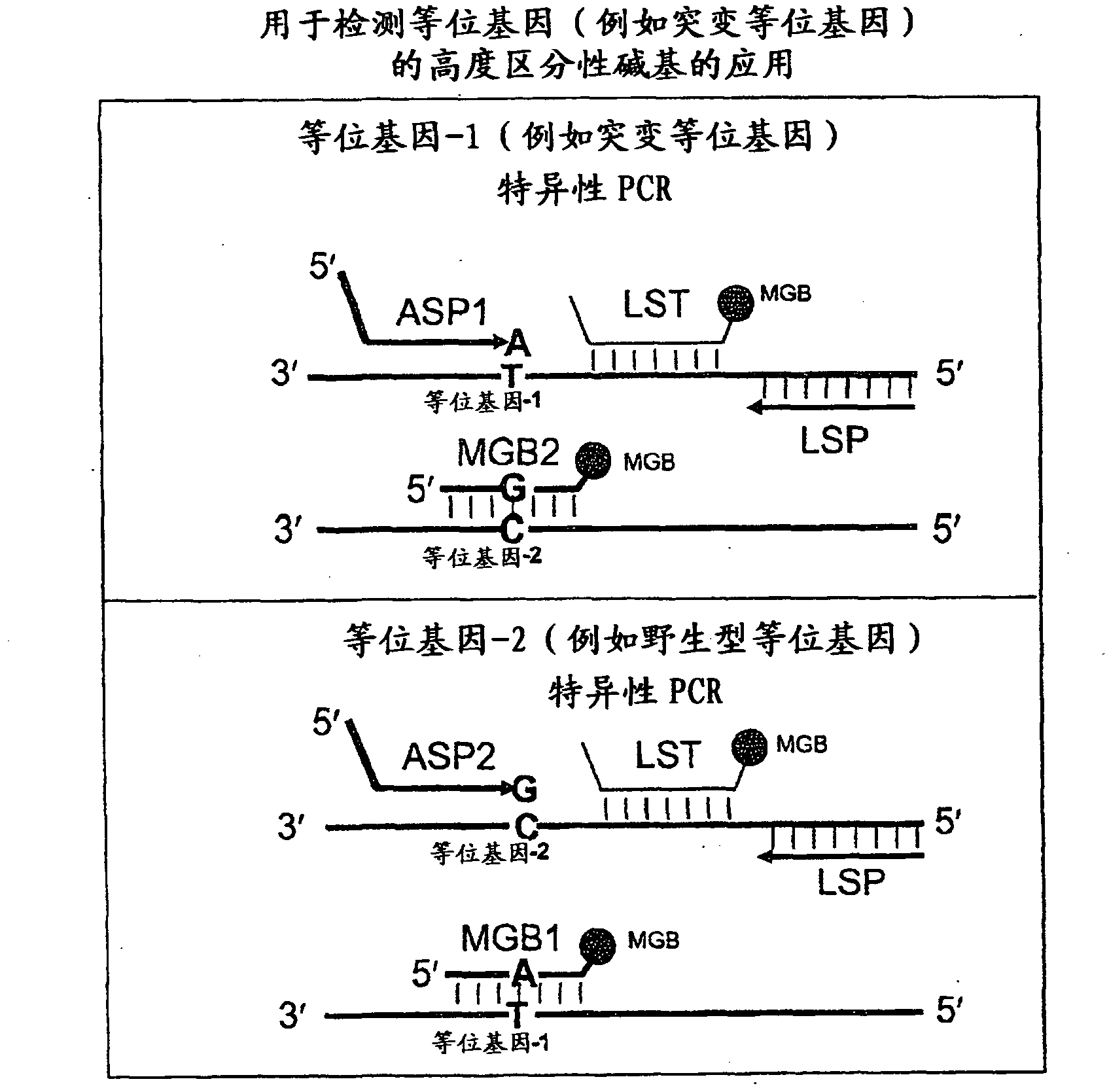
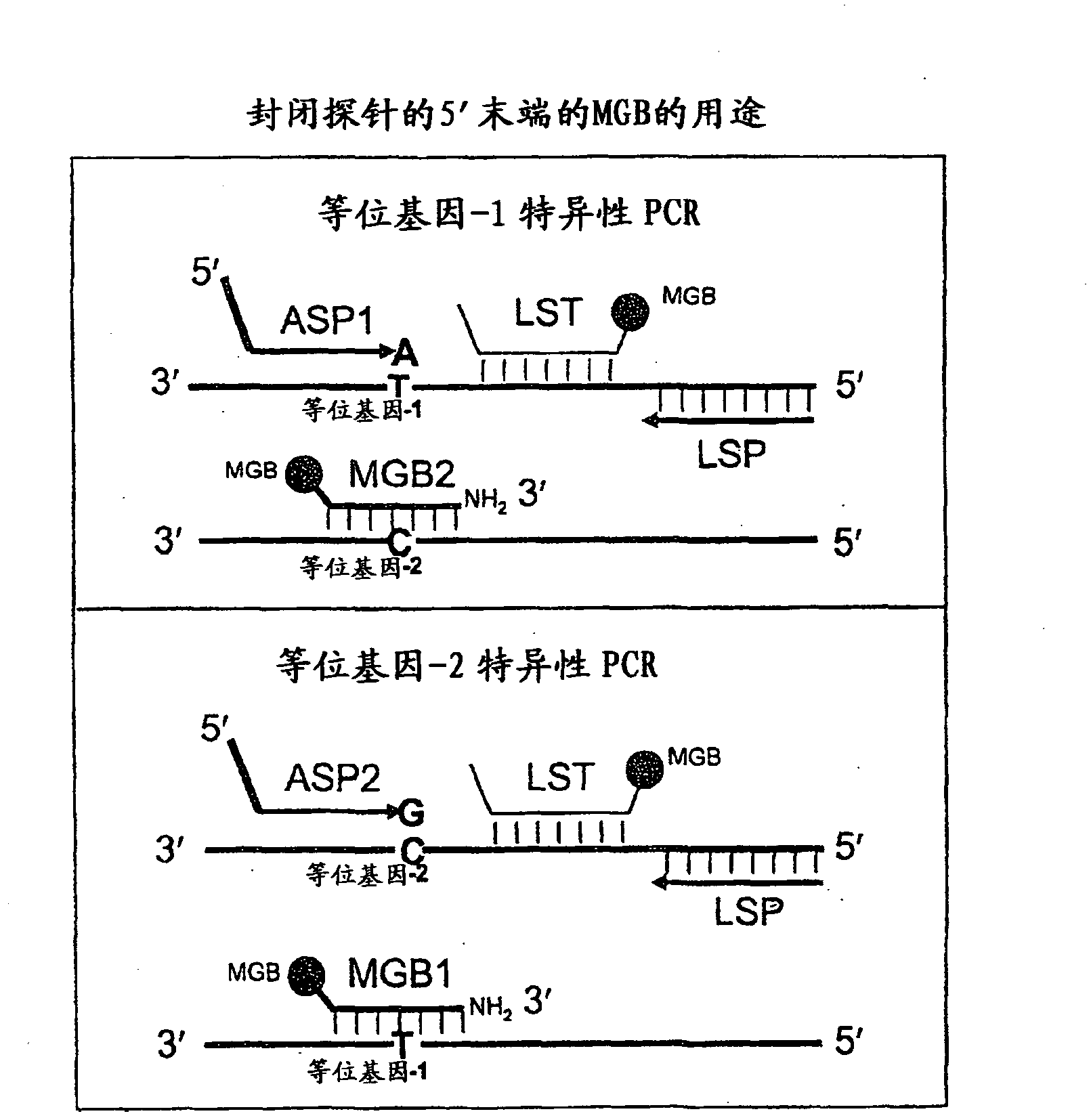
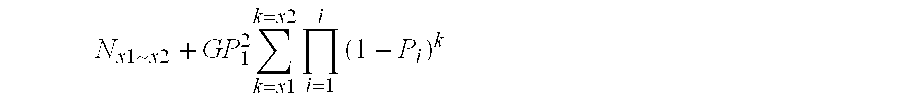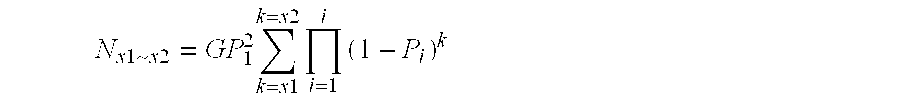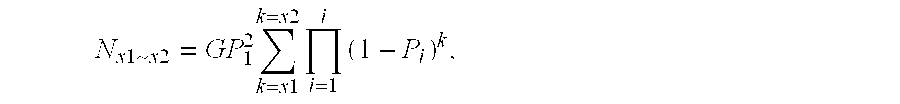Patents
Literature
134 results about "Sequence variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
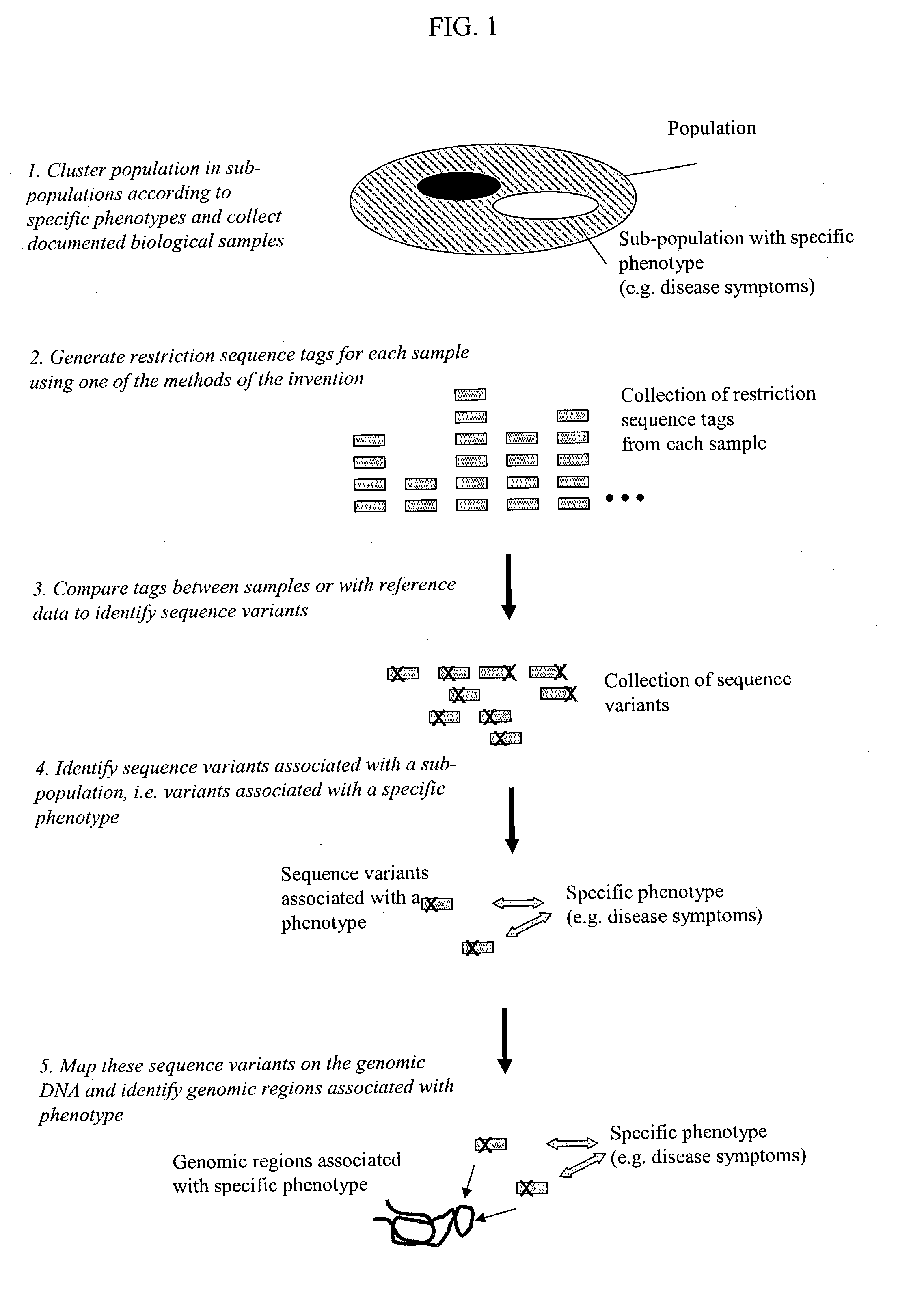
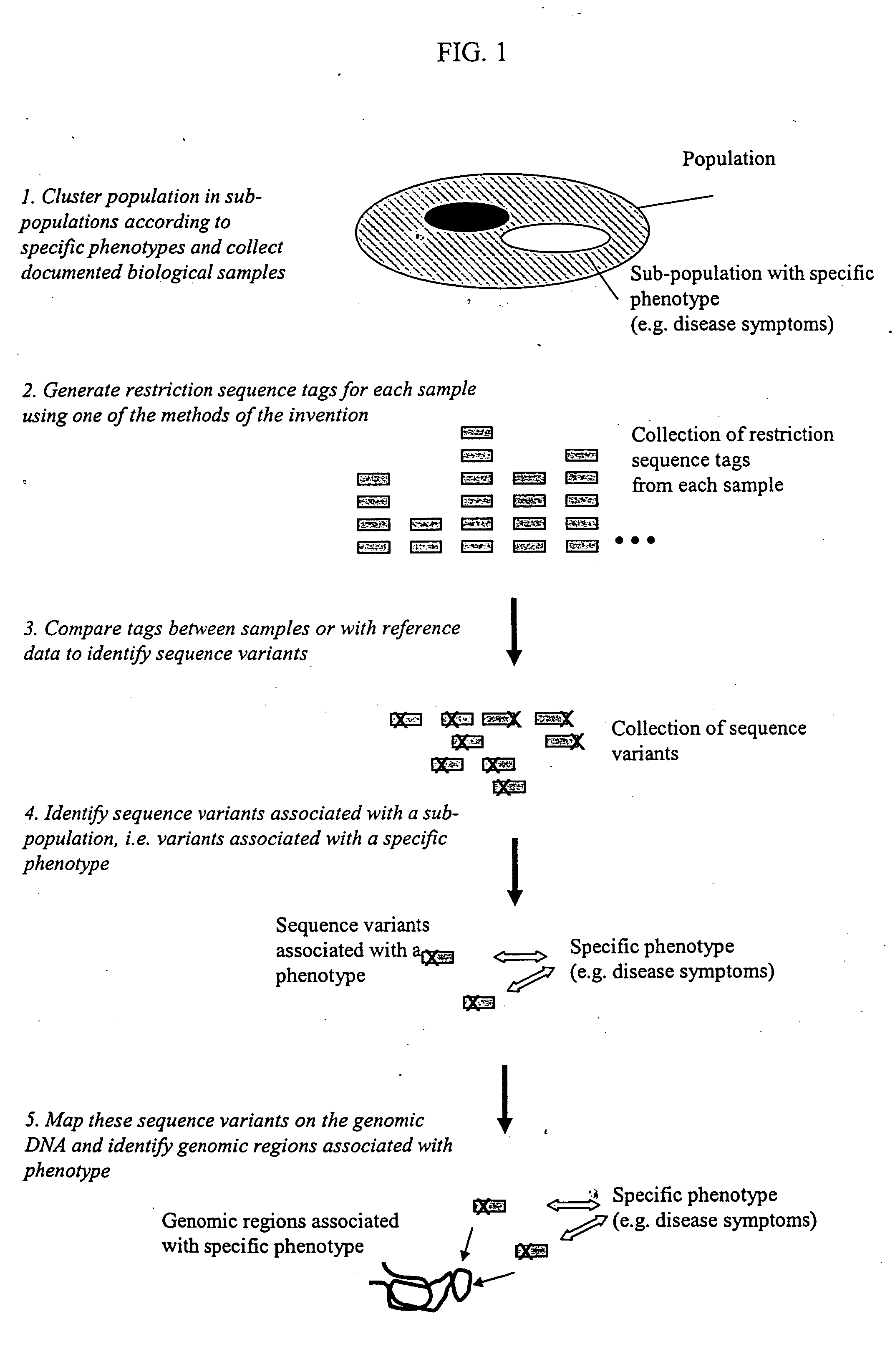
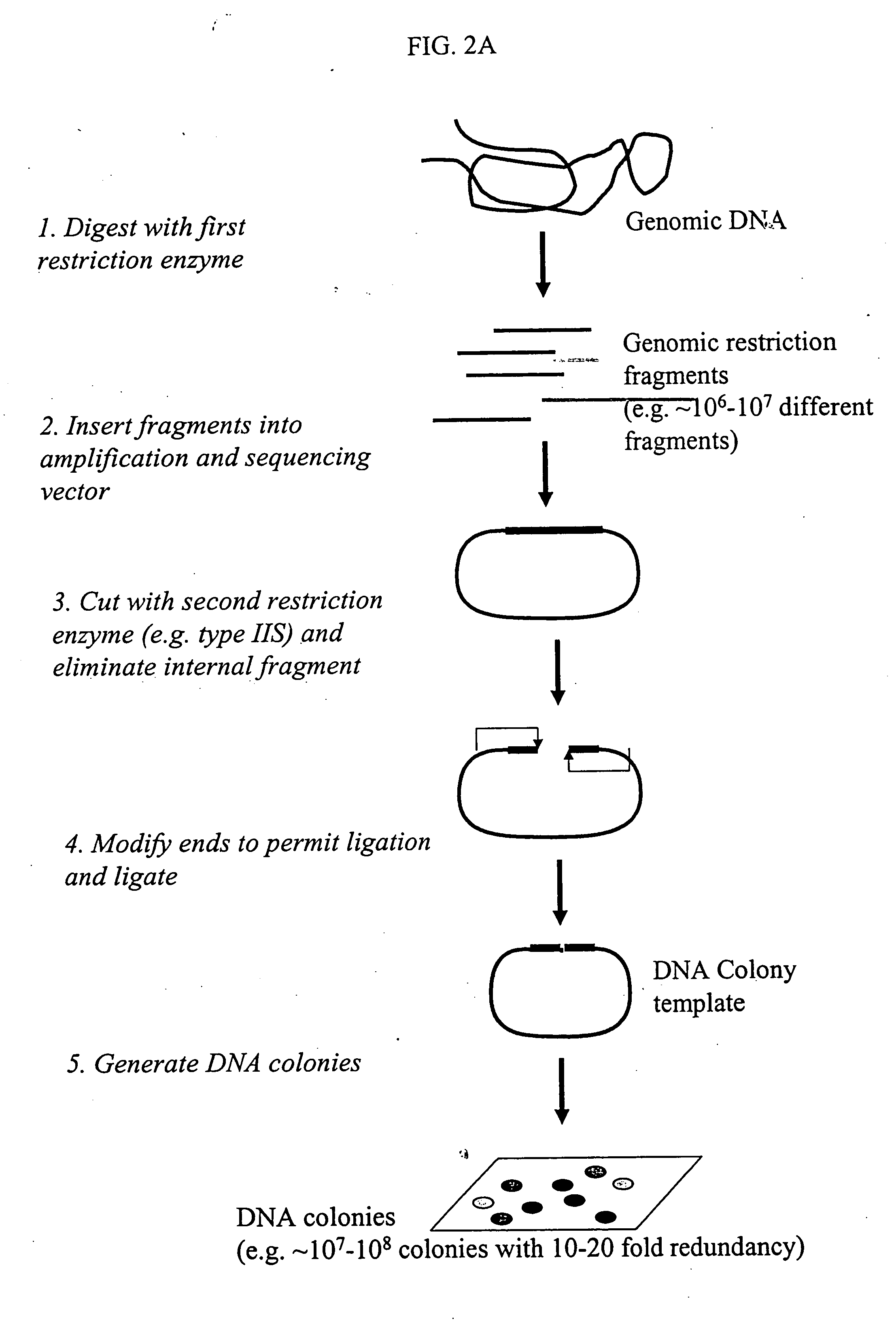
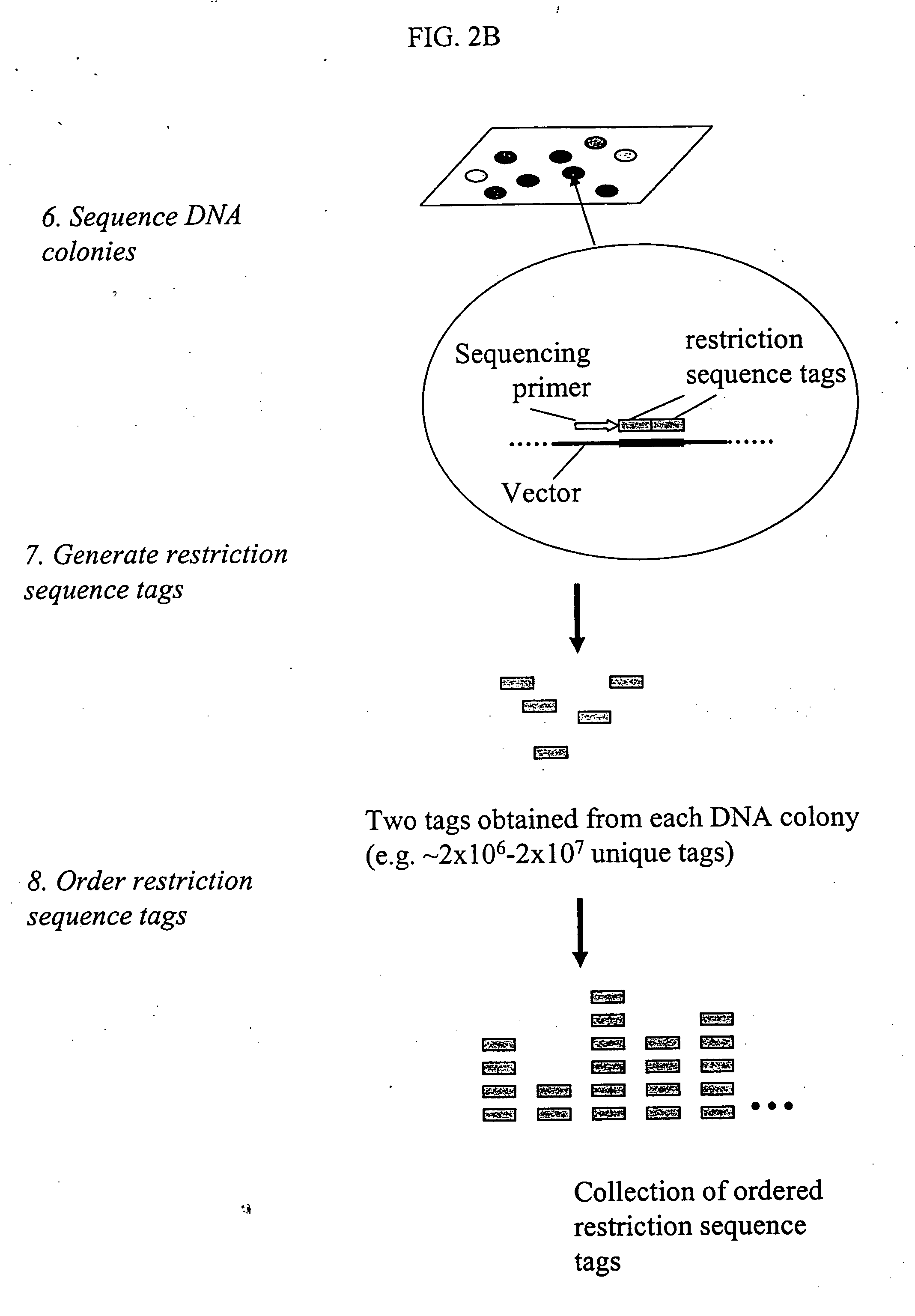
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
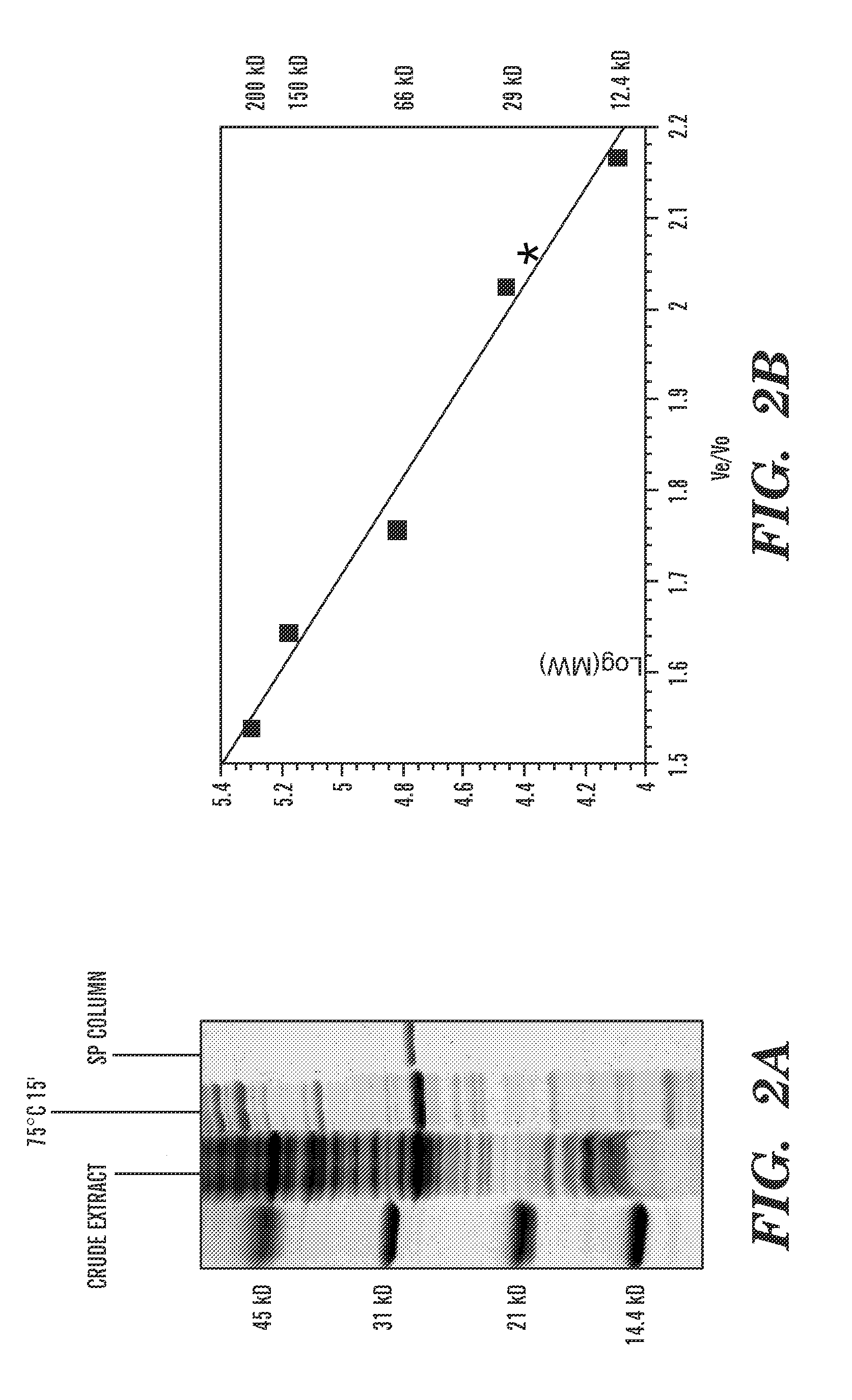
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
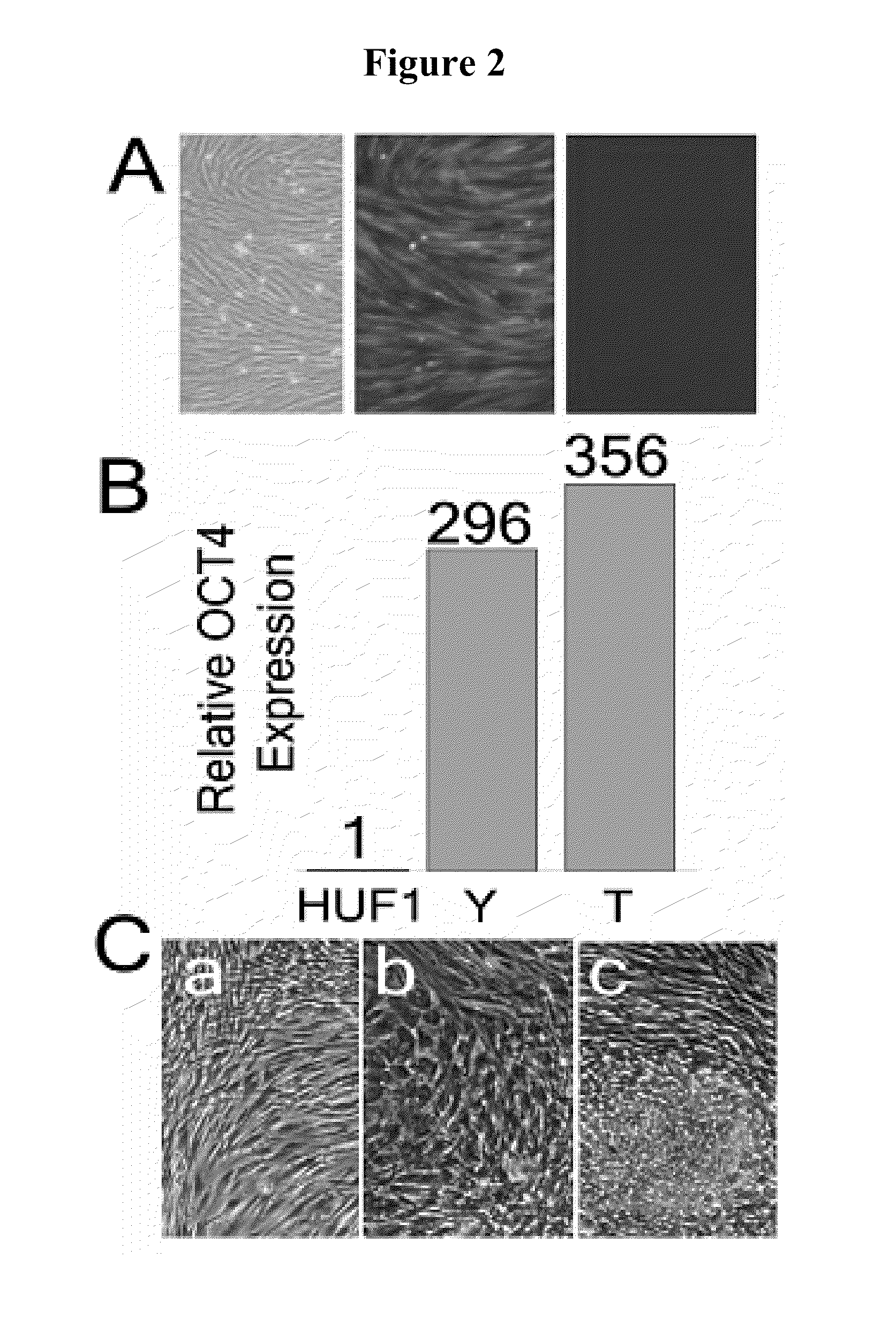
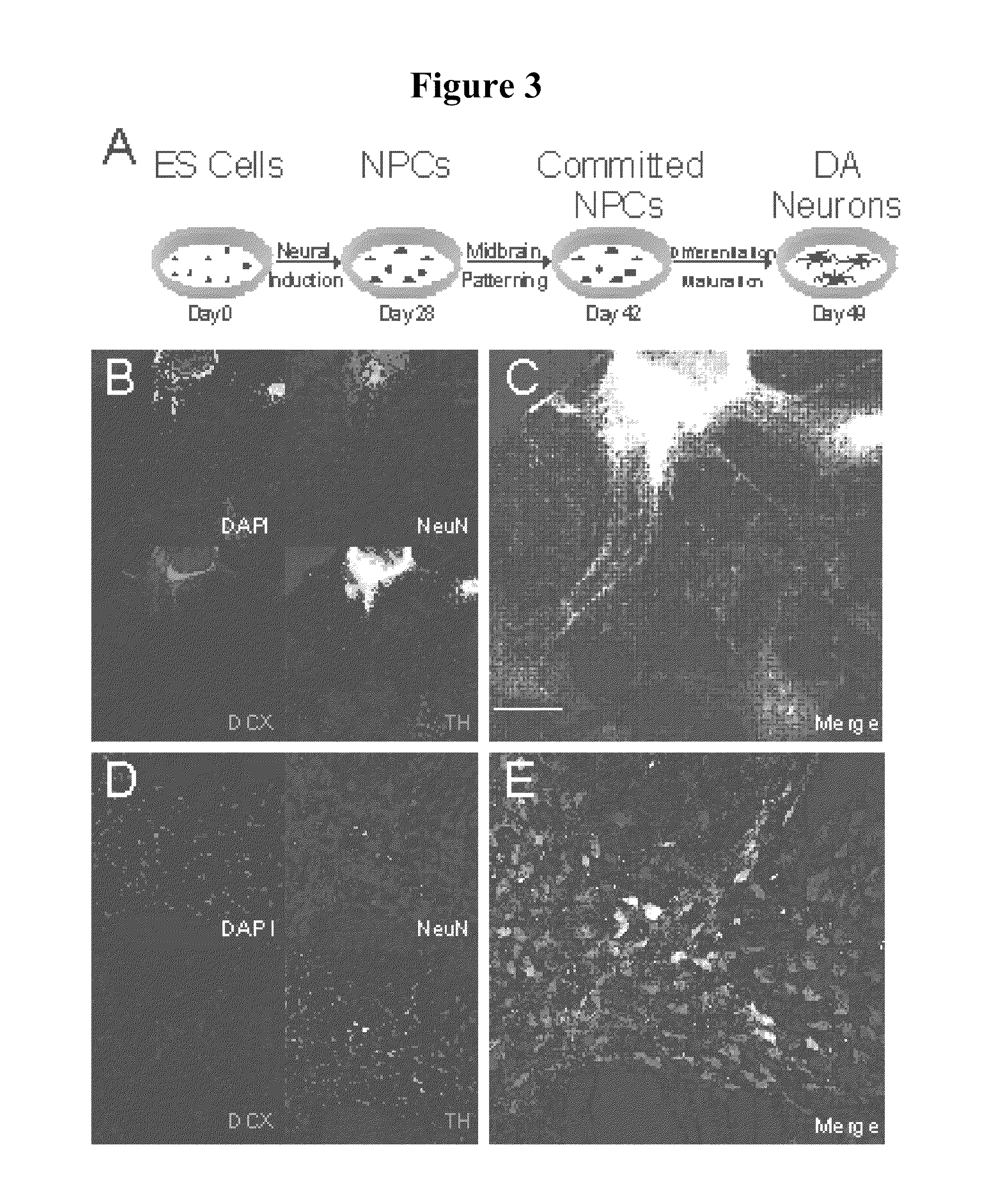
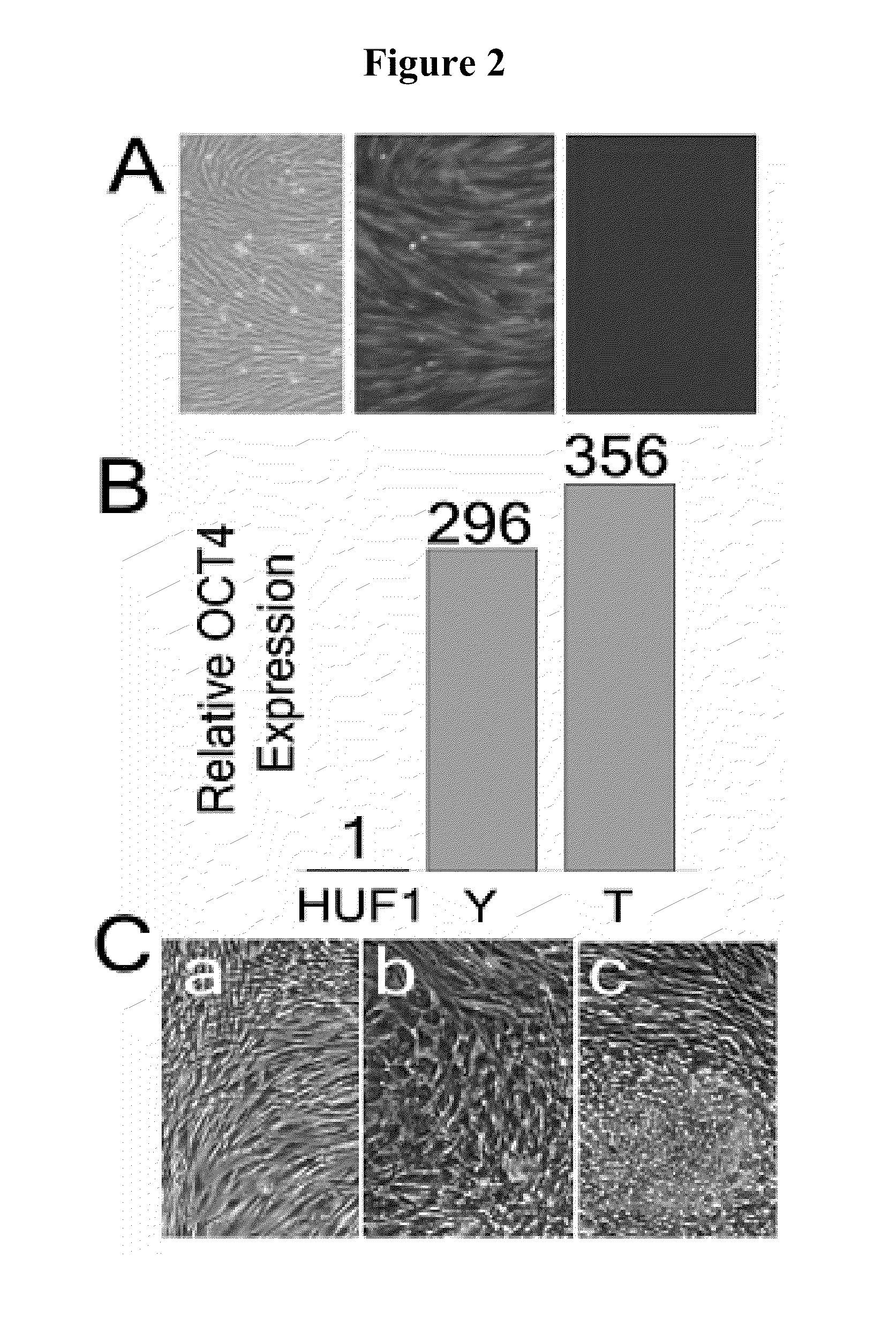
Pluripotent cell lines and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20100167286A1Microbiological testing/measurementDrug screeningSequence variationBioinformatics
Methods of generating cell lines with a sequence variation or copy number variation of a gene of interest, methods of use thereof, and cell lines with a sequence variation or copy number variation of a gene of interest are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
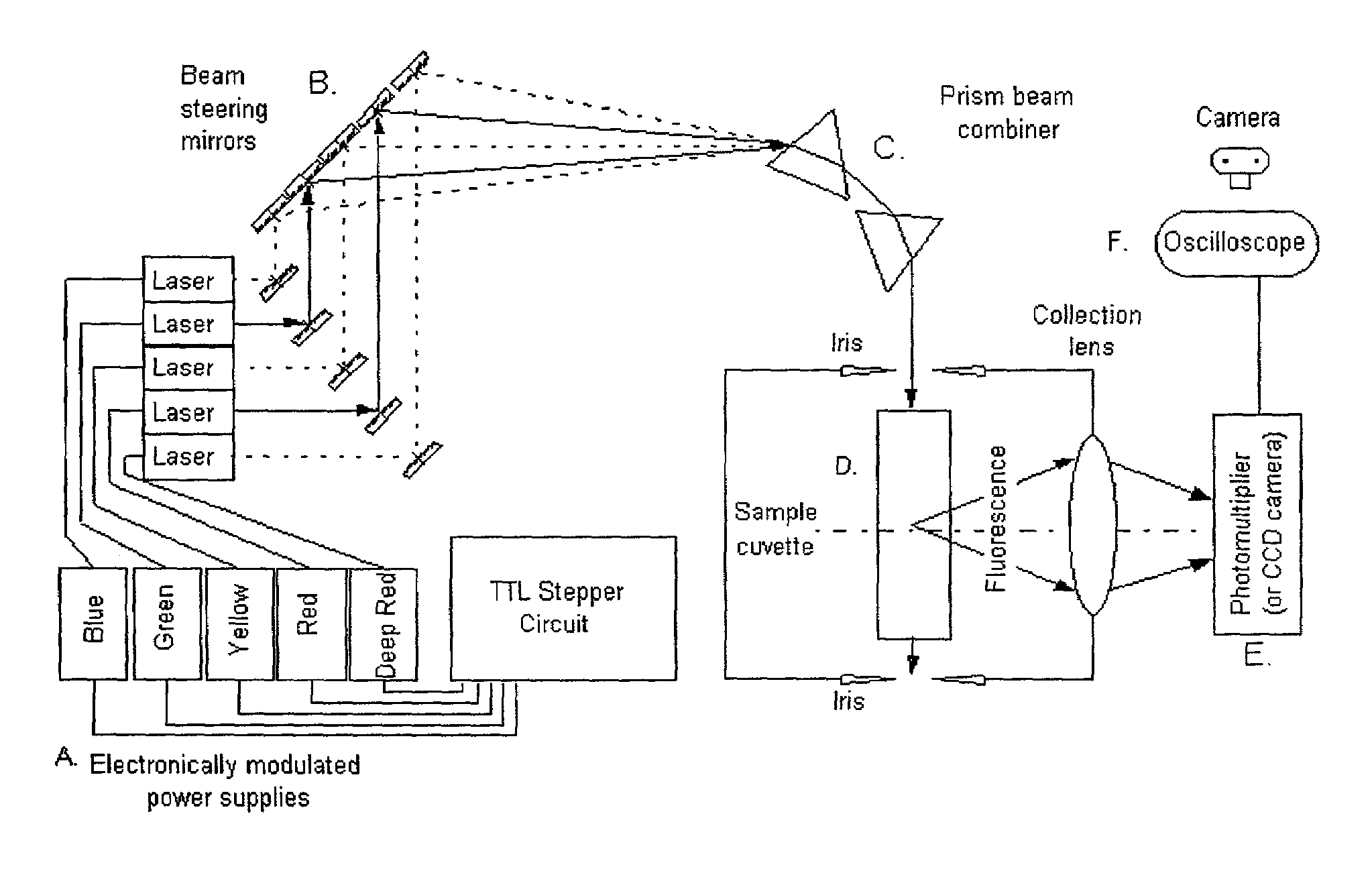
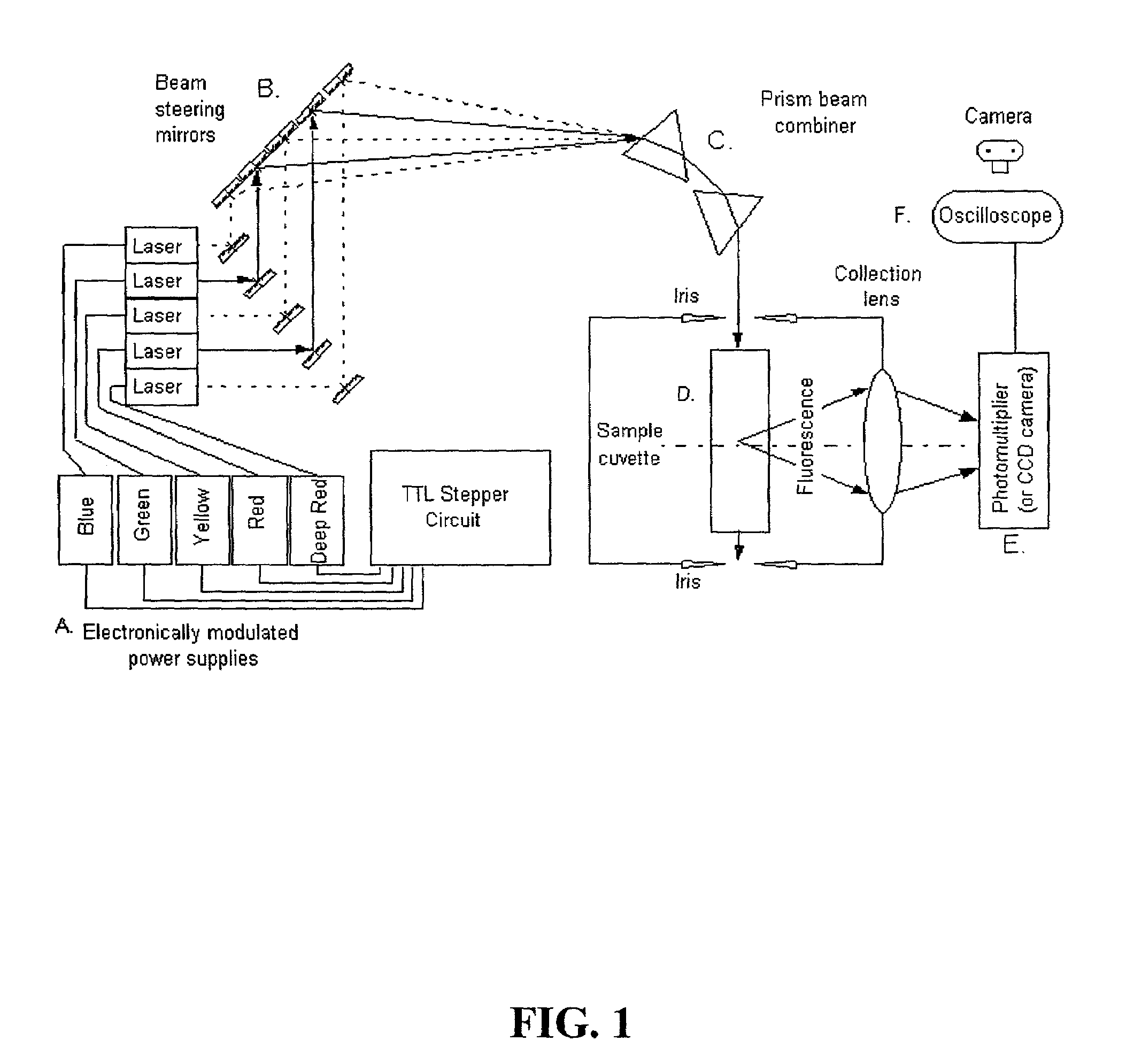
Pulsed-multiline excitation for color-blind fluorescence detection
InactiveUS6995841B2Accurate diagnosisImproved prognosisRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryFluorophoreCrowds
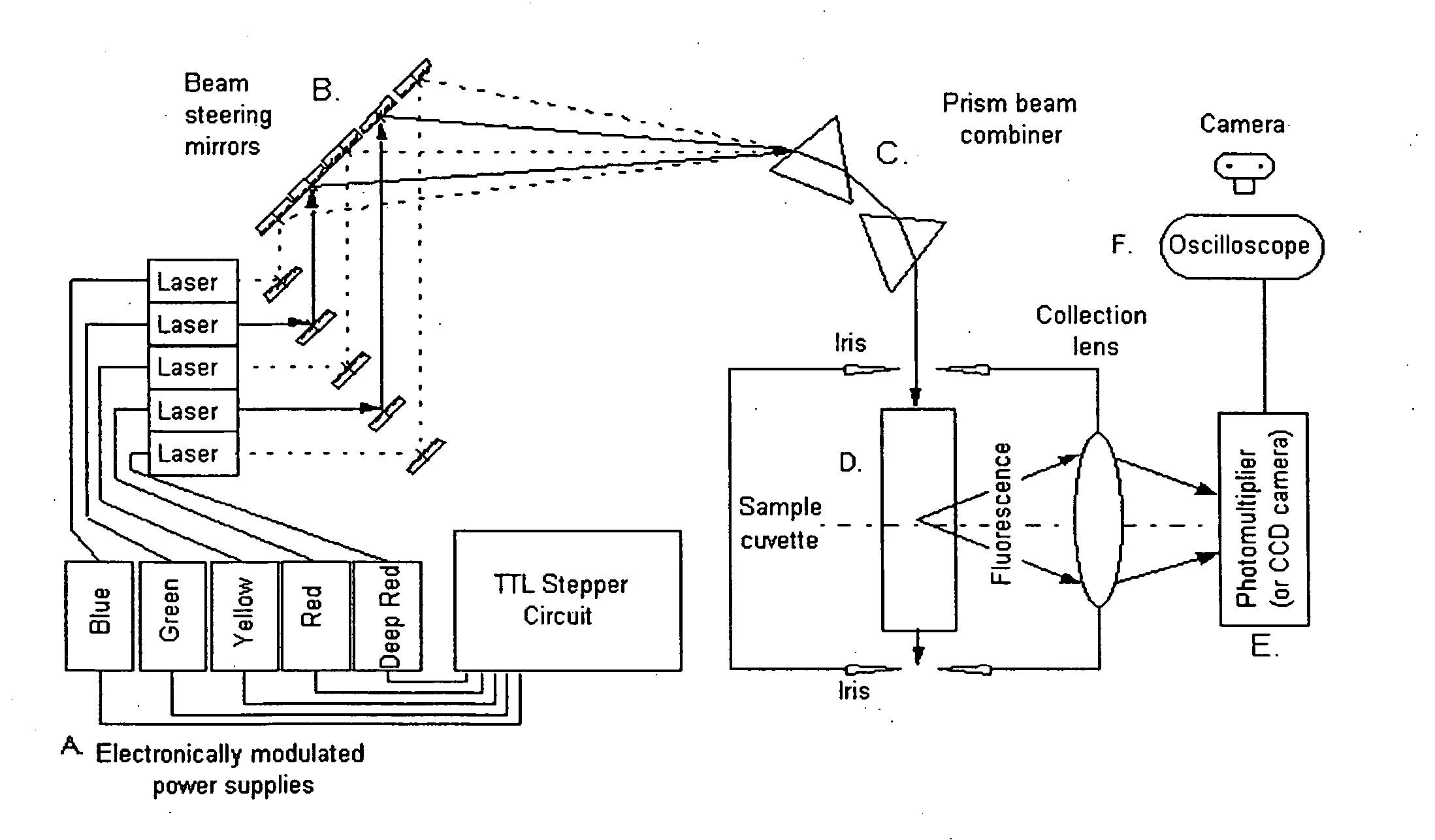
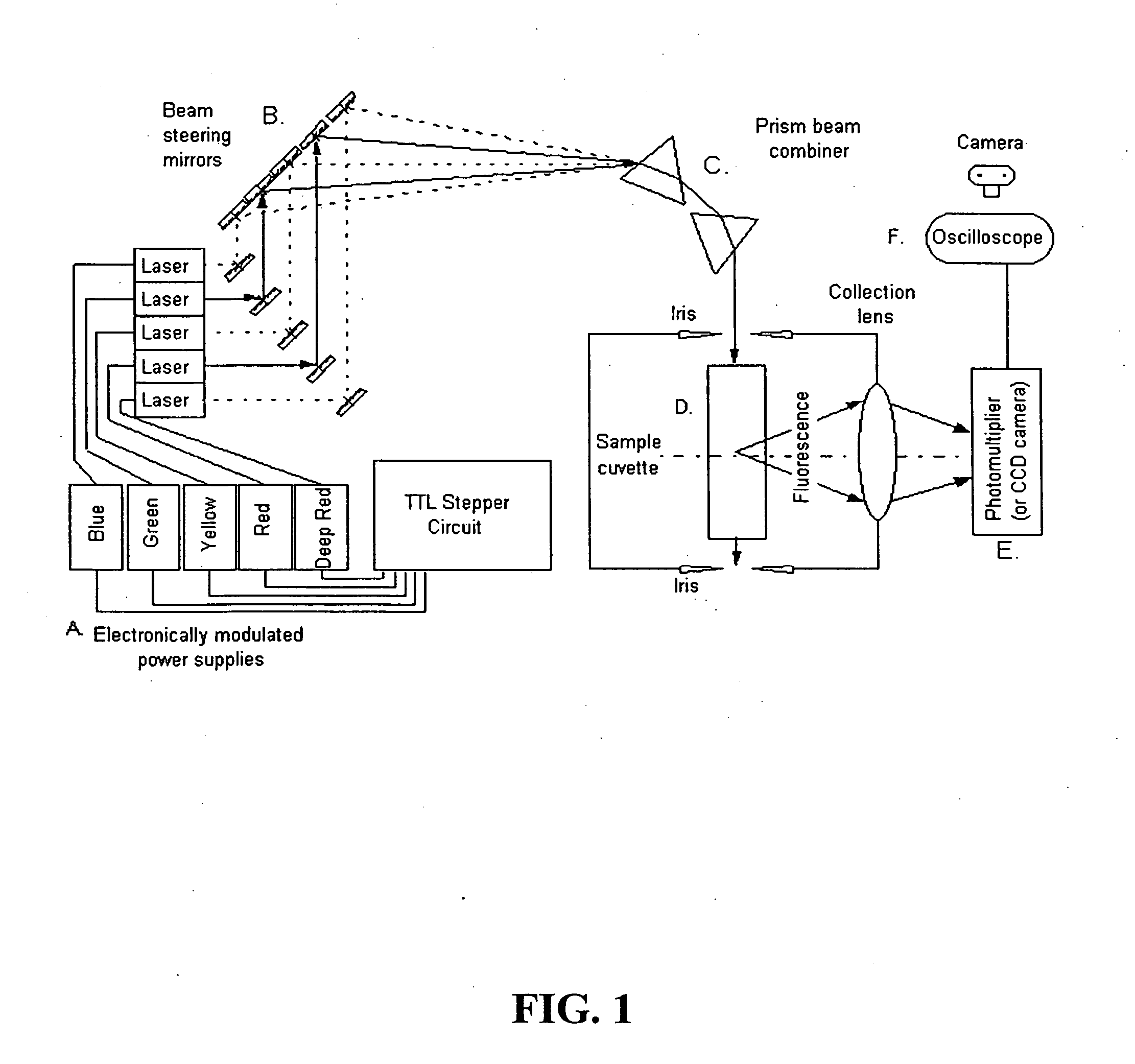
The present invention provides a technology called Pulse-Multiline Excitation or PME. This technology provides a novel approach to fluorescence detection with application for high-throughput identification of informative SNPs, which could lead to more accurate diagnosis of inherited disease, better prognosis of risk susceptibilities, or identification of sporadic mutations. The PME technology has two main advantages that significantly increase fluorescence sensitivity: (1) optimal excitation of all fluorophores in the genomic assay and (2) “color-blind” detection, which collects considerably more light than standard wavelength resolved detection. Successful implementation of the PME technology will have broad application for routine usage in clinical diagnostics, forensics, and general sequencing methodologies and will have the capability, flexibility, and portability of targeted sequence variation assays for a large majority of the population.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Systems and methods for identifying sequence variation
InactiveUS20130345066A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesRecognition sequenceContext specific
Systems and method for determining variants can receive mapped reads, align flow space information to a flow space representation of a corresponding portion of the reference. Reads spanning a position with a potential variant can be evaluated in a context specific manner. A list of probable variants can be provided.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Nucleic acid library design and assembly
InactiveUS20080064610A1Reduce solubilityImproving immunogenicityVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationSolubilityENCODE
Owner:CODON DEVICES
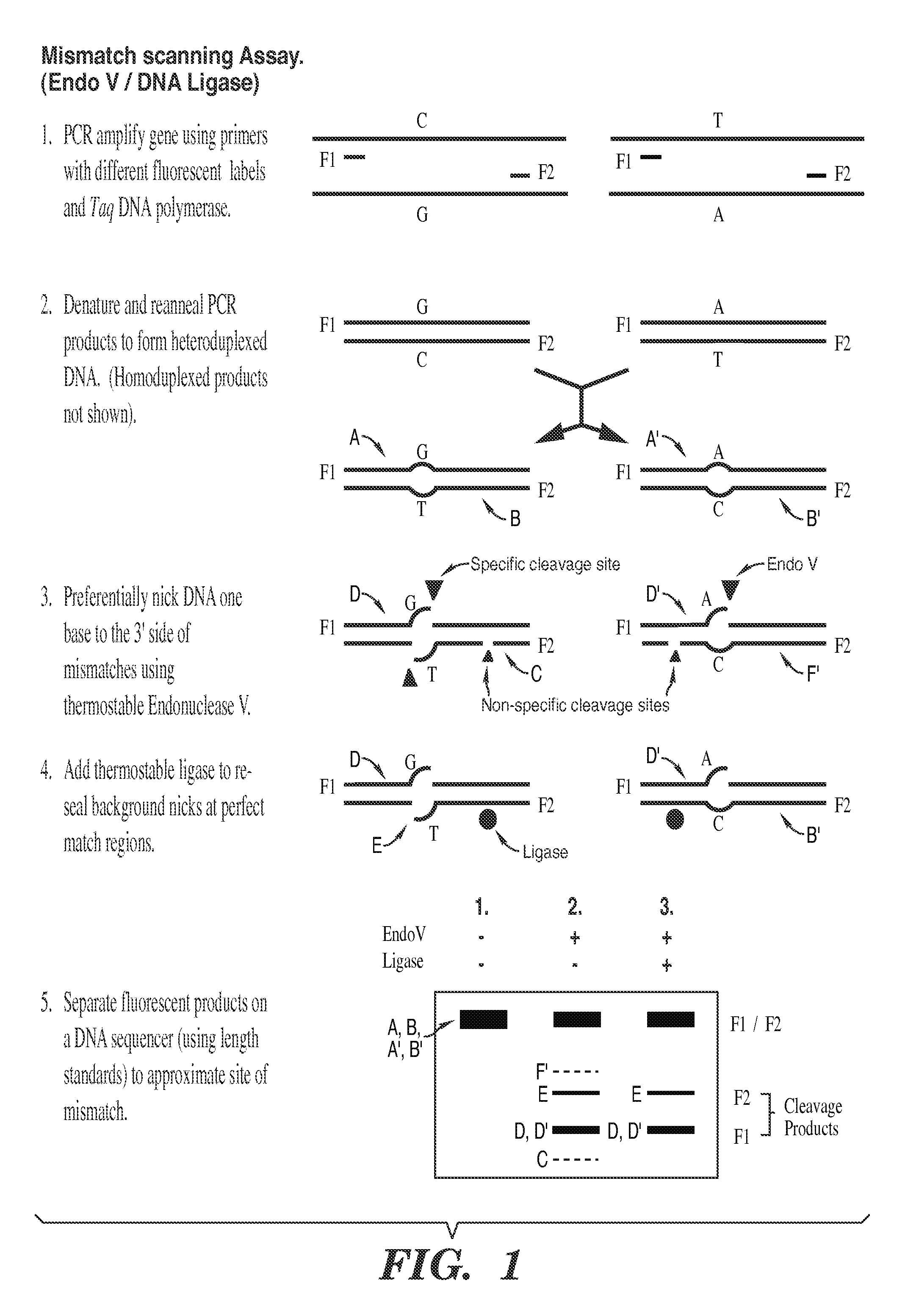
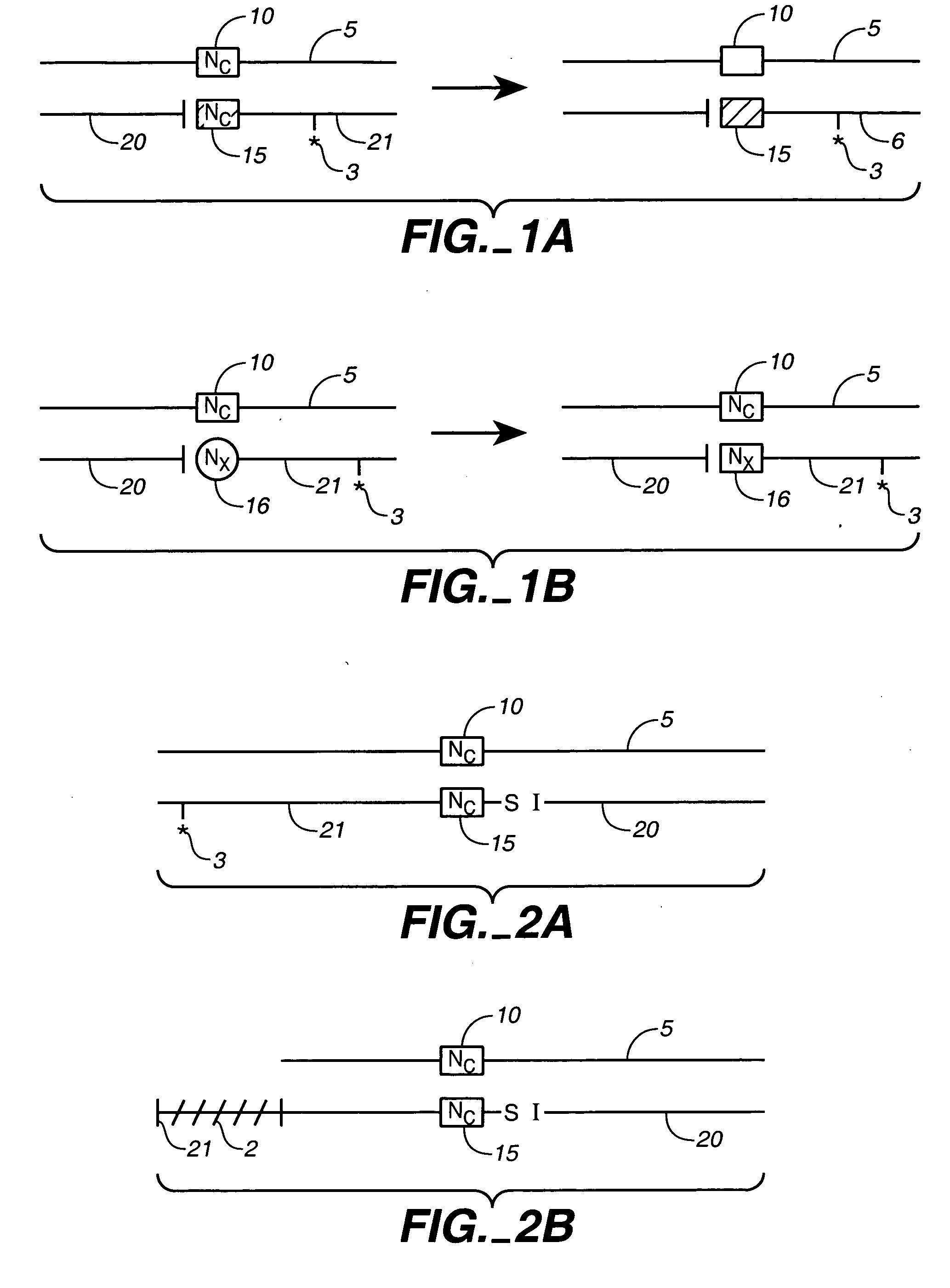
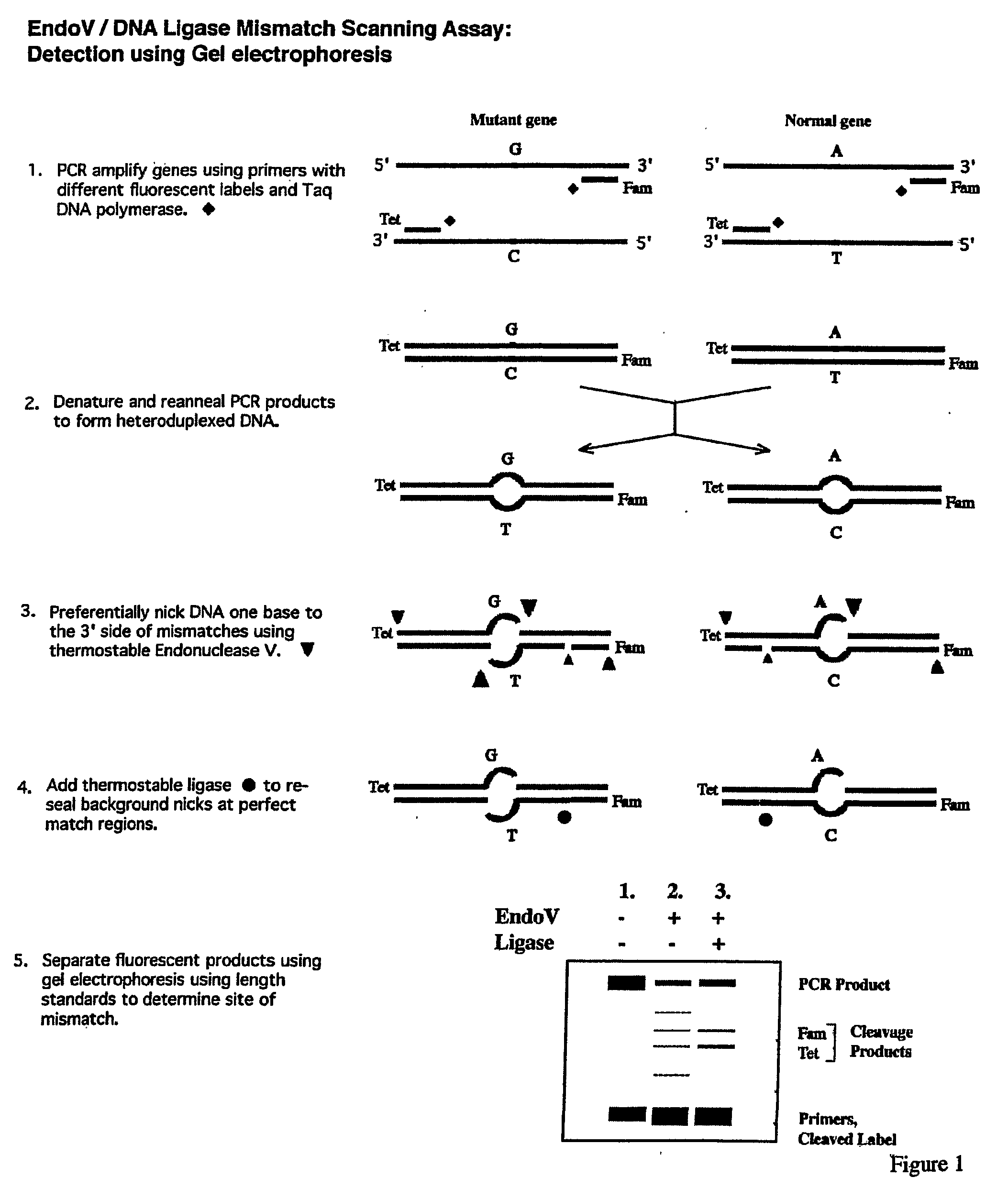
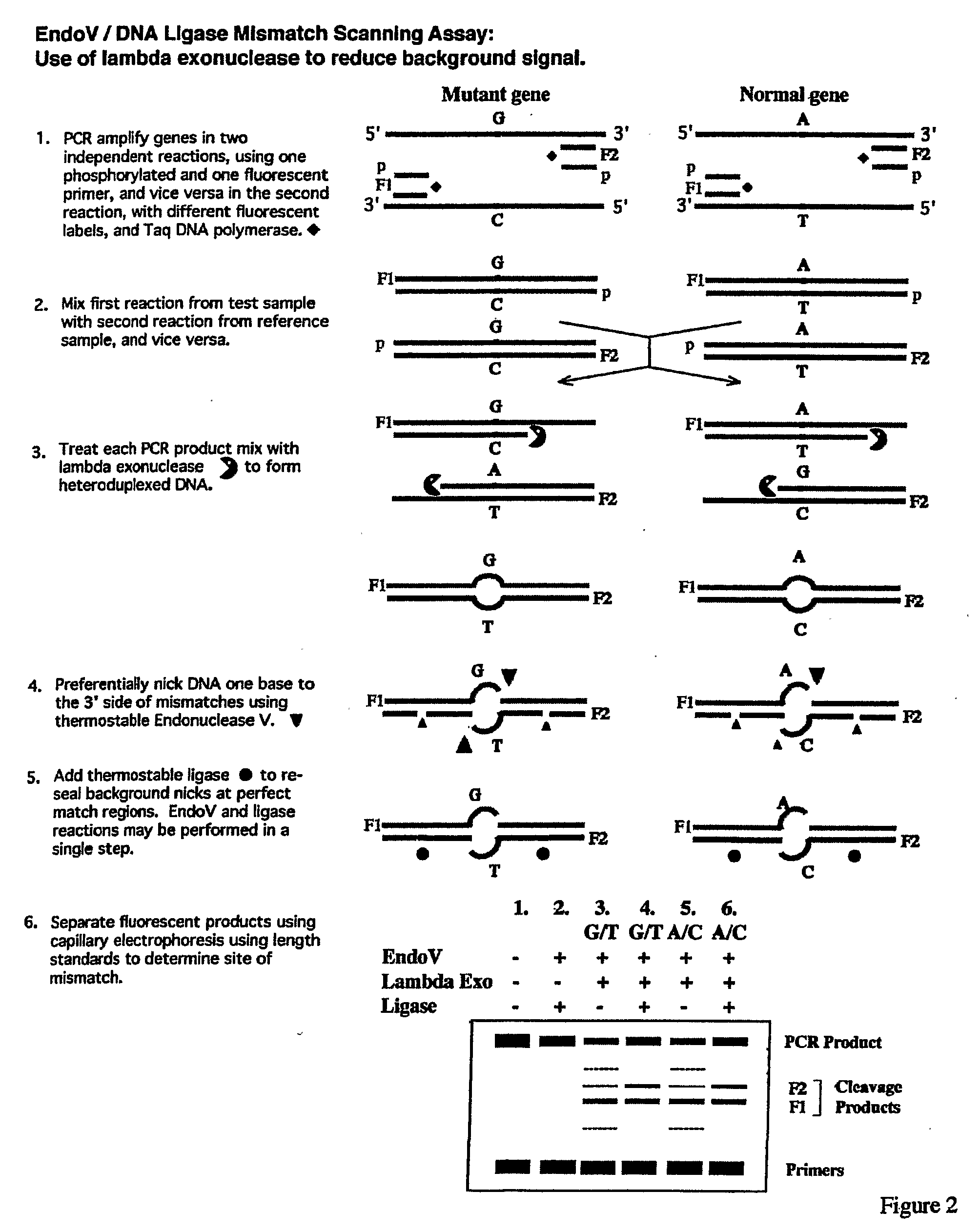
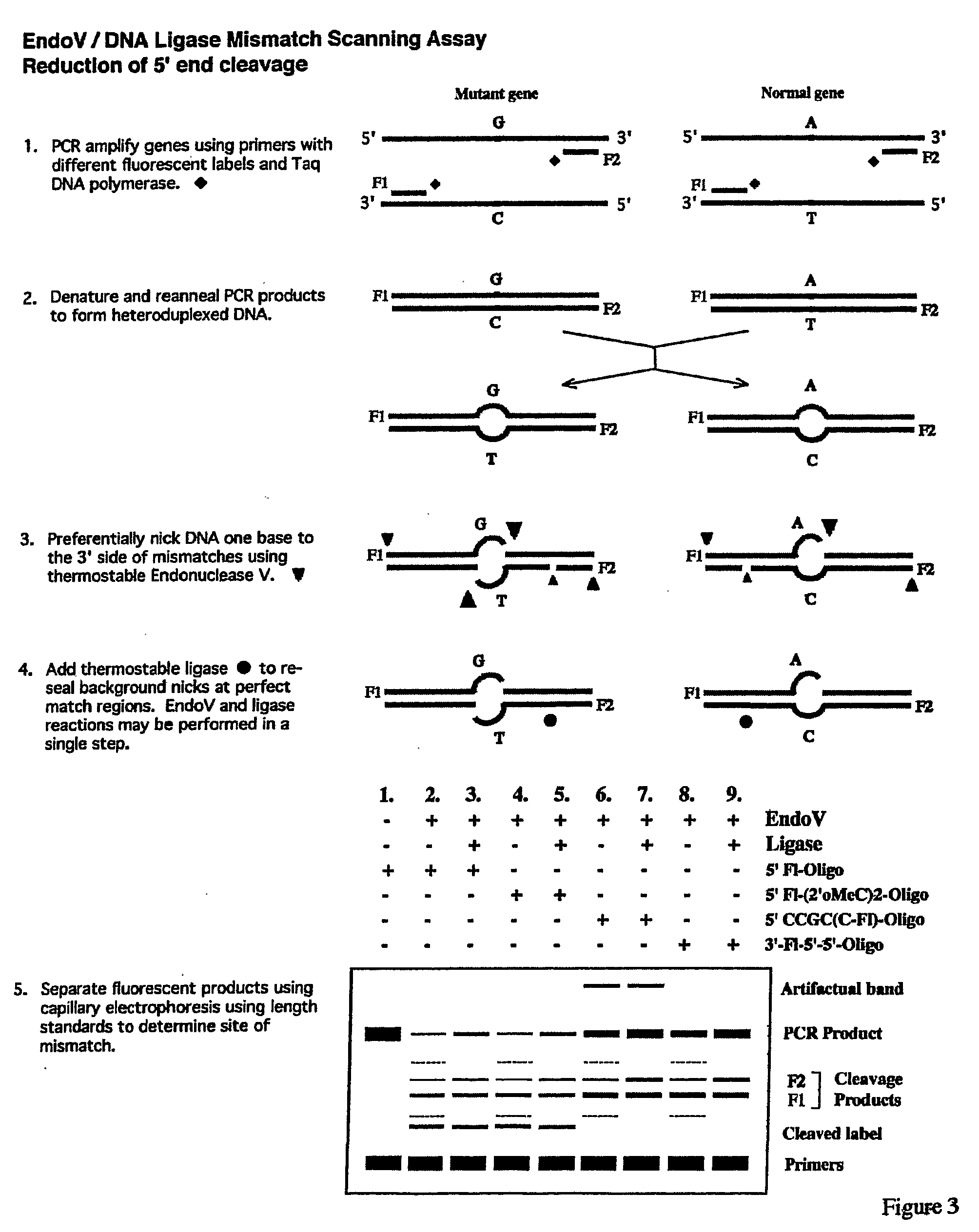
Detection of nucleic acid differences using combined endonuclease cleavage and ligation reactions
InactiveUS7807431B2Wide applicabilityImprove throughputSugar derivativesHydrolasesHeteroduplexSingle nucleotide mutation
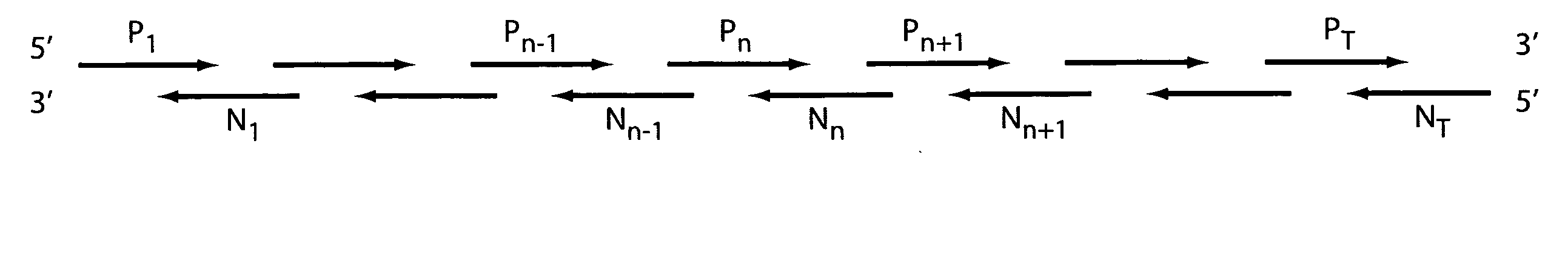
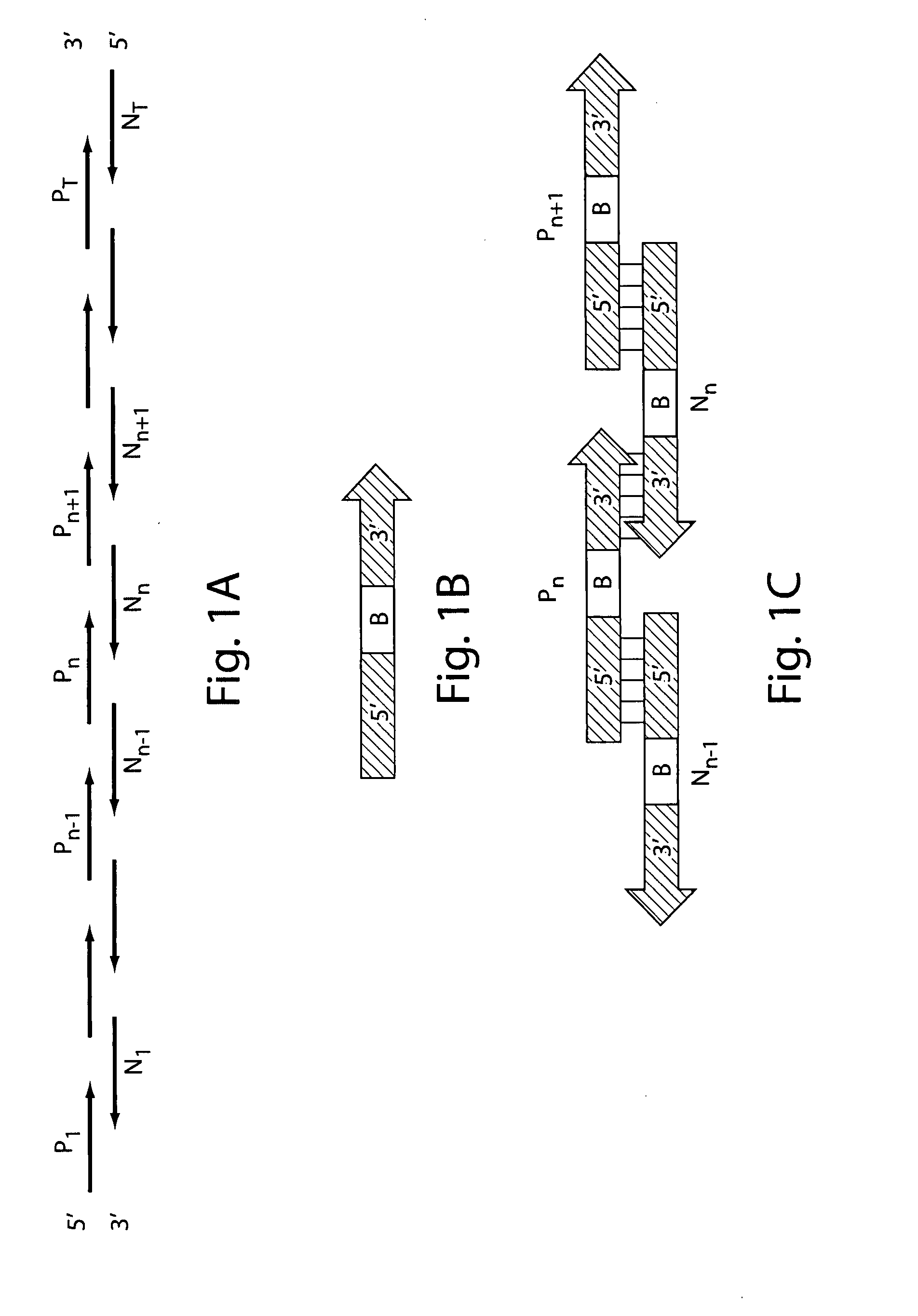
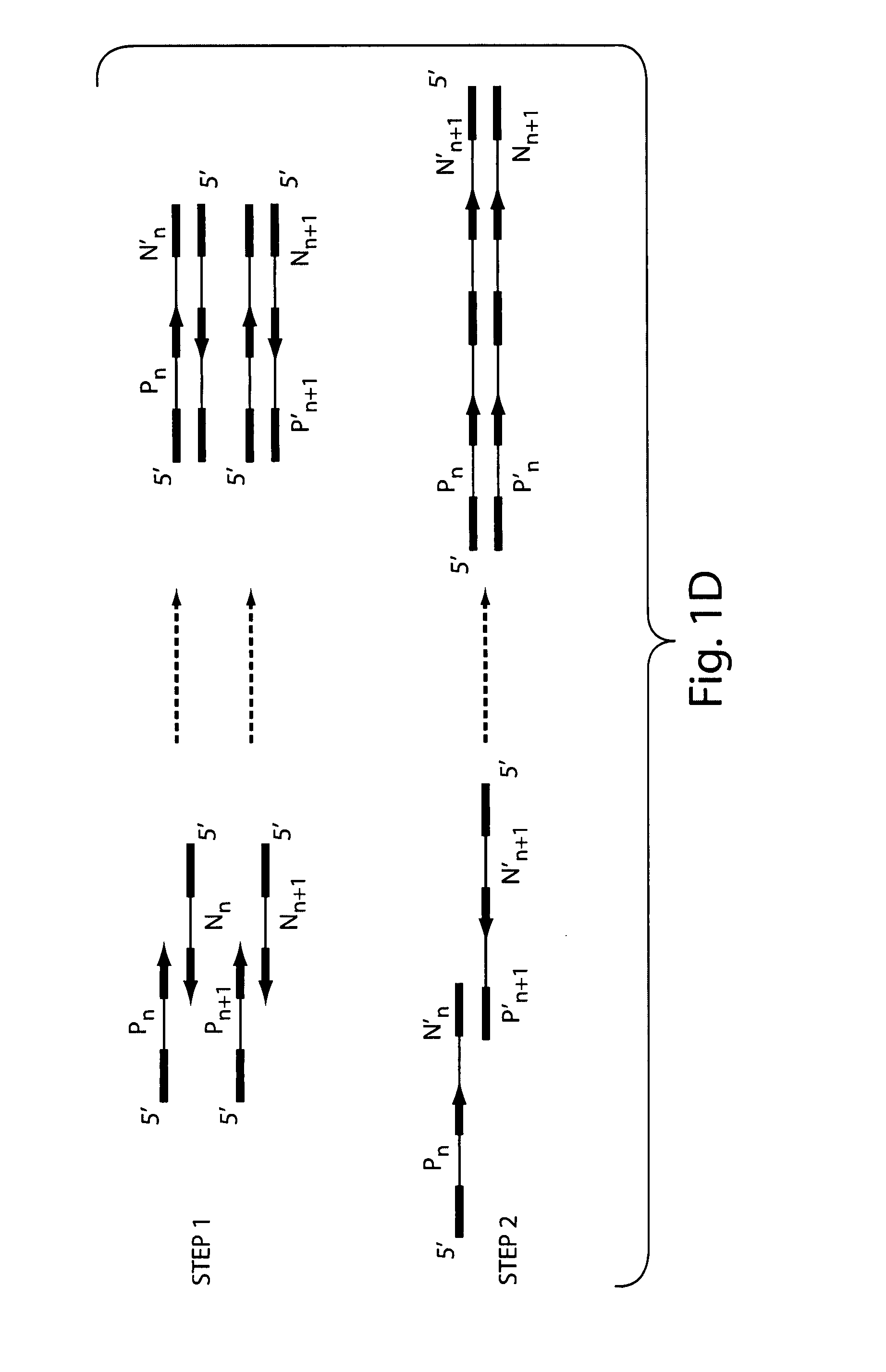
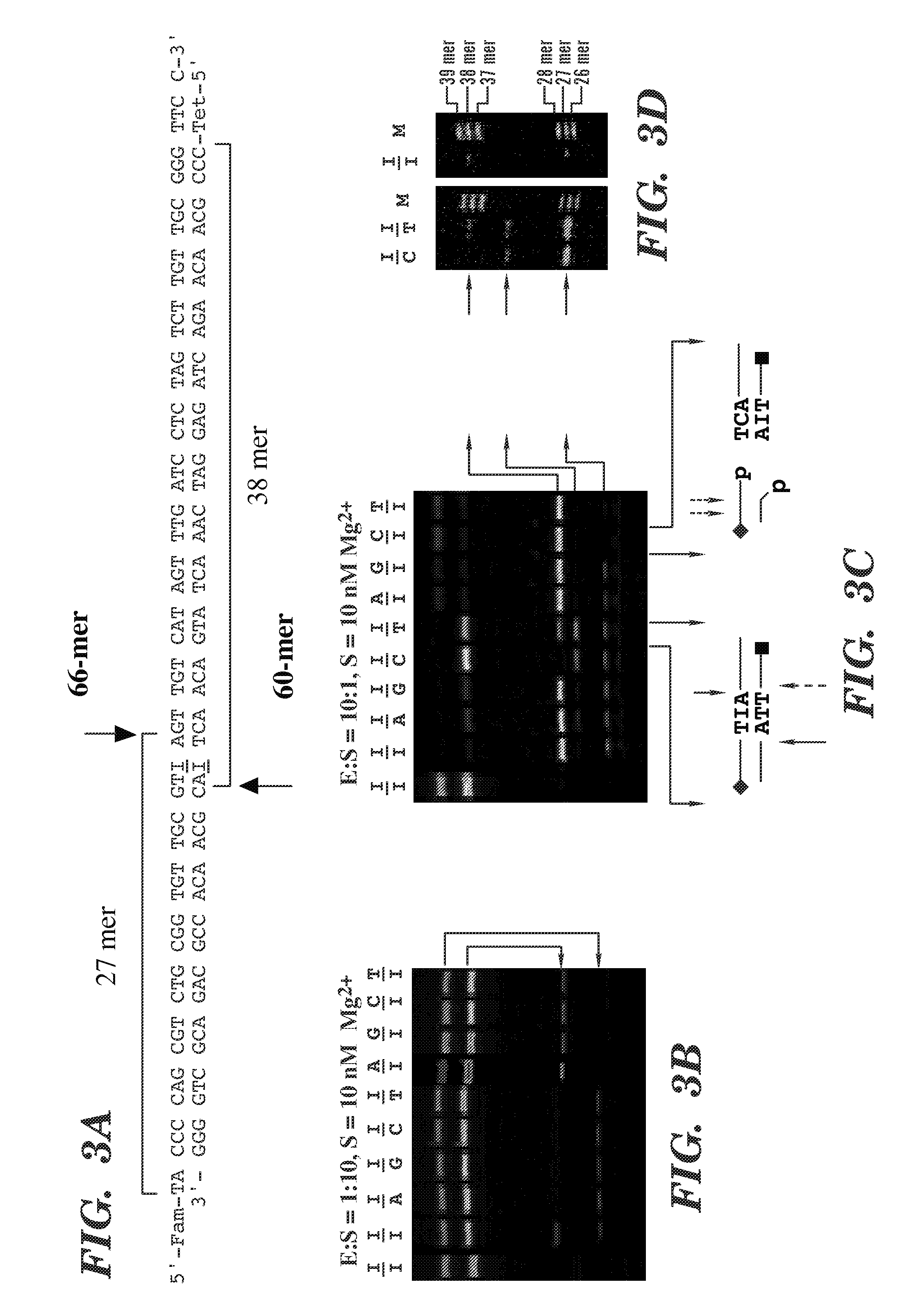
The present invention is a method for detecting DNA sequence differences including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Systems and methods for identifying sequence variation
Systems and method for determining variants can receive mapped reads, and call variants. In embodiments, flow space information for the reads can be aligned to a flow space representation of a corresponding portion of the reference. Reads spanning a position with a potential variant can be grouped and a score can be calculated for the variant. Based on the scores, a list of probable variants can be provided. In various embodiments, low frequency variants can be identified where multiple potential variants are present at a position.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for detecting mutation information in multiplex amplification sequencing product of genome
ActiveCN106202991AEfficient identificationQuick identificationHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesNatural abundance
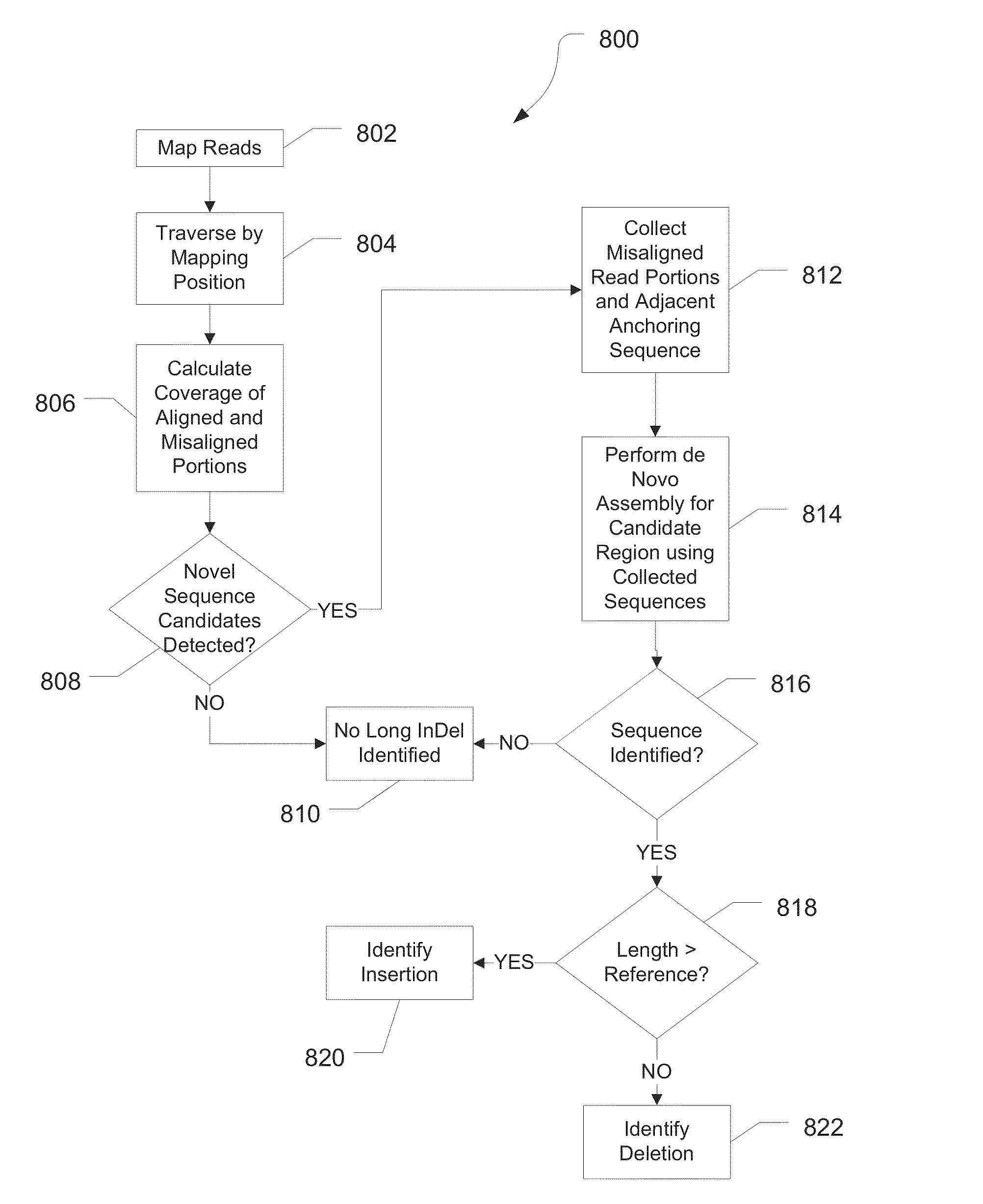
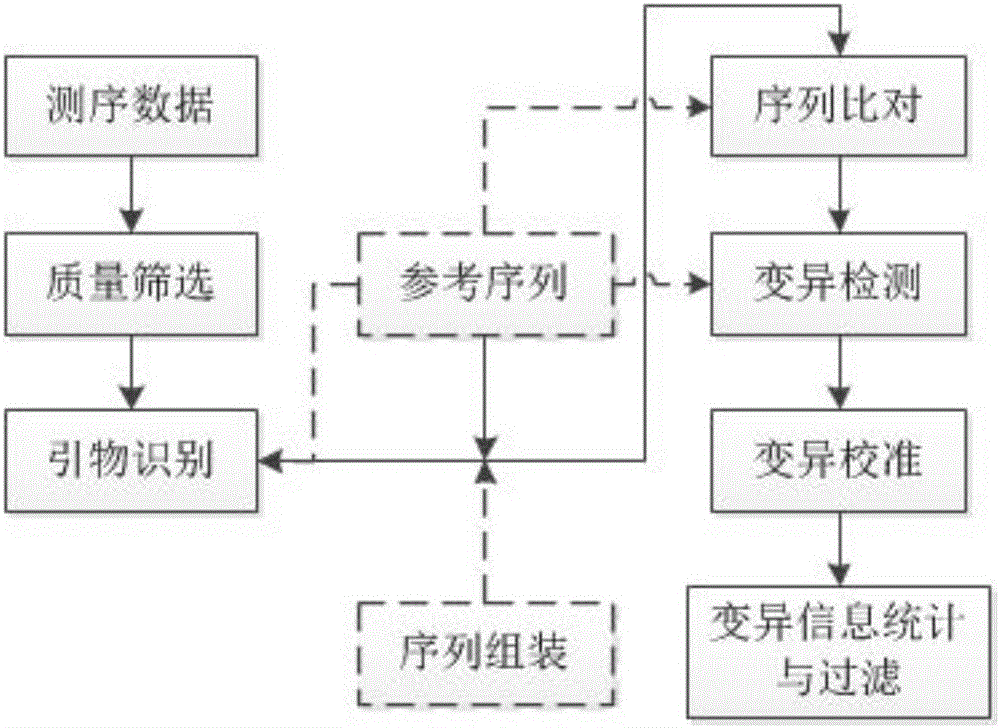
The invention discloses a method for detecting mutation information in a multiplex amplification sequencing product of a genome. The method comprises steps as follows: sequencing data are subjected to quality assessment and preprocessing; a recognizable sequencing sequence is selected for sequence assembling; the recognizable sequencing sequence or a sequence obtained through assembling is compared with a reference gene sequence, and preliminary variation information is obtained; fine calibration of sequence variation is performed according to different types of conditions; a calibrated sequencing fragment is obtained; the homozygosis or heterozygosis state of a target fragment is obtained according to the type of the sequencing fragment with the highest abundance; finally, the mutation information in the multiplex amplification sequencing product of the genome is obtained. By means of the method, the amplification product can be rapidly, efficiently and accurately recognized, and the calculation resources are saved; the sequence assembling process is compatible, and the problem of reduction of the quality value of basic groups produced in the sequencing process can be effectively solved; the homozygosis / heterozygosis state of variation information can be more effectively and stably judged, and random errors introduced in the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) process and the sequencing process are eliminated.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +1
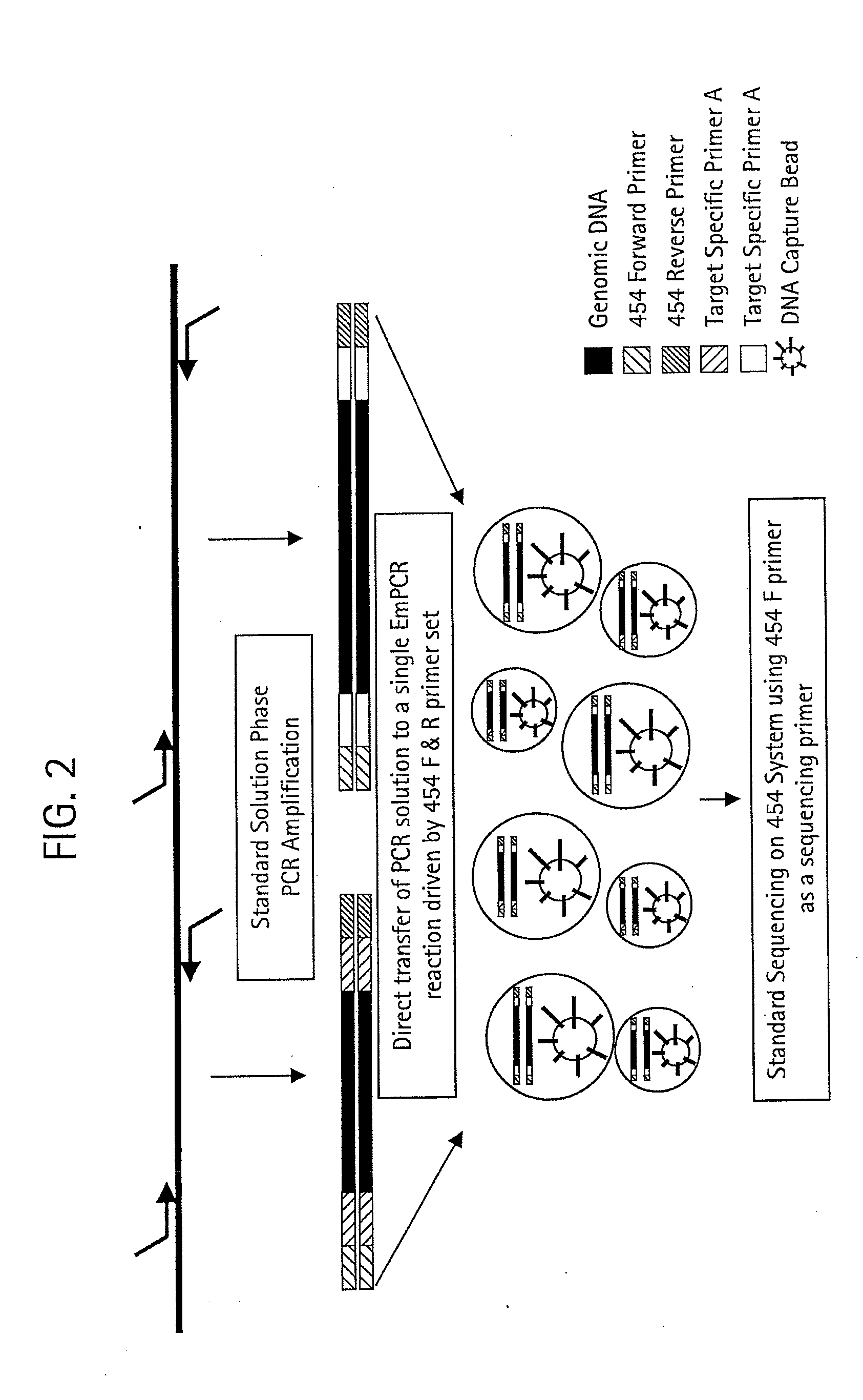
Methods for Determining Sequence Variants Using Ultra-Deep Sequencing
InactiveUS20120264632A1Reduce and effort and lossReduce and and product lossMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningUltra deep sequencingDirect sequencing
The claimed invention provides for new sample preparation methods enabling direct sequencing of PCR products using pyrophosphate sequencing techniques. The PCR products may be specific regions of a genome. The techniques provided in this disclosure allows for SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) detection, classification, and assessment of individual allelic polymorphisms in one individual or a population of individuals. The results may be used for diagnostic and treatment of patients as well as assessment of viral and bacterial population identification.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Chemical ligation of nucleic acids
The invention relates to the field of nucleic acid analysis. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions and methods used for the detection of sequence variations or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in a nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:CLINICAL MICRO SENSORS
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
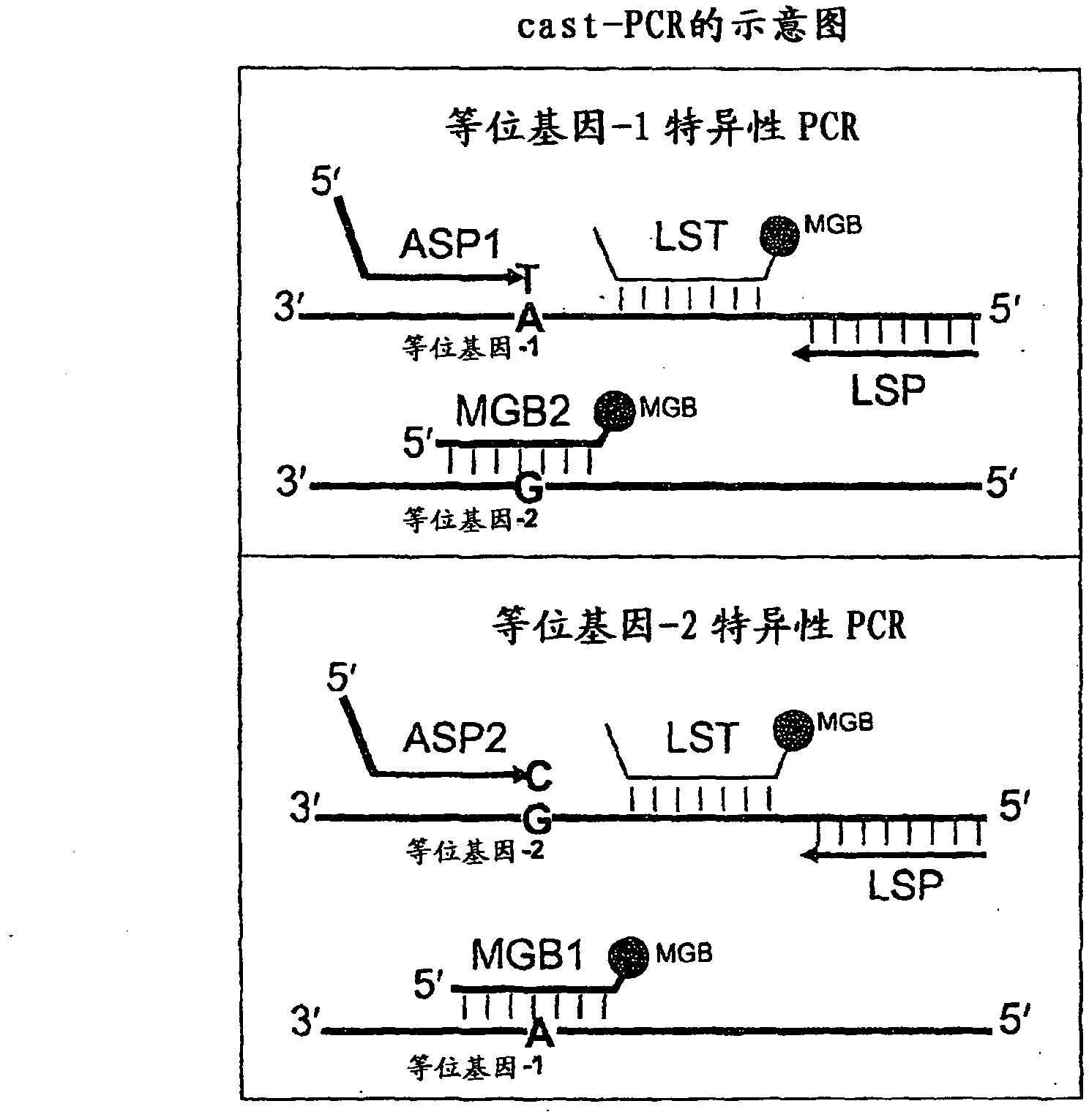
Methods, compositions, and kits for detecting allelic variants
ActiveCN102428190AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMutation detection
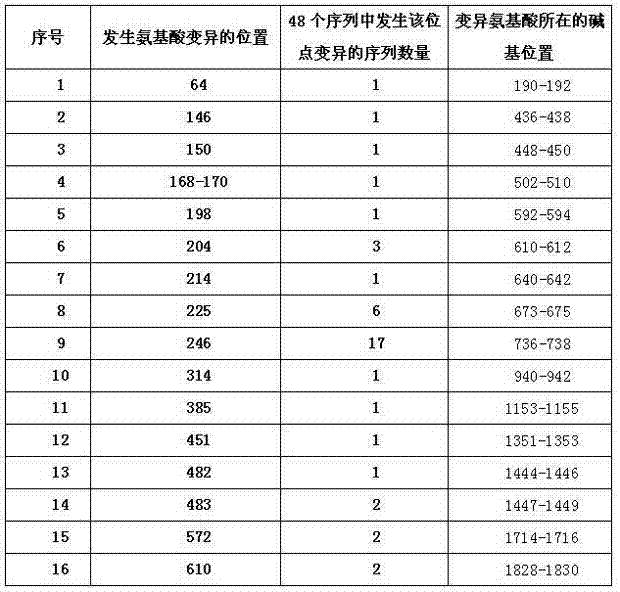
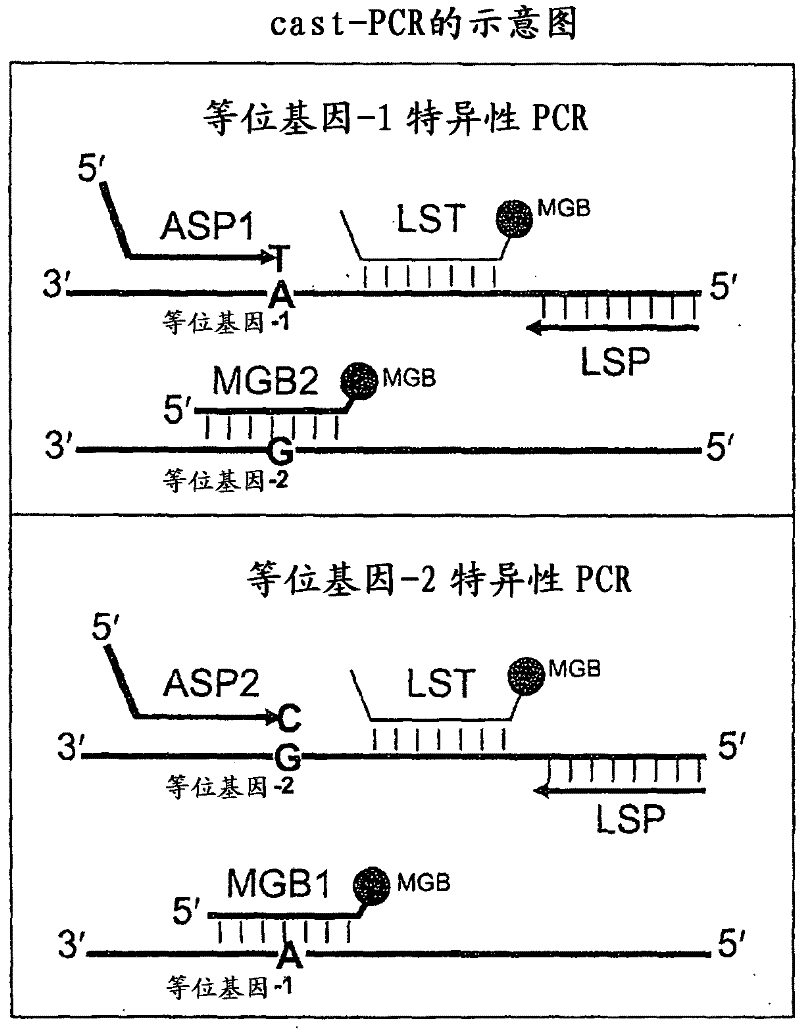
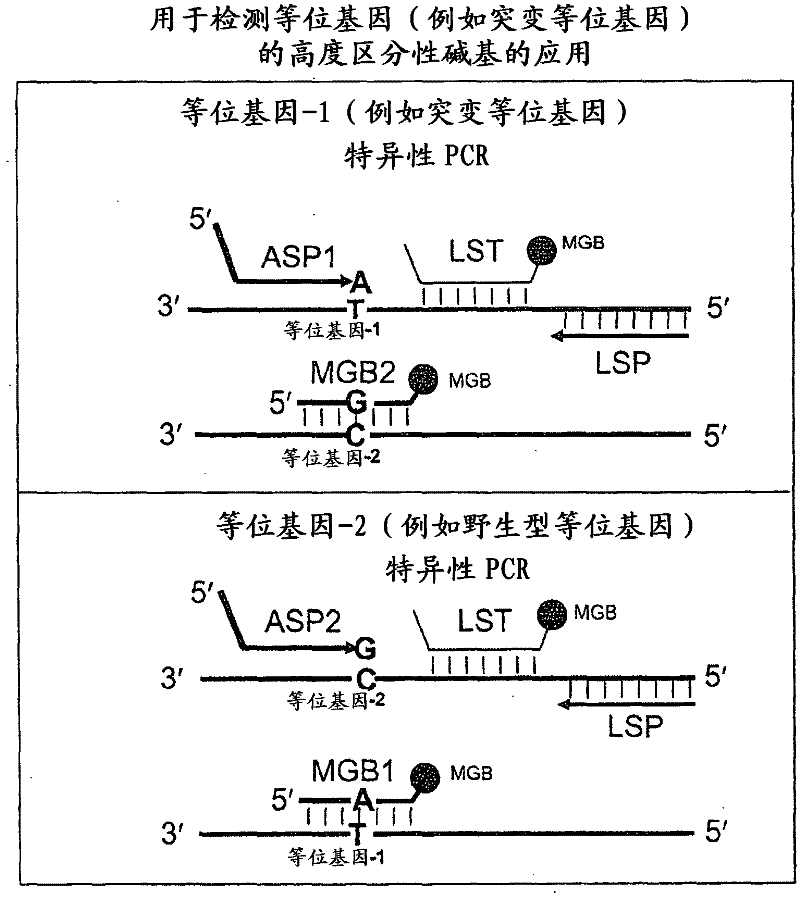
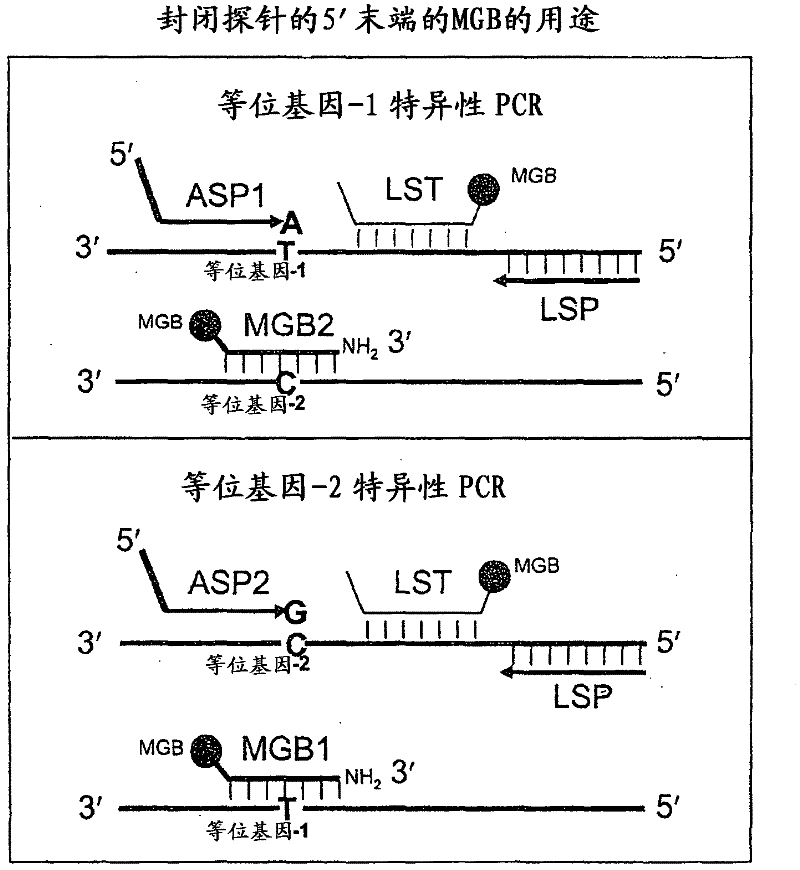
In some embodiments, the present inventions relates generally to compositions, methods and kits for use in discriminating sequence variation between different alleles. More specifically, in some embodiments, the present invention provides for compositions, methods and kits for quantitating rare (e.g., mutant) allelic variants, such as SNPs, or nucleotide (NT) insertions or deletions, in samples comprising abundant (e.g., wild type) allelic variants with high specificity and selectivity. In particular, in some embodiments, the invention relates to a highly selective method for mutation detection referred to as competitive allele-specific TaqMan PCR ('cast-PCR').
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
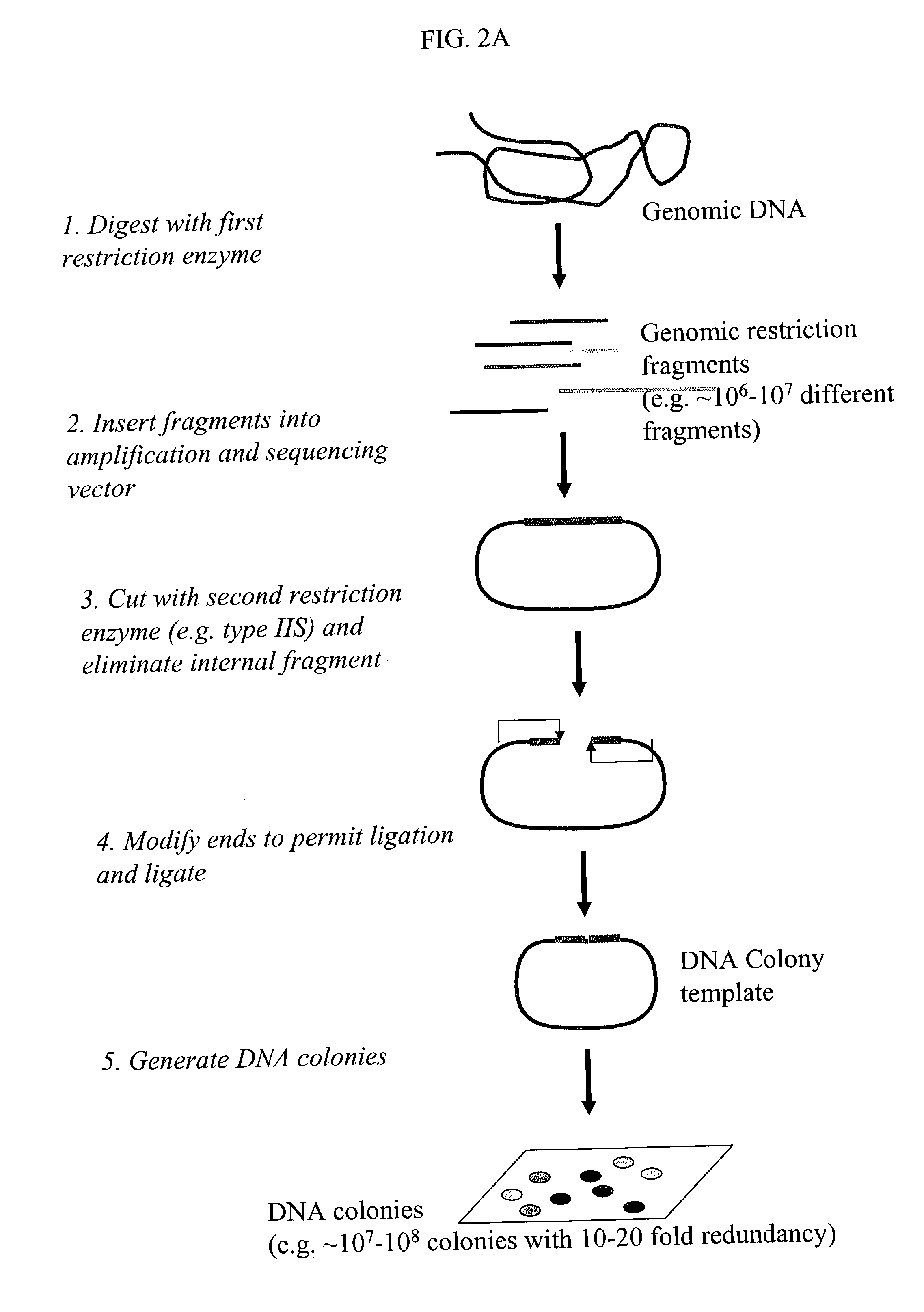
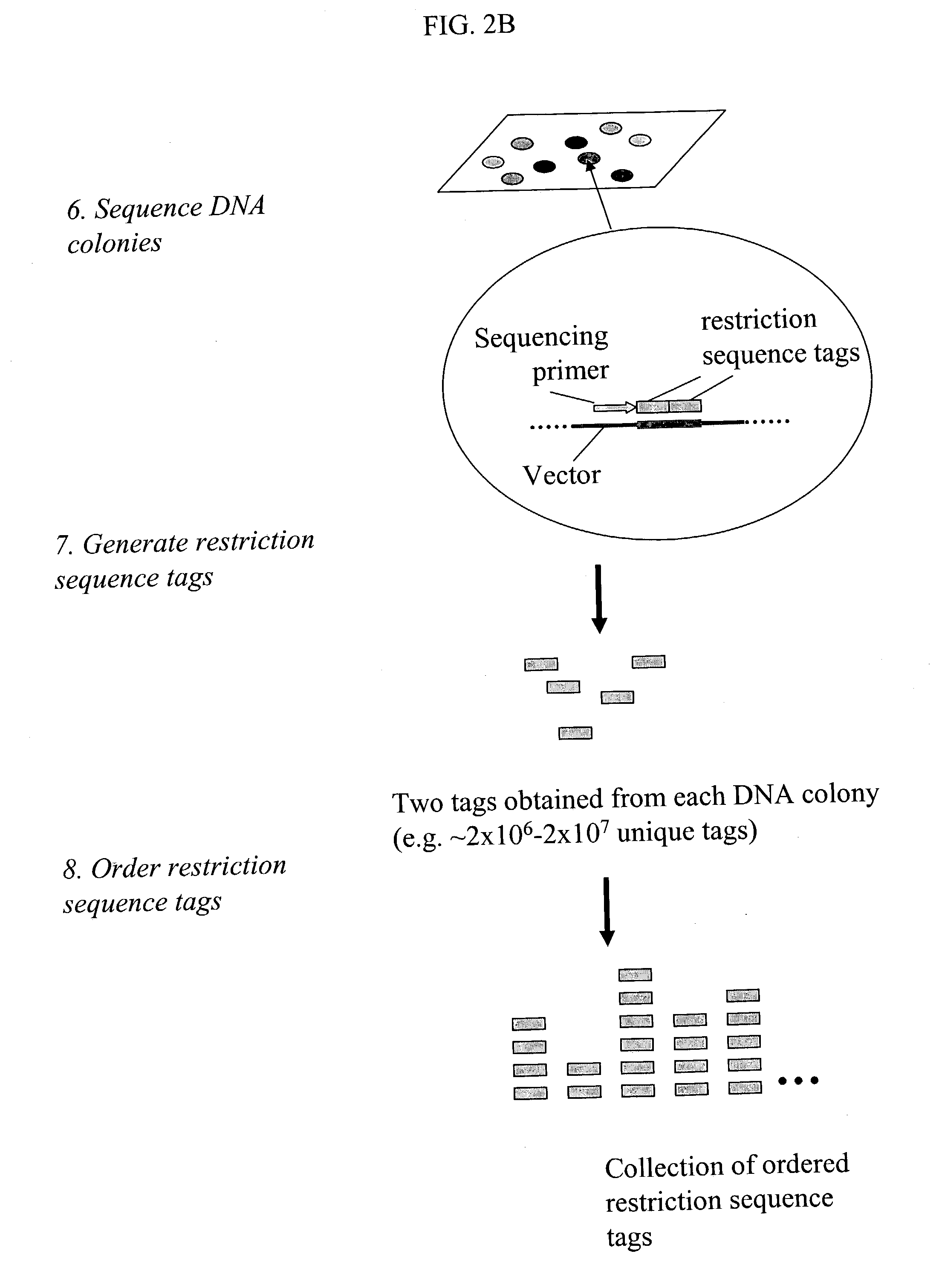
Genome partitioning
InactiveUS20060281082A1Reduce complexityHigh-throughput screeningSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypingSequence variation
This invention relates to ‘genome partitioning’ and nucleic library construction, for example for sequence variation discovery and screening. The method employs a plurality of restriction enzymes in order to reliably reproduce a representative partition of the entirety of a sample nucleic acid based on the restriction ends of one or more ‘layers’ of the fragments present. In preferred embodiments there is provided a method for producing a nucleic acid library, which library contains a plurality of different nucleic acid fragments, the method comprising: (i) digesting the sample nucleic acid with a plurality of different restriction enzymes to generate a plurality of different layers of fragments, wherein each layer is a group of fragments having a unique combination of restriction ends, and wherein the combination of layers represents the entirety of the sample nucleic acid, (ii) optionally purifying said fragments, (iii) selecting a desired sub-set of layers according to the unique restriction ends of said layers, (iv) ligating said sub-set of layers into vectors adapted to receive it, (v) transforming host cells with the vectors (vi) culturing said host cells to provide said library containing said partition of the sample nucleic acid. The invention also provides systems, methods and functions for designing and optimising such libraries, and genotyping ‘chips’ based on the genome partitioning methods.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
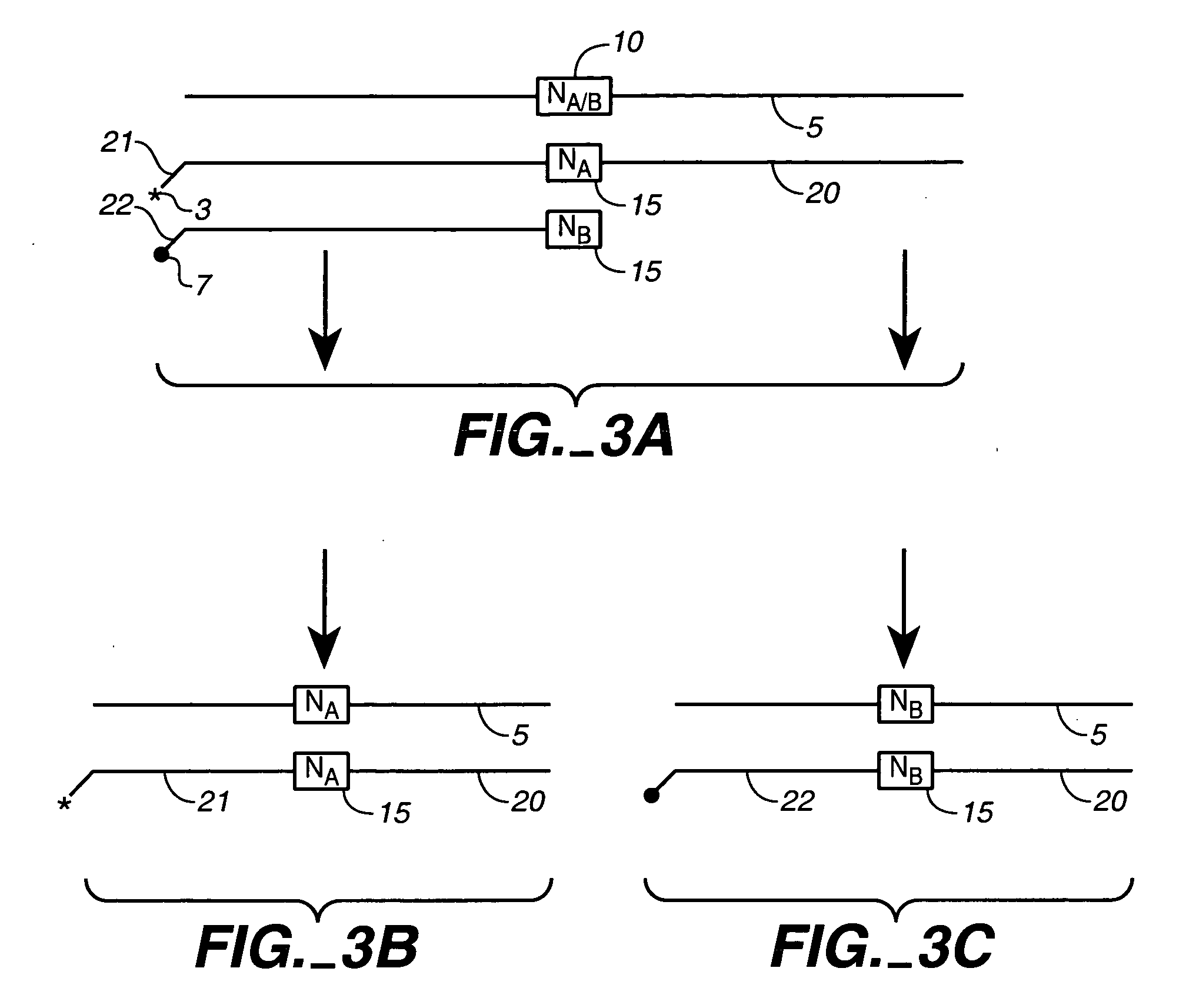
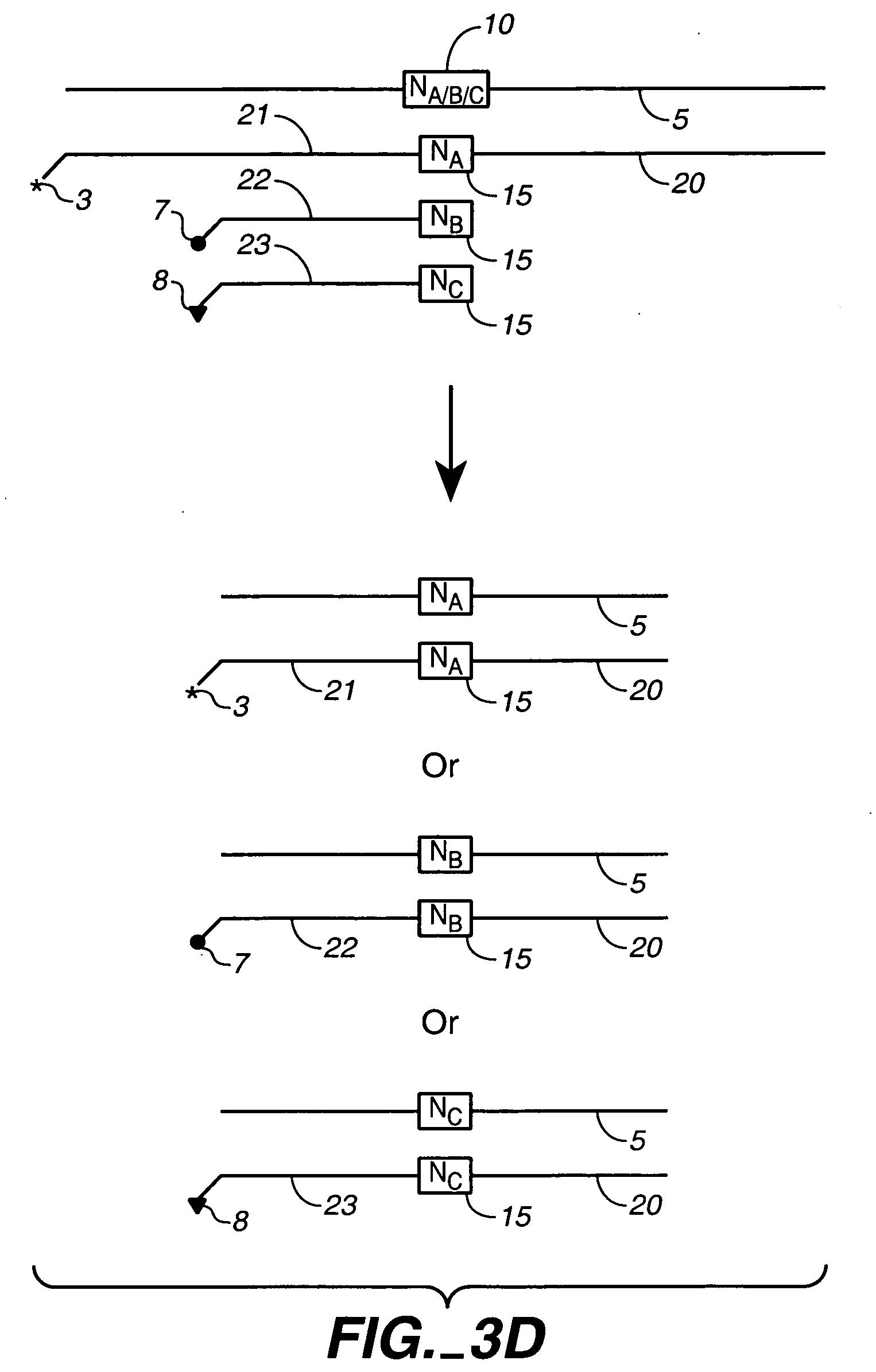
Polynucleotide sequence variants
InactiveUS20040142433A1High occurrenceGenetic material ingredientsFermentationHeterologousHomopolynucleotide
We describe here an in vitro method of redistributing sequence variations between non-identical polynucleotide sequences, by making a heteroduplex polynucleotide from two non-identical polynucleotides; introducing a nick in one strand at or near a base pair mismatch site; removing mismatched base(s) from the mismatch site where the nick occurred; and using the opposite strand as template to replace the removed base(s) with bases that complement base(s) in the first strand. By this method, information is transferred from one strand to the other at sites of mismatch.
Owner:NOVICI BIOTECH
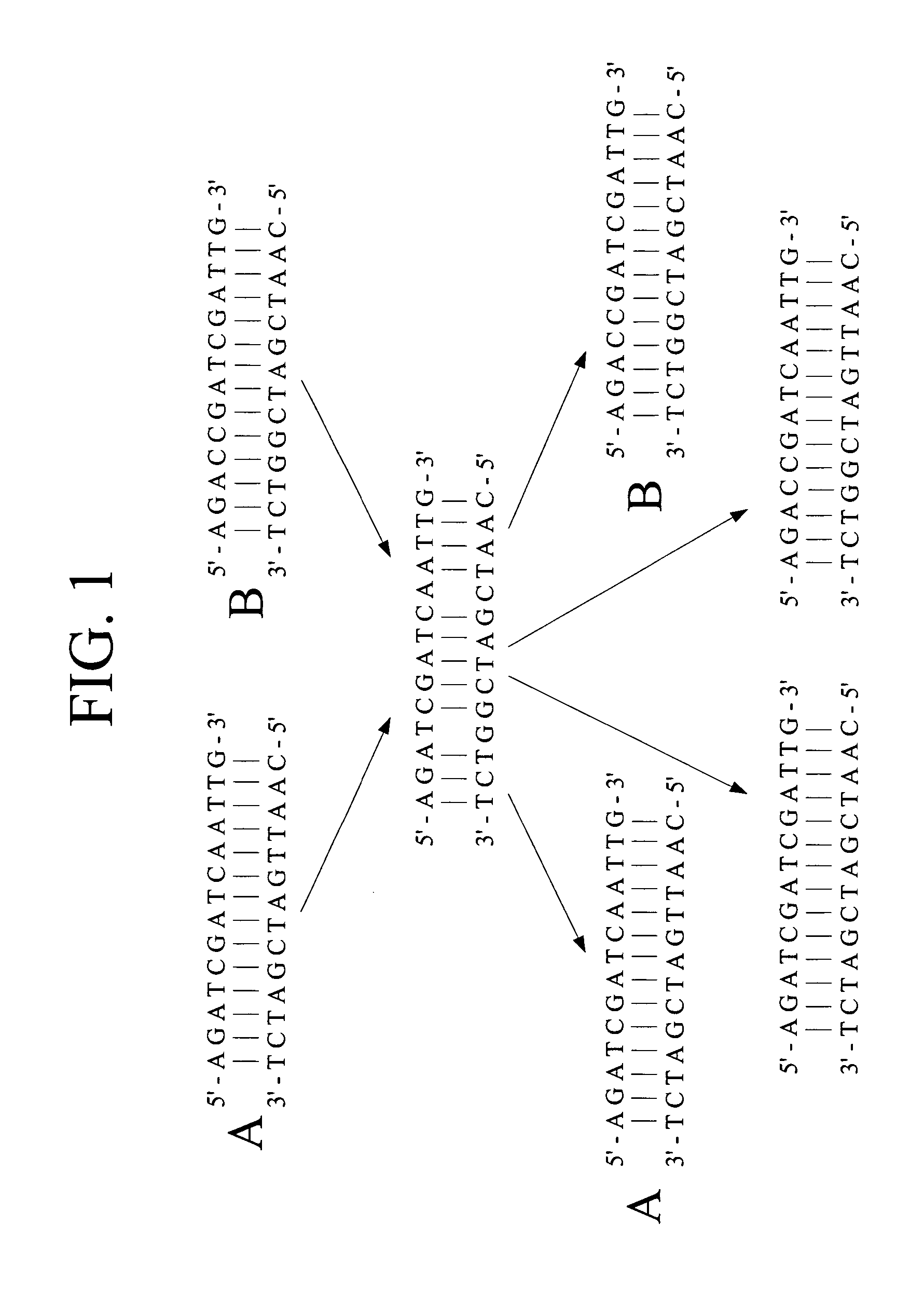
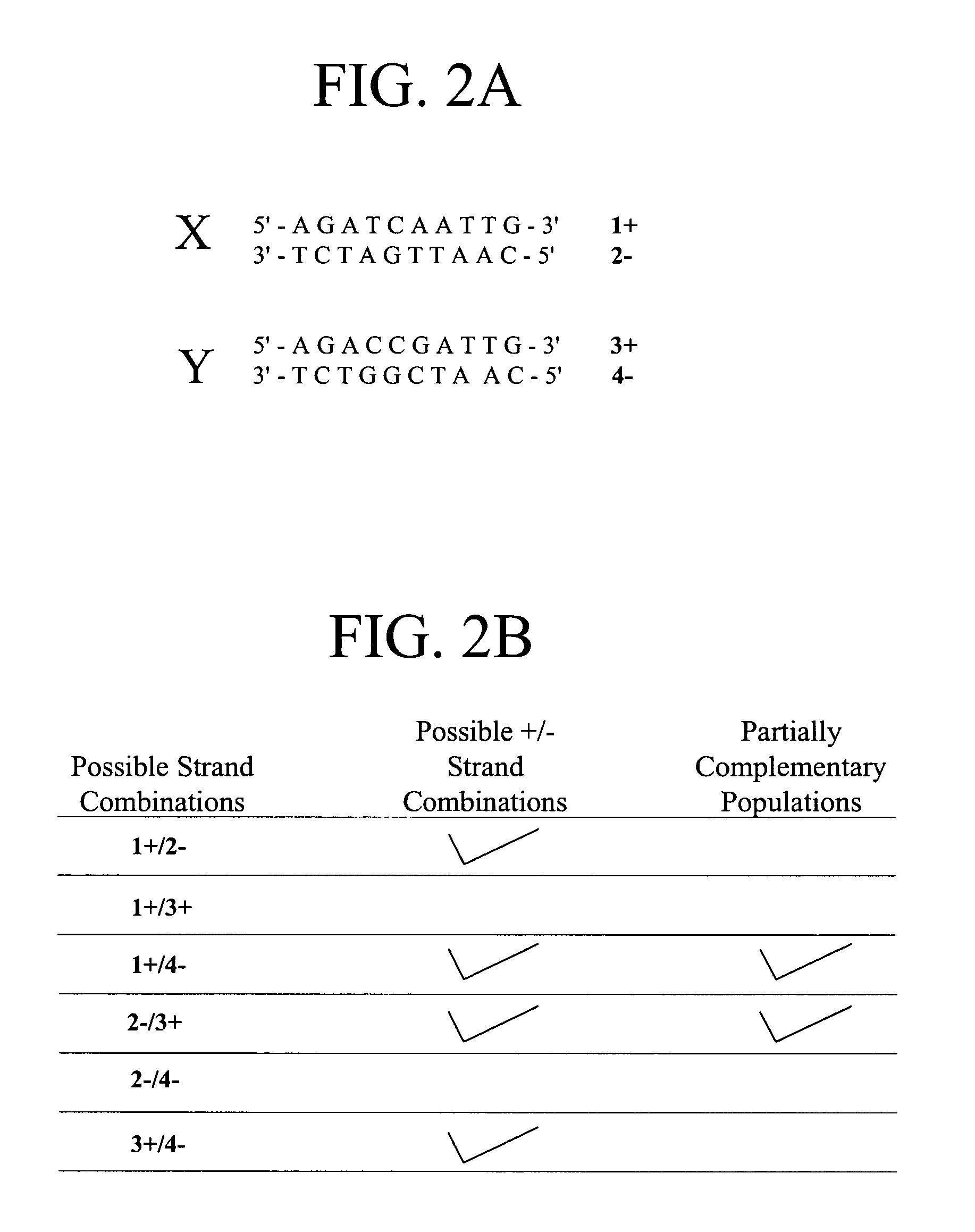
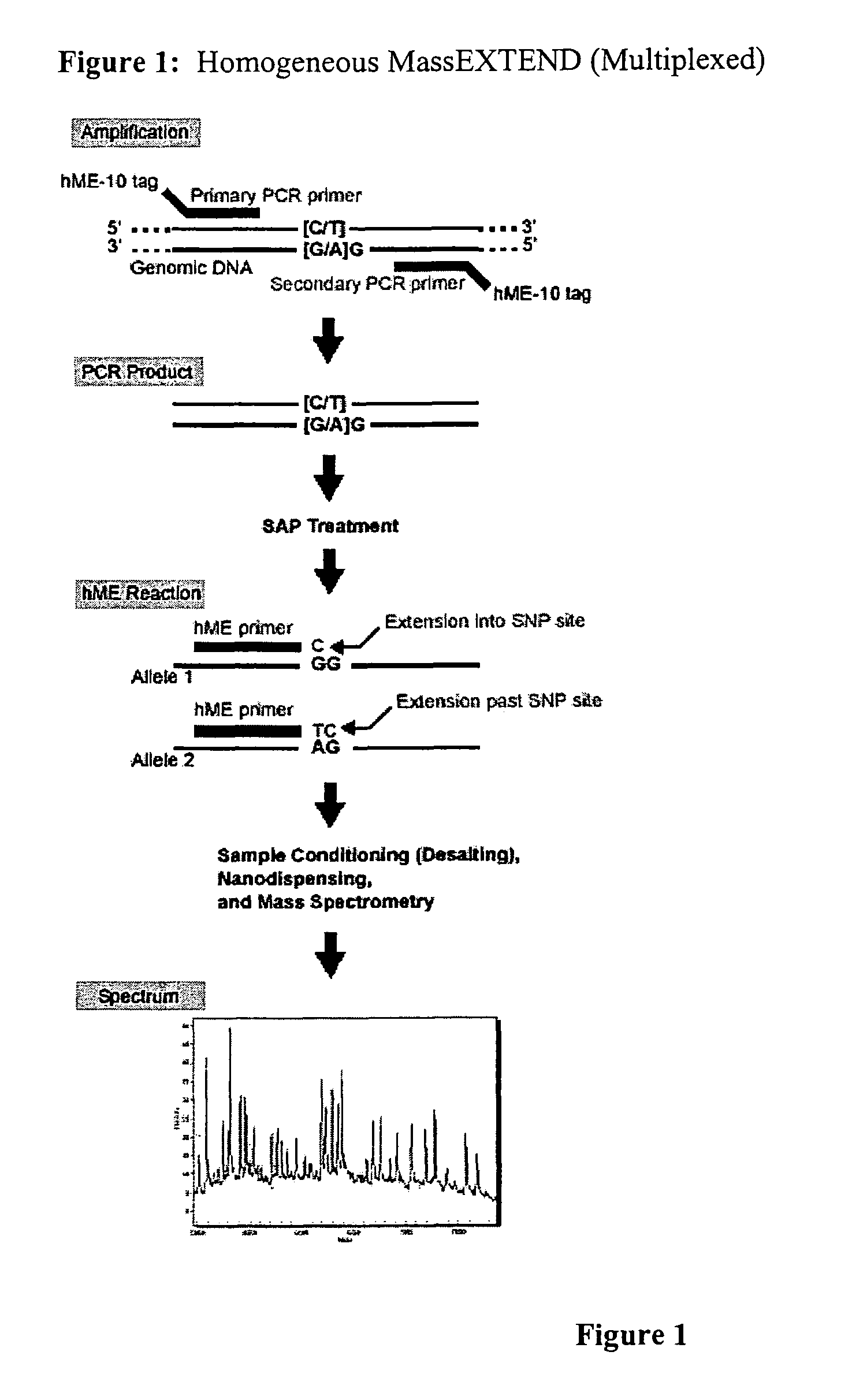
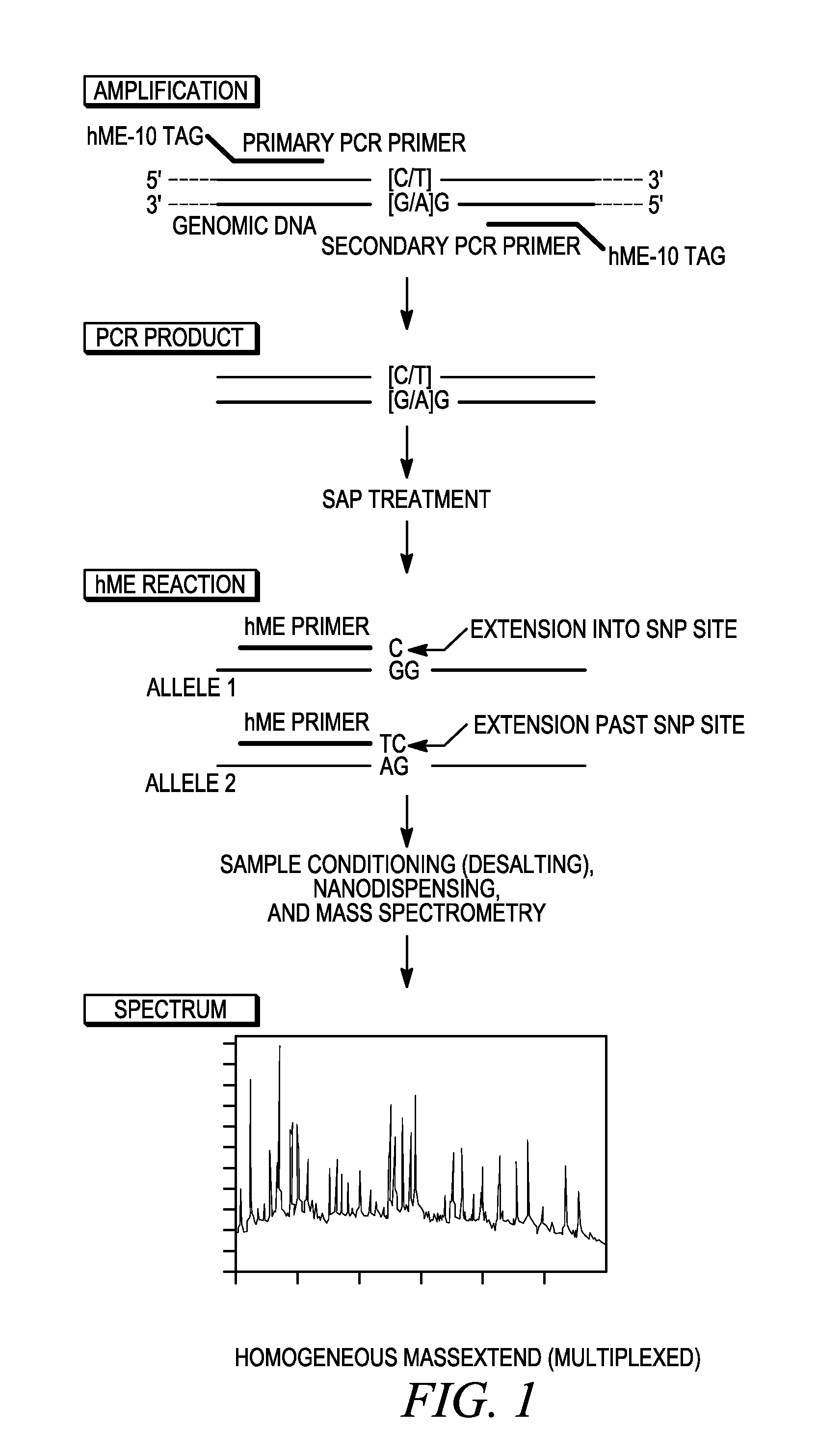
Methods for high level multiplexed polymerase chain reactions and homogeneous mass extension reactions
ActiveUS8003317B2Improve throughputLow costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSequence variation
Provided herein are optimized methods for performing multiplexed detection of a plurality of sequence variations. Also provided are methods for performing multiplexed amplification of target nucleic acid.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Allele-specific sequence variation analysis
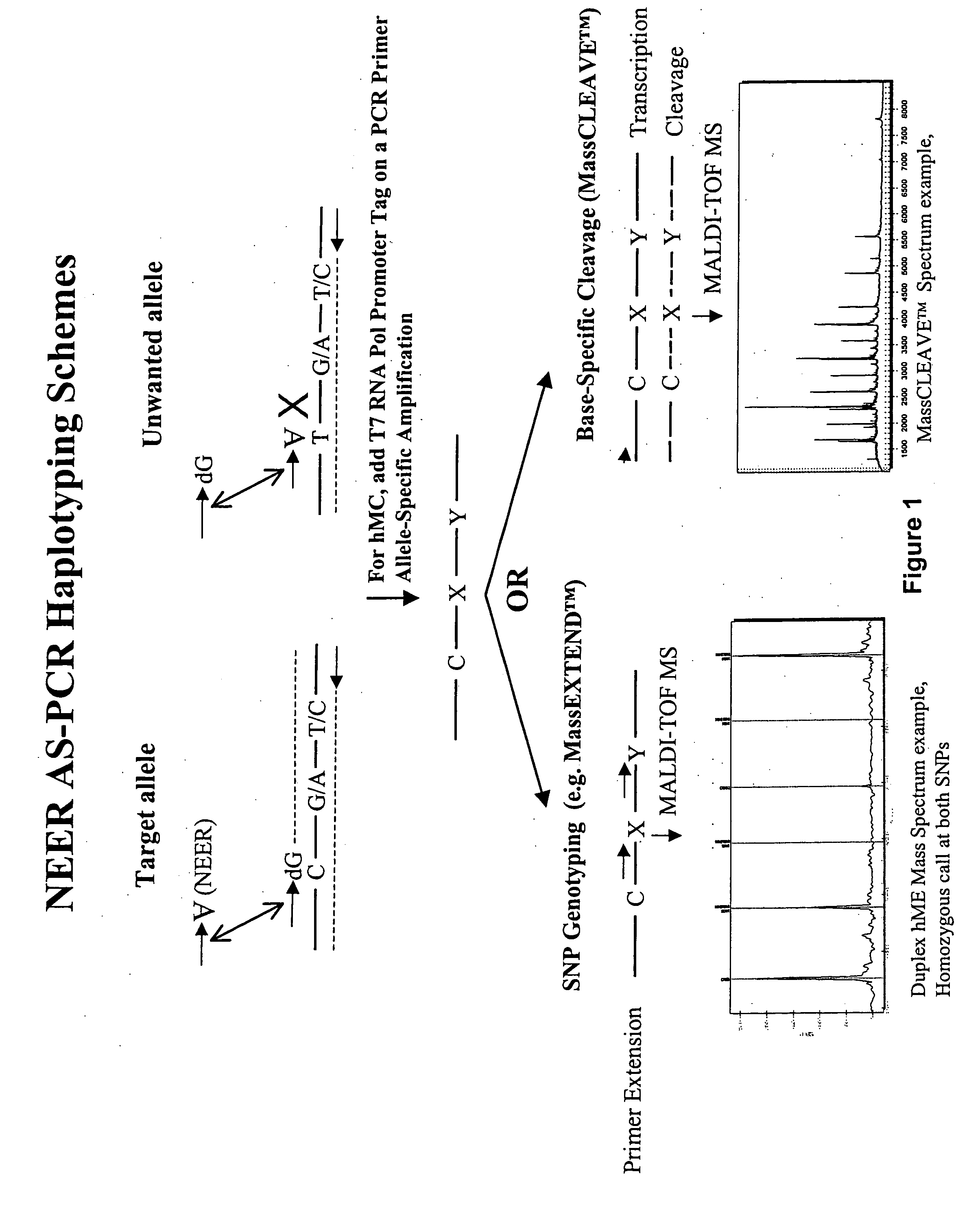
InactiveUS20050089904A1Reduce leakageImprove allele-specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomic DNAMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Fragmentation-based methods and systems, particularly mass spectrometry based methods and systems, for the analysis of sequence variations including haplotypes are provided. Also provided are methods for obtaining a specific allele from a nucleic acid mixture, such as genomic DNA.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Sequence Variants Associated with Prostate Specific Antigen Levels
InactiveUS20120150032A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigenProstate-specific antigen
Owner:DECODE GENETICS EHF
Pulsed-multiline excitation for color-blind fluorescence detection
InactiveUS20060139634A1Accurate diagnosisImproved prognosisRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyCrowdsFluorophore
The present invention provides a technology called Pulse-Multiline Excitation or PME. This technology provides a novel approach to fluorescence detection with application for high-throughput identification of informative SNPs, which could lead to more accurate diagnosis of inherited disease, better prognosis of risk susceptibilities, or identification of sporadic mutations. The PME technology has two main advantages that significantly increase fluorescence sensitivity: (1) optimal excitation of all fluorophores in the genomic assay and (2) “color-blind” detection, which collects considerably more light than standard wavelength resolved detection. This technology differs significantly from the current state-of-the-art DNA sequencing instrumentation, which features single source excitation and color dispersion for DNA sequence identification. Successful implementation of the PME technology will have broad application for routine usage in clinical diagnostics, forensics, and general sequencing methodologies and will have the capability, flexibility, and portability of targeted sequence variation assays for a large majority of the population.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method of detection of SP-A2 gene variants
The invention provides a method for predicting the susceptibility of an individual to pulmonary tuberculosis, the method comprising amplifying genomic DNA of pulmonary tuberculosis patients and normal control individuals using oligonuecleotide primers, sequencing the amplified PCR product and identifying the sequence variation computationally by comparing it with the already existing sequence of human SP-A2 gene.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20070015200A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
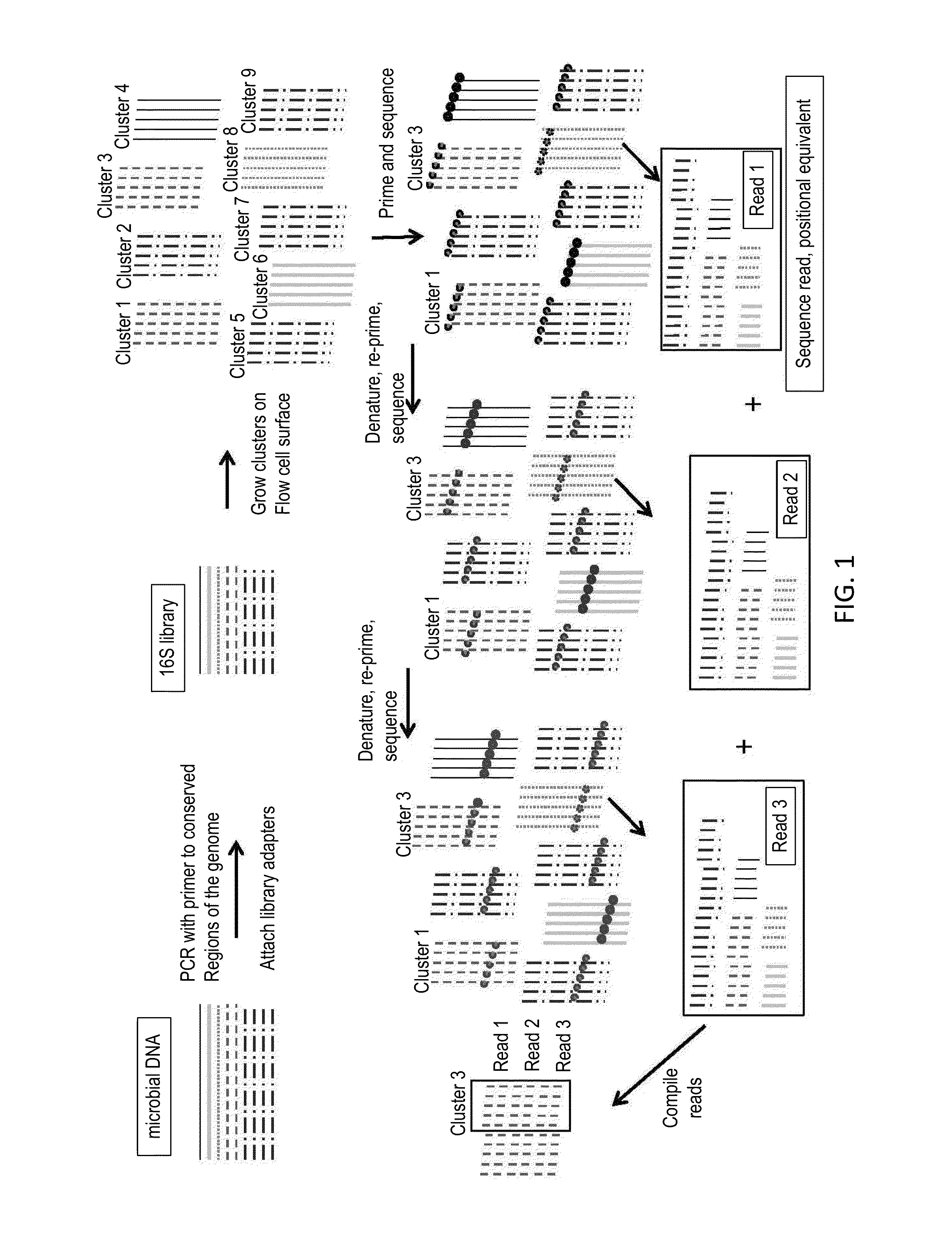
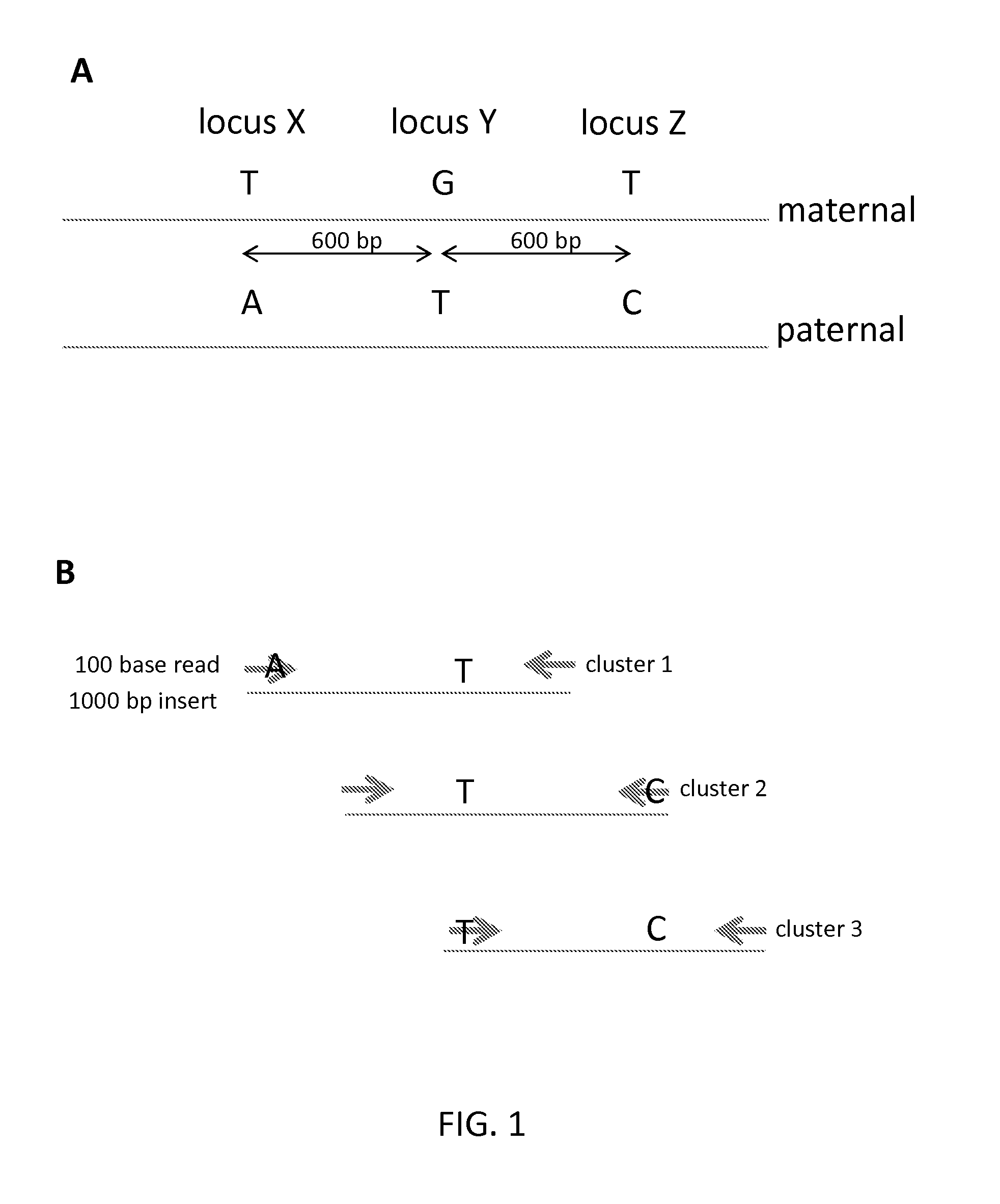
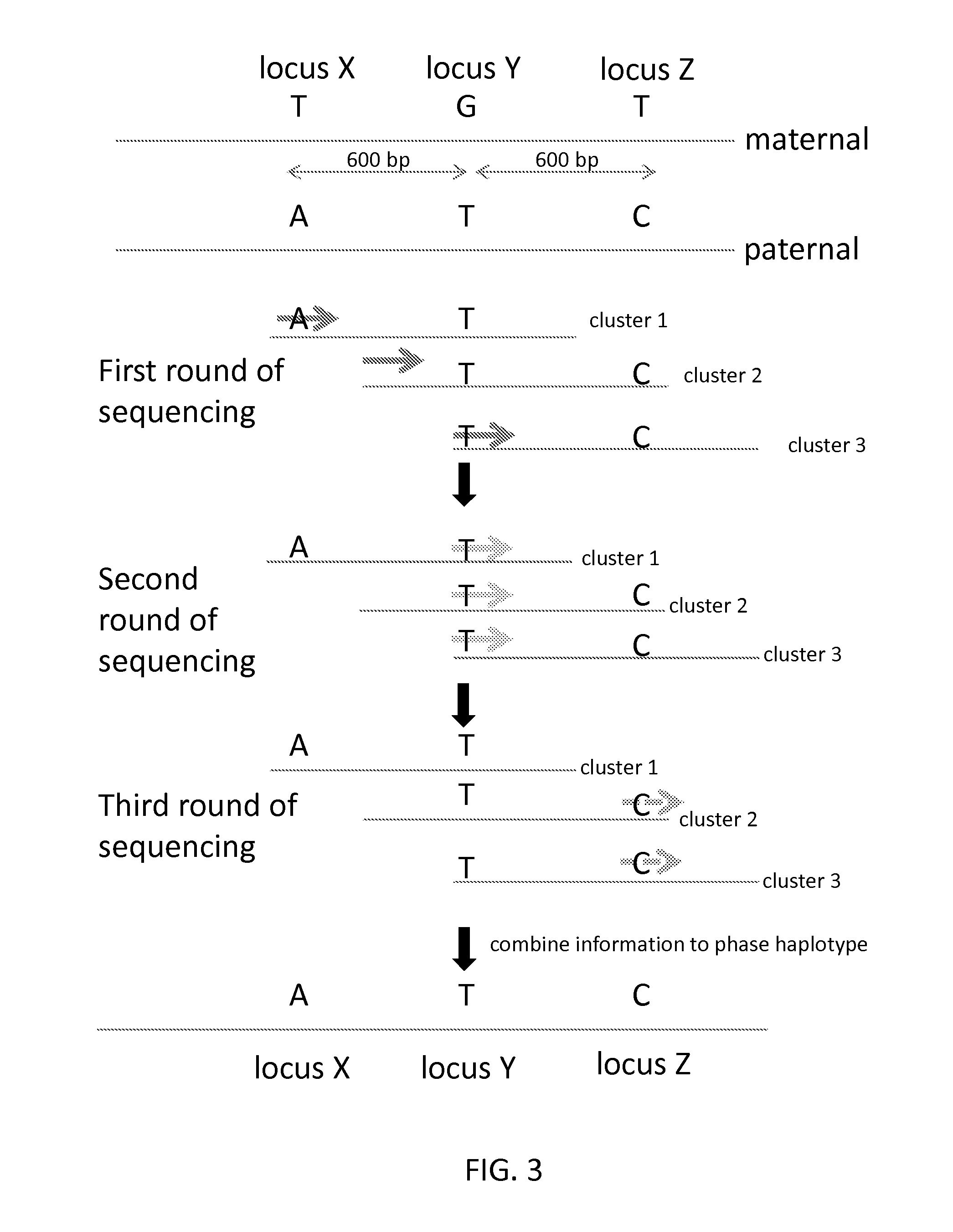
Sequential sequencing
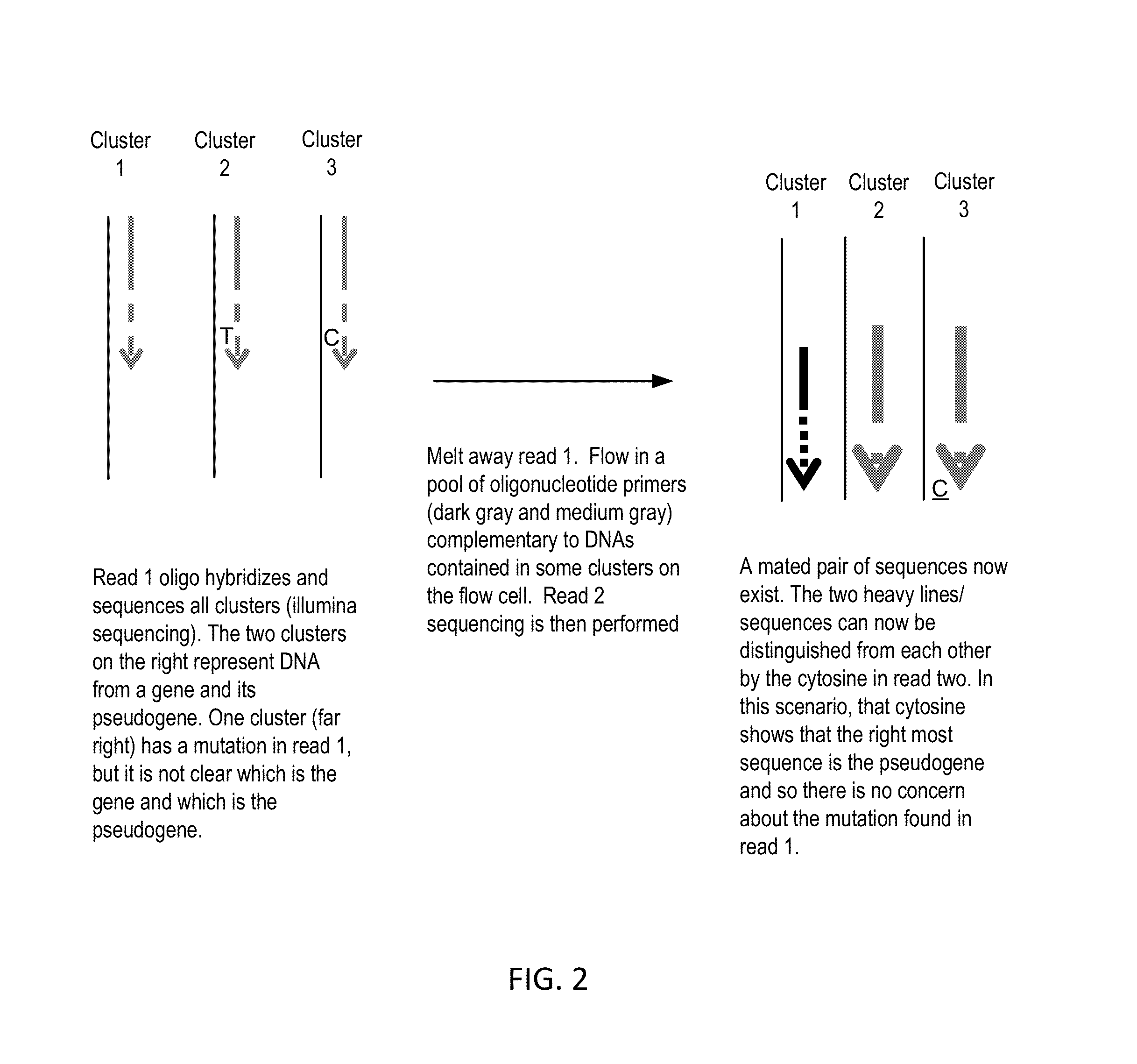
InactiveUS20140274738A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleic acid sequencingExon
The present invention provides improved methods, compositions and kits for short read next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits of the present invention enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (typically comprising regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information is obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein are useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Method for identifying variations in polynucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6048689AHigh speedSimple technologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThree stageDirect sequencing
A step-wise integrated process for identifying sequence variations in polynucleotide sequences is disclosed. The identification process is composed of three stages, including allele specific hybridization assays of known sequence variations (Stage I), sequence variation locating assays (Stage II), and direct sequencing (Stage III). The methods can be used for efficient and accurate detection of mutations in any test gene sample.
Owner:GENE LOGIC
Methods for high level multiplexed polymerase chain reactions and homogenous mass extension reactions
ActiveUS20120015826A1Low costNot adversely affecting the mass spectrometry analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSequence variationBioinformatics
Provided herein are optimized methods for performing multiplexed detection of a plurality of sequence variations. Also provided are methods for performing multiplexed amplification of target nucleic acid.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Pluripotent cell lines and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS8669048B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSequence variationBioinformatics
Methods of generating cell lines with a sequence variation or copy number variation of a gene of interest, methods of use thereof, and cell lines with a sequence variation or copy number variation of a gene of interest are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Sequential sequencing
ActiveUS20160251711A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingExon
Described herein are improved methods, compositions and kits for next generation sequencing (NGS). The methods, compositions and kits described herein enable phasing of two or more nucleic acid sequences in a sample, i.e. determining whether the nucleic acid sequences (which can comprise regions of sequence variation) are located on the same chromosome and / or the same chromosomal fragment. Phasing information can be obtained by performing multiple, successive sequencing reactions from the same immobilized nucleic acid template. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein can be useful, for example, for haplotyping, SNP phasing, or for determining downstream exons in RNA-seq.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
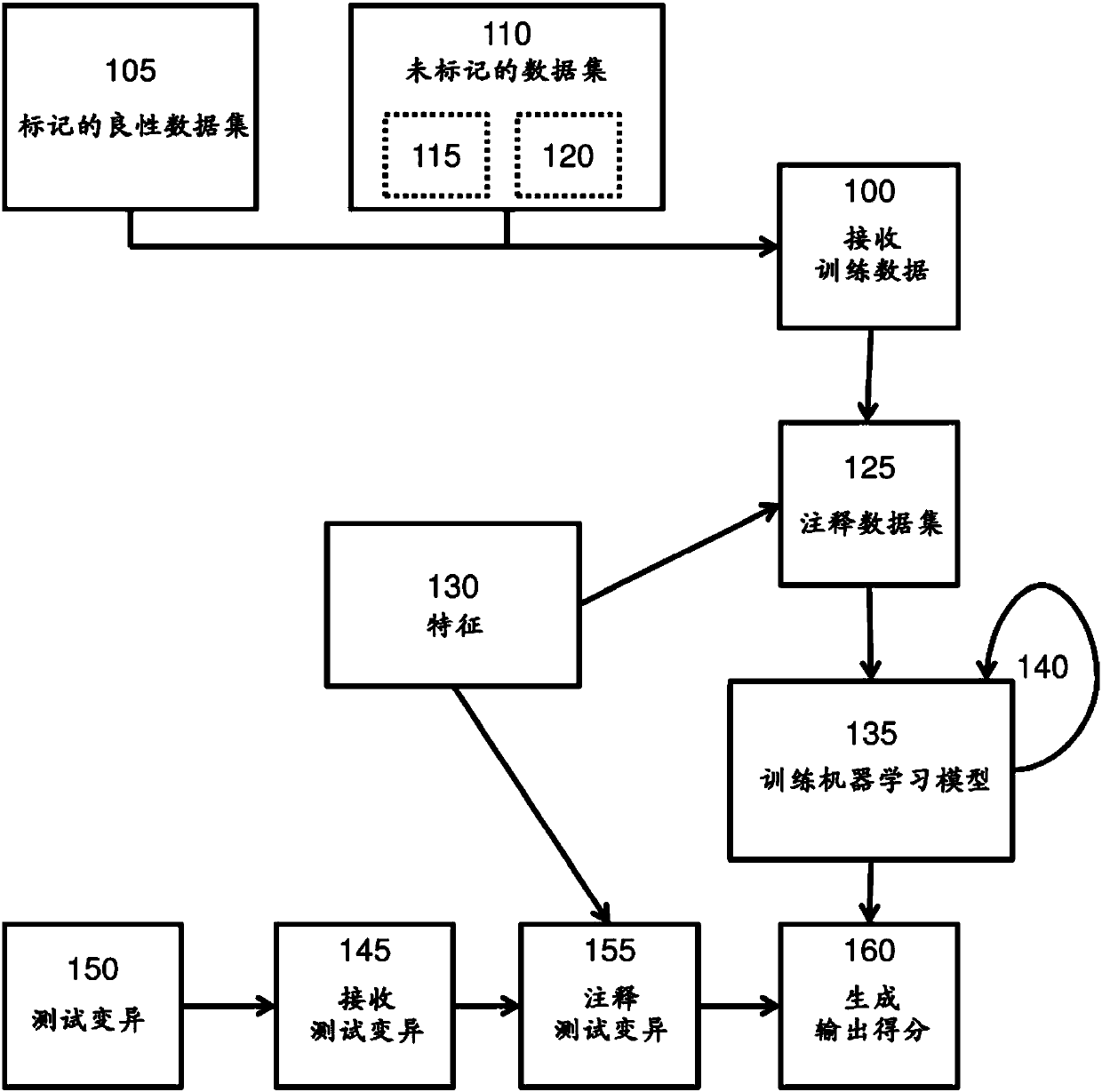
Methods of predicting pathogenicity of genetic sequence variants
Recent developments in cost-effective DNA sequencing allows for individualized genomic screening of a subject for genetic sequence variants. Training a pathogenicity prediction model using semi-supervised training methods produces a better model for predicting the pathogenicity of a test genetic sequence variant. Provided herein are methods for predicting the pathogenicity of a test genetic sequence variant by utilizing a training data set comprising labeled benign genetic sequence variants unlabeled genetic sequence variants, the unlabeled genetic sequence variants comprising a mixture of benign genetic sequence variants and pathogenic genetic sequence variants. The genetic sequences are annotated with one or more features and a machine learning model is trained in a semi-supervised process based on the training data. The test genetic sequence is then annotated using the one or more features and the probability that the test genetic sequence variant is pathogenic is predicted based onthe trained machine learning model.
Owner:COUNSYL INC
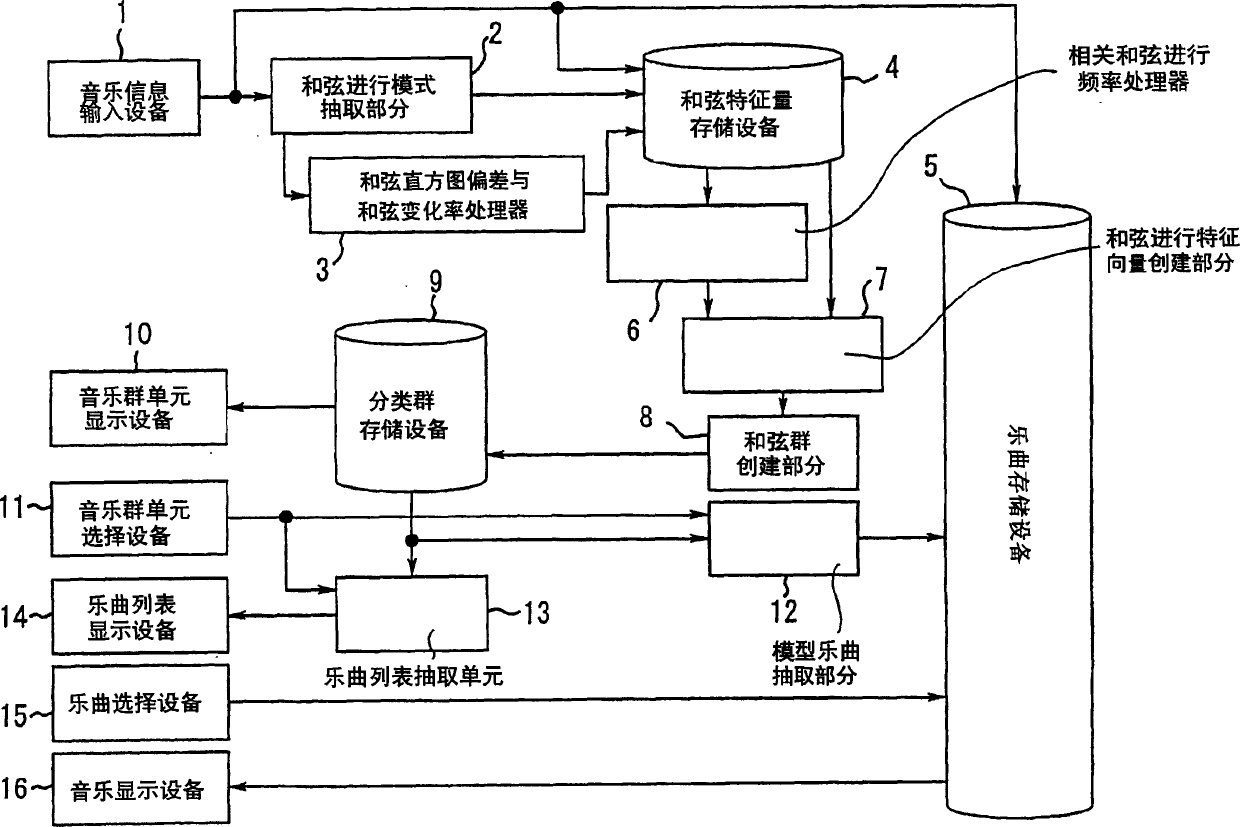
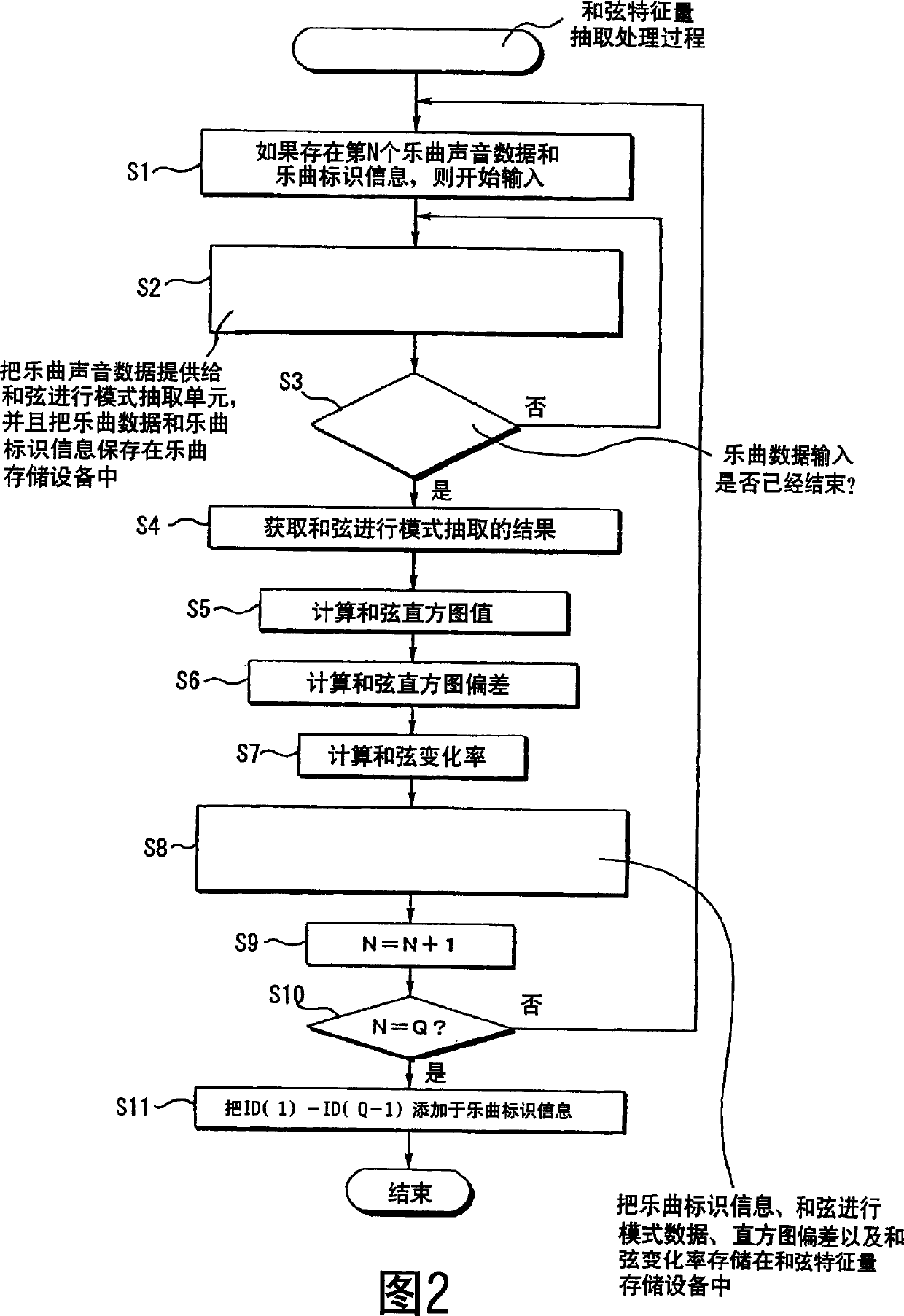
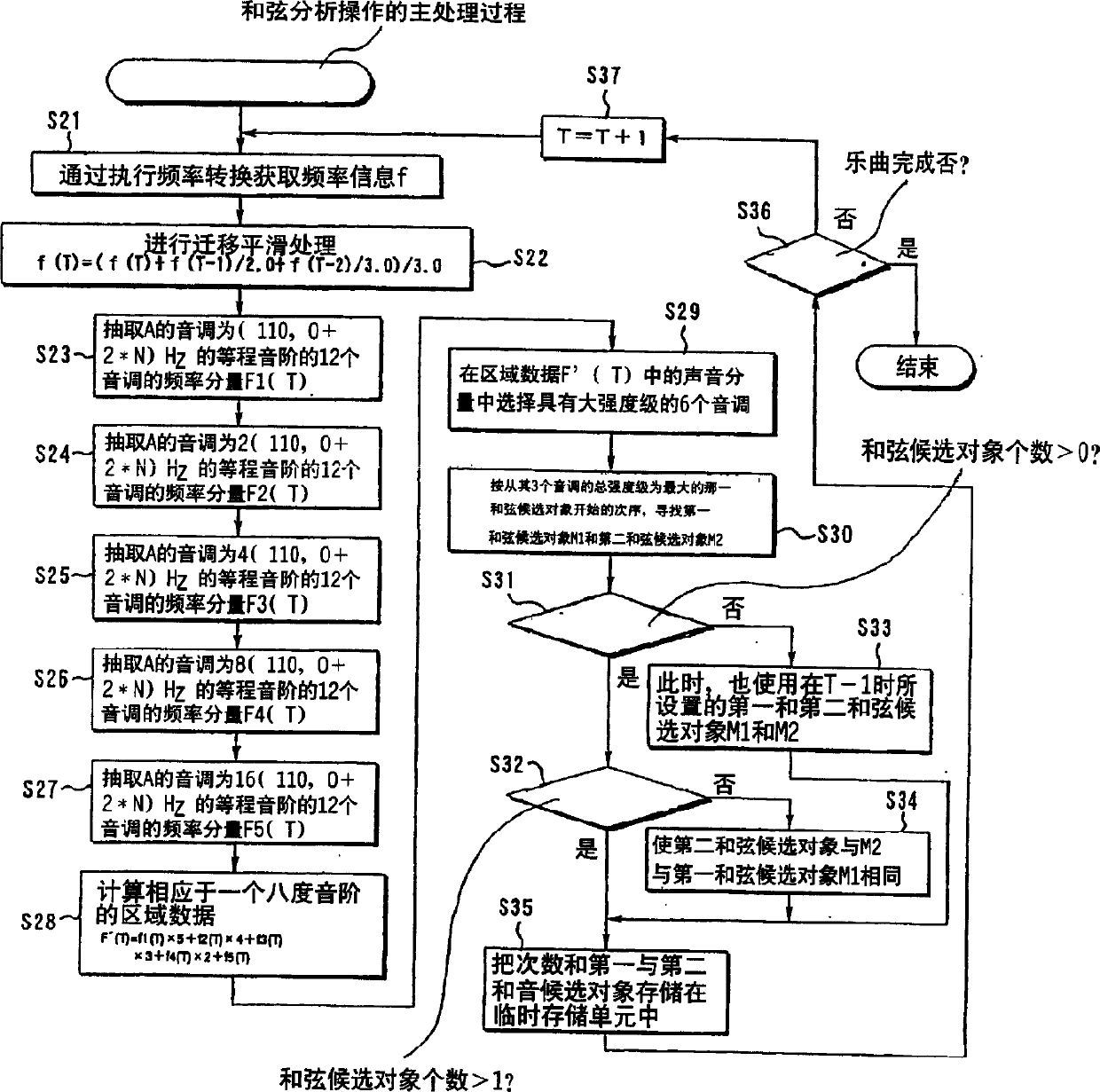
Automatic musical composition classification device and method
InactiveCN1619640AElectrophonic musical instrumentsSound producing devicesSequence variationSpeech recognition
An automatic musical composition classification device and method that allow automatic classification of a plurality of musical compositions based on melodic similarity. storing chord progression pattern data representing a chord progression sequence for each of the plurality of musical pieces, extracting a chord progression change feature amount for each of the plurality of musical pieces based on the chord progression pattern data, And according to the chord progression sequence and the chord progression change feature quantity represented by the chord progression pattern data of each of the plurality of music pieces, the multiple pieces of music are grouped.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
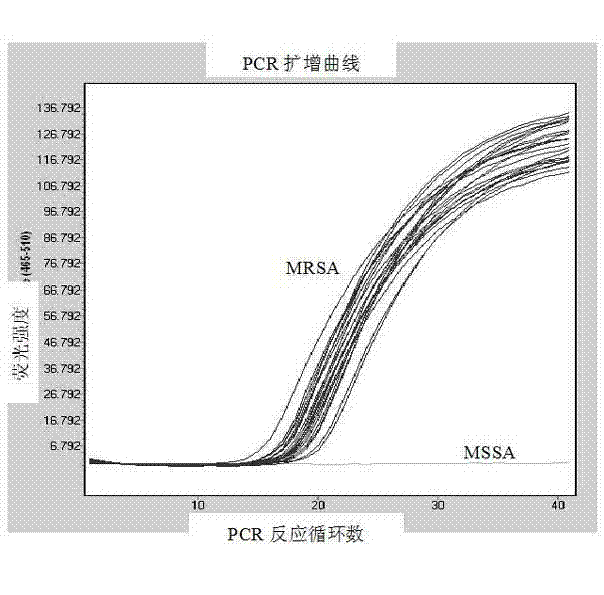
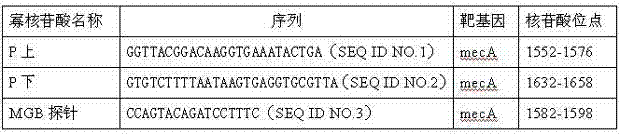
Primer and probe for detecting drug resistance genes mecA in methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN103173561AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMethicillin resistance geneConserved sequence
The invention provides a primer and a probe for detecting drug resistance genes mecA in methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The invention also provides a method and a detection kit for detecting drug resistance genes mecA in MRSA. According to the invention, the conserved sequence part of drug resistance genes mecA is directly detected without being affected by the mecA gene variation of strains, and a result is a gold standard of MRSA diagnosis. The specific primer and the probe provided by the invention are applicable to currently known strains containing sequence variation.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUTUO DISTRICT PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Methods, compositions and kits for detecting allelic variants
InactiveCN102301005ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionNucleotide
In some embodiments, the present invention generally relates to compositions, methods and kits for distinguishing sequence differences between different alleles. More specifically, in some embodiments, the present invention provides methods for quantifying rare (e.g., mutant) alleles in samples containing abundant (e.g., wild-type) allelic variants with high specificity and selectivity. Compositions, methods and kits for genetic variants such as SNP or nucleotide (NT) insertion or deletion. In particular, in some embodiments, the present invention relates to a highly selective method for detecting mutations known as competitive allele-specific TaqMan PCR ("cast-PCR").
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
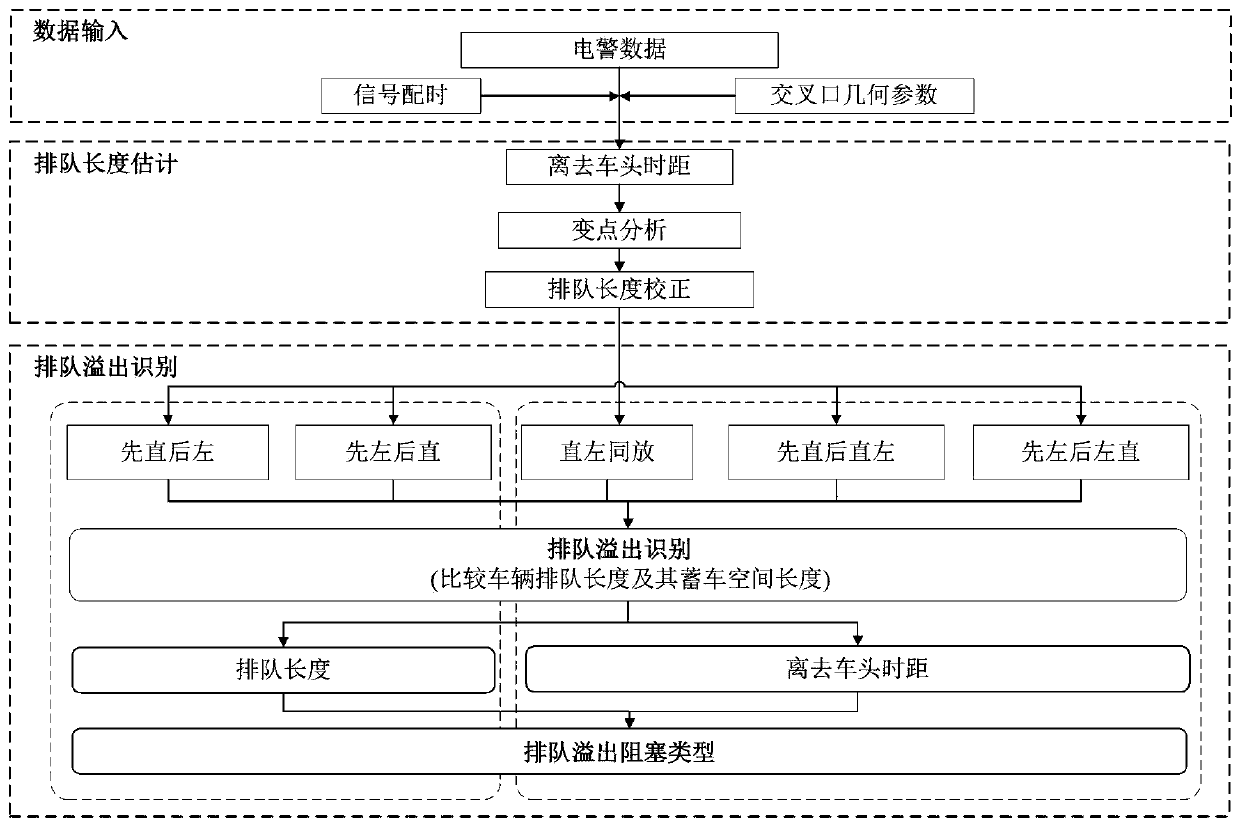
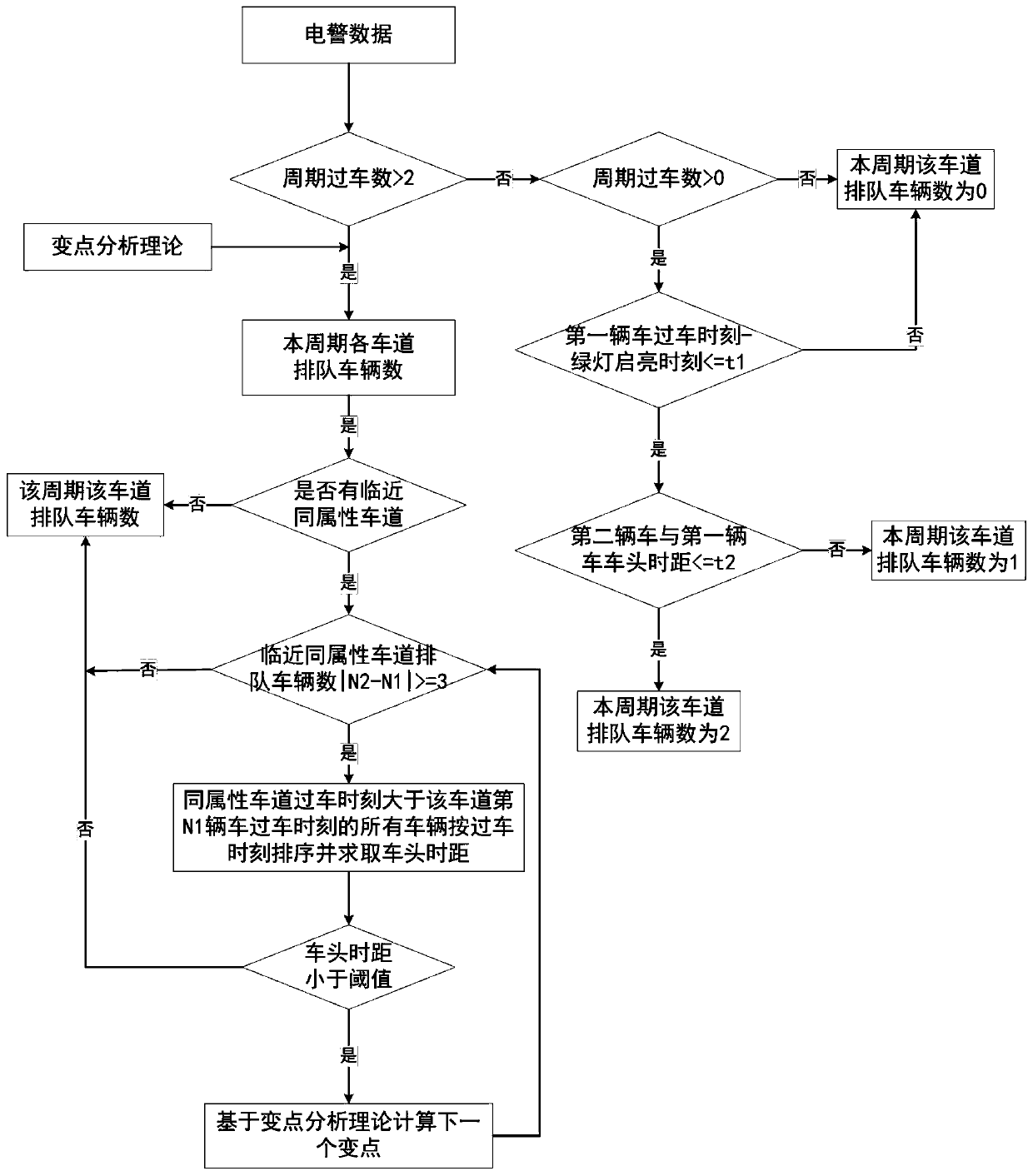
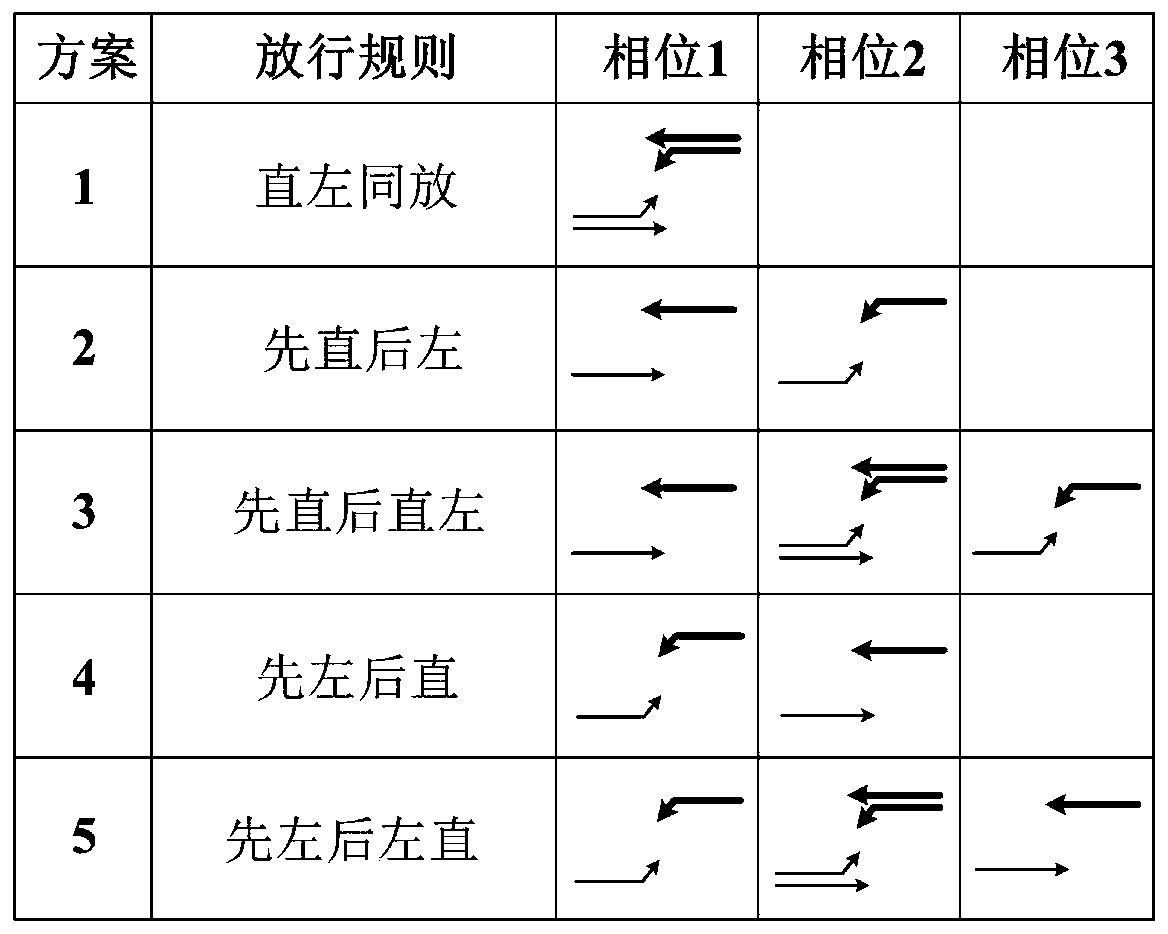
Intersection short-lane queue overflow identification method based on electric police data
InactiveCN109767625ALess input dataWide applicabilityDetection of traffic movementTimestampTime headway
The invention relates to an intersection short-lane queue overflow identification method based on electric police data. The intersection short-lane queue overflow identification method based on the electric police data comprises the steps of: (1), obtaining the electric police data, and calculating the departure time headway of a vehicle; (2), in combination with the timestamp information that thevehicle passes through a parking line and the departure time headway obtained by calculation, describing double characteristics of proximity spacing and time headway fluctuation, so that a departuretime headway sequence variation point is identified, and estimating the vehicle queue length on each lane; and (3), analyzing a possible queue overflow type of an intersection in a condition that a left-turn short lane and an adjacent straight lane are different in queue length; and furthermore, performing subdivision by judging whether driving of a vehicle on an adjacent lane is blocked or not. The queue length of each lane is obtained by calculation based on a variable point analyzing theory; under different phase release rules, queue overflow identification algorithms based on rules are respectively established; therefore, queue overflow states in different types can be identified; and the intersection short-lane queue overflow identification method based on the electric police data inthe invention has the advantages of being definite in queue overflow classification, little in input data, wide in applicability and the like.
Owner:苏州易通交通科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com