Patents
Literature
625results about "Indirect and direct heating destructive distillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
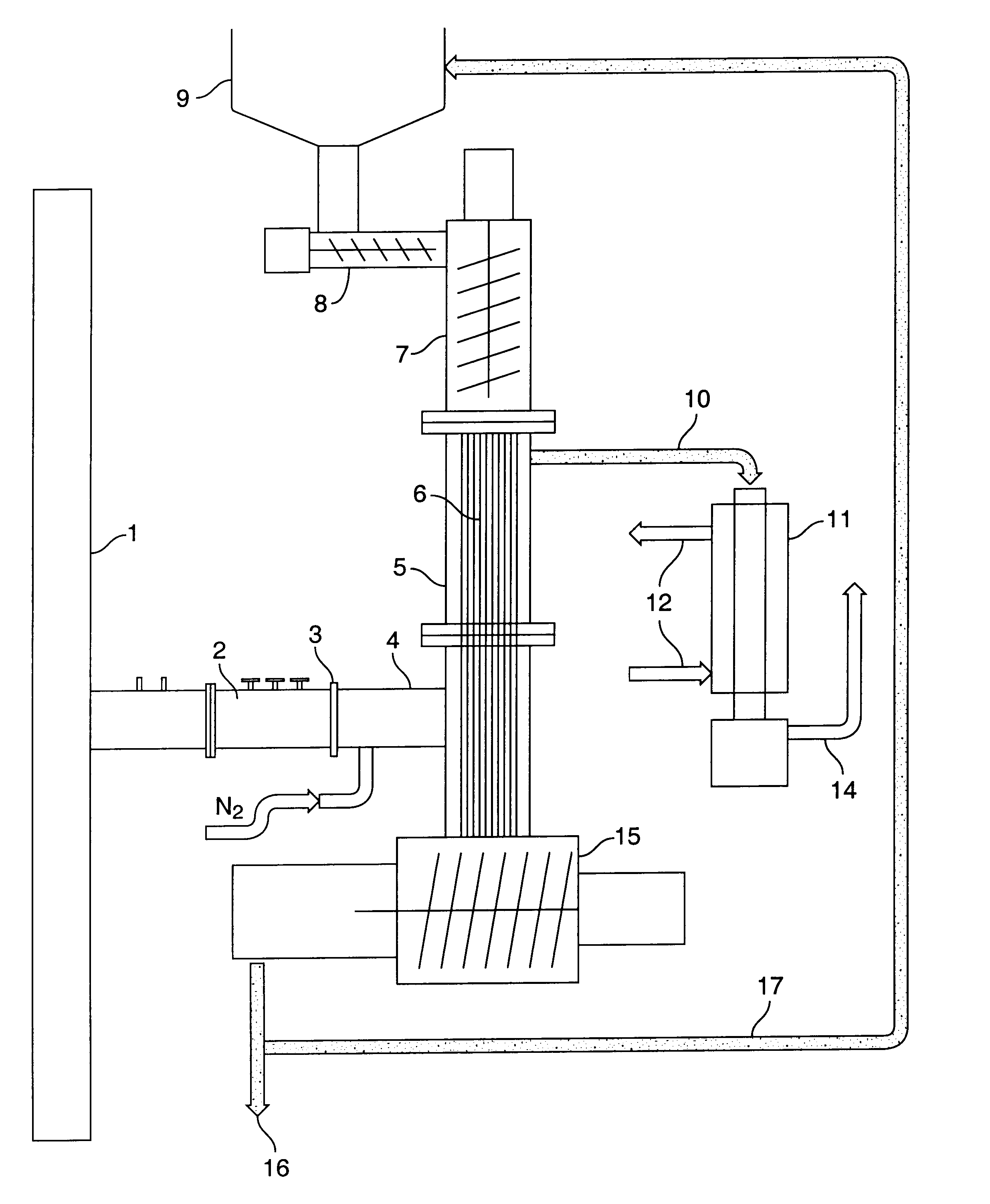
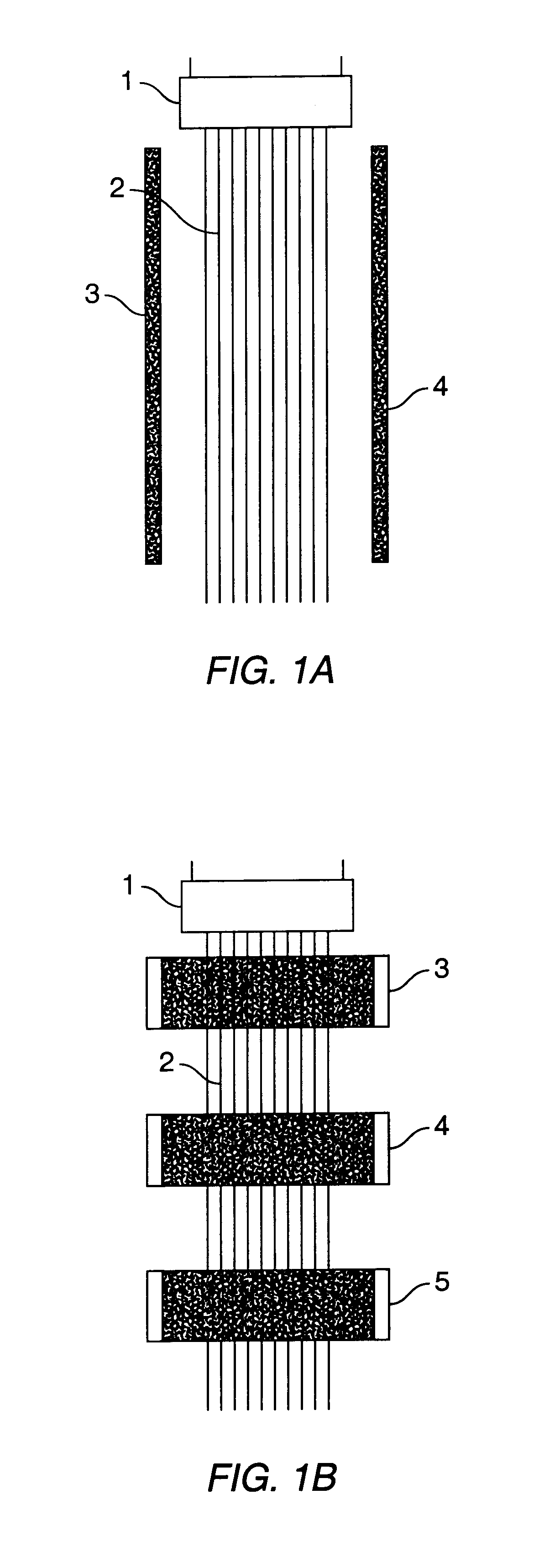
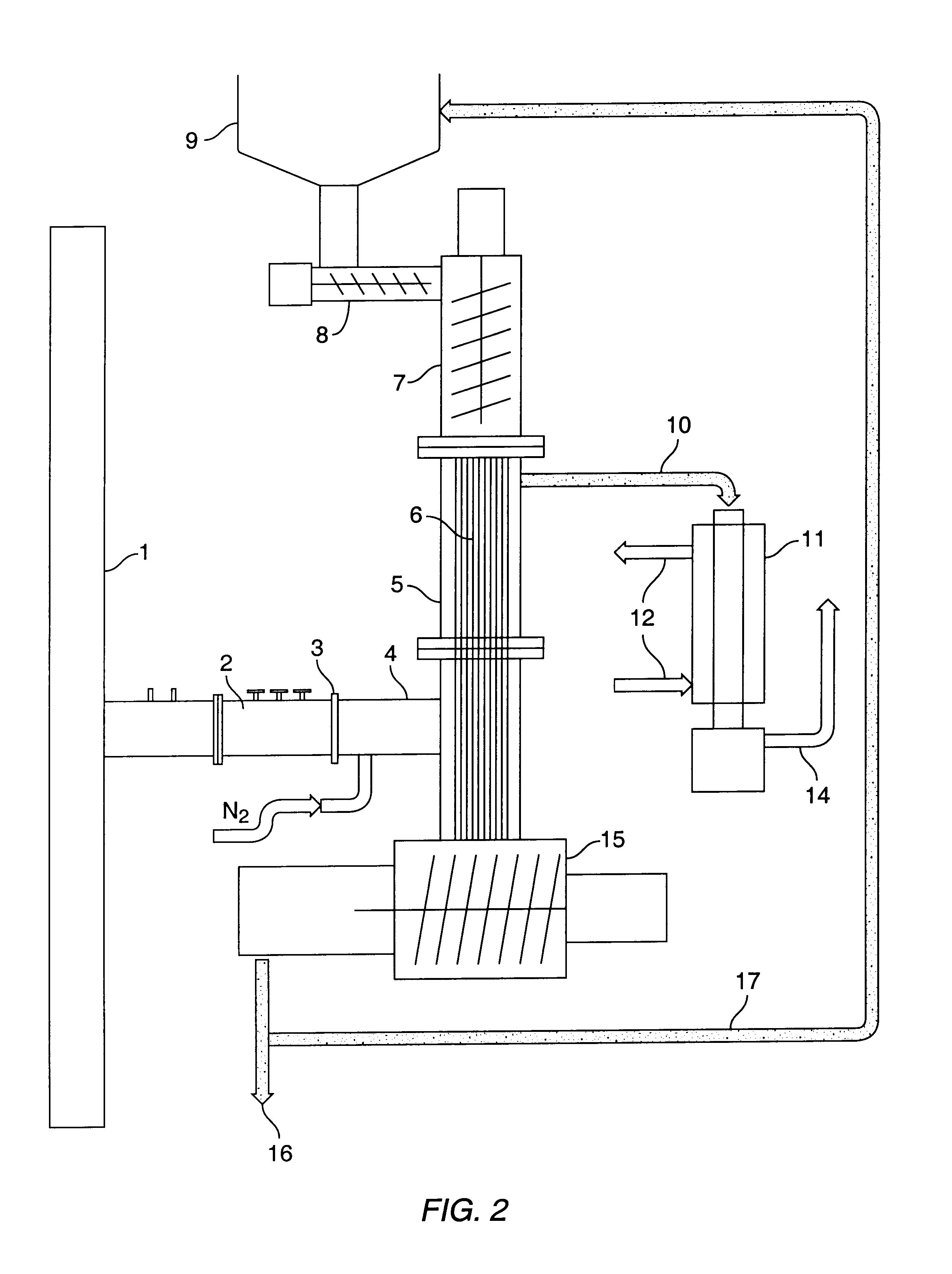
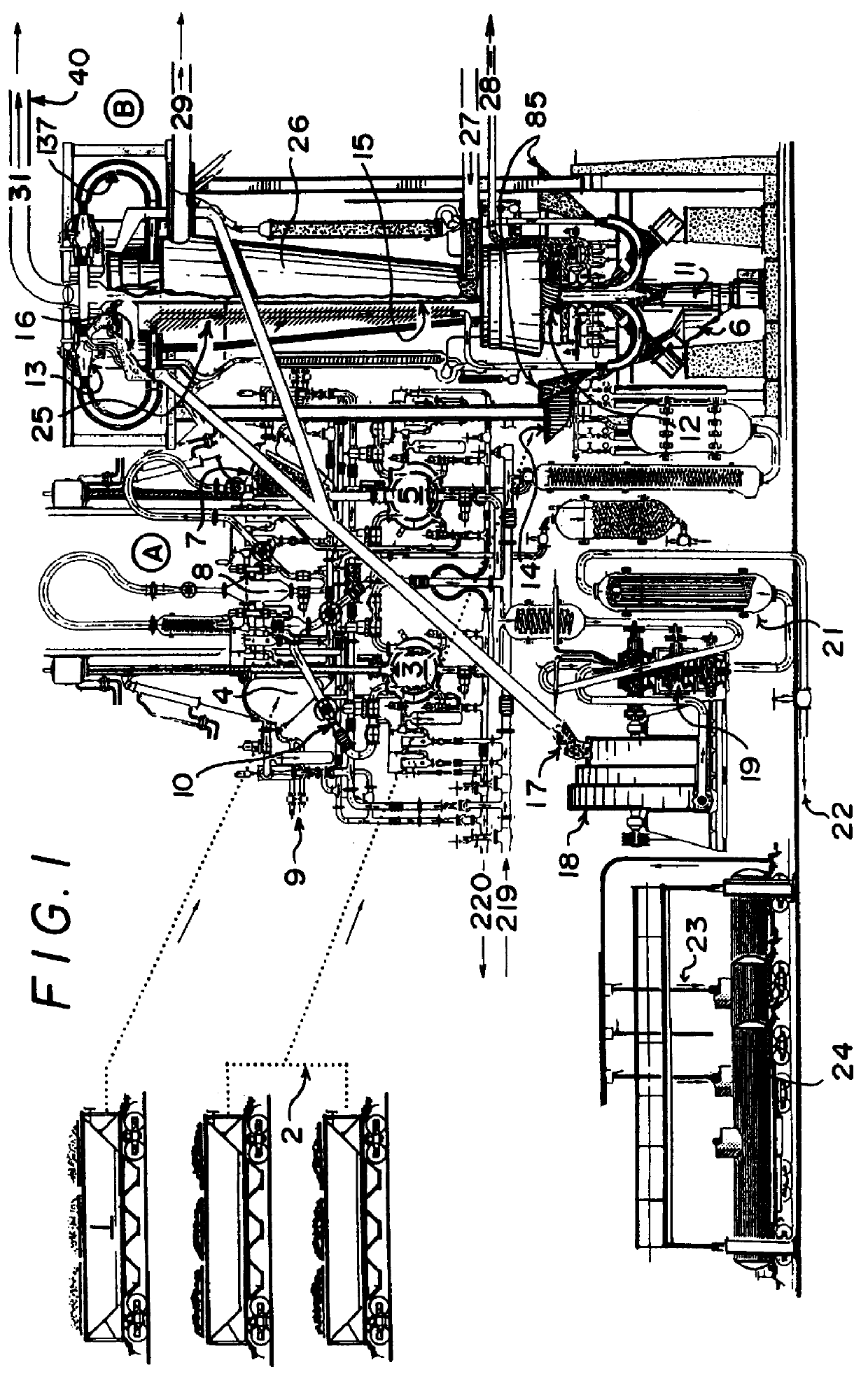
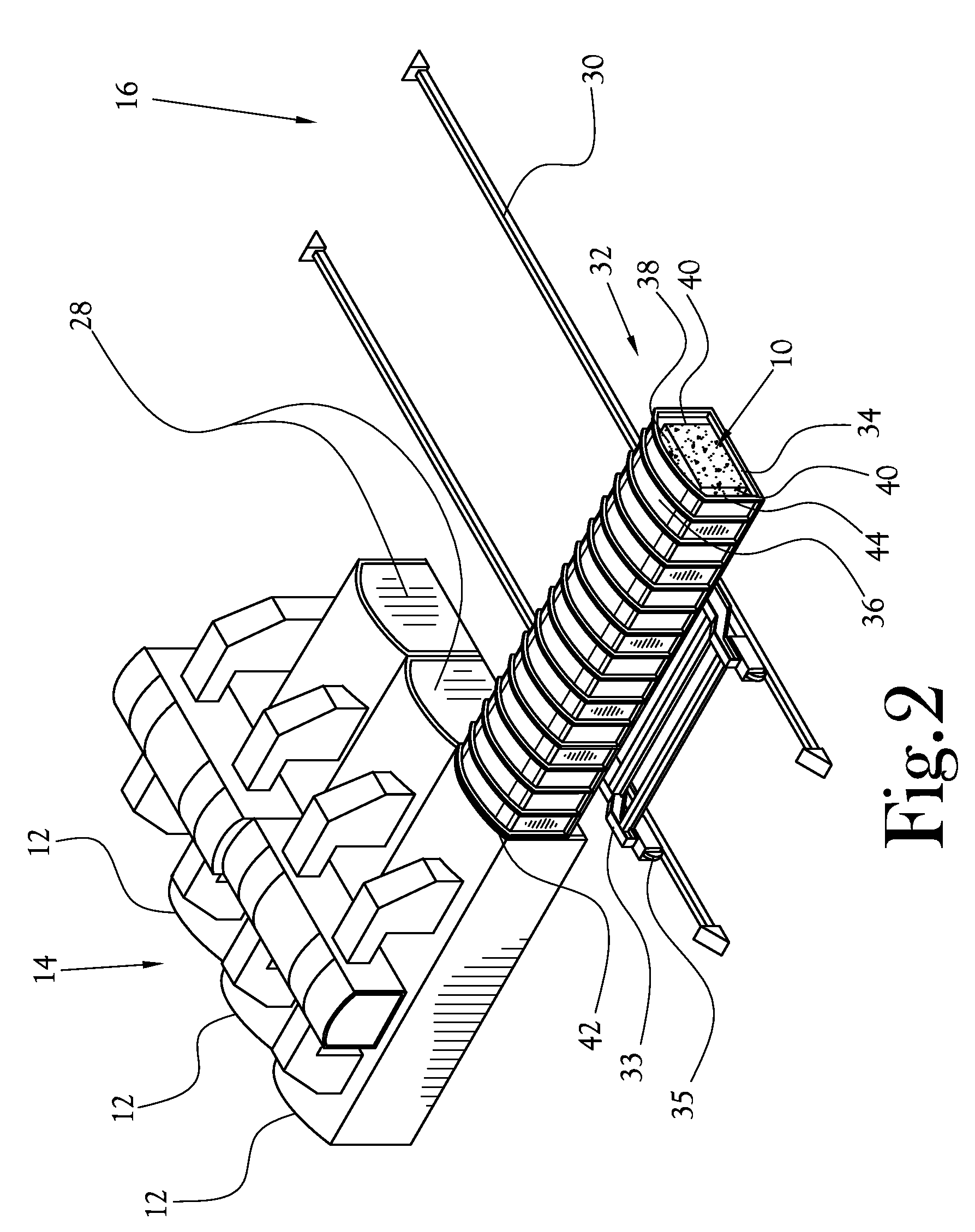
Process and reactor for microwave cracking of plastic materials
InactiveUS6184427B1Indirect and direct heating destructive distillationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionRadio frequency energyPlastic materials
A process of activated cracking of high molecular organic waste material which includes confining the organic waste material in a reactor space as a mixture with a pulverized electrically conducting material (sensitizer) and / or catalysts and / or "upgrading agents" and treating this mixture by microwave or radio frequency electro-magnetic radiation. Organic waste materials include hydrocarbons or their derivatives, polymers or plastic materials and shredded rubber. The shredded rubber can be the source of the sensitizer and / or catalyst material as it is rich in carbon and other metallic species. This sensitizer can also consist of pulverized coke or pyrolytically carbonized organic feedstock and / or highly dispersed metals and / or other inorganic materials with high dielectric loss which absorb microwave or radio frequency energy.
Owner:HIGHWAVE ACQUISITION
Apparatus for converting coal to hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6013158ALess producedLow costCombustible gas coke oven heatingDirect heating destructive distillationParticulatesSuspended particles
An apparatus for forming liquid hydrocarbons from solid coal. The coal is pulverized to provide a particulate coal feed, which is then extruded to provide a hollow tube of compressed coal supported inside of a support tube. A clay feed is extruded to provide a hollow tube of compressed clay supported inside of the coal tube and a combustible fuel is burned inside of the clay tube. The temperature of combustion is sufficient to fire the extruded clay and pyrolyze the extruded coal to produce hydrocarbon gases and coal char. The support tube has holes for releasing the hydrocarbon gases, which contain suspended particles formed during combustion. The suspended particles are removed from the hydrocarbon gases to provide clean gases, which are passed through an ionizing chamber to ionize at least a portion thereof. The ionized gases are then passed through a magnetic field to separate them from each other according to their molecular weight. Selected portions of at least some of the separated gases are mixed, and the mixed gases are cooled to provide at least one liquid hydrocarbon product of predetermined composition. Portions of the separated gases may also be mixed with the coal char and other input streams, such as waste plastics, and further treated to provide other hydrocarbon products.
Owner:WOOTTEN WILLIAM A
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
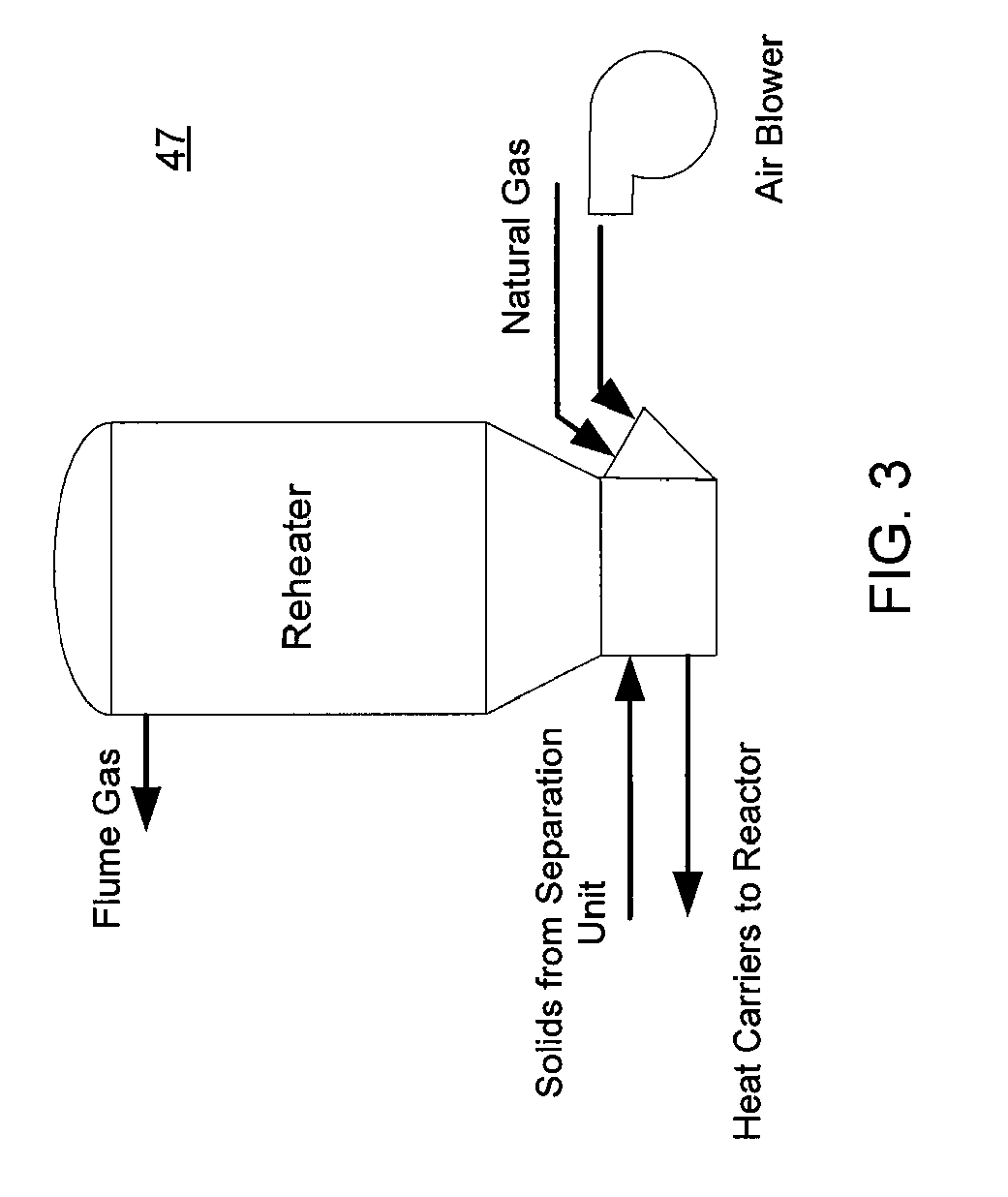
ActiveUS7905990B2Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingSolid waste disposalLiquid productHeat carrier
A rapid thermal conversion process for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. Biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. The liquid product may itself be used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Iron-based ionic liquid catalysts for hydroprocessing carbonaceous feeds
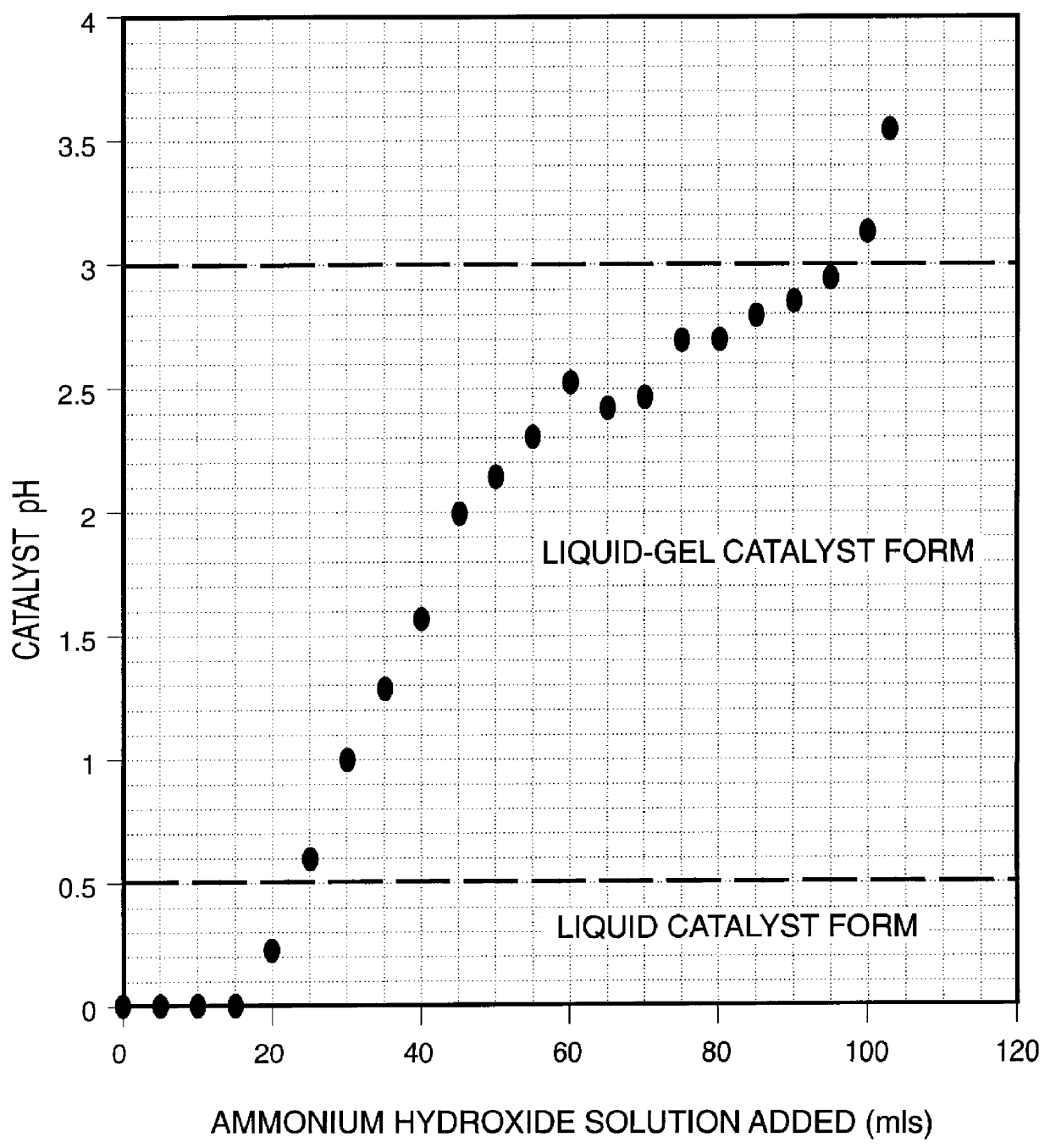
InactiveUS6139723AIncrease hydrocracking ability of catalystIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationCatalyst activation/preparationLiquid productIron salts
A highly dispersed iron-based ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst which may be anion-modified and metals-promoted has high catalytic activity, and is useful for hydrocracking / hydrogenation reactions for carbonaceous feed materials. The catalyst is produced by aqueous precipitation from saturated iron salt solutions such as ferric sulfate and ferric alum, and may be modified during preparation with anionic sulfate (SO42-) and promoted with small percentages of at least one active metal such as cobalt, molybdenum, palladium, platinum, nickel, or tungsten or mixtures thereof. The resulting catalyst may be used in a preferred ionic liquid form or in a liquid-gel form, and either fluidic form can be easily mixed and reacted with carbonaceous feed materials such as coal, heavy petroleum fractions, mixed plastic waste, or mixtures thereof. The invention includes methods for making the ionic liquid or liquid-gel catalyst, and processes for using the fluidic catalysts for hydroprocessing the carbonaceous feed materials to produce desirable low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid products.
Owner:HEADWATERS CTL
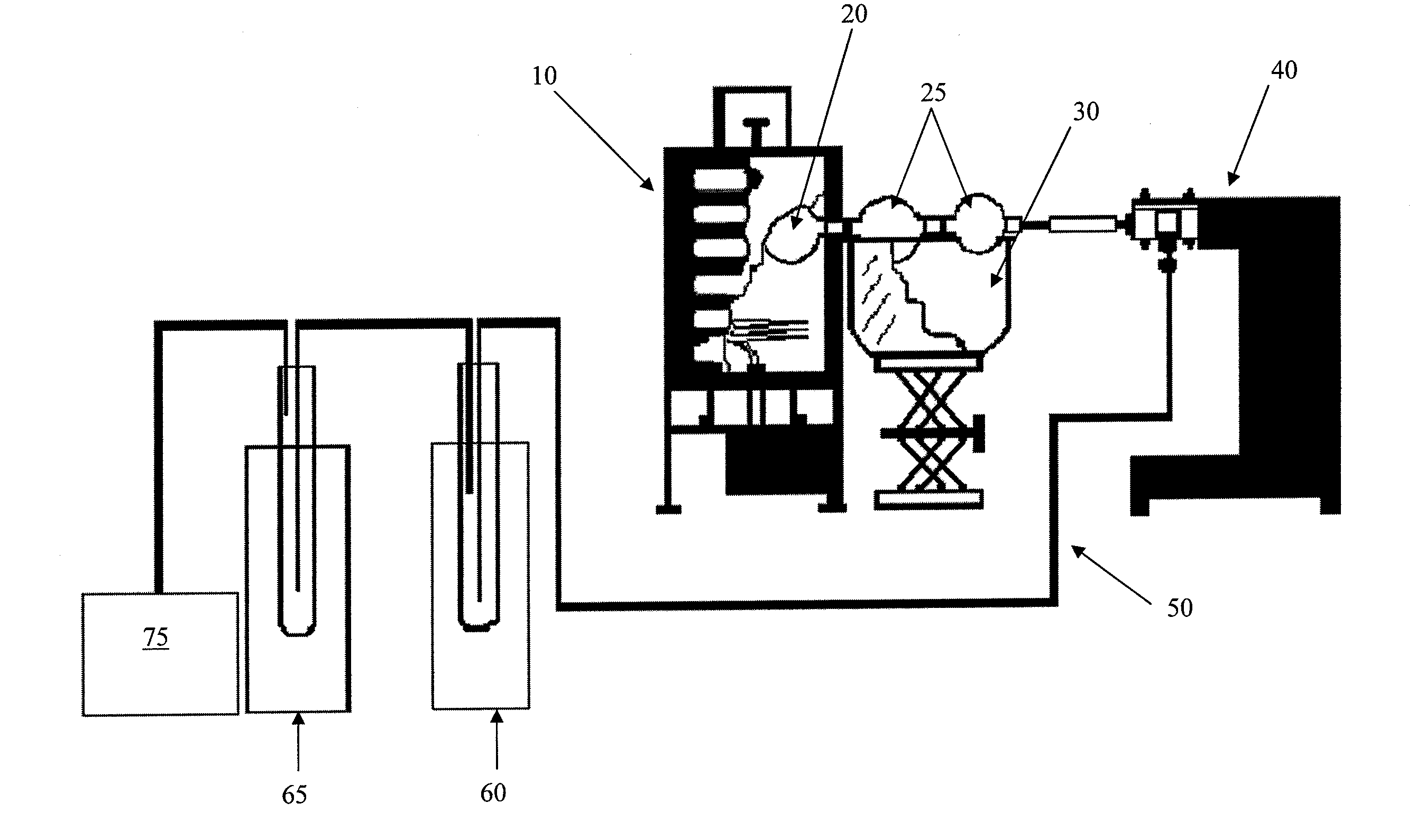
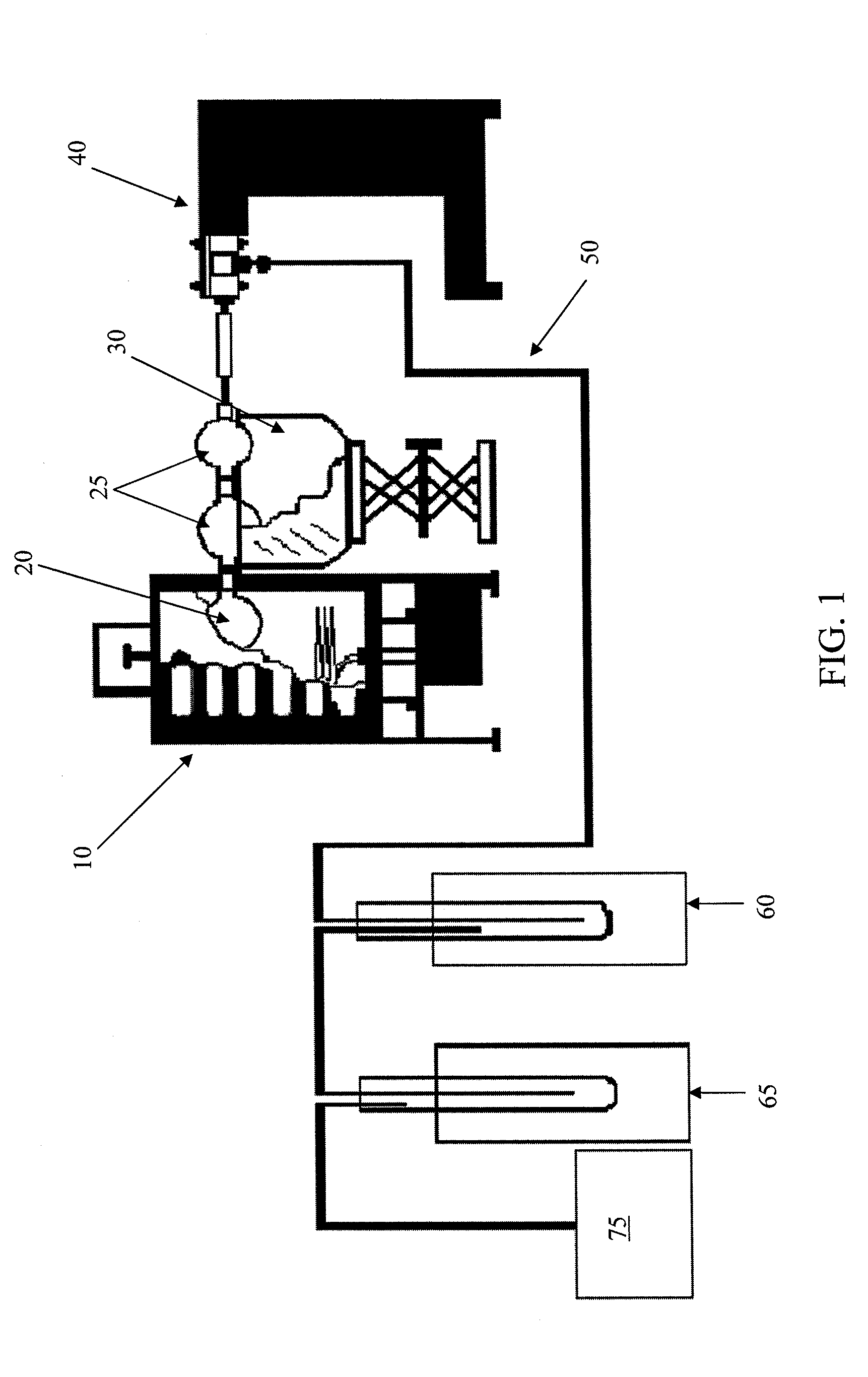
Methods and apparatus for converting waste materials into fuels and other useful products
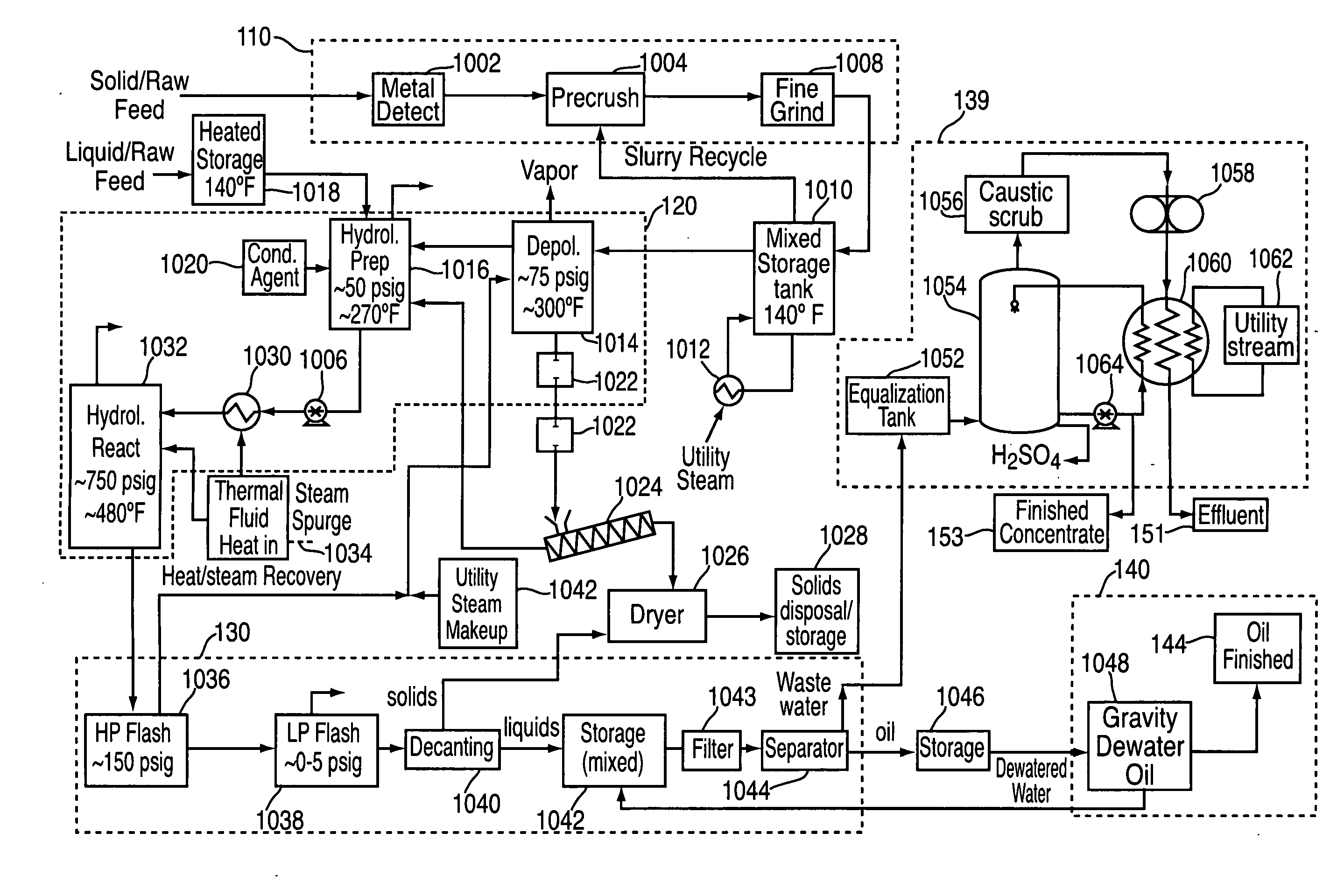
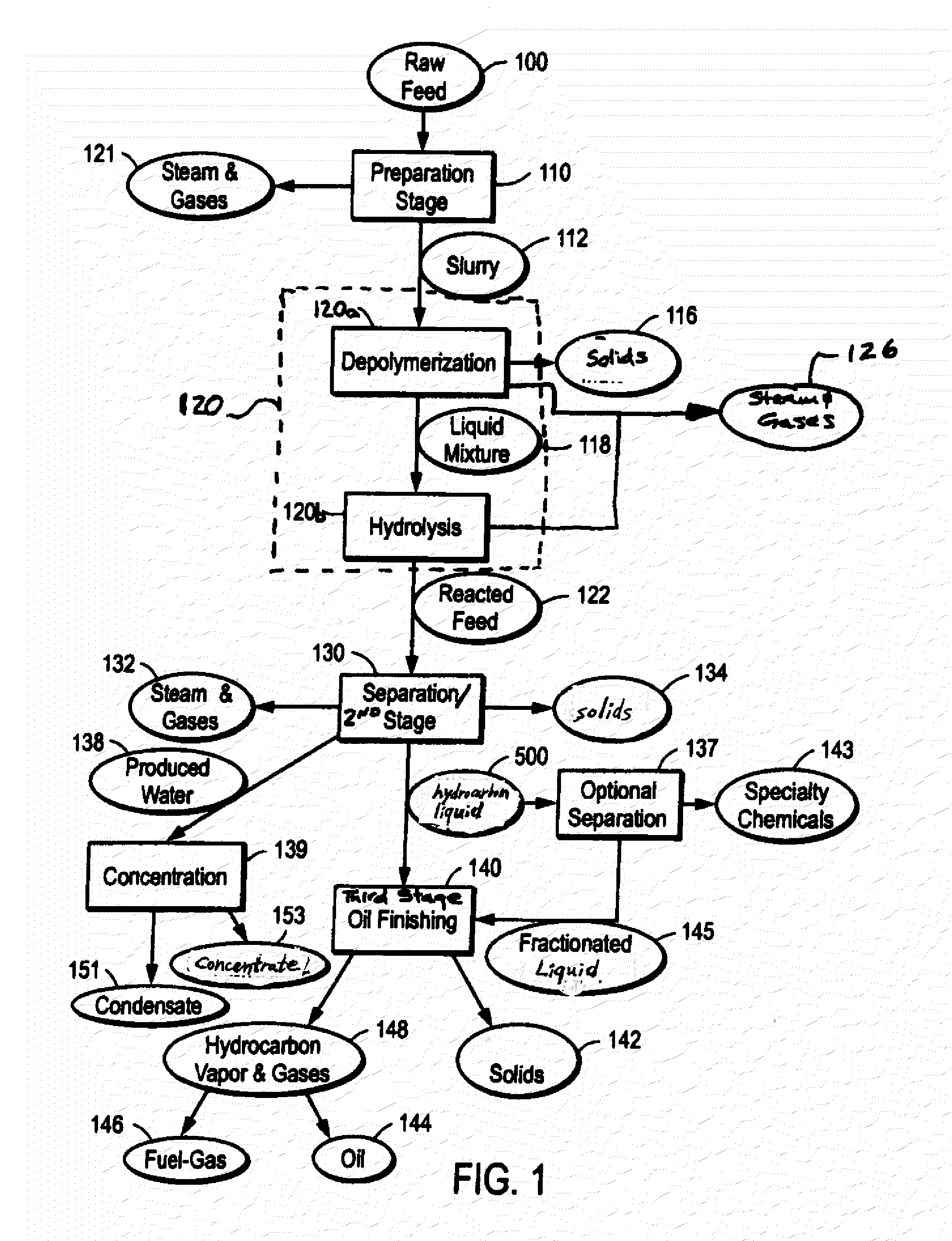
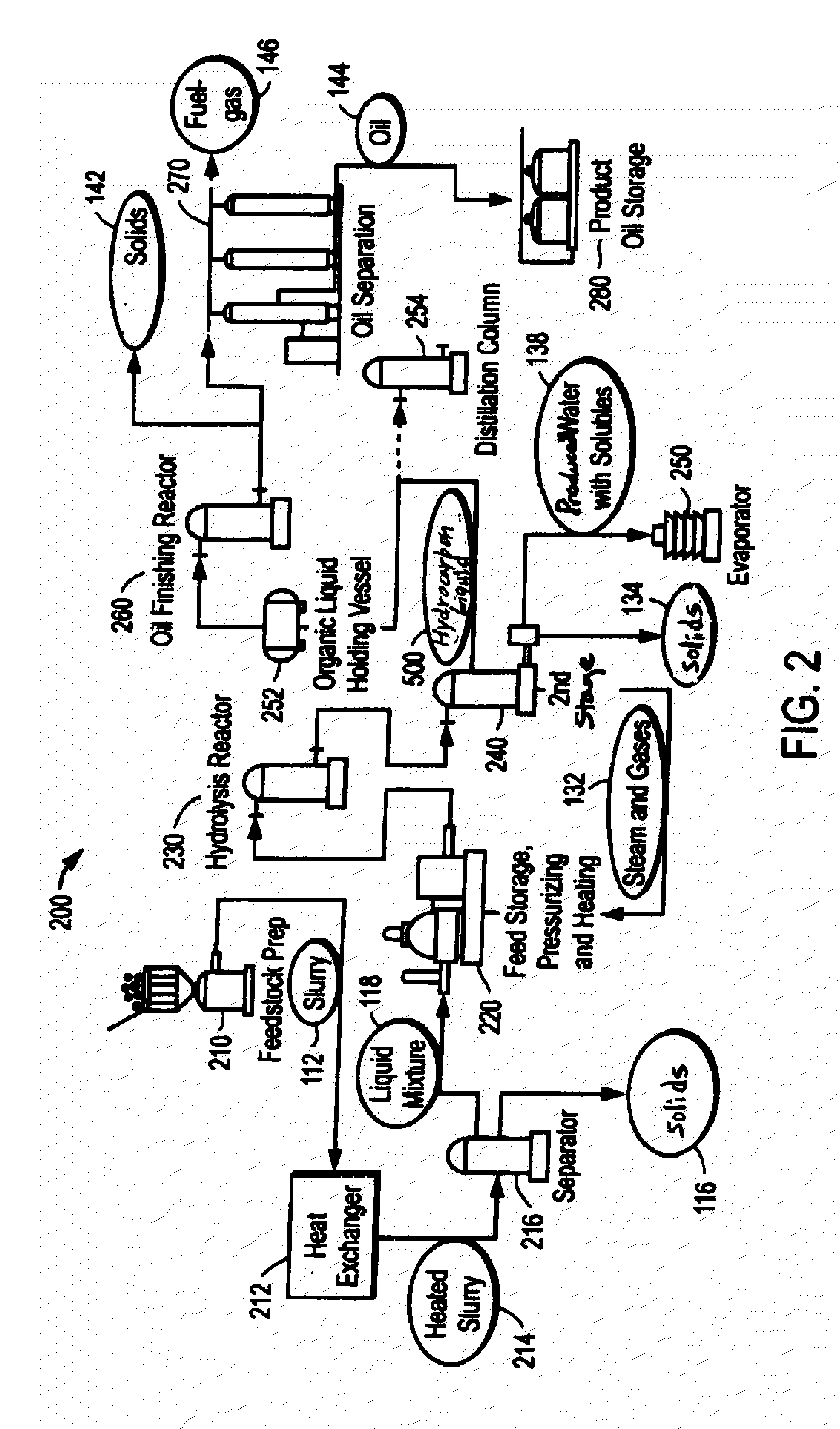
ActiveUS20090062581A1Effectively handle problematic wasteFree of contaminantsTransportation and packagingSolid waste disposalSpeciality chemicalsBiological waste
Conversion of waste and other organic feedstock into sustainable energy, feed, fertilizer, and other useful products of reliable purities is accomplished using water, heat, and pressure. More specifically, the invention provides methods and apparatus that handle mixed streams of various feedstocks, e.g. agricultural waste, biological waste, municipal solid waste, municipal sewage sludge, and shredder residue, to yield gas, oil, specialty chemicals, and carbon solids that can be used as is or are further processed. Useful products can be diverted at various points of the process or internalized to enhance the efficiency of the system.
Owner:SYNPET TEKNOLOJI GELISTIRME
Waste conversion process
InactiveUS20060280669A1Good yieldMinimization requirementsBiofuelsIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationEnvironmental engineeringSand granules
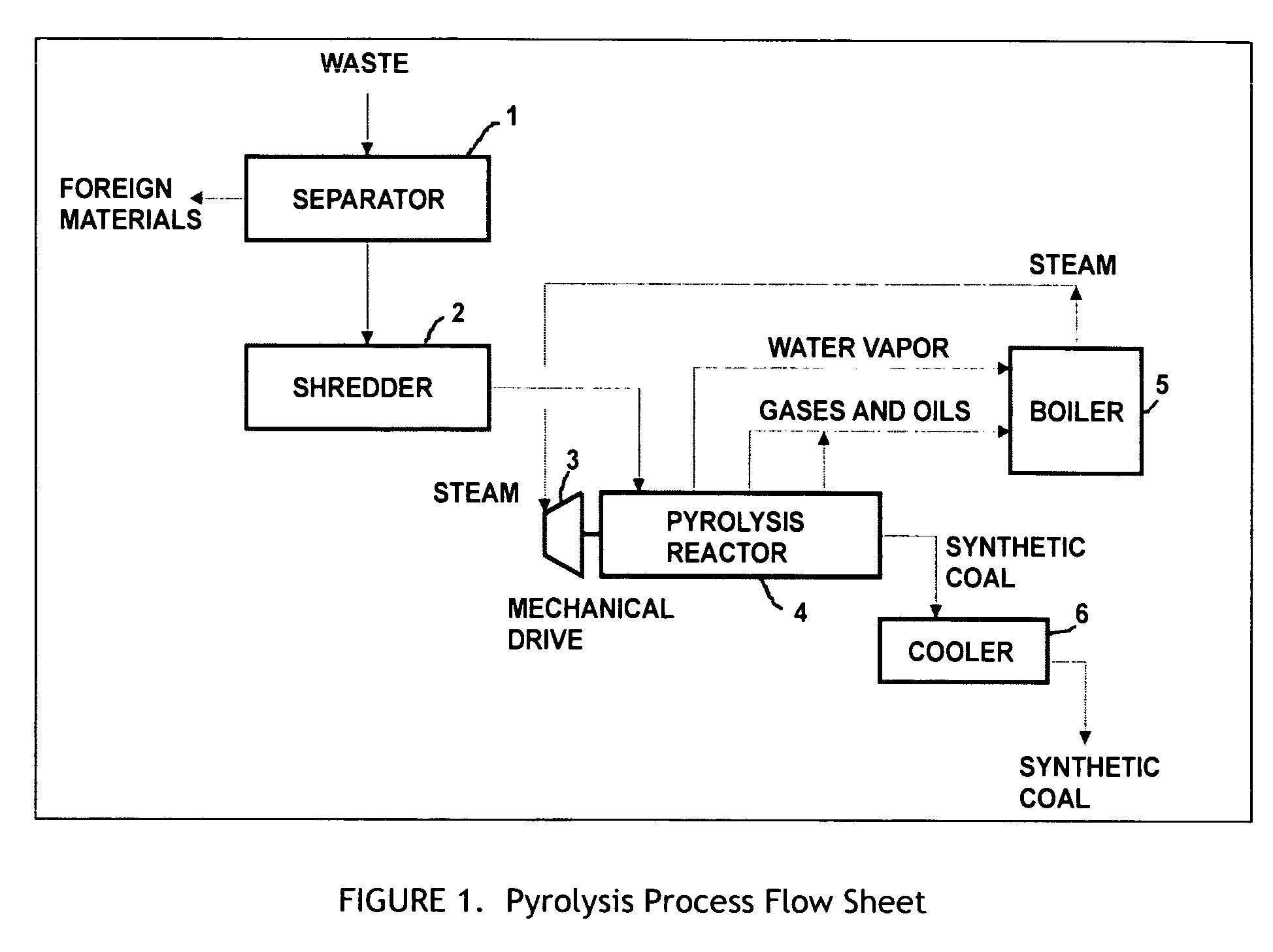
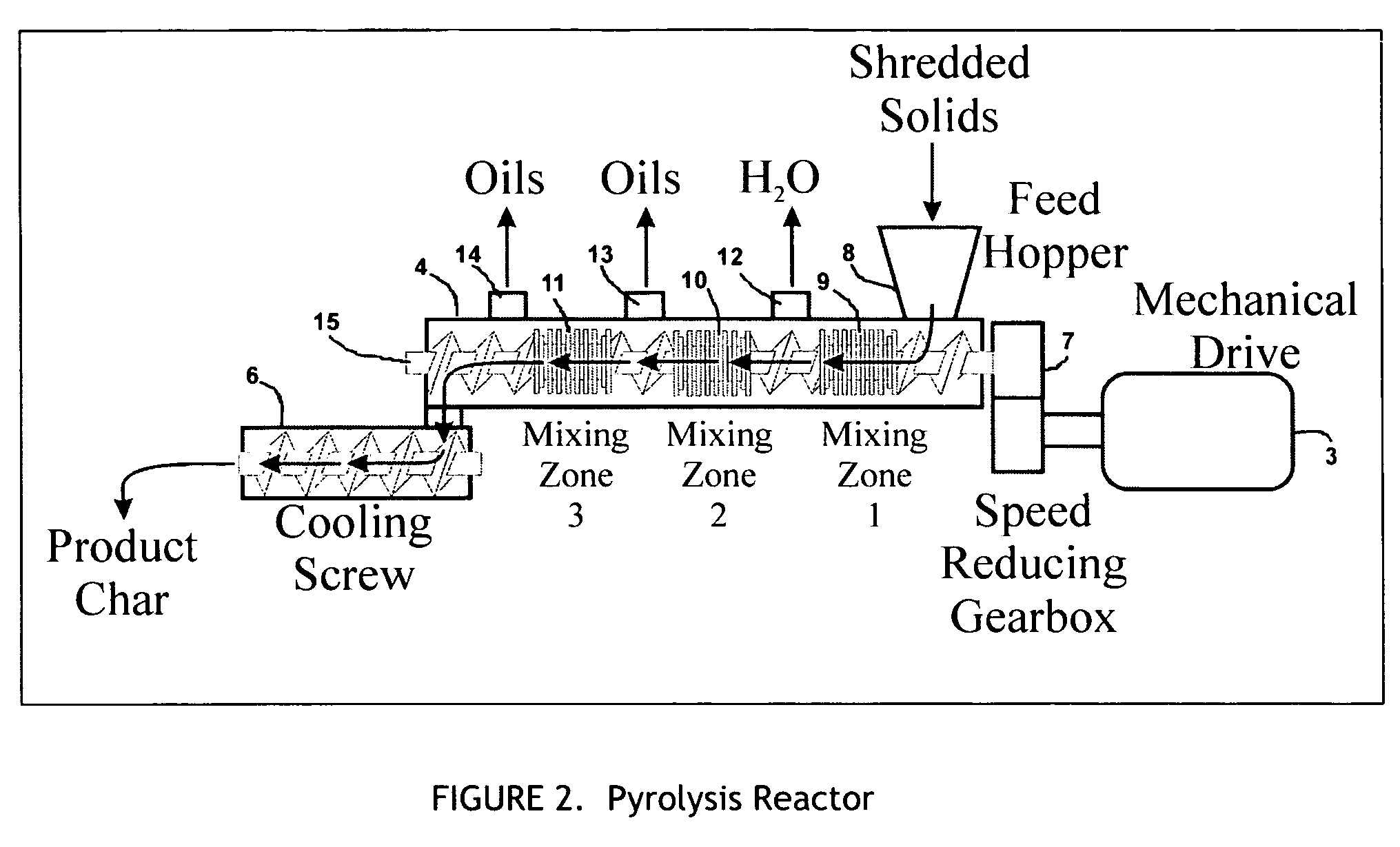
A process for the preparation of high quality char from organic waste materials. The waste is first sorted to remove recyclable inorganic materials of economic value (metals, glass) and other foreign materials that would be detrimental to the quality of the final product (stone, sand, construction debris, etc.). After size reduction, the waste is pyrolyzed at a temperature range of 250 to 600° F., in a high capacity, continuous mixer reactor, using in-situ viscous heating of the waste materials, to produce a highly uniform, granular synthetic product similar in energy content and handling characteristics to, but much cleaner burning than, natural coal.
Owner:ENTROPIC TECH CORP
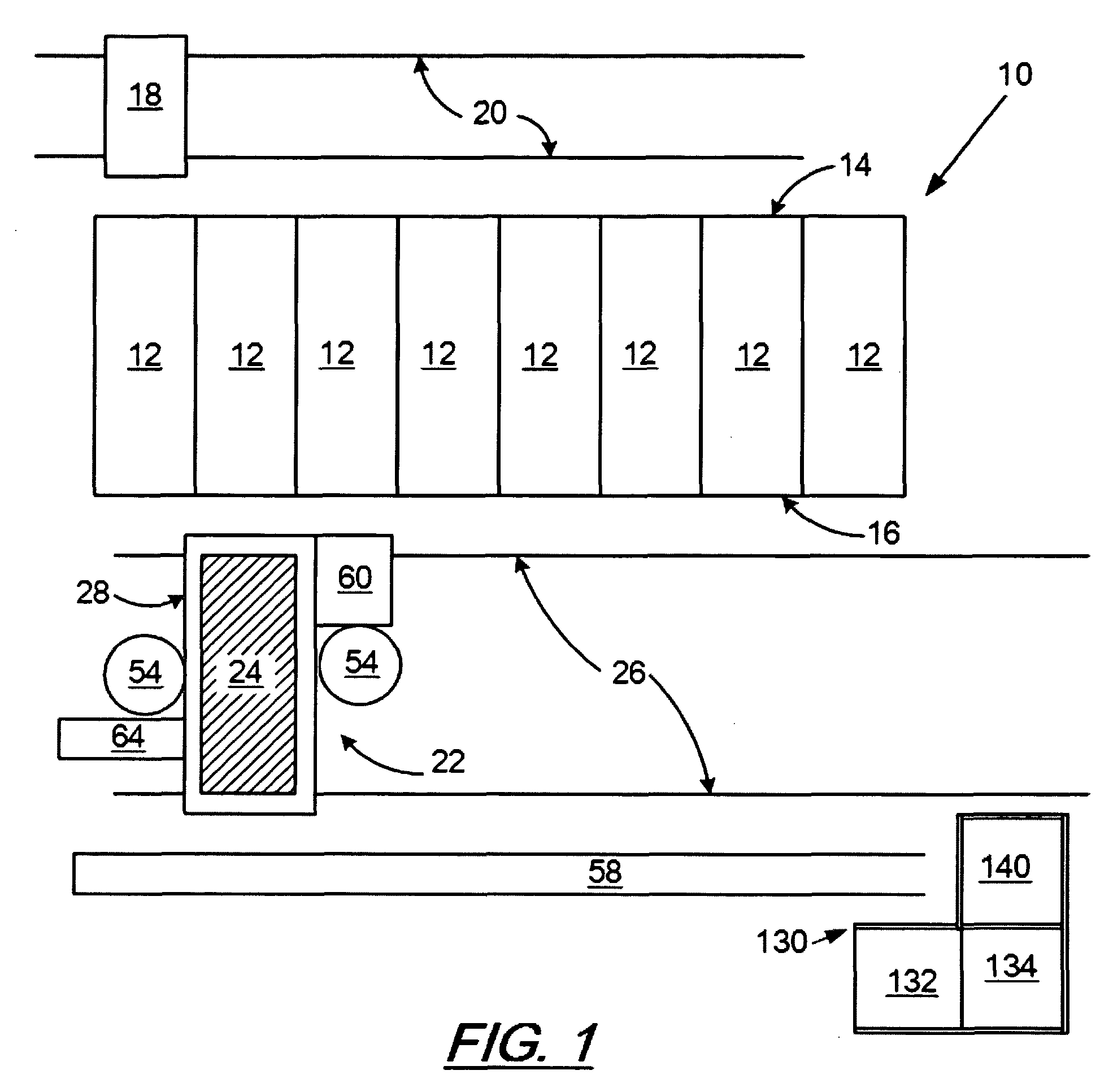
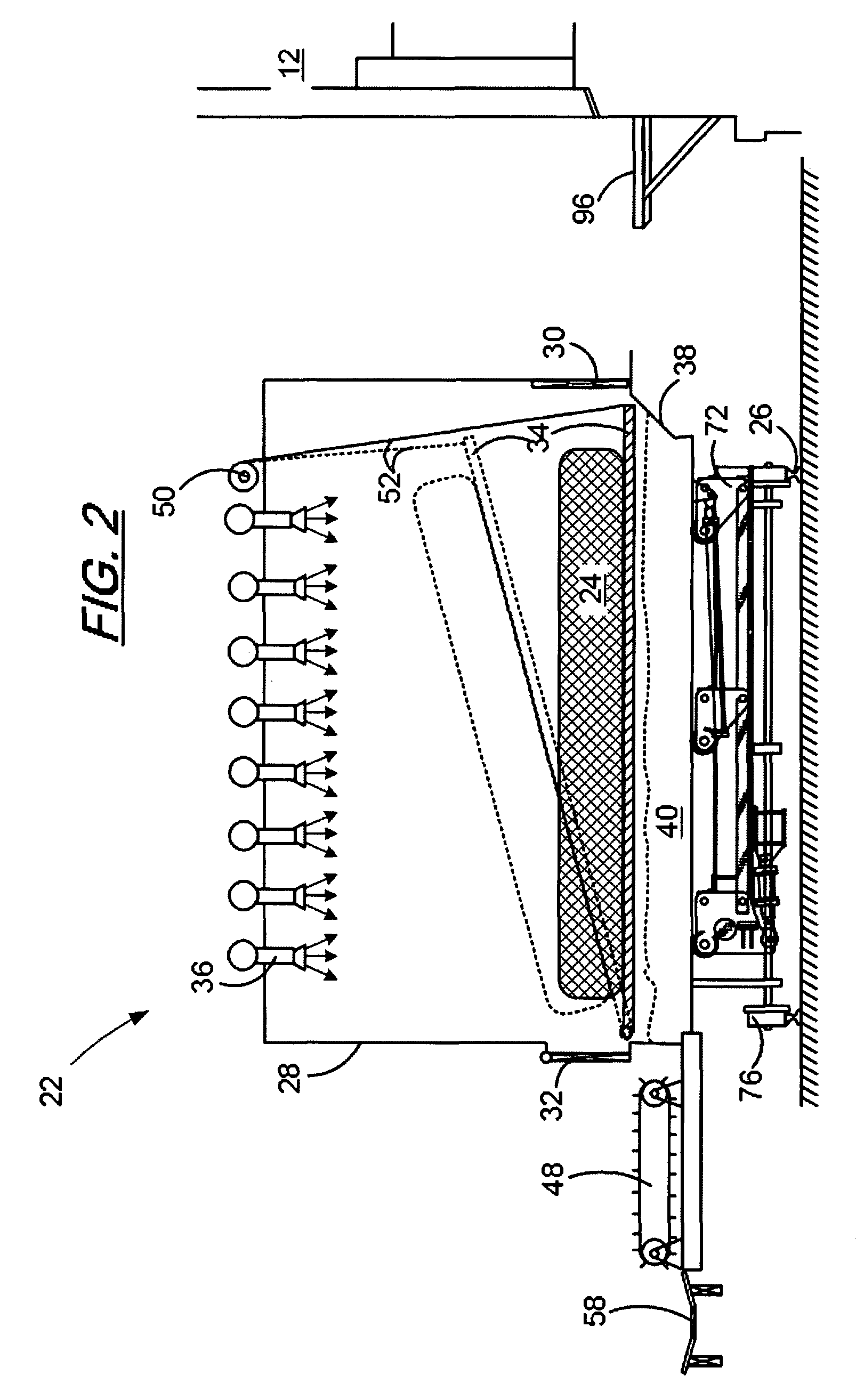
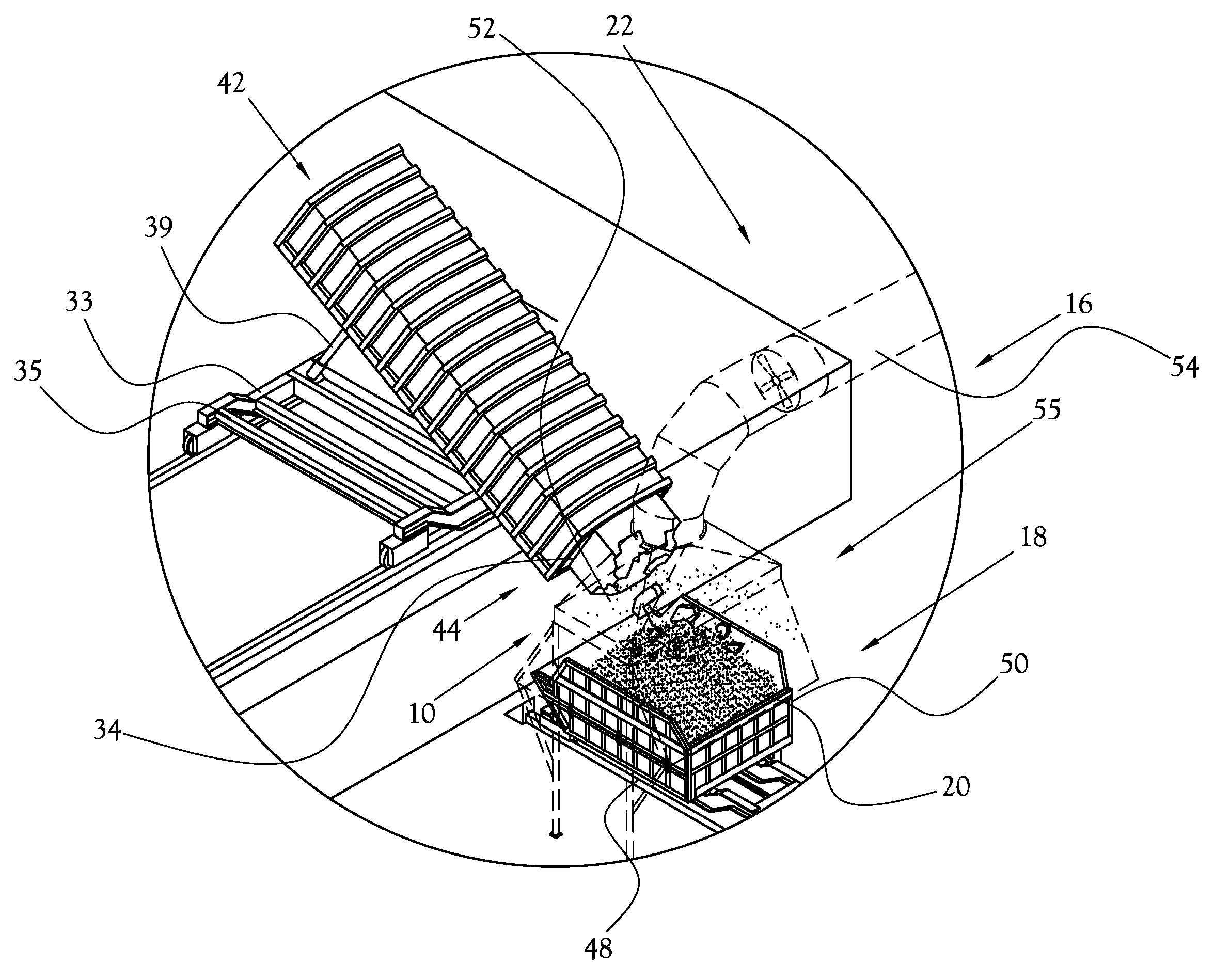
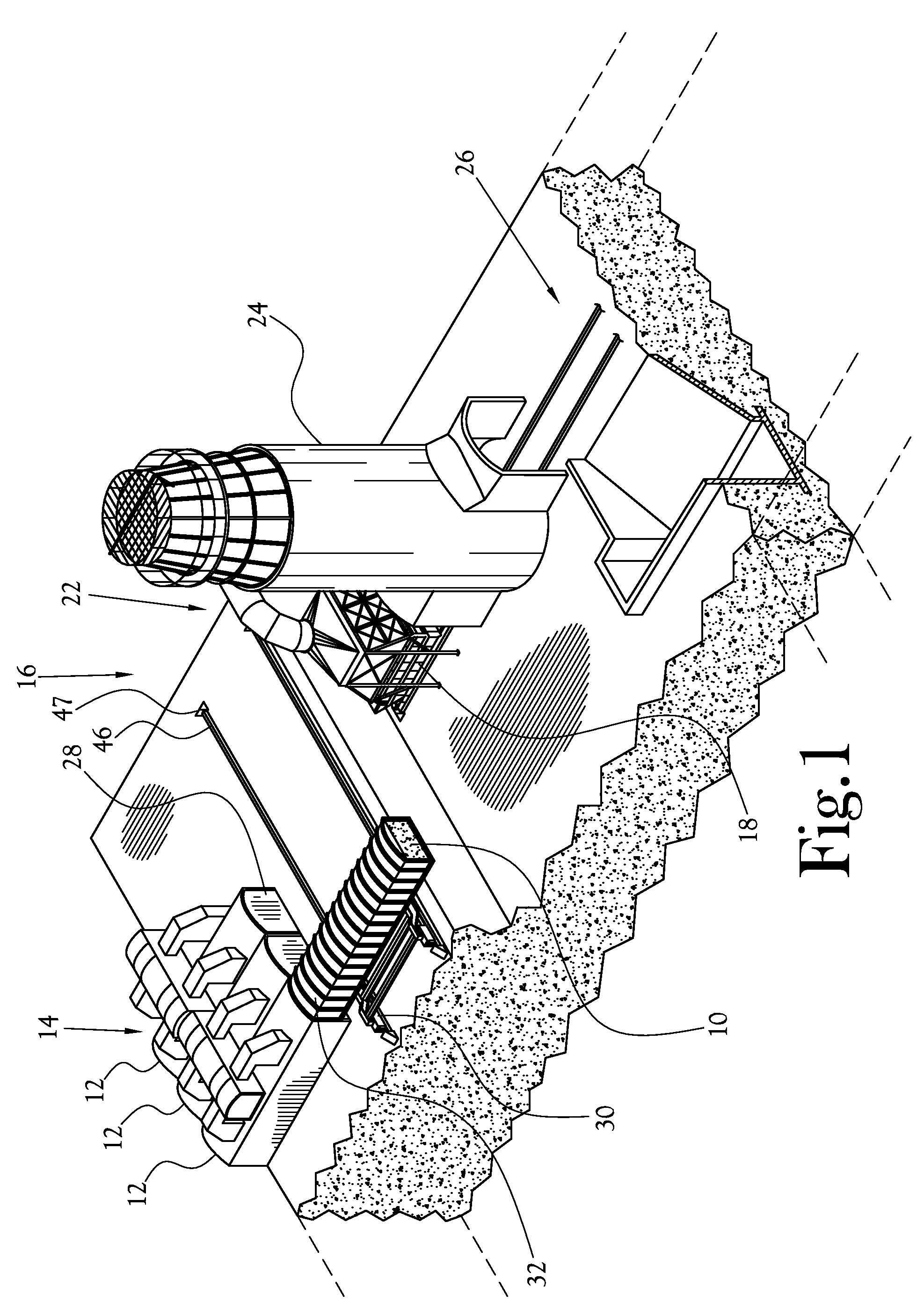
Coal bed vibration compactor for non-recovery coke oven
InactiveUS6059932AMechanical conveying coke ovensCharging-discharging device combinationsEngineeringCoke oven
A coal compaction system and method for a non-recovery coke oven having refractory roof, floor, side walls and end doors for coal charging and coke discharge provides an improved coal charging machine carrying a coal conveyor supported intermediate the ends of the conveyor to avoid conveyor sagging and non-uniform depth of a deposited coal bed, a number of pressurized fluid-driven vibratory compactors mounted on an end of the charging machine and spaced-apart across the width of the coal bed and serving to compact the coal bed on a retraction stroke of the charging machine, a pivoted lifting frame mounted on the charging machine above the compactors and from which the compactors individually are suspended and are provided with individual supply of pressurized fluid, and a coke pusher head mounted on the charging machine behind the compactors and serving, when the lifting frame and associated compactors are raised, to push finished coke from the coke oven.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA COKE TECH
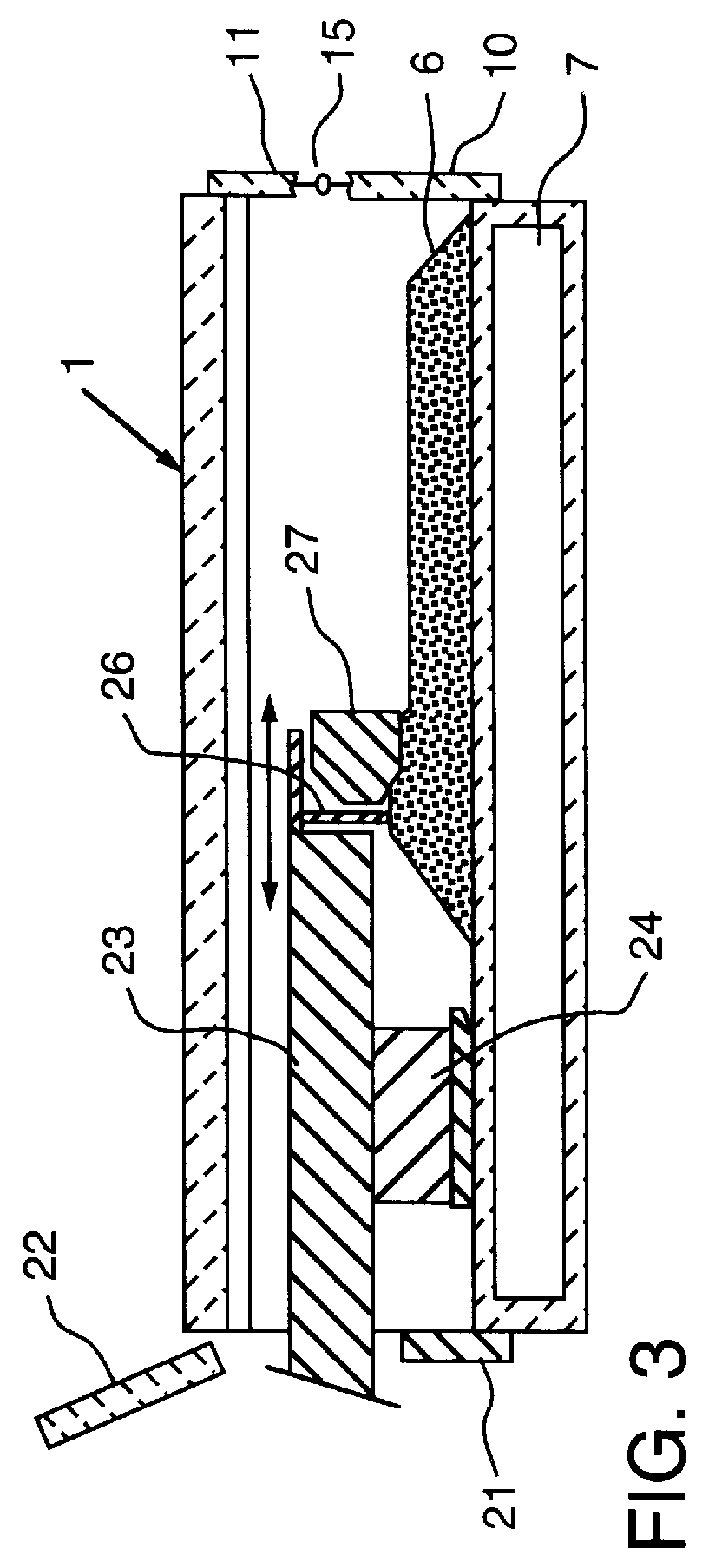
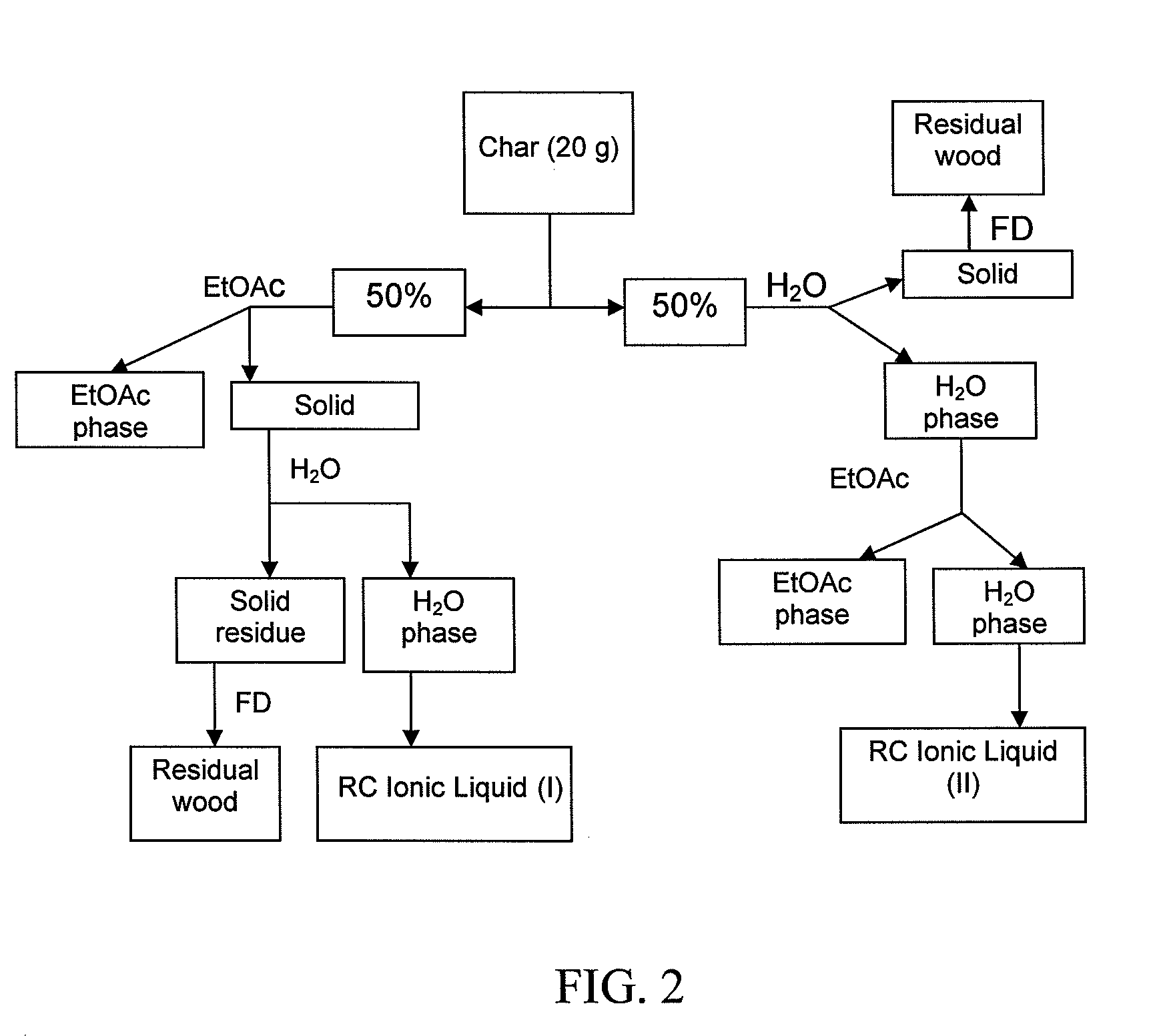
Product preparation and recovery from thermolysis of lignocellulosics in ionic liquids
InactiveUS20080185112A1Increase productionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentCoal charges mechanical treatmentCelluloseIonic liquid
The present invention provides methods for the thermolysis of lignocellulosic materials, such as wood, cellulose, lignin, and lignocellulose. In specific embodiments, the methods comprise combining the lignocellulosic material with an ionic liquid and subjecting the mixture of the lignocellulosic material and the ionic media to pyrolytic conditions to form a recoverable product, such as a commodity chemical.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
ActiveUS20090139851A1Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingCoke quenchingLiquid productHeat carrier
The present invent provides improved rapid thermal conversion processes for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. In an embodiment, biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. In one embodiment, the liquid product itself is used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Conversion of carbonaceous materials to synthetic natural gas by pyrolysis, reforming, and methanation
InactiveUS20080016769A1Reduce the temperatureCombustible gas chemical modificationProductsSyngasSteam reforming
The production of synthetic natural gas from a carbonaceous material, preferably a biomass material, such as wood. The carbonaceous material is first pyrolyzed, then subjected to steam reforming to produce a syngas, which is then passed to several clean-up steps then to a methanation zone to produce synthetic natural gas.
Owner:CLEAN ENERGY LLC
Method and apparatus for reclaiming oil from waste plastic
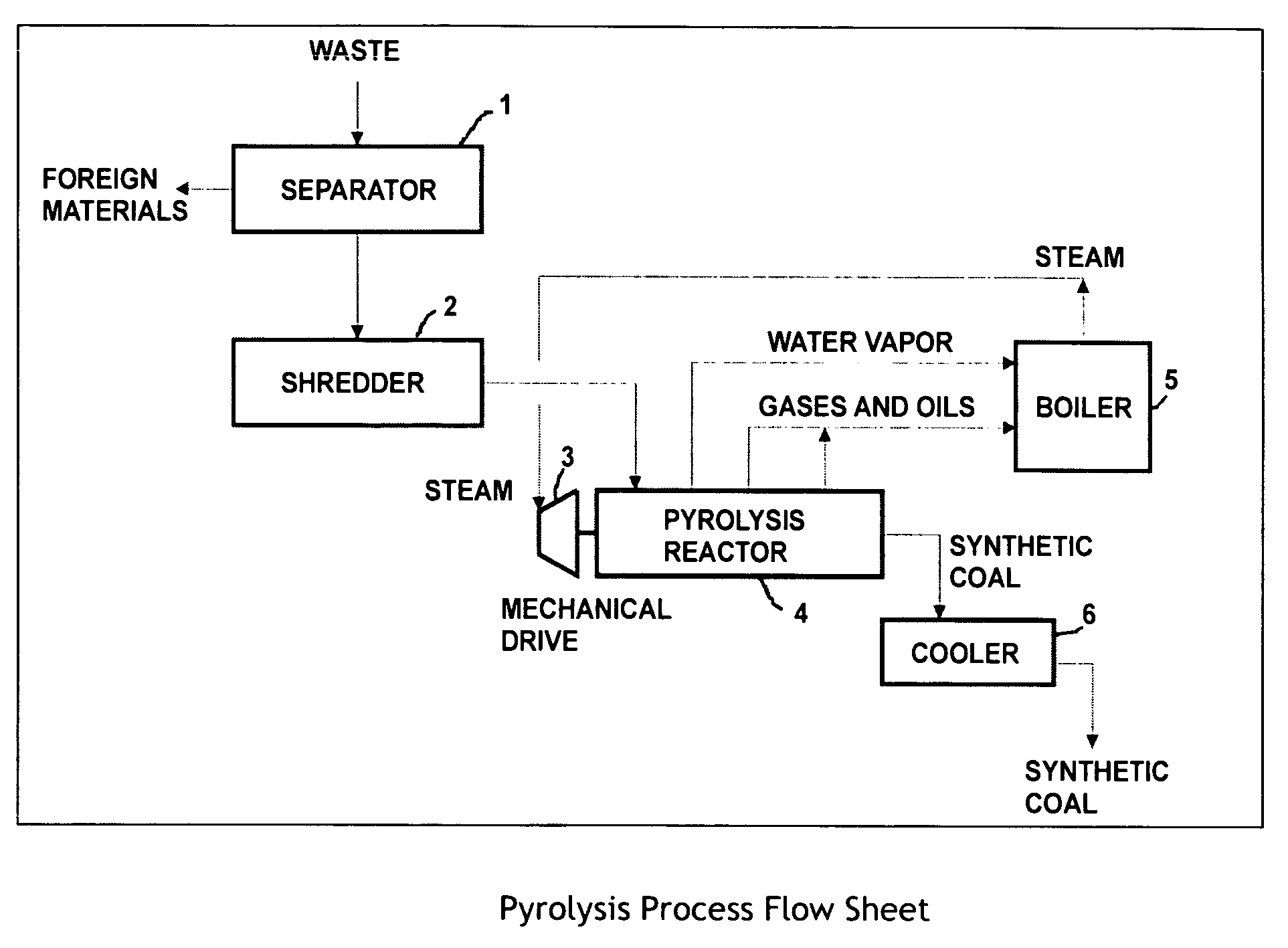
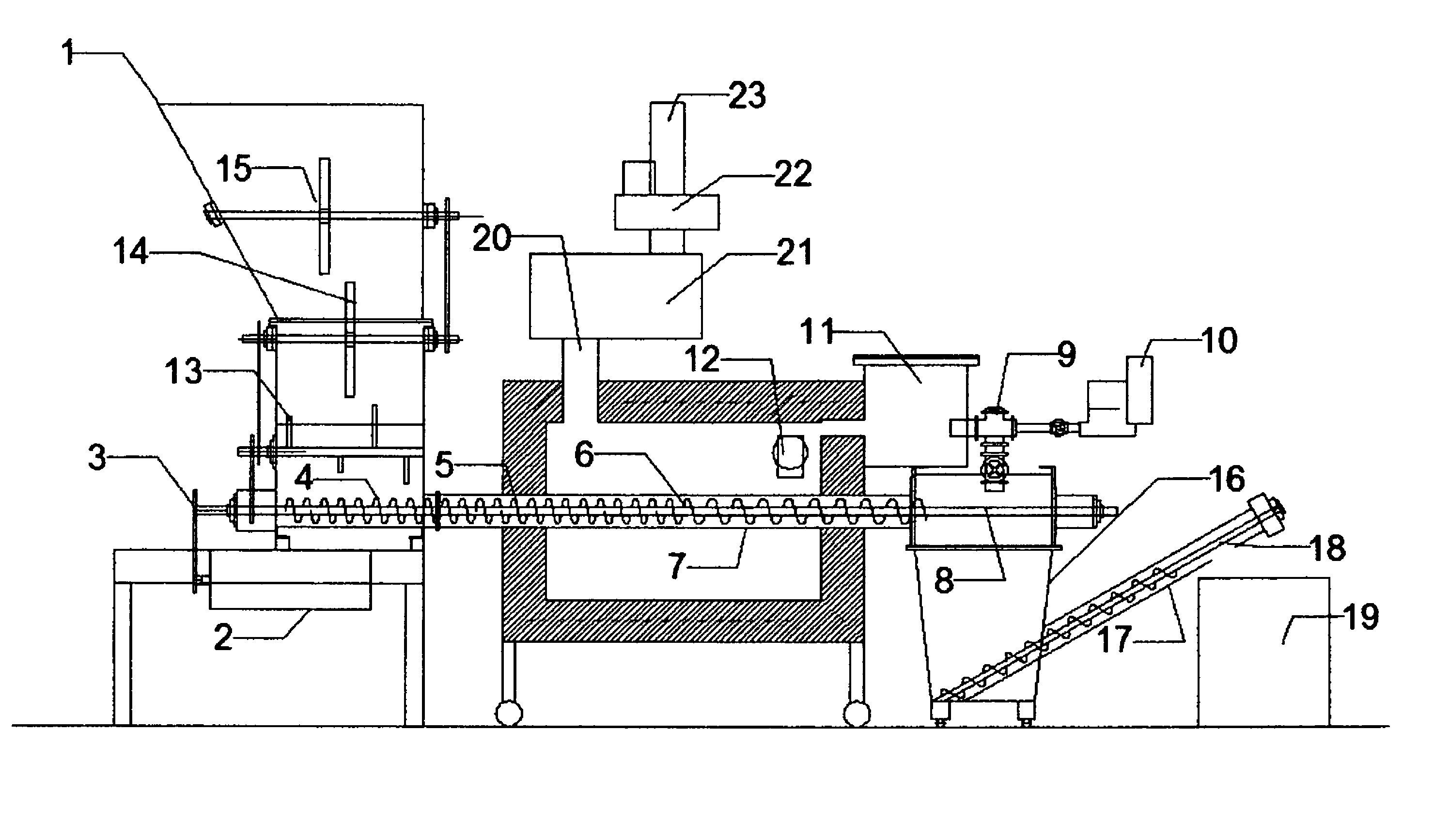
InactiveUS6011187AIncrease productionContinuous operationPlastic recyclingIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationForeign matterBoiling point
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 00572 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 8, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 8, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 27, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 31990 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 4, 1997This invention provides a method for reclaiming oil from waste plastic in such a way that thermosetting resins and solid foreign matter in the plastic will not pose a problem. This method greatly reduces the burden of presorting the garbage or industrial waste. To achieve this objective when oil is to be reclaimed from a waste plastic containing chlorine compounds, such as vinyl chloride, the plastic must first be stripped of chlorine. Prior to pyrolysis, while being conveyed forward in a continuous stream, the plastic is mixed with heated sand and / or an additive agent to raise its temperature to 250-350 DEG C. This creates a product which is comprised of a mixture of sand and substantially dechlorinated plastic. The product is mixed with heated sand to heat it directly to a temperature of 350-500 DEG C. It is maintained at this temperature until pyrolysis occurs. In order to obtain high-quality oil with a low boiling point, a first gas / liquid separation process separates the product obtained from the aforesaid pyrolysis into liquid high-boiling point oil, gaseous low-boiling point oil and low molecular-weight gases, and recirculates the liquid high-boiling point oil to the pyrolysis process, and a second gas / liquid separation process separates the gaseous low-boiling point oil and low molecular-weight gases into liquid low-boiling point oil and low molecular-weight gases. The first and second gas / liquid separation process are connected in sequence.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method and apparatus for compacting coal for a coal coking process
InactiveUS7497930B2Minimize amount of timeUniform bulk densityCoke quenchingCharging-discharging device combinationsEngineeringCoke oven
Relatively high speed methods for increasing the bulk density of coal particles, apparatus for increasing the bulk density of coal particles and methods for making metallurgical coke. Once such method includes depositing coal particles onto a charging plate external to a coking oven to provide an elongate bed of dry, uncompacted coal having an upper surface of the charging plate. The charging plate has side walls, and at least one movable end wall An impact pressure is applied to the upper surface of the bed of dry, uncompacted coal while degassing the coal to provide a dry, compacted coal bed having a bulk density ranging from about 960 to about 1200 kilograms per cubic meter.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
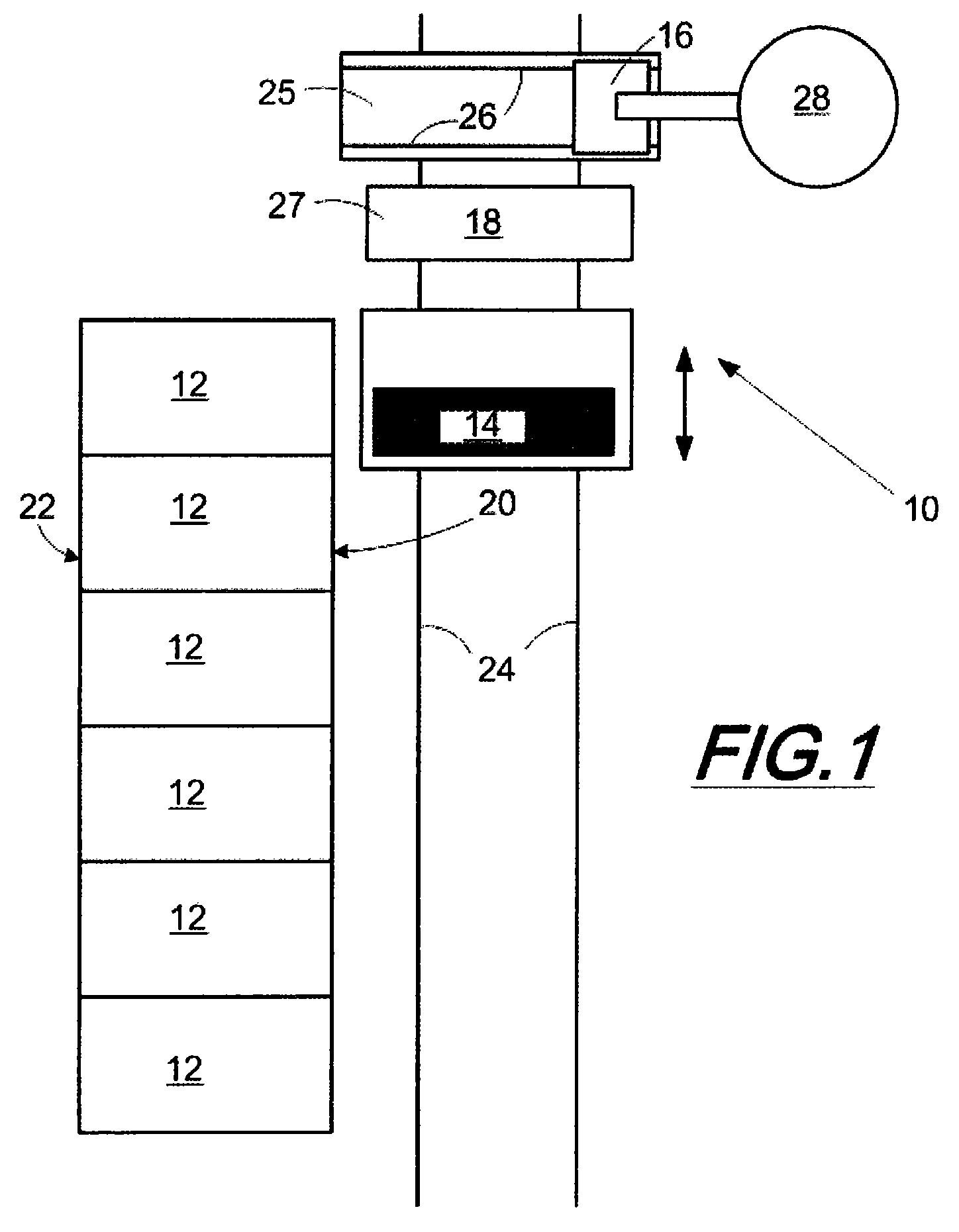
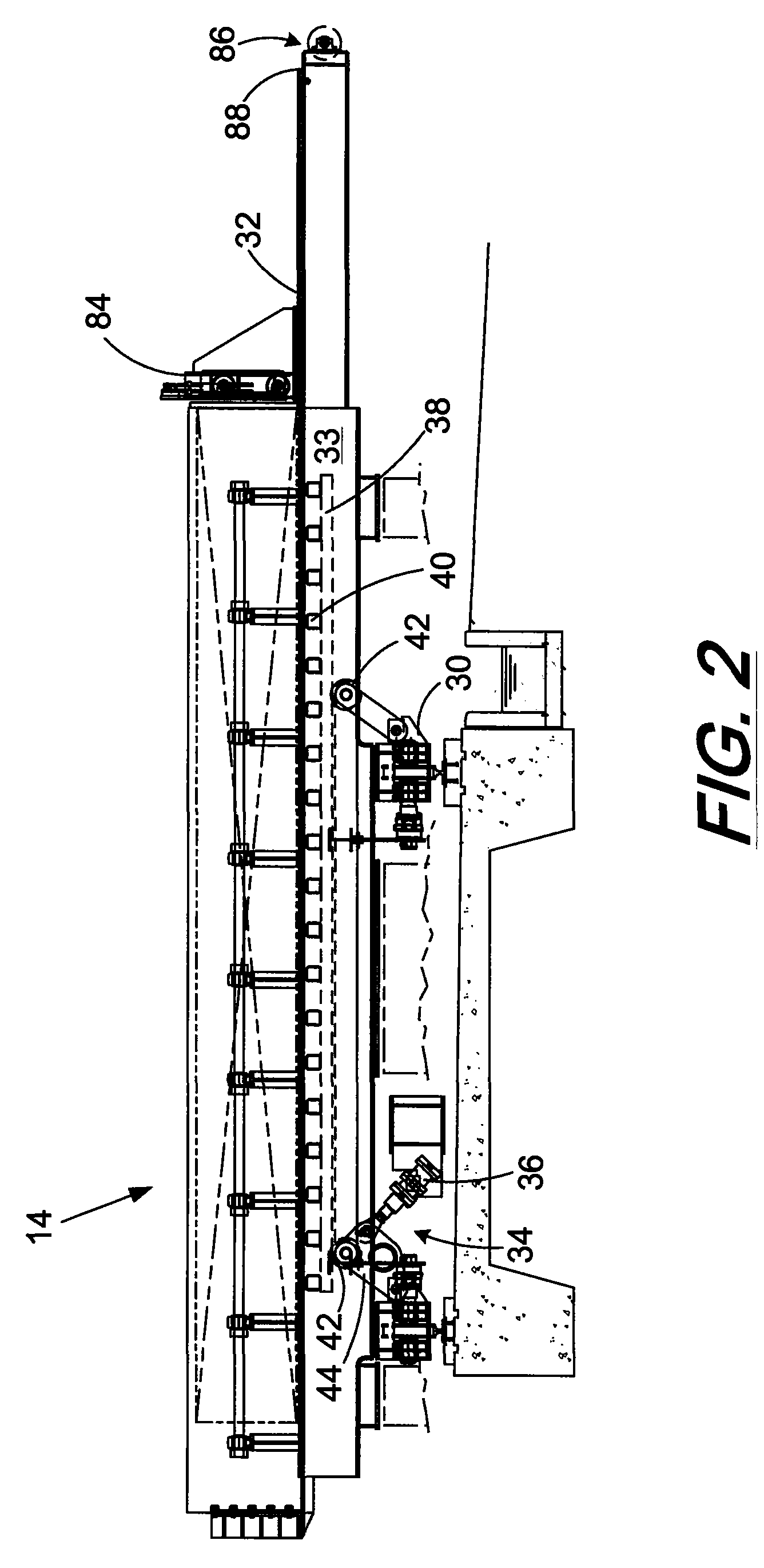
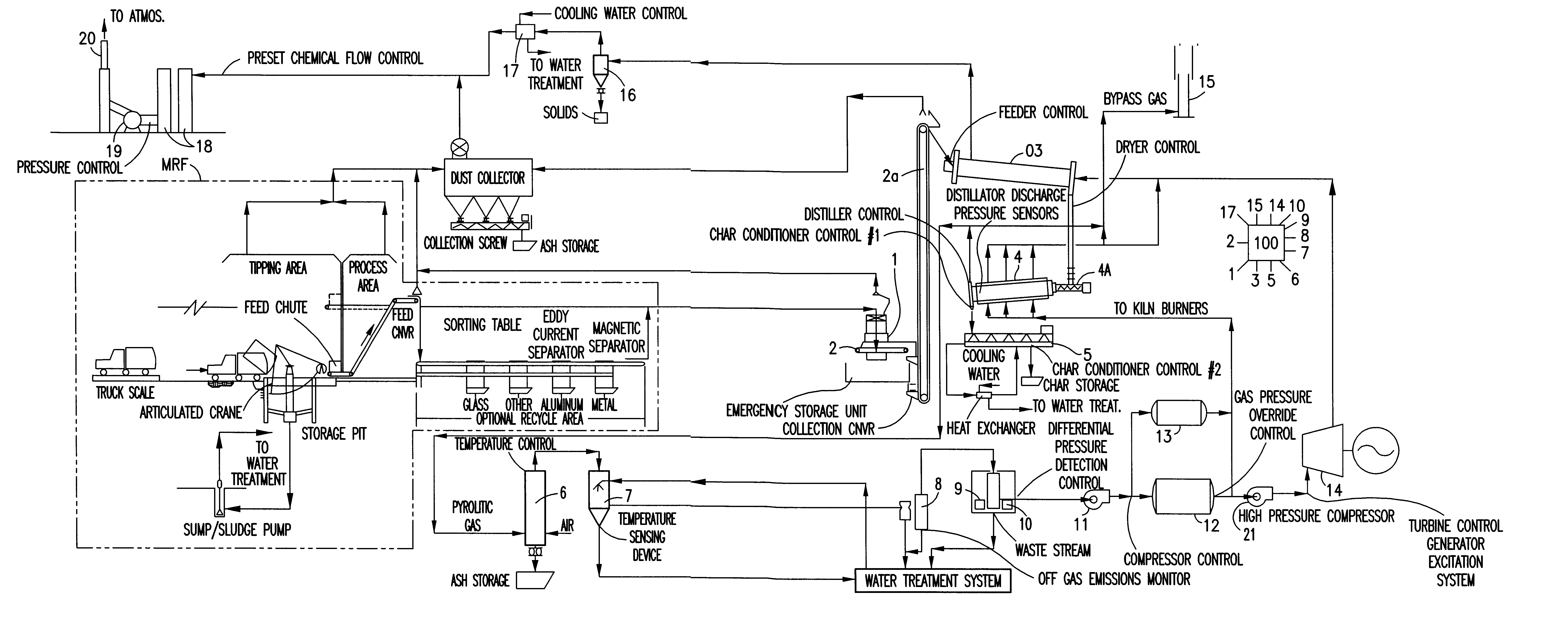
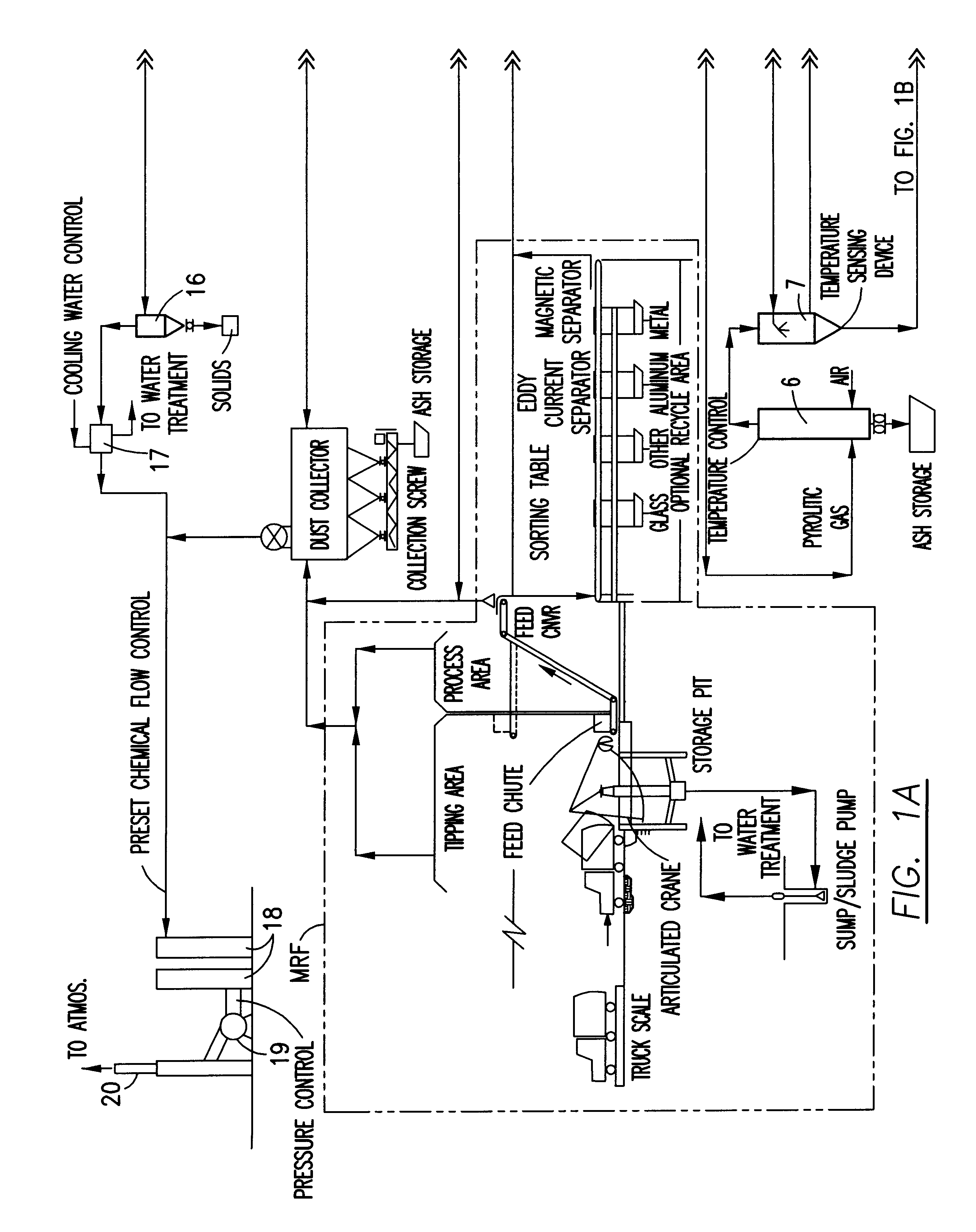
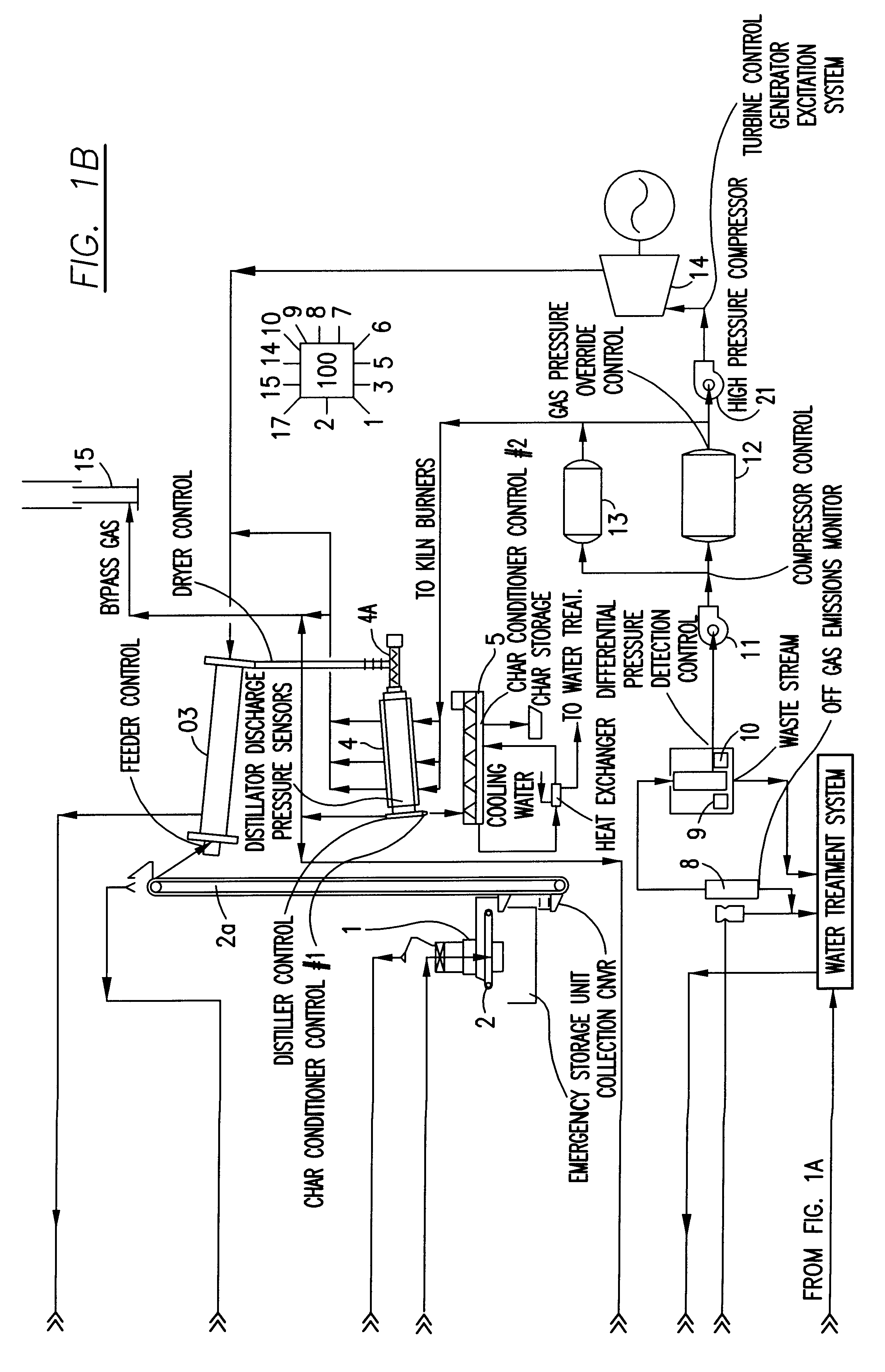
Integrated control and destructive distillation of carbonaceous waste
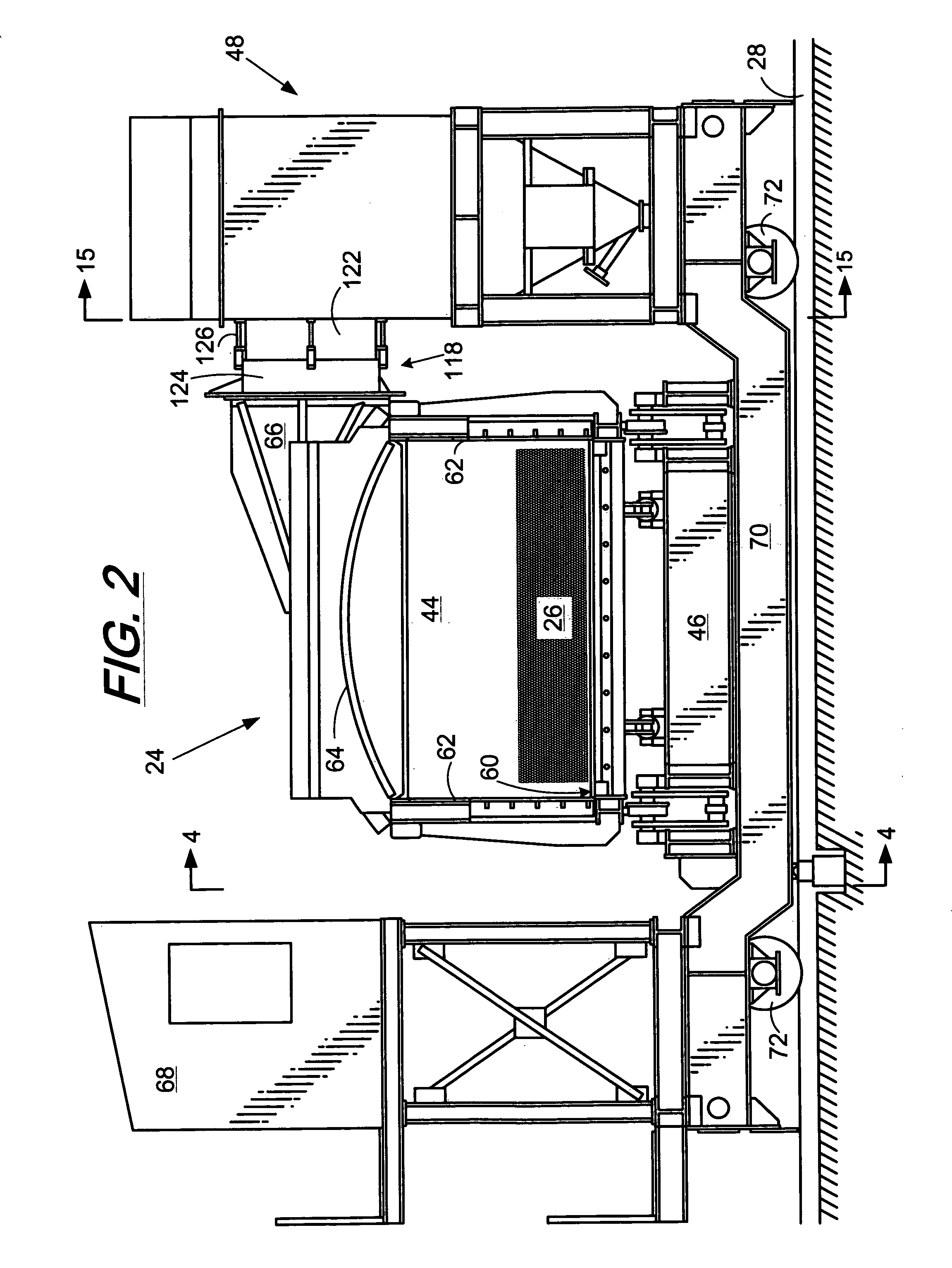
InactiveUS6182584B1High quantity and qualityEnhanced yield quantity and qualityHorizontal chamber coke ovensEmission preventionComputer control systemWaste stream
A system and process to provide integrated control for the pyrolytic composition of organic (biomass) waste products especially for municipal solid waste systems. The system includes integrated control that monitors biomass waste stream throughout the entire system and the products produced therefrom and includes presorting, controlling the amount of material processed in a continuous manner, shredding, removing moisture in a continuous process that is controlled and providing the waste stream to the distillation unit for pyrolytic action where it is converted into gaseous fuel and a char residue. The gaseous fuel is scrubbed clean and monitored and stored and reused to provide heat to the system. The entire system may be self-sustaining and continuous with very little or no human intervention. An integrated real time computer control system includes sensors and measuring devices with all the major components to ensure integrated efficiency.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SOLUTIONS & TECH
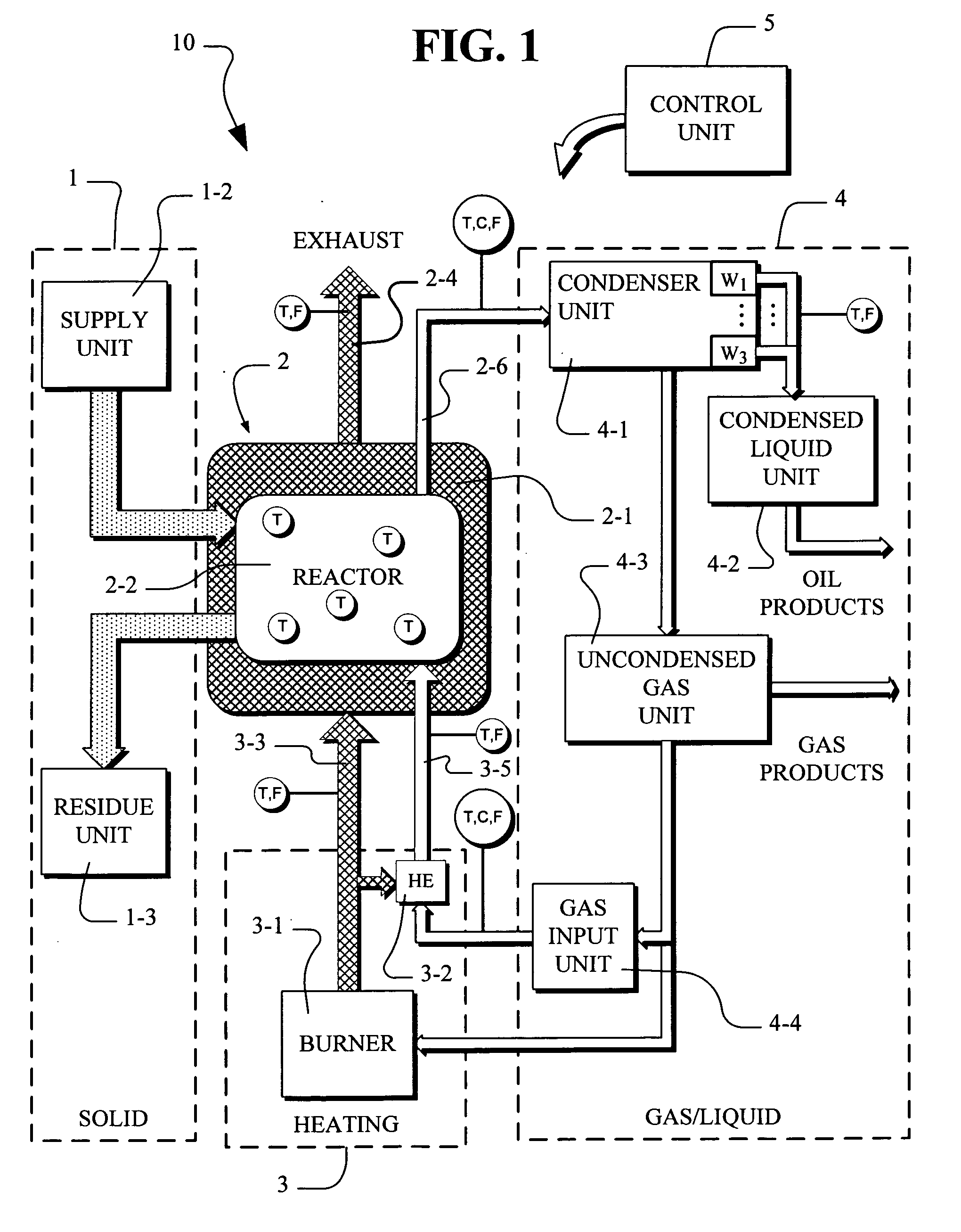
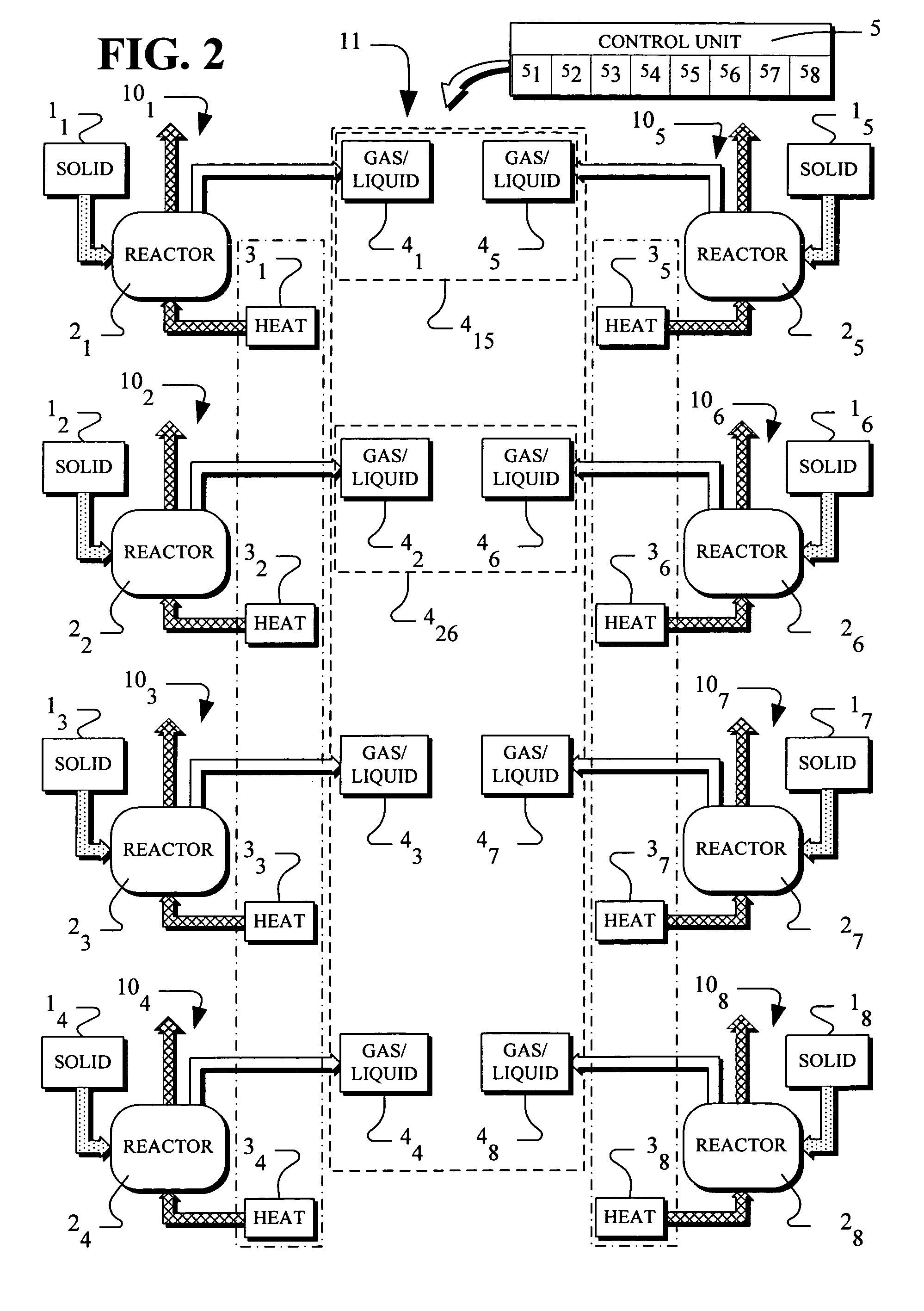
Batch pyrolysis system
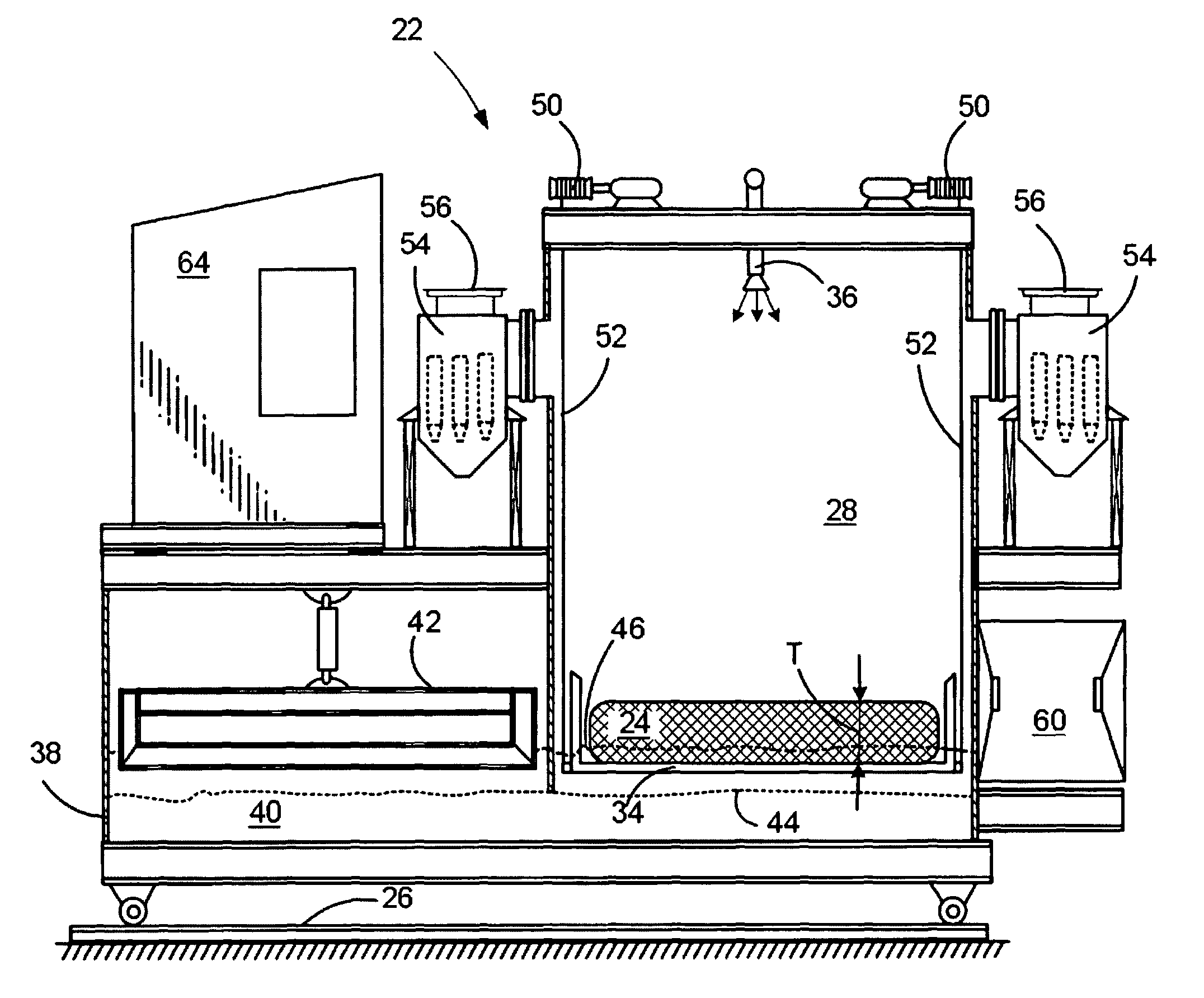
InactiveUS20060163053A1Quality improvementImprove throughputProductsBeehive ovensBatch processingProcess engineering
Disclosed is a scaleable pyrolysis system for batch processing of waste vehicle tires and other waste to provide pyrolysis products. The core pyrolysis system includes one or more batch reactors, heating units, solids processing units, gas / liquid processing units and control units. In operation, the temperature gradients internal to the reactor are controlled by preferential channeling of heat to provide pyrolysis products that are of high quality, and hence commercially advantageous, while facilitating high throughput.
Owner:ERSHAG BENGT STURE
Method of producing hodge carbonyls and oligomeric lignin
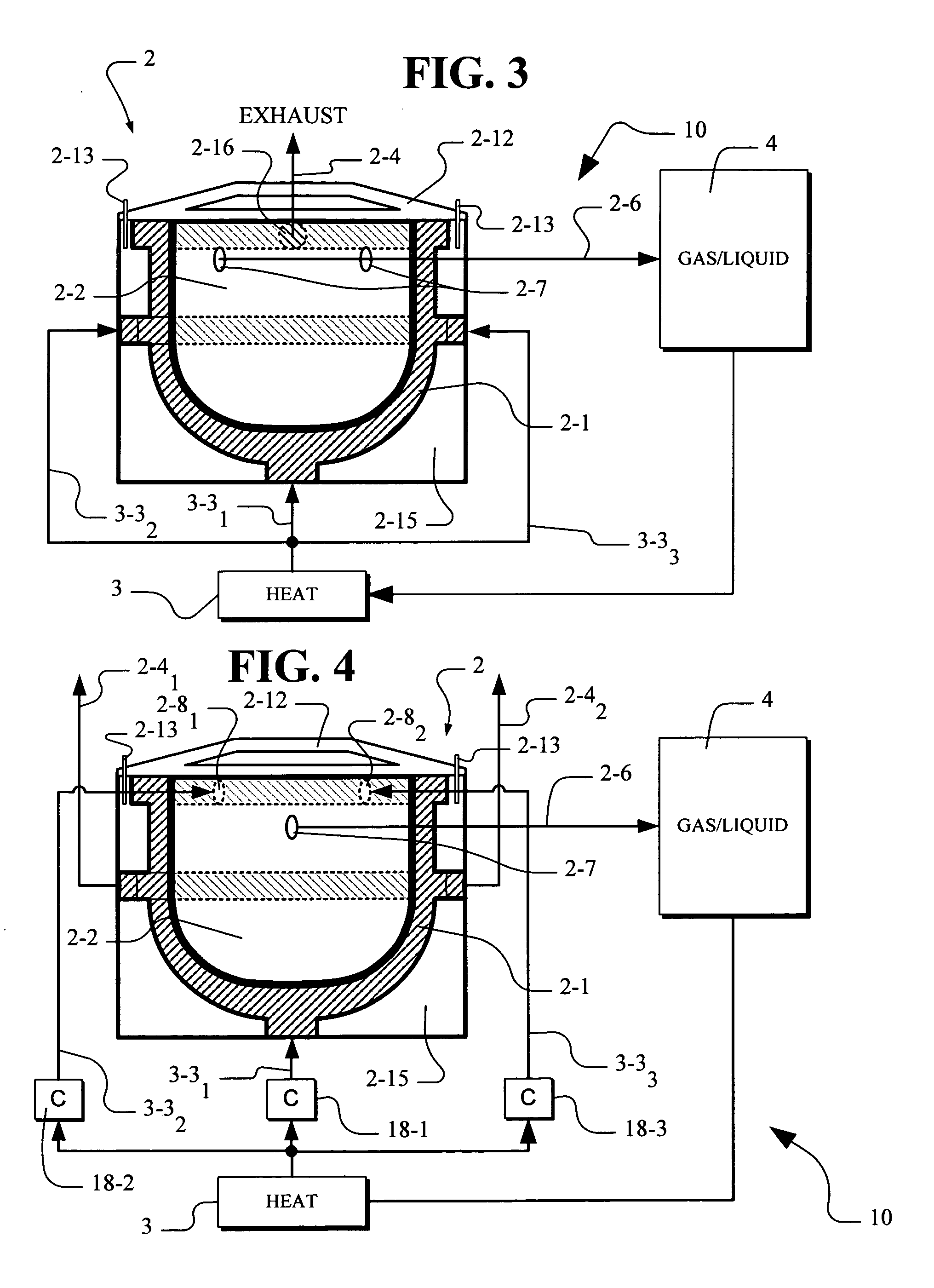
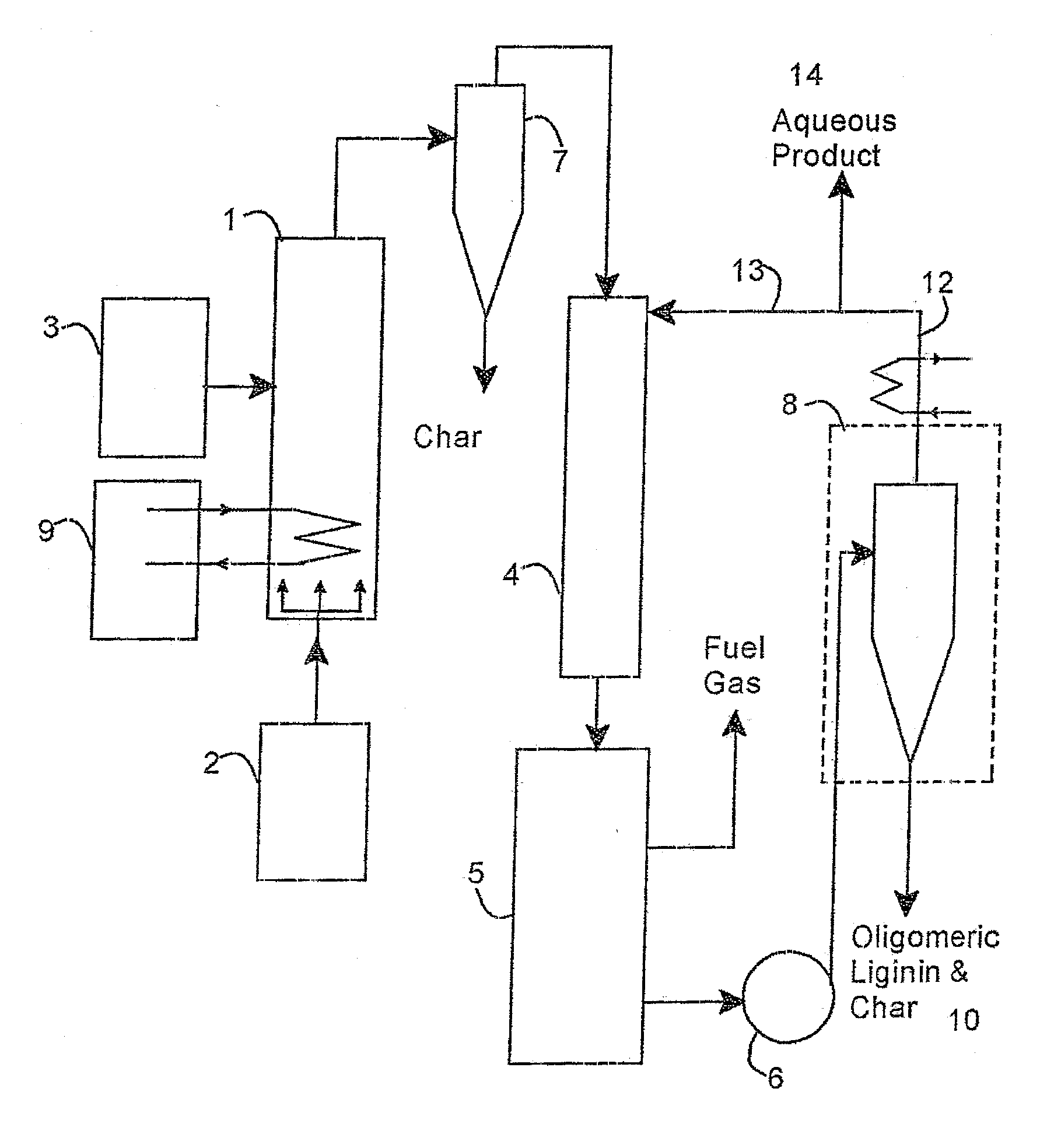
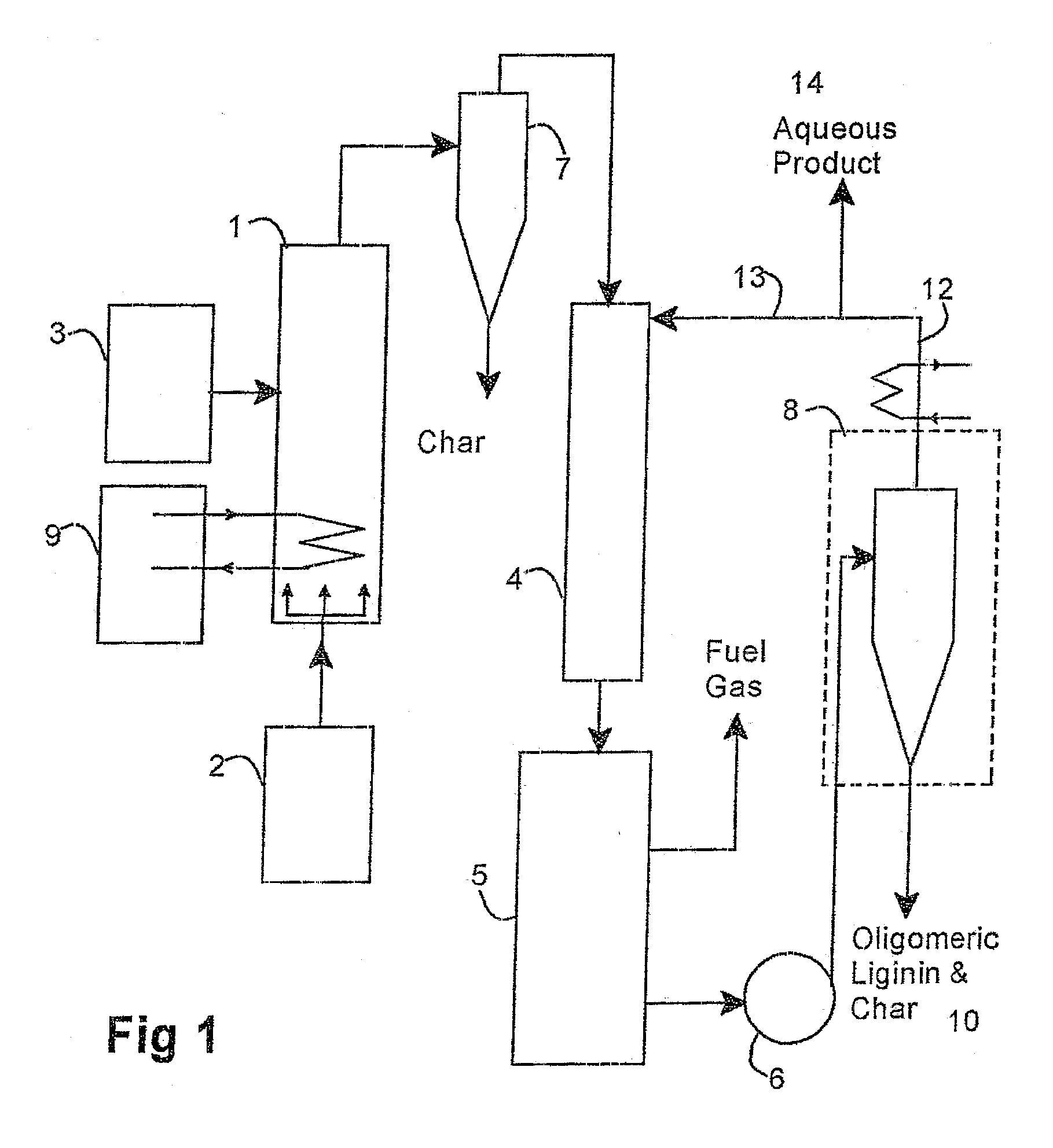
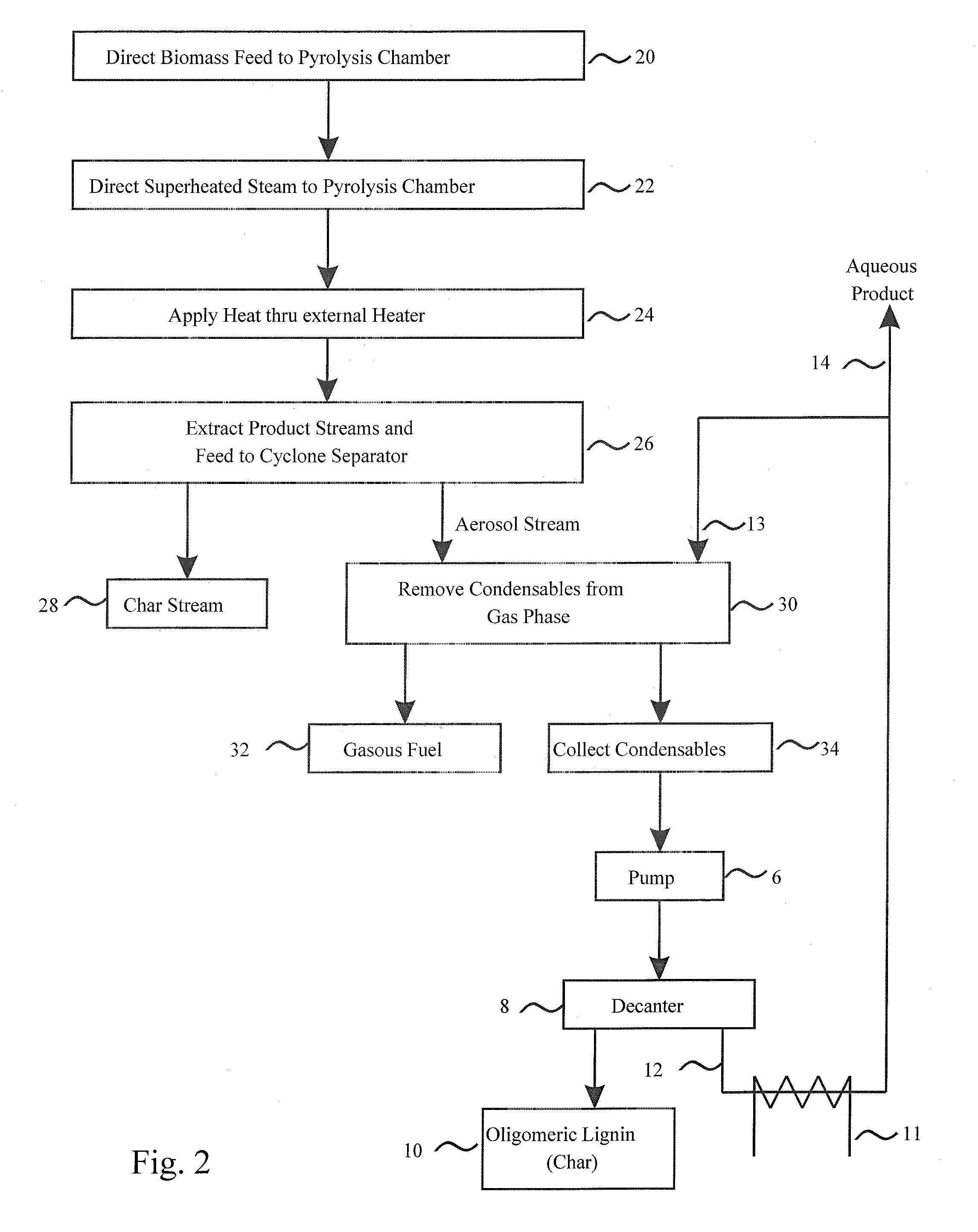
ActiveUS20090126433A1Low lignin contentBiofuelsIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationSufficient timeProcess engineering
A method of treating biomass feed by pyrolyzing it in the presence of superheated steam at a selected temperature for a sufficient time to produce at least one product stream.
Owner:KERRY GRP SERVICES INT
Flash-pyrolysis in a cyclone
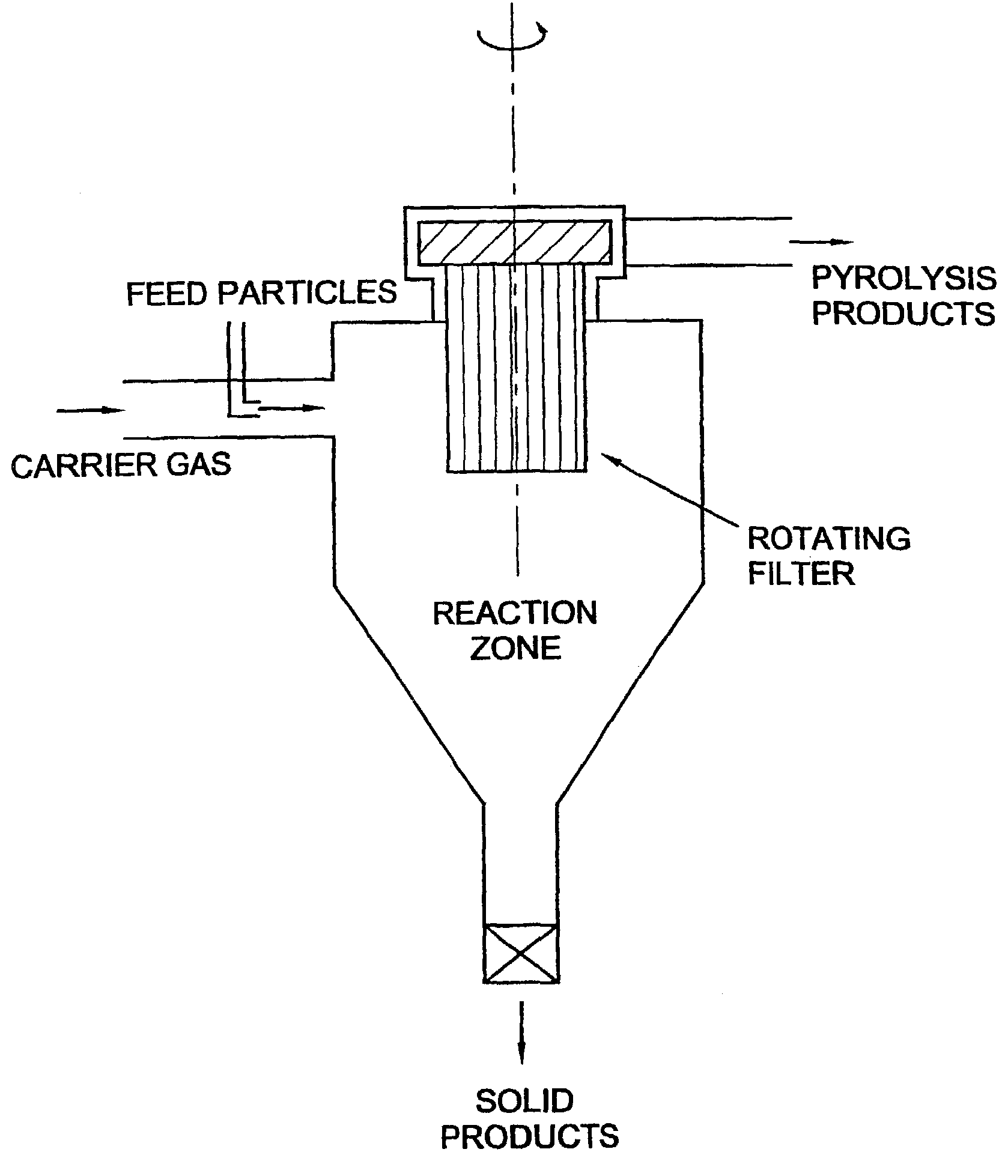
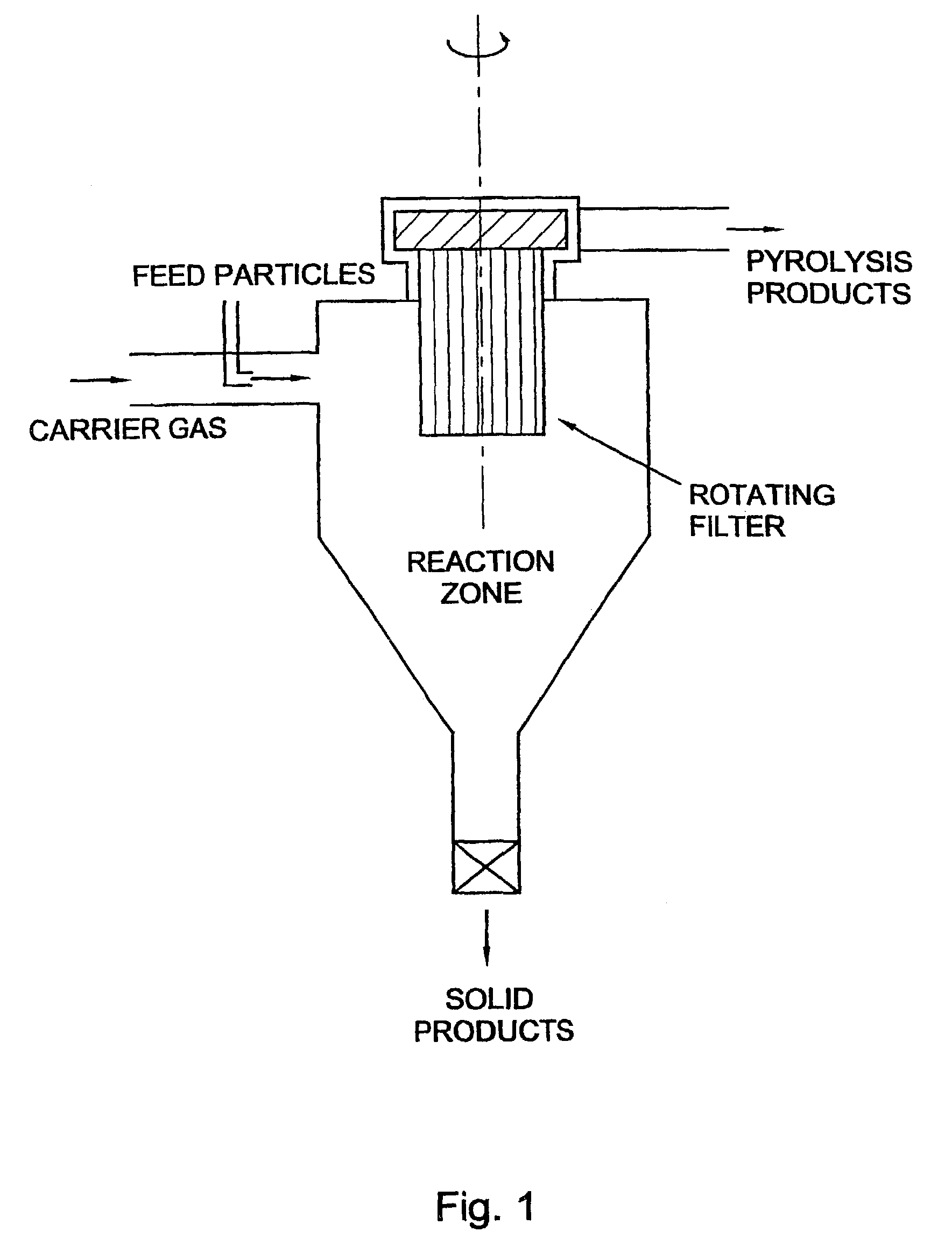
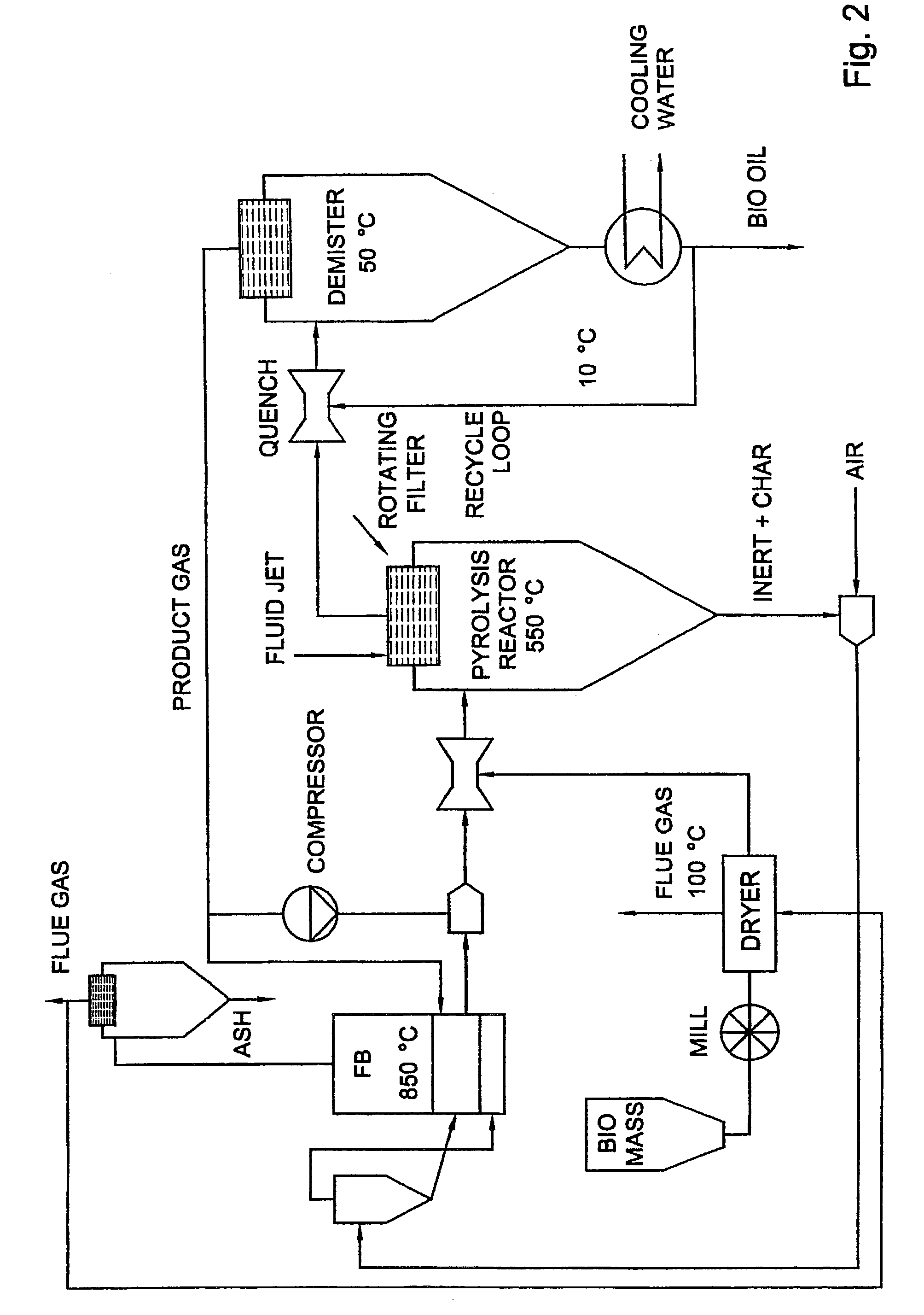
InactiveUS7202389B1Excessive crackingCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesCyclone
A process for the pyrolysis of carbonaceous material is carried out in a cyclone reactor which is fitted with enhanced filtering equipment. In addition the invention relates to the use of a cyclone fitted with a rotating filter as a pyrolysis reactor. By using a cyclone of the rotating separator type as a pyrolysis reactor, carbonaceous material, such as biomass, can effectively be converted in a product having excellent chemical properties and which product is free from particulate matter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
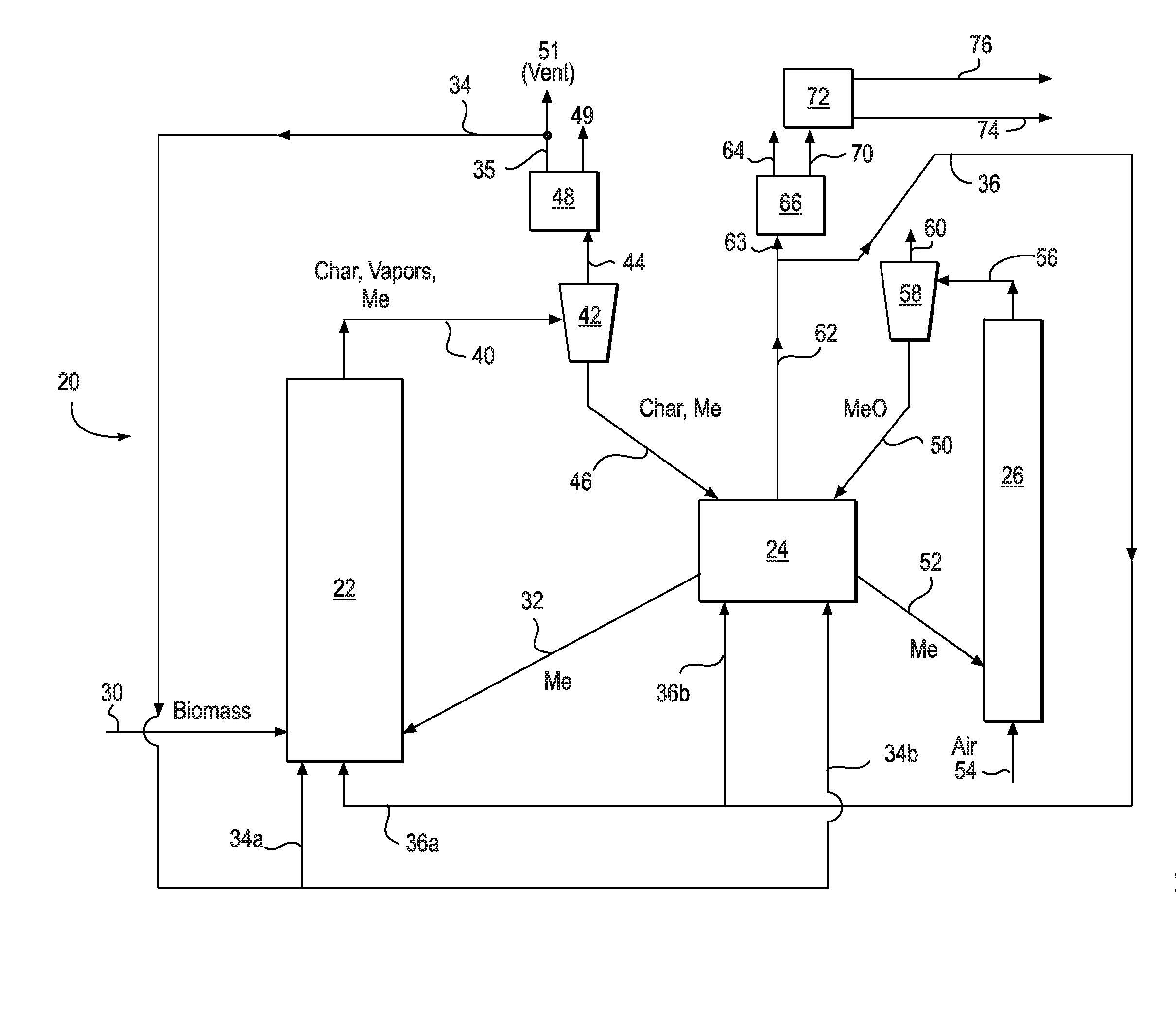
Method and system for capturing carbon dioxide from biomass pyrolysis process
A system and method for biomass pyrolysis utilizing chemical looping combustion of a produced char to capture carbon dioxide is disclosed. The system includes a biomass pyrolysis reactor, a char combustor, and oxidation reactor and a separator for separating carbon dioxide from flue gas produced by the char combustion. The pyrolysis reactor pyrolyzes biomass in the presence of reduced metal oxide sorbents producing char and pyrolysis oil vapor. The char is separated and combusted in the char combustor, in the presence of oxidized metal oxide sorbents, into a gaseous stream of carbon dioxide and water vapor. The carbon dioxide and water are separated so that a stream of carbon dioxide may be captured. The oxidation reactor oxidizes, in the presence of air, a portion of reduced metal oxide sorbents into oxidized metal oxide sorbents that are looped back to the char combustor to provide oxygen for combustion. A second portion of the reduced metal oxide sorbents is recycled from the char combustor to the pyrolysis reactor to provide heat to drive the pyrolysis. Pyrolysis oil upgrading catalyst particles may be used in addition to the metal oxide sorbents as heat energy carrier particles to improve the quality of the pyrolysis oil vapors produced in the pyrolysis reactor. Also, the metal oxide sorbents may have metals incorporated therein which serve to upgrade the pyrolysis vapors produced during pyrolysis. Non-limiting examples of such metals include Ni, Mo, Co, Cr, W, Rh, Ir, Re, and Ru.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
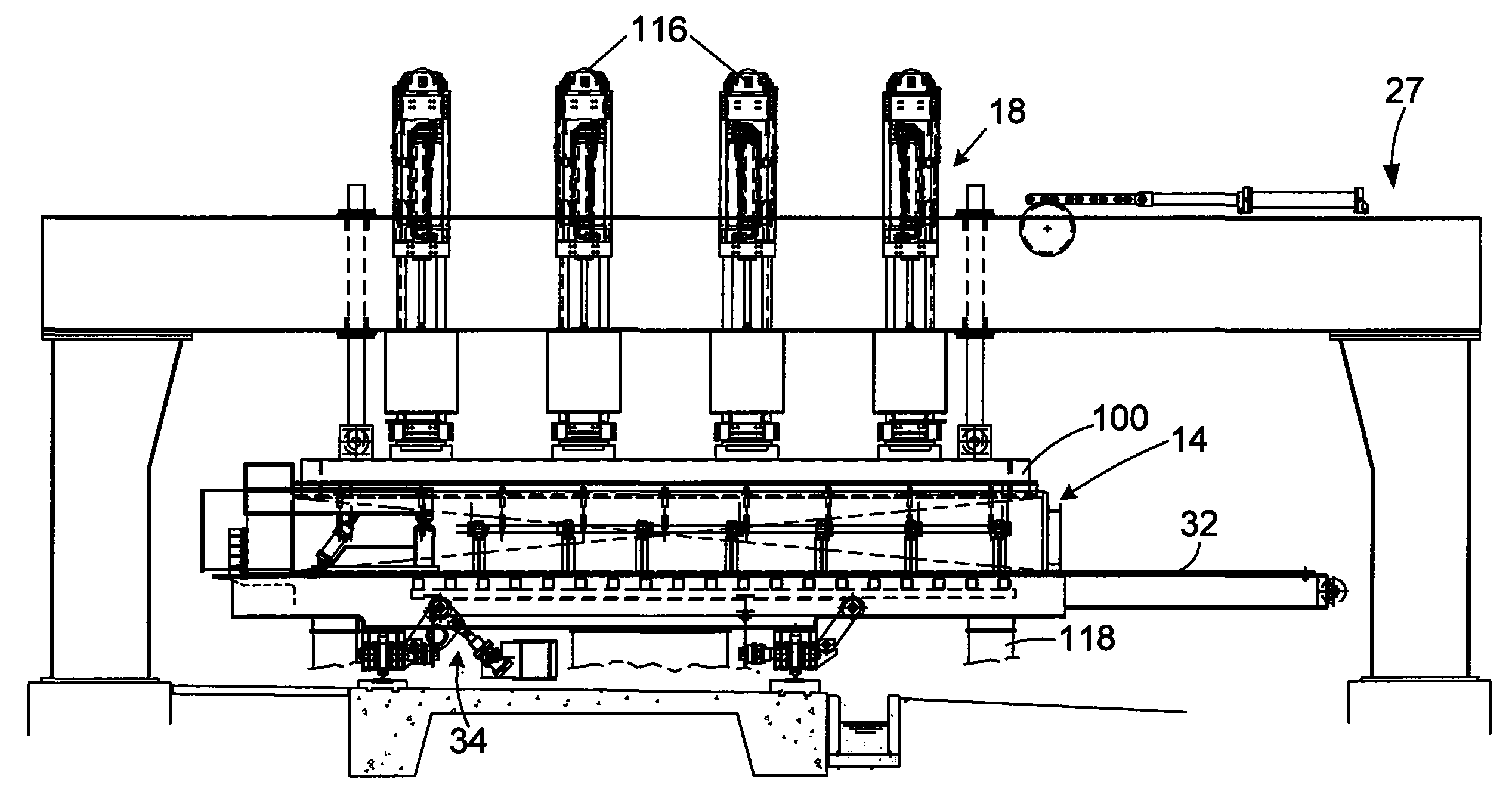
Process and plant for conversion of waste material to liquid fuel
ActiveUS20070179326A1Easy to wasteEasy feedingCatalytic crackingIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationEnvironmental engineeringLiquid fuel
A process and plant for the thermocatalytic conversion of waste materials into reusable fuels and a fuel produced by the process, involving the steps of delivering melted waste material (11) to one or more pyrolysis chambers (26) via heated and valved manifolds (22) and effecting pyrolysis of the waste material into a gascous state in an oxygen purged and pressure controlled environment. Pyrolytic gases are, then transferred to a catalytic converter (29) where the molecular structure of the gaseous material is altered in structure and form, with gases then transferred to one or more condensers (30a) to distil and cool gases in to their respective fractions. After post pyrolysis treatment, fuel fractions thon form a useable fuel. Includes the melting of waste (plastic) material (11) before delivery into any of the pyrolysis chambers (26), making the movement of material into the catalytic tower (29) a semi-continuous operation, directing melted waste material into one or more, but preferably four, pyrolysis chambers (26a, b, c, d), making each chamber capable of independent operation, optionally mechanically removing waste char from the pyrolysis chamber (107) by use of an internet auger (112) or other suitable means.
Owner:FUTURE ENERGY INVESTMENTS PTY LTD
Pyrolyzing gasification system and method of use
InactiveUS20050109603A1High gasifier discharge temperatureEfficient processGasifier mechanical detailsBiofuelsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesExternal combustion engine
Pyrolyzing gasification system and method of use including primary combustion of non-uniform solid fuels such as biomass and solid wastes within a refractory lined gasifier, secondary combustion of primary combustion gas within a staged, cyclonic, refractory lined oxidizer, and heat energy recovery from the oxidized flue gas within an indirect air-to-air all-ceramic heat exchanger or external combustion engine. Primary combustion occurs at low substoichoimetric air percentages of 10-30 percent and at temperatures below 1000 degrees F. Secondary combustion is staged and controlled for low NOx formation and prevention of formation of CO, hydrocarbons, and VOCs. The gasifier includes a furnace bed segmented into individual cells, each cell is independently monitored using a ramp temperature probe, and provided with controlled air injection. Gasifier air injection includes tuyere arrays, lances, or both. The oxidizer includes three serially aligned stages separated by air injecting baffles, and ability to adjust the exit air temperature.
Owner:HEAT TRANSFER INT
Method and apparatus for producing coke
ActiveUS8152970B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce moisture contentSpeed controllerCoke quenchingMetallurgyMetallurgical coke
A method and apparatus for quenching metallurgical coke made in a coking oven. The method includes pushing a unitary slab of hot coke onto a substantially planar receiving surface of a hot car. The hot car containing the coke is then transported to a quench car station. The unitary slab of hot coke is pushed onto a substantially planar receiving surface of a quench car at the quench car station. Quenching of the slab of hot coke is conducted in the quench car with a predetermine amount of water. After quenching, the quenched coke is dumped onto a receiving pad for collection thereof.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
Process and device for the pyrolysis of feedstock
InactiveUS7947155B1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCombustible gas coke oven heatingVolatilesEngineering
This invention involves pyrolysis of feedstock by introducing carbonaceous feedstock, into a hopper and moving it into a reactor tube enclosed in an oven, generating heat within the oven that is in part transferred to the feedstock, heating it to sufficient temperature to pyrolyze the feedstock into useful volatiles and char. A Venturi system produces a negative pressure directing volatiles into a pyro-gas oven producing heat necessary for pyrolysis and generating useful excess heat. The extruded pyrolysis char has uses including charcoal fuel, soil amendments, and activated charcoal while liquids can be produced for processing into fuels. Excess heat may be used to heat water, steam, and air, may be used in air heating and cooling systems, perform mechanical work with a Stirling engine or generate electricity on the order of 100 kW and higher. The system may be operated in a carbon neutral or even carbon negative manner, allowing sequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Owner:GREEN LIQUID & GAS TECH
Coker feed method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080179165A1Reduces drum/vessel thermal stressReduce thermal stressThermal non-catalytic crackingCombustible gas coke oven heatingEngineeringVertical axis
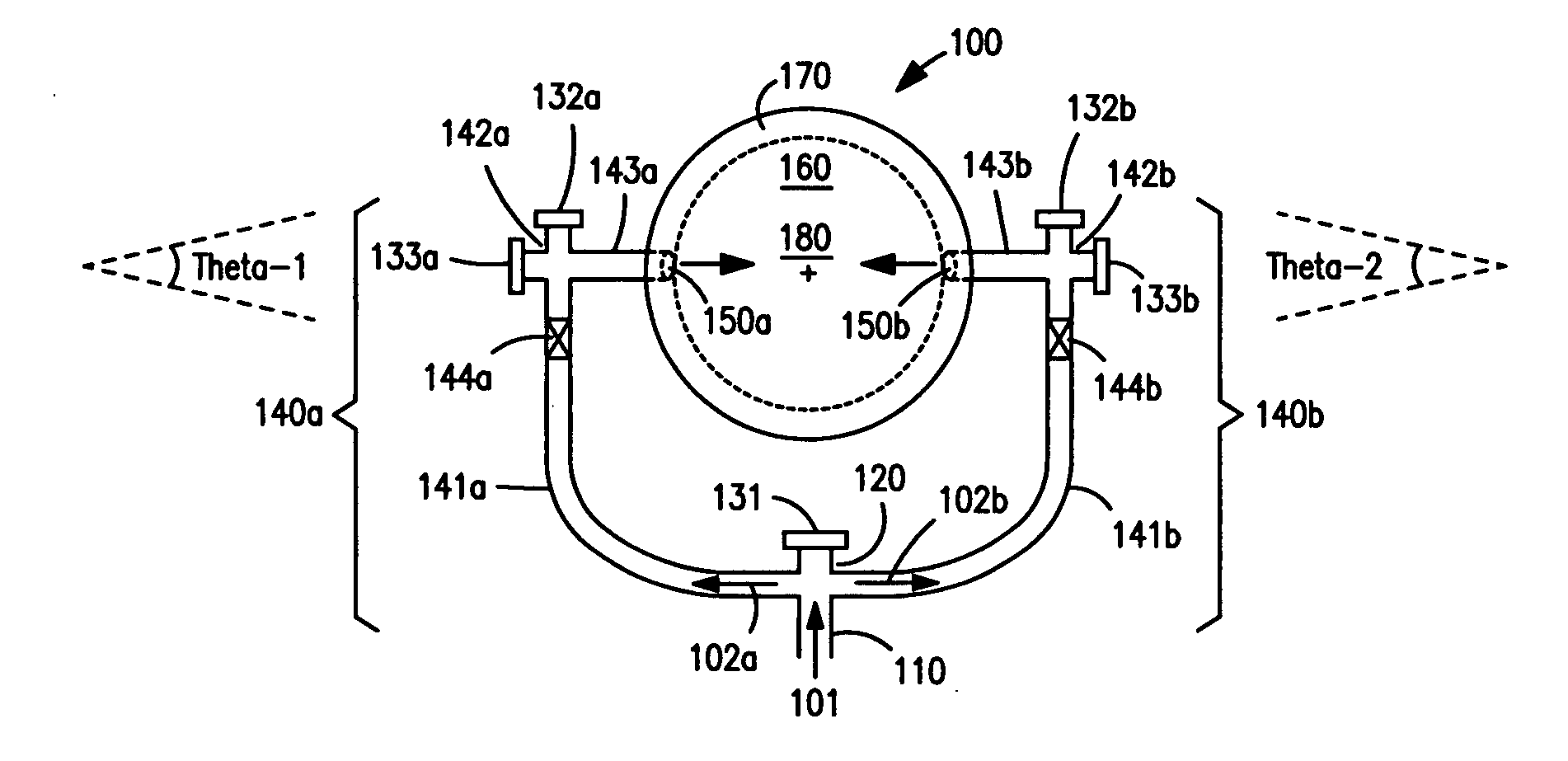
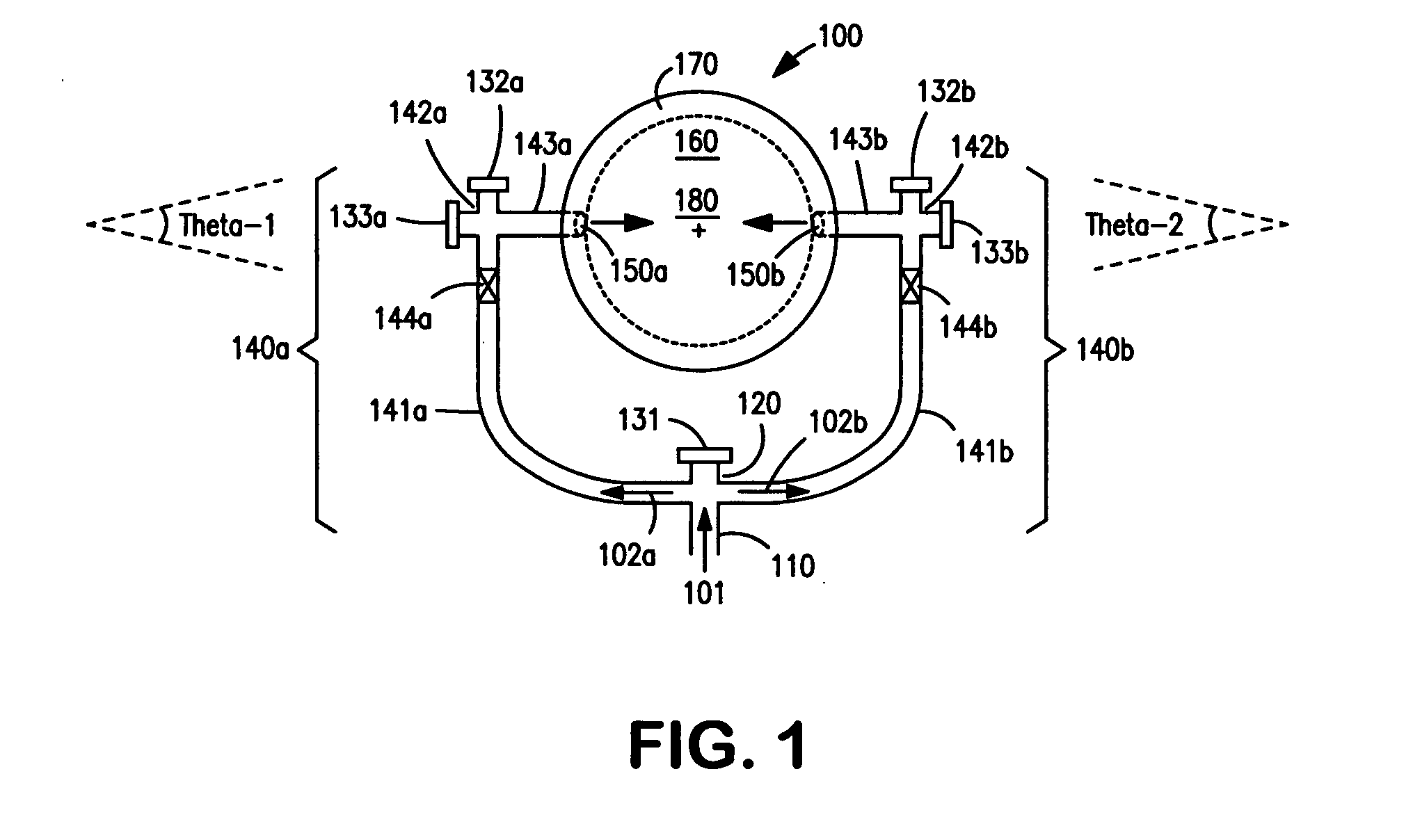
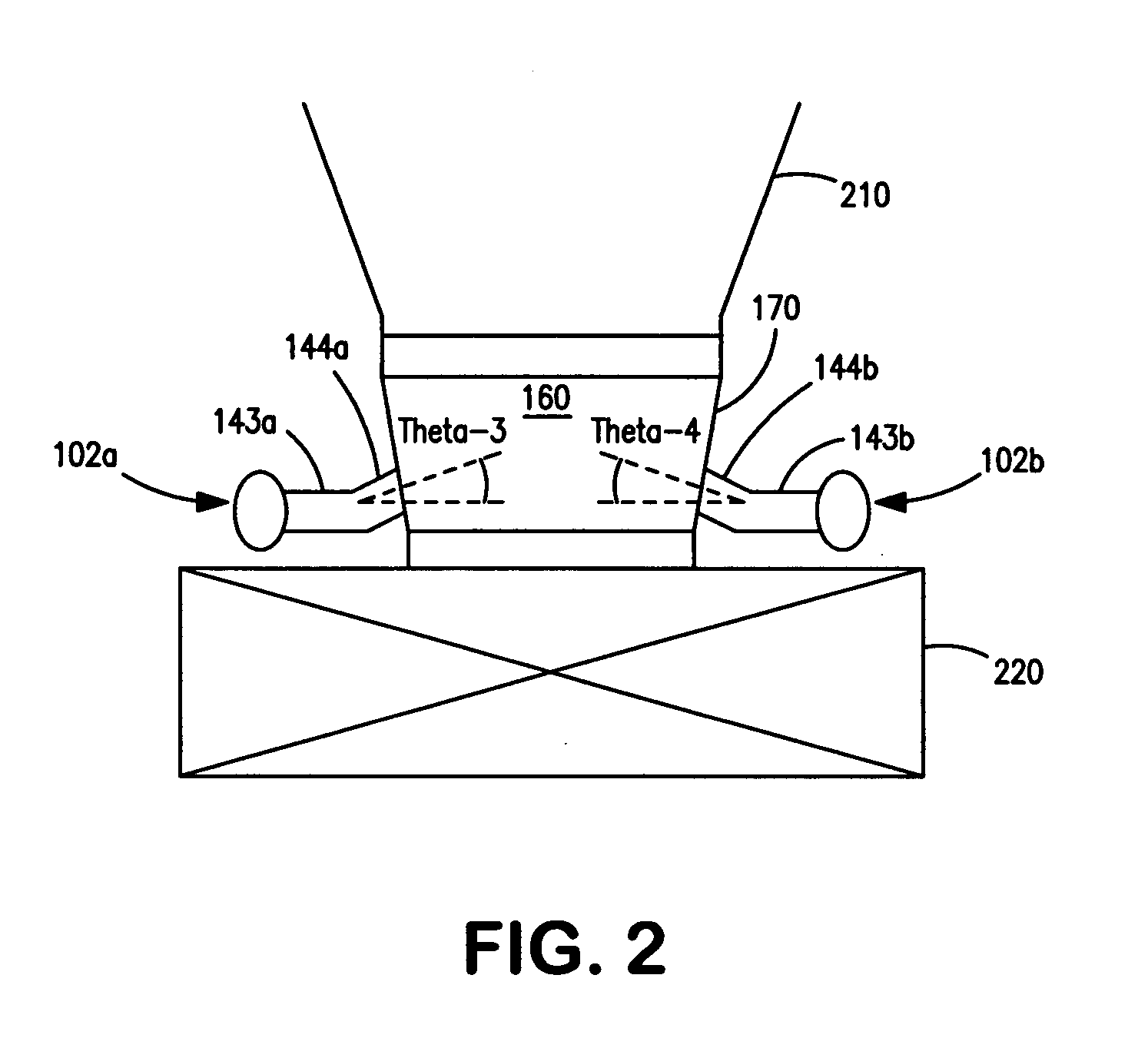
Described herein are methods and mechanisms for laterally dispensing fluid to a coke drum in a predictable and maintainable manner that alleviates thermal stress. In one embodiment, the methods and mechanisms utilize a split piping system to dispense fluid through two or more inlets into a spool that is connected to a coke drum and a coke drum bottom deheader valve. A combination of block valves and clean out ports provides a more effective means to clean the lines and allows fluid to be laterally dispensed in a controllable and predictable manner. The fluid is preferably introduced to the spool in opposing directions toward a central vertical axis of the spool at equal but opposing angles ranging from minus thirty (−30) to thirty (30) degrees relative to a horizontal line laterally bisecting the spool. Alternatively, however, fluid can be introduced to the spool tangentially.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Flat push coke wet quenching apparatus and process
InactiveUS7998316B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove efficiencyCoke quenchingDirect heating destructive distillationCoke ovenWater level
A method and apparatus for quenching metallurgical coke made in a coking oven. The method includes pushing a unitary slab of incandescent coke onto a substantially planar receiving surface of an enclosed quenching car so that substantially all of the coke from the coking oven is pushed as a unitary slab onto the receiving surface of the quenching car. The slab of incandescent coke is quenched in an enclosed environment within the quenching car with a plurality of water quench nozzles while submerging at least a portion of the slab of incandescent coke by raising a water level in the quenching car. Subsequent to quenching the coke, the planar receiving surface is tilted to an angle sufficient to slide the quenched coke off of the planar receiving surface and onto a product collection conveyer and sufficient to drain water from the quenched coke.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
Process for transporting and quenching coke
ActiveUS8236142B2Emission minimizationMinimize timeCoke quenchingDirect heating destructive distillationDust controlProcess engineering
A method and apparatus for transporting and quenching coke, useful in quenching a batch of coke produced in one of a plurality of coke ovens forming a coke oven battery, is disclosed. A hot car defining a substantially planar receiving surface is positioned adjacent a coke oven of the coke oven battery, and a unitary cake of unquenched coke is placed onto the hot car receiving surface. The hot car and unquenched coke are transported to a transfer station having a dust collection system. A quenching car is positioned at the transfer station adjacent the hot car, under the dust collection system. The unitary cake of unquenched coke is dumped into the quenching car receptacle, thereby separating the unitary cake. At least a portion of the dust generated by separation is collected. The quench car is then transported to a quenching station, where the separated coke is quenched.
Owner:WESTBROOK THERMAL TECH
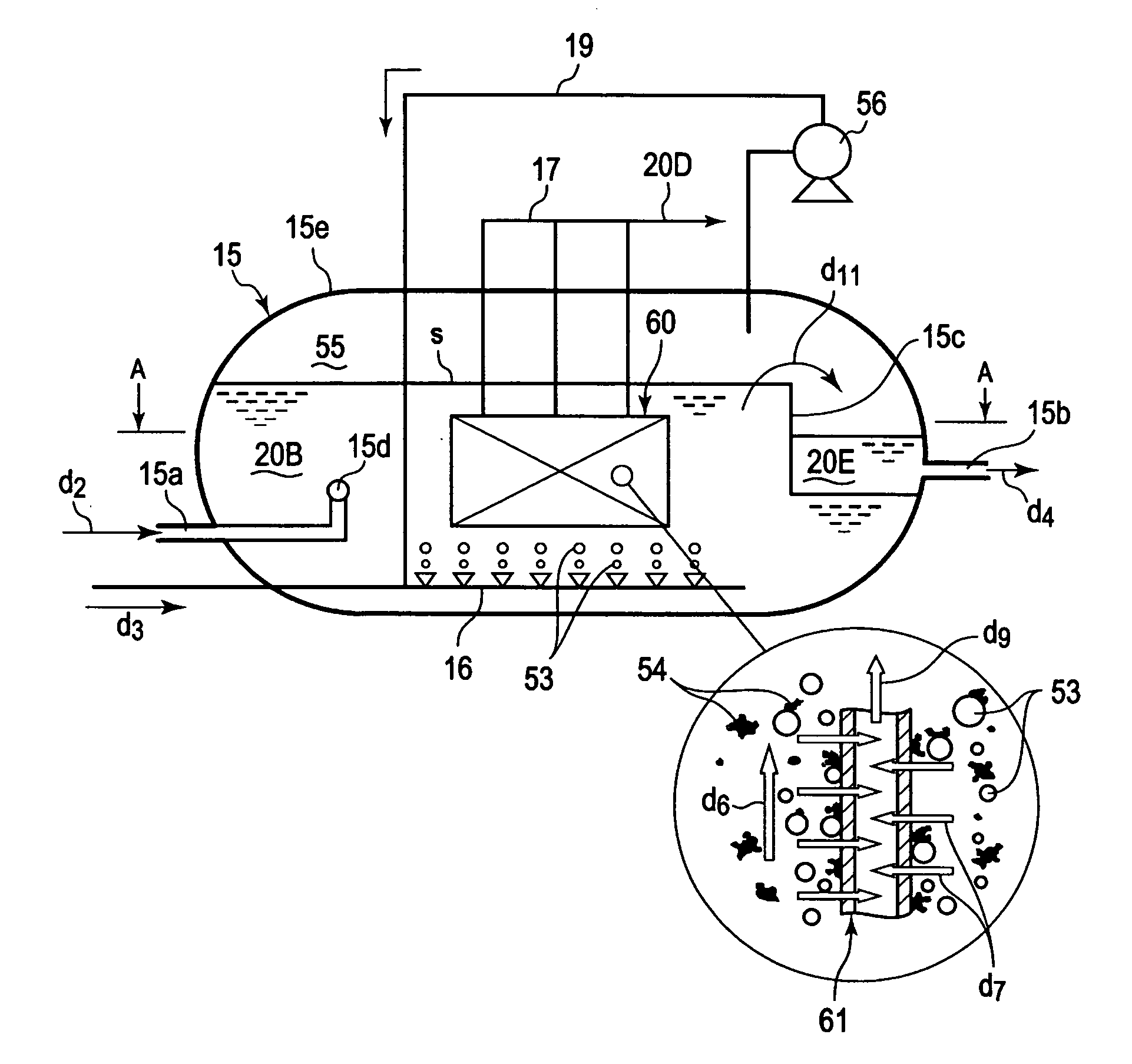
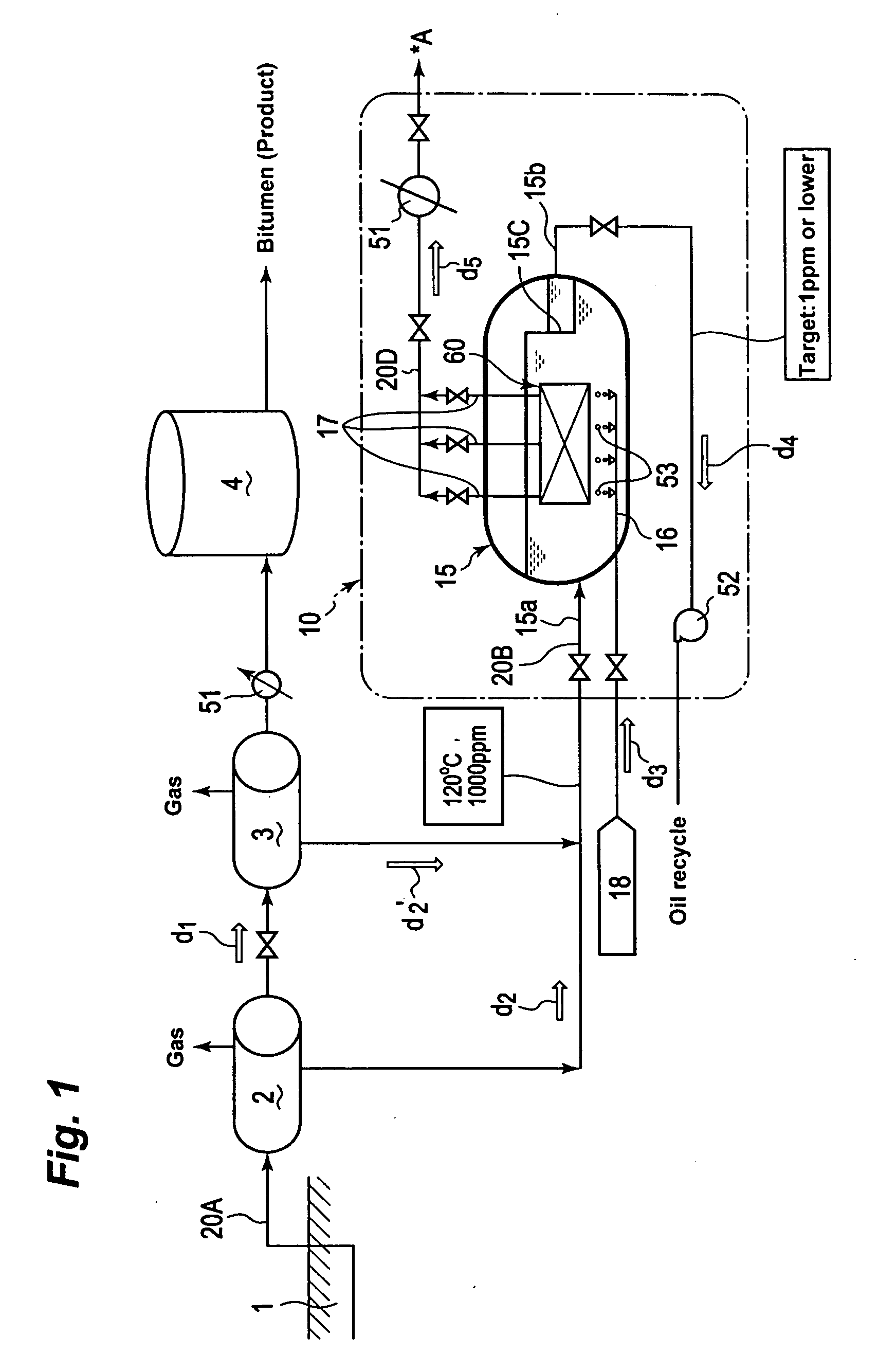
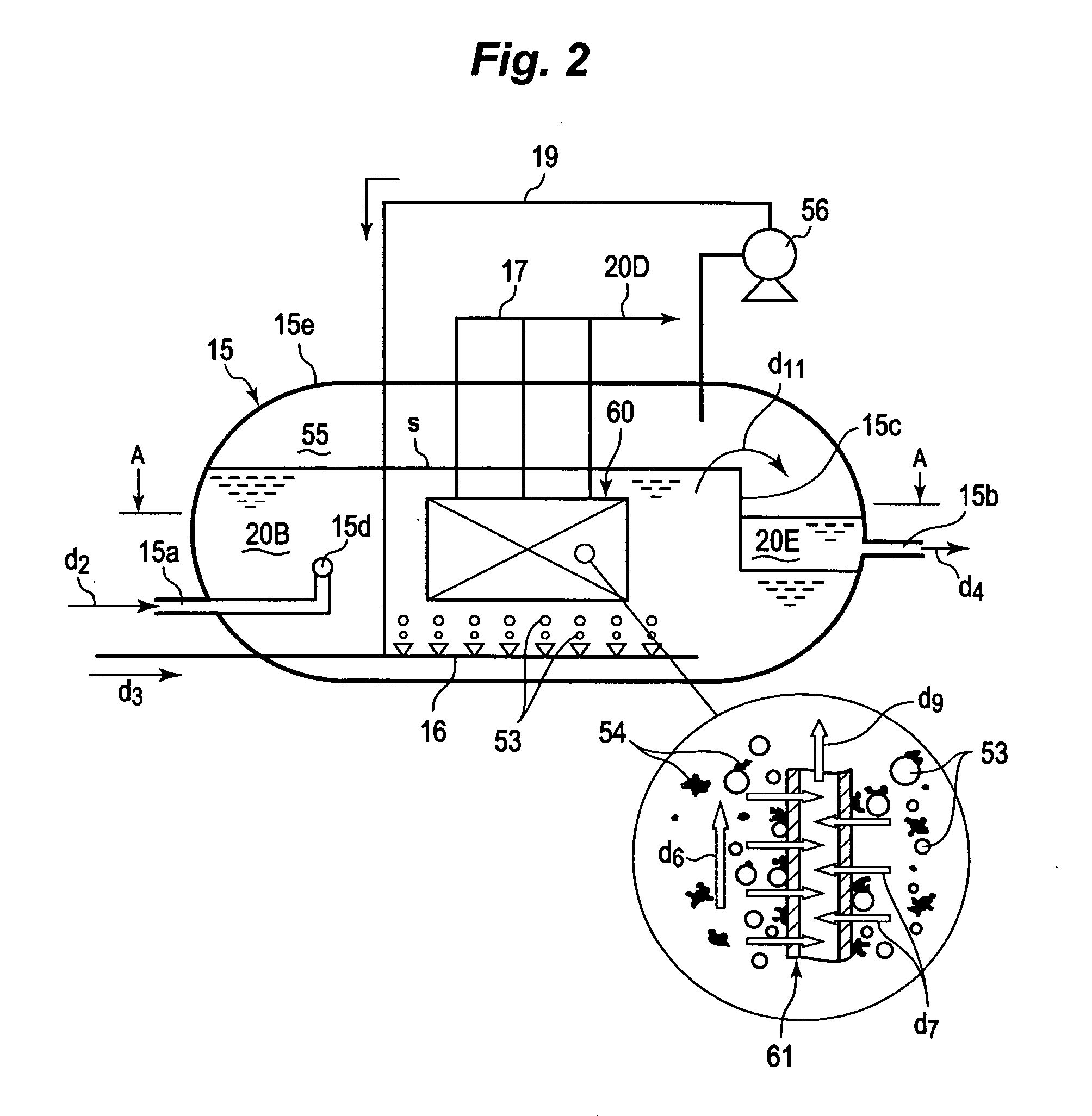
Apparatus of produced water treatment, system and method of using the apparatus, and method of water reuse by using the same
An apparatus of produced water treatment, to be adopted in an in-situ recovery method of producing bitumen from oil sand, the apparatus capable of removing the oil from produced water, the produced water of being left by separating the bitumen from bitumen-mixed fluid having been recovered from the oil sand, the apparatus having: a vessel for receiving the produced water; a submerge type filtration membrane module, installed in the vessel, for filtering the produced water in the condition of the membrane being submerged in the produced water; and a bubble generator for generating bubbles to be forwarded toward the submerged filtration membrane in the produced water.
Owner:TOYO ENG CORP +1
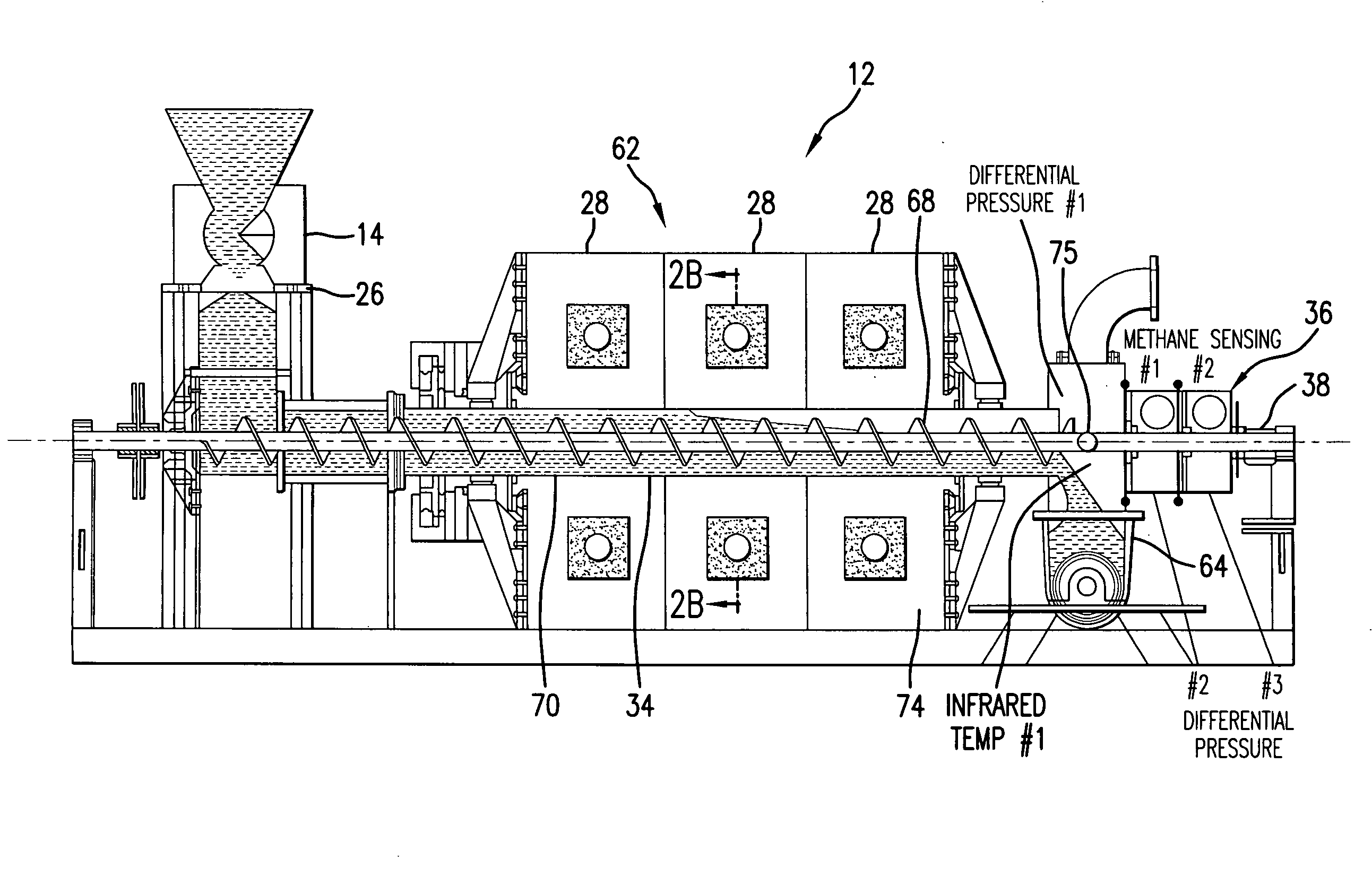
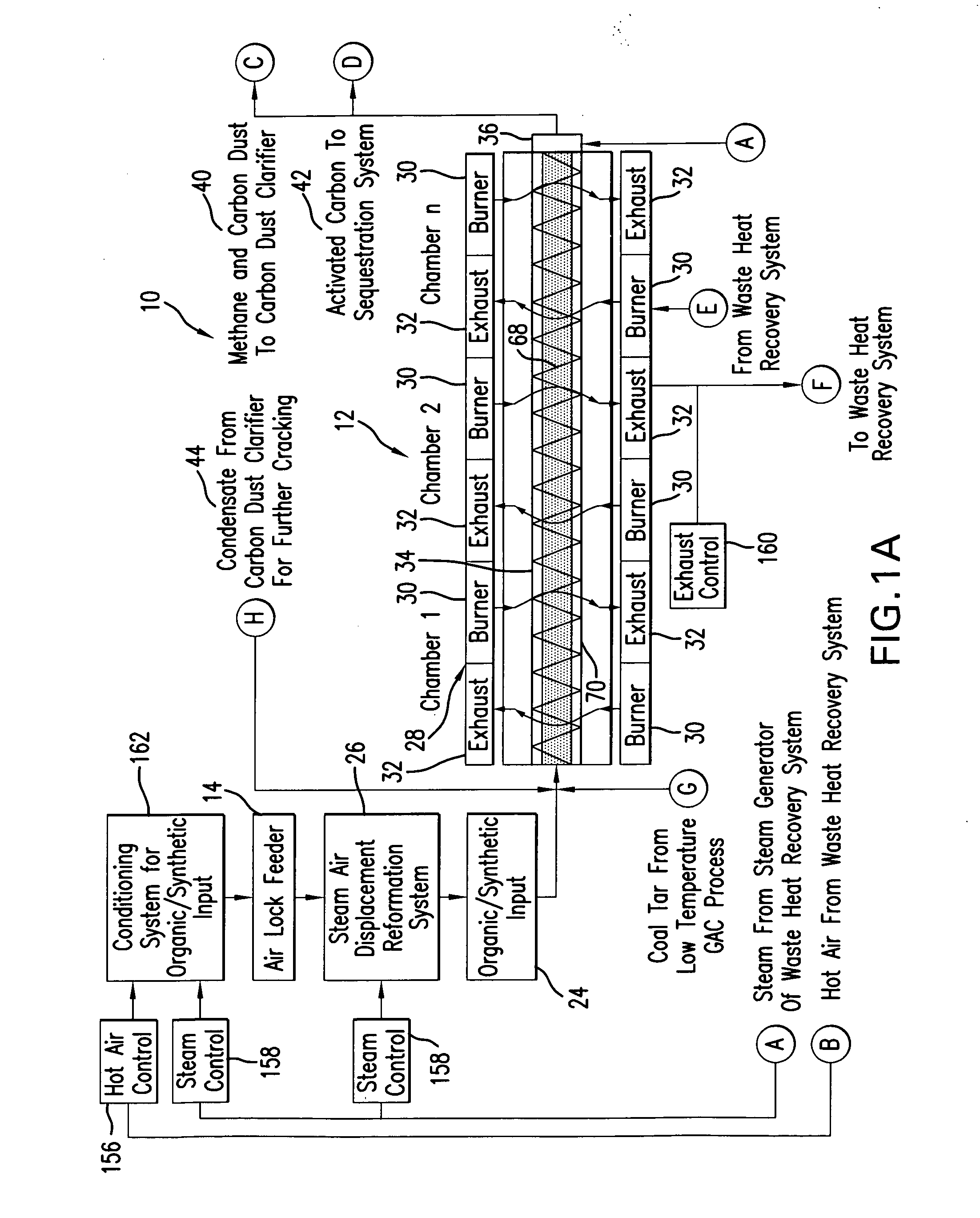
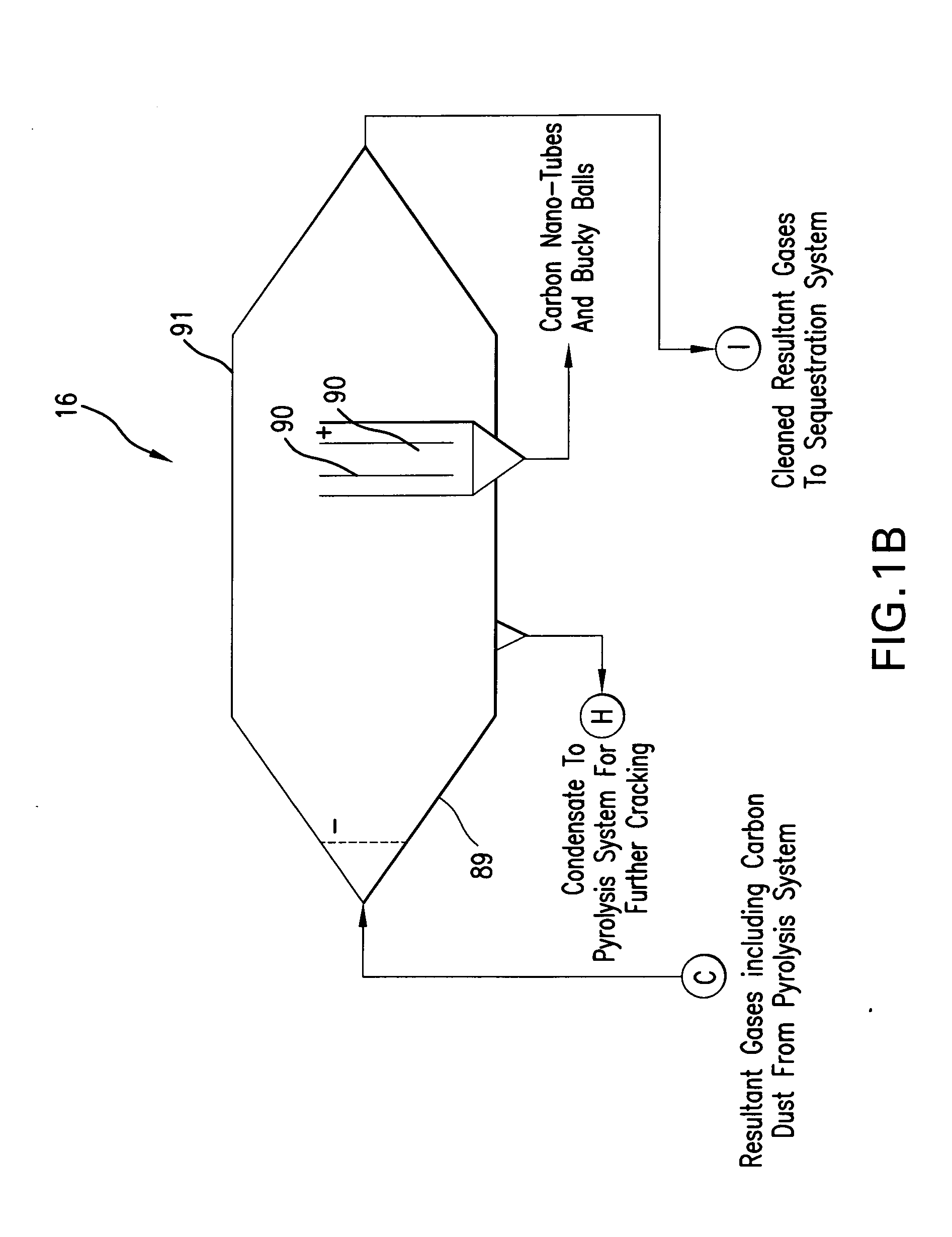
Pyrolysis Systems, Methods, and Resultants Derived Therefrom
ActiveUS20080286557A1Fit closelyWithout undesired degradation of communication system performanceLayered productsUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbon filtrationSilicon dioxide
A system and process for gasification of a carbonaceous feedstock uses pyrolysis to produce a gas product, which may include methane, ethane, and other desirable hydrocarbon gases, and a solids product, which includes activated carbon or carbon. The gas product may then be filtered using at least a portion of the activated carbon from the solids product as a filtering medium. In an embodiment, at least some of the noxious chemicals are sequestered or removed from the gas product in one or more filtering steps using the activated carbon as a filtering medium. In a further embodiment, the filtering steps are performed in stages using activated carbon at different temperatures. A high-temperature pyrolysis system that produces activated carbon may be combined with another high-temperature pyrolysis system that does not produce activated carbon to provide filtering of noxious compounds using activated carbon from the first high-temperature pyrolysis system. A high-temperature pyrolysis system may be combined with one or more low-temperature feedstock conversion processes such that waste heat from the high-temperature pyrolysis system is used to operate the low-temperature process. A novel non-wetting carbon having pores fused with silica can be produced from using the system and process.
Owner:TUCKER RICHARD D
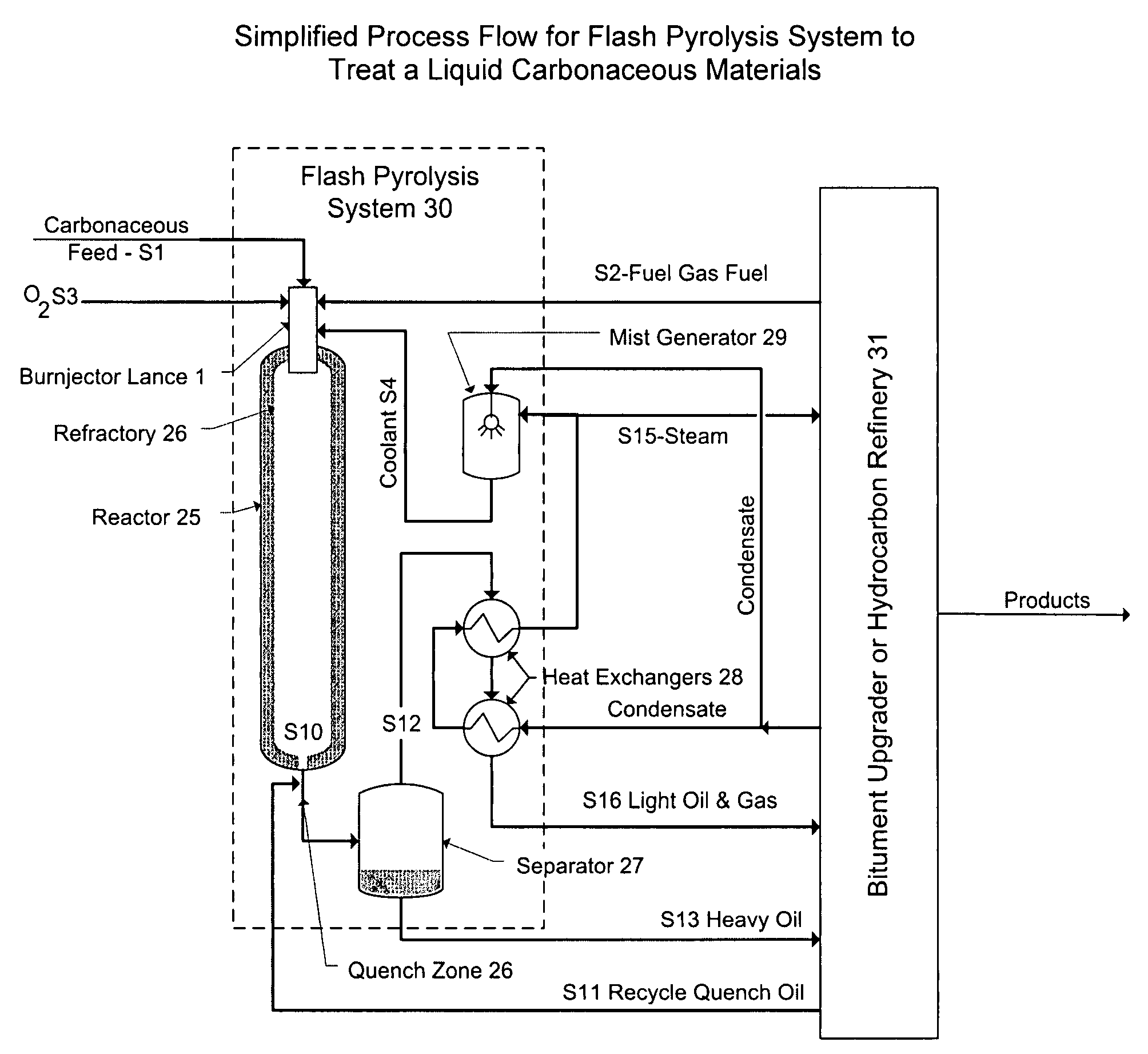
Flash pyrolosis method for carbonaceous materials
InactiveUS20070272538A1Efficient transferFast heatingThermal non-catalytic crackingDirect heating destructive distillationSufficient timeBoiling point
Methods are disclosed for pyrolizing carbonaceous materials to carbonaceous materials having lower boiling points by heating the carbonaceous material to a desired reaction temperature and holding the carbonaceous material in contact with the heat for a sufficient time to achieve the desired reaction to a lower boiling point carbonaceous materials, then rapidly cooling the desired reaction products. The heating source is a jet which will provide hot and high velocity gas streams to the carbonaceous material to be heated.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Apparatus and process for the pyrolysis of agricultural biomass
InactiveUS7943014B2Avoid cloggingPrevent escapeFluidized bed combustionCombustible gas coke oven heatingCombustion chamberFluidized bed
An integrated combustion chamber and fluidized bed pyrolysis reactor. In one embodiment, the combustion chamber is cylindrical and the pyrolysis reactor is provided annularly about the combustion chamber with an annular wall that provides a common surface for heat transfer. A lift tube in fluid communication with the pyrolysis reactor is provided within the combustion chamber for circulating biomass and an inert fluidizable media upwardly through the lift tube; this advantageously increases heat transfer and leads to more rapid pyrolysis. The media and biomass exit the lift tube into either a freeboard area of the pyrolysis reactor or into a low density region of the fluidized bed. A condensable gaseous product is produced during pyrolysis that has economic value. The apparatus and process are especially well suited to the pyrolysis of low density agricultural biomass. The apparatus is compact and particularly well suited to mobile operation.
Owner:AGRI THERM
Carbonization and gasification of biomass and power generation system
InactiveUS20050247553A1Increase temperatureHigh thermal efficiencyBeehive ovensCombustible gas catalytic treatmentCarbonizationTar
Biomass, including waste biomass, is gasified by a process in which the biomass is first carbonized, and the char and pyrolysis gas from the carbonizer are respectively fed to a high temperature gasifying part and a gas reformer part of a two-stage gasifier. A gasifying agent is continuously fed to the gasifying part, and intermittently fed to the gas reformer, to maintain the temperature required to avoid tar formation in the gas reformer stage. Multiple carbonization chambers are operated in rotation. When the carbonization / gasification apparatus is used to provide fuel to an electric power generator set, exhaust heat from the generator power plant is fed back to the carbonizer, and can be supplemented by exchange of heat from the gas delivered to generator power plant from the outlet of the gasifier.
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY +1
Coke oven flue gas sharing
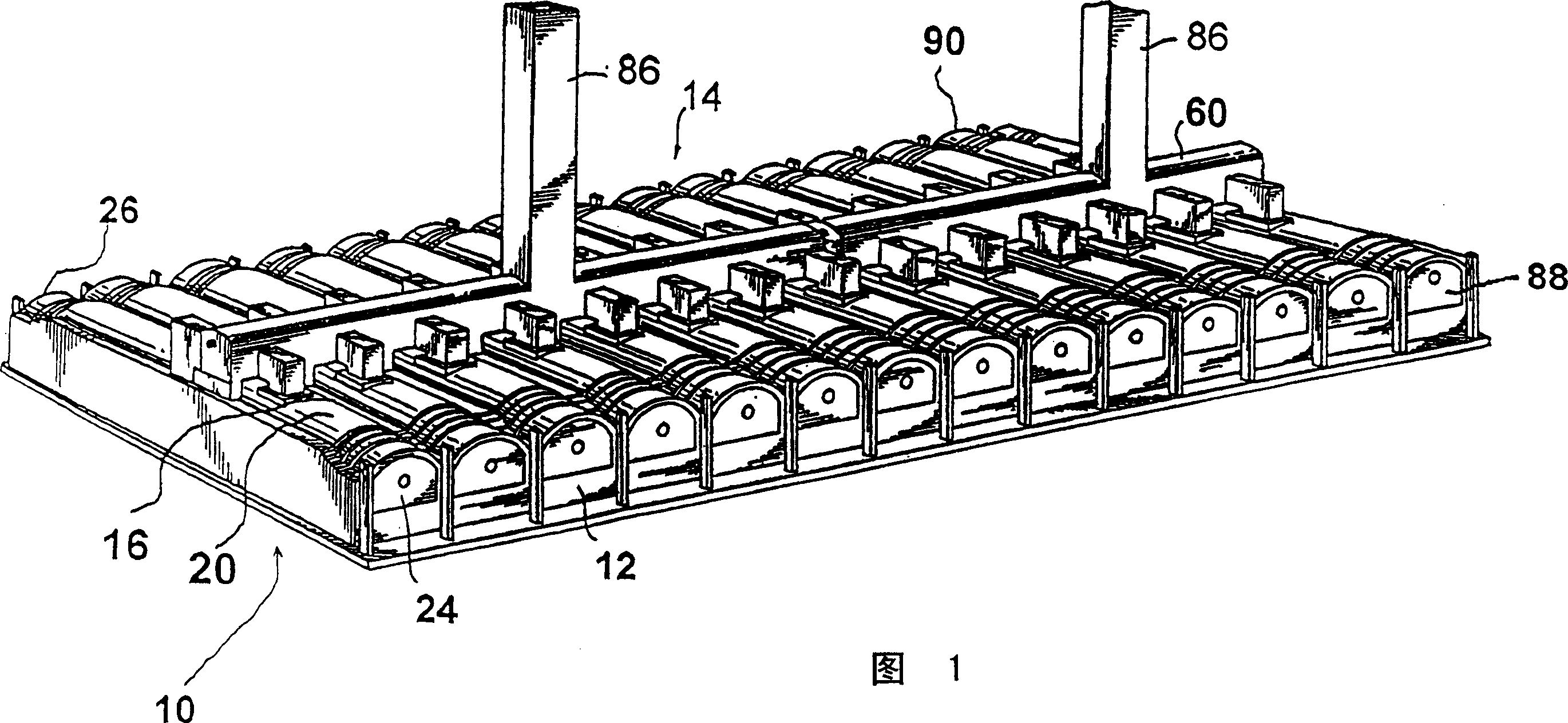
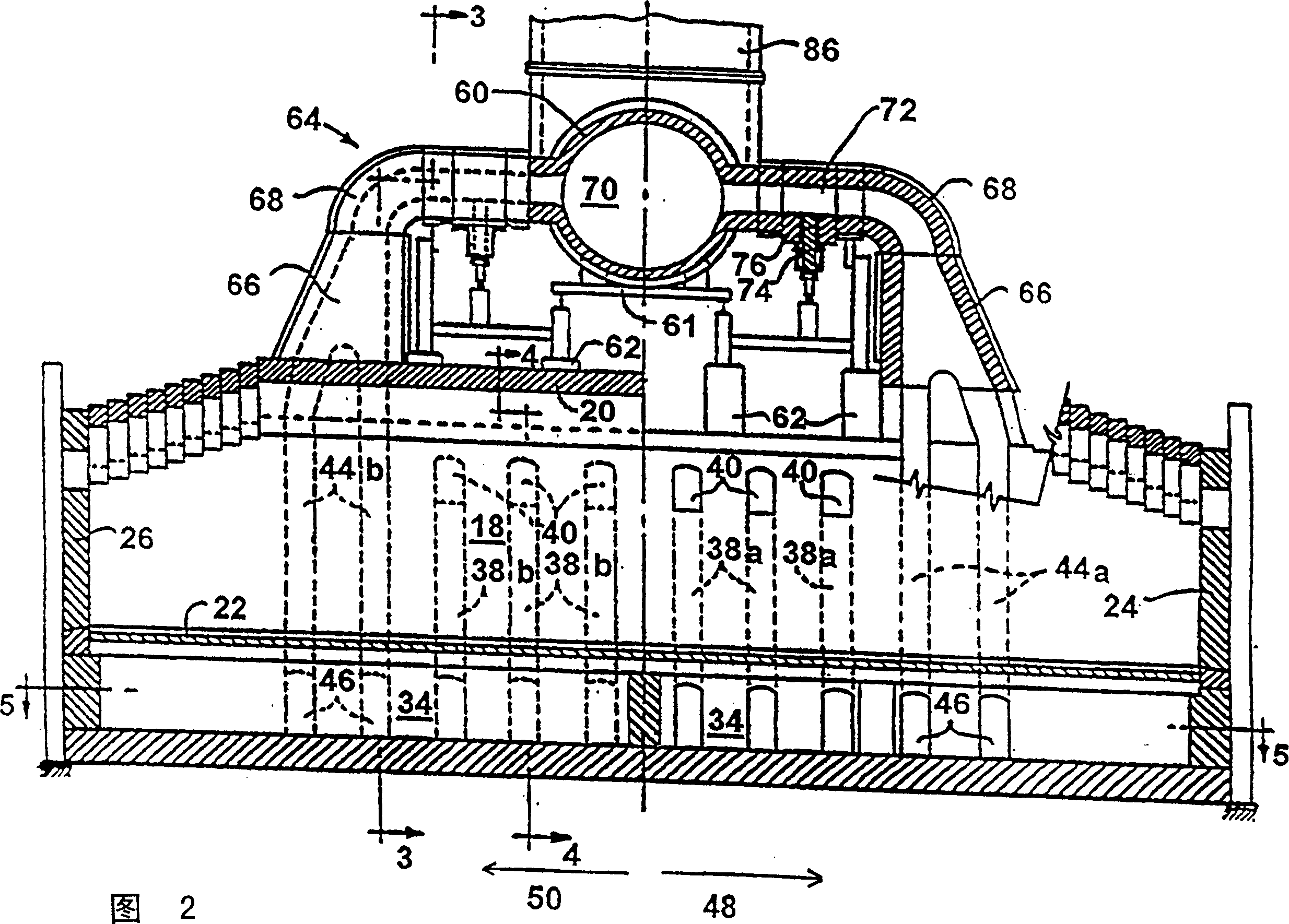
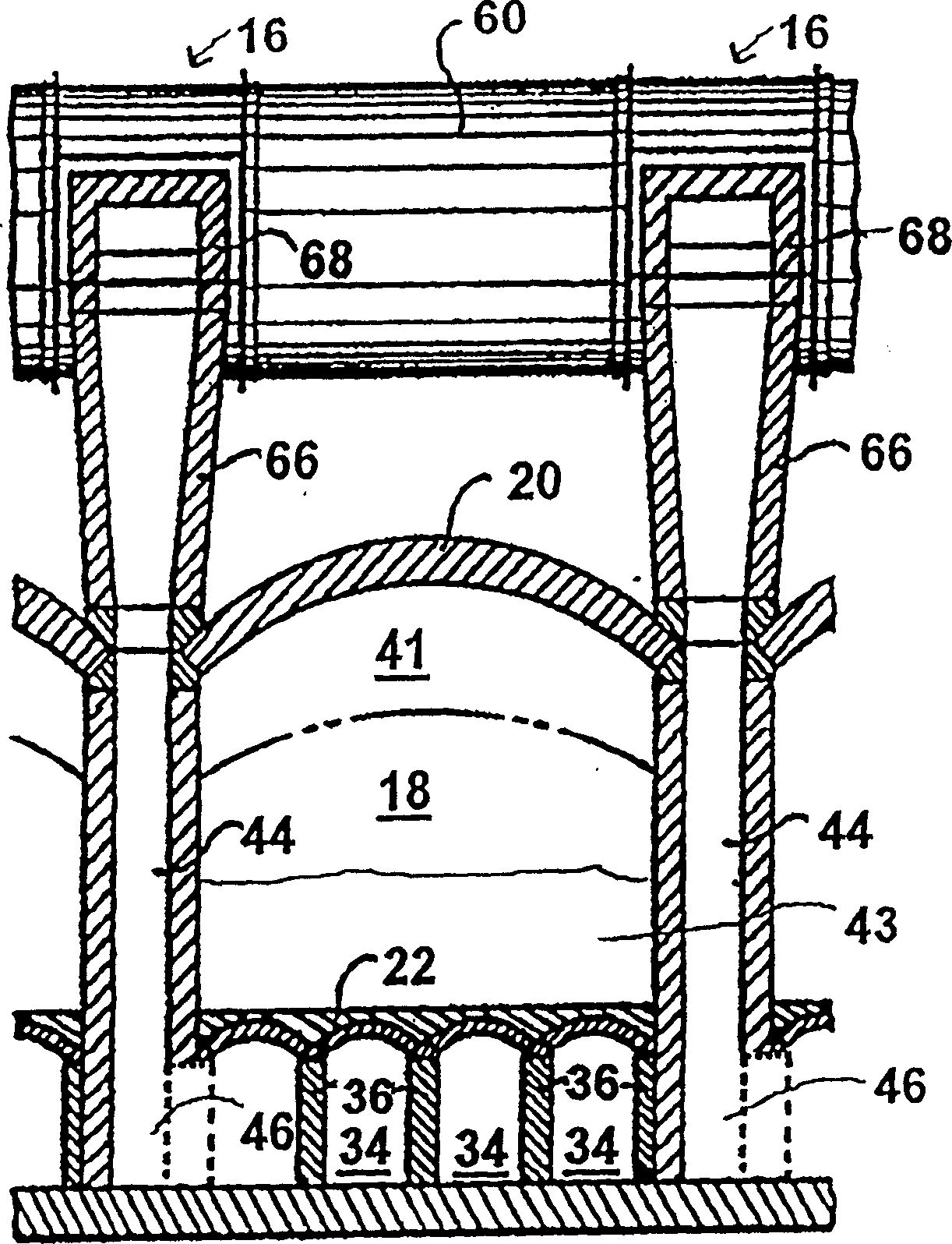
InactiveCN1527872AExtend your lifeReduce the gas flow rateCombustible gas coke oven heatingBeehive ovensFlue gasProduct gas
The invention provide a method and apparatus for decreasing gas flow rates in a sole flue gas system for a coke oven during at least an initial coking operation after charging a coking oven with coal (43). The method includes providing a duct system (96, 98) between a first coke oven having a first coking chamber (18) and a second coke oven having a second coking chamber (18) to direct at least a portion of gas from a gas space (41) in first coking chamber (18) to the second coke oven thereby reducing a gas flow rate in the first sole flue gas system of the first coke oven. Reduction in sole flue gas flow rates has a beneficial effect on product throughput, the life of the coke oven and environmental control of volatile emissions from coke ovens.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com