Patents
Literature
284 results about "O-Xylene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
O-Xylene (ortho-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C₆H₄(CH₃)₂. with two methyl substituents bonded to adjacent carbon atoms of a benzene ring (the ortho configuration). It is a constitutional isomer of m-xylene and p-xylene, the mixture being called xylene or xylenes. o-Xylene is a colorless slightly oily flammable liquid.
Process for the removal of impurities from combustion fullerenes
InactiveUS6923915B2Without incurring undo costEfficient removalMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesO-XylenePurification methods
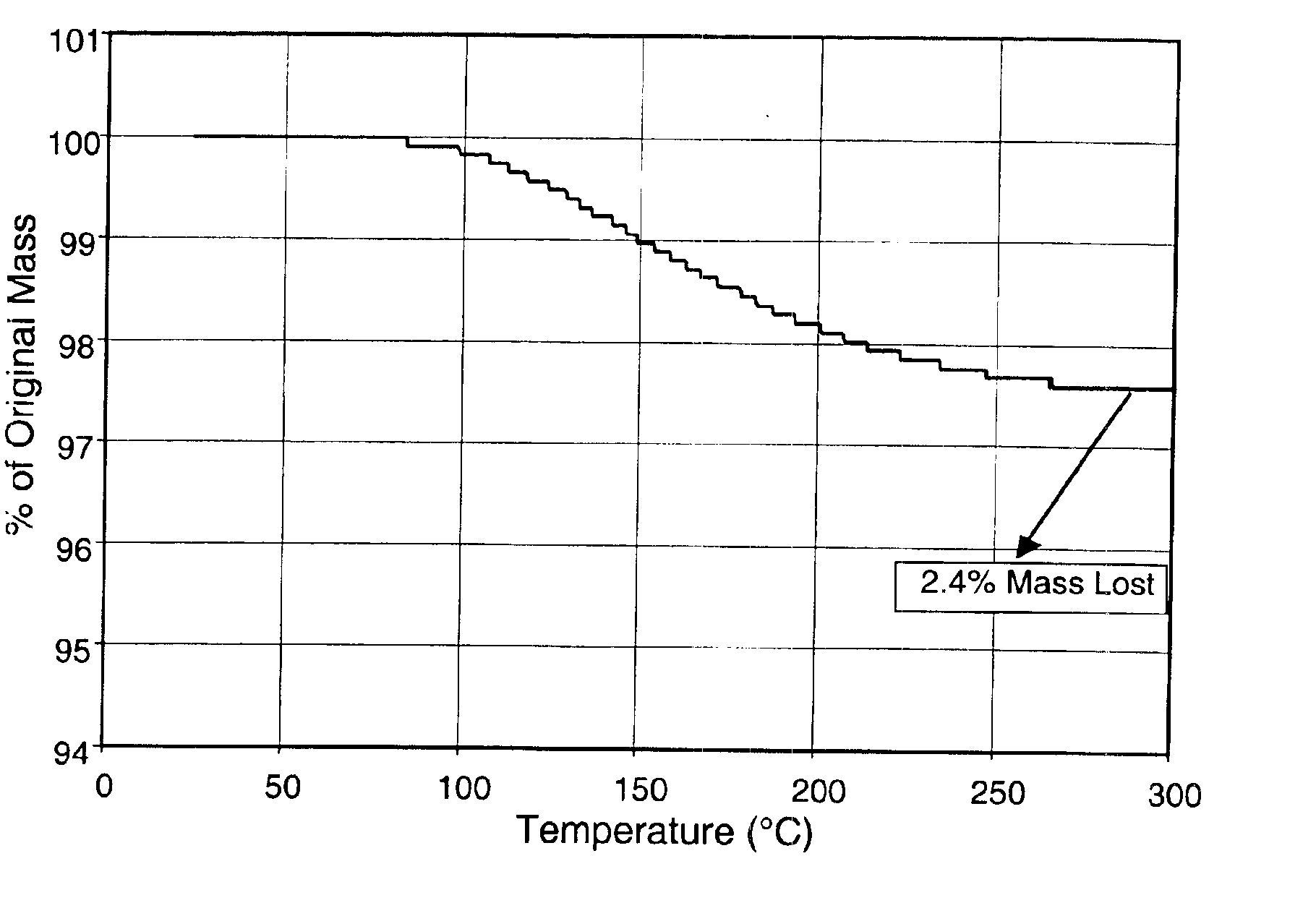
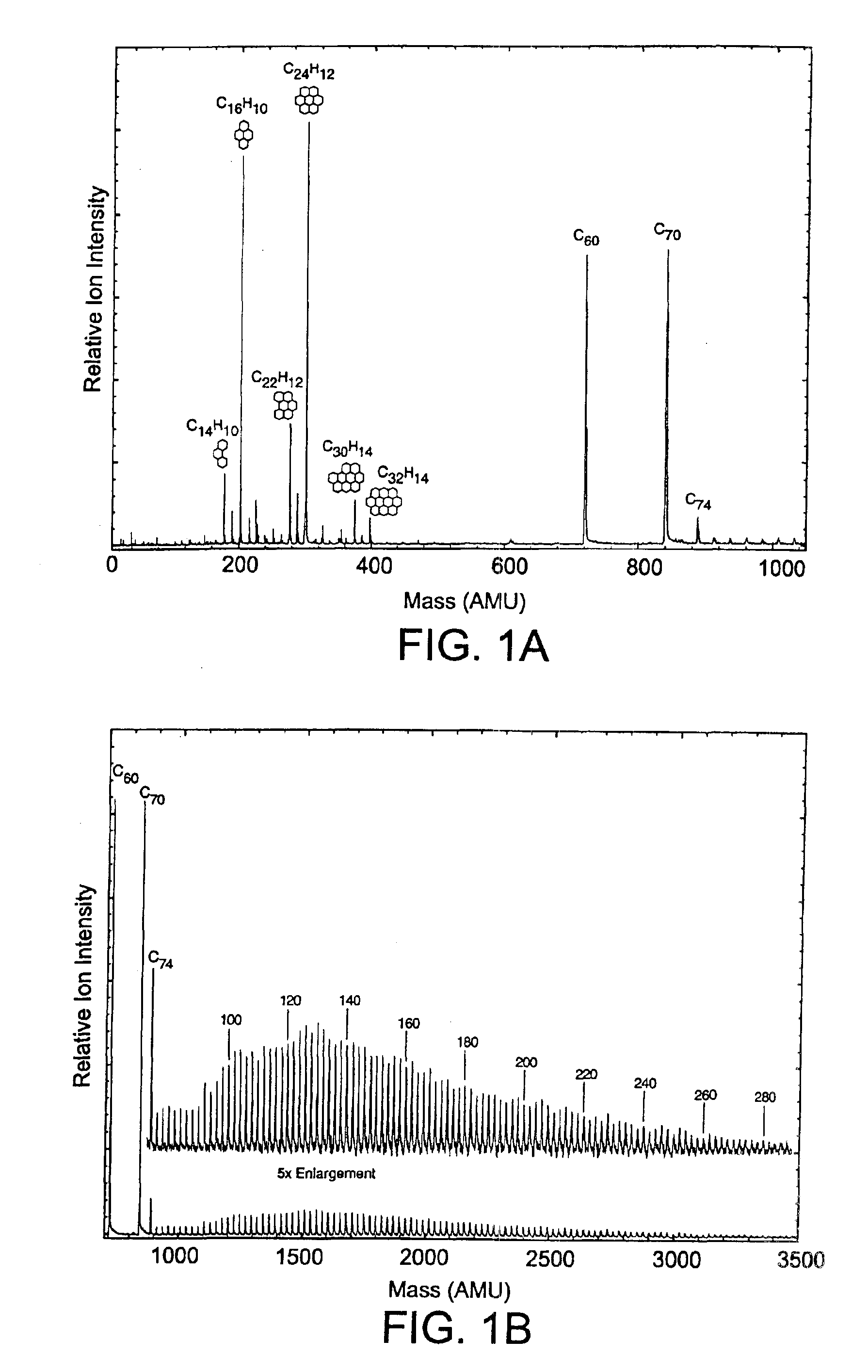
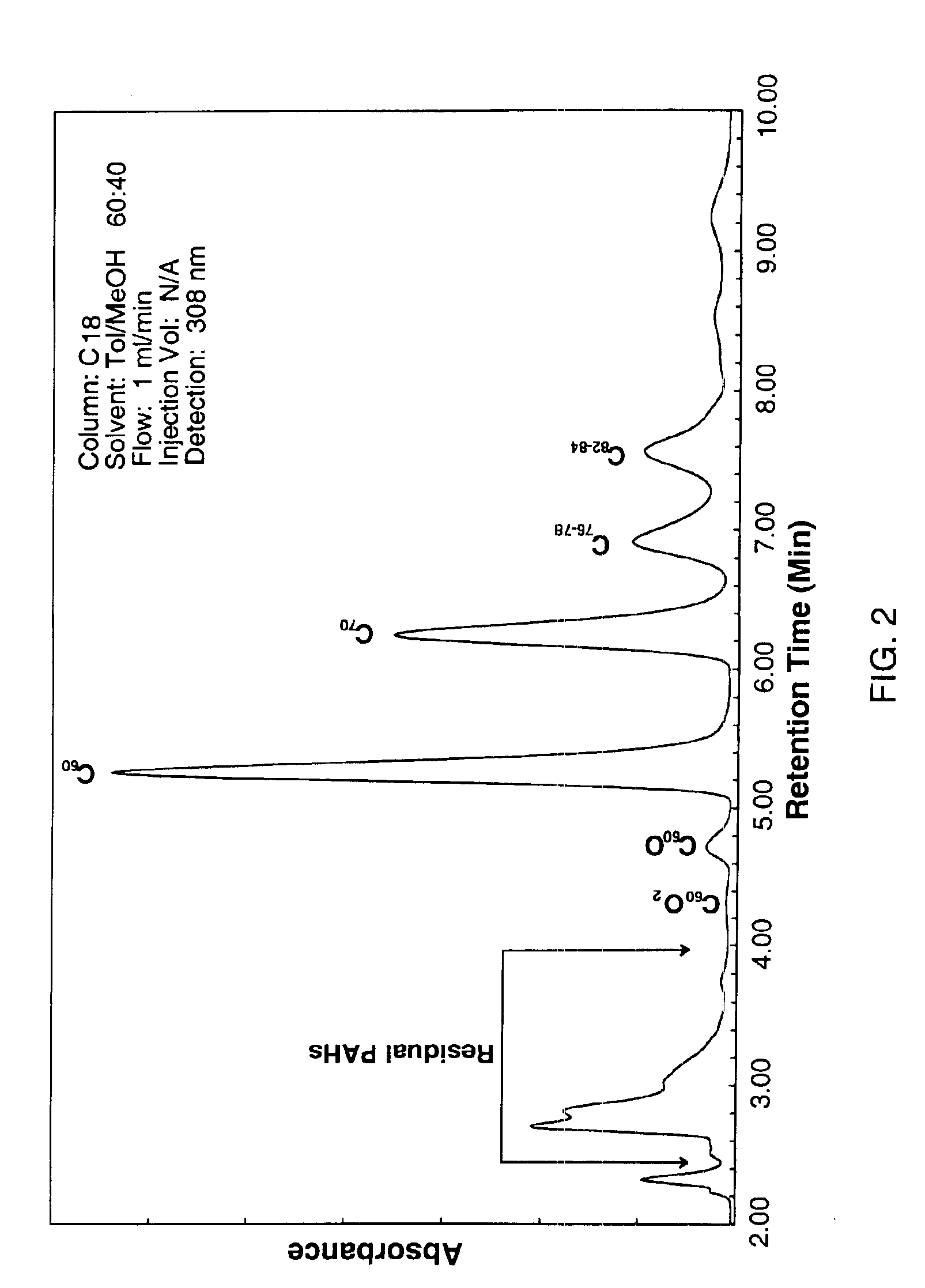
The invention generally relates to purification of carbon nanomaterials, particularly fullerenes, by removal of PAHs and other hydrocarbon impurities. The inventive process involves extracting a sample containing carbon nanomaterials with a solvent in which the PAHs are substantially soluble but in which the carbon nanomaterials are not substantially soluble. The sample can be repeatedly or continuously extracted with one or more solvents to remove a greater amount of impurities. Preferred solvents include ethanol, diethyl ether, and acetone. The invention also provides a process for efficiently separating solvent extractable fullerenes from samples containing fullerenes and PAHs wherein the sample is extracted with a solvent in which both fullerenes and PAHs are substantially soluble and the sample extract then undergoes selective extraction to remove PAHs. Suitable solvents in which both fullerenes and PAHs are soluble include o-xylene, toluene, and o-dichlorobenzene. The purification process is capable of treating quantities of combustion soot in excess of one kilogram and can produce fullerenes or fullerenic soot of suitable purity for many applications.
Owner:FRONTIER CARBON CORP
Production of a xylene isomer in three stages: separation, isomerization with a catalyst with an EUO zeolite base and transalkylation with recycling of C10-aromatic compounds
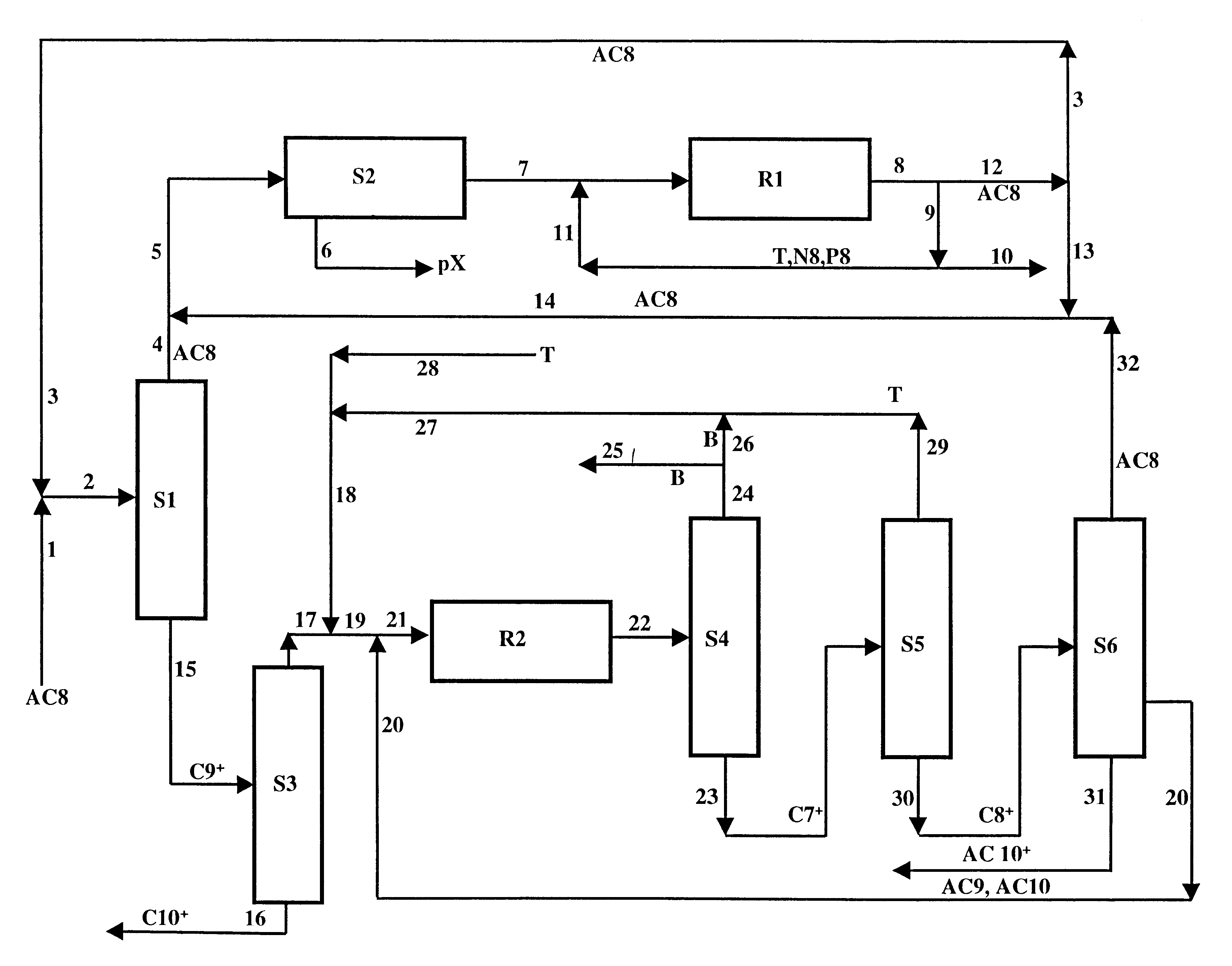
A process for the production of at least one xylene isomer, paraxylene, metaxylene or orthoxylene from an aromatic feedstock that has 7 to 10 carbon atoms per molecule. The process comprises a stage for transalkylation of C7- and C9-aromatic compounds, a stage for separation of xylenes and a stage for isomerization of xylenes. The isomerization catalyst used in the process comprises at least one EUO zeolite composition whose crystals are grouped in aggregates that have a grain size with a value of Dv,90 less than or equal to 500 microns and at least one element of group VIII.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Method for adsorbing-crystal separation of paraxylene and ethylbenzene from C8 aromatic
ActiveCN101045671ALarge amount of processingHigh purityAdsorption purification/separationCrystallisation purification/separationO-XyleneIsomerization
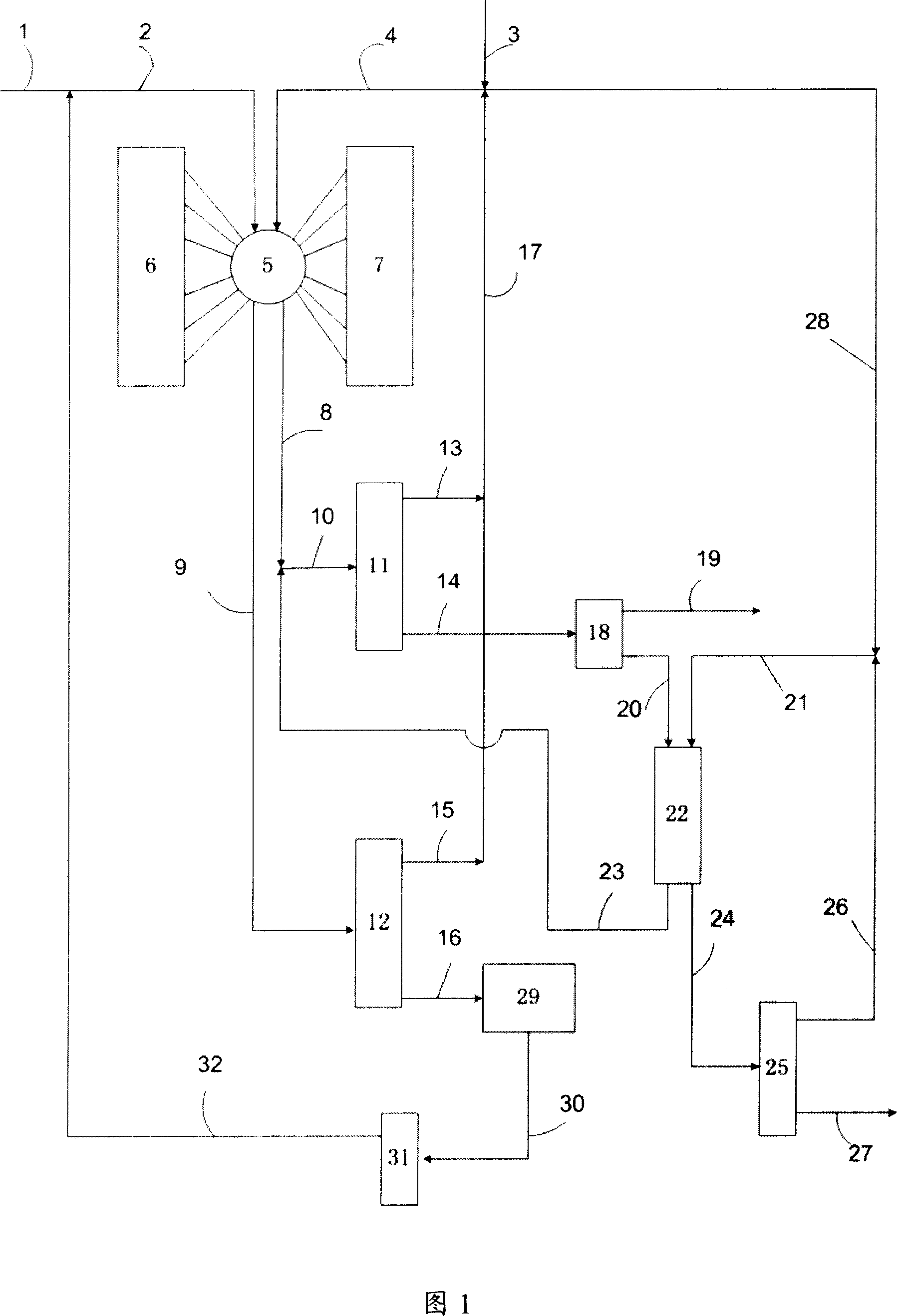
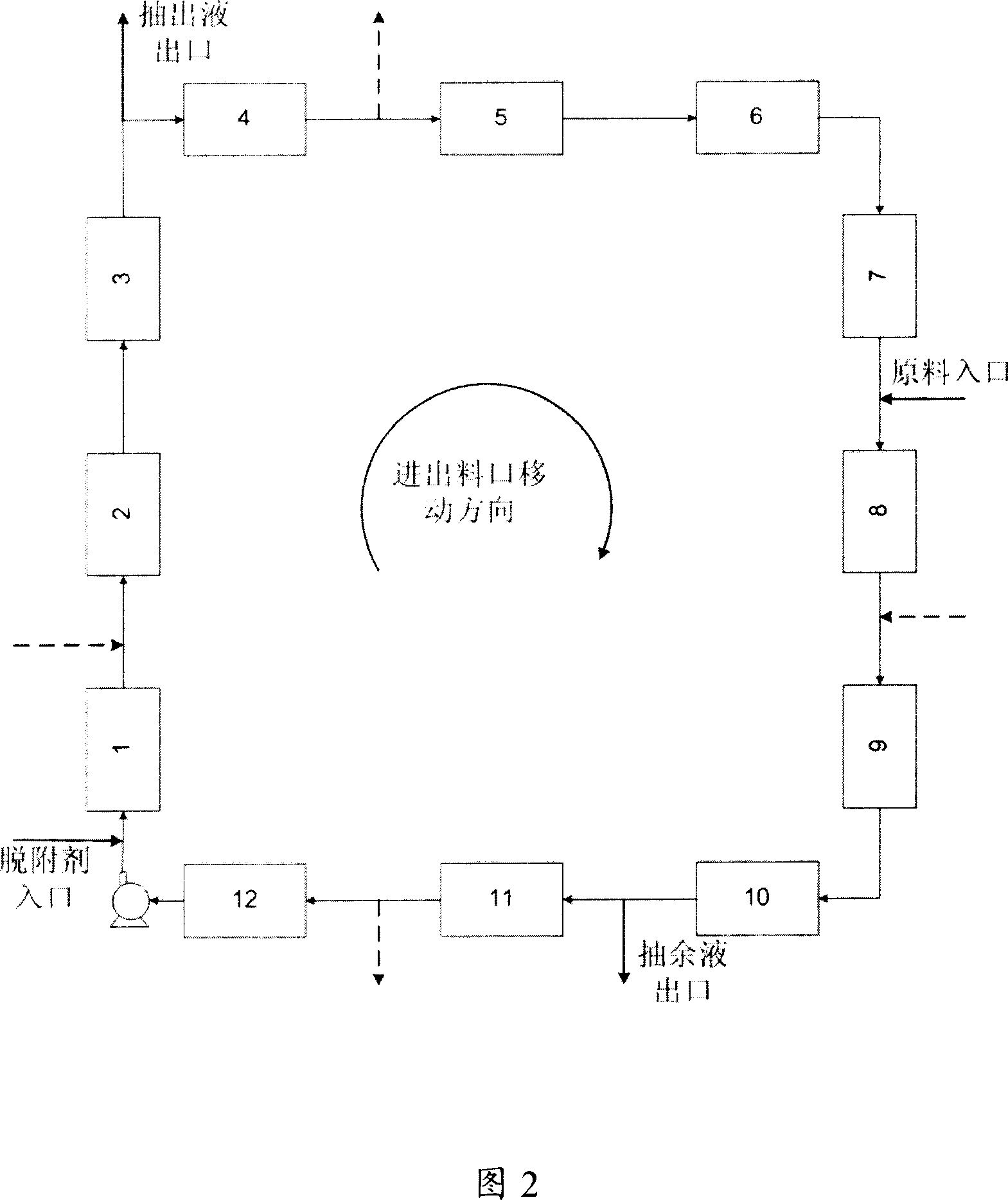
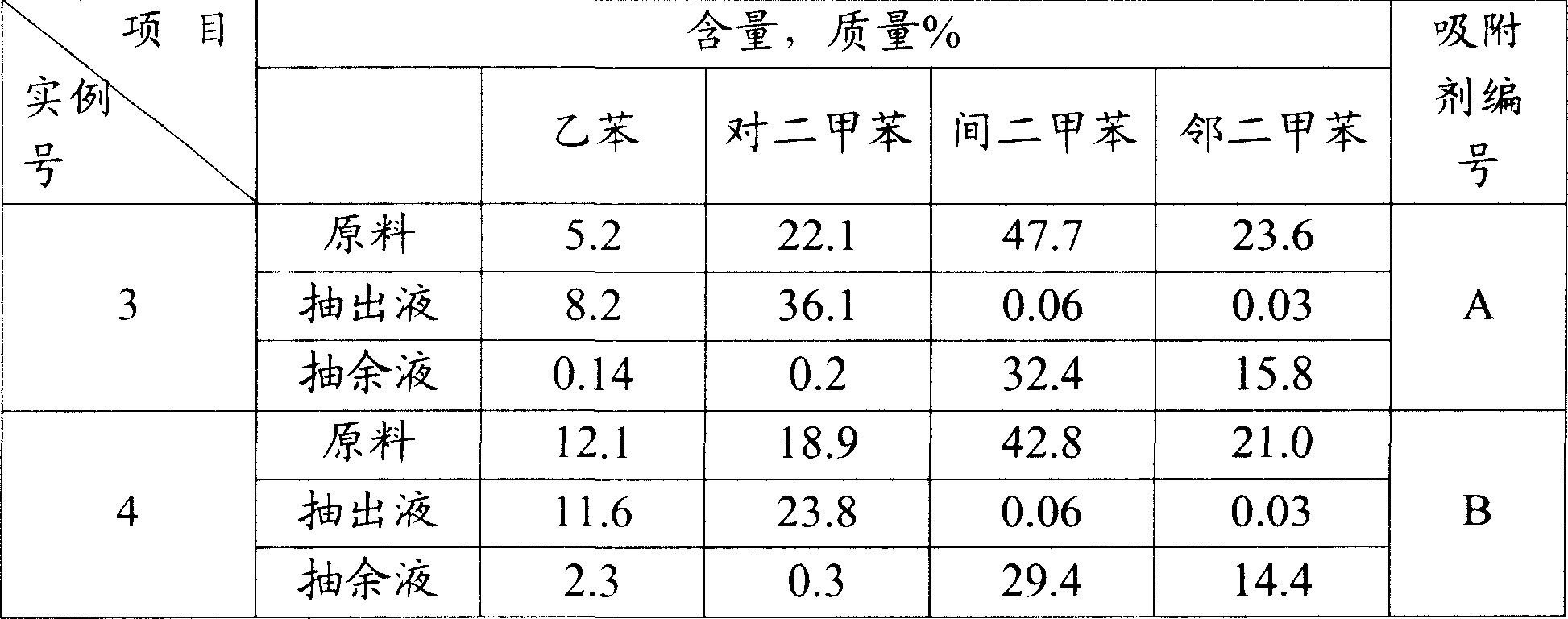
An adsorbing-crystallizing process for separating p-xylene and ethylbenzene from C8 arylhydrocarbon includes such steps as adsorptive separation to obtain the first material flow containing ethylbenzene and p-xylene and the second material flow containing meta-xylene and o-xylene, crystallizing for separating p-xylene from the first material flow, and adsorbing for separating ethylbenzene from the residual mother liquid.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) diphthalic anhydride
ActiveCN101696199AOvercoming the Factors Affecting Industrial Safety ProductionHigh yieldOrganic chemistryAlkyl transferO-Xylene
The invention discloses a preparation method of 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) diphthalic anhydride (6-FDA), belonging to the technical field of liquid crystal materials. The main technical scheme is achieved as follows: o-xylene and 2,2-dichloro-hexafluoropropane undergo alkylation reaction in an ionic liquid under the catalytic action of Lewis acids (AlCl3, ZnCl2) to obtain 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) di(2-xylene); then the 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) di(2-xylene) is oxidized by permanganic acid TEBA triethylbenzylammonium salts to obtain 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) diphthalandione; and finally, the 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) diphthalandione is dehydrated by acetic oxide to obtain the 4,4'-(Hexafluoroisopropylidene) diphthalicanhydride (6-FDA). The preparation method has the advantages of mild reaction condition, less three-waste emission and high yield.
Owner:天津众泰材料科技有限公司
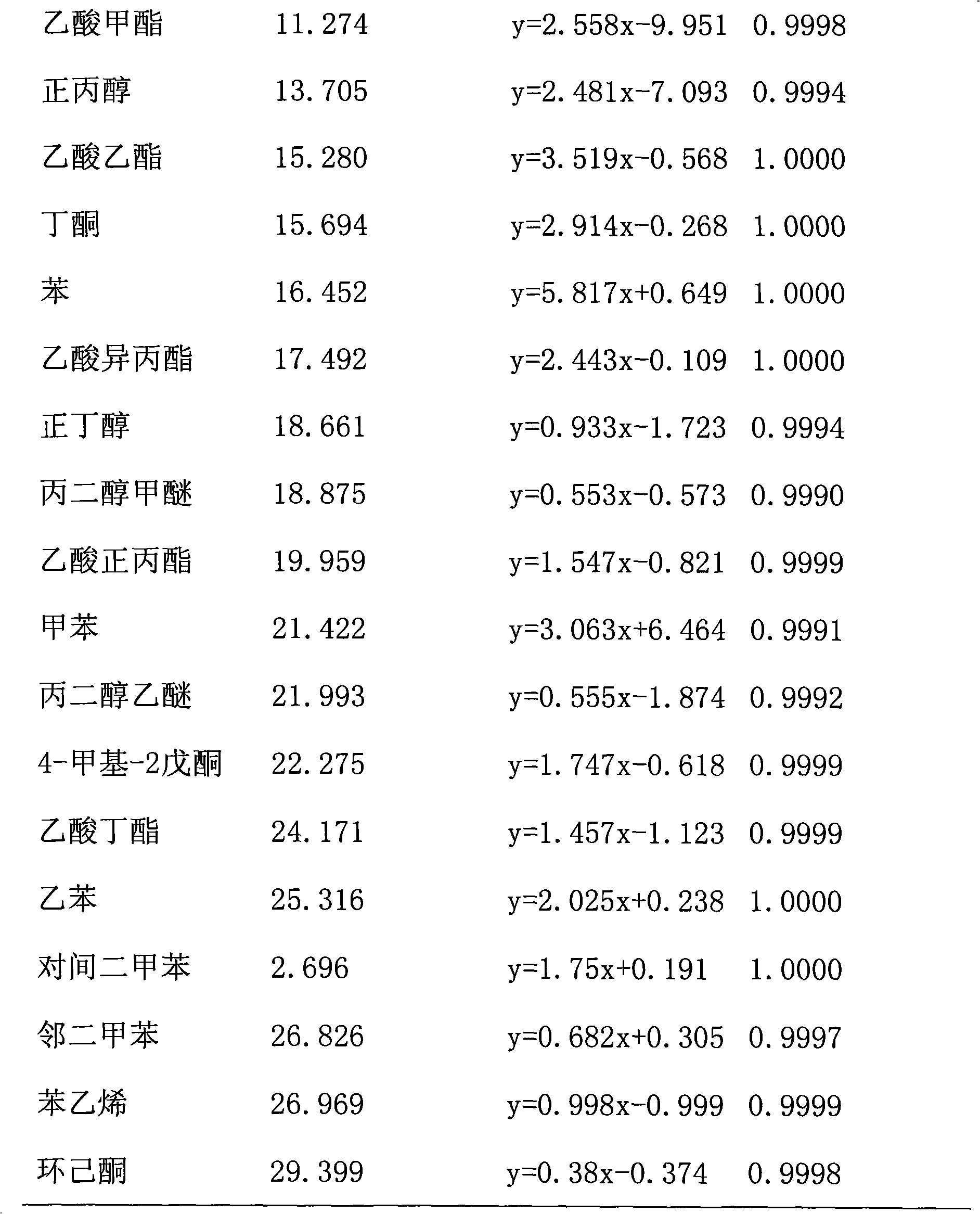
Method for detecting 21 volatile organic compounds (VOC) in tobacco packing box
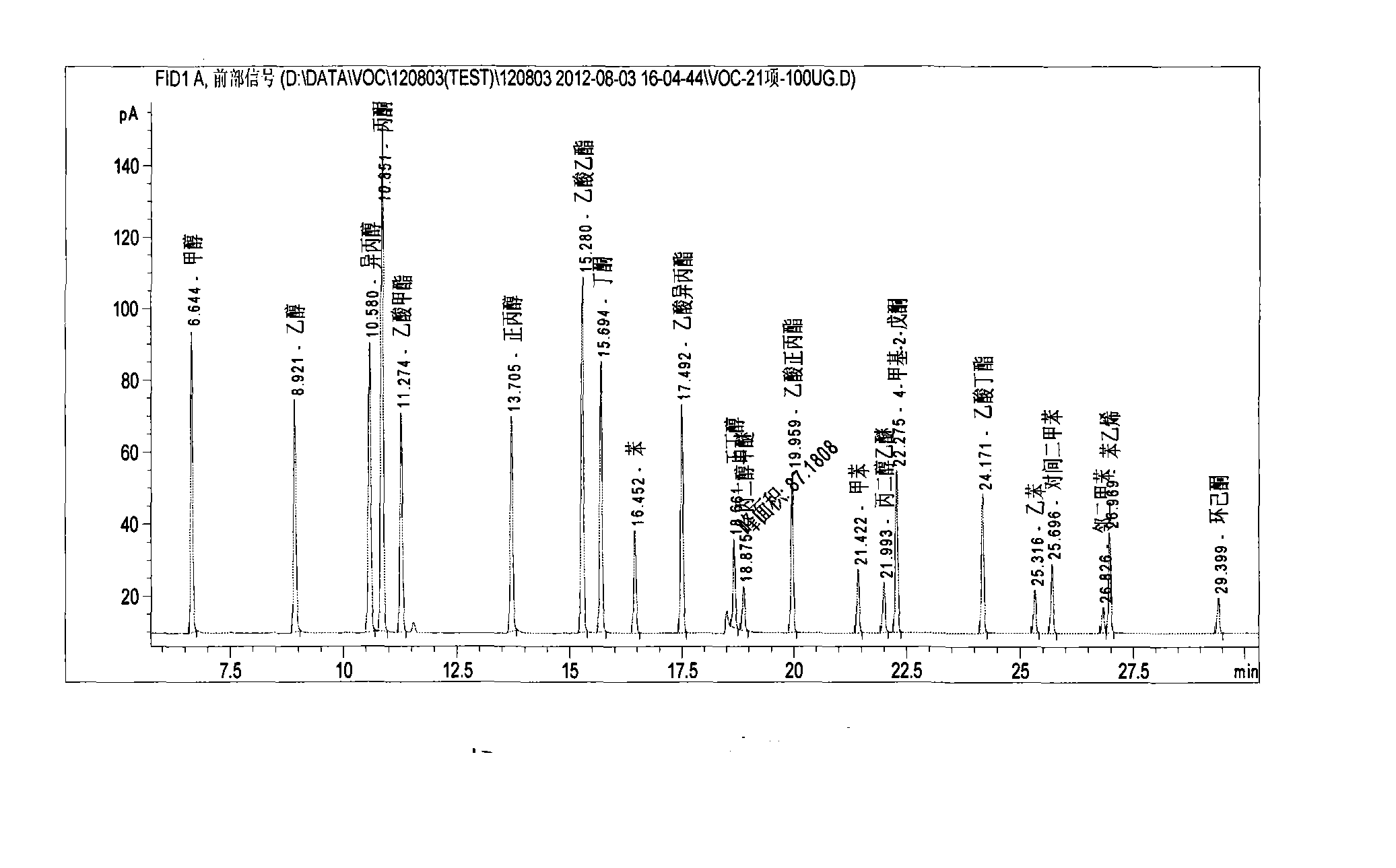
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco packing box, and in particular relates to a method for detecting contents of 21 volatile organic compounds (VOC), including benzene, methyl benzene, p-xylene, m-xylene, o-xylene, styrene, methanol, ethanol, acetone, isopropyl alcohol, methyl acetate, normal propyl alcohol, ethyl acetate, butanone, acetic acid isopropyl ester, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol monomethyl ether, n-propyl acetate, propylene glycol monoethyl ether, 4-methyl-2-pentanone, butyl acetate, cyclohexanone in a tobacco packing box. The method for detecting 21 volatile organic compounds in the tobacco packing box disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: sample pretreatment: preparing a piece of hard box packing paper; cutting and reserving a main packing surface by an area of 22.0cm*5.5cm; rolling the printing surface of the sample inwards to obtain a barrel-shaped part; putting the barrel-shaped part in a headspace bottle; adding 1000mu l of glycerol triacetate; sealing, and implementing a headspace-gas chromatography detection. The method disclosed by the invention is high in sensitivity, high in recovery rate, and excellent in precision of detecting result.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PONY TESTING TECH
Preparation of polymeric resins and carbon materials
Methods for making carbon materials are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, the method can include combining one or more polymer precursors with one or more liquids to produce a mixture. The mixture can be an emulsion, dispersion, or a suspension. The liquid can include hexane, pentane, cyclopentane, benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, diethyl ether, ethylmethylketone, dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, mineral oils, paraffin oils, vegetable derived oils, or any mixture thereof. The method can also include aging the mixture at a temperature and time sufficient for the polymer precursor to react and form polymer gel particles having a volume average particle size (Dv,50) of the polymer particles in gel form greater than or equal to 1 mm. The method can also include heating the polymer gel particles to produce a carbon material.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CHEM LLC
Method for preparing diphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride
ActiveCN101659647ASimple and fast operationSuitable for large-scale productionOrganic chemistryO-XyleneOxidizing agent
The invention relates to a method for preparing diphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride. The diphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride is prepared by taking o-xylene as a raw material through halogenating, coupling, oxidation and dehydration. In the method, the conversion rate of the o-xylene is 100 percent; and the total yield of the diphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride is 55 percent, the melting range is between 298 and 301 DEG C, and the purity is between 99.5 and 99.8 percent. The diphenyl tetracarboxylic dianhydride uses the o-xylene as the raw material instead of chloro-anhydride by coupling first and then oxidizing, so the experimental route and the method are simple, economic and easy to operate. At the same time, because potassium permanganate with low price is adopted as an oxidant, an industrial preparation method, which is simple, convenient and economic and has low requirements on equipment, is provided.
Owner:常熟华虞环境科技有限公司
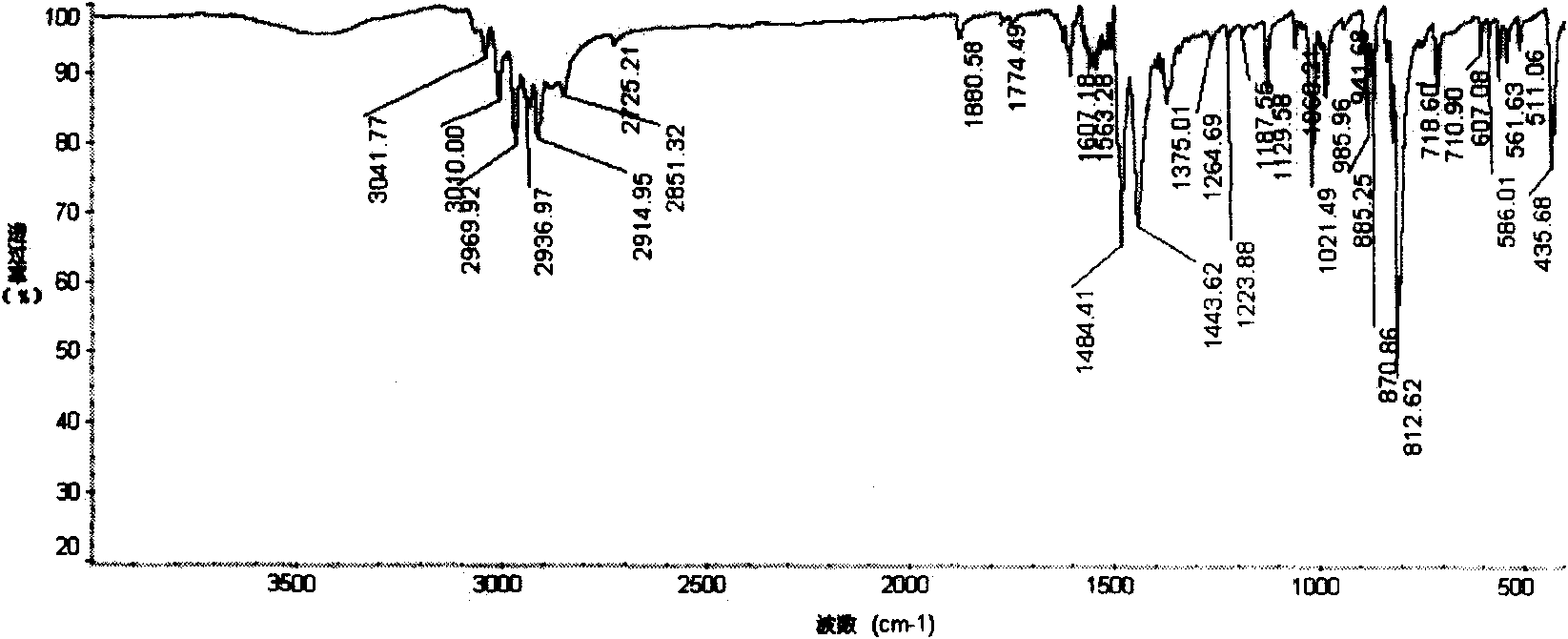
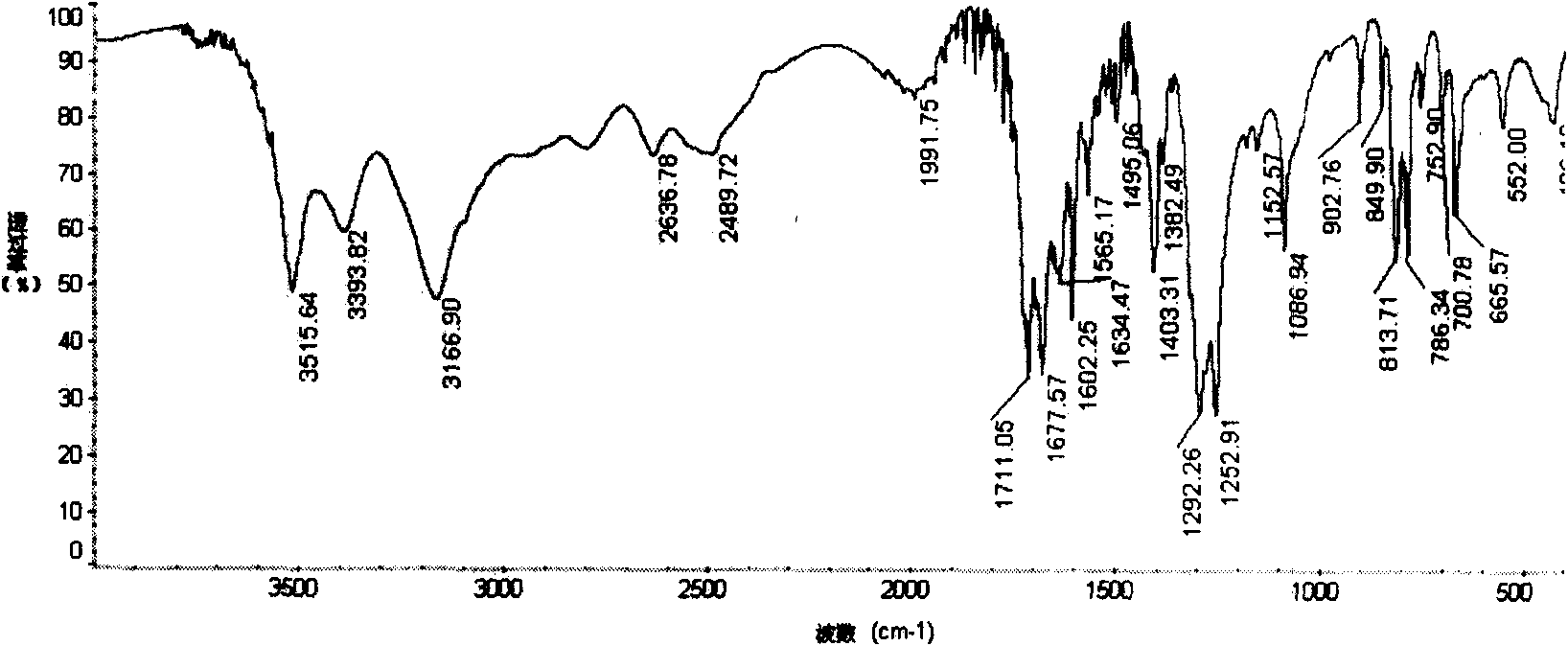
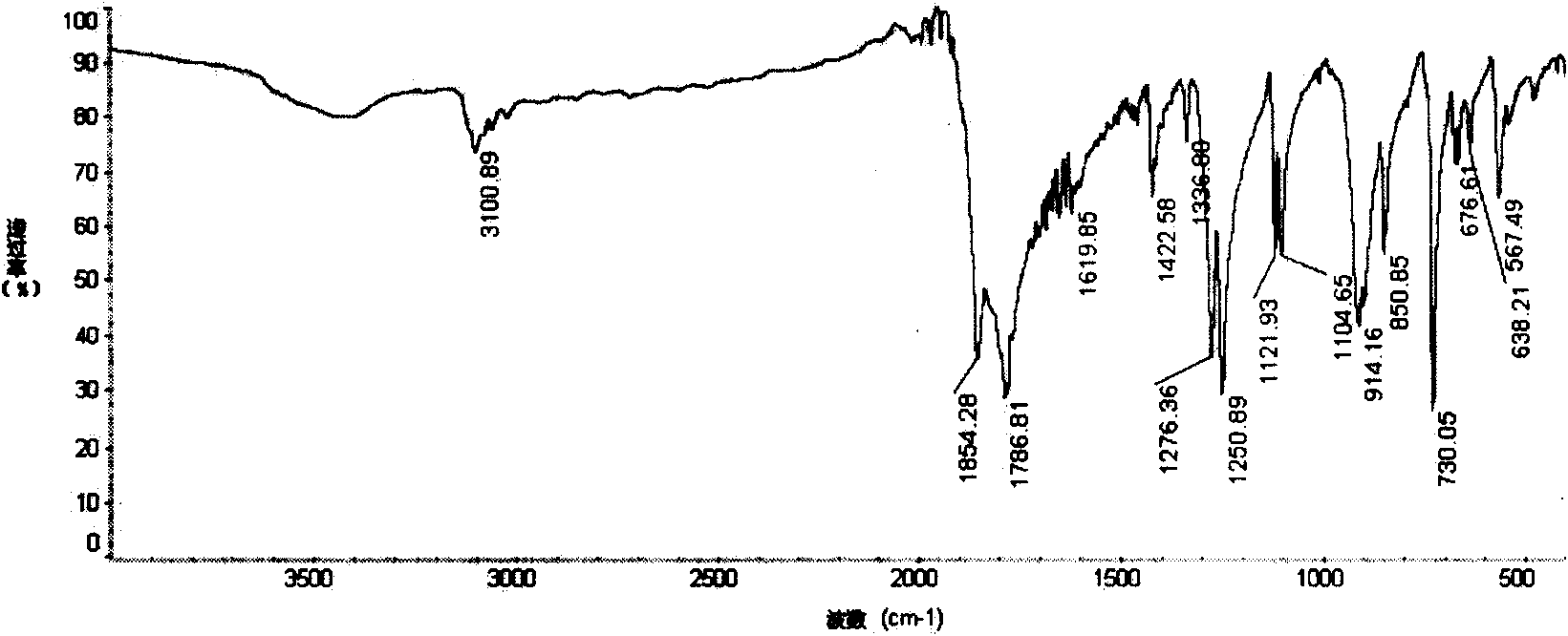
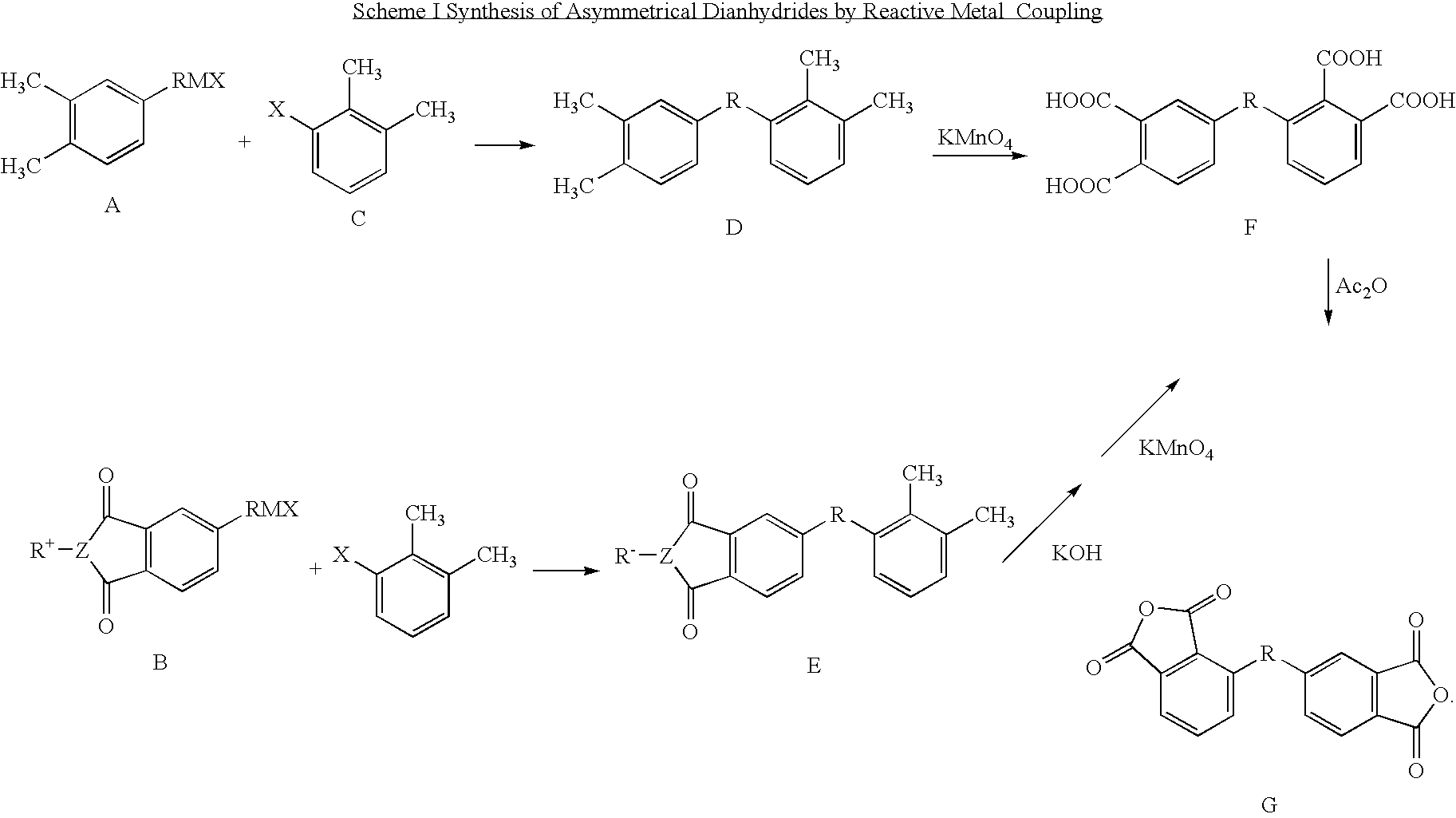
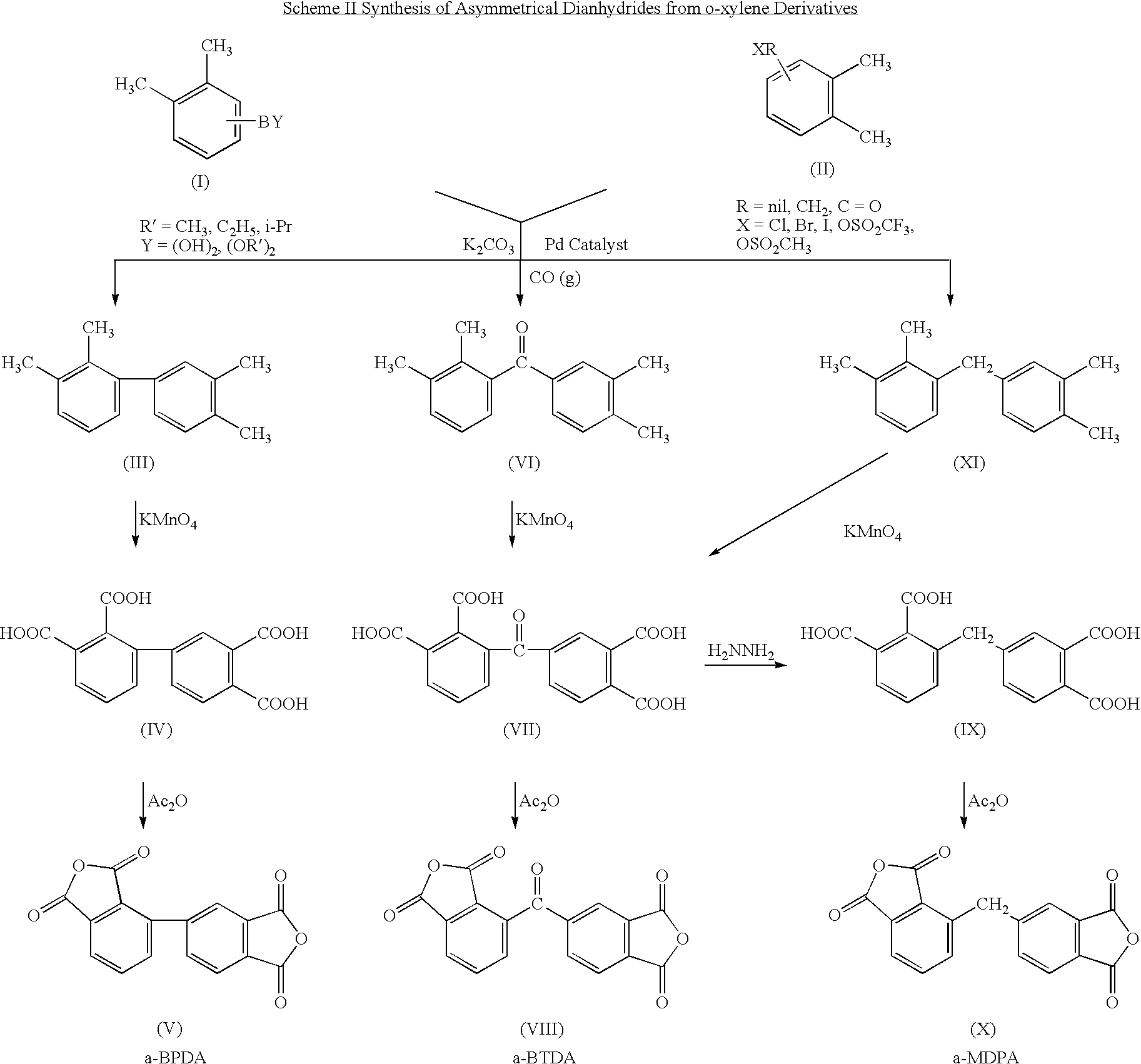
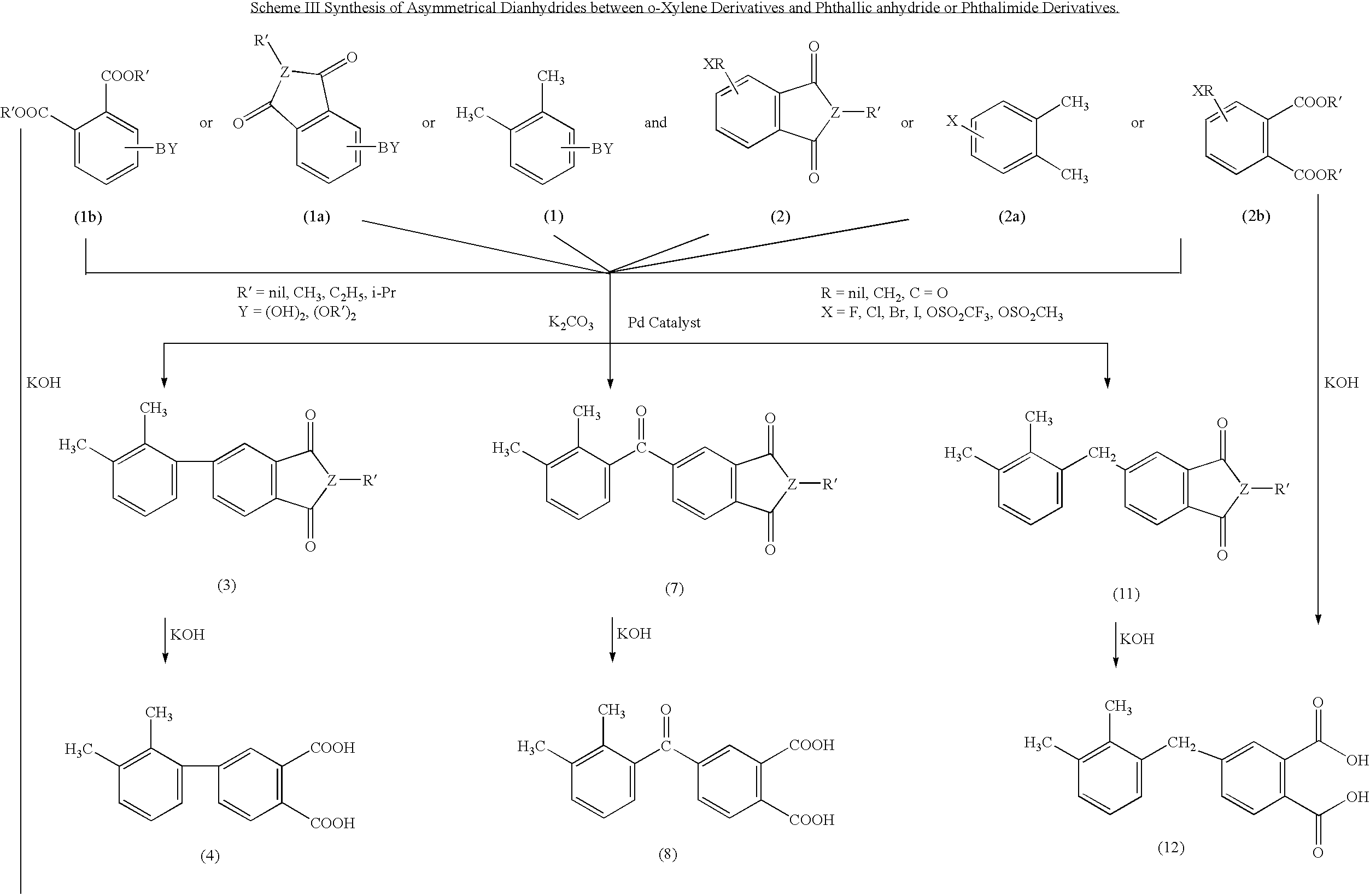
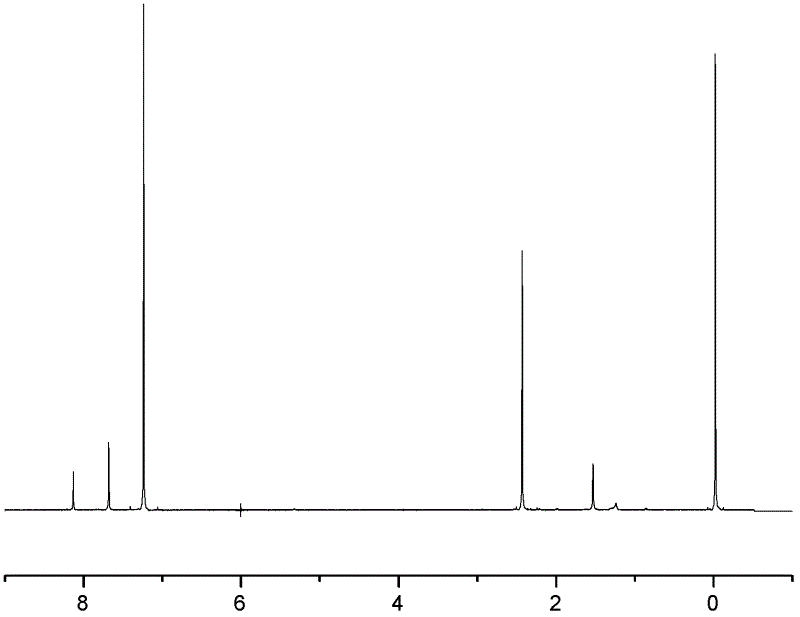
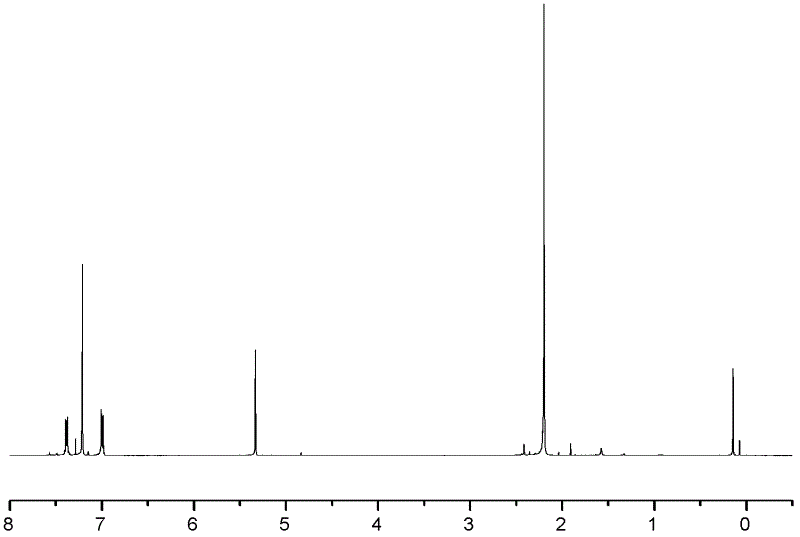
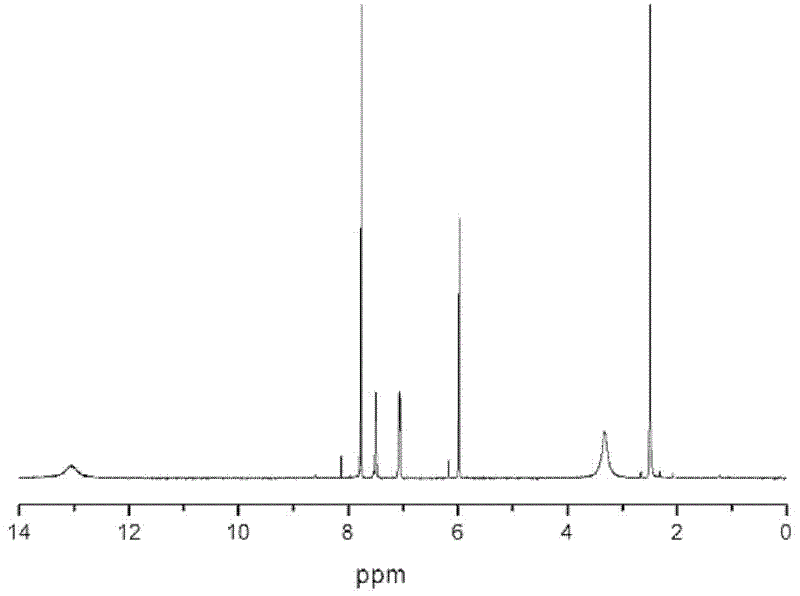
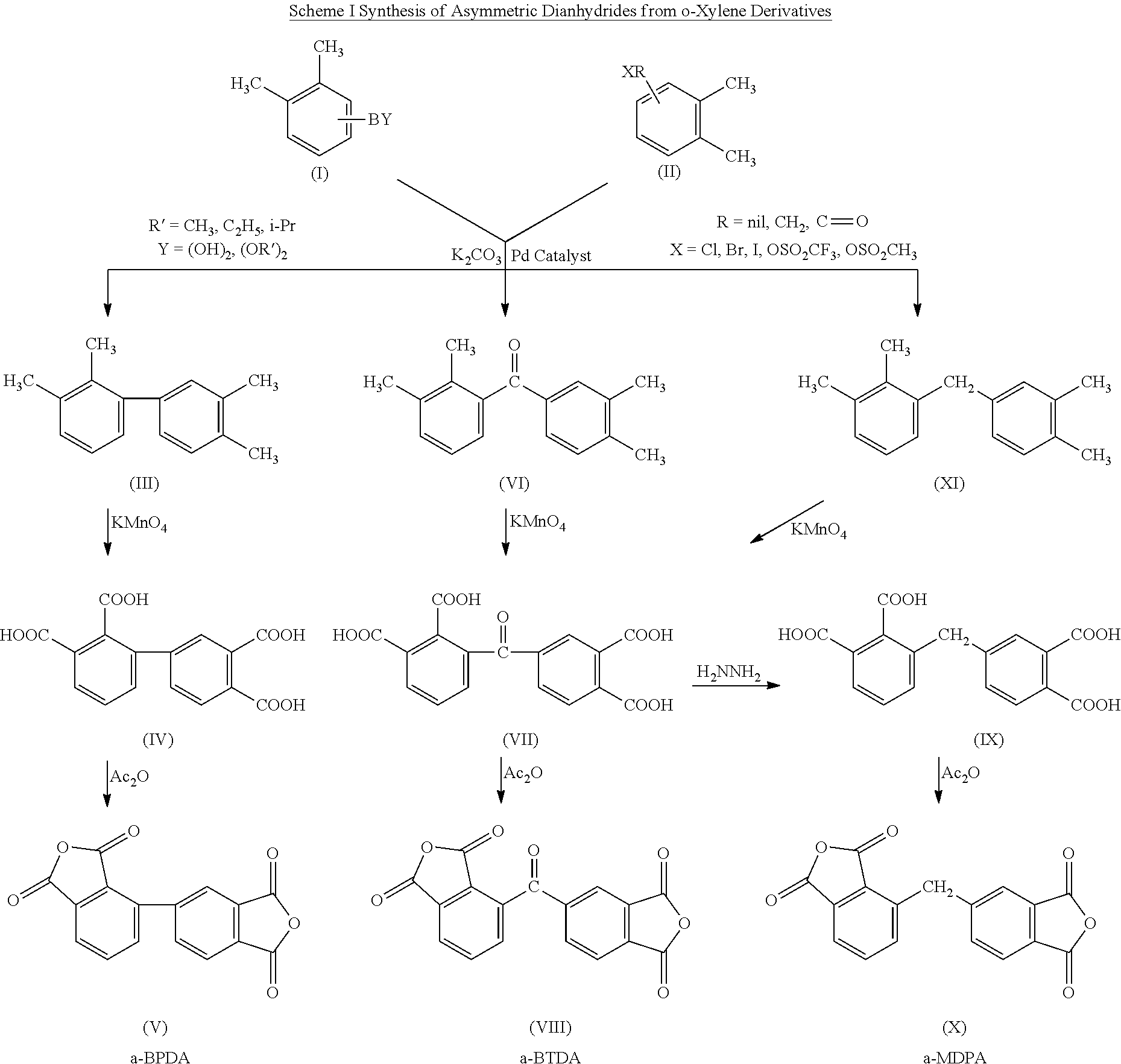
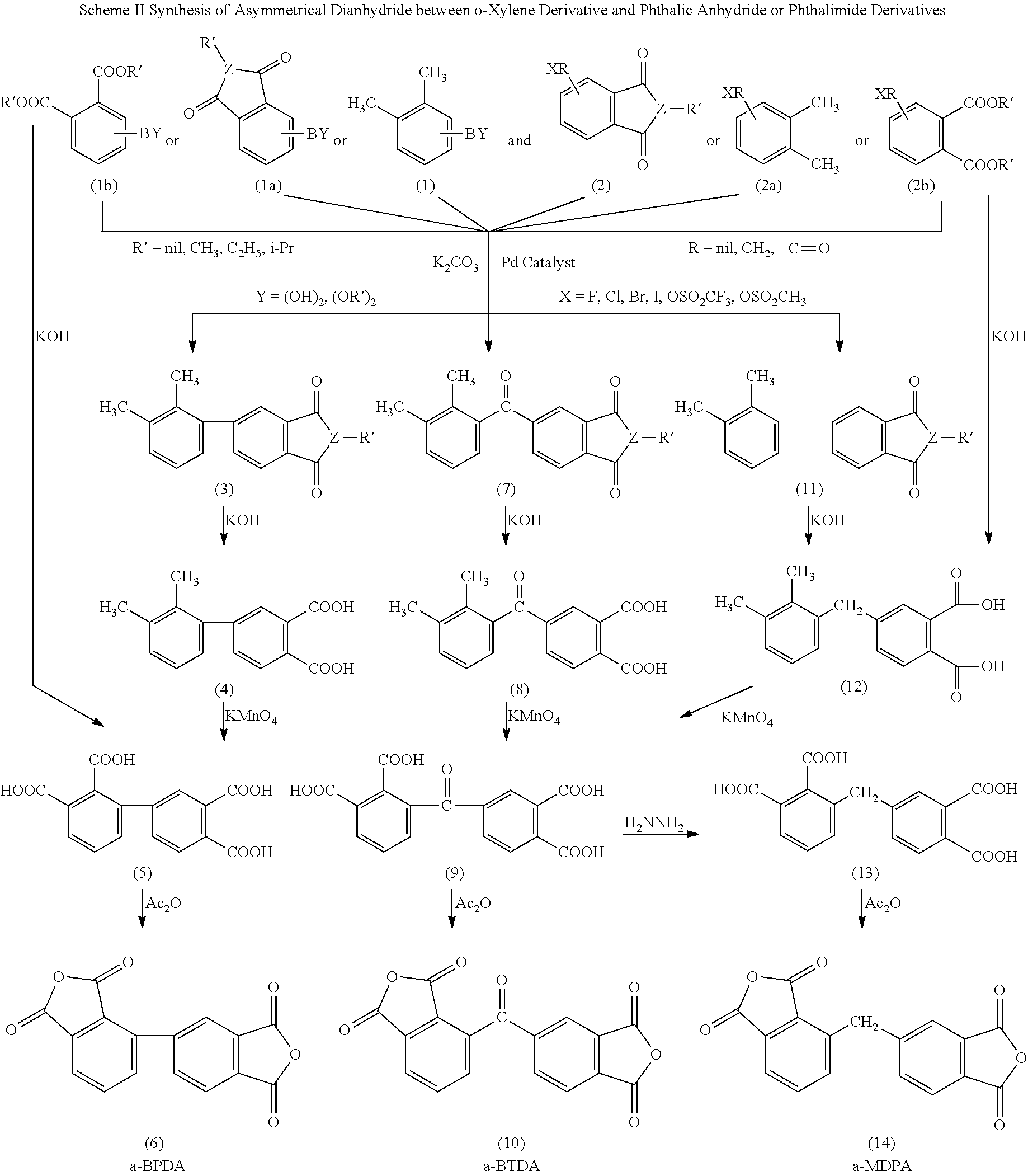
Synthesis of asymmetric tetracarboxylic acids and corresponding dianhydrides
ActiveUS7425650B1High yieldOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid amidesO-XyleneBPDA
This invention relates to processes for preparing asymmetrical biphenyl tetracarboxylic acids and the corresponding asymmetrical dianhydrides, namely 2,3,3′,4′-biphenyl dianhydride (a-BPDA), 2,3,3′,4′-benzophenone dianhydride (a-BTDA) and 3,4′-methylenediphthalic anhydride (-MDPA). By cross-coupling reactions of reactive metal substituted o-xylenes or by cross-coupling o-xylene derivatives in the presence of catalysts, this invention specifically produces asymmetrical biphenyl intermediates that are subsequently oxidized or hydrolyzed and oxidized to provide asymmetric biphenyl tetracarboxylic acids in comparatively high yields. These asymmetrical biphenyl tetracarboxylic acids are subsequently converted to the corresponding asymmetrical dianhydrides without contamination by symmetrical biphenyl dianhydrides.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT ADMINSRATOR OF NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE
Preparation method of tetramethyl biphenyl
ActiveCN103086838AIncrease concentrationLower reaction costHydrocarbon from halogen organic compoundsSolventRaw material
The invention provides a preparation method of tetramethyl biphenyl, which comprises the following steps: mixing halogenated o-xylene, magnesium metal, iodine, ether and transition metal catalyst, and reacting to obtain the tetramethyl biphenyl, wherein the mol ratio of ether to magnesium metal is (0.5-3):1. Compared with the prior art of synthesizing tetramethyl biphenyl from halogenated o-xylene, the invention has the following advantages: by using the raw material halogenated o-xylene as the solvent, the preparation of the format reagent and the coupling reaction are carried out in the initial raw material, so that the addition of abundant anhydrous solvent as the reaction medium is not needed, thereby lowering the reaction cost and simplifying the production technique; the magnesium metal is directly added into the halogenated o-xylene to obtain the format reagent, so the process is simple and the conditions are mild and controllable; and the raw material, the concentration of which in the reaction system is high, is used as the solvent and participates in the oxidation-reduction process in the coupling reaction, no oxidizer is needed, so the reaction conditions are mild and controllable.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vanadium-containing catalysts, process for manufacturing and use of the same
InactiveUS6281378B1Efficient preparationGood dispersionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationBenzoic acidPartial oxidation
Vanadium-containing catalysts are obtained by using polyvanadic acid as a source of vanadium. Vanadium-containing catalysts are obtained by mixing catalyst components other than vanadium, or their precursors, with a polyvanadic acid sol which is formed by ion-exchanging a metavanadic acid aqueous solution with a proton-type cation-exchange resin and performing polycondensation, and by drying and / or calcining the mixture. Such vanadium-containing catalysts can fully exhibit their catalytic activity under mild reaction conditions, and can be suitably used for various reactions, such as synthesis of phthalic anhydride by the partial oxidation of o-xylene, synthesis of benzaldehyde by the partial oxidation of toluene, synthesis of benzoic acid by the partial oxidation of toluene, synthesis of anisaldehyde by the partial oxidation of p-methoxy toluene, synthesis of propylene by the oxidative dehydrogenation of propane, synthesis of isobutene by the oxidative dehydrogenation of isobutane, synthesis of methyl formate by the oxidative dehydrogenation of methanol, and synthesis of acrylonitrile by the ammoxidation of propane.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Method for adsorbing and separating paraxylene and ethylbenzene from C8 aromatic components
ActiveCN104418698AReduce the difficulty of separationHigh purityHydrocarbon by isomerisationAdsorption purification/separationO-XyleneIsomerization
The invention discloses a method for adsorbing and separating paraxylene and ethylbenzene from C8 aromatic components. The method comprises the following steps: performing liquid-phase adsorption and separation on C8 aromatic hydrocarbons, thereby obtaining extracted oil rich in paraxylene and raffinate oil rich in ethylbenzene, m-xylene and o-xylene; introducing the raffinate oil into a gas phase adsorption and separation column, adsorbing ethylbenzene from the raffinate oil under the conditions of 190-270 DEG C, 0.4-0.8MPa and gas phase, allowing the non-adsorbed components to flow out of the gas phase adsorption and separation column to serve as adsorption residues, and purging an adsorbent bed layer by using purge gas under the pressure not less than the adsorption pressure, wherein the purged intermediate components is used as gas phase adsorption feedstock; reducing the pressure to 0.1-0.3 MPa, introducing the purge gas to desorb the adsorbed ethylbenzene so as to obtain the aspirate, performing xylene isomerization on the adsorption residues, wherein the isomerization products are taken as raw materials of the above liquid phase adsorption and separation. According to the method, the high-purity paraxylene and ethylbenzene can be separated from the C8 aromatic components, the adsorption residues hardly contain ethylbenzene, and isomerization can be performed under the non-hydrogen and low-temperature conditions.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for synthesizing BTX aromatic methyl into unsym-trimethyl benzene
ActiveCN101654394ALow costConvenient sourceHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationMethylating AgentM-Xylene
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing BTX aromatic methyl into unsym-trimethyl benzene. The method takes BTX aromatic hydrocarbon (comprising any one or more of benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene and mixed xylenes) and a methylating agent (selected from one or more of methyl alcohol, dimethyl ether and methane chloride) as raw materials to prepare unsym-trimethyl benzene by a methylation reaction under the catalytic action of an acid catalyst. The acid catalyst is selected from any one of halide, liquid acid, complexacid, heteropolyacid, solid super acid, acidic ion exchange resin, acidic oxide, hydrogenous zeolite molecular sieve or supported acid catalyst. The pressure of the methylation reaction is 0.01-10.0Mpa, the temperature is 30-700 DEG C, the mass space velocity of raw material liquid is 0.1-10.0h<-1>, and the mole ratio of the aromatic hydrocarbon and the methylating agent is 1:10 to 10:1. The methylation reaction can adopt a continuous fixed bed reaction or continuous stirred-tank reaction. The method has rich raw material resources, low cost, mild reaction condition as well as higher once-through conversion of the raw materials and yield of the unsym-trimethyl benzene.
Owner:SHANGHAI NOVEL CHEM TECH
2-methyl-3-methoxybenzoyl chloride synthesizing process
InactiveCN109384667AImprove separabilitySolve the problem of raw materialsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationO-XyleneSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a 2-methyl-3-methoxybenzoyl chloride synthesizing process. According to the present invention, low-cost o-xylene is used as a starting raw material, the product is synthesizedby using a conventional synthesis method comprising nitrification, esterification, reduction, diazotization, methylation, acyl chlorination and other steps, and the total yield is controlled at more than 65%; the esterification of the intermediate product improves the separation degree of the intermediate; the reaction solvent is added in the diazotization step, such that the process parameters are relatively easy to control, and the purity of the intermediate in the diazotization step is more than 96% so as to provide the guarantee for the quality of the subsequent product; and with the synthesis process, the product quality is stable and reliable, and the cost is low.
Owner:JIANGSU YONGAN CHEM CO LTD
Anaerobic biodegradation of unsaturated, saturated, aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons
An apparatus and method for anaerobic biodegradation, bioremediation or bioprocessing of hydrocarbons dissolved in an aqueous matrix, such as wastewater, groundwater, or slurry. Dissolved alkanes (saturated hydrocarbons), alkenes (unsaturated hydrocarbons), aromatic hydrocarbons and / or halogenated hydrocarbons are metabolized or cometabolized. In one form, the invention involves introducing an aqueous stream comprising at least one dissolved aromatic hydrocarbon (such as benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene, phenol, o-cresol, m-cresol, or p-cresol) and a dissolved oxide of nitrogen [such as nitrate (NO3-), nitrite (NO2-), nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O)] to a reactor, and operating said reactor under conditions that support denitrification of the aromatic hydrocarbon. Alternatively, the aqueous stream may comprise at least one alkane (such as ethane) and / or at least one alkene (such as ethene or ethylene) and biodegradation of these compounds is accomplished. In a preferred form, the aqueous stream also comprises at least one dissolved halogenated hydrocarbon (such as tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, or 1,1,1-trichloroethane) and dehalogenation of the halogenated hydrocarbon is accomplished. The reactor may be a continuous stirred tank reactor, a batch (or sequencing batch) reactor, a plug-flow reactor, a fixed-film reactor, or a pore space in an underground aquifer in situ. The reactor is operated in such a way that molecular oxygen is excluded from the space or zone in which the biodegradation is occurring and the other requirements of denitrifying bacteria are met. In some implementations, kinetic control (control of mean cell residence time) is used to enrich a denitrifying culture in the reactor.
Owner:YESTECH
Synthesis method for 2,3,6,7-triptycene tetracarboxylic dianhydride
InactiveCN102617587AHigh yieldHigh product purityOrganic chemistryChromatographic separationAcetic anhydride
The invention discloses a synthesis method for 2,3,6,7-triptycene tetracarboxylic dianhydride. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing 2,3,6,7-tetramethylanthracene from o-xylene and benzyl alcohol or methylene chloride under the catalysis of anhydrous aluminum trichloride; 2) diazotizing the 2,3,6,7-tetramethylanthracene, anthranilic acid and amyl nitrite to generate a crude product 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl triptycene; 3) performing chromatographic separation on the crude product 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl triptycene, and flushing the separated 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl triptycene by using a mixed eluting agent to obtain 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl triptycene; 4) oxidizing the 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl triptycene in a mixed solvent consisting of potassium permanganate, pyridine and water under a reflux condition to generate 2,3,6,7-triptycene tetracarboxylic acid; and 5) refluxing and dehydrating the 2,3,6,7-triptycene tetracarboxylic acid in acetic anhydride to generate the 2,3,6,7-triptycene tetracarboxylic dianhydride. The method has the characteristics of readily available and low-cost raw materials, high yield and high product purity.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
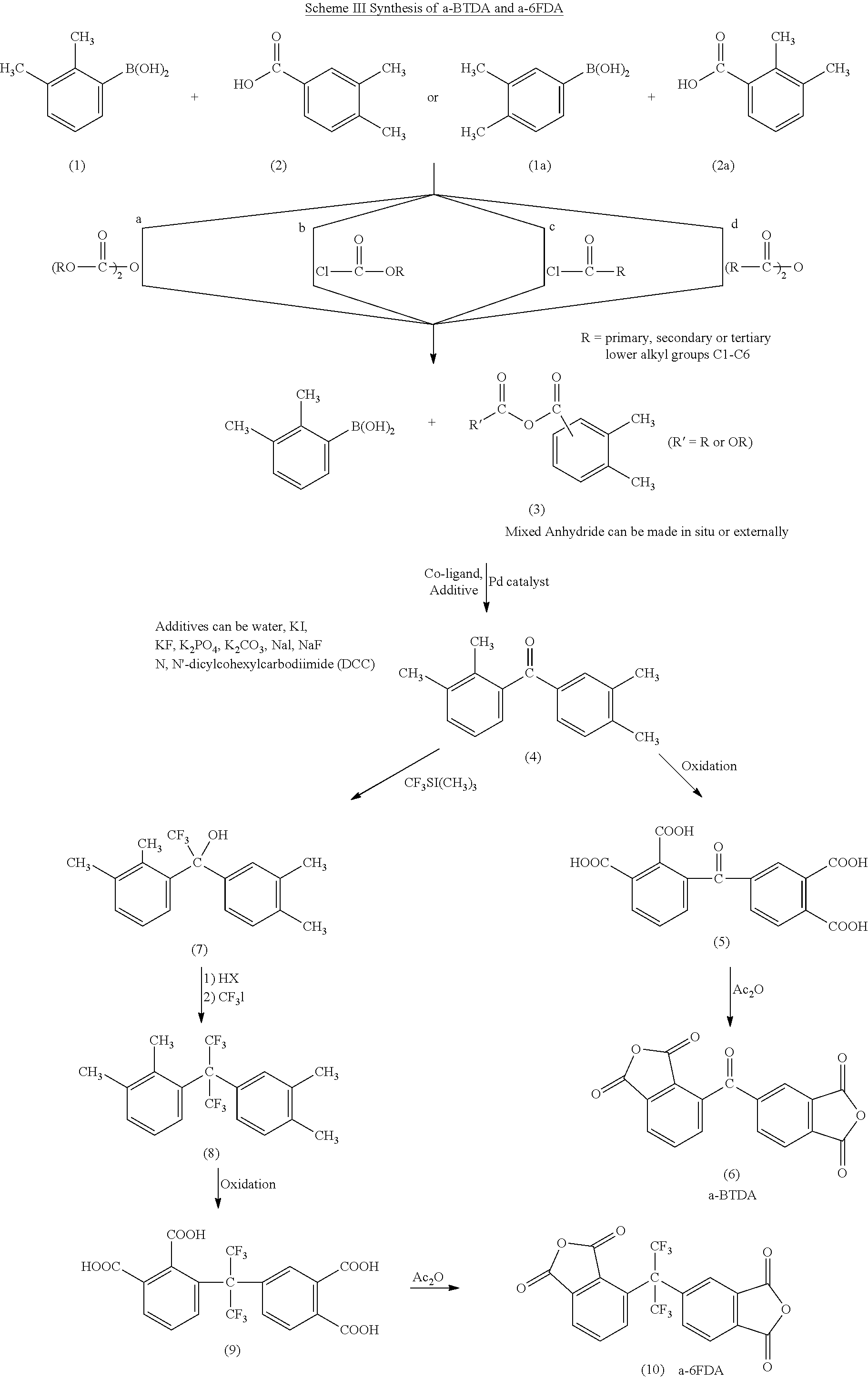
Polyimides derived from novel asymmetric dianhydrides
ActiveUS8093348B1Improve wear resistanceImprove adhesionOrganic chemistryTrifluoromethylationO-Xylene
This invention relates to the compositions and processes for preparing thermoset and thermoplastic polyimides derived from novel asymmetrical dianhydrides: specifically 2,3,3′,4′ benzophenone dianhydride (a-BTDA), and 3,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic anhydride (a-6FDA). The a-BTDA anhydride is prepared by Suzuki coupling with catalysts from a mixed anhydride of 3,4-dimethylbenzoic acid or 2,3-dimethylbenzoic acid with 2,3-dimethylphenylboronic acid or 3,4-dimethylphenylboronic acid respectively, to form 2,3,3′,4′-tetramethylbenzophenone which is oxidized to form 2,3,3′,4′-benzophenonetetracarboxylic acid followed by cyclodehydration to obtain a-BTDA. The a-6FDA is prepared by nucleophilic triflouoromethylation of 2,3,3′,4′-tetramethylbenzophenone with trifluoromethyltrimethylsilane to form 3,4′-(trifluoromethylmethanol)-bis(o-xylene) which is converted to 3,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene-bis(o-xylene). The 3,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)-bis(o-xylene) is oxidized to the corresponding tetraacid followed by cyclodehydration to yield a-6FDA.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT ADMINSRATOR OF NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION
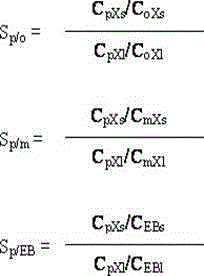
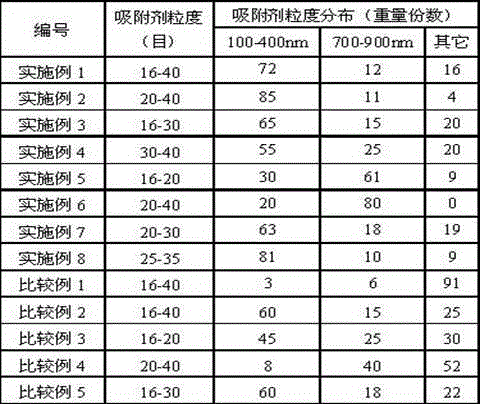
High-silicon MFI zeolite adsorbent without adhesive and preparation method thereof
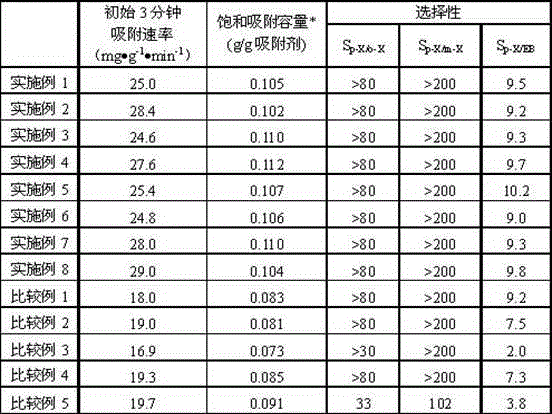
The invention relates to a high-silicon MFI zeolite adsorbent without adhesive and a preparation method thereof, which mainly aim at solving the problems of small adsorption capacity of an adsorbent for PX in mixed xylene C8, as well as low adsorption rate and poor separation effect in the prior art. The high-silicon zeolite adsorbent without adhesive is prepared through the steps of adding high-silicon MFI powder in specific grain size distribution into a silicon adhesive for forming and performing crystal transformation, wherein the grain size of the adsorbent is 16-40 meshes; at room temperature, when a solid-liquid ratio is 3 to 5, the adsorption capacity of per gram of adsorbent for p-xylene in a 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene solution containing 10% of p-xylene based on weight percent is greater than 0.102g, the selectivity coefficient of p-xylene for ethylbenzene, o-xylene and m-xylene is higher than 9.0, and within initial three minutes, the adsorption rate of the per gram of adsorbent for p-xylene is greater than 22mg / minute. By virtue of the technical scheme, the technical problems are well solved and the high-silicon MFI zeolite adsorbent without adhesive can be used for separation of p-xylene in C8 arene.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High-purity ptyltetracid dianhydride and synthesis method thereof, and polyimides synthesized on basis of ptyltetracid dianhydride
The invention discloses a high-purity ptyltetracid dianhydride and a synthesis method thereof, and polyimides synthesized on the basis of the ptyltetracid dianhydride. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out Friedel-Crafts reaction on cheap accessible industrial dichloromethane and o-xylene by using anhydrous AlCl3 as a catalyst to obtain 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl anthracene, carrying out D-A addition on the 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl anthracene and anthranilic acid or equivalent thereof to obtain 2,3,6,7-tetramethyl triptycene and derivative thereof tetramethylptycene, and oxidizing to obtain high-value ptyltetraformic acid; and carrying out high-temperature high-pressure solvothermal synthesis on the ptyltetraformic acid to obtain the corresponding high-purity high-yield ptyltetracid dianhydride. The solvothermal method for synthesizing dianhydride is suitable for dianhydride which can not be easily purified under normal pressure, and has the advantages of low loss and high yield. The ptyltetracid dianhydride and biphenyl diamines with different substituent groups are polycondensed by a one-step process to obtain a series of novel polyimides.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
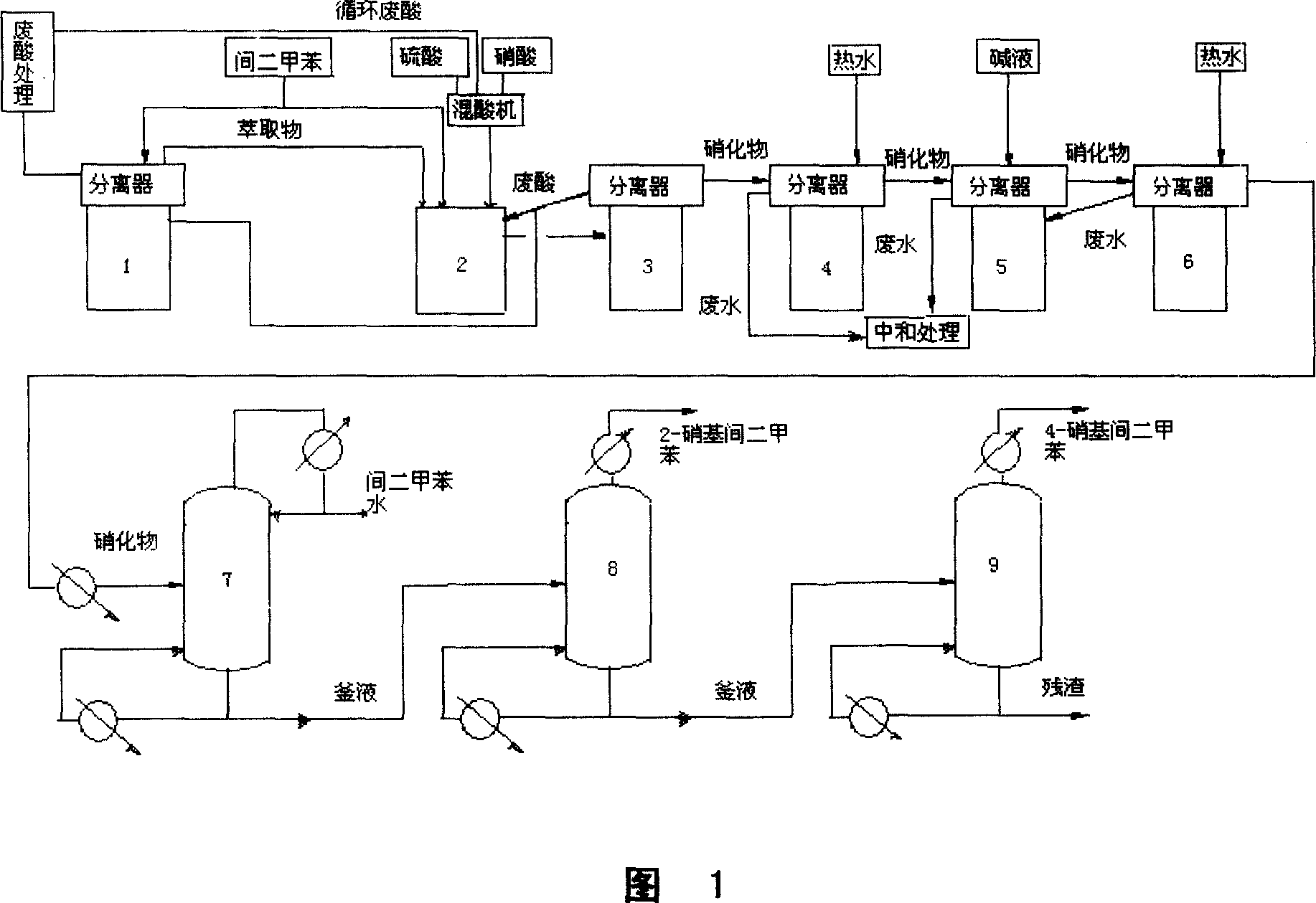
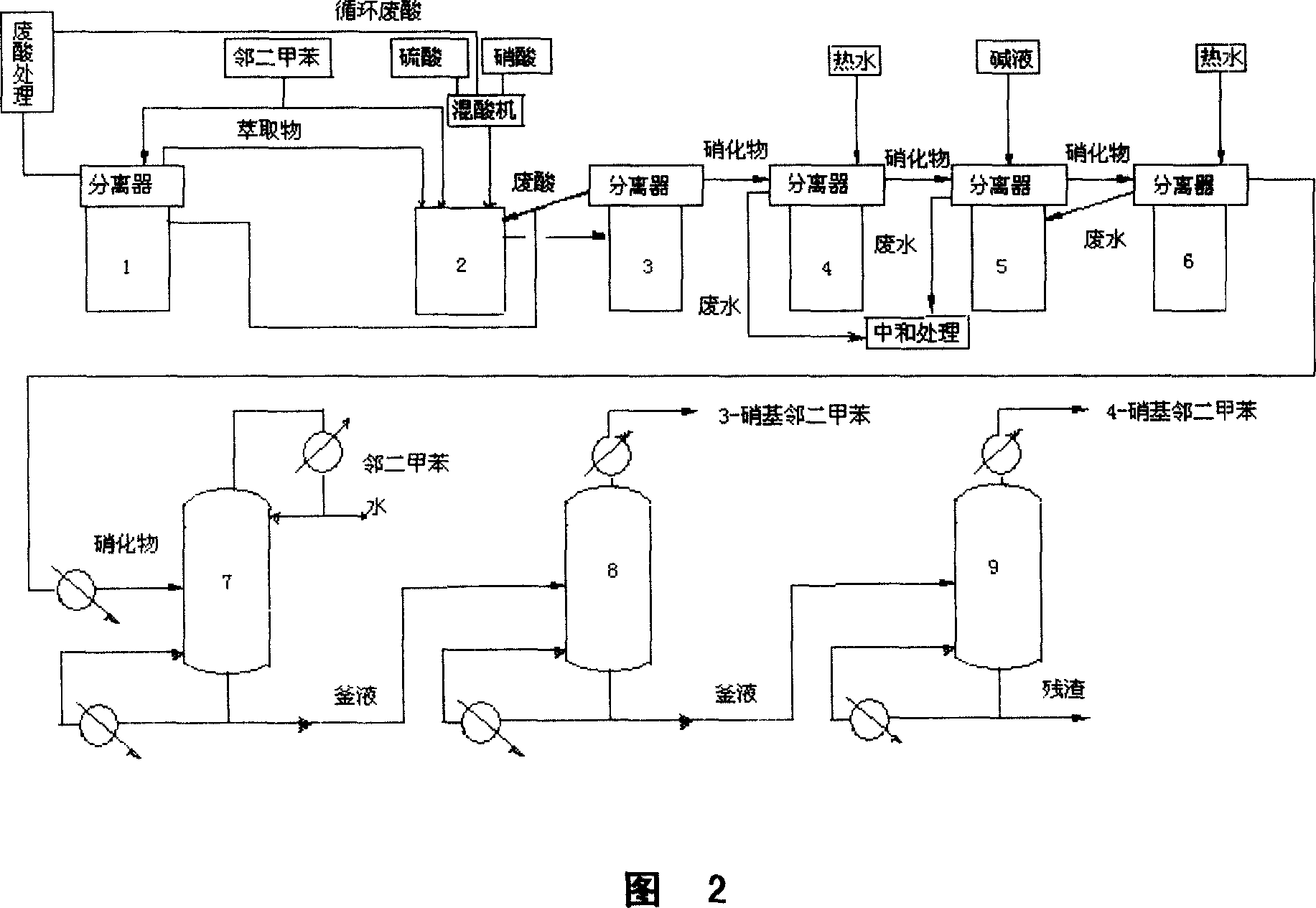
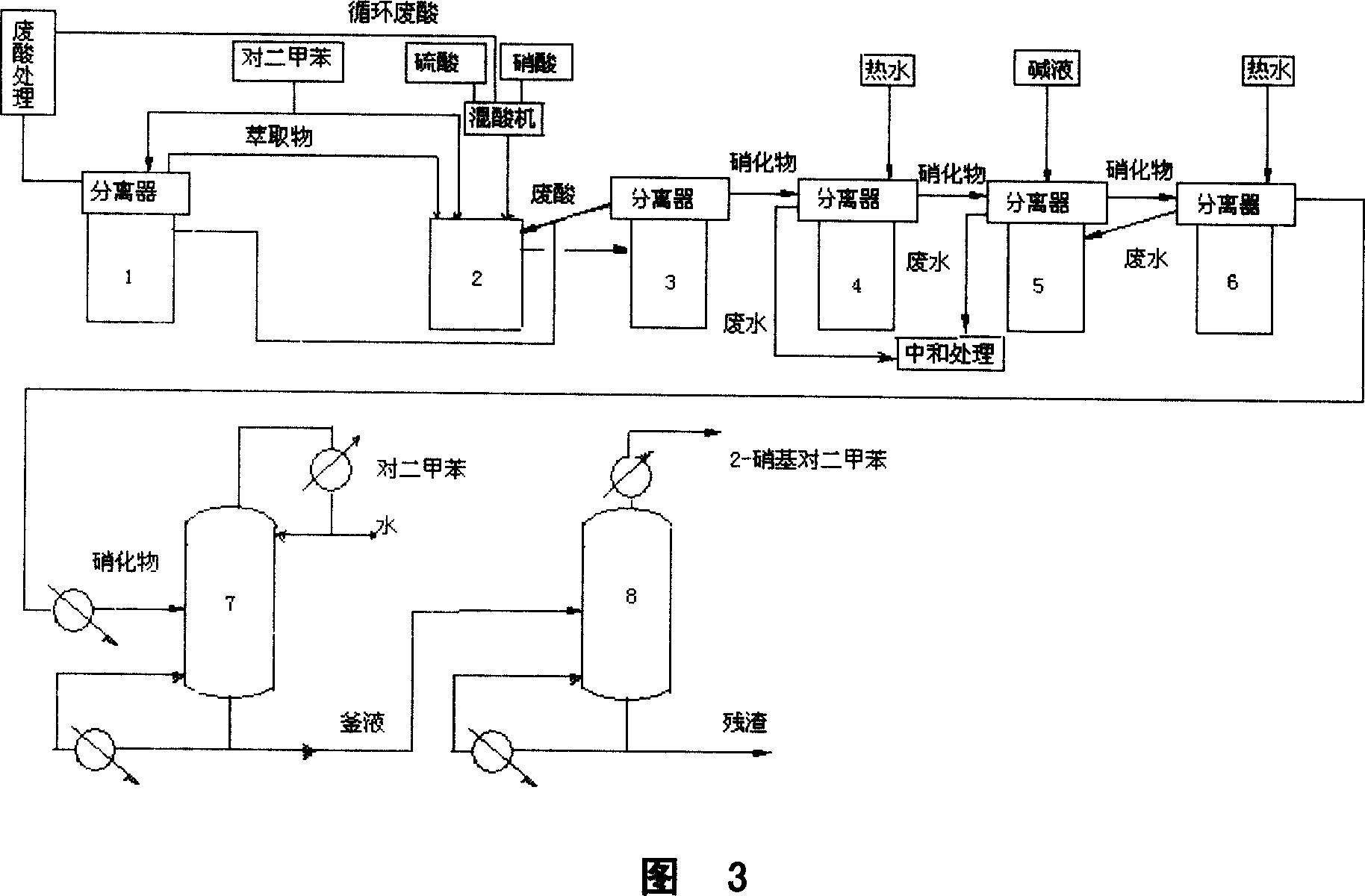
Process for continuously preparing nitro-xylene isomer monomer
The present invention is continuous xylene isomer monomer nitrifying and rectifying process with sulfuric acid and nitric acid mixture to obtain nitro xylene isomer monomer. The optimized process has product yield over 97 %; consumption of xylene, nitric acid and sulfuric acid of 750kg / ton, 465kg / ton and 40kg / ton separately; and purity of the 2, 6-dimethyl nitrobenzene, 2, 4-dimethyl nitrobenzene, 3, 4-dimethyl nitrobenzene, 2, 3-dimethyl nitrobenzene and 2, 5-dimethyl nitrobenzene up to 99.5 %. When the process has the material changed from xylene to o-xylene or p-xylene and the technological conditions changed correspondingly, 3, 4-dimethyl nitrobenzene, 2, 3-dimethyl nitrobenzene and 2, 5-dimethyl nitrobenzene may be produced.
Owner:GANSU YINGUANG CHEM IND GRP CO LTD
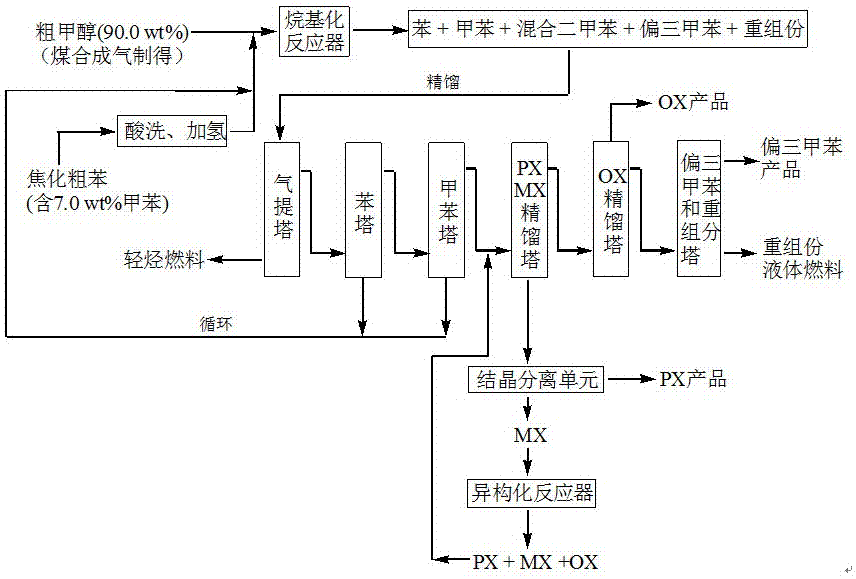
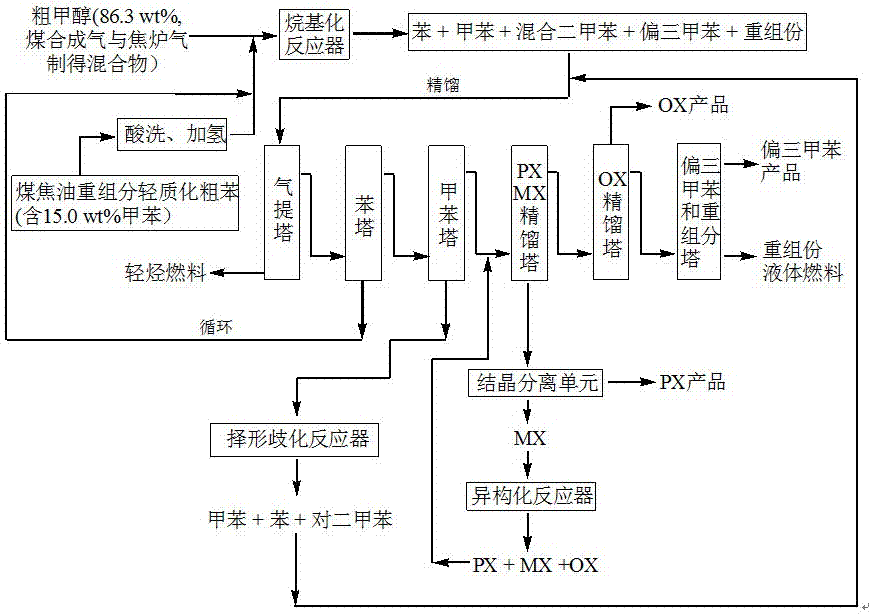
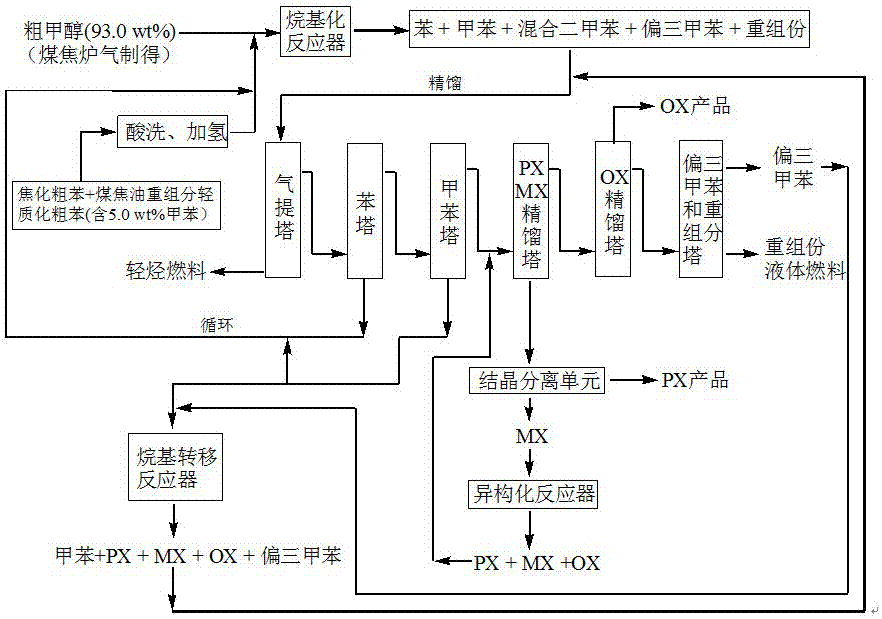
Method for producing p-xylene, o-xylene and 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene from coal-based raw materials
InactiveCN107473918AFlexible Adjustment StructureReduce coking and carbon depositionHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationFixed bed
The invention relates to a method for producing p-xylene, o-xylene and 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene from coal-based raw materials. P-xylene, o-xylene and 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene are produced from raw materials including crude benzene and crude methanol by acid pickling, hydrogenation pretreatment, alkylation reaction, rectification, crystal separation and isomerization reaction by virtue of an alkylation catalyst having large outer specific surface area and mainly adopting weak acid and medium-strong acid as main components as well as an anti-coking alkylation reaction medium; the used catalyst is flake-like MCM-56, nanometer needle-like ZSM-5, flake-like MCM-49 or a nanometer Beta molecular sieve modified by two metal oxides or a compound thereof; and a novel special molecular sieve based catalyst is also used for isomerization, alkyl transfer and shape selective disproportionation reaction which are all carried out in a fixed bed reactor. By using the method, the production costs of p-xylene, o-xylene and 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene can be effectively reduced, and the aim of producing aromatic products according to a non-petroleum raw material route is thoroughly achieved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
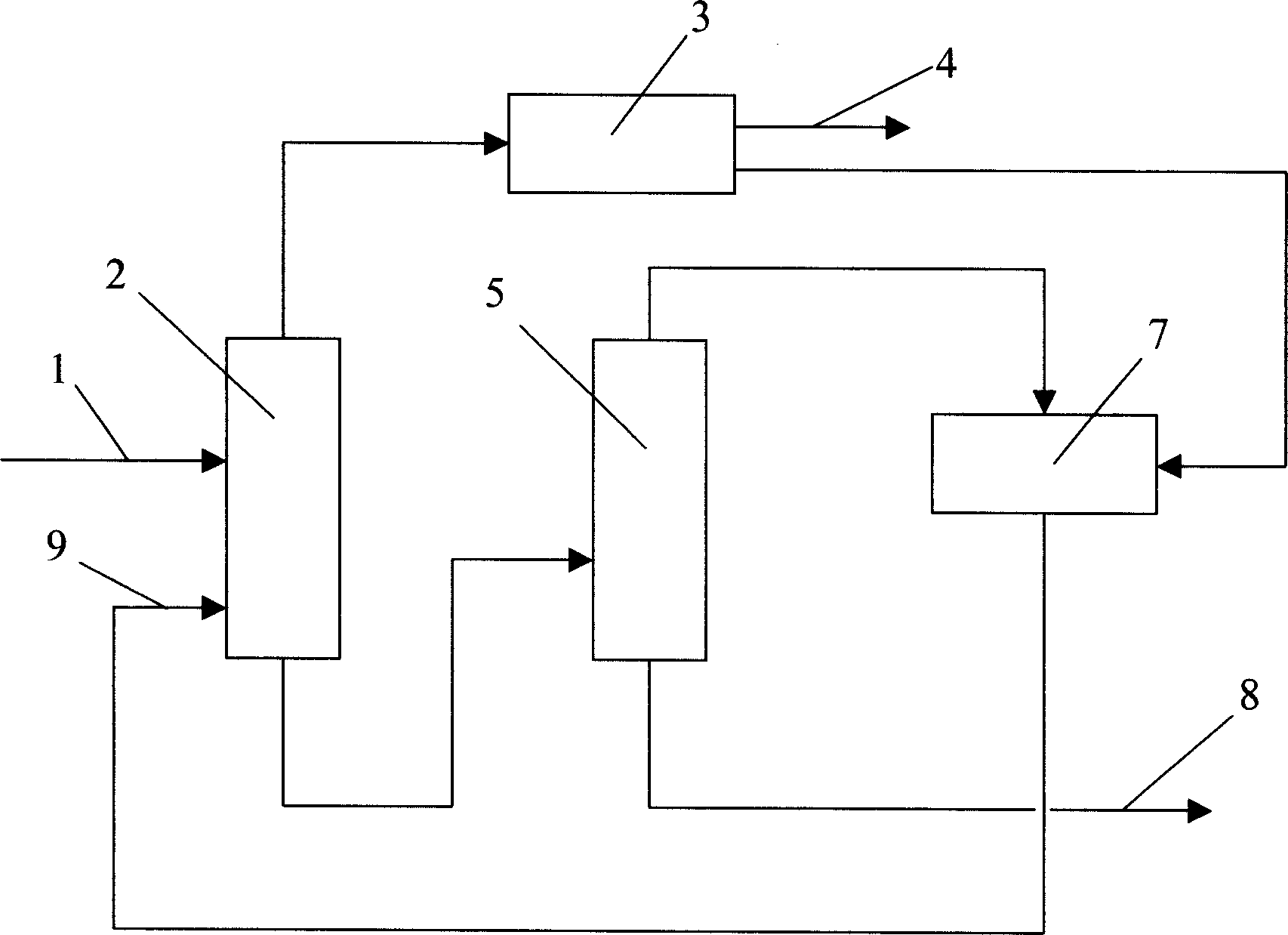
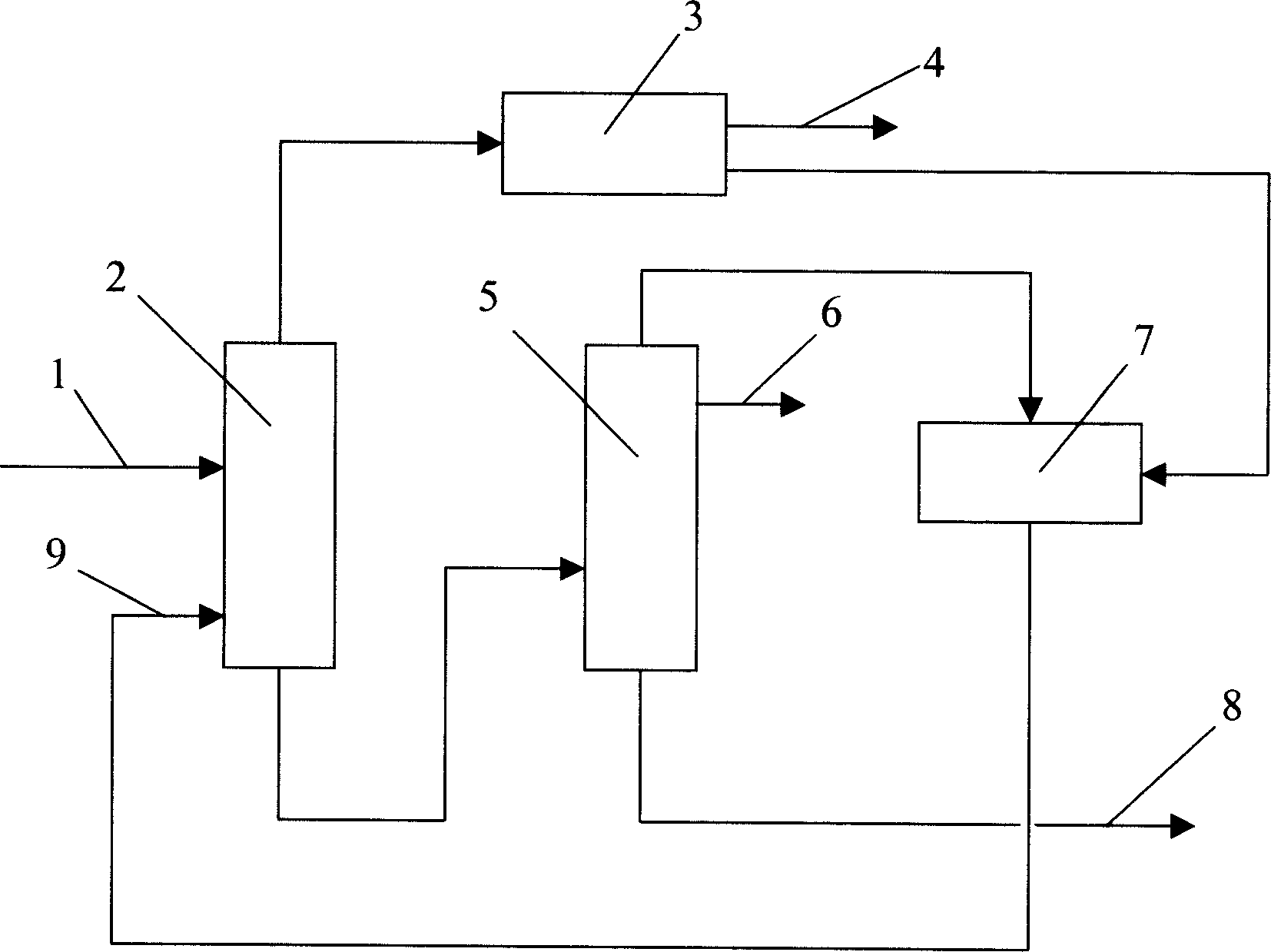
P-xylene producing process
The p-xylene producing process is superior to available technology, which has the demerits of o-xylene tower with single function, limited o-xylene product, too large size of xylene tower, etc. The p-xylene producing process includes making fresh C8+ arene material and isomeric C8+ arene from the isomerizing unit enter the xylene tower, extracting C8 arene from the tower top, adsorpting and separating in the adsorption and separation unit to obtain p-xylene product, feeding the raffinate from the adsorption and separation unit to the isomerizing unit, making C8+ arene containing o-xylene from the tower bottom to the o-xylene tower, and making the o-xylene tower top product enter to the adsorption and separation unit directly or after mixing with the raffinate from the adsorption and separation unit.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Hyphantria cunea Drury attractant composition, its application and attracting core
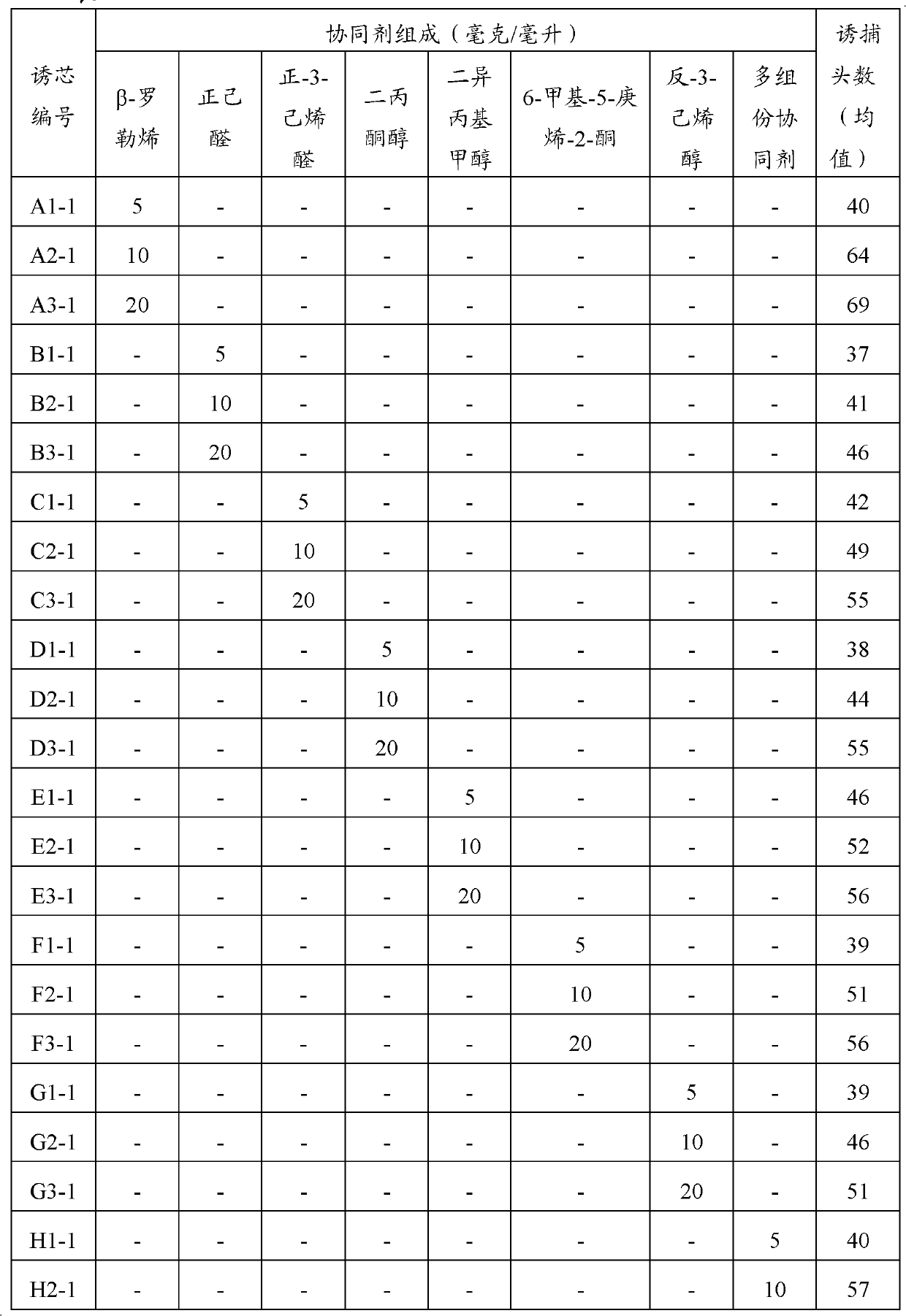
InactiveCN103315002AFlexible usageStrong autonomyBiocidePest attractantsDiacetone alcoholCis-3-Hexenal
The invention provides a Hyphantria cunea Drury attractant composition, its application and attracting core. The Hyphantria cunea Drury attractant composition includes Hyphantria cunea Drury sex pheromone and its synergistic agent. The synergistic agent contains one or more of the following plant source smell components: beta-ocimene, hexanal, cis-3-hexenal, diacetone alcohol, diisopropylcarbinol, 6-methyl-5-heptene-2-one, trans-3-hexenol, o-xylene, hemimellitene, trans-2-hexenal, and limonene. The attractant composition provided in the invention can be prepared into an attracting core so as to be used cooperatively with the existing Hyphantria cunea Drury sex pheromone. The invention provides the attracting core containing the Hyphantria cunea Drury attractant composition to prevent, control and detect Hyphantria cunea Drury, so that the defects of high cost and difficult popularization of imported and domestic Hyphantria cunea Drury sex pheromone attracting cores in the prior art are solved. The attracting core provided in the invention has the advantages of low cost, flexible use, and higher trapping efficiency.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
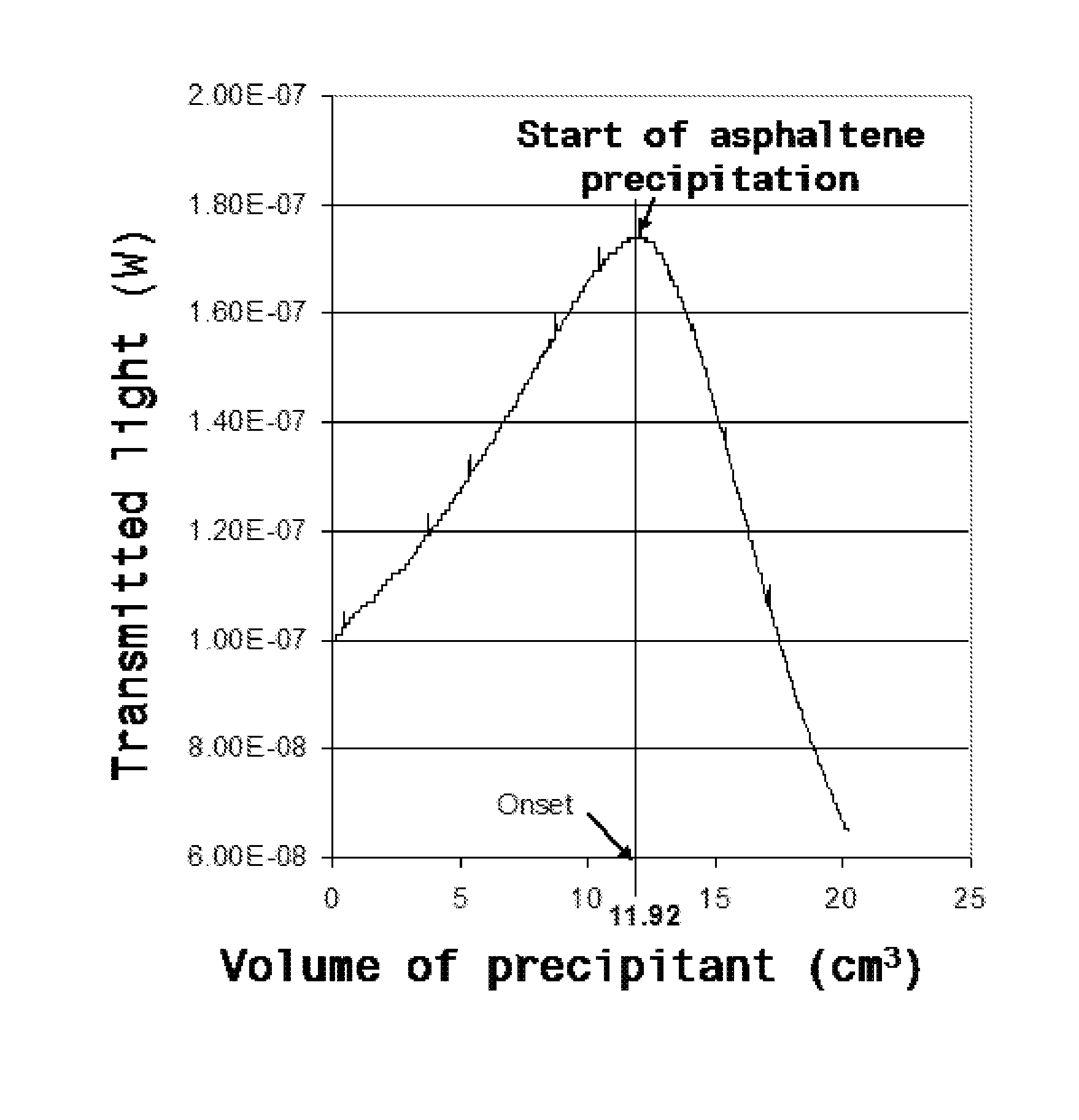
Multifunctional composition base 1,3-oxazinan-6-ones with corrosion inhibition and heavy organic compounds inhibition and dispersants and obtaining process
ActiveUS20110269650A1Control foulingAvoid corrosionAmino-carboxyl compound preparationFlushingPropanoic acidKerosene
Base compounds including 1,3-oxazinan-6-one derivatives of N-alkyl or N-alkenyl or N-cycloalkyl or N-aryl propionic acids and paraformaldehyde, and their application as corrosion inhibitors with multifunctional properties serving as inhibitory / dispersant of asphaltene in production processes, transportation, refining and storage of crude oil and derivatives. The corrosion inhibitor with inhibitory / dispersant of asphaltenes properties comprises an active substance base of 1,3-oxaninan-6-ones and hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, toluene, mixed xylenes, o-xylene, m-xylene and p -xylene, diesel, kerosene, jet fuel, alcohols, aliphatic branched and unbranched alcohols containing from 3 to 10 carbon atoms, such as isopropanol, butanol and pentanol, and mixtures of hydrocarbon solvents with aliphatic branched or unbranched liquid fuels. In addition, a process for obtaining 1,3-oxazinan-6-ones derivatives of N-alkyl or N-alkenyl or N-cycloalkyl or N-aryl propionic acids and paraformaldehyde is described.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Asphaltene-dispersing/inhibiting additive based on oxazolidines derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides
The present invention relates to formulations of asphaltenes' inhibitor-dispersant additives based on oxazolidine derived from polyalkyl or polyalkenyl N-hydroxyalkyl succinimides. Said formulations can contain inert organic solvents, preferably including: toluene, mixtures of xylene, o-xylene, p-xylene, kerosene, turbo-fuel; or inert hydrocarbon solvents having boiling points within the range of gasoline and diesel; or inert hydrocarbon or organic solvents having a boiling point within a range from 75 to 300° C. The ratio in weight of inert organic solvents to additive that prevents and controls the precipitation and deposition of asphaltenes ranges from 1:9 to 9:1, preferably from 1:3 to 3:1.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
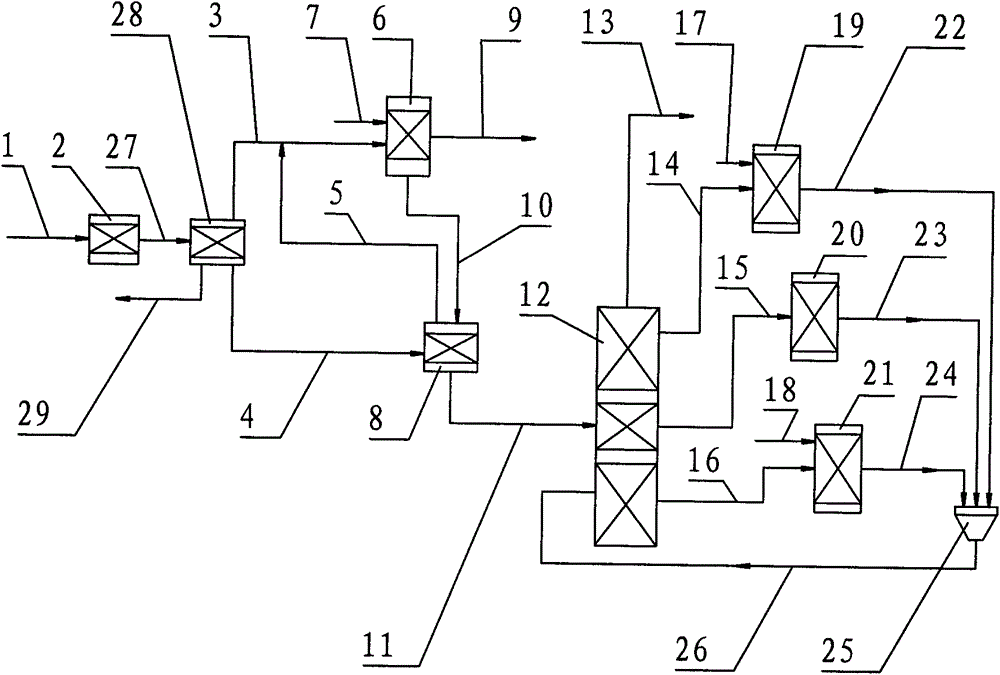
Method and apparatus for preparing p-xylene from methanol
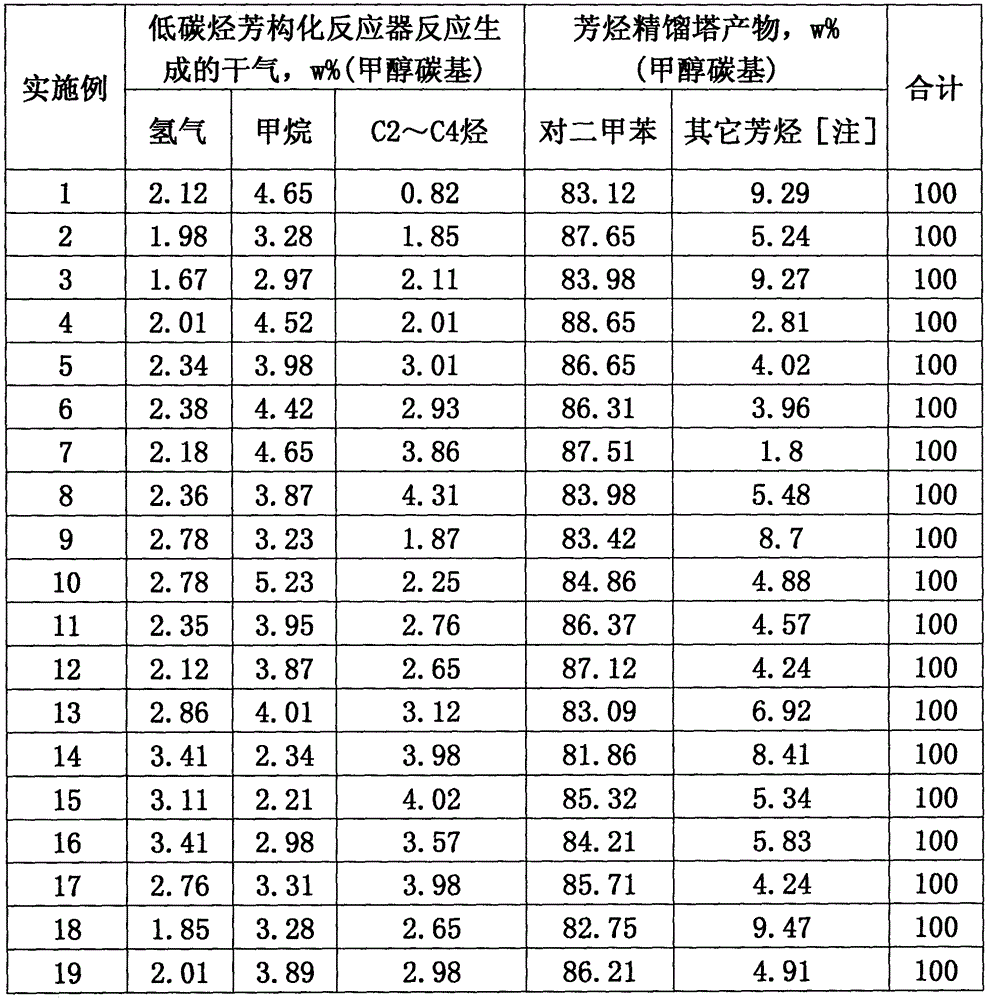
ActiveCN104892346AHigh yieldFlexible processHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsO-XyleneIsomerization
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus for preparing p-xylene from methanol. The method is mainly characterized in that first methanol feedstock produces a methanol aromatization reaction in a methanol aromatization reactor (2), and liquefied gas feedstock, a methanol aromatization gas product and non-aromatic raffinate oil separated from an aromatic hydrocarbon extraction apparatus produce a low-carbon hydrocarbon aromatization reaction in a low-carbon hydrocarbon aromatization reactor (6); second methanol feedstock as well as benzene and methylbenzene separated from an aromatic hydrocarbon rectifying tower (12) produce an alkylation reaction in an alkylation reactor (19), o-xylene, m-xylene and ethylbenzene separated from the aromatic hydrocarbon rectifying tower produce an isomerization reaction in an isomerization reactor (20), and fresh raw material benzene as well as C9 and aromatic hydrocarbons separated from the aromatic hydrocarbon rectifying tower produce a transalkylation reaction in a transalkylation reactor (21). P-xylene (13) separated from the aromatic hydrocarbon rectifying tower serves as a product. The present invention discloses the related apparatus. The method and the apparatus can produce p-xylene as much as possible.
Owner:LUOYANG PETROCHEMICAL ENG CORP SINOPEC +1
Green synthesis method of tetramethyl biphenyl isomer compounds
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
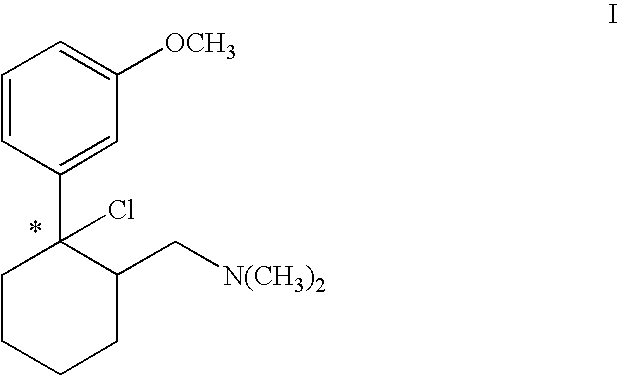
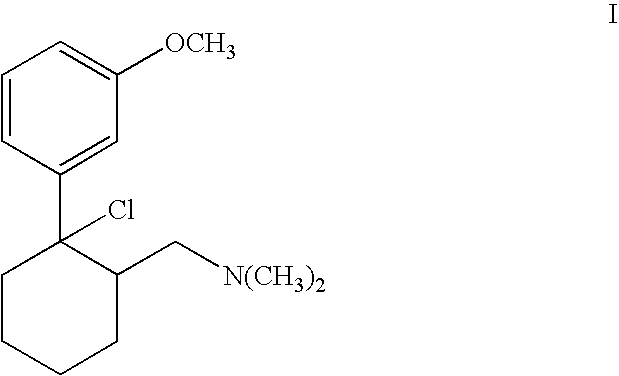
Process for chlorinating tertiary alcohols
InactiveUS20050119349A1Possible to separateReduce in quantityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSimple Organic CompoundsO-Xylene
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
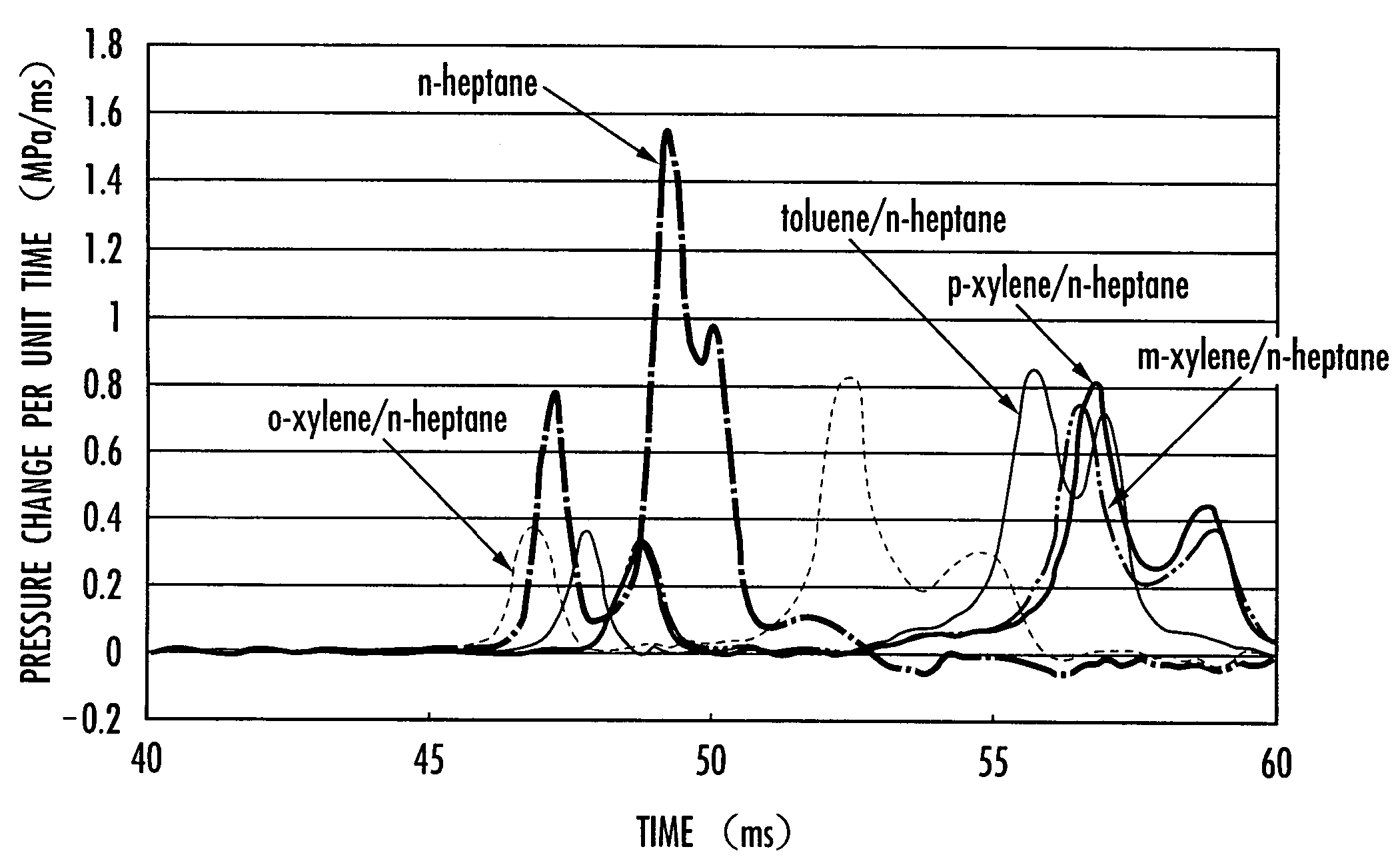
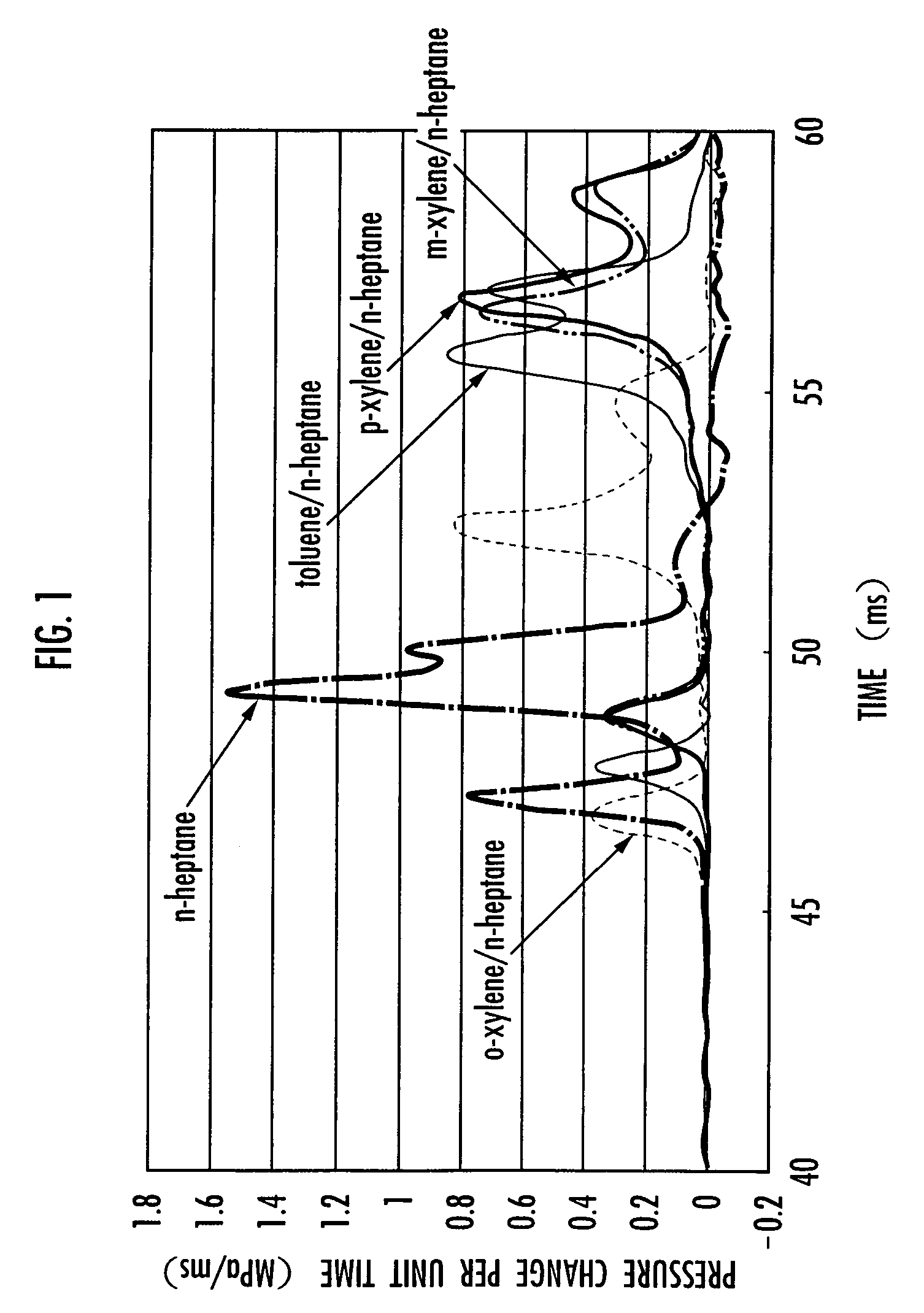
Internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7367309B2Guaranteed uptimeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionHydrocarbon
An internal combustion engine is provided which can operate by either the homogeneous charge compression ignition system or the spark ignition system using a single fuel. In the internal combustion engine using a fuel containing a hydrocarbon, the fuel contains o-xylene of 10 to 70 wt. % of the total weight, and the engine operates by either homogeneous charge compression ignition or spark ignition depending on the load. The fuel contains o-xylene of 30 to 50 wt. % of the total weight. The fuel contains, for example, n-heptane as the base fuel, and o-xylene of 10 to 70 wt. %, preferably 30 to 50 wt. %, of the total base fuel. The internal combustion engine operates by homogeneous charge compression ignition at low or medium load and by spark ignition at high load.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Preparation method of biphenyl derivatives
InactiveCN104262234AImprove recycling ratesThe process is conducive to energy saving and environmental protectionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsXylyleneNickel salt
The invention discloses a preparation method of biphenyl derivatives. According to the method, the biphenyl derivatives are generated by carrying out coupling reaction by taking non-water-soluble alkyl-substituted tetrahydrofuran as a solvent, halogenated O-xylene, halogenated alkyl phthalate and halogenated phthalimide as raw materials, manganese, aluminum or zinc as a reducing agent and nickel salt, cobalt salt, palladium salt, iron salt, copper salt or a complex compound composed of the salts, organic phosphorus and organic amine as a catalyst.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com