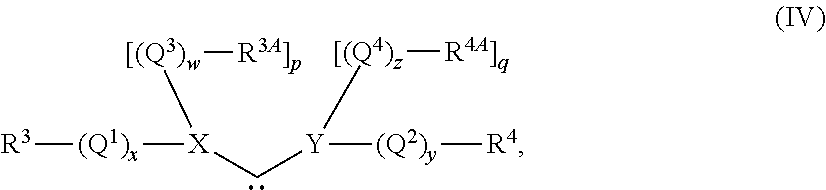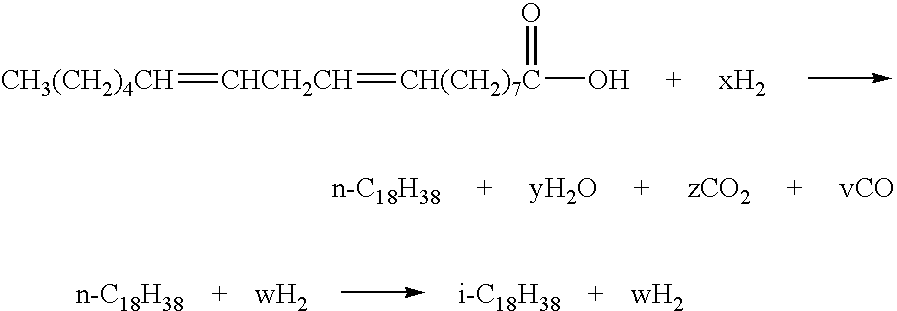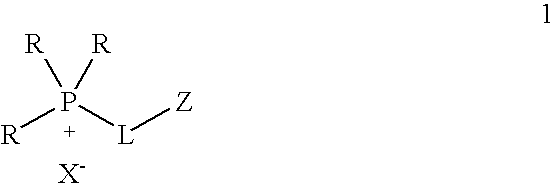Patents
Literature
6624results about "Hydrocarbon oils refining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Composite molecular sieve and hydrodesulfurization catalyst prepared with composite molecular sieve as carrier
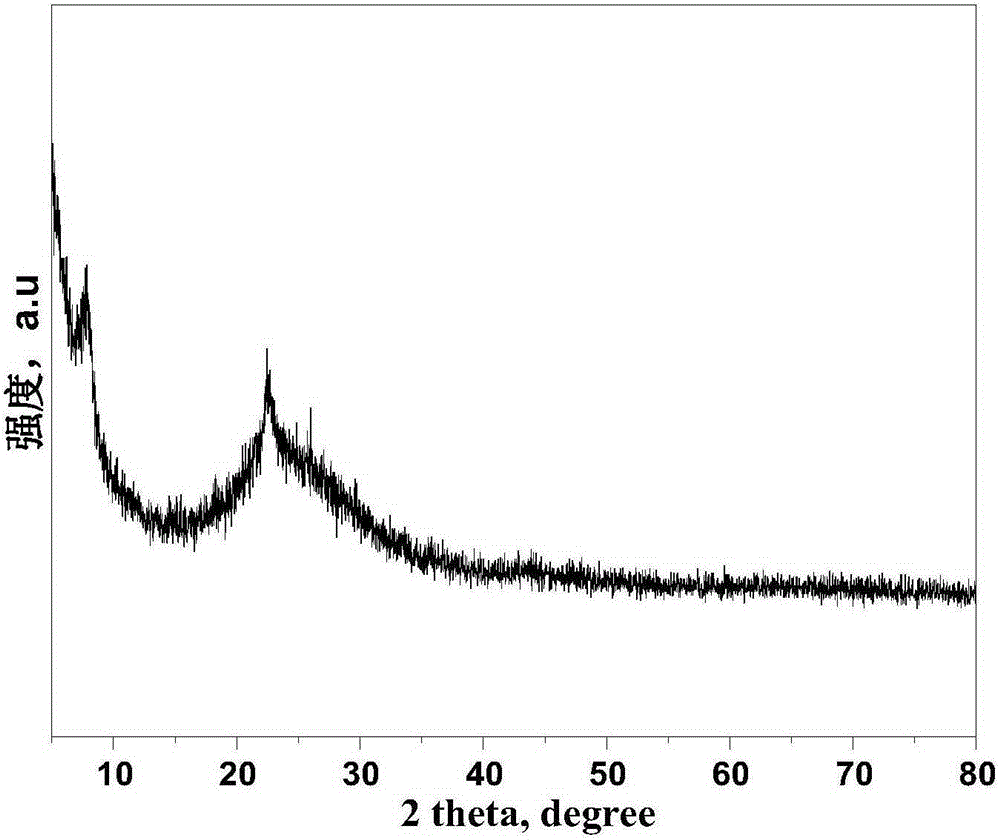
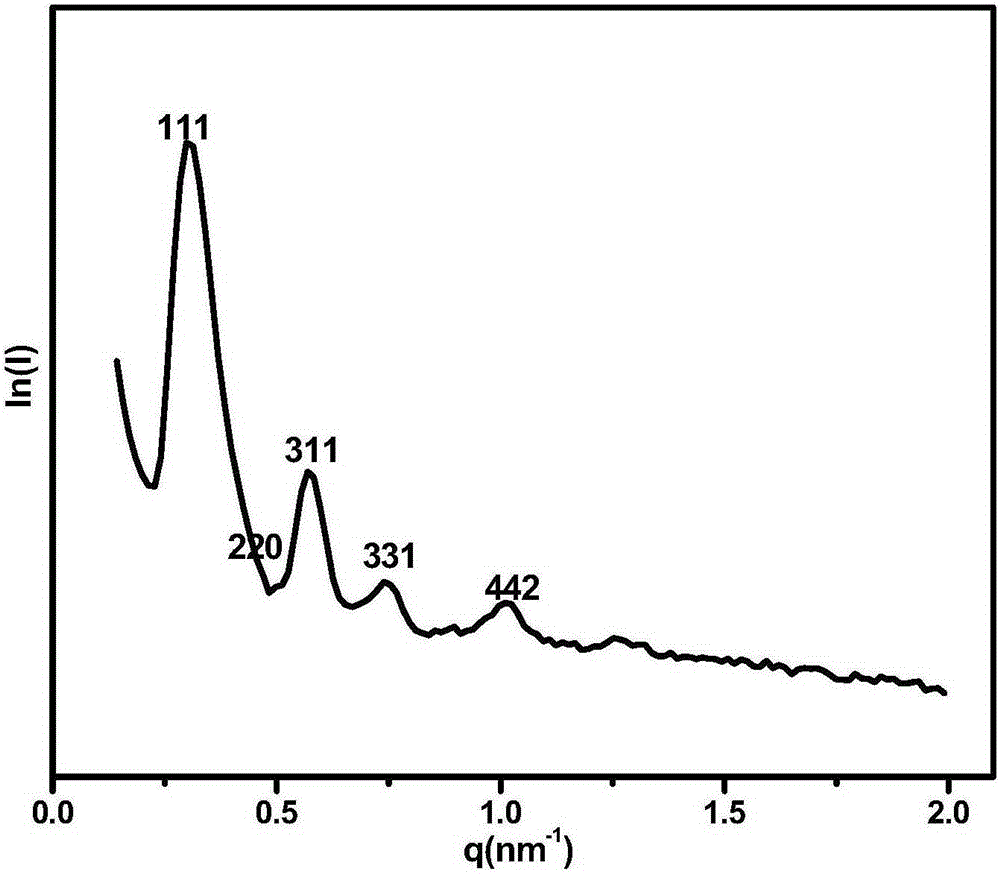
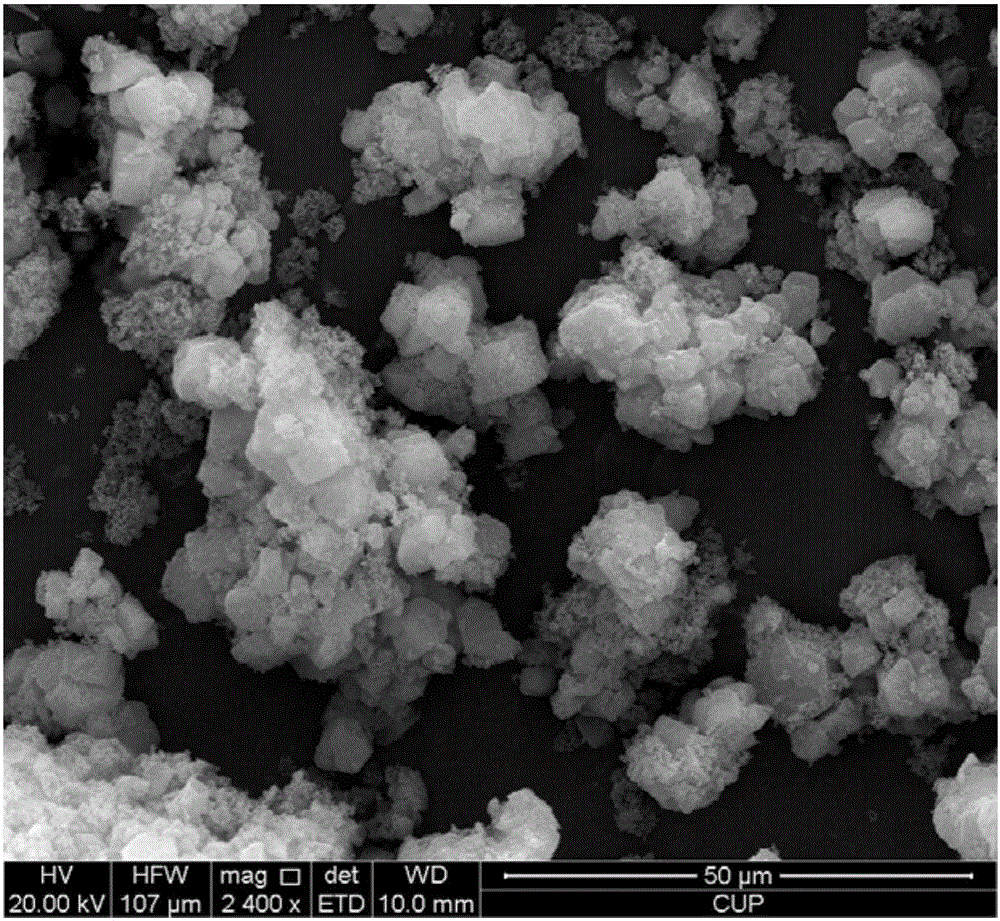
ActiveCN105251527AGood dispersionModerate dispersionMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningMolecular sieveSulfur
The invention provides a composite molecular sieve and a hydrodesulfurization catalyst prepared with the composite molecular sieve as a carrier. According to the composite molecular sieve and the hydrodesulfurization catalyst, the Beta-FDU-12 composite molecular sieve is of a bimodal porous structure, namely a Beta micropore and an FDU-12 mesoporous, the superficial area of the composite molecular sieve is 800-1000m<2>.g<-1>, the pore diameter is 14-25 nm, and the pore volume is 0.4-0.9 cm<3>.g<-1>.The hydrodesulfurization catalyst prepared with the Beta-FDU-12 composite molecular sieve as the carrier is outstanding in performance, the yield of FCC diesel oil can be higher than 99%, the denitrification percent can be higher than 98%, and the sulphur content is lower than 10 ppm.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Production of diesel fuel from vegetable and animal oils
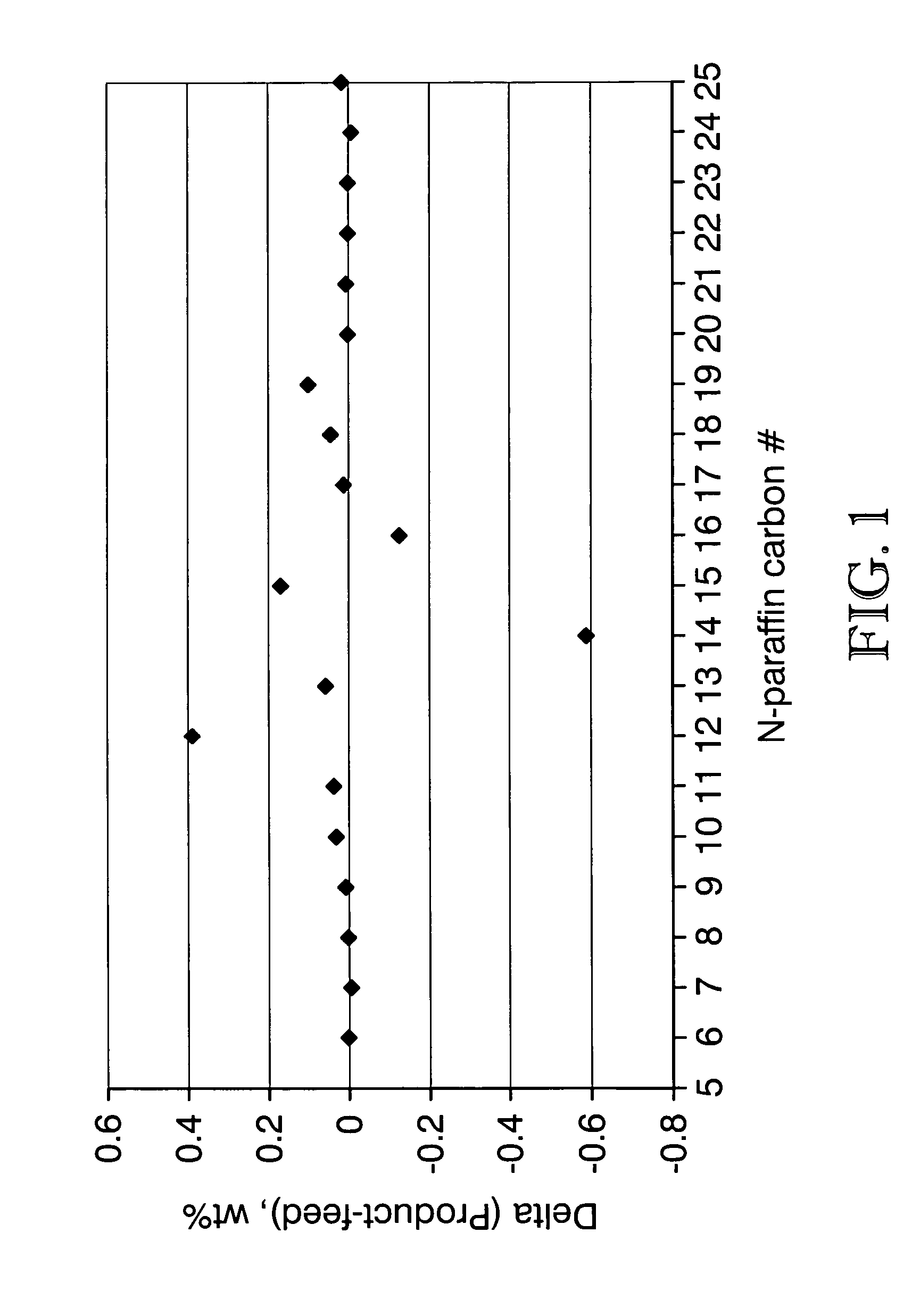
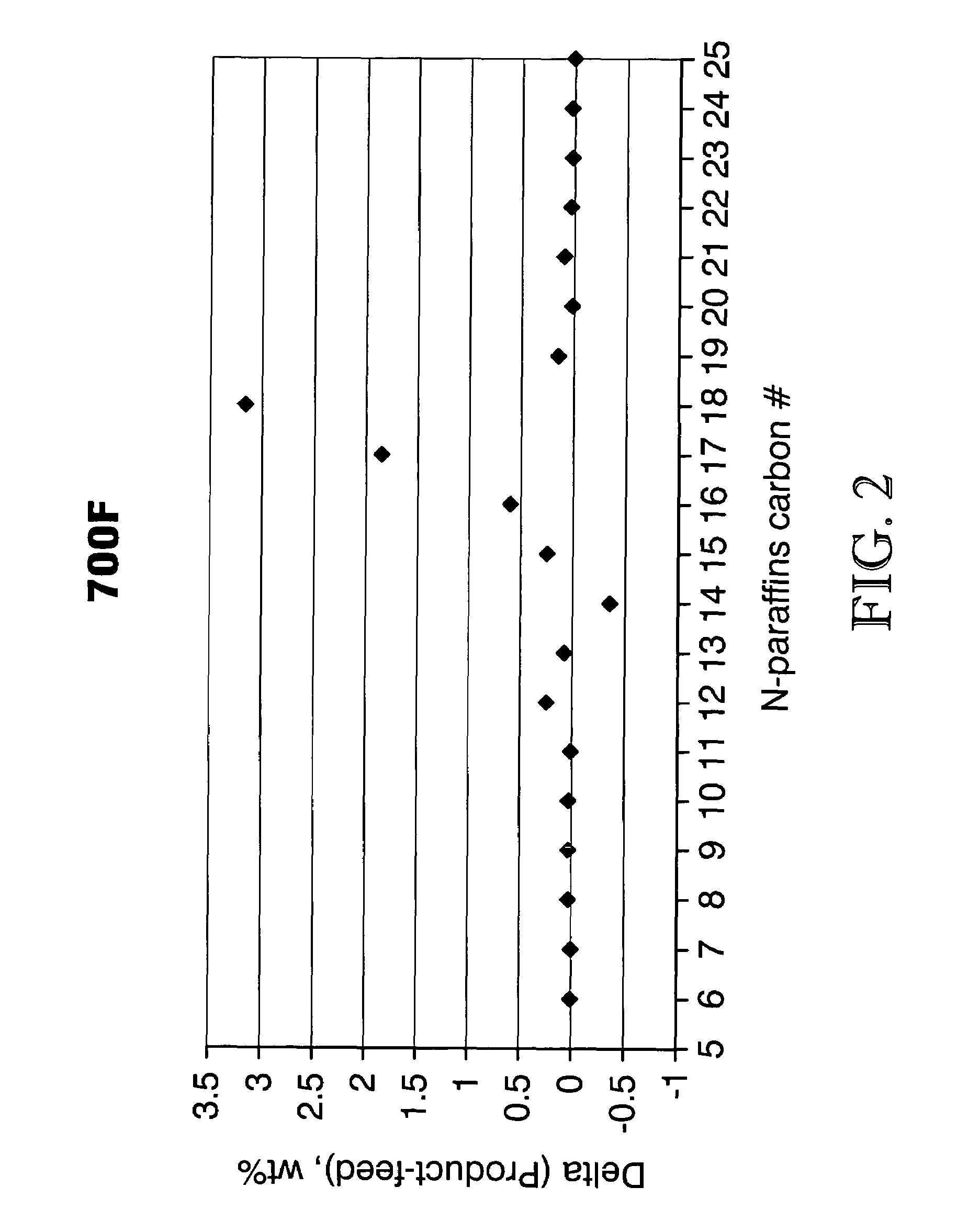
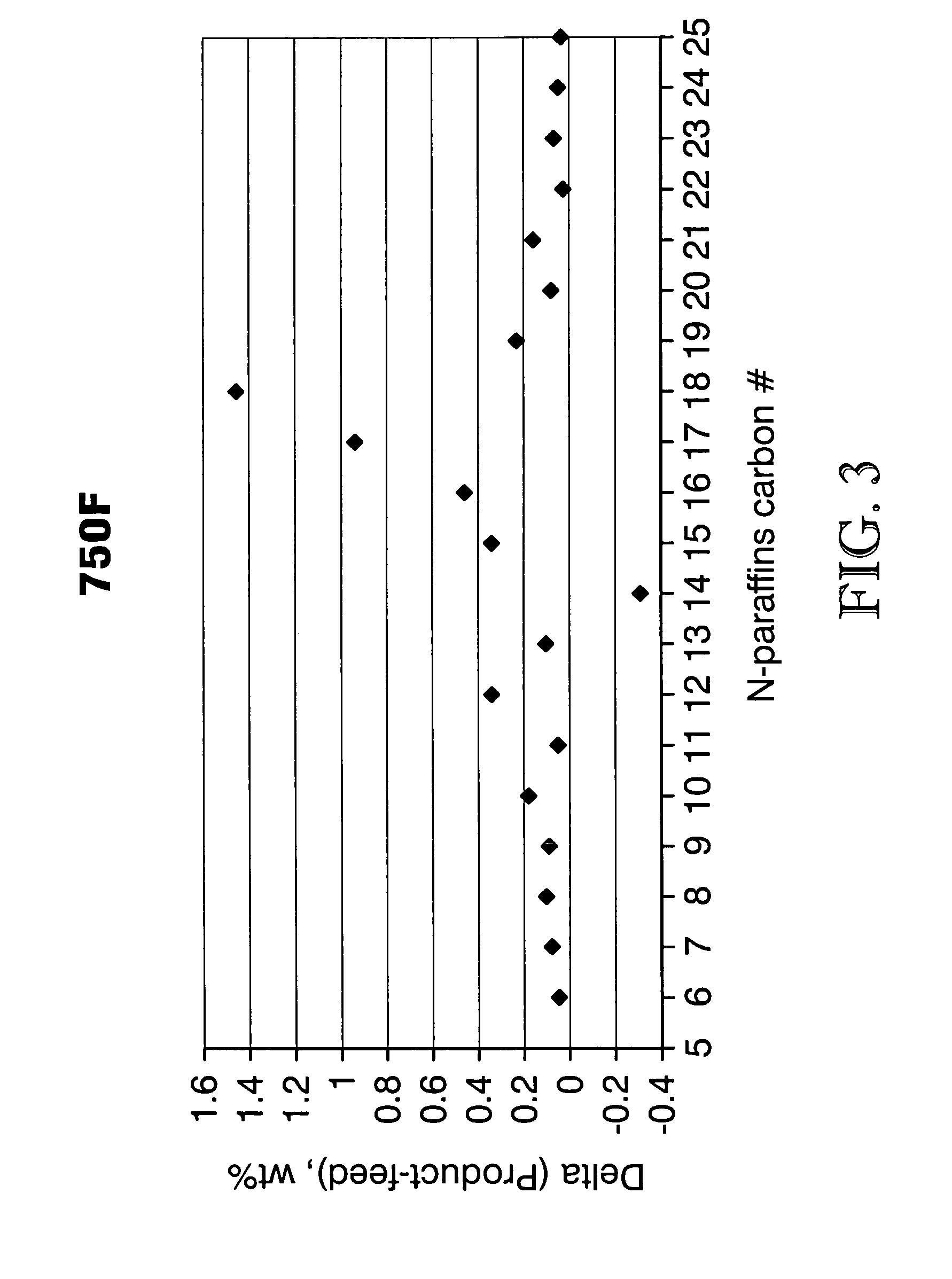
A process for producing a fuel composition from vegetable and / or animal oil comprises hydrodeoxygenating and hydroisomerizing the oil in a single step. The fuel composition has acceptable lubricity and comprises a mixture of C14 to C18 paraffins having a ratio of iso to normal paraffins of 2 to 8 and less than 5 ppm sulfur.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
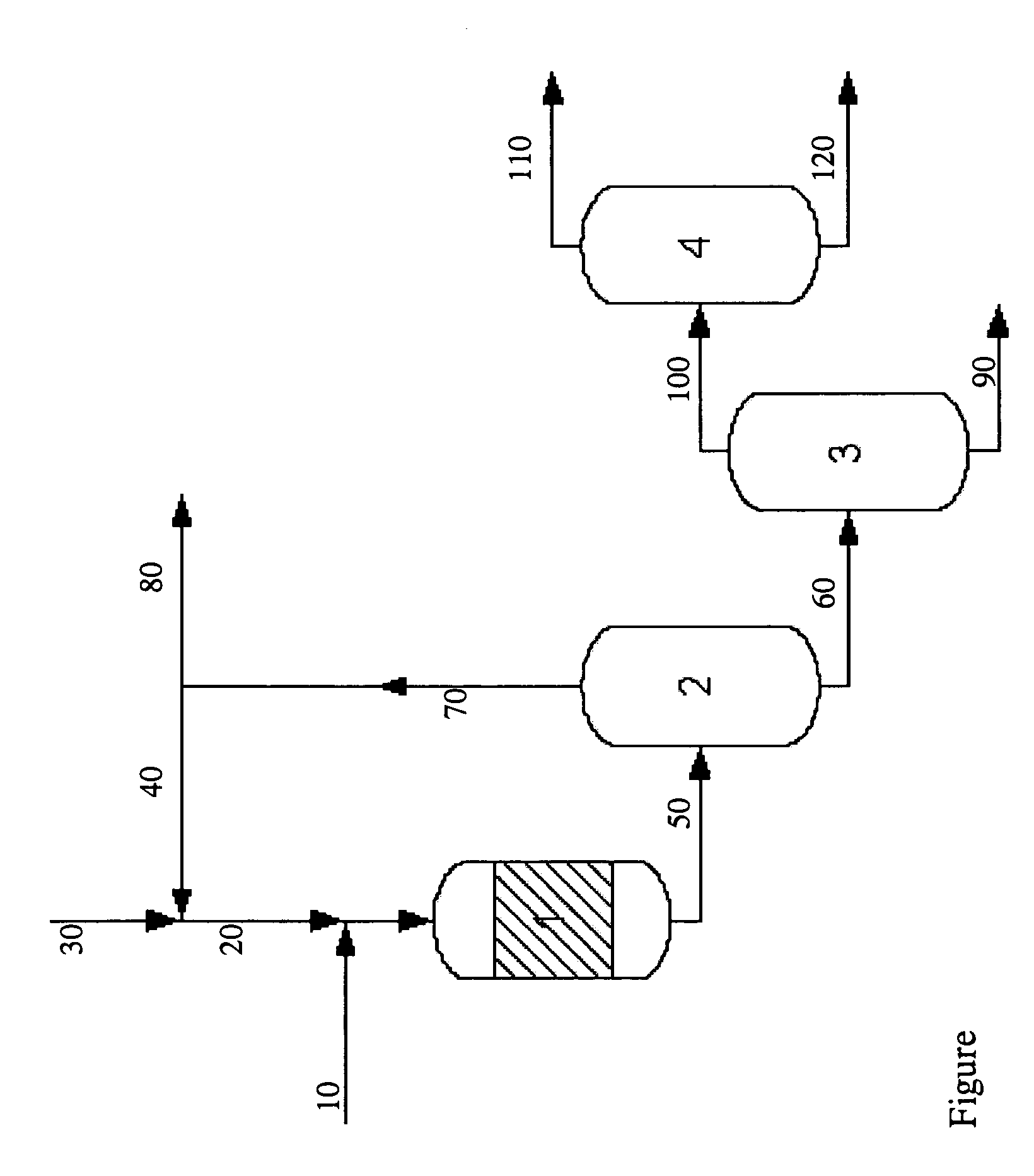
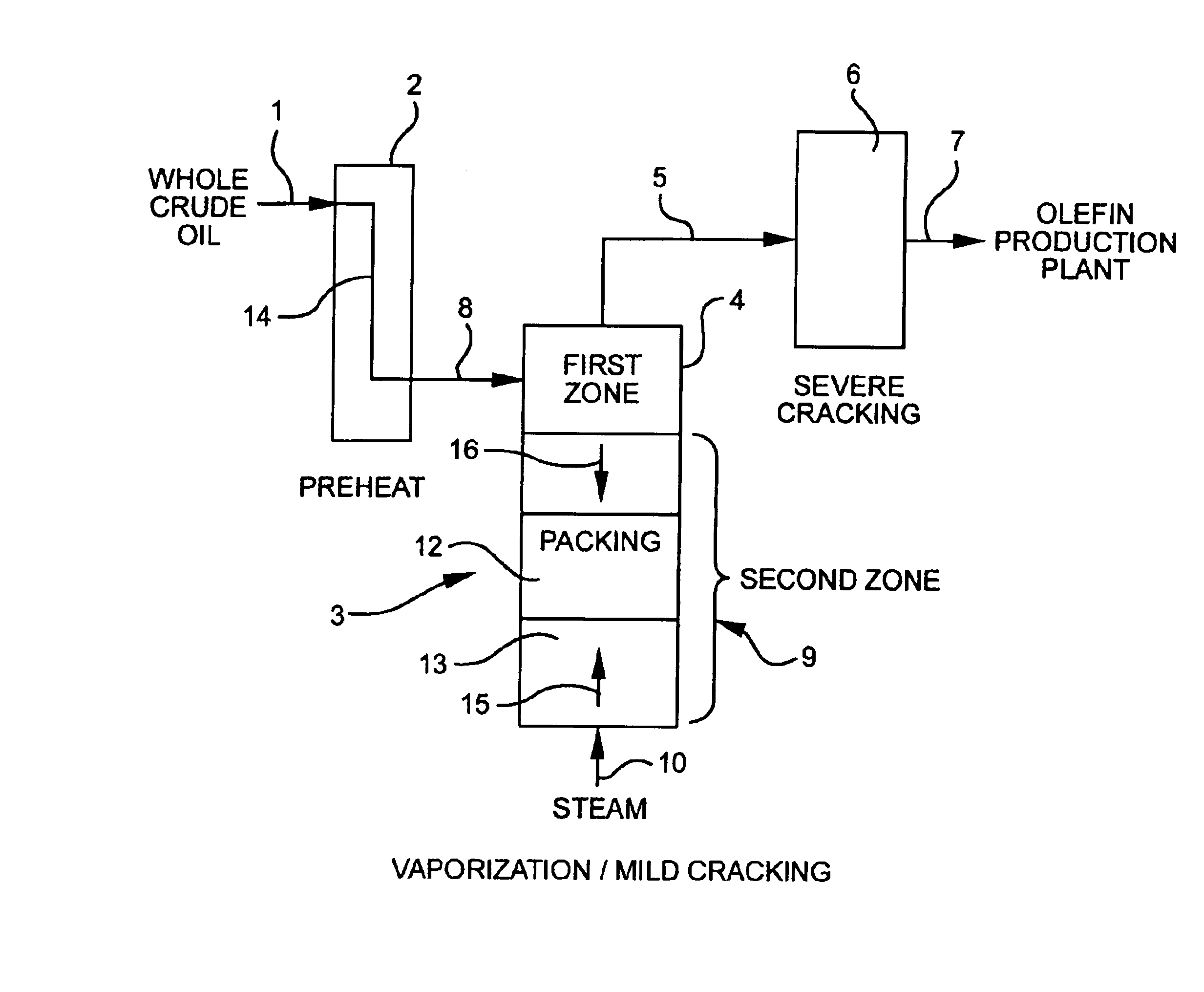
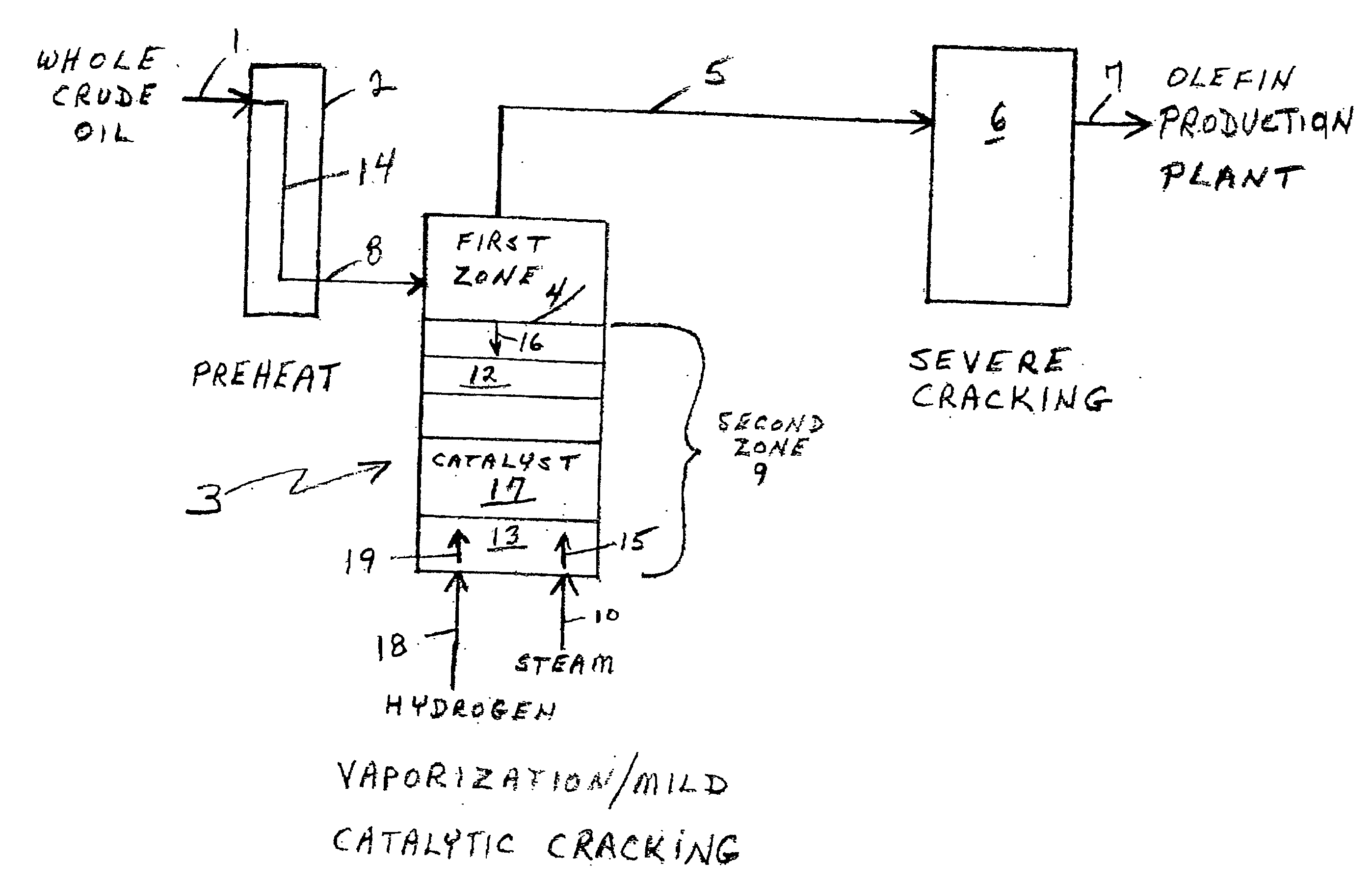
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil
InactiveUS6743961B2Lower temperature rangeReduce molecular weightThermal non-catalytic crackingHydrocarbonsOil productionAlkene
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild cracking conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors from mild cracking being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Chemical methods for treating a metathesis feedstock
ActiveUS20110160472A1Reduce starting peroxide valueFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationChemical treatmentNatural oils
Owner:WILMAR TRADING PTE LTD
Process for manufacturing lubricating base oil with high monocycloparaffins and low multicycloparaffins
InactiveUS20050133409A1Improve Oxidation StabilityHigh viscosity indexTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAdditivesSyngasMolecular sieve
A process for manufacturing a lubricating base oil by: a) performing Fischer-Tropsch synthesis on syngas to provide a product stream; b) isolating from said product stream a substantially paraffinic wax feed having less than about 30 ppm total nitrogen and sulfur, and less than about 1 wt % oxygen; c) dewaxing said feed by hydroisomerization dewaxing using a shape selective intermediate pore size molecular sieve comprising a noble metal hydrogenation component, wherein the hydroisomerization temperature is between about 600° F. (315° C.) and about 750° F. (399° C.), to produce an is dimerized oil; and d) hydrofinishing said isomerized oil to produce a lubricating base oil having specific desired properties.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
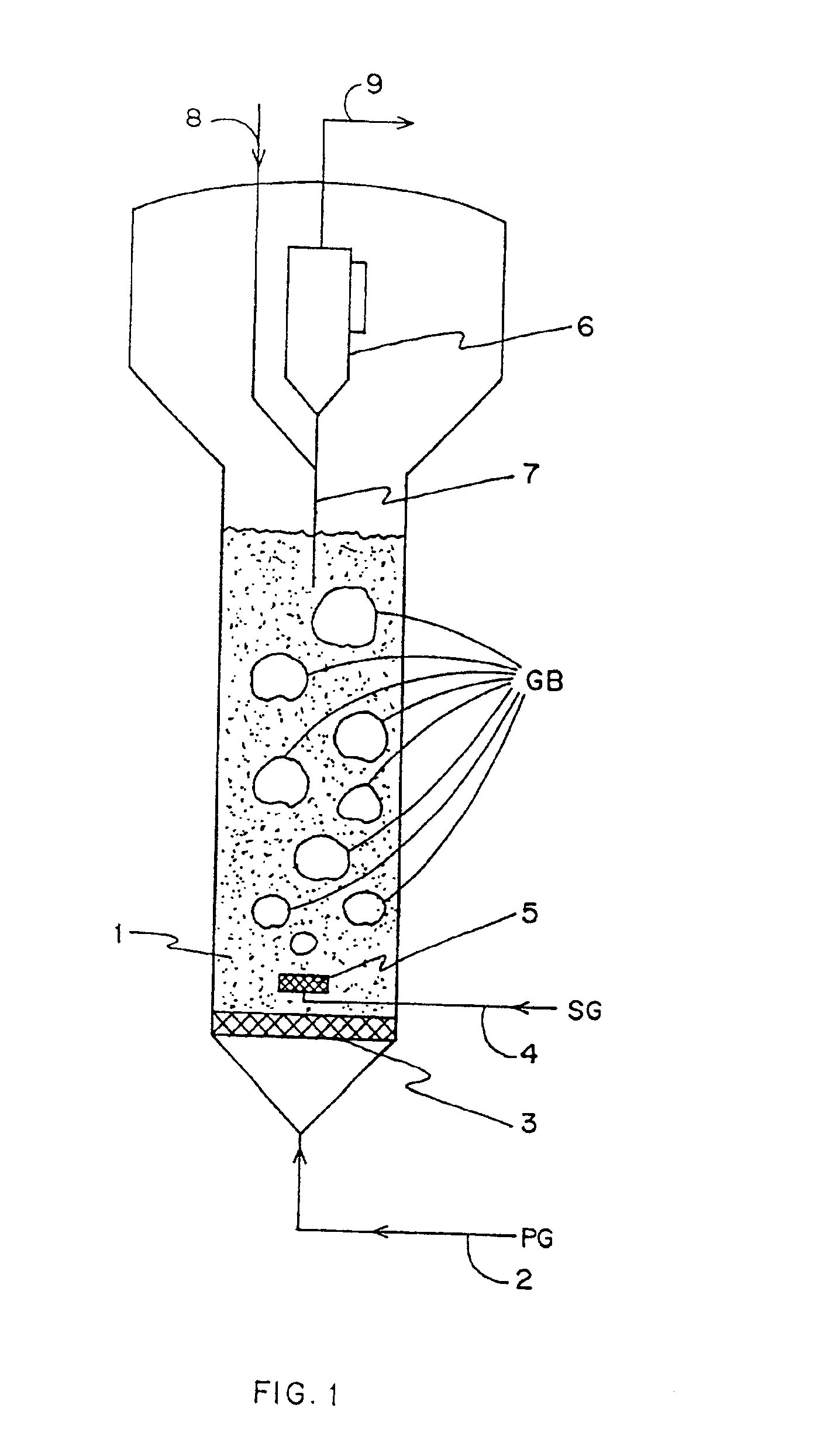
Method for gas-solid contacting in a bubbling fluidized bed reactor
InactiveUS6894183B2Eliminate and drastically reduce bypassEffective contactThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingForming gasSolid particle
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
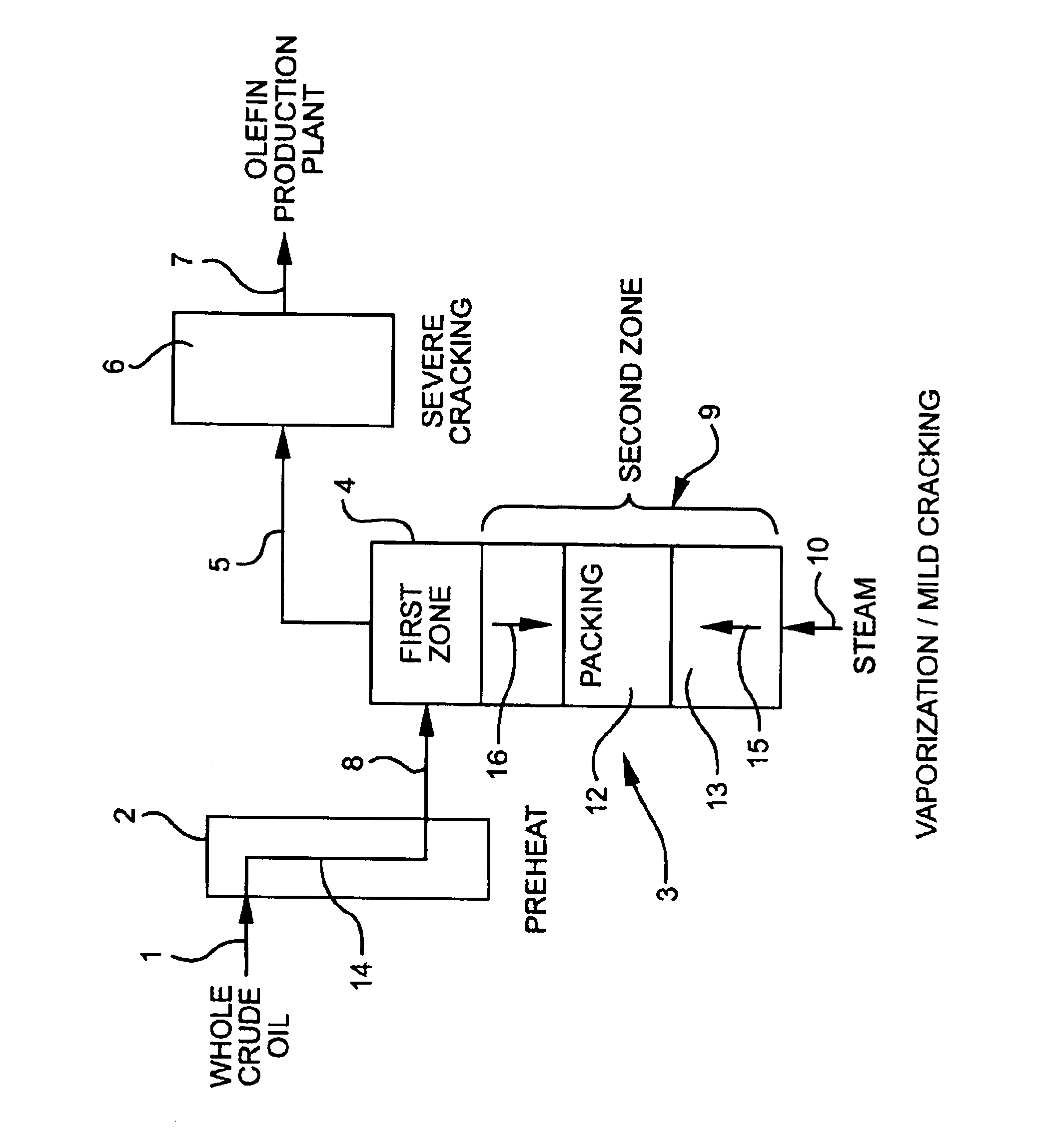
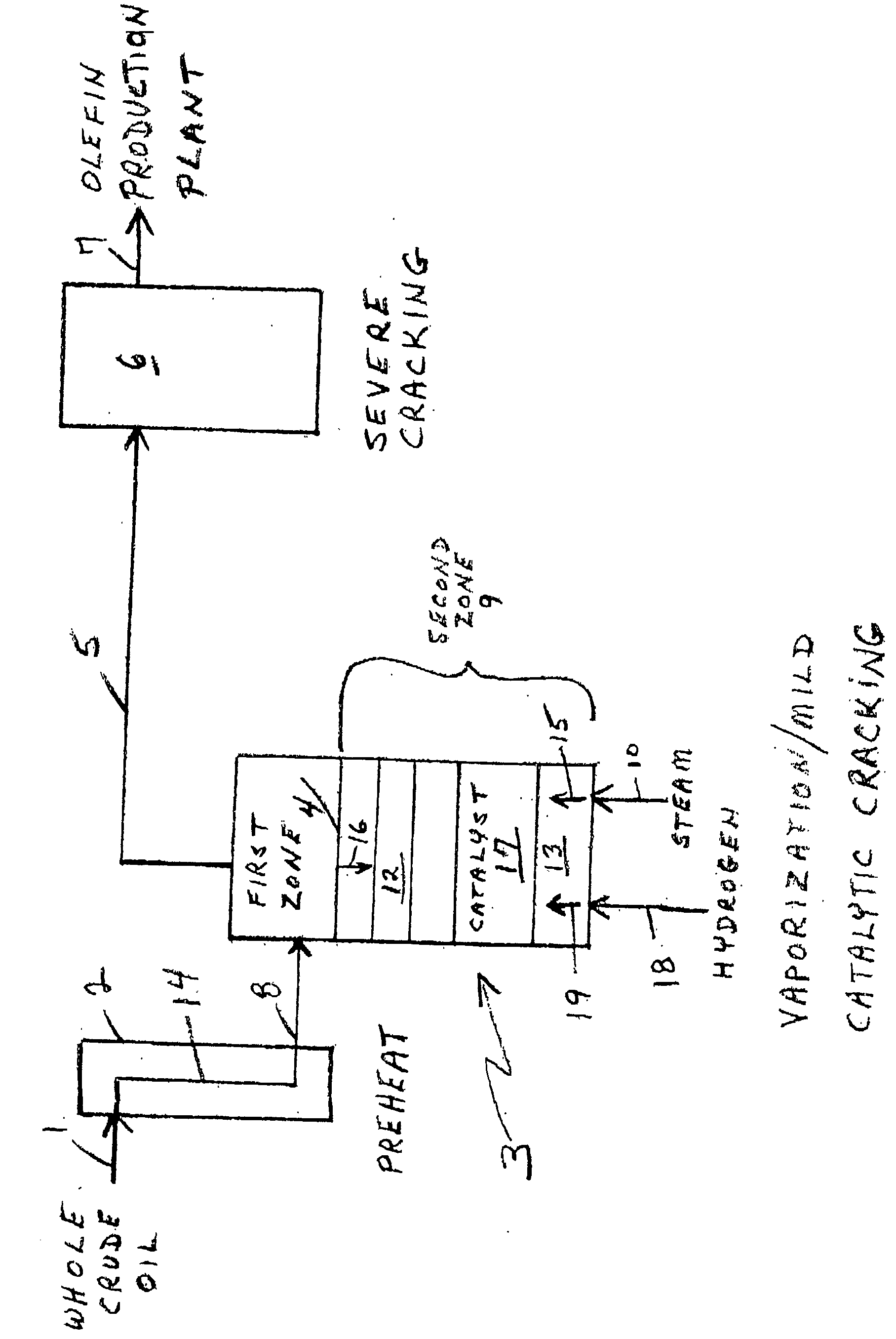
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil and mild catalytic cracking
InactiveUS20040054247A1Lower temperature rangeImproved vaporizationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingChemistryPyrolysis
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild catalytic cracking conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors from the mild catalytic cracking being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Process for Co-Producing Jet Fuel and LPG from Renewable Sources
ActiveUS20080244962A1Improve cold flowHydrocarbon by hydrogenationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionEngineeringRenewable resource
The present invention generally relates to a method for producing an isoparaffinic product useful as jet fuel from a renewable feedstock. The method may also include co-producing a jet fuel and a liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fraction from a renewable feedstock. The method includes hydrotreating the renewable feedstock to produce a hydrotreating unit heavy fraction that includes n-paraffins and hydroisomerizing the hydrotreating unit heavy fraction to produce a hydroizomerizing unit heavy fraction that includes isoparaffins. The method also includes recycling the hydroisomerizing unit heavy fraction through the hydroisomerization unit to produce an isoparaffinic product that may be fractionated into a jet fuel and an LPG fraction. The present invention also relates to a jet fuel produced from a renewable feedstock having improved cold flow properties.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Catalyst and process of paraffin hydrocarbon conversion
InactiveUS20040077914A1Improve solubilityEasy to useHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationAlkanePtru catalyst
A catalyst composition and process for the conversion of linear and / or branched paraffin hydrocarbons based on the use of an ionic liquid catalyst in combination with a Brønsted Acid, which provides a catalytic composition with an increased activity compared with said ionic liquid. Under suitable reaction conditions this conversion is leading to paraffin hydrocarbon fraction with higher octane number.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
Process for the manufacture of diesel range hydro-carbons
ActiveUS20070006523A1Improve low temperature performanceBig ratioBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsChemical industryAlkane
The invention relates to chemical industry and is directed to the production of middle distillate from vegetable oils. In the first step of the production method, the fatty acids or triglycerides of said vegetable oils are hydrogenated to give n-paraffins, and in the second step, the n-paraffins are catalytically converted to paraffins with branched chains. Using this process having two steps, a high-quality middle distillate useful as a component of diesel fuels without any particular specifications may be produced.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
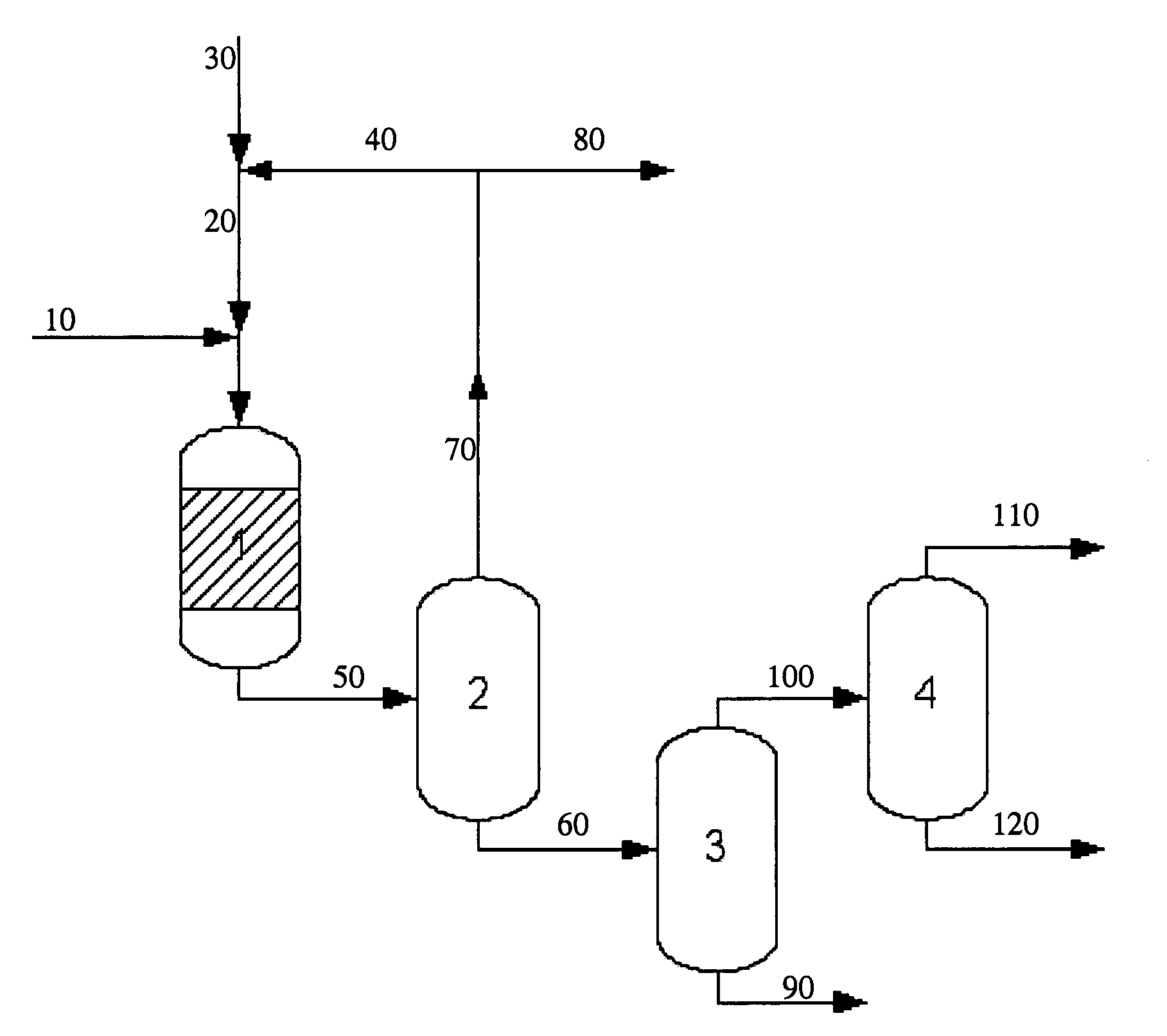
Heavy distillate oil hydrotreating method
ActiveCN101348732AQuality improvementQuality assuranceHydrocarbon oils refiningGasoline stabilisationWaxOil and grease
The invention relates to a method for hydrotreating heavy oil, in particular to the method for hydrotreating heavy oil, which improves the quality of diesel oil. Heavy distillate oil and animal and vegetable oil are used as raw material oil; under the hydrotreatment condition, the raw material oil and hydrogen gas are mixed and pass through a hydrotreatment reaction region; hydrogen-rich gas which is obtained by separating oil generated by hydrotreatment is circulated and utilized; and liquid obtained by separation is distillated to prepare a diesel oil product and hydrogenated wax oil. Compared with the prior art, the method can effectively improve the material source of a wax oil hydrotreatment device, ensure the quality of the hydrogenated wax oil, substantially increase the quality ofthe hydrotreated diesel oil and improve the storage stability of the animal and vegetable oil as fuel oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Control of mercury emissions from solid fuel combustion
InactiveUS6848374B2Remove pollutantsEasy to captureCombination devicesGas treatmentSorbentSolid fuel
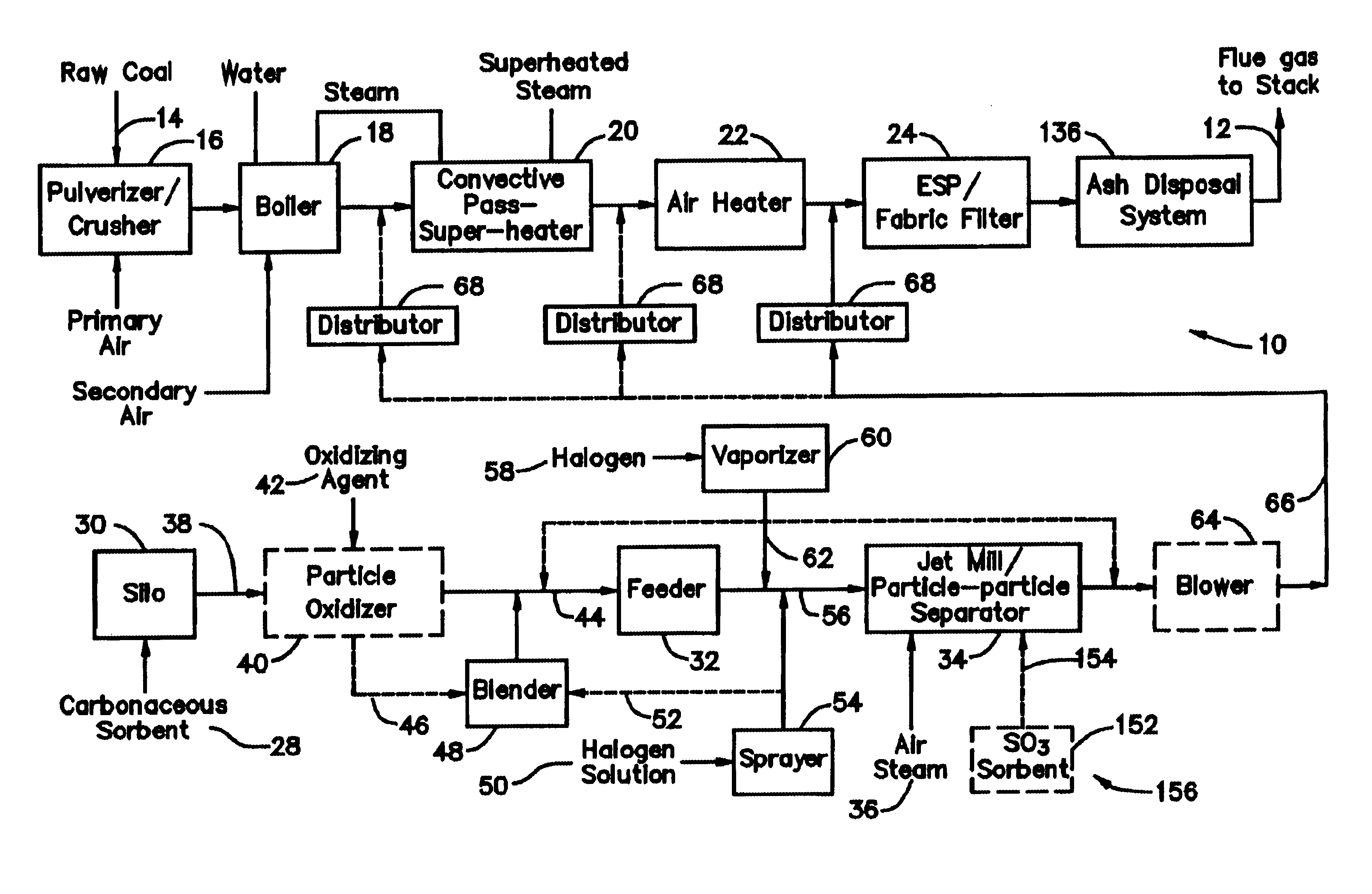
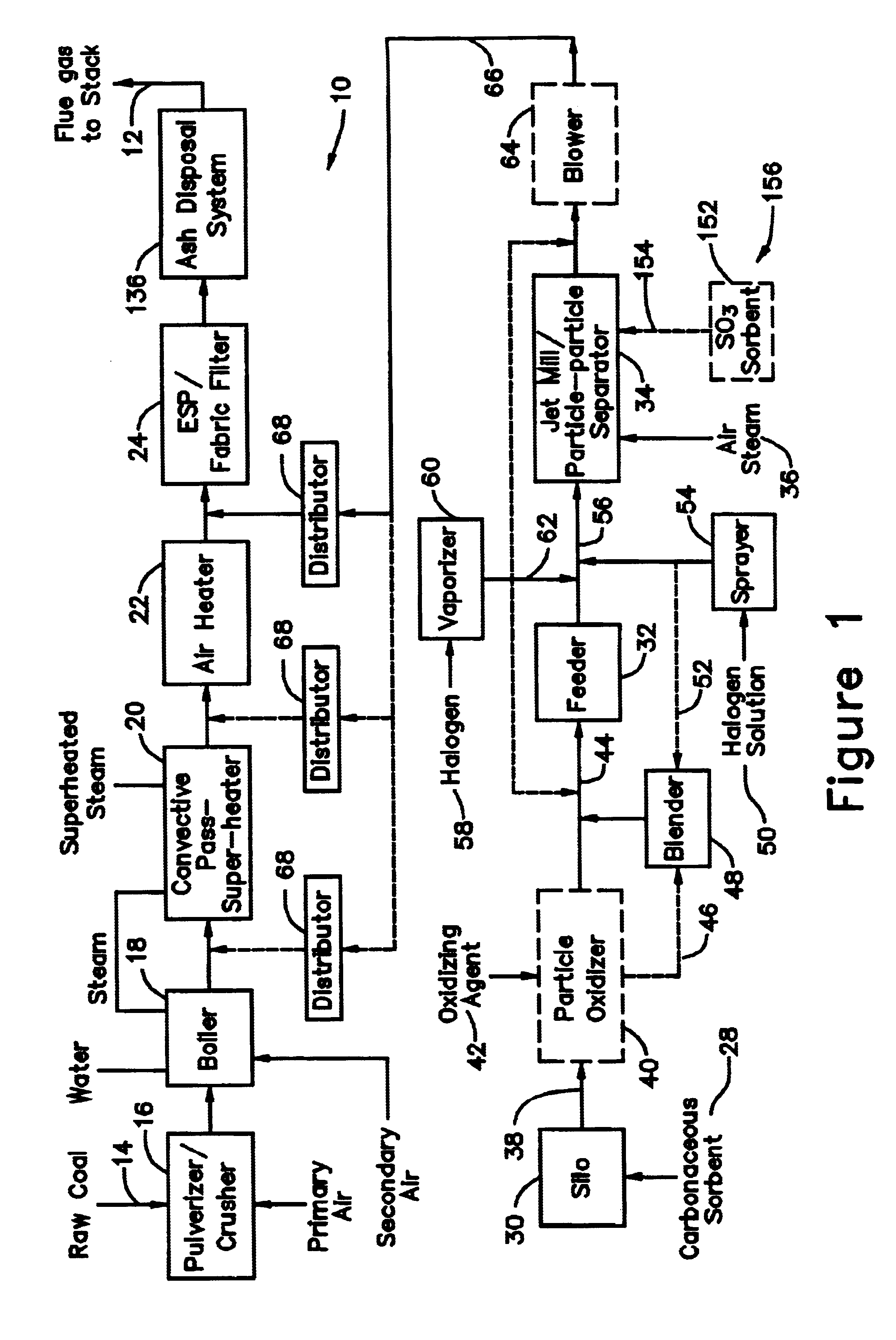
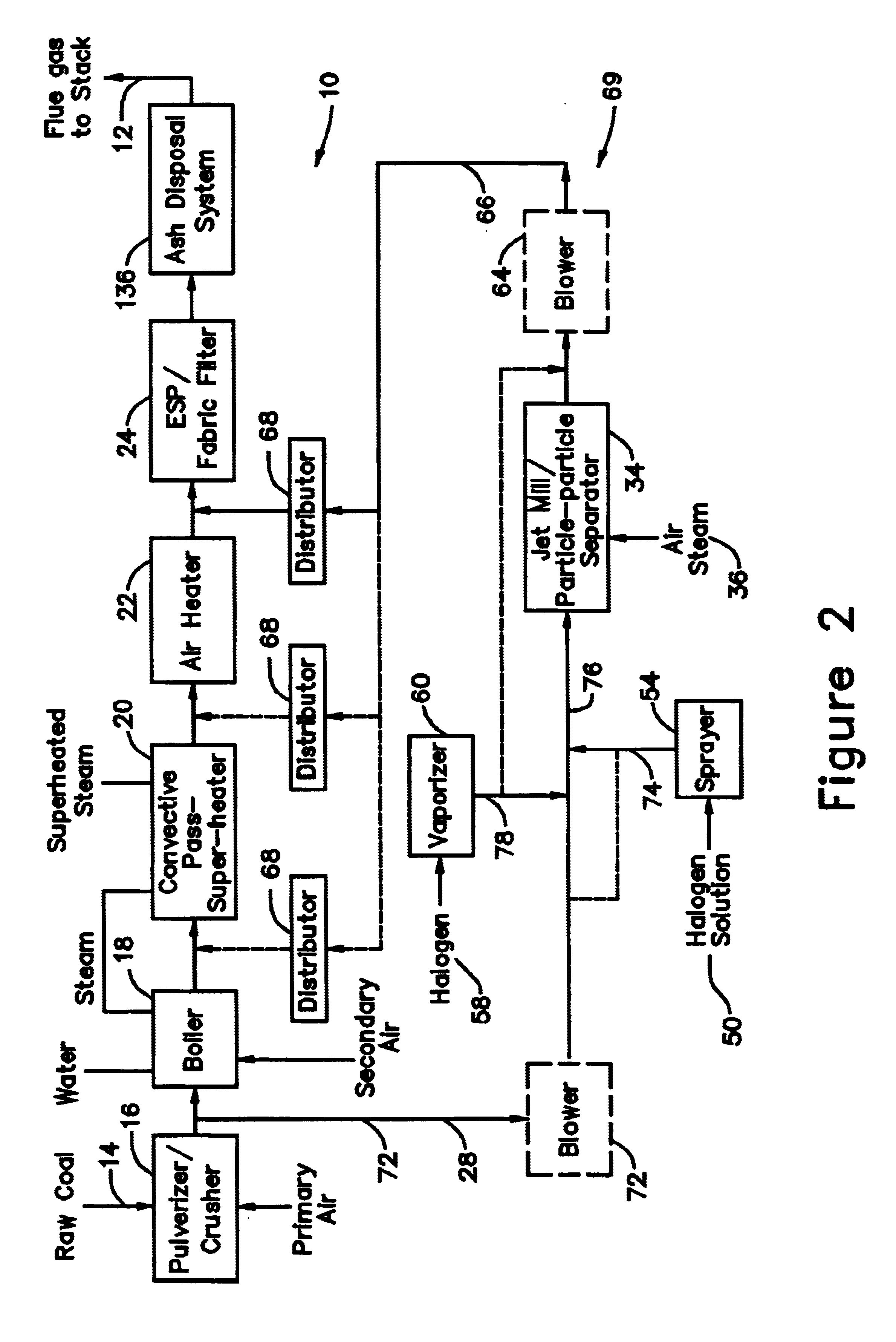
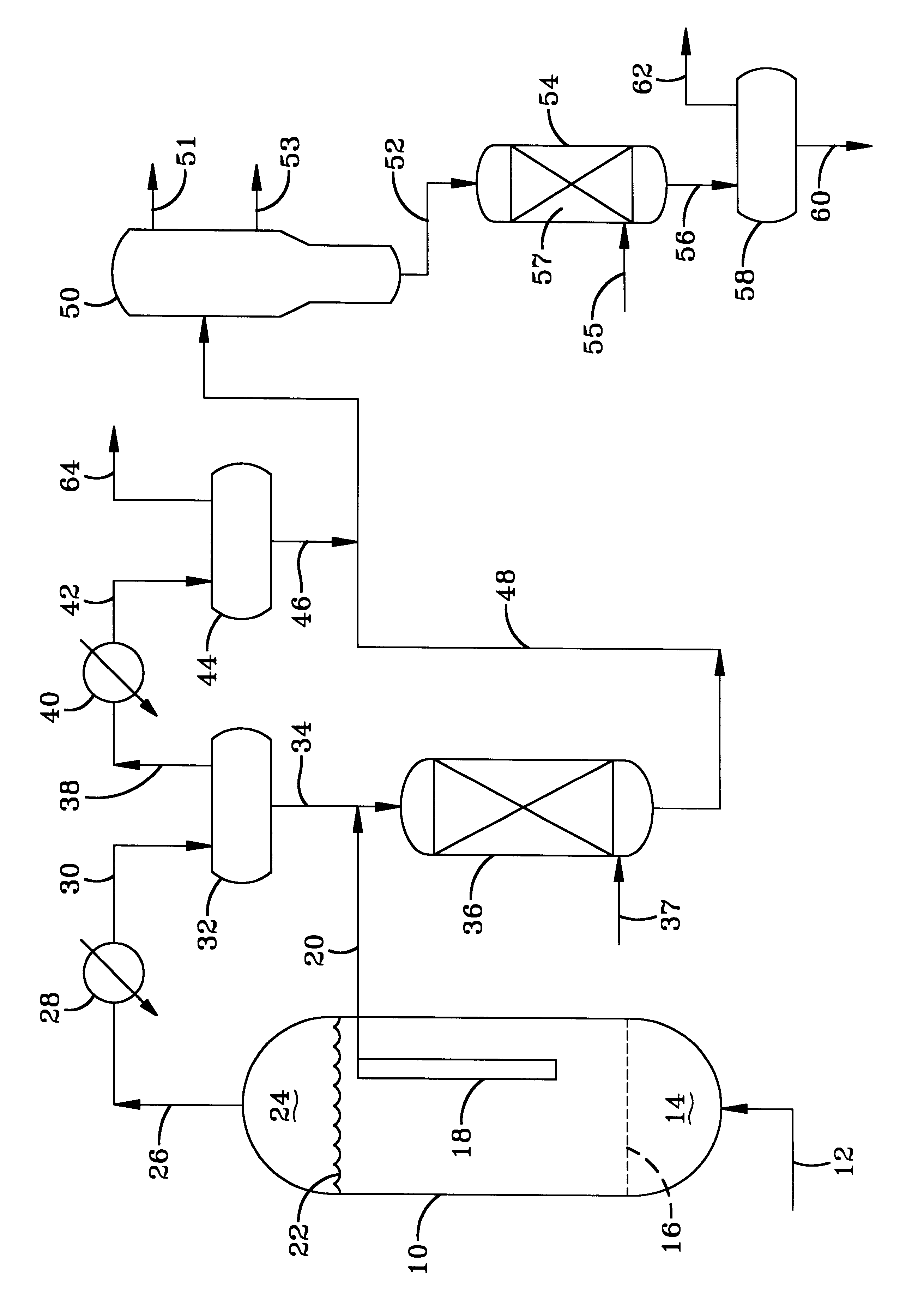
A system 26 for removing elemental mercury or mercury compounds handles carbonaceous sorbent 28 of a starter batch stored in a silo 30 in an agglomerated state. The sorbent 28 is fed by a feeder 32 to a separation device 34, which comminutes (if necessary) and de-agglomerates the sorbent particles 28 to their primary size distribution. This device 34 may be a particle-particle separator or a jet mill, where compressed air or high-pressure steam is the energy source. The de-agglomerated sorbent 28 of a contact batch created from the starter batch is conveyed by an airsteam for injection at a contact location 66 in a flue gas duct whereat carbonaceous sorbent of the contact batch adsorbs mercury from the flue gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Systems and methods for carbon capture and sequestration and compositions derived therefrom
ActiveUS20090143211A1Promote formationCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesNitrogen compoundsInterior spaceProduct formation
A method of sequestering a greenhouse gas is described, which comprises: (i) providing a solution carrying a first reagent that is capable of reacting with a greenhouse gas; (ii) contacting the solution with a greenhouse gas under conditions that promote a reaction between the at least first reagent and the greenhouse gas to produce at least a first reactant; (iii) providing a porous matrix having interstitial spaces and comprising at least a second reactant; (iv) allowing a solution carrying the at least first reactant to infiltrate at least a substantial portion of the interstitial spaces of the porous matrix under conditions that promote a reaction between the at least first reactant and the at least second reactant to provide at least a first product; and (v) allowing the at least first product to form and fill at least a portion of the interior spaces of the porous matrix, thereby sequestering a greenhouse gas.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
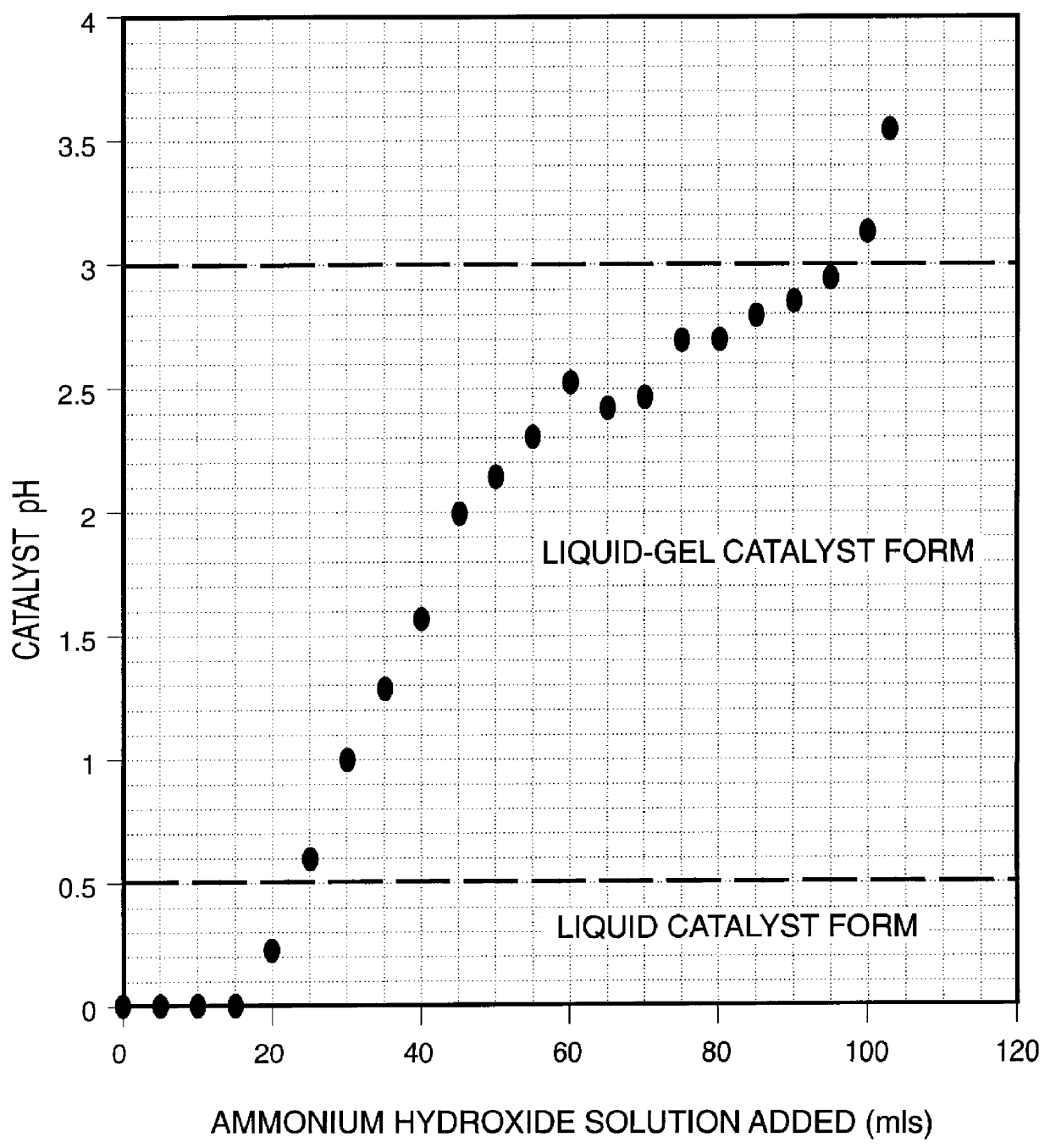
Iron-based ionic liquid catalysts for hydroprocessing carbonaceous feeds
InactiveUS6139723AIncrease hydrocracking ability of catalystIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid productIron salts
A highly dispersed iron-based ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst which may be anion-modified and metals-promoted has high catalytic activity, and is useful for hydrocracking / hydrogenation reactions for carbonaceous feed materials. The catalyst is produced by aqueous precipitation from saturated iron salt solutions such as ferric sulfate and ferric alum, and may be modified during preparation with anionic sulfate (SO42-) and promoted with small percentages of at least one active metal such as cobalt, molybdenum, palladium, platinum, nickel, or tungsten or mixtures thereof. The resulting catalyst may be used in a preferred ionic liquid form or in a liquid-gel form, and either fluidic form can be easily mixed and reacted with carbonaceous feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, mixed plastic waste, or mixtures thereof. The invention includes methods for making the ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst, and processes for using the fluidic catalysts for hydroprocessing the carbonaceous feed materials to produce desirable low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
Process for producing bio-derived fuel with alkyl ester and iso-paraffin components
InactiveUS20080163543A1Improve low temperature performanceImprove the lubrication effectBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlkaneParaffin oils
A process for producing a diesel fuel of biological origin. The process includes a biological component to be trans-esterified into a fatty acid alkyl ester. A fraction of the fatty acid alkyl ester is hydrodeoxygenated and hydroisomerized to produce an iso-paraffinic hydrocarbon. The fatty acid alkyl ester and the iso-paraffin components are combined into a middle distillate product suitable for direct use as diesel or jet fuel.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
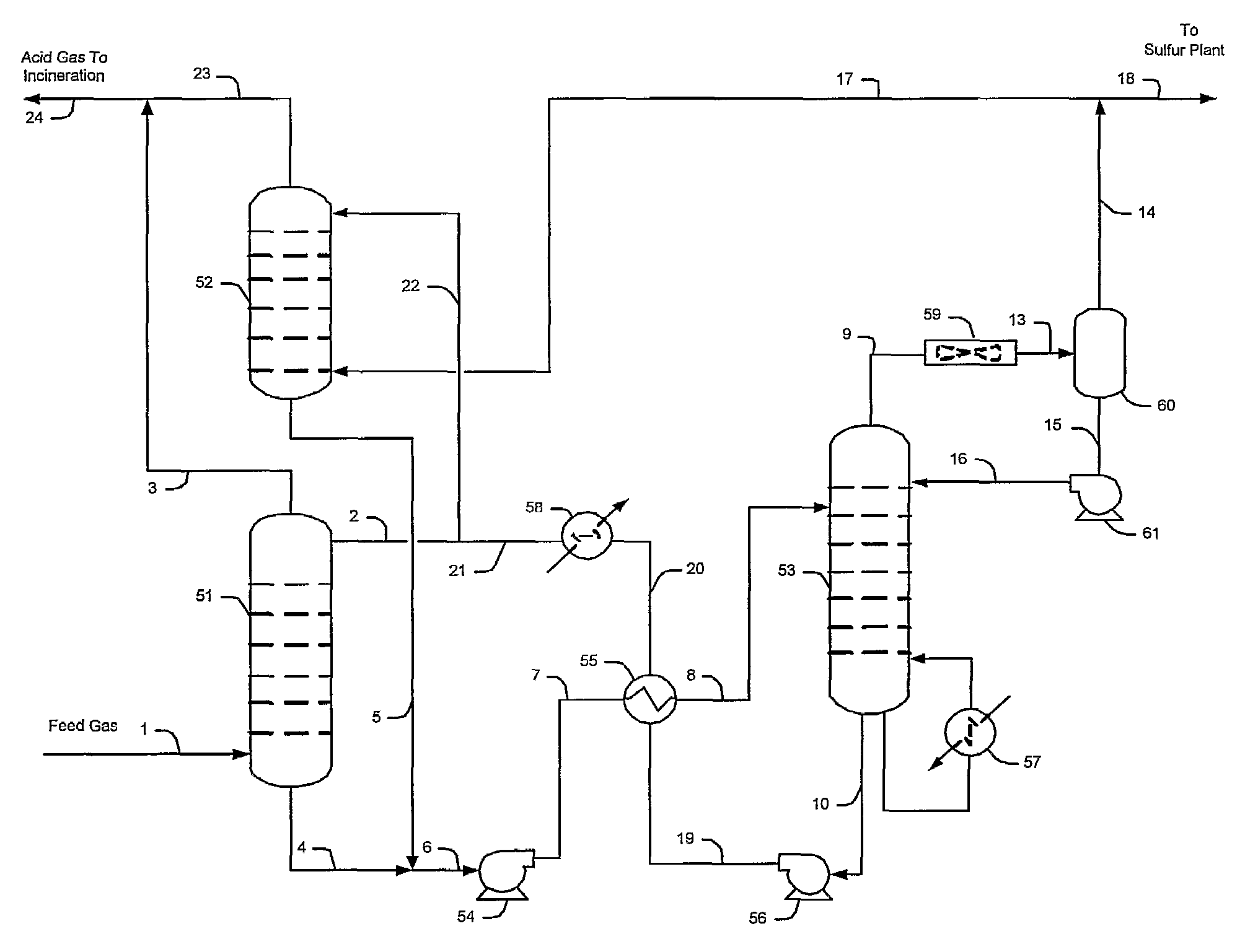
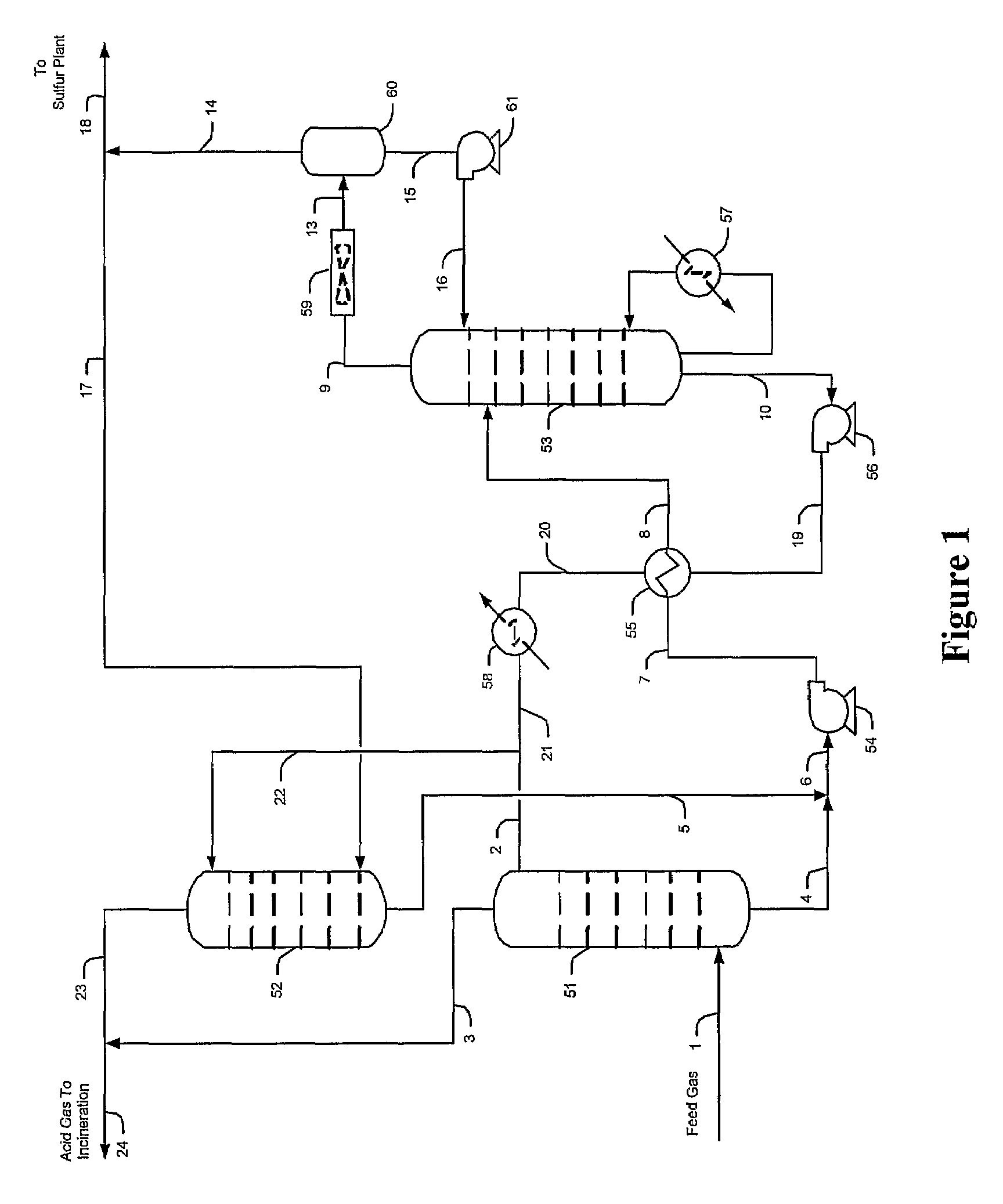
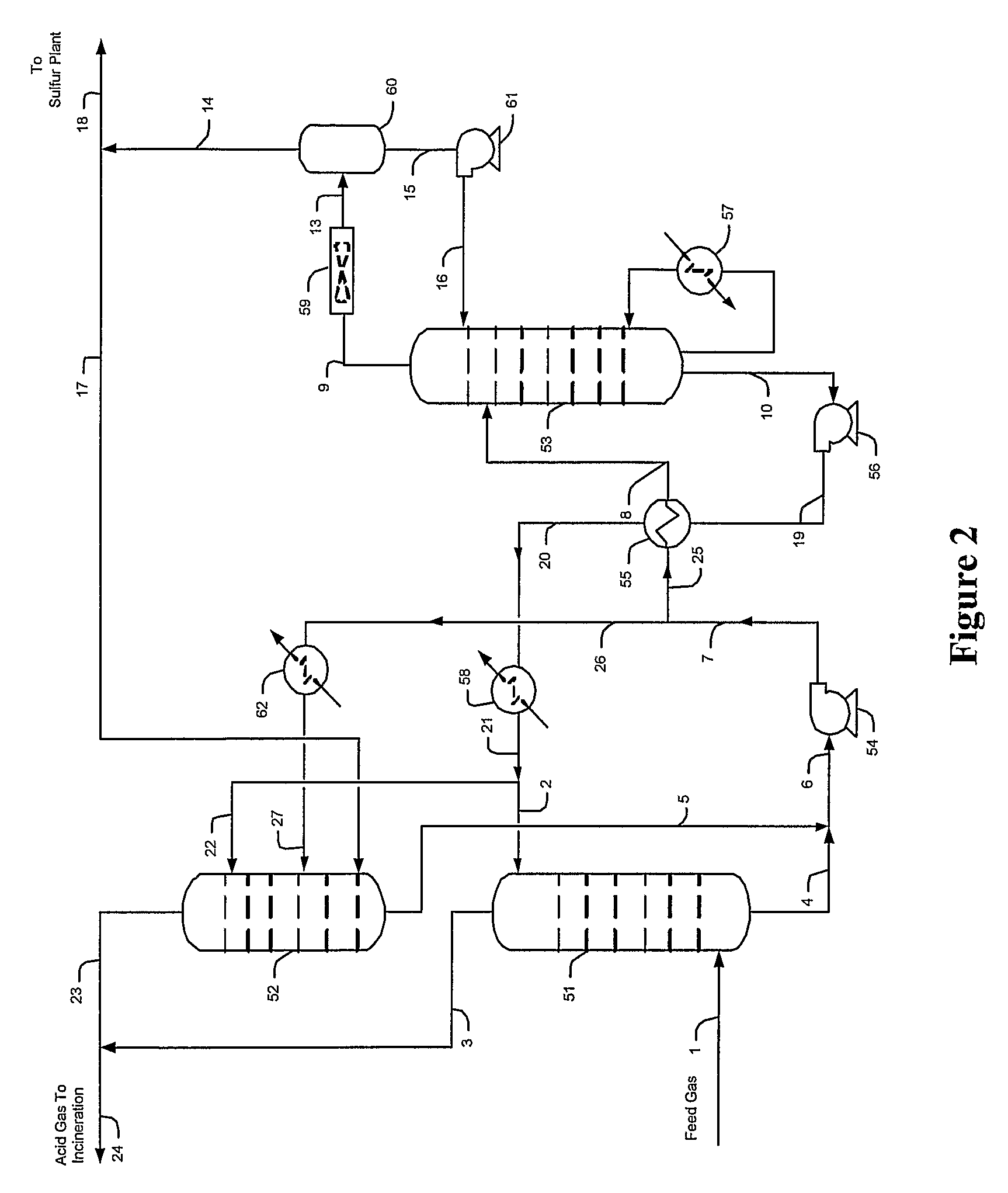
Methods and configurations for acid gas enrichment
ActiveUS7635408B2Increase the concentration of hydrogen sulfideSmall sizeGas treatmentCarbon compoundsSolventCarbon dioxide
Hydrogen sulfide is selectively enriched from an acid gas (1) that comprises relatively large quantities of carbon dioxide using a configuration in which a portion of an isolated hydrogen sulfide stream is introduced into an absorber (51) operating as a carbon dioxide rejecter. The resulting concentrated hydrogen sulfide enriched solvent (4) is then further used (directly or indirectly) to absorb hydrogen sulfide from an acid feed gas.
Owner:FLUOR ENTERPRISES
Isoparaffinic base stocks by dewaxing fischer-tropsch wax hydroisomerate over Pt/H-mordenite
A high VI and low pour point lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing a high purity, waxy, paraffinic Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction having an initial boiling point in the range of 650-750° F., followed by catalytically dewaxing the hydroisomerate using a dewaxing catalyst comprising a catalytic platinum component and an H-mordenite component. The hydrocarbon fraction is preferably synthesized by a slurry Fischer-Tropsch using a catalyst containing a catalytic cobalt component. This combination of the process, high purity, waxy paraffinic feed and the Pt / H-mordenite dewaxing catalyst, produce a relatively high yield of premium lubricant base stock.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for converting triglycerides to hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20070175795A1High reaction yieldIncrease cetane numberBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBoiling pointHydrocotyle bowlesioides
Processes for the conversion of hydrocarbons boiling in the temperature range of from about 80° F. to about 1000° F. to diesel boiling range hydrocarbons, and processes for increasing the cetane number and amount of n-C17 hydrocarbon products in such processes. Diesel boiling range hydrocarbons may be produced by contacting a hydrocarbon boiling in the above-mentioned boiling range with a triglyceride-containing compound to form a mixture, and then contacting the mixture with a hydrotreating catalyst under suitable reaction conditions.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
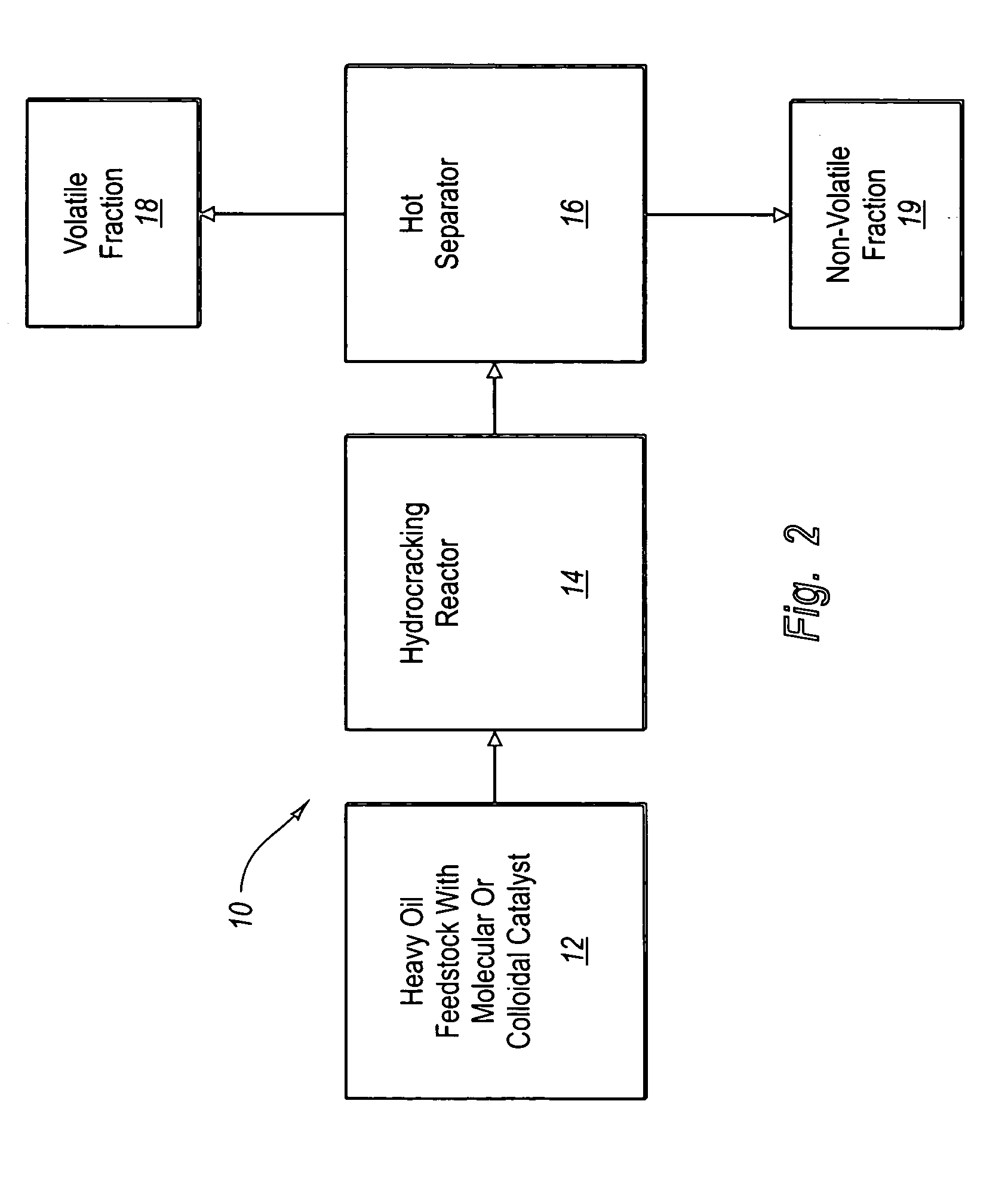
Hydroprocessing method and system for upgrading heavy oil using a colloidal or molecular catalyst
ActiveUS20050241993A1Inhibits eliminates formationEasy to useCatalyst regeneration/reactivationCatalyst activation/preparationColloidFuel oil
Methods and systems for hydroprocessing heavy oil feedstocks to form an upgraded material involve the use of a colloidal or molecular catalyst dispersed within a heavy oil feedstock, a hydrocracking reactor, and a hot separator. The colloidal or molecular catalyst promotes hydrocracking and other hydroprocessing reactions within the hydrocracking reactor. The catalyst is preferentially associated with asphaltenes within the heavy oil feedstock, which promotes upgrading reactions involving the asphaltenes rather than formation of coke precursors and sediment. The colloidal or molecular catalyst overcomes problems associated with porous supported catalysts in upgrading heavy oil feedstocks, particularly the inability of such catalysts to effectively process asphaltene molecules. The result is one or more of reduced equipment fouling, increased conversion level, and more efficient use of the supported catalyst if used in combination with the colloidal or molecular catalyst.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION LLC
Methods for producing a total product in the presence of sulfur
Methods of producing a total product are described. A method includes continuously contacting a feed with a hydrogen source in the presence of one or more inorganic salt catalysts and steam to produce a total product, wherein the feed has at least 0.02 grams of sulfur, per gram of feed; and producing a total product that includes coke and the crude product. The crude product has a sulfur content of at most 90% of the sulfur content of the feed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Systems and methods of producing a crude product
Contact of a crude feed with one or more catalysts produces a total product that includes a crude product. The crude feed has a residue content of at least 0.2 grams of residue per gram of crude feed. At least a portion of the crude product may be produced as a vapor. The crude product is a liquid mixture at 25° C. and 0.101 MPa. One or more properties of the crude product may be changed by at least 10% relative to the respective properties of the crude feed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Wide-cut synthetic isoparaffinic lubricating oils
A wide-cut lubricant base stock is made by hydroisomerizing and then catalytically dewaxing a waxy Fischer-Tropsch synthesized hydrocarbon fraction feed and comprises the entire dewaxate having an initial boiling point in the 650-75O° F.+ range. Formulated lubricating oils made by admixing the base stock with a commercial automotive additive package meet all specifications, including low temperature properties, for multigrade internal combustion engine crankcase oils. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the 650-750° F. range and continuously boils to an end point of at least 1050° F.+. Lower boiling hydrocarbons produced by the process are separated from the base stock by simple flash distillation. The base stock comprises the entire dewaxate having an initial boiling point in the 650-750° F. range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for the removal of nitrogen compounds from a fluid stream
ActiveUS7205448B2Increase capacityReduce accumulationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsMolecular sieveNitrite
At lower temperatures an acidic molecular sieve adsorbent preferentially adsorbs water and basic organic nitrogen compounds over weakly basic organic nitrogen compounds such as nitrites. Elevated temperatures improve the capacity of acidic molecular sieve adsorbents to adsorb nitrites in the presence of water.
Owner:UOP LLC
Process for converting triglycerides to hydrocarbons
ActiveUS7550634B2High reaction yieldIncrease cetane numberBiofuelsSolid fuelsBoiling pointTG - Triglyceride
Processes for the conversion of hydrocarbons boiling in the temperature range of from about 80° F. to about 1000° F. to diesel boiling range hydrocarbons, and processes for increasing the cetane number and amount of n-C17 hydrocarbon products in such processes. Diesel boiling range hydrocarbons may be produced by contacting a hydrocarbon boiling in the above-mentioned boiling range with a triglyceride-containing compound to form a mixture, and then contacting the mixture with a hydrotreating catalyst under suitable reaction conditions.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
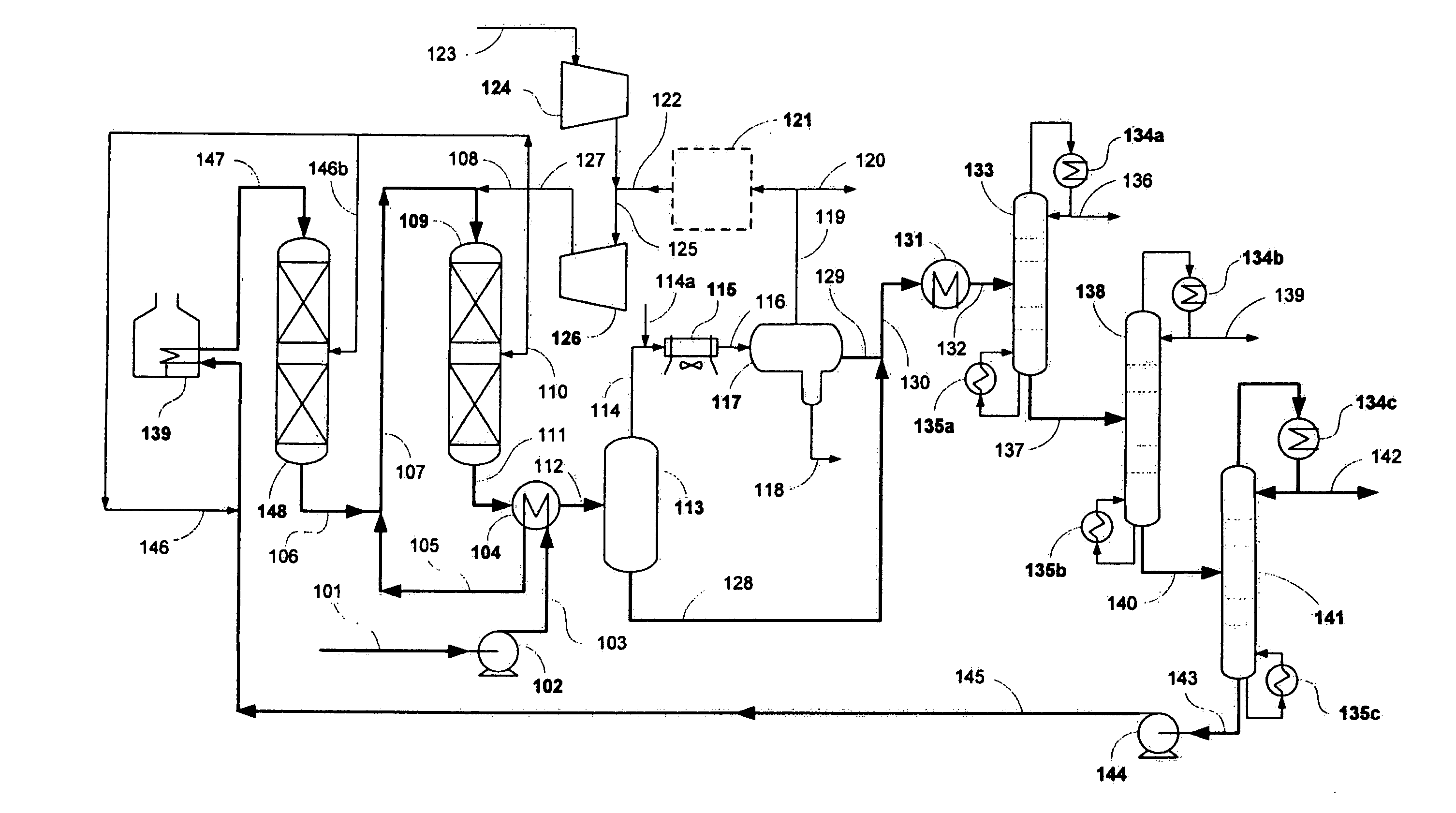
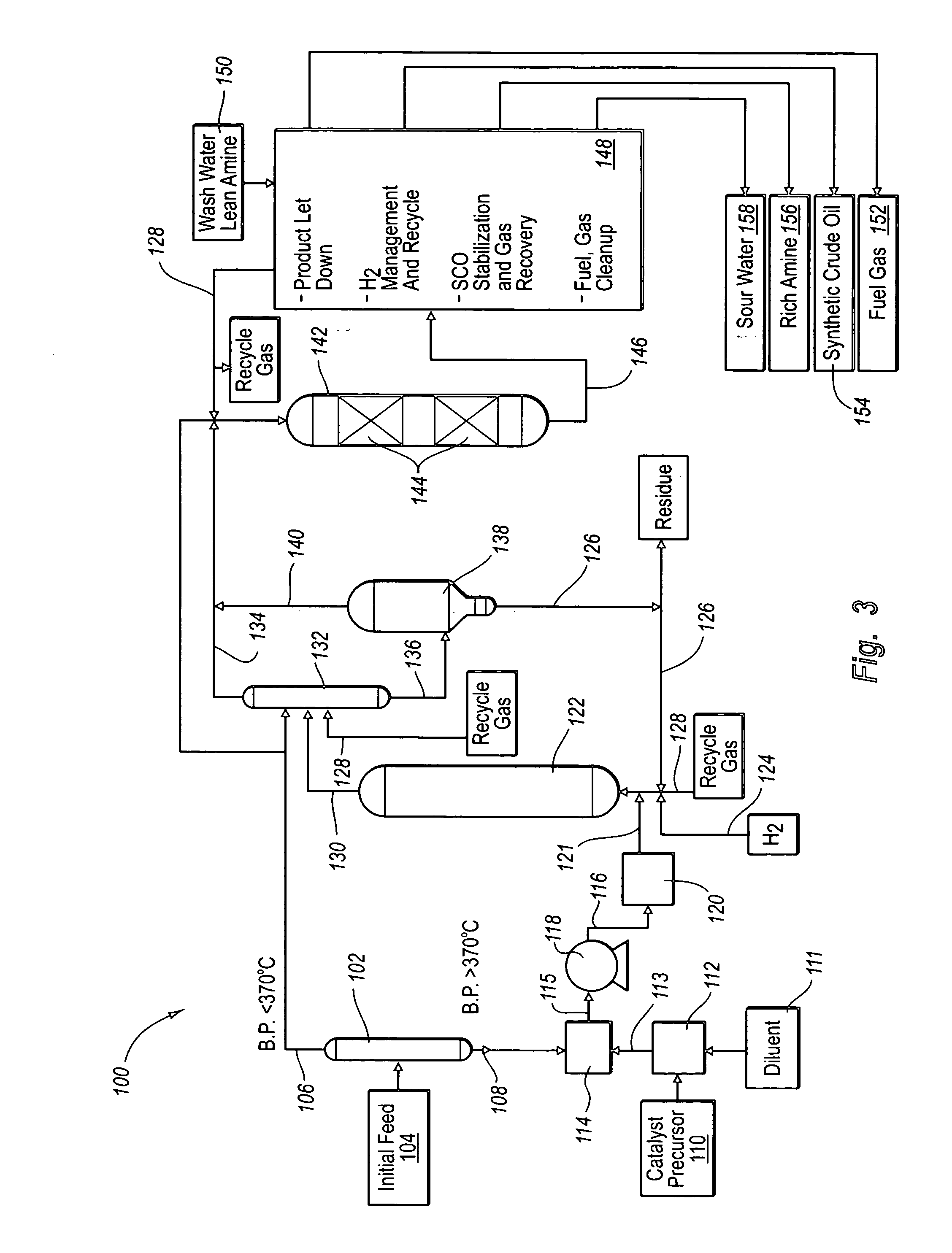
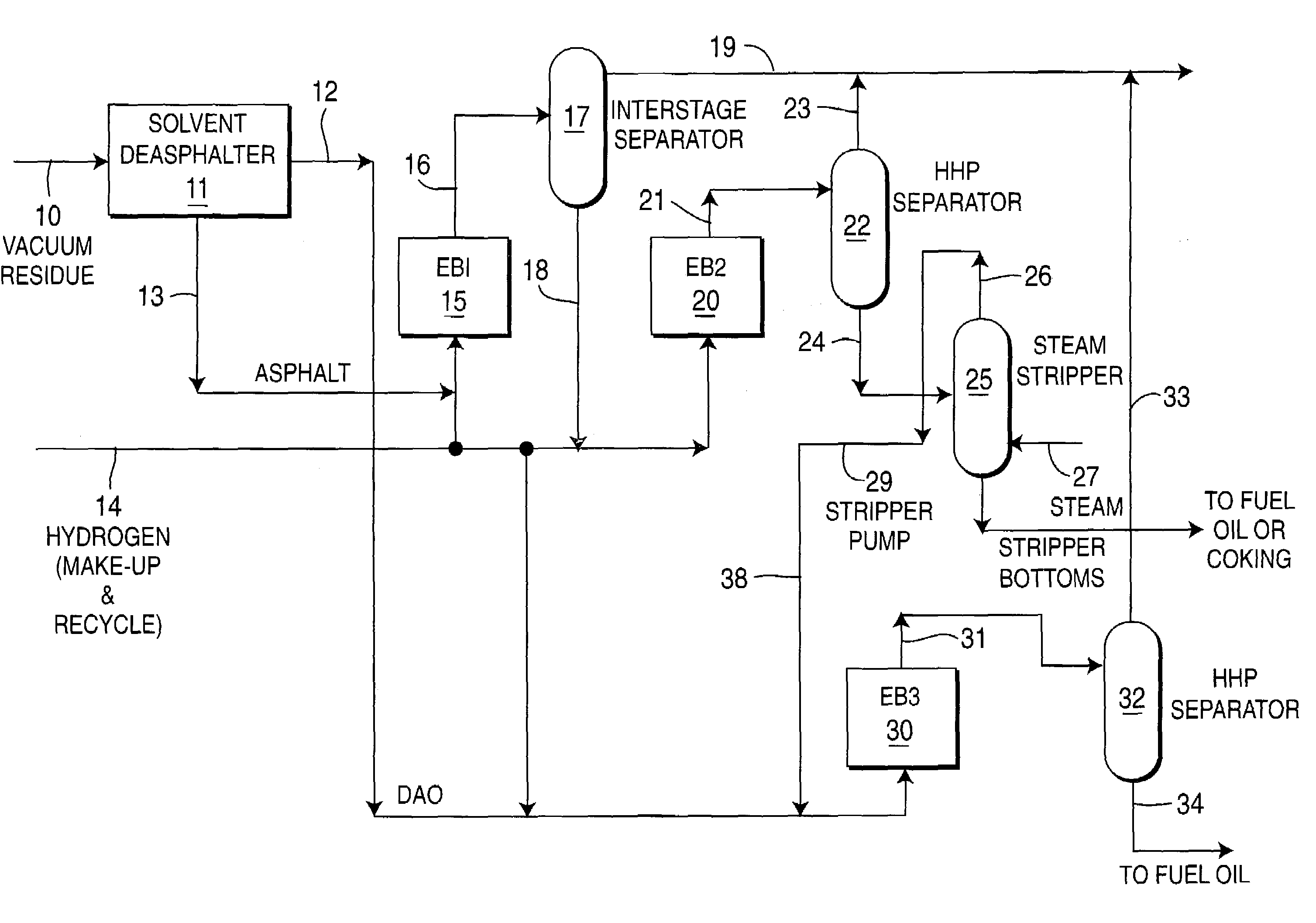
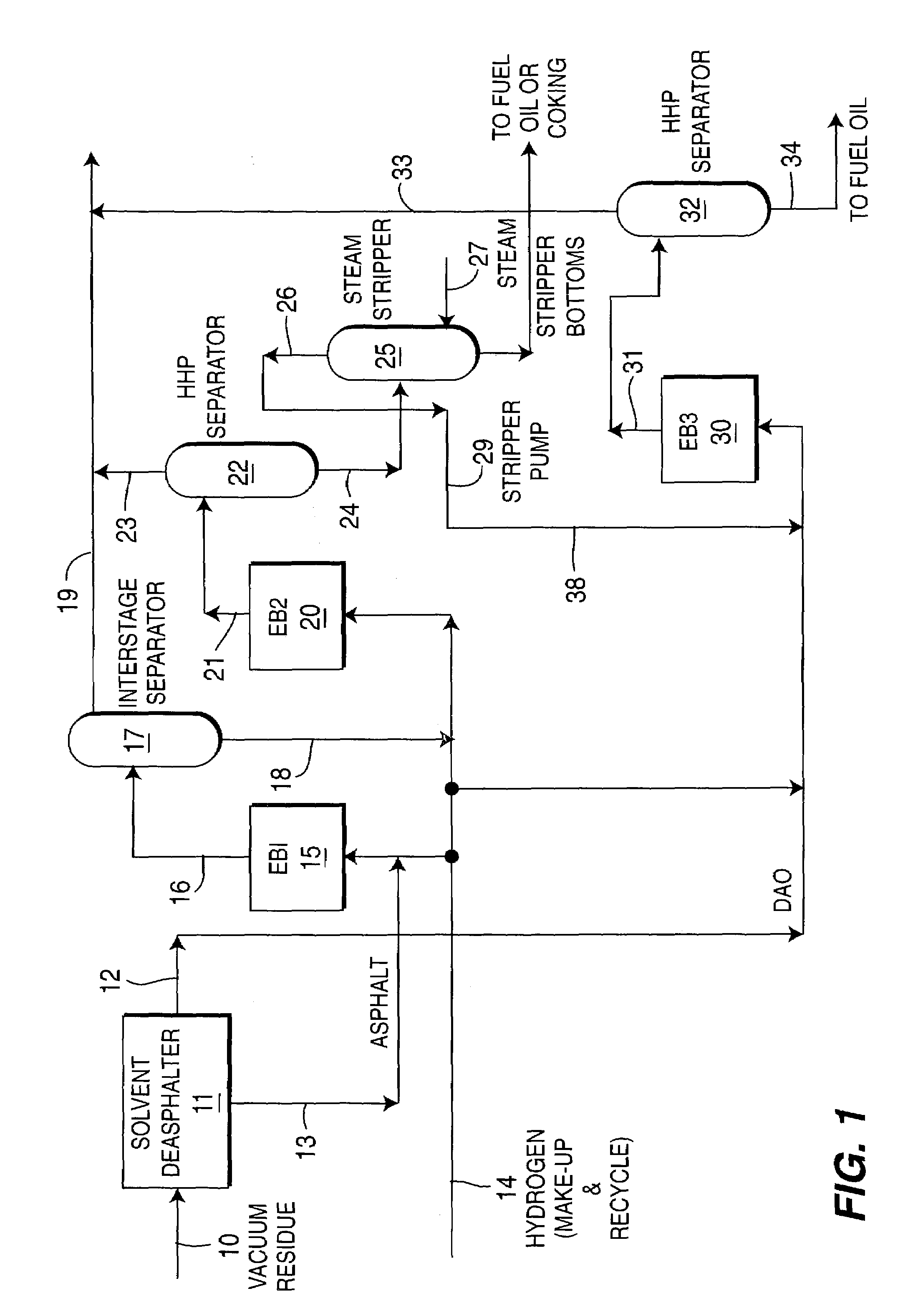
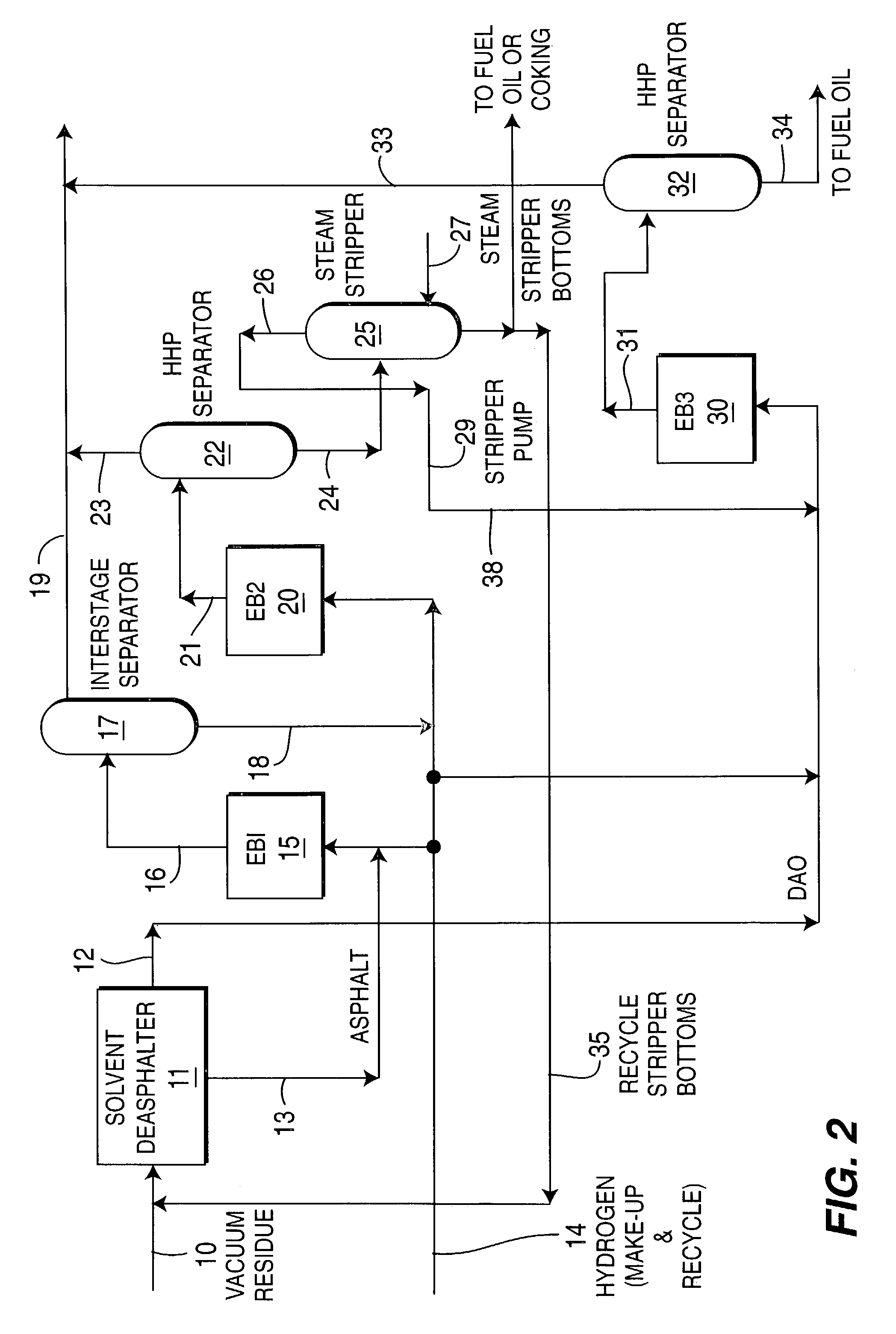
Effective integration of solvent deasphalting and ebullated-bed processing
InactiveUS7214308B2Reduced light gas yieldImprove hydrogen efficiencyTreatment with plural parallel cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural parallel stages onlyReactor systemHeavy crude oil
This invention relates to a novel method for economically processing vacuum residue from heavy crude oils by selectively processing the difficult and easy components in reactors whose design and operating conditions are optimized for the specific feed. The process utilizes an integrated solvent deasphalting (SDA) / ebullated-bed design wherein the heavy vacuum residue feedstock is initially sent to an SDA unit operated with C4 / C5 solvent to achieve a high deasphalted oil (DAO) yield. The resulting SDA products, namely asphaltenes and DAO are separately treated in ebullated-bed reactor(s) systems whose design and operating conditions are optimized for a particular feedstock. The resulting net conversion, associated distillate yield and product qualities are greatly improved relative to treatment of the entire residue feedstock in a common ebullated-bed reactor system.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Polyalphaolefin & fischer-tropsch derived lubricant base oil lubricant blends
InactiveUS20060199743A1Increase frictionImproved wear propertyTreatment with hydrotreatment processesAdditivesBase oilViscosity
Blended lubricant base oils and blended finished lubricants comprising ≧70 weight percent Fischer-Tropsch derived lubricant base oils comprising ≧6 weight % molecules with monocycloparaffinic functionality and less than 0.05 weight % molecules with aromatic functionality; at least one polyalphaolefin lubricant base oil with a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. greater than about 30 cSt and less than 150 cSt are provided. These blended lubricant base oils and blended finished lubricants exhibit superior friction and wear properties, in addition to other highly desired properties. Also provided are processes for making these blended lubricant base oils and blended finished lubricants.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process to produce biofuels from biomass
Biofuels can be produced by: (i) providing a biomass containing celluloses, hemicelluloses, lignin, nitrogen compounds and sulfur compounds; (ii) removing sulfur compounds and nitrogen compounds from the biomass by contacting the biomass with a digestive solvent to form a pretreated biomass containing carbohydrates and having less than 35% of the sulfur content and less than 35% of the nitrogen content of untreated biomass on a dry mass basis; (iii) contacting the pretreated biomass directly with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenolysis catalyst to form a plurality of oxygenated intermediates, and (vi) processing at least a portion of the oxygenated intermediates to form a liquid fuel.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Functionalized ionic liquids, and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to ionic liquids comprising a pendant Bronsted-acidic group, e.g., a sulfonic acid group. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of an ionic liquid comprising a pendant Bronsted-acidic group to catalyze a Bronsted-acid-catalyzed chemical reaction. A third aspect of the present invention relates to ionic liquids comprising a pendant nucleophilic group, e.g., an amine. Still another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of an ionic liquid comprising a pendant nucleophilic group to catalyze a nucleophile-assisted chemical reaction. A fifth aspect of the present invention relates to the use of an ionic liquid comprising a pendant nucleophilic group to remove a gaseous impurity, e.g., carbon dioxide, from a gas, e.g., sour natural gas.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH ALABAMA
High activity ZSM-48 and methods for dewaxing
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for removing polar impurities from hydrocarbons and mixtures of hydrocarbons
InactiveUS7553406B2Improve efficiencyMild process conditionsOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationSolvent extractionHydrocotyle bowlesioidesIonic liquid
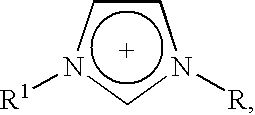
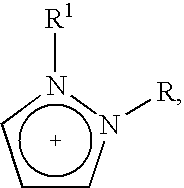
This invention relates to a process for removing polarizable impurities from hydrocarbons and mixtures of hydrocarbons using ionic liquids as an extraction medium. By way of extraction, the degree of contamination of the hydrocarbon or mixture of hydrocarbons is reduced to a low or very low level. The specific ionic liquids are compounds of the Formula 1, which are organic salts that are liquid or can be melted to form a liquid and that can form at least a biphasic mixture with a hydrocarbon. The process is suitable for purifying a wide range of hydrocarbons under a wide range of process conditions.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com