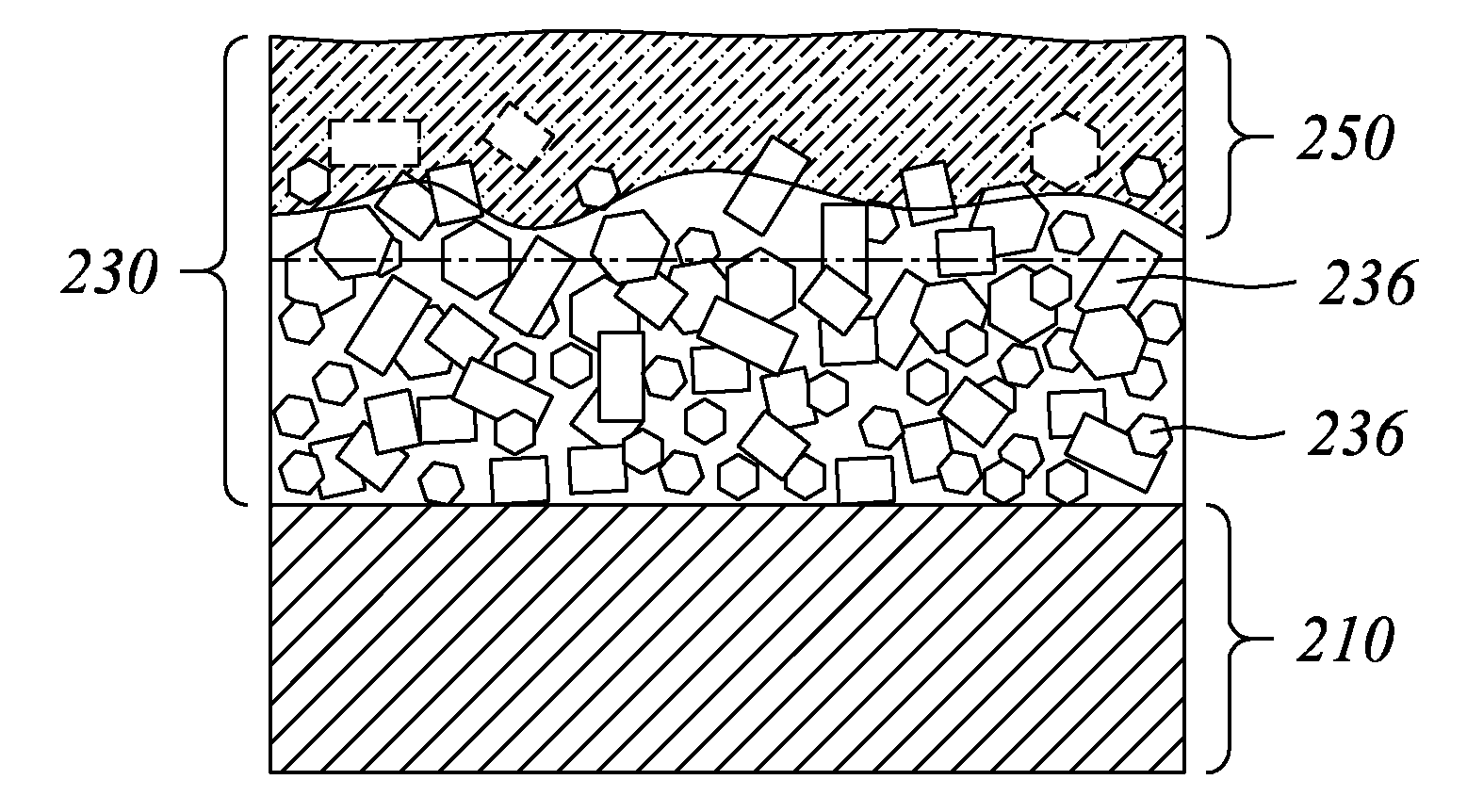
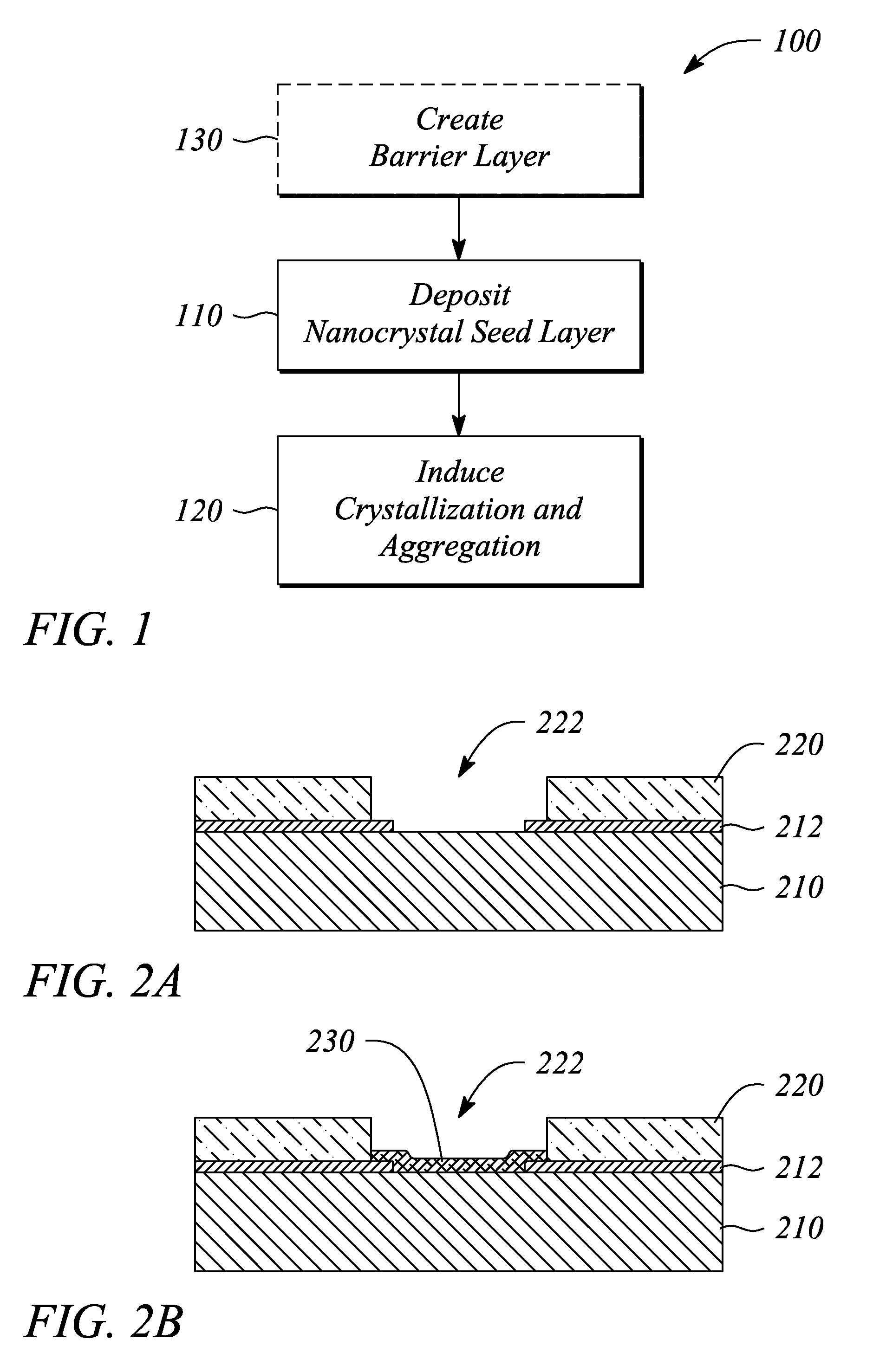
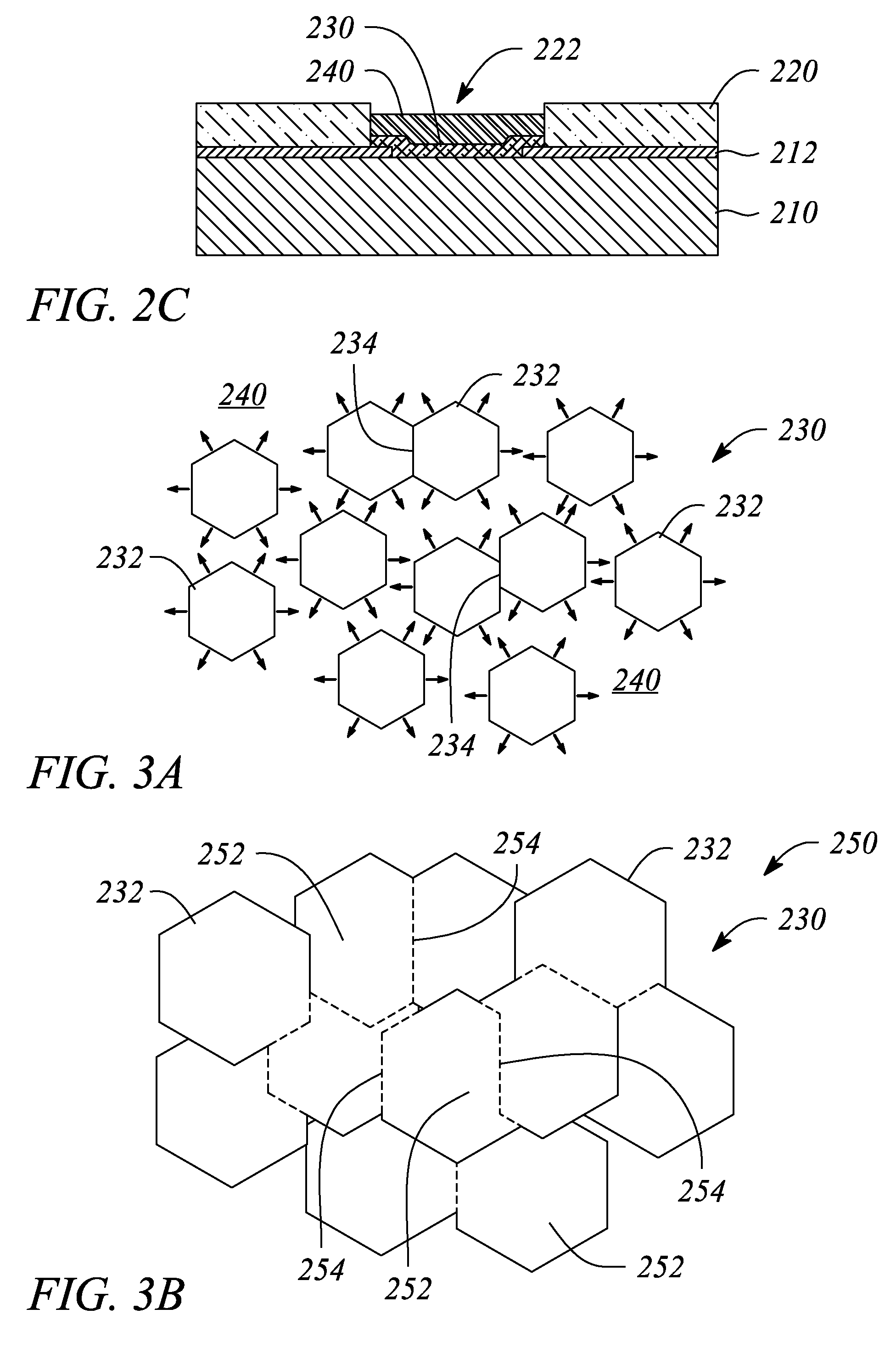
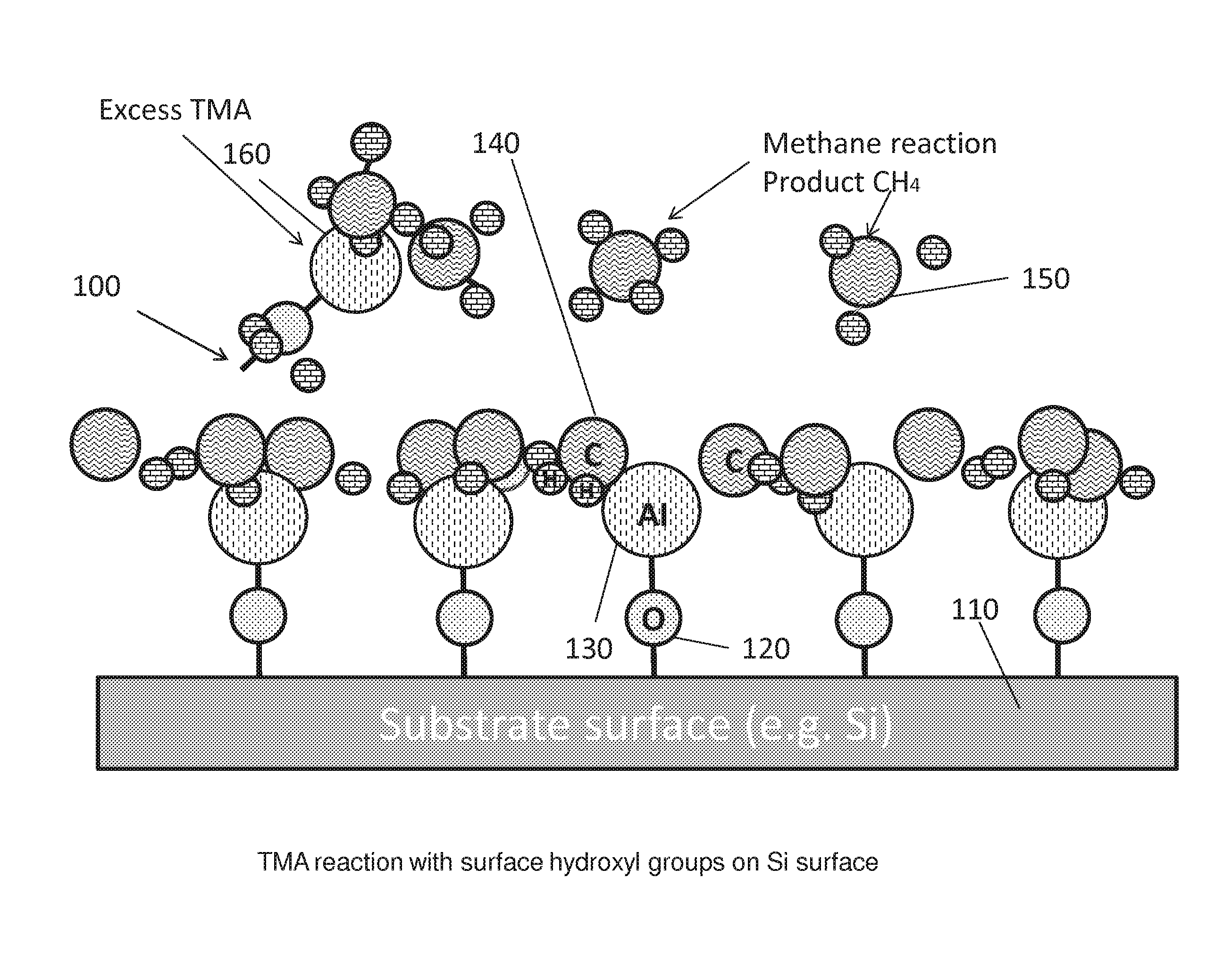
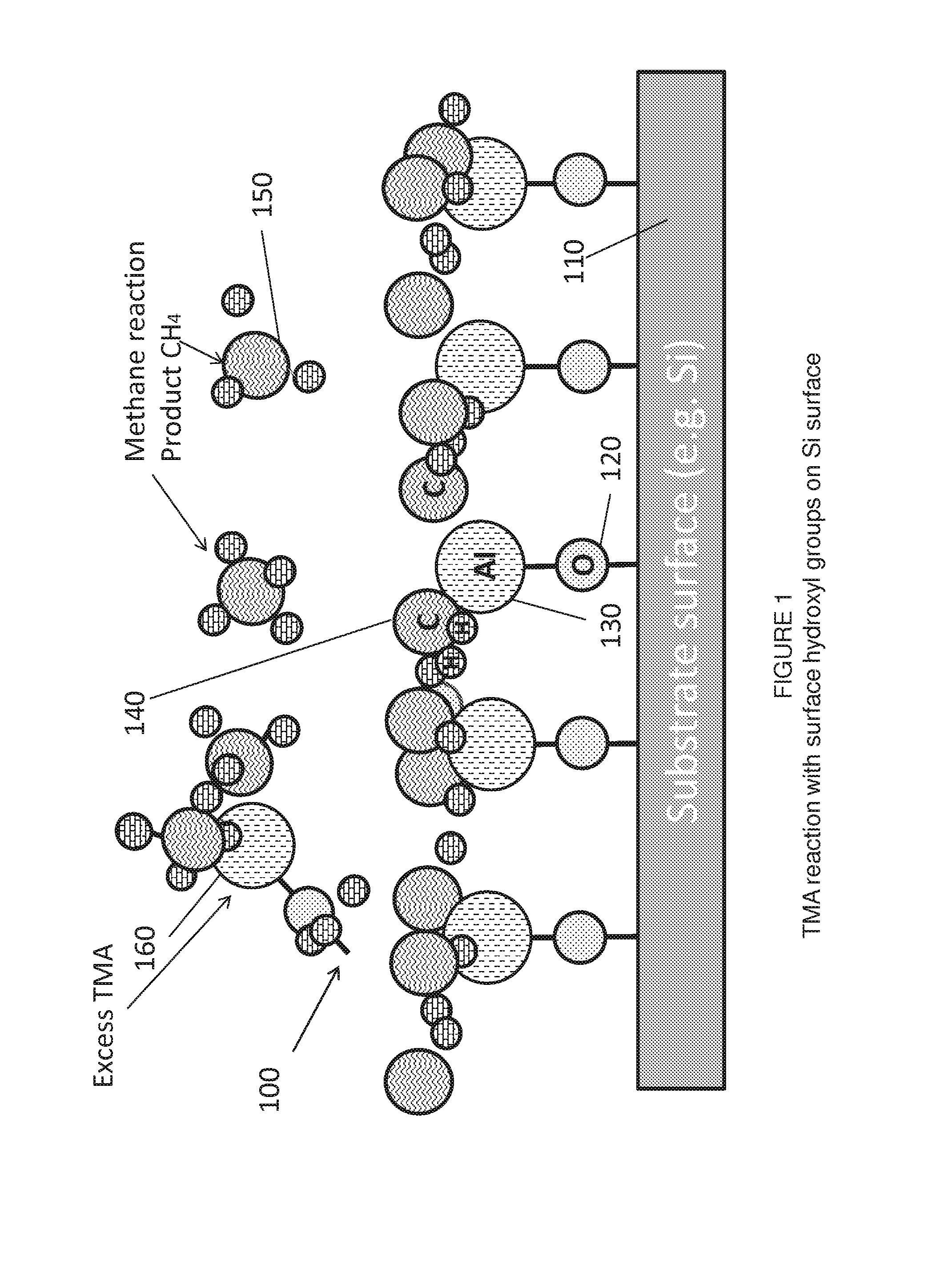
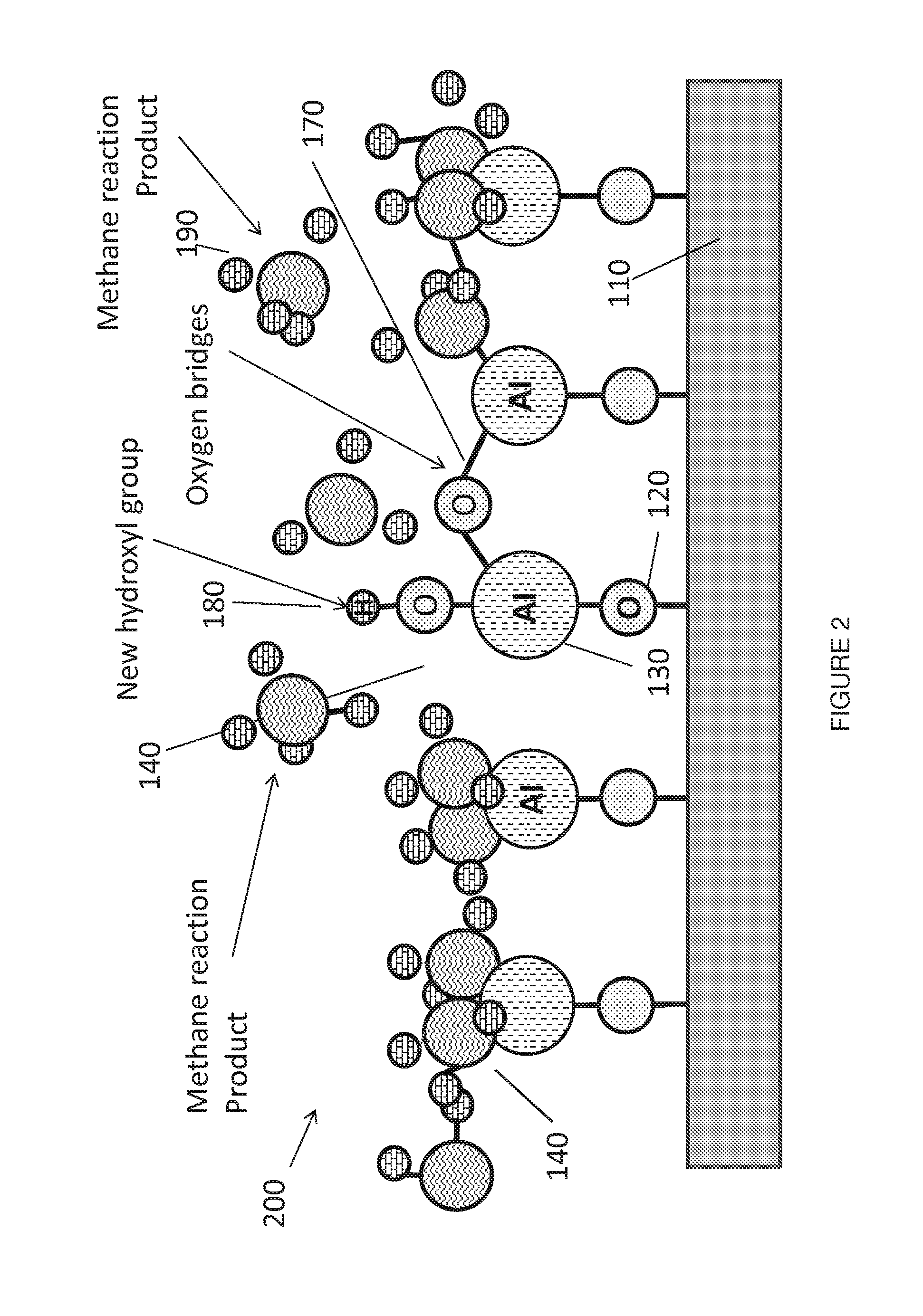
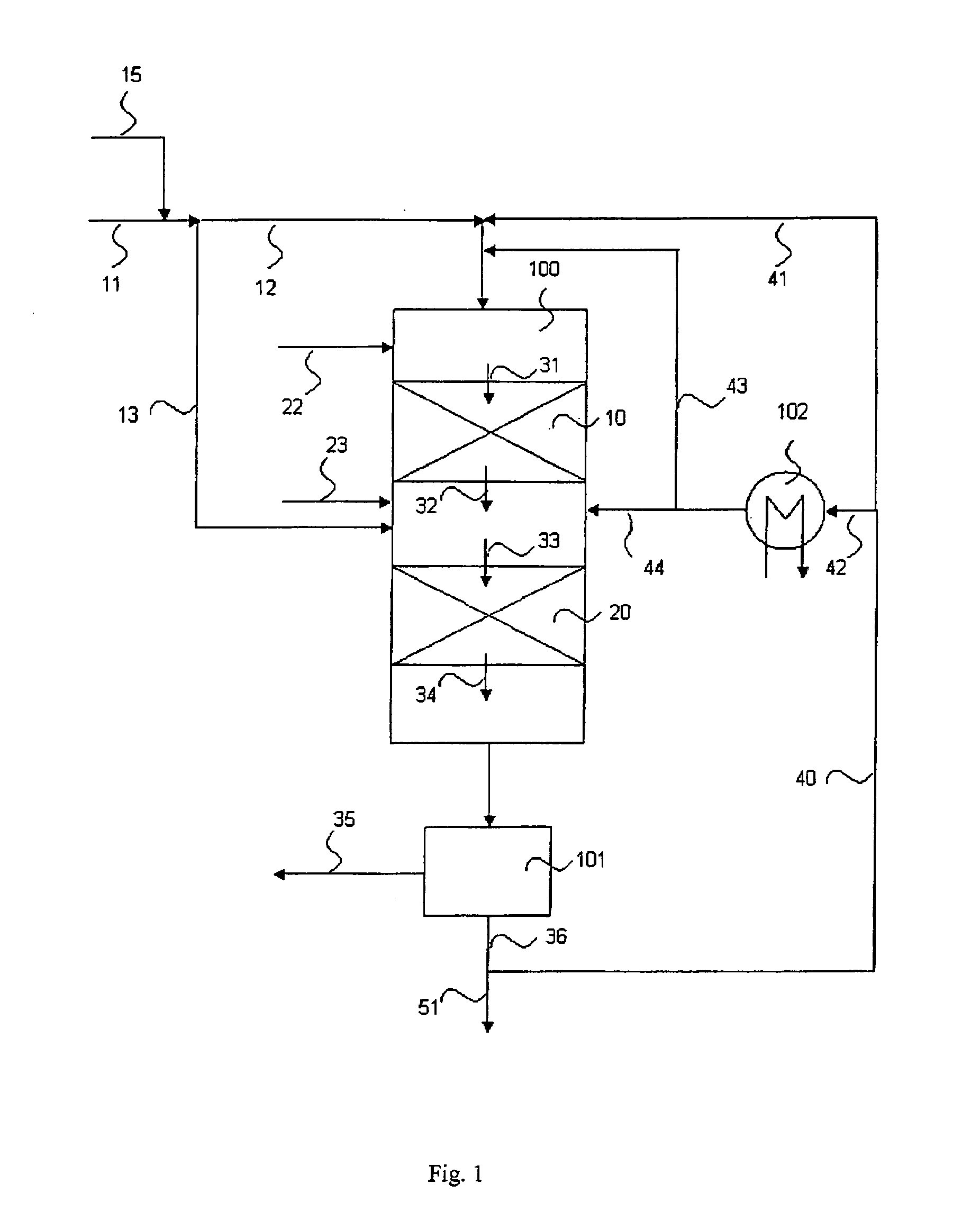
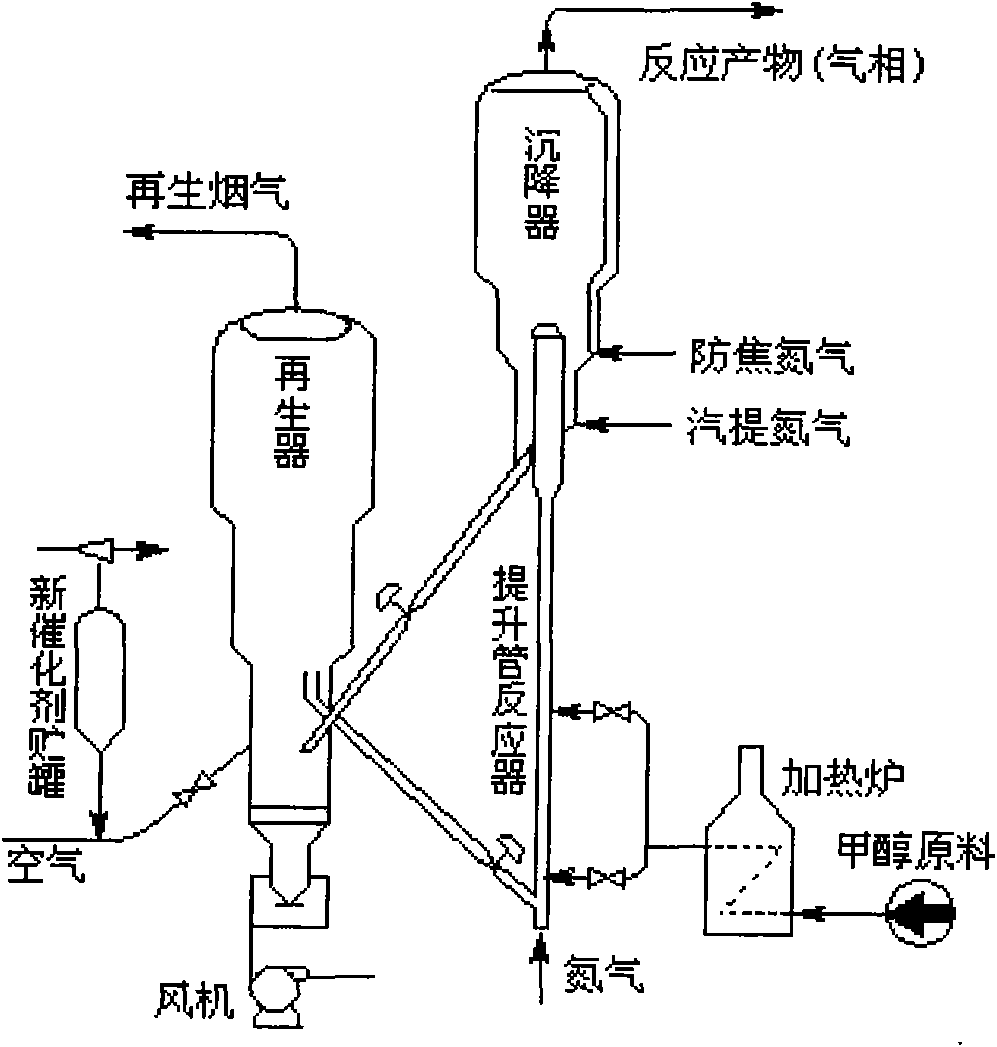
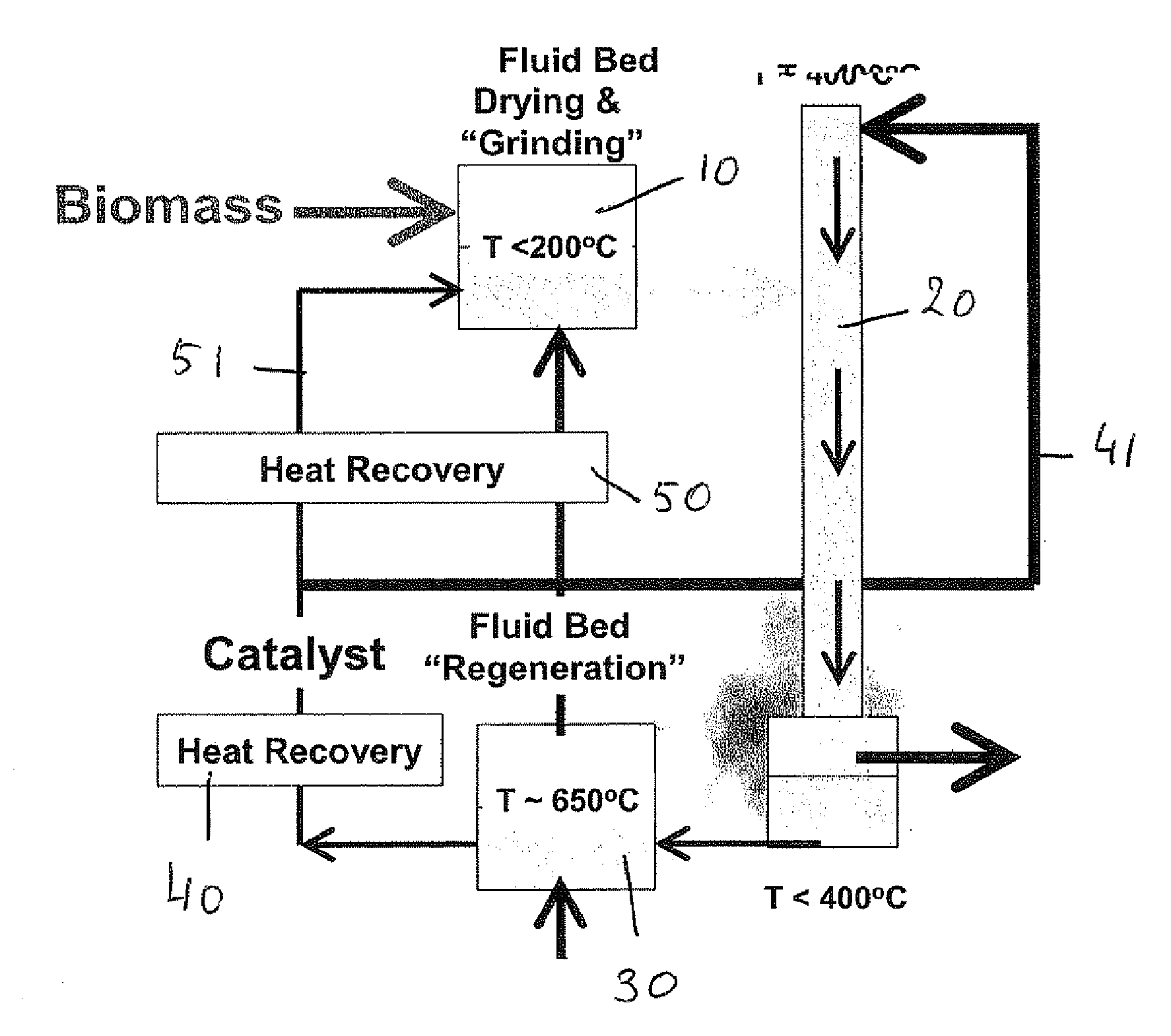
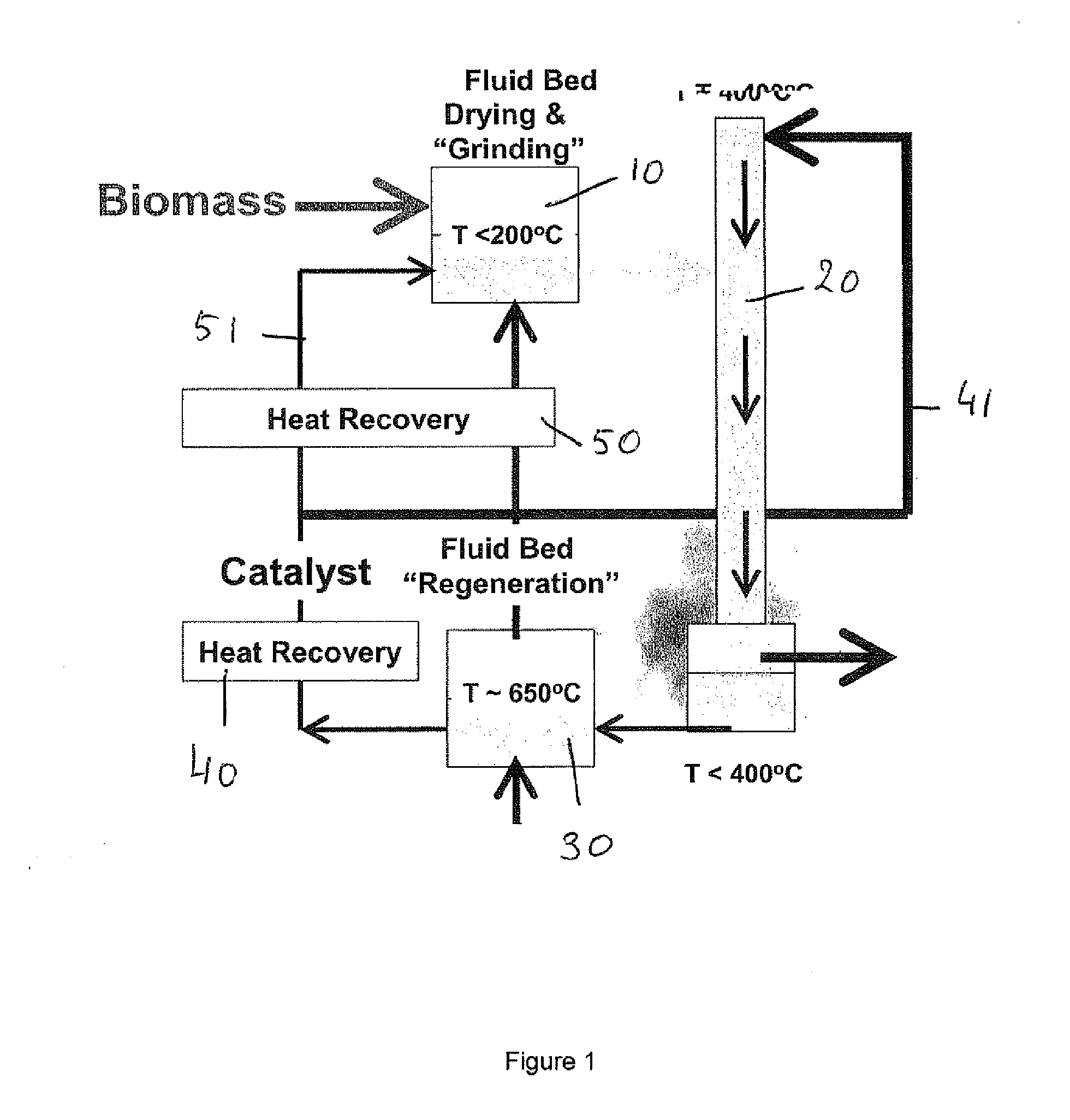
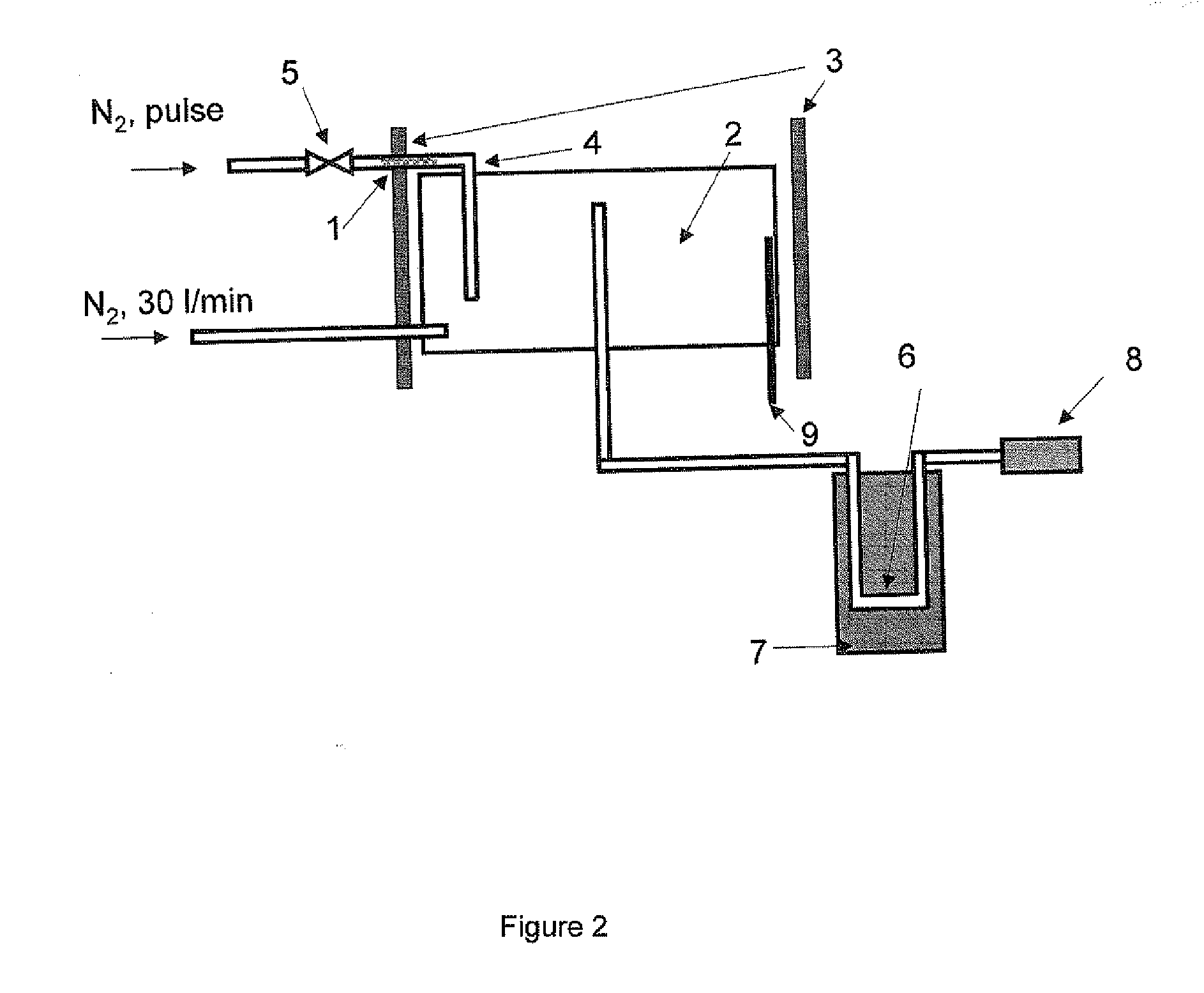
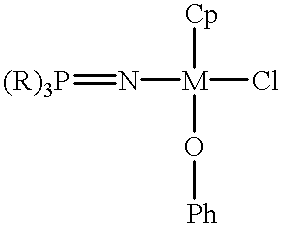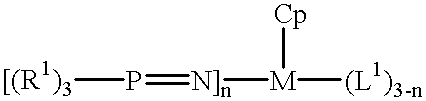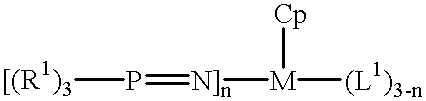Patents
Literature
29596 results about "Reaction temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Temperature is one of the effects that influence on the rates of reaction. By increasing. the temperature, the rate of a reaction proportionally increases until it reach the limits where. another factors might disturb the reaction from more increases. While the time taken for the. reaction is shorter at a higher temperature.
Fused nanocrystal thin film semiconductor and method
A thin film semiconductor and a method of its fabrication use induced crystallization and aggregation of a nanocrystal seed layer to form a merged-domain layer. The nanocrystal seed layer is deposited onto a substrate surface within a defined boundary. A reaction temperature below a boiling point of a reaction solution is employed. A thin film metal-oxide transistor and a method of its production employ the thin film semiconductor as a channel of the transistor. The merged-domain layer exhibits high carrier mobility.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Pre-passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus, and passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus during the initial reacation
ActiveUS20100282645A1Reduce operational riskReduce contentThermal non-catalytic crackingPhysical/chemical process catalystsLiquid productReaction temperature
The present invention relates to a pre-passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus prior to the reaction, or a passivation process for a continuous reforming apparatus during the initial reaction, comprising loading a reforming catalyst into the continuous reforming apparatus, starting the gas circulation and raising the temperature of a reactor, injecting sulfide into the gas at a reactor temperature ranging from 100-650° C., controlling the sulfur amount in the recycle gas within a range of 0.5-100×10−6 L / L so as to passivate the apparatus.The process of the present invention may also comprise the following steps:(1) loading a reforming catalyst into the continuous reforming apparatus, starting the gas circulation and raising the temperature of a reactor, feeding the reforming feedstock into the reaction system when the temperature of the reactor is increased to 300-460° C., introducing sulfide into the reaction system while or after the reforming feedstock is fed, controlling the ratio of the total sulfur amount introduced into the system to the reforming feedstock within the range of 0.5 μg / g-50 μg / g, reducing the content of sulfide introduced into the system when hydrogen sulfide concentration in the recycle gas reaches to 2.0 μL / L˜30 μL / L; and(2) maintaining the reforming reactor at a temperature of 460-490° C., controlling the ratio of the total sulfur amount introduced into the system to the reforming feedstock within the range of 0.2 μg / g-0.5 μg / g, adjusting the amount of the reforming feedstock to the design value of the apparatus, increasing the reforming reaction temperature to 490-545° C. according to the requirements on the octane number of the liquid product, and letting the reforming apparatus run under normal operating conditions.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Method of forming oxynitride film or the like and system for carrying out the same
InactiveUS6884295B2High film forming ratePromote oxidationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWater heatersReaction temperatureProduct gas
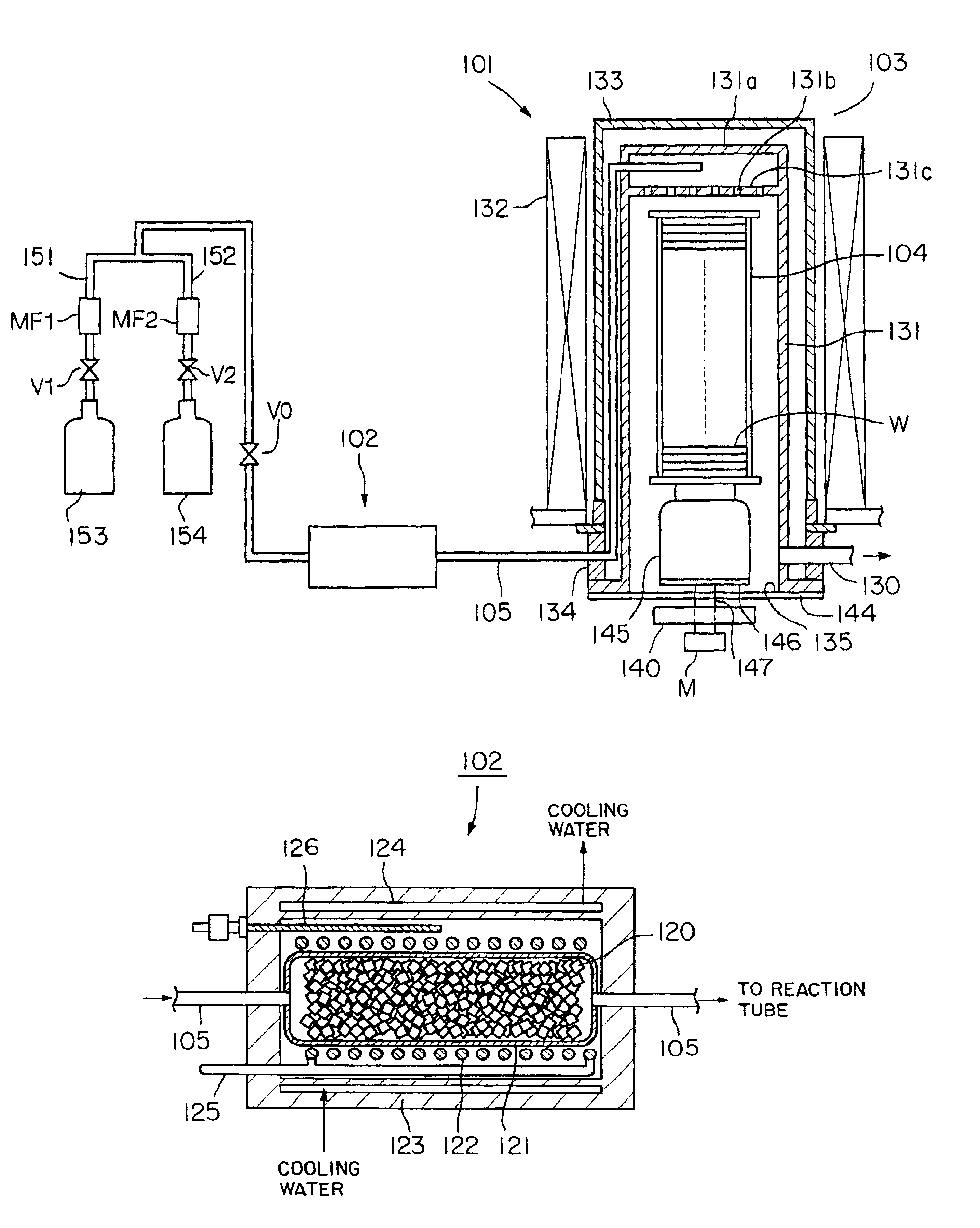
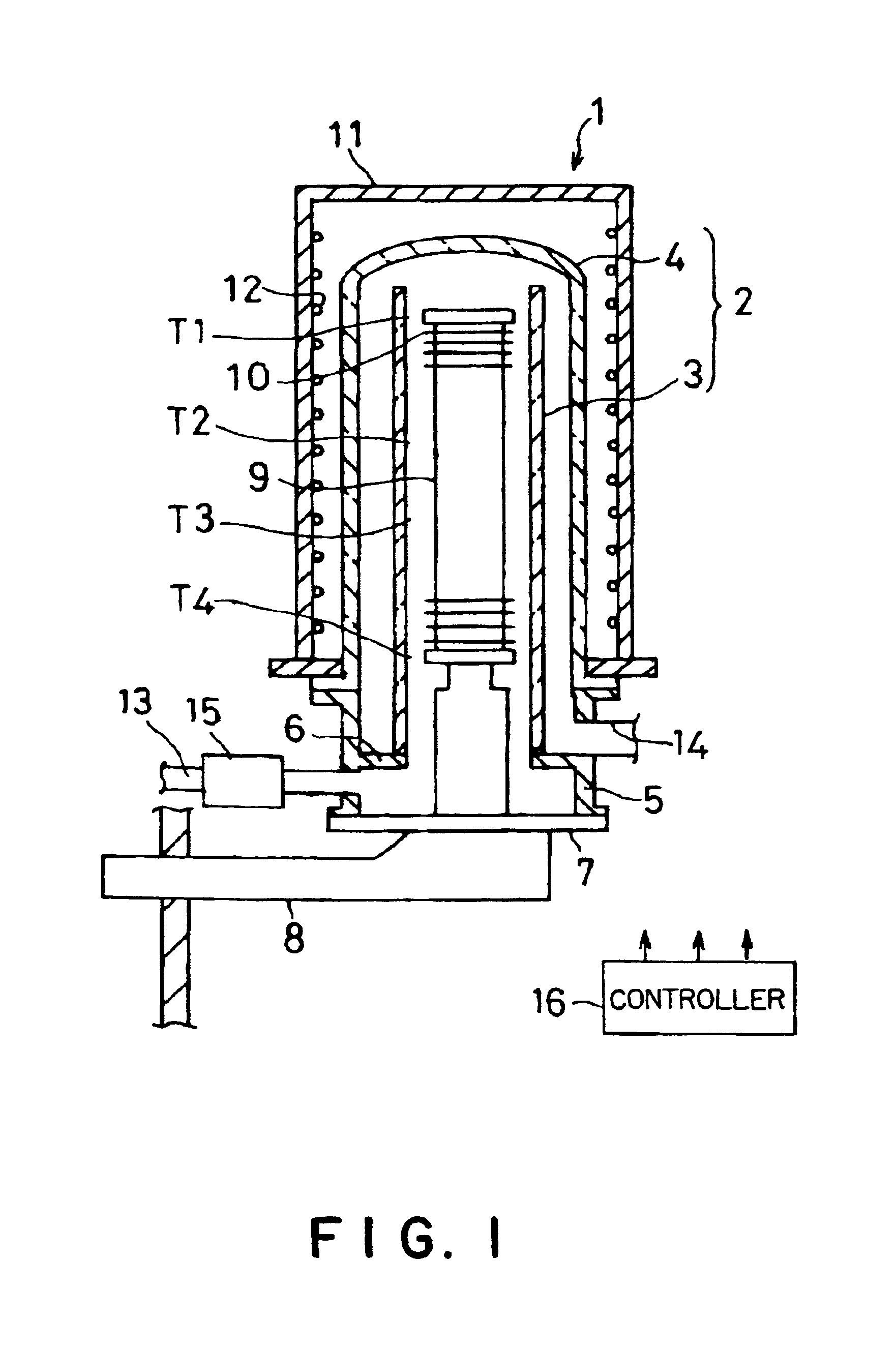
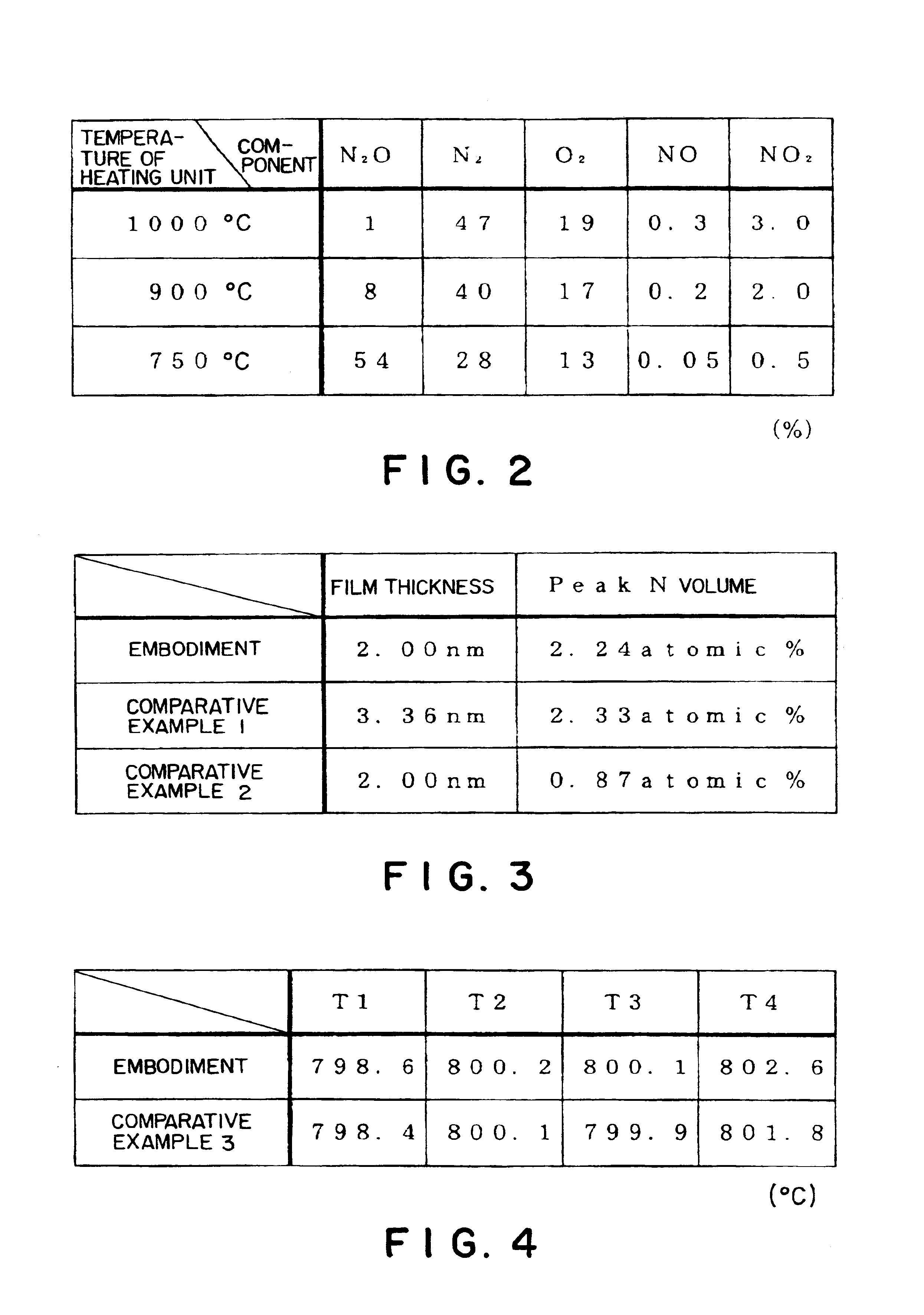
This invention is an oxynitride film forming method including: a reaction chamber heating step of heating a reaction chamber to a predetermined temperature, the reaction chamber containing an object to be processed; a gas heating step of heating a process gas to a temperature not lower than a reaction temperature at which an oxynitride film can be formed, the process gas consisting of dinitrogen oxide gas; and a film forming step of forming an oxynitride film on the object to be processed by supplying the heated process gas into the heated processing chamber. The temperature to which the reaction chamber is heated in the reaction chamber heating step is set at a temperature below a temperature at which the process gas undergoes a reaction.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Formation of heteroepitaxial layers with rapid thermal processing to remove lattice dislocations
InactiveUS20160155629A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesReaction temperatureGallium nitride
Method and devices are disclosed for device manufacture of gallium nitride devices by growing a gallium nitride layer on a silicon substrate using Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) followed by rapid thermal annealing. Gallium nitride is grown directly on silicon or on a barrier layer of aluminum nitride grown on the silicon substrate. One or both layers are thermally processed by rapid thermal annealing. Preferably the ALD process use a reaction temperature below 550° C. and preferable below 350° C. The rapid thermal annealing step raises the temperature of the coating surface to a temperature ranging from 550 to 1500° C. for less than 12 msec.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
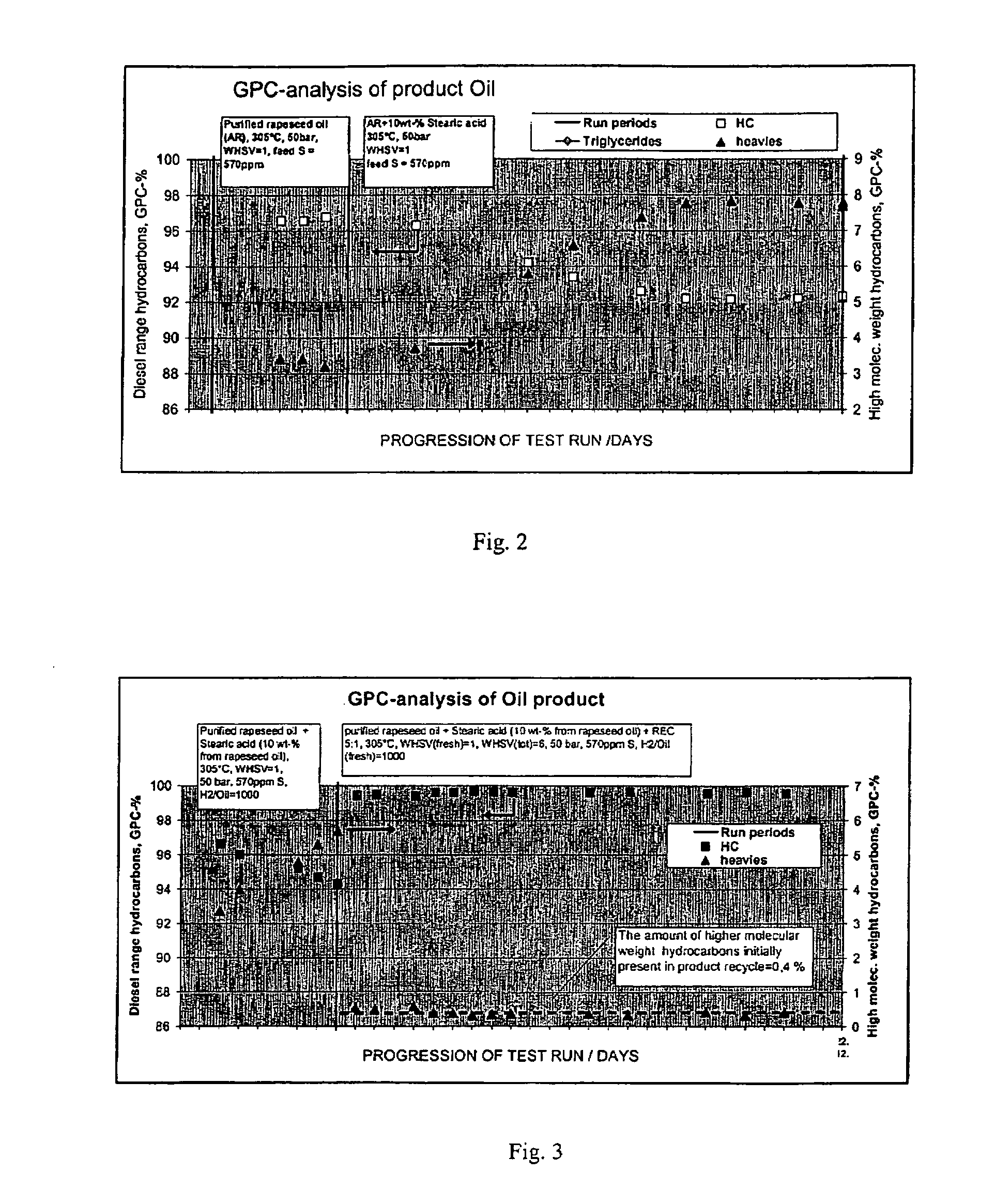
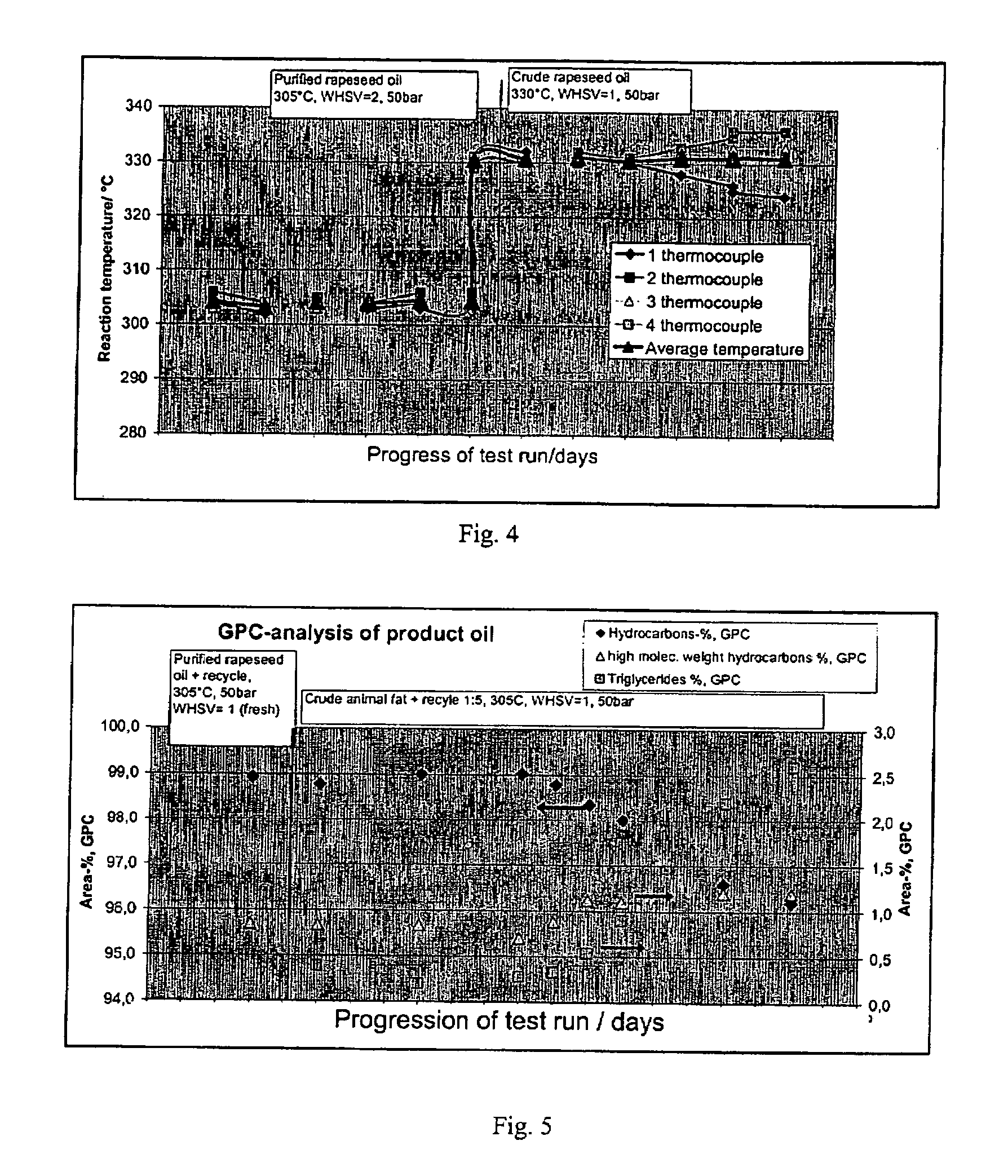
Process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20070010682A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationReaction temperature
The invention relates to a process for the manufacture of diesel range hydrocarbons wherein a feed is hydrotreated in a hydrotreating step and isomerised in an isomerisation step, and a feed comprising fresh feed containing more than 5 wt % of free fatty acids and at least one diluting agent is hydrotreated at a reaction temperature of 200-400° C., in a hydrotreating reactor in the presence of catalyst, and the ratio of the diluting agent / fresh feed is 5-30:1.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
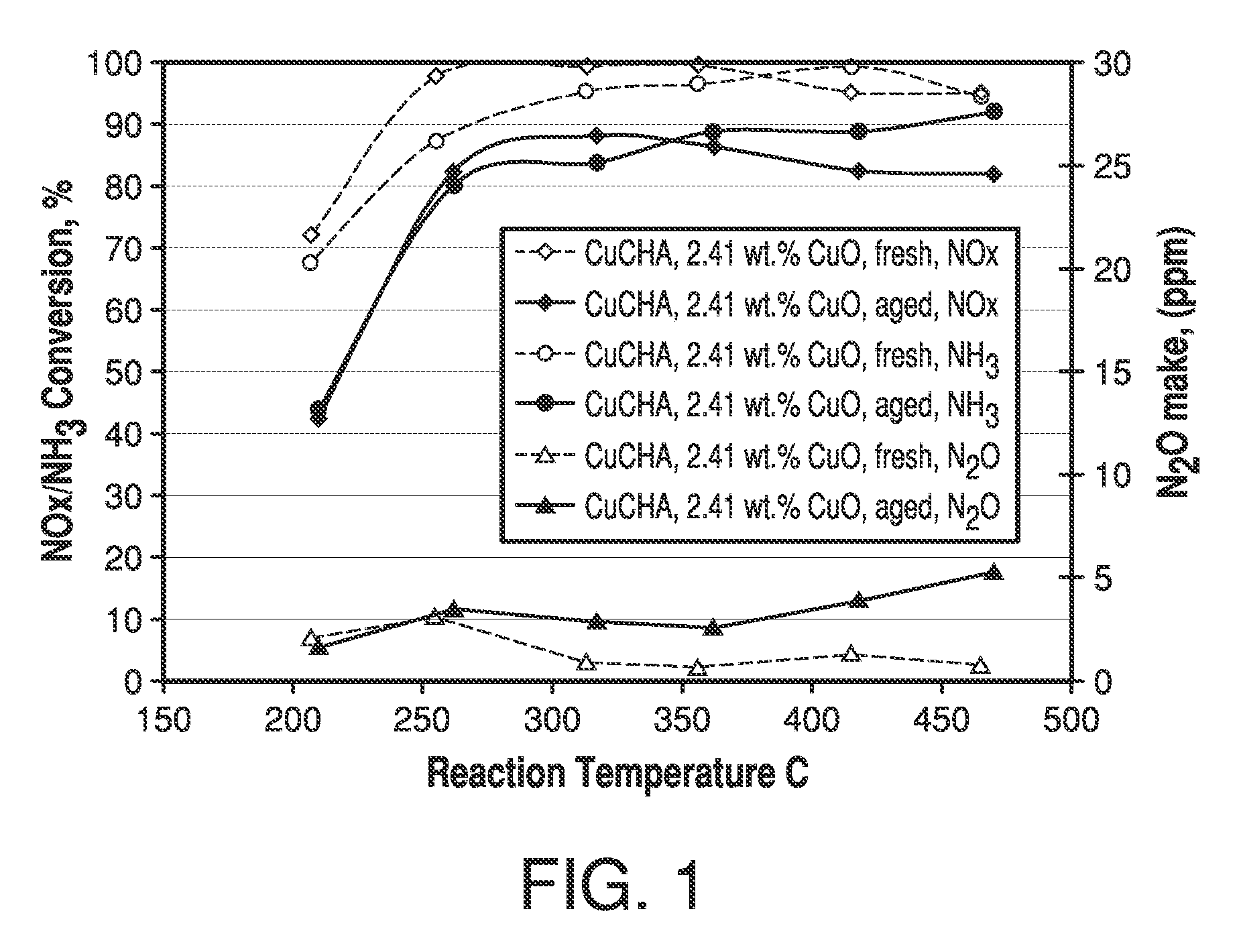
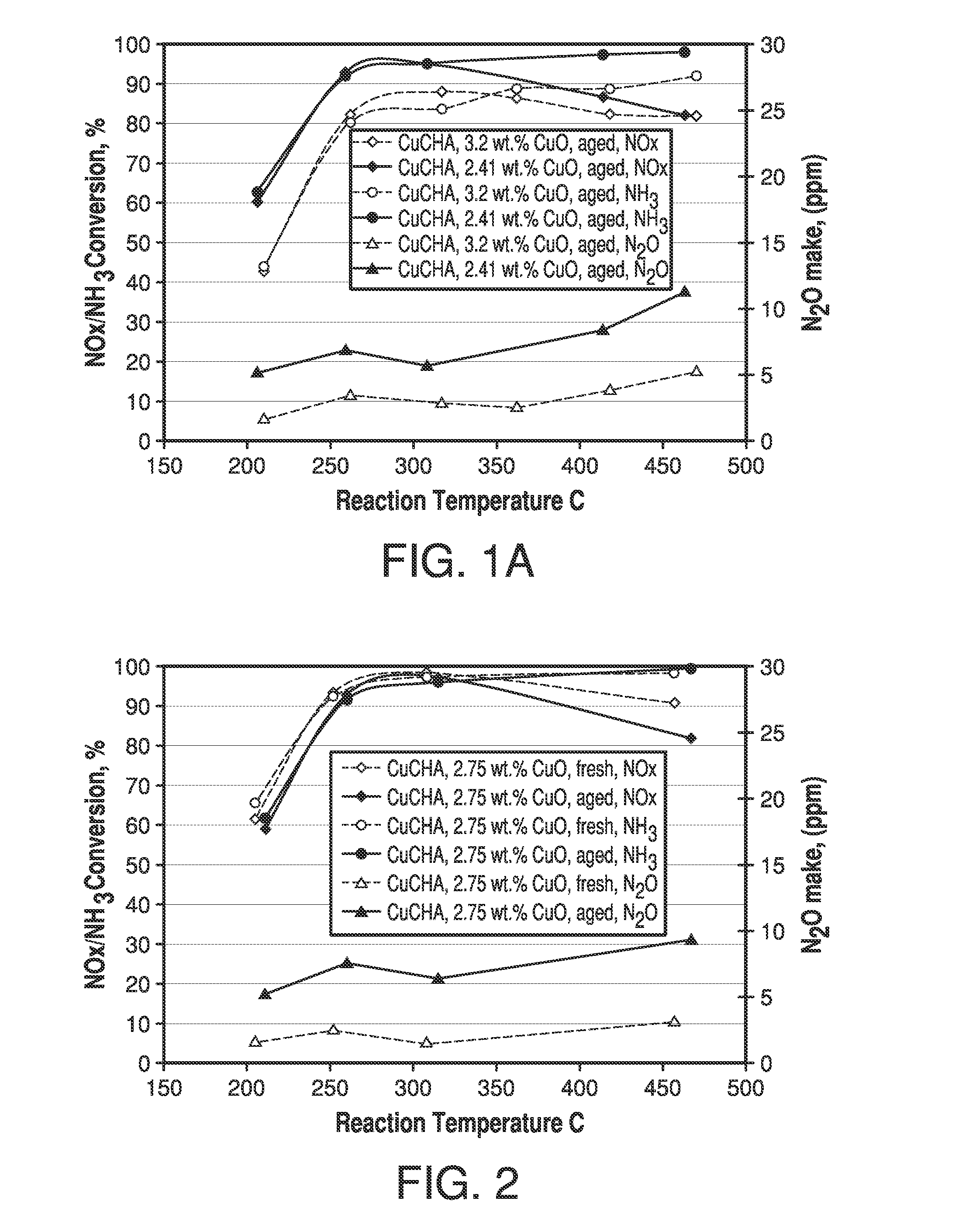
Copper CHA zeolite catalysts
ActiveUS7601662B2Good hydrothermal stabilityHigh catalytic activityCombination devicesAluminium compoundsReaction temperatureCrystal structure
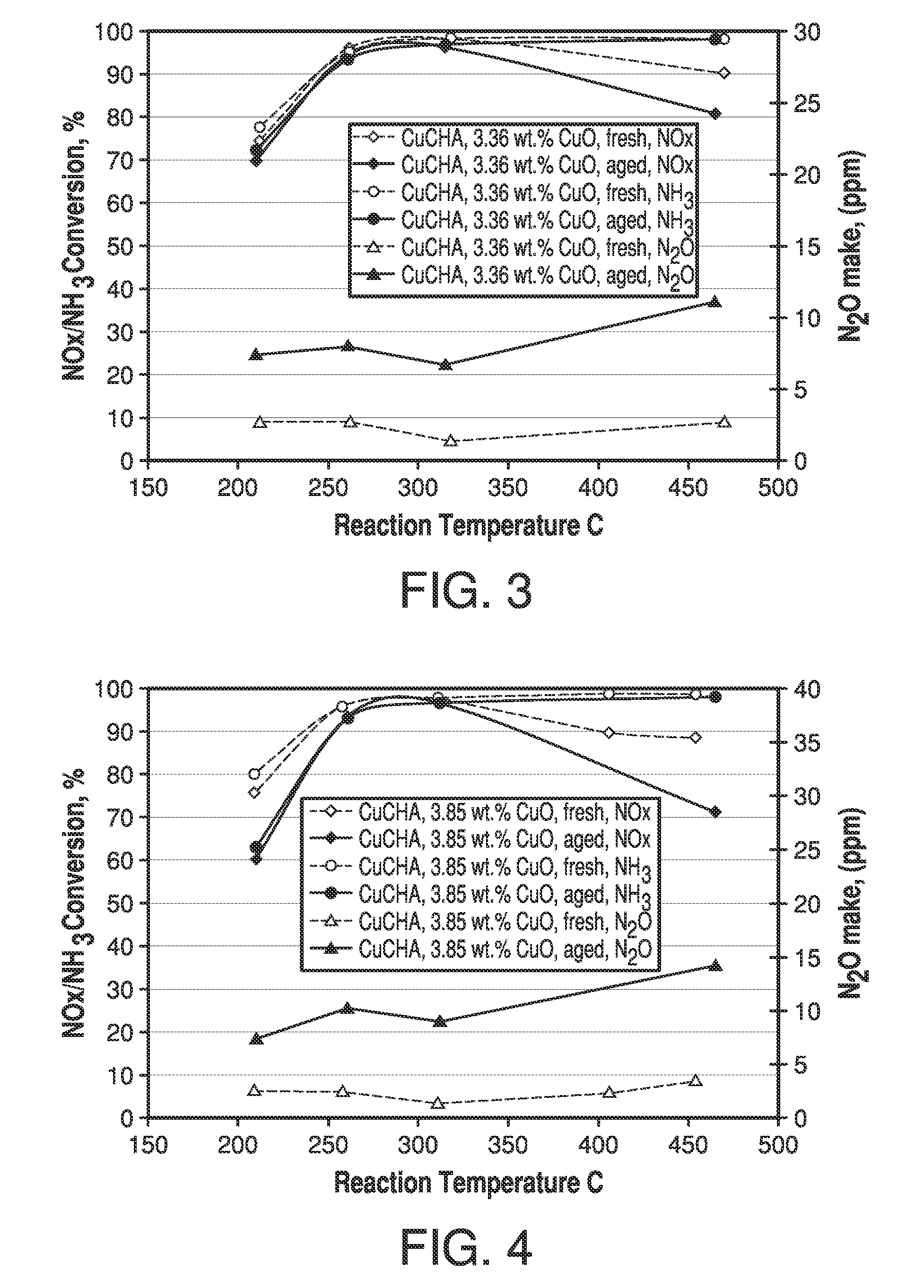
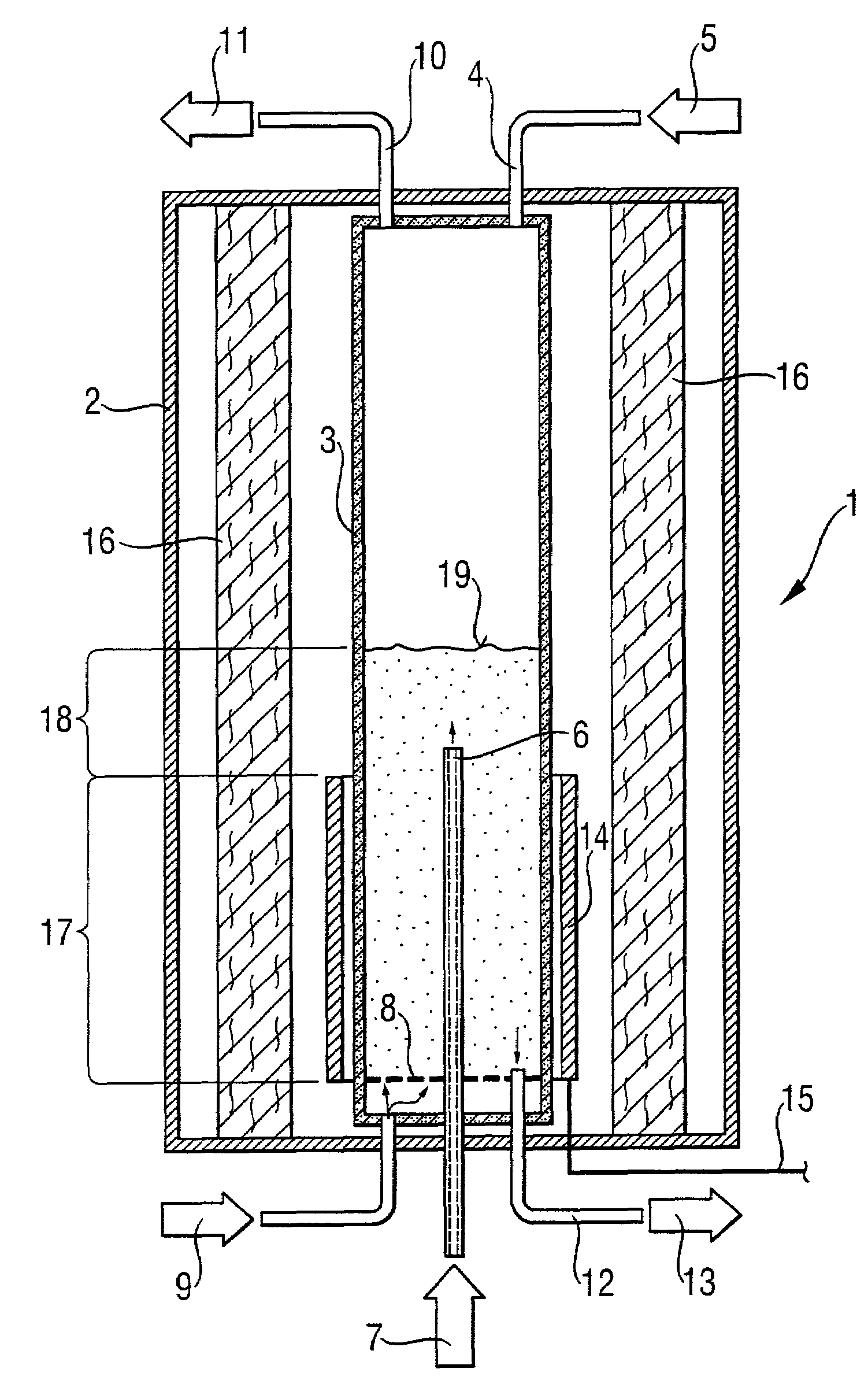
Zeolite catalysts and systems and methods for preparing and using zeolite catalysts having the CHA crystal structure are disclosed. The catalysts can be used to remove nitrogen oxides from a gaseous medium across a broad temperature range and exhibit hydrothermal stable at high reaction temperatures. The zeolite catalysts include a zeolite carrier having a silica to alumina ratio from about 15:1 to about 256:1 and a copper to alumina ratio from about 0.25:1 to about 1:1.
Owner:BASF CORP
Radiation-heated fluidized-bed reactor
InactiveUS7029632B1Low levelHigh puritySiliconFluidised-bed furnacesFluidized bedReaction temperature
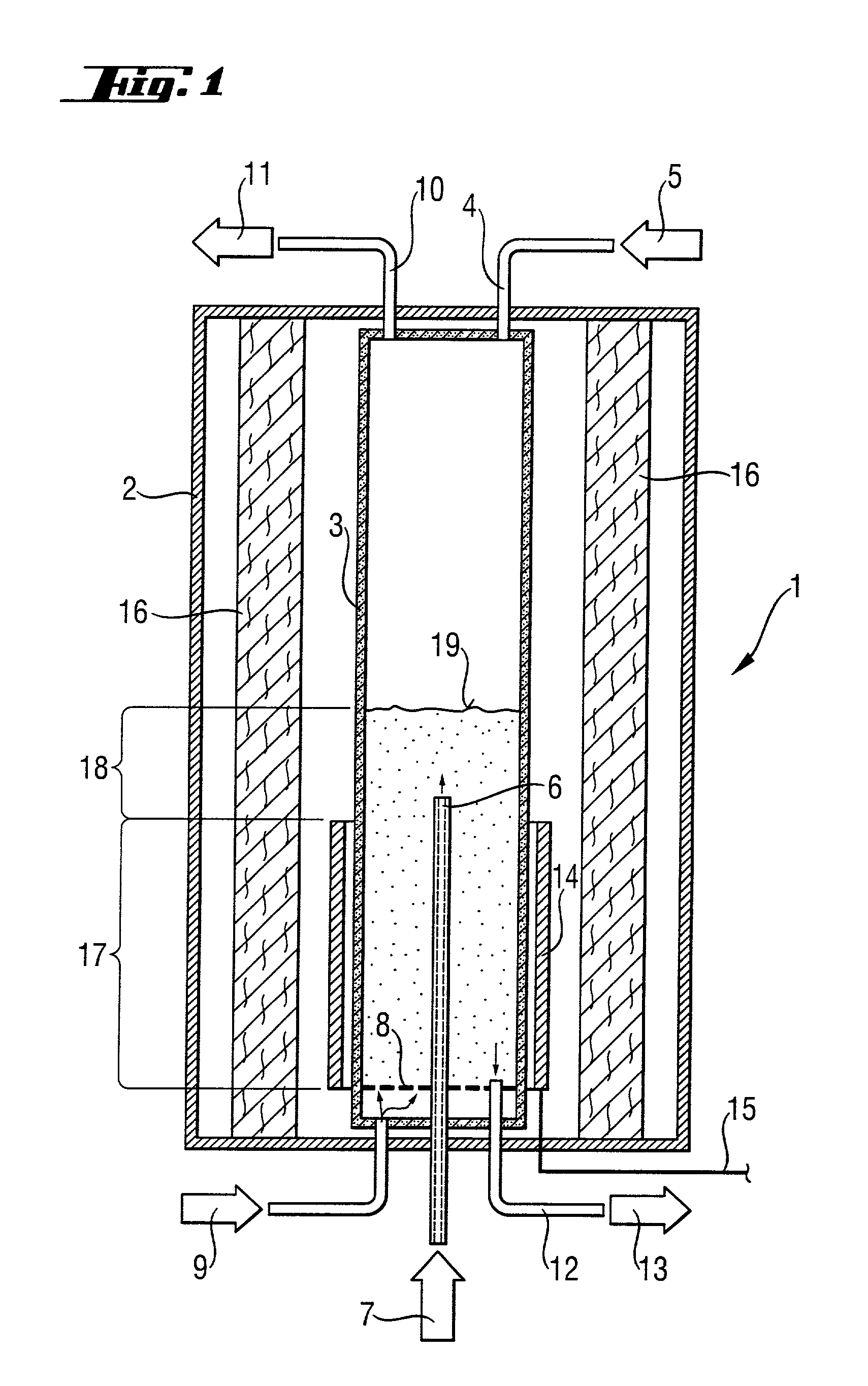
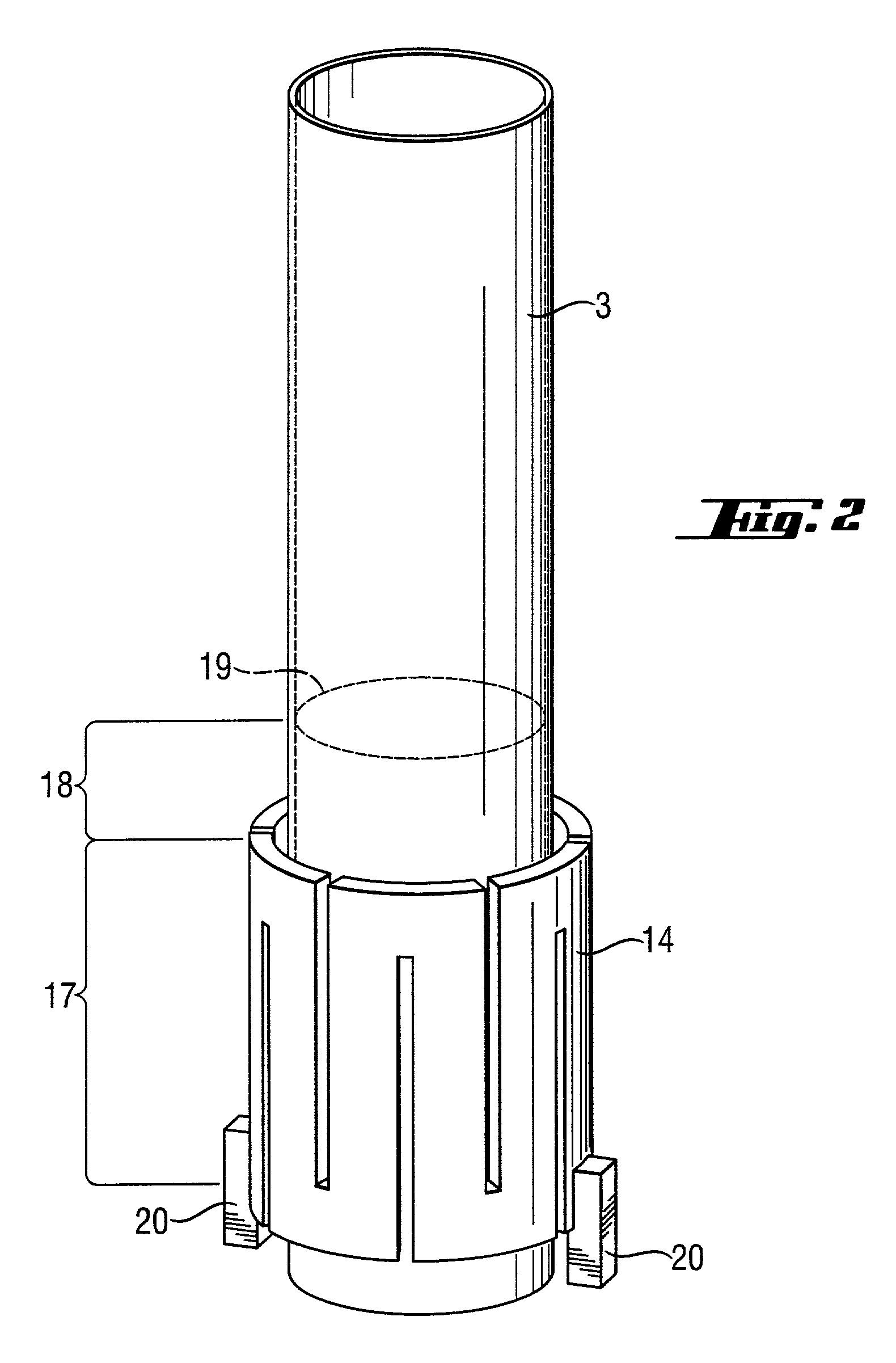
A radiation-heated fluidized-bed reactor and a process for producing high-purity polycrystalline silicon by using this reactor are provided. In this reactor, a heater device (14) is a radiation source for thermal radiation which is arranged outside the inner reactor tube and as a cylinder around the heater zone, without being in direct contact with the inner reactor tube. The inner reactor tube is designed in such a manner that it uses thermal radiation to heat the silicon particles in the heating zone to a temperature which is such that the reaction temperature is established in the reaction zone.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Process for production of surface-treated particulate water-absorbent resin
ActiveUS7201941B2Improve the level ofLittle cause gel blockingElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingParticulatesReaction temperature
An object of the present invention is to provide an excellent process for production of a surface-treated particulate water-absorbent resin wherein the process adopts a surface-treatment process that can enhance the properties (which the water-absorbent resin is desired to have) to extremely high levels, and also can solve the prior problems in such as safety, and further can sufficiently carry out the treatment even at a reaction temperature near room temperature. As a means of achieving this object, the process according to the present invention for production of a surface-treated particulate water-absorbent resin is characterized by comprising the steps of: adding a treating liquid to a particulate water-absorbent resin as a base polymer, wherein the treating liquid contains a radically polymerizable compound; and then irradiating the particulate water-absorbent resin with active energy rays while fluidizing the particulate water-absorbent resin, thereby surface-treating it.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Process for preparing arene selectivity by enhancing methanol aromatizatian and process for preparation of catalyst thereof
ActiveCN101550051AImprove methodHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationMolecular sieveFixed bed
The invention relates to a process for preparing arene selectivity by enhancing methanol aromatizatian. The process uses methanol as raw material, compositely modifies HZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst by active ions like Ga, Zn, Cu, Cr and Ag for catalyzing methanol aromatizatian, employs the fixed bed continuous process or the floating bed continuous process, wherein the reaction pressure is 0.1-3.5MPa; the reaction temperature is 380-500 DEG C; the space velocity of raw material liquid is 0.1-10.0 h; and N2 space velocity is 120-800 h. The advantages of the invention lie in collocation combination of mixing ion modification, and arene selectivity reaches to 70%.
Owner:TIANJI COAL CHEM IND GROUP +1
Process for converting carbon-based energy carrier material
InactiveUS20090308787A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
A process is disclosed process for converting a solid or highly viscous carbon-based energy carrier material to liquid and gaseous reaction products, said process comprising the steps of: a) contacting the carbon-based energy carrier material with a particulate catalyst material b) converting the carbon-based energy carrier material at a reaction temperature between 200° C. and 450° C., preferably between 250° C. and 350° C., thereby forming reaction products in the vapor phase. In a preferred embodiment the process comprises the additional step of: c) separating the vapor phase reaction products from the particulate catalyst material within 10 seconds after said reaction products are formed; In a further preferred embodiment step c) is followed by: d) quenching the reaction products to a temperature below 200° C.
Owner:MARD INC
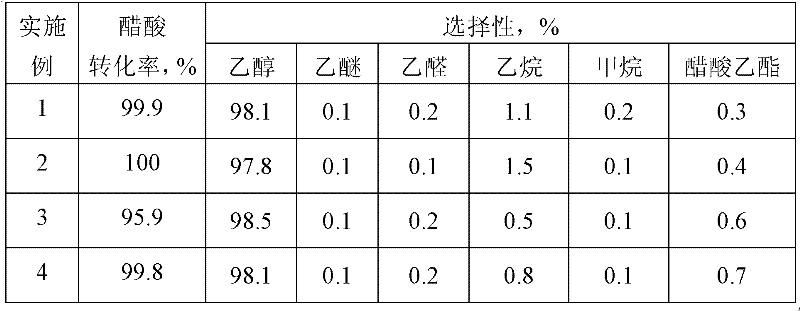
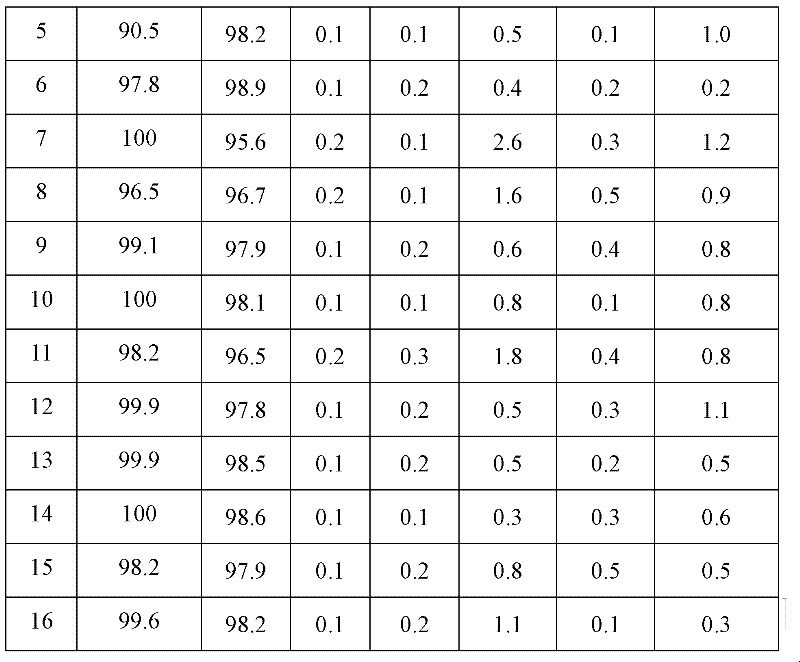
Method for preparing alcohol by acetic acid gas phase hydrogenation
ActiveCN102229520ALow reaction pressureReduce reaction energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationACETIC ACID LIQUIDGas phase
The invention relates to a method for preparing alcohol by acetic acid gas phase hydrogenation. A reaction system comprises acetic acid, hydrogen and a catalyst; the reaction temperature is 120-300 DEG C; the reaction pressure is 1.0-20.0MPa; the space velocity of acetic acid liquid is 0.5-10.5h<-1>; the molar ratio of H2 to acetic acid is 1-250; the catalyst takes activated carbon as a carrier; and main active components comprise one or two of transitional metals such as W and Mo. The addition agent is one of or more of precious metals such as Pd, Re, Pt, Rh and Ru and the like; and the acetic acid and the hydrogen can be converted into alcohol with high activity and selectivity under the action of the catalyst.
Owner:JIANGSU SOPO CHEM +1
Method of producing ethyl acetate
InactiveUS20090005588A1Good dispersionWell mixedOrganic compound preparationRotary stirring mixersAcetic acidReaction temperature
Methods and systems for the production of ethyl acetate are described herein. The methods and systems incorporate the novel use of a high shear device to promote dispersion and mixing of a carbonyl co-reactant (e.g. acetic acid, acetaldehyde) with ethanol. The high shear device may allow for lower reaction temperatures and pressures and may also reduce reaction time with existing catalysts.
Owner:HRD CORP
Full-automatic biochemical analyzer and analysis method thereof
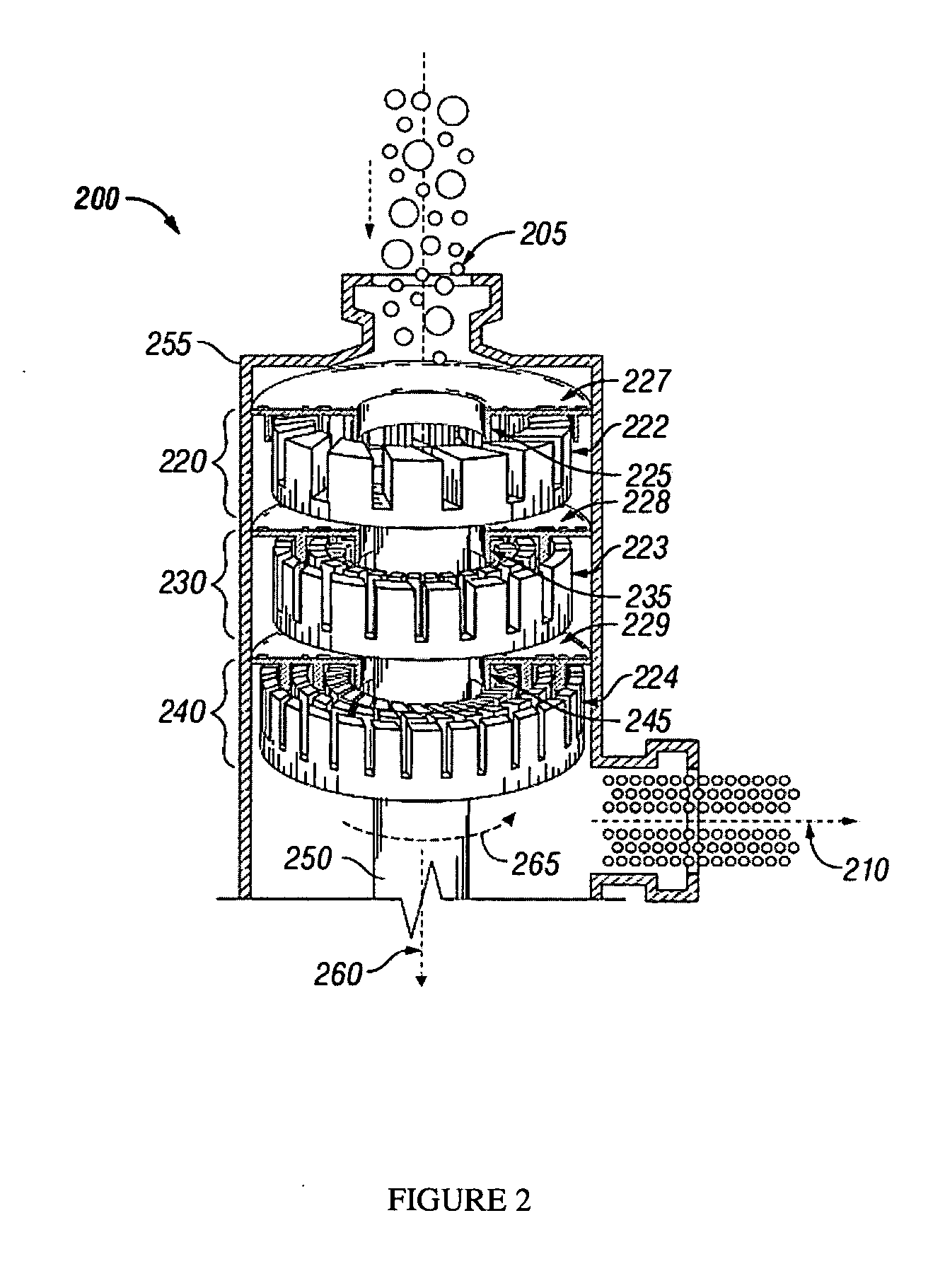
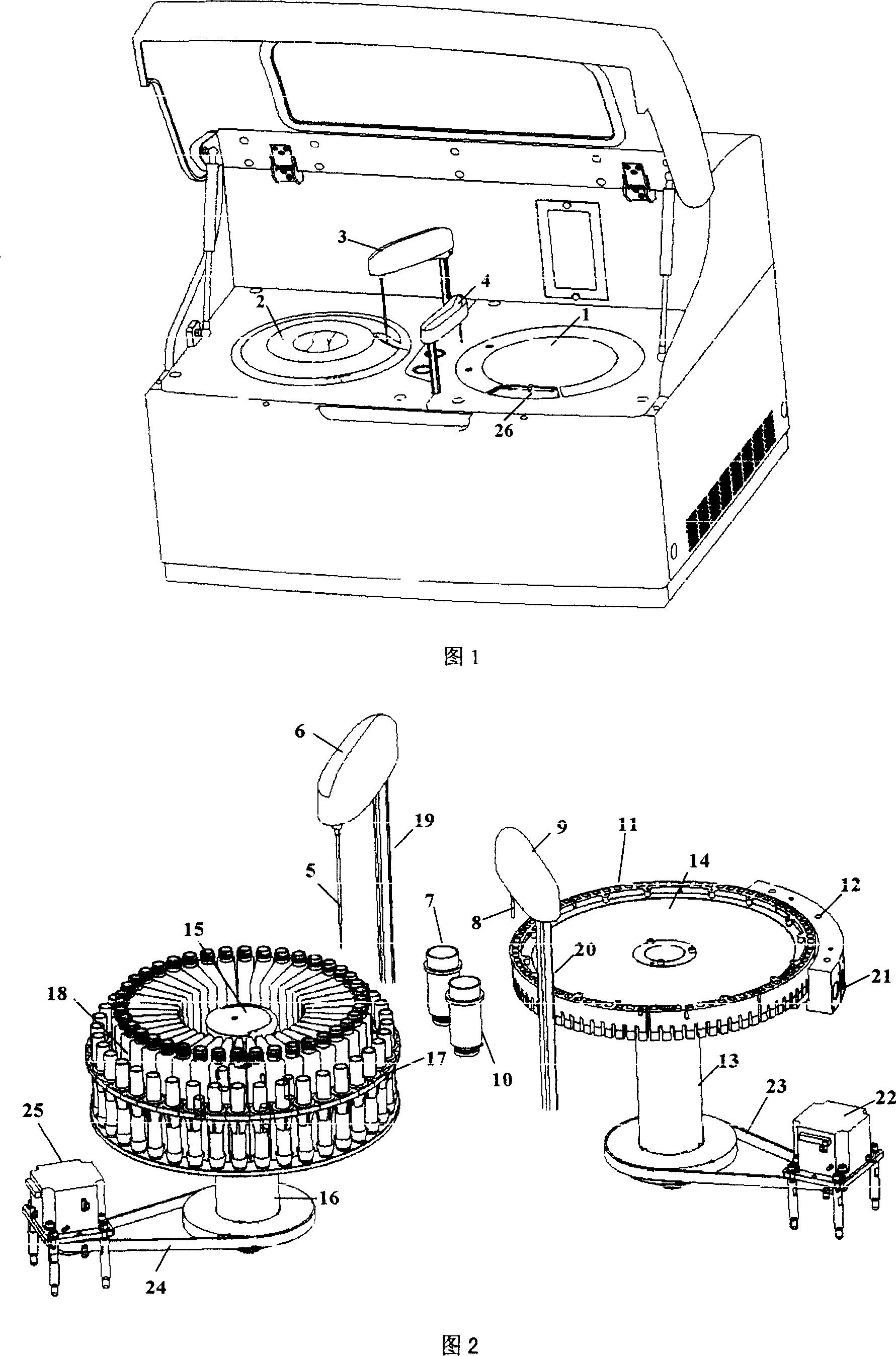
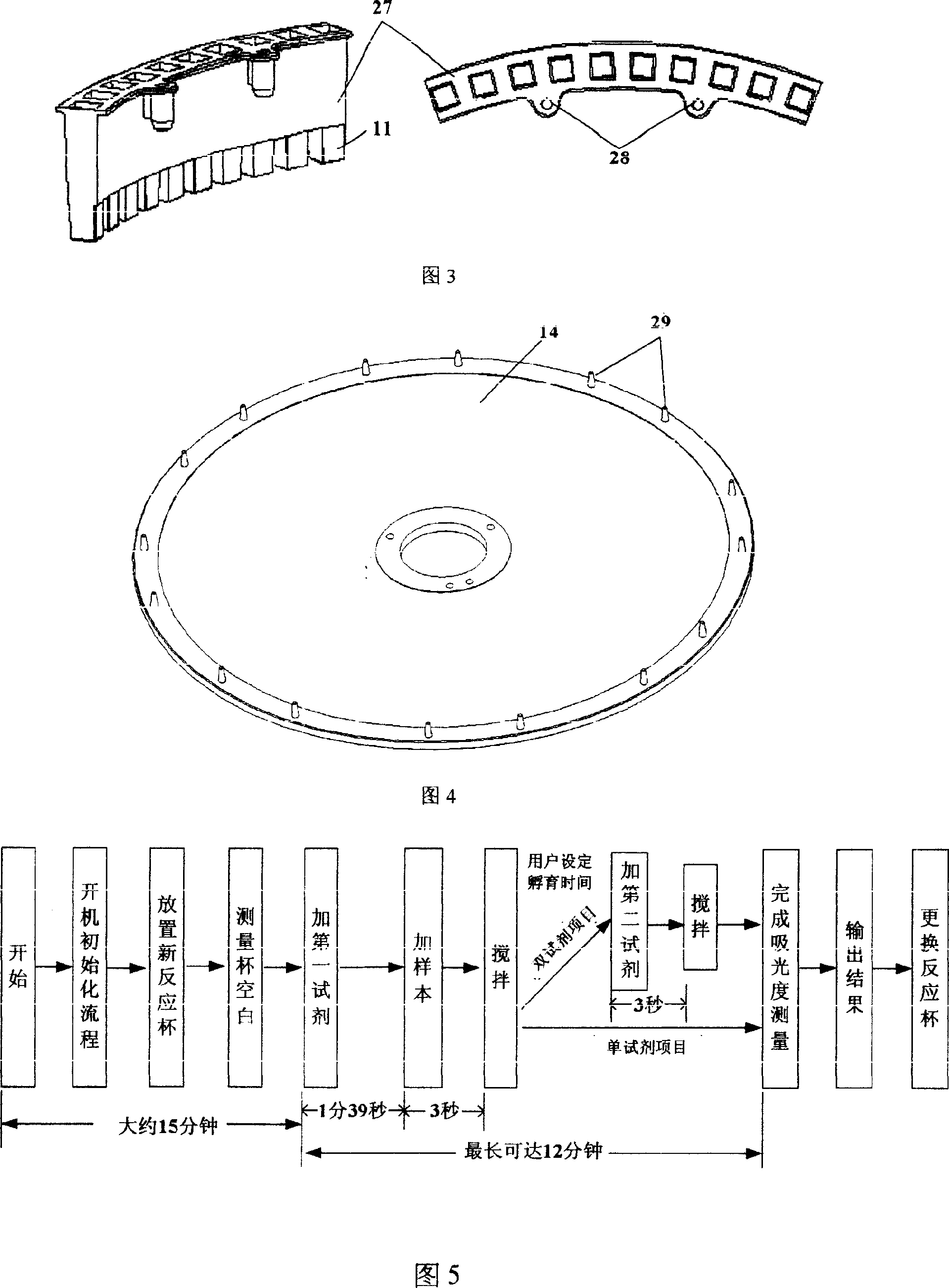
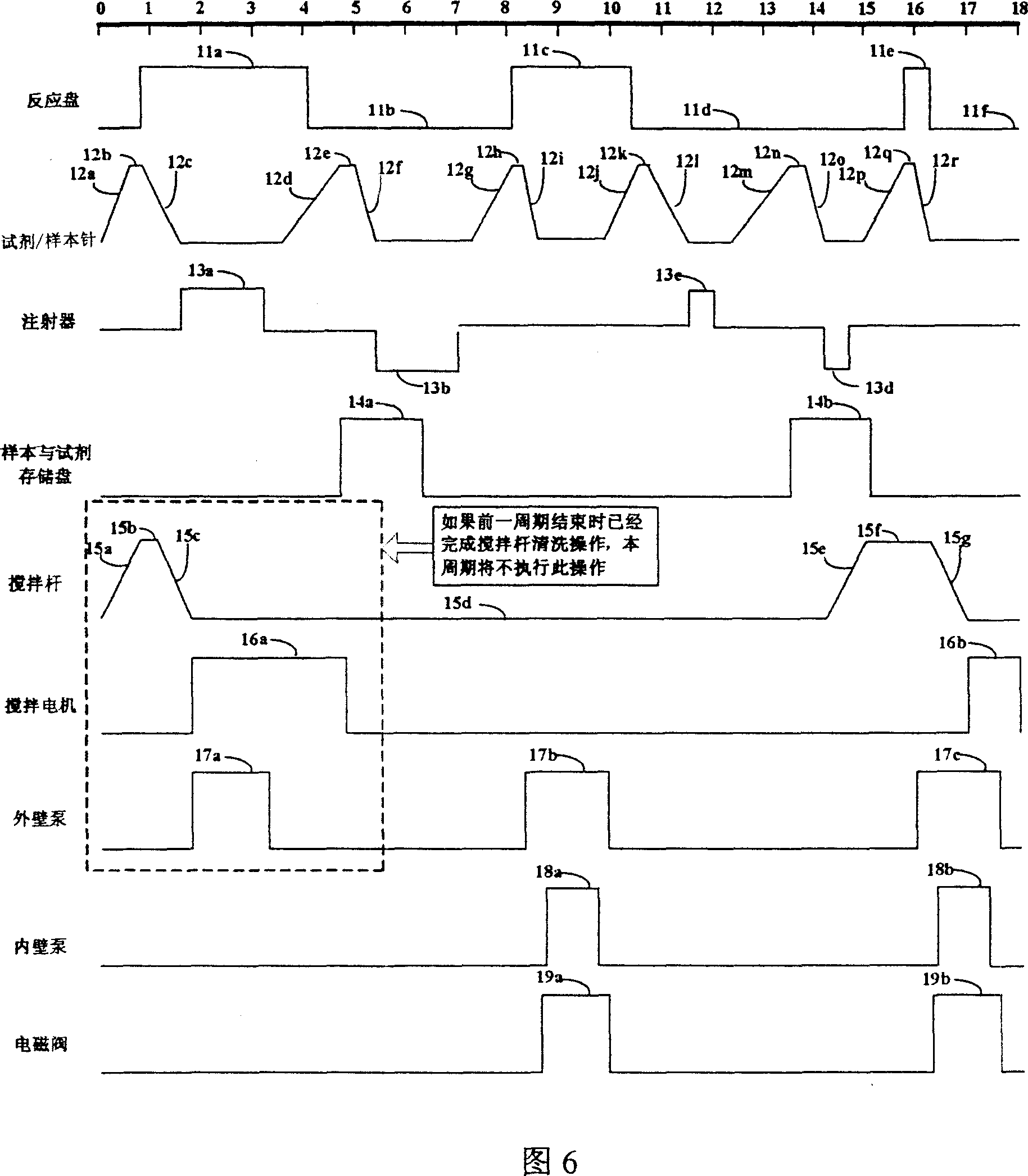
ActiveCN1963527APreserve the variance of sample loading timeKeep the differenceSamplingColor/spectral properties measurementsPhysical chemistryReaction temperature
This invention relates to composite multiple channel total automatic biological analyzers, which comprises reaction disc element, sample and agent memory disc elements, sample in element and mixture bar element. The invention can use one piece of liquid drawing probe for adding agent and sample, wherein, the fix probe mechanic arm is set with heating block to draw probe agent for pre-heating to achieve best reaction temperature as human once reaction cup.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Catalyst composition of ethylene oligomerization and the application
ActiveCN101032695AHigh activityGood choiceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionAryl1-Octene
The present invention relates to catalyst composition for oligomerizing ethylene and its application. The catalyst composition includes complex of acetylacetone chromium, tetrahydrofuran chromium chloride and / or chromium isooctanate; ligand containing P and N; activator of methyl aluminoxane, ethyl aluminoxane, propyl aluminoxane and / or butyl aluminoxane; and promoter of X1R6X2, where, each of X1 and X2 is F, Cl, Br, I or alkoxyl, and R6 is alkyl or aryl group; with the molar ratio of the complex, the ligand, the activator and the promoter being 1 to 0.5-10 to 50-3000 to 0.5-10. The catalyst composition is used in oligomerizing reaction of ethylene to prepare 1-octene, and has high catalytic activity and high 1-octene selectivity.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
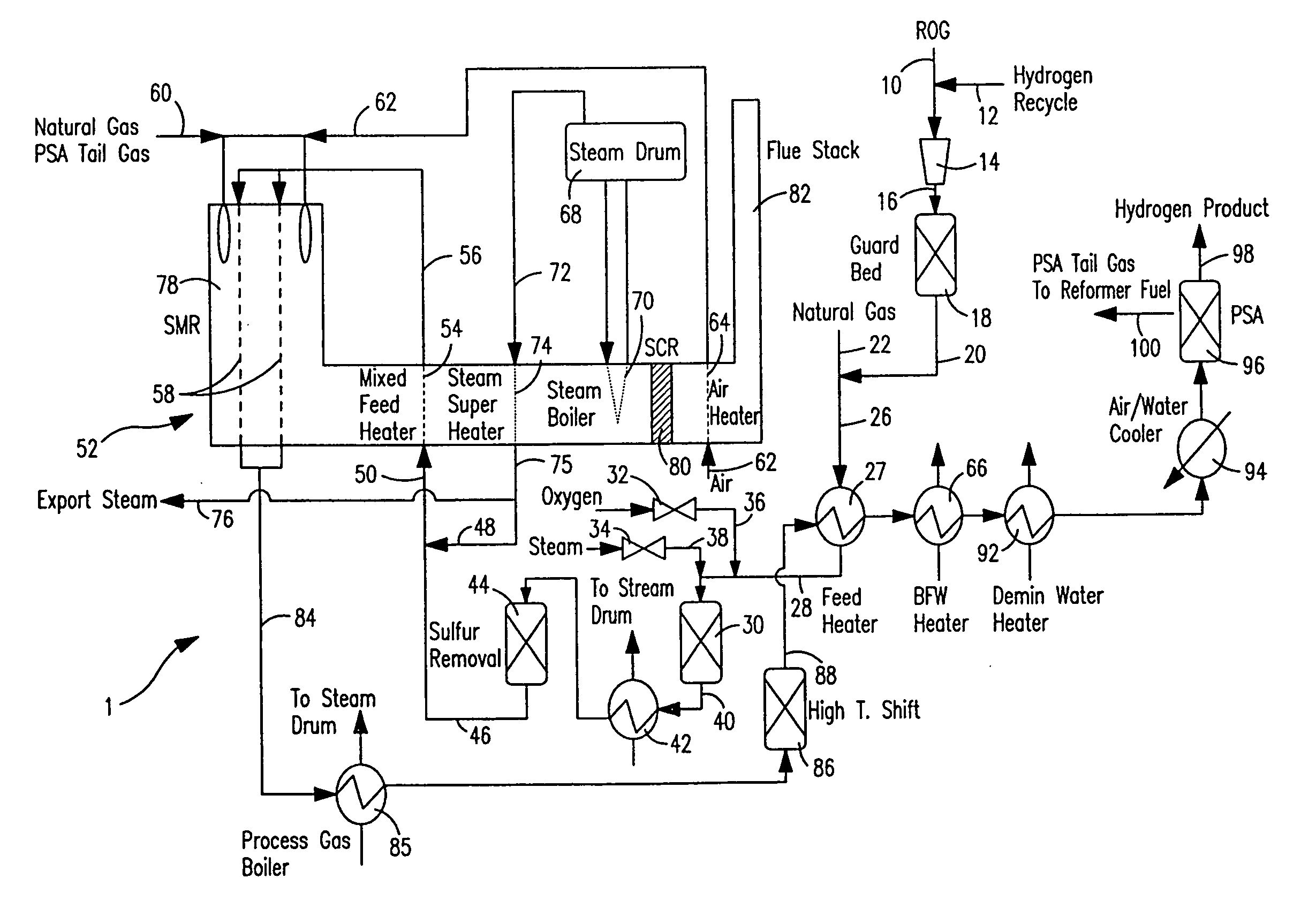
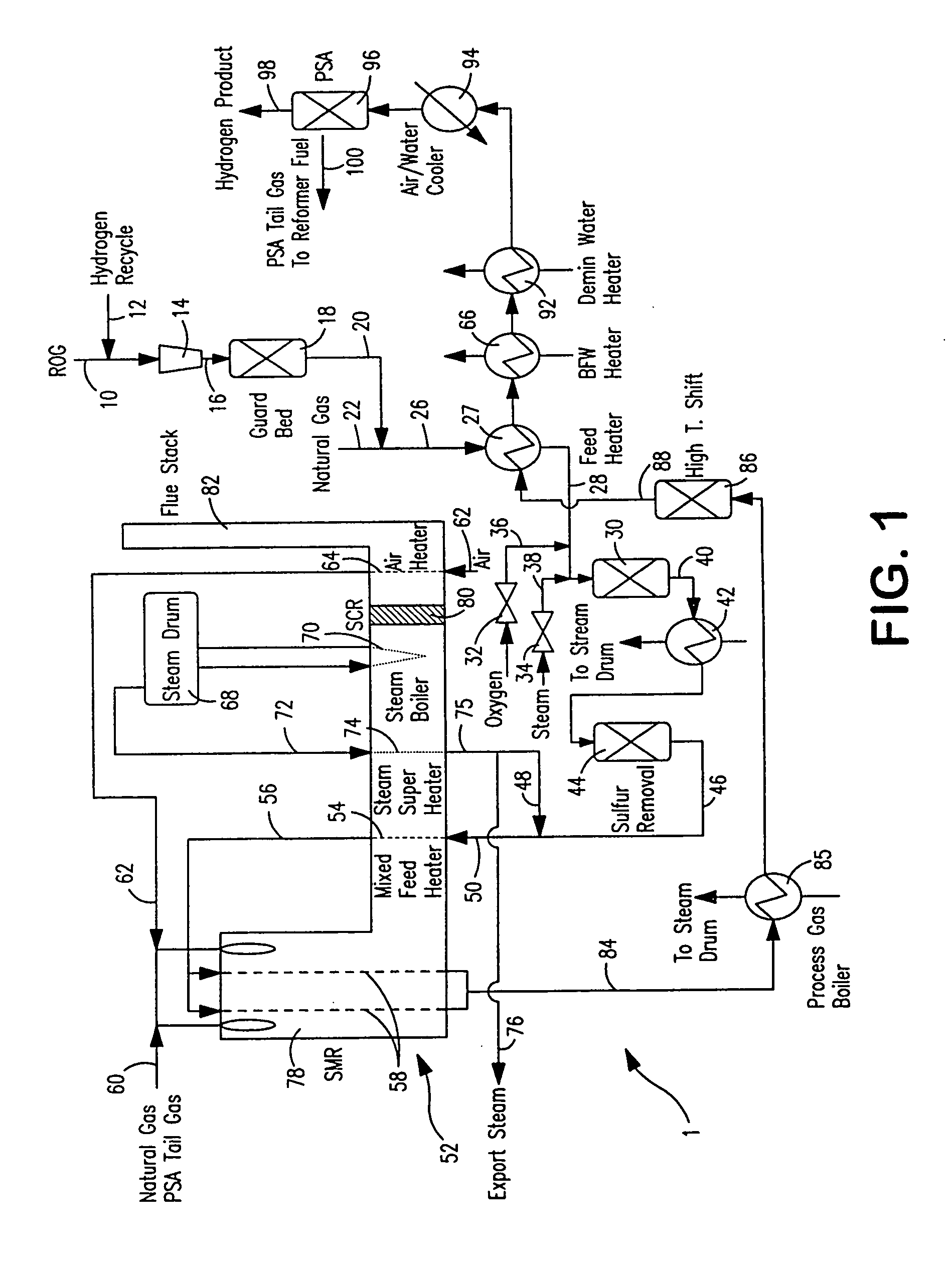
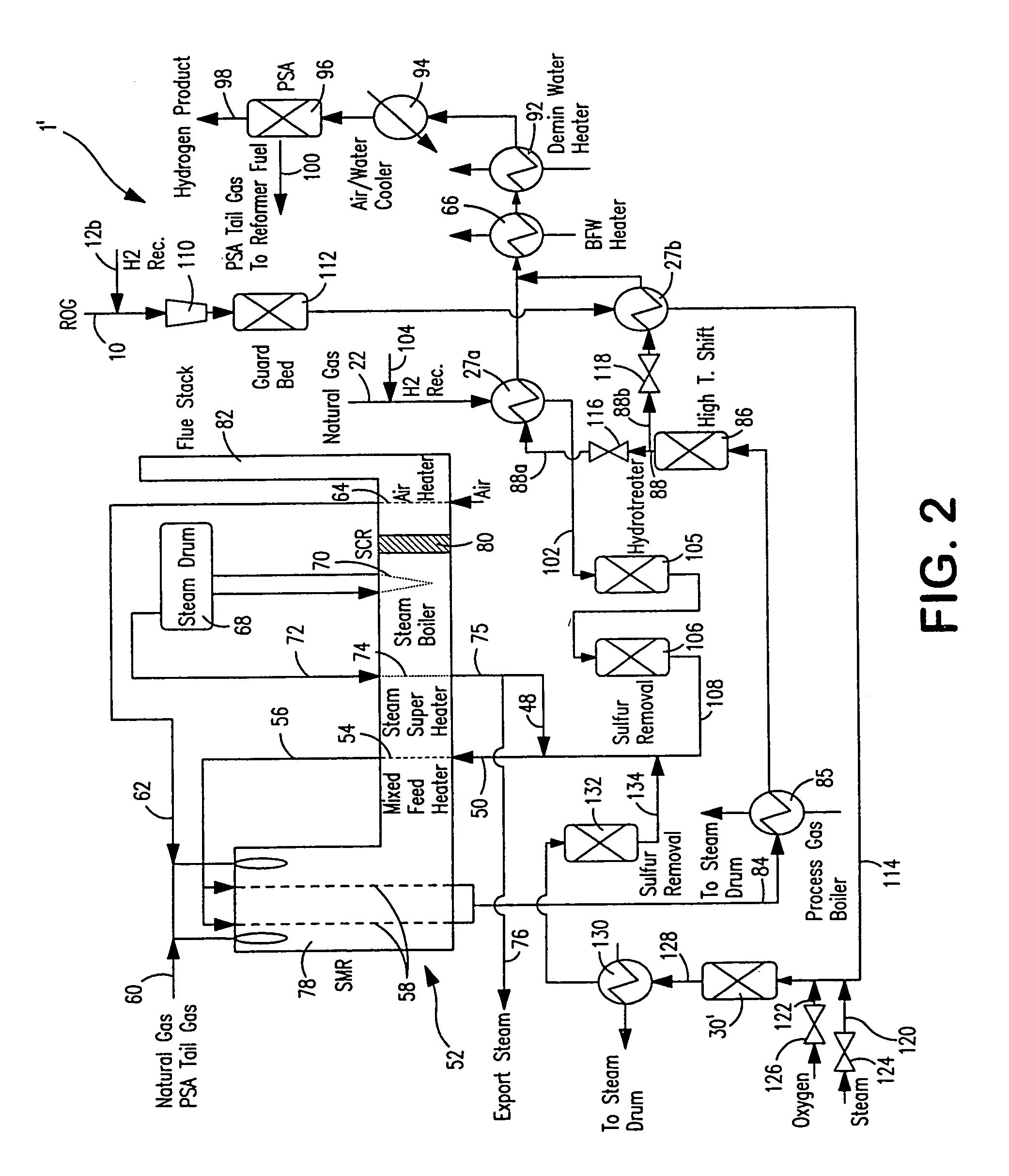
Steam methane reforming method
ActiveUS7037485B1Reduce fuel usageReduce firing rateHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesHydrogen separation using solid contactMethane reformerAlkane
A steam methane reforming method in which a feed stream is treated in a reactor containing a catalyst that is capable of promoting both hydrogenation and partial oxidation reactions. The reactor is either operated in a catalytic hydrogenation mode to convert olefins into saturated hydrocarbons and / or to chemically reduce sulfur species to hydrogen sulfide or a catalytic oxidative mode utilizing oxygen and steam to prereform the feed and thus, increase the hydrogen content of a synthesis gas produced by a steam methane reformer. The method is applicable to the treatment of feed streams containing at least 15% by volume of hydrocarbons with two or more carbon atoms and / or 3% by volume of olefins, such as a refinery off-gas. In such case, the catalytic oxidative mode is conducted with a steam to carbon ratio of less than 0.5, an oxygen to carbon ratio of less than 0.25 and a reaction temperature of between about 500° C. and about 860° C. to limit the feed to the steam methane reformer to volumetric dry concentrations of less than about 0.5% for the olefins and less than about 10% for alkanes with two or more carbon atoms.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
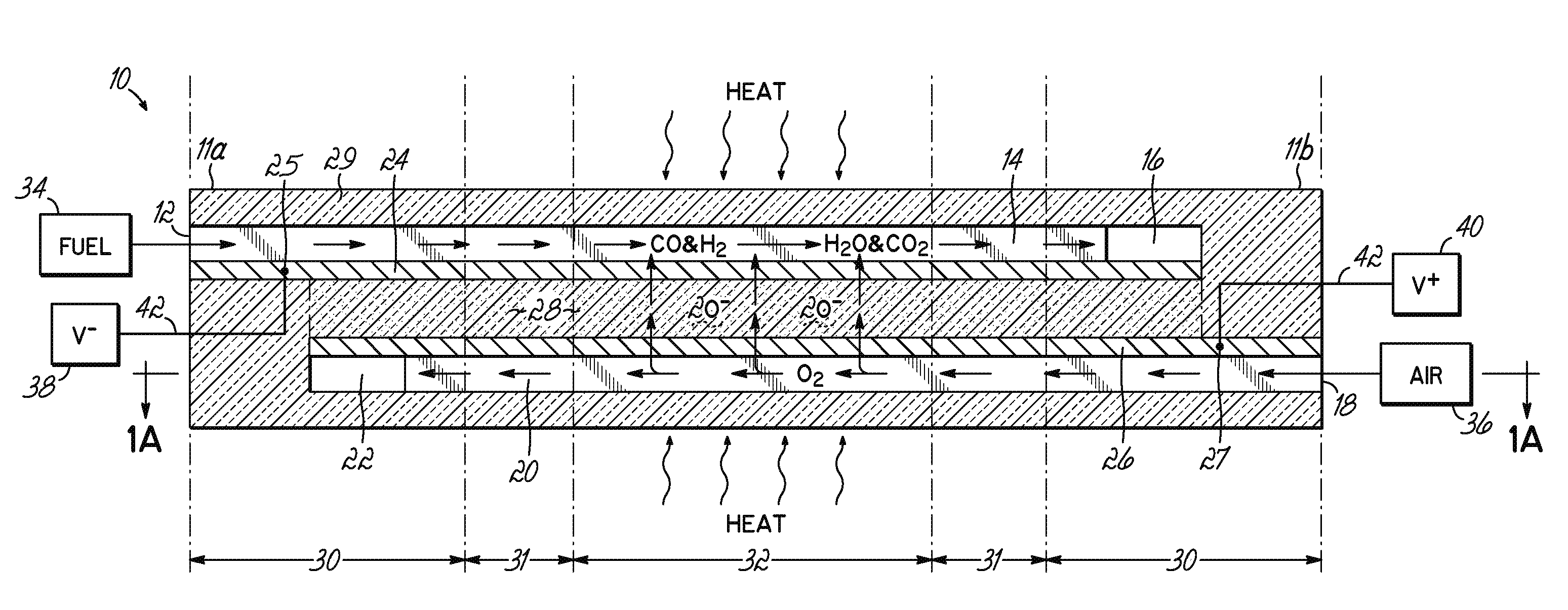
Integrated solid oxide fuel cell and reformer
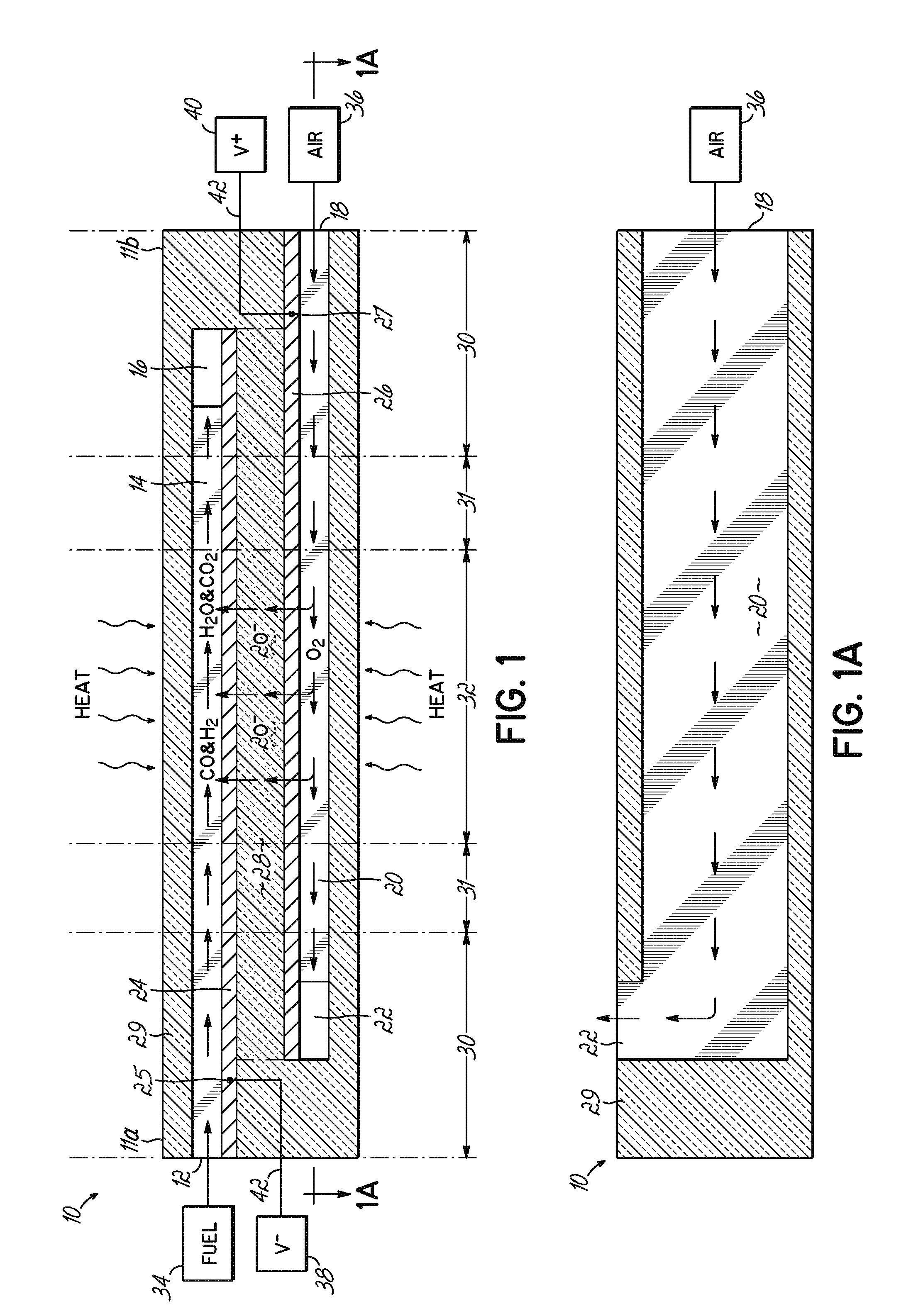
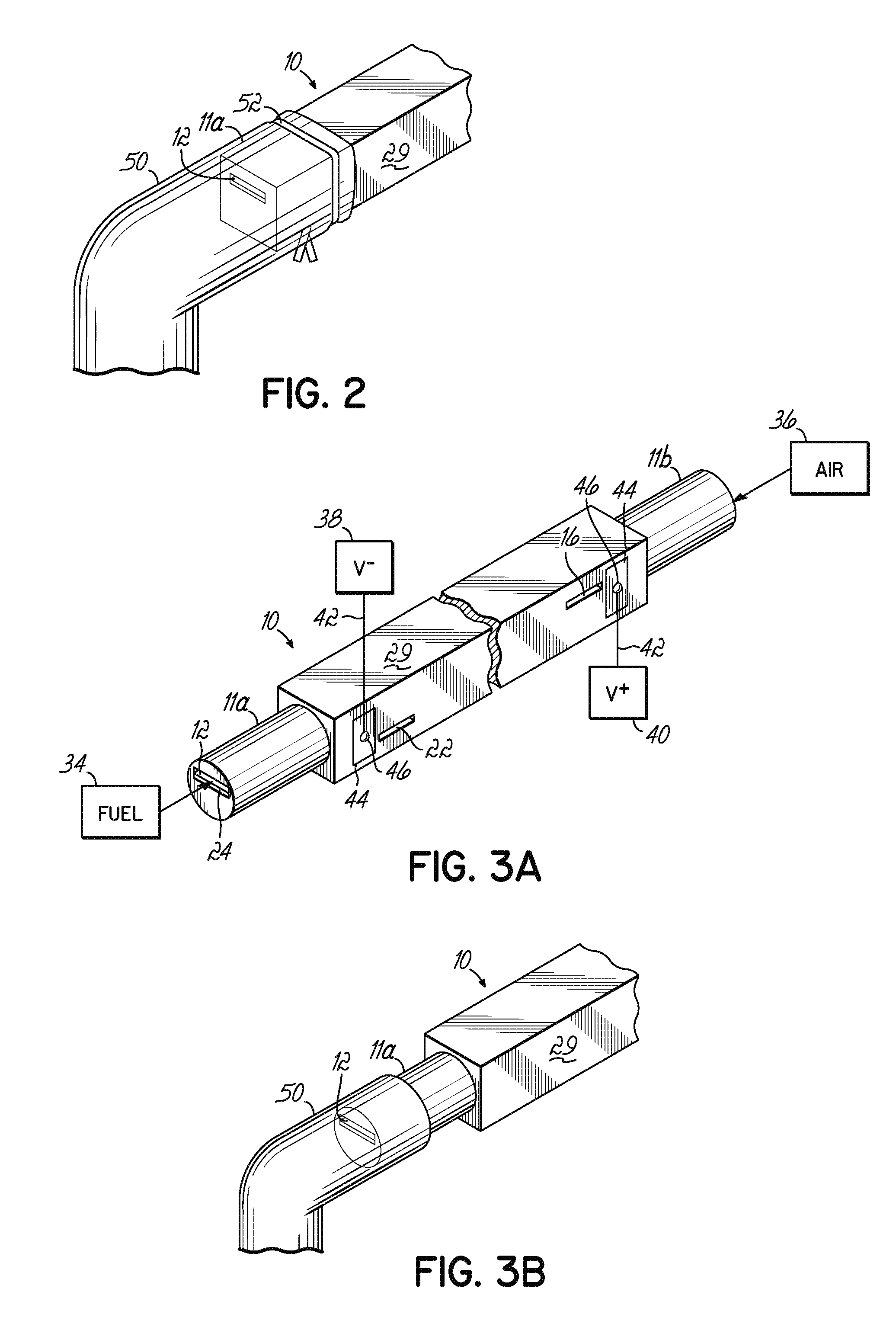
A disclosed apparatus for generating electrical power has, according to one embodiment of the invention, a plurality of tubular solid oxide fuel cells contained in a reaction chamber. The fuel cells are secured at one end thereof in a manifold block, the other ends thereof passing freely through apertures in a baffle plate to reside in a combustion chamber. Reaction gases are supplied to the insides of the tubular fuel cells from a plenum chamber below the manifold block and to the reaction chamber surrounding the outsides of the fuel cells through an annular inlet path, which may include a reformation catalyst. The gases inlet path to the plenum chamber, and the annular inlet path surround the reaction chamber, are both in heat conductive relation with the reaction chamber and the combustion chamber, and raise the gases to formation and reaction temperatures as appropriate.
Owner:ACUMENTRICS
High temperature solution polymerization process with phosphinimine cyclopentadienyl metal (GRP IV) complex
This invention is a solution process for the preparation of high molecular weight ethylene copolymers comprising contacting olefin monomers, with a catalyst system at a polymerization temperature at or above about 80 DEG C. with a catalyst system comprising an unbridged Group 4 metal compound having a monocyclopentadienyl ligand, a phosphinimine ligand and at least one uninegative, activation reactive ligand. The process can be practiced at a reaction temperature of at least 80 DEG C. to obtain high number average molecular weight polymer.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Process for making durable rutile titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatment
The present invention relates to a process for making durable titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatments on the titanium dioxide particle surface by reacting titanium tetrachloride vapor, an oxygen containing gas and aluminum chloride in a plug flow reactor to form a product stream containing titanium dioxide particles; and introducing silicon tetrachloride into the reactor at a point down stream of the point where the titanium tetrachloride and oxygen were contacted and where at least 97% of the titanium tetrachloride has been converted to titanium dioxide or where the reaction temperature is no greater than about 1200° C., and preferably not more than about 1100° C.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Method for synthesizing epoxypropane
ActiveCN101279959AHigh selectivityExtend your lifeOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionAlcoholReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method to synthesize propylene oxide, which is characterized in that alcohol with low content of carbon, propylene and oxydol(mol ratio 1-15:0.5-5:1) are put into a reactor which is fed with catalyzer; the propylene and the oxydol react and produce propylene oxide, and the condition for the reaction includes: temperature 30-90 DEG C, pressure 0.5-4.5MPa, ph value of the solution 5,0-8.0, and airspeed of the solution 0.1-7h-1; wherein the temperature and ph value of the solution in the whole process are adjusted according to the conversion rate of the oxydol, and once the conversion rate of the oxydol drops to 88.5%, the ph value and the temperature of the solution are increased. The method is simple in process, mild in condition, the conversion rate of the oxydol is high and the propylene oxide is of selectivity; meanwhile, the life of the catalyzer is prolonged to over 1200h through the adjustment of the ph value and the temperature of the solution.
Owner:HUNAN CHANGLING PETROCHEM SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD +2
Method for quick-speed preparing aerogel by hydro-thermal synthesis at low cost
InactiveCN101456569AReduce surface tensionIntegrity guaranteedSilicaAlkali metal silicatesReaction temperatureHydrothermal synthesis
The invention discloses a method for preparing aerogel materials by combining hydrothermal synthesis technology and sol-gel technology. The prepared aerogel comprises one or more of alumina aerogel, silica aerogel, zirconia aerogel and titania aerogel. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a reactant and a structure-directing agent according to certain proportion, and adding a pH value control agent to adjust the pH value; sealing hydrothermal reaction equipment, heating the mixture to be between 50 and 280 DEG C, making the mixture stand for 0 to 72 hours, raising the temperature to be between 60 and 300 DEG C, and continuously reacting for 0.1 to 72 hours; and cooling gel, taking out the gel, drying the gel and obtaining the aerogel. Compared with the prior art, the method has low reaction temperature and pressure, small equipment investment and simple and controllable technology, reduces potential safety hazards, greatly improves the preparation speed of the aerogel, saves the production cost, and is favorable to realize commercial mass production.
Owner:纳诺科技有限公司 +1
Method for using low-temperature plasma to prepare supported metal sulfide catalyst
InactiveCN103495427AGood dispersionAvoid exposureMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsDispersityReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for using low-temperature plasma to prepare a supported metal sulfide catalyst and belongs to the technical field of material science. The method is characterized by including: allowing ionization of hydrogen sulfide gas or gas containing hydrogen sulfide through gas discharge to form the low-temperature plasma distributed evenly, and using the low-temperature plasma to interact with supported metal salt precursor to generate metal sulfide. Due to the fact that the catalyst is avoided from being exposed in excessively high temperature, the prepared catalyst is free of thermal agglomeration, so that the catalyst is smaller in particle size and higher in dispersity. The method is suitable for preparation of various sulfide catalysts, metal sulfide can be supported on different materials to prepare various supported catalysts. The method has the advantages of low reaction temperature, low energy consumption, short preparation time and the like. In addition, processing objects are common metal salt, wide involve range is achieved, and the prepared catalyst is applicable to various common heterogeneous reactions.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis gas process comprising partial oxidation using controlled and optimized temperature profile
ActiveUS7261751B2Low selectivityRisk of explosion can be minimizedHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisPartial oxidationFixed bed
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
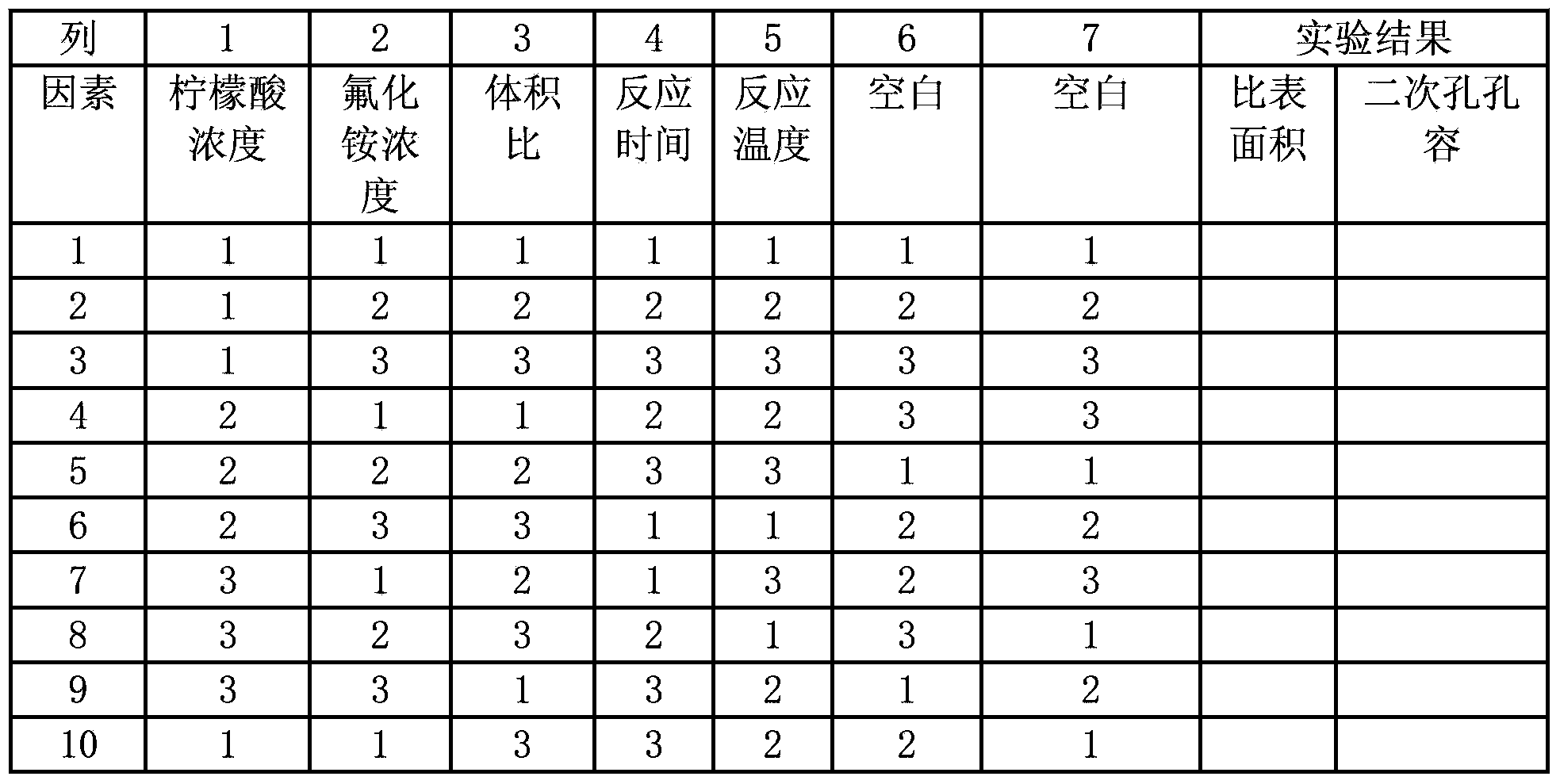
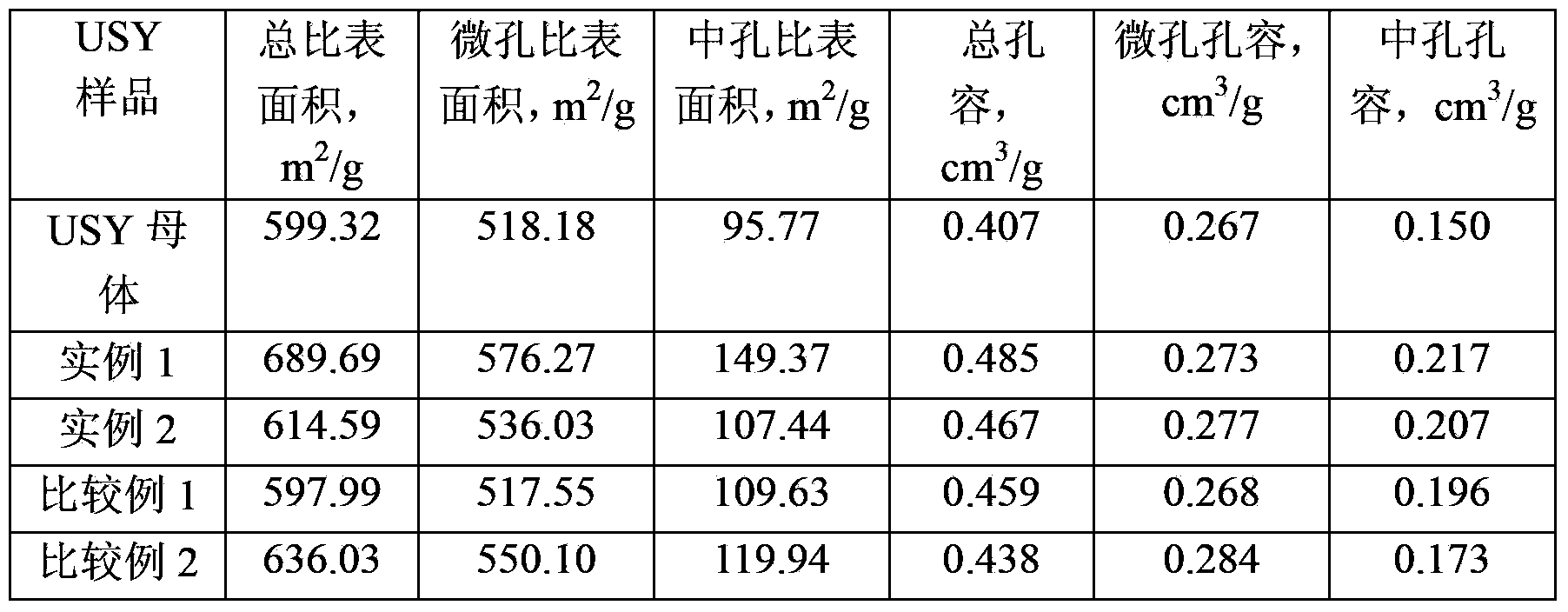
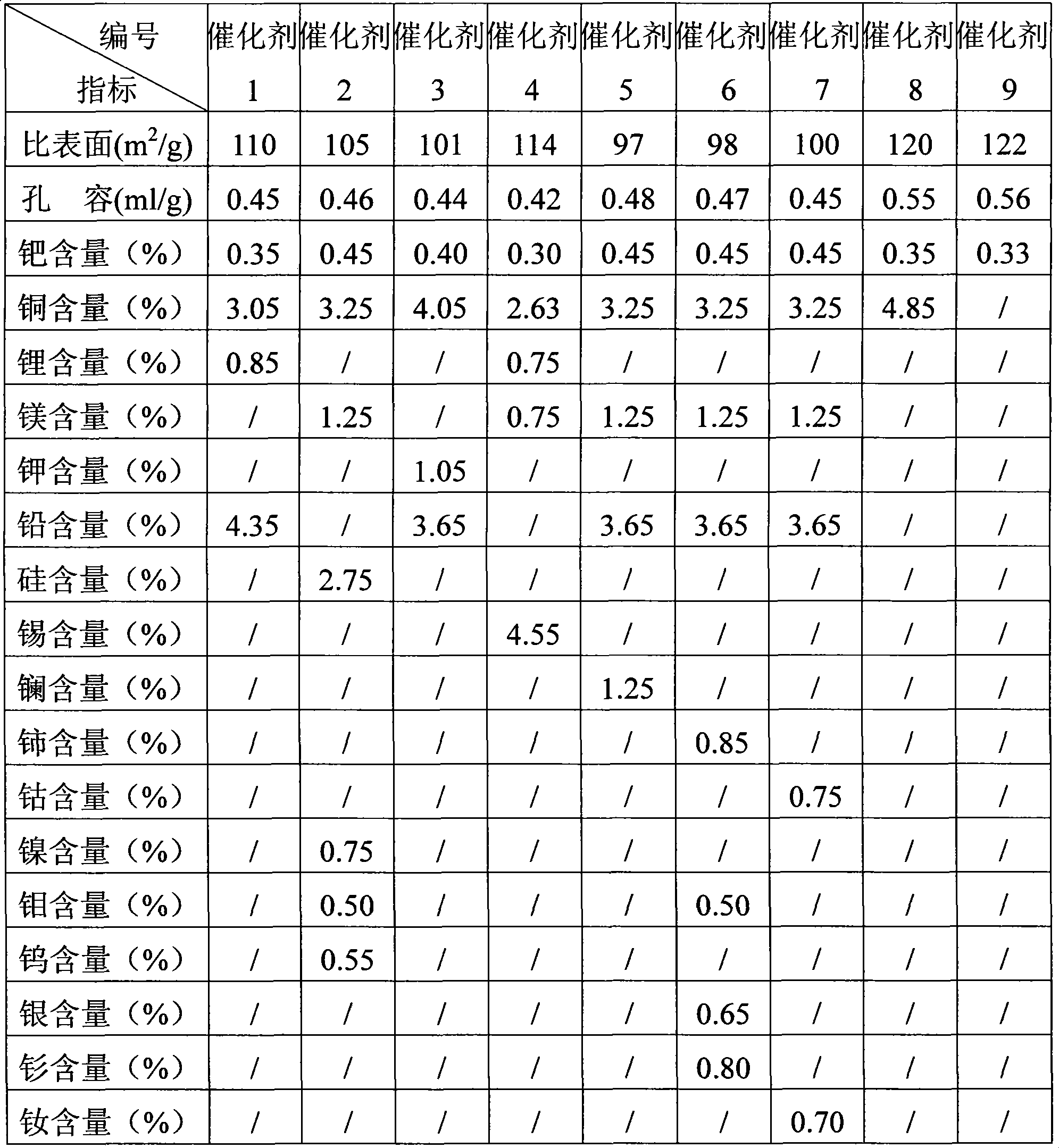
Method for modifying mesoporous-rich USY (Ultra-Stable Y) molecular sieve in combined manner
InactiveCN104229823ASmall cell constantIncreased secondary pore contentFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteInorganic saltsMolecular sieve
The invention relates to a method for modifying a USY (Ultra-Stable Y) molecular sieve. The method is characterized in that organic acid and an inorganic salt dealuminizing reagent are simultaneously added in a modifying process for organic acid-inorganic salt combined modification, and optimum process conditions, namely optimum concentration, volume ratio, reaction time, reaction temperature and the like, of an organic acid and an inorganic salt solution are determined by virtue of an orthogonal test. Compared with an industrial USY molecular sieve, the USY molecular sieve obtained by adopting the method disclosed by the invention is obviously increased in secondary pore content, can be kept at higher crystallinity and is enhanced in silica-alumina ratio, reduced in lattice constant and suitable for high-medium oil type hydrocracking catalyst carriers.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Acetylene hydrocarbon selective hydrogenation method
ActiveCN101434508AGood hydrogenation effectImprove hydrogenation activityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationHydrocarbon purification/separationButadiene DioxideUnsaturated hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a selective hydrogenation method of high unsaturated hydrocarbons in C4 fractions, which is characterized in that salvage stores which are rich in acetylene hydrocarbon and prepared by extracting butadiene are used as the material, and a fixed bed reactor is adopted to obtain 1, 3-budiene by selective hydrogenation under the existence of a catalyst. The adopted process conditions are as follows: the reaction temperature is between 30 DEG C and 90 DEG C, the reaction pressure is between 1.0 MPa and 4.0 MPa and the liquid space velocity is 7 to 20h<-1>. The catalyst is preferably a palladium system catalyst with alumina as a carrier, the specific surface is 50 to 150m<2> / g and the specific pore volume is 0.25 to 1.0ml / g. The method has remarkable good effects on reducing waste of resources and improving economic benefits by effectively utilizing the salvage stores rich in acetylene hydrocarbon and prepared by extracting butadiene.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Catalyzer used for low carbon alkane catalytic dehydrogenation and method of manufacturing propylene by paraffin hydrocarbons catalytic dehydrogenation with the same as catalyzer
InactiveCN101108362AReactiveMitigation of heightened demandMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkaneReaction temperature
The invention relates to a catalyst used for catalyzing and dehydrogenation of low-carbon alkane and the method of producing propylene by alkane catalyzing and dehydrogenation with the catalyst. The former catalyst used for catalyzing and dehydrogenation of low-carbon alkane, each molecule of the hydrocarbon has about 2 to 8 carbon atom, which is characterized in that: the catalyst makes a molecular sieve the carrier, the Pt family metal is loaded on the carrier as the active component, makes the IVA family metal element and alkalinity metal element as additional agent and high temperature standing inorganic oxide as connection agent; when the catalyst is used in producing propylene by alkane catalyzing and dehydrogenation, the reaction temperature is 500 to 700 DEG C., the pressure is 0 to 0.2Mpa, the quality air speed is 2 to 5h to 1, the regenerating temperature of the catalyst is 500 to 700 DEG C., the air speed is 100 to 1000h to 1, the pressure is 0 to 1.0MPa. With adopting the invention, the reaction of producing propylene by alkane catalyzing and dehydrogenation is good, the average transforming rate is 30 per cent, the selectivity above 95 per cent can keep for 50 days.
Owner:SINOPEC JINLING PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
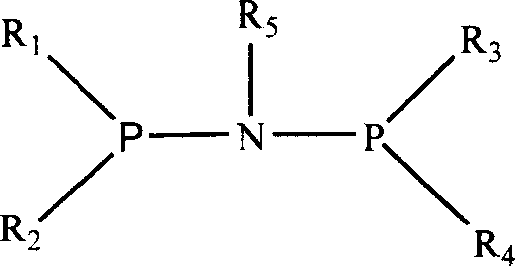
Polymerization catalyst having a phosphinimine ligand
InactiveUS6342463B1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
This invention is a solution process for the preparation of high molecular weight ethylene copolymers comprising contacting olefin monomers, with a catalyst system at a polymerization temperature at or above about 80° C. with a catalyst system comprising an unbridged Group 4 metal compound having a monocyclopentadienyl ligand, a phosphinimine ligand and at least one uninegative, activation reactive ligand. The process can be practiced at a reaction temperature of at least 80° C. to obtain high number average molecular weight polymer.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
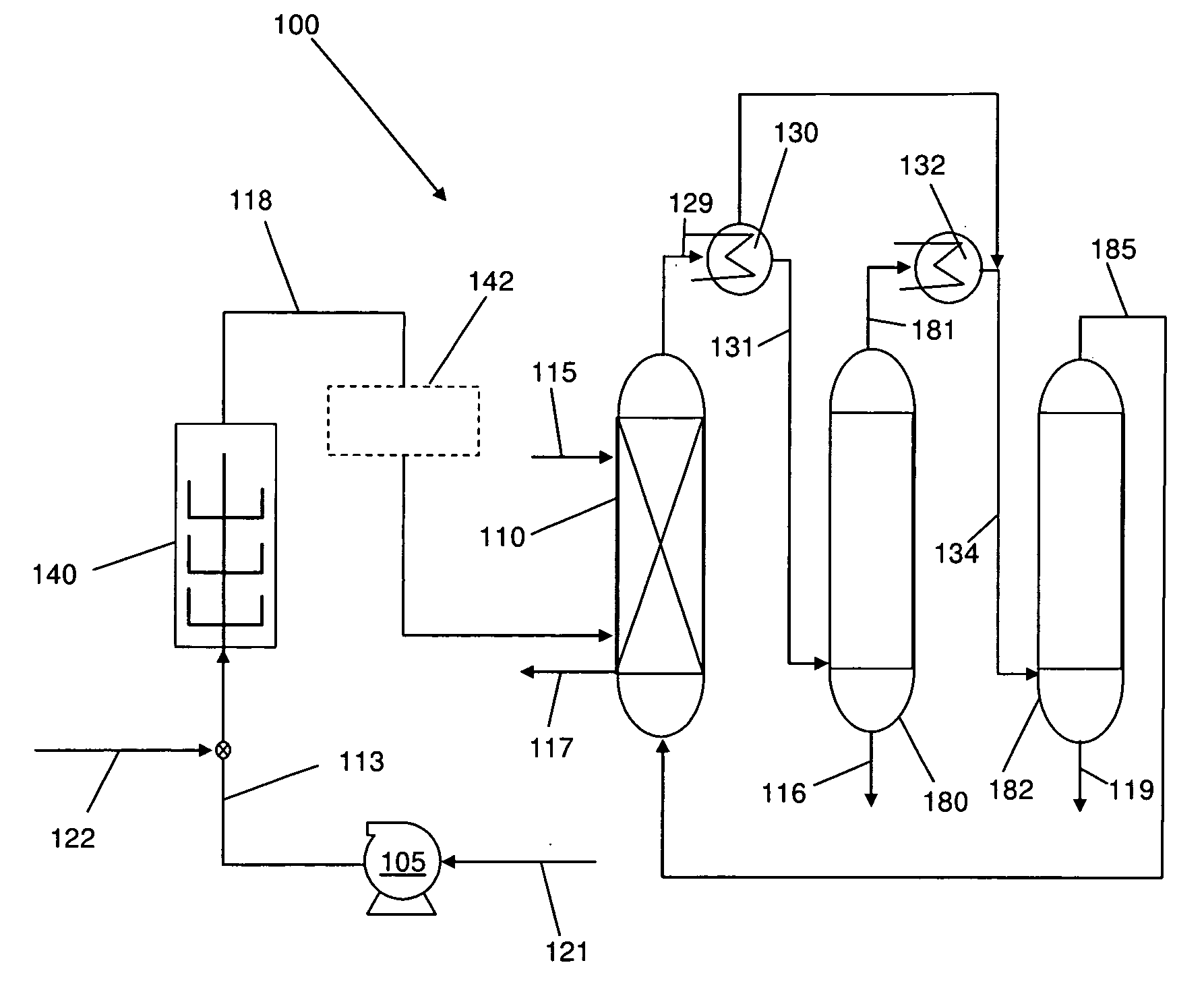
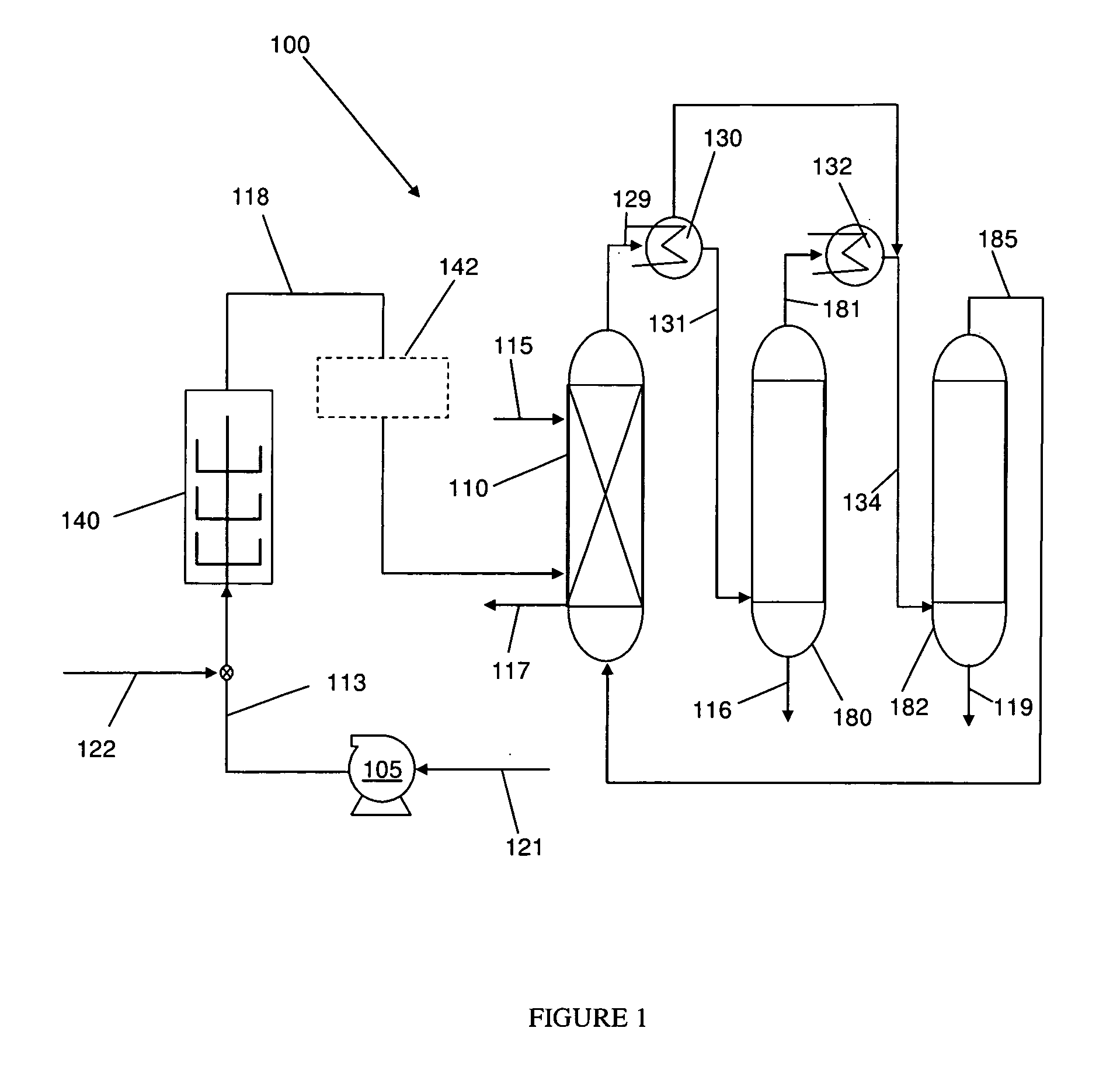
Method for preparing ethanol by hydrogenation of acetic ester
ActiveCN102093162AHigh activityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationReaction temperatureBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Device and System
The invention provides solid oxide fuel cell devices and a fuel cell system incorporating a plurality of the fuel devices, each device including an elongate substrate having a reaction zone for heating to an operating reaction temperature, and at least one cold zone that remains at a low temperature below the operating reaction temperature when the reaction zone is heated. An electrolyte is disposed between anodes and cathodes in the reaction zone, and the anode and cathode each have an electrical pathway extending to an exterior surface in a cold zone for electrical connection at low temperature. In one embodiment, the device is a multi-layer anode-cathode structure, and in another embodiment, the device is an electrode-supported device. The system further includes the devices positioned with their reaction zones in a hot zone chamber and their cold zones extending outside the hot zone chamber. A heat source is coupled to the hot zone chamber to heat the reaction zones to the operating reaction temperature, and fuel and air supplies are coupled to the substrates in the cold zones.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Method for synthesizing polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether. The invention mainly solves the following problems of the prior art that: in the process of synthesizing polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether, catalyst separation is difficult, the material conversion rate is low, and product selectivity is poor. The method adopts methanol and trioxymethylene as materials, the reactiontemperature is 70 DEG C to 200 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 0.5MPa to 6MPa, the materials react with super solid acidic catalyst by way of contact, so that the polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether CH3O(CH2O)nCH3 is produced, wherein the used catalyst is selected from solid superacids. By weight part, the polyoxymethylene dimethyl ethe comprises the following components: (a) 20 to 70 parts of acid selected from sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid or peroxosulfuric acid or at least one of salt thereof; (b) 30 to 80 parts of carrier selected from at least one of ZrO2, TiO2, SiO2, Fe2O3, SnO2, WO3 andAl203. The method effectively solves the problems, and can be used in the industrial production of polyoxymethylene dimethyl ether.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process and systems for the epoxidation of an olefin
A process for the epoxidation of an olefin, which process comprises reacting a feed comprising the olefin, oxygen and a reaction modifier in the presence of a highly selective silver-based catalyst at a reaction temperature T, and with the reaction modifier being present in a relative quantity Q which is the ratio of an effective molar quantity of active species of the reaction modifier present in the feed to an effective molar quantity of hydrocarbons present in the feed, and which process comprises the steps of:operating at a first operating phase wherein the value of T is T1 and the value of Q is Q1, andsubsequently operating at a second operating phase at a reaction temperature which is different from the reaction temperature employed in the first operating phase, such that the value of T is T2 and the value of Q is substantially Q2, whereby Q2 is determined by calculation and Q2 is defined by the formulaQ2=Q1+B(T2−T1),wherein B denotes a constant factor which is greater than 0; a reaction system suitable for performing the process for the epoxidation of an olefin; a computer program product which comprises a computer readable program recorded on a computer readable medium, suitable for instructing a data processing system of a computer system to execute calculations for the process for the epoxidation of an olefin; and a computer system which comprises the computer program product and a data processing system.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com