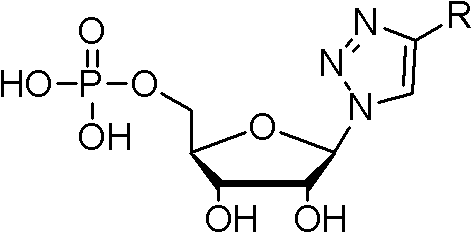
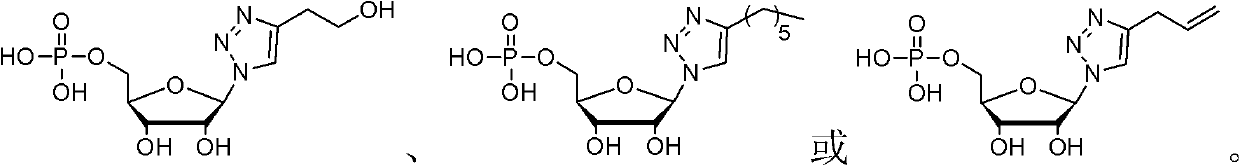
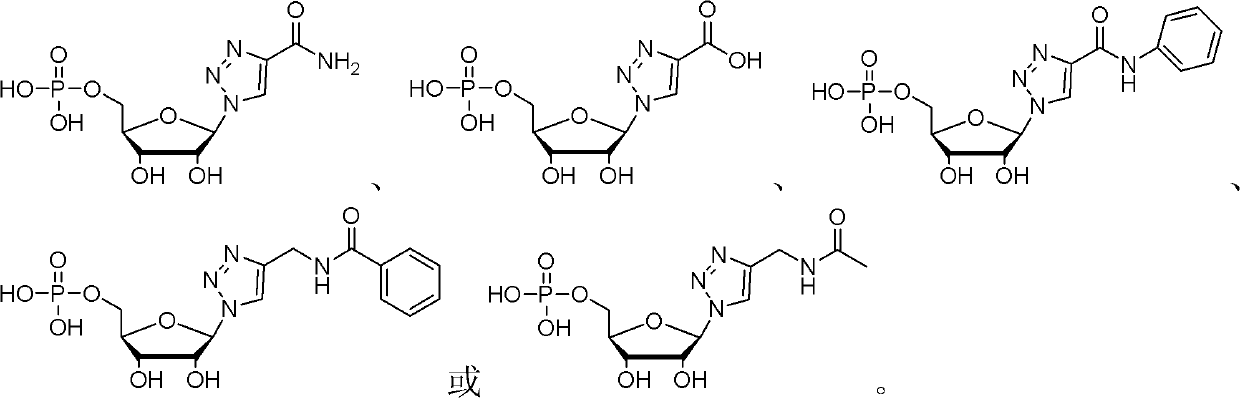
Nucleotide analogue and synthesis and application thereof
An analog and nucleotide technology, applied in the field of nucleotide analog synthesis, can solve the problems of unsuitable nucleotide analogs, increase selective protection and deprotection, etc., and achieve easy product separation and high yield , the effect of high substrate selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 2,3,5-triacetyl-1-azido-ribose (2mmol) was dissolved in 44ml of phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) containing 10% (volume content) DMF, added lipase (derived from Candida rugosa) to a concentration of 5000U / ml, reacted at 37°C for 1.5 hours, ethyl acetate Extraction, concentrated silica gel column chromatography to get 5-hydroxy-2,3-diacetyl-1-azido ribose Yield 90%; The 5-hydroxyl-2,3-diacetyl-1-azido ribose (1mmol), dissolved in anhydrous 4ml tetrahydrofuran, added triethylamine (1.2mmol), added dropwise phosphorus oxychloride (1.2mmol) at 0°C, and stirred for 24h. Add 2ml of water, stir at room temperature, and concentrate to obtain 5-phospho-2,3-diacetyl-1-ribose azido
[0038] Synthetic 5-phospho-2,3-diacetyl-1-azido-ribose (1mmol), in 10ml containing the aqueous solution of 80% methanol, add phenylacetylene (1.1mmol), copper sulfate (0.1mmol) and sodium ascorbate (0.6mmol), stir reaction at 60 ℃ for 36 hours, through silica gel column chromatography, The product ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The same method as in Example 1; the difference from Example 1 is that the alkyne used is 4-methoxyphenylacetylene, and in an aqueous solution containing 90% methanol, 5-phosphoric acid-2,3-diacetyl-1-alkyne The molar ratio of nitrogen ribose, phenylacetylene, copper sulfate and sodium ascorbate is 1:1.5:0.2:0.6, and the yield is 92%.
[0047]
[0048] 1 H NMR (D 2 O, 400MHz) δ (ppm) 8.17 (s, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.4Hz, 2H), 6.96 (d, J = 8.4Hz, 2H), 5.95 (d, J = 4.6Hz, 1H) , 4.51 (dd, J 1 =J 2 = 4.6Hz, 1H), 4.34(dd, J 1 =J 2 =4.6Hz, 1H), 4.23(m, 1H), 3.99(m, 2H), 3.59(s, 3H). 13 C NMR (D 2 O, 100.6MHz) δ (ppm) 158.8, 147.3, 126.8, 121.9, 119.3, 114.1, 92.2, 84.2 (d, J=8.5Hz), 75.0, 70.5, 64.3, 55.2. 31 P NMR (D 2 O, 162MHz) δ (ppm) 4.11. HRMS (ESI) calcd for (C 14 h 18 N 3 o 8 P) - 386.0753, found 386.0763.
[0049] Inhibition of Escherichia coli growth assay
[0050] The method is the same as in Example 1, except that the difference from Example 1 is th...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The same method as in Example 1; the difference from Example 1 is that the concentration of lipase in the reaction system is 1000U / ml, and the yield of 5-hydroxyl-2,3-diacetyl-1-ribose azide is 50%. The alkyne used is 4-fluorophenylacetylene, in aqueous solution containing 50% ethanol, the reaction temperature is 40°C, the reaction time is 24h, and the yield is 98%.
[0055]
[0056] 1 H NMR (D 2 O, 400MHz) δ (ppm) 8.27 (s, 1H), 7.54 (m, 2H), 7.00 (m, 2H), 6.02 (d, J = 4.8Hz), 4.53 (dd, J 1 =J 2 = 4.8Hz, 1H), 4.37(dd, J 1 =J 2 =4.8Hz, 1H), 4.26(m, 1H), 4.11(m, 2H). 13 C NMR (D 2 O, 100.6MHz) δ(ppm) 163.7(d, J=245.6Hz), 146.9, 127.5(d, J=8.2Hz), 125.3, 119.8, 115.8(d, J=21.9Hz), 92.3, 84.3(d , J=8.3Hz), 75.2, 70.4, 64.3. 31 P NMR (D 2 O, 162MHz) δ (ppm) 4.13. 19 F NMR (D 2 O, 376.5MHz) δ (ppm)-114.2. HRMS (ESI) calcd for (C 13 h 15 N 3 o 7 FP) - 374.0553, found 374.0566.
[0057] Inhibition of Escherichia coli growth assay
[0058] The method is the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com