Patents
Literature
1192results about "Coking carbonaceous materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
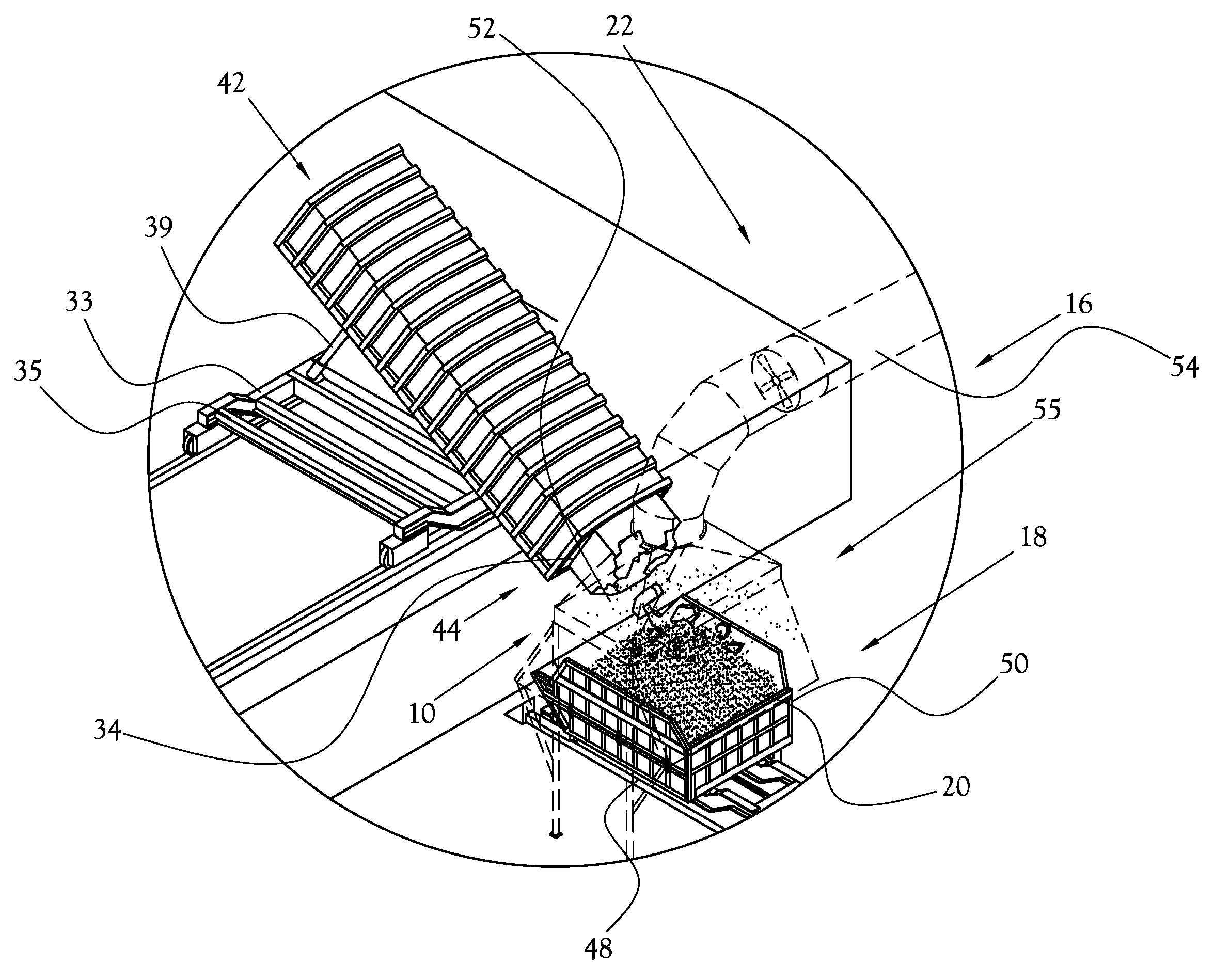
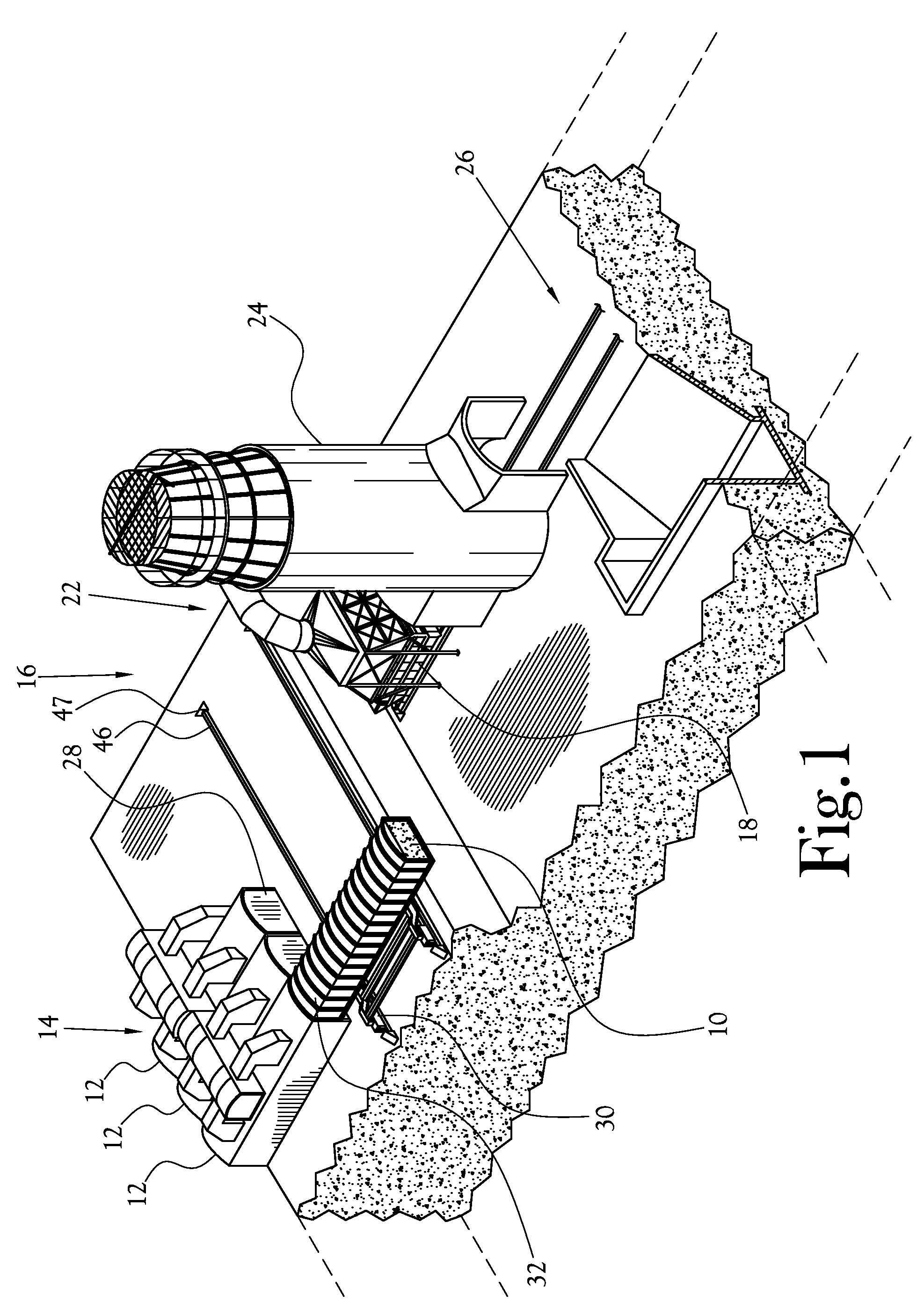
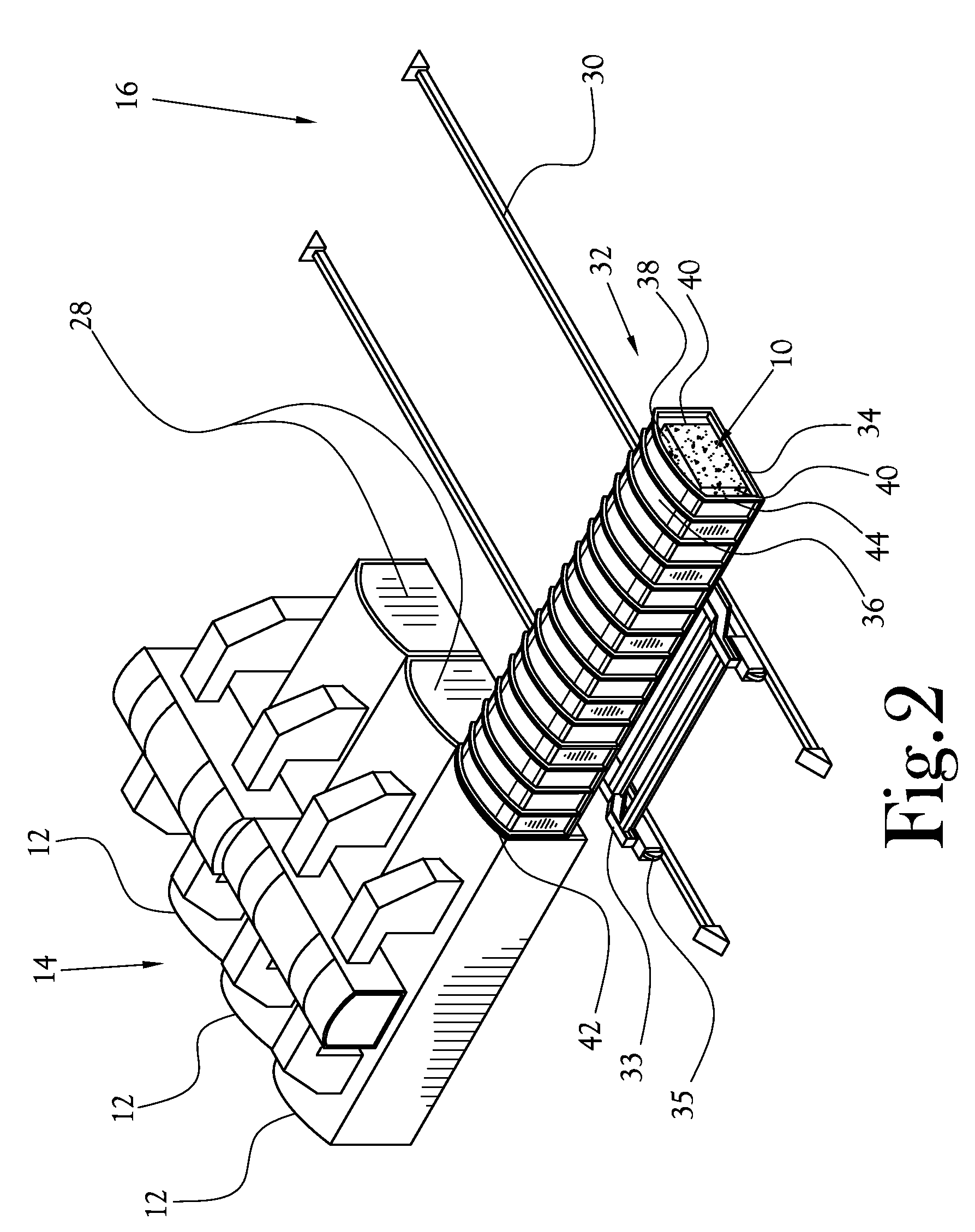
Mixing arrangement for atomizing nozzle in multi-phase flow
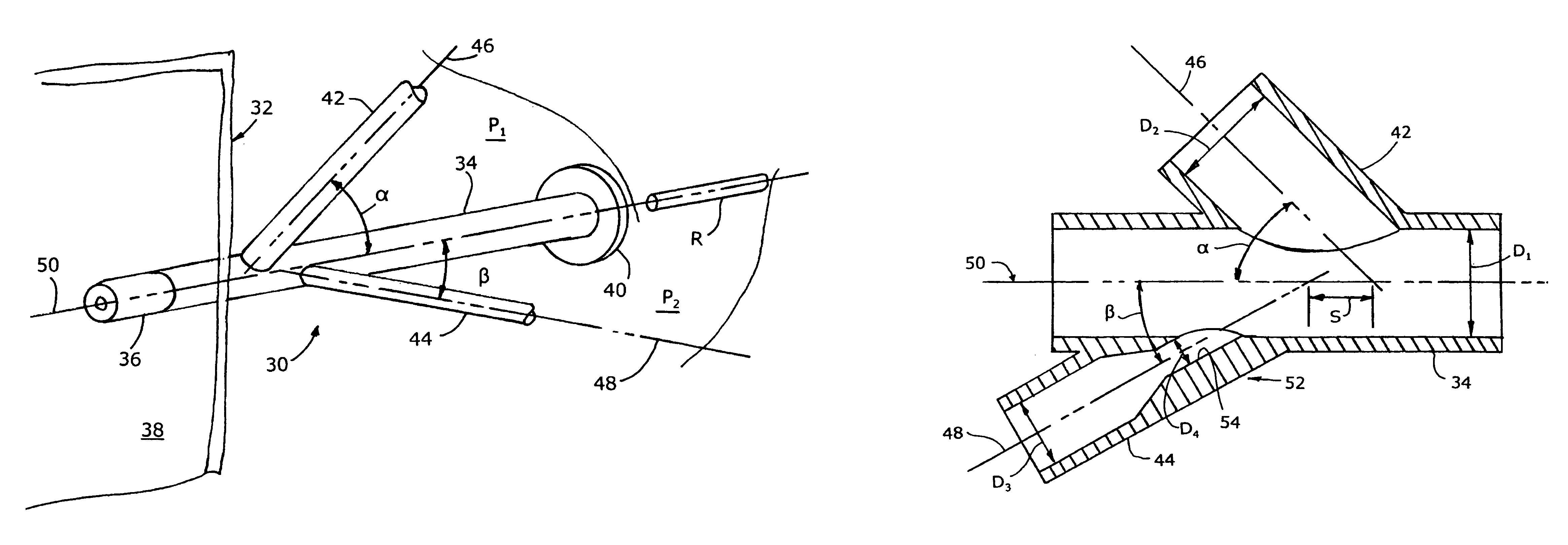
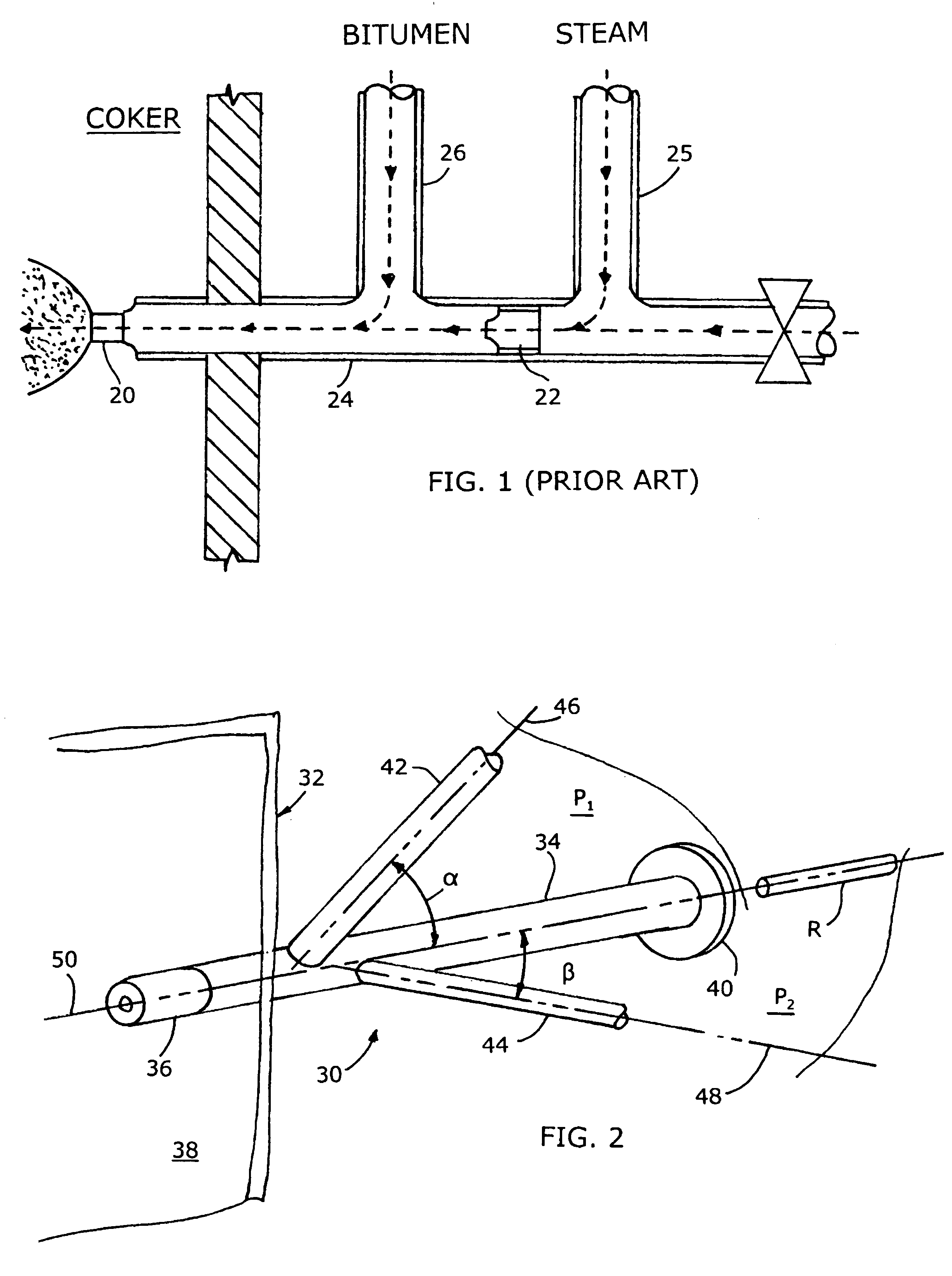
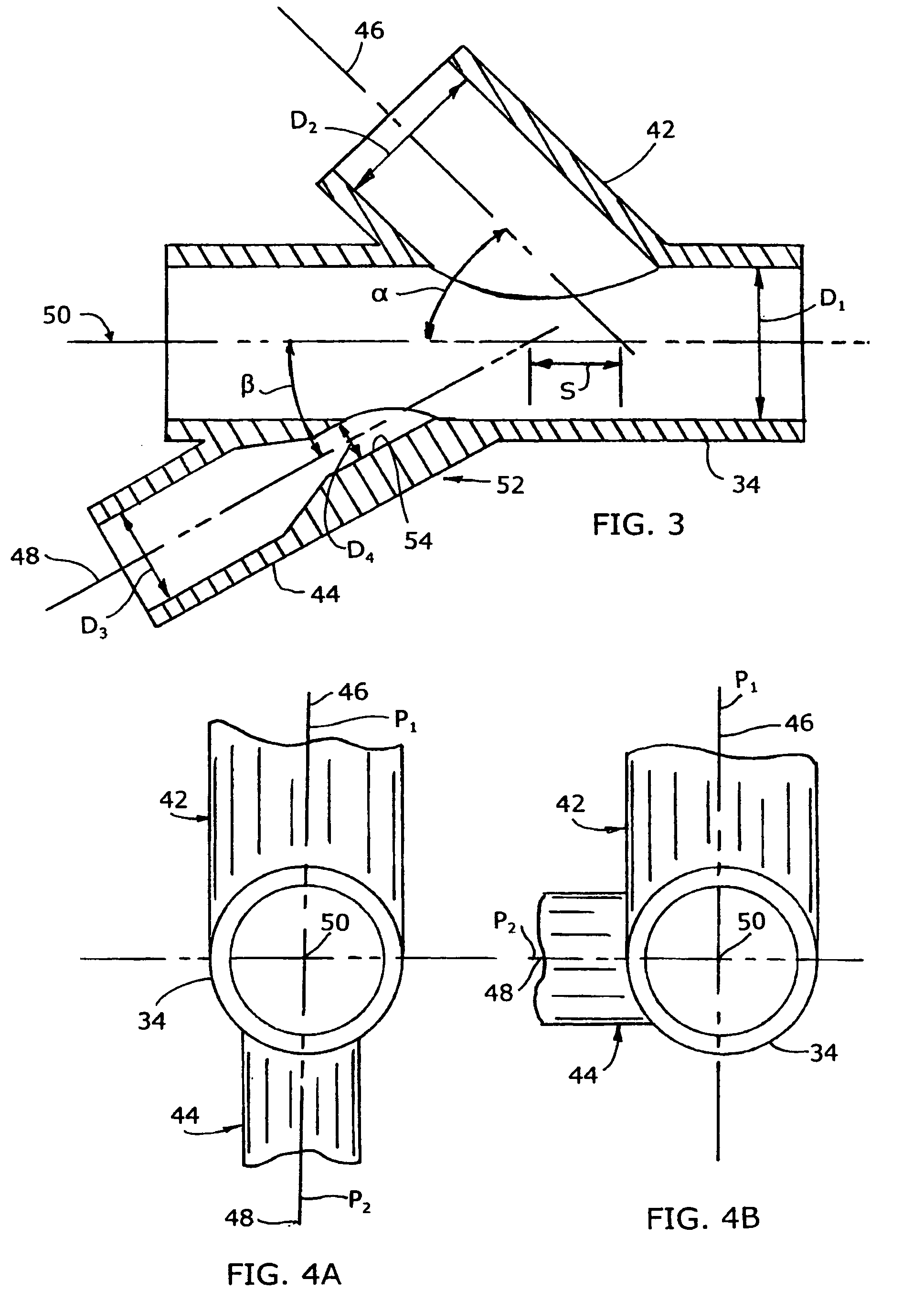
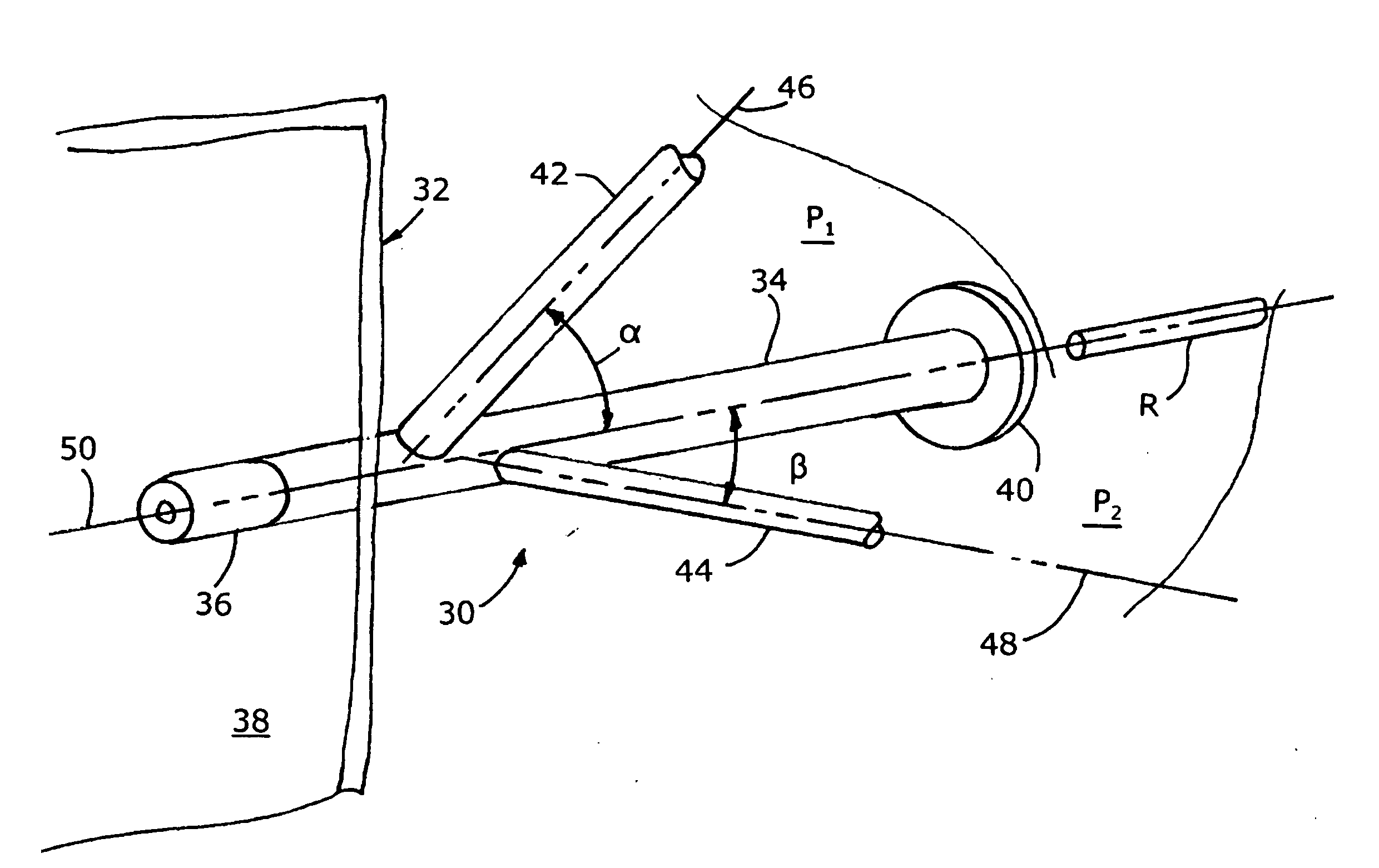
ActiveUS7140558B2Smooth transitionEasy to processCharging-discharging device combinationsFlow mixersAcute angleShortest distance
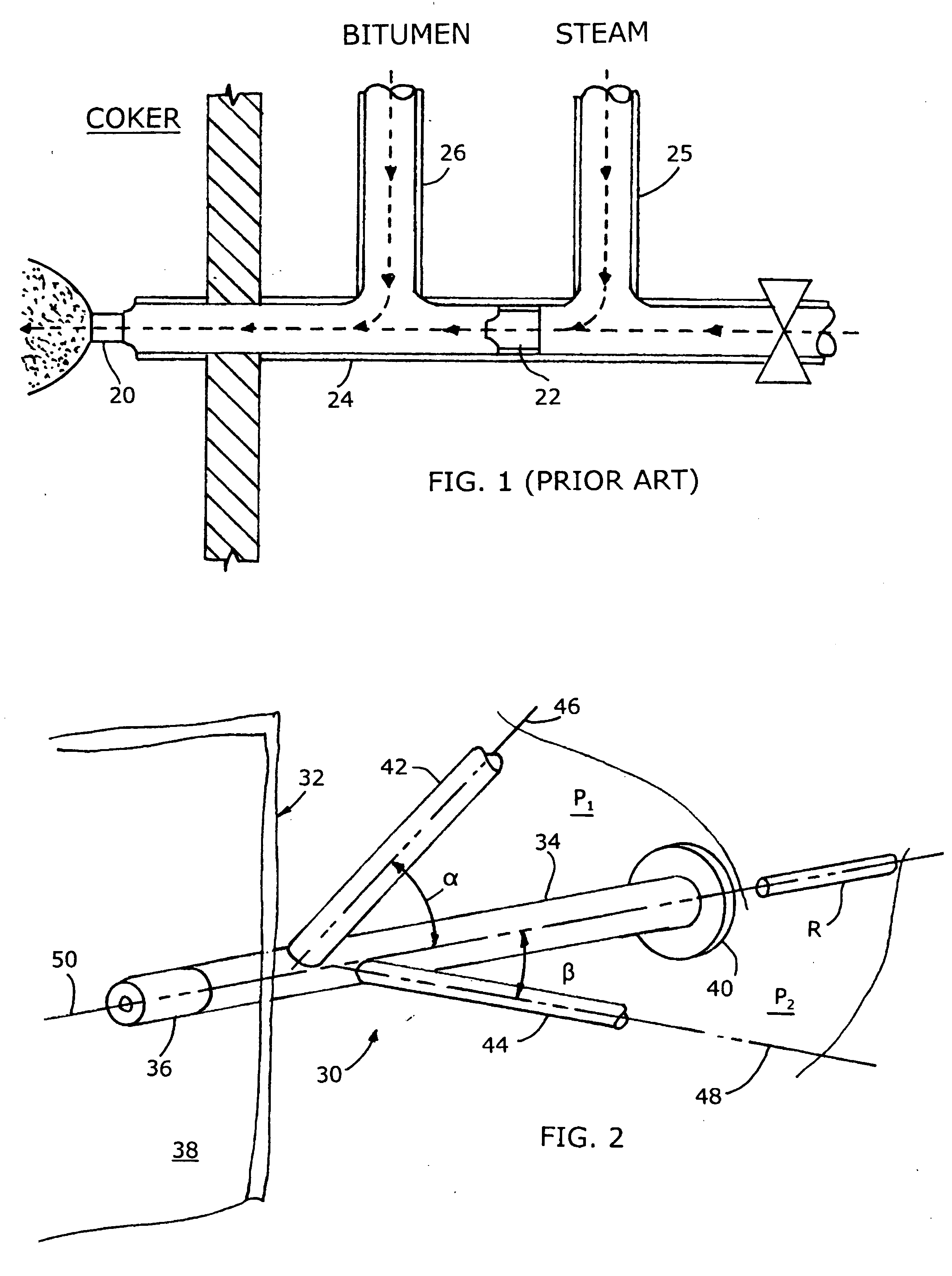
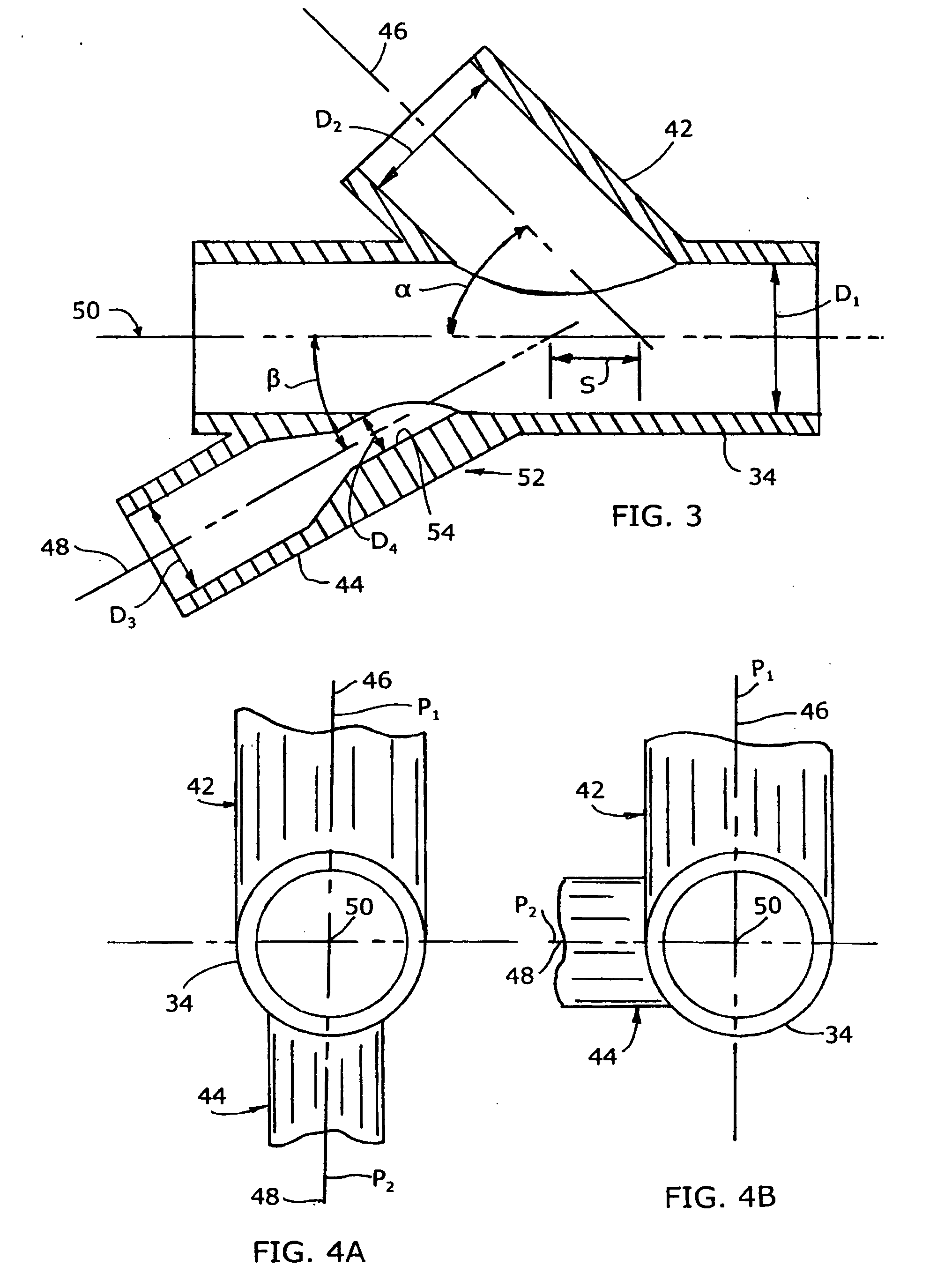
The invention relates to an improved mixing arrangement for, primarily, moving bitumen in steam from sources of such bitumen and steam to a reactor or coker for further processing of the bitumen into petroleum products. The invention provides a main conduit connected to an atomizing nozzle mounted in a wall of the reactor and first and second conduits for flowing bitumen and steam respectively into the main conduit. The first conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 45° and the second conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 30°. The second conduit is positioned upstream of the first conduit by a short distance of about 23 mm and may be angled radially relative to the first conduit by any angle, although a 90° angle is preferred. A flow accelerating nozzle is located in the second conduit adjacent the entrance therefrom into the main conduit The arrangement of the invention improves the flow characteristics of 2-phase material flowing to the atomizing nozzle, reducing pulsations in the main conduit and improving the resulting atomization of the bitumen in the reactor.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +1
Mixing arrangement for atomizing nozzle in multi-phase flow
ActiveUS20050001062A1Smooth transitionEasy to processCharging-discharging device combinationsFlow mixersAcute angleShortest distance
The invention relates to an improved mixing arrangement for, primarily, moving bitumen in steam from sources of such bitumen and steam to a reactor or coker for further processing of the bitumen into petroleum products. The invention provides a main conduit connected to an atomizing nozzle mounted in a wall of the reactor and first and second conduits for flowing bitumen and steam respectively into the main conduit. The first conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 45° and the second conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 30°. The second conduit is positioned downstream of the first conduit by a short distance of about 23 mm and may be angled radially relative to the first conduit by any angle, although a 90° angle is preferred. A flow accelerating nozzle is located in the second conduit adjacent the entrance therefrom into the main conduit. The arrangement of the invention improves the flow characteristics of 2-phase material flowing to the atomizing nozzle, reducing pulsations in the main conduit and improving the resulting atomization of the bitumen in the reactor.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +1
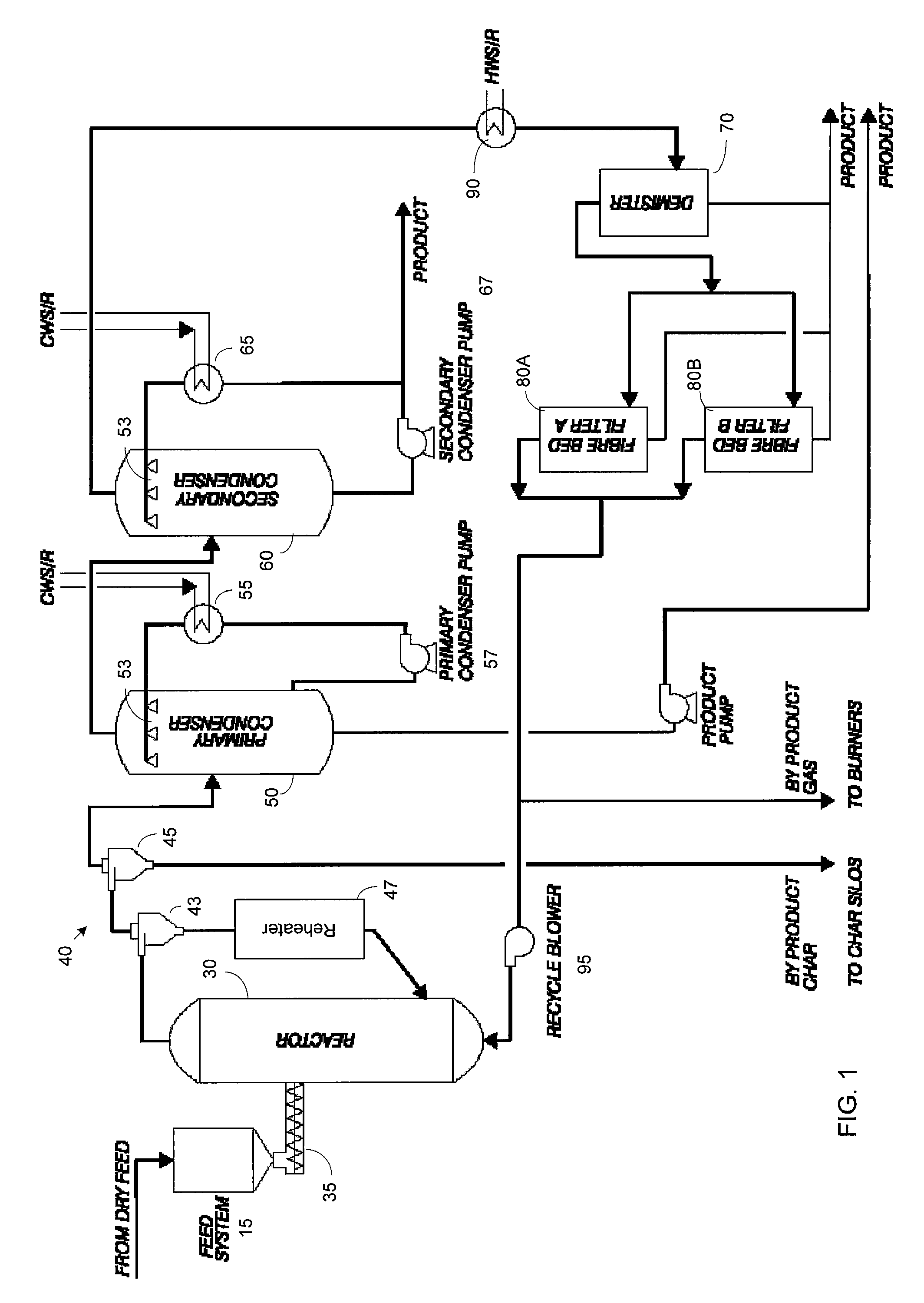
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
ActiveUS7905990B2Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingSolid waste disposalLiquid productHeat carrier
A rapid thermal conversion process for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. Biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. The liquid product may itself be used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
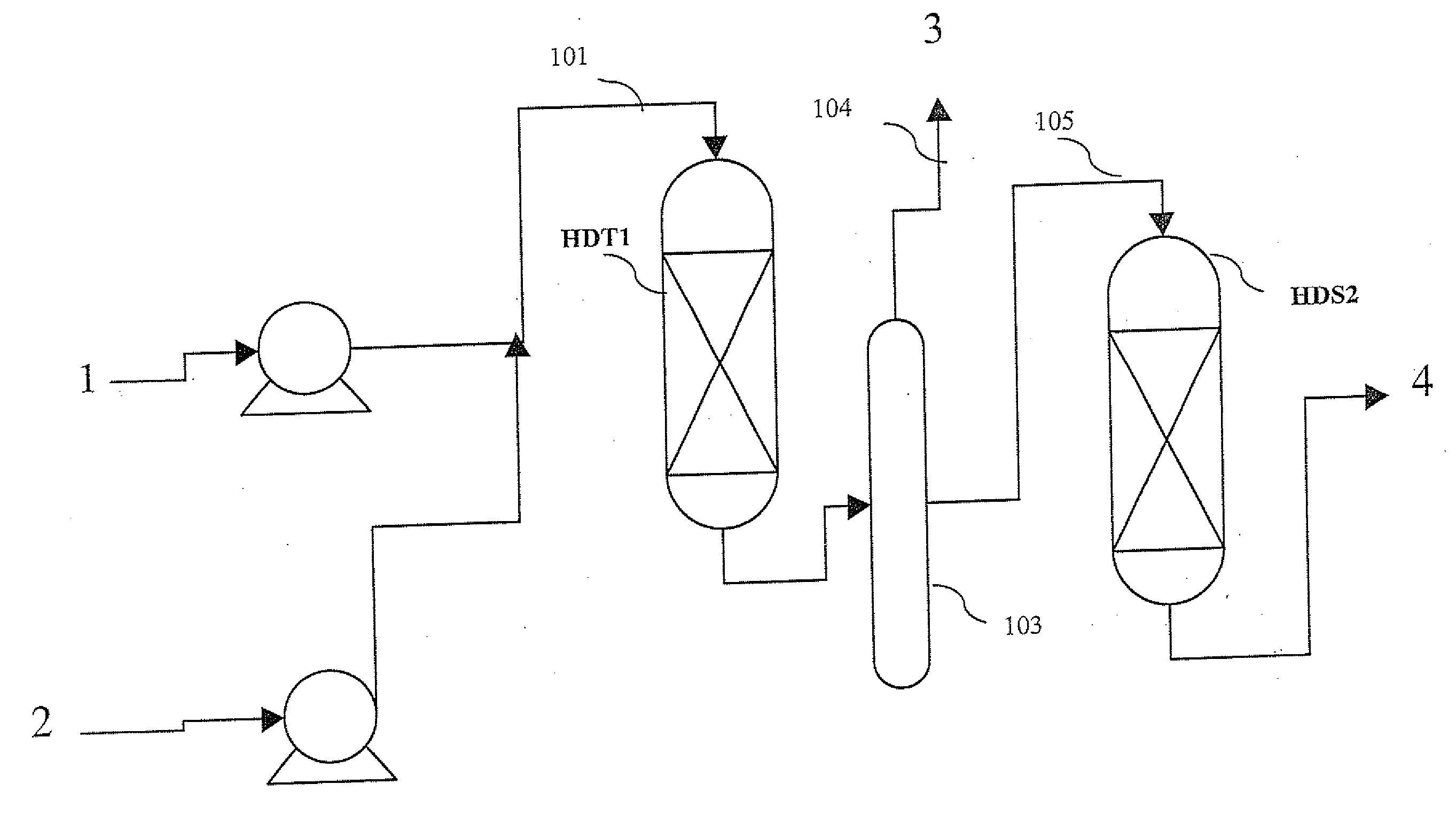
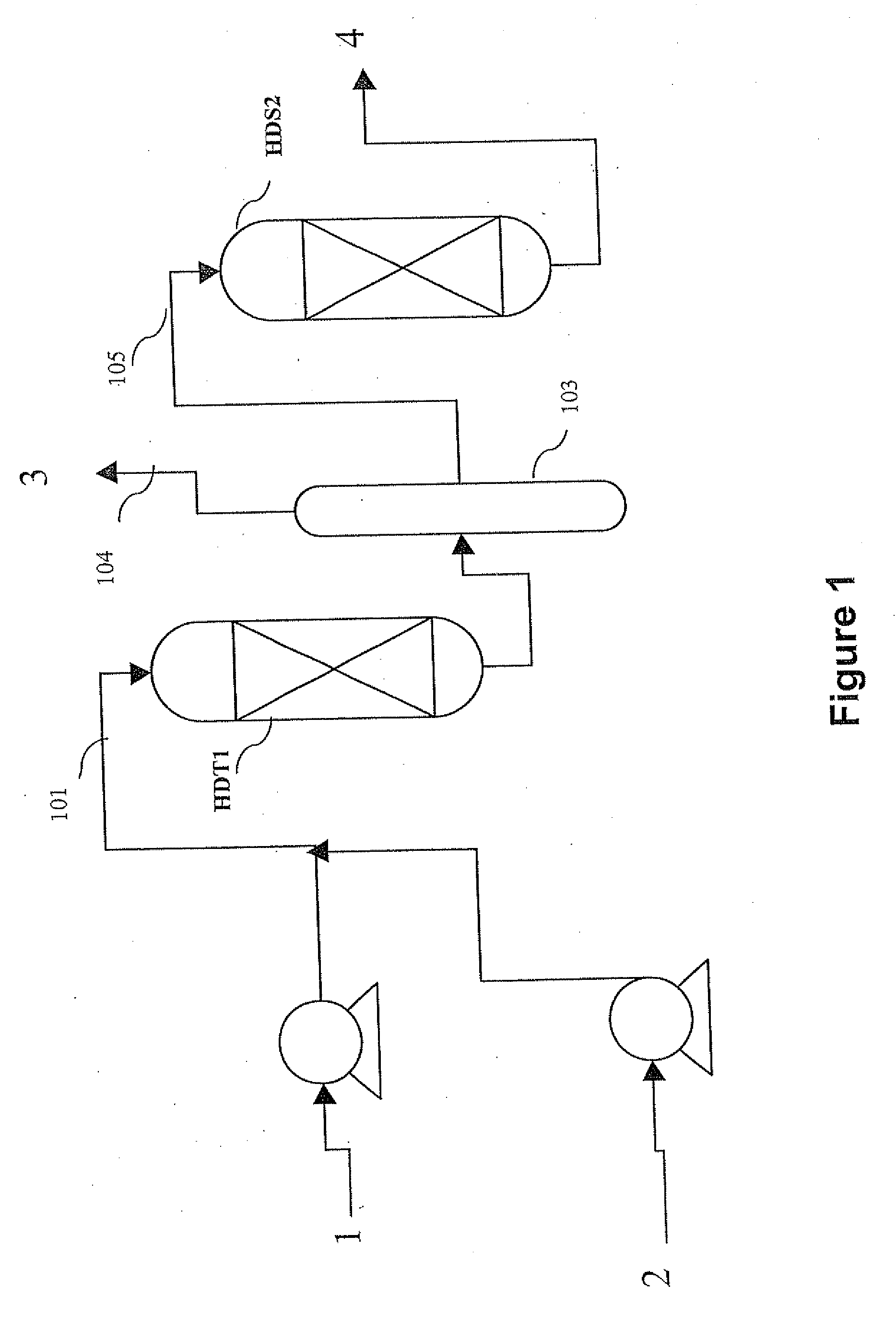
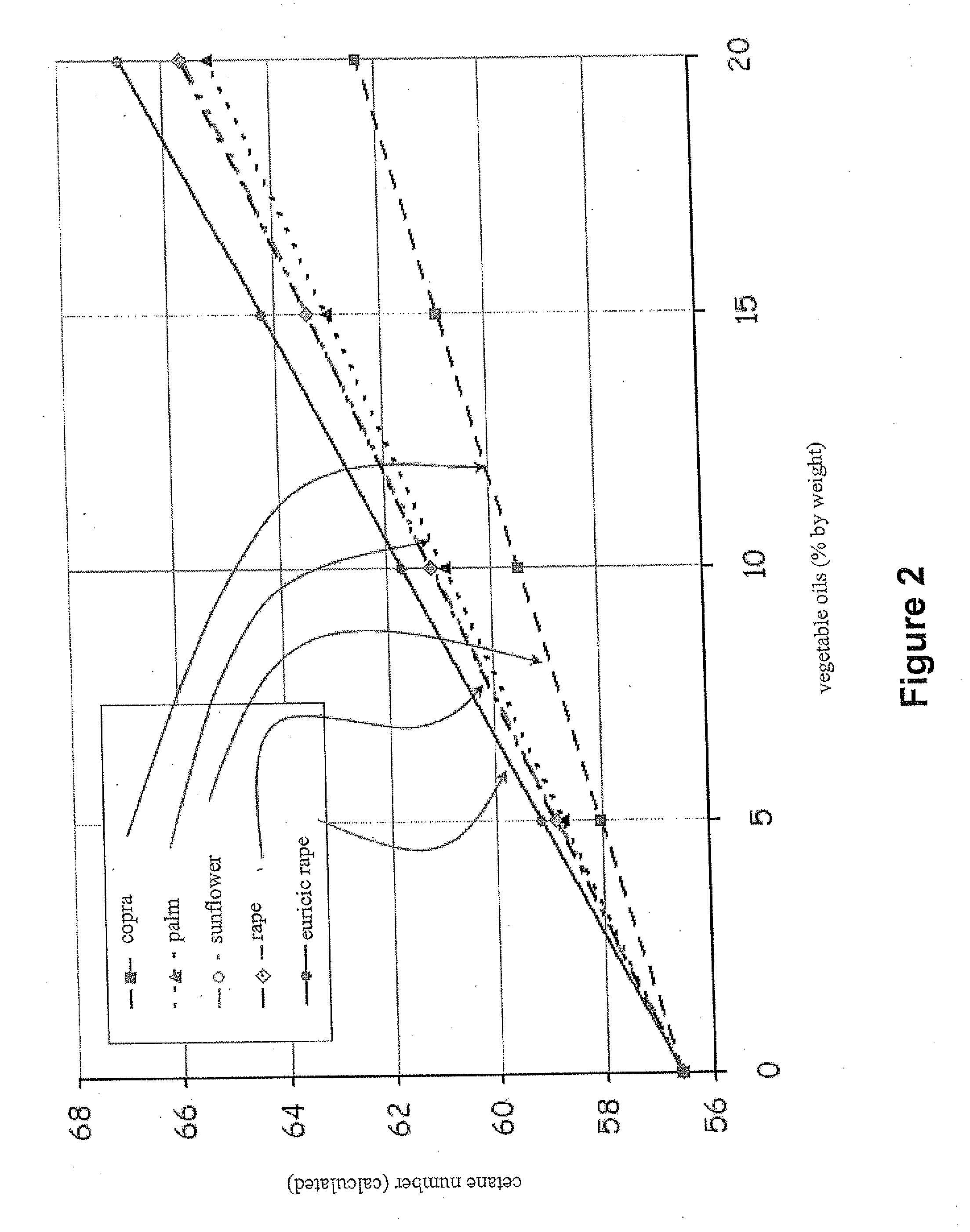
Methods of hydrotreating a mixture made up of oils of animal or vegetable origin and of petroleum cuts with intermediate stripping
ActiveUS20080161614A1Low costLimit consumption of hydrogenThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingVegetable oilVolumetric Mass Density
The invention relates to a hydrotreating method (HDT) using two plants working under different operating conditions with an intermediate stripping for co-treating a mixture made up of oils of vegetable or animal origin and petroleum cuts (gas oil cuts (GO) and middle distillates) in order to produce gas oil fuel bases meeting specifications. The first plant (HDT1) is more particularly dedicated to the reactions concerning oils of vegetable or animal origin in comixture while pretreating the hydrocarbon feed, whereas the second plant (HDS2) works under more severe conditions to obtain diesel fuel according to standards, in particular in terms of effluent sulfur content, density and cold properties. The process economy, the activity and the stability of the catalyst of the second plant are greatly improved by the intermediate stripping.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
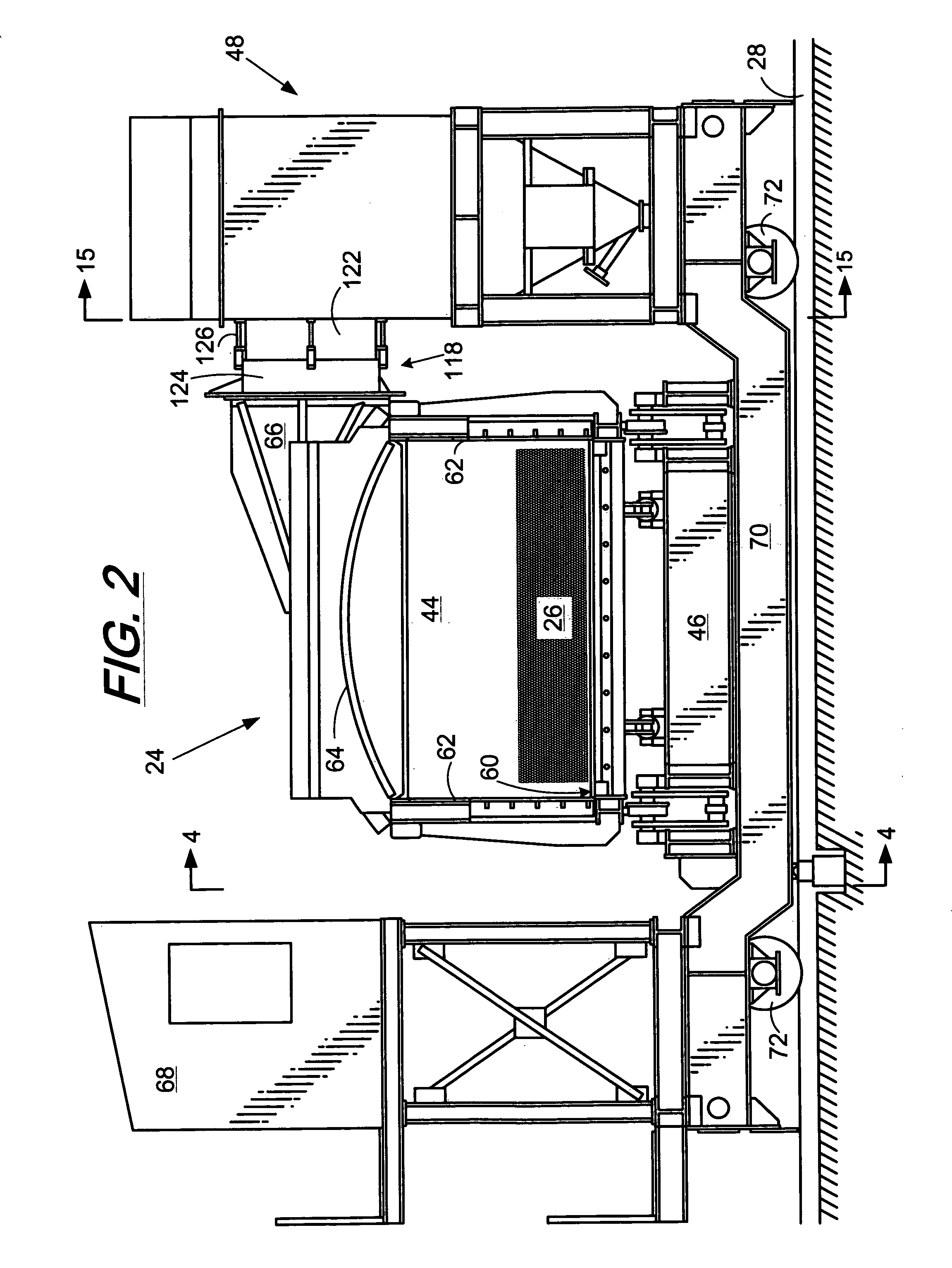
Coal bed vibration compactor for non-recovery coke oven
InactiveUS6059932AMechanical conveying coke ovensCharging-discharging device combinationsEngineeringCoke oven
A coal compaction system and method for a non-recovery coke oven having refractory roof, floor, side walls and end doors for coal charging and coke discharge provides an improved coal charging machine carrying a coal conveyor supported intermediate the ends of the conveyor to avoid conveyor sagging and non-uniform depth of a deposited coal bed, a number of pressurized fluid-driven vibratory compactors mounted on an end of the charging machine and spaced-apart across the width of the coal bed and serving to compact the coal bed on a retraction stroke of the charging machine, a pivoted lifting frame mounted on the charging machine above the compactors and from which the compactors individually are suspended and are provided with individual supply of pressurized fluid, and a coke pusher head mounted on the charging machine behind the compactors and serving, when the lifting frame and associated compactors are raised, to push finished coke from the coke oven.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA COKE TECH
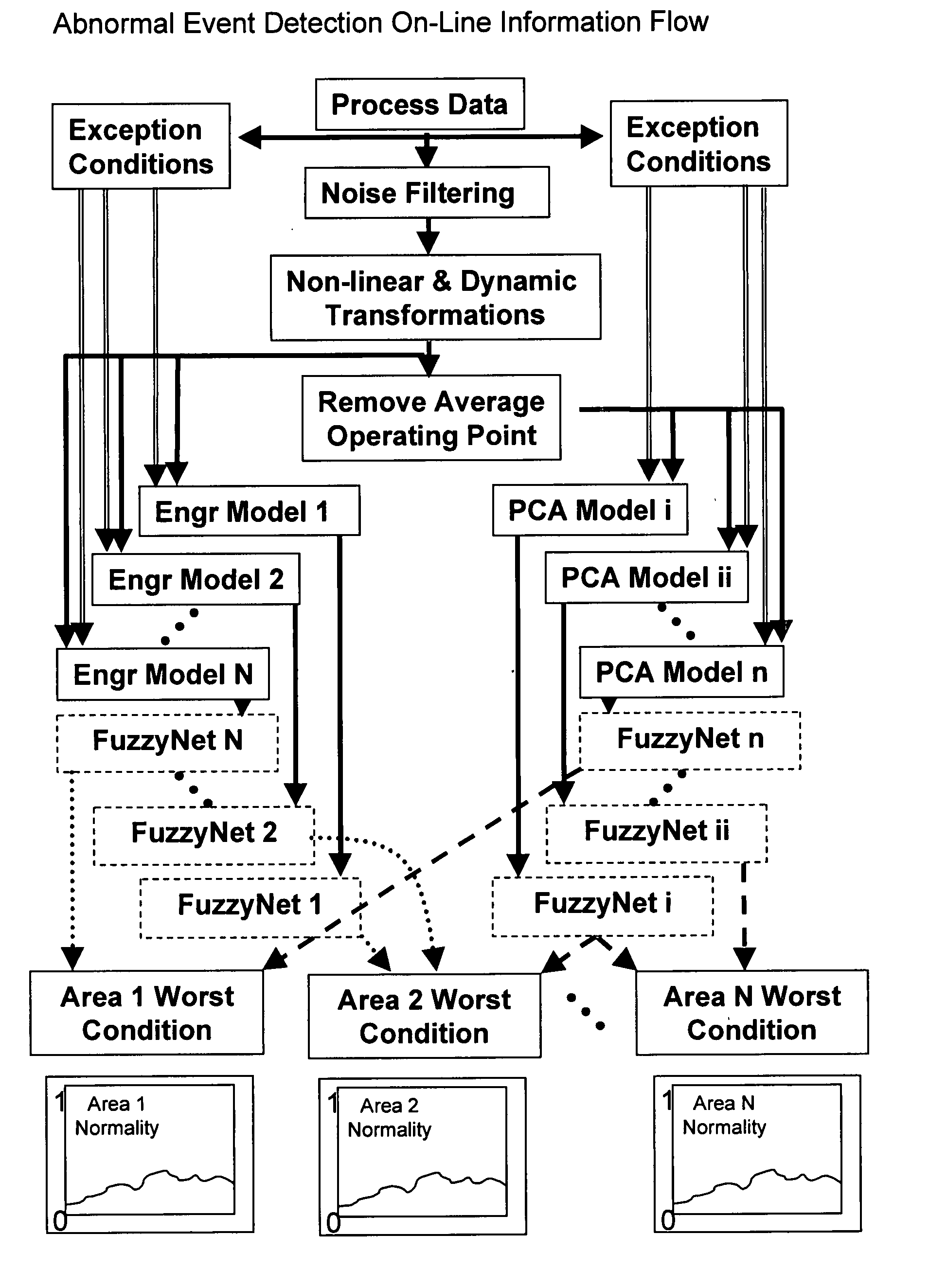
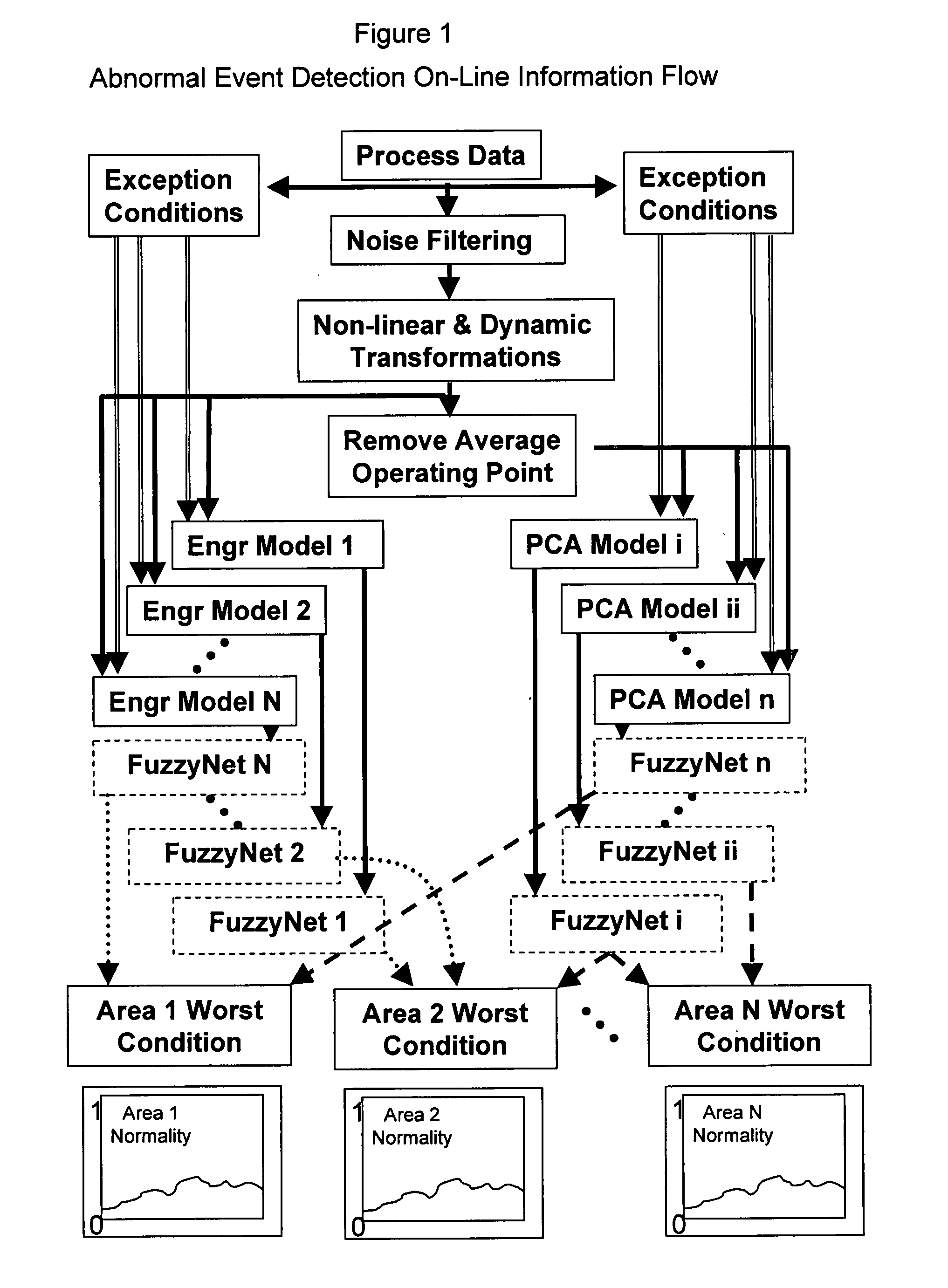
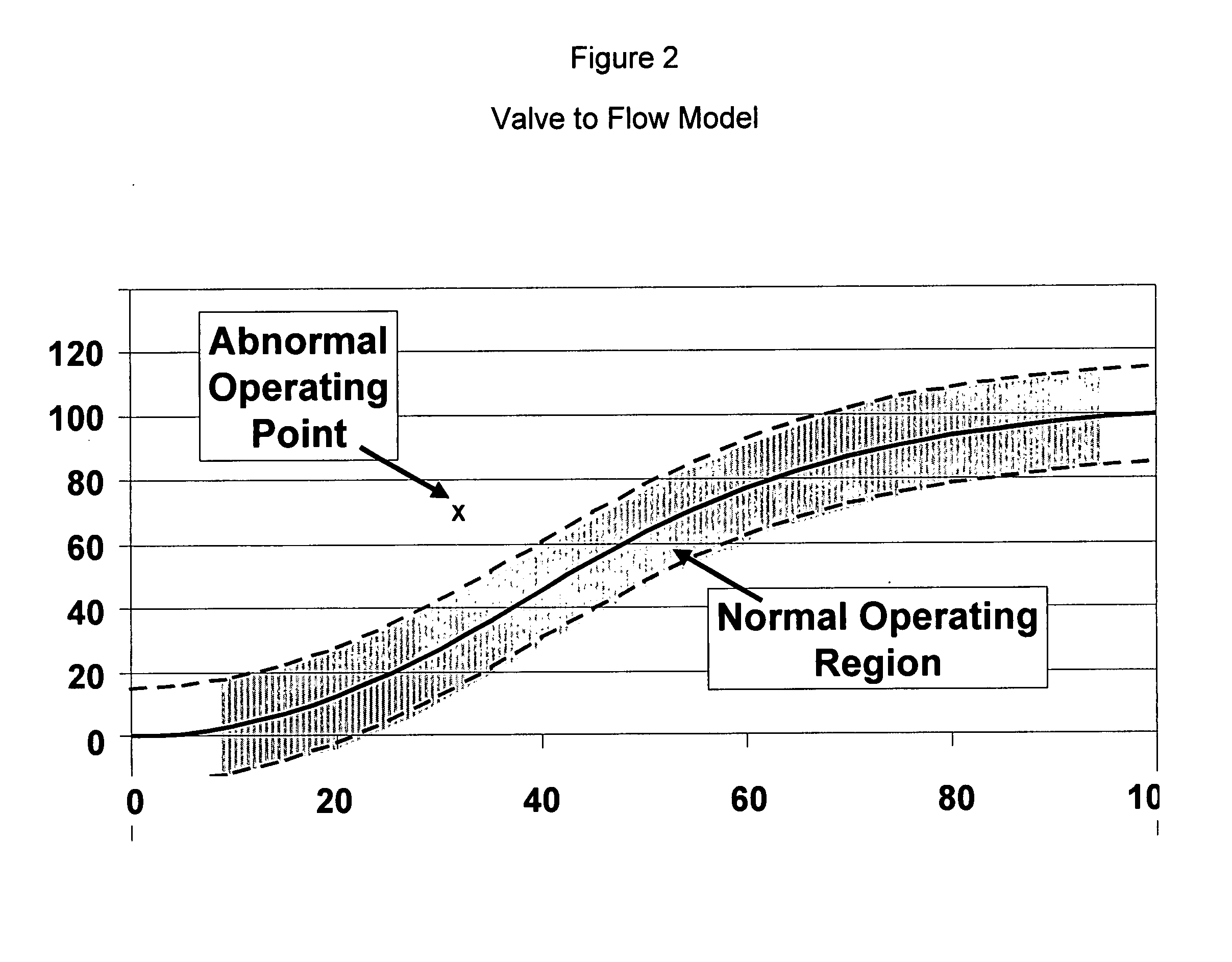
Application of abnormal event detection technology to delayed coking unit
ActiveUS20070250292A1Efficiently presentedPlug gaugesMeasurement arrangements for variablePrincipal component analysisCorrelation analysis
The present invention is a method for detecting an abnormal event for process units of a Delayed Coking Unit. The method compares the operation of the process units to statistical and engineering models. The statistical models are developed by principal components analysis of the normal operation for these units. The engineering models are based statistical and correlation analysis between variables. If the difference between the operation of a process unit and the normal model result indicates an abnormal condition, then the cause of the abnormal condition is determined and corrected.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
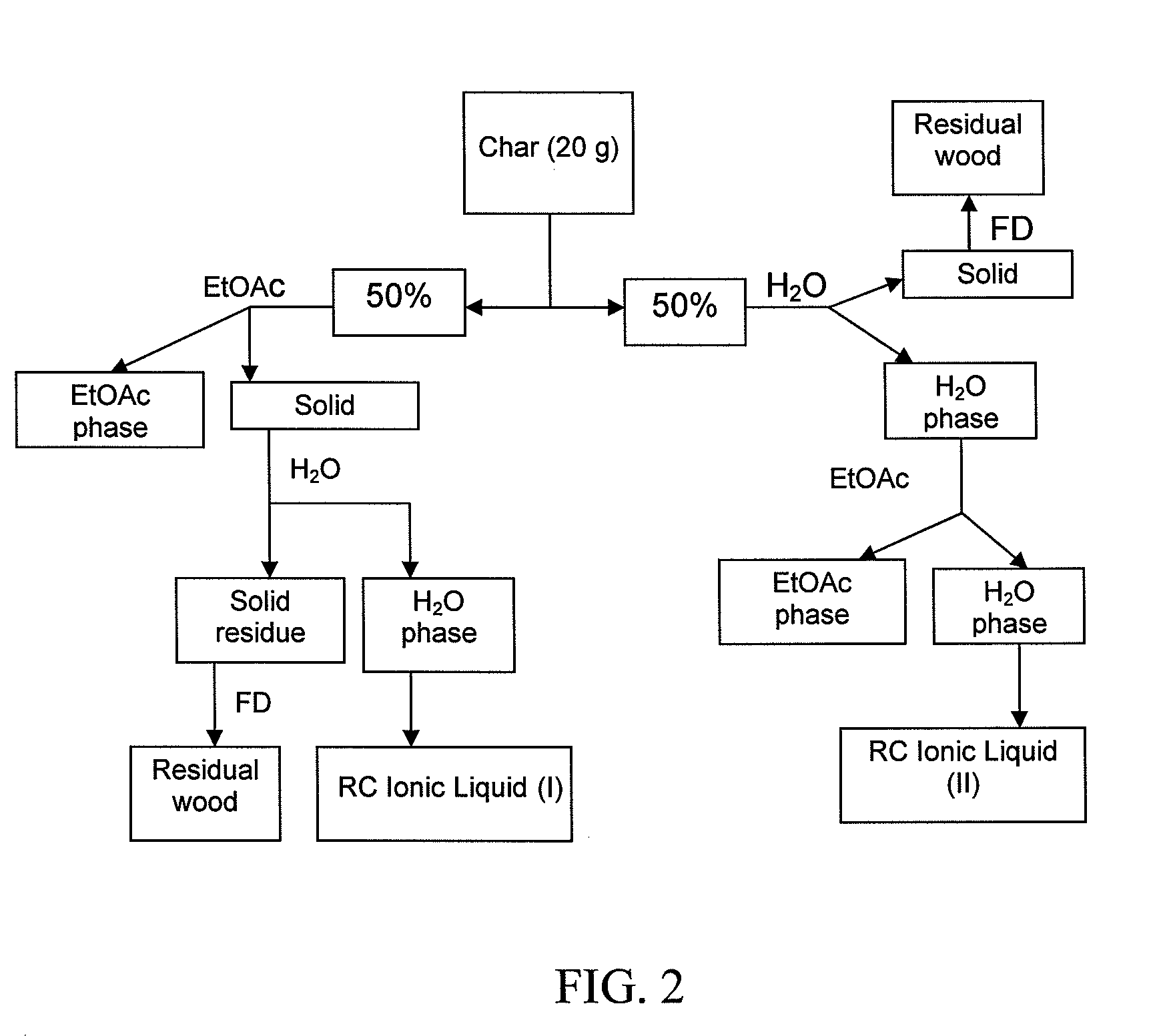
Product preparation and recovery from thermolysis of lignocellulosics in ionic liquids
InactiveUS20080185112A1Increase productionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentCoal charges mechanical treatmentCelluloseIonic liquid
The present invention provides methods for the thermolysis of lignocellulosic materials, such as wood, cellulose, lignin, and lignocellulose. In specific embodiments, the methods comprise combining the lignocellulosic material with an ionic liquid and subjecting the mixture of the lignocellulosic material and the ionic media to pyrolytic conditions to form a recoverable product, such as a commodity chemical.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Production and use of a premium fuel grade petroleum coke
InactiveUS20060032788A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingLiquid organic insulatorsCombustionSufficient time
A premium “fuel-grade” petroleum coke is produced by modifying petroleum coking technology. Coking process parameters are controlled to consistently produce petroleum coke within a predetermined range for volatile combustible material (VCM) content. The invention includes a process of producing a coke fuel, the method comprising steps: (a) obtaining a coke precursor material derived from crude oil and having a volatile organic component; and (b) subjecting the coke precursor material to a thermal cracking process for sufficient time and at sufficient temperature and under sufficient pressure so as to produce a coke product having volatile combustible materials (VCMs) present in an amount in the range of from about 13% to about 50% by weight. Most preferably, the volatile combustible materials in the coke product typically may be in the range of from about 15% to about 30% by weight. The present invention also provides methods for (1) altering the coke crystalline structure, (2) improving the quality of the coke VCM, and (3) reducing the concentration of coke contaminants. Fuels made from the inventive coke product and methods of producing energy through the combustion of such fuels are also included. Finally, novel environmental control techniques are developed to take optimal advantage of the unique characteristics of this upgraded petroleum coke.
Owner:ETTER ROGER G
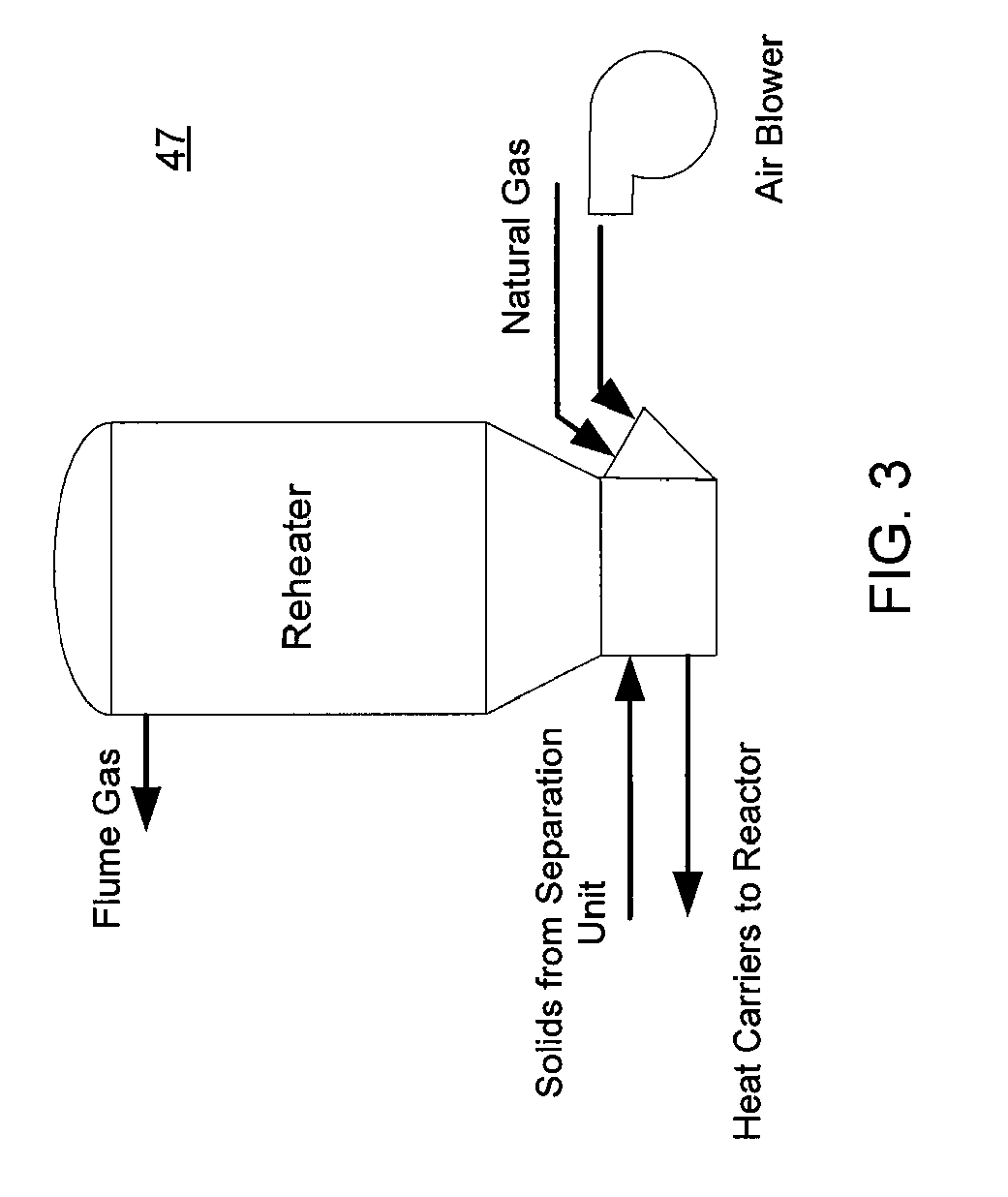
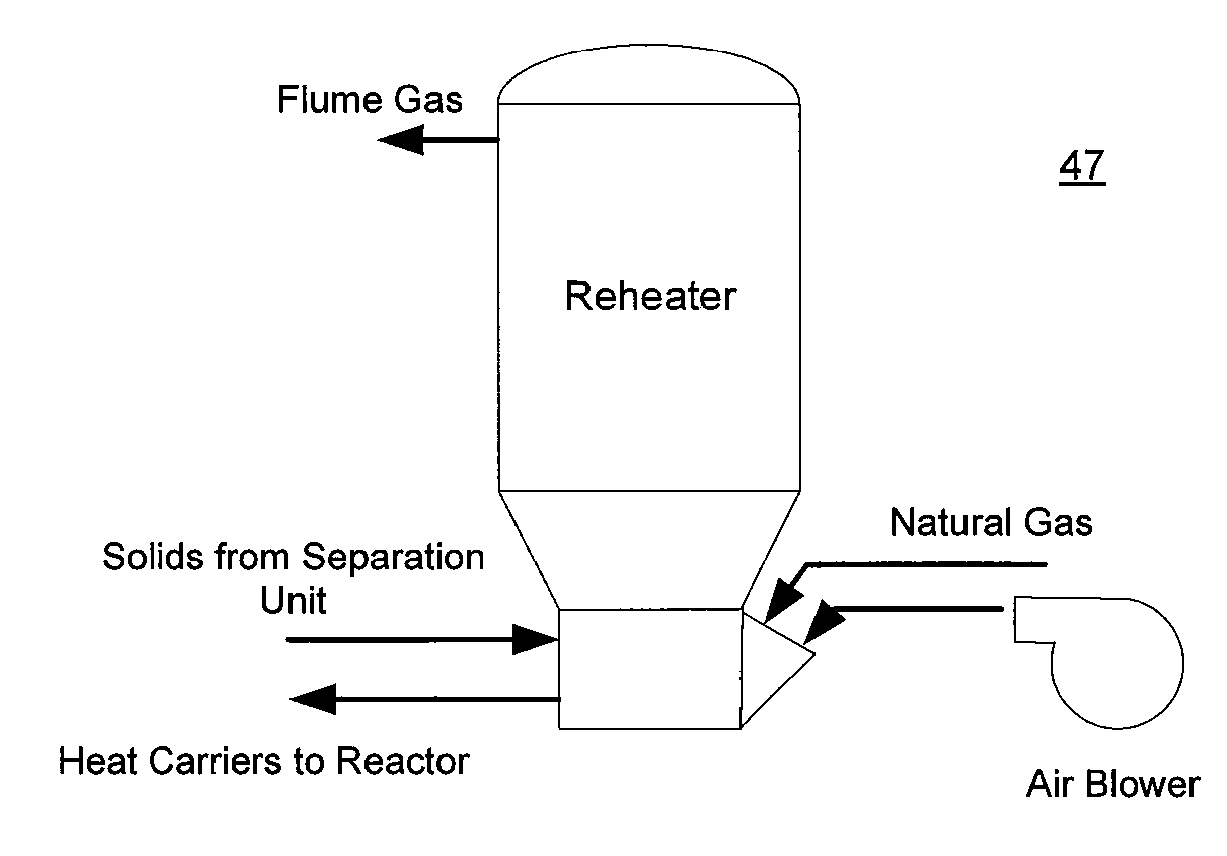
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
ActiveUS20090139851A1Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingCoke quenchingLiquid productHeat carrier
The present invent provides improved rapid thermal conversion processes for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. In an embodiment, biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. In one embodiment, the liquid product itself is used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
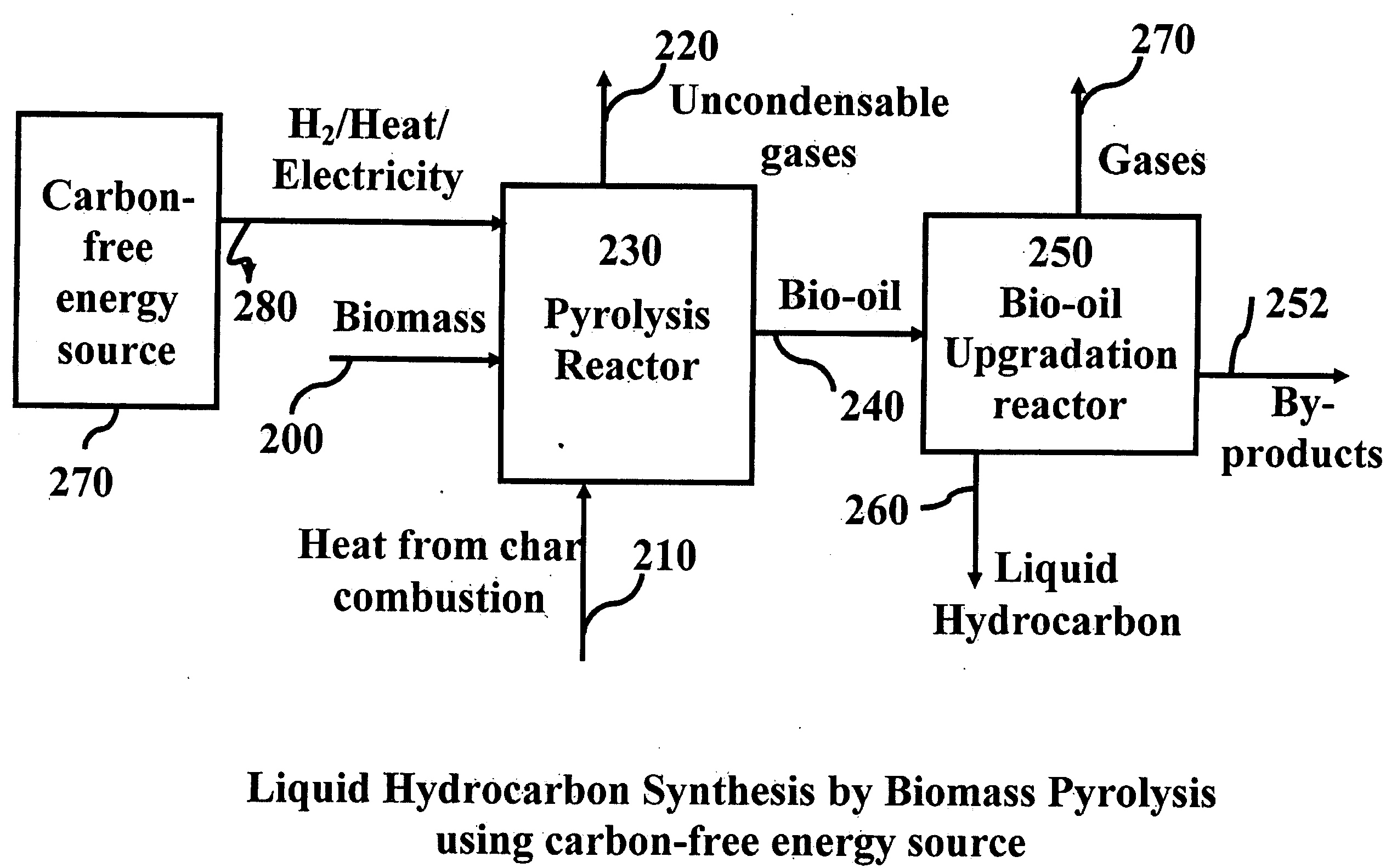
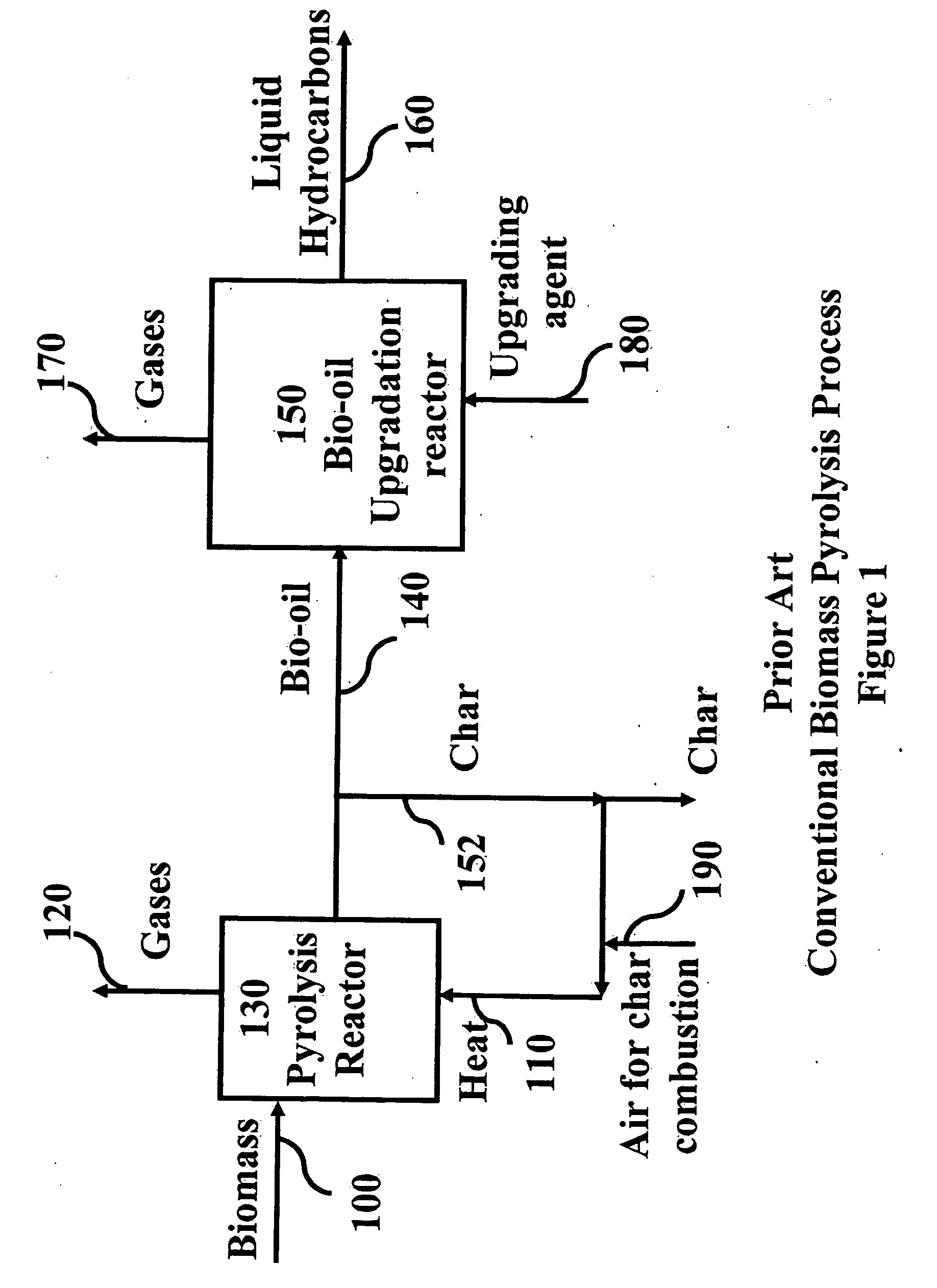
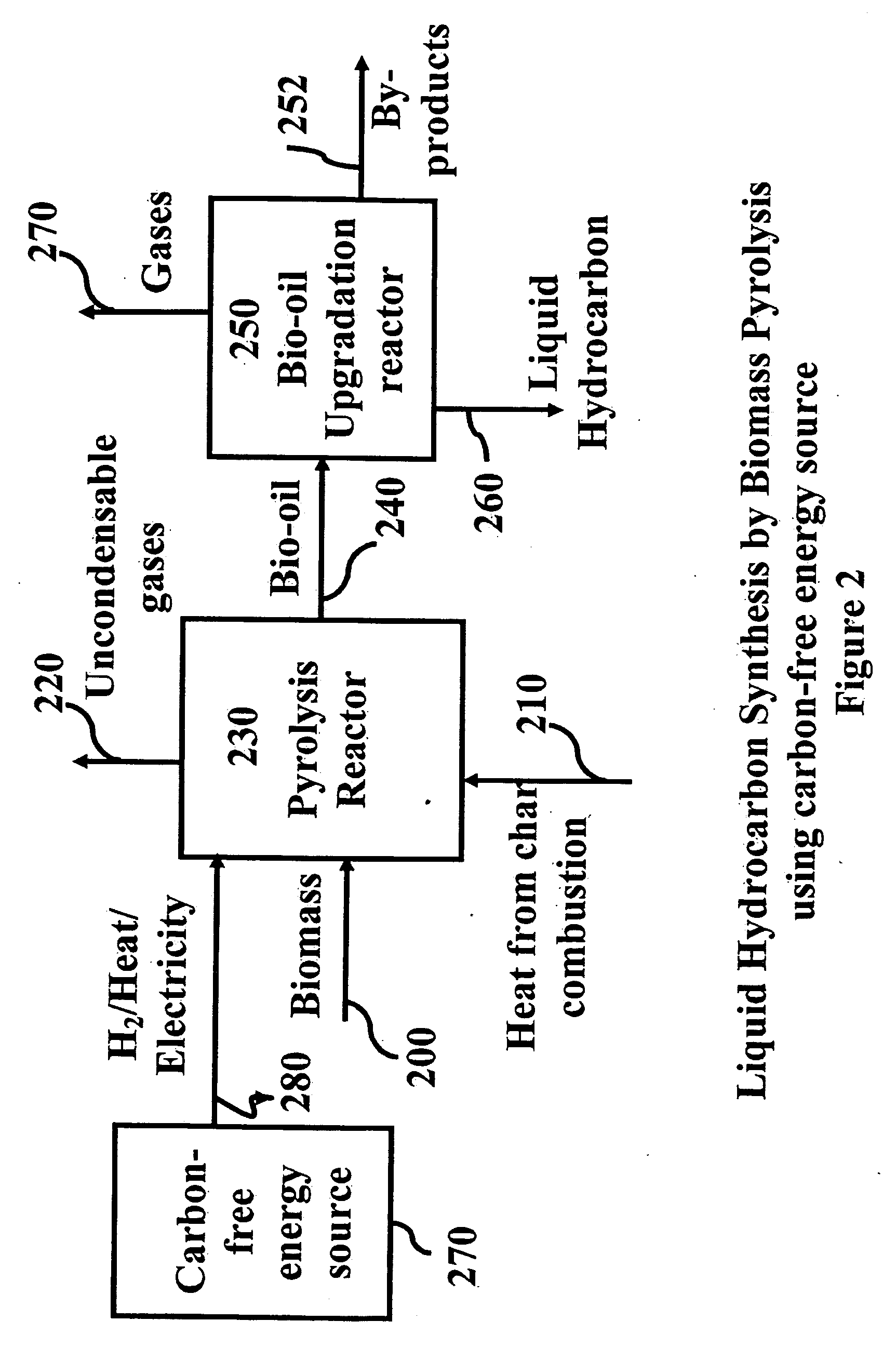
Novel process for producing liquid hydrocarbon by pyrolysis of biomass in presence of hydrogen from a carbon-free energy source
ActiveUS20090082604A1Process stabilityIncrease energy contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlkaneHydrogen
In at least one embodiment of the present invention, a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons from biomass is provided. The method comprises pyrolizing the biomass with hydrogen (H2) to form bio-oil. The bio-oil comprises alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, aromatics, hydrocarbons or mixtures thereof. The H2 is formed from a carbon-free energy source.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Alternative Process for Treatment of Heavy Crudes in a Coking Refinery
ActiveUS20110083996A1Increasing API gravityReduce the amount of metalThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining with metalsFuel oilPre treatment
The present invention relates to a process for the pretreatment of heavy oils using a catalytic hydrotreating process prior to introduction to a refinery. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of an HDM reactor and an HDS reactor in order to improve the characteristics of the heavy oil, such that when the oil is introduced into the refinery, the refinery can achieve improved throughputs, increased catalysts life, increased life cycles, and a reduction in overall operation costs.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Upgrading of tar using POX/coker
ActiveUS8083931B2Reduce and eliminate needThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyNaphthaPartial oxidation
The invention is directed to a process wherein a feedstock or stream comprising steam cracker tar is passed to a vacuum pipestill. A deasphalted cut of tar is obtained as an overhead (or sidestream) and a heavy tar asphaltenic product is obtained as bottoms. In preferred embodiments, at least a portion of the bottoms product is sent to a partial oxidation unit (POX) wherein syn gas may be obtained as a product, and / or at least a portion of the bottoms product is used to produce a light product stream in a coker unit, such as coker naphtha and / or or coker gas oil. In another preferred embodiment at least a portion of the overheads product is added to refinery fuel oil pools and in yet another preferred embodiment at least a portion of the overheads product is mixed with locally combusted materials to lower soot make. Two or more of the aforementioned preferred embodiments may be combined.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
System and method for atmospheric carbon sequestration
ActiveUS20100257775A1Increase carbon emissionsLiquid surface applicatorsSolid waste disposalCarbon sequestrationCoal
This invention relates to systems and methods for converting biomass into highly inert carbon. Specifically, some embodiments densify the carbon into anthracite-style carbon aggregations and store it in geologically stable underground deposits. The use of certain embodiments yield a net effect of removing atmospheric carbon via the process of photosynthesis and converting it into hard coal, which can be stored in underground beds that mimic existing coal deposits which are known to be stable for thousands of years.
Owner:COOL PLANET ENERGY SYST
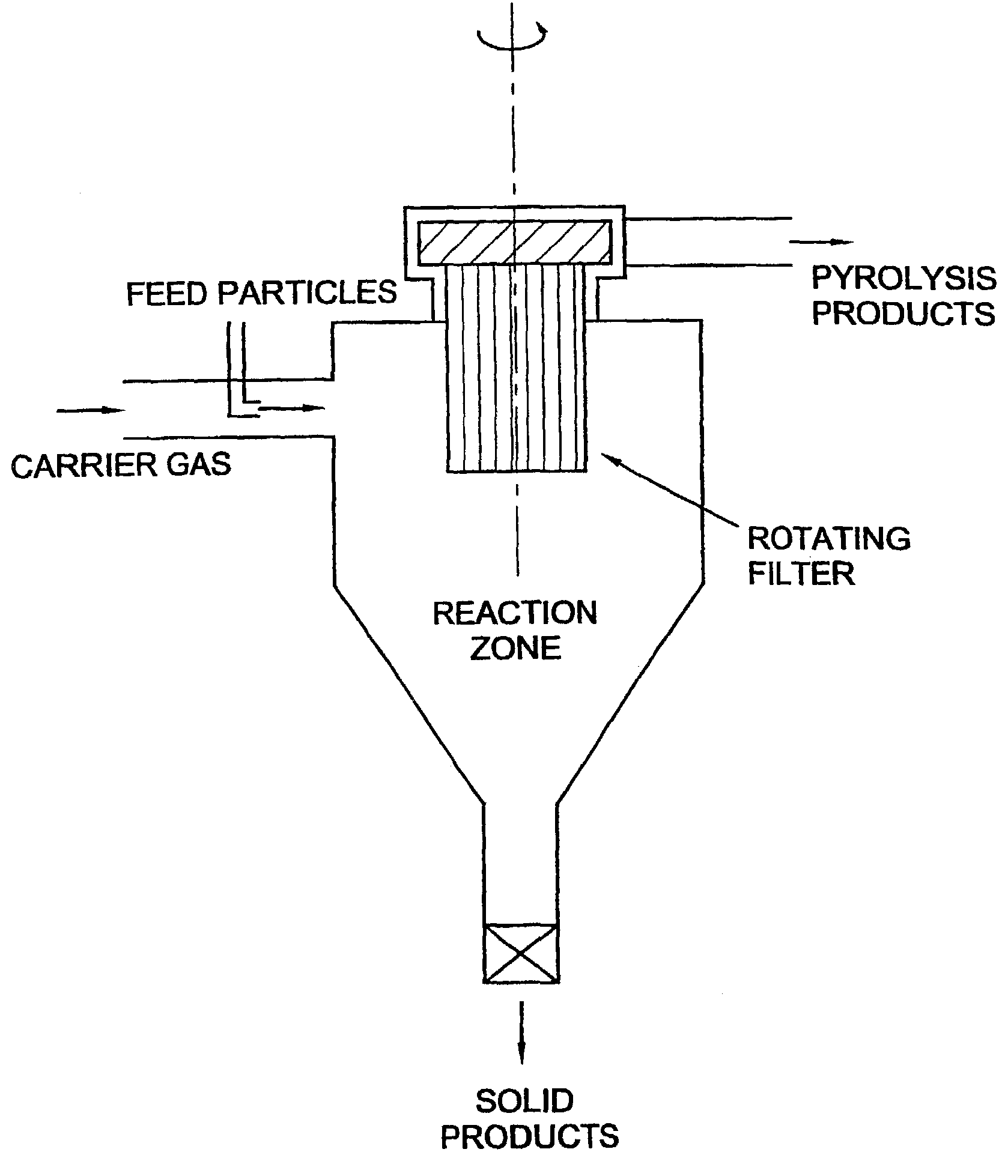
Flash-pyrolysis in a cyclone
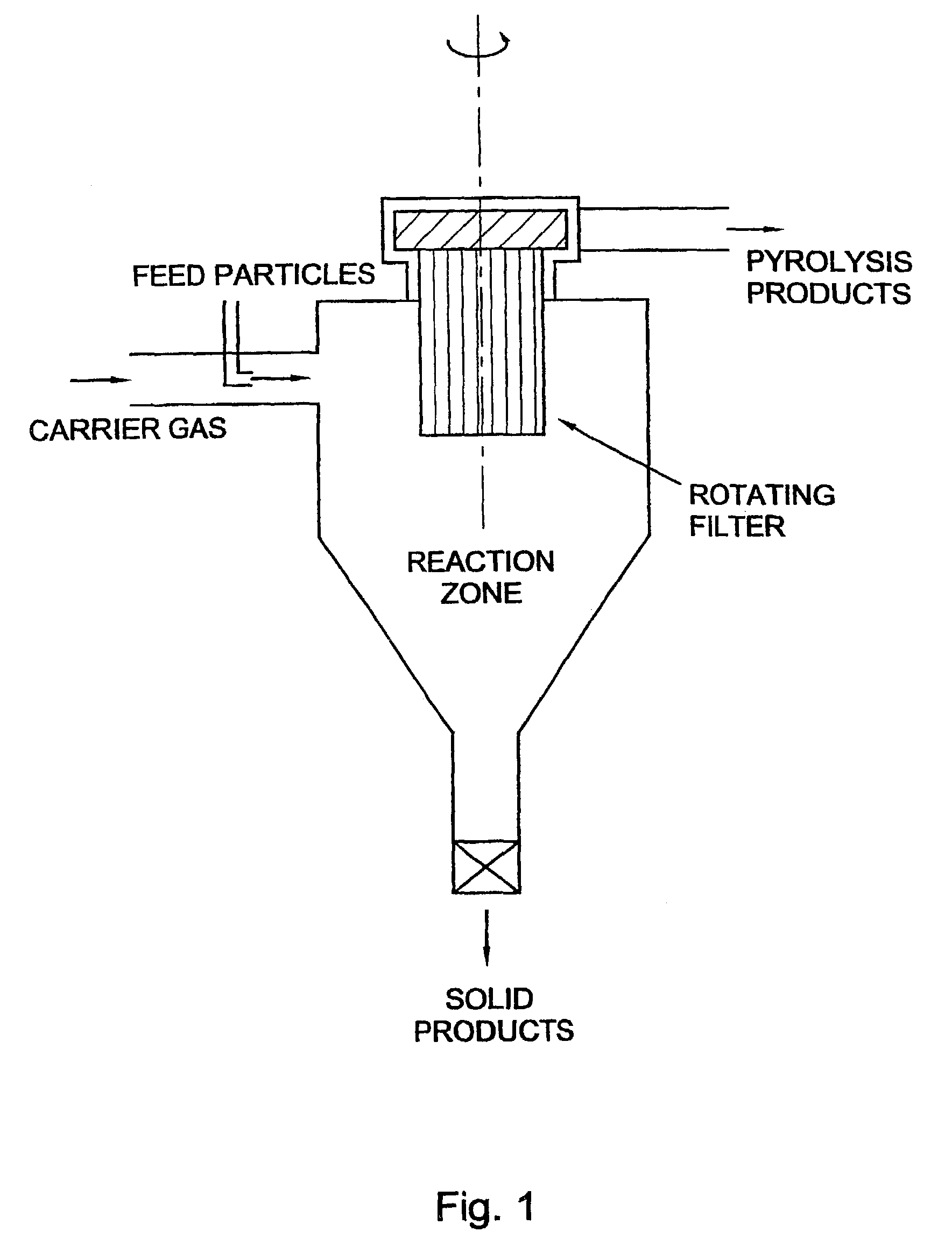
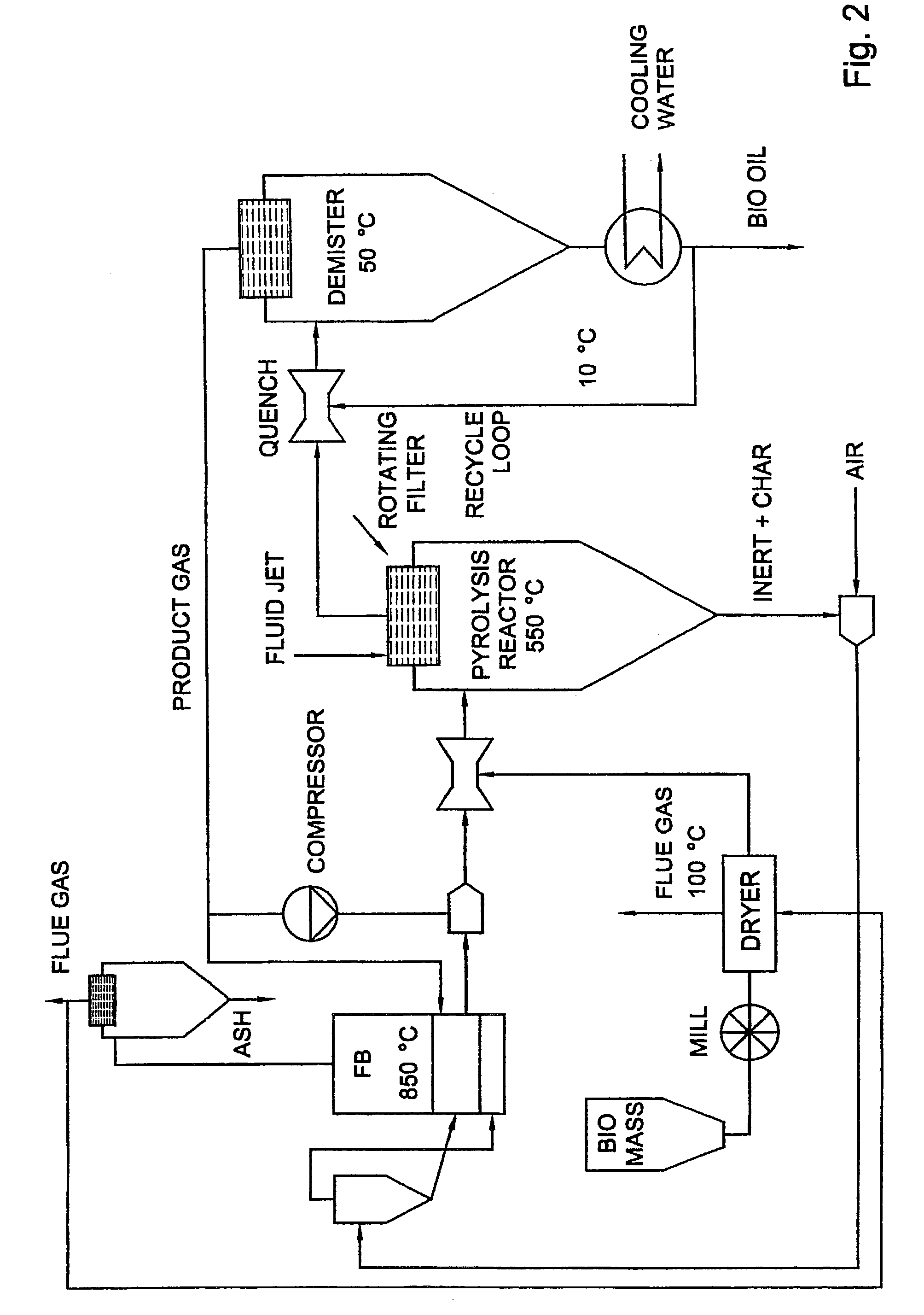
InactiveUS7202389B1Excessive crackingCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesCyclone
A process for the pyrolysis of carbonaceous material is carried out in a cyclone reactor which is fitted with enhanced filtering equipment. In addition the invention relates to the use of a cyclone fitted with a rotating filter as a pyrolysis reactor. By using a cyclone of the rotating separator type as a pyrolysis reactor, carbonaceous material, such as biomass, can effectively be converted in a product having excellent chemical properties and which product is free from particulate matter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
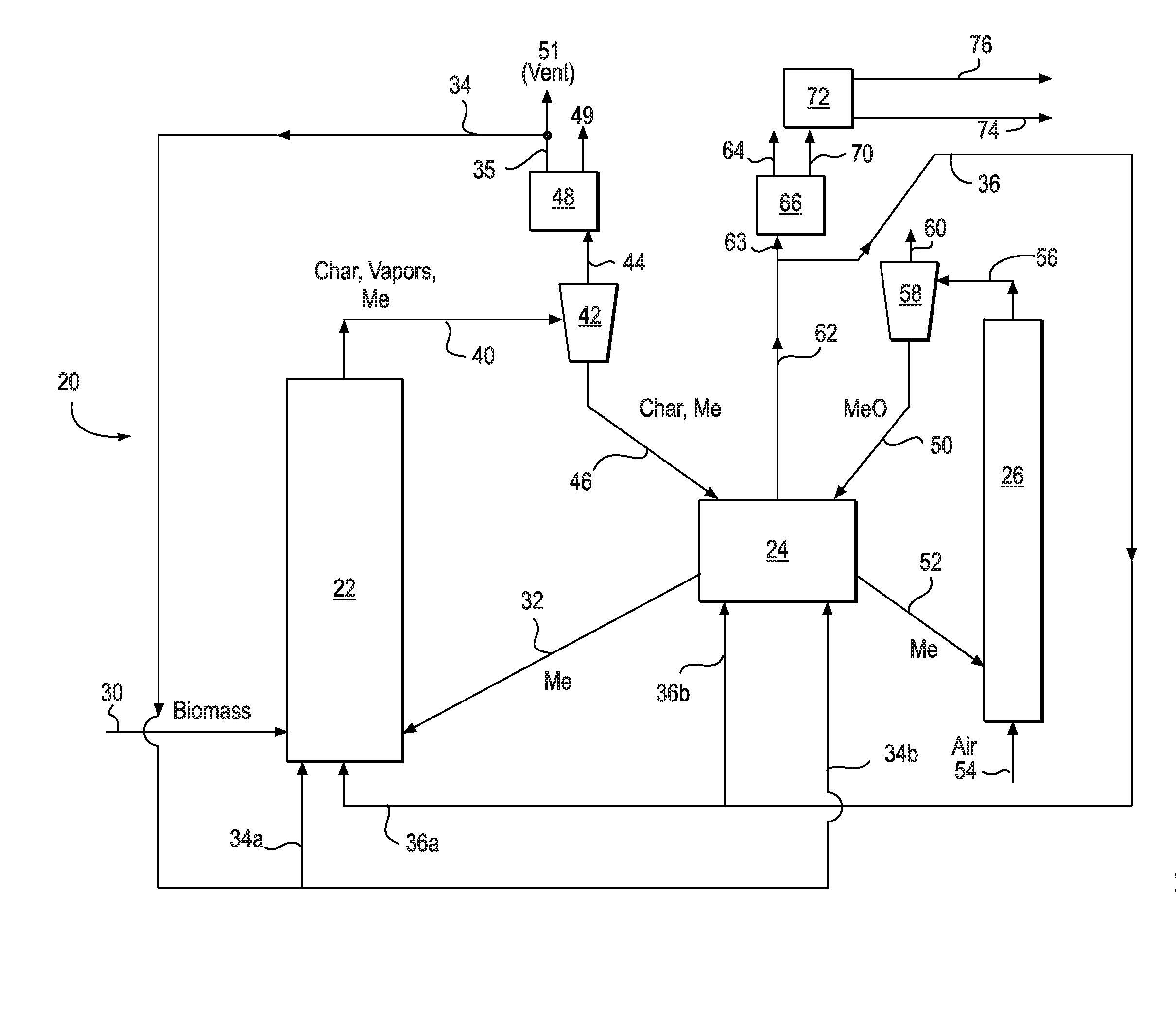
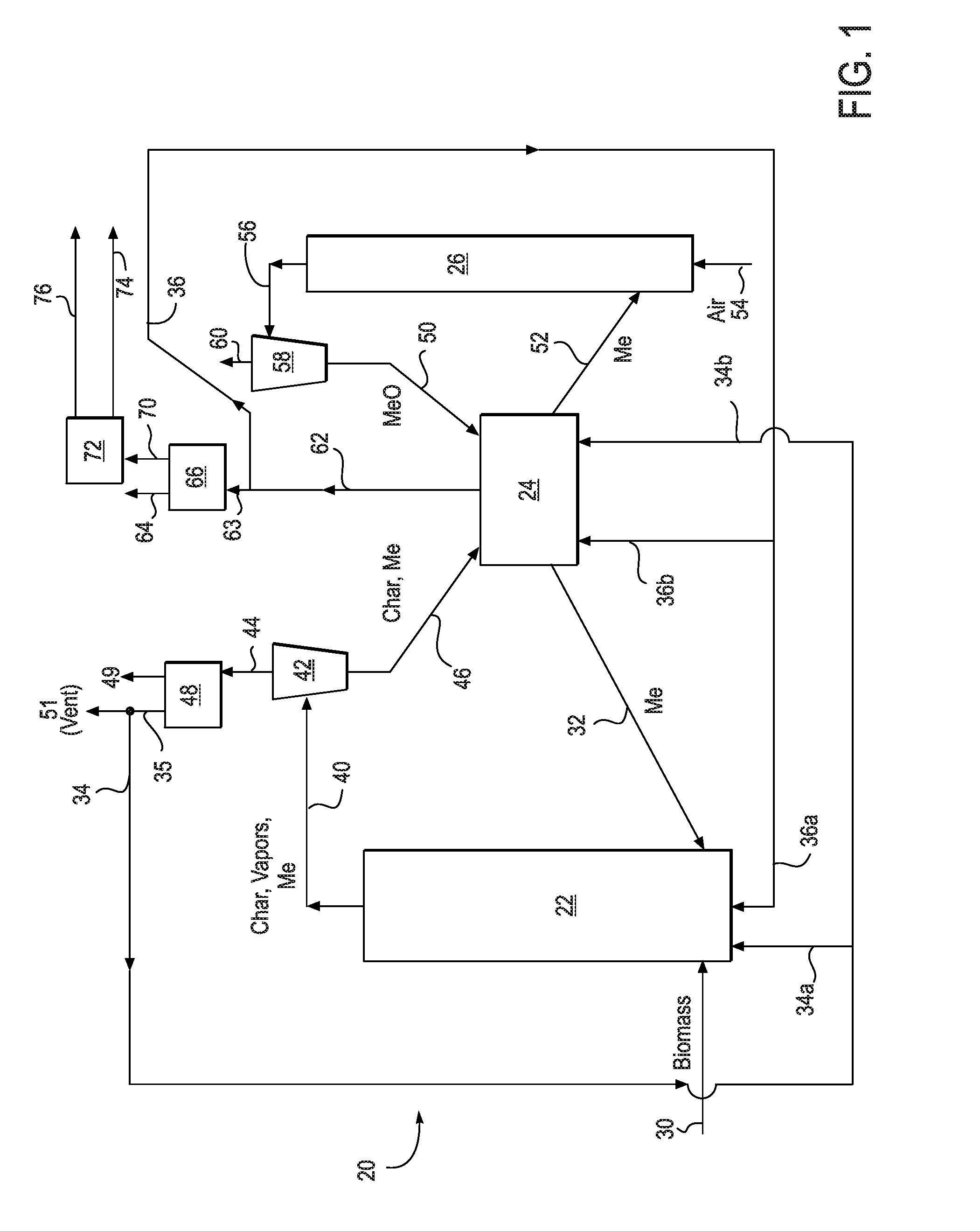
Method and system for capturing carbon dioxide from biomass pyrolysis process
A system and method for biomass pyrolysis utilizing chemical looping combustion of a produced char to capture carbon dioxide is disclosed. The system includes a biomass pyrolysis reactor, a char combustor, and oxidation reactor and a separator for separating carbon dioxide from flue gas produced by the char combustion. The pyrolysis reactor pyrolyzes biomass in the presence of reduced metal oxide sorbents producing char and pyrolysis oil vapor. The char is separated and combusted in the char combustor, in the presence of oxidized metal oxide sorbents, into a gaseous stream of carbon dioxide and water vapor. The carbon dioxide and water are separated so that a stream of carbon dioxide may be captured. The oxidation reactor oxidizes, in the presence of air, a portion of reduced metal oxide sorbents into oxidized metal oxide sorbents that are looped back to the char combustor to provide oxygen for combustion. A second portion of the reduced metal oxide sorbents is recycled from the char combustor to the pyrolysis reactor to provide heat to drive the pyrolysis. Pyrolysis oil upgrading catalyst particles may be used in addition to the metal oxide sorbents as heat energy carrier particles to improve the quality of the pyrolysis oil vapors produced in the pyrolysis reactor. Also, the metal oxide sorbents may have metals incorporated therein which serve to upgrade the pyrolysis vapors produced during pyrolysis. Non-limiting examples of such metals include Ni, Mo, Co, Cr, W, Rh, Ir, Re, and Ru.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for extracting heavy liquefaction oil and intermediate-phase bitumen matter from coal liquefaction residuals and application thereof
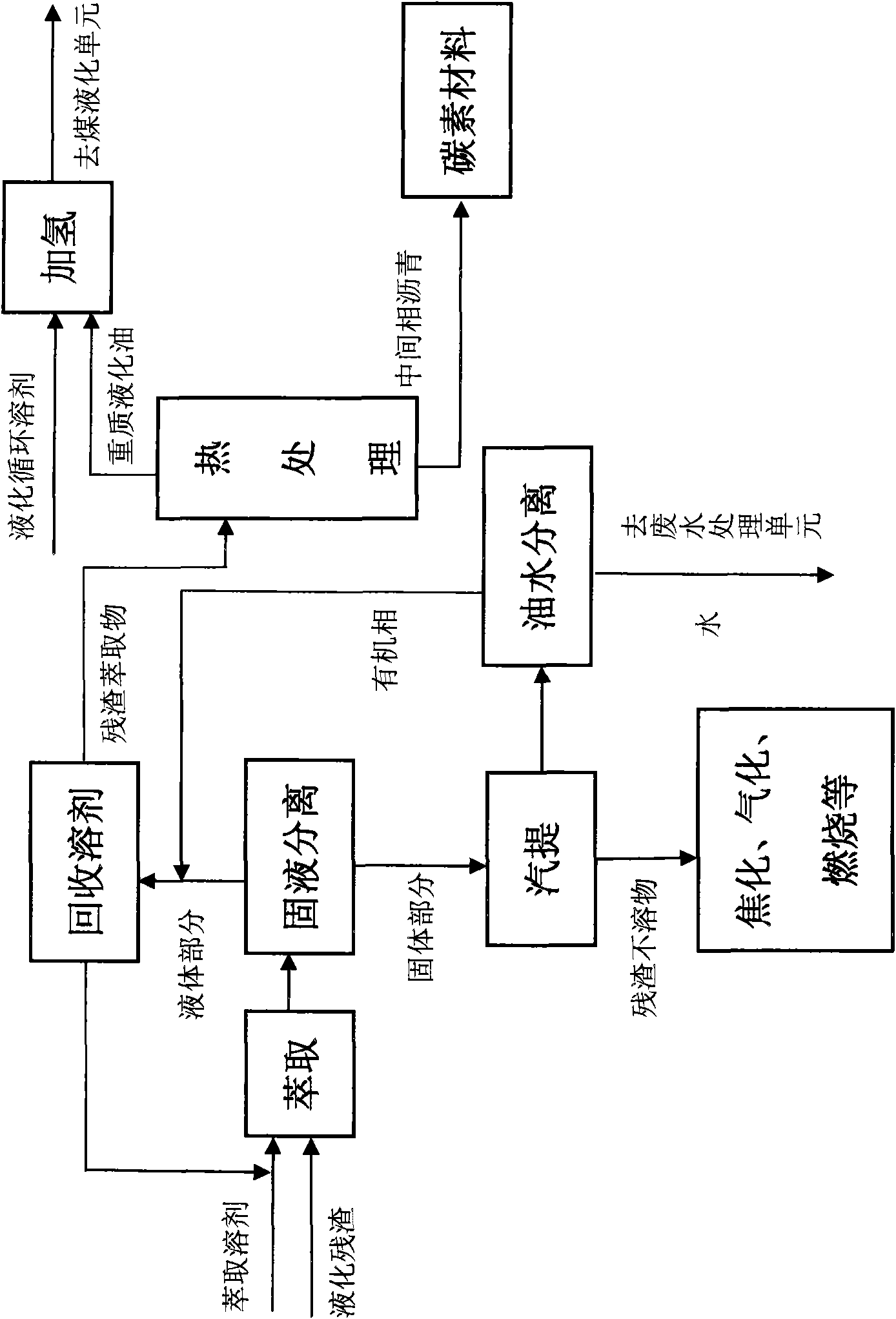
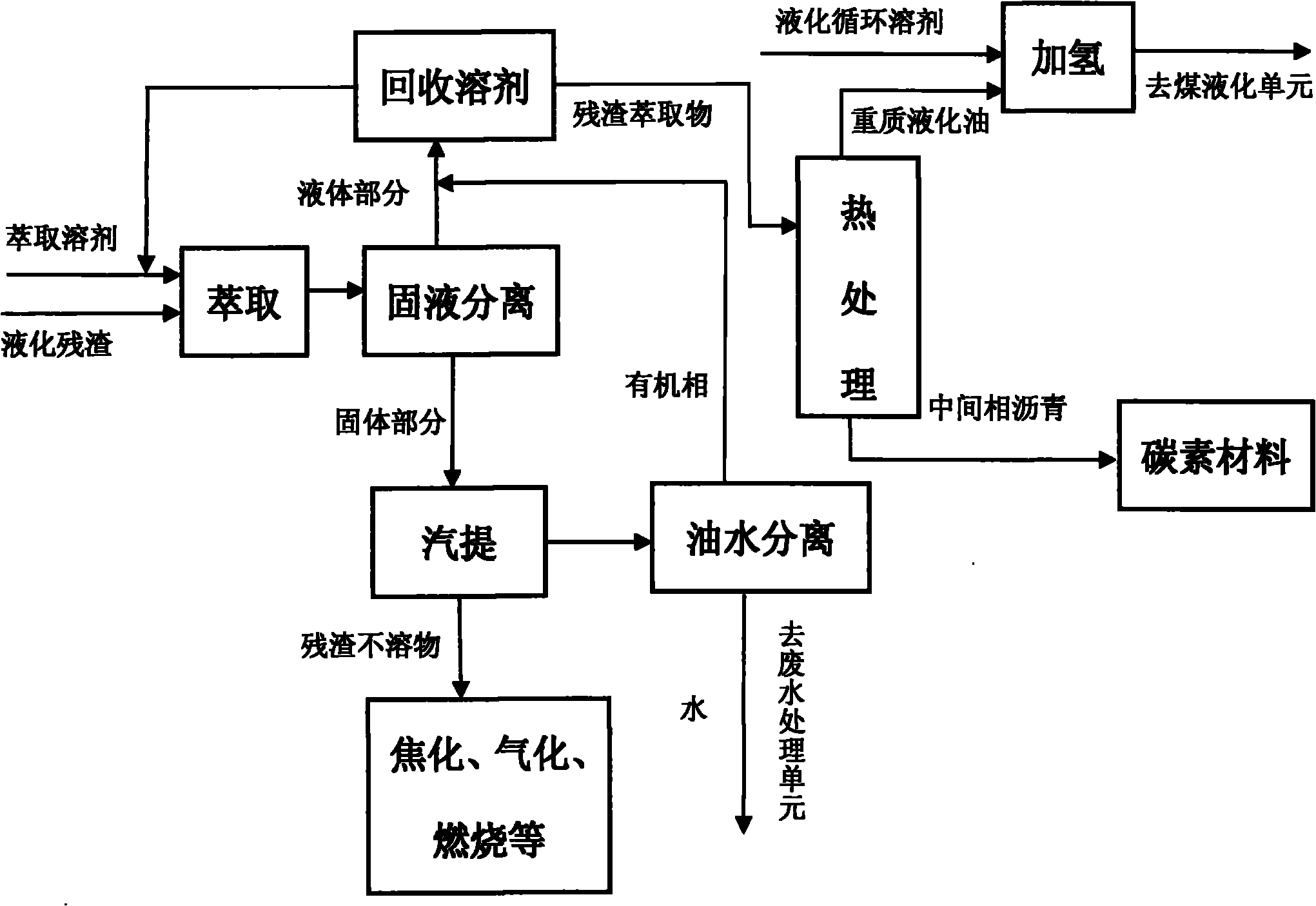
ActiveCN101885976ARealize rationalityRealization of high value-added utilizationThermal non-catalytic crackingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionEvaporationOil water
The invention provides a method for extracting heavy liquefaction oil and an intermediate-phase bitumen matter from coal liquefaction residuals and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: adding coal liquefaction residual powder and an extraction solvent to a stirring kettle together for extraction to obtain extraction liquid and extraction residues; carrying out solid-liquid separation on the obtained extraction liquid and extraction residues; carrying out steam stripping on the obtained extraction residues, and recovering an organic phase after oil-water separation; mixing the extraction liquid with the organic phase, and then delivering into a solvent recovery unit; recovering the extraction solvent for recycling use or being returned to a liquefaction productprocessing unit by using a distillation method and / or an evaporation method, wherein residuals obtained after the extraction solvent is recovered are liquefaction residual extractives; delivering theobtained liquefaction residual extractives into a heat treatment unit, and separating the heavy liquefaction oil from the intermediate-phase bitumen matter by using a heating dry distillation method;and adding the obtained heavy liquefaction oil and other recycling solvents in a direct liquefaction process to a coal liquefaction solvent hydrogenation unit together.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +2
Method for producing blast furnace coke through coal compaction in a non-recovery or heat recovery type oven
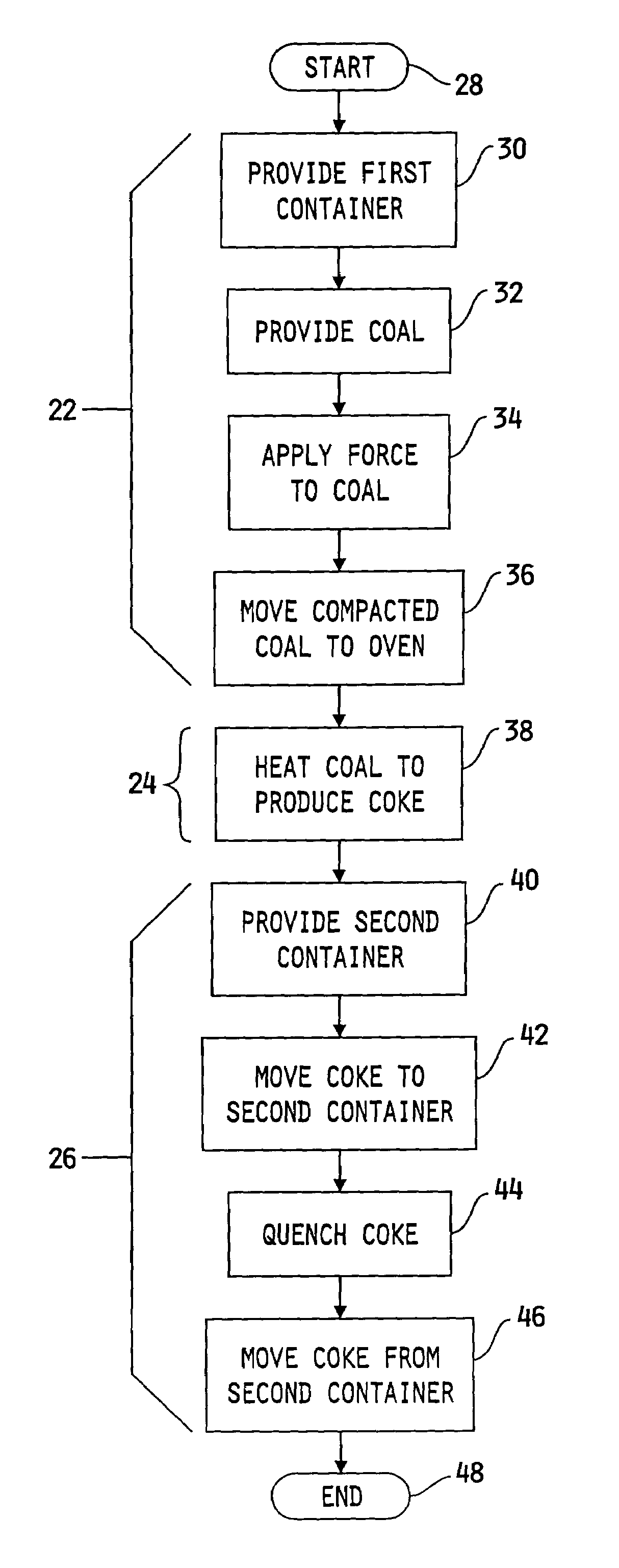
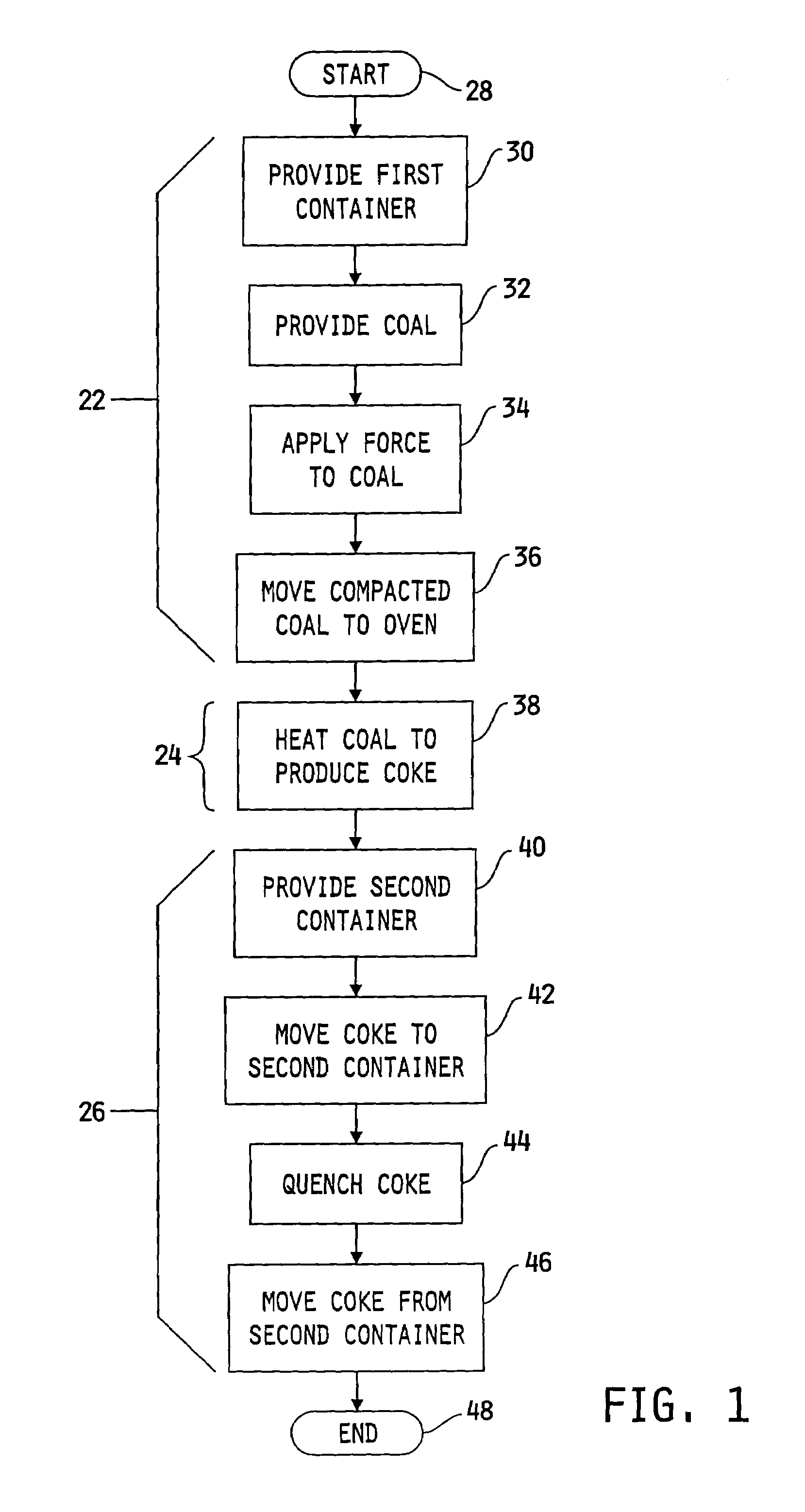
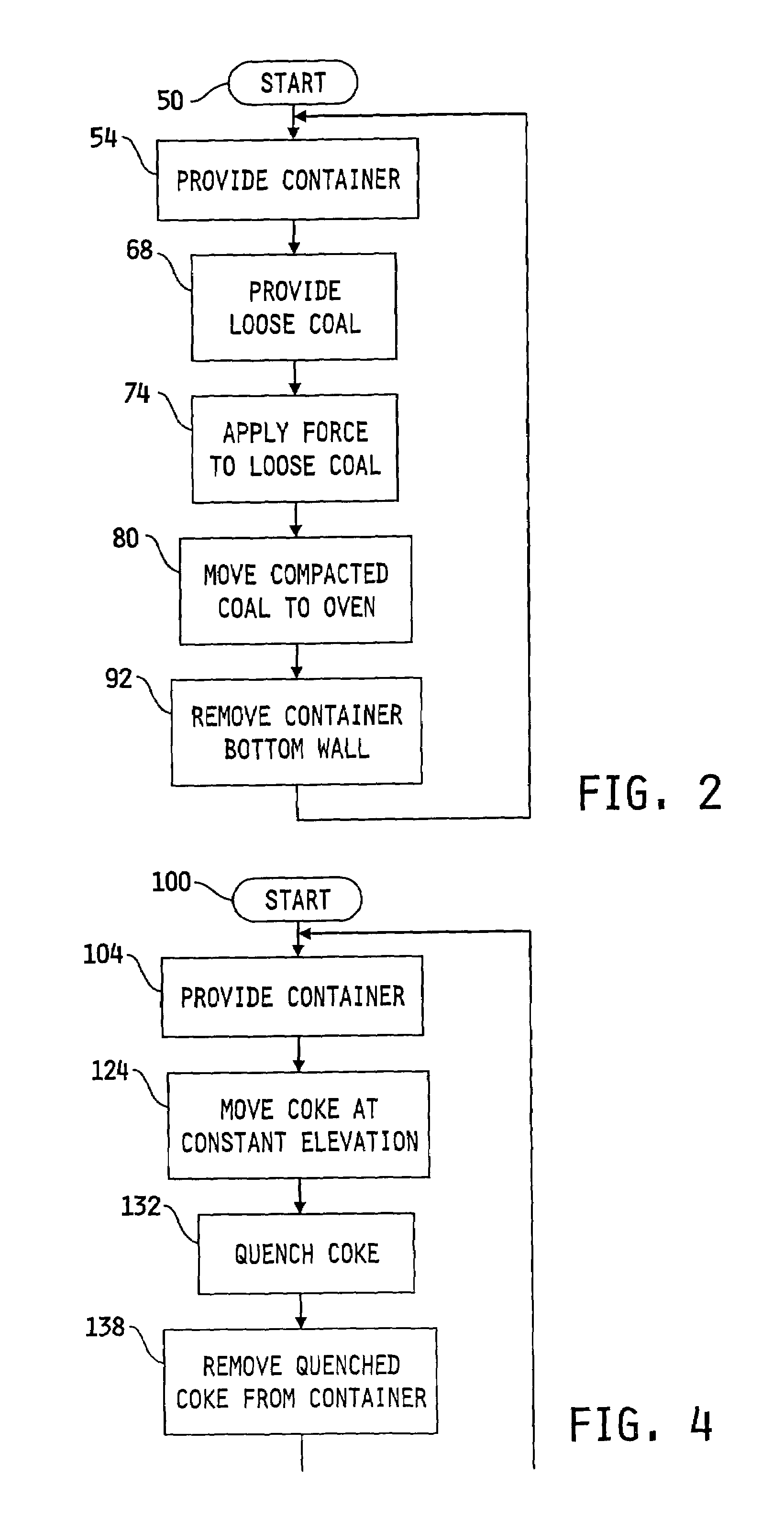
A method for producing non-recovery / heat recovery coke may include the steps of providing a container, disposing a volume of loose coal into the container such that a vertical dimension of the volume of loose coal in the container is smaller than a horizontal dimension of the volume of loose coal, applying a force to the coal in the container to produce a volume of compacted coal having a substantially uniform density which is larger than that of the loose coal, disposing the compacted coal into a non-recovery / heat recovery type oven, and heating the compacted coal to produce coke. The method may also include the steps of providing a container, and moving the non-recovery / heat recovery coke mass from the oven at a substantially constant elevation to the container, quenching the coke mass in the container to produce a quenched coke mass, and removing the quenched coke mass from the container.
Owner:ARCELORMITTAL INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO SL
Method and apparatus for producing coke
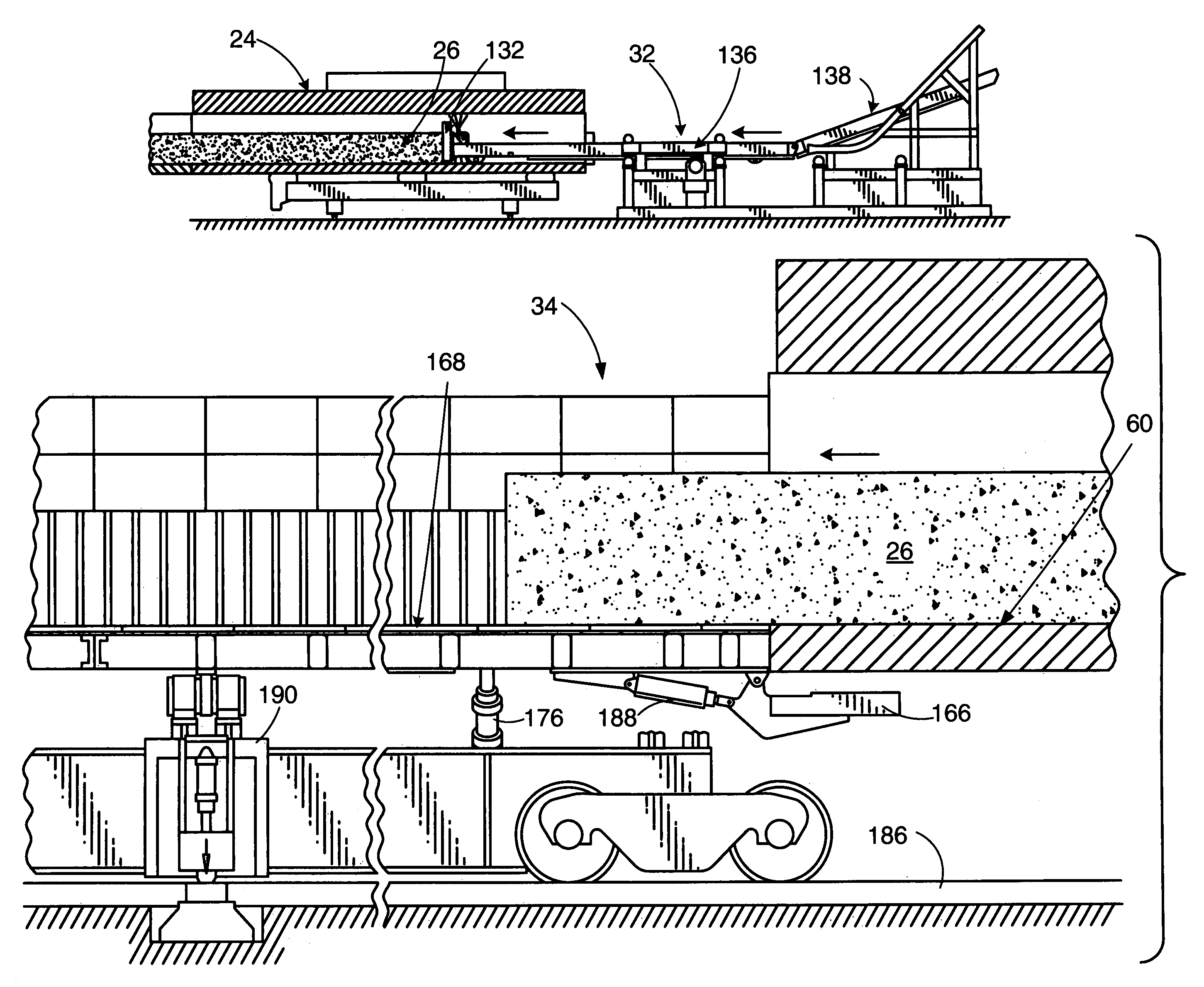
ActiveUS8152970B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce moisture contentSpeed controllerCoke quenchingMetallurgyMetallurgical coke
A method and apparatus for quenching metallurgical coke made in a coking oven. The method includes pushing a unitary slab of hot coke onto a substantially planar receiving surface of a hot car. The hot car containing the coke is then transported to a quench car station. The unitary slab of hot coke is pushed onto a substantially planar receiving surface of a quench car at the quench car station. Quenching of the slab of hot coke is conducted in the quench car with a predetermine amount of water. After quenching, the quenched coke is dumped onto a receiving pad for collection thereof.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
Hydrocarbon thermal cracking using atmospheric distillation
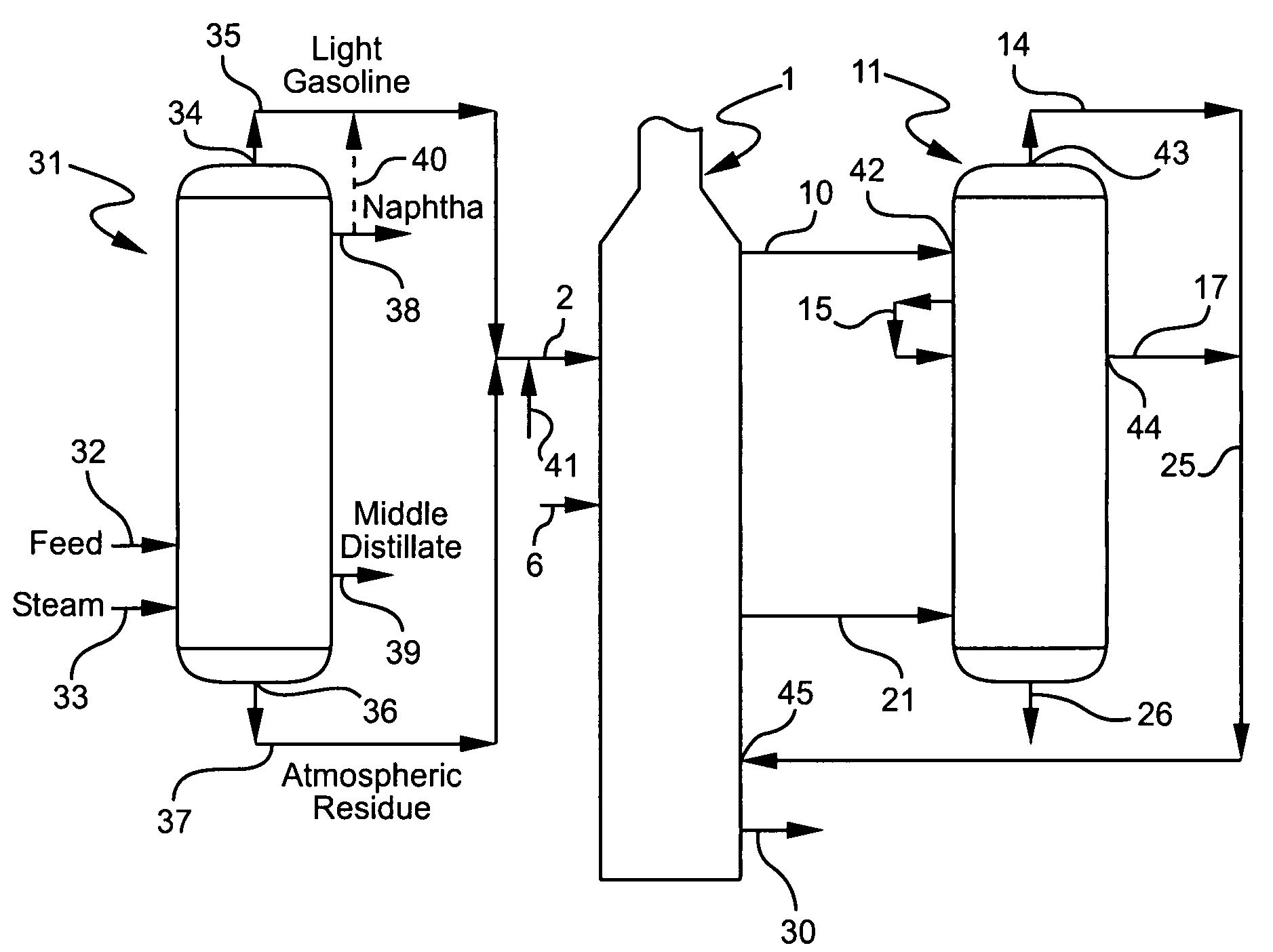
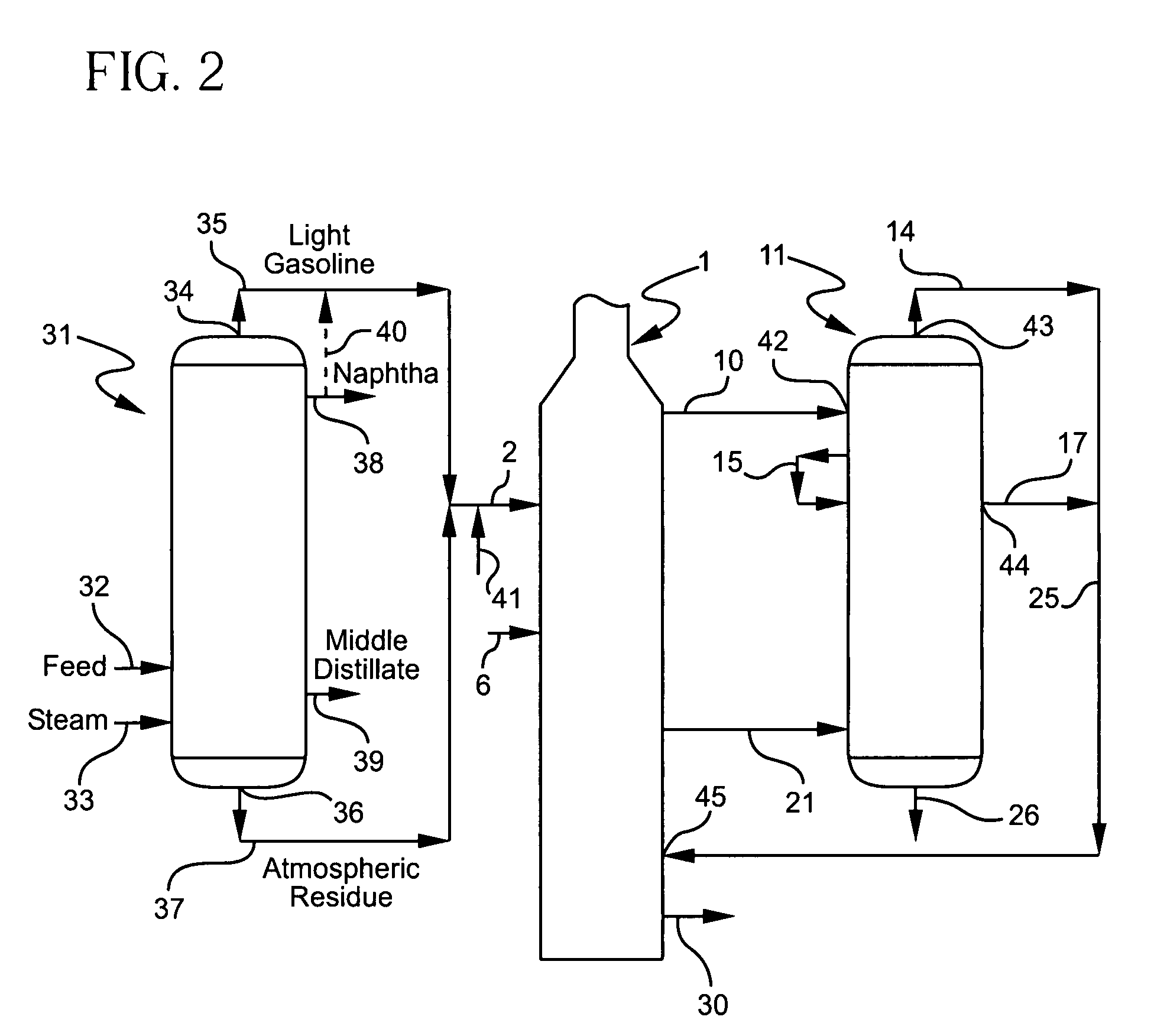
ActiveUS7404889B1Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyDistillationGasoline
A method for thermally cracking a hydrocarbonaceous feed wherein the feed is first processed in an atmospheric thermal distillation step to form a light gasoline and atmospheric residuum mixture. The light gasoline / residuum combination is gasified at least in part in a vaporization step, and the gasified product of the vaporization step is thermally cracked.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Process and device for the pyrolysis of feedstock
InactiveUS7947155B1Thermal non-catalytic crackingCombustible gas coke oven heatingVolatilesEngineering
This invention involves pyrolysis of feedstock by introducing carbonaceous feedstock, into a hopper and moving it into a reactor tube enclosed in an oven, generating heat within the oven that is in part transferred to the feedstock, heating it to sufficient temperature to pyrolyze the feedstock into useful volatiles and char. A Venturi system produces a negative pressure directing volatiles into a pyro-gas oven producing heat necessary for pyrolysis and generating useful excess heat. The extruded pyrolysis char has uses including charcoal fuel, soil amendments, and activated charcoal while liquids can be produced for processing into fuels. Excess heat may be used to heat water, steam, and air, may be used in air heating and cooling systems, perform mechanical work with a Stirling engine or generate electricity on the order of 100 kW and higher. The system may be operated in a carbon neutral or even carbon negative manner, allowing sequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Owner:GREEN LIQUID & GAS TECH
Coker feed method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080179165A1Reduces drum/vessel thermal stressReduce thermal stressThermal non-catalytic crackingCombustible gas coke oven heatingEngineeringVertical axis
Described herein are methods and mechanisms for laterally dispensing fluid to a coke drum in a predictable and maintainable manner that alleviates thermal stress. In one embodiment, the methods and mechanisms utilize a split piping system to dispense fluid through two or more inlets into a spool that is connected to a coke drum and a coke drum bottom deheader valve. A combination of block valves and clean out ports provides a more effective means to clean the lines and allows fluid to be laterally dispensed in a controllable and predictable manner. The fluid is preferably introduced to the spool in opposing directions toward a central vertical axis of the spool at equal but opposing angles ranging from minus thirty (−30) to thirty (30) degrees relative to a horizontal line laterally bisecting the spool. Alternatively, however, fluid can be introduced to the spool tangentially.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Flat push coke wet quenching apparatus and process
InactiveUS7998316B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove efficiencyCoke quenchingDirect heating destructive distillationCoke ovenWater level
A method and apparatus for quenching metallurgical coke made in a coking oven. The method includes pushing a unitary slab of incandescent coke onto a substantially planar receiving surface of an enclosed quenching car so that substantially all of the coke from the coking oven is pushed as a unitary slab onto the receiving surface of the quenching car. The slab of incandescent coke is quenched in an enclosed environment within the quenching car with a plurality of water quench nozzles while submerging at least a portion of the slab of incandescent coke by raising a water level in the quenching car. Subsequent to quenching the coke, the planar receiving surface is tilted to an angle sufficient to slide the quenched coke off of the planar receiving surface and onto a product collection conveyer and sufficient to drain water from the quenched coke.
Owner:SUNCOKE TECH & DEV LLC
Process for transporting and quenching coke
ActiveUS8236142B2Emission minimizationMinimize timeCoke quenchingDirect heating destructive distillationDust controlProcess engineering
A method and apparatus for transporting and quenching coke, useful in quenching a batch of coke produced in one of a plurality of coke ovens forming a coke oven battery, is disclosed. A hot car defining a substantially planar receiving surface is positioned adjacent a coke oven of the coke oven battery, and a unitary cake of unquenched coke is placed onto the hot car receiving surface. The hot car and unquenched coke are transported to a transfer station having a dust collection system. A quenching car is positioned at the transfer station adjacent the hot car, under the dust collection system. The unitary cake of unquenched coke is dumped into the quenching car receptacle, thereby separating the unitary cake. At least a portion of the dust generated by separation is collected. The quench car is then transported to a quenching station, where the separated coke is quenched.
Owner:WESTBROOK THERMAL TECH
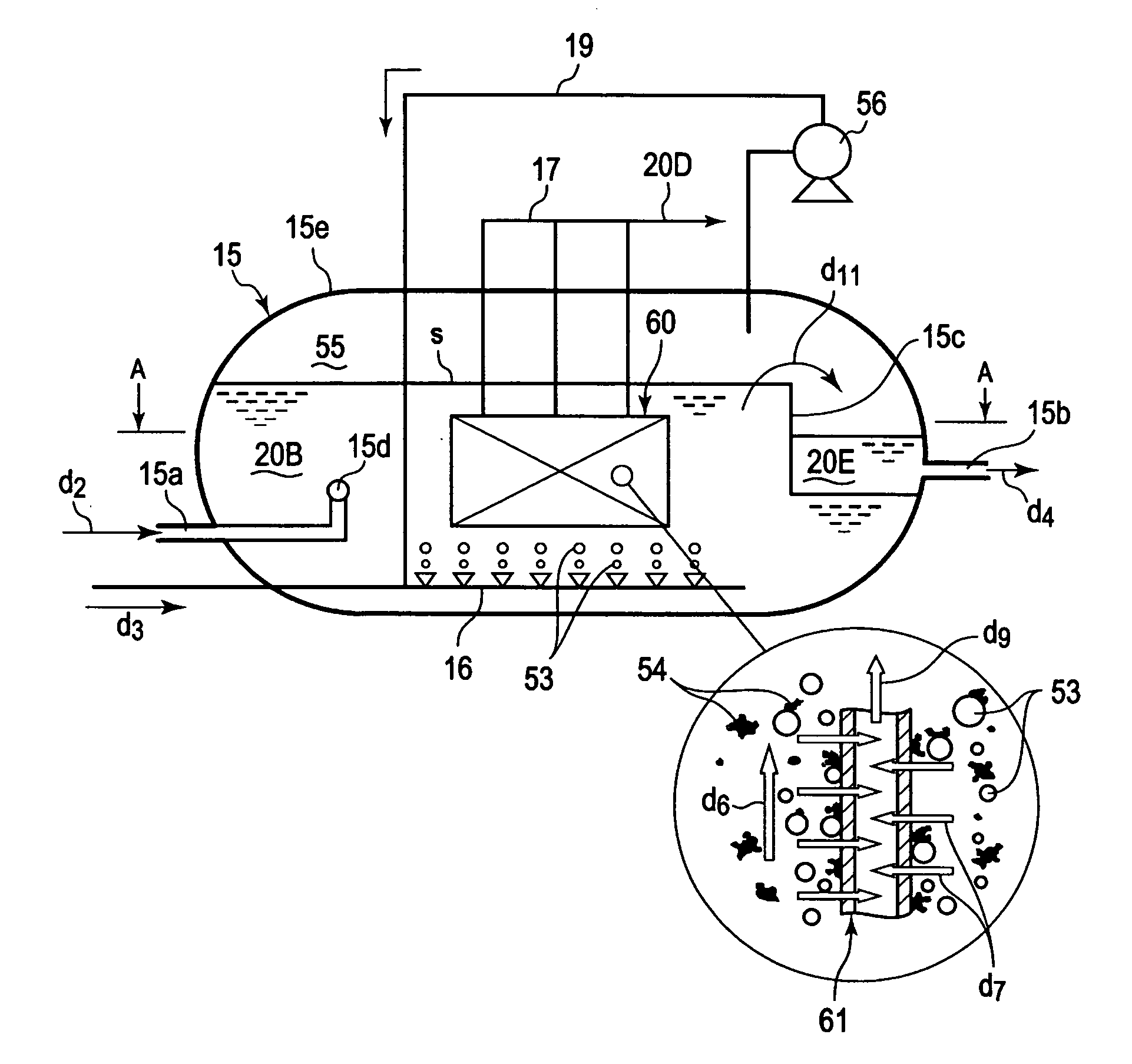
Apparatus of produced water treatment, system and method of using the apparatus, and method of water reuse by using the same
An apparatus of produced water treatment, to be adopted in an in-situ recovery method of producing bitumen from oil sand, the apparatus capable of removing the oil from produced water, the produced water of being left by separating the bitumen from bitumen-mixed fluid having been recovered from the oil sand, the apparatus having: a vessel for receiving the produced water; a submerge type filtration membrane module, installed in the vessel, for filtering the produced water in the condition of the membrane being submerged in the produced water; and a bubble generator for generating bubbles to be forwarded toward the submerged filtration membrane in the produced water.
Owner:TOYO ENG CORP +1
Pyrolysis Systems, Methods, and Resultants Derived Therefrom
ActiveUS20080286557A1Fit closelyWithout undesired degradation of communication system performanceLayered productsUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbon filtrationSilicon dioxide
A system and process for gasification of a carbonaceous feedstock uses pyrolysis to produce a gas product, which may include methane, ethane, and other desirable hydrocarbon gases, and a solids product, which includes activated carbon or carbon. The gas product may then be filtered using at least a portion of the activated carbon from the solids product as a filtering medium. In an embodiment, at least some of the noxious chemicals are sequestered or removed from the gas product in one or more filtering steps using the activated carbon as a filtering medium. In a further embodiment, the filtering steps are performed in stages using activated carbon at different temperatures. A high-temperature pyrolysis system that produces activated carbon may be combined with another high-temperature pyrolysis system that does not produce activated carbon to provide filtering of noxious compounds using activated carbon from the first high-temperature pyrolysis system. A high-temperature pyrolysis system may be combined with one or more low-temperature feedstock conversion processes such that waste heat from the high-temperature pyrolysis system is used to operate the low-temperature process. A novel non-wetting carbon having pores fused with silica can be produced from using the system and process.
Owner:TUCKER RICHARD D
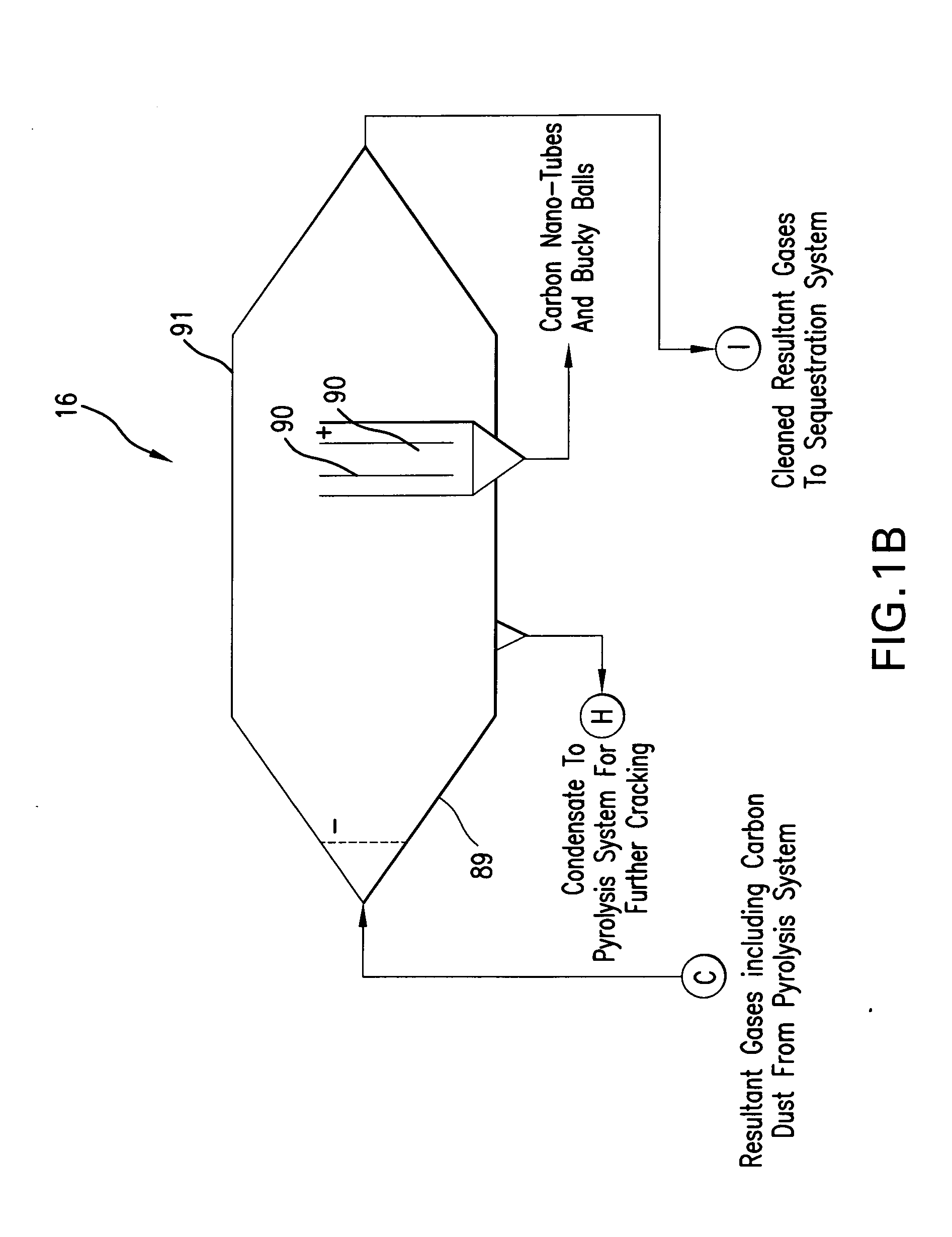
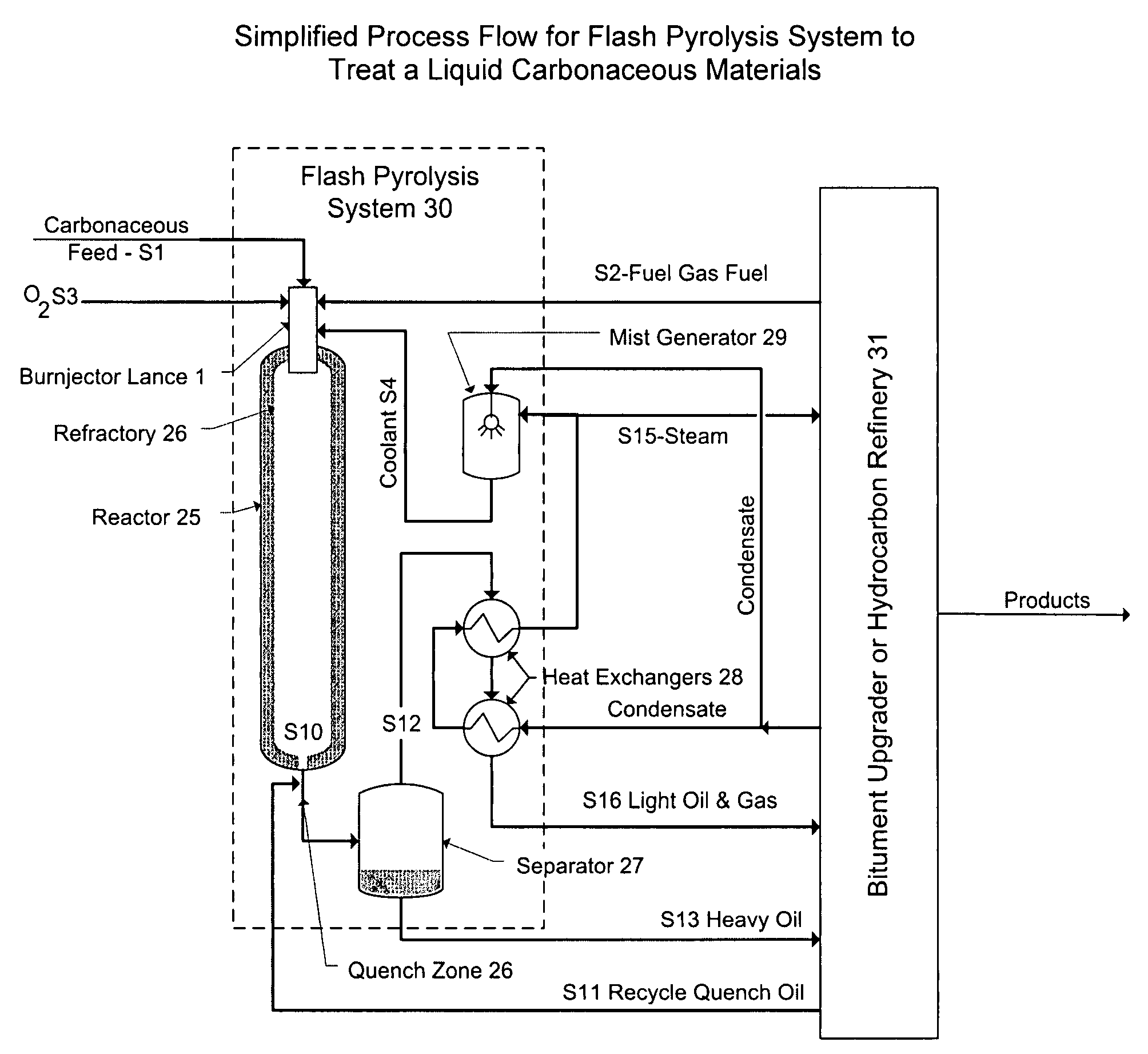
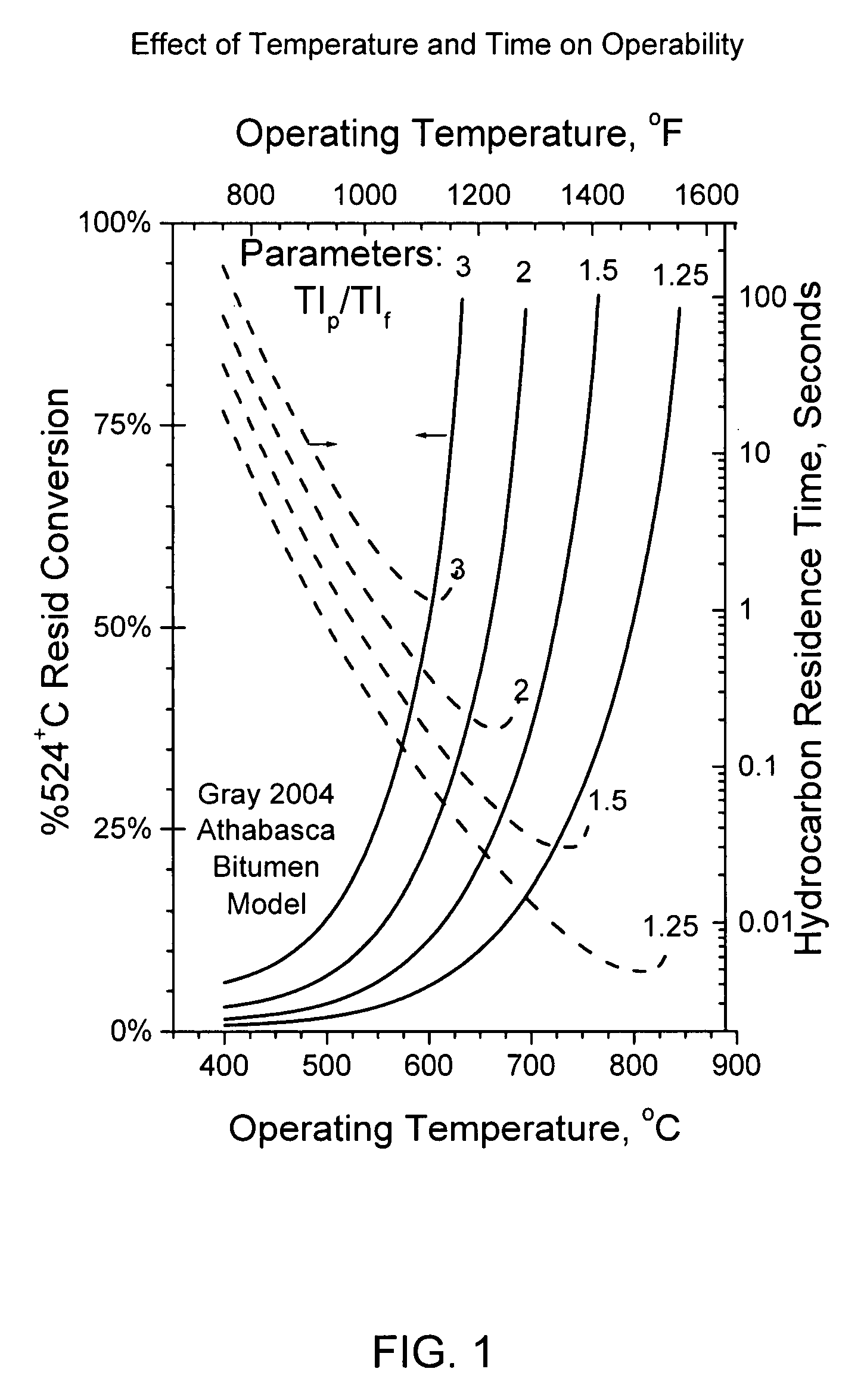
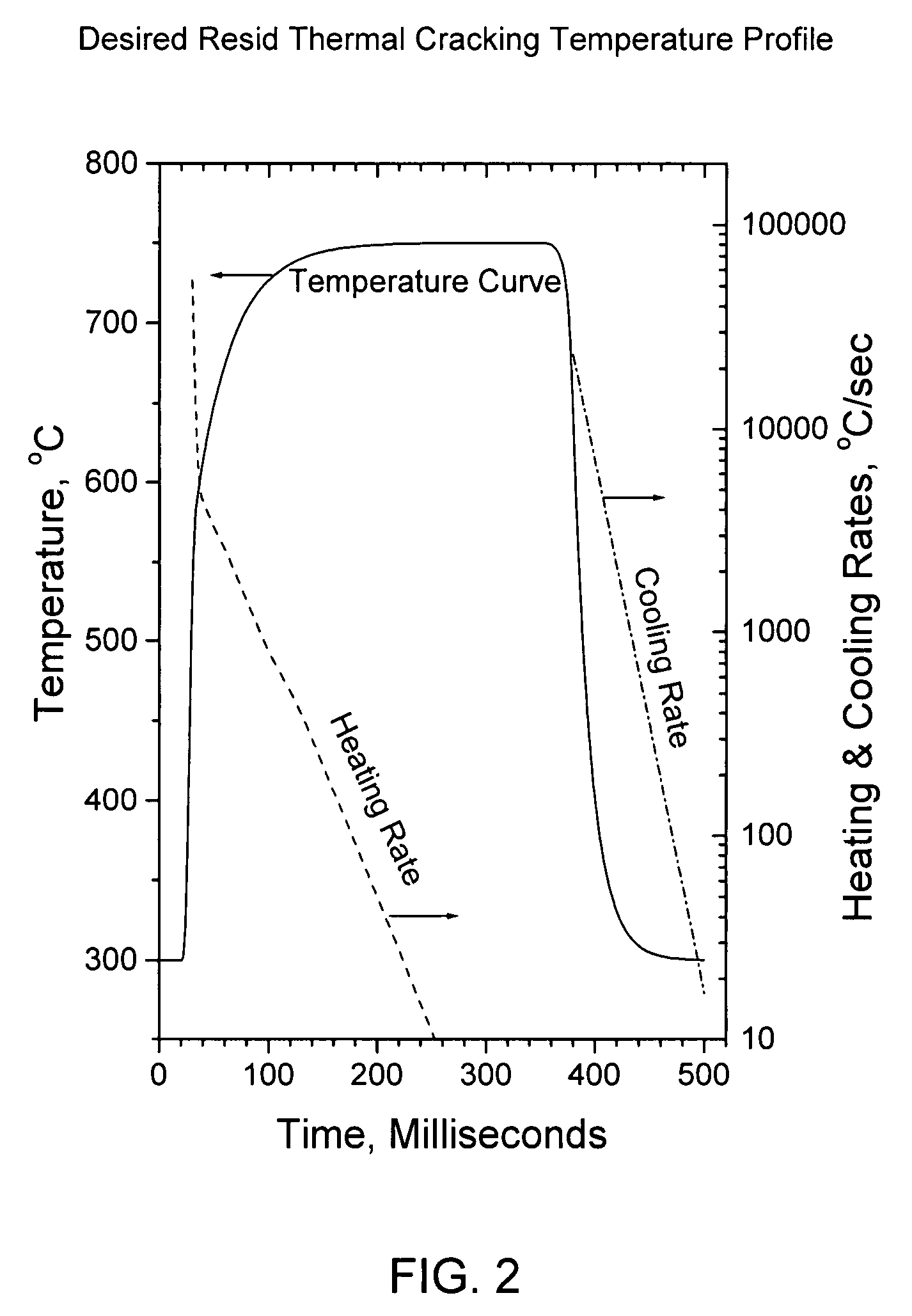
Flash pyrolosis method for carbonaceous materials
InactiveUS20070272538A1Efficient transferFast heatingThermal non-catalytic crackingDirect heating destructive distillationSufficient timeBoiling point
Methods are disclosed for pyrolizing carbonaceous materials to carbonaceous materials having lower boiling points by heating the carbonaceous material to a desired reaction temperature and holding the carbonaceous material in contact with the heat for a sufficient time to achieve the desired reaction to a lower boiling point carbonaceous materials, then rapidly cooling the desired reaction products. The heating source is a jet which will provide hot and high velocity gas streams to the carbonaceous material to be heated.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Apparatus and process for the pyrolysis of agricultural biomass
InactiveUS7943014B2Avoid cloggingPrevent escapeFluidized bed combustionCombustible gas coke oven heatingCombustion chamberFluidized bed
An integrated combustion chamber and fluidized bed pyrolysis reactor. In one embodiment, the combustion chamber is cylindrical and the pyrolysis reactor is provided annularly about the combustion chamber with an annular wall that provides a common surface for heat transfer. A lift tube in fluid communication with the pyrolysis reactor is provided within the combustion chamber for circulating biomass and an inert fluidizable media upwardly through the lift tube; this advantageously increases heat transfer and leads to more rapid pyrolysis. The media and biomass exit the lift tube into either a freeboard area of the pyrolysis reactor or into a low density region of the fluidized bed. A condensable gaseous product is produced during pyrolysis that has economic value. The apparatus and process are especially well suited to the pyrolysis of low density agricultural biomass. The apparatus is compact and particularly well suited to mobile operation.
Owner:AGRI THERM
Method of converting pyrolyzable organic materials to biocarbon
InactiveUS20100300866A1Simple methodWidespread benefit to the efficiency of the method and the biocarbon qualityCombustible gas coke oven heatingCarbon compoundsVolatilesCarbonization
A method of forming a pyrolysed biocarbon from a pyrolyzable organic material is delineated. The method involves the conversion of pyrolyzable organic materials to biocarbon for subsequent use. A carbonization circuit is employed with individual feedstock segments being advanced through the circuit. The method facilitates user manipulation of rate of advancement of the feedstock through the circuit, selective collation of volatiles from pyrolyzing feedstock, selective exposure of predetermined feedstock segments to collated volatiles as well as thermal recovery and redistribution as desired by the user. This results in the capacity for a customizable biocarbon product, the latter being an auxiliary feature of the methodology.
Owner:ALTERNA ENERGY
Method of producing charcoal, conditioned fuel gas and potassium from biomass
InactiveUS7226566B2Reduce productionSuitable for useLiquid degasificationSolid waste disposalPotassiumProcess engineering
Owner:CSA ENERGY
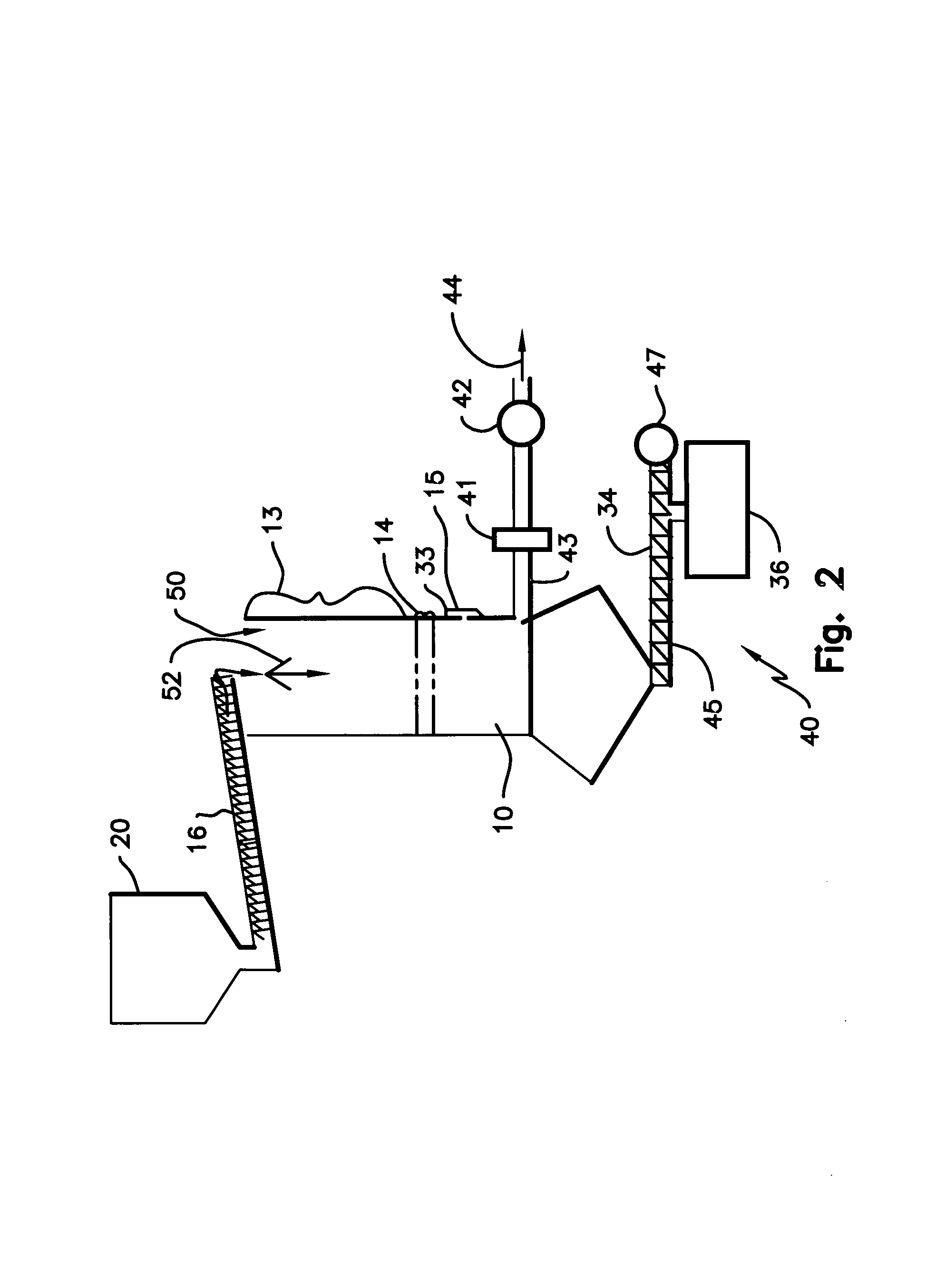
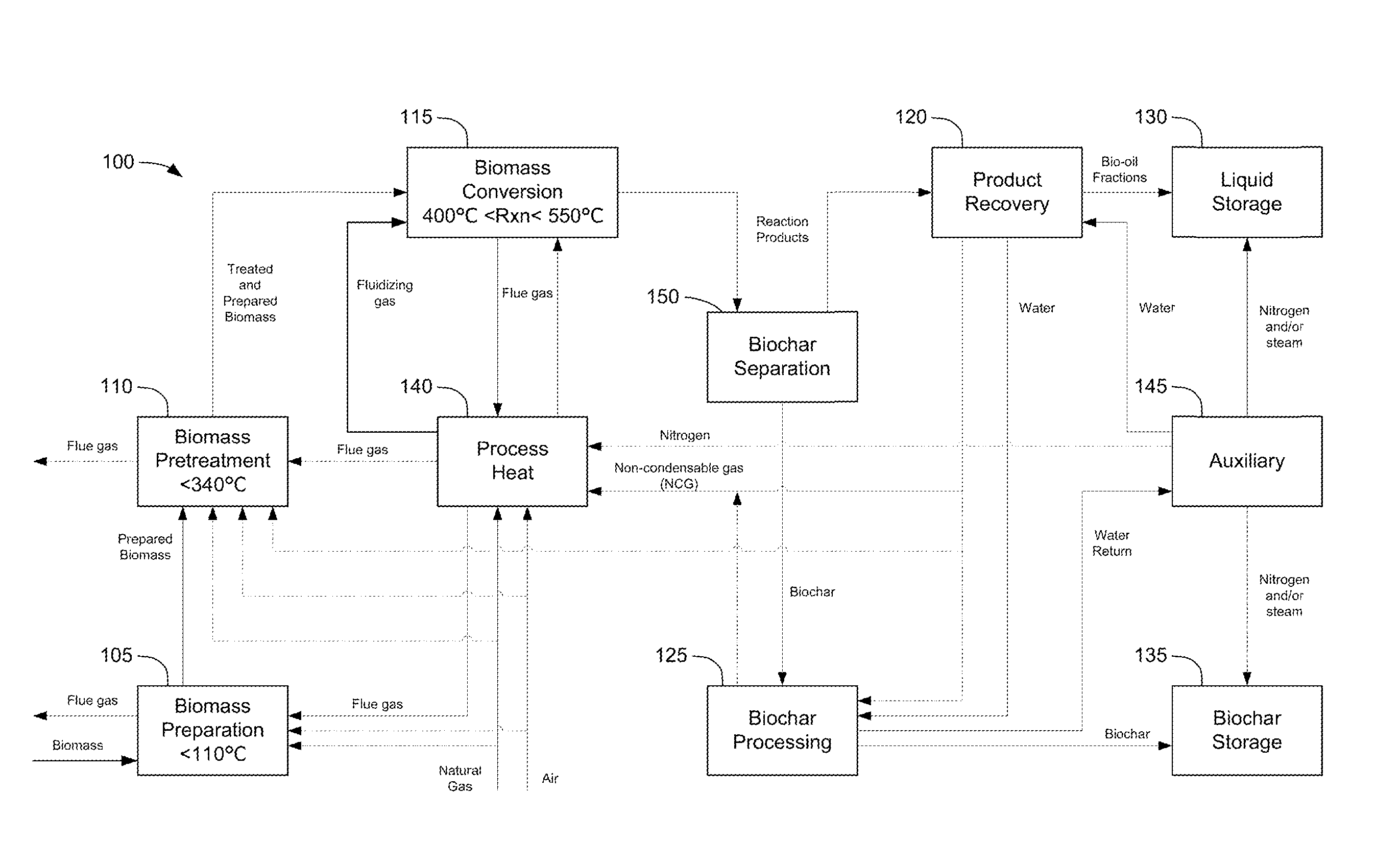
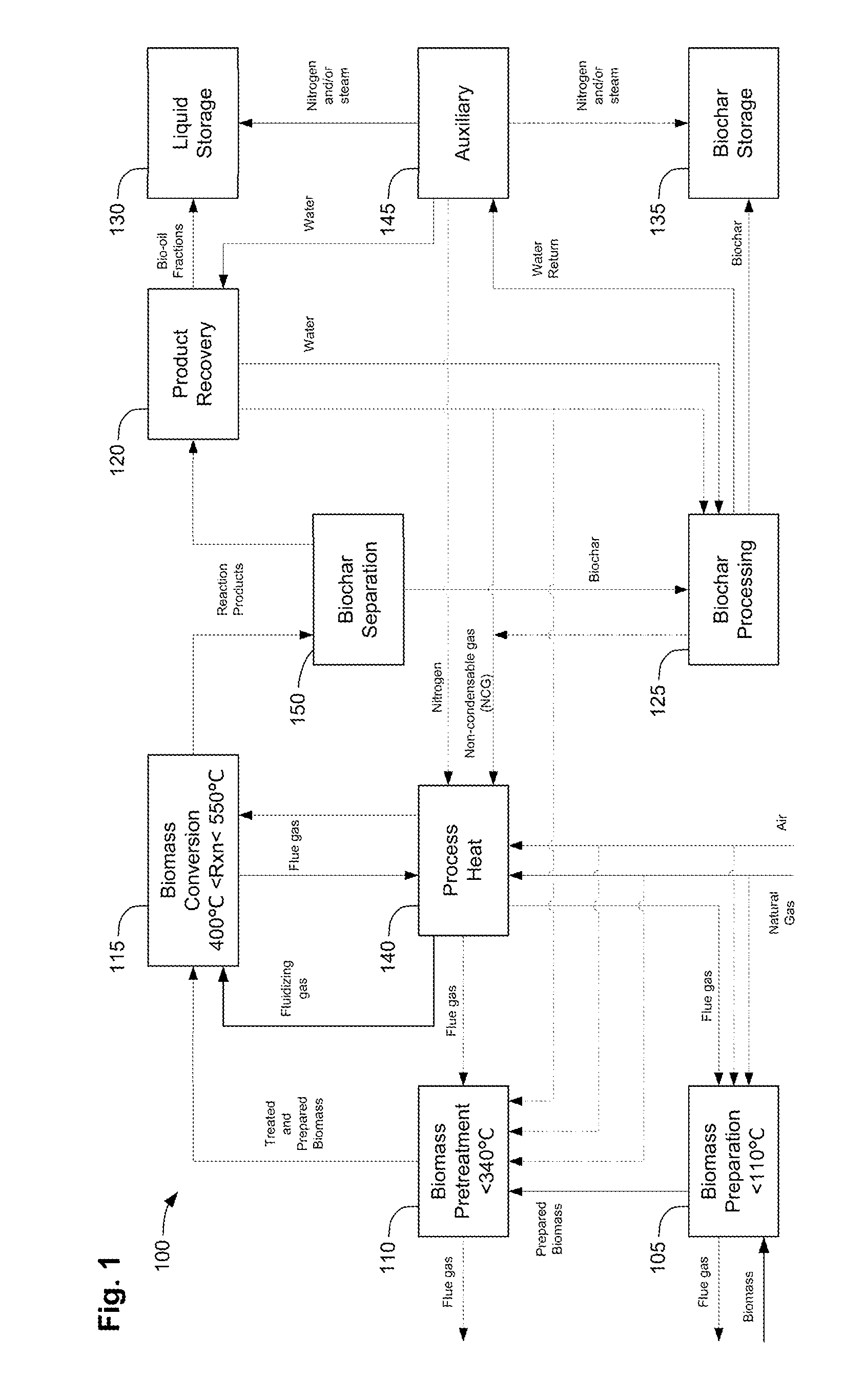
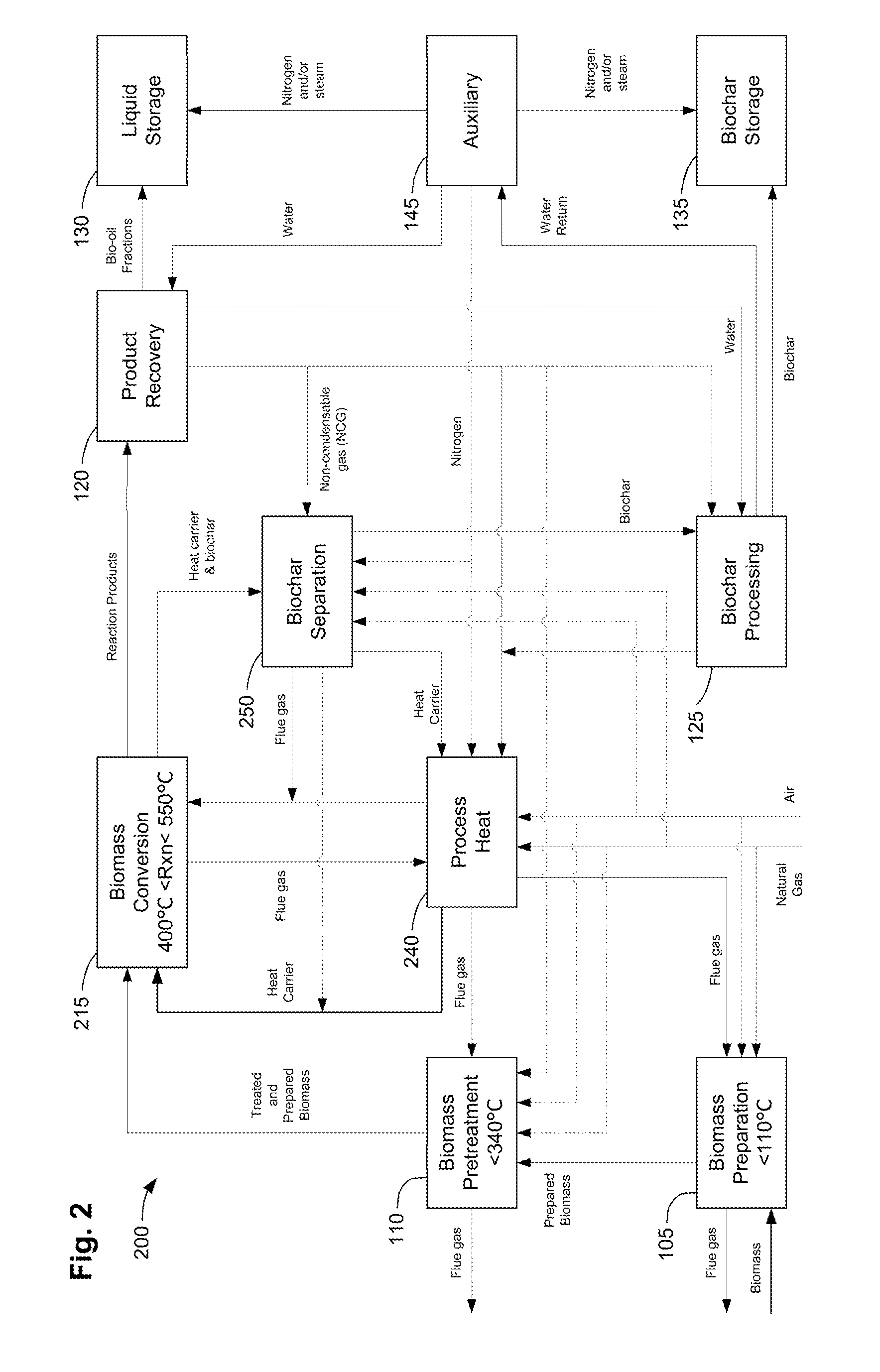
Methods for integrated fast pyrolysis processing of biomass
ActiveUS8100990B2Minimizes water contentImprove collection efficiencyDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsPre treatmentSafe handling
Methods, process, apparatus, equipment, and systems are disclosed for converting biomass into bio-oil fractions for chemicals, materials, feedstocks and fuels using a low-cost, integrated fast pyrolysis system. The system improves upon prior art by creating stable, bio-oil fractions which have unique properties that make them individually superior to conventional bio-oil. The invention enables water and low-molecular weight compounds to be separated into a final value-added fraction suitable for upgrading or extracting into value-added chemicals, fuels and water. Initial bio-oil fractions from the process are chemically distinct, have low-water content and acidity which reduces processing costs normally associated with conventional bio-oil post-production upgrading since fewer separation steps, milder processing conditions and lower auxiliary inputs are required. Biochar is stabilized so that it can be handled safely. The integrated fast pyrolysis process includes biomass storage, preparation, pretreatment, and conversion, product recovery and processing to create and store stable biochar and bio-oil fractions.
Owner:AVELLO BIOENERGY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com