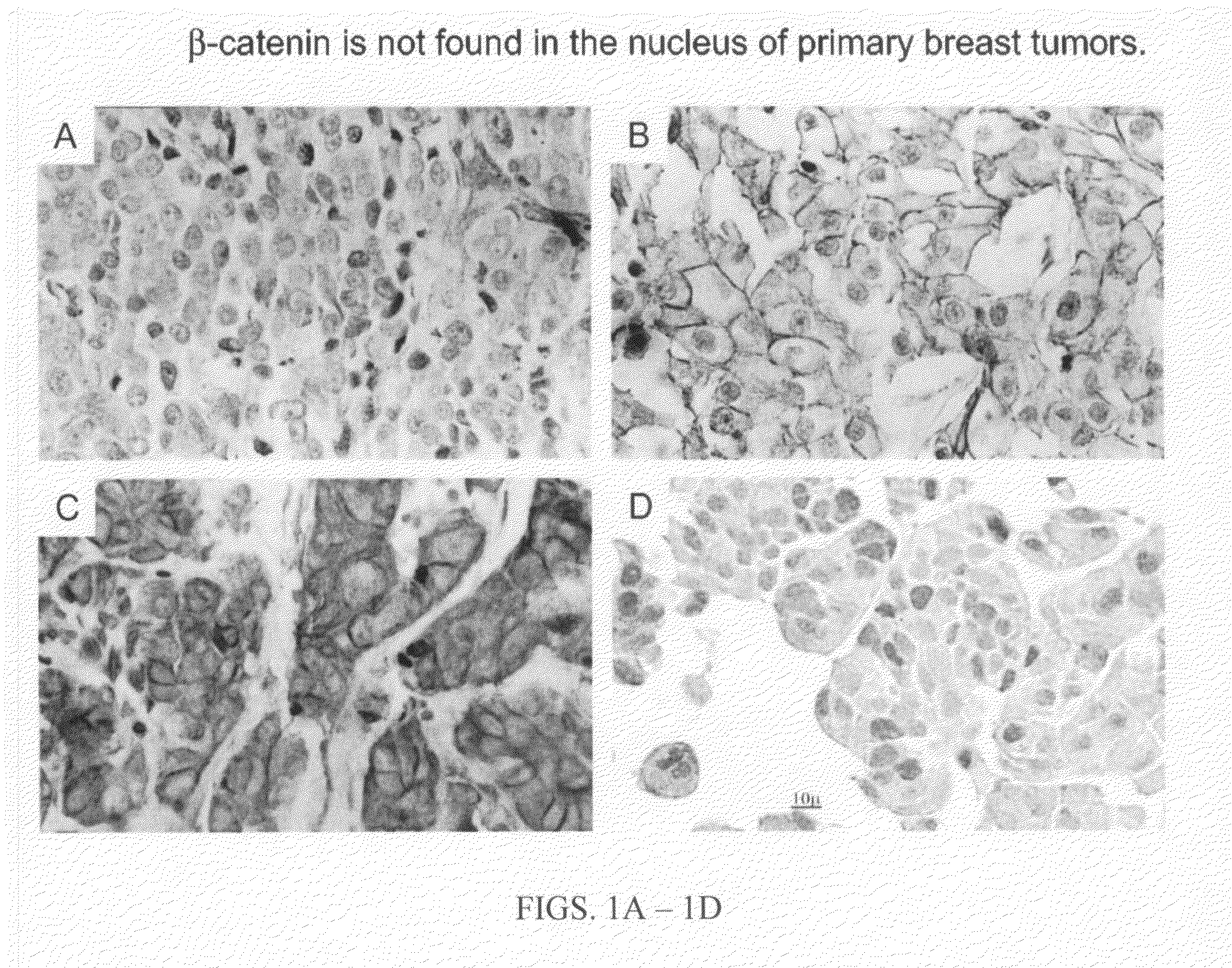Patents
Literature
38 results about "Outcome measures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Outcome measure. Determination and evaluation of the results of an activity, plan, process, or program and their comparison with the intended or projected results.
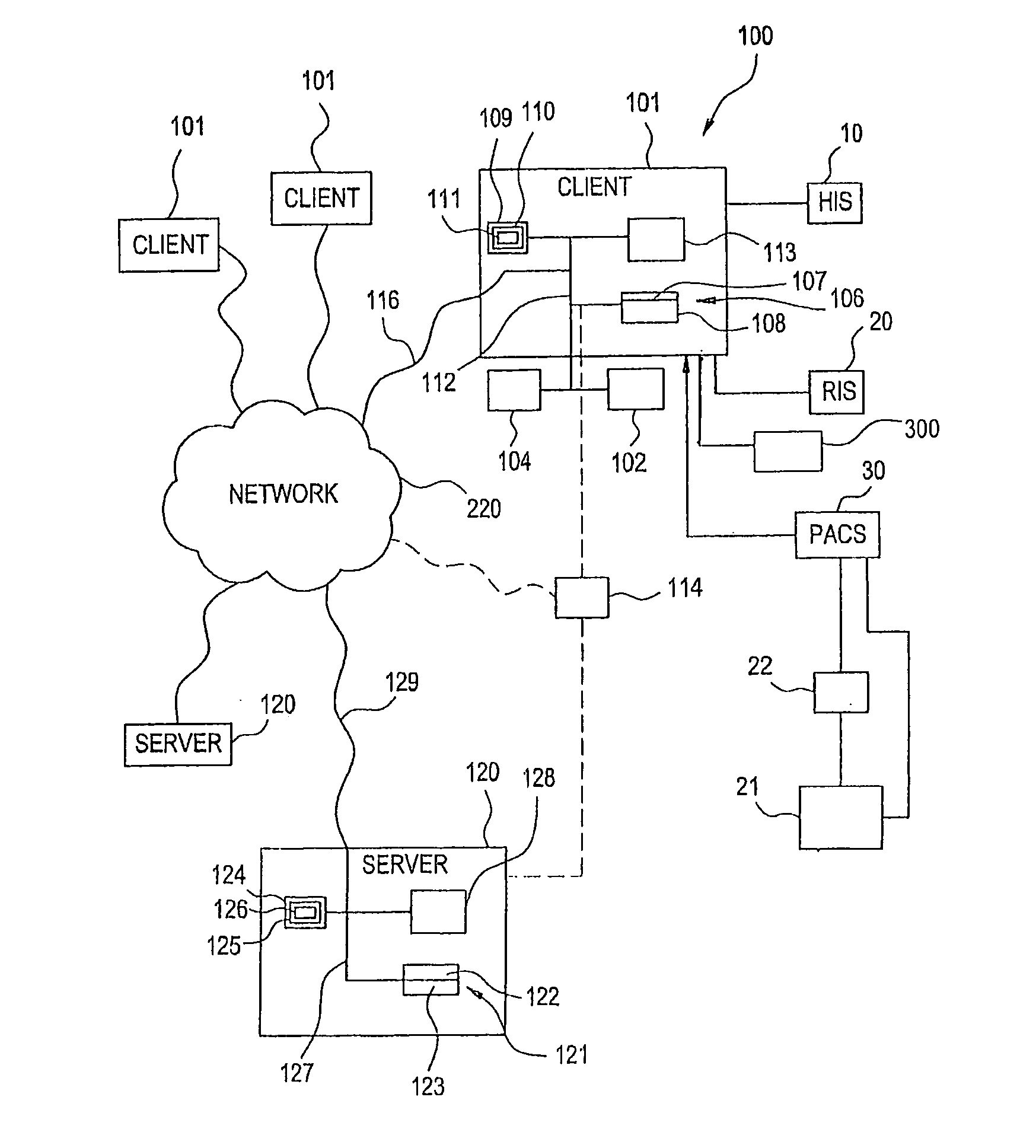
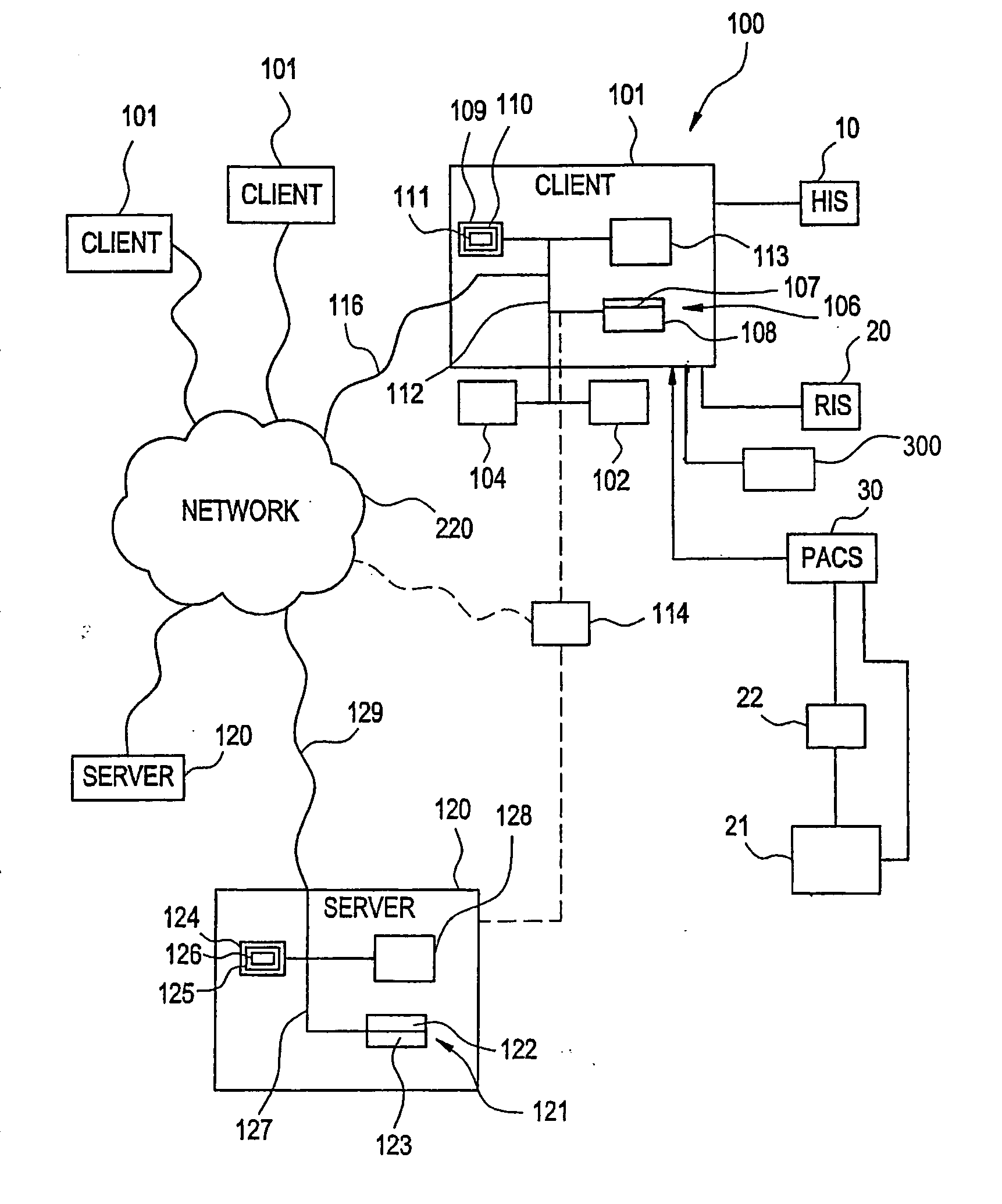
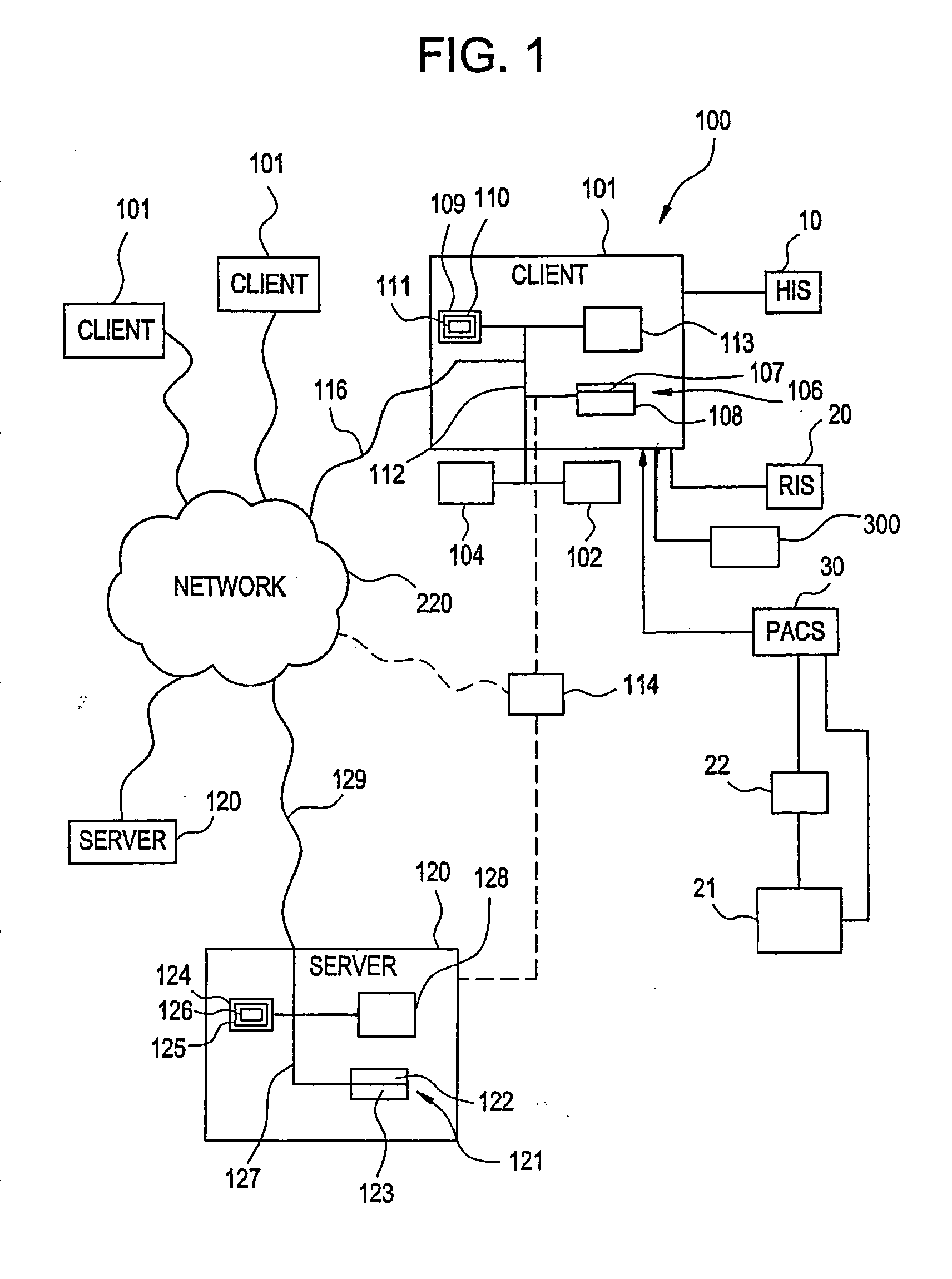
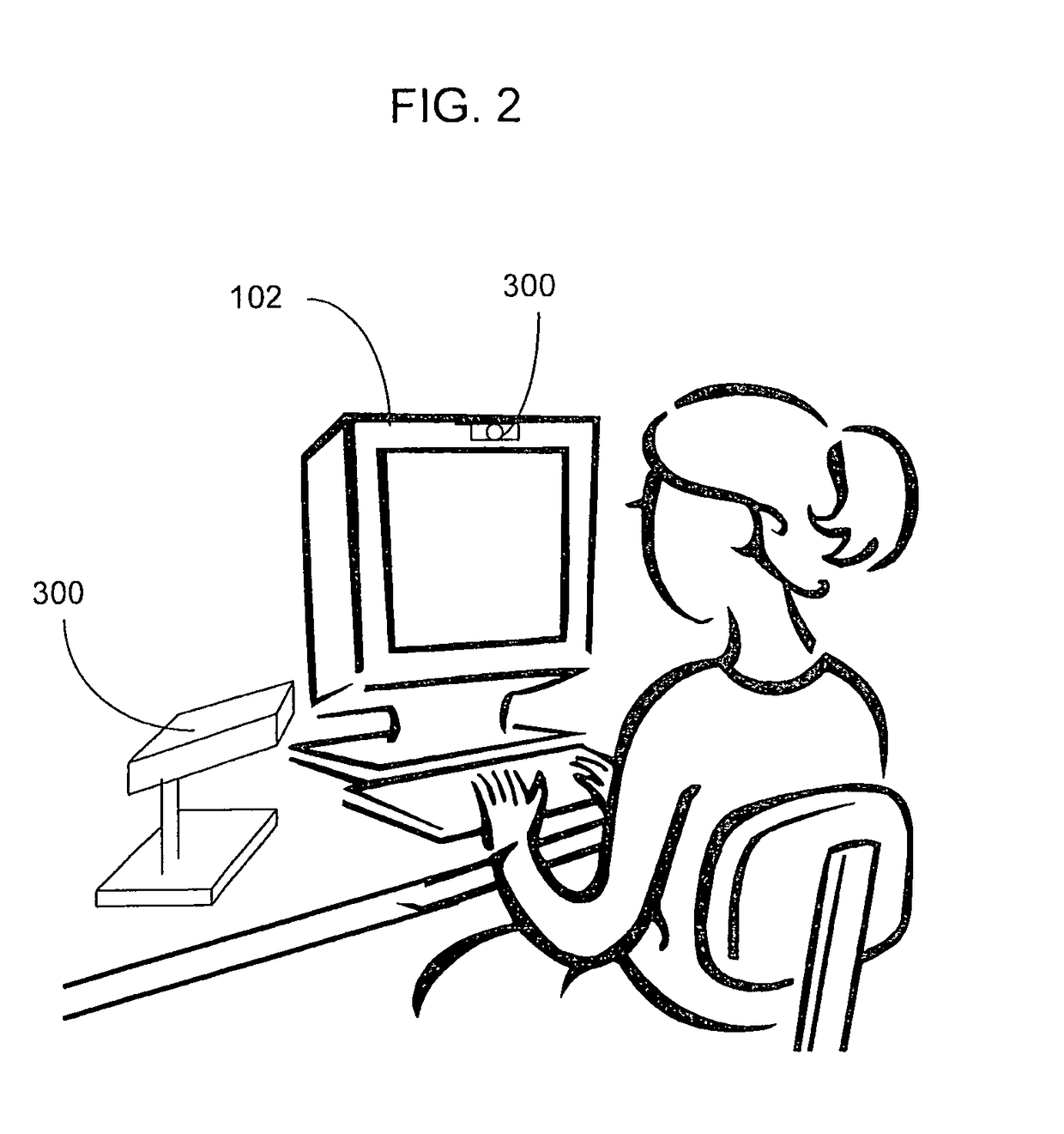
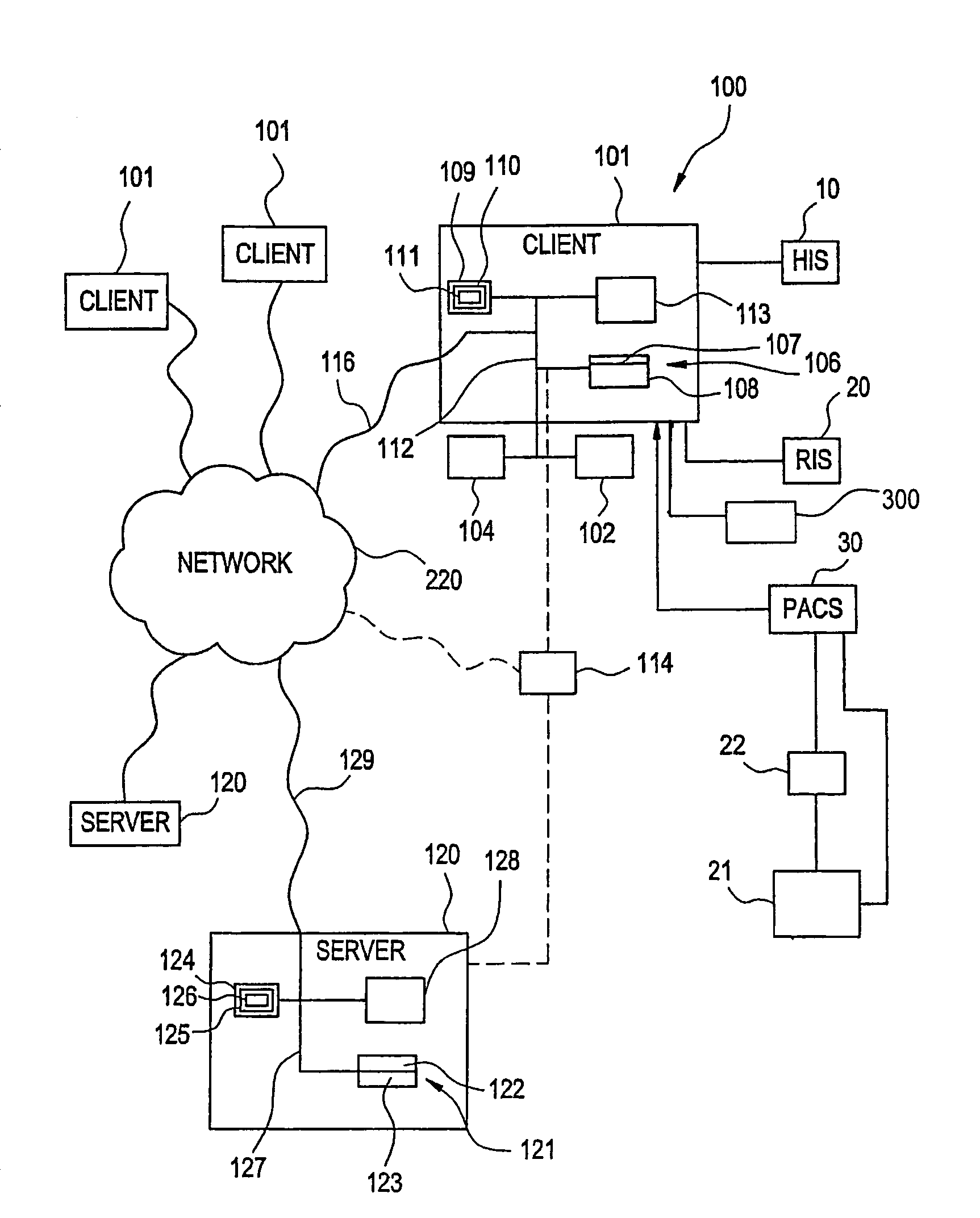
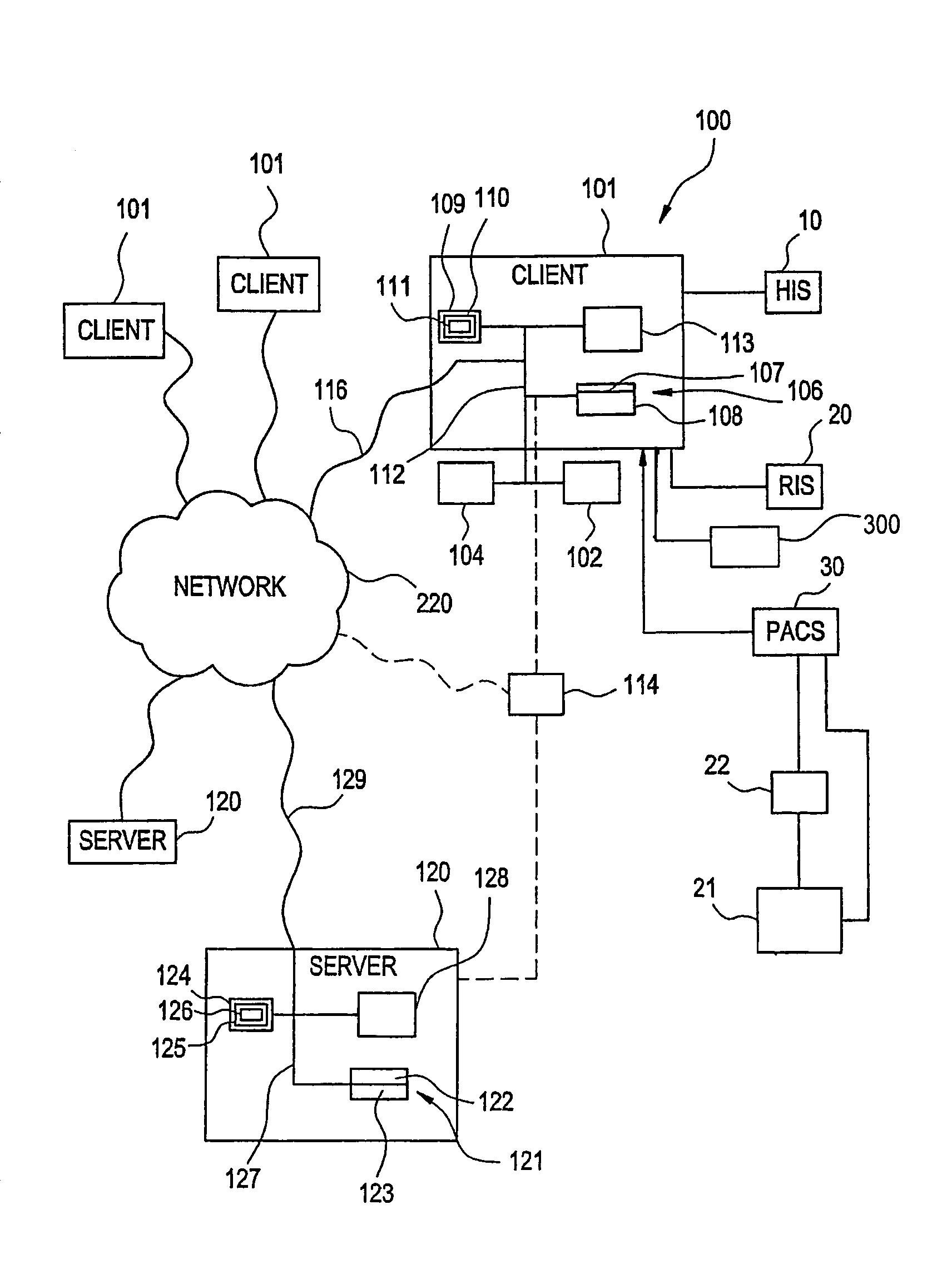
Visually directed human-computer interaction for medical applications
InactiveUS20110270123A1Faster and intuitive human-computer inputFaster and more intuitive human-computer inputDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGuidelineApplication software
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus of utilizing an eye detection apparatus in a medical application, which includes calibrating the eye detection apparatus to a user; performing a predetermined set of visual and cognitive steps using the eye detection apparatus; determining a visual profile of a workflow of the user; creating a user-specific database to create an automated visual display protocol of the workflow; storing eye-tracking commands for individual user navigation and computer interactions; storing context-specific medical application eye-tracking commands, in a database; performing the medical application using the eye-tracking commands; and storing eye-tracking data and results of an analysis of data from performance of the medical application, in the database. The method includes performing an analysis of the database for determining best practice guidelines based on clinical outcome measures.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
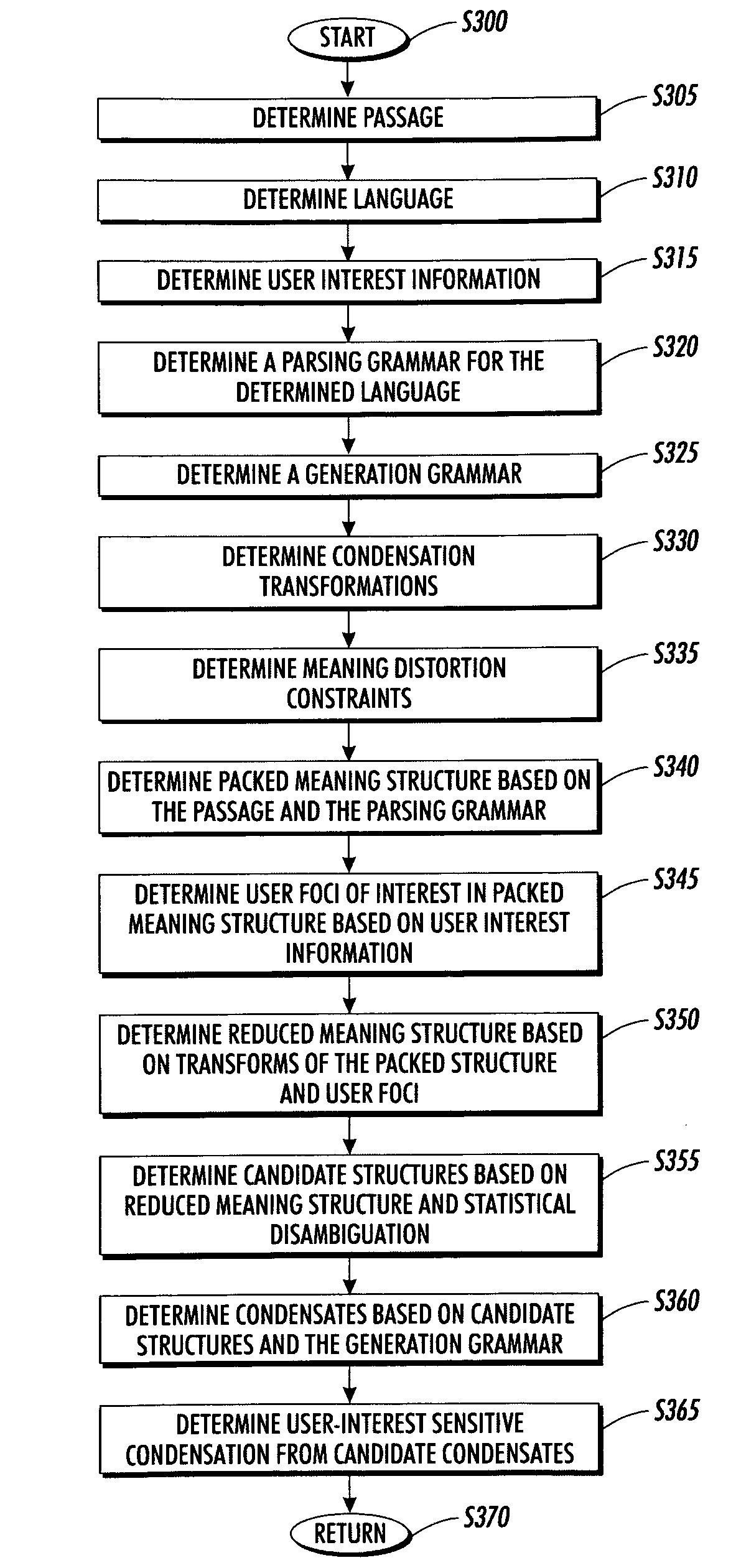
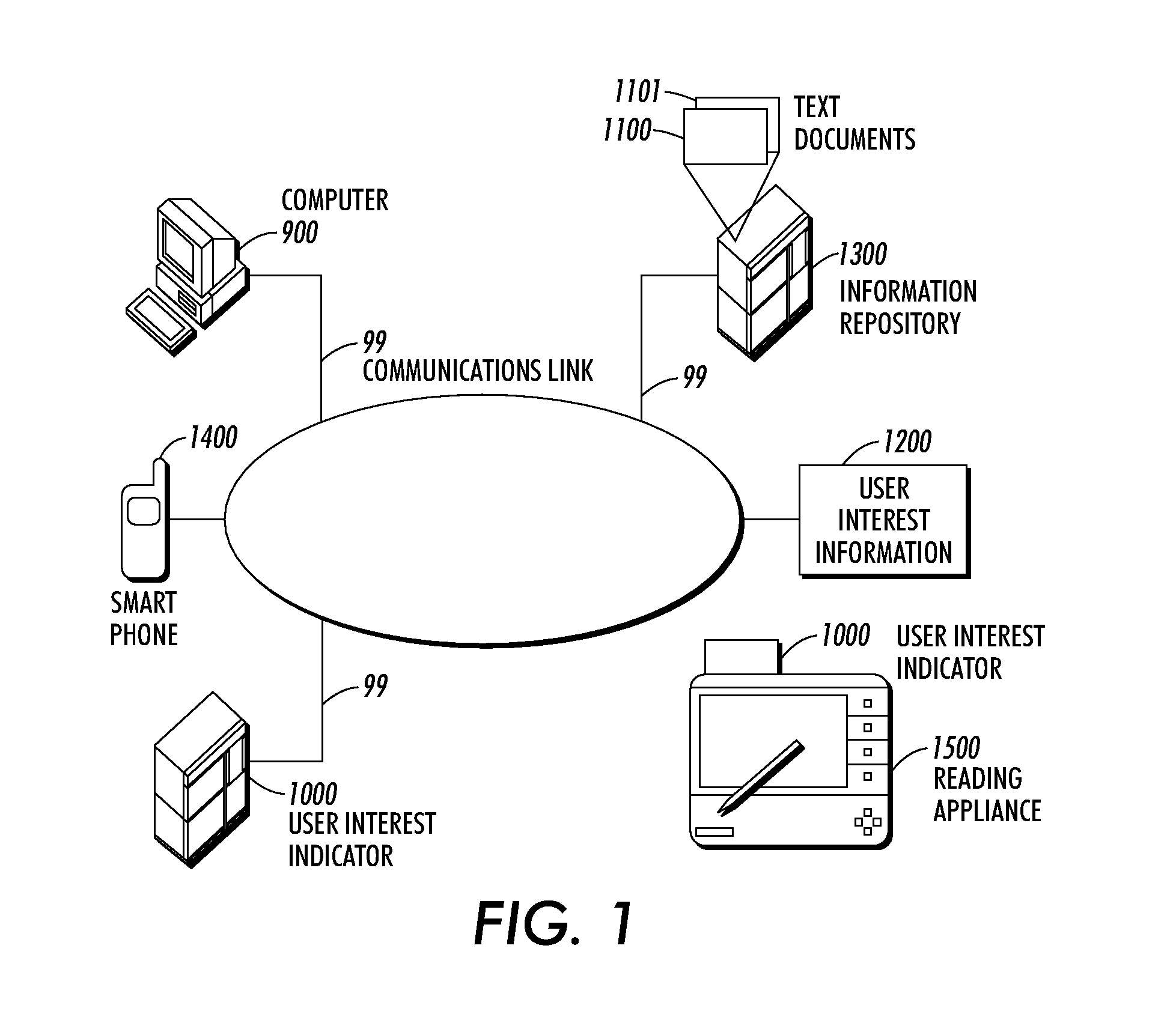
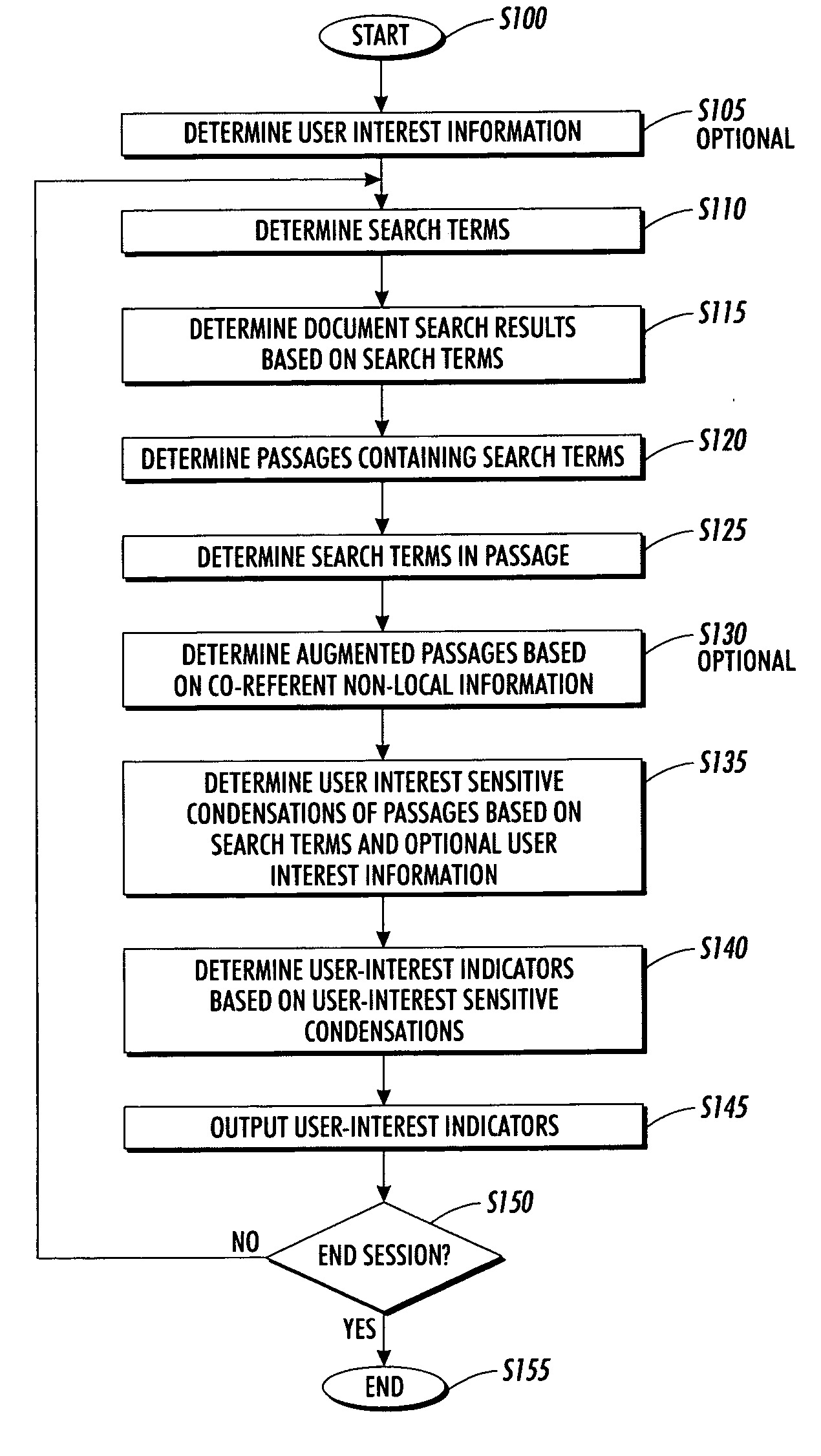
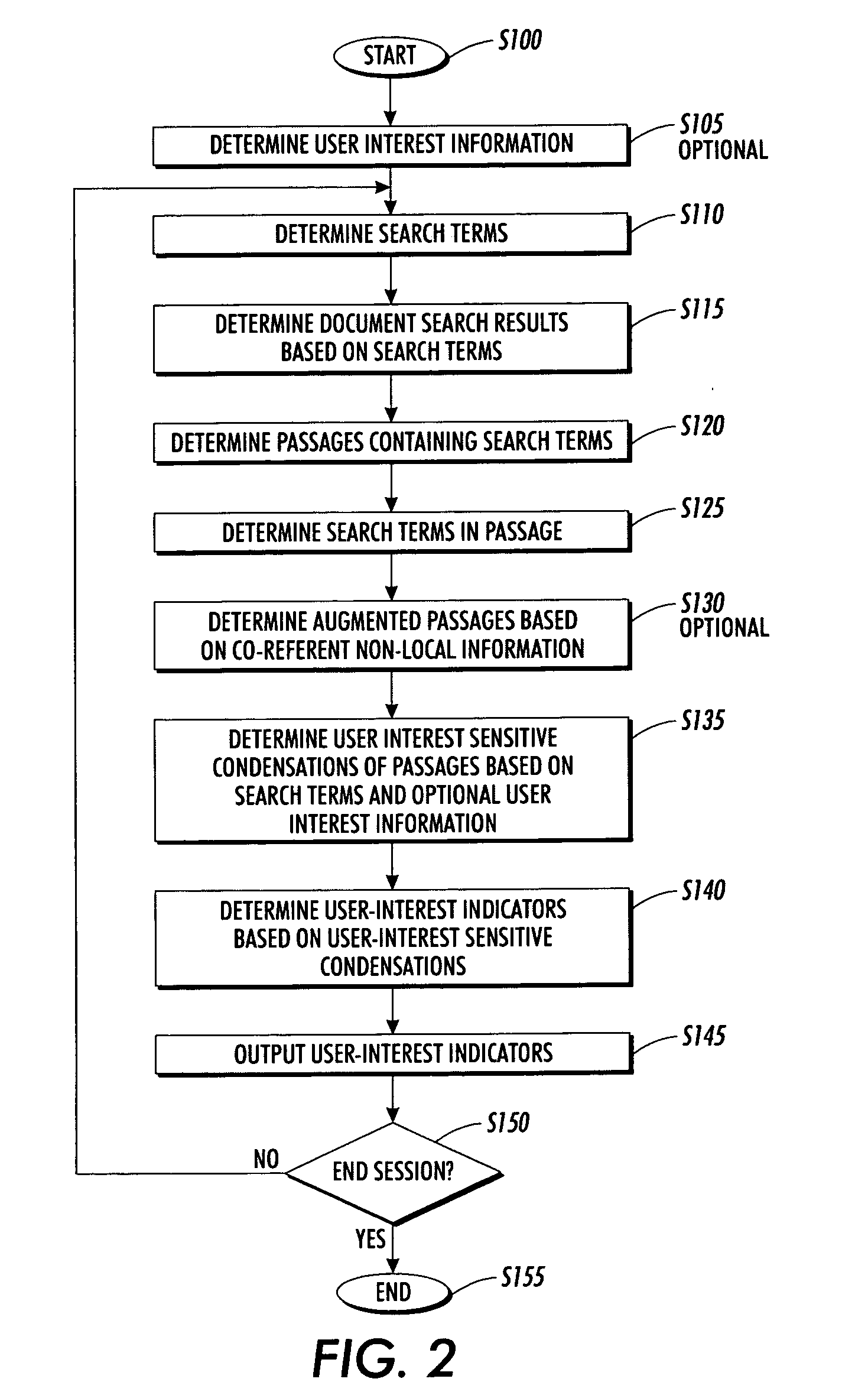
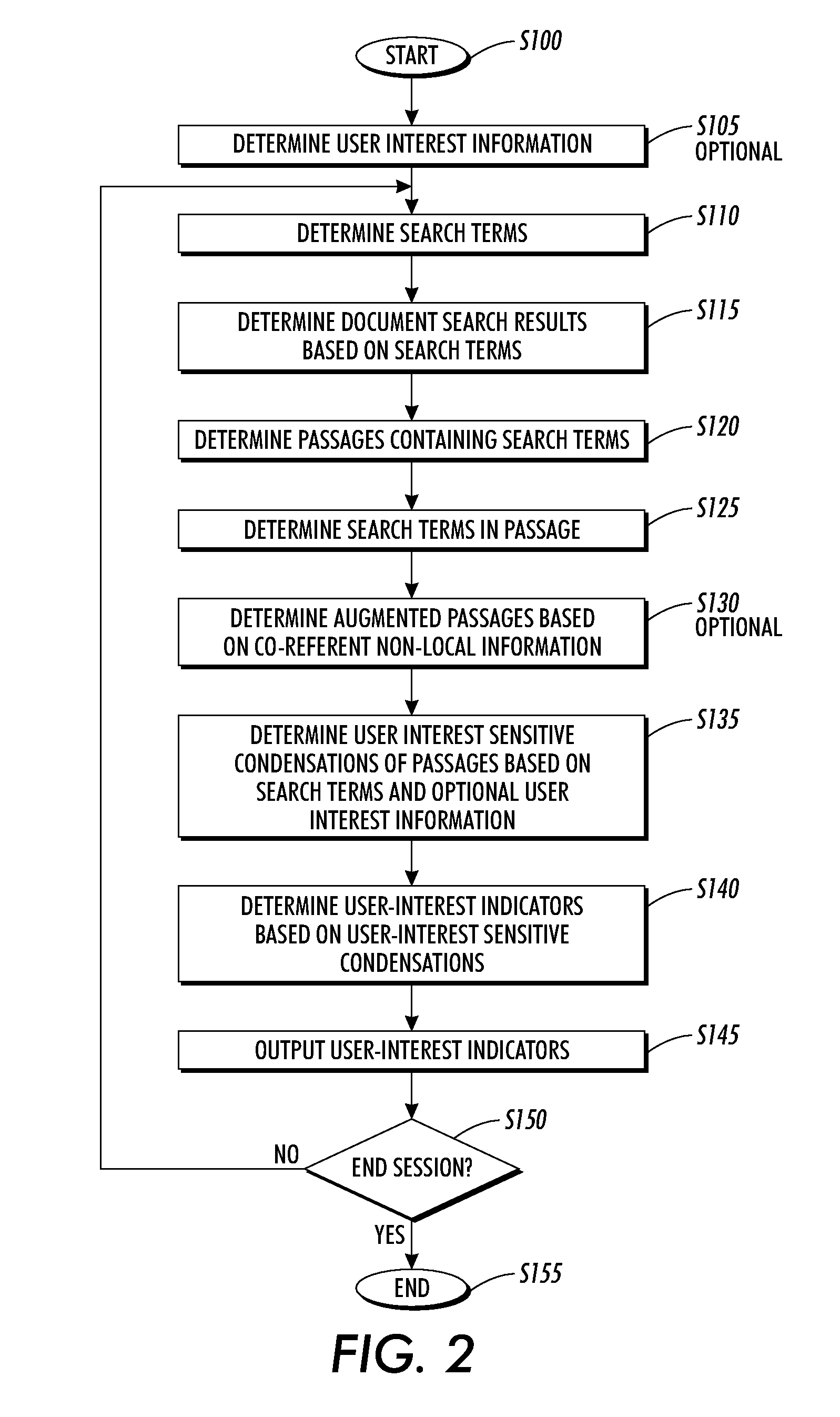
Systems and methods for using and constructing user-interest sensitive indicators of search results
InactiveUS7401077B2Reduce overheadData processing applicationsWeb data indexingOutcome measuresDocumentation
Techniques are provided to construct and use user-interest sensitive indicators of search results. A set of documents is determined based on one or more search terms. Passages within each selected document are identified based on the search terms. Condensation transformations applied to the passages to preferentially retain elements of the passage based on the search terms and user interest information. The resultant indicator is provides a user-interest sensitive signal of the meaning of the passage.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
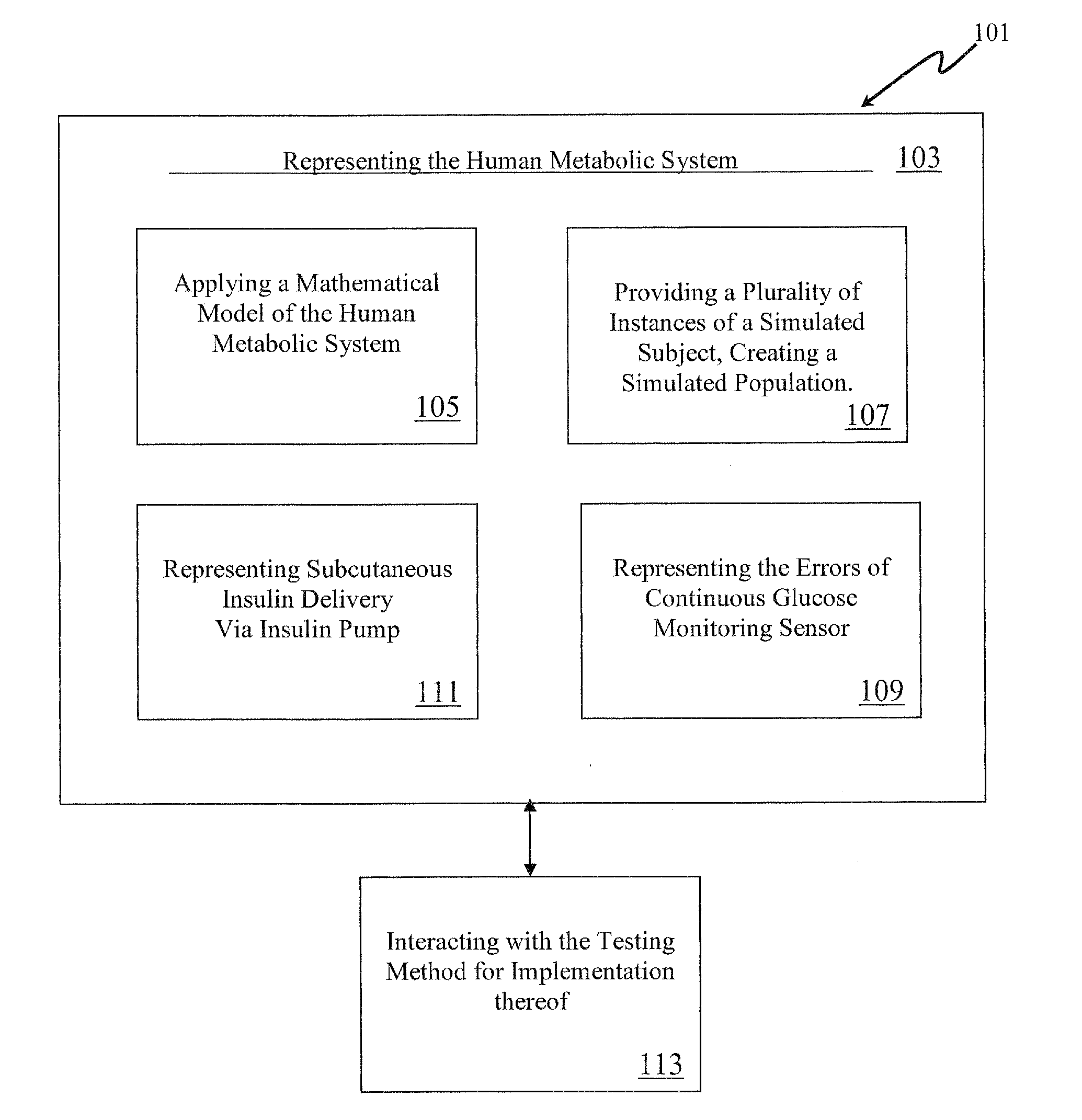
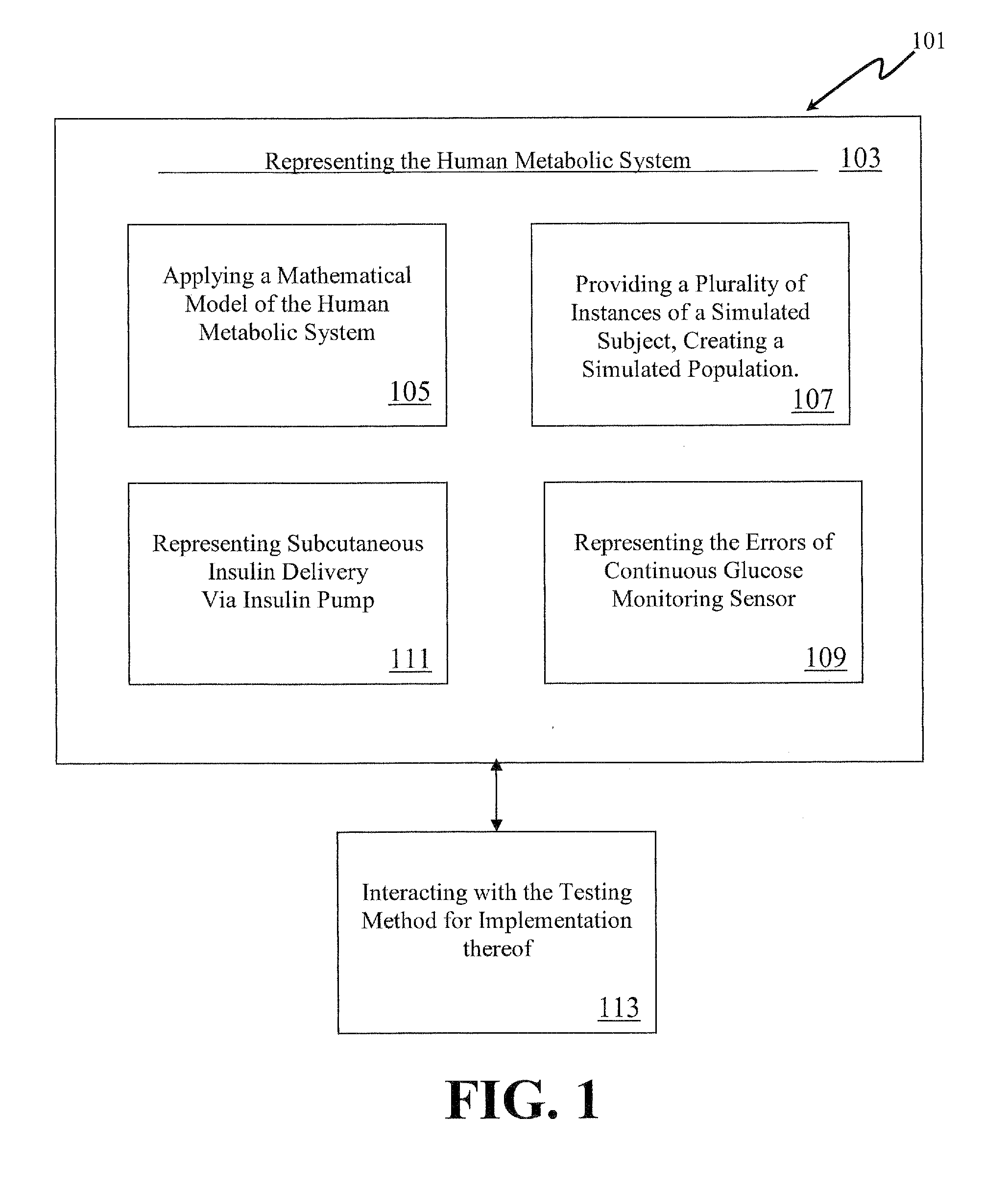
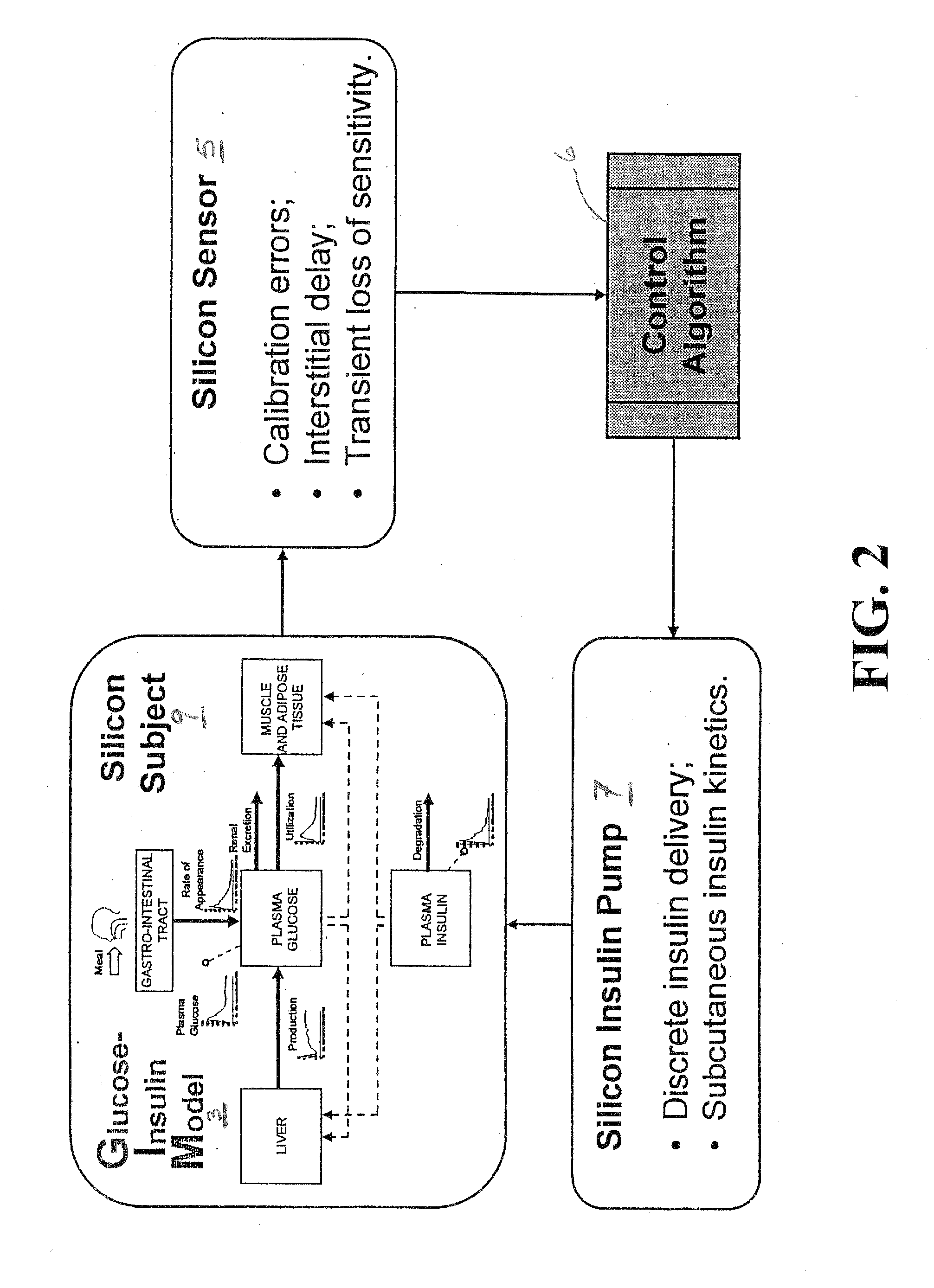
Method, System and Computer Simulation Environment for Testing of Monitoring and Control Strategies in Diabetes
A simulation environment for in silico testing of monitoring methods, open-loop and closed-loop treatment strategies in type 1 diabetes. Some exemplary principal components of the simulation environment comprise, but not limited thereto, the following: 1) a “population” of in silico “subjects” with type 1 diabetes in three age groups; 2) a simulator of CGM sensor errors; 3) a simulator of insulin pumps and discrete insulin delivery; 4) an interface allowing the input of user-specified treatment scenarios; and 5) a set of standardized outcome measures and graphs evaluating the quality of the tested treatment strategies. These components can be used separately or in combination for the preclinical evaluation of open-loop or closed-loop control treatments of diabetes.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Respiration training machine enabling grasp of result
InactiveUS20090170664A1Easy to masterIncrease motivationGymnastic exercisingRespiratory organ evaluationOutcome measuresBreathing process
A breathing exerciser includes: a guide unit for guiding an exercise pattern of breathing to a user; a breathing sensor for detecting breathing of the user; a breathing index calculating unit for calculating, based on a signal from the breathing sensor, a breathing index at least one of before and after an exercise period during which the exercise pattern is guided, the breathing index representing a characteristic of a breathing state of the user; and an outcome index calculating unit for calculating an outcome index based on at least two breathing indices, the outcome index representing an outcome of breathing exercise; and an informing unit for informing the outcome index to the user.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD +1
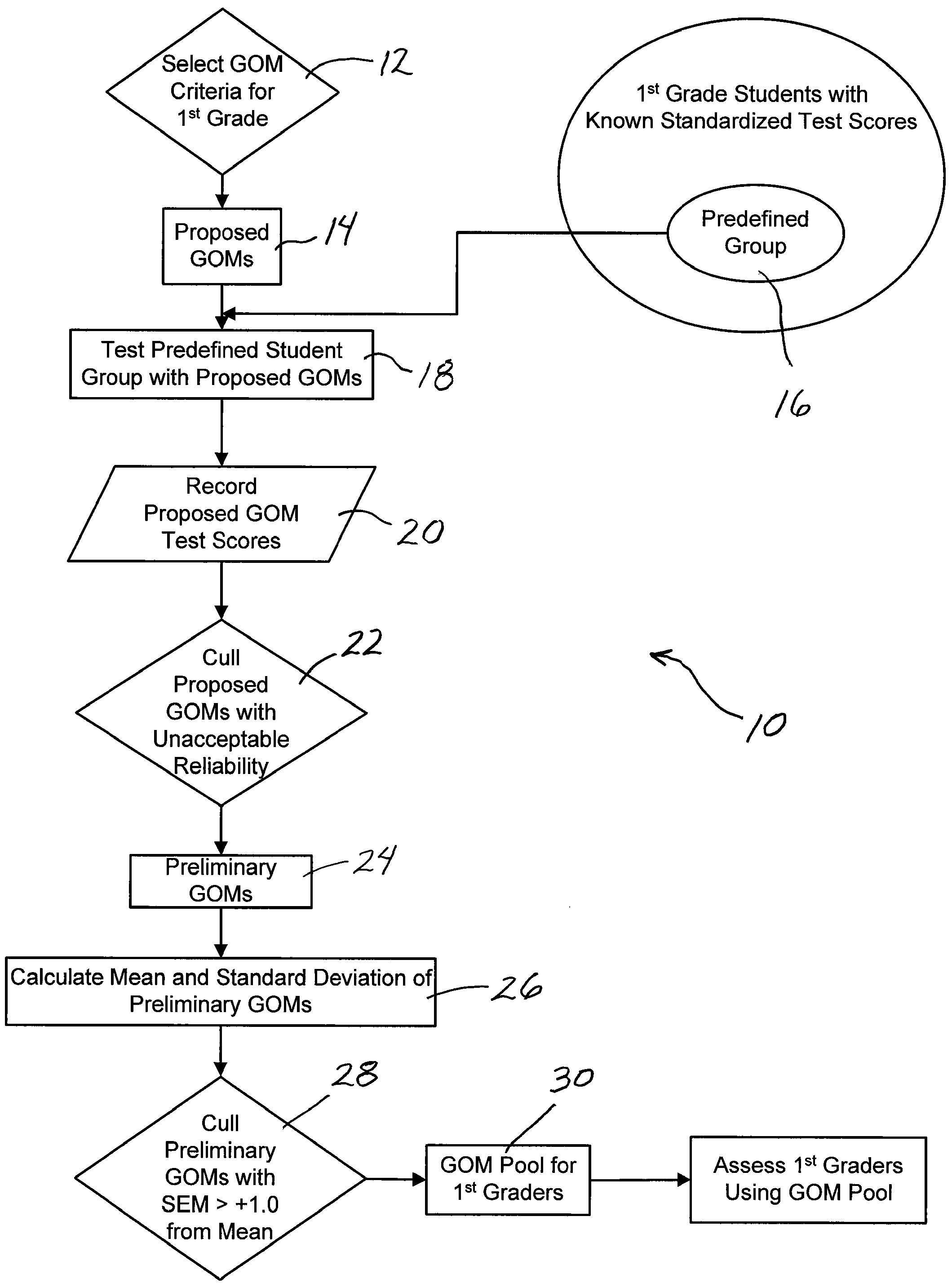
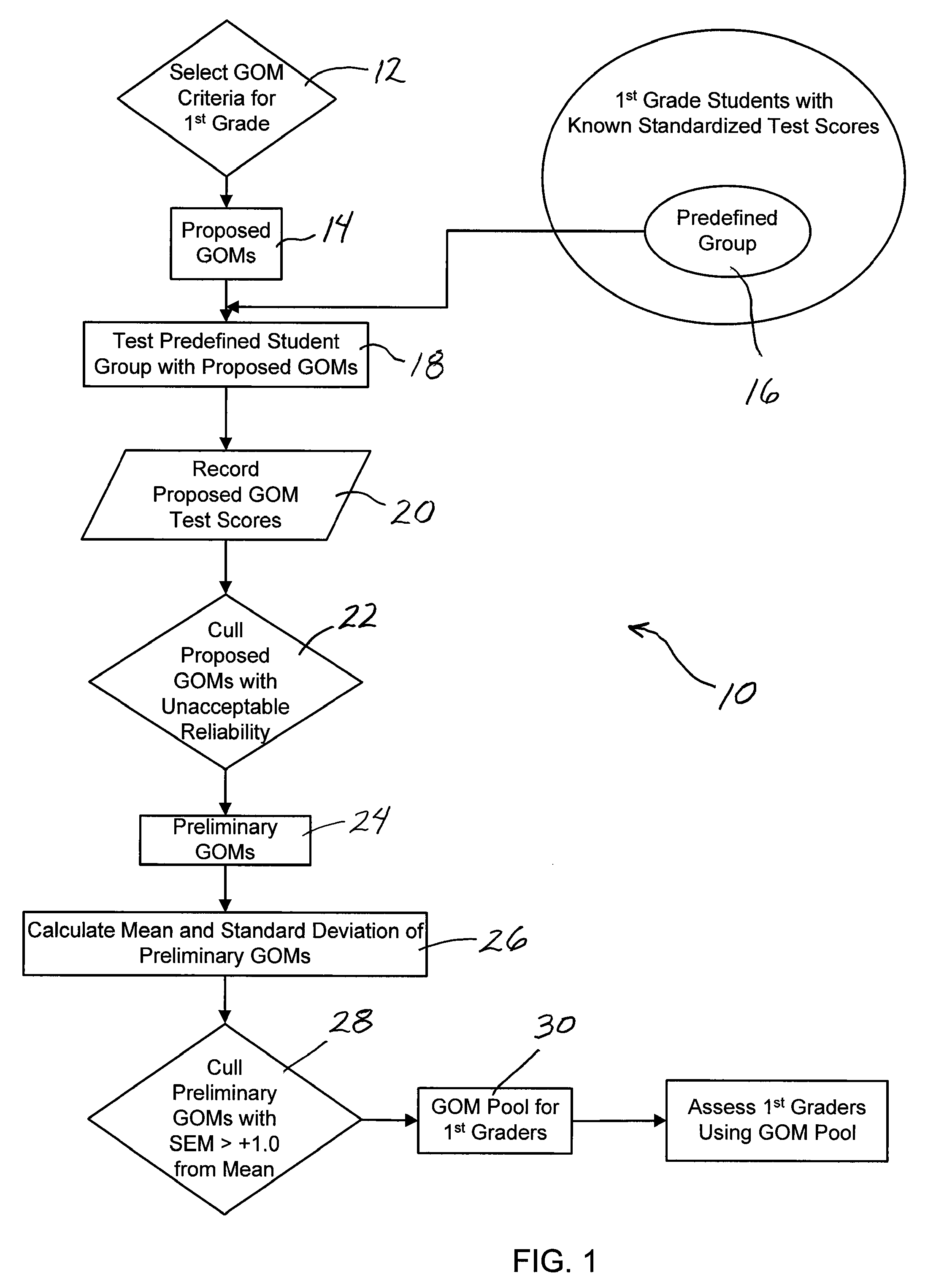
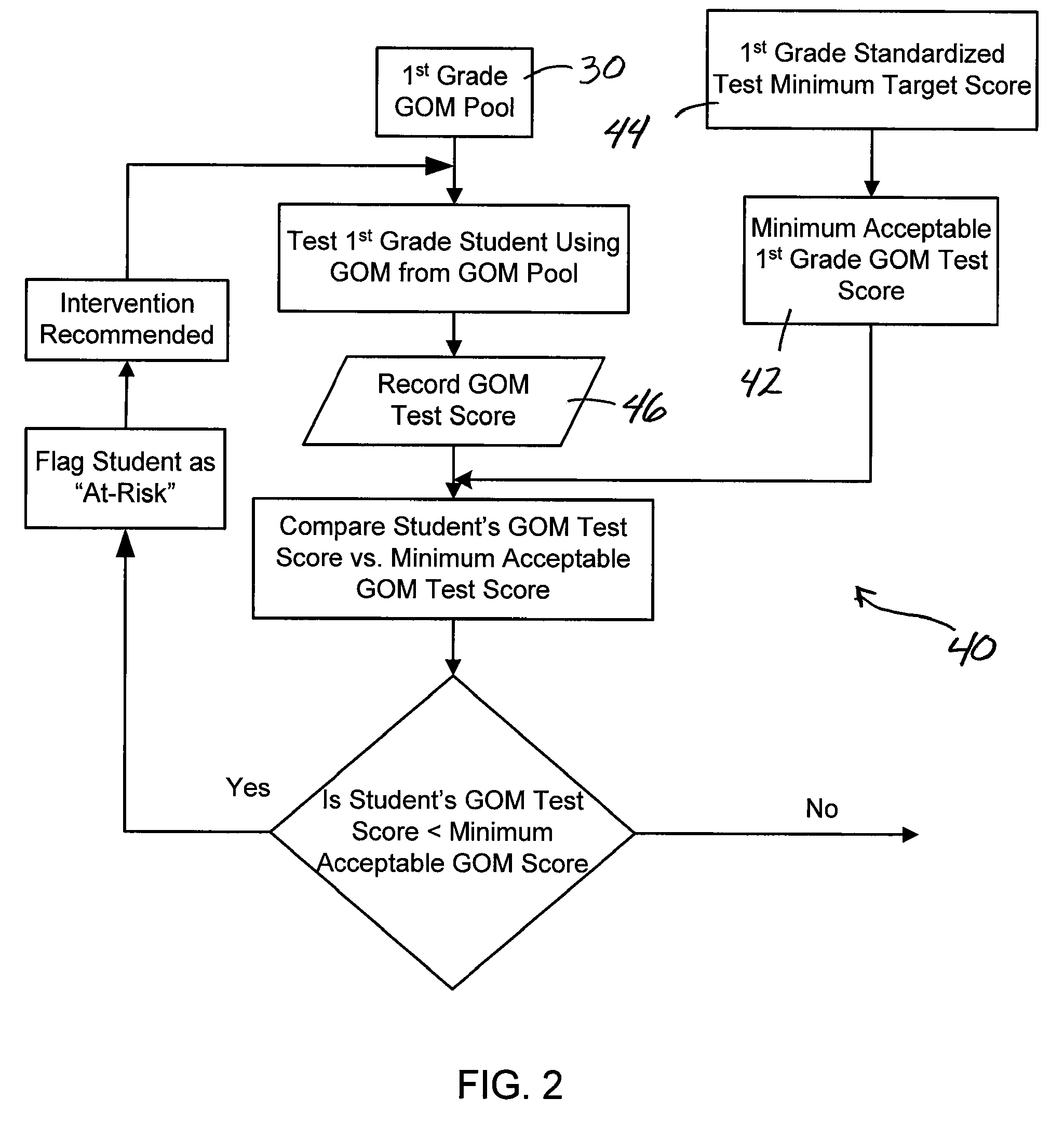
System and method assessing student achievement
A system and method for assessing and monitoring student academic achievement levels for purposes of identifying students at risk for not meeting minimum academic standards as measured using standardized tests, and for tracking or monitoring student academic performance levels. The system and method of the present invention comprises producing a pool of curriculum-independent General Outcome Measures (GOMs) of substantially equal difficulty for a particular grade level, and further comprises a system and method of assessing and monitoring students in that grade level using the pool of GOMs for the purpose of identifying those students at risk for not meeting minimum standardized test target scores and for tracking or monitoring student academic performance levels. The system comprises a database accessible remotely by authorized users through a network and user interface in which authorized users can remotely input student academic performance information and selectively retrieve that information for display through the user interface.
Owner:PSYCHOLOGICAL CORPORATION
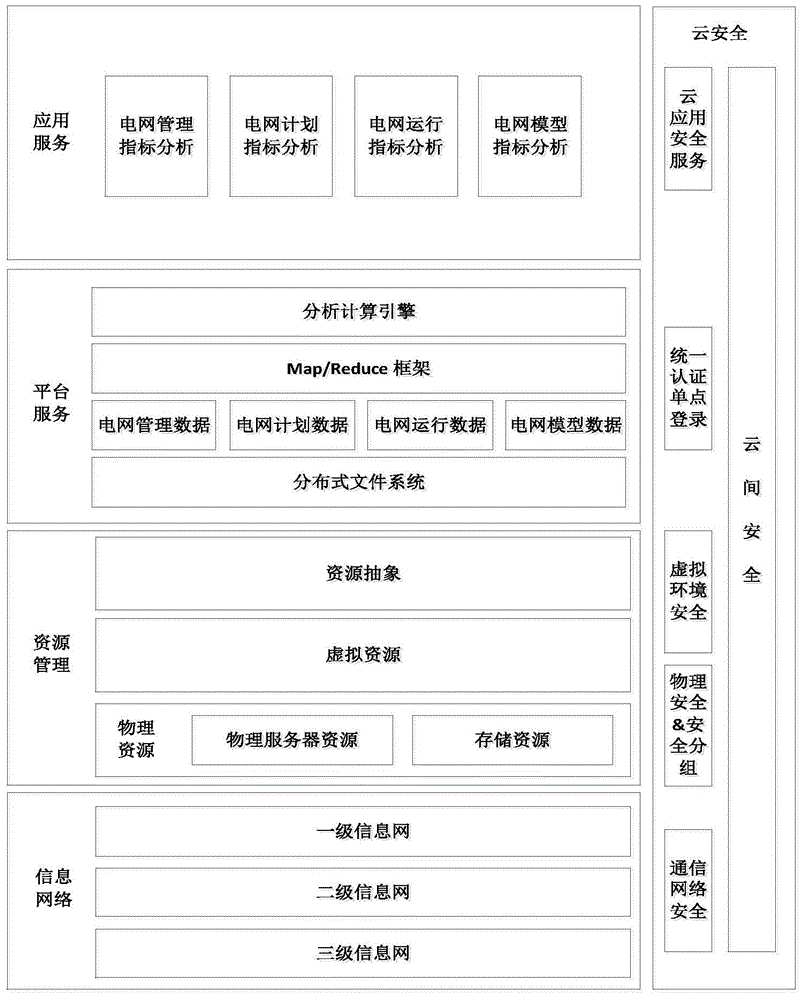
Power dispatching production management system based on cloud computing and realization method of power dispatching production management system
InactiveCN104156810AImprove perceptionRapid responseResourcesManufacturing computing systemsIsomerizationPower dispatch
The invention discloses a power dispatching production management system based on cloud computing and a realization method of the power dispatching production management system. The system supports panoramic real-time presentation of diversified and isomerous mass data; the real-time panoramic data presentation refers to real-time visualization of various result indexes obtained through analysis of operating data, display design provides a friendly visualization mode for user experience and adapts to characteristics of diversity and isomerization of a current terminal, so as to develop an omnibearing monitoring and analyzing system on the basis of a visualization technology, therefore, the sensory ability of dispatching persons to power grid states can be improved, and the dispatching persons can rapidly and effectively respond to emergency situations; the power dispatching production management system can schedule maintenance plans in a rolling manner and has the functions of monthly plan high-class statistic analysis display and automatic generation of power failure information.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
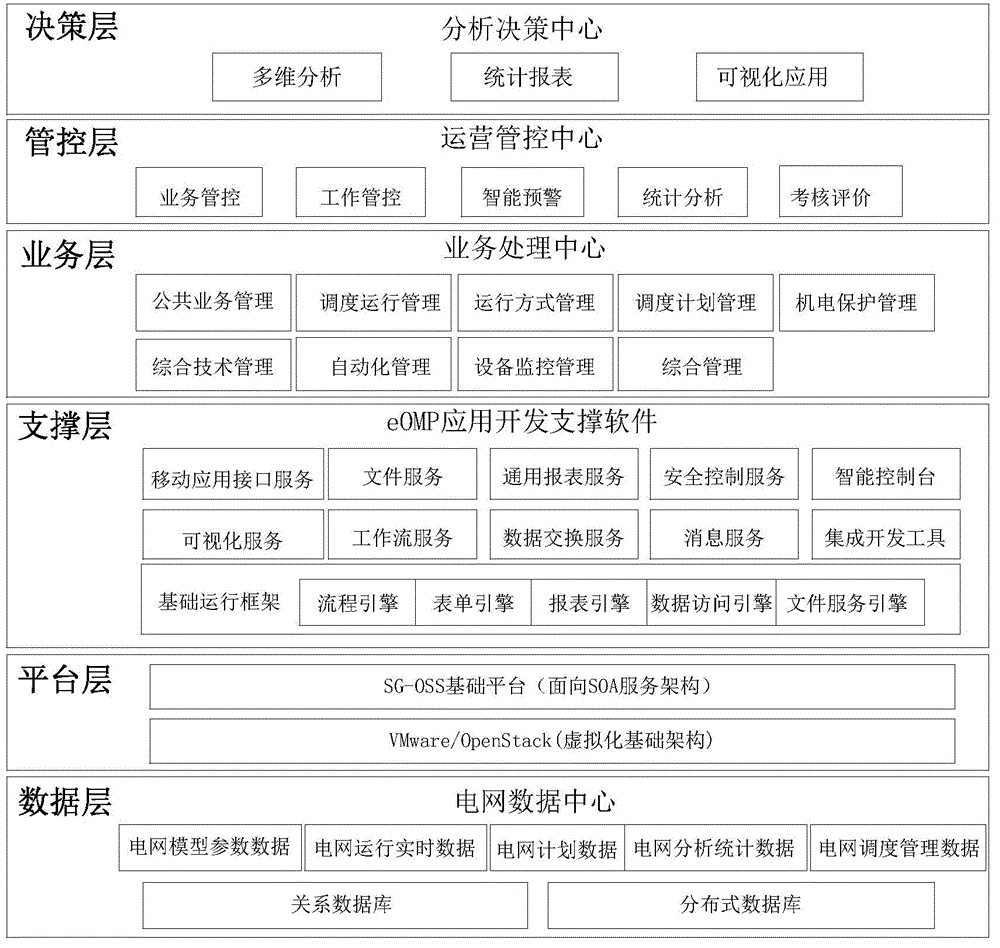
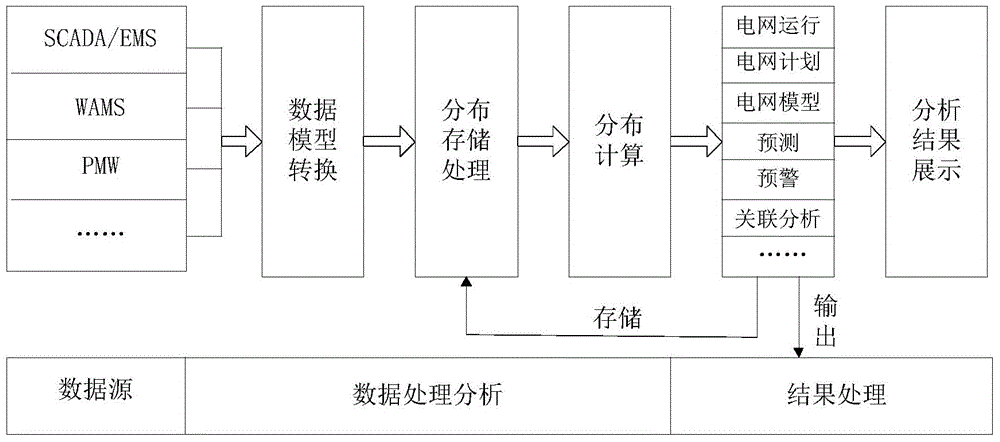
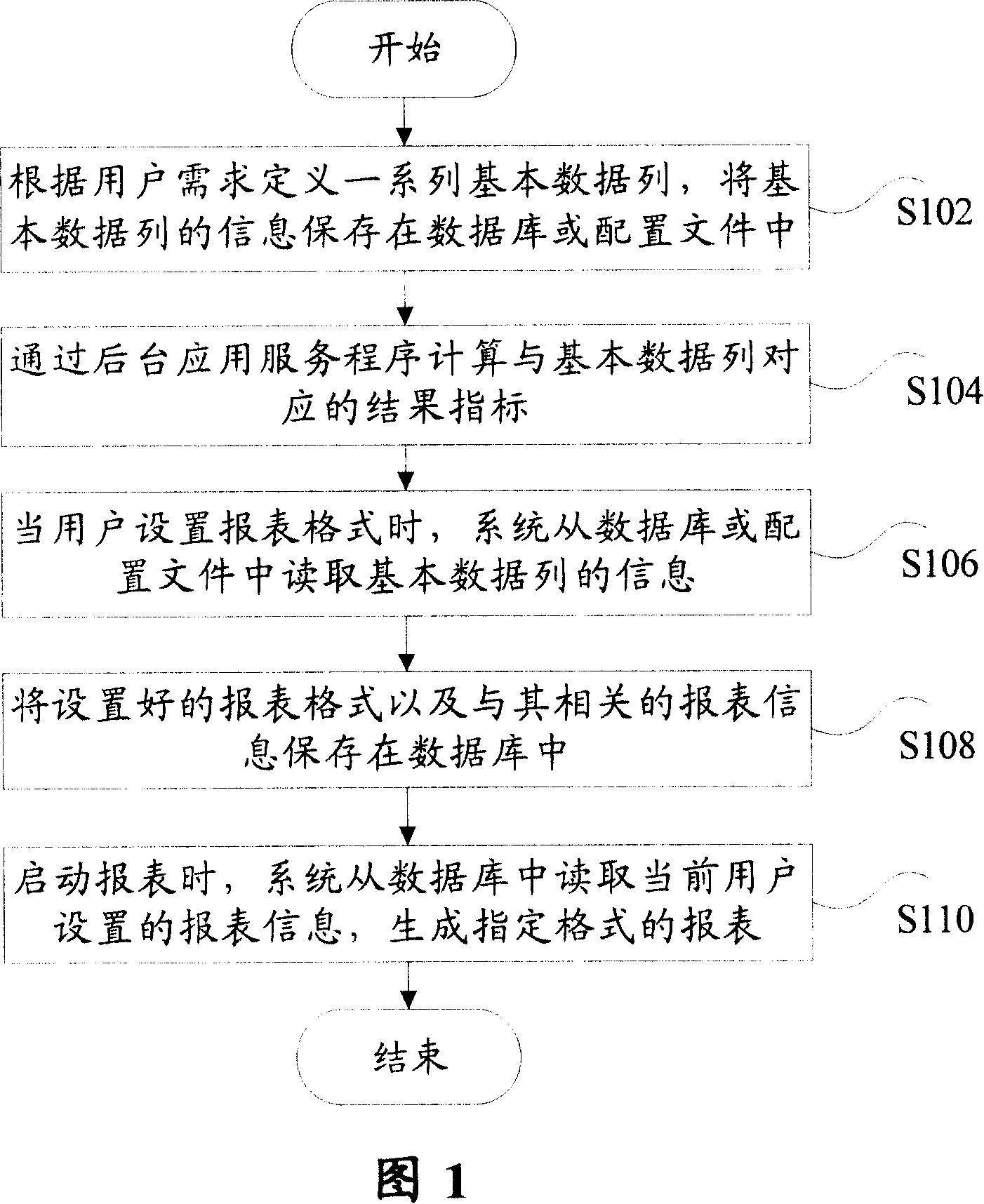
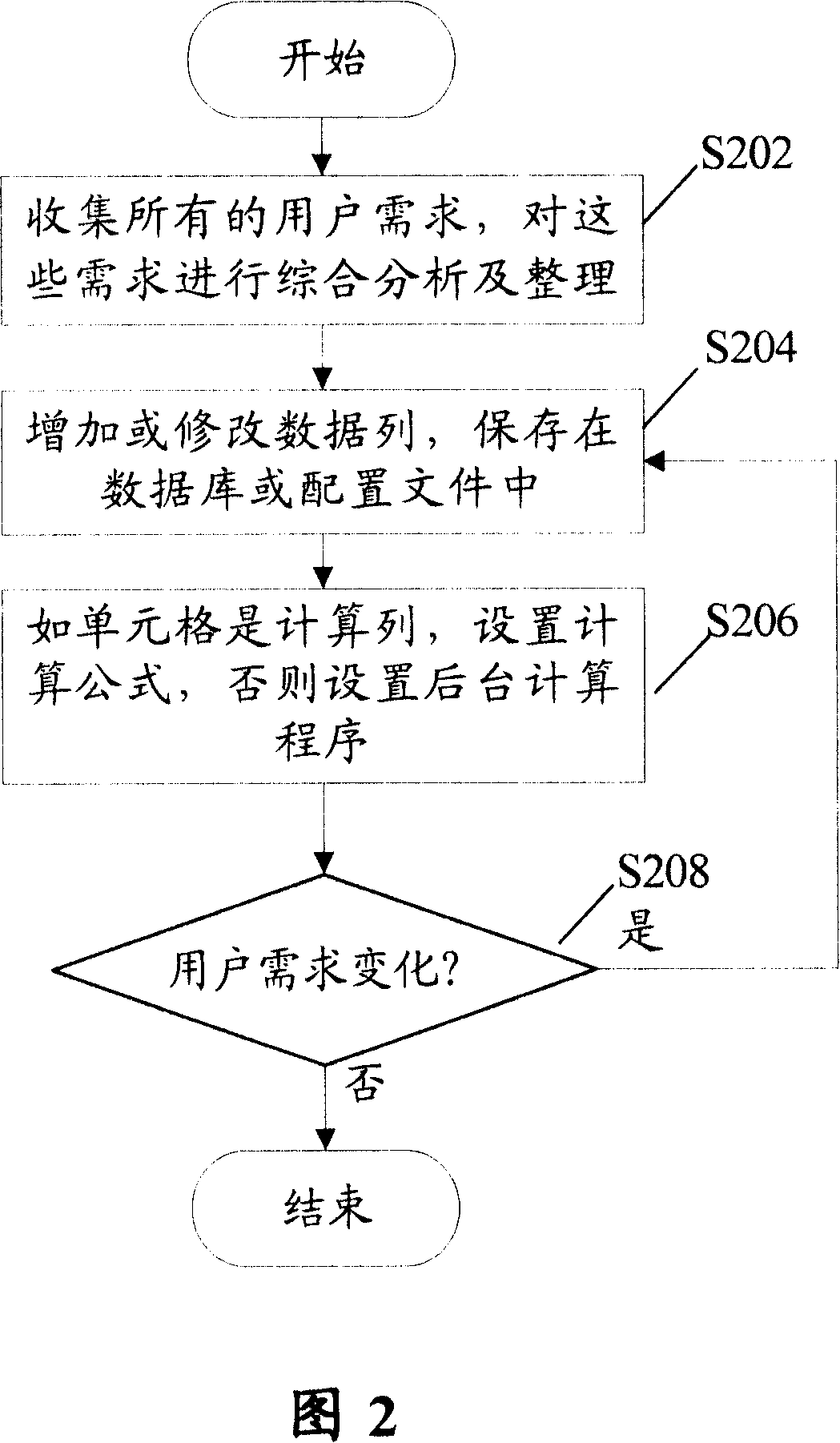
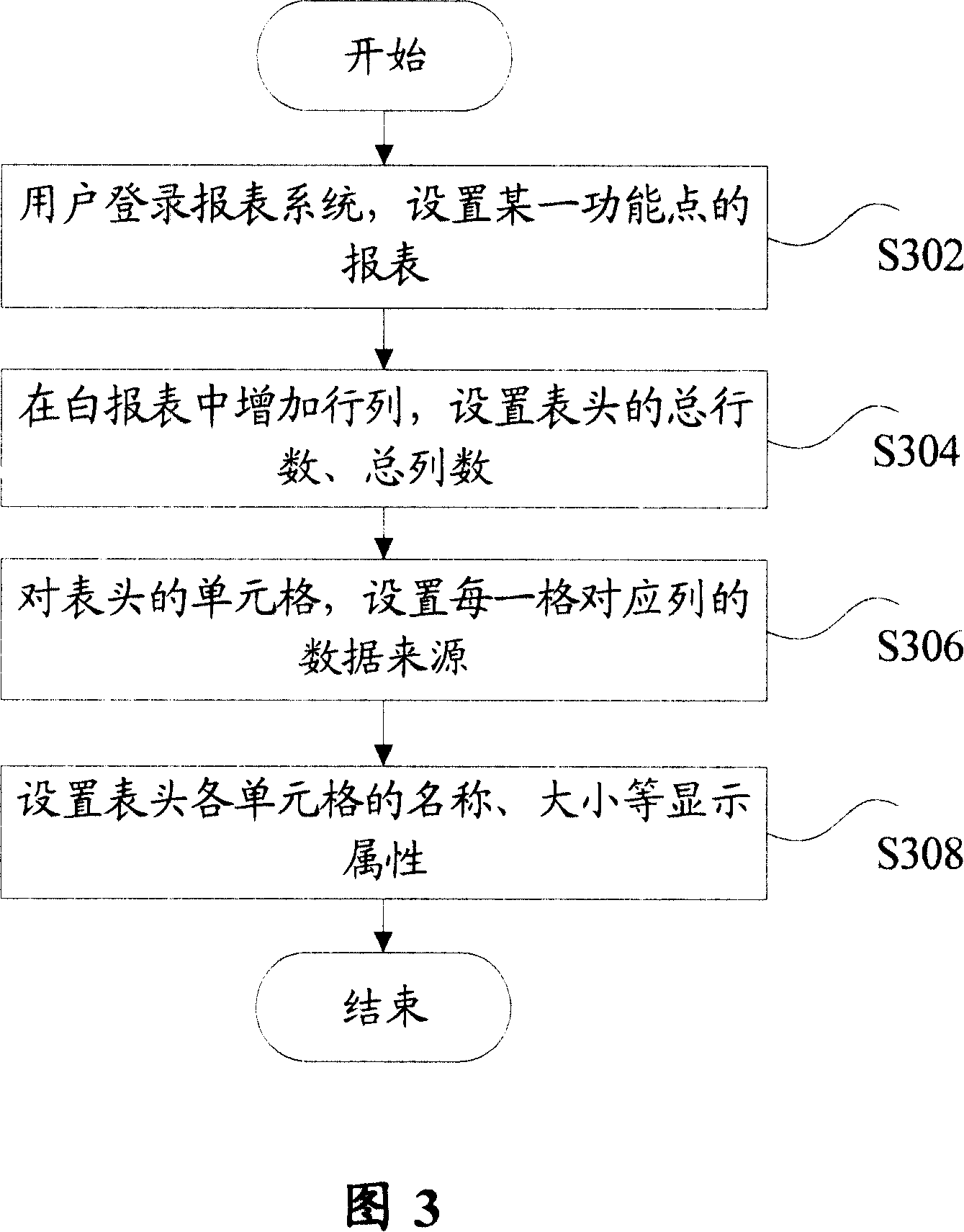
Method for realizing user-defined report forms
InactiveCN101140562ASolve inflexibilityReduce difficultySpecial data processing applicationsUser needsOutcome measures
The invention discloses a self-defined statement fulfilling method, which comprises: Step S102, define a serial basic data list according to users' demands, and save the information of the basic data list into a database or a configuration file; and Step S104, utilize a background application service program to calculate results indexes corresponding with the basic data. Utilization of the invention can create specific format statements according to users' demands, and save the corresponding configuration information into a database or a configuration file, so as to effectively overcome inflexibility and not easy expansibility due to statements in fixed formats; meanwhile, the invention can reduce difficulties in development and maintenance for statements.
Owner:ZTE CORP
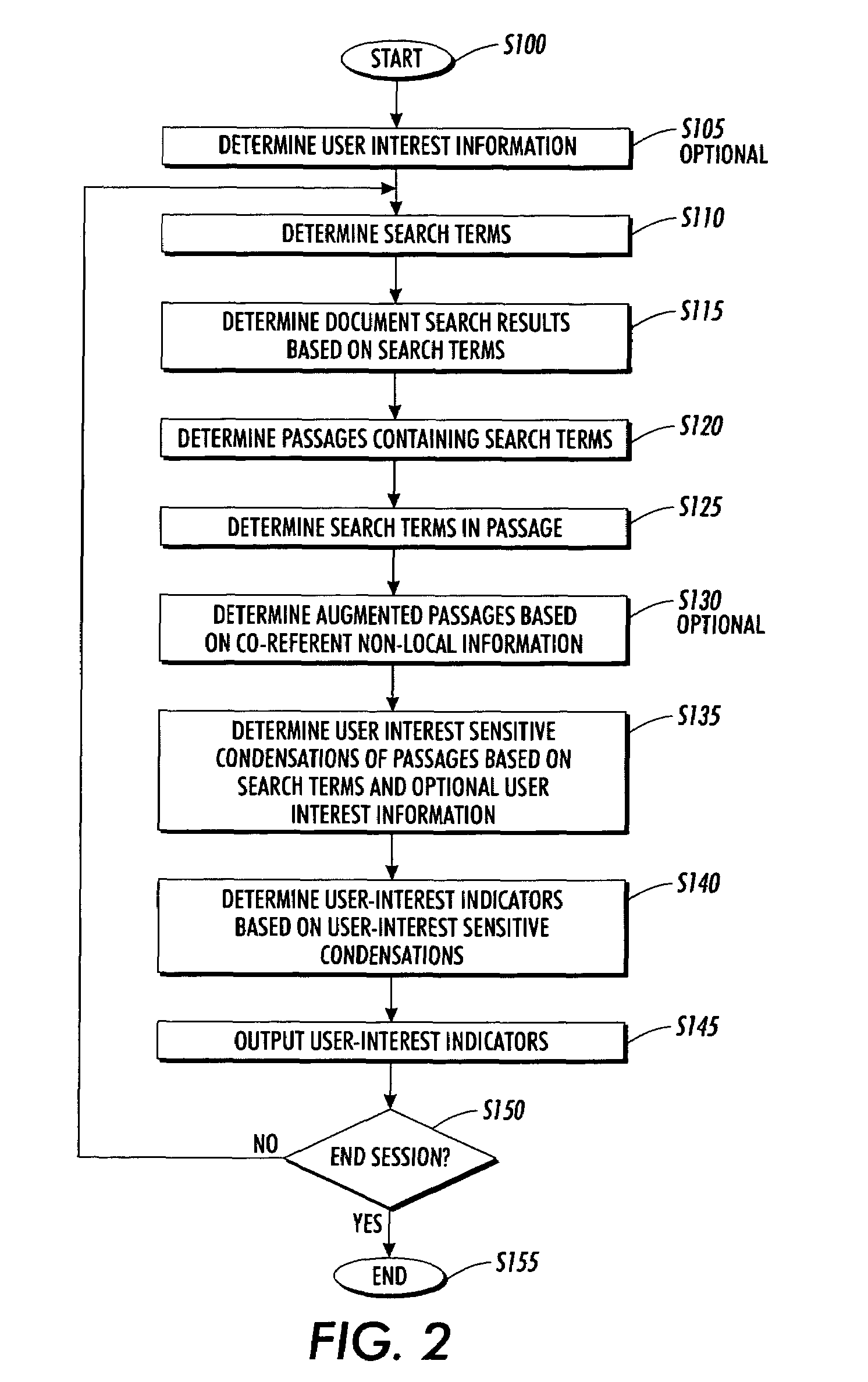
Systems and methods for using and constructing user-interest sensitive indicators of search results
InactiveUS20060136385A1Low cognitive overheadReduce overheadWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsOutcome measuresPaper document
Techniques are provided to construct and use user-interest sensitive indicators of search results. A set of documents is determined based on one or more search terms. Passages within each selected document are identified based on the search terms. Condensation transformations applied to the passages to preferentially retain elements of the passage based on the search terms and user interest information. The resultant indicator is provides a user-interest sensitive signal of the meaning of the passage.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Kit for fast culture, identification and drug sensitivity test of helicobacter pylori (Hp) and examination method therefor
ActiveCN102888442ARapid cultivationEliminate dependenciesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGrowth promotingThermostat
The invention belongs to the technical field of helicobacter pylori (Hp) examination and discloses a kit for fast culture, identification and a drug sensitivity test of Hp and an examination method therefor. The kit comprises a first culture tube, an identification reagent device and a drug sensitivity test unit. Through the first culture tube of Hp, bedside inoculation of a specimen is realized and the traditional sample transport and preservation processes are avoided; ordinary thermostat culture is realized and dependence on a CO2 incubator is eliminated; an Hp growth result is represented by a color change so that a result can be determined accurately by laypeople; through the combination of a growth promoting agent and a growth indicator, culture time is shortened and fast culture of Hp is realized; an Hp identification reagent, fast combination identification of Hp is realized; and through the drug sensitivity test unit of Hp, fast and accurate examination of drug sensitivity of Hp is realized. The kit and the examination method therefor can realize fast and accurate examination of Hp.
Owner:CHONGQING CORETECH MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method of data mining in medical applications
InactiveUS20110218815A1Increase productivityQuality improvementMedical data miningFinanceData dredgingPersonalization
The present invention relates to a method of creating databases for data mining in medical applications. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to providing a data-driven objective reimbursement model incorporating performance and quality measures, tied to patient, exam, context, and provider-specific variables. In another embodiment, the present invention creates standardized databases where context, patient, provider, and technology specific variables are used to create an objective quantitative measure of exam complexity, which can be correlated with performance times and outcomes measures for iterative refinement. In another embodiment, through the combined analysis of examination complexity, interpretation accuracy, and interpretation times, specific to each individual radiologist, external pacers are created which can be customized to a radiologist's individual needs and preferences. The derived data is used to identify best practice patterns and end-user performance, which can be used by radiologists for individualized education and training.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
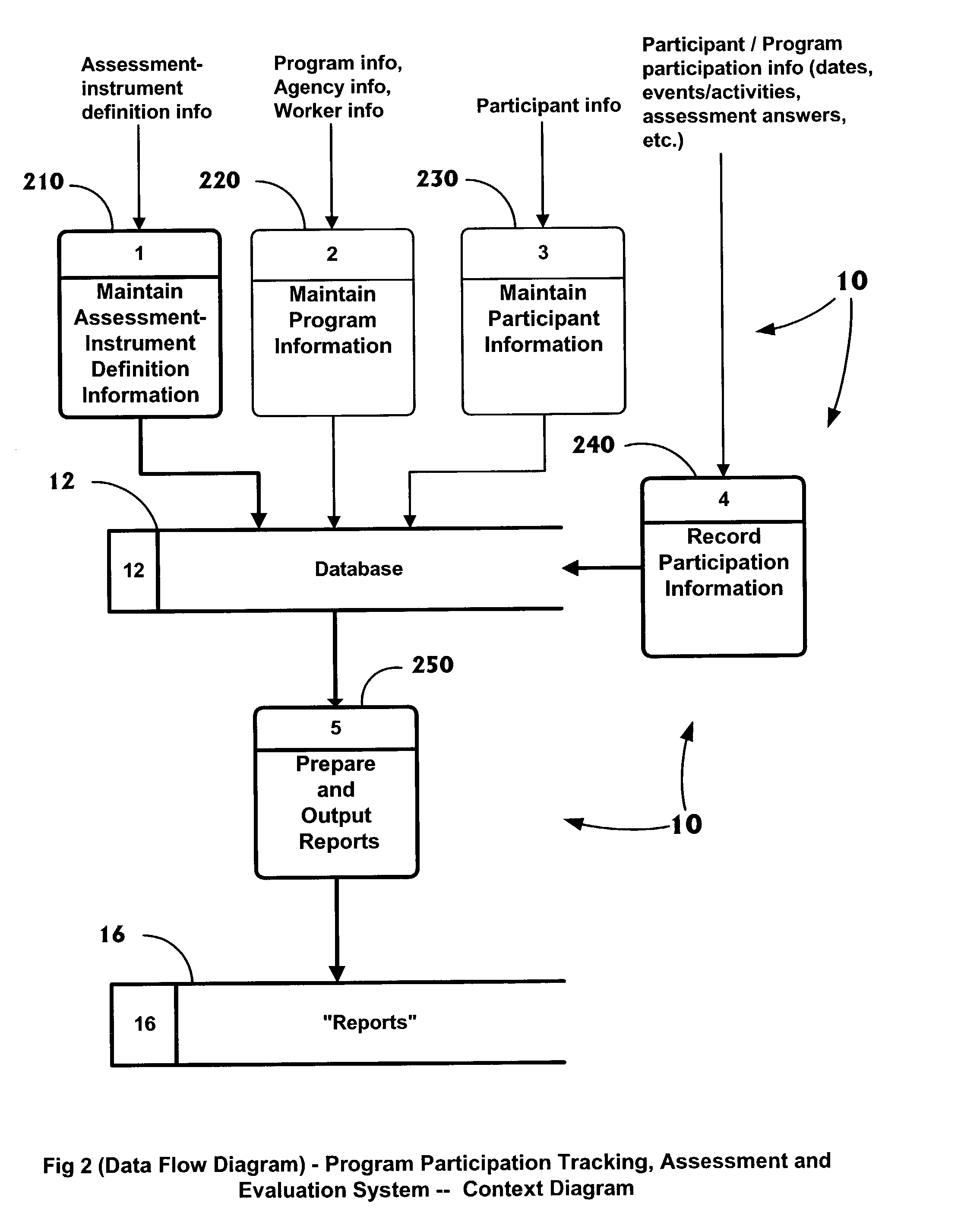
Method for tracking and assessing program participation
InactiveUS7269579B2Flexible and convenientEasy activityDigital data processing detailsChaos modelsOutcome measuresRelational database
Disclosed is a computerized decision support system and method for a) tracking participation within programs, b) capturing participant's participation activity and assessment information in a format that can be easily analyzed and c) distilling the participation and assessment data into useful management and evaluation information. The repository of longitudinal data can be analyzed and reported for case-management and program-evaluation purposes. An assessment module enables analyzable assessment instruments to be custom-defined by the system user, e.g. a program manager. The customized assessment instrument is used to provide answer-restricted questions during an assessment interview, enabling virtually any data item to be tracked historically. The system captures date / time-stamped participation information at various levels of detail and stores this information in a way that can be easily retrieved and analyzed for program and participant-focused analysis. A set of industry-standard participation events can be tracked, with supporting detail, as well as less-data-intensive ad hoc user-defined activities. The data model underlying the system, and the implementation of this model within a relational database system, provides a great degree of flexibility, adaptability and efficient navigation through the database for analysis and reporting. Though numerous program-evaluation reports are provided, a set of intermediary aggregations of data is also available for efficient evaluation of additional program outcome measures.
Owner:LOVEGREN VICTORIA M
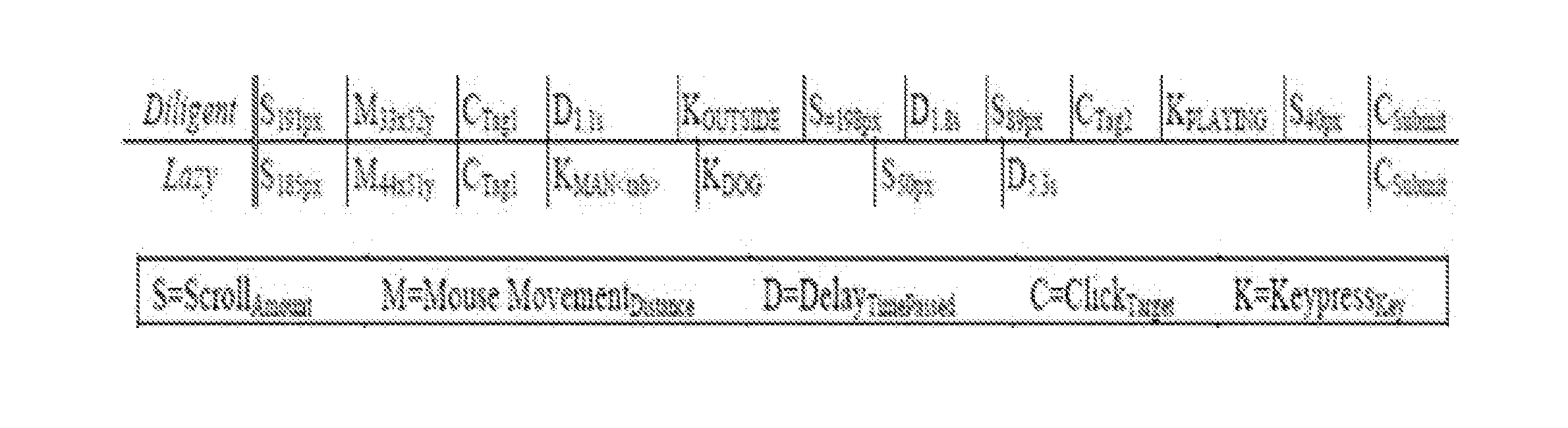
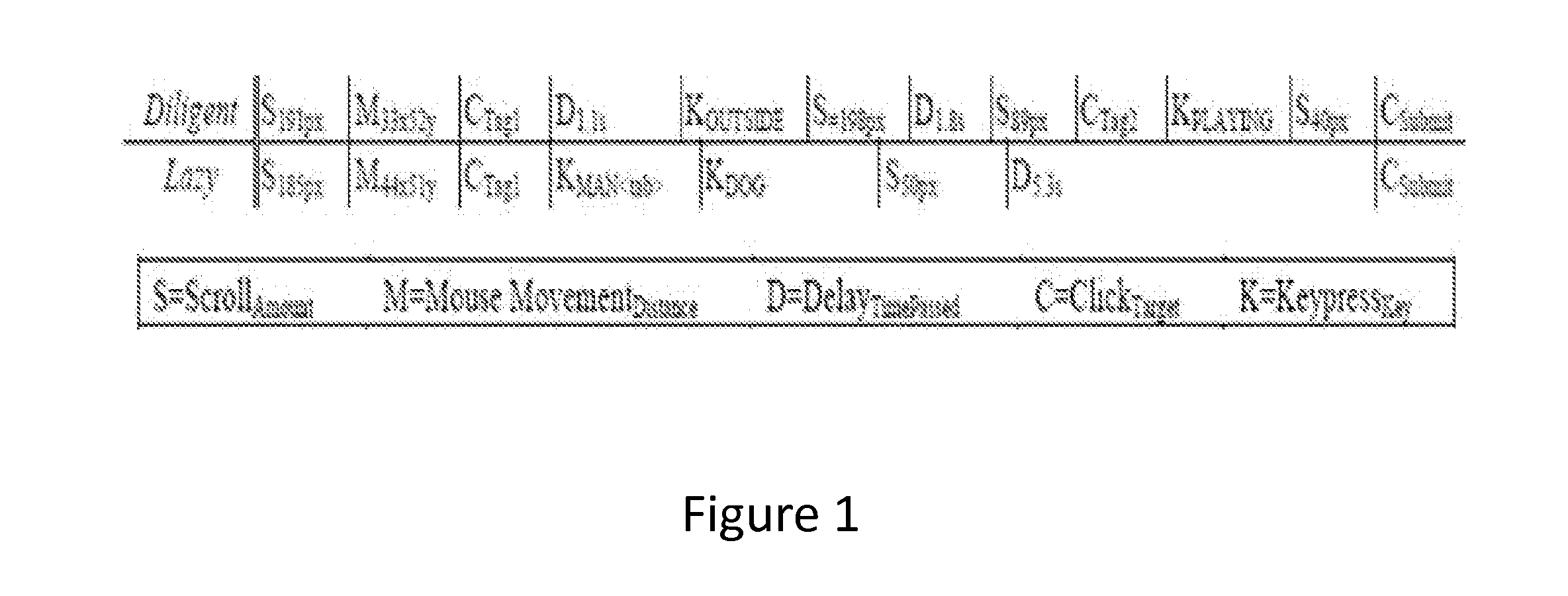
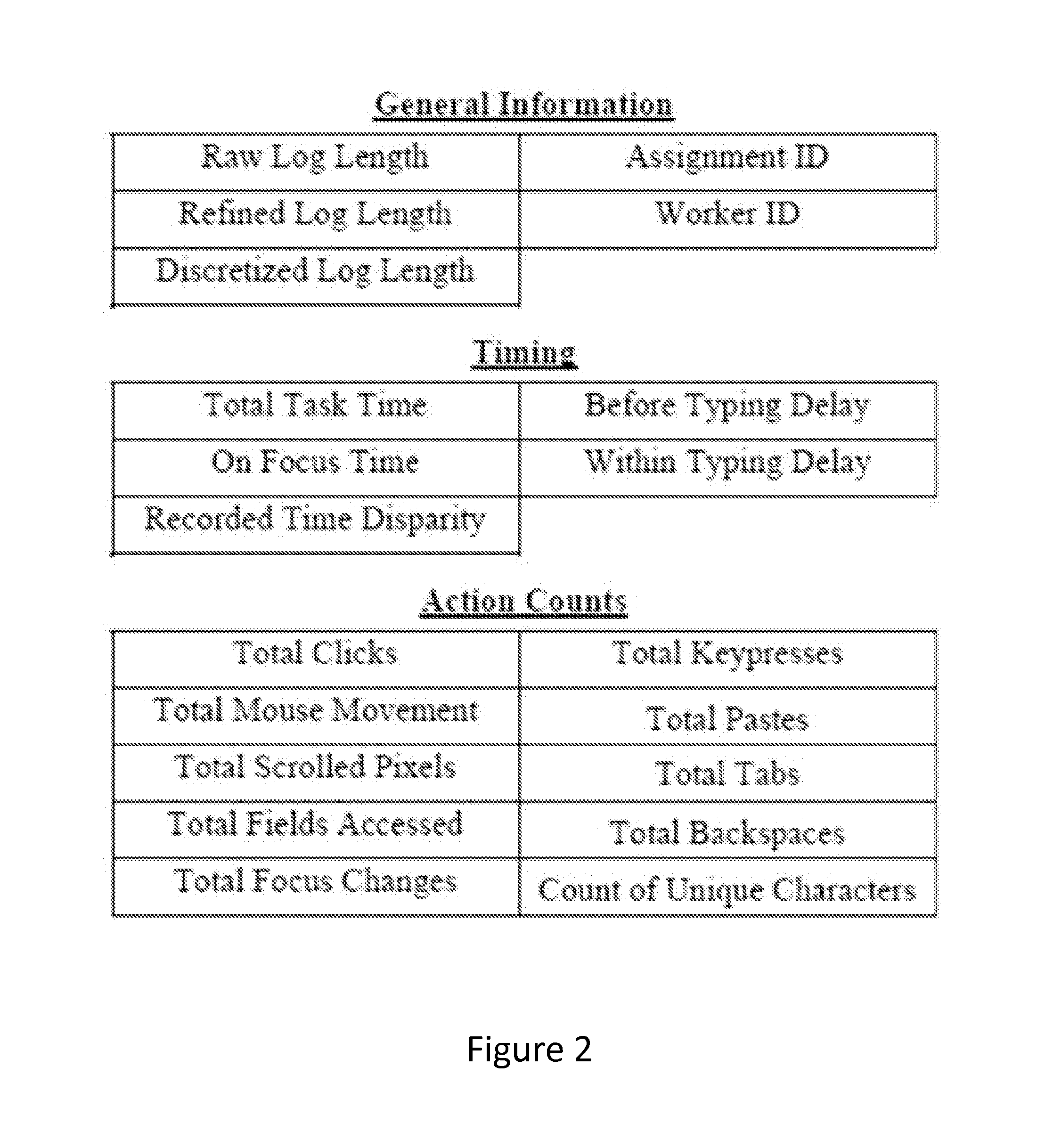
System and Method of Using Task Fingerprinting to Predict Task Performance
A novel method of using task fingerprinting to predict outcome measures such quality, errors, and the likelihood of cheating, particularly as applied to crowd sourced tasks. The technique focuses on the way workers work rather than the products they produce. The technique captures behavioral traces from online crowd workers and uses them to build predictive models of task performance. The effectiveness of the approach is evaluated across three contexts including classification, generation, and comprehension tasks.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Method and apparatus for presenting bingo gaming results using multiple prize distributions
ActiveUS20070060290A1Large prizeImprove distributionApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesOutcome measuresEngineering
A method includes operating a bingo player station in a first play mode in which the result for a respective bingo game play initiated through the bingo player station is assigned according to a first pattern list. In response to detecting a trigger event, the bingo player station is switched from the first play mode to a second play mode and then the bingo player station is operated in this second play mode. In the second play mode, the result for a respective bingo game play initiated through the bingo player station is assigned according to a second pattern list. The bingo player station is switched from the second play mode to the first play mode in response to a return event. Both the first pattern list and the second pattern list may share at least one result level and at least one common result indicator. However, the two pattern lists are different so that a given bingo pattern correlated to a prize in one of the pattern maps may correlate to a different prize or no prize in the other pattern map.
Owner:EVERI GAMES
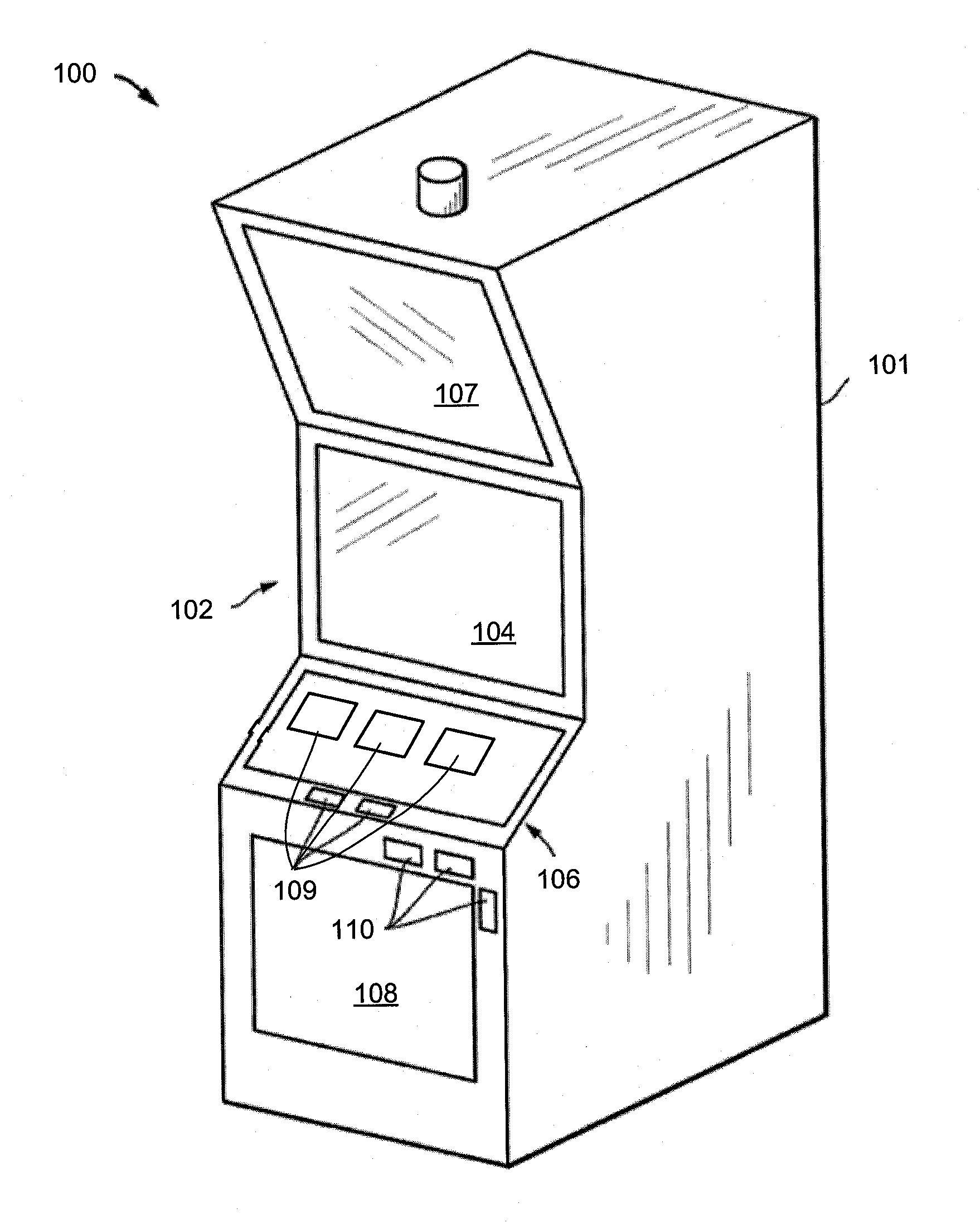
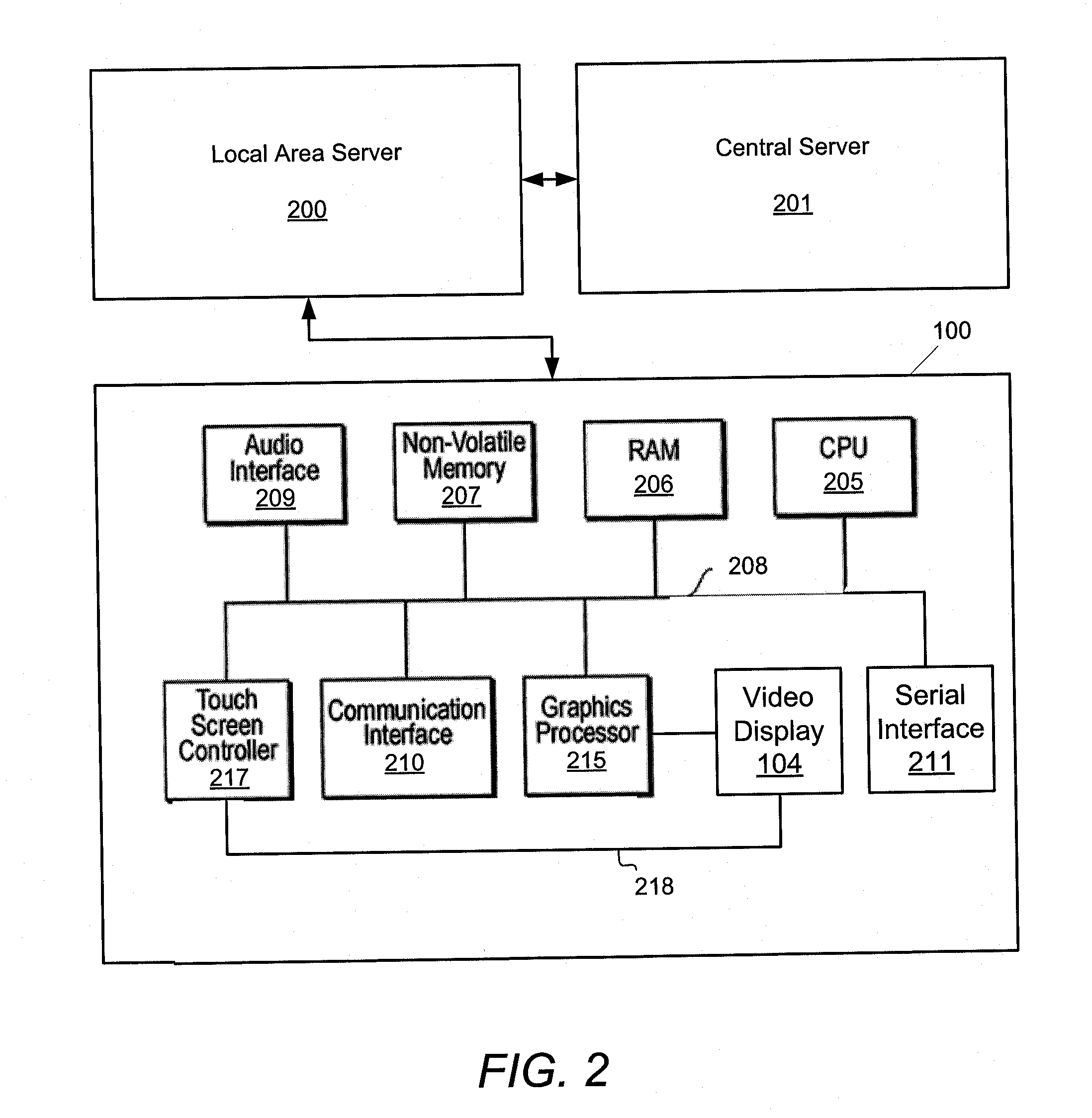
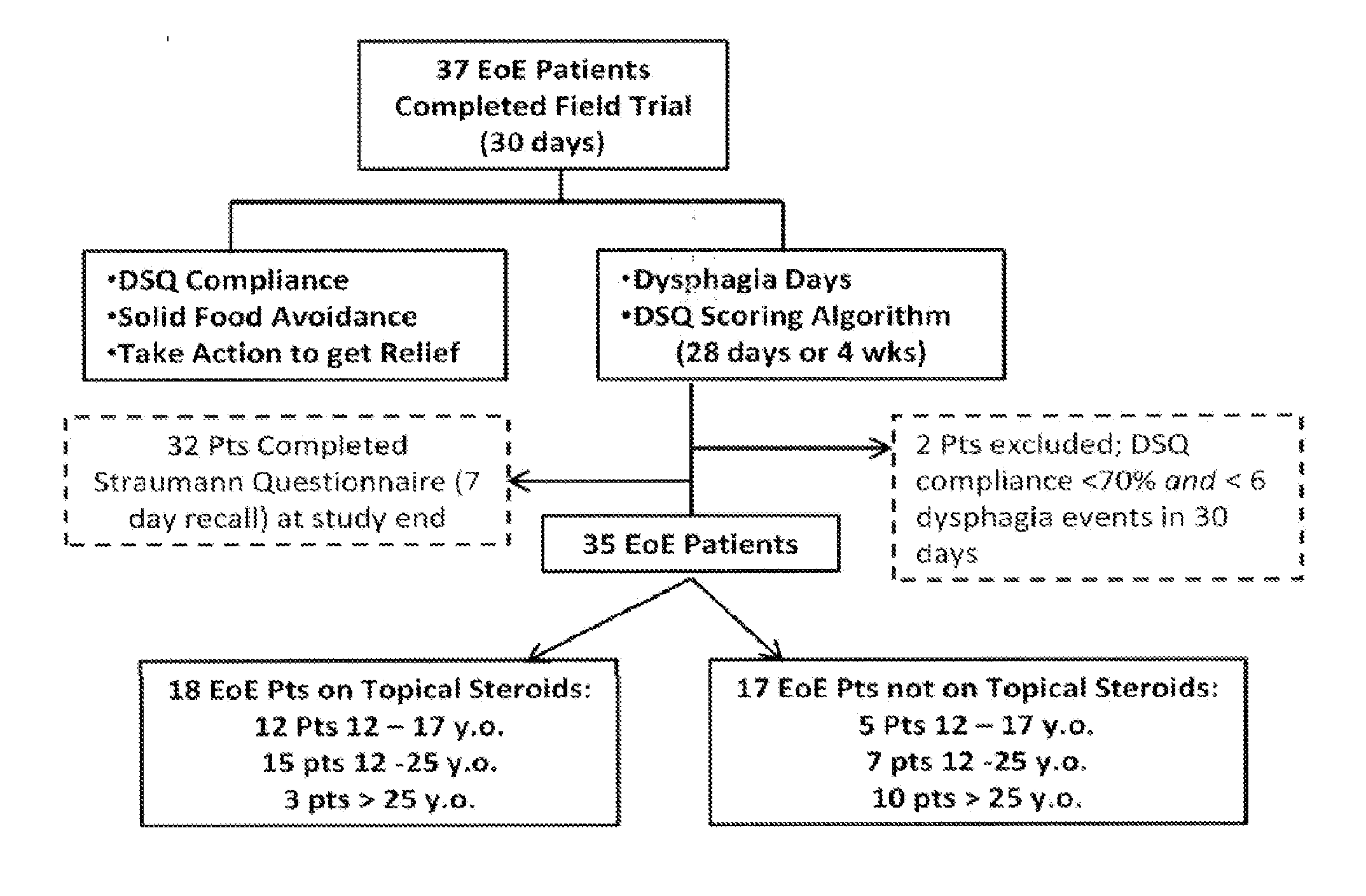
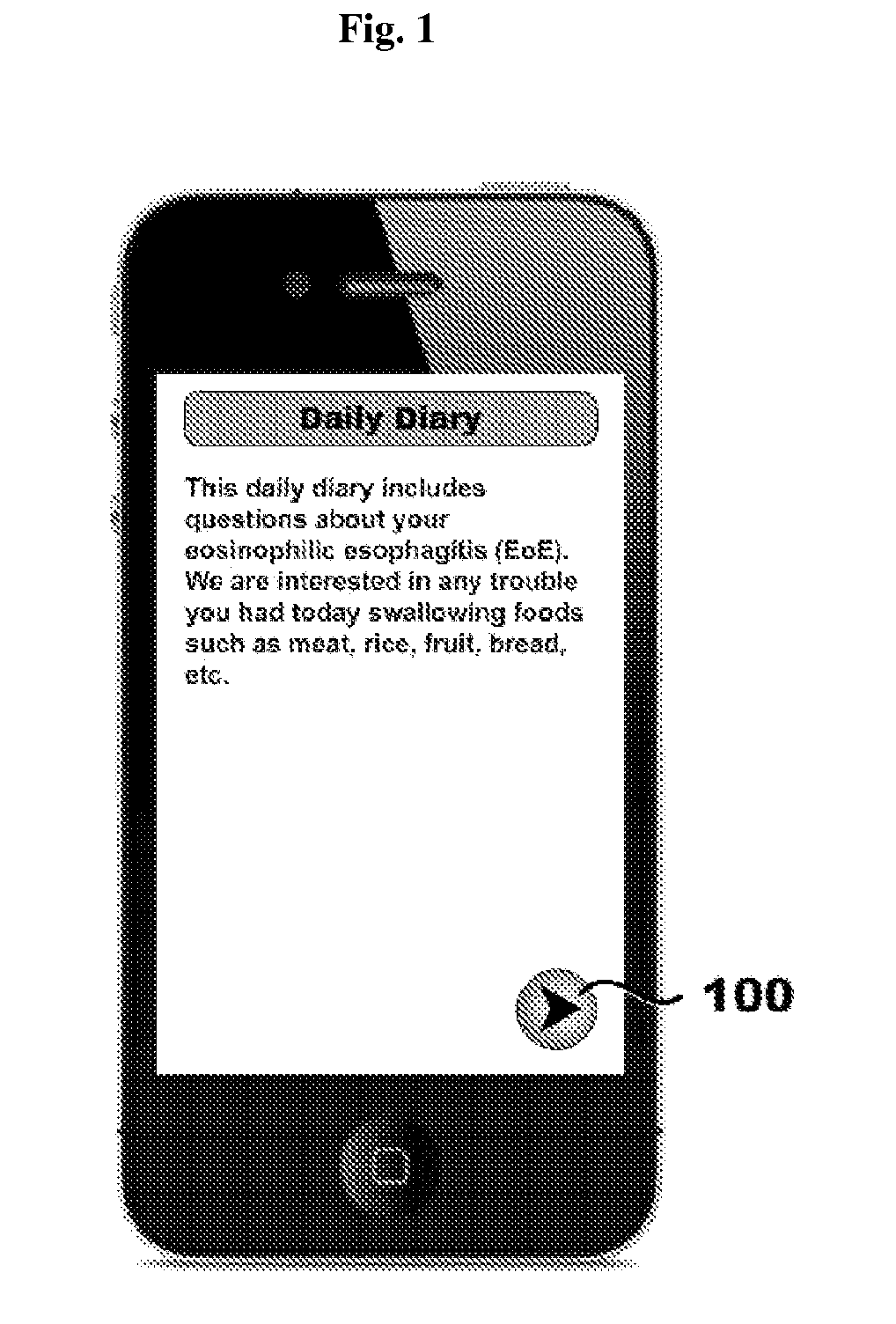
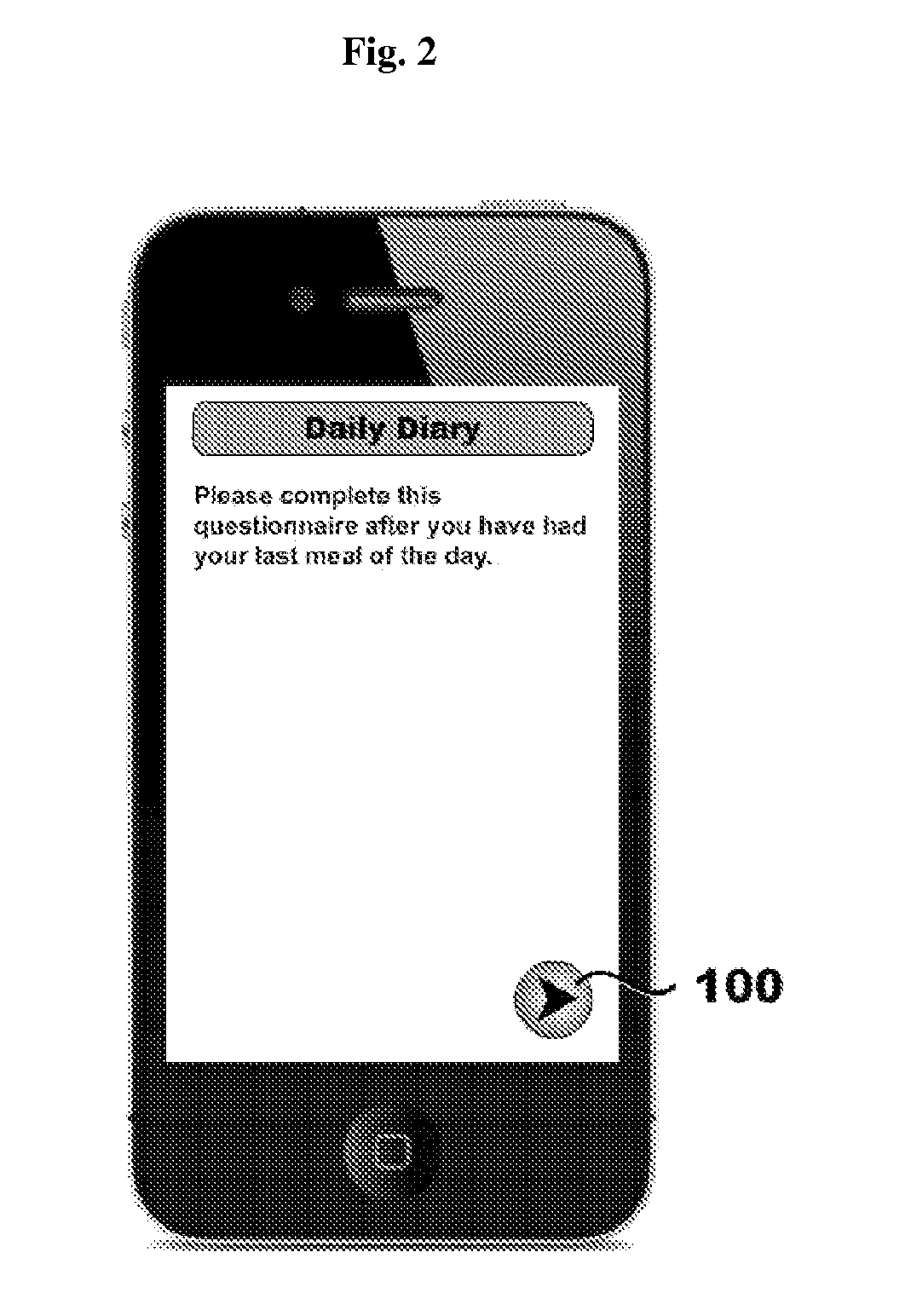
Systems, methods, and software for providing a patient-reported outcome measure of dysphagia patients with eosinophilic esophagitis
ActiveUS20160078186A1Reduction in esophageal inflammationData processing applicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionPatient questionnaireSwallow food
Provided herein are computer-based systems, software, and methods of using the same including a daily patient questionnaire, the questionnaire comprising: a question for determining whether the patient avoided solid food; a question for determining whether the patient had difficulty swallowing solid food; a question for determining what action the patient took to correct or relieve difficulty swallowing food; a question for determining the amount of pain the patient experienced while swallowing food; and a software module configured to apply an algorithm to answers to one or more of said questions to determine a score, wherein said score illustrates one or more selected from the group consisting of: (1) severity, intensity, or frequency of patient dysphagia; (2) suitability of a patient for a particular diagnostic tool, diagnostic method, or therapy for dysphagia; and (3) efficacy of a particular therapy for dysphagia.
Owner:VIROPHARMA HLDG
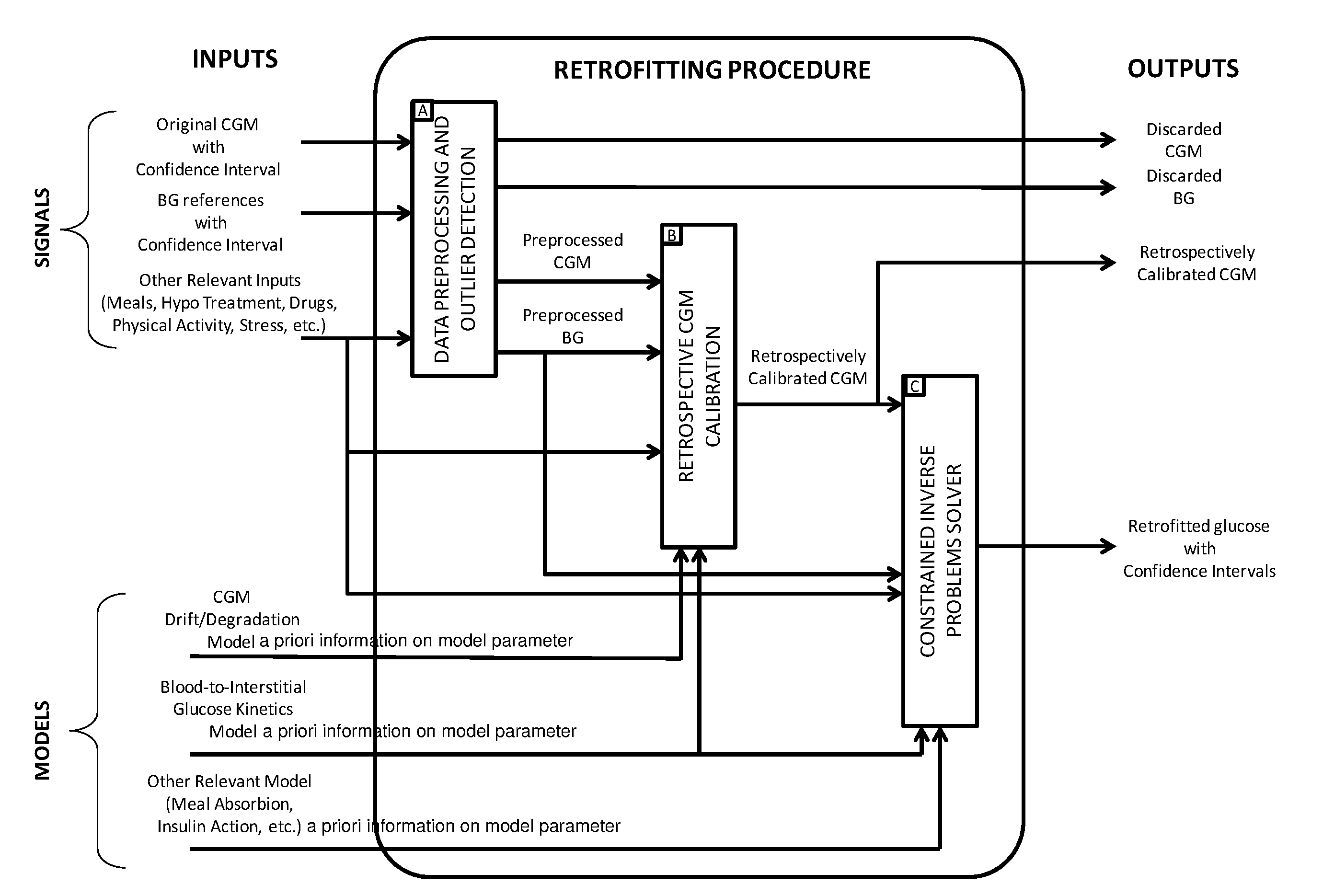
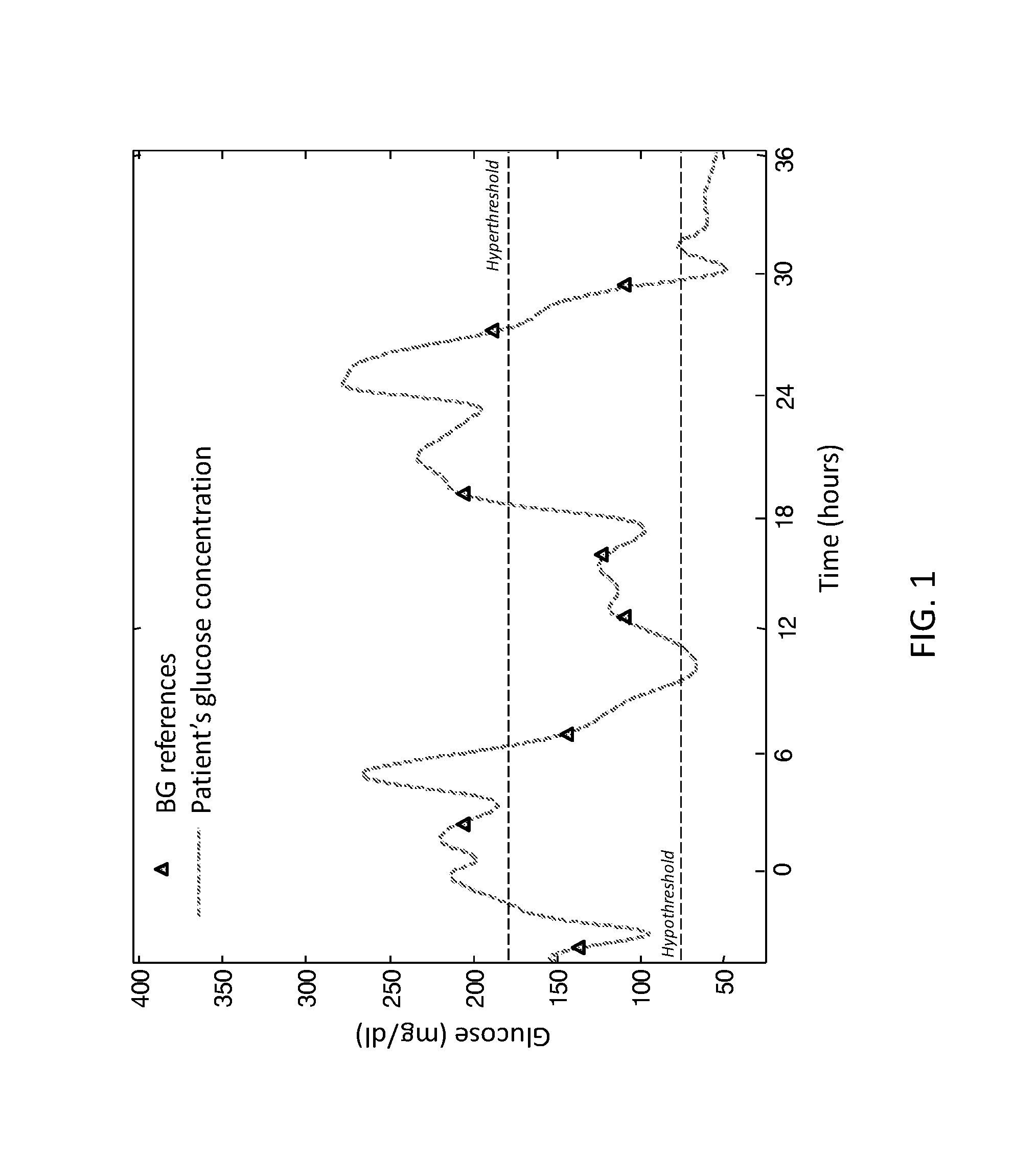
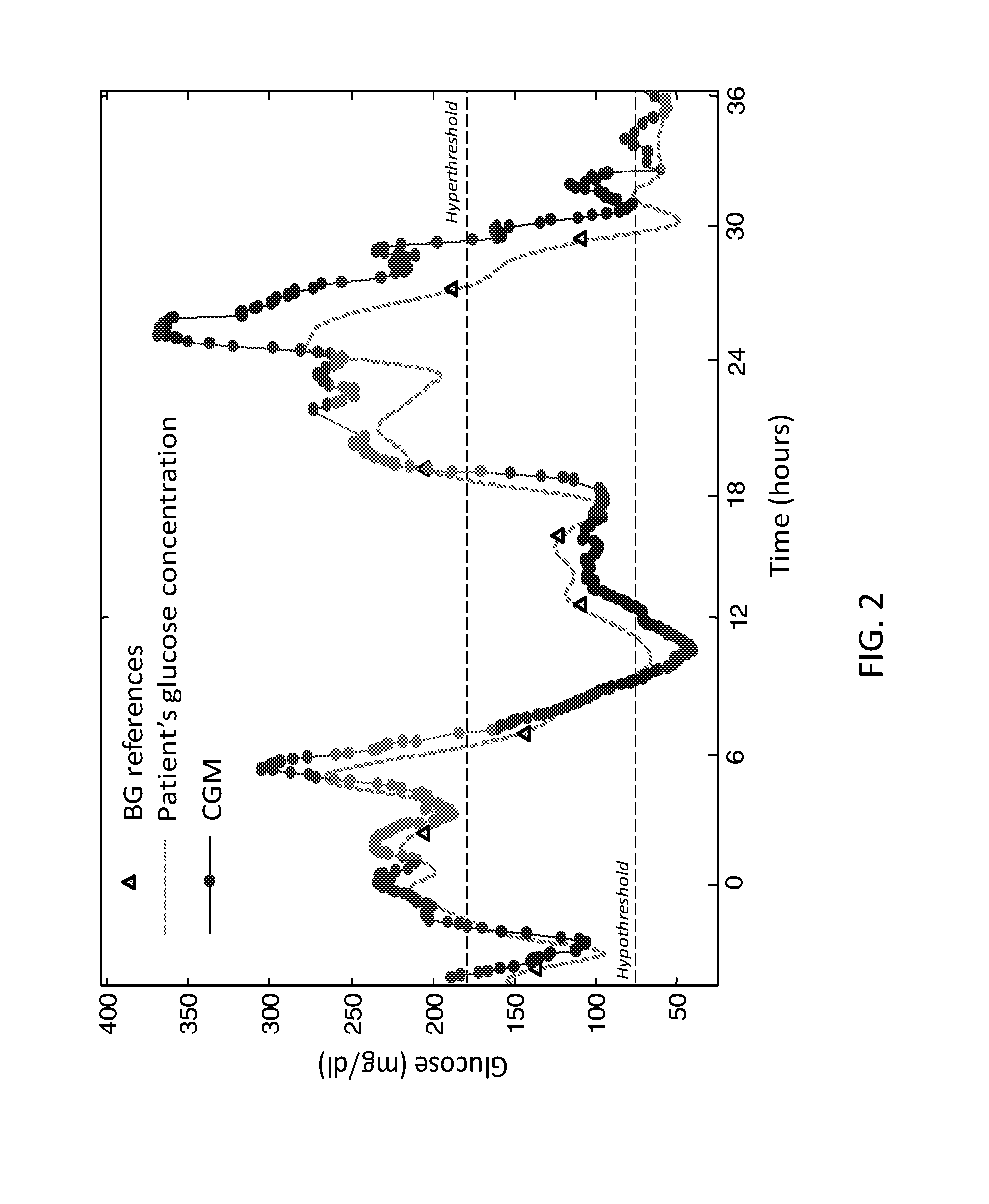
Retrospective retrofitting method to generate a continuous glucose concentration profile by exploiting continuous glucose monitoring sensor data and blood glucose measurements
ActiveUS20160073964A1Reducing delays/distortionsHigh precisionHealth-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisConcentrations glucoseConfidence interval
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices provide glucose concentration measurements in the subcutaneous tissue with limited accuracy and precision. Therefore, CGM readings cannot be incorporated in a straightforward manner in outcome metrics of clinical trials e.g. aimed to assess new glycaemic-regulation therapies. To define those outcome metrics, frequent Blood Glucose (BG) reference measurements are still needed, with consequent relevant difficulties in outpatient settings. Here we propose a “retrofitting” algorithm that produces a quasi continuous time BG profile by simultaneously exploiting the high accuracy of available BG references (possibly very sparsely collected) and the high temporal resolution of CGM data (usually noisy and affected by significant bias). The inputs of the algorithm are: a CGM time series; some reference BG measurements; a model of blood to interstitial glucose kinetics; and a model of the deterioration in time of sensor accuracy, together with (if available) a priori information (e.g. probabilistic distribution) on the parameters of the model. The algorithm first checks for the presence of possible artifacts or outliers on both CGM datastream and BG references, and then rescales the CGM time series by exploiting a retrospective calibration approach based on a regularized deconvolution method subject to the constraint of returning a profile laying within the confidence interval of the reference BG measurements. As output, the retrofitting algorithm produces an improved “retrofitted” quasi-continuous glucose concentration signal that is better (in terms of both accuracy and precision) than the CGM trace originally measured by the sensor. In clinical trials, the so-obtained retrofitted traces can be used to calculate solid outcome measures, avoiding the need of increasing the data collection burden at the patient level.
Owner:DEXCOM
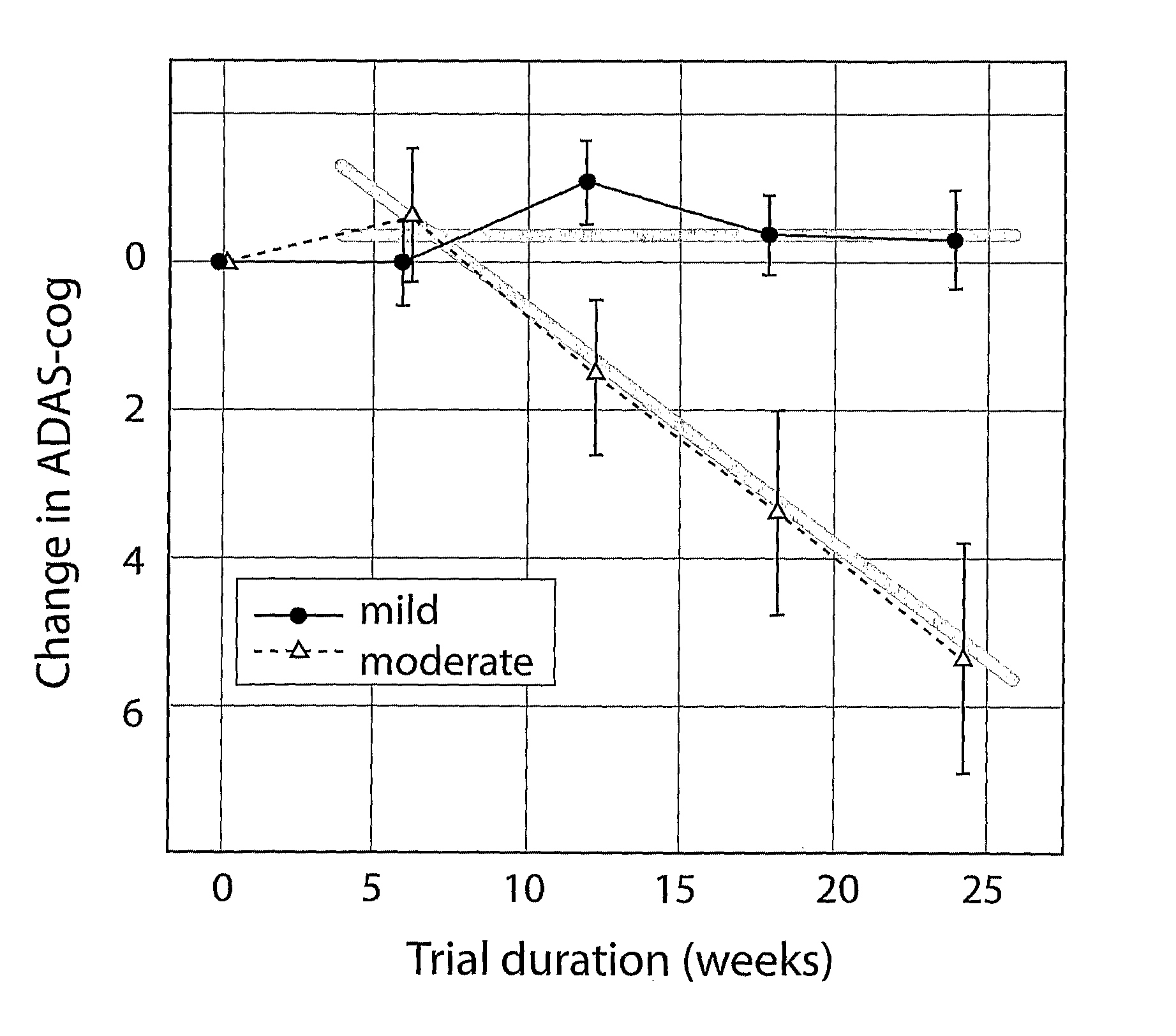
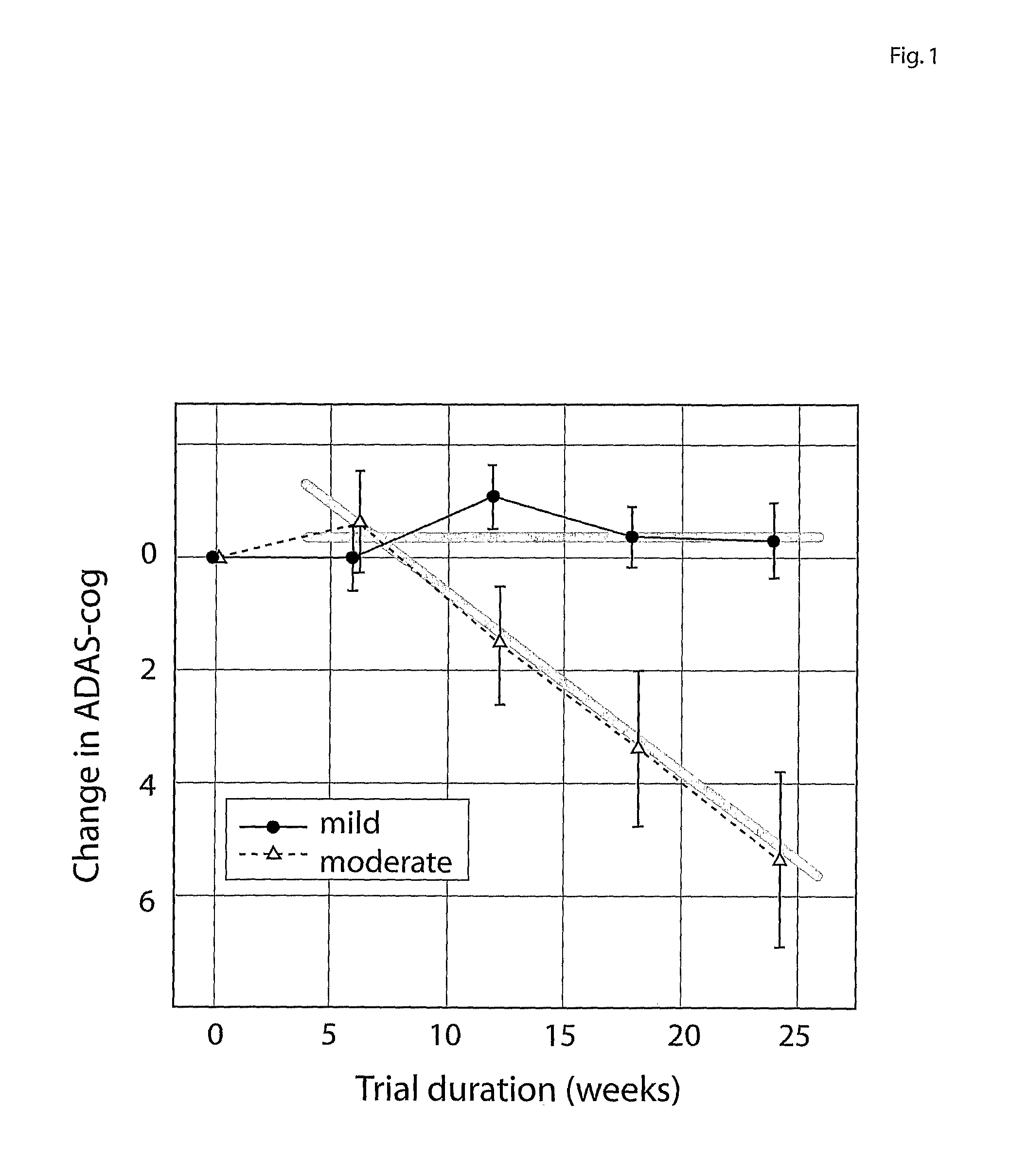
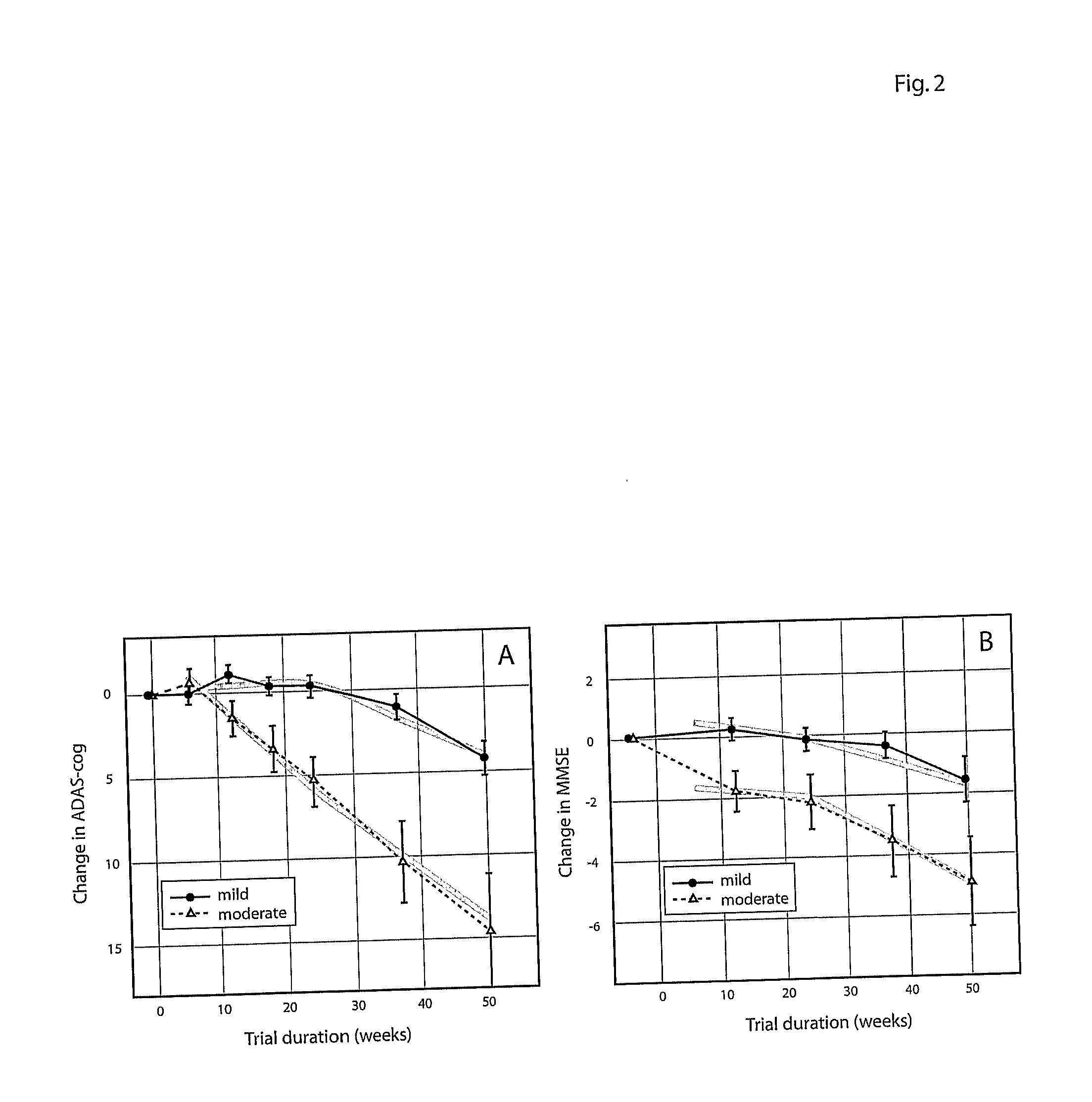
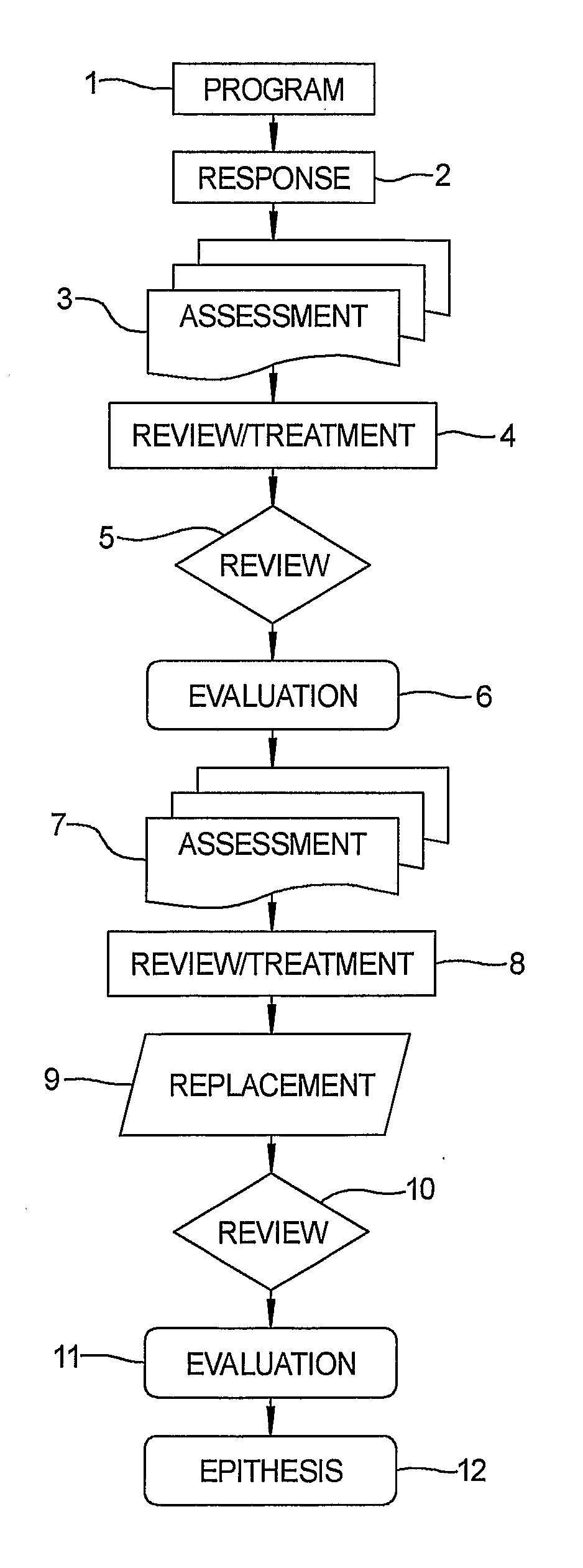
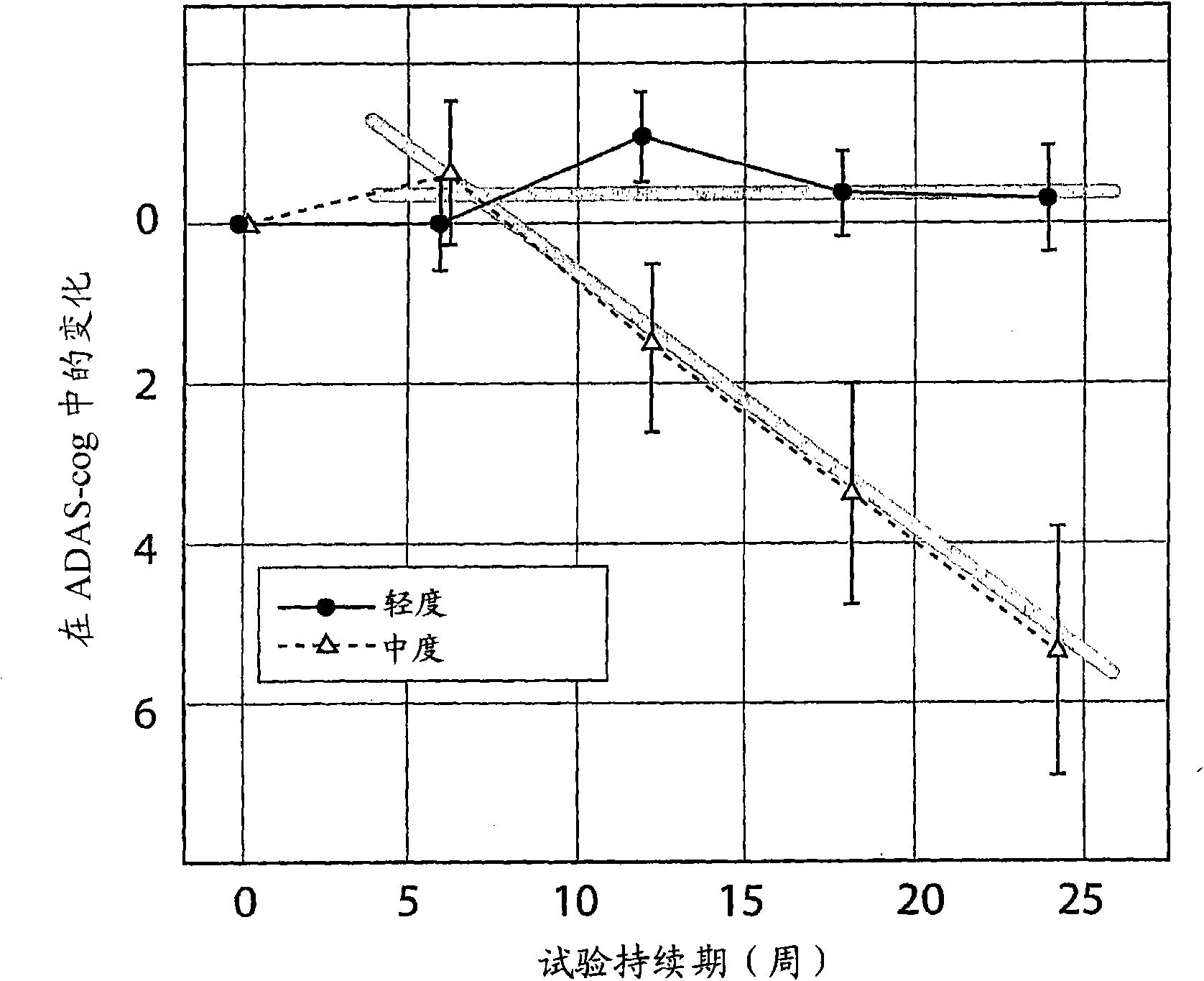
Systems for clinical trials
InactiveUS20100280975A1Medical simulationData processing applicationsBaseline IndicatorTreatment Arm
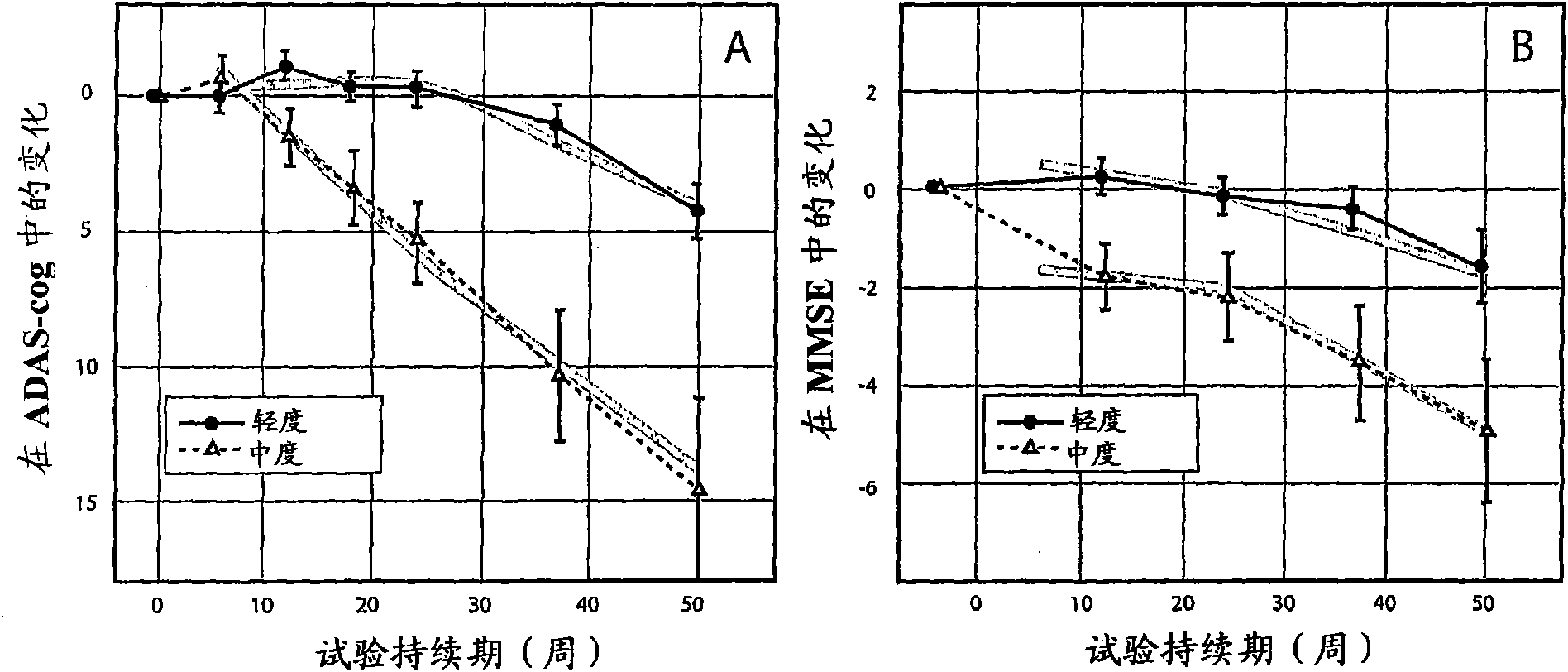
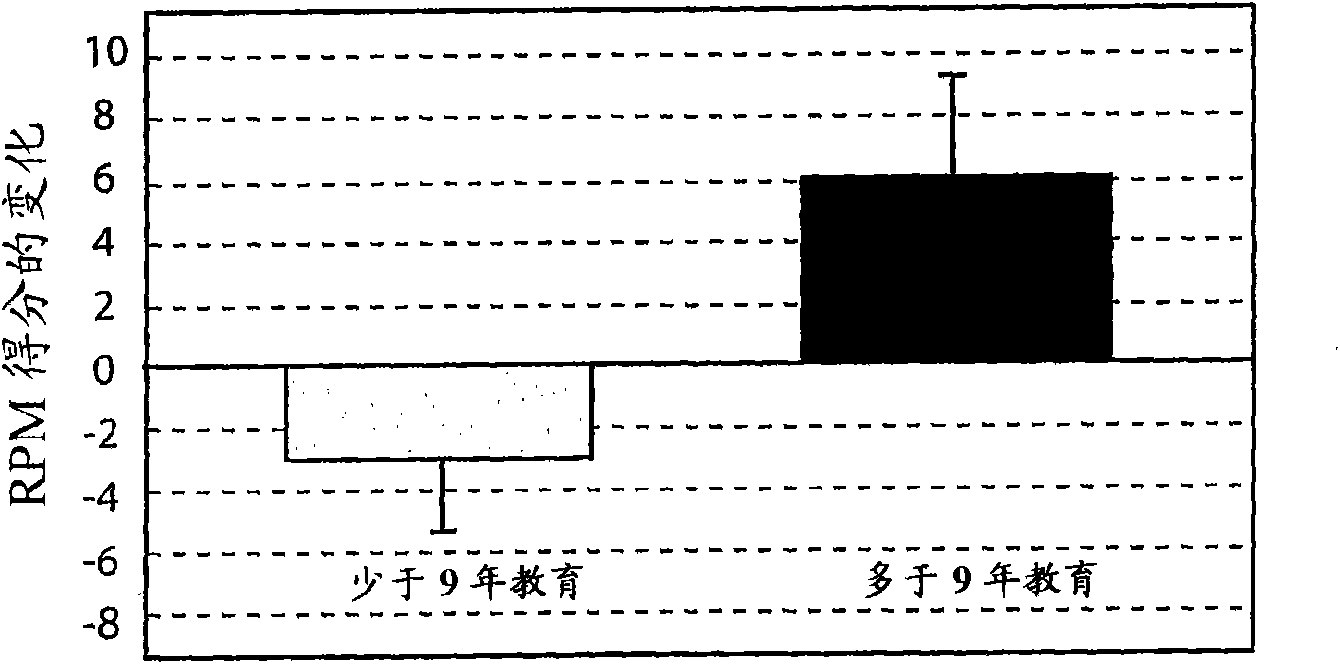
The invention provides methods and systems for assessing the efficacy of a pharmaceutical which is putatively disease modifying of a cognitive disorder, for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of that cognitive disorder, the method comprising the steps of: (1) stratifying a subject group into at least 2 sub-groups according to a baseline indicator of likely disease progression, (2) treating members of each subject group with the pharmaceutical for a treatment time frame, (3) deriving psychometric and optionally physiological outcome measures for each treated patient group, (4) comparing the outcomes at (3) with a comparator arm of said sub-groups which is optionally a placebo or minimal efficacy comparator arm, (5) using the comparison in (4) to derive an efficacy measure for the pharmaceutical. The methods and systems of the invention address problems such as low rate of decline over the treatment time-frame of patients who have mild-disease severity at baseline and biased withdrawal, particularly in the placebo / comparator treatment arm.
Owner:WISTA LAB LTD
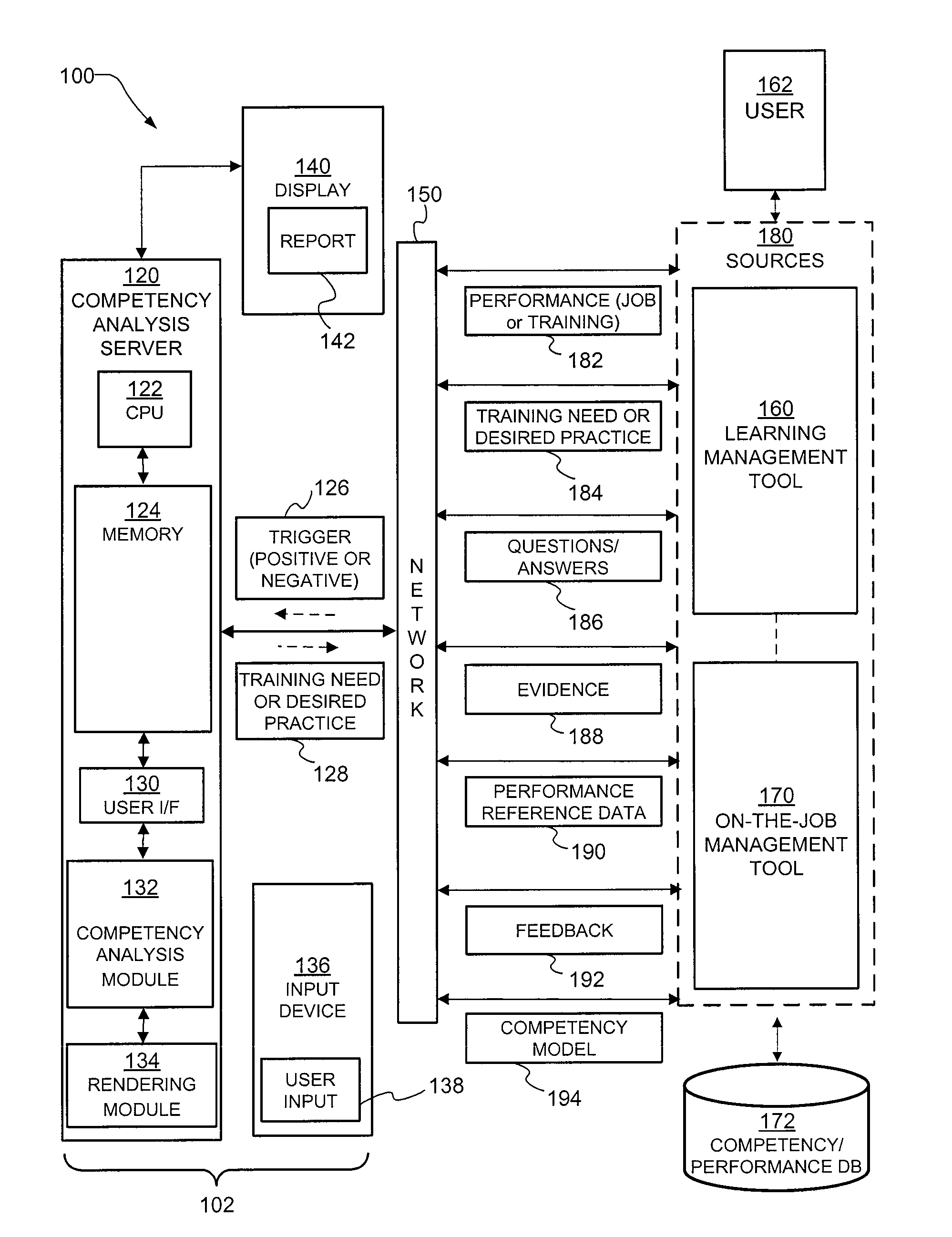
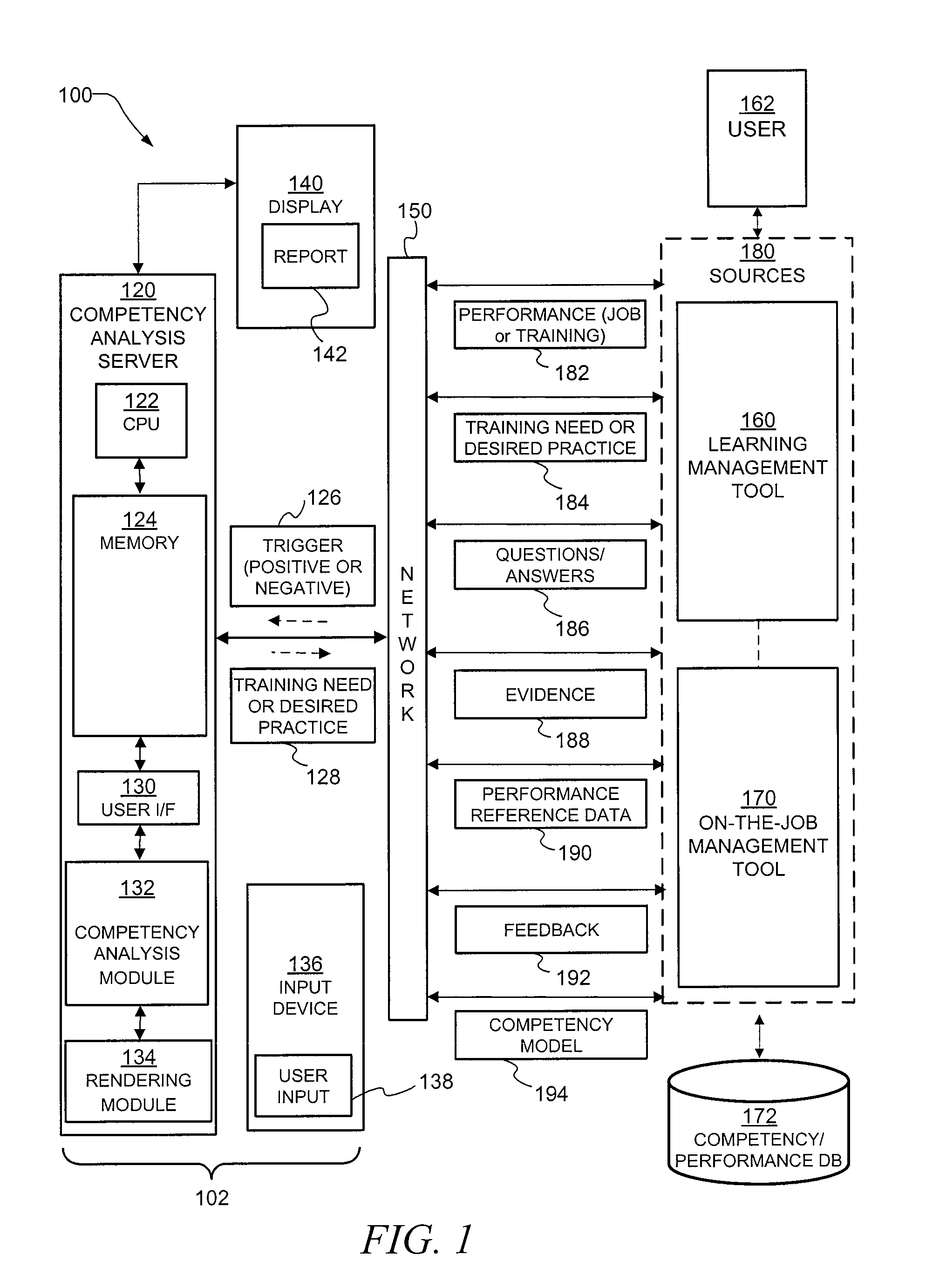
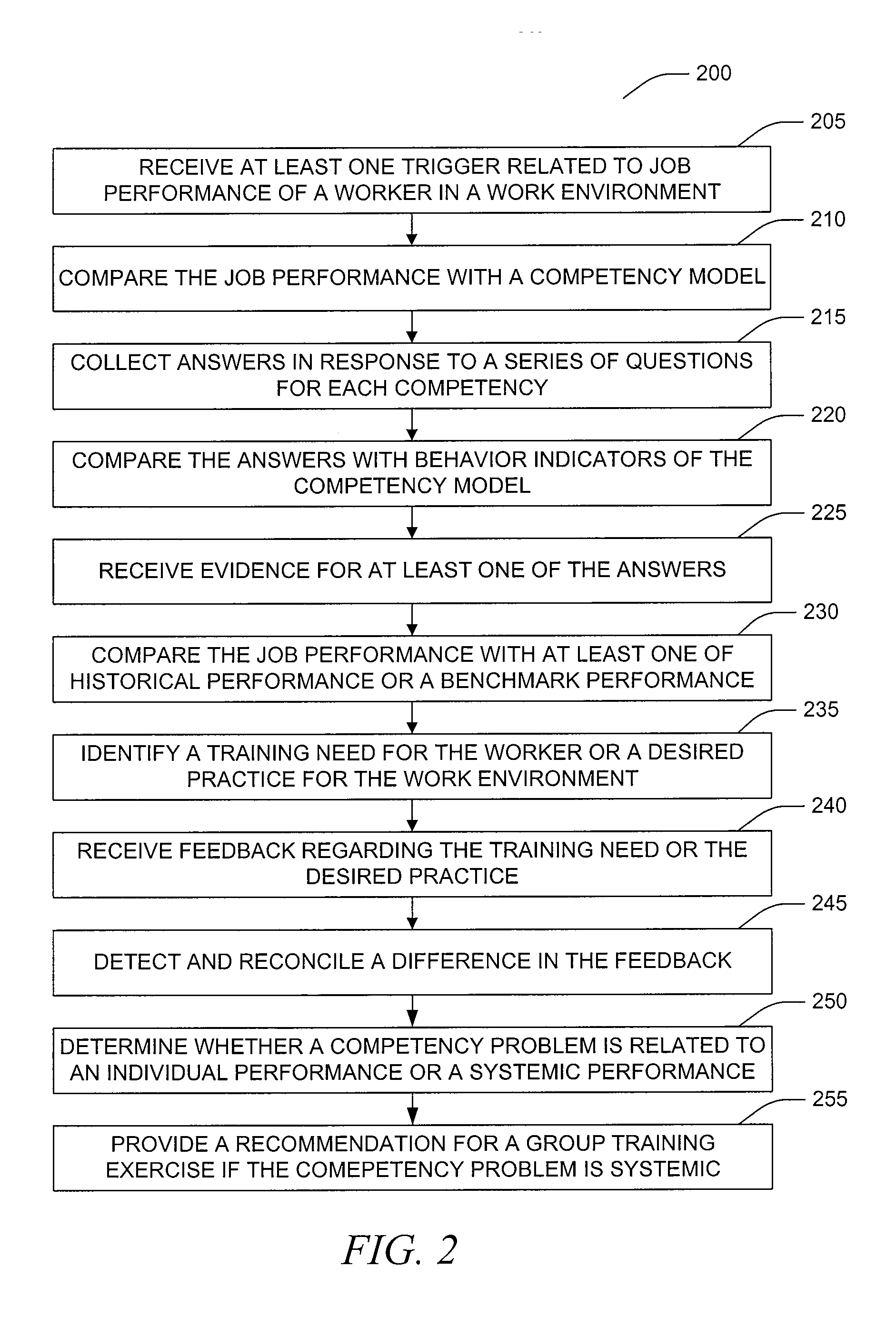
Decision aid tool for competency analysis
A computer implemented method and system include receiving a trigger in the computer related to job performance in a work environment. The system compares job performance related to the trigger to a worker competency model having behavior indicators of good performance. The comparison of job performance to the worker competency model, behavior indicators, and outcome measures is used to provide an indication of good and poor job performance for a variety of situations. Training, best practices, and effective strategies may also be automatically identified.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Systems, methods, and software for providing a patient-reported outcome measure of dysphagia patients with eosinophilic esophagitis
ActiveUS10176301B2Medical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsPatient questionnaireSwallow food
Provided herein are computer-based systems, software, and methods of using the same including a daily patient questionnaire, the questionnaire comprising: a question for determining whether the patient avoided solid food; a question for determining whether the patient had difficulty swallowing solid food; a question for determining what action the patient took to correct or relieve difficulty swallowing food; a question for determining the amount of pain the patient experienced while swallowing food; and a software module configured to apply an algorithm to answers to one or more of said questions to determine a score, wherein said score illustrates one or more selected from the group consisting of: (1) severity, intensity, or frequency of patient dysphagia; (2) suitability of a patient for a particular diagnostic tool, diagnostic method, or therapy for dysphagia; and (3) efficacy of a particular therapy for dysphagia.
Owner:VIROPHARMA HLDG
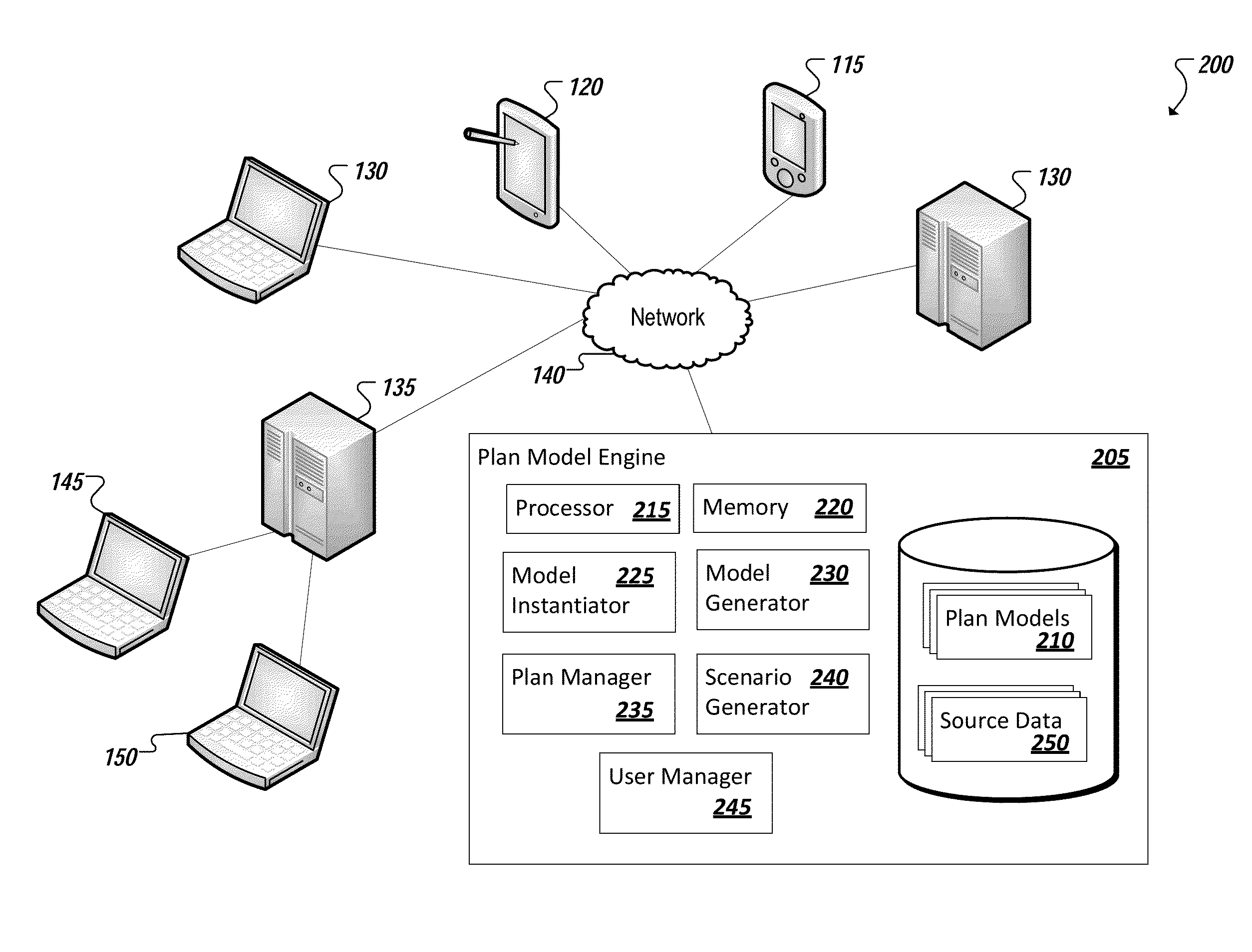
Plan modeling
InactiveUS20140058712A1ResourcesAnalogue processes for specific applicationsOutcome measuresProgram planning
A plan model is identified that is adapted to model business outcomes for a particular domain, the plan model including a respective scope model defining the particular domain. A value can be identified of an input driver or outcome measure of the plan model. A scenario can be generated from the plan model for the particular domain based on the identified value. In some instances, business outcomes of plan models are expressed as one or more respective outcome measures. Each plan model can further include one or more input drivers representing variables influencing the one or more outcome measures, a respective scope model defining the domain of the plan model, and a sensitivity model corresponding to the domain and defining one or more dependencies between the input drivers and outcome measures.
Owner:O9 SOLUTIONS
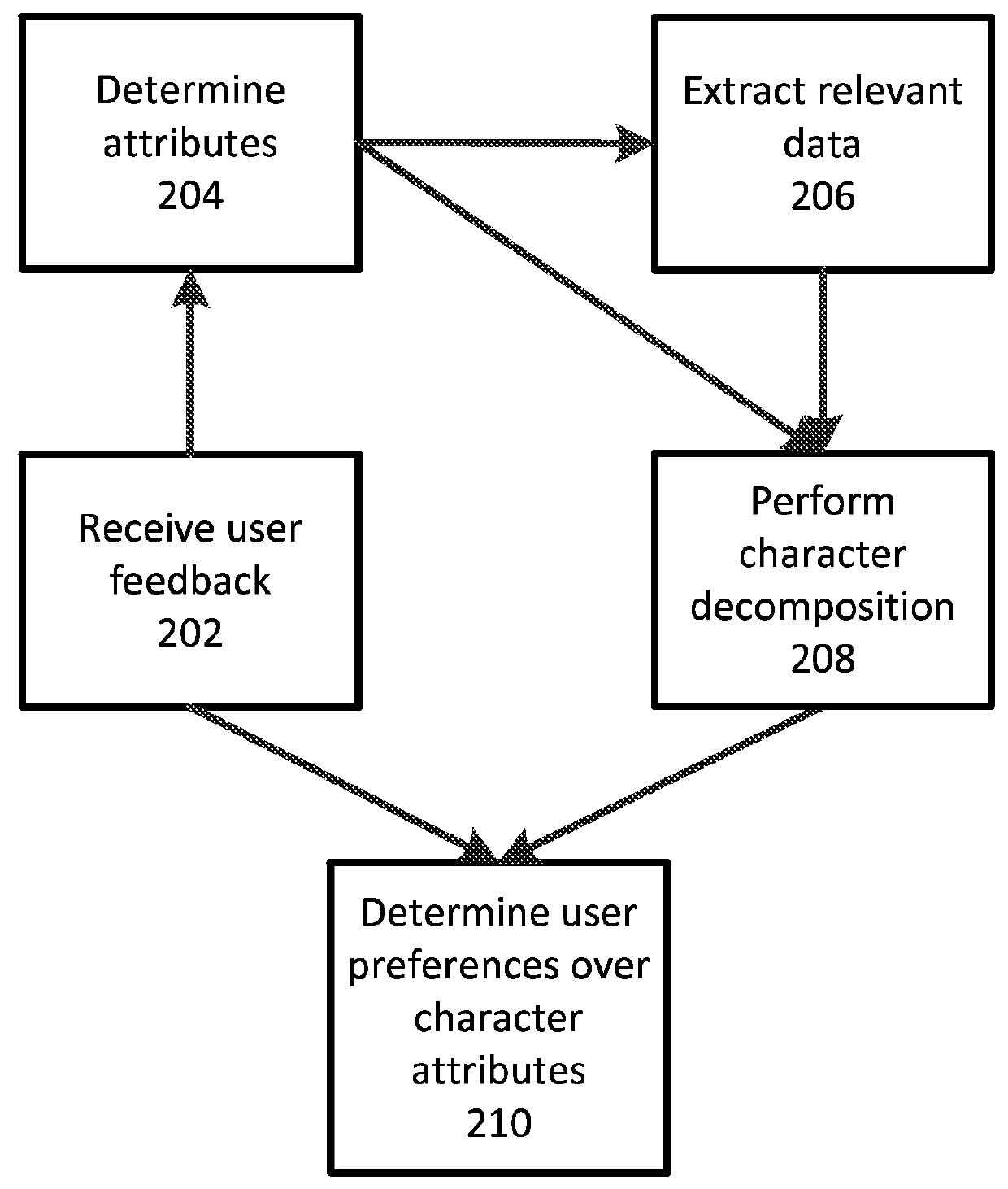
Character based media analytics
Techniques for analyzing media content are described. One technique generally comprises performing a regression analysis for characters in a plurality of media content based on user demographics, content outcome measure, and character models. The technique determines an attribute of significance. In some embodiments, the technique selects media content for display that depicts a character having at least a threshold value of the attribute of significance. In some embodiments, the technique displays media analytics for the attribute of significance determined based on a value of the attribute of significance exceeding a threshold significance value.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC
Visually directed human-computer interaction for medical applications
InactiveUS9841811B2Faster and more intuitive human-computer inputInput/output for user-computer interactionEye diagnosticsGuidelineContext specific
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus of utilizing an eye detection apparatus in a medical application, which includes calibrating the eye detection apparatus to a user; performing a predetermined set of visual and cognitive steps using the eye detection apparatus; determining a visual profile of a workflow of the user; creating a user-specific database to create an automated visual display protocol of the workflow; storing eye-tracking commands for individual user navigation and computer interactions; storing context-specific medical application eye-tracking commands, in a database; performing the medical application using the eye-tracking commands; and storing eye-tracking data and results of an analysis of data from performance of the medical application, in the database. The method includes performing an analysis of the database for determining best practice guidelines based on clinical outcome measures.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
Method of data mining in medical applications
InactiveUS8249892B2Enhance decisionImprove educationMedical data miningFinanceData dredgingPersonalization
The present invention relates to a method of creating databases for data mining in medical applications. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to providing a data-driven objective reimbursement model incorporating performance and quality measures, tied to patient, exam, context, and provider-specific variables. In another embodiment, the present invention creates standardized databases where context, patient, provider, and technology specific variables are used to create an objective quantitative measure of exam complexity, which can be correlated with performance times and outcomes measures for iterative refinement. In another embodiment, through the combined analysis of examination complexity, interpretation accuracy, and interpretation times, specific to each individual radiologist, external pacers are created which can be customized to a radiologist's individual needs and preferences. The derived data is used to identify best practice patterns and end-user performance, which can be used by radiologists for individualized education and training.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
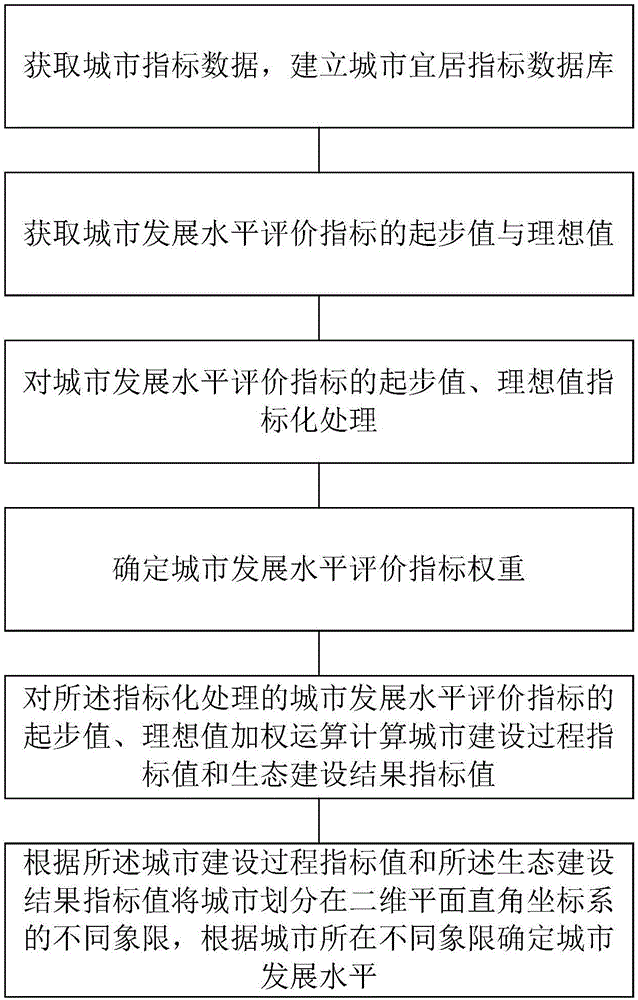
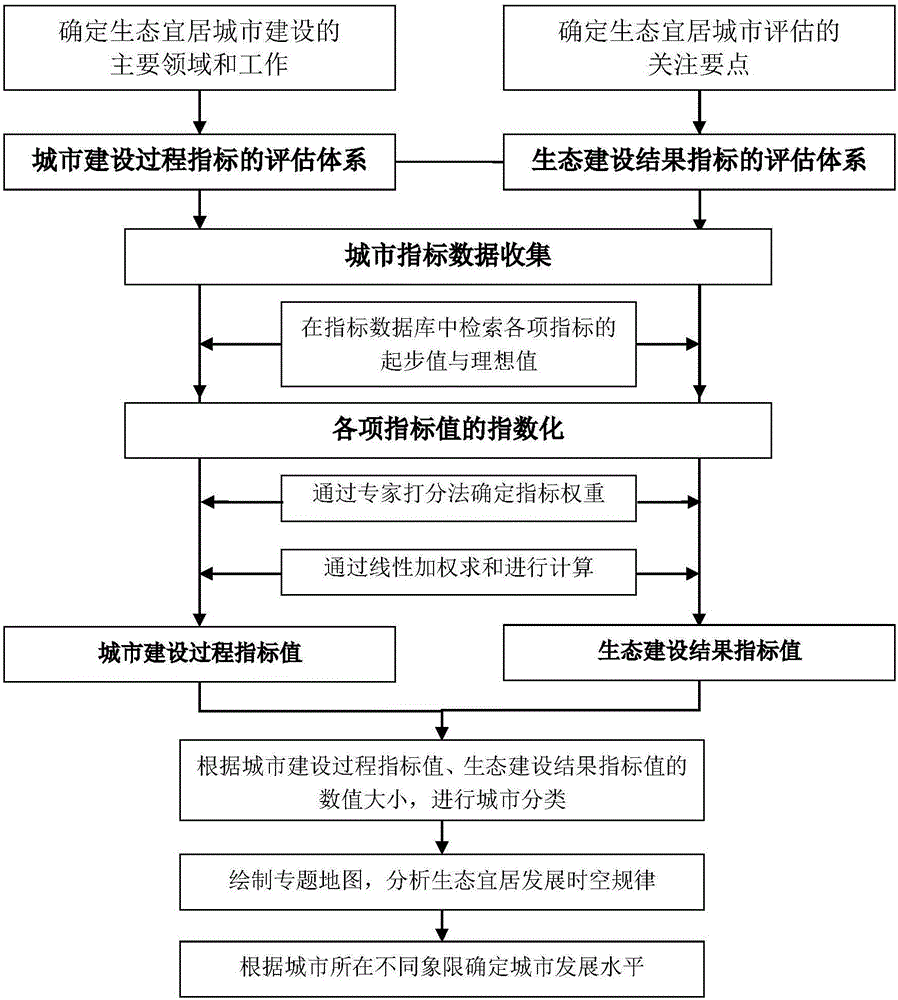
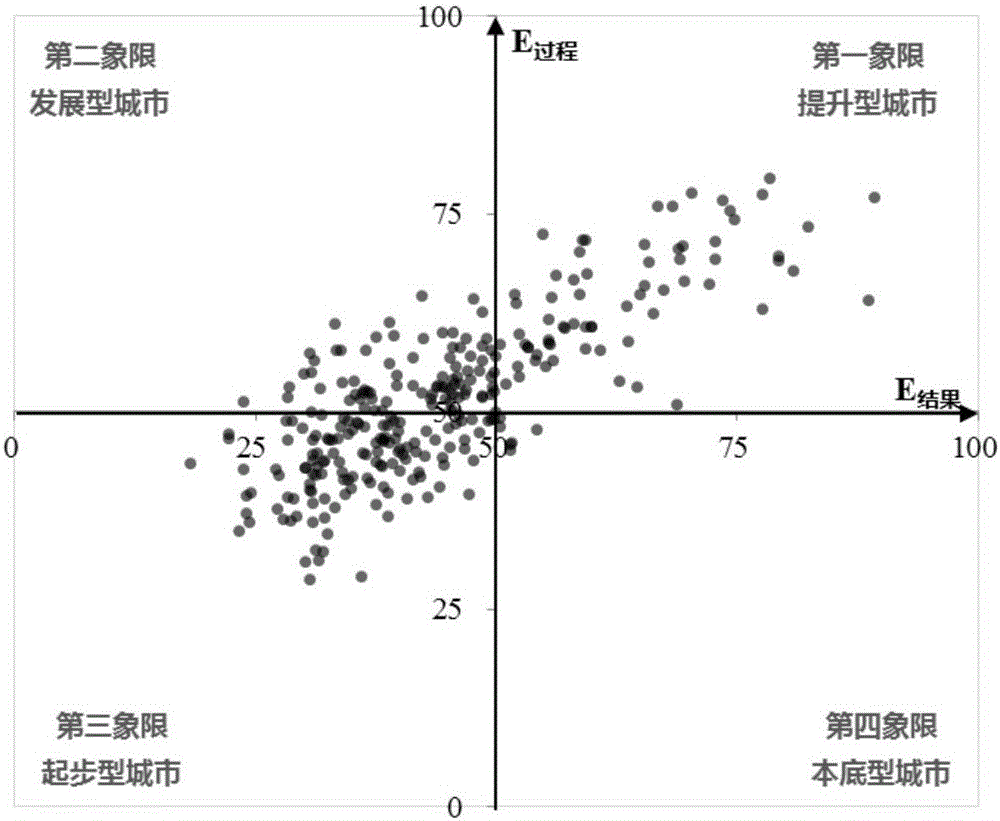
City development level calculation method
InactiveCN106845749AAvoid complex and bulky disadvantagesEasy to compareResourcesFour quadrantsOutcome measures
The invention relates to a city development level calculation method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining city index data and establishing a city livable index database; obtaining a starting value and an ideal value of a city development level evaluation index and performing indexing processing; determining a weight of the city development level evaluation index; performing weighted calculation on the starting value and the ideal value, subjected to the indexing processing, of the city development level evaluation index to calculate a city construction process index value and an ecological construction result index value; and including a city in different quadrants of a two-dimensional plane rectangular coordinate system according to the city construction process index value and the ecological construction result index value, and determining a city development level according to the different quadrants where the city is located, wherein the starting value is a minimum value of the city development level evaluation index, and the ideal value is an optimal value of the city development level evaluation index. According to the method, the shortcomings of complexity and hugeness of a conventional index system are overcome, and the city development level is not only limited to simplex numerical ranking; and city ecological livable development results are represented by four quadrants, so that the city position can be clearly determined more quickly.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF BUILDING RES
Systems and methods for using and constructing user-interest sensitive indicators of search results
ActiveUS20070240078A1Reduce overheadData processing applicationsWeb data indexingOutcome measuresPaper document
Techniques are provided to construct and use user-interest sensitive indicators of search results. A set of documents is determined based on one or more search terms. Passages within each selected document are identified based on the search terms. Condensation transformations applied to the passages to preferentially retain elements of the passage based on the search terms and user interest information. The resultant indicator is provides a user-interest sensitive signal of the meaning of the passage.
Owner:XEROX CORP
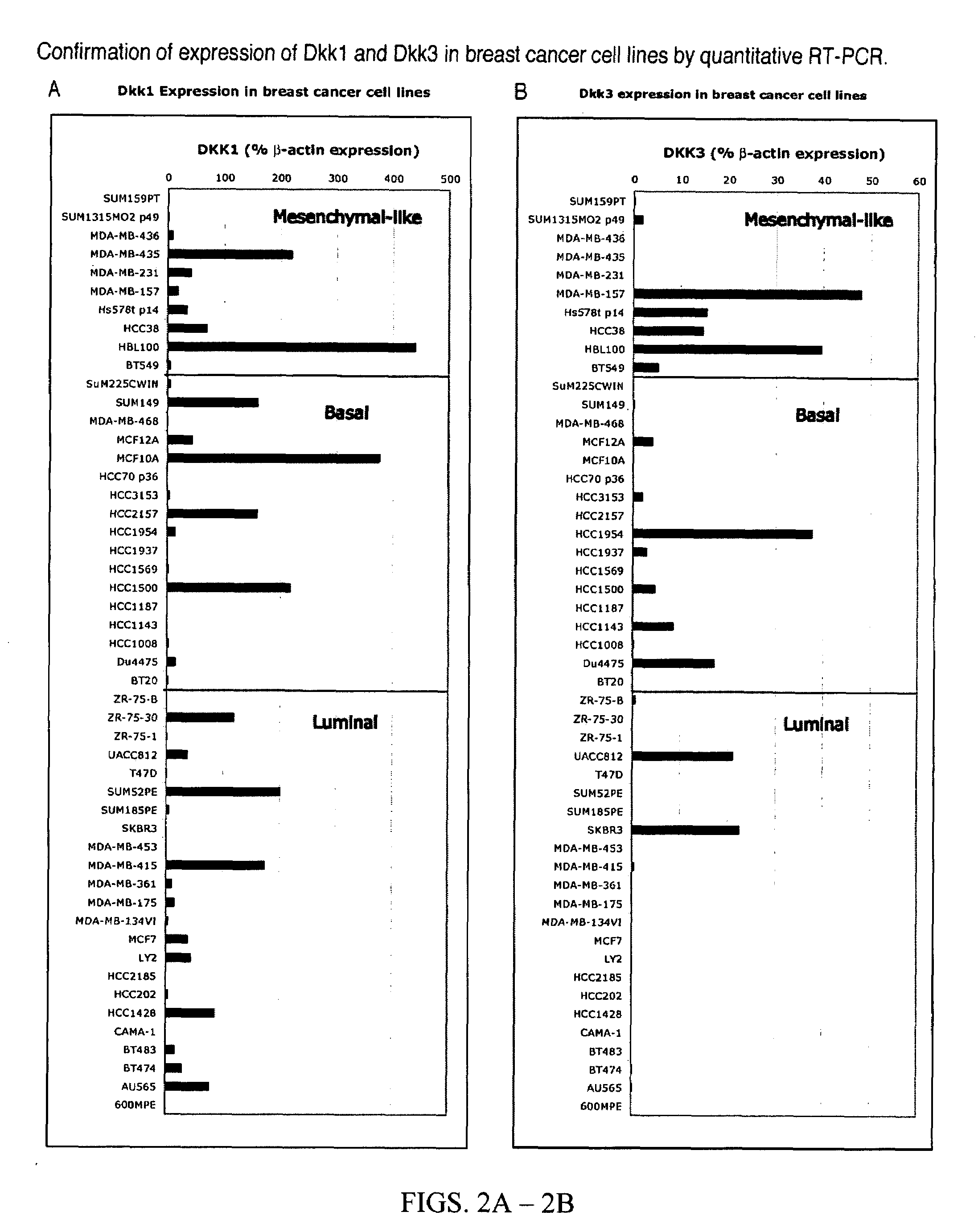
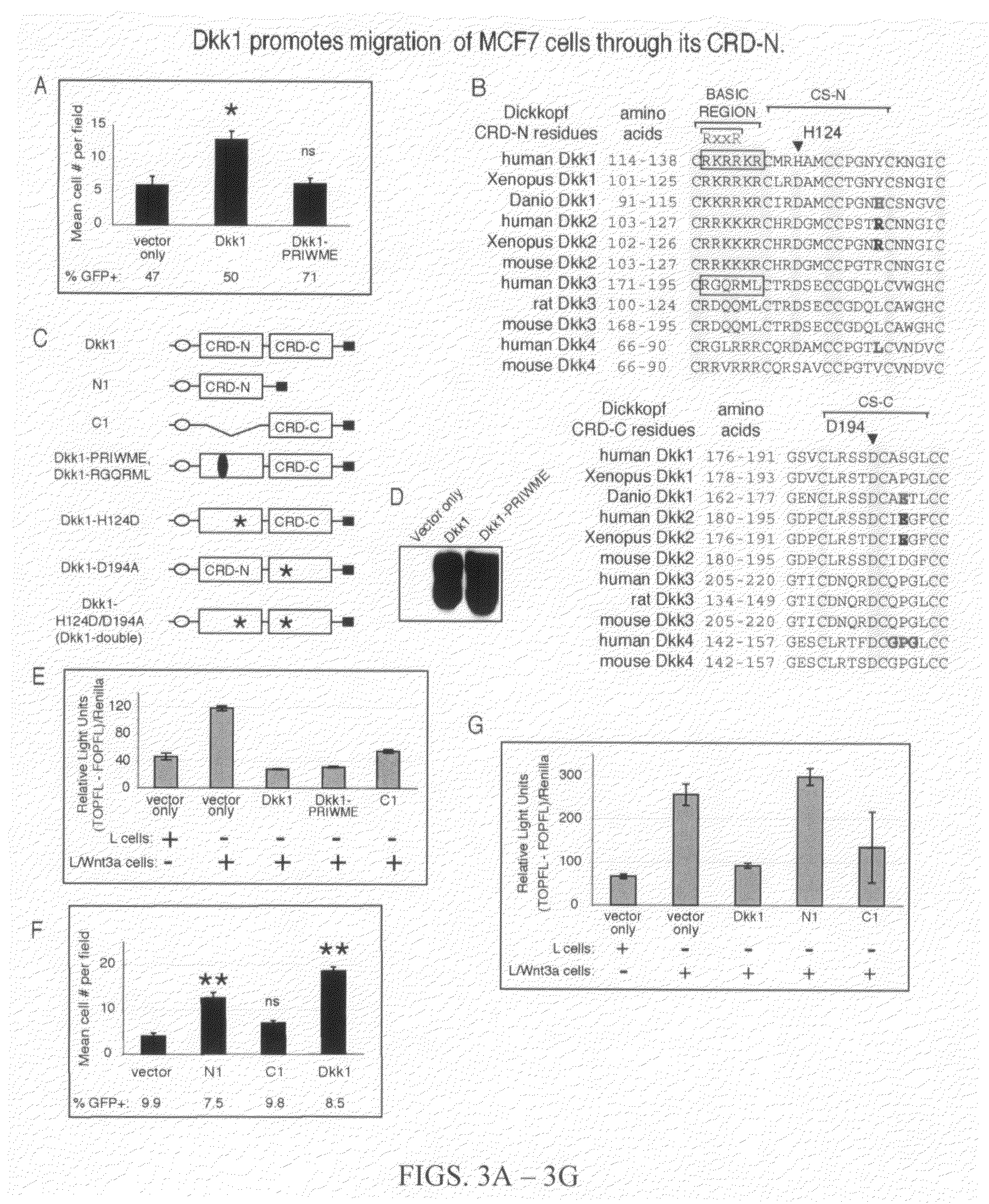
Compositions and methods for inhibiting cell migration
InactiveUS7465585B1Dkk activity is elevatedDecrease Dkk activityPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological testingGood prognosisOutcome measures
The finding that Dickkopf1 (Dkk1) is a dual function protein demonstrates a mechanism for the coordination of cell migration and antagonism of Wnt / β-catenin signaling during developmental and pathological processes. The profile of Dkk proteins expressed by human breast cancers correlates with indicators of outcome: Dkk1 associates with markers of poor prognosis whereas expression of single function Dkk2 or Dkk3 (which inhibit Wnt / β-catenin signaling and promote migration, respectively) correlates with phenotypes reflective of good prognosis. Therefore, the pro-migratory activities of Dkk1 and 3 identified here offer new insights into breast cancer progression and a potential avenue for therapeutic intervention.
Owner:BURNHAM INST THE
Business method for hair replacement and maintenance
InactiveUS20110166882A1Promote lowerImprove microcirculationTherapiesCommercePersonalizationOutcome measures
The quality of hair maintenance and replacement services in commercial personal grooming service companies provided by an organization to a customer is assured. Initial multiphasic assessment with progressive reviews and client input and acceptance of a mutually derived solution is performed, undertaken and measured. Episodic client assurance reviews, assessment of mutually designated outcome metrics and collective modifications are made to heighten client commitment, satisfaction and quality assurance. Process and final deliverable reviews are performed to assure customer need satisfaction. The invention is a method comprised of an array of multiple comprehensive steps individualized to the specific characteristics of the client with their completion measured, reported and agreed upon to assure consistent and acceptable quality levels.
Owner:RAGAZZI CESARE
Systems for clinical trials
The invention provides methods and systems for assessing the efficacy of a pharmaceutical which is putatively disease modifying of a cognitive disorder, for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of that cognitive disorder, the method comprising the steps of: (1) stratifying a subject group into at least 2 sub-groups according to a baseline indicator of likely disease progression, (2) treating members of each subject group with the pharmaceutical for a treatment time frame, (3) deriving psychometric and optionally physiological outcome measures for each treated patient group, (4) comparing the outcomes at (3) with a comparator arm of said sub-groups which is optionally a placebo or minimal efficacy comparator arm, (5) using the comparison in (4) to derive an efficacy measure for the pharmaceutical. The methods and systems of the invention address problems such as low rate of decline over the treatment time-frame of patients who have mild-disease severity at baseline and biased withdrawal, particularly in the placebo / comparator treatment arm.
Owner:WISTA LAB LTD
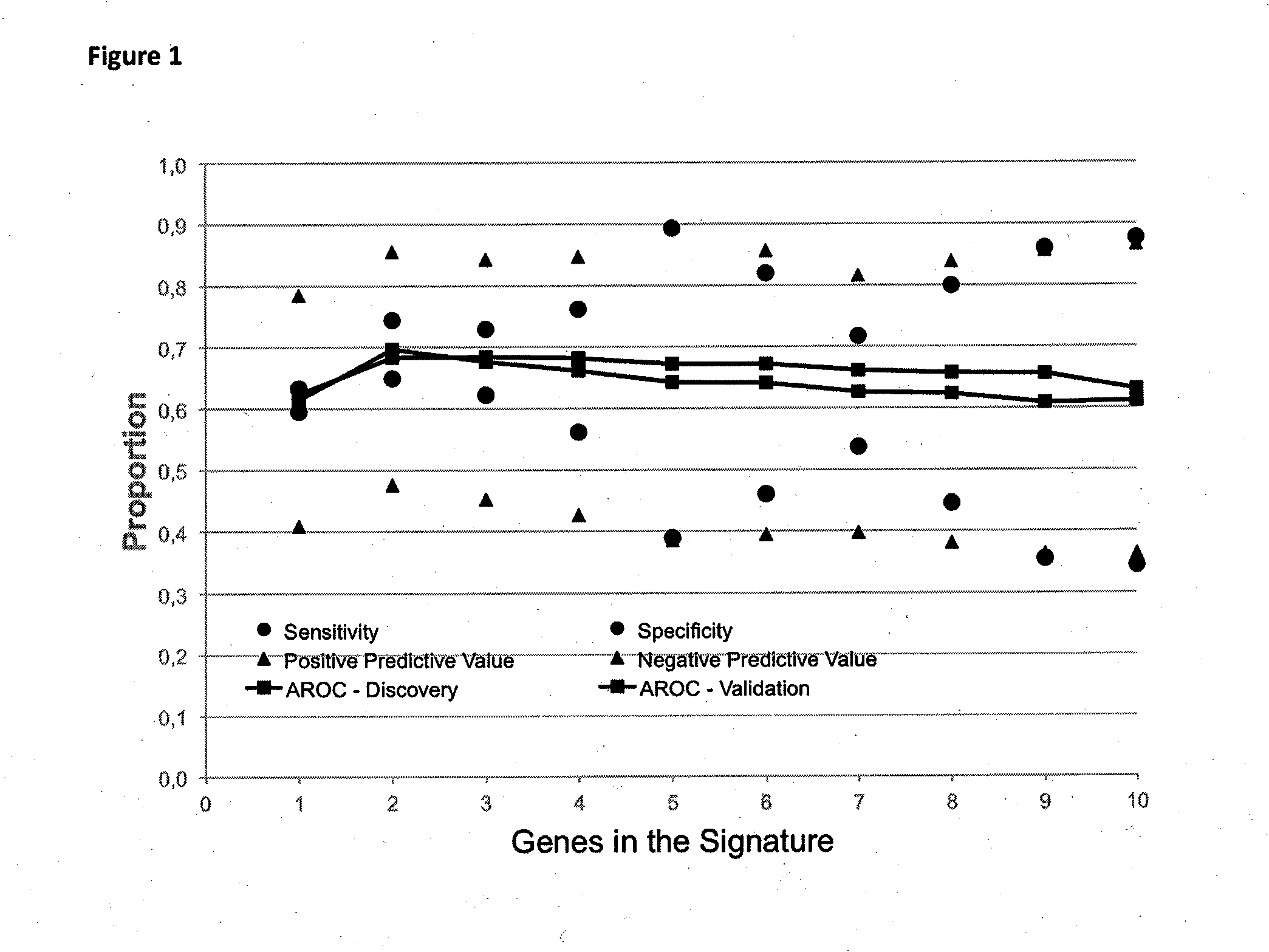
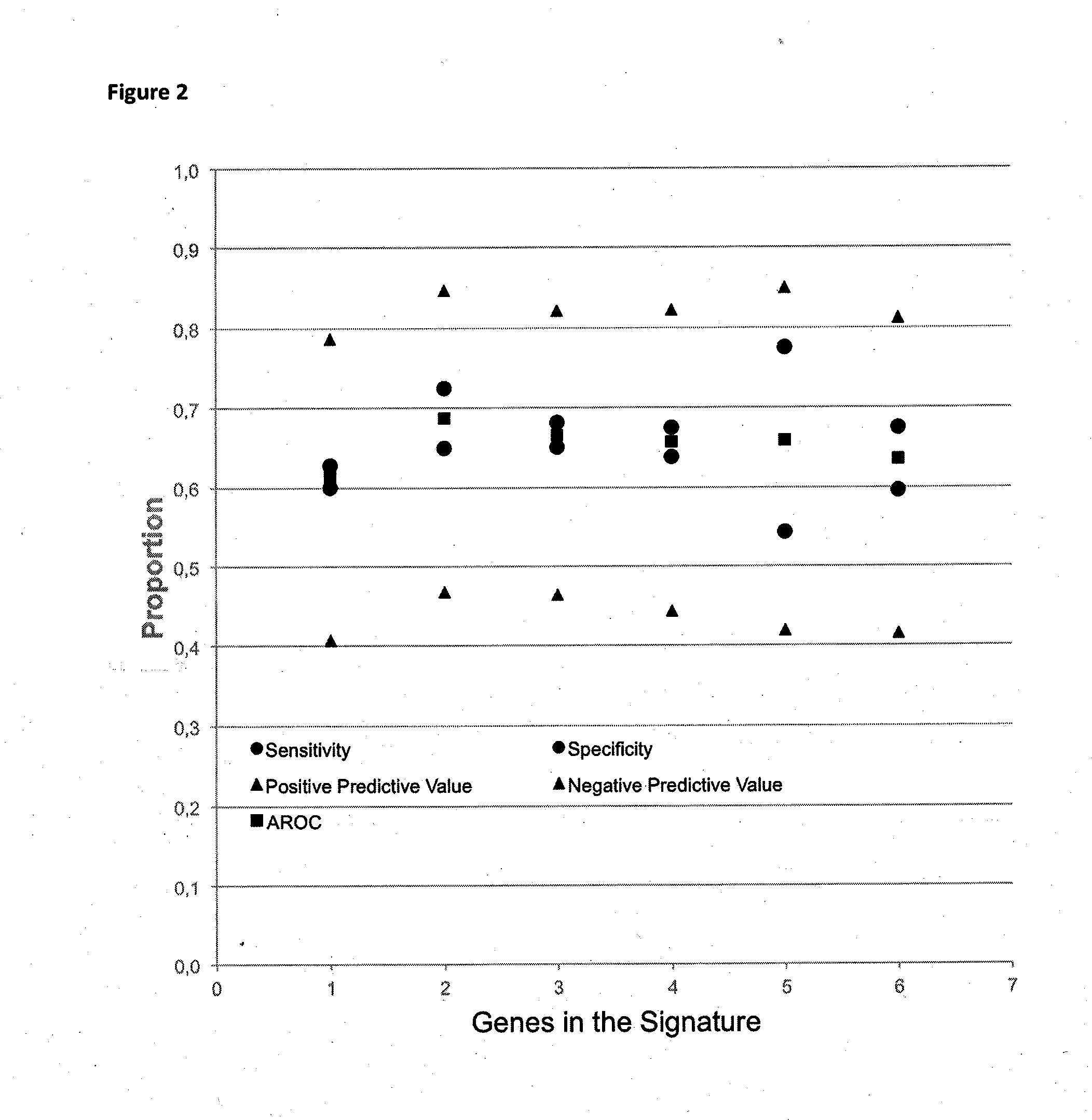
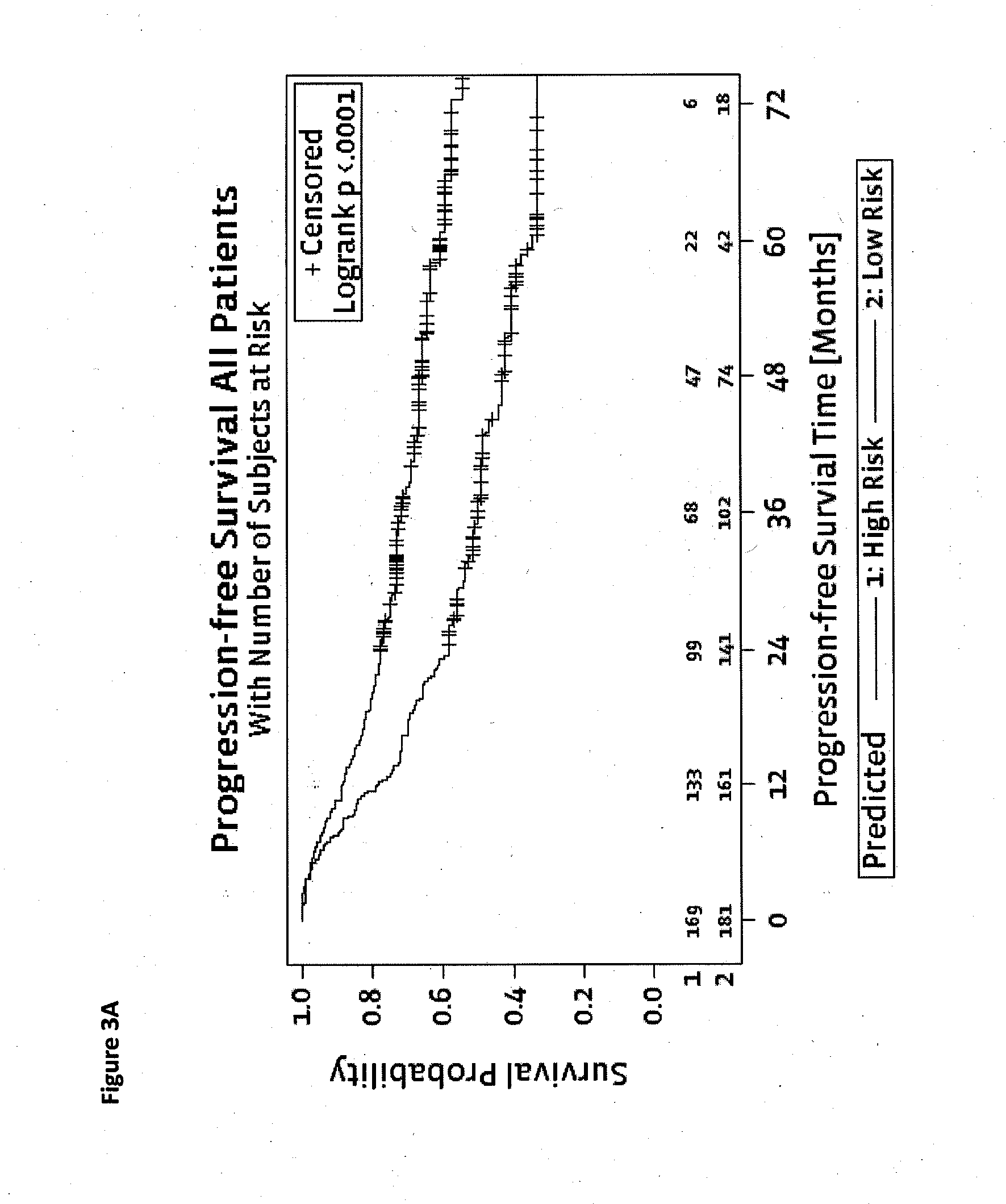
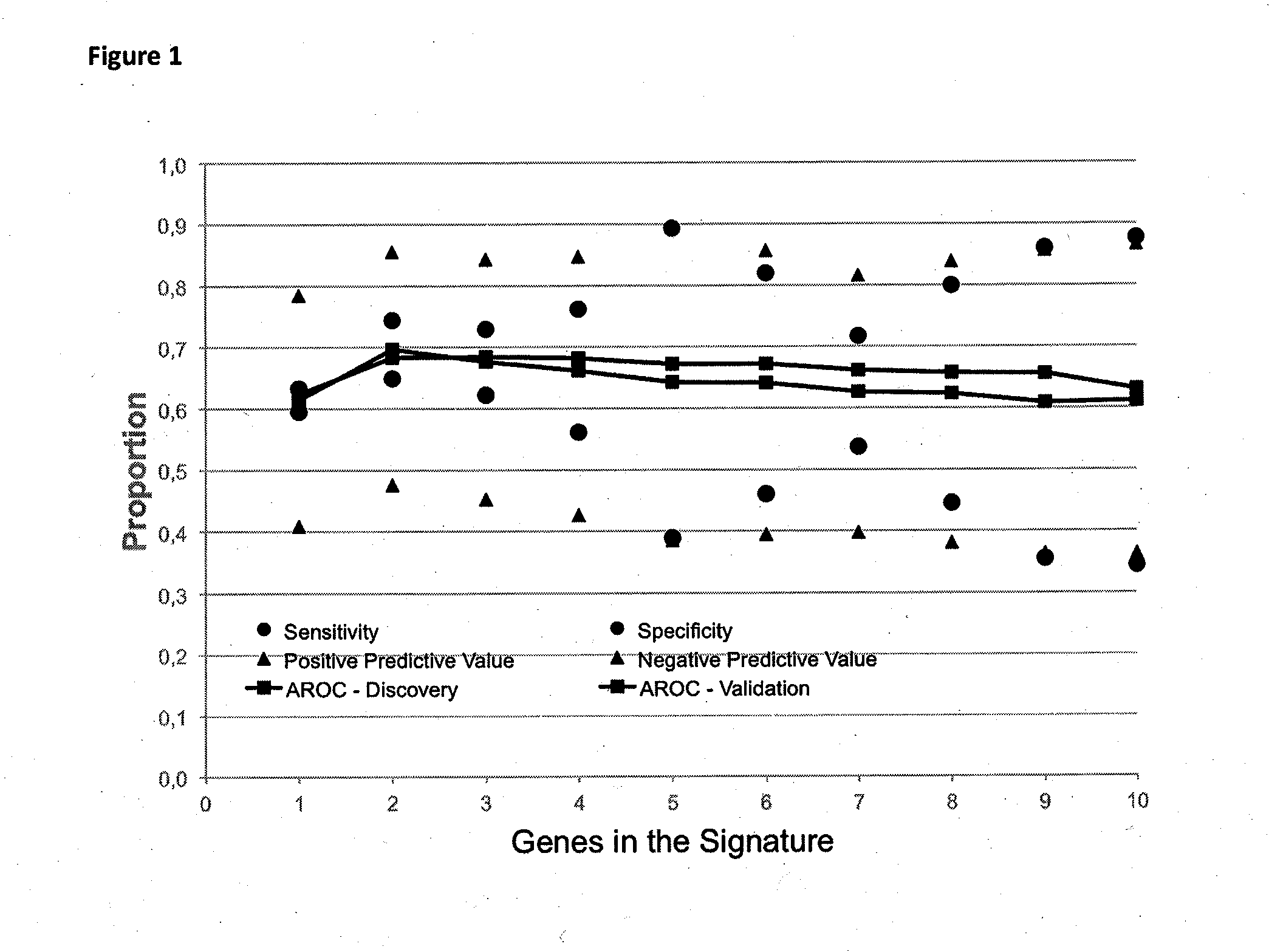
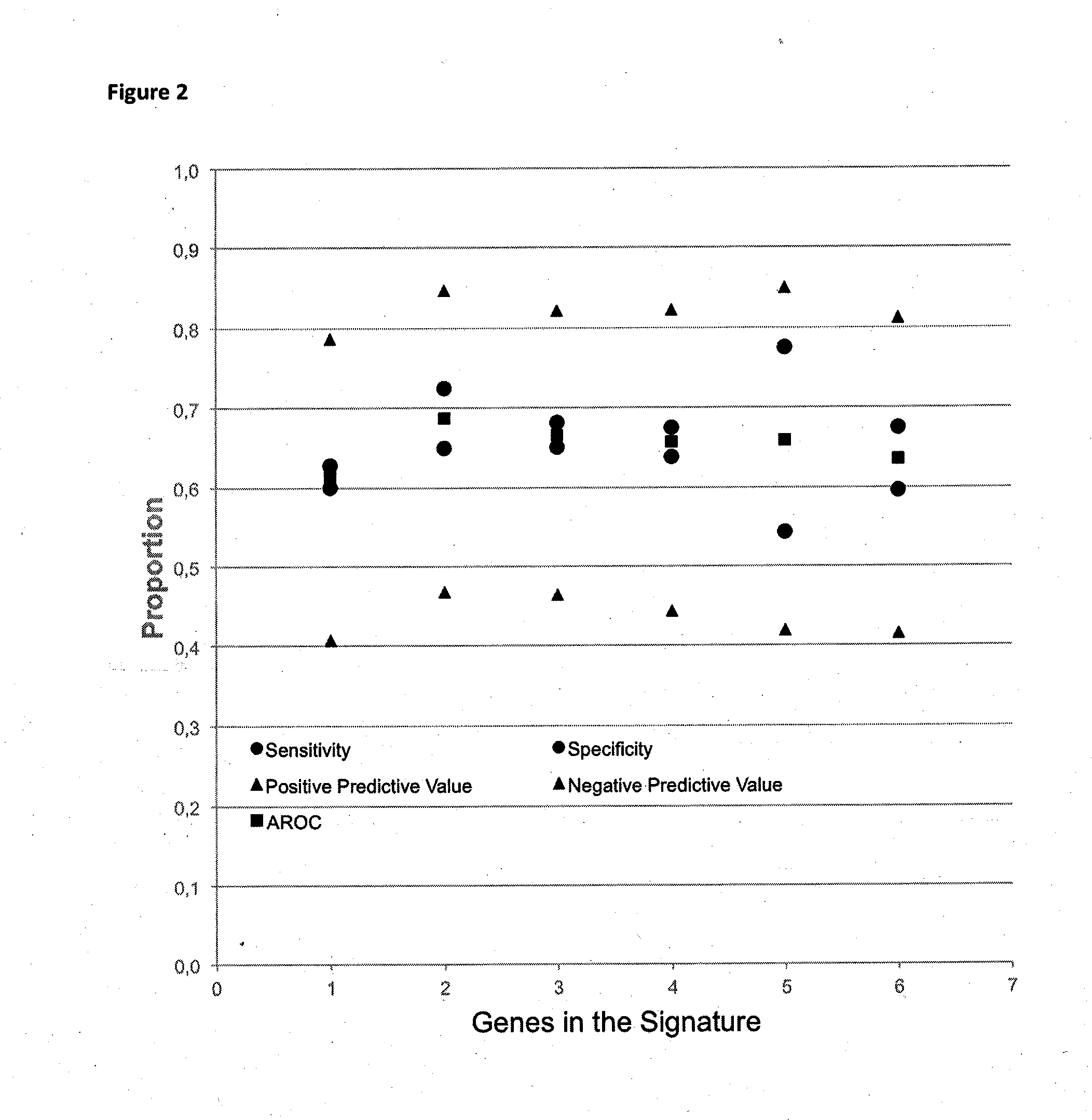
Method for predicting a manifestation of an outcome measure of a cancer patient
InactiveUS20160153032A9Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOutcome measuresTissue sample
The invention pertains to a method for predicting a manifestation of an outcome measure of a cancer patient based on a tumor DNA containing tissue sample from the cancer patient, comprising, firstly, determining an existence of a sequence variation within segments of at least two genes of the tumor DNA as Present, if at least one significant sequence variation can be determined, or as Absent, if no significant sequence variation can be determined, wherein the at least two genes of the tumor DNA are associated with the outcome measure of the patient; secondly, combining the existence of sequence variations of the at least two genes using a logical operation (prediction function), and thirdly, predicting based on the results of the logical operation the manifestation of an outcome measure of the patient.
Owner:SIGNATURE DIAGNOSTICS
High-efficiency cooperative work realization method and system thereof
InactiveCN106485463AImprove interactivityGuaranteed timelinessOffice automationTask completionOutcome measures
The invention discloses a high-efficiency cooperative work realization method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of associating a flow influencing a task progress / a result with a task and generating task and flow association information; and sending the task and flow association information to a task participant and a process handler so as to carry out assessment and processing. The high-efficiency cooperative work solution scheme provided in the invention is based on an OKR assessment standard, a subtask, a subproject and a correlation flow are taken as intermediate key results which influence a final result. Through using instant communication, timeliness of task and flow participant information acquisition is guaranteed so that task management, a work flow and the instant communication are tightly associated. An examination mode of a traditional KPI which only concerns a result index is destroyed and a purpose of high-efficiency cooperation is reached. Timeliness of cooperation information communication is greatly increased, task completion effectiveness is guaranteed and interaction among the flow, the instant communication and a task management module is increased.
Owner:深圳市青柠互动科技开发有限公司
Method for predicting a manifestation of an outcome measure of a cancer patient
InactiveUS20140342925A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOutcome measuresLogical operations
The invention pertains to a method for predicting a manifestation of an outcome measure of a cancer patient based on a tumor DNA containing tissue sample from the cancer patient, comprising, firstly, determining an existence of a sequence variation within segments of at least two genes of the tumor DNA as Present, if at least one significant sequence variation can be determined, or as Absent, if no significant sequence variation can be determined, wherein the at least two genes of the tumor DNA are associated with the outcome measure of the patient; secondly, combining the existence of sequence variations of the at least two genes using a logical operation (prediction function), and thirdly, predicting based on the results of the logical operation the manifestation of an outcome measure of the patient.
Owner:SIGNATURE DIAGNOSTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com