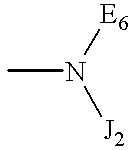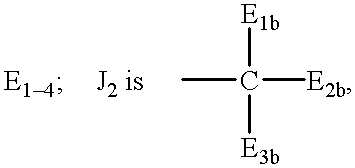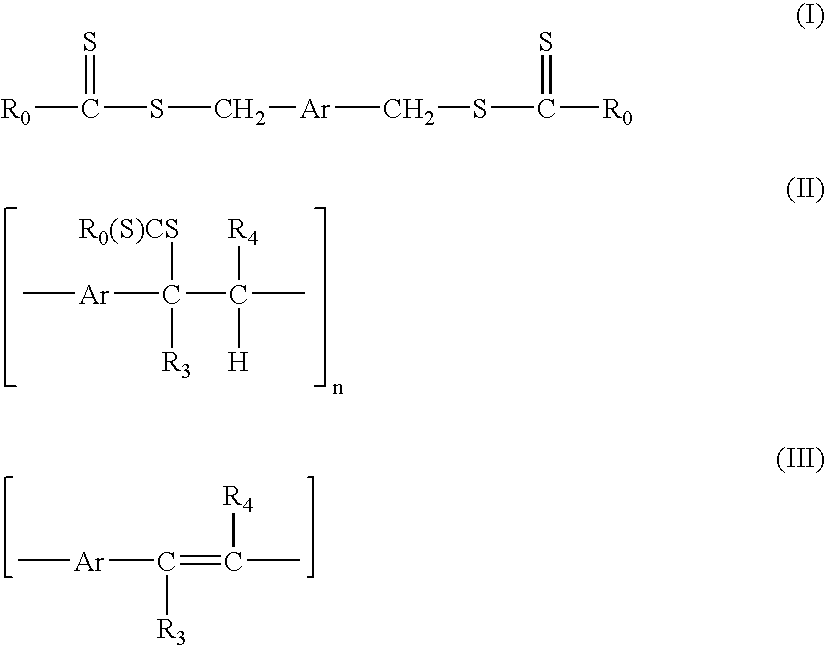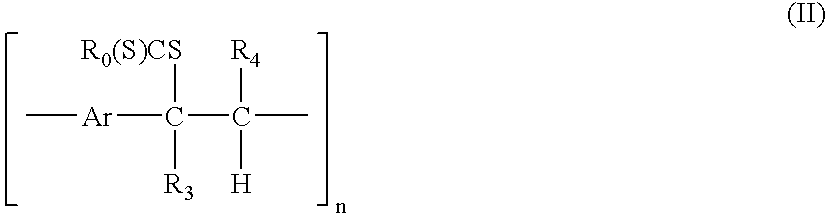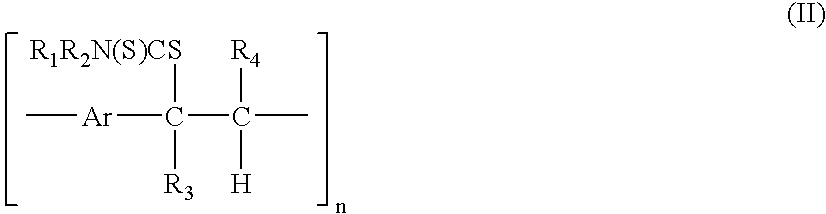Patents
Literature
677 results about "Leaving group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a leaving group is a molecular fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. Leaving groups can be anions or neutral molecules, but in either case it is crucial that the leaving group be able to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl⁻, Br⁻, and I⁻, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO⁻). Fluoride (F⁻) functions as a leaving group in the nerve-agent sarin gas. Common neutral molecule leaving groups are water and ammonia. Leaving groups may also be positively charged cations (such as H⁺ released during the nitration of benzene); these are also known specifically as electrofuges.
Catalyst composition, method of polymerization, and polymer therefrom
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
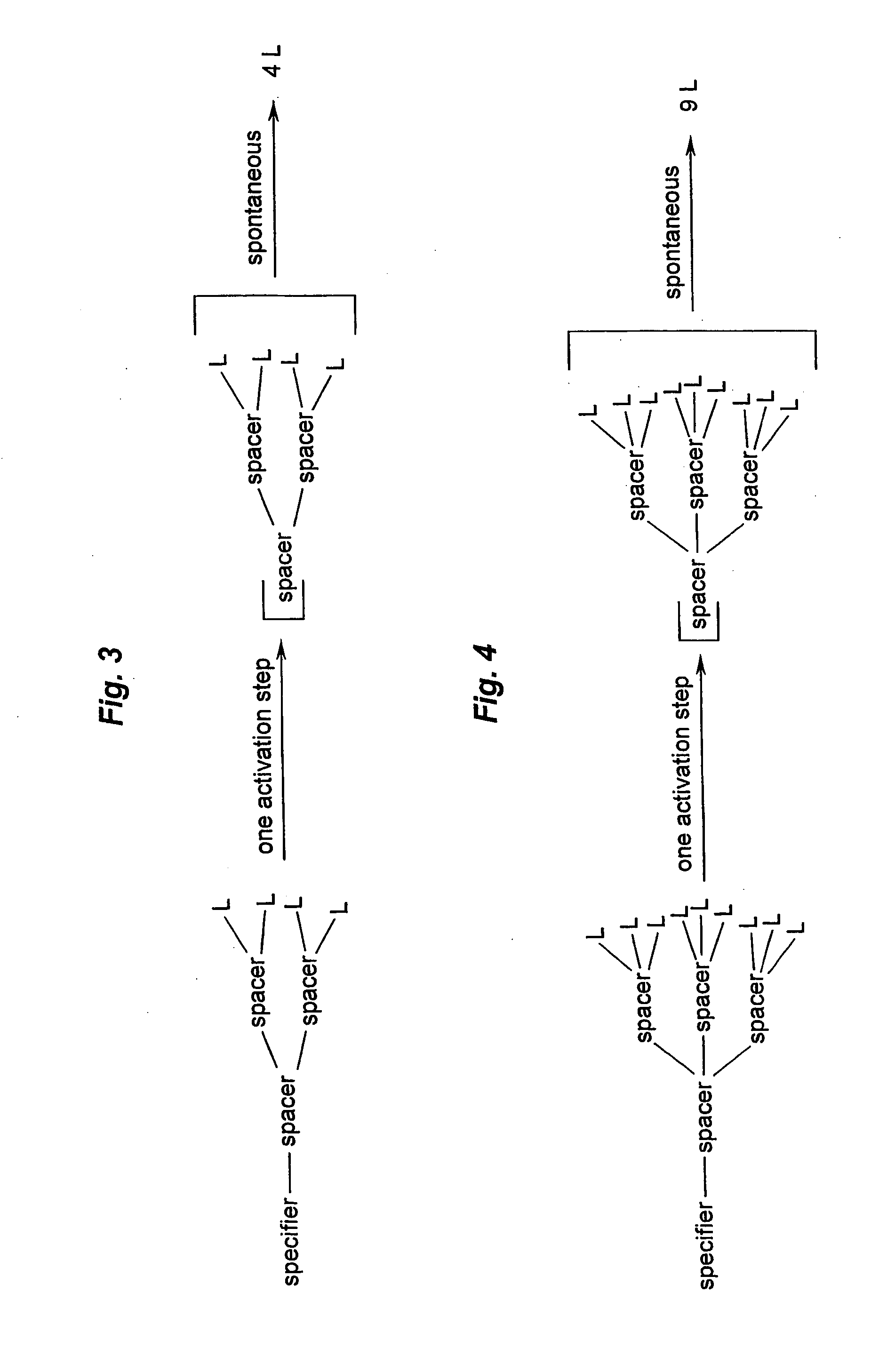
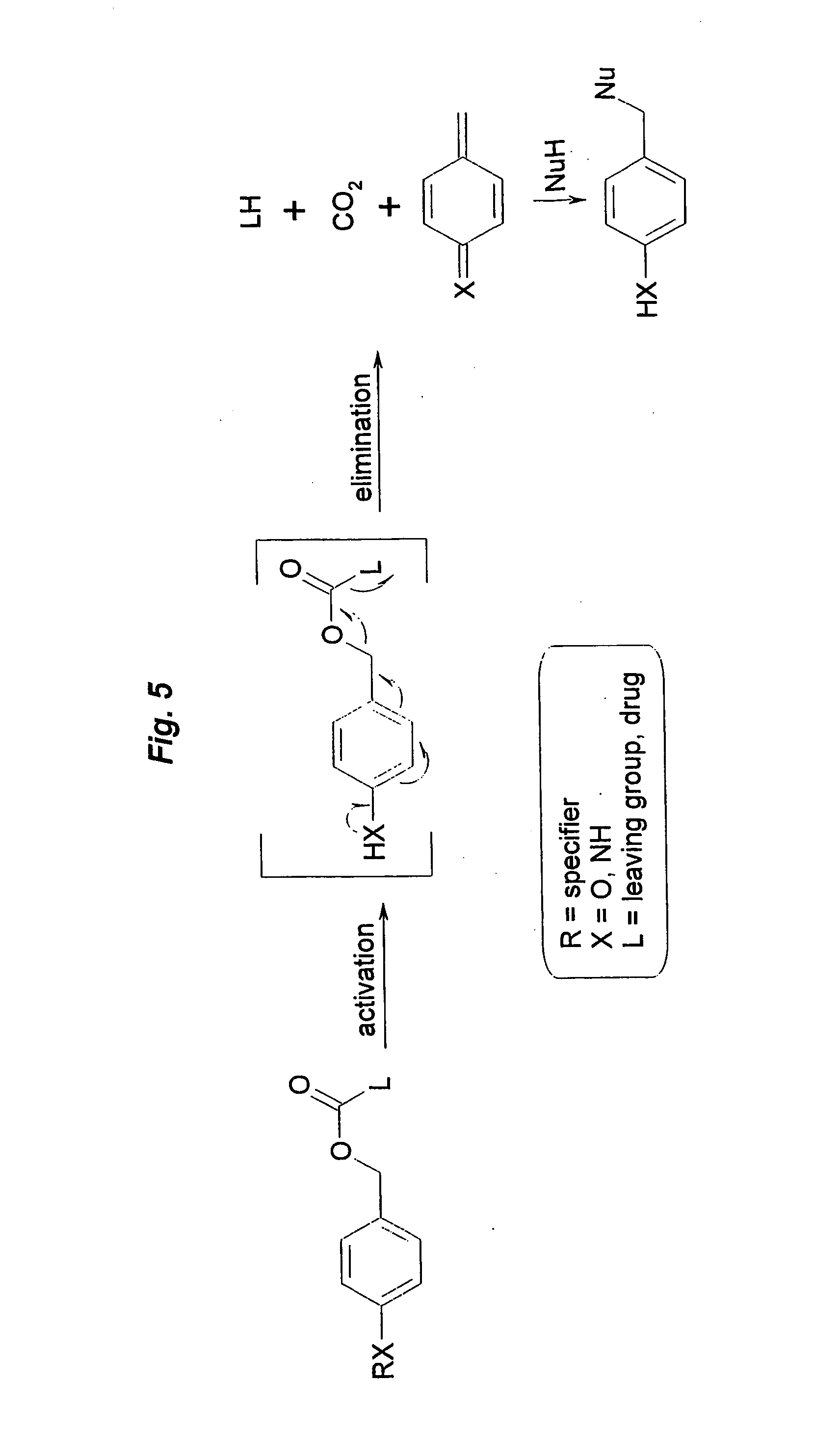
Prodrugs built as multiple self-elimination-release spacers
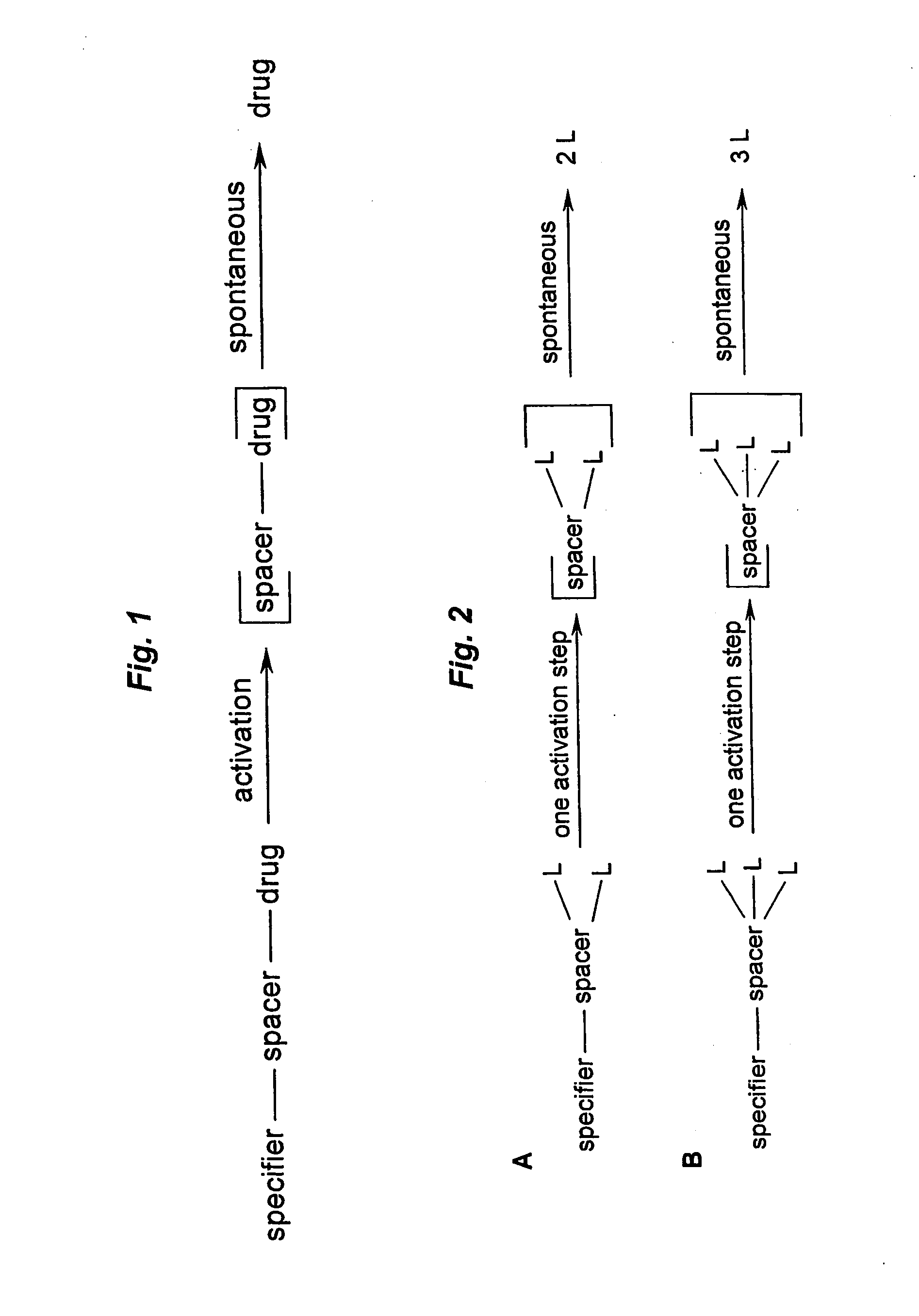
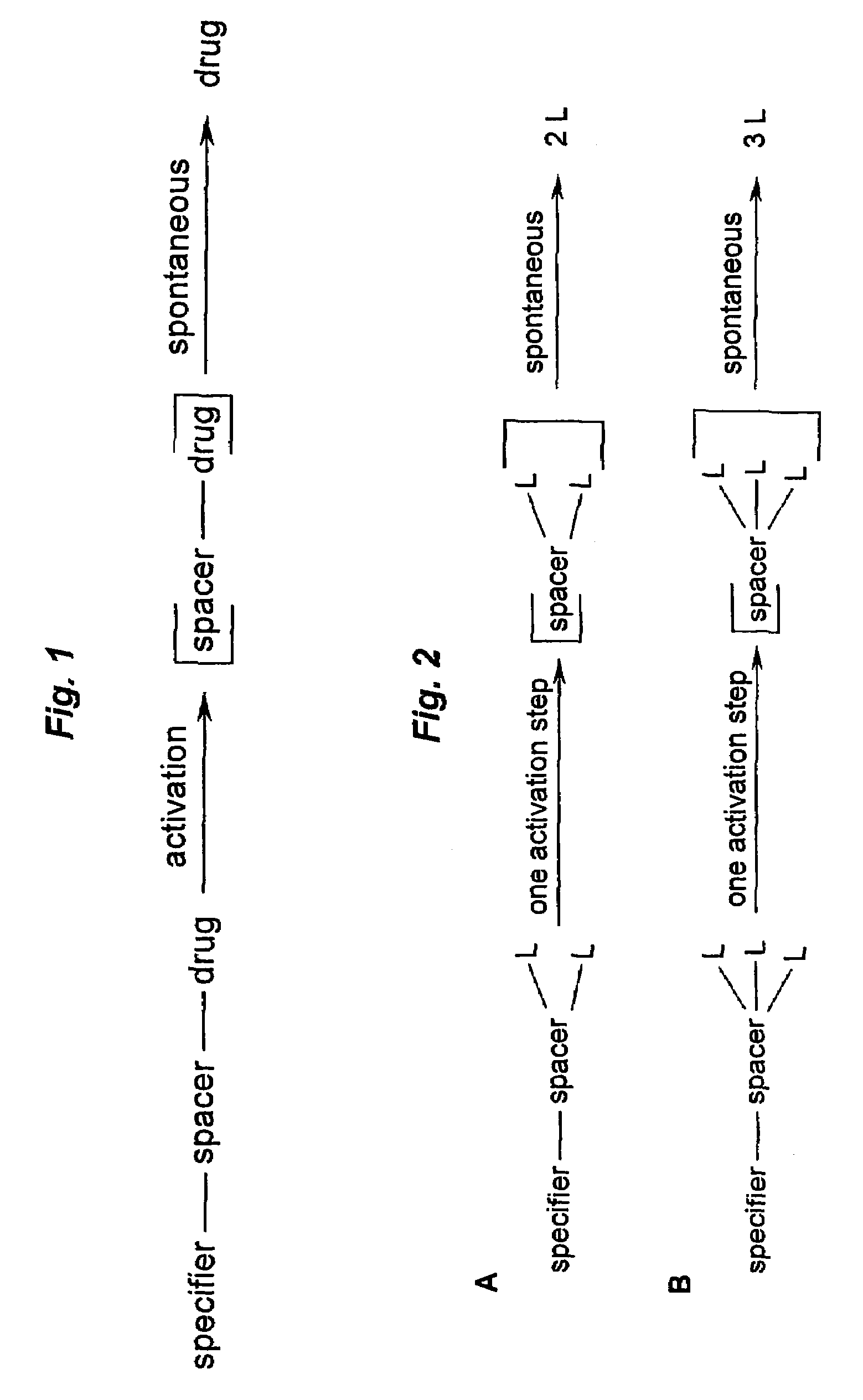
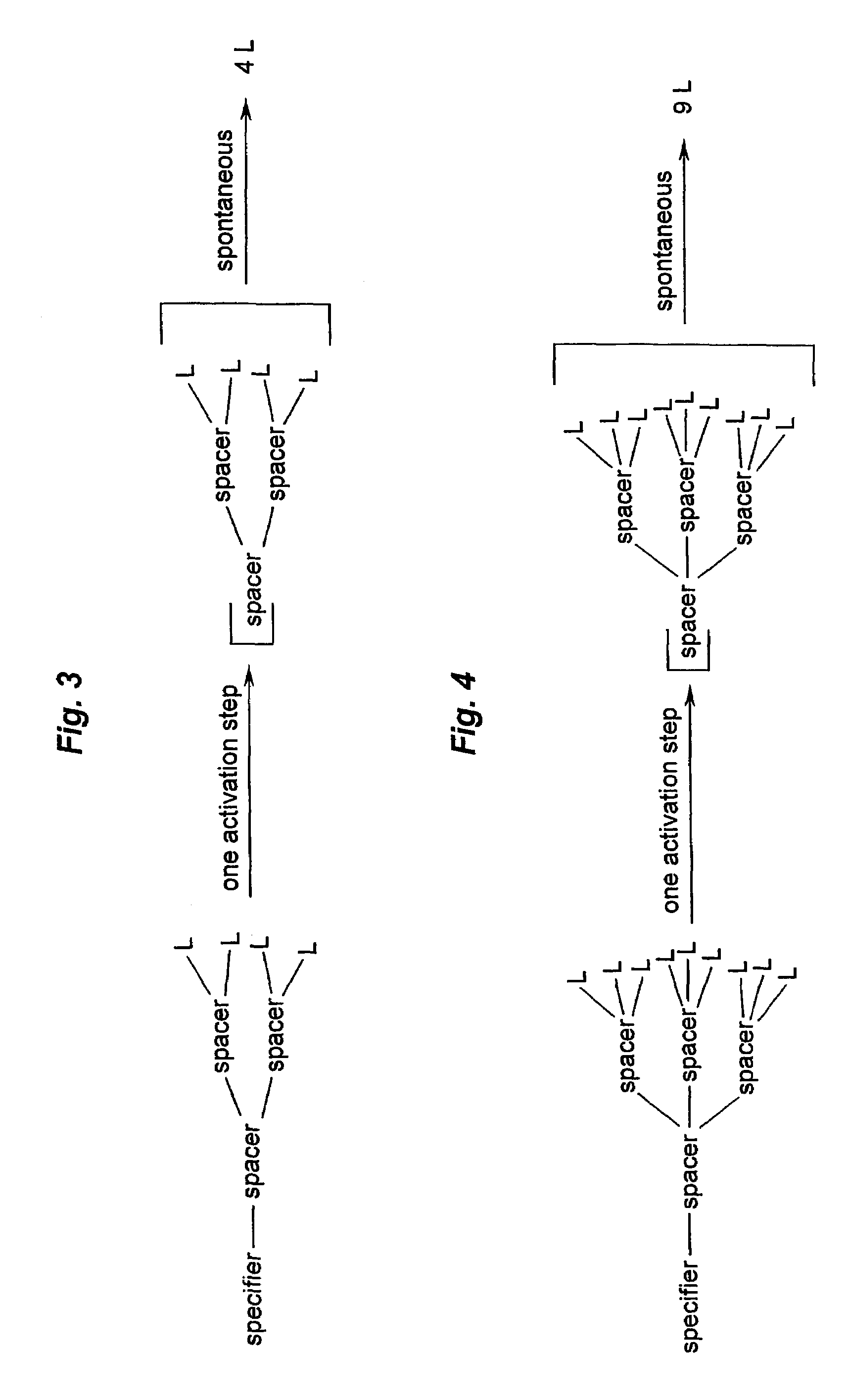
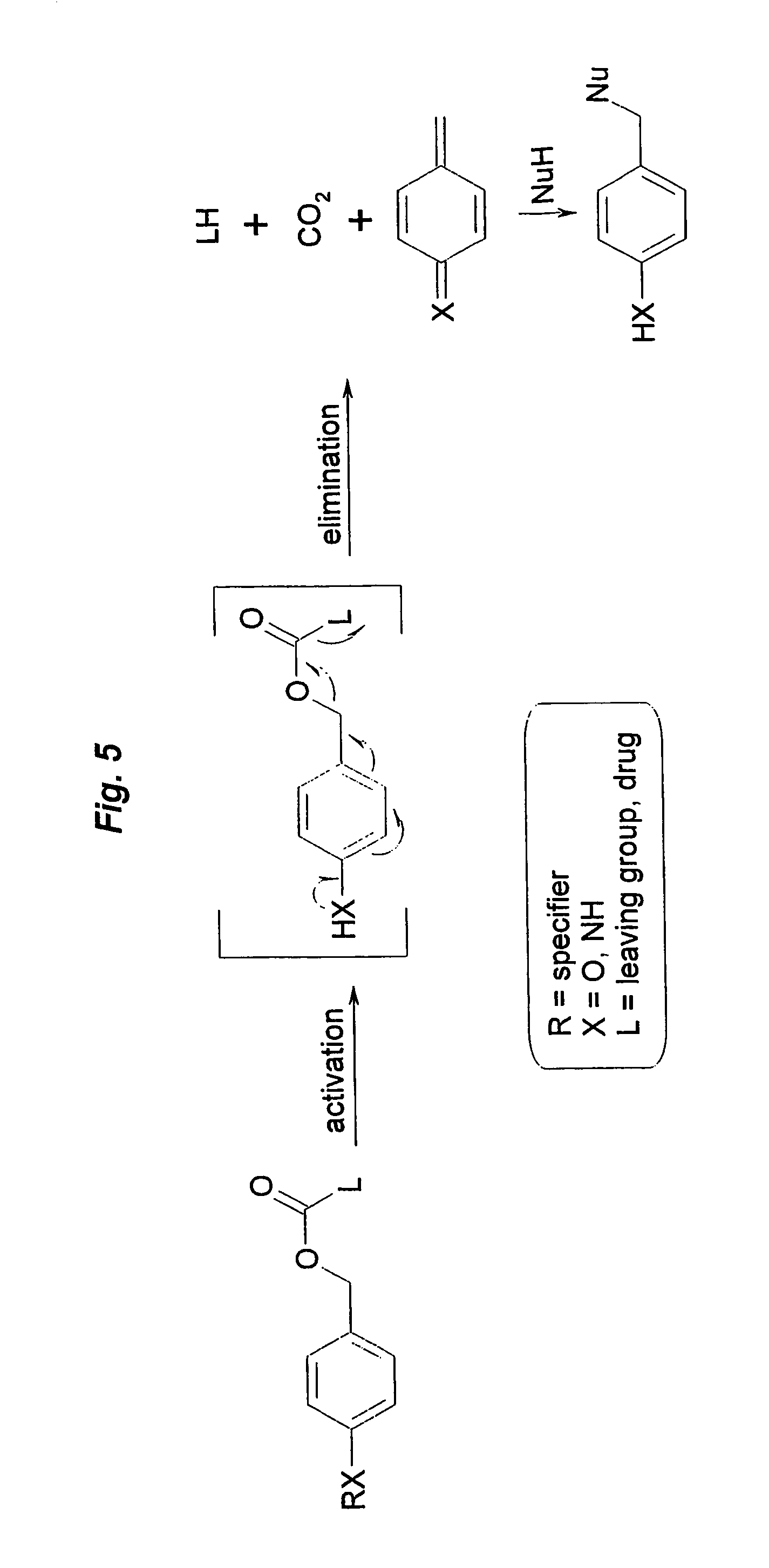
This invention concerns multiple release spacers and spacer systems, which release multiple leaving groups following a single activation. It concerns compounds comprising a specifier linked to two or more of the same or different leaving groups (L in the figure) via a self-eliminating multiple release spacer or spacer system, which compounds upon a single activation step, in particular removal or transformation of the specifier, release at least two leaving groups.
Owner:SYNTARGA BV
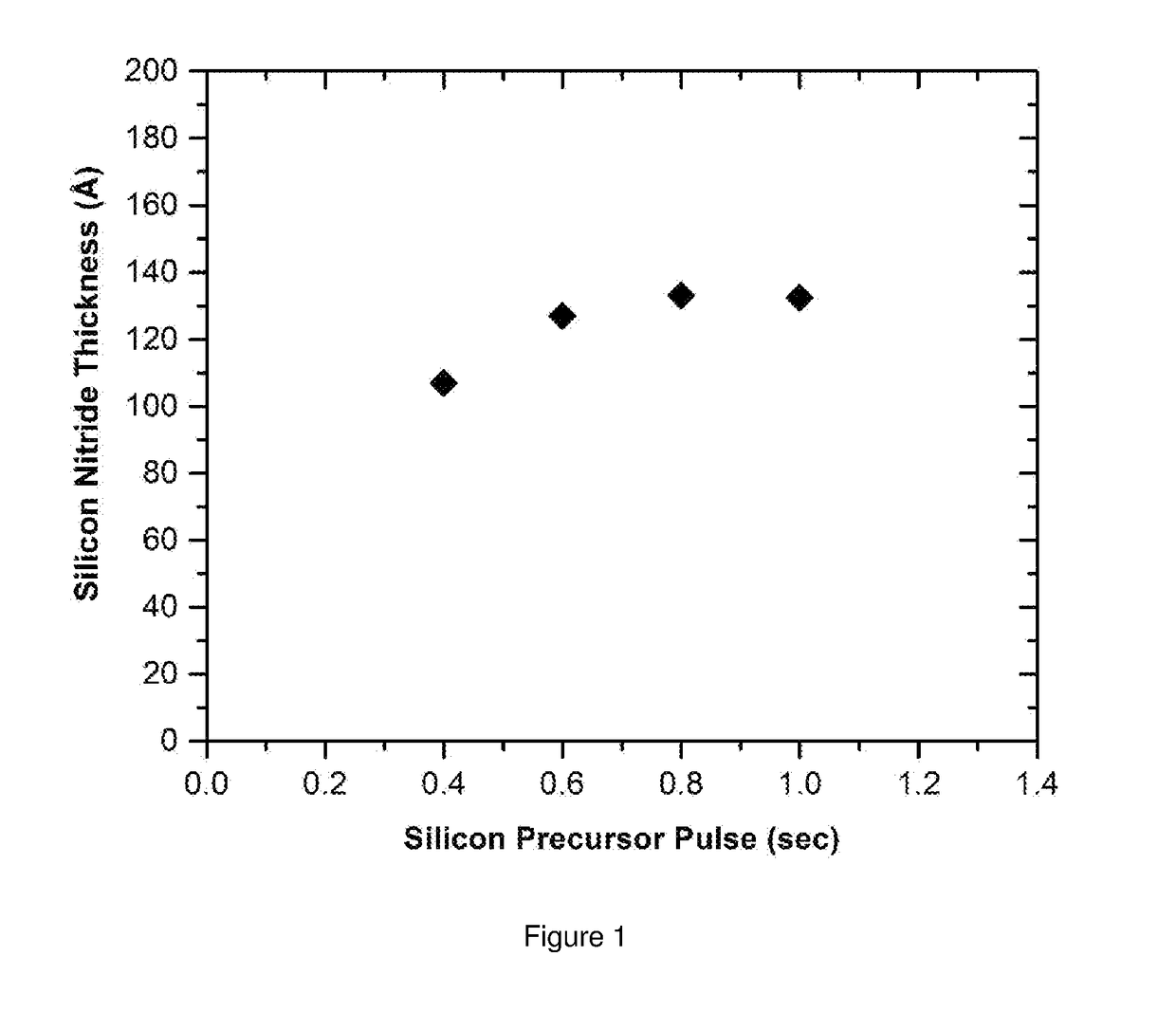
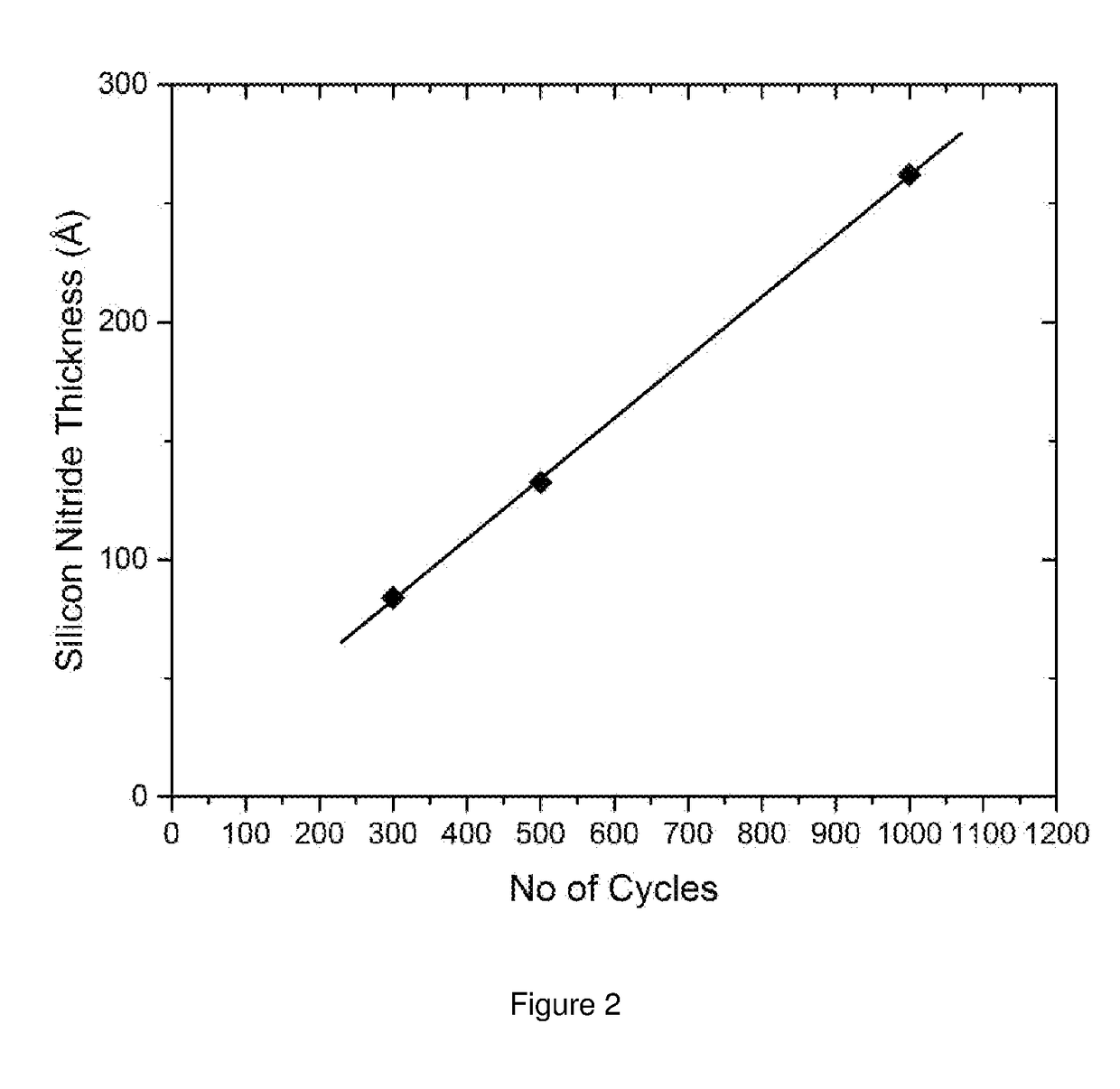
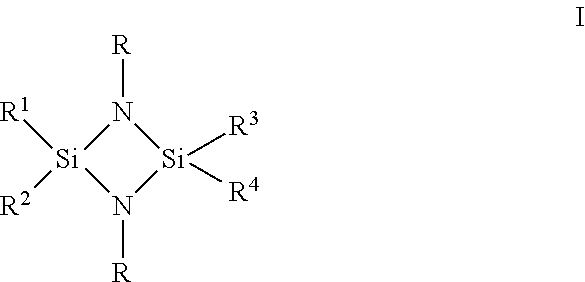
Compositions and methods for depositing silicon nitride films
ActiveUS20190085451A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingLeaving groupReactive site
Described herein are compositions, silicon nitride films and methods for forming silicon nitride films using at least on cyclodisilazane precursor. In one aspect, there is provided a method of forming a silicon nitride film comprising the steps of: providing a substrate in a reactor; introducing into the reactor an at least one cyclodisilazane comprising a hydrocarbon leaving group and two Si—H groups wherein the at least one cyclodisilazane reacts on at least a portion of the surface of the substrate to provide a chemisorbed layer; purging the reactor with a purge gas; introducing a plasma comprising nitrogen and an inert gas into the reactor to react with at least a portion of the chemisorbed layer and provide at least one reactive site wherein the plasma is generated at a power density ranging from about 0.01 to about 1.5 W / cm2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
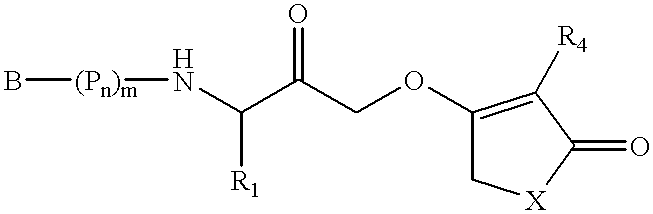
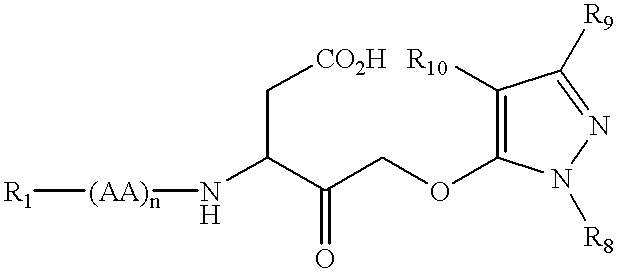
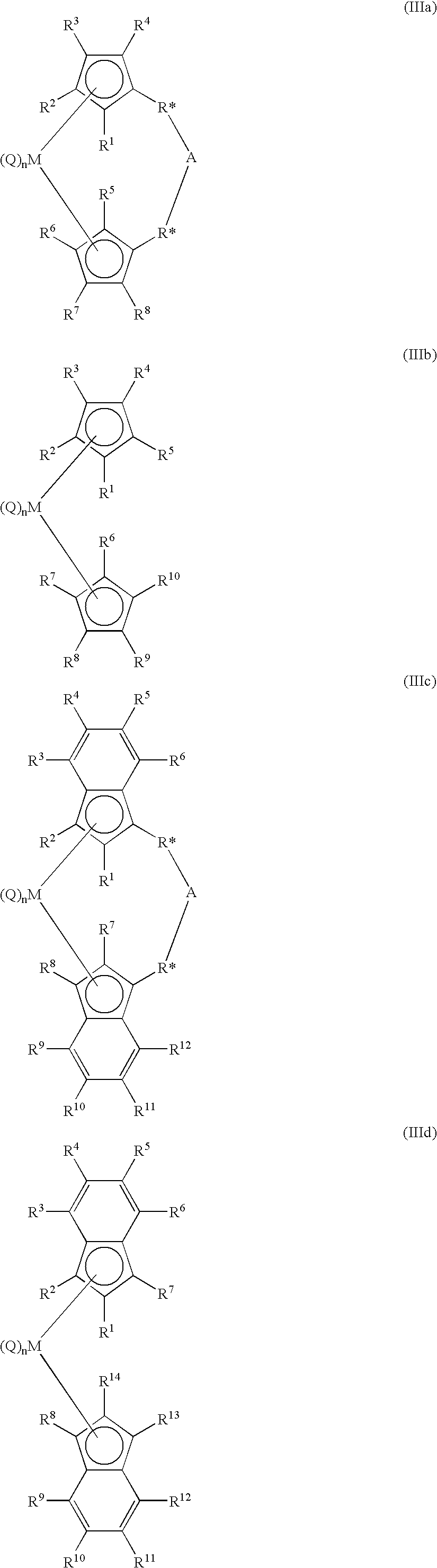
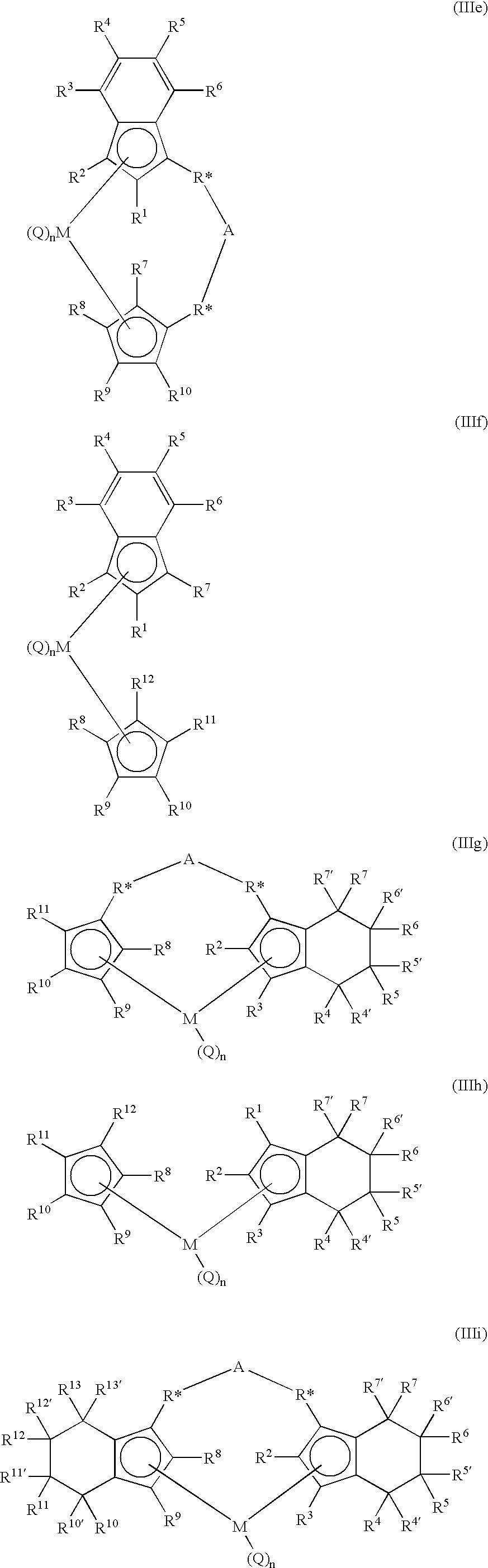
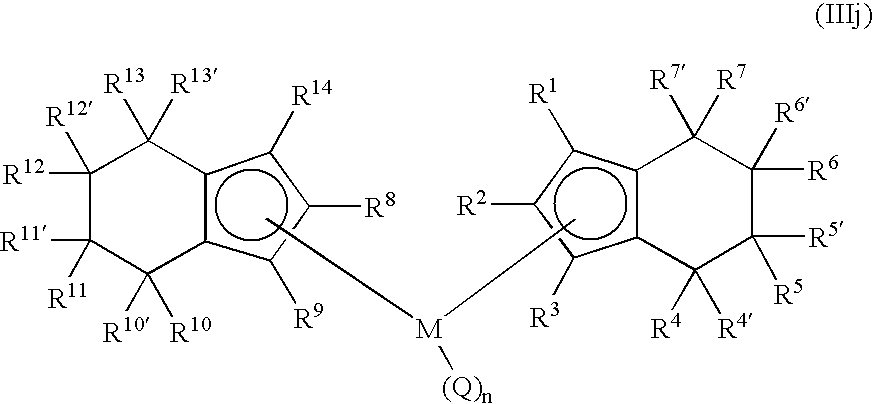
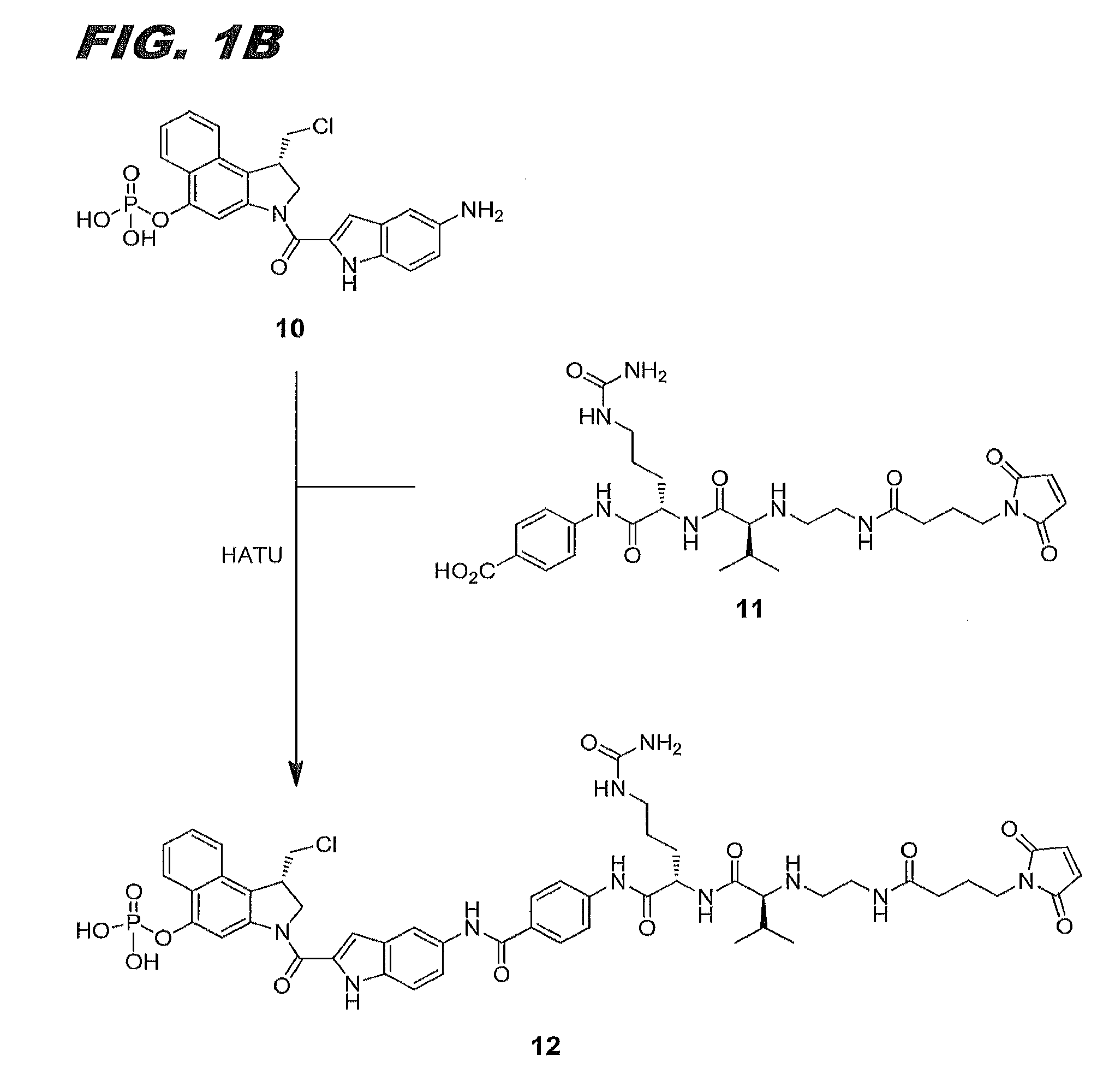
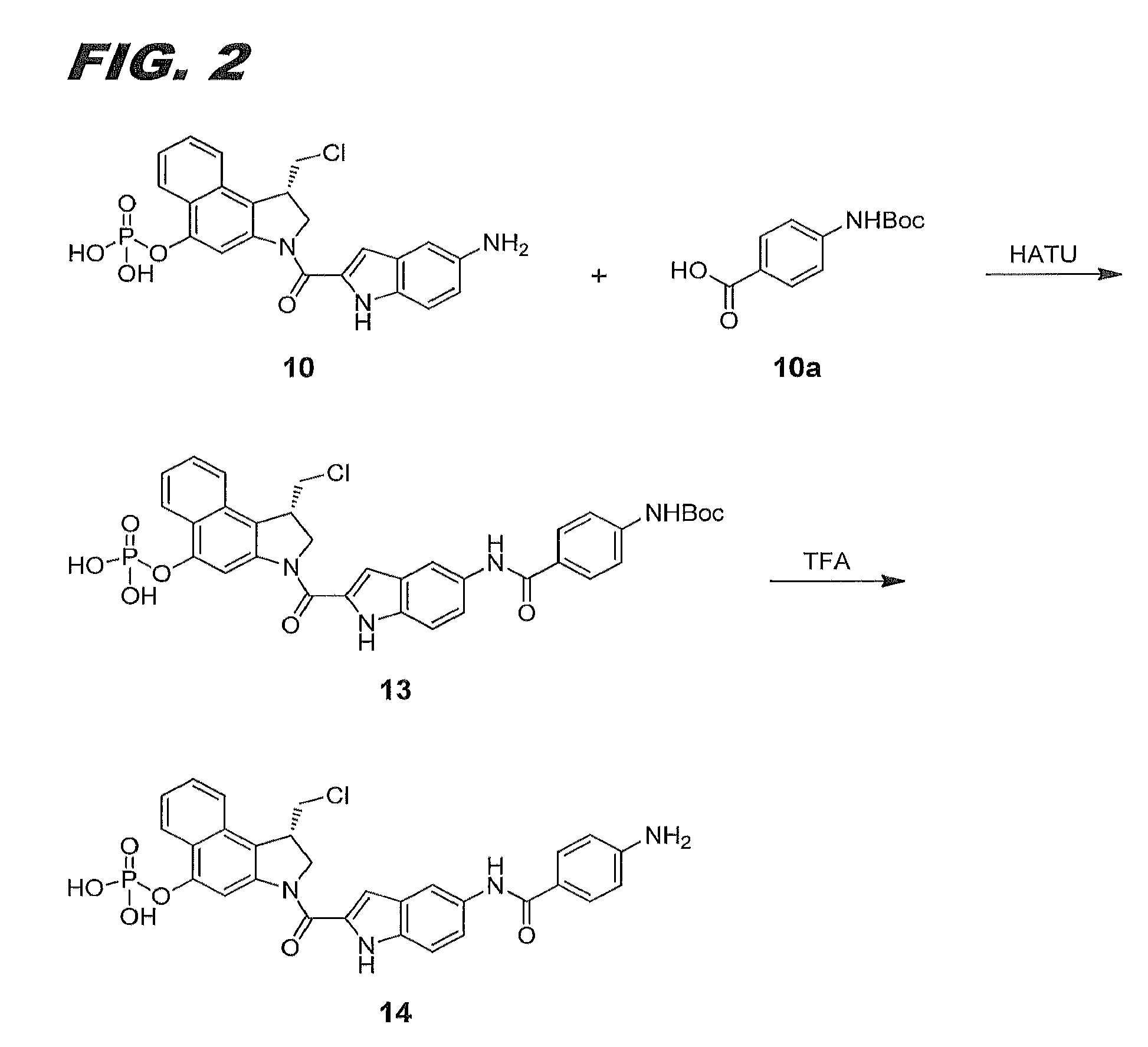
11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines
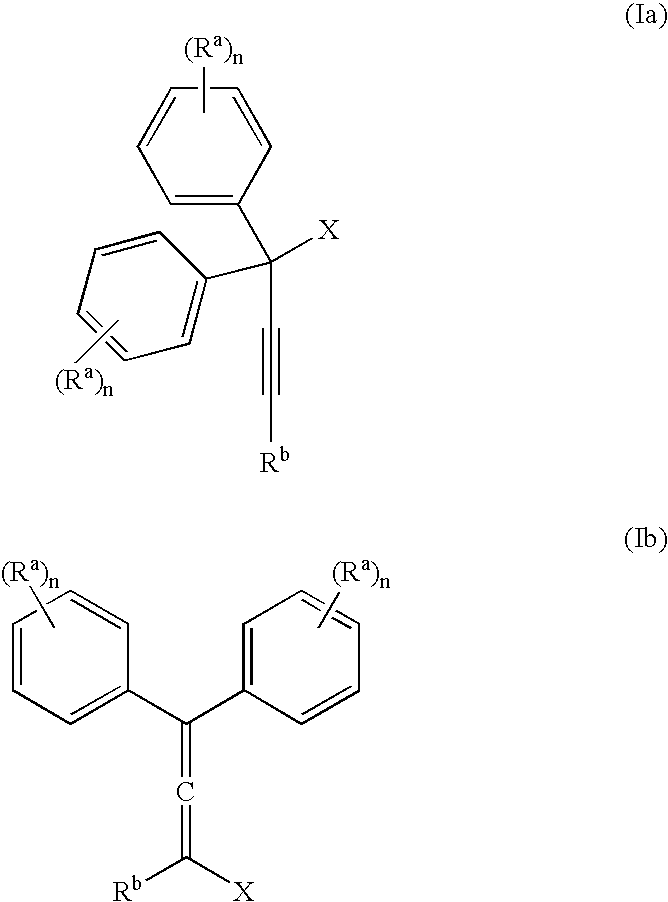
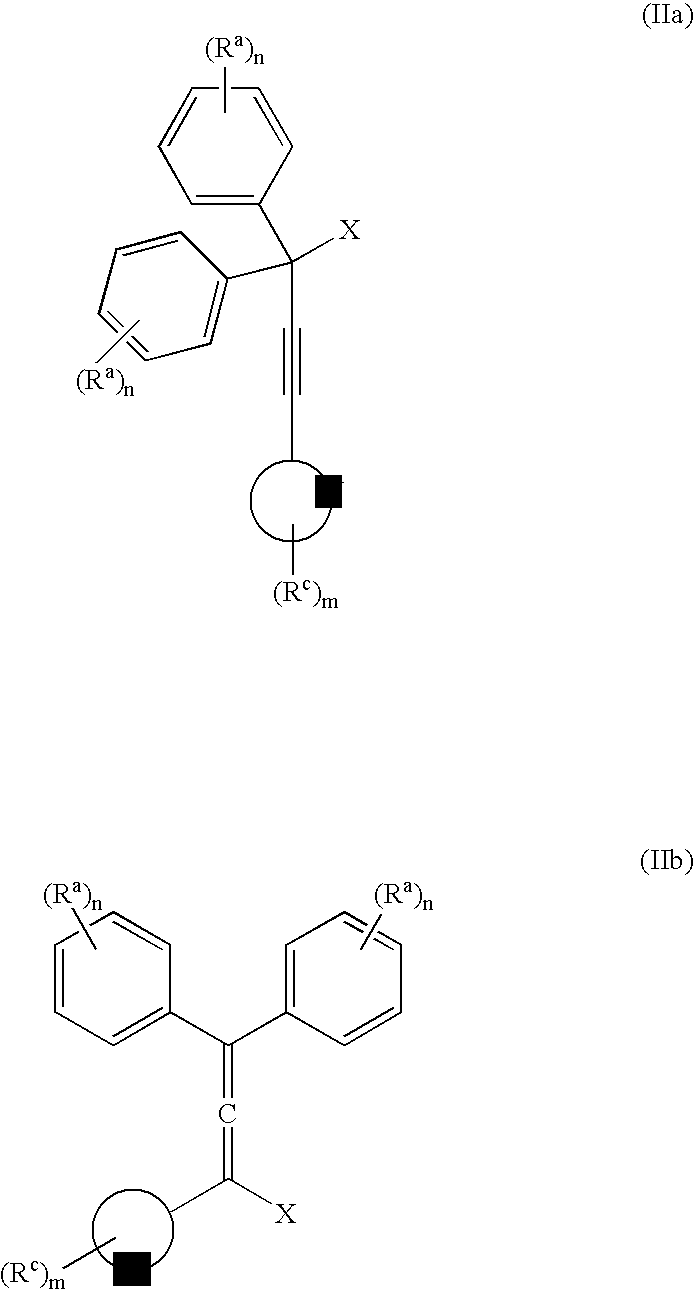
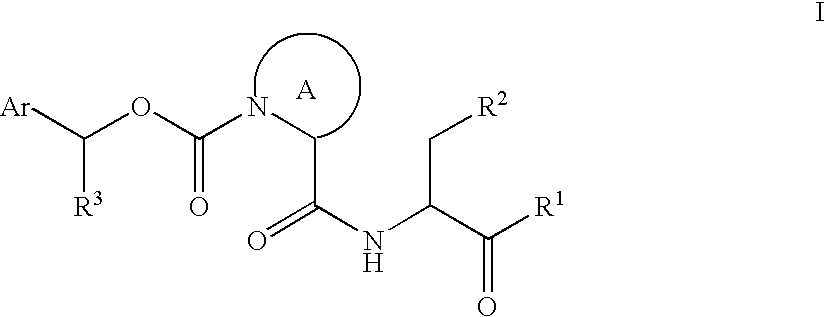
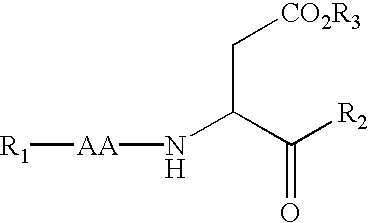
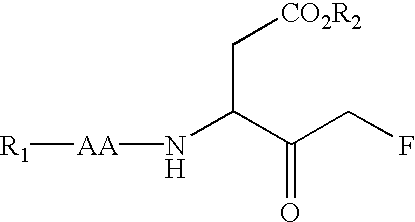
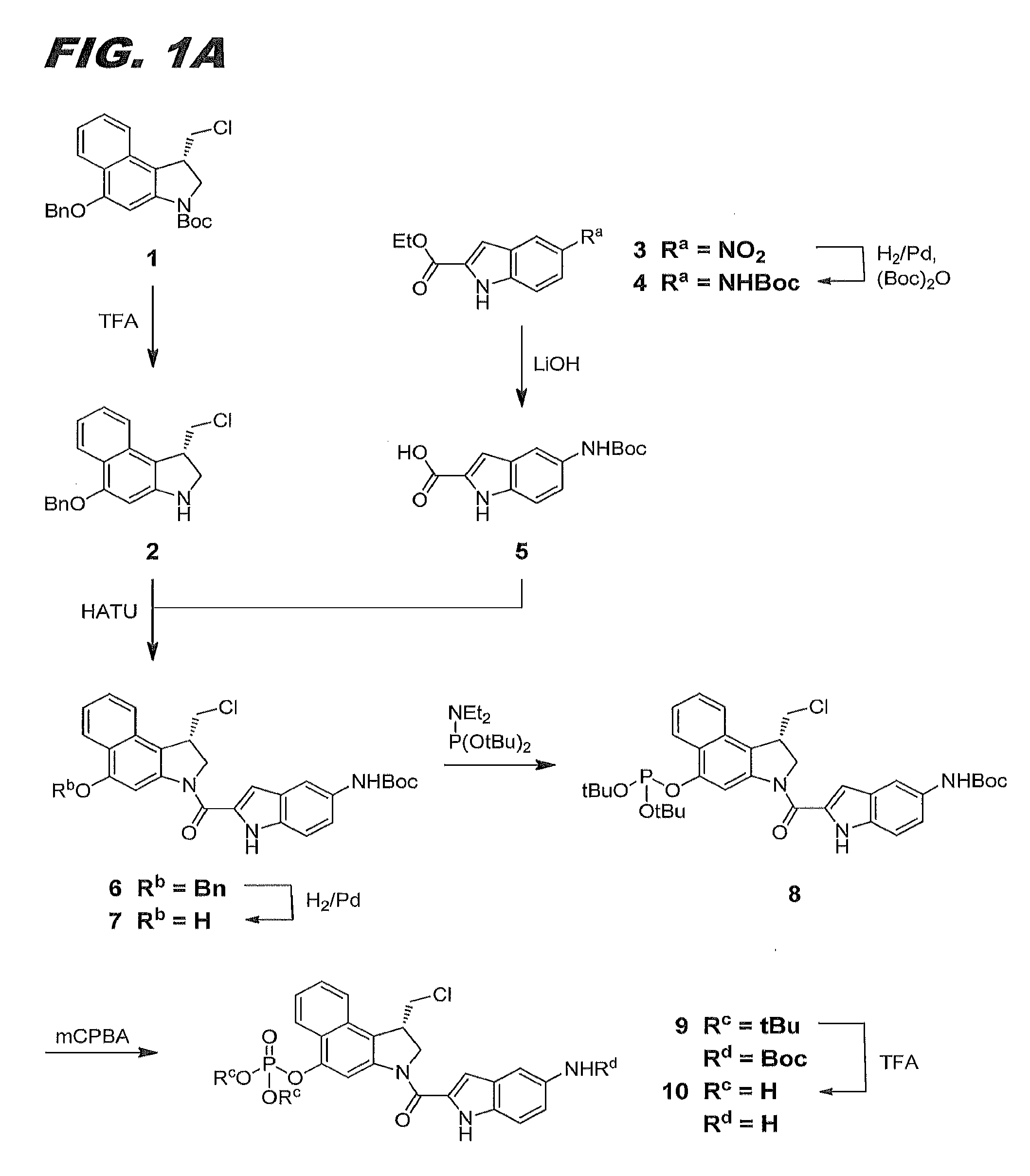
The present inventors have developed a key intermediate for the production of C2 substituted PBDs, which has a leaving group at the C2 position, a carbamate protecting group at the N10 position and a protected hydroxy group at the C11 position. In a first aspect, the present invention comprises a compound with a the formula (I), wherein: R10 is a carbamate-based nitrogen protecting group; R11 is an oxygen protecting group; and R2 is a labile leaving group. In a further aspect, the present invention comprises a method of synthesising a compound of formula (III), or a solvate thereof, from a compound of formula (I) as defined in the first aspect, R16 is either O—R11, wherein R11 is as defined in the first aspect, or OH, or R10 and R16 together form a double bond between N10 and C11; and R15 is R. The other substituents are defined in the claims. Further aspects of the present invention relate to compounds of formula (III) (including solvates thereof when R10 and R16 form a double bond between N10 and C11, and pharmaceutical salts thereof), pharmaceutical compositions comprising these, and their use in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a proliferative disease.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Polymerization process using a metallocene catalyst system
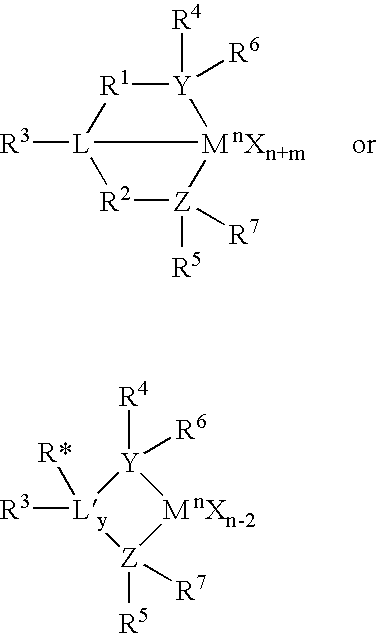
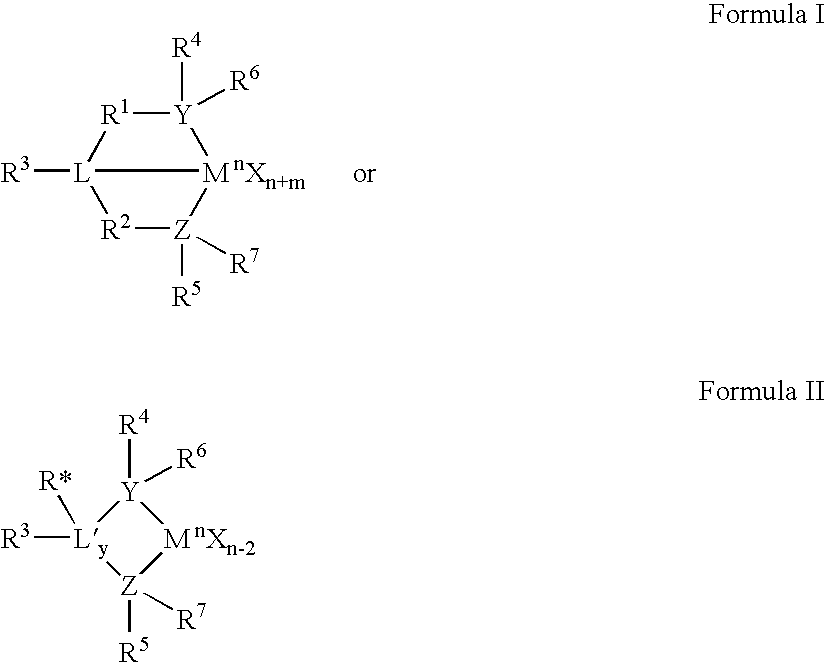
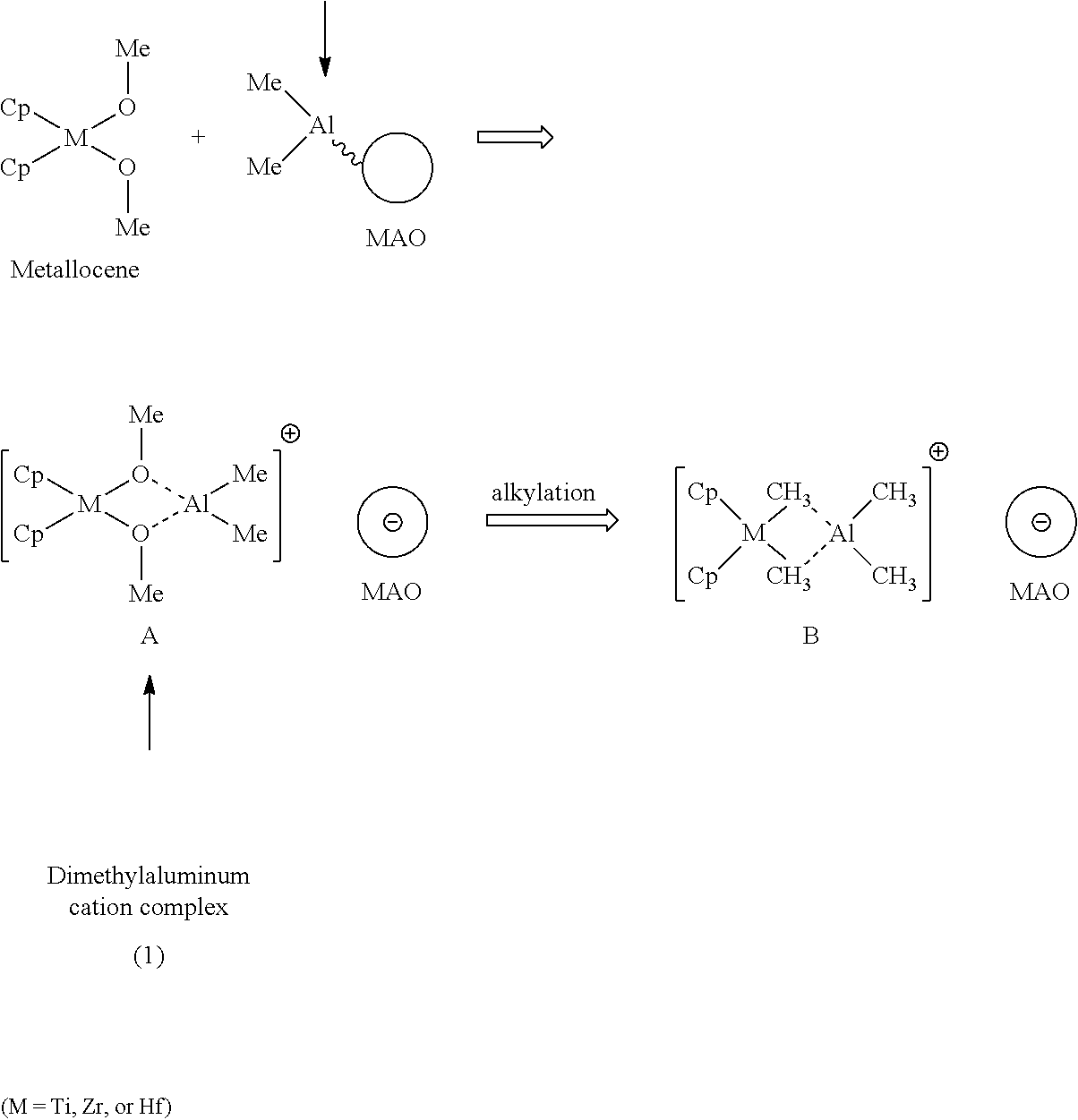
InactiveUS6894131B2Improved reactor performanceReducing and eliminating needOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationLeaving groupFluoride
Provided is a process for polymerizing olefins in the presence of a metallocene catalyst compound having at least one fluoride or fluorine containing leaving group. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process and catalyst composition having improved reactor performance, reducing or eliminating the need for anti-fouling additives to the catalyst composition and / or the reactor. In one embodiment, the invention is a process of polymerizing olefins comprising contacting ethylene and at least one comonomer with a supported catalyst system comprising a metallocene catalyst compound, the metallocene catalyst compound comprising at least one fluoride ion or fluorine containing leaving group; and wherein the supported catalyst system comprises an inorganic oxide support having an average particle size of from 35 μm or less and a pore volume of from 1 to 2 cm3 / g. The polymer product resulting therefrom is, in one embodiment, a copolymer having a density in the range of from 0.910 g / cm3 to 0.940 g / cm3; a molecular weight distribution of from 1.8 to 4; and an I2 of from 0.1 dg / min to 10 dg / min and is suitable for such articles as films.
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
Prodrugs built as multiple self-elimination-release spacers
This invention concerns multiple release spacers and spacer systems, which release multiple leaving groups following a single activation. It concerns compounds comprising a specifier linked to two or more of the same or different leaving groups (L in the figure) via a self-eliminating multiple release spacer or spacer system, which compounds upon a single activation step, in particular removal or transformation of the specifier, release at least two leaving groups.
Owner:SYNTARGA BV
Immunoconjugates, compositions for making them, and methods of making and use
ActiveUS20120301490A1Adequate levelOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntigenDNA Minor Groove Binding Agent
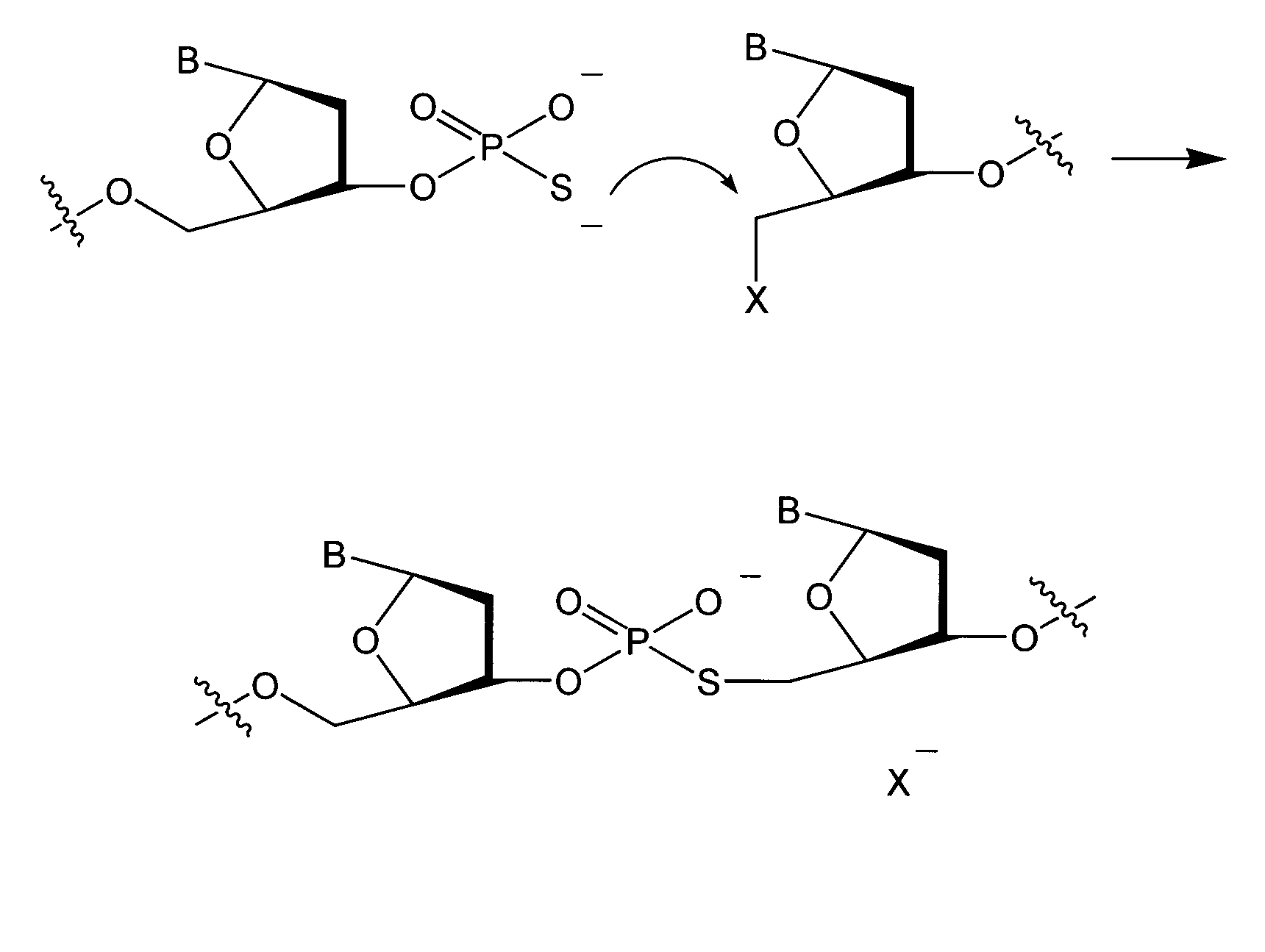
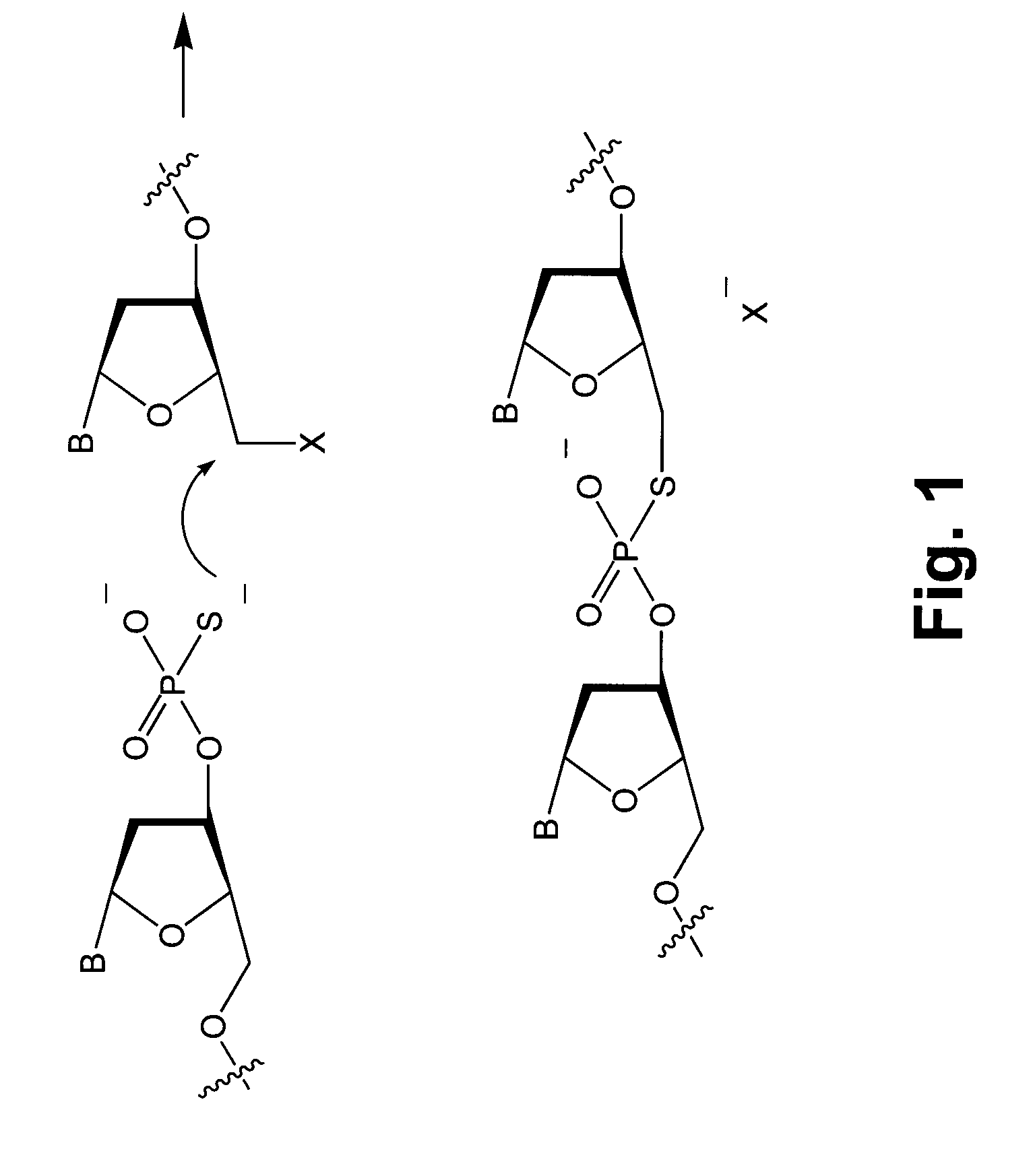
An immunoconjugate in which a phosphate-prodrugged DNA minor groove binding agent of formula (I), where X is a nucleophilically displaceable leaving group, is conjugated to an antibody or an antigen binding fragment of an antibody, and compounds that can be used for making such immunoconjugates, and uses of such immunoconjugates.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
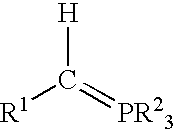
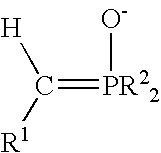
Process for preparing functional group-containing olefinic compounds
ActiveUS6838576B1High yieldStereoselectivity can be controlledPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationCompound aLeaving group
A process for preparing functional group-containing olefinic compounds comprises the steps of (a) reacting at least one alkylidene phosphorane with at least one carbonyl-containing compound that comprises at least one group that is a leaving group, or that is capable of subsequent conversion to a leaving group, to form an olefinic compound that comprises at least one leaving group, the carbonyl-containing compound being selected from the group consisting of ketones and aldehydes; and (b) reacting the olefinic compound with at least one functional group-containing nucleophile to form a functional group-containing olefinic compound.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aluminoxane Catalyst Activators Containing Carbocation Agents, and use thereof in Polyolefin Catalysts
ActiveUS20130345376A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolyolefinLeaving group
This invention relates to an activator composition comprising (i) an organoaluminum compounds; (ii) a carbocation compound of the formula R1 (X)n; wherein R1 is a hydrocarbyl; n is from 1 to the number of possible substitutions of the hydrocarbyl group and each X is a labile leaving group; and (iii) an aluminoxane. The activator composition may also contain a carrier support. This invention also provides a catalyst composition comprising the activator composition described above and a transition metal component. This invention also provides methods of polymerizing monomer comprising carrying out such polymerization in the presence of one or more catalyst composition according to this invention.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Synthesis of polymerization catalyst components
InactiveUS6869903B2Increasing and decreasing reaction temperatureLarge influenceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationLeaving groupHalogen
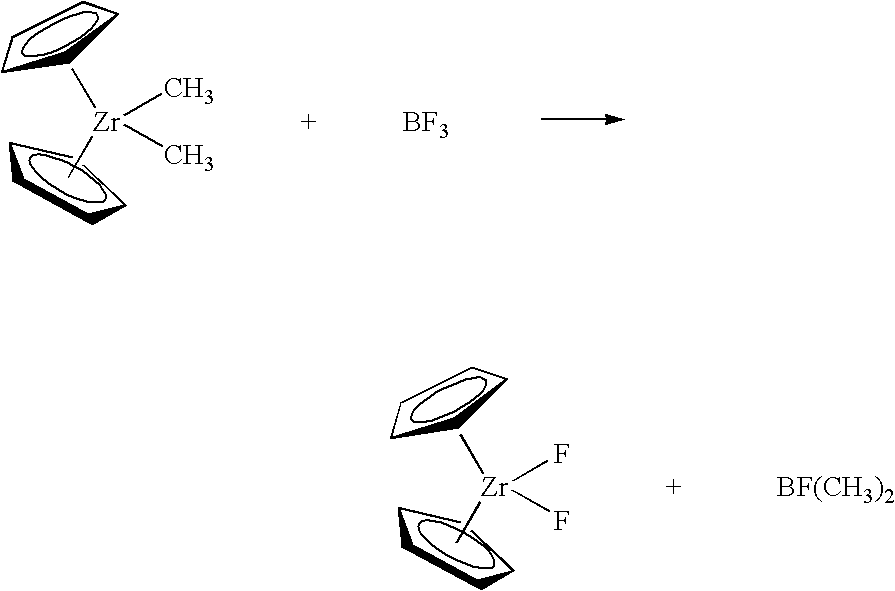
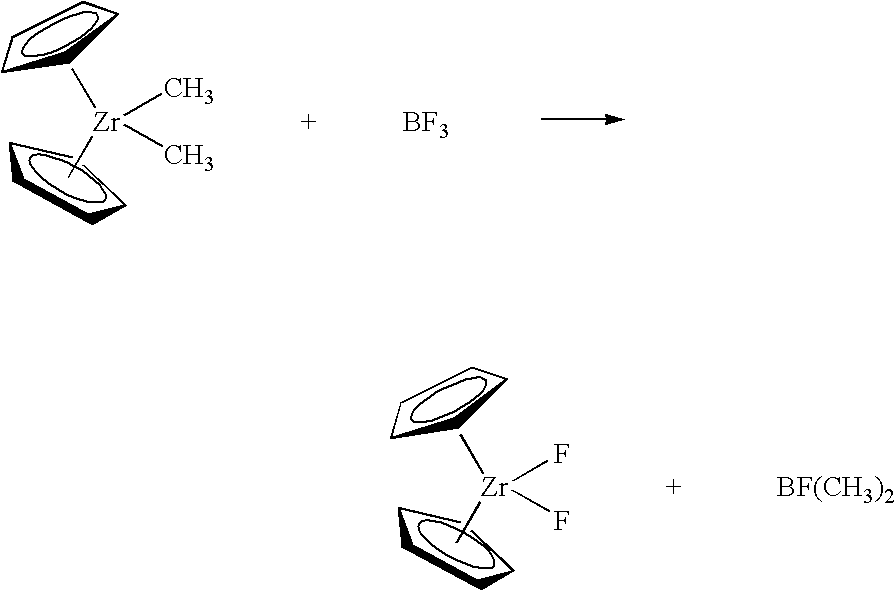
The present invention provides a method of synthesizing fluorided metallocene catalyst components comprising contacting at least one fluoriding agent comprising fluorine with one or more alkylated metallocene catalyst components comprising one or more non-halogen leaving groups to produce a fluorided catalyst component; wherein from less than 3 equivalents of fluorine are contacted for every equivalent of leaving group. The method of the invention is exemplified by the following reaction which takes place in a non-coordinating diluent such as pentane: wherein one or both of the “Cp” rings may be substituted with an R group as described herein, and may be bridged. The reaction can be run at any desirable temperature, desirably between 10° C. and 35° C. The reaction product of the BF3 and dimethyl zirconocene is the fluorided zirconocene. The mole ratio of the BF3 fluoriding agent and the starting metallocene is less than 2:1 (fluoriding agent:metallocene) in one embodiment, and less than or equal to 1.6:1 in a particular embodiment, and less than or equal to 1.5:1 in a more particular embodiment, and less than or equal to 1.2:1 in yet a more particular embodiment.
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
Positive resist compositions and patterning process
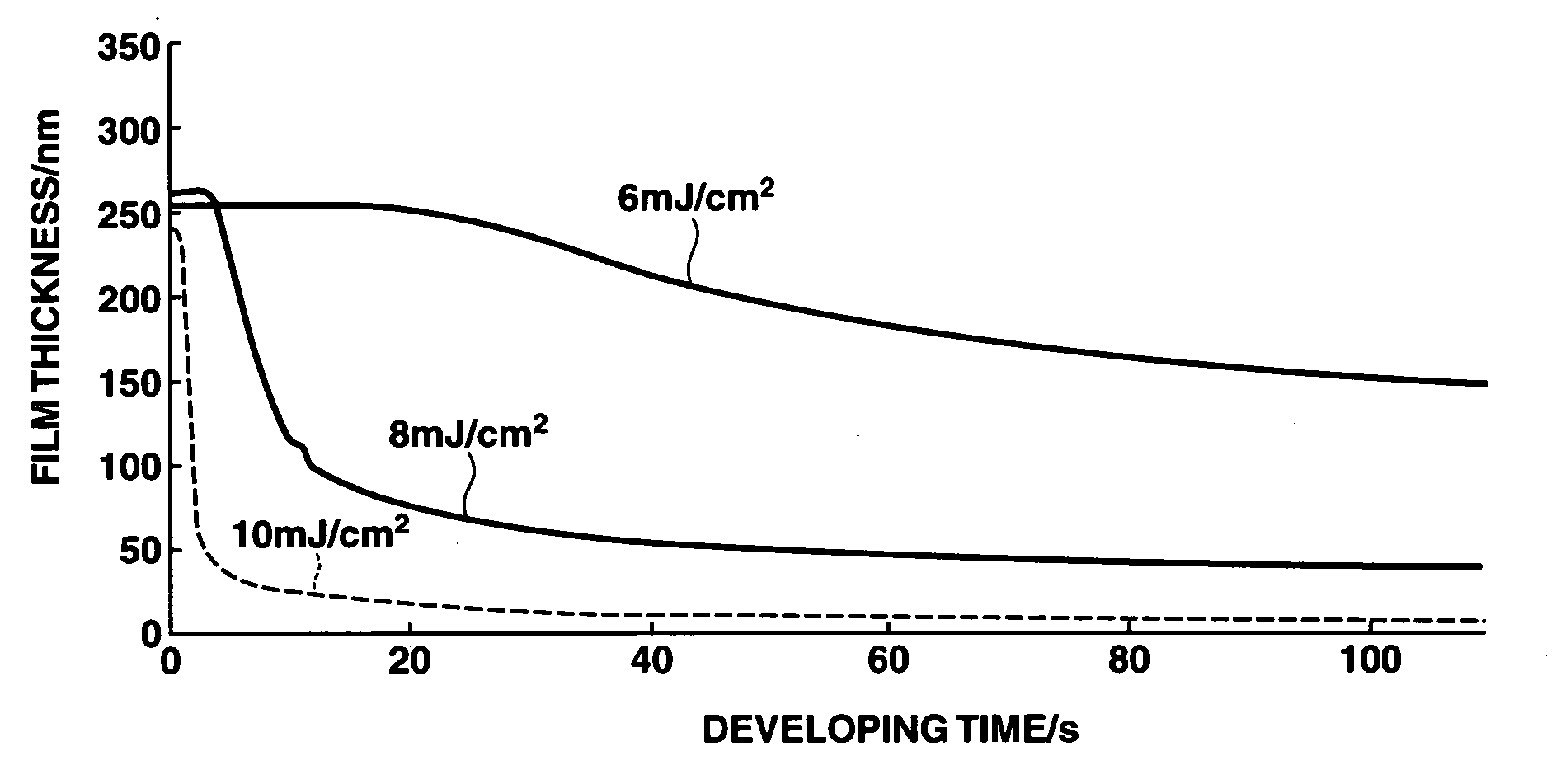
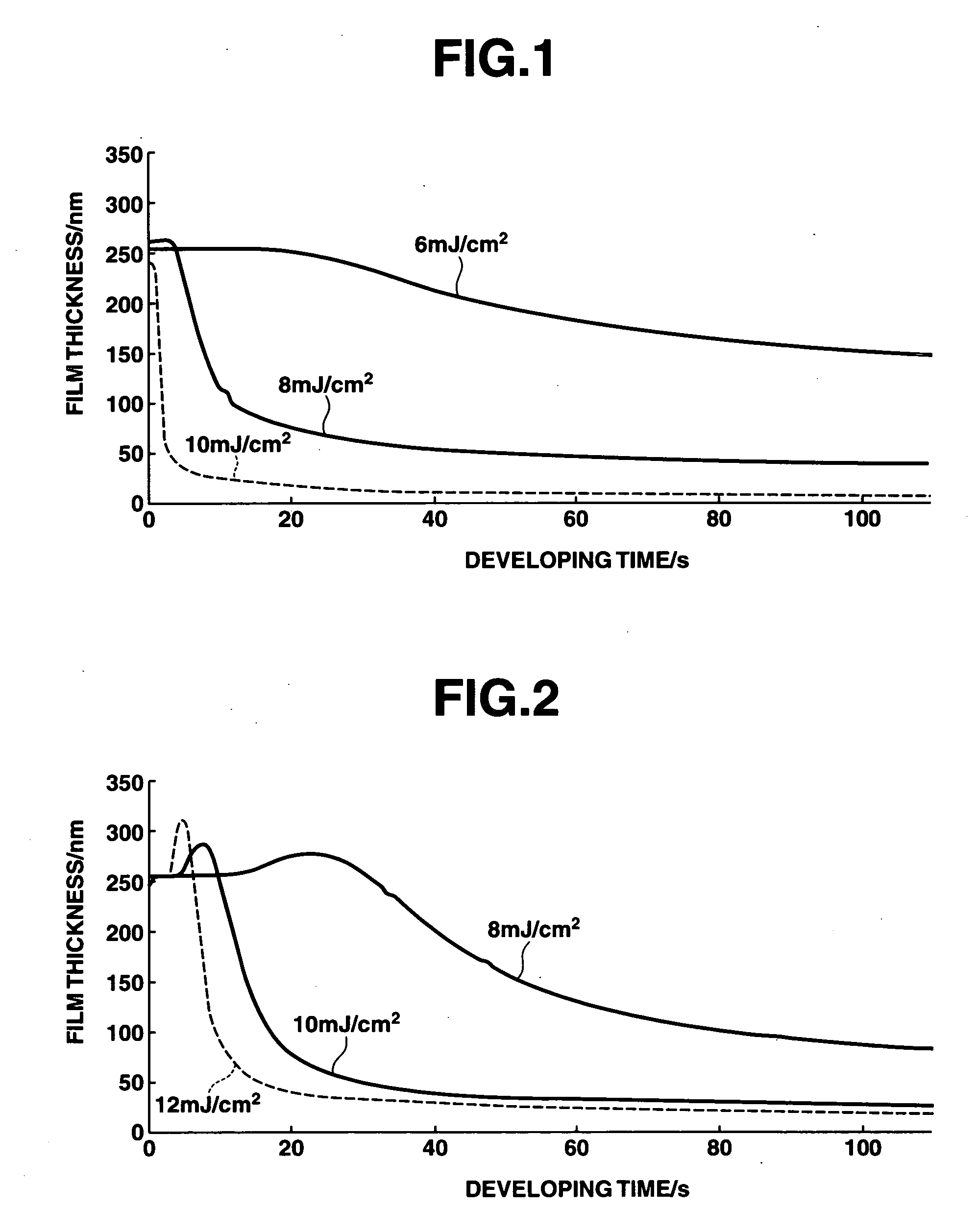
ActiveUS20050227174A1Minimal line edge roughnessHigh sensitivityAgricultural machinesRadiation applicationsMeth-Leaving group
A polymer which is obtained from a combination of (meth)acrylate having a bridged ring lactone group and (meth)acrylate having an acid leaving group with a hexafluoroalcohol group is used as a base resin to formulate a positive resist composition which when exposed to high-energy radiation and developed, exhibits a high sensitivity, a high resolution, and a minimal line edge roughness due to controlled swell during development. The composition also has excellent dry etching resistance.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Compounds and kits for preparing imaging agents and methods of imaging
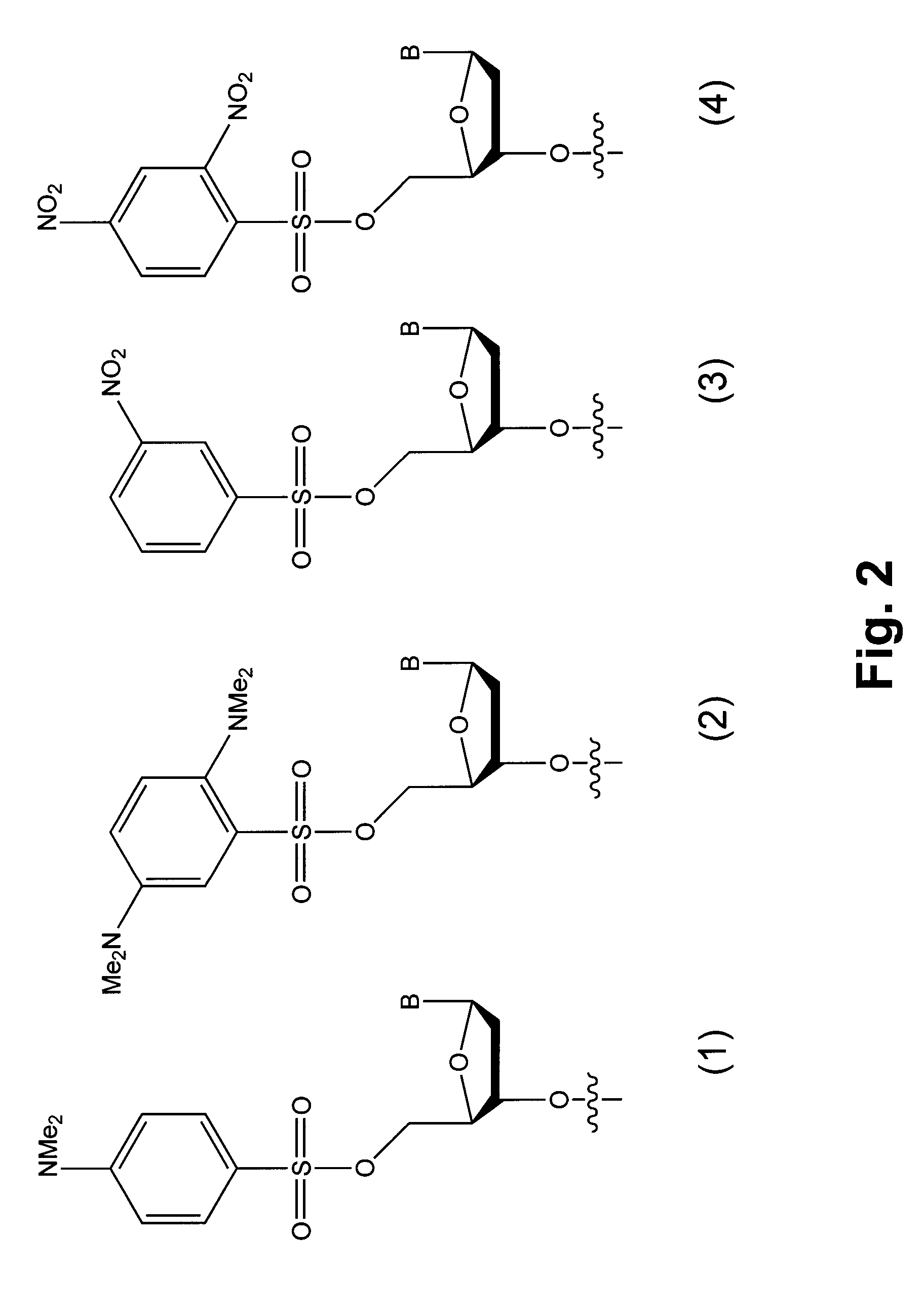
InactiveUS20050049487A1Improve isolationRadioactive preparation carriersRadiation diagnosticsLeaving groupRegioselectivity
Compounds that include a targeting moiety bound to a regioselective leaving group are useful for preparing imaging agents. The imaging agents can be isolated from by-products derived from the leaving group based on differences in the chemical attributes (e.g., net charge or polarity) of the molecules or physical attributes of the molecules through the use of a solid support. Methods of producing an imaging agent include the steps of providing a compound that includes a targeting moiety bound to a support via a linker group that contains a site for regioselective substitution of a detectable species, contacting the compound with a solution containing the detectable species, and recovering the imaging agent. Kits which include a first container having therein a solution containing a detectable species and a second container having therein a compound that includes a targeting moiety bound to a support via a leaving group that contains a site for regioselective substitution of the detectable species are also useful for preparing imaging agents.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
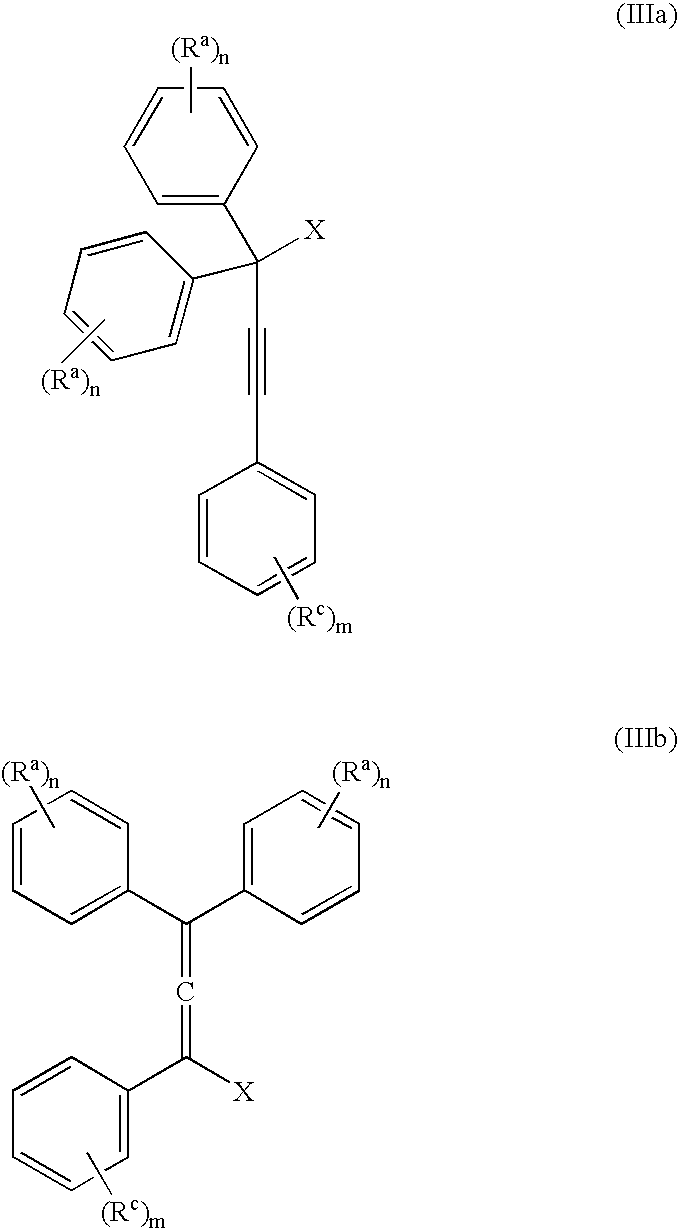
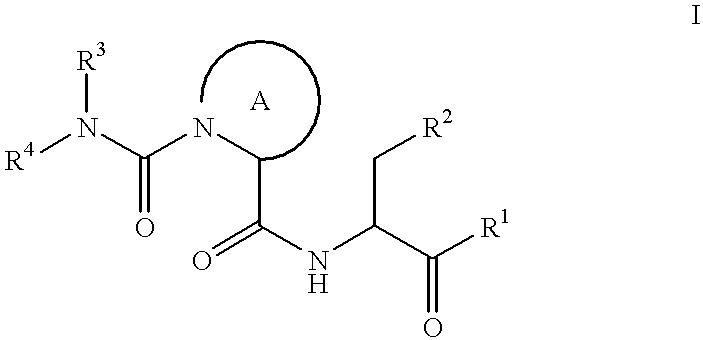
11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines
The present inventors have developed a key intermediate for the production of C2 substituted PBDs, which has a leaving group at the C2 position, a carbamate protecting group at the N10 position and a protected hydroxy group at the C11 position. In a first aspect, the present invention comprises a compound with a the formula (I), wherein: R10 is a carbamate-based nitrogen protecting group; R11 is an oxygen protecting group; and R2 is a labile leaving group. In a further aspect, the present invention comprises a method of synthesising a compound of formula (III), or a solvate thereof, from a compound of formula (I) as defined in the first aspect, R16 is either O-R11, wherein R11 is as defined in the first aspect, or OH, or R10 and R16 together form a double bond between N10 and C11; and R15 is R. The other substituents are defined in the claims. Further aspects of the present invention relate to compounds of formula (III) (including solvates thereof when R10 and R16 form a double bond between N10 and C11, and pharmaceutical salts thereof), pharmaceutical compositions comprising these, and their use in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a proliferative disease.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
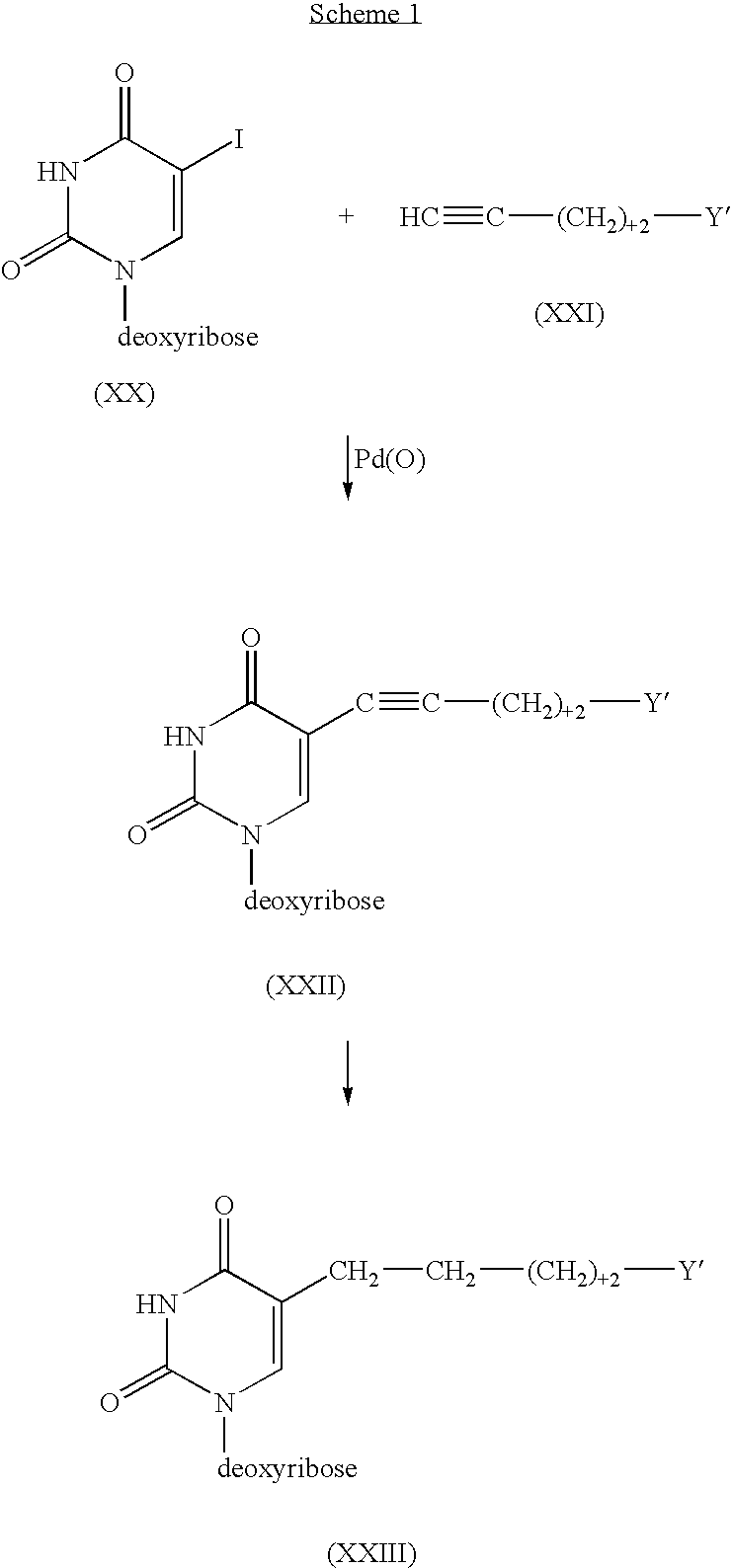
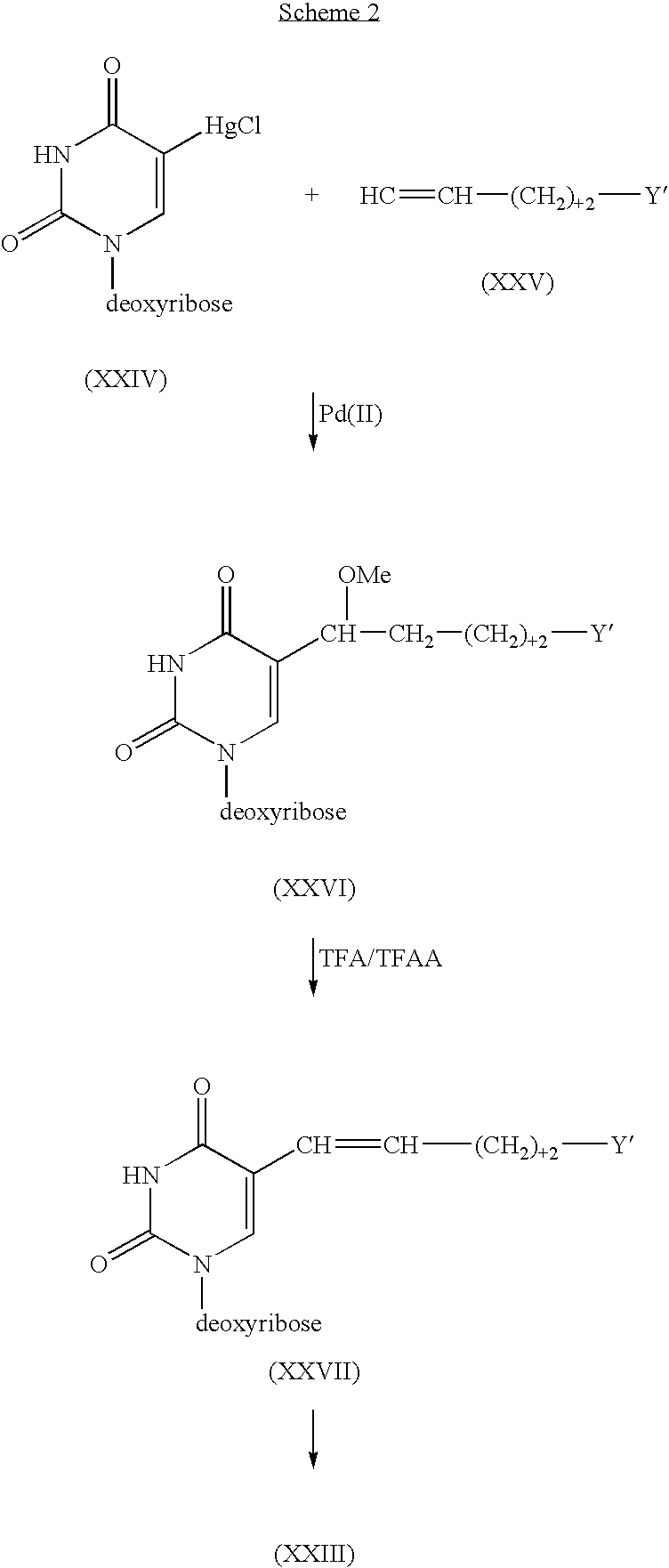
Pyrimidine nucleoside compounds and oligonucleoside compounds containing same
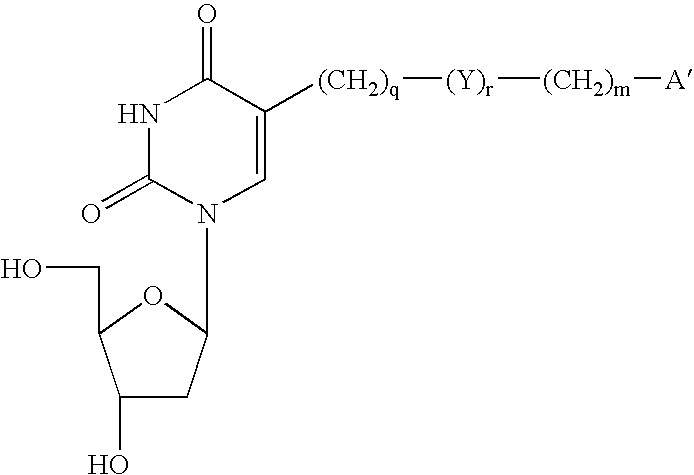
InactiveUS6060592AEffective activityImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrosoSilylene
Novel 2- and 4-substituted pyrimidine nucleosides and oligonucleosides are provided, as are methods and intermediates useful in preparing same. In preferred embodiments, one of the 2- and 4-substituents is =O, =NH, or =NH2+ and the other is Q, =C (RA)-Q, C(RA)(RB)-C(RC)(RD)-Q, C (RA)=C(RC)-Q or C 3BOND C-Q, where RA, RB, RC and RD independently are H, SH, OH, NH2, or C1-C20 alkyl, or one of (RA)(RB) or (RC)(RD) is =O, and Q is halogen, hydrogen, C1-C20 alkyl, C1-C20 alkylamine, C1-C20 alkyl-N-phthalimide, C1-C20 alkylimidazole, C1-C20 alkylbis-imidazole, imidazole, bis-imidazole, amine, N-phthalimide, C2-C20 alkenyl, C2-C20 alkynyl, hydroxyl, thiol, keto, carboxyl, nitrates, nitro, nitroso, nitrile, trifluoromethyl, trifluoromethoxy, O-alkyl, S-alkyl, NH-alkyl, N-dialkyl, O-aralkyl, S-aralkyl, NH-aralkyl, azido, hydrazino, hydroxylamino, isocyanato, sulfoxide, sulfone, sulfide, disulfide, silyl, O-(hydroxyl protecting group), a leaving group, a heterocycle, an intercalator, a reporter molecule, a conjugate, a polyamine, a polyamide, a polyethylene glycol, a polyether, or a depurination enhancing group.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Synthesis process
ActiveUS20060025617A1The method is simple and fastHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAlcoholLeaving group
A process for synthesizing a single isomer of a naphthacene compound comprises the steps of: (a) reacting a symmetrically substituted 1,1-diarylpropargyl alcohol compound with a reagent capable of forming a leaving group to form a reaction mixture containing a intermediate; and then (b) heating the intermediate in the presence of a solvent and in the absence of any oxidizing agent to form a single naphthacene compound.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Caspase inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20020058630A1Enhanced inhibitory effectGood effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCaspase inhibitorsAryl
Described herein are compounds that are useful as caspase inhibitors having the formula: wherein Ring A is an optionally substituted piperidine, tetrahydroquinoline or tetrahydroisoquinoline ring; R1 is hydrogen, CN, CHN2, R, or CH2Y; R is an optionally substituted group selected from an aliphatic group, an aryl group, or an aralkyl group; Y is an electronegative leaving group; R2 is CO2H, CH2CO2H, or esters, amides or isosteres thereof; and R3 is hydrogen, an optionally substituted aryl group, an optionally substituted aralkyl group, or an optionally substituted C1-6 aliphatic group, R4 is an optionally substituted group selected from an aryl group or a heterocyclyl group, or R3 and R4 taken together with the nitrogen to which they are attached optionally form a substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic, bicyclic or tricyclic ring.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
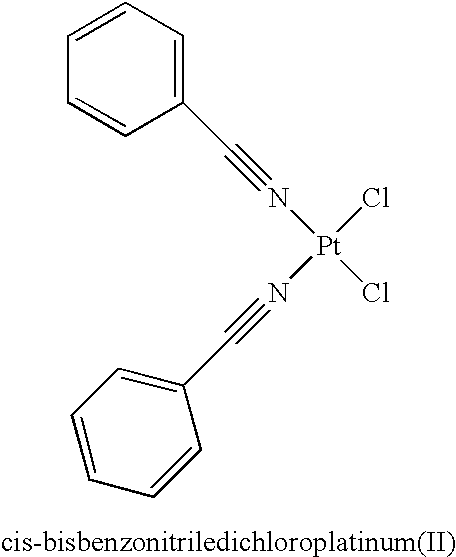
Monoazole ligand platinum analogs
InactiveUS7759488B2Easily transported into tumor cellStrong hydrogen bondingOrganic active ingredientsPlatinum organic compoundsPurinePt element
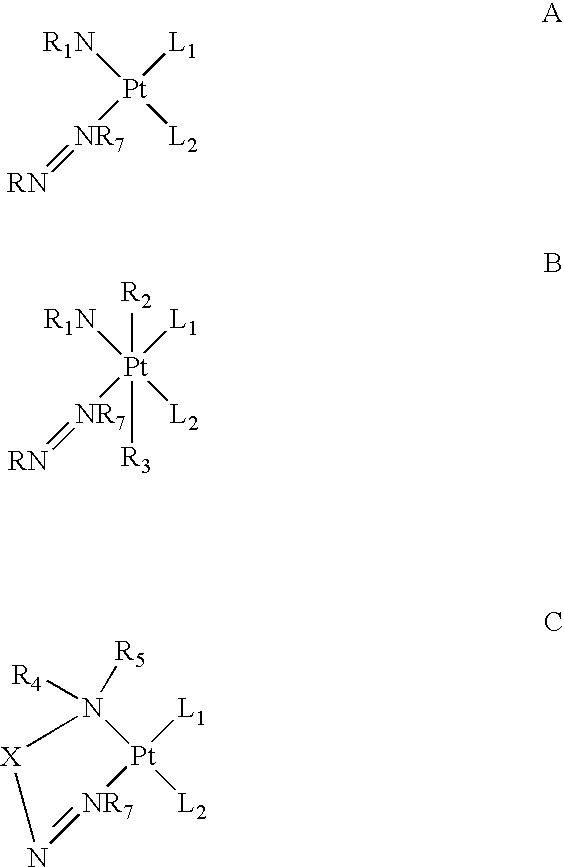
Disclosed herein are novel platinum-based analogs with a single substituted azole ligand: RN═NR7, wherein the RN═NR7 functional group is covalently bonded to the platinum through nitrogen of NR7. The analogs also have nitrogen donor ligands capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the bases in DNA or RNA, and one or more leaving groups which can be displaced by water, hydroxide ions or other nucleophiles, which is thought to form active species in vivo, and then, form cross-linked complexes between nucleic acid strands, principally between purines in DNA (or RNA), i.e., at the Guanine or Adenine bases, thereof. These platinum analogs may also be more easily transported into tumor cells, due to their increased lipophilicity and are likely to be useful as anti-neoplastic agents, and in modulating or interfering with the synthesis or replication or transcription of DNA or translation or function of RNA in vitro or in vivo, as they are potentially capable of forming a platinum coordinate complex with an intact or nascent DNA or RNA and thereby interfering with cellular synthesis, transcription or replication of nucleic acid polynucleotides.
Owner:BIONUMERIK PHARMA INC
Process for the preparation of alogliptin
The present invention is based on the discovery of a process for preparing pyrimidin- dione compounds, especially alogliptin and its derivatives, which comprises the reaction of a urea derivative of formula (VIII) with a malonic acid or its derivatives to form intermediates of formulae (VII) or (VII-A), which are subsequently converted to a compound of formula (II) upon introduction of a leaving group X. Compound (II) then reacts with an amine to form compound (I), which is optionally converted to its salts of formula (IV).
Owner:MAPI PHARMA
Organic field effect transistor and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060081880A1Uniformity of film thickness can be impairedLow mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesLeaving groupHydrogen atom
There is provided a method for producing a field effect transistor with a high field-effect mobility using a simple method for forming an organic semiconductor layer. A method for producing an organic field effect transistor comprising an organic semiconductor layer, comprising a step of forming the organic semiconductor layer by the photodecomposition of a bicyclic compound containing in a molecule thereof at least one bicyclic ring represented by formula (1): wherein R1 and R3 each denotes a group for forming an aromatic ring or a heteroaromatic ring which may have a substituent, together with a group to be bonded to R1 or R3; R2 and R4 each denotes a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an ester group or a phenyl group; and X is a leaving group which denotes carbonyl group or —N═.
Owner:CANON KK
Terminally-branched polymeric linkers containing extension moieties and polymeric conjugates containing the same
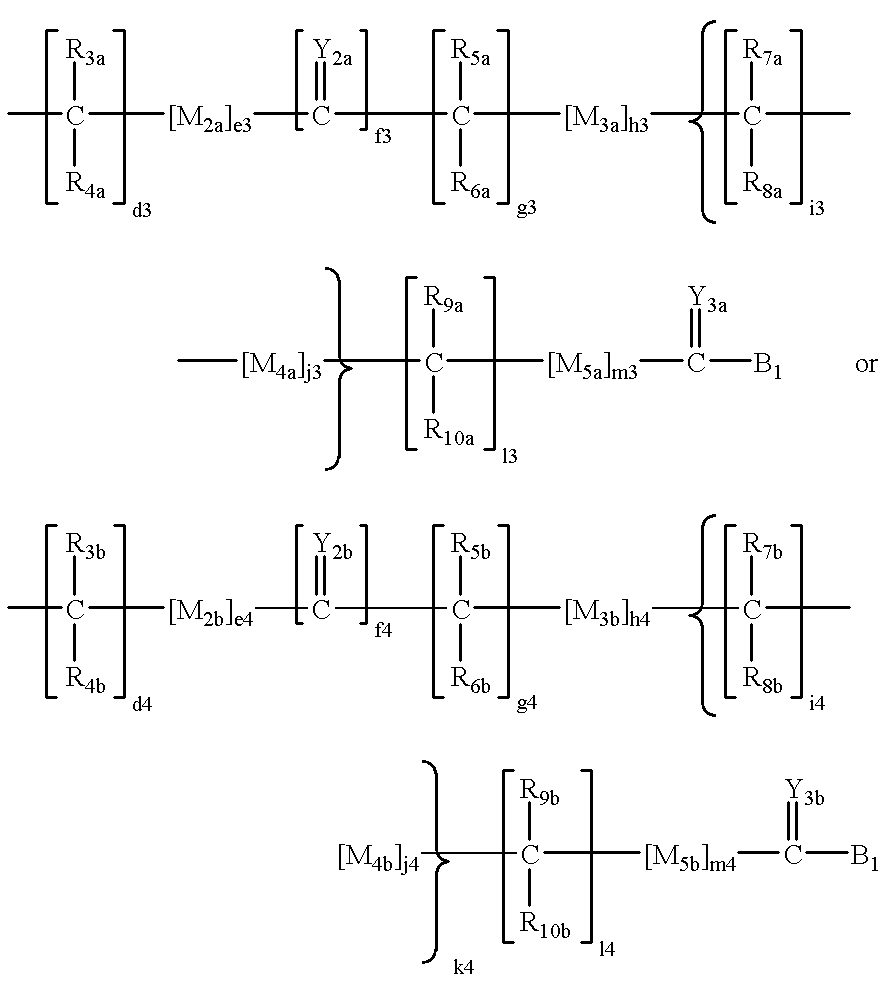
E1a-3a are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-6 alkyls, C3-12 branched alkyls, C3-8 cycloalkyls, C1-6 substituted alkyls, C3-8 substituted cycloalkyls, aryls, substituted aryls, aralkyls, C1-6 heteroalkyls, substituted C1-6 heteroalkyls, C1-6 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-6heteroalkoxy, wherein B1 is a leaving group, OH, a residue of a hydroxyl-containing moiety or a residue of an amine-containing moiety or wherein E6 is independently selected from the same group which defines wherein E1b-3b are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-6 alkyls, C3-12 branched alkyls, C3-8 cycloalkyls, C1-6 substituted alkyls, C3-8 substituted cycloalkyls, aryls, substituted aryls, aralkyls, C1-6 heteroalkyls, substituted C1-6 heteroalkyls, C1-6 alkoxy, phenoxy, C1-6 heteroalkoxy, wherein B2 is a leaving group, OH, a residue of a hydroxyl-containing moiety or a residue of an amine-containing moiety; G is a polymeric residue; Y1-3, Y2a-d and Y3a-d are each independently O, S or NR11a M1-4, M2a-2d, M3a-3d, and M4a-4d are each independently O, S or NR11b; M5 and M5a-d are each independently X or Q, wherein X is an electron withdrawing group and Q is a moiety containing a free electron pair positioned three to six atoms from C(=Y3) or C(=Y3a-d); R1-10, R1a-11a, R1b-11b, R1c-10c and R1d-10d are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-6 alkyls, C3-12 branched alkyls, C3-8 cycloalkyls, C1-6 substituted alkyls, C3-8 substituted cycloalkyls, aryls, substituted aryls, aralkyls, C1-6 heteroalkyls, substituted C1-6 heteroalkyls, C1-6 alkoxy, phenoxy and C1-6 heteroalkoxy; and a, b, c, d1-d6, e1-e6, f1-f6, g1-g6, h1-h6, i1-i6, j1-j6, k1-k6, l1-l6, m1-m6 are each independently zero or a positive integer.
Owner:BELROSE PHARMA
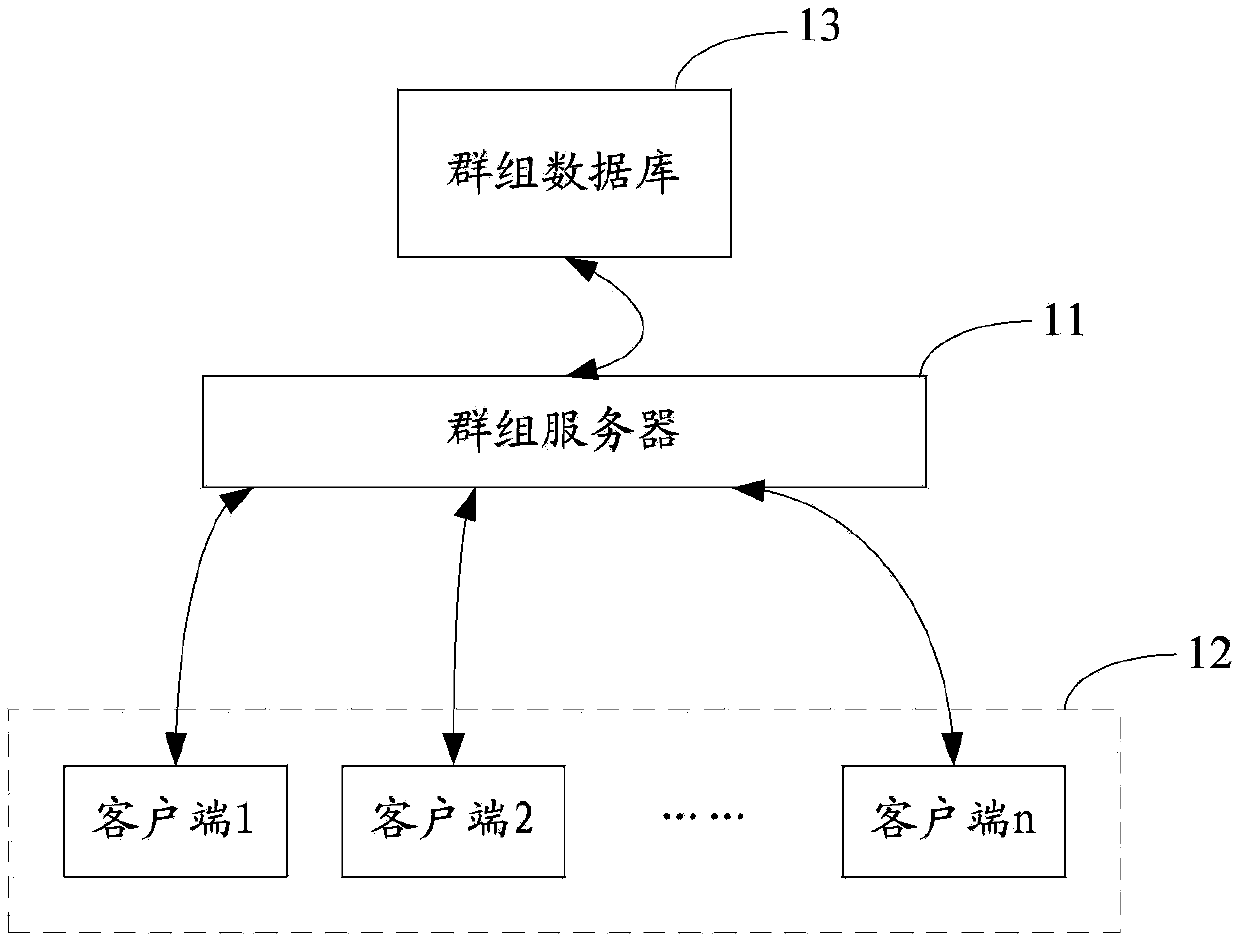
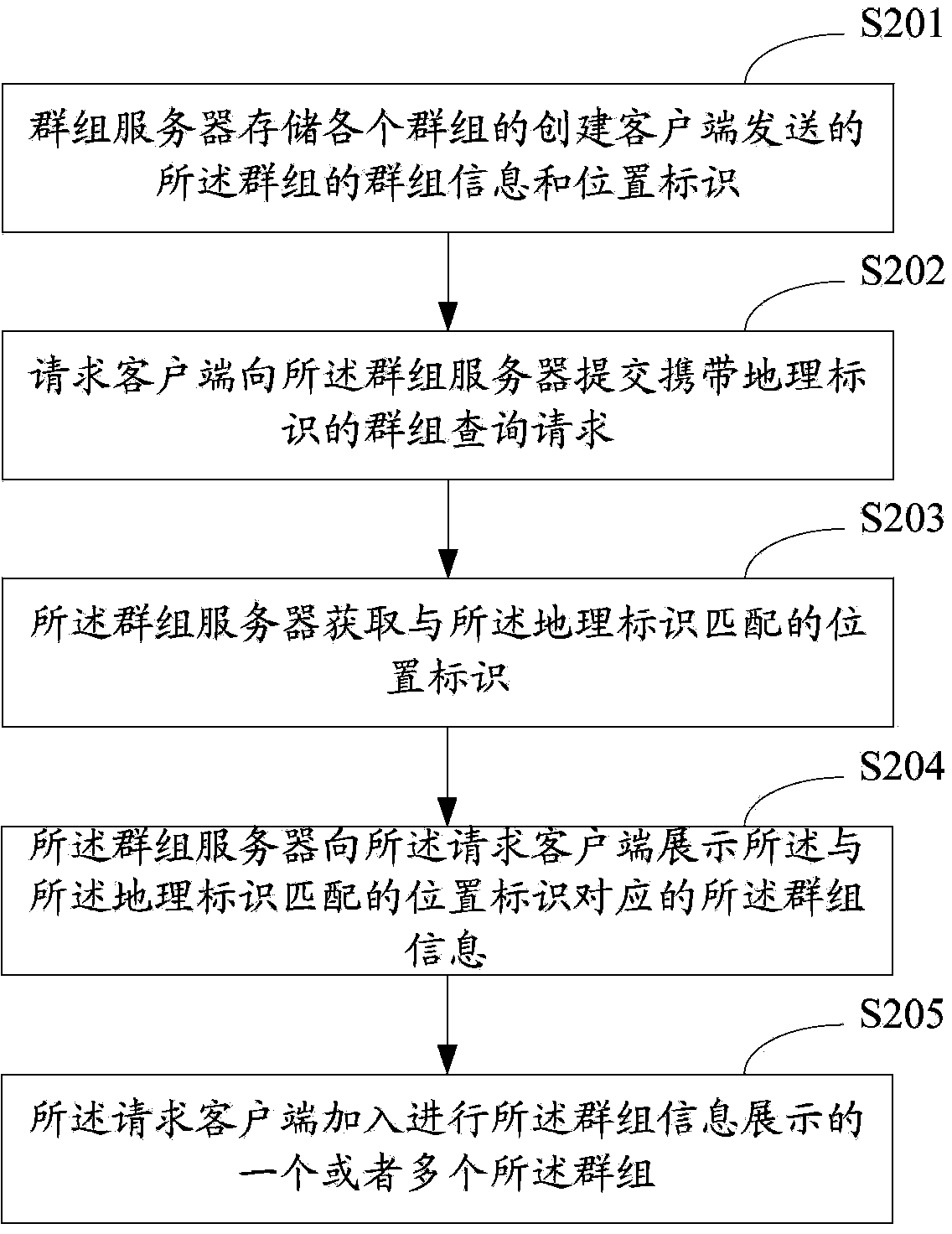
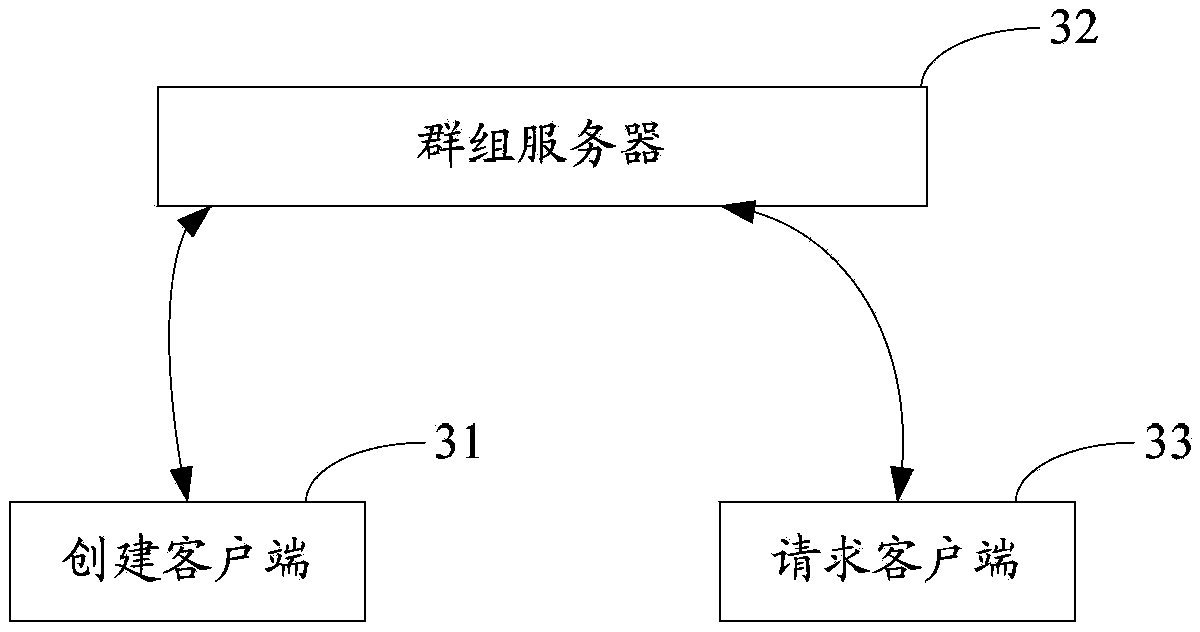
Group joining method and system
PendingCN103873269AGuaranteed continuous activityEnsure sustainable expansionSpecial service provision for substationBroadcast service distributionLeaving groupClient-side
The invention is suitable for the field of network technologies, and provides a group joining method and system. The method includes: a group server stores group information and position identifiers of groups sent by creation client sides of the groups; a client side is requested to submit a group query request carrying geographical identifiers to the group server; the group server obtains position identifiers matched with the geographical identifiers; the group server demonstrates group information corresponding to the position identifiers matched with the geographical identifiers to the requested client side; and the requested client side joins one or more groups demonstrated by the group information. Through the group joining method provided by the invention, expansibility of the groups is not invalid due to the creation client sides of the groups leaving group creation positions, thereby ensuring sustainable expansion of a group relationship chain, and further ensuring continuous degrees of activity of the groups.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
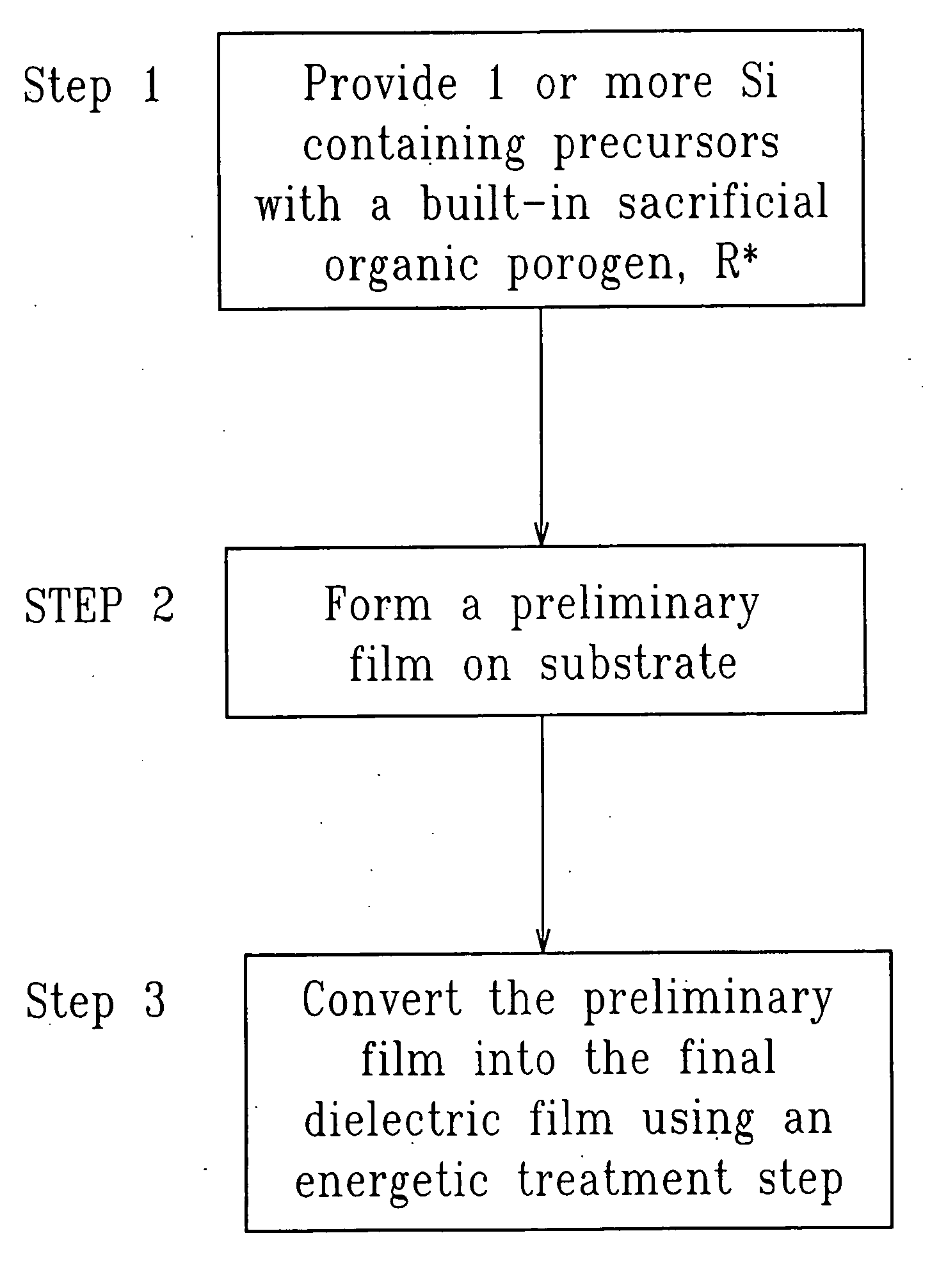
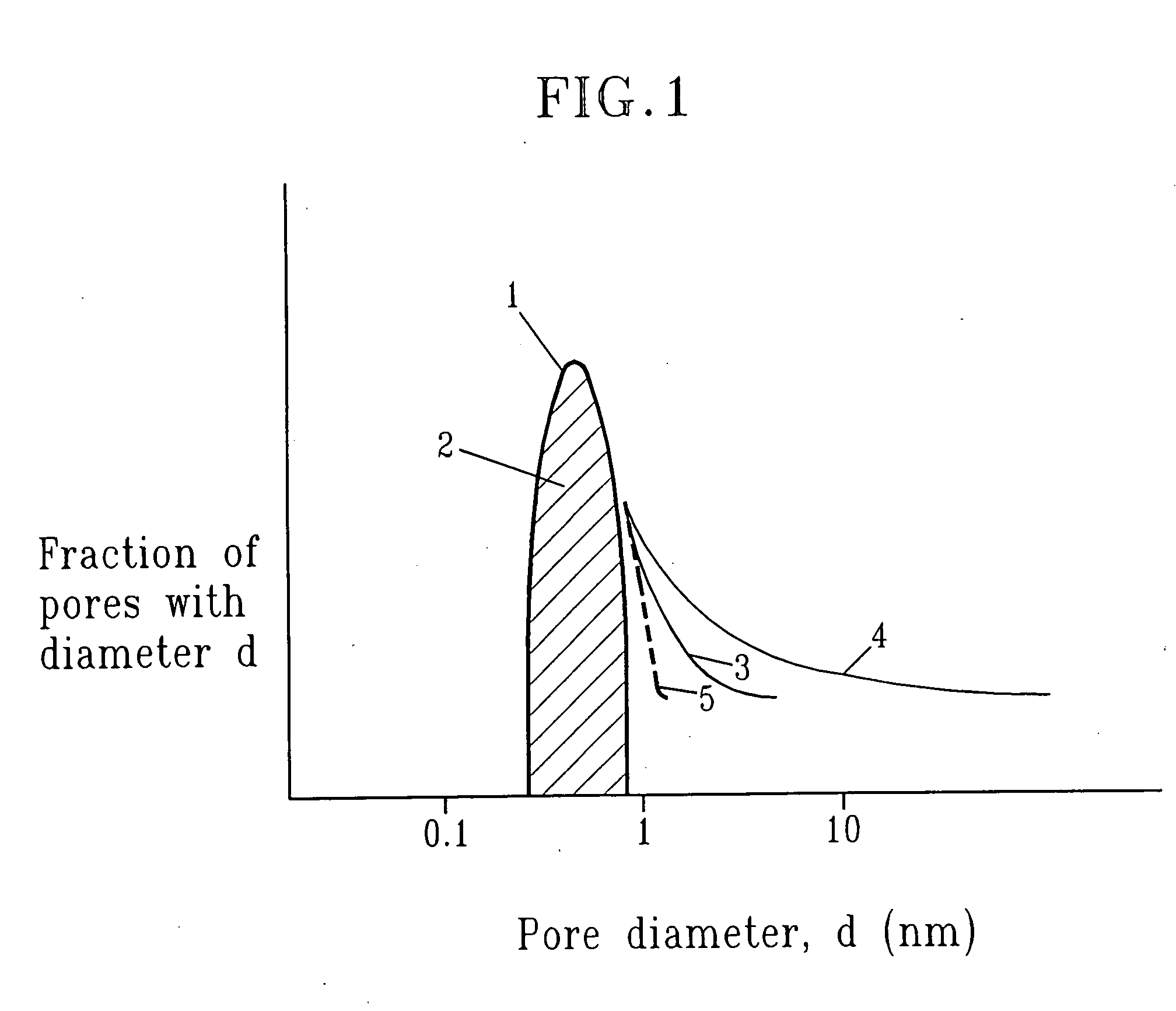
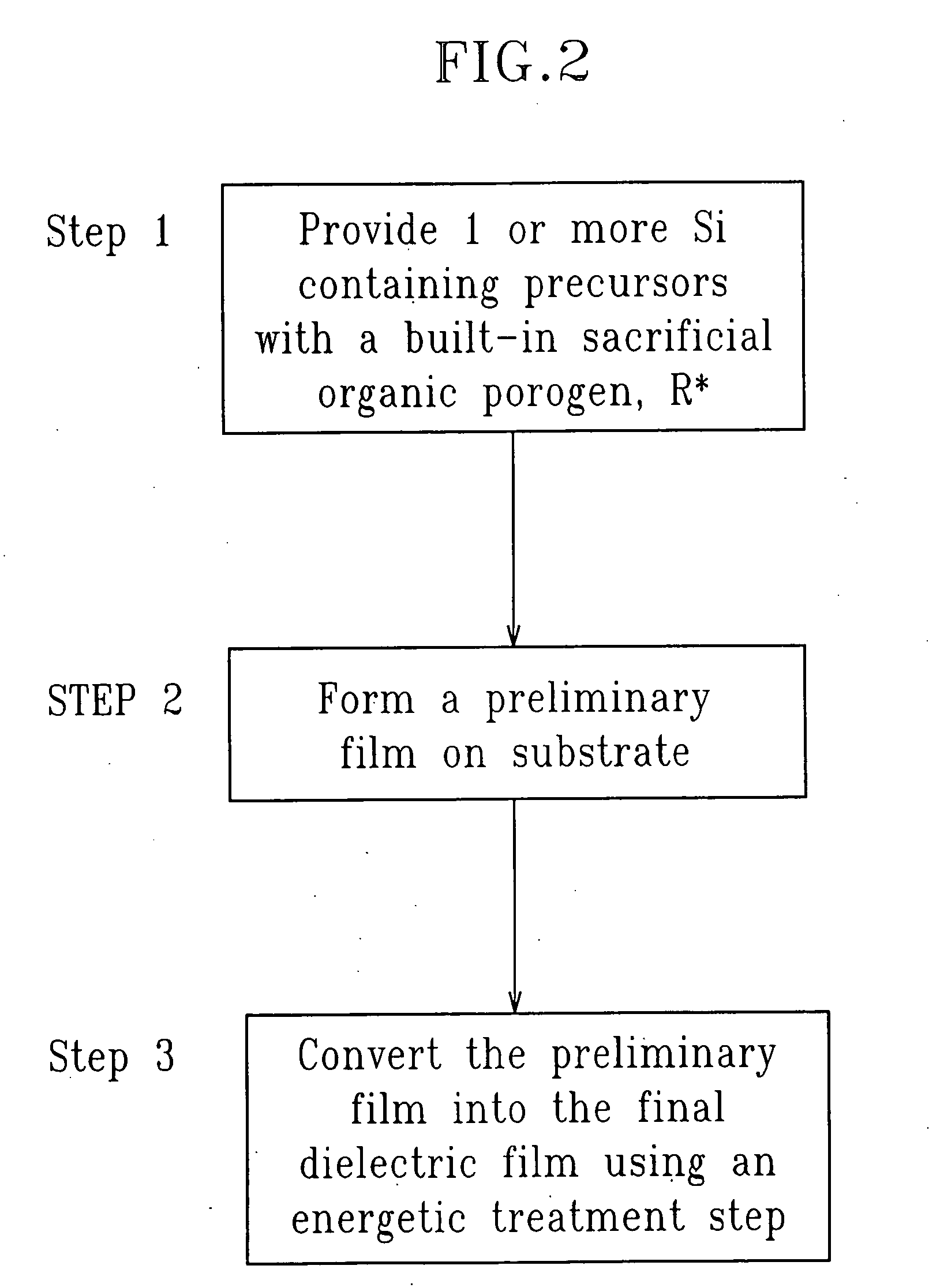
SiCOH film preparation using precursors with built-in porogen functionality
ActiveUS20070161256A1Improve film propertiesEasy to controlLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPorosityLeaving group
A method of fabricating a dielectric material that has an ultra low dielectric constant (or ultra low k) using at least one organosilicon precursor is described. The organosilicon precursor employed in the present invention includes a molecule containing both an Si—O structure and a sacrificial organic group, as a leaving group. The use of an organosilicon precursor containing a molecular scale sacrificial leaving group enables control of the pore size at the nanometer scale, control of the compositional and structural uniformity and simplifies the manufacturing process. Moreover, fabrication of a dielectric film from a single precursor enables better control of the final porosity in the film and a narrower pore size distribution resulting in better mechanical properties at the same value of dielectric constant.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Click chemistry method for synthesizing molecular imaging probes
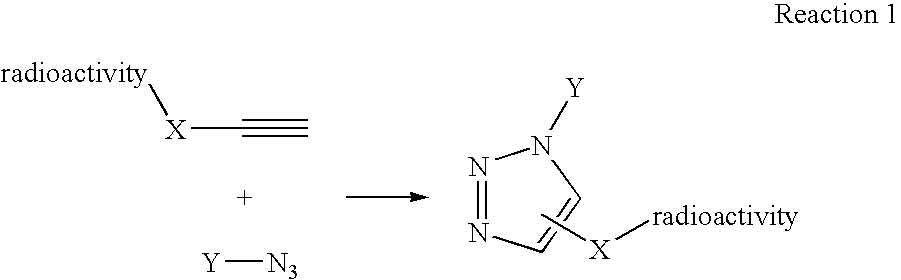
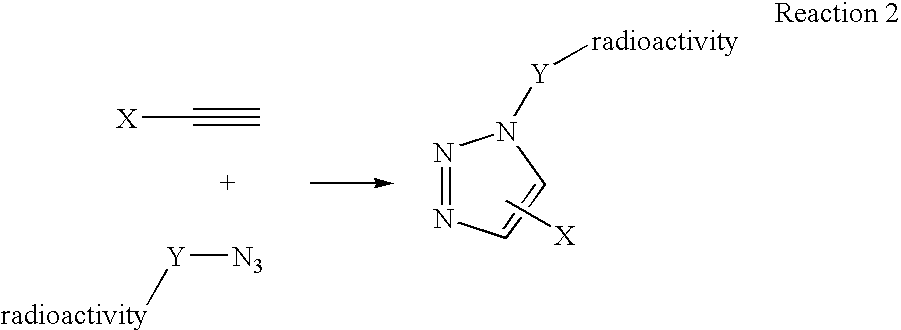
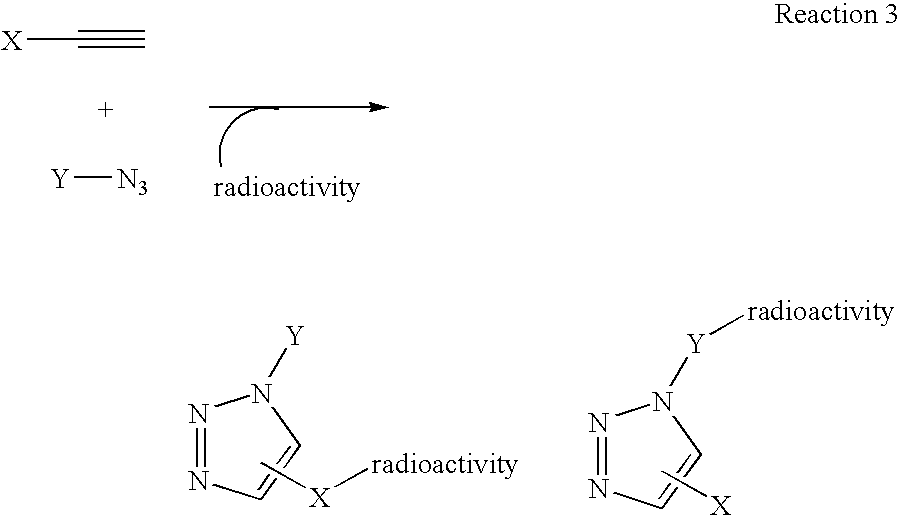
InactiveUS20060263293A1High reaction specificityEfficiently labeledSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLeaving groupChemical reaction
The present disclosure provides a method for preparing a radioactive ligand or radioactive substrate having affinity for a target biomacromolecule, the method comprising: (a) reacting a first compound comprising a first functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction, with a radioactive reagent under conditions sufficient to displace the leaving group with a radioactive component of the radioactive reagent to form a first radioactive compound; (b) providing a second compound comprising a second complementary functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction with the first functional group; (c) reacting the first functional group of the first radioactive compound with the complementary functional group of the second compound via a click chemistry reaction to form the radioactive ligand or substrate; and (d) isolating the radioactive ligand or substrate.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
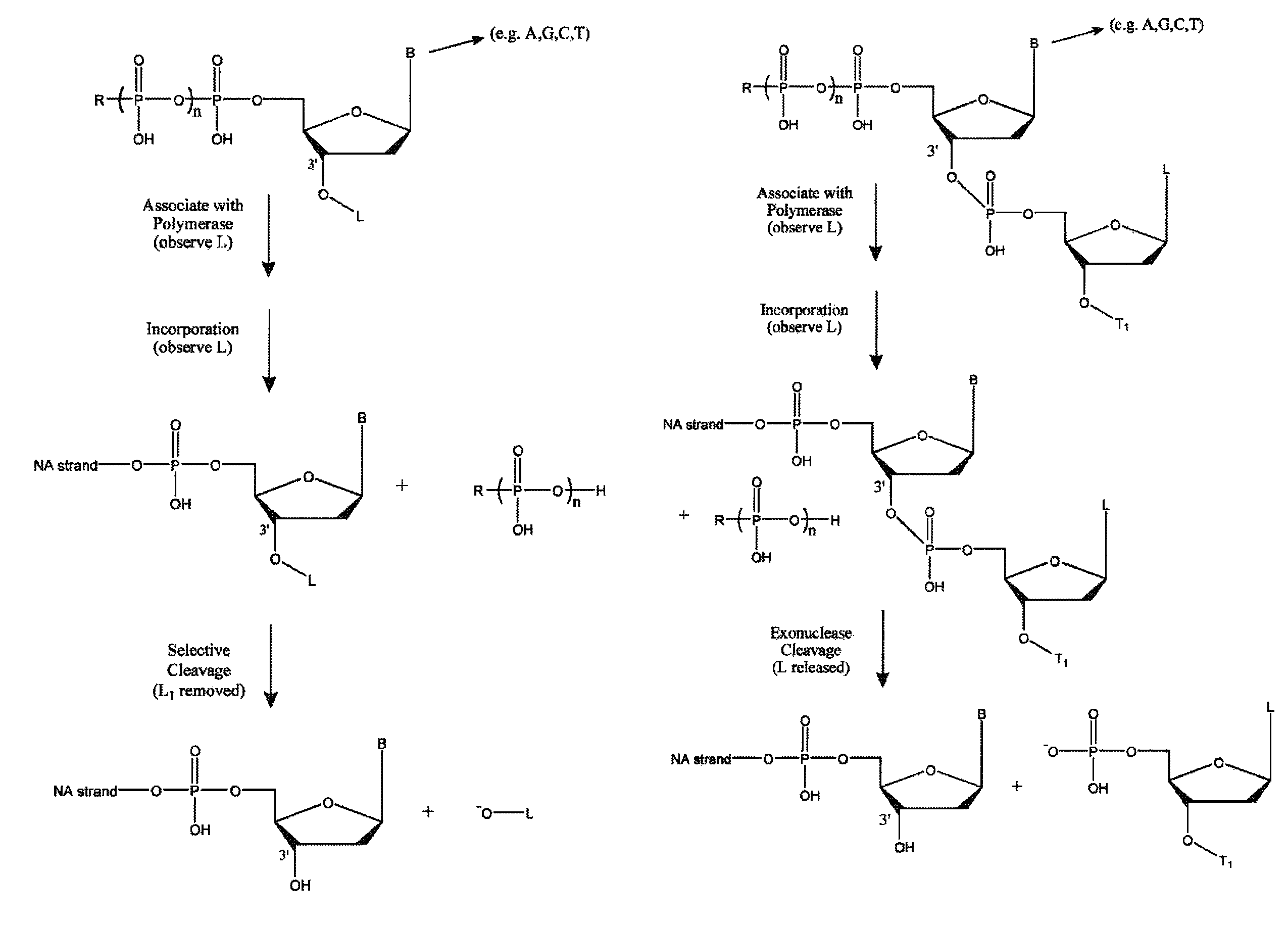
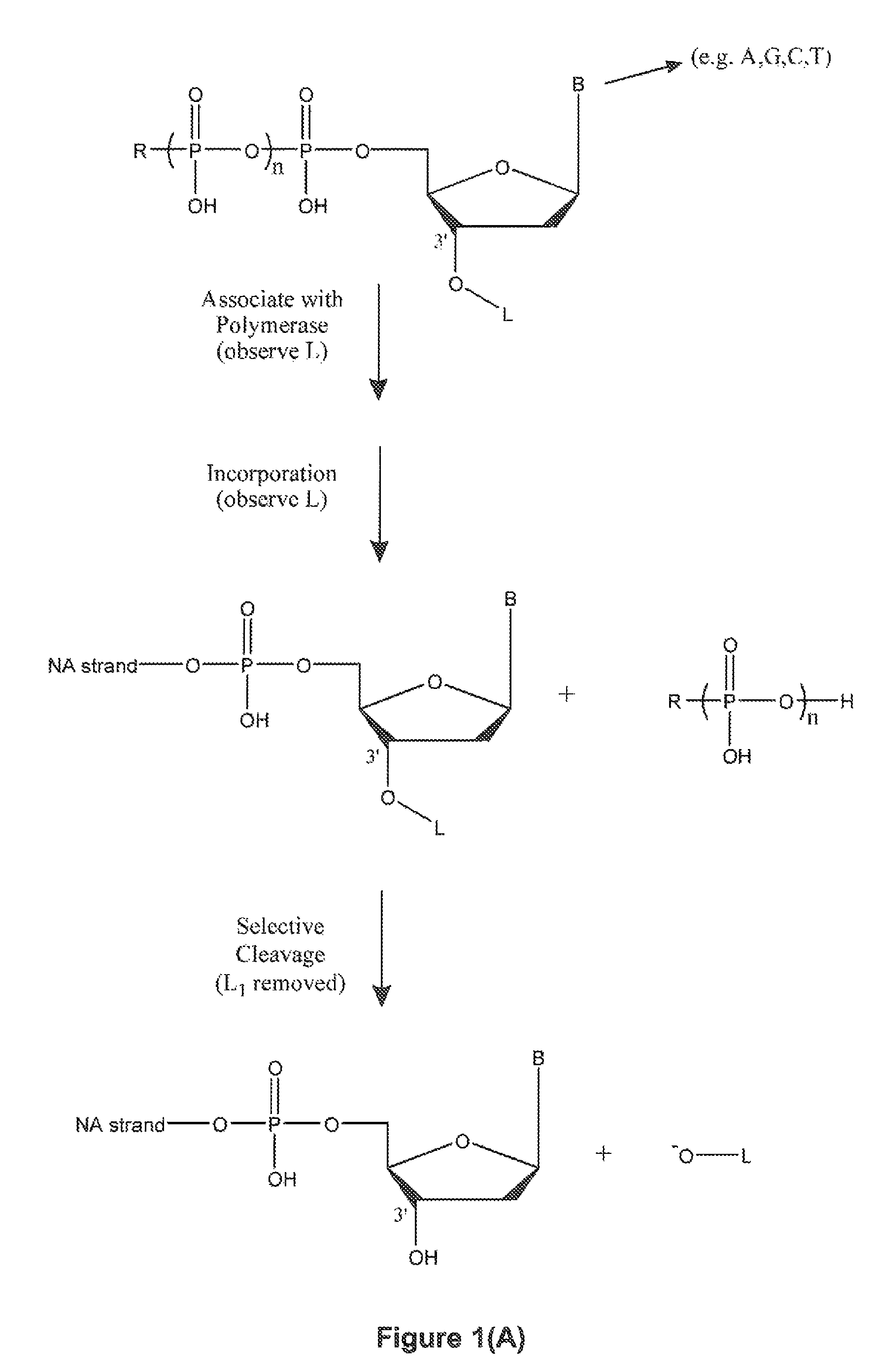
Cross-linking oligonucleotides
Owner:DRUG ROYALTY TRUST 9
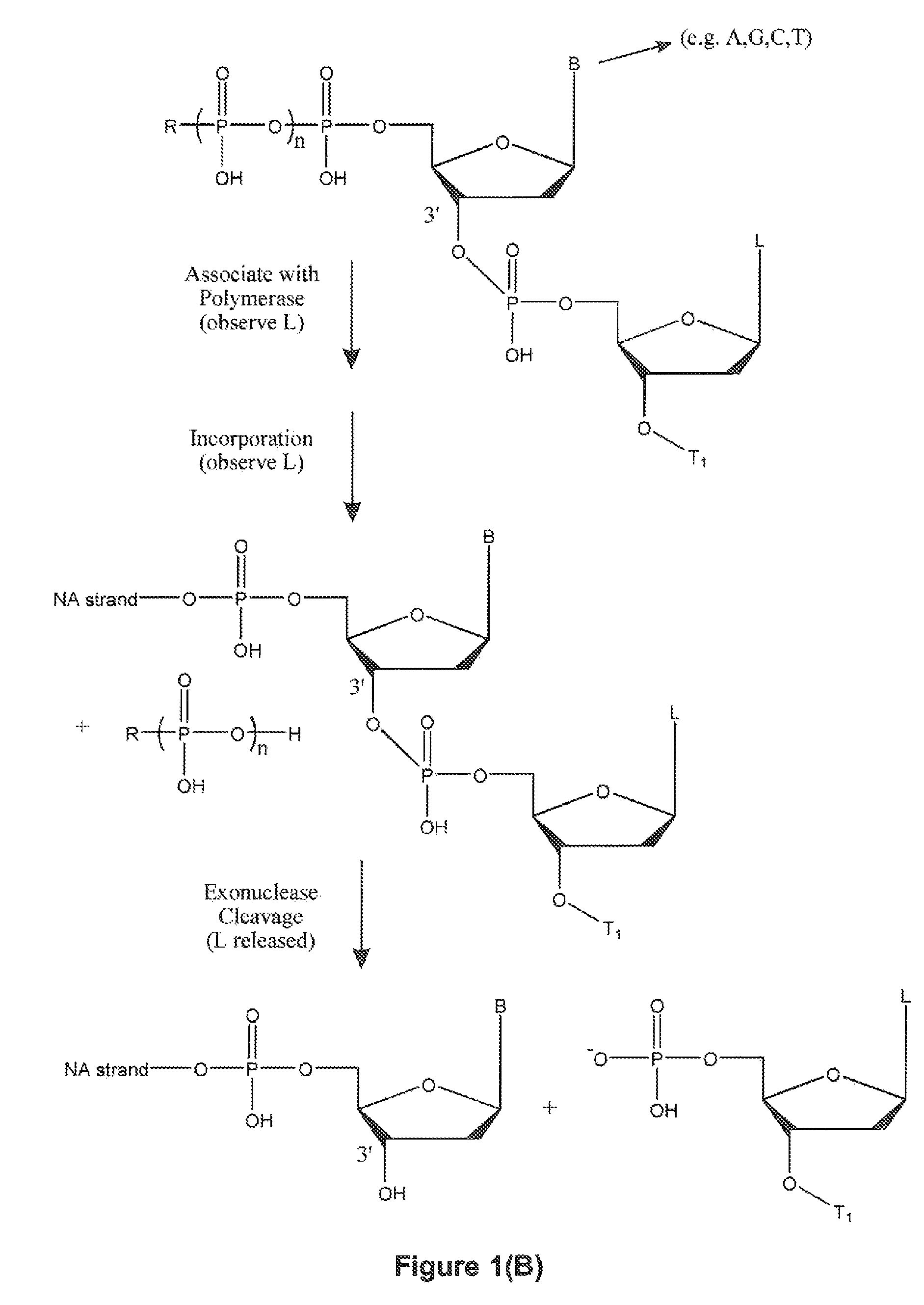
Single molecule sequencing with two distinct chemistry steps
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method for the poduction of cyclic molecules
InactiveUS20070184516A1High yieldImprove reaction speedPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclaseThioester synthesis
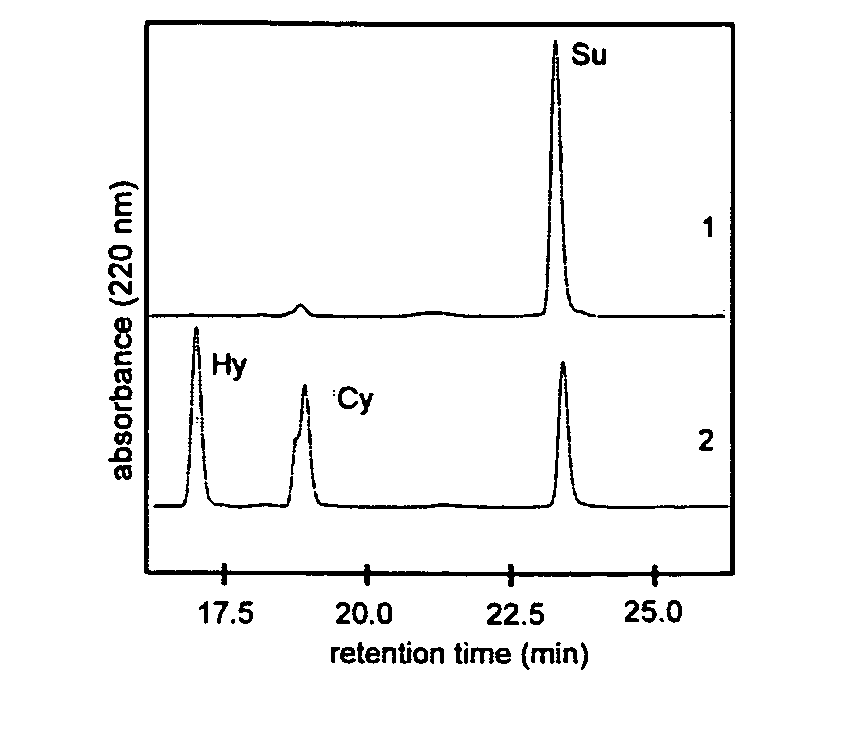
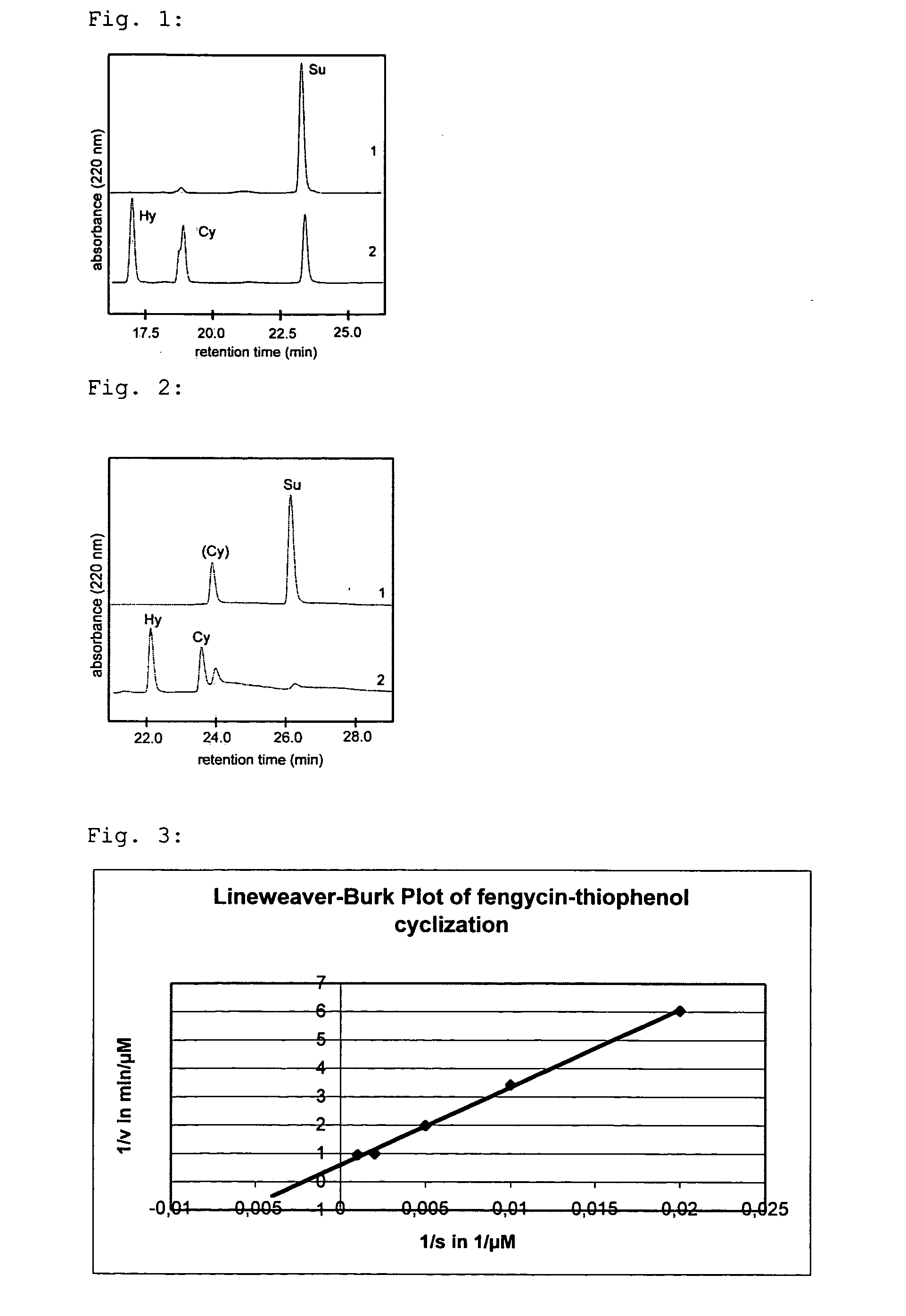
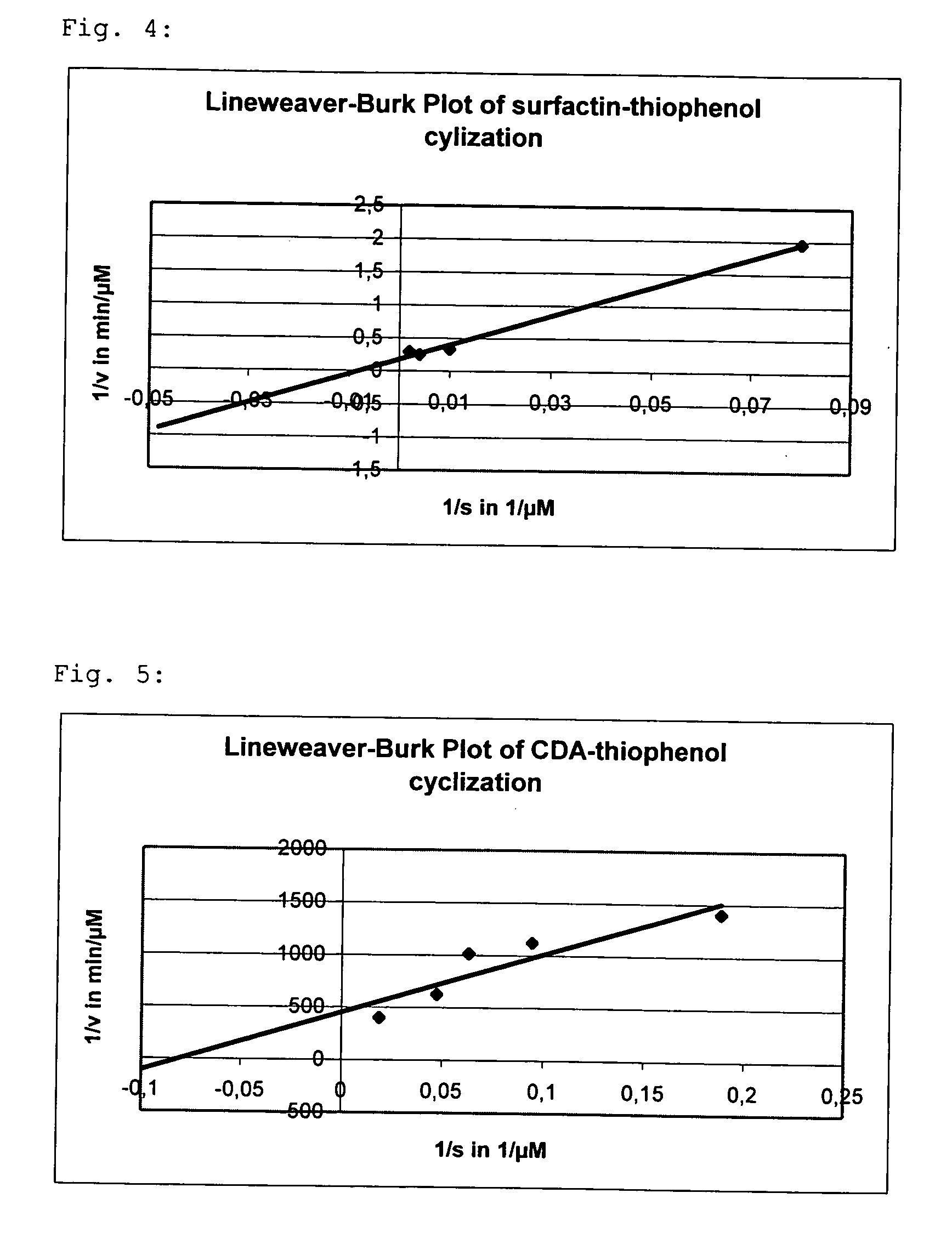
The invention at hand describes a method for the cyclization of peptides and proteins in which linear thioesters serve as substrates. The cyclization is catalyzed by thioesterase domains of NRPS or PKS cyclases. The substrates according to the present invention are composed of one linear peptide on which a charge-stabilized aromatic, heteroaromatic or araliphatic leaving group is bound. These substrates lead to higher yields and reaction rates than linear peptides able to be cyclized with methods known so far and, furthermore, allow the cyclization of such peptides which were previously not able to be cyclized.
Owner:ZYRUS BET GMBH & CO PATENTE I KG
Detection of chemical ligation using fluorescence quenching leaving groups
InactiveUS20040259102A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical ligationLeaving group
Novel compounds having a fluorescence quencher as a leaving group are disclosed. Nucleic acids and other molecules containing a fluorophore and a fluorescence quencher are disclosed as an embodiment of this invention. The use of the oligonucleotides in enzyme-free oligonucleotide ligation reactions results in an increase in fluorescence when the oligonucleotide also contains a nearby fluorophore. The ligation reactions can be performed in solution, on surfaces, or in cells.
Owner:SANDFORD UNIV +1
Synthetic process for trans-aminocyclohexyl ether compounds
InactiveUS20050038256A1Organic compound preparationHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsLeaving groupAcyl group
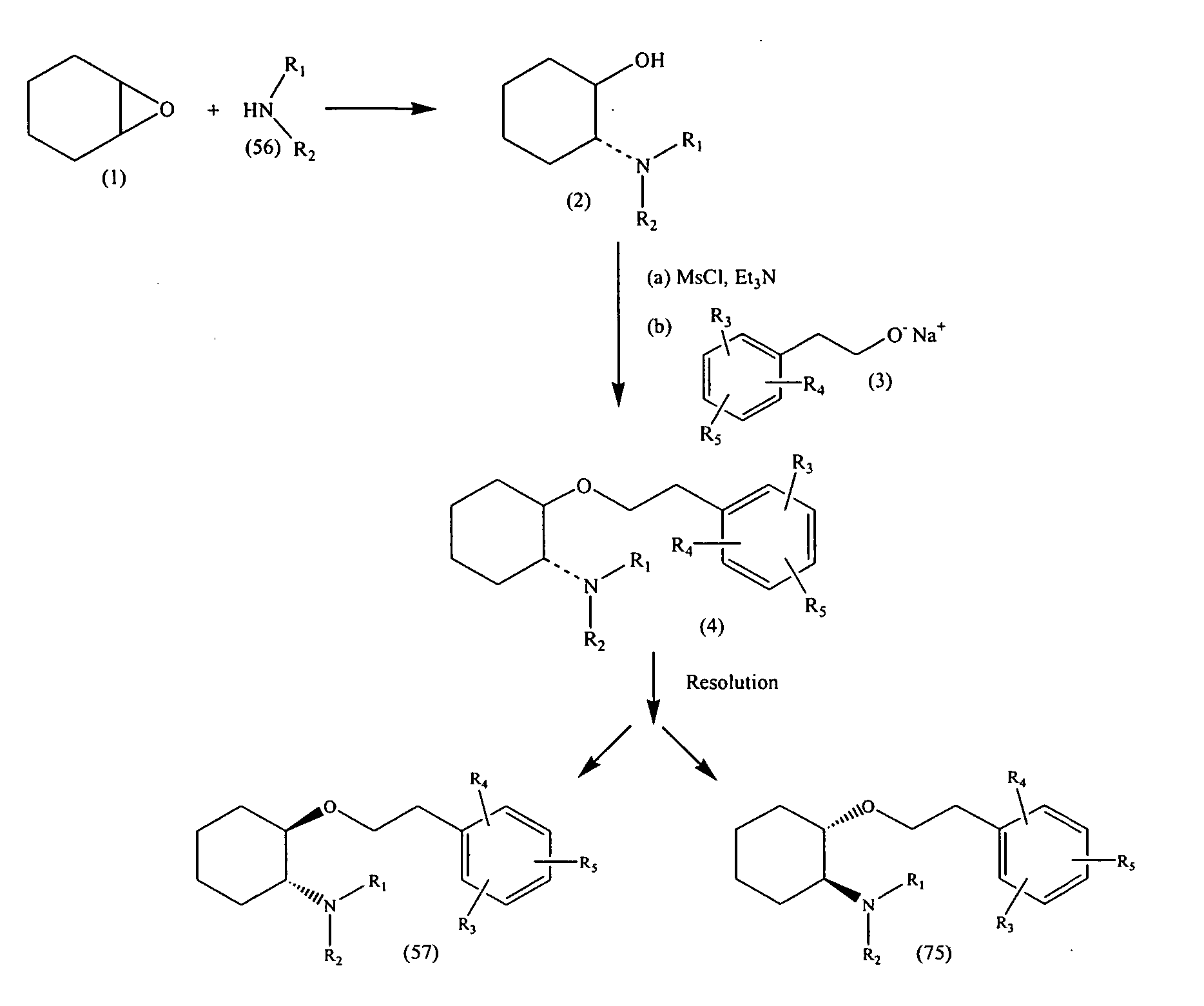
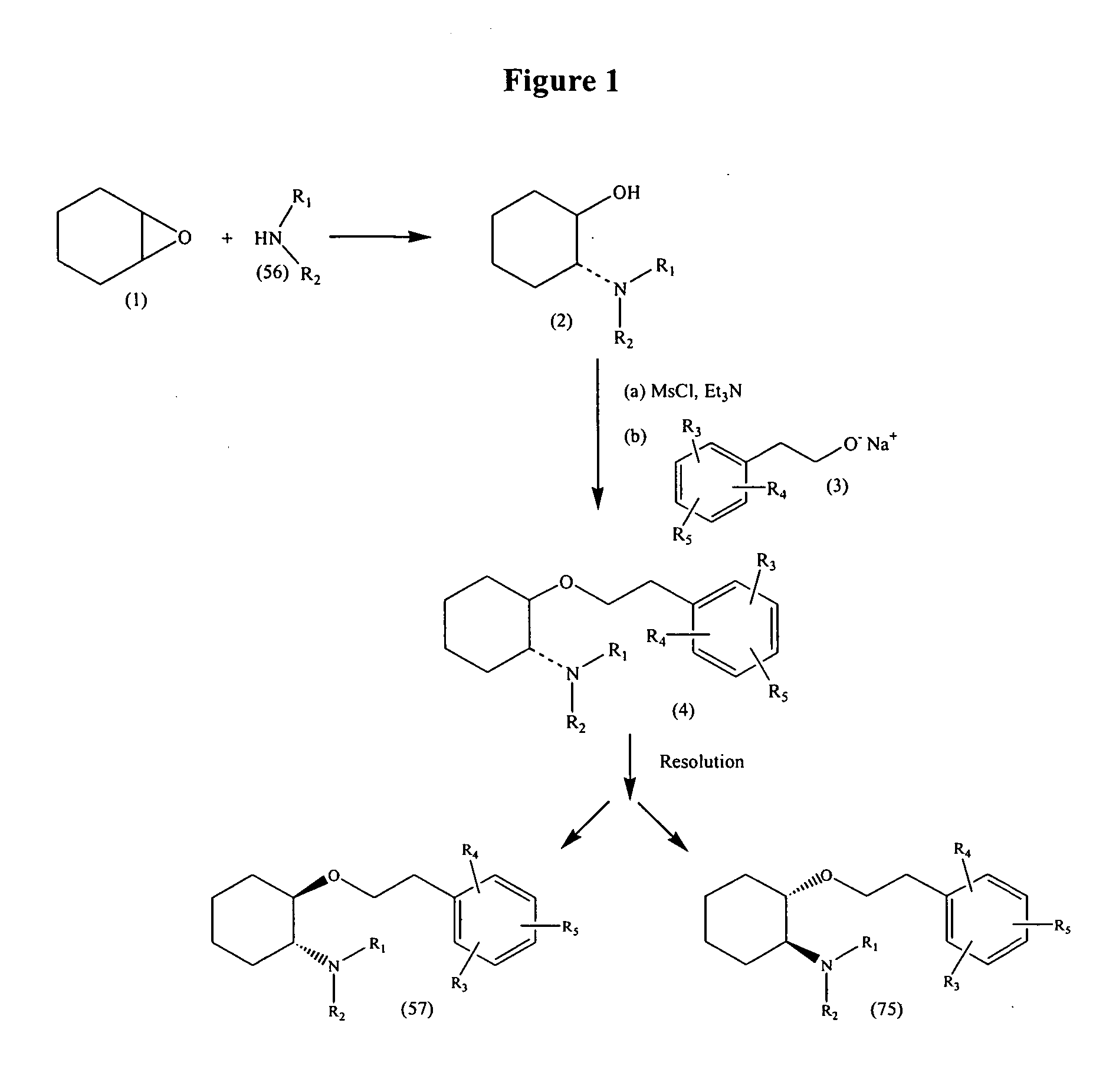
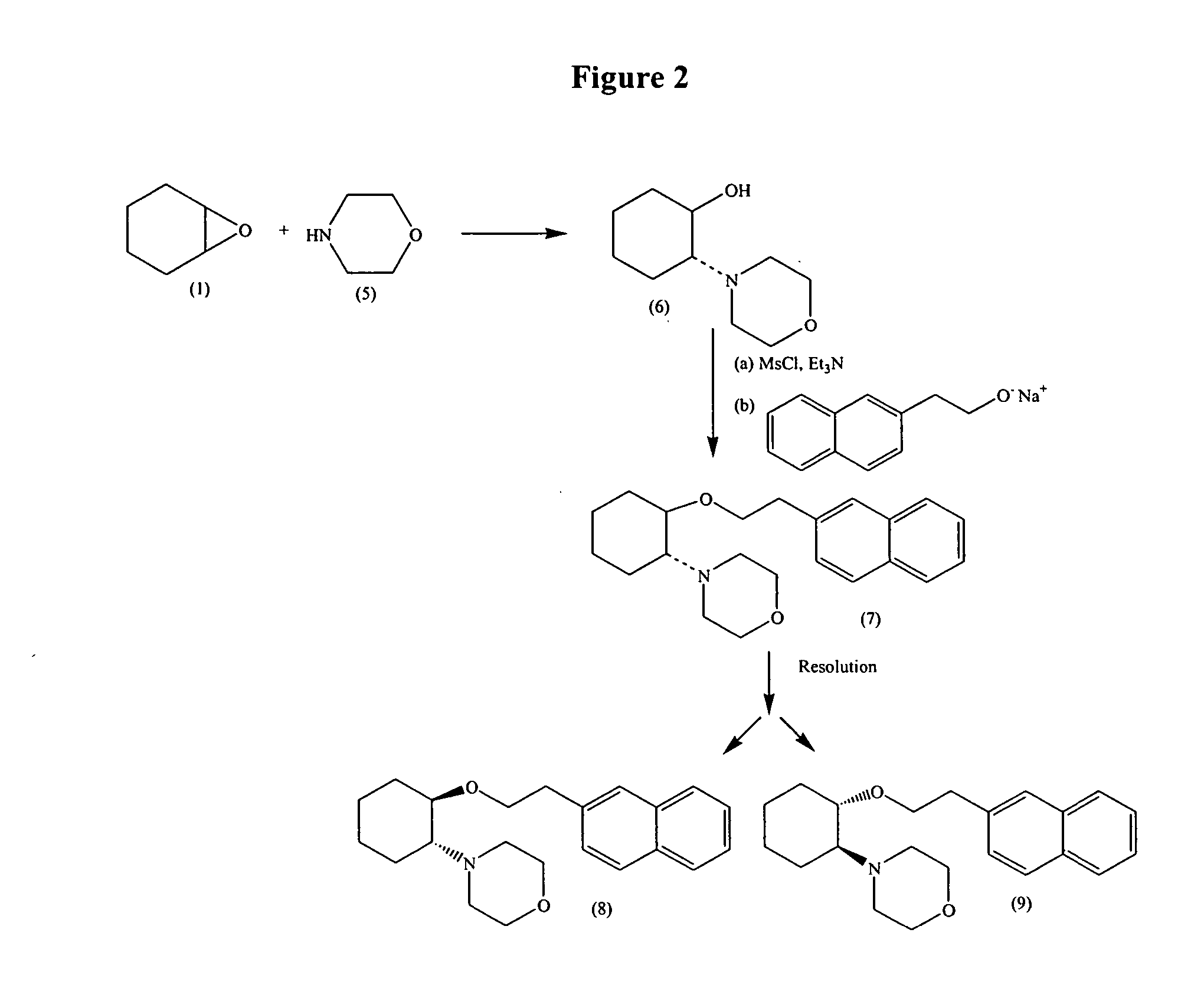
A method of stereoselectively making an aminocyclohexyl ether comprises, for example, reacting to form the aminocyclohexyl ether having the formula respectively, wherein independently at each occurrence, R1 and R2 are independently hydrogen, C1-C8alkyl, C3-C8alkoxyalkyl, C1-C8hydroxyalkyl, or C7-C12aralkyl; or R1 and R2 are independently C3-C8alkoxyalkyl, C1-C8hydroxyalkyl, and C7-C12aralkyl; or R1 and R2, when taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are directly attached in formula (57) or (75), form a ring denoted by formula (I): wherein the ring of formula (I) is formed from the nitrogen as shown as well as three to nine additional ring atoms independently carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur; where any two adjacent ring atoms may be joined together by single or double bonds, and where any one or more of the additional carbon ring atoms may be substituted with one or two substituents selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxy, C1-C3hydroxyalkyl, oxo, C2-C4acyl, C1-C3alkyl, C2-C4alkylcarboxy, C1-C3alkoxy, and C1-C20alkanoyloxy, or may be substituted to form a spiro five- or six-membered heterocyclic ring containing one or two oxygen and / or sulfur heteroatoms; or any two adjacent additional carbon ring atoms may be fused to a C3-C8carbocyclic ring, and any one or more of the additional nitrogen ring atoms may be substituted with substituents selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C6alkyl, C2-C4acyl, C2-C4hydroxyalkyl and C3-C8alkoxyalkyl; or R1 and R2, when taken together with the nitrogen atom to which they are directly attached in formula (I), may form a bicyclic ring system selected from the group consisting of 3-azabicyclo[3.2.2]nonan-3-yl, 2-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl, 3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-3-yl, and 3-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptan-3-yl; and wherein R3, R4 and R5 are independently bromine, chlorine, fluorine, carboxy, hydrogen, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, methanesulfonamido, nitro, cyano, sulfamyl, trifluoromethyl, C2-C7alkanoyloxy, C1-C6alkyl, C1-C6alkoxy, C2-C7alkoxycarbonyl, C1-C6thioalkyl, aryl or N(R6,R7) where R6 and R7 are independently hydrogen, acetyl, methanesulfonyl or C1-C6alkyl; or R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen, hydroxy or C1-C6alkoxy; with the proviso that R3, R4 and R5 cannot all be hydrogen; and wherein O-J is a leaving group. Methods of making intermediates are also disclosed.
Owner:CARDIOME PHARMA CORP
Method of preparing derivatives of polyarylene vinylene and method of preparing an electronic device including same
InactiveUS20050159581A1High yieldHigh molecular weightSolid-state devicesDomestic articlesPolymer scienceLeaving group
A technique is described for the preparation of polymers according to a process in which the starting compound of formula (I) is polymerized in the presence of a base in an organic solvent. No end chain controlling agents are required during the polymerisation to obtain soluble precursor polymers. The precursor polymer such obtained comprises structural units of the formula (II). In a next step, the precursor polymer (II) is subjected to a conversion reaction towards a soluble or insoluble conjugated polymer by thermal treatment. The arylene or heteroarylene polymer comprises structural units of the formula III. In this process the dithiocarbamate group acts as a leaving group and permits the formation of a precursor polymer of structural formula (II), which has an average molecular weight from 5000 to 1000000 Dalton and is soluble in common organic solvents. The precursor polymer with structural units of formula (II) is thermally converted to the conjugated polymer with structural formula (III).
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Caspase inhibitors and uses thereof
InactiveUS7053057B2Enhanced inhibitory effectGood effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAryl
This invention provides caspase inhibitors having the formula:wherein Ring A is an optionally substituted piperidine, tetrahydroquinoline or tetrahydroisoquinoline ring; R1 is hydrogen, CHN2, R, or —CH2Y; R is an optionally substituted group selected from an aliphatic group, an aryl group, an aralkyl group, a heterocyclic group, or an heterocyclylalkyl group; Y is an electronegative leaving group; R2 is CO2H, CH2CO2H, or esters, amides or isosteres thereof; Ar is an optionally substituted aryl group; and R3 is hydrogen, an optionally substituted C1-6 alkyl, F2, CN, aryl or R3 is attached to Ar to form an unsaturated or partially saturated five or six membered fused ring having 0–2 heteroatoms. The compounds are useful for treating caspase-mediated diseases in mammals.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
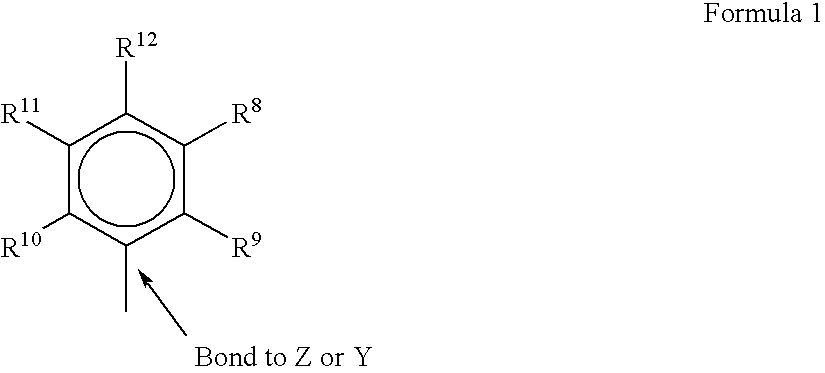
![11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines 11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/dfe0bdc2-9bfe-4984-a8af-93415b268a91/US07741319-20100622-C00001.png)
![11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines 11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/dfe0bdc2-9bfe-4984-a8af-93415b268a91/US07741319-20100622-C00002.png)
![11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines 11-hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/dfe0bdc2-9bfe-4984-a8af-93415b268a91/US07741319-20100622-C00003.png)
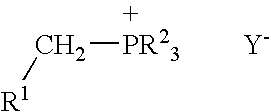


![11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines 11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a5abc81f-2574-4753-bd1c-679d59be3015/US20070173497A1-20070726-C00001.png)
![11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines 11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a5abc81f-2574-4753-bd1c-679d59be3015/US20070173497A1-20070726-C00002.png)
![11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines 11-Hydroxy-5h-pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4] benzodiazepin-5-one derivatives as key intermediates for the preparation of c2 substituted pyrrolobenzodiazepines](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a5abc81f-2574-4753-bd1c-679d59be3015/US20070173497A1-20070726-C00003.png)