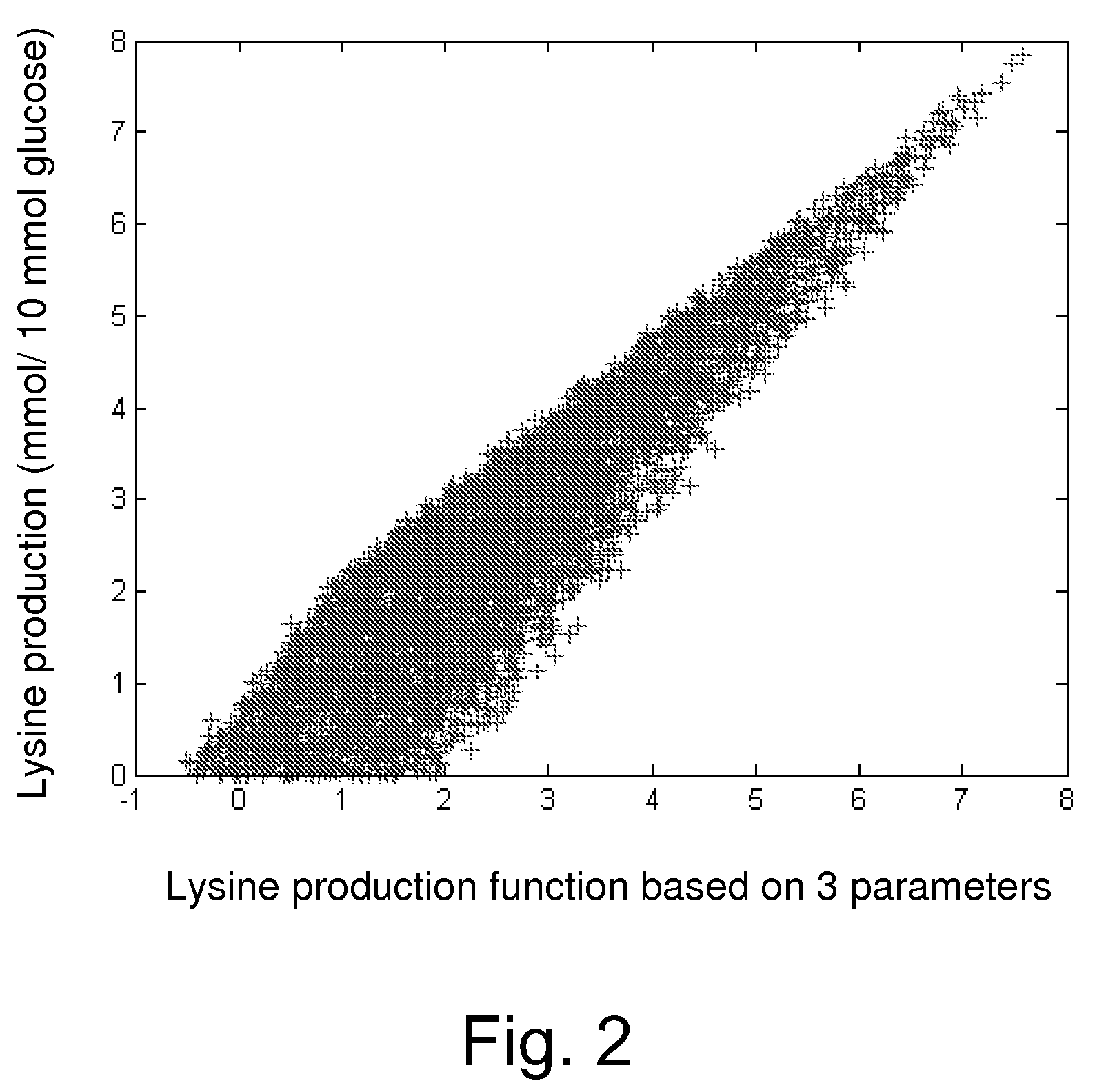
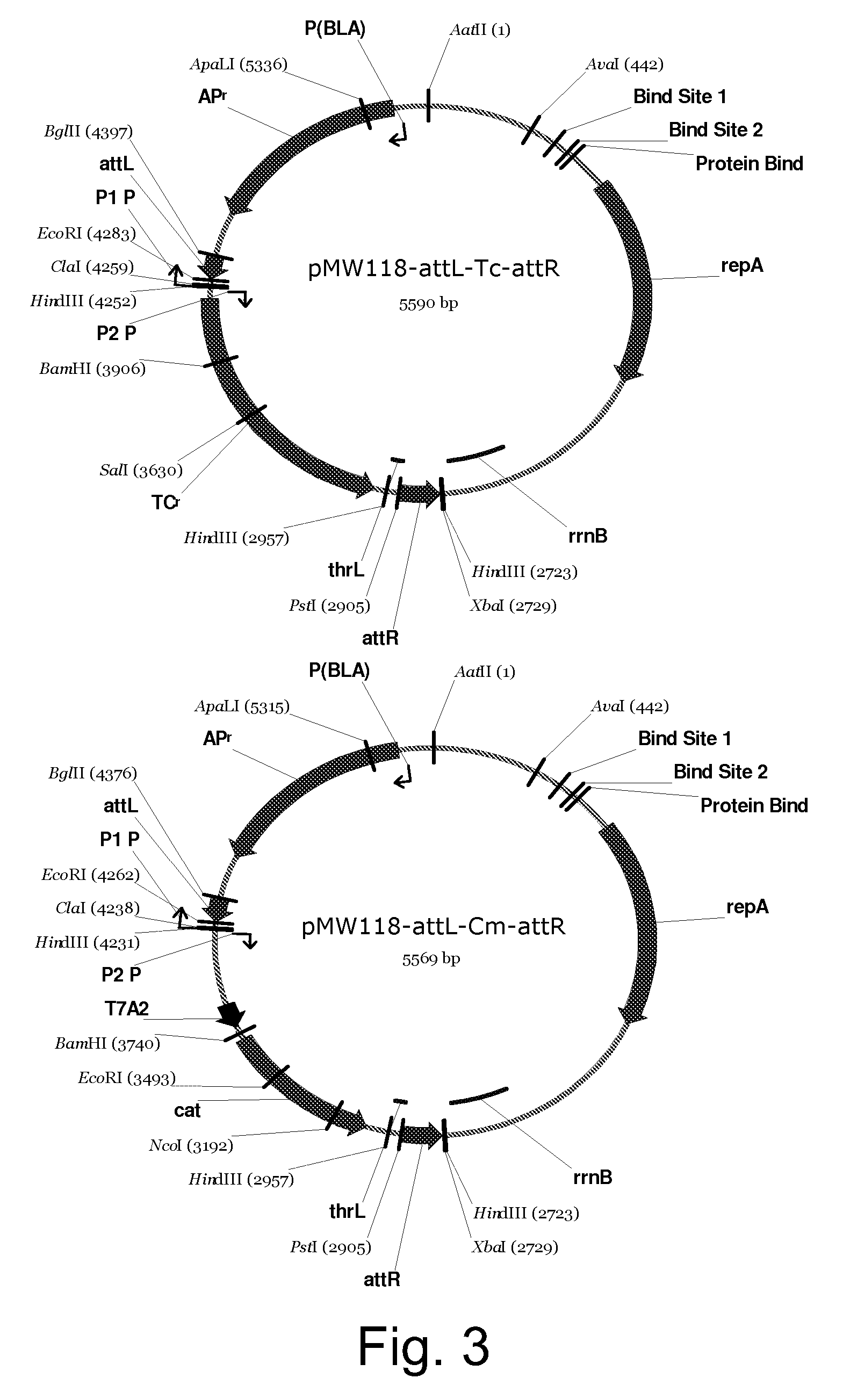
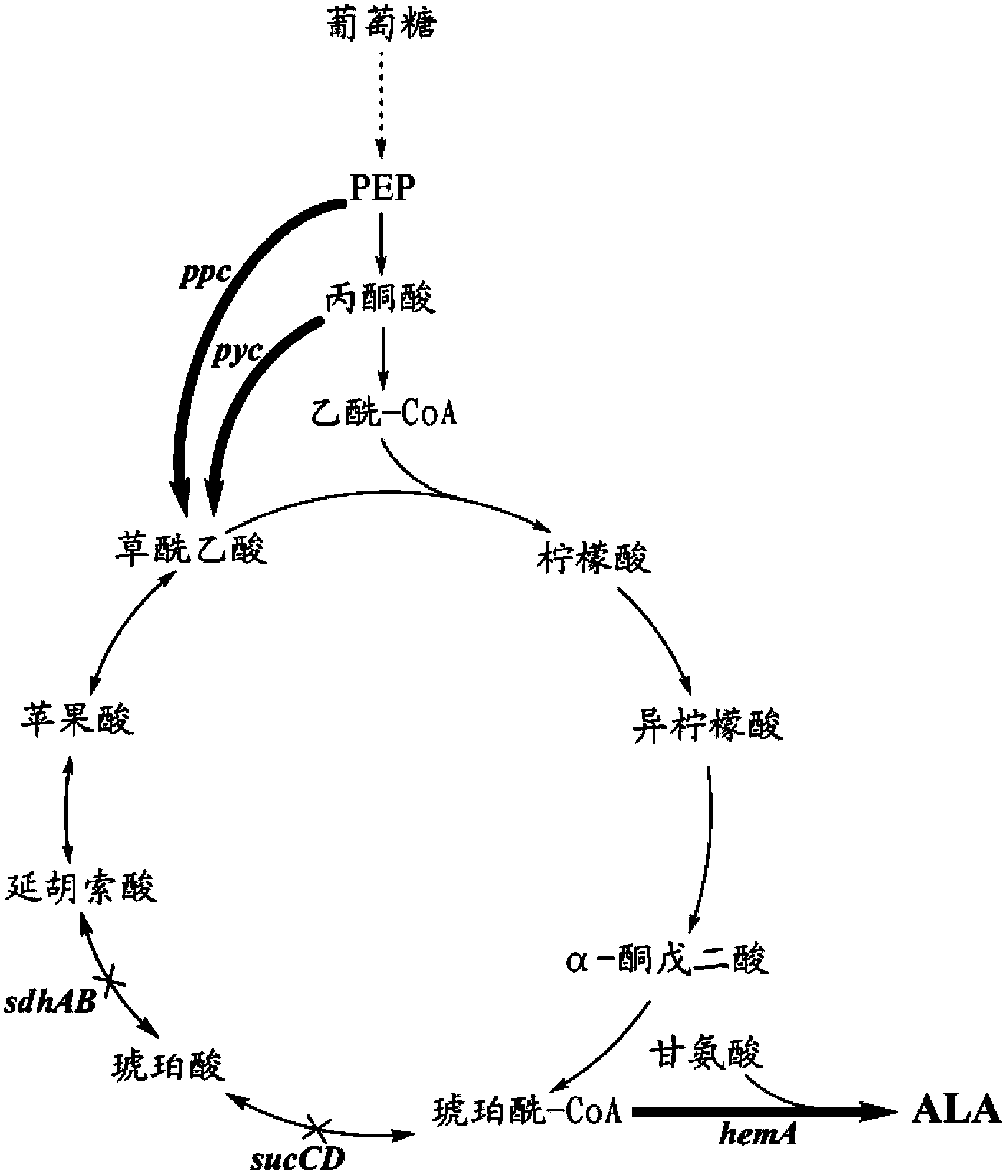
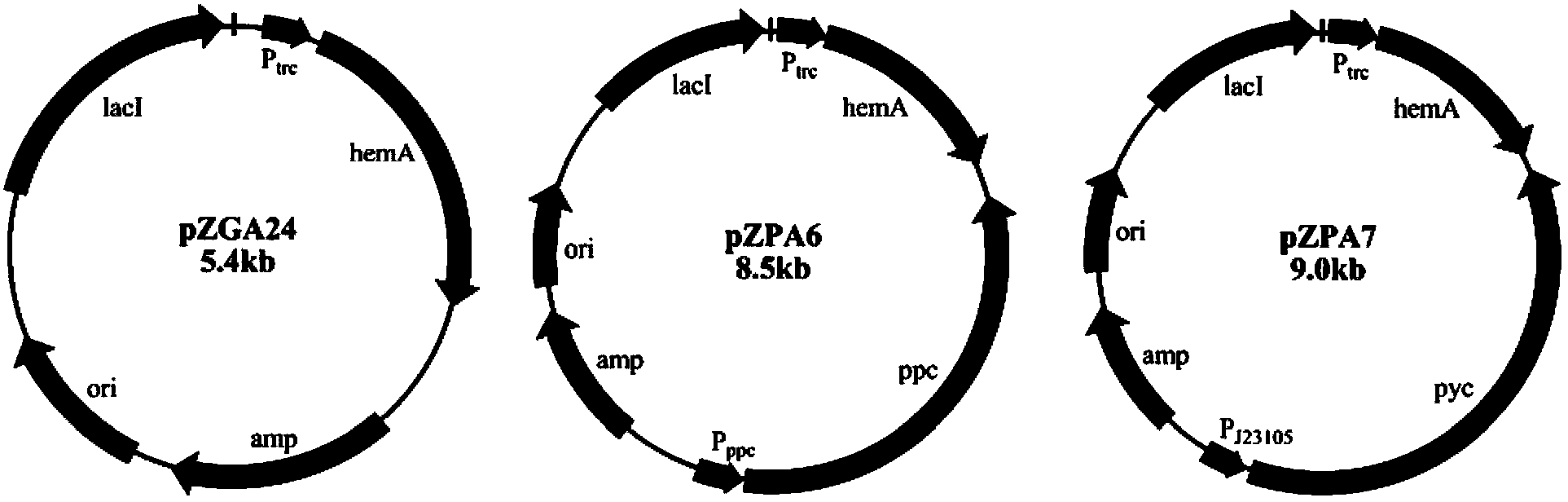
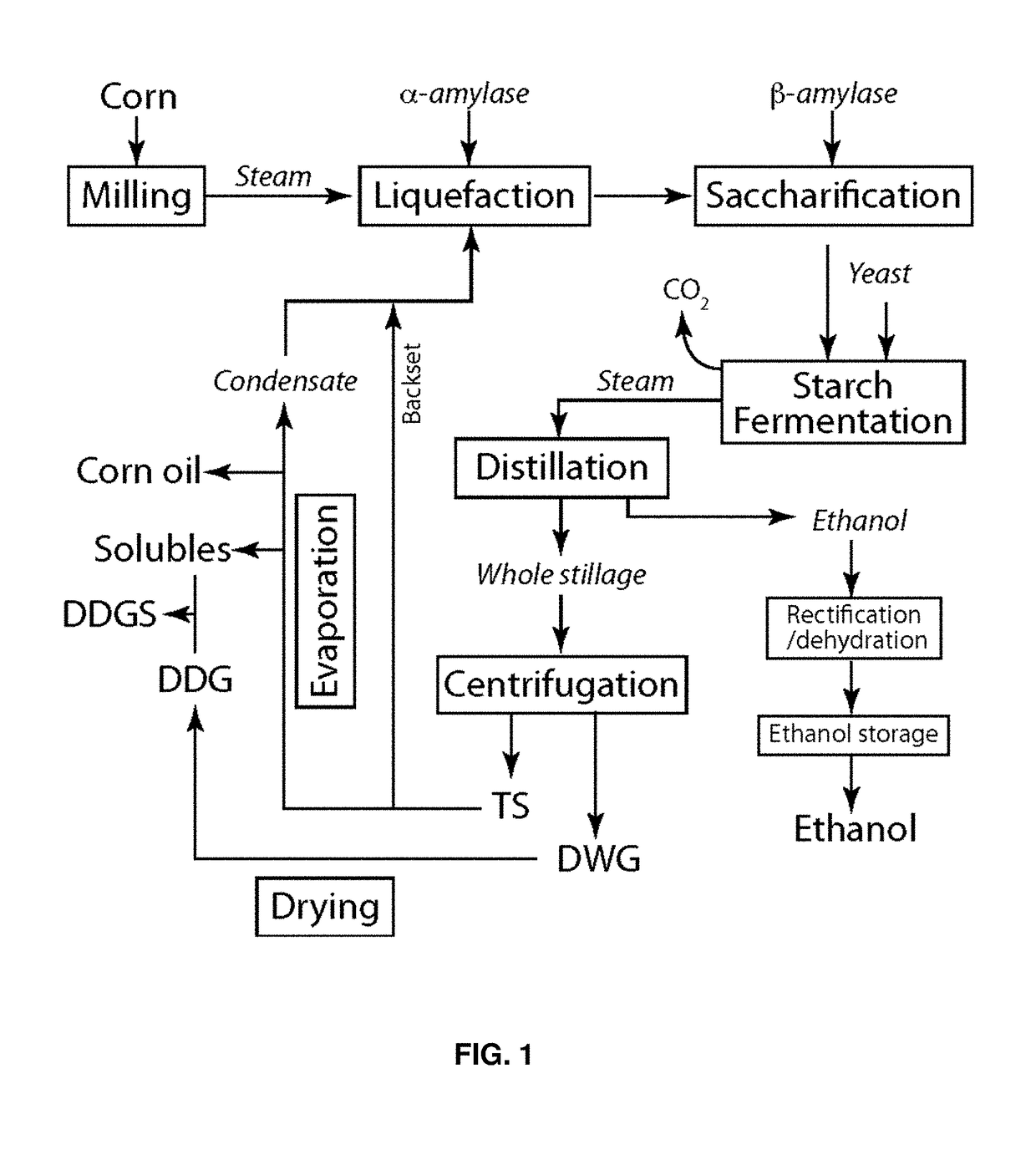
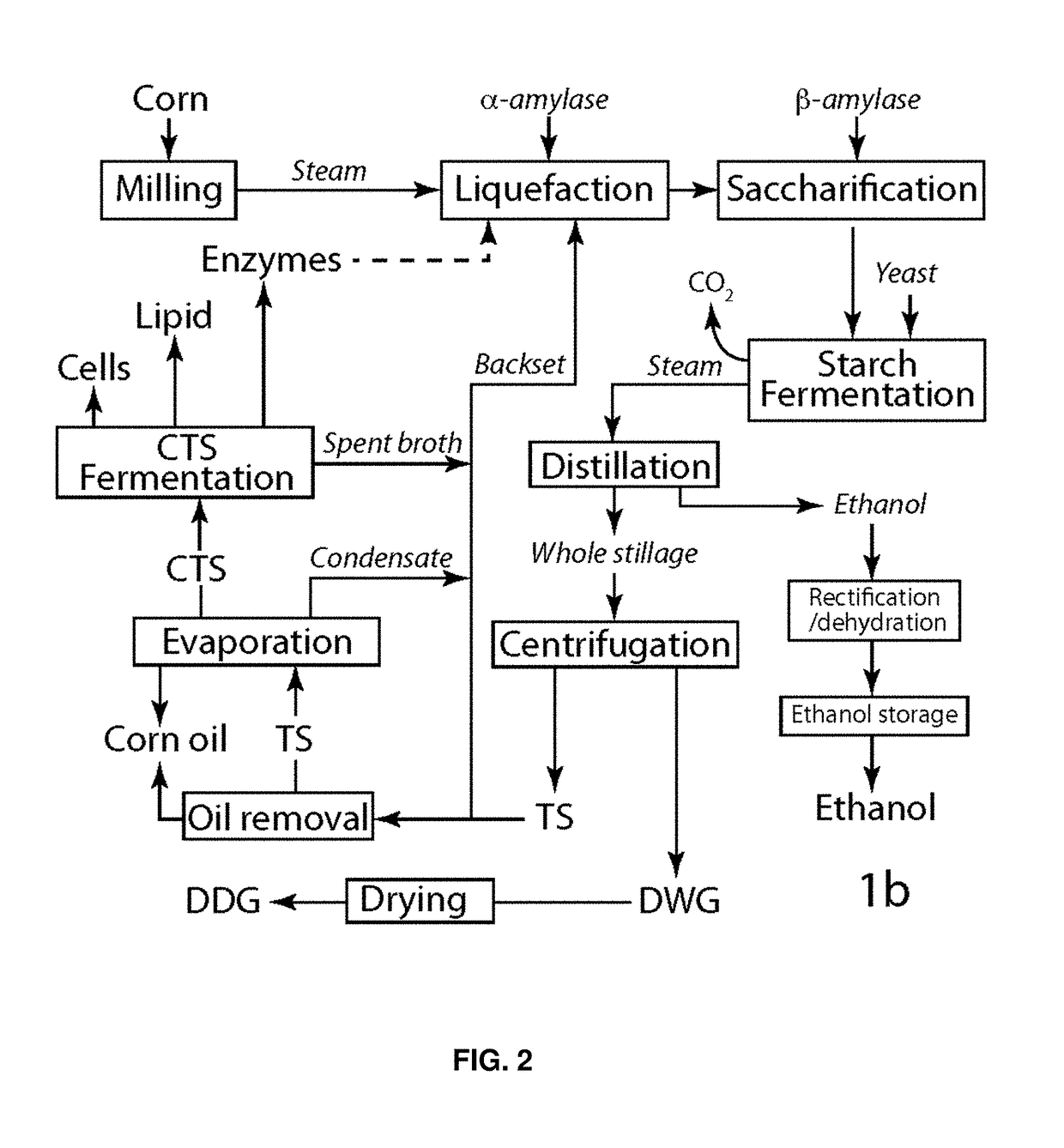
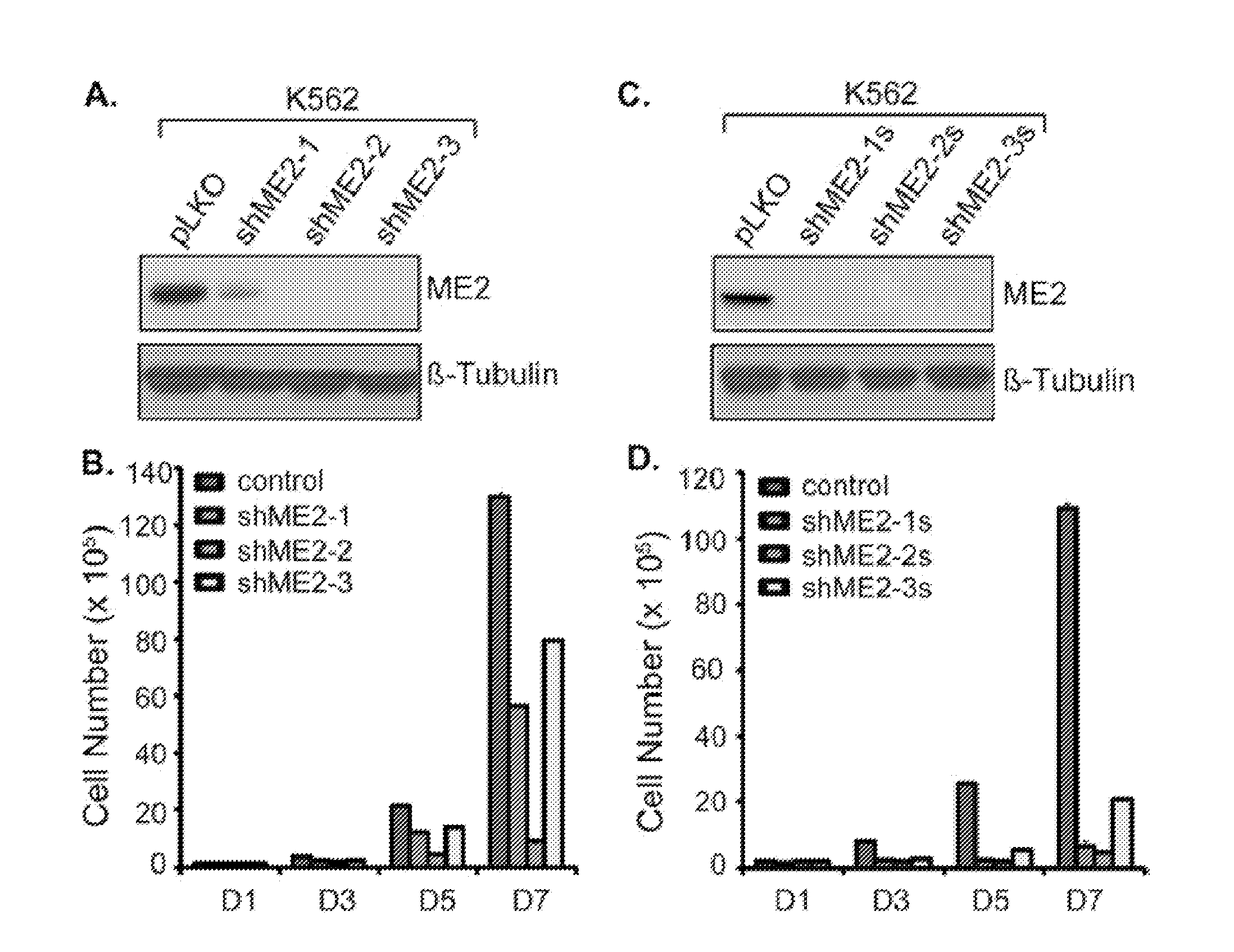
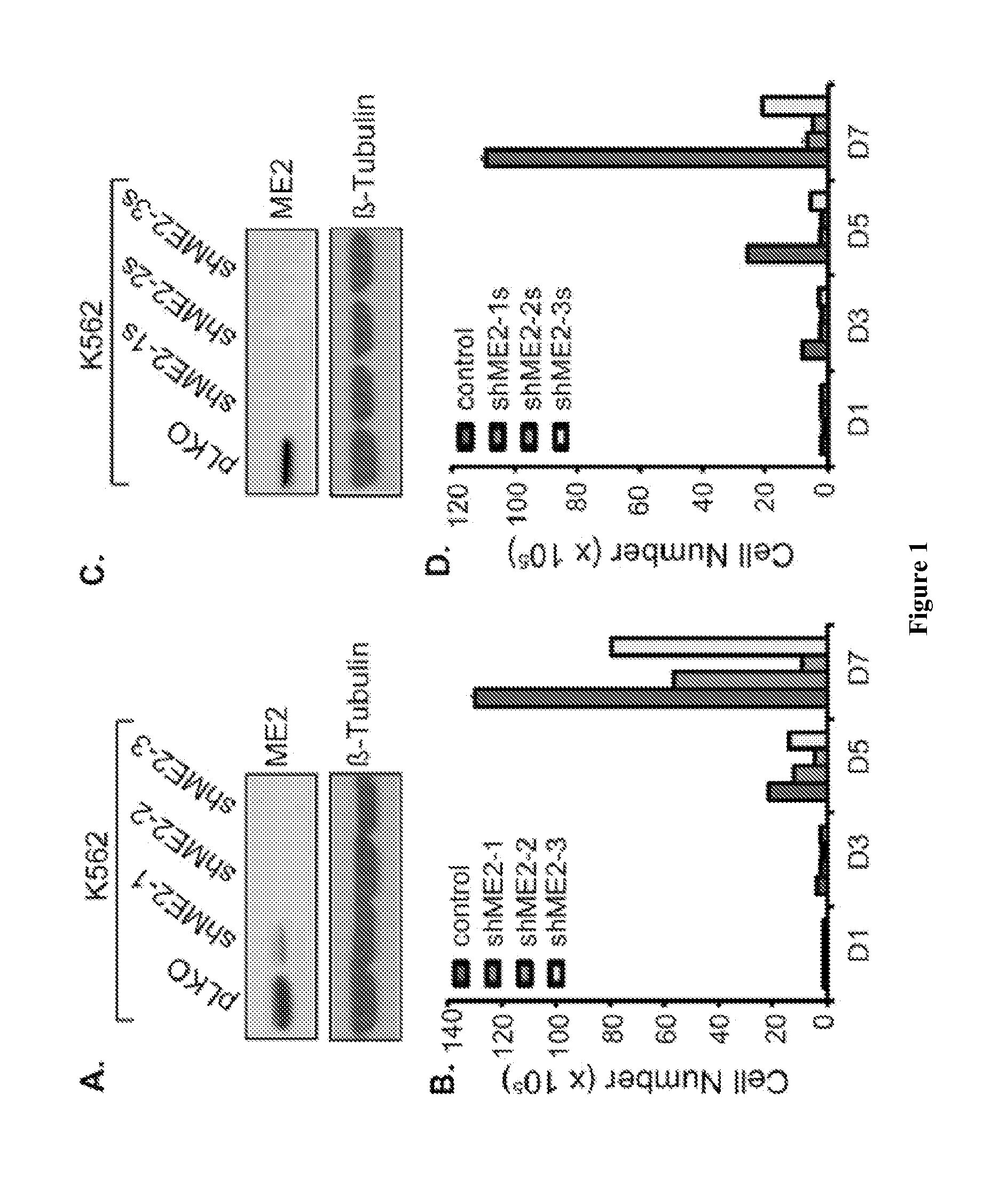
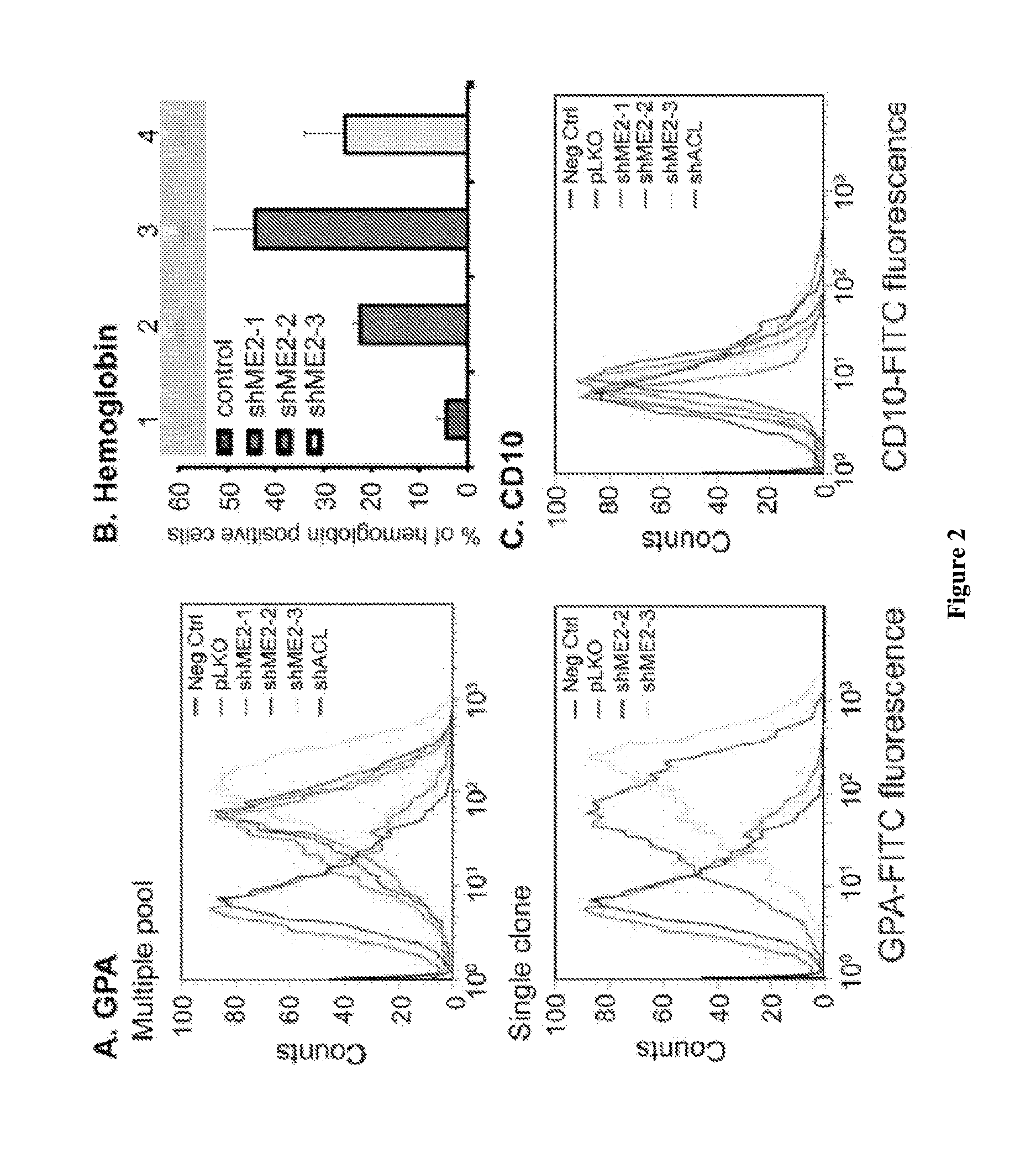
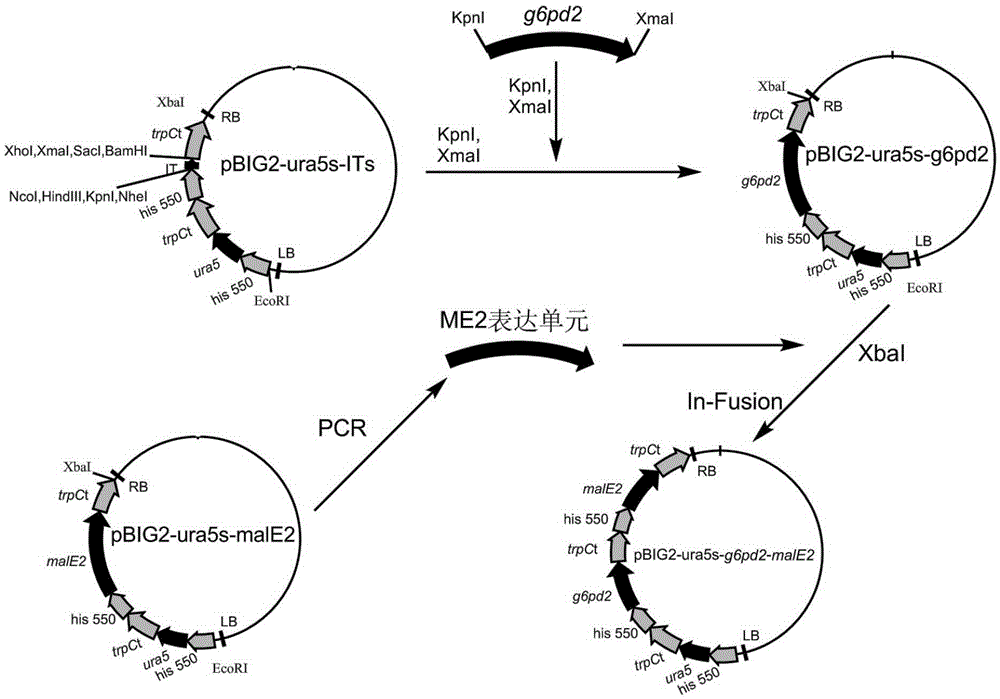
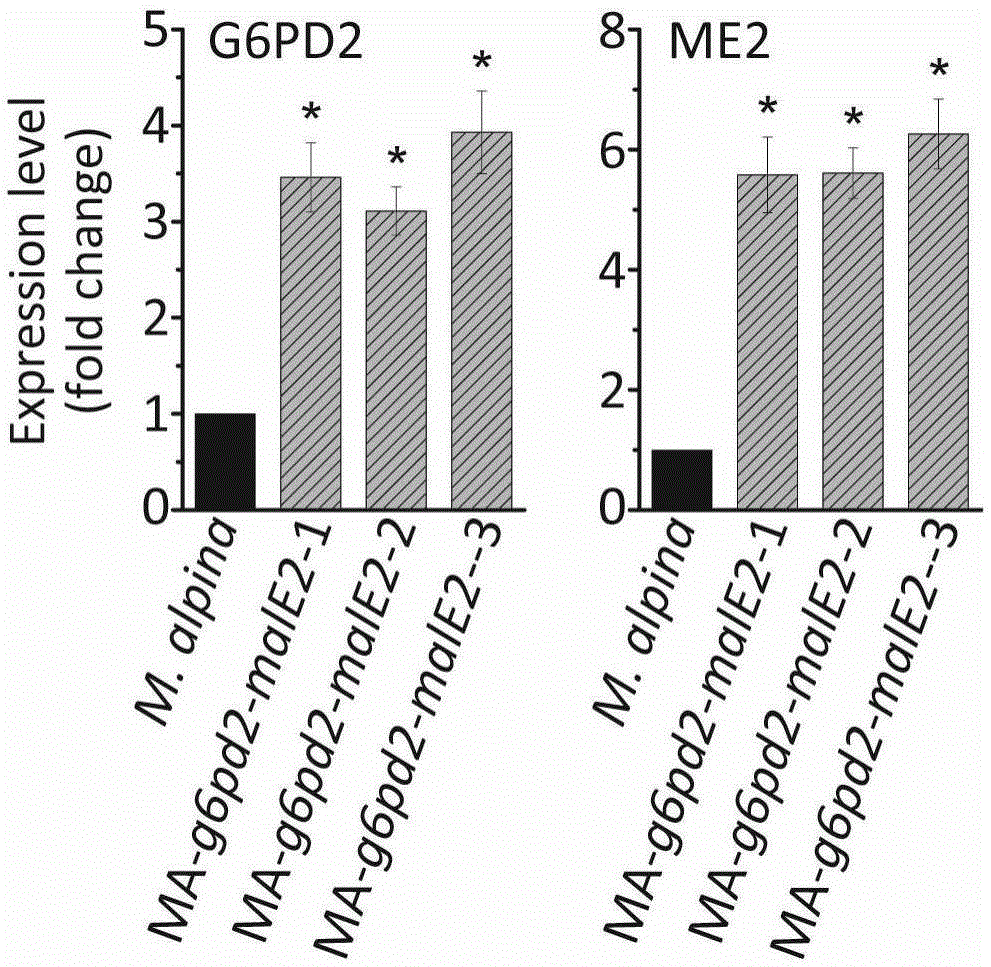
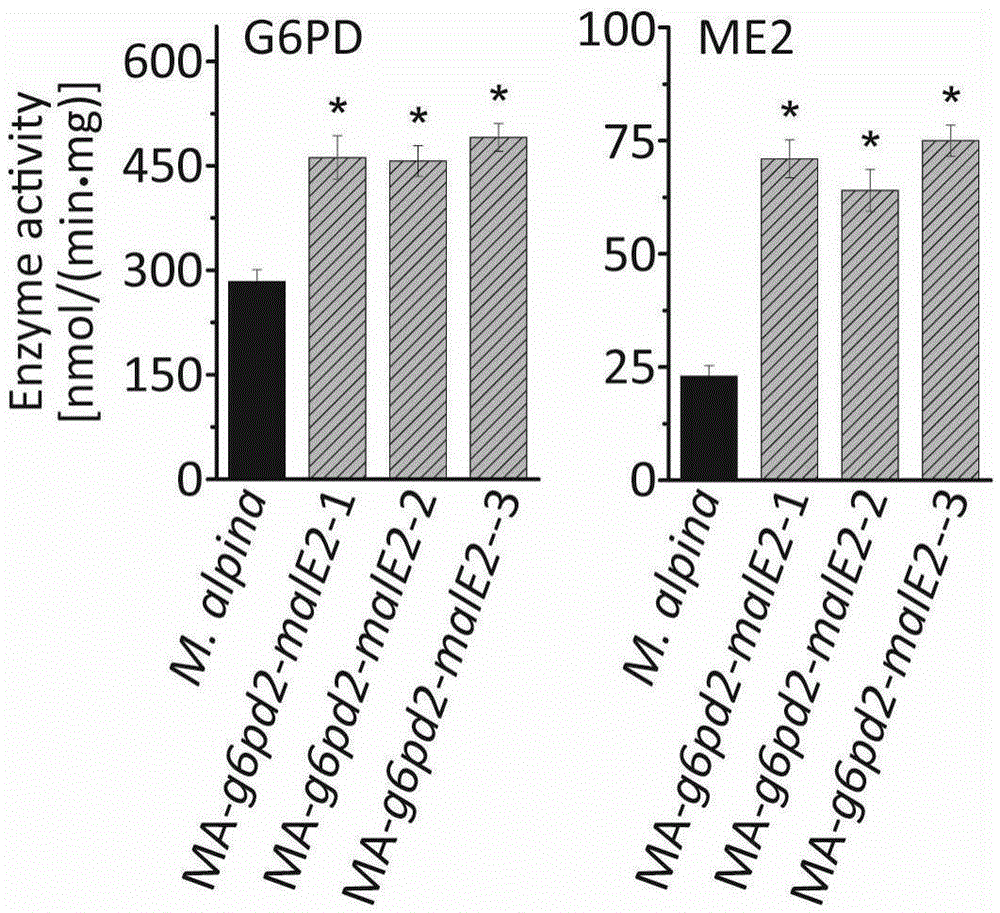
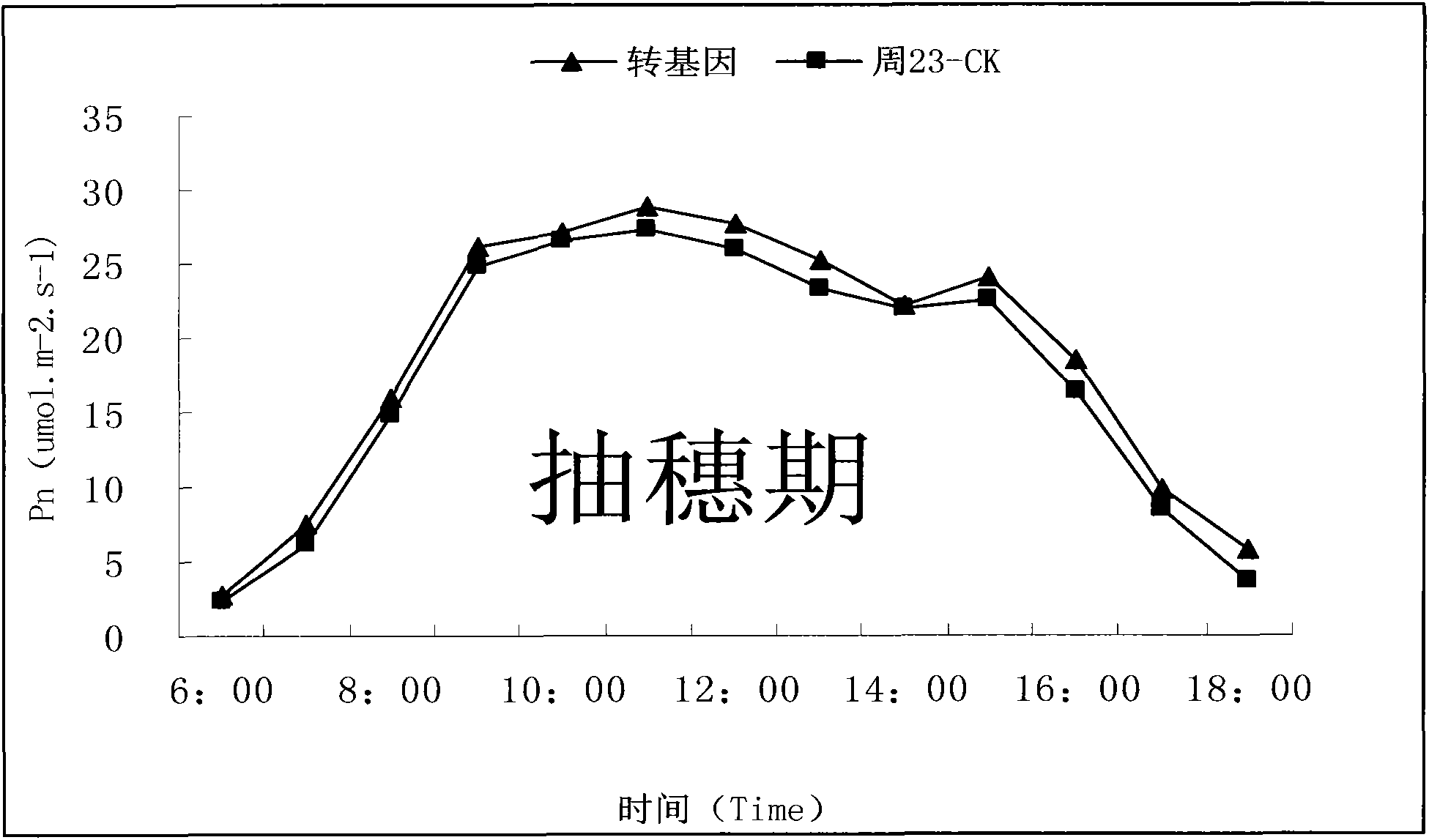
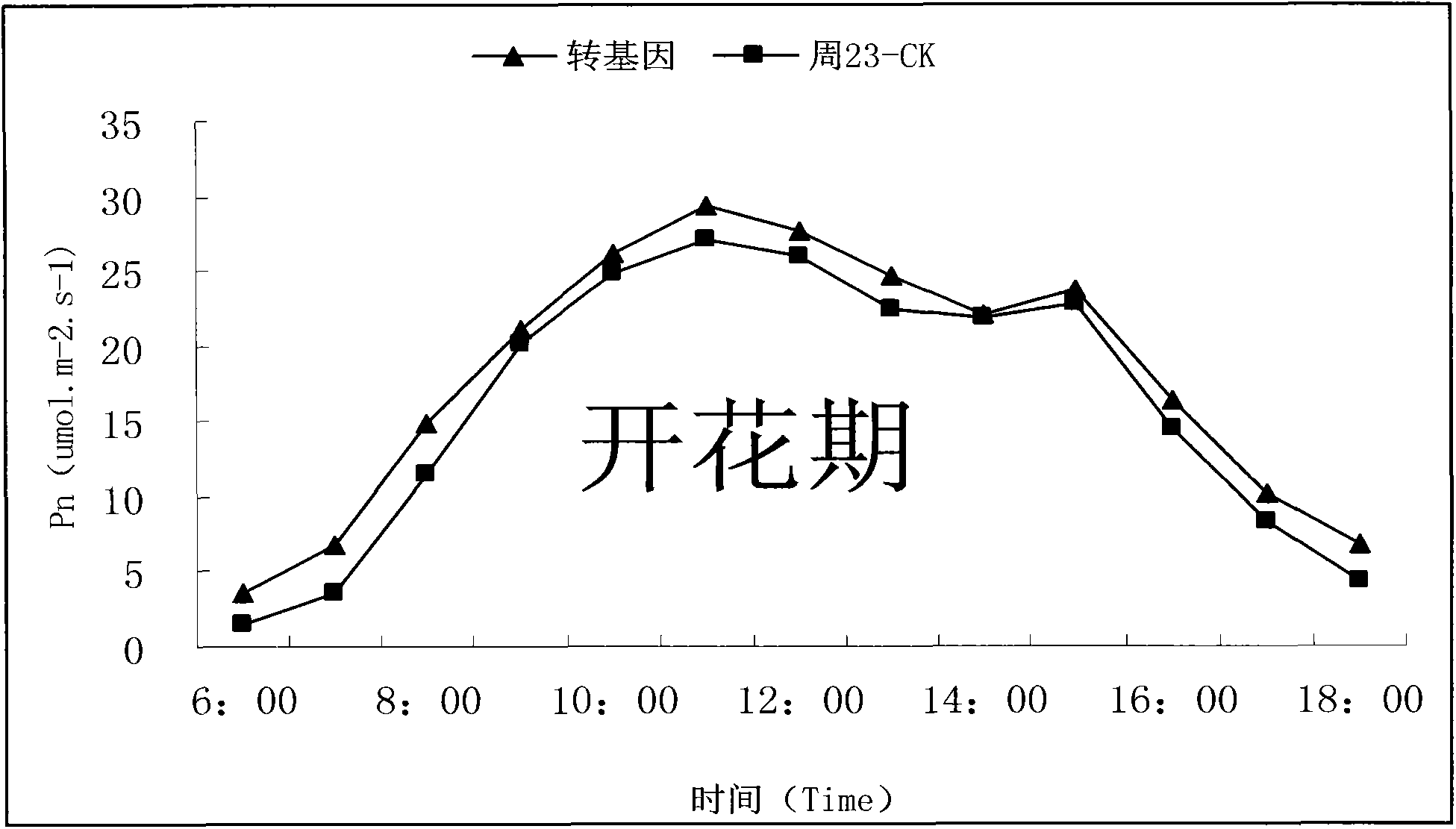
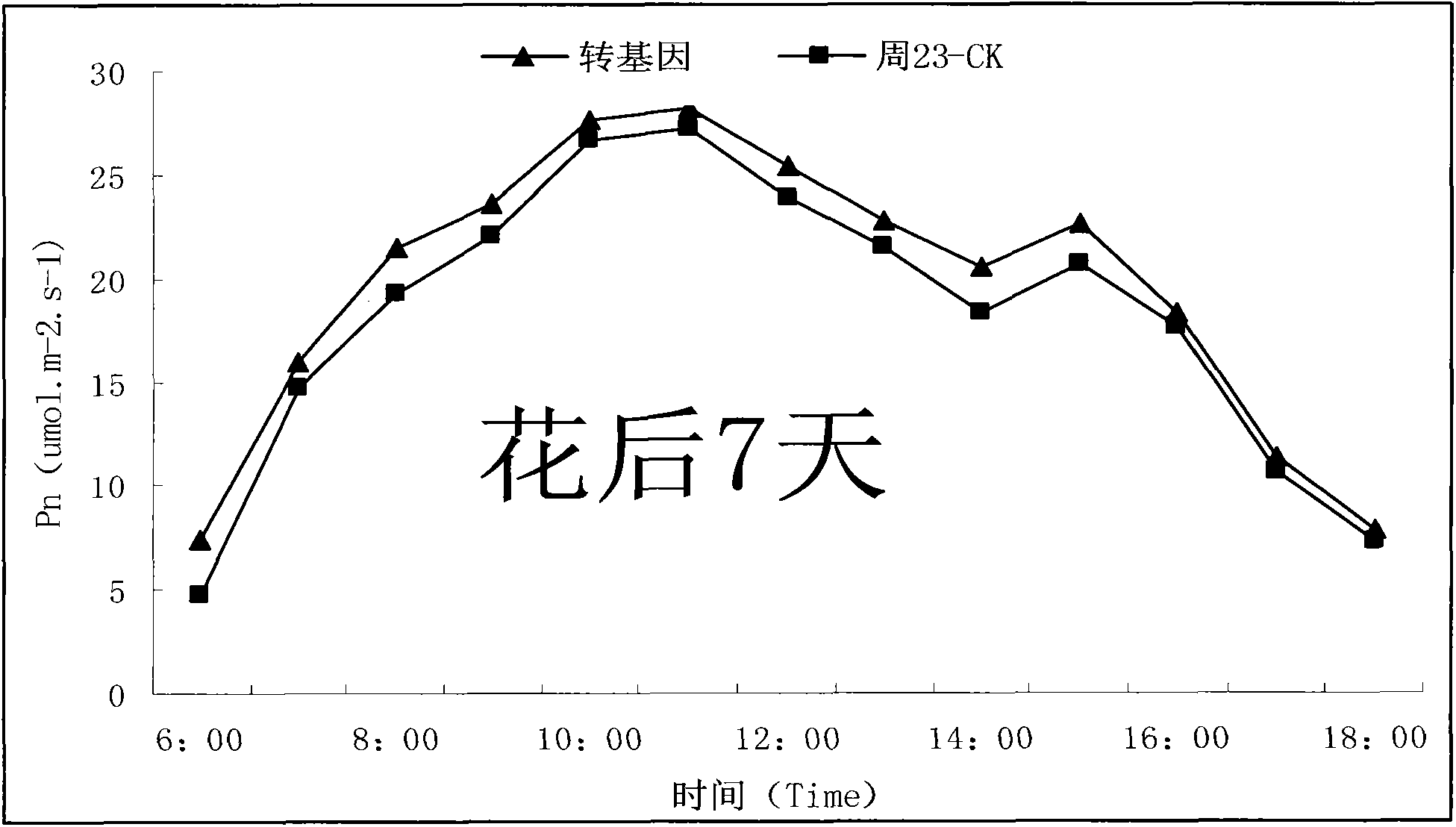
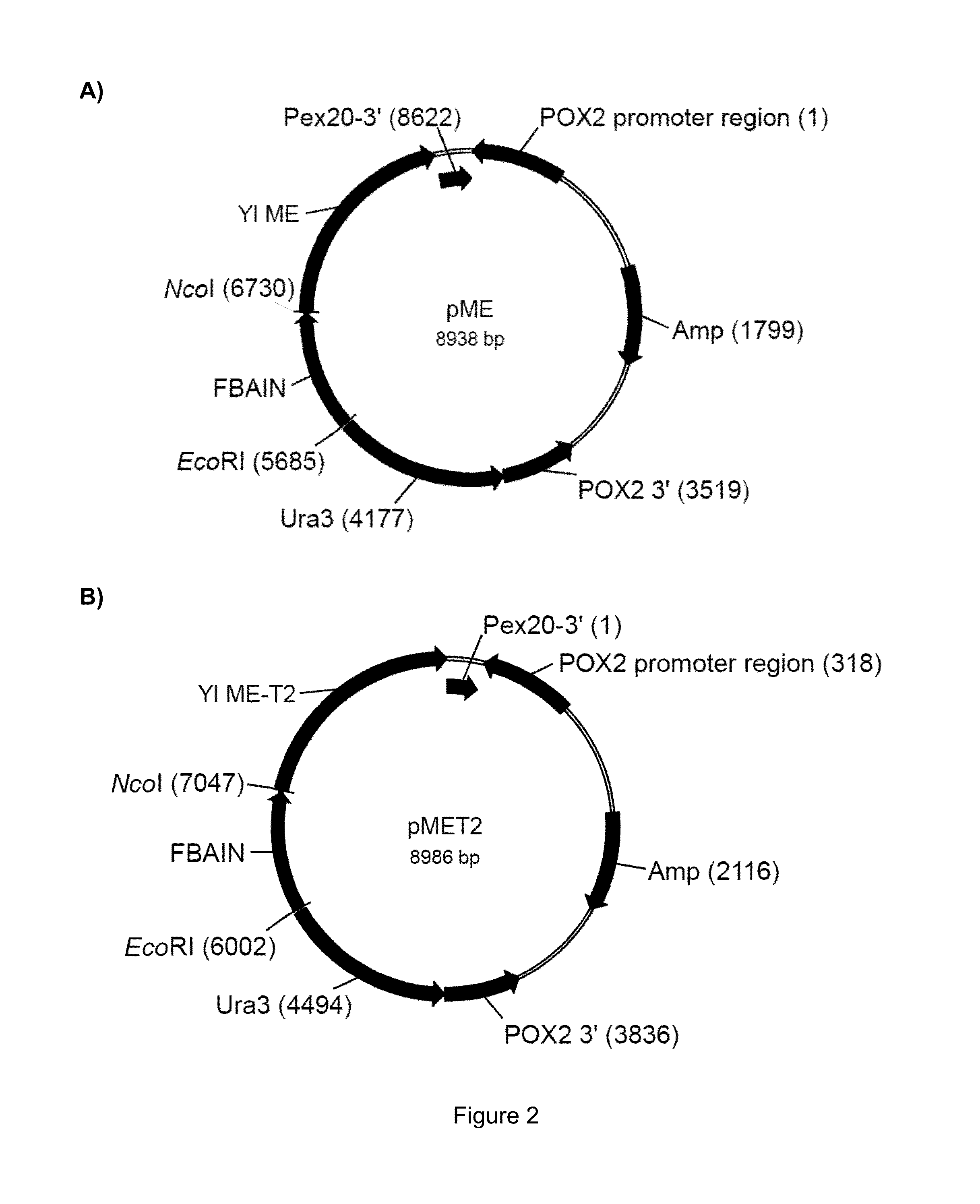
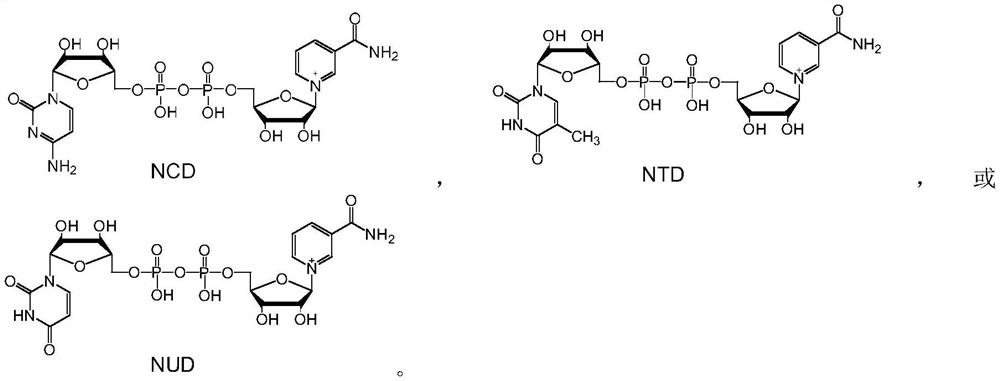
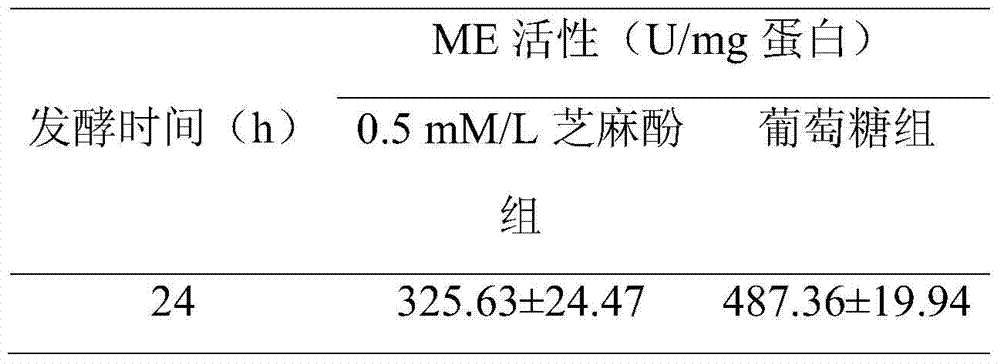
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Malic enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
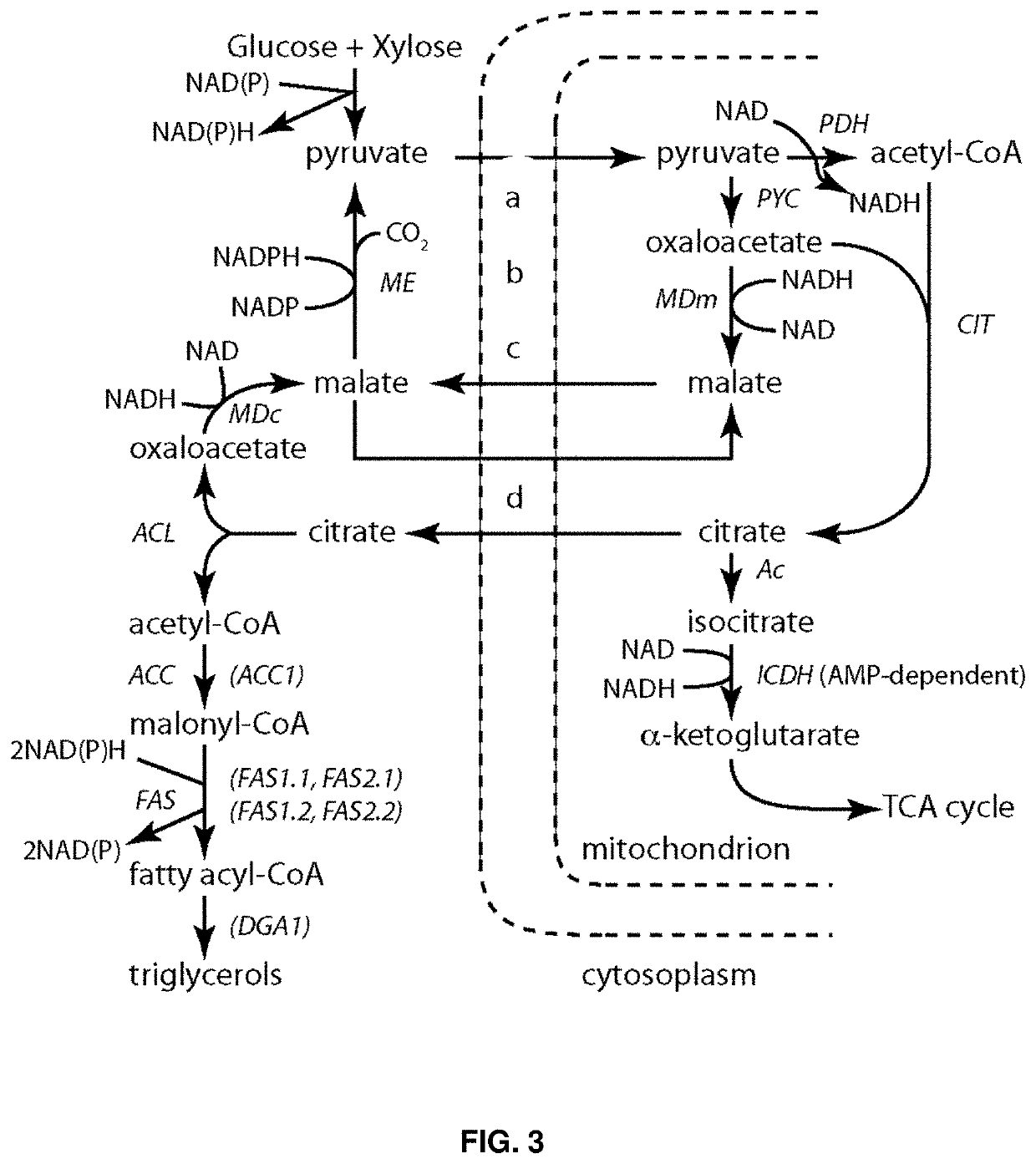
Malic enzyme may refer to decarboxylating malate dehydrogenases: Malate dehydrogenase or NAD-malic enzyme Malate dehydrogenase, another NAD-malic enzyme Malate dehydrogenase or NADP-malic enzyme including D-malate dehydrogenase
Novel gene encoding malic enzyme and method for preparing succinic acid using the same
ActiveUS20070042476A1Increase productionLightweight productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismNucleotide
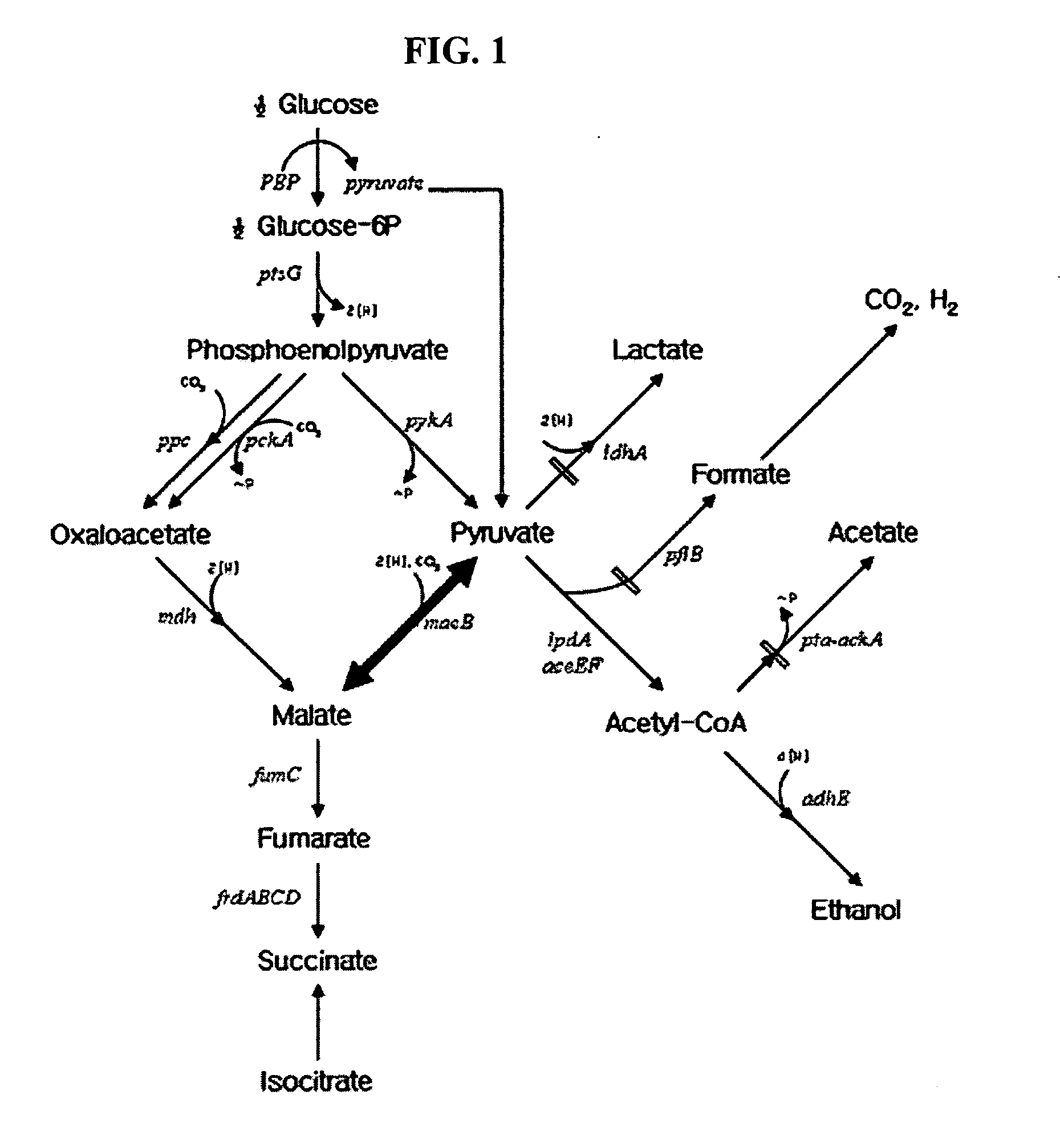
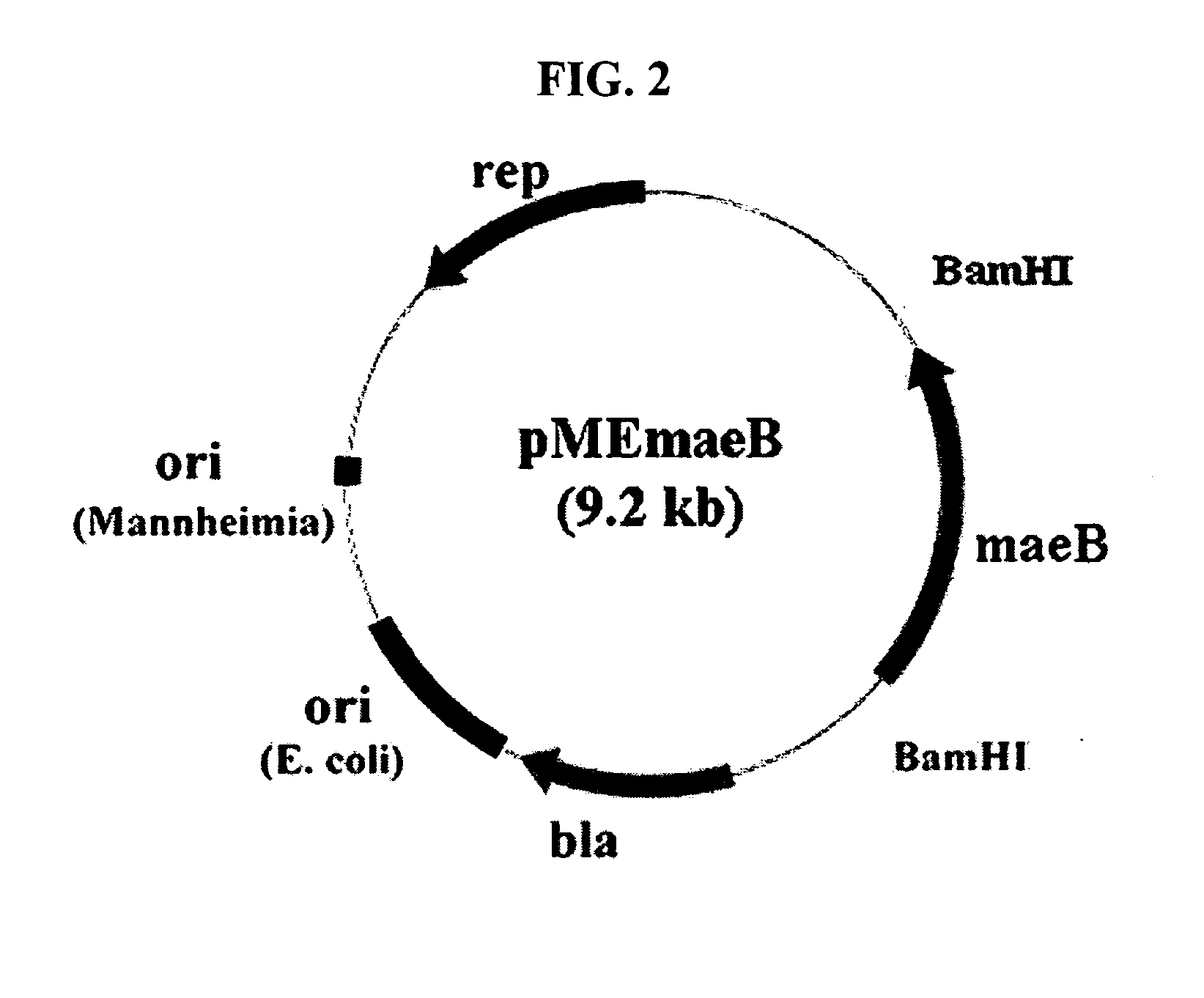
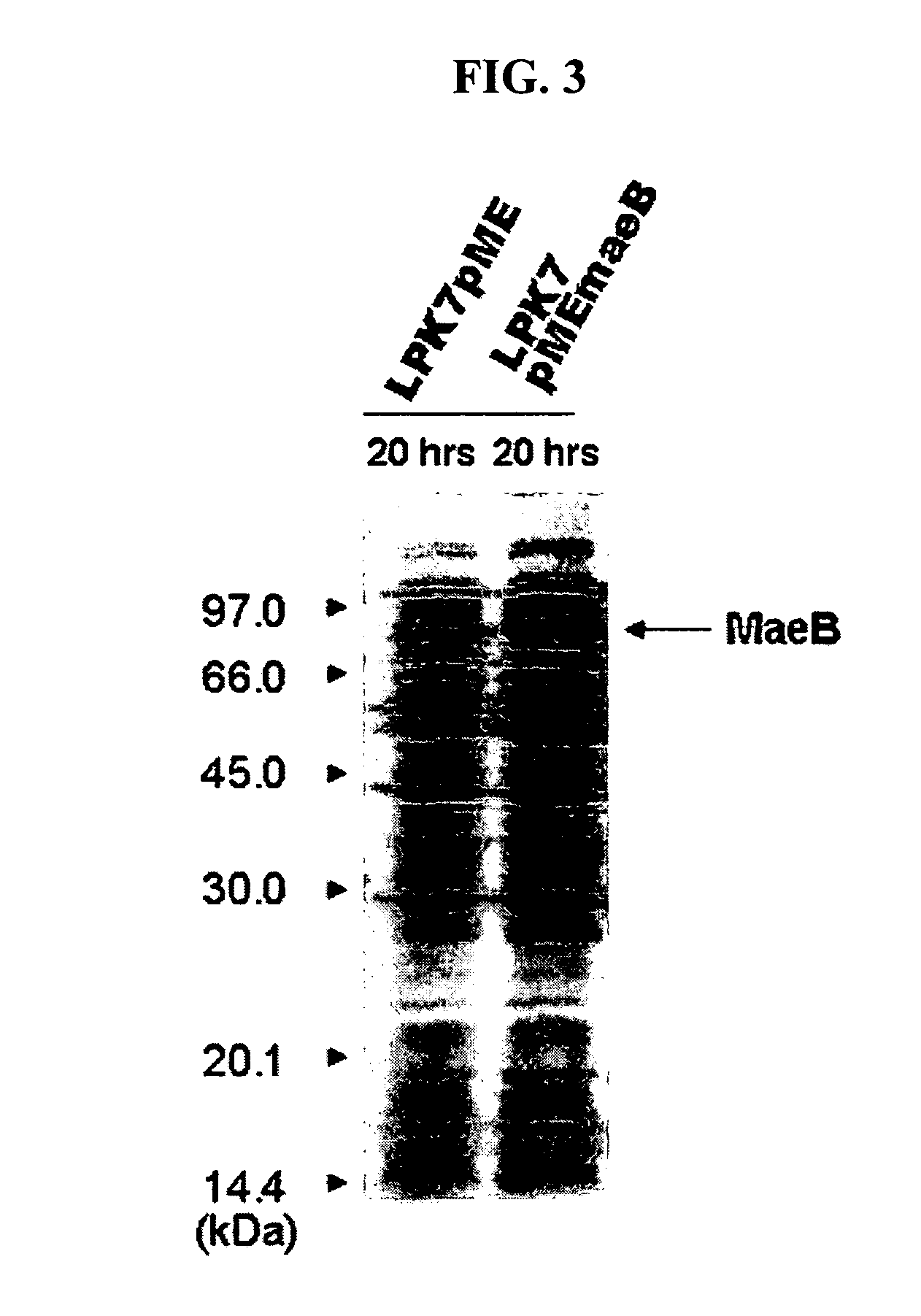
A nucleotide sequence encoding a malic enzyme and a method for preparing succinic acid using the same, more particularly, a maeB nucleotide sequence encoding a malic enzyme B having the activity of converting pyruvic acid or pyruvate to malic acid or malate, or vice versa, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a microorganism transformed with the recombinant vector, and a method for preparing succinic acid using the transformed microorganism.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
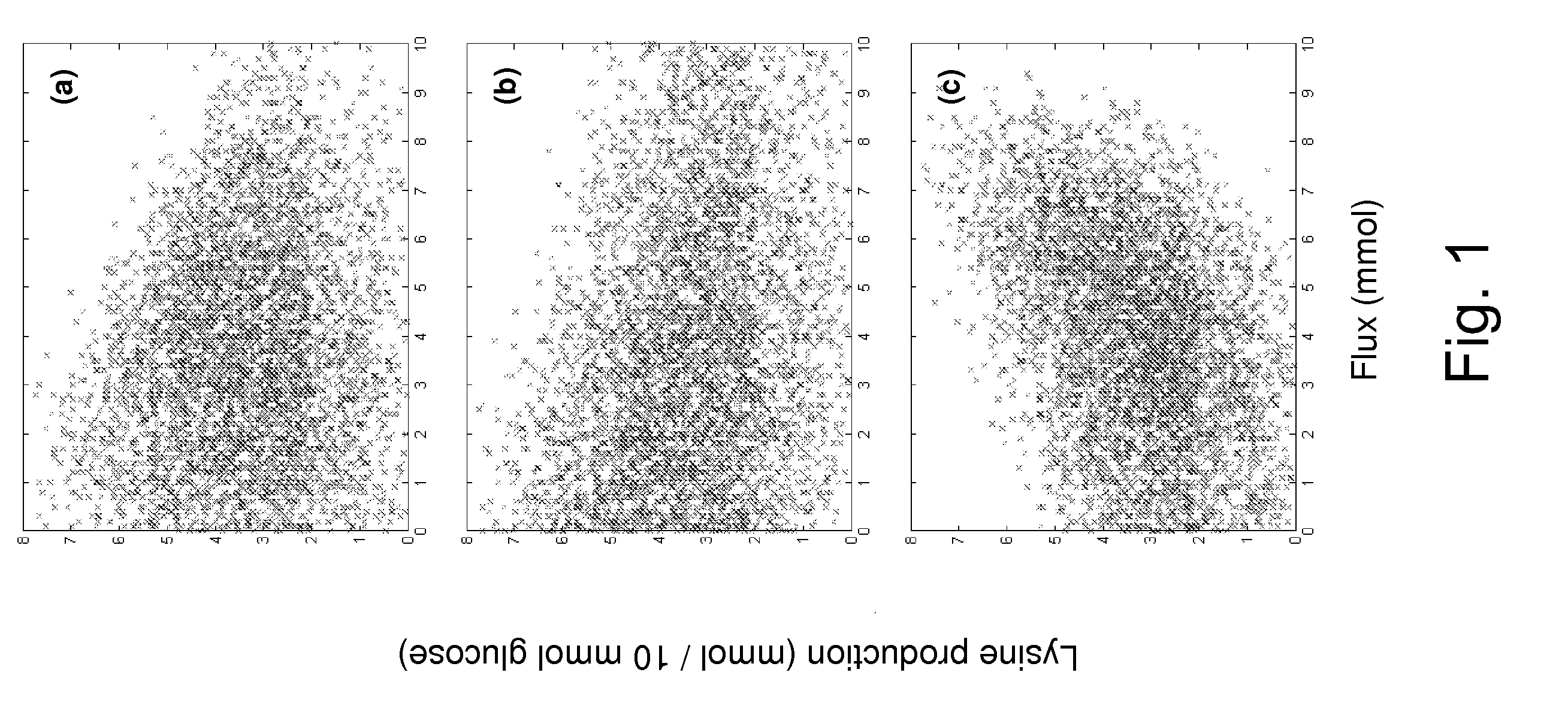
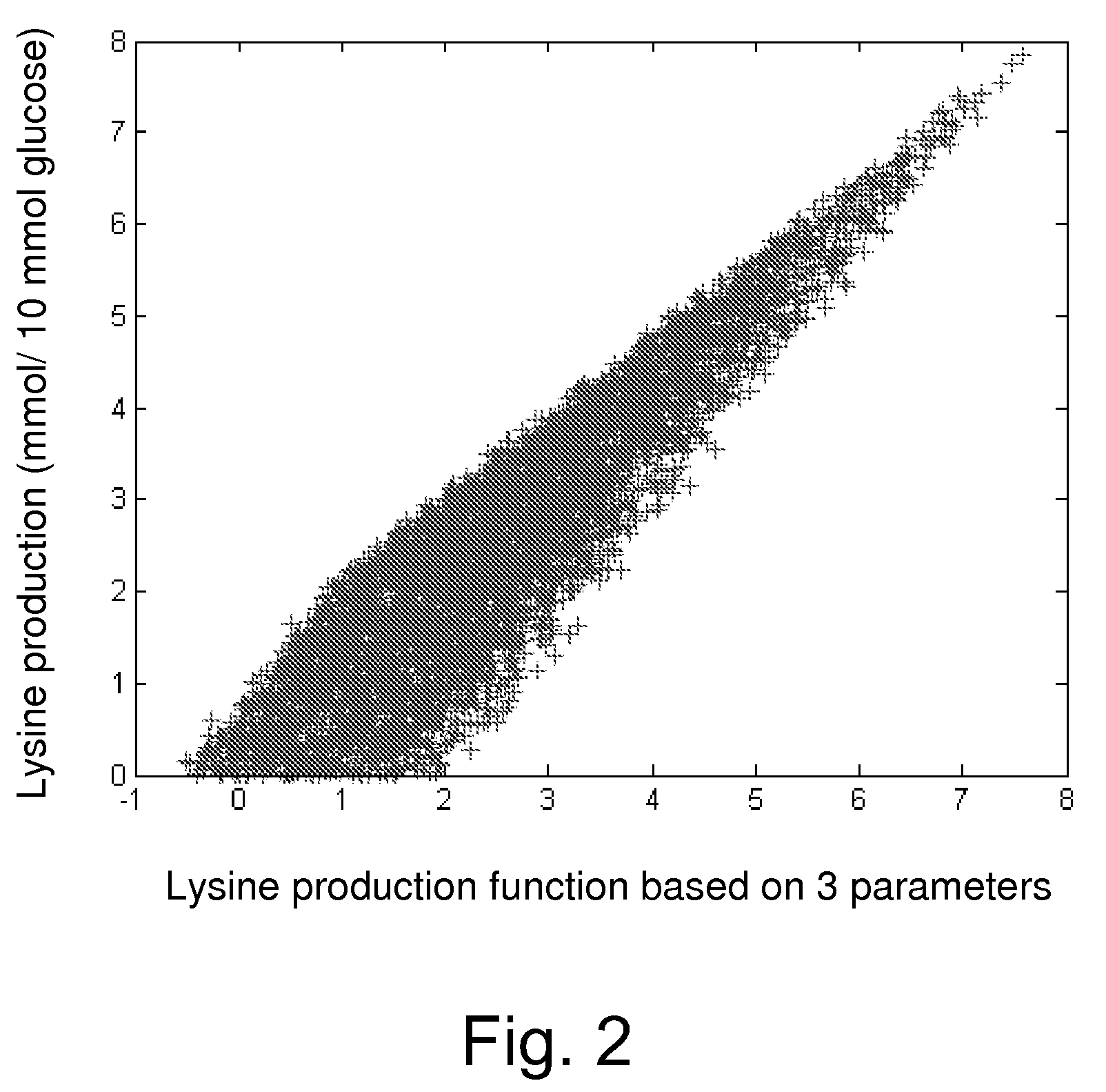
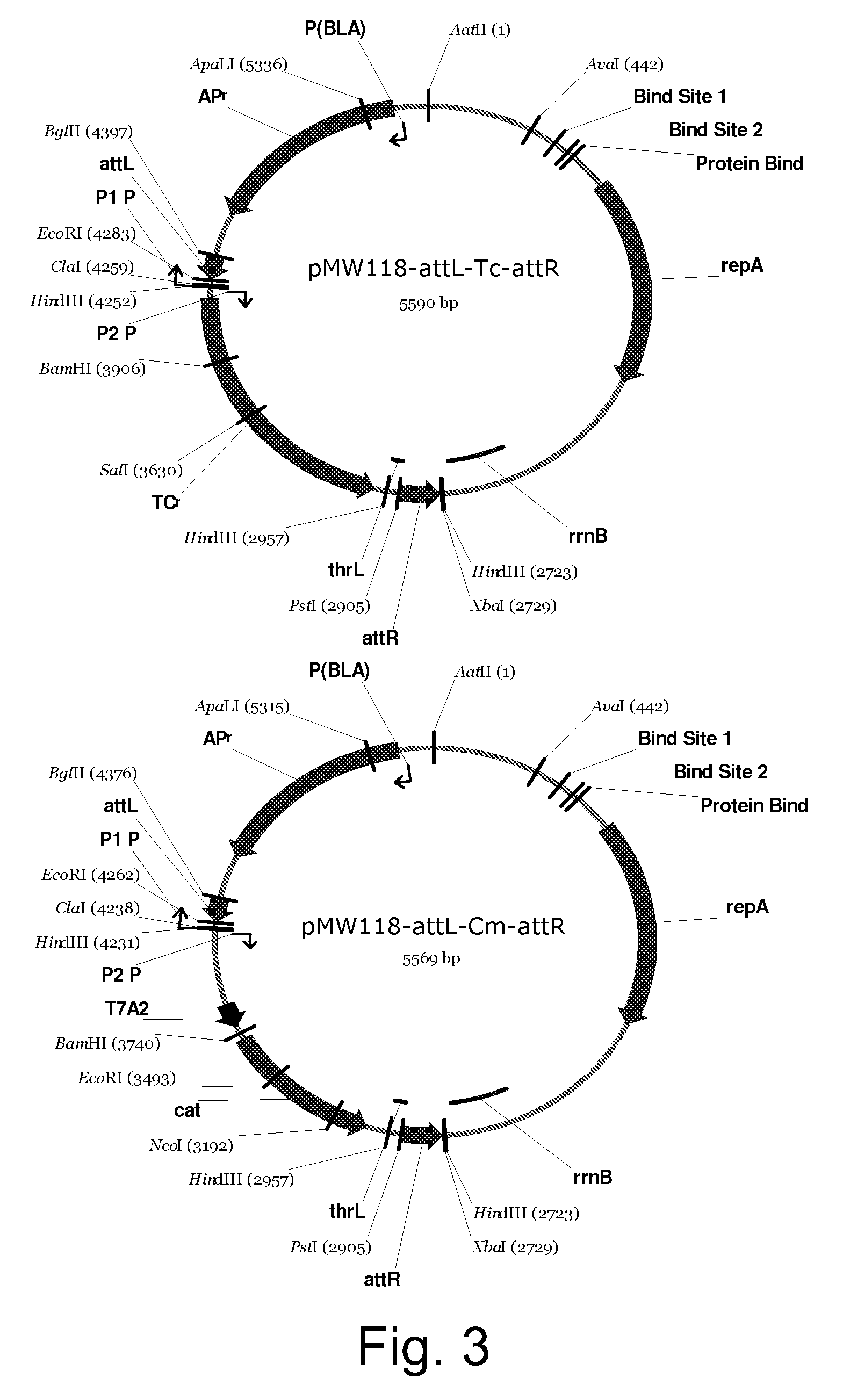
Method for producing L-lysine or L-threonine
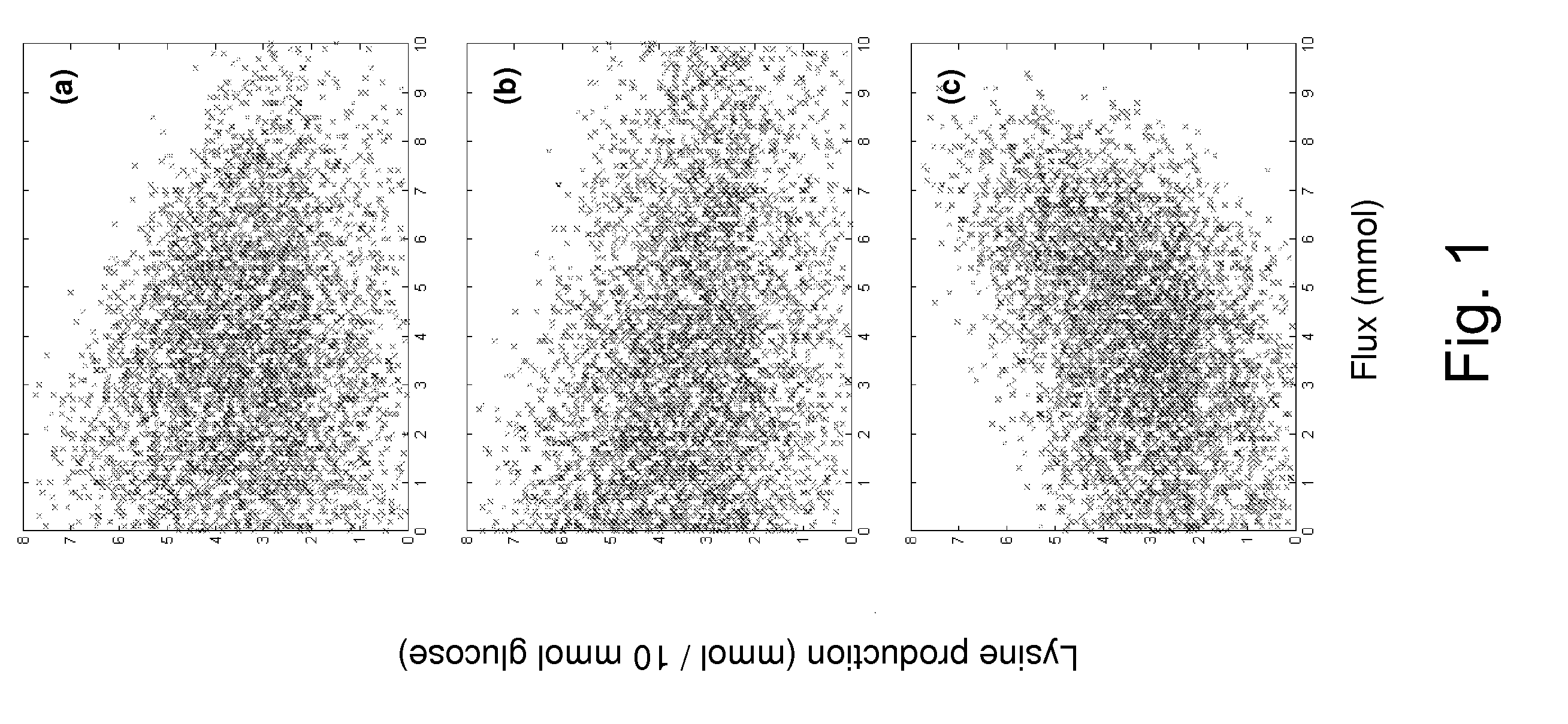
A bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia which has an ability to produce L-lysine or L-threonine and which is modified so that a malic enzyme does not function normally in a cell, and a method for producing L-lysine or L-threonine, comprising culturing the bacterium in a medium to produce and cause accumulation of L-lysine or L-threonine, and collecting the L-lysine or L-threonine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for improving glycerol microbial fermentation production of 1,3-propanediol by constructing gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN102199570APromote conversionPromote circulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTricarboxylic acid
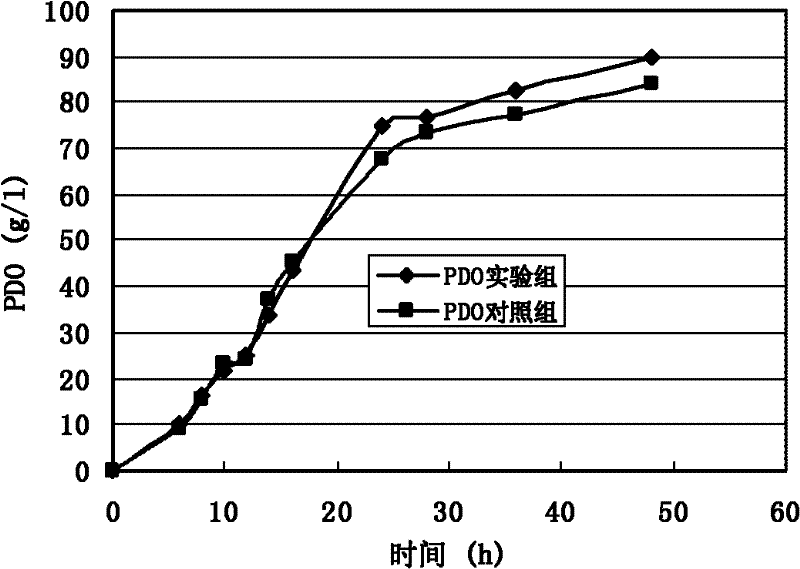
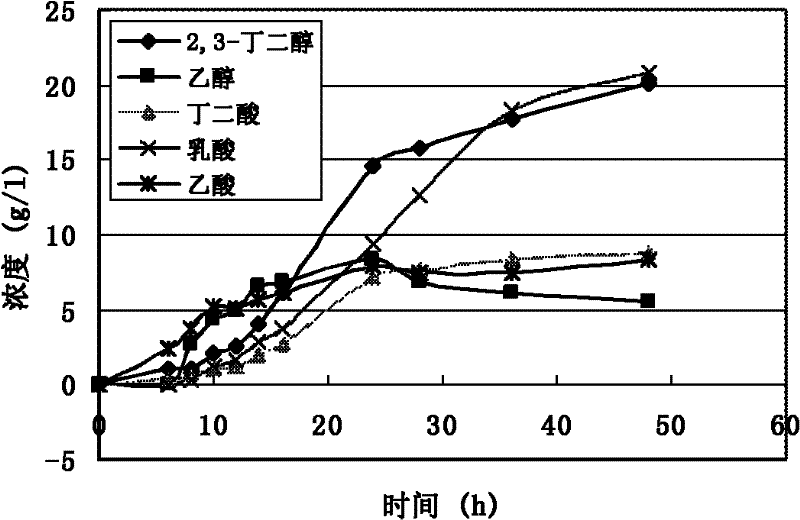
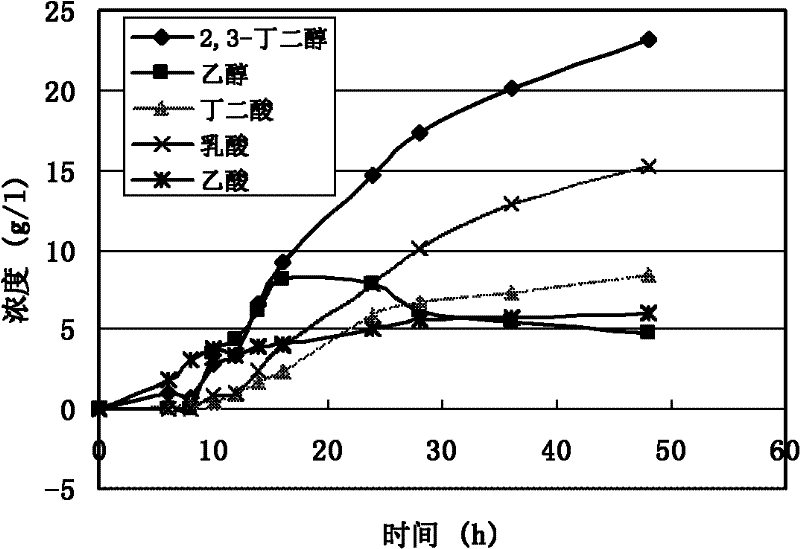
The invention provides a method for improving the microbial production of 1,3-propanediol by constructing a gene engineering bacterium. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an expression vector with the inserted malic enzyme gene; delivering the expression vector in host bacteria generating 1,3-propanediol; adding an inducer to induce the overexpression of the malic enzyme gene in the fermentation and culture process; and adopting the aerobic fermentation means and performing the fed batch of substrate glycerol to produce 1,3-propanediol. The method is characterized in that the constructed gene engineering bacterium can express more malic enzyme than the original strain in the fermentation process, thus the convertion from pyruvic acid to malic acid can be promoted, the circulation of tricarboxylic acid can be promoted, the bacterium can generate more nicotinamide adenine dinueleotide (NADH) and energy (ATP), the activity of 1,3-propanediol oxidation-reduction enzymein the bacterium and the glycerol conversion rate can be increased. The invention has the following advantages: the substrate glycerol utilization rate of the producing bacterium can be increased, the concentration and production strength of the fermented 1,3-propanediol can be obviously increased, the yield of 1,3-propanediol can be increased and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Microbial synthesis method of gamma-linolenic acid oil
InactiveCN101445815AIncrease productivityLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationContinuous fermentationTO-18
A method for producing gamma-linolenic acid oil by microbial fermentation comprises the following process steps: culturing high-level expression strains of malic enzyme and gamma-linolenic acid synthetase; performing activation and amplification culture on original strains; then performing primary fermentation, secondary fermentation, third-stage fermentation and a fourth-stage fermentation; dehydrating, drying and extracting the oil. The method has the advantages of good strains, high yield, high dry bacteria yield up to 10-30%, good oil yield up to 35-55%, satisfactory gamma-linolenic acid yield up to 18-29% and low production cost. The method can help reduce the cost of raw materials for the production process by 50-70%. The semi-continuous fermentation or continuous fermentation process is advanced, scientific and mature, can be used for large scale industrialized production, and achieve 50-500t fourth-stage fermentation level.
Owner:北京有容建业科技发展有限责任公司
Method for producing l-lysine or l-threonine
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for promoting synthesis of DHA in schizochytrium limacinum grease
ActiveCN104450809AInhibitory activityPathway metabolic flux reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCarboxylic acidBiology
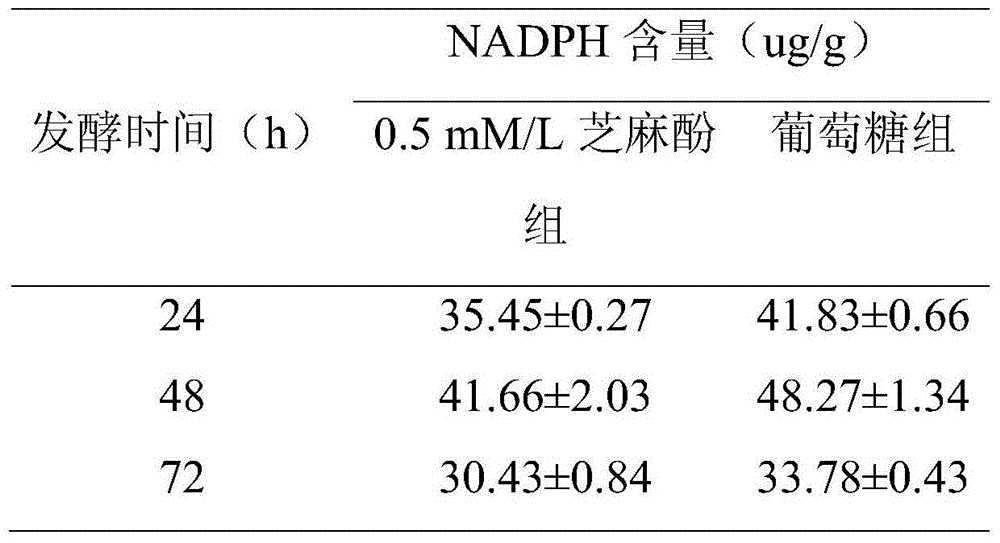
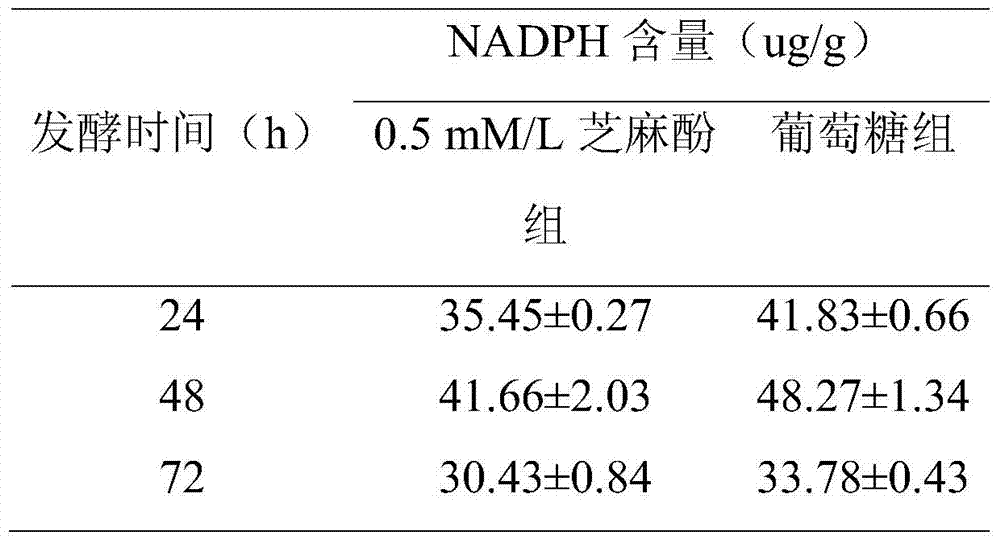
The invention relates to a method for promoting synthesis of DHA in schizochytrium limacinum grease, and particularly relates to a method for prompting synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in schizochytrium limacinum grease. The method is characterized in that the activity of malic enzyme in a tricarboxylic acid transport system is inhibited by adding an exogenous control factor, so that the content of the NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the exogenous control factor is sesamol. According to the method, a fermentable carbon source also can be selected to reduce metabolic flux of a pentose phosphate pathway in the bacteria, so that the content of NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the largest content of the DHA in the grease of final bacteria can reach 55.3 percent. The method is simple, easy, obvious in effect, capable of greatly increasing the content of DHA in the bacteria grease and is likely to realize the industrialized application.
Owner:WUHAN HUASHITE IND BIOTECH DEV
Construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid
ActiveCN110951660APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPhosphorous acid
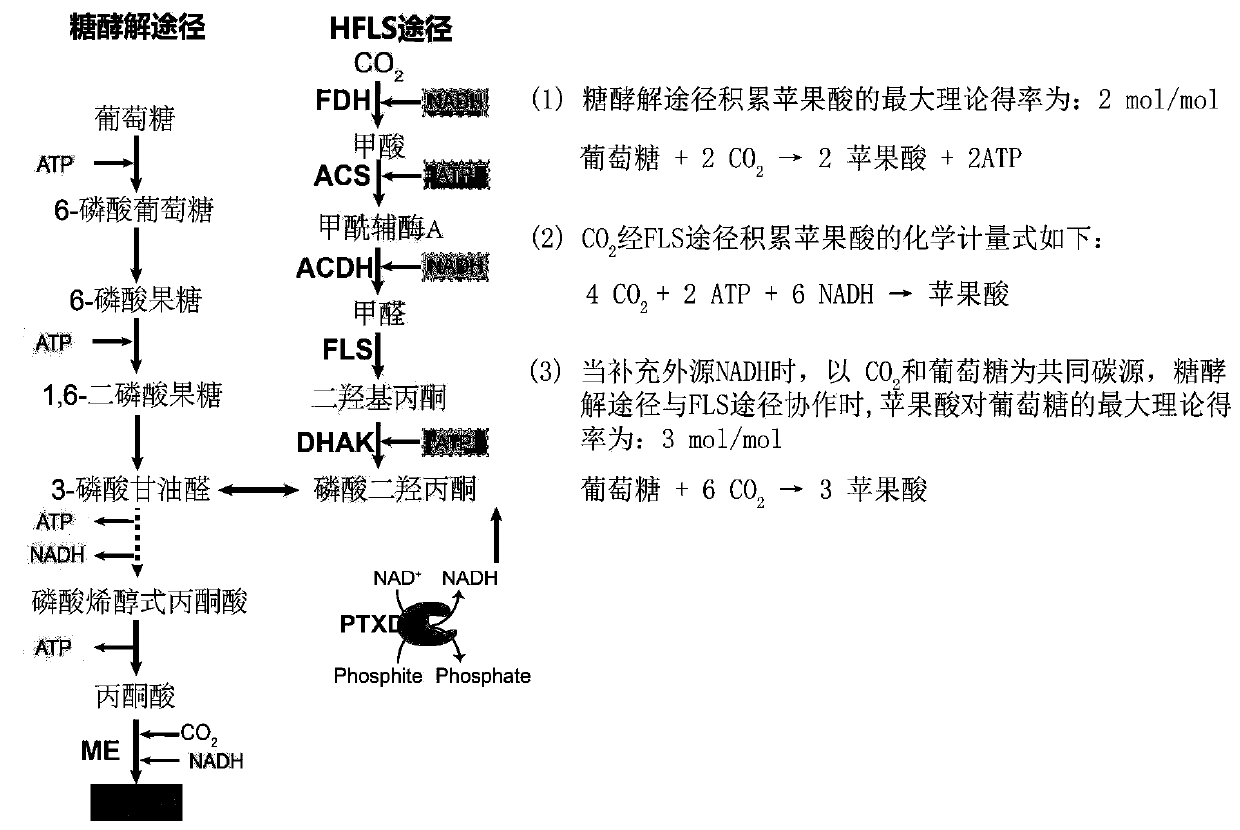
The invention discloses construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation. The engineeringbacterium is a strain obtained by carrying out gene engineering modification on Escherichia coli MG1655. The genetic engineering transformation is as follows: 1, knocking out a fumarate reductase gene, a fumarase gene, a lactic dehydrogenase gene and an ethanol dehydrogenase gene, and carrying out free over-expression on formate dehydrogenase, acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, acylated acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, formaldehyde lyase, dihydroxyacetone kinase, malic enzyme and phosphorous acid oxidordeuctase so as to obtain a strain GH0407. The strain is used for fermentation production of malic acid, CO2 and glucose are used as co-substrates for anaerobic fermentation for 72 h, the malic acid yield reaches 39 g / L, the yield is 1.53 mol / mol, and malic acid is not accumulated in an original starting strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
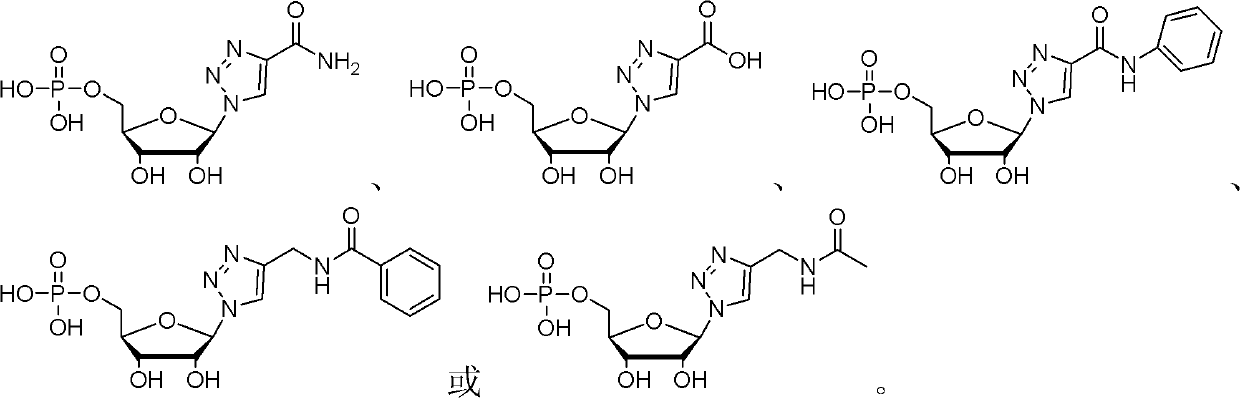
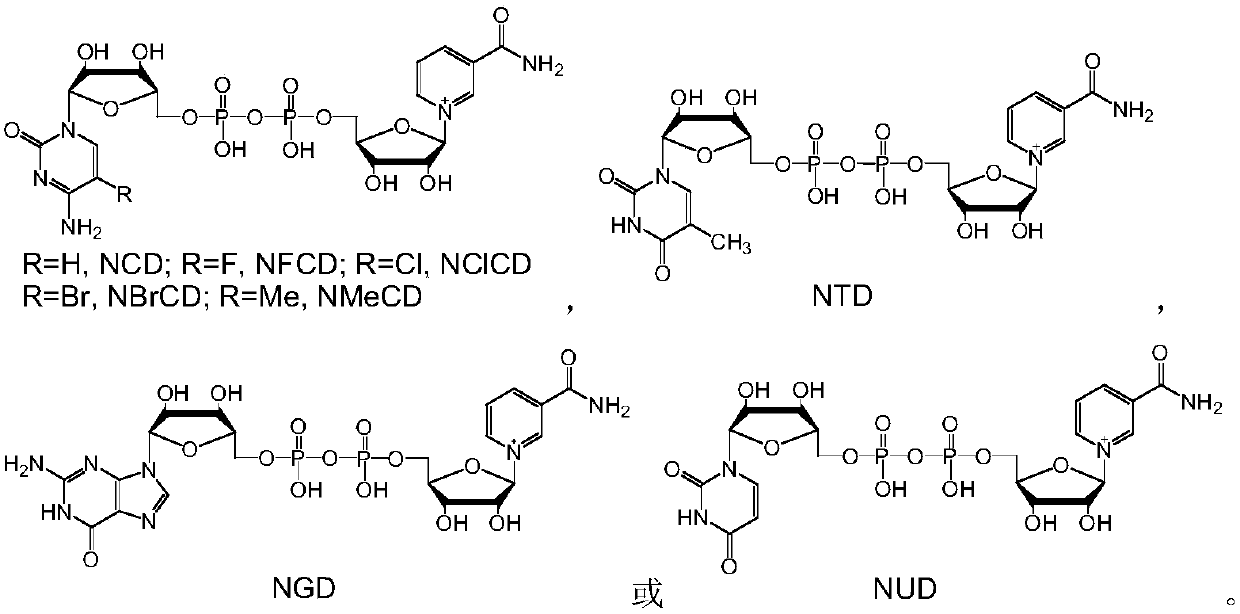
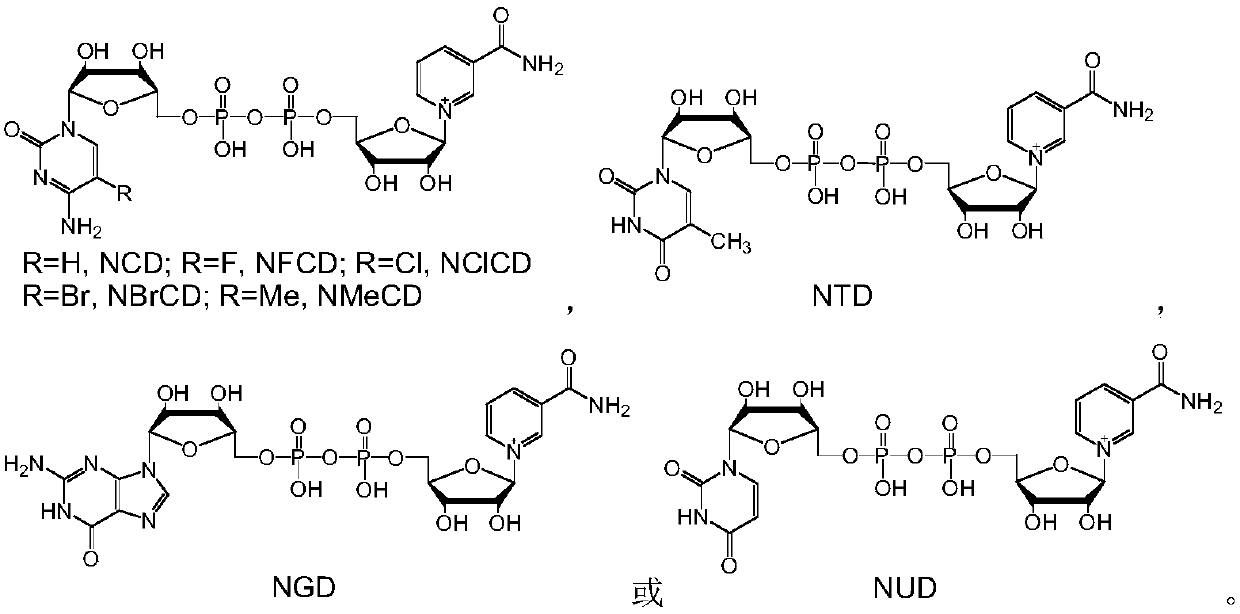
Nucleotide analogue and synthesis and application thereof
InactiveCN102558261AConducive to synthetic structural diversityConducive to structural diversityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliMalic enzyme
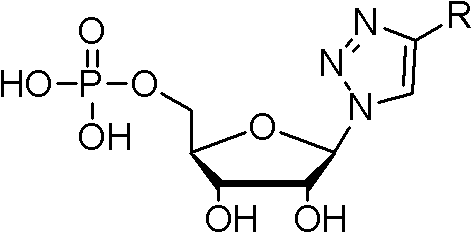
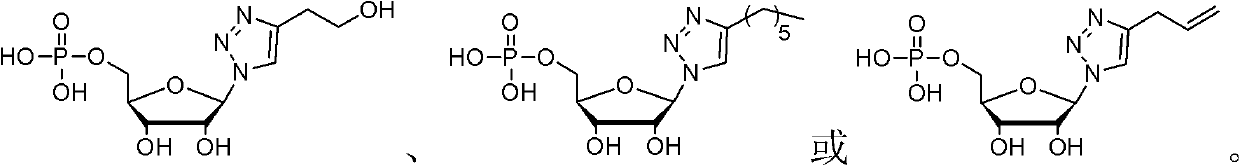
The invention discloses a nucleotide analogue and a synthesis and a application thereof. The constitutional formula of the nucleotide analogue is that: Tetra-O-Acetyl-D-Ribose is adopted as a raw material and generates the nucleotide analogue containing a triazole ring formwork through four steps of reaction, wherein R is C2-C15 saturated or unsaturated alkyl, or C2-C10 saturated or unsaturated alkyl containing hetero atoms; or R is R1 which is hydroxyl, alkoxy, amino or substituent amido; or R is R2 which is aryl or saturated or unsaturated alkyl; or R is R3 which is halogen, amono, methoxyl, methyl or other substituent. The nucleotide analogue can restrain the growth of microorganism such as escherichia coli, and can be used as an inhibitor of dehydrogenase such as malate dehydrogenase.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
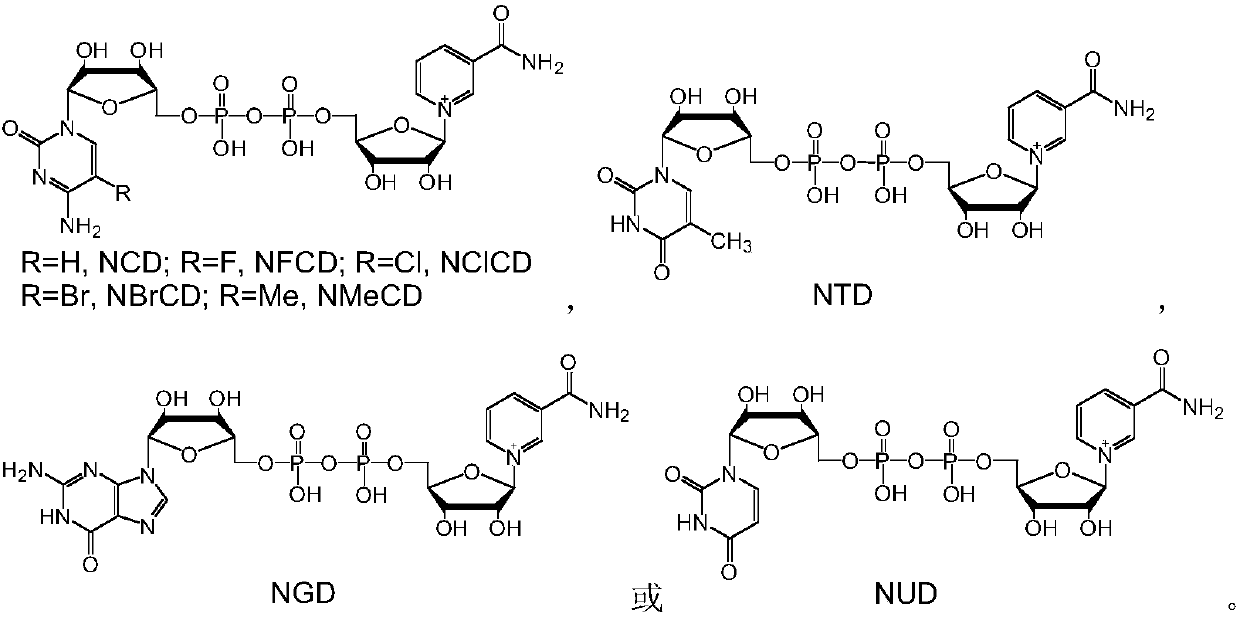
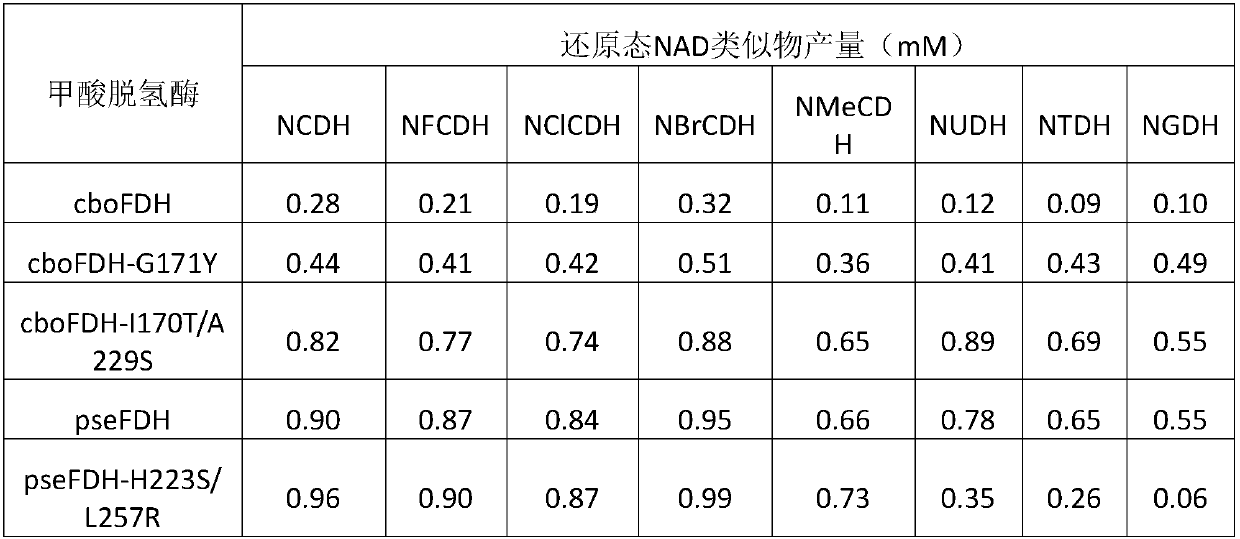
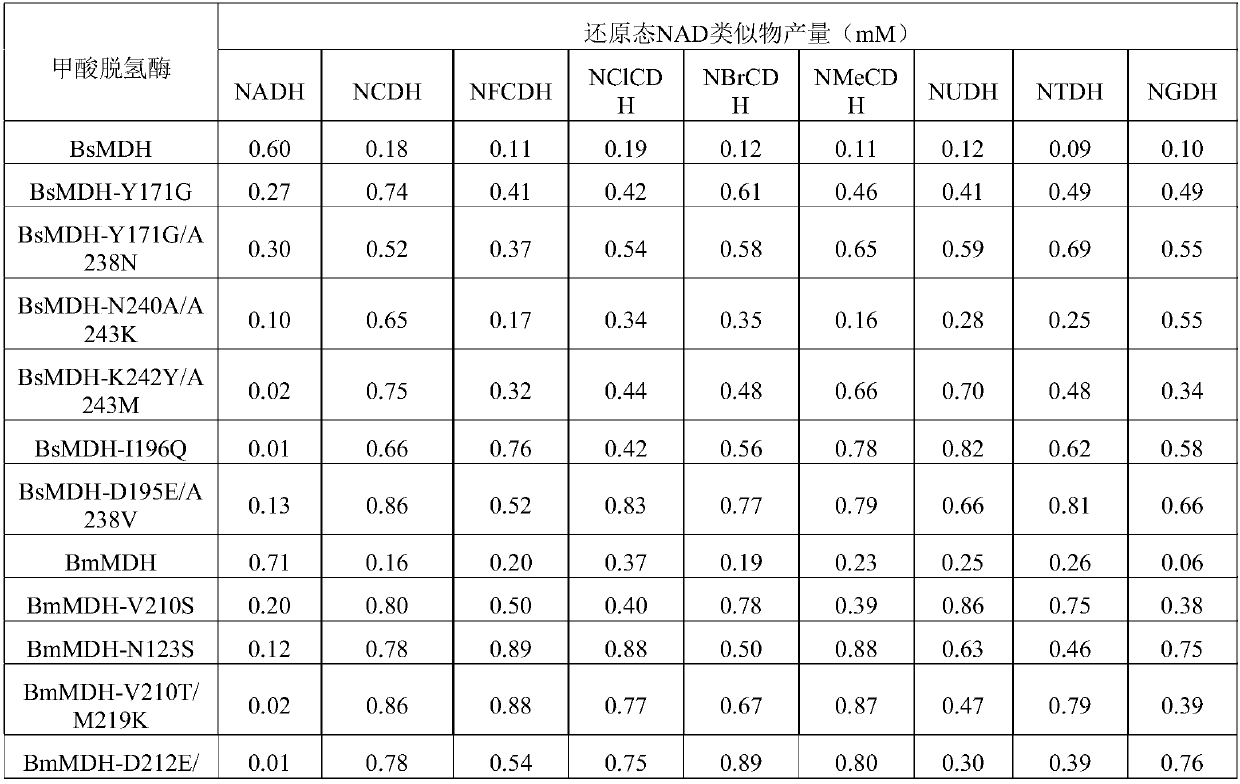
Reduction method of NAD analog
The invention discloses a reduction method of a NAD analog and an application of the reduction method. According to the method, a reducing agent is a formic acid compound, a catalyst is hydrogenlyasewhich can use the formic acid compound, and when the hydrogenlyase is used for oxidating the formic acid compound, the NAD analog is converted into a reducing state. The method can be used for producing the reducing state NAD analog or a deuterated reducing state analog, and can also be used for providing reducing power for an enzyme reaction consuming the reducing state NAD analog, and the reducing state NAD analog can also be used as coenzyme to be used for a reduction reaction of enzyme catalysis of malic enzyme ME-L310R / Q401C, D-lactate dehydrogenase DLDH-V152R, saccharomyces cerevisiae alcohol dehydrogenase and the like. Wide application of the NAD analog is facilitated. According to the reducing method of the NAD analog, under the mild condition, the regenerated reducing state NAD analog can be used for preparing malic acid or lactic acid, and can also be used as oxidation-reduction power for adjusting and controlling the metabolism intensity of the malic acid or the lactic acidin microorganisms.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant microorganisms for enhanced production of mevalonate, isoprene, and isoprenoids
ActiveUS20160032323A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesHeterologousCitrate synthase
The invention features compositions and methods for the increased production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids in microorganisms by engineering a microorganism for increased carbon flux towards mevalonate production in the following enzymatic pathways: (a) citrate synthase, (b) phosphotransacetylase, (c) acetate kinase, (d) lactate dehydrogenase, (e) malic enzyme, and (f) pyruvate dehydrogenase such that one of more of the enzyme activity is modulated. In addition, production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids can be further enhanced by the heterologous expression of the mvaE and mvaS genes (such as, but not limited to, mvaE and mvaS genes from the organisms Listeria grayi DSM 20601, Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus gallinarum EG2, and Enterococcus casseliflavus).
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
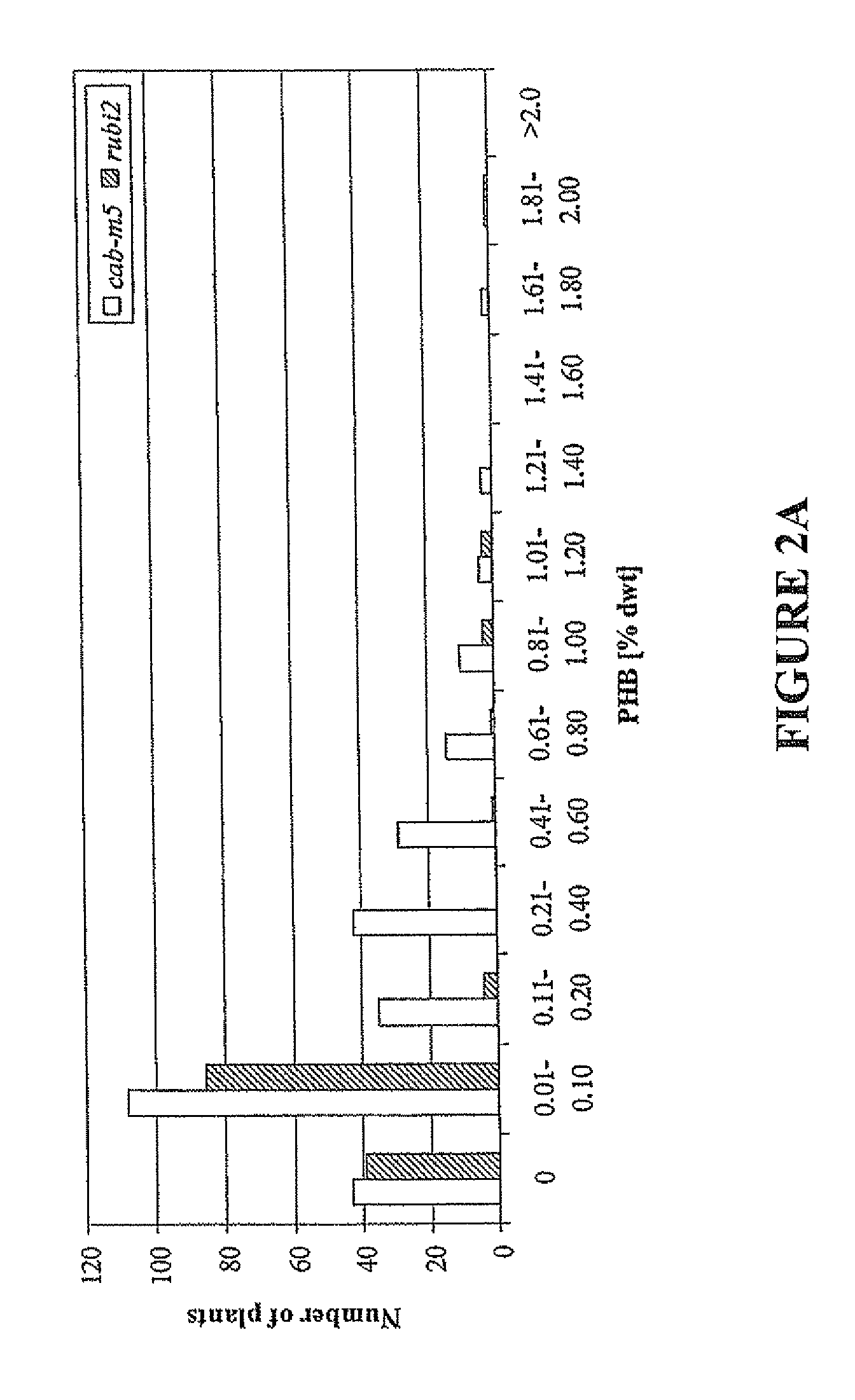
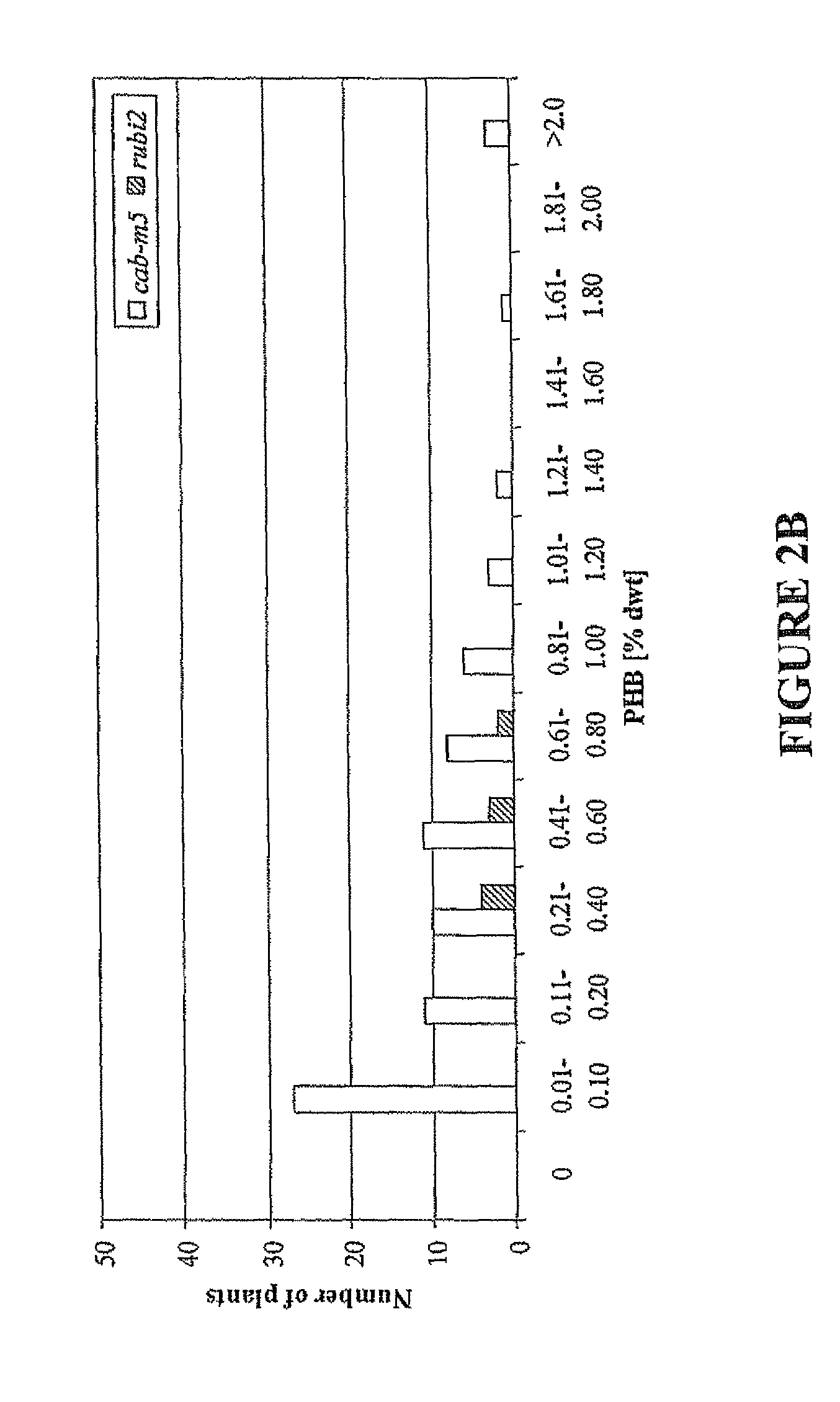
Production of polyhydroxybutyrate in switchgrass
InactiveUS8487159B2Improve conversion efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesPlant cellGenetically engineered
Transgenic plants, plant material, and plant cells for synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates, preferably poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (also referred to a as PHB) are provided. Preferred plants that can be genetically engineered to produce PHB include plants that do not normally produce storage products such as oils and carbohydrates, and plants that have a C4 NAD-malic enzyme photosynthetic pathway. Such plants also advantageously produce lignocellulosic biomass that can be converted into biofuels. An exemplary plant that can be genetically engineered to produce PHB and produce lignocellulosic biomass is switchgrass, Panicum virgatum L. A preferred cultivar of switchgrass is Alamo. Other suitable cultivars of switchgrass include but are not limited to Blackwell, Kanlow, Nebraska 28, Pathfinder, Cave-in-Rock, Shelter and Trailblazer.
Owner:METABOLIX
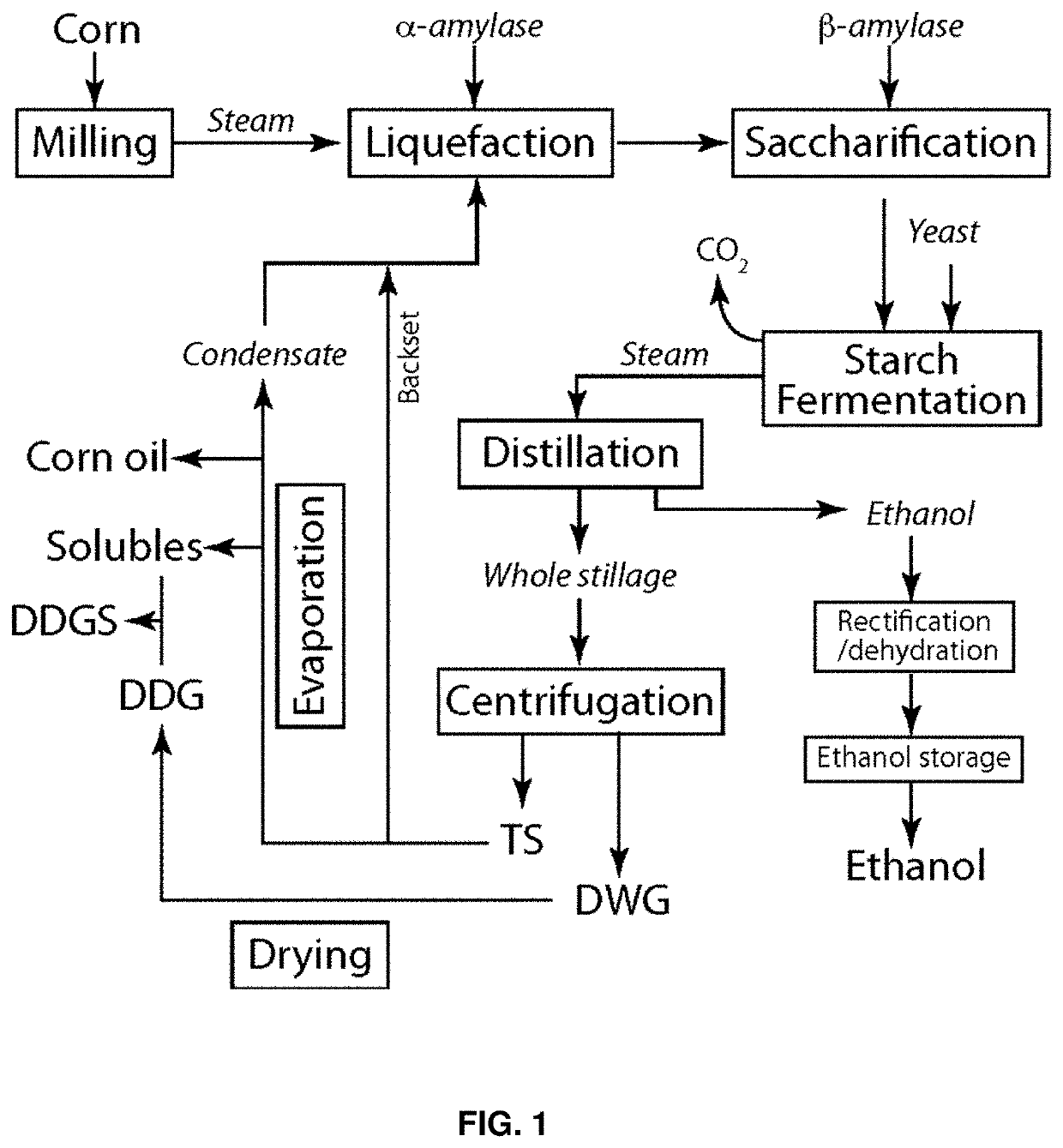
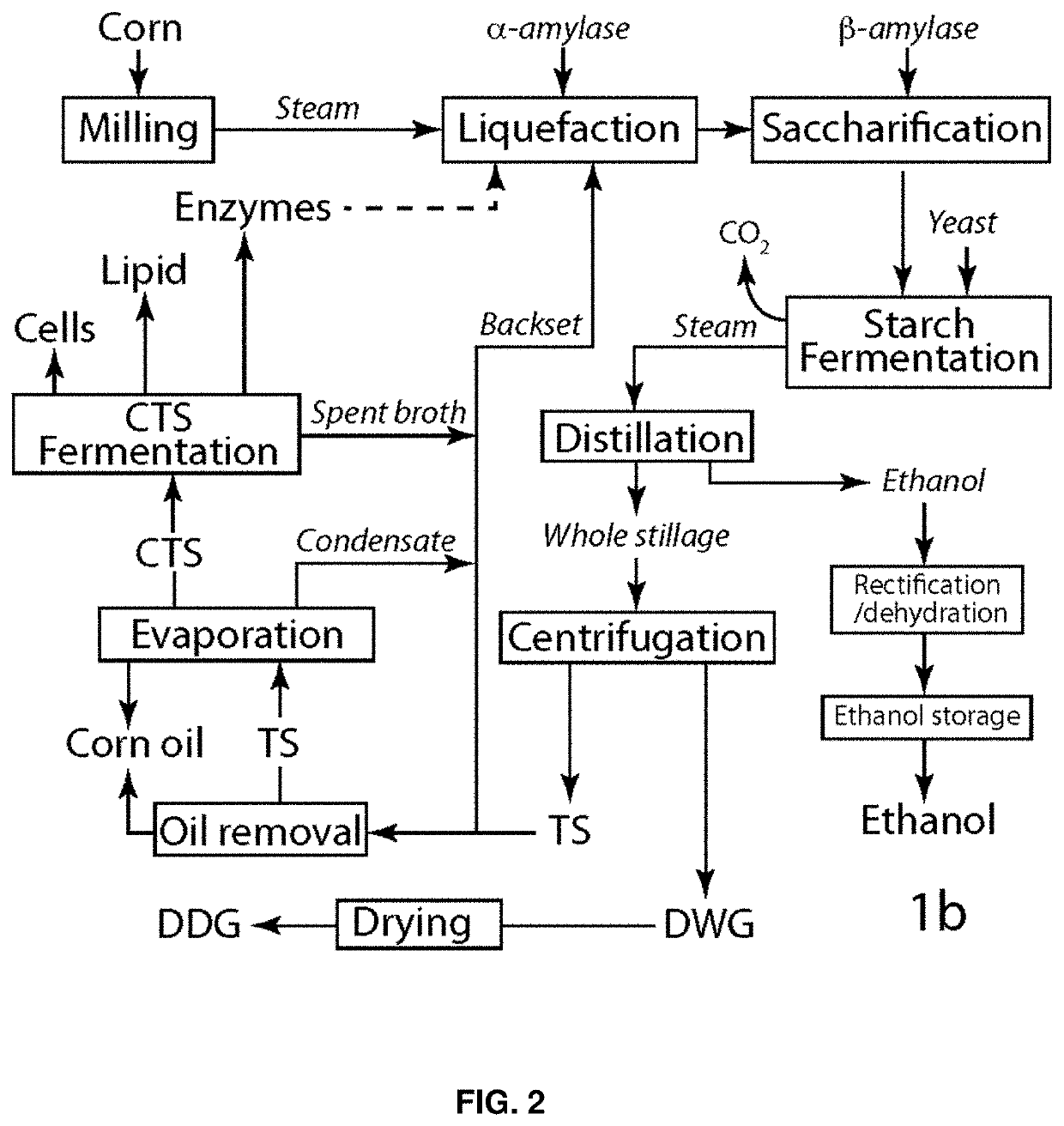
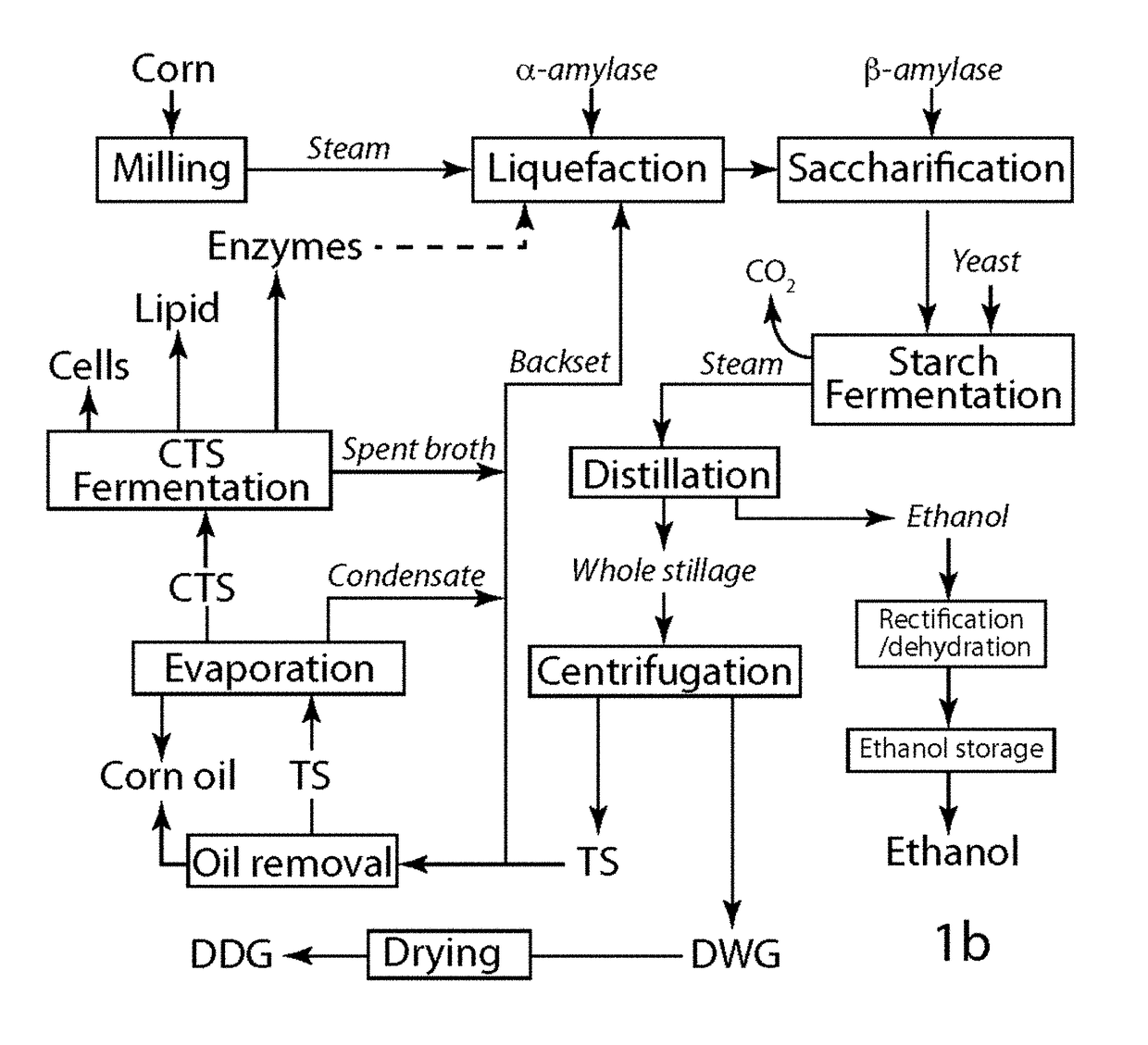
Compositions and methods for producing lipids and other biomaterials from grain ethanol stillage and stillage derivatives
ActiveUS10662448B2Conducive to liquefactionIncrease ratingsFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementPhospholipidAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
Lipogenic yeasts bioengineered to overexpress genes for lipid production, and methods of use thereof. The yeasts are modified to express, constitutively express, or overexpress an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, an alpha-amylase, an ATP citrate lyase, a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a fatty acid synthase, a glycerol kinase, a 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, a malic enzyme, a fatty acyl-CoA reductase, a delta-9 acyl-CoA desaturase, a glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, a lysophosphatidate acyltransferase, a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, a beta-glucosidase, a hexose transporter, a glycerol transporter, a glycoside hydrolase enzyme, an auxiliary activity family 9 enzyme, or combinations thereof. The yeasts in some cases are also modified to reduce or ablate activity of certain proteins. The methods include cultivating the yeast to convert low value soluble organic stillage byproducts into lipids suitable for biodiesel production and other higher value uses.
Owner:XYLOME CORP
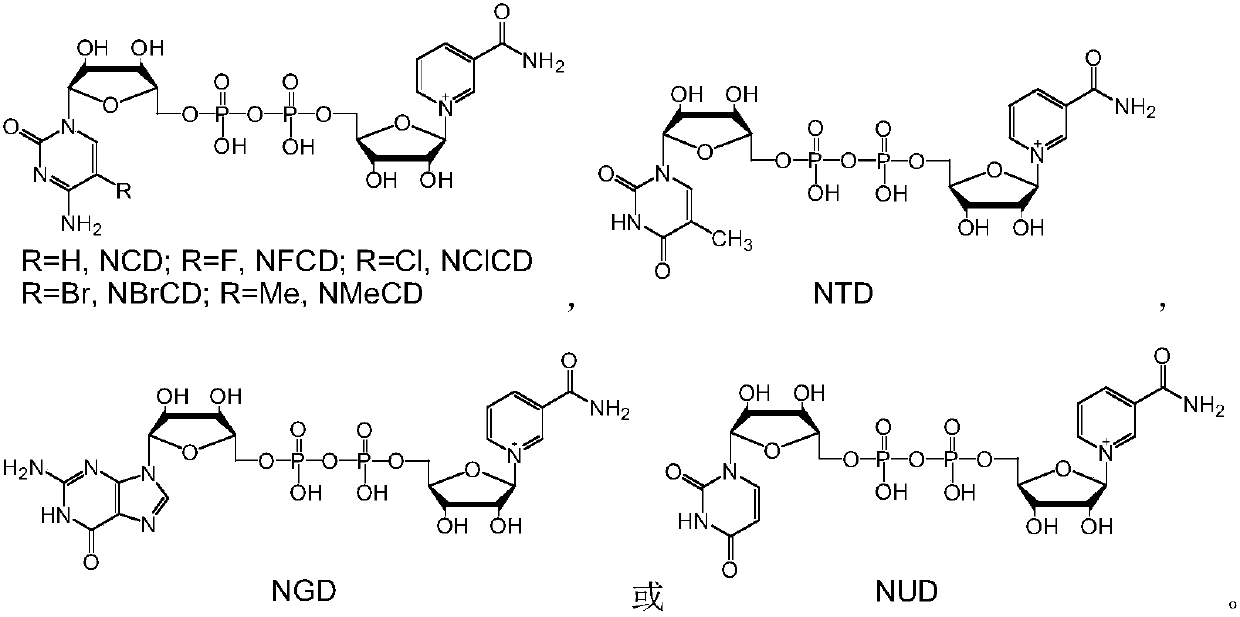
Method for reducing NAD analogues by utilizing methanol
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
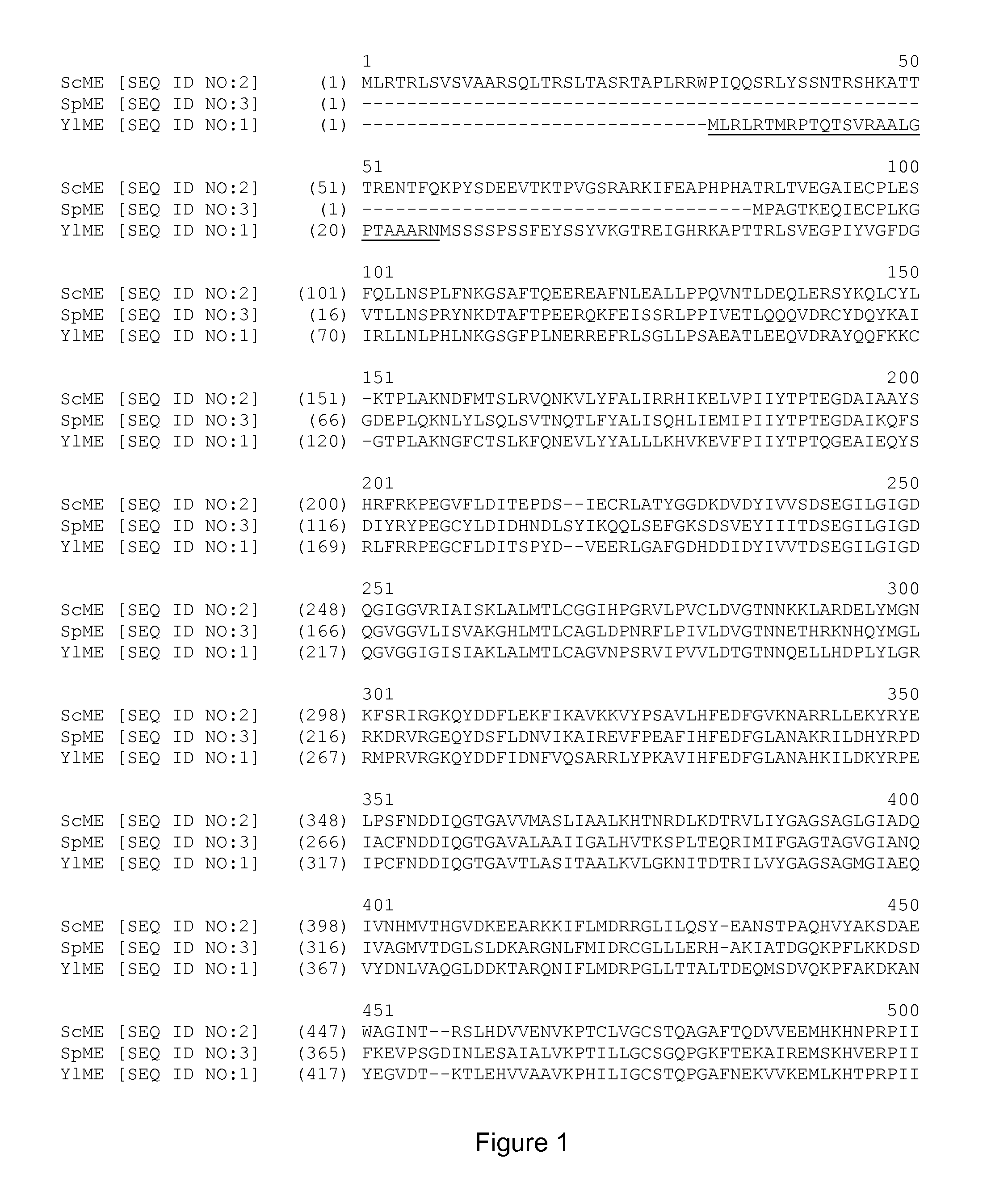
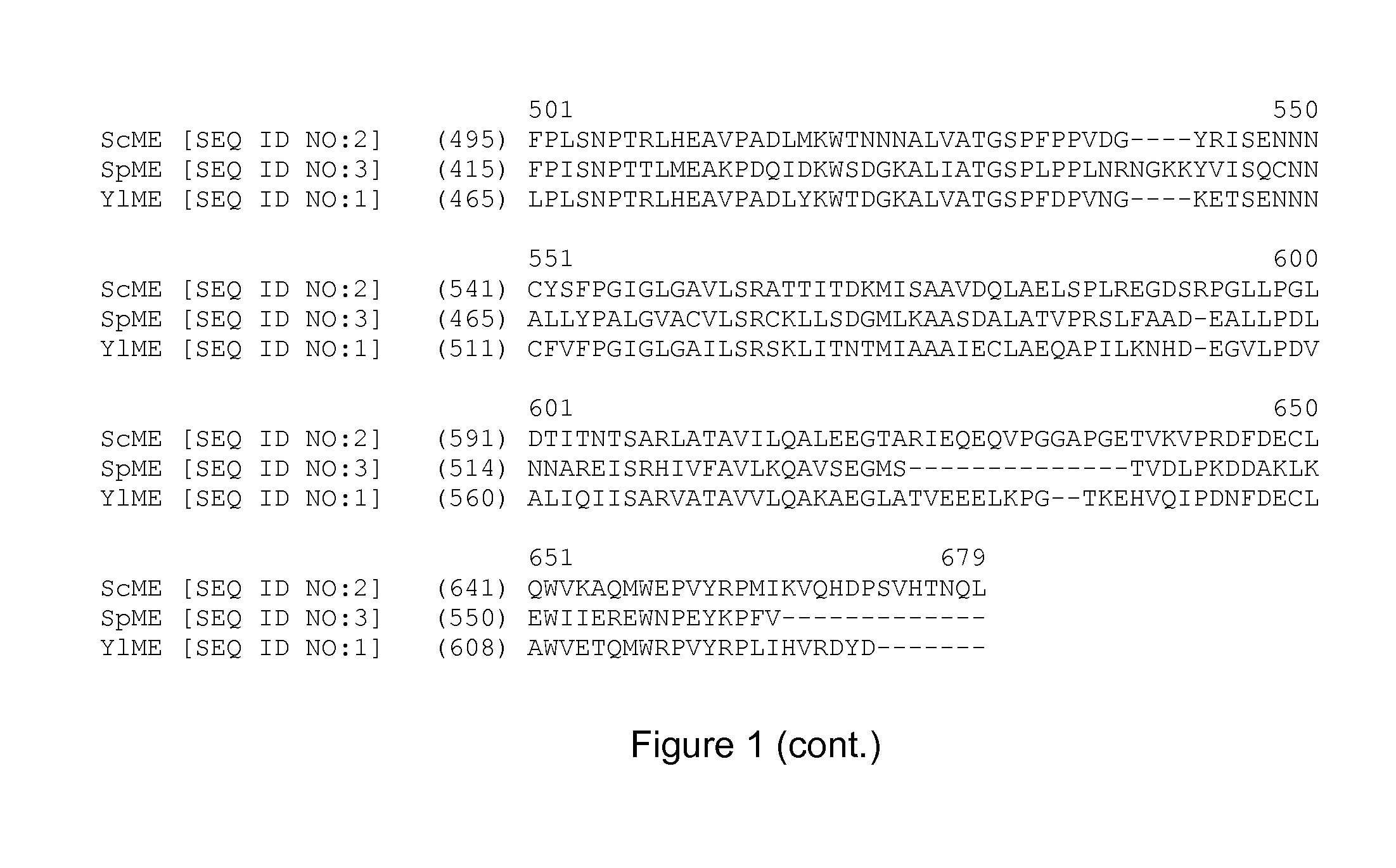
Malic enzyme gene SgME1 as well as application thereof
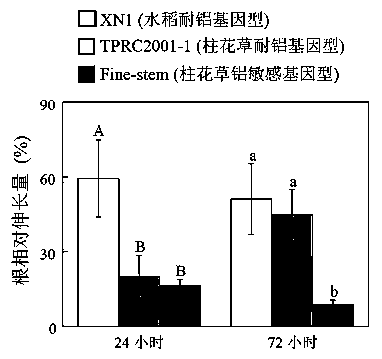
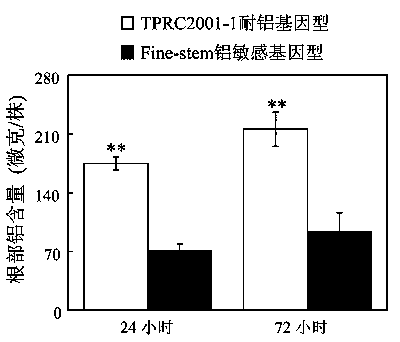
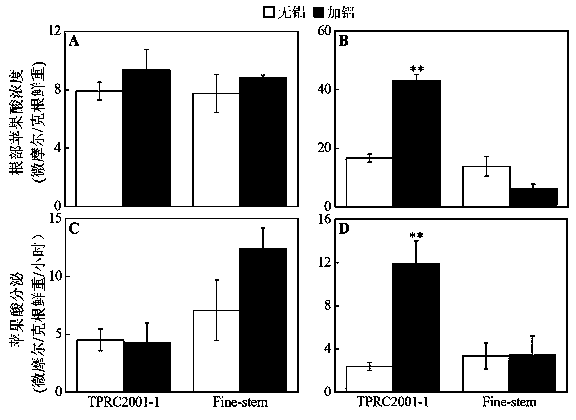
The invention discloses a gene SgME1 which codes malic enzyme as well as an application of the gene SgME1. The nucleotide sequence of the malic enzyme gene SgME1 is shown as SEQIDNO:1, and the amino acid sequence of coded proteins is shown as SEQIDNO:2. The SgME1 gene has the functions of regulating and controlling synthesis of malic acid of stylosanthes guianensis, and over-expressing the SgME1 to accelerate synthesis of malic acid of yeasts, hairy roots of beans and Arabidopsis and increasing the aluminum tolerance of the SgME1.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
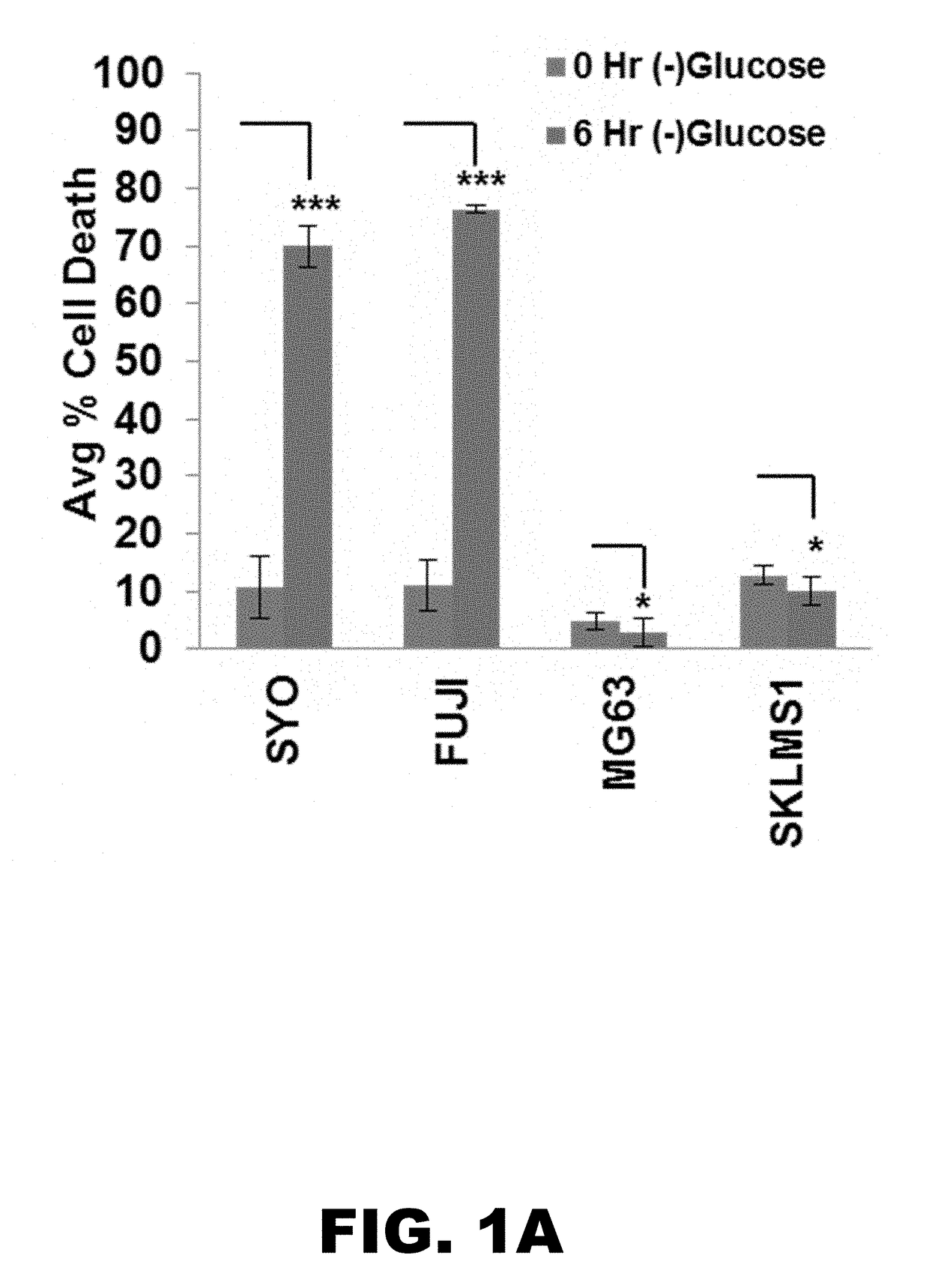
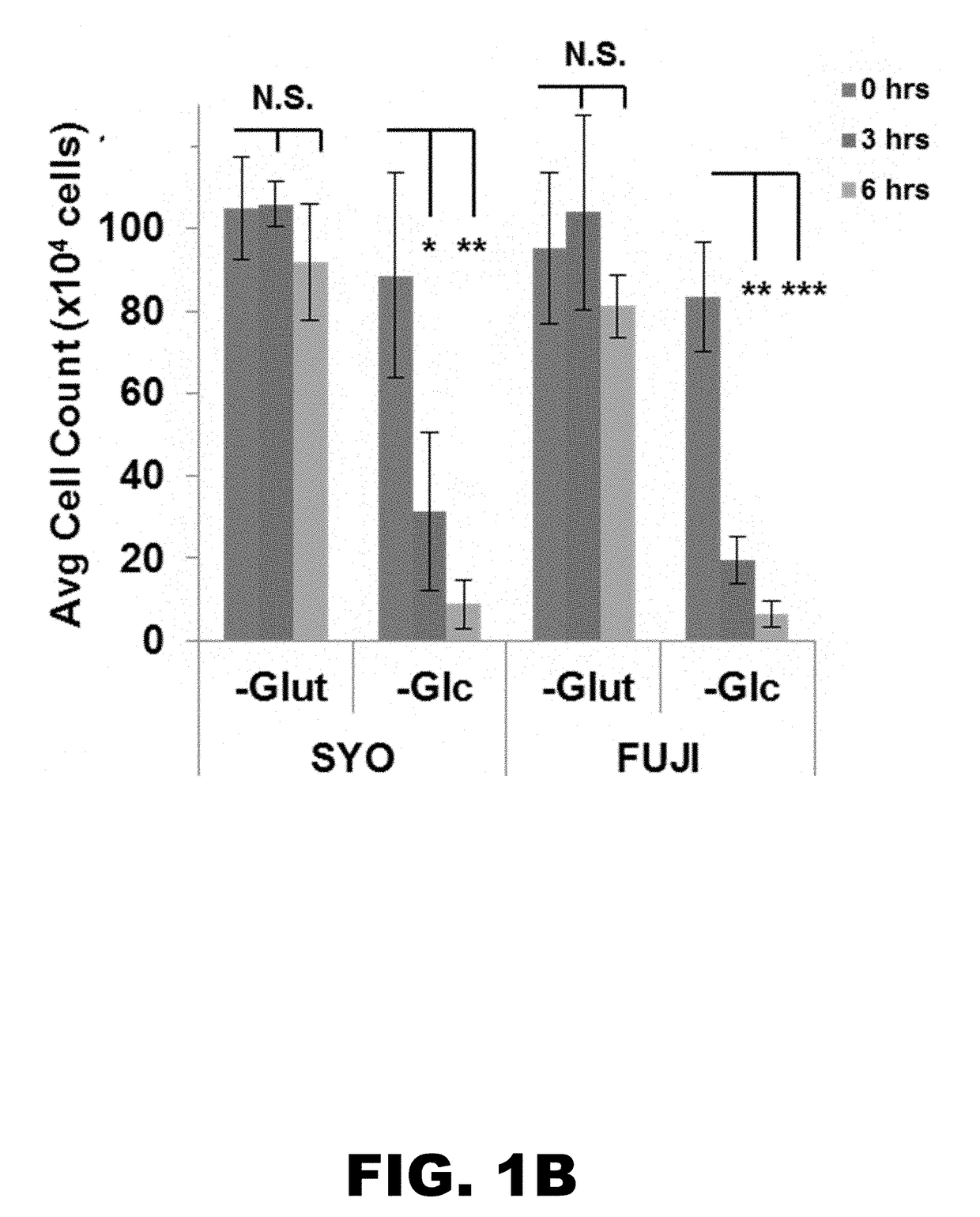
Methods of treating proliferative disorders with malate or derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20150056215A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntiangiogenic agents
The present invention relates to methods, compositions, and diagnostic tests for treating and diagnosing proliferative disorders, such as cancel-, that result in dysregulation of malic enzyme 2. In particular, the methods and compositions include monotherapy with malate, or a derivative thereof, as well as combination therapy, such as malate, or a derivative thereof, combined with another therapeutic agent, such as a malic enzyme 2 inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent, a glycolysis inhibitor, an antiangiogenic agent, an immunomodulatory agent, an antibody, or a cytokine.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Methods of diagnosing and treating cancer comprising me1
The present disclosure provides a method of determining treatment for cancer comprising identifying the absence of malic enzyme 1 (ME1) and treating with an inducer of ferroptosis.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method for increasing content of docosahexaenoic acid in schizochytrium limacinum grease
ActiveCN104480152APathway metabolic flux declinePathway metabolic flux reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationTricarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
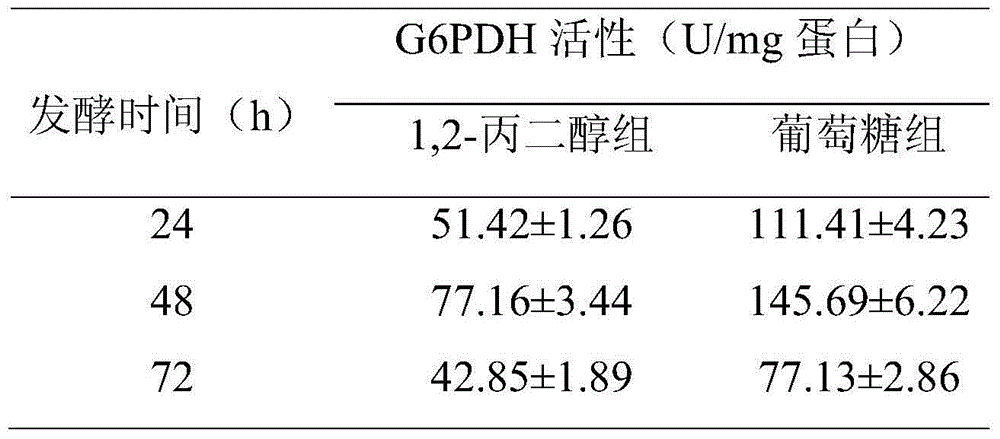
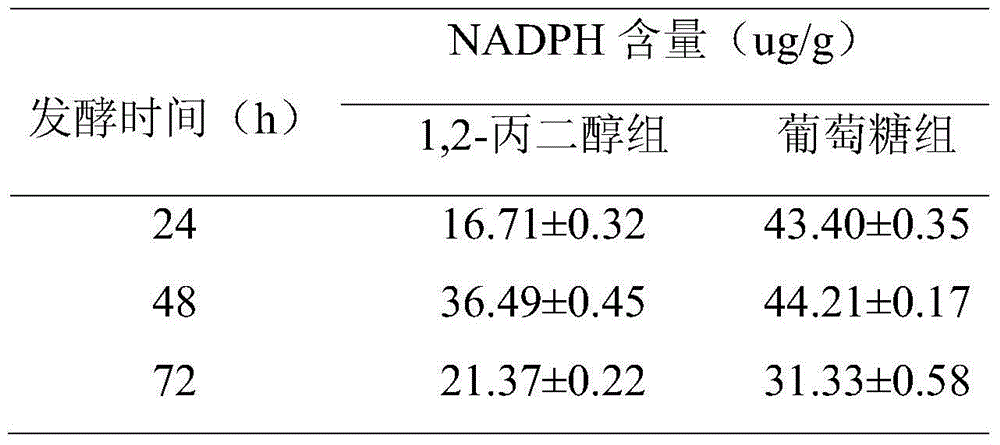
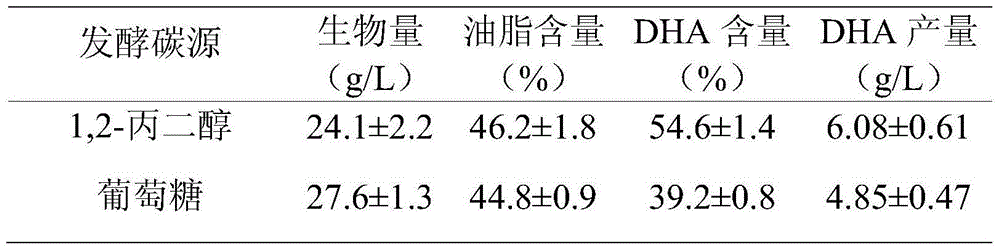
The invention relates to a method for increasing content of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in schizochytrium limacinum grease. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: lowering metabolic flux of a pentose phosphate pathway in thallus by selecting a fermentable carbon source, and lowering the metabolic flux of the pentose phosphate pathway in thallus by further adding an exogenous regulation factor; inhibiting the activity of malic enzyme in a tricarboxylic acid transfer system to greatly lower the content of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) in the schizochytrium limacinum thaluus, promote the large-scale synthesis of DHA and enable the content of DHA in the grease of the obtained thallus to be as high as 55.3%, wherein the fermentation carbon source is 1,2-propylene glycol or any one or a mixture of 1,2-propylene glycol and acetate, the exogenous regulation factor is preferably sesamol which is added after filtering and degerming when a fermentation culture medium is sterilized, and the addition amount of the sesamol is 0.5-3.0mM / L. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to perform, obvious in effect, capable of greatly increasing the content of DHA in the thallus grease and easy for industrial application.
Owner:WUHAN HUASHITE IND BIOTECH DEV +1
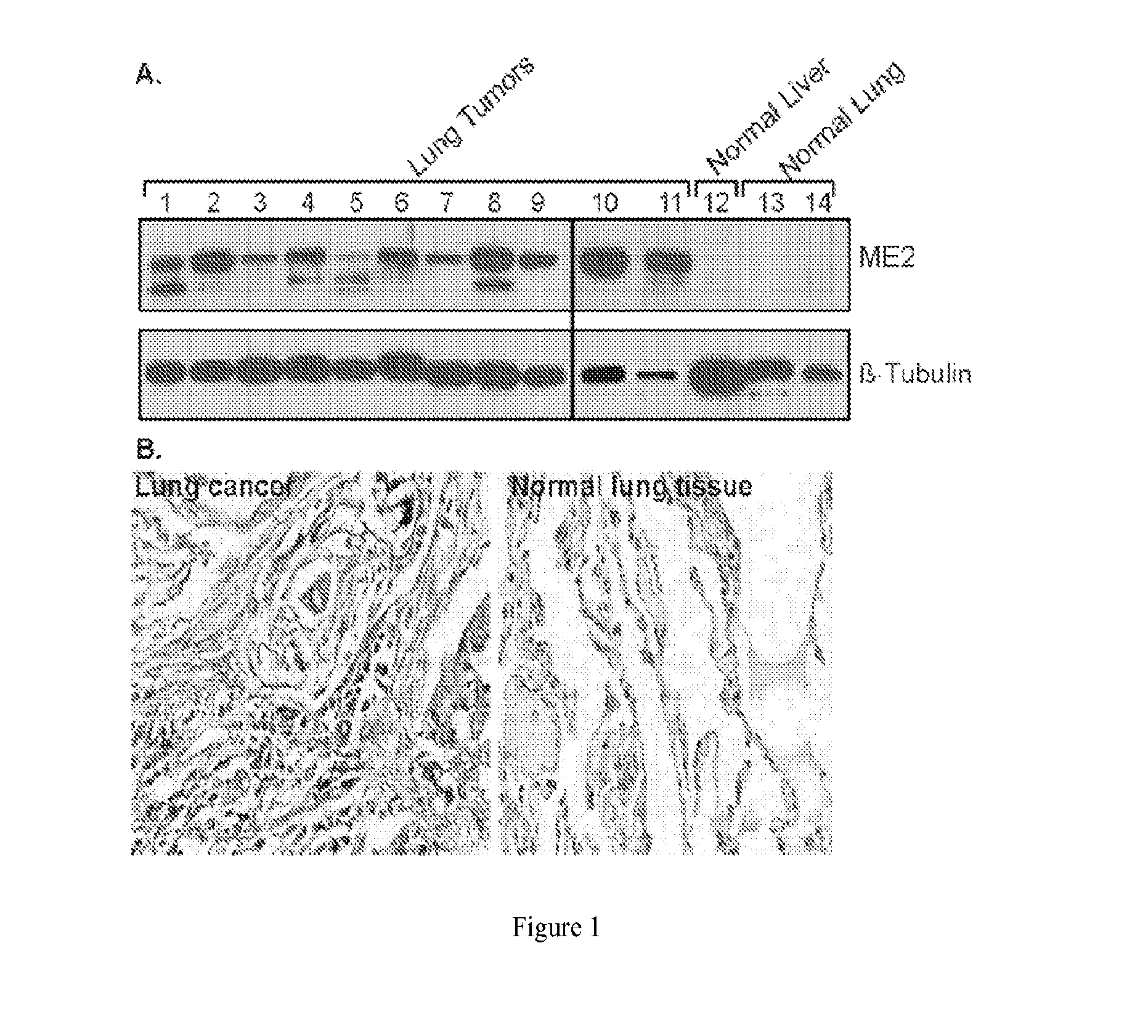
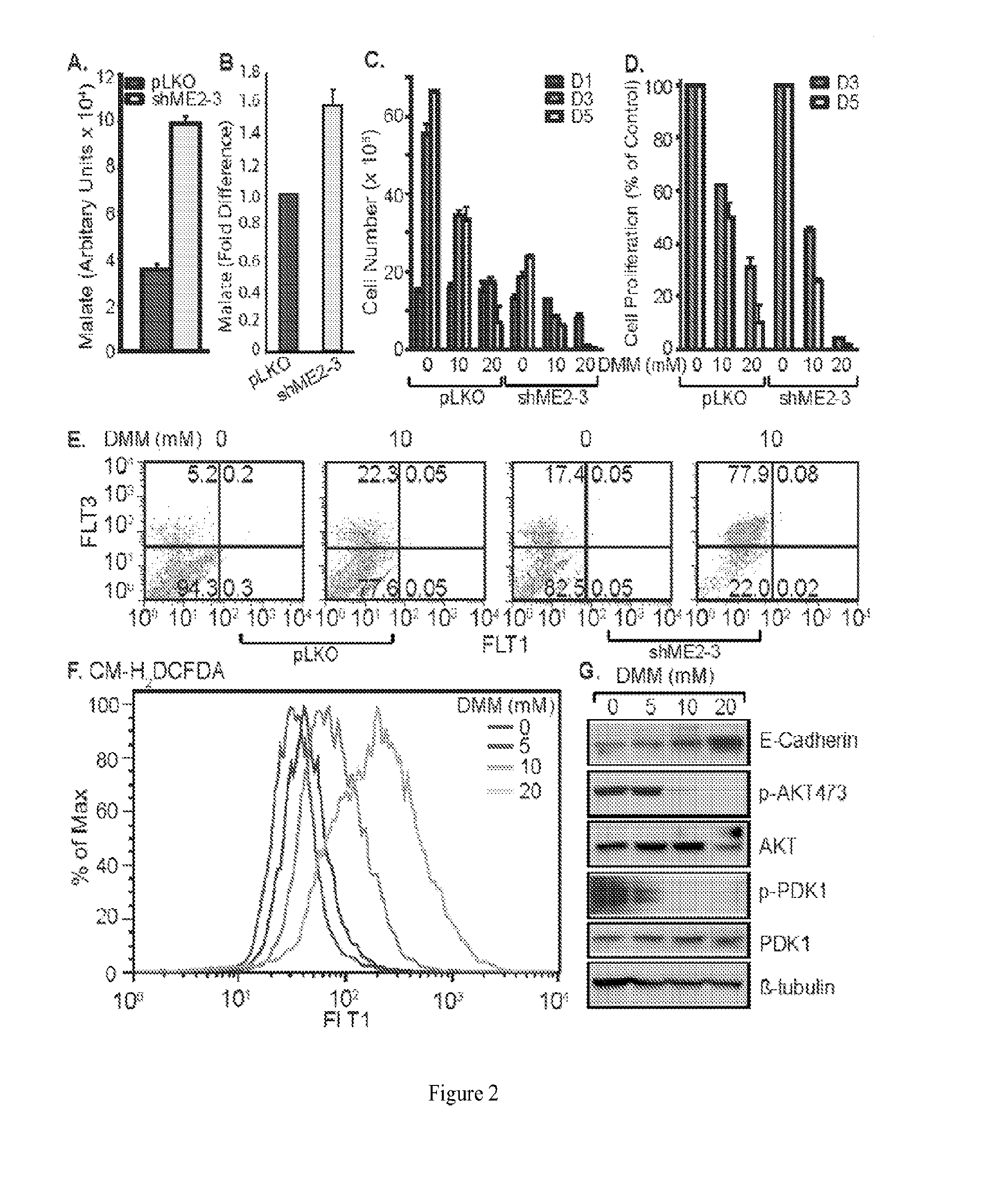
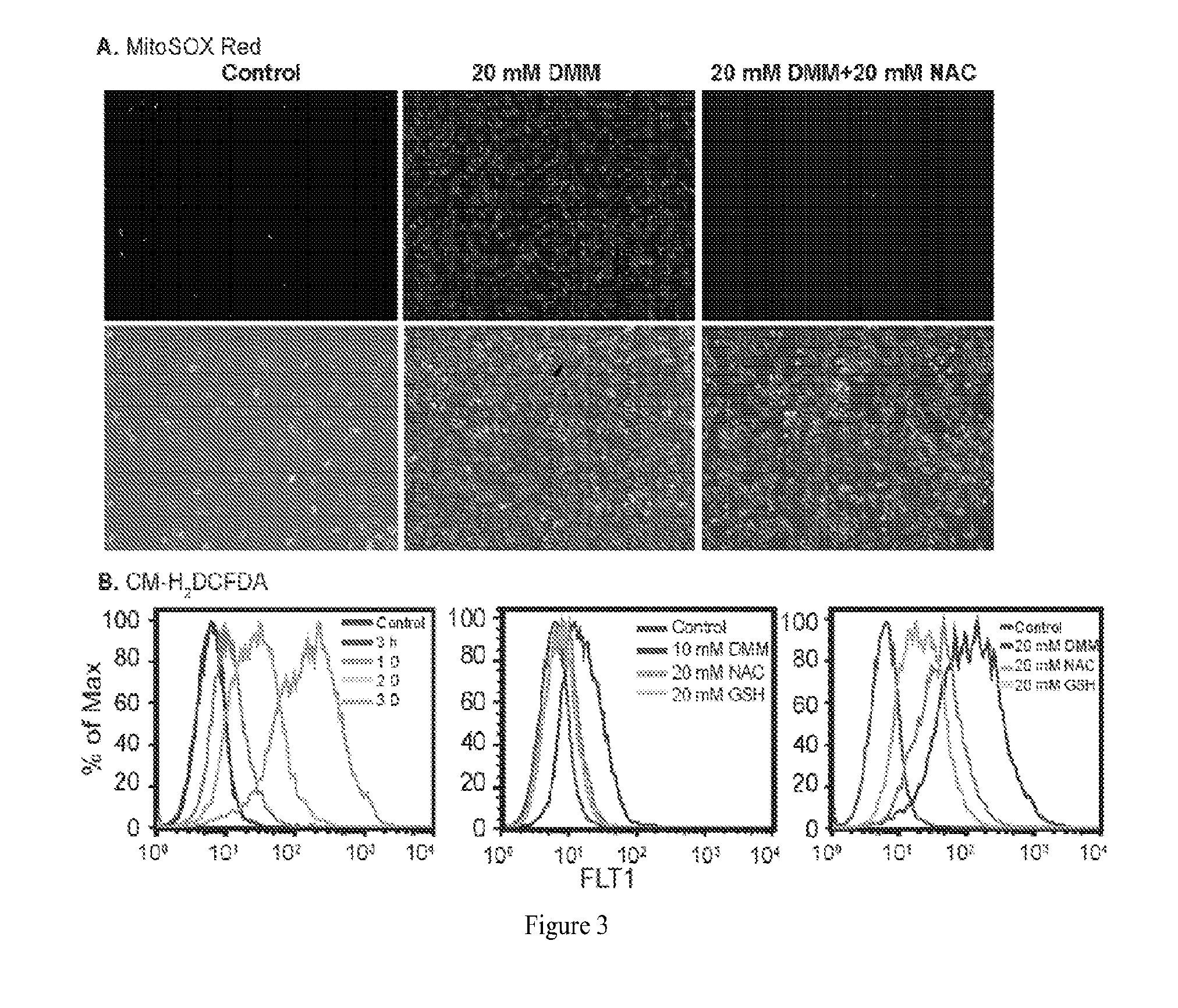
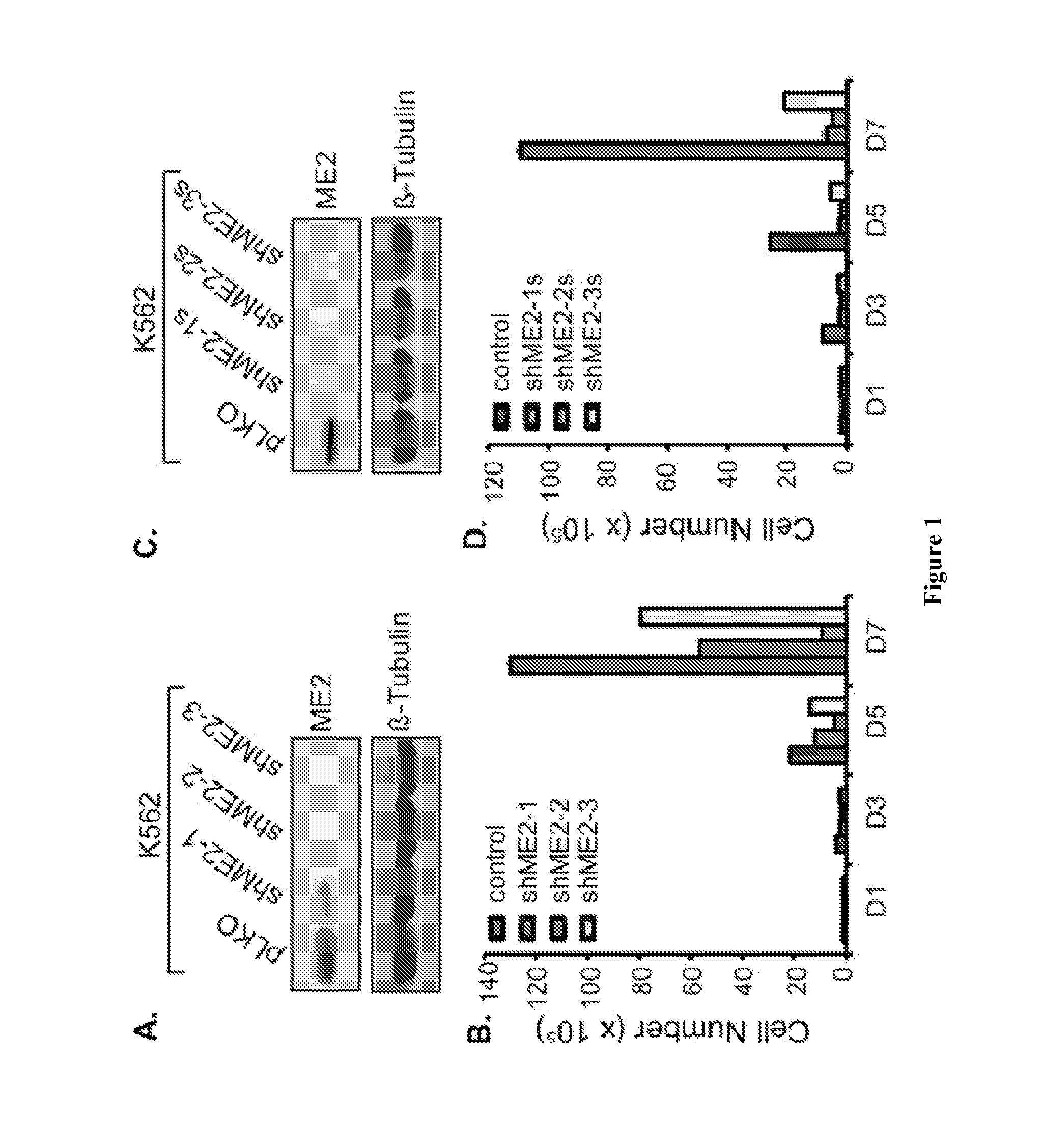
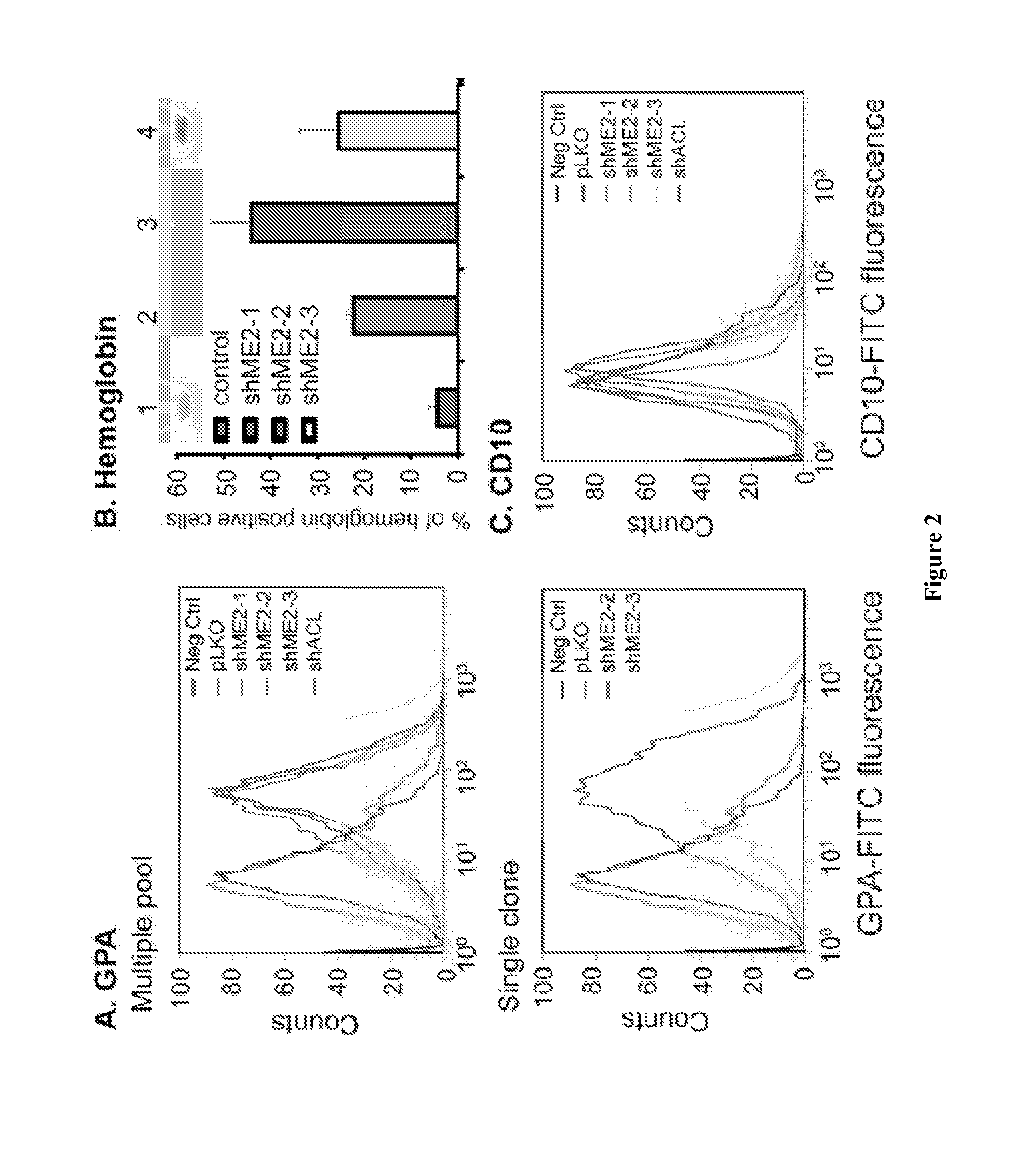
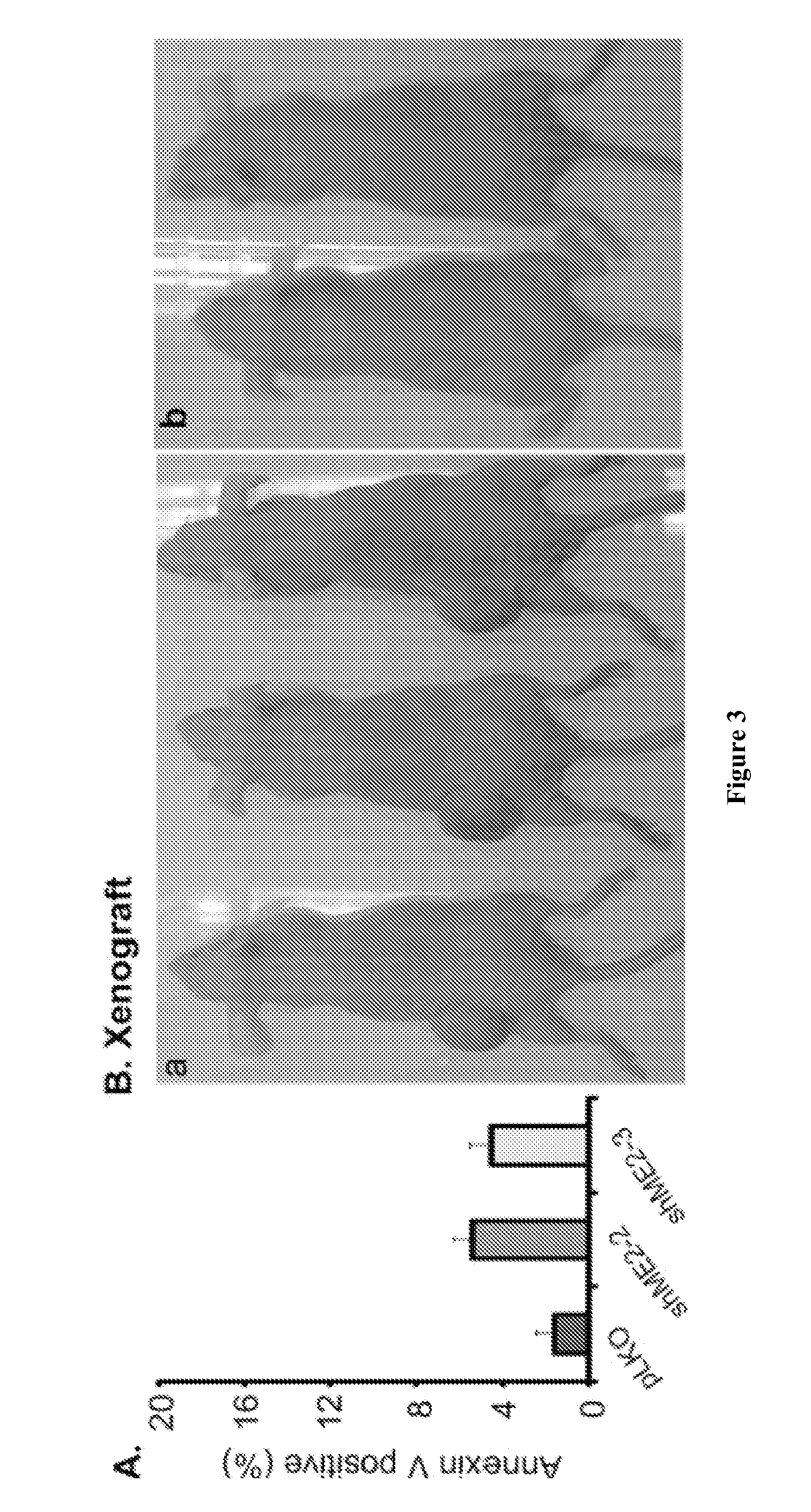
Methods and compositions for malic enzyme 2 (ME2) as a target for cancer therapy
ActiveUS20130209488A1Diminishment of extentAvoid spreadingHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to methods, compositions, and diagnostic tests for treating and diagnosing cancer and other related diseases that result in dysregulation of malic enzyme 2. In particular, the methods and compositions include combination therapy, such as with a combination of two or more ME2 inhibitors or a combination of an ME2 inhibitor and an anticancer agent.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Compositions and methods for producing lipids and other biomaterials from grain ethanol stillage and stillage derivatives
ActiveUS20180245109A1Increase profit marginDecreasing thin stillage viscosityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBio engineeringLysophospholipid Acyltransferase
Lipogenic yeasts bioengineered to overexpress genes for lipid production, and methods of use thereof. The yeasts are modified to express, constitutively express, or overexpress an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, an alpha-amylase, an ATP citrate lyase, a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a fatty acid synthase, a glycerol kinase, a 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, a malic enzyme, a fatty acyl-CoA reductase, a delta-9 acyl-CoA desaturase, a glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, a lysophosphatidate acyltransferase, a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, a beta-glucosidase, a hexose transporter, a glycerol transporter, a glycoside hydrolase enzyme, an auxiliary activity family 9 enzyme, or combinations thereof. The yeasts in some cases are also modified to reduce or ablate activity of certain proteins. The methods include cultivating the yeast to convert low value soluble organic stillage byproducts into lipids suitable for biodiesel production and other higher value uses.
Owner:XYLOME CORP
Methods and compositions for malic enzyme 2 (ME2) as a target for cancer therapy
ActiveUS9539323B2Lower Level RequirementsDiminishment of extentHeavy metal active ingredientsCompound screeningDiseaseAnticarcinogen
The present invention relates to methods, compositions, and diagnostic tests for treating and diagnosing cancer and other related diseases that result in dysregulation of malic enzyme 2. In particular, the methods and compositions include combination therapy, such as with a combination of two or more ME2 inhibitors or a combination of an ME2 inhibitor and an anticancer agent.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and malic enzyme coordinate-expressed recombinant mortierella alpine strain, constructing method thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant bacterium for coordinately expressing glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)2 and malic enzyme (ME)2 in mortierella alpine, and further relates to a constructing method of the strain and an application of the strain. According to the recombinant bacterium, the constructing method and the application, the high-arachidonic-acid-yield mortierella alpine gene recombinant strain is constructed with mortierella alpine uracil auxotroph as a material; the important effects of the G6PD2 and the ME2 in the fatty acid synthesis process and the fatty acid desaturation process are verified; due to coordinate and ectopic expression of the two genes, the effects of increasing the yield and the desaturation degree of fatty acid are effectively achieved at the same time, the proportion of ARA in the total fatty acid is remarkably increased, fermentation time is effectively shortened, and the recombinant bacterium is of great significance in lipid synthesis basic principle researching and product development of the oil-producing fungus in mortierella alpine ATCC 32222.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Malic enzyme (NADP-ME) gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103614396AImprove photosynthetic efficiencyIncreased breeding yield levelsOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetically modified wheat
The invention discloses a malic enzyme (NADP-ME) gene and application thereof. The novel NADP-ME gene provided by the invention can be stably expressed and inherited in wheat, thus obviously improving photosynthetic efficiency compared with an acceptor material. Therefore, the NADP-ME gene provides a significant gene source and parent material support for improving photosynthetic efficiencies of C3 crops through a C4 high-photosynthetic efficiency gene and for selecting a high-photosynthetic efficiency transgenic wheat variety which substantially improves yield level.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI XIAOMAI INST
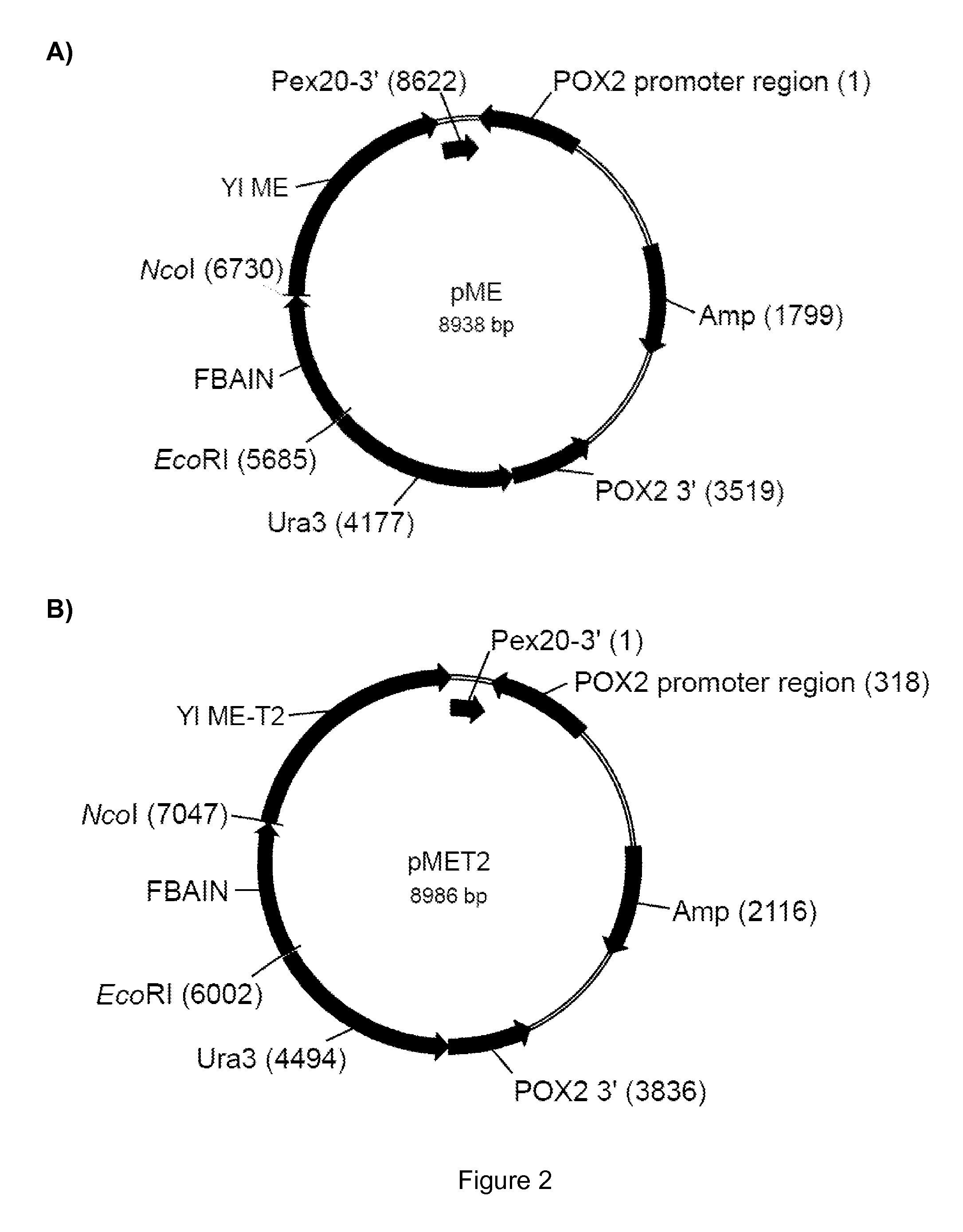
Expression of cytosolic malic enzyme in transgenic Yarrowia to increase lipid production
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for reducing NAD analogue by using methanol
The invention discloses a method for reducing an NAD analogue by using methanol and application of the method. In the method, the methanol is taken as a reducing agent, methanol dehydrogenase capableof utilizing the methanol is taken as a catalyst, and the NAD analogue is transformed into a reduction state while the methanol is oxidized by the methanol dehydrogenase. The method can be used for producing a reduction-state NAD analogue or a deuterated reduction-state analogue, and can also provide reduction-state coenzyme for an enzymatic reaction consuming the reduction-state NAD analogue; thereduction-state NAD analogue can be used as a coenzyme to be applied to reduction reactions catalyzed by enzymes such as malic enzyme ME-L310R / Q401C, D-lactic dehydrogenase DLDH-V152R, and saccharomyces cerevisiae alcohol dehydrogenase, and wide application of the NAD analogue is facilitated. According to the NAD analogue reduction method, the reduction-state NAD analogue can be regenerated undera mild condition for preparing malic acid or lactic acid; and the reduction-state NAD analogue can also serve as an oxidation-reduction force to regulate the metabolic intensity of malic acid or lactic acid in microorganisms.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for promoting the synthesis of DHA in Schizochytrium oil
ActiveCN104450809BInhibitory activityPathway metabolic flux reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSchizochytriumCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a method for promoting synthesis of DHA in schizochytrium limacinum grease, and particularly relates to a method for prompting synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in schizochytrium limacinum grease. The method is characterized in that the activity of malic enzyme in a tricarboxylic acid transport system is inhibited by adding an exogenous control factor, so that the content of the NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the exogenous control factor is sesamol. According to the method, a fermentable carbon source also can be selected to reduce metabolic flux of a pentose phosphate pathway in the bacteria, so that the content of NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the largest content of the DHA in the grease of final bacteria can reach 55.3 percent. The method is simple, easy, obvious in effect, capable of greatly increasing the content of DHA in the bacteria grease and is likely to realize the industrialized application.
Owner:WUHAN HUASHITE IND BIOTECH DEV
Expression of cytosolic malic enzyme in transgenic yarrowia to increase lipid production
InactiveUS20130260427A1Lipid content can be increasedMicroorganismsOxidoreductasesLipid contentPolynucleotide
Transgenic Yarrowia species are disclosed herein that comprise a polynucleotide encoding a cytosolic malic enzyme, a lipid content that is at least about 35% by weight of the dry cell weight of the Yarrowia species, and an engineered polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) biosynthetic pathway, wherein overexpression of the cytosolic malic enzyme increases lipid content.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Genetic biochemical site marker for cerebral ischemia inbred line meriones unguiculatus and application of biochemical site marker
ActiveCN107870190AEasy to operateFast intuitive homozygosityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHemoglobin Beta ChainTranslocase
The invention relates to a genetic biochemical site marker for cerebral ischemia inbred line meriones unguiculatus and application of the biochemical site marker. The genetic biochemical site marker for the cerebral ischemia inbred line meriones is selected from at least one of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-1, esterase-3, carbonic anhydrase-2, alkaline phosphatase-1, isocitrate dehydrogenase-1, malic enzyme-1, glucose phosphate translocase-1, renal catalase-2, peptidase-3, glucose phosphate isomerase-1, hemoglobin-beta chain, transferring, esterase-1, esterase-10, glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase-1, beta-glucuronidase-1, esterase-2, lactic dehydrogenase regulator-1, serum protein-1, amylase-1, esterase-6, esterase-8, esterase-9, esterase-4, catalase-1 and esterase-12.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Recombinant vector over-expressing malic enzyme gene, and its application
InactiveCN104131024AReduce sizeEasy to cloneUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHomologous Sequences
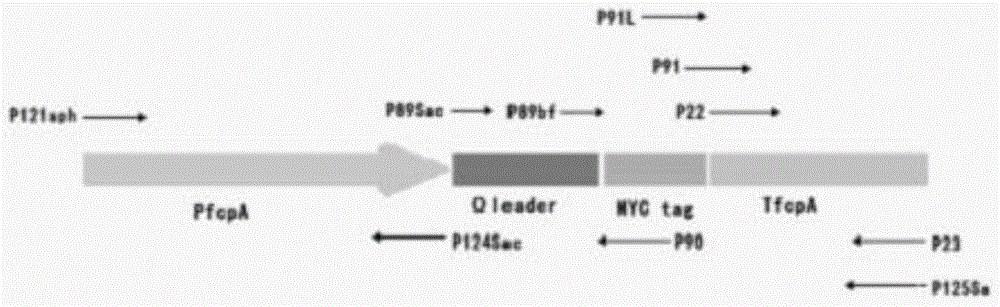
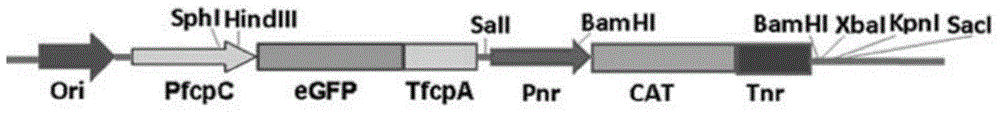
The invention discloses a recombinant vector over-expressing a malic enzyme gene, and its application. The recombinant vector comprises a screening labeled gene expression cassette and a target gene expression cassette; the screening labeled gene expression cassette comprises a resistance screening gene, the upstream of the resistance screening gene is fused with an Escherichia coli P1 promoter, and the downstream of the resistance screening gene is fused with an Escherichia coli ccdB terminator; and the target gene expression cassette comprises a Phaeodactylum tricornutum fcpC gene promoter, the malic enzyme gene, a Phaeodactylum tricornutum fcpA gene terminator and an Omega leader sequence, and the Omega leader sequence is in the downstream of the Phaeodactylum tricornutum fcpC gene promoter. The recombinant vector is small, is suitable for converting, is easy to operate, is a homologous sequence of the Phaeodactylum tricornutum, and benefits for expression. The over-expression of the malic enzyme gene can substantially improve the content of lipids in micro-algal cells, and lays the foundation for the researches of biological energy.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com