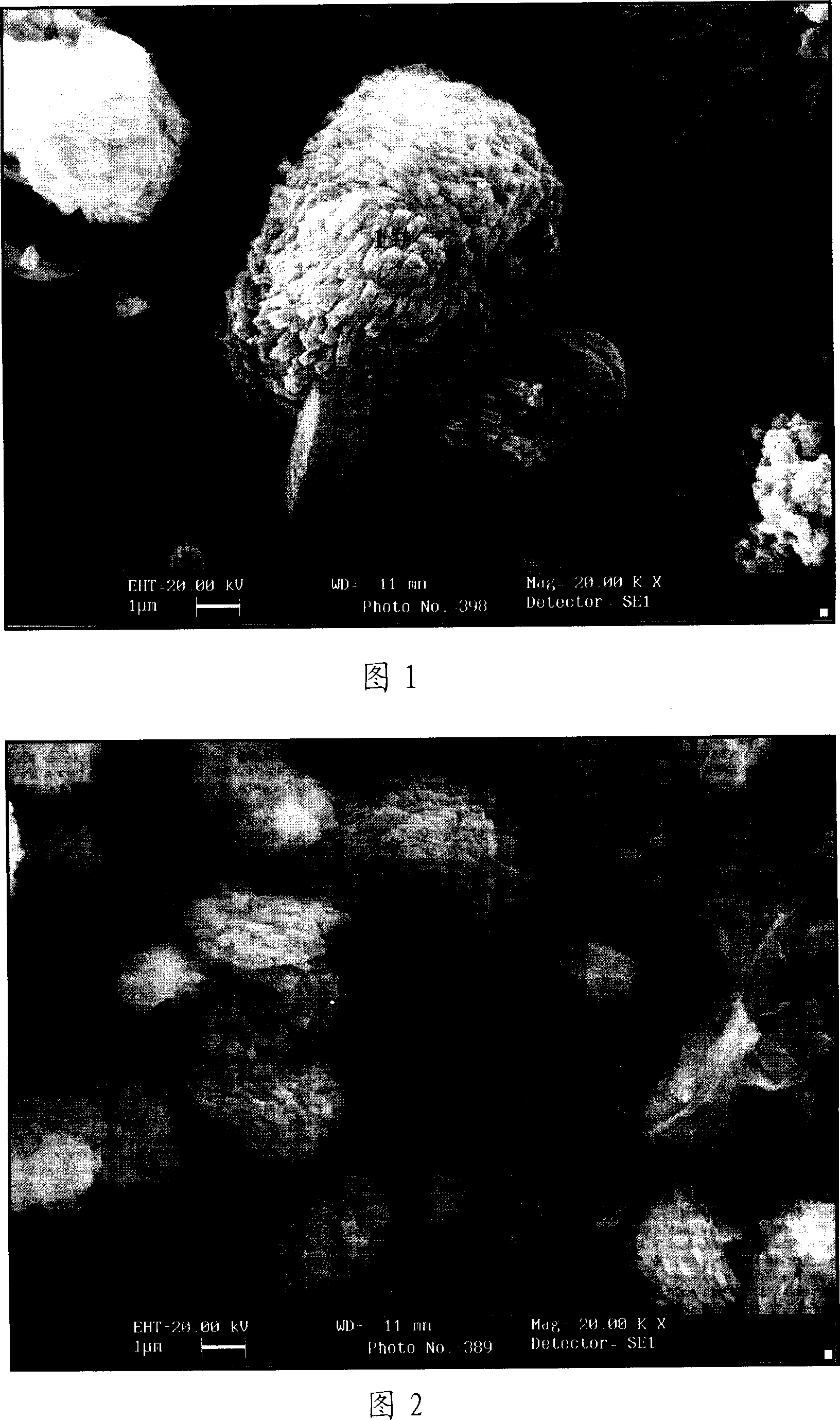
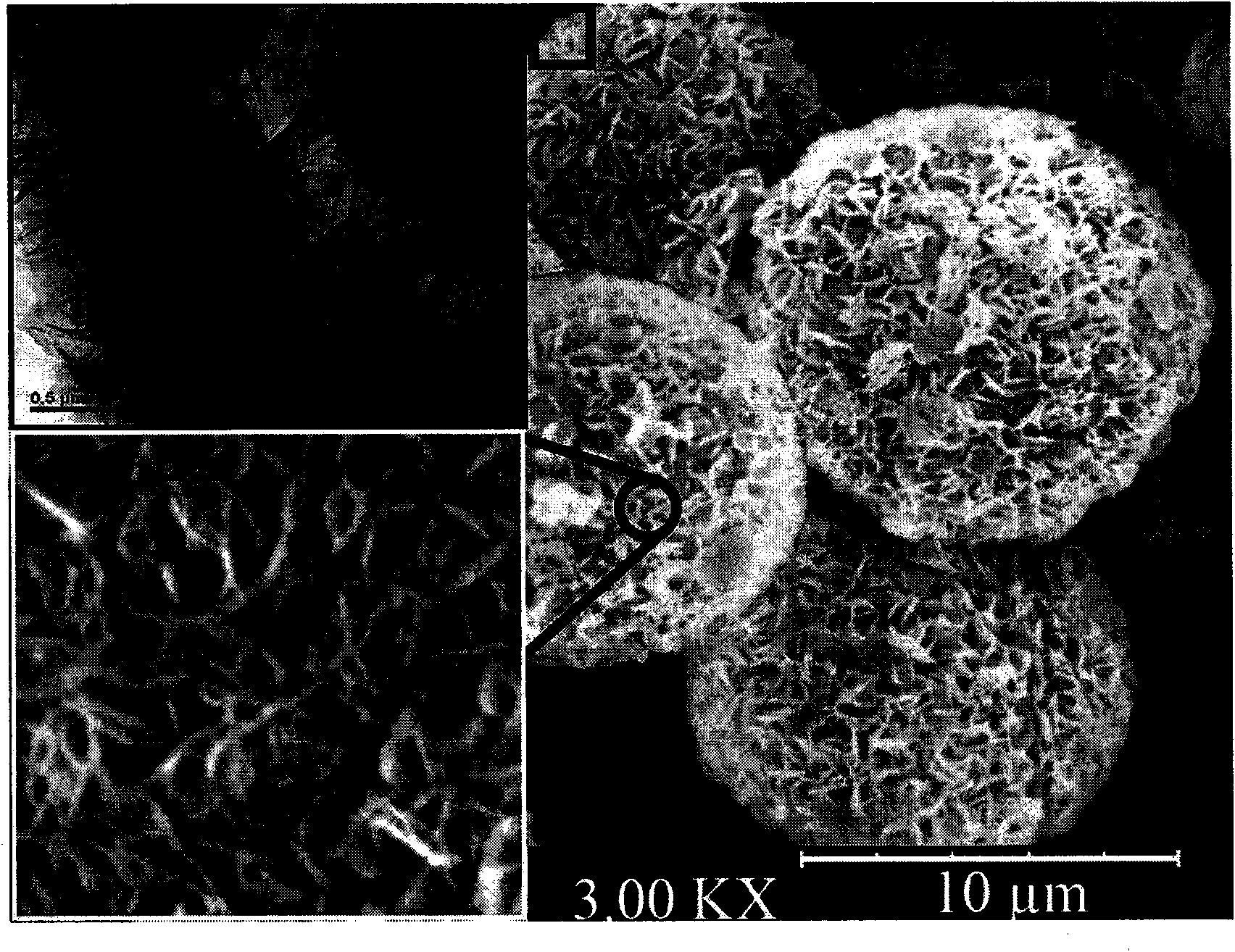
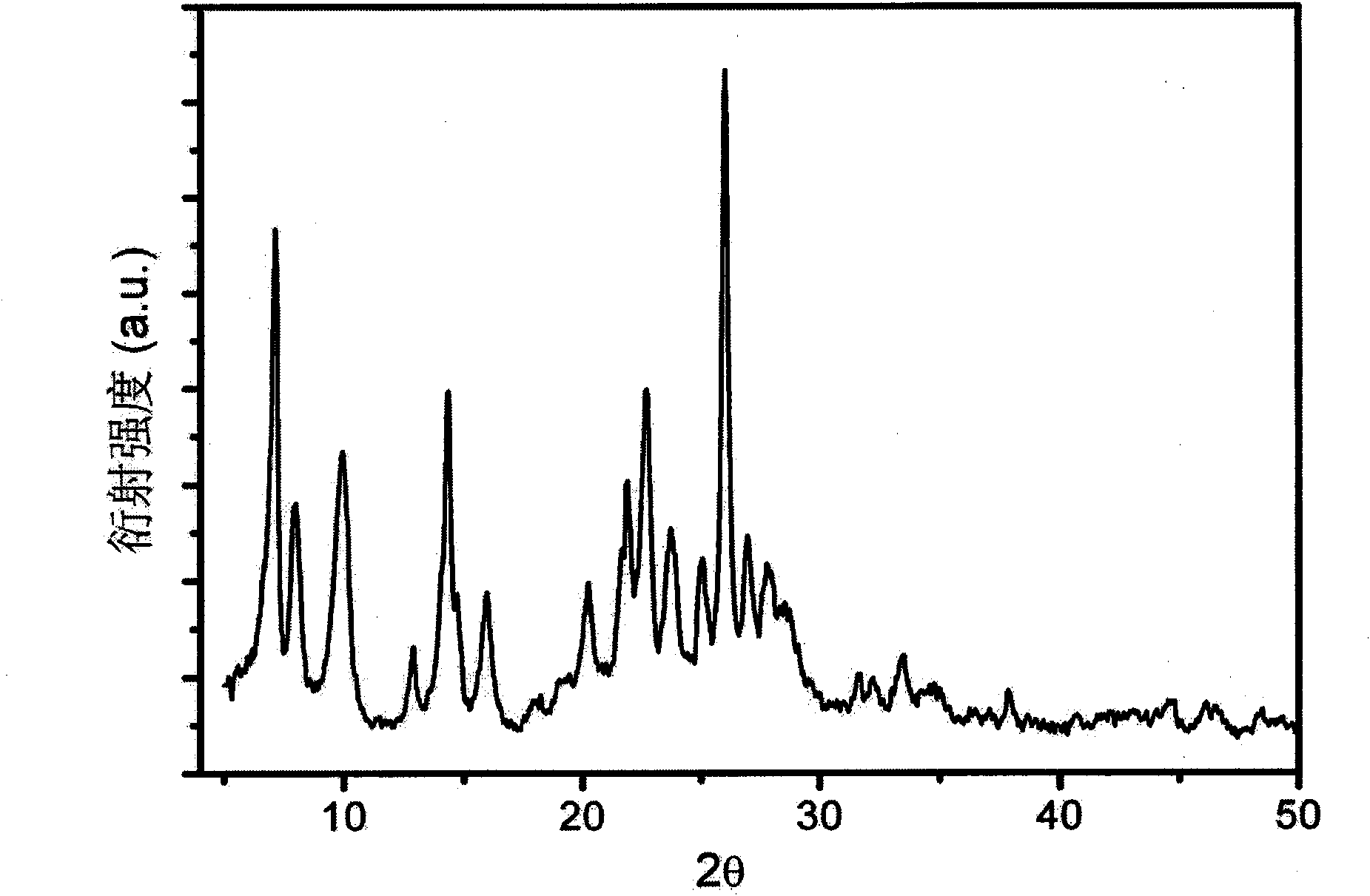
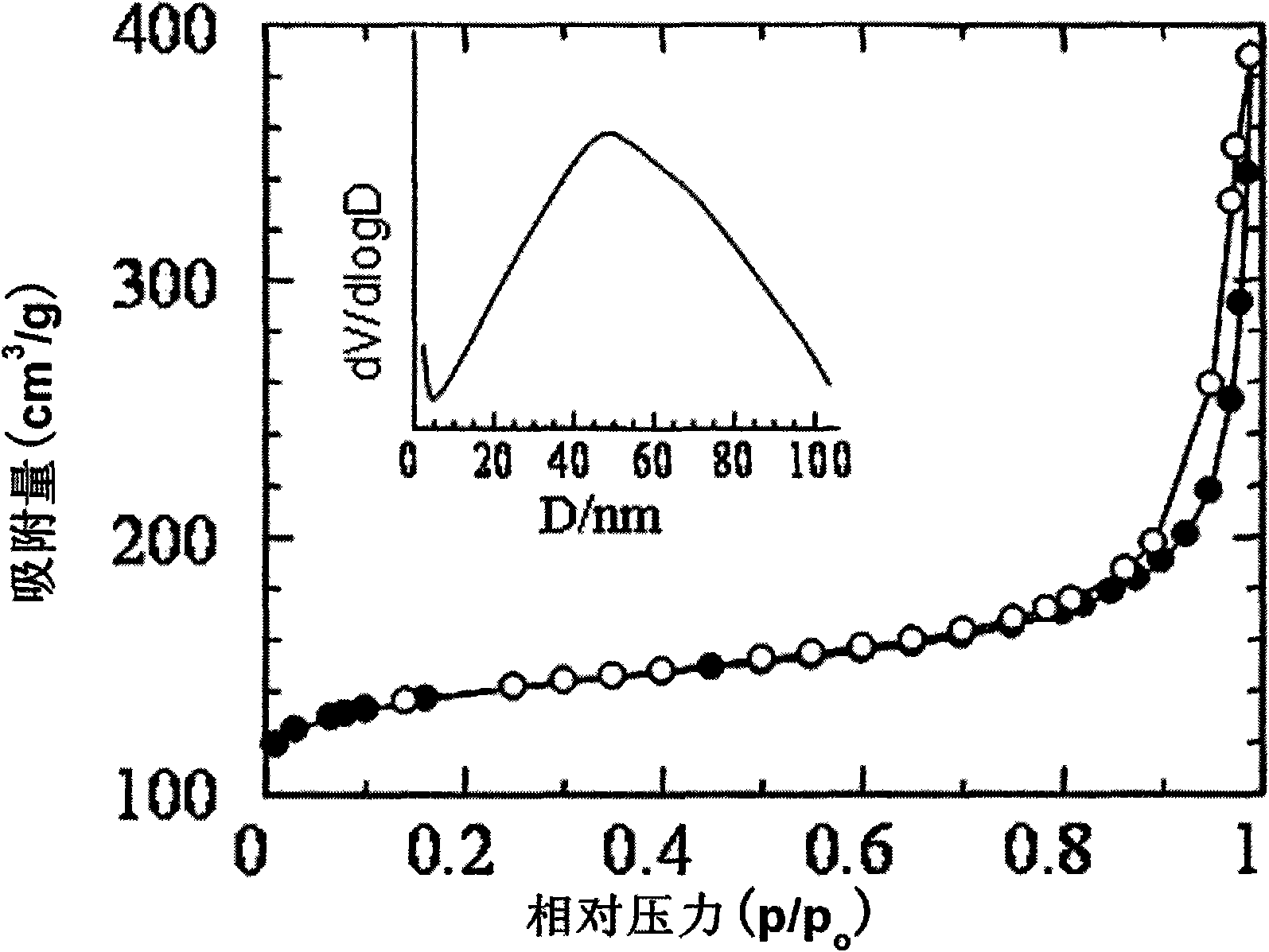
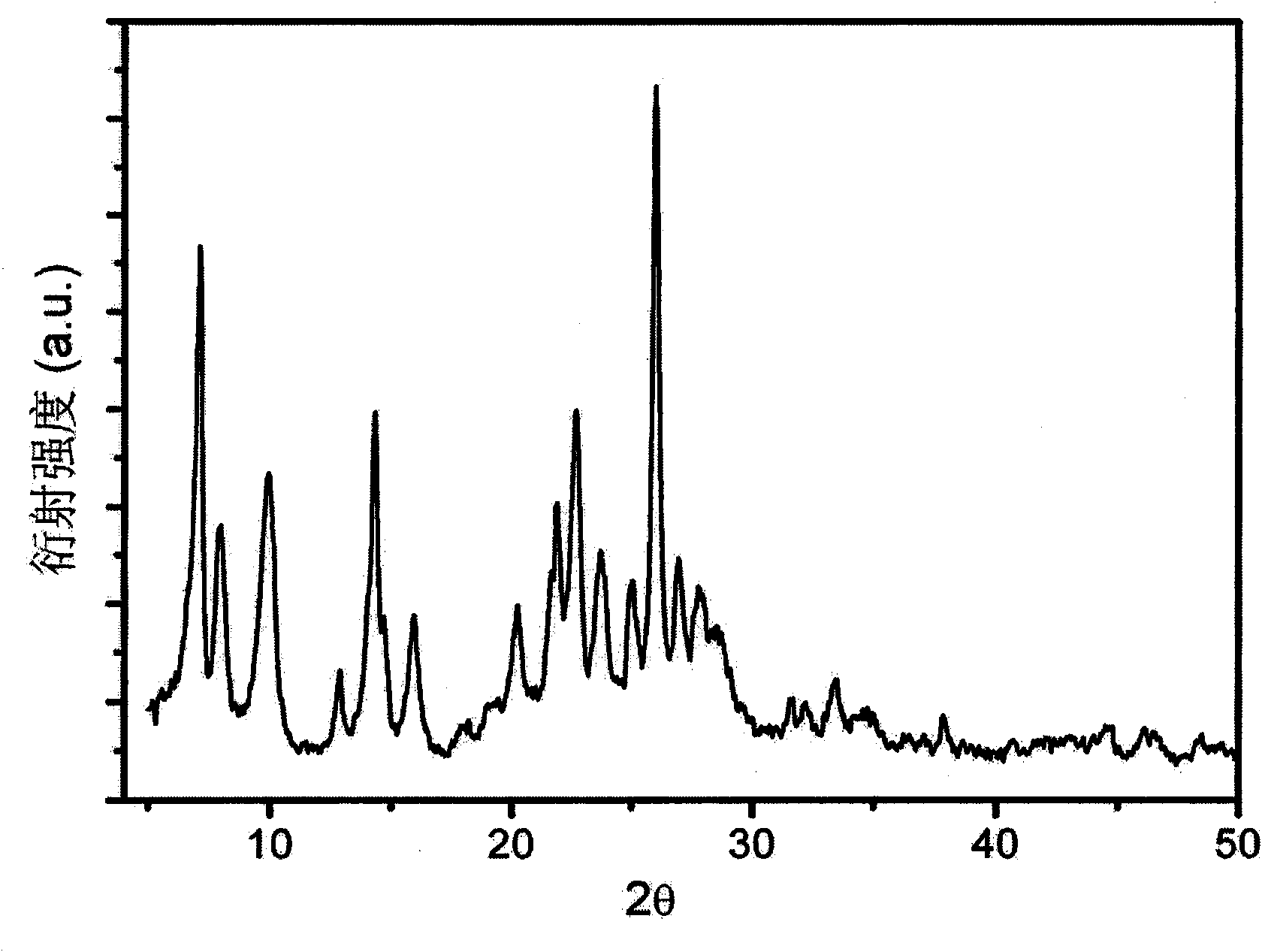
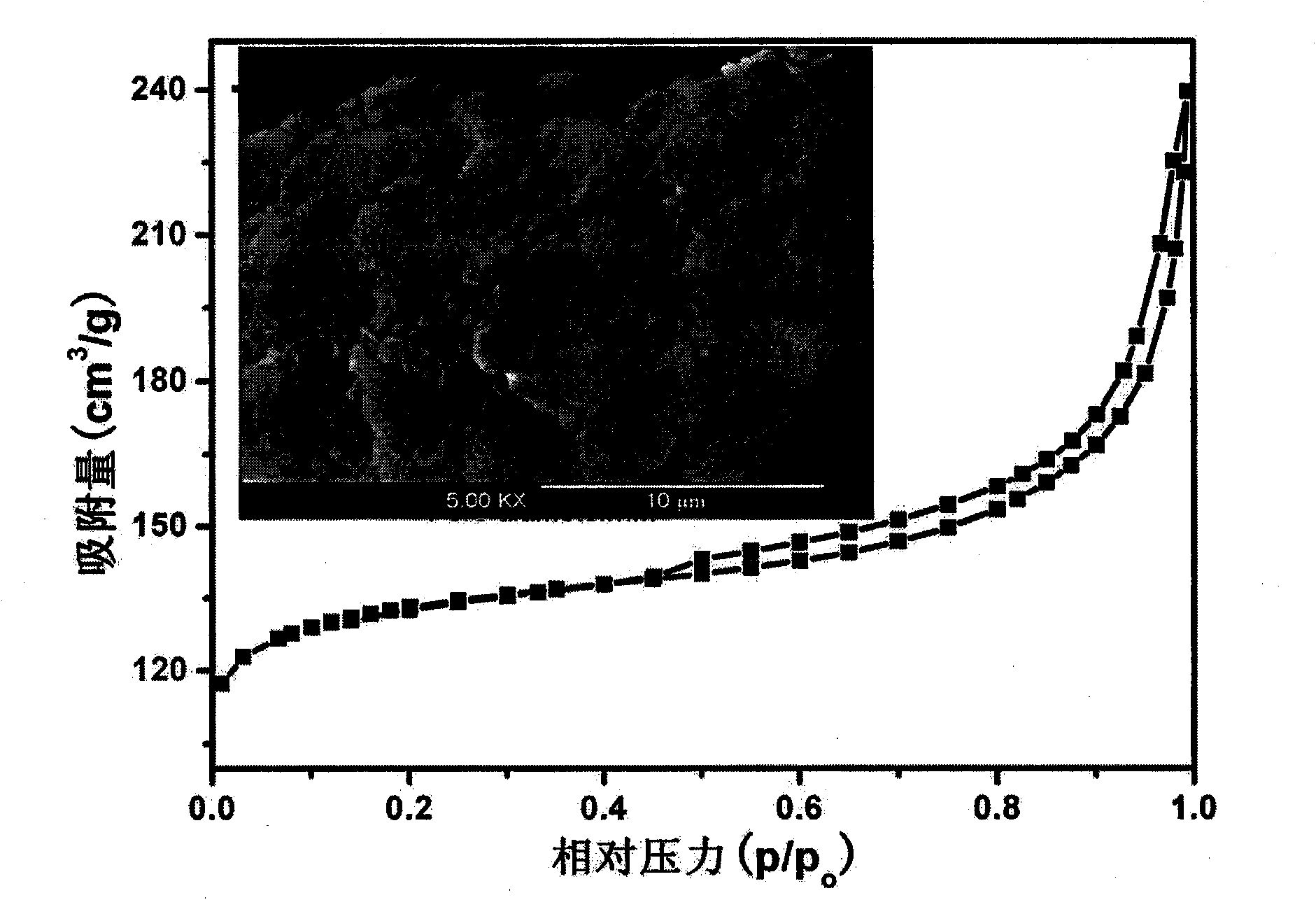
Patents
Literature
1945 results about "Aromatization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aromatization is a chemical reaction in which an aromatic system is formed from a single nonaromatic precursor. Typically aromatization is achieved by dehydrogenation of existing cyclic compounds, illustrated by the conversion of cyclohexane into benzene. Aromatization includes the formation of heterocyclic systems.
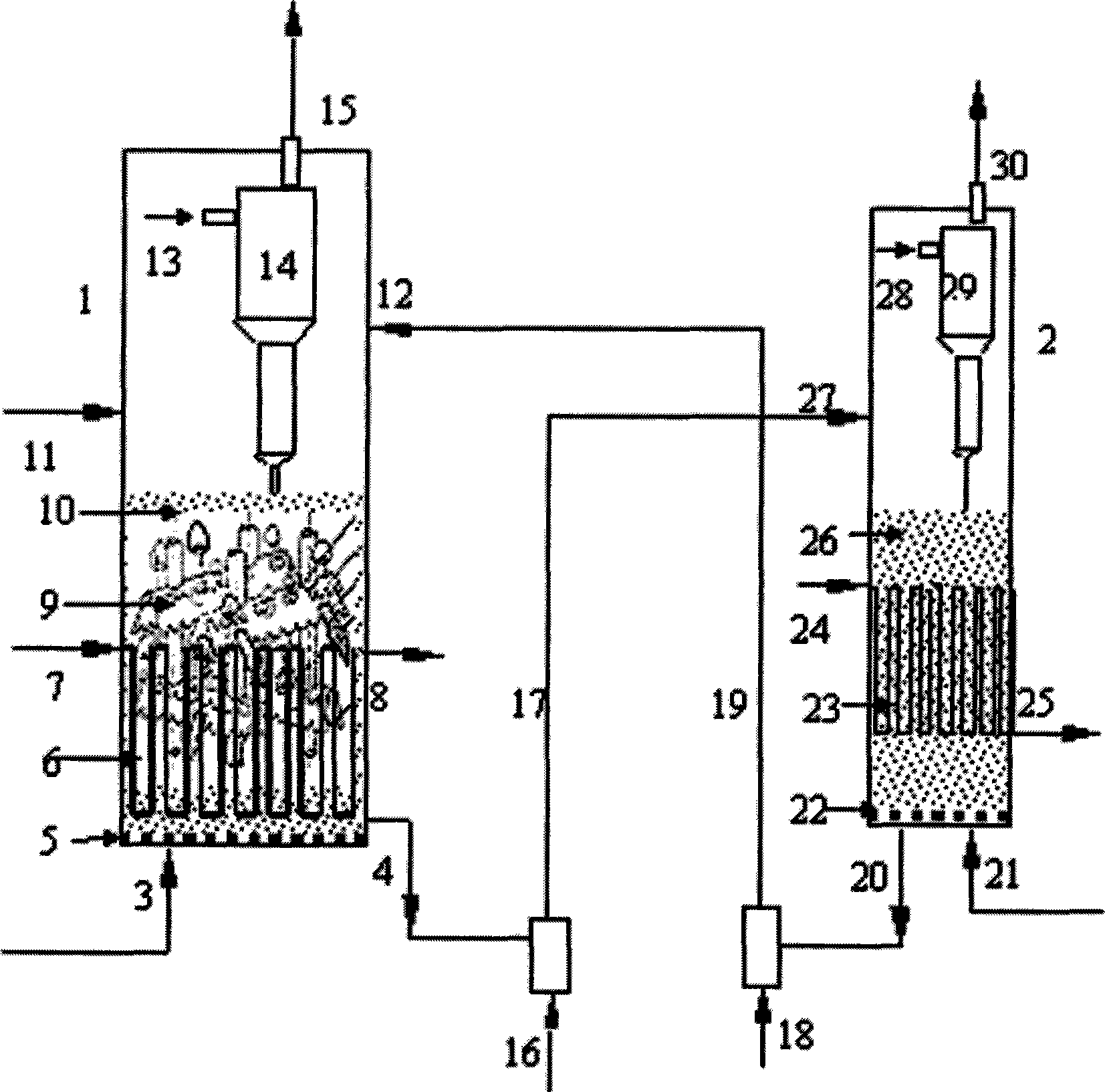
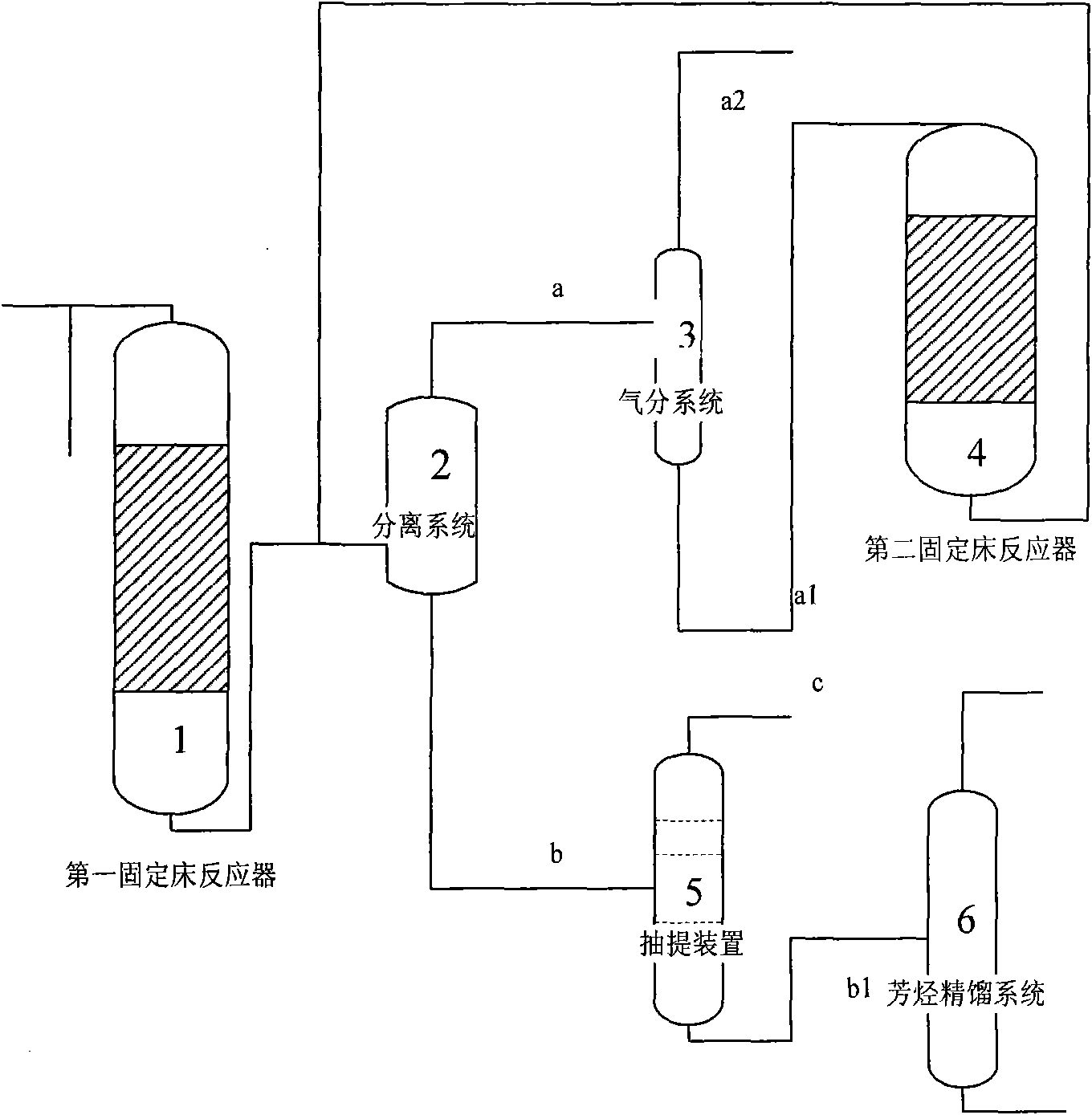
Continuous aromatization and catalyst regeneration device and method thereof
ActiveCN101244969ANo temperature fluctuationsDoes not affect aromatization reactionMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst regeneration/reactivationFluidized bedAromatization
The invention discloses and belongs to the chemical equipment field, which more particularly relates to a C1-C2 hydrocarbon or methanol aromatization and catalyst regeneration fluidized bed device (comprising an aromatization fluidized bed, a catalyst continuous regeneration fluidized bed, a pipeline used for catalyst transportation and a solid transportation device which are arranged between the two fluidized beds), and an aromatization catalyst which is suitable for the fluidized bed operations and the operation methods of aromatization reaction, catalyst regeneration and the device. The device, the catalyst and the method are used for regulating the coking status of the catalyst in an aromatization reactor at any time, thus achieving the aim of transforming the C1-C2 hydrocarbon or the methanol continuously and efficiently and generating aromatics with high selectivity. The C1-C2 hydrocarbon or methanol aromatization and catalyst regeneration fluidized bed device of the invention with adjustable catalyst activity and selectivity can improve the purity and yield of the aromatics, can lead the aromatization reactor operates continuously without stopping at the same time, can improve the strength of aromatics production, and lower the operation cost of the catalyst regeneration when stopping and restarting the whole system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
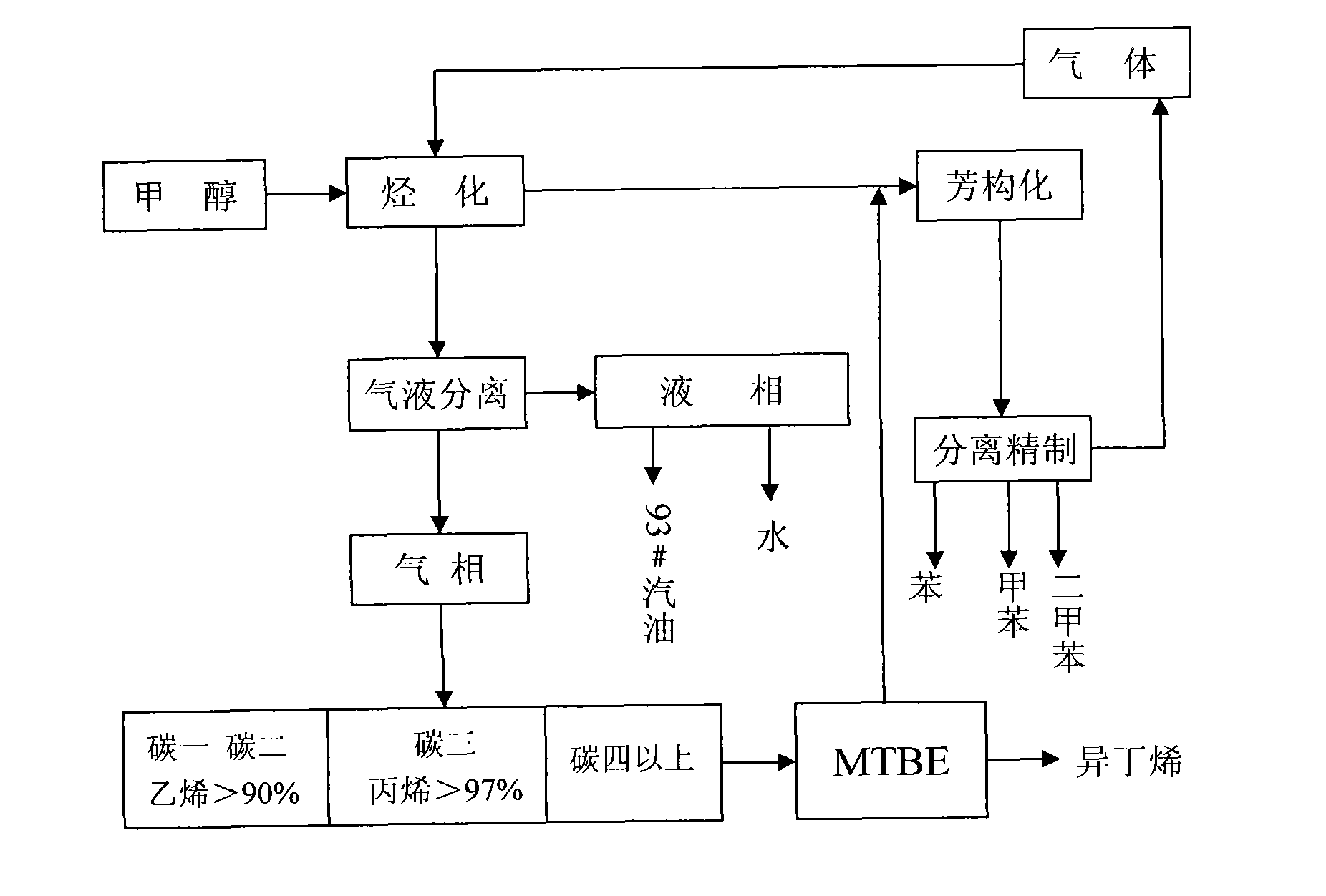
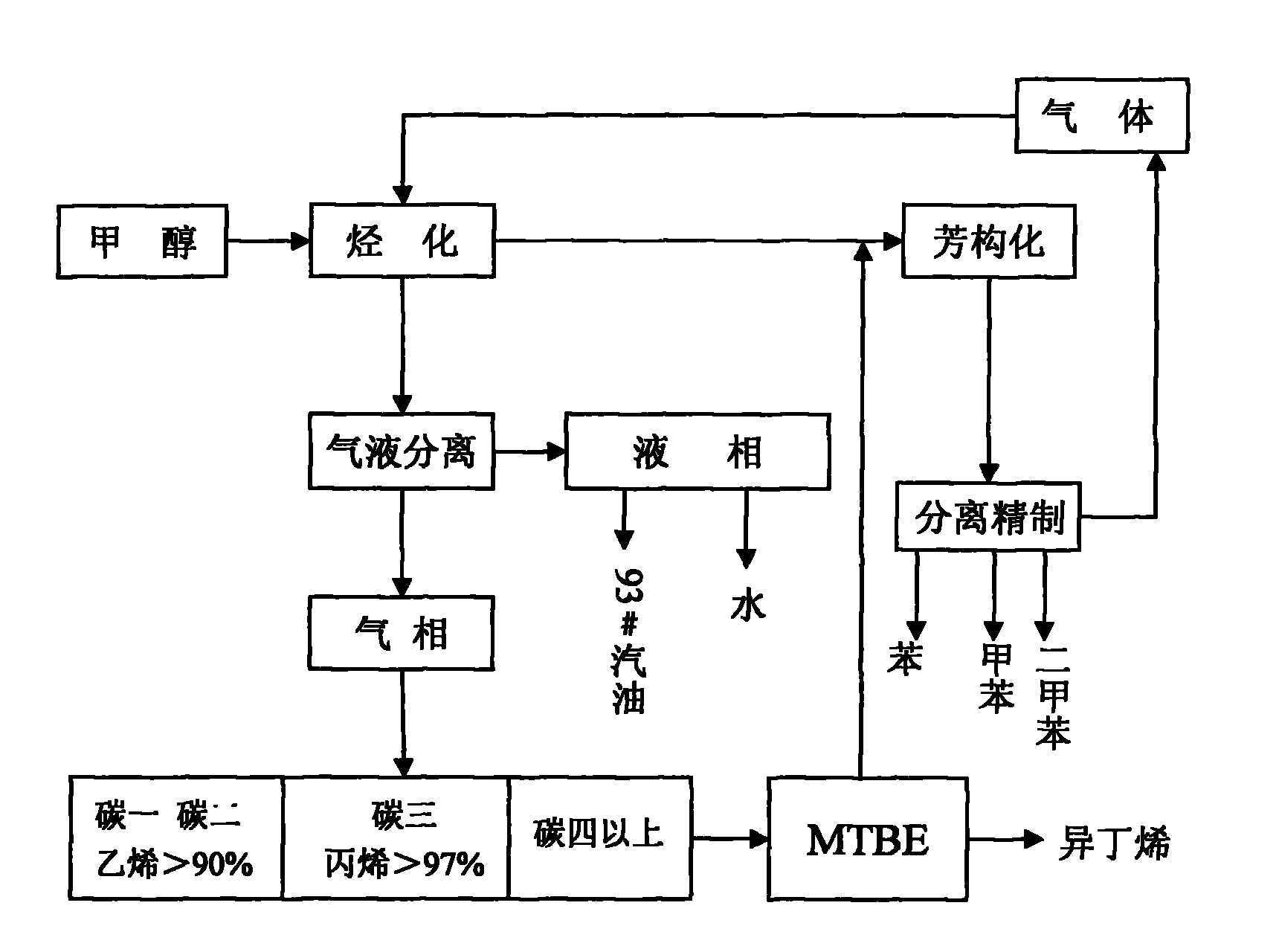
System and process for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by converting methanol or dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101823929AHigh yieldHigh selectivityHydrogen separation using liquid contactHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsAromatizationAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a system and a process for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by converting methanol or dimethyl ether and belongs to the technical field of aromatic hydrocarbon production. The methanol or the dimethyl ether serving as a raw material firstly reacts in an aromatization reactor; a reaction product is separated; H2, methane, mixed C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and partial C9s + hydrocarbons serving as products are output from the system; and C2+ non-aromatic hydrocarbon and aromatic hydrocarbons except the mixed C8 aromatic hydrocarbon and the partial C9s + hydrocarbons are take as a circular material flow and return to corresponding reactors for further aromatization reaction. By separating and recycling the product obtained in the process of aromizing the methanol or the dimethyl ether, the system and the process improve the yield and selectivity of the aromatic hydrocarbon; and moreover, the process is flexible, and target products can be changed according to market demands.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Slow release of fragrant compounds in perfumery using 2-benzoyl benzoates, 2-alkanoyl benzoates or alpha -keto esters
A fragrance delivery system which releases fragrant alcohols upon exposure to light. The system comprises 2-benzoyl benzoates of general formulae which can comprise various subtituents R1-R5 as defined in the application and a substituted R* which is the organic part of a fragrant alcohol.
Owner:FIRMENICH SA
Process for preparing dimethylbenzene by aromatization of methanol
ActiveCN101671226AHigh yieldExtend the life cycleHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsHydrocarbon by hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon condensationMolecular sieveAlkyl transfer
A process for preparing dimethylbenzene by aromatization of methanol relates to a process for preparing dimethylbenzene by conducting aromatization reaction in a methanol aromatization reactor with methanol and hydrocarbon as raw materials. The process uses a metal-modified molecular sieve composite material as catalyst and causes the mixture of methanol and one or a plurality of C1-C12 hydrocarbons to conduct aromatization reaction in the methanol aromatization reactor. By adjusting the ratio between methanol and hydrocarbons in the raw material, the process regulates and controls the coordination between aromatization and alkylation reaction and realizes the purposes of effectively improving the yield of the target product dimethylbenzene and prolonging the service cycle of catalyst.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and propylene simultaneously employing methanol/dimethyl ether
InactiveCN101607858AHigh selectivityIncrease added valueMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolecular sieveFixed bed
The invention discloses a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons and propylene simultaneously employing methanol / dimethyl ether, comprising the following steps: 1) placing raw materials containing methanol or / and dimethyl ether, metals and molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified through silanizing in a first fixed bed reactor to perform catalytic reaction; 2) separating the products obtained in step 1) to obtain propylene, then placing propylene in a second fixed bed reactor with molecular sieve based catalyst which is modified by using metals to react, then performing aromatization on the obtained product in step 1) and obtaining aromatic hydrocarbons; then separating to obtain toluene and sending toluene back to the outlet of the first fixed bed reactor as a raw material. In the method, methanol is converted and prepared to aromatic hydrocarbons while propylene is produced at the same time and the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is high. In the products prepared by the method, the content of propylene can reach above 20%, the content of aromatic hydrocarbons can reach above 58wt% and the content of paraxylene in aromatic hydrocarbons is more than 35wt%.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
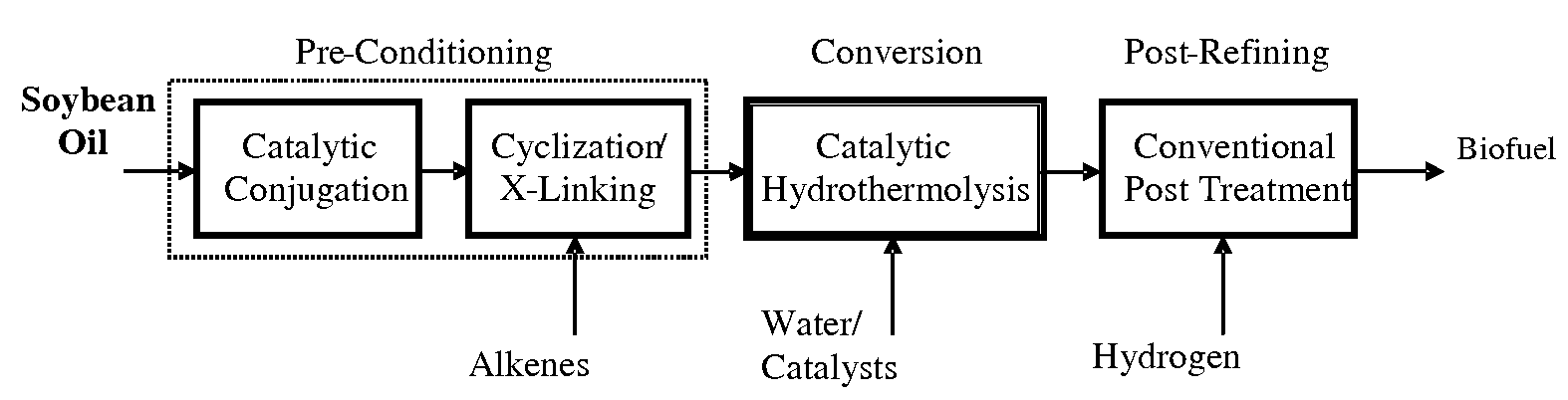
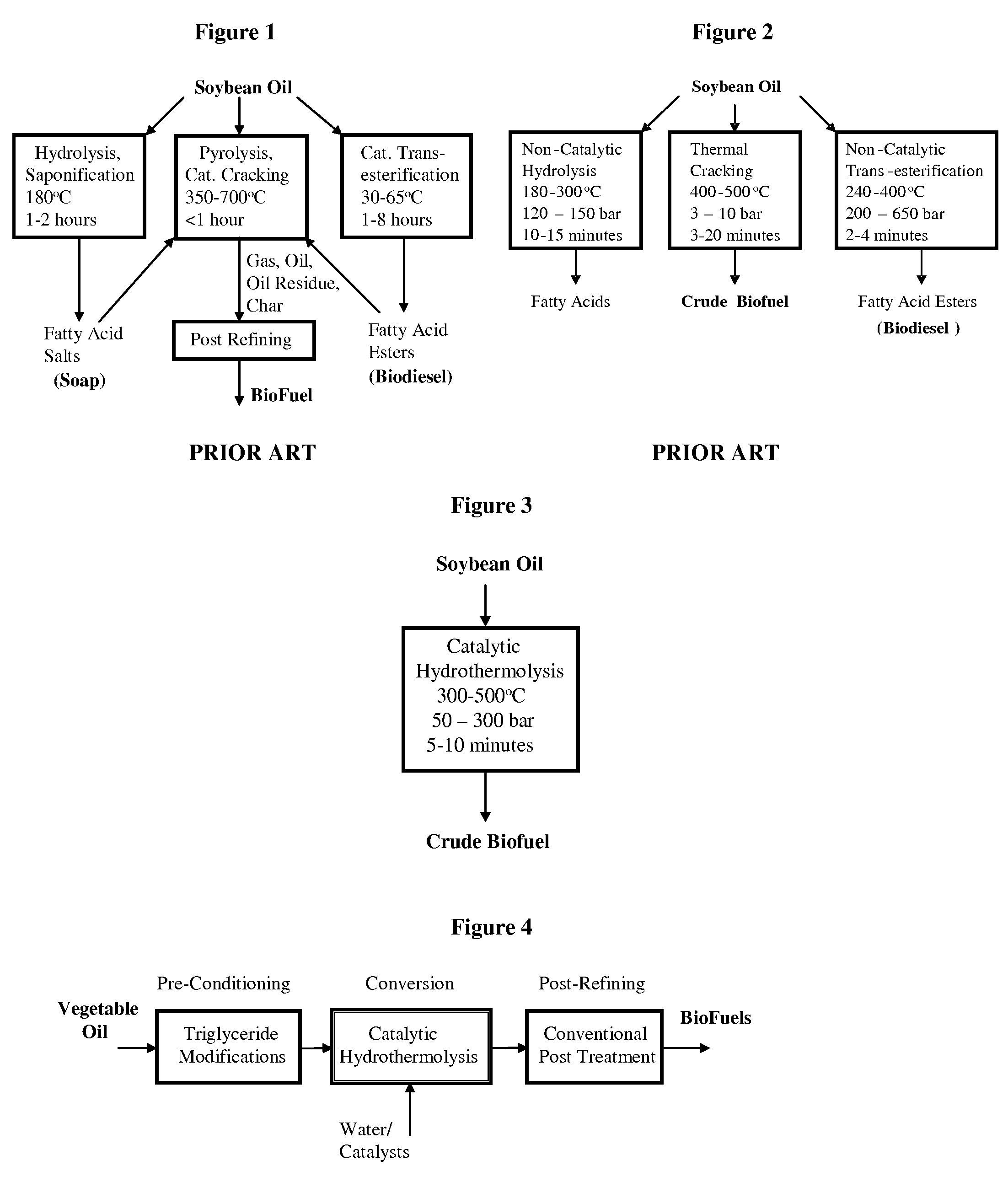
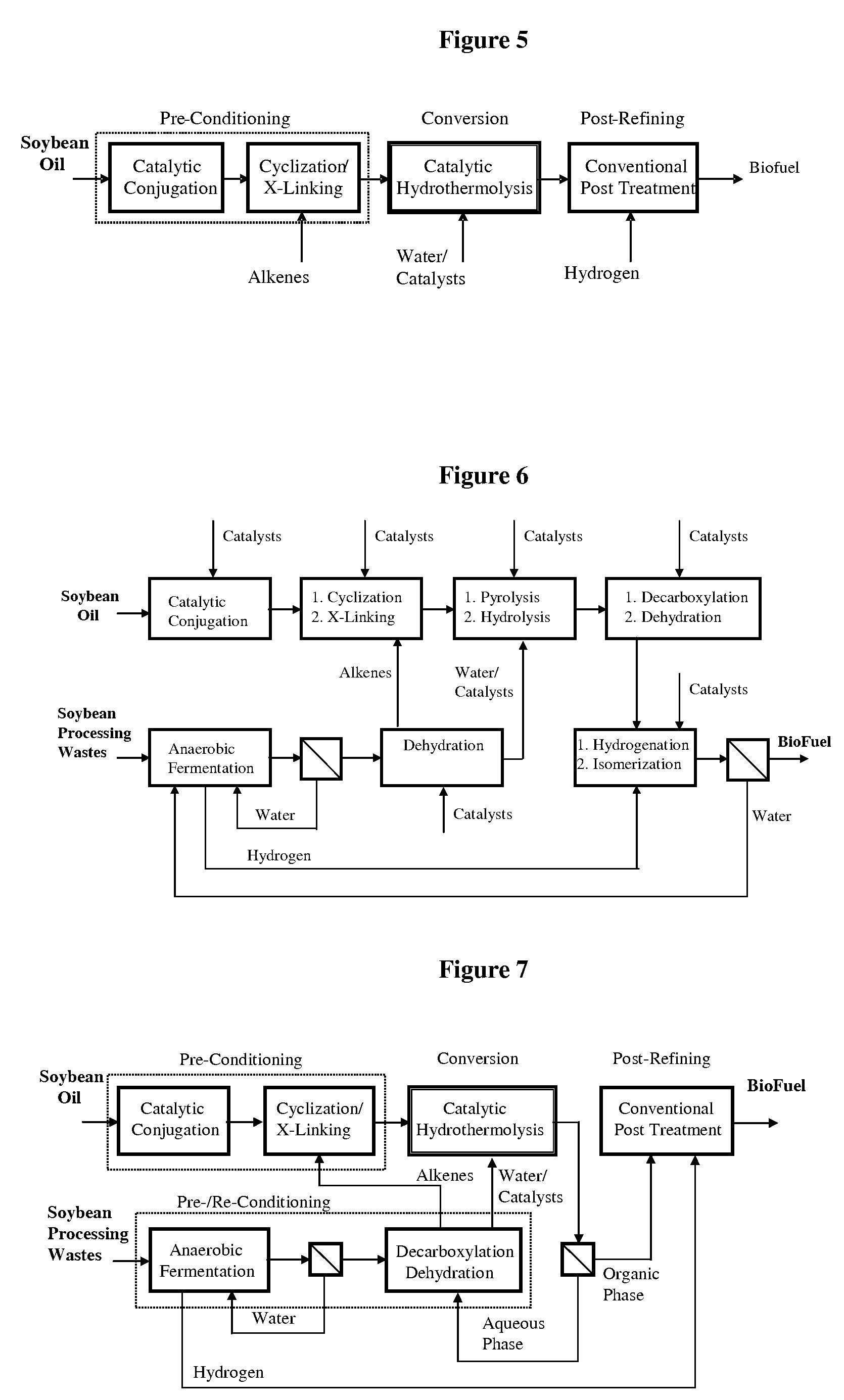
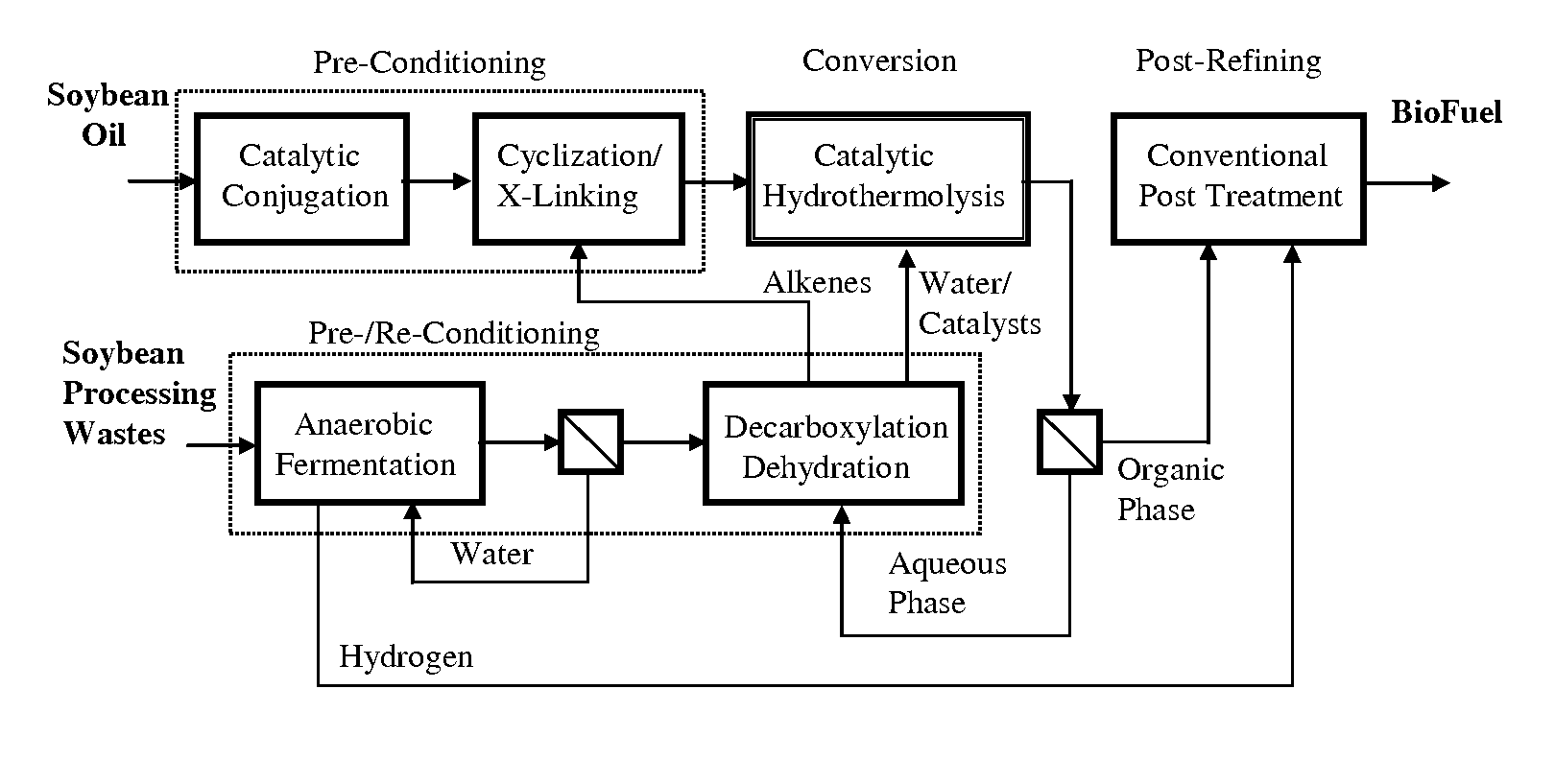
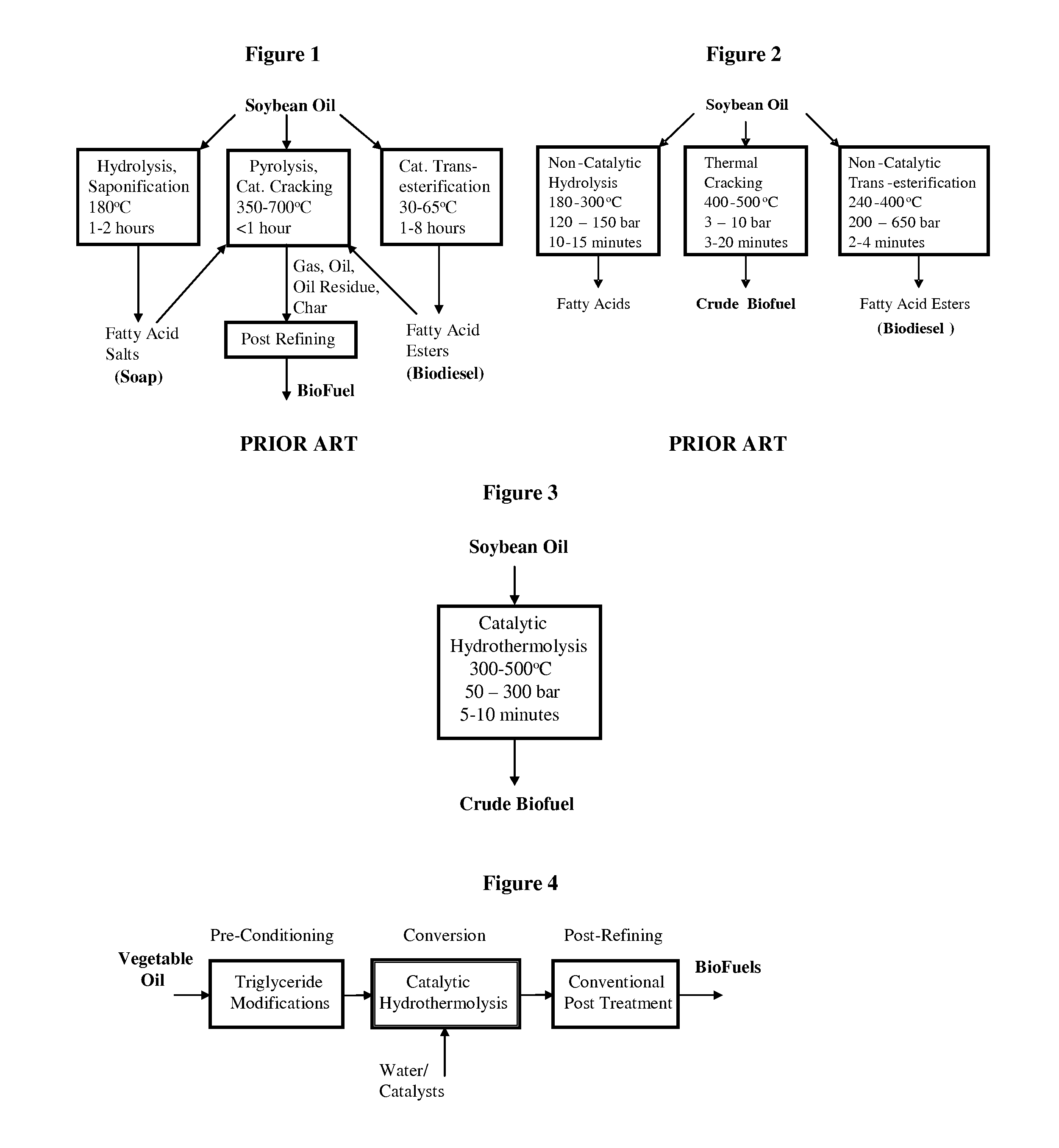
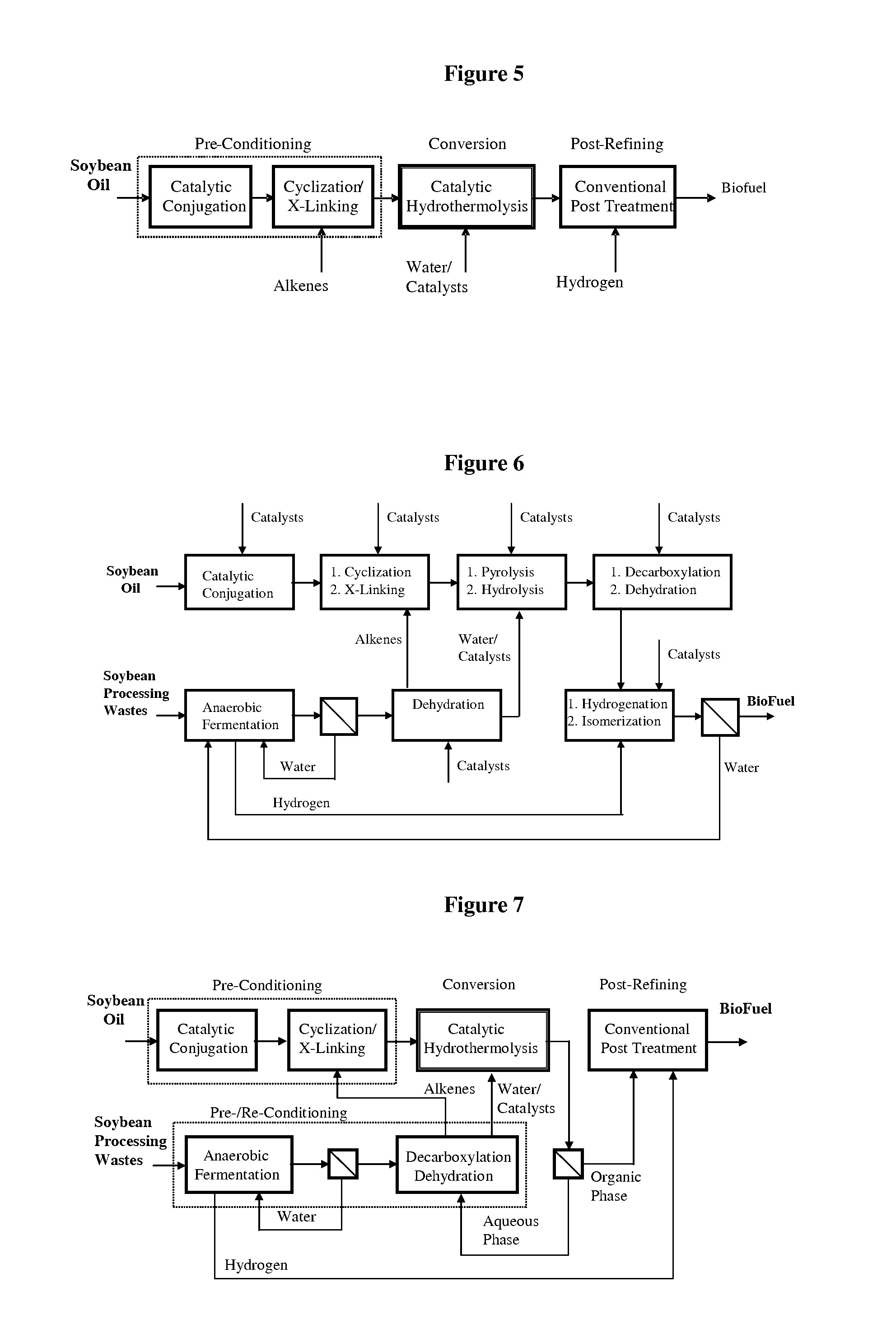
Method of converting triglycerides to biofuels
ActiveUS7691159B2Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkIsomerization
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Process for producing low carbon olefin and arene parallel cogeneration gasoline by using methanol as raw material
InactiveCN102146010ALow costReduce energy consumptionHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionEnvironmental resistanceCogeneration
The invention discloses a process for producing low carbon olefin and arene parallel cogeneration gasoline by using methanol as a raw material. In the process, the methanol is used as the raw material and a molecular sieve catalyst is adopted to produce the low carbon olefin and arene parallel cogeneration gasoline by a methanol alkylation reaction and aromatization. In the process, the coal-based methanol is used as the raw material and can replace the conventional petroleum raw material to cogenerate a basis organic chemical raw material, and thus, the dependence degree of the conventional petrochemical industry on the petroleum can be reduced. Meanwhile, the process is also beneficial for reducing the foreign dependence degree of national petroleum, the strategic safety of energy and resources is improved, the production process of the process has low discharge, low pollution and low energy consumption, the requirements on green and environment protection are met, and the process has the advantages of low production cost and strong market competitiveness.
Owner:江苏煤化工程研究设计院有限公司 +2
Catalyst for C4 liquefied petroleum gas aromatization and its preparing method
InactiveCN1586721ALess modification stepsLow costMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionHigh carbonFixed bed
The present invention belongs to the field of catalyst preparation in petrochemical technology, and especially one kind of catalyst for the aromatization of liquefied C4 petroleum gas in fixed bed reactor and its preparation process. Technologically, the catalyst features that its mother substance is high-silicon zeolite with crystal granulation of 10-500 nm and the zeolite is alumina formed and prepared into the hydrogen type catalyst via conventional process, and the hydrogen type catalyst is vapor treated to regulate the acidity and acid treated to expand the pores and restore the pore passage. The catalyst is used in the aromatization of liquefied C4 petroleum gas, and has low reaction temperature, high olefin converting rate and high carbon deposition resistance.
Owner:DALIAN LIGONG QIWANGDA CHEM TECH
Aromatization catalyst, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN1651141ALipophilicHigh aromatization activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsMolecular sieveAdhesive
An aromatizing catalyst for molifying poor gasoline to prepare high-octane gaseline component or arylhydrocarbon is prepared from the Zn, P and RE metal modified HZSM-5 molecular sieve, Y-type molecular sieve, carrier and adhesive proportionally.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Process for alkane aromatization using platinum-zeolite catalyst
InactiveUS20050143610A1Formation is suppressedHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAlkanePlatinum
Aromatization of alkanes having one to four carbon atoms per molecule to aromatics, such as benzene, toluene and xylenes (BTX), uses a catalyst of a crystalline zeolite on which platinum has been deposited, specifically a platinum-containing ZSM-5. A byproduct of the process is a light gas fraction of methane and ethane. The use of a platinum-containing ZSM-5 catalyst in an alkane aromatization process, such as the Cyclar process, suppresses the formation of methane and increases selectivity to BTX. The high content of ethane relative to methane in the light gas fraction allows this process effluent to be a feedstream for a cracker.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Zeolite composite, method for making and catalytic application thereof
A catalytic material includes microporous zeolites supported on a mesoporous inorganic oxide support. The microporous zeolite can include zeolite Beta, zeolite Y (including “ultra stable Y”—USY), mordenite, Zeolite L, ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-12, ZSM-20, Theta-1, ZSM-23, ZSM-34, ZSM-35, ZSM-48, SSZ-32, PSH-3, MCM-22, MCM-49, MCM-56, ITQ-1, ITQ-2, ITQ-4, ITQ-21, SAPO-5, SAPO-11, SAPO-37, Breck-6, ALPO4-5, etc. The mesoporous inorganic oxide can be e.g., silica or silicate. The catalytic material can be further modified by introducing some metals e.g. aluminum, titanium, molybdenum, nickel, cobalt, iron, tungsten, palladium and platinum. It can be used as catalysts for acylation, alkylation, dimerization, oligomerization, polymerization, hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, aromatization, isomerization, hydrotreating, catalytic cracking and hydrocracking reactions.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Method of Converting Triglycerides to Biofuels
ActiveUS20080071125A1Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationBiofuelsIsomerizationPtru catalyst
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
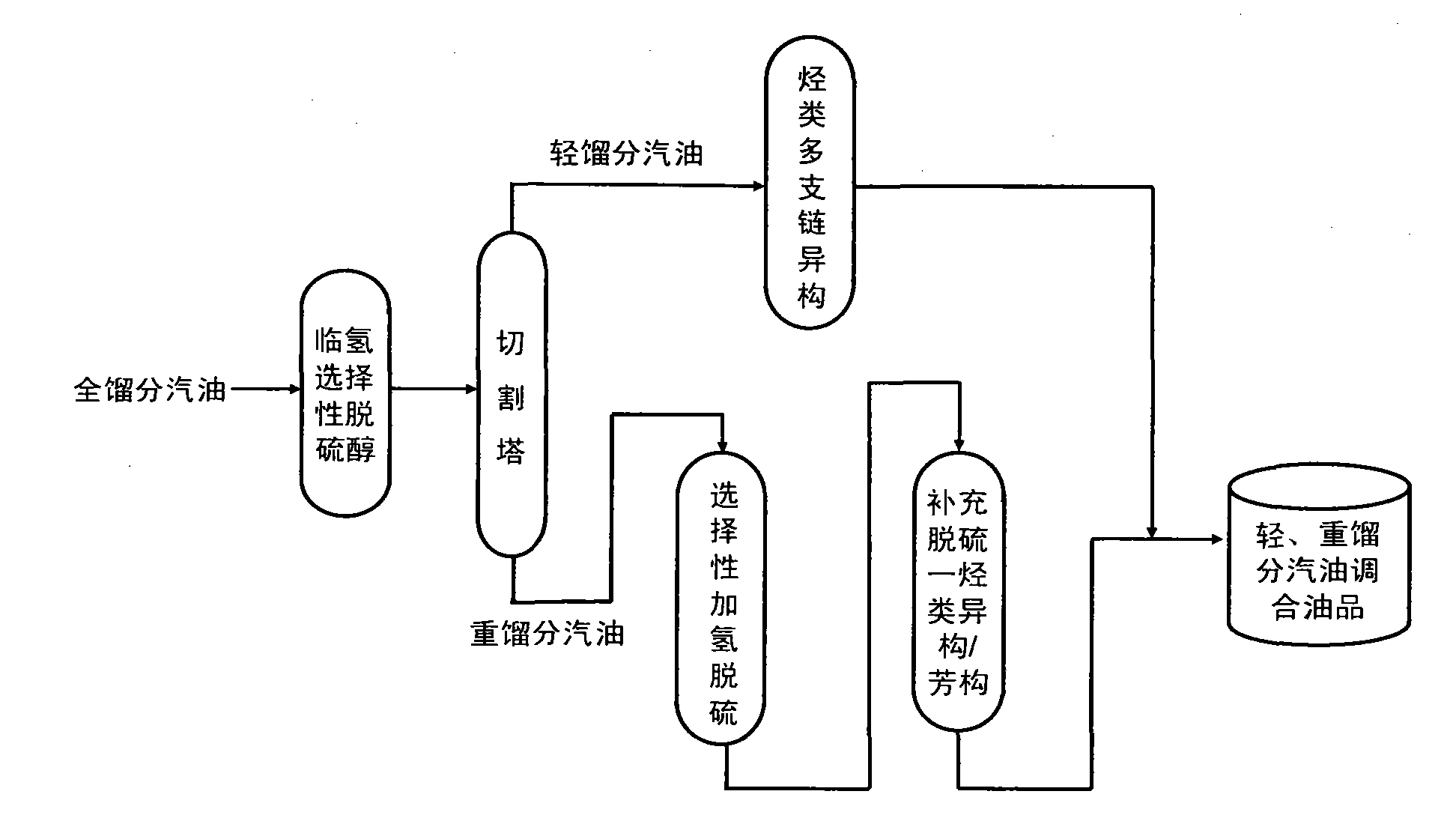
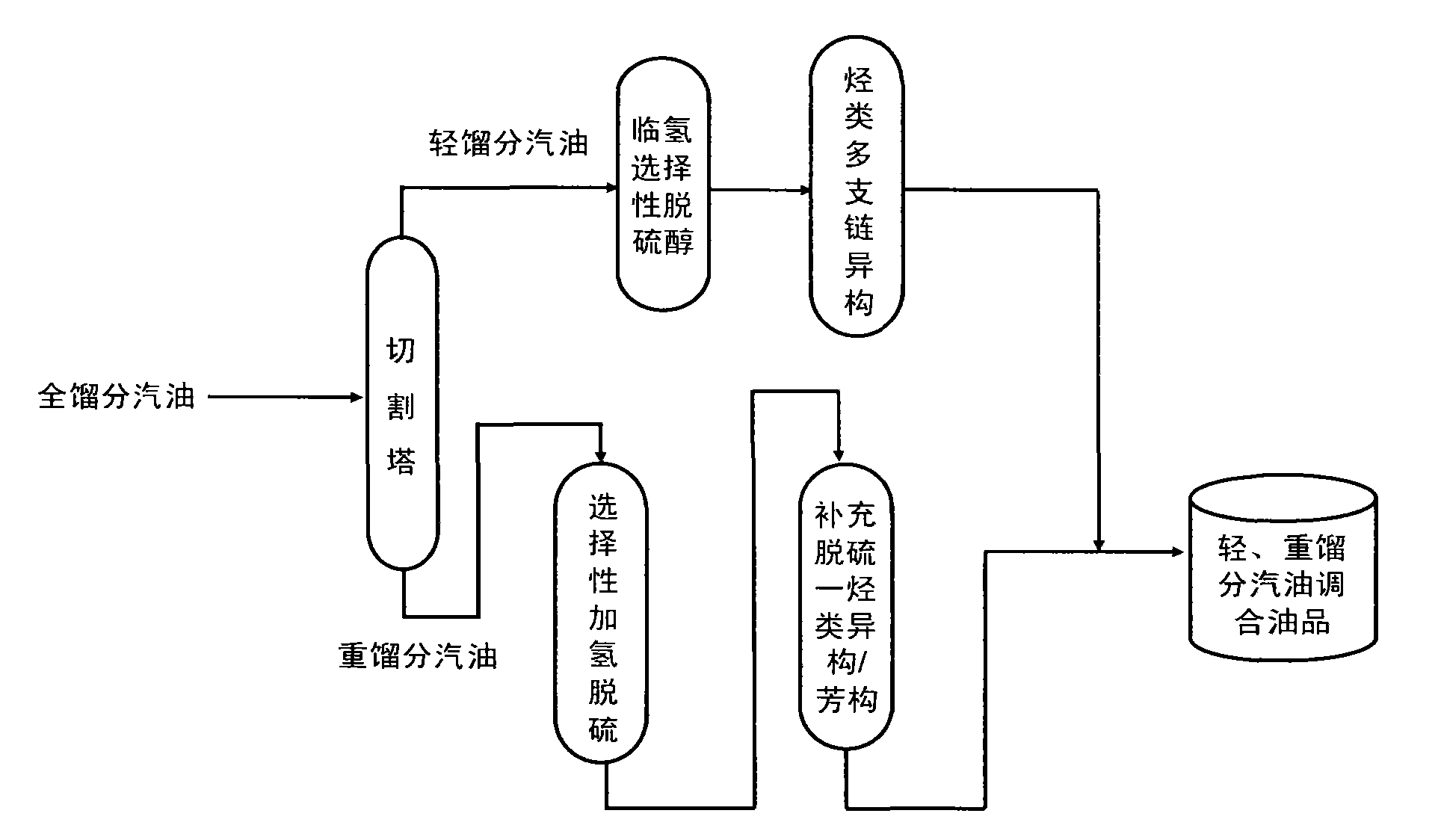
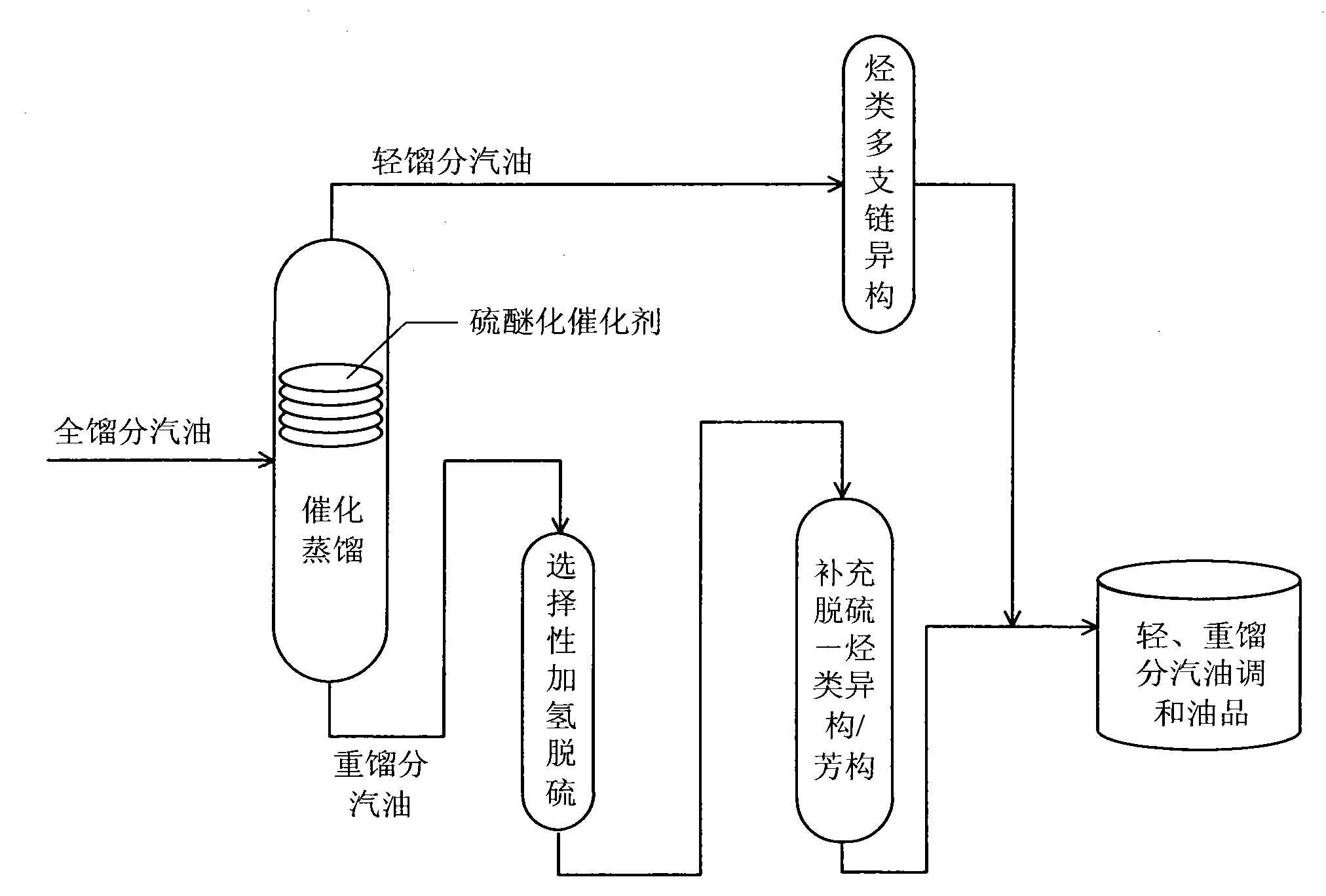
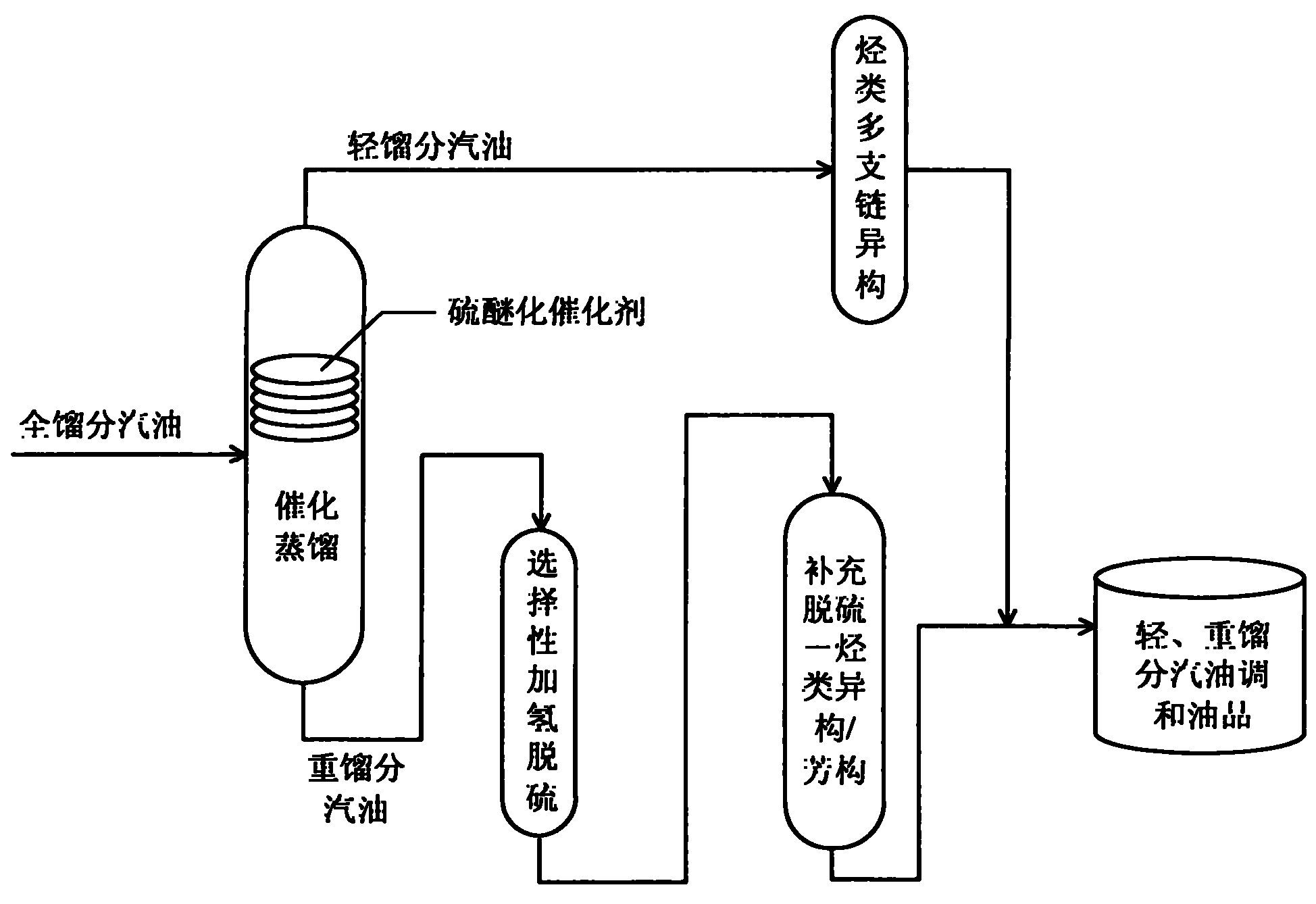
Efficient coupling hydro-upgrading method for producing gasoline with ultra-low sulfur and high octane number
ActiveCN101885983AImprove octaneOctane recoveryTreatment with hydrotreatment processesIsomerizationAlcohol
The invention relates to an efficient coupling hydro-upgrading method for producing gasoline with ultra-low sulfur and a high octane number. The method comprises the following steps of: distilling inferior full cut gasoline at 50-90 DEG C to obtain light cut gasoline and heavy cut gasoline; making the light cut gasoline contact with a hydrocarbon multi-branched isomerization catalyst; making the heavy cut gasoline contact with a selective hydrogenation desulfurization catalyst and a complement desulfurization isomerization / aromatization catalyst sequentially; and finally, mixing the treated light cut gasoline with the treated heavy cut gasoline to obtain the gasoline with the ultra-low sulfur and the high octane number. The method further comprises the step of: before the distillation, making the inferior full cut gasoline contact with a hydro-selective desulfurization alcohol catalyst, or, before making the light cut gasoline contact with a hydrocarbon multi-branched isomerization catalyst, making the light cut gasoline contact with the hydro-selective desulfurization alcohol catalyst. The efficient coupling hydro-upgrading method is suitable for the hydro-upgrading treatment of inferior gasoline with ultrahigh sulfur and high olefin, reduces the sulfur content after the upgrading treatment to below 5mu g / g (no sulfur substantially) and can maintain the octane number and higher yield of products.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Process for alkane aromatization using platinum-zeolite catalyst
InactiveUS7186871B2Formation is suppressedHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAlkanePlatinum
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
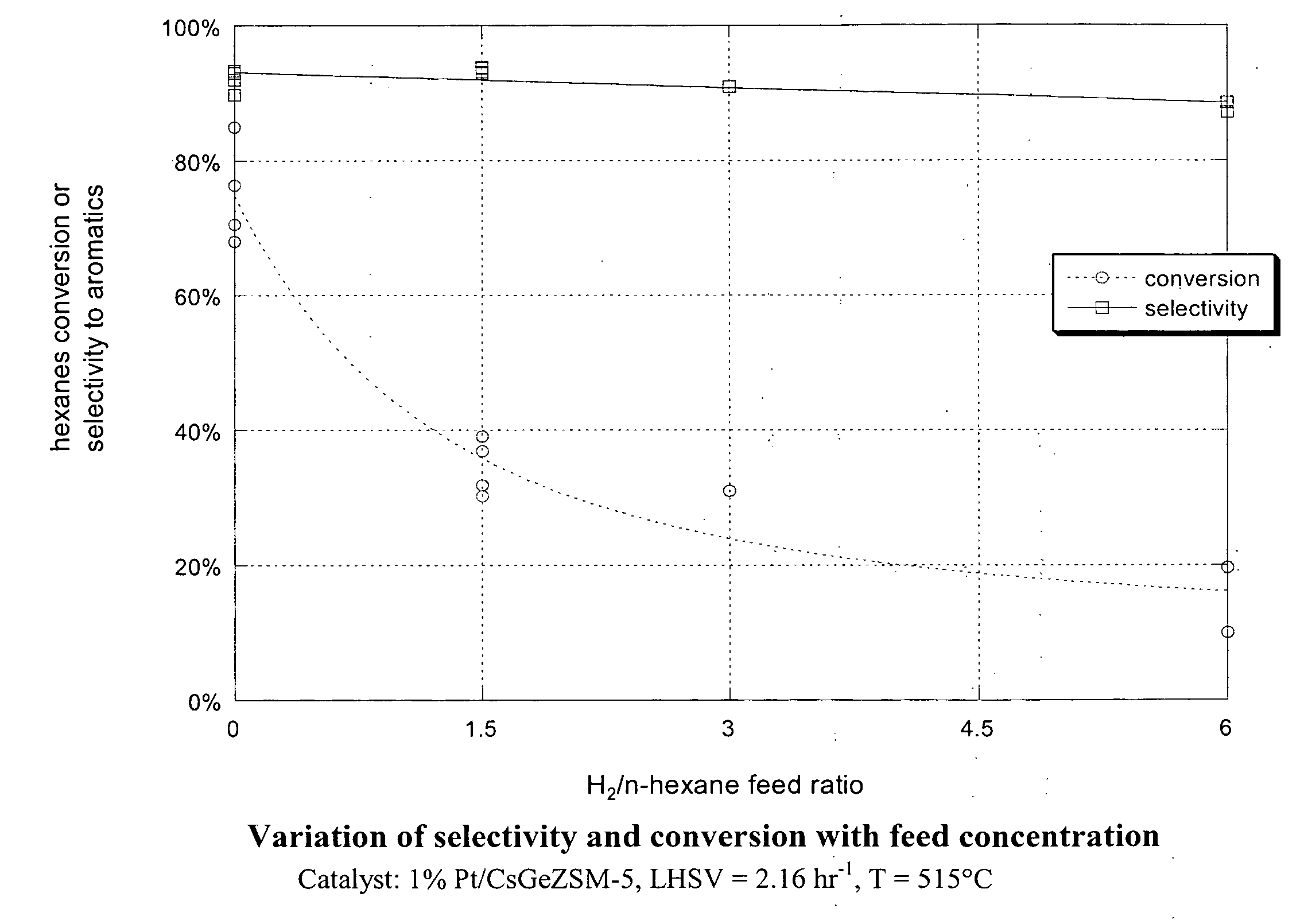
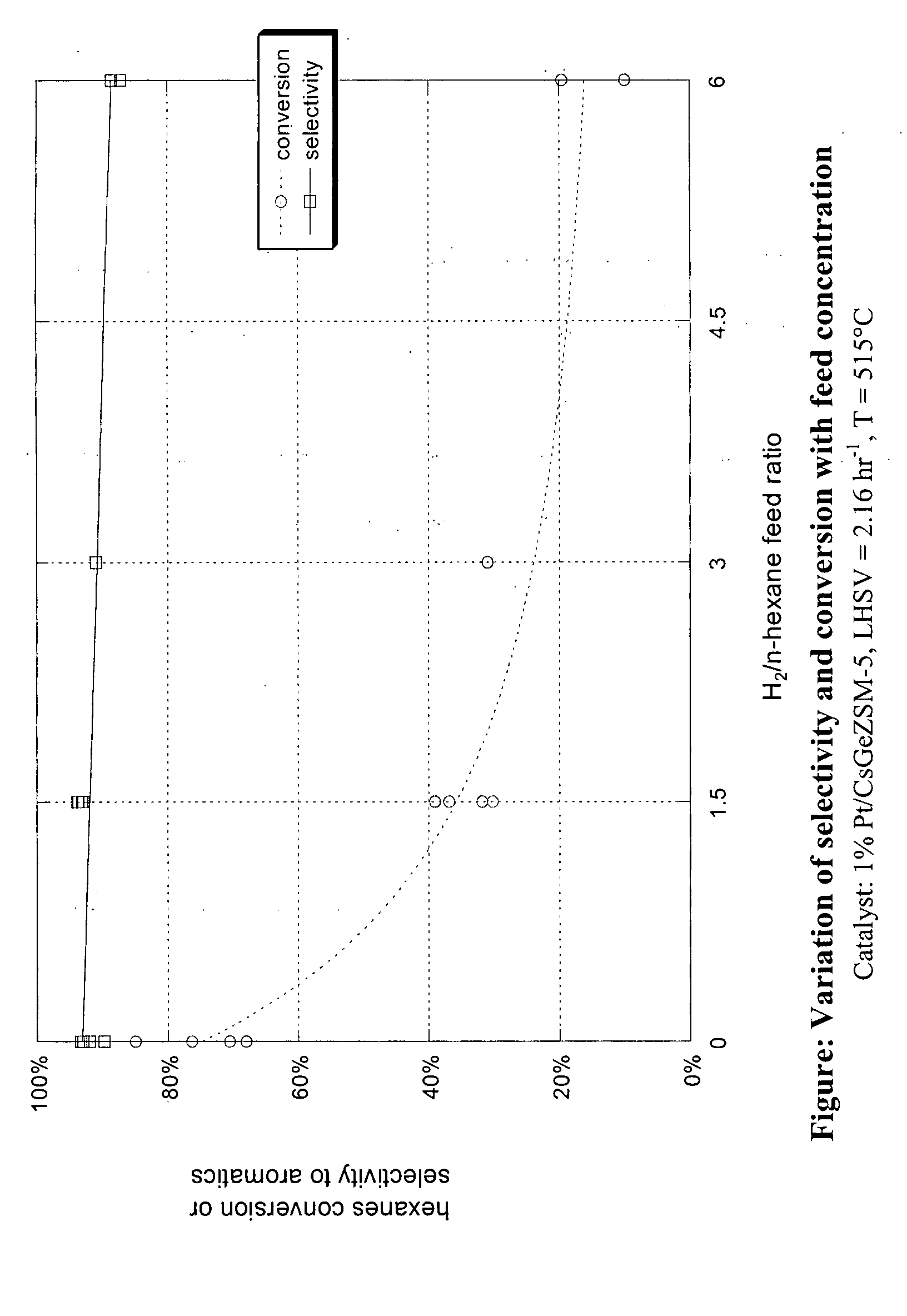
Aromatization of alkanes using a germanium-zeolite catalyst
ActiveUS20080255398A1Molecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonAlkaneAlkaline earth metal
This invention relates to a process for the aromatization of C6 to C12 alkanes, such as hexane, heptane and octane, to aromatics, such as benzene, ethyl benzene, toluene and xylenes, with a germanium-containing zeolite catalyst. The catalyst is a non-acidic aluminum-silicon-germanium zeolite on which a noble metal, such as platinum, has been deposited. The zeolite structure may be of MFI, BEA, MOR, LTL or MTT. The zeolite is made non-acidic by being base-exchanged with an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal, such as cesium, potassium, sodium, rubidium, barium, calcium, magnesium and mixtures thereof, to reduce acidity. The catalyst is sulfur tolerant and may be pretreated with a sulfur compound, i.e., sulfided. The hydrocarbon feed may contain sulfur up to 1000 ppm. The present invention could be applicable to a feedstream which is predominantly paraffinic and / or low in naphthenes. Lowering the hydrogen to hydrocarbon ratio increases conversion and aromatics selectivity.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
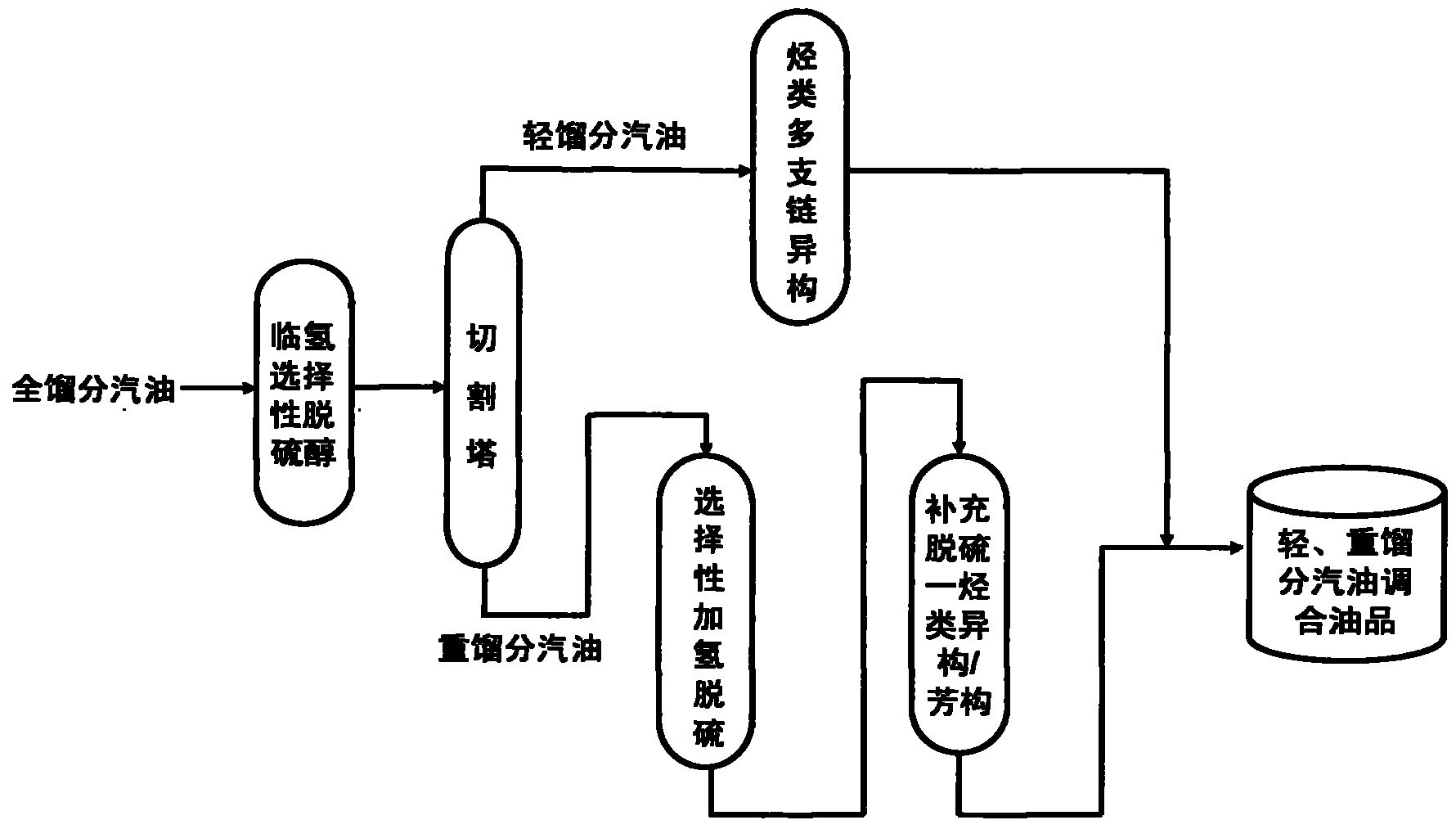
Production method for ultra-low sulfur and high-octane number gasoline
ActiveCN101885985ATake advantage ofIncrease temperatureTreatment with hydrotreatment processesIsomerizationHydrodesulfurization
The invention relates to a production method for ultra-low sulfur and high-octane number gasoline. The method comprises the following steps of: filling a poor-quality full range gasoline raw material in a reaction distillation column to contact the material with a sulfoether catalyst to perform a sulfur ether reaction and fraction cutting so that low-boiling point sulfides, such as thiol and thiophene, are converted into high-boiling point sulfoether which is then transferred into heavy fraction gasoline, wherein the cutting fractionation temperature of light fraction gasoline and the heavy fraction gasoline is 50 to 90 DEG C; contacting the light fraction gasoline with a hydrocarbon highly branched isomerization catalyst; contacting the heavy fraction gasoline with a selective hydrodesulfurization catalyst and a desulfurization-hydrocarbon isomerization / aromatization catalyst; and mixing the treated light fraction gasoline and the heavy fraction gasoline to obtain the ultra-low sulfur and high-octane number gasoline. The method is suitable for modifying poor-quality gasoline, can reach better desulfurization and olefin reduction effects on ultra-high sulfur and high-olefin poor-quality catalytic gasoline, and can maintain or increase the octane number of the product and keep a higher product yield after reaction.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method for deep desulfurization olefin hydrocarbon reduction of inferior gasoline
ActiveCN101492608AStructuring reaction does not affectReduce olefin contentRefining to eliminate hetero atomsCatalytic pyrolysisHydrogen
The invention discloses a gasoline deep desulphurization and olefin reduction method, comprising that the gasoline raw material and hydrogen are contacted with hydrogenation absorption desulphurization and olefin aromatization difunctional catalyst to remove sulfur in the gasoline and reduce the olefin content in the gasoline product. The method of the invention can produce gasoline product with the sulfur content lower than 50 micrograms per gram, and can further produce gasoline product with the sulfur content lower than 10 micrograms per gram while the olefin content is lower than 20v%, and meanwhile the antiknock quality index loss is low. The method of the invention can be applied to deep desulphurization and olefin reduction process of FCC gasoline, catalytic pyrolysis gasoline, coker gasoline, pyrolysis gasoline and pressure gasoline or the mixed gasoline raw material thereof.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
ZSM-5/SAPO-11 composite zeolite and catalytically cracked gasoline hydrogenation quality-improved catalyzer and the methoer for preparing the same
ActiveCN101081370AImprove product qualityEquilibrium HydrodesulfurizationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningIsomerizationHydrodesulfurization
The present invention is one kind of catalyst with ZSM-5 / SAPO-11 composite zeolite for hydrogenating and modifying catalytically cracked gasoline and its preparation process. The composite zeolite is prepared through compounding solution A with aluminum sulfate, sulfuric acid and water; compounding solution B with water glass, tetraethyl ammonium hydroxide and water; mixing solution A and solution B to form homogeneous colloid; crystallizing the colloid mixture at 150-180 deg.c for 24-72 hr; adding phosphoric acid, pseudoboehite, silica sol and SAPO-11 synthesizing template agent; and final crystallizing at 170-200 deg.c for 24-48 hr to obtain sodium type composite zeolite. The catalyst with the composite zeolite as carrier has excellent hydrogenating and desulfurizing performance, high stability, high gasoline yield, high isomerization activity and certain aromatization activity, and may be applied in producing high quality clean gasoline product.
Owner:BEIJING CUP GREEN CATALYTIC TECH
Aromatization modifying catalyst for catalytic gasoline and preocess
InactiveCN1488724AHigh yieldReduce carbon depositionRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonLanthanideRare earth
The present invention relates to a technological process for producing low-sulfur low-olefin clean gasoline by using catalytic cracked gasoline and catalyst used by said process. Said invention adopts hydrofinishing and aromatization combined process, in which the aromatization adopts small-grain hydrogen type molecular sieve catalyst including IA group metal, transition metal and lanthanide series rare-earth metal oxide, and the crystal grain size of the molecular sieve is in the range of 20nm-800 nm. Said invented catalyst can reduce cracking reaction and can raise the yield of the gasoline.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing molecular sieve catalyst used in carbon 4 liquid gas aromatization reaction
InactiveCN101530813AHigh aromatization performanceMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionMolecular sieveWater vapor
The invention relates to a method for preparing a molecular sieve catalyst used in carbon 4 liquid gas aromatization reaction. The concrete steps of the method are as follows: 1. the prepared rare earth-ZSM5 / ZSM11 co-crystallization molecular sieve, alumina and water are mixed uniformly, extruded and molded, dried and baked; 2. the above product is put in alkali solution with the concentration of 0.05 to 2.0M and air-bubble-stirred for 1 to 10 hours at 45 to 100 DEG C; 3. the product in step 2 is washed to neutrality, exchanged by ammonium nitrate solution, dried and baked into H-type molecular sieve; and 4. the product in step 3 is processed by high-temperature water vapor and loaded with metal zinc, thus obtaining the catalyst. The method has the advantages that the modified molecular sieve catalyst shows better carbon 4 liquid gas aromatization reaction performance compared with catalyst that is not alkali-treated.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Encapsulation of bulky fragrance molecules
The present invention relates to a fragrance composition to be incorporated into the core of a core shell capsule comprising:I) 60-100% by weight of at least 5 fragrance compounds, 20-100% by weight of said fragrance compounds comprising at least 3 bulky molecules having a molecular weight of less than 325 atomic mass units, conforming to the following structures:a) molecules containing more than one ring, each ring having between 3 and 8 atoms of any of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur in any ring and atoms being shared by any of the rings;b) molecules having at least two rings, each ring having between 3 and 8 atoms of any of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur in which any rings share a common atom;c) molecules having at least two rings, each ring having between 3 and 8 atoms of any carbon, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur in which any two rings share at least two adjacent common atoms;d) molecules containing a single alicyclic ring which contains at least 5 atoms, but no more than 8 atoms, of any of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur in which at least one of the carbon atoms of the ring has two substituents, or a carbon atom alpha to the ring is tertiary carbon atom, or the ring has substituents on at least three of the atoms which make up the ring;e) molecules containing at least one macrocyclic ring, which is a ring having more greater than eight atoms of any of carbon, nitrogen oxygen or sulfur in the ring;f) molecules containing at least one substituted aromatic ring containing at least 5 atoms of any of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur, but in which at least one substituents has a tertiary carbon in a position alpha or beta to the ring;g) molecules containing a substituted aromatic ring comprising at least 5 atoms with at least 3 substituents groups on the ring all of which must contain at least 2 atoms from among carbon, oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur; andII) 0-40% by weight of pro-fragrances, solvents, and other benefit agents which possess any of the structural features a) to g) but are not constrained by the molecular weight restrictions.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
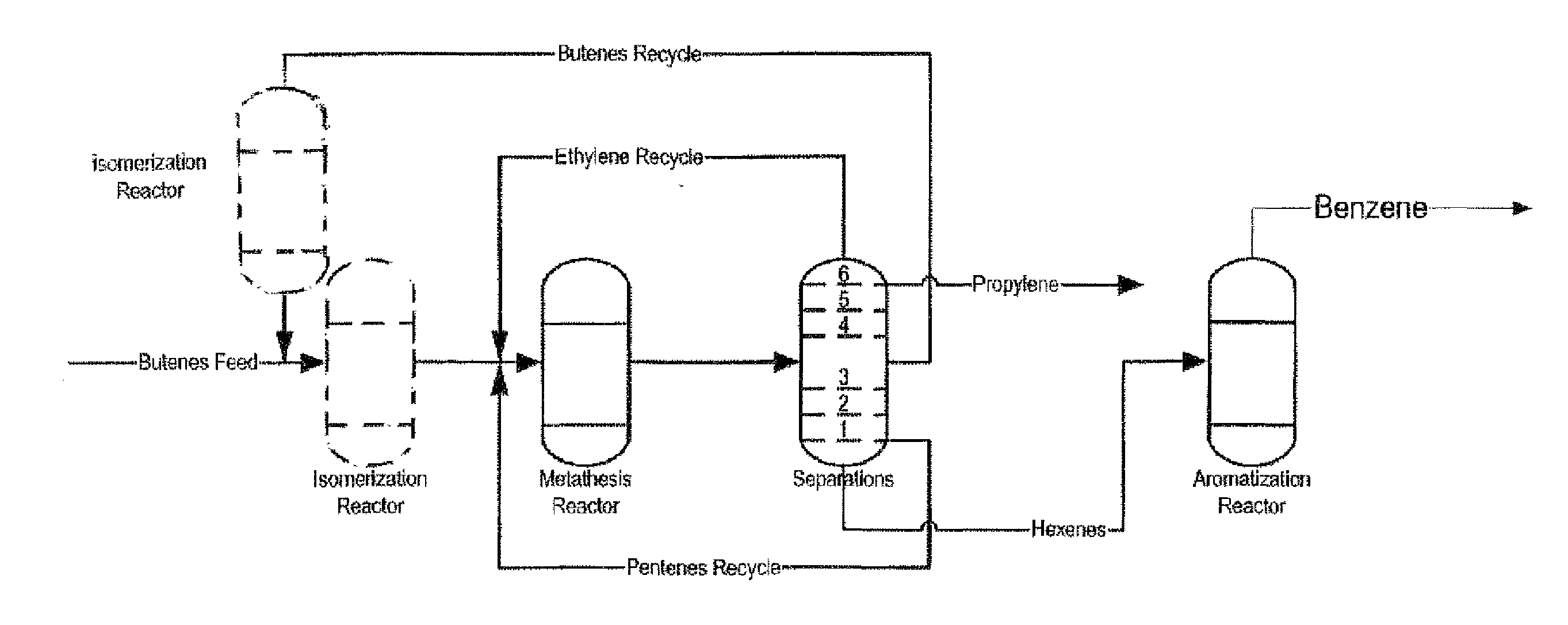
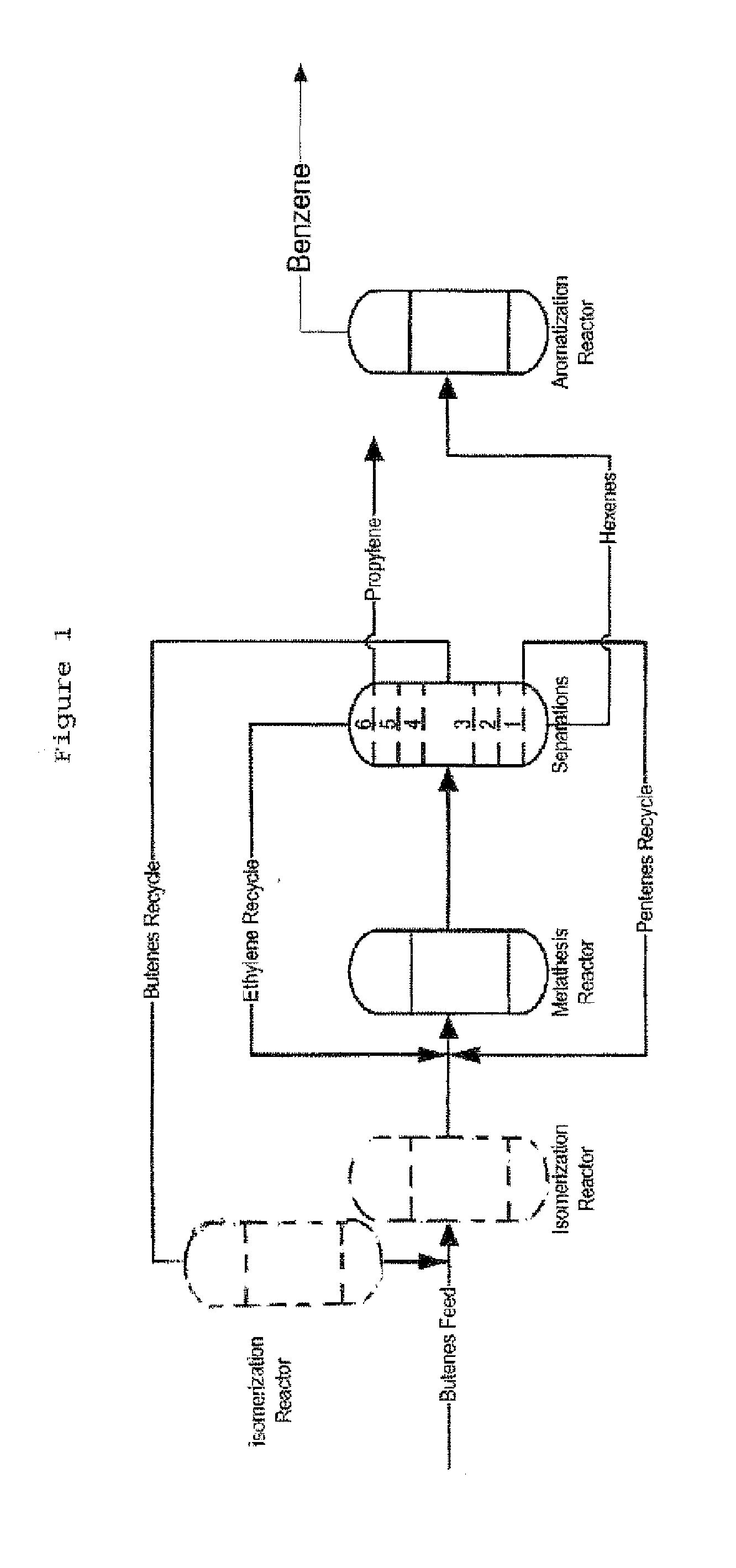
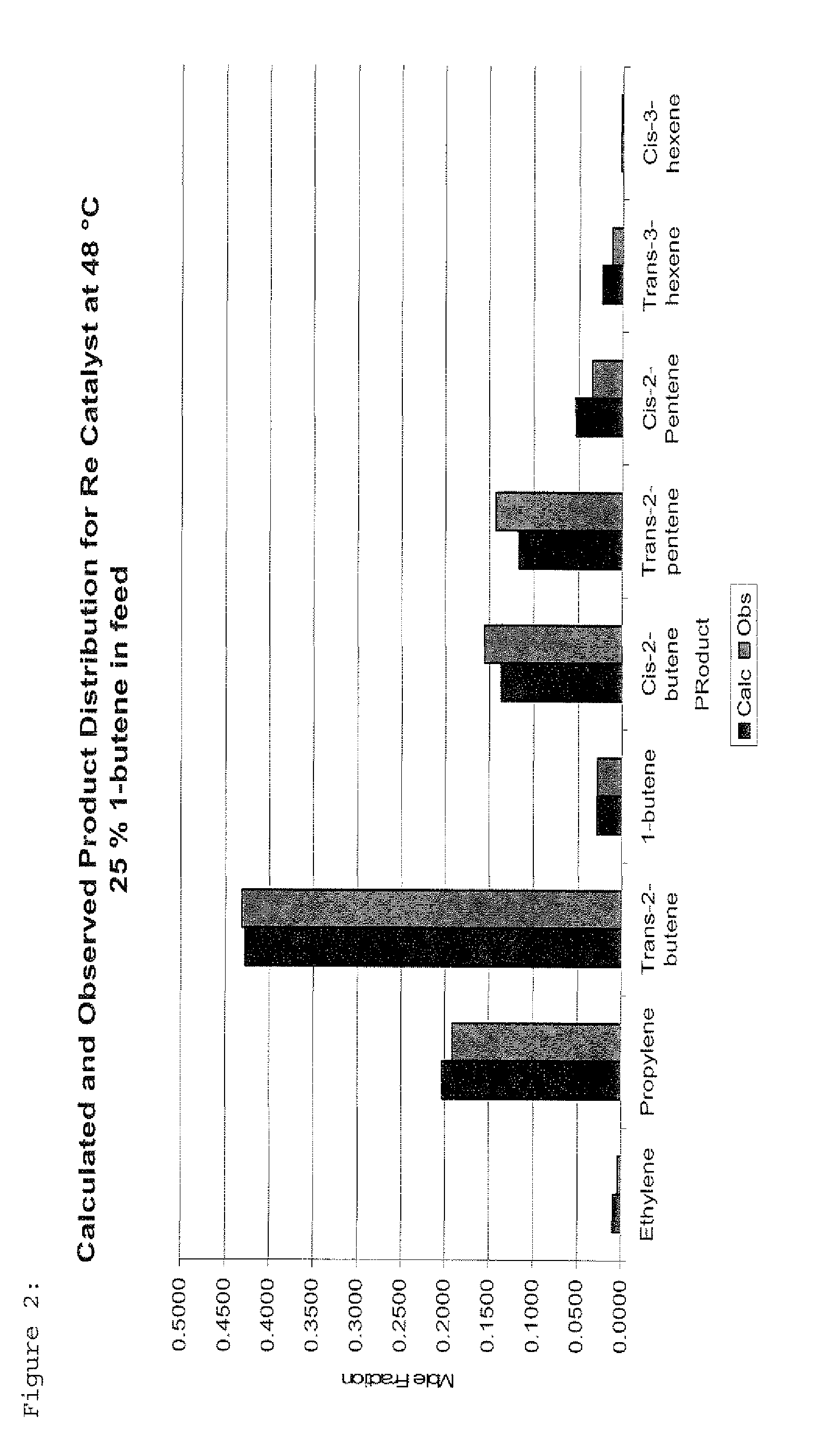
Process for Producing Propylene and Aromatics from Butenes by Metathesis and Aromatization
InactiveUS20110263917A1Molecular sieve catalystDistillation purification/separationIsomerizationOctene
The invention is for a process for producing propylene and hexene (along with ethylene, pentenes, product butenes, heptenes and octenes) by metathesis from butenes (iso-, 1- and cis and trans 2-) and pentenes and then aromatizing the hexenes (along with higher olefins, such as heptenes and octenes) to benzene (along with toluene, xylenes, ethylbenzene and styrene). Since the desired products of the metathesis reaction are propylene and hexene, the feed to the metathesis reaction has a molar ratio for 1-butene:2-butene which favors production of propylene and 3-hexene with the concentration of hexenes and higher olefins in the metathesis product being up to 30 mole %. An isomerization reactor may be used to obtain the desired molar ratio of 1-butene:2-butene for the feed composition into the metathesis reactor. After the metathesis reaction, of hexene and higher olefins are separated for aromatization to benzene and other aromatics.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
Modifying method for naphtha and light hydrocarbon aromatization
ActiveCN101747933ALower end pointReduce carbon deposition rateCatalytic naphtha reformingLiquid productHydrogen
A modifying method for naphtha and light hydrocarbon aromatization comprises: contacting naphtha and C3-C5 light hydrocarbon with aromatization catalyst in the presence of hydrogen-containing gas to carry out aromatization modifying reaction, wherein the reaction temperature is 250-600 DEG C, and the volume ratio of hydrogen to naphtha is 20-400. The method can convert naphtha with low octane value and low-carbon hydrocarbon into gasoline component with high octane value and excellent liquefied gas, the final distilling point of liquid product and the carbon-accumulating speed of catalyst areobviously reduced, and the service life of catalyst is prolonged.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve based catalyst and preparation and use methods
ActiveCN104941695AShorten the diffusion pathEasy to spreadMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsStrong acidsZSM-5
The invention discloses a nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve based catalyst and preparation and use methods. The molecular sieve catalyst consists of molecular sieves and metal components, wherein the molecular sieves are nano ZSM-5 molecular sieves with a short b-axis, a medium high silica-alumina ratio, less strong acid, high Lewis acid content, and resistance to hydrothermal deactivation. The preparation method is as follows: mixing a silicon source, an aluminum source, a template agent, a structure promoter, an additive and alkali with water, and stirring to prepare a precursor solution, then crystallizing, separating solid from liquid, and calcinating to obtain molecular sieve raw powder; mixing the molecular sieve raw powder with an ammonium salt solution, stirring, filtering, mixing with the ammonium salt solution for several times, stirring, filtering, and calcinating to obtain hydrogen-type ZSM-5 molecular sieves; mixing with the metal precursor solution, drying and calcinating to obtain the aromatization catalyst. The use method is as follows: transforming oxy-compound raw materials to aromatic hydrocarbon through the catalyst under the reaction conditions. The nano ZSM-5 molecular sieve based catalyst has the characteristics of being high in aromatics yield (reaching up to 99%) and long in service life (the catalyst is alive after 300 hours, and the aromatics selectivity reaches up to 70% after the catalyst is subjected to hydrothermal aging at 760 DEG C for 4 hours).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Metal supported MCM-22 molecular sieve hollow sphere bifunctional catalyst preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101618336AHigh reactivityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMolecular sieveActive component
The invention relates to a metal supported MCM-22 molecular sieve hollow sphere bifunctional catalyst preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the molecular sieve catalysis technology. The method is characterized in that carbon black sphere particles are used as template, molecular sieve hollow spheres with multi-stage pore path structure is prepared by rotation hydrothermal crystallization and by using metal active components the prepared molecular sieve hollow spheres are loaded and modified. The prepared Mo / HMCM-22 molecular sieve hollow sphere bifunctional catalyst can be used in methane non-oxidative aromatization reaction system. The effect and the benefit of the invention is that the preparation method of the molecular sieve hollow spheres has simple operation and low cost, and the prepared hollow sphere catalyst has excellent catalytic performance in the methane non-oxidative aromatization reaction, high methane conversion rate and aromatics yield and very long catalyst life.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Process for hydrogenating modifying faulty gasoline
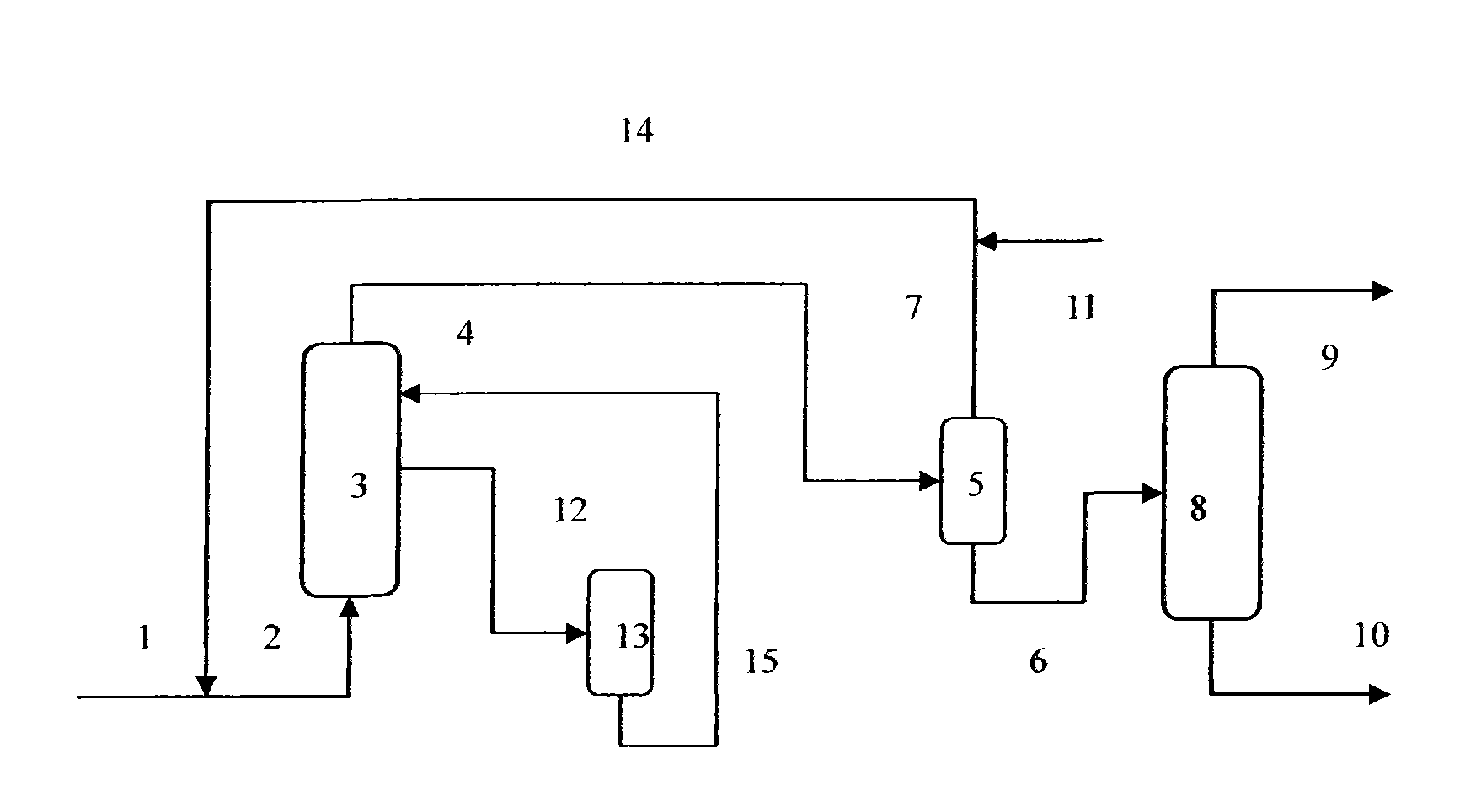
ActiveCN1597865ASimple processEasy to operateTreatment with hydrotreatment processesOrganic sulfide compoundIsomerization
The invention provides a process method for making hydrodesulfation and alkene reduction on the bad gasoline, like all-fractional FCC gasoline, etc. Under the conditions of hydrogen gas existence and temperature gradually rising, to contact with three catalysts forms three reaction regions. The first reaction region has lower temperature and uses hydrofining catalyst and mainly eliminates di-alkene in the gasoline; the second reaction region has higher temperature and uses selective hydrodesulfation catalyst and mainly eliminates organic sulfide and some alkenes; the third reaction region has the highest temperature, uses gasoline modifying catalyst and makes the modifying reactions including aromatization, isomerization and benzene alkylation, increasing octane number of gasoline and improving product quality. It has the advantages of simple flow, being easy to operate, fully using reaction heat, prolonging the operating cycle of catalyst, high liquid yield, low hydrogen consumption.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for improving catalytic property of methane aromatization catalyst
InactiveCN101618337AImprove catalytic performanceImprove bindingMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsLevel structureActive component
The invention relates to a method for improving the catalytic property of methane aromatization catalyst, belonging to the technical field of molecular sieve catalysis. The invention is characterized in that on the condition of no-second template, the crystal growth of zeolite molecular sieve is controlled by reasonablely controlling zeolite molecular sieve synthesis conditions such as synthesis formulation, charging sequence, ageing time, crystallization temperature, crystallization time and the like, small molecular sieve crystal is used for assembly and intergrowth to form MCM-22 and ZSM-5 molecular sieve assembly with multi-stage pore path structure, Mo or Re used can be adopted as active component to perform loading and modification to the prepared molecular sieve assembly, and the invention provides Mo-based MCM-22 and ZSM-5 molecular sieve assembly catalysts and an application thereof in methane non-oxidative aromatization reaction. The effects and the benefits of the invention is that the operation is simple, the cost is low and in methane non-oxidative aromatization reaction, the multi level structure assembly catalyst prepared by the method of the invention has better catalytic performance compared with the traditional catalyst.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for depolymerizing lignin into aromatic compounds under conditions of no additional hydrogen
The invention relates to a method for depolymerizing lignin into aromatic compounds under the conditions of no additional hydrogen. According to the method, biomass-base alcohol compound reformation hydrogen production reaction and lignin hydrodepolymerization reaction are combined; and in the reaction process, the biomass-base alcohol compounds are subjected to in-situ reformation hydrogen production, and meanwhile, the hydrogen is used for hydroepolymerizing lignin. The lignin is selectively cracked into C6-C9 aromatic compounds of phenolic group, guaiacol group, lilac group or other derivatives under the action of the catalyst. The conversion rate of the raw materials is up to higher than 50%, and the content of the guaiacol-group and lilac-group aromatic compounds in the cracked product can reach higher than 90%. The method uses the hydrogen prepared by biomass-base alcohol in-situ reformation as the hydrogen source, and avoids using high-pressure hydrogen in the preparation route; and thus, the method has the characteristics of high safety coefficient in the reaction process, high yield of the aromatic compounds, and mild reaction conditions.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons through hydrogenation of carbon dioxide
ActiveCN107840778AEasy to prepareRaw materials are cheap and easy to getHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveCarbon dioxide production
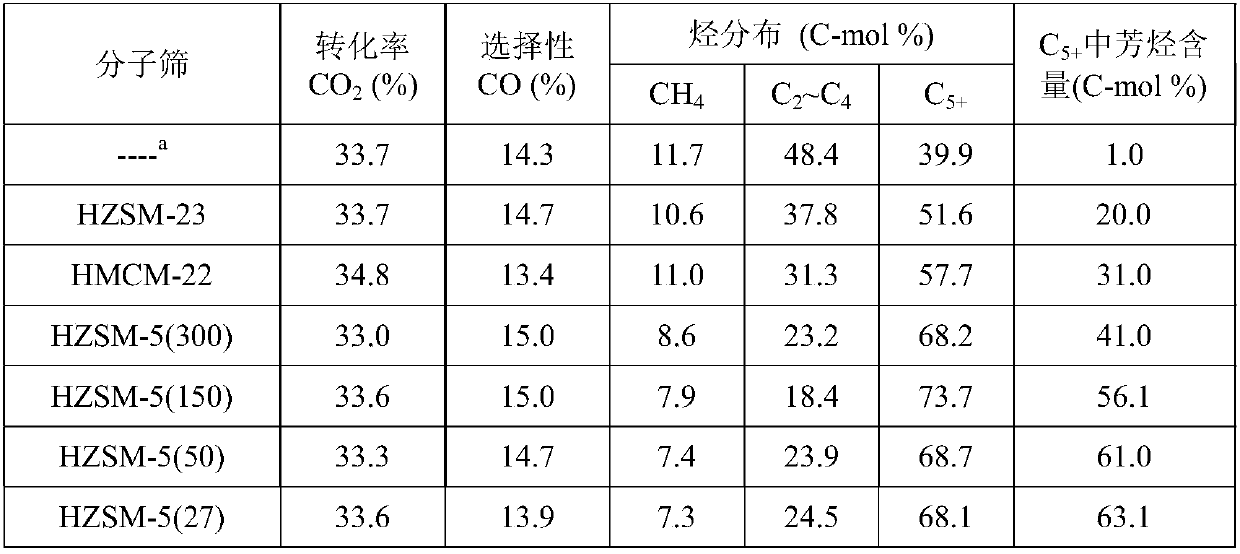
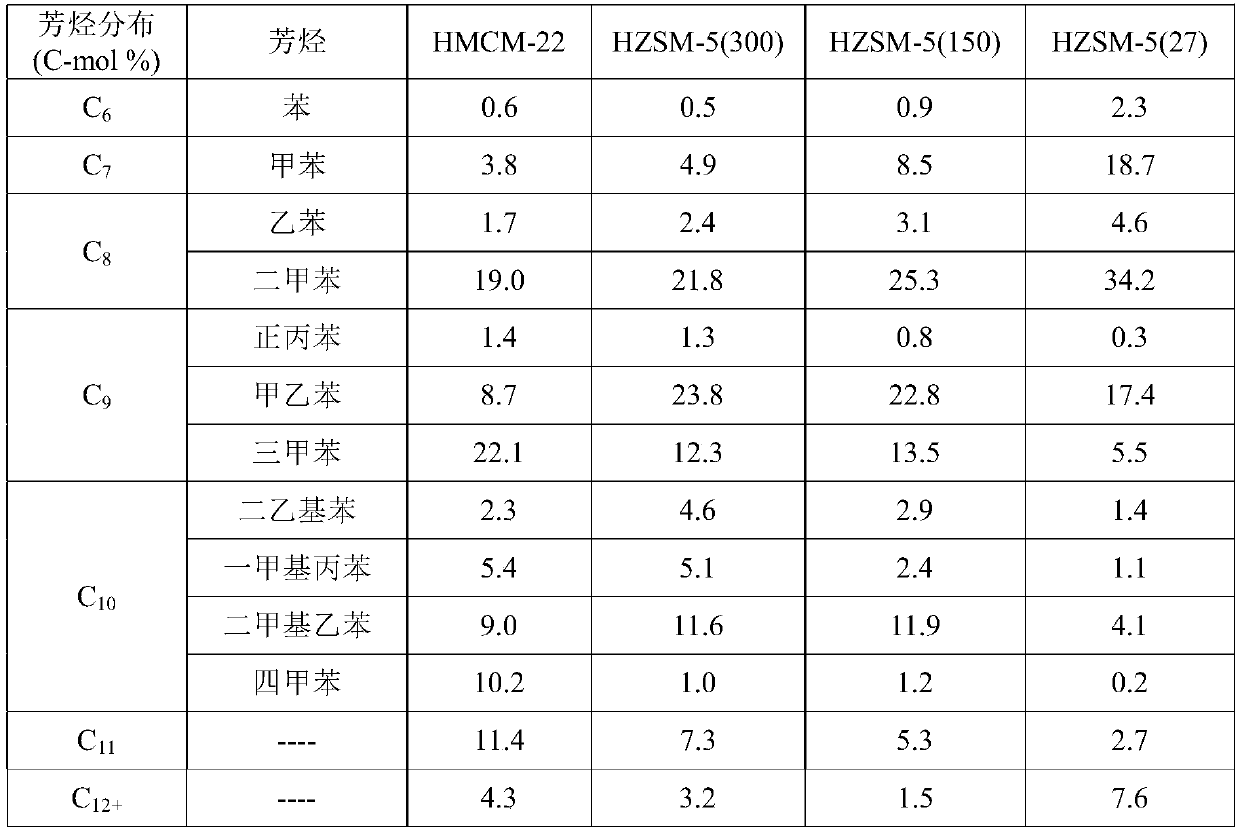
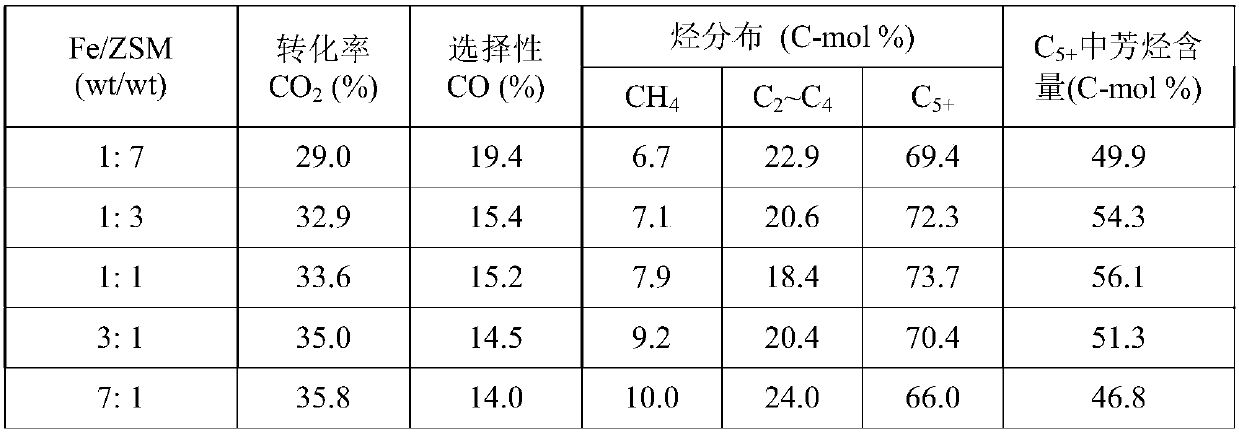
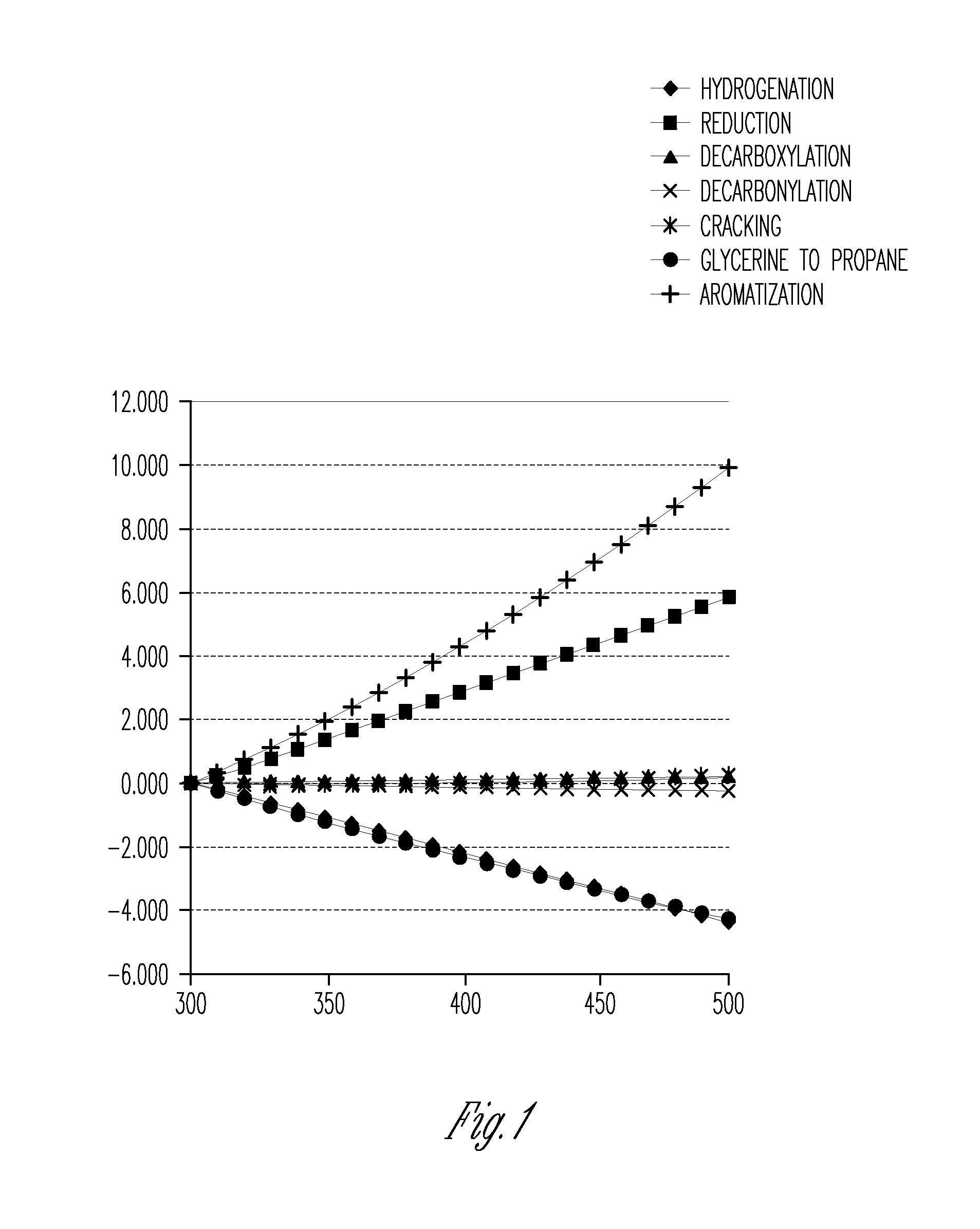
The invention provides a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbons through hydrogenation of carbon dioxide. A gas mixture composed of carbon dioxide and hydrogen is directly converted under the catalysis of a multifunctional composite catalyst under the reaction conditions of a temperature of 250 to 450 DEG C, a pressure of 0.01 to 10.0 MPa, space velocity of 500 to 50000 mL / (h.g<cat>) and a H<2> / CO<2> mol ratio of 0.5 to 8.0 so as to produce the aromatic hydrocarbons. The composite catalyst is prepared by mixing a first component with a second component, wherein the first component is a Fe-based catalyst for preparation of low-carbon olefins through hydrogenation of carbon dioxide, and the second component is one or more than two selected from a group consisting of molecular sieves modified or unmodified by metals and mainly exerting aromatization effect on olefins. According to the method, the one-way CO2 conversion rate can reach 33% or above; the selectivity of hydrocarbon products can be controlled to be 80% or above; the content of methane in hydrocarbon products is lower than 8%; the content of C<5+> hydrocarbons is higher than 65%; and the aromatic hydrocarbons account for63% or more of the C<5+> hydrocarbons. The method opens up a novel route for production of aromatic hydrocarbons from carbon dioxide.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Process for the conversion of renewable oils to liquid transportation fuels
InactiveUS20120157734A1Efficient reductionEfficient processingBiofuelsSolid fuelsIsomerizationKerosene
The present invention relates to production of fuels or fuel blendstocks from renewable sources. Various embodiments provide a method of producing a hydrocarbon product by hydrotreating a feedstock including at least one of a renewable triacylglyceride (TAG), renewable free fatty acid (FFA), and renewable fatty acid C1-C5 alkyl ester (C1-C5 FAE) in the presence of a nonsulfided hydrotreating catalyst to produce a first product including hydrocarbons. In some examples, the first product can be subjected to further chemical transformations such as aromatization, cracking, or isomerization to produce a second product including hydrocarbons. In various embodiments, the first or second hydrocarbon product with minimal or substantially no further processing can be suitable as a liquid transportation fuel or fuel blendstock, including fuels such as gasoline, naptha, kerosene, jet fuel, and diesel fuels.
Owner:ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES CENT FOUNDATIO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com