Patents
Literature
117results about "Beehive ovens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
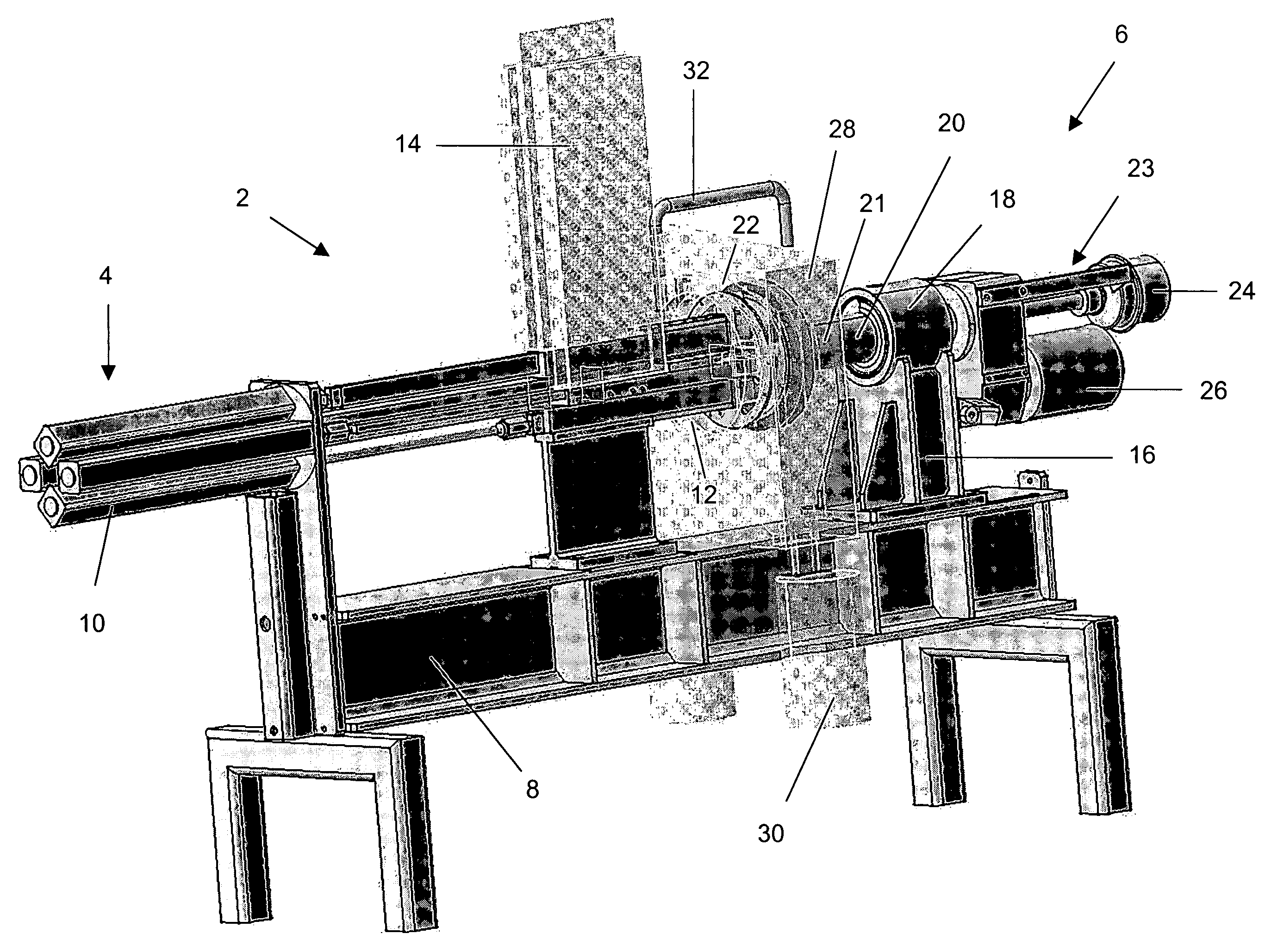
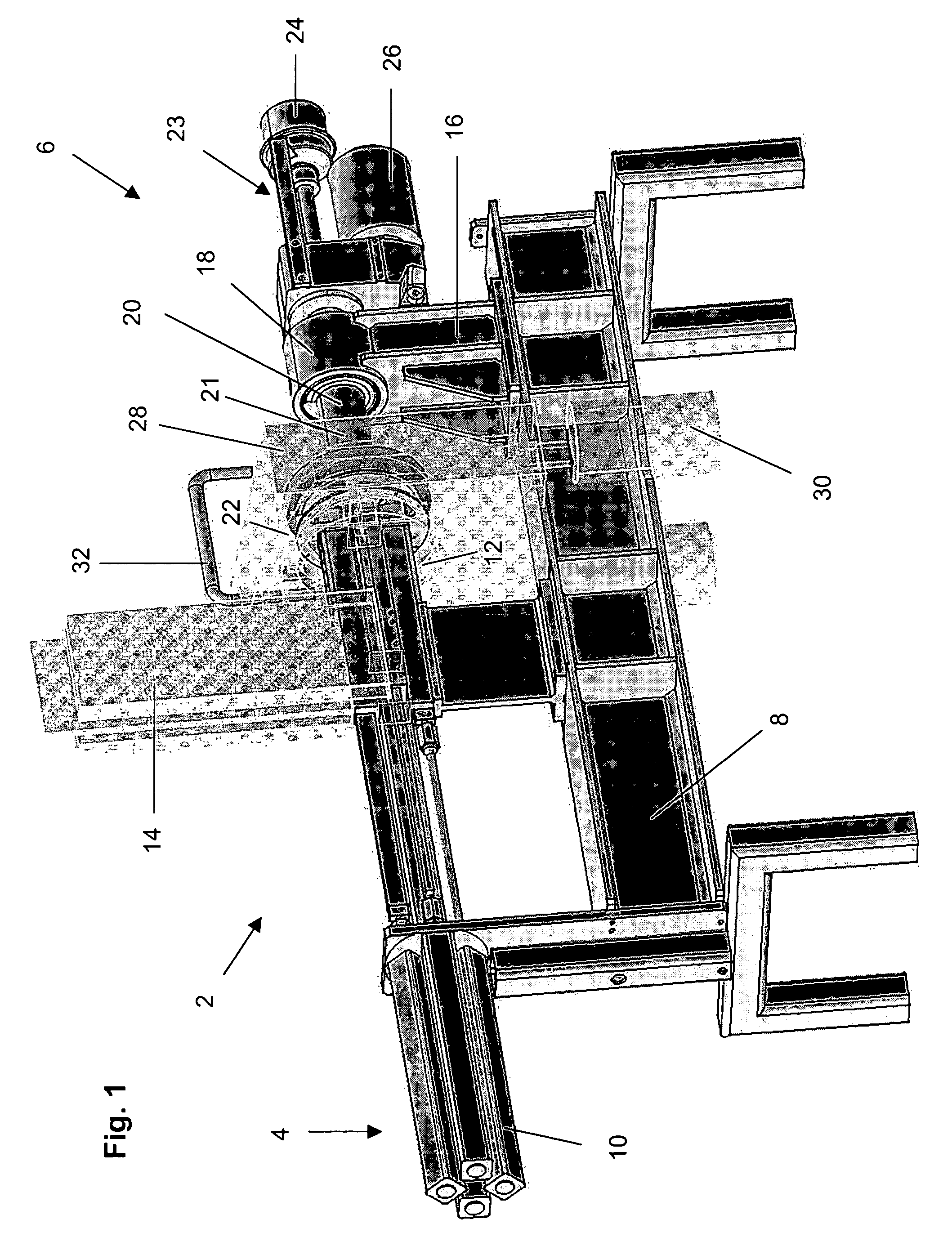
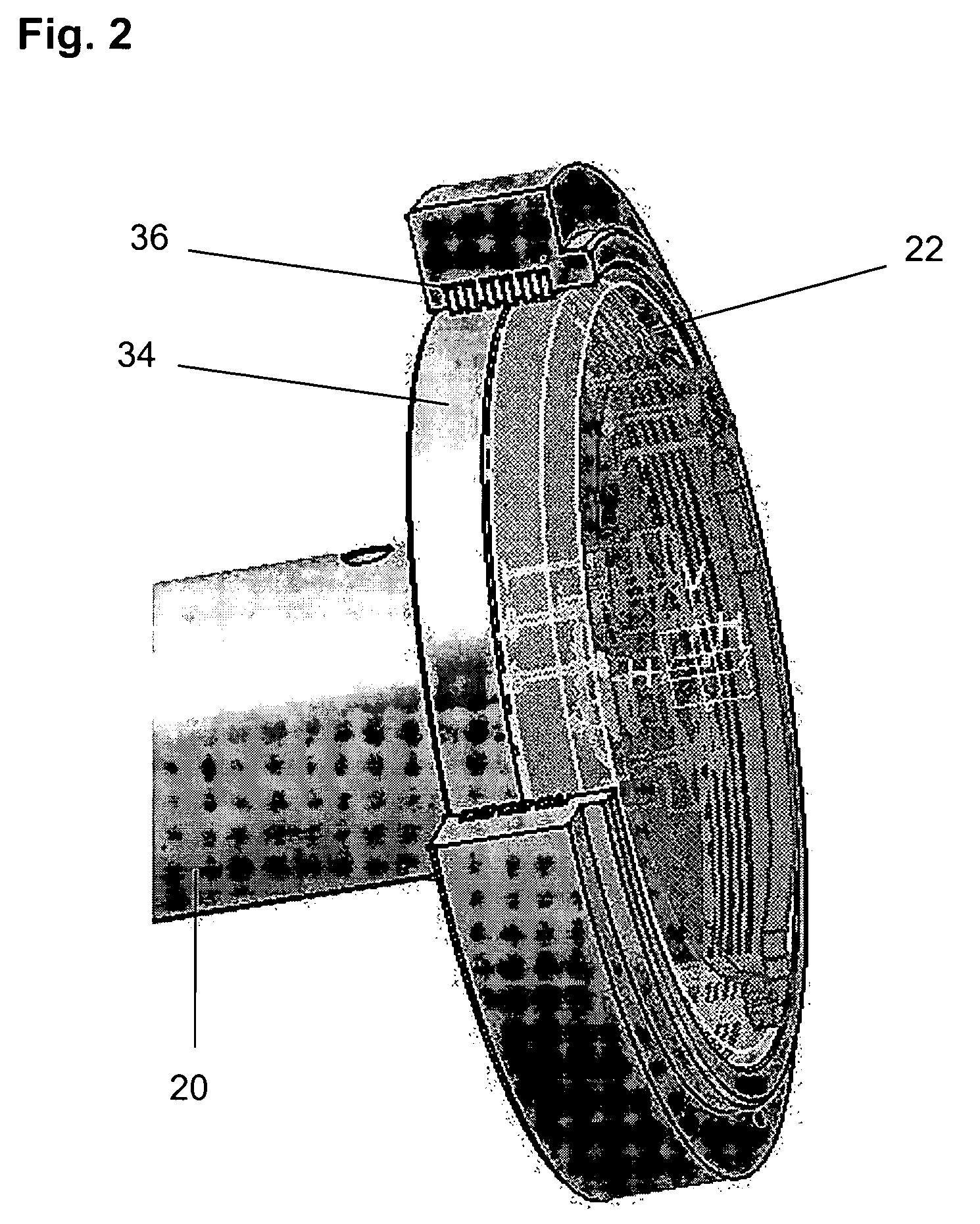
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
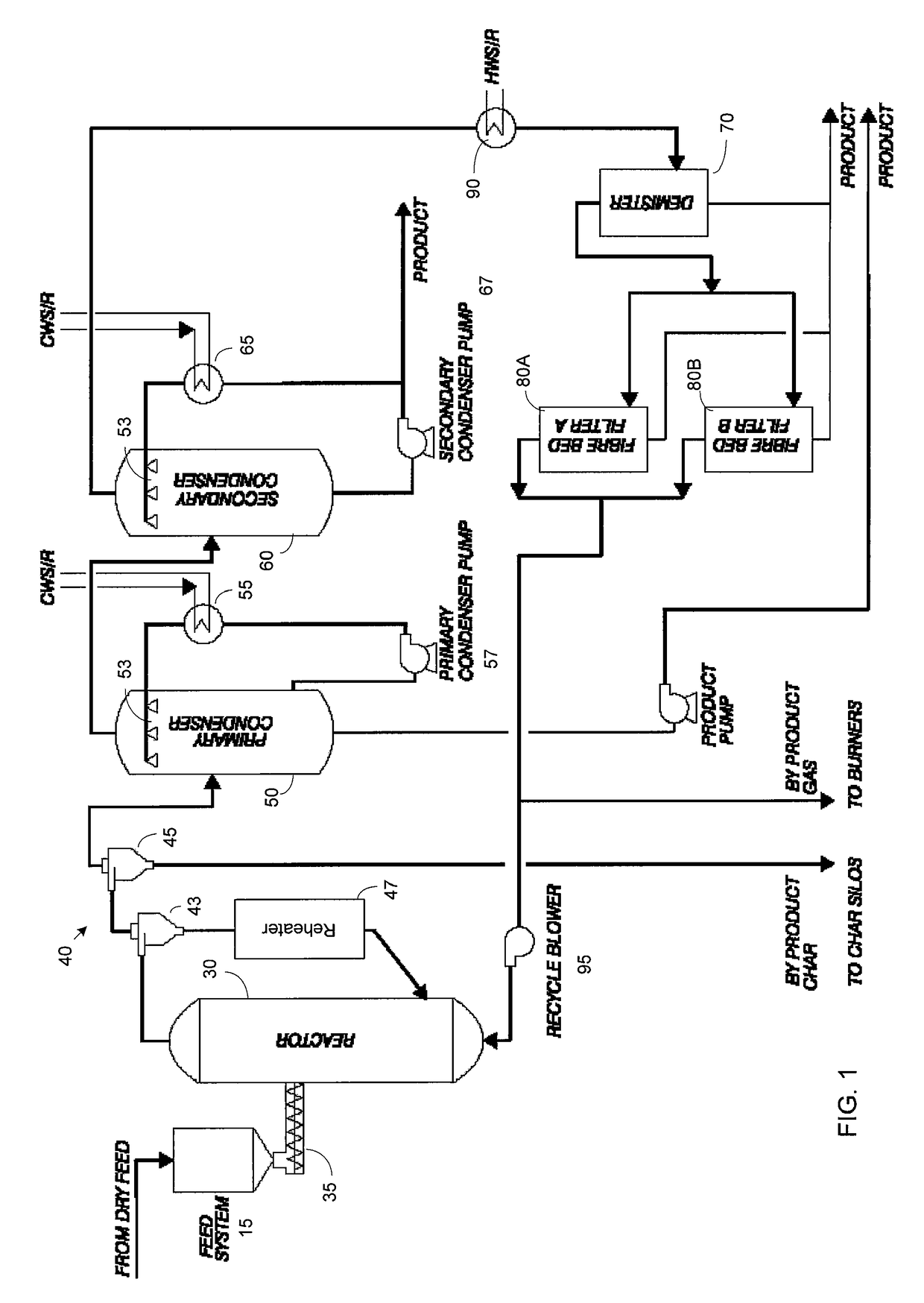
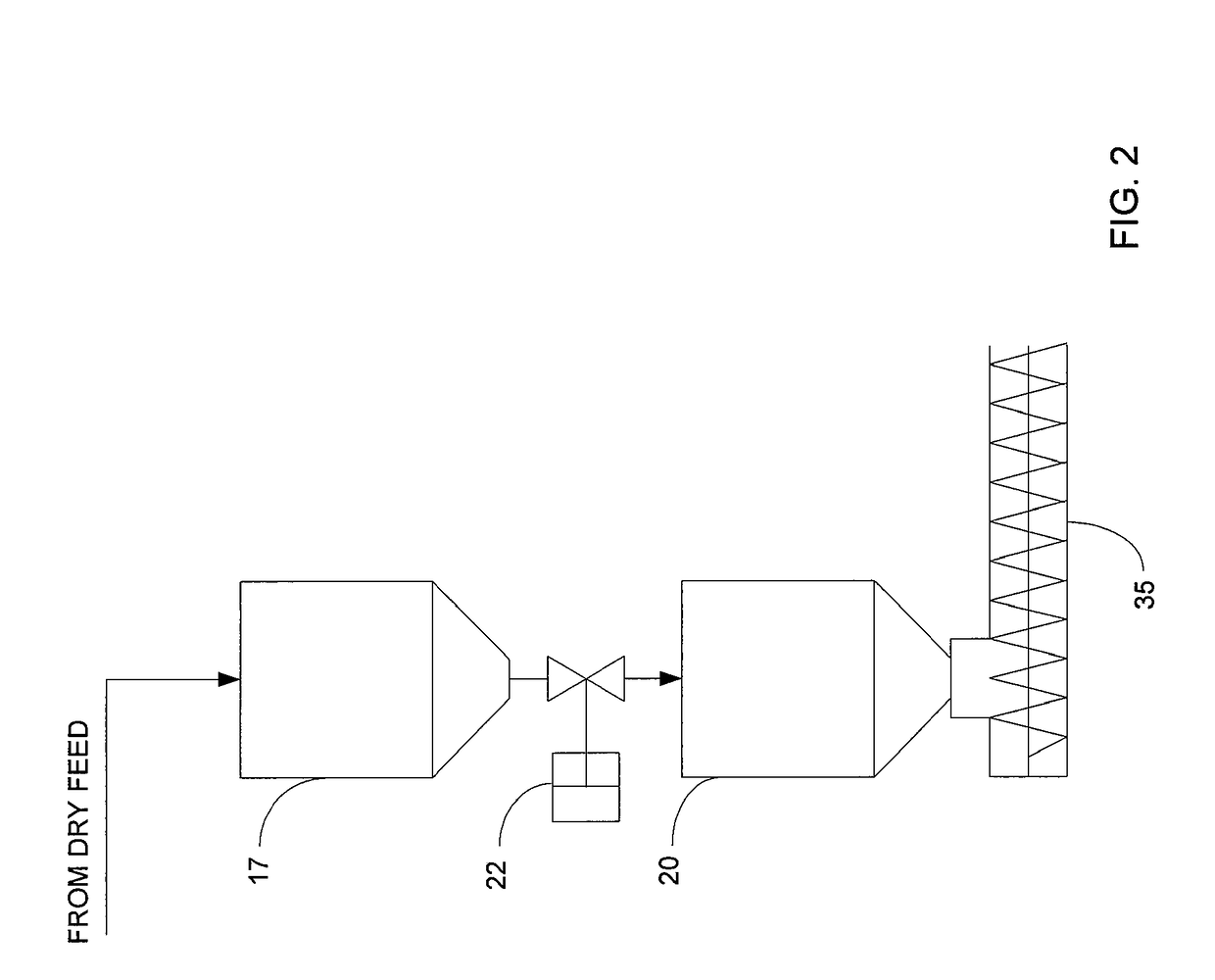
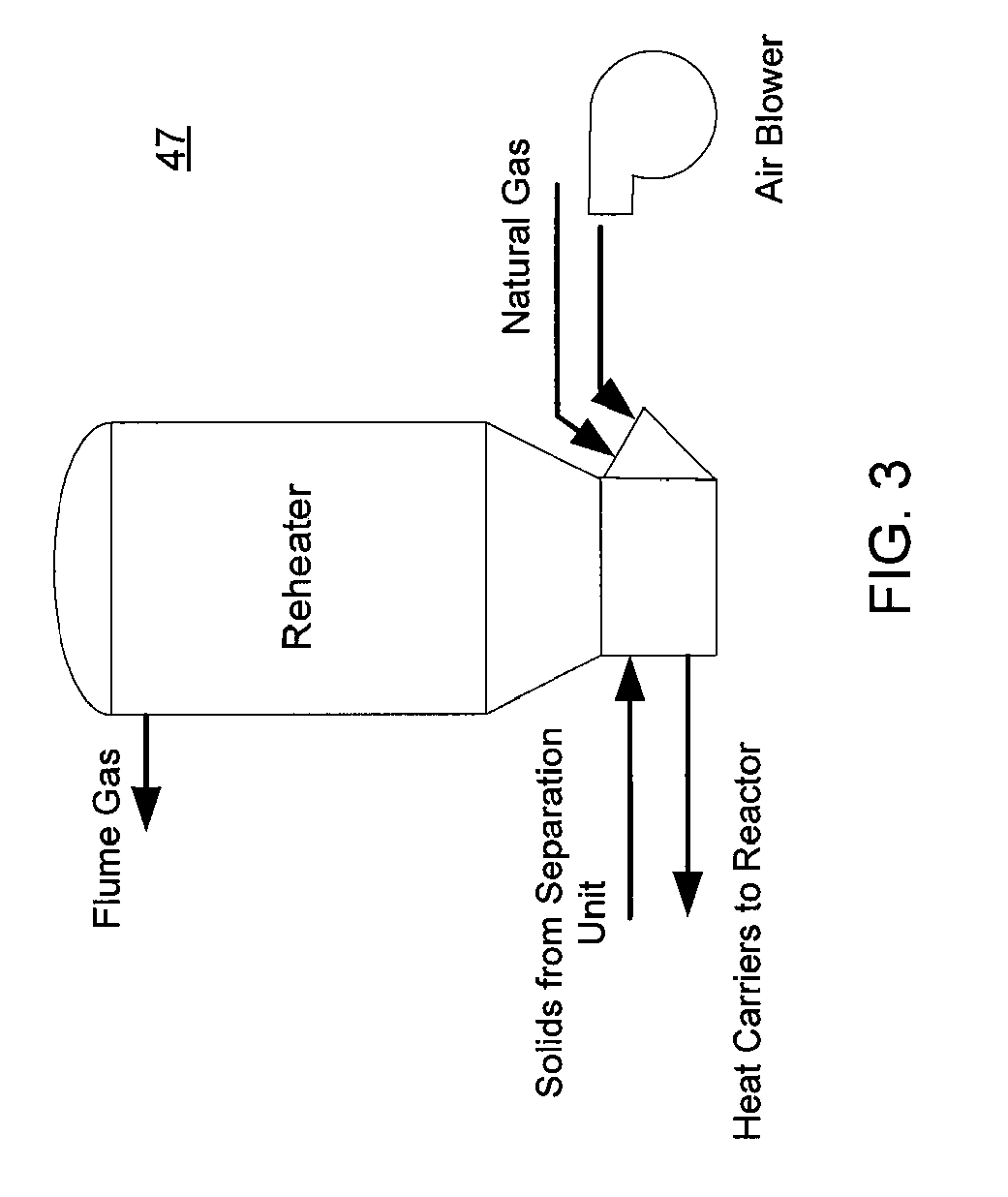
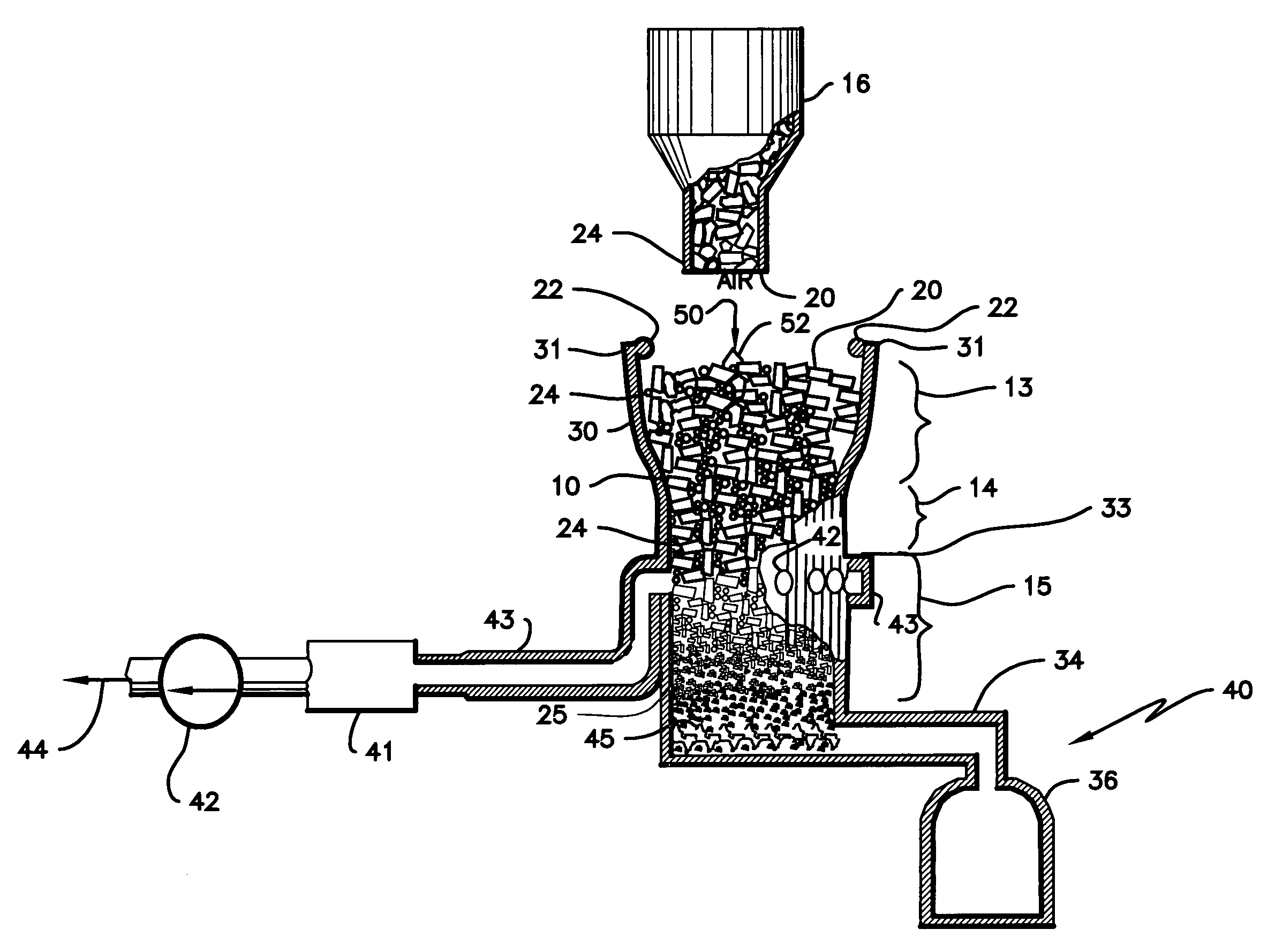
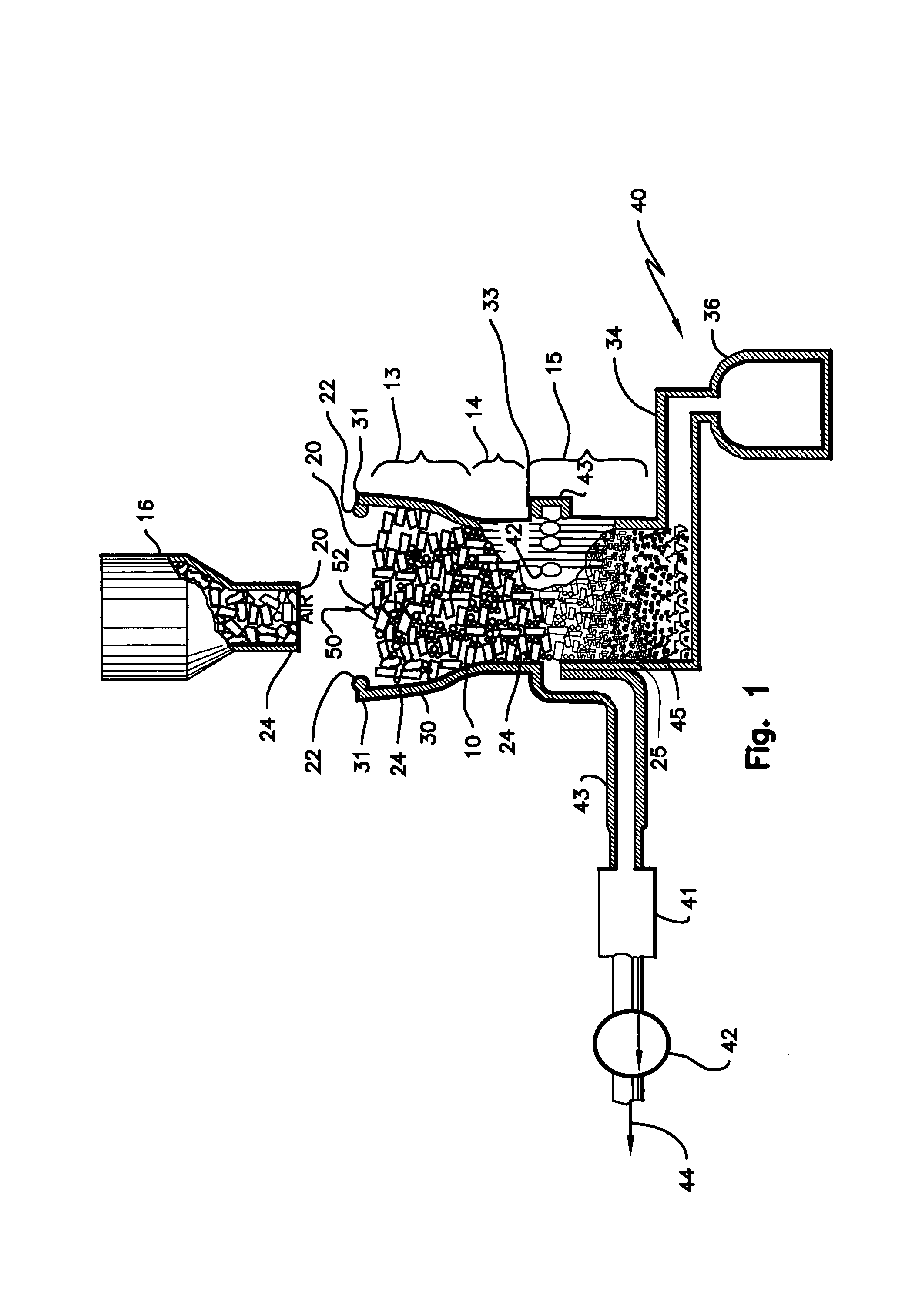
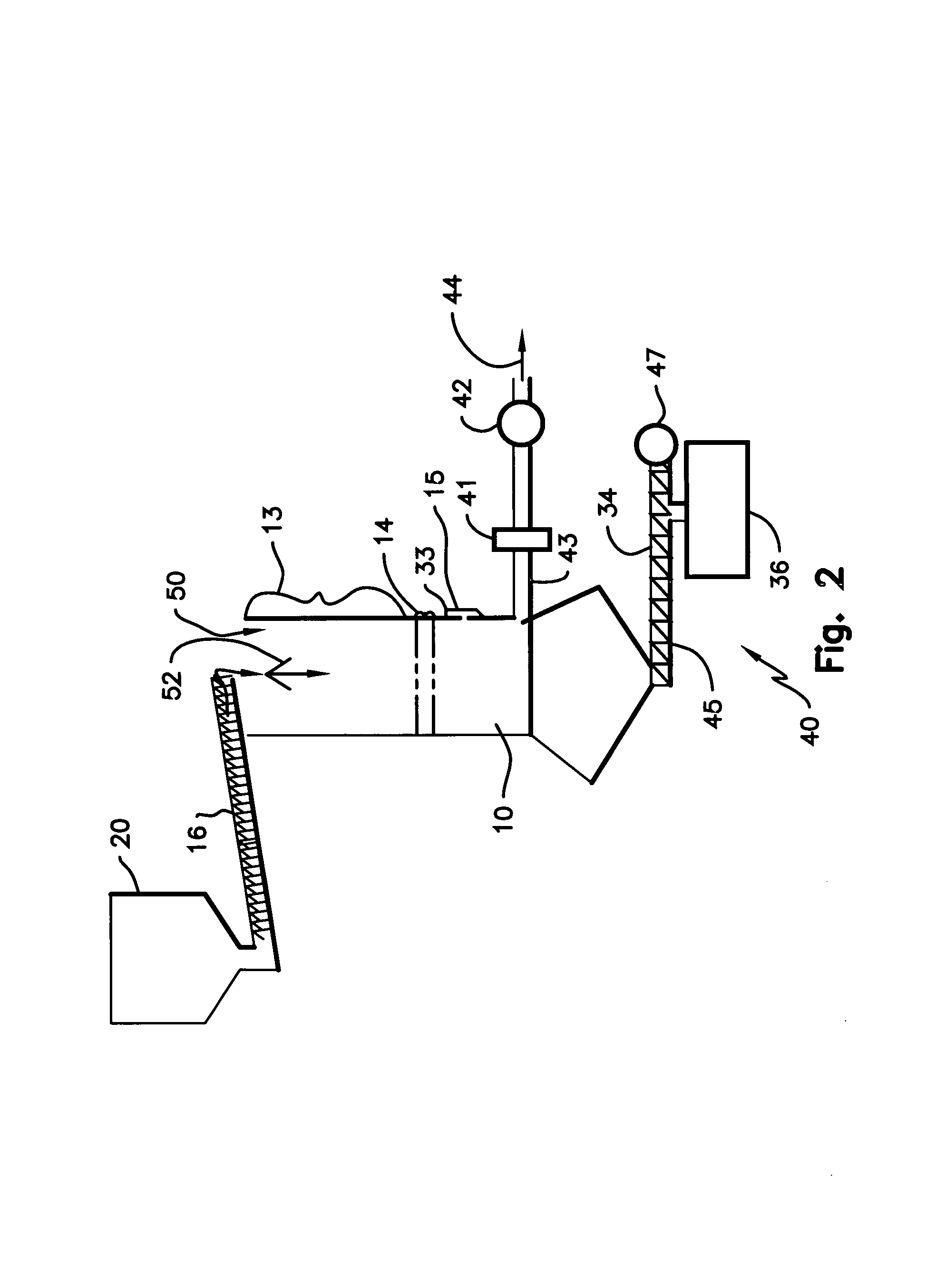
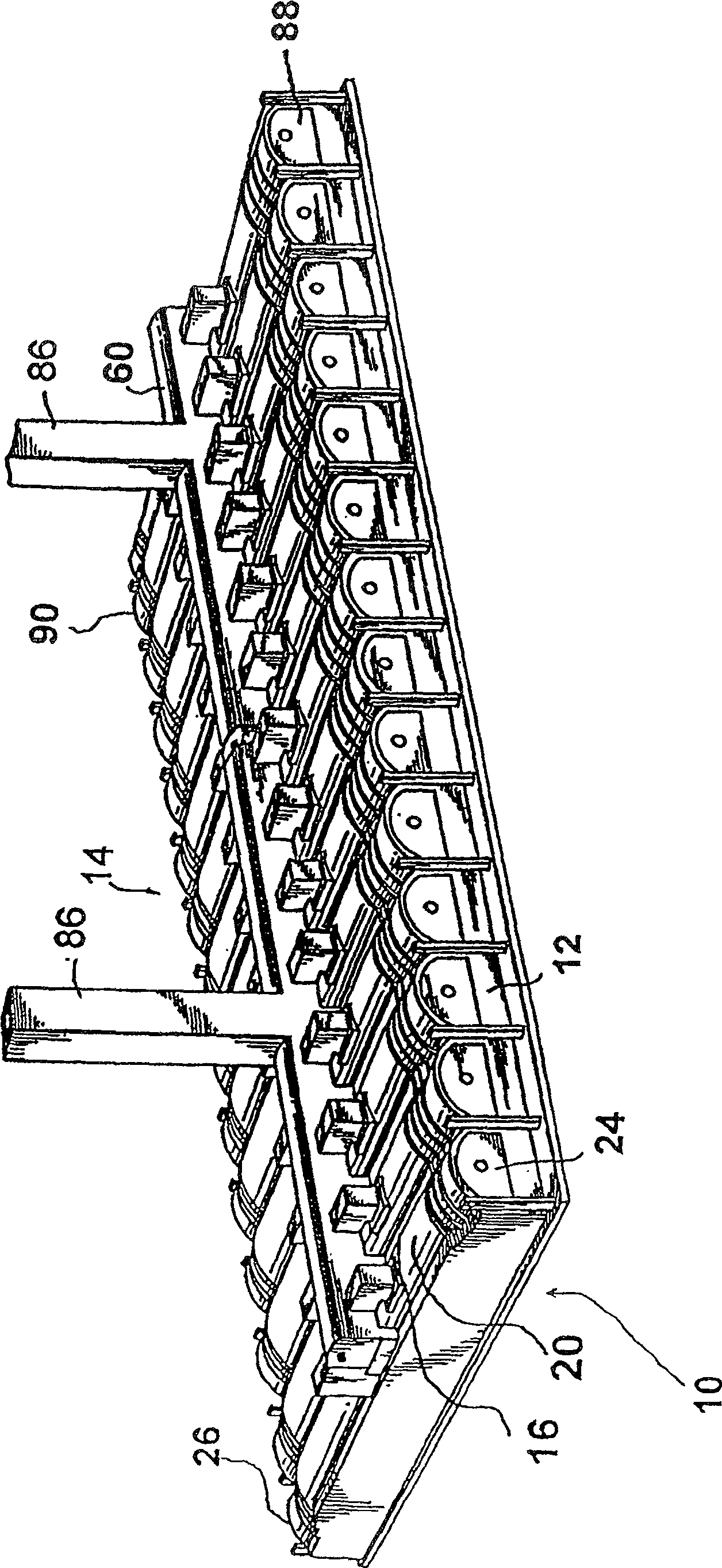
ActiveUS7905990B2Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingSolid waste disposalLiquid productHeat carrier
A rapid thermal conversion process for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. Biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. The liquid product may itself be used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Waste conversion process
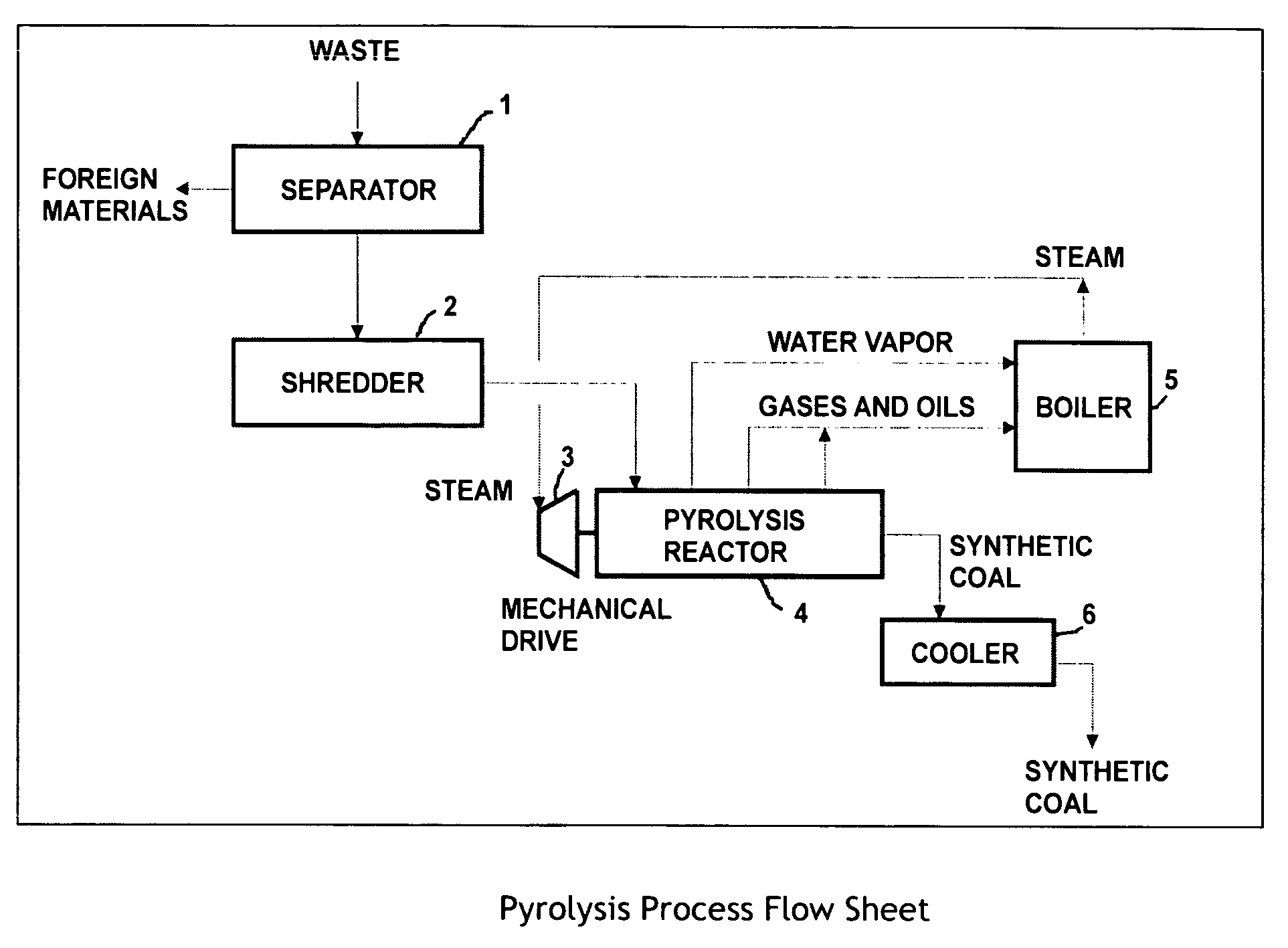
InactiveUS20060280669A1Good yieldMinimization requirementsBiofuelsIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationEnvironmental engineeringSand granules
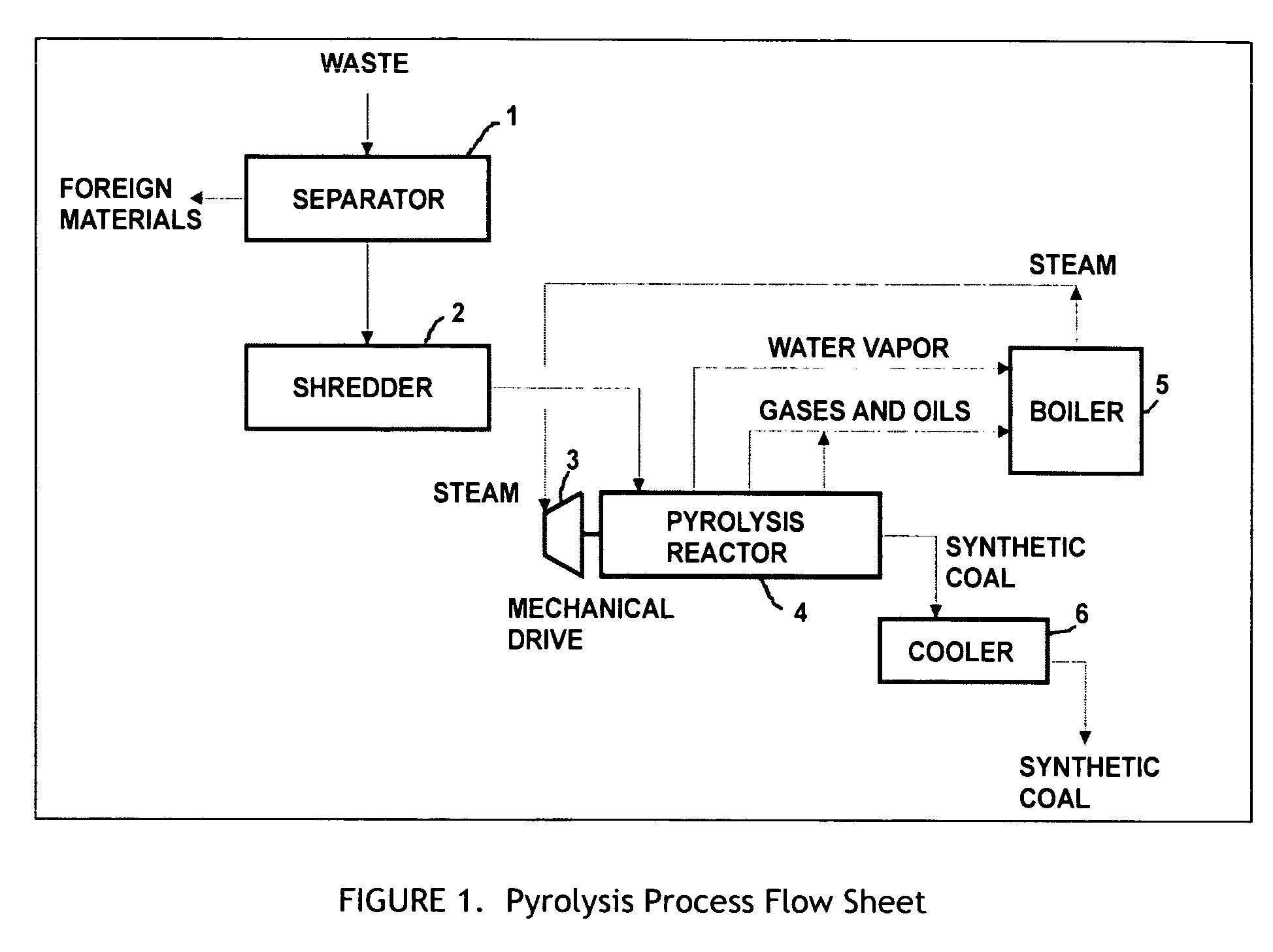
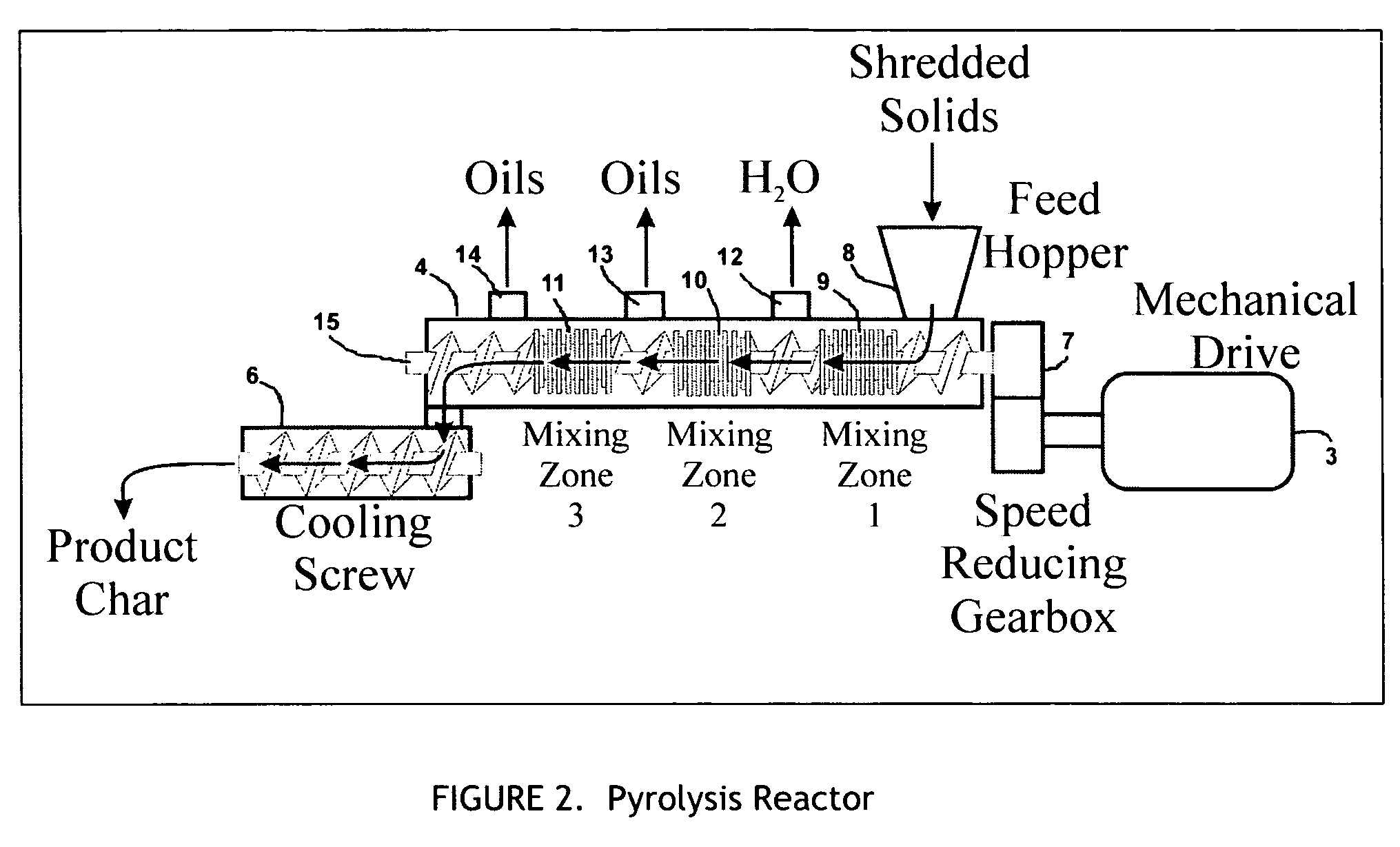
A process for the preparation of high quality char from organic waste materials. The waste is first sorted to remove recyclable inorganic materials of economic value (metals, glass) and other foreign materials that would be detrimental to the quality of the final product (stone, sand, construction debris, etc.). After size reduction, the waste is pyrolyzed at a temperature range of 250 to 600° F., in a high capacity, continuous mixer reactor, using in-situ viscous heating of the waste materials, to produce a highly uniform, granular synthetic product similar in energy content and handling characteristics to, but much cleaner burning than, natural coal.
Owner:ENTROPIC TECH CORP
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
ActiveUS20090139851A1Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingCoke quenchingLiquid productHeat carrier
The present invent provides improved rapid thermal conversion processes for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. In an embodiment, biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. In one embodiment, the liquid product itself is used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Batch pyrolysis system
InactiveUS20060163053A1Quality improvementImprove throughputProductsBeehive ovensBatch processingProcess engineering
Disclosed is a scaleable pyrolysis system for batch processing of waste vehicle tires and other waste to provide pyrolysis products. The core pyrolysis system includes one or more batch reactors, heating units, solids processing units, gas / liquid processing units and control units. In operation, the temperature gradients internal to the reactor are controlled by preferential channeling of heat to provide pyrolysis products that are of high quality, and hence commercially advantageous, while facilitating high throughput.
Owner:ERSHAG BENGT STURE
Interlocking floor brick for non-recovery coke oven
An improved non-recovery coke oven floor constructed of a single layer of refractory bricks including, for each oven sole flue, a pair of trunnion bricks and a center bridge brick spanning the width of the flue, having lower brick surfaces in the form of an arch, and joined end-to-end by a tapered tongue-and-groove joint disposed approximately perpendicular to the direction of a compression load transmitted by the center bridge brick to the trunnion bricks.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA COKE TECH
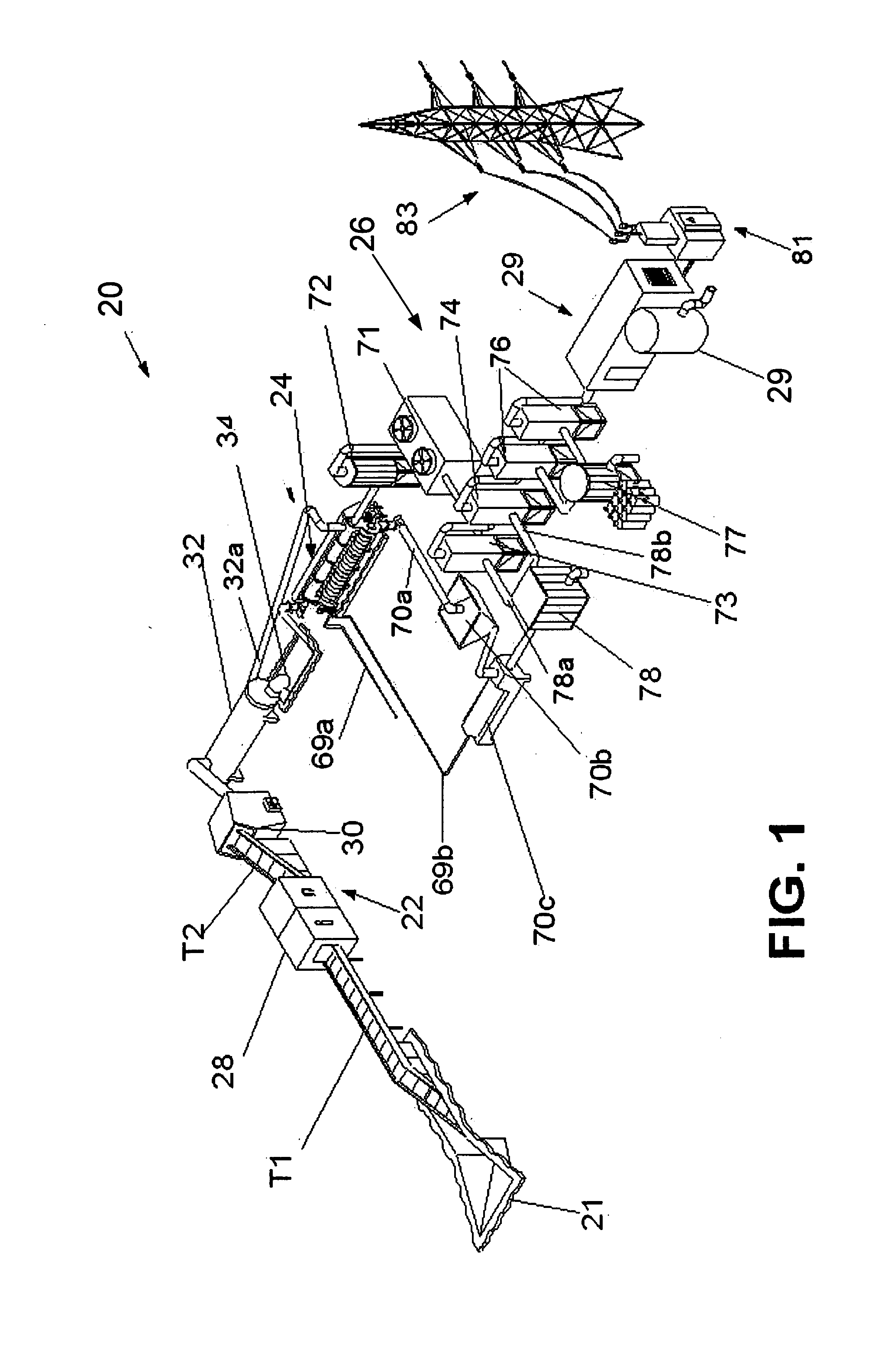
Process and device for the pyrolysis of feedstock
InactiveUS7947155B1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCombustible gas coke oven heatingVolatilesEngineering
This invention involves pyrolysis of feedstock by introducing carbonaceous feedstock, into a hopper and moving it into a reactor tube enclosed in an oven, generating heat within the oven that is in part transferred to the feedstock, heating it to sufficient temperature to pyrolyze the feedstock into useful volatiles and char. A Venturi system produces a negative pressure directing volatiles into a pyro-gas oven producing heat necessary for pyrolysis and generating useful excess heat. The extruded pyrolysis char has uses including charcoal fuel, soil amendments, and activated charcoal while liquids can be produced for processing into fuels. Excess heat may be used to heat water, steam, and air, may be used in air heating and cooling systems, perform mechanical work with a Stirling engine or generate electricity on the order of 100 kW and higher. The system may be operated in a carbon neutral or even carbon negative manner, allowing sequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Owner:GREEN LIQUID & GAS TECH
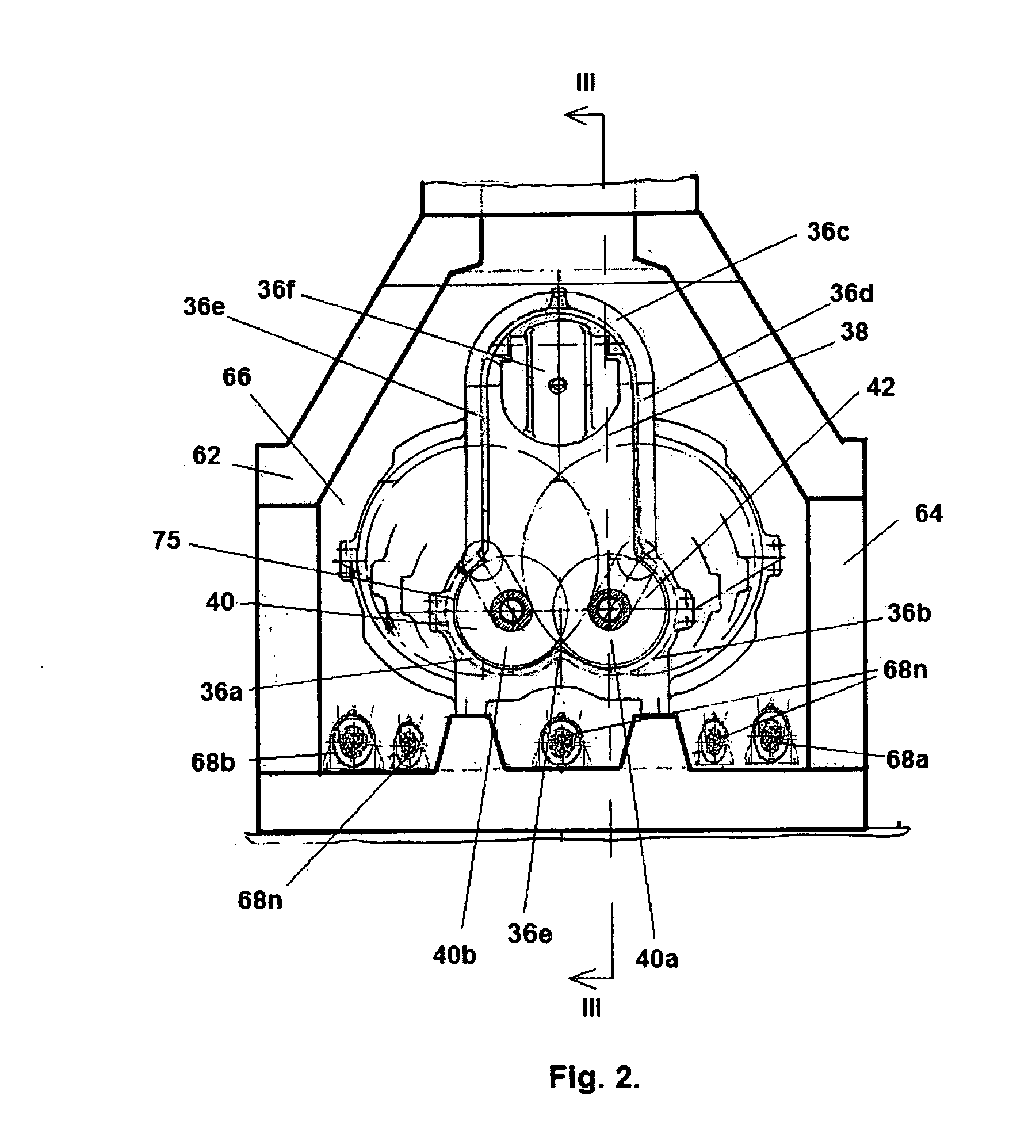
Carbonization and gasification of biomass and power generation system
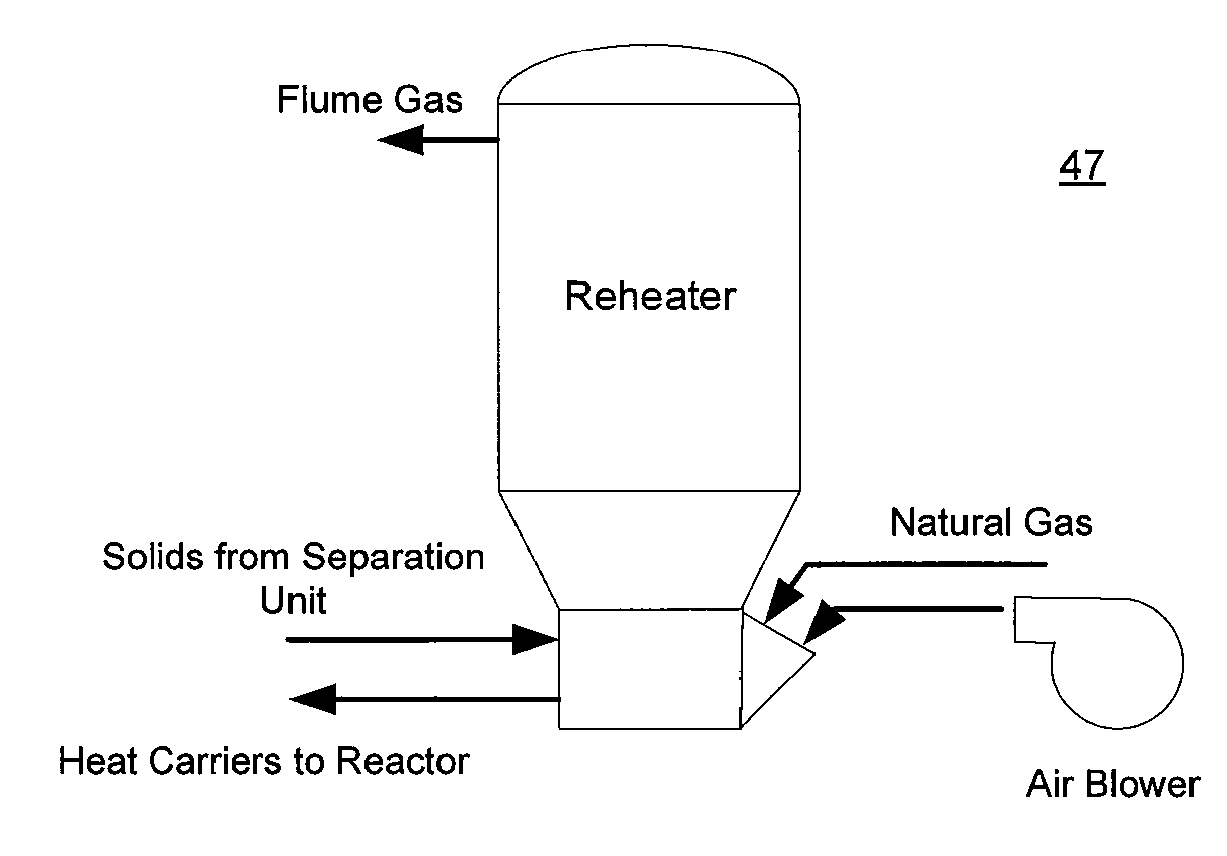
InactiveUS20050247553A1Increase temperatureHigh thermal efficiencyBeehive ovensCombustible gas catalytic treatmentCarbonizationTar
Biomass, including waste biomass, is gasified by a process in which the biomass is first carbonized, and the char and pyrolysis gas from the carbonizer are respectively fed to a high temperature gasifying part and a gas reformer part of a two-stage gasifier. A gasifying agent is continuously fed to the gasifying part, and intermittently fed to the gas reformer, to maintain the temperature required to avoid tar formation in the gas reformer stage. Multiple carbonization chambers are operated in rotation. When the carbonization / gasification apparatus is used to provide fuel to an electric power generator set, exhaust heat from the generator power plant is fed back to the carbonizer, and can be supplemented by exchange of heat from the gas delivered to generator power plant from the outlet of the gasifier.
Owner:CENTRAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF ELECTRIC POWER INDUSTRY +1
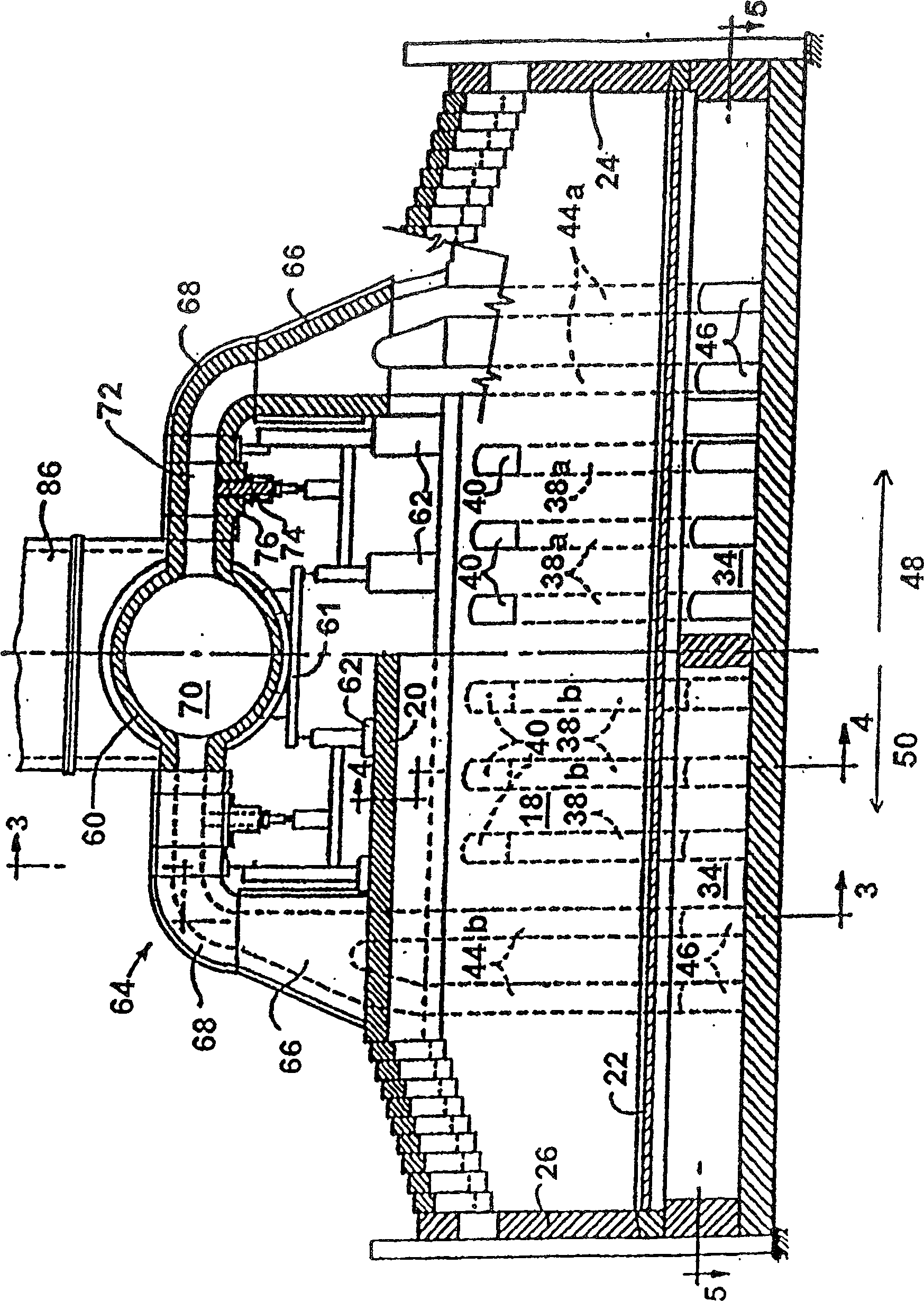
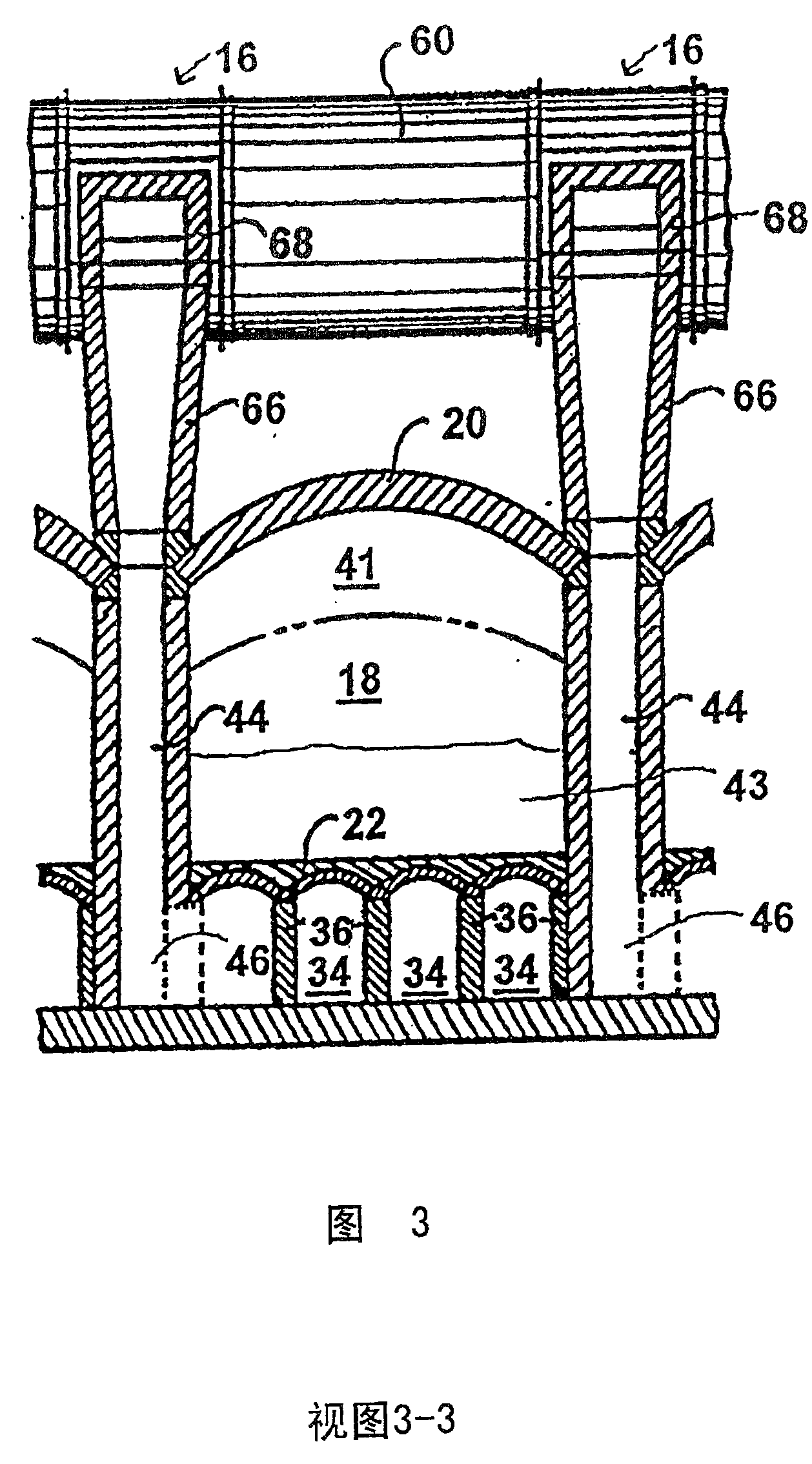
Coke oven flue gas sharing
InactiveCN1527872AExtend your lifeReduce the gas flow rateCombustible gas coke oven heatingBeehive ovensFlue gasProduct gas
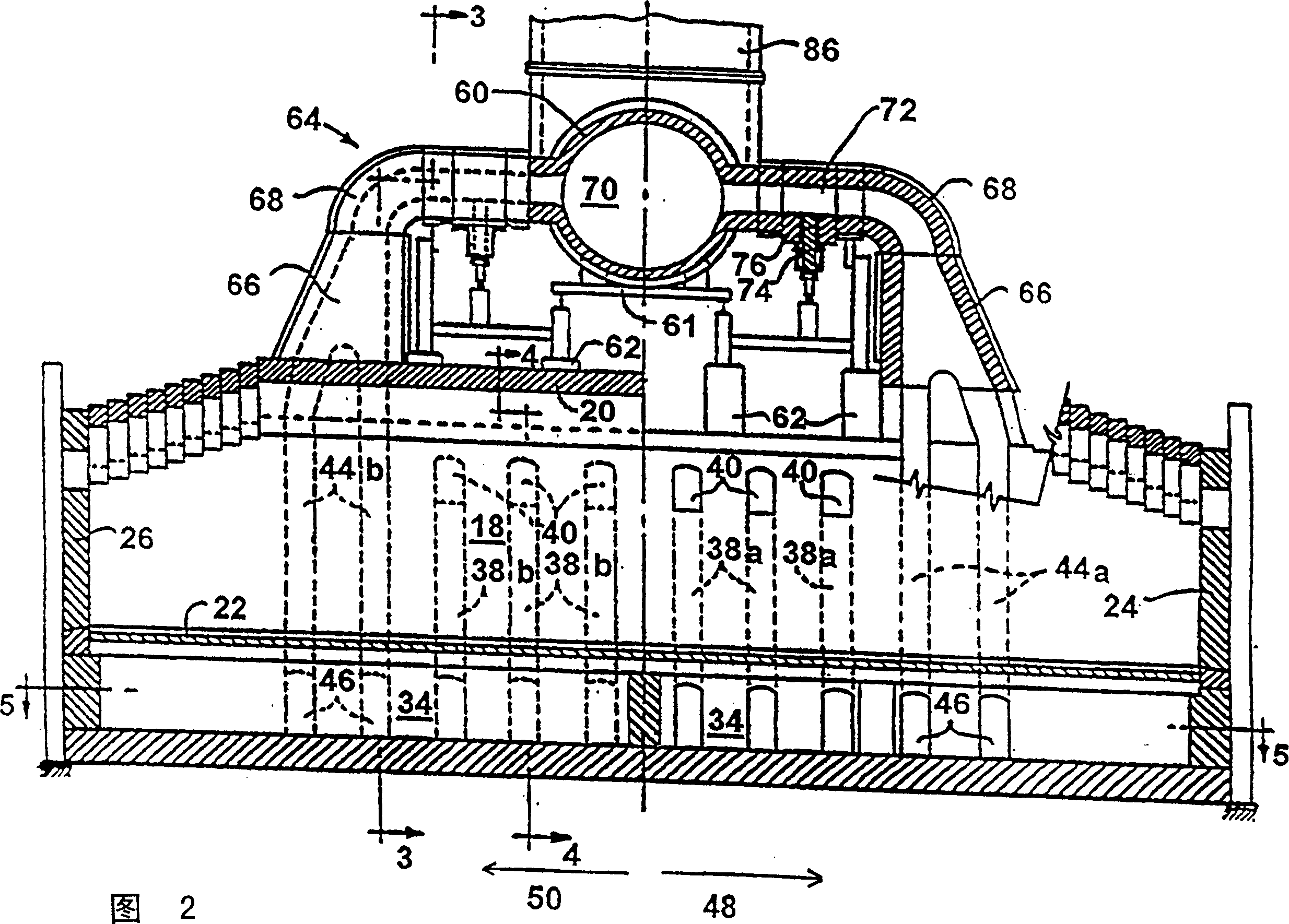
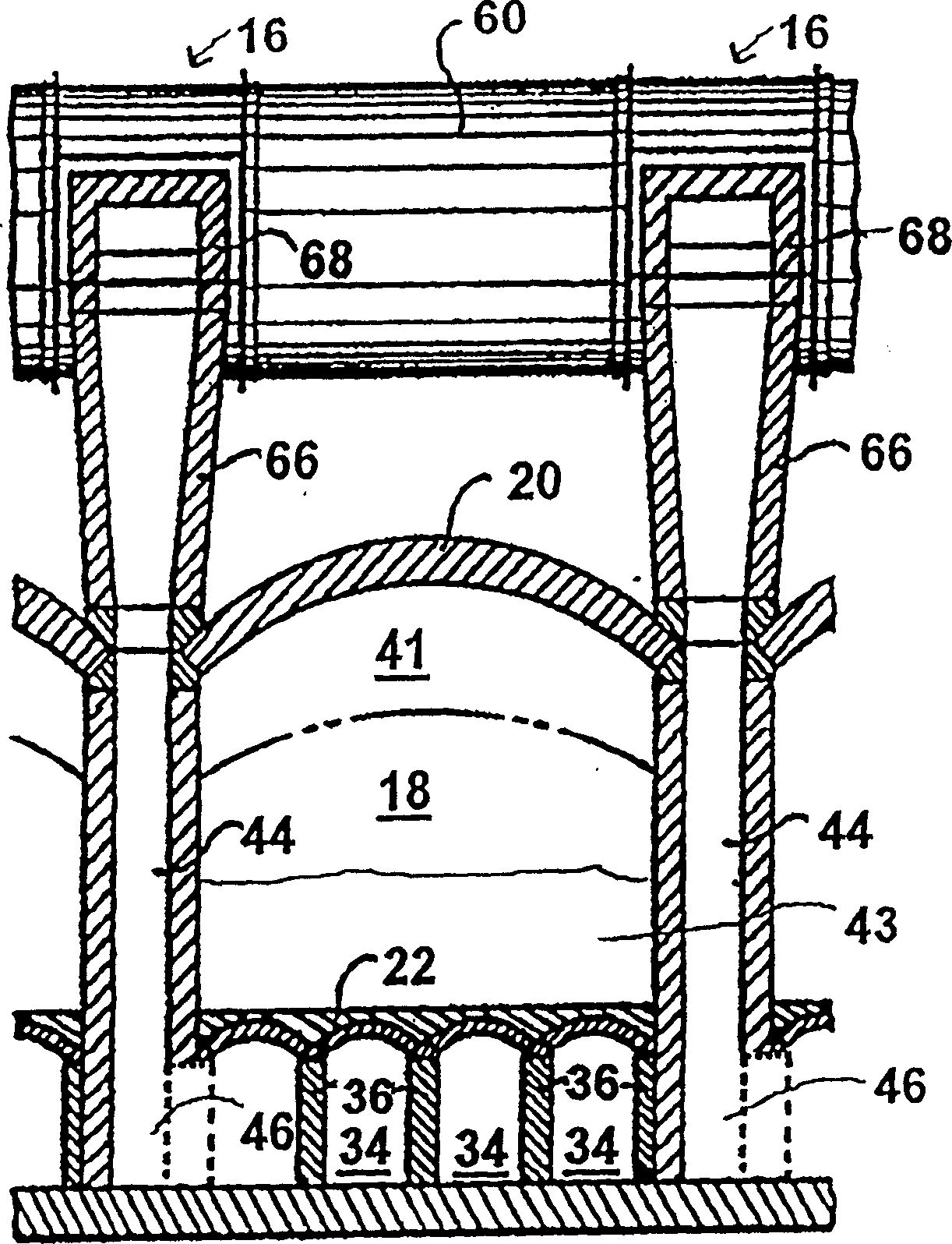
The invention provide a method and apparatus for decreasing gas flow rates in a sole flue gas system for a coke oven during at least an initial coking operation after charging a coking oven with coal (43). The method includes providing a duct system (96, 98) between a first coke oven having a first coking chamber (18) and a second coke oven having a second coking chamber (18) to direct at least a portion of gas from a gas space (41) in first coking chamber (18) to the second coke oven thereby reducing a gas flow rate in the first sole flue gas system of the first coke oven. Reduction in sole flue gas flow rates has a beneficial effect on product throughput, the life of the coke oven and environmental control of volatile emissions from coke ovens.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
Method of producing charcoal, conditioned fuel gas and potassium from biomass
InactiveUS7226566B2Reduce productionSuitable for useLiquid degasificationSolid waste disposalPotassiumProcess engineering
Owner:CSA ENERGY
Coke oven flue gas sharing
InactiveCN100510004CExtend your lifeReduce the gas flow rateCombustible gas coke oven heatingBeehive ovensCoke Oven EmissionFlue gas
The invention provides a method and apparatus for reducing the gas flow velocity in the bottom flue gas system of a coke oven during at least one initial coking operation after the coke oven has been charged with coal (43). The method includes providing a ductwork (96, 98) between a first coke oven having a first coking chamber (18) and a second coke oven having a second coking chamber (18) for transferring at least a portion of the gas from The gas space (41) in the first coking chamber (18) is led into the second coking oven, thereby reducing the gas flow velocity in the first bottom flue gas system of the first coking oven. Reducing the gas flow velocity in the bottom flue has beneficial effects on product yield, coke oven life and environmental control of coke oven volatile emissions.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
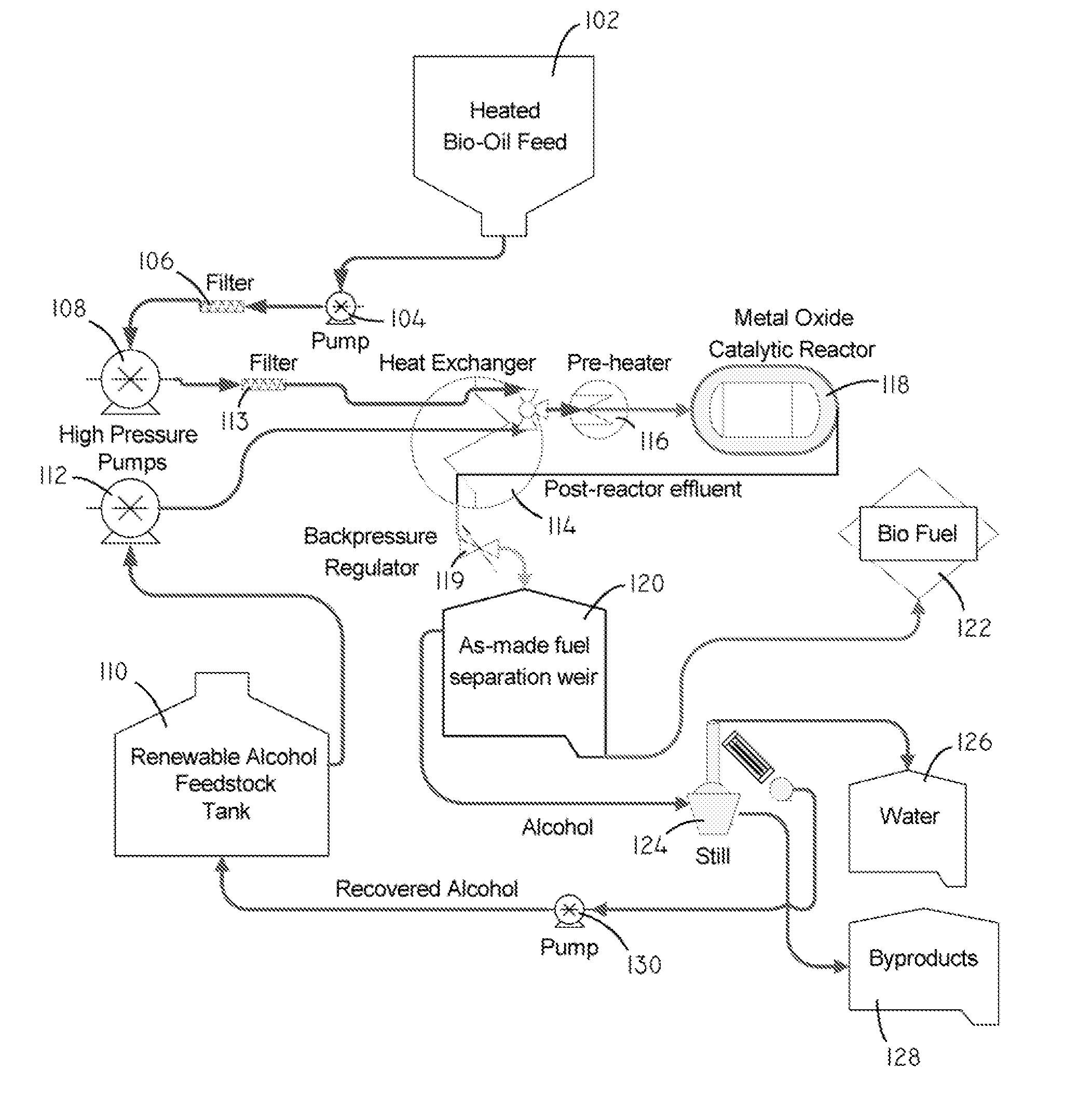
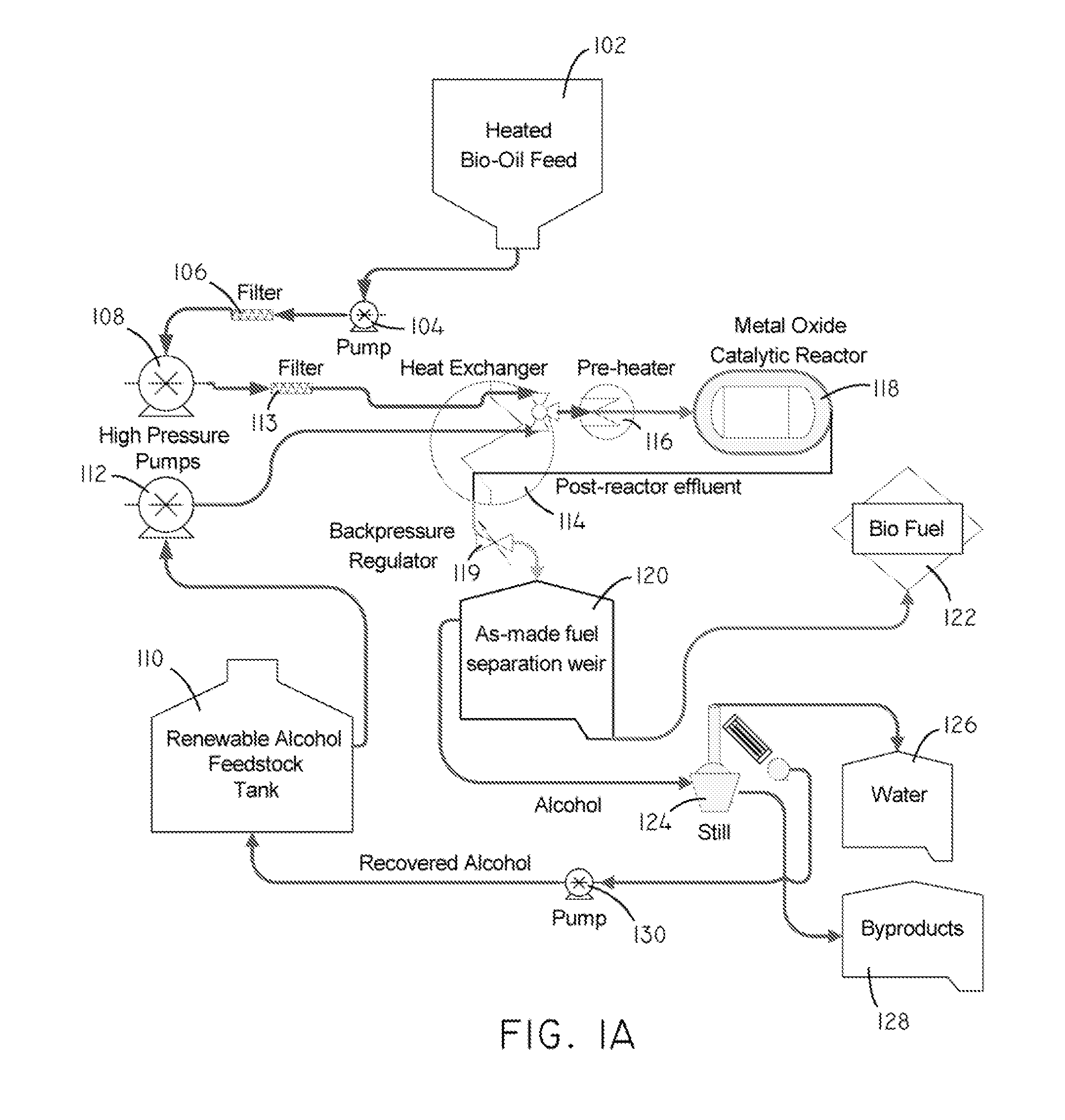
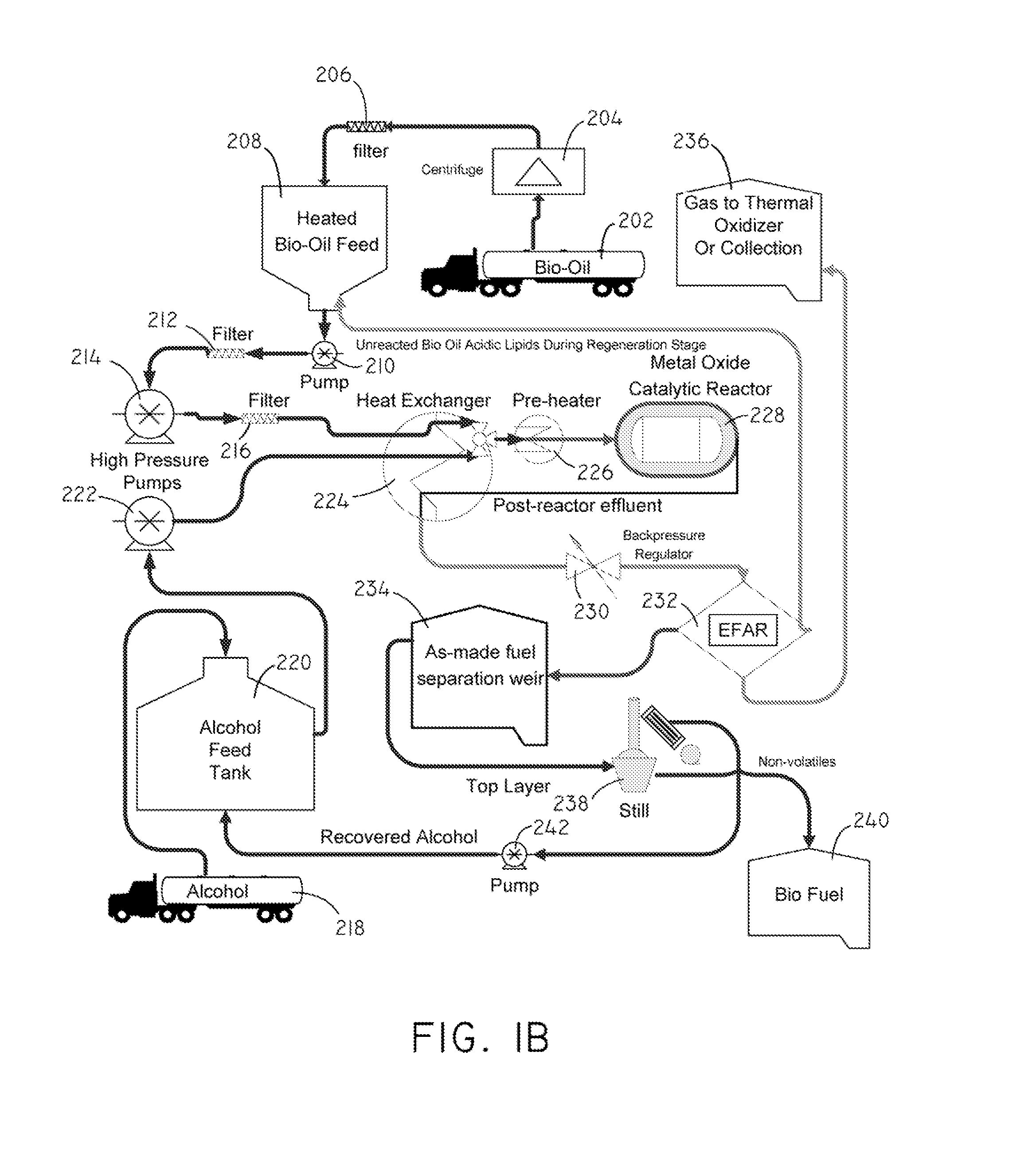
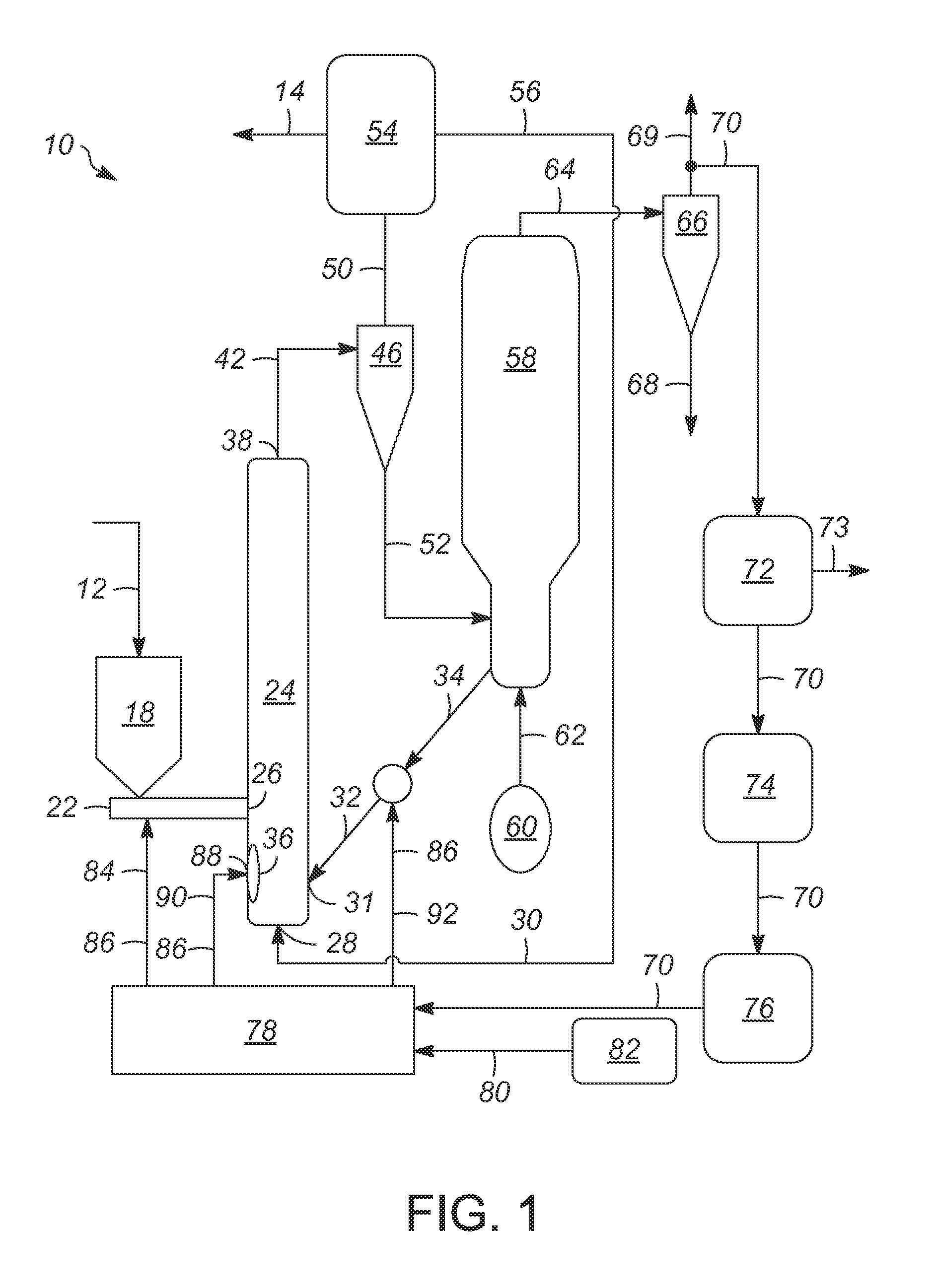
Systems and methods for producing fuels from biomass
The present invention relates to systems and methods for producing fuels. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of producing a diesel-equivalent fuel, including pyrolyzing biomass to form a pyrolysis oil and contacting the pyrolysis oil and an alcohol with a metal oxide catalyst at a temperature of greater than about 60 degrees Celsius. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of refining pyrolysis oil including contacting pyrolysis oil and an alcohol with a metal oxide catalyst at a temperature of greater than about 60 degrees Celsius. In an embodiment, the invention includes a system for processing biomass into fuel including a pyrolysis chamber defining an interior volume; a first heating element configured to heat the pyrolysis chamber; a refining chamber in selective fluid communication with the pyrolysis chamber, the refining chamber defining an interior volume, a metal oxide catalyst disposed within the interior volume; and a second heating element configured to heat the refining chamber. Other embodiments are also described herein.
Owner:SARTEC
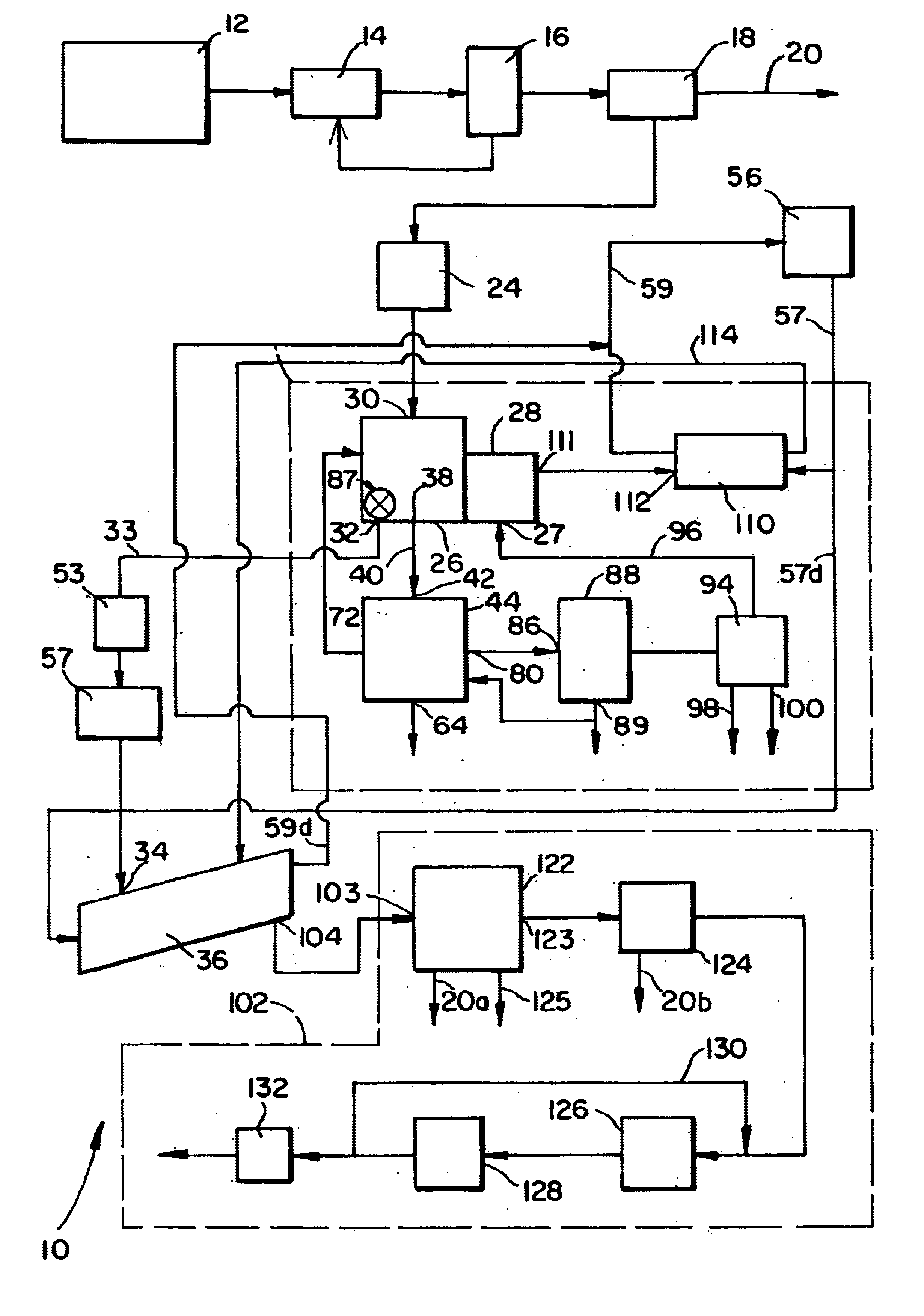
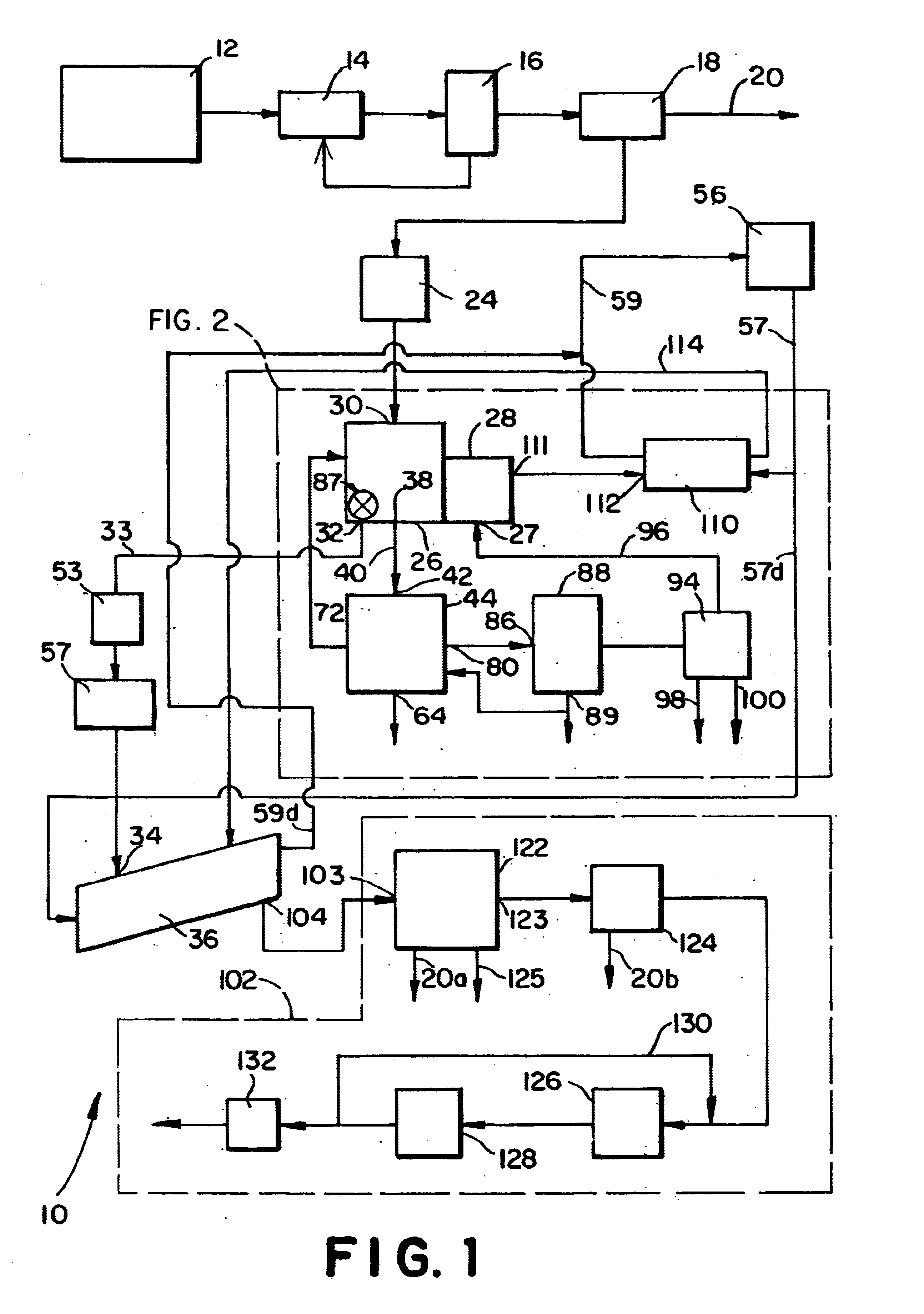
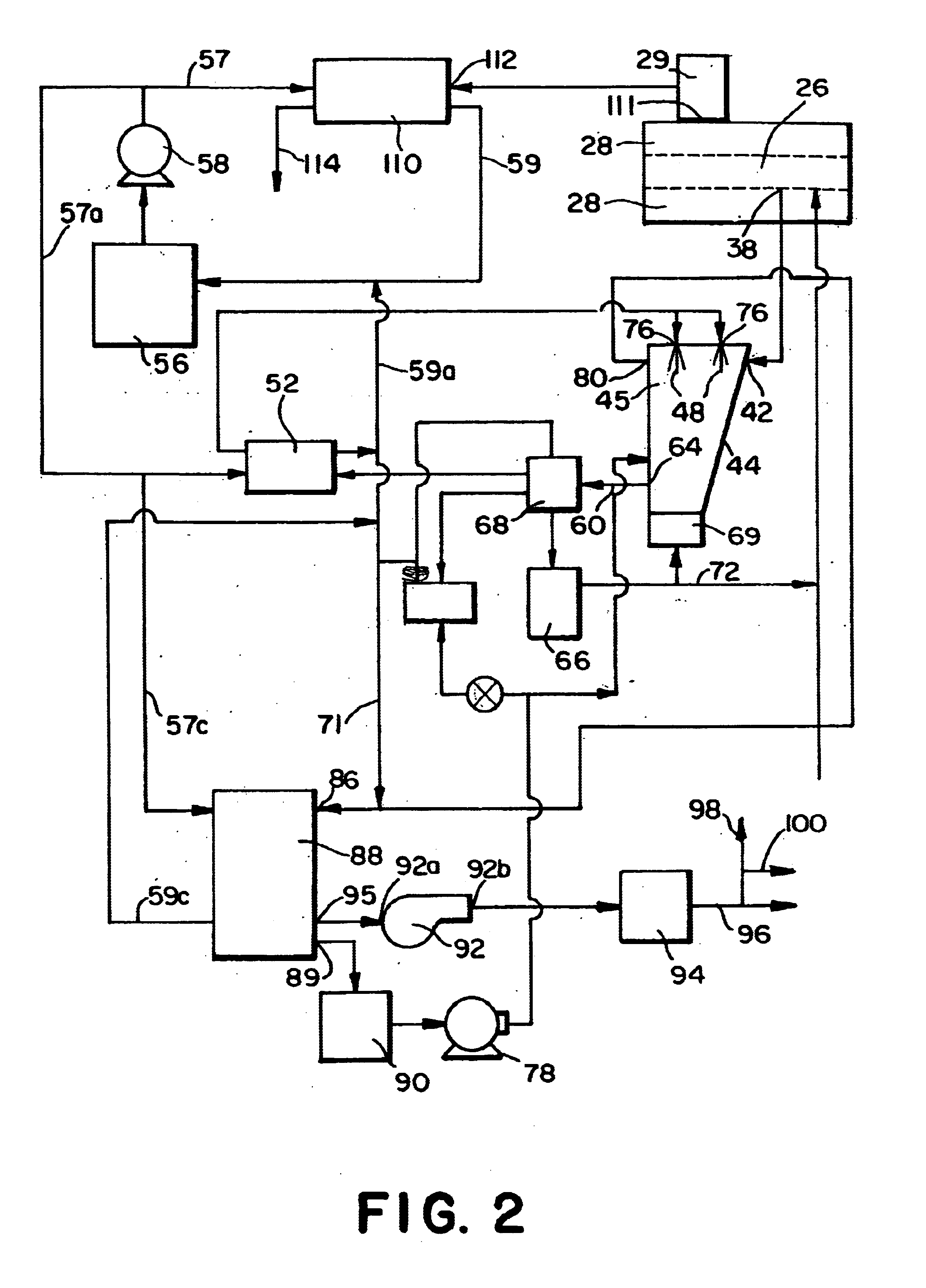
Process for pyrolyzing tire shreds and tire pyrolysis systems
Tire pyrolysis systems and processes are provided which include feeding tire shreds to a pyrolysis reactor, pyrolyzing the shreds in a pyrolysis reactor to produce a hydrocarbon-containing gas stream and carbon-containing solid, removing the carbon-containing solid from the reactor, directing the hydrocarbon-containing gas stream into a separator, contacting the hydrocarbon-containing gas stream with an oil spray in the separator thereby washing particulate from the hydrocarbon-containing gas stream and condensing a portion of the gas stream to oil, removing and cooling the oil from the separator, directing non-condensed gas from the gas stream away from the separator, and directing a portion of the cooled oil removed from the separator to an inlet of the separator for use as the separator oil spray. A process is also provided in which solids from the pyrolysis reactor are directed to an auger having a pressure which is greater than the pressure in the pyrolysis reactor, and in which non-condensed gas from the gas stream after condensing a portion of the gas is directed to at least one burner in heat exchange relation with the pyrolysis reactor, and burned to heat the reactor and generate an effluent flue gas, a portion of which effluent flue gas is cooled and injected into the auger which is a trough auger in one embodiment.
Owner:RENAISSANCE ENERGY GROUP
Method and device for thermal ablative pyrolysis of biomass
InactiveUS7438785B2Available heating surfaceWithdrawal of pyrolysis products is moreover simplifiedCombustible gas coke oven heatingSolid waste disposalProcess engineeringMaterial supply
Owner:PYTEC THERMOCHEM ANLAGEN
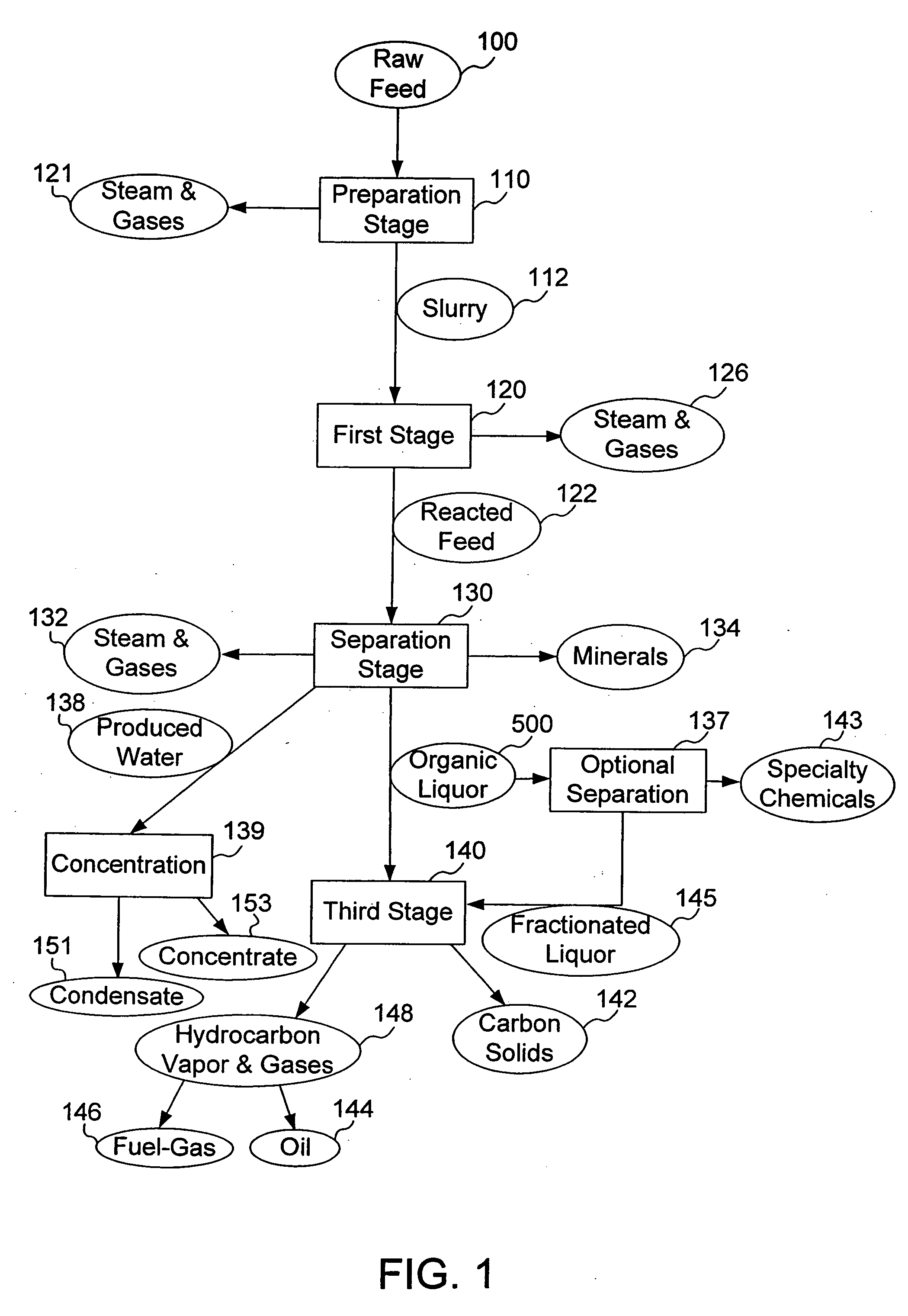
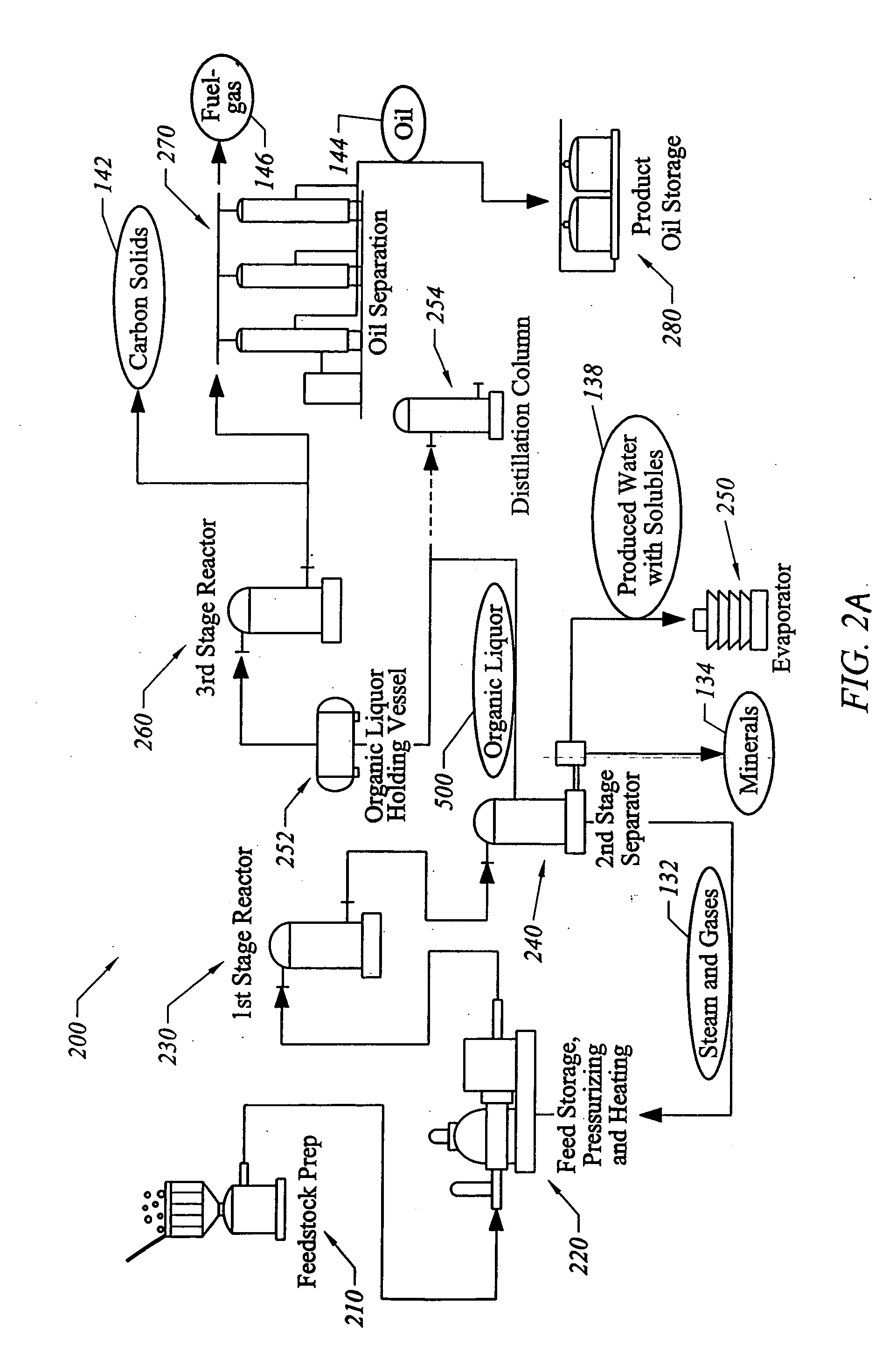
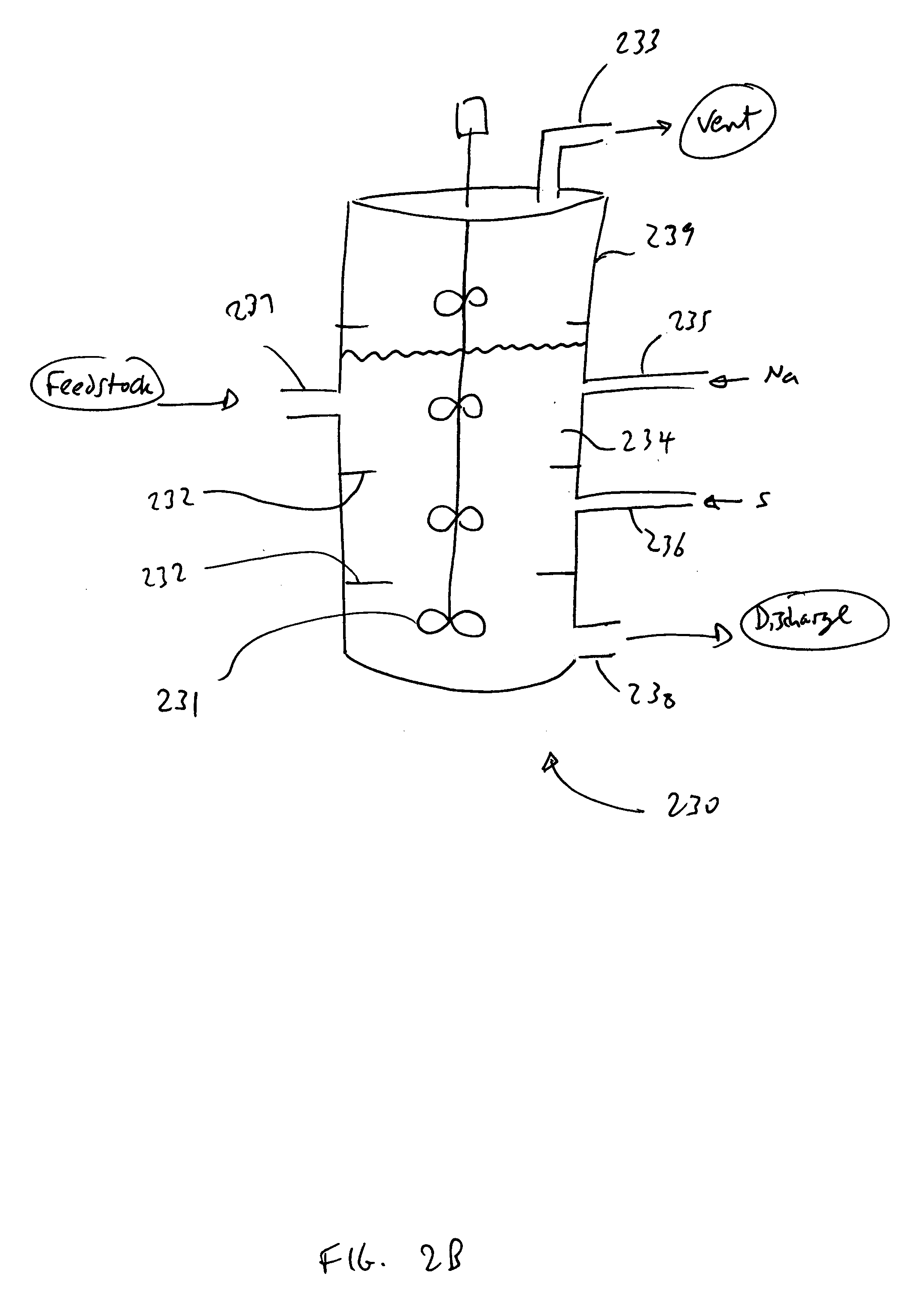
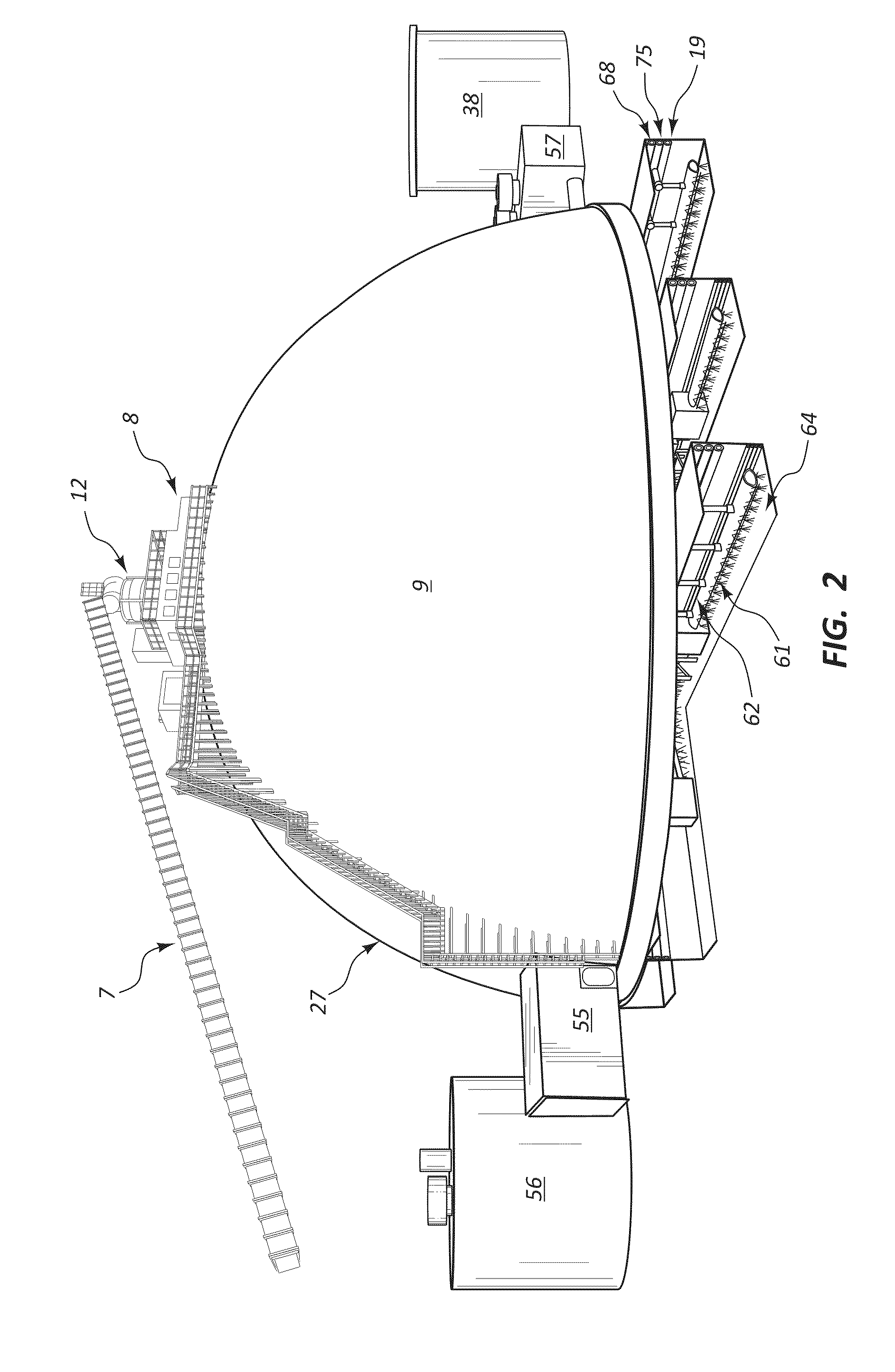
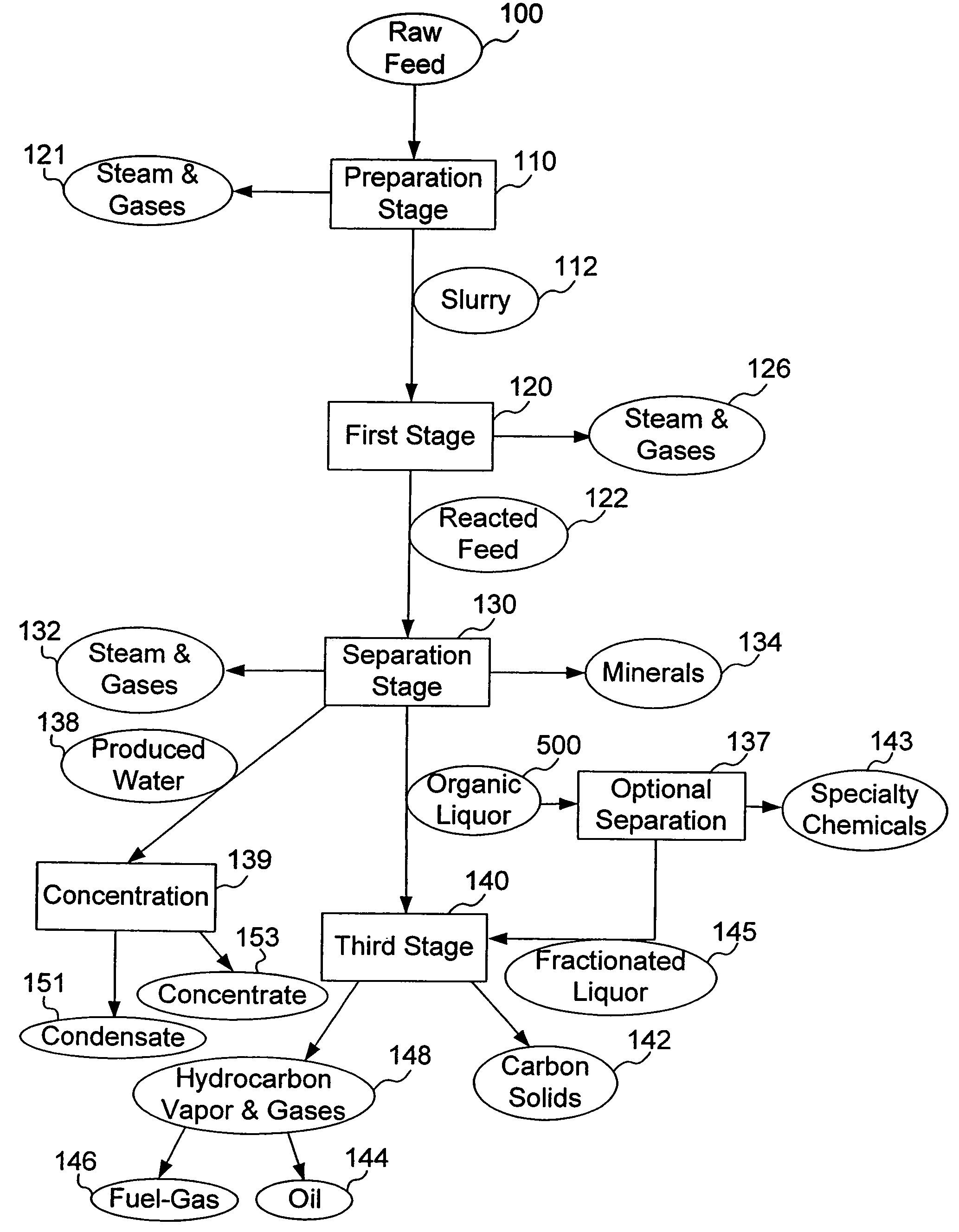
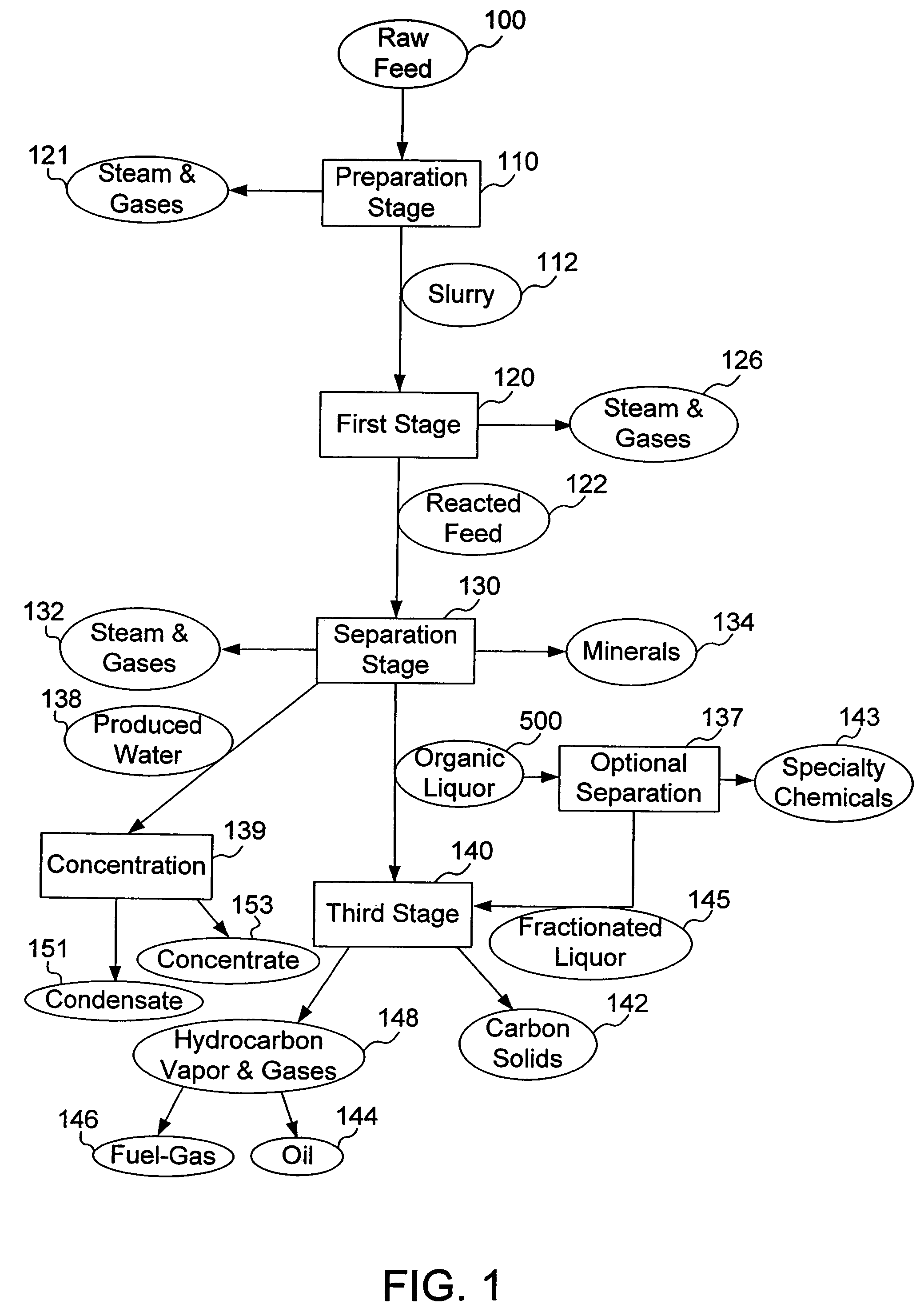
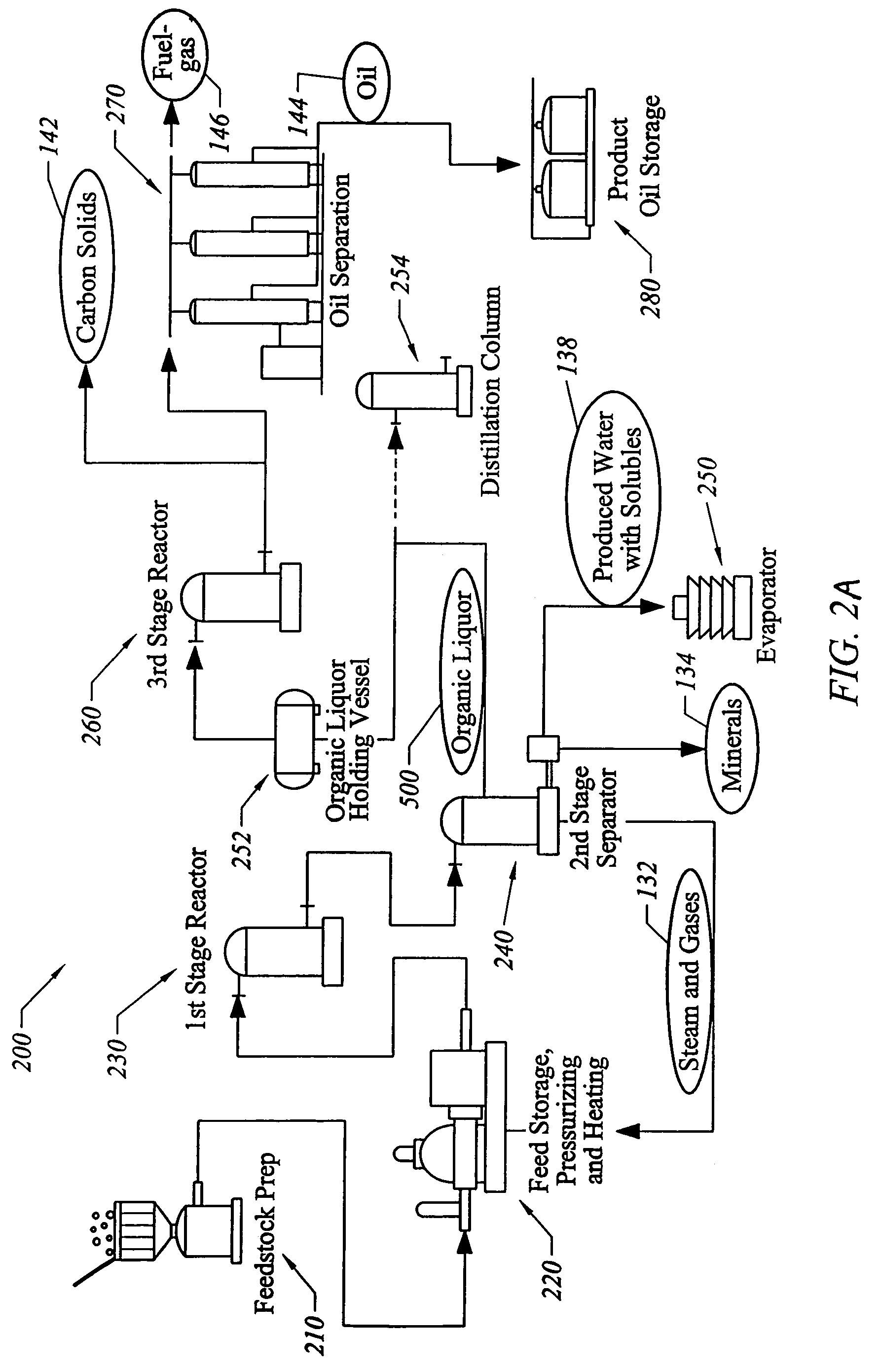
Process for conversion of organic, waste, or low-value materials into useful products
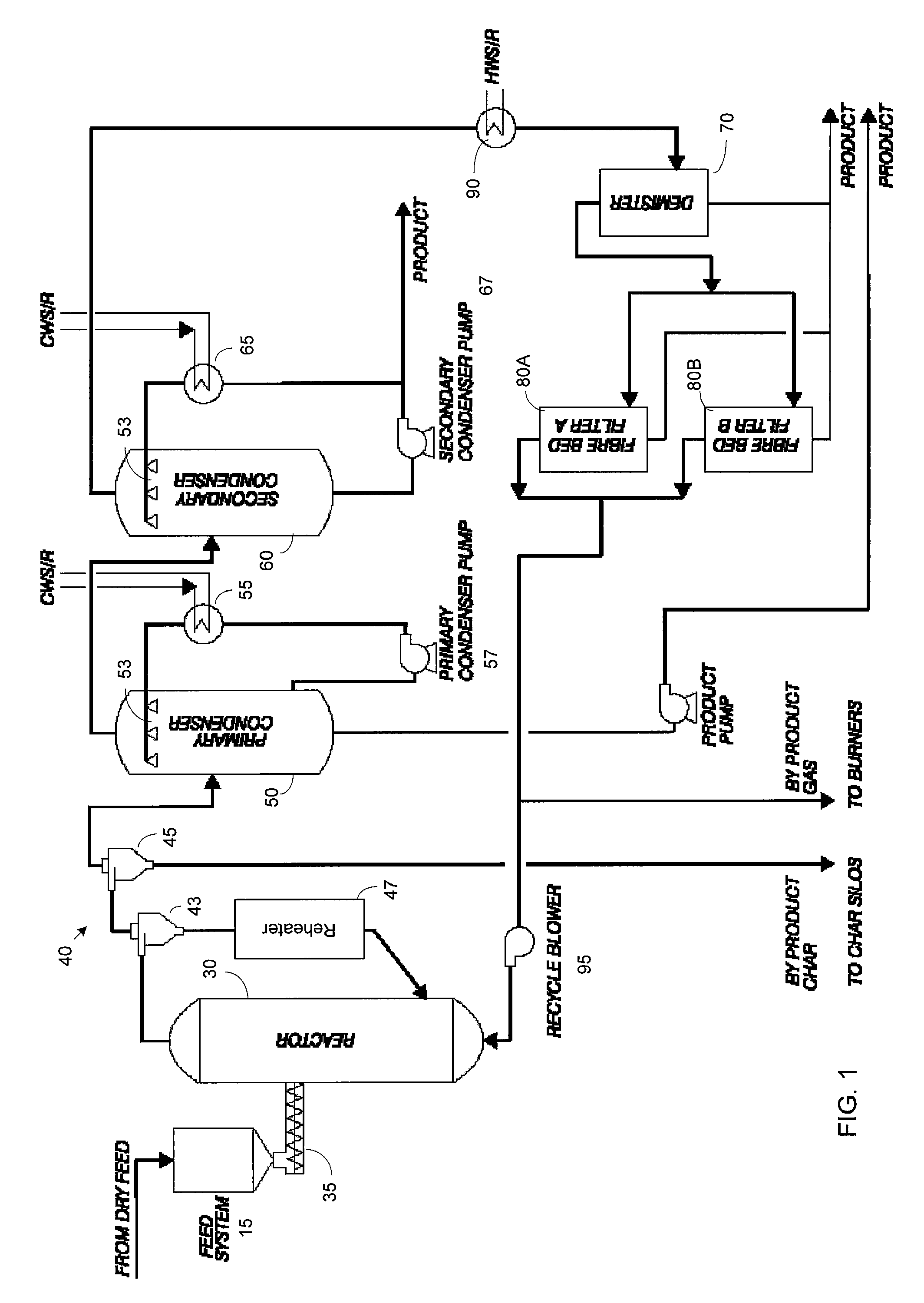
ActiveUS20060004237A1Low viscosityHydrocarbon purification/separationIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationHigh energySulfur
The present invention addresses the processing of waste and low-value products to produce useful materials in reliable purities and compositions, at acceptable cost, and with high energy efficiency. In particular, the invention comprises a multi-stage process that converts various feedstocks such as offal, animal manures, municipal sewage sludge, that otherwise have little commercial value, to useful materials including gas, oil, specialty chemicals, and carbon solids. The process subjects the feedstock to heat and pressure in a reducing environment accomplished by controlled addition of sulfur and sodium, separates out various components, then further applies heat and pressure to one or more of those components. The invention further comprises an apparatus for performing a multi-stage process of converting waste products into useful materials, and at least one oil product that arises from the process.
Owner:SYNPET TEKNOLOJI GELISTIRME
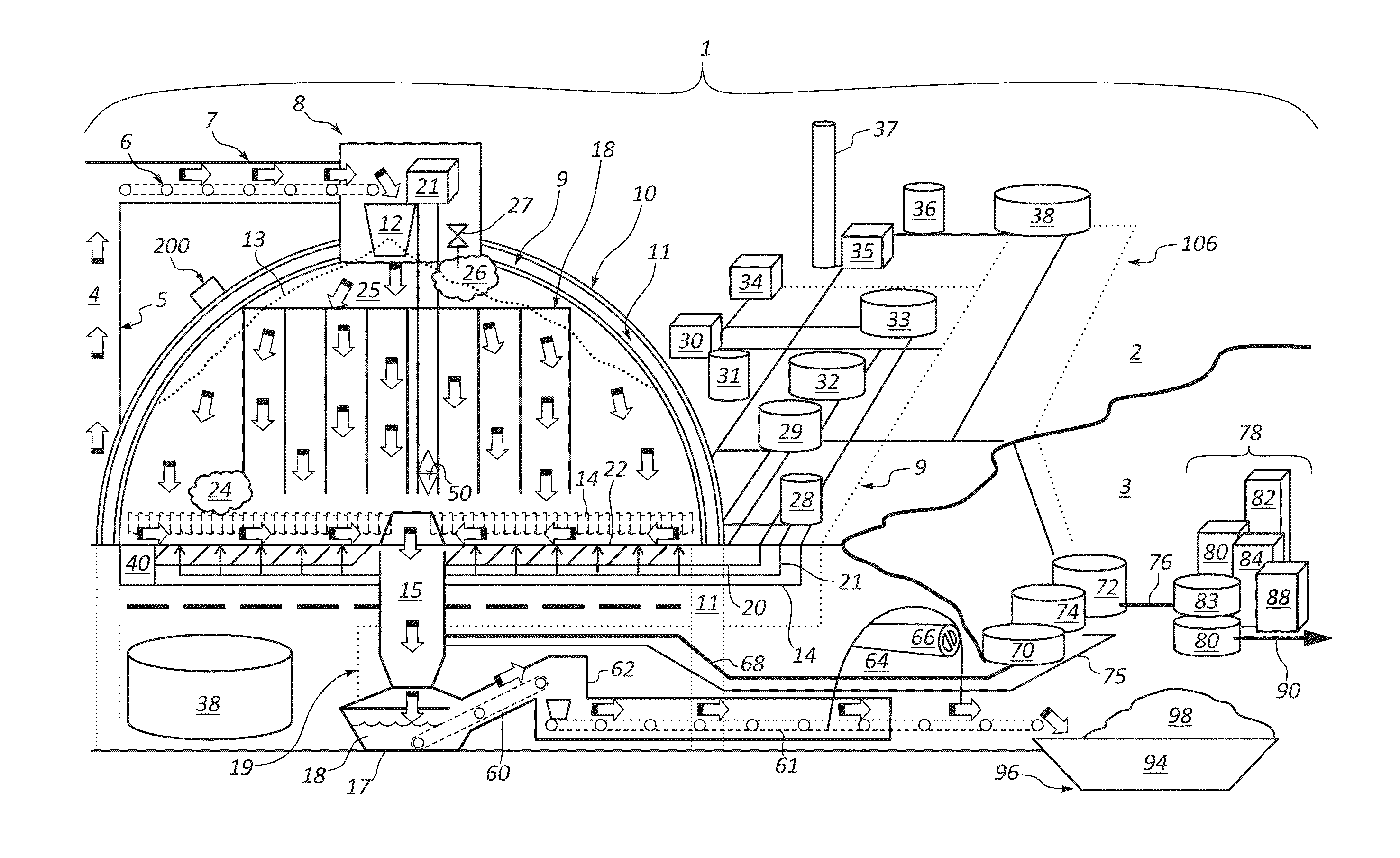
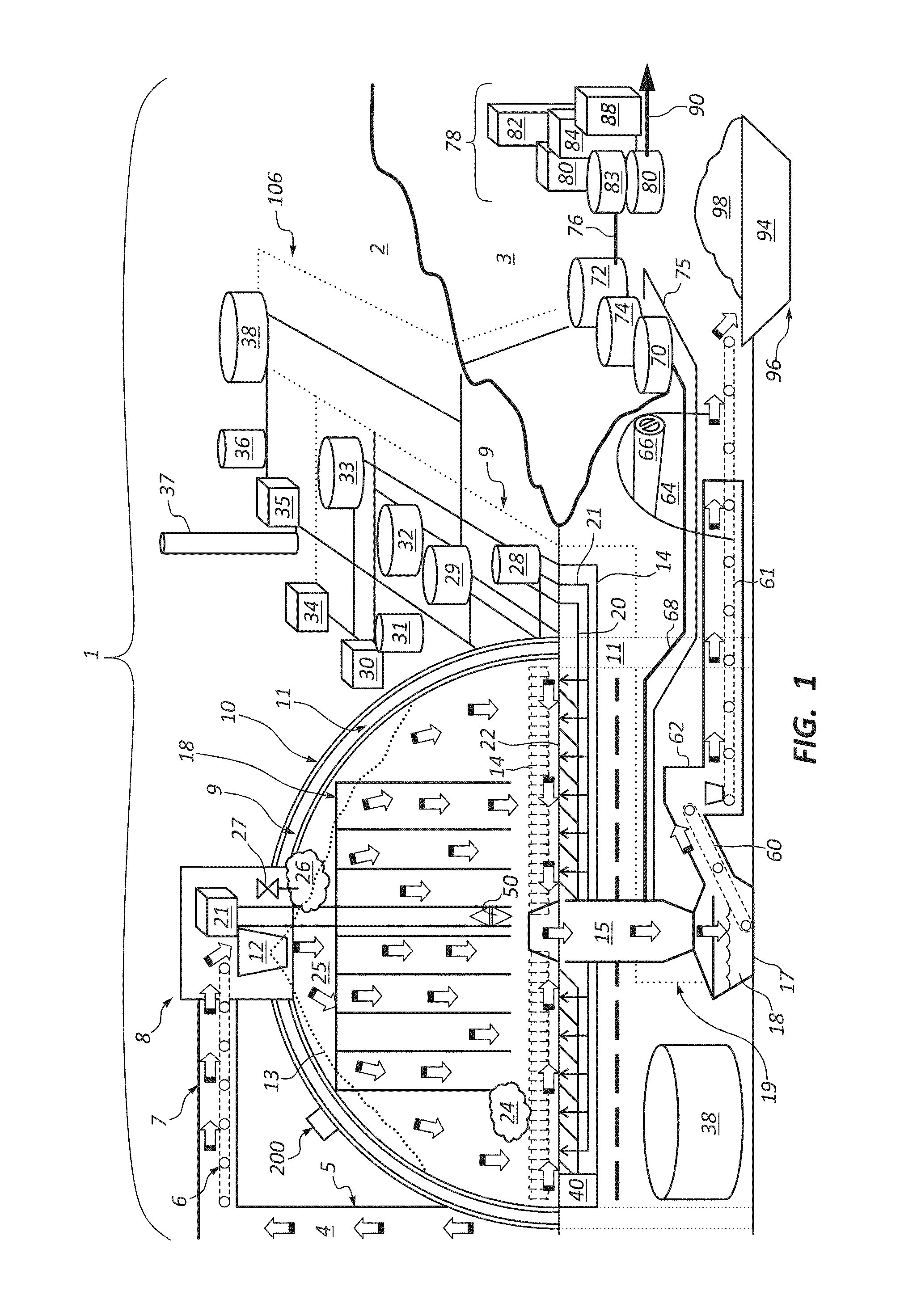
Systems, Apparatus and Methods of a Dome Retort
InactiveUS20110313218A1Increased material throughputLower cost of capitalPressurized chemical processDirect heating destructive distillationBasementControl system
A system, apparatus and method for hydrocarbon extraction from feedstock material that is or includes organic material, such as oil shale, coal, lignite, tar sands, animal waste and biomass. A retort system including at least one retort vessel may include a monolithic dome structure surrounded by a process isolation barrier, the dome structure being sealingly engaged with the process isolation barrier. The dome structure and the process isolation barrier define a retort chamber, at least a portion of which may comprise a subterranean chamber. A lower end of the dome retort structure provides an exit for collected hydrocarbons and spent feedstock material. Systems may include a plurality of such dome retort structures. A control system may be used for controlling one or more operating parameters of a retorting process performed within such a dome retort structure for extraction and collection of hydrocarbons.
Owner:DANA TODD C
Process for conversion of organic, waste, or low-value materials into useful products
ActiveUS7301060B2Low viscosityHydrocarbon purification/separationIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationSpeciality chemicalsHigh energy
Owner:SYNPET TEKNOLOJI GELISTIRME
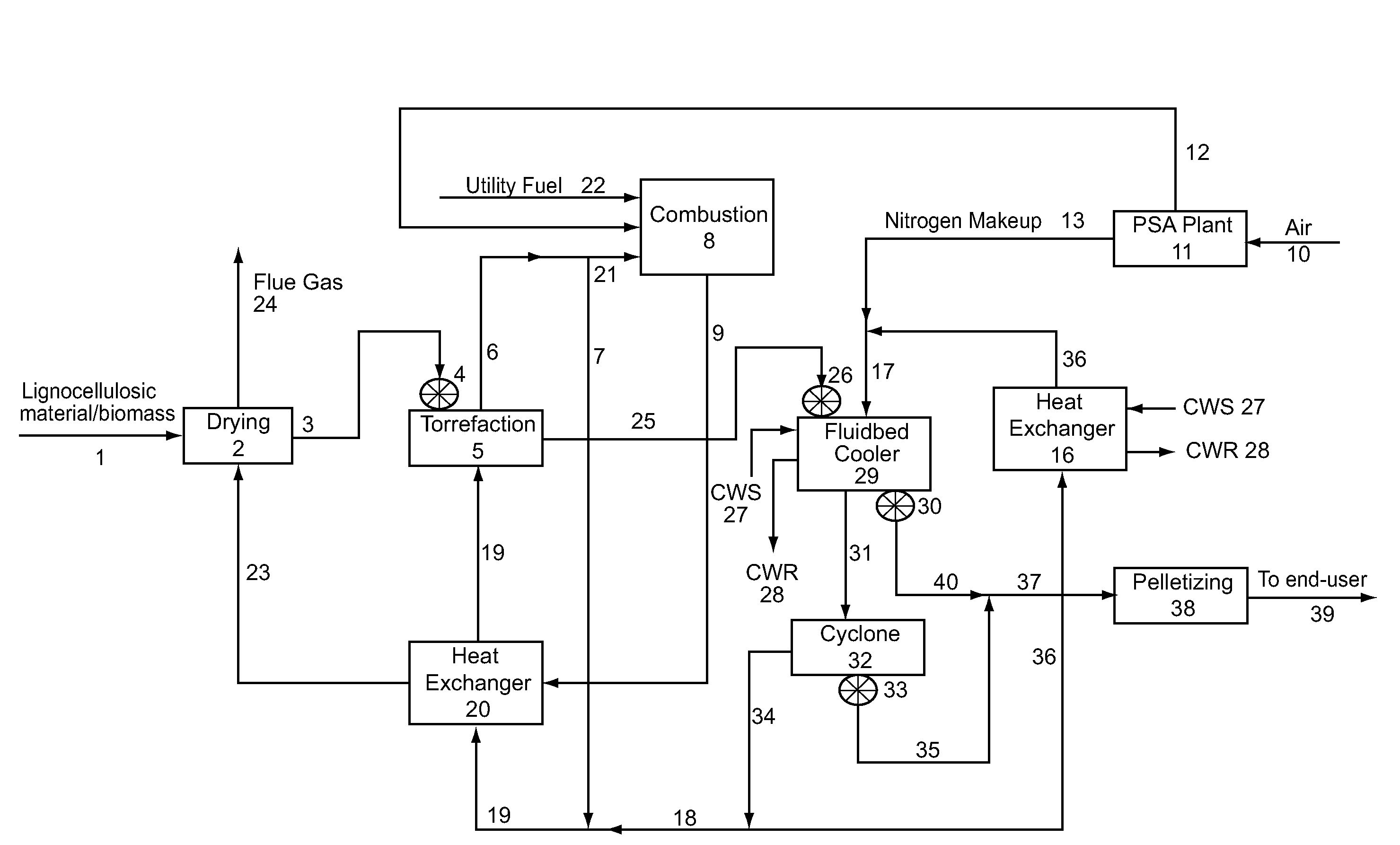
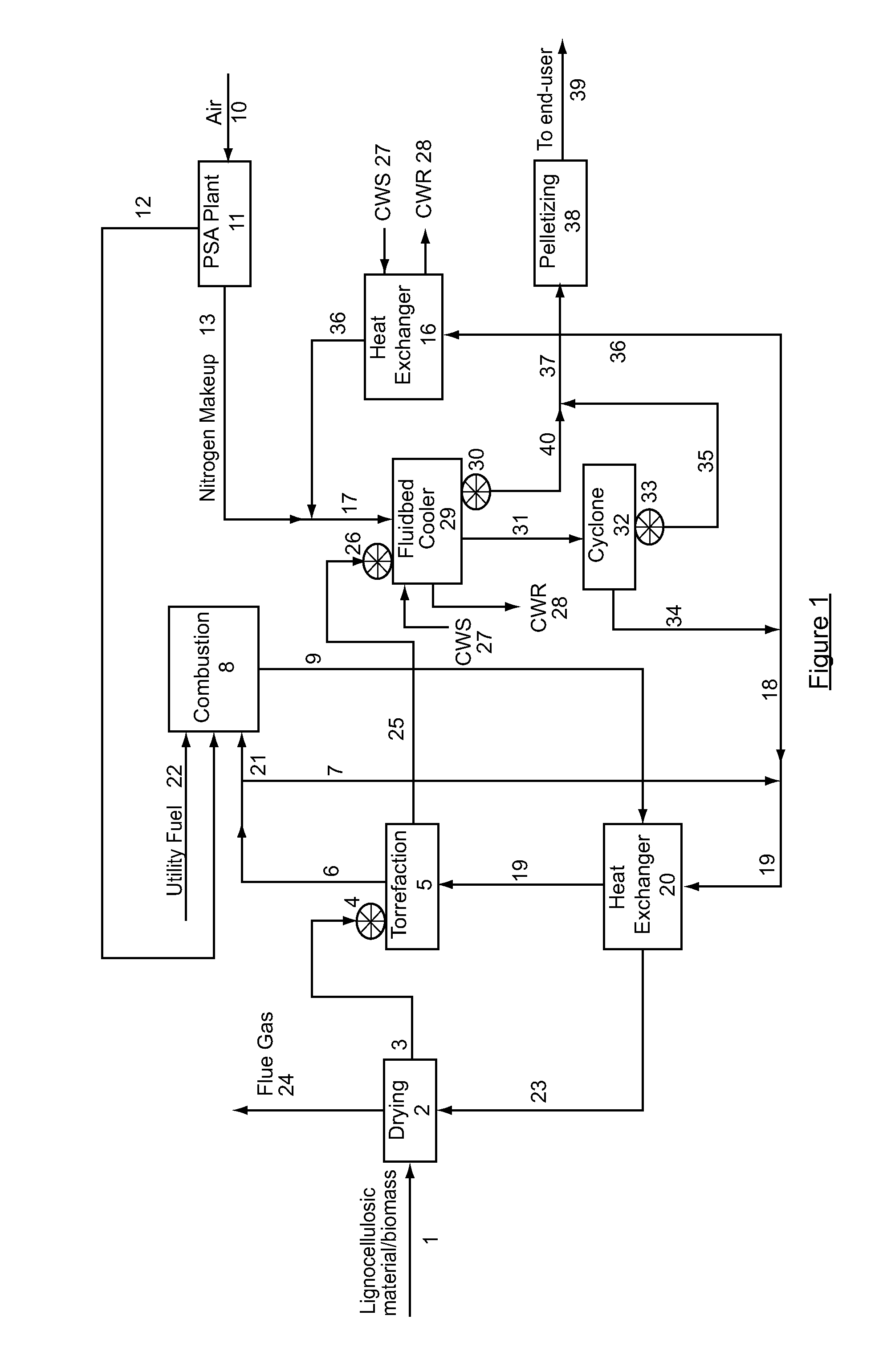
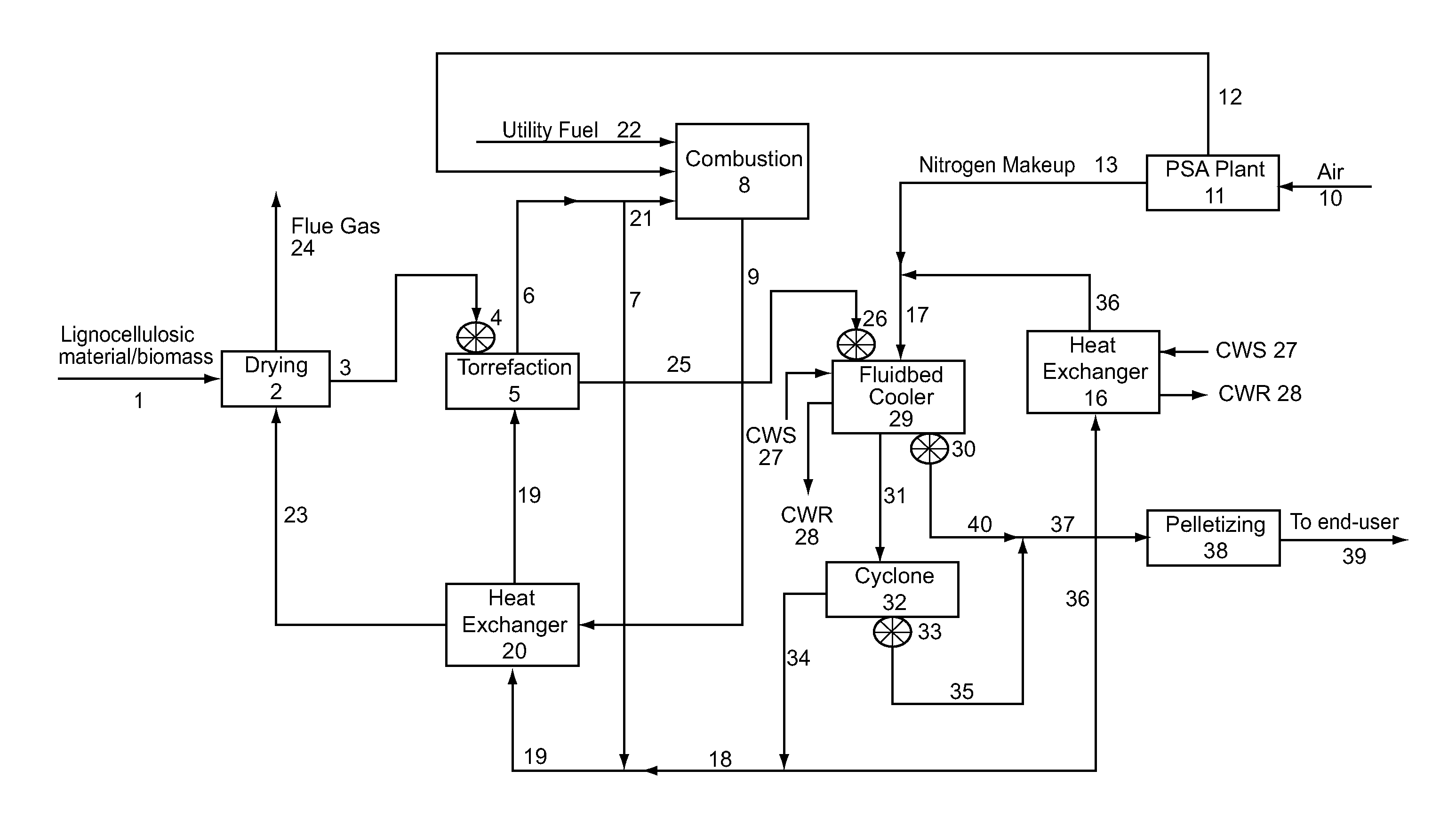
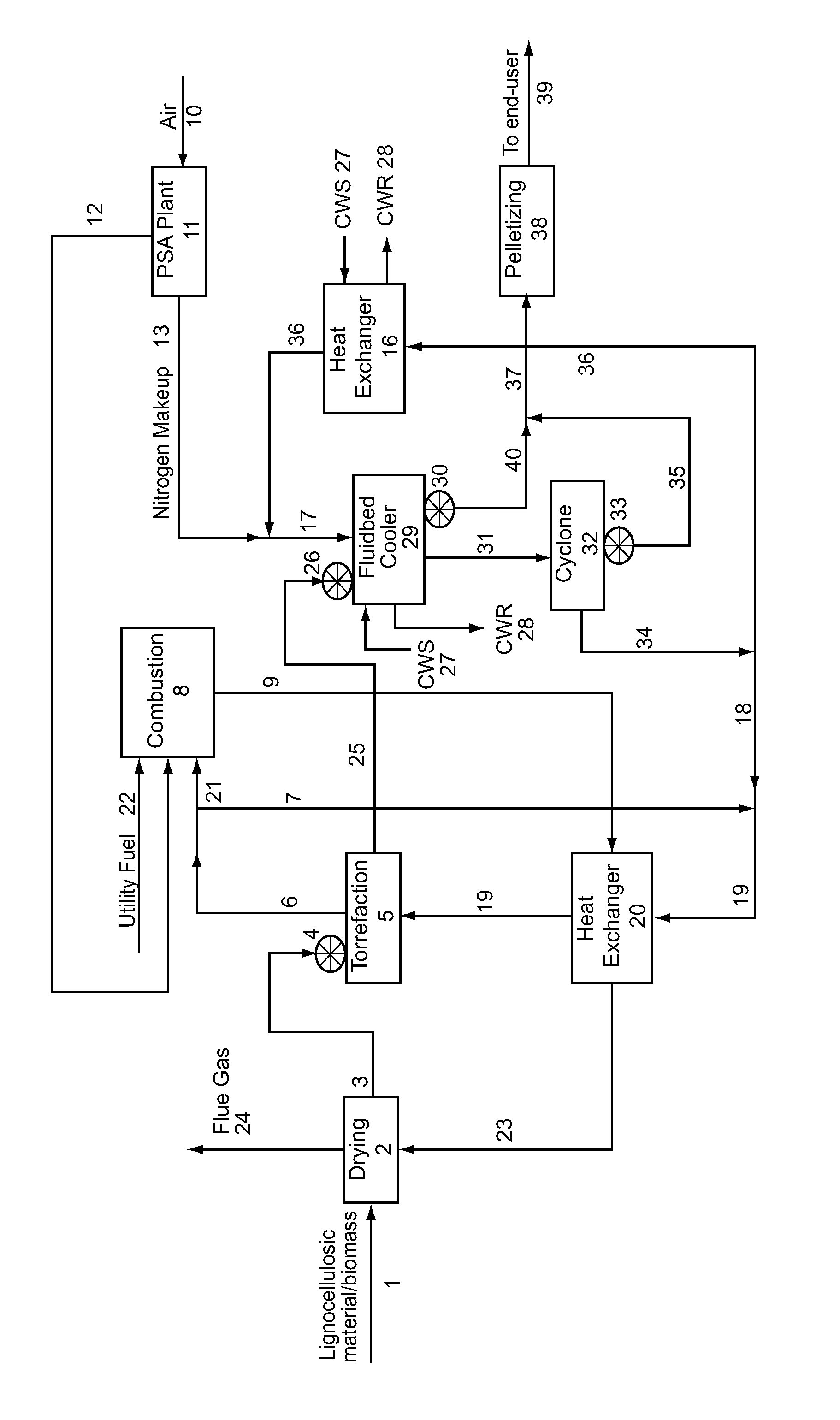
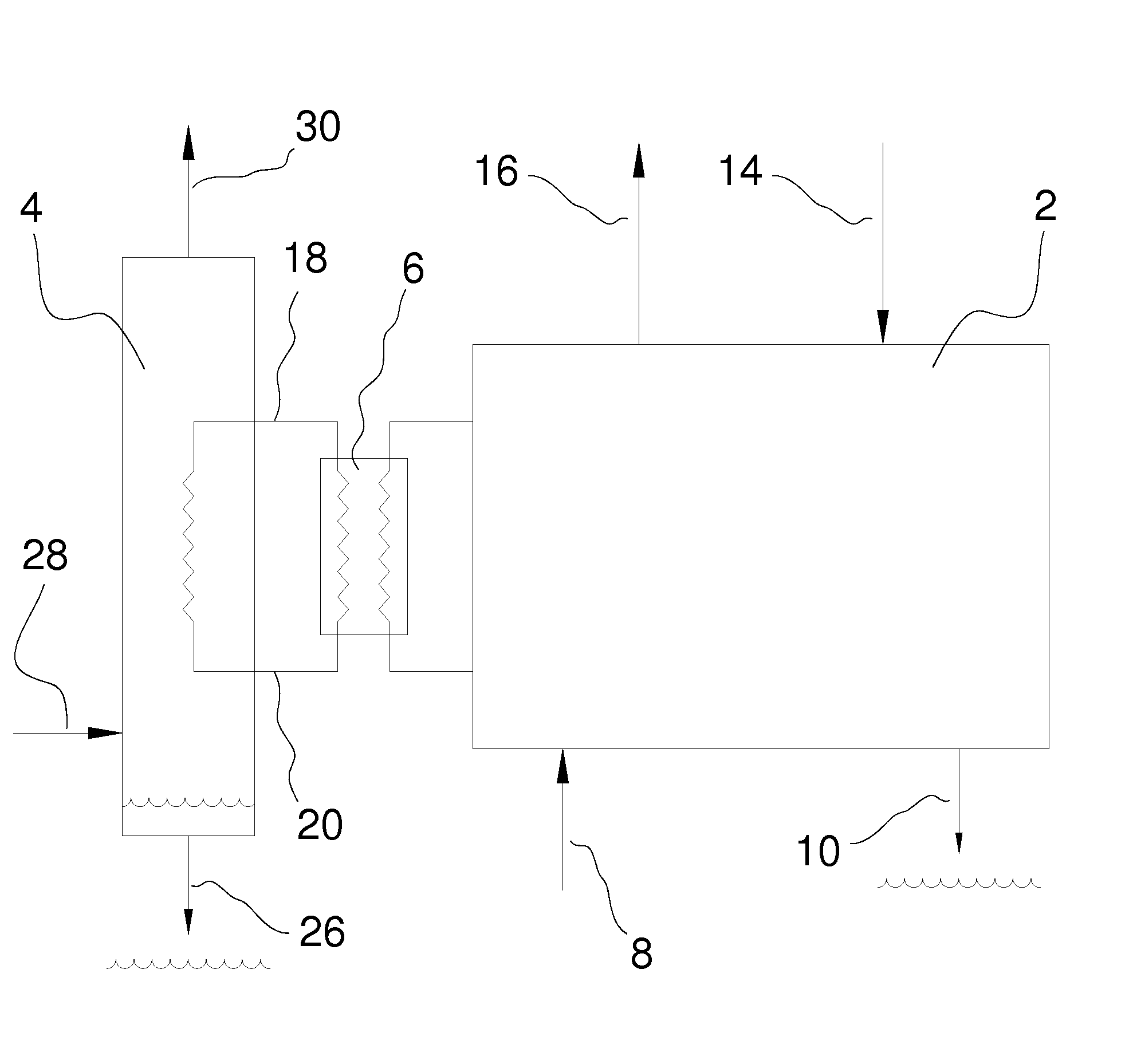
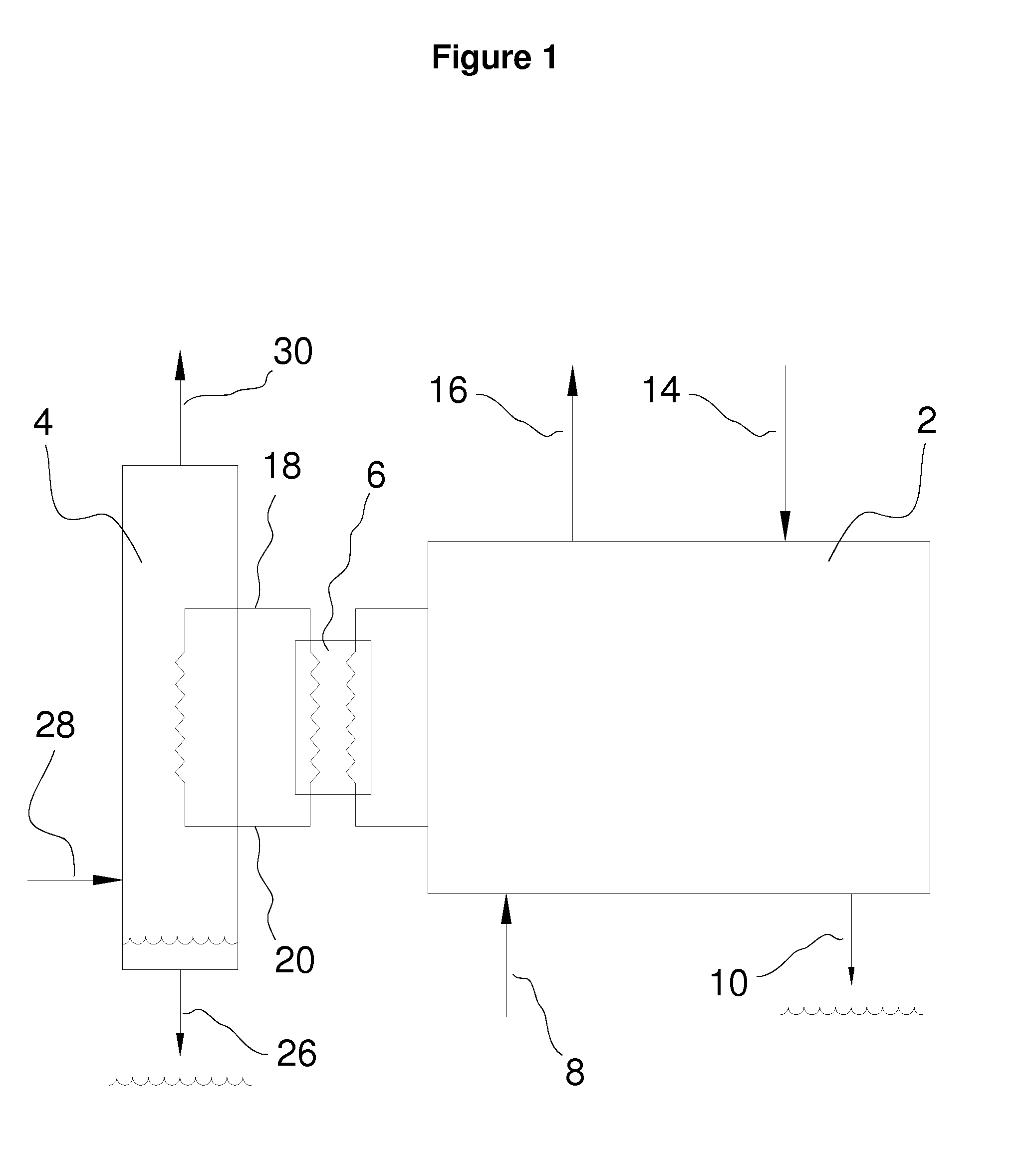
Method and system for the torrefaction of lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20110041392A1BiofuelsIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationCelluloseProcess engineering
Owner:ANDRITZ TECH & ASSET MANAGEMENT
Vacuum Pyrolytic Gasification And Liquefaction To Produce Liquid And Gaseous Fuels From Biomass
InactiveUS20110011721A1Facilitate heavy fuel distillation operationBiofuelsIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationRare-earth elementVacuum pressure
A biofuel production method, catalyst and system. The method may include combining a feedstock comprising a carbonaceous material with a consumable catalyst to produce a feedstock / catalyst mixture, and subjecting the feedstock / catalyst mixture to a vacuum pyrolytic gasification and liquefaction process to produce one or more biofuels. The catalyst includes effective amounts of various catalyst constituents, which may include some or all of kaolin, zeolite, amorphous silica, alumina aluminum phosphate and rare earth elements. The system may include apparatus for heating the feedstock / catalyst mixture under selected temperature and vacuum pressure conditions to produce a gaseous effluent comprising one or more hydrocarbon fractions, and additional distillation and condensation apparatus to produce one or more liquid and gaseous fuels.
Owner:CHAMPAGNE GARY E
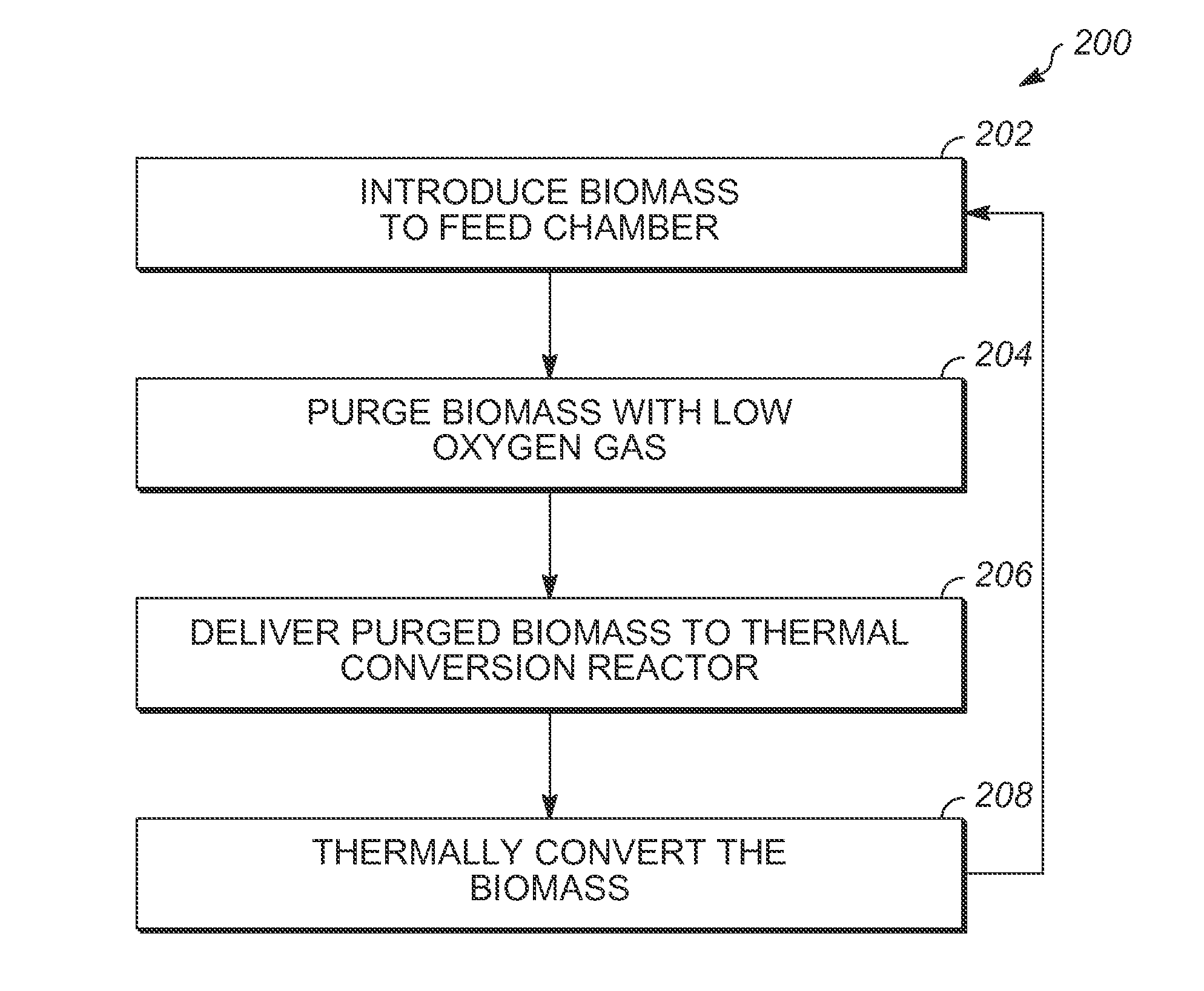
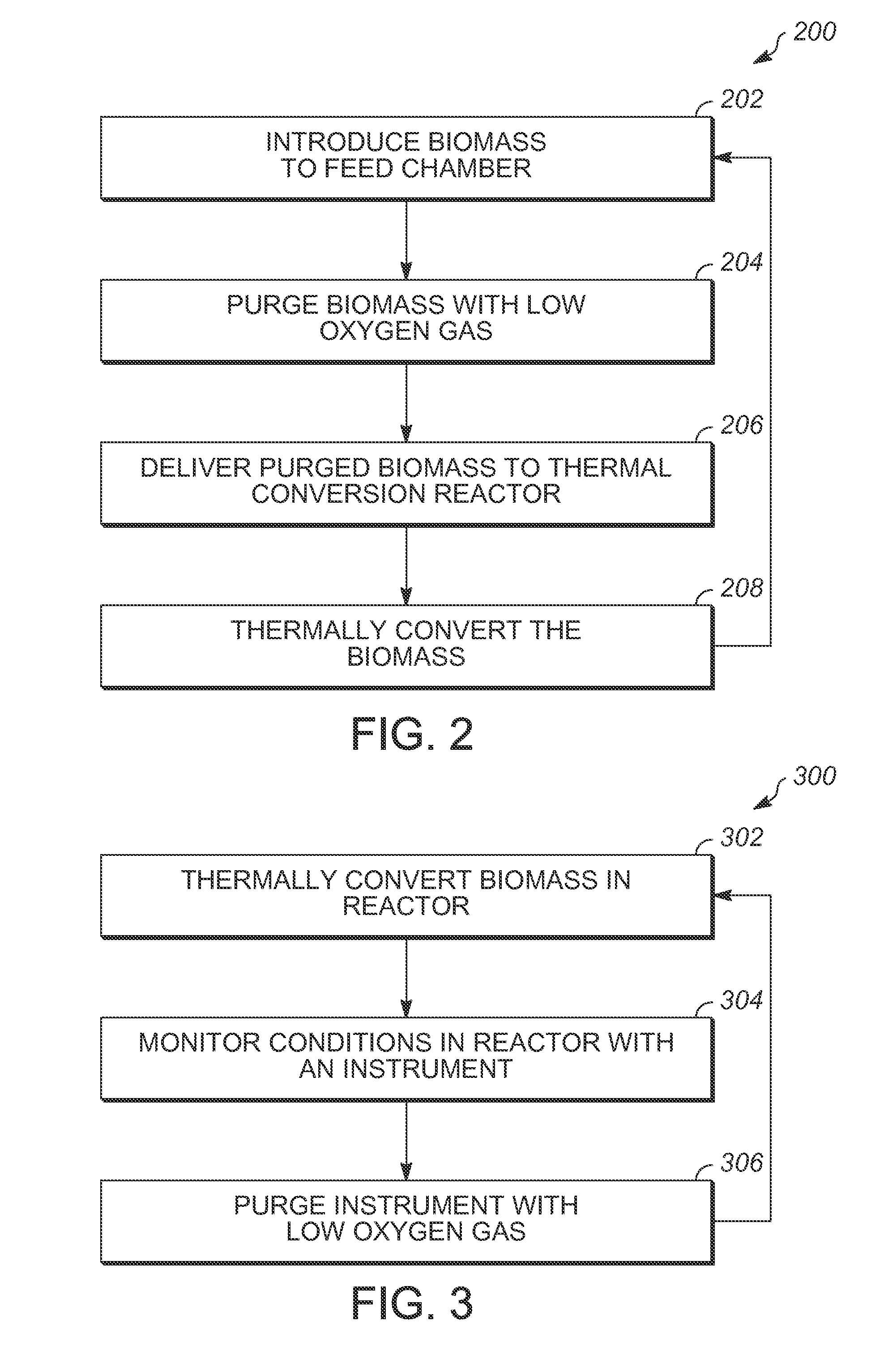
Methods and apparatuses for thermally converting biomass
Methods and apparatuses for thermally converting or pyrolyzing biomass are provided. In one embodiment, a method of thermally converting biomass includes introducing the biomass to a reactor feed chamber. The method provides for flowing a low oxygen gas into the reactor feed chamber to purge the reactor feed chamber and biomass of oxygen. The method also includes delivering the purged biomass to a thermal conversion reactor and thermally converting the biomass in the thermal conversion reactor.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Staged biomass pyrolysis process and apparatus
InactiveUS20110278149A1Low heating rateReduce tar contentProductsBeehive ovensOxygenThermal treatment
Owner:ASTON UNIV
Successive pyrolysis system of waste synthetic-highly polymerized compound
InactiveUS20060076224A1Maximizes operating rateProductsCombustible gas coke oven heatingCombustion chamberBoiling point
Disclosed is a successive pyrolysis system of waste synthetic-highly polymerized compound for successively pyrolizing combustible waste by indirect heating at a pyrolysis chamber maintaining an anaerobic or hypoxic environment, and producing refined oil like heavy oil and light oil according to boiling points at a distillation column to be used as heat source for the pyrolysis of the waste. The successive pyrolysis system comprises a hopper; an automatic waste injection device, which discharges a predetermined amount of waste from the hopper; a pyrolysis chamber for maintaining a high-temperature and hypoxic environment, and successively pyrolizing the waste by indirect heating; a gas burning chamber for burning noncondensable gas among pyrolysis gas produced at the time of the pyrolysis of the waste, and providing heat of a predetermined temperature to the outer surface of the pyrolysis chamber to be used as heat source for the pyrolysis of the waste; a refined oil producing means for producing refined oil from the pyrolysis gas reformed after going through catalyst reaction and providing residual noncondensable gas to the gas burning chamber; and an automatic discharging device for successively discharging ashes transported after being pyrolized from the pyrolysis chamber.
Owner:ALPO
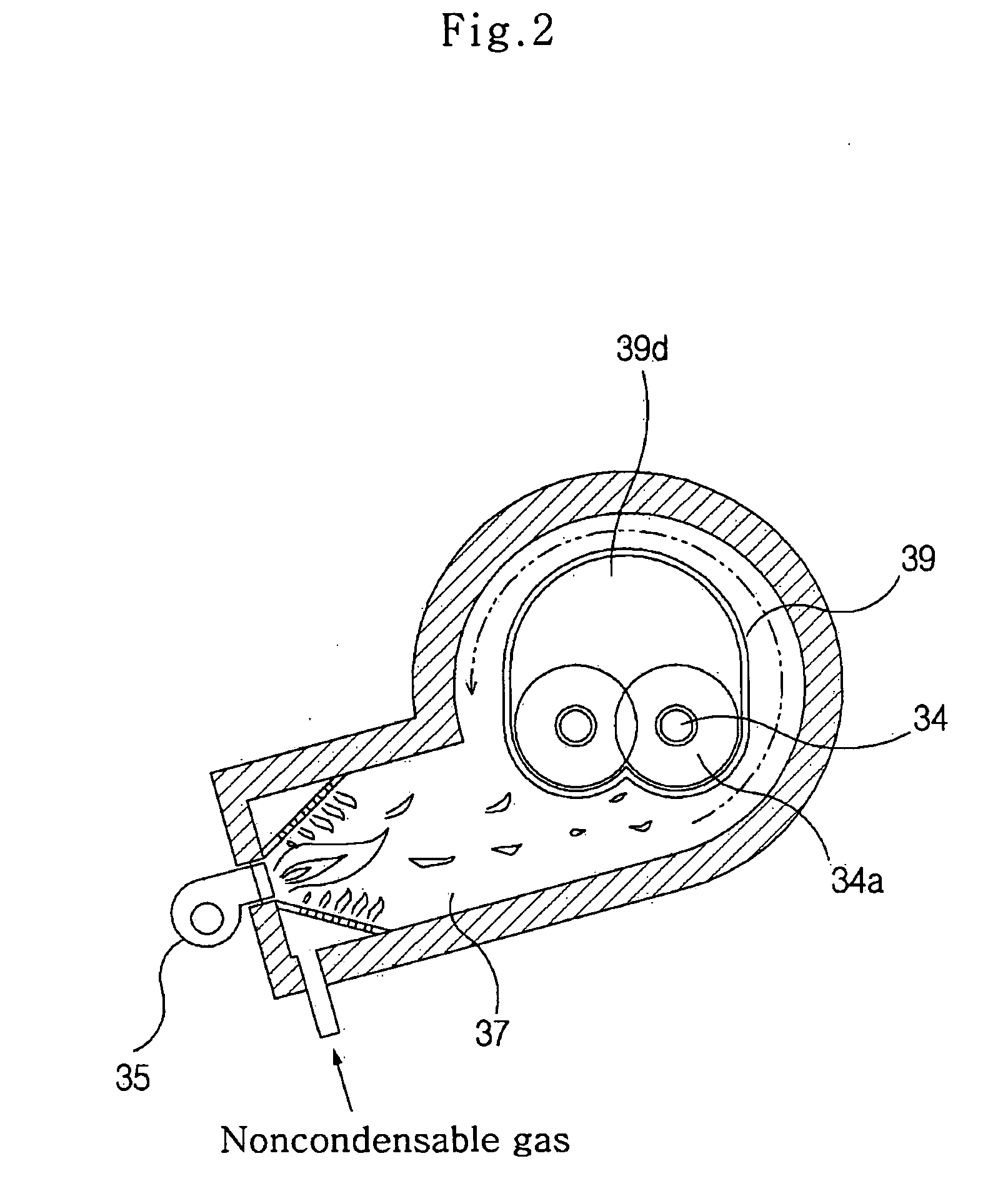
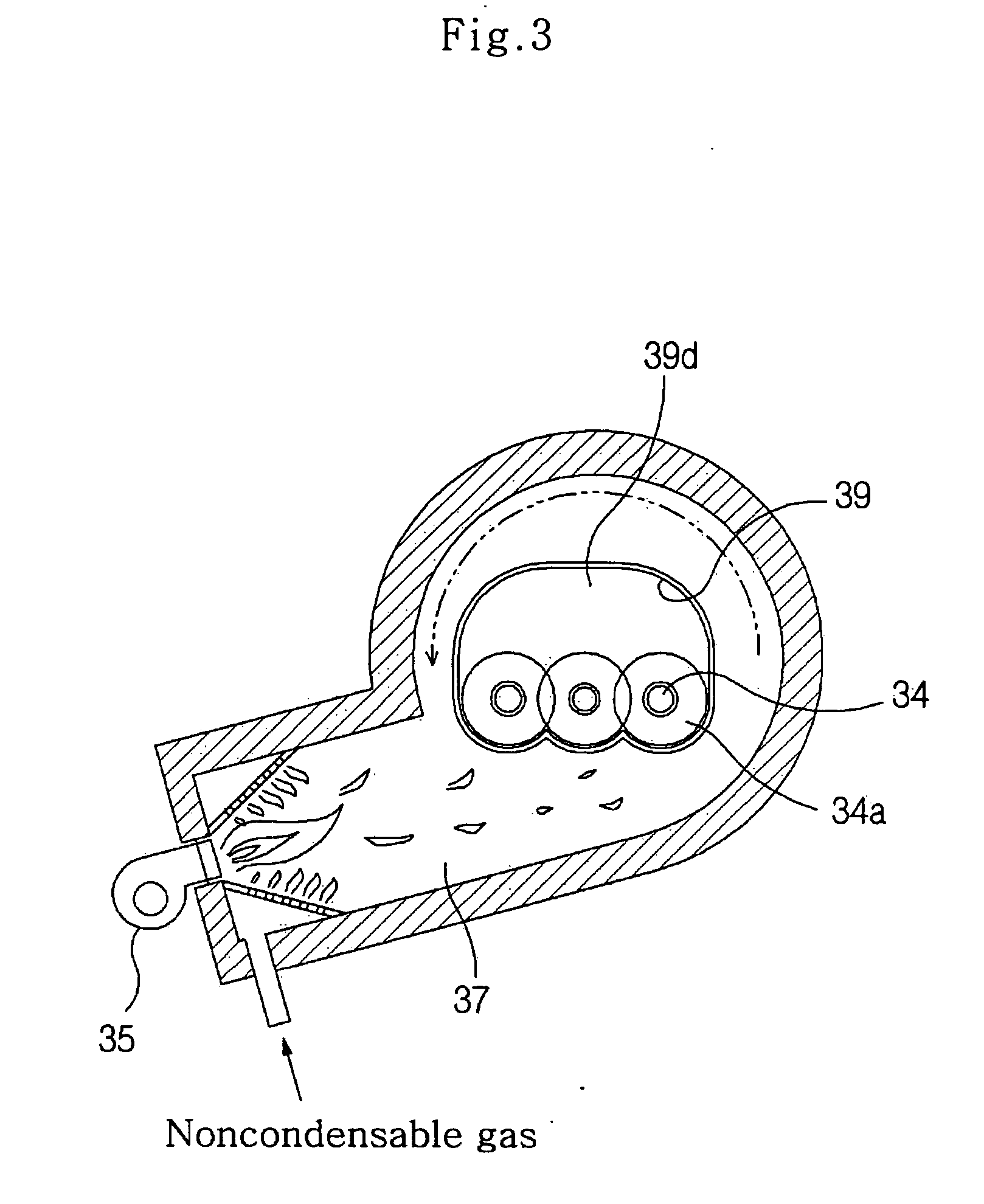
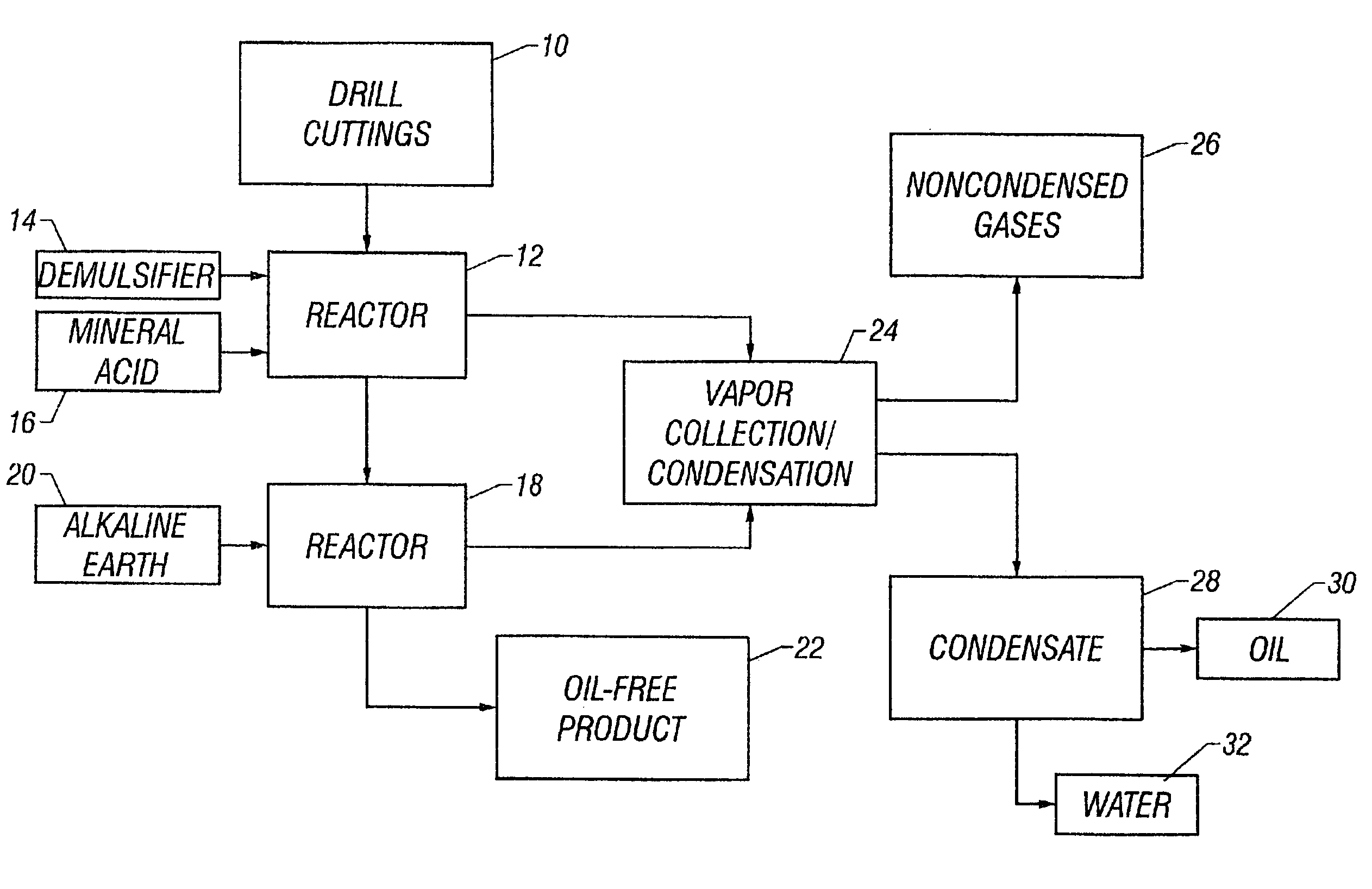
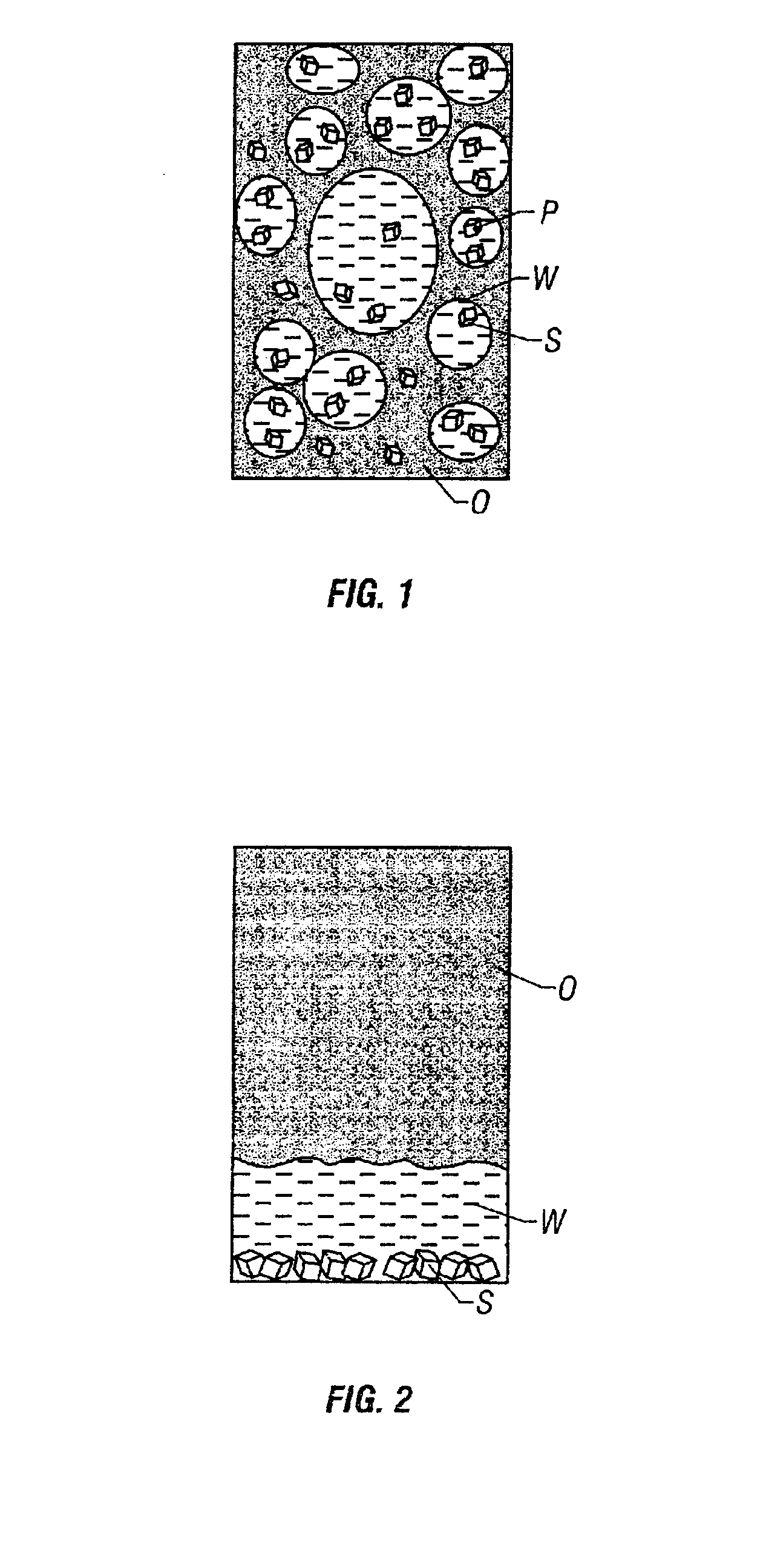
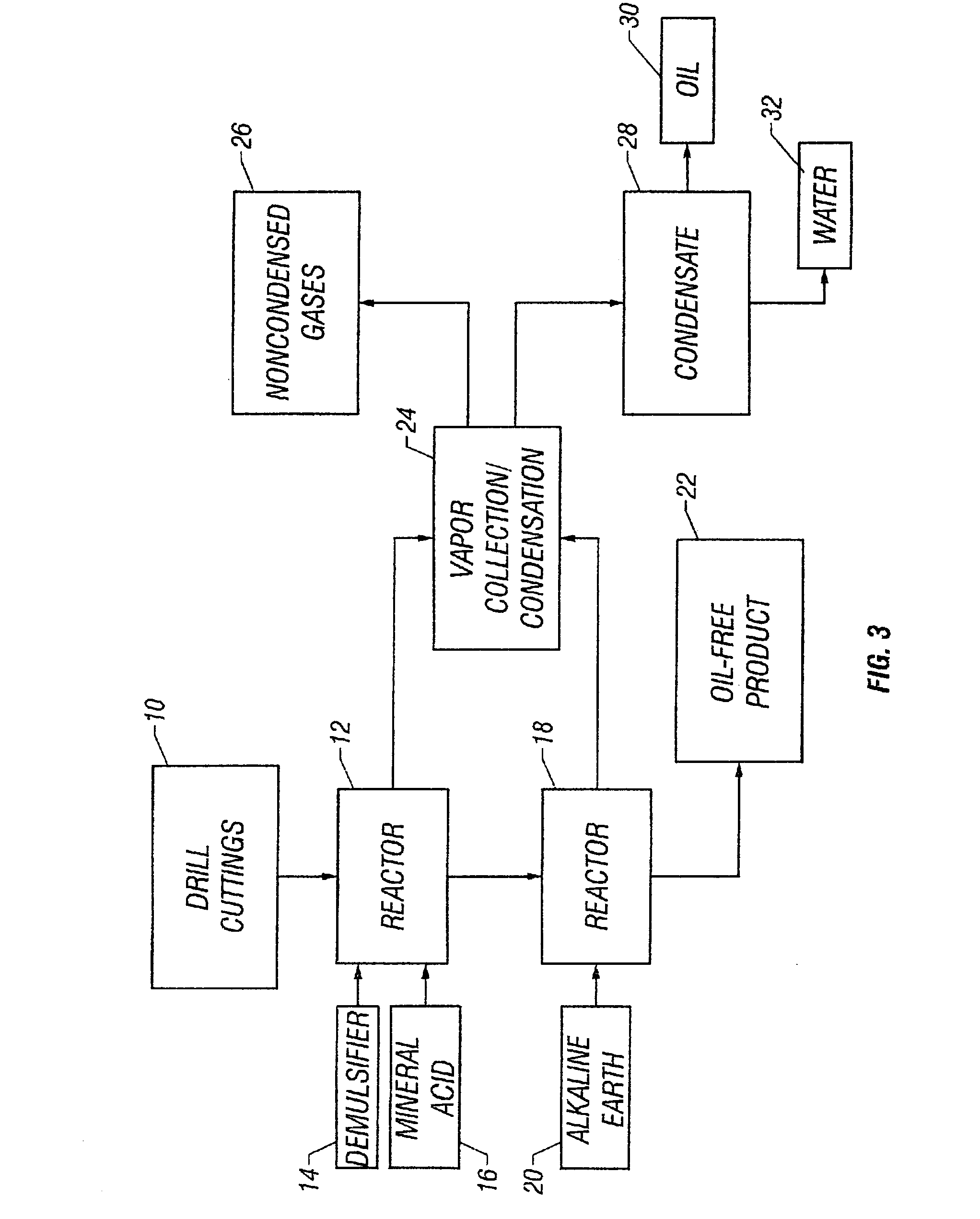
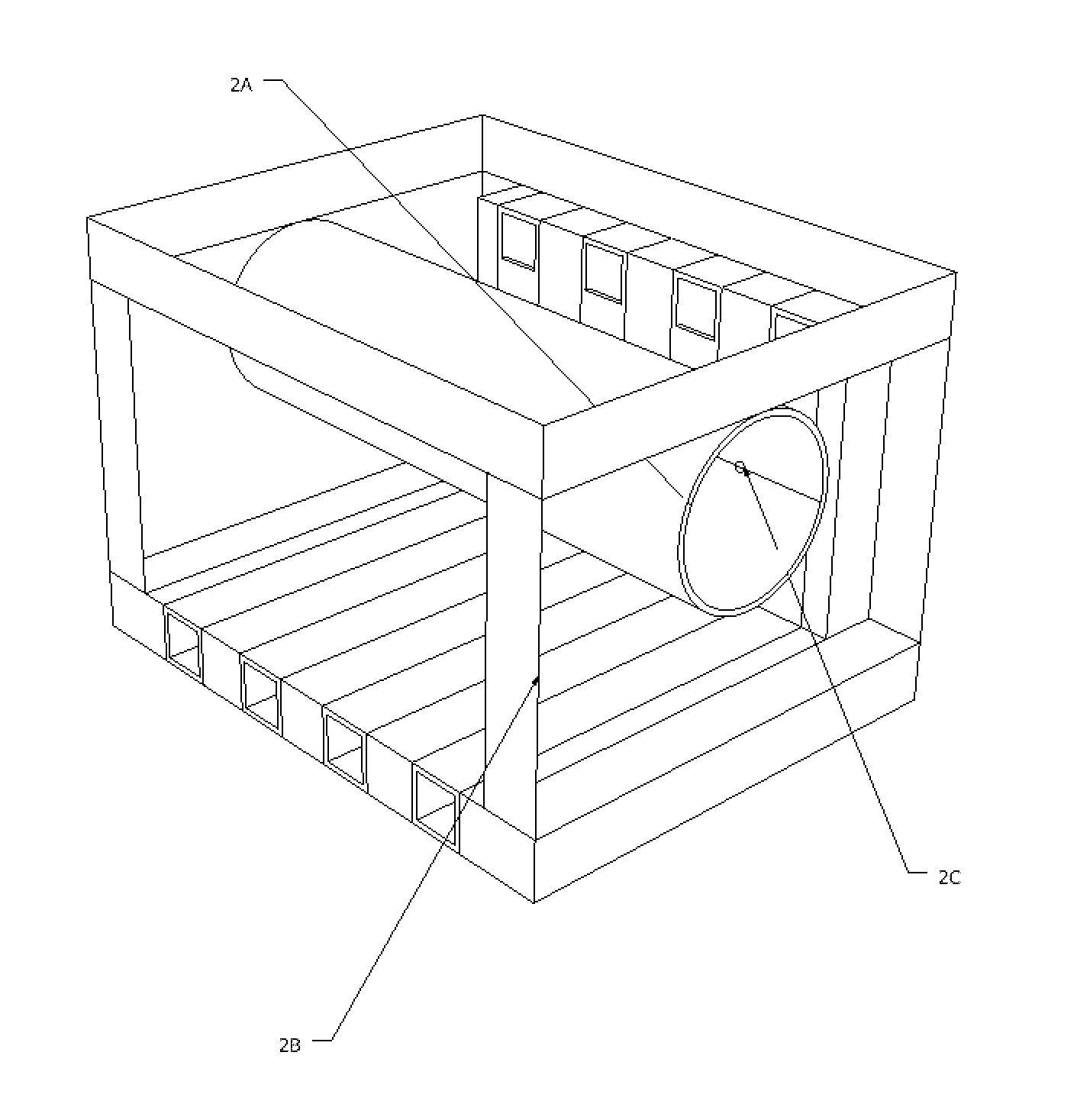
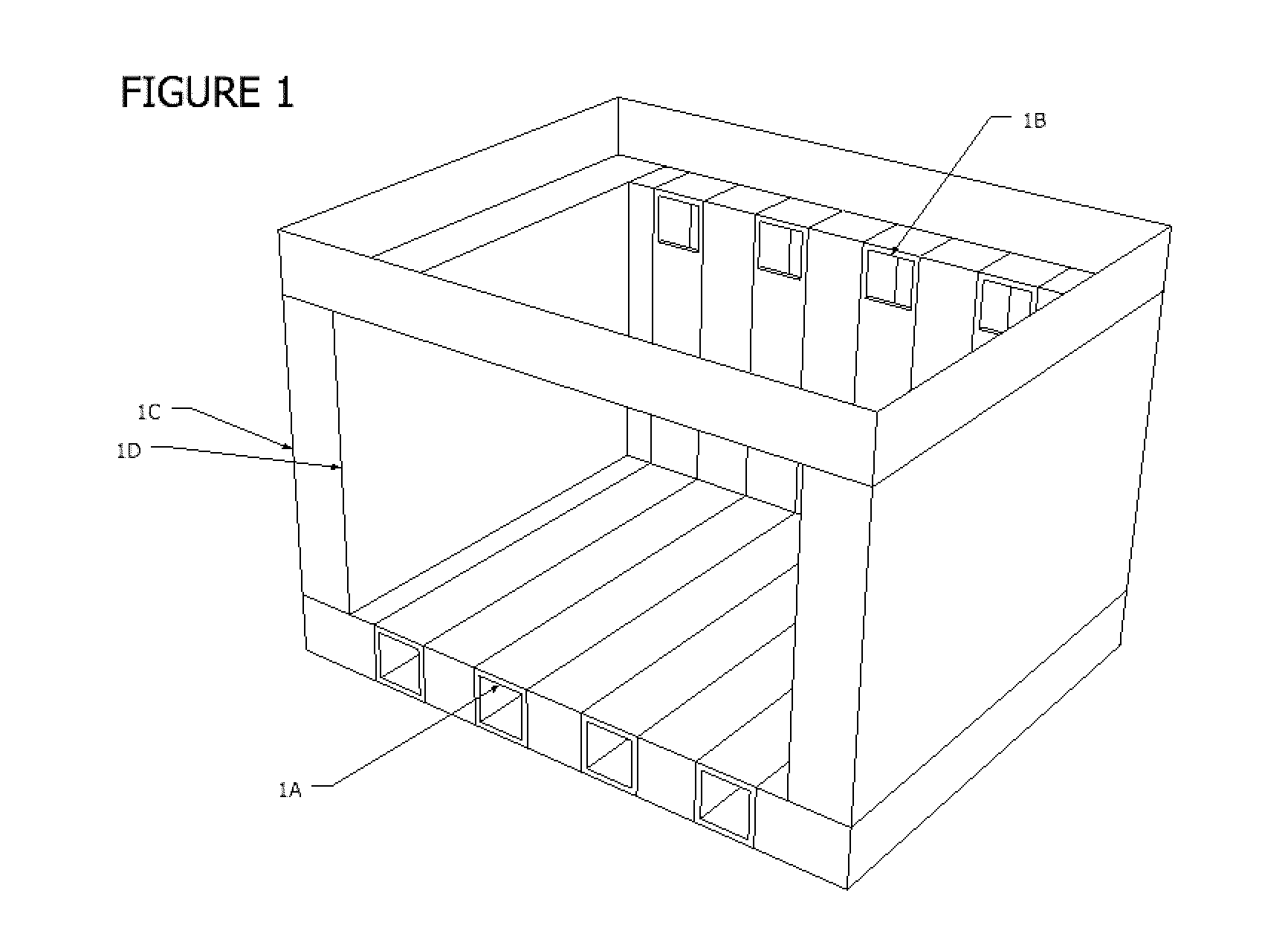
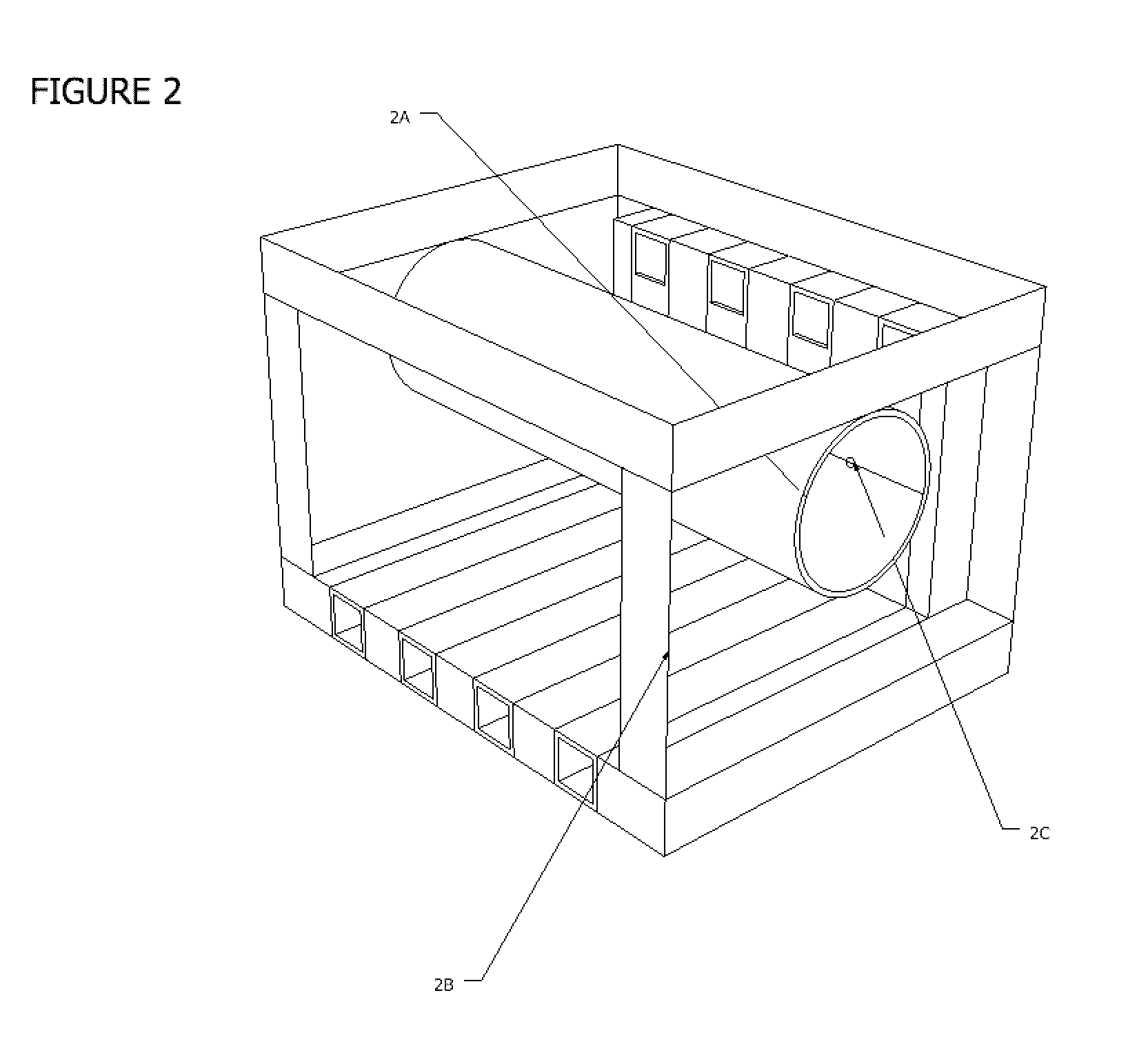
Drill cutting treatment method
InactiveUS6668947B2Easy to removeRapid and extensive and costsLighting and heating apparatusTransportation and packagingOrganic acidEmulsion
A method and apparatus for treating for disposal oil-contaminated clay substrates such as drill cuttings from drilling with an oil-based mud. If necessary, the substrate is pretreated with an aqueous emulsion breaker such as alkylbenzenesulfonic acid. The substrate is mixed under high shear conditions with a mineral acid such as sulfuric acid. This can be done in an agitated reactor with sequential addition of the organic and inorganic acids. The substrate is then mixed with alkaline earth such as lime in a second agitated reactor. The reactions between the acid(s), alkaline earth and substrate are exothermic and provide heat to vaporize the oil, reaction products and water. Recoverable constituents in the vapor can be condensed in a vapor collection system. The treated substrate is essentially free of oil and has a controlled water content.
Owner:RACIONAL ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT
Biochar retort kiln
Systems and methods for a biochar retort kiln are disclosed herein. A method for making biochar includes placing waste bio mass in a cylindrical retort chamber. The retort chamber extends outwardly at a first end and a second end from a fire box. Pyrolysis is fueled by igniting the waste biomass. Syngasses are evacuated through one or more holes defined by the cylindrical retort chamber, such that the syngasses are driven out of the biomass and out of the retort chamber to be consumed by a fire in the firebox. The byproduct of the described method is biochar.
Owner:SHEPARD BRITTON
Method and system for the torrefaction of lignocellulosic material
Owner:ANDRITZ TECH & ASSET MANAGEMENT
System and method for wastewater reduction and freshwater generation
InactiveUS20080277262A1Reduction of environmental liabilityImprove reliabilityBeehive ovensAuxillariesEvaporative coolerFresh water organism
A process whereby freshwater is generated and wastewater is eliminated through the employ of waste combustion gas; wherein combustion gas is cooled below dewpoint, via the effects of a wastewater fed evaporative cooler, resulting in the combined benefits of freshwater generation from the combustion gas and evaporative reduction of the wastewater.
Owner:LAYNE CHRISTENSEN COMPANY
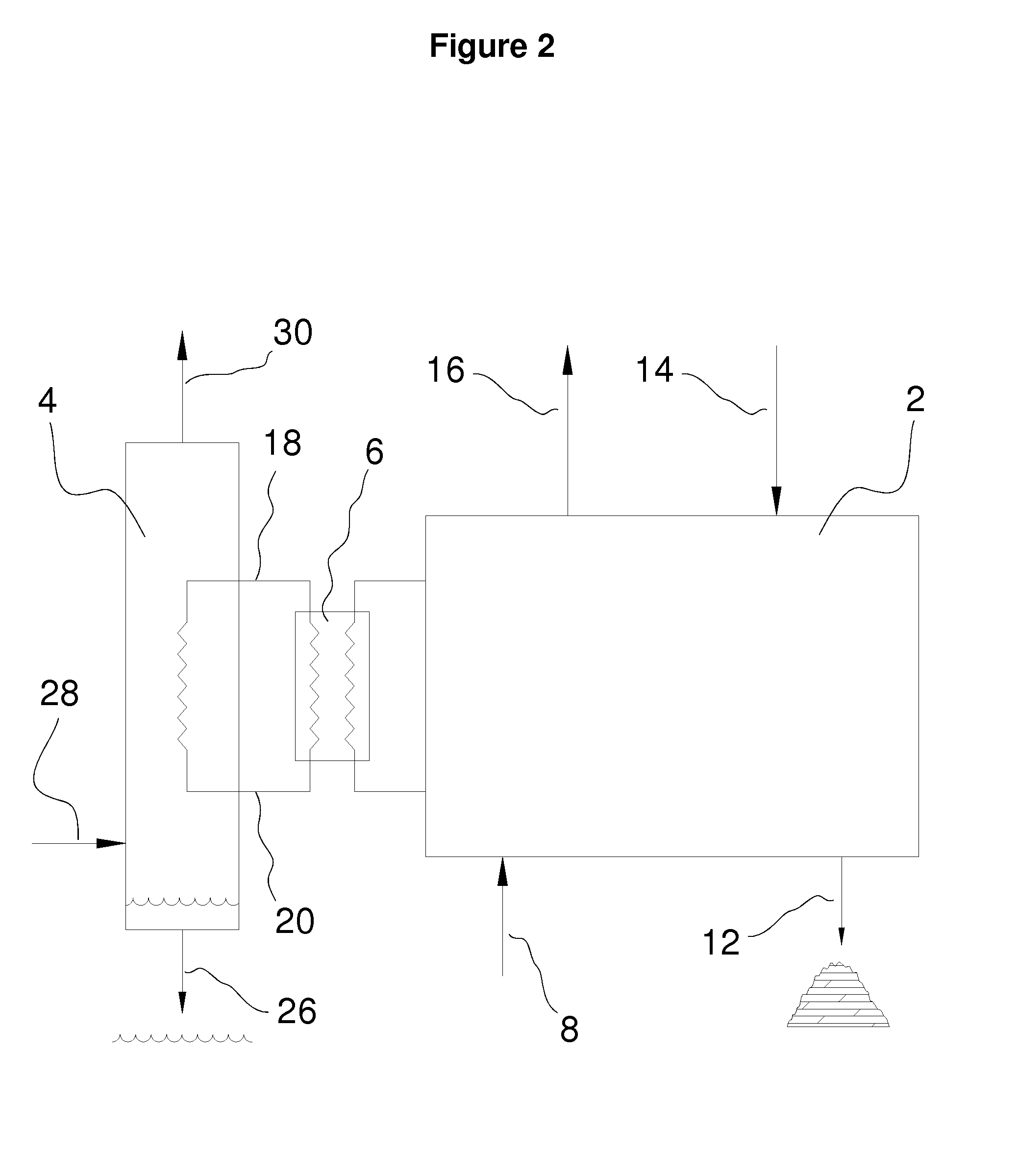
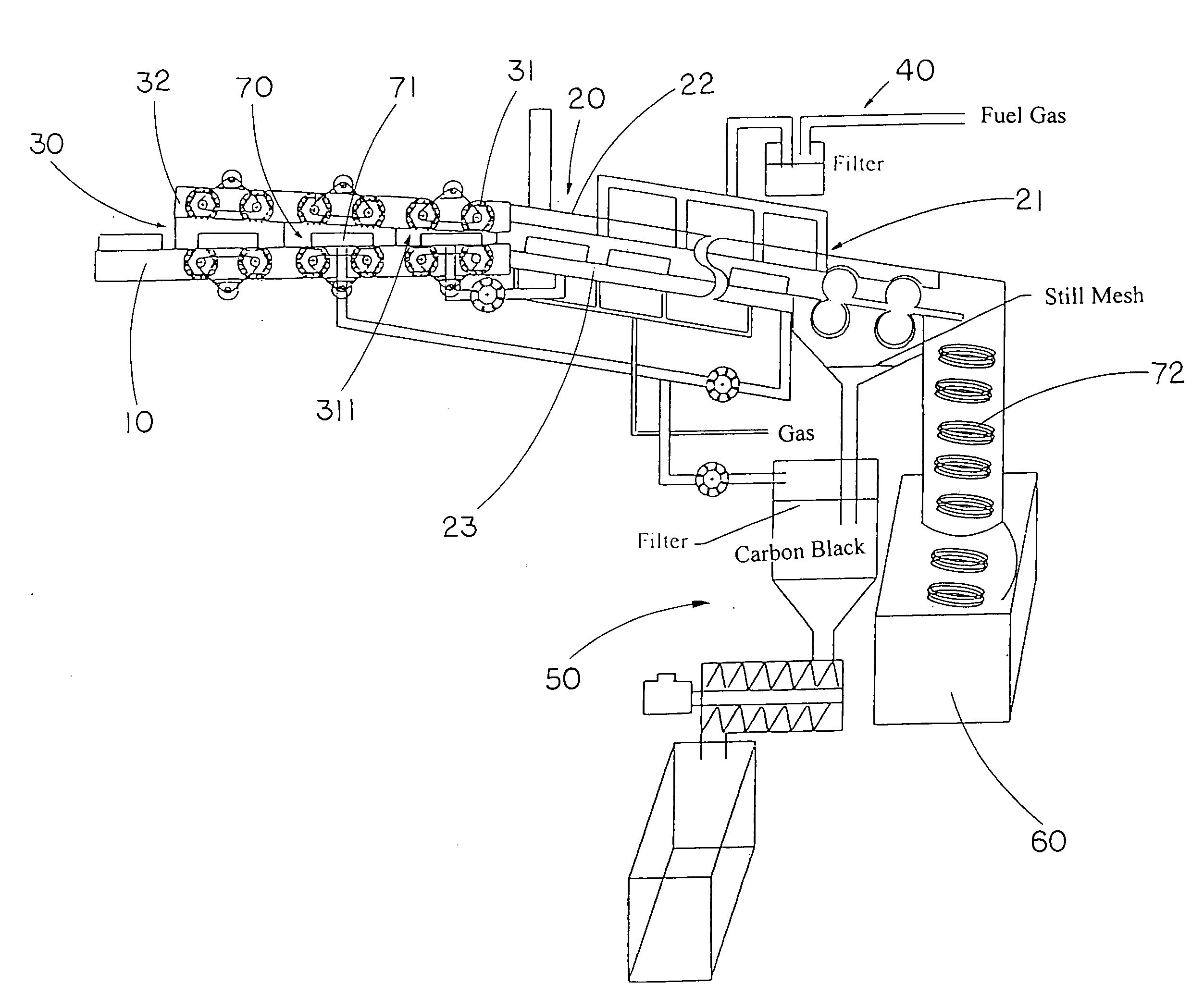
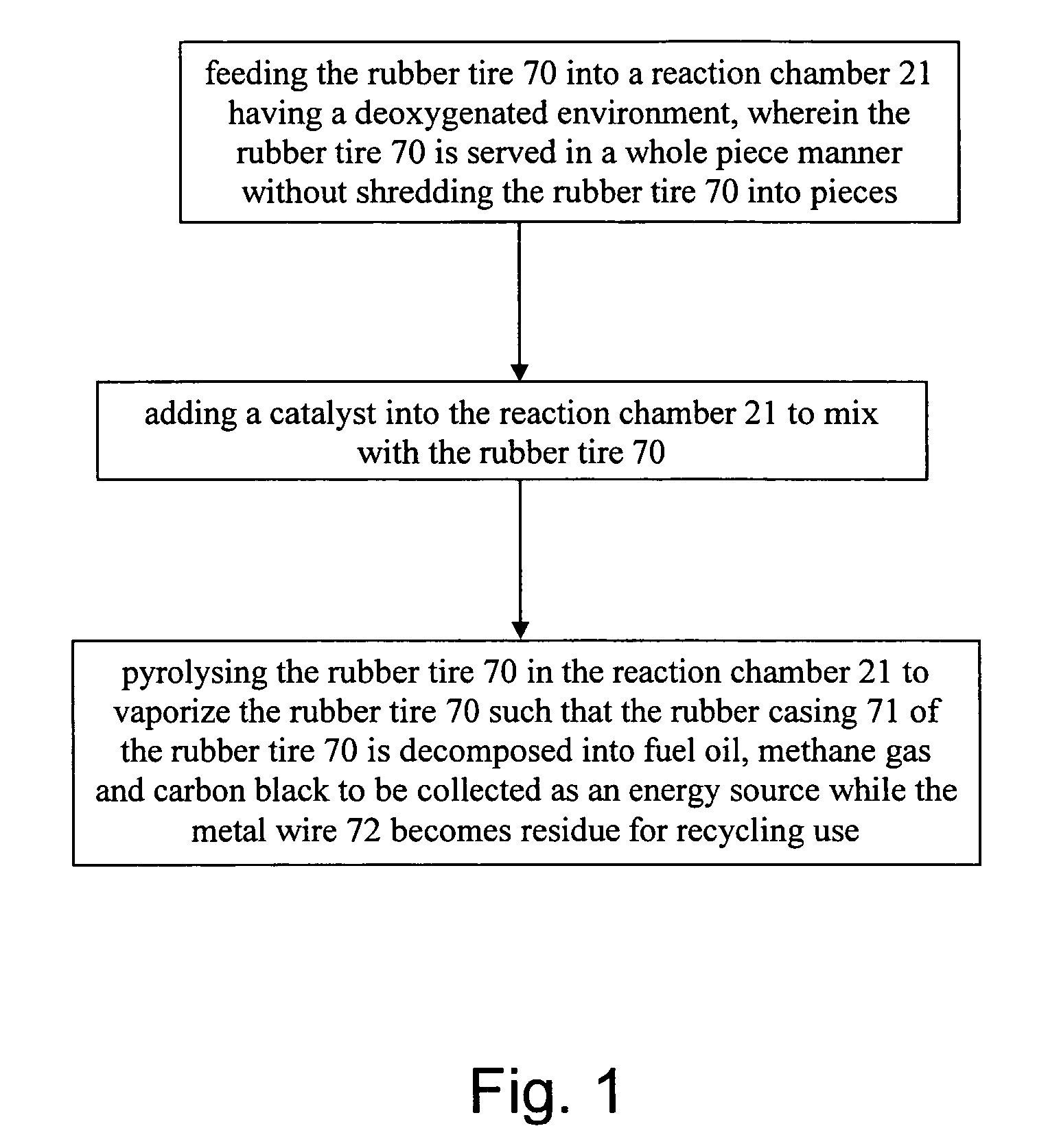
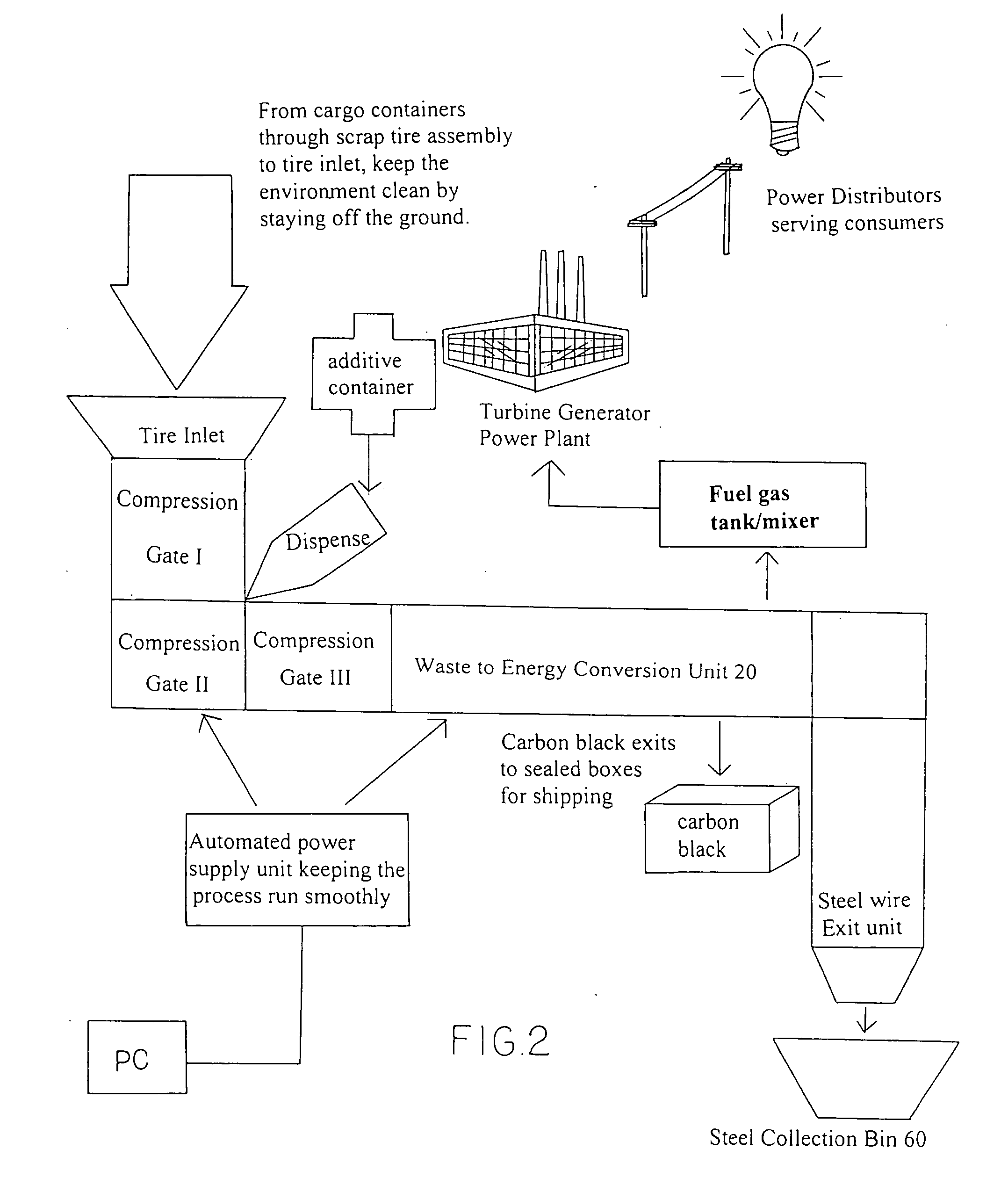
Rubber tire to energy pyrolysis system and method thereof
InactiveUS20060211899A1Maximize applicationLow costIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationRetortsFuel oilMethane gas
The present invention provides a pyrolysis system and method thereof which are capable of converting an entire rubber tire into several energy resources in an environmentally-friendly manner. The system includes a tire transporting unit, a waste to energy conversion unit, and a energy collection unit. The waste to energy conversion unit includes a conversion housing having a reaction chamber for receiving the rubber tire for pyrolysis processing to decompose the rubber tire into fuel oil, methane gas and carbon black, while metal wire from the rubber tire are resided for recycling use.
Owner:LEE ERNEST
Method and system for wasteless processing and complete utilization of municipal and domestic wastes
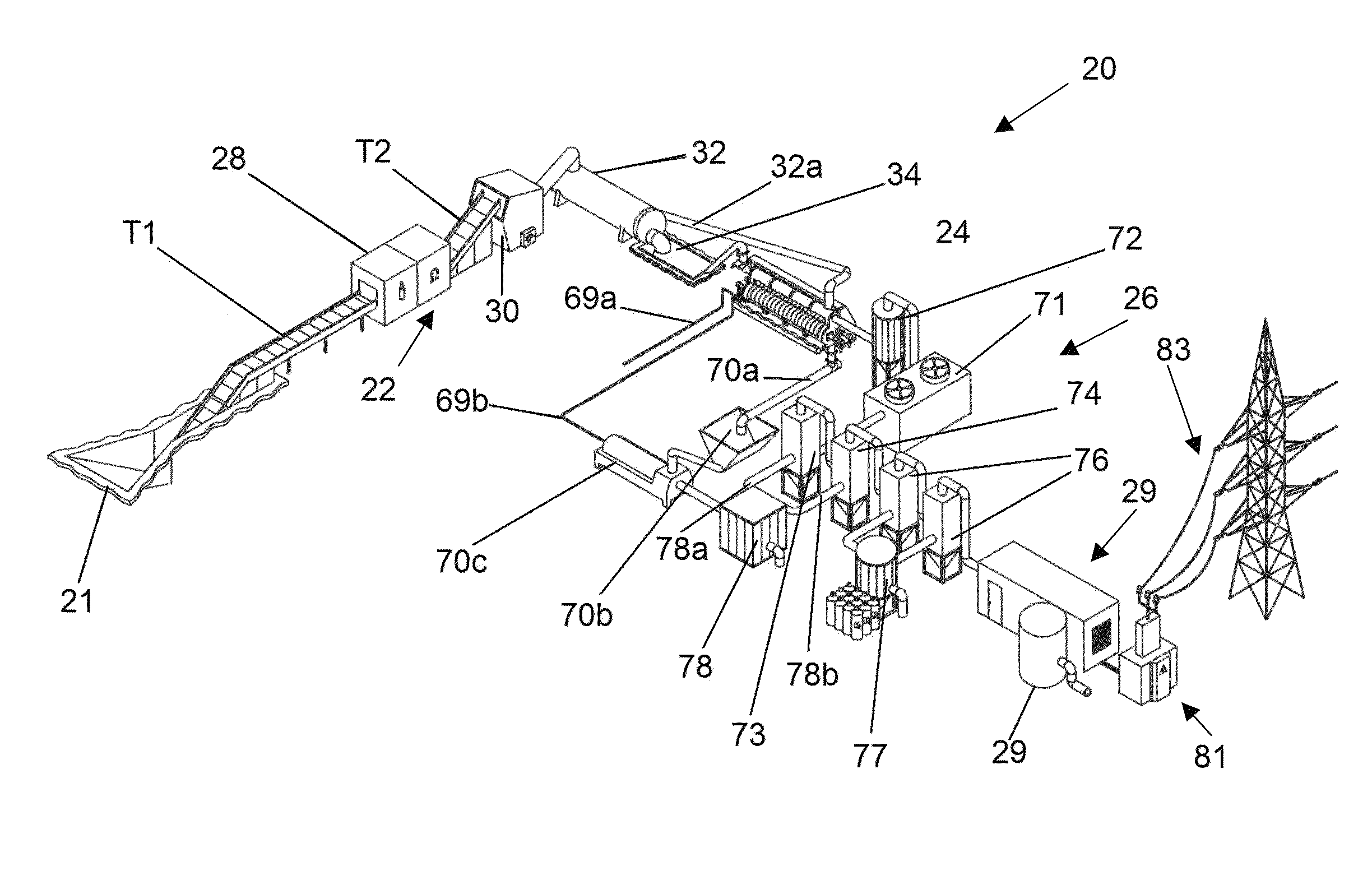
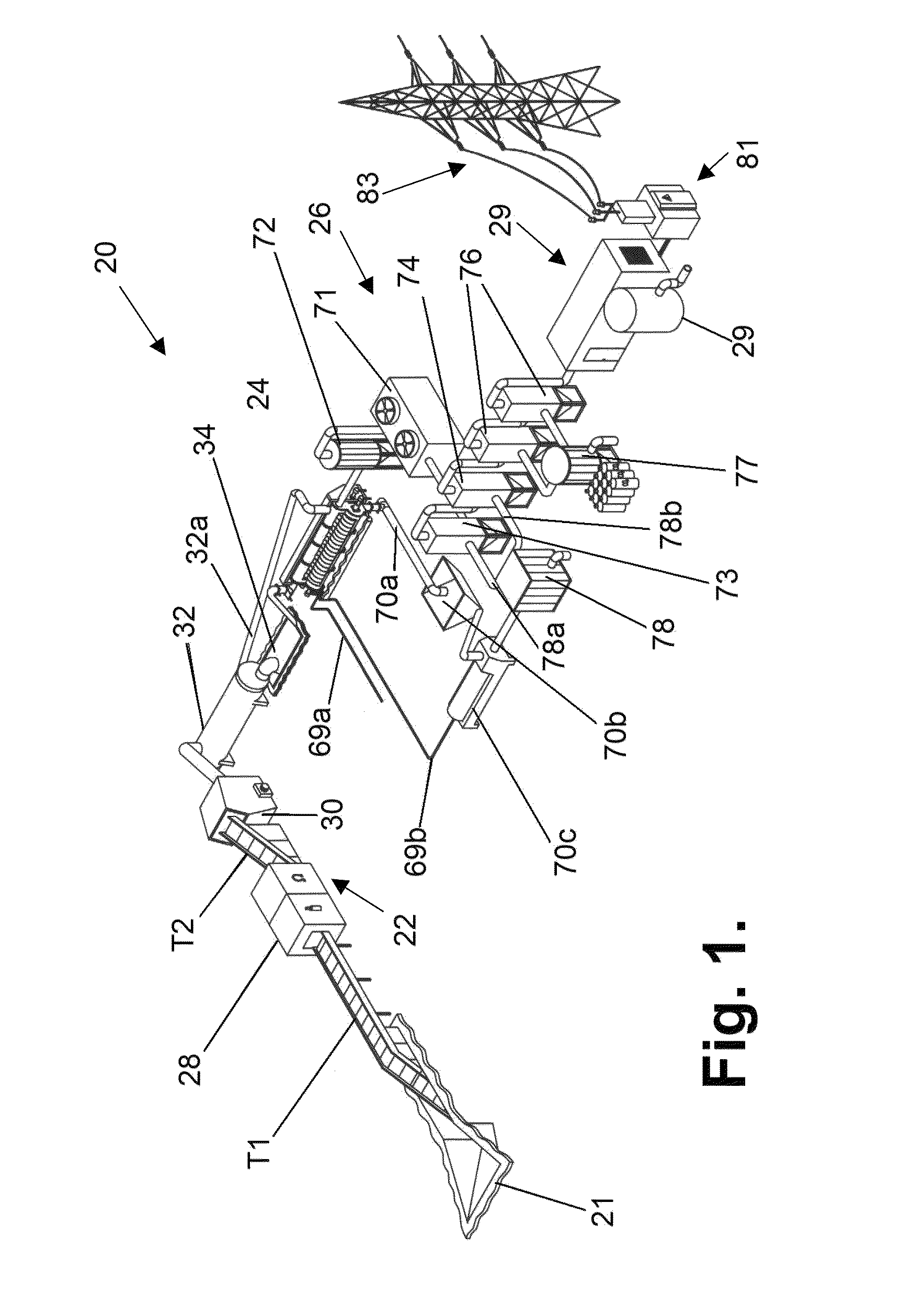
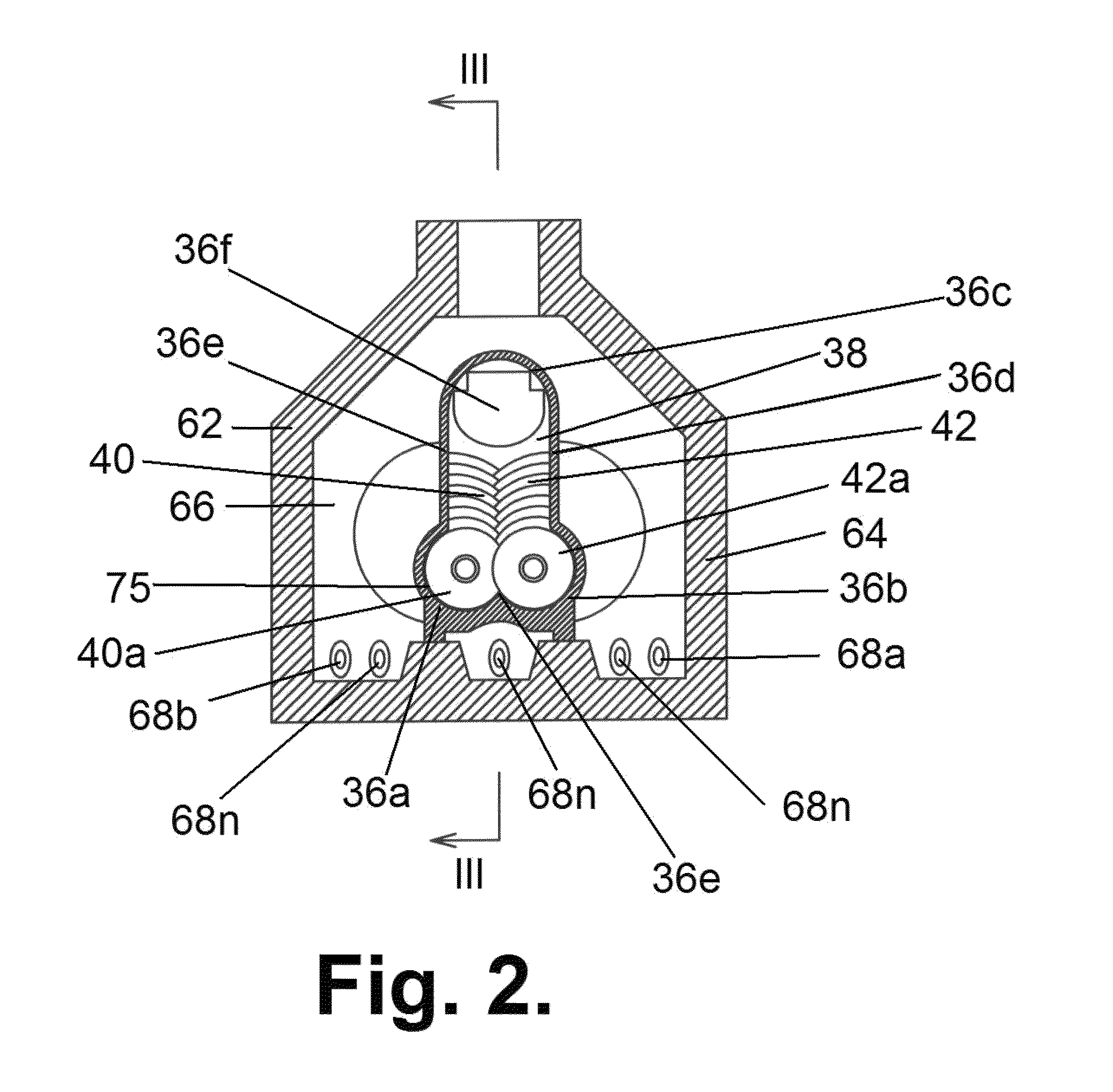
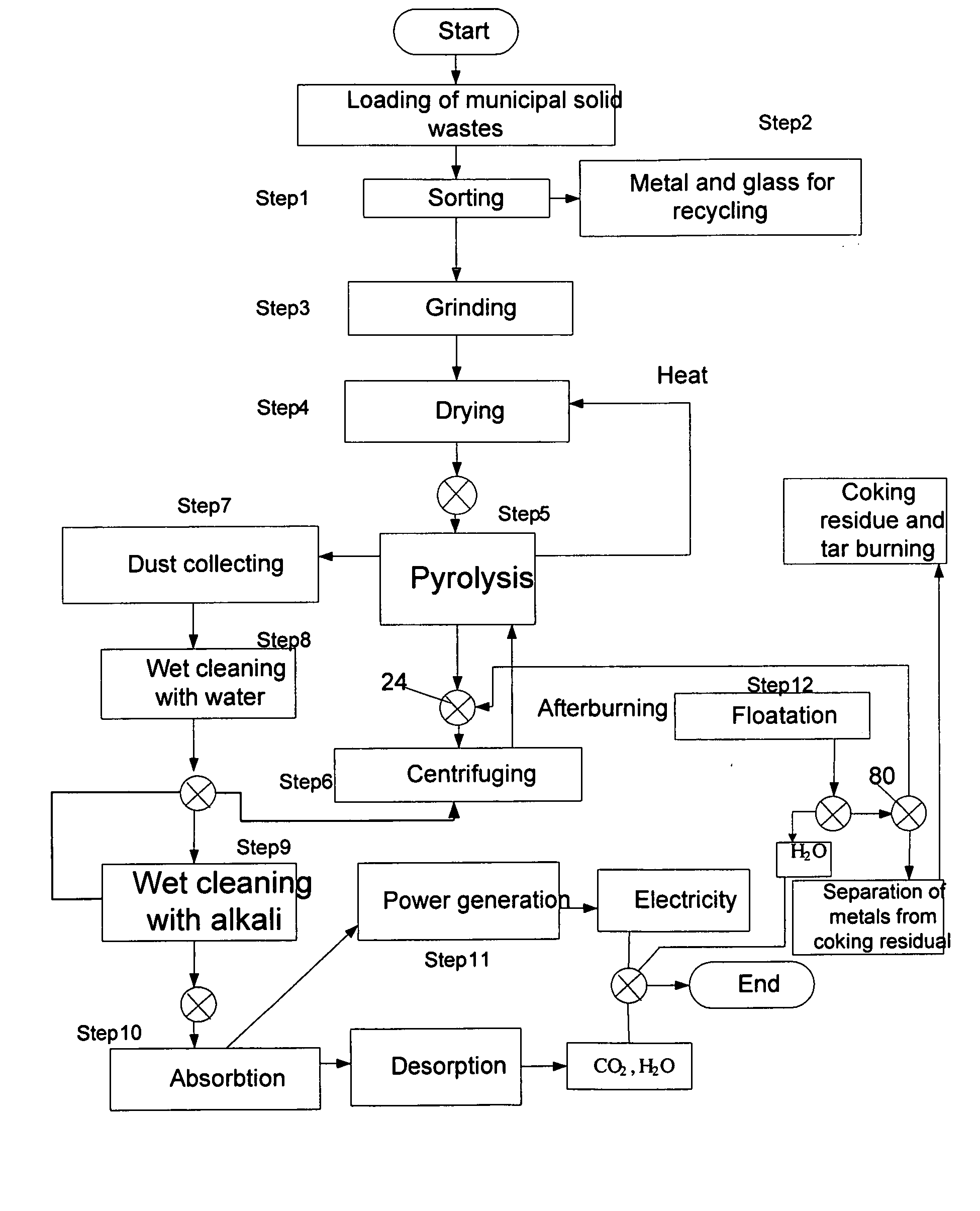
ActiveUS8419902B2Efficient use ofHigh degreeThermal non-catalytic crackingCharging-discharging device combinationsElectricitySyngas
Proposed are a system and method for wasteless pyrolytic processing and complete utilization of municipal and domestic wastes. The wastes are sequentially passed through units of sorting, grinding, drying, accumulating, and sending to a pyrolysis reactor for pyrolytic treatment. The syngas produced in the pyrolysis is passed through dry cleaning, dust catching, a first wet cleaning with water, a second wet cleaning with alkali, and a floatation unit for separation of water which is purified to an extent sufficient for technical use. The purified syngas is also passed through an absorber and is then used as a working medium for a power generation unit such as a gas turbine co-generator that generates electricity. Solid products of the pyrolysis reaction, such as coke, are returned to the reactor for afterburning, and the heat of the reaction can be utilized in a dryer, or the like.
Owner:GREENLIGHT ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Method and system for wasteless processing and complete utilization of municipal and domestic wastes
ActiveUS20100293853A1Wasteless pyrolytic processingComplete utilizationThermal non-catalytic crackingCharging-discharging device combinationsSyngasElectricity
Proposed are a system and method for wasteless pyrolytic processing and complete utilization of municipal and domestic wastes. The wastes are sequentially passed through units of sorting, grinding, drying, accumulating, and sending to a pyrolysis reactor for pyrolytic treatment. The syngas produced in the pyrolysis is passed through dry cleaning, dust catching, a first wet cleaning with water, a second wet cleaning with alkali, and a floatation unit for separation of water which is purified to an extent sufficient for technical use. The purified syngas is also passed through an absorber and is then used as a working medium for a power generation unit such as a gas turbine co-generator that generates electricity. Solid products of the pyrolysis reaction, such as coke, are returned to the reactor for afterburning, and the heat of the reaction can be utilized in a dryer, or the like.
Owner:GREENLIGHT ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Process for producing fuel from plastic waste material by using dolomite catalyst
A process for producing fuel by cracking a plastics-derived liquid, which is obtained from a pyrolysis process, using a dolomite catalyst. The plastics-derived liquid is produced by the pyrolysis of plastic waste, such as of one or more of polyethylene, polystyrene or polypropylene. The plastic-derived liquid is first subjected to a semi-batch catalytic cracking reaction over a very low cost dolomite catalyst to obtain high quality oil for fuel, which comprises mainly light and heavy naphtha. Moreover, the catalytic cracking reaction is conducted at operating temperatures lower than 320° C.
Owner:SRINAKRUANG JUMLUCK
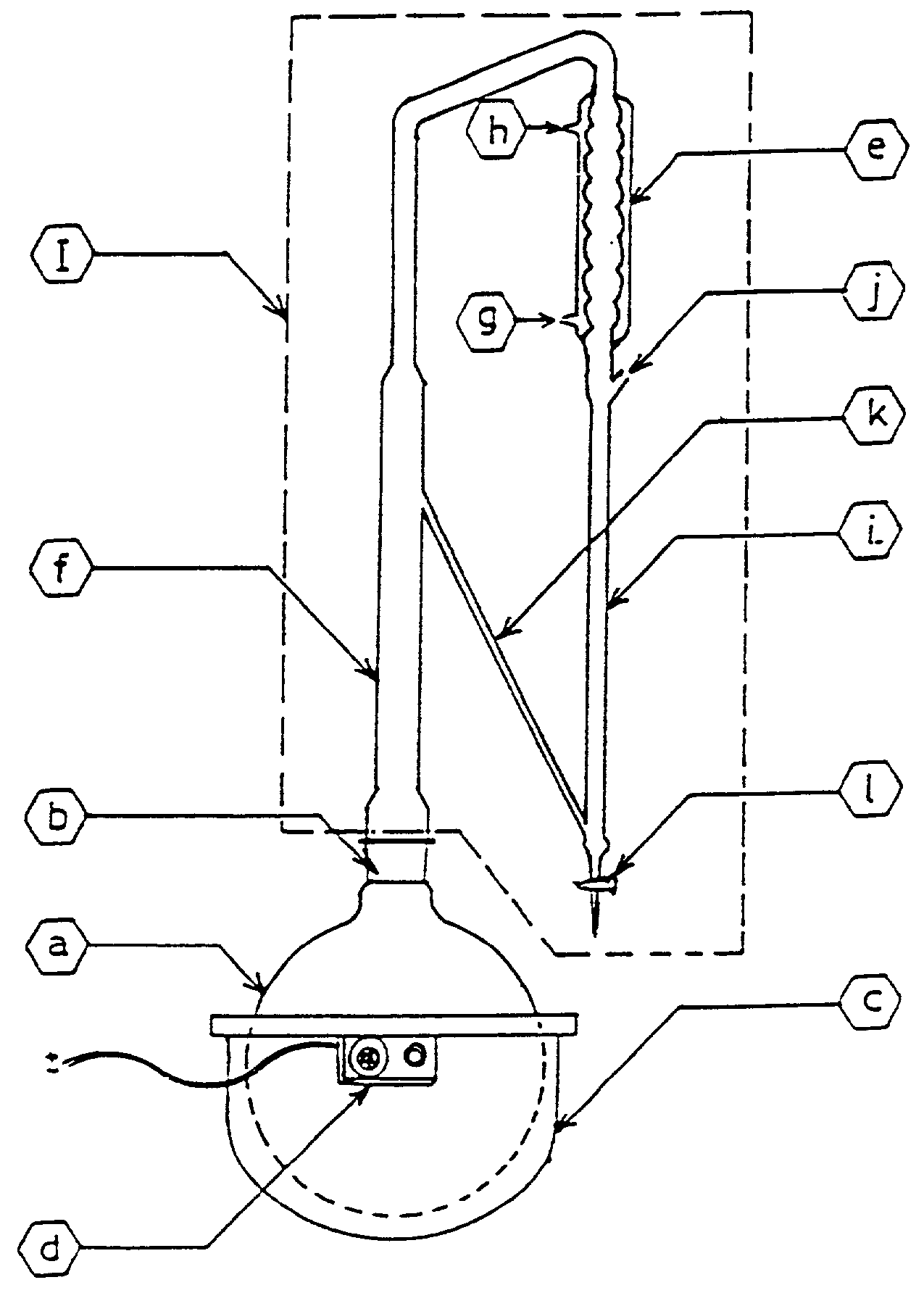
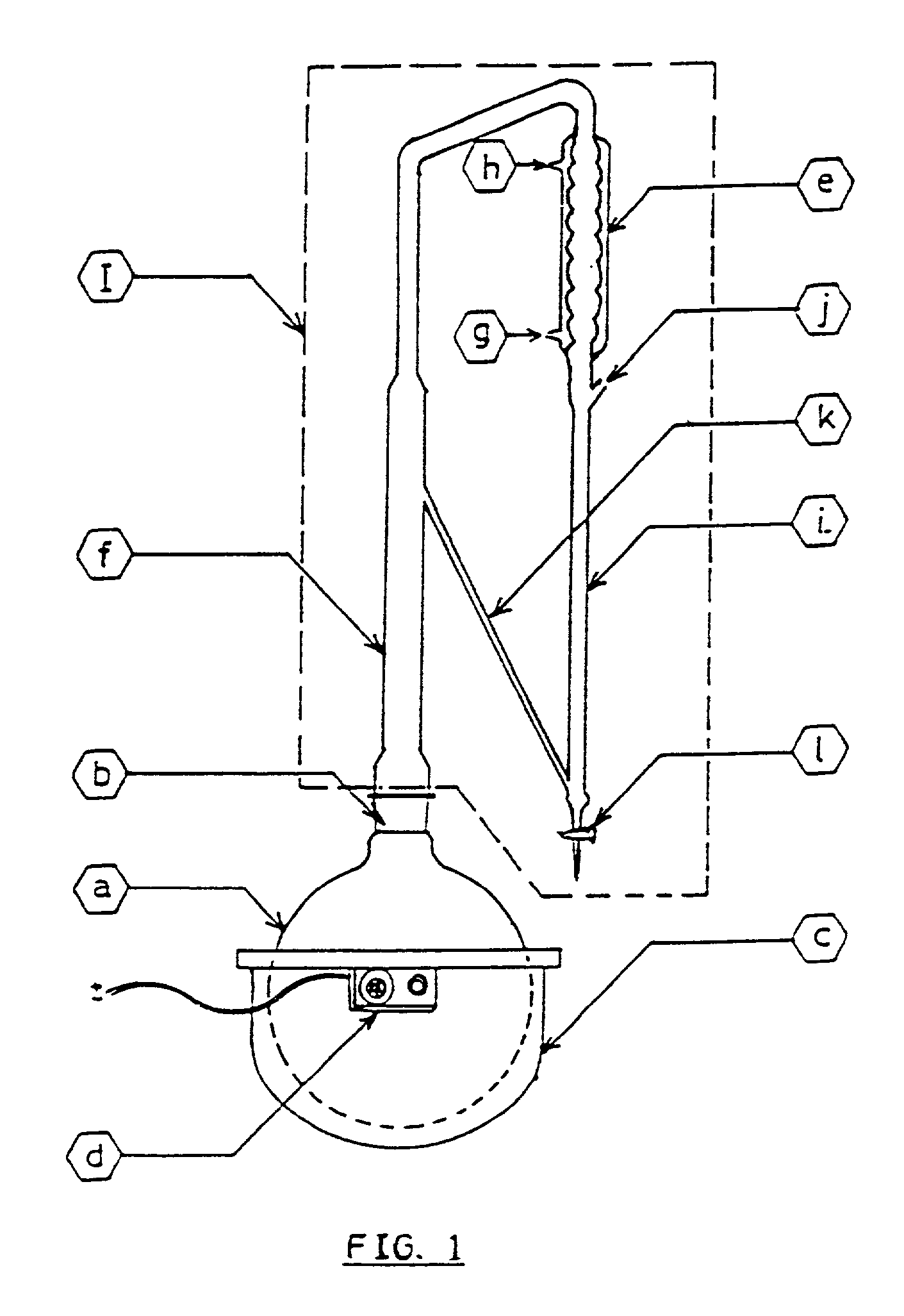
Simple portable mini distillation apparatus for the production of essential oils and hydrosols
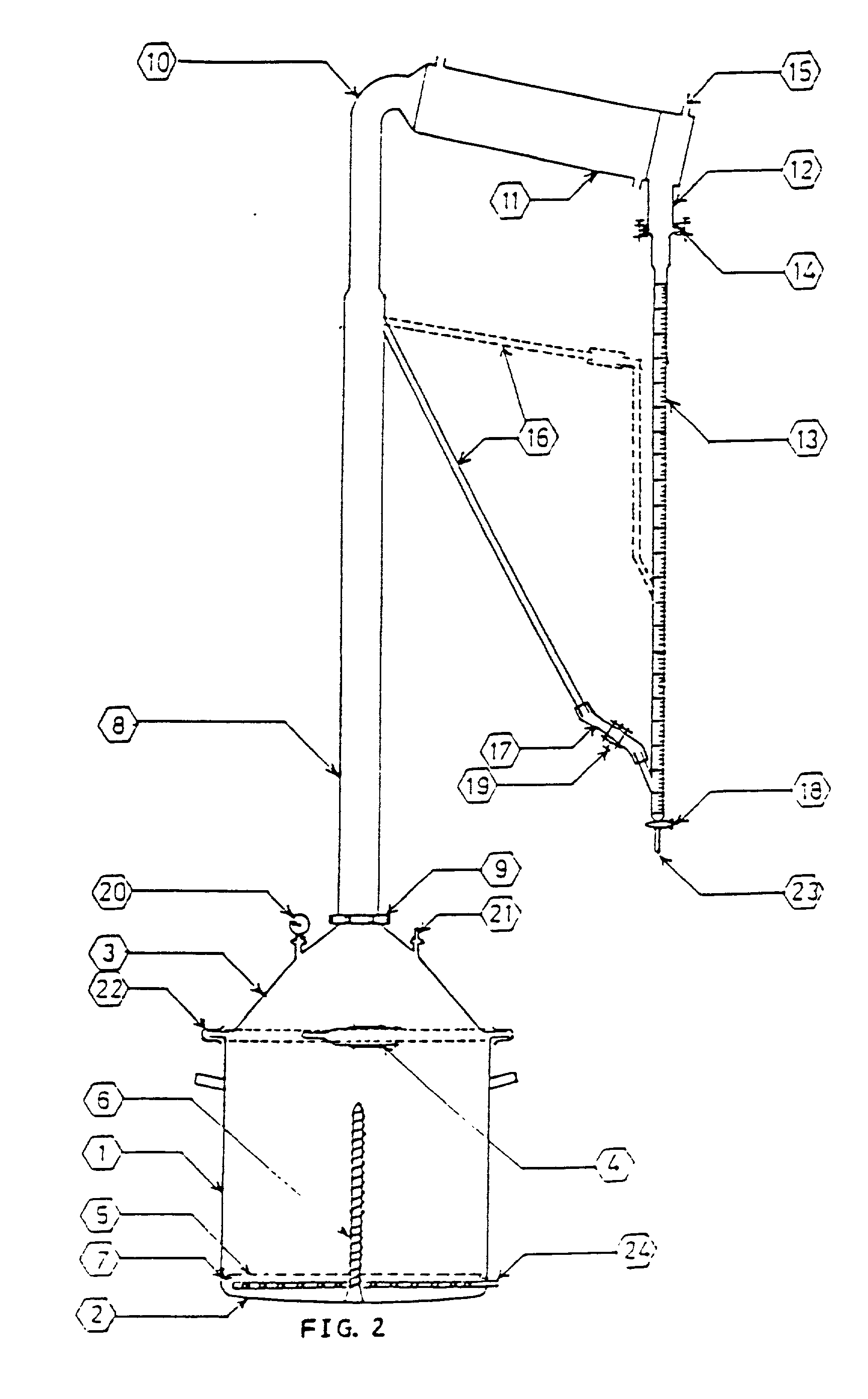
This invention relates to a simple, convenient, portable mini-distillation apparatus for the production of essential oils and hydrosols, said apparatus is useful to distill essential oils and hydrosols such as rose water, ajowain water from fresh and dried plant material like leaves, flowers, roots and rhizomes by water distillation, water and steam distillations and as an optional, steam distillation can also be performed at atmospheric pressure as well as slightly higher and lower than atmospheric pressure, said apparatus can be heated on brick-clay furnace with small agro-waste, LPG cooking gas, electrically heated stove or kerosene / diesel burner etc. and requires minimum attention during handling; since the apparatus is made of stainless steel and glass, the essential oil distilled is of better quality.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com