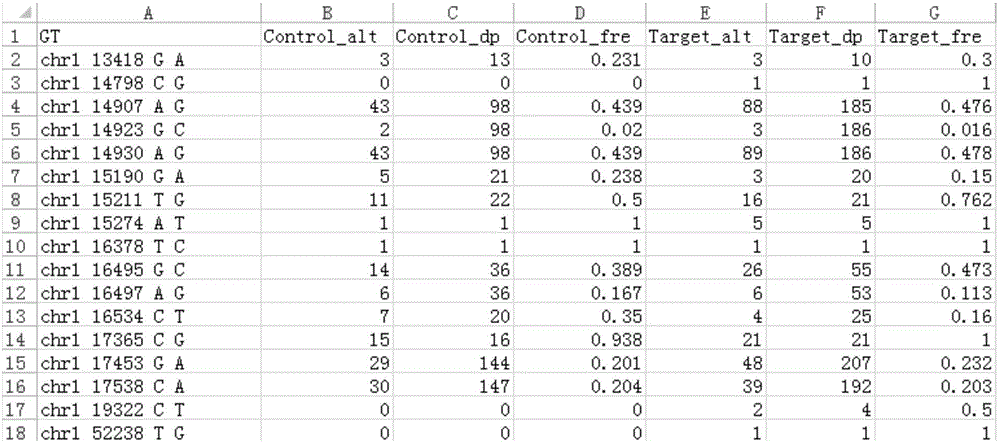
The invention provides a tumor mutation site screening and mutual exclusion gene mining method, which comprises the following steps: (1) filtering a vcf file and an output file of ANNOVAR annotation software; (2) carrying out the descriptive analysis of different experimental groups of mutation sites; (3) constructing a mutation gene matrix; and (4) carrying out mutual exclusion and joint mutation analysis on the generated mutation gene matrix on the basis of a Fisher exact test to determine a mutual exclusion and joint mutation gene. The mutation site is filtered by the annotation information of the mutation site and basic parameters including a sequencing read number, site sequencing depth and the like, and then, the obtained mutation site is subjected to the descriptive analysis of different experimental groups of mutation modes and the mining of a mutual exclusion and joint mutation gene set.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
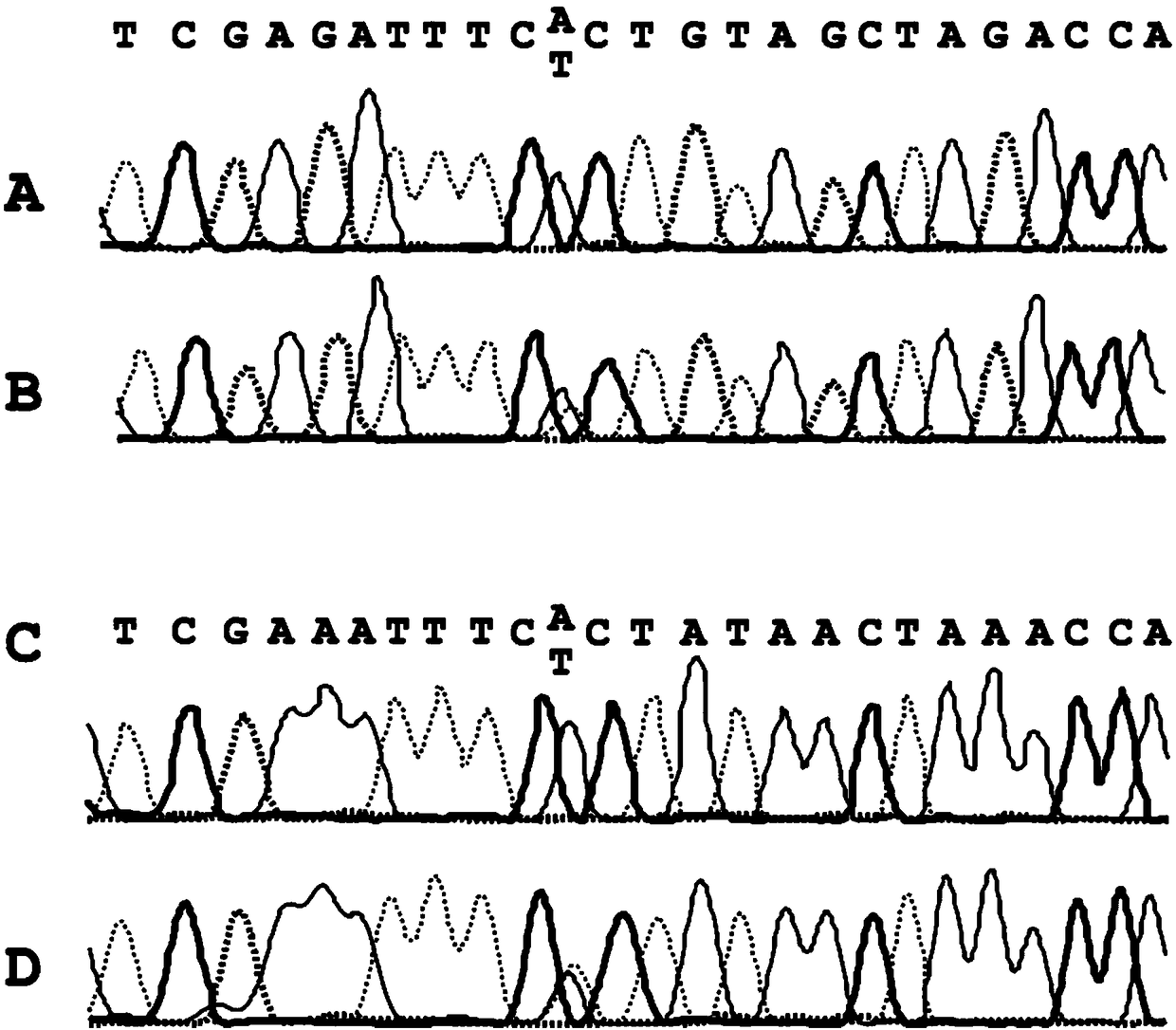
Mutational analysis
A method for analysing genetic mutations, and in particular single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and / or somatic mutations, is described, as well as methods for preferentially amplifying one allelic form compared with another form. The methods use an oligonucleotide probe which hybridises to a first allele with a lower melting temperature (Tm) than that with which it hybridises to a second allele, together with amplification primers which flank the oligonucleotide probe binding site and which bind to the sample with a higher Tm than that of the probe and the first allele. An amplification reaction may be carried out at a temperature such that the probe is preferentially hybridised to the second allele, thereby amplifying the first allele. The amplified sequences may be detected using the same probe as acted as the blocking probe during amplification.
Owner:EPISTEM
Bap1 mutational analysis in determining susceptibility to, prognosis of, and treatment of melanocytic neoplasia
InactiveUS20140011696A1Increased riskMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMelanocytomaNeoplasm
Methods and compositions for diagnosing and prognosing neoplasms, particularly malignant melanomas, and for identifying patients at high risk for melanocytic nevi and / or melanomas or other cancers are provided. Methods for distinguishing between nevi at high and low risk for malignant transformation and for characterizing or classifying lesions or nevi are also disclosed. Assays and kits for prognosis of melanoma in a human subject comprising assessment of BAP1 protein and / or BAP1 nucleic acid are provided.
Owner:MEDICAL UNIV OF GRAZ +1
Tumor mutation site screening and mutual exclusion gene mining system
InactiveCN106022001AFacilitate biological interpretationBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGene miningAnnotation
The invention provides a tumor mutation site screening and mutual exclusion gene mining system. The system comprises a filtering module which is used for filtering a vcf file and an ANNOVAR software output file in an exome processing process; an analysis module which is used for carrying out description analysis on different experiment group mutation sites; a gathering module which is used for gathering mutation genes of each sample and establishing a mutation gene matrix according to an experiment group mutation gene list; and a mining module which is used for carrying out Fisher precise checking based mutual exclusion and co-mutation analysis on the generated mutation gene matrix, thereby determining mutual exclusion and co-mutation genes. According to system, the mutation sites are filtered according to basic parameters such as annotation information of the mutation sites, the sequencing read number and site sequencing depth; and description analysis of different experiment group mutation modes and mining of co-mutation and mutual exclusion gene sets are carried out on the obtained mutation sites.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Mutation detection and identification
ActiveUS20030194724A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMutation detectionAllele
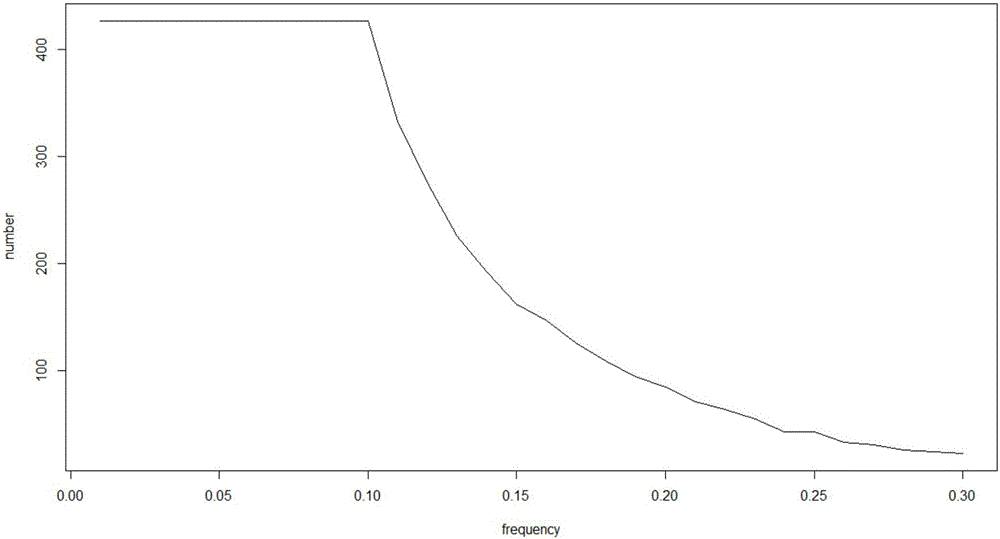
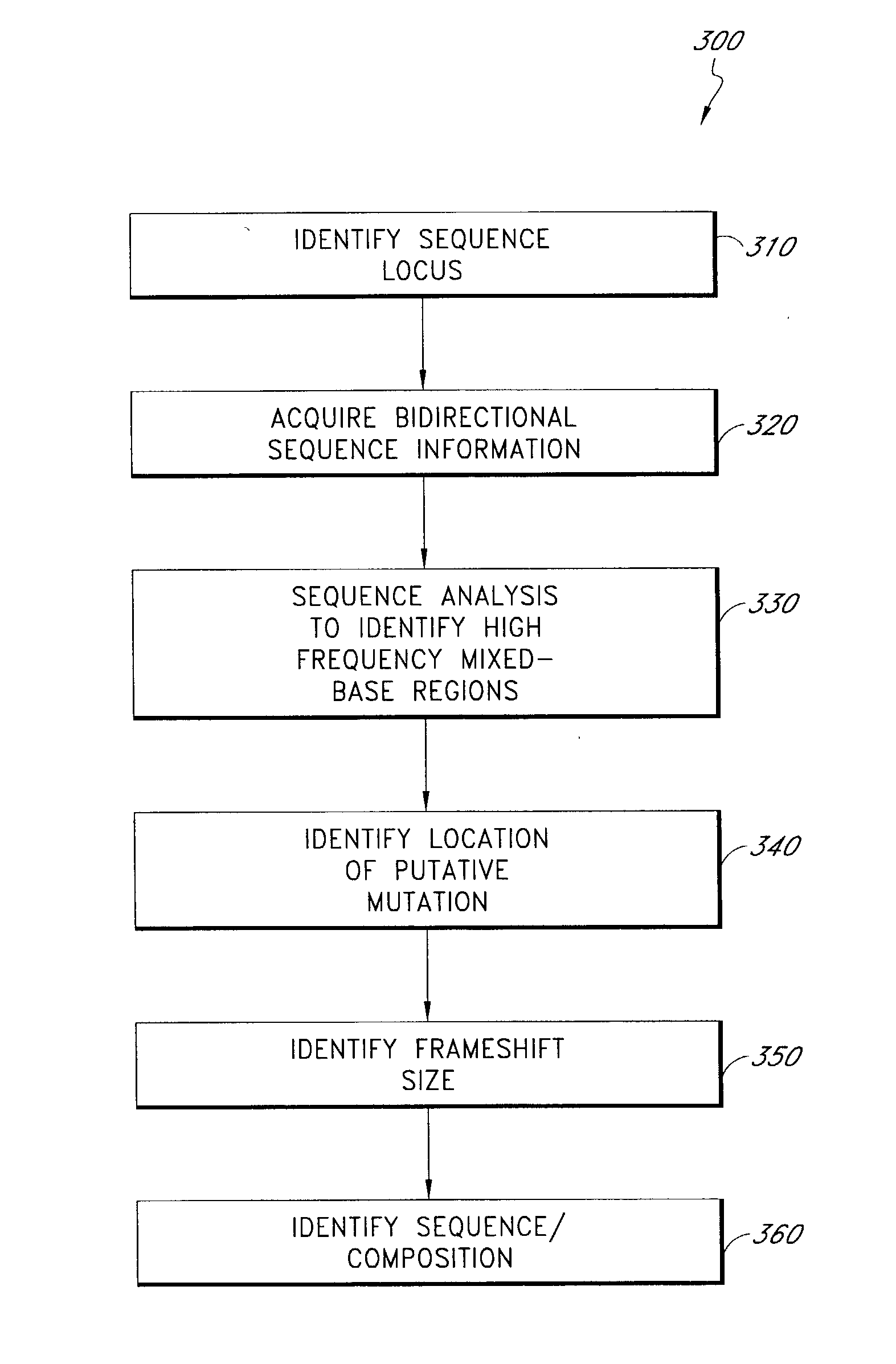
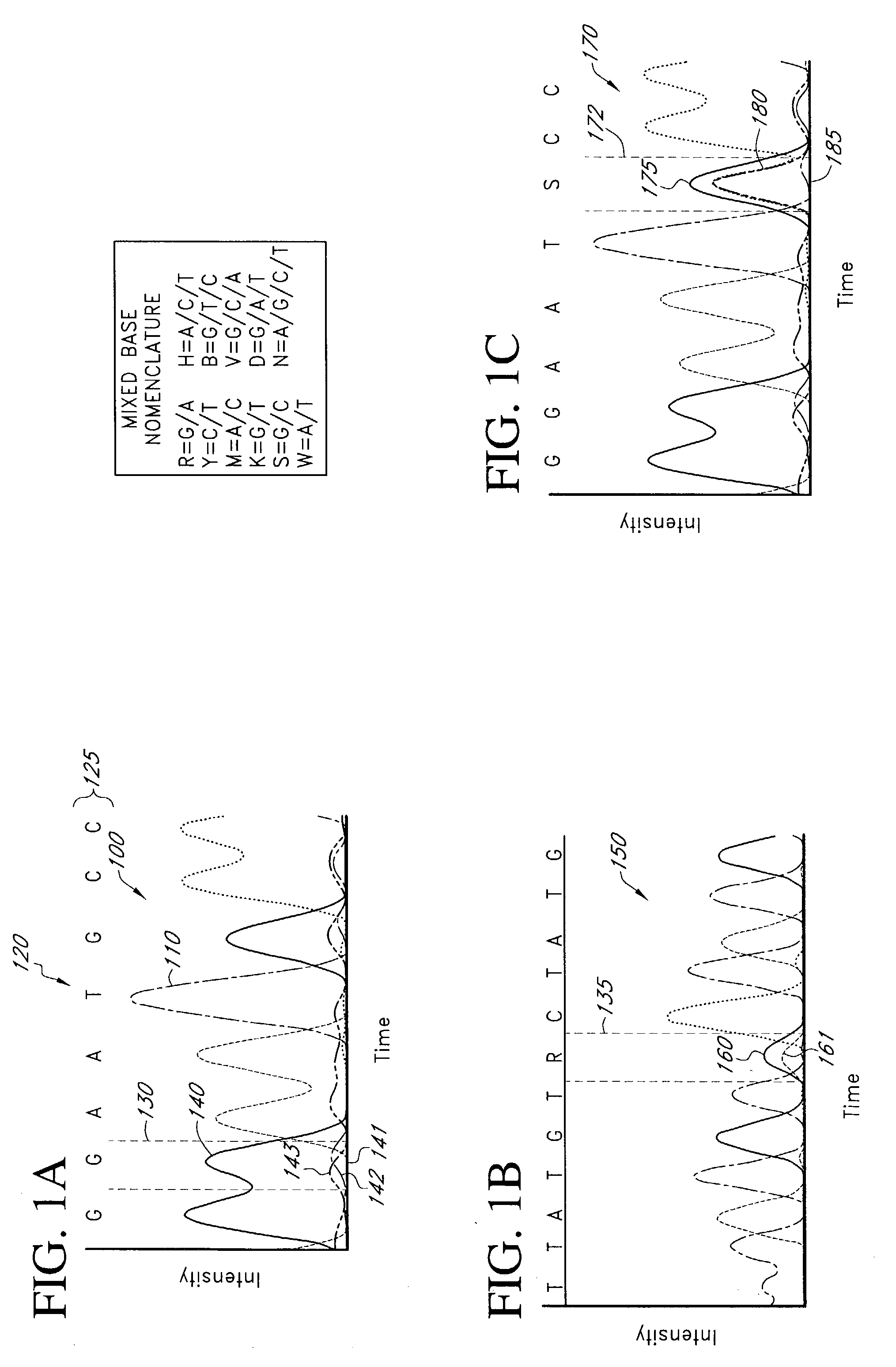
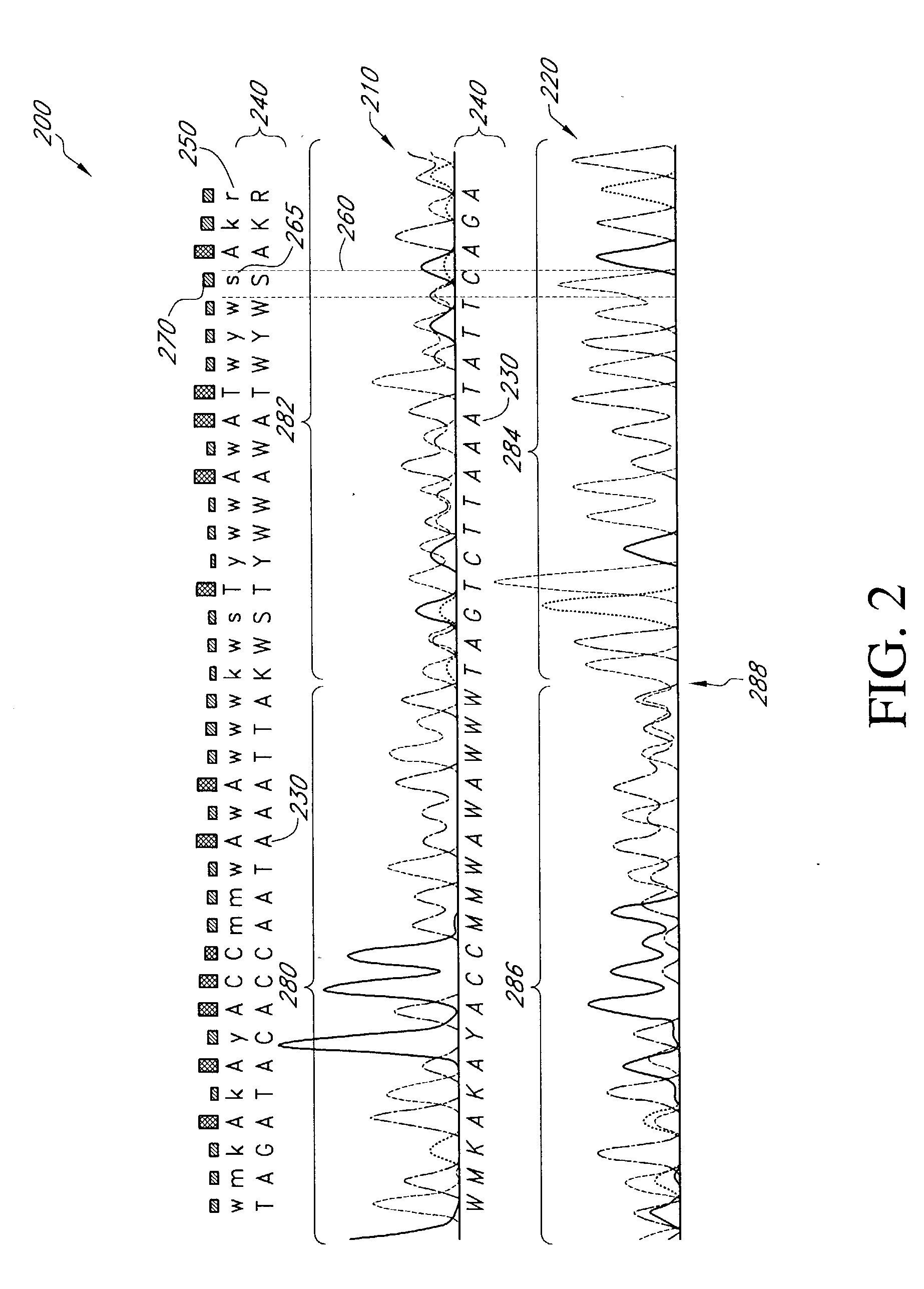
The present teachings disclose methods for evaluation of sequence information to characterize putative heterozygous indel mutations. The mutation analysis methods utilize sequence and trace information to identify mixed-base presence resulting from allelic differences. These methods may be applied to identify and resolve single nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions, deletions, and other mutational events.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
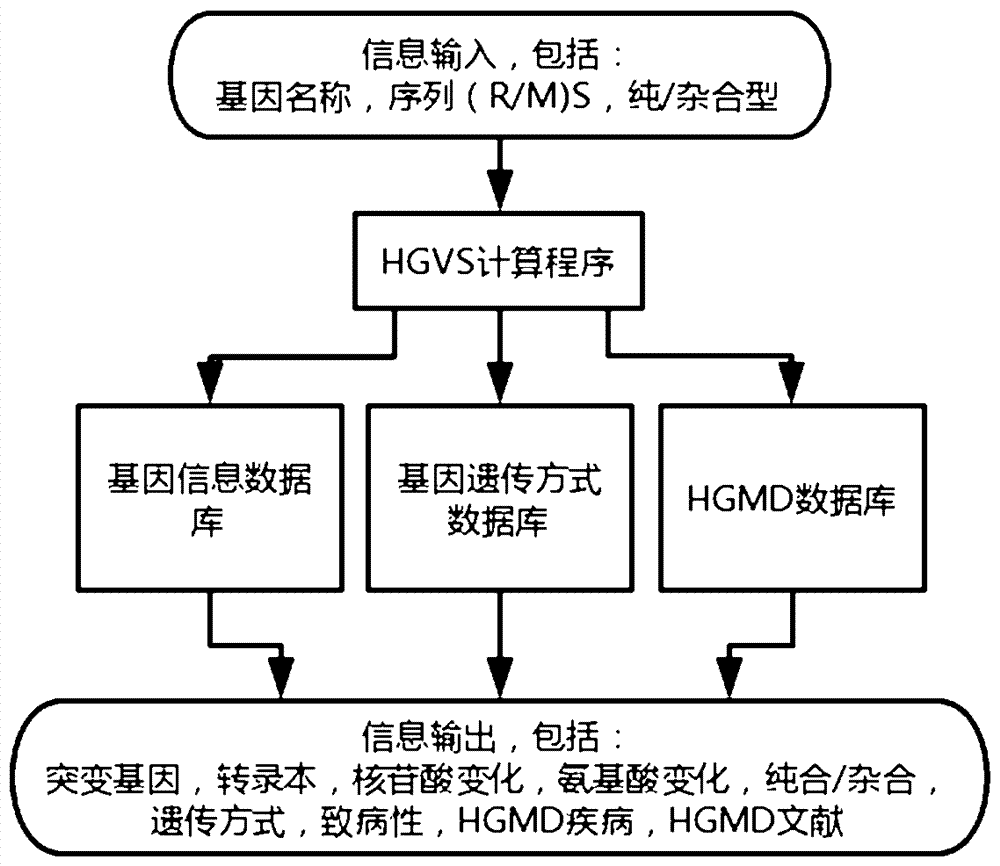
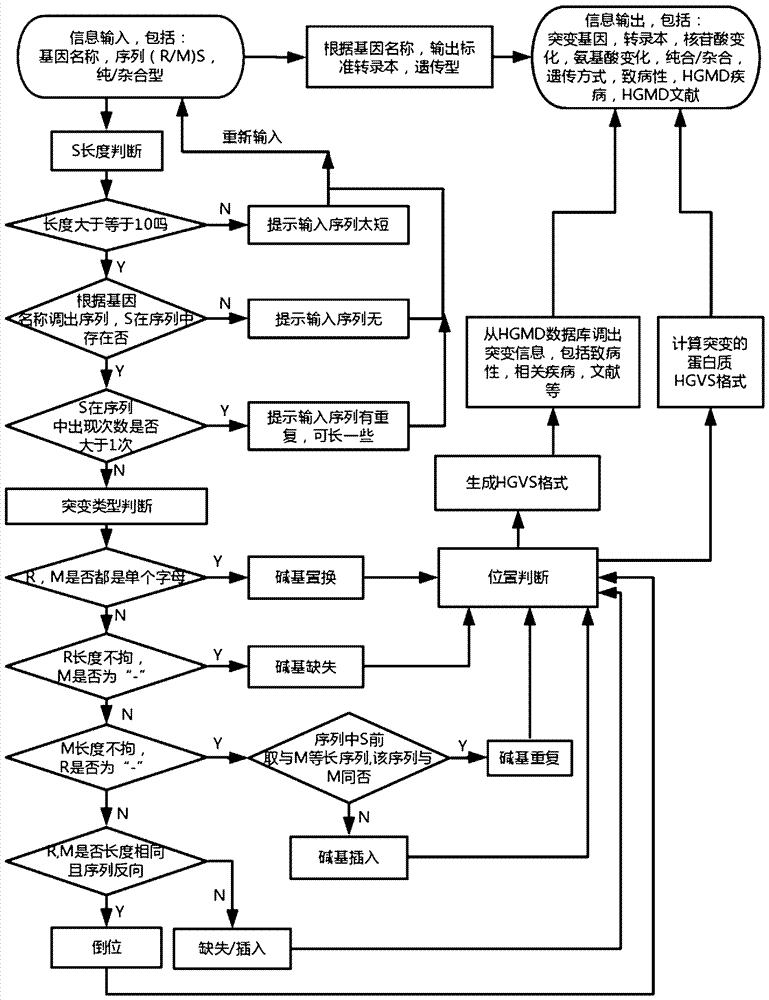
Implementation method for HGVS (Human Geome Variation Society) name generation and analysis system of human gene mutation
The invention discloses an algorithm for the automatic generation module of the HGVS (Human Geome Variation Society) name of gene mutation. The algorithm comprises the following elements: 1) describing a mutation site by a ''gene(R / M)Sz / c'' format, wherein the meaning of the gene(R / M)Sz / c is a gene name, one segment of sequence after a (mutation site reference sequence / mutation site mutation sequence) mutation site and whether the mutation site is a homozygotic type or a hybrid type, and the three parts are separated by a space so as to describe mutation discovered by sequencing; 2) the format is input into a mutation analysis system, a gene information database, a gene inheritance pattern way database, an HGMD database and the like are called through an HGVS calculation program for calculation; and 3) the HGVS name of the gene mutation and relevant information based on the HGVS information are obtained. Through tests, a human gene mutation system based on the algorithm can analyze of mutation of more than 6000 human genes so as to meet the analysis requirements of gene mutation including common genetic diseases, cancers and the like.
Owner:江阴检汇生物科技有限公司
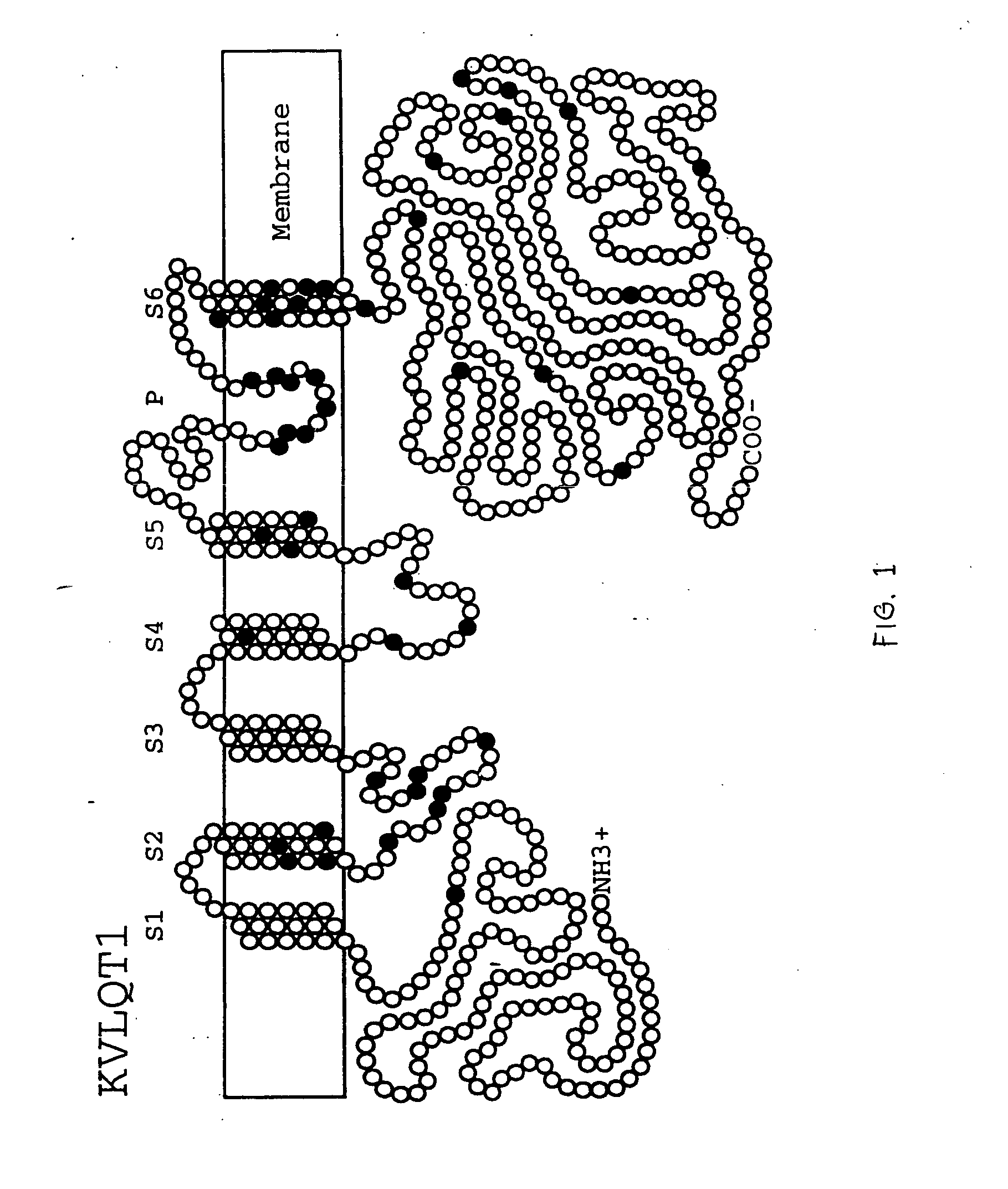
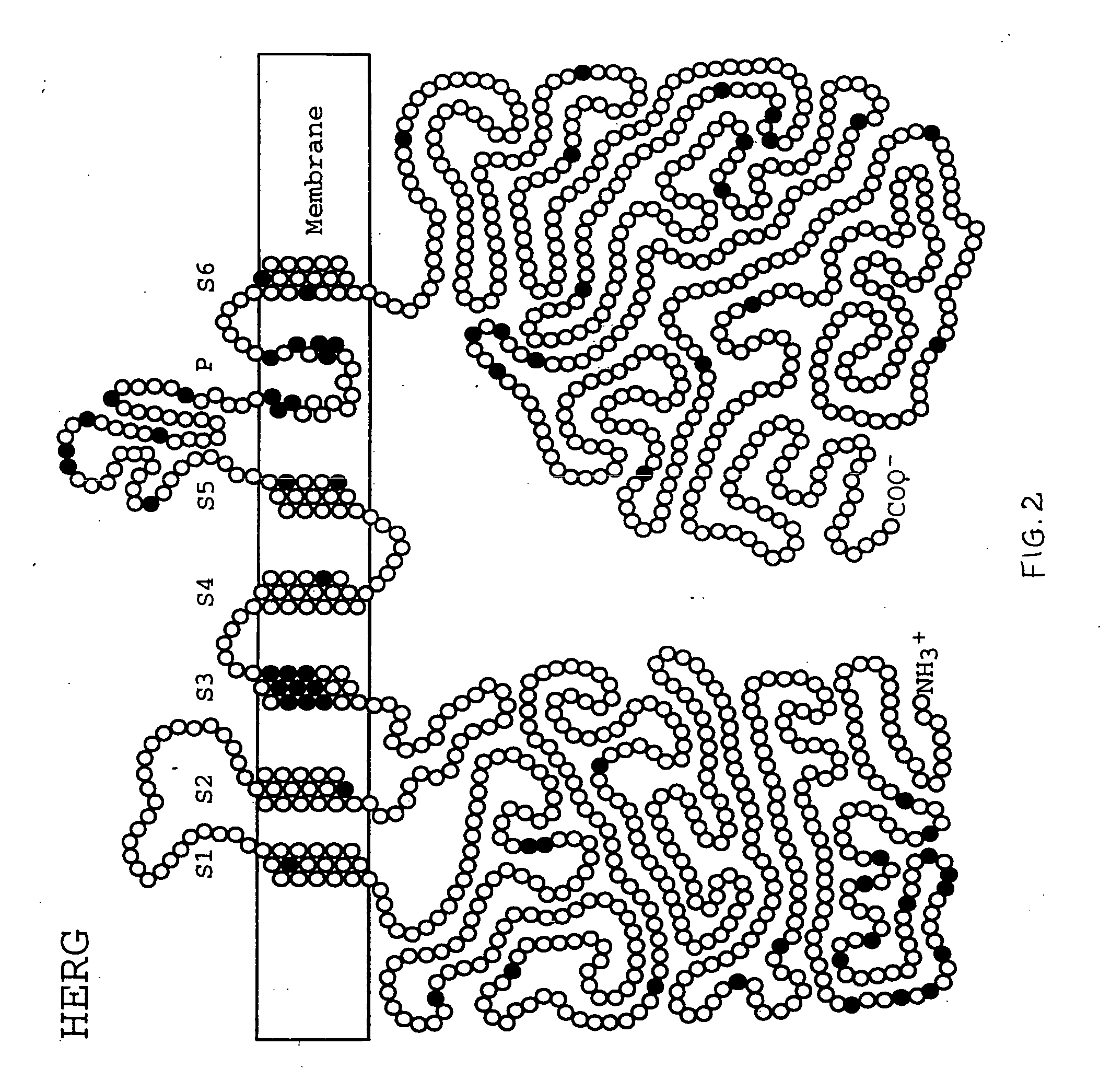
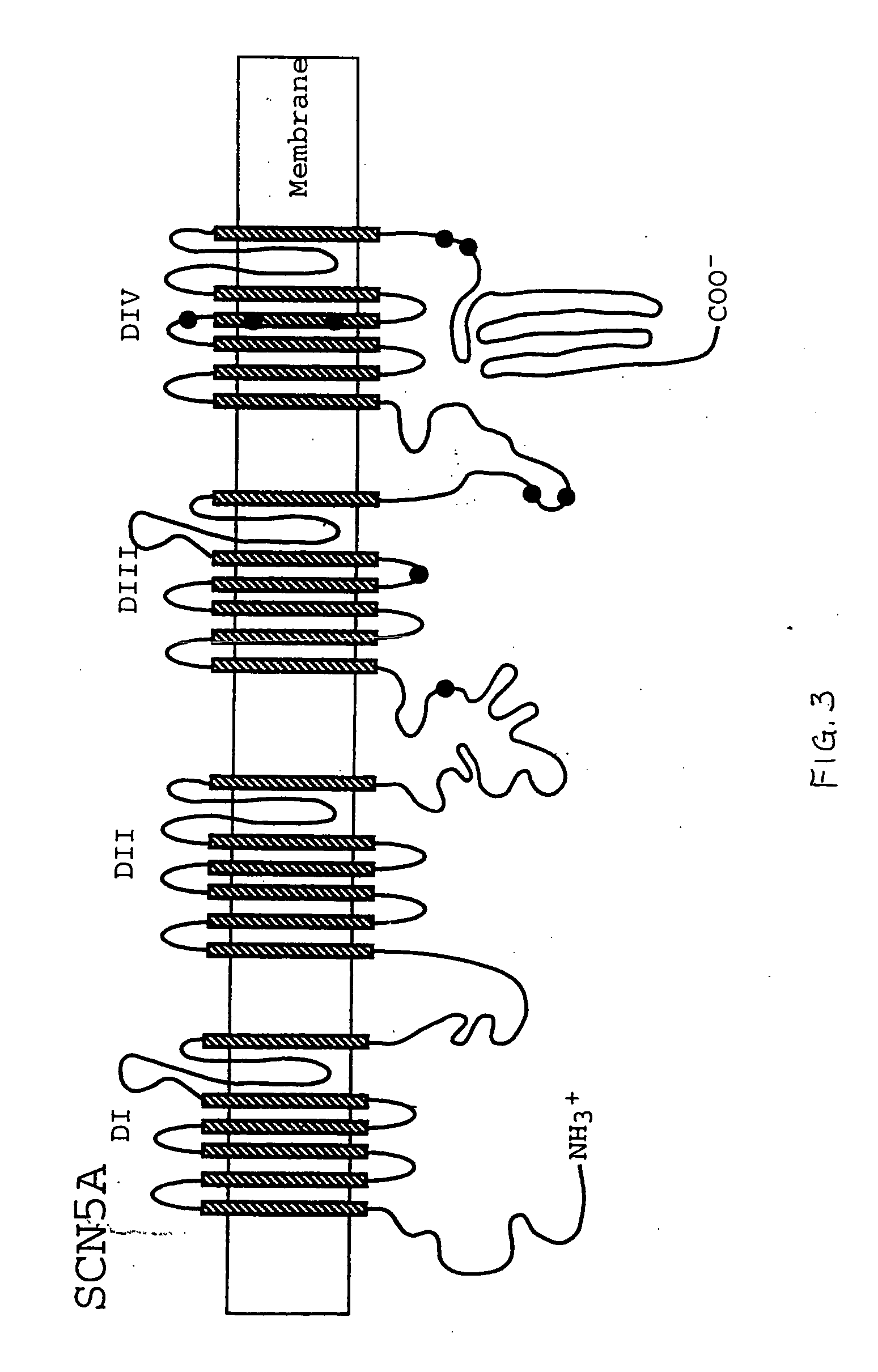
Alterations in the long QT syndrome genes KVLQT1 and SCN5A and methods for detecting same
Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is a cardiovascular disorder characterized by prolongation of the QT interval on electrocardiogram and presence of syncope, seizures and sudden death. Five genes have been implicated in Romano-Ward syndrome, the autosomal dominant form of LQTS. These genes are KVLQT1, HERG, SCN5A, KCNE1 and KCNE2. Mutations in KVLQT1 and KCNE1 also cause the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, a form of LQTS associated with deafness, a phenotypic abnormality inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. Mutational analyses were used to screen 262 unrelated individuals with LQTS for mutations in the five defined genes. A total of 134 mutations were observed of which eighty were novel.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method for determining a mutation in genomic dna, use of the method and kit for carrying out said method
Disclosed is a method for determining a mutation in genomic DNA. The method is characterised in that the mutation analysis is carried out using genomic DNA in which at least one portion of the cytosine contained therein has previously been converted into uracil or into another base with a base pair behaviour or molecular weight that differs from cytosine.
Owner:迪莫迪特里希
Measurement of mutation load using the p53 gene in human cells from paraffin embedded tissues
InactiveUS20070020648A1Assessing cancer riskAssessing prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCarcinogenMutated protein
A method for determining mutation load in a somatic cell is determined by mutation analysis of the p53 gene. The p53 gene has been found to be a useful indicator of predisposition to spontaneous mutations or prior carcinogen exposure. Cells that contain mutated p53 tend to accumulate the mutant protein. Thus, DNA from a cell identified by p53 accumulation is amplified and the amplification product further analyzed for mutations in the p53 gene.
Owner:SOMMER STEVEN S +2
Method for knocking out AAV receptor, HEK293 cell strain with AAV receptor knocked out and application
ActiveCN107245475AReduce lossesIncrease final yieldCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVectorsCytologyCell strain
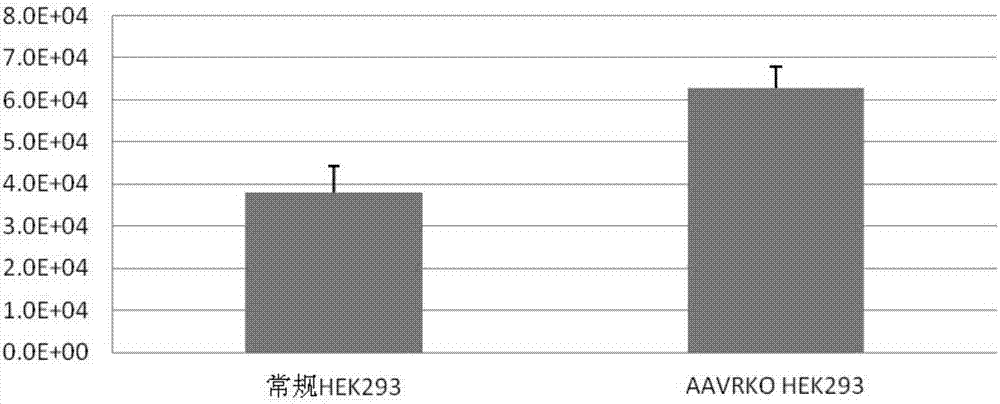
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering and cytology, in particular to an AAV receptor knocking out method, an HEK293 cell strain with an AAV receptor being knocked out and an application. The knocked-out AAV receptor is KIAA0319L. The knocking out method comprises the following steps: establishing a sgRNA carrier of a targeted AAVR genome sequence; carrying out transfection for a 293 T-cell, and culturing to obtain each clonal cell; carrying out Suveyor gene mutation analysis test; selecting AAVR mutant monoclone; then selecting an AAVR mutant cell strain with high yield of AAV; identifying a mutation condition of other potential mutant site; and enlarging the cell strain without other mutant sites, and establishing a library for production. The final yield of the AAV produced by the HEK293 cell strain of the knocked-out AAV receptor is about 50 percent higher than the yield of the conventional HEK293.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PACKGENE BIOTECH CO LTD
Mutational analysis
ActiveUS9005932B2Rapidly and easily analyzedSimple procedureMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBinding siteNucleotide
A method for analysing genetic mutations, and in particular single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and / or somatic mutations, is described, as well as methods for preferentially amplifying one allelic form compared with another form. The methods use an oligonucleotide probe which hybridises to a first allele with a lower melting temperature (Tm) than that with which it hybridises to a second allele, together with amplification primers which flank the oligonucleotide probe binding site and which bind to the sample with a higher Tm than that of the probe and the first allele. An amplification reaction may be carried out at a temperature such that the probe is preferentially hybridised to the second allele, thereby amplifying the first allele. The amplified sequences may be detected using the same probe as acted as the blocking probe during amplification.
Owner:EPISTEM
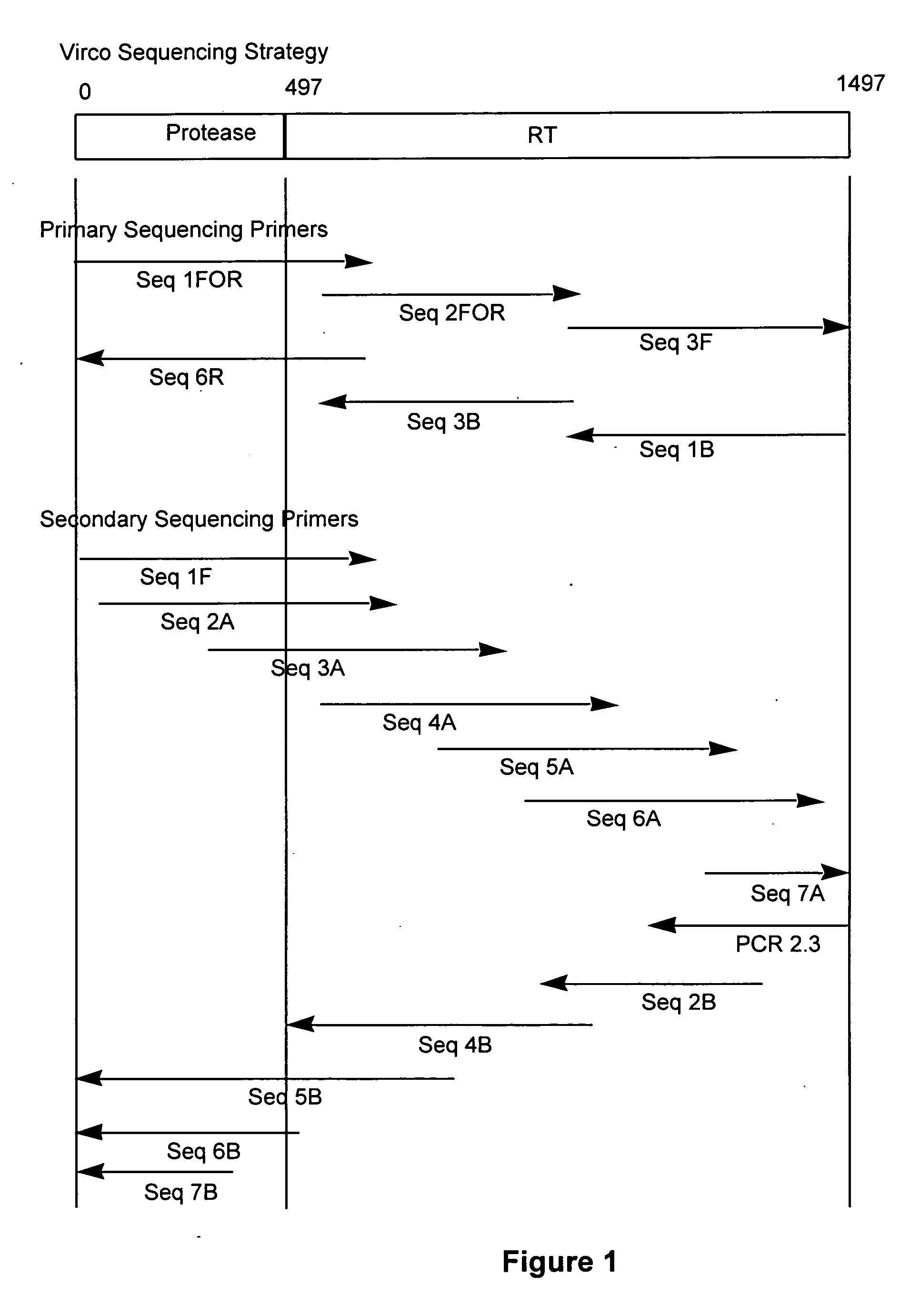
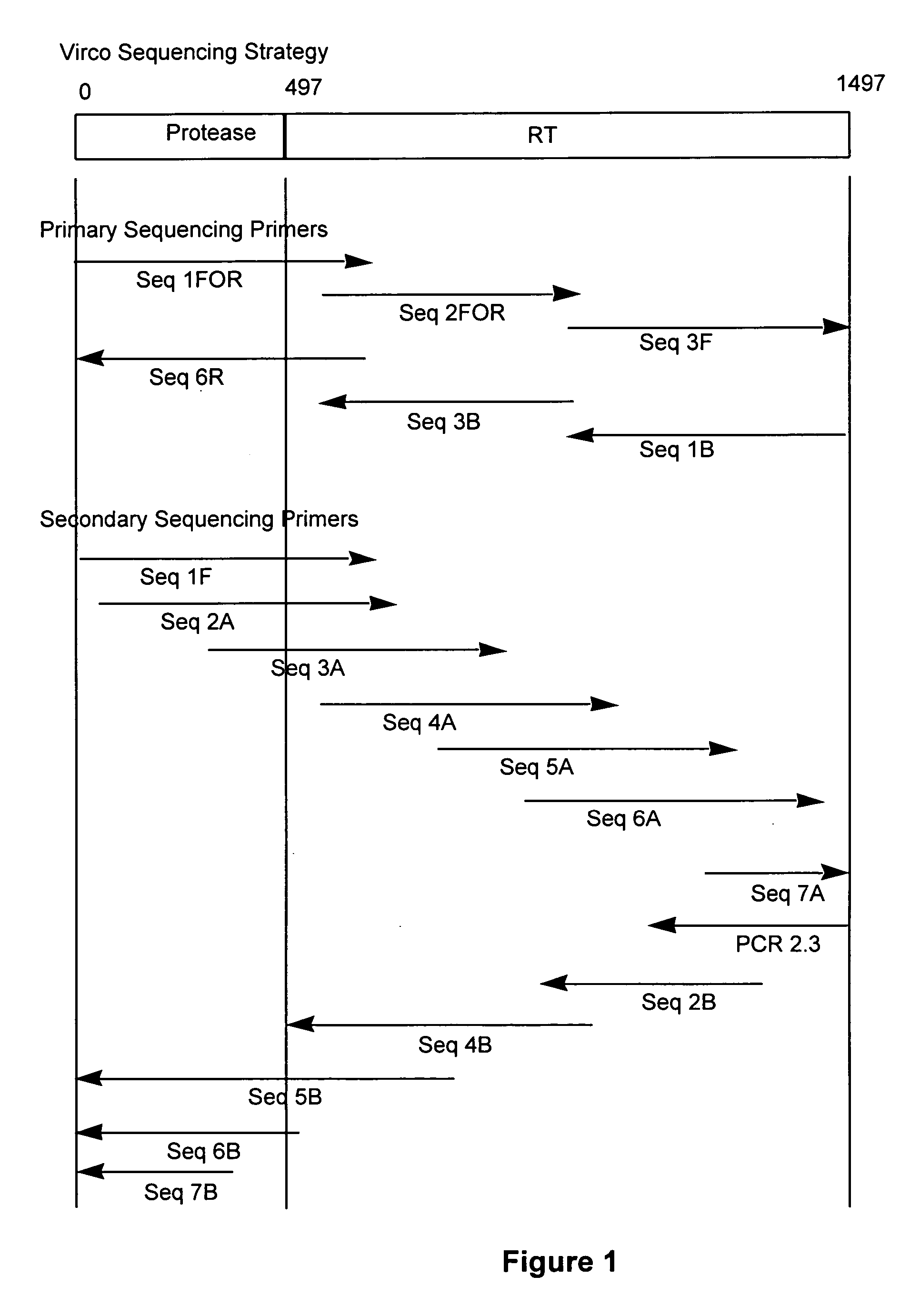
Method for mutation detection in hiv using pol sequencing
InactiveUS20050058981A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionOligonucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for mutation analysis of the HIV pol gene of HIV virions comprising amplifying virion RNA or DNA via nested PCR using outer primers as represented in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2, amplifying said PCR product via nested PCR using a 5′ and 3′ primer chosen from the inner primers SEQ ID No. 3, 4, 5, and 6, and sequencing this secondary obtained PCR product using at least one sequencing primer chosen from any of SEQ ID No. 7 to 12 or variants thereof. In the alternative, at least one secondary sequencing primer may be used chosen from any of SEQ ID No. 13 to 24. The benefit of the sequences present in the invention resides in the fact that, with the aid of the oligonucleotides, the sequences of all presently known HIV subtypes and all mutations of the pol gene presently known to yield resistance towards antiretroviral therapy can be determined. The present invention also relates to kits for performing such a method as well as primers for performing the same.
Owner:VIRCO NV
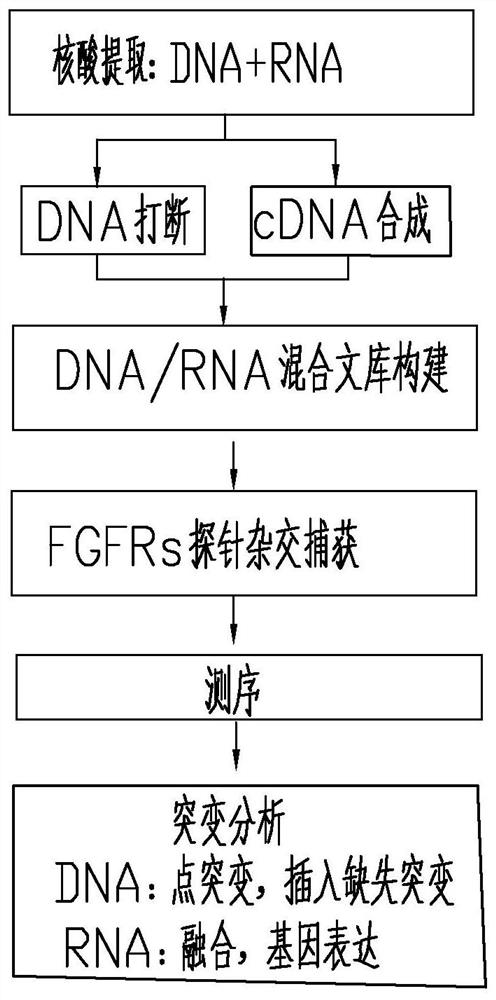
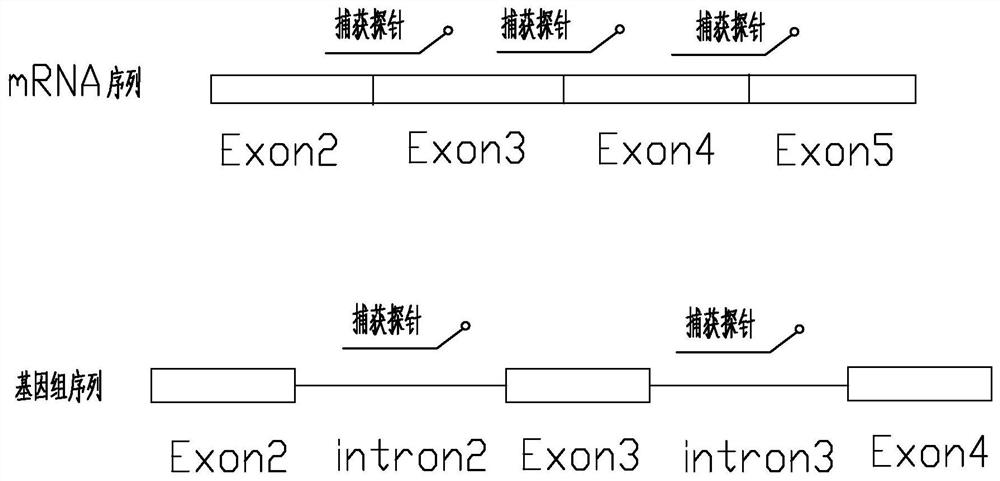
Method and probe sequence for detecting FGFRs gene mutation based on high-throughput sequencing
ActiveCN112301115AMeet testing needsGuaranteed detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JTotal rna
The invention relates to a method and probe sequence for detecting FGFRs gene mutation based on high-throughput sequencing. The method comprises the following steps of 1) co-extracting genome DNA andtotal RNA of a sample; 2) fragmenting the genome DNA and recovering the fragmented DNA; 3) performing total RNA interruption and / or primer hybridization according to the total RNA quality control condition; 3) synthesizing a first strand of cDNA; 4) synthesizing a second strand of the cDNA; 5) mixing the fragmented DNA with the cDNA to construct a mixed library; 6) performing hybridization and capture by adopting a capture probe; 7) performing library amplification and purification after capture; and 8) performing high-throughput sequencing and mutation analysis. According to the invention, single base mutation, insertion and deletion mutation, fusion mutation and relative expression quantity analysis of FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4 genes can be detected.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Mutational analysis of JAK2
An assay for mutations in JAK2 is described. The assay uses selective amplification of mutant alleles with a blocker probe which preferentially hybridises to wild type alleles. The same probe is then used to detect presence or absence of wild type sequences. It is not necessary to know the specific mutant sequence beforehand.
Owner:EPISTEM
Mutation analysis using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20020162622A1High sensitivityReduce molecular weightSugar derivativesSamplingChemical treatmentFree form
The invention presents a method for examining genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) to detect the presence of pre-known mutations, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), using mass spectrometry with ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). The invention uses nucleoside triphosphates with modified sites for the method of primer extension in a duplicating, enzymatic reaction and at least partially removal of primers from the extension product, in combination with product neutralization by chemical treatment of the modified sites, so that the resulting DNA products can be, by using special matrix materials, preferredly ionized in an adduct-free form over other constituents in the reaction solution without any further cleaning. The method is particularly suitable for simultaneous identification of several mutations by multiplexing.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
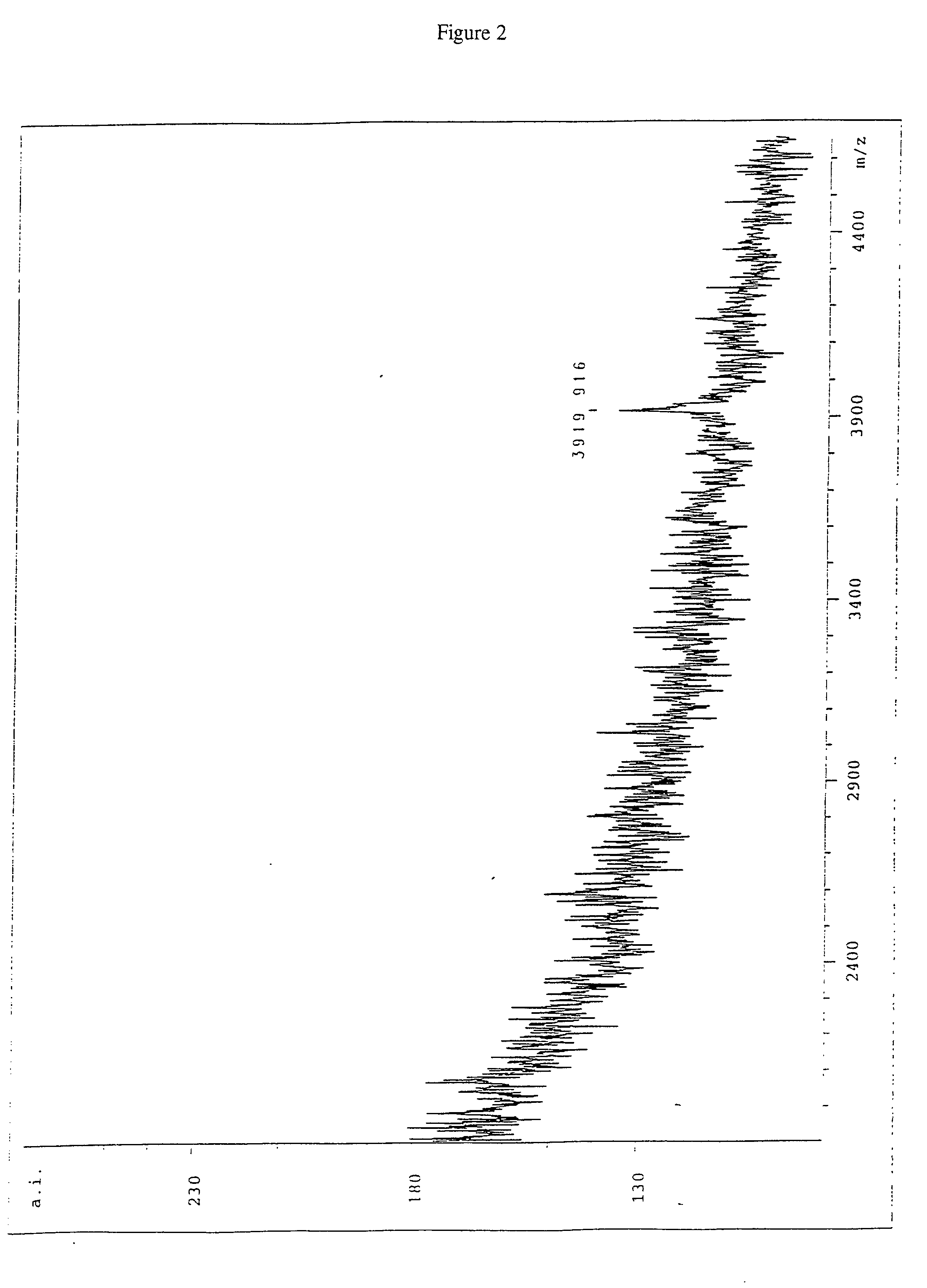
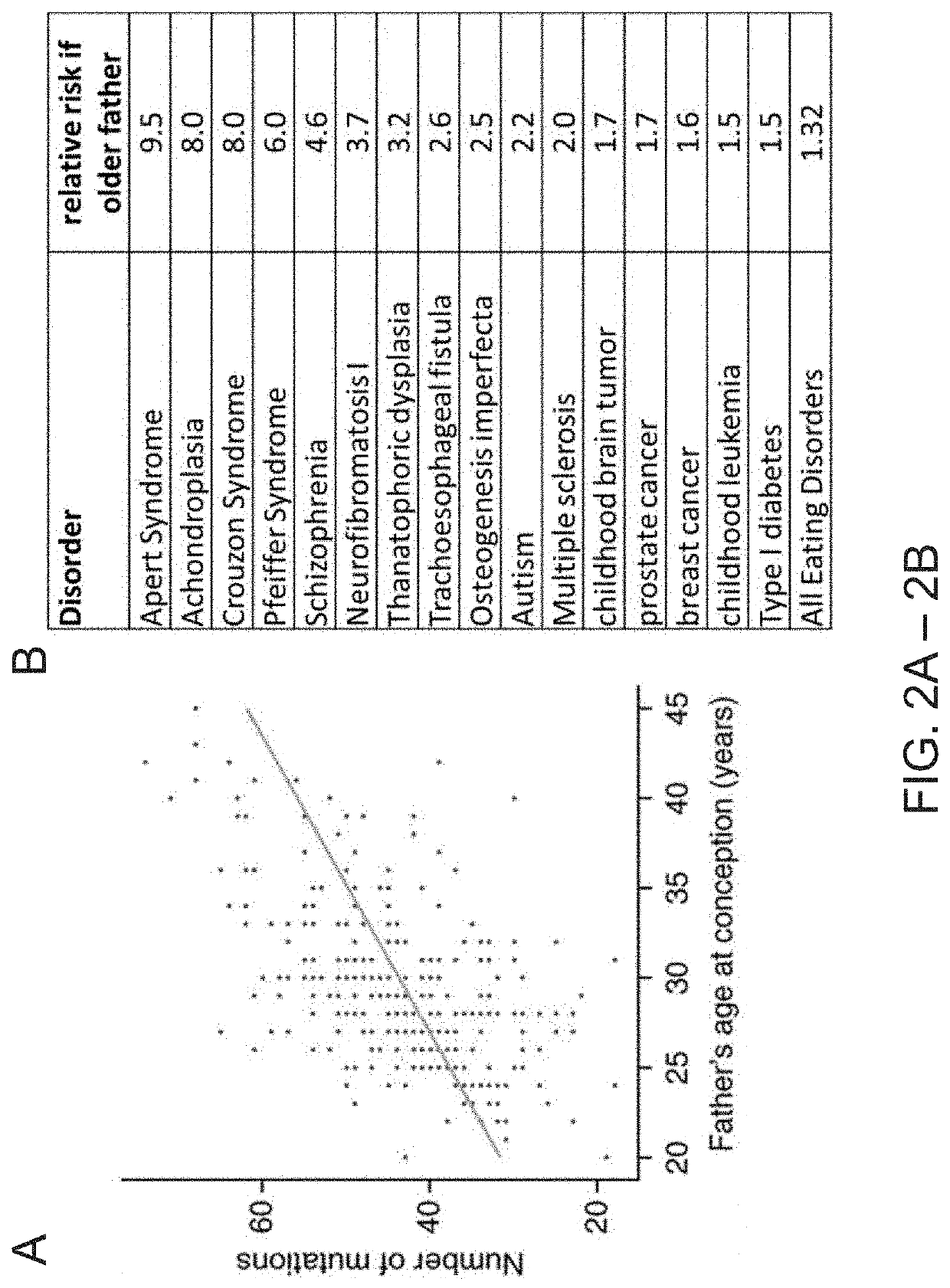
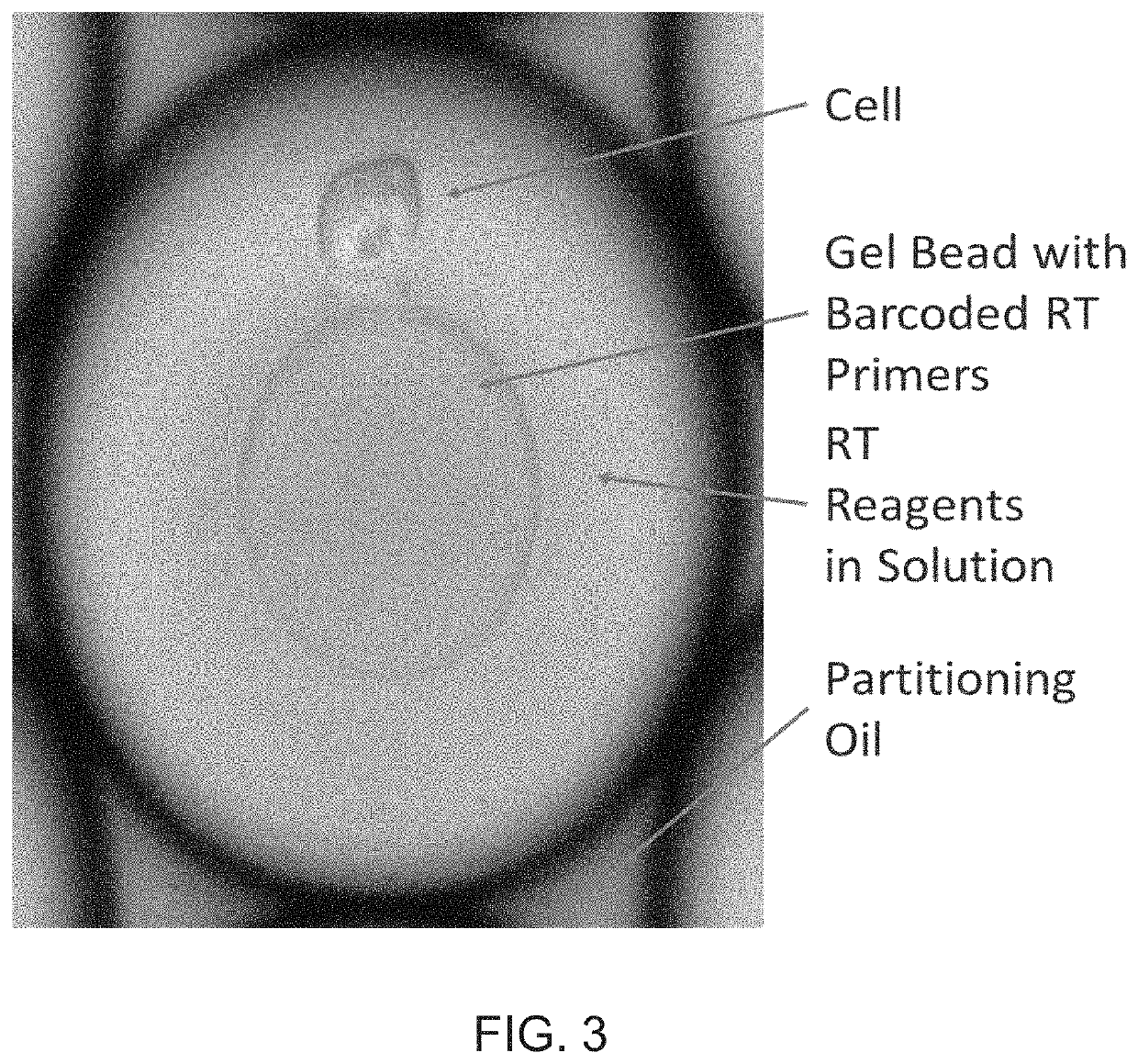
Single sperm gene expression and mutation anaylsis for prediction of diseases
PendingUS20200010896A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologySpermatid
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
DNA methylation and mutational analysis methods for bladder cancer surveillance
PendingCN110621788AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDNA methylationGenes mutation
The present disclosure relates to methods of monitoring bladder cancer patients and analyzing patient samples for presence of methylated DNA and optionally particular gene mutations. In some embodiments, analysis results are correlated with clinical outcome measures such as risk of bladder cancer recurrence.
Owner:基美健有限公司
Topographic genotyping for determining the diagnosis, malignant potential, and biologic behavior of pancreatic cysts and related conditions
InactiveUS20140296103A1Easy to analyzeEasy diagnosisHealth-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular analysisMicrosatellite
The application relates to a method of a predicting the presence of invasive pancreatic cancer or high grade dysplasia, pre-cancerous pancreatic states and non-neoplastic conditions comprising detailed molecular analysis incorporating DNA quality and quantity, K-ras mutational analysis and a broad spectrum of tumor suppressor gene linked microsatellite LOH. Methods of diagnosing, determining prognosis of and determining a course of treatment for pancreatic cancer or high grade dysplasia, pre-cancerous pancreatic states and non-neoplastic conditions are also provided.
Owner:REDPATH INTEGRATED PATHOLOGY INC
Pyrophosphoric acid sequencing kit for detecting CYP3A4*4 genotyping
ActiveCN102719555AQualitatively accurateIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementO-Phosphoric AcidTaq polymerase
The invention discloses a kit for detecting CYP3A4*4 genetyping, belongs to the testing field of in-vitro nucleic acid, and particularly relates to a pyrophosphoric kit for detecting CYP3A4*4 genetyping. The pyrophosphoric kit for detecting CYP3A4*4 genetyping comprises uracil DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)glycosylase, Taq polymerase, a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplimer and a sequencing primer. The pyrophosphoric kit provided by the invention has high sensitivity and good specificity; and after simple treatment, a PCR product can be subjected to sequencing by utilizing phosphoric acid sequencing instrument, the operation is simple and convenient, the reaction time is short, the sequencing operation by adopting the pyrophosphoric kit provided by the invention has higher sensitivity when being compared with a gold-standard CE (capillary electrophoresis) sequencing operation, thus the pyrophosphoric kit is particularly suitable for mutation analysis.
Owner:韩勇
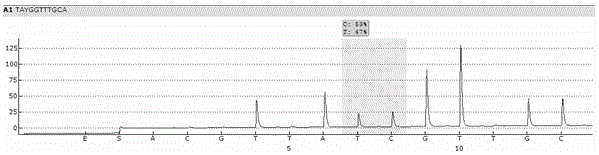
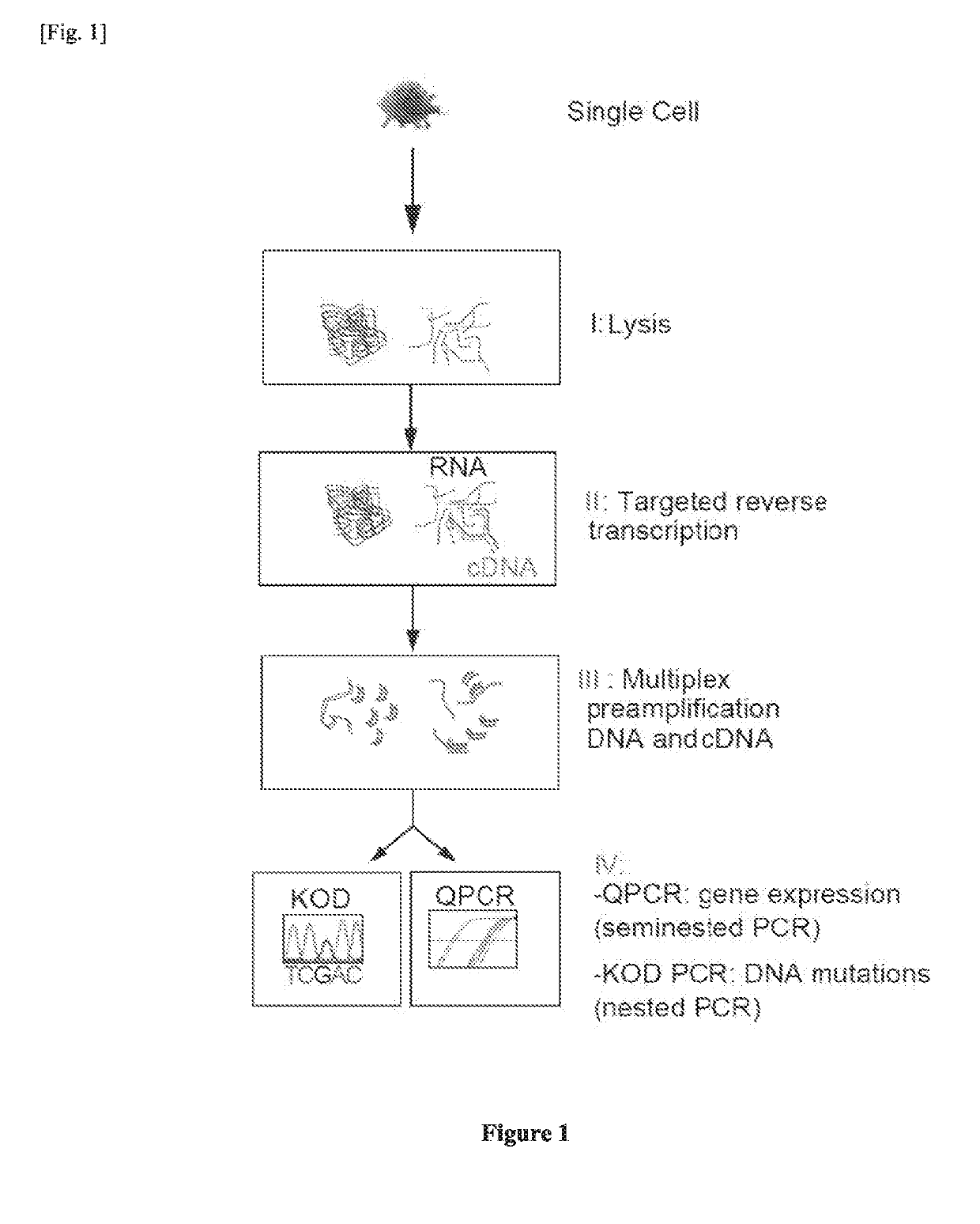
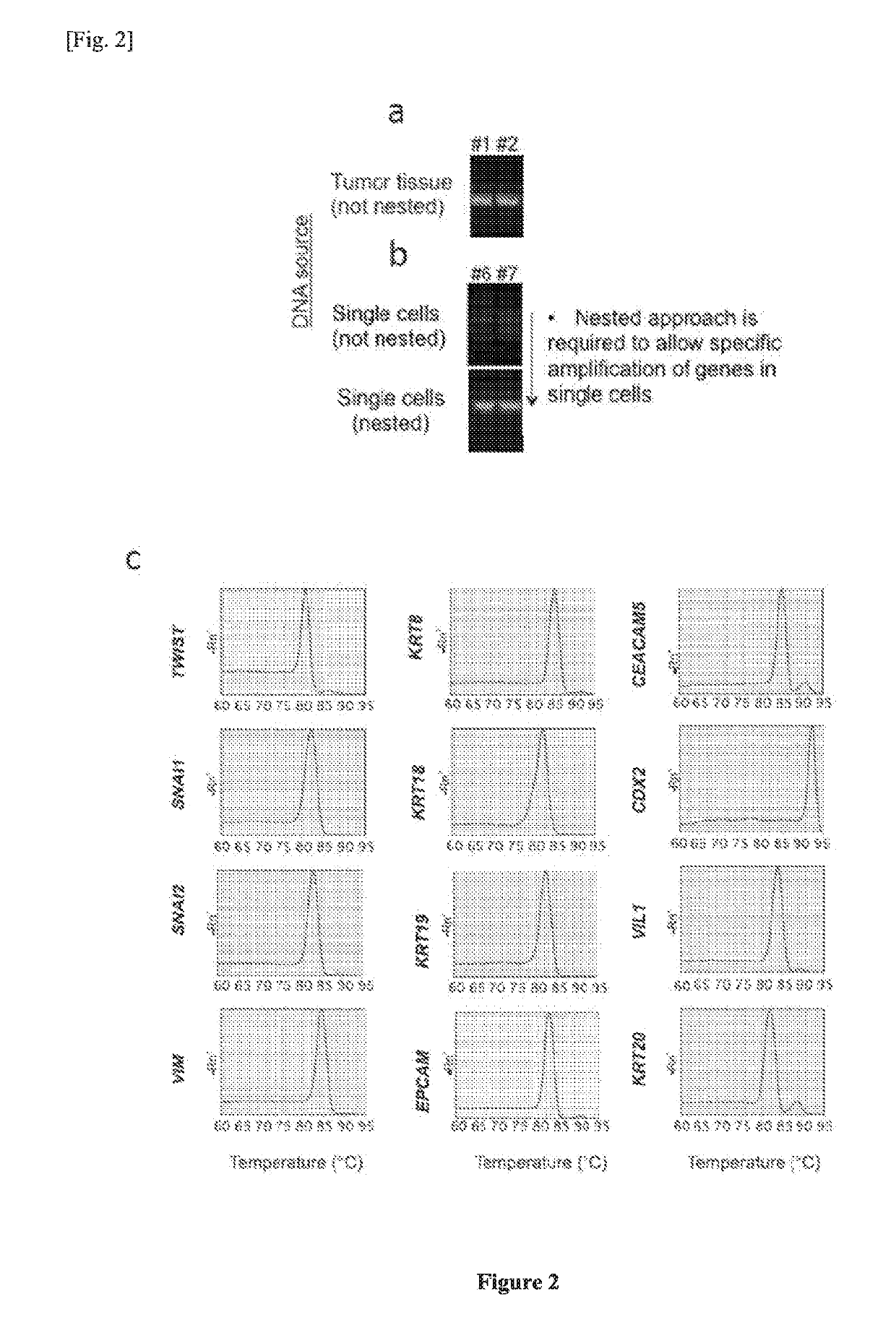
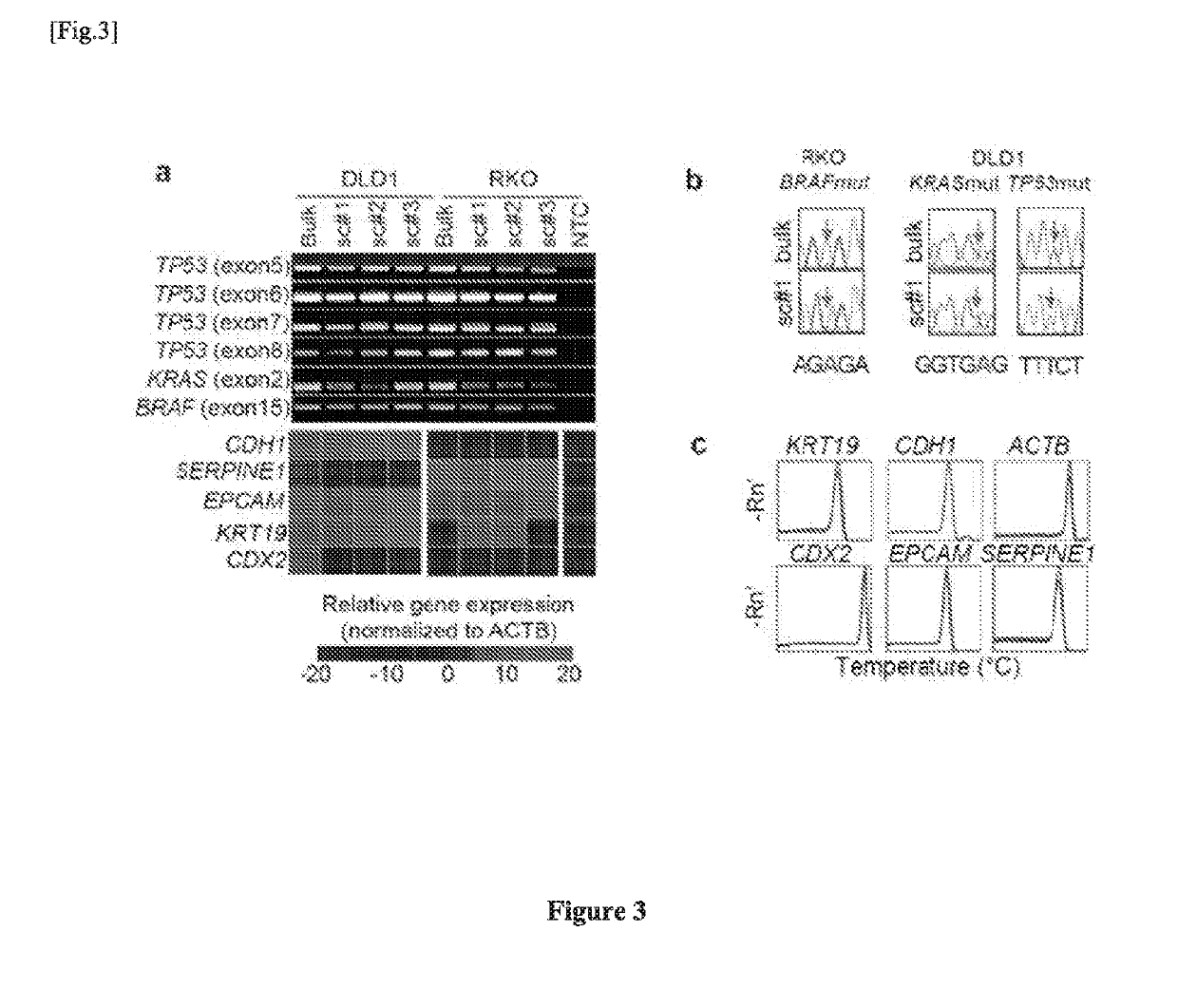
Single cell RNA and mutational analysis PCR (scrm-PCR): a method for simultaneous analysis of DNA and RNA at the single-cell level
A method of simultaneously analyzing RNA and DNA in a sample, the method comprising the step (a) contacting the sample with a reverse primer from a first primer pair directed to a target RNA region to effect reverse transcription of RNA into cDNA with a reverse transcriptase; (b) subsequently contacting the sample with (i) a forward primer from the first primer pair directed to a second cDNA region, (ii) a forward and a reverse primers from a second primer pair targeted to a DNA region, and (ii) a DNA polymerase to simultaneously amplify the target cDNA and target DNA region; and (c) analyzing the amplified target cDNA region and / or amplified target DNA region. Also encompassed are uses of the method to analyze gene expression and mutations, kits comprising primers, enzymes, buffers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for mutation detection in HIV-1 using pol sequencing
The present invention relates to a method for mutation analysis of the HIV pol gene of HIV virions comprising amplifying virion RNA or DNA via nested PCR using outer primers as represented in SEQ ID No. 1 and 2, amplifying said PCR product via nested PCR using a 5′ and 3′ primer chosen from the inner primers SEQ ID No. 3, 4, 5, and 6, and sequencing this secondary obtained PCR product using at least one sequencing primer chosen from any of SEQ ID No. 7 to 12 or variants thereof. In the alternative, at least one secondary sequencing primer may be used chosen from any of SEQ ID No. 13 to 24. The benefit of the sequences present in the invention resides in the fact that, with the aid of the oligonucleotides, the sequences of all presently known HIV subtypes and all mutations of the pol gene presently known to yield resistance towards antiretroviral therapy can be determined. The present invention also relates to kits for performing such a method as well as primers for performing the same.
Owner:VIRCO NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com