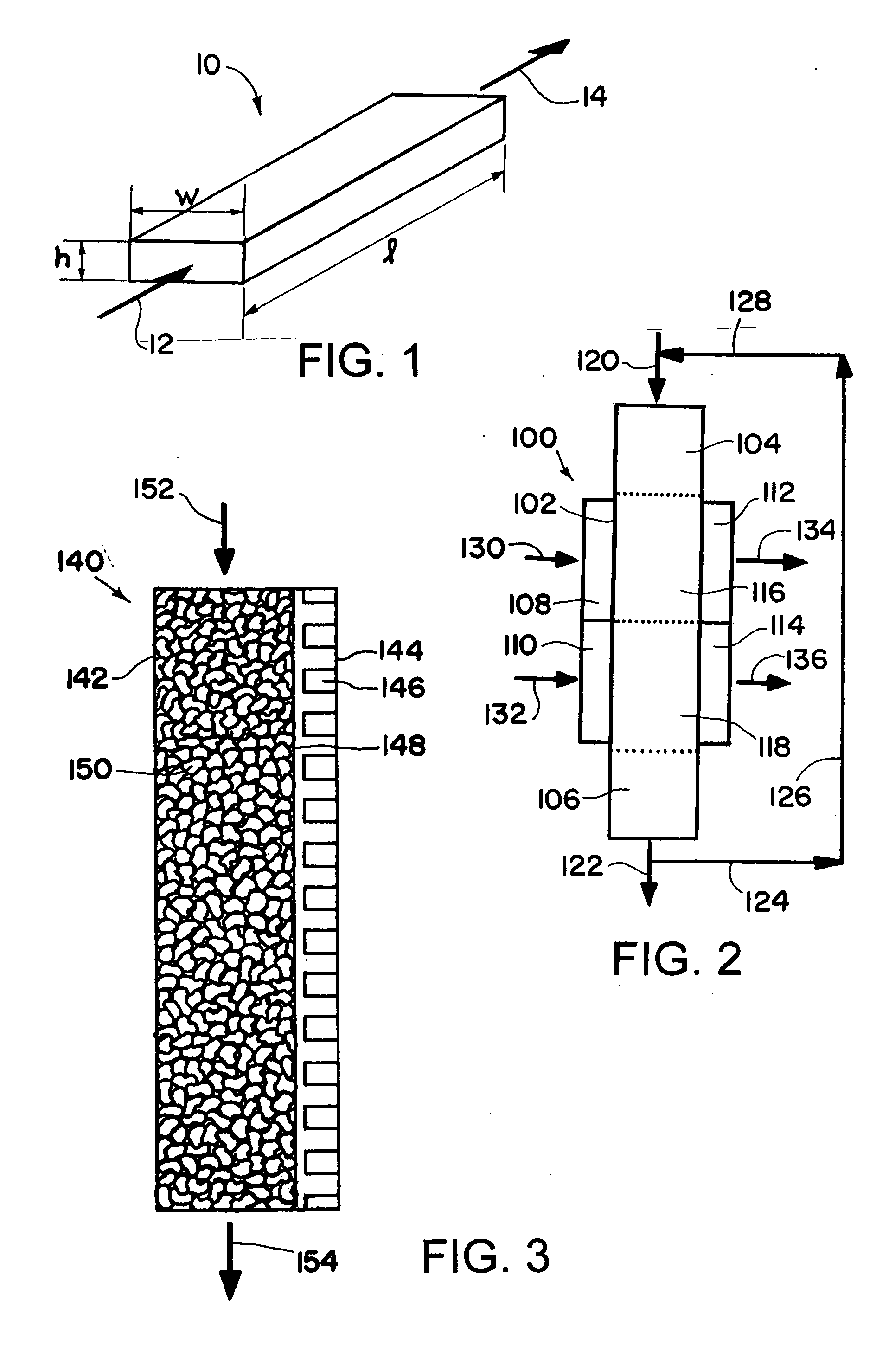
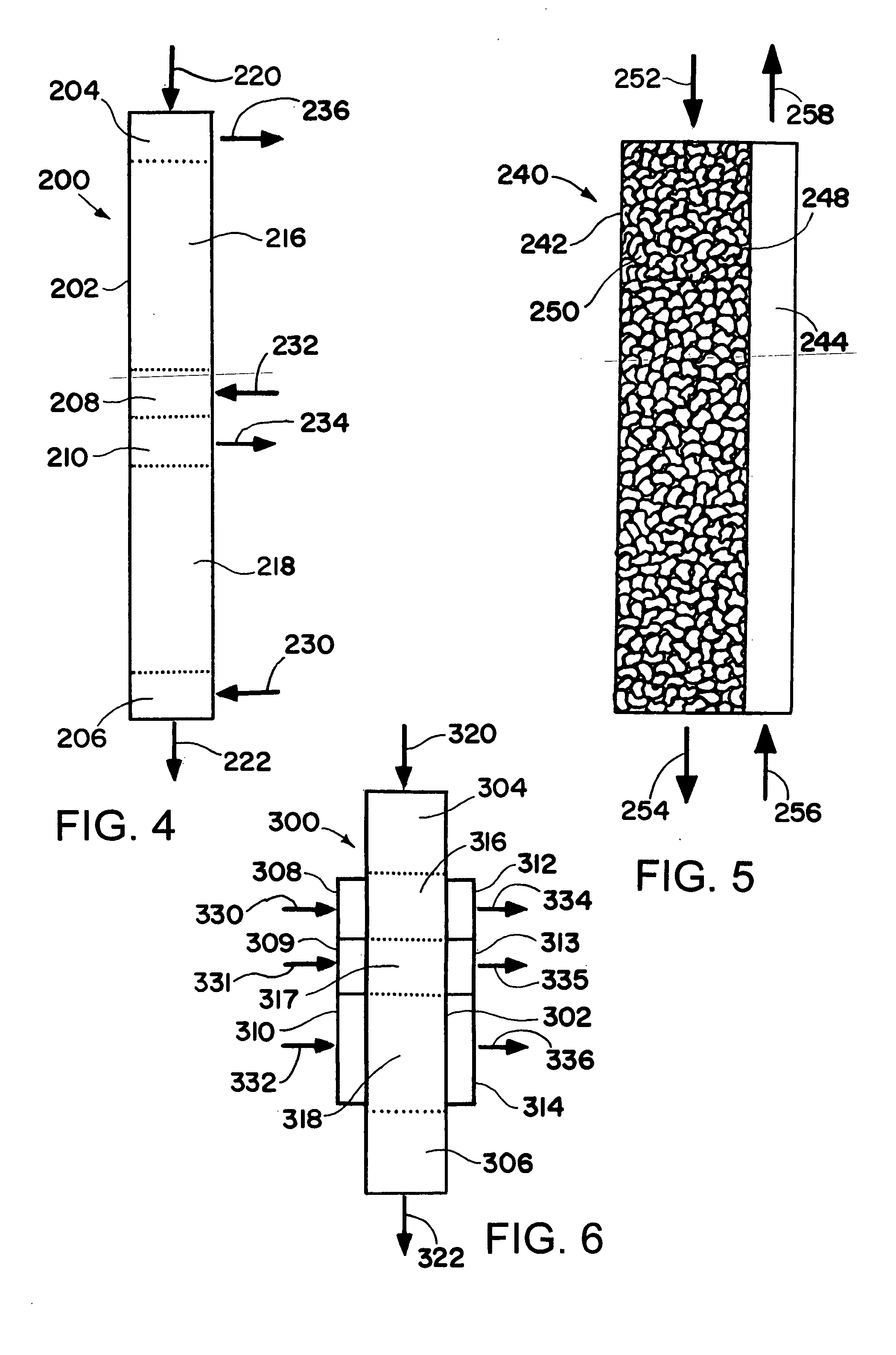
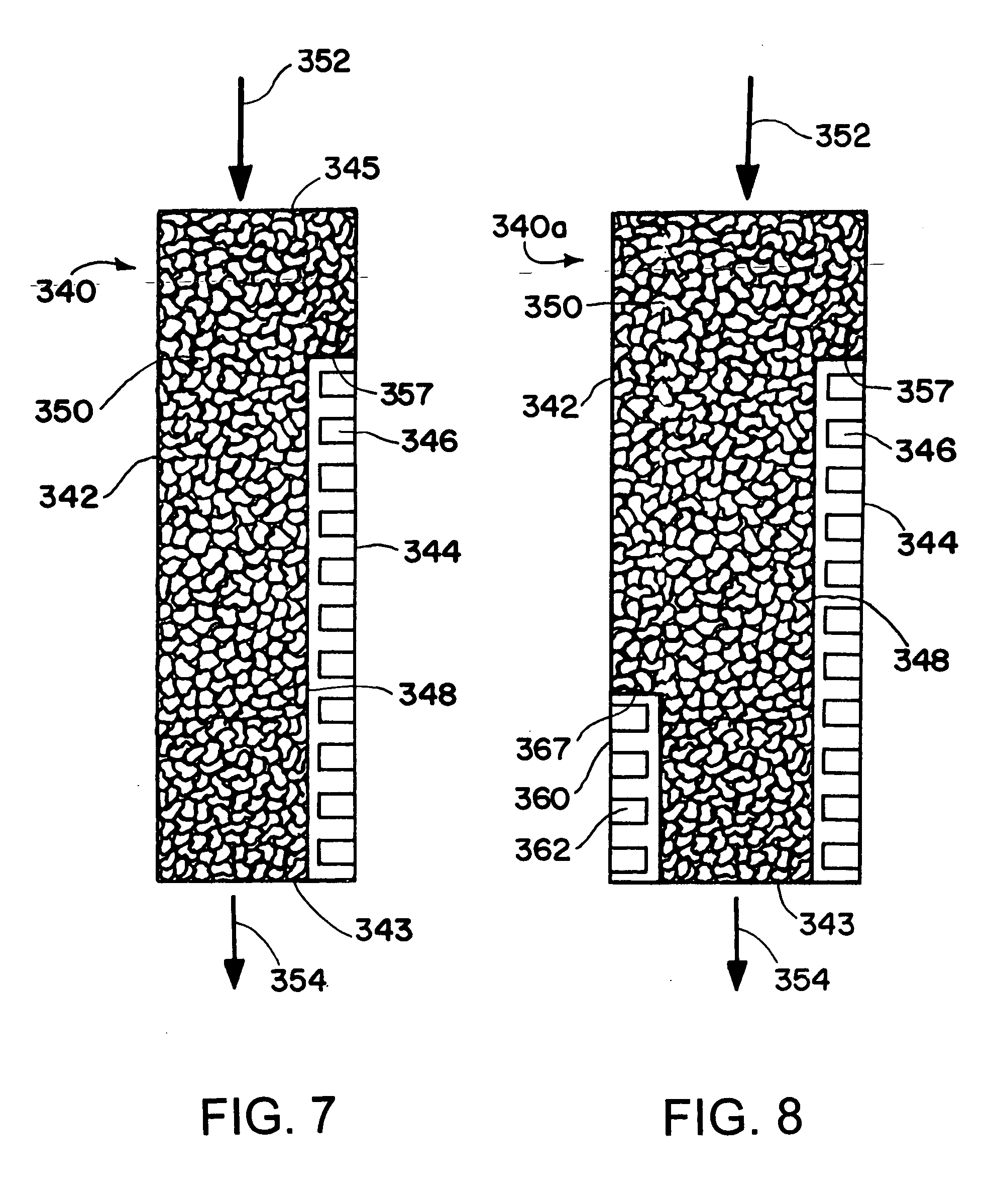
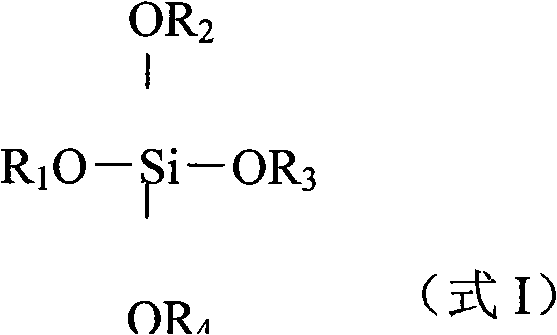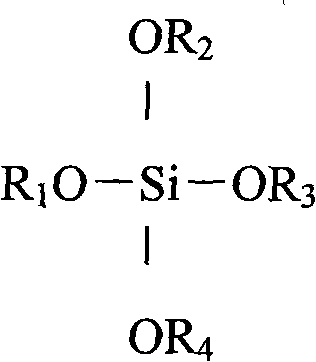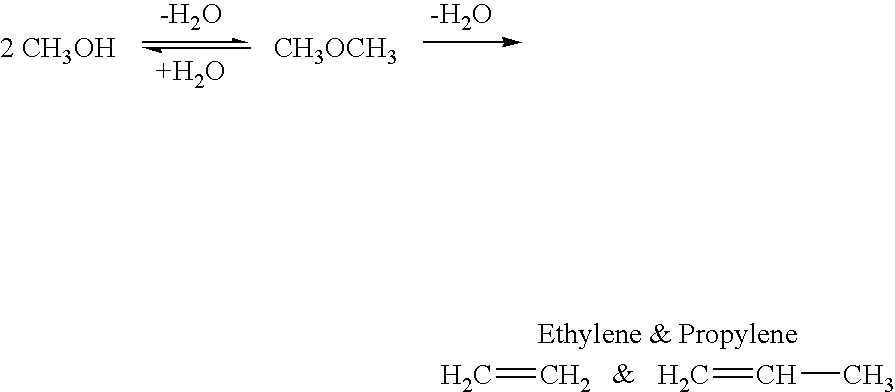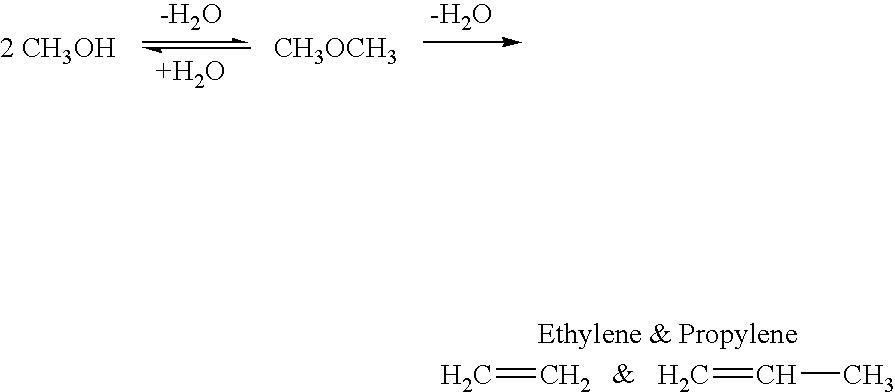Patents
Literature
3994 results about "Dimethyl ether" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dimethyl ether (DME, also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH₃OCH₃, simplified to C₂H₆O. The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor to other organic compounds and an aerosol propellant that is currently being demonstrated for use in a variety of fuel applications. It is an isomer of ethanol.
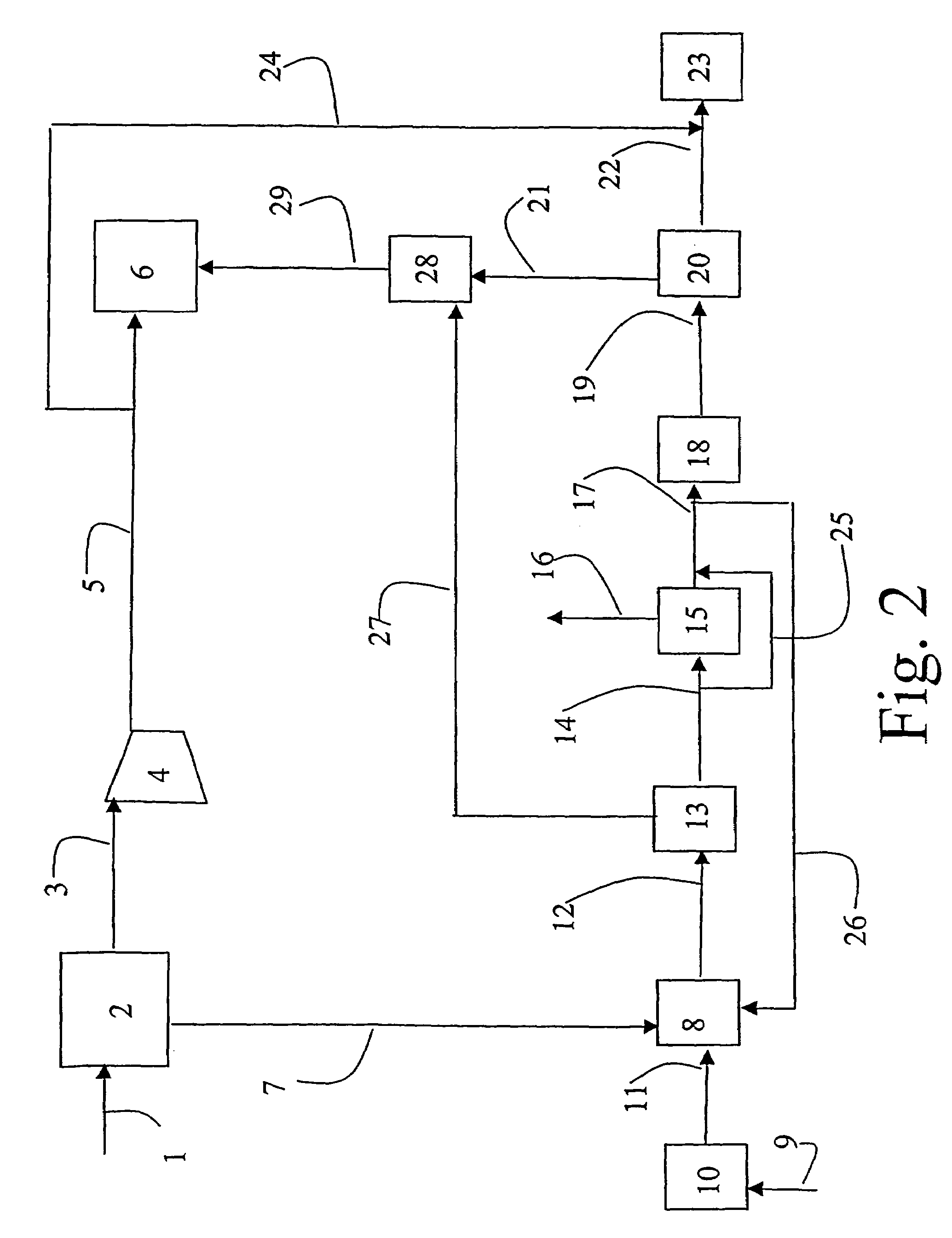
Low water methanol carbonylation process for high acetic acid production and for water balance control
ActiveUS7005541B2High acetic acid production rateIncrease chanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionWater methanolAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a process for the production of acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol, and reactive derivatives thereof, in a reaction mixture using a rhodium-based catalyst in low water conditions. The process is used to achieve reaction rates of at least 15 g mol / l / hr. The high rate reactions proceed at water concentrations of less than 2.0 wt. %. Under certain conditions, the water concentration in the reaction mixture of the process is maintained at a desired concentration by at least one process step including adding a compound such as methyl acetate, dimethyl ether, acetic anhydride, or mixtures of these compounds to the reaction system. The process step of adding the components to the reaction mixture may be combined with other process steps for controlling water concentrations in reaction mixtures for the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7208624B2Easy to separateFacilitate phase separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateFormate Esters
An improved process is disclosed for producing acetic acid, including the following steps: reacting a carbonylatable reactant such as methanol, methyl acetate, methyl formate or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in a reaction medium containing water, methyl iodide, and a catalyst to produce a reaction product that contains acetic acid; separating the reaction product to provide a volatile phase containing acetic acid, water, and methyl iodide and a less volatile phase; distilling the volatile phase to produce a purified acetic acid product and a first overhead containing water, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide; phase separating the first overhead to provide a first liquid phase containing water and a second liquid phase containing methyl iodide; and adding dimethyl ether to the process in an amount effective to enhance separation of the first overhead to form the first and second liquid phases.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
System and process for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by converting methanol or dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101823929AHigh yieldHigh selectivityHydrogen separation using liquid contactHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAromatizationAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a system and a process for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by converting methanol or dimethyl ether and belongs to the technical field of aromatic hydrocarbon production. The methanol or the dimethyl ether serving as a raw material firstly reacts in an aromatization reactor; a reaction product is separated; H2, methane, mixed C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and partial C9s + hydrocarbons serving as products are output from the system; and C2+ non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbons except the mixed C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and the partial C9s + hydrocarbons are take as a circular material flow and return to corresponding reactors for further aromatization reaction. By separating and recycling the product obtained in the process of aromizing the methanol or the dimethyl ether, the system and the process improve the yield and selectivity of the aromatic hydrocarbon; and moreover, the process is flexible, and target products can be changed according to market demands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing methyl acetate by carbonylating dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101613274AImprove stabilityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMolecular sieveMethyl acetate
The invention discloses a catalyst modification method for preparing methyl acetate by carbonylating dimethyl ether. The method is applied to the reaction process in which the dimethyl ether reacts with the carbon monoxide to high selectively form methyl acetate in the presence of an acid molecular sieve catalyst, particularly a mordenite molecular sieve. Pyridine organic amines are utilized to modify the mordenite molecular sieve and modify a channel structure and the acidity of the molecular sieve, thereby effectively inhibiting carbon deposition and greatly improving the stability of catalysts. The use of the catalysts by the method can catalyze the carbonylation of dimethyl ether to obtain methyl acetate under mild conditions. The conversion rate of dimethyl ether is between 10 and 60percent, the selectivity of the methyl acetate is over 99 percent, and the activity of the catalysts is kept steady after the reaction is performed for 48 hours.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
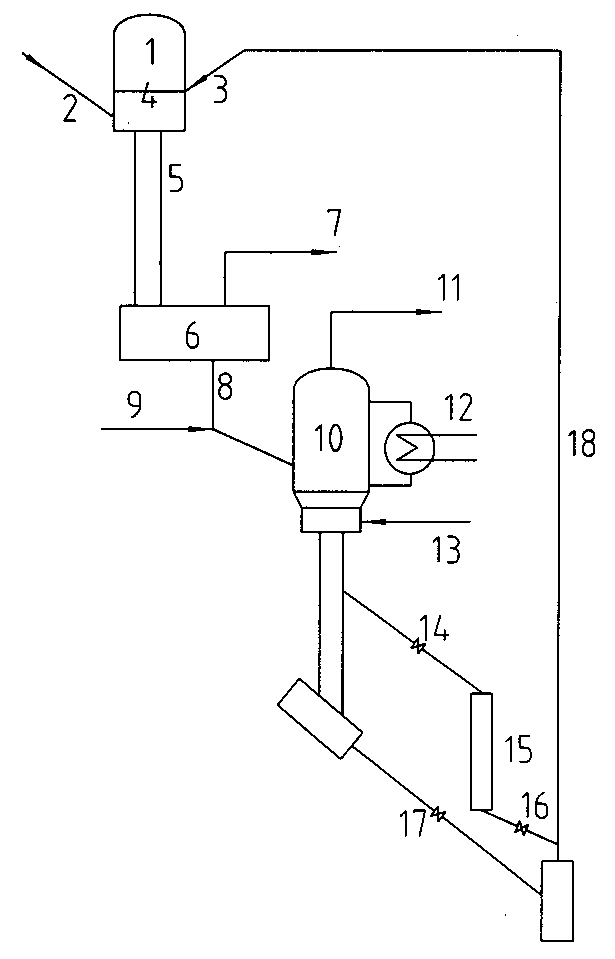
Method and plant or increasing oil recovery by gas injection
A method and a plant for simultaneous production of a gas for injection into an oil field and production of methanol, dimethyl ether and / or other oxygenated hydrocarbons or production of higher hydrocarbons from natural gas is disclosed. An air separation unit (ATR) for production of pure nitrogen for injection and pure oxygen for production of synthesis gas (“syngas”) by authermal reformation of a natural gas is an essential part of the method and plant.
Owner:DEN NORSKE STATS OLJESELSKAP AS
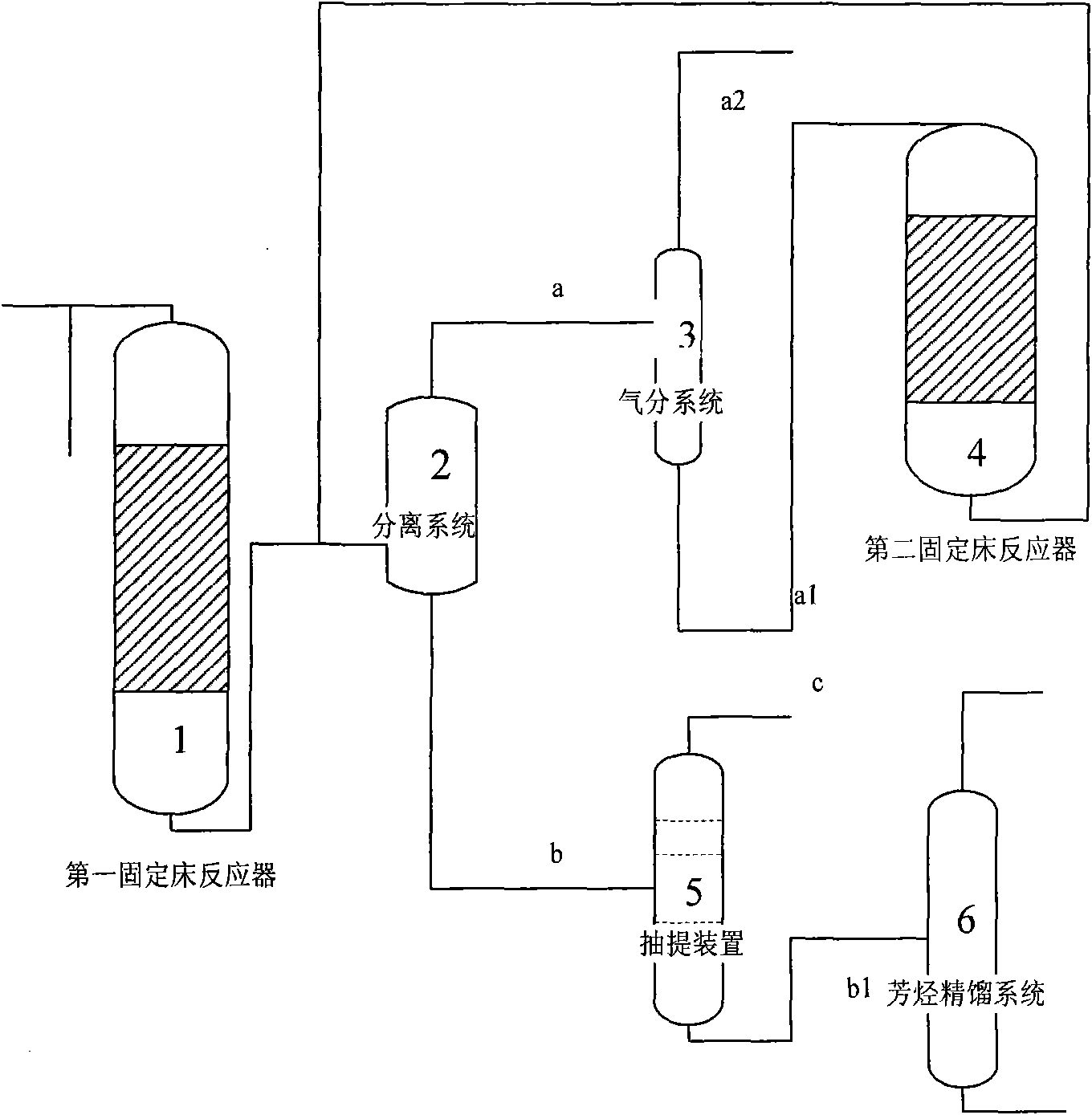
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and propylene simultaneously employing methanol/dimethyl ether
InactiveCN101607858AHigh selectivityIncrease added valueMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolecular sieveFixed bed
The invention discloses a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and propylene simultaneously employing methanol / dimethyl ether, comprising the following steps: 1) placing raw materials containing methanol or / and dimethyl ether, metals and molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified through silanizing in a first fixed bed reactor to perform catalytic reaction; 2) separating the products obtained in step 1) to obtain propylene, then placing propylene in a second fixed bed reactor with molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified by using metals to react, then performing aromatization on the obtained product in step 1) and obtaining aromatic hydrocarbons; then separating to obtain toluene and sending toluene back to the outlet of the first fixed bed reactor as a raw material. In the method, methanol is converted and prepared to aromatic hydrocarbons while propylene is produced at the same time and the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is high. In the products prepared by the method, the content of propylene can reach above 20%, the content of aromatic hydrocarbons can reach above 58wt% and the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is more than 35wt%.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Catalyst for manufacturing hydrogen or synthesis gas and manufacturing method of hydrogen or synthesis gas
InactiveUS6361757B1Produce hydrogenEfficient productionIron compoundsCobalt compoundsIridiumForming gas
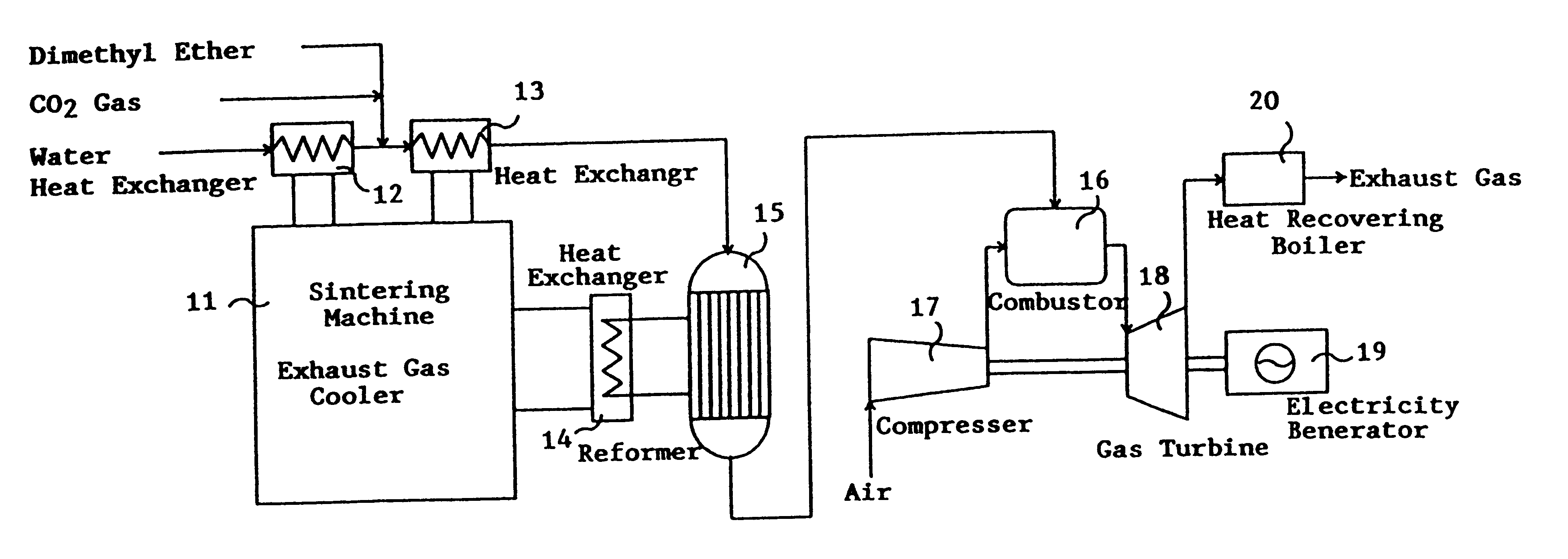
This invention provides a catalyst for producing hydrogen gas from a mixed gas comprising dimethyl ether and water vapor or carbon dioxide gas, which comprises copper, iron, cobalt, palladium, iridium, platinum, rhodium, or nickel as an active component, and a method of producing synthesis gas or hydrogen gas in a high yield at a low temperature. By using the catalyst, a fuel cell, electricity generation, reduction of iron ore and the like can be carried out.
Owner:NIPPON KOKAN KK
Olefin production via oxygenate conversion
InactiveUS20070155999A1Improved arrangementImproved processing schemeOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationSyngasOxygen compound
Improved processing for the production of light olefins via oxygenate conversion processing is provided. Synthesis gas conversion such as to produce an effluent including at least methanol can be integrated with oxygenate conversion processing such as to produce an oxygenate conversion reactor effluent including at least light olefins and dimethyl ether. At least a portion of the oxygenate conversion reactor effluent can be contacted with such produced methanol to effect recovery of dimethyl ether from the oxygenate conversion reactor effluent.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for producing light olefins
InactiveUS6046372AMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAlkyl transferCrystalline materials
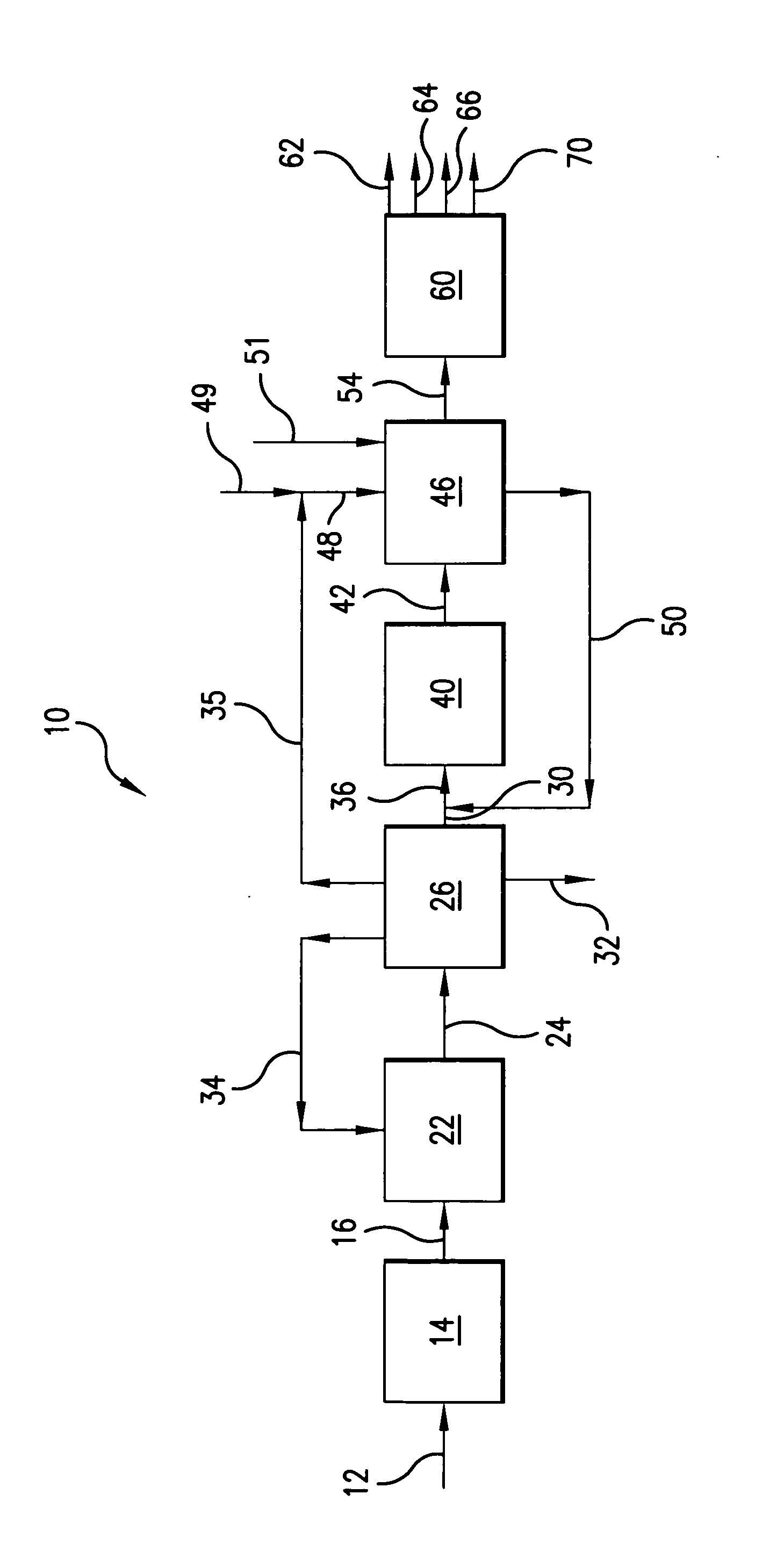
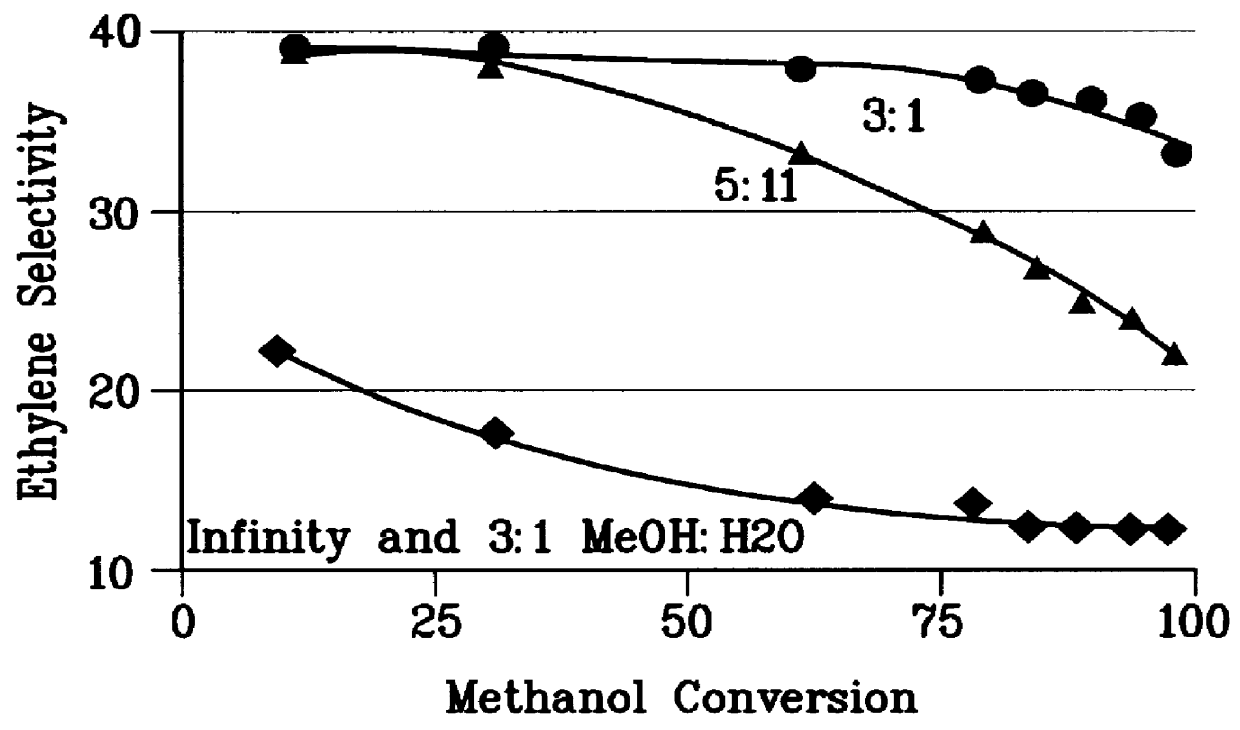
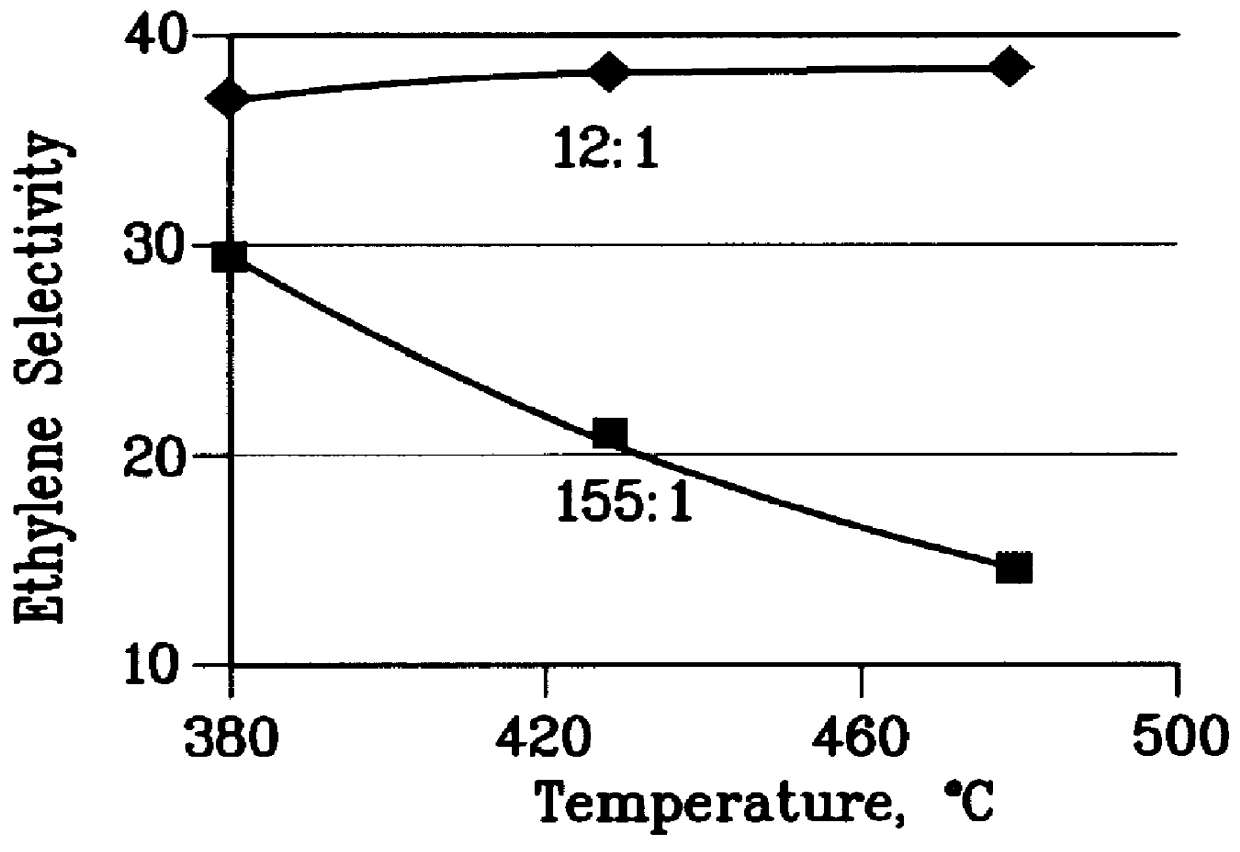
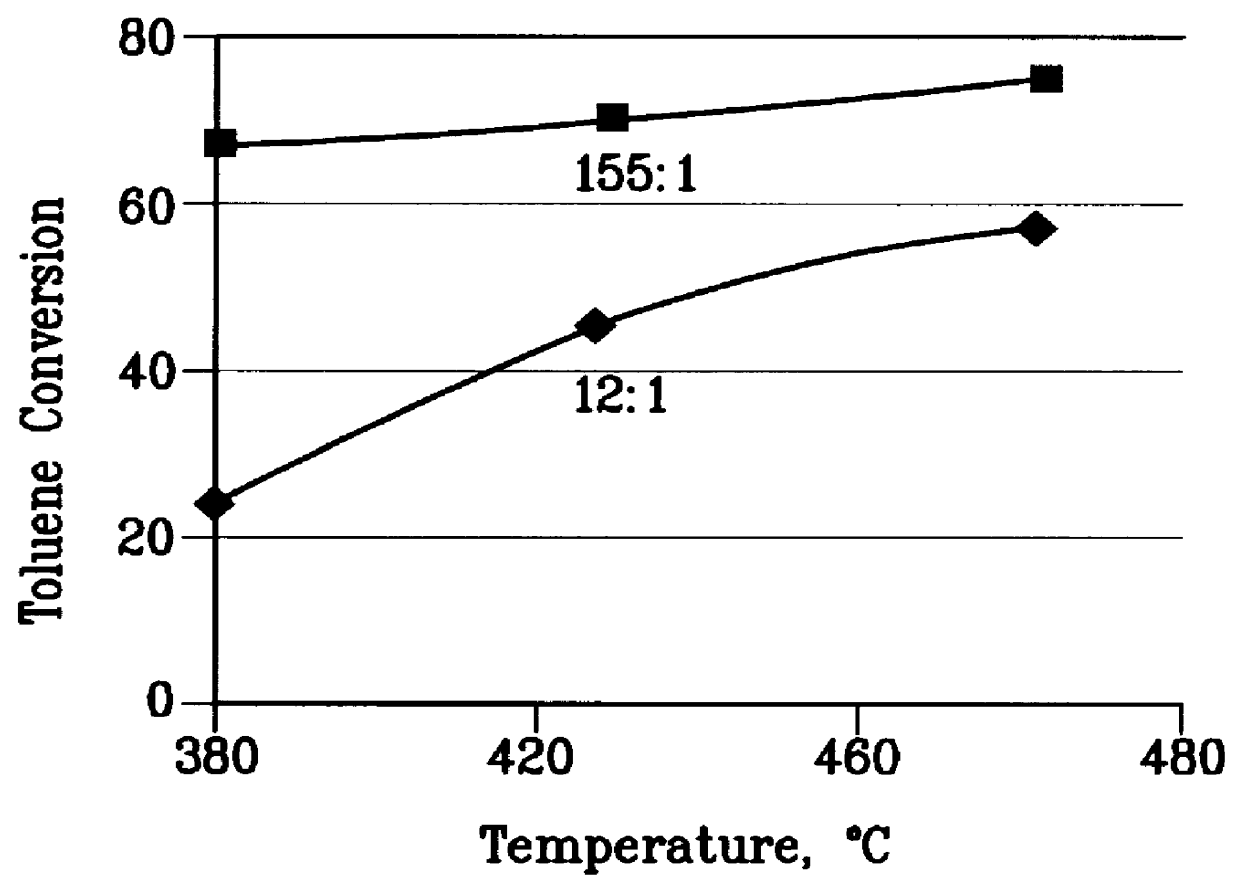
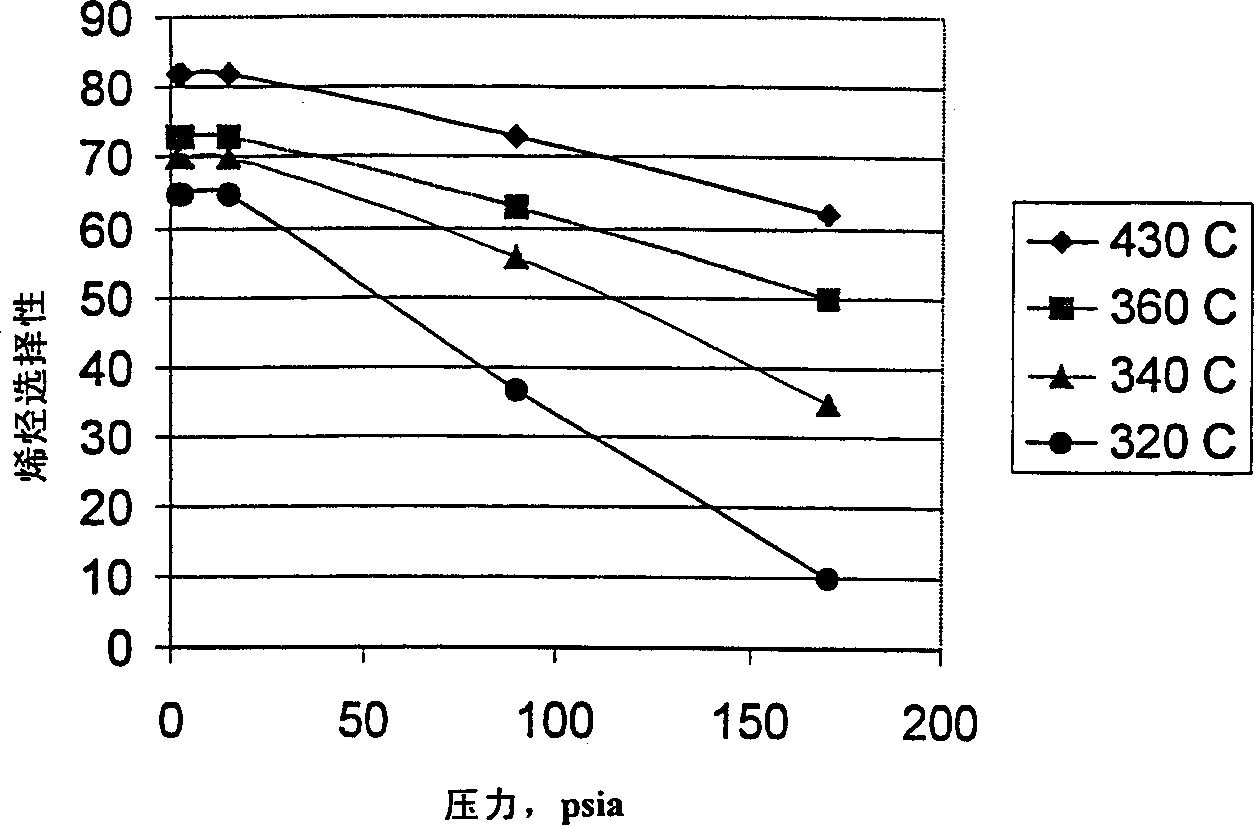
There is provided a process for converting methanol and / or dimethyl ether to a product containing C2 to C4 olefins which comprises the step of contacting a feed which contains methanol and / or dimethyl ether with a catalyst comprising a porous crystalline material, said contacting step being conducted in the presence of an aromatic compound under conversion conditions including a temperature of 350 DEG C. to 480 DEG C. and a methanol partial pressure in excess of 10 psia (70 kPa), said porous crystalline material having a pore size greater than the critical diameter of the aromatic compound and the aromatic compound being capable of alkylation by the methanol and / or dimethyl ether under said conversion conditions.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
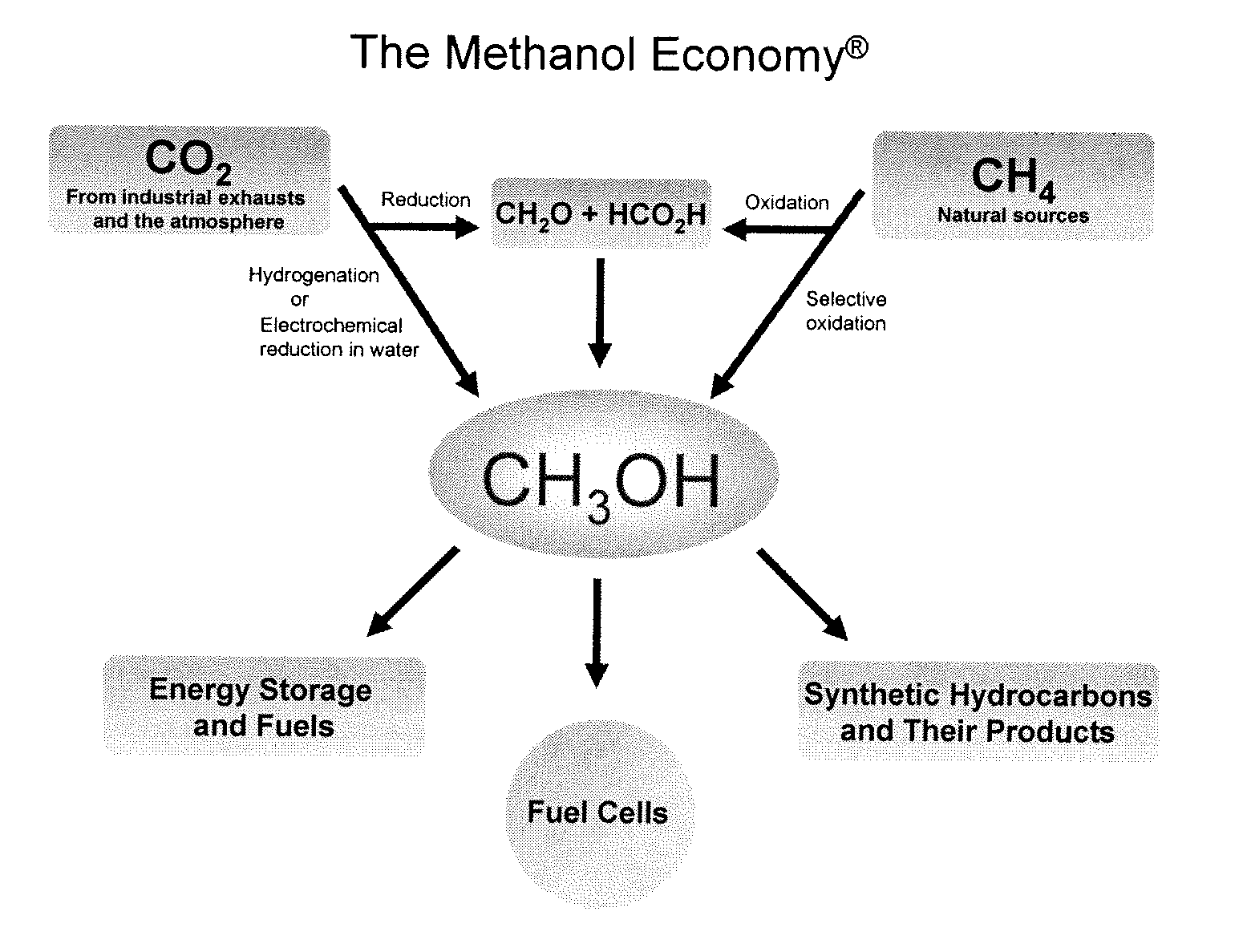
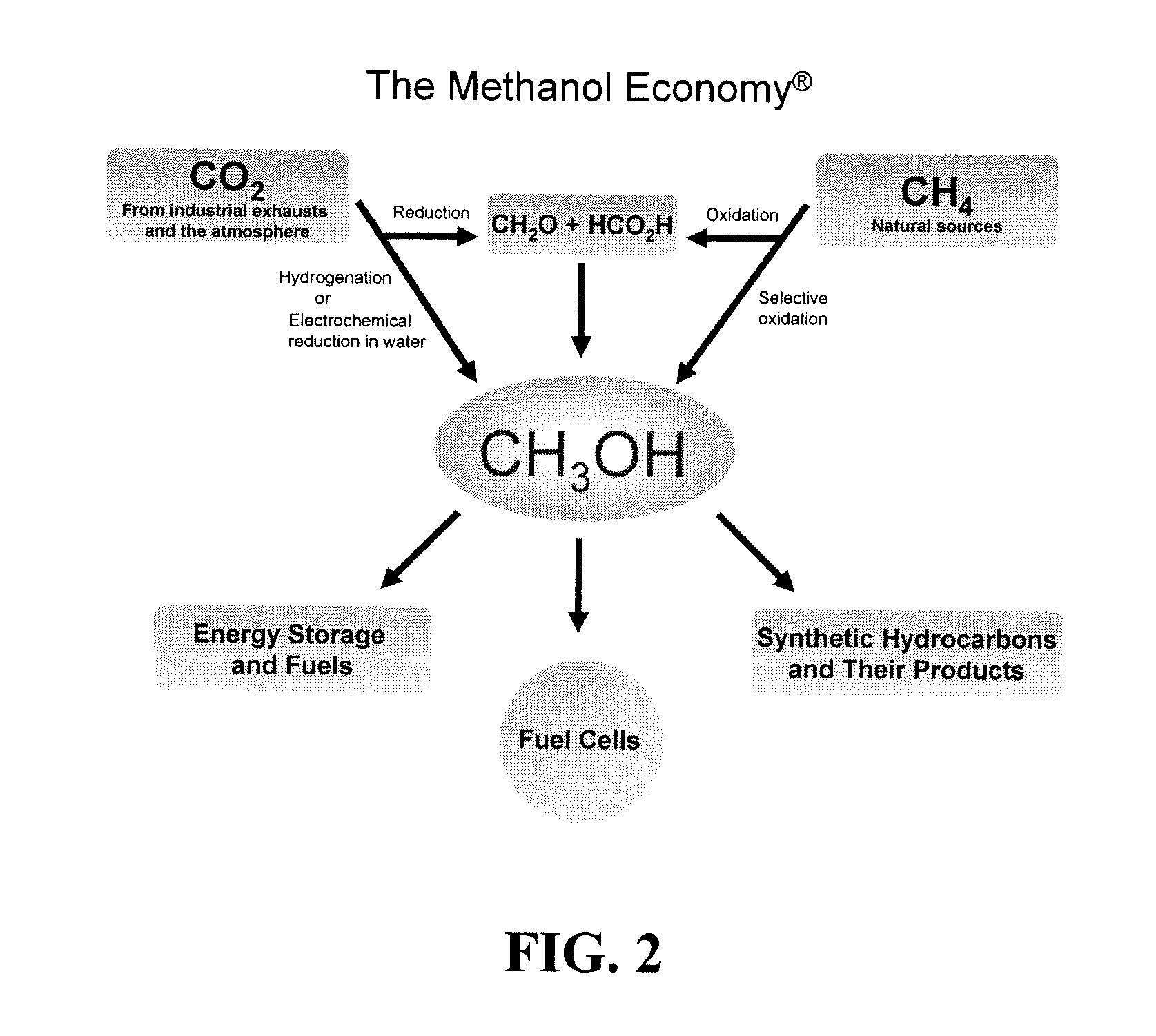
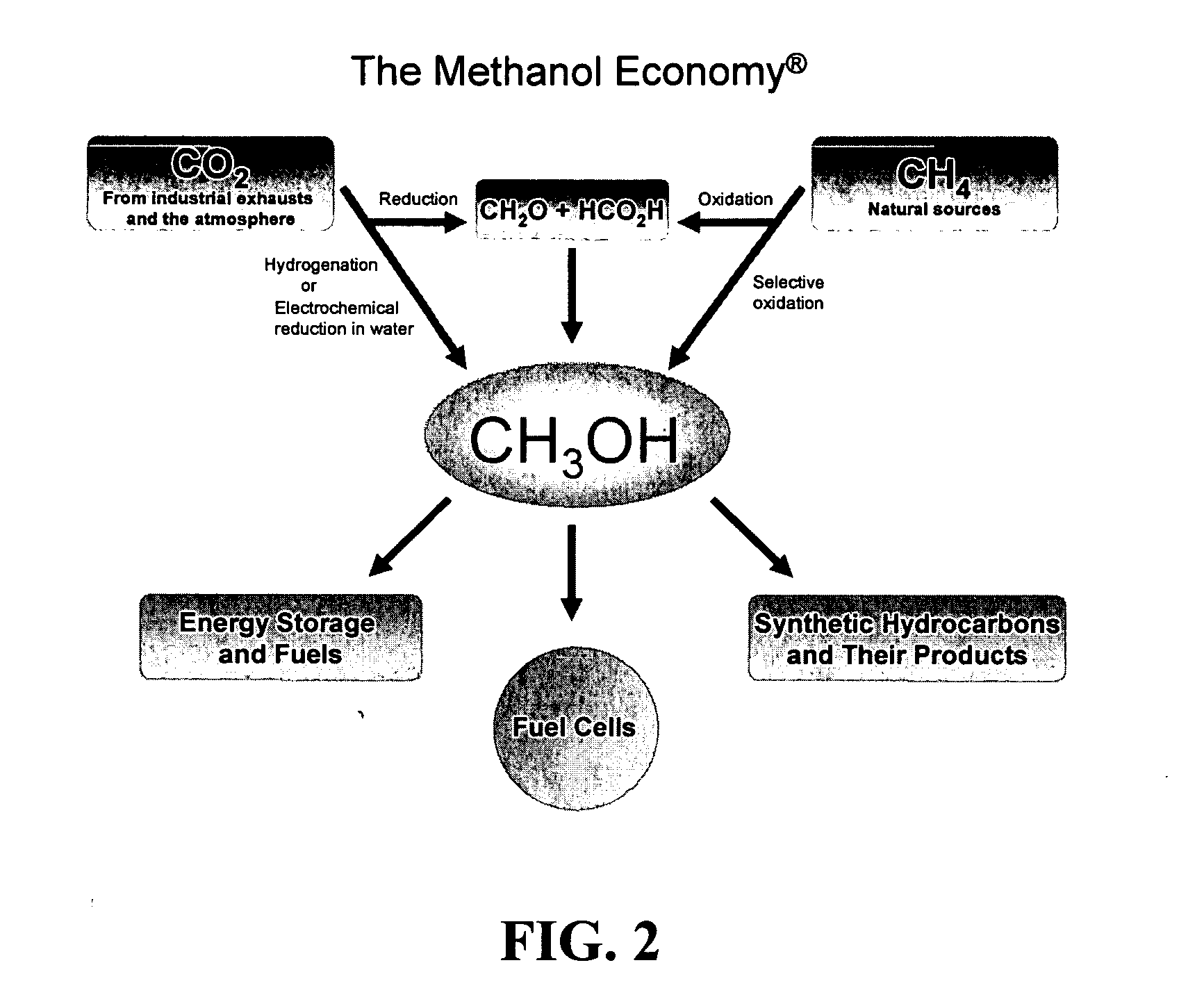
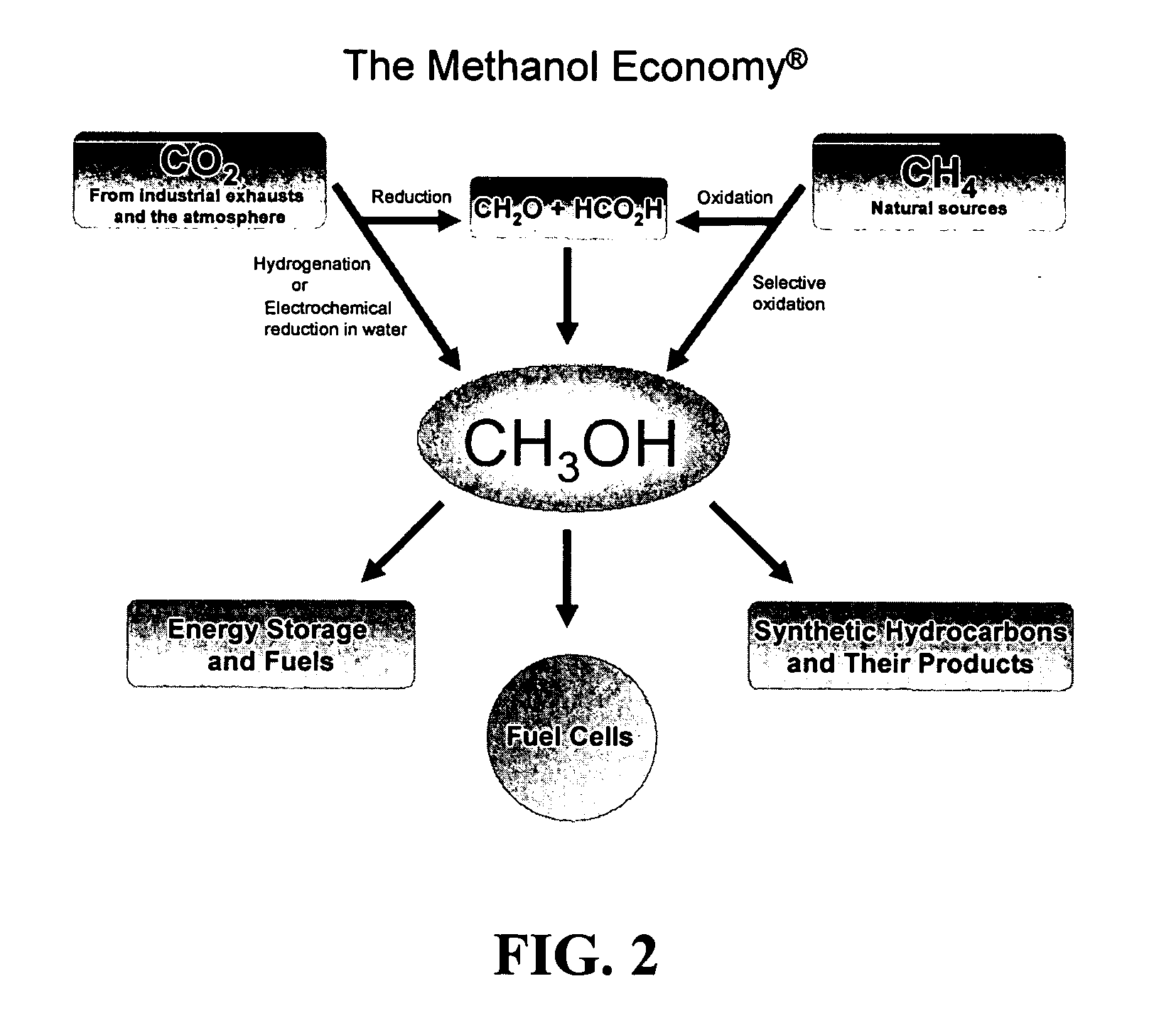
Efficient and selective chemical recycling of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20070254969A1Avoid emissionsElectrolysis componentsOxygen compounds purification/separationElectrochemistryDimethyl ether
An efficient and environmentally beneficial method of recycling and producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by chemical or electrochemical reduction secondary treatment to produce essentially methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Catalyst and process for converting methanol to hydrocarbons
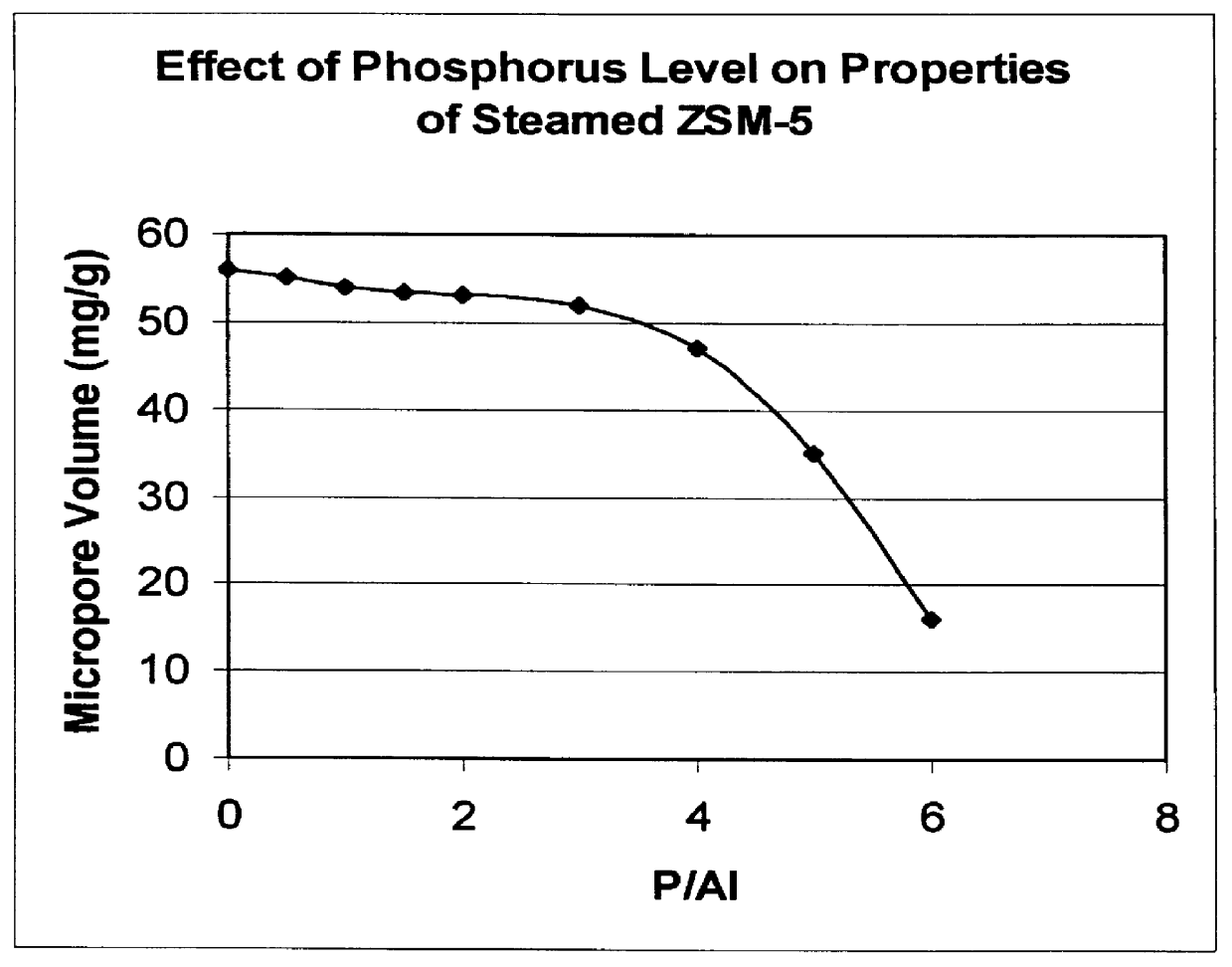
InactiveUS6048816AMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystCrystalline materialsDimethyl ether
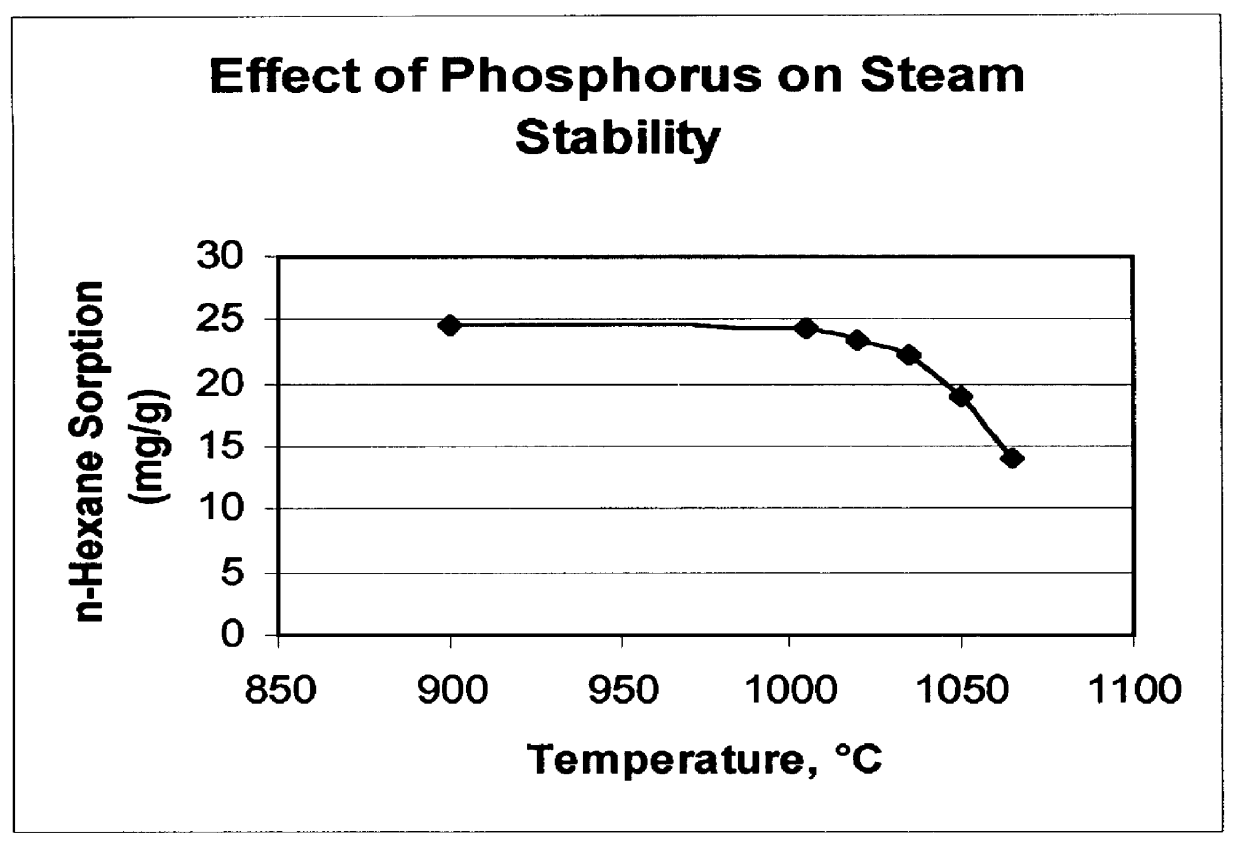
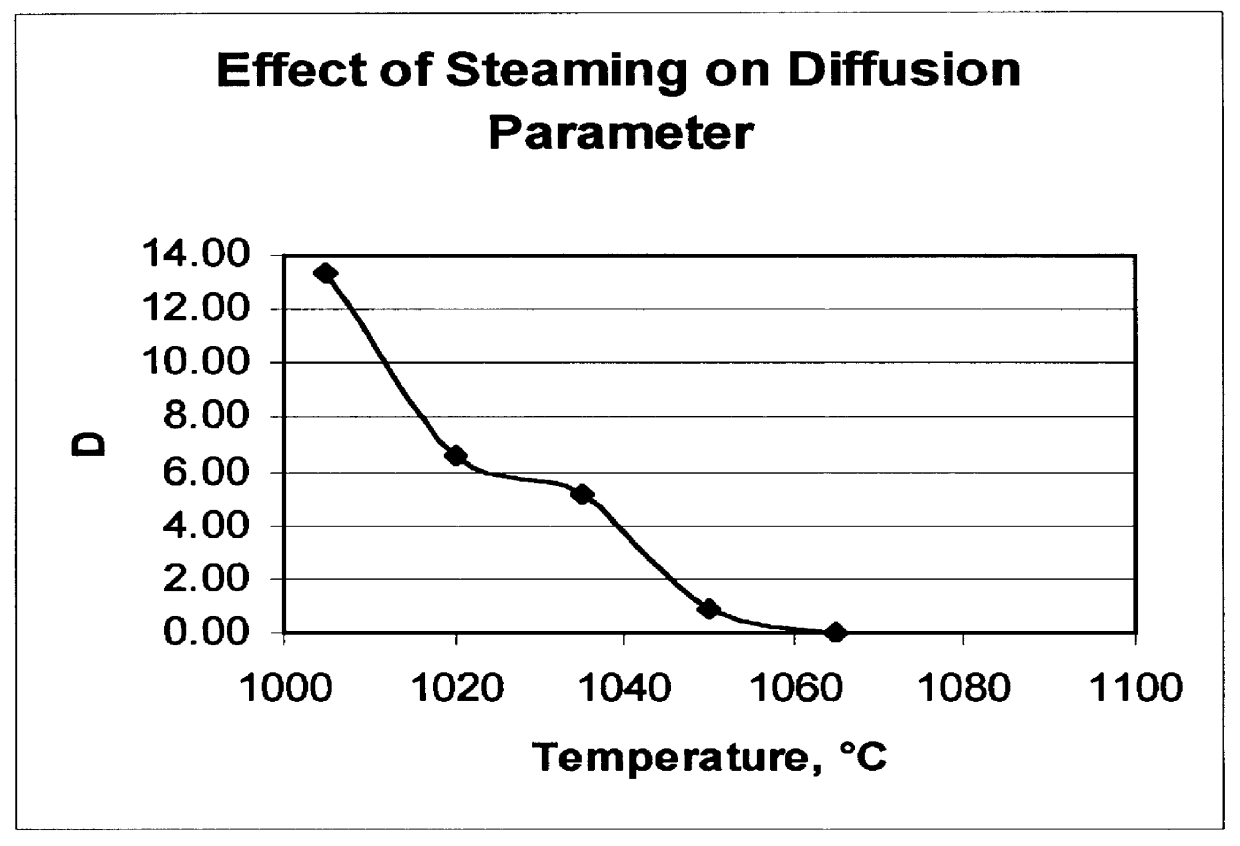
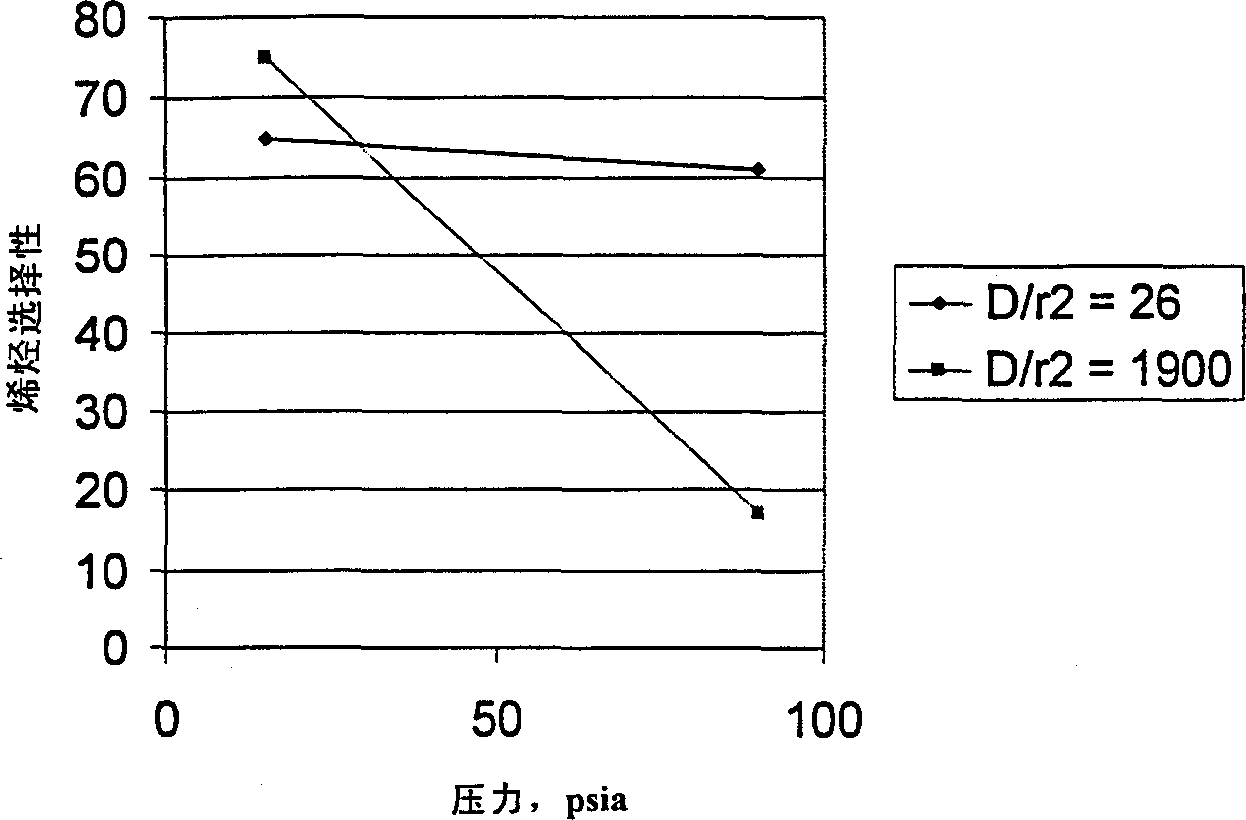
There is provided a catalyst and a process for converting methanol or dimethyl ether to a product containing C2 to C4 olefins. The catalyst comprises a porous crystalline material having a Diffusion Parameter for 2,2-dimethylbutane of about 0.1-20 sec-1 when measured at a temperature of 120 DEG C. and a 2,2-dimethylbutane pressure of 60 torr (8 kPa). In addition, the catalyst is characterized by a hydrothermal stability such that, after steaming the catalyst at 1025 DEG C. for 45 minutes in 1 atmosphere steam, the catalyst exhibits a methanol conversion activity of at least 50% when contacted with methanol at a methanol partial pressure of 1 atmosphere, a temperature of 430 DEG C. and 0.5 WHSV. The porous crystalline material is preferably a medium-pore zeolite, particularly ZSM-5, which contains phosphorus and has been severely steamed at a temperature of at least 950 DEG C.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP
Efficient and selective conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20060235091A1Minimize or eliminate the disadvantages or dangers inherentElectrolysis componentsCarbon compoundsHydrogenFlue gas
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by electrochemical reduction produces formic acid acid and some formaldehyde and methanol mixtures. The formic acid can be used as source of carbon as well as hydrogen to produce methanol, dimethyl ether and other products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Light olefin production via dimethyl ether
InactiveUS20070203380A1Improved arrangementImproved processing schemeOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionOlefin synthesisDimethyl ether
Improved processing for the production of light olefins is provided involving synthesis gas conversion to form an effluent including product dimethyl ether, subsequent separation of the product dimethyl ether and conversion thereof to the desired light olefins. The synthesis gas conversion effluent may also desirably include methanol and at least a portion of such methanol may be employed to effect the separation of the product dimethyl ether.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process and system for preparing low-carbon olefin from methanol or dimethylether
InactiveCN1356299AReduce wearReduce aggregationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsChemical recyclingAlkaneGas solid
A process for preparing low-carbon olefin from methanol or dimethyl ether includes loading its raw material and silicon aluminium phosphate (SAPO34) molecular sieve as catalyst into gas-solid parallel down-flowing fluidized bed reactor, super-short contact, reaction, fast gas-solid separation to separating resultant from catalyst to prevent secondary reaction, and regerating catalyst for cyclic use. Its advantages include high output rate (93%), high conversion rate of raw material, and less by-product.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
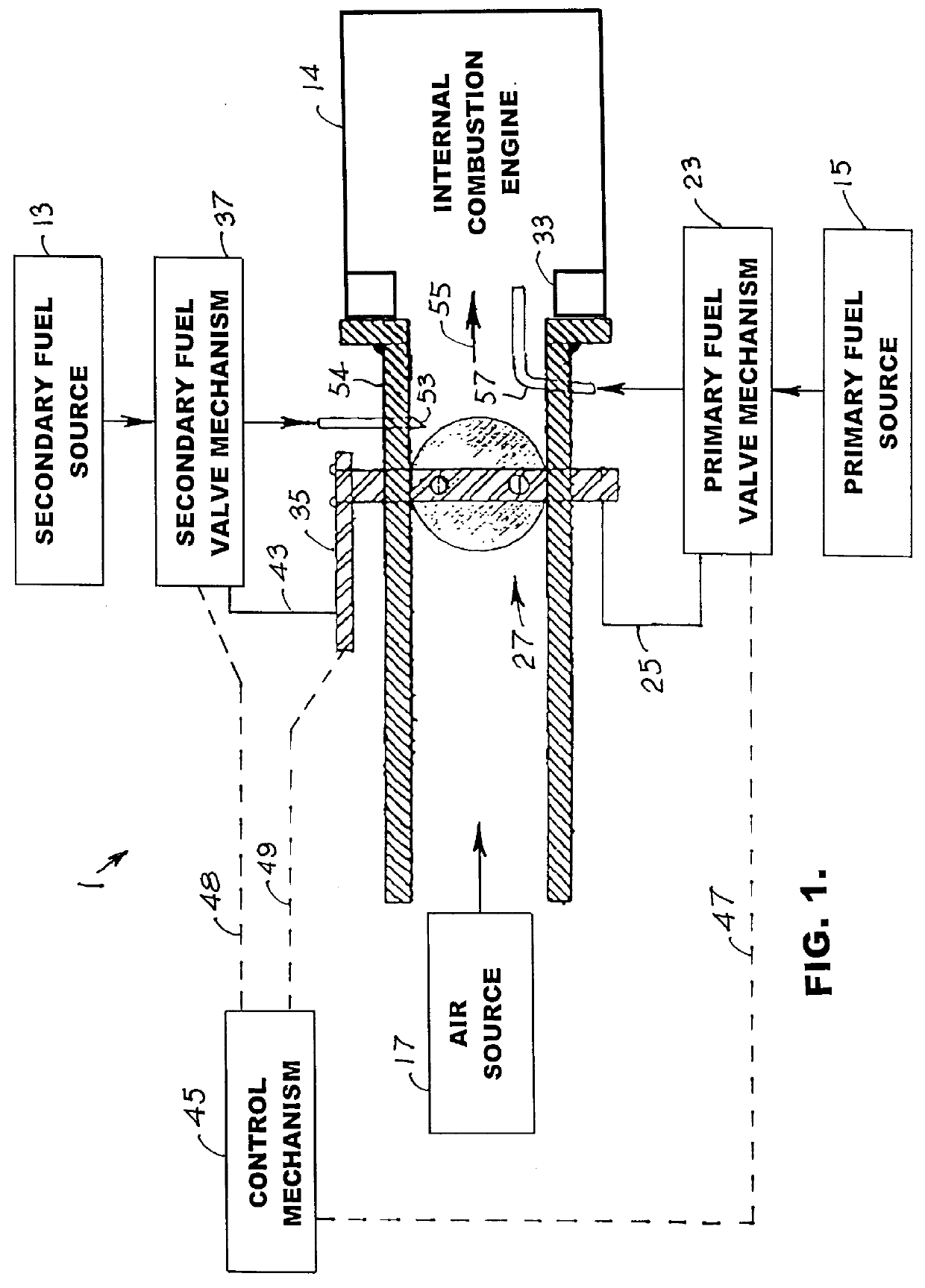
Internal combustion system using acetylene fuel
InactiveUS6076487AInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCarbon chainInternal combustion engine
An environmentally clean dual fuel for an internal combustion engine, comprising acetylene as a primary fuel and a combustible fuel, such as one or more fluids selected from an alcohol such as ethanol, methanol or any other alcohol or alcohols from the group comprising C1-C20 carbon chains, ethers such as from the group comprising dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, ethyl t-butyl ether, t-amyl methyl ether, di-isopropyl ether and the like, low-molecular-weight esters such as from the group comprising methyl formate, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl propionate and the like, or other suitable combustible fluid such as mineral spirits and the like, as a secondary fuel for operatively preventing early ignition and knock arising from the primary fuel. The dual fuel, internal combustion system, which generally utilizes a two-stage process for start-up and operation and can be operated with air- or liquid-cooling, is environmentally clean with hydrocarbon, CO, NOx, and SOx emissions substantially eliminated.
Owner:GOTEC
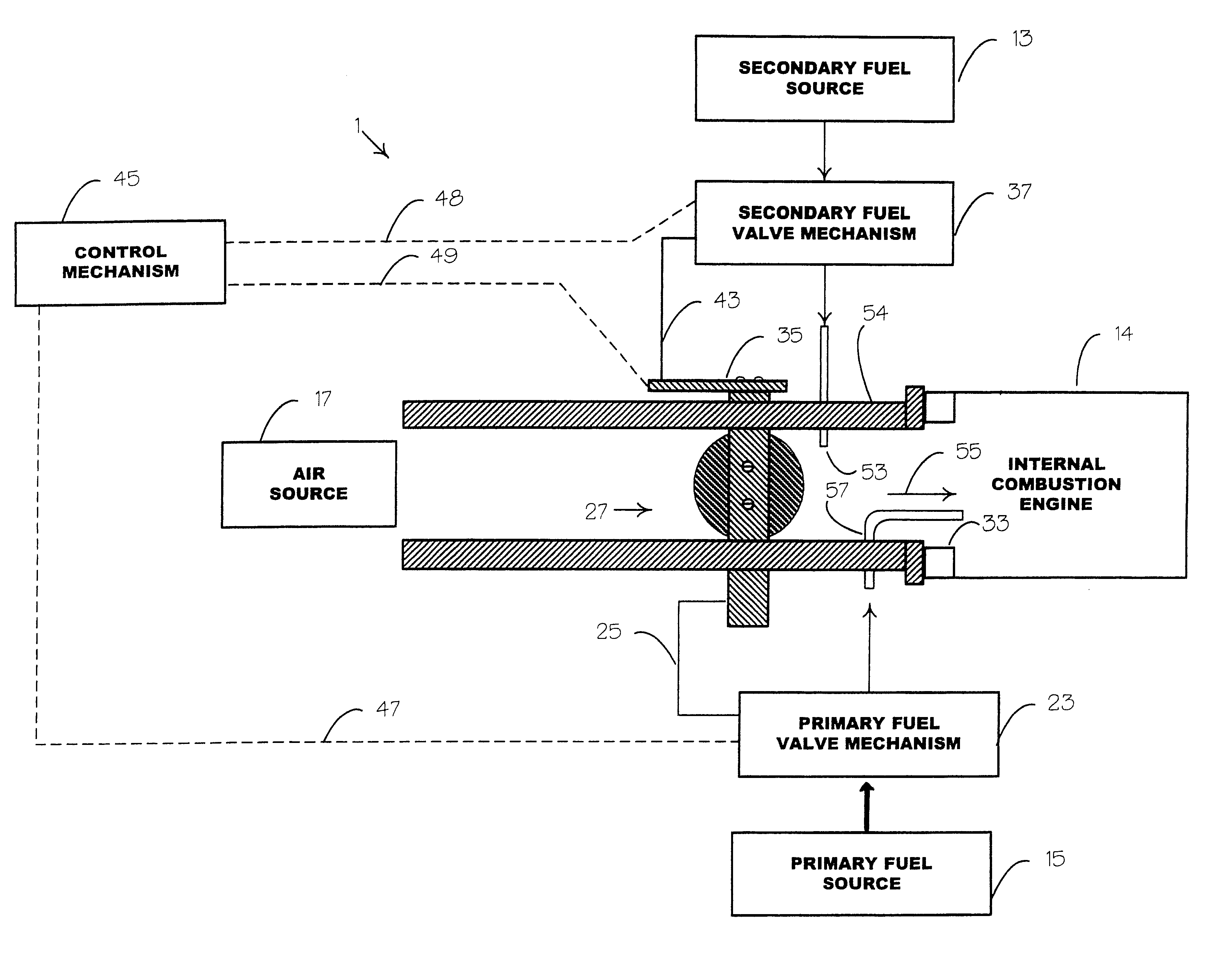
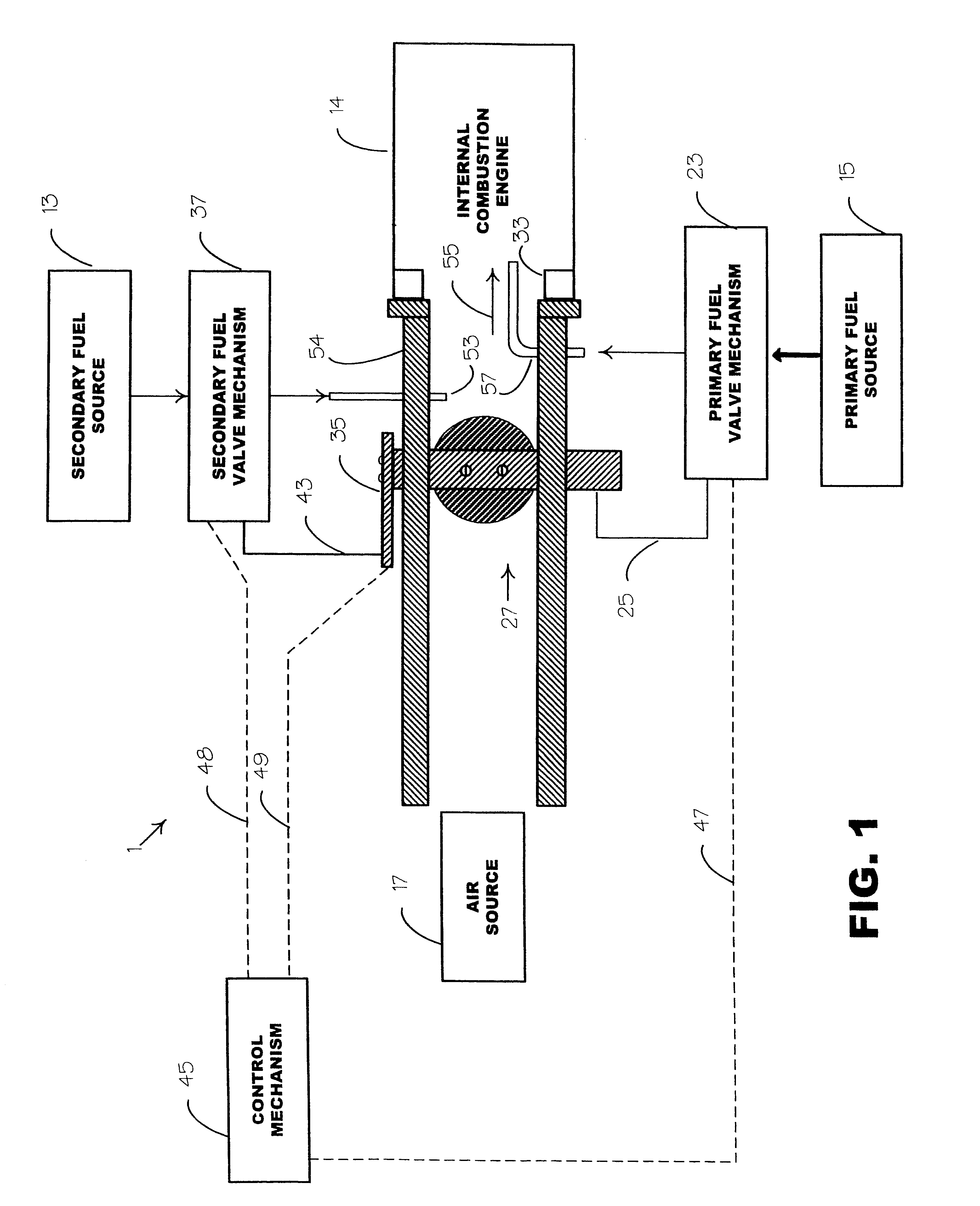
Internal combustion system adapted for use of a dual fuel composition including acetylene
InactiveUS6575147B2Easy to operateImprove performanceNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesCarbon chainMineral spirit
An internal combustion engine adapted to use an environmentally clean multi-fuel composition, comprising acetylene as a primary fuel and a combustible fuel, such as one or more fluids selected from an alcohol such as ethanol, methanol or any other alcohol or alcohols from the group comprising C1-C12 carbon chains, ethers such as from the group comprising dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, ethyl t-butyl ether, t-amyl methyl ether, di-isopropyl ether and the like, low-molecular-weight esters such as from the group comprising methyl formate, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl propionate, ethyl malate, butyl malate, and the like, or other suitable combustible fluid such as mineral spirits and the like, as a secondary fuel for operatively preventing early ignition and knock arising from the primary fuel.
Owner:GOTEC INC
Processes for converting oxygenates to olefins at reduced volumetric flow rates
InactiveUS20060020155A1Reduction in effluent volumetric flow rateMolecular sieve catalystCatalystsSyngasMolecular sieve
This invention provides processes for forming light olefins from methanol and / or from syngas through a dimethyl ether intermediate. Specifically, the invention is to converting methanol and / or syngas to dimethyl ether and water in the presence of a first catalyst, preferably comprising γ-alumina, and converting the dimethyl ether to light olefins and water in the presence of a second catalyst, preferably a molecular sieve catalyst composition.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for producing liquid fuel from carbon dioxide and water
ActiveUS20070244208A1Combustible gas chemical modificationOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesLiquid fuel
A process for producing high octane fuel from carbon dioxide and water is disclosed. The feedstock for the production line is industrial carbon dioxide and water, which may be of lower quality. The end product can be high octane gasoline, high cetane diesel or other liquid hydrocarbon mixtures suitable for driving conventional combustion engines or hydrocarbons suitable for further industrial processing or commercial use. Products, such as dimethyl ether or methanol may also be withdrawn from the production line. The process is emission free and reprocesses all hydrocarbons not suitable for liquid fuel to form high octane products. The heat generated by exothermic reactions in the process is fully utilizes as is the heat produced in the reprocessing of hydrocarbons not suitable for liquid fuel.
Owner:CRI EHF
Method for producing methanol, dimethyl ether, derived synthetic hydrocarbons and their products from carbon dioxide and water (moisture) of the air as sole source material
InactiveUS7378561B2High activityImprove surface activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsNano structuringWater source
A method for producing methanol and dimethyl ether using the air as the sole source of materials is disclosed. The invention relates to a method for separating the water (i.e., the moisture in the air) and carbon dioxide content of atmospheric air for their use in the subsequent production of methanol, dimethyl ether and derived synthetic hydrocarbons as products. The method includes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water under conditions sufficient to produce methanol and / or dimethyl ether. Methanol and / or dimethyl ether can be used as fuel or fuel additives or further converted to synthetic hydrocarbons and their products. Carbon dioxide is captured on a suitable absorbent, preferentially polyethyleneimine supported on nano-structured fumed silica. The process can also involve hydrogenation with hydrogen produced by electrolysis of water obtained from the air or from any other water source. Methanol can be dehydrated to produce dimethyl ether or further processed to produce synthetic hydrocarbons, polymers, and products derived from them by other known methods.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing propylene and aromatic hydrocarbon by virtue of conversion of methanol
ActiveCN102190546AHigh yieldHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsEthylene productionLiquid productGas phase
The invention relates to a method for preparing propylene and aromatic hydrocarbon by virtue of conversion of methanol, and the method is mainly used for solving the problem that the methanol is just converted into propylene and the aromatic hydrocarbon can not be co-produced in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: 1) converting above 80% of methanol into dimethyl ether by virtue of pre-reaction; 2) feeding the generated diamethyl ether and residual methanol into a device for producing propylene from the methanol for reaction so as to obtain a material flow I which mainly comprises the propylene, ethylene and C4, C5, C6 and over-C6 hydrocarbons; 3) after the material flow I is separated, returning the ethylene back to the device for producing the propylene from the methanol for cycling reaction, and feeding C4 and C5 hydrocarbons into an aromatizing device for reaction so as to obtain a material flow II containing aromatic hydrocarbon; and 4) cooling the material flow II, separating a gas-phase product low-carbon hydrocarbons from a liquid-phase product, and separating the liquid product from the material flow I so as to obtain C6 and over-C6 hydrocarbons, mixing, extracting and separating so as to obtain the aromatic hydrocarbon and non-aromatic hydrocarbon. By using the technical scheme, the problem is well solved; and the method can be used in industrialproduction for preparing the ethylene and the aromatic hydrocarbon by virtue of conversion of methanol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing bio-fuel that integrates heat from carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions to drive biomass gasification reactions
ActiveUS20070225383A1Improve thermal efficiencyImprove economyCatalytic crackingBiofuelsSyngasBiodiesel
A low-temperature catalytic process for converting biomass (preferably glycerol recovered from the fabrication of bio-diesel) to synthesis gas (i.e., H2 / CO gas mixture) in an endothermic gasification reaction is described. The synthesis gas is used in exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions, such as Fischer-Tropsch, methanol, or dimethylether syntheses. The heat from the exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction is integrated with the endothermic gasification reaction, thus providing an energy-efficient route for producing fuels and chemicals from renewable biomass resources.
Owner:VIRENT +1
Selective oxidative conversion of methane to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20060235088A1Minimize or eliminate the disadvantages or dangers inherentPreparation by oxidation reactionsElectrolysis componentsFormate EstersDimethyl ether
The present invention relates to a method of producing methanol from a methane source by oxidizing methane under conditions sufficient to a mixture of methanol and formaldehyde while minimizing the formation of formic acid and carbon dioxide. The oxidation step is followed by treatment step in which formaldehyde is converted into methanol and formic acid which itself can further be converted into methanol via catalytic hydrogenation of intermediately formed methyl formate.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Process for converting methanol or dimethyl ether to olefins
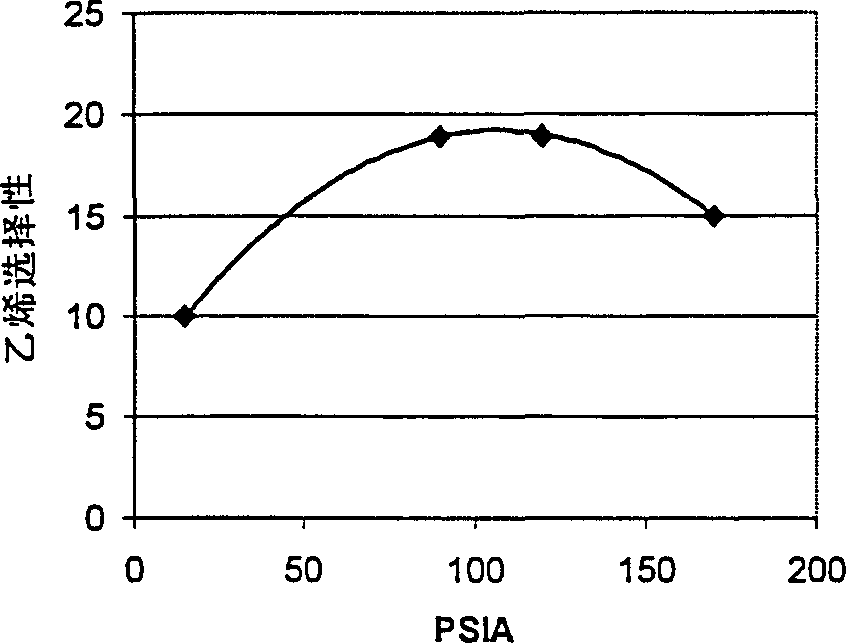
There is provided a process for converting methanol or dimethyl ether to a product containing C2 to C4 olefins, which comprises the step of contacting a feed containing methanol or dimethyl ether with a catalyst which comprises a zeolite having 10-ring intersecting channels, such as ZSM-5, and which has a Diffusion Parameter for 2,2-dimethylbutane of less than 100 sec-1 when measured at a temperature of 120 DEG C. and a 2,2-dimethylbutane pressure of 60 torr (8 kPa). The contacting step is conducted at a temperature of 370 to 480 DEG C., a methanol partial pressure of 30 to 150 psia and a methanol conversion per pass of less than 95%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
Process for conducting an equilibrium limited chemical reaction using microchannel technology
InactiveUS20050176832A1Large specific surface areaIncrease heatOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationChemical reactionDimethyl ether
The disclosed invention relates to a process for conducting an equilibrium limited chemical reaction in a microchannel reactor. The process involves the use of active heat exchange and is suitable for conducting exothermic and endothermic reactions. The process is particularly suitable for synthesizing methanol and dimethyl ether.
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
Integral supported carbon molecular sieve catalyst, preparing method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101224432AReduce the number of growthSave raw materialsMolecular sieve catalystsEther preparation by compound dehydrationGas phaseCarbon nanotube
A catalyst for an integrated supported carbon modular sieve comprises an integrated beehive cordierite, a carbon-nano tube and an HZSM-5 modular sieve, wherein the carbon-nano tube takes 7-20 proportions, HZSM-5 takes 10-30 proportions, and cordierite tales 60-80 proportions. The preparation method is that: carbon-nano tube is produced in situ on the integrated beehive cordierite by using chemical vapor deposition firstly, and the carbon-nano tube is taken as carrier, then the ZSM-5 modular sieve is developed on the carrier by using a secondary growth method. The catalyst for an integrated supported carbon-modular sieve can be used for the gas-phase synthesis of dimethyl ether DME by the dehydration of methanol.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Recuperative combustion system
InactiveUS20110041740A1Reducing and eliminating amount of oxygenSolid fuel combustionIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationOxygenDimethyl ether
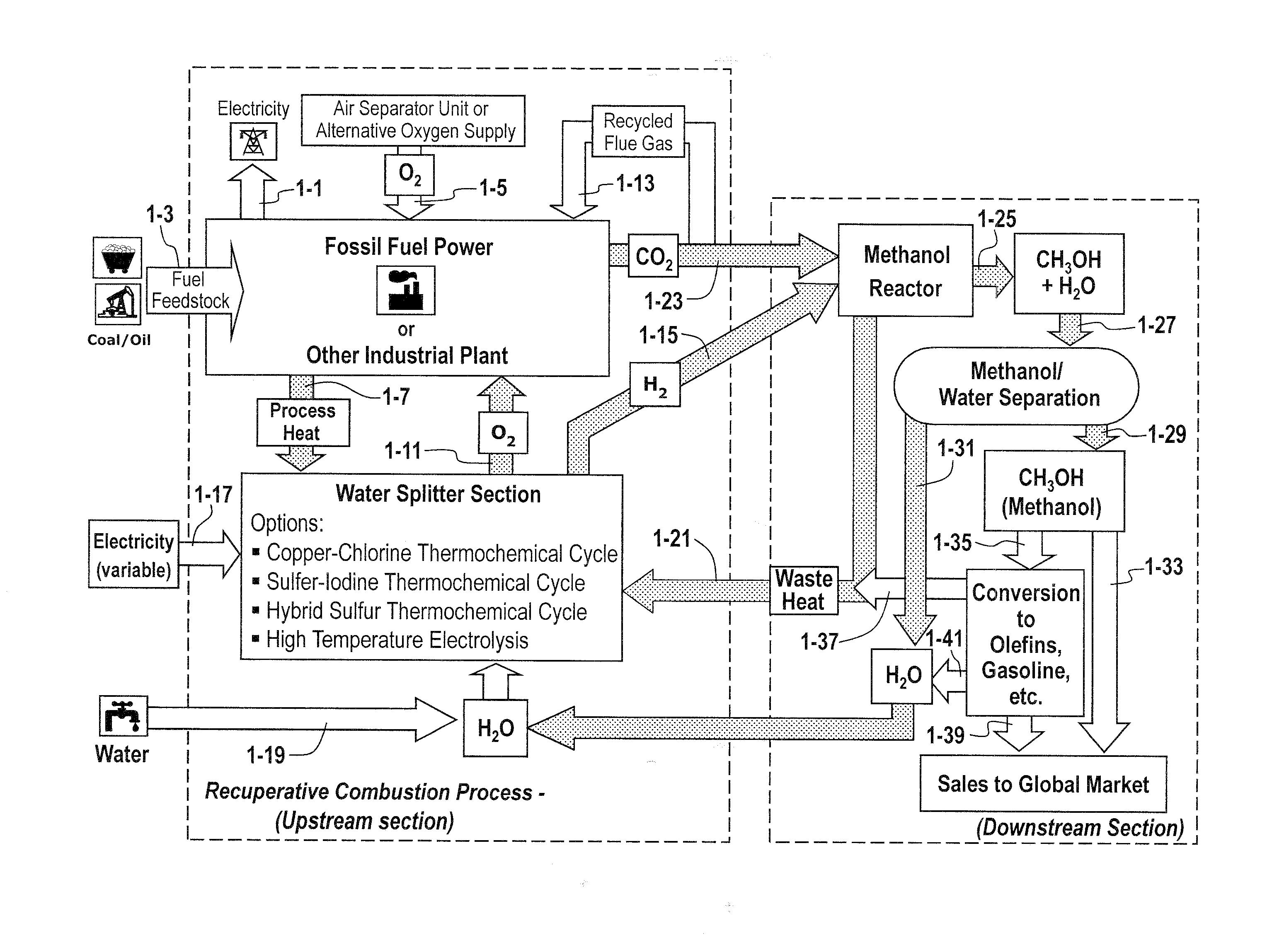
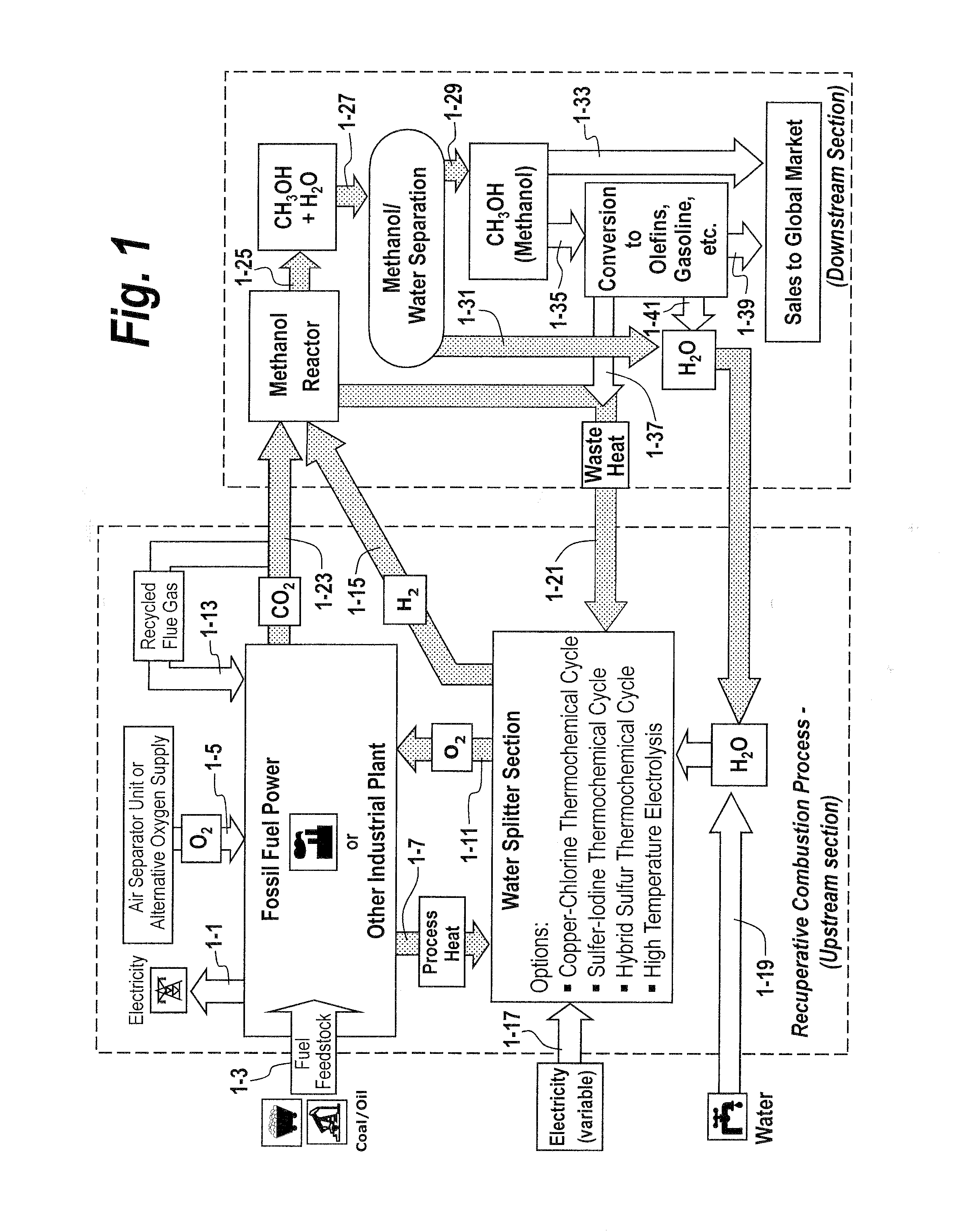
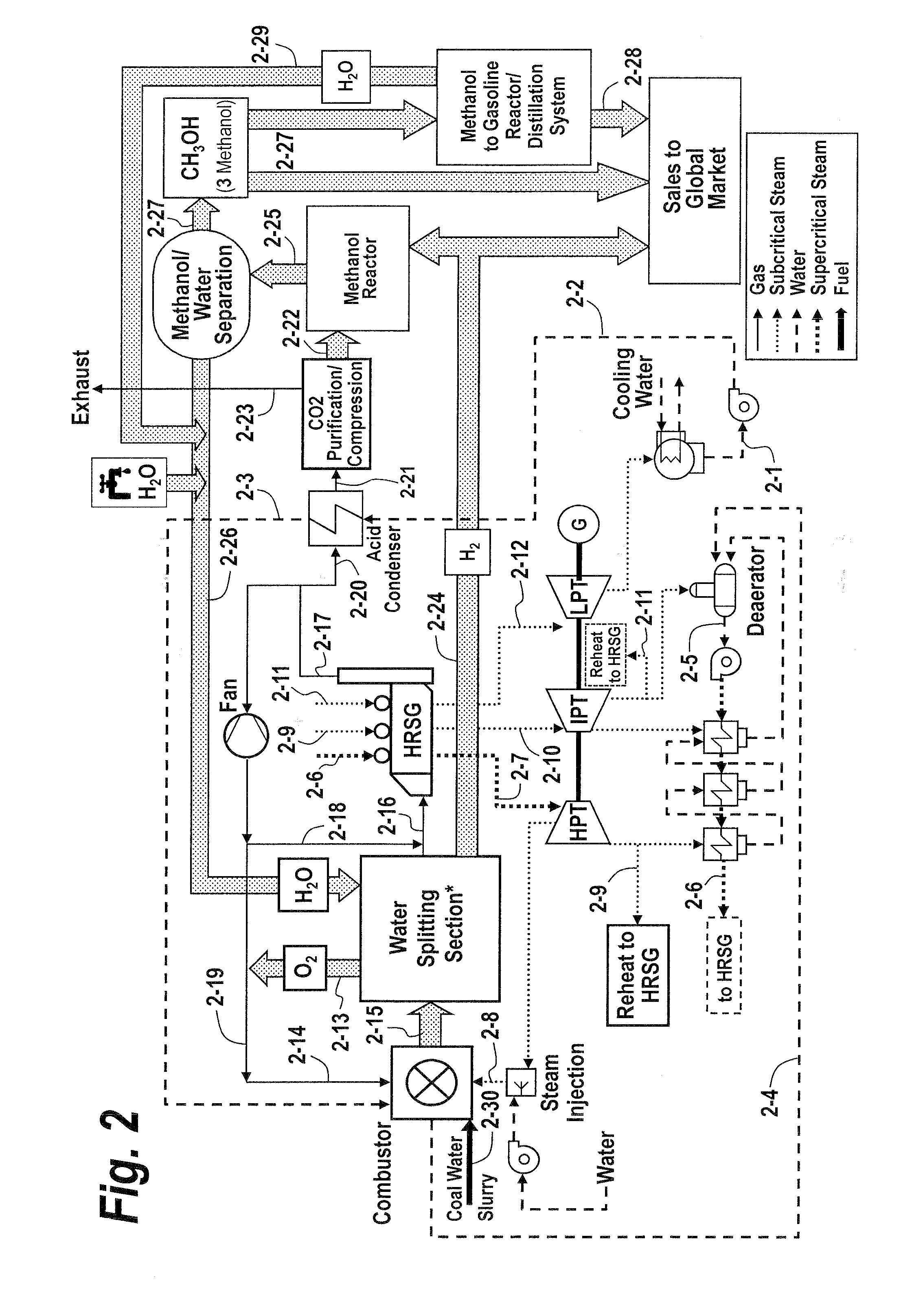
The methods and systems described herein relate to a recuperative combustion system that recuperates energy from fuel combustion that would otherwise be lost. The recuperative combustion system minimizes or eliminates the need for an air separator unit through the use of a clean water splitter section, consisting of a thermochemical cycle or high-temperature electrolysis. Water is split into its component hydrogen and oxygen, primarily with process heat from the combustion process. The oxygen produced by the water splitter provides oxygen necessary for oxy-fuel combustion, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for the power intensive air separator unit and / or external oxygen source, significantly increasing the efficiency of the oxy-fuel combustion cycle. Hydrogen produced by the water splitter may be used for a variety of industrial uses, or combined with carbon dioxide (captured from the flue gases produced by said combustion process) to produce methanol. Methanol can further be refined in a methanol to gasoline reactor to produce dimethyl ether, olefins or high grade gasoline. Described herein are methods and systems that 1) increase oxy-fuel combustion efficiency, 2) produce hydrogen for a suite of industrial / energy uses, and 3) capture carbon dioxide and convert it to high value hydrocarbons.
Owner:REILLY TIMOTHY J
Electrolyte additives for lithium sulfur rechargeable batteries
ActiveUS9160036B2Improve Coulombic efficiencyAvoid reactionLi-accumulatorsLithium–sulfur batteryLithium sulfur
An electrolyte solution for a lithium sulfur battery contains a lithium oxalatoborate compound in a 0.05-2 M solution in conventional lithium sulfur battery electrolyte solvents, optionally with other lithium compounds. Examples of solvents include dimethoxyethane (DME), dioxolane, and triethyleneglycol dimethyl ether (TEGDME). Electrochemical cells contain a lithium anode, a sulfur-containing cathode, and a non-aqueous electrolyte containing the lithium oxalatoborate compound. Lithium sulfur batteries contain a casing enclosing a plurality of the cells.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
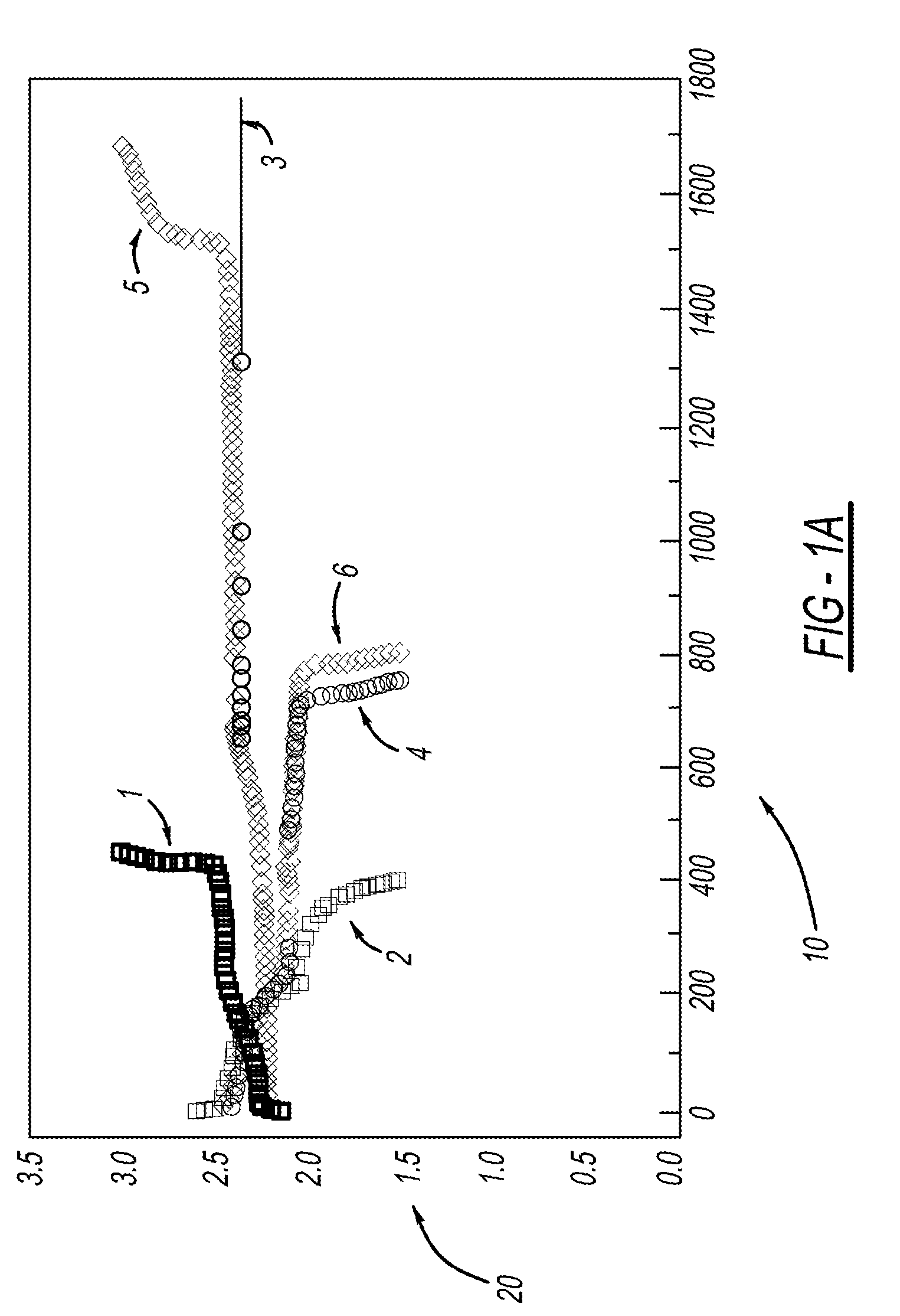
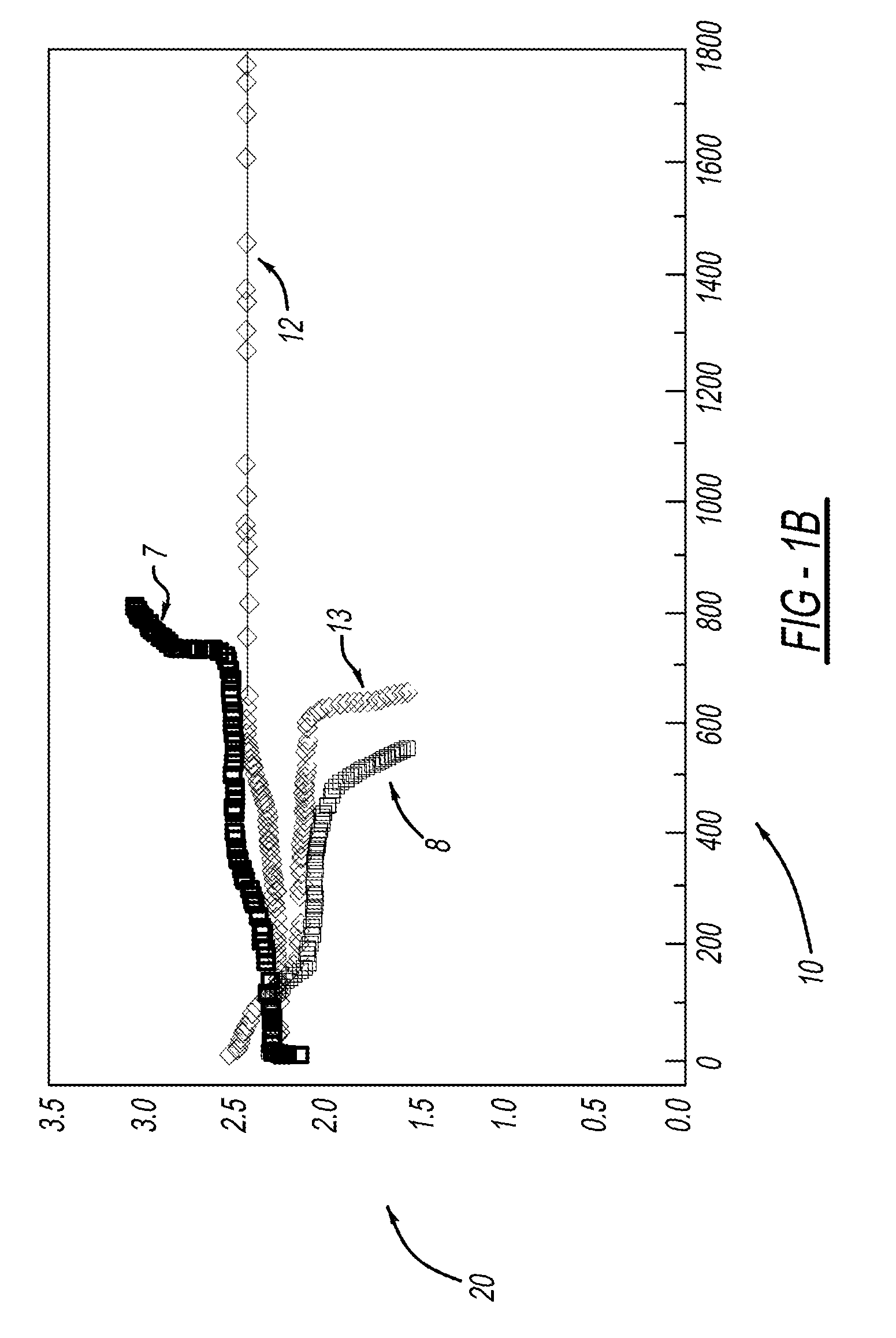
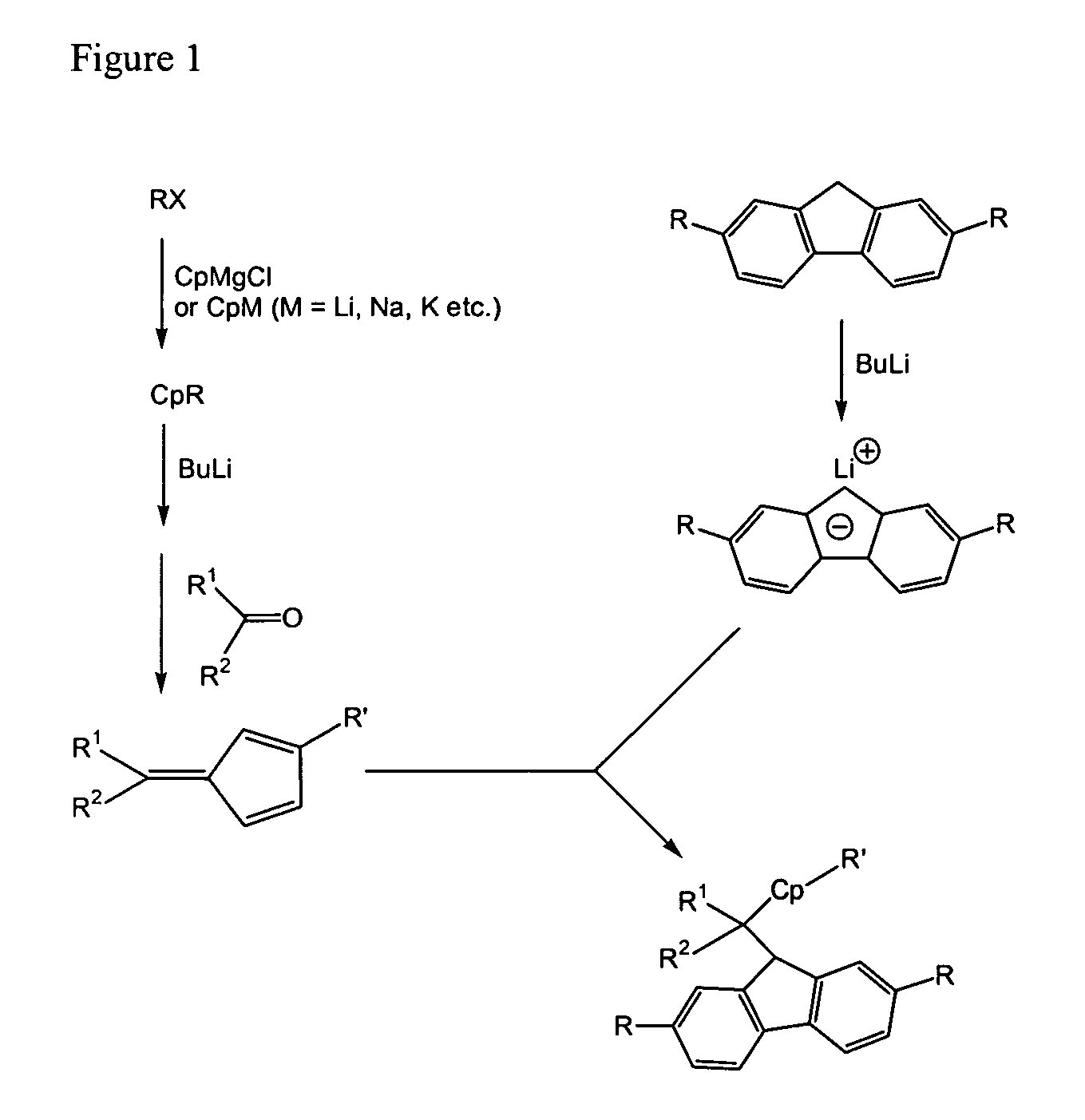
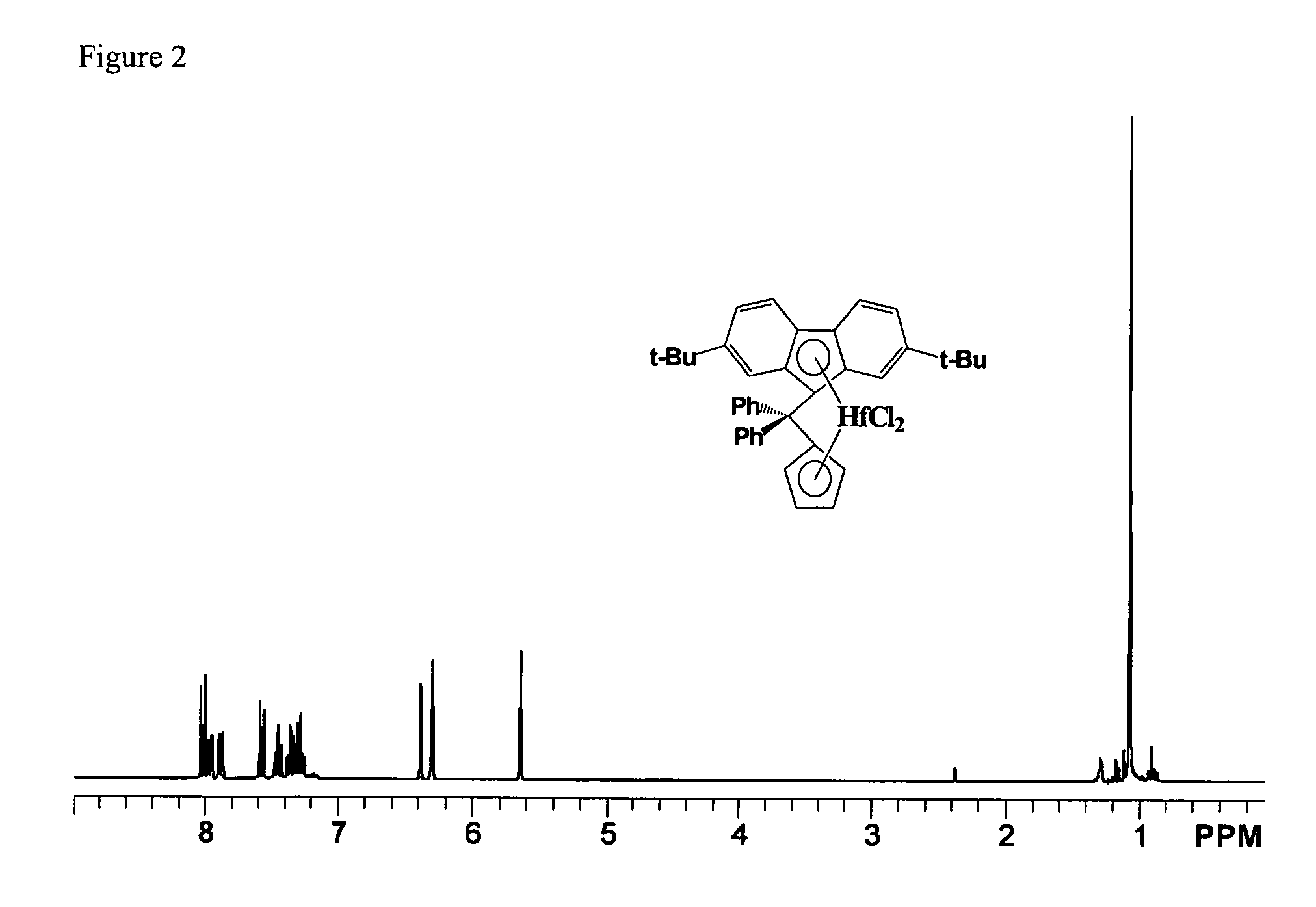
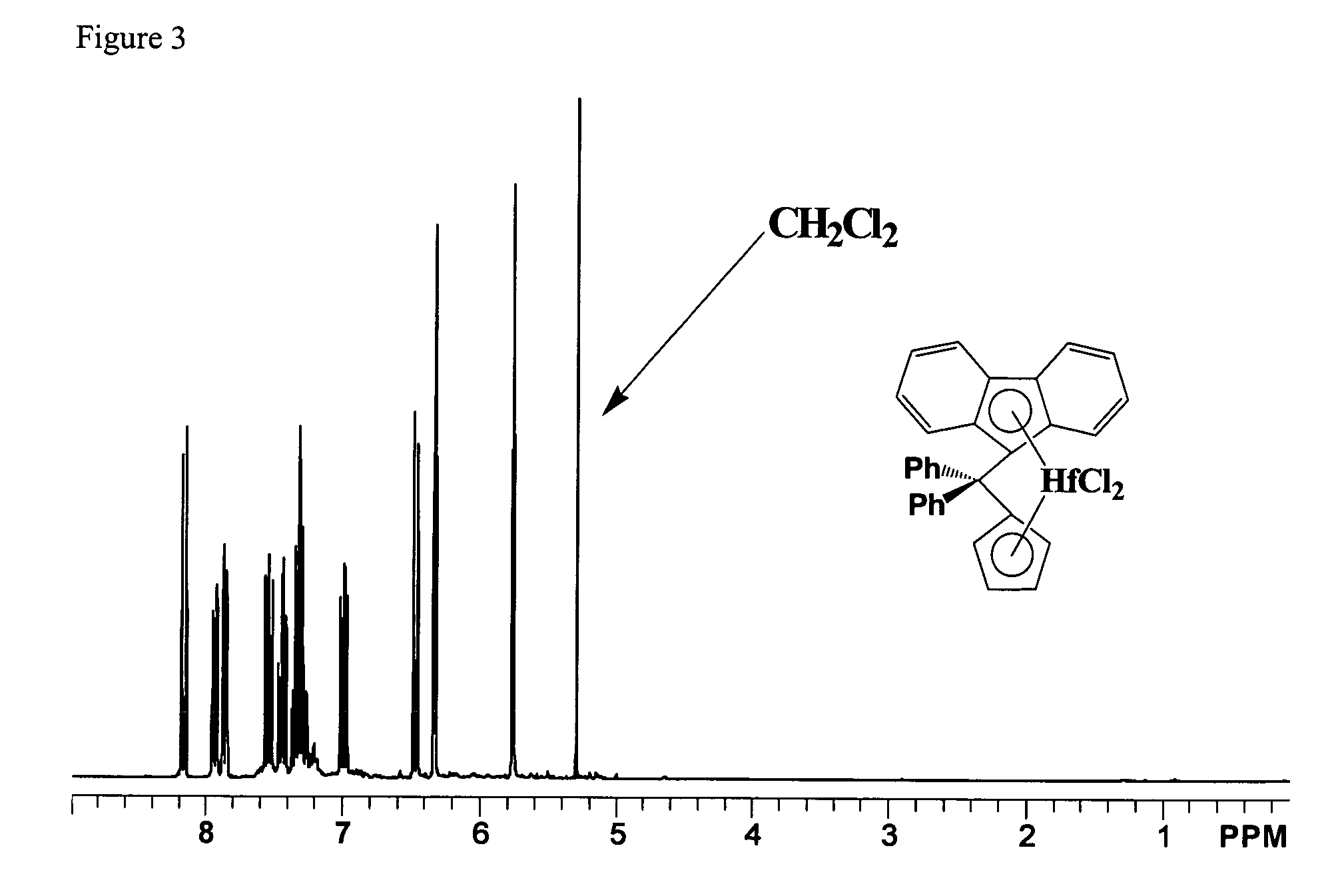
Process for one-pot synthesis of 1,1-diphenyl-1-(3-substituted-cyclopentadienyl)-1-(2,7-di-t-butyl-fluoren-9-yl)methane type ligands
ActiveUS7468452B1Silicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAnsa-metallocenePhenyl group
The present invention is directed to a method of making a ligand which can be used to form an ansa-metallocene. Further, the present invention is directed to a method of making the ansa-metallocene. In both methods the process steps employed to form the ligand are conducted in the presence of tetrahydrofuran, a substituted tetrahydrofuran, tetrahydropyran, a substituted tetrahydropyran or ethylene glycol dimethyl ether.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Method for continuous production of polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether
InactiveCN102786397ARealize industrial productionImprove stabilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystDistillation
The invention provides a method for continuous production of polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a) feeding dimethoxymethane and hot-melted paraformaldehyde into a fixed bed reactor and adopting an acidic resin catalyst, so as to prepare polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether (DMM3-8), wherein the reaction temperature is 120-180 DEG C and the pressure is 0.1-10 MPa; b) cooling the reaction product, and then performing adsorptive separation through a dehydrating tower, so as to obtain polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether of which most water, cytidine glycol and hemiacetal are desorbed; c) feeding the polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether subjected to desorption into a distillation tower for separation, wherein most of a low-boiling component (dimethoxymethane (DMM)), poly-di-formaldehyde dimethyl ether (DMM2), a by-product (methanol) and triformol are extracted first, and then the materials in a tower kettle are fed into a rectifying tower in the next step, so as to extract the rest of the DMM2 and the triformol; and d) returning the low-boiling component (dimethoxymethane (DMM)), the methanol, the DMM2 and the triformol, which are evaporated out by the distillation tower and the rectifying tower in the last step, into the fixed bed reactor to continue to react to prepare polyformaldehyde dimethyl ether.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Method for synthesizing dimethyl ether by adopting biomass indirect liquification one-step process
InactiveCN1477090ASelf-heating reactionOvercoming the deficiency of hydrogen contentEther preparationSyngasPetroleum
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing dimethyl ether by high-effectively cleanly utilizing biomass. It utilizes the gasified gas produced by catalytic gasification of biomass air-water vapor, and makes the gasified gas undergo the process of methane reformation to prepare synthetic gas, and utilizes the synthetic gas to directly synthesize clean fuel dimethyl ether.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com