Patents
Literature
1867results about "Solid separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
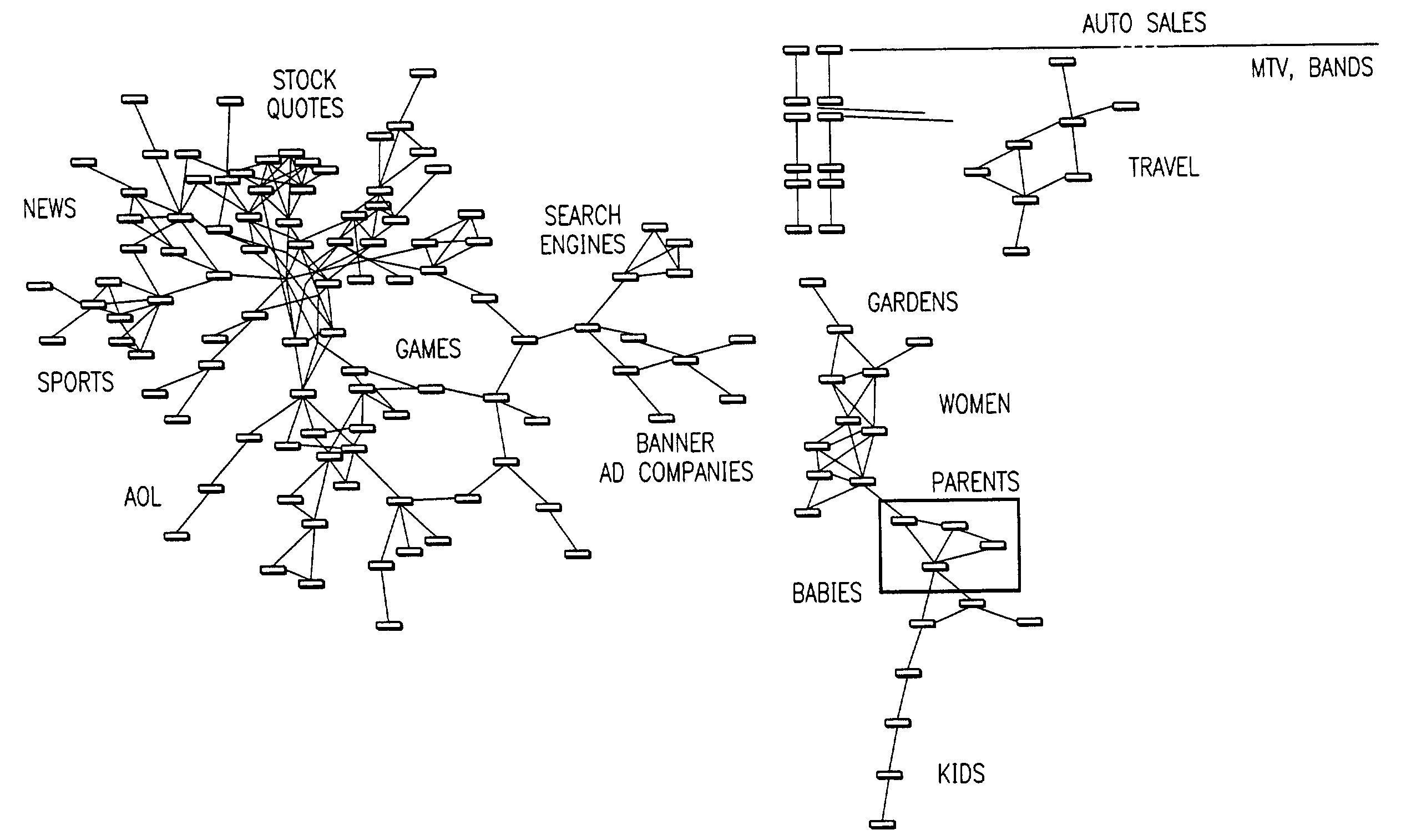
Visualization and analysis of user clickpaths
Methods and data processing system readable media have been created to graph user clickstream data over a network or at a network site to yield meaningful and visually esthetic information. In one set of embodiments, the method can comprise (i) performing a significance test on data from a network log and generating significance results. The method can also comprise (ii) determining which of network addresses and clicktrails between network addresses meet a traffic flow criterion. The data that meet a significance criterion, traffic criterion, or both can form (iii) graphable addresses and relationships. The method can further comprise (iv) generating statistics about the graphable addresses and relationships. The method can still further comprise (v) generating a graph based on the statistics about the graphable addresses and relationships, and (vi) changing any or all of the traffic flow, significance criterion, and statistics being computed, and regenerating the graph.
Owner:OPEN TEXT SA ULC
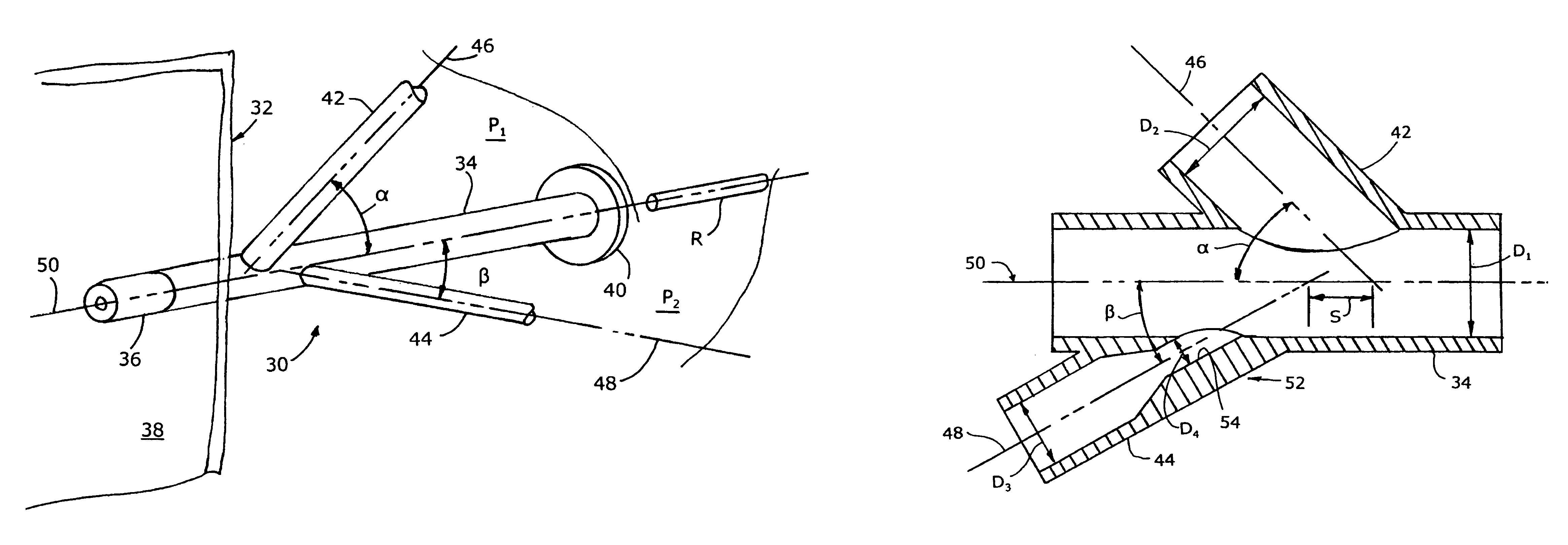
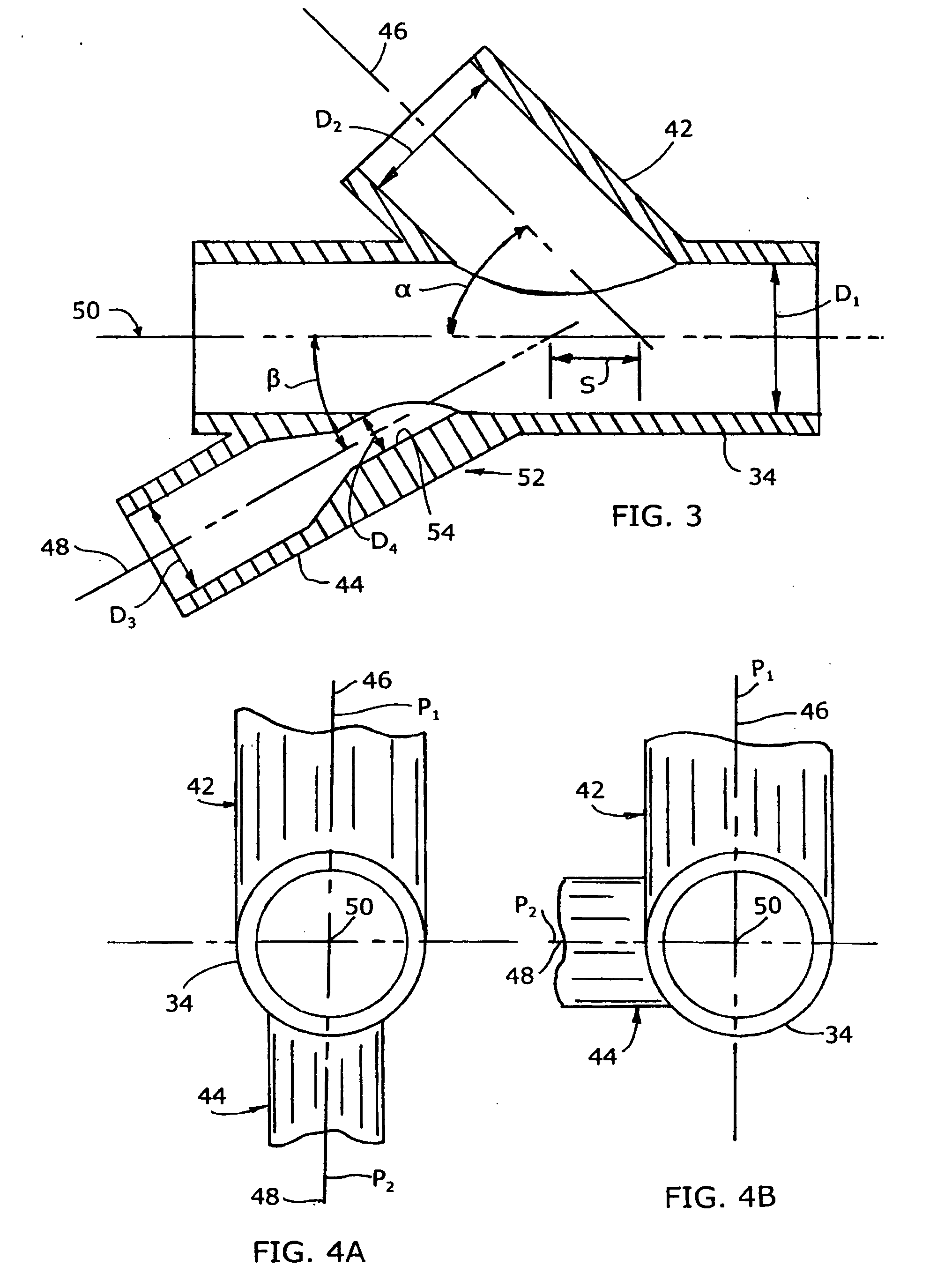
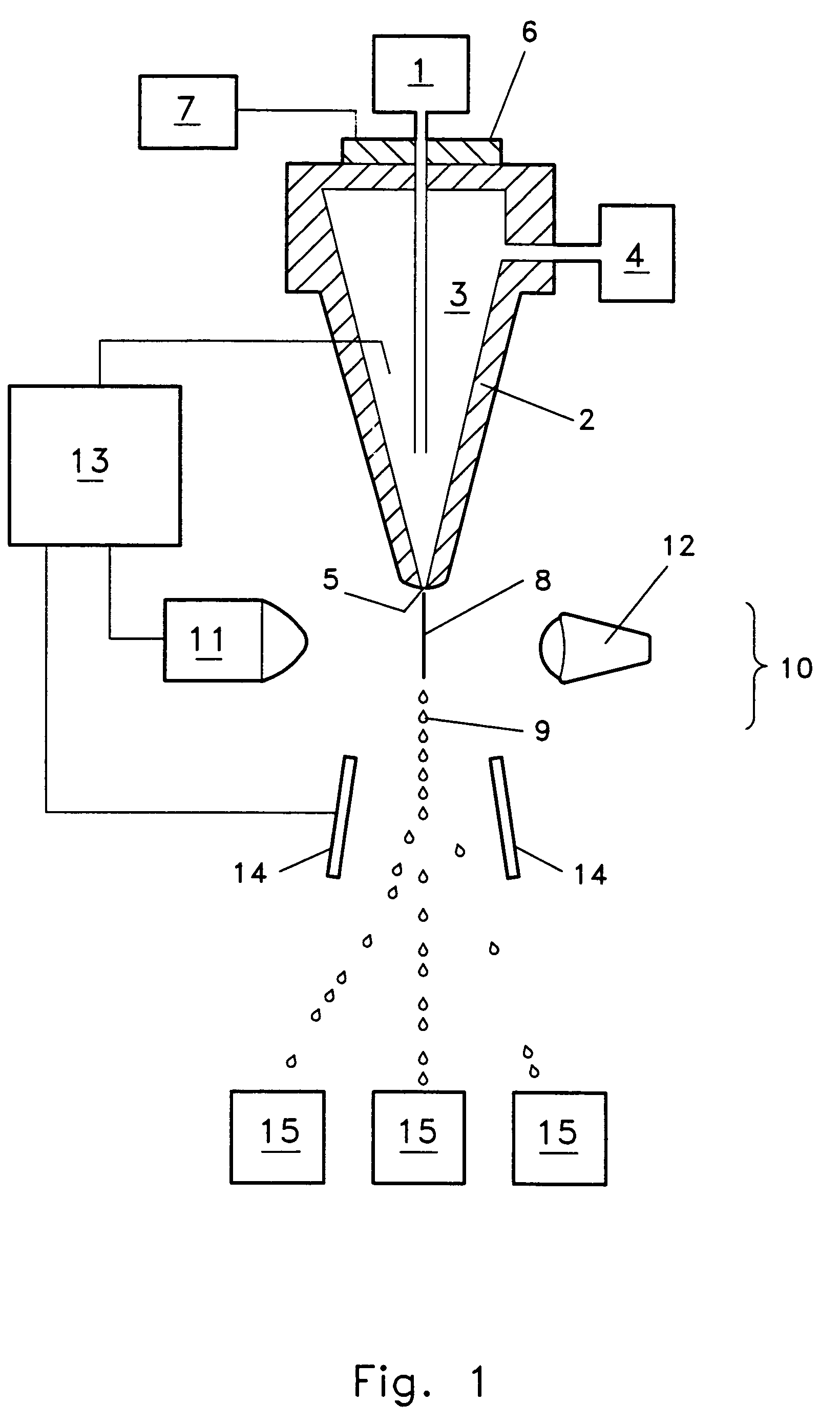
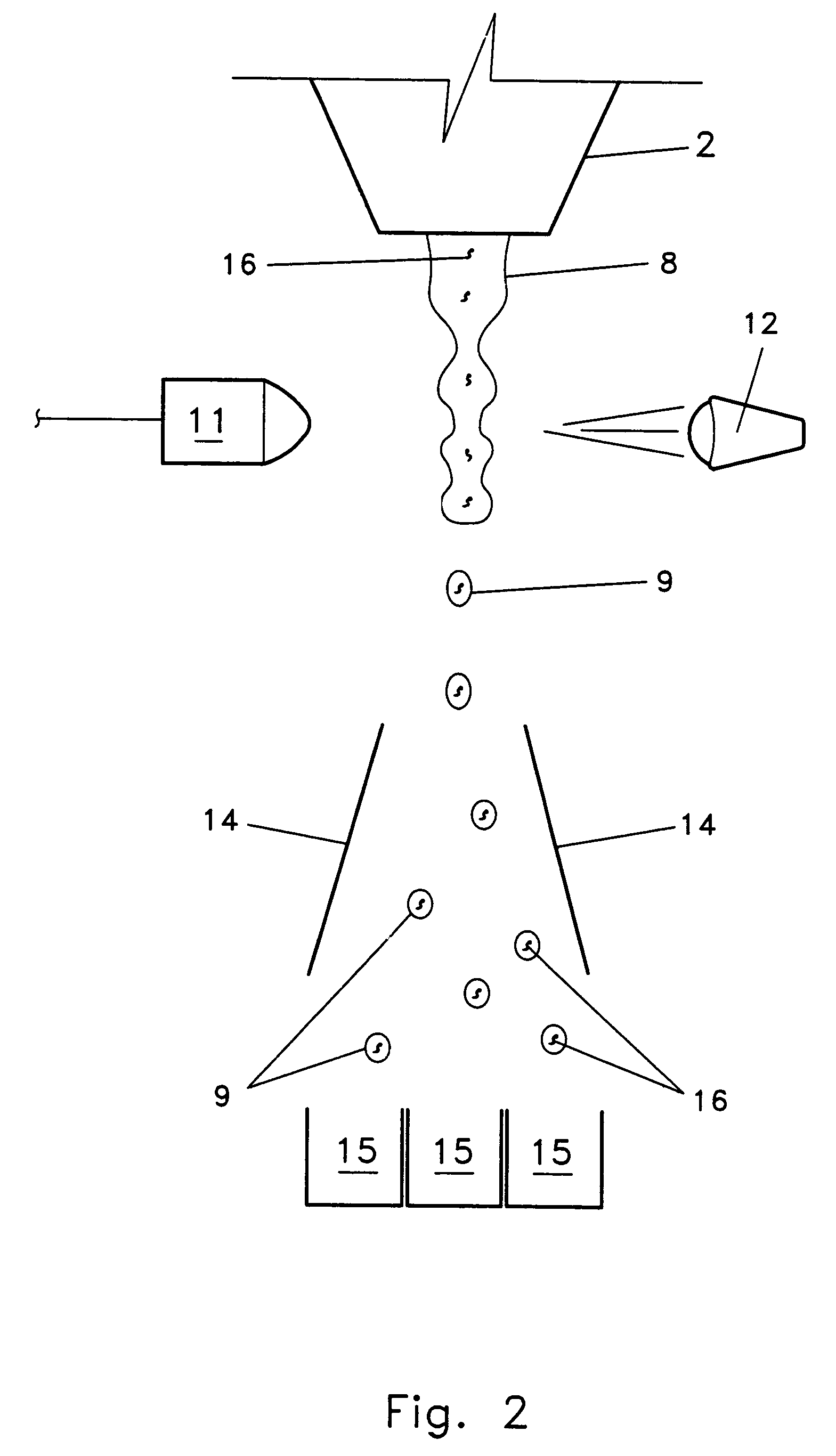
Mixing arrangement for atomizing nozzle in multi-phase flow
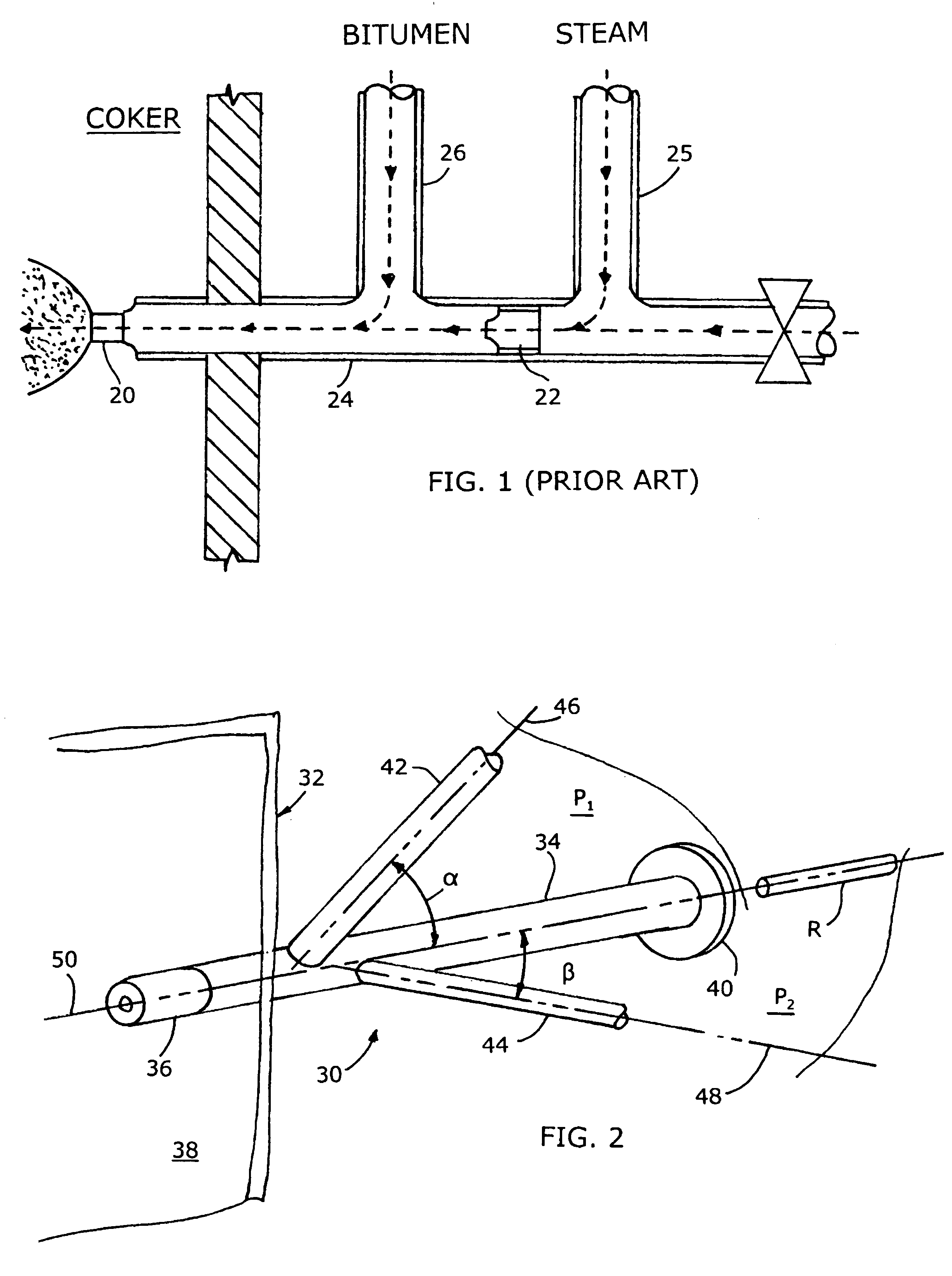
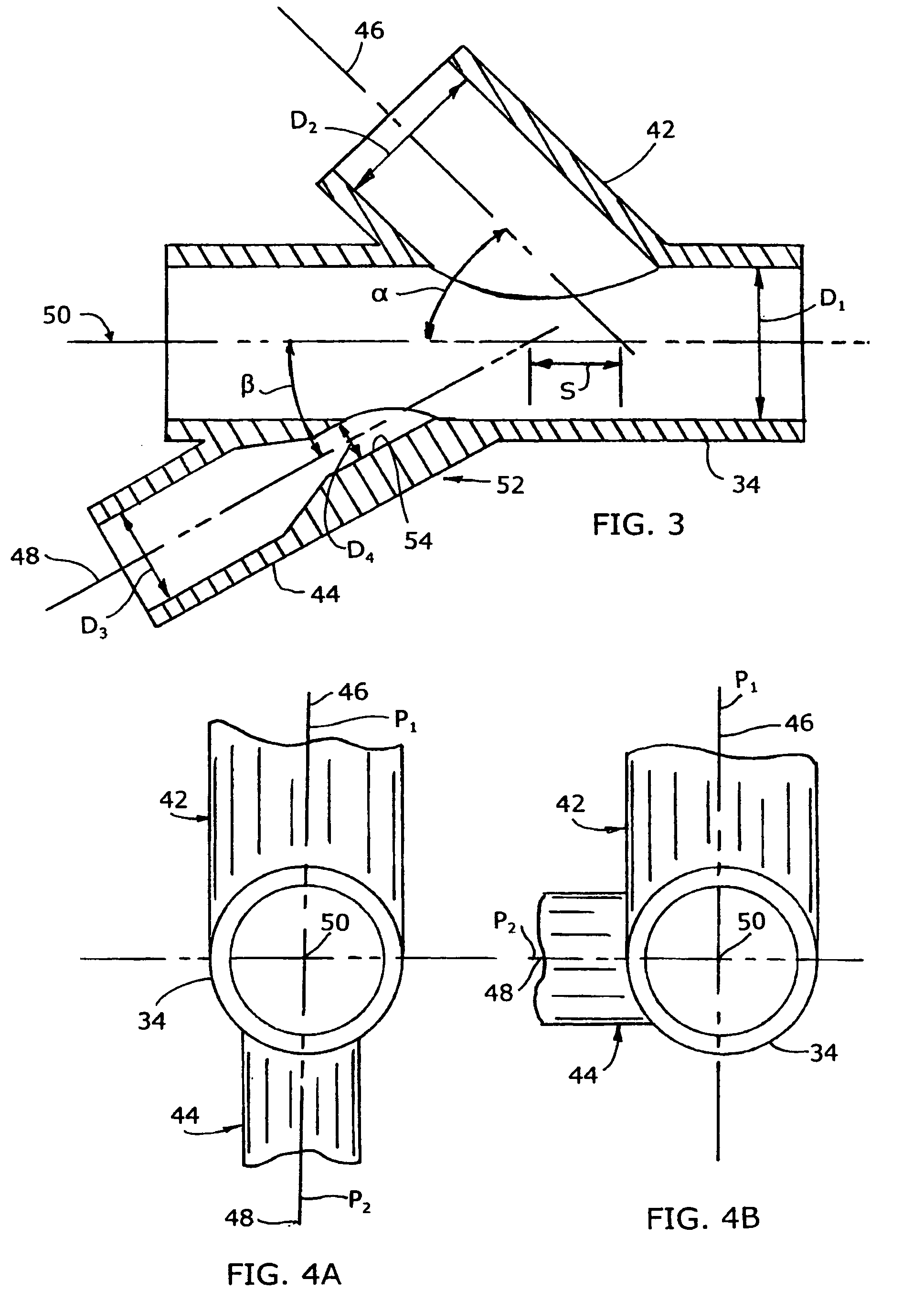
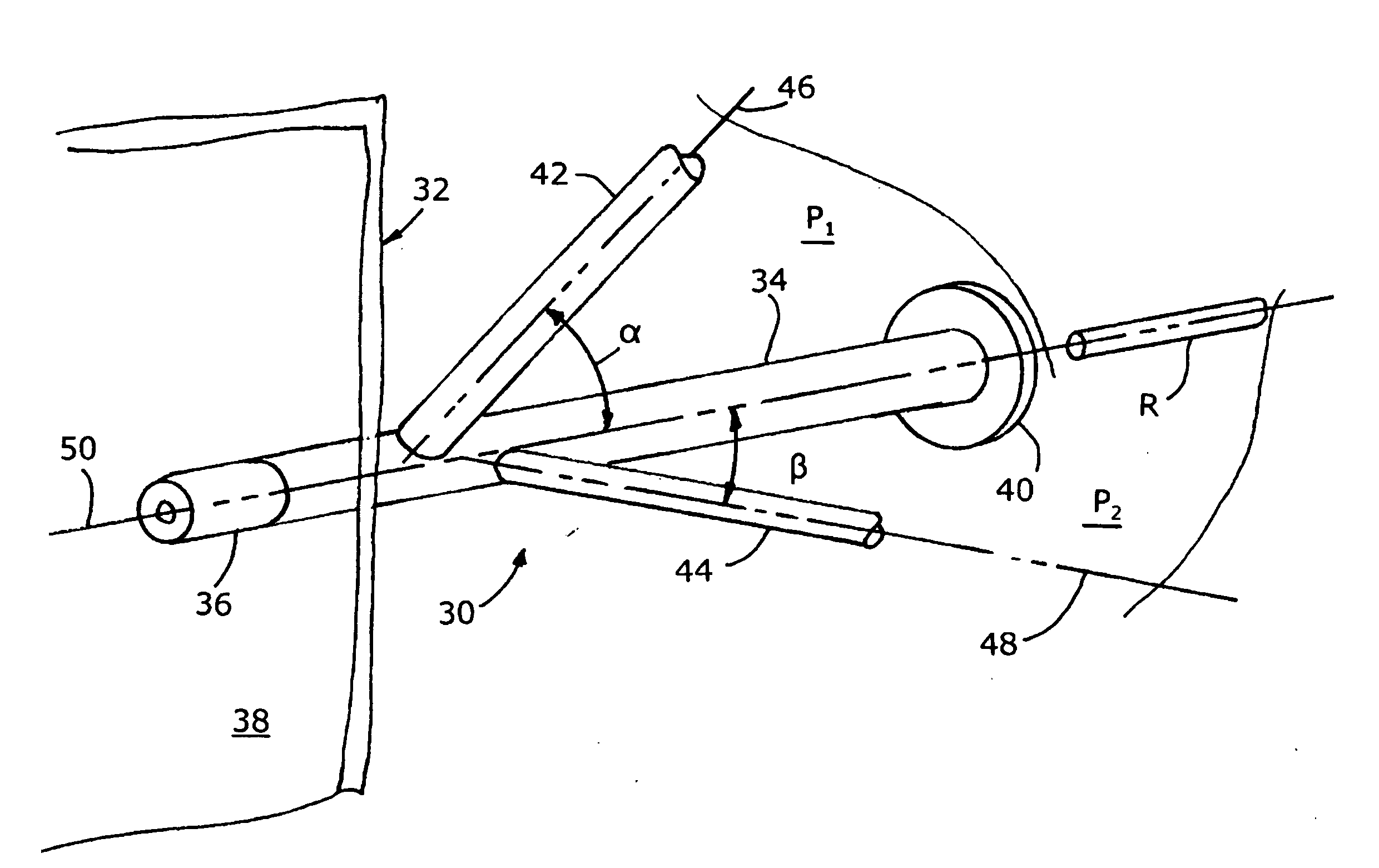
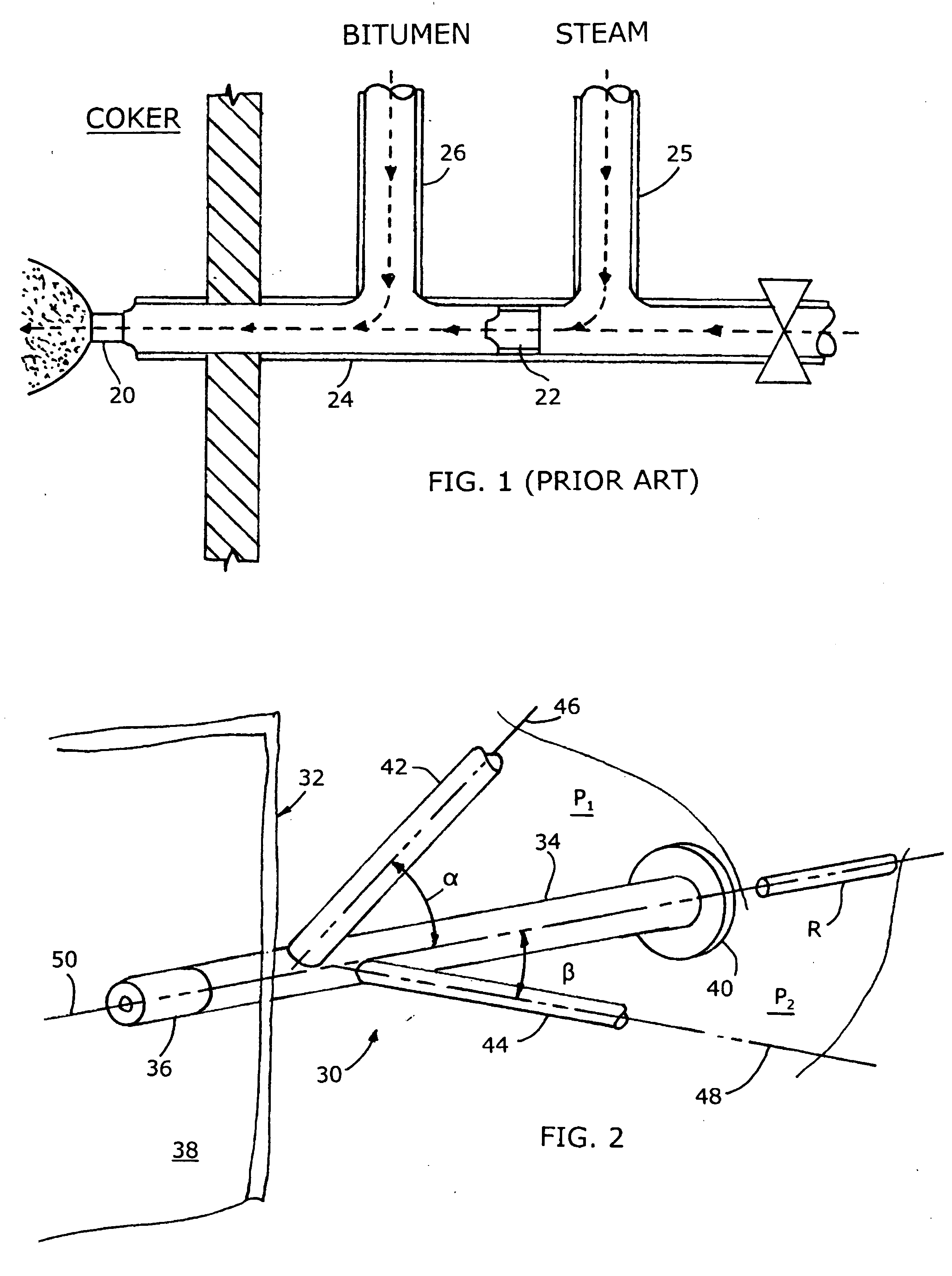
ActiveUS7140558B2Smooth transitionEasy to processCharging-discharging device combinationsFlow mixersAcute angleShortest distance
The invention relates to an improved mixing arrangement for, primarily, moving bitumen in steam from sources of such bitumen and steam to a reactor or coker for further processing of the bitumen into petroleum products. The invention provides a main conduit connected to an atomizing nozzle mounted in a wall of the reactor and first and second conduits for flowing bitumen and steam respectively into the main conduit. The first conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 45° and the second conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 30°. The second conduit is positioned upstream of the first conduit by a short distance of about 23 mm and may be angled radially relative to the first conduit by any angle, although a 90° angle is preferred. A flow accelerating nozzle is located in the second conduit adjacent the entrance therefrom into the main conduit The arrangement of the invention improves the flow characteristics of 2-phase material flowing to the atomizing nozzle, reducing pulsations in the main conduit and improving the resulting atomization of the bitumen in the reactor.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +1
Mixing arrangement for atomizing nozzle in multi-phase flow
ActiveUS20050001062A1Smooth transitionEasy to processCharging-discharging device combinationsFlow mixersAcute angleShortest distance
The invention relates to an improved mixing arrangement for, primarily, moving bitumen in steam from sources of such bitumen and steam to a reactor or coker for further processing of the bitumen into petroleum products. The invention provides a main conduit connected to an atomizing nozzle mounted in a wall of the reactor and first and second conduits for flowing bitumen and steam respectively into the main conduit. The first conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 45° and the second conduit is angled relative to the main conduit at an acute angle of about 30°. The second conduit is positioned downstream of the first conduit by a short distance of about 23 mm and may be angled radially relative to the first conduit by any angle, although a 90° angle is preferred. A flow accelerating nozzle is located in the second conduit adjacent the entrance therefrom into the main conduit. The arrangement of the invention improves the flow characteristics of 2-phase material flowing to the atomizing nozzle, reducing pulsations in the main conduit and improving the resulting atomization of the bitumen in the reactor.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +1
Reversible electrodeposition devices and associated electrochemical media
InactiveUS7193764B2Improve electrochemical performanceSolid separationTenebresent compositionsEngineeringConductive materials
The present invention is directed to a reversible electrodeposition device comprising: a first substrate having an electrically conductive material associated therewith; a second substrate having an electrically conductive material associated therewith; a nucleation layer at least partially covering at least one of the electrically conductive materials of the first and second substrates; an electrochemical medium contained within a chamber positioned between the first and second substrates.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
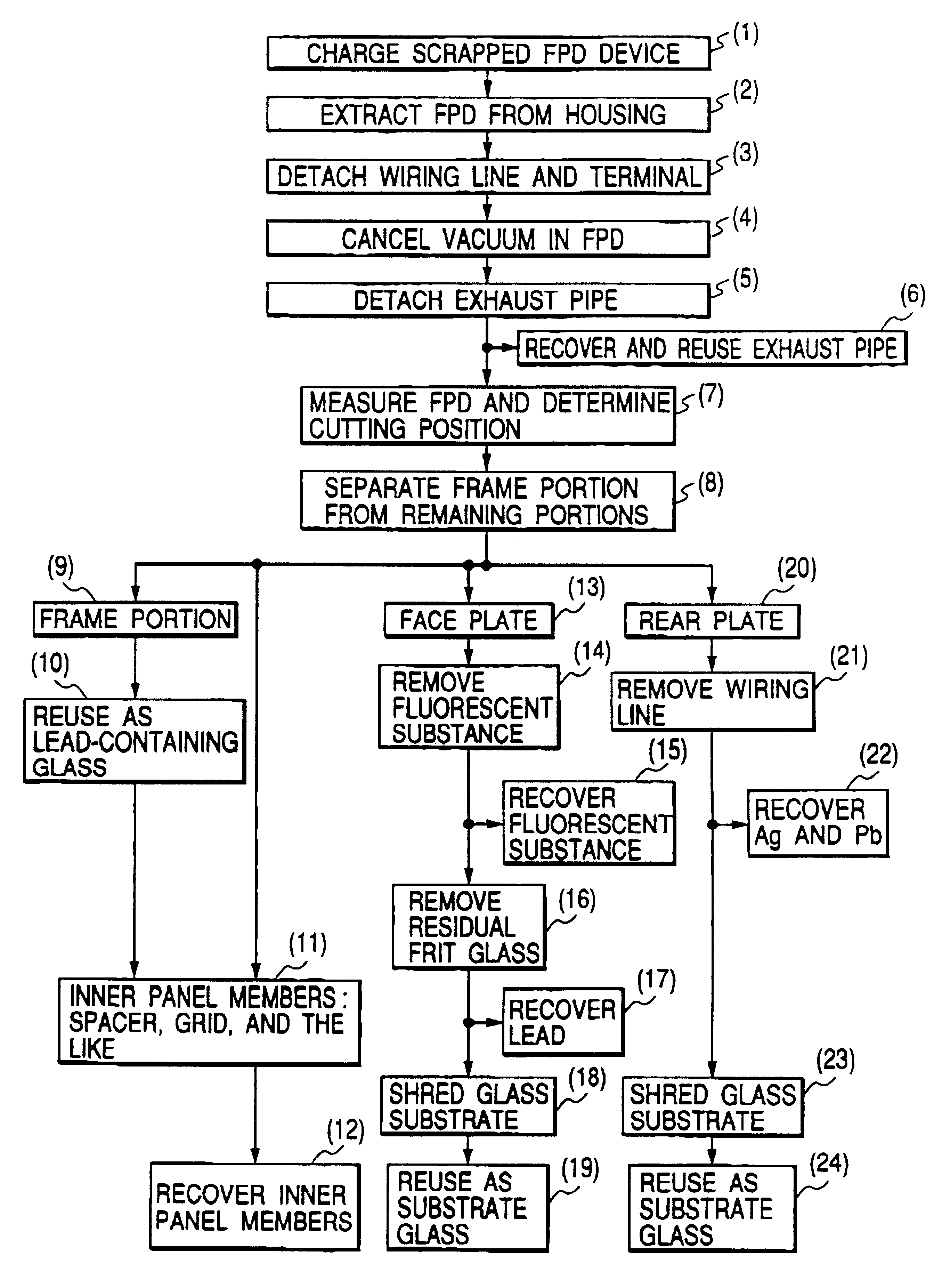
Image display apparatus, disassembly processing method therefor, and component recovery method
InactiveUS6632113B1No pressureAvoid secondary damageElectric discharge tubesGlass recyclingRecovery methodFrit
To reuse glass used in a flat panel display, processing suitable for global environment such as processing of separating a lead component must be realized. A disassembly processing method for a flat panel display having a structure in which a face plate and rear plate mainly containing glass are airtightly joined via a frame with frit glass is characterized by including the step of separating the face plate and rear plate joined with the frit glass. The separation step is characterized by separating the face plate and rear plate by cutting, dissolution, or melting.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CANON KK
Process and apparatus for treating tailings
ActiveUS20050150844A1Easy to separateMaximize efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolid separationSolventOil sands
Processes and apparatus for the treatment of product streams from mineral processing operations, including the treatment of tailings which result from oil sand processing operations. The processes and apparatus relate to the recovery of a diluent solvent from bitumen froth tailings and to the thickening of tailings from a bitumen froth stream and a middlings stream resulting from an oil sand extraction process. In one aspect the processes and apparatus relate particularly to the recycling of product streams to maximize process efficiencies. In a second aspect the processes and apparatus relate particularly to the thickening of tailings to produce an underflow component, a clarified overflow component and an unclarified overflow component.
Owner:TRUENORTH ENERGY CORP
Apparatus and process for mediated electrochemical oxidation of materials
A unique apparatus unique apparatus and process that uses mediated electrochemical oxidation (MEO) for: (1) Destruction of: a) nearly all organic solid, liquid, and gases materials, except fluorinated hydrocarbons; b) all biological solid, liquid, and gases materials; c) and / or dissolution and decontamination (such as cleaning equipment and containers, etc.) of nearly all inorganic solid, liquid, or gas where higher oxidation states exist which includes, but is not limited to, halogenated inorganic compounds (except fluorinated), inorganic pesticides and herbicides, inorganic fertilizers, carbon residues, inorganic carbon compounds, mineral formations, mining tailings, inorganic salts, metals and metal compounds, etc.); and d) combined materials (e.g. a mixture of any of the foregoing with each other); henceforth collectively referred to as materials. (2) Sterilization / disinfection of equipment, glassware, etc., by destroying all existing infectious materials. (3) Dissolution of transuranic / actinide materials and / or destruction of the oxidizable components in the hazardous waste portion of mixed waste. (4) Generation of hydrogen and oxygen from MEO of materials. (5) Alteration of organic, biological, and inorganic materials by MEO to produce other compounds from these materials. The materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the materials with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the materials molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable material species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100° C. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Method and Apparatus for Microwave Reduction of Organic Compounds
InactiveUS20070102279A1Maximum protectionElectrical coke oven heatingSolid waste disposalEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
The invention described herein generally pertains to utilization of high power density microwave energy to reduce organic compounds to carbon and their constituents, primarily in a gaseous state. The process includes, but is not limited to, scrap tires, plastics, asphalt roofing shingles, computer waste, medical waste, municipal solid waste, construction waste, shale oil, and PCB / PAH / HCB-laden materials. The process includes the steps of feeding organic material into a microwave applicator and exposing the material to microwave energy fed from at least two linear polarized sources in non-parallel alignment to each other, and collecting the material. The at least two sources of microwave energy are from a bifurcated waveguide assembly, whose outputs are perpendicular to each other and fed through waveguide of proper impedance, such that the microwave sources are physically and electrically 90° out of phase to each other. The microwave frequency is between 894 and 1000 MHz, preferably approximately 915 MHz.
Owner:NOVAK JUDITH
Method and Device for Separating Particles
InactiveUS20080217259A1Other blood circulation devicesWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsSonificationHarmonic
The invention relates to a method and a device for separating particles using ultrasonic standing waves which are switched between two different frequencies. A second order harmonic standing wave is used together with the fundamental standing wave. If the particles are exposed to the fundamental standing wave, the forces act to collect particles at the centre. If the particles are exposed to the second order harmonic standing wave, the forces act to collect particles at the two pressure nodes at the sides. By switching the frequency between the second order harmonic standing wave and the fundamental standing wave, particles with different properties will be exposed to different accelerations and are separated into two streams.
Owner:SPECTRONIC
High purity x-chromosome bearing and y-chromosome bearing populations of spermatozoa
InactiveUS20040053243A1Improve apparent resolutionMinimizes coincidenceAnimal reproductionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysiologyLight beam
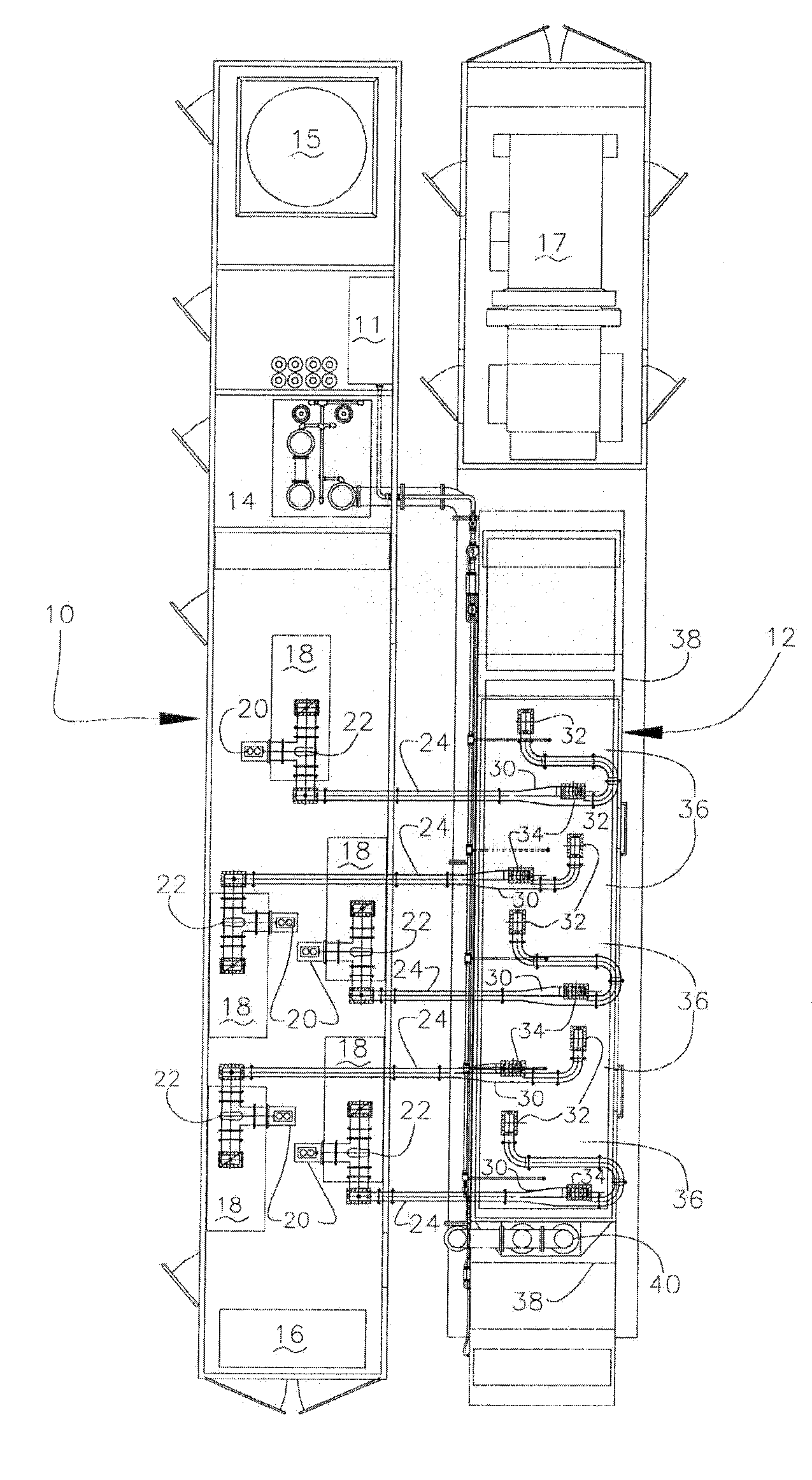
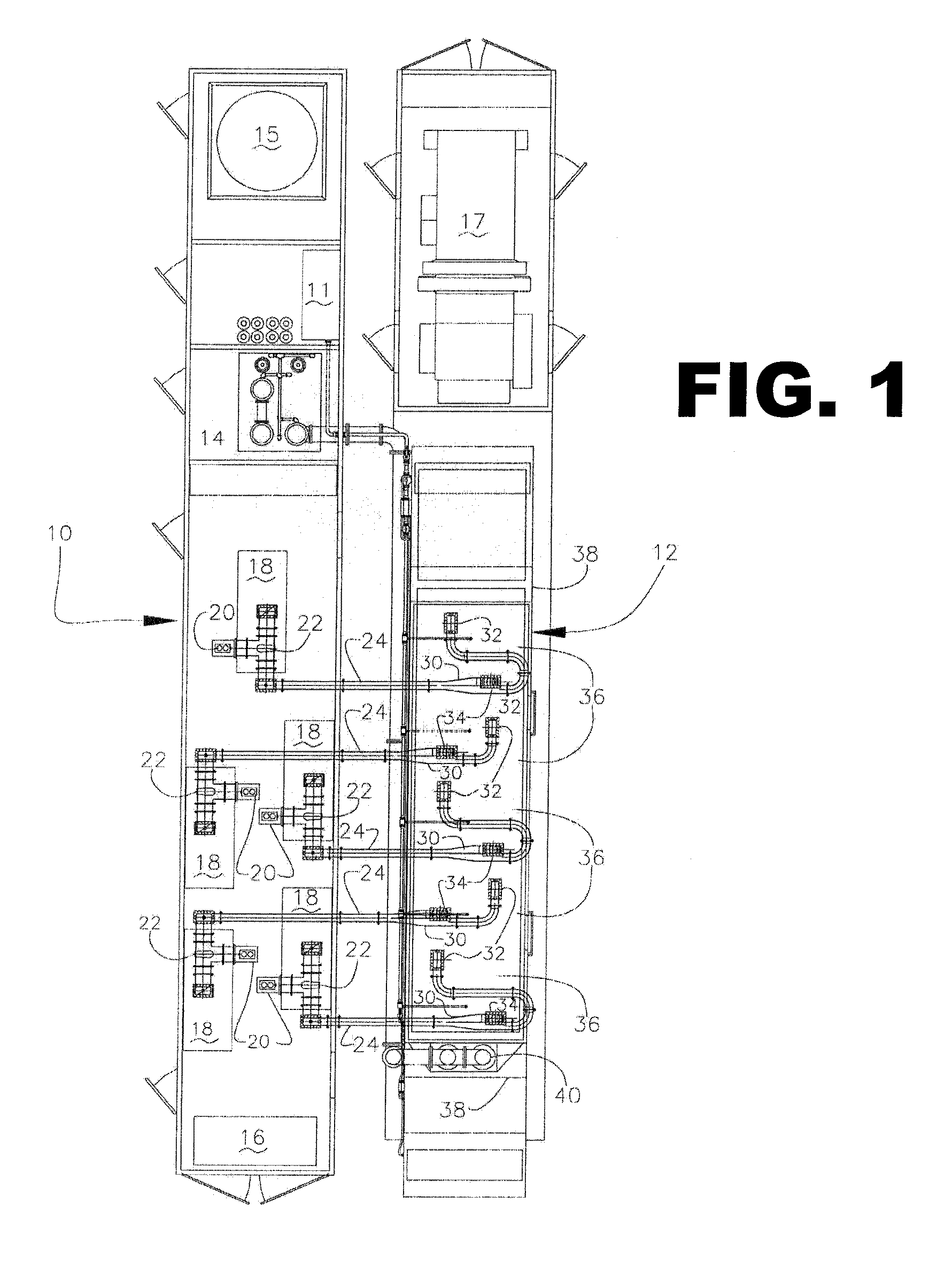
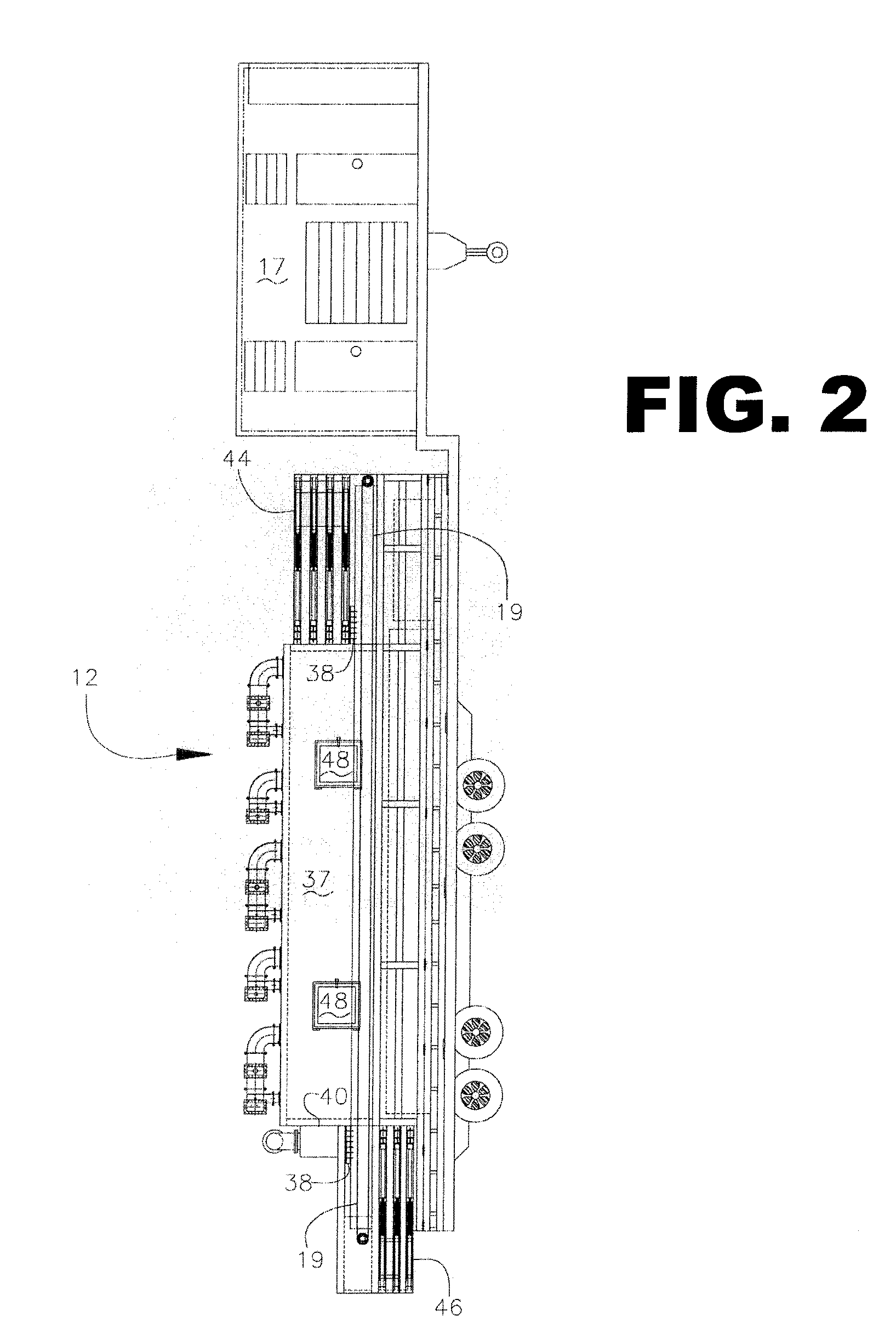
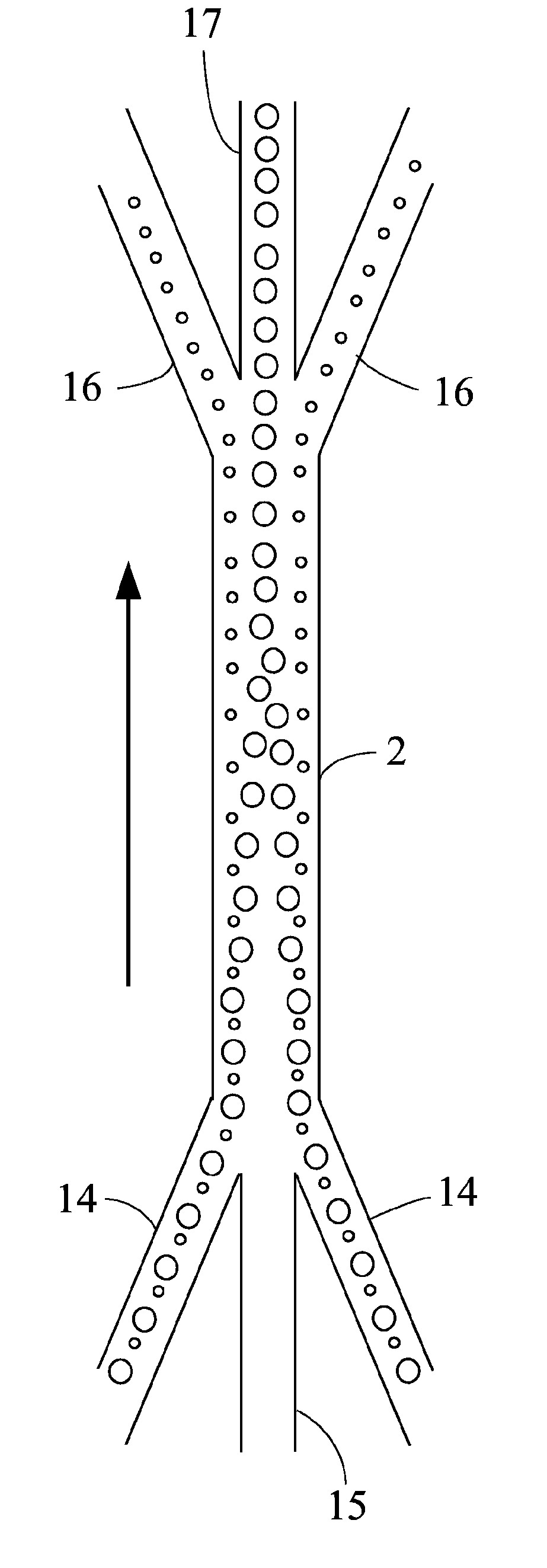
Isolated non-naturally occurring populations of spermatozoa (15) having high purity and technologies to differentiate spermatozoa (28) based on characteristics such as mass, volume, orientation, or emitted light including methods of analysis and apparatus such as beam shaping optics (30) and detectors (32).
Owner:XY
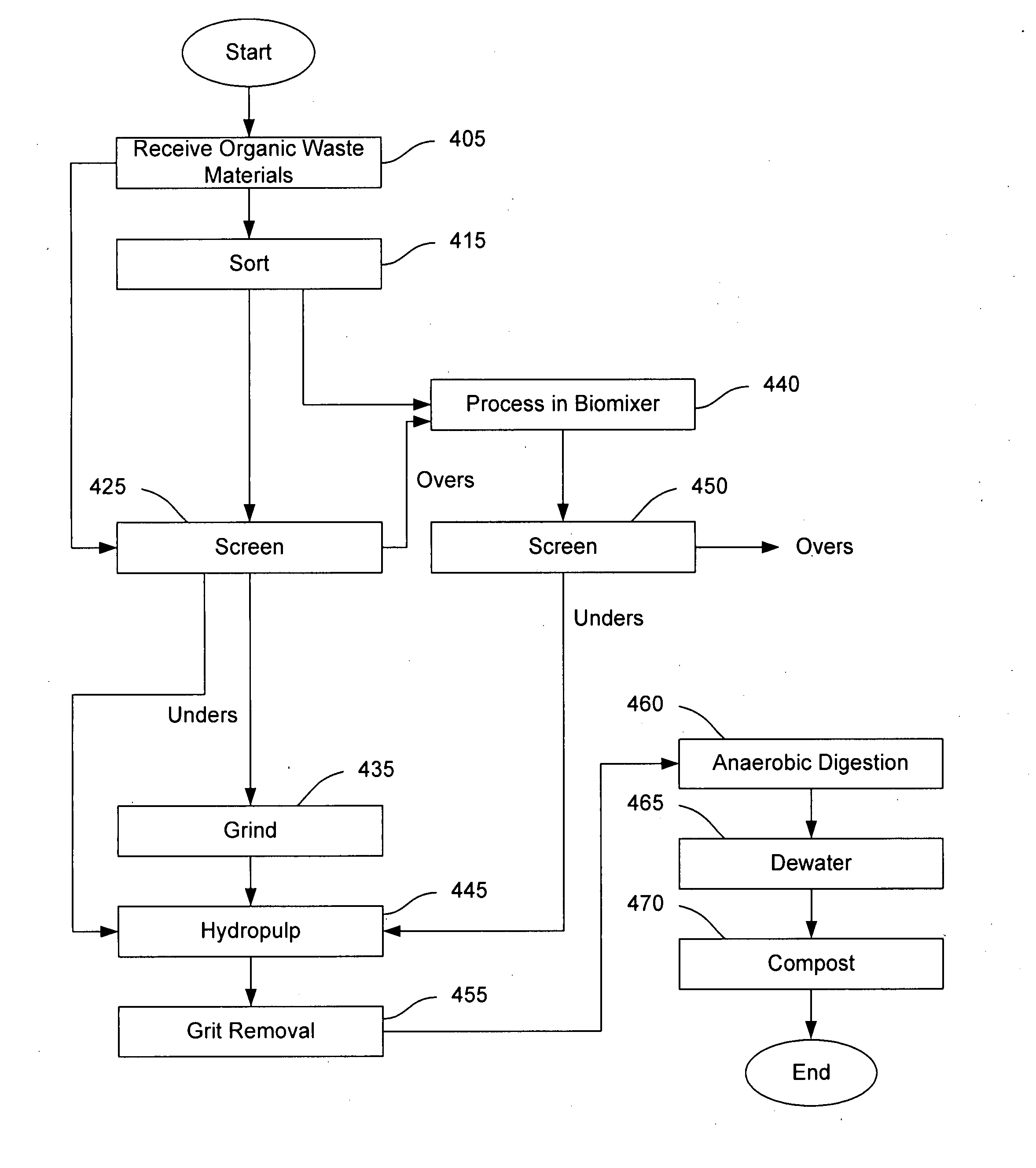
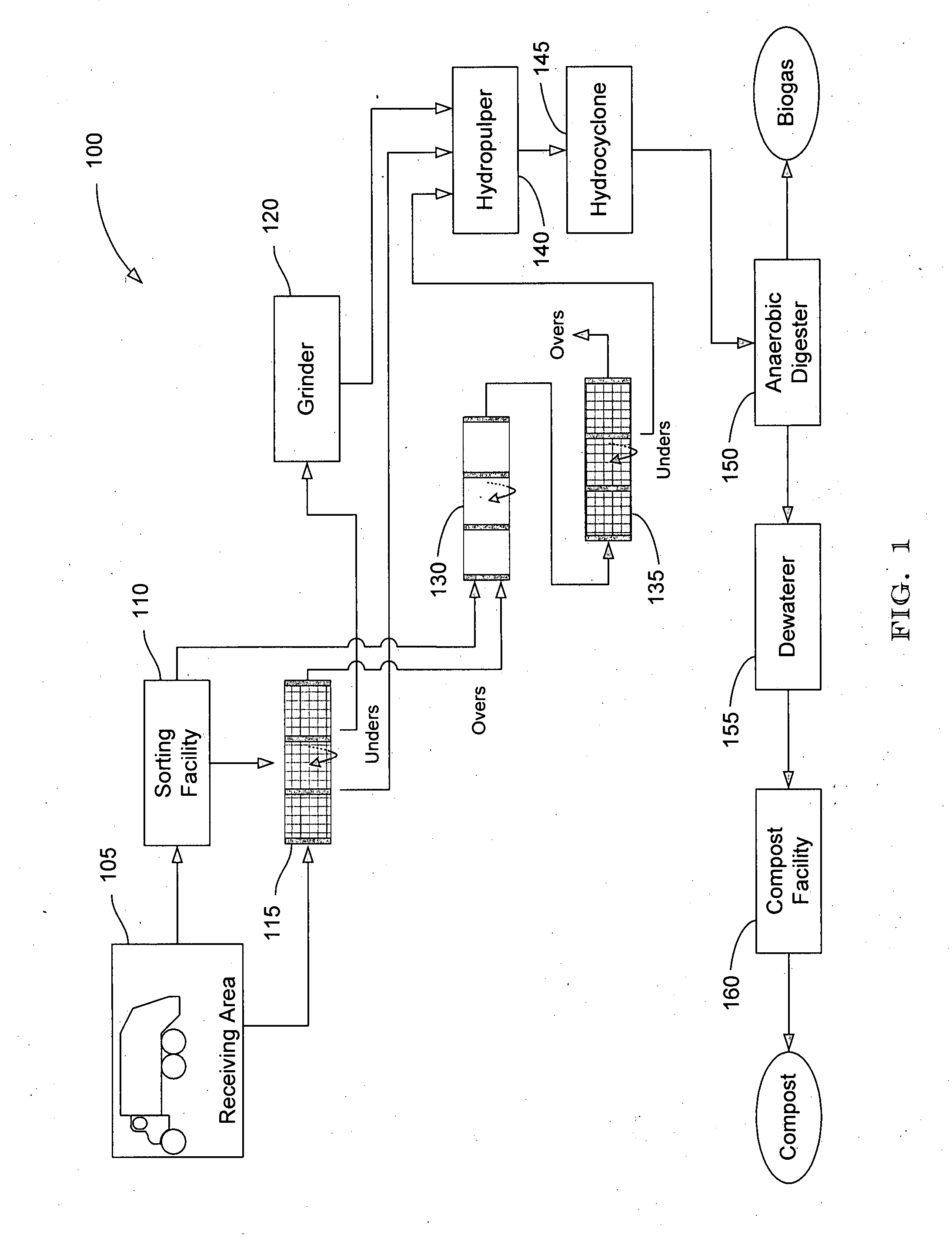
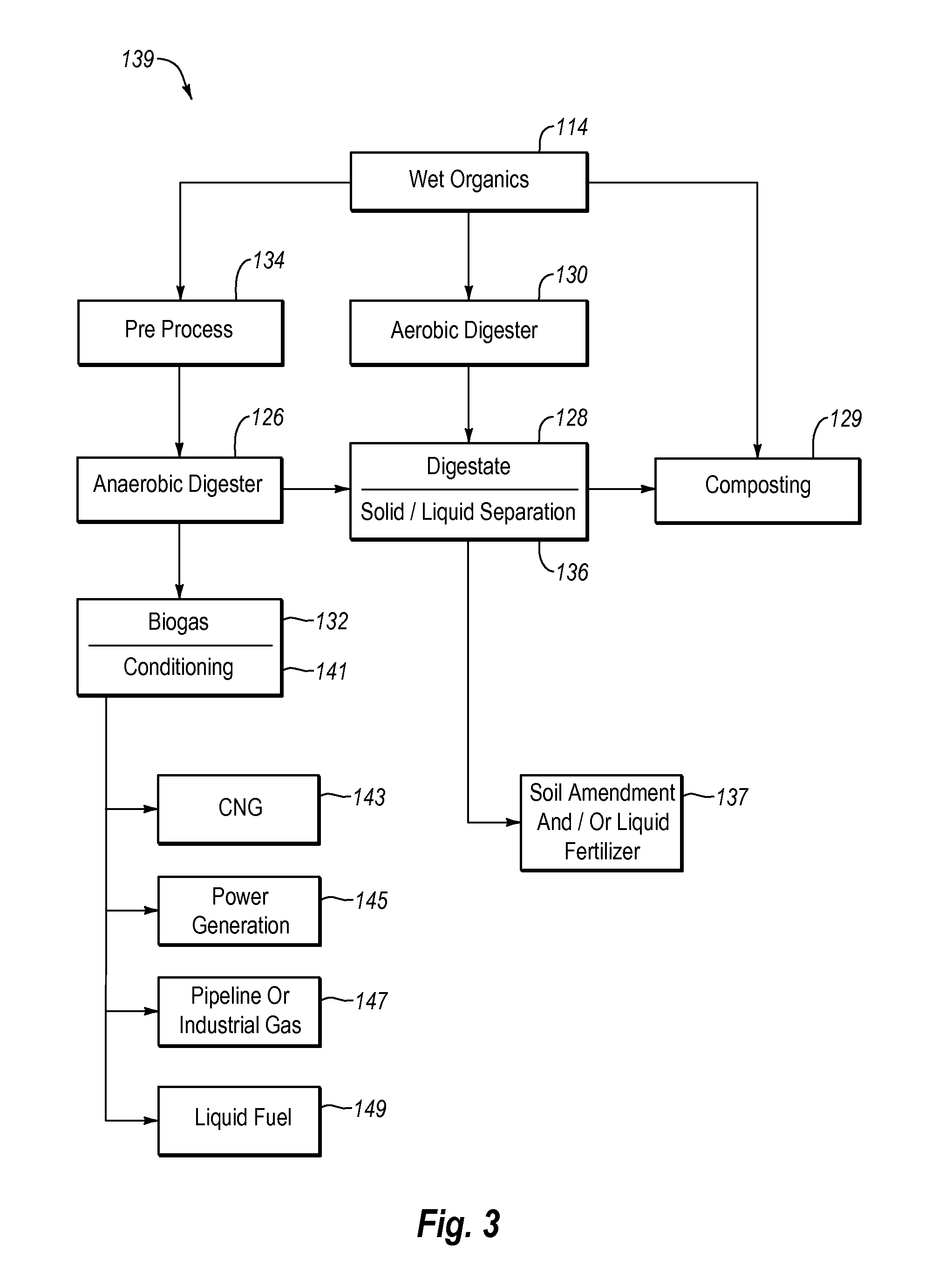
Systems and methods for converting organic waste materials into useful products
ActiveUS20080020456A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fractionProduct system
Systems and methods are provided for converting organic waste materials from a municipal waste stream to useful products. Organic waste materials having a wide range of compositions such as, for example, yard waste, food waste, paper, and the organic fraction of municipal solid waste are converted into a uniform biomass that is suitable for conversion to useful products, such as fuels. Through the use of a biomixer and a hydropulper, as well as through sorting and screening, the organic waste materials are progressively reduced in size and cleaned of contamination. The resulting uniform biomass is suitable for anaerobic digestion to produce biogas and a residual solid that is suitable for producing a high quality compost.
Owner:RECOLOGY
High purity X-chromosome bearing and Y-chromosome bearing populations of spermatozoa
InactiveUS7371517B2Image distortionHigh refractive indexAnimal reproductionMaterial analysis by optical meansX chromosomeAnalysis method
Isolated non-naturally occurring populations of spermatozoa (15) having high purity and technologies to differentiate spermatozoa (28) based on characteristics such as mass, volume, orientation, or emitted light including methods of analysis and apparatus such as beam shaping optics (30) and detectors (32).
Owner:XY
Reversible electrodeposition devices and associated electrochemical media
ActiveUS20050111070A1Improve electrochemical performanceSolid separationNon-linear opticsEngineeringConductive materials
The present invention is directed to a reversible electrodeposition device comprising: a first substrate having an electrically conductive material associated therewith; a second substrate having an electrically conductive material associated therewith; a nucleation layer at least partially covering at least one of the electrically conductive materials of the first and second substrates; an electrochemical medium contained within a chamber positioned between the first and second substrates.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
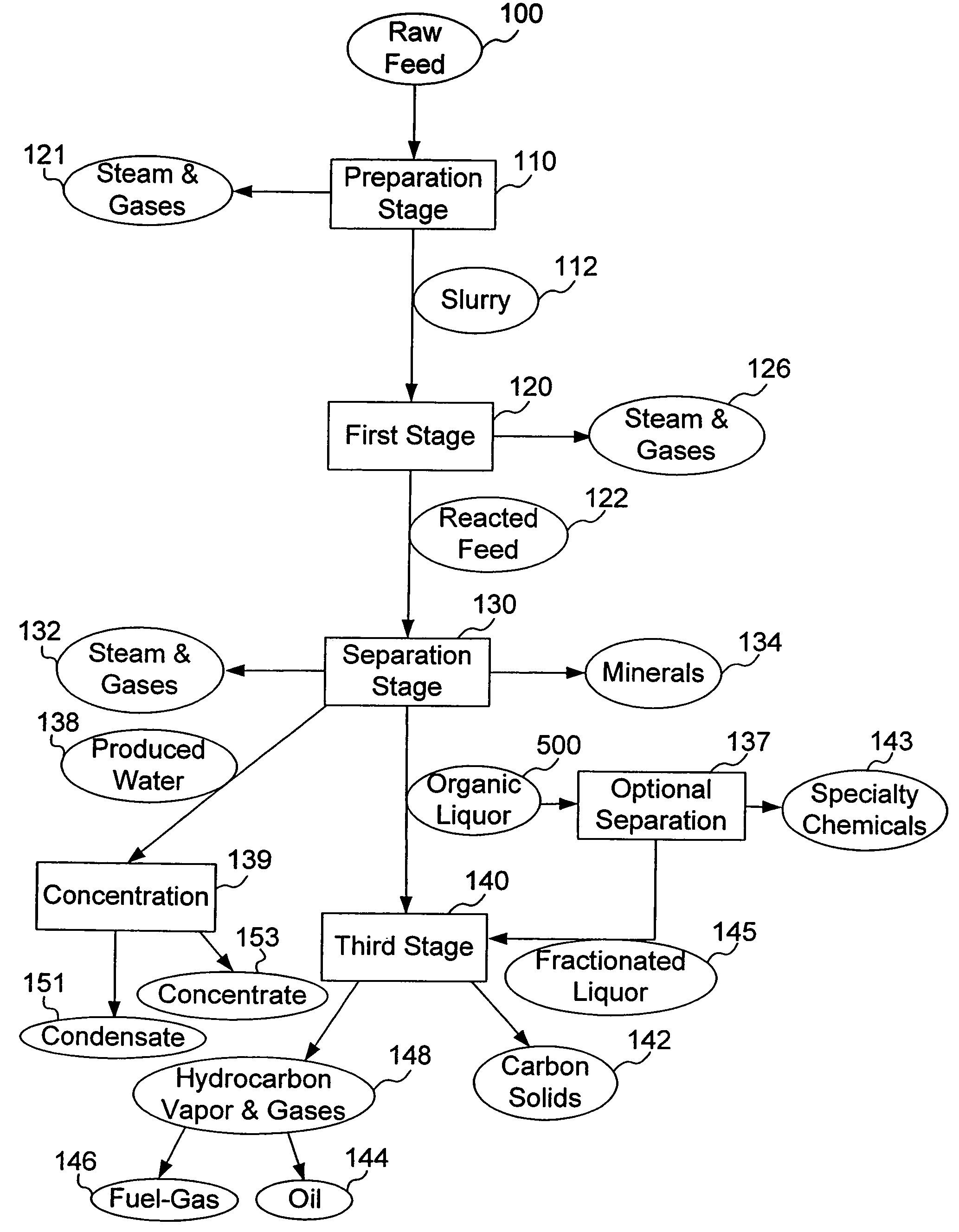
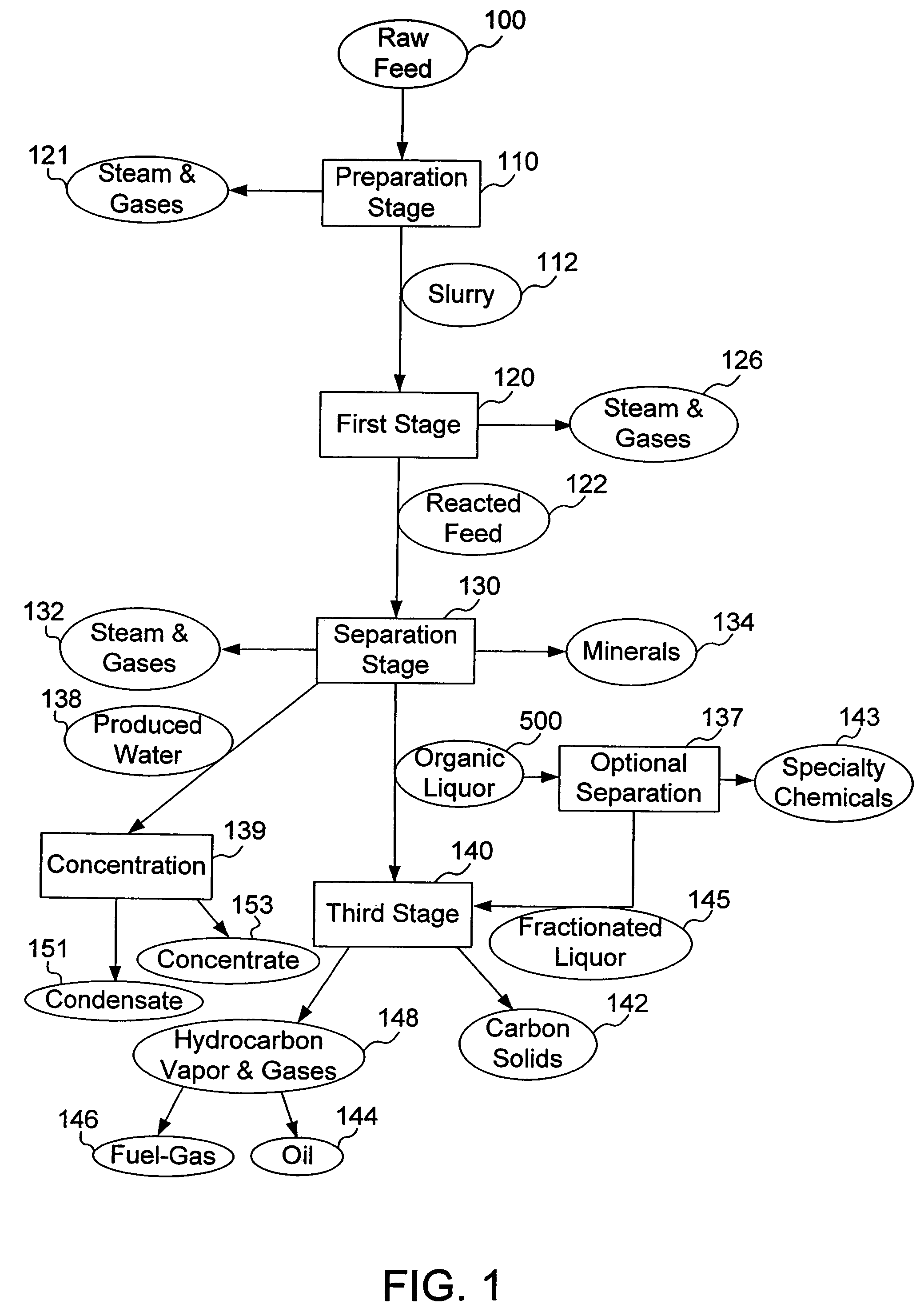
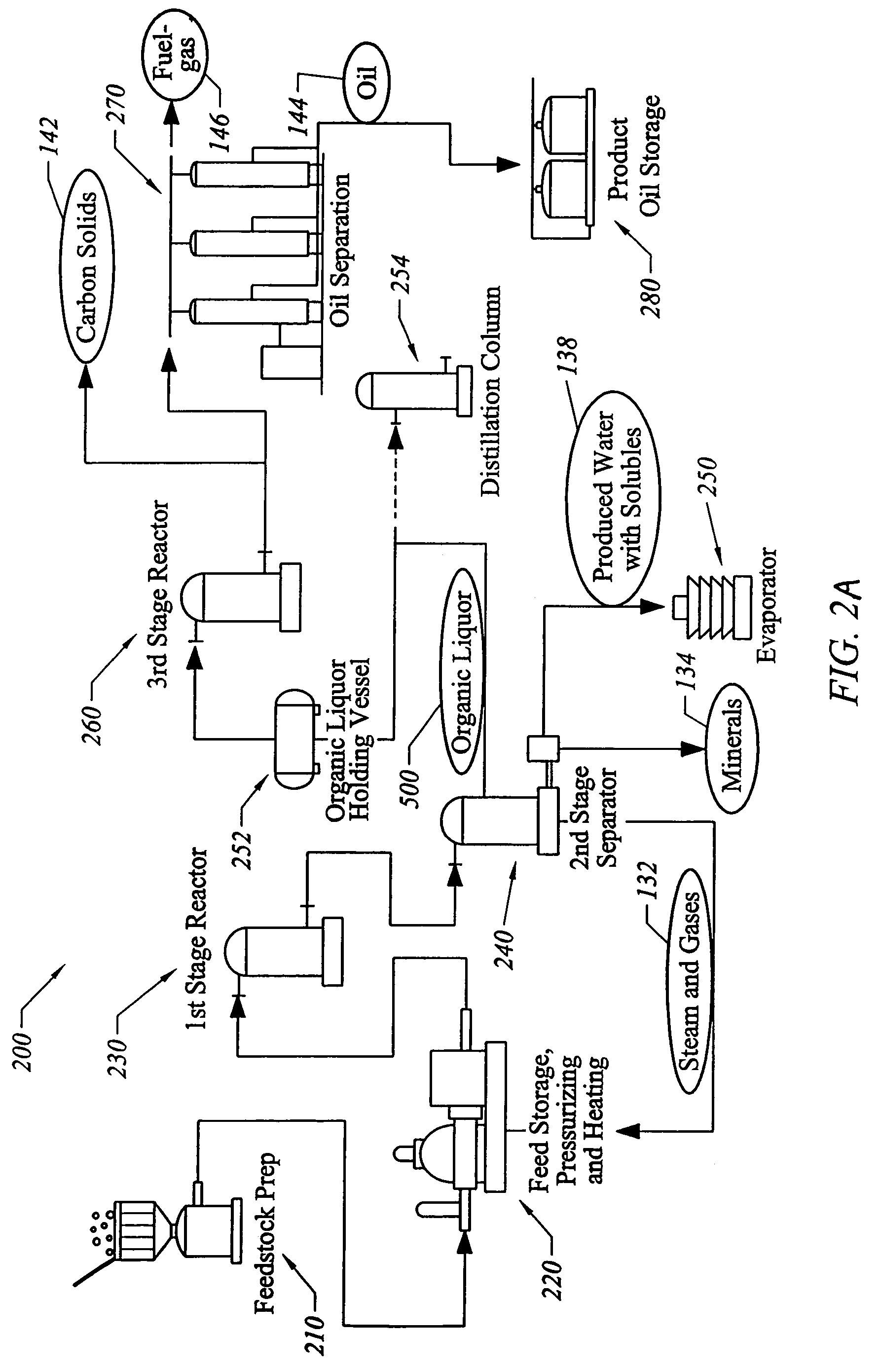
Process for conversion of organic, waste, or low-value materials into useful products
ActiveUS20060004237A1Low viscosityHydrocarbon purification/separationIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationHigh energySulfur
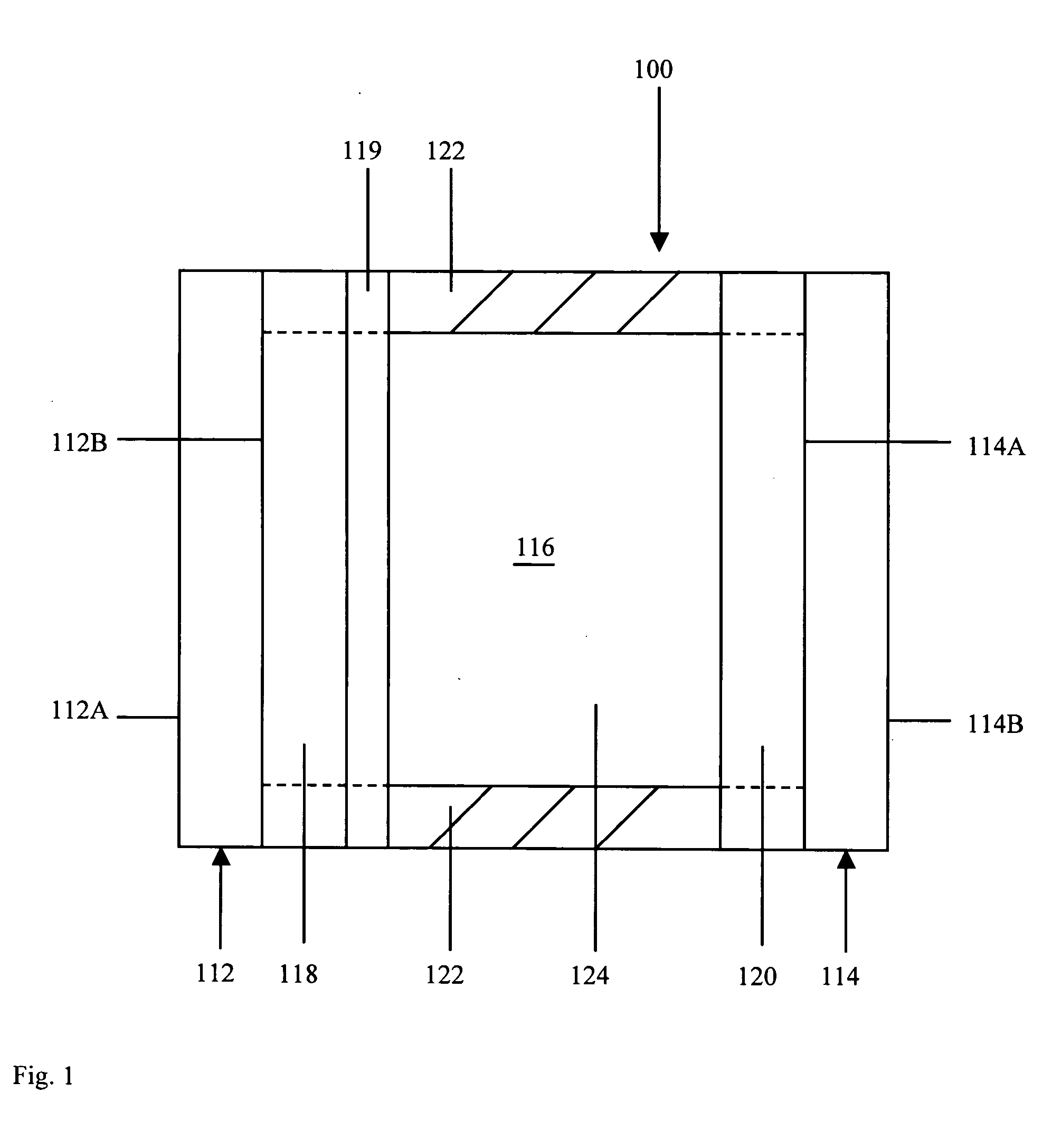
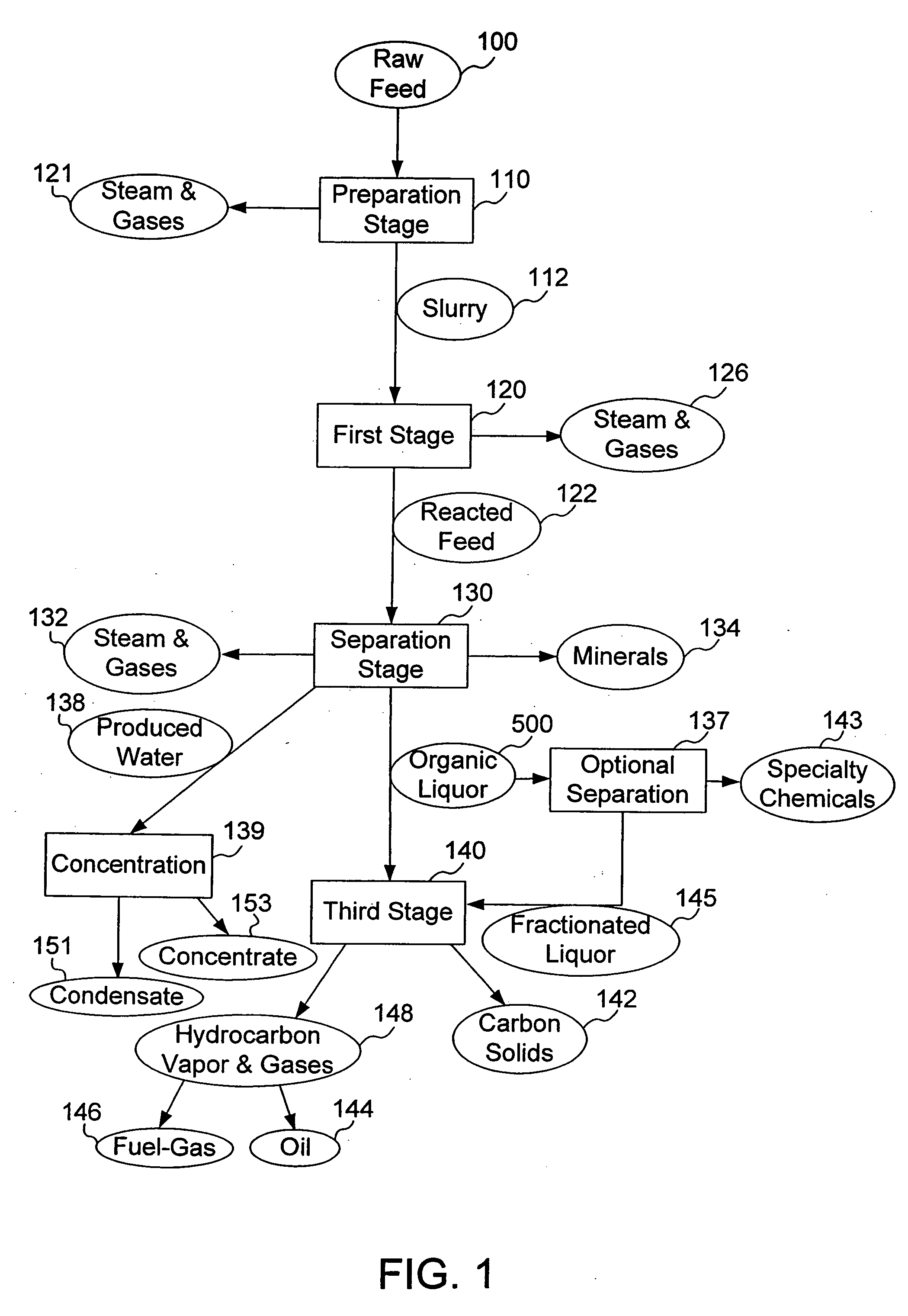
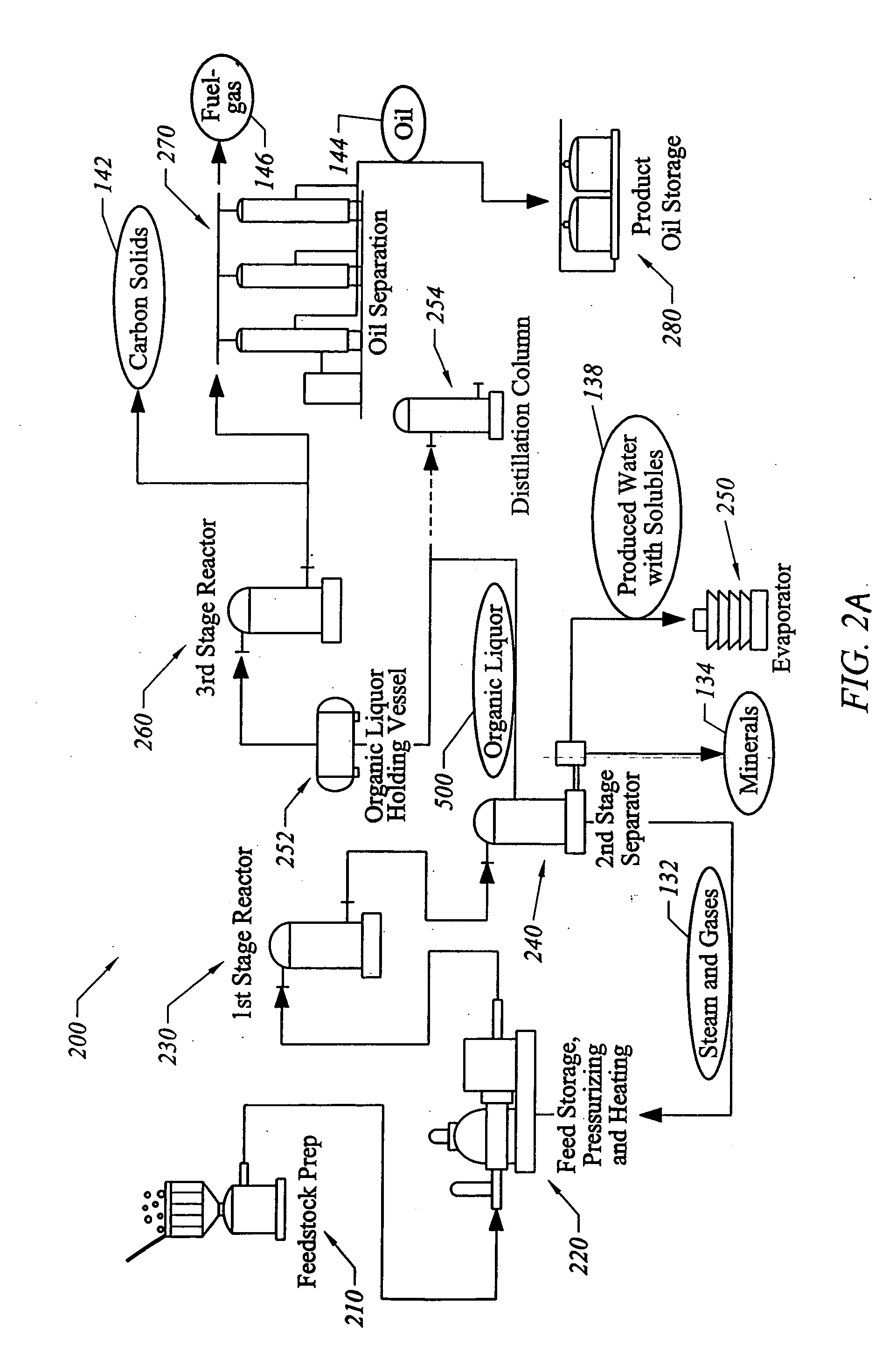
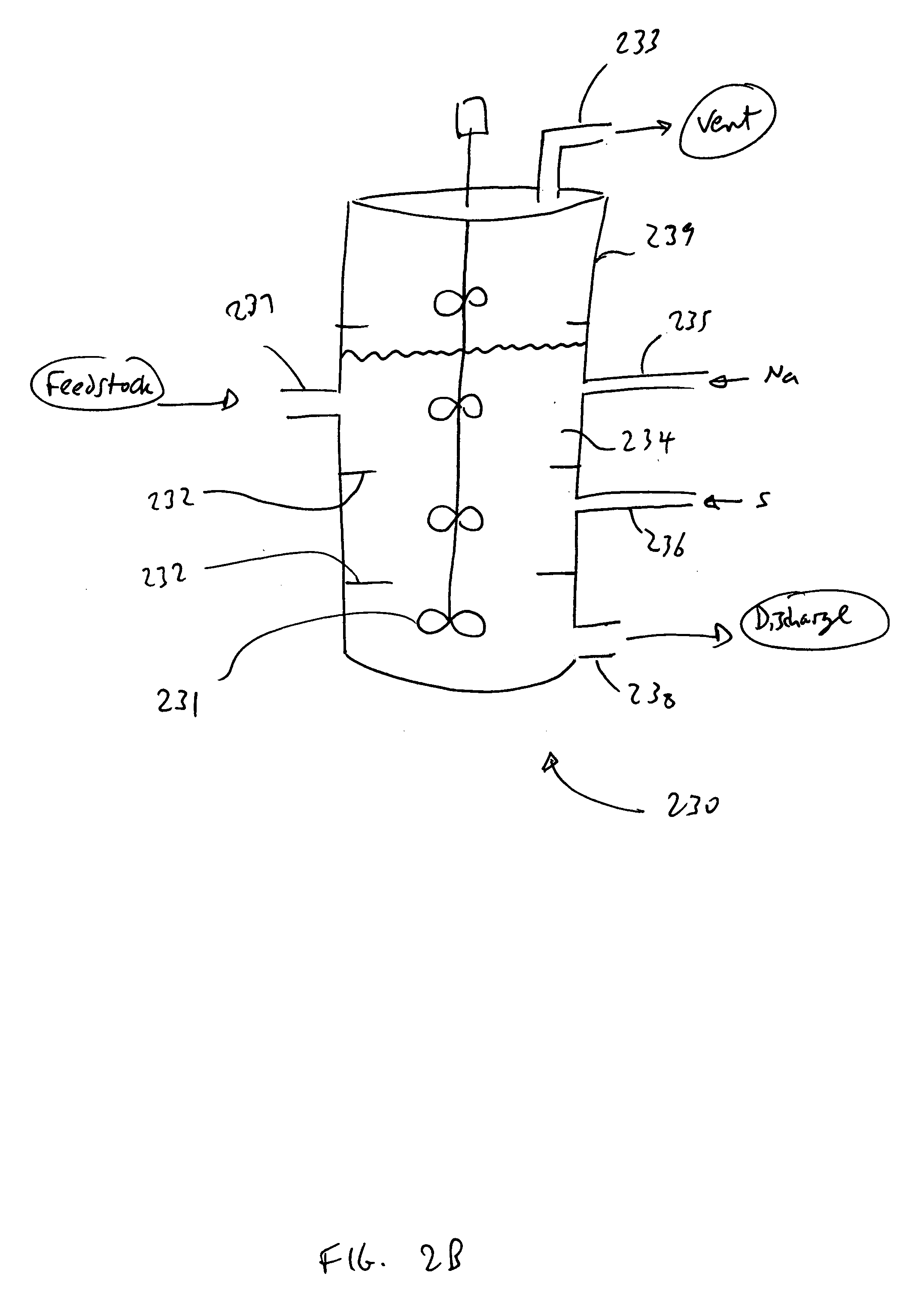
The present invention addresses the processing of waste and low-value products to produce useful materials in reliable purities and compositions, at acceptable cost, and with high energy efficiency. In particular, the invention comprises a multi-stage process that converts various feedstocks such as offal, animal manures, municipal sewage sludge, that otherwise have little commercial value, to useful materials including gas, oil, specialty chemicals, and carbon solids. The process subjects the feedstock to heat and pressure in a reducing environment accomplished by controlled addition of sulfur and sodium, separates out various components, then further applies heat and pressure to one or more of those components. The invention further comprises an apparatus for performing a multi-stage process of converting waste products into useful materials, and at least one oil product that arises from the process.
Owner:SYNPET TEKNOLOJI GELISTIRME
Combined mailing streams
A method of combining mail streams in a printing finishing process including the acts of generating a master mailing list having a sequence, forming a fist mail stream, forming a second mail stream, and combining the first mail stream and the second mail stream according to the sequence of the master mailing list.
Owner:QUAD GRAPHICS
Systems and methods for processing mixed solid waste
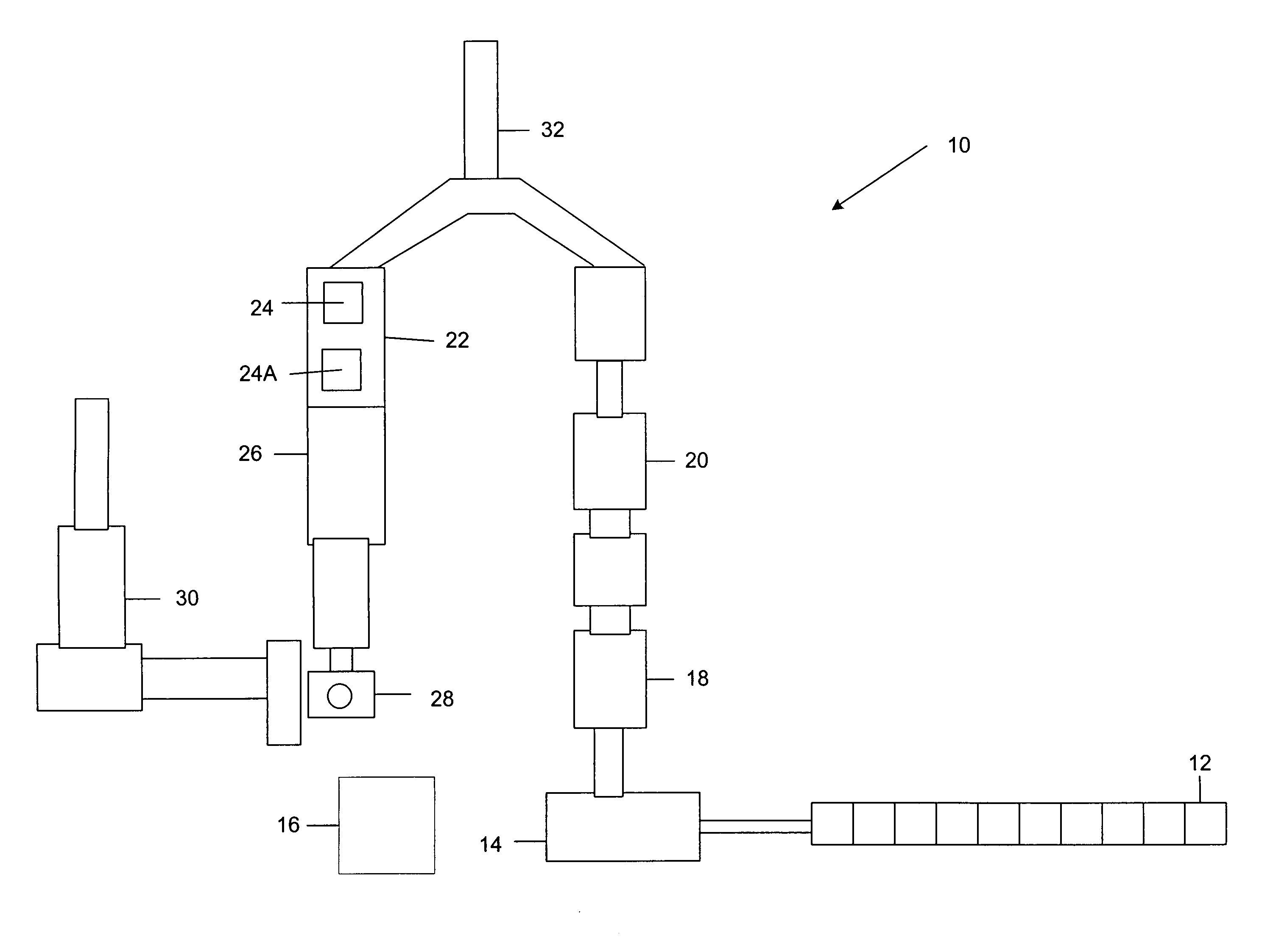
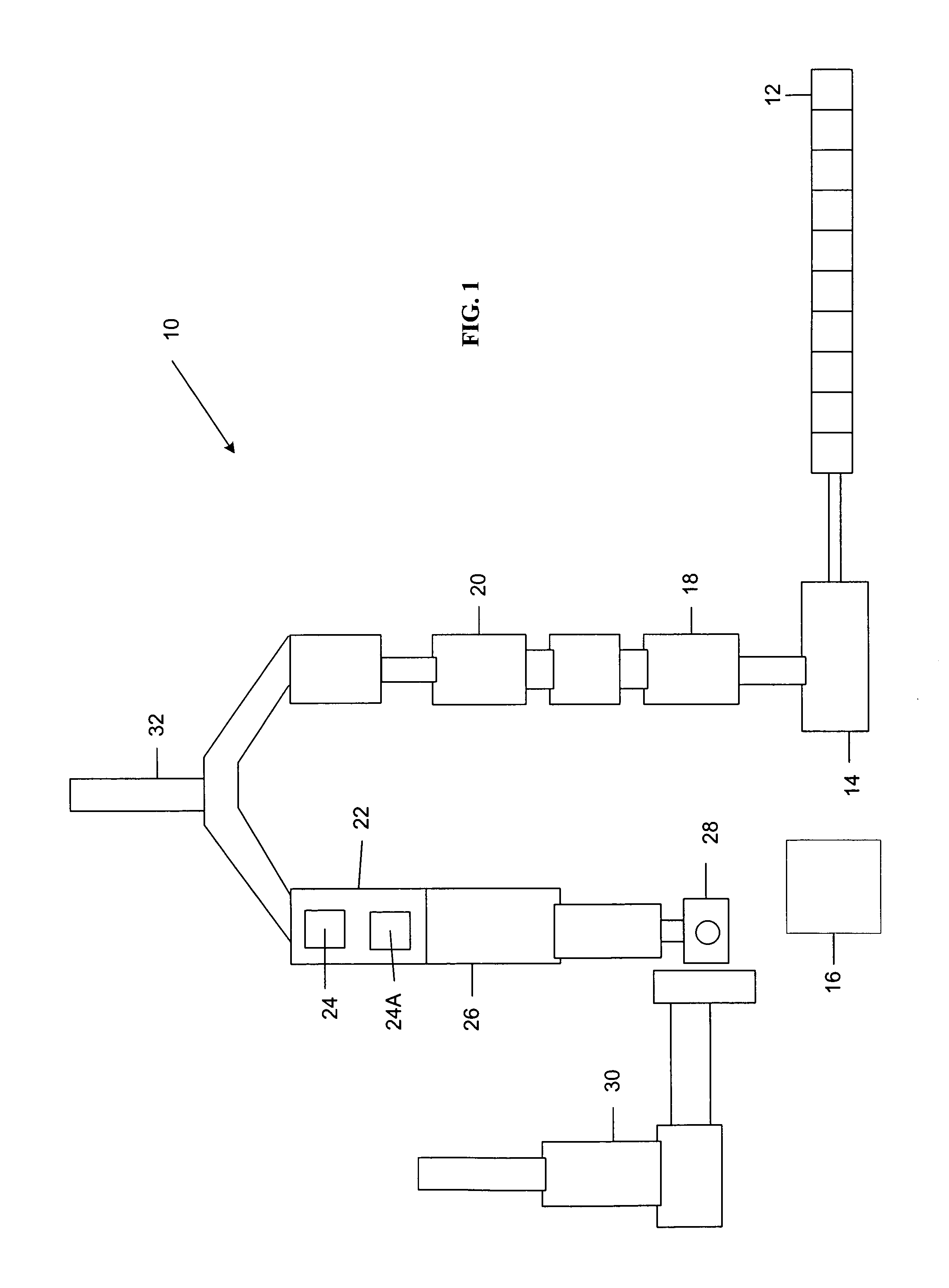
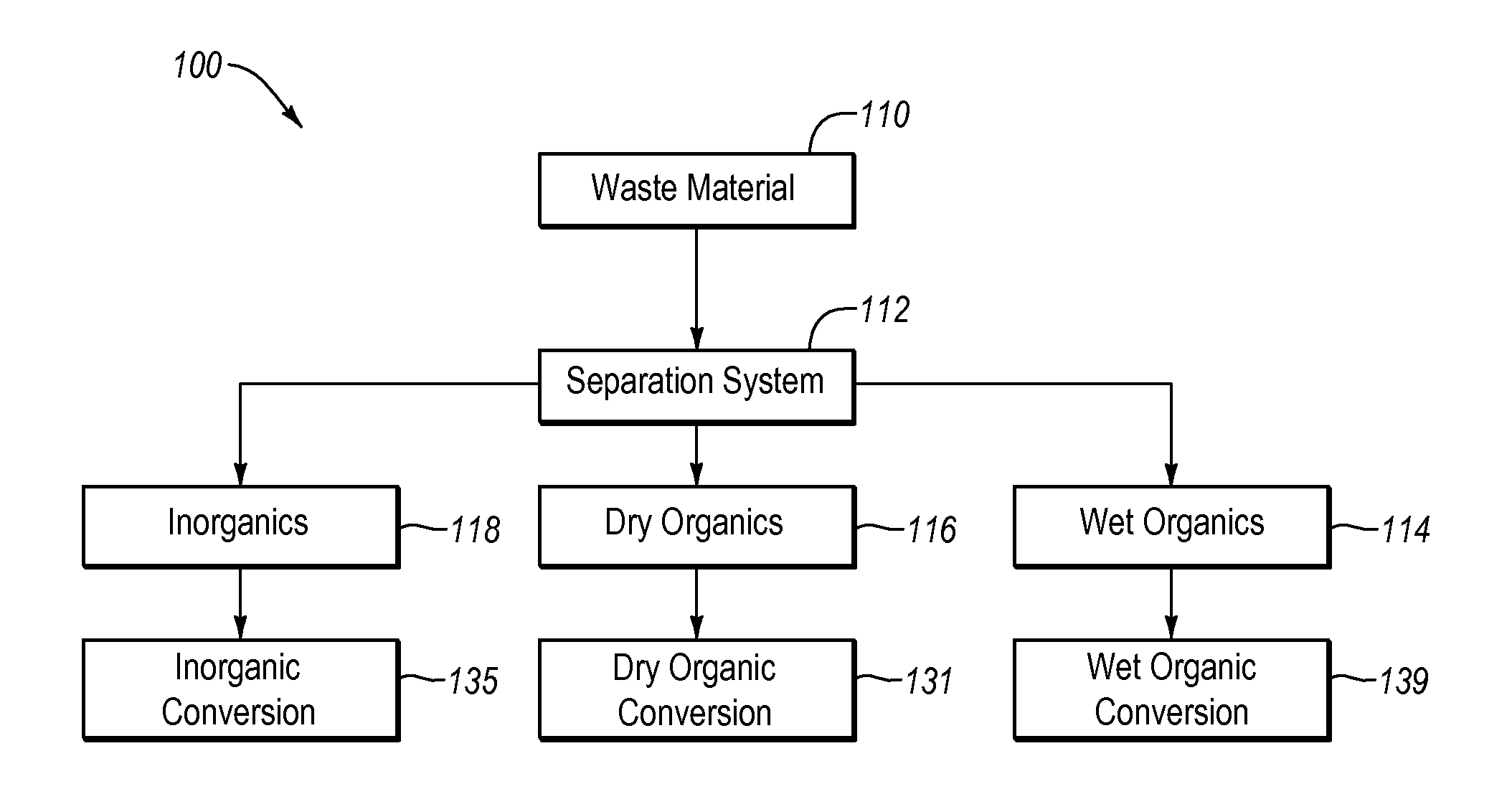
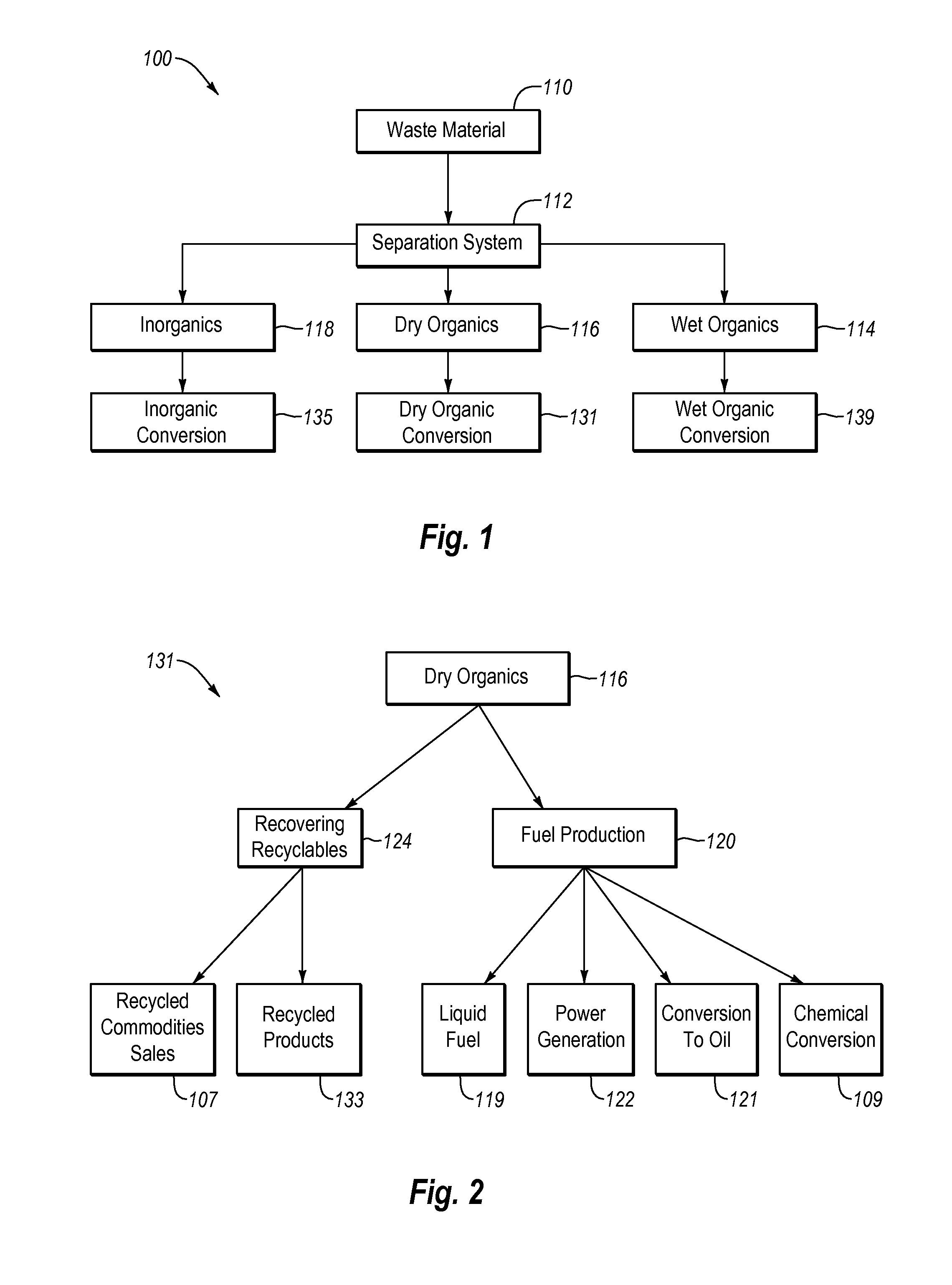
ActiveUS20120190102A1Efficient extractionMaximize efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesWaste processingEnvironmental chemistry
Solid waste that includes a mixture of wet organic material and dry organic material can be are separated using mechanical separation to produce a wet organic stream enriched in wet organics and a dry organic stream enriched in dry organics. The separated wet organic stream and dry organic stream are separately converted to renewable or recyclable products using different conversion techniques particularly suited for the separated wet and dry organic streams.
Owner:UPLAND ROAD IP HOLDCO LLC +2
Process for conversion of organic, waste, or low-value materials into useful products
ActiveUS7301060B2Low viscosityHydrocarbon purification/separationIndirect and direct heating destructive distillationSpeciality chemicalsHigh energy
Owner:SYNPET TEKNOLOJI GELISTIRME
Acoustic methods for separation of cells and pathogens
InactiveUS20160363579A1High sensitivityLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid separationParticulatesMicrobubbles
Devices and methods for inspecting, detecting, isolating, monitoring, characterizing, or separating pathogens in blood containing blood cells are disclosed. The devices include a flow chamber having a solvent inlet, at least one host-fluid inlet, a particulate outlet, at least one residual outlet, and a reflector. The methods include trapping the pathogens in the acoustic standing wave, introducing a solvent into the flow chamber, and removing the pathogens from the device. Devices and methods for inspecting, detecting, isolating, monitoring, characterizing, or separating specialized circulating cells in blood containing blood cells are also disclosed. The devices include a flow chamber having at least one inlet and at least one outlet, and a microscope objective and a cover glass. The methods include driving the transducer to create an acoustic standing wave in the flow chamber and microbubbles in the blood.
Owner:FLODESIGN SONICS
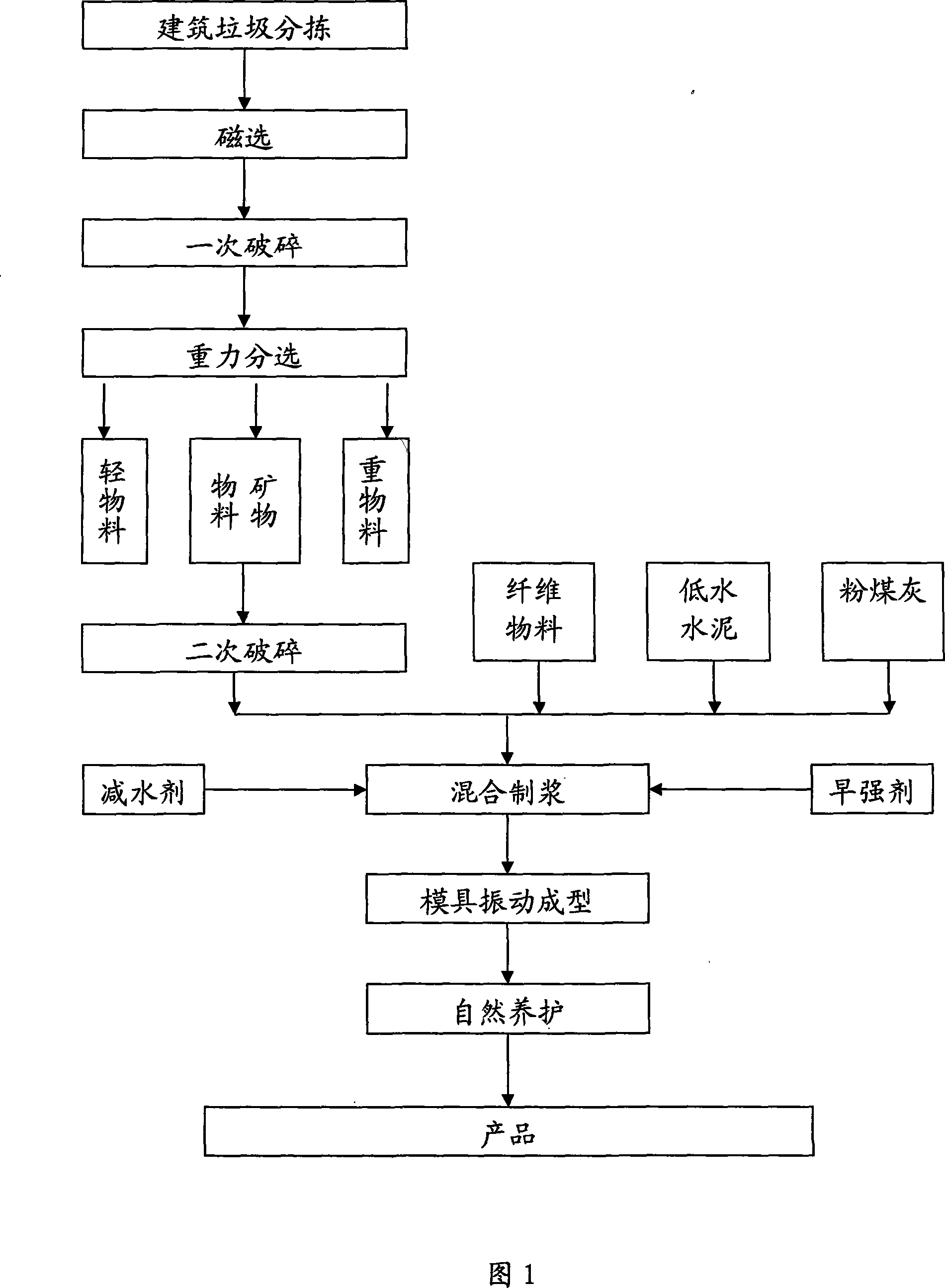
Method for manufacturing building material from building garbage
InactiveCN101239804AReduce final emissionsReduce dosageConstruction waste recoveryTransportation and packagingFiberBrick
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing the building material with the building garbage, the method executes sorting, magnetic separation, primary crushing and gravity sorting to the city building material, and the building material is separated to heavy material, light material and mineral material, the mineral material is used for manufacturing the building material after the secondary crushing, and the raw material of the building material comprises the following components: fiber material 5-10 parts, mineral material 40-60 parts, low-water cement 20-30 parts and other material 0-30 parts, the production process of the building material comprises the steps of mixing the fiber material, mineral material and other material to uniform, then adding the low-water cement for mixing to uniform, adding water and stirring to slurry, placing into the mold for jolt molding or extrusion molding, and forming the building used sheet material after natural curing. The method of the invention has the advantages of full utilization of the mineral material comprising the major component of the building garbage, saving the material resource, reducing the final discharging amount of the building garbage, and the method can be used for manufacturing the building materials such as hollow brick, hollow block, partition plate and the like.
Owner:BEIJING HENGYECUN S&T
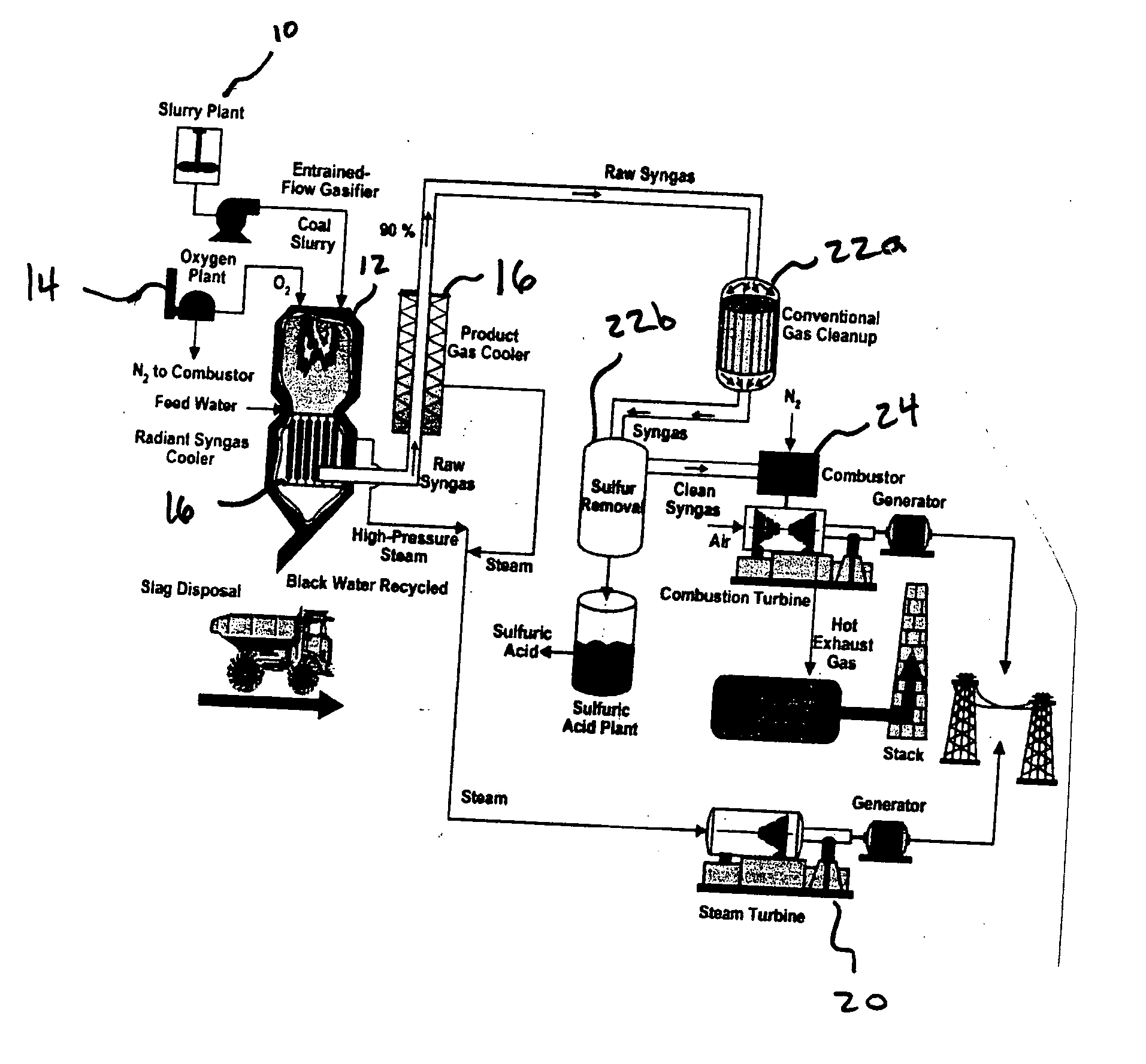
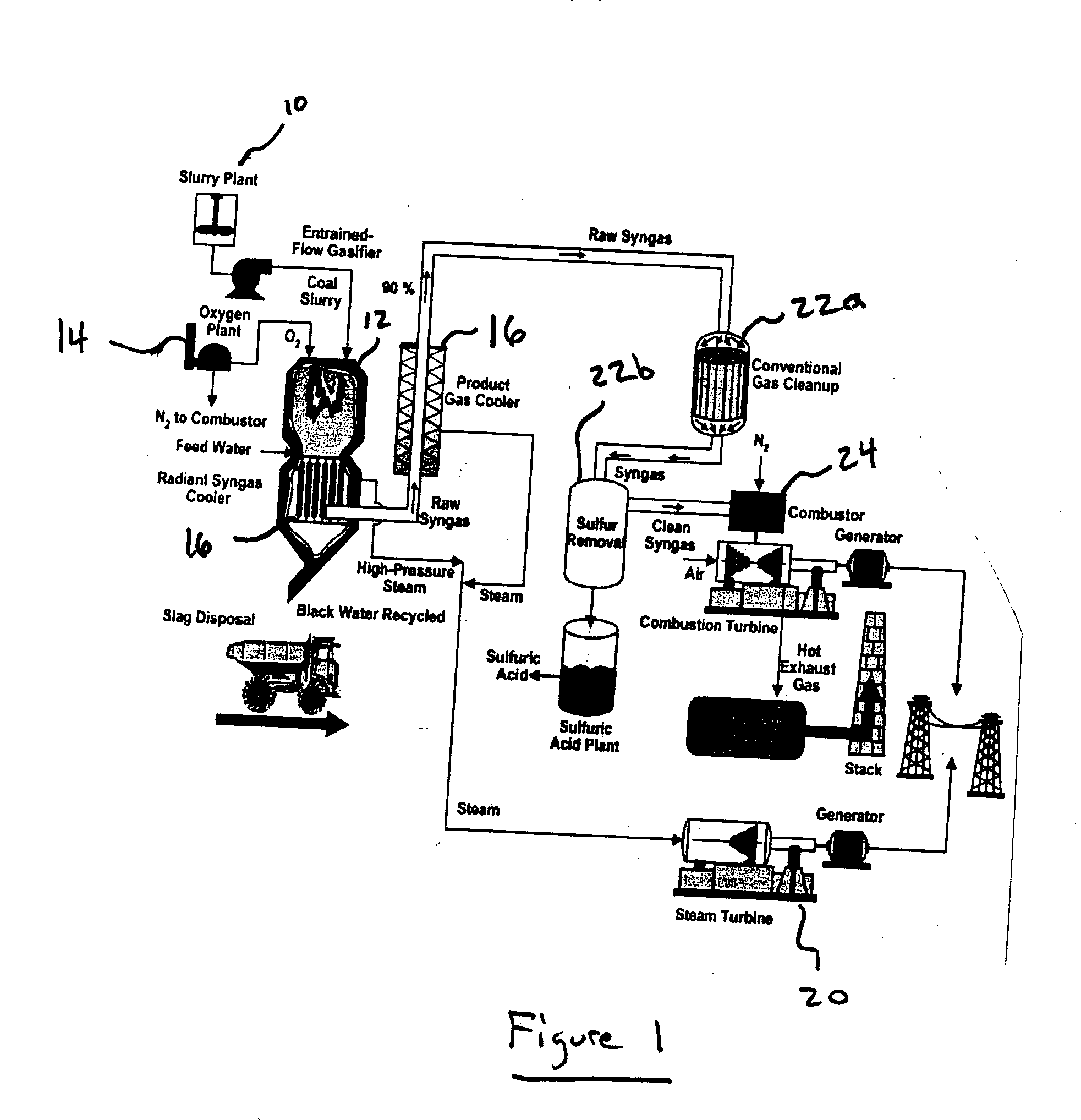
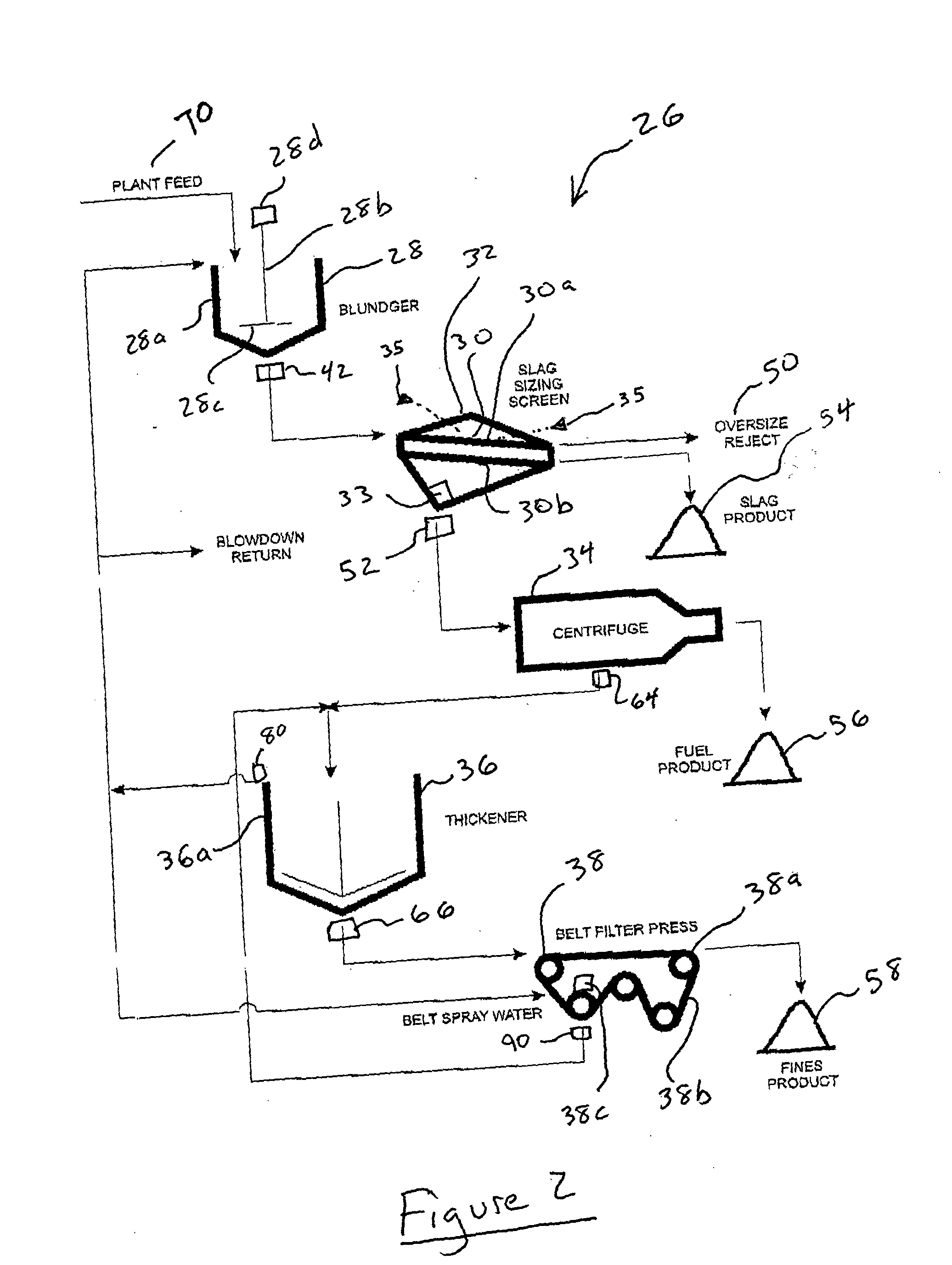
Method and system for beneficiating gasification slag
ActiveUS20050051500A1Improve propertiesGreat potentialWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesSlagSlurry
The present invention provides a method of beneficiating slag, including mixing the slag with water to form a slurry. The slurry is screened through a first screen to remove a first portion of material and then screened through a second screen to remove a second portion of material. In one embodiment, the second portion of material has a carbon content less than about 5% and, more preferably, a carbon content less than about 1%.
Owner:CHARAH LLC
Sack packer for automatically collecting grain
InactiveCN102745348APrevent throwingAchieve one-offSolid separationSolid materialTransmission systemEngineering
The invention discloses a sack packer for automatically collecting grain. The sack packer comprises a leaked grain cleaning device, an auger, a grain poking device, a lift conveyer, a wind impurity removing device, a grain feeding mechanism, a vibrating screen and a magnetic impurity removing device, a barn, a quantitative packing and conveying system, an automatic bag sealing system, and a power and transmission system, wherein all devices are fixed on the frame, and cooperate to finish automatic the collecting, automatic cleaning, quantitative packing, and automatic bag sealing functions of the grain; the grain poking device (the leaked grain cleaning device is started when a field is not smooth) collects the grain paved on a seasoning yard into the auger when working; the auger conveys the grain to the lift conveyor; the lift conveyor lifts the grain to a grain feeding mechanism; the wind impurity removing device absorbs light impurity mixed in the grain in the process that the grain falls off, and plays a certain airing role; the vibrating screen and the magnetic impurity removing device remove and collect different sizes and properties of impurities, and the grain is quantitatively packed and automatically sealed after entering into the barn.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for separating particles
InactiveUS7674630B2Little travelConvenient travelOther blood circulation devicesWithdrawing sample devicesSonificationHarmonic
The invention relates to a method and a device for separating particles using ultrasonic standing waves which are switched between two different frequencies. A second order harmonic standing wave is used together with the fundamental standing wave. If the particles are exposed to the fundamental standing wave, the forces act to collect particles at the center. If the particles are exposed to the second order harmonic standing wave, the forces act to collect particles at the two pressure nodes at the sides. By switching the frequency between the second order harmonic standing wave and the fundamental standing wave, particles with different properties will be exposed to different accelerations and are separated into two streams.
Owner:SPECTRONIC
Apparatus and process for treating waste
ActiveUS20130029394A1Easy to separateEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDigestionInternal combustion engine
A method for treating municipal solid waste and other waste is provided which comprises: introducing said waste into a rotary autoclave which is downwardly inclined towards its discharge end and has a door at the discharge end; and injecting steam through said door into said autoclave to treat the load. A method is also provided for treating waste, comprising steam autoclaving the waste, anaerobically digesting an organic-rich fraction of the autoclaved waste, recovering methane-containing gas from anaerobic digestion, internally combusting the methane-containing gas to generate power and exhaust gas, and generating steam for autoclaving using the waste heat. A plant for treating the waste may comprise at least one autoclave for steam treating the waste, at least one anaerobic digestion tank for digesting an organic-rich fraction of the autoclaved waste, a recovery system for recovering methane-containing gas from the or each digestion tank, at least one internal combustion engine for combusting the methane-containing gas and generating power, and a steam generator fed with combustion gas from the internal combustion engine for generating and accumulating steam for supply to said at least one autoclave. Also provided is a method of treating waste material in a rotary autoclave, which comprises: loading the waste material into a top opening of the autoclave whilst rotating the autoclave in a first direction in which screw flights within the autoclave convey the waste forwardly along a downwardly inclined body of the autoclave towards a base of the autoclave; rotating the autoclave in a second direction opposite to the first direction so as to establish a circulation of the loaded material between the upper and lower ends of the autoclave to facilitate vacuum and / or steam treatment thereof; and monitoring the load imparted by the autoclave adjacent upper and lower ends thereof during the reverse rotation, increase of the load adjacent the upper end of the autoclave providing an indication of effective load circulation. A door structure for a commercial-scale autoclave based on a castellated door and a locking ring with lock blocks of inwardly facing U-structure is also provided.
Owner:AEROTHERMAL GROUP
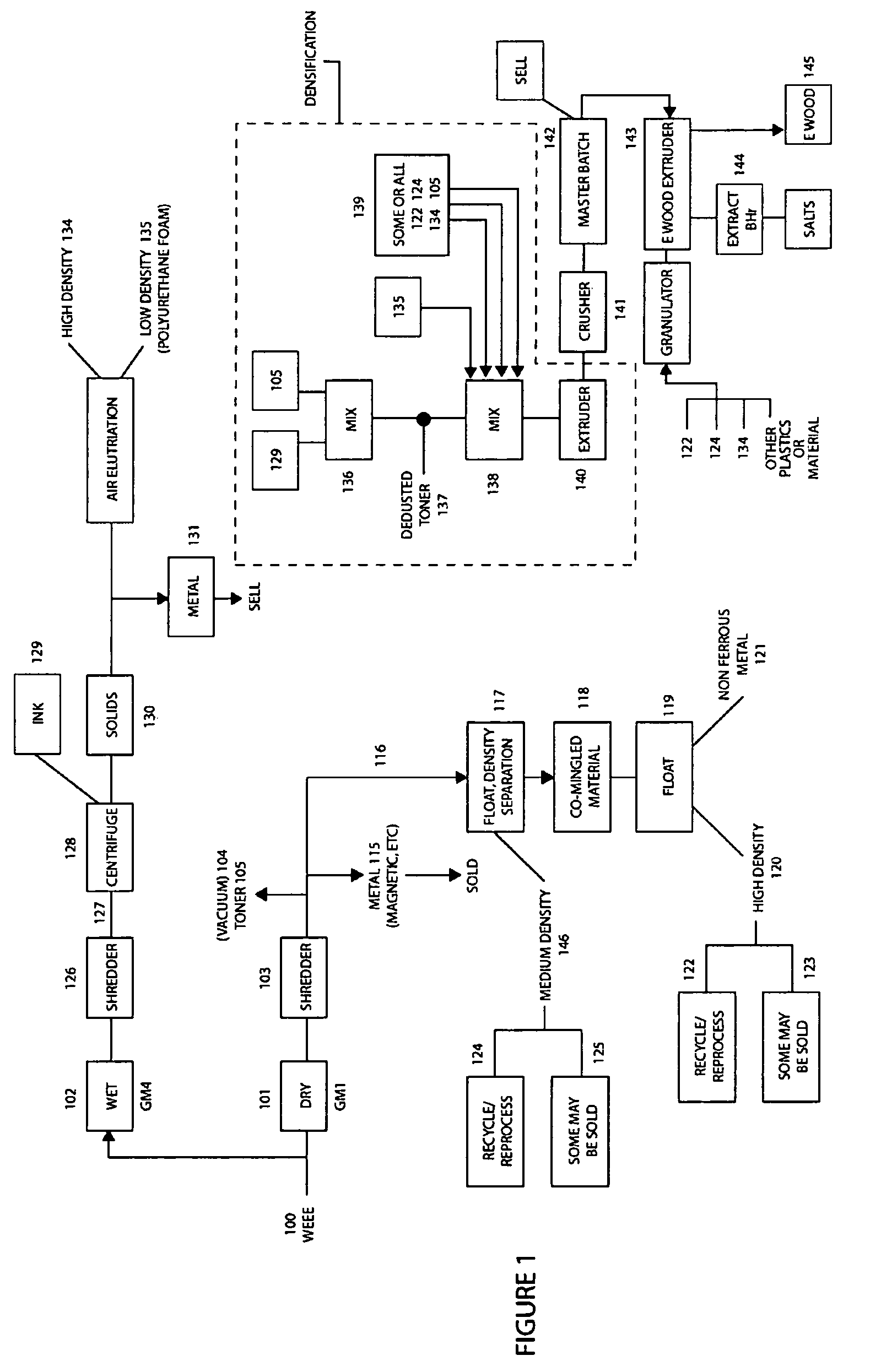
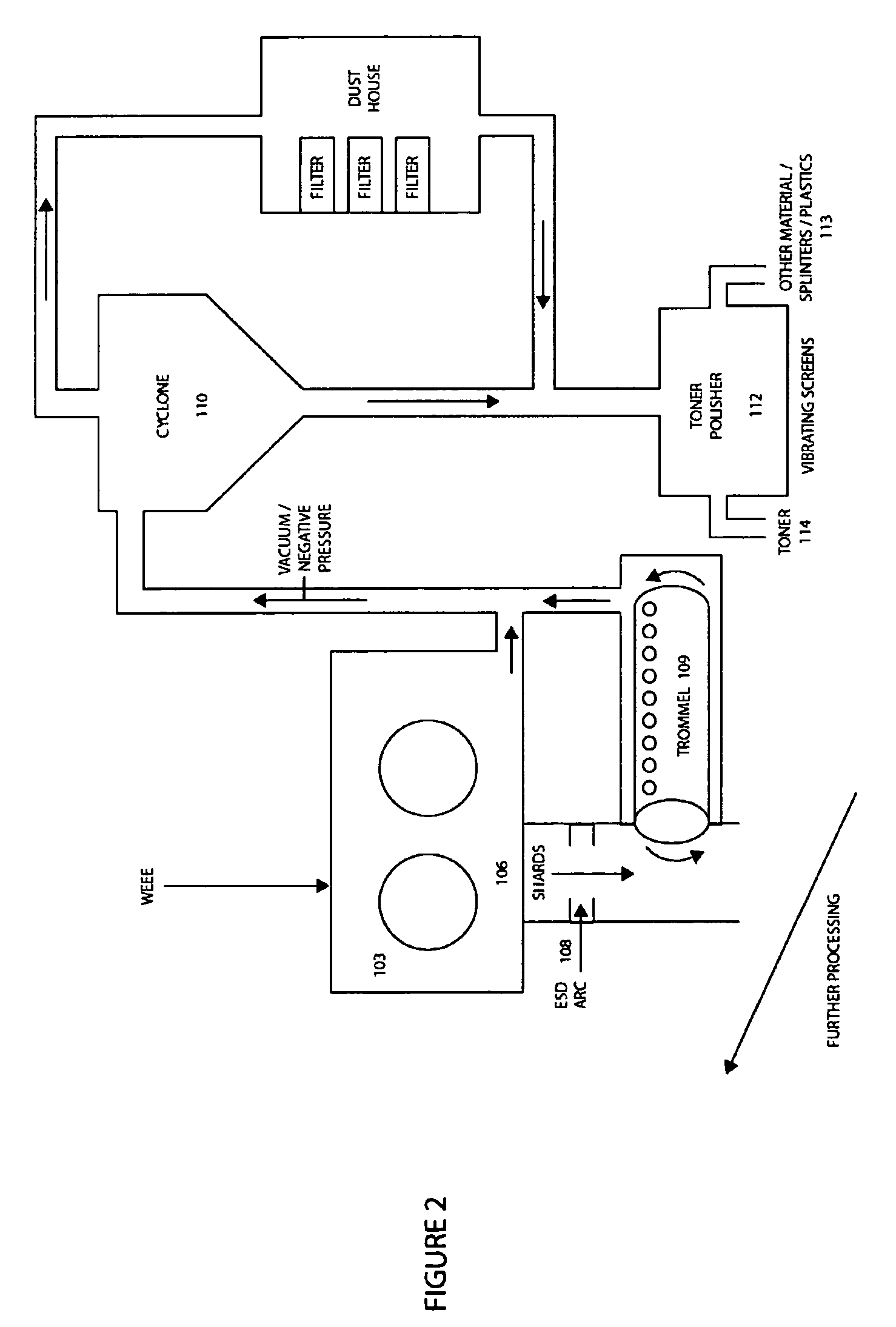
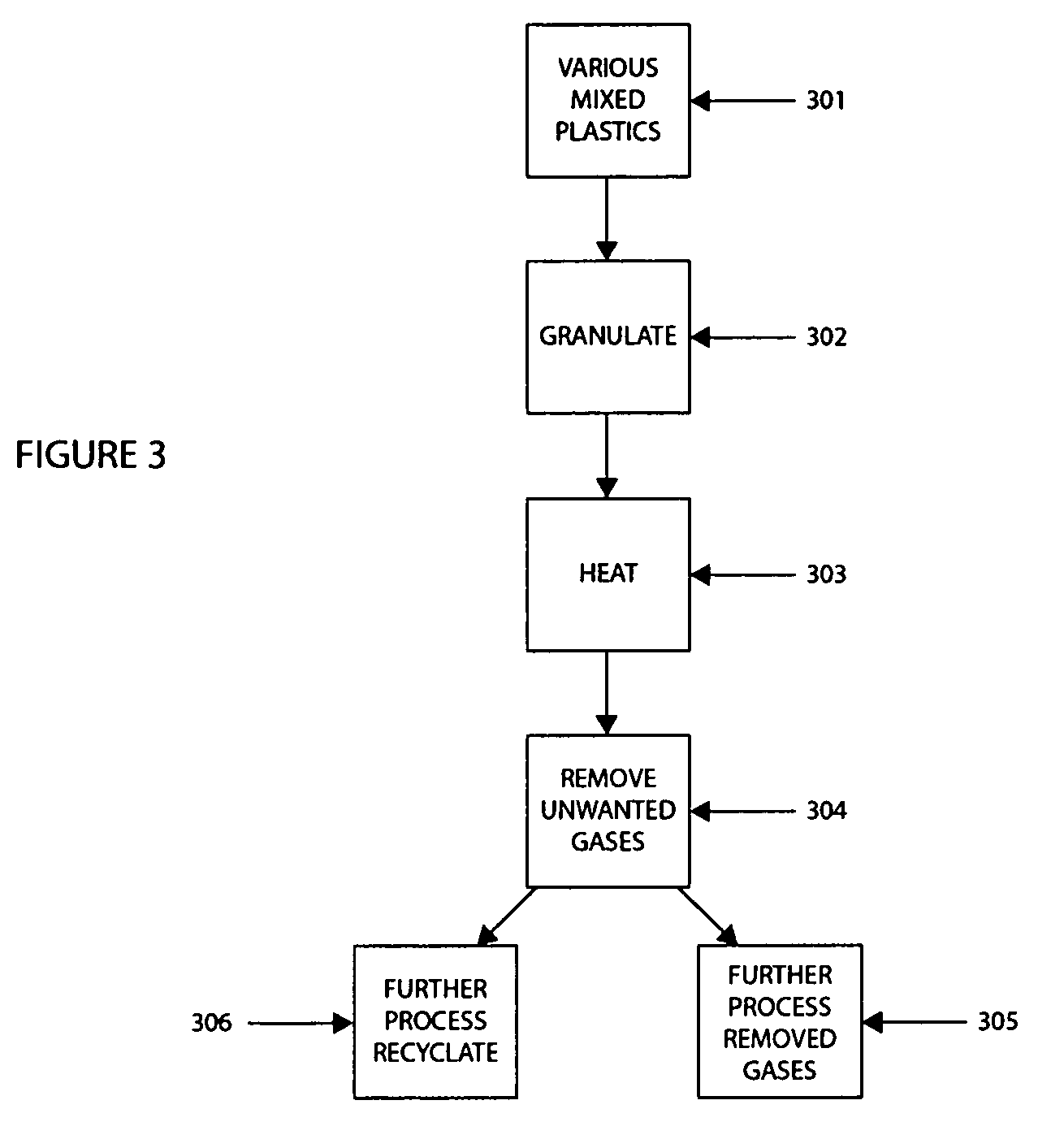
Method of recycling mixed streams of ewaste (WEEE)
The present invention relates to the recycling of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Preferably, the present invention relates to the substantial recycling of all material forming the WEEE, thus providing substantially zero landfill. In yet another form, the invention relates to an additive and / or method of providing an additive. In still another form, the invention relates to recycling ink, toner, and / or PU foam from imaging consumables, forming part of the WEEE. In another form, the invention relates to the recycling of plastic materials containing flame retardants, including the recycling of plastics materials, such as plastics materials containing brominated flame retardants generally based on styrenics (e.g. PS, HIPS, ABS, PPO / PS, PPE / PS, ABS / PC) and polyamides (Nylon 6, nylon 6,6, nylon 12) and other engineering plastics such as polyacetal, polycarbonate, PET, PBT, liquid crystal polymers.
Owner:CLOSE THE LOOP TECH
Method for treating an exhausted glycol-based slurry
InactiveUS7223344B2Efficient regenerationUseful life of componentLiquid separation auxillary apparatusReversed direction vortexParticulatesSolid particle
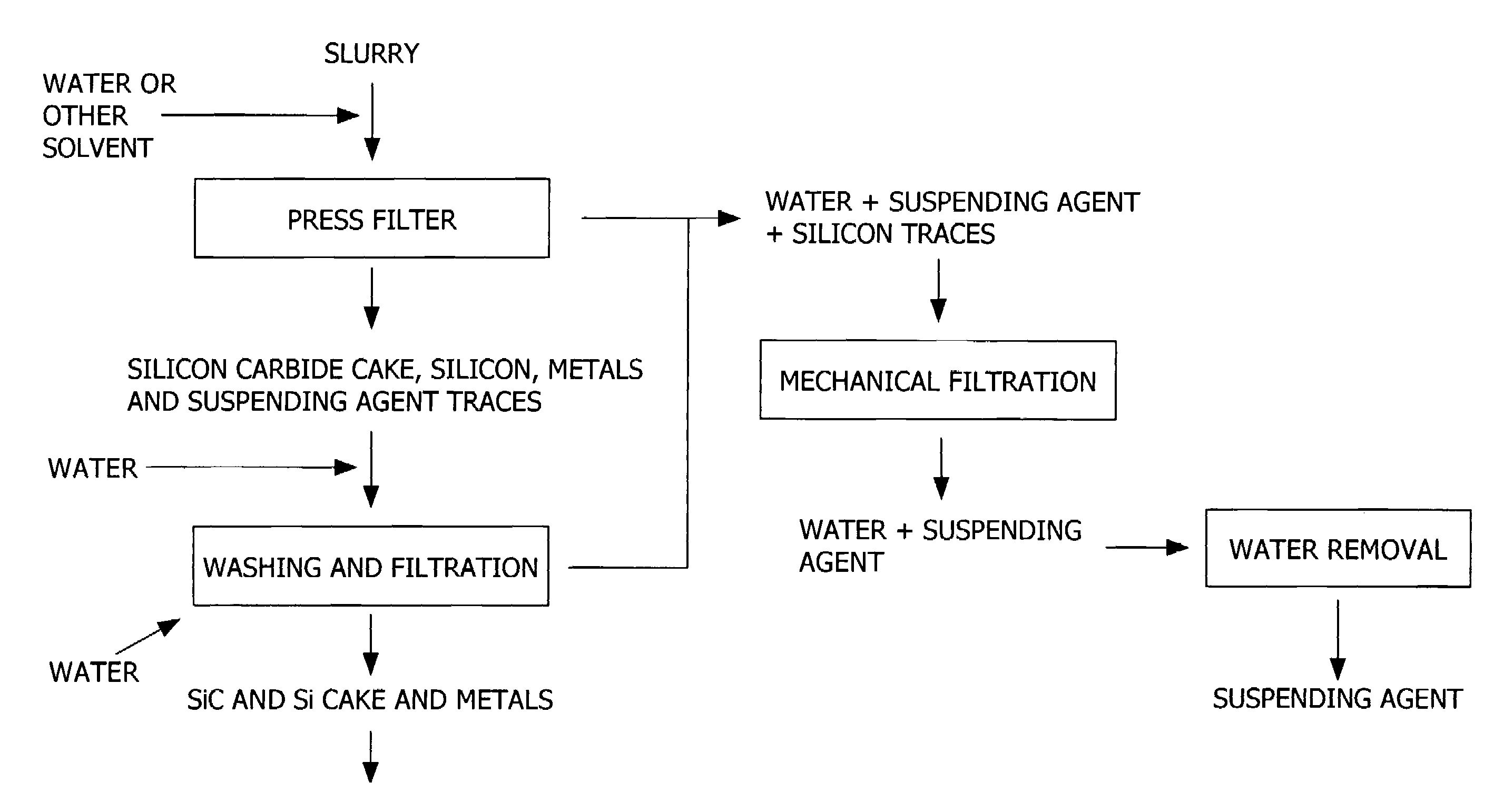
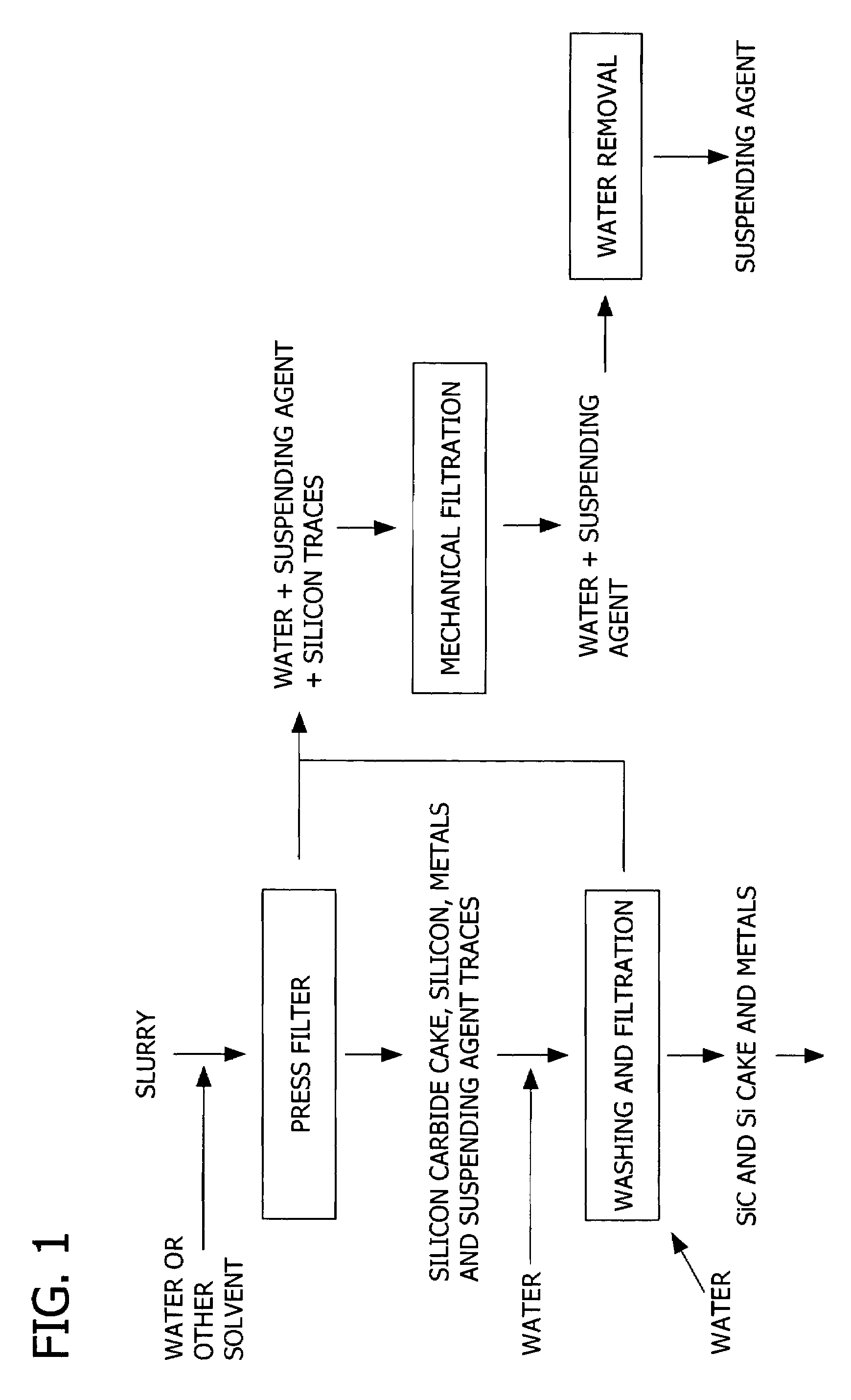
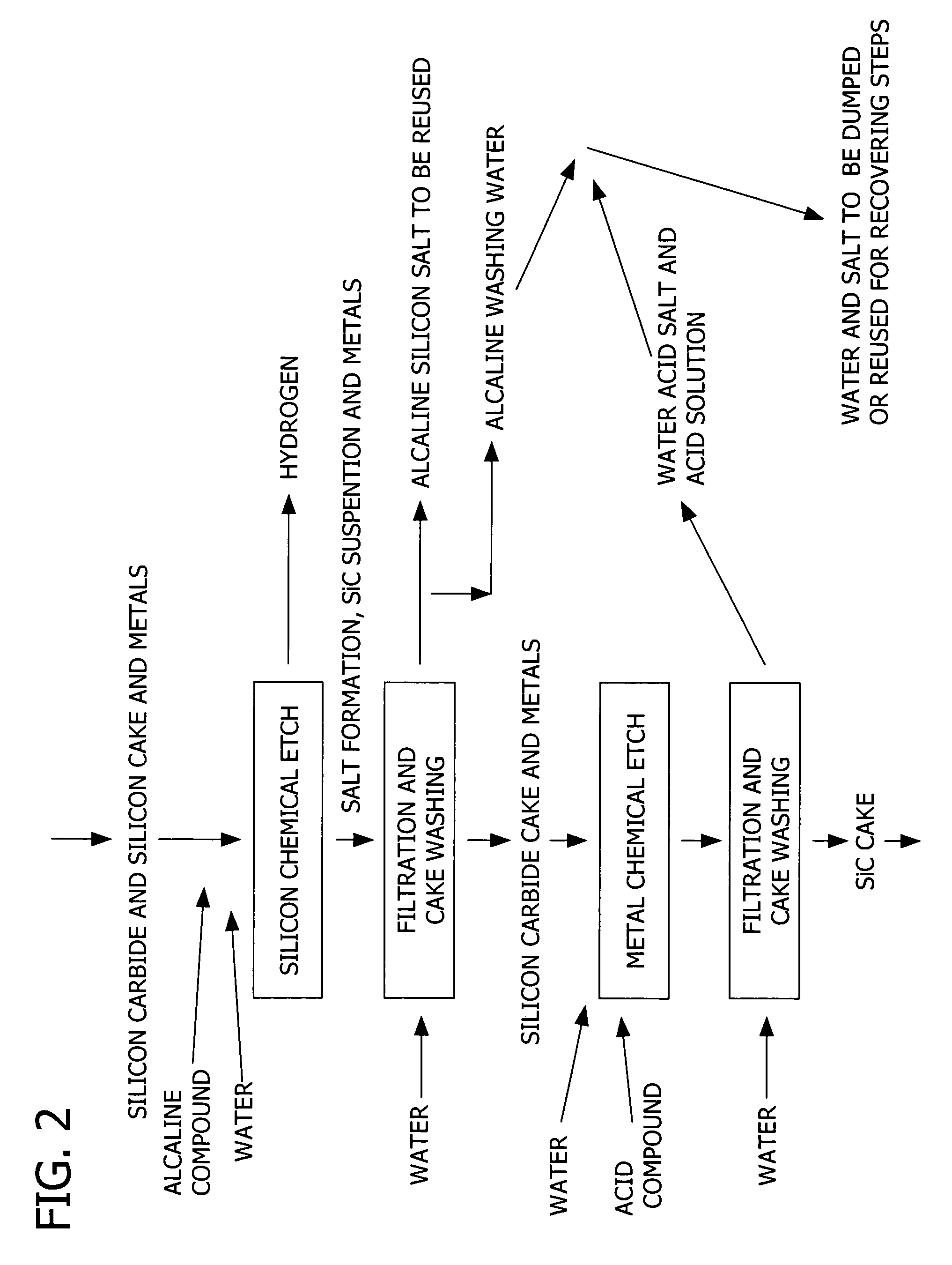
A method of separating, recovering and reusing components of an exhausted slurry used in slicing silicon wafers from a silicon ingot. In the method, the solid particles and lubricating fluid of the exhausted slurry are separated without decreasing the viscosity of the exhausted slurry. The separated lubricating fluid may be collected and reused in the preparation of a fresh slurry. Additionally, the silicon particulate and metal slicing wire particulate are dissolved and separated from the abrasive grains. The abrasive grains are separated into spent abrasive grains and unspent abrasive grains. The separated unspent abrasive grains are suitable for reuse in the preparation of a fresh slurry.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD +1
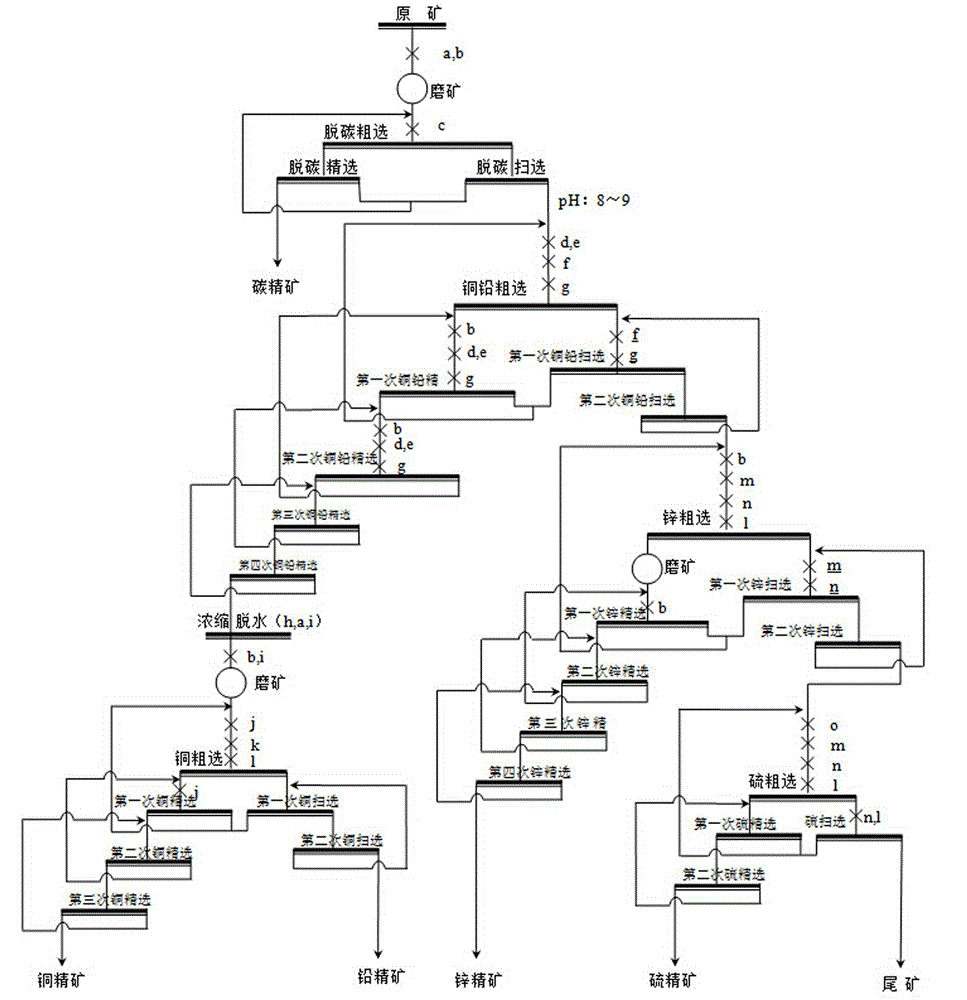
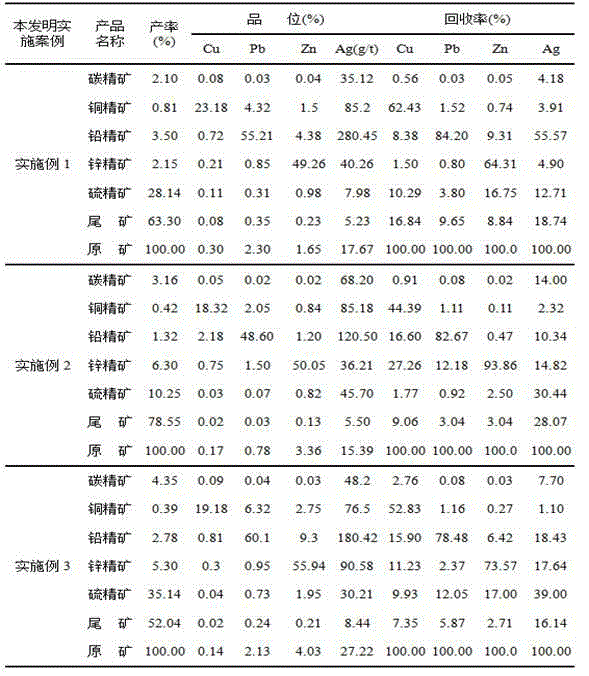
Beneficiation method for cu-pb-zn polymetallic ores
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for cu-pb-zn polymetallic ores, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal beneficiation. According to the technical scheme, the characteristic of complex cu-pb-zn-sulfur polymetallic ores with embedded fine-grained carbon level is utilized, a technological process of carbon-removing, cu-pb partial bulk flotation, cu-pb separation and zn-and-sulfur choosing in tailings is adopted, a concentration and fine grinding mode is adopted to achieve deep reagent removal, the influence of slurry on flotation is effectively eliminated, efficient collectors A8 and depressors T721 for cu-pb separation are used in the cu-pb partial bulk flotation process, separation and recovery of copper, lead, zinc and sulfur are effectively achieved, and concentrate mixing is obviously lowered.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
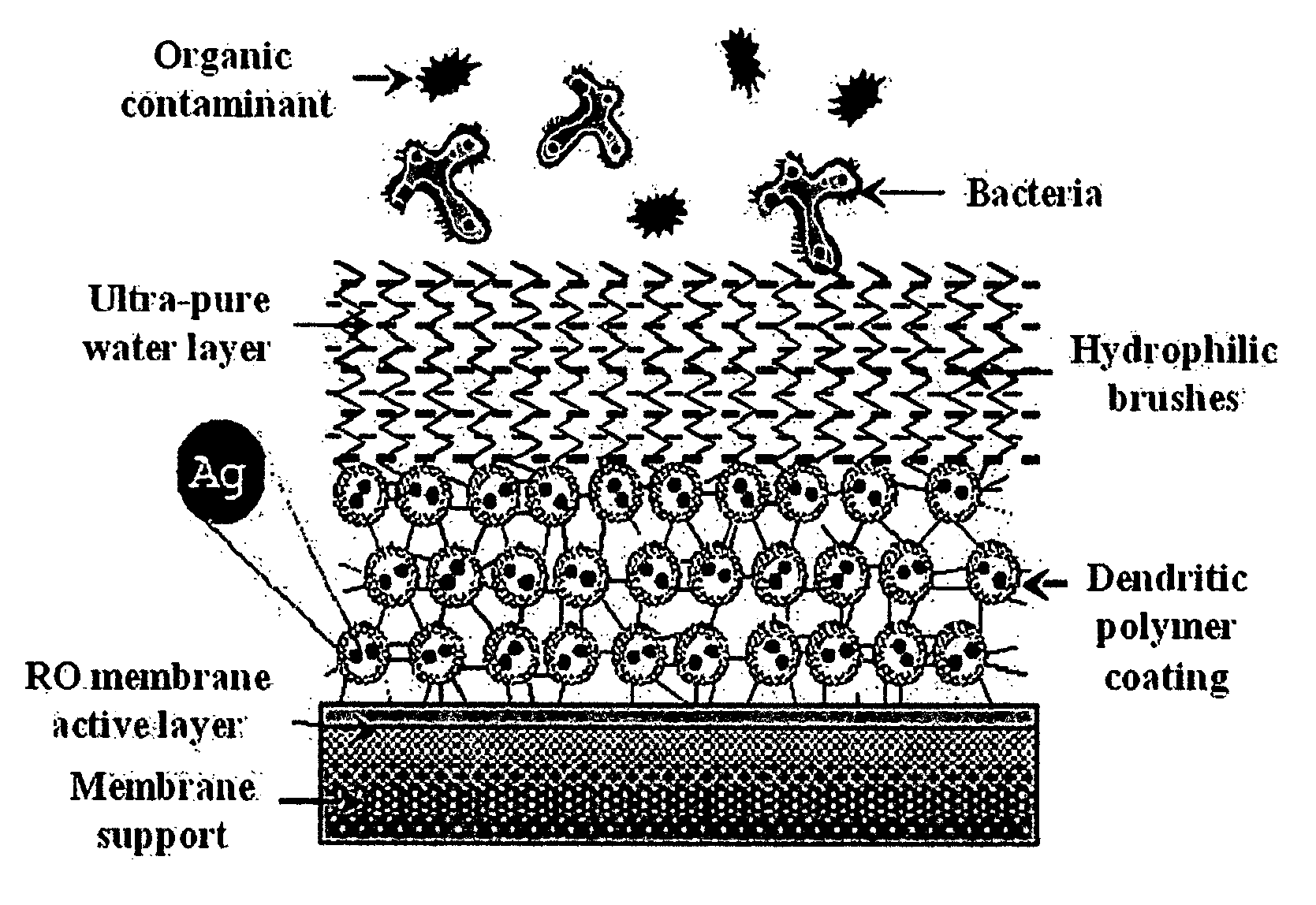
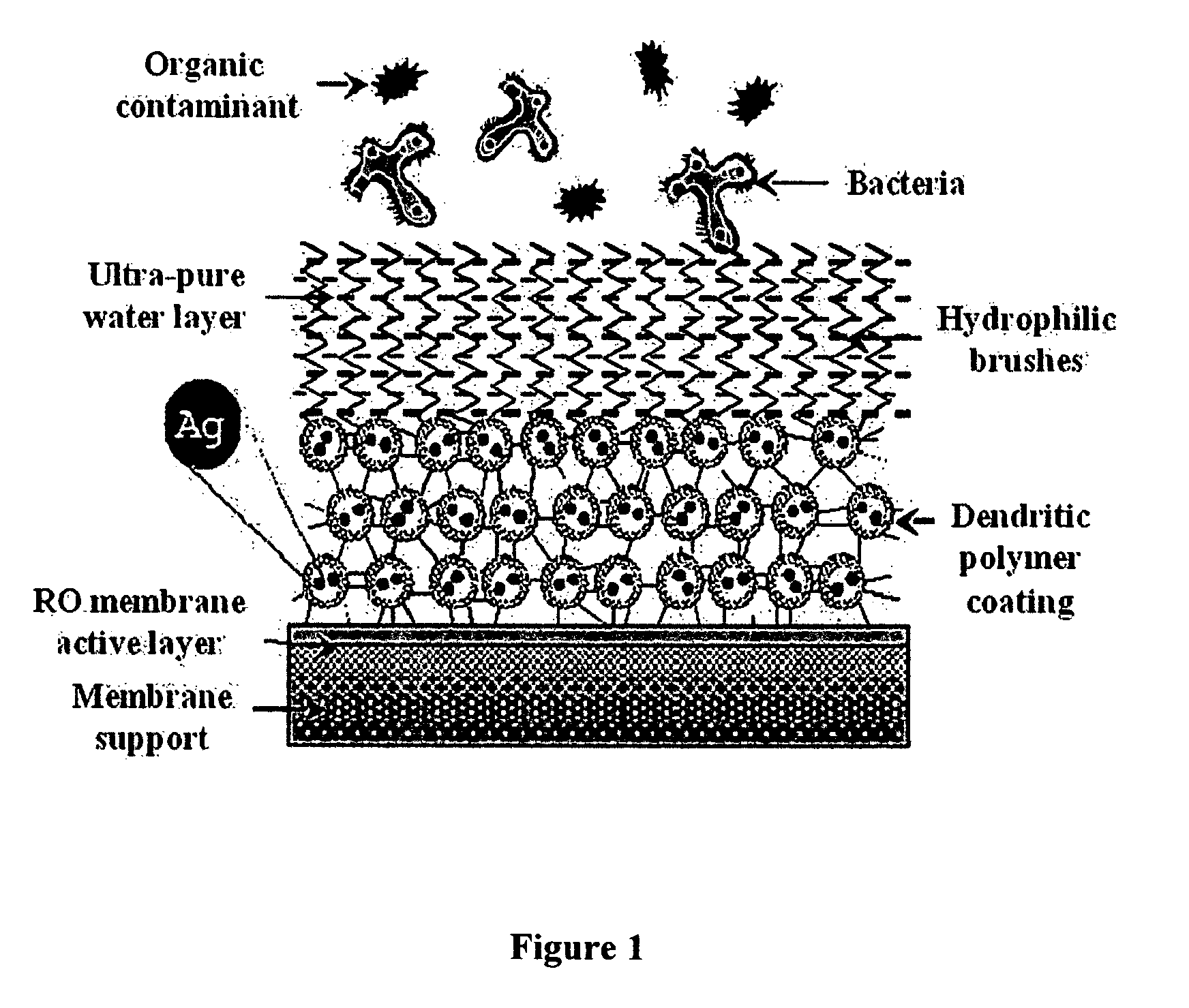
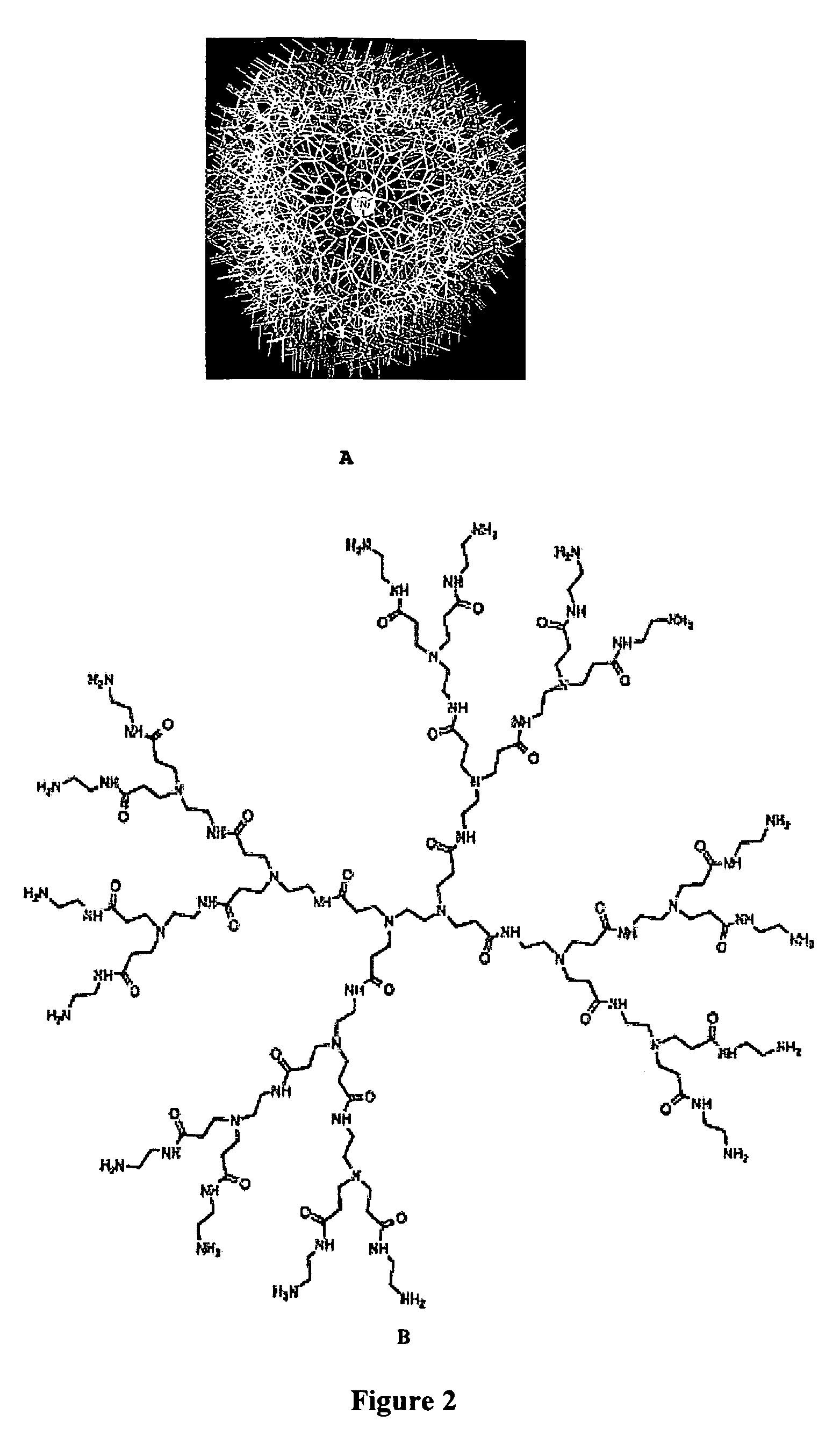
Surface modification of polyamide reverse osmosis membranes
InactiveUS8505743B2Improve hydrophilicityPrevent subsidenceMembranesSolid separationDendrimerCoated membrane
The present invention relates to surface modification of reverse osmosis membranes to introduce antifouling properties without compromising the separation properties of the original membranes. This approach utilizes: providing a coated membrane surface having enhanced hydrophilic characteristics that prevents the biofoulants from settling; have a surface that consists of hydrophilic brushes that unsettle any biofoulants that get through; and having antimicrobial ions present in the membrane coatings and able to remove or minimize any remaining biofoulants without leaching into the permeate. These coatings are made using dendritic polymers such as hyperbranched polymers or dendrimers.
Owner:MICHIGAN MOLECULAR INST
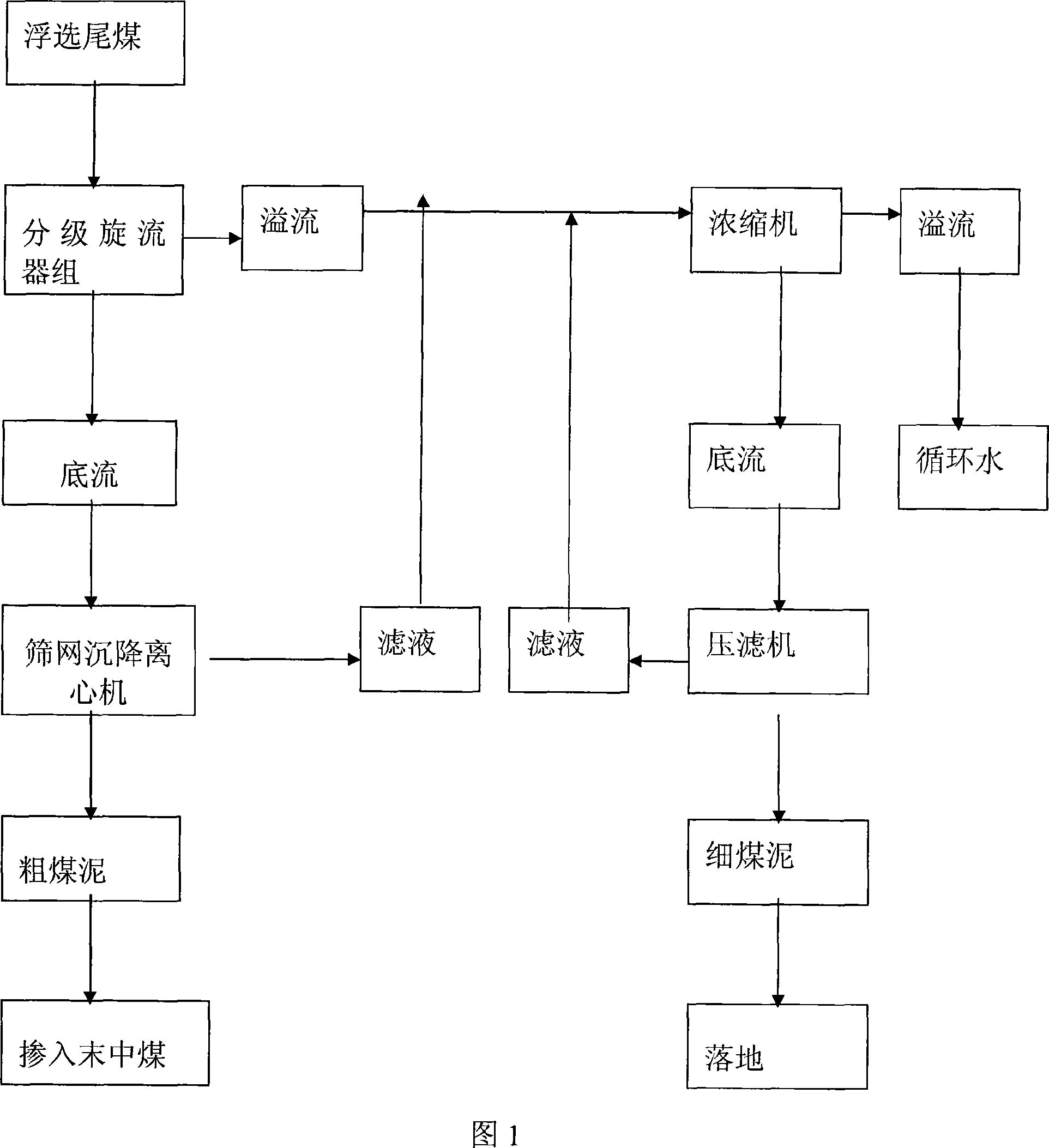
Floating tail-coal graded recovering process
The invention relates to a technology method of flotation tailings classification recovery process, belongs to solid-liquid separation technology area, used to solve maximize recovery of flotation tailings issue. It uses classification Cyclone group to grade flotation tailings, the products moisture after dehydration is 14-18%, the particle size of recovery is 0.045-3mm, it occupy55-60% of floatation tailings quantity; the pressure filter recover fine fuel, the product after dehydration occupy 40-45% of floatation tailings quantity. The invention method filled the flotation tailings bank of use the technology at home and abroad, supplies a low input, high efficiency, simple process, a high degree automation of flotation tailings recovery method, has a simple system, low-moisture products, a bulk materials, can into the coal or other late Medium steam coal advantages. Six months can recover the investment, with good economic and social benefits.
Owner:开滦(集团)有限责任公司煤业分公司
Polymeric film for water soluble package
InactiveUS7083047B2Organic detergent compounding agentsSolid separationPolymer thin filmsBackbone chain
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH +1
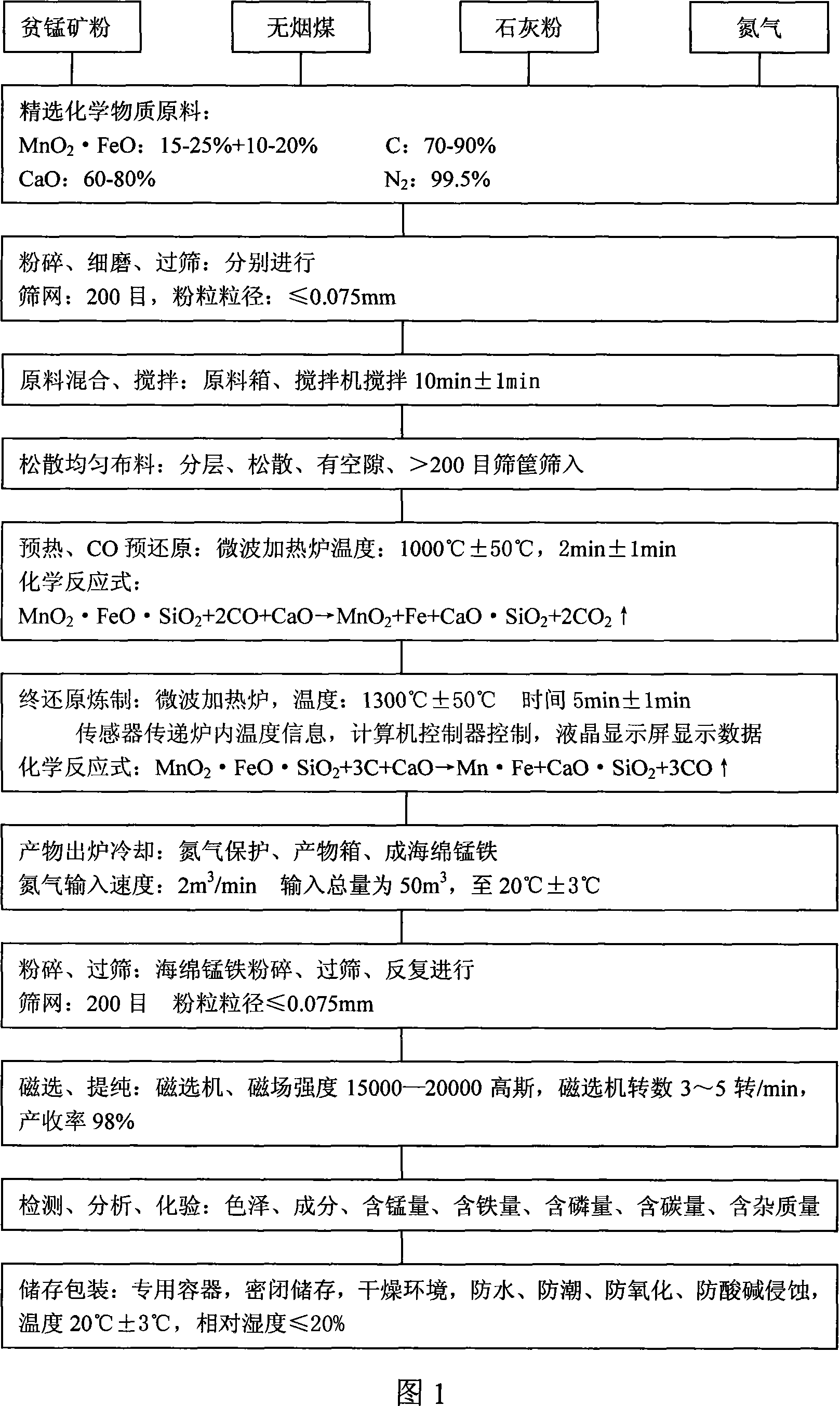
Method for preparing low-carbon metal manganese iron by using manganese-poor powdered ore
The invention relates to a low-carbon ferromanganese production method using low-grade manganese mineral powder. The low-grade manganese mineral powder which has rich reserves is heated by a micro-wave oven, reduced by carbon, smelted at high temperature, purified by magnetic separation to directly prepare low-carbon ferromanganese. And the production method saves sintered agglomeration process with large energy consumption and serious pollution. The low-carbon ferromanganese with high purity is made through the steps that: the material is carefully chosen, crushed, fine- grinded, sieved, mixed, stirred, preheated by the micro-wave oven, pre-reduced through carbon monoxide, finally reduced, smelted at high temperature, cooled under the protection of nitrogen and purified by magnetic separation. The preparation method has the advantages of short technological process, less using equipment, being suitable for large- scale industrialization production, the yield rate can reach 98 percent, wherein manganese content is 75 percent and iron content is 20 percent, and the content of carbon is less than 0.5 percent; the content of harmful material sulfur is also less than 0.5 percent; the content of phosphor is less than 0.2 percent. The products have the advantages of low carbon, low phosphor and sulfur containing, no agglomeration, no pollution to environment. The method is the ideal ferromanganese direct production method using low-grade manganese mineral powder and fills up a scientific research blank in the field in China.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com