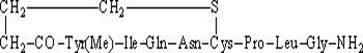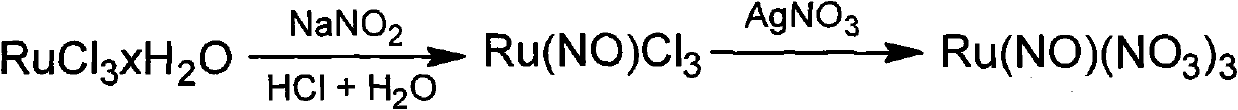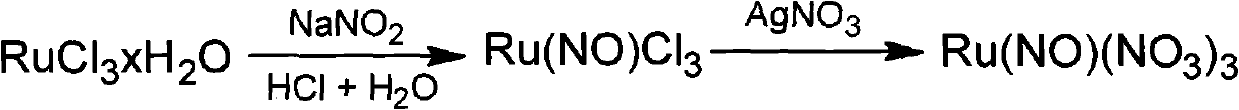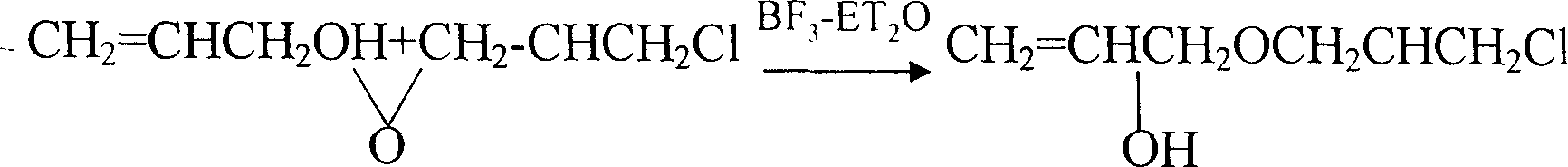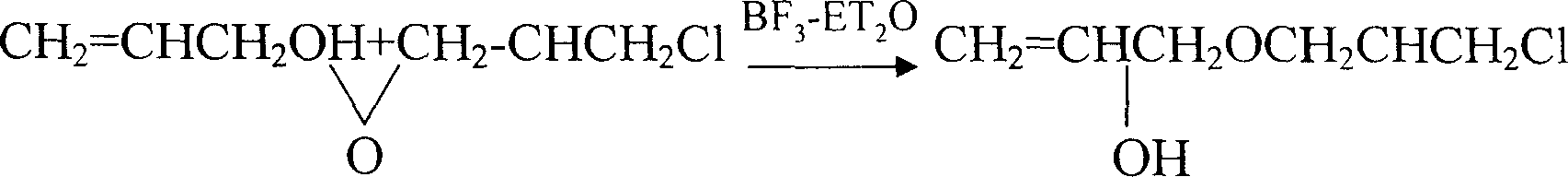Patents
Literature
2635 results about "Diethyl ether" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula (C₂H₅)₂O, sometimes abbreviated as Et₂O (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colorless, highly volatile flammable liquid. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories and as a starting fluid for some engines. It was formerly used as a general anesthetic, until non-flammable drugs were developed, such as halothane. It has been used as a recreational drug to cause intoxication. It is an isomer of butanol.
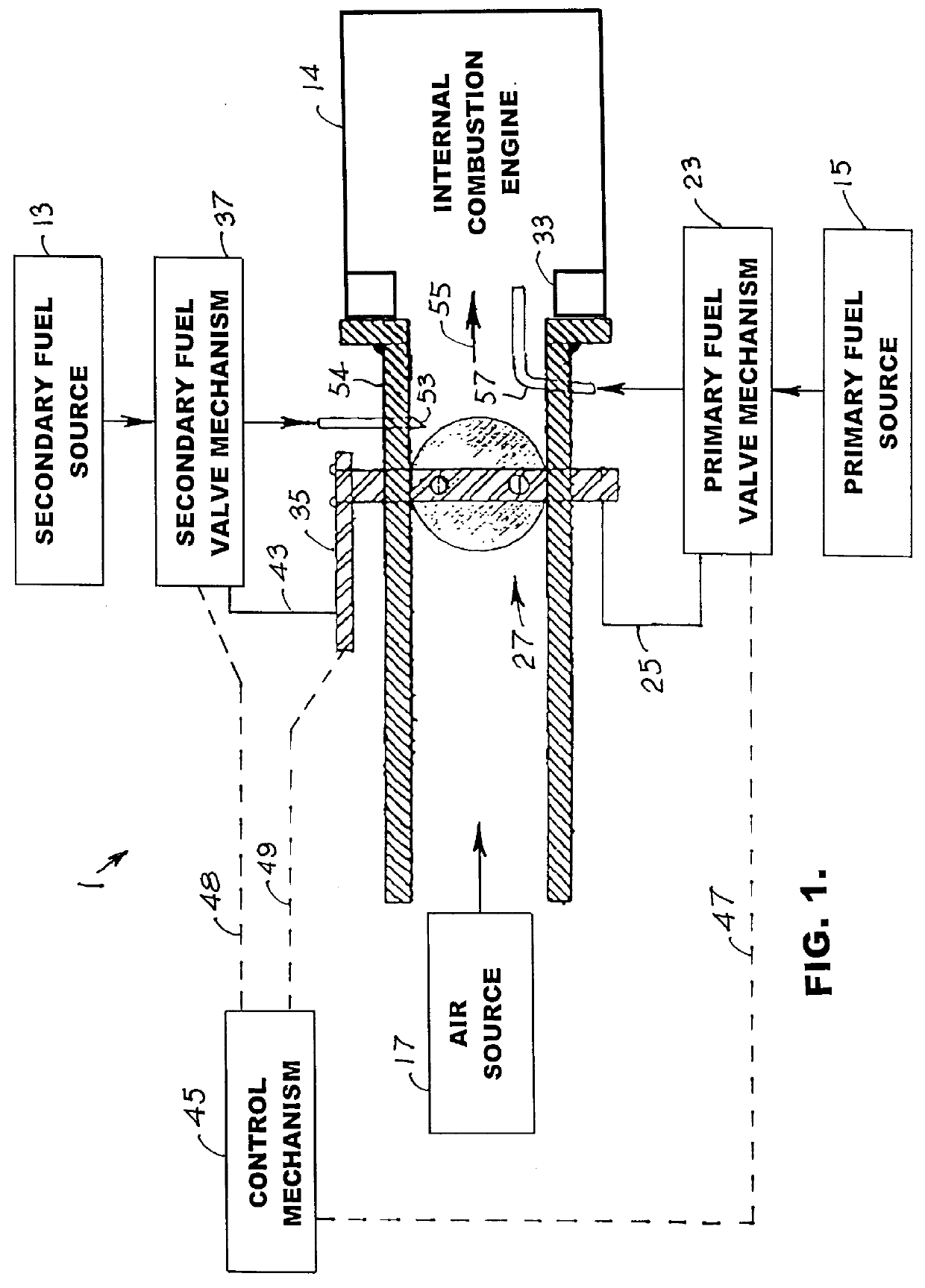
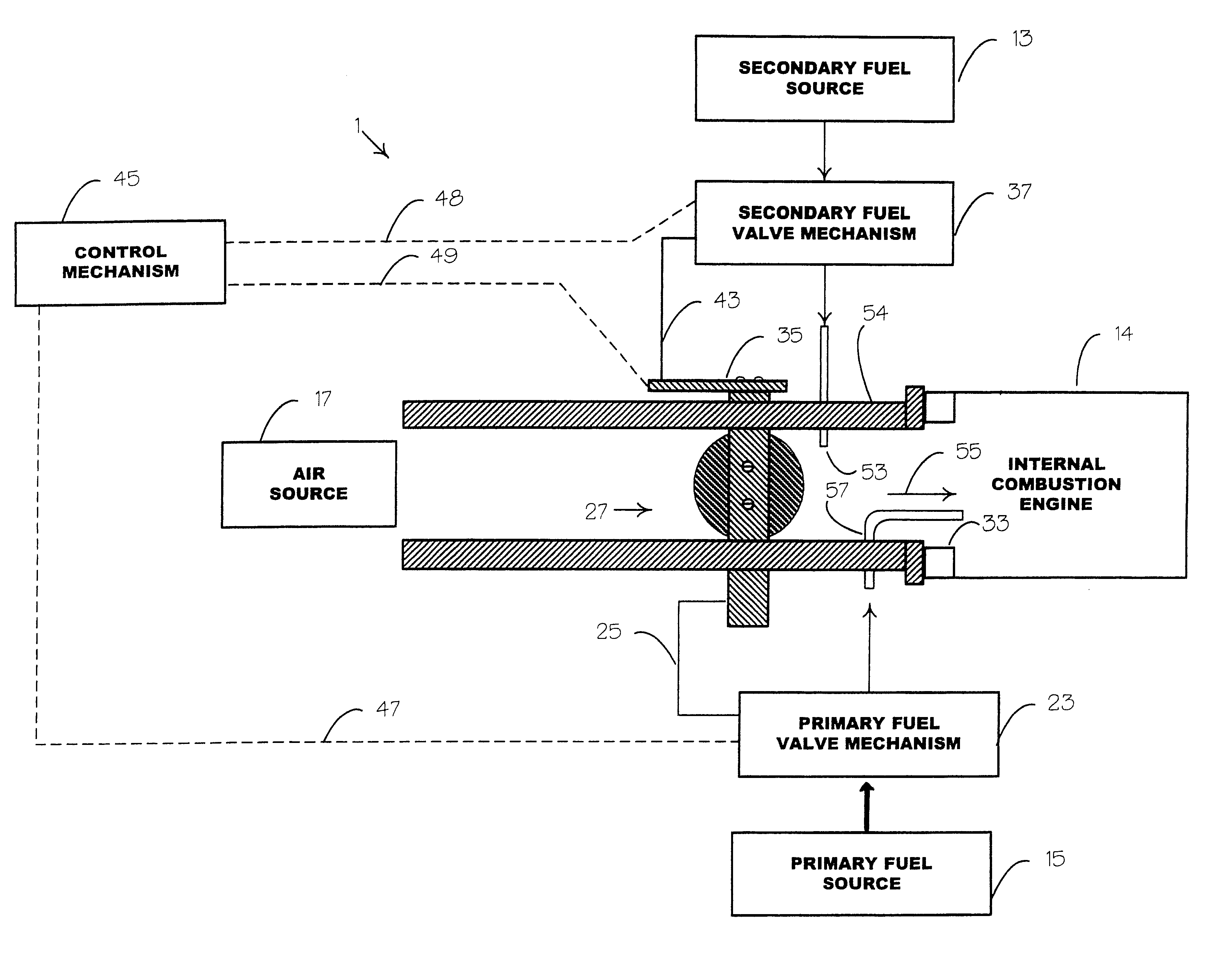
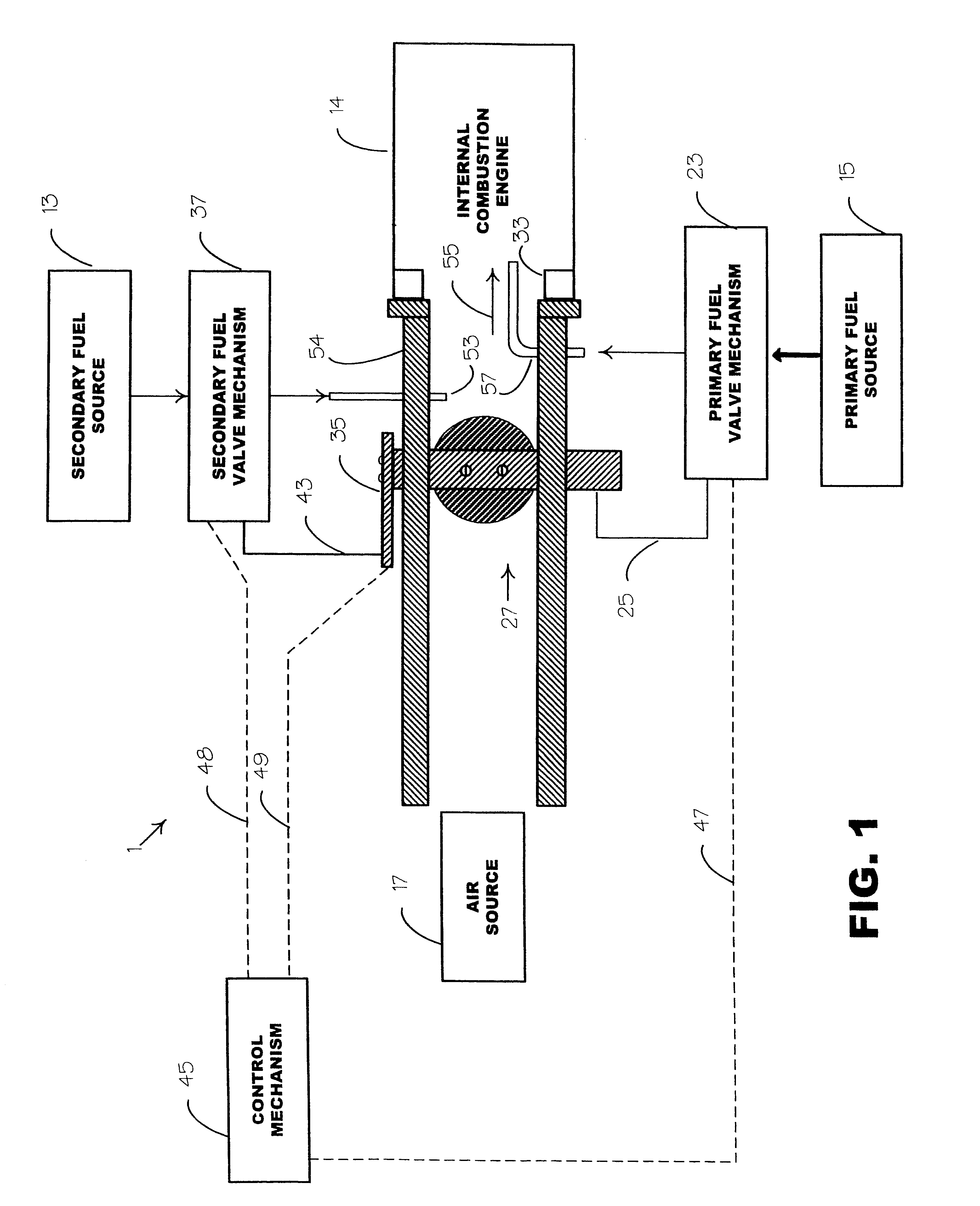
Internal combustion system using acetylene fuel
InactiveUS6076487AInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCarbon chainInternal combustion engine
An environmentally clean dual fuel for an internal combustion engine, comprising acetylene as a primary fuel and a combustible fuel, such as one or more fluids selected from an alcohol such as ethanol, methanol or any other alcohol or alcohols from the group comprising C1-C20 carbon chains, ethers such as from the group comprising dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, ethyl t-butyl ether, t-amyl methyl ether, di-isopropyl ether and the like, low-molecular-weight esters such as from the group comprising methyl formate, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl propionate and the like, or other suitable combustible fluid such as mineral spirits and the like, as a secondary fuel for operatively preventing early ignition and knock arising from the primary fuel. The dual fuel, internal combustion system, which generally utilizes a two-stage process for start-up and operation and can be operated with air- or liquid-cooling, is environmentally clean with hydrocarbon, CO, NOx, and SOx emissions substantially eliminated.
Owner:GOTEC
Internal combustion system adapted for use of a dual fuel composition including acetylene
InactiveUS6575147B2Easy to operateImprove performanceNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesCarbon chainMineral spirit
An internal combustion engine adapted to use an environmentally clean multi-fuel composition, comprising acetylene as a primary fuel and a combustible fuel, such as one or more fluids selected from an alcohol such as ethanol, methanol or any other alcohol or alcohols from the group comprising C1-C12 carbon chains, ethers such as from the group comprising dimethyl ether, diethyl ether, methyl t-butyl ether, ethyl t-butyl ether, t-amyl methyl ether, di-isopropyl ether and the like, low-molecular-weight esters such as from the group comprising methyl formate, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, methyl propionate, ethyl propionate, ethyl malate, butyl malate, and the like, or other suitable combustible fluid such as mineral spirits and the like, as a secondary fuel for operatively preventing early ignition and knock arising from the primary fuel.
Owner:GOTEC INC
Internal combustion engine system
InactiveUS20070221163A1Improve efficiencyEmission reductionNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionFuel tank
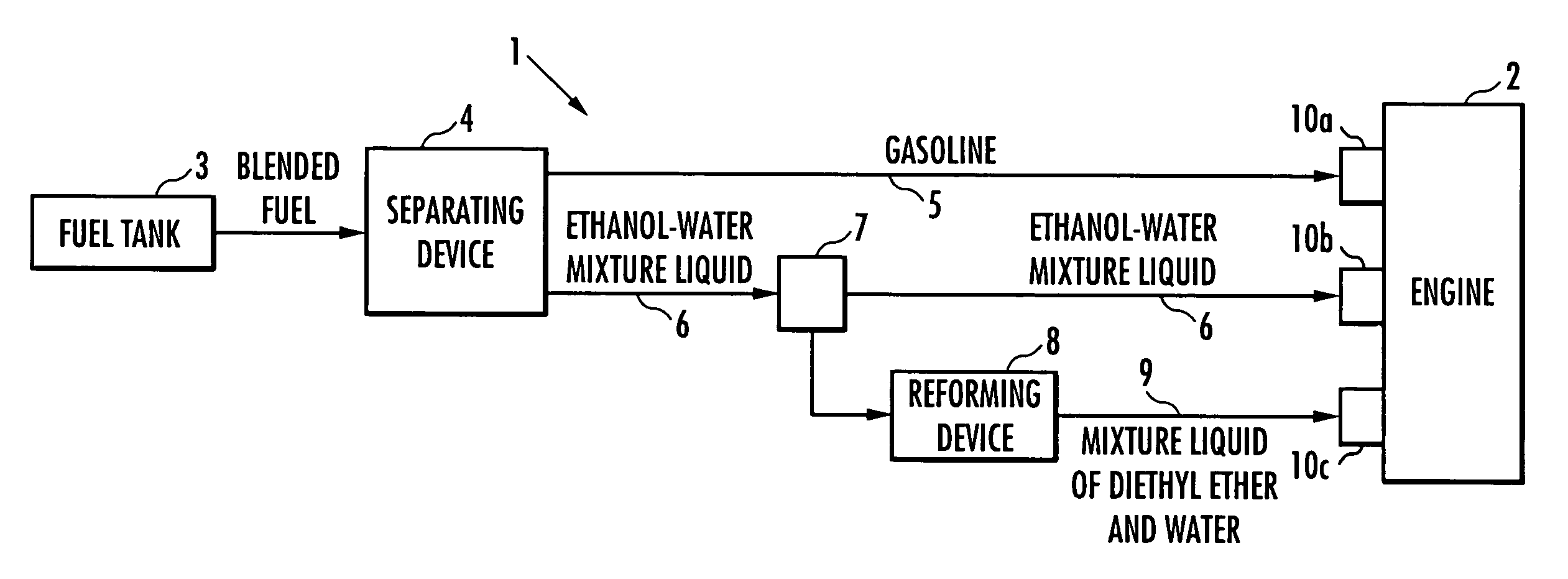
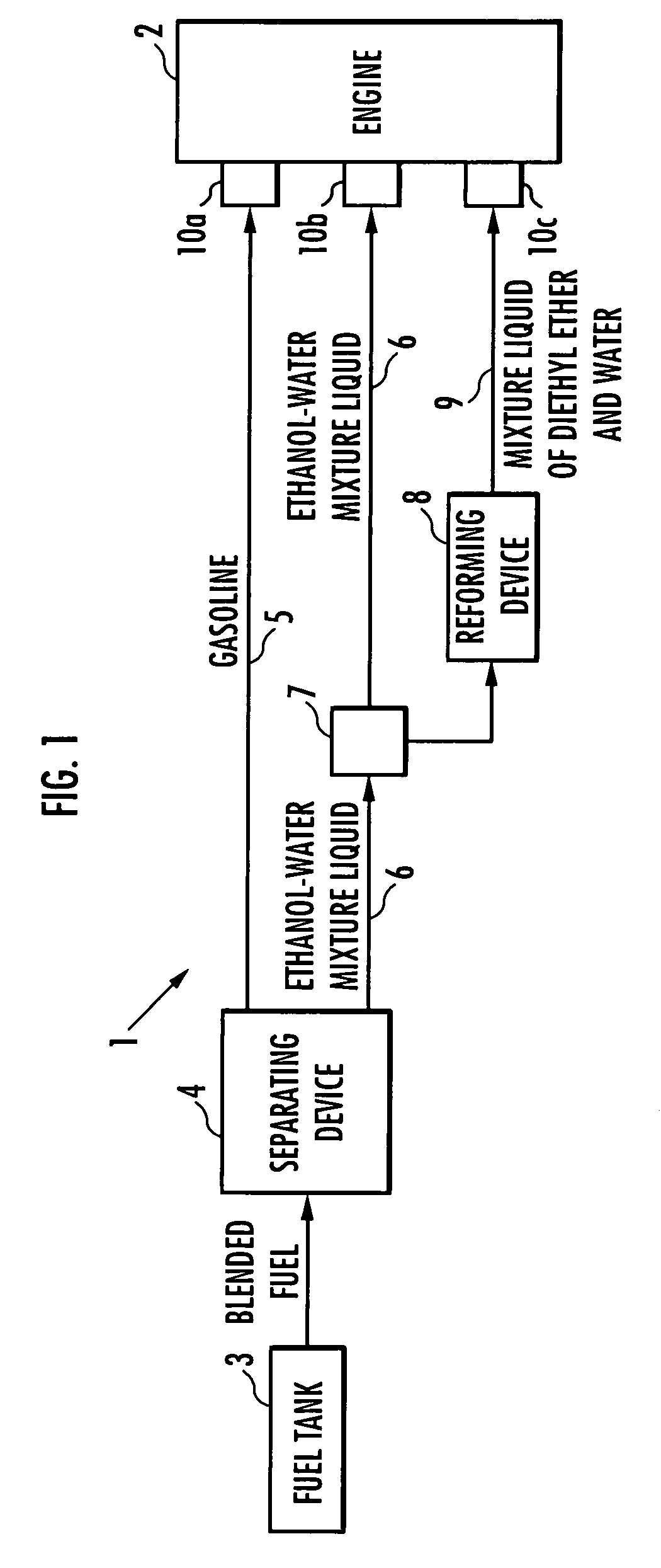
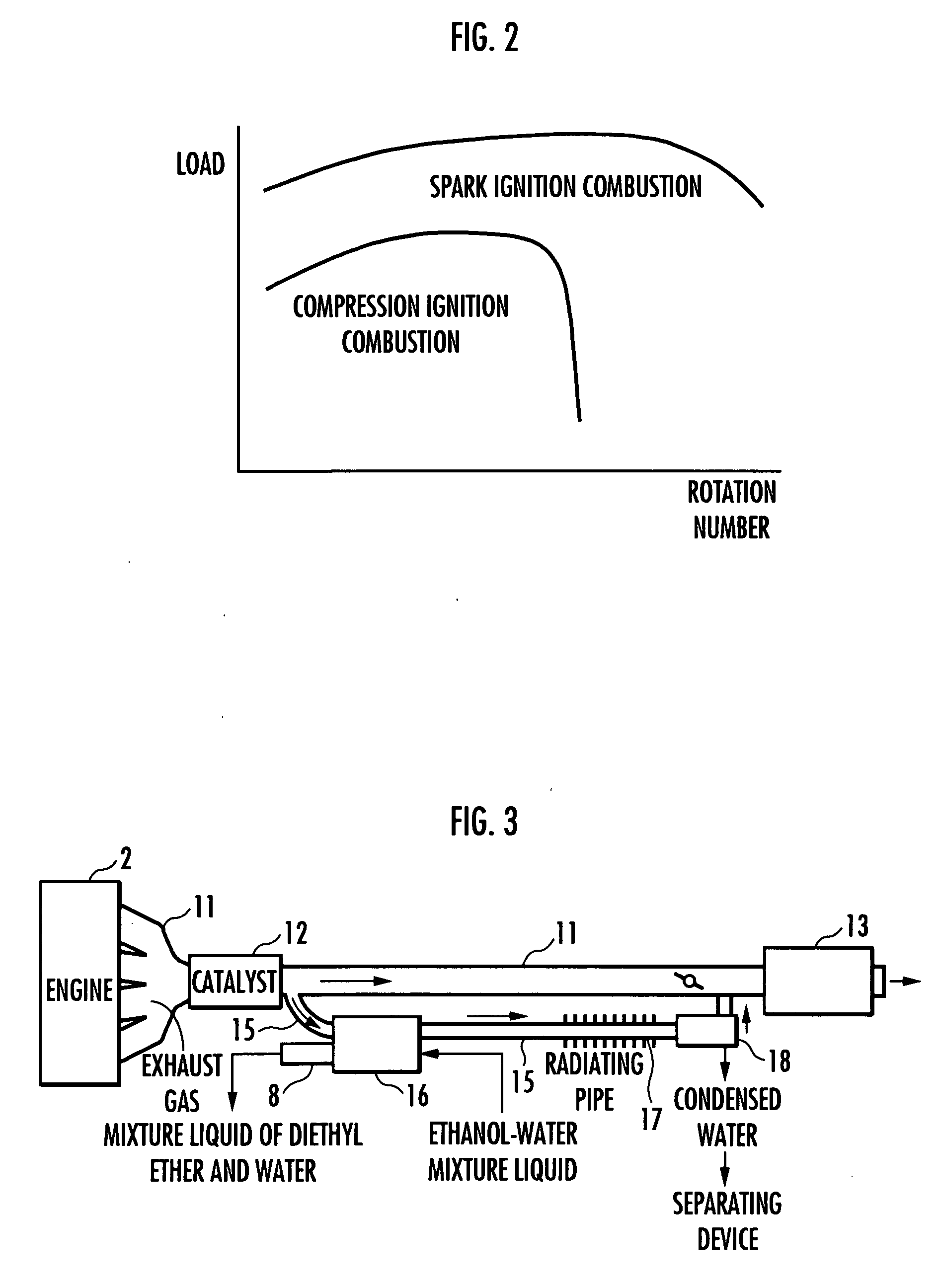
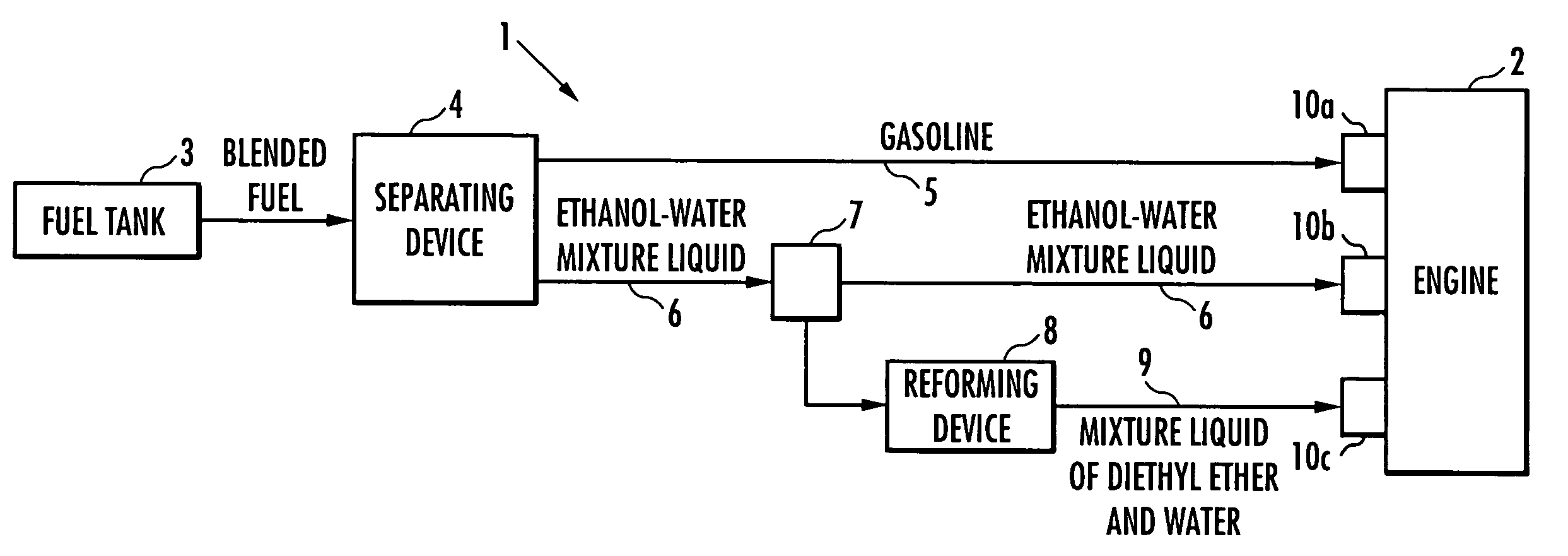
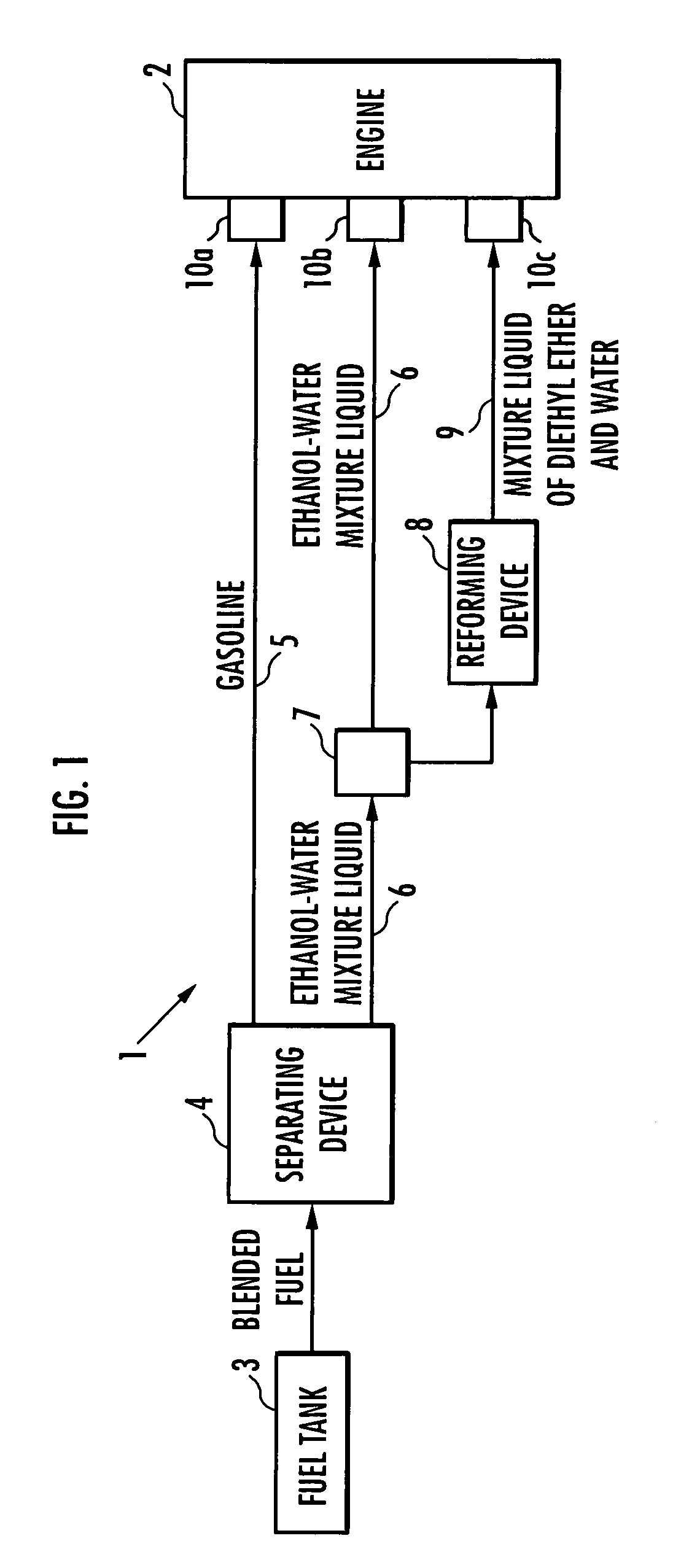
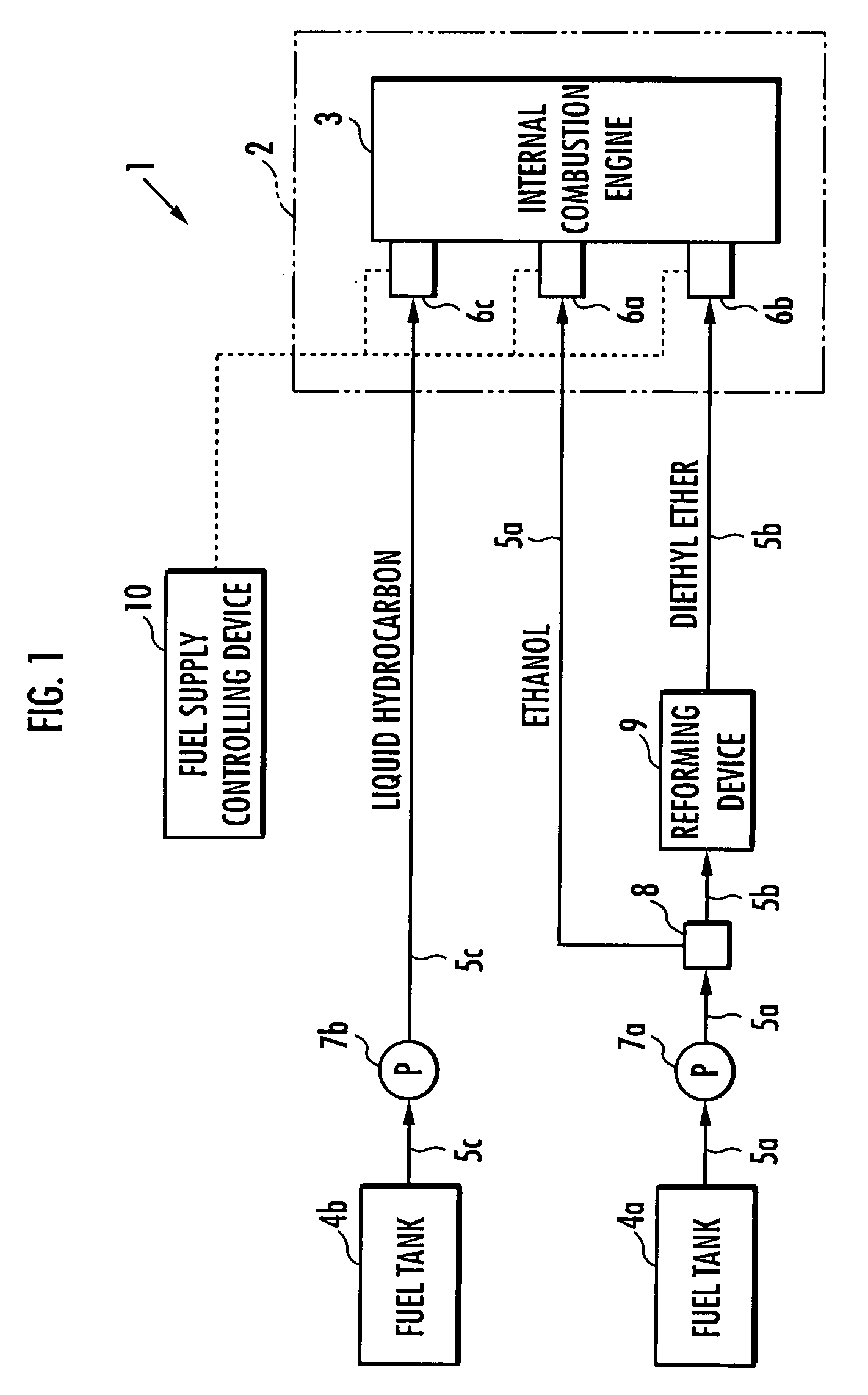
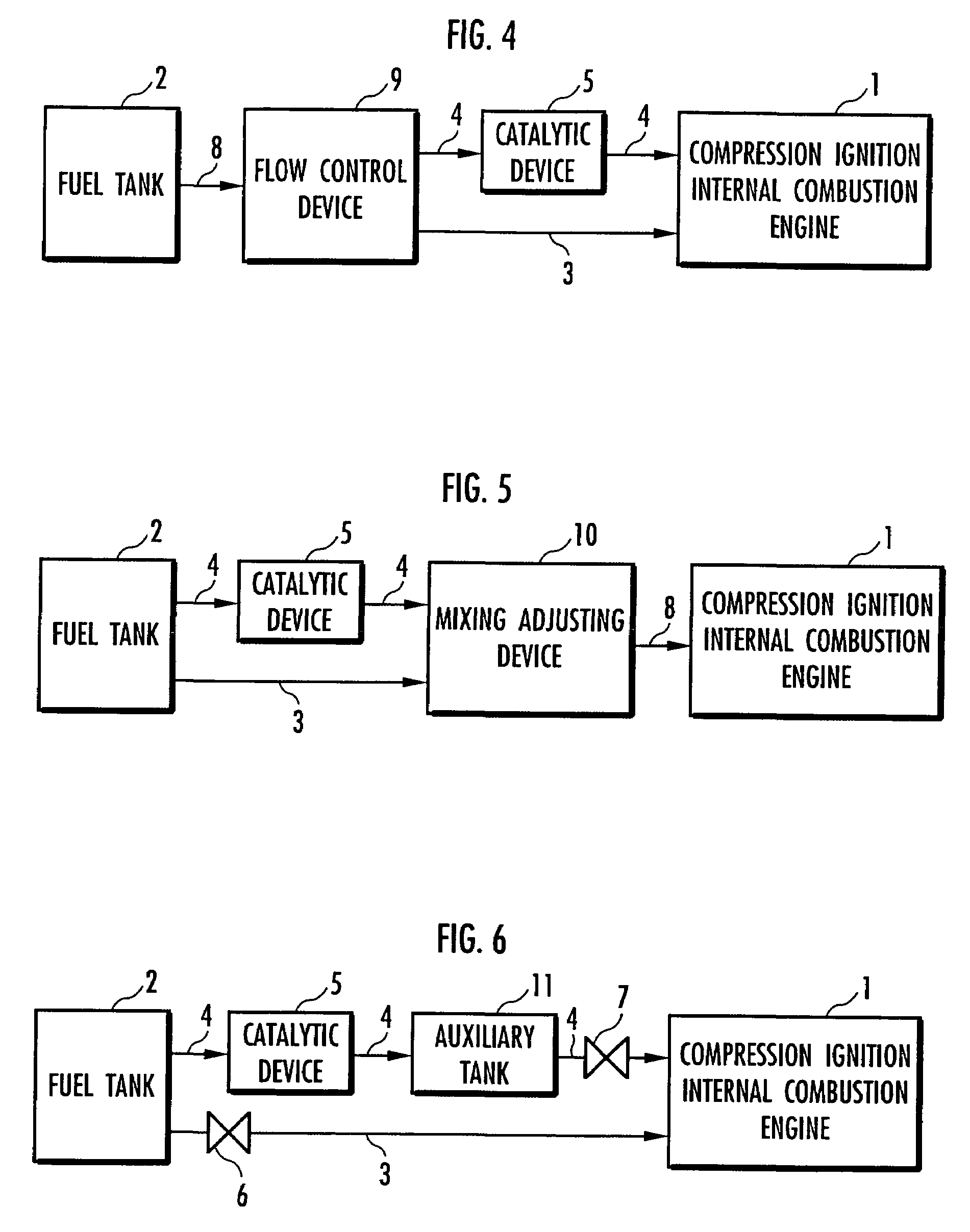
The present invention provides an internal combustion engine system which uses a blended fuel of gasoline and ethanol, operates with high efficiency, and can inhibit nitrogen oxide and the like from being discharged. The internal combustion engine system comprises: a fuel tank 3 that accommodates a blended fuel having an octane number of 80 to 100, which has been prepared by blending gasoline having the octane number of 30 to 85 and ethanol into a weight ratio between 9:1 and 6:4; separating means 4 for adding water to the blended fuel to separate the blended fuel into the gasoline and an ethanol-water mixture liquid; reforming means 8 for reforming one part of the ethanol-water mixture liquid to produce a mixture liquid of diethyl ether and water; and fuel injectors 10a, 10b and 10c which independently inject each of the gasoline, the ethanol-water mixture liquid and the mixture liquid of diethyl ether and water. The internal combustion engine system conducts spark ignition combustion when a load is high, and conducts homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion when the load is low.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Process for the removal of impurities from combustion fullerenes
InactiveUS6923915B2Without incurring undo costEfficient removalMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesO-XylenePurification methods
The invention generally relates to purification of carbon nanomaterials, particularly fullerenes, by removal of PAHs and other hydrocarbon impurities. The inventive process involves extracting a sample containing carbon nanomaterials with a solvent in which the PAHs are substantially soluble but in which the carbon nanomaterials are not substantially soluble. The sample can be repeatedly or continuously extracted with one or more solvents to remove a greater amount of impurities. Preferred solvents include ethanol, diethyl ether, and acetone. The invention also provides a process for efficiently separating solvent extractable fullerenes from samples containing fullerenes and PAHs wherein the sample is extracted with a solvent in which both fullerenes and PAHs are substantially soluble and the sample extract then undergoes selective extraction to remove PAHs. Suitable solvents in which both fullerenes and PAHs are soluble include o-xylene, toluene, and o-dichlorobenzene. The purification process is capable of treating quantities of combustion soot in excess of one kilogram and can produce fullerenes or fullerenic soot of suitable purity for many applications.
Owner:FRONTIER CARBON CORP
Internal combustion engine system
InactiveUS7370609B2Improve efficiencyEmission reductionNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesFuel tankNitrogen oxide
An internal combustion engine system uses a blended fuel of gasoline and ethanol, operates with high efficiency, and can inhibit nitrogen oxide and the like from being discharged. The internal combustion engine system includes: a fuel tank 3 that accommodates a blended fuel having an octane number of 80 to 100, which has been prepared by blending gasoline having the octane number of 30 to 85 and ethanol into a weight ratio between 9:1 and 6:4; A separating device for adding water to the blended fuel to separate the blended fuel into the gasoline and an ethanol-water mixture liquid; A reforming device for reforming one part of the ethanol-water mixture liquid to produce a mixture liquid of diethyl ether and water; and fuel injectors which independently inject each of the gasoline, the ethanol-water mixture liquid and the mixture liquid of diethyl ether and water.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Internal combustion engine system
InactiveUS20080098985A1Accurate timingElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHomogeneous charge compression ignitionNaphtha
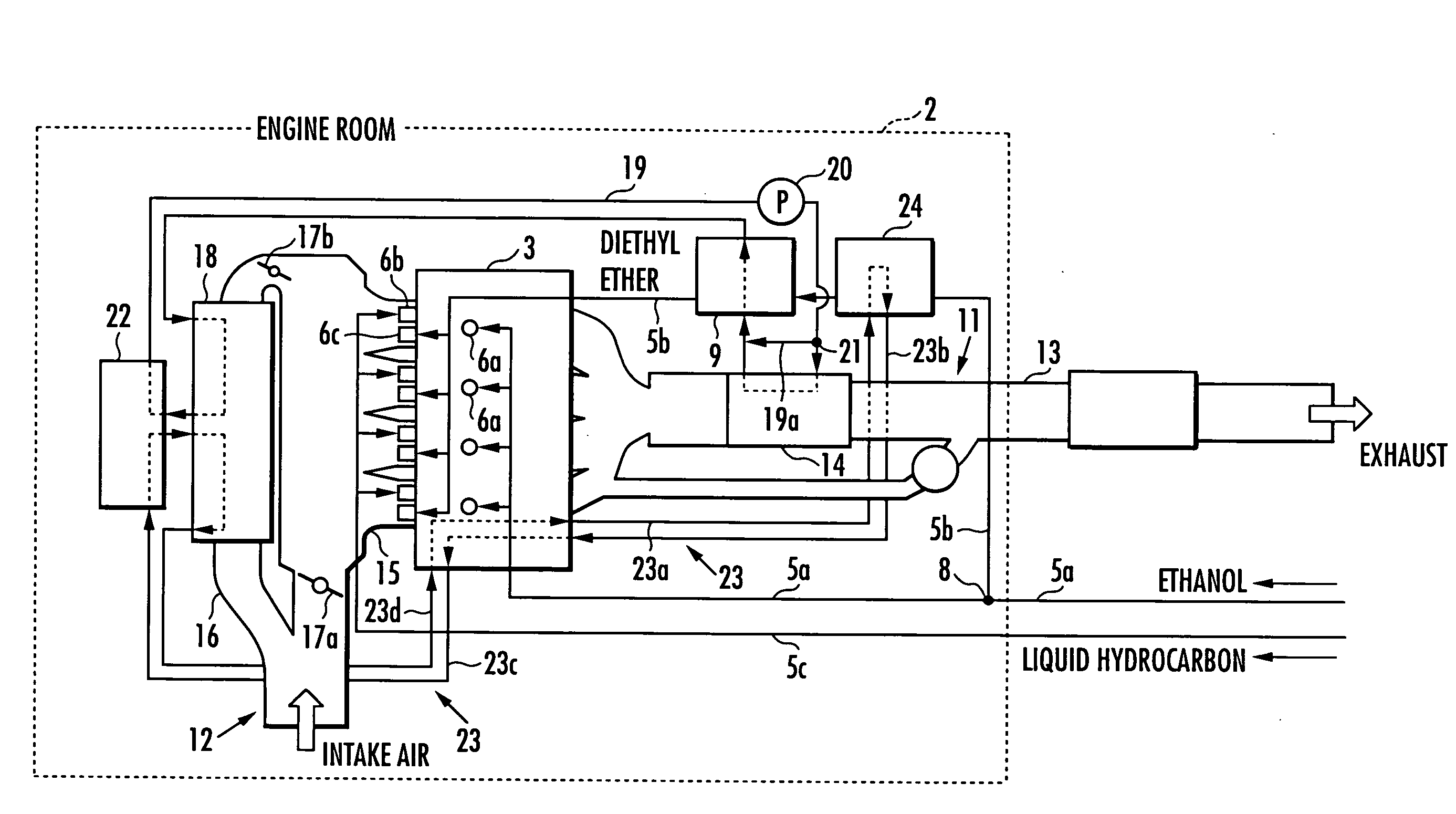
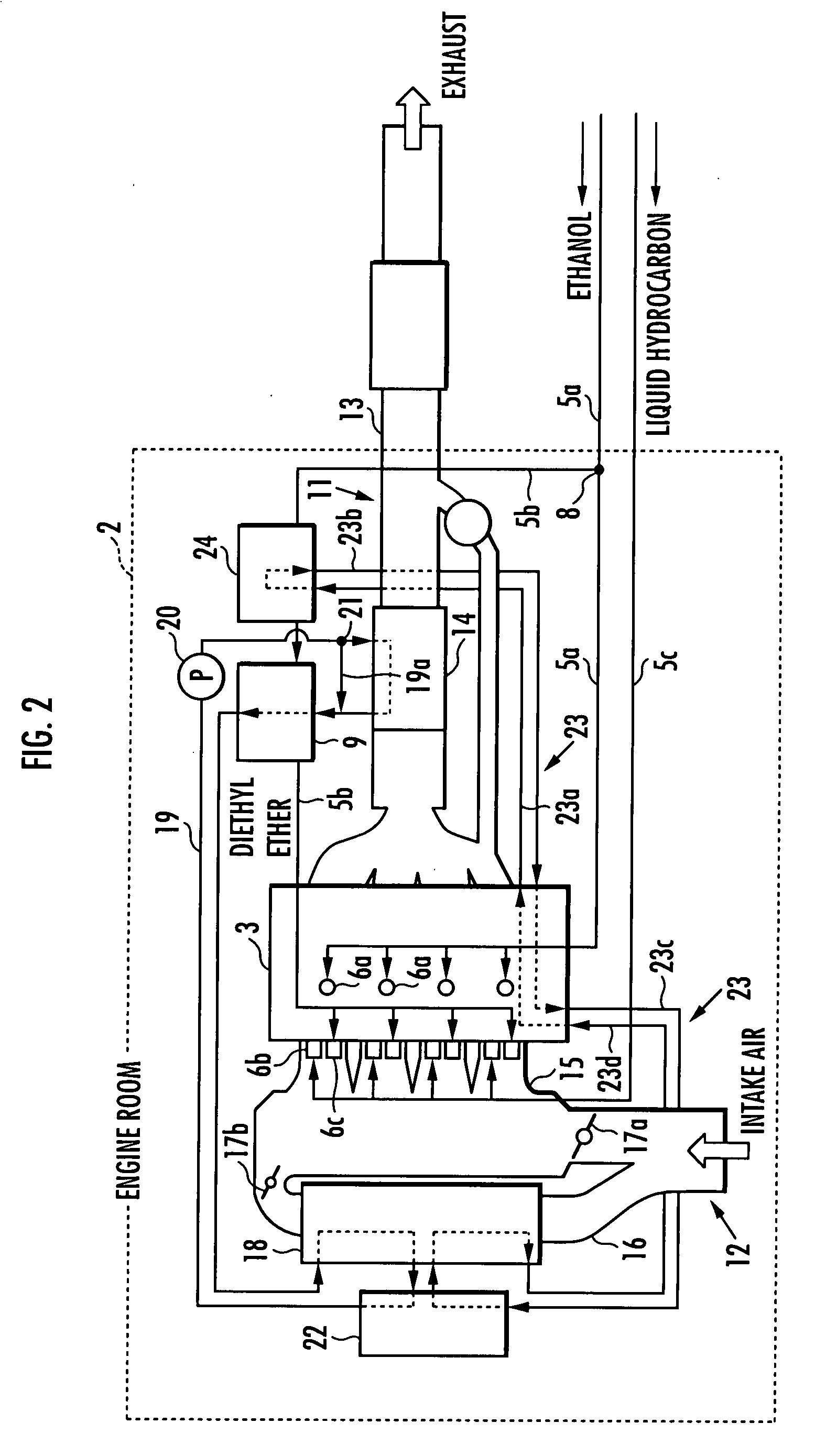
The present invention provides an internal combustion engine system that can precisely control ignition timing on homogeneous charge compression ignition. The internal combustion engine system includes a fuel tank 4a containing ethanol, a fuel tank 4b containing at least one of gasoline and GTL naphtha, a reforming device 9 for reforming ethanol to obtain diethyl ether, a heat exchange device 14 for heating a heating medium, an ethanol heater 9b for heating ethanol with the heating medium, and a fuel supply controlling device 10 for controlling a mixture ratio of the fuel. The internal combustion engine system further includes an intake air heater 18 for heating intake air with the heating medium. The internal combustion engine system further comprises an adiabatic storage container 29 for storing the heating medium during a halt of an internal combustion engine 3. The internal combustion engine system further comprises a flow controlling device 27 for flowing the heating medium to the adiabatic storage container 29 only when a temperature detected by a thermal detector 30a is higher than a temperature detected by a thermal detector 30b during an operation of the internal combustion engine 3. The internal combustion engine system further comprises a fuel tank 42 containing a mixed fuel, and a separating device 43 for separating the mixed fuel into an ethanol-water mixture, gasoline and GTL naphtha by adding water to the mixed fuel.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
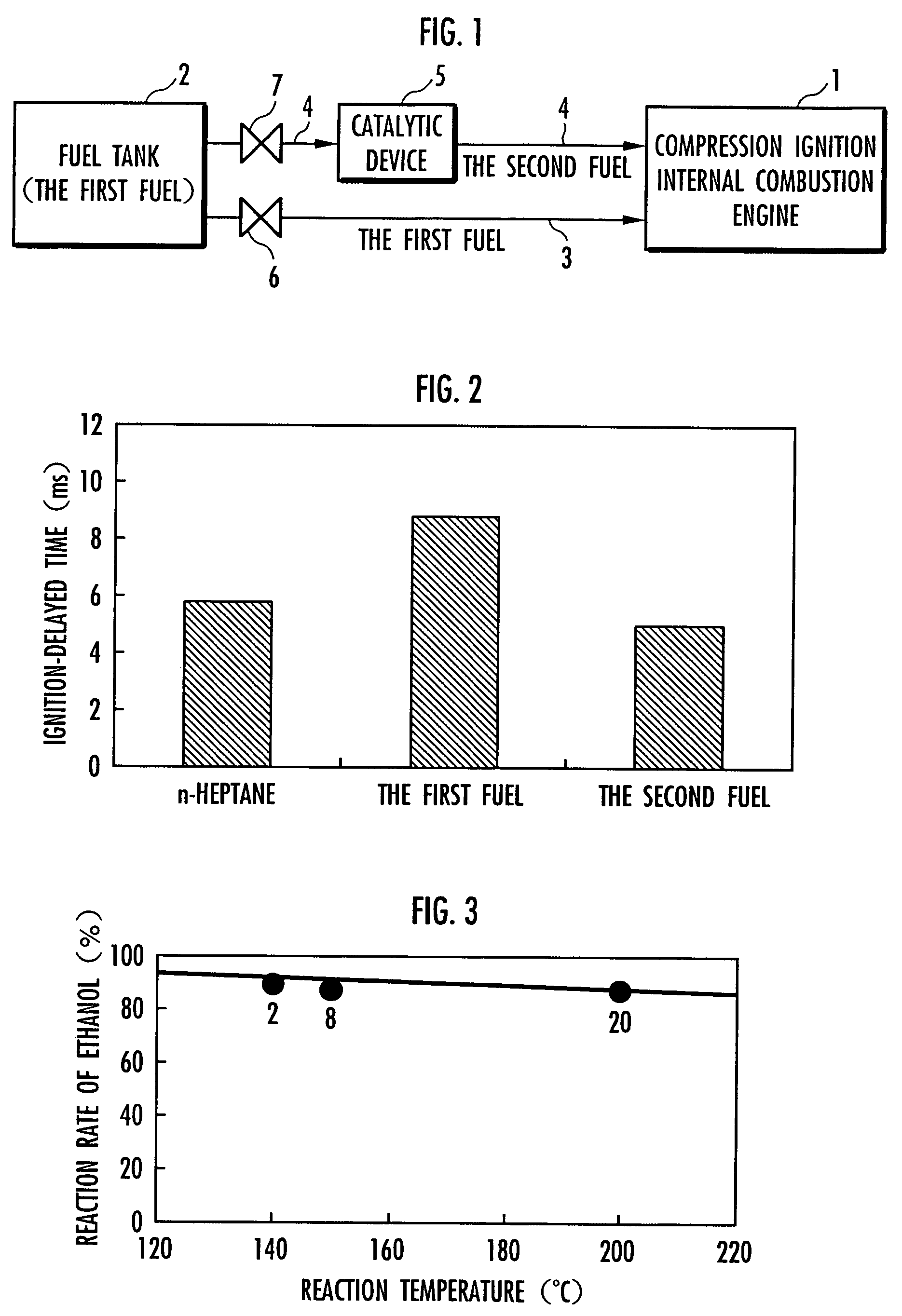
Method for controlling compression ignition internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7261065B2Improve flammabilityRaise the possibilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRoom temperatureInternal combustion engine
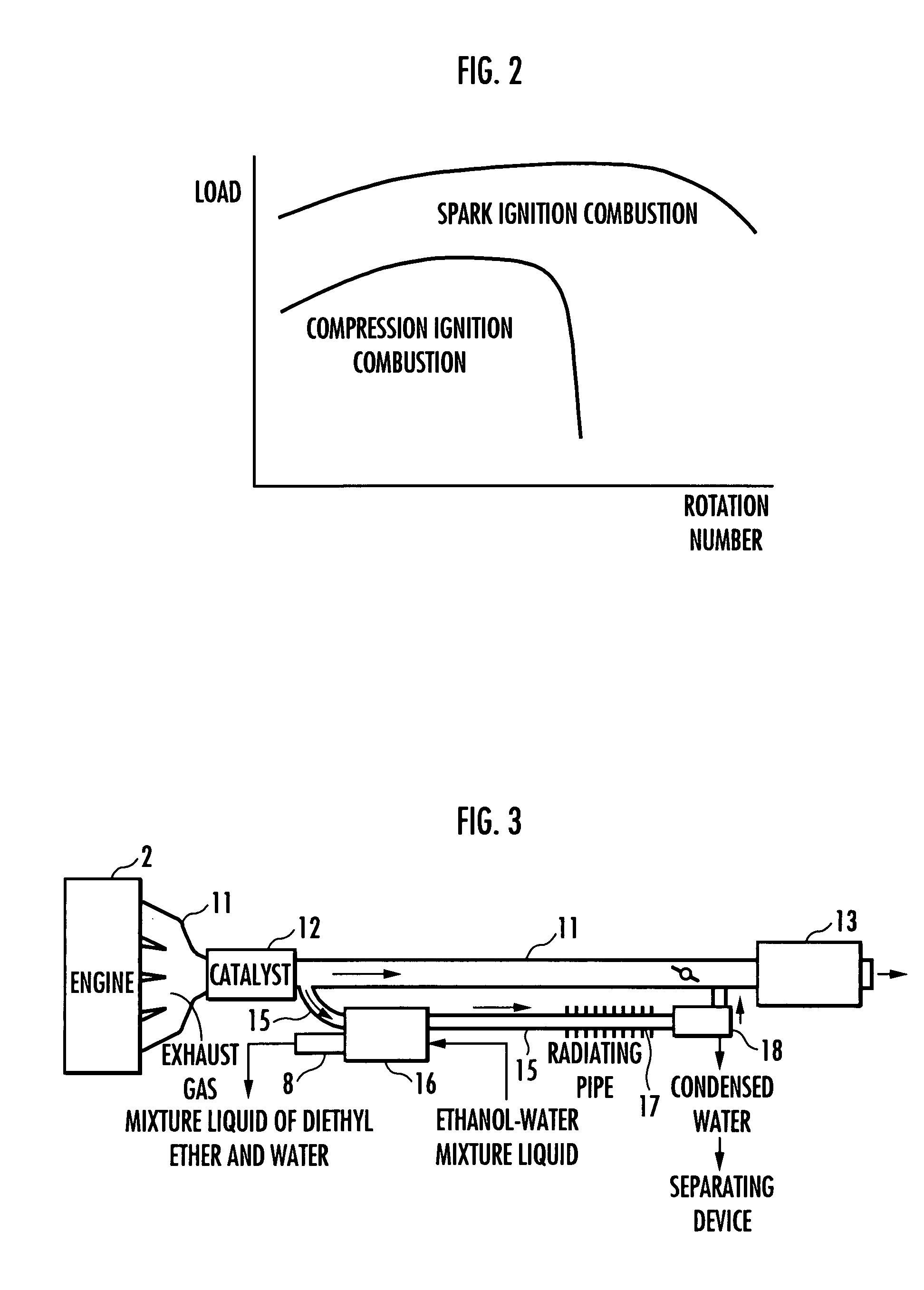
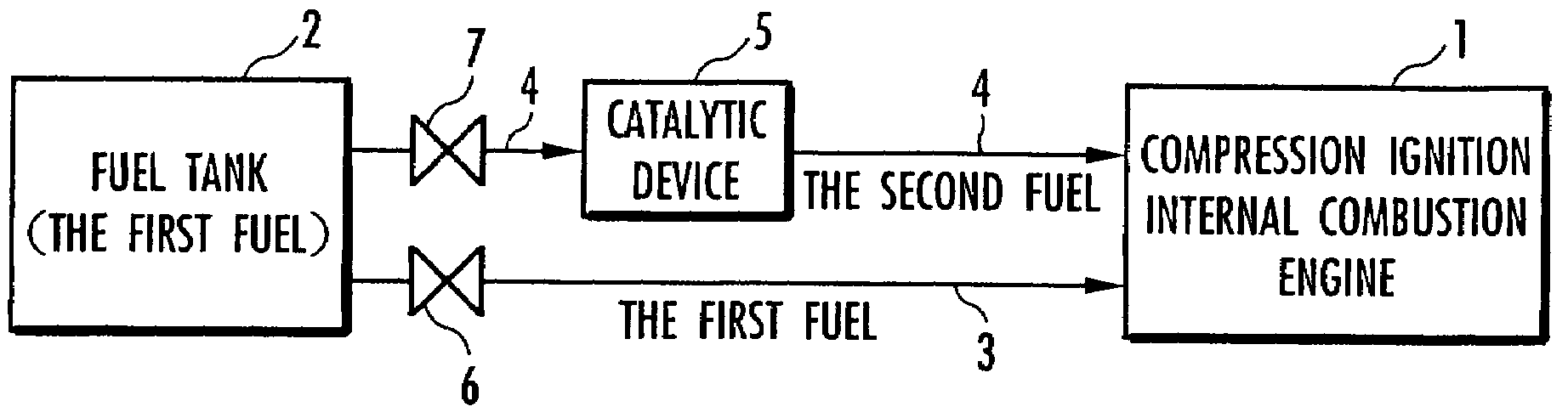
The present invention provides a method for controlling a compression ignition internal combustion engine, which can easily cope with a wide range of demand loads. The compression ignition internal combustion engine 1 has a first fuel 2 containing ethanol, and reforming means 5 for reforming the first fuel into a second fuel having higher ignitability than the first fuel, by converting at least one part of ethanol contained in the first fuel 2 to diethyl ether, and each amount of the first fuel and the second fuel to be supplied to the compression ignition internal combustion engine is varied, in accordance with the change of a load required to the compression ignition internal combustion engine 1. Thus, the proportion of the first fuel to the total fuels supplied to the internal combustion engine 1 is increased, with the increase of the demand load, while the proportion of the second fuel to the total fuels supplied to the internal combustion engine 1 is increased, with the decrease of the demand load. The first fuel 2 contains ethanol and a hydrocarbon which is liquid at room temperature.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
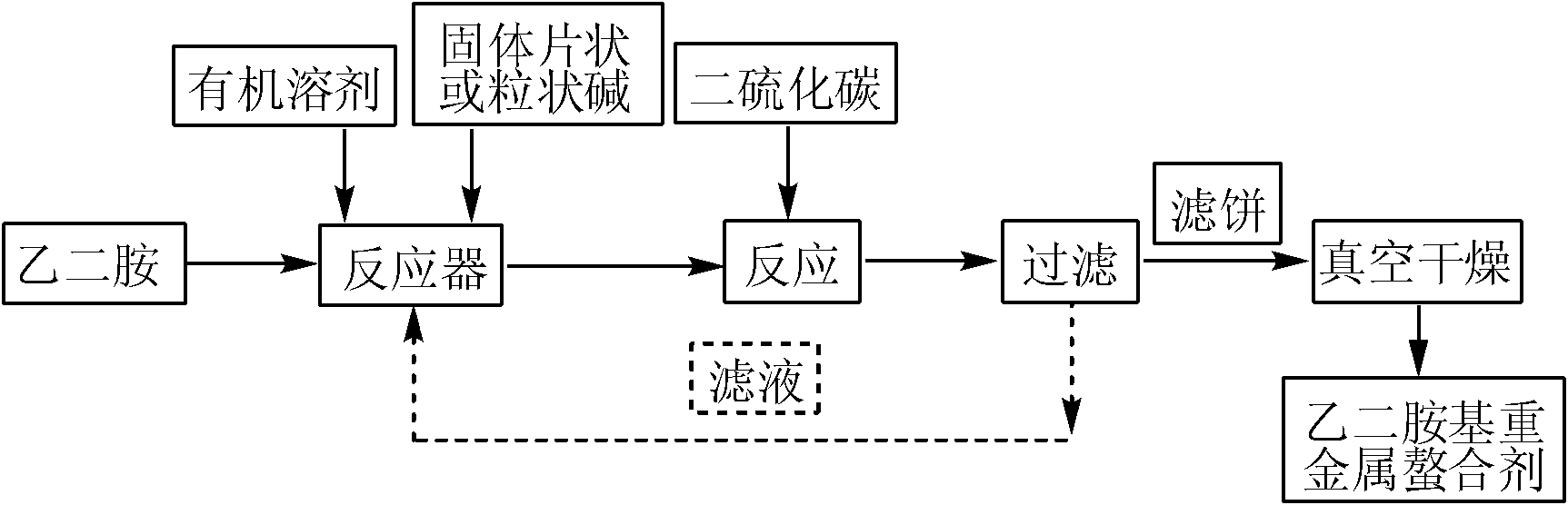
Ethylenediamine-based heavy metal chelating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101857296AOvercoming the defect of spatial mismatchOvercome the defects of large steric hindrance and difficulty in reaching the standard concentration of residual heavy metal ionsWater/sewage treatmentEthylenediamineHeavy metal chelation
The invention belongs to the technical field of removal, purification and entrapment of heavy metal ions in a water body, and in particular relates to an ethylenediamine-based heavy metal chelating agent and a preparation method thereof. The ethylenediamine-based heavy metal chelating agent is prepared by directly reacting ethylenediamine, carbon disulfide and solid alkali in absolute ethyl alcohol or a mixed solvent consisting of absolute ethyl alcohol and diethyl ether in a certain volume ratio. The method overcomes the defect of steric effect of polymer chains when the conventional polymeric chelating agent chelates the heavy metal ions, and also overcomes the defect that floccules have excessive negative charge to obstruct the further growth of the floccules because of mismatched space of chelation groups of small molecules with multiple functional groups. The product is solid powder, has high stability and is convenient to store and transport. The method has the advantages of simple synthetic process, mild reaction conditions, easy operation and control, high reaction speed, high efficiency, recyclable solvent, high utilization rate of raw materials, less discharge of three wastes, environmental-friendly technical process, conventional equipment and easy industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
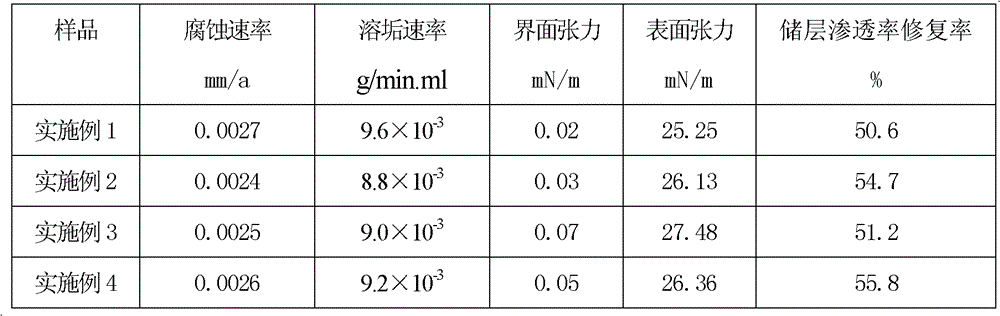
Blocking remover of gas well shaft
The invention relates to a blocking remover of a gas well shaft. The blocking remover comprises, by weight, 5-25% of an alcohol ether compound, 0.5-10% of a dispersant, 1-10% of a cleaning agent, and 0.5-5% of chelating agent, with the balance being a nitrogen-containing polar solvent, wherein the nitrogen-containing polar solvent is one selected from N,N dimethyl formamide, N,N dimethyl acetamide, and N-methyl pyrrolidone, the alcohol ether compound is one selected from glycol-ether, glycol-propyl ether, glycol-butyl ether, and diglycol-ether, the disperant whose micelle particle size is from 20nm to 100nm is a middle-phase microemulsion-type dispersant mixed by kerosene, water, a surfactant and a cosurfactant, the cleaning agent is one selected from allene diamine, acetonitrile and pentylamine, and the chelating agent is one selected from sodium citrate and EDTA. The blocking remover has the advantages that corrosivity is weak, that the speed of dissolving blockage is fast, that the product performance is stable in high temperatures, and that the blocking remover can reduce damages caused by water locking and fouling in areas close to gas wells, and can recover the permeability of storing layers.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
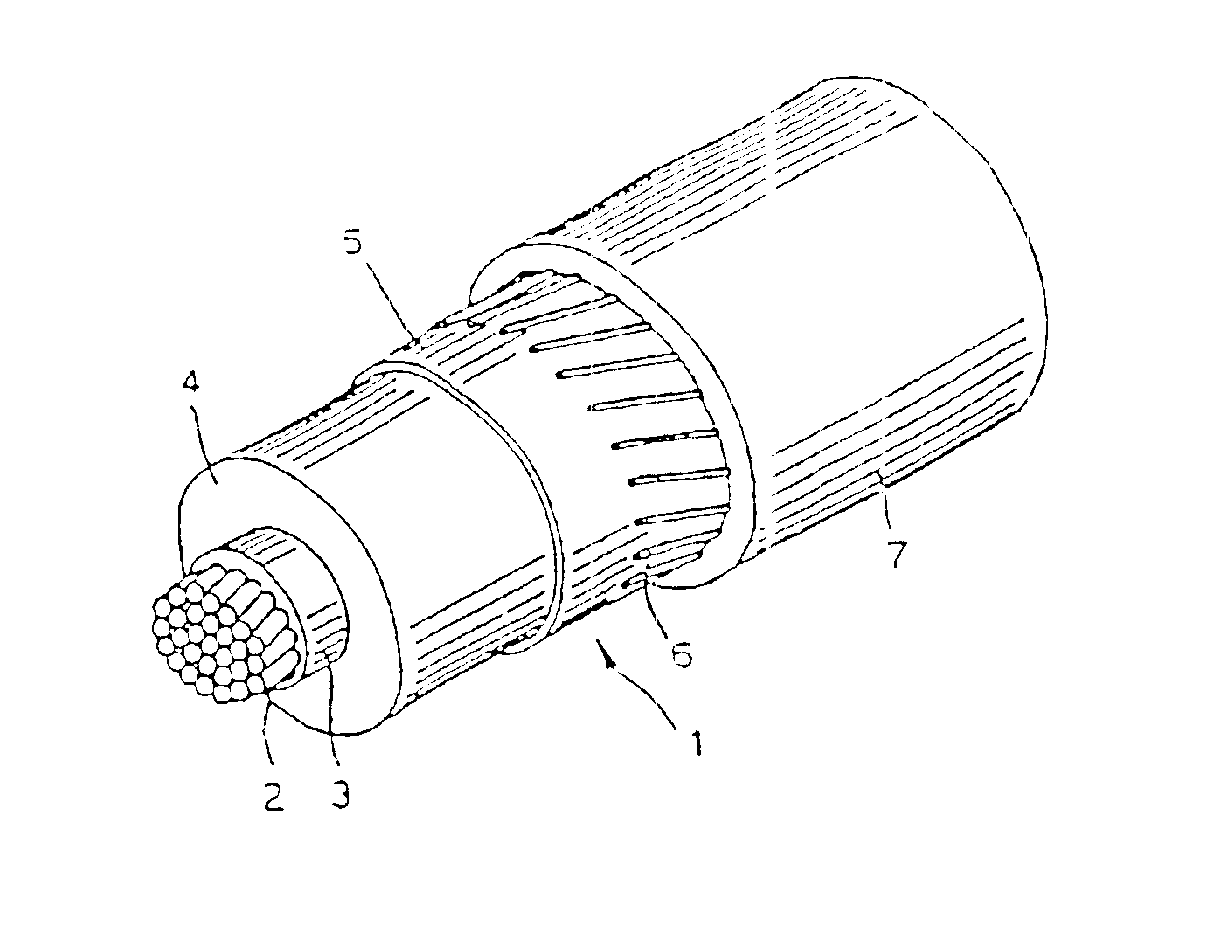
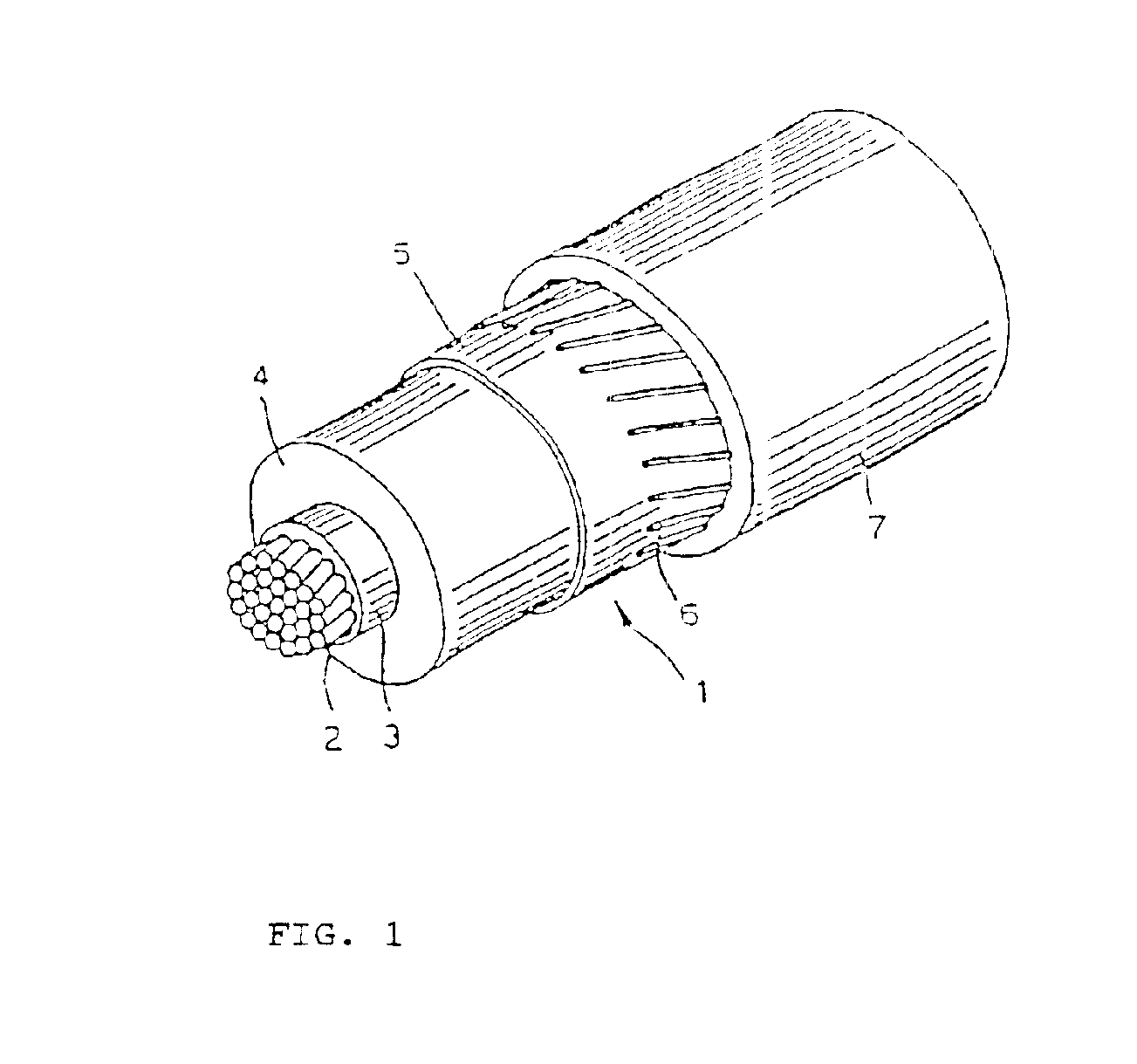
Cable with recyclable covering
InactiveUS6861143B2Improve performanceGood flexibilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical conductorEthylene Homopolymers
A cable includes at least one conductor and at least one covering layer. The at least one covering layer includes a thermoplastic polymer material. The polymer material includes a propylene homopolymer or a copolymer of propylene with an olefin comonomer. The olefin comonomer is ethylene, one or more α-olefins other than propylene, or ethylene and one or more α-olefins other than propylene. The homopolymer or copolymer has a melting point between 140° C. and 165° C., a melting enthalpy between 30 J / g and 80 J / g, a boiling diethyl ether soluble fraction less than or equal to 12 wt % and melting enthalpy less than or equal to 4 J / g, a boiling n-heptane soluble fraction between 15 wt % and 60 wt % and melting enthalpy between 10 J / g and 40 J / g, and a boiling n-heptane insoluble fraction between 40 wt % and 8 wt % and melting enthalpy greater than or equal to 45 J / g.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA +1
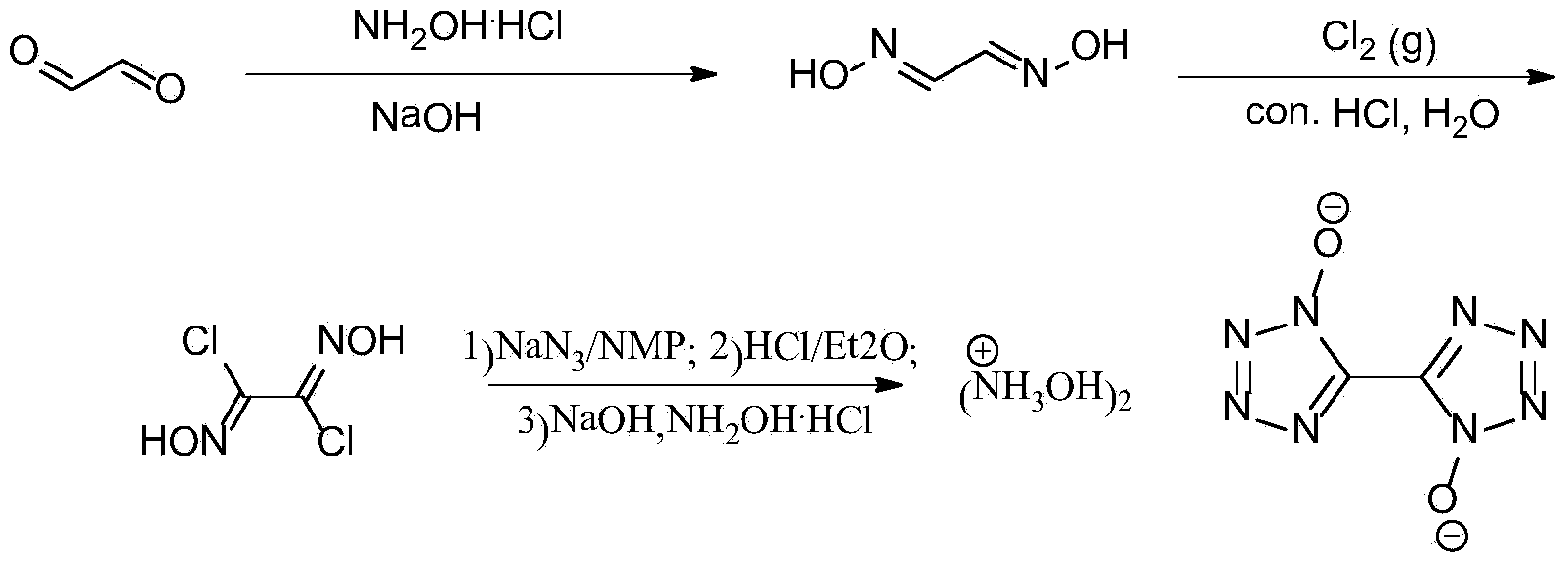
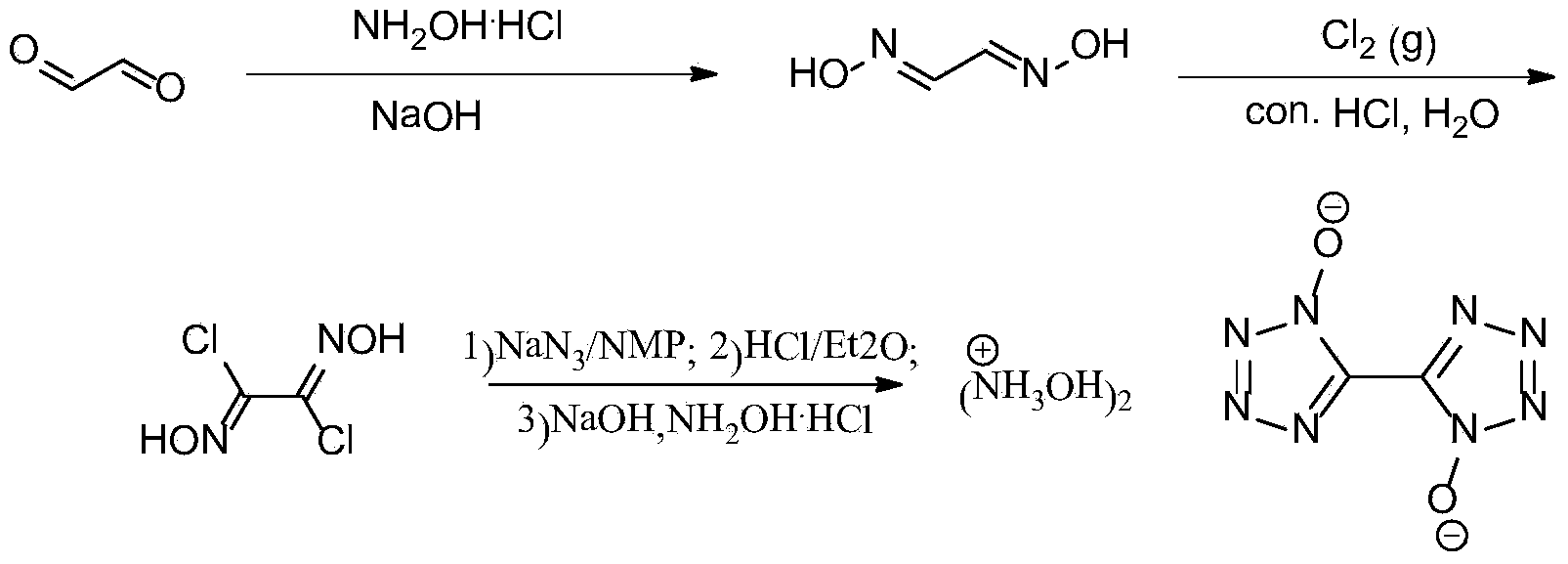
Synthetic method of 5, 5'-bistetrazole-1, 1'-dioxo hydroxyl ammonium salt (TKX-50)
InactiveCN103524444AAvoid purification processEasy to operateOrganic chemistryFiltrationOrganic synthesis
The invention provides a method for preparing 5, 5'-bistetrazole-1, 1'-dioxo hydroxyl ammonium salt (TKX-50), and belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the steps as follows: step one, glyoxime is prepared, and the yield is 62%; step two, a product obtained in the step one is dissolved in water and concentrated hydrochloric acid, chlorine is introduced at the temperature of 0 DEG C for a reaction for a period of time, and dichloroglyoxime is obtained; and finally, a product obtained in the step two is dissolved in a solvent, and the product and sodium azide have a reaction at the temperature of 0 DEG C for a period of time; after that, the mixture is transferred into diethy ether, and sealed for a reaction at the room temperature overnight after HCl is introduced for a period of time; and after diethyl ether and most HCl gas are volatilized, pH of an aqueous NaOH solution is regulated to be about 8, reflux cooling is performed, filtered and separated solids are dissolved in hydroxylamine hydrochloride to have a reaction for a period of time, and TKX-50 is obtained. According to the method, glyoxal is adopted as a raw material, water is adopted as a solvent for preparation of dichloroglyoxime in the step two, and only direct filtration is required in postprocessing, so that the tedious purification process is prevented, and the cost is reduced; and besides, a target product TKX-50 is synthetized through three steps of reactions, the total yield is up to 34%, the reaction condition is mild, the operation is simple and convenient, and the industrialization is easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Non-irritating solvent-borne polymeric coatings for application to the skin
InactiveUS20070048355A1Accelerate the rate of drying of such coatingsStinging and burning problem isBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLiquid mediumKetone
A method and composition for reducing or eliminating stinging that may accompany application of topical solution of a skin-compatible polymeric material to a skin wound, abrasion, burn or other skin injury. The topical solution may contain one or more skin-irritating chemicals, such as diethyl ether, ethanol, ethyl acetate, methyl acetate, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone and combinations thereof. The method includes: (i) providing a composition that contains between 1% and 10% by weight of the skin-compatible polymeric material dissolved in a liquid medium suitable for human topical use in which the liquid medium includes less than 20% combined weight of skin-irritating chemicals, and at least 45% combined weight of at least one volatile solvent and / or volatile co-solvent, in which the molecules constituting this 45% combined weight portion of the liquid medium contain at least 5 carbon atoms, and the liquid medium has an initial boiling point at 1 atmosphere of greater than 35° C. and less than 150° C., and causes little or no stinging when applied to a skin injury, and (ii) applying the composition to the skin of a patient at the site of the skin injury.
Owner:PERLMAN DANIEL
Room temperature synthesis of GaN nanopowder
InactiveUS20070297969A1Yield andIncrease ratingsMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsReaction rateRoom temperature
In the direct production of GaN by the metathesis of Li3N and GaCl3 or GaBr3 or GaI3, the reaction rate and yields can be greatly enhanced by including diethyl ether in the reaction system.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Preparation method of polypeptide synthesis carbetocin
ActiveCN102167723AConvenient sourceHigh peptide yieldPeptide preparation methodsCarbetocinDiethyl ether
The invention discloses a preparation method of polypeptide synthesis carbetocin. The technical scheme of the method comprises the steps of taking Rink Amide MBHA (methylbenzene hydrogen amine) resin as an initial raw material; taking Fmoc-protected amino acid as a monomer; sequentially connecting amino acid, wherein Cys adopts Fmoc-Cys (CH2CH2CH2COOR)-OH, and the last amino acid uses Fmoc-Tyr (Me)-OH, and obtaining protected nonapeptide resin; removing the Fmoc azyl protected group of Tyr; cutting straight chain peptide from the resin by peptide cutting reagents such as FTA (fault tree analysis) and the like; precipitating a straight chain peptide rough product by adding diethyl ether; performing ring formation reaction by adding BOP (butyl octyl phthalate) / HOBt (oxhydryl benzotriazole) / DMF (dimethyl formamide); and purifying the preparation type HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) in a separating way to obtain a target product. After the method is used, the each-step peptide connecting yield is more than 99%, the peptide cutting yield is 96.2%, and the gross yield is as high as more than 35%. The preparation method is convenient to industrial implementation, and has a higher industrial prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA
New method for preparing ruthenium nitrosylnitrate solid
ActiveCN102167405AReduce usageHigh purityRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsDiethyl etherSodium nitrite
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Foamed polyhydroxyalkanoate resin particles and method of producing the foamed particles
InactiveUS20090176900A1Good environmental compatibilityEasy-to-use, energy-saving and economicalDiethyl etherCopolymer
It is intended to provide an easy-to-use, energy-saving and economical method of producing foamed resin particles having a high environmental compatibility by using an ether, which generates neither sulfur oxide nor sot in the course of disposal and incineration and enables considerable reduction in nitrogen oxide formation, and further using a resin which originates in a plant and contributes to the carbon dioxide fixation. Namely, a method of producing foamed P3HA resin particles comprising the step of feeding particles of a resin containing a copolymer, which is produced by a microorganism and has a repeating unit represented by the general formula (1) [-CHR-CH2-CO-O-] (wherein R represents an alkyl group represented by CnH2n+1 and n is an integer of from 1 to 15), and a foaming agent into an airtight container, and the step of heating the mixture until the resin particles become softening, then releasing one end of the airtight container and discharging the resin particles into an atmosphere with a pressure lower than the pressure in the airtight container to thereby foam the resin particles and give foamed particles. In this method of producing foamed P3HA resin particles, the foaming agent is at least one member selected from the group consisting of dimethyl ether, diethyl ether and methyl ethyl ether.
Owner:MERIDIAN
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
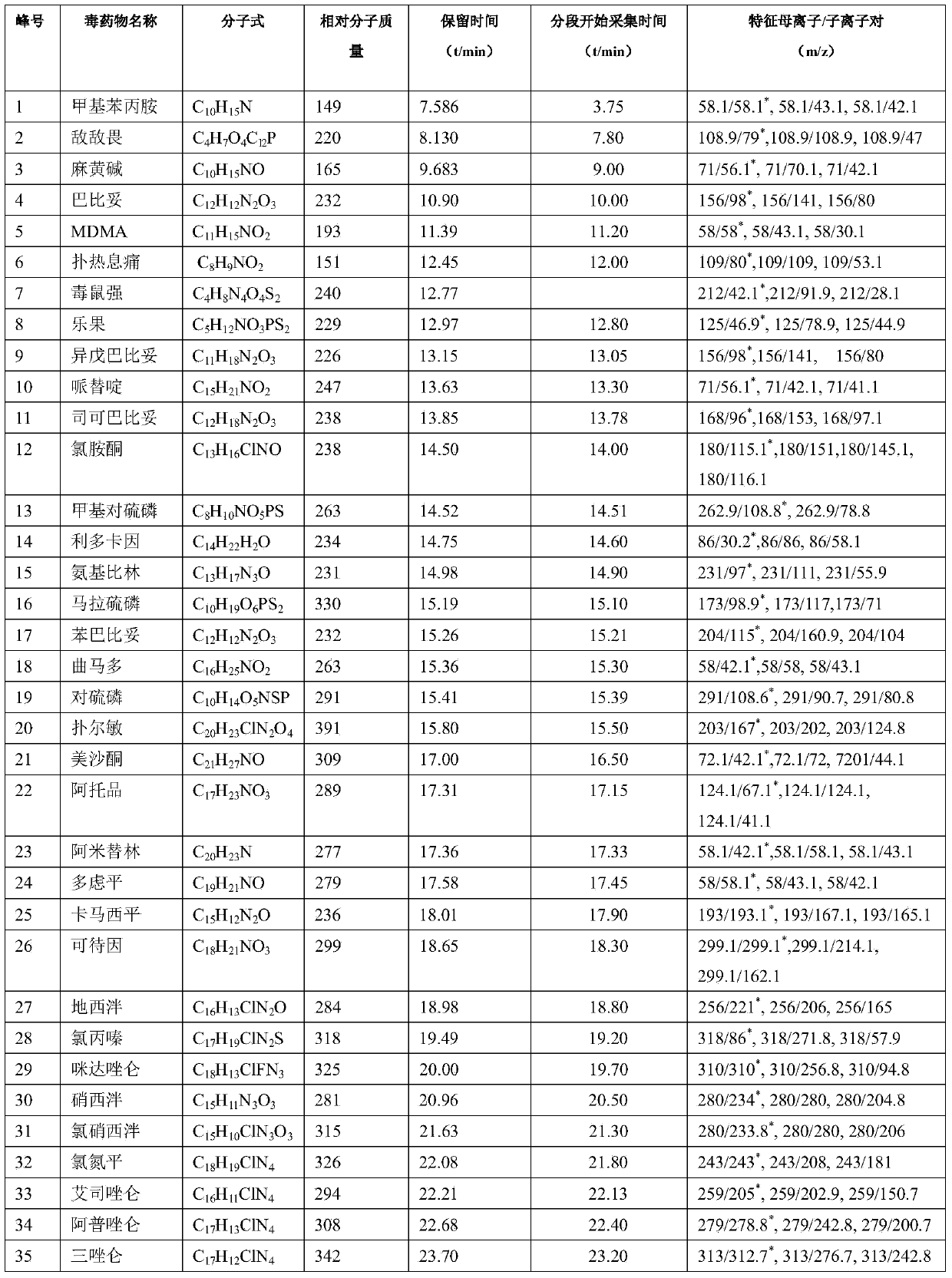
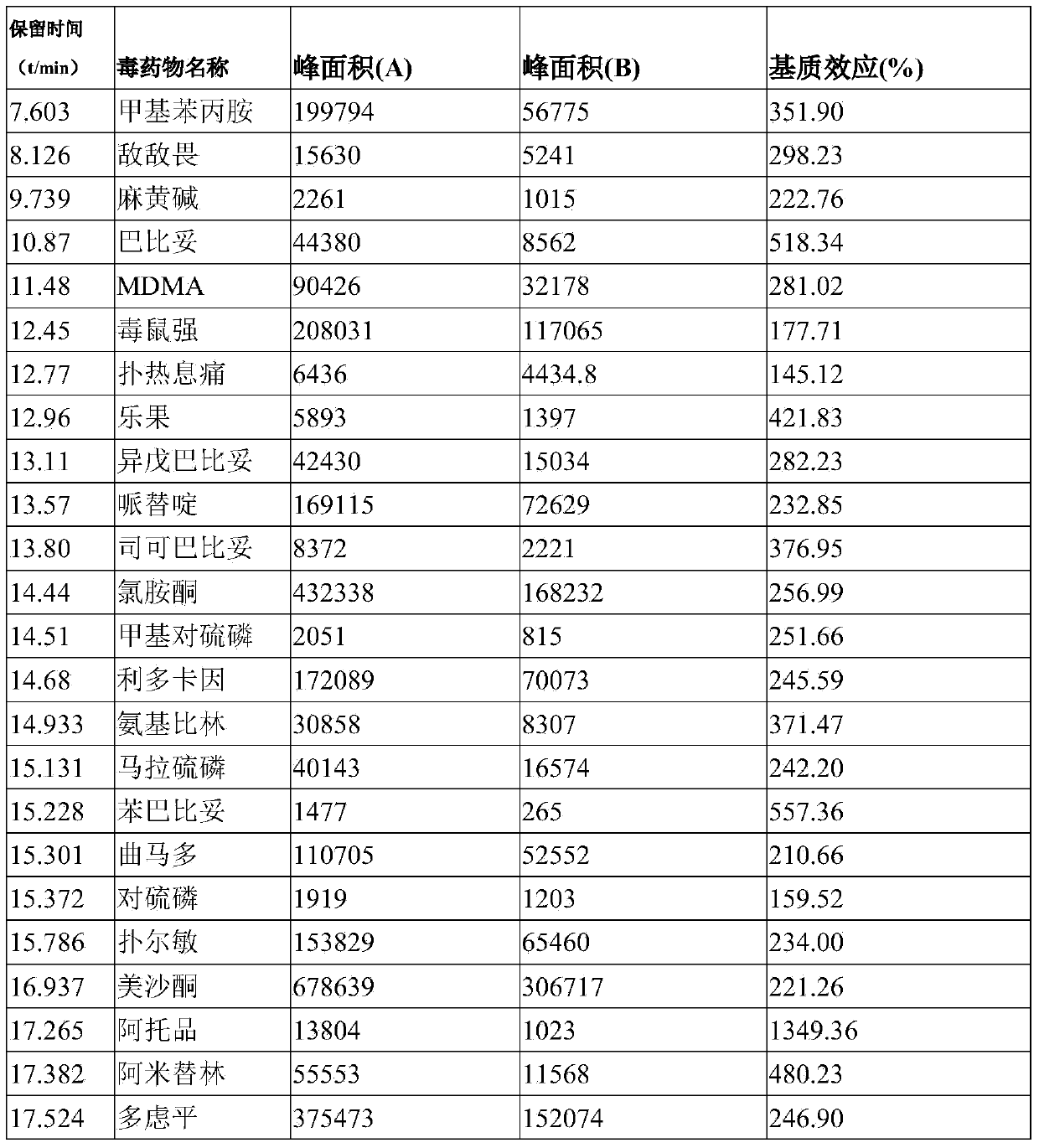
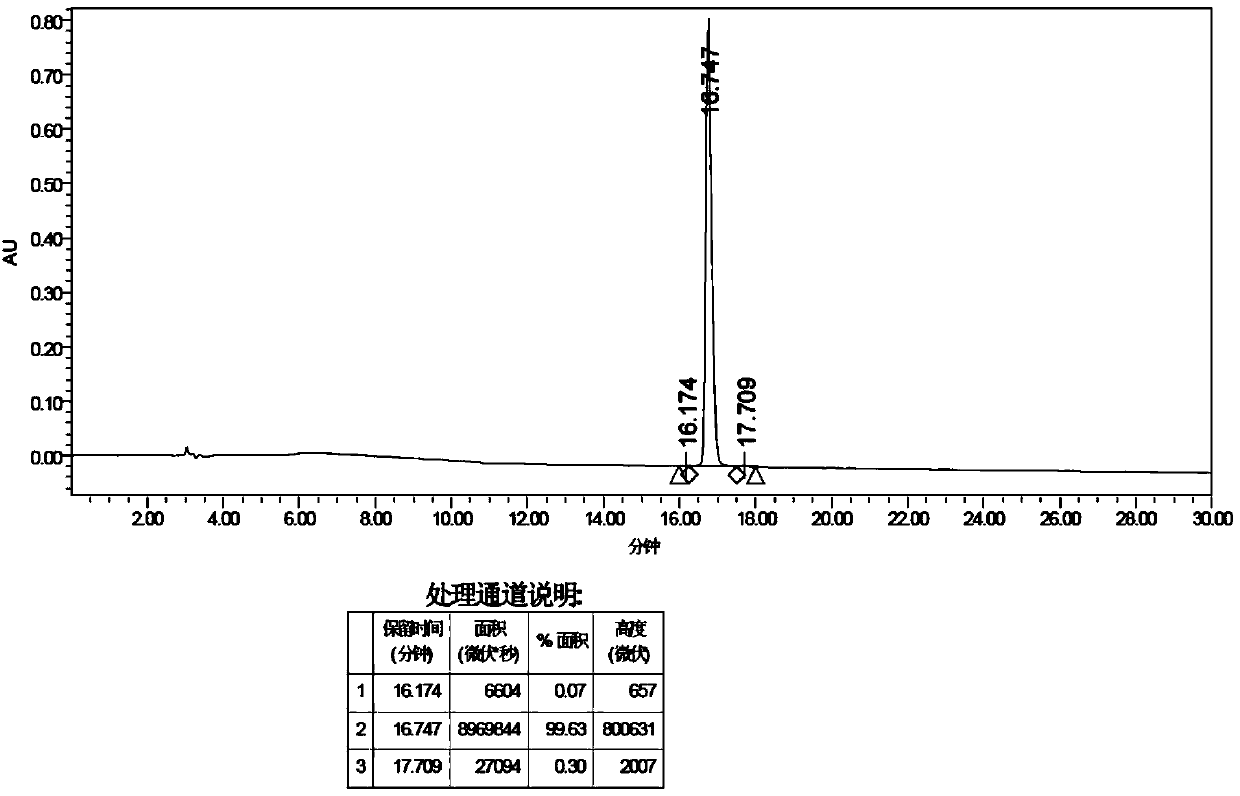
Series quadrupole-rod gas-chromatographic mass spectrometry detection method for 35 toxic medicaments in urine
InactiveCN103808846AAccurate Qualitative and Quantitative AnalysisEliminate distractionsComponent separationGas phaseRetention time
The invention discloses a series quadrupole-rod gas-chromatographic mass spectrometry detection method for 35 toxic medicaments in urine. The series quadrupole-rod gas-chromatographic mass spectrometry detection method comprises the steps of constructing a multiple-reaction detection method on a series quadrupole-rod gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer through standard substances of 35 toxicants (medicines), and determining 2-3 pairs of feature parent ions and daughter ions and the retention time of each toxicants (medicines); extracting a urine sample to be detected through diethyl ether, performing ultrasonic and centrifugal treatment, blow-drying and dissolving, and then qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing the toxicants (medicines) through a tandem mass spectrum MRM. By the adoption of a series quadrupole-rod gas-chromatographic-mass spectrometry / mass spectrometry method (GC-MS / MS), the method disclosed by the invention can quickly screen 35 conventional toxicants (medicines) in the urine of a human body; a detection result is accurate, sensitive and quick; the recycling rate of toxicants (medicines) is 80.82-118.56 percent; the detection limit is up to 0.0014-1.8 micrograms per microliter.
Owner:FUJIAN INT TRAVEL HEALTH CARE CENT
Aluminum electroplating solution
InactiveUS20130168258A1Accelerated precipitationImprove film thickness uniformitySolubilityAluminum metal
Owner:HITACHI LTD
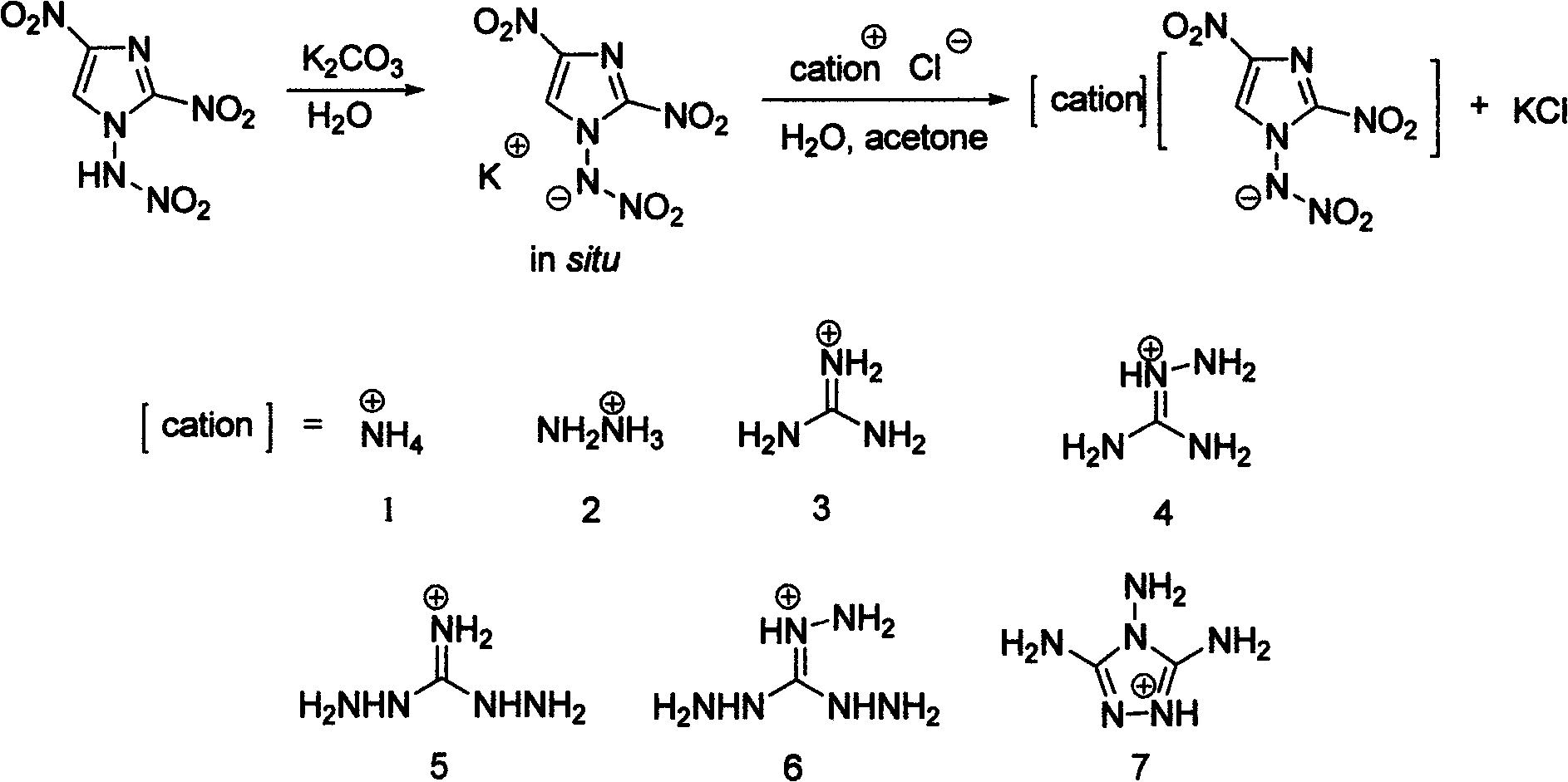
Energetic ion salts of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103483264AExcellent detonation speed and pressure performanceThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationNitroimidazoleHydrazine compound
The invention discloses energetic ion salts of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of energetic materials. The synthetic method is as follows: dissolving the 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe in deionized water to obtain a pale yellow clear liquid, adding with stirring 0.5 time molar equivalent of potassium carbonate at room temperature for in-situ generation of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe potassium salt, then adding one time molar equivalent of ammonium chloride, hydrazine hydrochloride, guanidine hydrochloride, monoaminoguanidine hydrochloride, diaminoguanidine hydrochloride, triaminoguanidine hydrochloride and 3, 4, 5-triamino-1, 2, 4-triazole hydrochloride, stirring to precipitate a pale yellow solid precipitate, after about 1 hour of reaction, filtering the pale yellow precipitate, further recrystallizing a coarse product by use of an acetone and diethyl ether mixed solvent to obtain a pure product. The synthetic method of the invention is simple, mild in condition and high in yield, and is environmental friendly due to using of the deionized water as a solvent. The density of involved seven salts is 1.70-1.93g cm<-3>, the detonation velocity calculated by EXPLO software is between 8370 and 9209 m s<-1>, the detonation pressure is between 29.3 and 40.5 GPa, the actually measured impact sensitivity is 4-40J, the detonation performance is excellent, and the energetic ion salts are potential energetic materials.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Solid-phase synthesis method of degarelix
ActiveCN103992392AThe process steps are simpleMild conditionsLuteinising hormone-releasing hormonePeptide preparation methodsAcetic anhydrideDiethyl ether
The invention discloses a solid-phase synthesis method of degarelix. The solid-phase synthesis method of degarelix comprises the following steps: on the basis of taking Fmoc-amino resin as a solid-phase carrier, replacing orotic acid fragments connected with an alanine benzene ring in the fifth site and an amino in the fourth site with ivdde, and performing sequential condensation reaction from the end C to the end N so as to connect 10 protected amino acids, thereby obtaining a full-protective peptide resin; then removing the Fmoc protecting group of end N D-Nal, acetylating by using acetic anhydride and pyridine, replacing ivDde with Hor, cutting the peptide resin by using a splitting agent, and precipitating by using frozen diethyl ether to obtain crude peptide. Besides, the invention also relates to a method for synthesizing a raw material Fmoc-Aph(ivDde)-OH by use of ivDde-OH and Fmoc-Aph-OH. The solid-phase synthesis method of degarelix has the advantages that the ivDde is introduced to synthesize decapeptide firstly and then the Hor is used as a substitute to avoid a rearrangement side reaction; the solid-phase synthesis method is simple in process steps, easy to control, low in influence on a human body and the environment, high in yield, and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:NANTONG SHIMEIKANG PHARMA CHEM
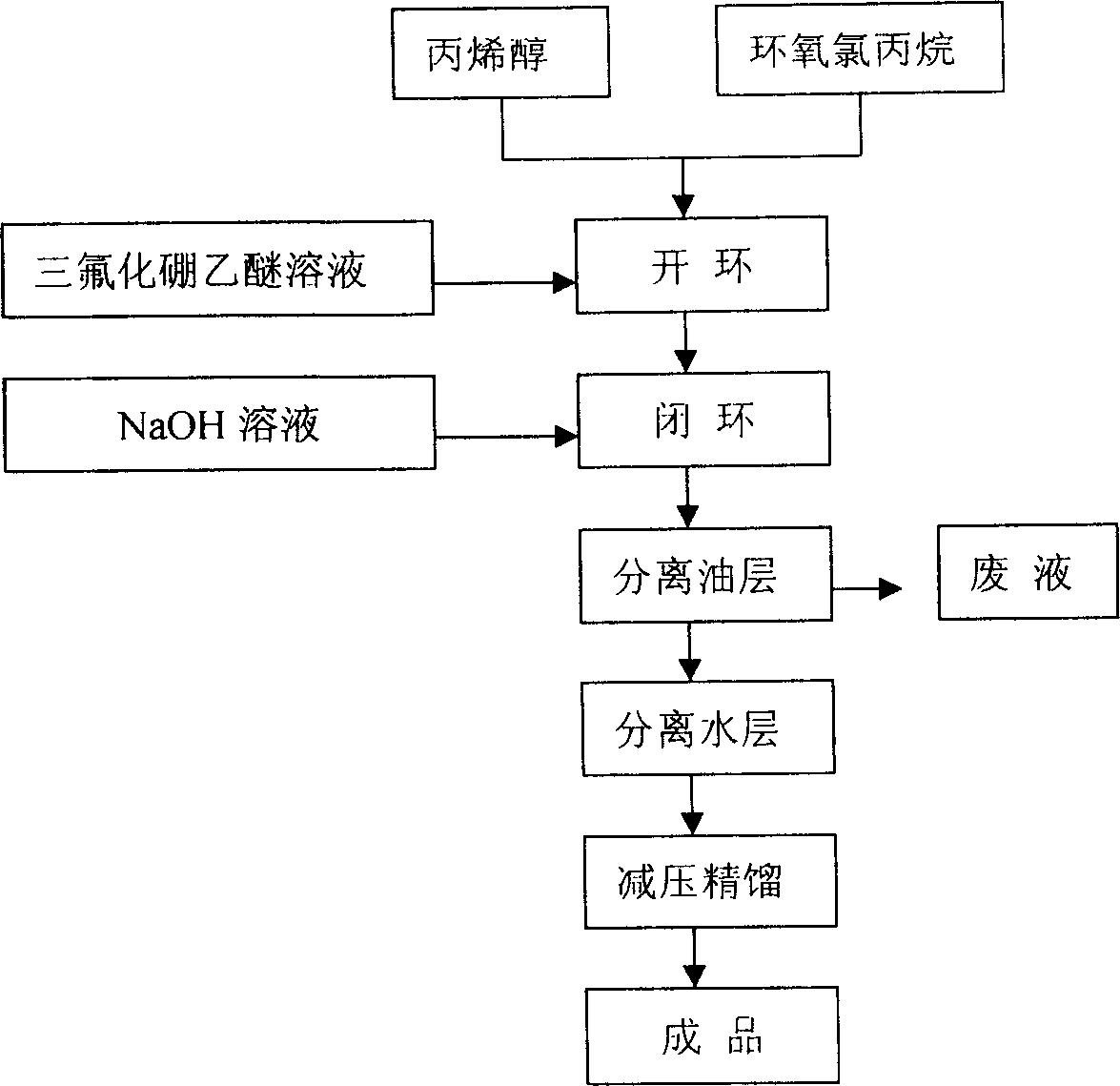
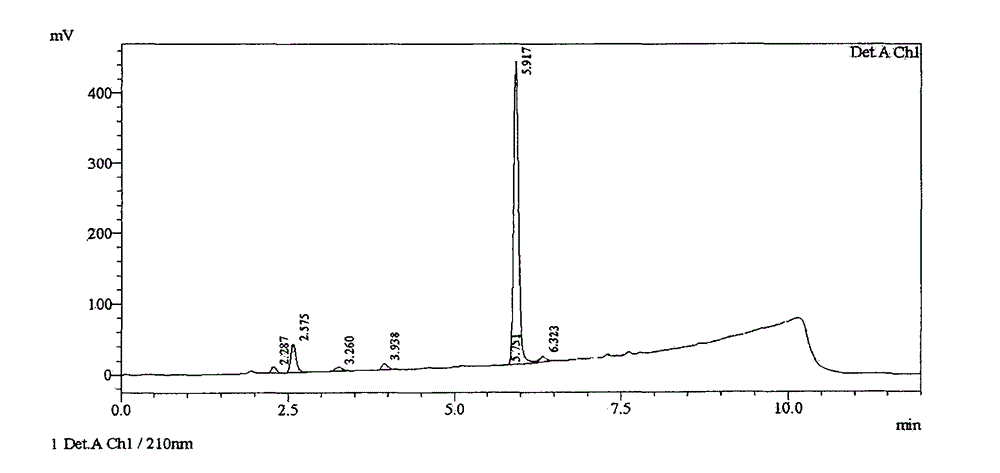
Process of industrialized preparing allyl glycidol ether
This invention provides an allyl glycidyl ether industrialized preparation method. It uses Boron trifluoride diethyl ether comoles compound as catalyst, propylene alcohol and epichlorohydrin as raw material, pass through the condensation ring-opening reactions generate 1-chloro-2-hydroxy-3- allyloxy propane, then under alkaline conditions through close-loop to obtain allyl glycidyl ether; the product yield rate is 78%, the content of 98%.
Owner:樊福定
Butylphthalide synthesis method and purification technology
The invention relates to a butylphthalide synthesis method. The method comprises the steps that methyl 2-formyl benzoic acid is adopted as a starting material, THF is adopted as a solvent to react with an n-butyl magnesium chloride Grignard reagent, and acid regulation is performed to prepare a butylphthalide product. The invention further relates to a technology for preparing high-purity butylphthalide. The obtained crude butylphthalide product is subjected to hydrolysis treatment by an alkaline substance, acid regulation is performed to separate out solids, and filtering is performed to obtain a butylphthalide midbody; the acid regulation and alkali regulation processes are executed repeatedly, and finally ring closure and decompression desolvation are performed to obtain high-purity butylphthalide. According to the synthesis method, low-flash diethyl ether is prevented from being adopted as a solvent, the purification technology is easy to implement, the reagent can be purchased in bulk easily, column chromatography product purification and reduced pressure distillation under high temperature and high vacuum degree are not needed, and industrial enlarged production is easy.
Owner:福建省宝诺医药研发有限公司
Processes for Producing Cellooligosaccharide
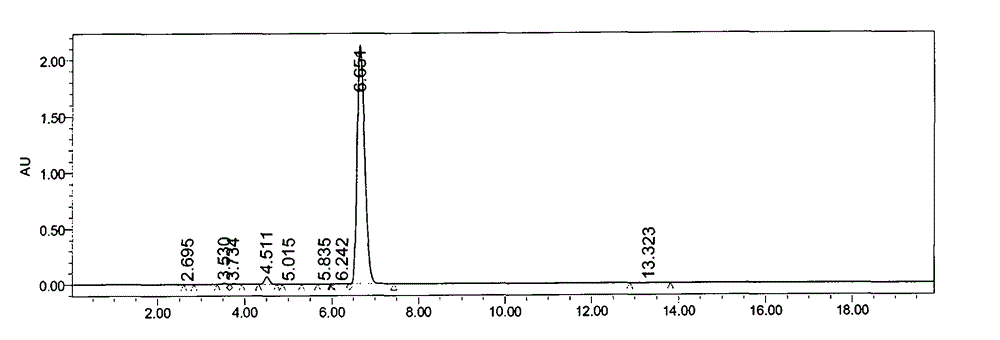
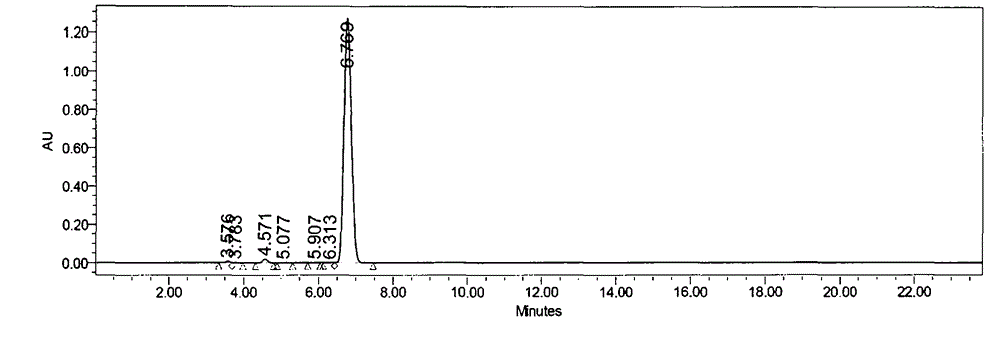
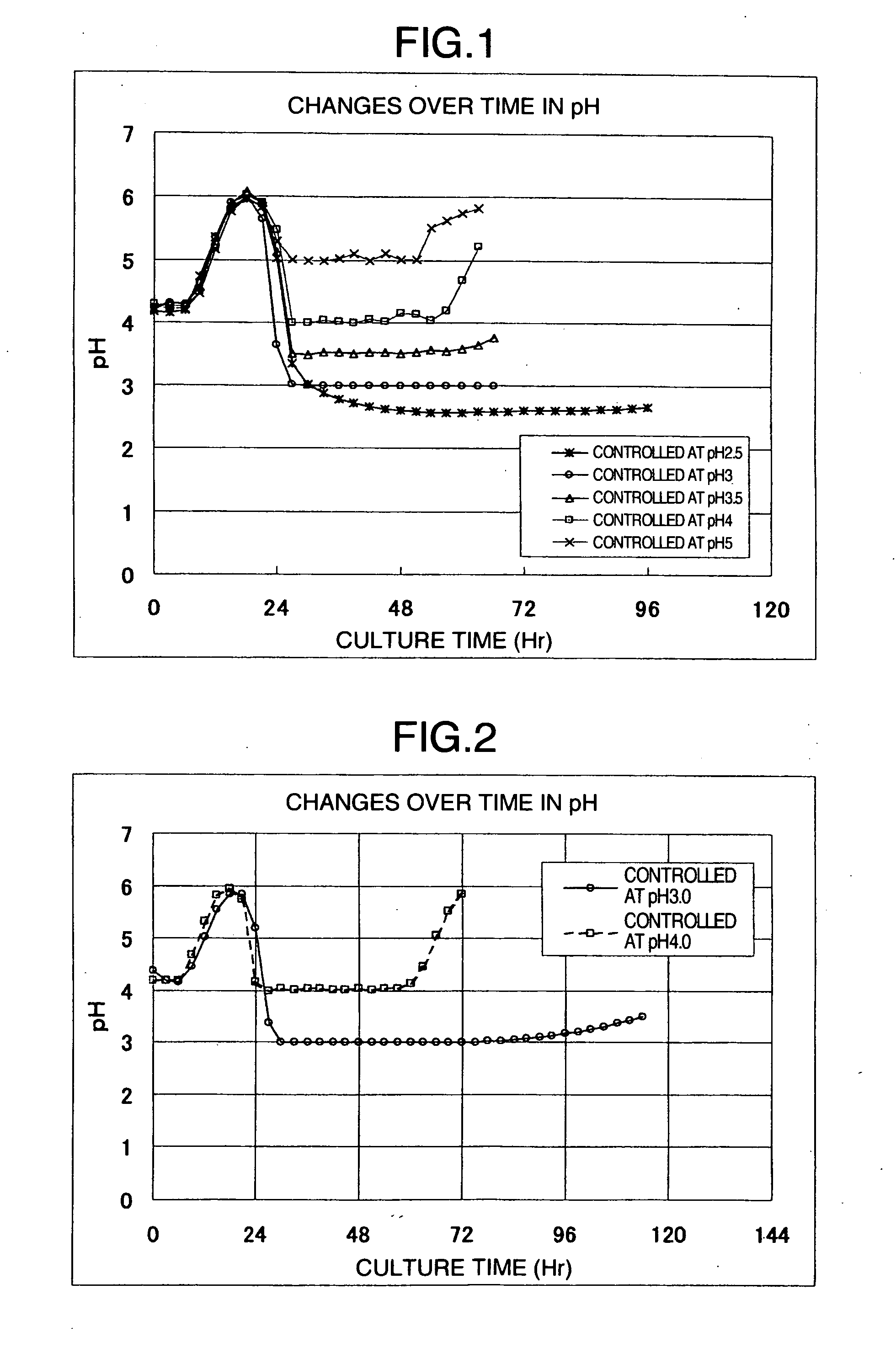
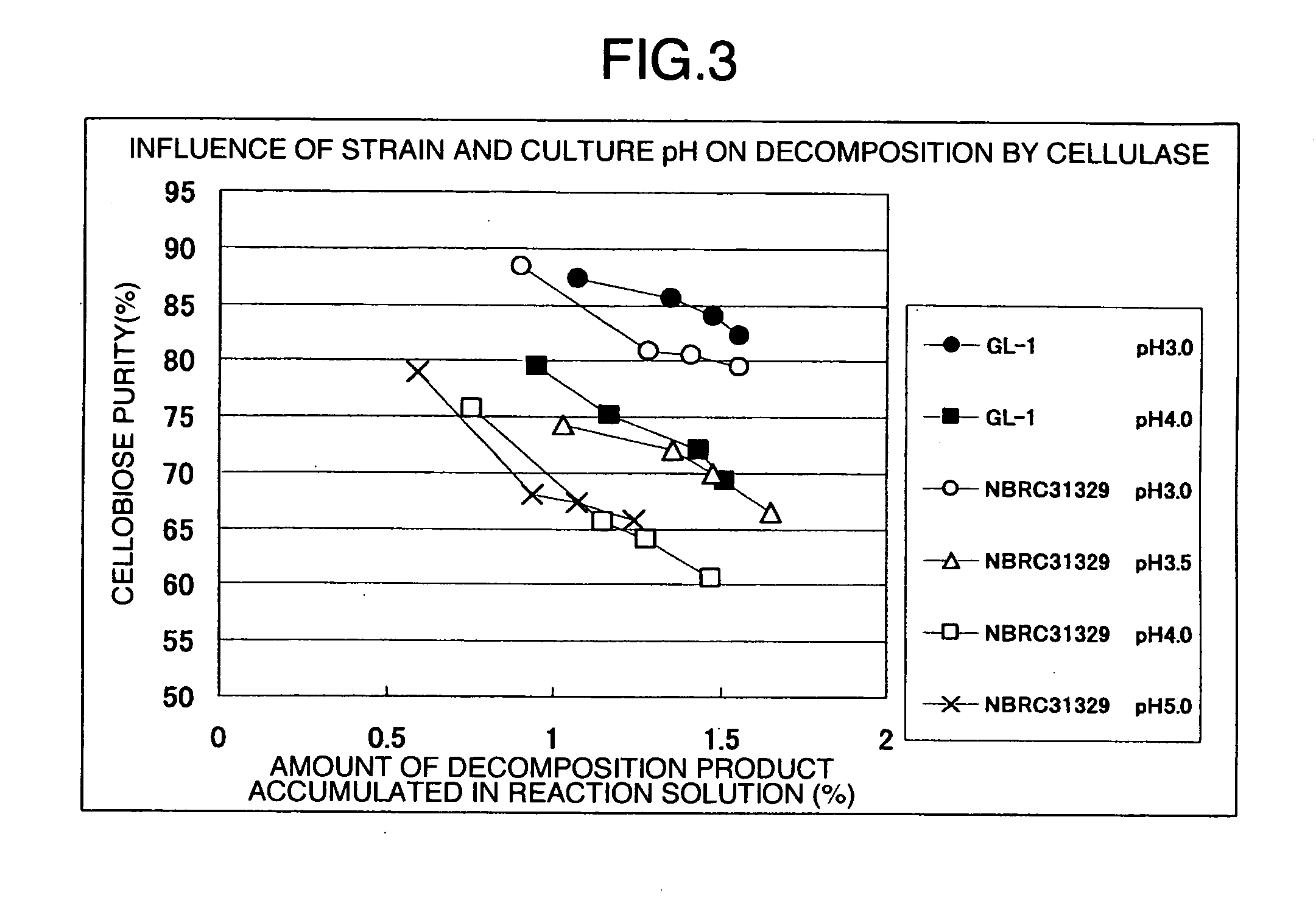
InactiveUS20070207108A1High yieldImprove decomposition rateCosmetic preparationsBiocideFiberPolymer science
A process of producing cellooligosaccharide, comprising enzymatically decomposing, in the presence of cellulase, a water-insoluble natural cellulosic material having an average degree of polymerization not greater than 700, an average particle size not greater than 100. A process of producing cellooligosaccharide, comprising enzymatically decomposing, in the presence of cellulase, a water-insoluble natural cellulosic material having an average degree of polymerization not greater than 700, containing 10% or more by mass of a colloidal cellulose component and a diethyl ether-soluble substance content less than 1% by mass.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Extracting device for giant salamander skin mucus and extracting method
ActiveCN104223121ANo damageExtract safeProtein composition from fishAnimal proteins working-upGiant salamanderEngineering
The invention discloses an extracting device for giant salamander skin mucus. The extracting device is characterized by comprising a collecting tank (1) and a sealing tank cover (2), wherein corn angles formed by connecting four side walls and the bottom surface of the collecting tank (1) are chamfered, one corner of the sealing tank cover (2) has a diethyl ether injection hole (3), an absorbent ball (4) is fixed at the bottom surface of the collecting tank (1) right below the diethyl ether injection hole (3). The invention further provides an extracting method for extracting giant salamander skin mucus by using the device, wherein the giant salamander is stimulated and narcotized by using diethyl ether. The extracting method is harmless to the giant salamander when being used for collecting mucus, diethyl ether easily volatilizes, stains in the body for a short time, and is little in residue, therefore, the extracting method is safe, effective, and is capable of continuously extracting mucus.
Owner:CHONGQING KUIXU BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
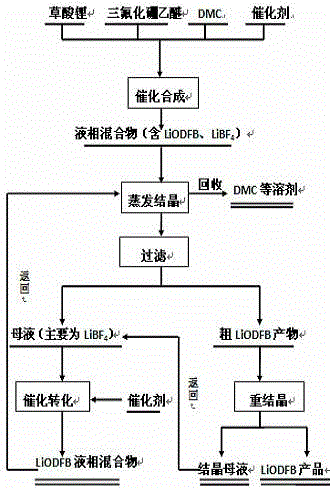
Preparation method of lithium ion battery electrolyte salt LiODFB (lithium oxalyldifluroborate)
InactiveCN104628754AAvoid wastingIncrease profitGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFiltrationSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of lithium ion battery electrolyte salt LiODFB (lithium oxalyldifluroborate). The method comprises the following steps: performing catalytic synthesis of lithium oxalate and boron trifluoride diethyl ether in a solvent of DMC (dimethyl carbonate) and the like to obtain a liquid-phase mixture and a little unreacted lithium oxalate solid, performing filtration, and then performing evaporative crystallization to obtain crude LiODFB; recrystallizing the crude LiODFB to meet the requirement of lithium ion battery electrolyte salt; and collecting filtered mother liquid and crystallization mother liquid, adding oxalate and a catalyst, performing catalytic conversion to obtain a liquid-phase mixture which mainly contains LiODFB, and performing evaporative crystallization again. The technological process is low in cost, the purity of the prepared LiODFB is above 99.9%, the yield is above 90%, and the method is convenient to operate, has favorable economic benefits and environmental benefits and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN ZHENGYUAN ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS & DEVICE INST +1
Novel red BODIPY fluorescent dye and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102702768ANarrow absorbencyNarrow fluorescence emission spectrumMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical reaction1,4-Benzoquinone
The invention relates to a novel red BODIPY fluorescent dye with the chemical formula of C10+mH7+nBF2N2+xOy, wherein m, n, x and y are integers from 0 to 100. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving pyrrole with substituent groups R1, R2 and R3 in an organic solution; adding ethyl glyoxylate together with nitrogen to the organic solution for a chemical reaction by using trifluoroacetic acid or toluenesulfonic acid as a catalyst; adding 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone oxidative dehydrogenation; and adding organic amine and a boron trifluoride diethyl ether solution for another reaction. After the reaction solution is concentrated, chromatography is performed with a silicagel column to obtain the fluorescent dye. The fluorescent dye can be used for cell imaging, fluorescent probe or laser dye. The fluorescent dye has the advantages that the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum and the fluorescence emission spectrum of the fluorescent dye are narrow; fluorescent quanta has high efficiency and good light stability; and the fluorescent dye has simple molecular structure and can be synthesized easily, so as to facilitate popularization and application.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method of preparing poly-pyrrole/polythiofuran derivative composite conductive macromolecule material for super electrical condenser
InactiveCN101492545AIncrease specific volumeImprove cycle stabilityCapacitor electrodesPolymer sciencePolypyrrole
The invention relates to a preparation method for polypyrrole / polythiophene derivative compound conductive high polymer material, which comprises the following steps: firstly, boron trifluoride diethyl ether and aether are blended, and then added with ionic liquid to obtain A solution; pyrrole and thiofuran derivative monomer are added into the A solution to prepare B solution; the B solution is added into an electrolytic cell equipped with three electrodes; and electrochemical polymerization is carried out under the protection of nitrogen; polymerized current density is 1-10 mA / cm2; a layer of uniform polypyrrole / polythiophene derivative complex film can be obtained on a working electrode after polymerization is finished; the working electrode is taken out for washing and dried in the temperature of 60 DEG C. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the composite electrode material prepared by the invention has about 200 F / g of bulking value and an electrical potential widow with about 0-2.8 width in organic solvent, and still has higher specific capacity and better circulation stability when discharging in high power.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Extraction of natural capsaicine
InactiveCN1439630ACrystal stableOperating conditions are easy to controlCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationDiethyl etherEthyl acetate
A process for extracting natural capsicine from hot pepper powder or the hot pepper extract as the by-product obtained after extracting rutilant pigment from hot pepper features that the alcohol, ethylether, acetone, petroleum ether, or ethyl acetate is used as extractant, a separation accelerator is used to prevent the generation of the third phase, a saponifying activator is used for speeding up saponifying reaction at low temp (28-35 deg.C) and a cleaner is used for stable crystallizing. Its advantages are high purity (more than 99%), and low cost.
Owner:贵州慧博科技开发有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com