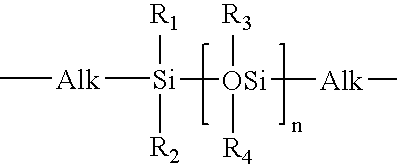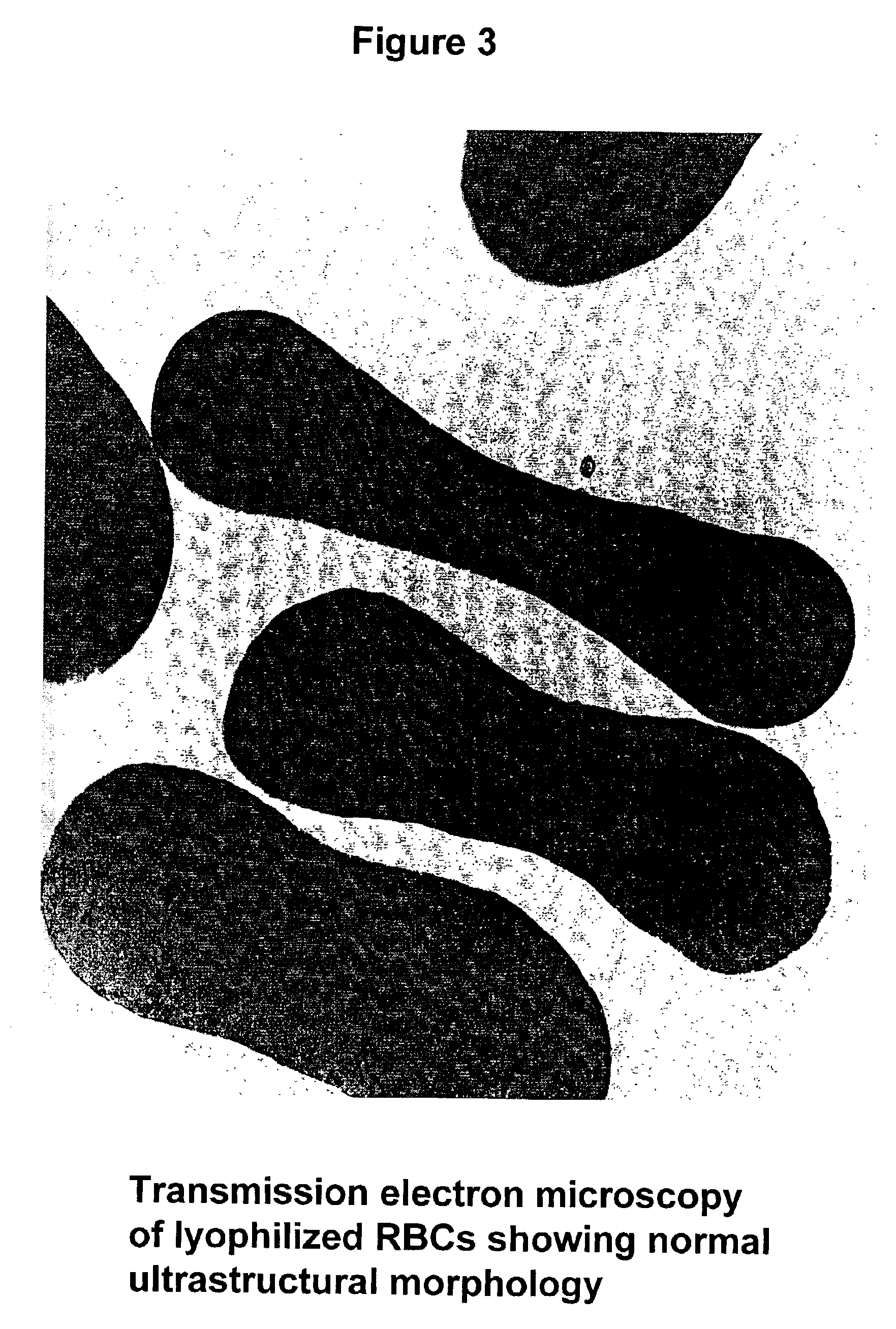Patents
Literature
196 results about "Chemical ligation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
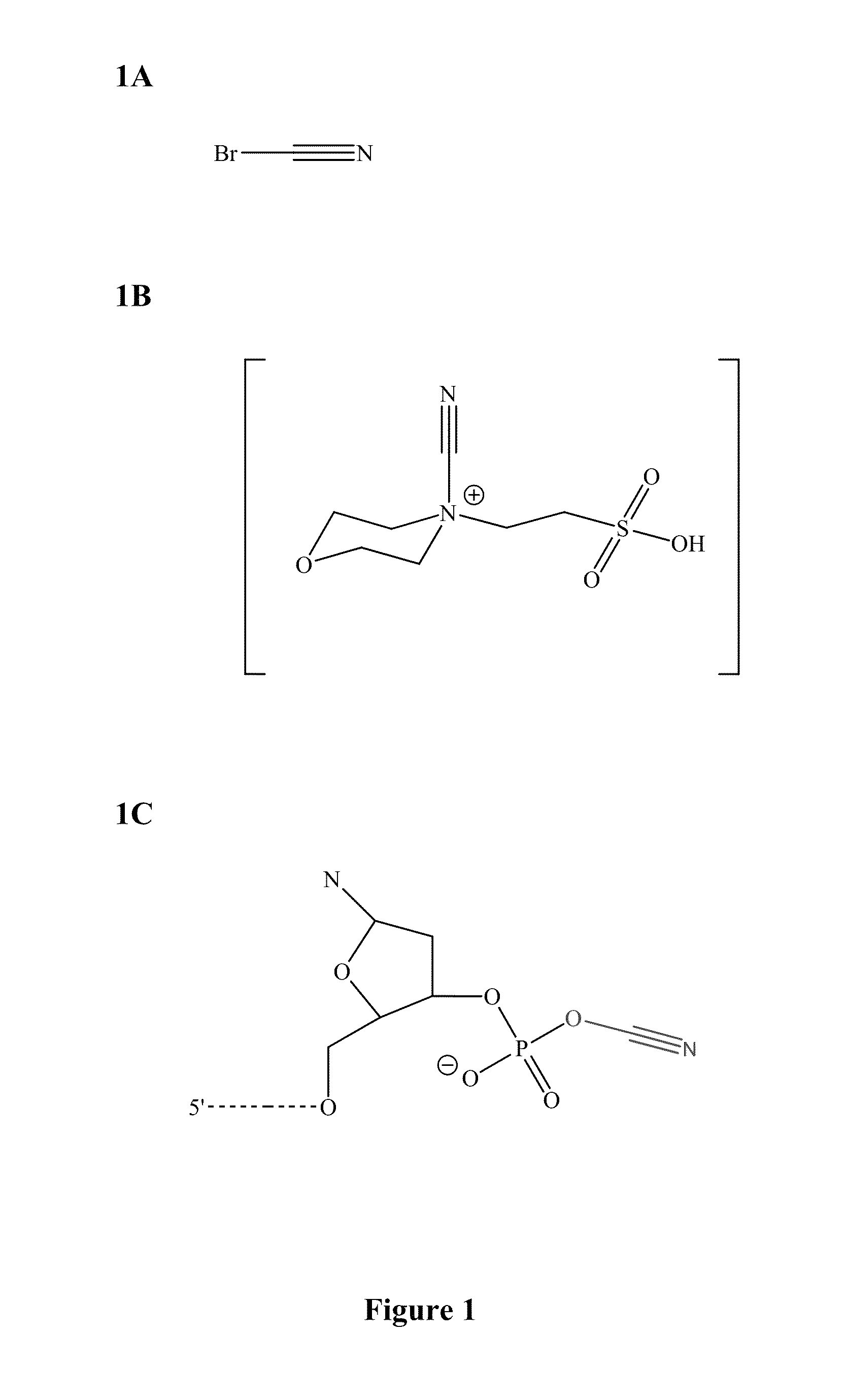
Chemical ligation is a set of techniques used for creating long peptide or protein chains. It is the second step of a convergent approach. First, smaller peptides containing 30-50 amino acids are prepared by conventional chemical peptide synthesis. Then, they are completely deprotected. Chemical ligation is the technique of coupling these peptides by chemoselective reaction to give a unique reaction product, usually in aqueous solution. With several coupling steps, proteins of up to 200-300 amino acids can be produced.
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS20020172963A1High precisionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
Novel recombinant proteins with N-terminal free thiol
InactiveUS20050170457A1Extended half-lifeIncreases circulating serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCysteine thiolateHalf-life
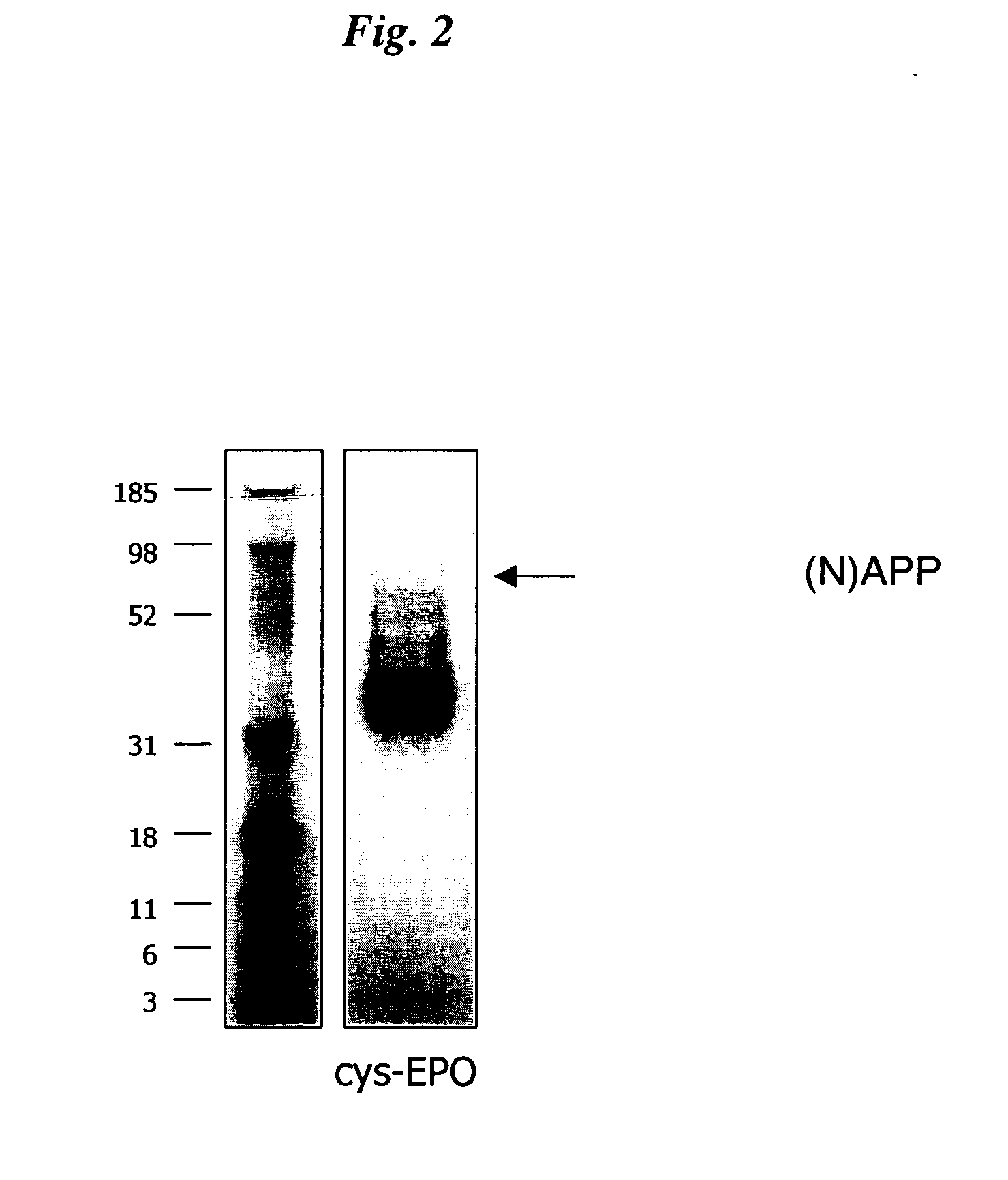
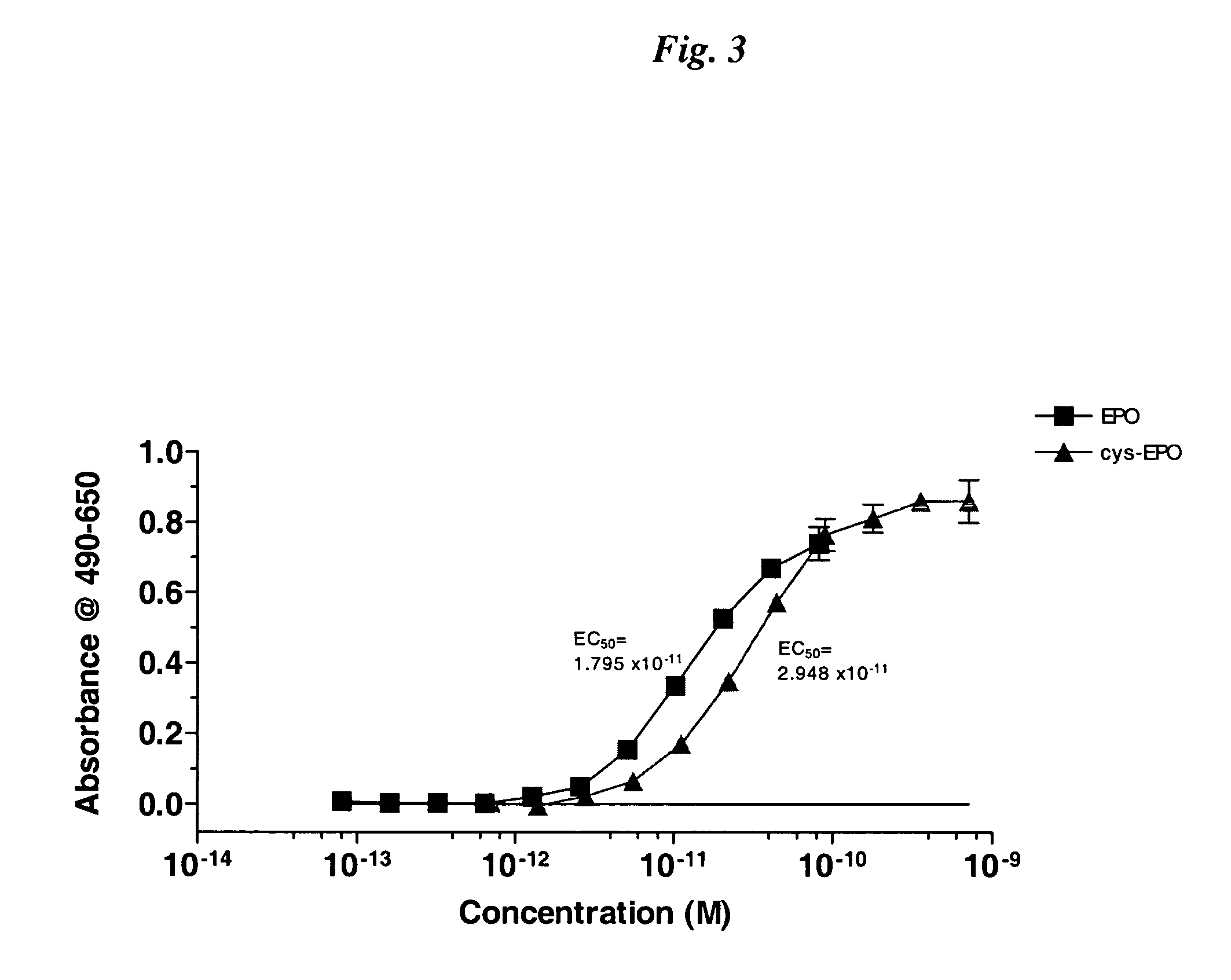
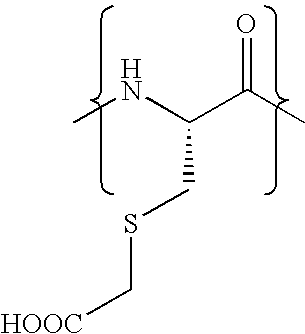
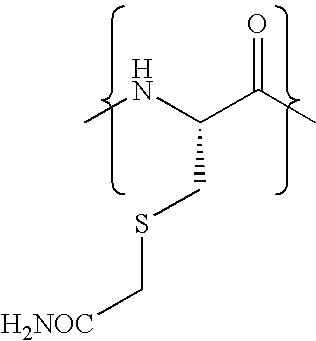
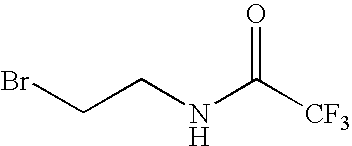
The present invention relates to novel modified proteins having N-terminal free thiols that can be produced by recombinant methods and are ready for further chemical derivatization. In particular, the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds having altered biochemical, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. More particularly, one embodiment of the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds of the formula: (M)n-X-A-cys-EPO (I) where EPO is an erythropoeitin moiety selected from erythropoietin or an erythropoietin variant having at least one amino acid different from the wild-type human EPO, or any pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives thereof having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of red blood cells; cys represents the amino acid cysteine and occurs at position −1 relative to the amino acid sequence of the erythropoietin moiety; A indicates the structure of the residual moiety used to chemically attach X to the thiol group of −1Cys; X is a water soluble polymer such as a polyalkylene glycol or other polymer; M is an organic molecule (including peptides and proteins) that increases the circulating half-life of the construct; and N is an integer from 0 to 15.
Owner:CENTOCOR
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS6958216B2High sensitivityImprove portabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
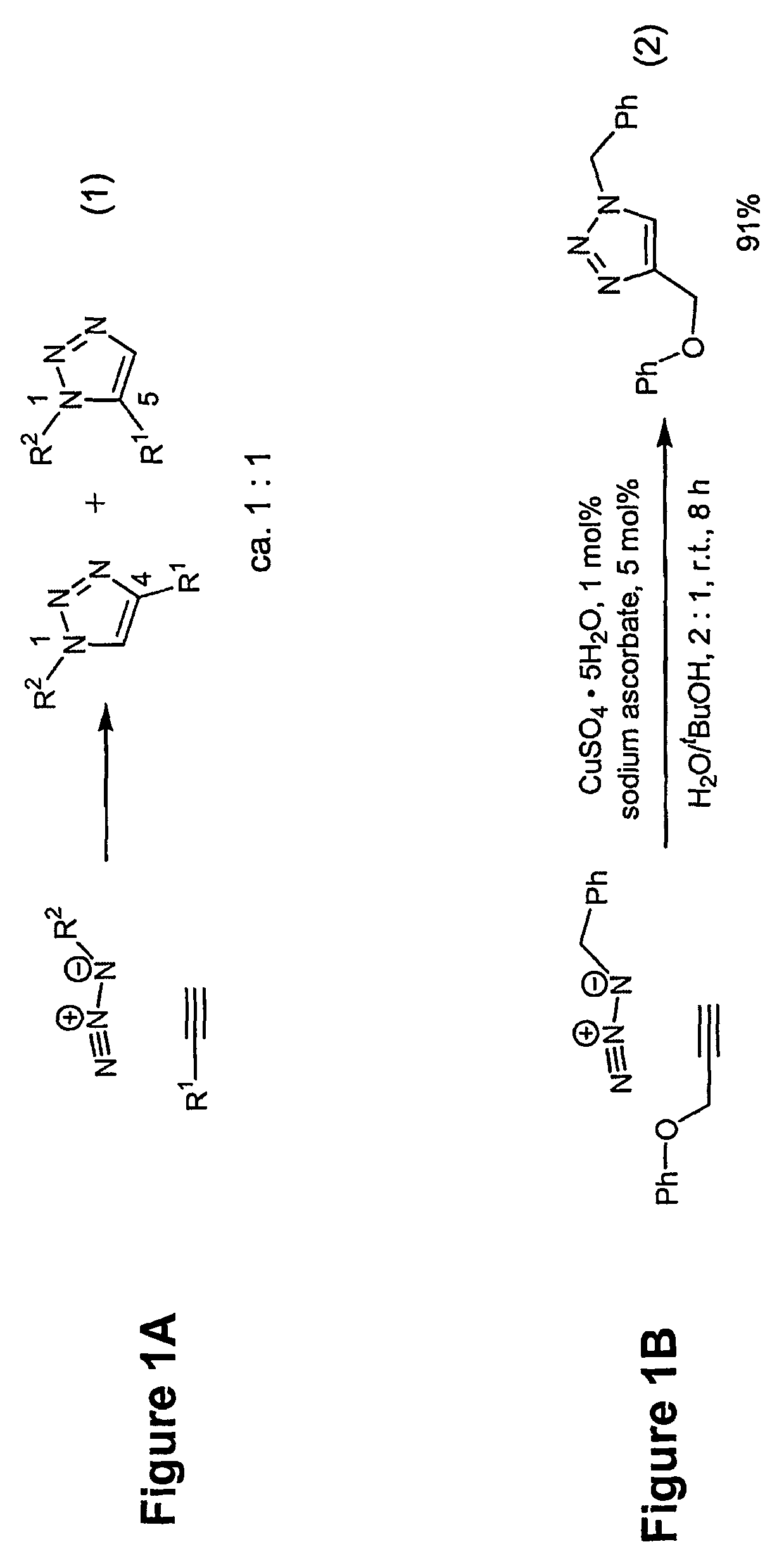
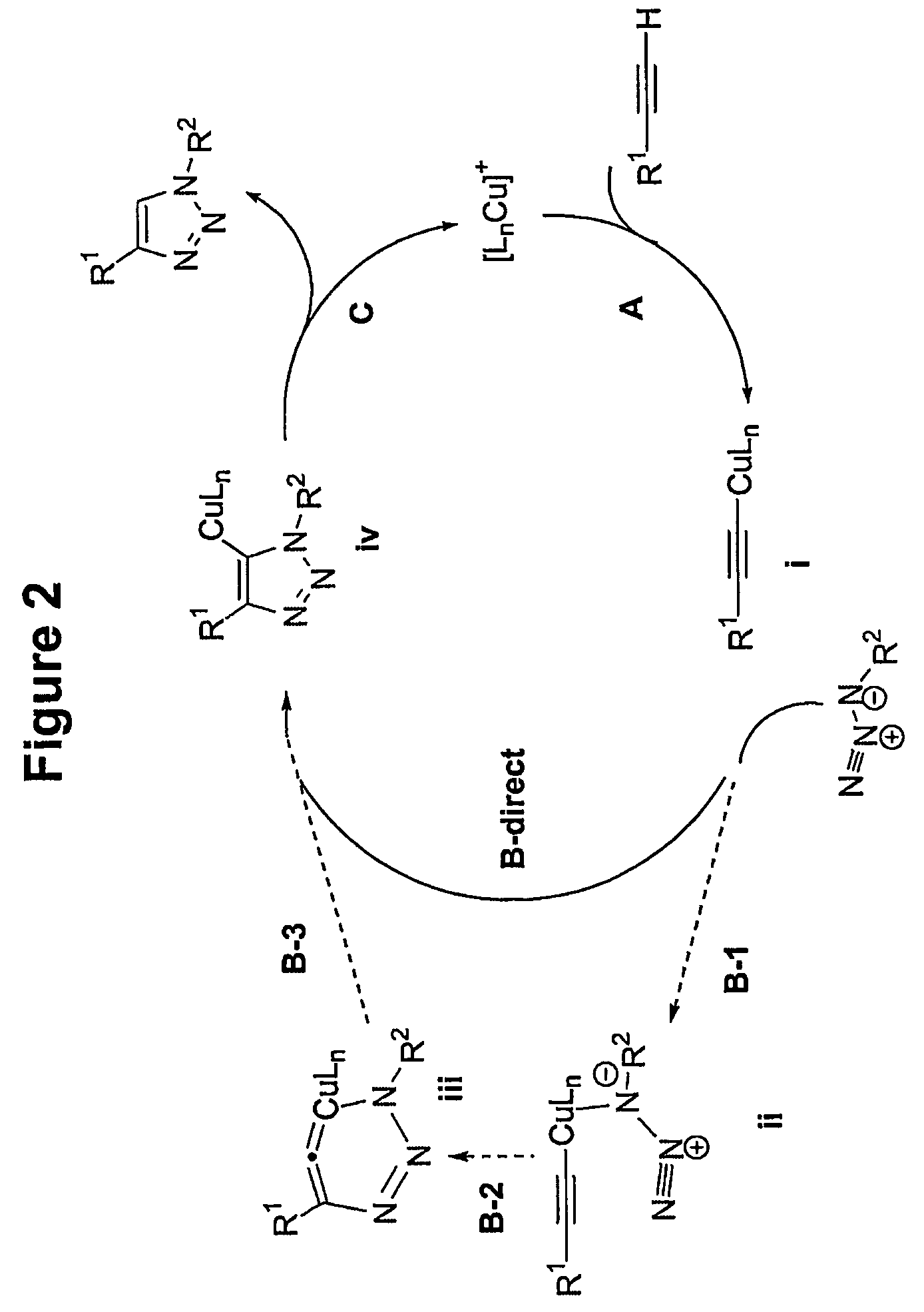
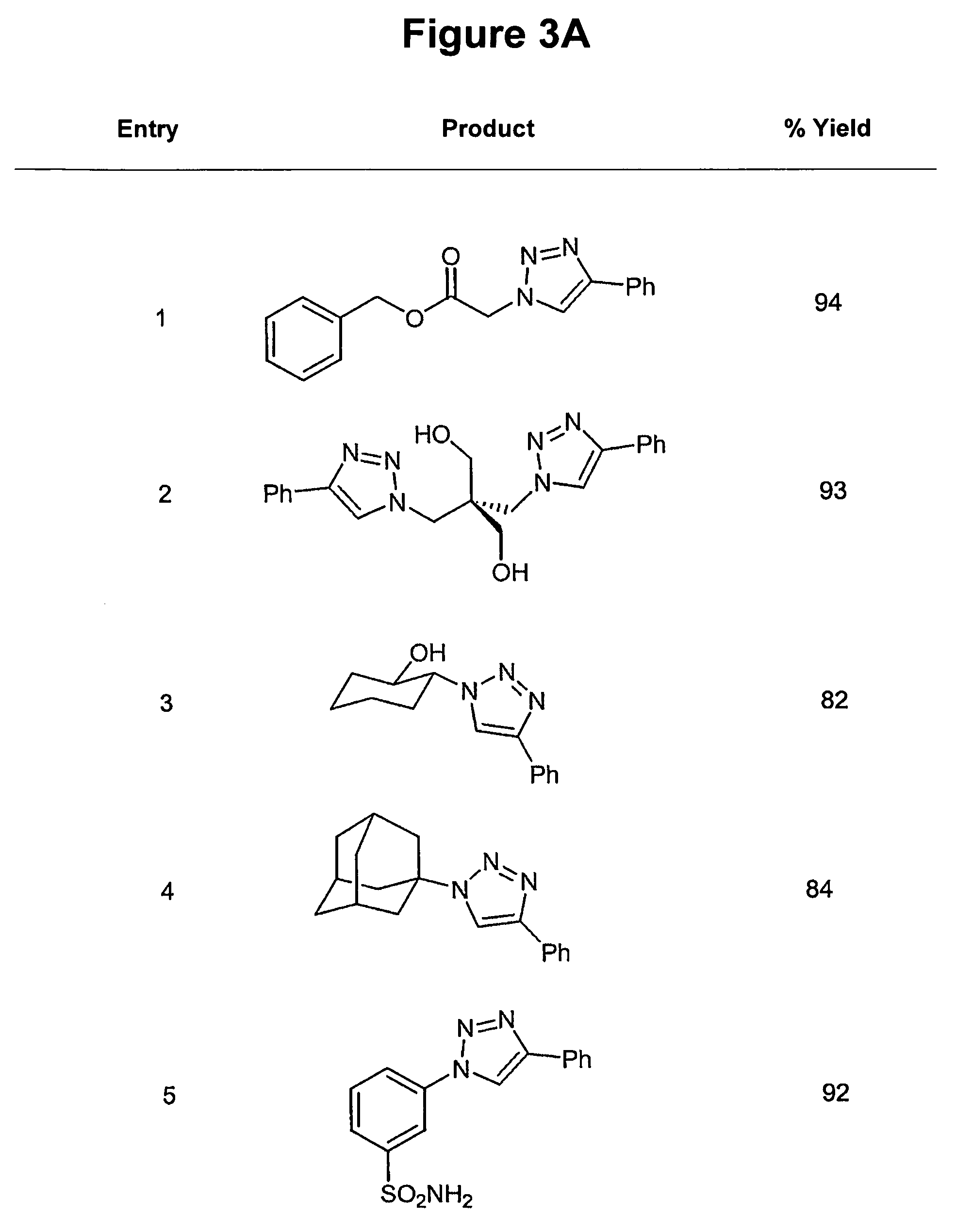
Copper-catalysed ligation of azides and acetylenes
InactiveUS7763736B2Organic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical ligationAqueous alcohol
A copper catalyzed click chemistry ligation process is employed to bind azides and terminal acetylenes to provide 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole triazoles. The process comprises contacting an organic azide and a terminal alkyne with a source of reactive Cu(I) ion for a time sufficient to form by cycloaddition a 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole. The source of reactive Cu(I) ion can be, for example, a Cu(I) salt or copper metal. The process is preferably carried out in a solvent, such as an aqueous alcohol. Optionally, the process can be performed in a solvent that comprises a ligand for Cu(I) and an amine.
Owner:TETARD INC
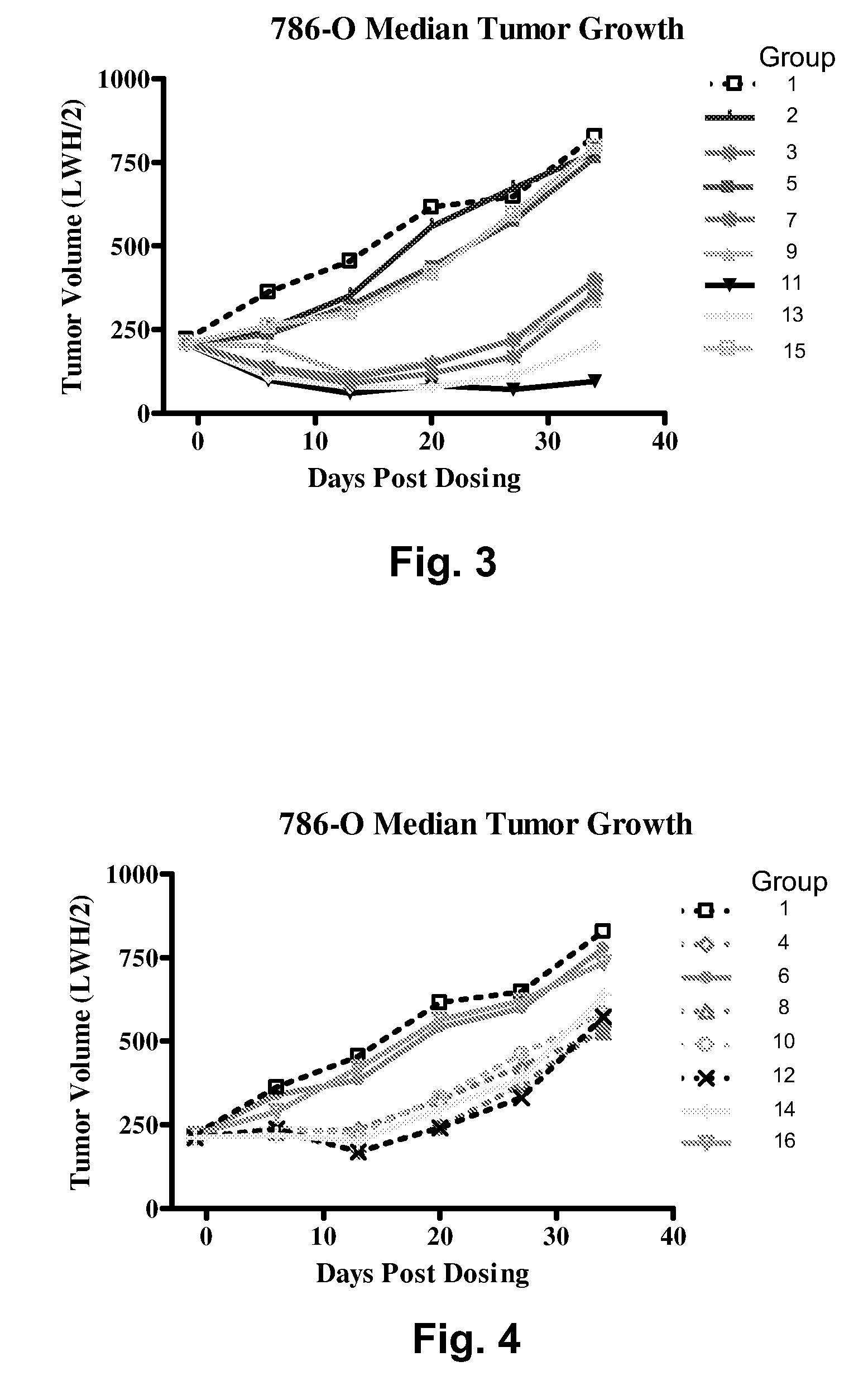
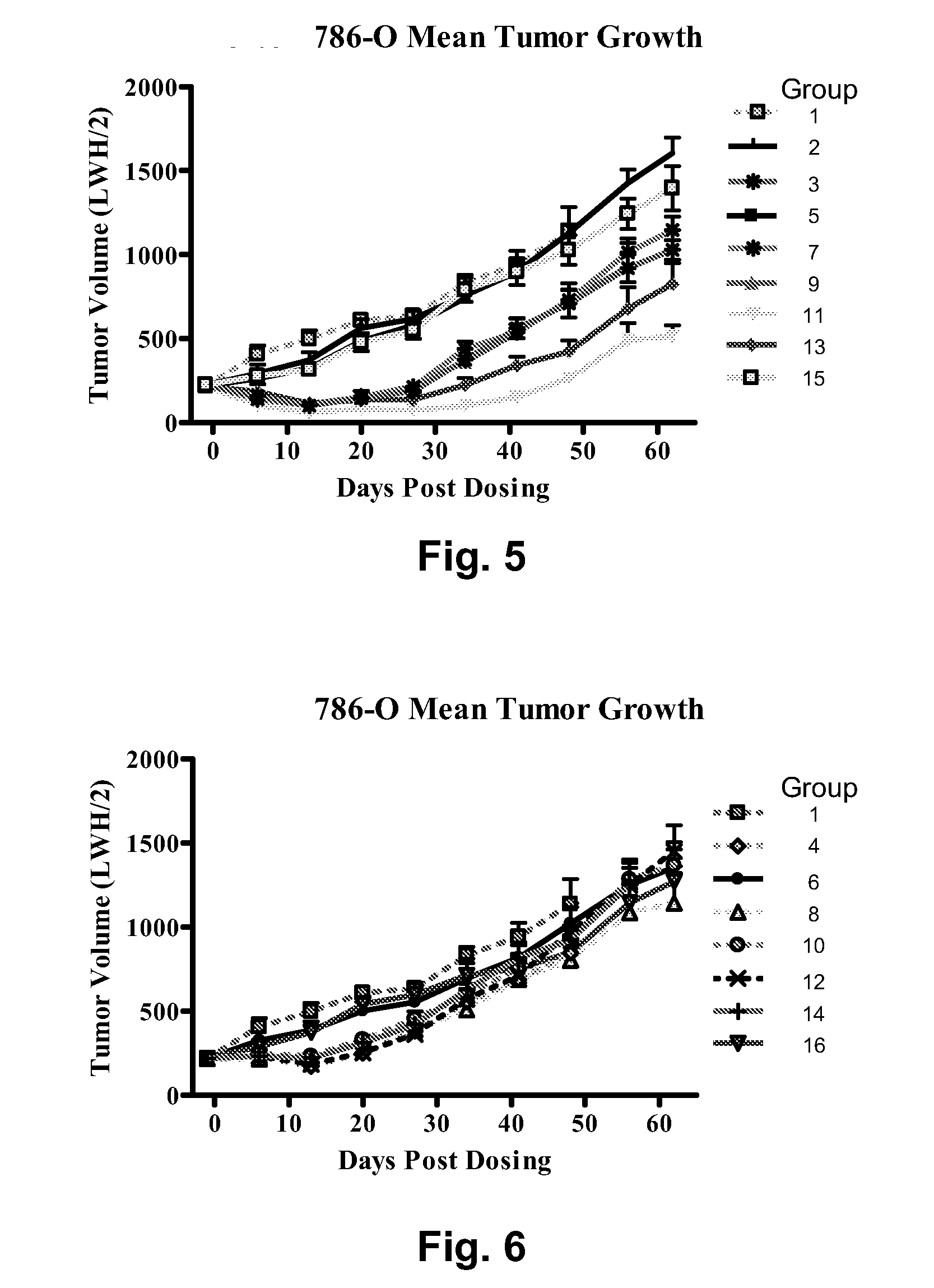
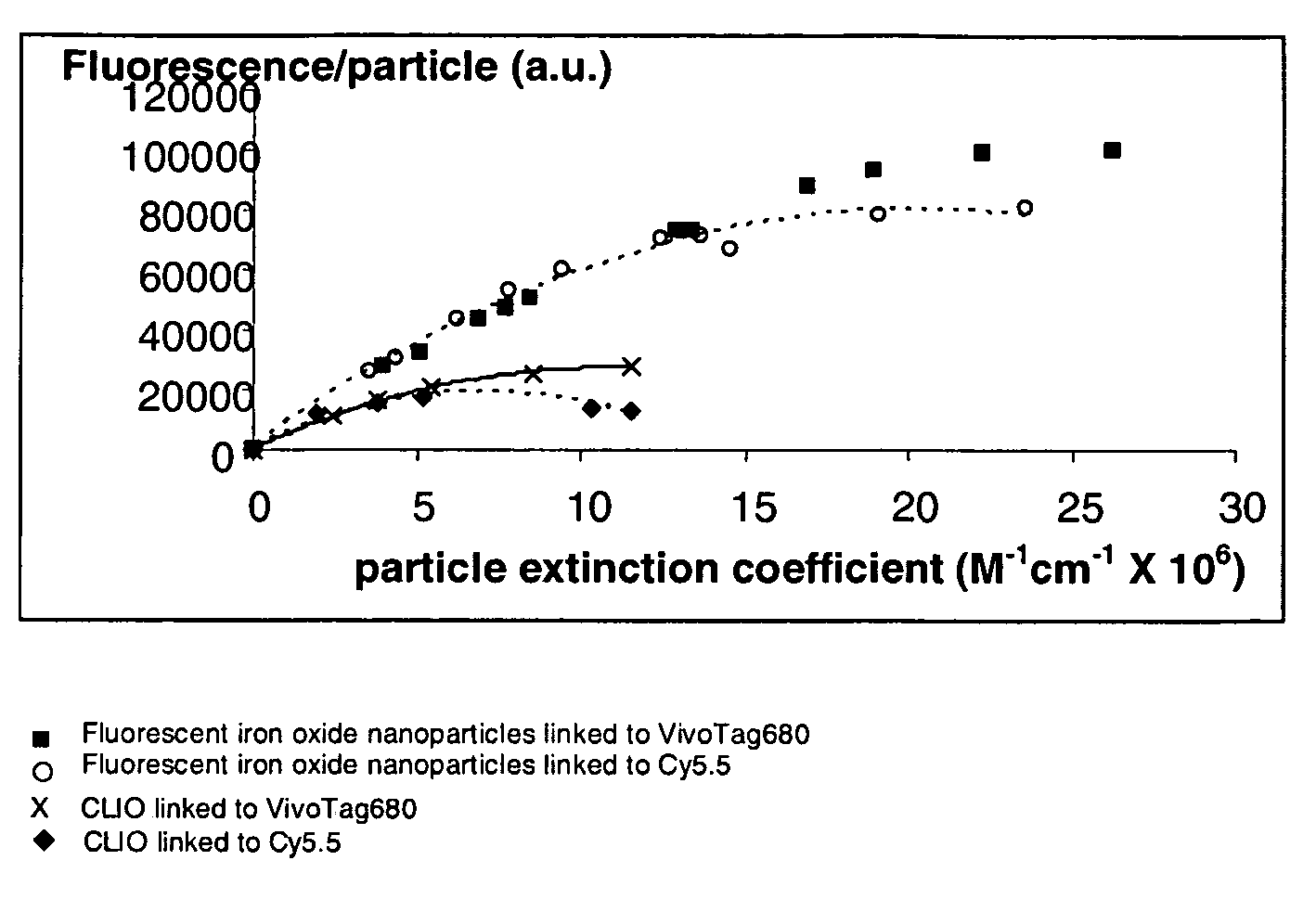
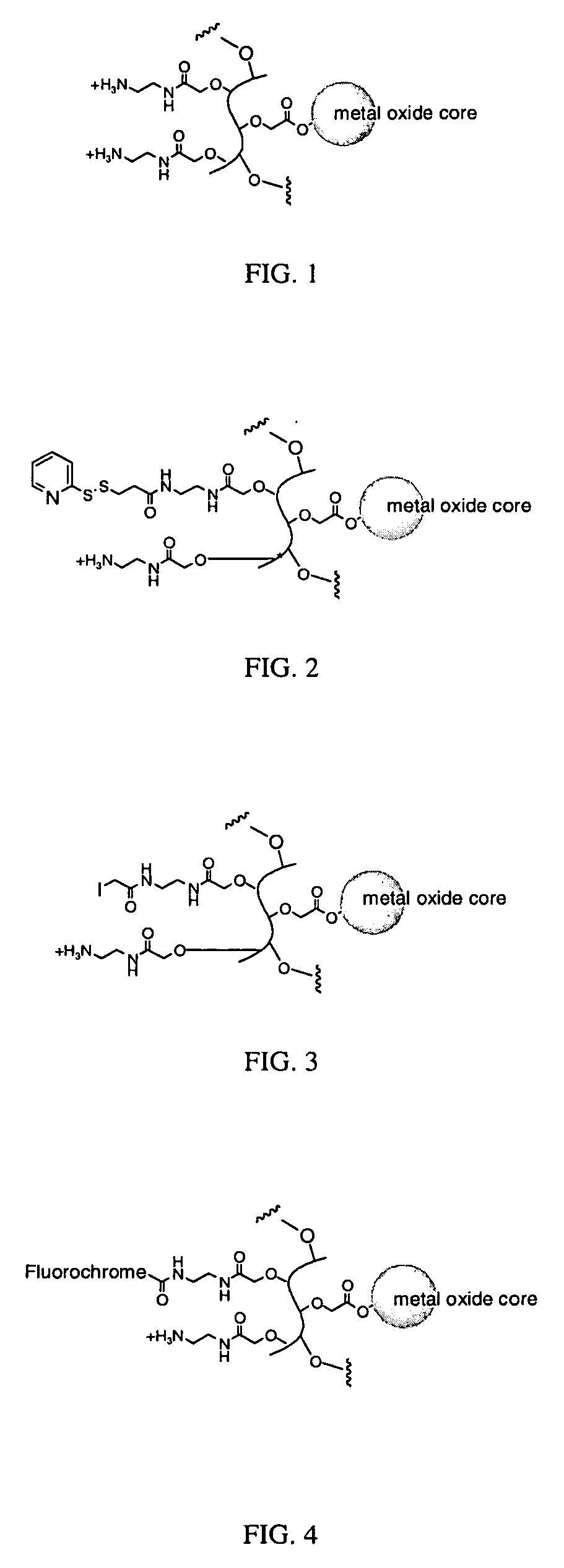
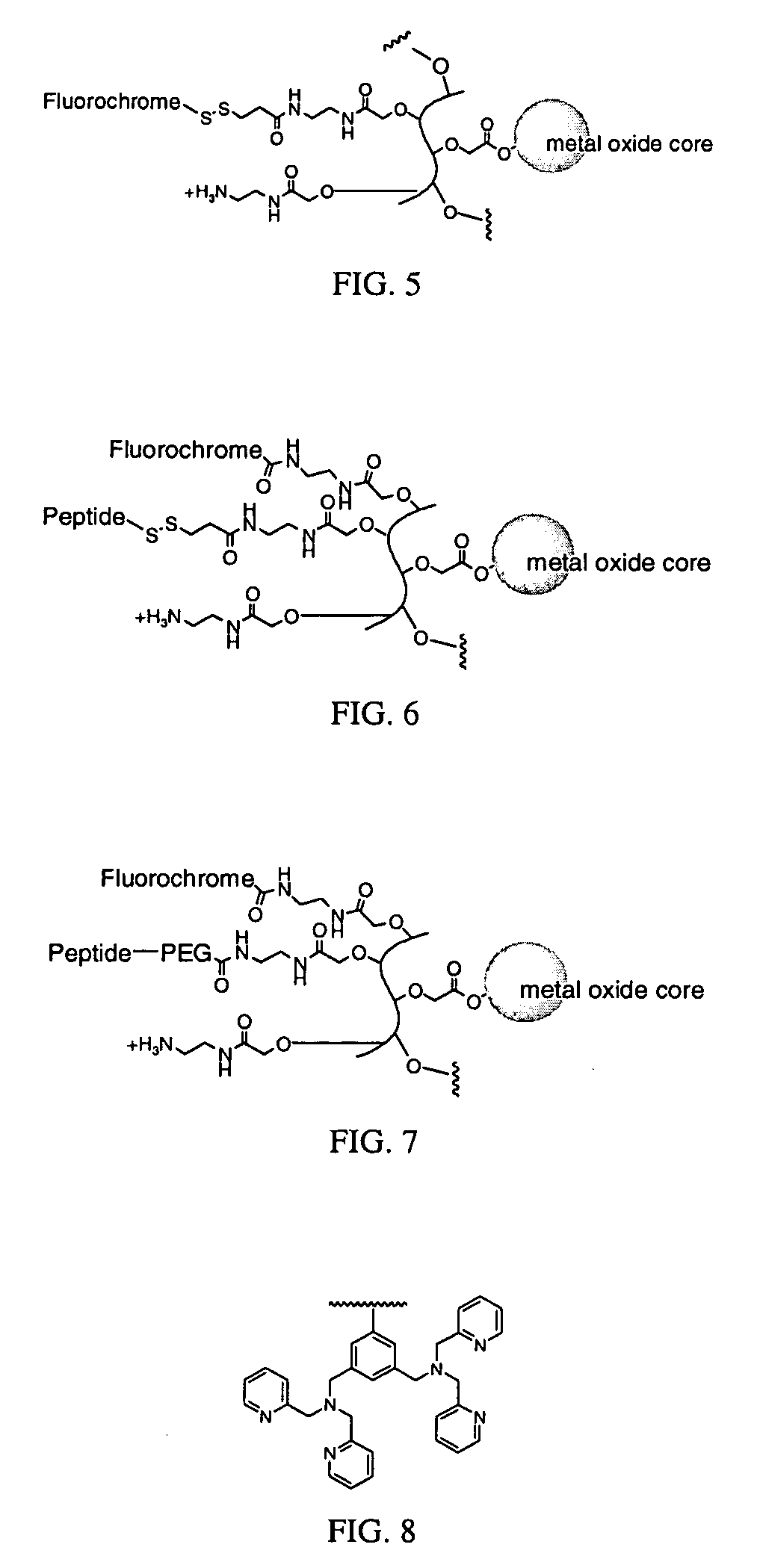
Biocompatible fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080226562A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryMetal oxide nanoparticlesChemical ligation
The invention relates to highly fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles to which biomolecules and other compounds can be chemically linked to form biocompatible, stable optical imaging agents for in vitro and in vivo applications. The fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles may also be used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), thus providing a multi modality imaging agent.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
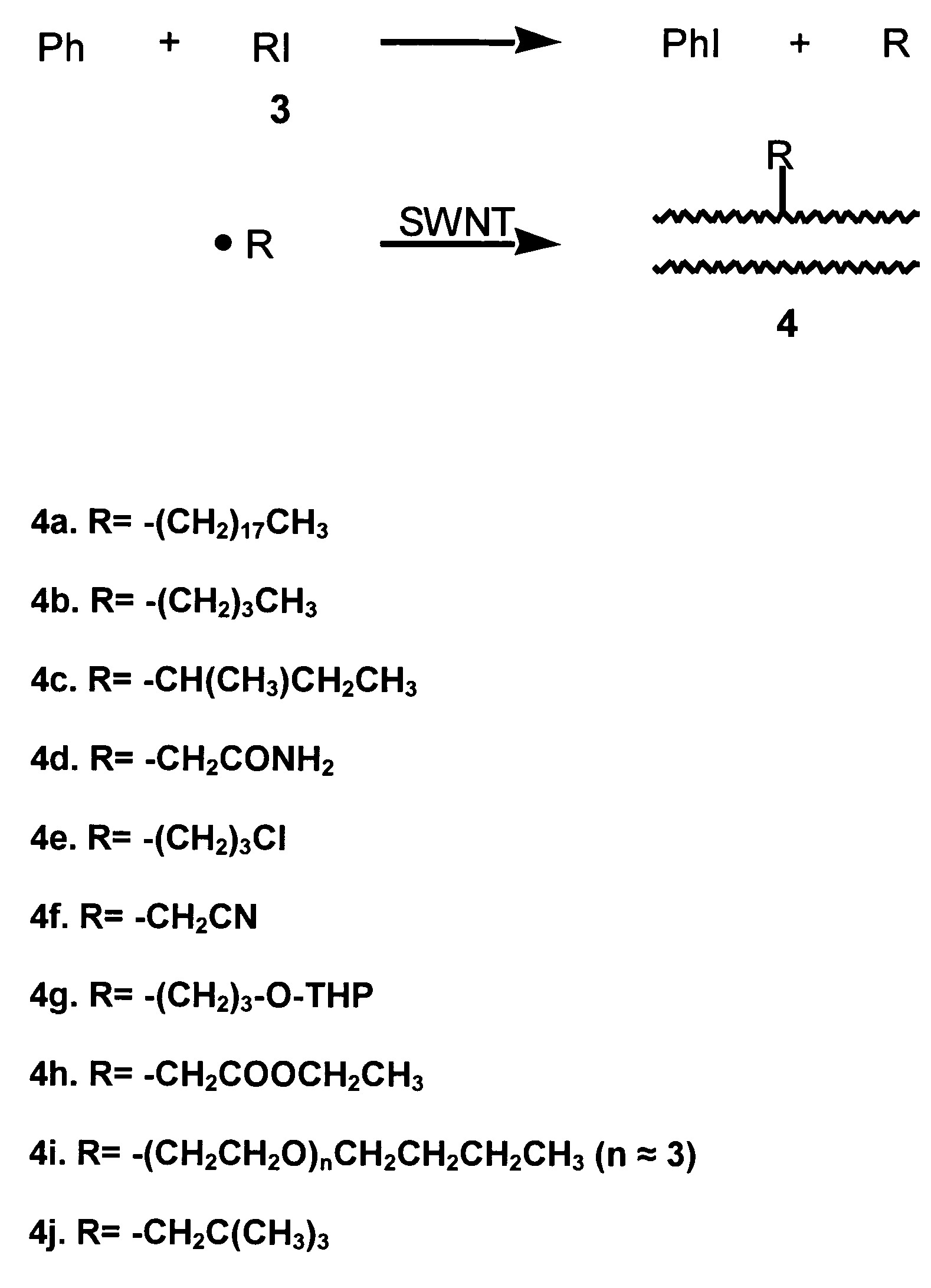
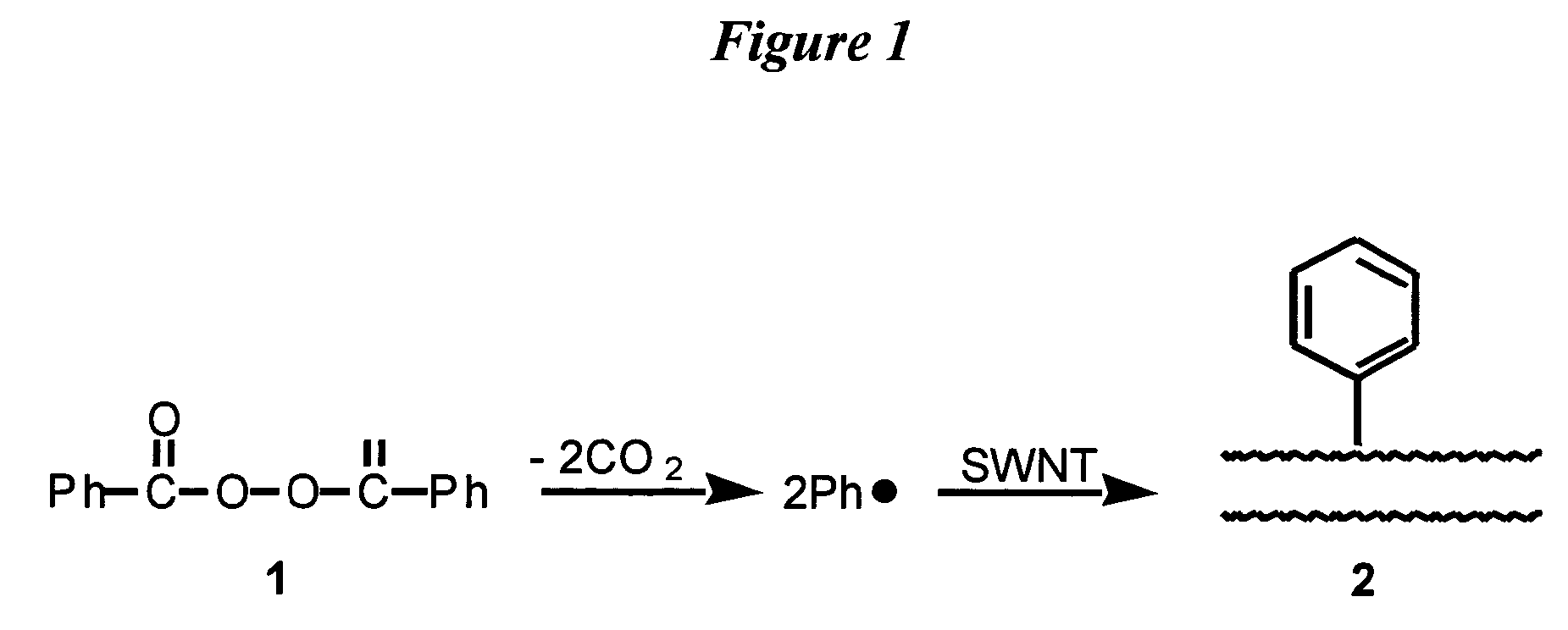
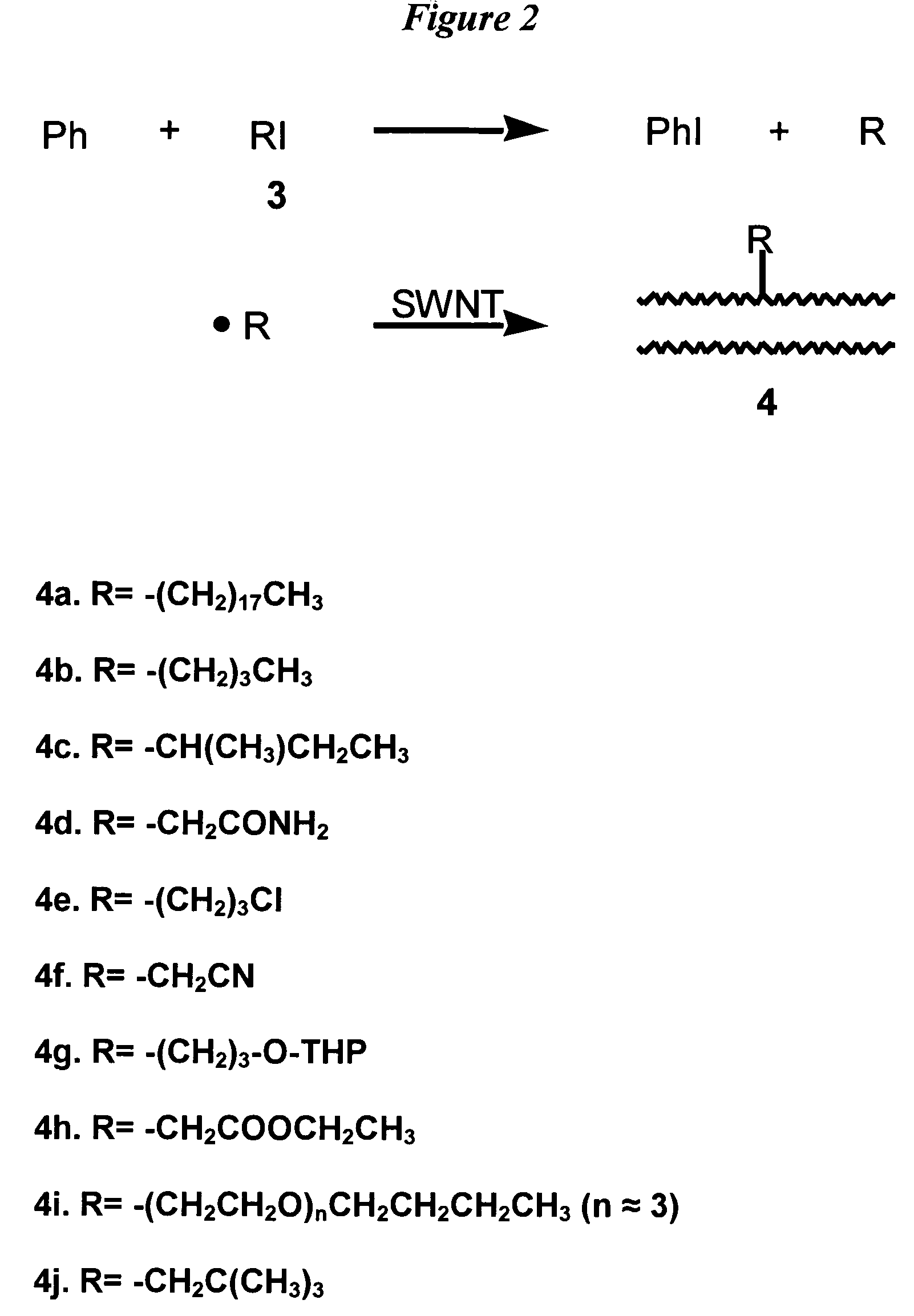
Method for functionalizing carbon nanotubes utilizing peroxides
ActiveUS7125533B2Good dispersionSimple materialMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentCarbon centered radicalsAcyl group
A method for functionalizing the wall of single-wall or multi-wall carbon nanotubes involves the use of acyl peroxides to generate carbon-centered free radicals. The method allows for the chemical attachment of a variety of functional groups to the wall or end cap of carbon nanotubes through covalent carbon bonds without destroying the wall or endcap structure of the nanotube. Carbon-centered radicals generated from acyl peroxides can have terminal functional groups that provide sites for further reaction with other compounds. Organic groups with terminal carboxylic acid functionality can be converted to an acyl chloride and further reacted with an amine to form an amide or with a diamine to form an amide with terminal amine. The reactive functional groups attached to the nanotubes provide improved solvent dispersibility and provide reaction sites for monomers for incorporation in polymer structures. The nanotubes can also be functionalized by generating free radicals from organic sulfoxides.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Implant improving local bone formation
InactiveUS20060188542A1Improve effectivenessBiocideDental implantsChemical LinkageCalcium biphosphate
A bone implant comprises an active agent on at least a portion thereof. The active agent is locally deliverable to bone proximate the implant in at least a two-phased release scheme. A first phase rapidly releases a first quantity of the active agent, and at least a second phase gradually releases a second quantity of the active agent, whereby bone formation stimulated by the active agent is modulated. In one embodiment, a porous implant comprises a porous portion coated with a calcium phosphate compound and which is contacted with a bisphosphonate compound to form a bisphosphonate layer chemically bound to the calcium phosphate at the surface of the porous portion and to form bisphosphonate molecules being non-chemically attached inside the pores of the porous portion. The non-chemically attached bisphosphonate molecules are released in the subject at a rate greater than that of the chemically bound bisphosphonate layer.
Owner:BOBYN JOHN DENNIS +1
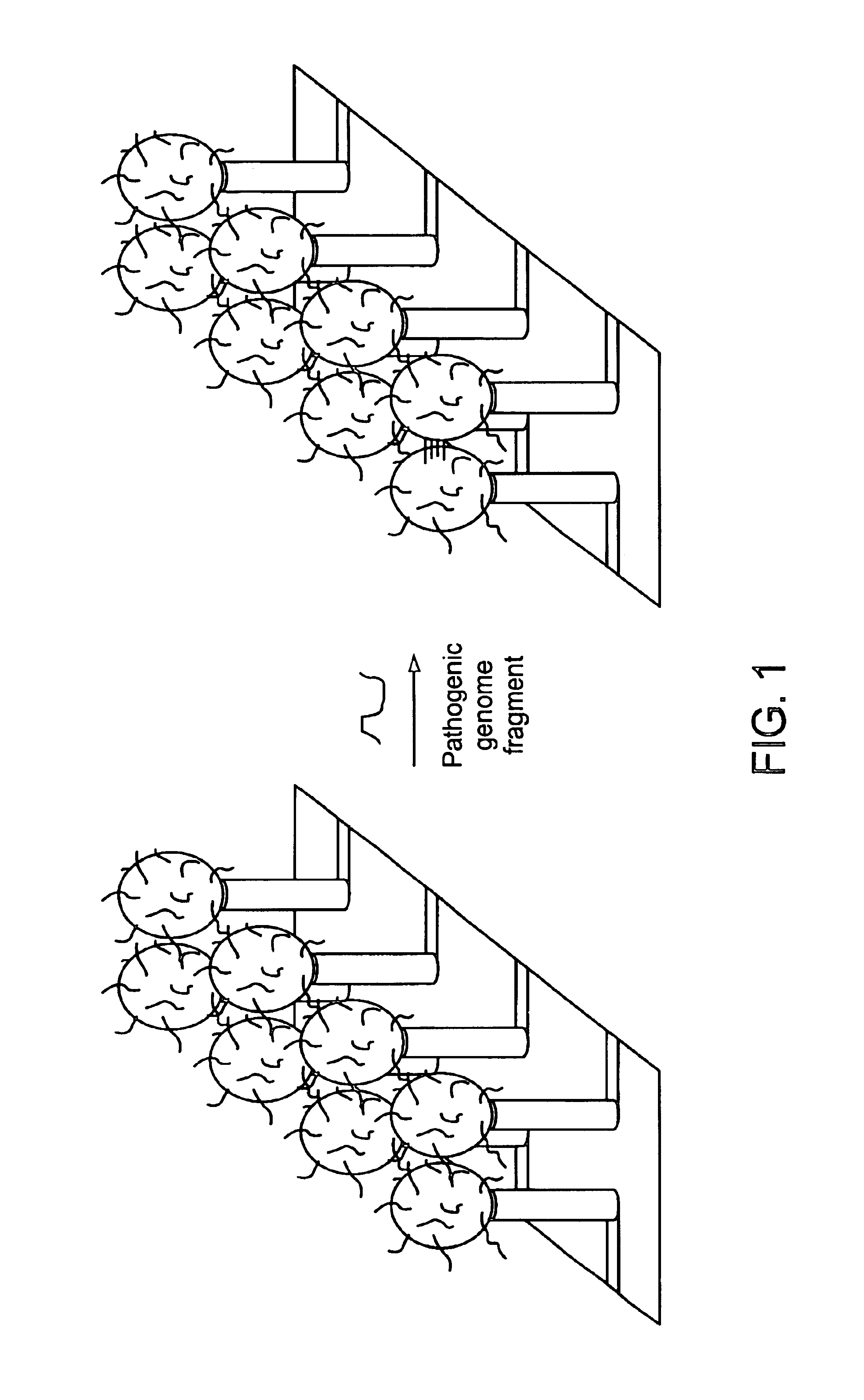
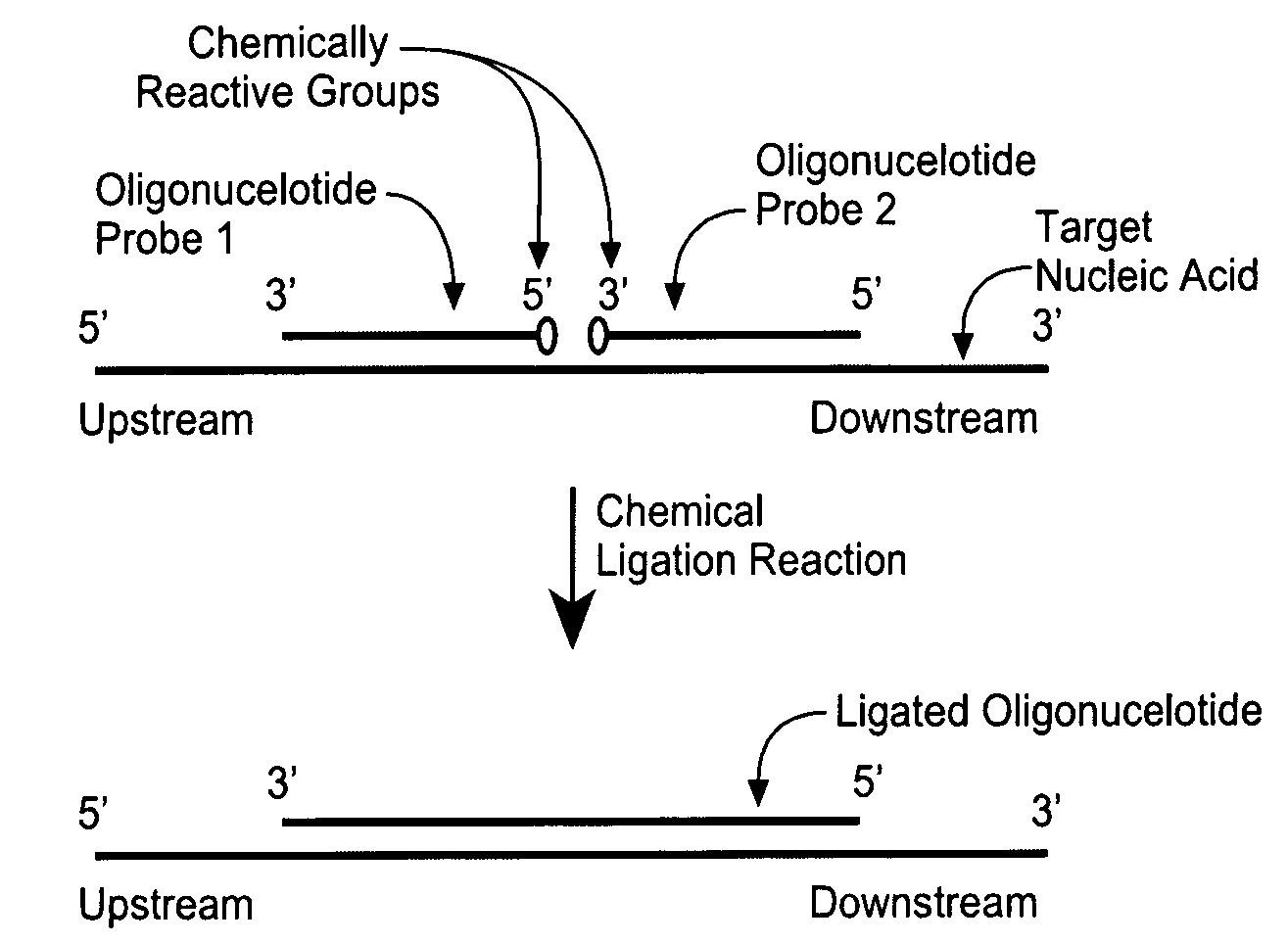
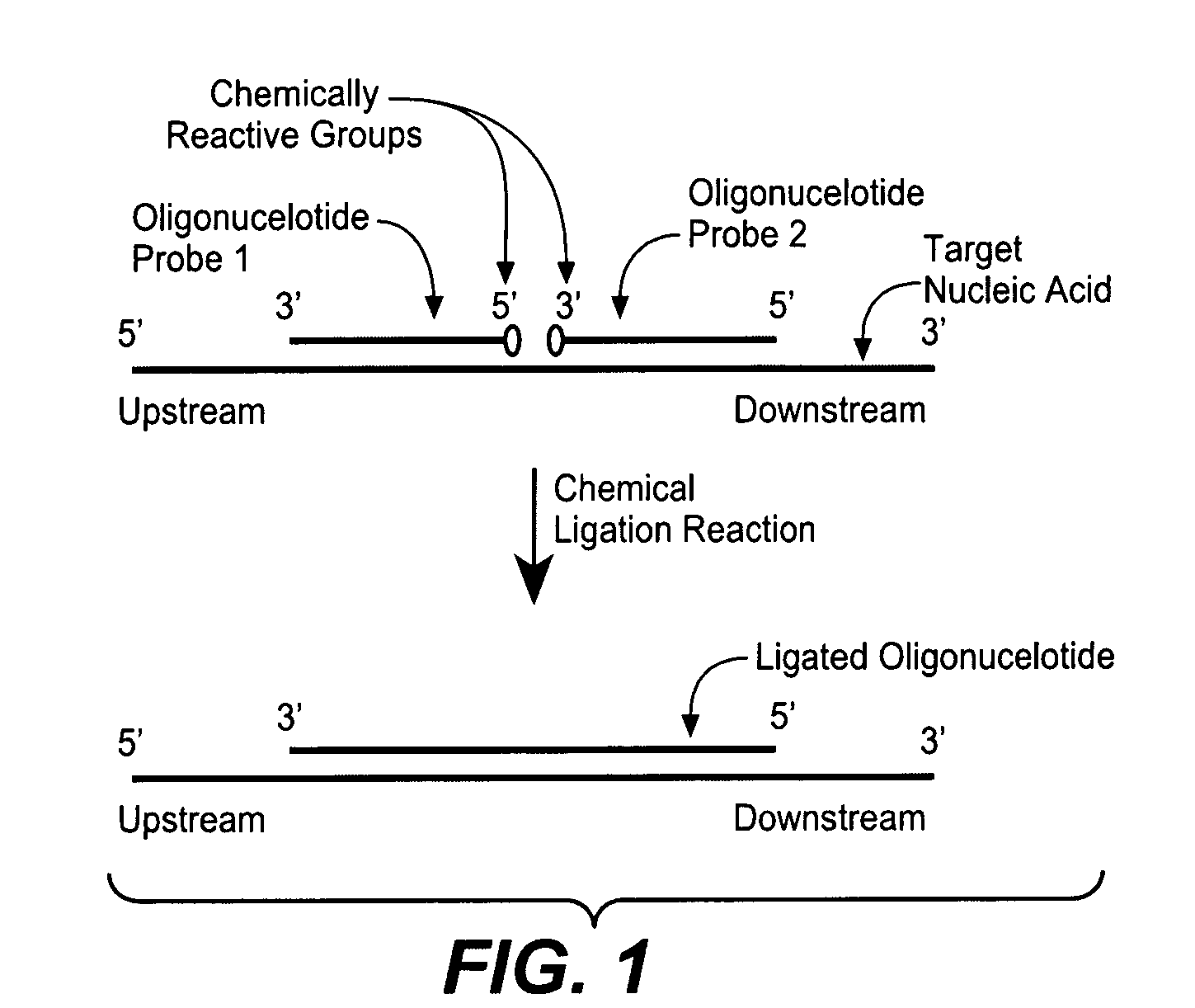
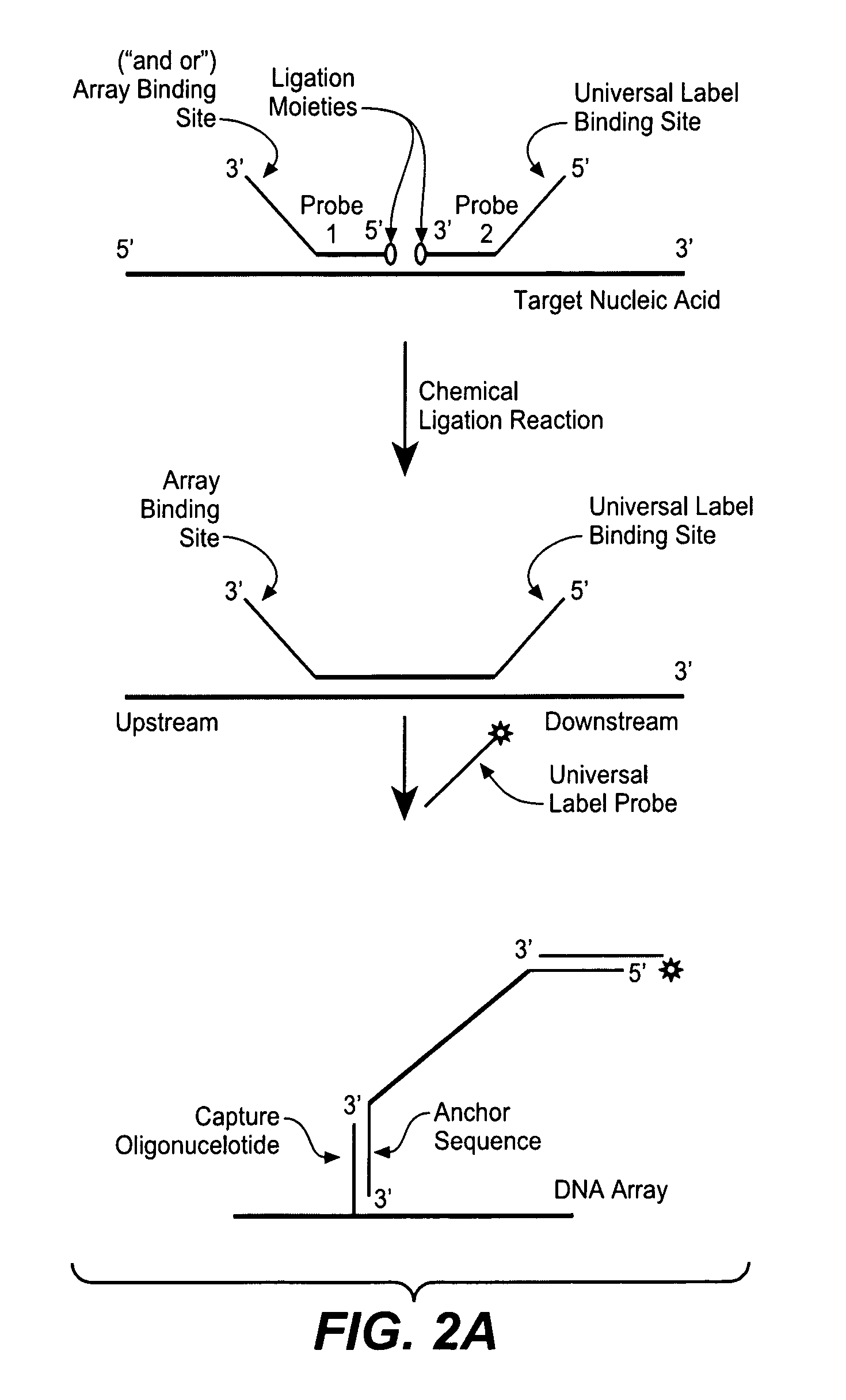
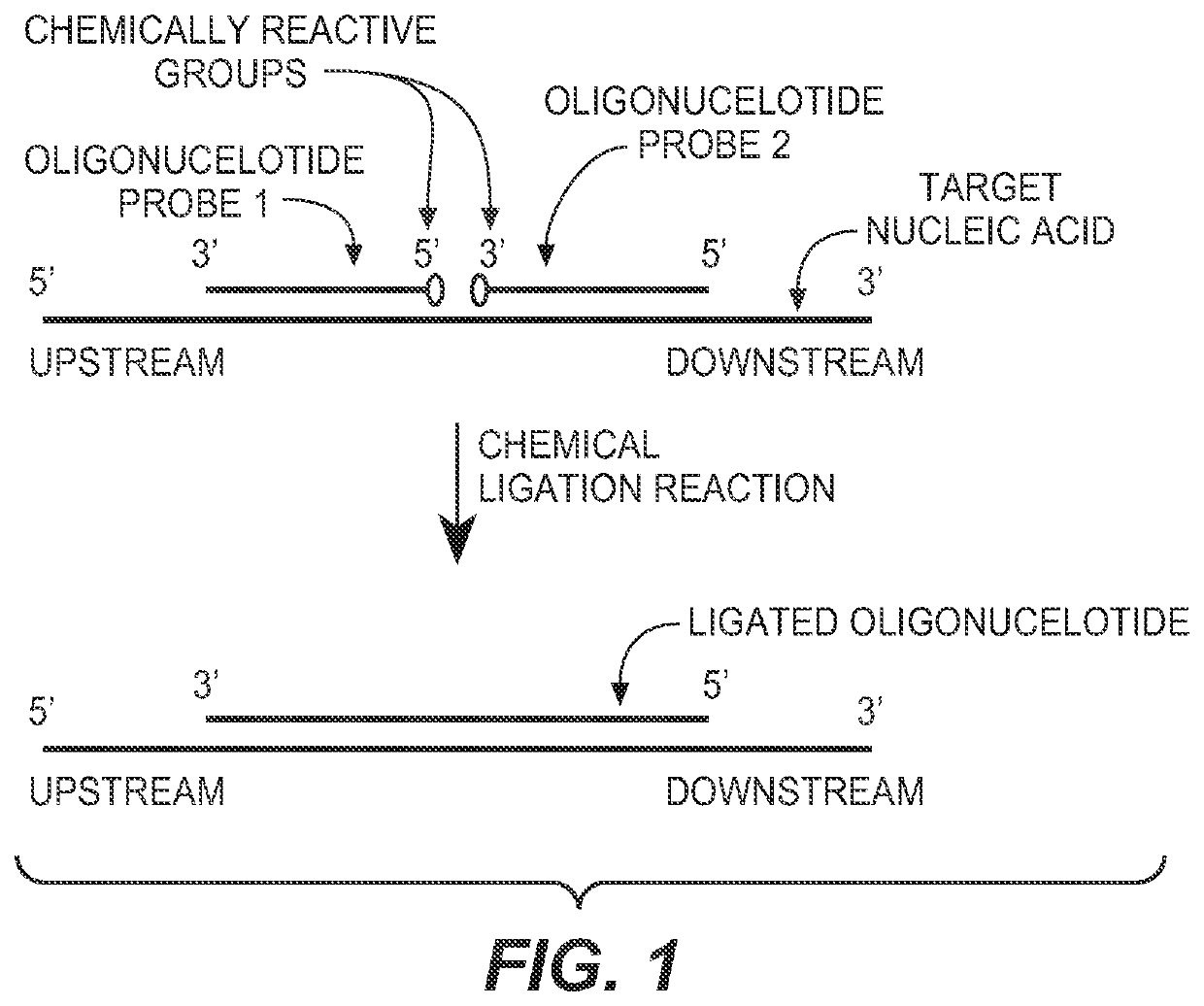
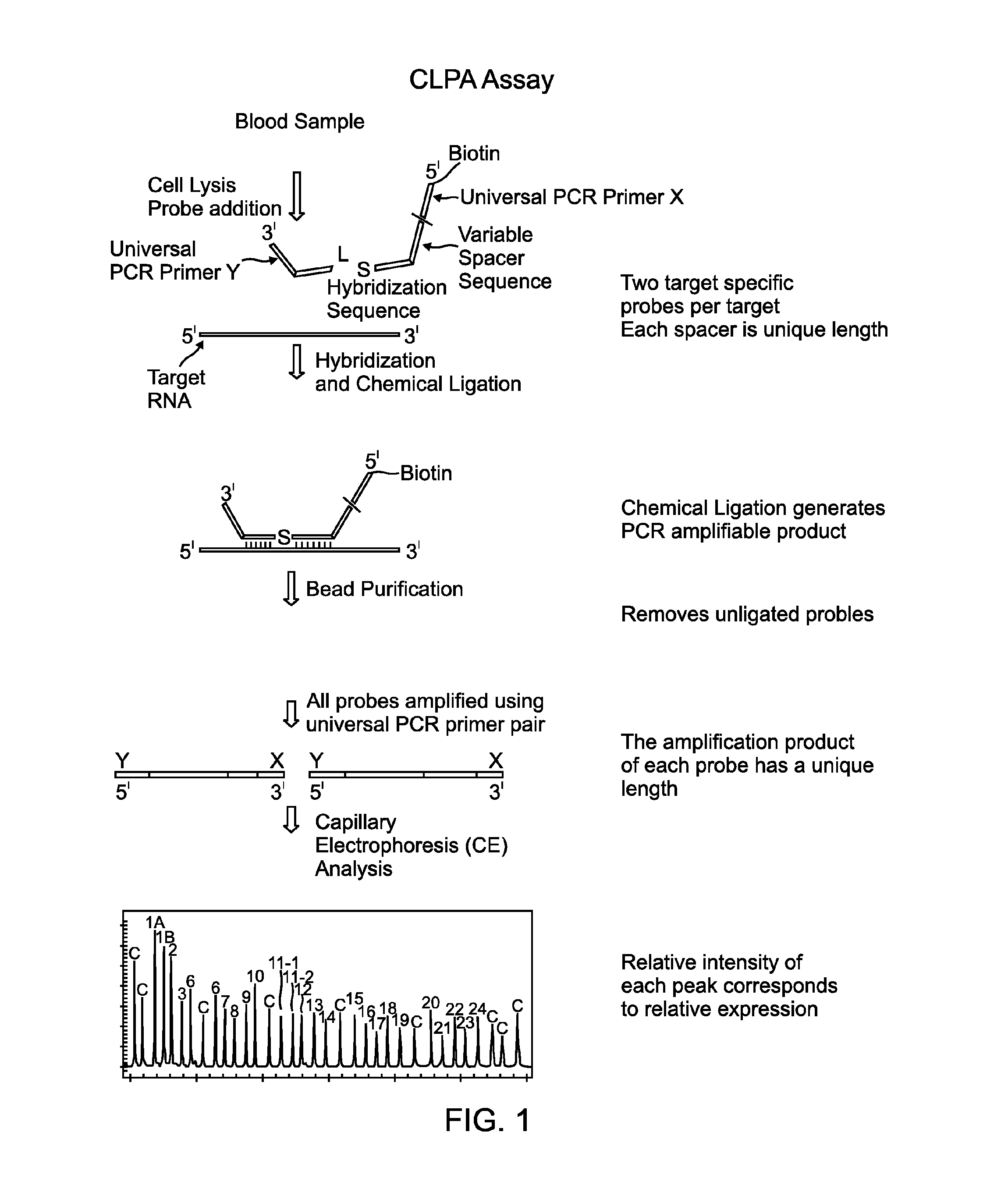
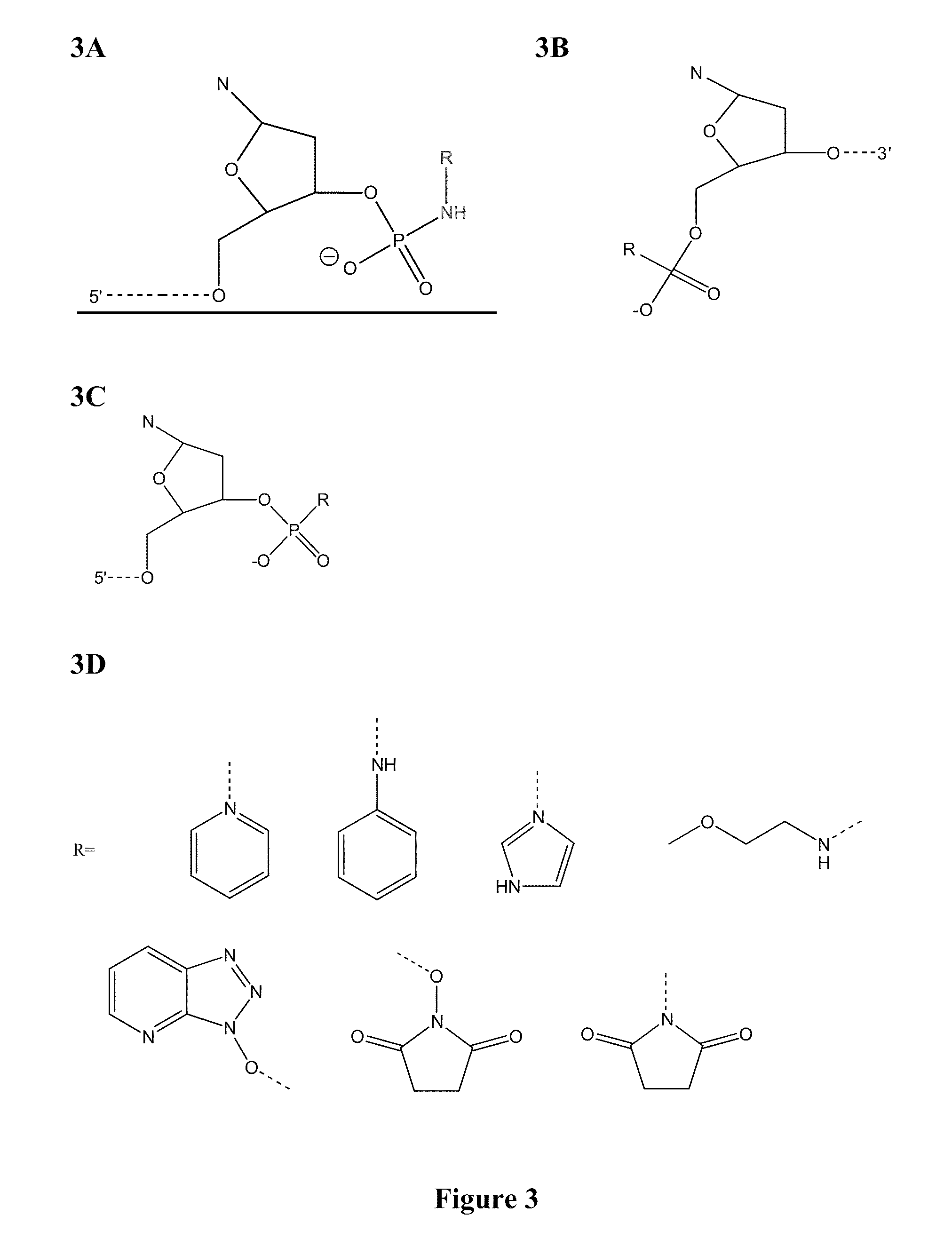
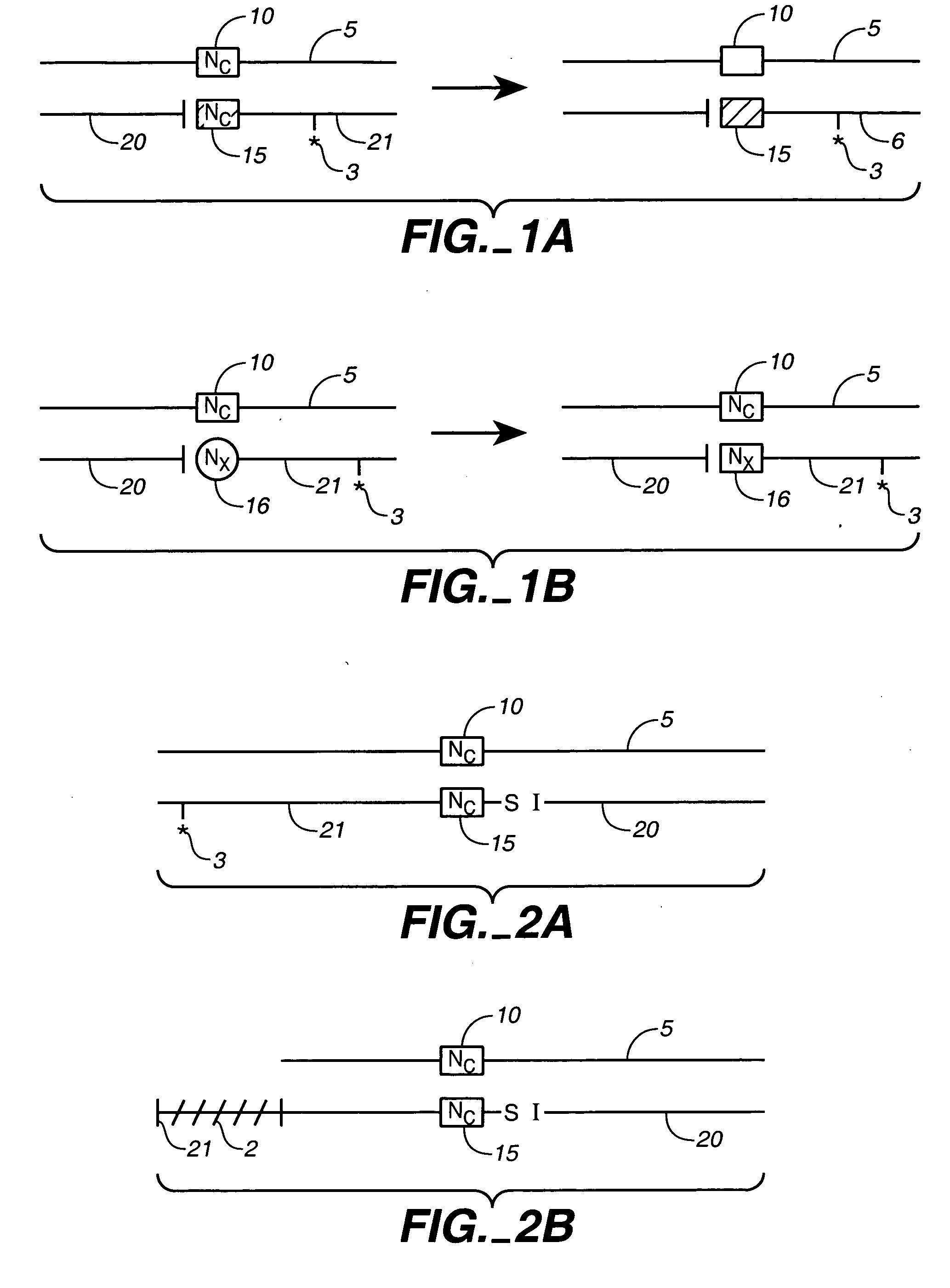
Detection of nucleic acid targets using chemically reactive oligonucleotide probes
ActiveUS20080124810A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical ligationChemical reaction
The present invention provides compositions, apparatuses and methods for detecting one or more nucleic acid targets present in a sample. Methods of the invention include utilizing two or more oligonucleotide probes that reversibly bind a target nucleic acid in close proximity to each other and possess complementary reactive ligation moieties. When such probes have bound to the target in the proper orientation, they are able to undergo a spontaneous chemical ligation reaction that yields a ligated oligonucleotide product. In accordance with the invention, the presence of the target(s) of interest can be determined by measuring the presence or amount of ligated oligonucleotide product.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
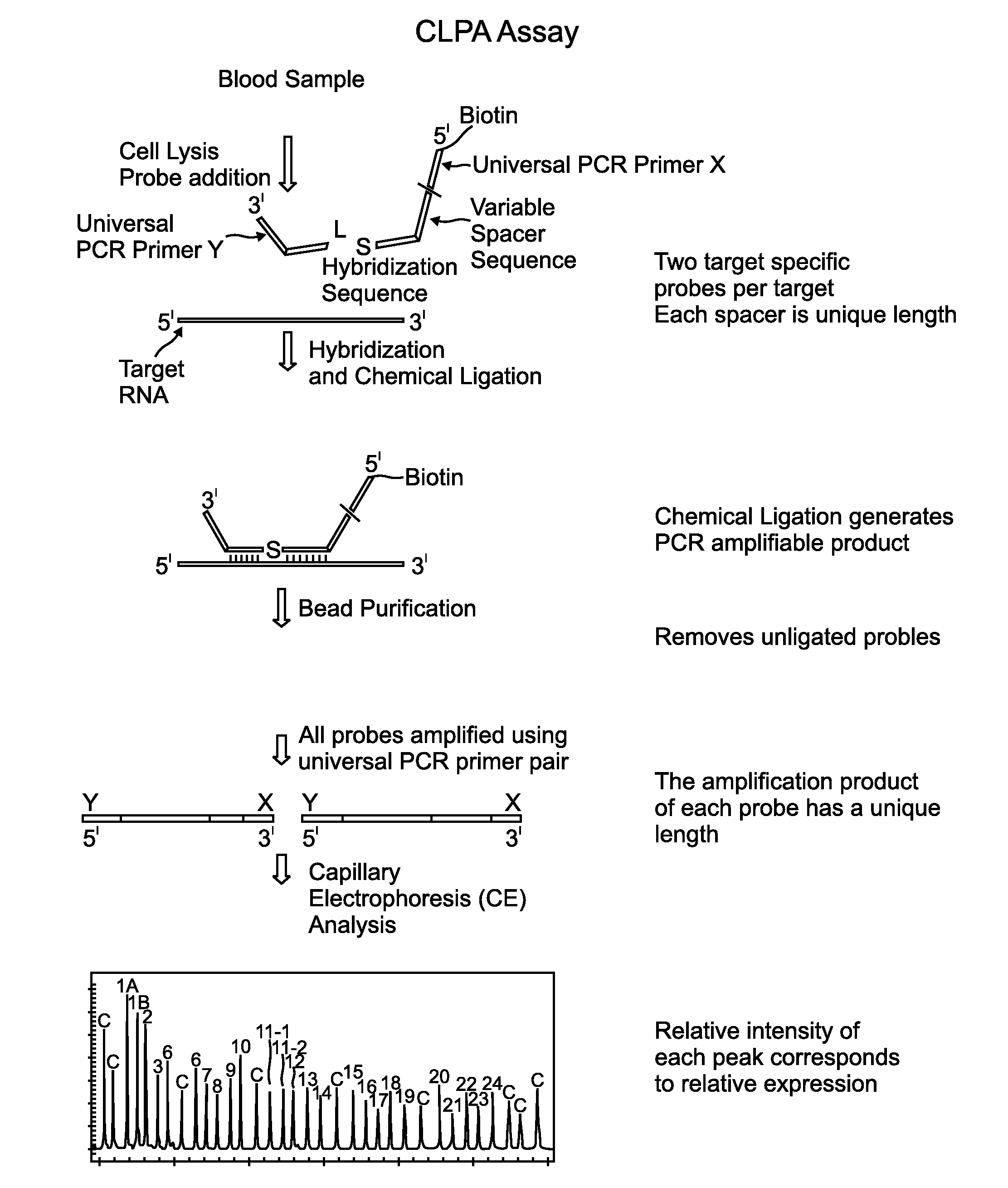
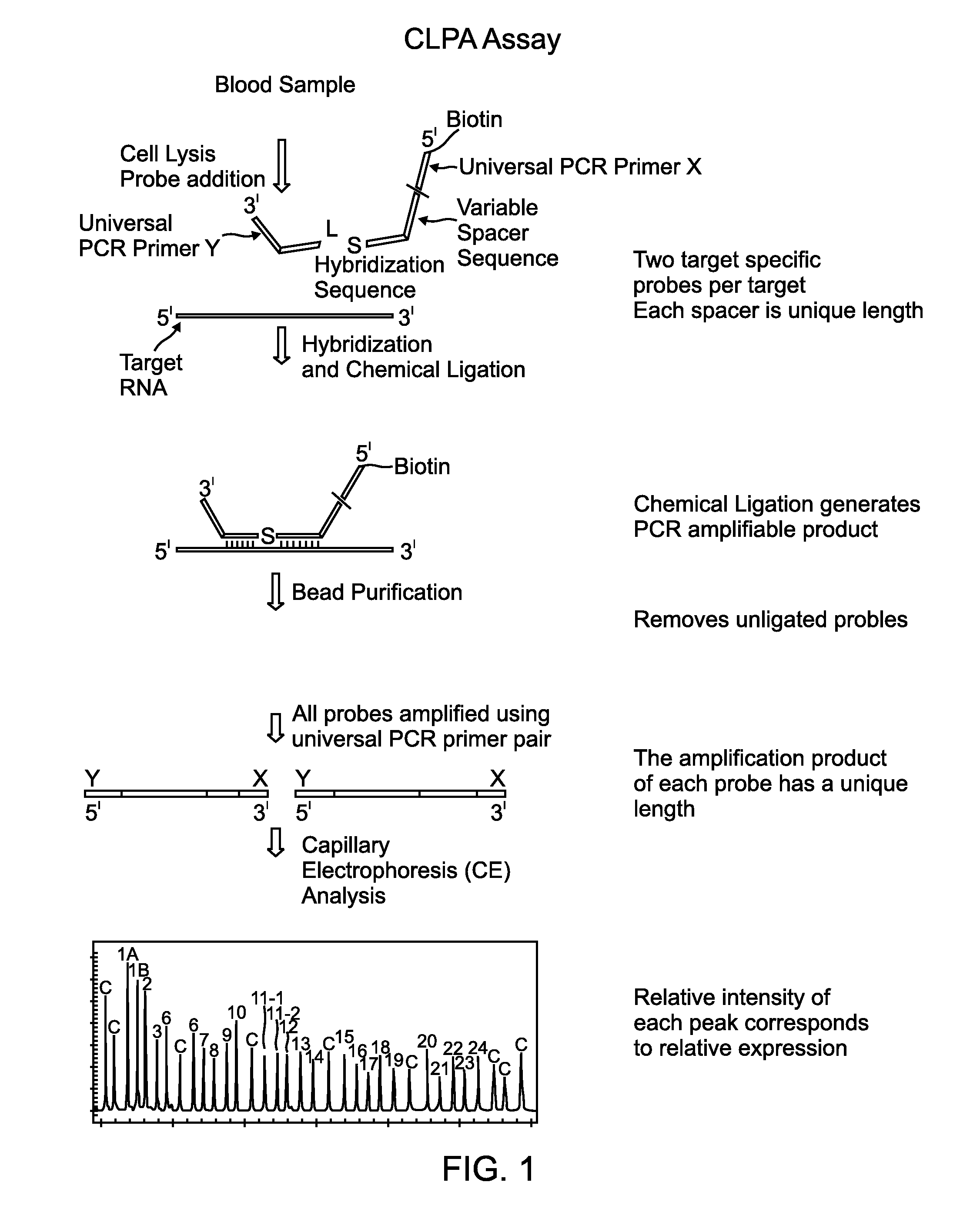
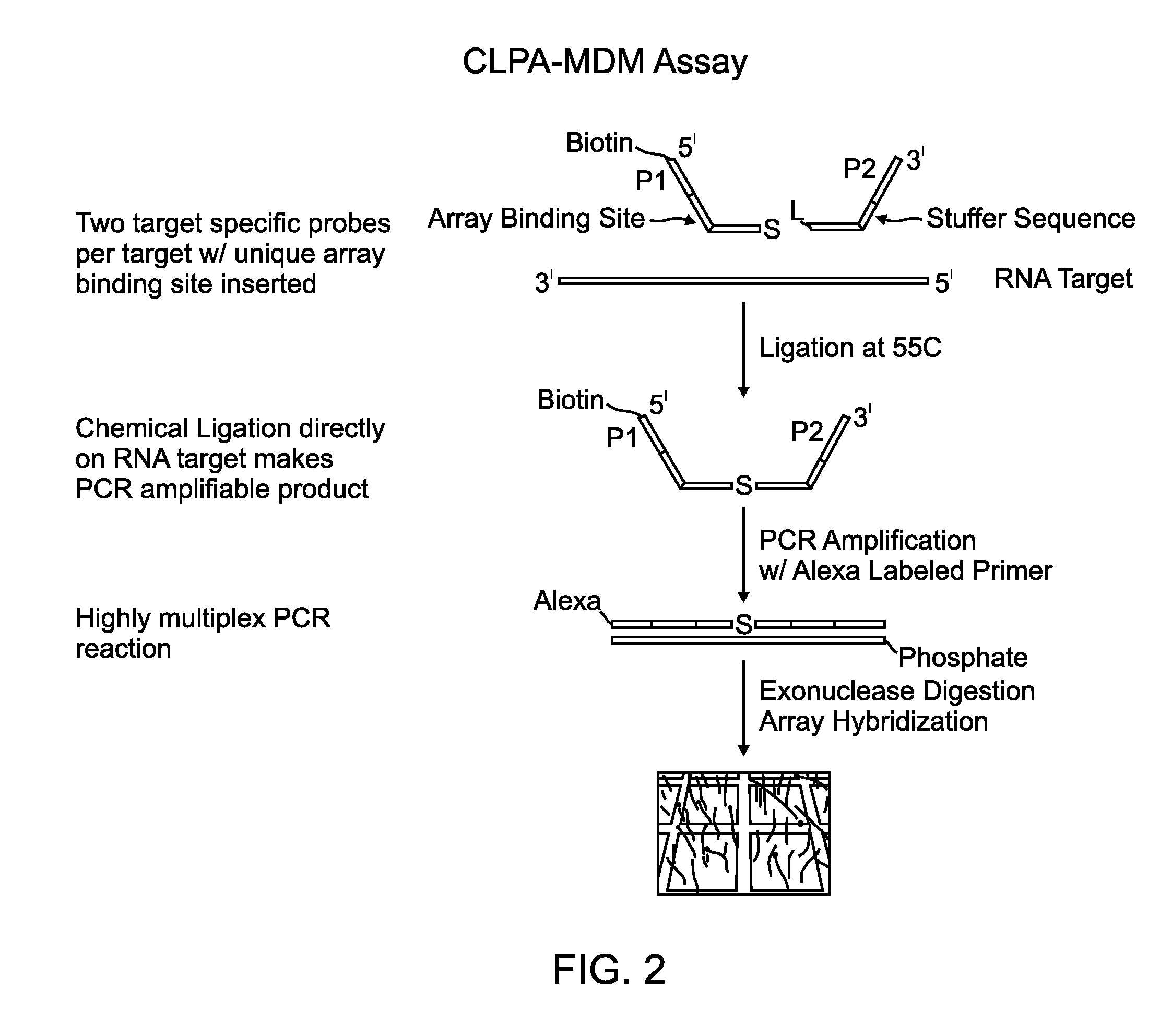
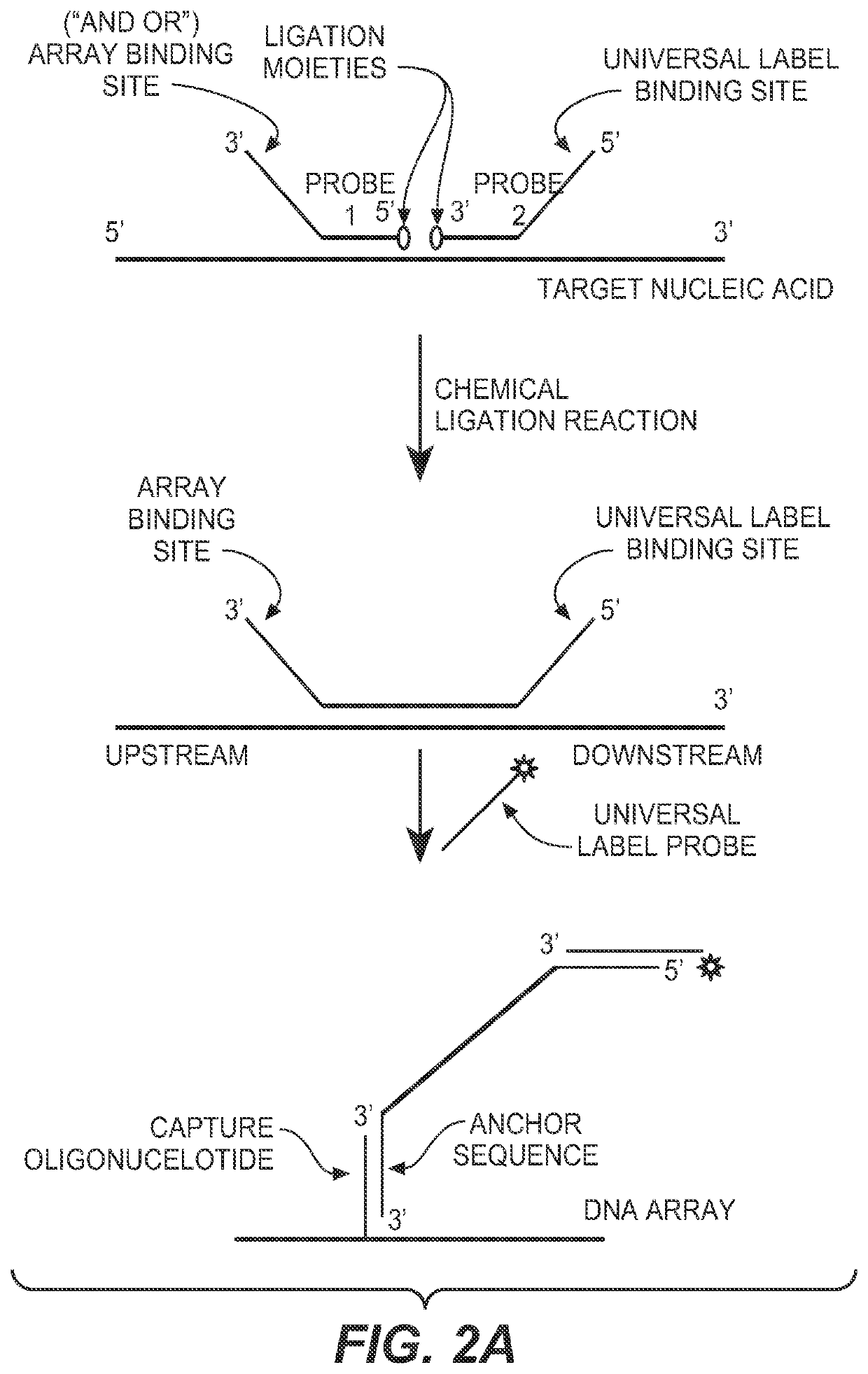
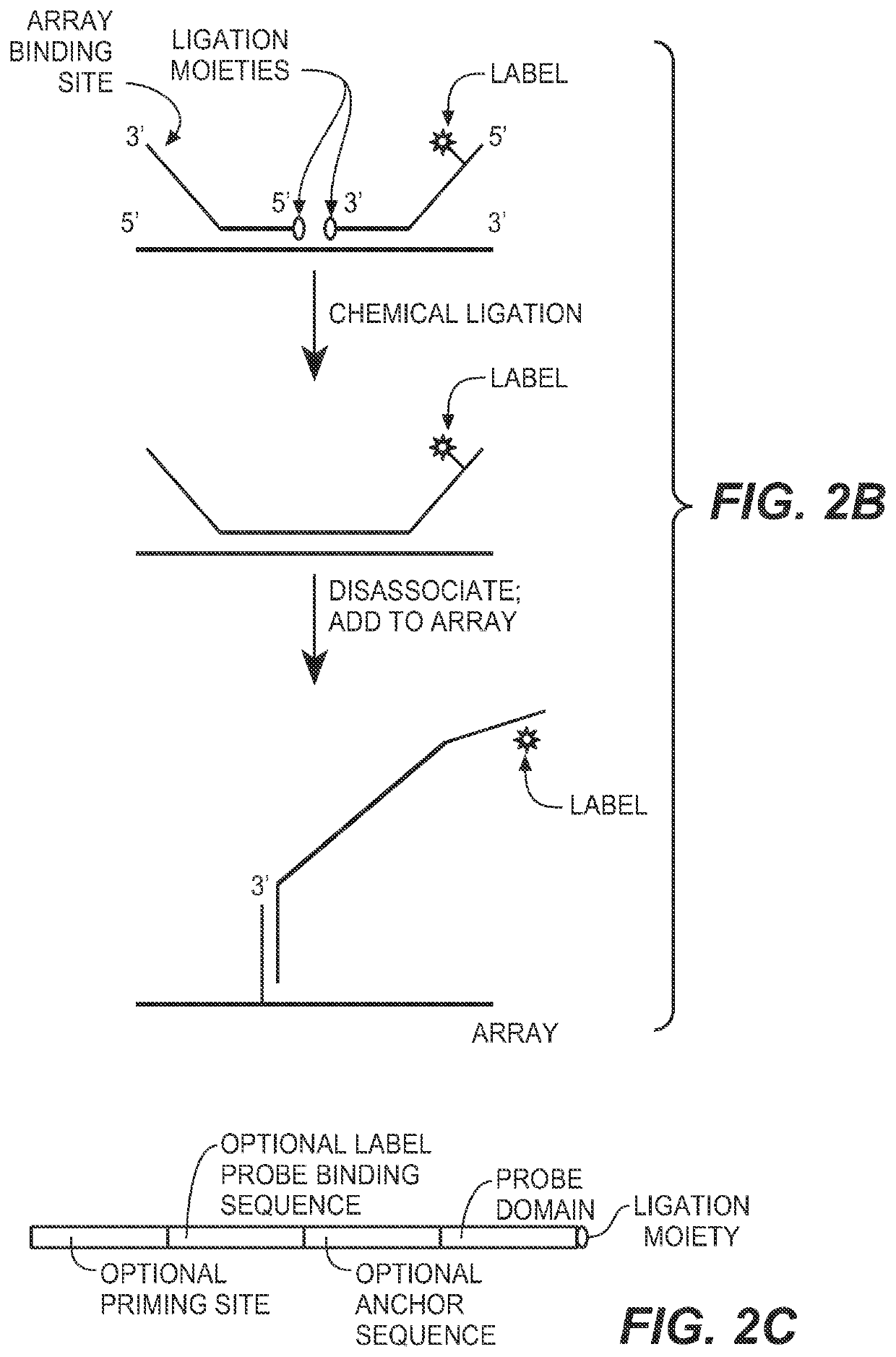
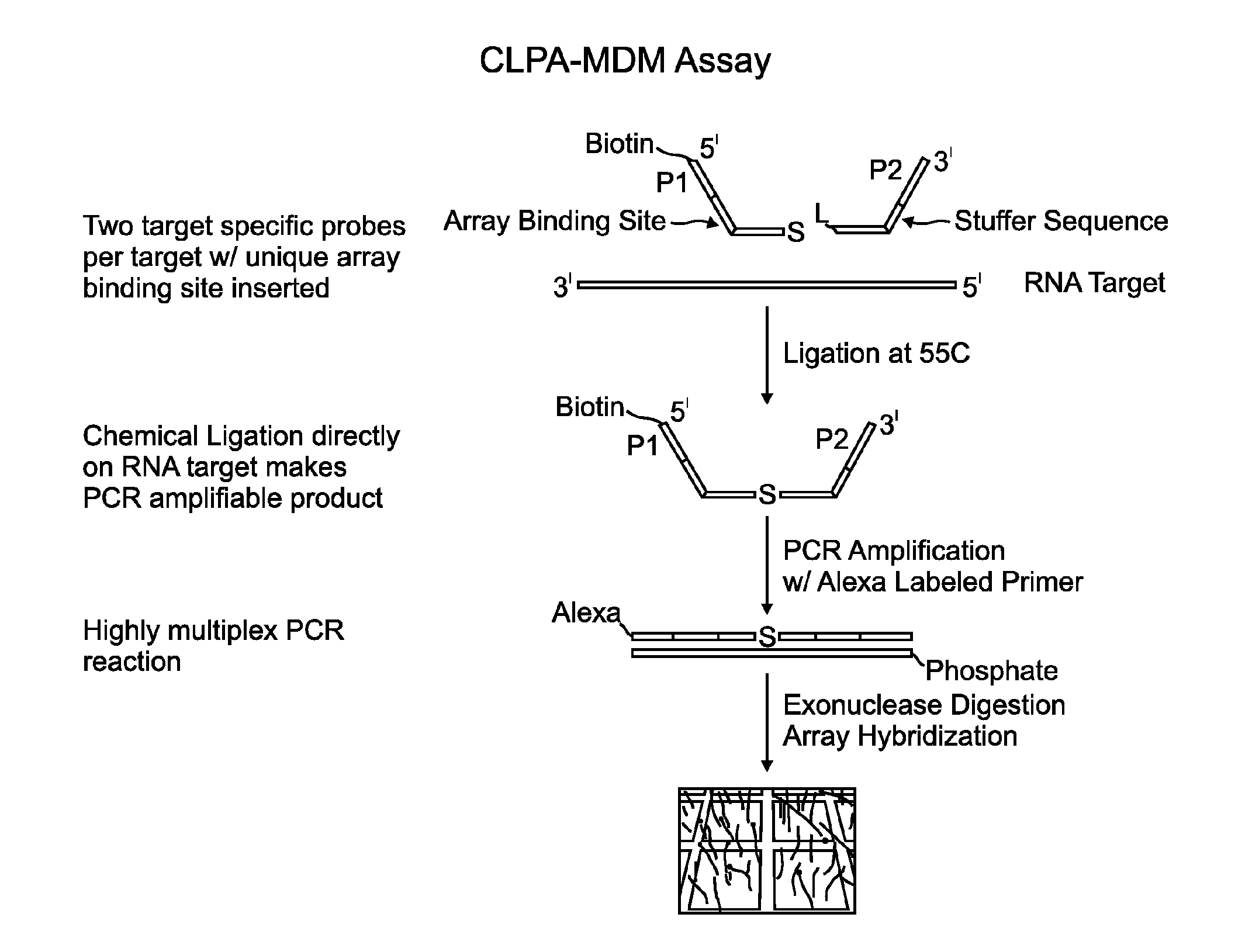
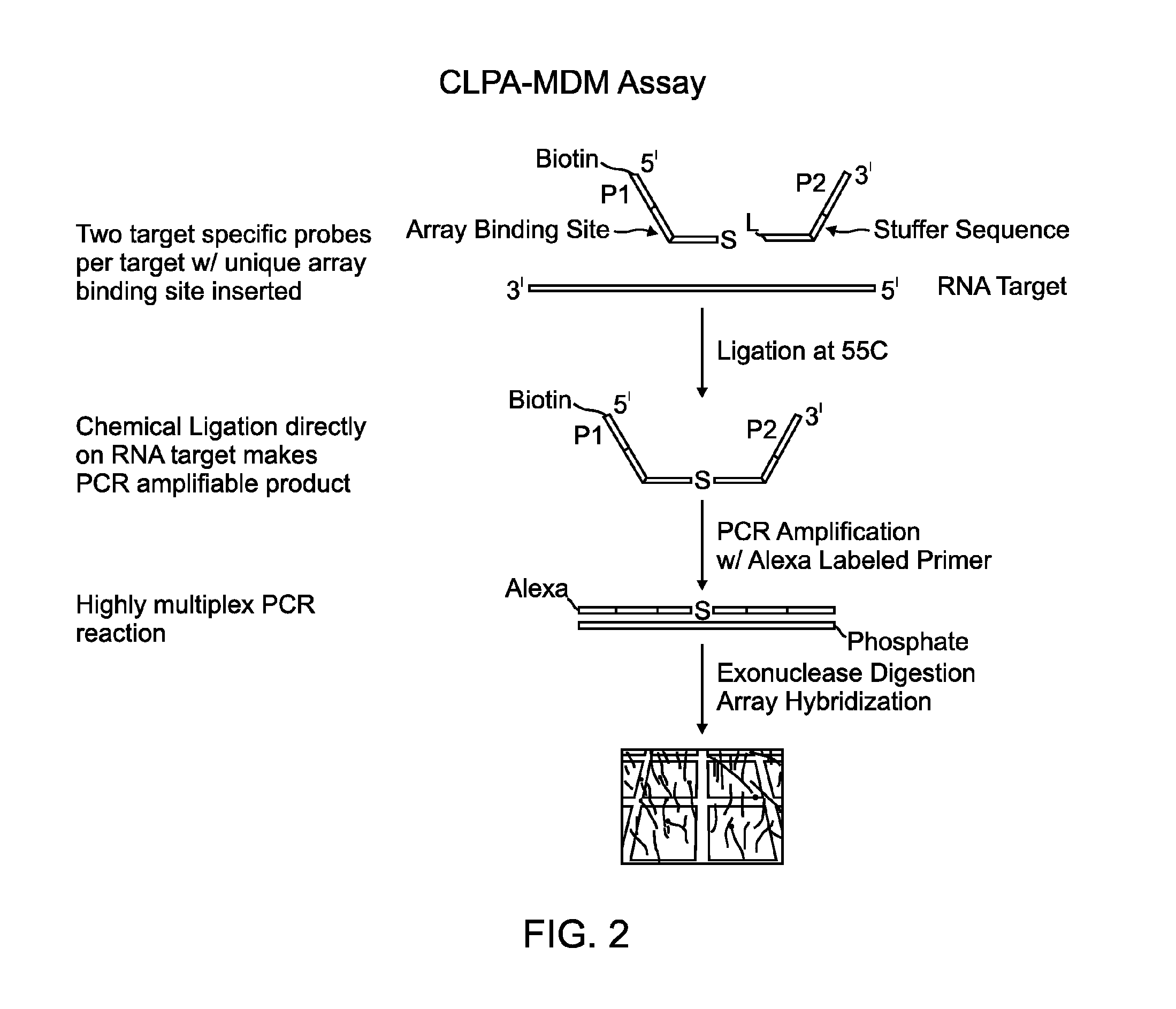
Chemical ligation dependent probe amplification (CLPA)
ActiveUS20100267585A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical ligationCapillary electrophoresis
The present invention provides compositions, apparatuses and methods for detecting one or more nucleic acid targets present in a sample. Methods of the invention include utilizing two or more oligonucleotide probes that reversibly bind a target nucleic acid in close proximity to each other and possess complementary reactive ligation moieties. When such probes have bound to the target in the proper orientation, they are able to undergo a spontaneous chemical ligation reaction that yields a ligated oligonucleotide product. In one aspect, the ligation product is of variable length that correlates with a particular target. Following chemical ligation, the probes may be amplified and detected by capillary electrophoresis or microarray analysis.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
Detection of nucleic acid targets using chemically reactive oligonucleotide probes
ActiveUS10829803B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical ligationChemical reaction
The present invention provides compositions, apparatuses and methods for detecting one or more nucleic acid targets present in a sample. Methods of the invention include utilizing two or more oligonucleotide probes that reversibly bind a target nucleic acid in close proximity to each other and possess complementary reactive ligation moieties. When such probes have bound to the target in the proper orientation, they are able to undergo a spontaneous chemical ligation reaction that yields a ligated oligonucleotide product. In accordance with the invention, the presence of the target(s) of interest can be determined by measuring the presence or amount of ligated oligonucleotide product.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
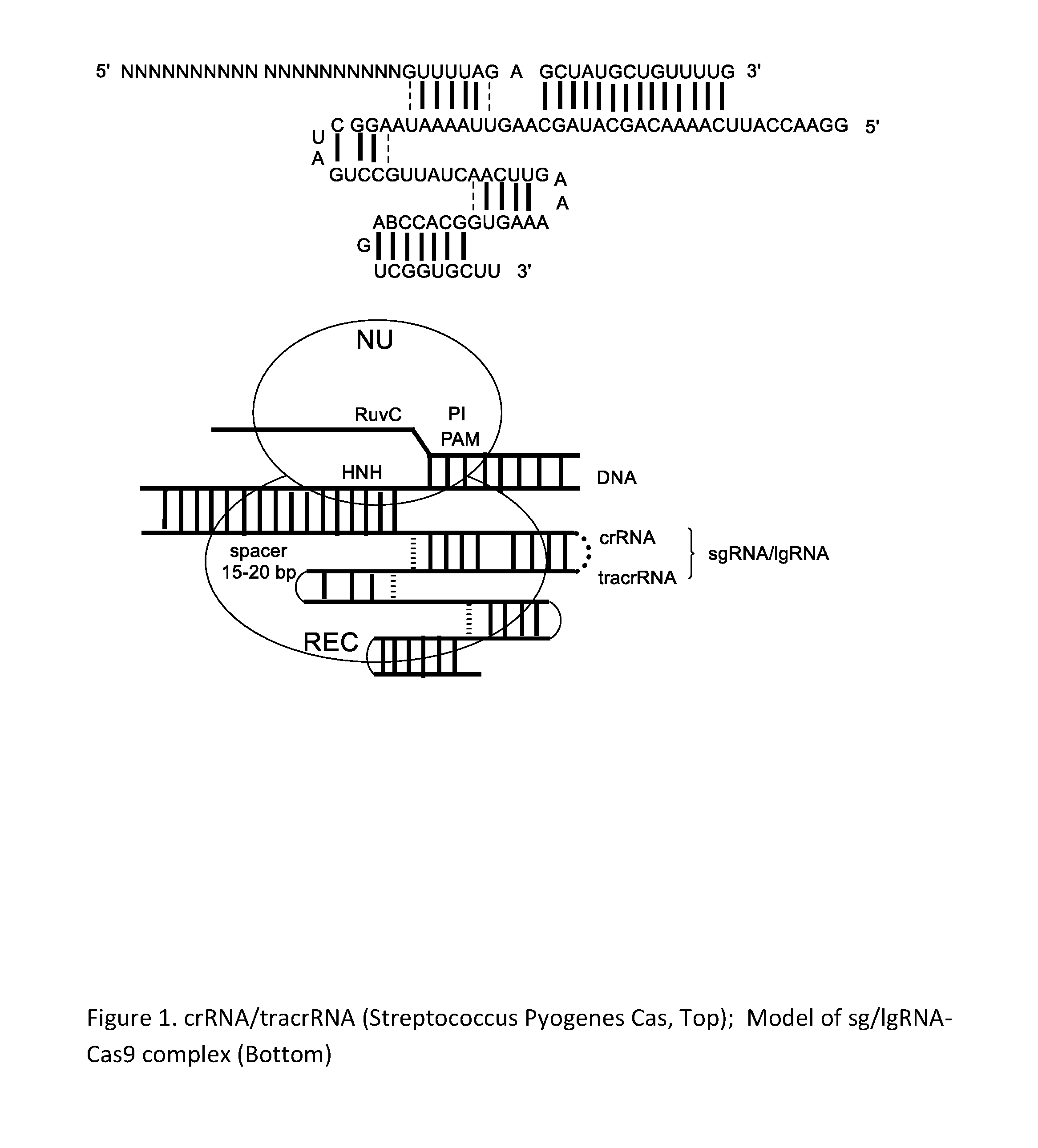
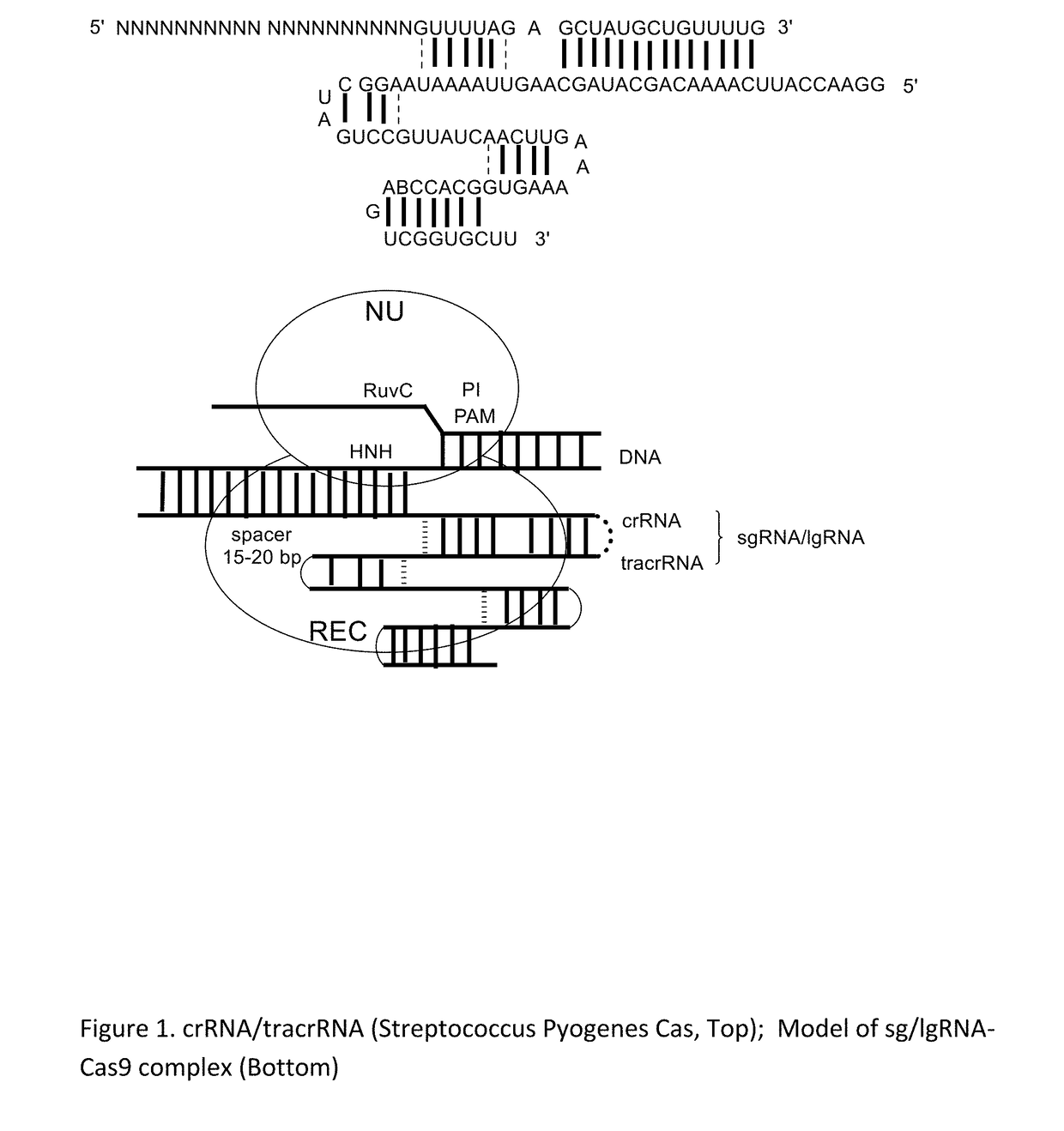
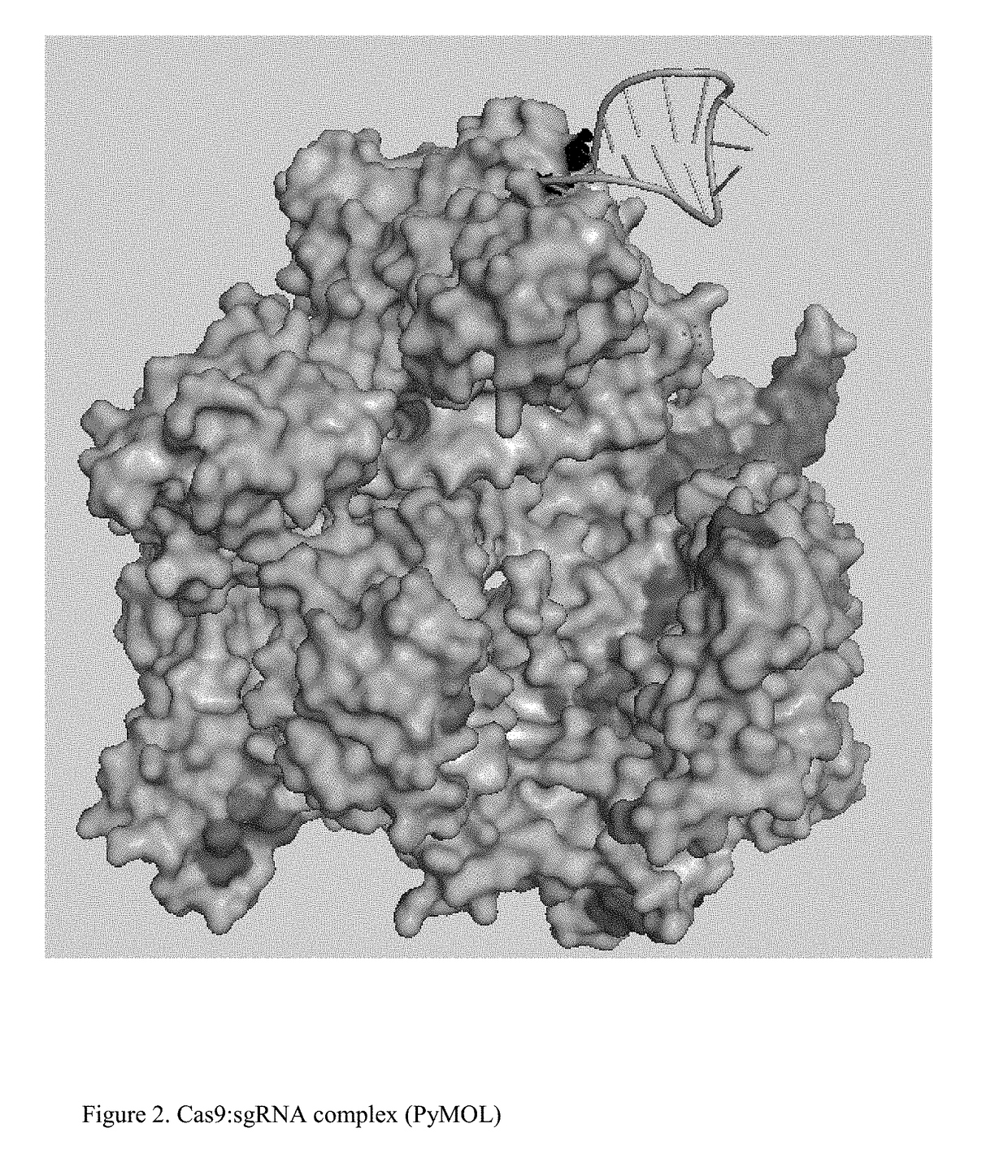
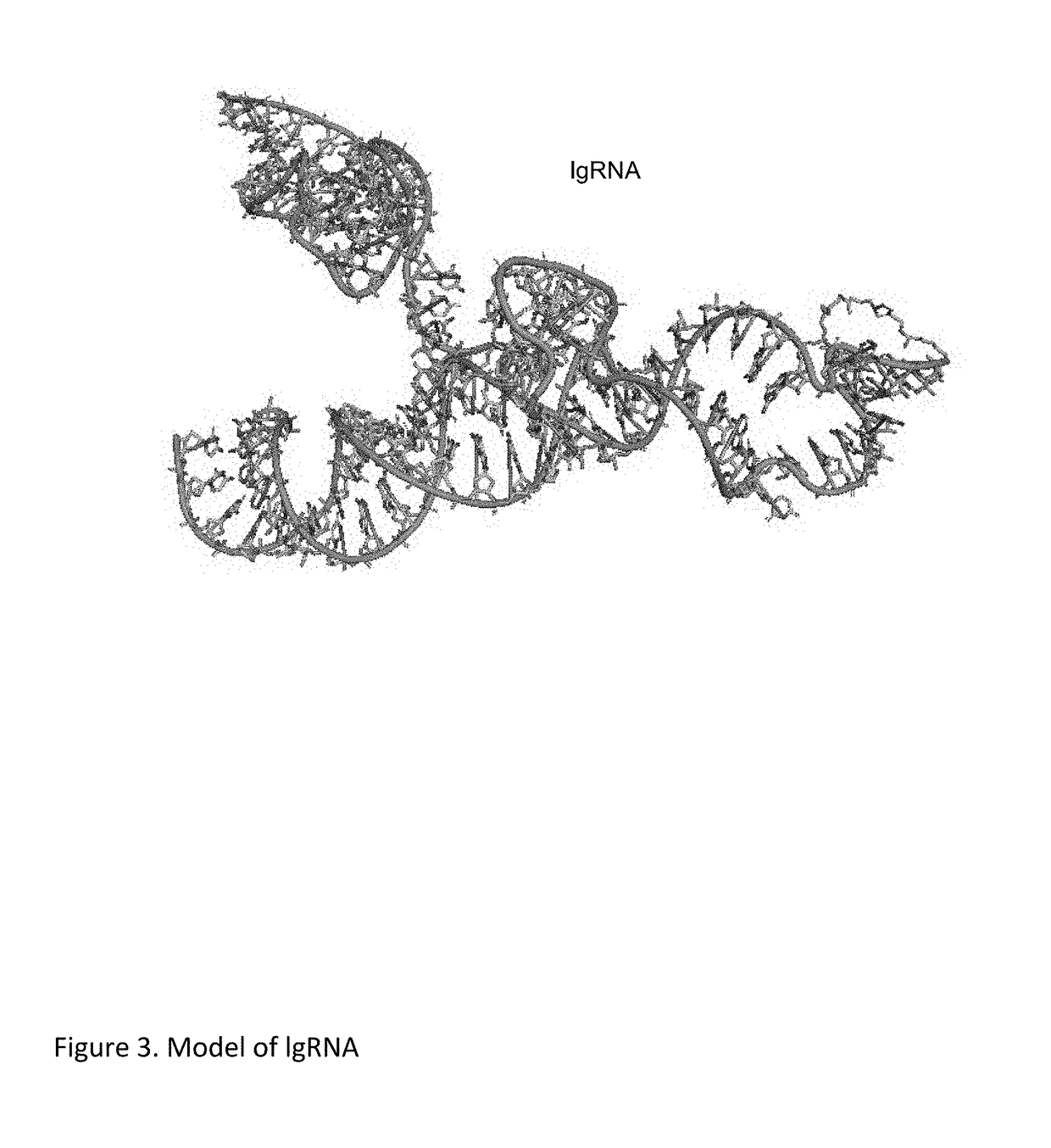
Chemically Ligated RNAs for CRISPR/Cas9-lgRNA Complexes as Antiviral Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20160215275A1Good effectMinimizing off-target cleavagesOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical ligationNucleotide
Provided herein are chemically ligated guide RNA oligonucleotides (lgRNA) which comprise two functional RNA modules (crgRNA and tracrgRNA) joined by non-nucleotide chemical linkers (nNt-linker), their complexes with CRISPR-Cas9, preparation methods of Cas9-lgRNA complexes, and their uses for treatments of viral infections in humans. Also disclosed are processes and methods for preparation of these compounds.
Owner:ZHONG MINGHONG
Methods and compositions for detecting target nucleic acids
ActiveUS20130005594A1Rapid target detectionSimple processNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical ligationBioinformatics
The present invention provides compositions, apparatuses and methods for detecting one or more nucleic acid targets present in a sample. Methods of the invention include utilizing two or more ligation probes that reversibly bind a target nucleic acid in close proximity to each other and possess complementary reactive ligation moieties. When such probes have bound to the target in the proper orientation, they are able to undergo a spontaneous chemical ligation reaction that yields a ligation product that is directly detected or that is amplified to produce amplicons that are then detected. The present invention also provides methods to stabilize sample RNA so that degradation does not significantly affect the results of the analysis.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
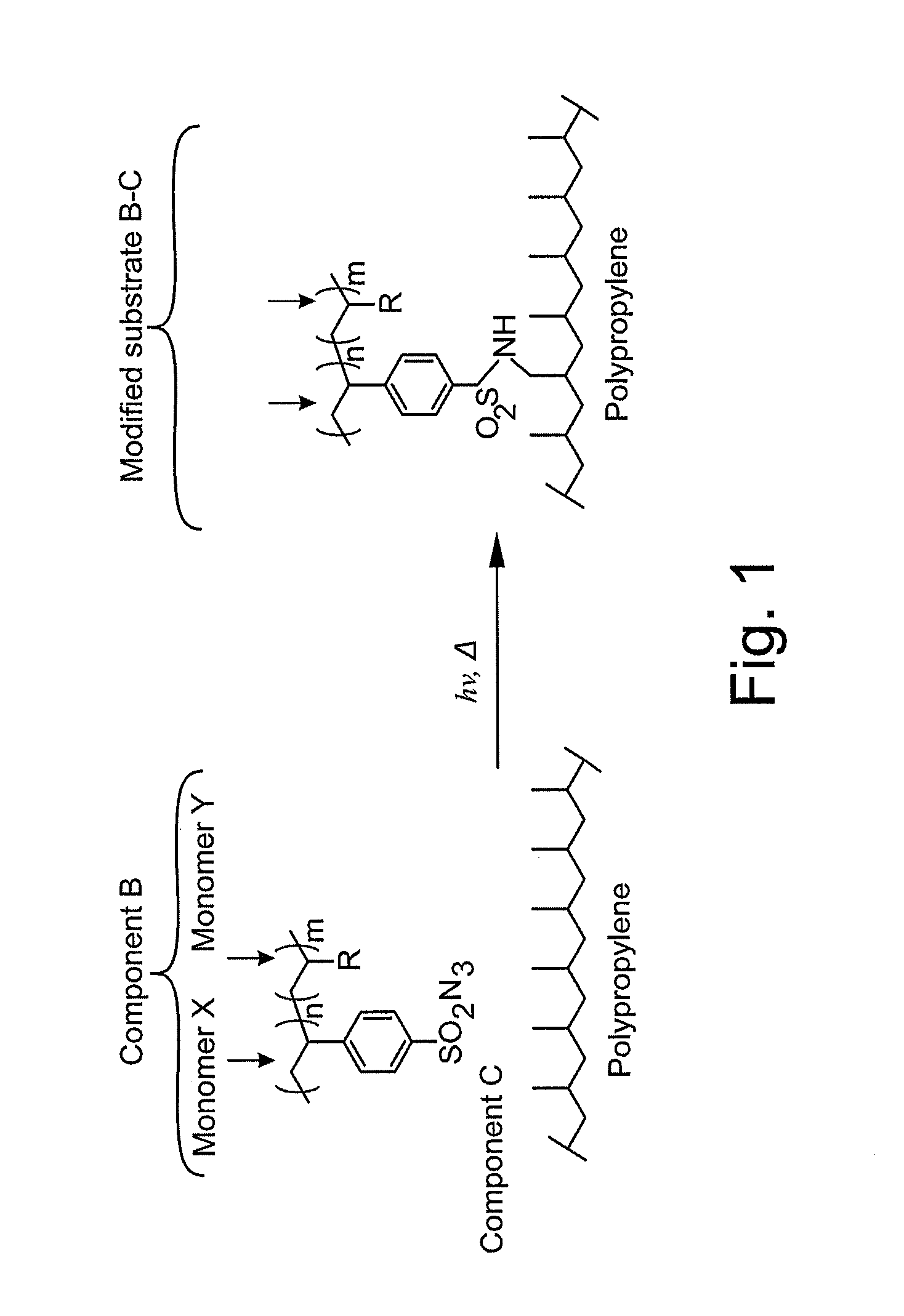
Process for surface modifying substrates and modified substrates resulting therefrom
The present invention generally relates to a method of modifying the surface of substrates such as contact lenses and other biomedical articles by at least partially coating the surfaces of such substrates with a polymeric tie layer having reactive sites. Various other moieties may then be chemically attached to the article surface by reaction of the other moieties with the reactive sites through classical chemical attachment mechanisms.
Owner:ALCON INC
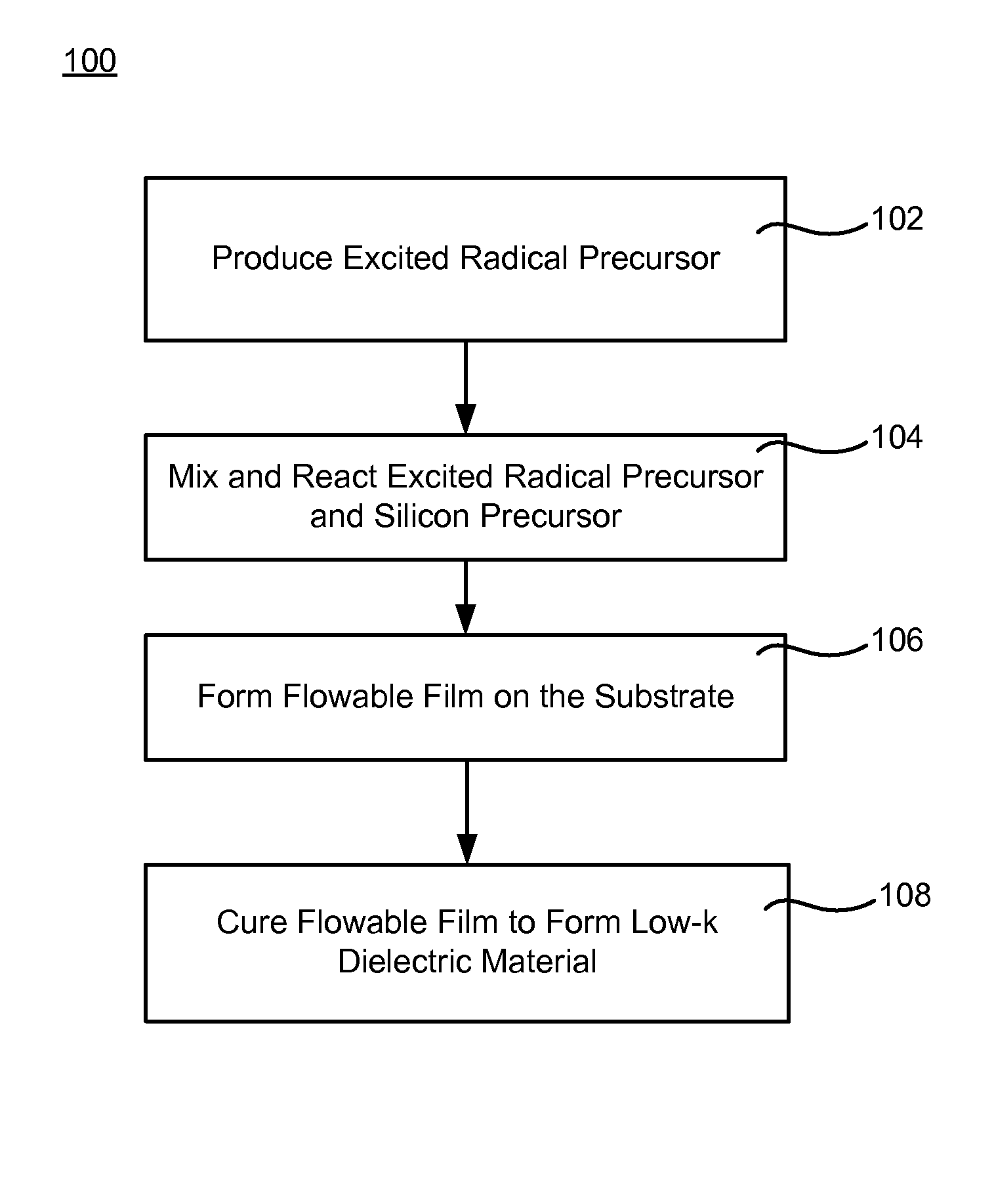
Chemical linkers to impart improved mechanical strength to flowable films
InactiveUS20140302690A1High mechanical strengthHigh strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaChemical ligation
Methods forming a low-κ dielectric material on a substrate are described. The methods may include the steps of producing a radical precursor by flowing an unexcited precursor into a remote plasma region, and reacting the radical precursor with a gas-phase silicon precursor to deposit a flowable film on the substrate. The gas-phase silicon precursor may include at least one silicon-and-oxygen containing compound and at least one silicon-and-carbon linker. The flowable film may be cured to form the low-κ dielectric material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
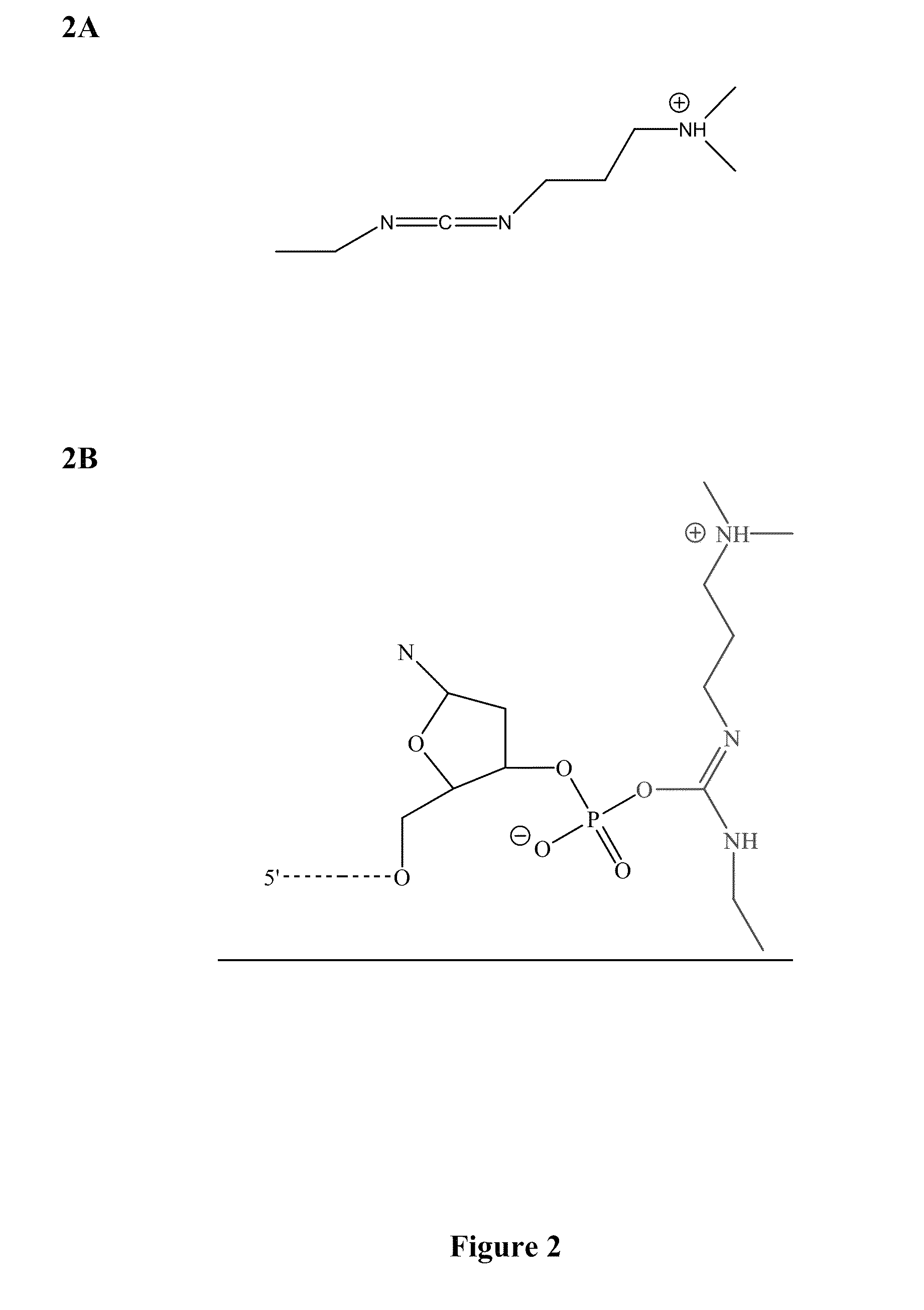
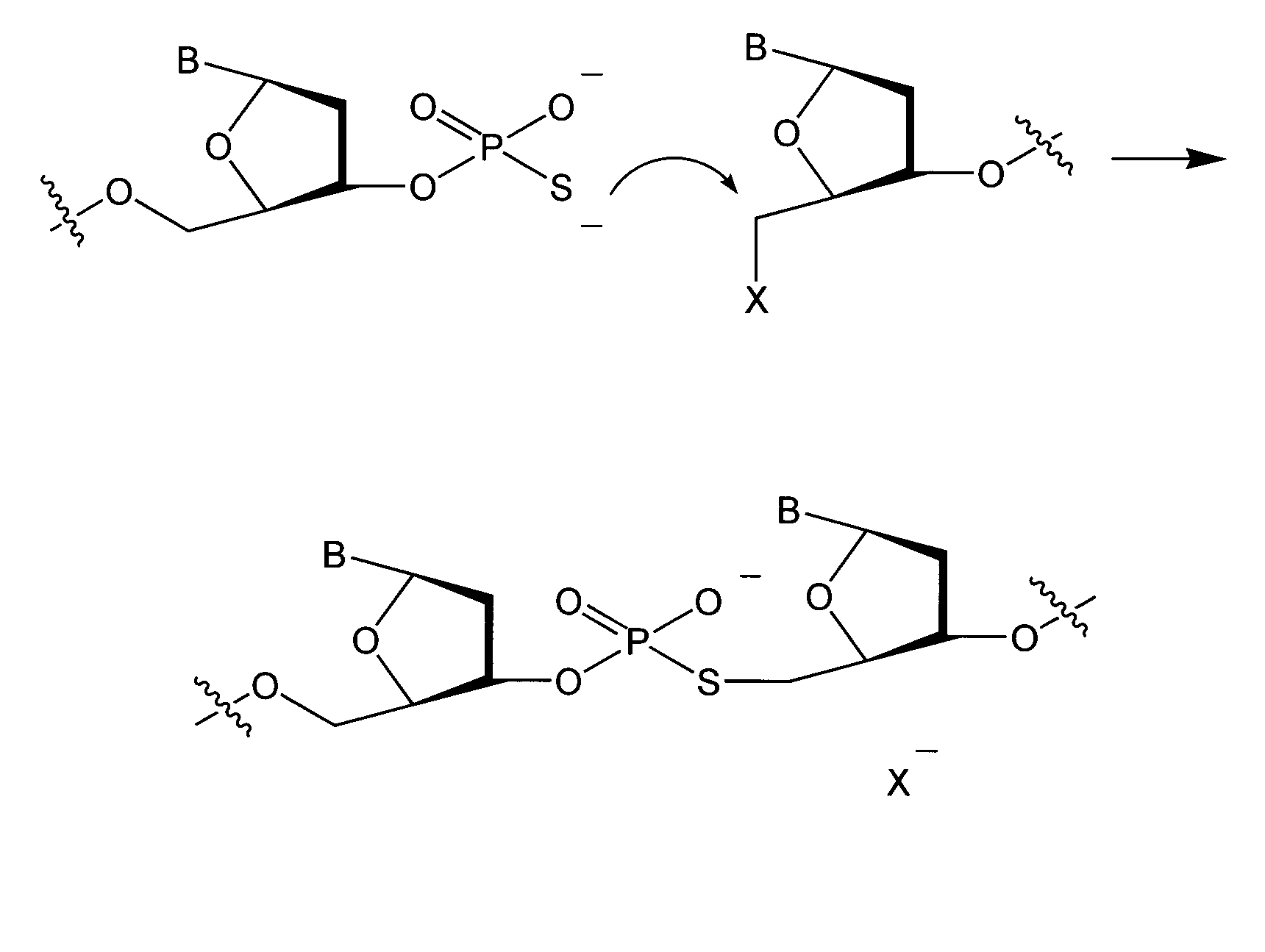
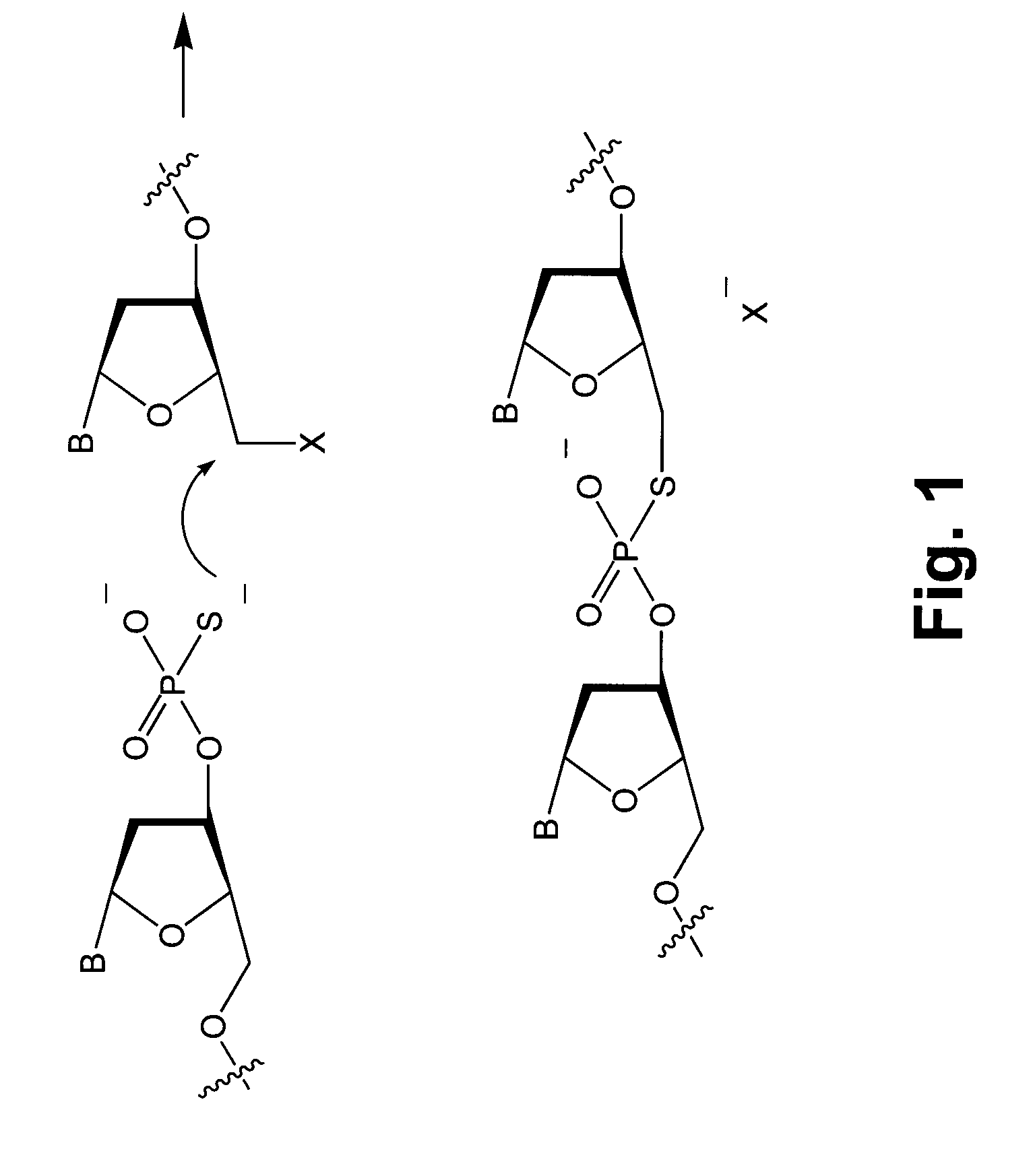
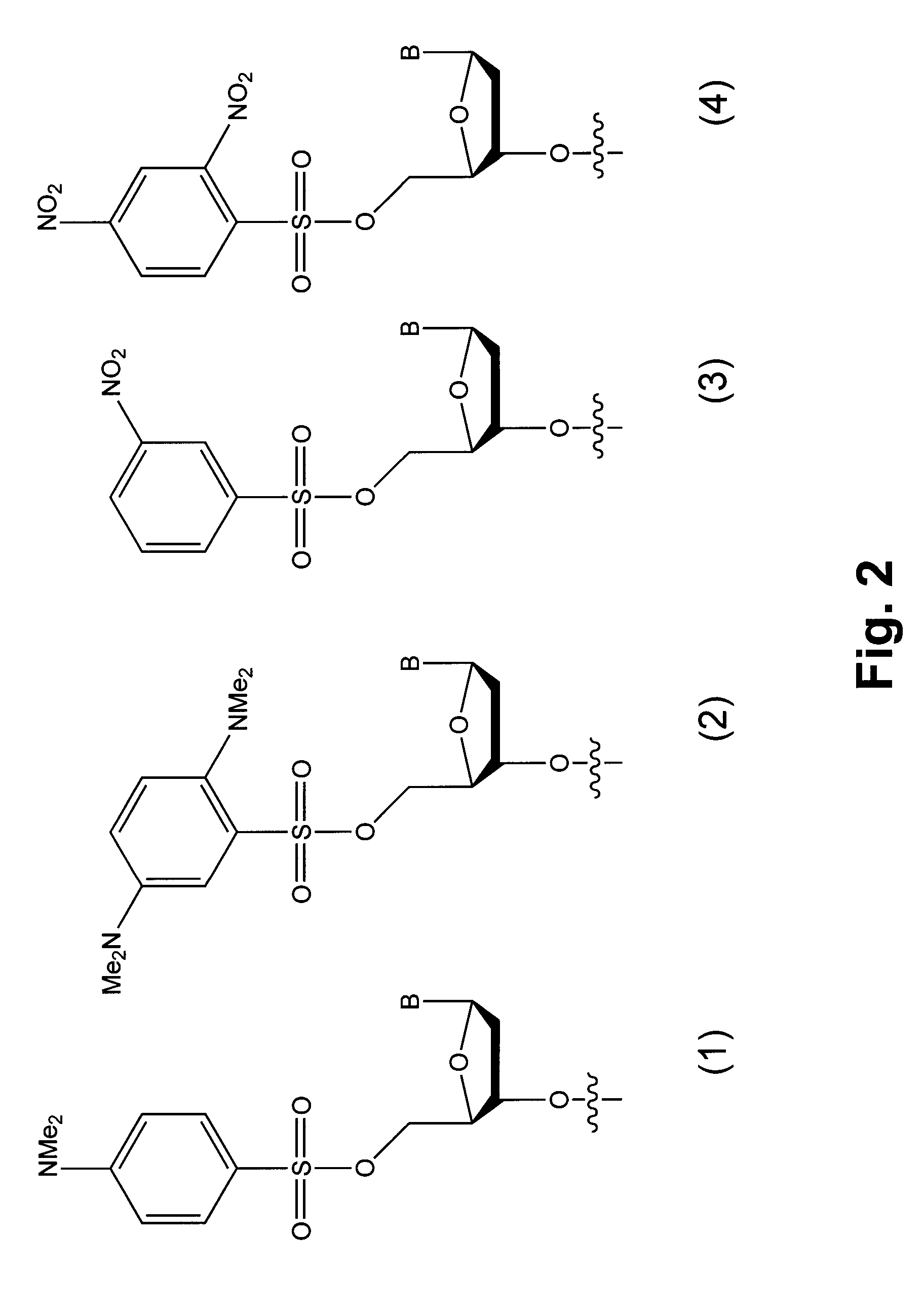
Methods and compounds for chemical ligation
ActiveUS8481258B2Eliminating risk of UV damageSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical ligationNucleic acid sequencing
Compositions and methods for chemical ligation are provided. Methods for nucleic acid sequencing, nucleic acid assembly and nucleic acid synthesis are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
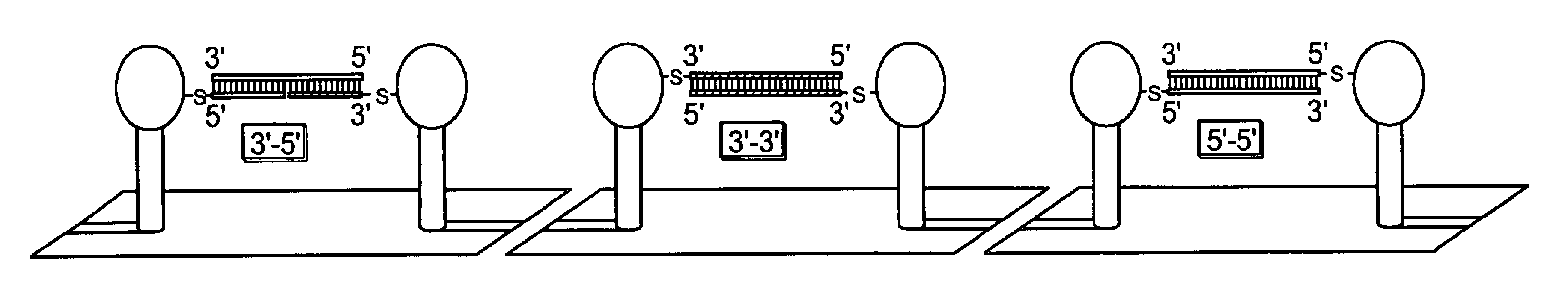
Chemical ligation of nucleic acids
The invention relates to the field of nucleic acid analysis. More particularly, the invention relates to compositions and methods used for the detection of sequence variations or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in a nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:CLINICAL MICRO SENSORS
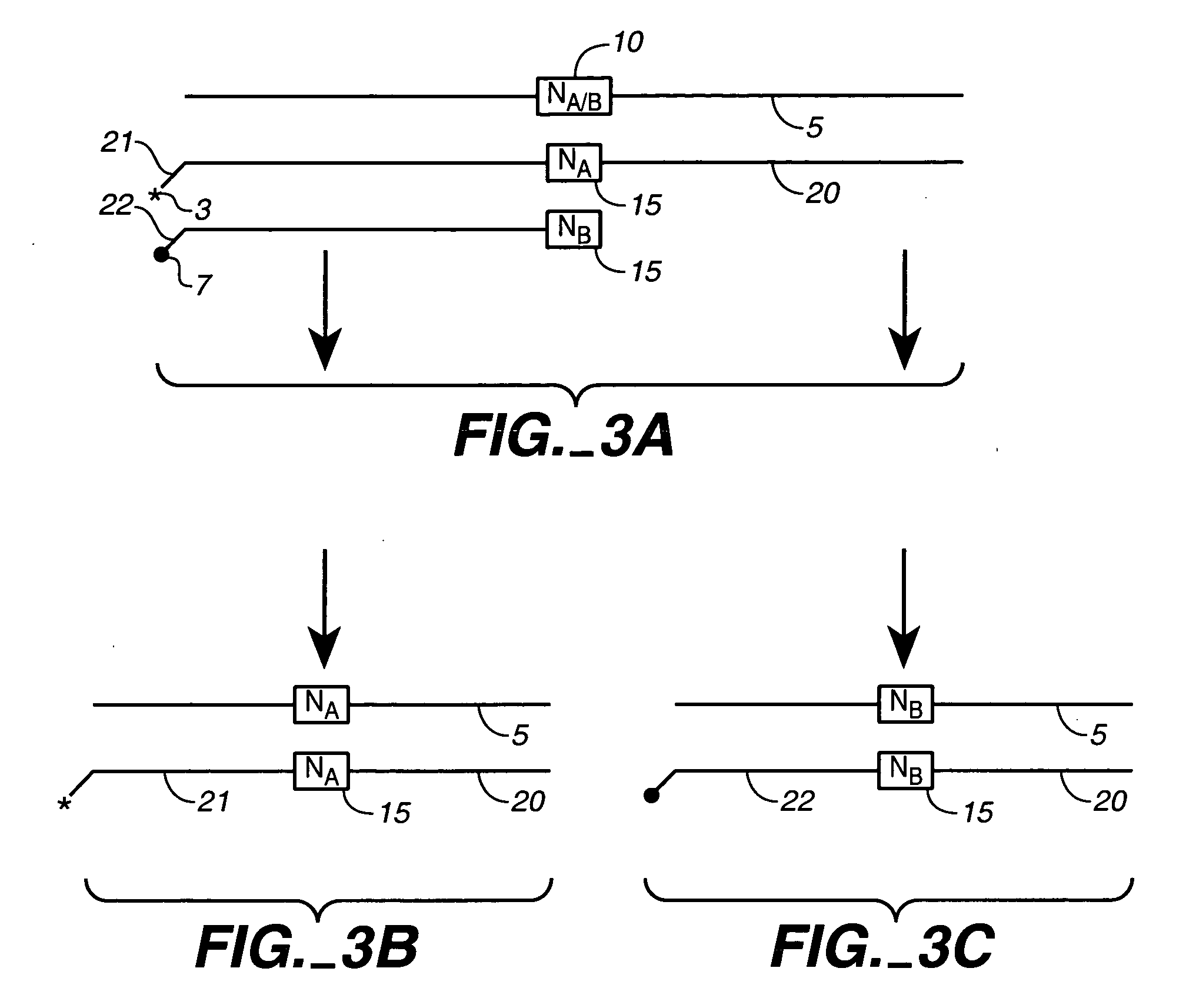
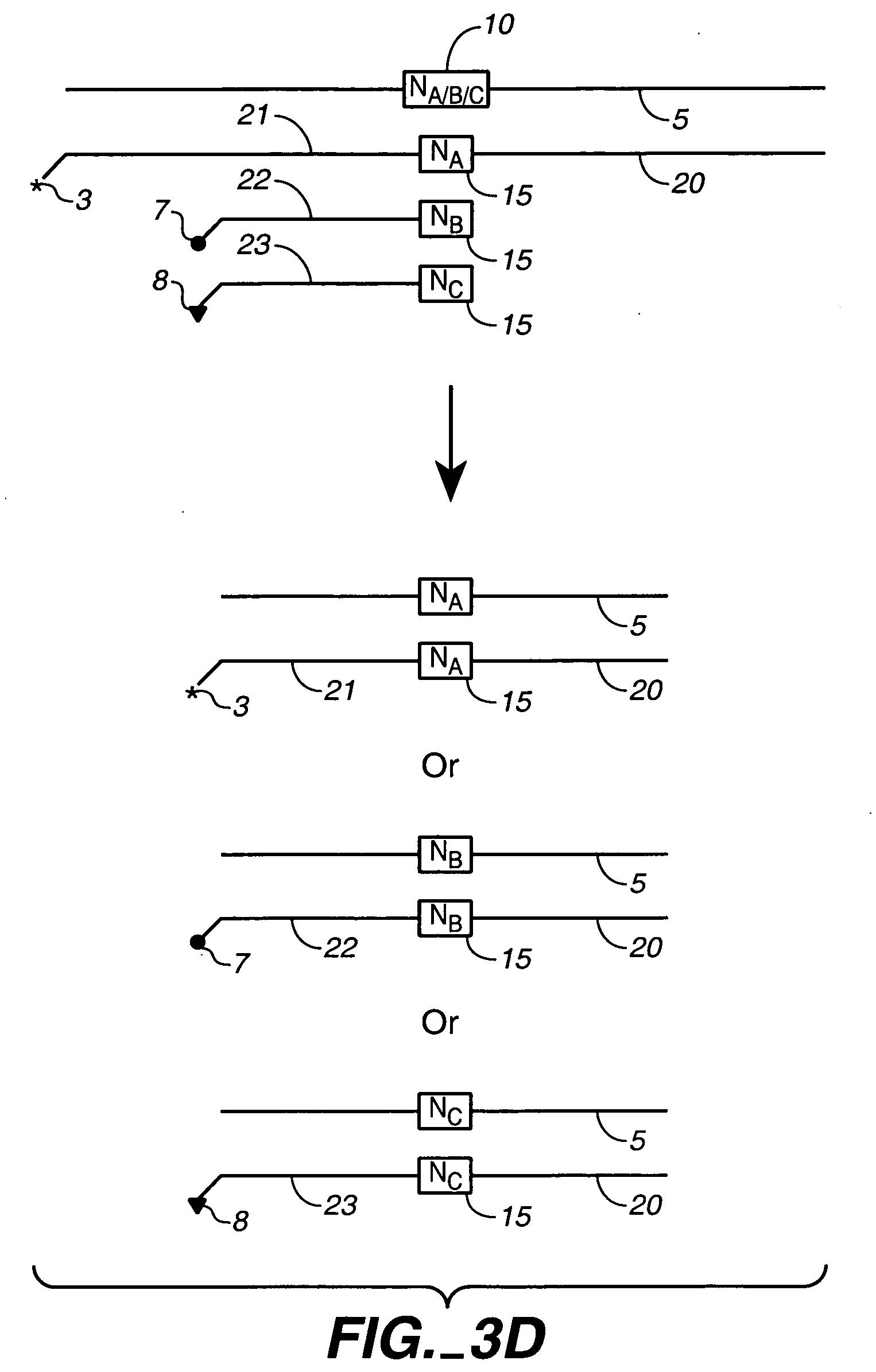
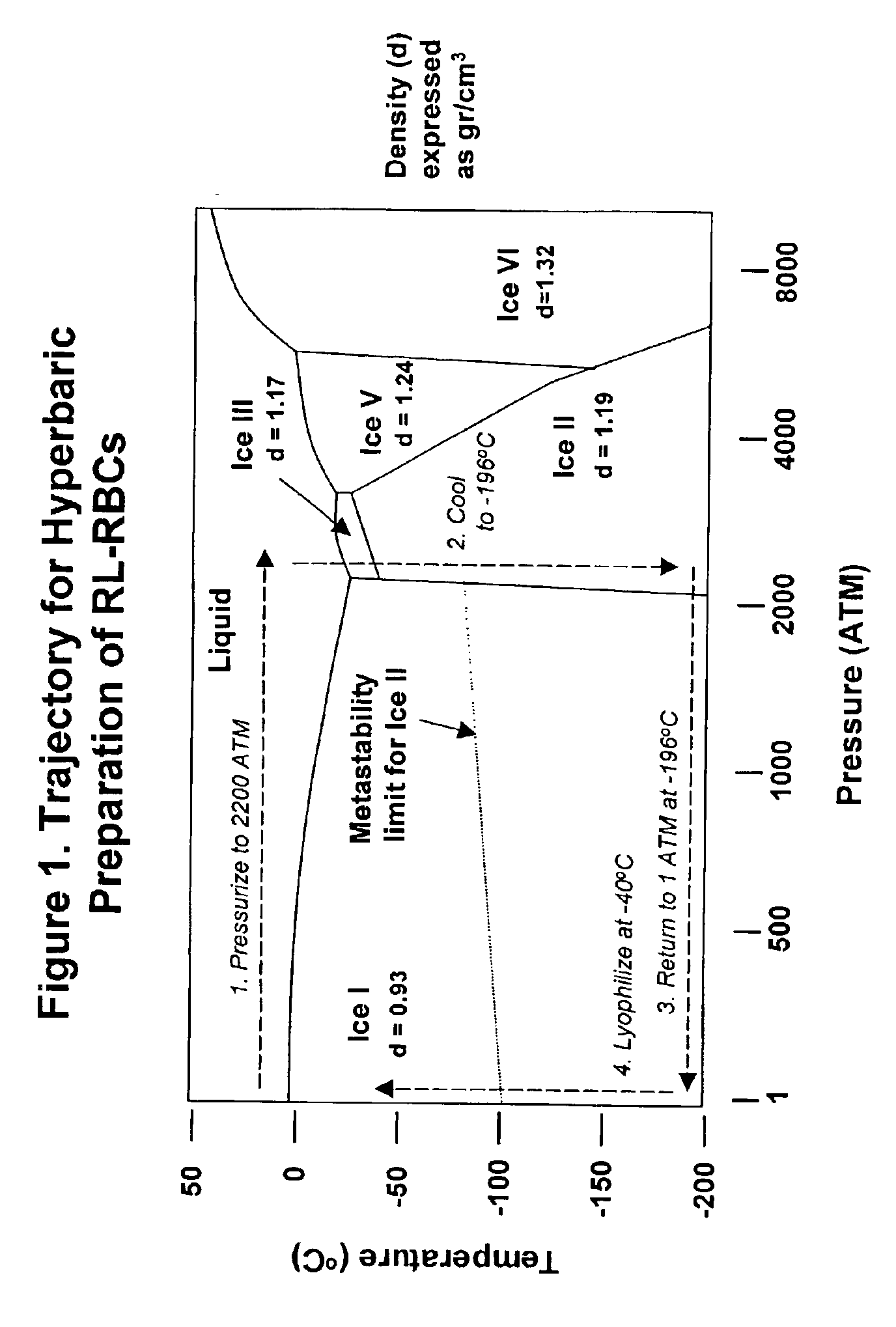
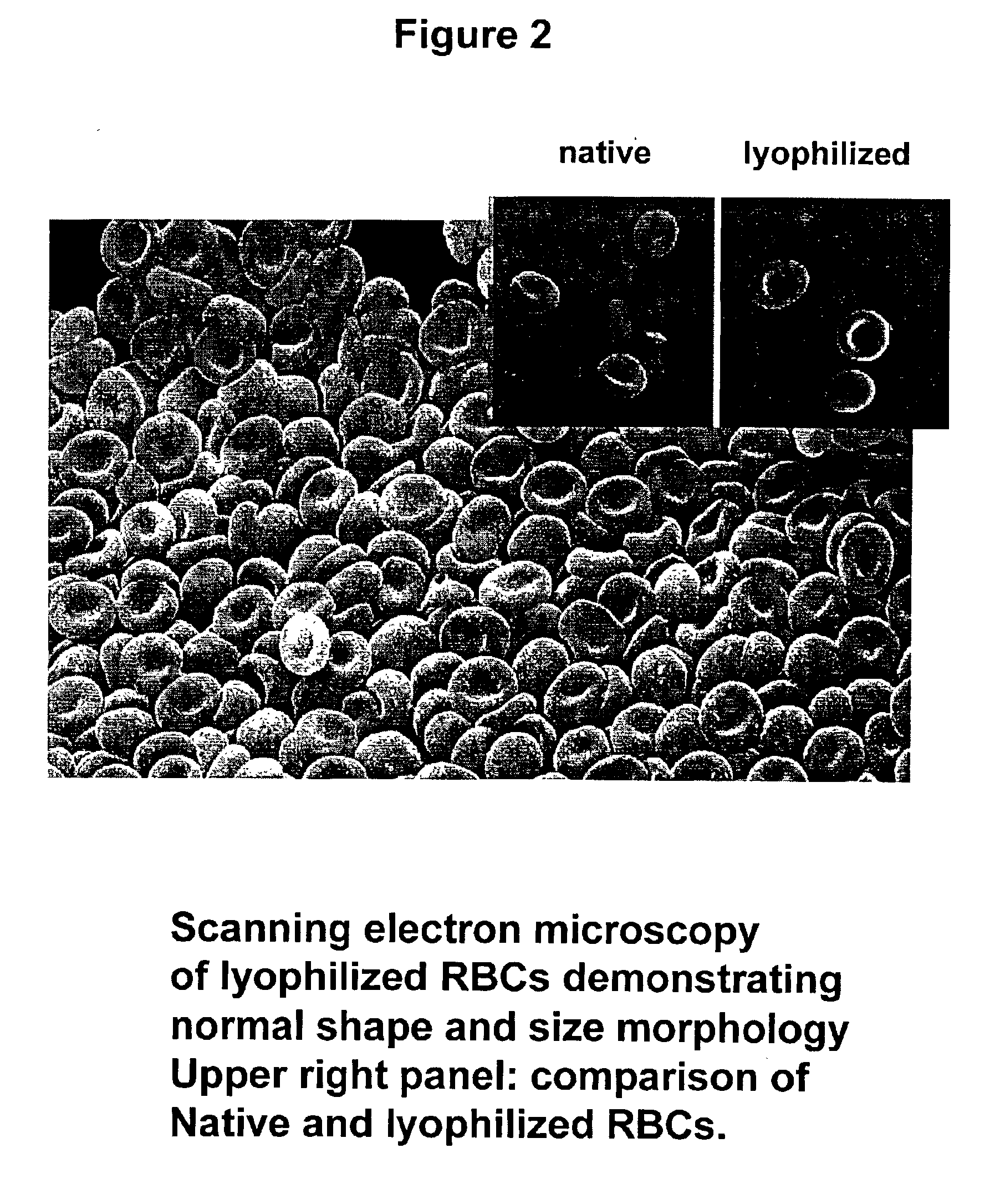
Fixed dried red blood cells and method of use
Fixed-dried red blood cells (RBCs), and processes for preparing the same are disclosed. The red blood cells, upon reconstitution with distilled water or appropriate buffer: bind oxygen with native affinities, have partial deformability, present minimal thrombogenicity to platelets, and have oblated blood group antigens. The RBCs are preferably fixed by means of cross-linkers with aldehyde functions such as paraformaldehyde or glutaraldehyde either alone or in combination. Native oxygen kinetics are achieved by preparing the red blood cells with 1,6-diphosphofructose. Blood group antigens and chemical functions that render the lyophilized RBCs thrombogenic are occluded by chemically attaching polyoxyethylene glycol polymers to the surface membrane of the red blood cells. The cross-linked red blood cells are preferably died by lyophilization.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Chemically Ligated RNAs for CRISPR/Cas9-lgRNA Complexes as Antiviral Therapeutic Agents
InactiveUS20180230464A1Good effectSmall sizeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical ligationNucleotide
Owner:ZHONG MINGHONG
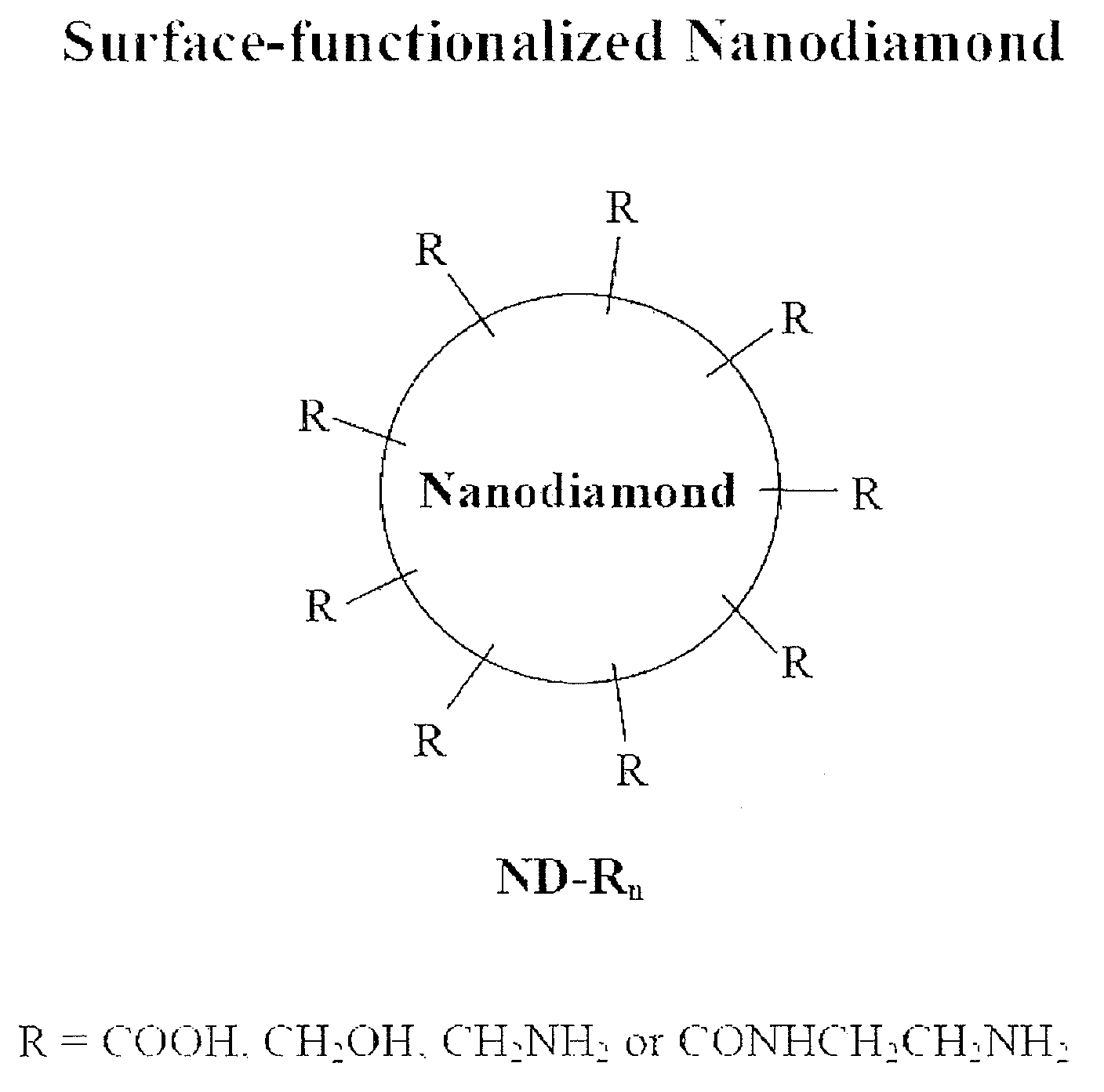
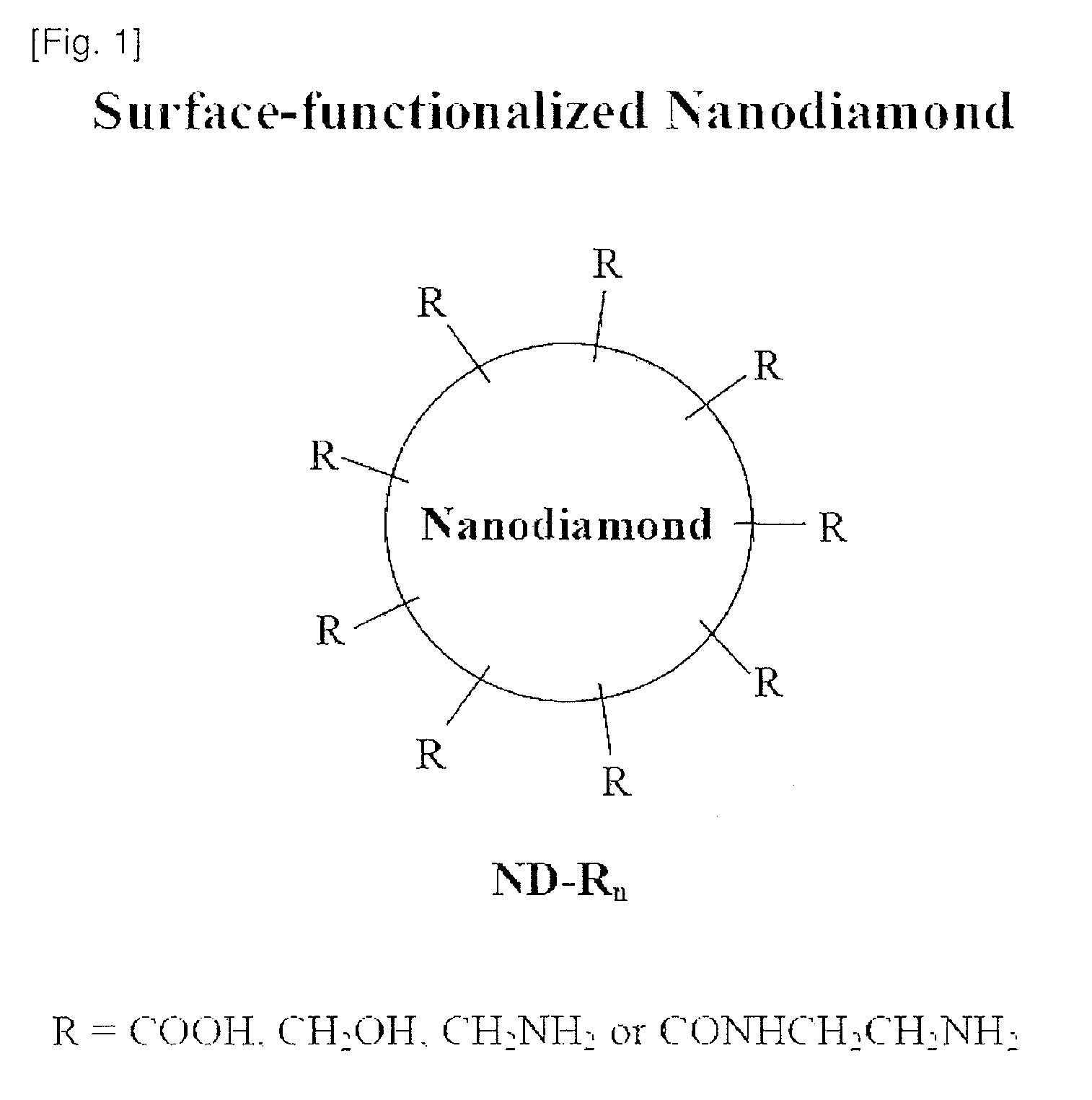
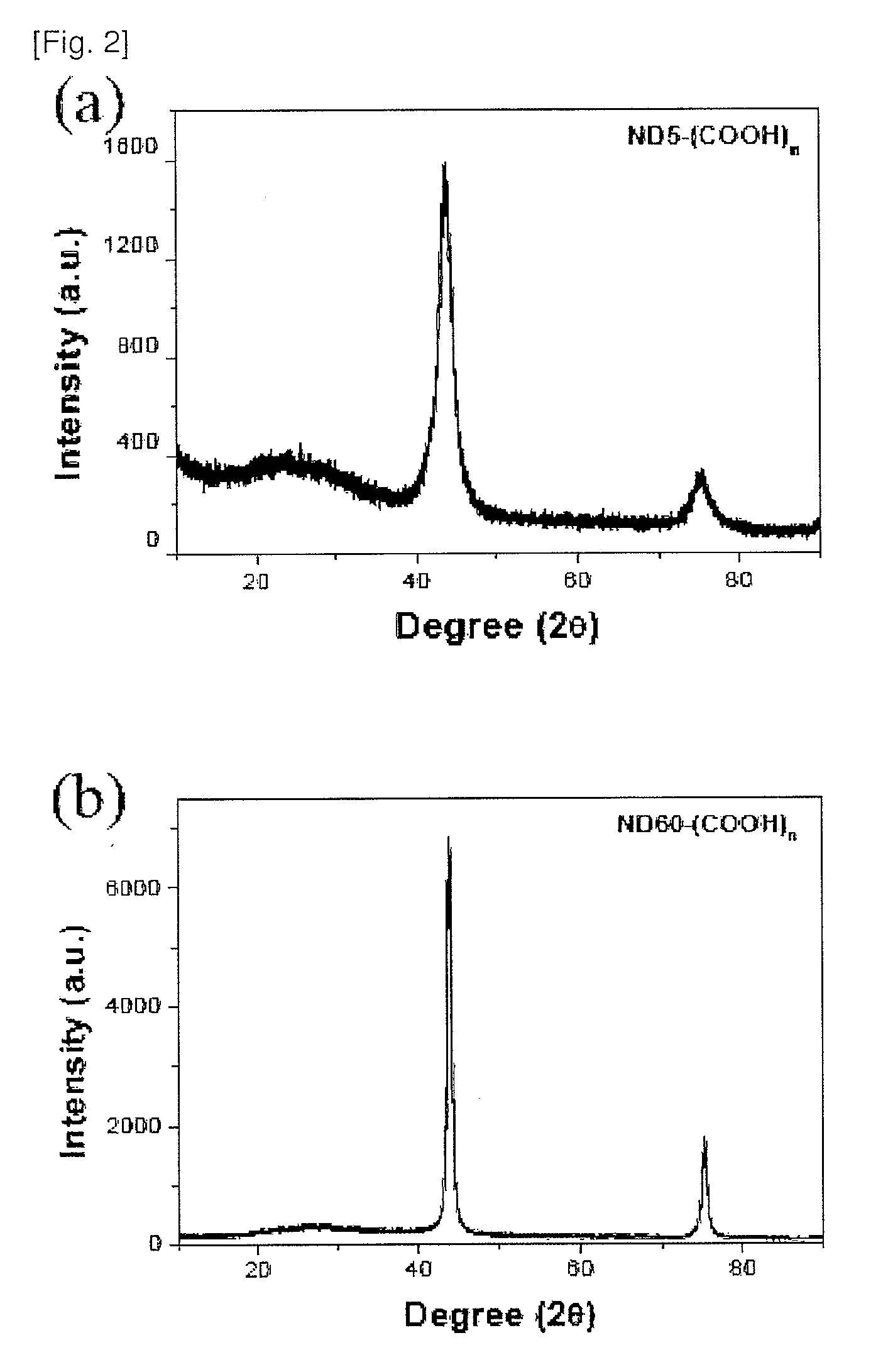
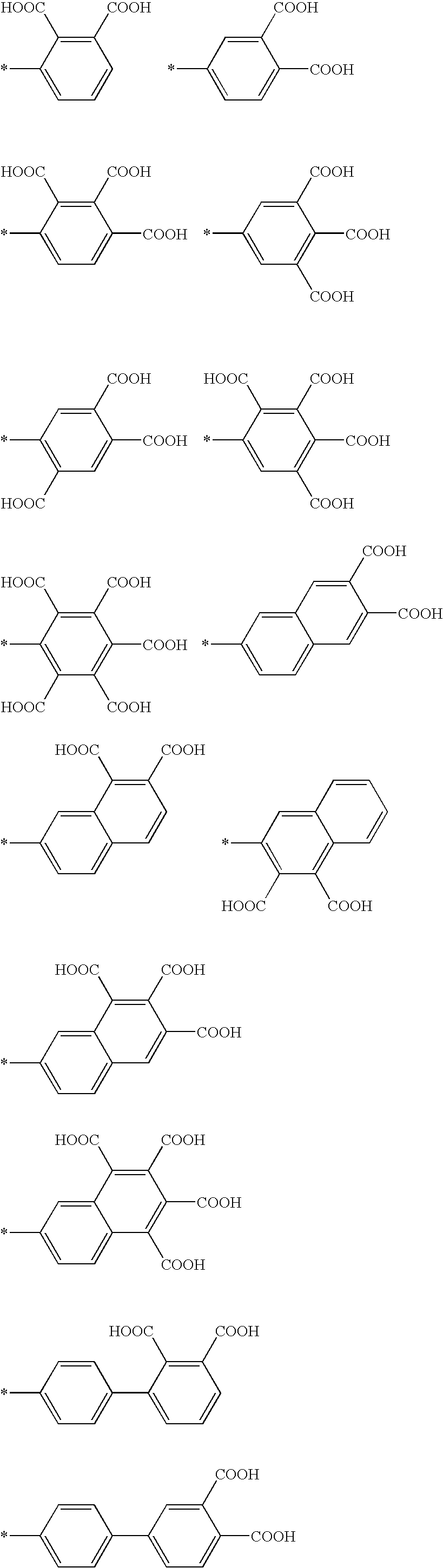
Nanodiamond compounds synthesized by surface functionalization
InactiveUS20100298600A1Improve solubilityMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen-containing compound preparationSolubilityStrong acids
Disclosed herein is a method for chemically attaching carboxyl, alcohol, amine or amide groups to the surface of nanodiamond (ND) in a liquid phase. Also disclosed herein are a functional ND compound obtained by the method and use thereof. The method includes treating synthetic ND with a size of 1 nm-1OO nm with sonication and a strong acid to provide ND-(COOH)n. The ND-(COOH)n compound is used as a starting material to provide ND compounds having alcohol, amine or amide groups attached to the surfaces thereof. The surface-functionalized ND compounds are characterized by using an X-ray diffractometer, FTIR, AFM, particle size analyzer and zeta sizer. The ND compounds show functionalities as well as high solubility to provide stable ND solutions in a liquid phase. Therefore, the ND compounds may be used as diamond coating agents. The powder of the ND compounds may be used as materials for producing composites of polymers, plastics, synthetic fibers, ceramics, etc., or as additives for toothpaste, shampoos, soap and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:NANODIAMOND
Ink-jet inks and ink sets exhibiting reduced bleed, wicking, and/or halo effect and associated methods
Compositions, systems, and methods for ink-jet printing having improved black to color bleed control, reduced wicking, and / or reduced halo are described. The composition can include a functionalized carbon pigment dispersed in an ink vehicle. The carbon pigment includes functional groups chemically attached thereto. Suitable functional groups includes an aromatic ring structure having multiple carboxyl groups (or salts thereof) attached to the aromatic ring structure, wherein at least two of the multiple carboxyl groups are positioned on adjacent carbon atoms of the aromatic ring structure.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering: fibrin formulations with peptides
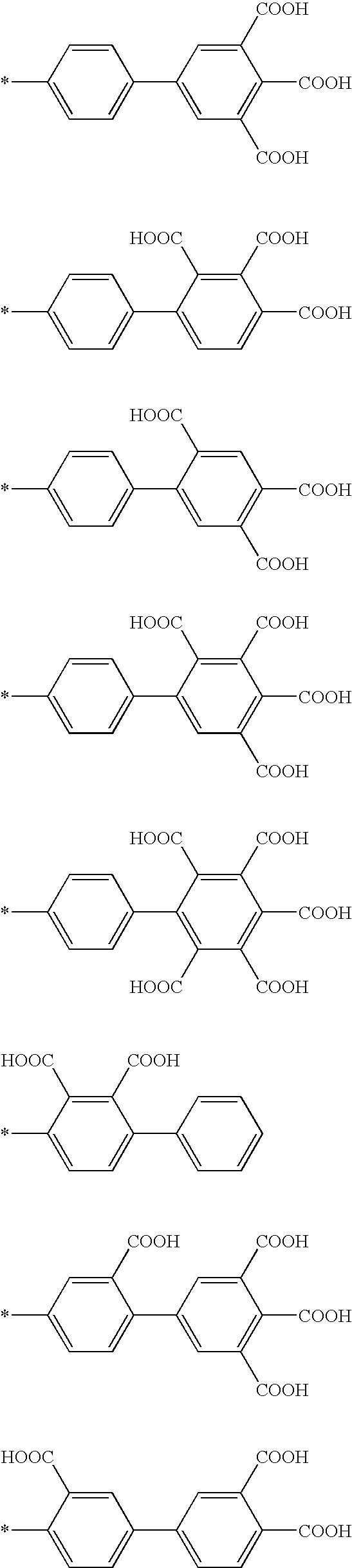
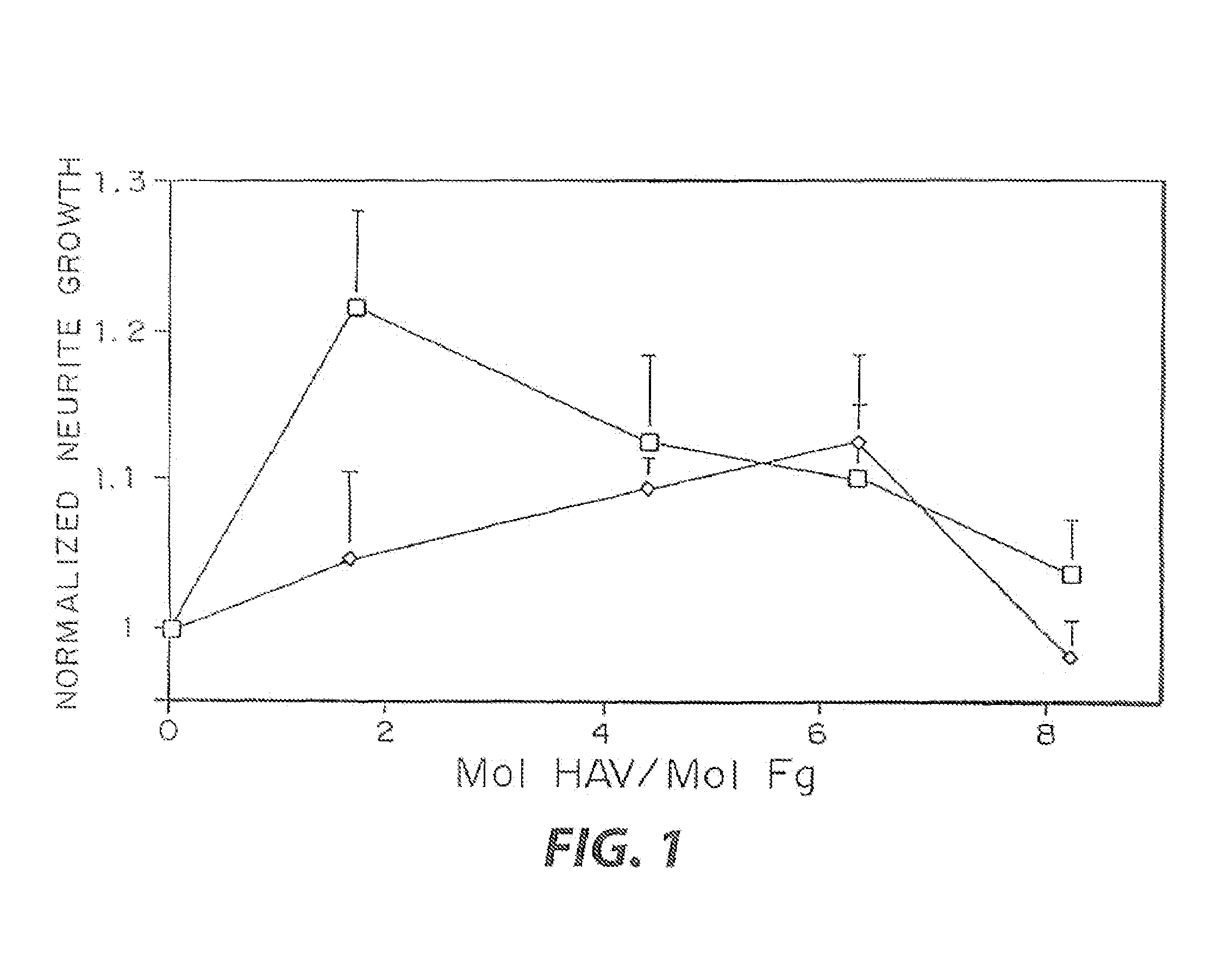
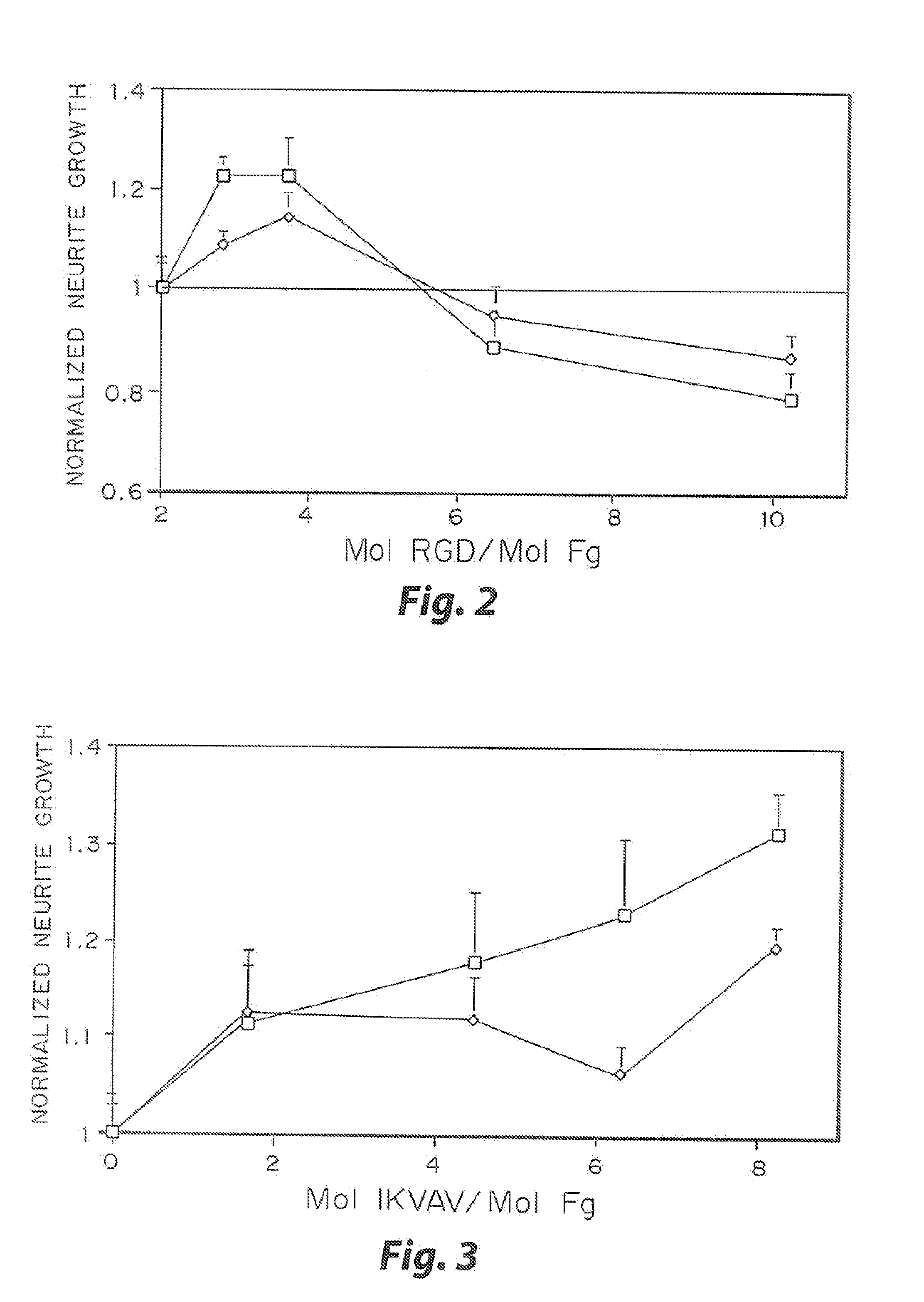
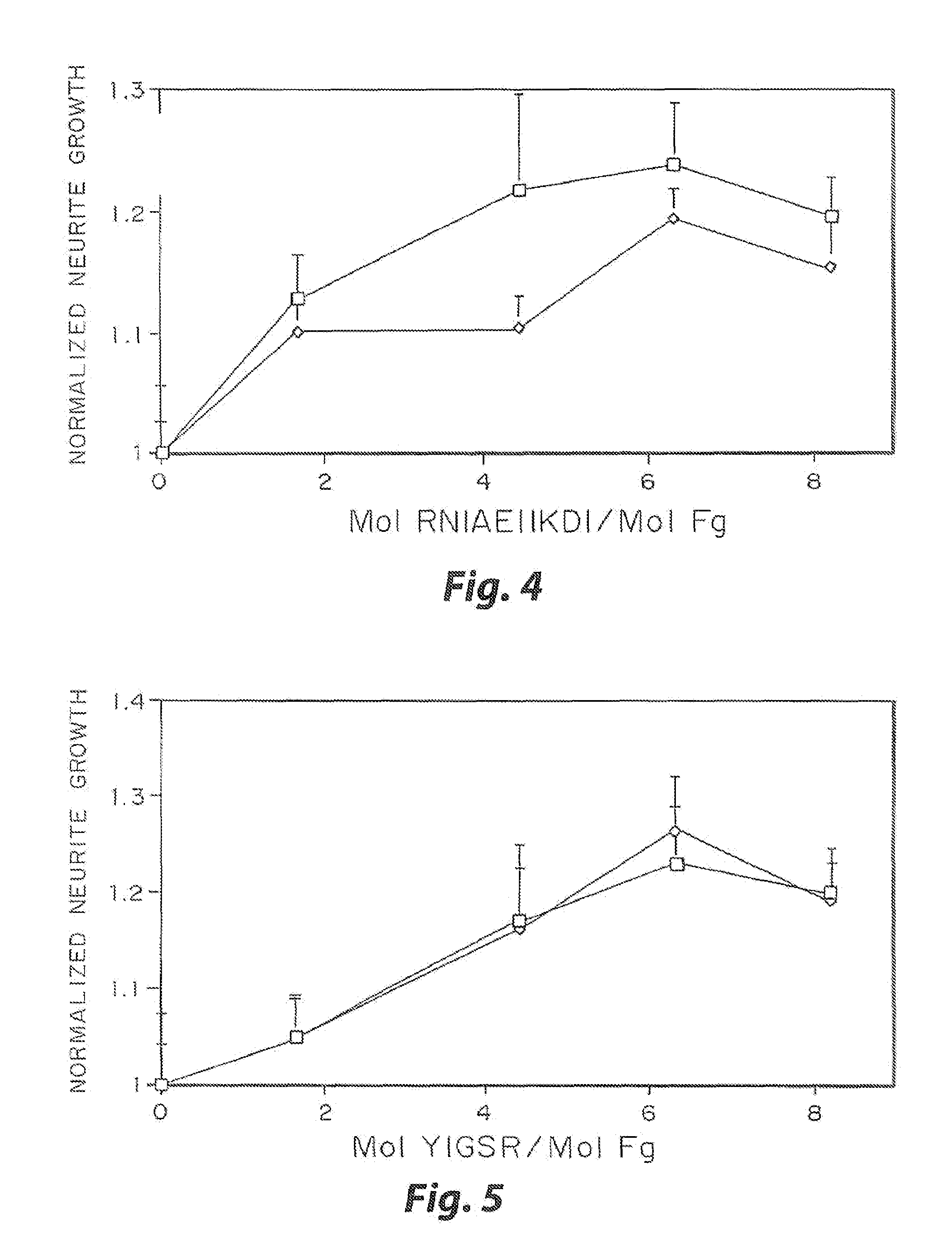
InactiveUS7241730B2Efficacious platformEnhanced andPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCell Surface ProteinsADAMTS Proteins
Heparin-binding regions of several proteins, such as neural cell adhesion molecule, fibronectin, laminin, midkine, and anti-thrombin III have been shown to promote neurite extension on two-dimensional surfaces. The effect of heparin-binding peptides on neurite extension through three-dimensional matrices was investigated by culturing embryonic chick dorsal root ganglia (DRG) within fibrin gels containing chemically attached heparin-binding peptide (HBP). The length of neurites within fibrin gels containing cross-linked HBP was increased by more than 70% over extension through fibrin gels containing no peptide. The HBP sequence of antithrombin III was incorporated into the fibrin gel as the C-terminal domain of a bidomian, chimeric peptide; the N-terminal second domain of this peptide contained the ∀2-plasmin inhibitor substrate for Factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa, a transglutaminase, was used to chemically attach the HBP-containing chimeric peptide to the fibrin gels during polymerization. The amount of HBP cross-linked into the fibrin gels was determined, after degradation by plasmin using gel permeation chromatography, to be approximately 8 moles of peptide per mole fibrinogen. A peptide (HBP), where the cross-linking glutamine was replaced with glycine, showed no increase in extension in comparison with fibrin gels. The additional of heparin to the gel percursors resulted in no increase in neurite extension in comparison with fibrin gels. HBPs promote neurite extension by binding to cell surface proteoglycans on the DRG.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Detection of chemical ligation using fluorescence quenching leaving groups
InactiveUS20040259102A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical ligationLeaving group
Novel compounds having a fluorescence quencher as a leaving group are disclosed. Nucleic acids and other molecules containing a fluorophore and a fluorescence quencher are disclosed as an embodiment of this invention. The use of the oligonucleotides in enzyme-free oligonucleotide ligation reactions results in an increase in fluorescence when the oligonucleotide also contains a nearby fluorophore. The ligation reactions can be performed in solution, on surfaces, or in cells.
Owner:SANDFORD UNIV +1
Ocular socket prosthesis
InactiveUS6346121B1Reduce riskOptical articlesTissue regenerationChemical ligationHydrophilic polymers
The invention provides an ocular socket prosthesis comprising a hydrogel consisting essentially of a biocompatible hydrophilic polymer onto which tissues can be directly sutured. Preferably the prosthesis comprises the polymer both in its homogeneous gel form and in its sponge form, and the two forms are chemically joined at their interface via an interpenetrating polymer network (IPN). However, it is also contemplated that the prosthesis of the invention may be made predominantly or entirely from the sponge form of the polymer. Methods of production of the prosthesis of the invention and of surgical implantation are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:LIONS EYE INST OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
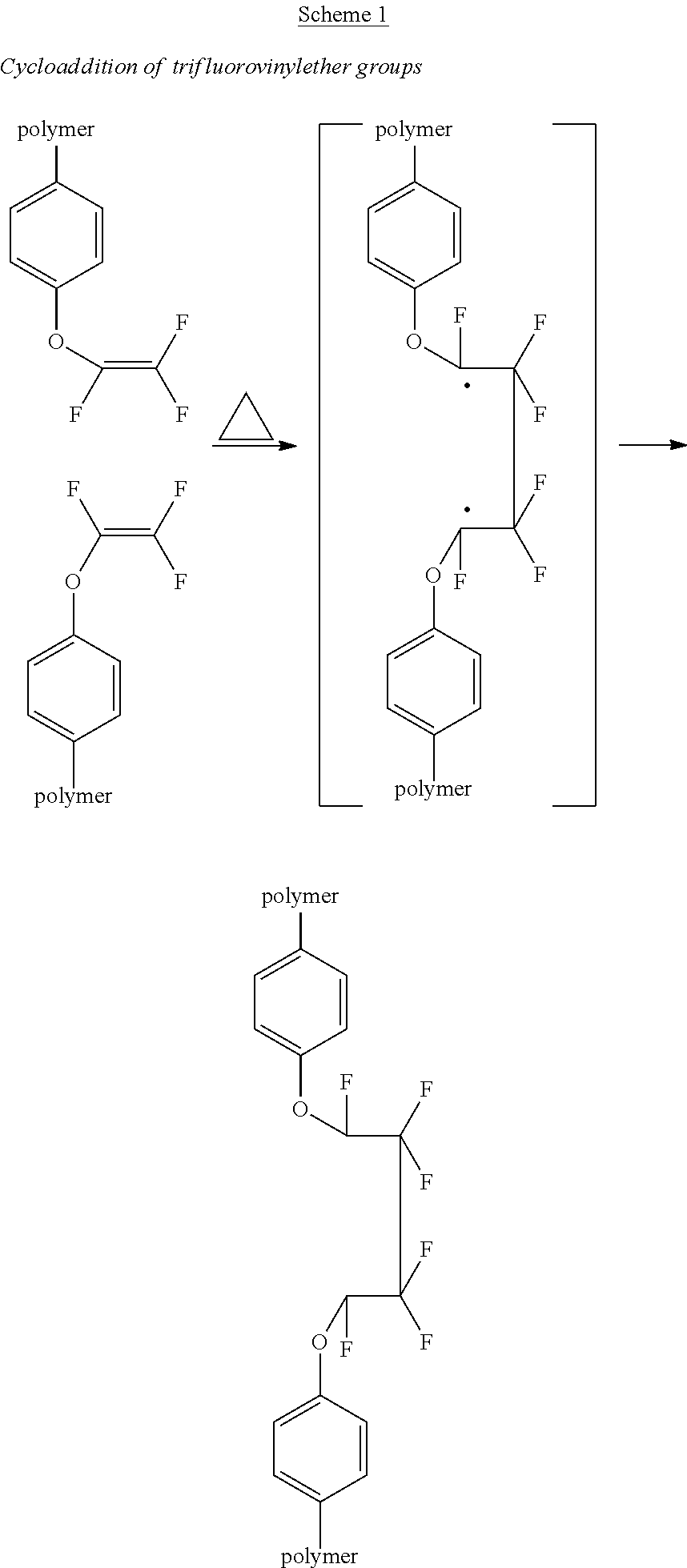
Perfluorocyclobutane crosslinked hydrogels
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Construction of paclitaxel-oleic acid small-molecular prodrug self-assembled nanoparticles
ActiveCN105833284AAchieve specific drug releasePromote enrichmentPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSide effectPolyethylene glycol
The invention designs and synthesizes a series of paclitaxel-oleic acid small-molecular prodrugs; with the application of a chemical connecting arm which is sensitive to an oxidation-deoxidation environment, the rapid release of the drugs in tumor cells is promoted. On the basis, small-molecular prodrug self-assembled nano-drug delivery systems are prepared. The small-molecular prodrug self-assembled nano-drug delivery systems have the advantages that by virtue of a one-step nano-precipitation method, nano-drug self-assembled nanoparticles are simple in preparation process and easy for industrialization; the nano-drug self-assembled nanoparticles are small and uniform in grain size (to 100nm), and the nano-drug self-assembled nanoparticles are enriched in a tumor part by virtue of an EPR (enhanced permeability and retention) effect; an ultrahigh drug-loading capacity is guaranteed, which is beneficial for reducing adverse reactions caused by auxiliary materials and biological materials; surface modification is easy to implement, and the intake of a reticuloendothelial system can be effectively avoided and the intake of the tumor cells to the nanoparticles can be improved by virtue of PEG (polyethylene glycol) and active targeting modification; and on the basis of the sensitivity of the chemical connecting arm to the oxidation-deoxidation microenvironment of the tumor cells, the specific drug release of paclitaxel in the tumor part is achieved, a curative effect is improved and toxic and side effects are reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY +1
Friction-reducing and abrasive composite materials with reactive nanometer inorganic particles/epoxy and production thereof
A reactive nanometer inorganic particle / epoxy resin abrasive composite material and its production are disclosed. The composite material consists of epoxy resin 90-99wt%, nanometer inorganic particle 1-10wt% and graft monomer 0.1-5%. The graft monomer is mixture of any kind or several kinds of methyl acrylic acid ethylene oxide ester, acrylic amide, phenylethylene, ethyl acrylate, methyl ethyl acrylate or butyl acrylate. The process is carried out by surface graft modifying nanometer grains, inducing reactive polymer, epoxy resin curing reacting and forming chemical connection between nanometer grains and resin matrix. It has better anti-friction and wear-resistant performances and is simple. It can be used for epoxy resin coating and various miniature devices.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Pseudo-native chemical ligation
InactiveUS20060149039A1Easily employedProduct is unsuitablePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticPolymer modifiedChemical ligation
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for extending the technique of native chemical ligation to permit the ligation of a wider range of peptides, polypeptides, other polymers and other molecules via an amide bond. The invention further provides methods and uses for such proteins and derivatized proteins. The invention is particularly suitable for use in the synthesis of optionally polymer-modified, synthetic bioactive proteins, and of pharmaceutical compositions that contain such proteins.
Owner:AMYLIN PHARMA INC
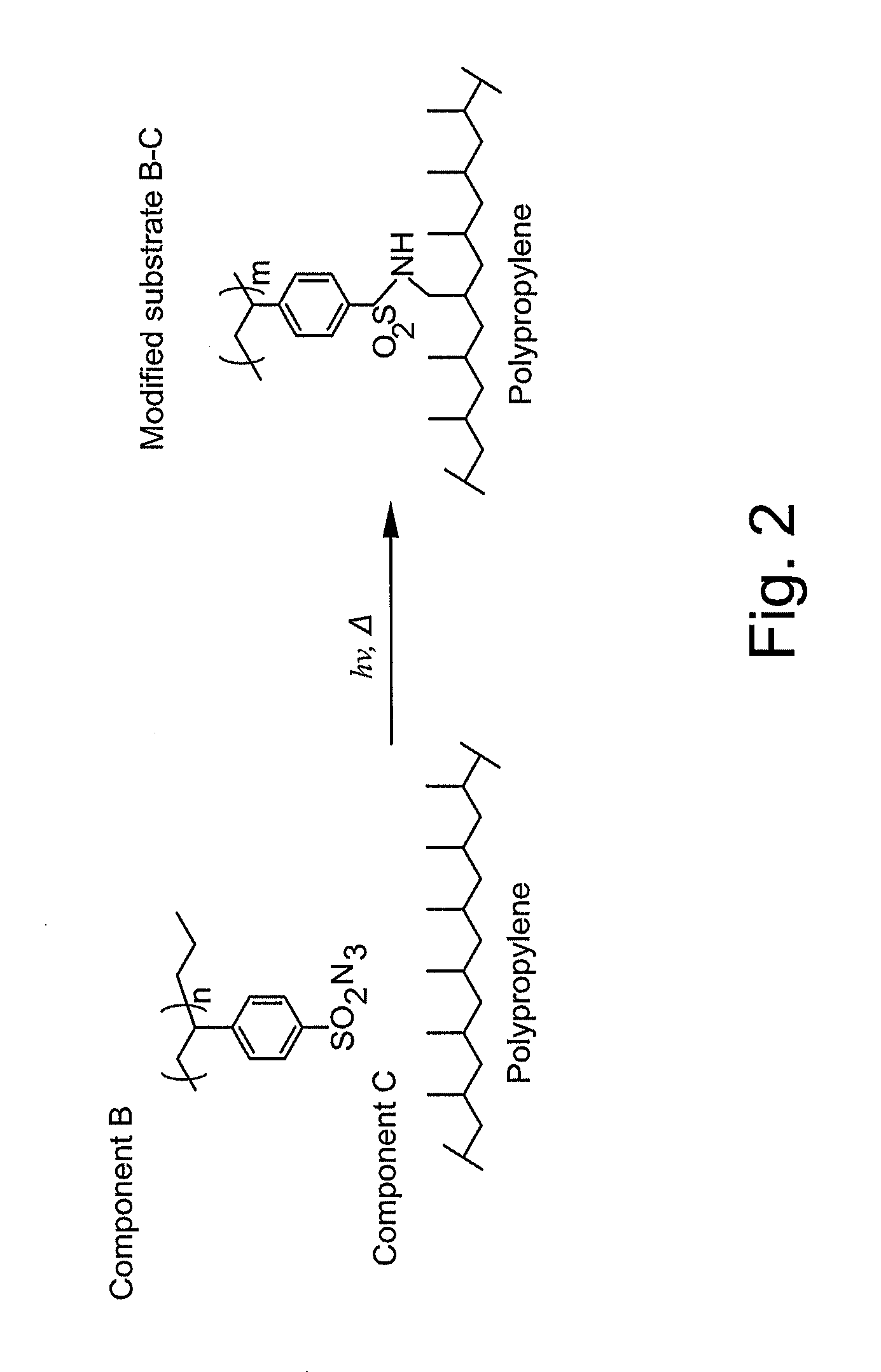
Surface modifying agents, modified materials and methods
The present invention relates to surface modifying agents for polymeric and / or textile materials, methods of making and / or using a surface modifying agent to modify and functionalize polymeric and / or textile materials, and / or methods of using surface modified or functionalized polymeric and textile materials, and / or products using or incorporating surface modified or functionalized polymeric and textile materials. For example, the surface modifying agent in precursor form can be styrene sulfonyl azide monomer, polymer or copolymer capable of undergoing a chemical reaction in the presence of heat or light to form one or more styrene sulfonated nitrene monomers, polymers or copolymers, which are capable of chemically reacting with the surface of a polymeric or textile material to endow a specific or desired chemical surface functionality to the surface of a polymeric or textile material. Furthermore, the present invention is possibly preferably directed to a surface modifying agent which comprises a styrene sulfonated nitrene monomer, polymer or polymer containing one or more nitrene functional groups, which are capable of chemically reacting via an insertion reaction into one or more carbon-hydrogen bonds on the surface of a polymeric or textile material in order to chemically attach a specific or desired chemical functionality to the surface of a polymeric or textile material.
Owner:CELGARD LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com