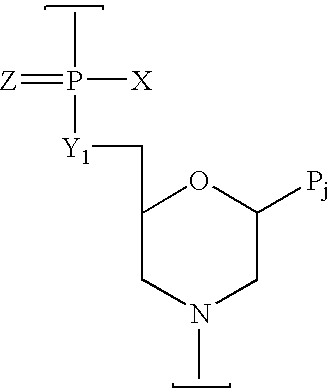
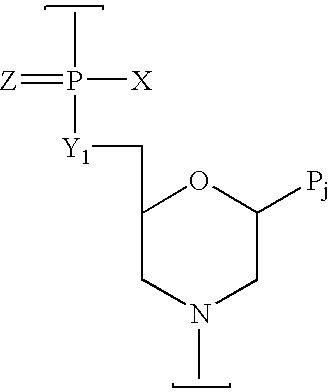
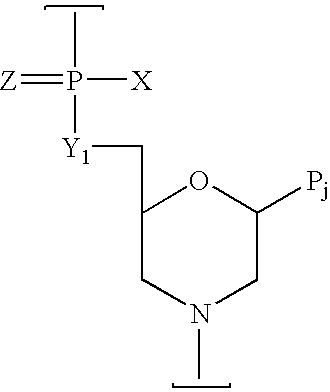
Peptide conjugated, inosine-substituted antisense oligomer compound and method
a technology of inosine substitution and antisense oligomer, which is applied in the field of antisense oligomer compound, can solve the problems of compound antisense activity and ability to purify the compound, and achieve the effect of enhancing the uptake of the compound and cellular uptak
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Peptide Synthesis and Conjugation to PMO
[0092] Peptides were synthesized by Fmoc Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis, referred to herein as SPPS. A p-benzyloxybenzyl alcohol resin was used for synthesis of peptides with a C-terminal acid, while a Rink Amide MBHA resin was used for peptide amides. Both resins are available from Novabiochem (San Diego, Calif.). A typical synthesis cycle began with N-terminal deprotection via 20% piperidine. Then, N-α-Fmoc-protected amino acids were coupled to the growing peptide chain by activation with 2-(1H-Benzotriazole-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HBTU) in the presence of N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIEA). Arginine side chains were protected with the 2,2,4,6,7-pentamethyldihydrobenzofuran-5-sulfonyl (Pbf) protecting group, cysteine with trityl, and lysine side chains with t-butoxycarbonyl (Boc). The cycle was repeated until all of the amino acids were added, in a carboxy-to-amino direction, in the desired sequence. Cleavage from...
example 2
G-Rich Oligomers form G-Tetraplex Aggregates when Conjugated to Arginine-Rich Peptides
[0096] This example details the development of an arginine-rich peptide-PMO conjugate that targets the c-myc gene for a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) clinical application. The goal of the project described in this example was to develop processes for the synthesis and purification of the conjugate with acceptable yield and purity. Furthermore, methods for analysis of the conjugate must characterize it and identify impurities throughout the synthetic process and in any formulations used in the clinic. Quantitation of the amount of free peptide remaining in the product is probably the most critical analytical capability as free peptide is potentially more toxic than conjugate or free PMO.
[0097] As will be shown below, it is clear that aggregation through the formation of intramolecular G-quartets is a major hurdle to overcome in the synthesis of arginine-rich peptides conjugated to G-rich PMO...
example 3
Inosine Substituted for Guanine Prevents Aggregation of G-Rich Oligomers Conjugated to Arginine-Rich Peptides
[0104] It has long been recognized that guanine-rich nucleic acid sequences can adopt intermolecular or intramolecular quadruplex structures that are stabilized by the presence of G-quartets (see FIG. 5). G-quartets are stacked planar hydrogen-bonded guanine tetramers and cause guanine-rich nucleic acids to form quadruplex structures. The potential roles of quadruplex formation in vivo have been investigated because some biologically important G-rich sequences are capable of forming G-quartets under physiological conditions in vitro. In addition, the number of reports describing specific G-quartet-binding proteins is now considerable (Shafer and Smirnov 2000).
[0105] G-rich oligomers (GROs) can form a variety of possible quadruplex structures, depending on both thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. The structures formed can be influenced by oligonucleotide base sequence ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com