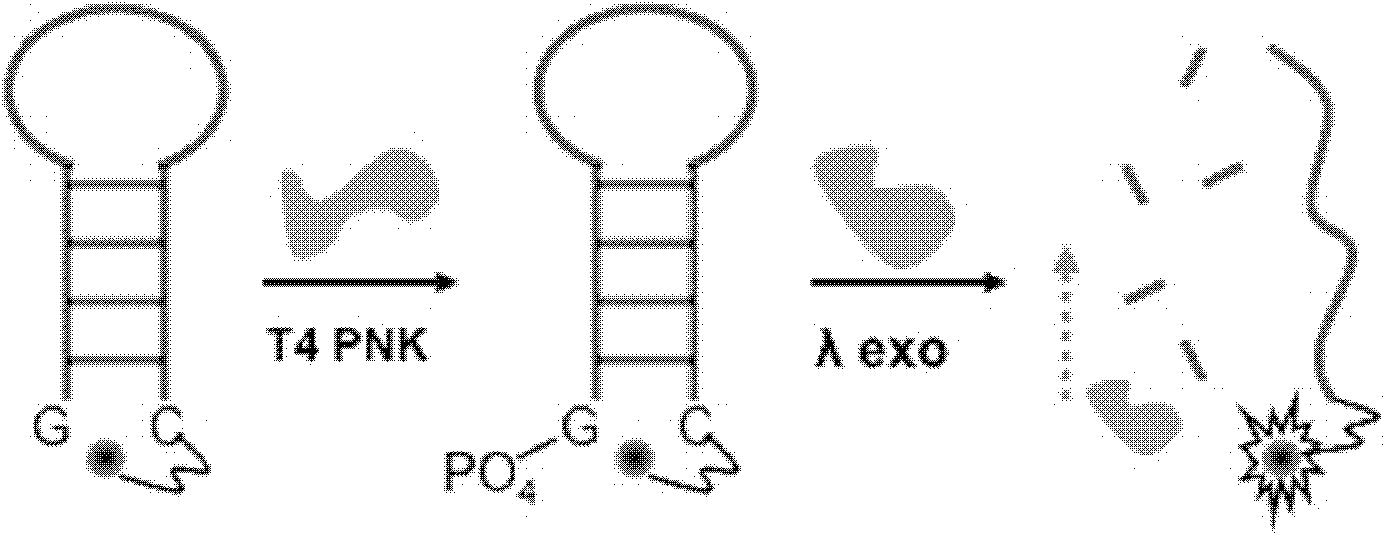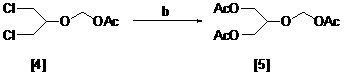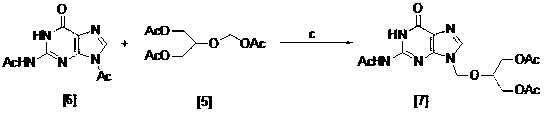Patents
Literature
570 results about "Guanine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Guanine (/ˈɡwɑːnɪn/; or G, Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine.
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20080113351A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
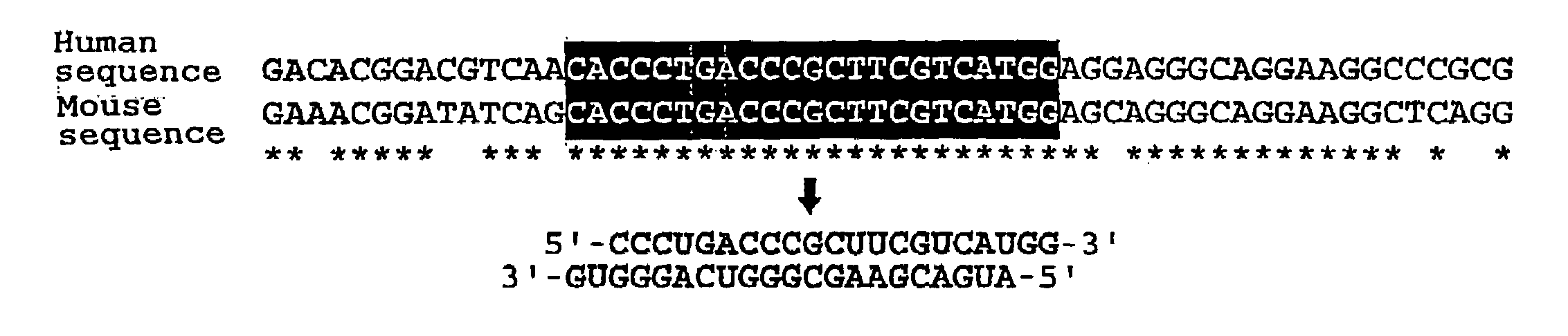
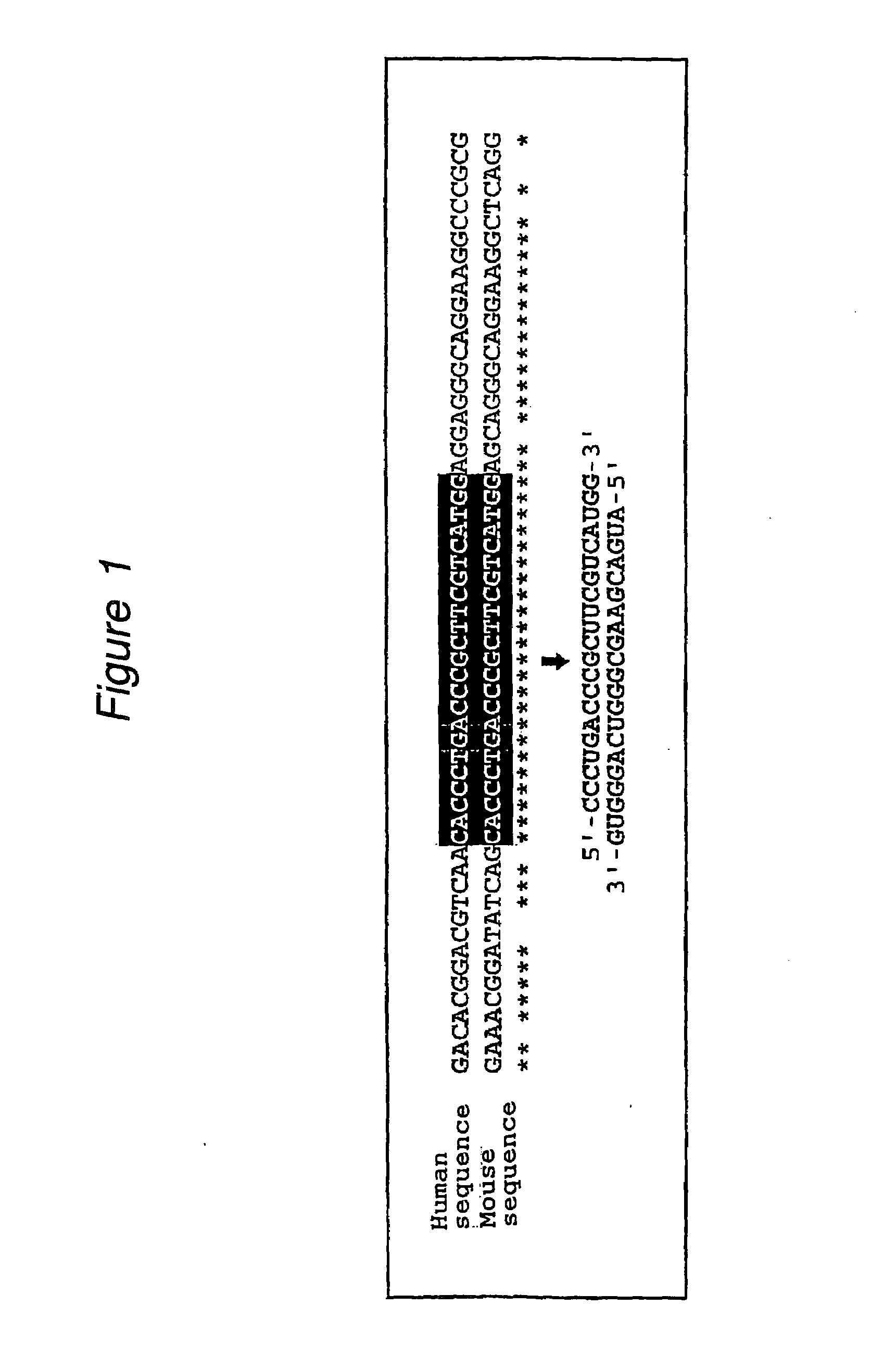
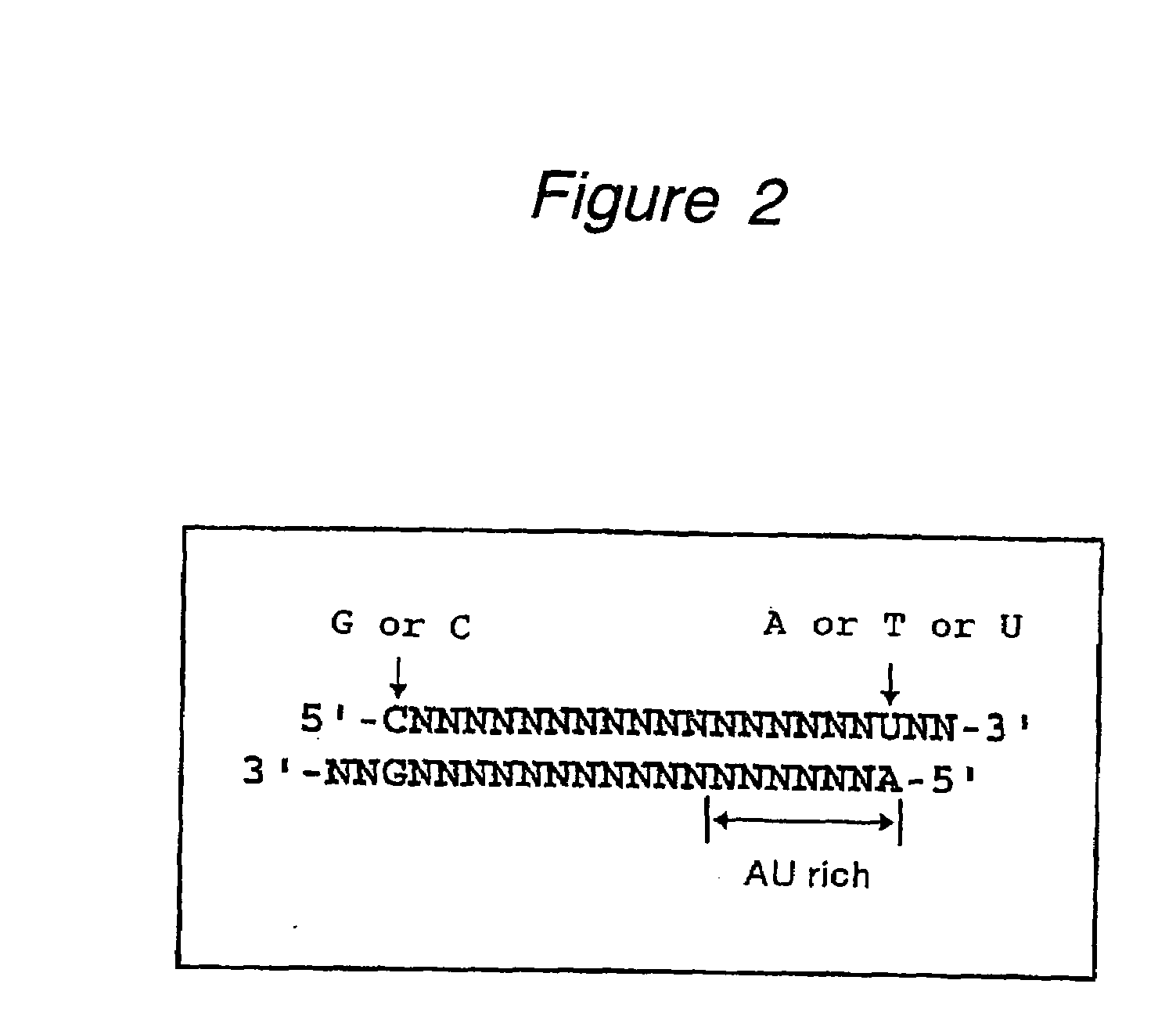
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:ALPHAGEN
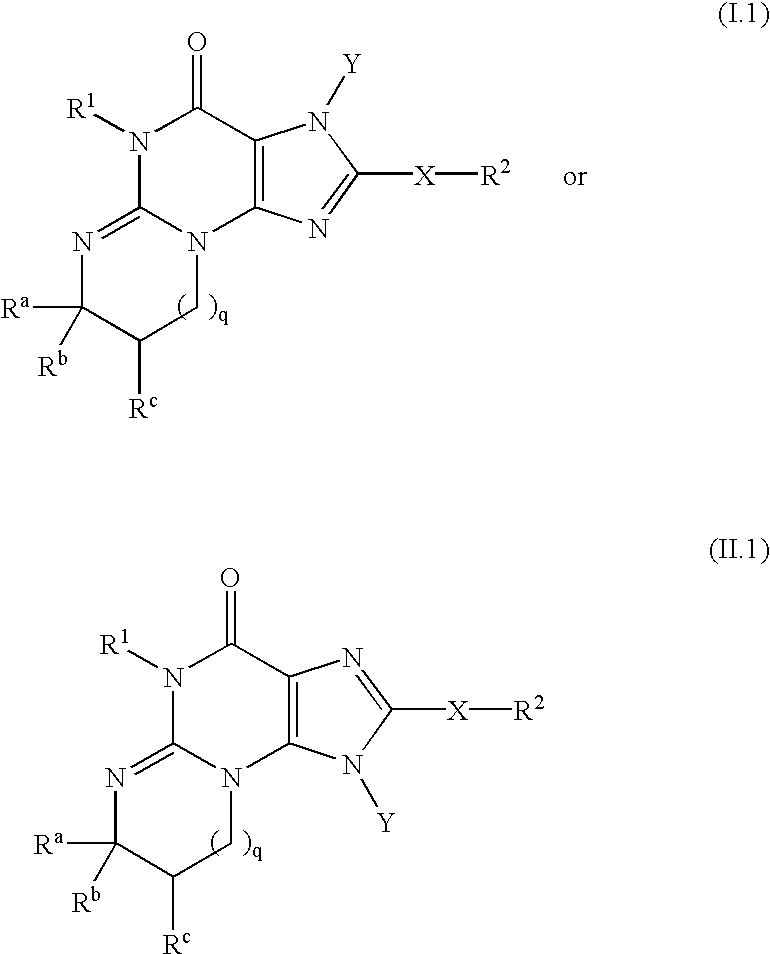
Substituted nucleosides, preparation thereof and use as inhibitors of RNA viral polymerases
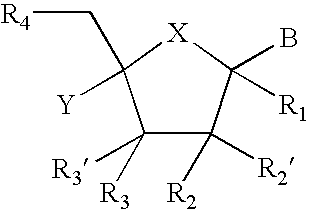
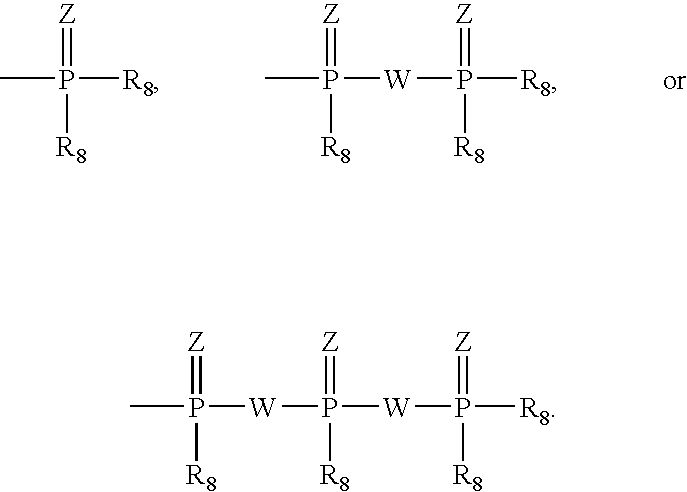
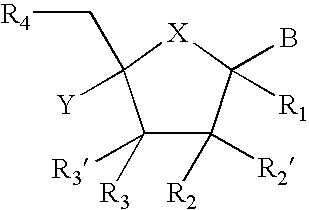
Provided are compounds represented by: X is O, S or NR6, R1 is H or (CH2)mR5, R2, R2', R3 and R3' are independently NO2, N3 or (CH2)mR5, OH R4 is H, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)nR7, R5 is H, halo, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)mR7, R6 and R6a are individually H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, aryl or substituted aryl, R7 is: R8 is H, F, SR9 or OR9, R9 is H, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl or hydroxyprotecting group, Y is H, CH3 or (CH2)mR5, Z is O or S W is CH2, CF2, CHF or O, m is 0-4, B is adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, thymine, modified purines and pyrimidines substituted pyridines, five membered heterocycles substituted by at least one of amines, substituted amines, amides, substituted amides, esters, halogens, alkyls, ethers; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and prodrugs thereof. These ring systems may be substituted.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Modified nucleosides and nucleotides and uses thereof
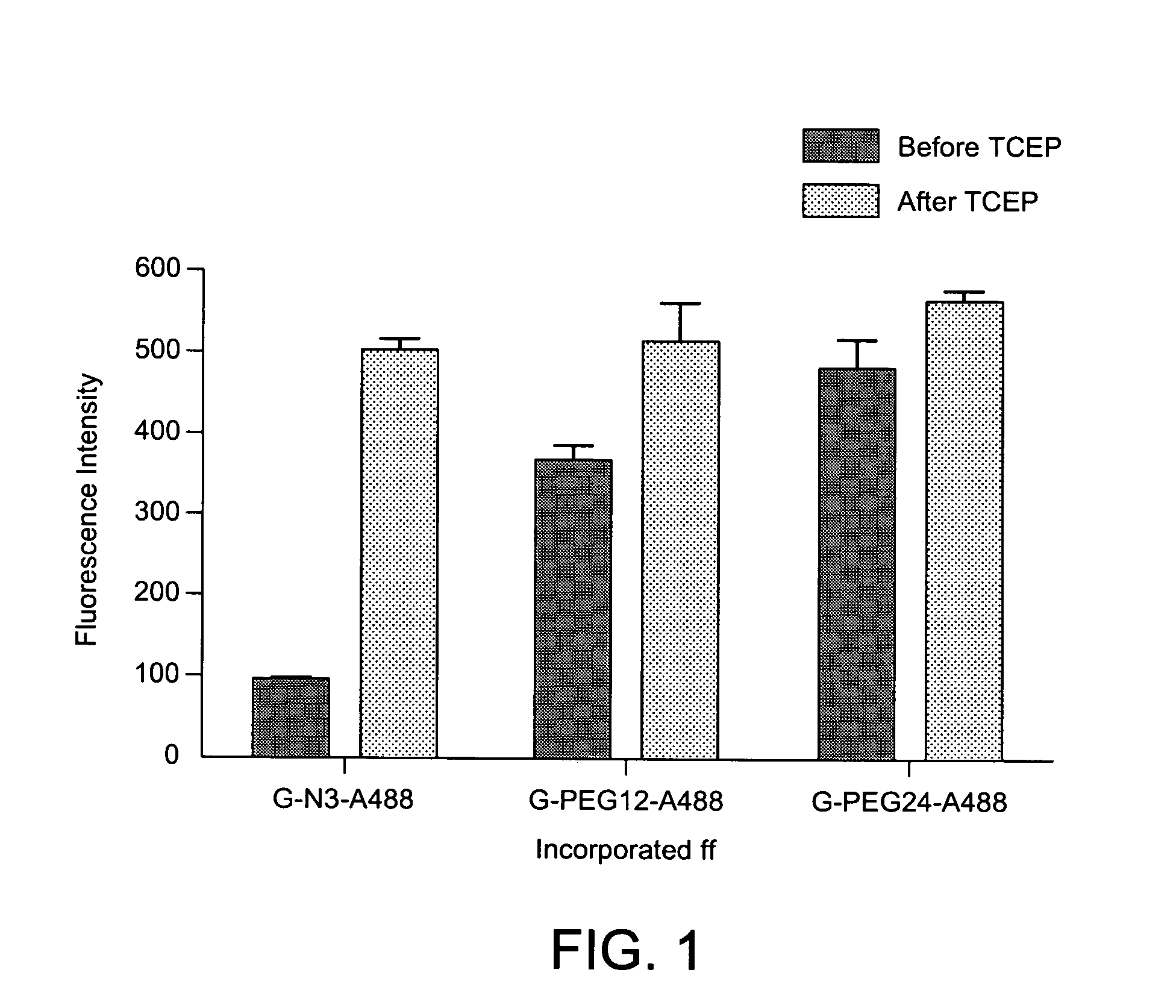
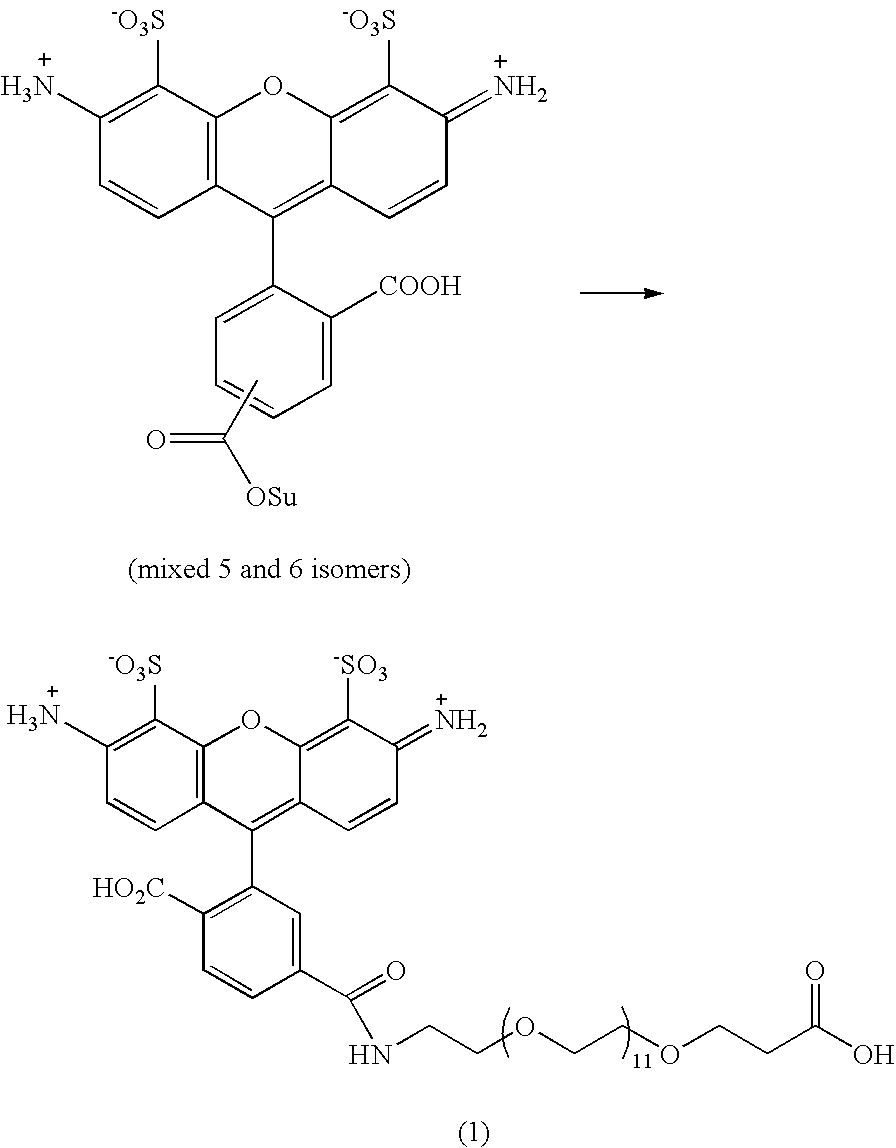
ActiveUS7592435B2Increase brightnessHigh fluorescence intensitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePurine
The invention is directed to modified guanine-containing nucleosides and nucleotides and uses thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to modified fluorescently labelled guanine-containing nucleosides and nucleotides which exhibit enhanced fluorophore intensity by virtue of reduced quenching effects.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Oligonucleotides including pyrazolo[3,4-D]pyrimidine bases, bound in double stranded nucleic acids
A triplex forming oligonucleotide is complementary pursuant to the G / T or A / G recognition motif to a homopurine, or substantially homopurine target sequence in double stranded nucleic acids, and at least one and preferably all of the guanine bases are replaced by their pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine analog, namely by 6-amino-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one. The oliginucleotides containing the pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine analog of guanine exhibit a lesser degree of self-association, and lack the nucleophilic nitrogen atom in the 7 position of guanine. The latter feature results in a diminished extent of self-crosslinking in ODNs which also have a covalently attached cross-linking agent.
Owner:EPOCH PHARMA
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20110054005A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:BIO THINKTANK
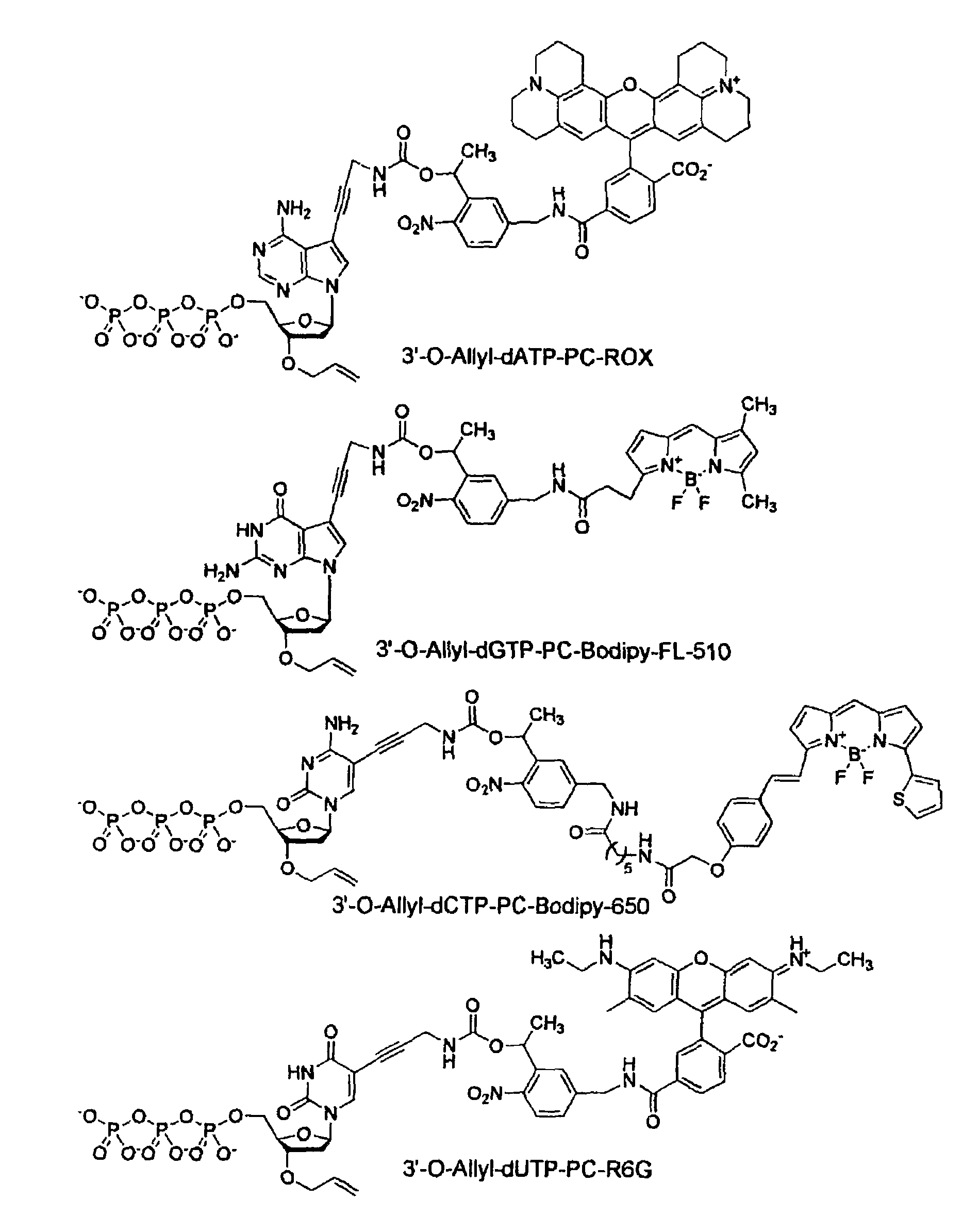
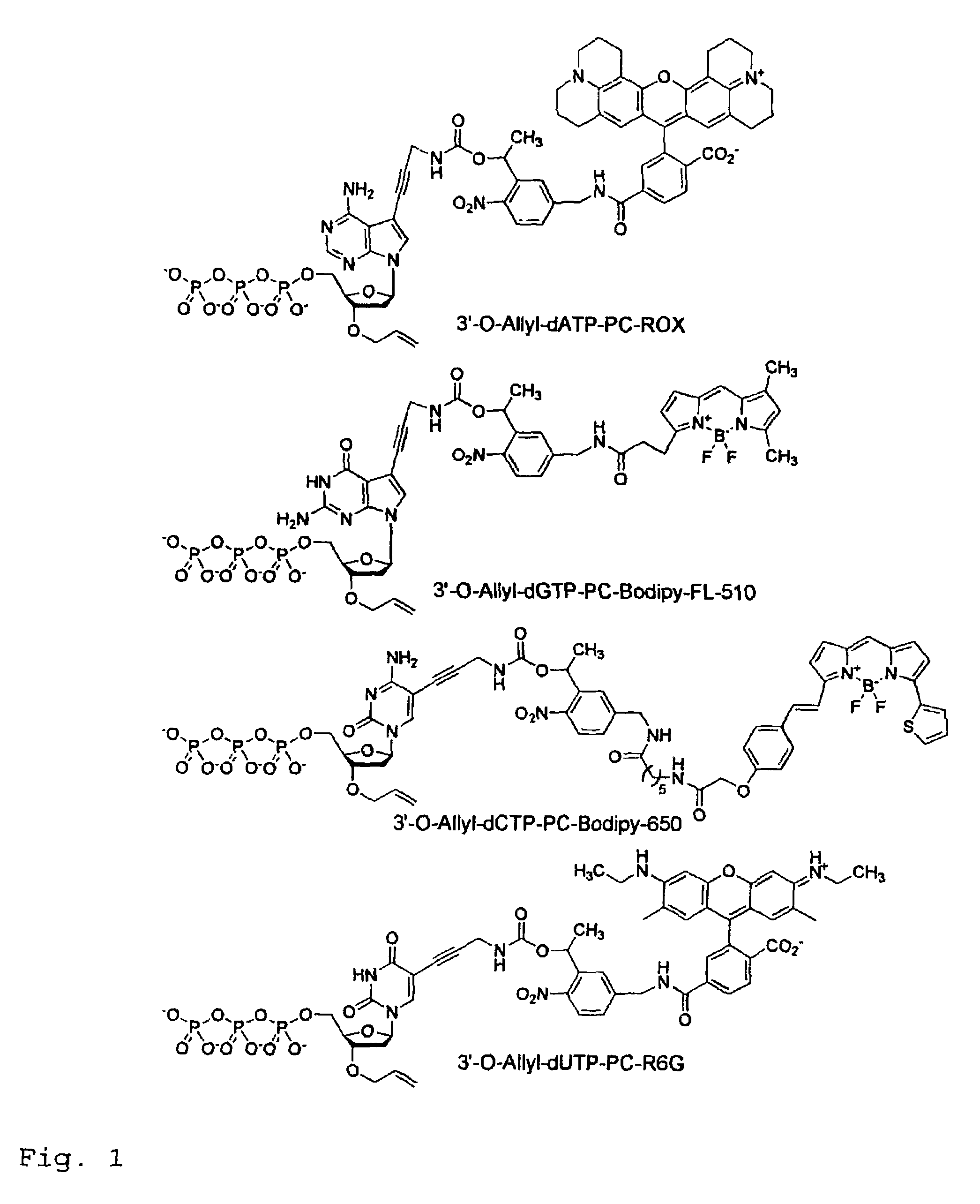
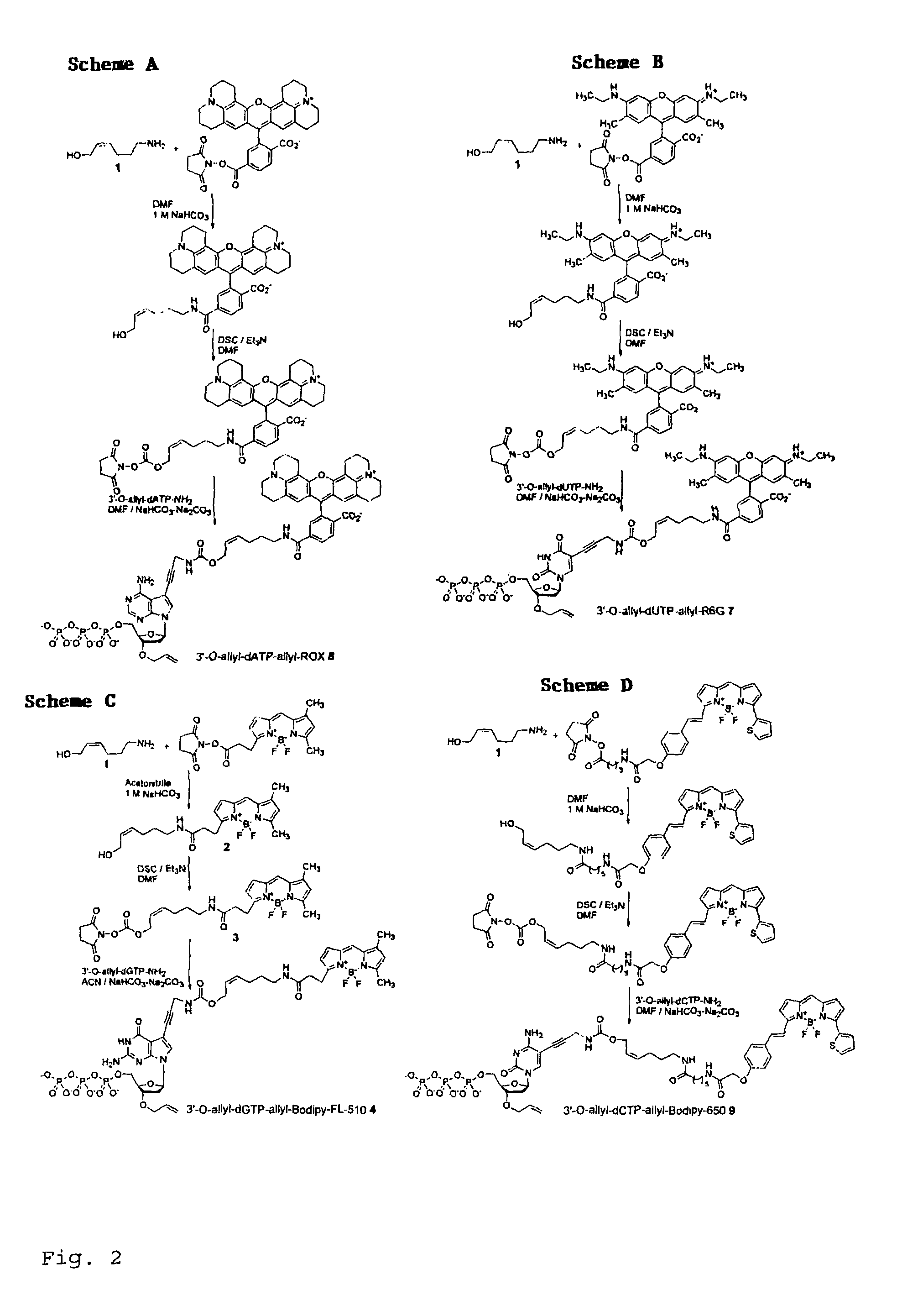
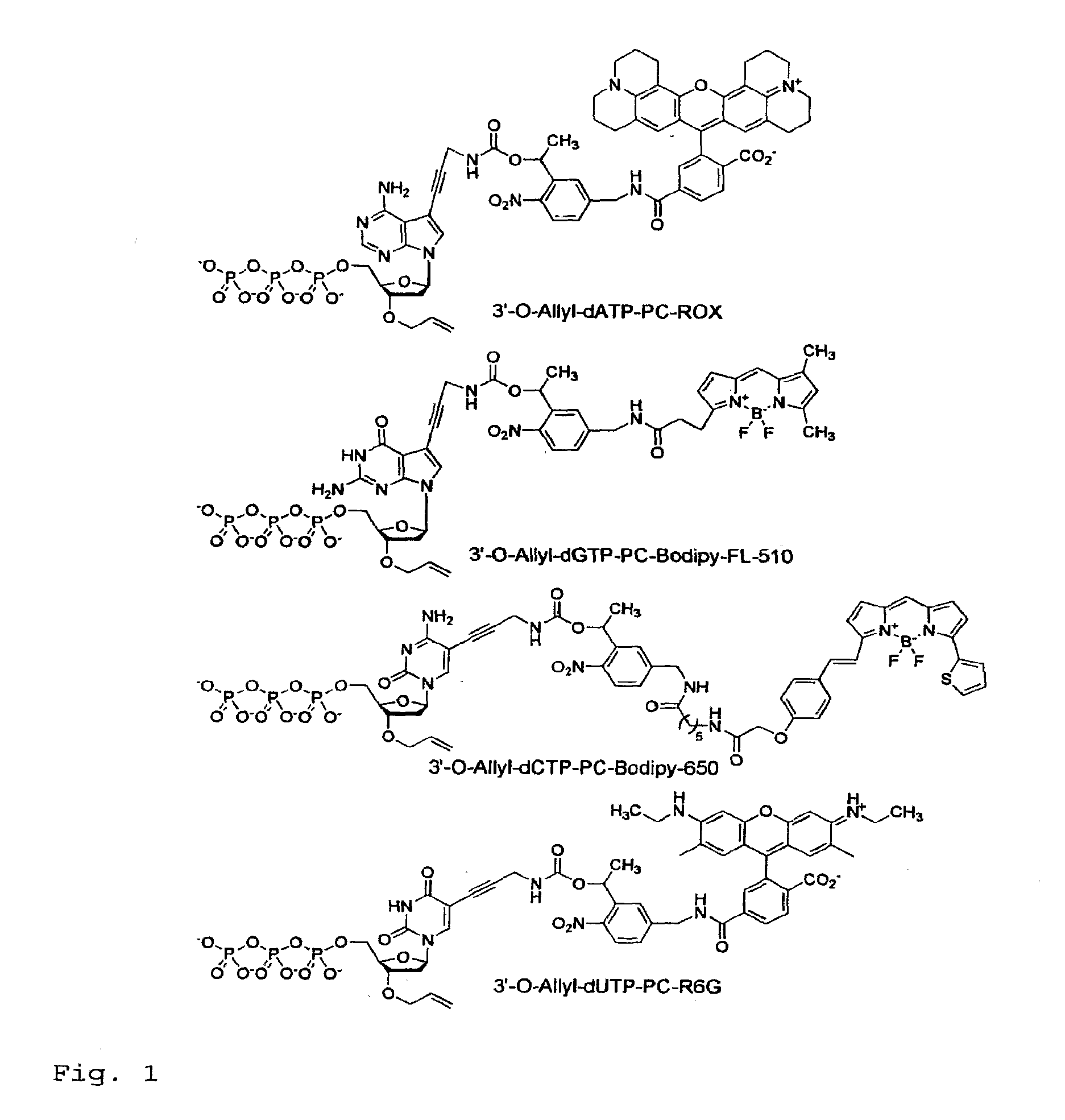
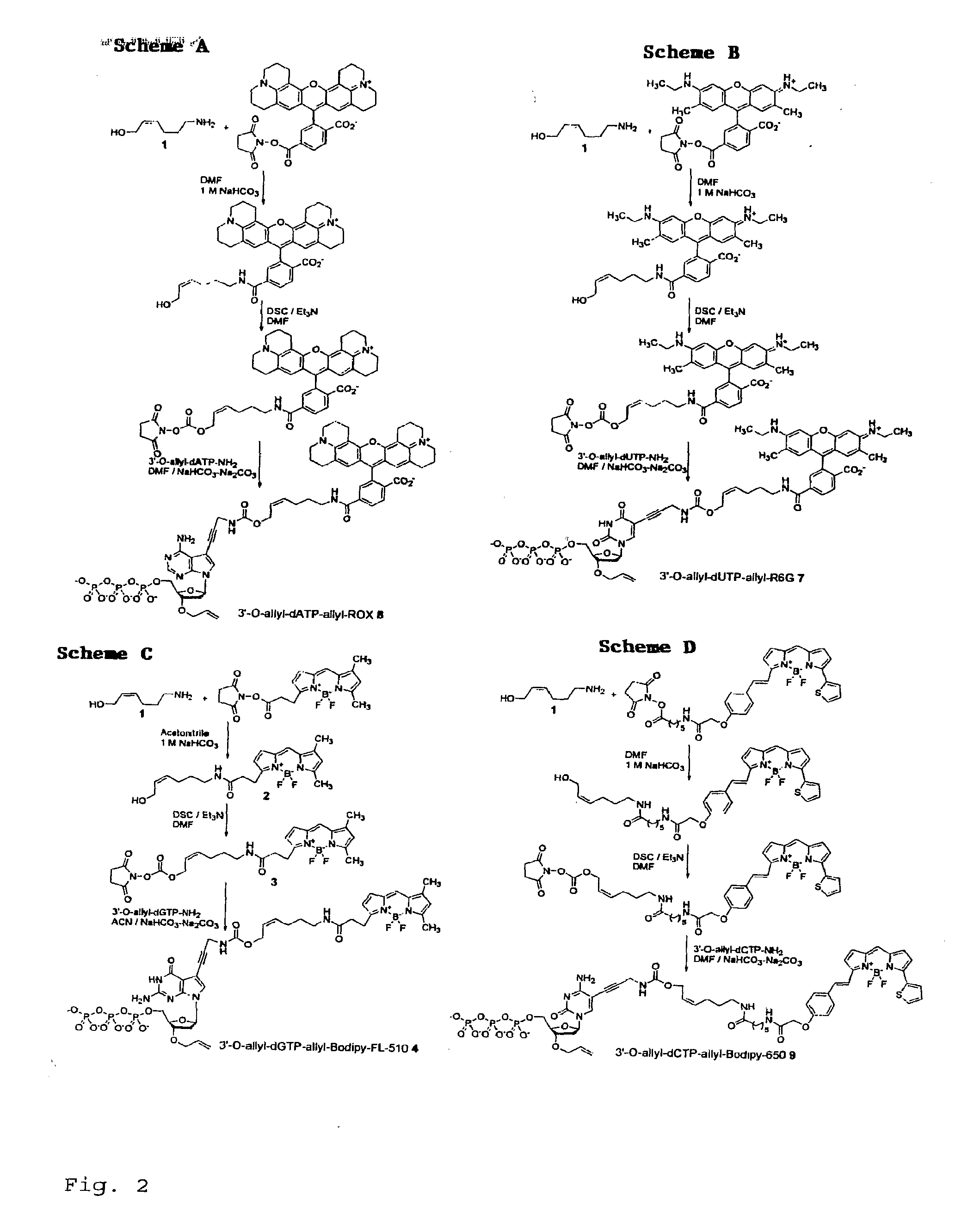
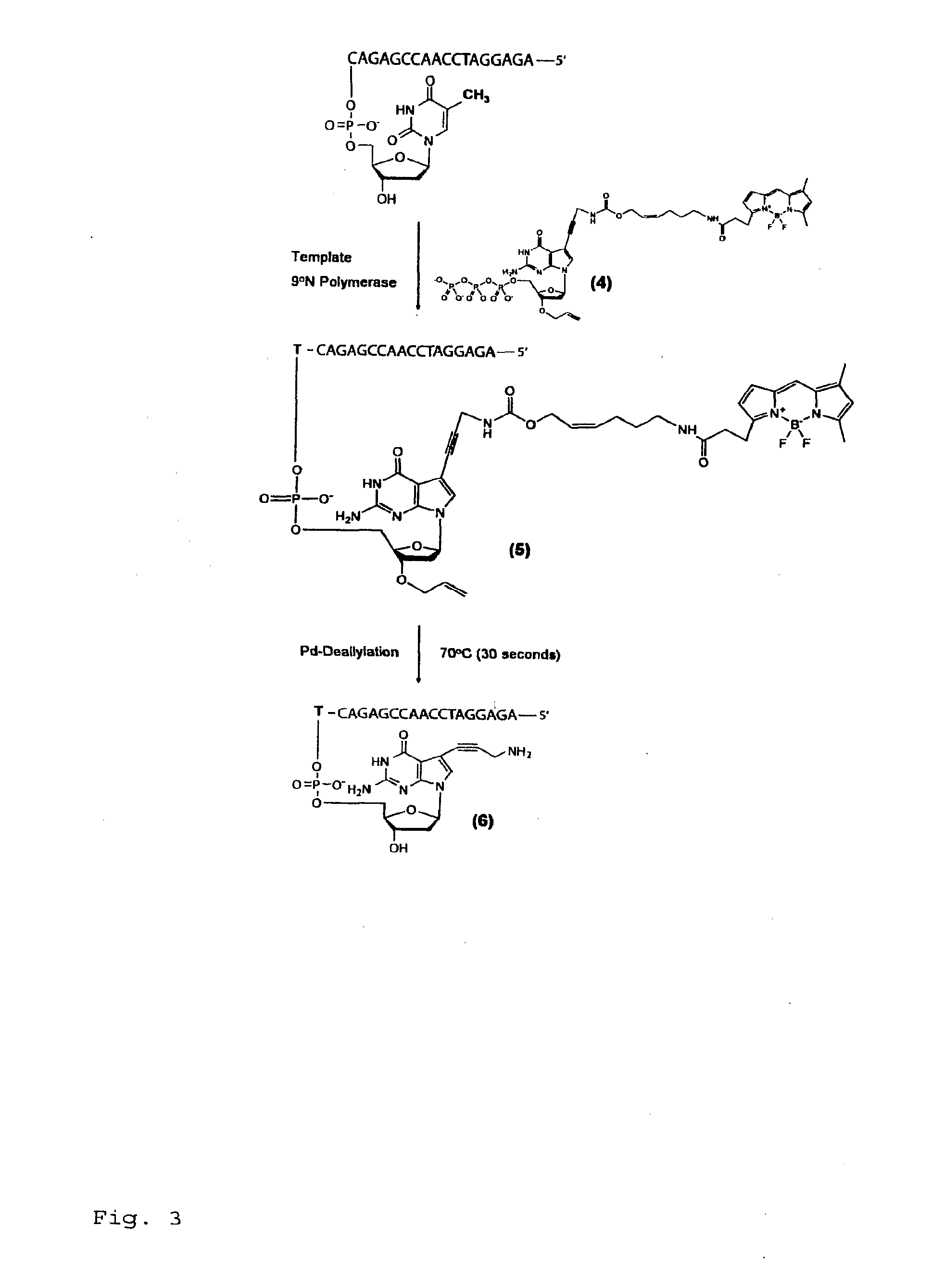
Chemically cleavable 3'-o-allyl-DNTP-allyl-fluorophore fluorescent nucleotide analogues and related methods
This invention provides a nucleotide analogue comprising (i) a base selected from the group consisting of adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil, (ii) a deoxyribose, (iii) an allyl moiety bound to the 3′-oxygen of the deoxyribose and (iv) a fluorophore bound to the base via an allyl linker, and methods of nucleic acid sequencing employing the nucleotide analogue.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
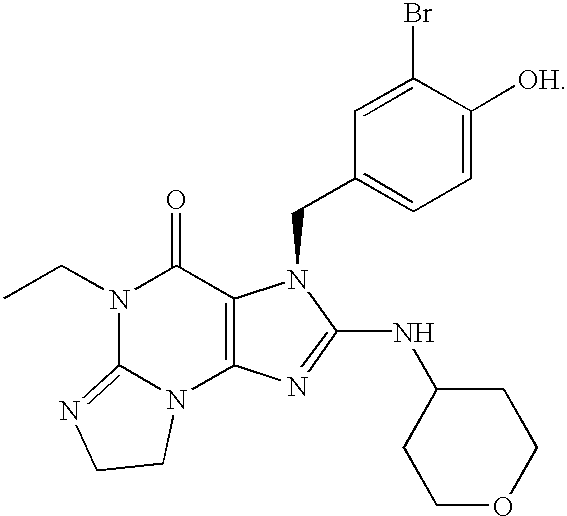
Polycyclic guanine phosphodiesterase V inhibitors
InactiveUS6969719B2High selectivityImprove side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicineSexual dysfunction
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Artificially synthesized DNA storage medium with coding information, storage reading method for information, and applications
ActiveCN104850760AEasy to synthesizeLower Sequencing CostsSpecial data processing applicationsCytosineA-DNA
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, specifically belongs to the technical field of DNA storage, more specifically an artificially synthesized DNA storage medium with coding information, a storage reading method for the information, and applications. Discarding DNA storage technology depended on a mature binary code or a ternary code in the prior art, the invention creatively discloses a DNA storage mode capable of coding directly. Through using storage method capable of coding directly, especially tetragenous basic group coding, the obtained DNA chain storing digit information is short in entire sequence and average content of guanine and cytosine in the sequence is relatively balanced. The method of the invention is in favour of synthesizing, convenient for decoding, and could reduce error rate. The method of the invention can be used for covering a plurality of character types such as English, figure, Chinese and punctuation marks with wide application range.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Methods and kits for characterizing GC-rich nucleic acid sequences
Methods and kits of characterizing a GC rich region of a nucleic acid of interest are provided. One method is effected by (a) contacting the nucleic acid of interest with an agent that modifies cytosine or guanine residues into residues complementary to adenine or thymine for obtaining a modified nucleic acid in which the cytosine or guanine residues are replaced by the residues complementary to adenine or thymine; (b) amplifying the modified nucleic acid by amplification primers being hybridizable with the modified nucleic acid and being designed for directing amplification of at least a portion of the modified nucleic acid, for obtaining an amplification product corresponding to the GC rich region; and (c) determining the size of the amplification product, thereby characterizing the GC rich region of the nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:GAMIDAGEN
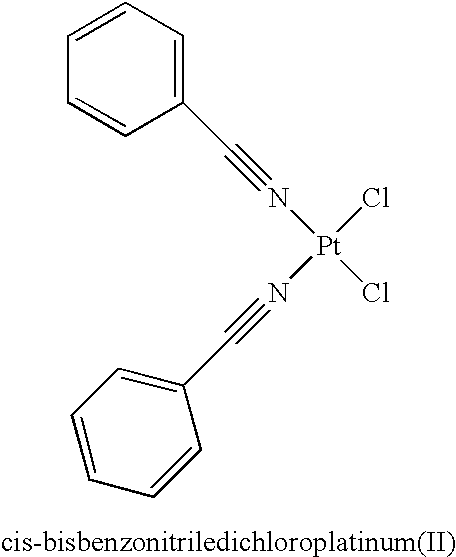
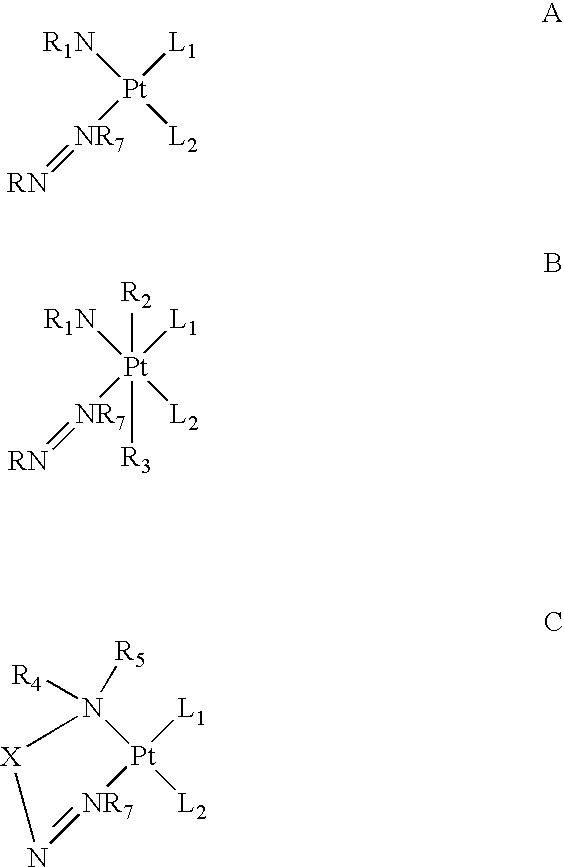
Monoazole ligand platinum analogs
InactiveUS7759488B2Easily transported into tumor cellStrong hydrogen bondingOrganic active ingredientsPlatinum organic compoundsPurinePt element
Disclosed herein are novel platinum-based analogs with a single substituted azole ligand: RN═NR7, wherein the RN═NR7 functional group is covalently bonded to the platinum through nitrogen of NR7. The analogs also have nitrogen donor ligands capable of forming hydrogen bonds with the bases in DNA or RNA, and one or more leaving groups which can be displaced by water, hydroxide ions or other nucleophiles, which is thought to form active species in vivo, and then, form cross-linked complexes between nucleic acid strands, principally between purines in DNA (or RNA), i.e., at the Guanine or Adenine bases, thereof. These platinum analogs may also be more easily transported into tumor cells, due to their increased lipophilicity and are likely to be useful as anti-neoplastic agents, and in modulating or interfering with the synthesis or replication or transcription of DNA or translation or function of RNA in vitro or in vivo, as they are potentially capable of forming a platinum coordinate complex with an intact or nascent DNA or RNA and thereby interfering with cellular synthesis, transcription or replication of nucleic acid polynucleotides.
Owner:BIONUMERIK PHARMA INC
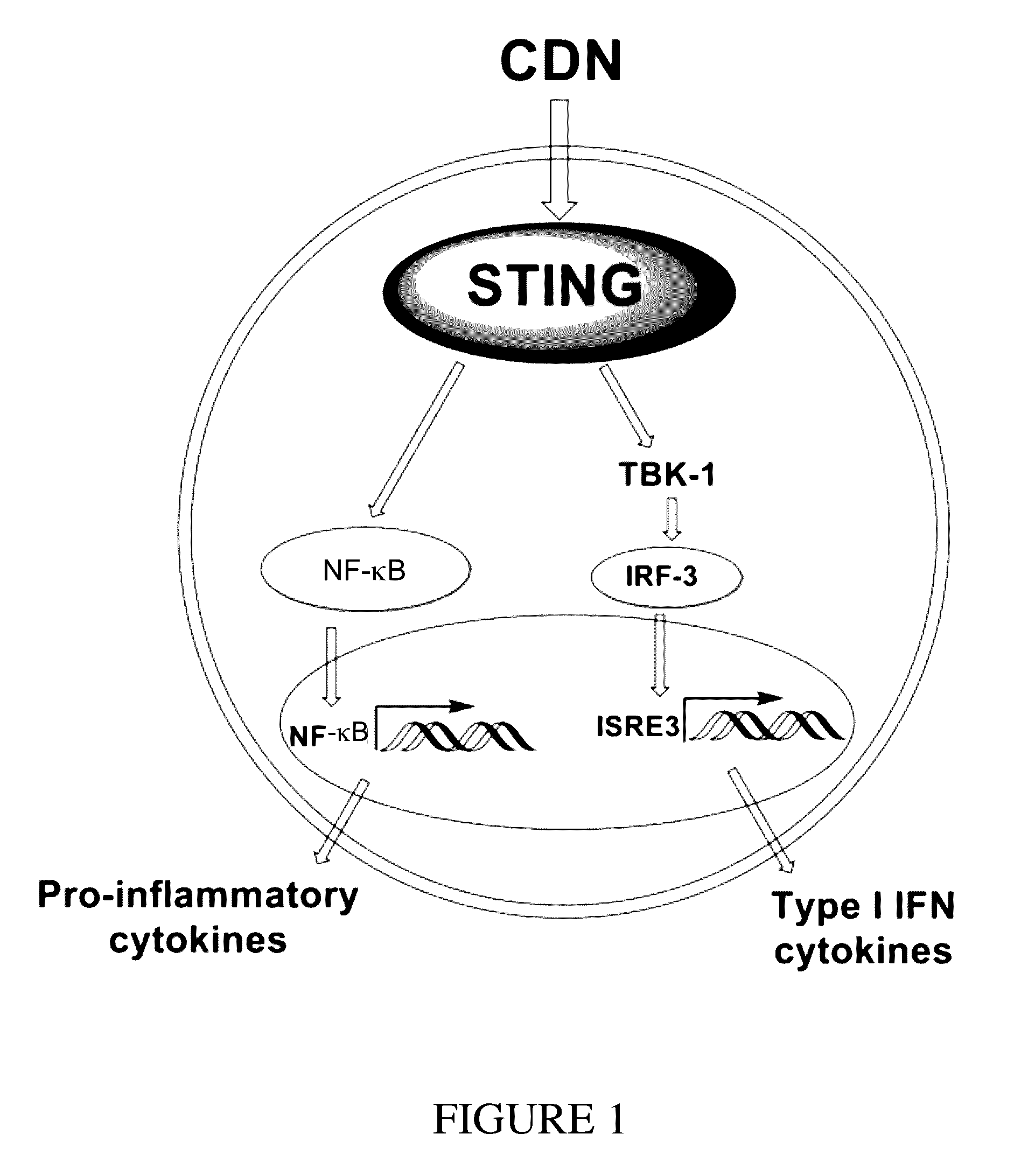
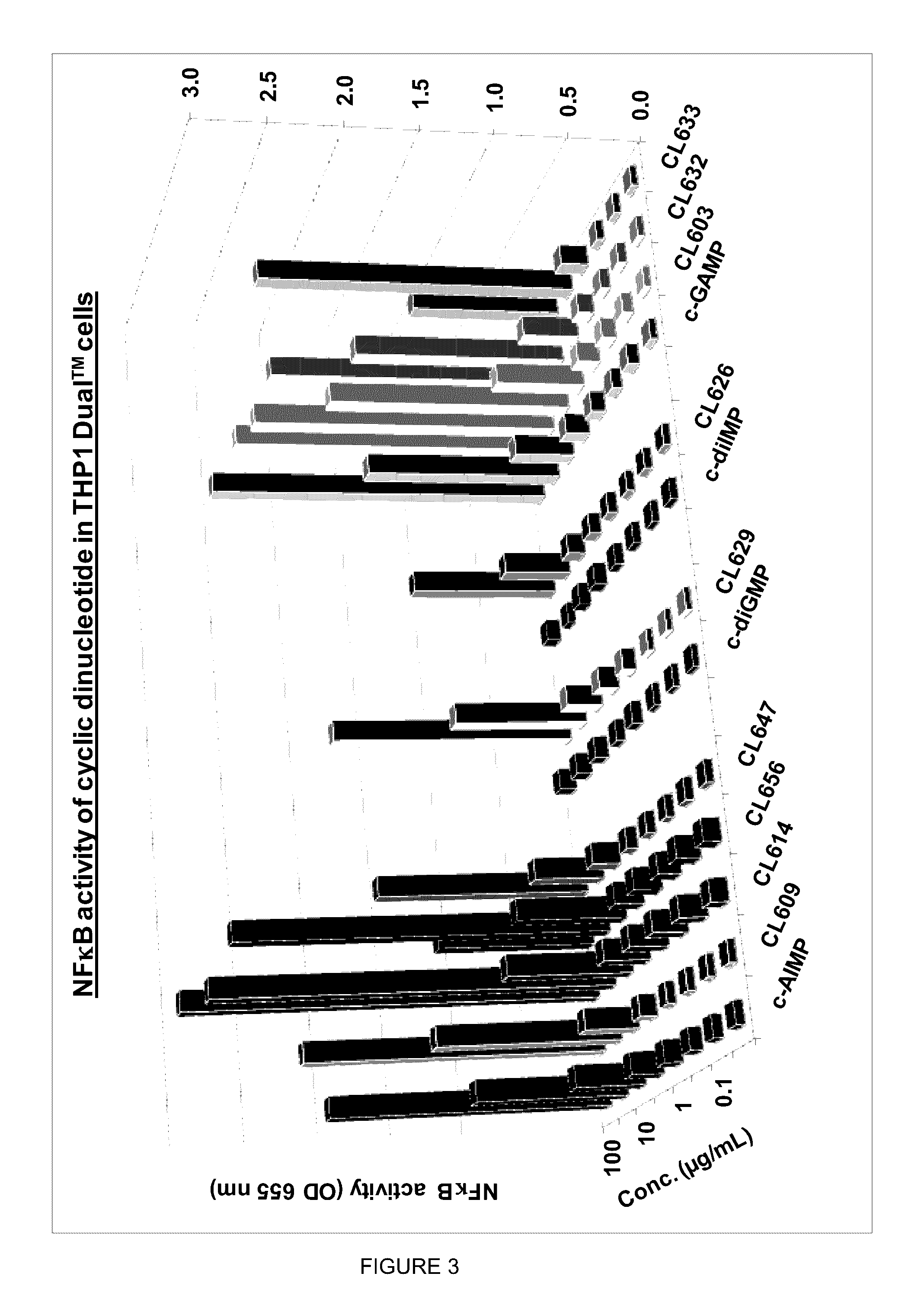
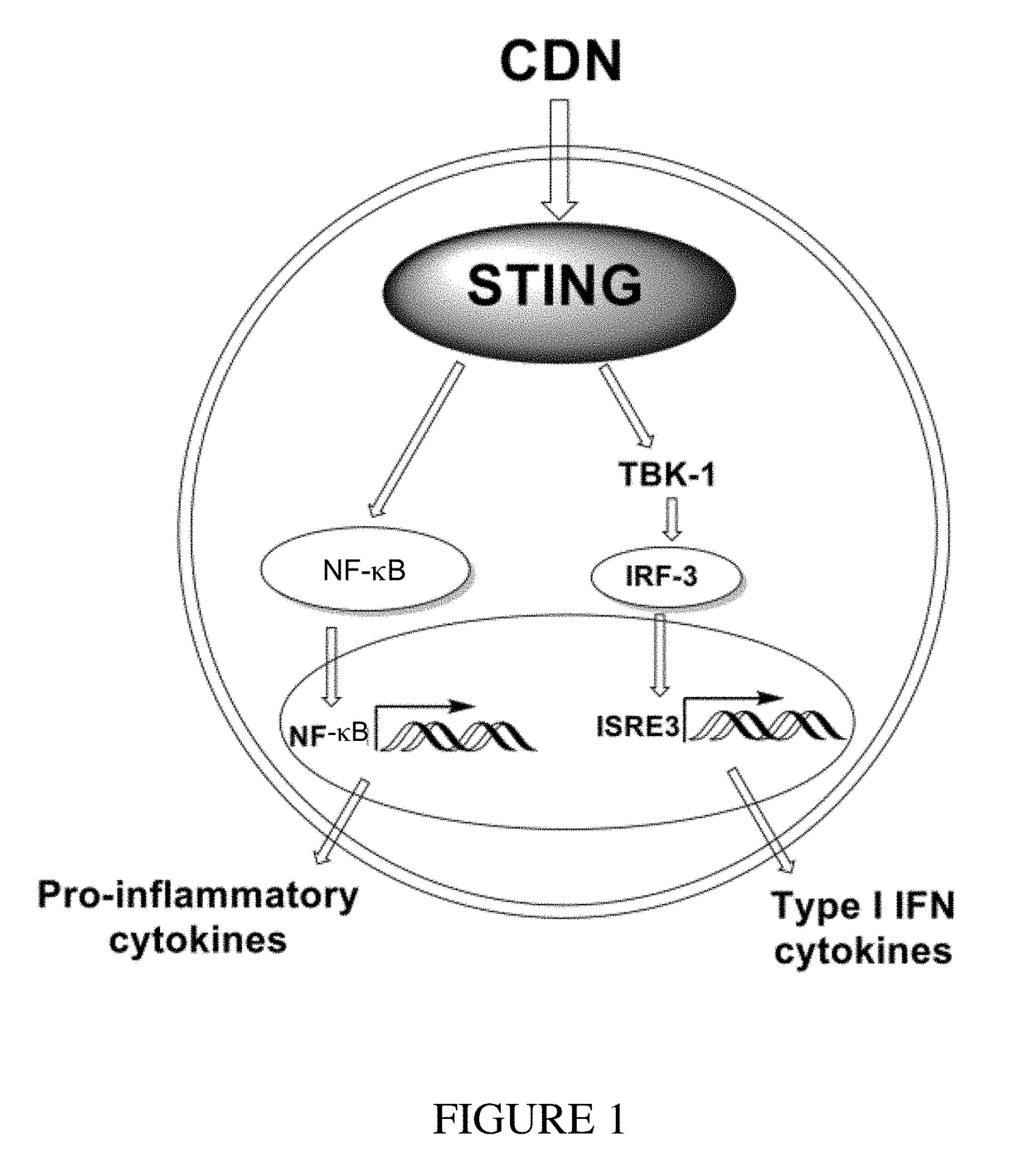
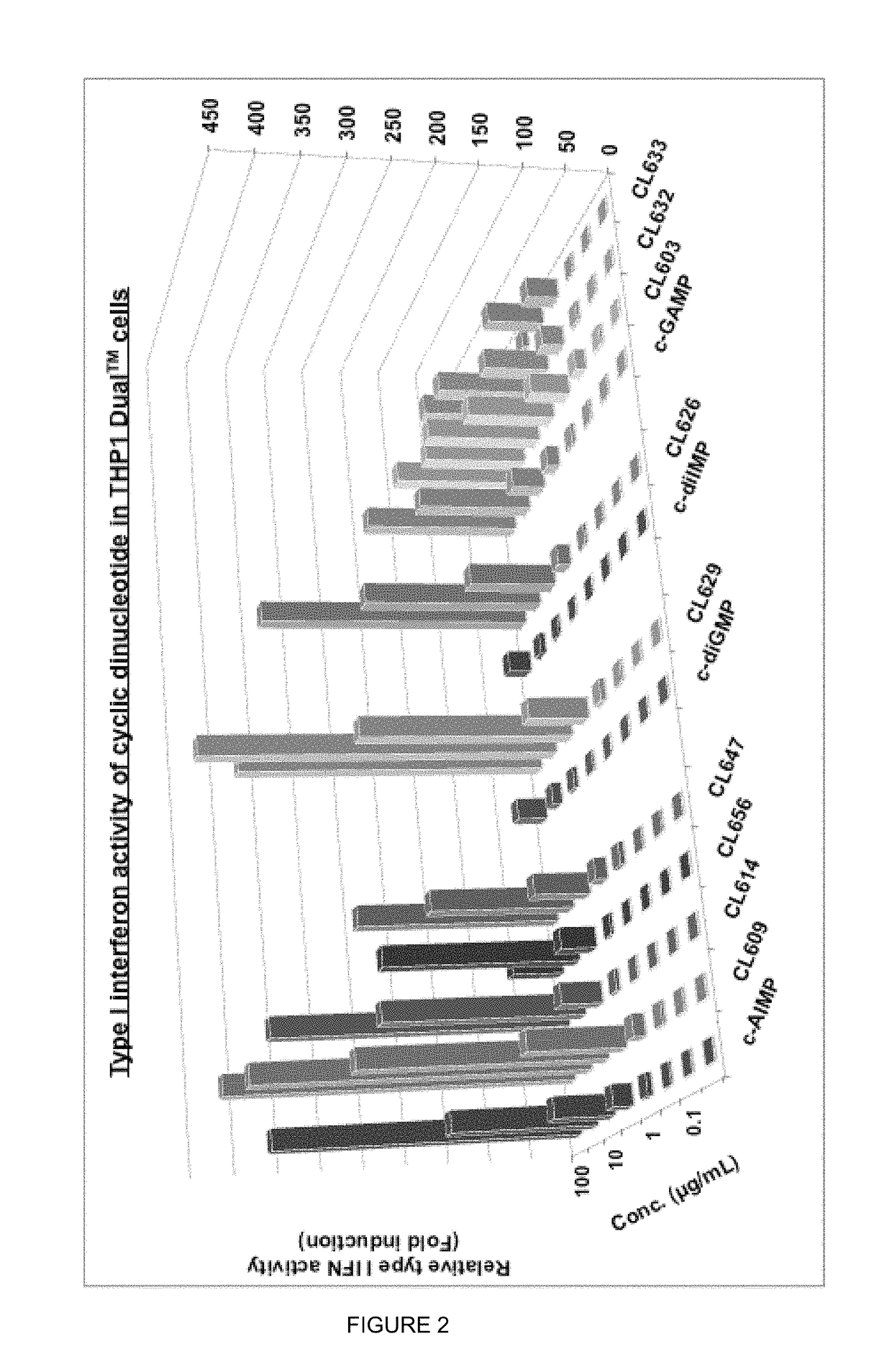
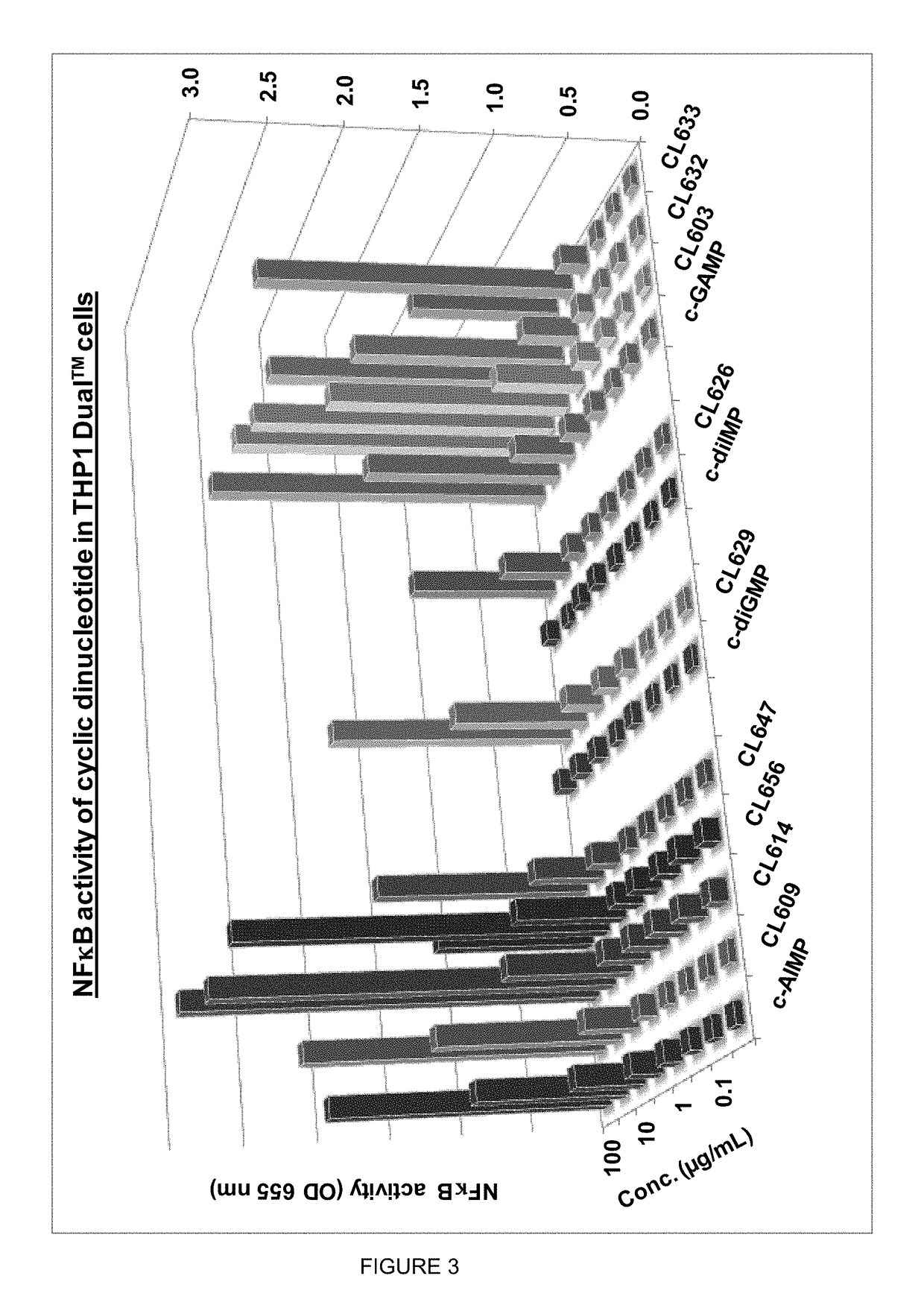
Cyclic dinucleotides for cytokine induction
ActiveUS20160362441A1Improve the immunityDelay EliminationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPurineIn vivo
A cyclic dinucleotide compound of Formula (I):wherein X1 is H or F; X2 is H or F; at least one among X1 and X2 is a fluorine atom; Z is OH, OR1, SH or SR1, wherein: R1 is Na or NH4, or R1 is an enzyme-labile group which provides OH or SH in vivo such as pivaloyloxymethyl; B1 and B2 are bases chosen from Adenine, Hypoxanthine or Guanine, and B1 is a different base than B2 and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions including the cyclic dinucleotide, as well as their use in the treatment of a bacterial infection, a viral infection or a cancer are also described.
Owner:KAYLA THERAPEUTICS
Agents for intravitreal administration to treat or prevent disorders of the eye
InactiveUS20050137124A1Reduce chancePotential damageBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsDiseaseUrea derivatives
Methods and preparations for treating disorders of the eye and / or causing posterior vitreous disconnection or disinsertion. Preparations containing a) urea, b) urea derivatives (e.g., hydroxyurea, thiourea), c) a non-steroidal anti-inflamatory agents, d) antmetabolites, e) urea, urea derivatives, non-enzymatic proteins, nucleosides, nucleotides and their derivatives (e.g., adenine, adenosine, cytosine, cytadine, guanine, guanitadine, guanidinium, thymidine, thimitadine, uradine, uracil, cystine), uric acid, calcium acetal salicylate, ammonium sulfate or other compound capable of causing non-enzymatic dissolution of the hyaloid membrane or e) any of the possible combinations thereof, are administered to the eye in therapeutically effective amounts.
Owner:KATO PHARMA
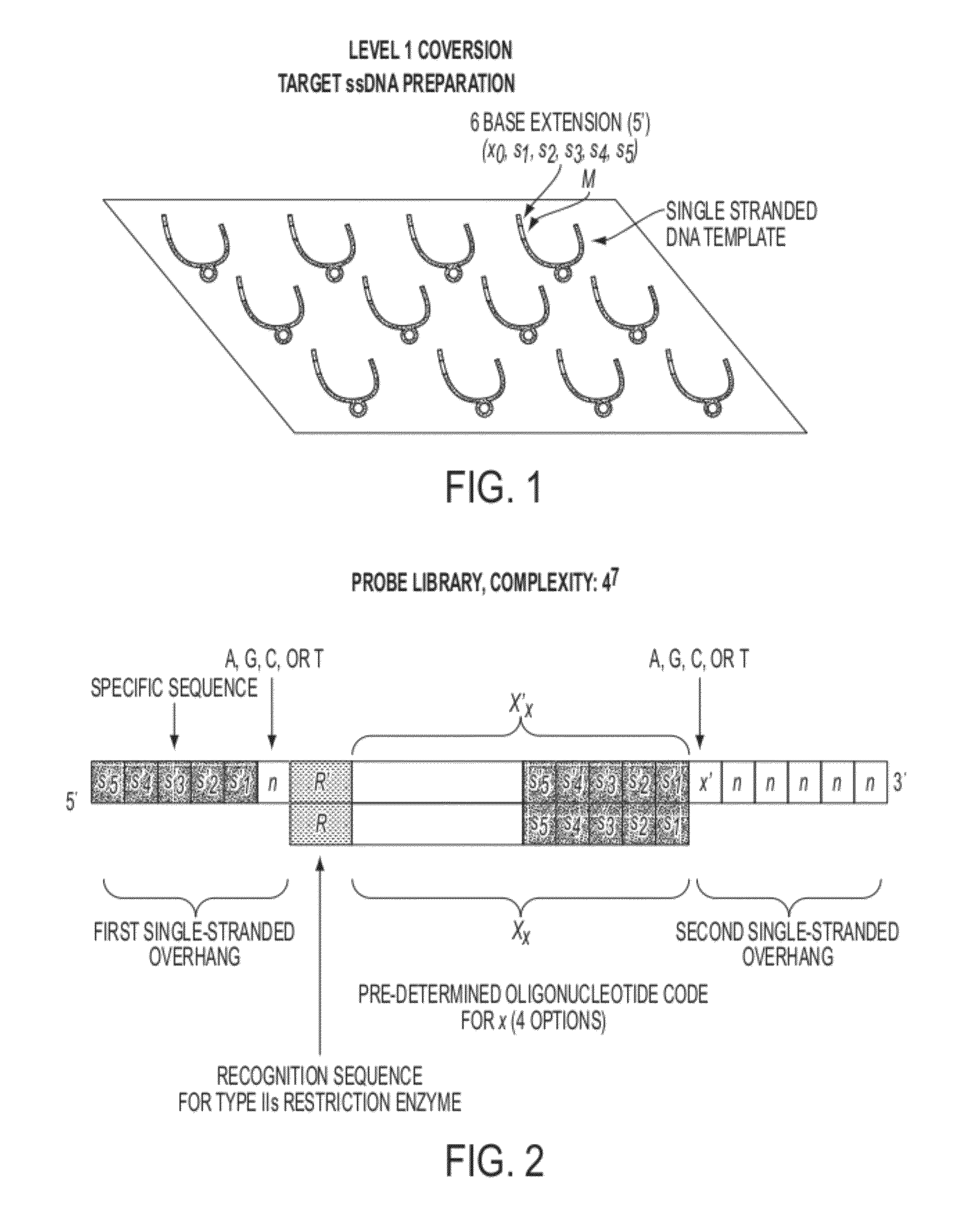
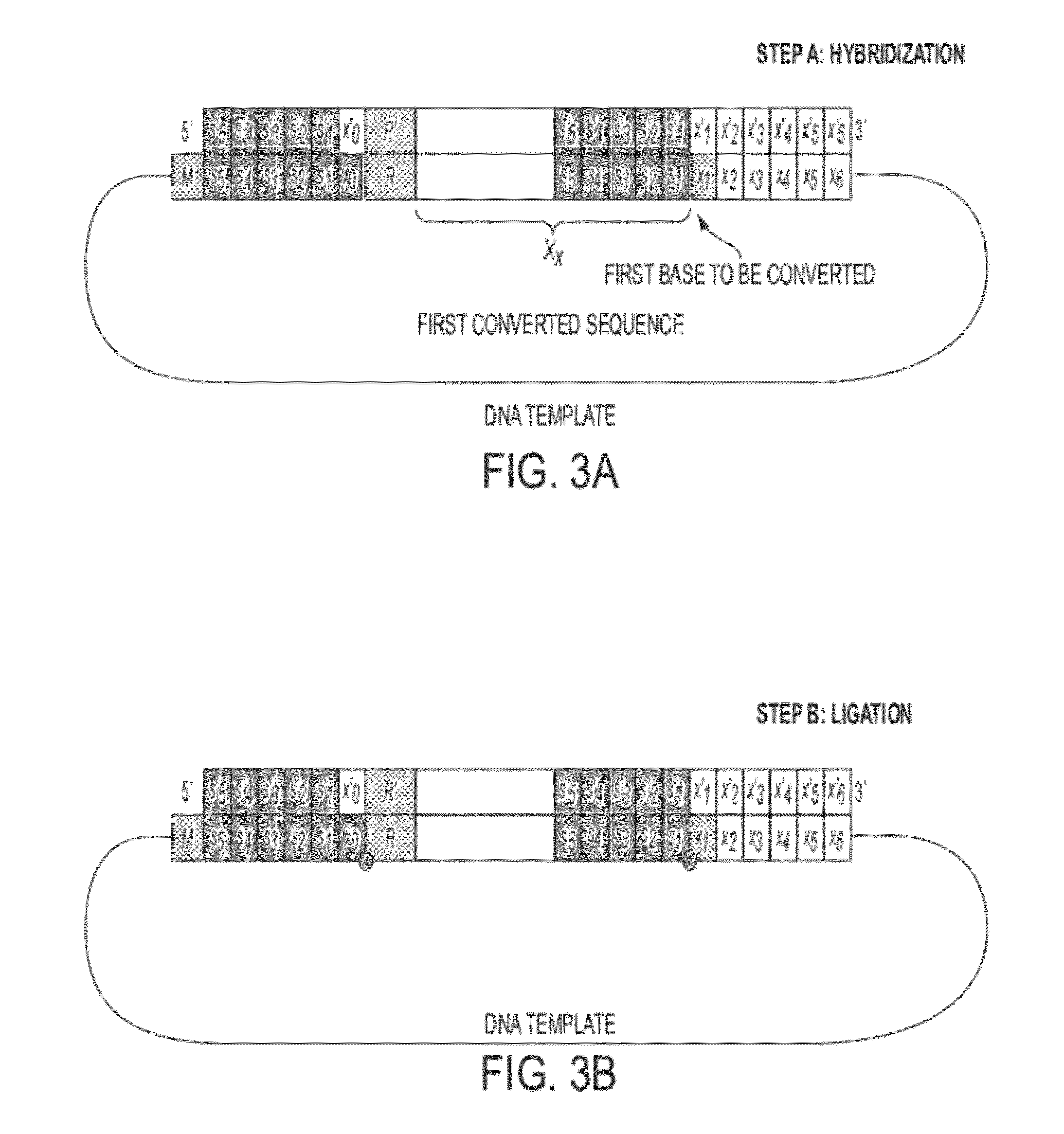
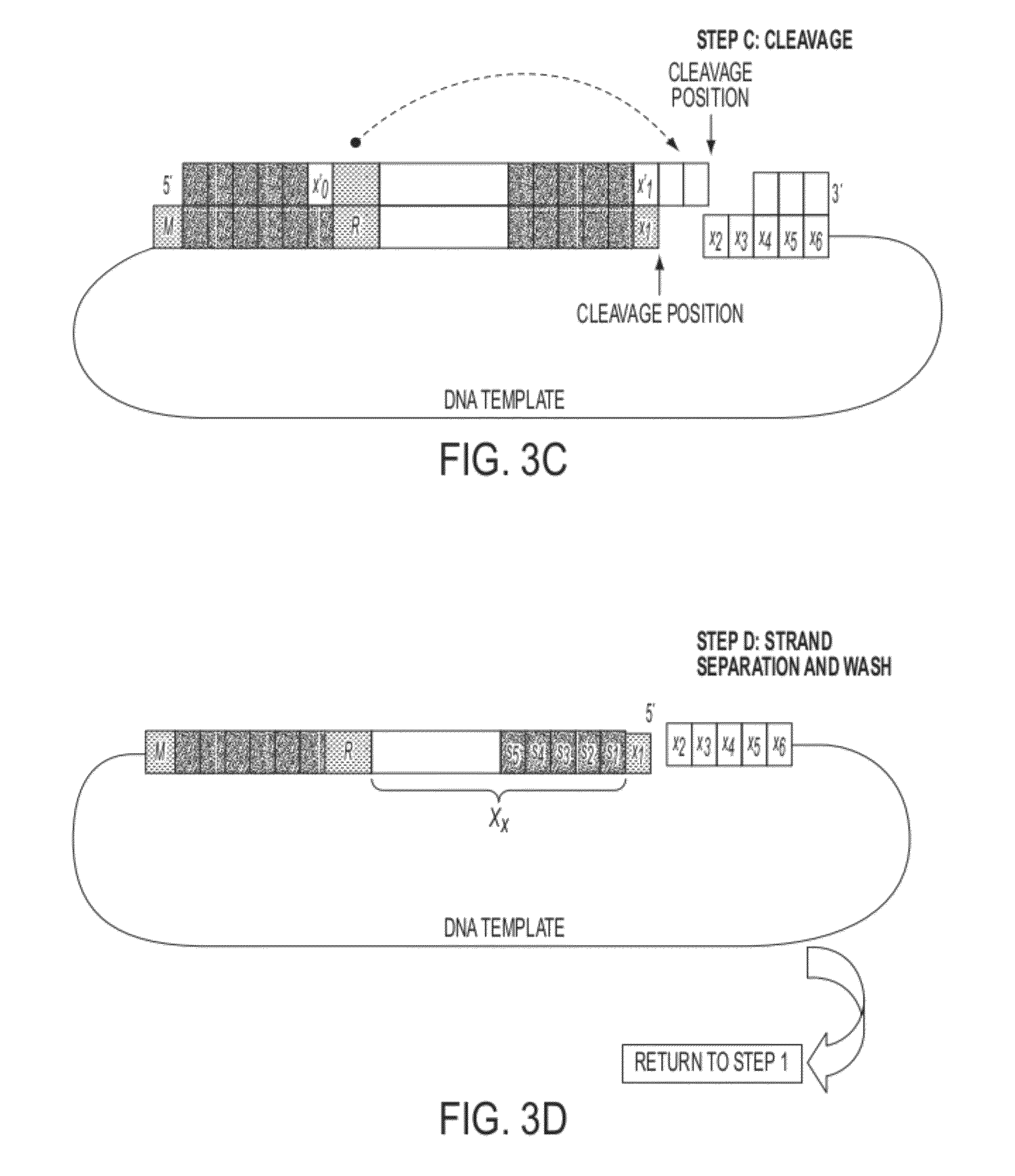
Sequence preserved DNA conversion
InactiveUS20120040869A1Eliminates introductionImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionCytosineThymine
Described herein are inexpensive high throughput methods to convert a target single stranded DNA (ssDNA) such that each nucleotide (or base) adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C) is converted to a pre-determined oligonucleotide code, with the sequential order preserved in the converted ssDNA, or RNA. The method does not require the use of DNA polymerases during the cycles and involves the use of an oligonucleotide probe library with repeated cycles of ligation and cleavage. At each cycle, one or more nucleotides on one end (e.g., either the 5′ end or the 3′ end) of a target, e.g., ssDNA, are cleaved and then ligated with the corresponding oligonucleotide code at the other end of the target ssDNA.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Cyclic dinucleotides for cytokine induction
ActiveUS10011630B2High activityImprove bioavailabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPurineIn vivo
A cyclic dinucleotide compound of Formula (I):wherein X1 is H or F; X2 is H or F; at least one among X1 and X2 is a fluorine atom; Z is OH, OR1, SH or SR1, wherein: R1 is Na or NH4, or R1 is an enzyme-labile group which provides OH or SH in vivo such as pivaloyloxymethyl; B1 and B2 are bases chosen from Adenine, Hypoxanthine or Guanine, and B1 is a different base than B2 and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions including the cyclic dinucleotide, as well as their use in the treatment of a bacterial infection, a viral infection or a cancer are also described.
Owner:KAYLA THERAPEUTICS
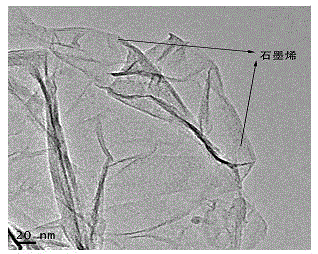
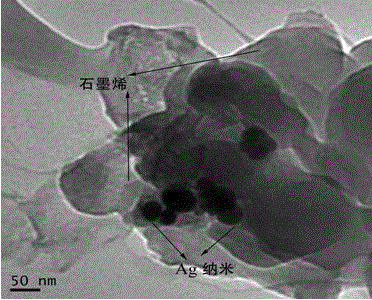
Silver-poly dopamine-graphene-modified electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102914580AHigh sensitivityImprove conductivityMaterial electrochemical variablesGraphiteElectrochemistry
The invention discloses a silver-poly dopamine-graphene-composite-modified electrochemical sensor which is mainly characterized in that a silver-poly dopamine-graphene composite membrane is coated on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode. A preparation method of the silver-poly dopamine-graphene-composite-modified electrochemical sensor includes: adding silver-poly dopamine-graphene into dimethylformamide for uniform dispersing so that silver-poly dopamine-graphene dispersion liquid is obtained, then coating the dispersion liquid on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, and evaporating solvent to obtain the needed sensor. A silver-poly dopamine-graphene composite is prepared only by mixing reactants and stirring at the room temperature. The preparation method is simple, mild in reaction conditions and low in cost. The prepared electrochemical sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, low detection limit and the like, and is capable of achieving rapid sensitivity determination of guanine and adenine, simple to operate, green and environment-friendly.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Peptide conjugated, inosine-substituted antisense oligomer compound and method
InactiveUS20050288246A1Enhancing the cellular uptakeImprove compoundSpecial deliveryAntiviralsBase JCytosine
A therapeutic oligomer-peptide conjugate, and methods of using the conjugate are disclosed. The conjugate includes (a) a substantially uncharged oligonucleotide analog compound having a base sequence that includes a string of bases that are complementary to four or more contiguous cytosine bases in a target nucleic acid region to which the compound is intended to bind, and (b) conjugated to the compound, an arginine-rich peptide effective to enhance the uptake of the compound into target cells. The string of bases in the compound includes at least one inosine base positioned in the string so as to limit the number of contiguous guanine bases in said string to three or fewer. The conjugate has greater cellular uptake than the compound alone, by virtue of the arginine-rich peptide, and substantially greater antisense activity greater activity than the conjugate in the absence of inosine-for guanine substitutions.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Microelectronic device for electrochemical detection of nucleic acid hybridization
InactiveUS7049068B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyRedoxNucleic acid hybridisation
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and method for detecting nuclease
ActiveCN102154489ASimple and fast operationDesign and synthesis cost reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceSide chain
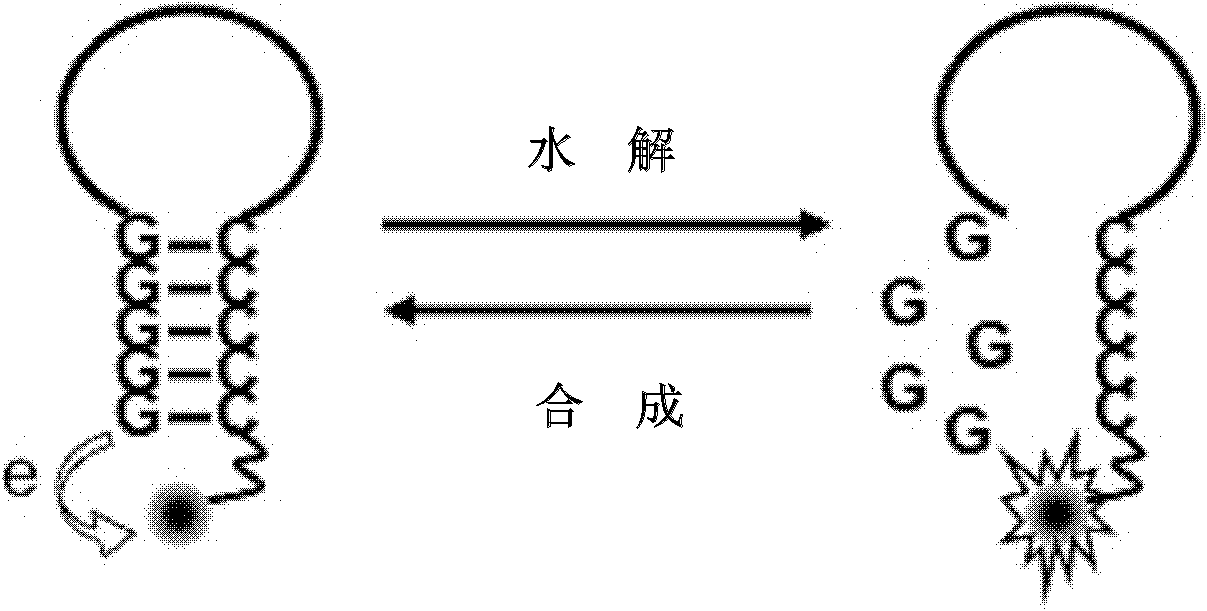
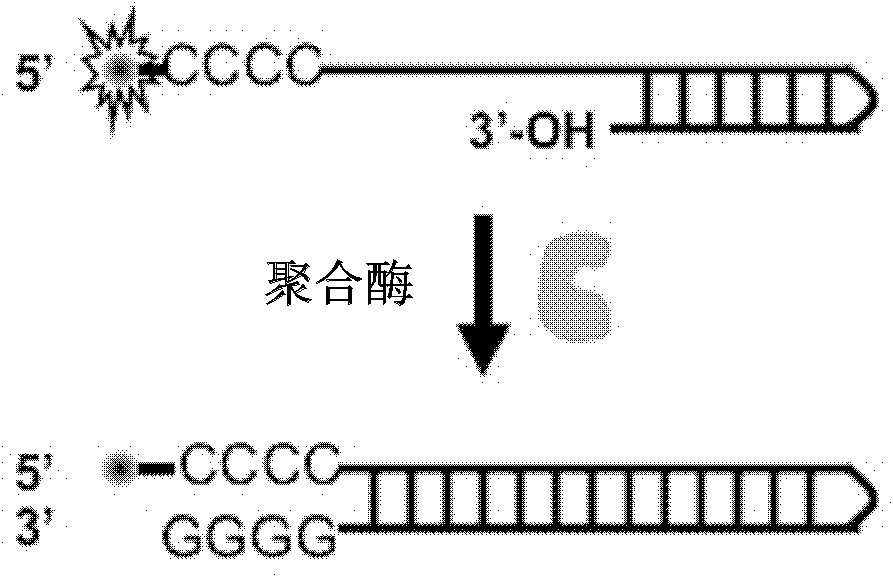
The invention discloses a singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and a method for detecting nuclease. The singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe has a stem loop structure, wherein a loop part consists of 5-24 nucleotide residues; a stem part is in a hydrolysis mode or a synthesis mode according to the activity of nuclease to be detected; in the hydrolysis mode, the stem part has a double-chain structure, the tail end is provided with at least three continuous G-C base pairs, the C base ends are labeled with fluorescence groups, the G base ends have quenching effects, one chain of the stem part is hydrolyzed under the action of the nuclease to release a fluorescence signal; and in the synthesis mode, the stem part consists of a section of double chains and a 5'-(dC)4-8side chain, the 5'- end is labeled with a fluorescence group, the 3'- end reacts with the nuclease, 4-8 continuous guanine deoxyribonucleotides are produced by polymerization extension, the fluorescence group at the 5'- end is quenched, and the activity of the nuclease to be detected is analyzed according to the change condition of the fluorescence signal.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Preparation of water-soluble luminous silver nano cluster with double-stranded DNA as template
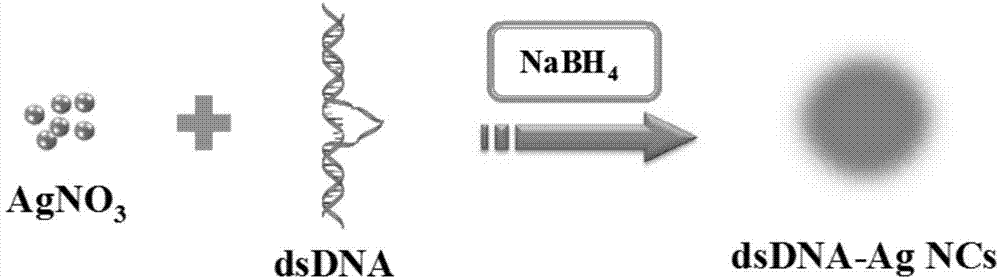
Provided is preparation of a water-soluble luminous silver nano cluster with double-stranded DNA as a template. Firstly, single-stranded DNA rich in cytosine base group is used, 6 cytosine base group loops are reserved in the single-stranded DNA, the total number of the cytosine base groups is 29, single-stranded DNA rich in guanine base group complements the single-stranded DNA and is added, the total number of the guanine base groups is 23, the double-stranded DNA with the 6 cytosine base group loops is formed through the annealing function and is used as the template, and synthesis is achieved through the method of adding sodium borohydride to restore silver nitrate. The preparation process is simple, easy to implement and environmentally friendly, and the preparation can be applied to the preparation of other luminous nano materials. In addition, new nano materials synthesized through the method have water solubility, a high quantum yield, light stability, good biocompatibility and other performance, and have potential wide application to the fields of biosensors, cell imaging, clinical medicine and the like.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
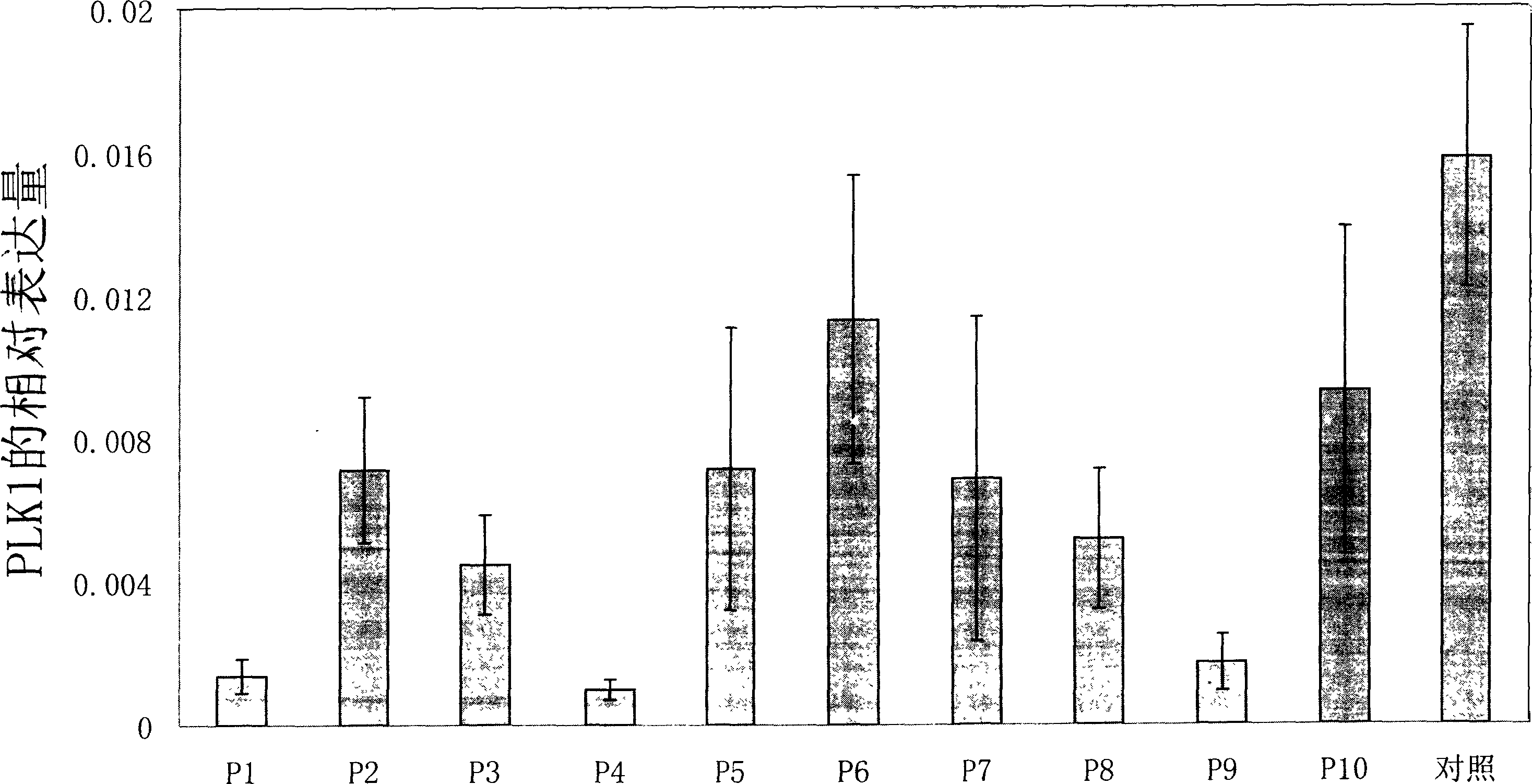
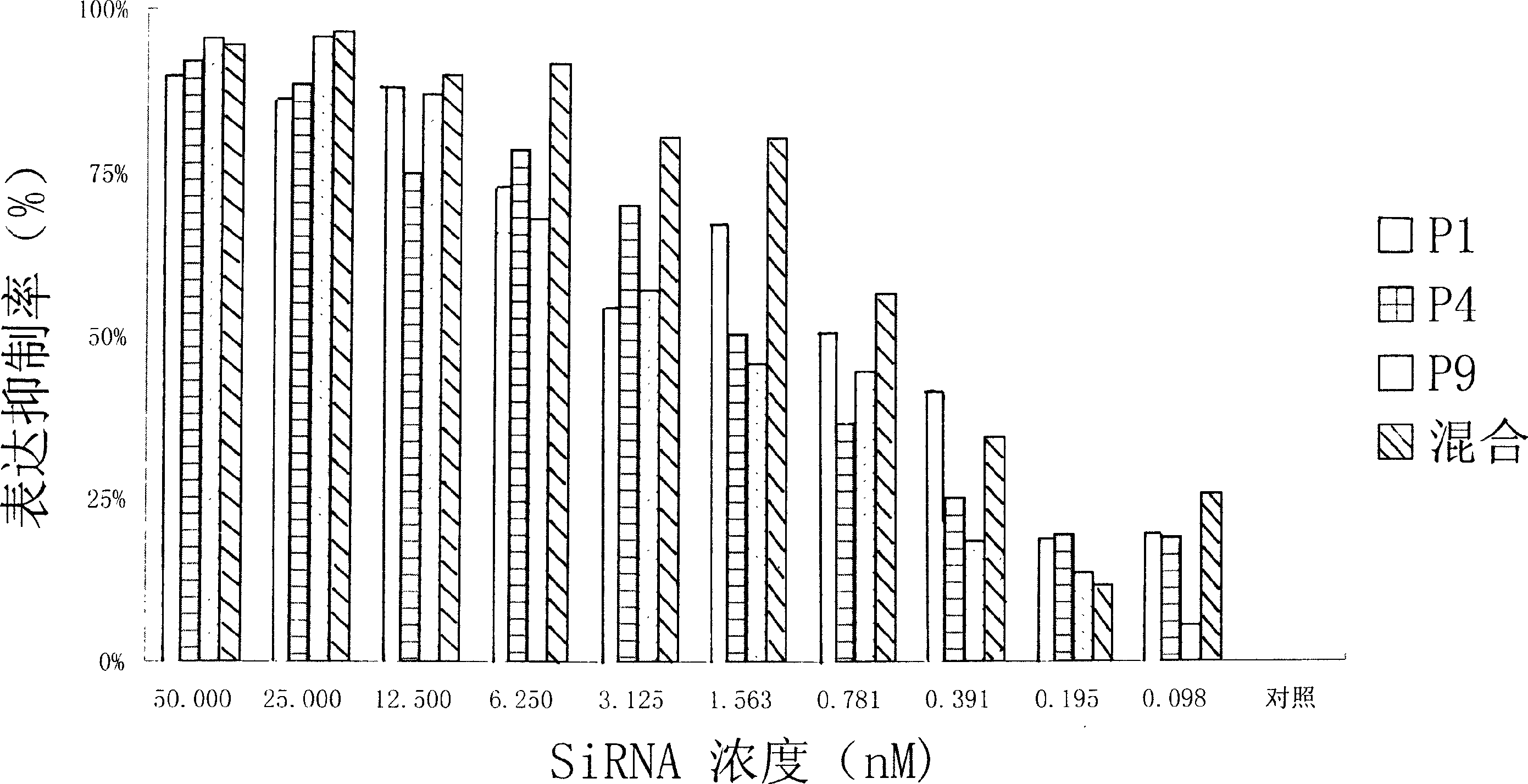
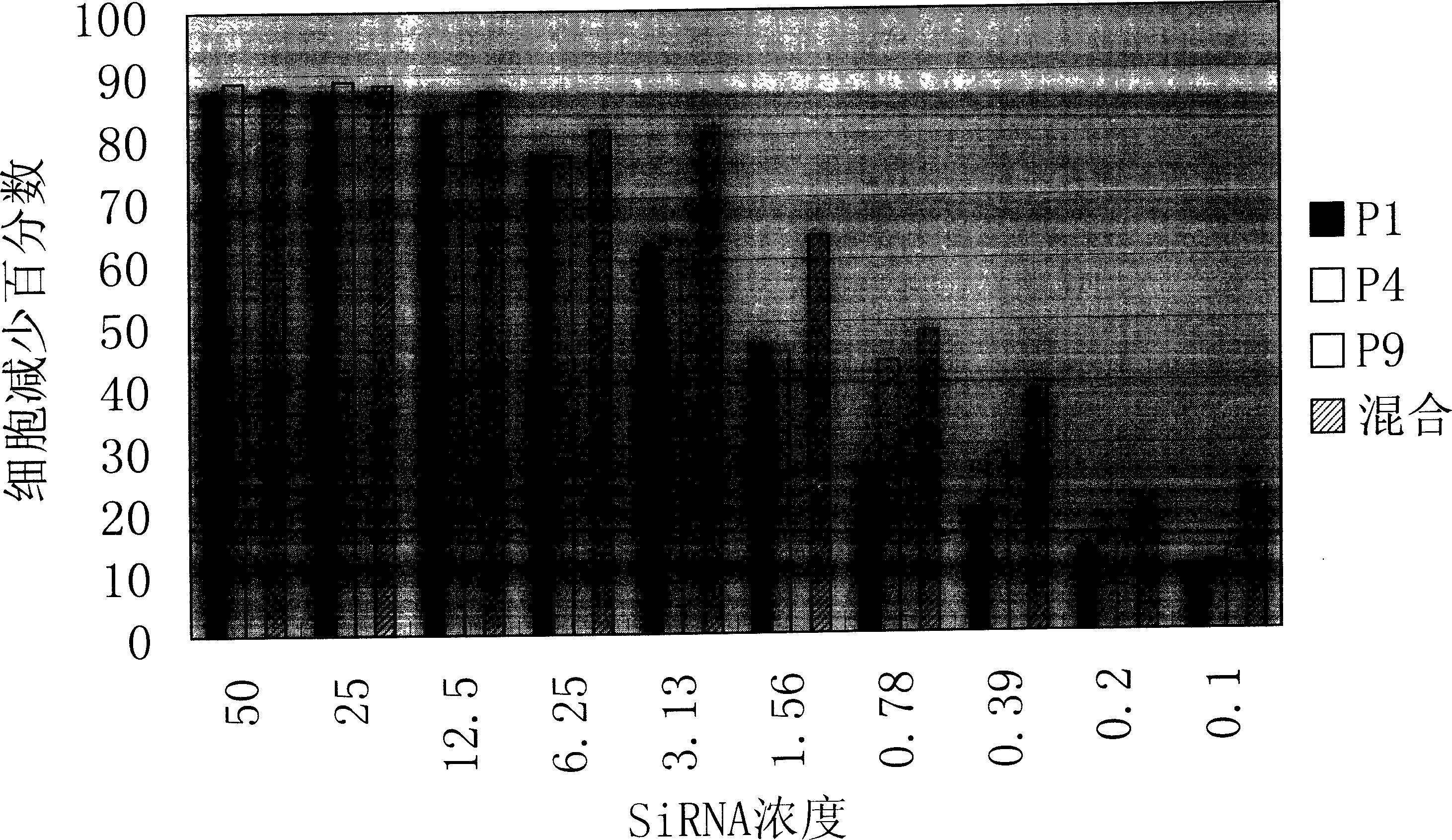
Small interference RNA molecule (SiRNA) capable of effectively killing and wounding tumour cell pointed at PLK1 mRNA, its mixture and use
InactiveCN1651450AAccurate removalLow maximum inhibitory concentrationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCytosineNucleotide
A small-interference RNA (SiRNA) molecular directed to PLKI mRNA for killing tumor cells, its mixture and its application are disclosed. It is a double-stranded RNA molecular. Its nucleoside sequence is also disclosed.
Owner:杭州新瑞佳生物医药技术开发有限公司
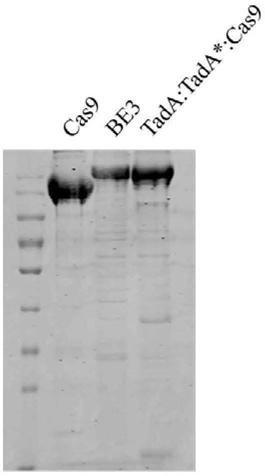
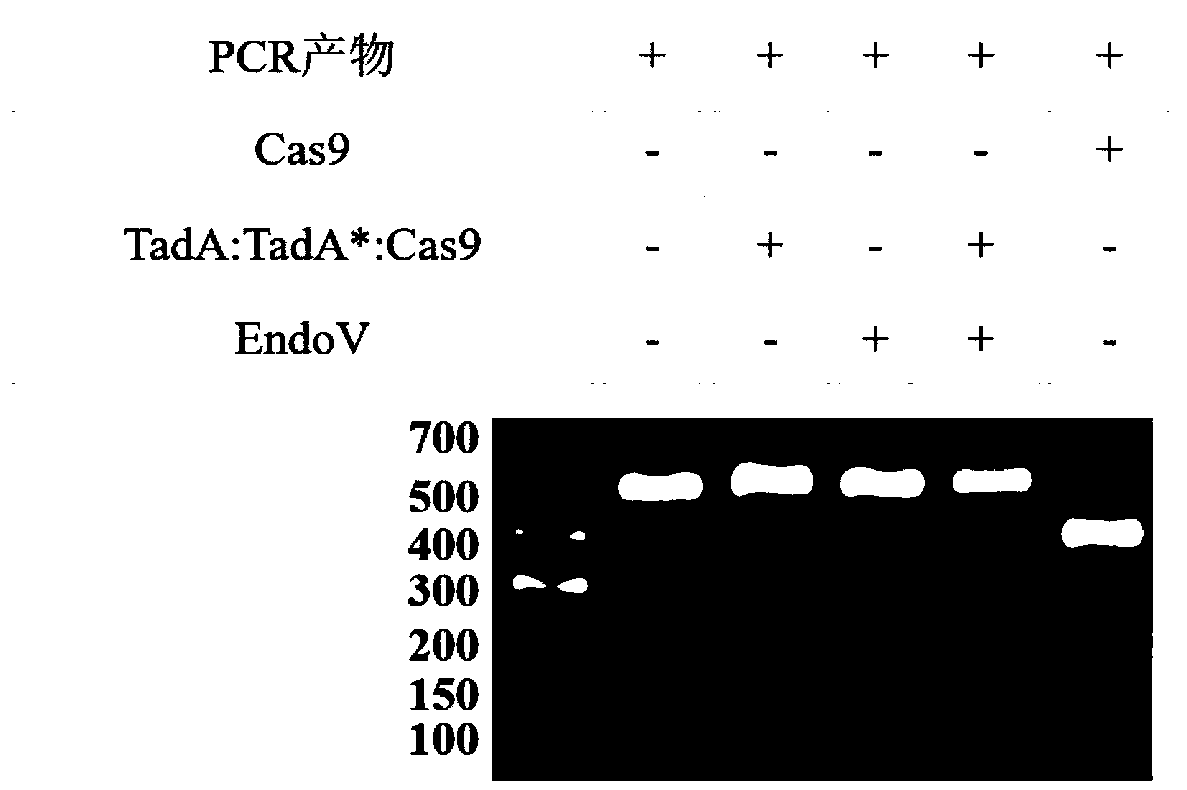
Method for detecting off-target effect of adenine base editor system based on whole genome sequencing, and its application in gene editing
PendingCN109295186AAccelerate cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesGenome editingWhole genome sequencing
The invention provides a method for detecting the off-target effect of an adenine base editor system based on whole genome sequencing, and its application in gene editing, The adenine base editor system comprises a TadA:TadA*:Cas9 fusion gene and gRNA. The system can catalyze the efficient replacement of adenine (A) at a target site with guanine (G), and has a broad application prospect in human disease gene editing therapy and disease model construction. The first method for detecting the off-target effect of the ABE system in a whole genome range, called EndoV-seq method for short, is developed in the invention. The EndoV-seq method provided by the invention has a broad application prospect in the field of gene editing, especially gene editing therapy.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
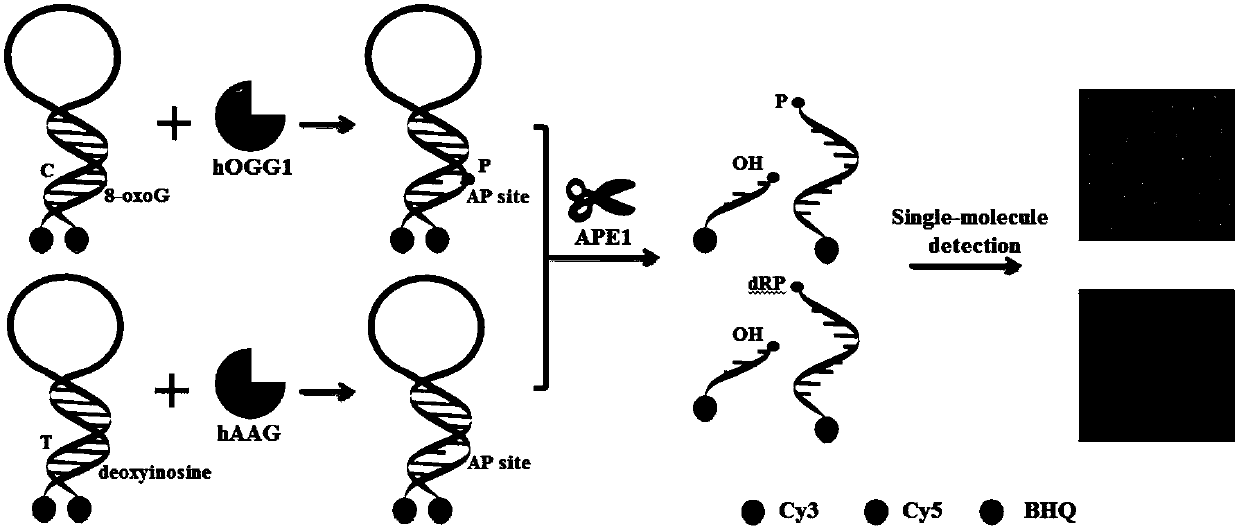
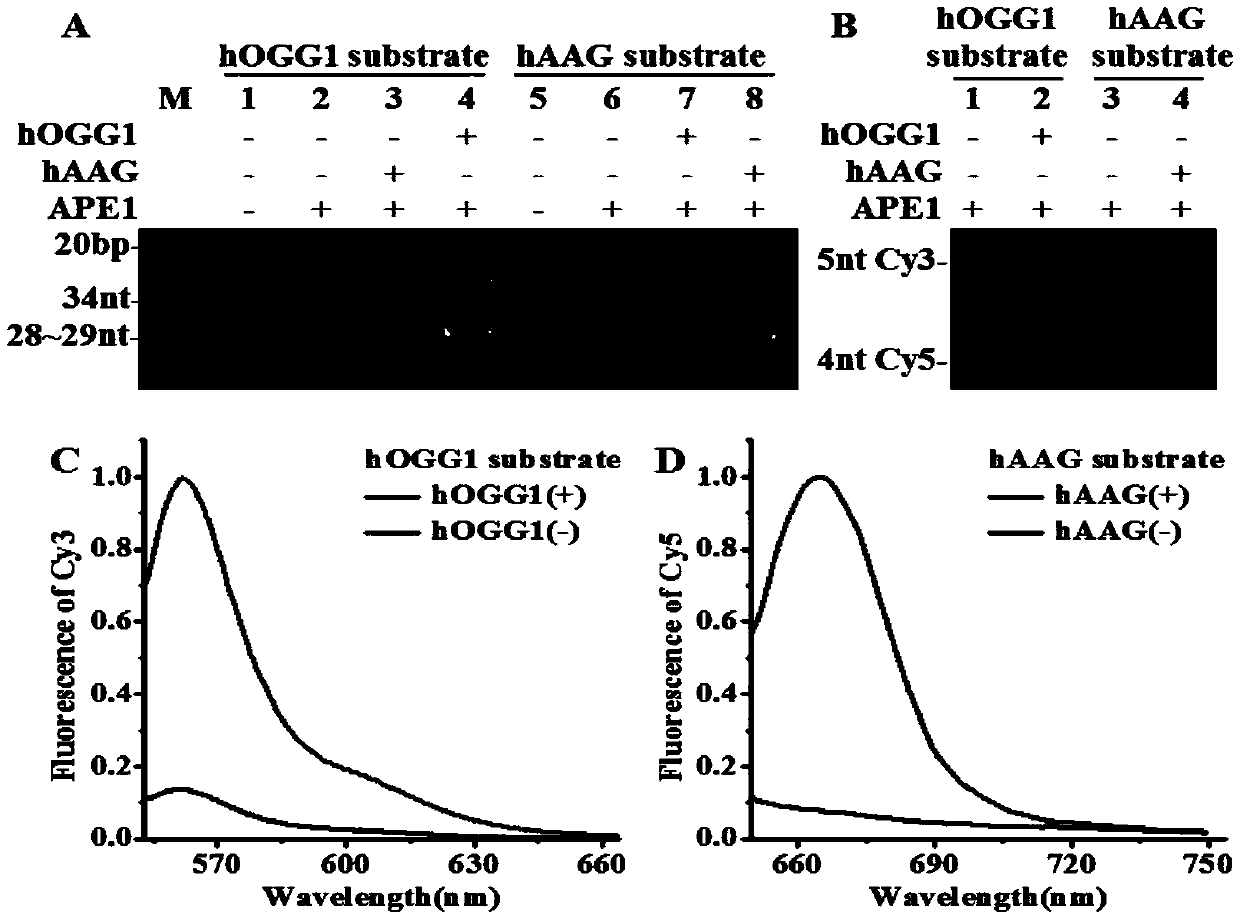
Fluorescence chemical sensor and method for simultaneously detecting diversified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylases on single-molecular levels and application of fluorescence chemical sensor
ActiveCN107723338AEasy to prepareThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMethylpurine DNA GlycosylaseMolecular level
The invention discloses a fluorescence chemical sensor and a method for simultaneously detecting diversified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylases on single-molecular levels and application of thefluorescence chemical sensor. The fluorescence chemical sensor, the method and the application have the advantages that the fluorescence chemical sensor is based on two different molecular beacons including a molecular beacon modified by 8-hydroxyl guanine and a molecular beacon modified by deoxygenated hypoxanthine, the tail end of the molecular beacon modified by the 8-hydroxyl guanine is labeled by cyanine 3 (Cy3) and quenching groups, the tail end of the molecular beacon modified by the deoxygenated hypoxanthine is labeled by cyanine 5 (Cy5) and quenching groups, the fluorescence chemicalsensor is used for detecting 8-hydroxyl guanine DNA glycosylases and N-methylpurine DNA glycosylases and is different from the traditional molecular beacons which can be severely affected by dynamicsand thermodynamics, signal restoration of the Cy3 and the Cy5 depends on molecular beacon splitting with the DNA glycosylases used as media, the DNA glycosylases can be simultaneously sensitively detected by the aid of the method without optional signal amplification, the activity of hOGG1 and hAAG can be detected by the aid of the method in an ultra-sensitive manner without optional signal amplification, the fluorescence chemical sensor can be easily, conveniently and quickly operated, and accurate and reliable test results can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
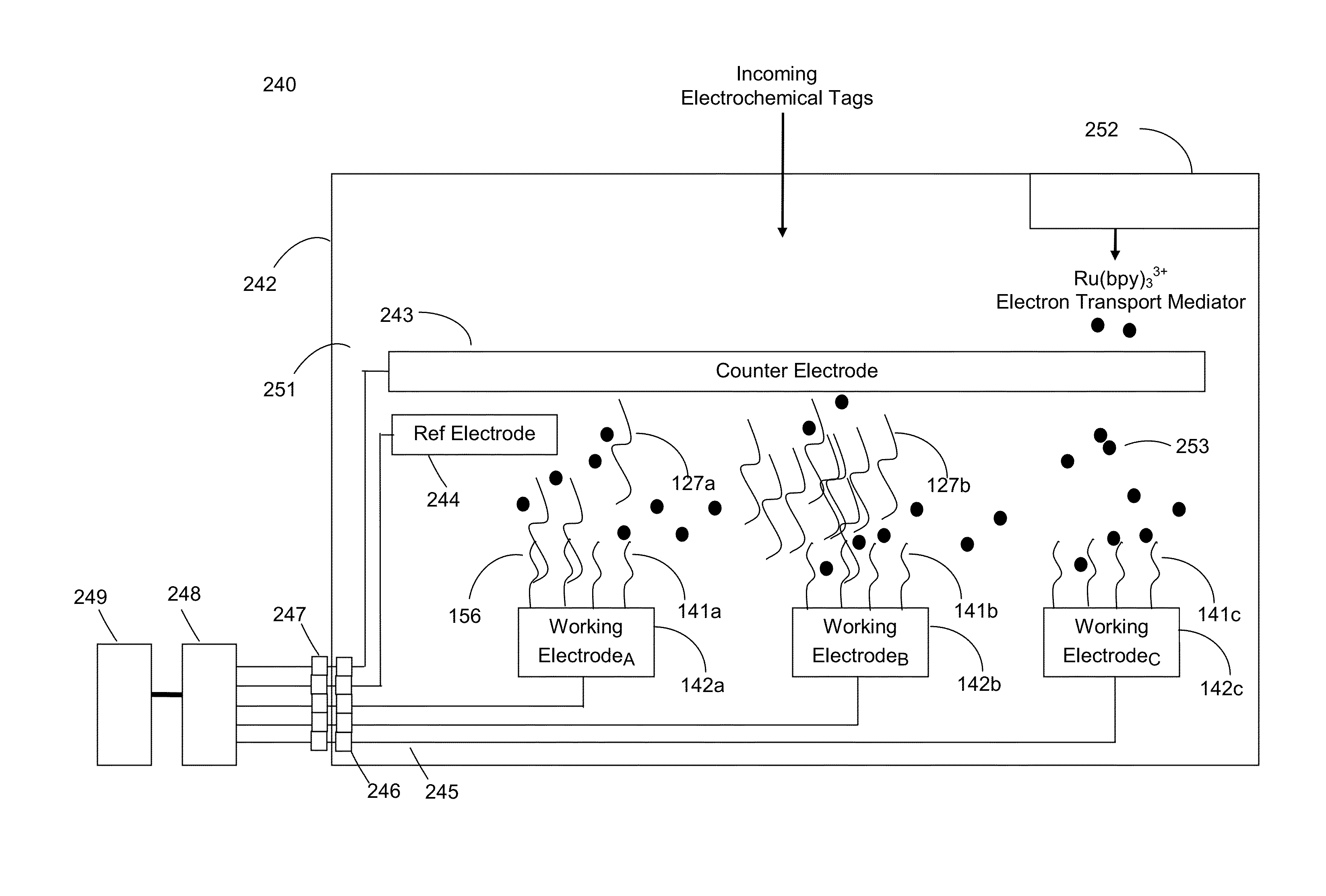
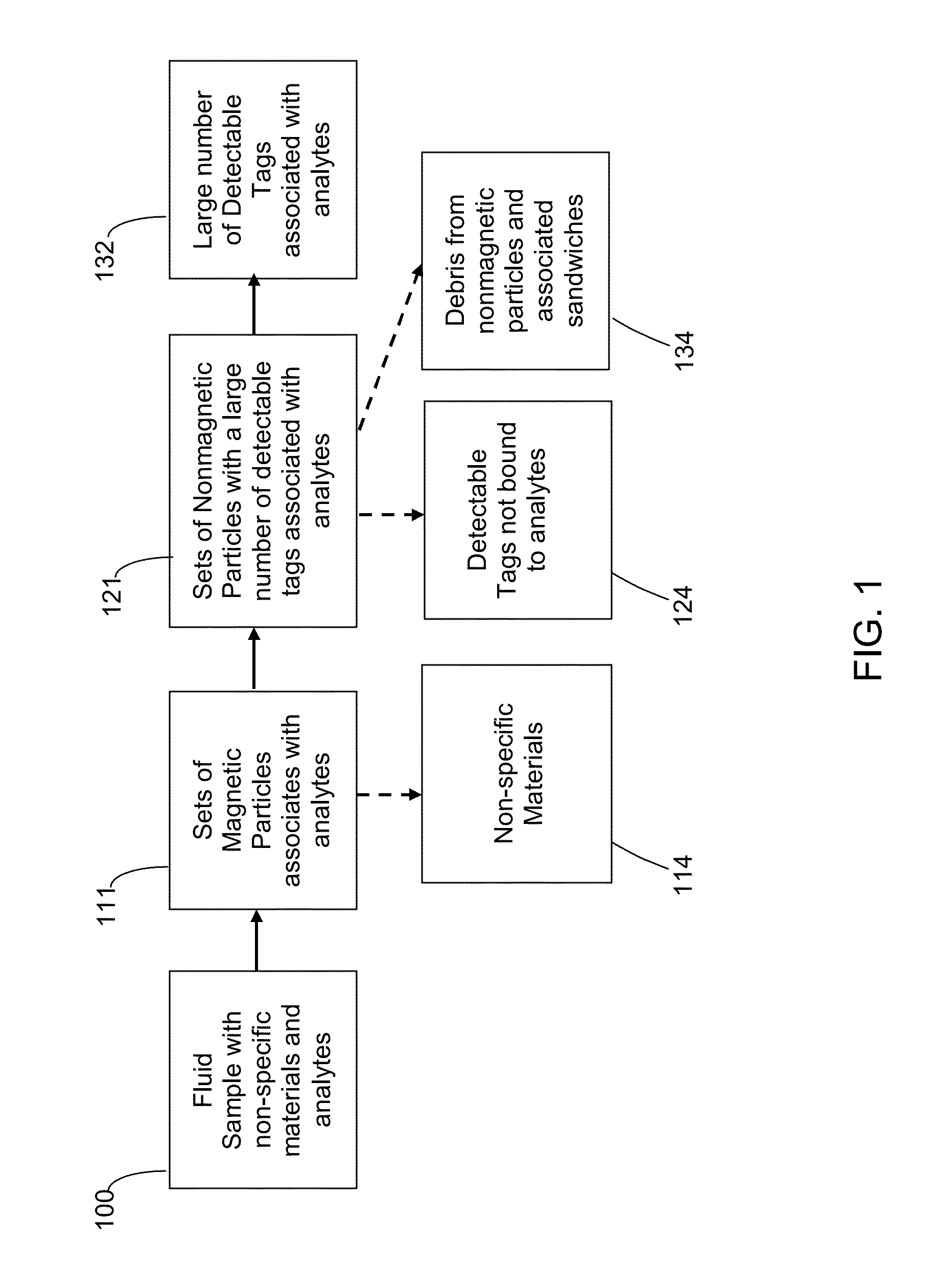
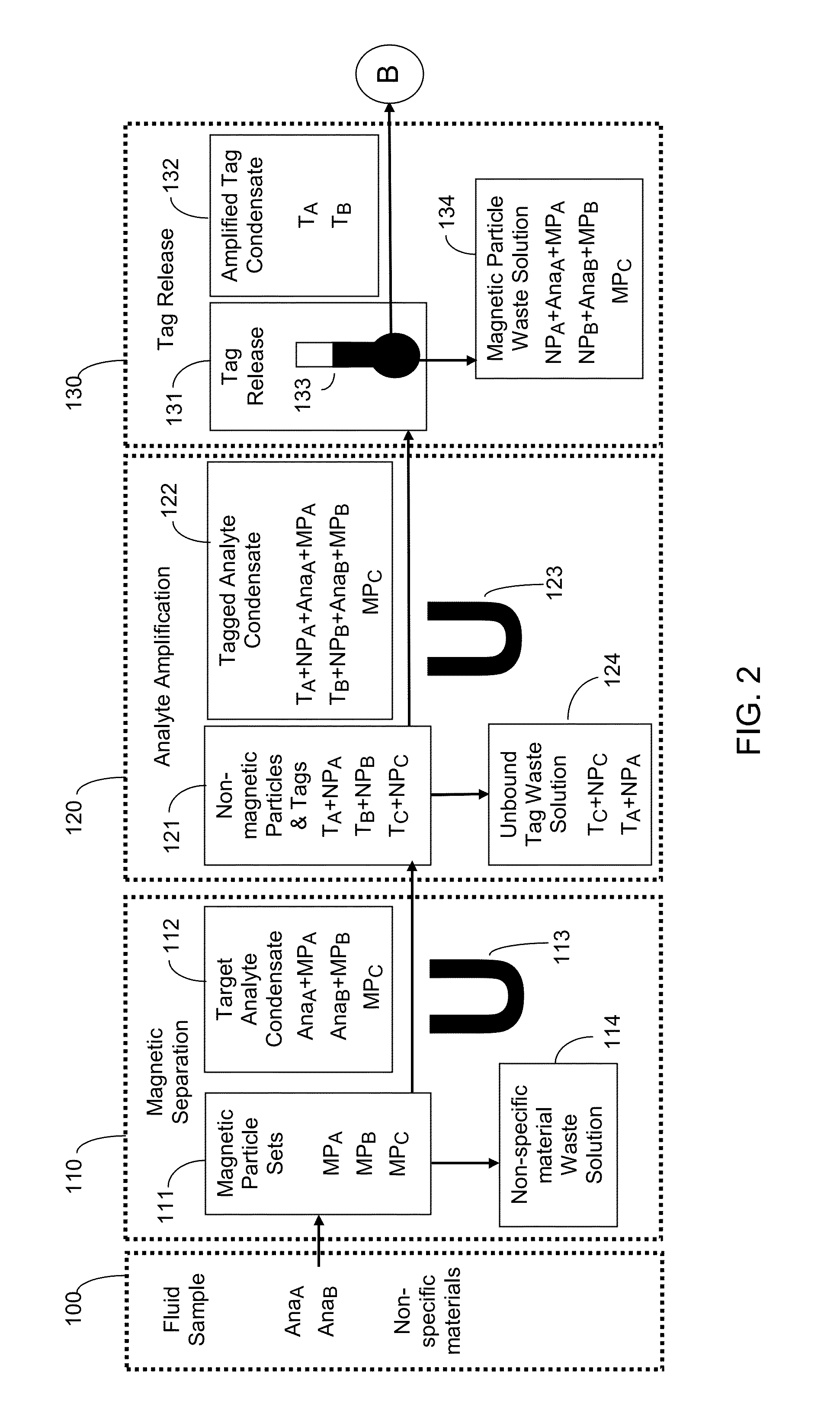
Ultra-sensitive detection of extremely low level biological analytes using electrochemical signal amplification and biosensor
ActiveUS20150141272A1Enhanced detection signalImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorUltra sensitive
This invention allows ultra-low levels of virtually any biological analyte to be detected and quantified rapidly, simply and inexpensively with an electrochemical biosensor using a novel electrochemical signal amplification technique. The invention amplifies detection signals from low level analytes using an innovative sandwich ELISA structure that replaces optical labels with a massive amount of electrochemically detectable guanine rich oligonucleotide tags. Selective binding is achieved with matched pairs of either commercial or custom analyte binding materials such as monoclonal antibodies or single stand DNA. The guanine tags are eluted from the sandwich structures and hybridize with complementary cytosine rich oligonucleotide recognition probes attached to the surface of a biosensor working electrode. An electrochemical technique generates a signal in proportion to the guanine level on the working electrode which is also proportional to the analyte level in the sample. Magnetic separation and a nanosensor are used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio for measuring analyte levels 1,000,000 times lower than enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Owner:GORDON NEIL
Method for preparing ganciclovir
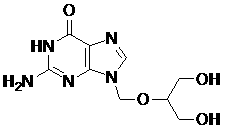
The invention relates to a method for preparing ganciclovir. The method comprises the following steps of: a, adding paraformaldehyde into 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol [2], reacting under the action of a catalyst to obtain hemiformal [3], and reacting with an acetic anhydride to obtain 1,3-dichloro-2-acetoxylmethoxylpropane [4]; b, making 1,3-dichloro-2-acetoxylmethoxylpropane [4] react with absolute postassium acetate or anhydrous sodium acetate in an organic solvent medium in the presence of a tetraalkyl ammonium bromide catalyst with 1-20 carbon atoms and an acetic anhydride serving as a dehydrating agent to obtain 1,3-diacetoxy-2-acetoxymethoxyl propane [5]; c, performing a condensation reaction on 1,3-diacetoxy-2-acetoxymethoxyl propane [5] and 2,9-diacetyl guanine [6] in an organic solvent medium in the presence of a catalyst and an acetic anhydride serving as a dehydrating agent to obtain triacetyl ganciclovir [7]; and d, hydrolyzing the triacetyl ganciclovir [7] to obtain ganciclovir [1]. The method has the advantages of easy and controllable preparation process, high utilization ratios of raw materials, low cost and high yield of a prepared ganciclovir product.
Owner:HUBEI GEDIAN HUMANWELL PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Chemically cleavable 3'-o-allyl-dntp-allyl-fluorophore fluorescent nucleotide analogues and related methods
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
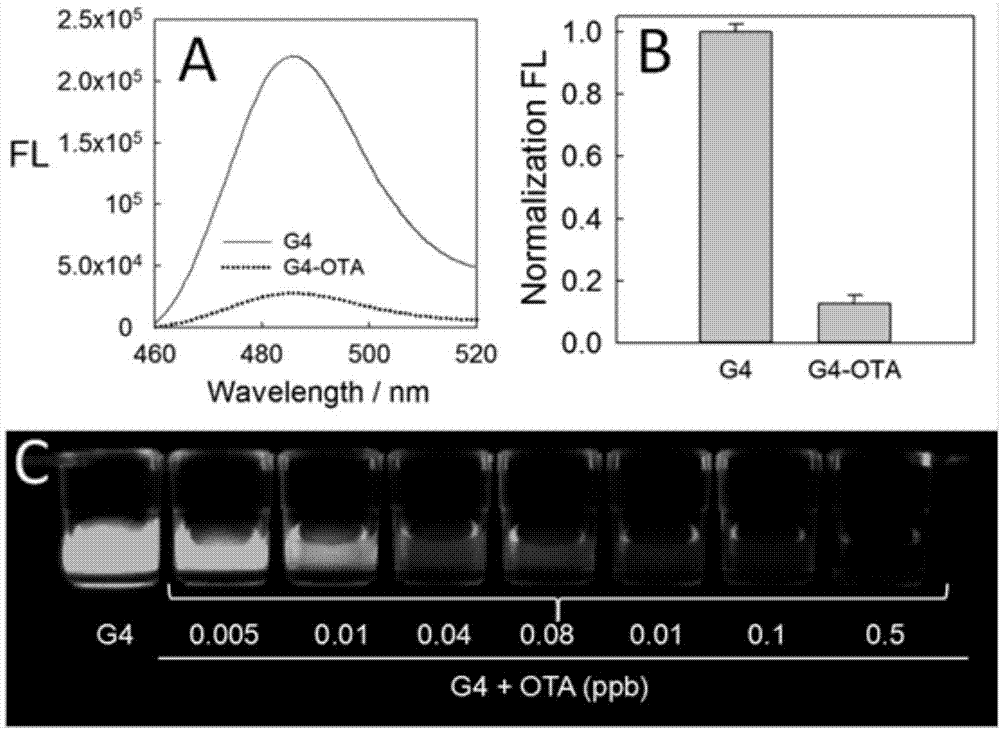
Method for detecting fungaltoxin through multiple signals and kit
ActiveCN107271668ARich identification methodsRich Signal TransformationBiological material analysisBiological testingFluorescenceUltraviolet
The invention discloses a method for detecting fungaltoxin through multiple signals. The method comprises the following steps: 1) combining fungaltoxin with aptamer: adding a to-be-detected sample after the reaction of the fungaltoxin aptamer and complementary sequence thereof, thereby acquiring a mixed solution A; 2) amplifying a digestion auxiliary signal: reacting the mixed solution A with restriction enzyme, thereby acquiring a mixed solution B; 3) preparing a guanine tetramer structure: reacting the mixed solution B with tail-end deoxynucleotide transferase and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate and reacting with ligand molecules, thereby acquiring a mixed solution C; and 4) detecting and analyzing: performing catalytic oxidation reaction on the mixed solution C and different substrates, generating ultraviolet, fluorescent and chemiluminescent signals and calculating the content of fungaltoxin in the to-be-detected sample according to the relation of the response strength of all the signals and the fungaltoxin concentration. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of quick and simple operation and treatment, short detection time, marker-free effect, low cost, high precision, high sensitivity, and the like.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
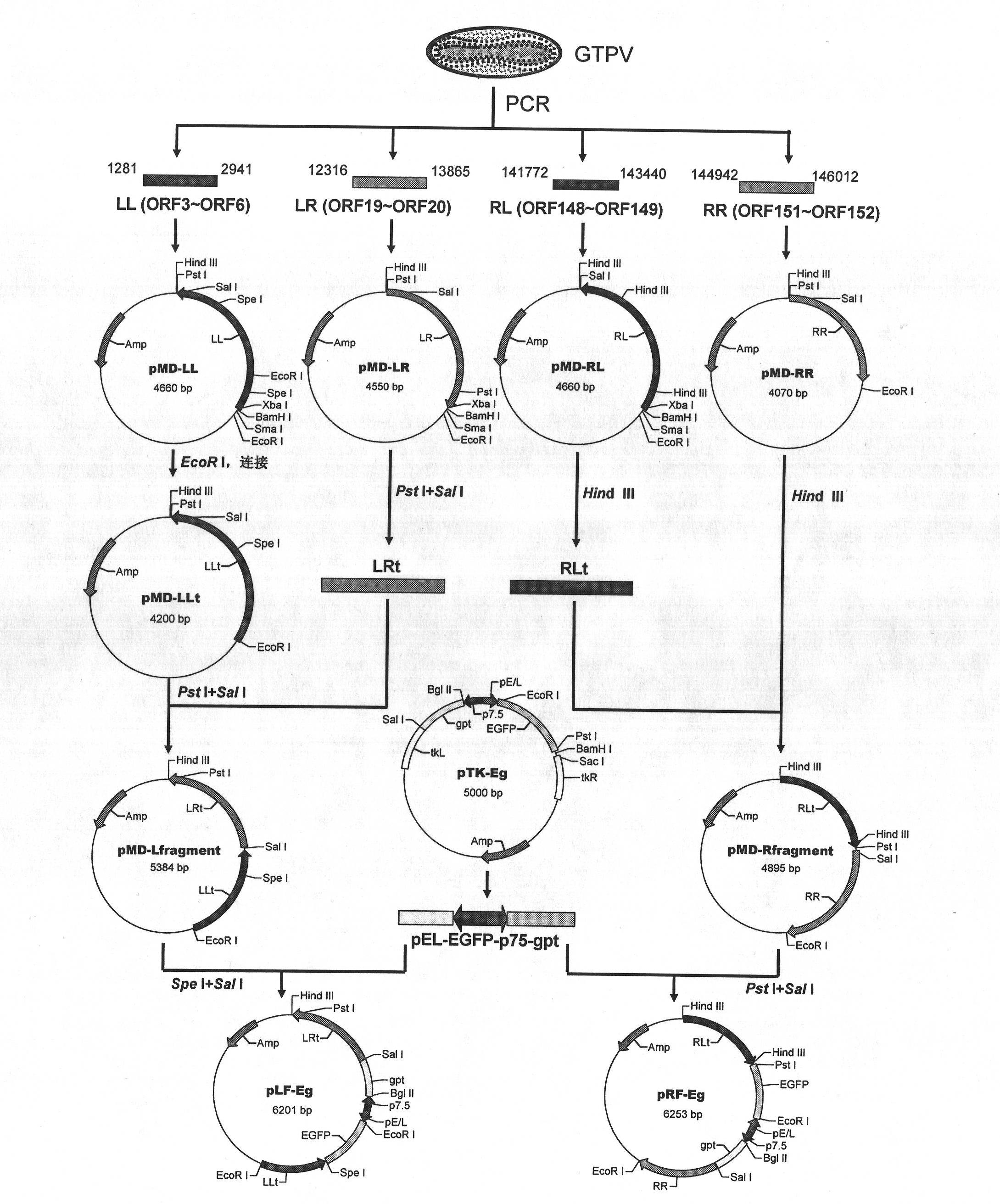
Method for screening non-essential regions for replication of goat pox virus and universal transfer vectors for same
InactiveCN102174508AImprove securitySmall virulent effectsViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodTransfer vector
The invention relates to a method for screening non-essential regions for replication of a goat pox virus and universal transfer vectors for same. The method comprises the steps of amplifying two-end gene segments of any two regions of a goat pox virus gene by using a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method; then, inserting an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene and a xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (gpt) gene expression cassette into the segments; establishing two universal transfer vectors of the goat pox virus; and acquiring a recombinant virus expressing an exogenous gene stably from the transfer vectors, thereby determining the selected regions to be non-essential regions for replication of the goat pox virus, wherein each universal transfer vector contains one unique restriction enzyme cutting site Sal I and allows gene expression cassettes of other items to insert in. The recombinant virus obtained by means of the two universal transfer vectors provided by the invention not only has a growth performance similar to a parent virus, but also has better safety because a plurality of toxicity related genes in a genome are knocked out in an orientation way, and has the potential to be developed into an attenuated vaccine strain for gene engineering.
Owner:广西壮族自治区动物疫病预防控制中心
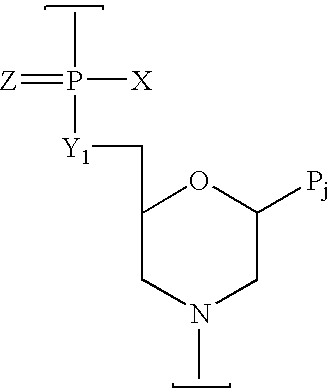
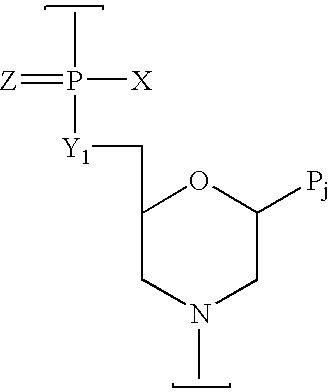
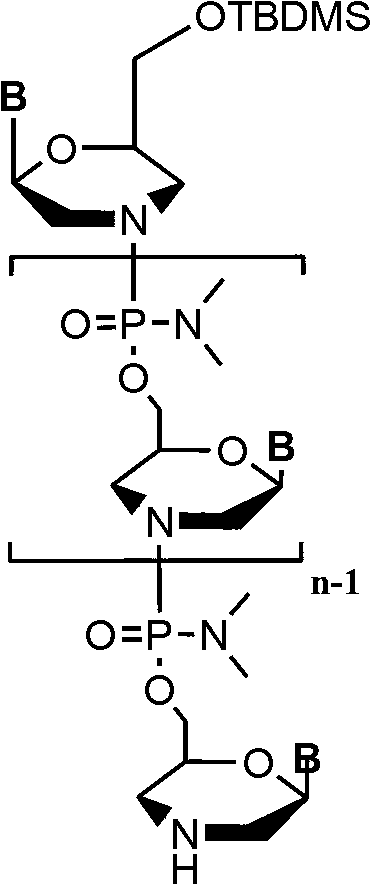
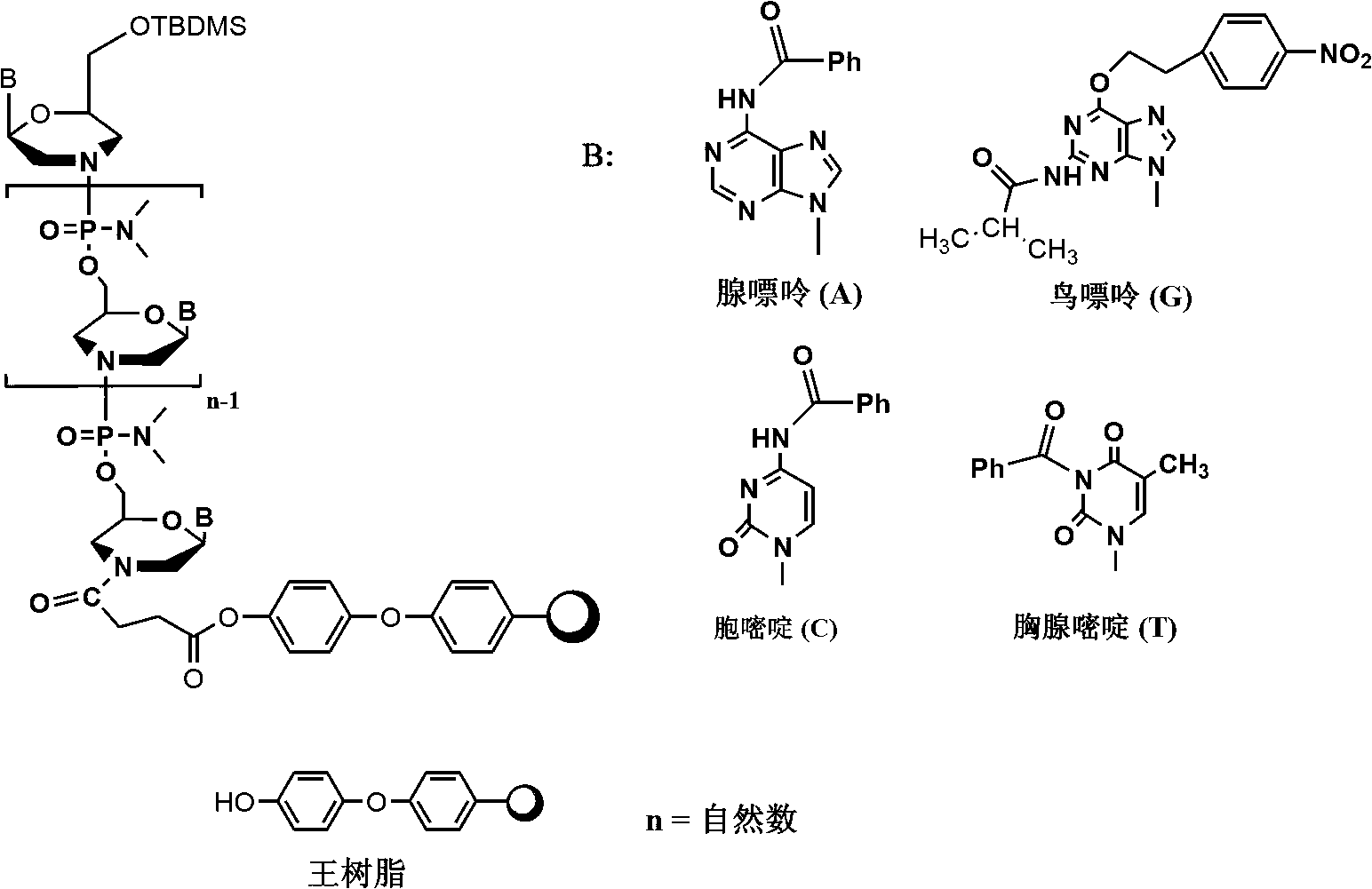
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer synthetized by solid phase and method thereof
The invention relates to a method for synthetizing phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer by solid phase. A cheap resin is utilized; Wang resin is as a solid phase carrier; the phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) structure of which terminal hydroxyl is protected by tert-butyl dimethyl silicon is shown in the description, wherein a structure of basic group B is any one of adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Compared with the existing solid phase synthetic technology, the method provided by the invention can greatly reduce synthetic cost, and can be suitable for mass production of phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer.
Owner:天津特安化学科技有限公司
Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid hybridization
InactiveUS20050233358A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementRedoxNucleic acid hybridisation
A method of detecting a nucleic acid (e.g., DNA, RNA) that contains at least one preselected base (e.g., adenine, guanine, 6-mercaptoguanine, 8-oxo-guanine, and 8-oxo-adenine) comprises (a) reacting the nucleic acid with a transition metal complex capable of oxidizing the preselected base in an oxidation-reduction reaction; (b) detecting the oxidation-reduction reaction; and (c) determining the presence or absence of the nucleic acid from the detected oxidation-reduction reaction at the preselected base. The method may be used in a variety of applications, including DNA sequencing, diagnostic assays, and quantitative analysis.
Owner:THORP H +5
Nitrogen-rich doped porous structural carbon material and preparation method and application thereof
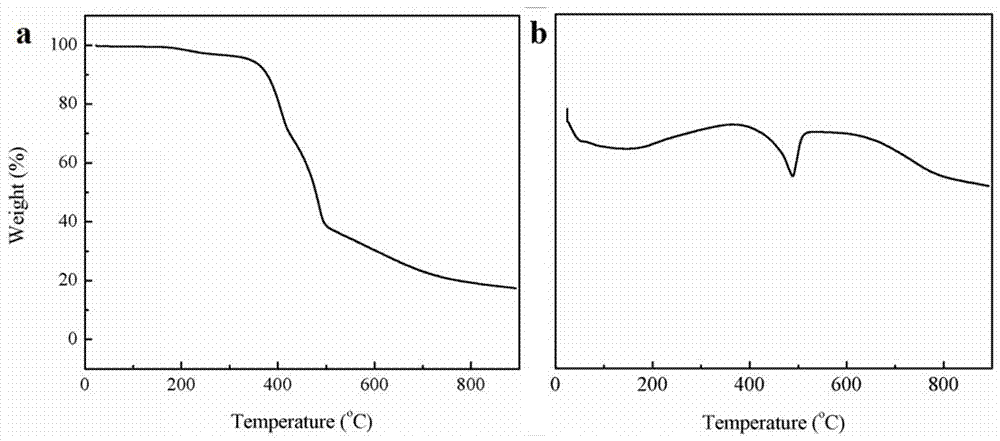
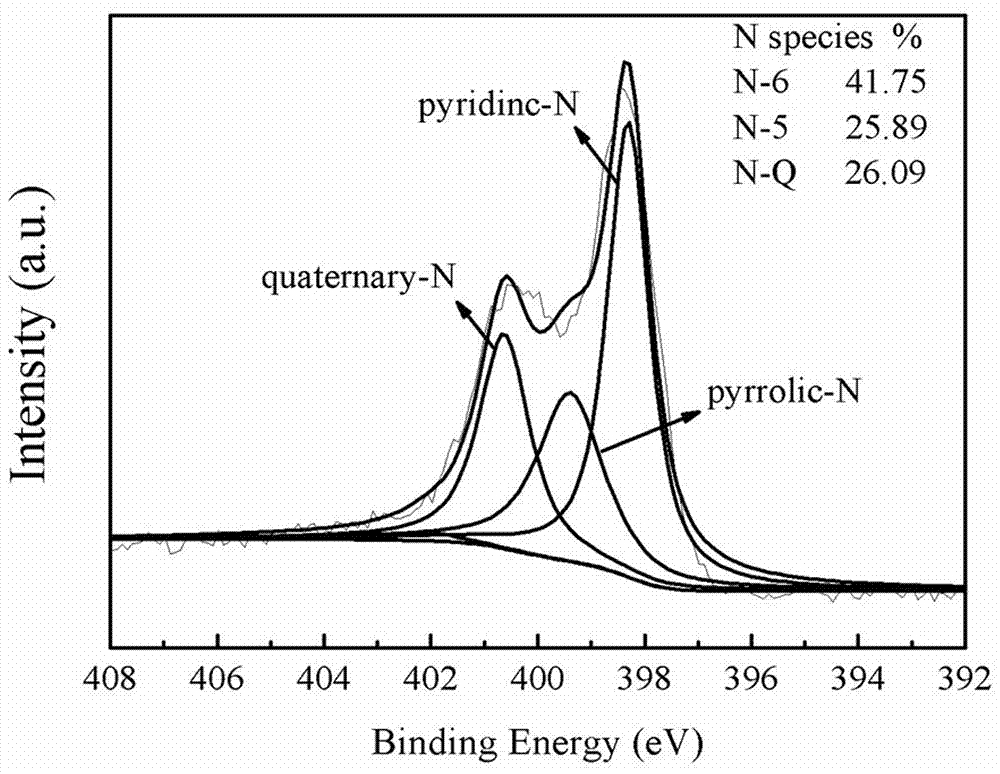
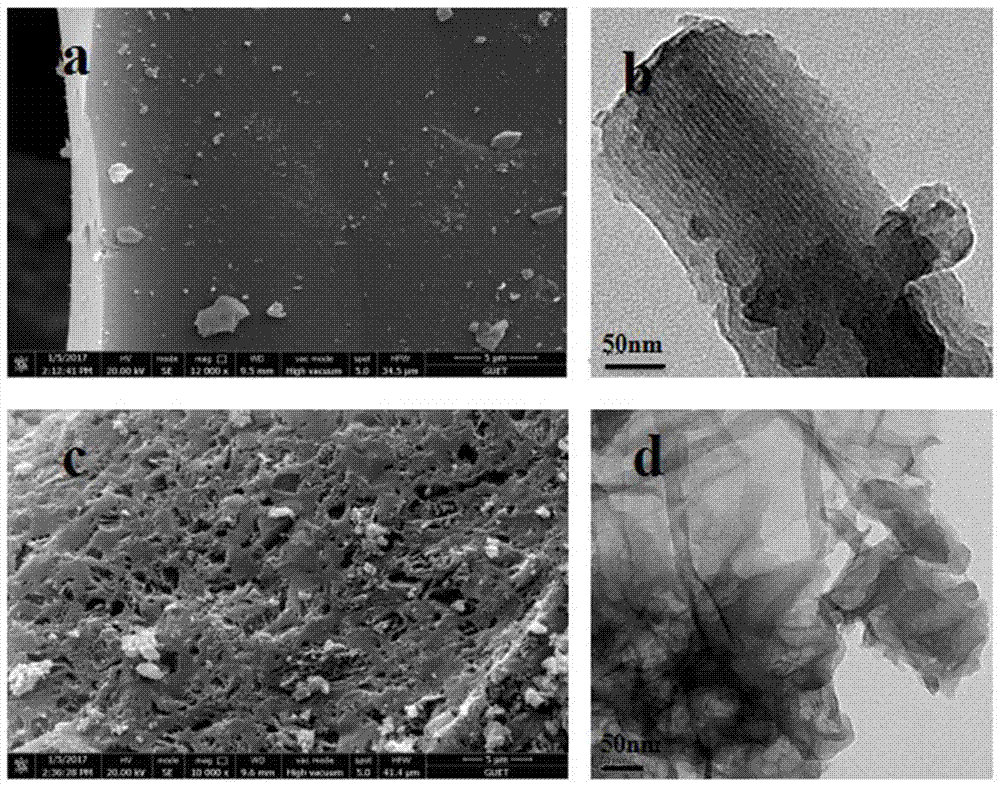
InactiveCN106910893AMany active sitesImprove lithium storage performanceHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesCapacitanceActive agent
The invention provides a nitrogen-rich doped porous structural carbon material which is prepared by mixing water soluble phenolic resin, a surfactant F127 and guanine by a solvent evaporation self assembly method. The preparation method comprises the steps: (1) obtaining a nitrogen-containing precursor from the surfactant F127, guanine and the water soluble phenolic resin through the evaporation self-assembly process; (2) carrying out pyrolysis of the nitrogen-containing precursor to obtain nitrogen-rich doped modified porous carbon material; and (3) washing the obtained porous carbon material, filtering, and drying to obtain the nitrogen-rich doped porous structural carbon material. With an application of the material as a negative electrode material for a lithium ion battery, when the current density is 100 mA*g<-1>, the specific capacity value is 607 mAh*g<-1>; with an application of the material as a super capacitor material, when the current density is 0.5 A*g<-1>, the specific capacitance is 218 F*g<-1>. The prepared carbon material has the advantages of large specific surface area, excellent electrochemical performance, simple preparation process and easy mass production, and has wide application prospects in electrochemistry and other fields.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com