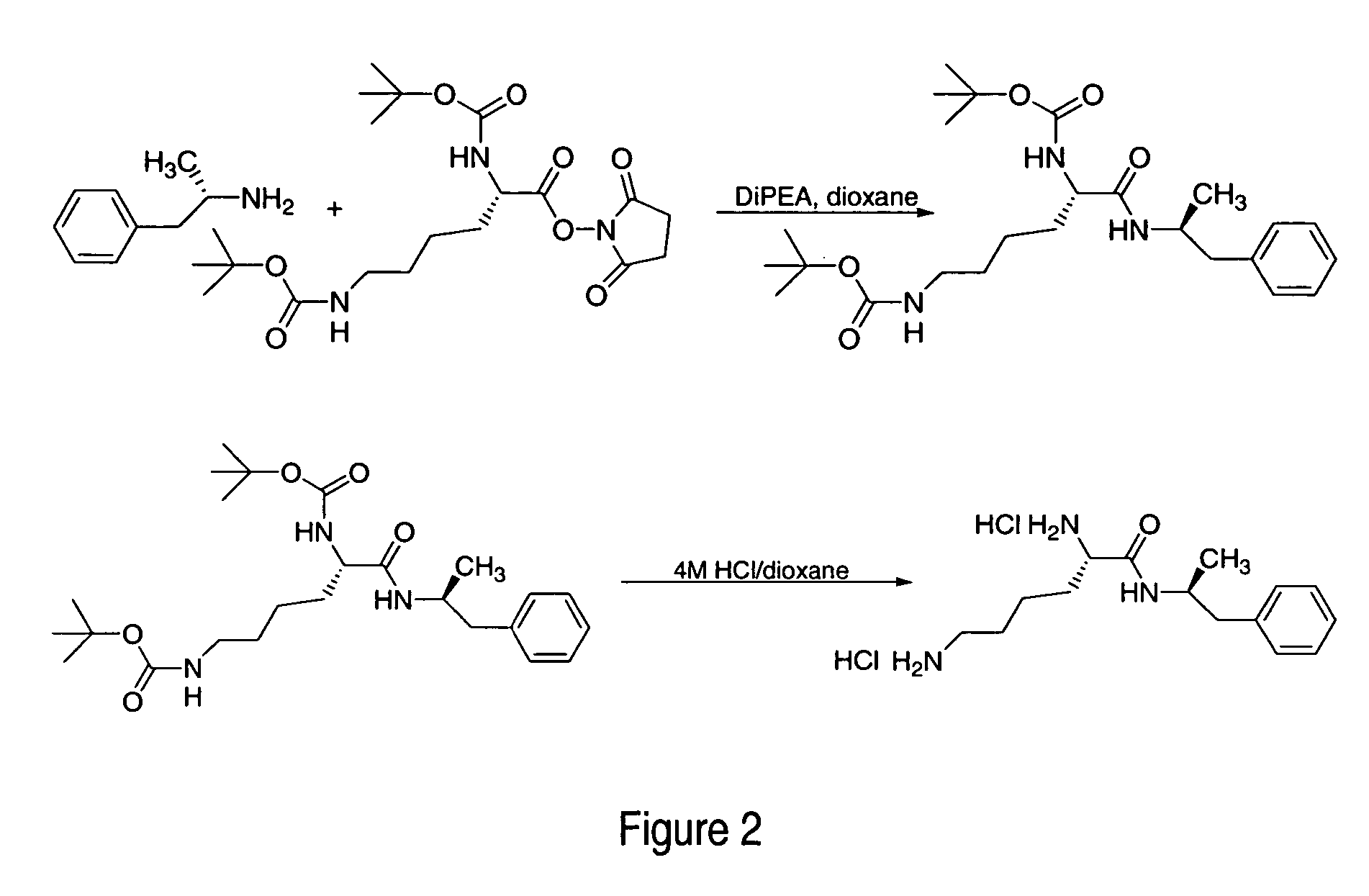
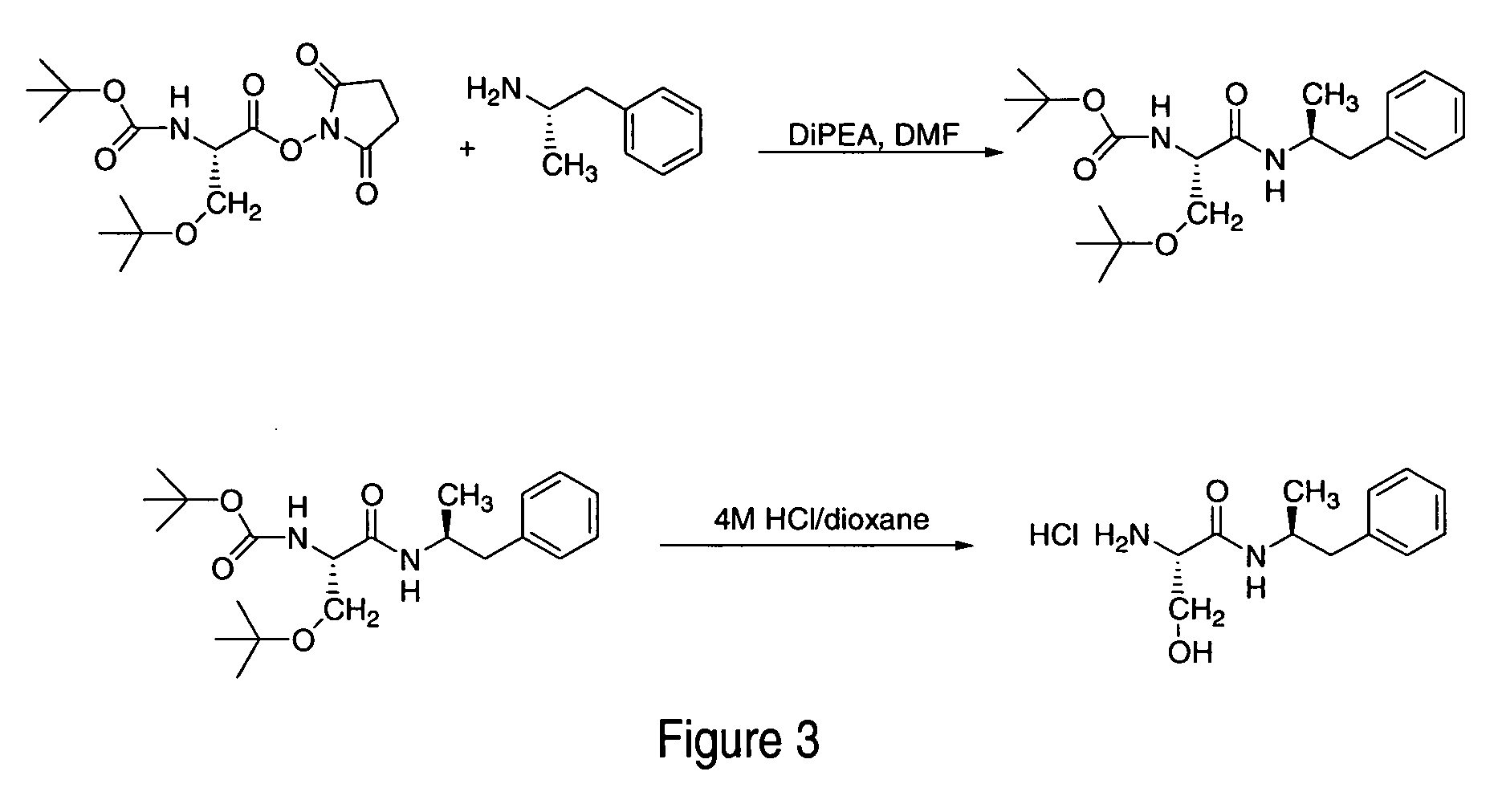
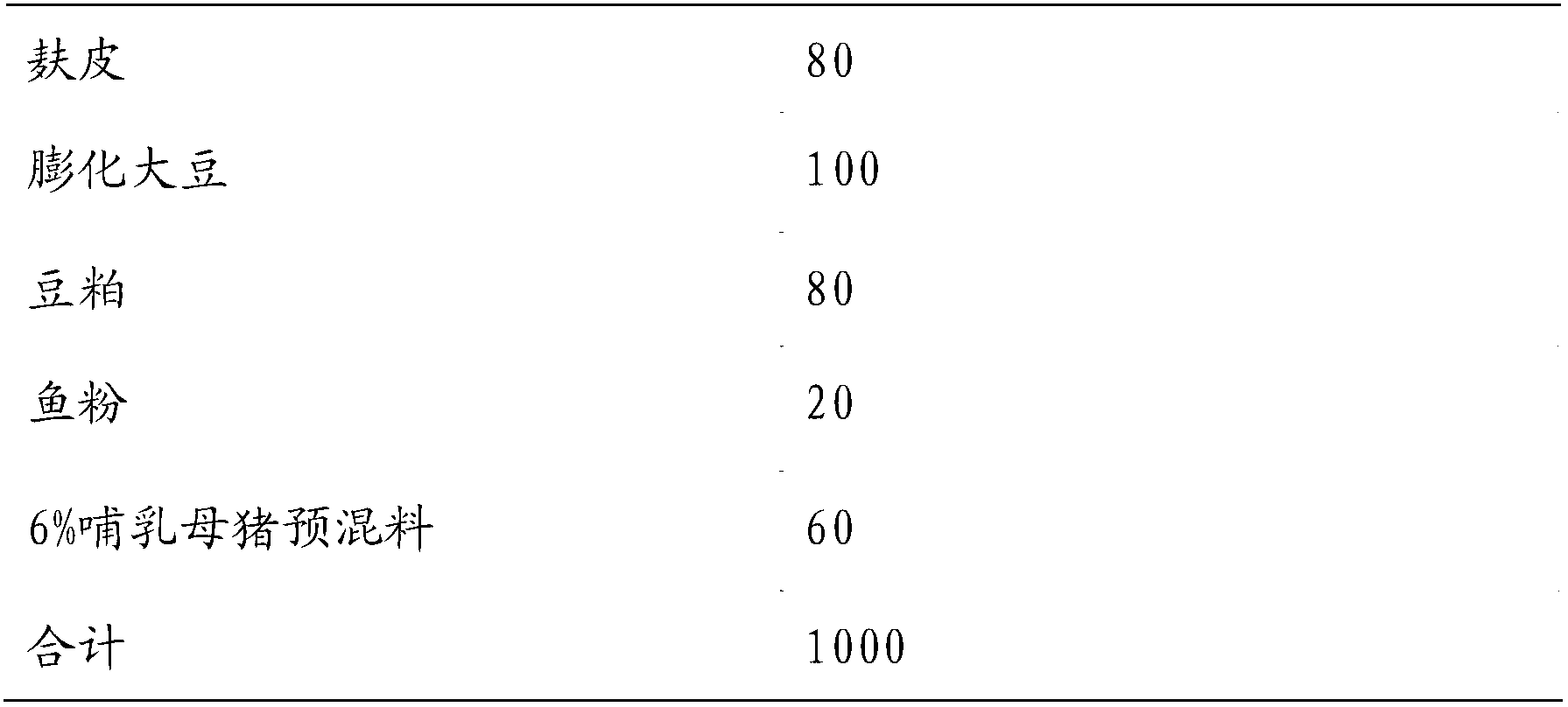Patents
Literature
6851 results about "Lysine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH₃⁺ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO⁻ form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH₂)₄NH₂), classifying it as a basic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons, AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the S configuration.
Methods of making amino acids using E. coli transformed with csc genes
An amino acid such as threonine, homoserine, isoleucine, lysine, valine and tryptophan is produced using a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has been constructed from sucorse non-assimilative strain belonging to the genus Escherichia and which harbors sucrose non-PTS (phosphoenol pyruvate-dependent sucrose-6-phosphotransferase system) genes and has an ability to produce the amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
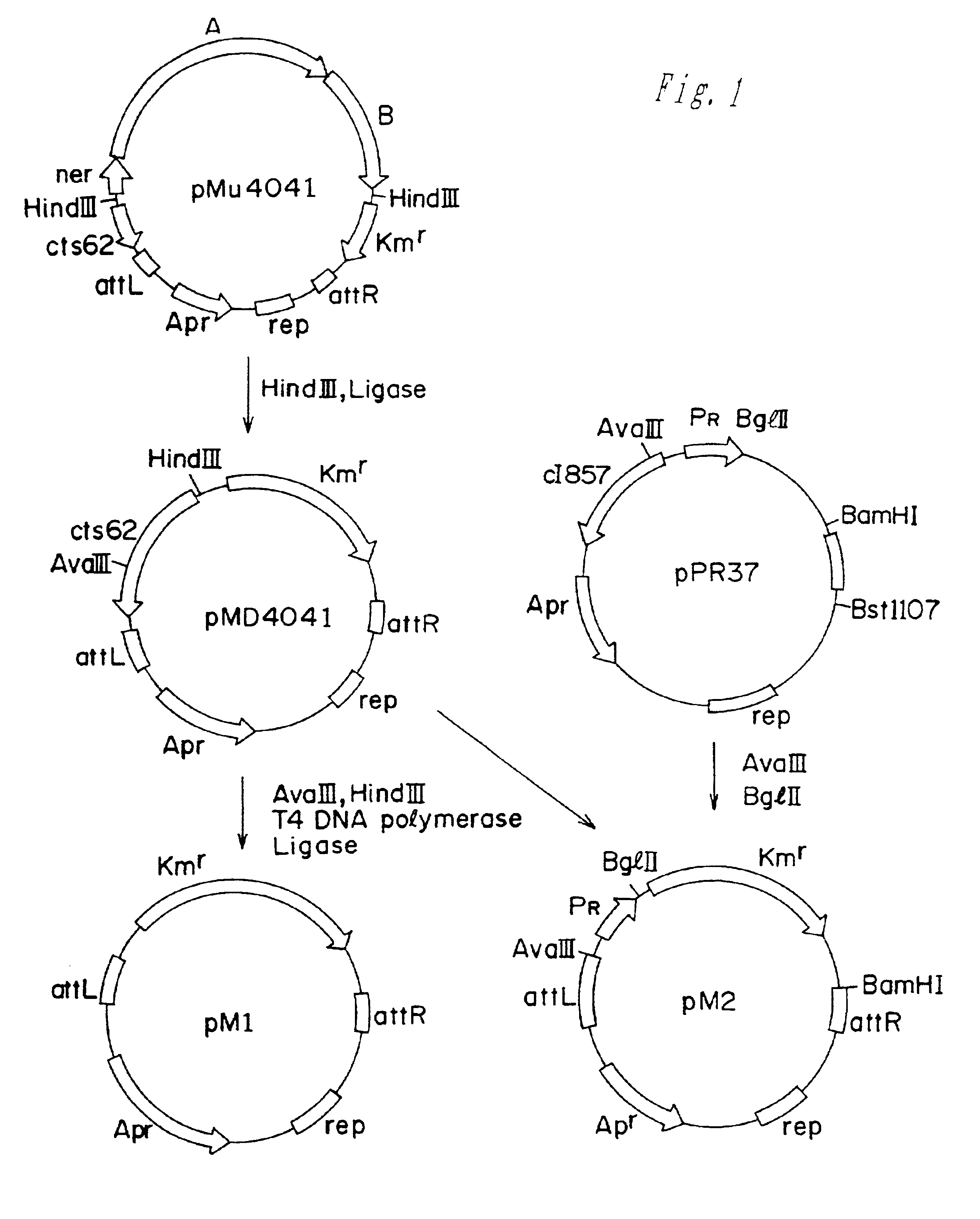
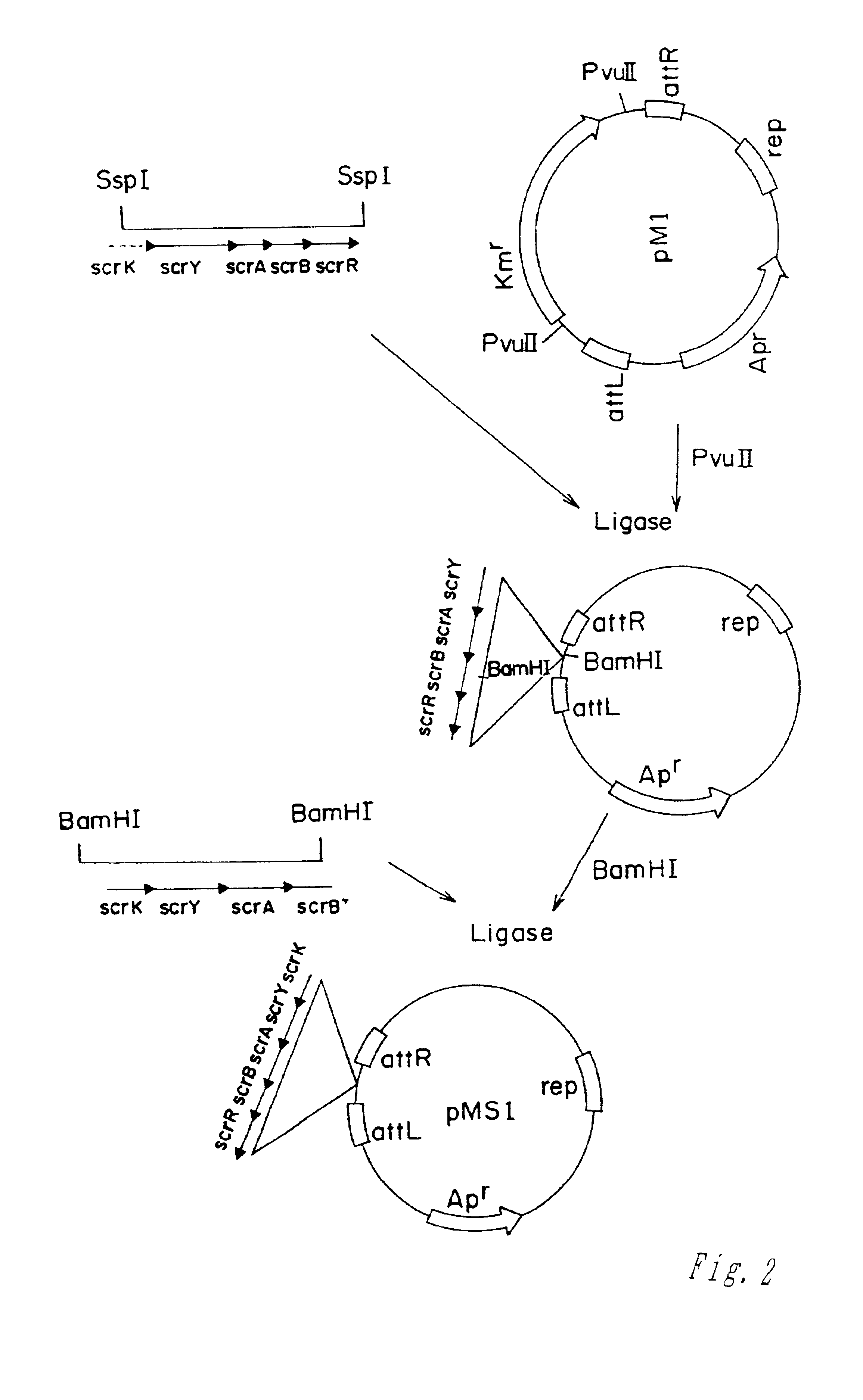
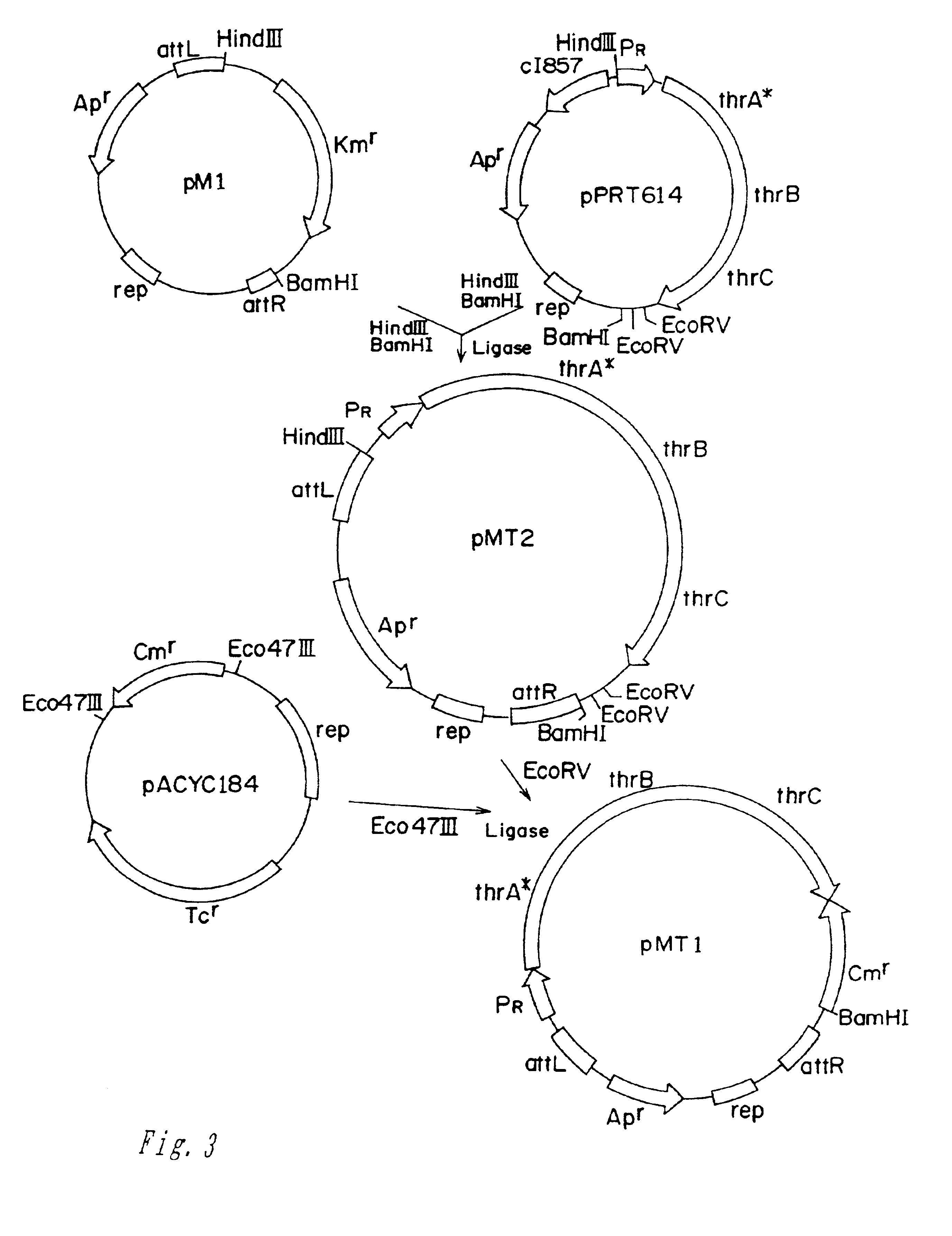
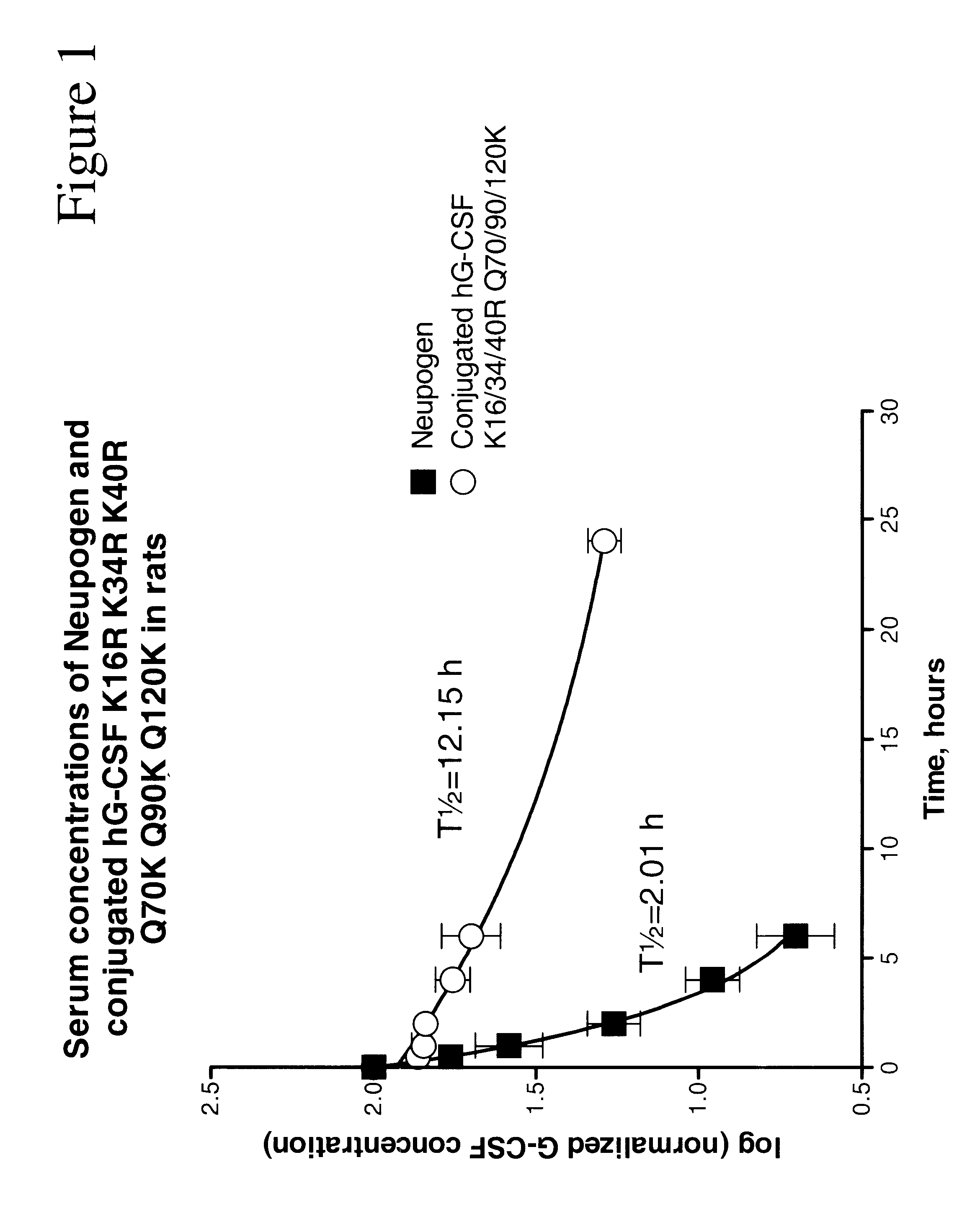
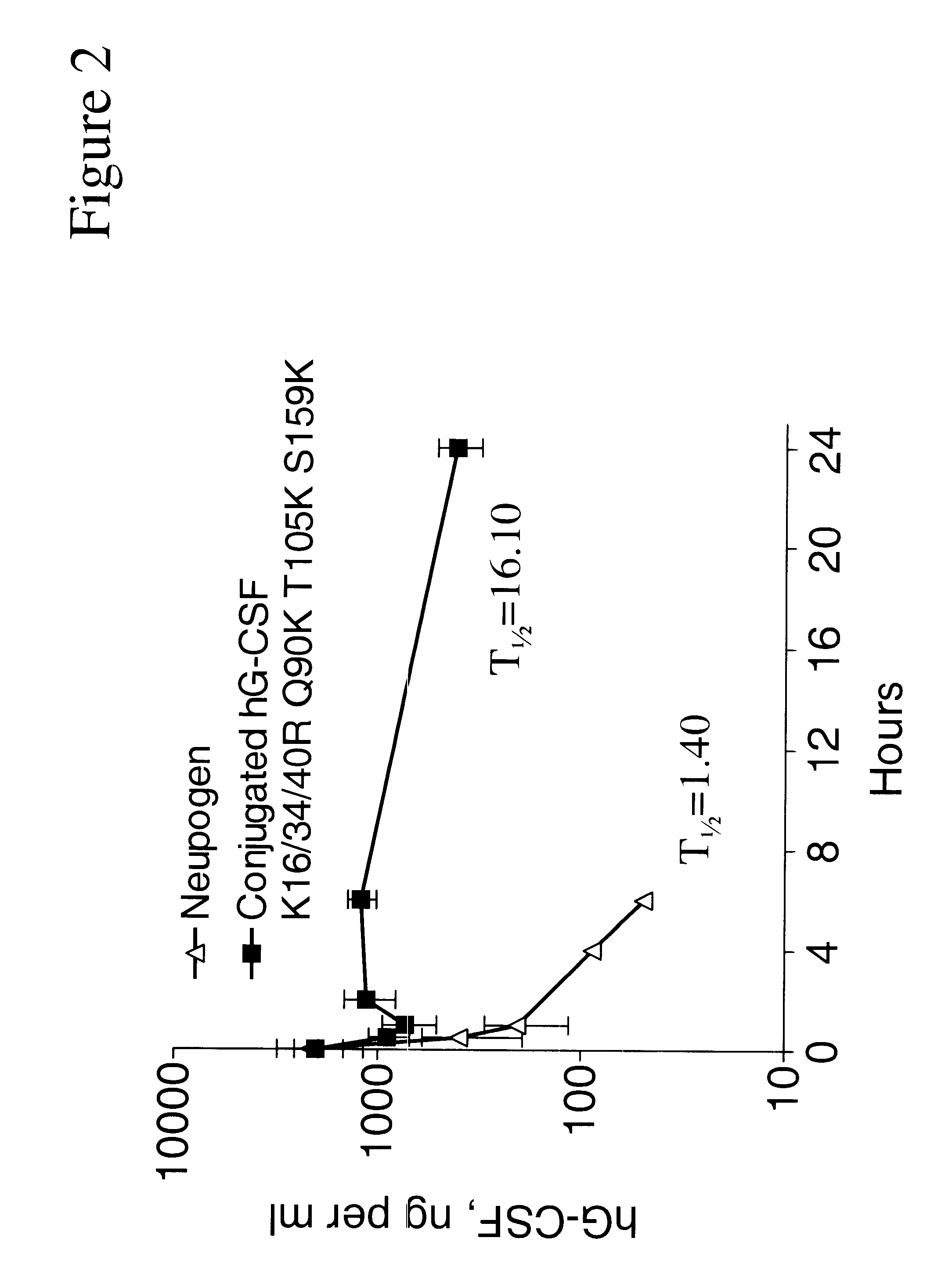
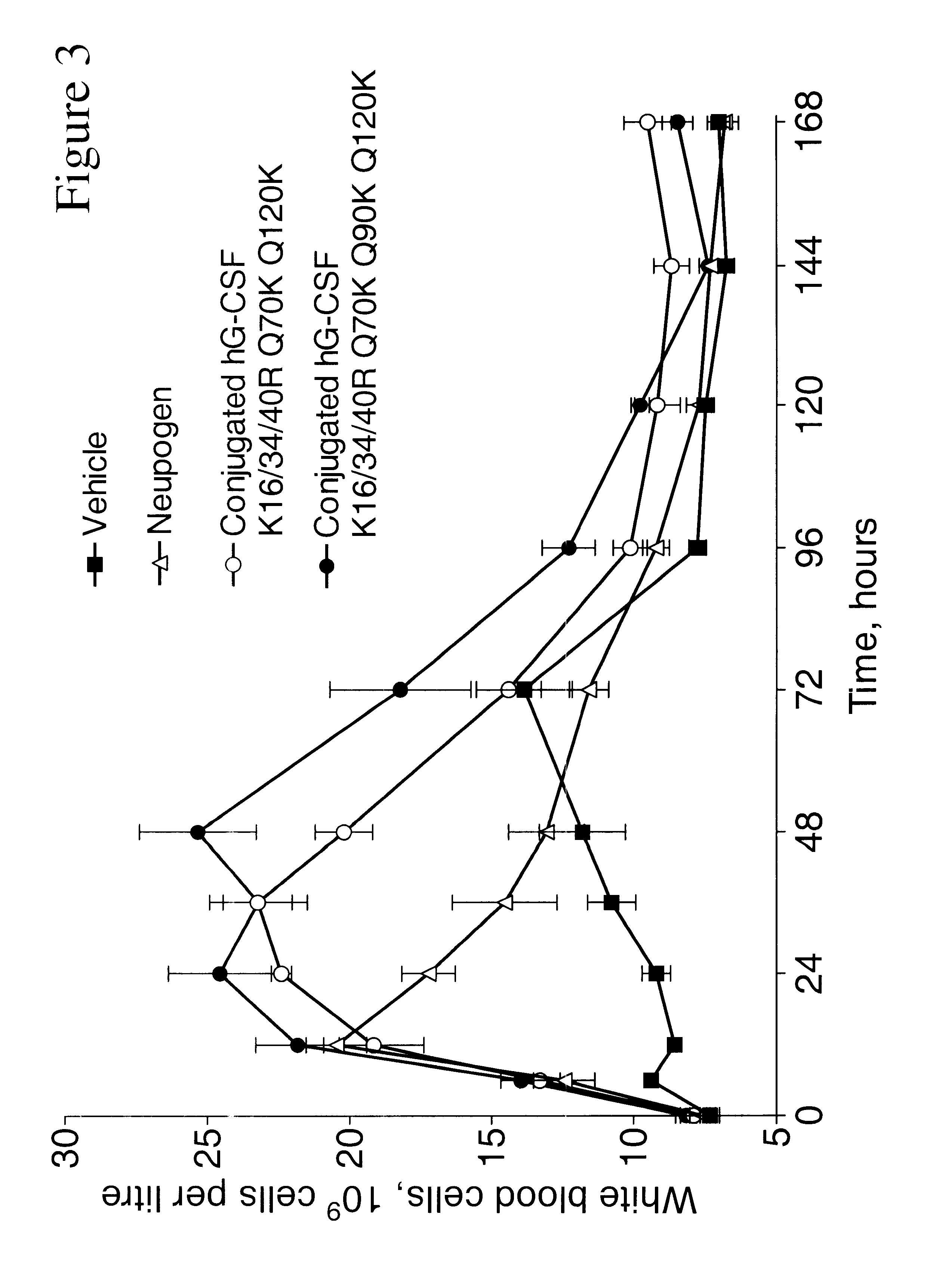
G-CSF conjugates
InactiveUS6555660B2Improved propertyReduced in vitroBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to polypeptide conjugates comprising a polypeptide exhibiting G-CSF activity and having an amino acid sequence that differs from the amino acid sequence of human G-CSF in at least one specified introduced and / or removed amino acid residue comprising an attachment group for a non-polypeptide moiety, and having at least one non-polypeptide moiety attached to an attachment group of the polypeptide. The attachment group may e.g. be a lysine, cysteine, aspartic acid or glutamic acid residue or a glycosylation site, and the non-polypeptide moiety may e.g. be a polymer such as polyethylene glycol or an oligosaccharide. The conjugate, which has a reduced in vitro bioactivity compared to hG-CSF, has one or more improved properties such as increased biological half-life and increased stimulation of neutrophils.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Crosslinked gels comprising polyalkyleneimines, and their uses as medical devices
ActiveUS20070196454A1Promote cell growthSoft tissue growthIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSurgical adhesivesCross-linkCysteine thiolate
One aspect of the present invention generally relates to methods of sealing a wound or tissue plane or filling a void splace. In a preferred embodiment, the wound is an ophthalmic, pleural or dural wound. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane comprises a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Treatment of the polyethyleneimine with a cross-linking reagent causes the polyethyleneimine polymers to polymerize forming a seal. In certain instances, the cross-linking reagent is a polyethylene glycol having reactive terminal groups. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the reactive terminal groups are isocyanates. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine has a lysine, cysteine, isocysteine or other nucleophilic group attached to the periphery of the polymer. In certain instances, the polyethyleneimine is mixed with a second polymer, such as a polyethylene glycol containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing electrophilic groups with a cross-linking reagent containing nucleophilic groups. In certain instances, the electrophilic groups on the polyalkyleneamine are activated esters, such as N-hydroxy succinimide ester. In certain instances, the compositions used to seal the wound or tissue plane are formed by reacting a polyalkyleneamine bearing photopolymerizable groups with ultraviolet or visibile light. Compositions used to seal the wound which contain PEI or a derivative of PEI are found to adhere tightly to the tissue. Other aspects of the present invention relate to methods of filling a void of a patient or adhering tissue. In certain instances, the methods use a polyalkyleneamine. In a preferred embodiment, the polyalkyleneamine is polyethyleneimine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a polymeric composition formed by exposing a polyalkyleneamine to an activated polyalkylene glycol. In certain instances, the composition is attached to mammalian tissue.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS20100300463A1Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArgininePhenylalanine
A method of thermally processing a tobacco material is provided, the method including the steps of (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof, to form a moist tobacco mixture; (ii) heating the moist tobacco mixture at a temperature of at least about 60° C. to form a heat-treated tobacco mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated tobacco mixture into a tobacco product. Heat-treated tobacco composition prepared according to the method are also provided, such as heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition comprising a tobacco material, water, flavorant, binder, and filler, the heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition having an acrylamide content of less than about 2000 ppb.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
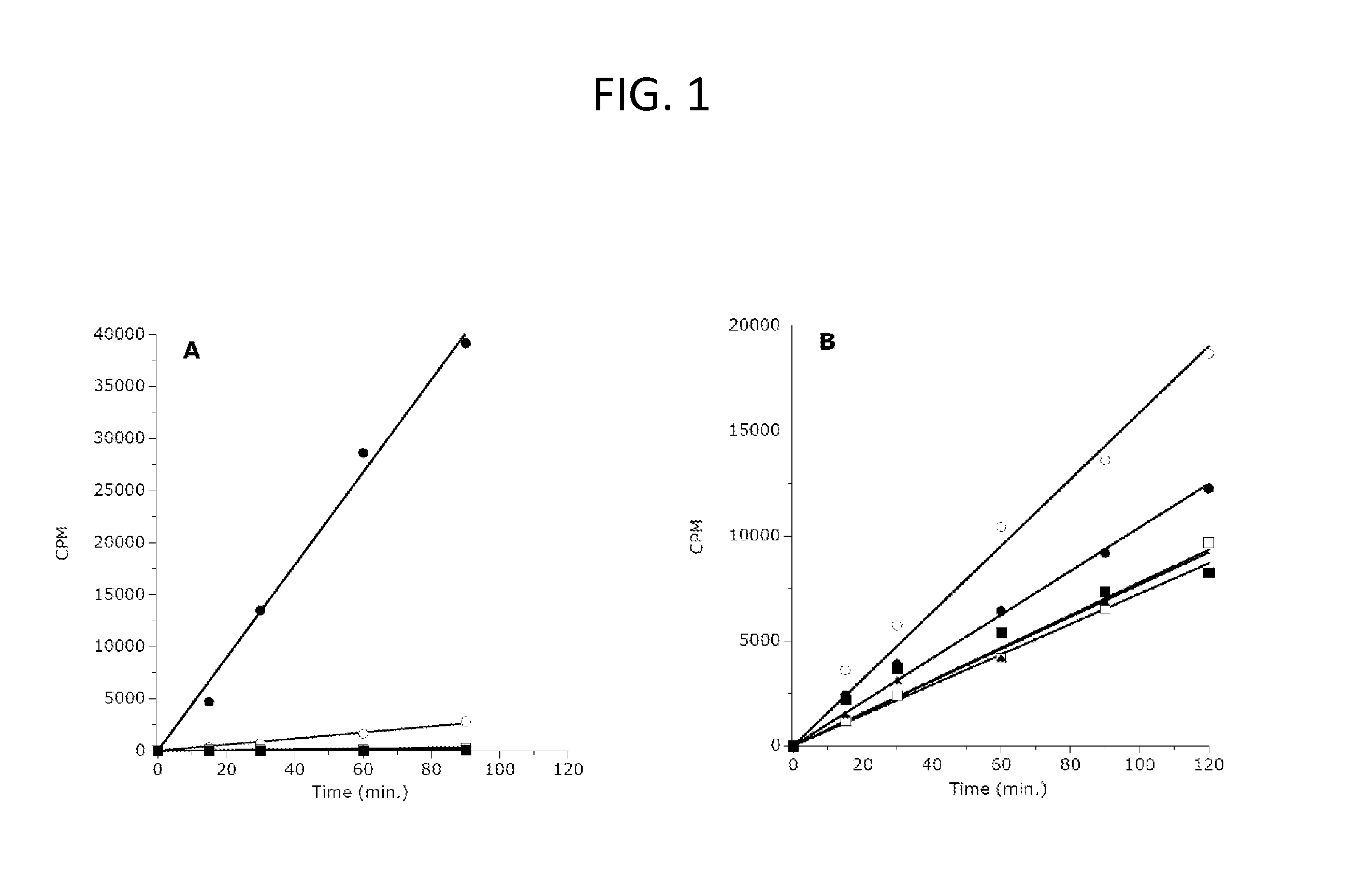
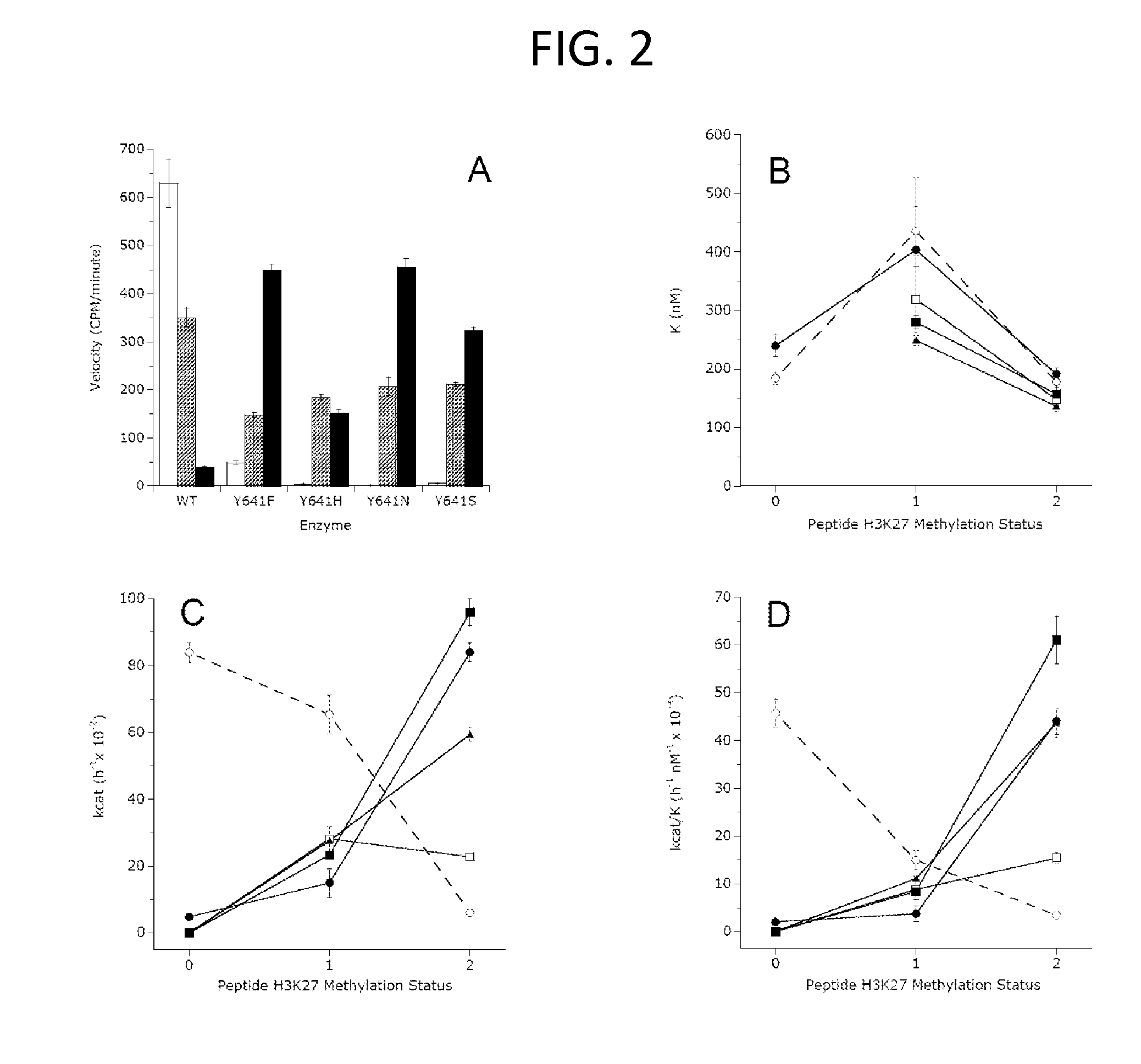
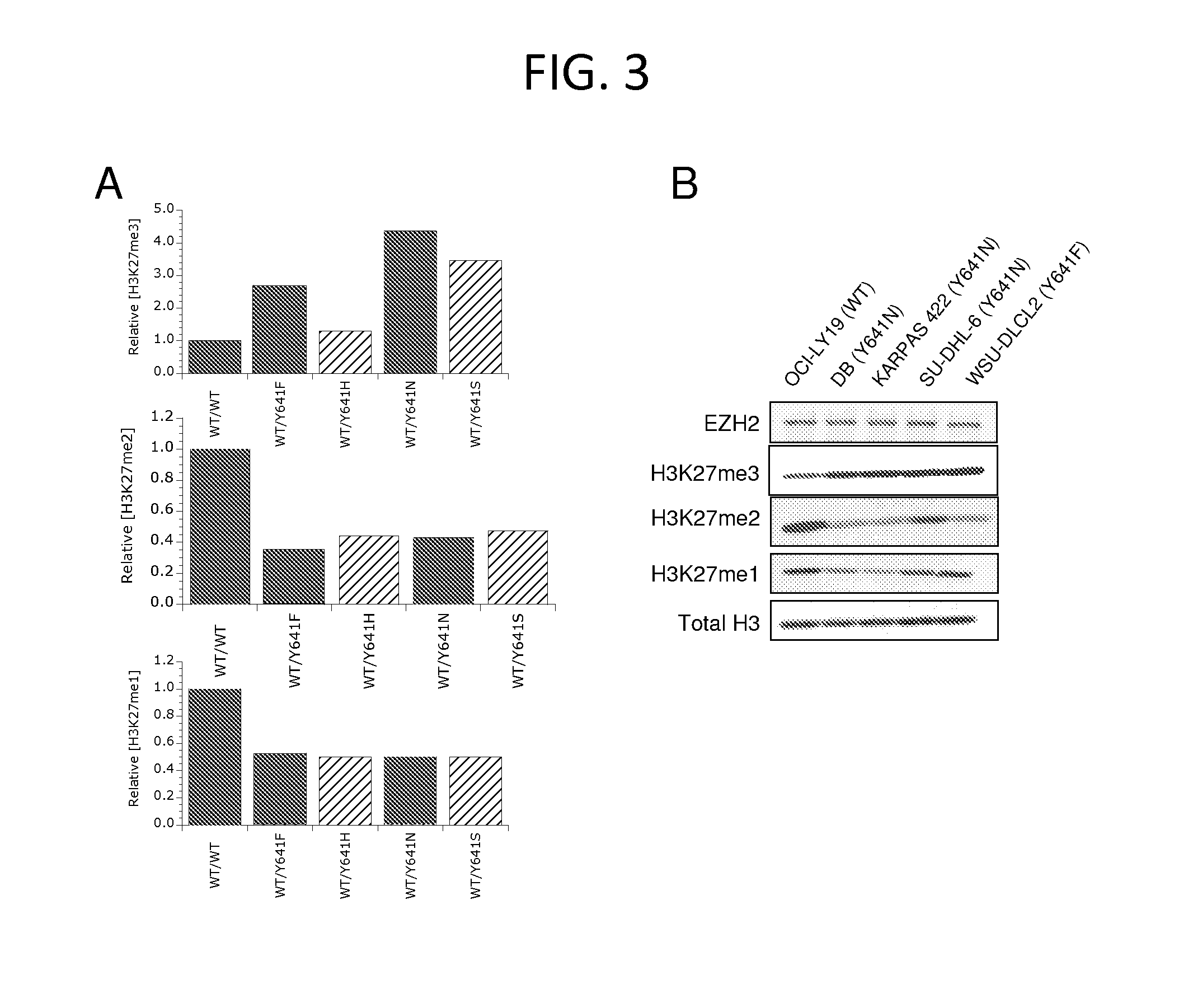
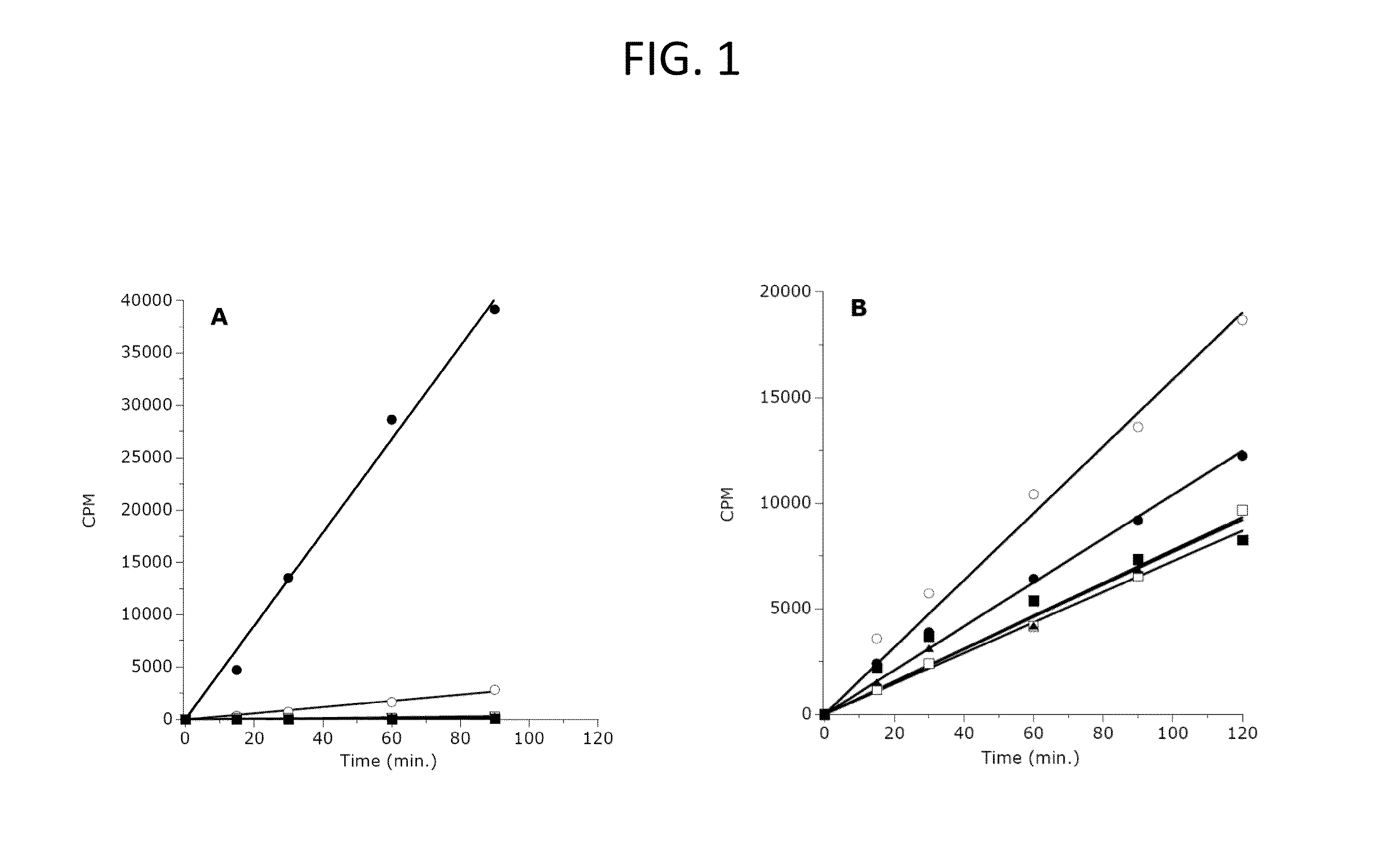
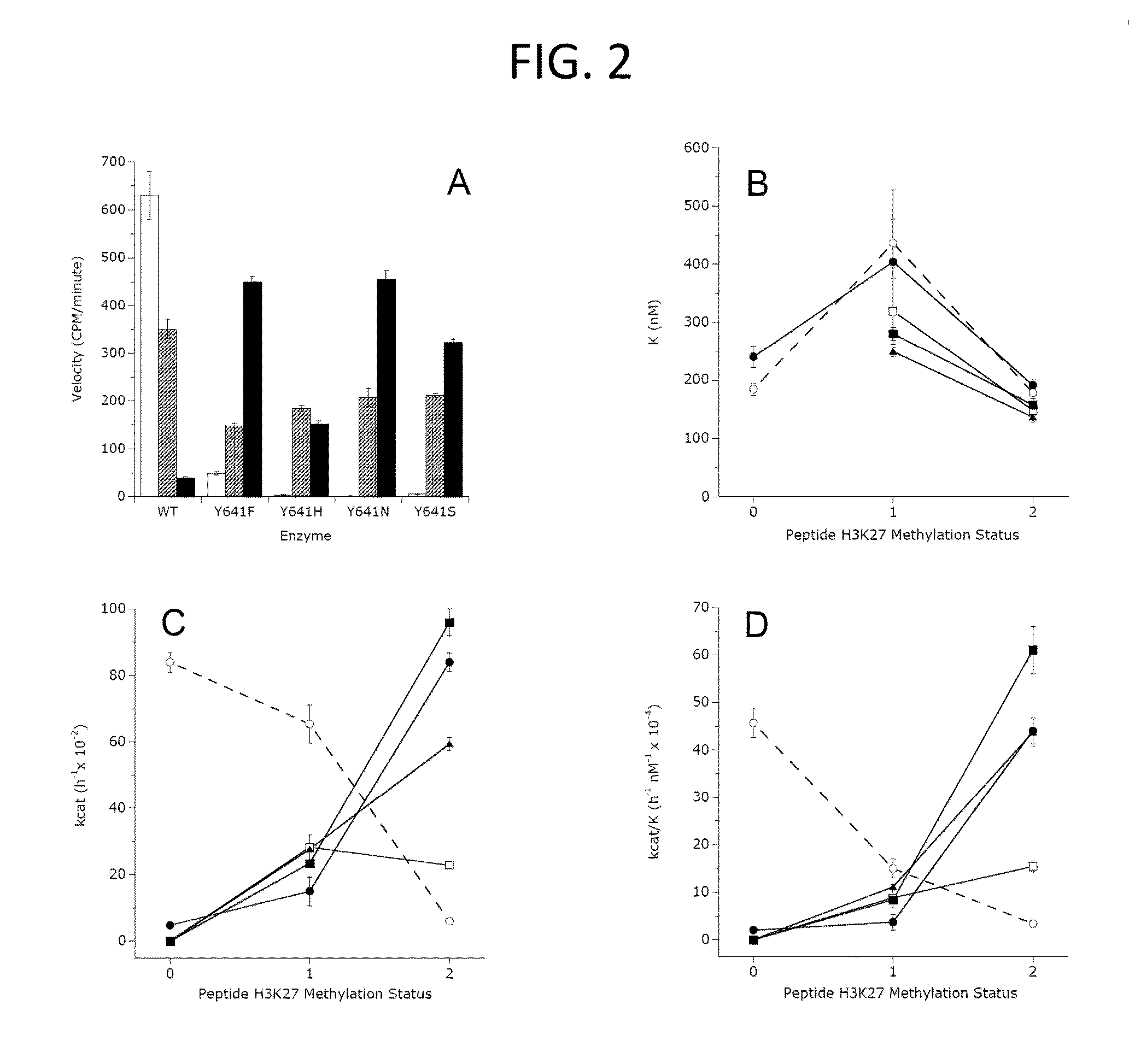
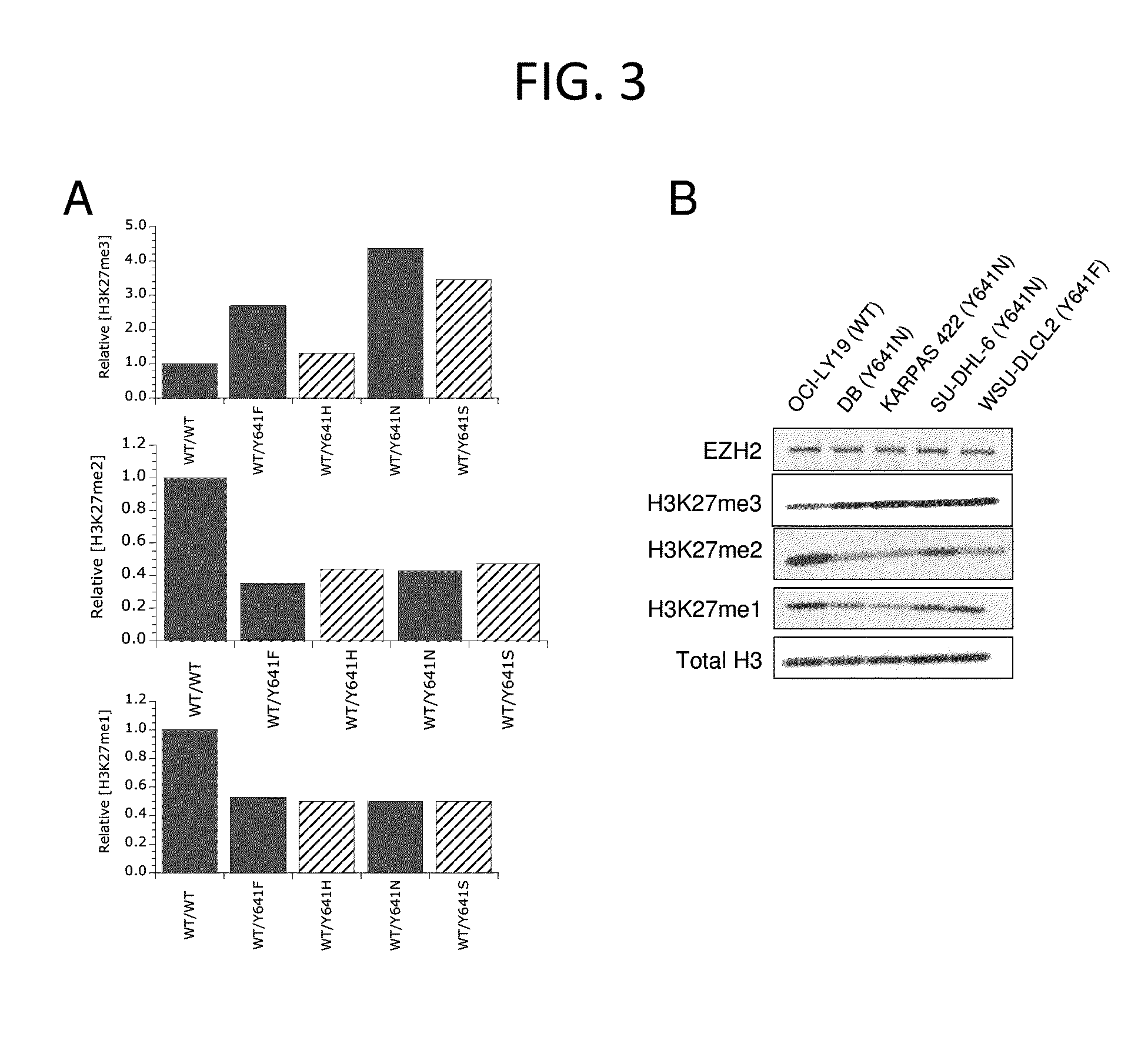
Inhibitors of Human EZH2 and Methods of Use Thereof
The invention relates to inhibition of wild-type and certain mutant forms of human histone methyltransferase EZH2, the catalytic subunit of the PRC2 complex which catalyzes the mono- through tri-methylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3-K27). In one embodiment the inhibition is selective for the mutant form of the EZH2, such that trimethylation of H3-K27, which is associated with certain cancers, is inhibited. The methods can be used to treat cancers including follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Also provided are methods for identifying small molecule selective inhibitors of the mutant forms of EZH2 and also methods for determining responsiveness to an EZH2 inhibitor in a subject.
Owner:EPIZYME
Inhibitors of Human EZH2, and Methods of Use Thereof
The invention relates to inhibition of wild-type and certain mutant forms of human histone methyltransferase EZH2, the catalytic subunit of the PRC2 complex which catalyzes the mono- through tri-methylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3-K27). In one embodiment the inhibition is selective for the mutant form of the EZH2, such that trimethylation of H3-K27, which is associated with certain cancers, is inhibited. The methods can be used to treat cancers including follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Also provided are methods for identifying small molecule selective inhibitors of the mutant forms of EZH2 and also methods for determining responsiveness to an EZH2 inhibitor in a subject.
Owner:EPIZYME
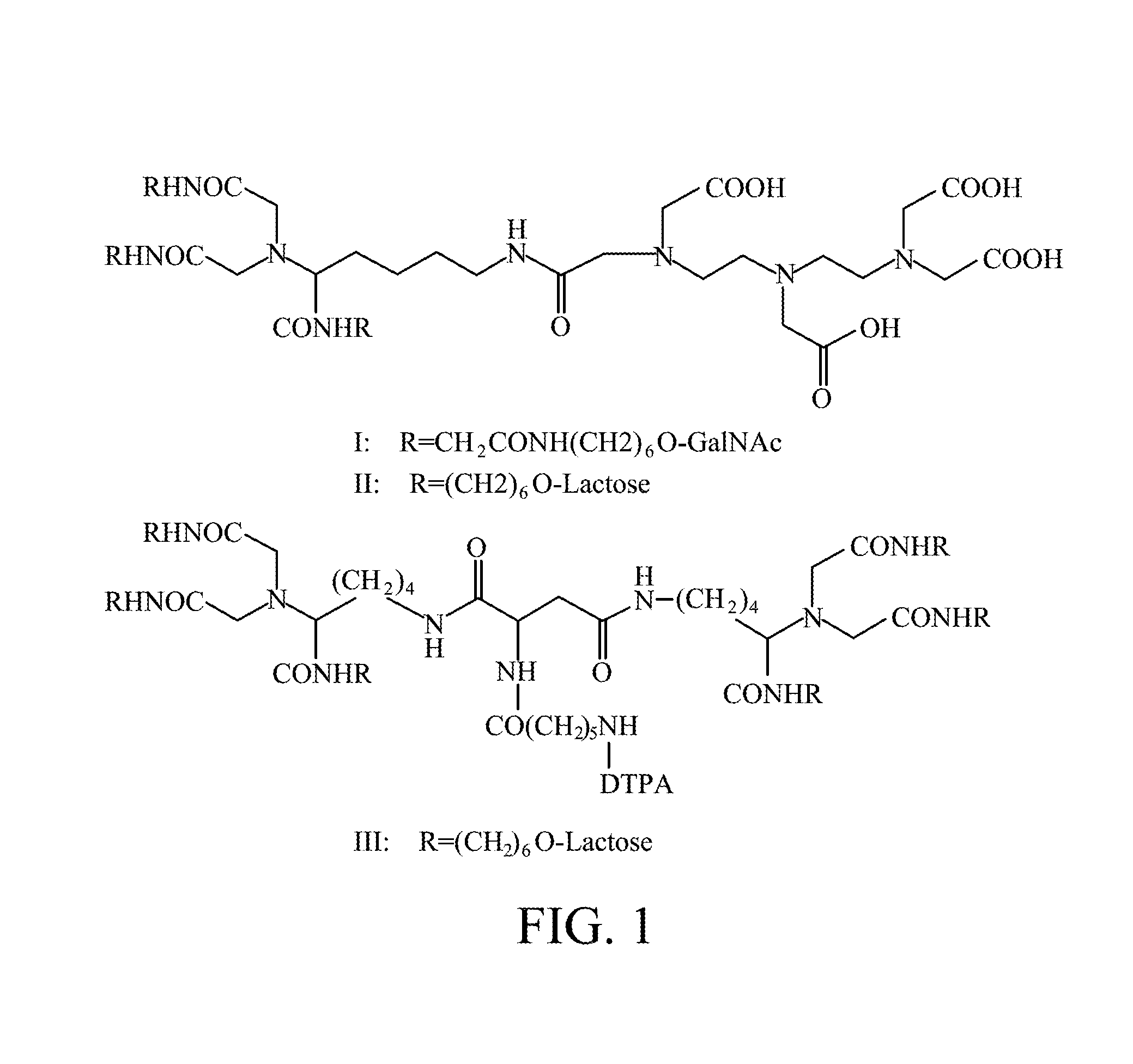
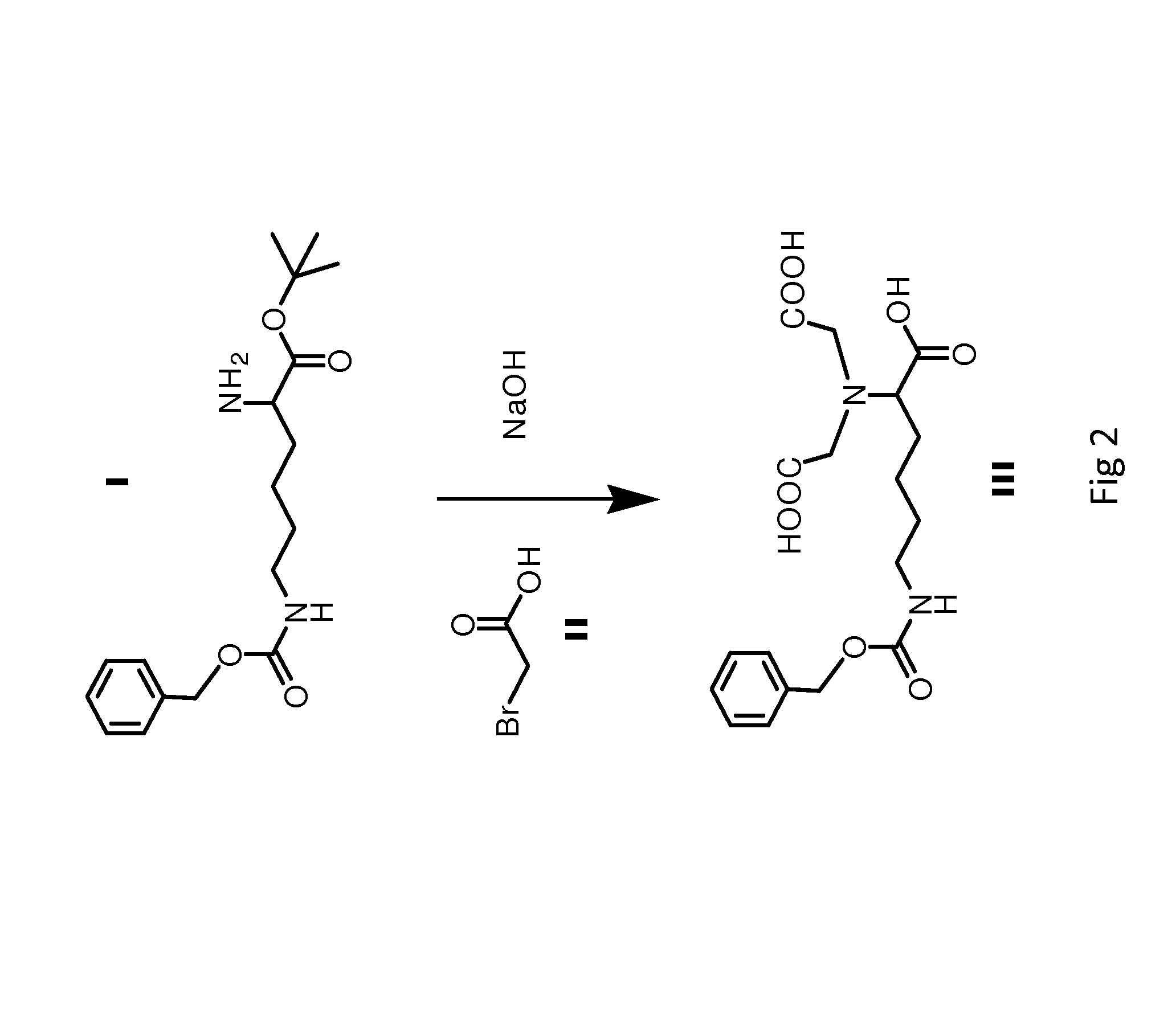
Liver-targeting agents and their synthesis
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Abuse resistant lysine amphetamine compounds
ActiveUS20050038121A1Prevents euphoriaLower potentialOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAlternative treatment
The present invention describes compounds, compositions and methods of using the same comprising lysine covalently attached to amphetamine. These compounds and compositions are useful for reducing or preventing abuse and overdose of amphetamine. These compounds and compositions find particular use in providing an abuse-resistant alternative treatment for certain disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), ADD, narcolepsy, and obesity. Oral bioavailability of amphetamine is maintained at therapeutically useful doses. At higher doses bioavailability is substantially reduced, thereby providing a method of reducing oral abuse liability. Further, compounds and compositions of the invention decrease the bioavailability of amphetamine by parenteral routes, such as intravenous or intranasal administration, further limiting their abuse liability.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Stabilized antibody-containing formulations
ActiveUS20090291076A1Good cakingIncrease of the viscosity of the high-concentration antibody-containing solutionAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsArginineThreonine
The present invention relates to antibody-containing lyophilized formulations free from reducing sugars, non-reducing sugars, sugar alcohols or polysaccharides as excipients and including one or more amino acid selected from the group consisting of arginine, histidine, lysine, serine, proline, glycine, alanine and threonine or a salt thereof.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20060088919A1Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedBacteriaDepsipeptidesL-threonineArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Stabilized Glycosaminoglycan Preparations and Related Methods
Compositions comprising a glycosaminoglycan (e.g., a hyaluronan, hyaluronic acid, hyaluronate, sodium hyaluronate, dermatan sulfate, karatan sulfate, chondroitin 6-sulfate, heparin, etc.) in combination with at least one component selected from; i) polyglycols (e.g., polyethylene glycol), ii) long chain hydroxy polyanionic polysaccharides (e.g., dextran, sodium alginate, alginic acid, propylene glycol alginate, carboxymethyl cellulose and carboxyethyl cellulose, hydroxyl ethyl starch, hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose, hydroxy propyl ethyl cellulose, hydroxy propyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, polylysine, polyhistidine, polyhydroxy proline, poly ornithine, polyvinyl pyrolidone, polyvinyl alcohol, chitosan, etc.) and iii) long chain Nitrogen containing polymers (e.g., Polylysine, Polyvinylpyrrolidone, and polyvinyl alcohol). The invention also includes methods for using such compositions (e.g., as substance delivery materials, tissue fillers or bulking agents, as moistening or hydrating agents, etc.)
Owner:S K PHARMA INC
Composition for long-acting peptide analogs
ActiveUS20090088387A1Increase perfusionImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeArginine
The invention describes compositions of peptide analogs that are active in blood or cleavable in blood to release an active peptide. The peptide analogs have a general formula: A-(Cm)x-Peptide, wherein A is hydrophobic moiety or a metal binding moiety, e.g., a chemical group or moiety containing 1) an alkyl group having 6 to 36 carbon units, 2) a nitrilotriacetic acid group, 3) an imidodiacetic acid group, or 4) a moiety of formula (ZyHisw)p, wherein Z is any amino acid residue other than histidine, His is histidine, y is an integer from 0-6; w is an integer from 1-6; and p is an integer from 1-6; wherein if A has alkyl group with 6 to 36 carbon units x is greater than 0; and Cm is a cleavable moiety consisting of glycine or alanine or lysine or arginine or N-Arginine or N-lysine, wherein x is an integer between 0-6 and N may be any amino acid or none. The peptide analogs are complexed with polymeric carrier to provide enhanced half-life.
Owner:PHARMAIN CORP
CATIONIC PEPTIDES FOR siRNA INTRACELLULAR DELIVERY
What is described is a composition for delivery of a RNA molecule to a cell, comprising: a double stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecule of about 15 to about 40 base pairs; and a polynucleotide delivery-enhancing peptide, comprising a region of alternating lysine and histidine residues, or of alternating D and L forms of arginine.
Owner:NASTECH PHARMA
Pharmaceutical composition and method for the transdermal delivery of calcium
InactiveUS20070292493A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce and prevent likelihoodHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsBiocideArginineTryptophan
The present invention relates to a method and transdermal pharmaceutical composition for preventing or reducing the likelihood of calcium deficiency or imbalances caused by calcium deficiency. The transdermal pharmaceutical composition includes a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of calcium and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier constituting a pluronic lecithin organogel. In addition to calcium, the transdermal pharmaceutical composition may also contain a therapeutically effective amount of: (1) a pharmaceutically acceptably salt of other minerals such as magnesium, zinc, selenium, manganese, or chromium; (2) a vitamin such as vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin C, vitamin E or B-complex vitamins, choline, lecithin, inositol, PABA, biotin, or bioflavomoids; (3) a carotenoid such as lycopene or lutein; (4) a hormone such as dehydroepiandrosterone, progesterone, pregnenolone, or melatonin; (5) an amino acid such as arginine, glutamine, lysine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, GABA, tryptophan, carnitine, or acetyl-l-carnitine; (6) a fatty acid such as a fish oil or flax seed oil; (7) a vita-nutrient such as coenzyme Q10; (8) a cartilage building nutrient such as glucosamine, chondroitin, or MSM, (9) a herb such as ginkgo biloba, echinacea, 5-HTP, St. John's wort, or saw palmetto; or (9) any combination thereof. The transdermal pharmaceutical composition may be topically administered to a human to prevent or reduce the likelihood of calcium deficiency or imbalances caused by calcium deficiency such as hypertension, high cholesterol, colon and rectal cancer, osteomalacia, rickets, osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, preeclampsia, tooth decay, and premenstrual syndrome.
Owner:BRIERRE BARBARA T
Gene products of bacillus licheniformis which form odorous substances and improved biotechnological production methods based thereon
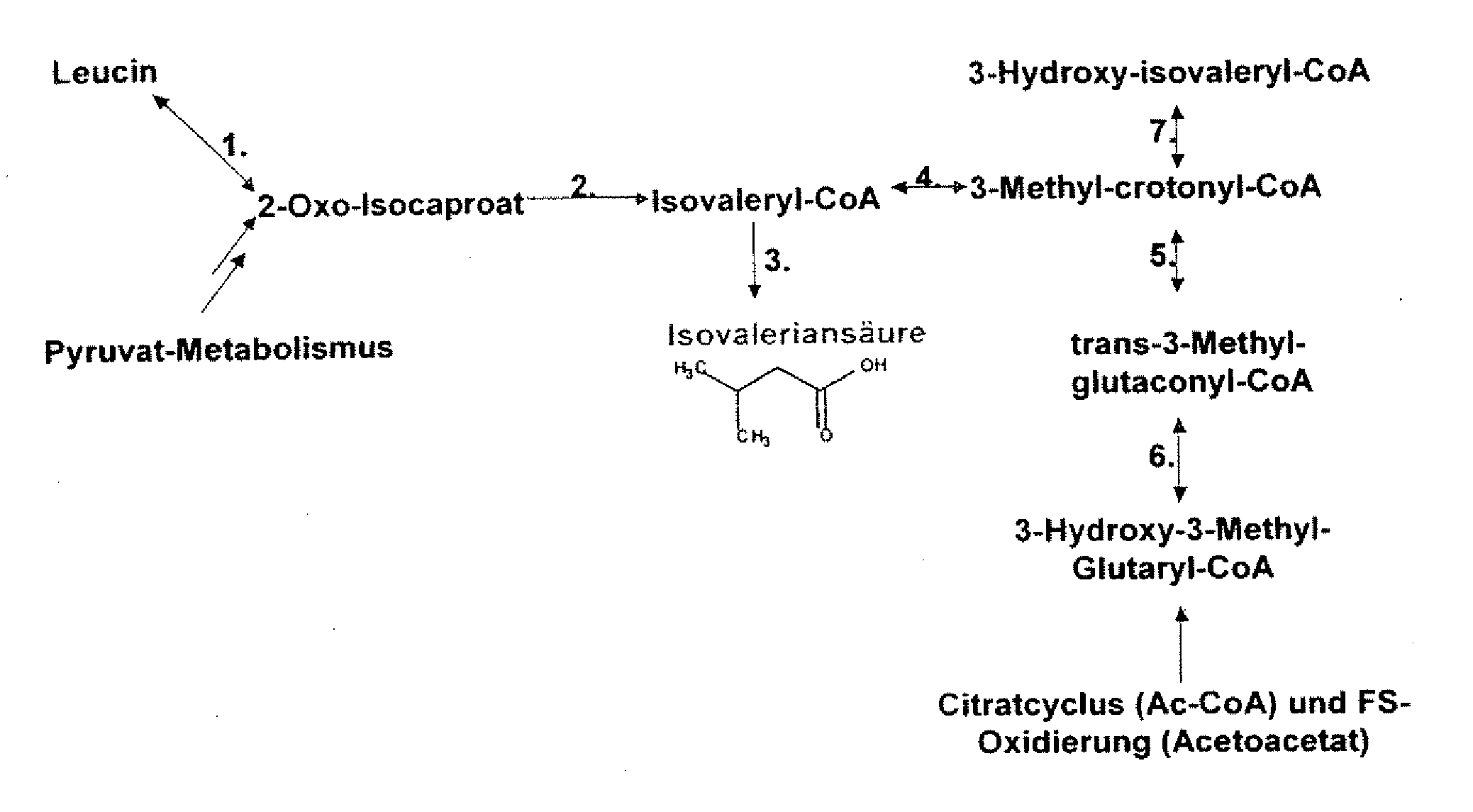
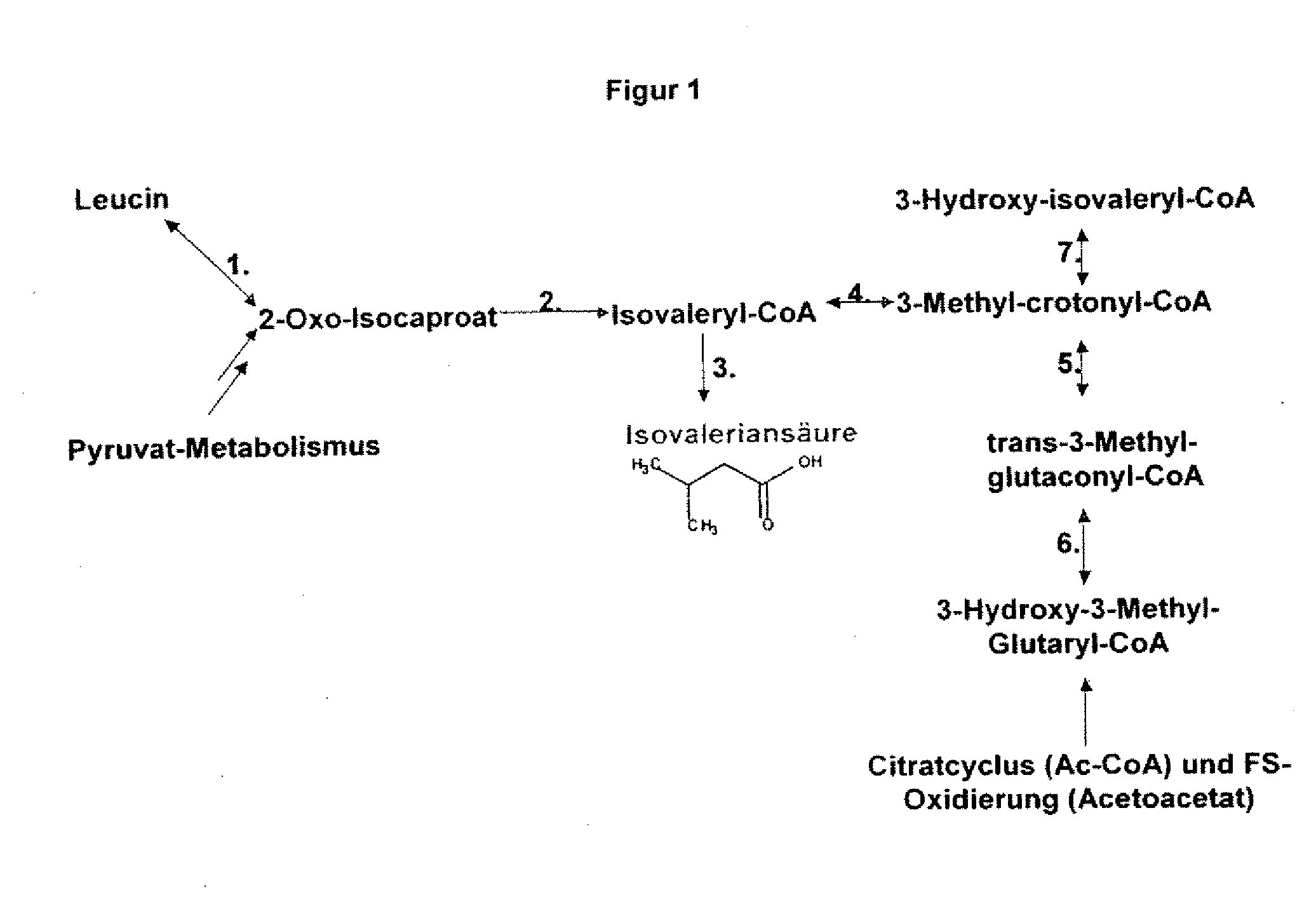
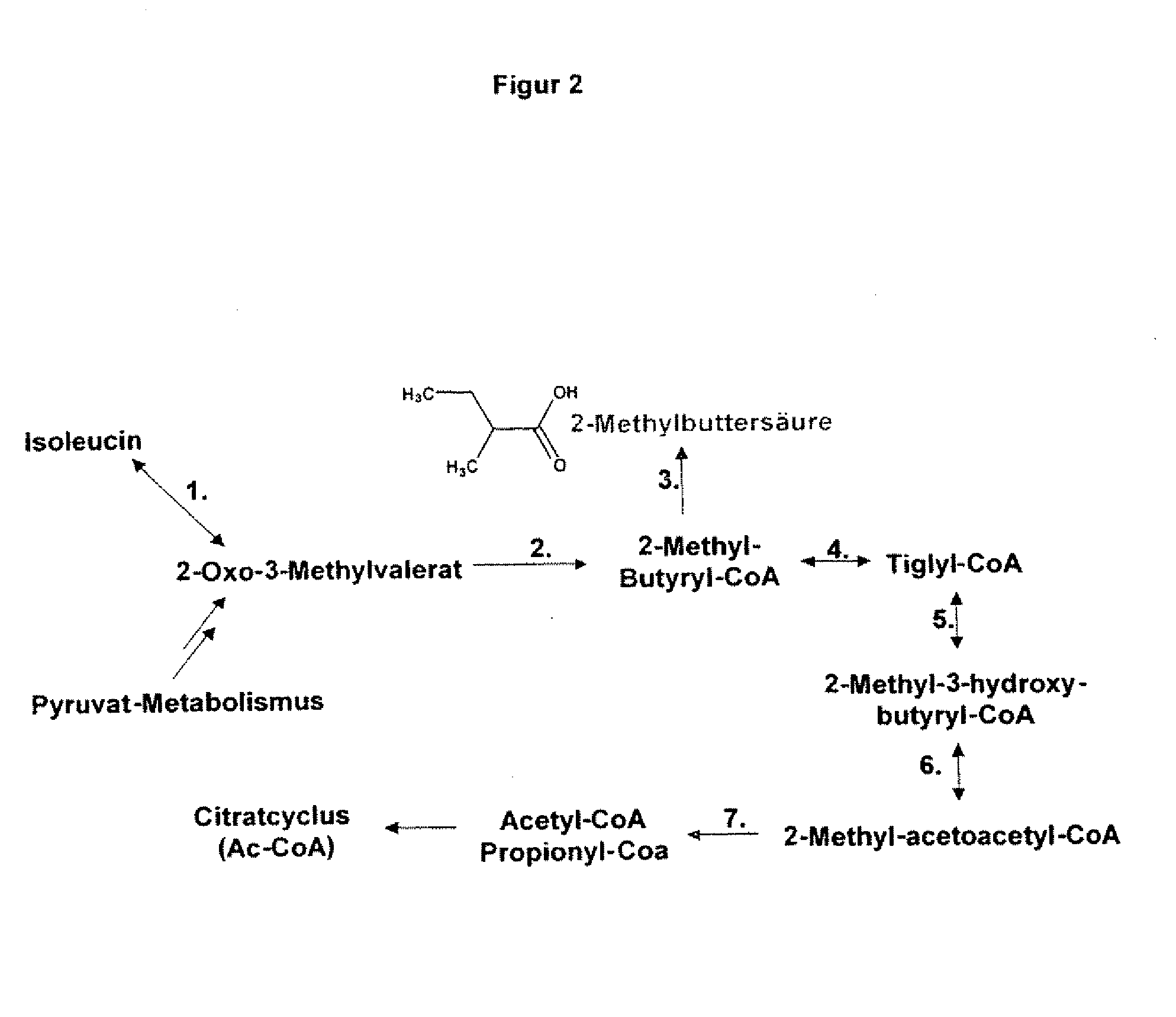
InactiveUS20070190605A1Reduce formationImprove filtering effectBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisPropanoic acid
The present invention relates to 25 hitherto undescribed genes of B. licheniformis and gene products derived therefrom and all sufficiently homologous nucleic acids and proteins thereof. They occur in five different metabolic pathways for the formation of odorous substances. The metabolic pathways in question are for the synthesis of: 1) isovalerian acid (as part of the catabolism of leucine), 2) 2-methylbutyric acid and / or isobutyric acid (as part of the catabolism of valine and / or isoleucine), 3) butanol and / or butyric acid (as part of the metabolism of butyric acid), 4) propyl acid (as part of the metabolism of propionate) and / or 5) cadaverine and / or putrescine (as parts of the catabolism of lysine and / or arginine). The identification of these genes allows biotechnological production methods to be developed that are improved to the extent that, to assist these nucleic acids, the formation of the odorous substances synthesized via these metabolic pathways can be reduced by deactivating the corresponding genes in the micro-organism used for the biotechnological production. In addition, these gene products are thus available for preparing reactions or for methods according to their respective biochemical properties.
Owner:BASF AG
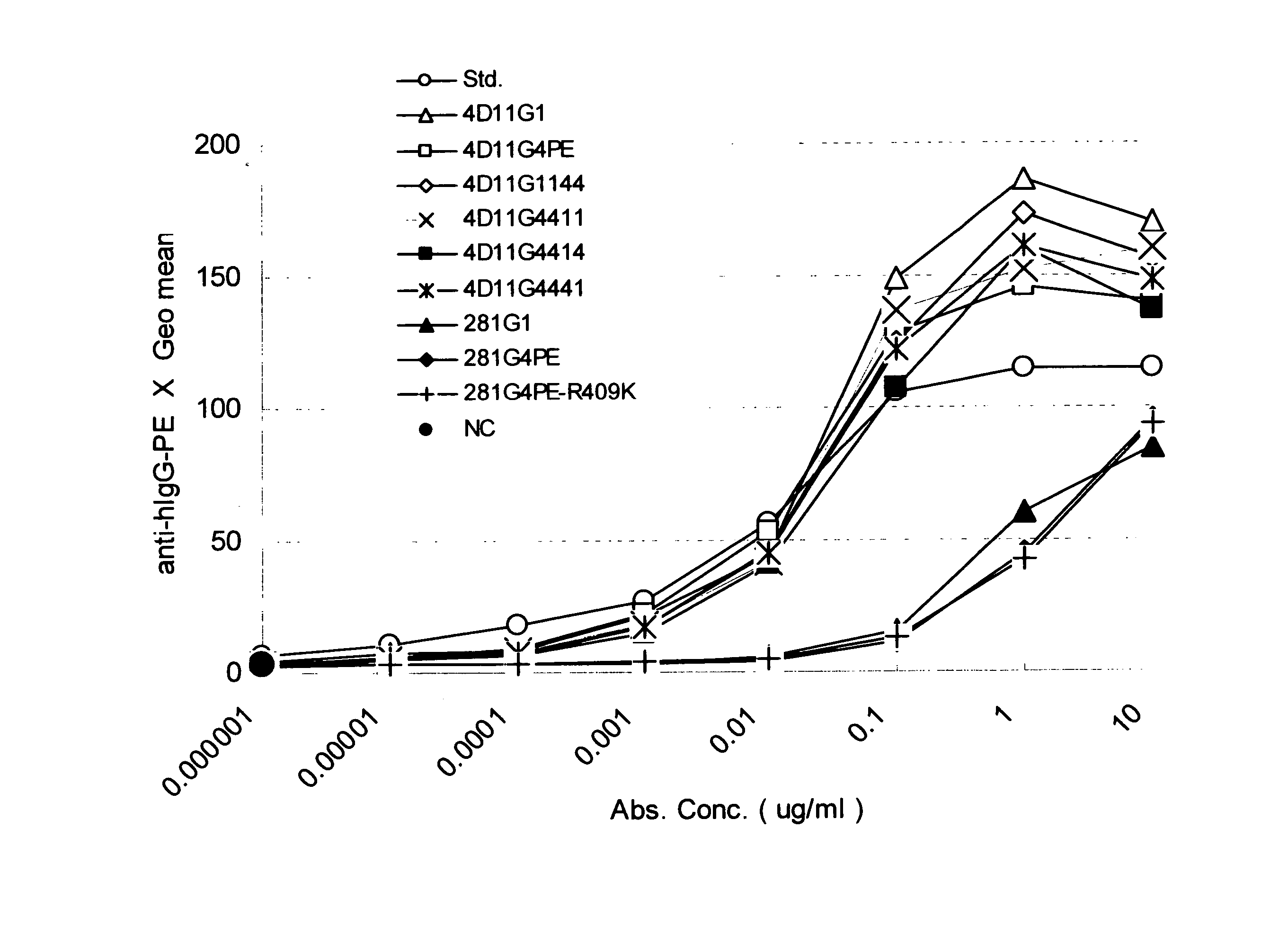
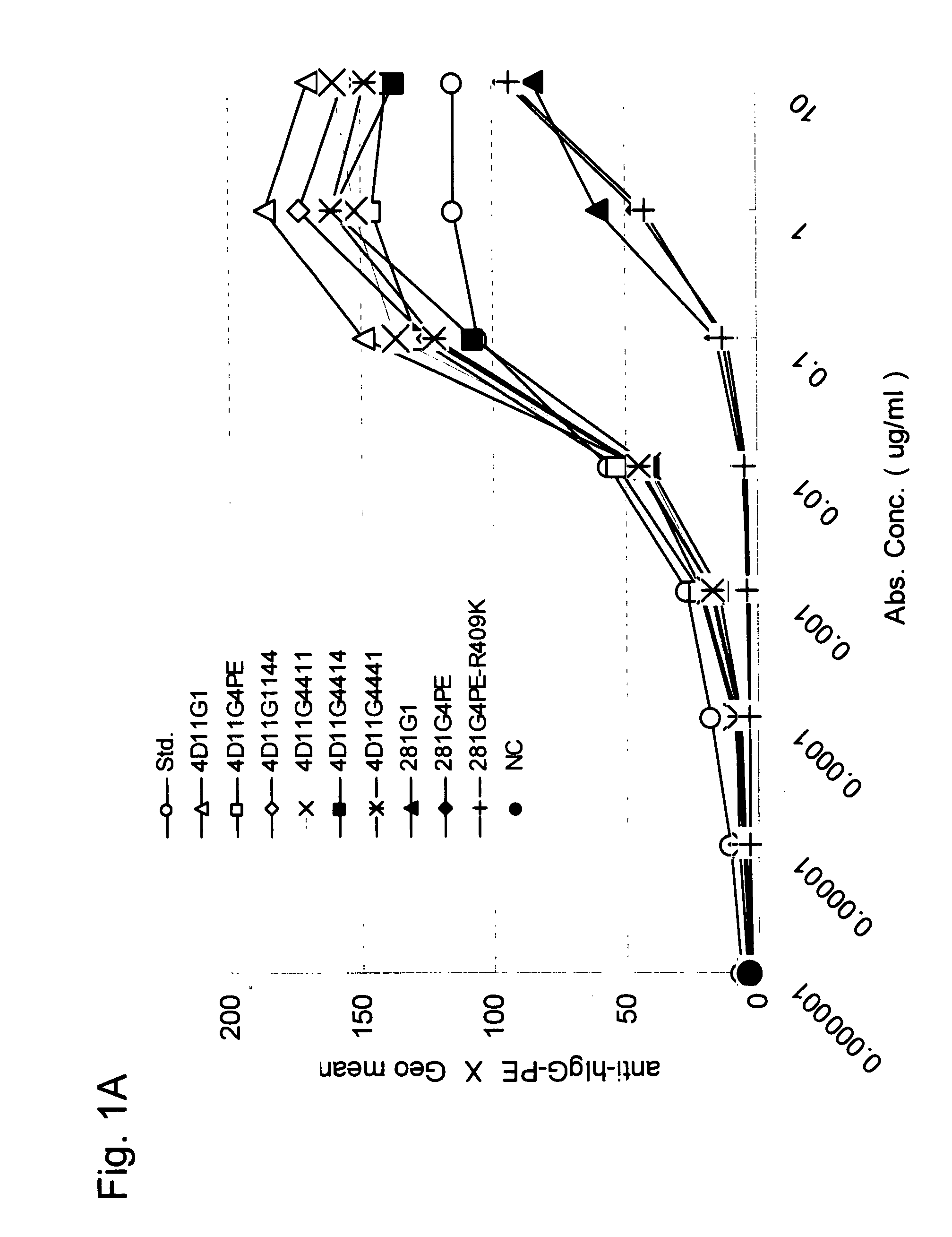
Stabilized Human Igg4 Antibodies
ActiveUS20080063635A1Stable productionReduce adverse effectsNervous disorderAntipyreticArginineMutant
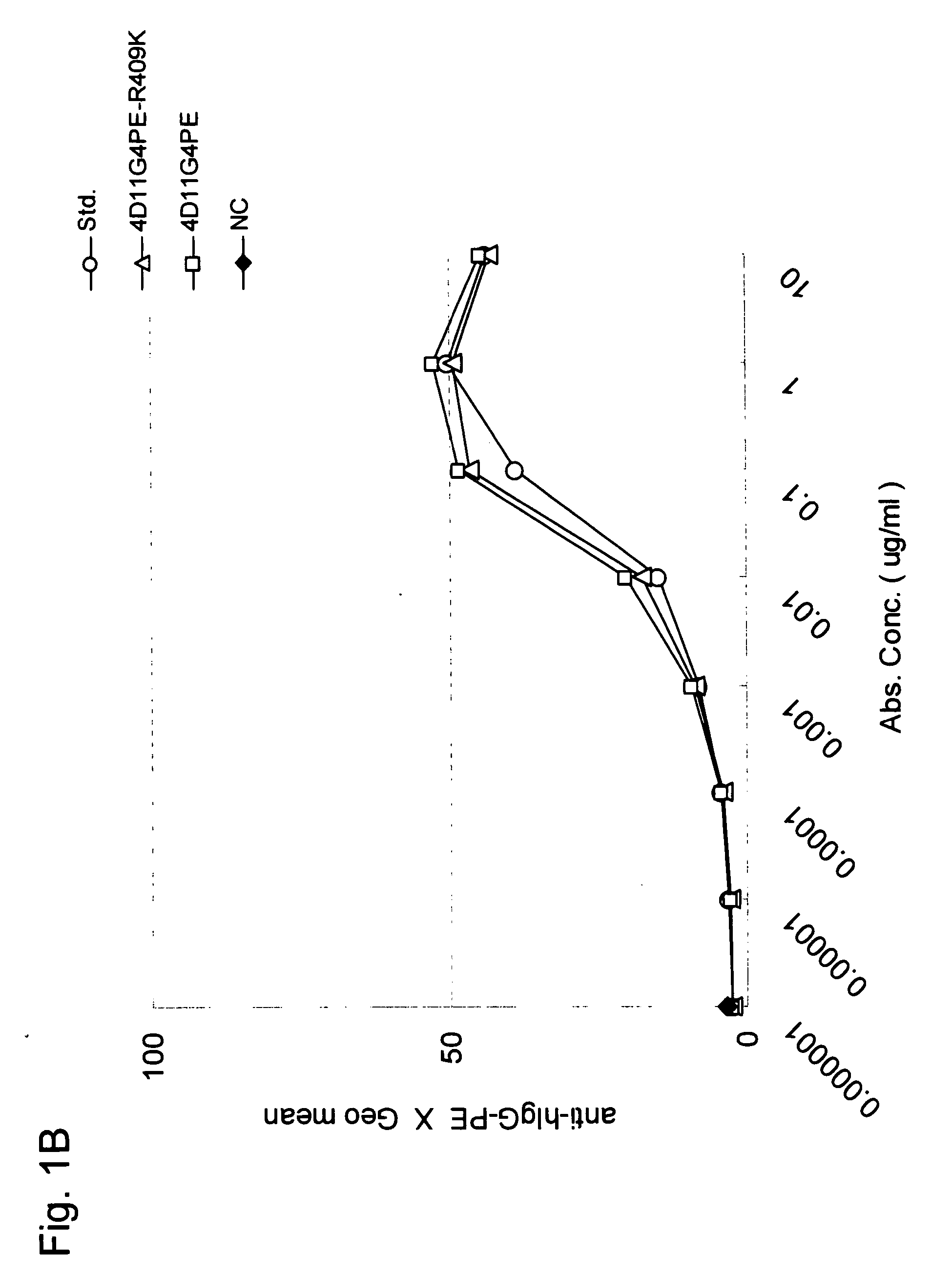
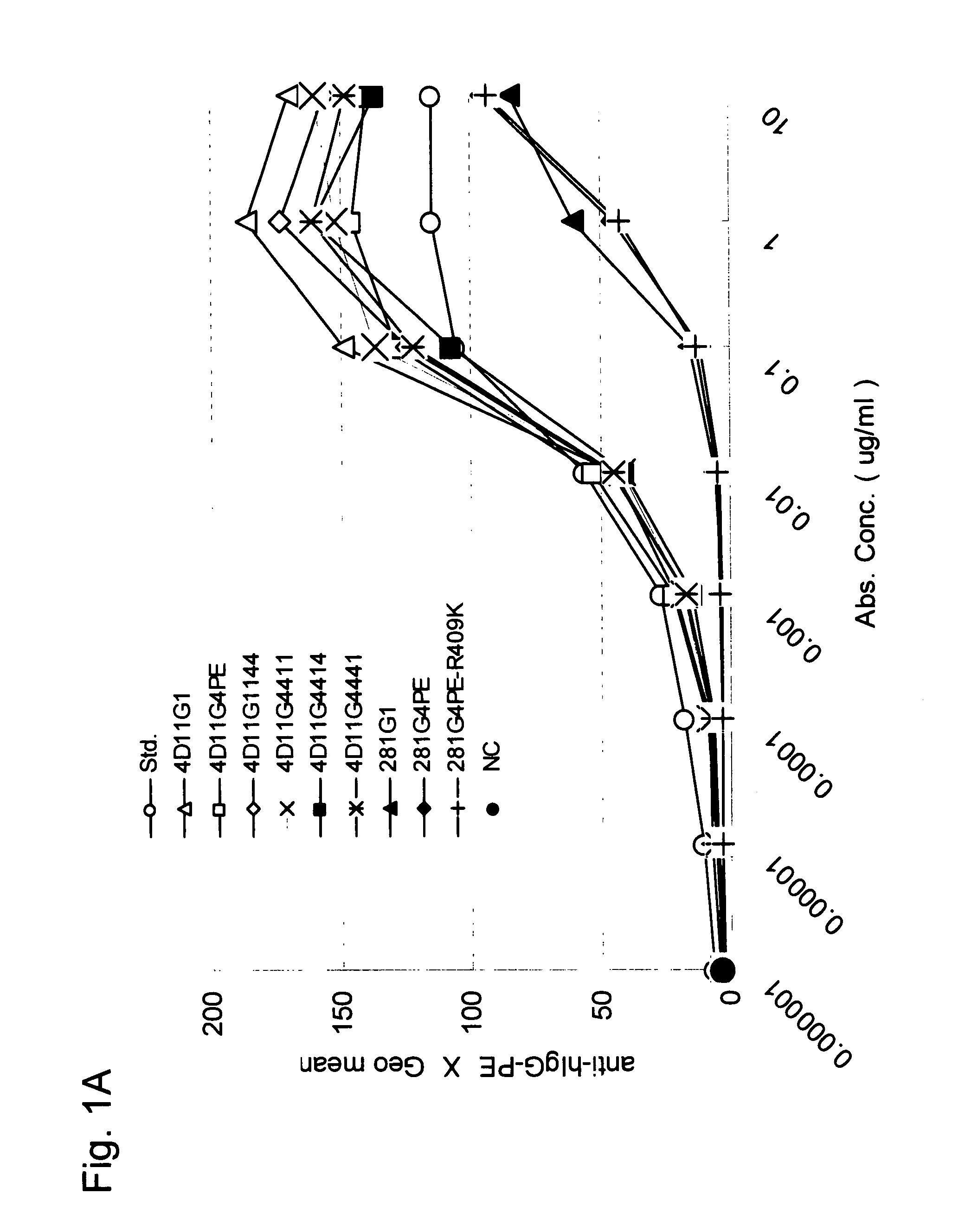
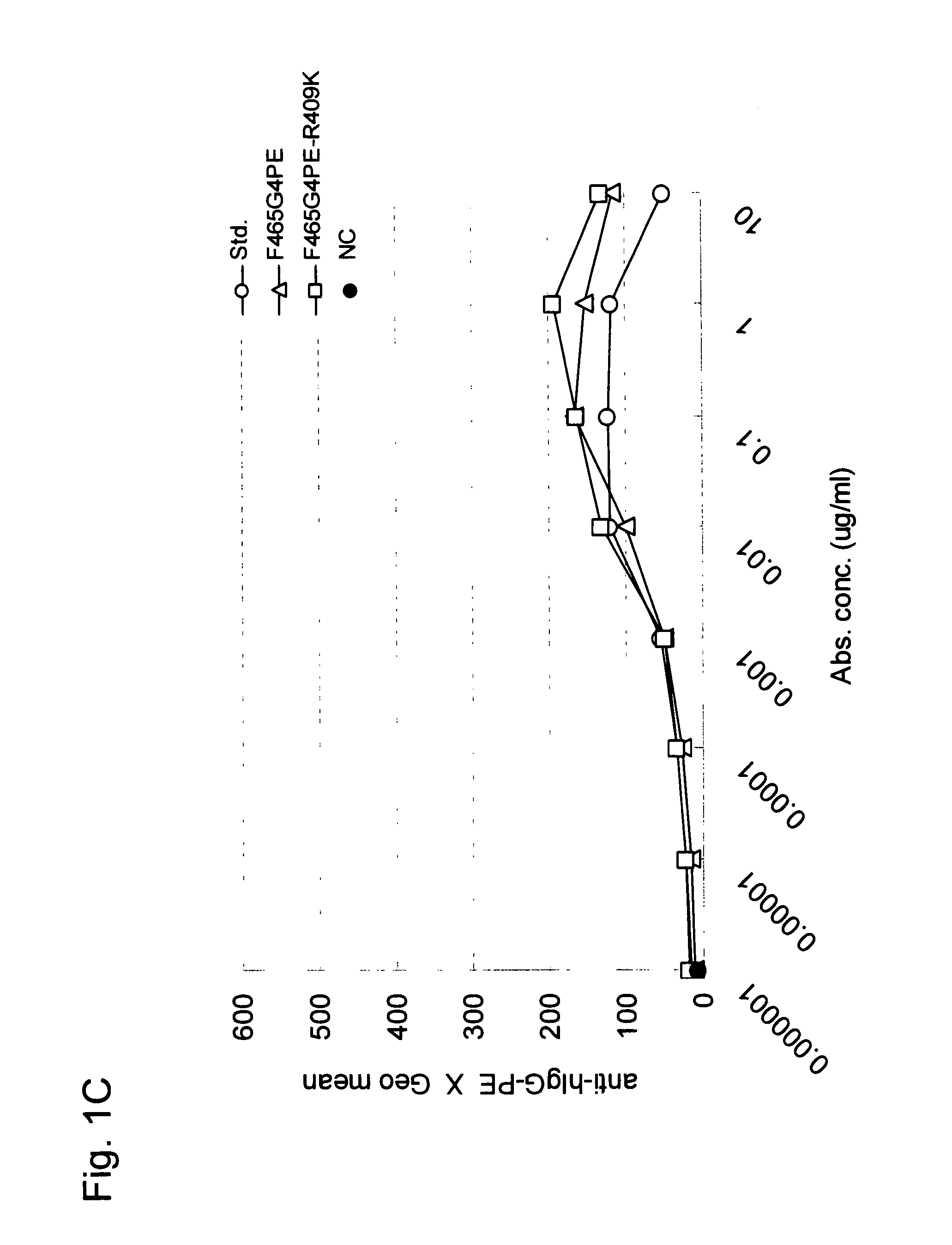
A highly stable mutant of human IgG4 antibody is provided. Such antibody is an antibody in which the CH3 domain of human IgG4 is substituted with the CH3 domain of human IgG1 and which exhibits inhibited aggregate formation, an antibody in which the CH3 and CH2 domains of human IgG4 are substituted with the CH3 and CH2 domains of human IgG1, respectively, or an antibody in which arginine at position 409 indicated in the EU index proposed by Kabat et al. of human IgG4 is substituted with lysine and which exhibits inhibited aggregate formation.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Mixed micellar delivery system and method of preparation
InactiveUS6221378B1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOctylphenoxy PolyethoxyethanolChamomile extract
A mixed micellar pharmaceutical formulation includes a micellar proteinic pharmaceutical agent, an lkali metal C8 to C22 alkyl sulphate, alkali metal salicylate, a pharmaceutically acceptable edetate and at least one absorption enhancing compounds. The absorption enhancing compounds are selected from the group consisting of lecithin, hyaluronic acid, pharmaceutically acceptable salts of hyaluronic acid, octylphenoxypolyethoxyethanol, glycolic acid, lactic acid, chamomile extract, cucumber extract, oleic acid, linolenic acid, borage oil, evening of primrose oil, trihydroxy oxo cholanylglycine, glycerin, polyglycerin, lysine, polylysine, triolein and mixtures thereof. The amount of each absorption enhancing compound is present in a concentration of from 1 to 10 wt. / wt. % of the total formulation, and the total concentration of absorption enhancing compounds are less than 50 wt. / wt. % of the formulation. Preferably, the formulation is administered, in combination with a propellant, to the buccal cavity, using a metered dose dispenser.
Owner:GENEREX PHARMA INC
Stabilized human Igg4 antibodies
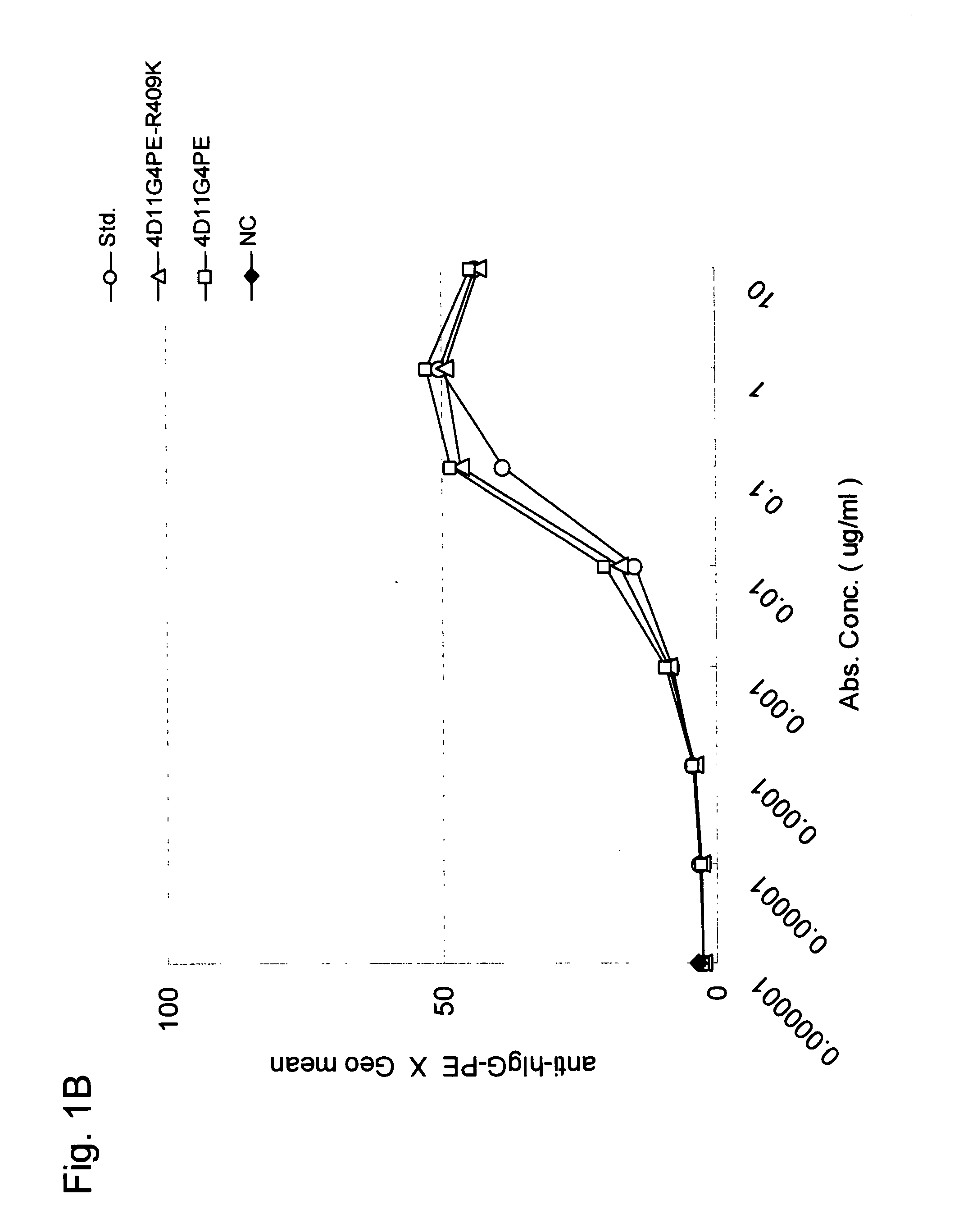
A highly stable mutant of human IgG4 antibody is provided. Such antibody is an antibody in which the CH3 domain of human IgG4 is substituted with the CH3 domain of human IgG1 and which exhibits inhibited aggregate formation, an antibody in which the CH3 and CH2 domains of human IgG4 are substituted with the CH3 and CH2 domains of human IgG1, respectively, or an antibody in which arginine at position 409 indicated in the EU index proposed by Kabat et al. of human IgG4 is substituted with lysine and which exhibits inhibited aggregate formation.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS8991403B2Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArginineTobacco product
A method of thermally processing a tobacco material is provided, the method including the steps of (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof, to form a moist tobacco mixture; (ii) heating the moist tobacco mixture at a temperature of at least about 60° C. to form a heat-treated tobacco mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated tobacco mixture into a tobacco product. Heat-treated tobacco composition prepared according to the method are also provided, such as heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition comprising a tobacco material, water, flavorant, binder, and filler, the heat-treated smokeless tobacco composition having an acrylamide content of less than about 2000 ppb.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
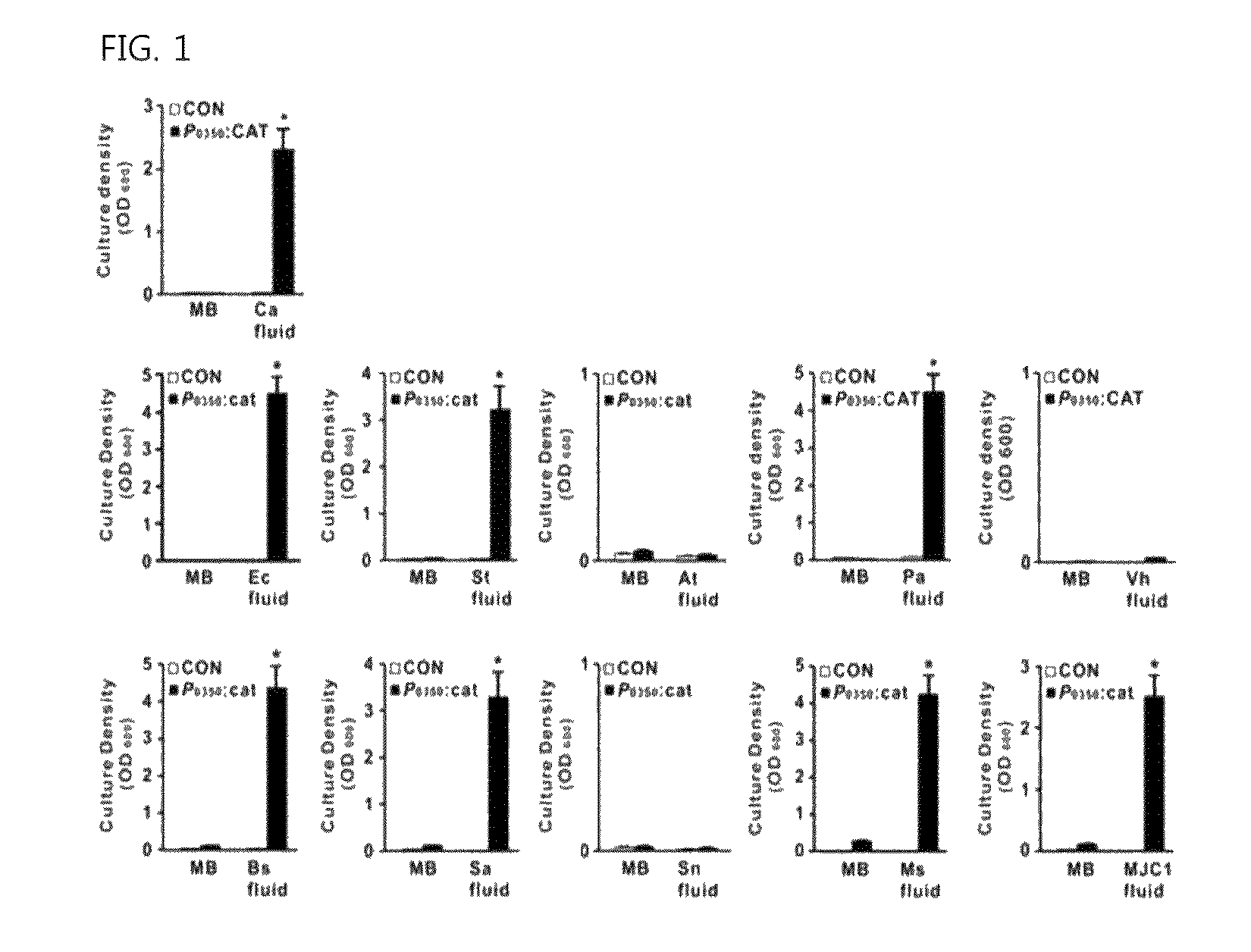
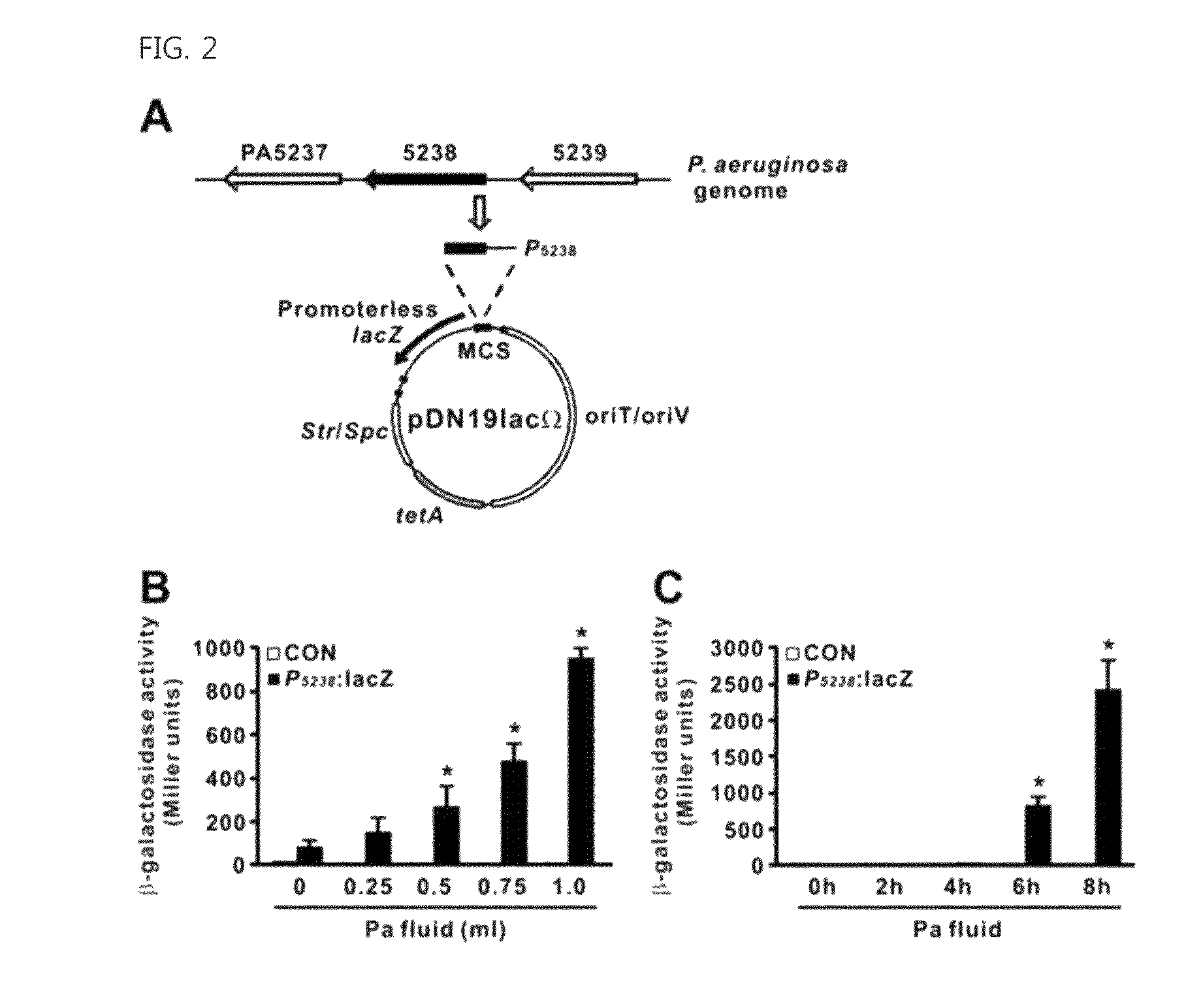
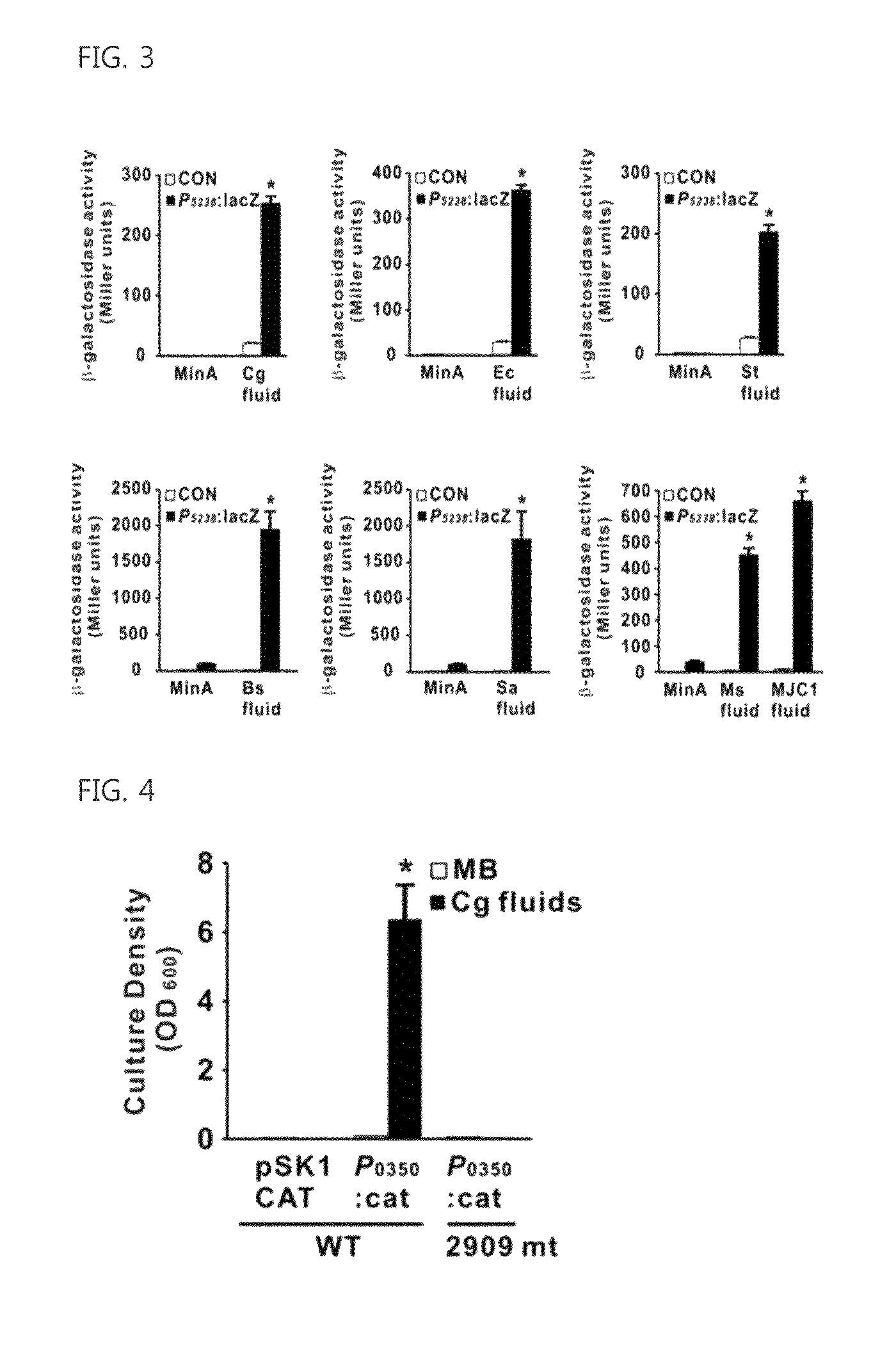
Genes encoding biofilm formation inhibitory proteins and a method for producing L-lysine using a bacterial strain with the inactivated genes
The present invention relates to a novel isolated gene (polynucleotide) which encodes a protein having a biofilm formation inhibitory activity derived from Coryneform bacteria, a L-lysine-producing strain in which the polynucleotide is inactivated, and a method for producing L-lysine using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
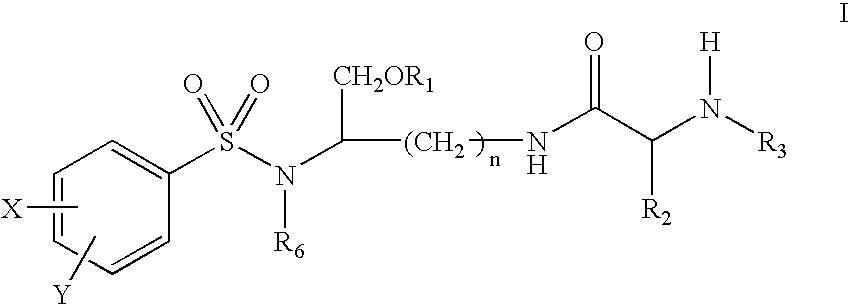
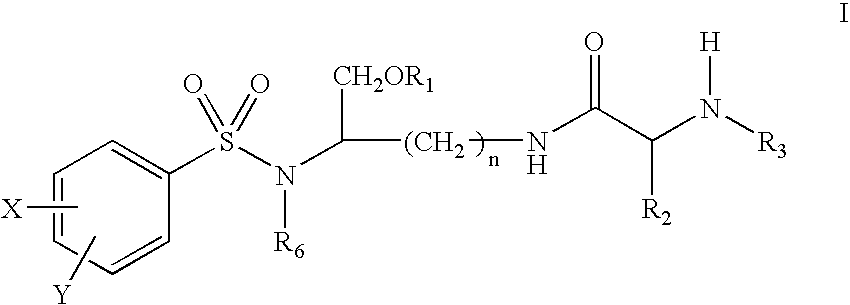
Lysine based compounds
ActiveUS20060025592A1Improve solubilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationStereochemistryAmmonium
The present invention provides lysine based compounds of the formula; and when the compound of formula I comprises an amino group, pharmaceutically acceptable ammonium salts thereof, wherein R1 may be, for example, (HO)2P(O)—, (NaO)2P(O)—, alkyl-CO— or cycloalkyl-CO—, wherein X may be, for example, F, Cl, and Br, and wherein R2 and R3 are as defined herein.
Owner:TAIMED BIOLOGICS
Aerosol formulations for buccal and pulmonary application
InactiveUS6436367B1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChamomile extractOleic Acid Triglyceride
A mixed micellar aerosol pharmaceutical formulation includes a micellar proteinic pharmaceutical agent, an alkali metal lauryl sulphate, at least three micelle forming compounds, a phenol and a propellant. The micelle forming compounds are selected from the group consisting of lecithin, hyaluronic acid, pharmaceutically acceptable salts of hyaluronic acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, chamomile extract, cucumber extract, oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, monoolein, monooleates, monolaurates, borage oil, evening of primrose oil, menthol, trihydroxy oxo cholanyl glycine and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, glycerin, polyglycerin, lysine, polylysine, triolein, polyoxyethylene ethers and analogues thereof, polidocanol alkyl ethers and analogues thereof. The amount of each micelle forming compound is present in a concentration of from 1 to 20 wt. / wt. % of the total formulation, and the total concentration of micelle forming compounds are less than 50 wt. / wt. % of the formulation. The propellant, e.g. a fluorocarbon propellant, provides enhanced absorption of the pharmaceutical agent.
Owner:GENEREX PHARMA
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS8944072B2Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArgininePhenylalanine
A method of preparing a tobacco material for use in a smoking article is provided, including (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof; (ii) heating the mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated mixture into a smoking article as a smokable material. A smoking article in the form of a cigarette is also provided that includes a tobacco material pre-treated to inhibit reaction of asparagine to form acrylamide in mainstream smoke. Upon smoking, the smoking article is characterized by an acrylamide content of mainstream smoke that is reduced relative to an untreated control smoking article.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
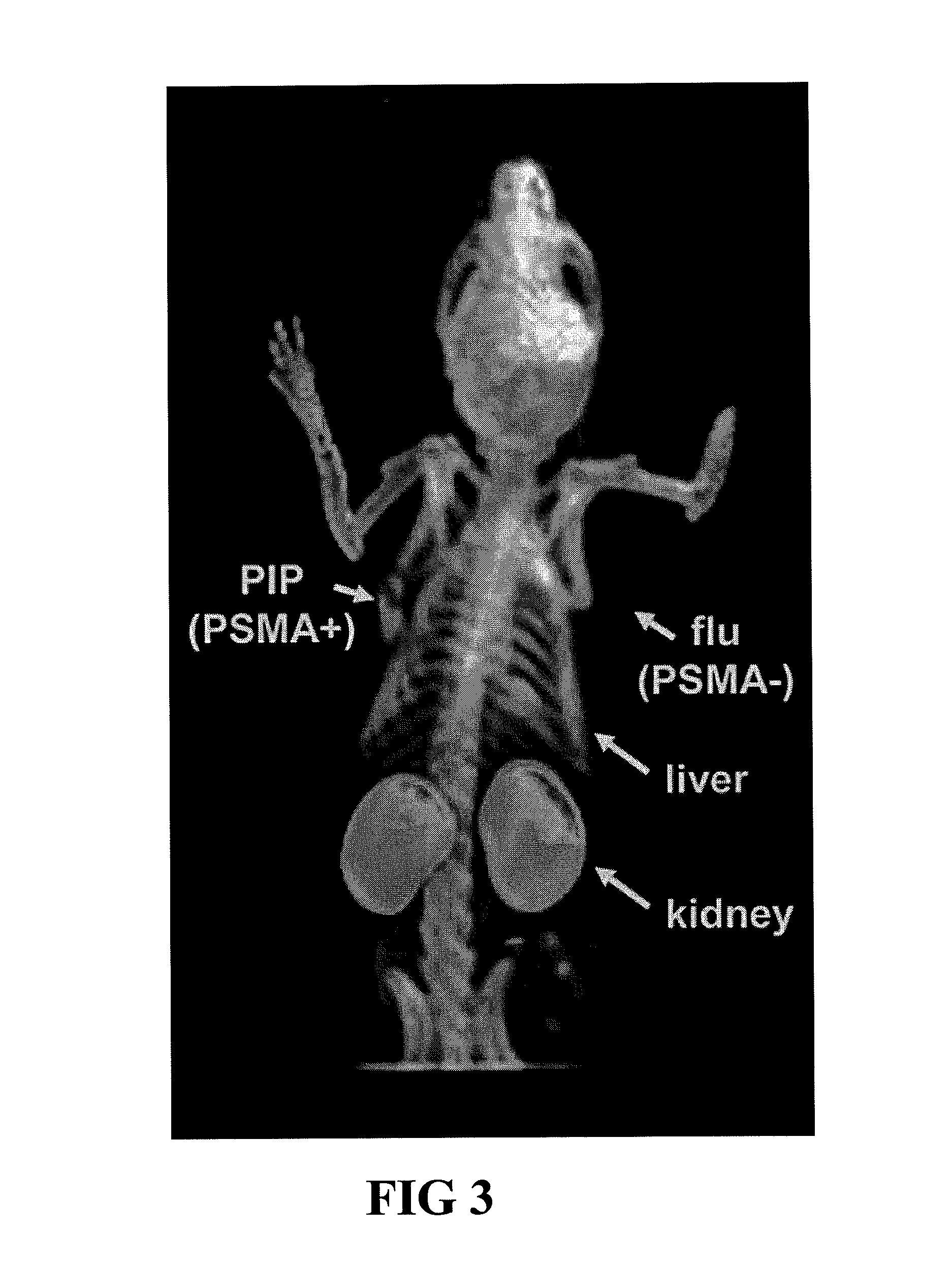
PSMA-binding agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS8778305B2Satisfies long standing and unmetSharp contrastGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsProstate cancer cellAntigen
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding compounds having radioisotope substituents are described, as well as chemical precursors thereof. Compounds include pyridine containing compounds, compounds having phenylhydrazine structures, and acylated lysine compounds. The compounds allow ready incorporation of radionuclides for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) for imaging, for example, prostate cancer cells and angiogenesis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
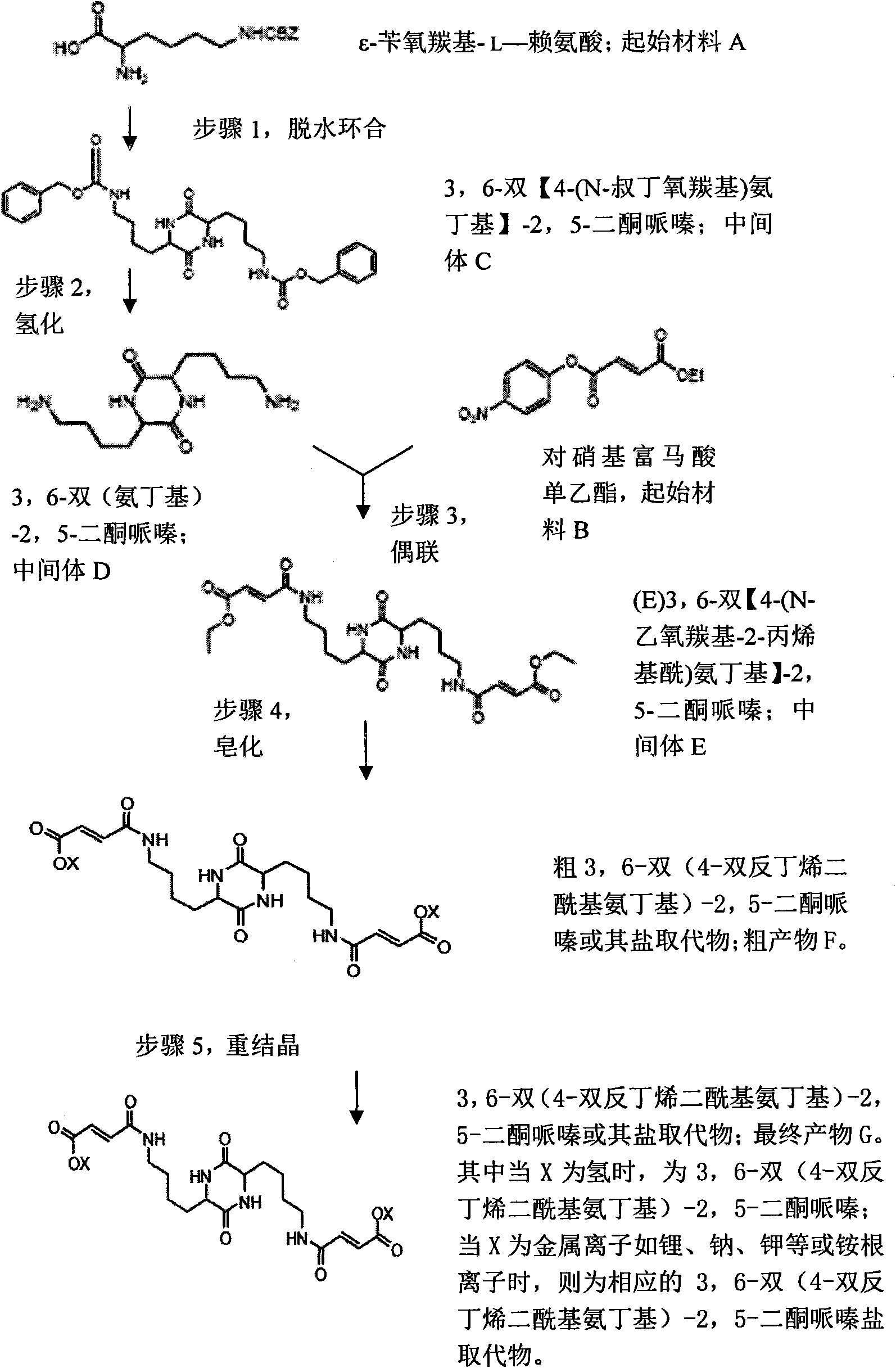
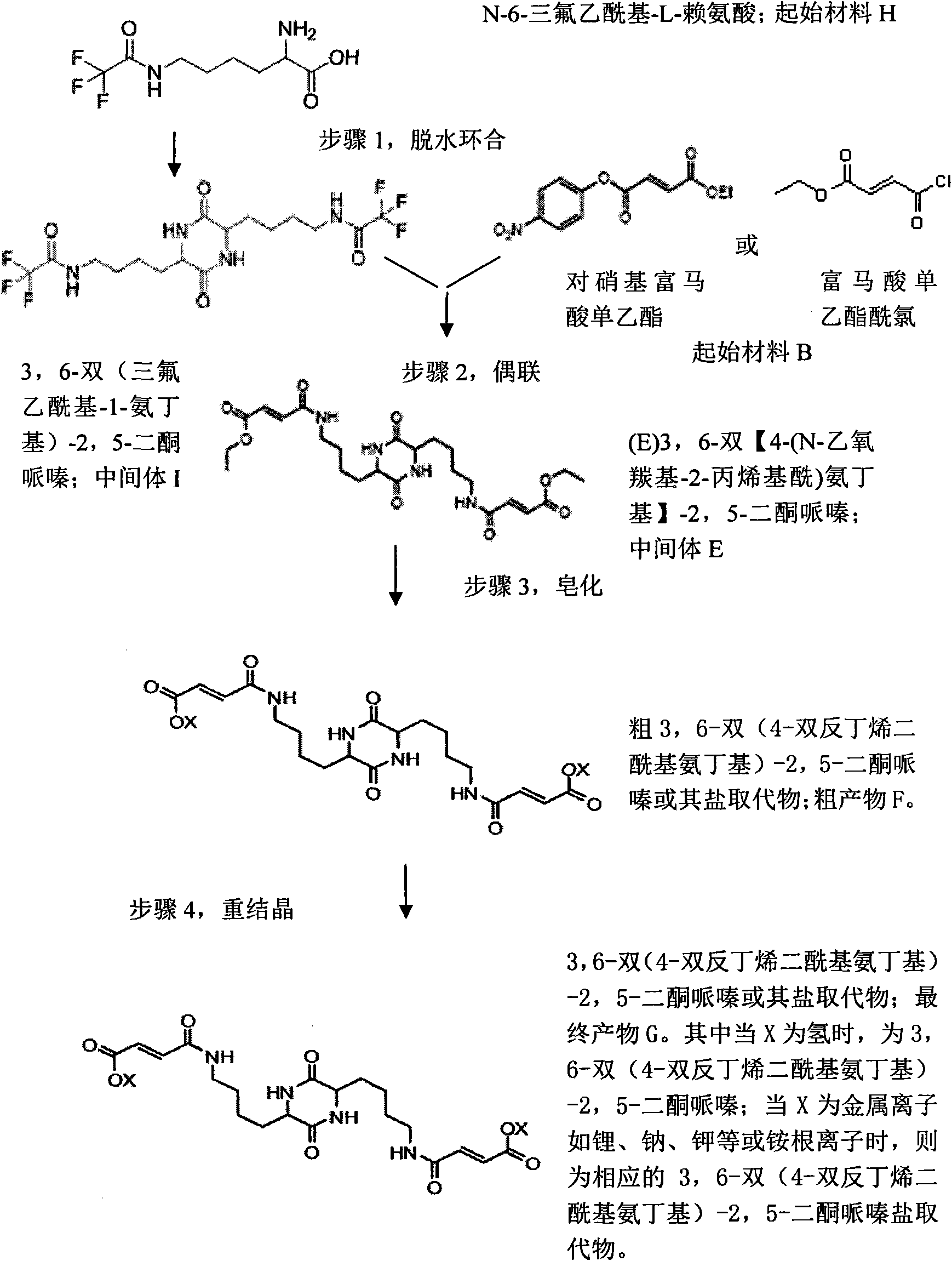
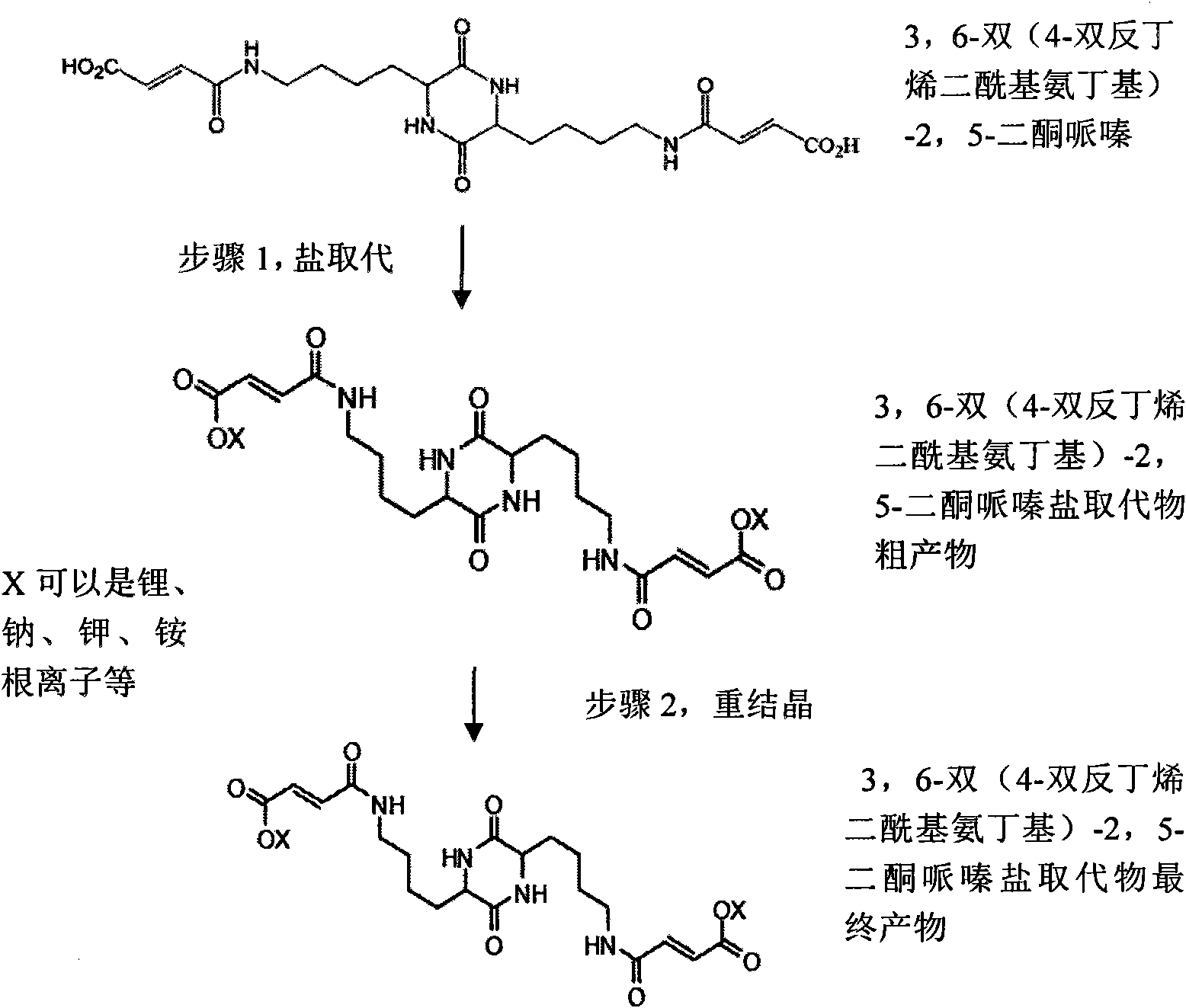
Synthetic methods of 3,6-bis(4-bisfumaroyl aminobutyl)-2,5-diketopiperazine and salt substitute thereof
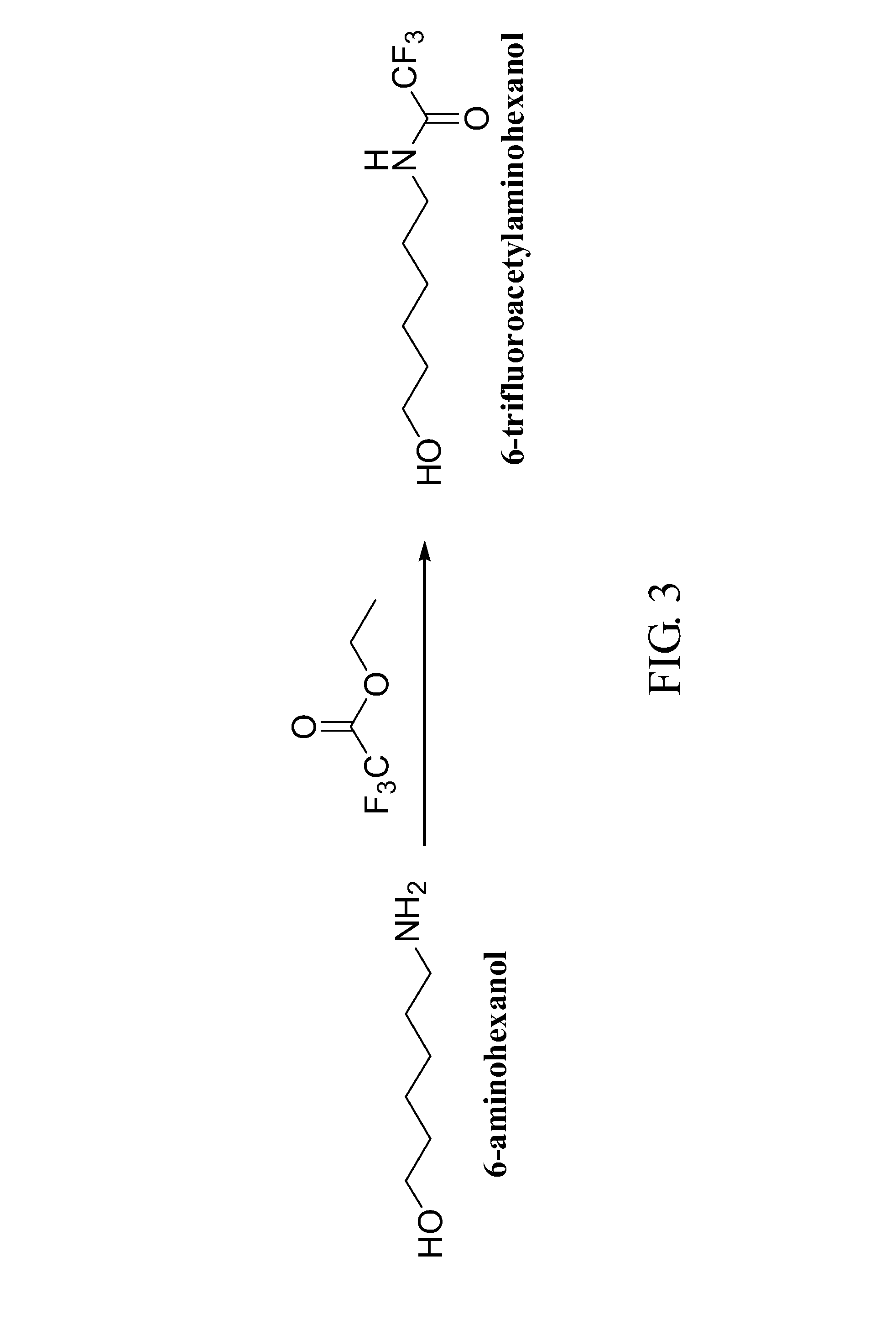
The invention relates to two synthetic methods of 3,6-bis(4-bisfumaroyl aminobutyl)-2,5-diketopiperazine and a salt substitute thereof. The first synthetic method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a final product through the steps of cyclodehydration, hydrogenation, coupling, saponification, recrystallization and the like by using epsilon-benzoyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine and p-nitryl monoethyl fumarate as starting materials. The second synthetic method comprises the following steps of: obtaining the final product through the steps of cyclodehydration, coupling, saponification, recrystallization and the like by using N-6-trifluoroacetyl-L-lysine and the p-nitryl monoethyl fumarate (or p-nitryl monoethyl fumarate acyl chloride) as the starting materials. Meanwhile, the salt substitute of the 3,6-bis(4-bisfumaroyl aminobutyl)-2,5-diketopiperazine can also be generated by directly carrying out substitution reaction on the 3,6-bis(4-bisfumaroyl aminobutyl)-2,5-diketopiperazine as a reaction product and corresponding salt.
Owner:于清
Durable thermoset binder compositions from 5-carbon reducing sugars and use as wood binders
ActiveUS20110263757A1Minimize formaldehyde contentWeaken energyCosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsTris(2-aminoethyl)amineParticle board
The present invention provides thermosetting aqueous binder compositions of (i) one or more diprimary diamine, e.g. lysine, or poly(primary amine), e.g. polyethylenimine and tris(2-aminoethyl)amine, and (ii) one or more 5-carbon reducing sugar, such as xylose. The binders are at least substantially formaldehyde free and cure rapidly at temperatures sufficiently low and with sufficiently little swelling to enable one to provide wood or woody material containing articles, such as particle board, oriented strand board and bamboo boards or articles.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Composition for an in vitro fertilization medium
InactiveUS6130086AImprove stabilityIncrease stimulationCulture processMedical devicesArginineTryptophan
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 02503 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 4, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08946 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 13, 1997The present invention aims to provide a medium composition for in vitro fertilization, in particular, a composition usable in the culture of ova or early embryos which are fertilized eggs, the preparation or culture of sperm, and the pre-treatment of ova or sperm. The composition comprises, as its essential components, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan, L-lysine, L-threonine, L-valine, L-methionine, L-isoleucine, L-leucine, L-proline, glycine, L-alanine, L-tyrosine, L-histidine, L-arginine, L-taurine, L-aspartic acid, L-serine, L-asparagine, L-glutamic acid, L-glutamine and L-cystine, provided that at least a part of the L-cystine may be replaced by L-cysteine.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
Method for producing L-lysine or L-threonine
A bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has an ability to produce L-lysine or L-threonine and which is modified so that a malic enzyme does not function normally in a cell, and a method for producing L-lysine or L-threonine, comprising culturing the bacterium in a medium to produce and cause accumulation of L-lysine or L-threonine, and collecting the L-lysine or L-threonine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Abuse resistant lysine amphetamine compounds
InactiveUS7223735B2Reduced activityRelease is diminished and eliminatedOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAlternative treatment
The present invention describes compounds, compositions and methods of using the same comprising lysine covalently attached to amphetamine. These compounds and compositions are useful for reducing or preventing abuse and overdose of amphetamine. These compounds and compositions find particular use in providing an abuse-resistant alternative treatment for certain disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), ADD, narcolepsy, and obesity. Oral bioavailability of amphetamine is maintained at therapeutically useful doses. At higher doses bioavailability is substantially reduced, thereby providing a method of reducing oral abuse liability. Further, compounds and compositions of the invention decrease the bioavailability of amphetamine by parenteral routes, such as intravenous or intranasal administration, further limiting their abuse liability.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Six percent-premix for lactating sows and wheat-type daily ration prepared from six percent-premix
ActiveCN103053852AImprove reproductive performanceIncrease feed intakeAnimal feeding stuffComposite electrolytePhytase
The invention belongs to the field of feeds, and particularly relates to a six percent-premix for lactating sows and a wheat-type daily ration prepared from the six percent-premix. The premix comprises multivitamins, composite trace elements, DL-methionine, lysine, threonine, L-arginine, valine, composite electrolyte, compound enzyme, 5000 IU of phytase, functional additives, feed attractants, calcium hydrogen phosphate, stone powder, salt, choline, antioxidants and defatted rice bran. On the whole, the daily ration for the lactating sows is capable of protecting the development of mammary glands of the sows, ensuring plentiful milk with high quality in the lactation period of the sows and increasing the survival rate of suckling piglets, and enables the piglets to have higher weaning weight.
Owner:河南宏展生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com