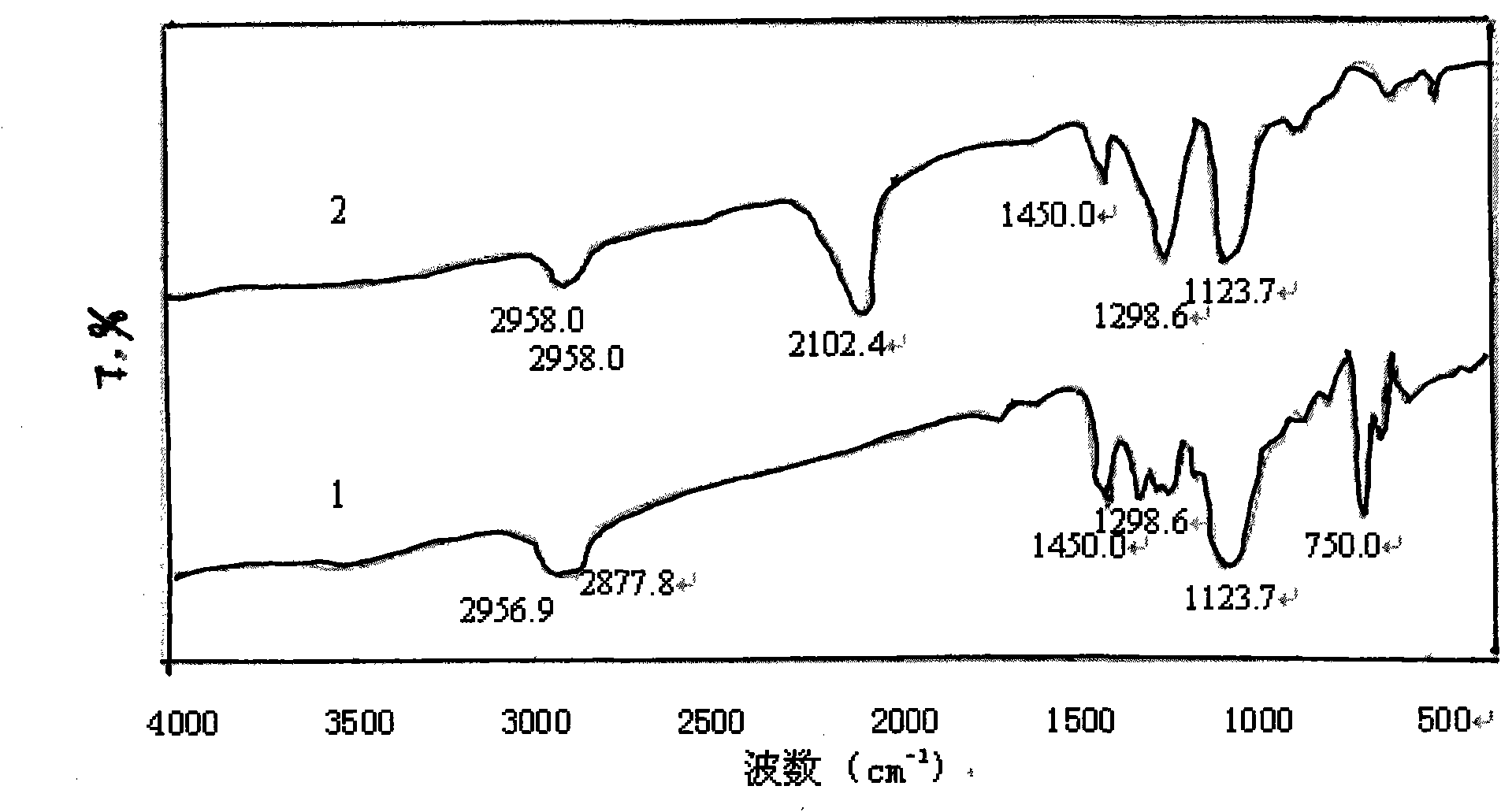
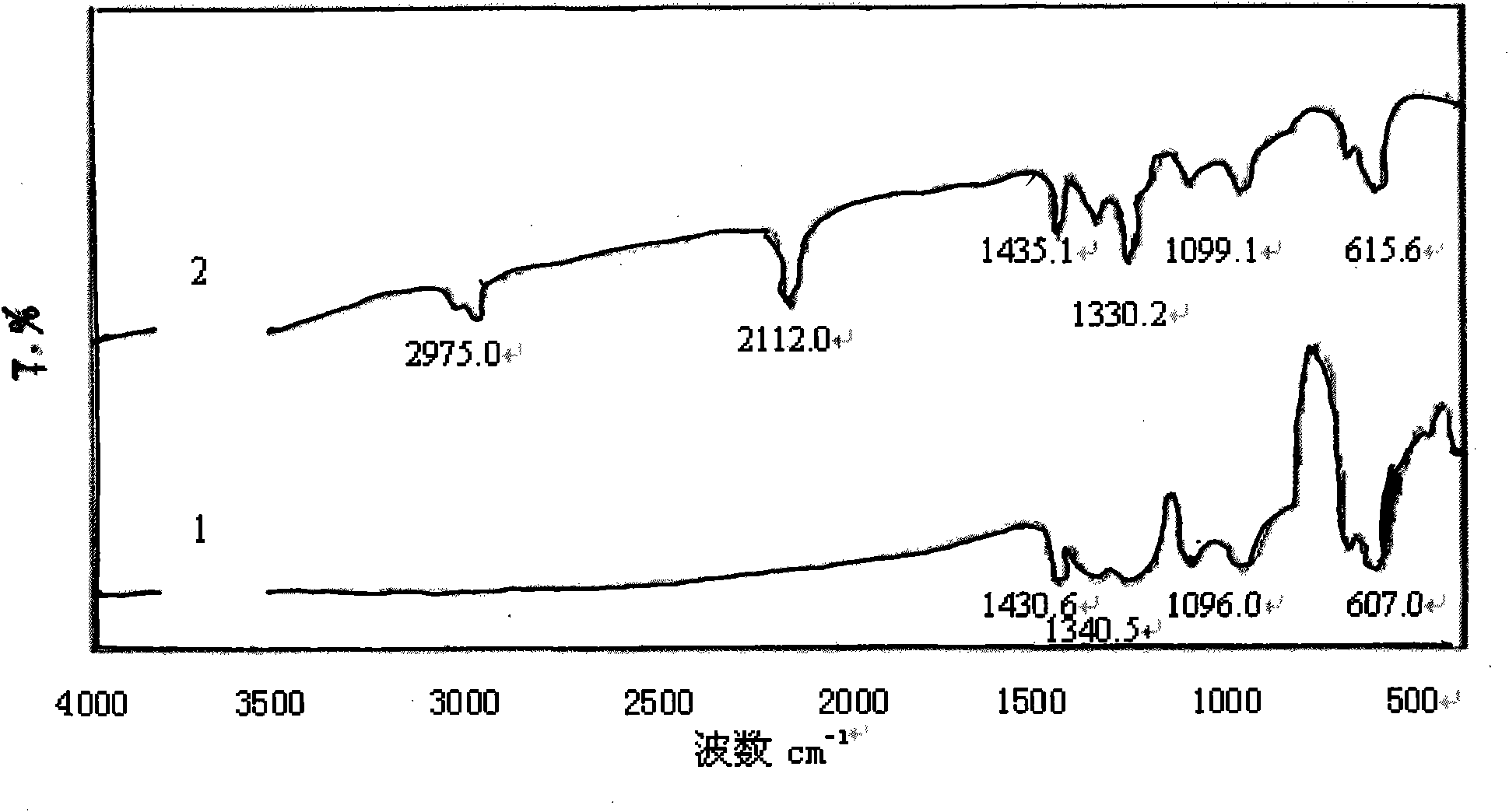
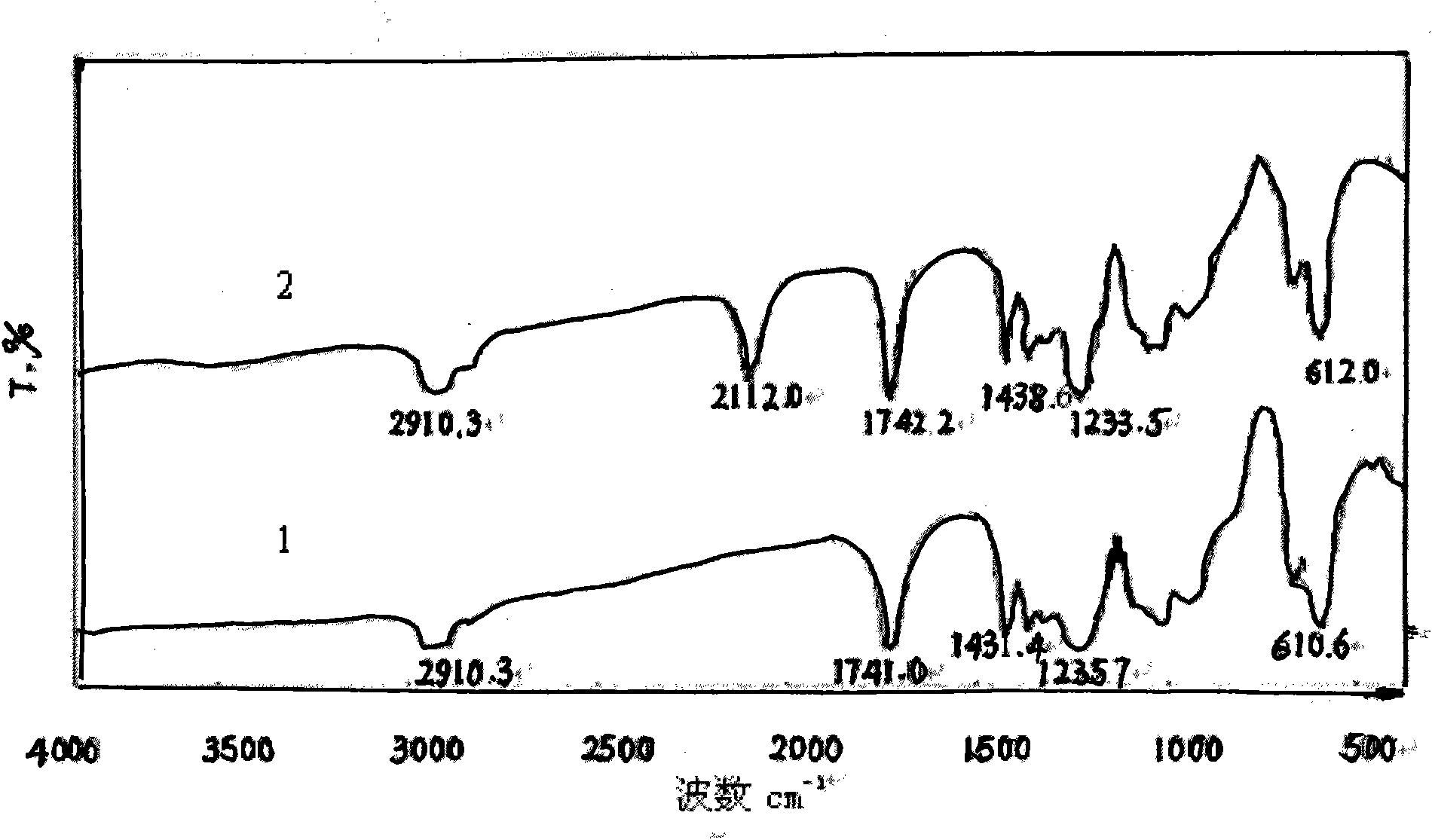
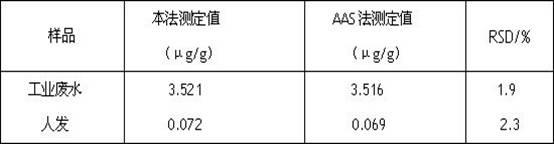
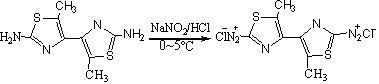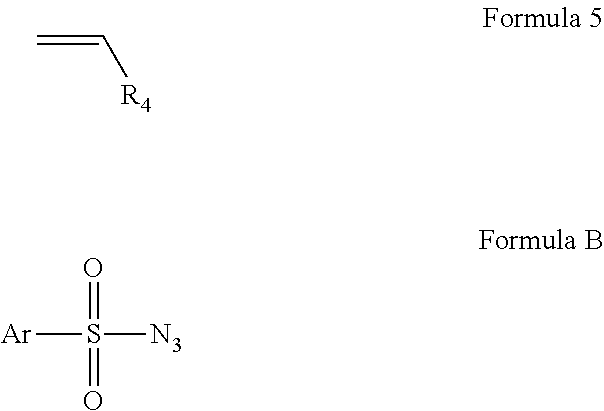Patents
Literature
47 results about "Nitrene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
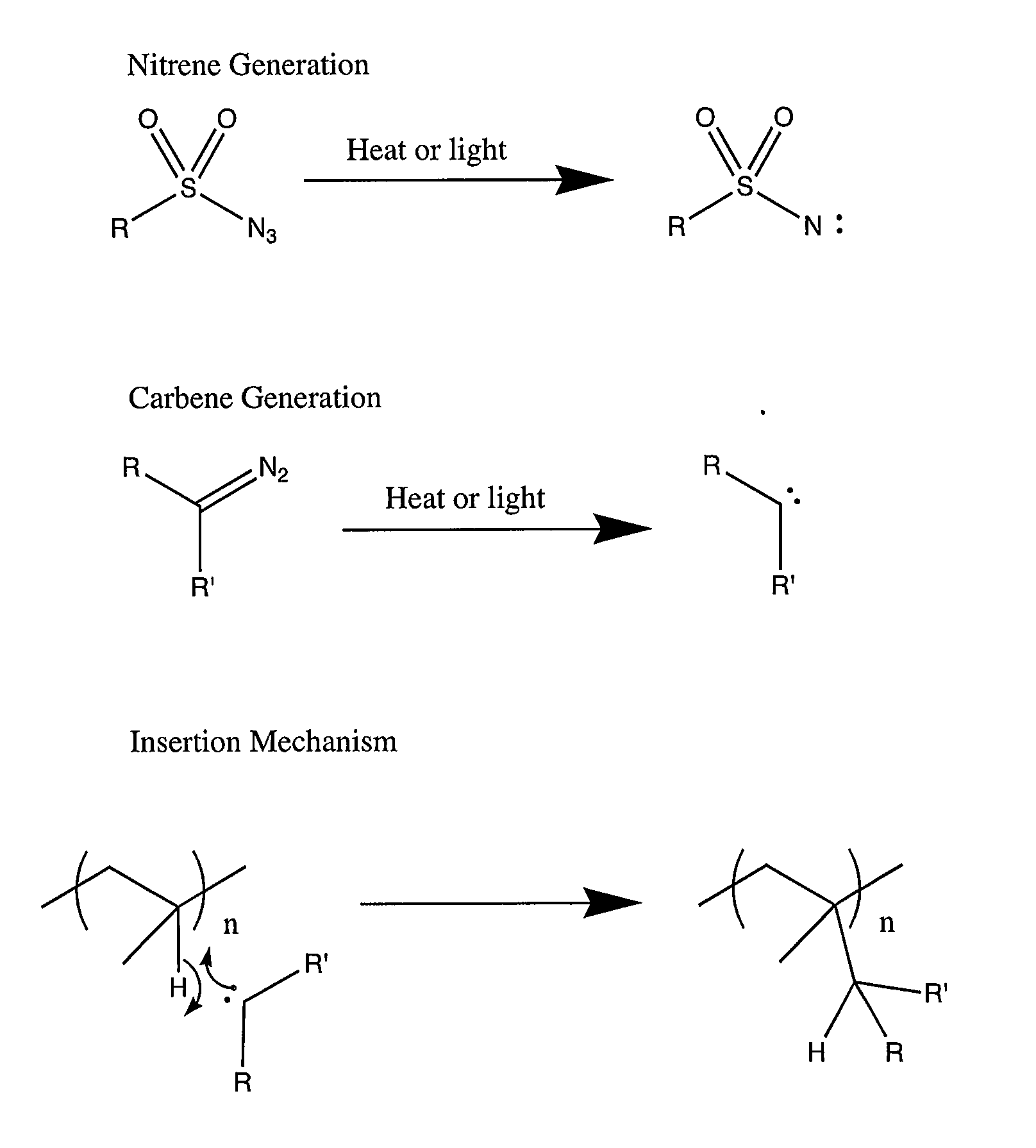
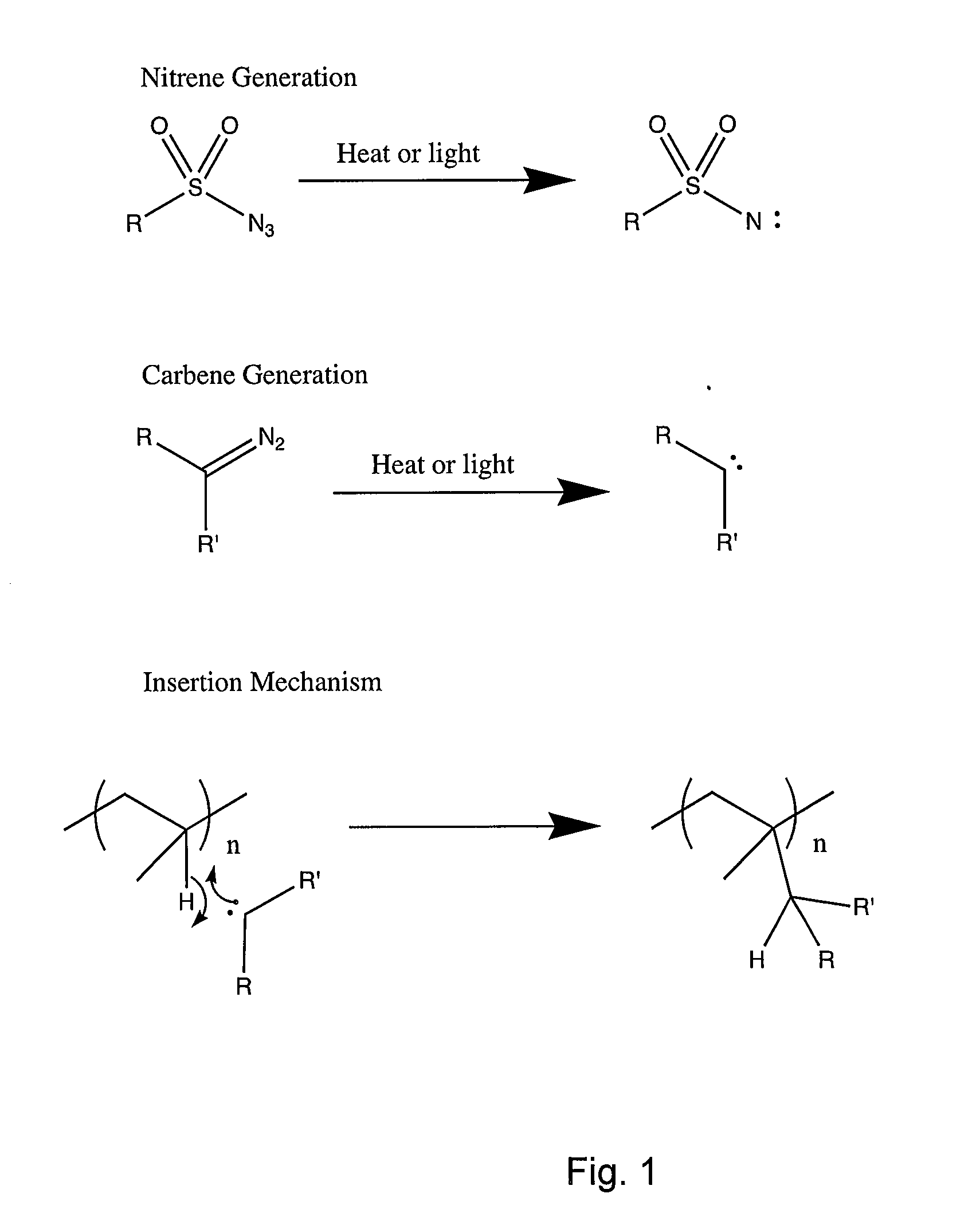
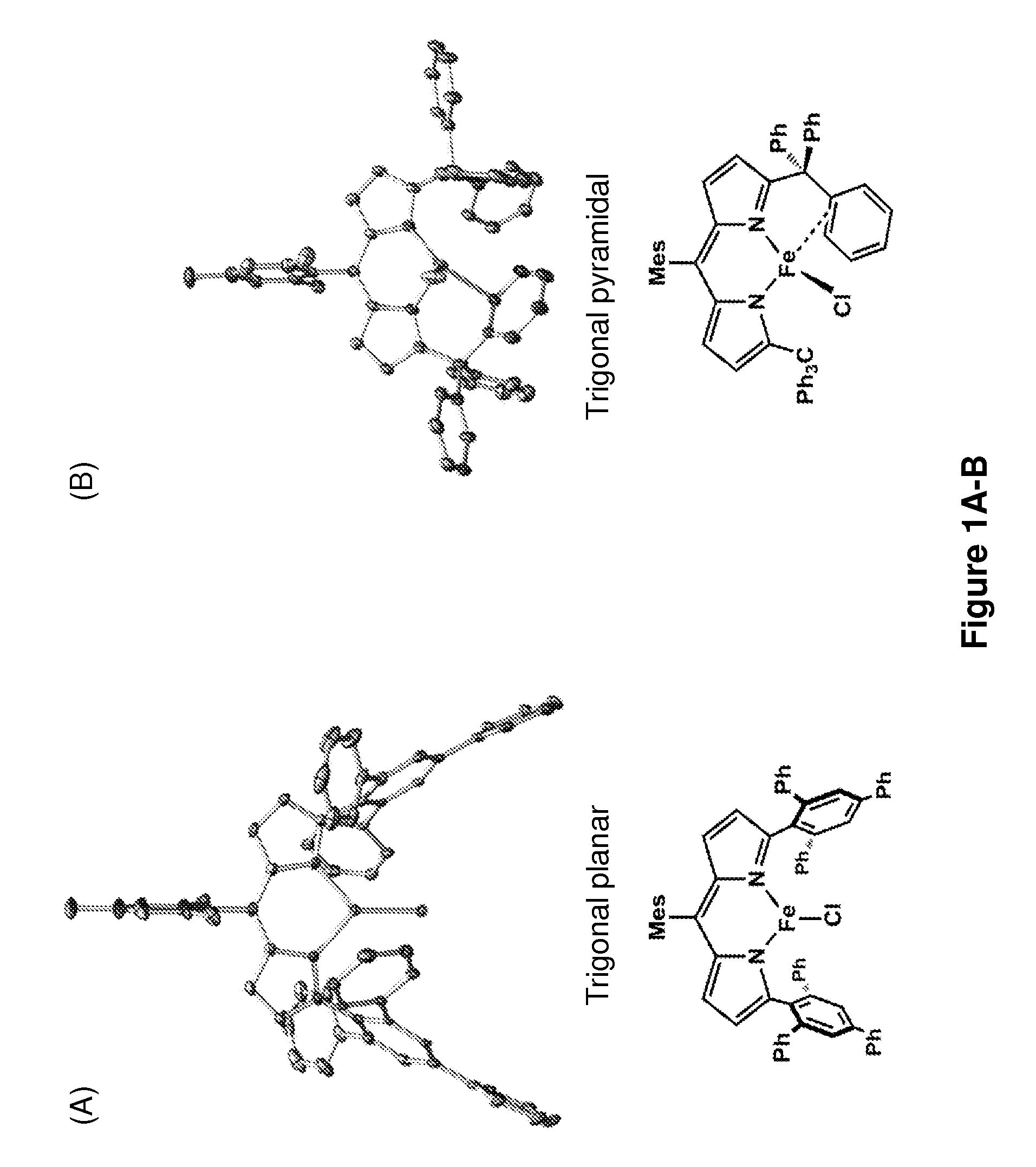
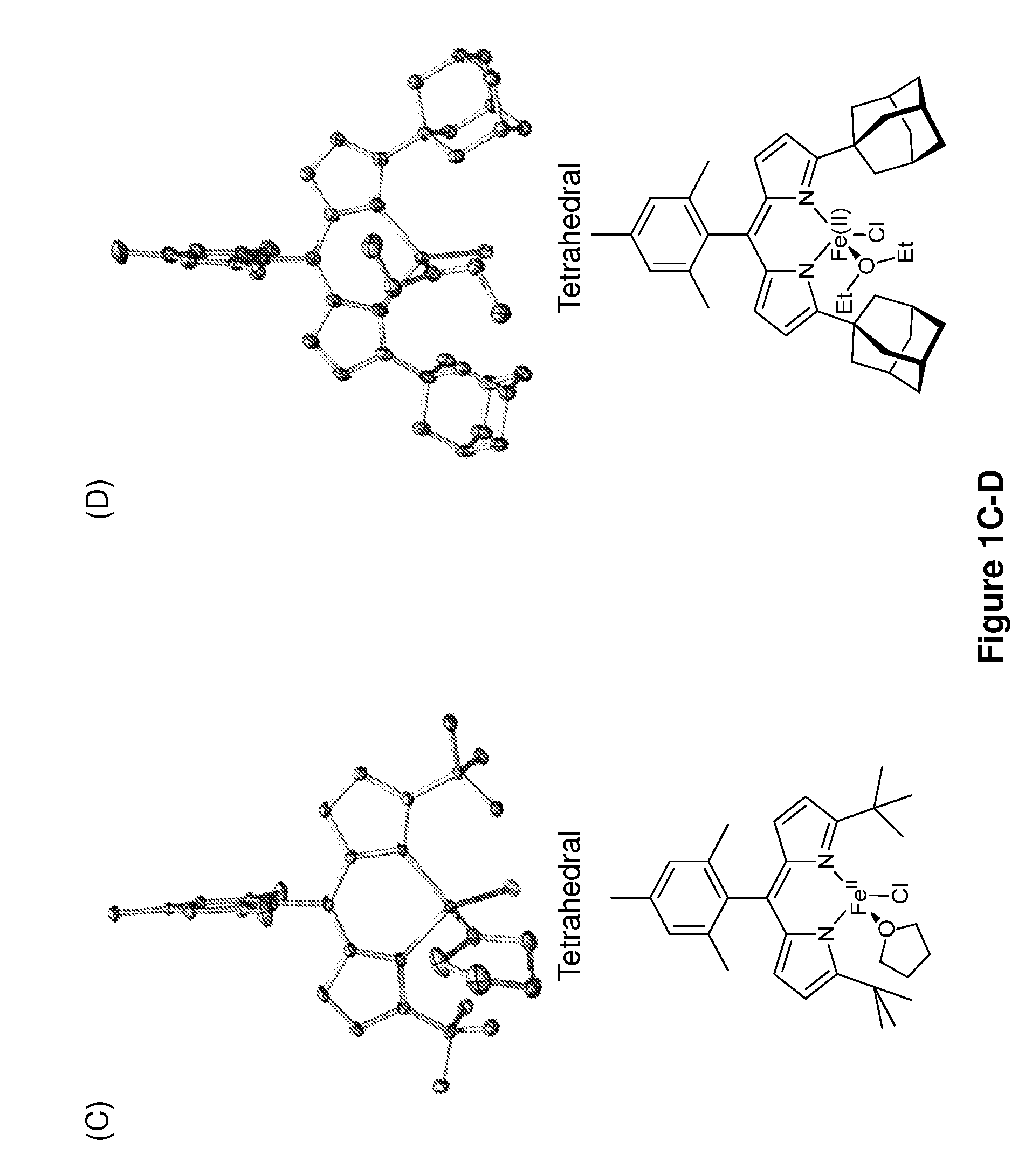
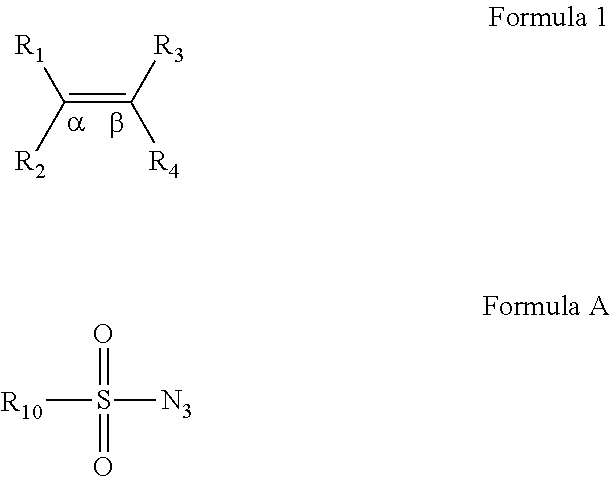
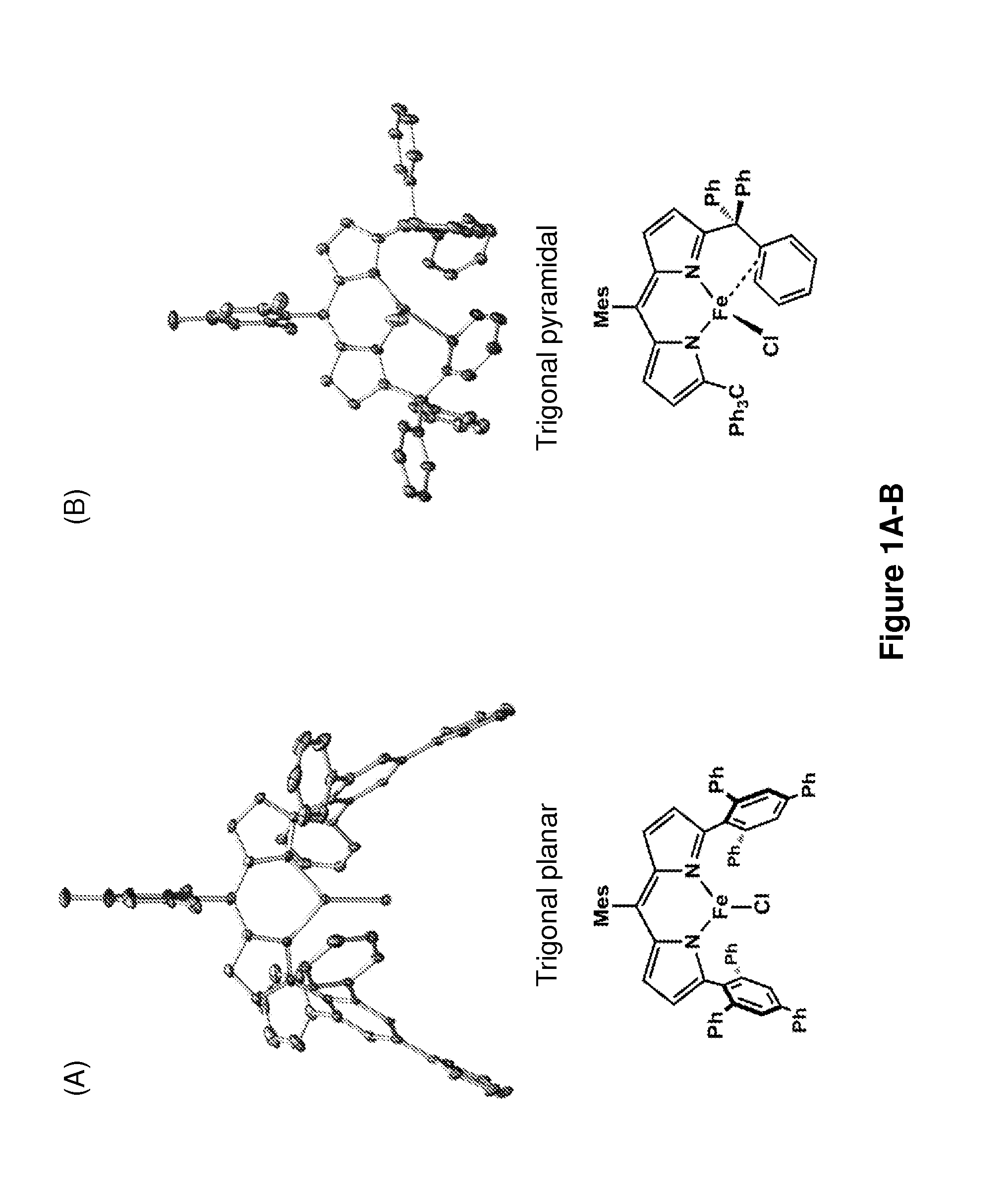
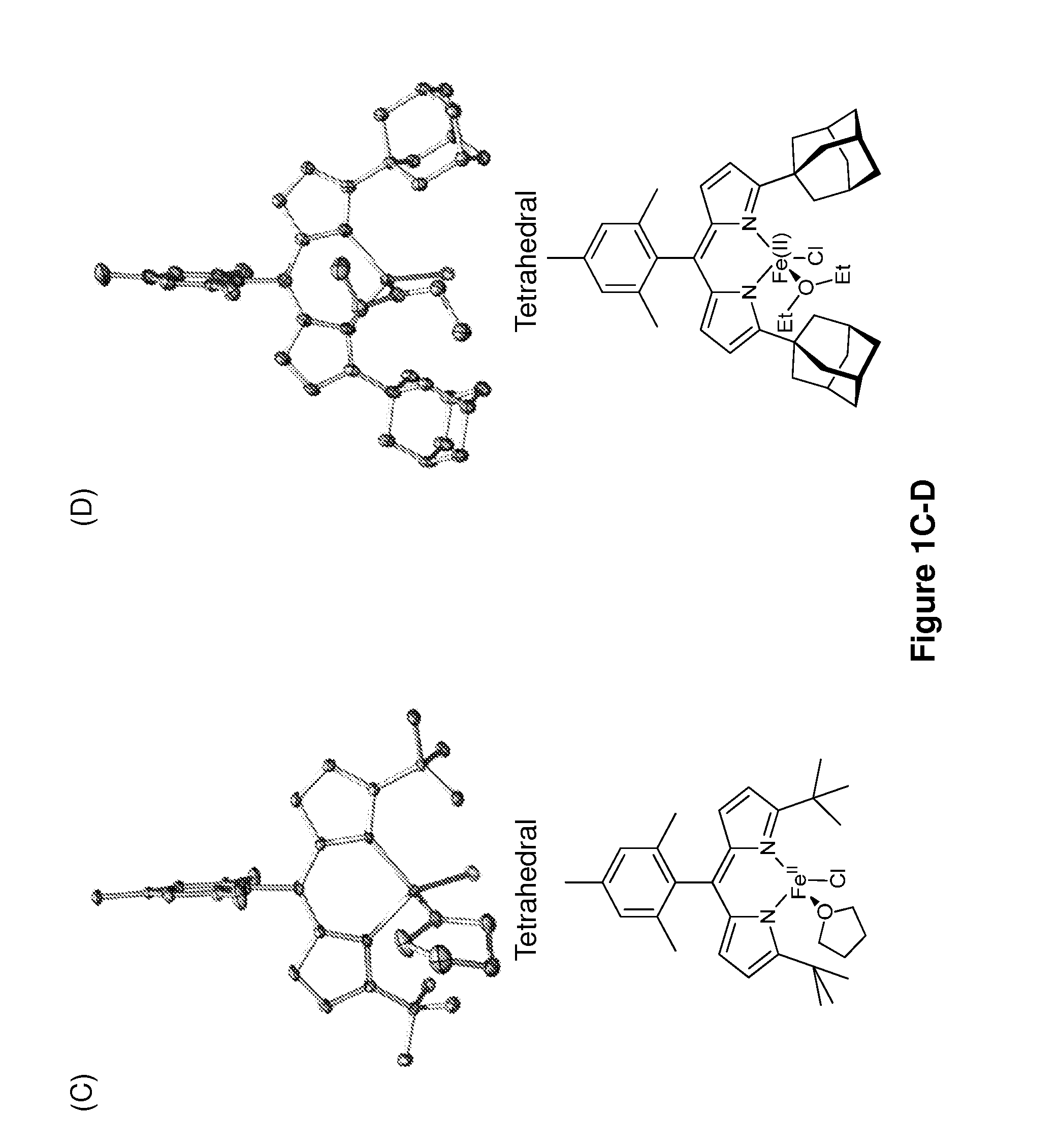
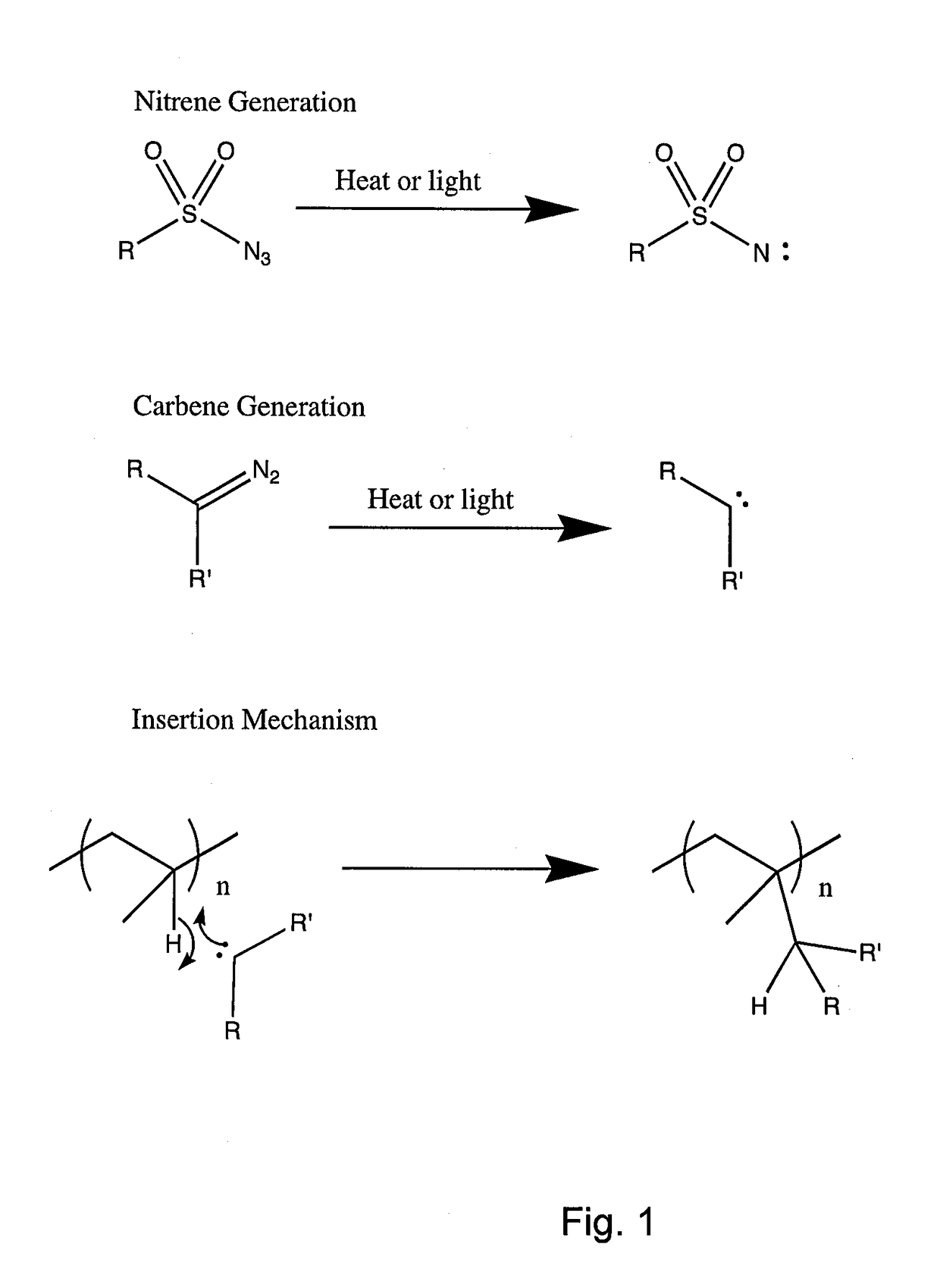
In chemistry, a nitrene (R–N) is the nitrogen analogue of a carbene. The nitrogen atom is uncharged and univalent, so it has only 6 electrons in its valence level—one covalent bond and four non-bonded electrons. It is therefore considered an electrophile due to the unsatisfied octet. A nitrene is a reactive intermediate and is involved in many chemical reactions. The simplest nitrene, HN, is called imidogen, and that term is sometimes used as a synonym for the nitrene class.
Covalent functionalization graphene and preparation method thereof
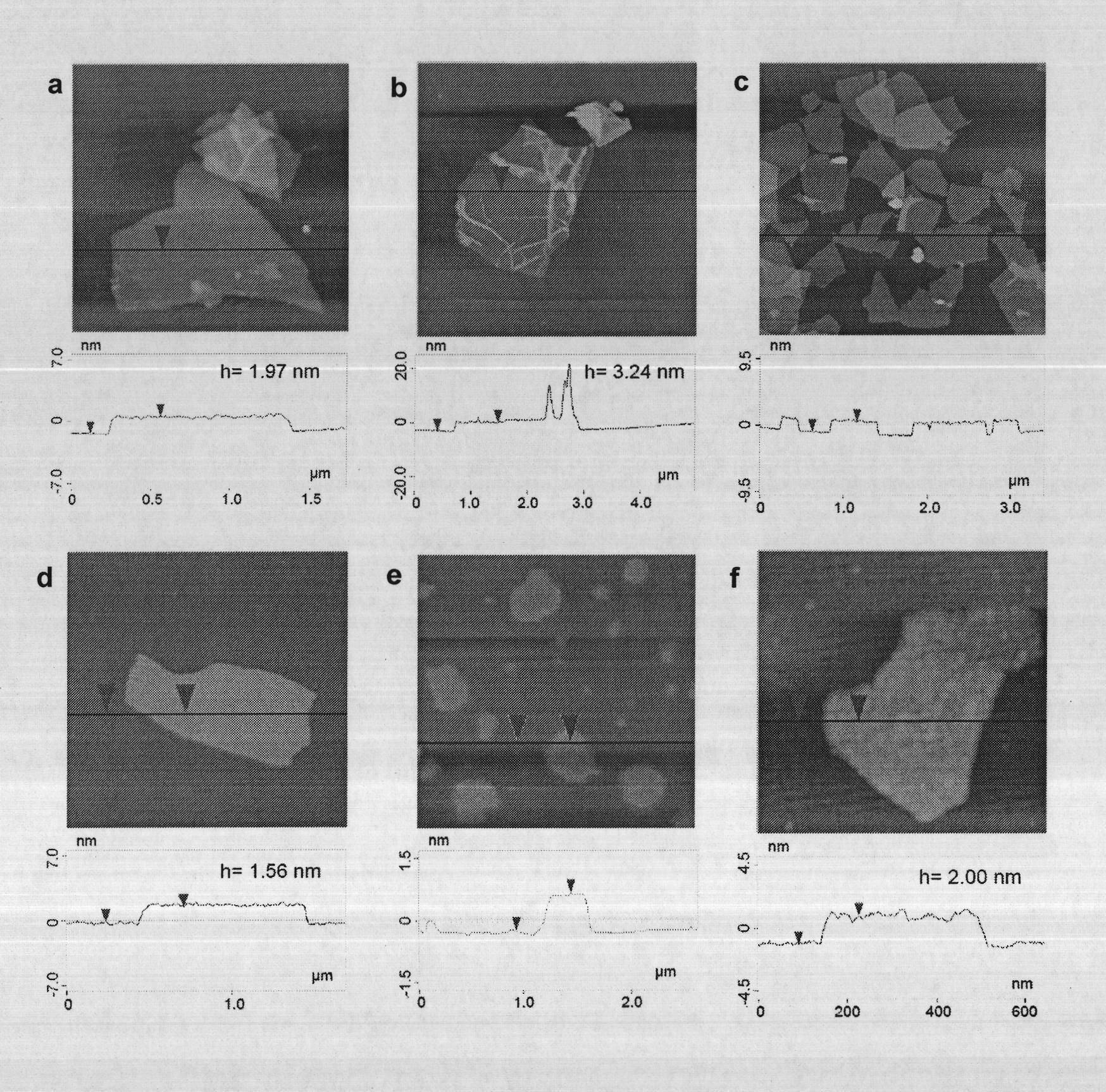
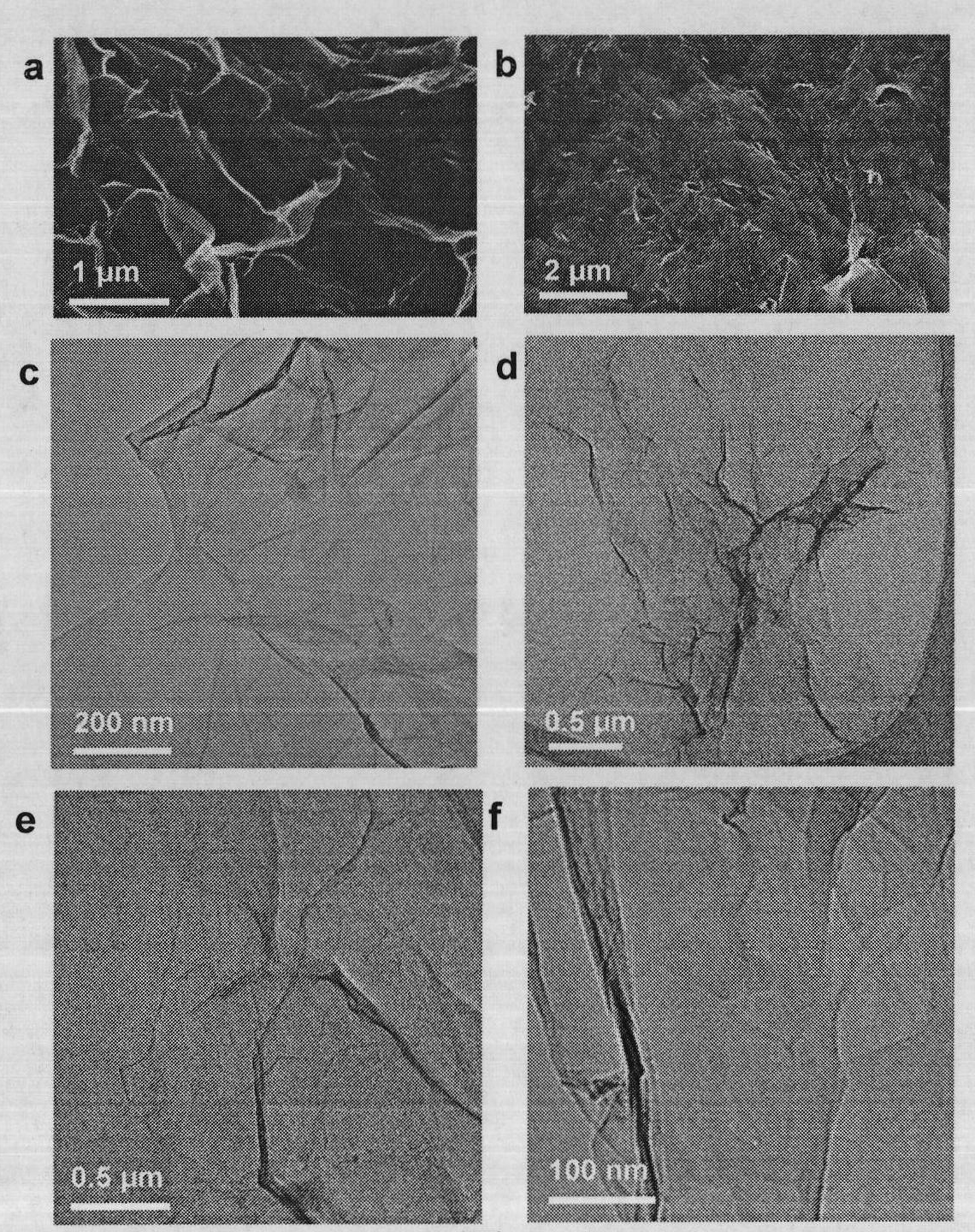
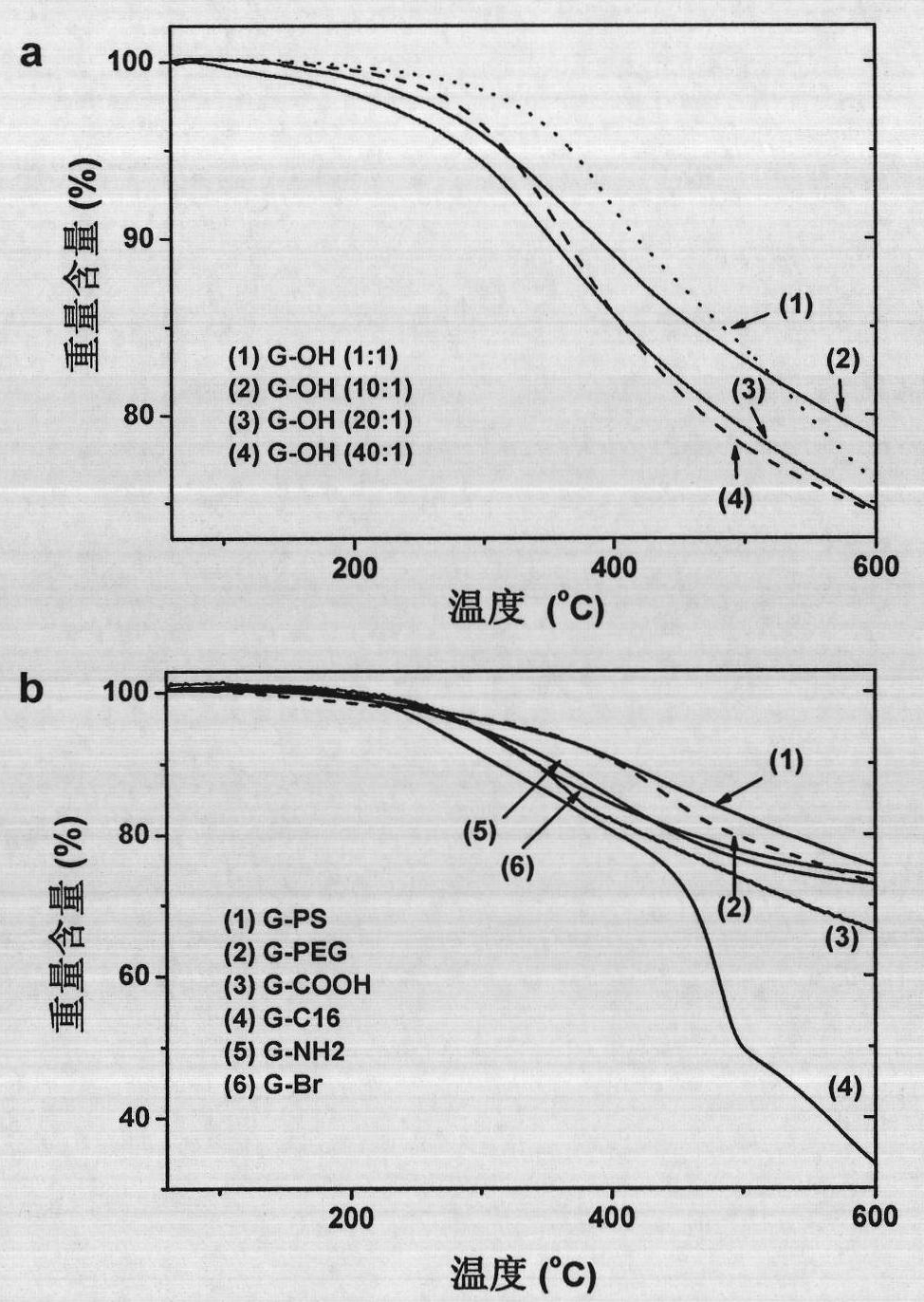
The invention discloses covalent functionalization graphene and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the covalent functionalization graphene comprises the following steps of: adding 1 part by weight of graphene oxide and 0.1-100 parts by weight of azido substances to a reactor; reacting for 0.1-72 hours in a hot bath at 100-220 DEG C; filtering, centrifugalizing, and washing to obtain the covalent functionalization graphene. In the invention, the graphene oxide is used as a raw material to directly react with an azido compound to prepare a covalently-modified functionalization graphene material based on nitrene chemistry by adopting a one-step method. The preparation method has simple and convenient method, simple process and large-scale production, is a general method and can enable multiple functional groups (such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, bromo and long alkyl group) and high polymers (such as polyethylene glycol and polystyrene) to be covalently connected to the graphene. The obtained covalent functionalization graphene has good solvent dispersity and conductivity, and can be processed in a solvent and widely used in the fields of micro-nano electron, machinery, chemical engineering, high performance materials, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
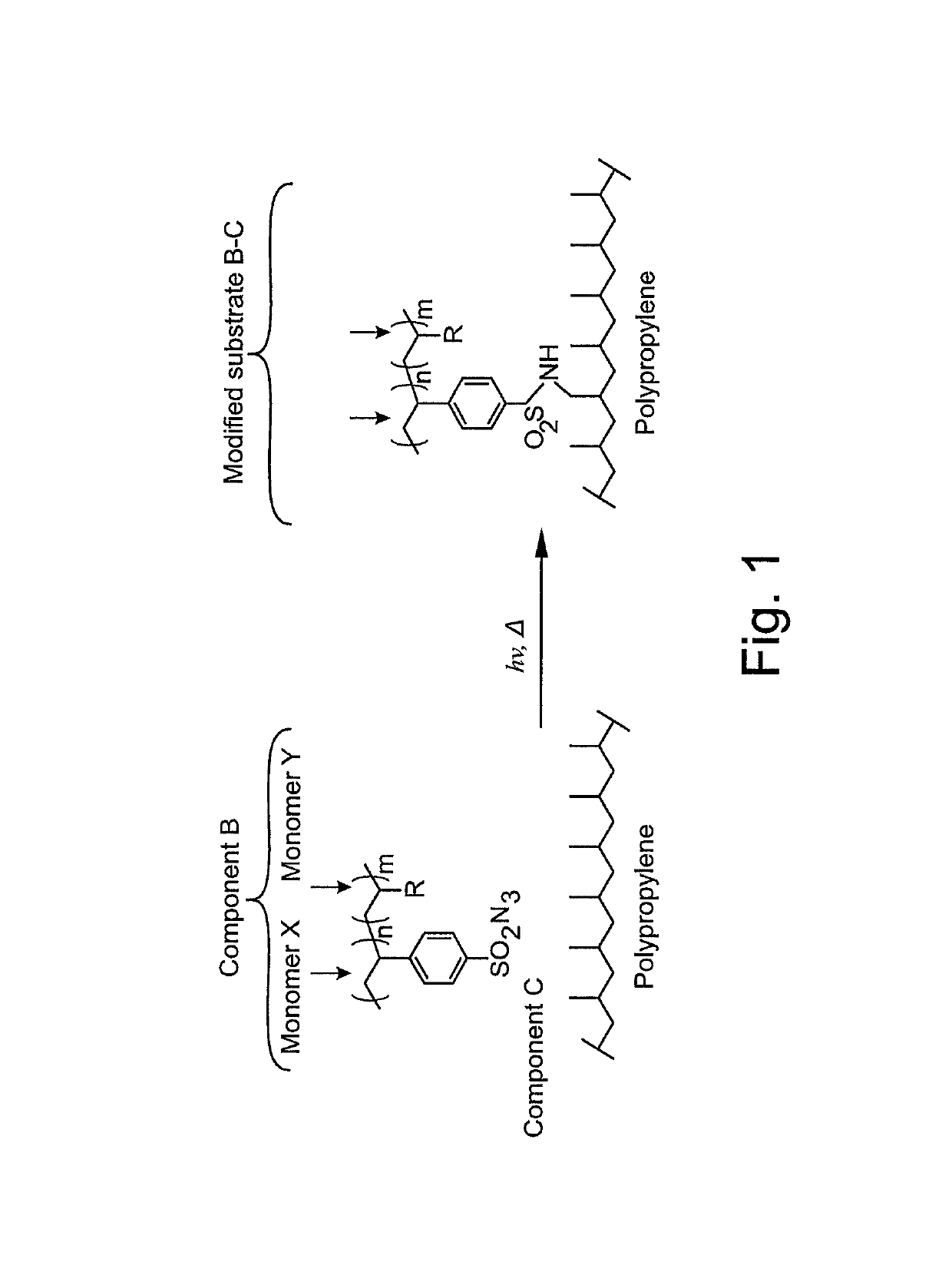
Surface modifying agents, modified materials and methods
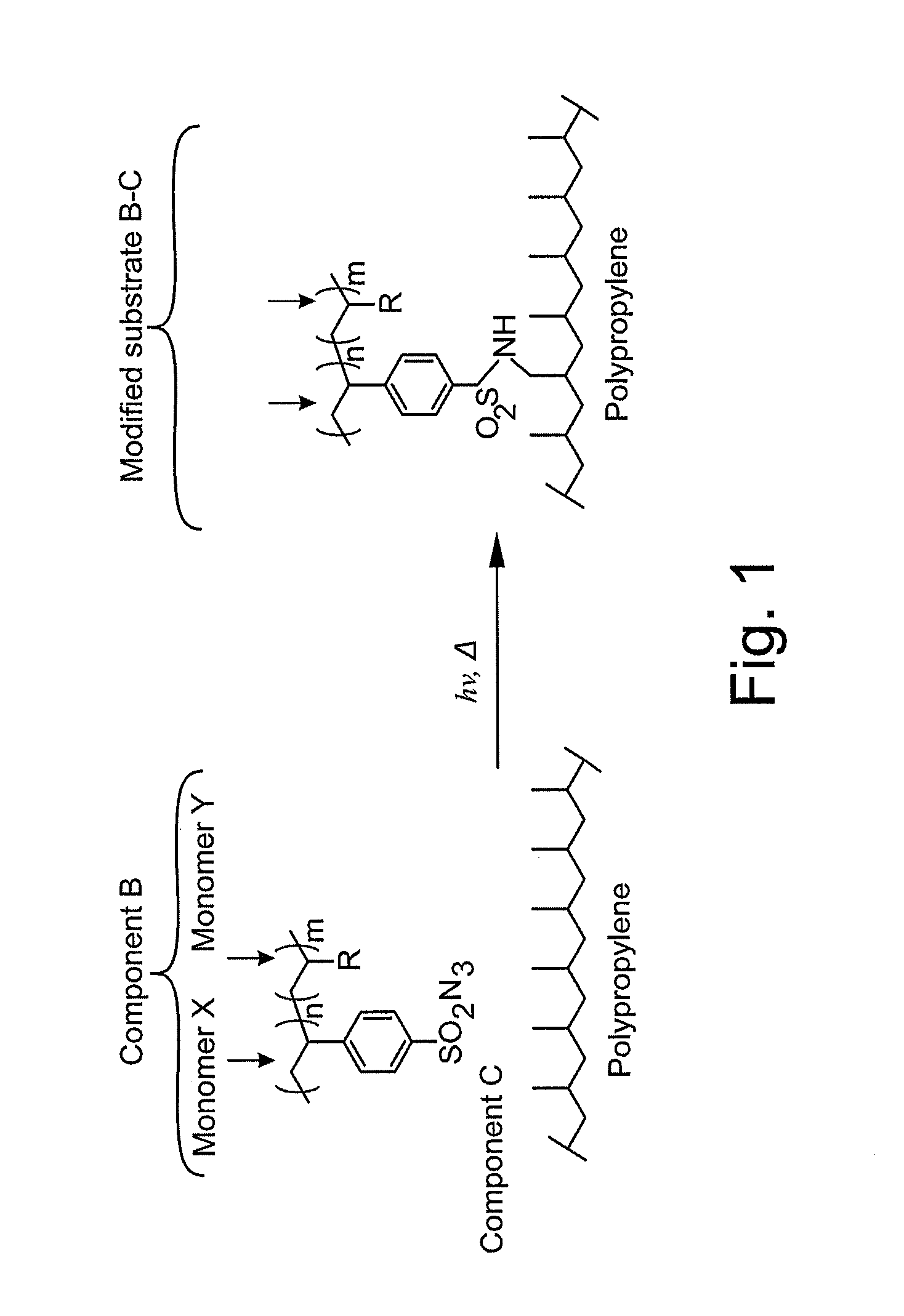
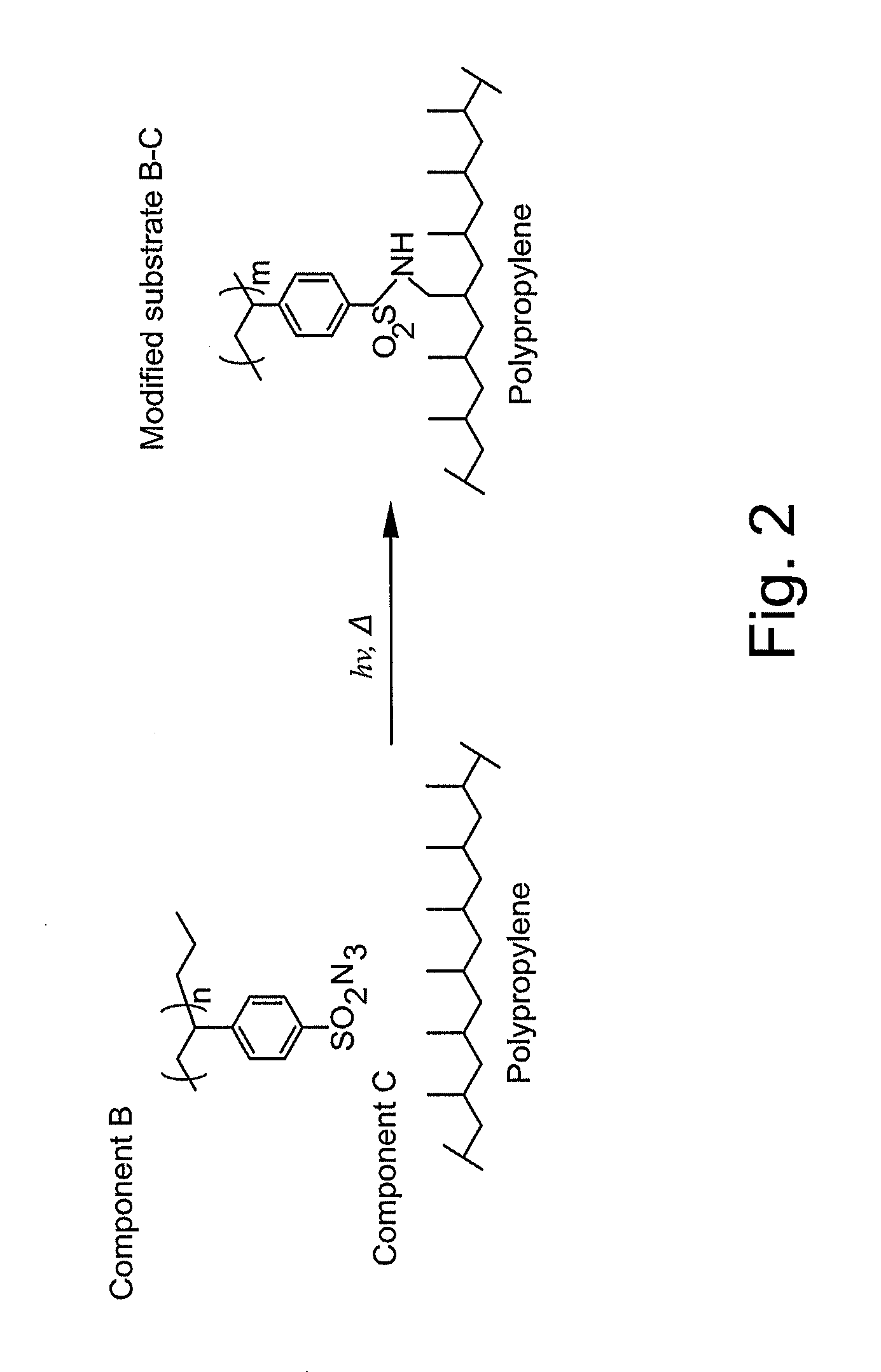
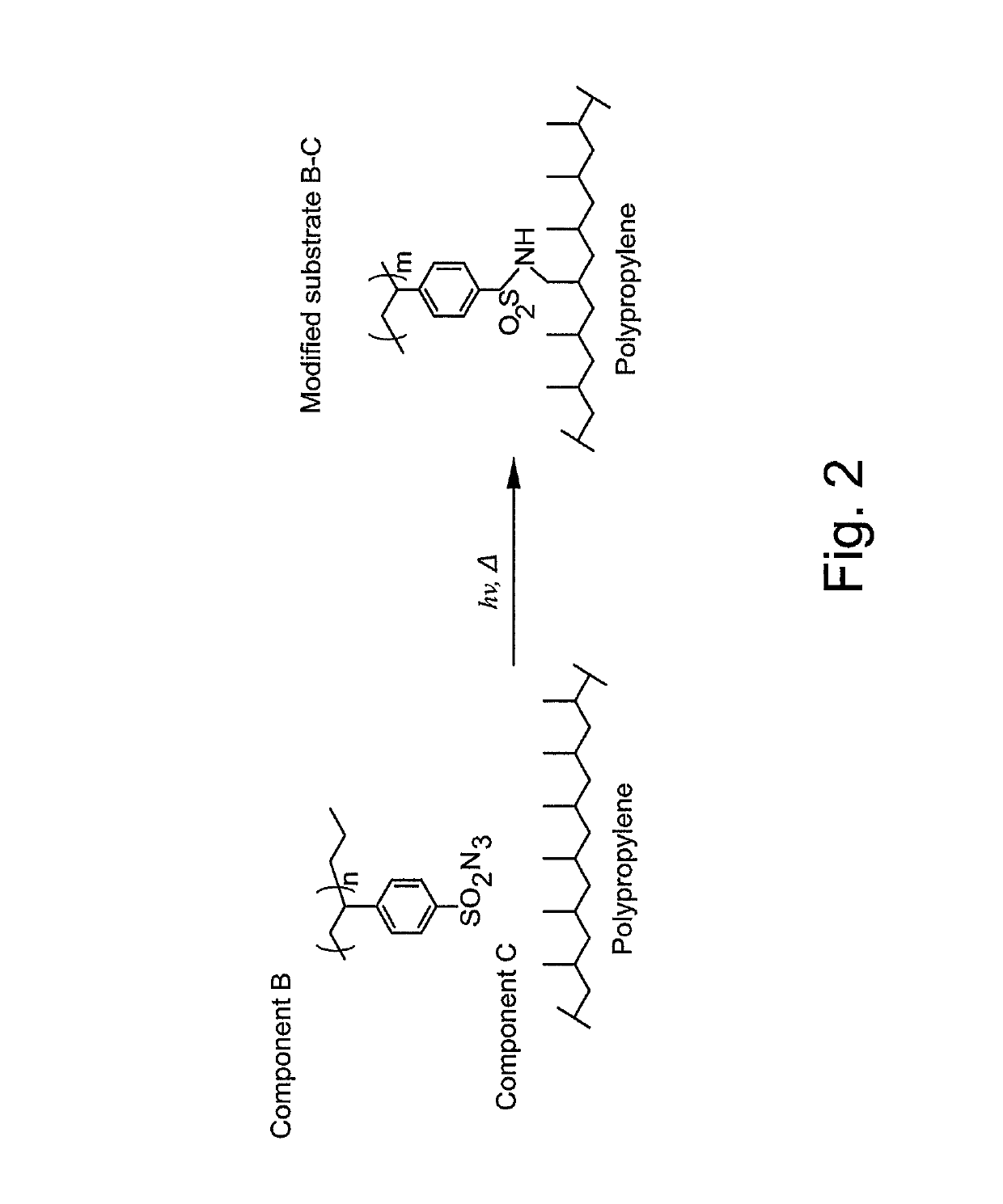
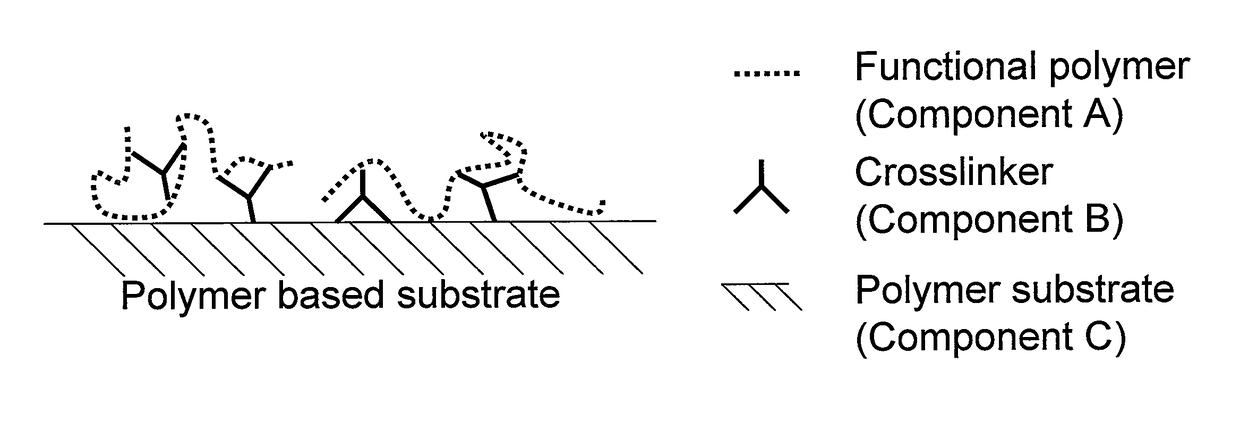
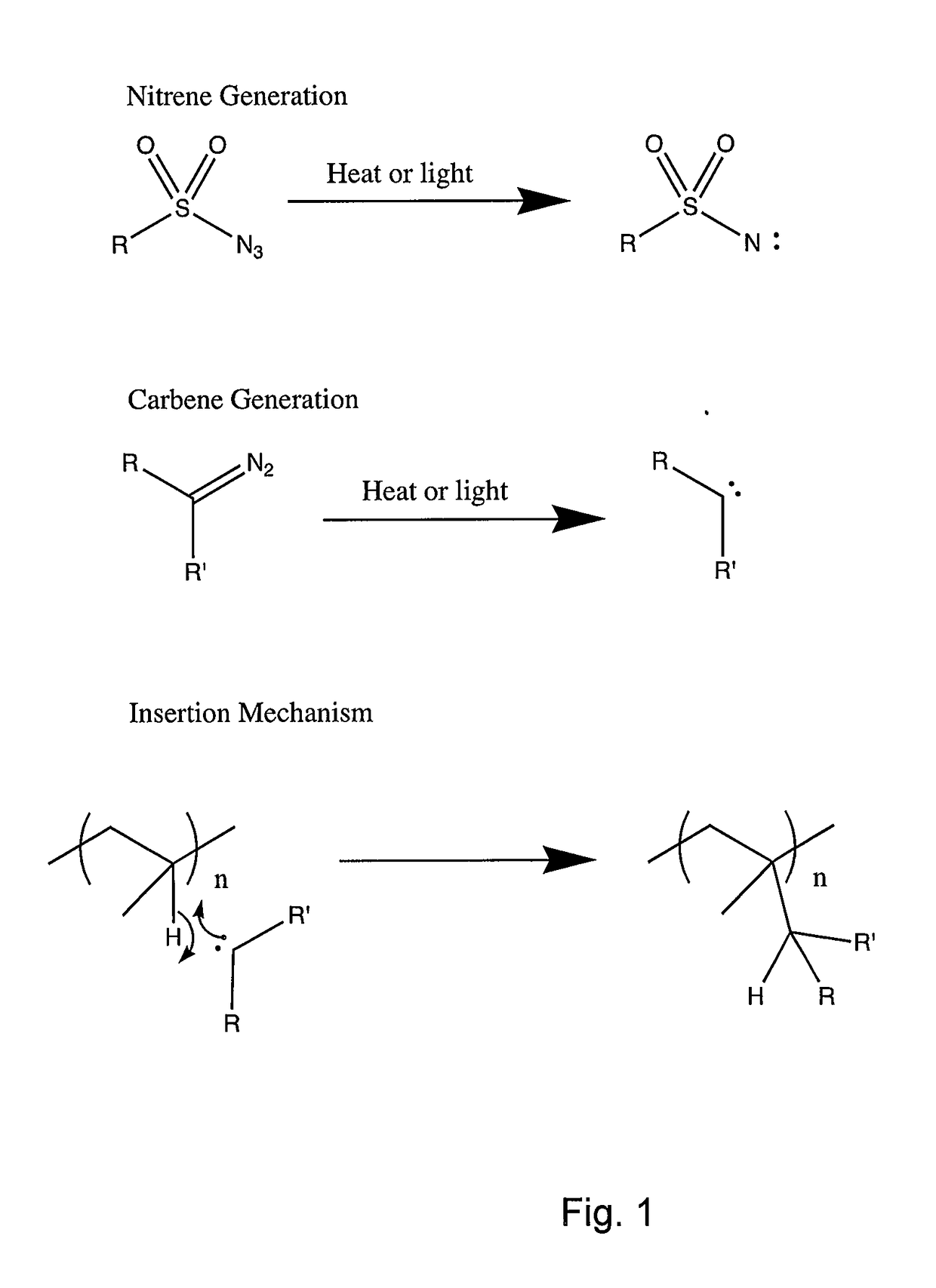
The present invention relates to surface modifying agents for polymeric and / or textile materials, methods of making and / or using a surface modifying agent to modify and functionalize polymeric and / or textile materials, and / or methods of using surface modified or functionalized polymeric and textile materials, and / or products using or incorporating surface modified or functionalized polymeric and textile materials. For example, the surface modifying agent in precursor form can be styrene sulfonyl azide monomer, polymer or copolymer capable of undergoing a chemical reaction in the presence of heat or light to form one or more styrene sulfonated nitrene monomers, polymers or copolymers, which are capable of chemically reacting with the surface of a polymeric or textile material to endow a specific or desired chemical surface functionality to the surface of a polymeric or textile material. Furthermore, the present invention is possibly preferably directed to a surface modifying agent which comprises a styrene sulfonated nitrene monomer, polymer or polymer containing one or more nitrene functional groups, which are capable of chemically reacting via an insertion reaction into one or more carbon-hydrogen bonds on the surface of a polymeric or textile material in order to chemically attach a specific or desired chemical functionality to the surface of a polymeric or textile material.
Owner:CELGARD LLC
Surface modified polymeric materials, modified functionalized polymers, functional polymers, and methods
ActiveUS20130022876A1Improve wettabilityImprove high temperature stabilityAnimal housingImmunoglobulinsFiberHollow fibre
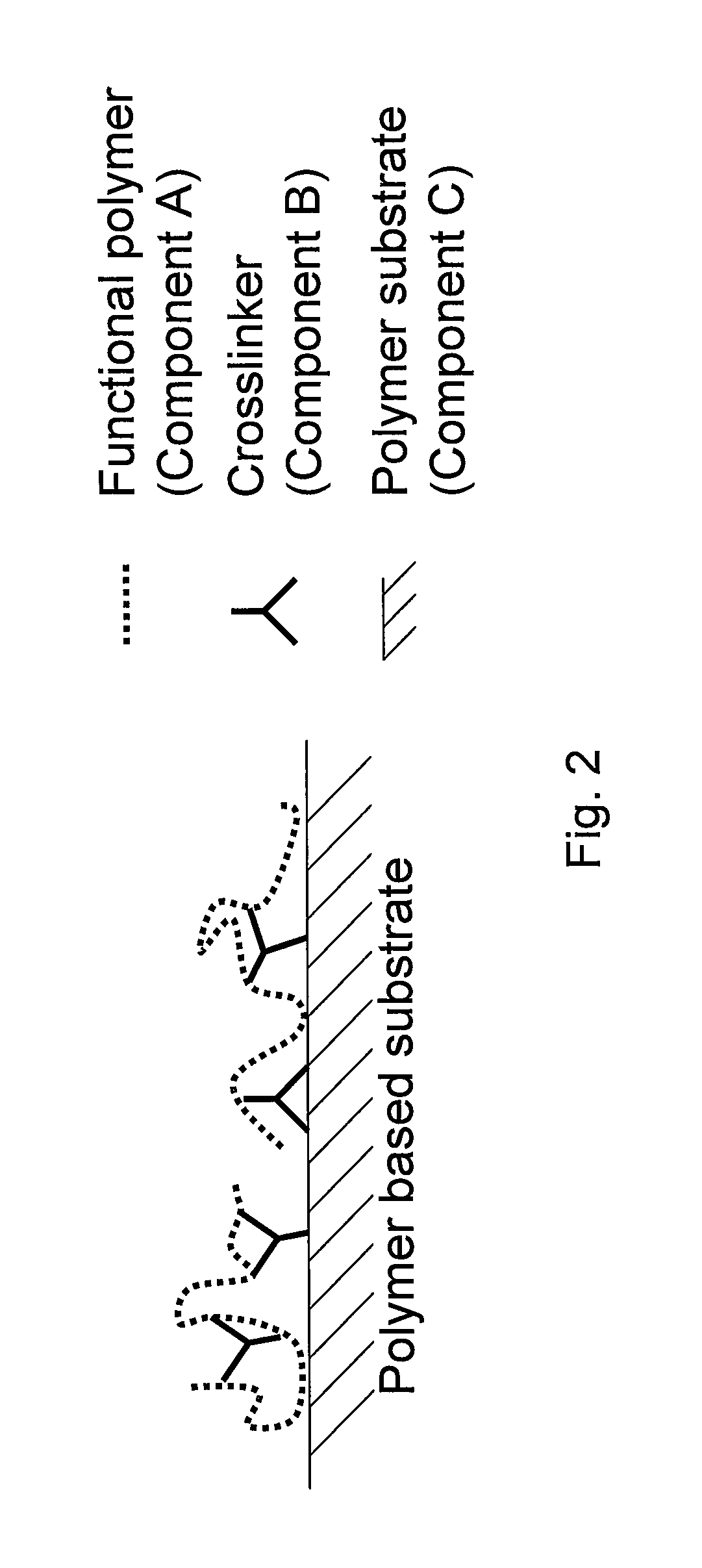
The present invention relates to new, improved or modified polymer materials, membranes, substrates, and the like and to new, improved or modified methods for permanently modifying the physical and / or chemical nature of surfaces of the polymer materials, membranes, or substrates for a variety of end uses or applications. For example, one improved method uses a carbene and / or nitrene modifier to chemically modify a functionalized polymer to form a chemical species which can chemically react with the surface of a polymer substrate and alter its chemical reactivity. Furthermore, this invention can be used to produce chemically modified membranes, fibers, hollow fibers, textiles, and the like.
Owner:CELGARD LLC
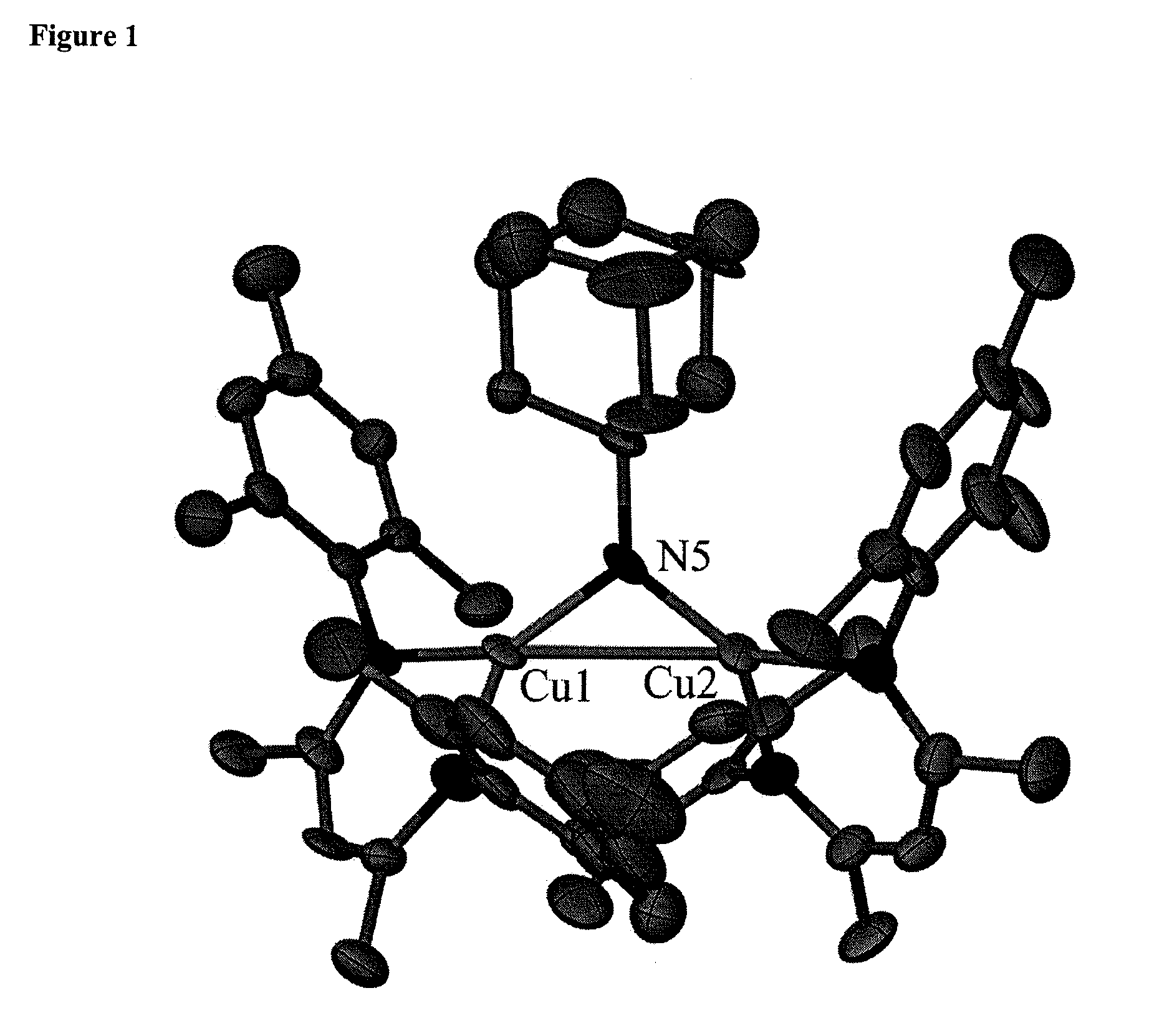
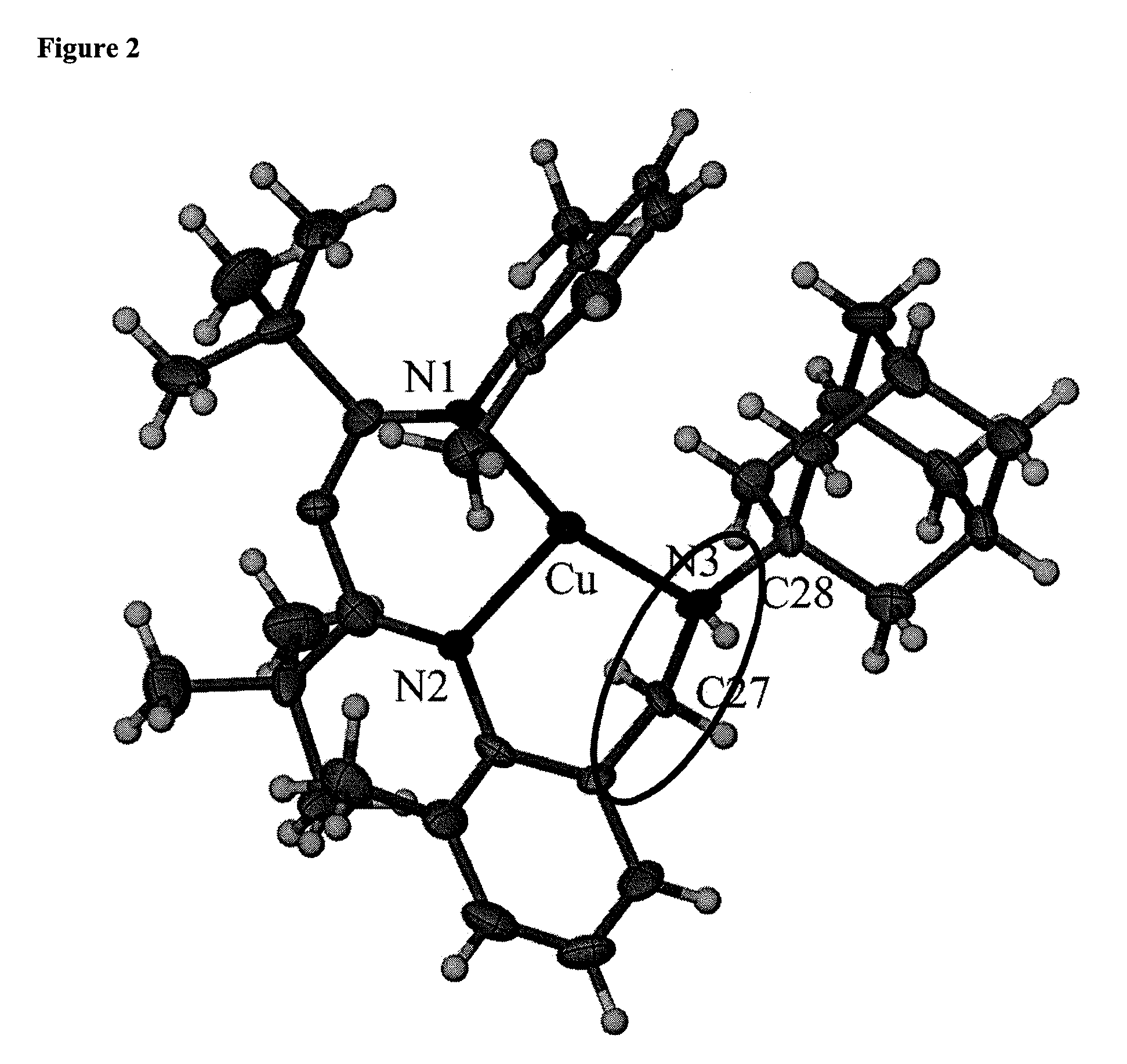
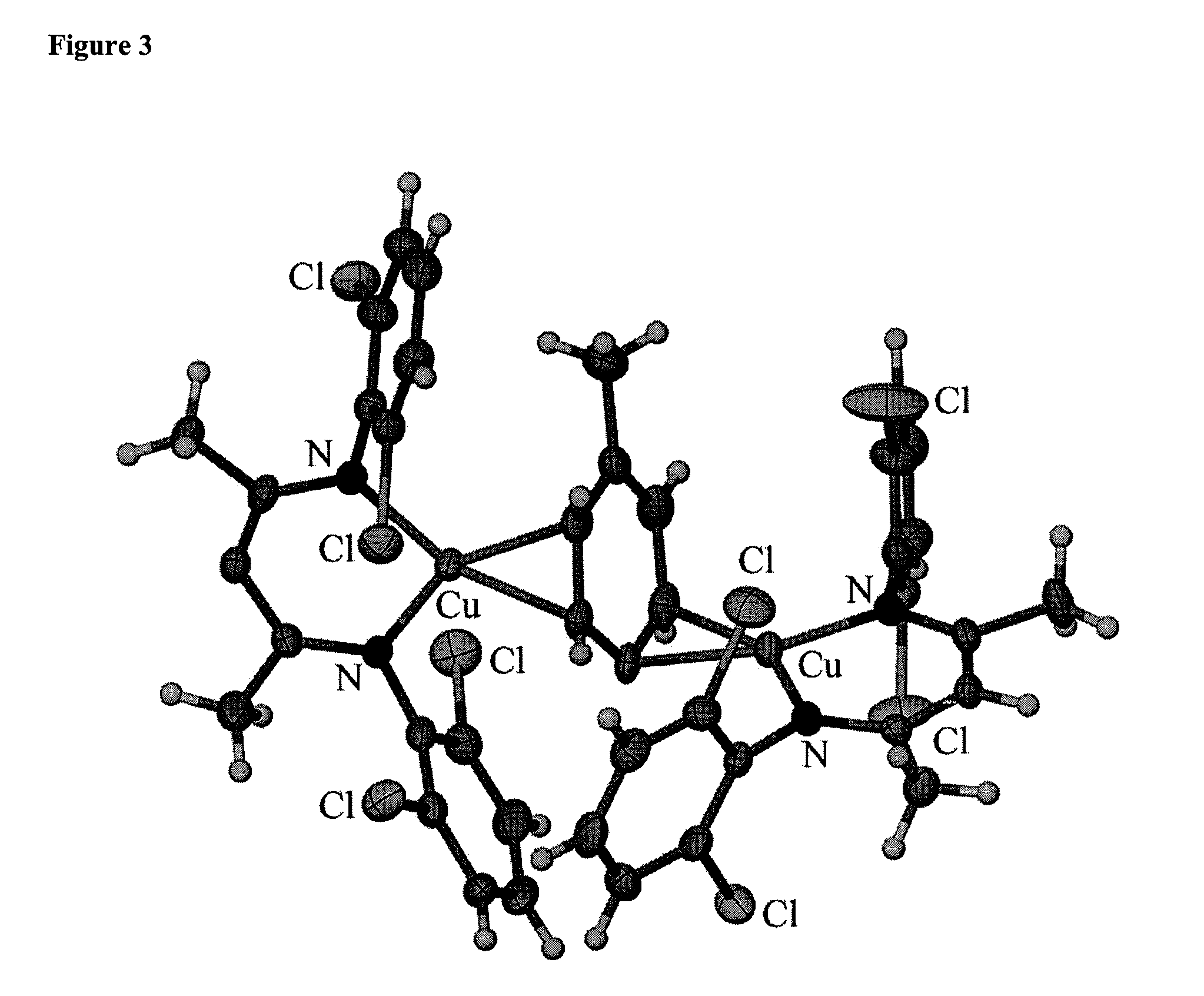
C-H Bond Amination and Olefin Aziridination with Beta-Diketiminato Copper Catalysts
ActiveUS20100056806A1Avoid it happening againEconomicalGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationMetal catalystNitrogen
One aspect of the present invention relates to a method for the transition metal (e.g., Cu(I)) mediated amidation of C—H bonds using electron-rich aliphatic azides. In certain embodiments, the methods are useful for the C—H insertion of nitrenes generated and stabilized by a β-diketiminato metal catalyst. In certain embodiments, said nitrenes are generated from organoazides, or by oxidation of the corresponding amine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to olefin aziridination using said β-diketiminato metal catalysts. In addition, the methods of the present invention include stereoselective C—H bond aminations and olefin aziridinatons. In certain embodiments, the methods are conducted in an aerobic environment. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to the use of O2 as an oxidant, wherein water is the byproduct of oxidation; this fact avoids the generation of toxic byproducts and renders the methods atom economical.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Methods and compositions for dual phototherapy
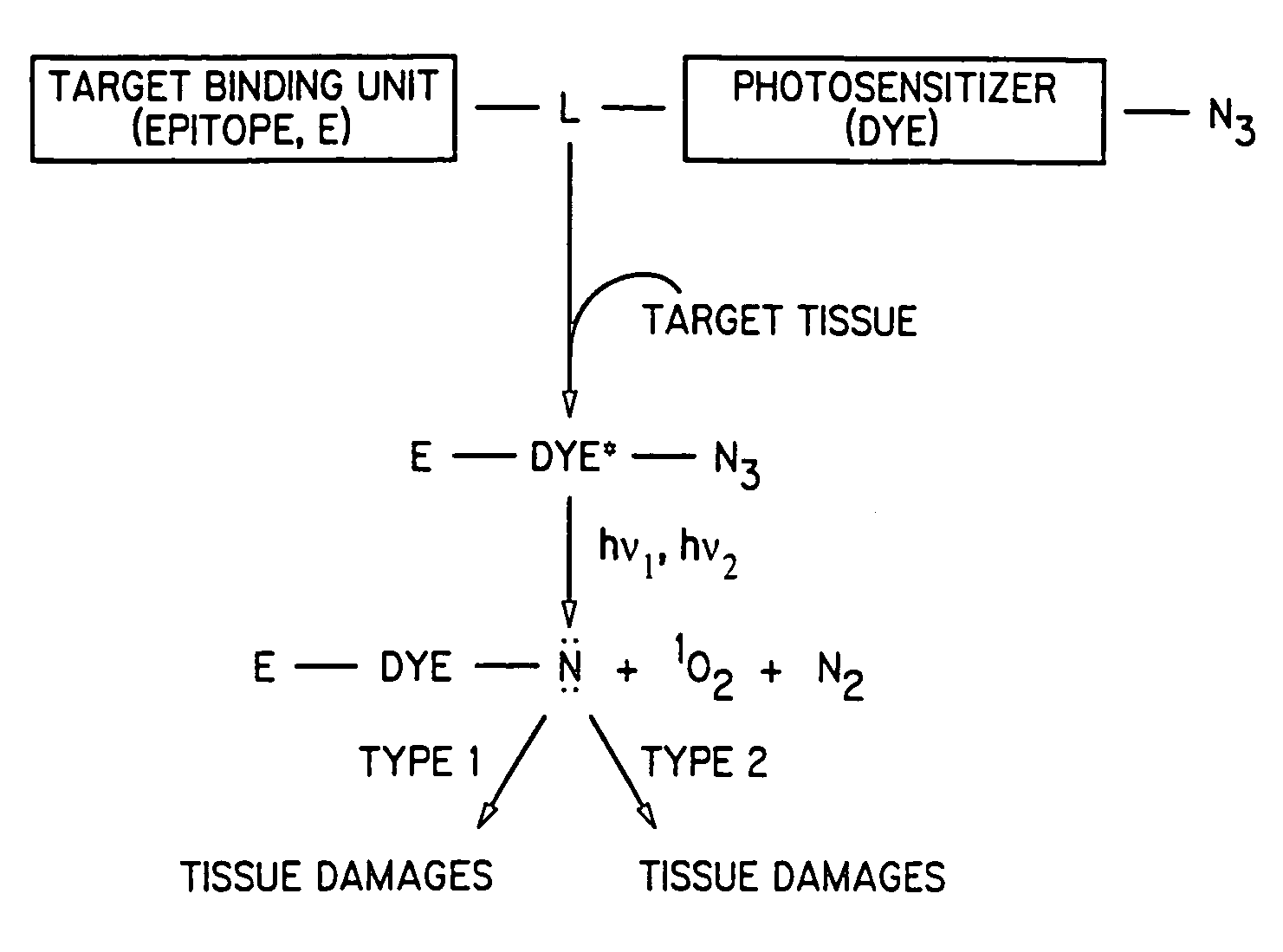
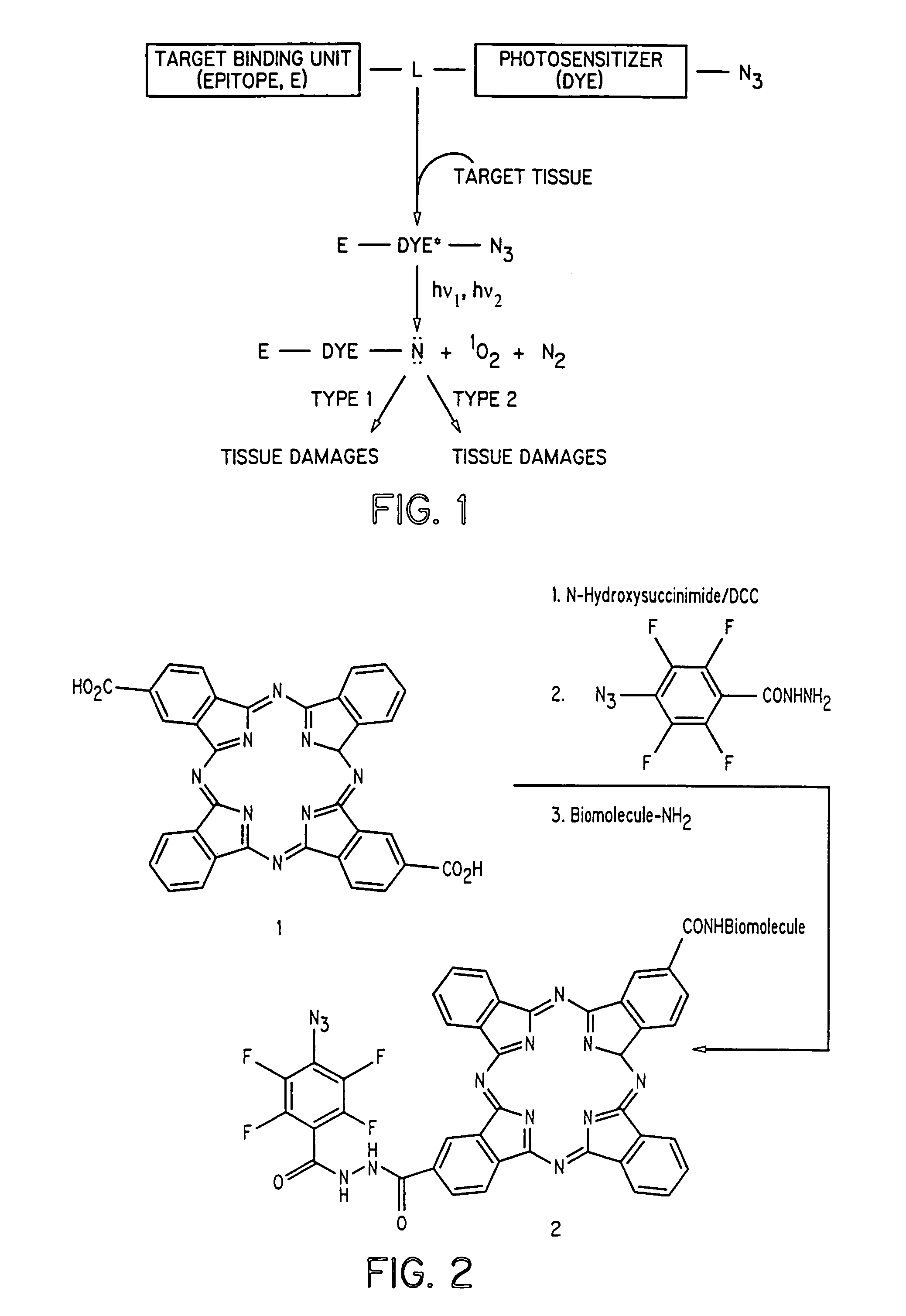
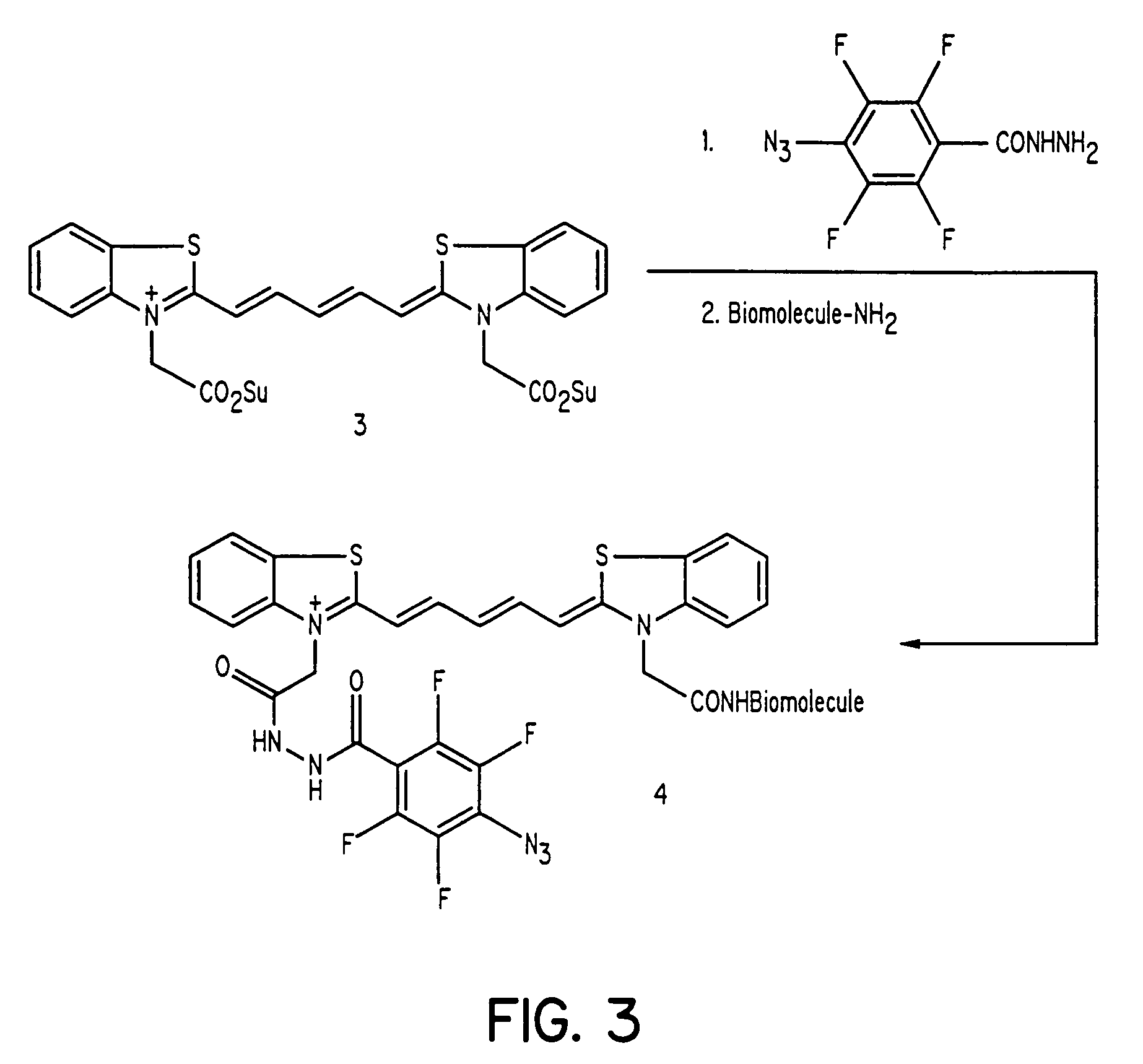
The present invention discloses dye-azide derivatives and their bioconjugates for dual phototherapy of tumors and other lesions. The compounds of the present invention may contain either a mixture of Type 1 and Type 2 agents or a single entity that integrates both units in the same molecules. The compounds are designed to produce both Type 1 and Type 2 phototherapeutic effect at once using dual wavelength light source that will produce singlet oxygen and nitrene at the lesion of interest.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
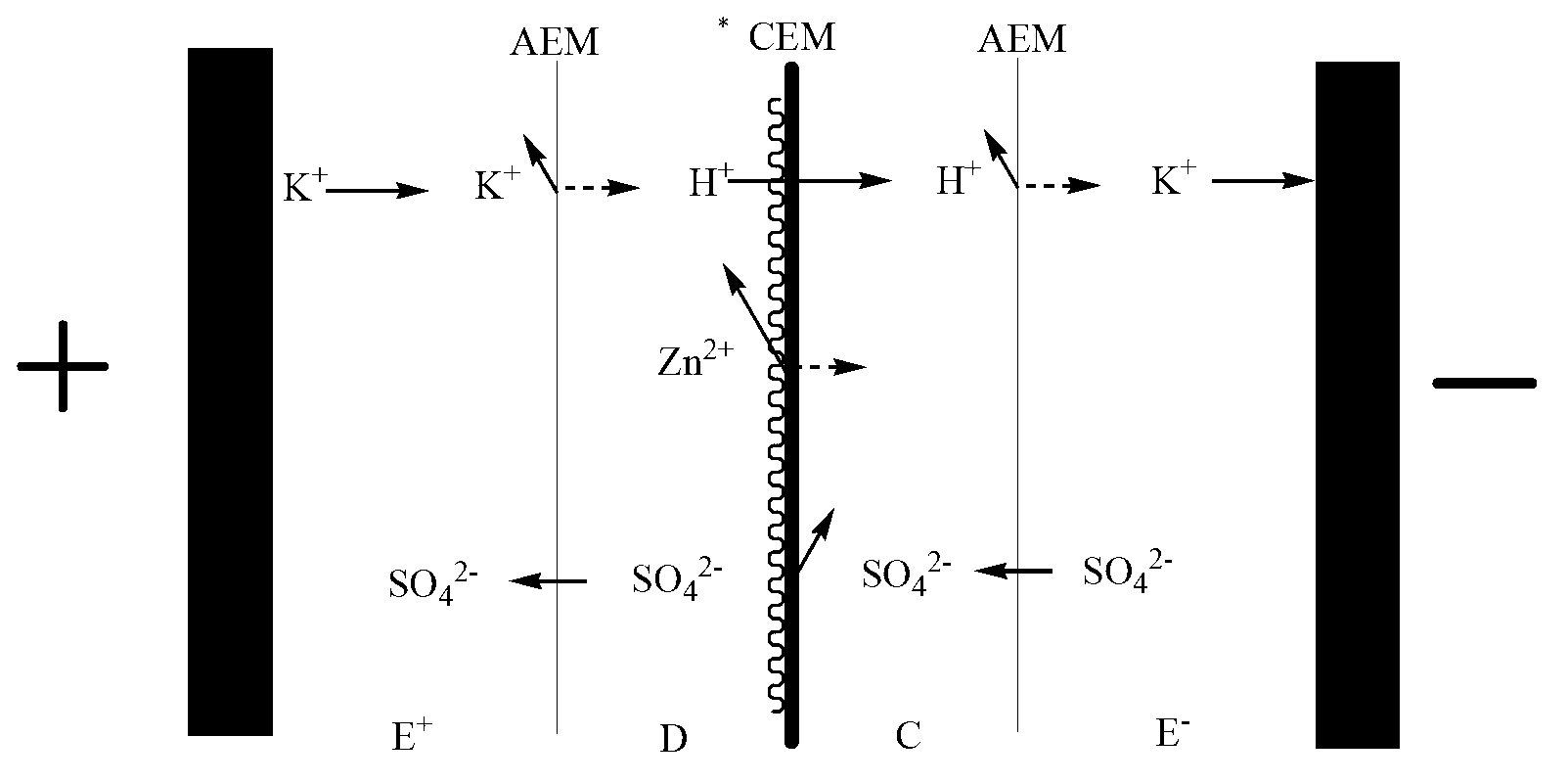
Method for preparing cation exchange membrane with monovalent preferential separation function
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cation exchange membrane with a monovalent preferential segregation function. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, attaching chitosan and / or an azide derivative solution thereof to the roughened surface of a conventional cation exchange membrane by embedded dipping at first; after the surface drains off away from light, irradiating the azide derivative of chitosan by ultraviolet light to initiate bond insertion reaction of nitrene to complete fixing of a covalent bond on the basement membrane surface; and finally, regulating the compactness and electrical charge density of a functional layer substrate and the attachment effect of the functional layer substrate on the basement membrane surface by crosslinking treatment and / or amination treatment so as to form a compact and even positively charged thin layer fixed by the covalent bond on the surface of the conventional cation exchange membrane. A series of electroosmosis experiments show that monovalent and multivalent cations are effectively and selectively separated by virtue of the aperture sifting effect of a functional layer, and the difference of electrostatic interactions between the functional layer and different valent cations in a separation process.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
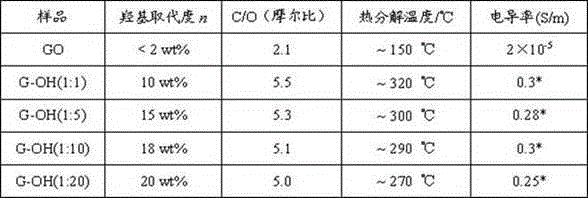
Preparation method of controllable high-substitution hydroxyl functionalized graphene
InactiveCN104370284AHigh degree of hydroxyl substitutionThe degree of substitution is controllableOrganic solventSodium azide
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of controllable high-substitution hydroxyl functionalized graphene. The preparation method of the controllable high-substitution hydroxyl functionalized graphene comprises the following steps: 1) adopting an improved Hummers method to oxidize original graphite by virtue of a strong oxidant, and then, preparing graphene oxide by diluting, washing and drying; 2) dispersing sodium azide and chloroethanol in different solvents, performing substitution reaction at a certain temperature to prepare a hydroxyl azide compound; and 3) at a high temperature, adopting nitrene with relatively high reaction activity to perform functionalization treatment on the graphene oxide to obtain the hydroxyl functionalized graphene. The hydroxyl functionalized graphene obtained by the preparation method disclosed by the invention can be stably dispersed in water and a plurality of organic solvents, has good dispersion stability and extensive use in the fields such as micronanoelectronics, machinery, electric wires and cables and high-performance composite materials.
Owner:JINCHENG POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER +1
Intramolecular C-H amination with sulfonyl azides
InactiveUS20100063277A1Good yieldFunctional group formation/introductionOrganic chemistryPyrenesulfonyl azideNitrogen gas
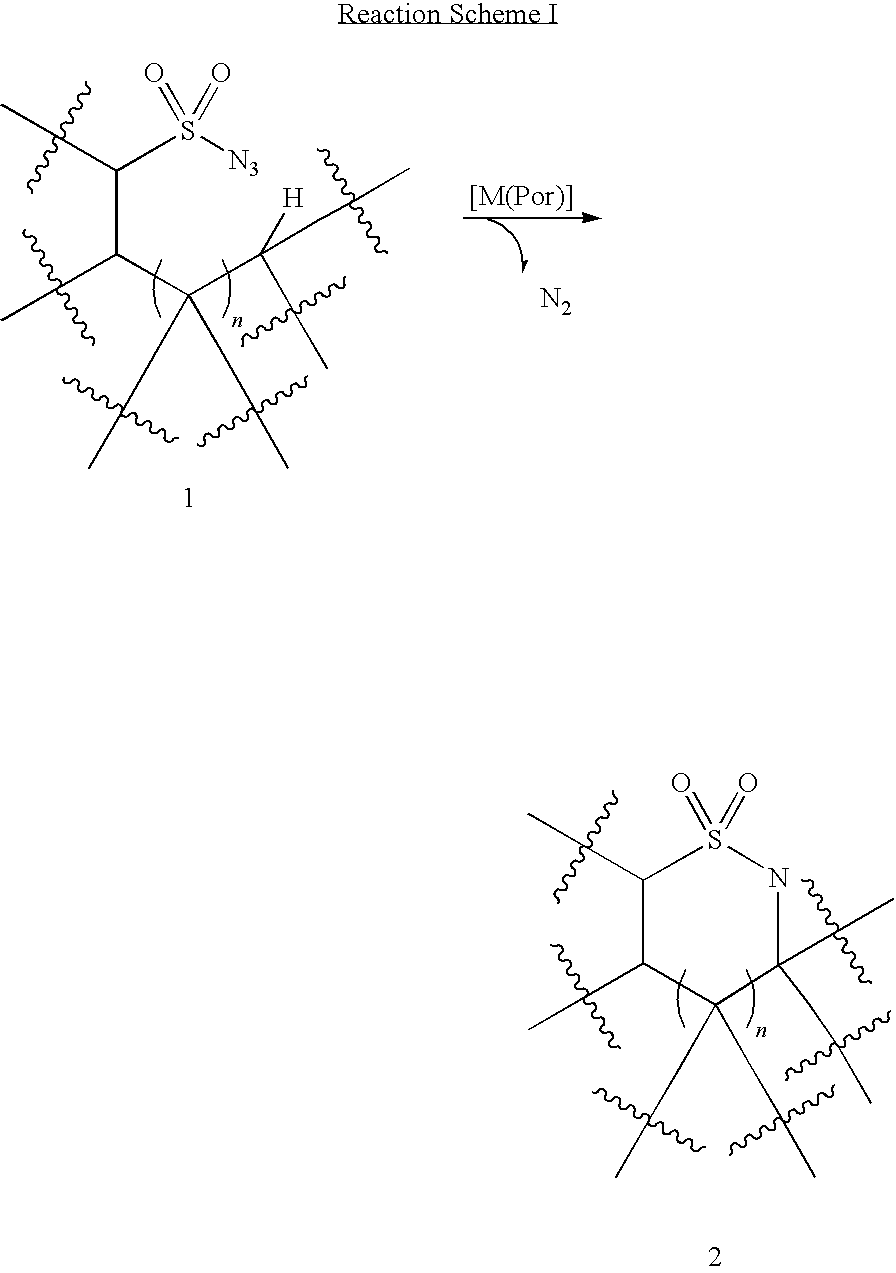
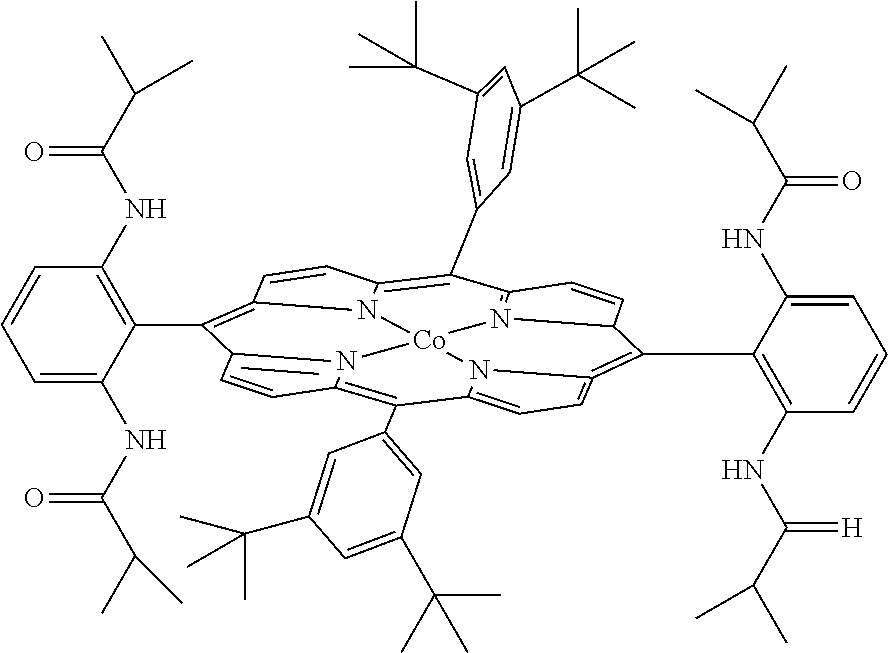
Cobalt (II) complexes of porphyrins are effective catalysts for intramolecular nitrene insertion of C—H bonds with arylsulfonyl azides. The cobalt-catalyzed process can proceed efficiently under mild and neutral conditions in low catalyst loading without the need of other reagents or additives, generating nitrogen gas as the only byproduct. Using the simple tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP) as the ligand, the cobalt-catalyzed intramolecular amidation can be applied to primary, secondary, and tertiary C—H bonds and suitable for a broad range of arylsulfonyl azides, leading to the syntheses of various benzosultam derivatives in excellent yields
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
POSS acrylate/p-vinylbenzylazide copolymer coat material and its preparation method
InactiveCN103087247AImprove thermal stabilityImprove adhesionCoatingsVegetal fibresMethacrylatePolymer science
The invention relates to a coat material rapidly cross-linking under the irradiation of ultraviolet and simultaneously containing a POSS component and an azide reaction group, and concretely relates to a POSS acrylate / p-vinylbenzylazide copolymer coat material and its preparation method. Free radical copolymerization of a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-containing (meth)acrylate monomer and an azido group-containing styrene monomer is carried out, the obtained copolymer is dissolved in a solvent to form a dispersion, and ultraviolet irradiation and solvent volatilization are carried out to obtain a coat having a good stability and a high adhesion. According to the invention, the azido group decomposes to a nitrene group having an extremely-high reaction activity under the irradiation of the ultraviolet, and the nitrene group can almost react with any C-H bonds or C=C bonds of an adjacent molecule, and can even be inserted into a O-H bond or an N-H bond, so the chemical modification of the surface of glass and a cotton fiber or a film in covalent bond is realized, and the process is simple and rapid.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Non-woven surface covalent bonding gelatin adsorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102059096AWide variety of sourcesWide adaptabilityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCellulosePolyester
The invention discloses a method for preparing a novel adsorption material by covalent bonding gelatin on the surface of a non-woven fabric, comprising the following steps of, with a synthetic or nature high polymer non-woven fabric (such as PP (Propene Polymer), PET (Polyester Terephthalate), cellulose and the like) as a substrate, dip-coating the synthetic or nature high polymer non-woven fabric with a polyazide solution to form an activated non-woven fabric substrate, and dip-coating a gelatin solution on the activated non-woven fabric substrate; and utilizing ultraviolet irradiation to photolyze an azide group to form active nitrene, covalently bonding gelatin molecules on the surface of the non-woven fabric through insertion reaction of the active nitrene, and generating partial crosslinking, and finally, removing unbonded or uncrosslinked gelatin by soaking with cold or hot water to prepare the adsorption material. The adsorption material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has stronger adsorption capacity to tannin, has the balance adsorption capacity of 59.5-134.2mg / g and can reach adsorption balance through about 3h.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
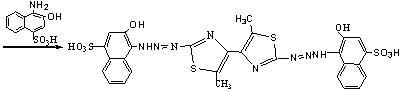
2,2'-bis(2-hydroxy-4-sulfonic-1-naphthylamine azoxyl)-5,5'-dimethyl-4,4'-bithiazole and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102311404AHigh sensitivityGood choiceOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorometric AnalysisNaphthalene
The invention relates to a bis-heterocyclic triazene compound, and specifically relates to a 2,2'-bis(2-hydroxy-4-sulfonic-1-naphthylamine azoxyl)-5,5'-dimethyl-4,4'-bithiazole and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparation of 2,5-dibromohexanedione; (2) preparation of 2,2'-diamino-5,5'-dimethyl-4,4'-bithiazole; (3) preparation of 5,5'-dimethyl-4,4'-bithiazole-2,2'- bis-diazonium salt; (4) preparation of an objective product BHSNAADMBT. The technical scheme of the invention connects bithiazole heterocycle and naphthalene ring derivative with fluorescence property together to synthesize a reagent with double functional-analytical groups and large steric hindrance; and the compound of the invention not only has high reaction sensitivity with metal ions, but also has good selectivity. The reagent is a good photometric analysis developer and a novel fluorescence analytical reagent with high sensitivity and good selectivity as well.
Owner:SHANXI DATONG UNIV
Adsorbing material for azide method coupling gelatin and preparation method of adsorbing material
InactiveCN104549178AOvercome water solubilityOvercome fragileOther chemical processesPolymer scienceCarboxyl radical
The invention discloses an adsorbing material for azide method coupling gelatin and a preparation method of the adsorbing material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: grafting an unsaturated monomer containing carboxyl on the surface of a macromolecular non-woven base material to introduce the carboxyl by employing an ultraviolet induction technology; introducing aromatic amino by employing electrostatic self-assembly of aromatic diamine diazonium salt and the carboxyl, and transforming into an azide group; decomposing into active nitrene under ultraviolet irradiation, fixing gelatin on a non-woven surface through inserting reaction of nitrene; and finally soaking in hot water, and removing uncoupled gelatin to prepare the absorbing material. The adsorbing material is relatively good in hydrophilia; the carrier content and the water absorption rate of the gelatin can be adjusted within a large range; and the adsorbing material has relatively high adsorption capacity on tannin, has a selective absorption effect on adsorption of the tannin in green tea and emblic leafflower fruit extracts, and also has the selective absorption effect on condensed tannin in the green tea extract.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Modification of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and azide cross-linked mixed-matrix membranes made therefrom
Disclosed is a method of modifying a metal-organic framework (MOF), the modified MOF, and methods for using the same. The method of modification can include heating a mixture comprising an azide compound and a MOF to generate a nitrene compound and nitrogen (N2) from the azide compound and covalently bonding the nitrene compound to the MOF to obtain the modified MOF.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
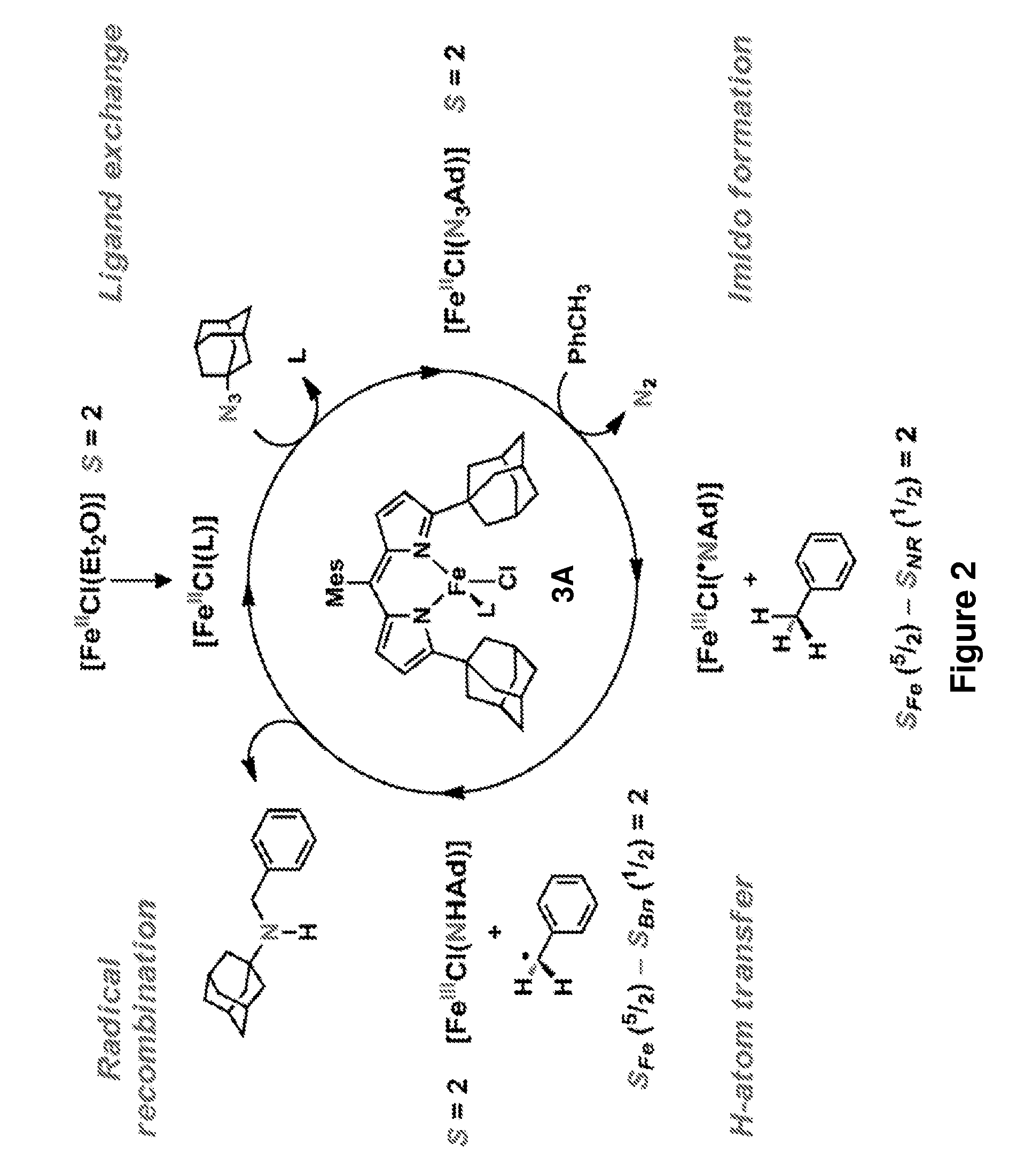
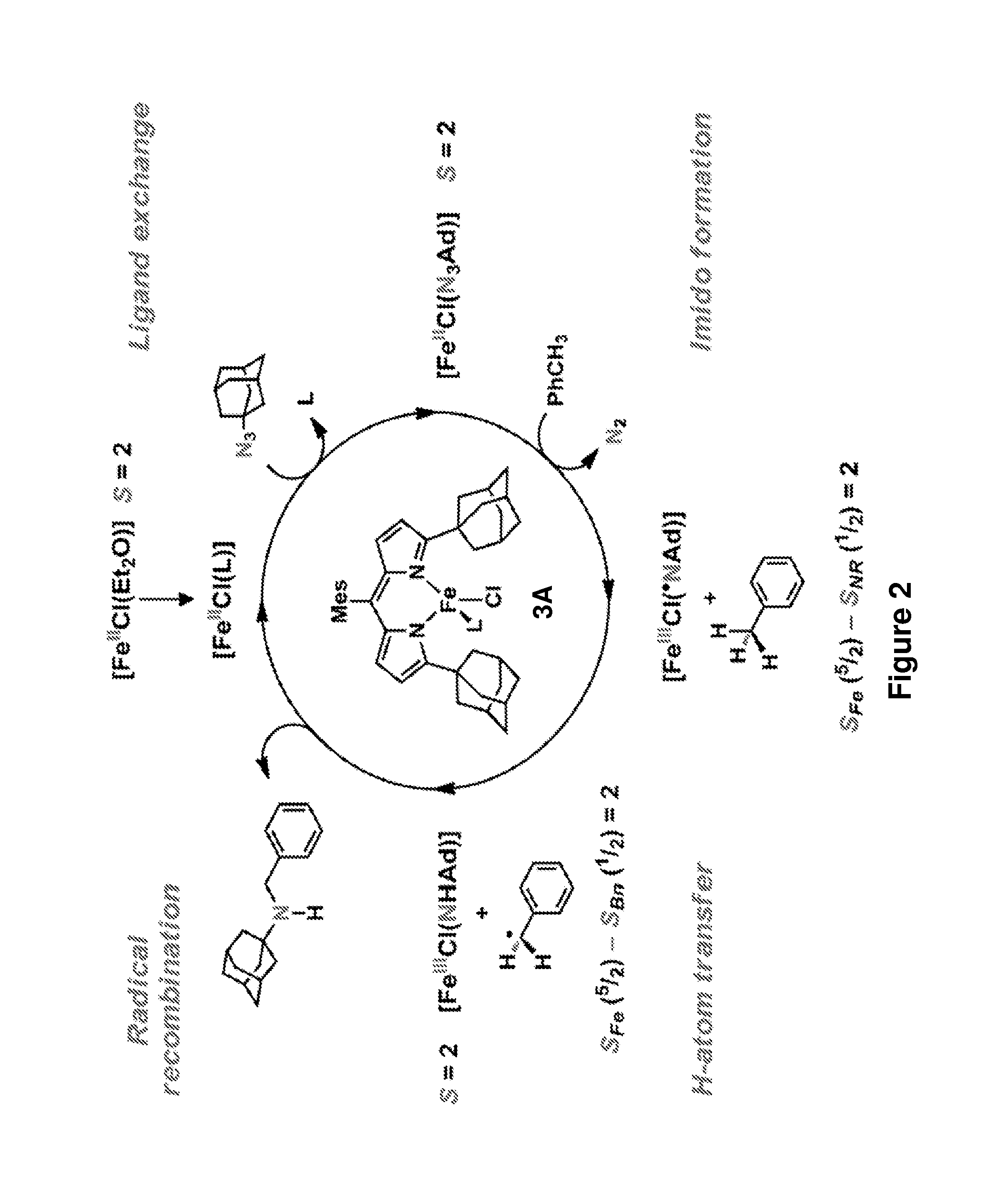
Synthesis of acyclic and cyclic amines using iron-catalyzed nitrene group transfer
InactiveUS9487472B2Poor economyAvoid great wasteOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAzideFerric
The present invention provides novel synthetic methods for making acyclic secondary amines by reacting an azide with a compound bearing one or more C—H groups, catalyzed by a FeII-dipyrromethene complex. The acyclic secondary amines are thought to be formed through an intermolecular nitrene transfer. Also provided herein are methods of synthesizing protected (e.g., Boc- or Fmoc-protected) cyclic secondary amines (e.g., 5-, 6-, and 7-membered cyclic secondary amines) by reacting an azide that bears one or more C—H groups, catalyzed by a FeII-dipyrromethene complex. The protected cyclic secondary amines are thought to be formed through an intramolecular nitrene transfer and may be subsequently deprotected to yield cyclic secondary amines.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nylon 66/polyaminated bismaleimide composite for inner sheaths of heat-resisting power lines and preparation method of nylon 66/polyaminated bismaleimide composite
InactiveCN105153694AImprove interface performanceImprove flame retardant performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSlagPotassium
The invention discloses a nylon 66 / polyaminated bismaleimide composite for inner sheaths of heat-resisting power lines and a preparation method of the nylon 66 / polyaminated bismaleimide composite. The nylon 66 / polyaminated bismaleimide composite comprises, by weight, 39-57 parts of nylon 66, 18-26 parts of polyaminated bismaleimide, 15-25 parts of poly(2(phenoxy) accidentally phosphorus nitrene), 24-32 parts of blast furnace water slag micro-powder, 2-4 parts of stannous chloride, 3-5 parts of N-methyl-p-toluenesulfonamide, 5-10 parts of potassium fluozirconate, 10-15 parts of dimethyl maleate, 4-8 parts of zinc hydroxystannate, 3-5 parts of cuproous bromide, 4-6 parts of oxidized polyethylene wax, 5-8 parts of perfluopolyether, 15-25 parts of colloidal graphite powder and 18-27 parts of flame retardant particles. The nylon 66 / polyaminated bismaleimide is good in mechanical property, wear-resisting property and aging resistance.
Owner:TIANCHANG FUXIN ELECTRONICS
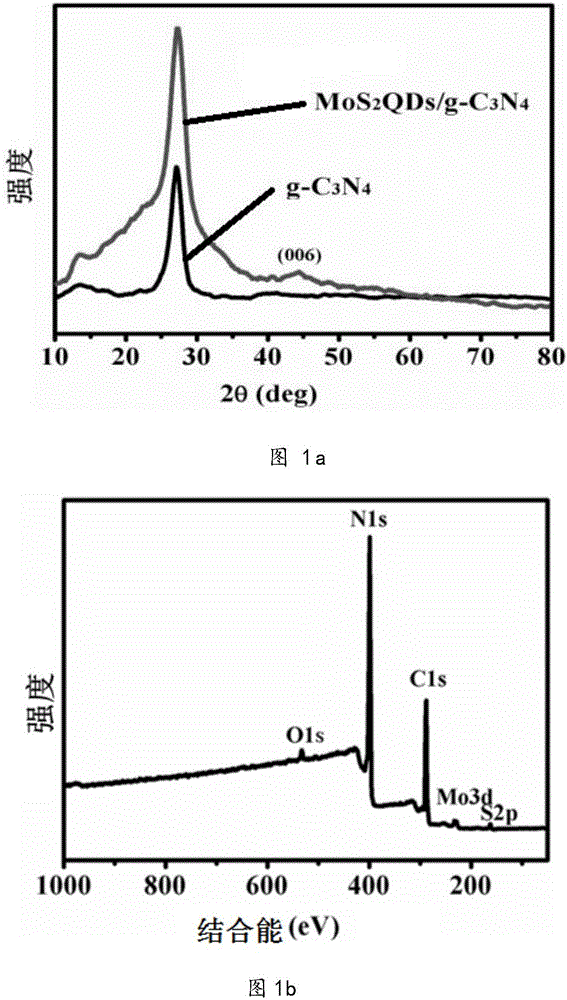
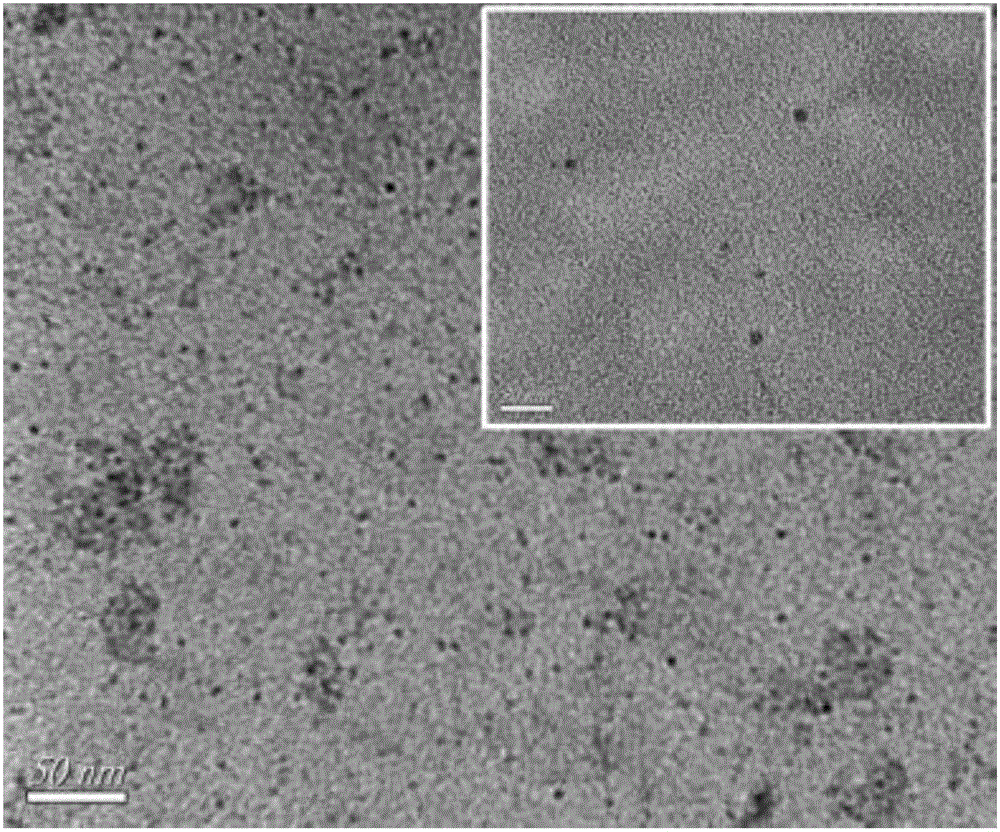
Molybdenum disulfide quantum dot modified graphite-like carbon nitrene as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107519909AImprove catalytic performanceImproved efficiency in degrading organic matterCatalyst activation/preparationSulfideMaterials science
The invention relates to molybdenum disulfide quantum dot modified graphite-like carbon nitrene as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. Carbon nitrene adopting a two-dimensional layered structure is modified with nanoscale molybdenum disulfide quantum dots, the content of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots is 1wt%-10wt%, and the balance is carbon nitrene. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: (1) soluble molybdenum salt, sulfur and hydrazine are subjected to a hydrothermal reaction, and the molybdenum disulfide quantum dots are produced; (2) g-C3N4 synthesized through solid phase sintering and the molybdenum disulfide quantum dots are dispersed in a microemulsion, and a MoS2QDs / g-C3N4 composite is synthesized with a microemulsion-ultrasonic method and has higher photocatalysis efficiency. The cost is low and the process is simple.
Owner:ZHENJIANG COLLEGE
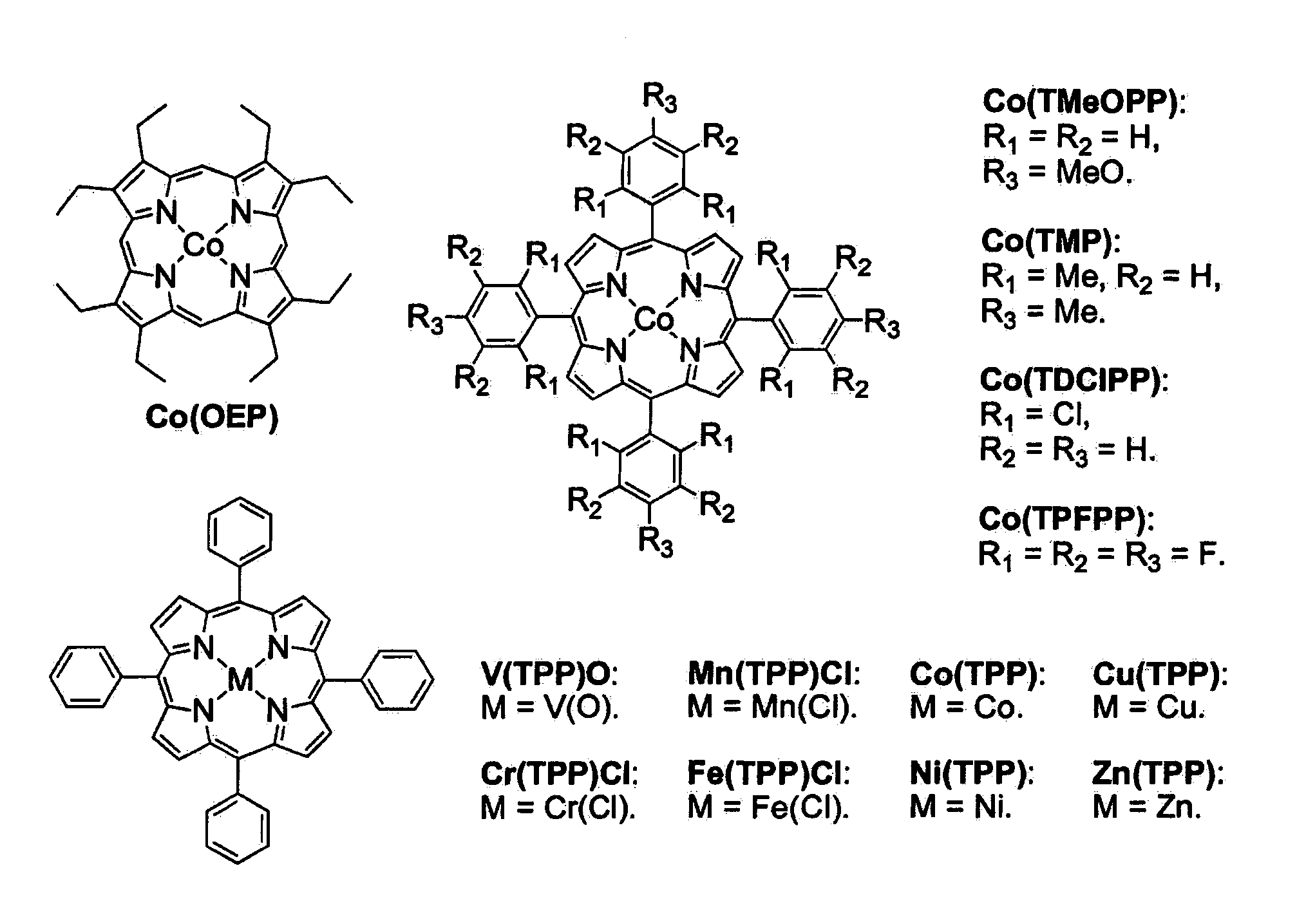
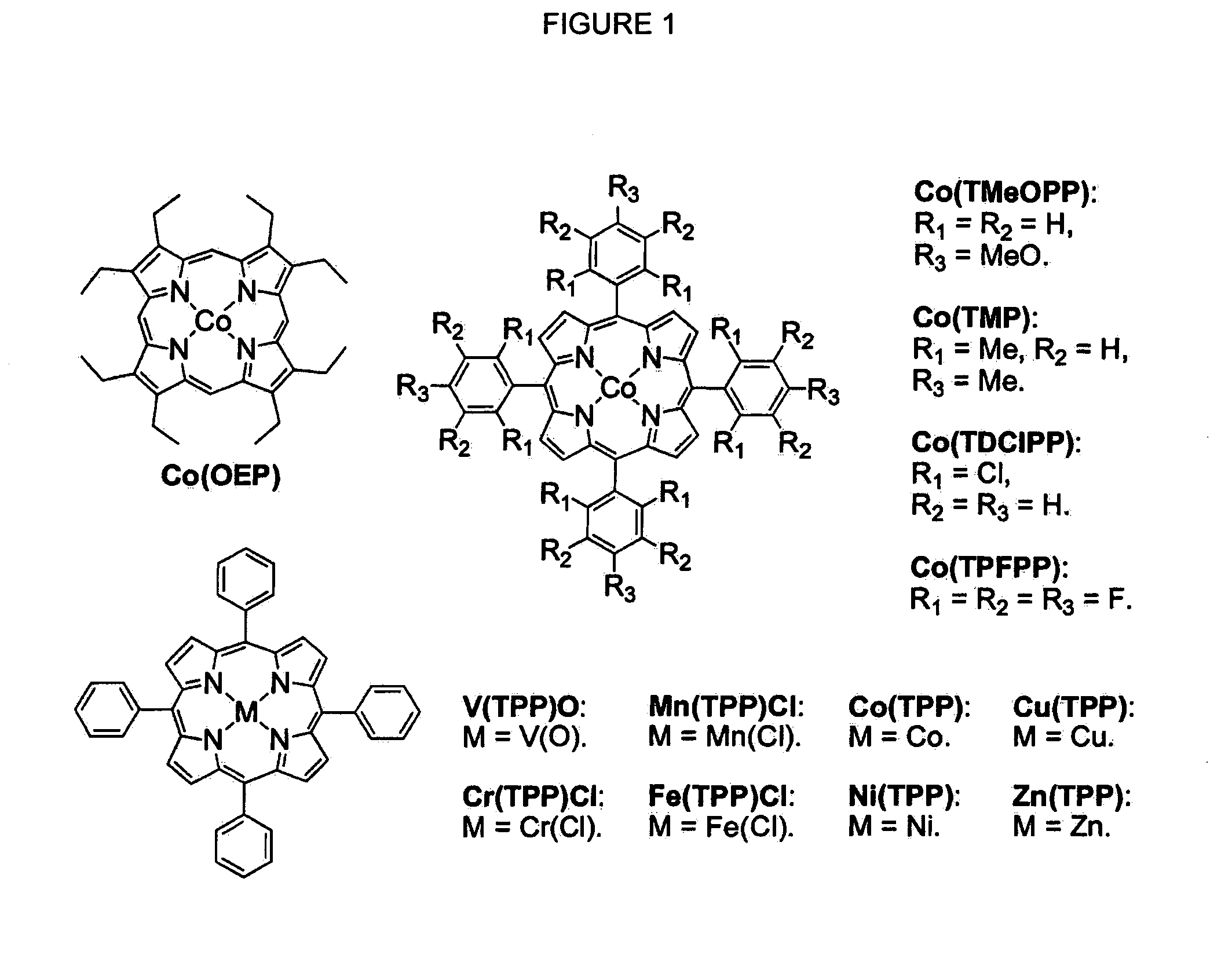
Metal Porphyrin Catalyzed Olefin Aziridination with Sulfonyl Azides
InactiveUS20110112288A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCobalt organic compoundsHydrogenPyrenesulfonyl azide
Cobalt(II) complex of P1 [Co(P1)], a new porphyrin that was designed on the basis of potential hydrogen bonding interactions in the metal-nitrene intermediate, is a highly active catalyst for olefin aziridination with azides. The [Co(P1)]-based system can be effectively employed for different combinations of aromatic olefins and arysulfonyl azides, synthesizing various sulfonylated aziridines in excellent yields. Besides its mild catalytic conditions, the Co-catalyzed aziridination process enjoys several attributes associated with the relatively low cost of cobalt and widely accessible arylsulfonyl azides. Furthermore, it generates stable dinitrogen as the only by-product.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
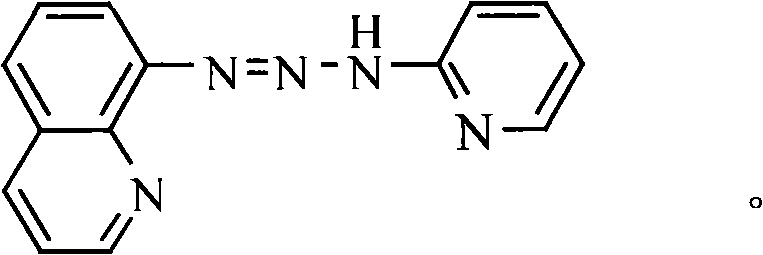
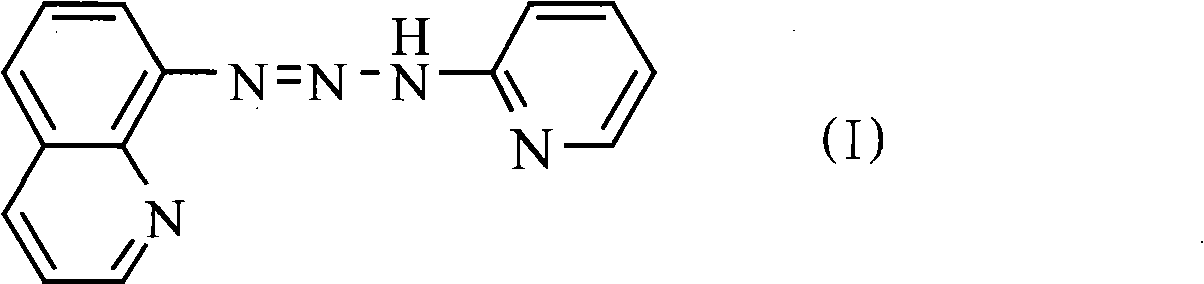
1-(8-chinoline)-3(2-pyridine)-triazene, preparation thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN101274930AHigh sensitivityGood choiceOrganic chemistryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAlcoholFluorescence
The invention relates to a triazene compound 1-(8-quinoline)-3-(2-pyridyl)-triazene (QPyT) which contains heterocycle. The preparation method of the invention comprises the steps: diazotizing 8-amino quinoline by using sodium nitrate under acidic condition and reacting with 2-aminopyridine in alcoholic solution. The compound is not only a good visualization reagent, but also a fluorescent reagent with high sensitivity and good selectivity, which can be used for fluoroscopic examination of metal ion, in particular for the examination of Pb (II) in alkaline medium.
Owner:SHANXI DATONG UNIV
Synthesis of acyclic and cyclic amines using iron-catalyzed nitrene group transfer
InactiveUS20160002145A1Poor economyAvoid great wasteOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAzideFerric
The present invention provides novel synthetic methods for making acyclic secondary amines by reacting an azide with a compound bearing one or more C—H groups, catalyzed by a FeII-dipyrromethene complex. The acyclic secondary amines are thought to be formed through an intermolecular nitrene transfer. Also provided herein are methods of synthesizing protected (e.g., Boc- or Fmoc-protected) cyclic secondary amines (e.g., 5-, 6-, and 7-membered cyclic secondary amines) by reacting an azide that bears one or more C—H groups, catalyzed by a FeII-dipyrromethene complex. The protected cyclic secondary amines are thought to be formed through an intramolecular nitrene transfer and may be subsequently deprotected to yield cyclic secondary amines.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
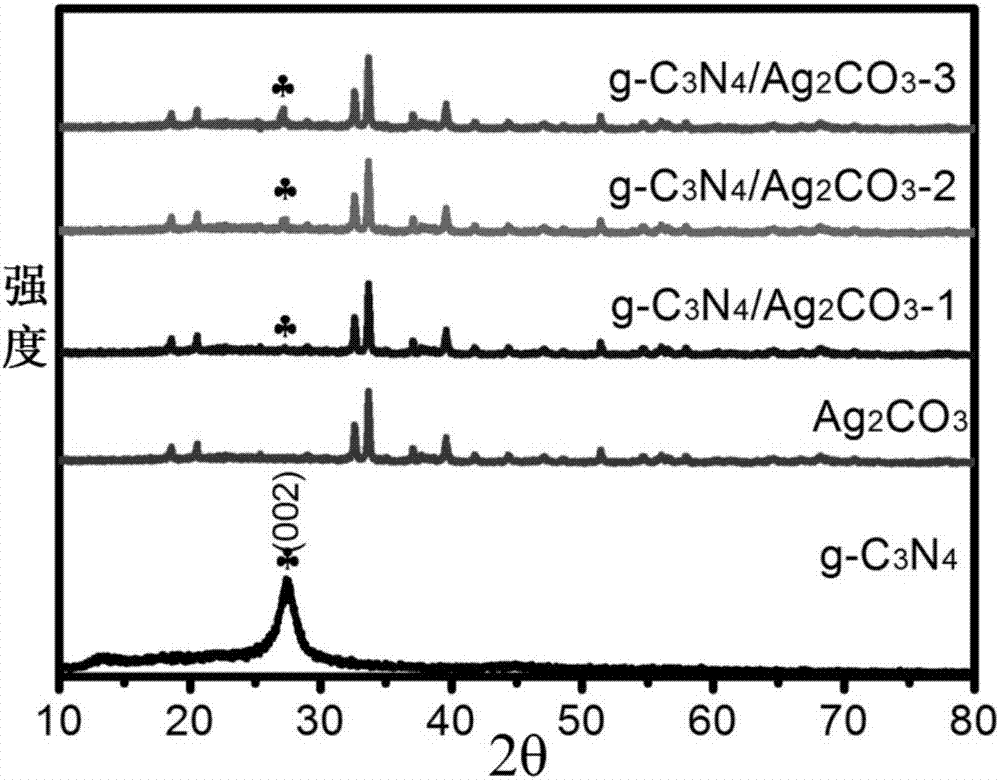
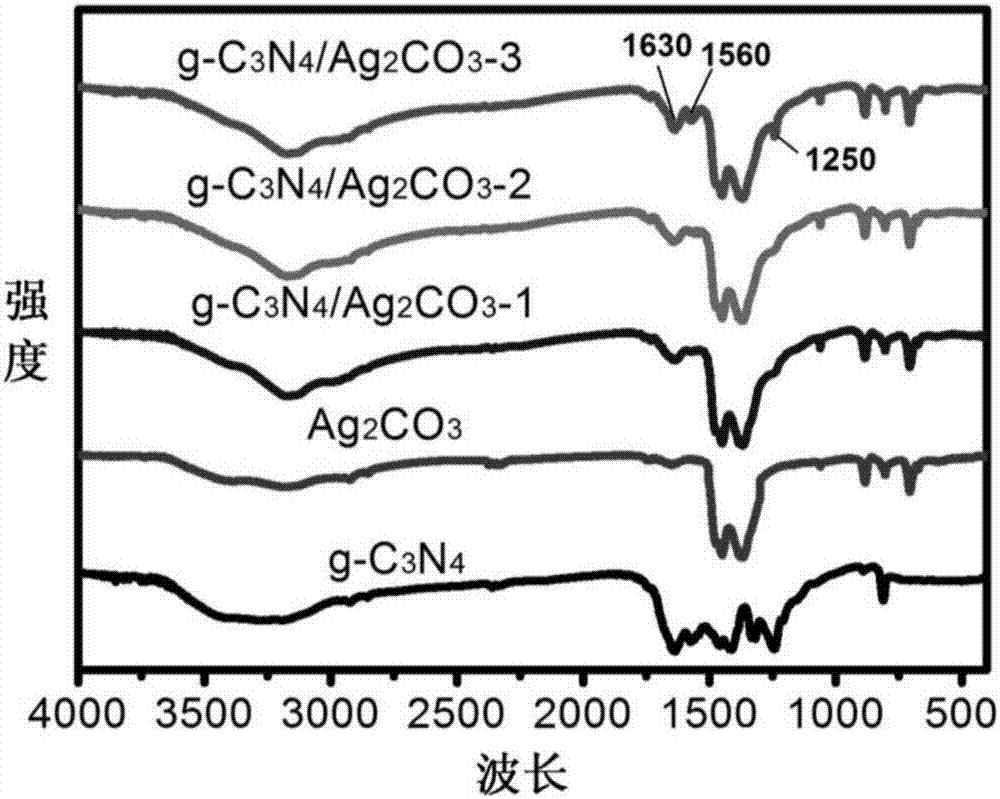
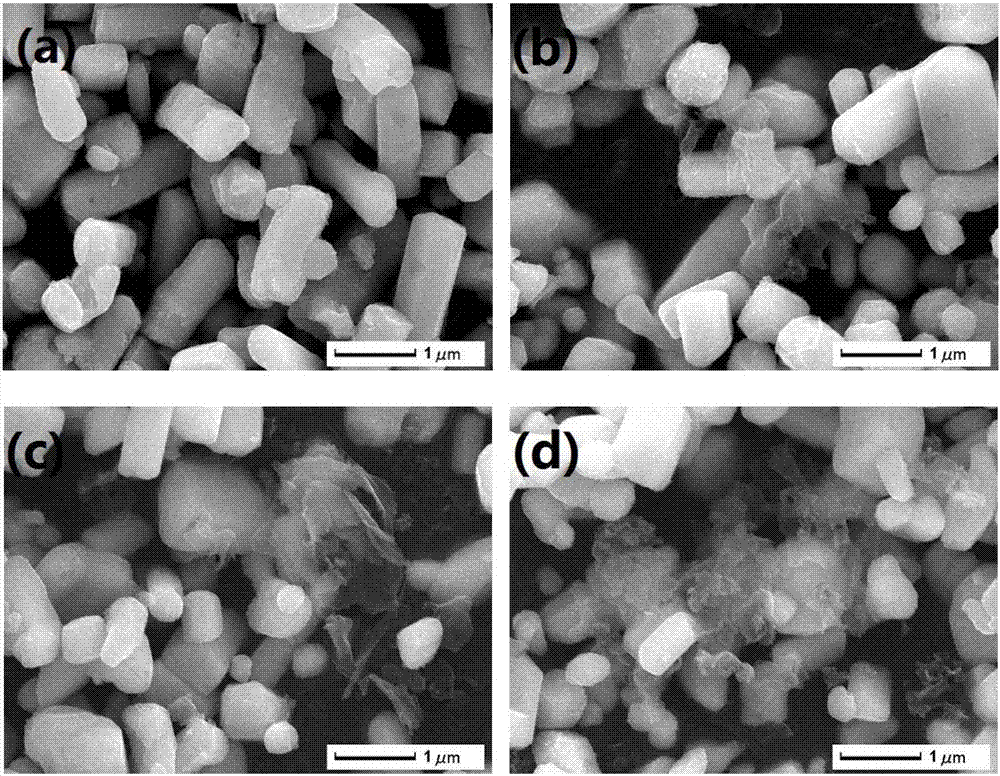
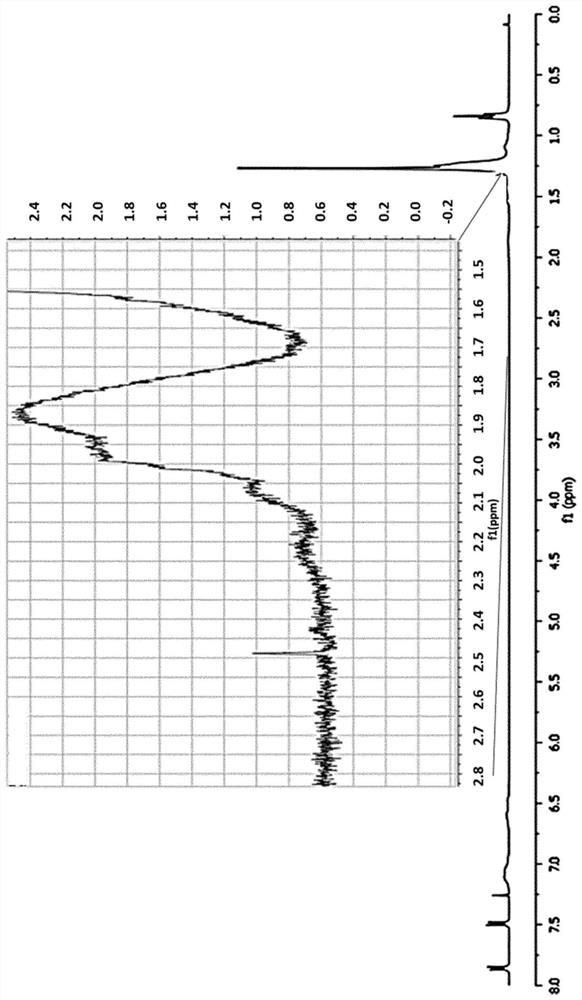
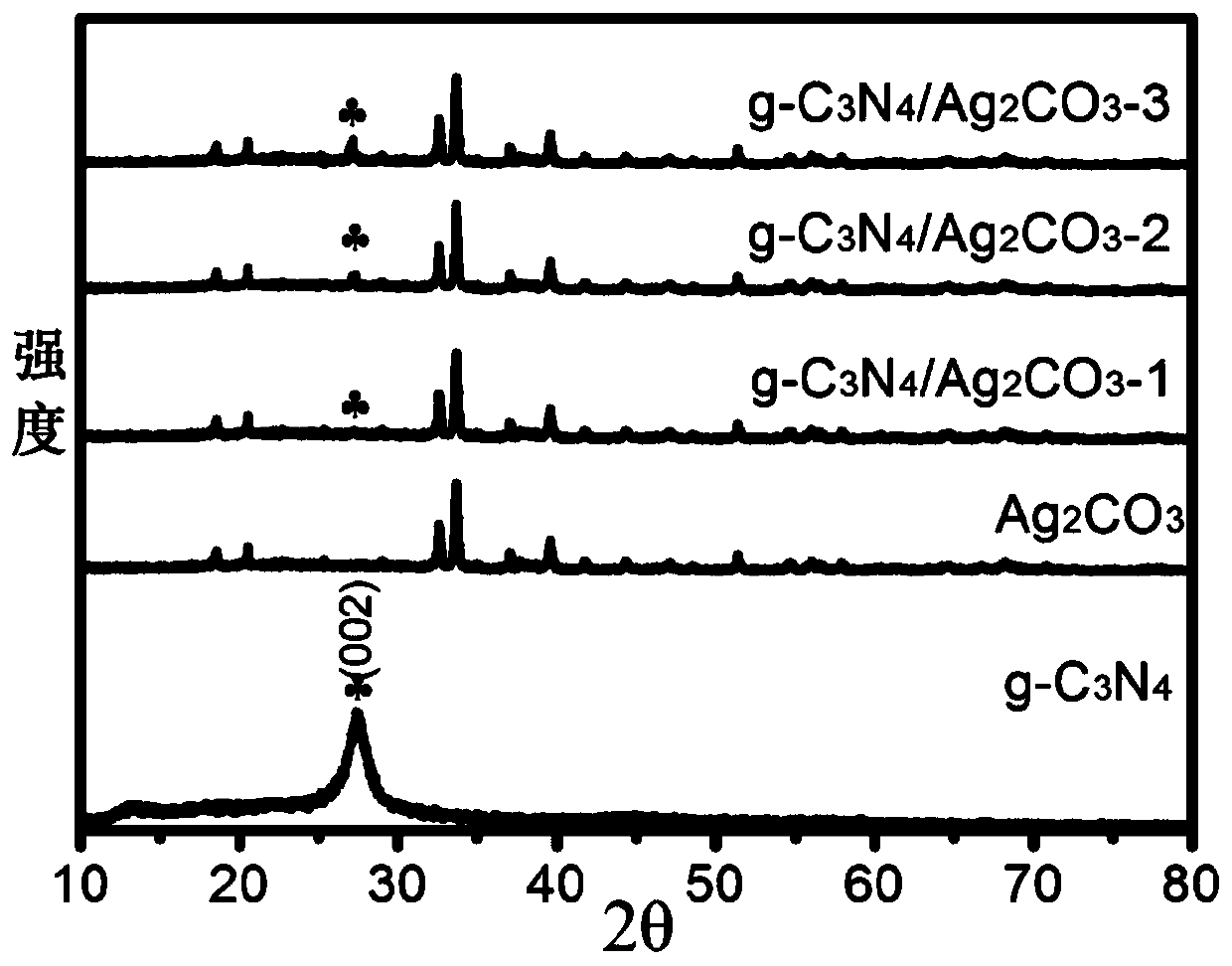
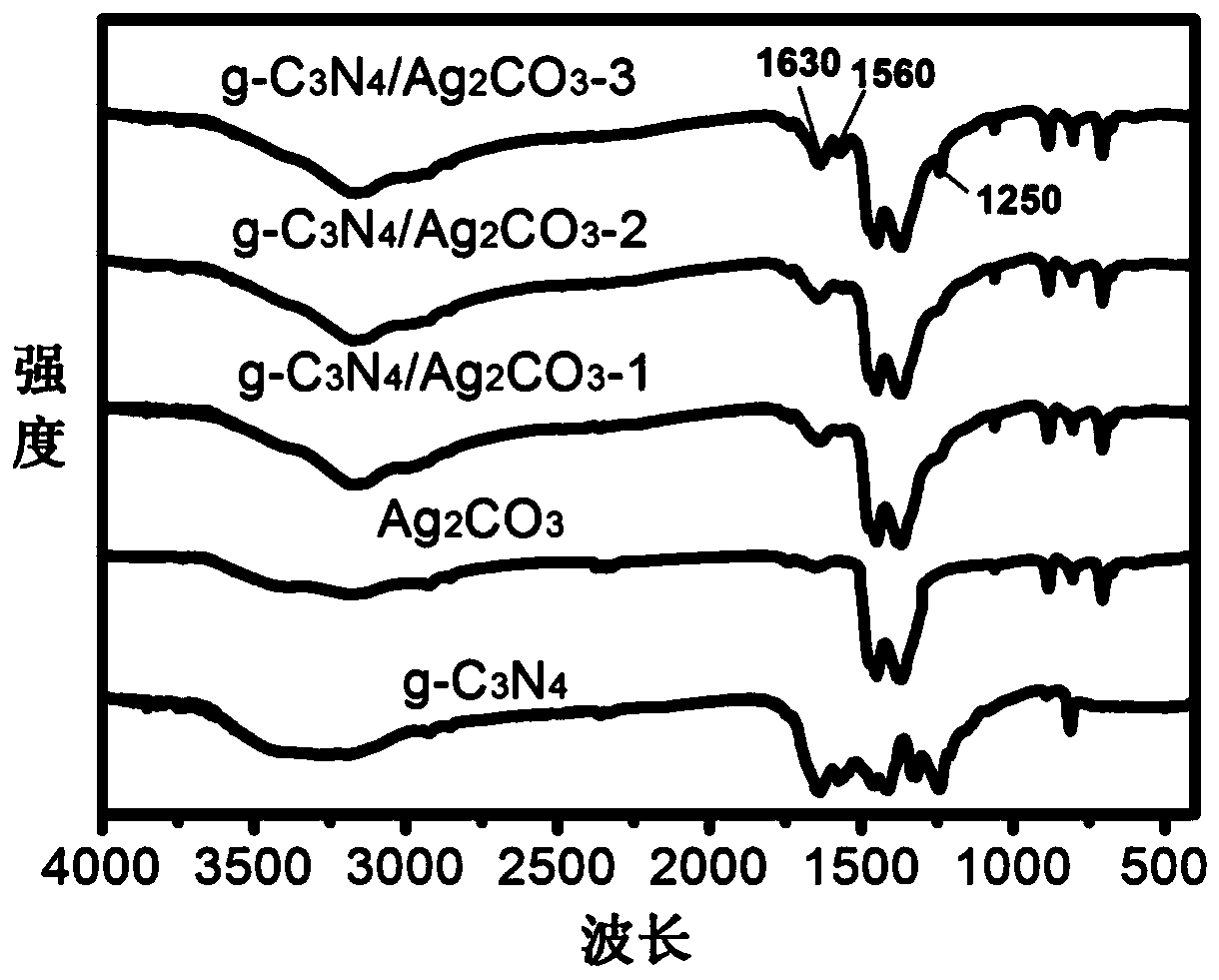
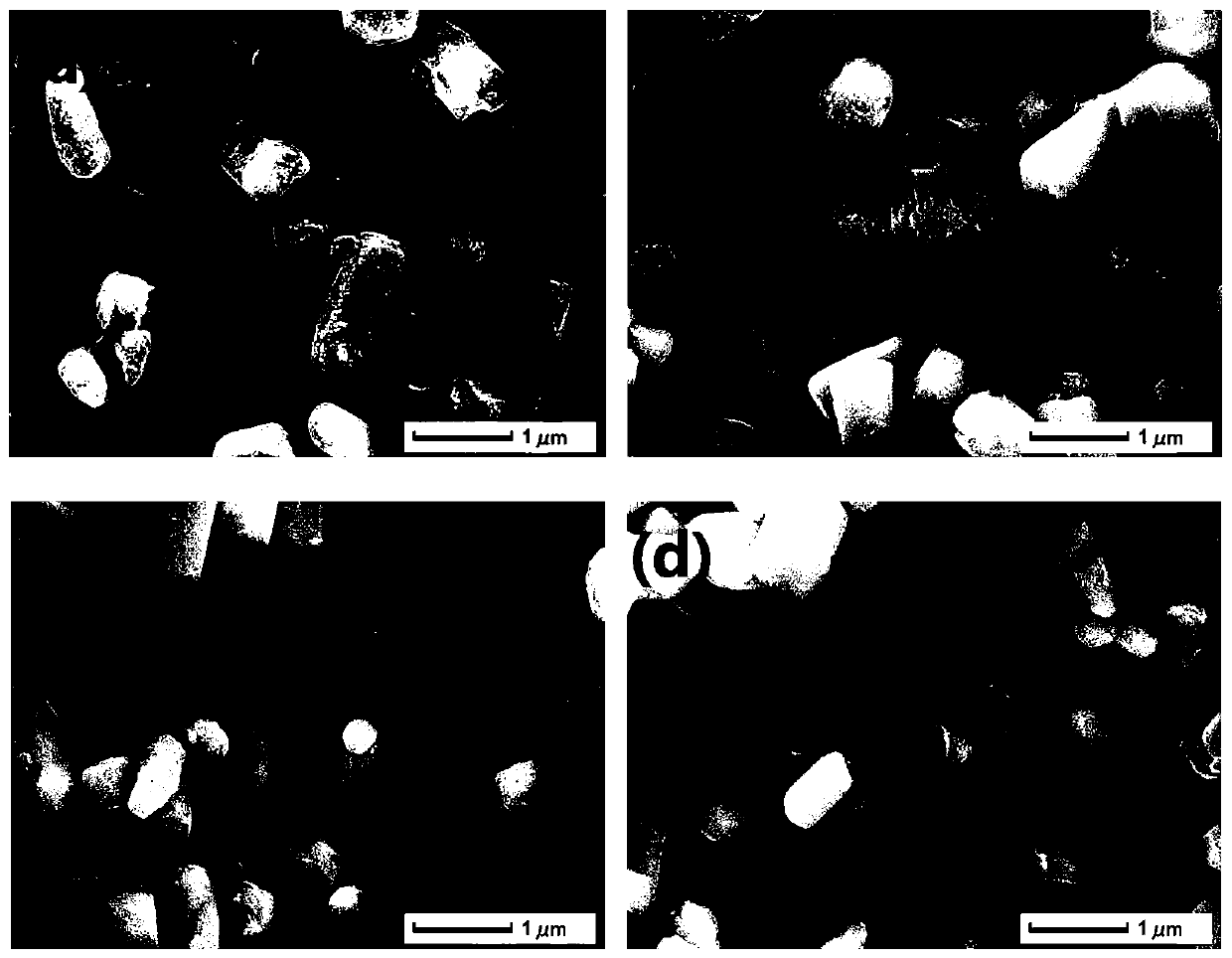
Carbine-nitrene/silver carbonate composite nano-material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107970965ALow costThe production process is simple and easy to controlGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsSilver carbonatePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention discloses a carbine-nitrene / silver carbonate composite nano-material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite nano-material comprises 1 to 10 wt% of g-C3N4, withthe balance being Ag2CO3, wherein Ag2CO3 microrods adhere to the surface of lamellar g-C3N4. The preparation method comprises the following steps: subjecting urea and melamine to solid phase sinteringin a tubular furnace so as to prepare a g-C3N4 nanosheet; dispersing the g-C3N4 nanosheet in deionized water under the action of stirring and supersonic waves; and then adding a soluble silver salt and a precipitating agent, allowing a solution to undergo a precipitation reaction at room temperature, and carrying out cleaning and drying so as to obtain a reaction product, i.e., the carbine-nitrene / silver carbonate composite nano-material which is applicable to treatment of organic waste water and organic pollutants in the air. Addition of the g-C3N4 effectively improves the photocatalytic degradation of organic matters.
Owner:ZHENJIANG COLLEGE
Method of using graphene composite material covalently modified by polymer with aggregation-induced emission characteristic to prepare solid film optical limiter
ActiveCN110452364AImprove solubilityExcellent optical propertiesLuminescent compositionsNon-linear opticsSolubilityPolymer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of using an organic light-emitting material, covalently modified graphene, and a composite material thereof to prepare a solid film optical limiter, specifically provides a method of using a using graphene composite material covalently modified by a polymer with an aggregation-induced emission characteristic to prepare a solid film optical limiter, andat the same time, provides a polymer with an aggregation-induced emission characteristic, graphene covalently modified by the polymer, and a preparation method of the polymer. The polymer is preparedby Suzuki coupling polymerization reactions, contains tetraphenyl ethylene and a fluorene functional group, and has an aggregation-induced emission characteristic. Through nitrene reactions, the polymer is covalently grafted to the surface of graphene, and the obtained graphene composite material is used to prepare a solid film optical limiter. The obtained graphene composite material has excellent dissolvability, outstanding optical properties, and a good charge transfer performance. The prepared solid film optical limiter has excellent optical response and thus has a wide application range in photo-electronic devices.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
C-H bond amination and olefin aziridination with β-diketiminato copper catalysts
ActiveUS8471051B2Good yieldAvoid it happening againOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal catalystNitrogen
One aspect of the present invention relates to a method for the transition metal (e.g., Cu(I)) mediated amidation of C—H bonds using electron-rich aliphatic azides. In certain embodiments, the methods are useful for the C—H insertion of nitrenes generated and stabilized by a β-diketiminato metal catalyst. In certain embodiments, said nitrenes are generated from organoazides, or by oxidation of the corresponding amine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to olefin aziridination using said β-diketiminato metal catalysts. In addition, the methods of the present invention include stereoselective C—H bond aminations and olefin aziridinatons. In certain embodiments, the methods are conducted in an aerobic environment. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to the use of O2 as an oxidant, wherein water is the byproduct of oxidation; this fact avoids the generation of toxic byproducts and renders the methods atom economical.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
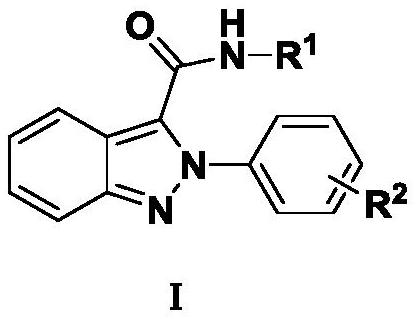
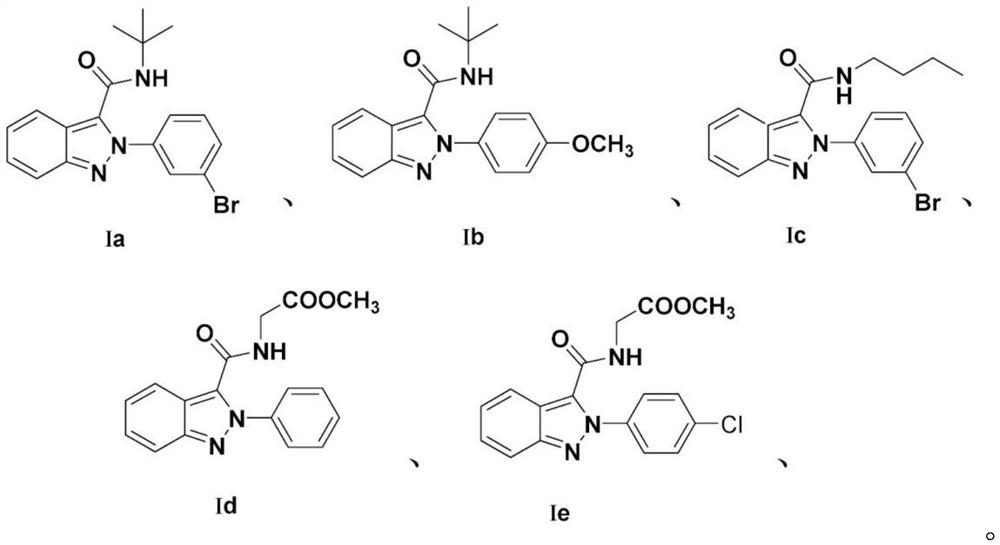
Indazole derivative and application thereof
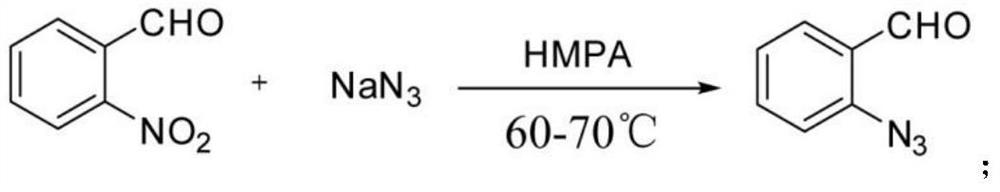
ActiveCN113372276AAchieve functional group transformationAchieve conversionAntibacterial agentsBiocideIsomerizationDehydrogenation
The invention discloses an indazole derivative and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting o-nitrobenzaldehyde with sodium azide to obtain o-azidobenzaldehyde; preparing an intermediate azide from the o-azidobenzaldehyde, an amine compound and an isonitrile compound; and adding the intermediate azide into a Schlenk tube, carrying out photoinduction to realize nitrene insertion, aromatic ring isomerization and dehydrogenation reaction, carrying out post-treatment, extracting with water and ethyl acetate, and carrying out organic phase column chromatography separation to obtain the indazole derivative. According to the reaction, a target compound with high yield can be obtained under sunlight. The compound can be selectively used as a bactericide, can be mixed with other carriers or diluents allowed by plant protection to obtain various common dosage forms, such as a mixture, granules and an emulsion in water, and can also be selectively mixed with other pesticides, such as an insecticide, a herbicide and a plant growth regulator for use or simultaneously used together with the pesticide, the herbicide and the plant growth regulator. In addition, the molecules containing the indazole skeleton have potential medicinal value.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Surface modifying agents, modified materials and methods
The present invention relates to surface modifying agents for polymeric and / or textile materials, methods of making and / or using a surface modifying agent to modify and functionalize polymeric and / or textile materials, and / or methods of using surface modified or functionalized polymeric and textile materials, and / or products using or incorporating surface modified or functionalized polymeric and textile materials. For example, the surface modifying agent in precursor form can be styrene sulfonyl azide monomer, polymer or copolymer capable of undergoing a chemical reaction in the presence of heat or light to form one or more styrene sulfonated nitrene monomers, polymers or copolymers, which are capable of chemically reacting with the surface of a polymeric or textile material to endow a specific or desired chemical surface functionality to the surface of a polymeric or textile material. Furthermore, the present invention is possibly preferably directed to a surface modifying agent which comprises a styrene sulfonated nitrene monomer, polymer or polymer containing one or more nitrene functional groups, which are capable of chemically reacting via an insertion reaction into one or more carbon-hydrogen bonds on the surface of a polymeric or textile material in order to chemically attach a specific or desired chemical functionality to the surface of a polymeric or textile material.
Owner:CELGARD LLC
Surface modified polymeric materials, modified functionalized polymers, functional polymers, and methods
ActiveUS20180358594A1Improve adhesionHigh surface energySynthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentFiberPolymer science
The present invention relates to new, improved or modified polymer materials, membranes, substrates, and the like and to new, improved or modified methods for permanently modifying the physical and / or chemical nature of surfaces of the polymer substrate for a variety of end uses or applications. For example, one improved method uses a carbene and / or nitrene modifier to chemically modify a functionalized polymer to form a chemical species which can chemically react with the surface of a polymer substrate and alter its chemical reactivity. Such method may involve an insertion mechanism to modify the polymer substrate to increase or decrease its surface energy, polarity, hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity, oleophilicity or oleophobicity, and / or the like in order to improve the compatibility of the polymer substrate with, for example, coatings, materials, adjoining layers, and / or the like. Furthermore, this invention can be used to produce chemically modified membranes, fibers, hollow fibers, textiles, and the like, for example, to produce polyolefin microporous battery separators or membranes having improved hydrophilicity or wettability, having crosslinking in the polyolefin which can improve the high temperature stability, and / or the like.
Owner:CELGARD LLC
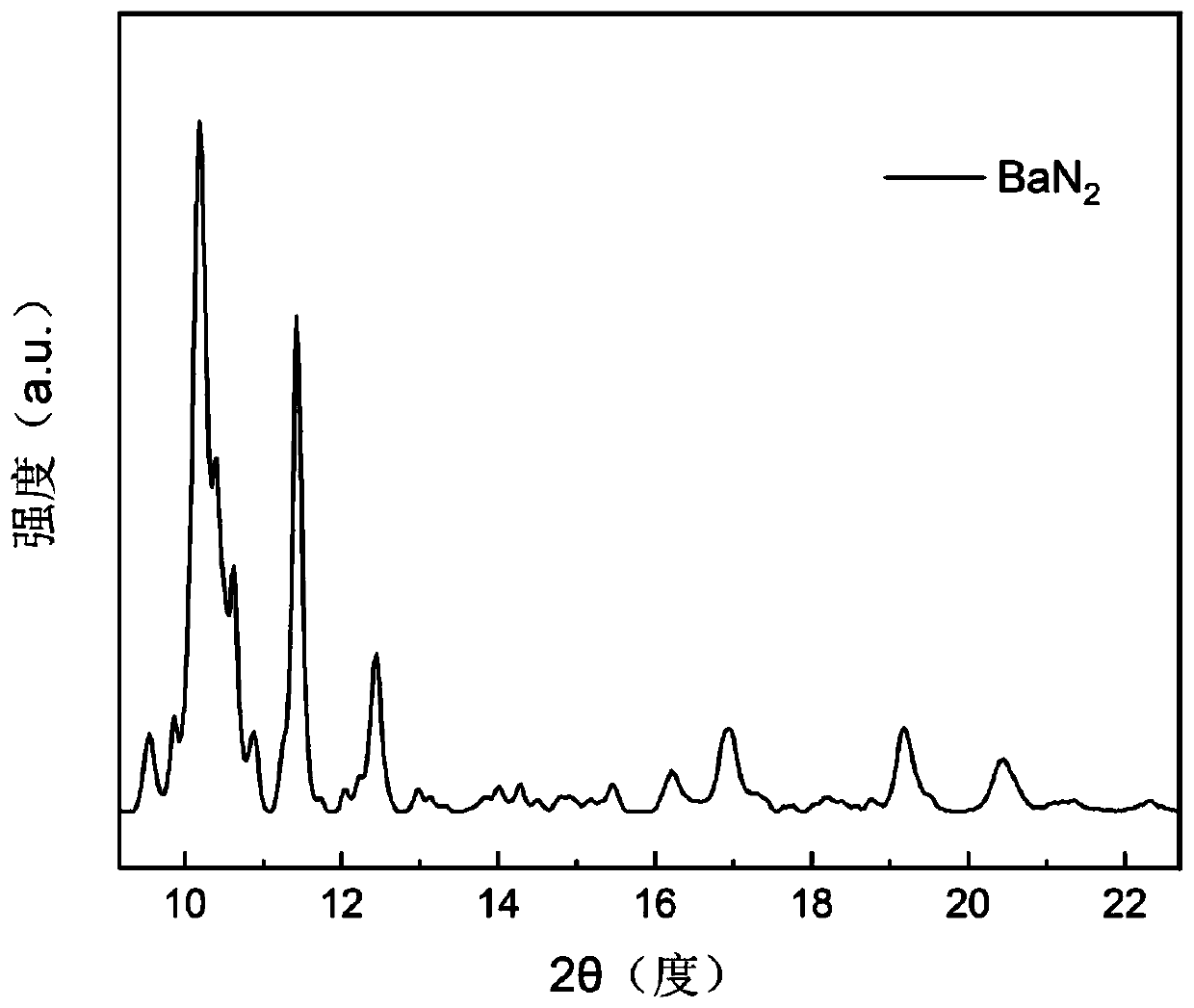
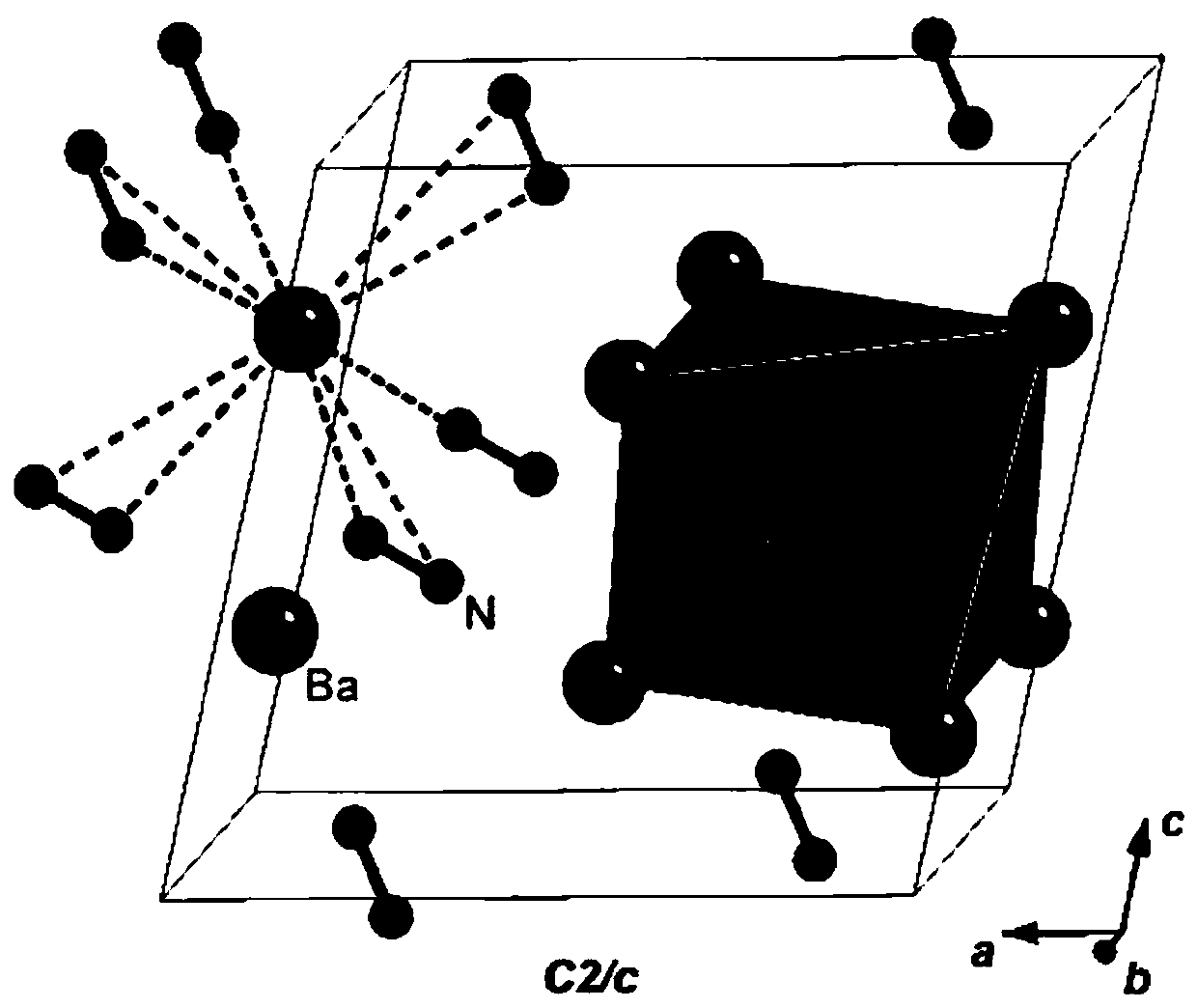
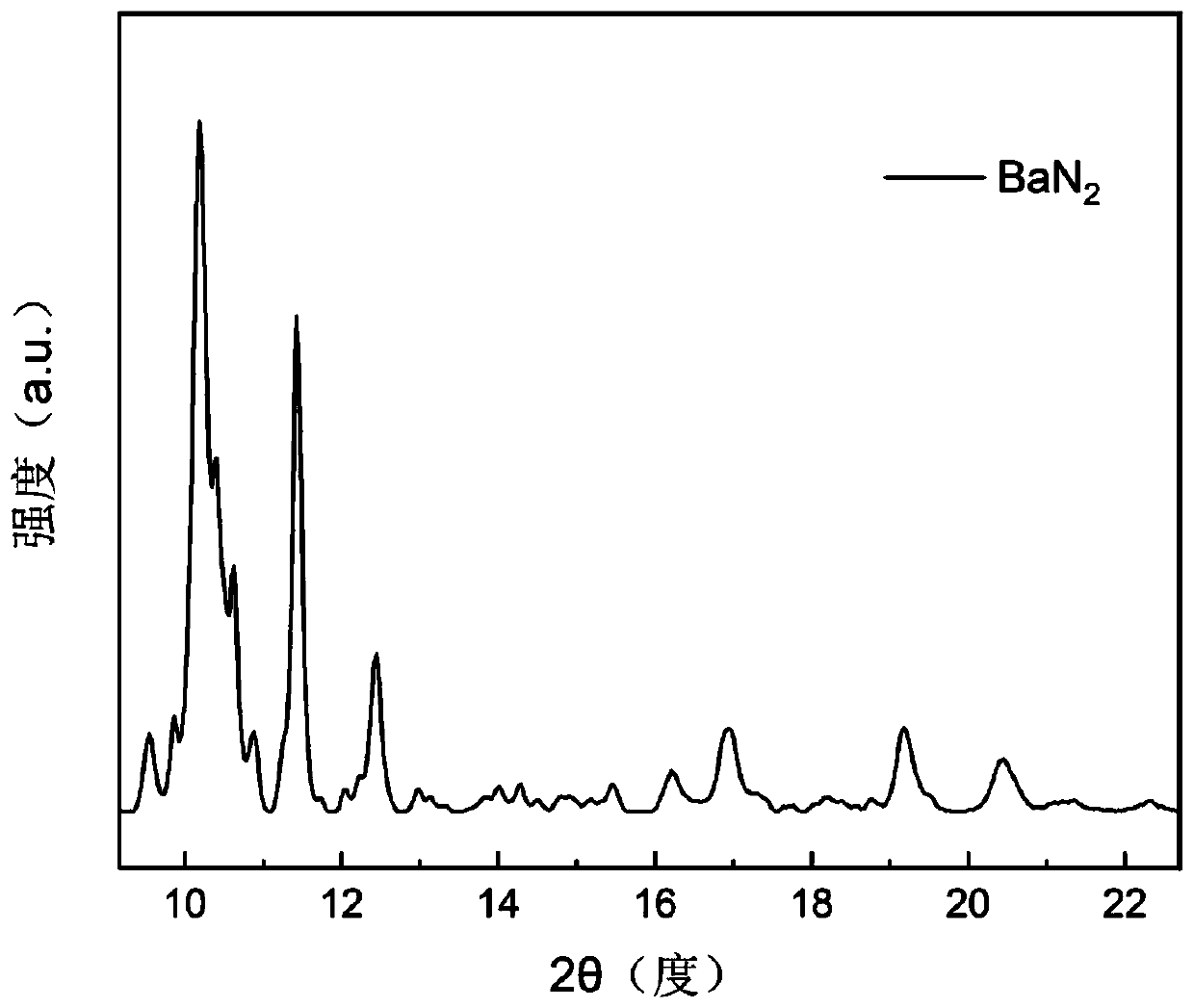
High-temperature and high-pressure preparation method of monoclinic-phase barium diazene
InactiveCN111170288AShort manufacturing timeAvoid problemsNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsAlkaline earth metalPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a high-temperature and high-pressure preparation method of monoclinic phase barium diazene, which belongs to the technical field of preparation of conductive energetic materials. With barium azide as a raw material through the technological processes of grinding, briquetting, assembling, high-temperature and high-pressure synthesis, and cooling and pressure relief, the monoclinic phase barium diazene is prepared. The monoclinic phase diazene barium is prepared by taking barium azide as a raw material and adopting a high-temperature and high-pressure synthesis method, sothat the preparation time is greatly shortened, and the method has certain experimental guidance significance for preparing the alkaline-earth metal diazene nitride.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Surface modified polymeric materials, modified functionalized polymers, functional polymers, and methods
ActiveUS10069126B2Improve adhesionHigh surface energySynthetic resin layered productsCell component detailsFiberPolymer science
Owner:CELGARD LLC
A kind of azide coupling gelatin adsorption material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104549178BFacilitated DiffusionAchieve captureOther chemical processesPolymer scienceCarboxyl radical
The invention discloses an adsorbing material for azide method coupling gelatin and a preparation method of the adsorbing material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: grafting an unsaturated monomer containing carboxyl on the surface of a macromolecular non-woven base material to introduce the carboxyl by employing an ultraviolet induction technology; introducing aromatic amino by employing electrostatic self-assembly of aromatic diamine diazonium salt and the carboxyl, and transforming into an azide group; decomposing into active nitrene under ultraviolet irradiation, fixing gelatin on a non-woven surface through inserting reaction of nitrene; and finally soaking in hot water, and removing uncoupled gelatin to prepare the absorbing material. The adsorbing material is relatively good in hydrophilia; the carrier content and the water absorption rate of the gelatin can be adjusted within a large range; and the adsorbing material has relatively high adsorption capacity on tannin, has a selective absorption effect on adsorption of the tannin in green tea and emblic leafflower fruit extracts, and also has the selective absorption effect on condensed tannin in the green tea extract.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Functionalized rubbers
PendingCN113227174AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer scienceChain scission
Owner:DYNASOL ELASTOMEROS
Carbonitrone/silver carbonate composite nanomaterial, its preparation method and its application
ActiveCN107970965BLow costThe production process is simple and easy to controlGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsSilver carbonatePhotocatalytic degradation
The invention discloses a carbonazene / silver carbonate composite nanomaterial, its preparation method and its application. Among the composite nanomaterials, g‑C 3 N 4 Accounting for 1wt%~10wt%, the balance is Ag 2 CO 3 , and Ag 2 CO 3 Micron rods attached to the sheet g‑C 3 N 4 s surface. The preparation method is: solid-phase sintering of urea and melamine in a tube furnace to prepare g‑C 3 N 4 Nanosheets; under stirring and ultrasonic conditions, g‑C 3 N 4 The nanosheets are dispersed into deionized water, and then soluble silver salts and precipitants are added. A solution precipitation reaction occurs at room temperature. After cleaning and drying, the reaction product is obtained, which can be used in organic wastewater treatment and the degradation of organic pollutants in the air. g‑C 3 N 4 The addition of can effectively improve the ability of photocatalytic degradation of organic matter.
Owner:ZHENJIANG COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com