Systems for clinical trials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example embodiments
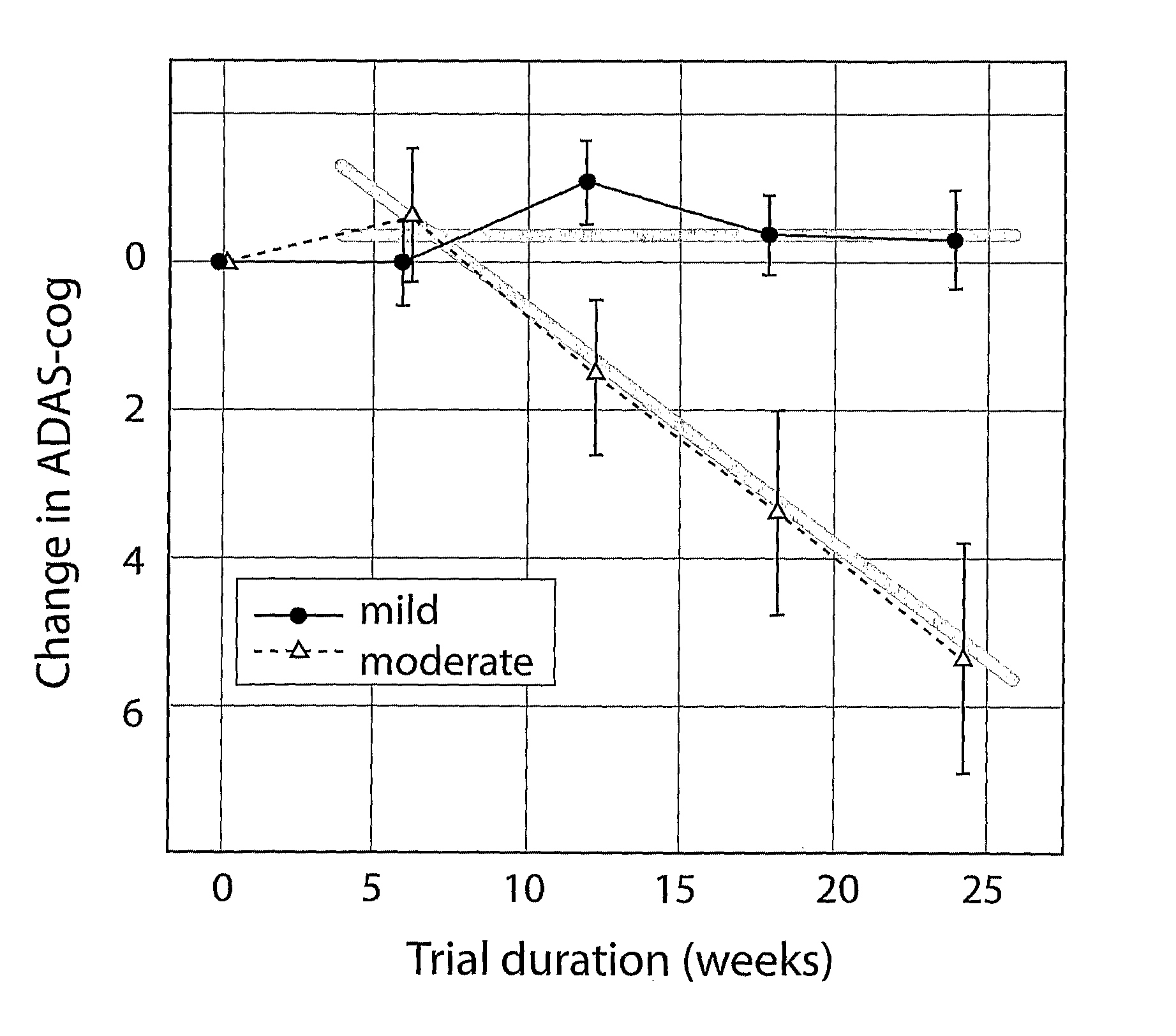
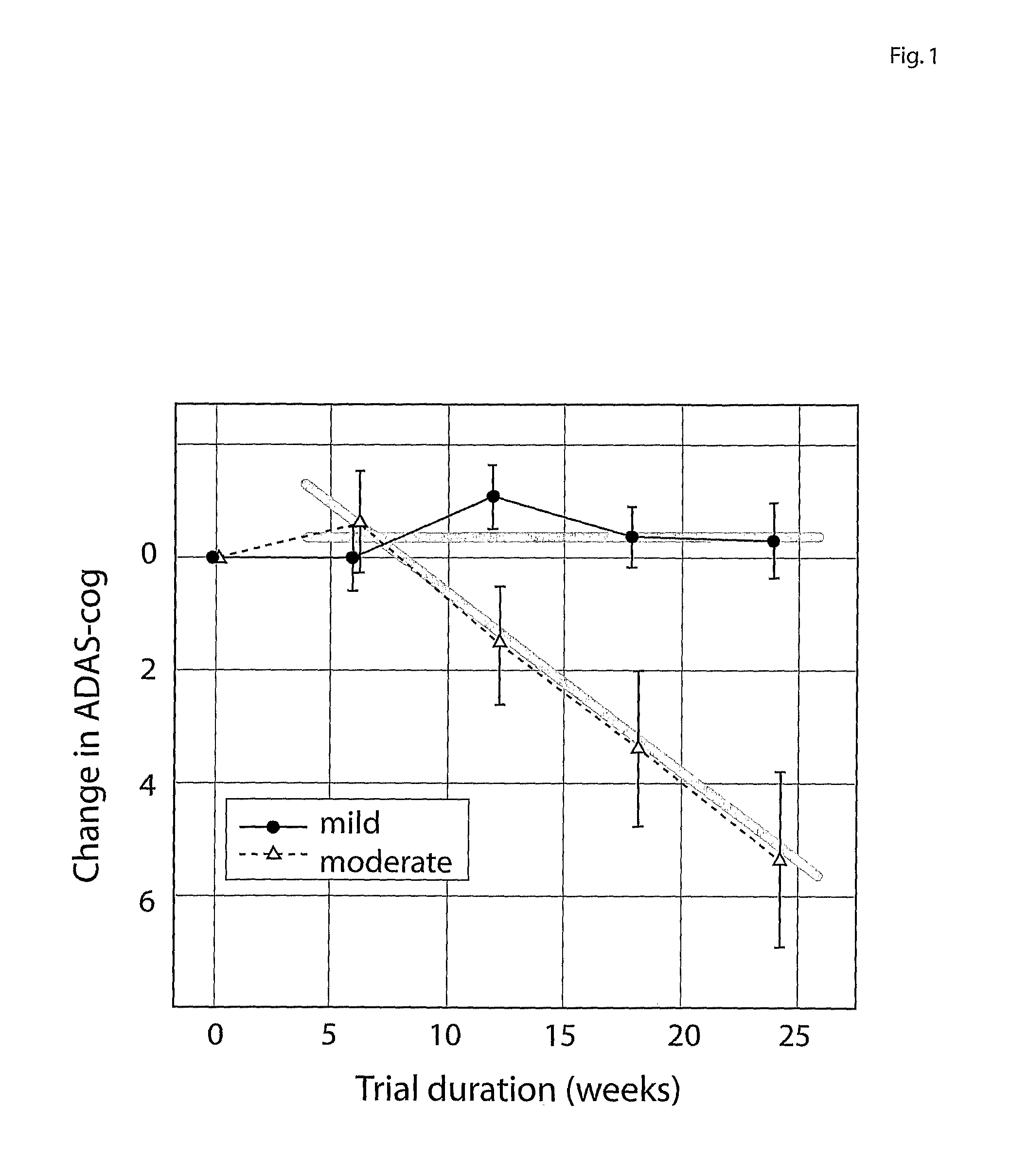
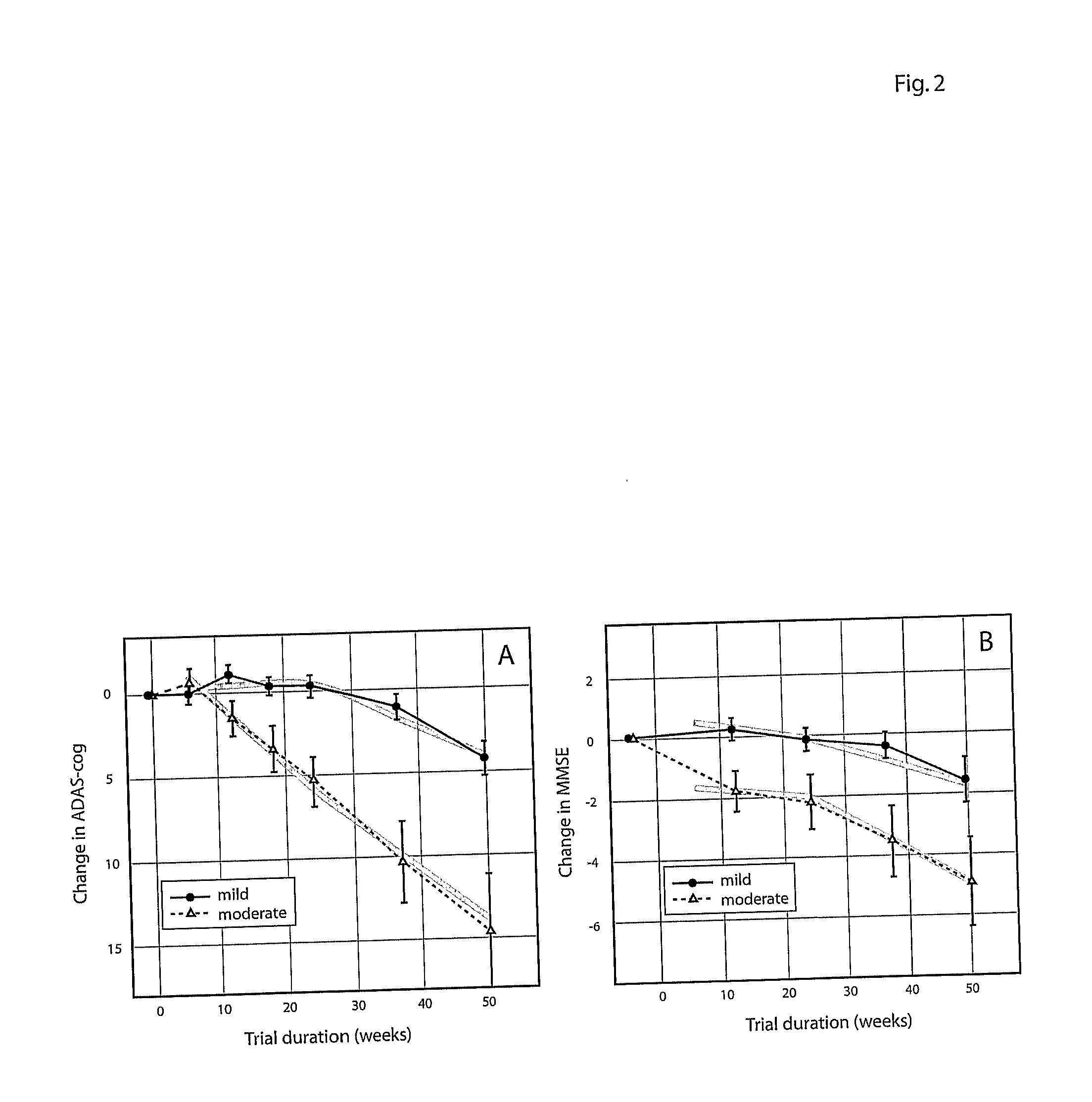
[0183]Thus in one embodiment the subject group is stratified into mild AD (CDR=1) and moderate AD (CDR=2). Another sub-group may be Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI as defined by agreed clinical criteria or CDR=0.5).
[0184]In the MCI and mild AD sub-group the time frame may be insufficient to expect, in the light of the results described herein, decline in the psychometric outcome measure (e.g. less than 6 months).
[0185]Thus physiological outcome measures are used in addition to psychometric outcome measures. These may be in the time frame up to 6 months for mild AD (e.g. 3 to 4 months), and even longer (6-12 months for MCI). As shown herein, efficacy demonstrated by such measures can predict future efficacy using clinical-psychometric end-points.
[0186]In mild or moderate AD, dosage strengths of a putative disease-modifying treatment, which may produce limited or no apparent therapeutic efficacy over 6 months, but which produces evidence of physiological efficacy over 6 months, can be ...
example 1
Disease Severity at Baseline and Rate of Disease Progression
[0200]It has been generally recognised in the literature that severity or stage of disease is an important predictor of disease progression (reviewed recently in Schaufele, M., Bickel, H., Weyerer, S. (2002) Which factors influence cognitive decline in older adults suffering from dementing disorders? International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 17:1055-1063).
[0201]However the rember™ study is the first in which CDR severity at baseline was pre-specified as a stratification covariate in the primary outcome analysis. Subjects were classified into two groups: those who were CDR-mild at baseline (including 3 [1% of total randomised] who were CDR-questionable at baseline) and those who were CDR moderate at baseline. Although CDR has been advocated previously as a staging instrument (Berg, L., Danziger, W. L., Storandt, M., Coben, L. A., Gado, M., Hughes, C. P., Knesevich, J. W., Botwinick, J. (1984) Predictive features in mild...
example 2
Cognitive Reserve
[0209]Although there is a general relationship between increased load of brain pathology and decline in cognitive function, this relationship does not explain all of the variance in the data. Attempts to explain the variability have been formulated in terms of the concepts of “brain reserve” or “cognitive reserve”, which relate to two different theoretical formulations (Stern, Y. (2002) What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 8:448-460). The first is the passive brain reserve model, where reserve is defined by brain size or neuronal count. It is described as passive because it is defined in terms of the amount of damage or burden an individual can withstand before clinical symptoms appear. The second, or active cognitive reserve model, suggests that the brain can compensate for pathological burden by recruiting other processes to perform tasks compromised by disease (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com