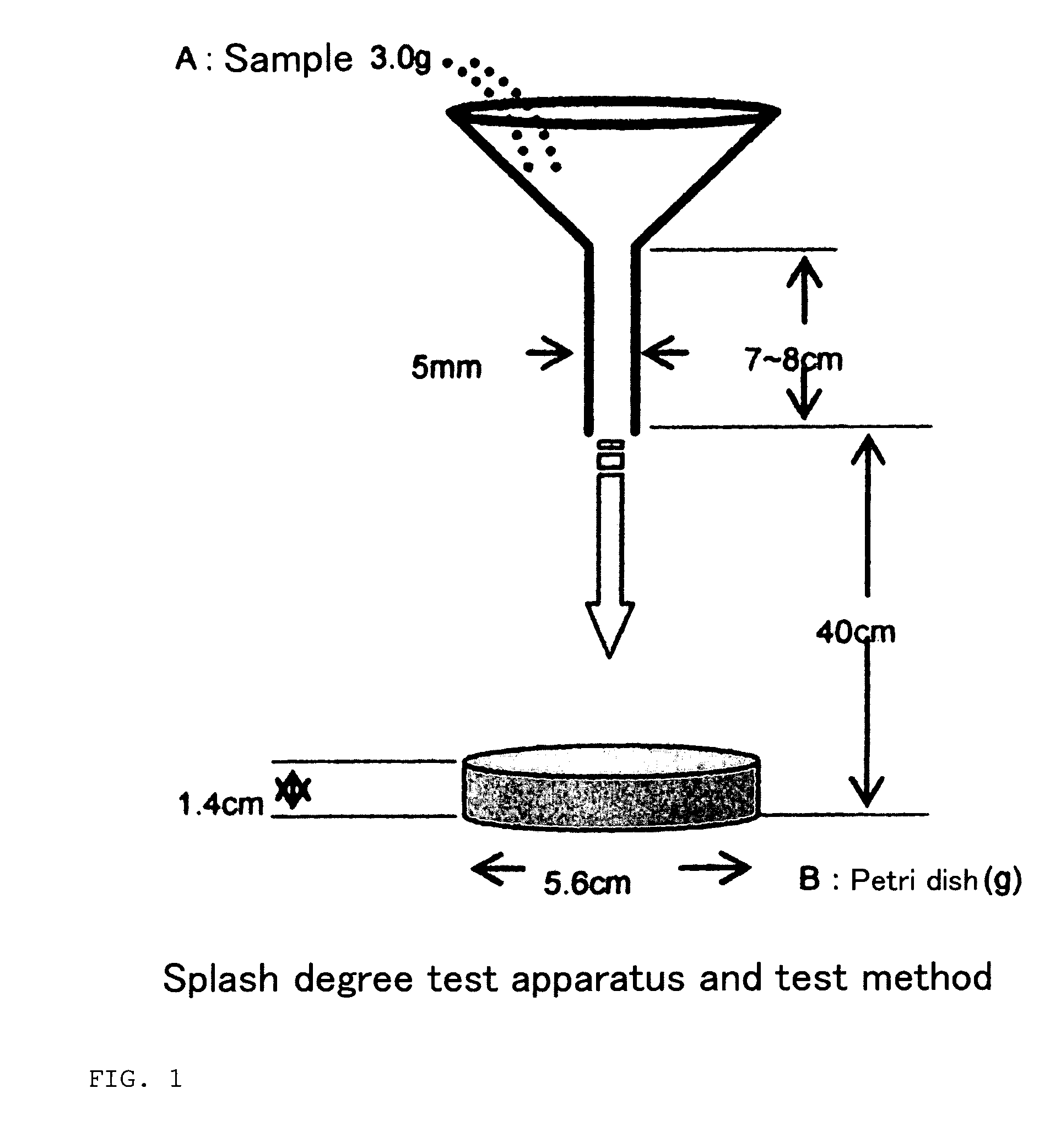
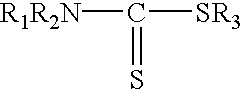
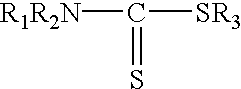
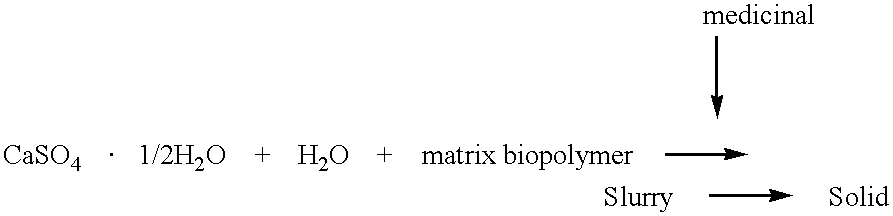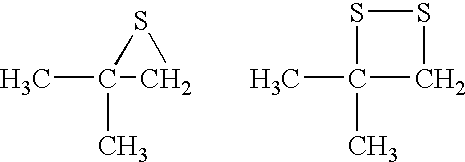Patents
Literature
1268 results about "Inorganic Carbon Compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the composition of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Inorganic compounds can be defined as any compound that is not organic compound. Some simple compounds that contain carbon are often considered inorganic.
Phosphor and light-emitting equipment using phosphor
ActiveUS20070007494A1Increase brightnessGood colorOther chemical processesNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsFluorescenceRare earth
An object of the present invention is to provide an inorganic phosphor having fluorescence properties emitting an orange or red light which has a longer wavelength as compared with the cases of conventional sialon phosphors activated with a rare earth. The invention relates to a design of white light-emitting diode rich in a red component and having good color-rendering properties by employing a solid solution crystal phase phosphor which uses as a host crystal an inorganic compound having the same crystal structure as that of a CaSiAlN3 crystal phase and to which M Element (wherein M Element is one or two or more elements selected from the group consisting of Mn, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb) is added as an emission center.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
Methods for removing organic compounds from nano-composite materials
InactiveUS6960327B2Conveniently producedAvoid calcinationAluminium compoundsSilicaLight waveSimple Organic Compounds
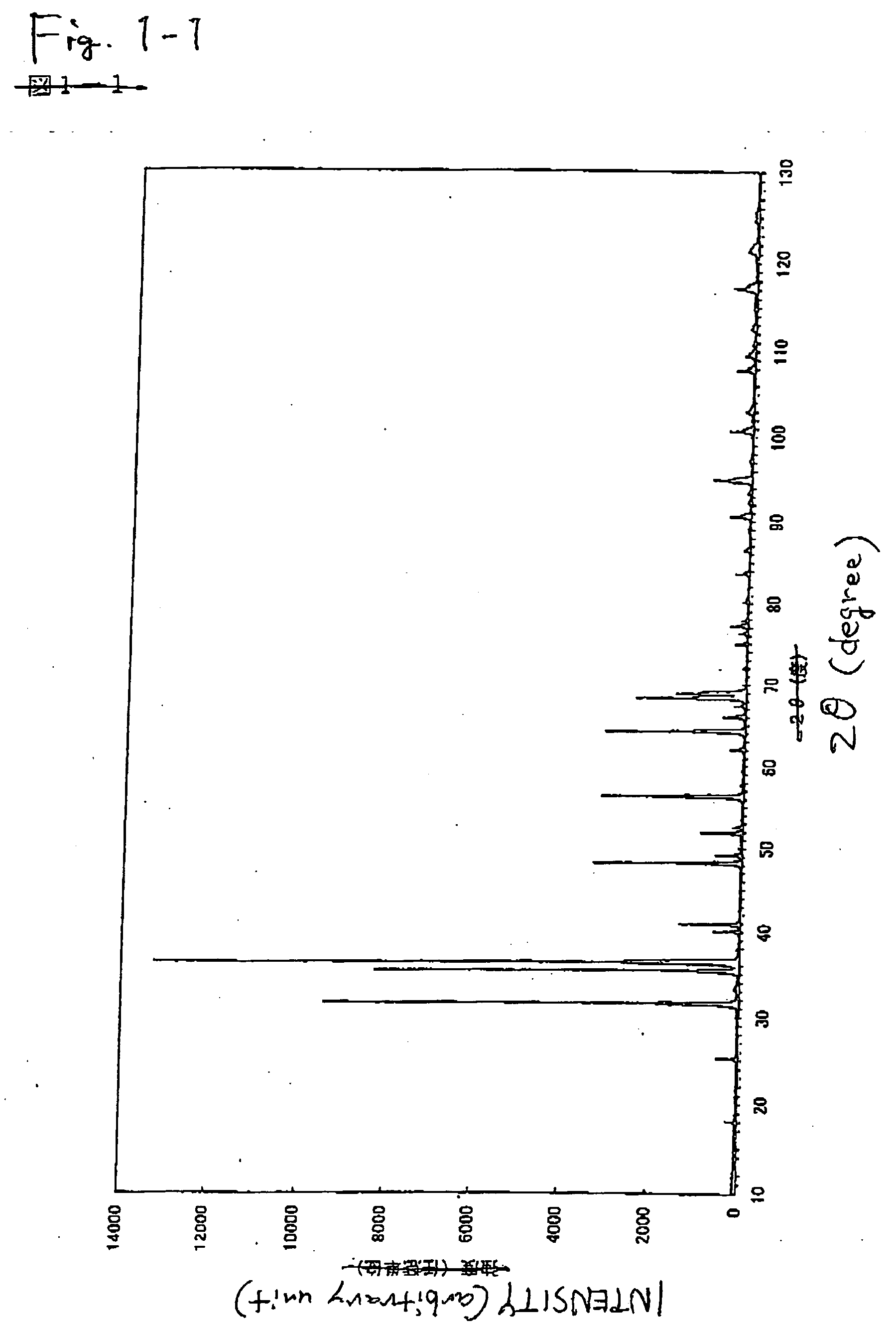
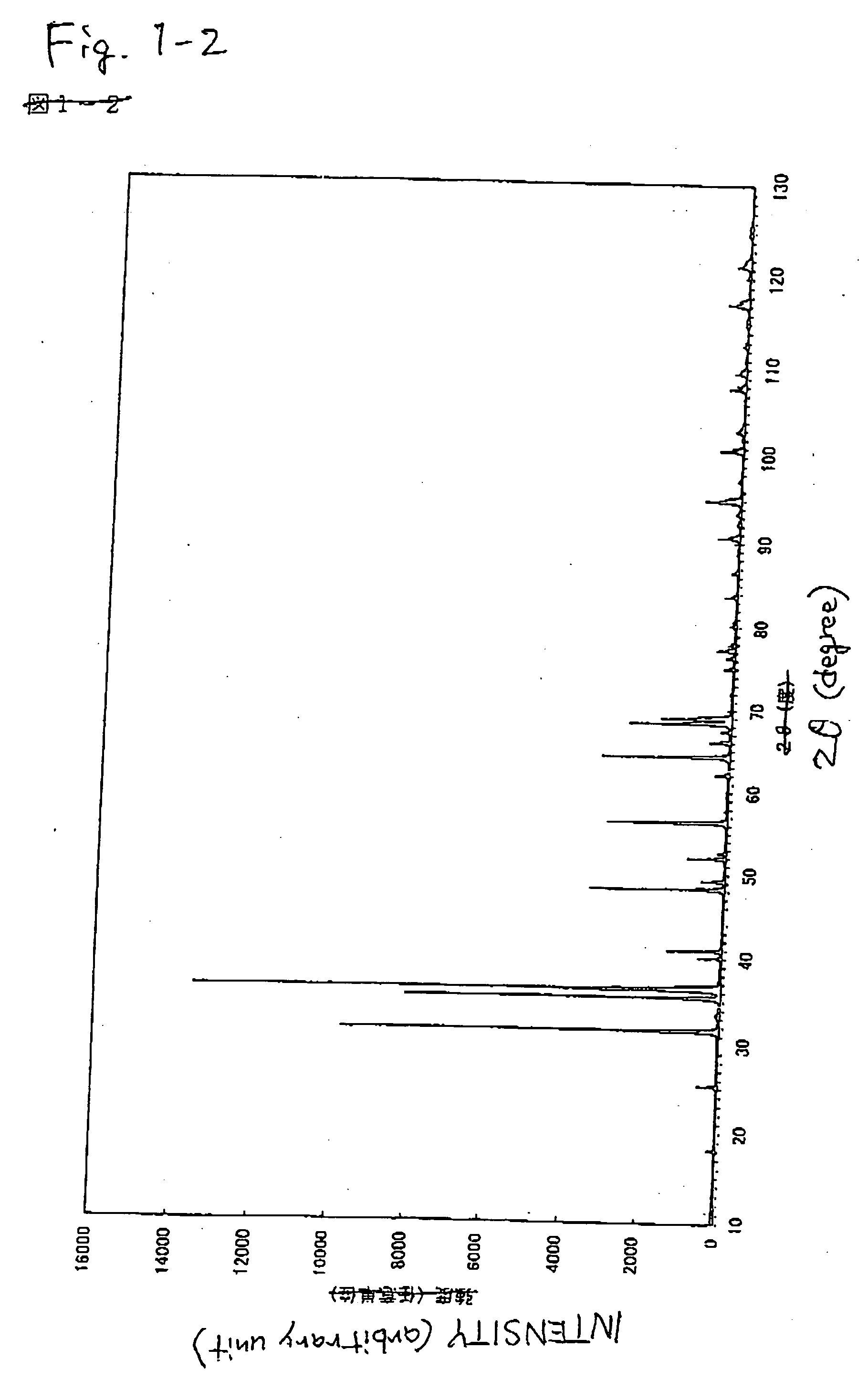
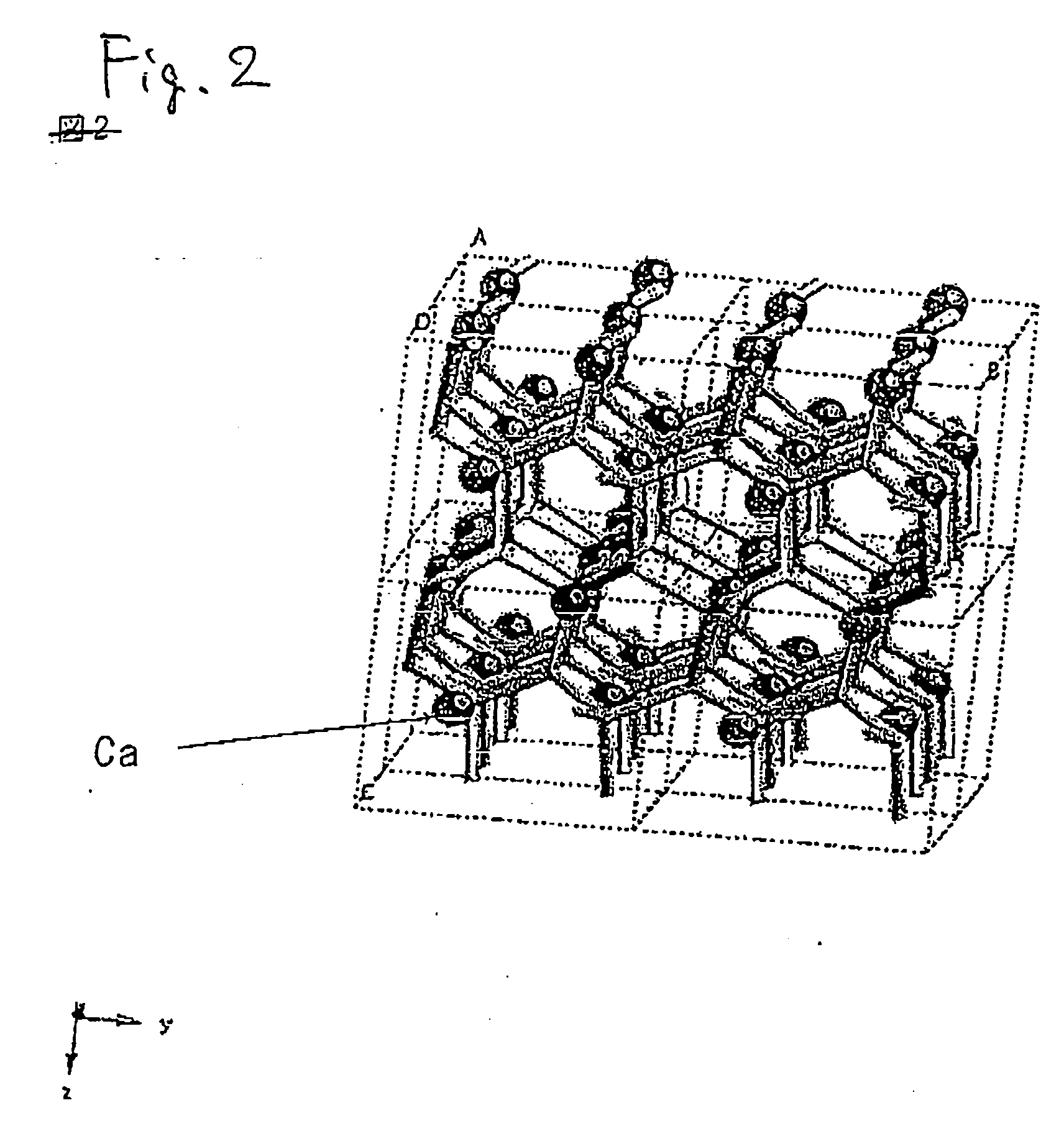
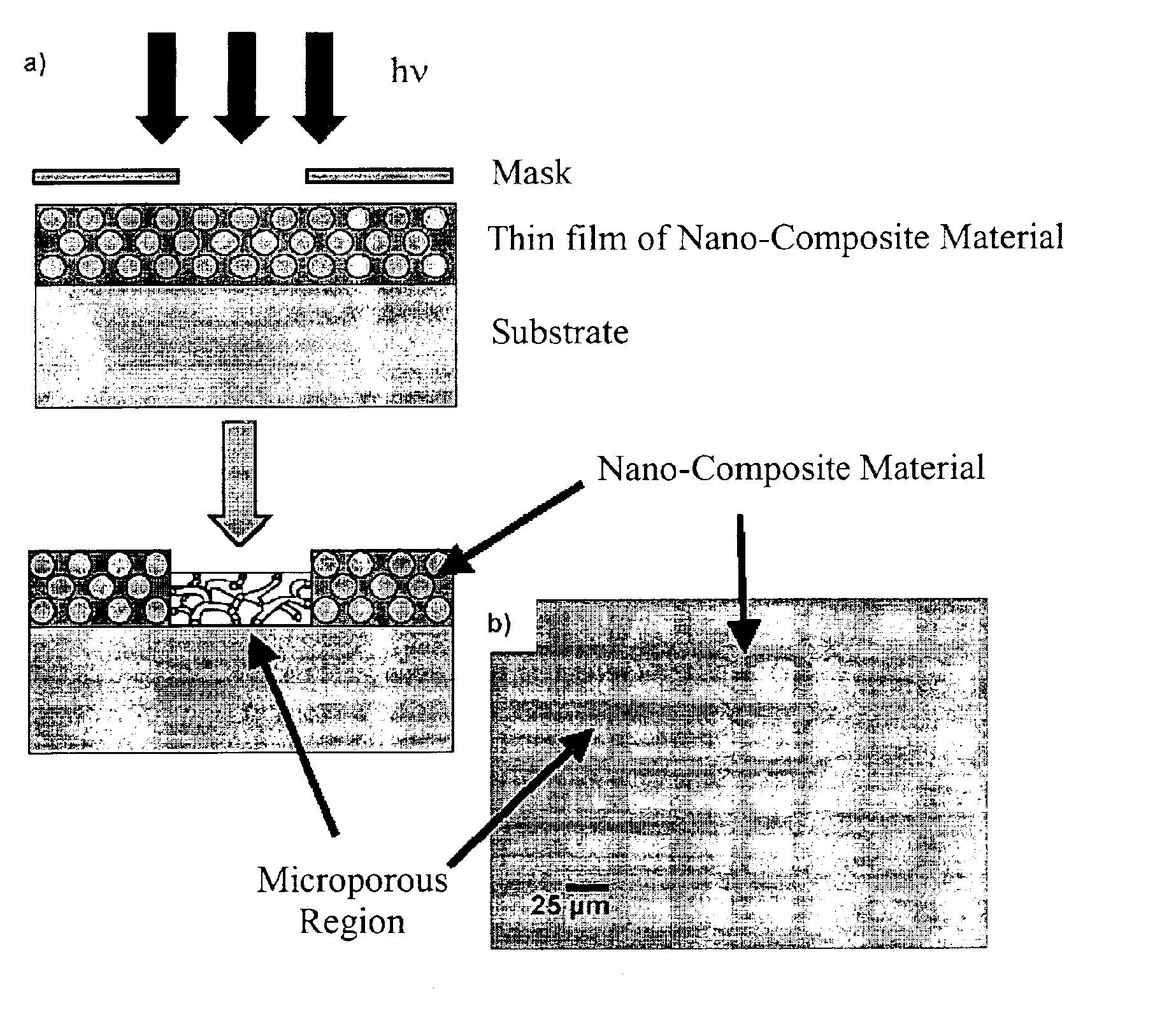
The present invention provides methods for selectively removing organic compound from a nano-composite material which comprises the organic compound that is dispersed within a solid inorganic compound structure. In particular, methods of the present invention comprise irradiating the nano-composite material with electromagnetic radiation wavelength that is shorter than the wavelength of visible light.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functions or binding specificities
ActiveUS20060228300A1Reduce exposureReduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAntibody fragmentsBinding peptide
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for stably tethered structures of defined compositions with multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. Particular embodiments concern stably tethered structures comprising a homodimer of a first monomer, comprising a dimerization and docking domain attached to a first precursor, and a second monomer comprising an anchoring domain attached to a second precursor. The first and second precursors may be virtually any molecule or structure, such as antibodies, antibody fragments, antibody analogs or mimetics, aptamers, binding peptides, fragments of binding proteins, known ligands for proteins or other molecules, enzymes, detectable labels or tags, therapeutic agents, toxins, pharmaceuticals, cytokines, interleukins, interferons, radioisotopes, proteins, peptides, peptide mimetics, polynucleotides, RNAi, oligosaccharides, natural or synthetic polymeric substances, nanoparticles, quantum dots, organic or inorganic compounds, etc. The disclosed methods and compositions provide a simple, easy to purify way to obtain any binary compound attached to any monomeric compound, or any trinary compound.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Chemical manufacture of nanostructured materials
InactiveUS6872330B2High strengthIncrease volumeMaterial nanotechnologyOxide/hydroxide preparationInorganic compoundTe element
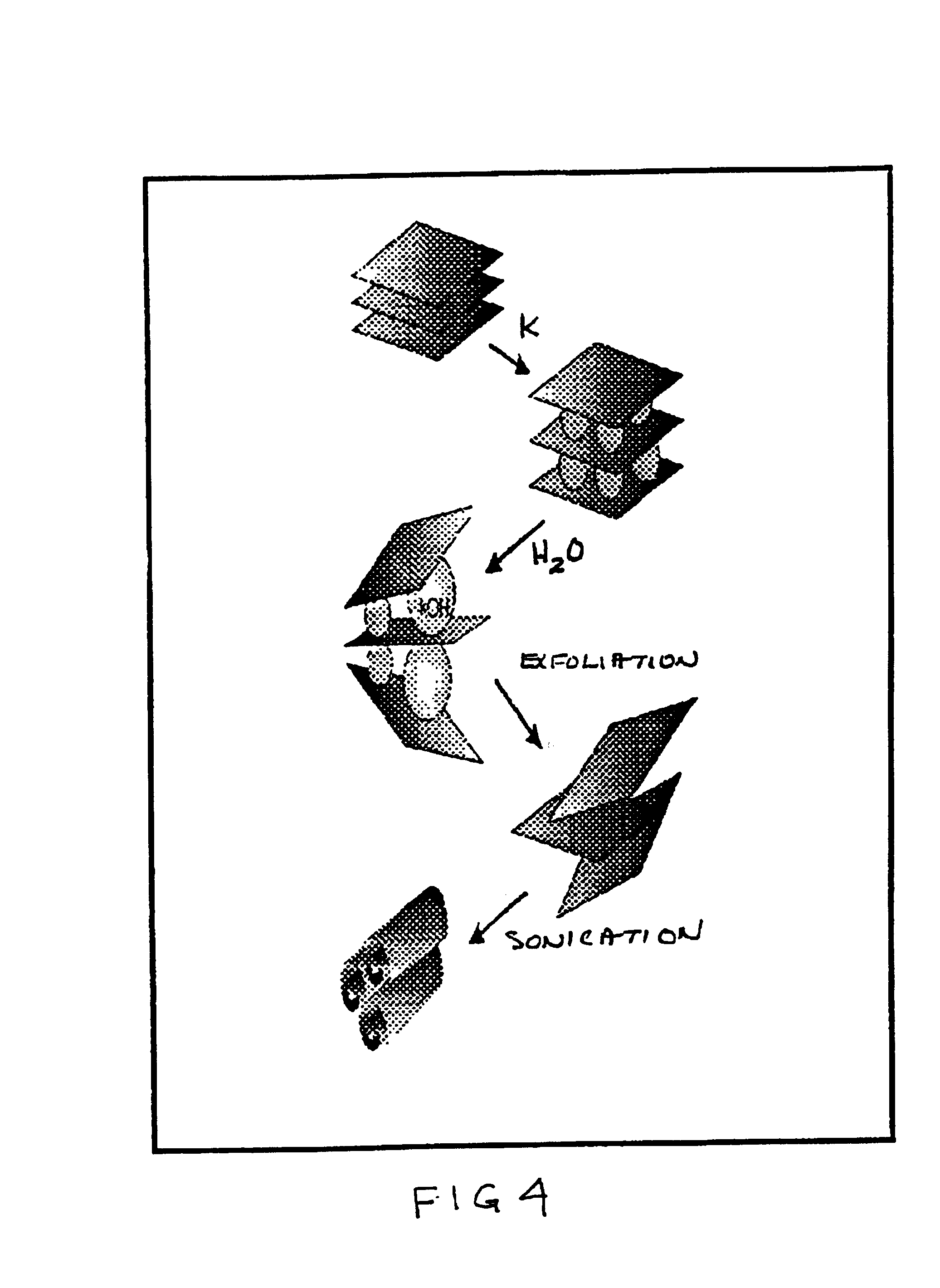
A low temperature chemical route to efficiently produce nanomaterials is described. The nanomaterials are synthesized by intercalating ions into layered compounds, exfoliating to create individual layers and then sonicating to produce nanotubes, nanorods, nanoscrolls and / or nanosheets. It is applicable to various different layered inorganic compounds (for example, bismuth selenides / tellurides, graphite, and other metal complexes, particularly transition metal dichalcogenides compounds including oxygen, sulfur, tellurium or selenium).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Organic electroluminescent device and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6416888B1Increased durabilityReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesInorganic compoundThin layer
An organic EL device having a low driving voltage and exhibiting high luminous brightness and superior durability, and a method of manufacturing the same. The organic EL device has an anode layer, an organic light-emitting layer, and a cathode layer. An inorganic thin layer, comprising an inorganic compound of Ge, Sn, Zn, Cd, etc. and an inorganic compound of an element of Group 5A to Group 8 in the periodic table in combination, is provided between the anode layer and the organic light-emitting layer and between the cathode layer and the organic light-emitting layer, or the anode layer or the cathode layer comprises a chalcogenide of Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, Ga, In, Zn, Cd, Mg, etc. and an inorganic compound of an element of Group 5A to Group 8 in the periodic table in combination.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Silicon composite particles, preparation thereof, and negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell
ActiveUS20050214644A1Improve cycle performanceMinimize changesSilicaNitrogen compoundsSilicon alloyInorganic compound
Silicon composite particles are prepared by sintering primary fine particles of silicon, silicon alloy or silicon oxide together with an organosilicon compound. Sintering of the organosilicon compound results in a silicon-base inorganic compound which serves as a binder. Each particle has the structure that silicon or silicon alloy fine particles are dispersed in the silicon-base inorganic compound binder, and voids are present within the particle.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Electrochemical methods, devices, and structures
ActiveUS20060102455A1Increase strainDeferred-action cellsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersInorganic compoundElectrochemistry
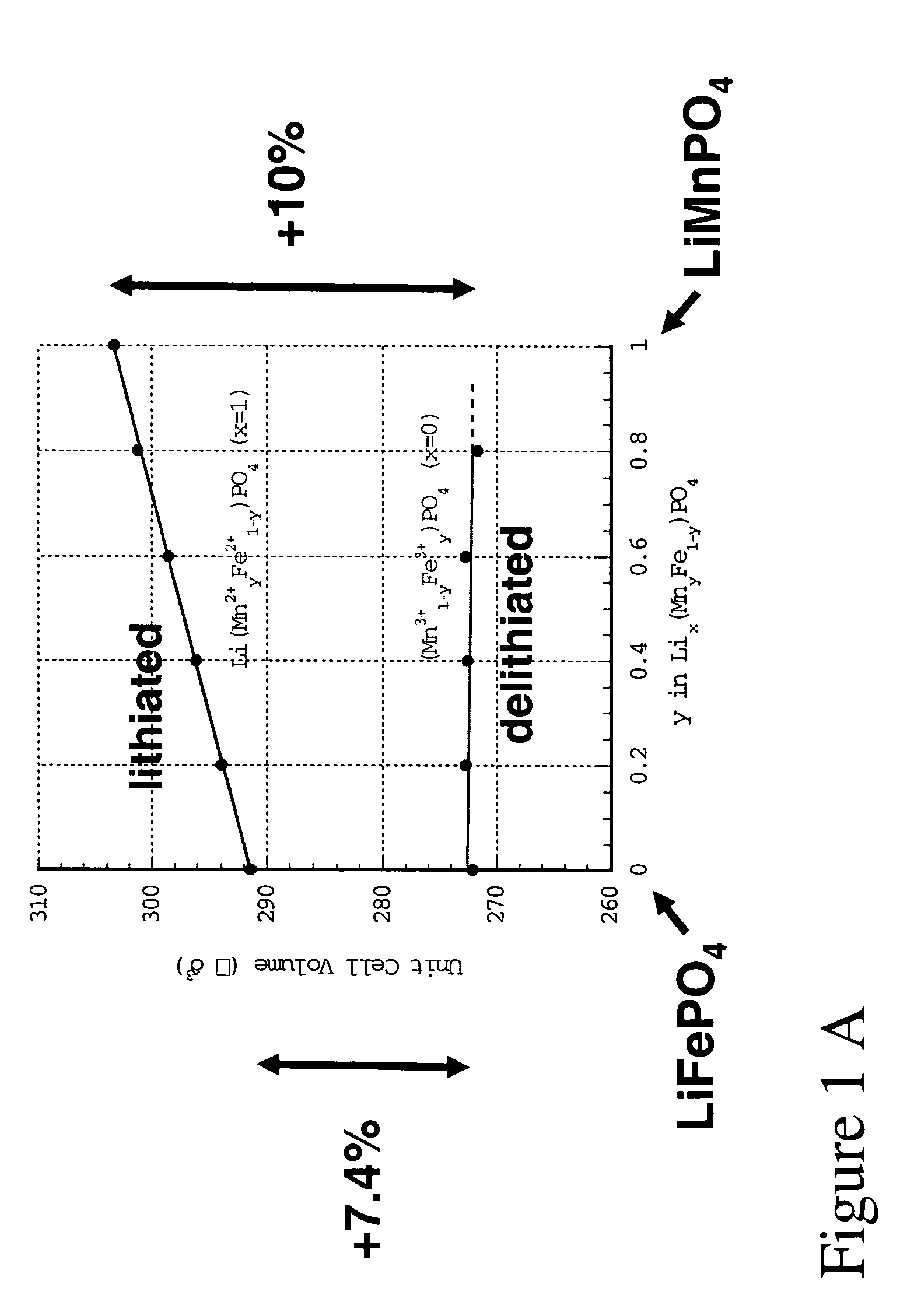
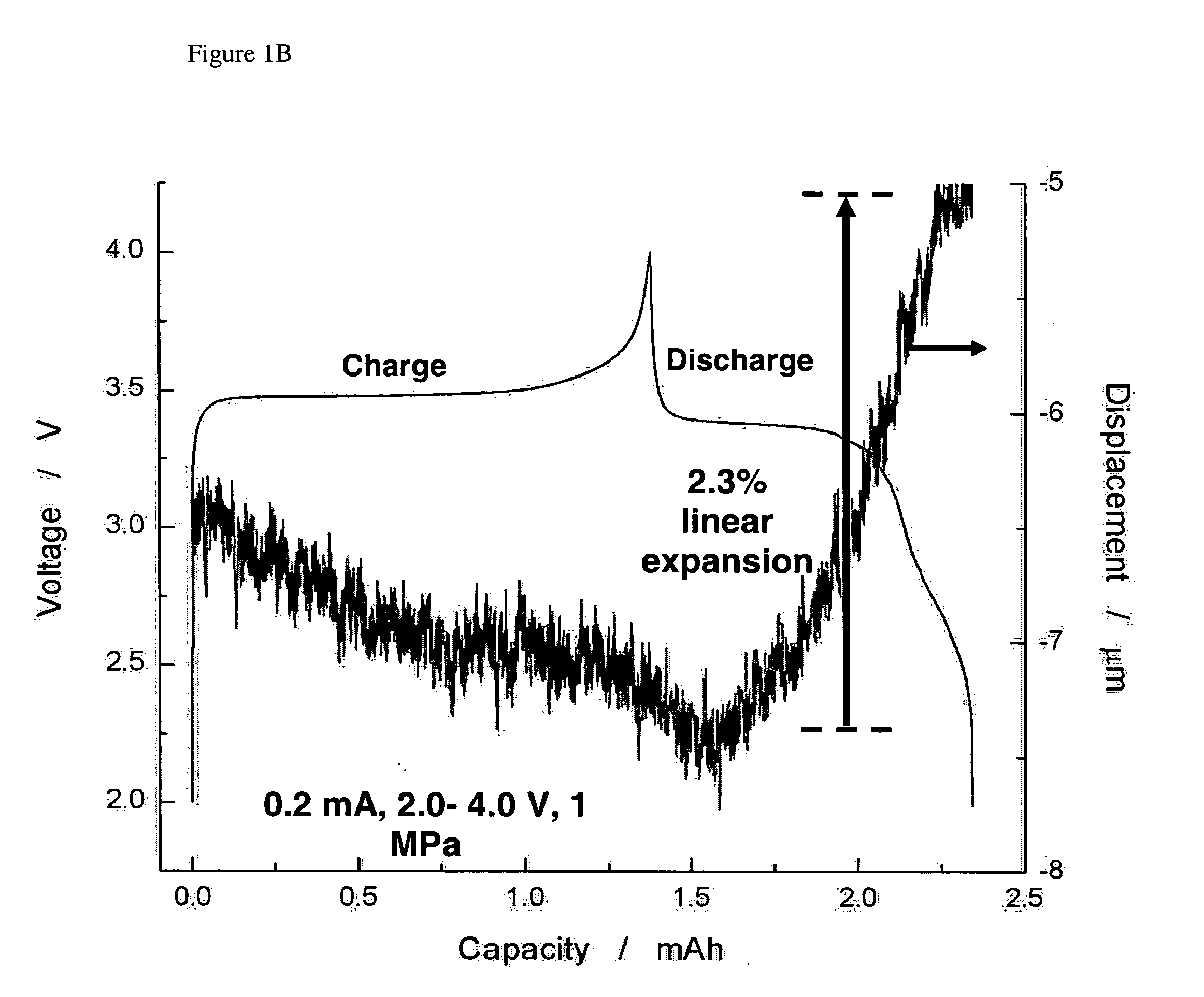
The present invention provides devices and structures and methods of use thereof in electrochemical actuation. This invention provides electrochemical actuators, which are based, inter-alia, on an electric field-driven intercalation or alloying of high-modulus inorganic compounds, which can produce large and reversible volume changes, providing high actuation energy density, high actuation authority and large free strain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
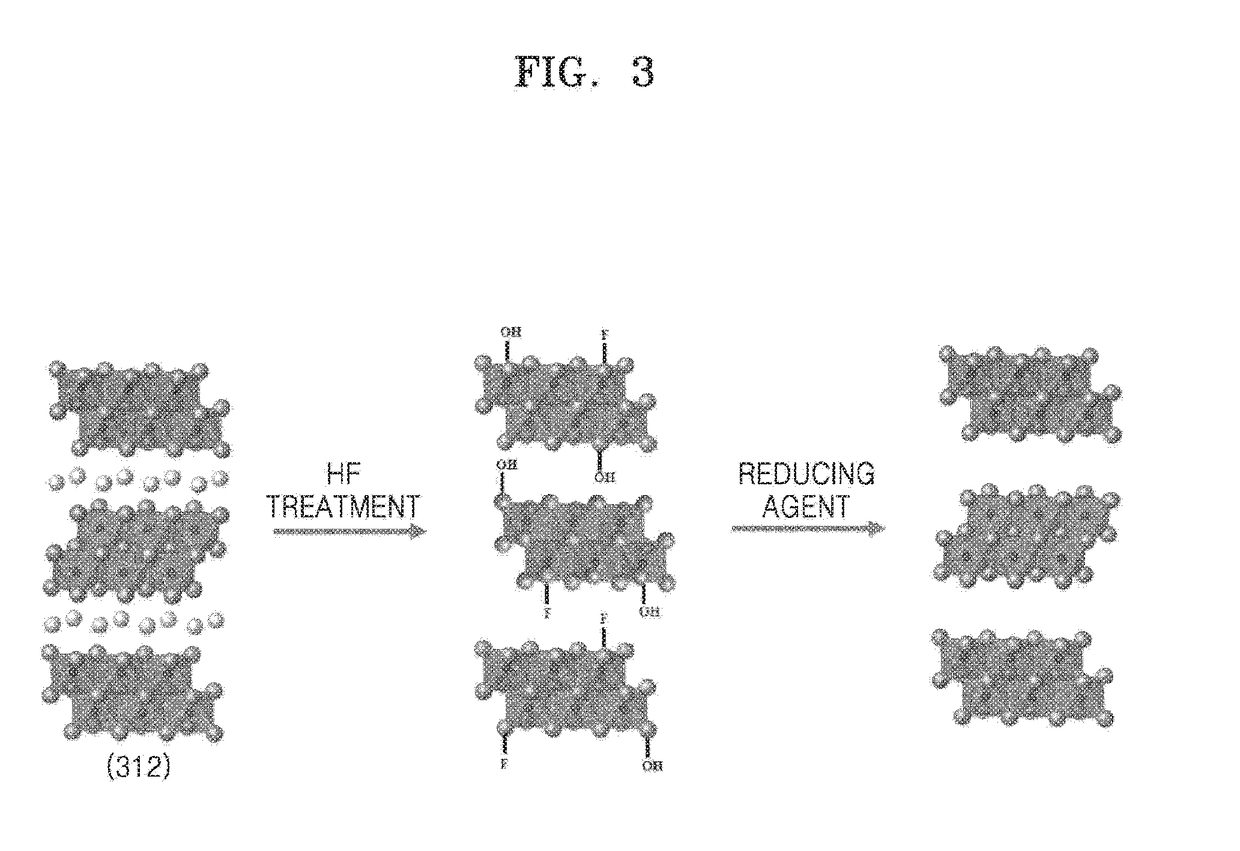
Mxene nanosheet and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20170088429A1Material nanotechnologyNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsIodideInorganic compound
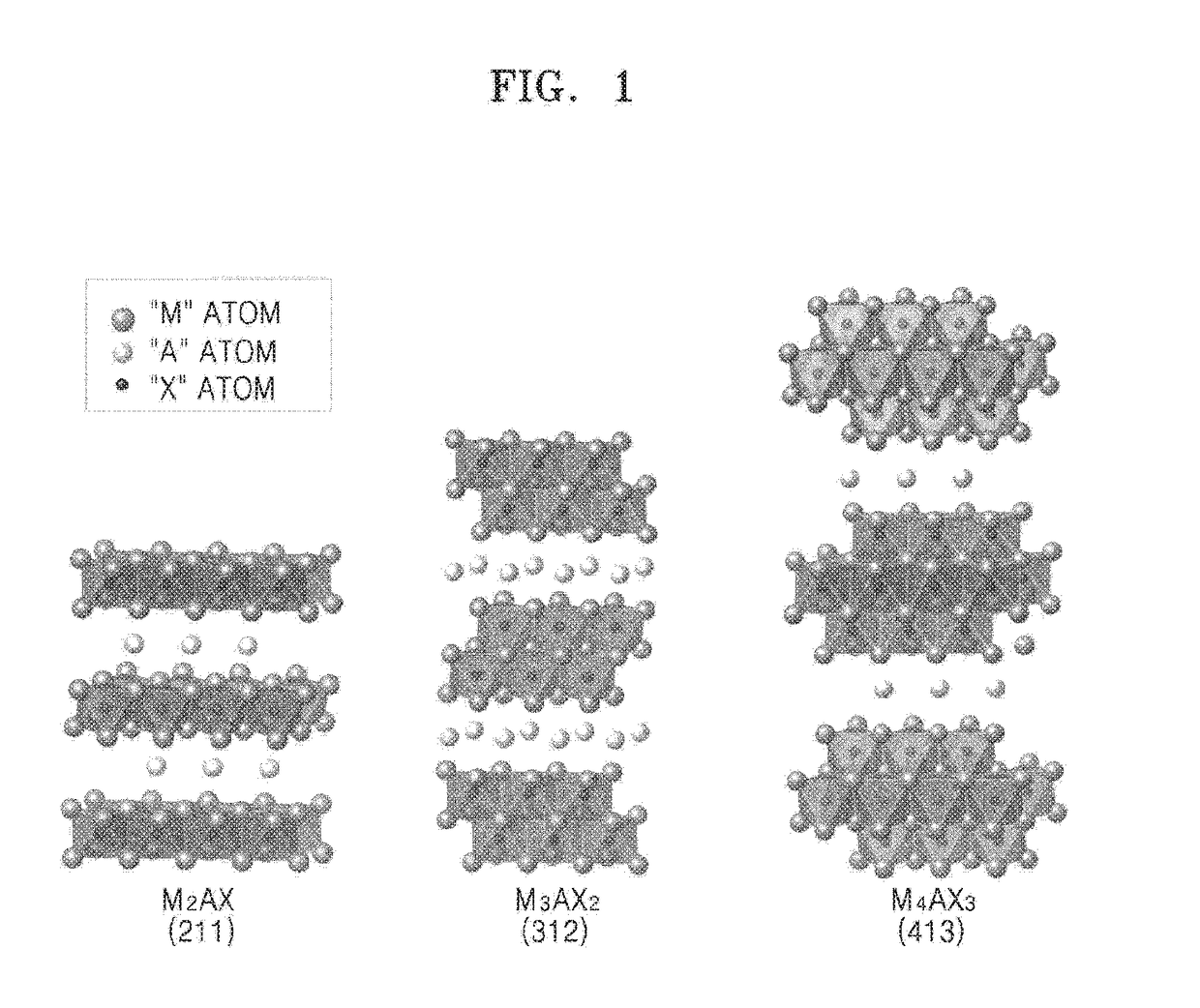
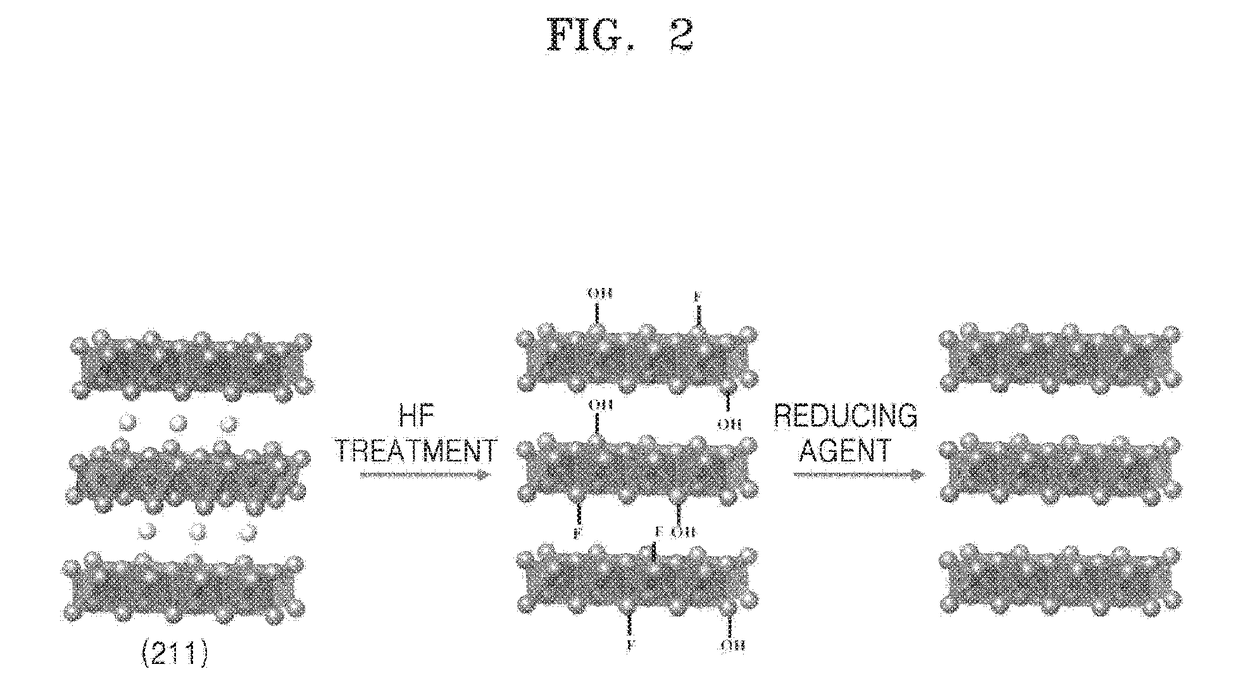
A method of manufacturing a MXene nanosheet includes removing an A atomic layer from an inorganic compound having a formula of Mn+1AXn to form a nanosheet, the nanosheet having a formula of Mn+1XnTs, and reducing the nanosheet having a formula of Mn+1XnTsto form an MXene nanosheet, the MXene nanosheet having a formula of Mn+1Xn, wherein M is at least one of Group 3 transition metal, Group 4 transition metal, Group 5 transition metal, and Group 6 transition metal, A is at least one of a Group 12 element, Group 13 element, Group 14 element, Group 15 element and Group 16 element, X is one of carbon (C), nitrogen (N) and a combination thereof, Ts is one of oxide (O), epoxide, hydroxide (OH), alkoxide having 1-5 carbon atoms, fluoride (F), chloride (Cl), bromide (Br), iodide (I), and a combination thereof, and n is one of 1, 2 and 3.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV +1
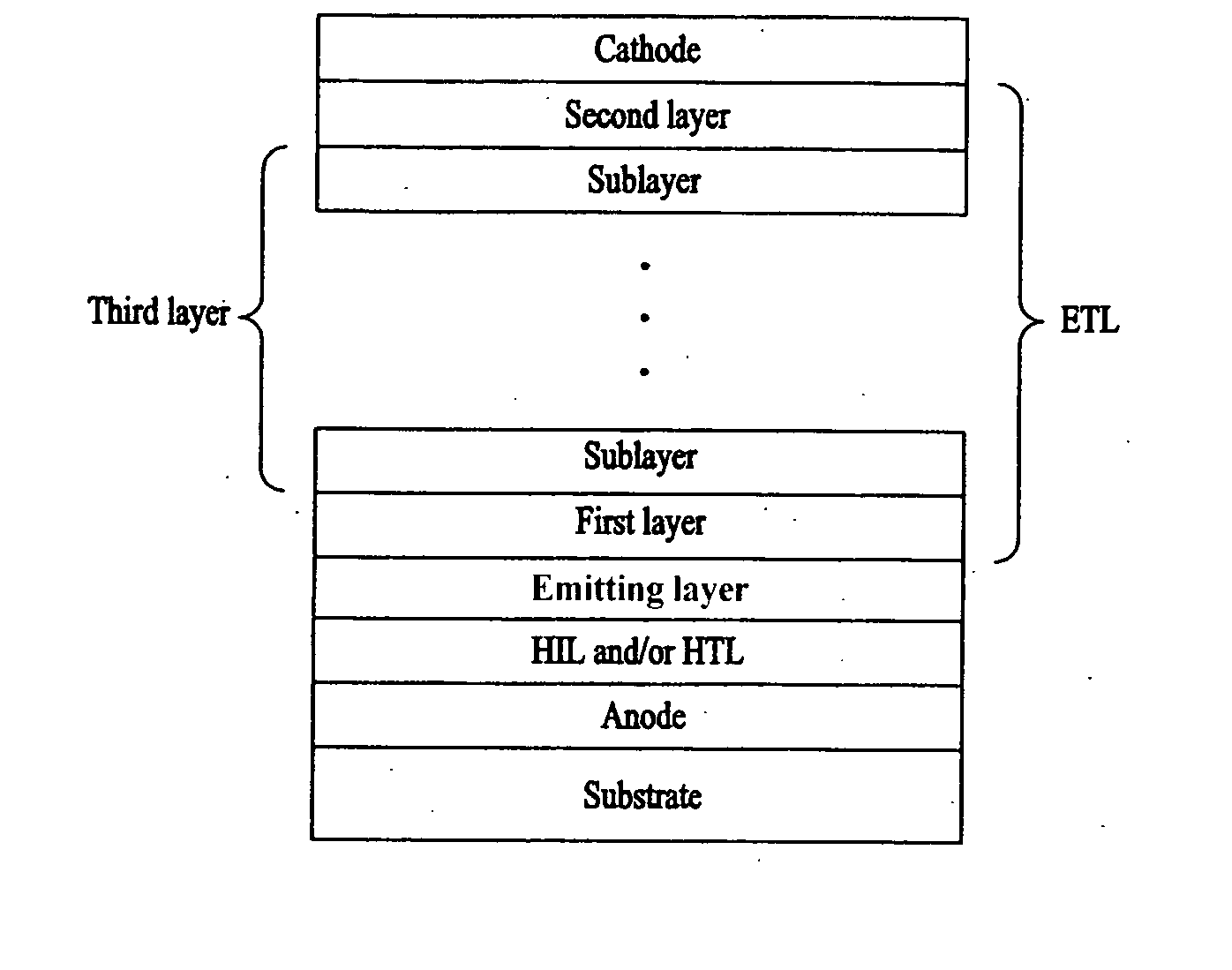
Organic electroluminescence device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070020483A1Improve efficiencyProlong lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsInorganic compound
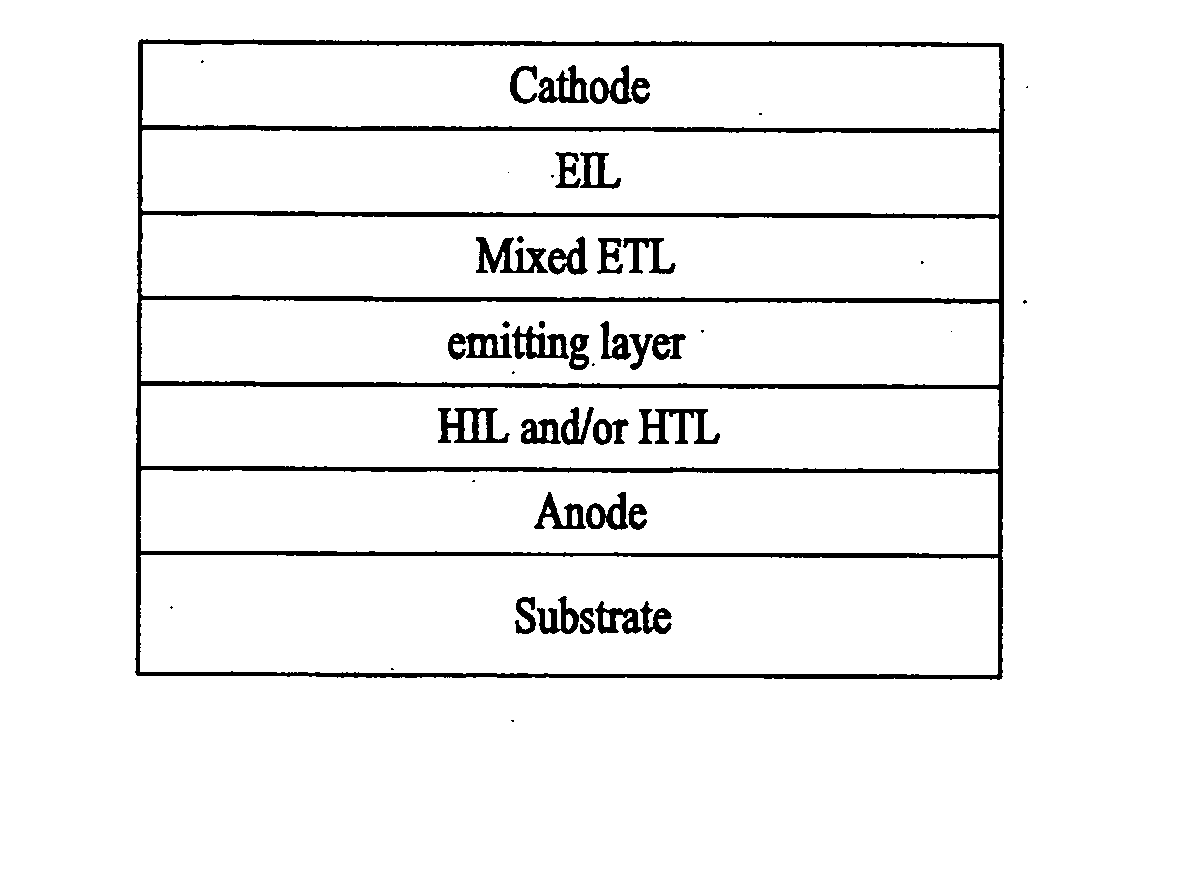
An organic electroluminescent (EL) device having improved efficiency and service life is provided. The organic electroluminescent device has a stack structure including an emitting layer and an electron-transport layer positioned between an anode and a cathode. The electron-transport layer includes a first layer adjacent to the emitting layer which may be a mixture of at least two materials, and a second layer adjacent to the cathode which may be a mixture of at least two materials. The mixture of at least two materials may be a mixture of an organic compound and one or more other organic compounds, or may be a mixture of a metal or inorganic compound and one or more other metal or inorganic compounds, or may be a mixture of one or more organic compounds and one or more metal or inorganic compounds.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Apparatus and process for mediated electrochemical oxidation of materials
A unique apparatus unique apparatus and process that uses mediated electrochemical oxidation (MEO) for: (1) Destruction of: a) nearly all organic solid, liquid, and gases materials, except fluorinated hydrocarbons; b) all biological solid, liquid, and gases materials; c) and / or dissolution and decontamination (such as cleaning equipment and containers, etc.) of nearly all inorganic solid, liquid, or gas where higher oxidation states exist which includes, but is not limited to, halogenated inorganic compounds (except fluorinated), inorganic pesticides and herbicides, inorganic fertilizers, carbon residues, inorganic carbon compounds, mineral formations, mining tailings, inorganic salts, metals and metal compounds, etc.); and d) combined materials (e.g. a mixture of any of the foregoing with each other); henceforth collectively referred to as materials. (2) Sterilization / disinfection of equipment, glassware, etc., by destroying all existing infectious materials. (3) Dissolution of transuranic / actinide materials and / or destruction of the oxidizable components in the hazardous waste portion of mixed waste. (4) Generation of hydrogen and oxygen from MEO of materials. (5) Alteration of organic, biological, and inorganic materials by MEO to produce other compounds from these materials. The materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the materials with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the materials molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable material species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100° C. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
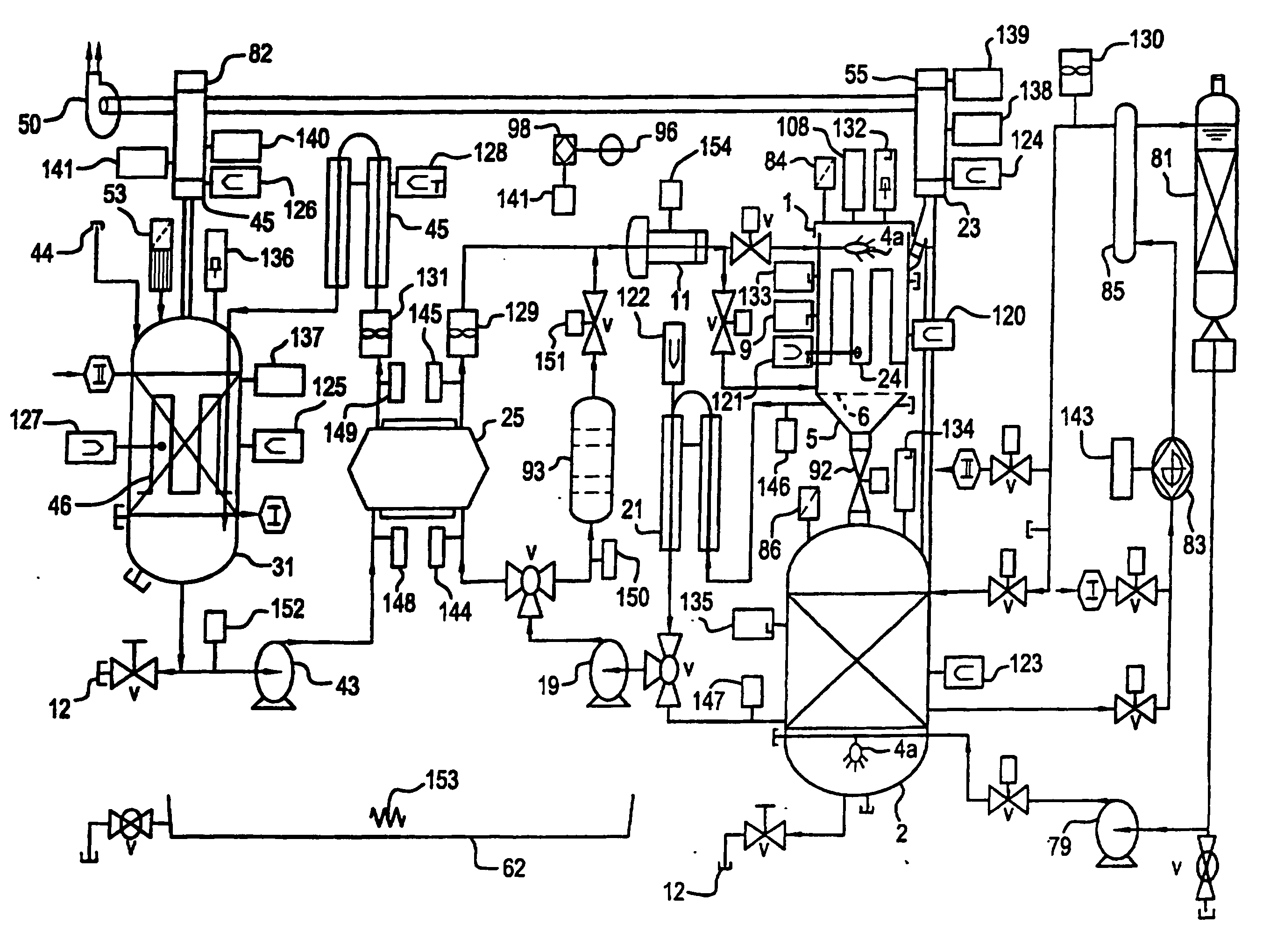
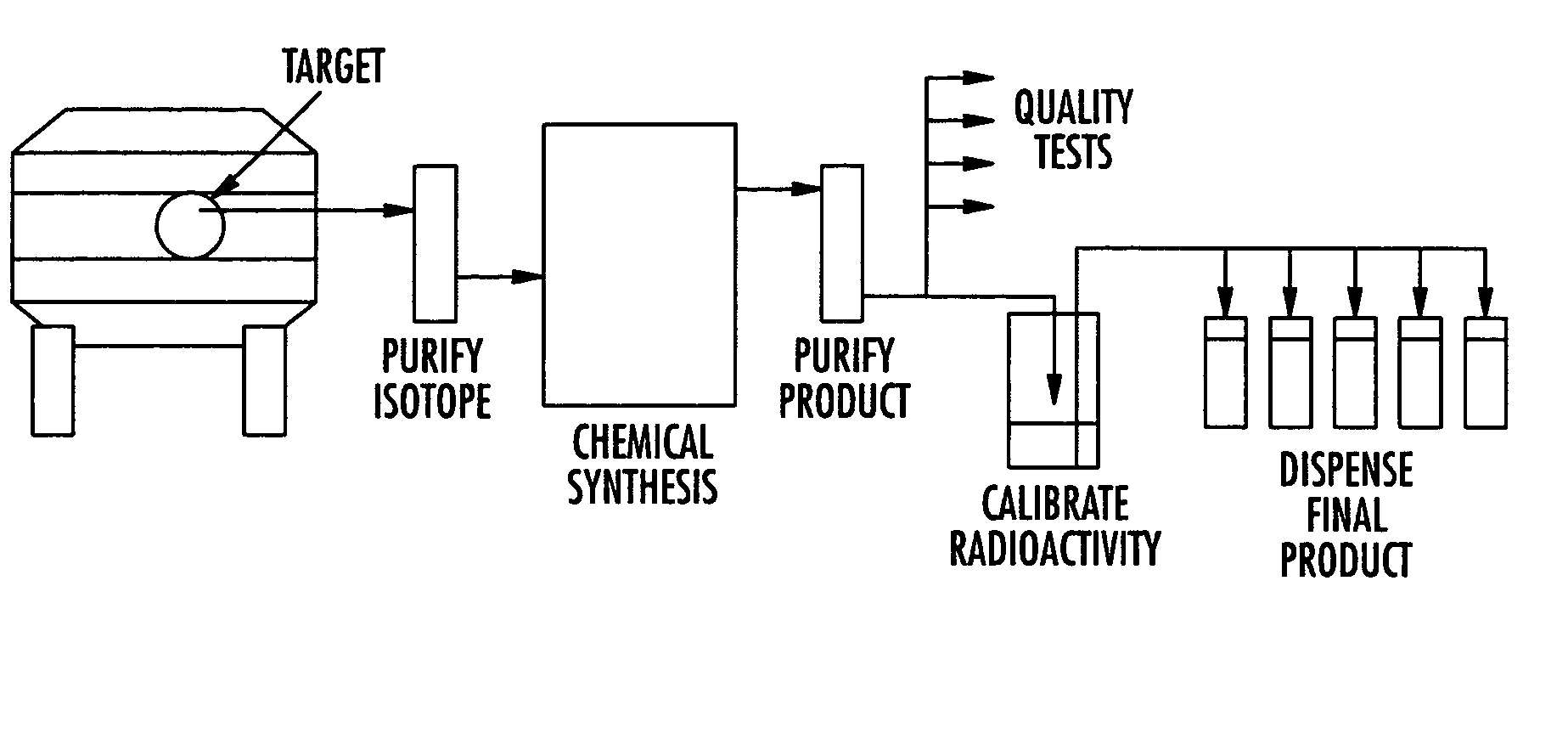
Microfluidic apparatus and method for synthesis of molecular imaging probes
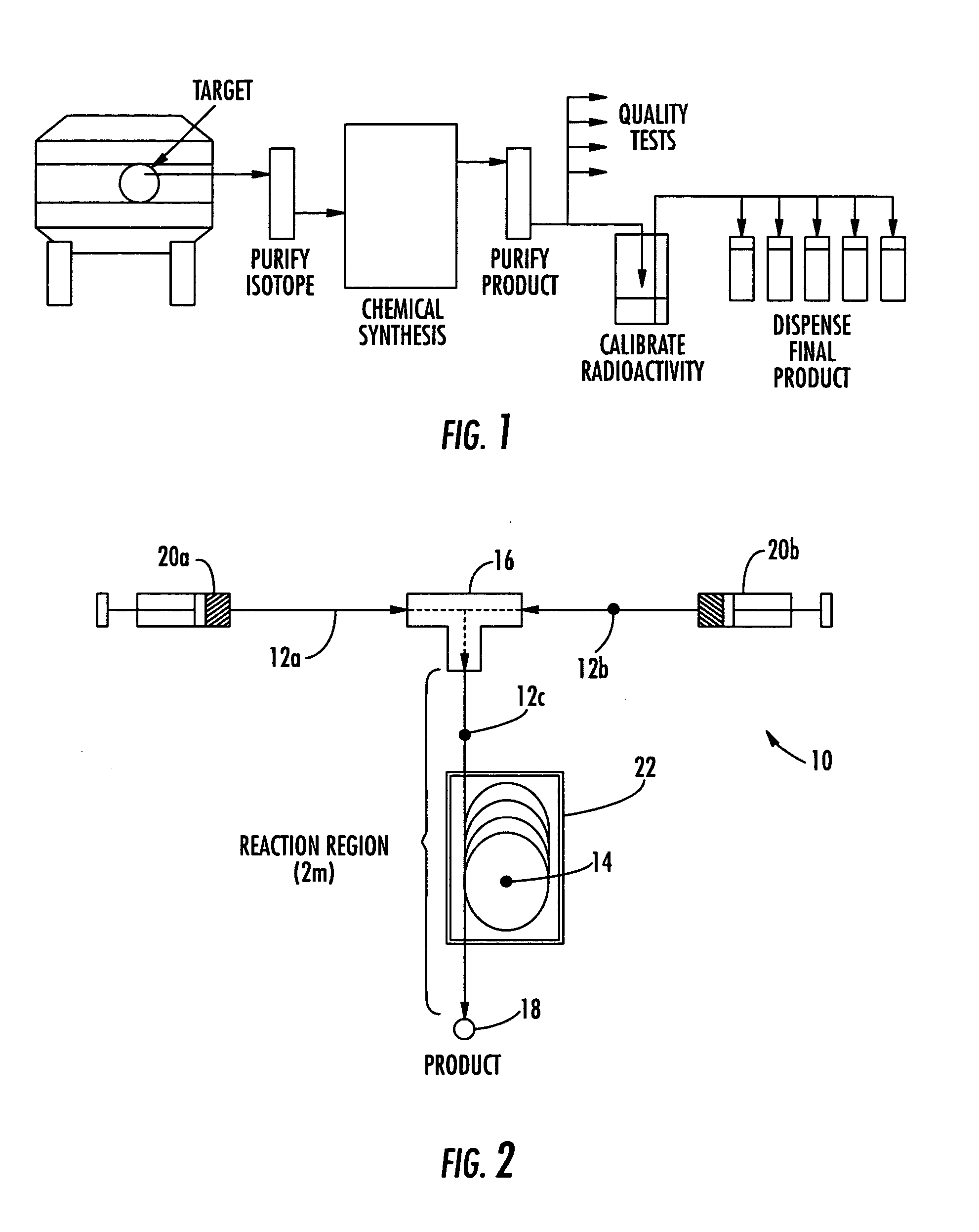
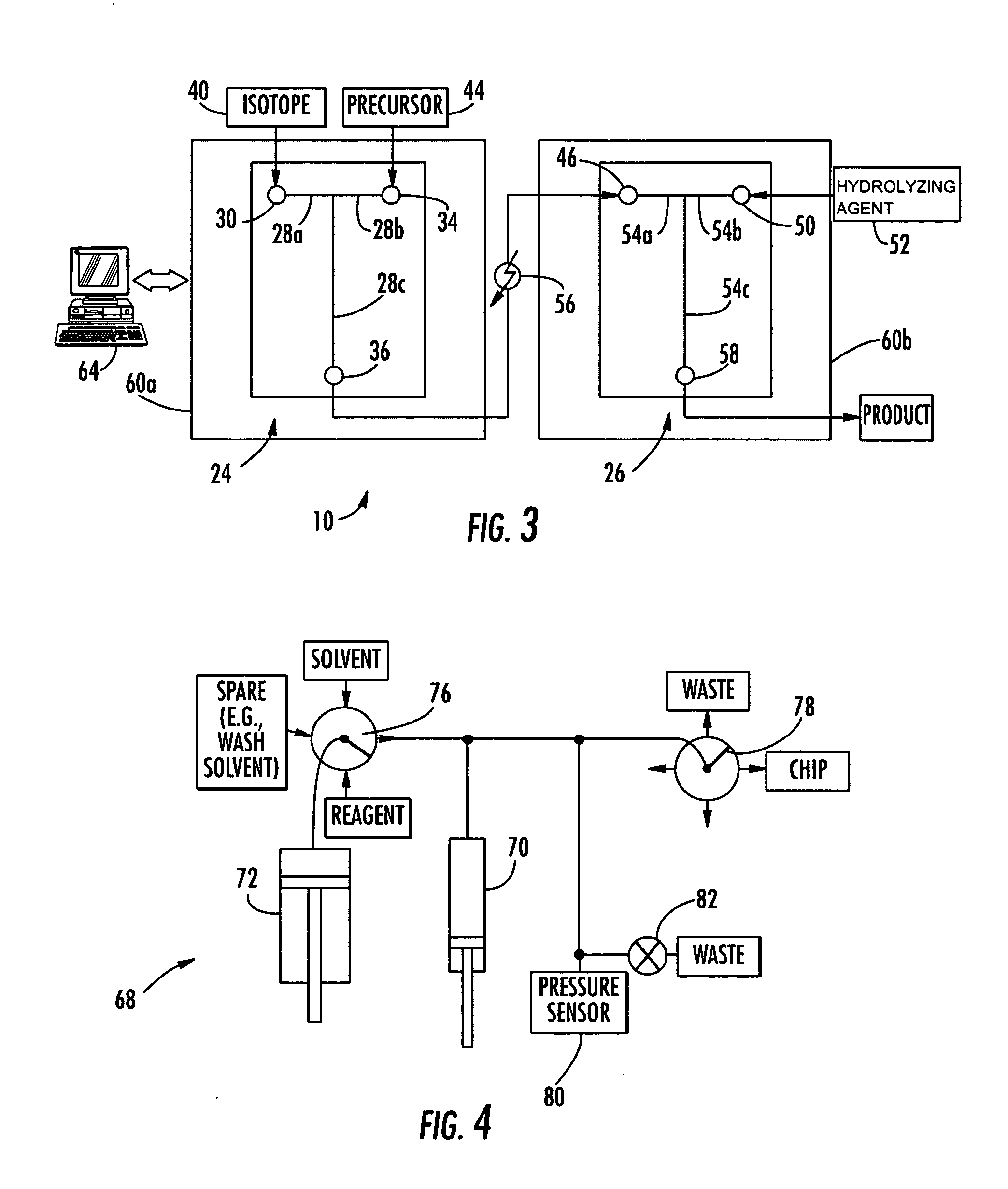
InactiveUS20050232387A1Fast synthesis timeHigh synthetic yieldIn-vivo radioactive preparationsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMicroreactorMolecular imaging
The invention provides a method and apparatus for preparation of radiochemicals, such as PET molecular imaging probes, wherein the reaction step or steps that couple the radioactive isotope to an organic or inorganic compound to form a positron-emitting molecular imaging probe are performed in a microfluidic environment. The method for synthesizing a radiochemical in a microfluidic environment comprises: i) providing a micro reactor comprising a first inlet port, a second inlet port, an outlet port, and at least one microchannel in fluid communication with the first and second inlet ports and the outlet port; ii) introducing a reactive precursor into the first inlet port of the micro reactor, the reactive precursor adapted for reaction with a radioactive isotope to form a radiochemical; iii) introducing a solution comprising a radioactive isotope into the second inlet port of the micro reactor; iv) contacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution in the microchannel of the micro reactor; v) reacting the reactive precursor with the isotope-containing solution as the reactive precursor and isotope-containing solution flow through the microchannel of the micro reactor, the reacting step resulting in formation of a radiochemical; and vi) collecting the radiochemical from the outlet port of the micro reactor.
Owner:MOLECULAR TECH
Inorganic-polymer complexes for the controlled release of compounds including medicinals
InactiveUS6391336B1Control releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsControlled releaseActive agent
This invention relates generally to the production and use of inorganic-polymer complexes for the controlled release of compounds including medicinals. The inorganic compound used is advantageously calcium sulfate-hemihydrate. The invention includes a composition for the controlled release of an active agent comprising: a) a hydrated or crystallized inorganic compound, and b) a matrix polymer which slows the release of the active agent, wherein the composition is a solid matrix due to the hydration or crystallization of the inorganic compound. Further included is a composition for the controlled release of an active agent comprising: a) a hydrated or crystallized inorganic compound, and b) a complexing agent which forms a salt or conjugate with the active agent, wherein the composition is a solid matrix due to the hydration or crystallization of the inorganic compound.
Owner:ROYER BIOMEDICAL INC
Fluorescent substance and light-emitting device employing the same
ActiveUS20100025632A1Improve quantum efficiencyHigh emission intensitySolid-state devicesLuminescent compositionsQuantum efficiencyFluorescence
The present invention provides a fluorescent substance excellent both in quantum efficiency and in temperature characteristics, and also provides a light-emitting device utilizing the fluorescent substance. This fluorescent substance contains an inorganic compound comprising a metal element M, a trivalent element M1 other than the metal element M, a tetravalent element M2 other than the metal element M, and either or both of O and N. In the inorganic compound, the metal element M is partly replaced with a luminescence center element R. The crystal structure of the fluorescent substance is basically the same as Sr3Al3Si13O2N21, but the chemical bond lengths of M1-N and M2-N are within the range of ±15% based on those of Al—N and Si—N calculated from the lattice constants and atomic coordinates of Sr3Al3Si13O2N21, respectively. The fluorescent substance emits luminescence having a peak in the range of 490 to 580 nm when excited with light of 250 to 500 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Display device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060091397A1Improve reliabilityHigh definitionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsDisplay device
It is an object of the invention to manufacture a highly reliable display device at a low cost with high yield. A display device of the invention includes: a first reflective electrode layer; and a second transparent electrode layer with an electroluminescent layer interposed therebetween, wherein the electroluminescent layer has a layer containing an organic compound and an inorganic compound, and the first electrode layer contains an aluminum alloy containing at least one or more selected from the group consisting of molybdenum, titanium, and carbon.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Non-alkaline micronized wood preservative formulations
Provided is a non-alkaline composition for the preservation of wood and other cellulosic materials. The composition comprises an aqueous dispersion of micronized inorganic compounds and / or organic biocides. Also provided is a method for making the composition.
Owner:OSMOSE
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070045621A1Reduce adhesionImprove adhesionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsDevice material
It is an object of the present invention to manufacture, with high yield, semiconductor devices in each of which an element which has a layer containing an organic compound is provided over a flexible substrate. A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device includes: forming a separation layer over a substrate; forming an element-forming layer by forming an inorganic compound layer, a first conductive layer, and a layer containing an organic compound over the separation layer, and forming a second conductive layer which is in contact with the layer containing an organic compound and the inorganic compound layer; and after attaching a first flexible substrate over the second conductive layer, separating the separation layer and the element-forming layer at the separation layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Composite particles and method for production thereof and use thereof
InactiveUS20060116279A1Improve photocatalytic activityImprove efficiencyPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyFiberUltraviolet
A composite particle comprised of a larger particle and, supported thereon, smaller particles wherein the smaller particles are photocatalyst-containing fine particles with an average particle diameter of 0.005-0.5 μm as calculated from a BET specific surface area, and the larger particle has an average particle diameter of 2-200 μm as measured by the laser diffraction-scattering particle size measuring method. The smaller particle is preferably a composite particle of titanium dioxide with an inorganic compound exhibiting no catalytic activity, such as silica, or a particle containing a Brφonsted acid salt, especially on the surface thereof; and an advantageous method for producing the above composite particles wherein the above larger particles and smaller particles are dry mixed by a ball-mill or mixed by rotation of blades or by shaking, with an energy constant controlled within a specific range. A composition comprising an organic polymer and the above composite particles can give a shaped article, such as fiber, film or a molding, exhibiting ultraviolet ray-screening function.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Enhanced boron nitride composition and compositions made therewith
A boron nitride composition having its surface treated with a coating layer comprising at least one of a silane, a siloxane, a carboxylic derivative, and mixtures thereof, wherein the coating layer adheres to at least 10% of the surface of the boron nitride. The boron nitride powder surface is first treated by either a calcination process, or by coating with at least an inorganic compound for the surface to have a plurality of reactive sites containing at least a functional group that is reactive to at least one functional group of the final coating layer.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS QUARTZ INC
Flame retardant composition with improved fluidity, flame retardant resin composition and molded products
ActiveUS20070176154A1Improve flame retardant performanceImproved powder property and hygroscopic propertyDyeing processMelamine phosphateAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a flame retardant composition comprising 1-99 weight parts of a salt of piperazine and an inorganic compound selected from among piperazine phosphate, piperazine pyrophosphate and piperazine polyphosphate, or a mixture of two or more of these piperazine salts (ingredient (A)), 99-1 weight parts of a salt of melamine and an inorganic compound selected from among melamine phosphate, melamine pyrophosphate and melamine polyphosphate, or a mixture of two or more of these melamine salts (ingredient (B) ) (wherein, the sum of ingredient (A) and ingredient (B) is 100 weight parts), 0-50 weight parts of an arbitrary ingredient (ingredient (C)), and 0.01-20 weight parts of a silicone oil having a viscosity at 25° C. of 5000 mm2 / s (ingredient (D)) which is added thereto. This flame retardant not only has superior flame retarding properties, but also has enhanced powder properties and anti-hygroscopic properties, and when it is added to a resin, there is little change of electrical resistance.
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Process for removing mercury from liquid hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6537443B1Reduce concentrationEasy maintenanceRefining with non-metalsRefining with metal saltsParticulatesNatural-gas condensate
Mercury is removed from crude oils, natural gas condensates and other liquid hydrocarbons by first removing colloidal mercury and solids that contain adsorbed mercury and then treating the hydrocarbons with an organic or inorganic compound containing at least one sulfur atom reactive with mercury. The sulfur compound reacts with dissolved mercury that contaminates the hydrocarbons to form mercury-containing particulates that are then removed from the hydrocarbons to produce a purified product having a reduced mercury content. Preferably, the treating agent is an organic sulfur-containing compound such as a dithiocarbamate or sulfurized isobutylene.
Owner:UNION OIL OF CALIFORNIA
Coating composition, coating film thereof, antireflection coating, antireflection film, image display, and intermediate product
InactiveUS20030096102A1Good dispersibilityGood dispersionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsMetallurgyRefractive index
A coating material capable of forming a high-quality thin film having a regulated refractive index; a coating film formed from the coating material; an antireflection coating comprising the coating film; an antireflection film to which the antireflection coating is applied; and an image display. The coating composition comprises (1) rutile-form titanium oxide having primary particle diameter of 0.01 to 0.1 mum and coated with an inorganic compound for reducing or eliminating the photocatalytic activity and with an organic compound having an anionic polar group and / or an organometallic compound, (2) a binder ingredient curable with an ionizing radiation, (3) a dispersant having an anionic polar group, and (4) an organic solvent. The coating film formed from the coating composition is suitable for forming a light-transmitting layer constituting or contained in a single- or multi-layer antireflection coating (17), in particular, a medium-refractive-index layer (18), high-refractive-index layer (19), or hard coat layer (16) having a high refractive index.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Biaxially stretched multilayer polypropylene film and use thereof
InactiveCN101160209ALow densityLow surface smoothnessSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsPolymer scienceFilm base
Disclosed is a biaxially stretched multilayer polypropylene film wherein a front layer and back layer composed of a propylene polymer (a1) are respectively arranged on both sides of a biaxially stretched polypropylene film base layer (B) which is composed of a propylene polymer composition (A) obtained by adding an inorganic compound powder (a2) to the propylene polymer (a1). This biaxially stretched multilayer polypropylene film is characterized in that the front and back layers have a surface roughness (three-dimensional center plane average roughness SRa) of less than 0.08 [mu]m and a glossiness (incident angle: 60 degrees) of not less than 114%, and the multilayer polypropylene film has a total light transmittance of not more than 20% and a density of 0.40-0.65 g / cm<3>.
Owner:TOHCELLO CO LTD (JP)
Resin composition
InactiveUS20050107497A1Improve barrier propertiesImprove moisture resistanceSpecial tyresRecord information storagePolymer scienceAdhesive belt
A resin composition, substrate material, sheet, laminated board, resin-bearing copper foil, copper-clad laminate, TAB tape, printed board, prepreg and adhesive sheet are provided which exhibit improved mechanical properties, dimensional stability, heat resistance and flame retardance, particularly high-temperature physical properties. A resin composition containing 100 parts by weight of a thermosetting resin and 0.1-65 parts by weight of an inorganic compound, the resin composition having a mean linear expansion coefficient (α2) of up to 17×10−3 [° C.−1] over the temperature range from a temperature 10° C. higher than a glass transition temperature of the resin composition to a temperature 50° C. higher than the glass transition temperature of the resin composition.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Organic electroluminescence device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070020484A1Improve efficiencyProlong lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsInorganic compound
An organic electroluminescent (EL) device is provided which uses an electron-transport layer including hole blocking capability. The device includes a stack structure, with an emitting layer and an electron-transport layer provided between an anode and a cathode. The electron-transport layer is a mixture of at least two materials. This mixture may include an organic compound and one or more other organic compounds, or may include a metal or inorganic compound and one or more other metal or inorganic compounds, or may include one or more organic compounds and one or more metal or inorganic compounds. By incorporating a hole blocking capability into the electron-transport layer, structure and fabrication of the device is simplified and efficiency is increased.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Absorbent polymer structure with improved retention capacity and permeability
ActiveUS20060029782A1Rotating receptacle mixersLiquid surface applicatorsPolymer scienceCross linker
A process for producing an absorbent polymer structure (Pa) by treating the outer portion of an untreated absorbent polymer structure (Pu1). The process includes the step of bringing the outer portion of the untreated absorbent polymer structure (Pu1) into contact with an aqueous solution including at least one chemical cross-linker and at least one inorganic compound in dispersed colloidal form. The process also includes the step of heating the absorbent polymer structure, of which the outer portion has been brought into contact with the aqueous solution, at a temperature within a range from about 40 to about 300° C., so that the outer portion of the absorbent polymer structure is more strongly cross-linked in comparison to the inner portion and the inorganic compound is at least partly immobilized in the outer portion of the absorbent polymer structure.
Owner:EVONIK SUPERABSORBER GMBH
Electroconductive laminate, electromagnetic wave shielding film for plasma display and protective plate for plasma display
InactiveUS20080174872A1Improve conductivitySmall resistivityMagnetic/electric field screeningLayered productsChemical compoundRefractive index
An electroconductive laminate comprising a substrate and an electroconductive film formed on the substrate, wherein the electroconductive film has a multilayer structure having a high refractive index layer containing an inorganic compound and a metal layer alternately laminated from the substrate side in a total layer number of (2n+1) (wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 12); the refractive index of the inorganic compound is from 1.5 to 2.7; the metal layer is a layer containing silver; the total thickness of all metal layer(s) is from 25 to 100 nm; and the resistivity of the electroconductive film is from 2.5 to 6.0 μΩcm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Formulations of bendamustine
InactiveUS20130210879A1Improve long-term stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAntioxidantMedicine
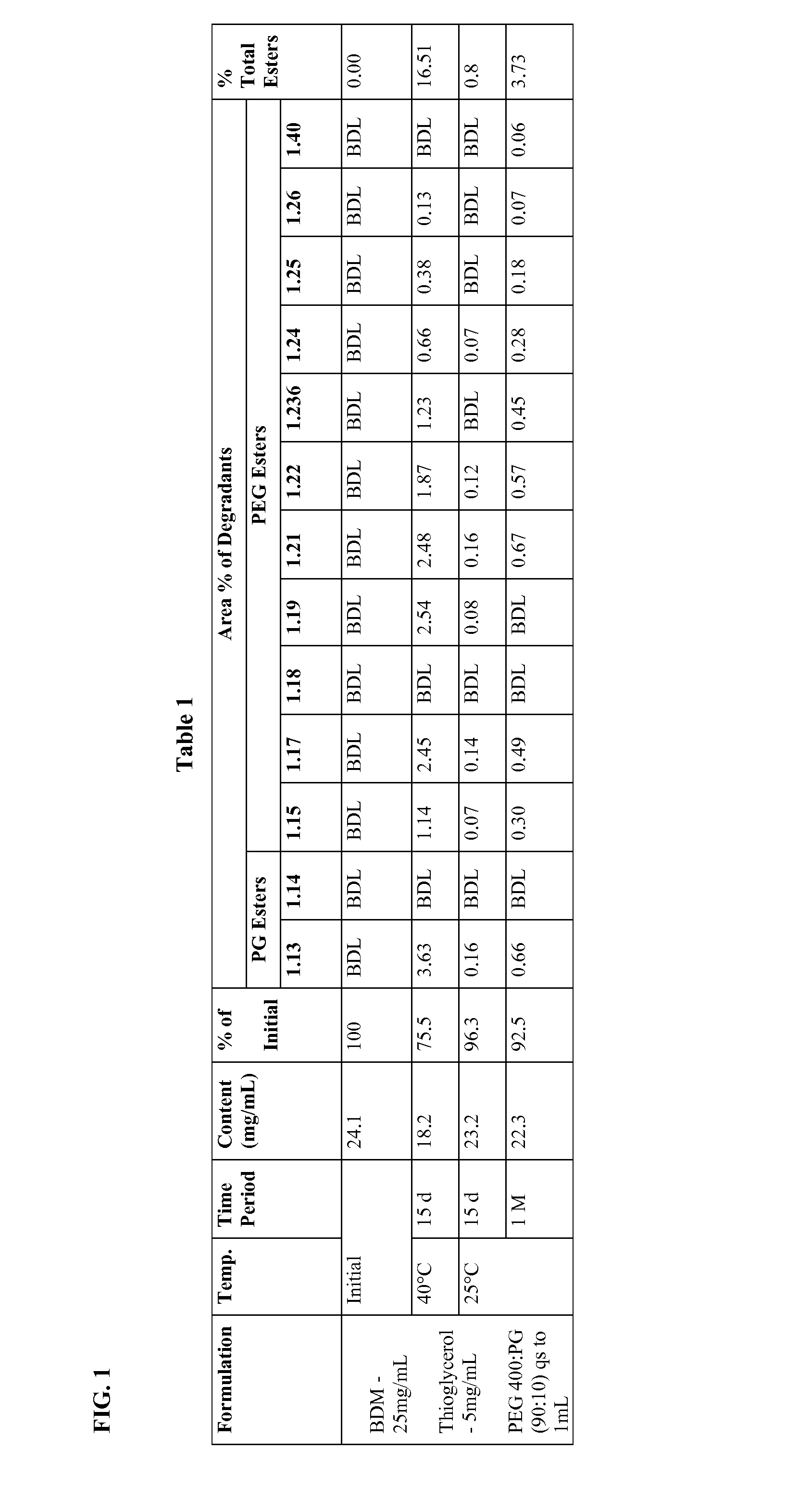
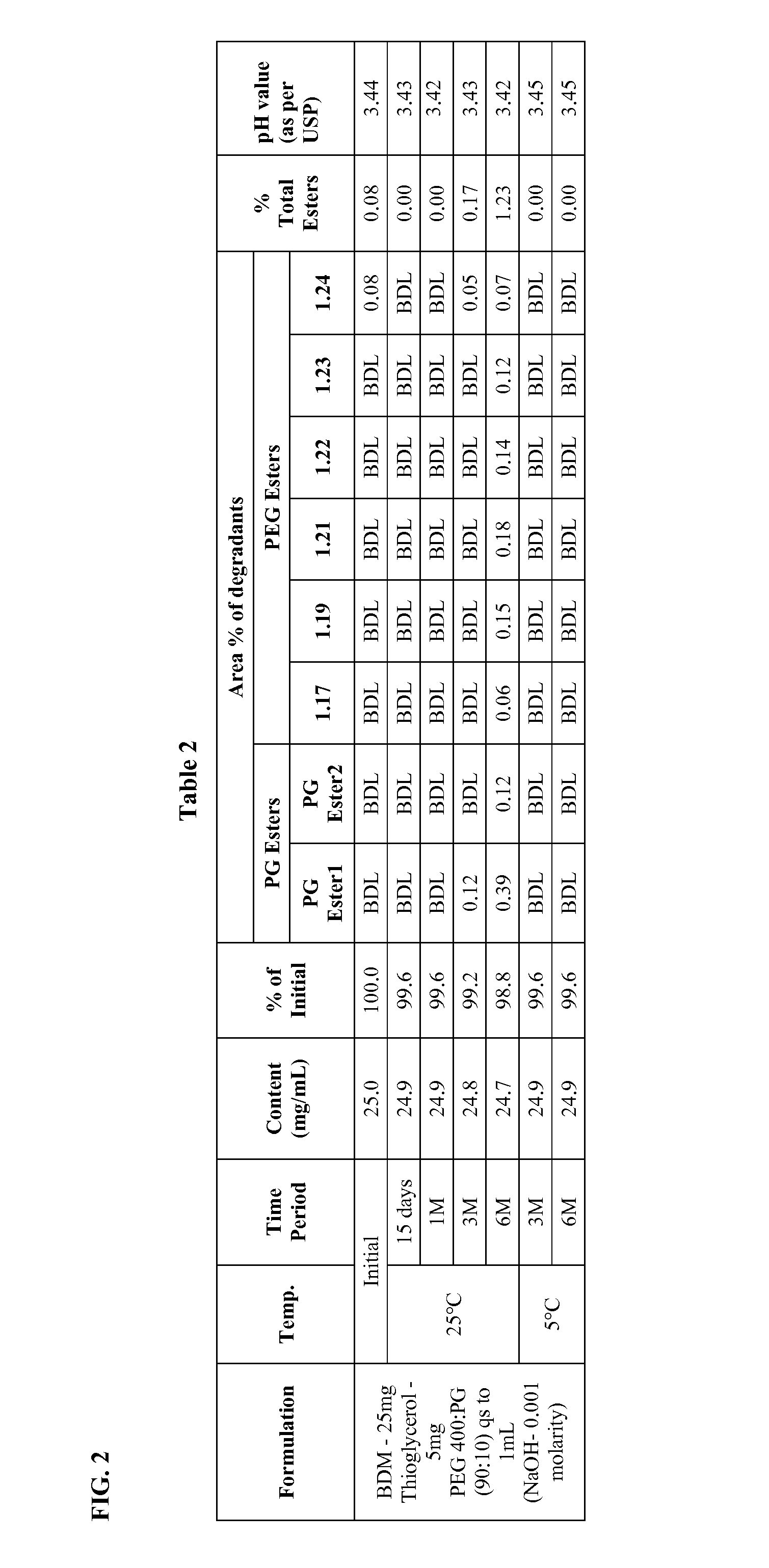
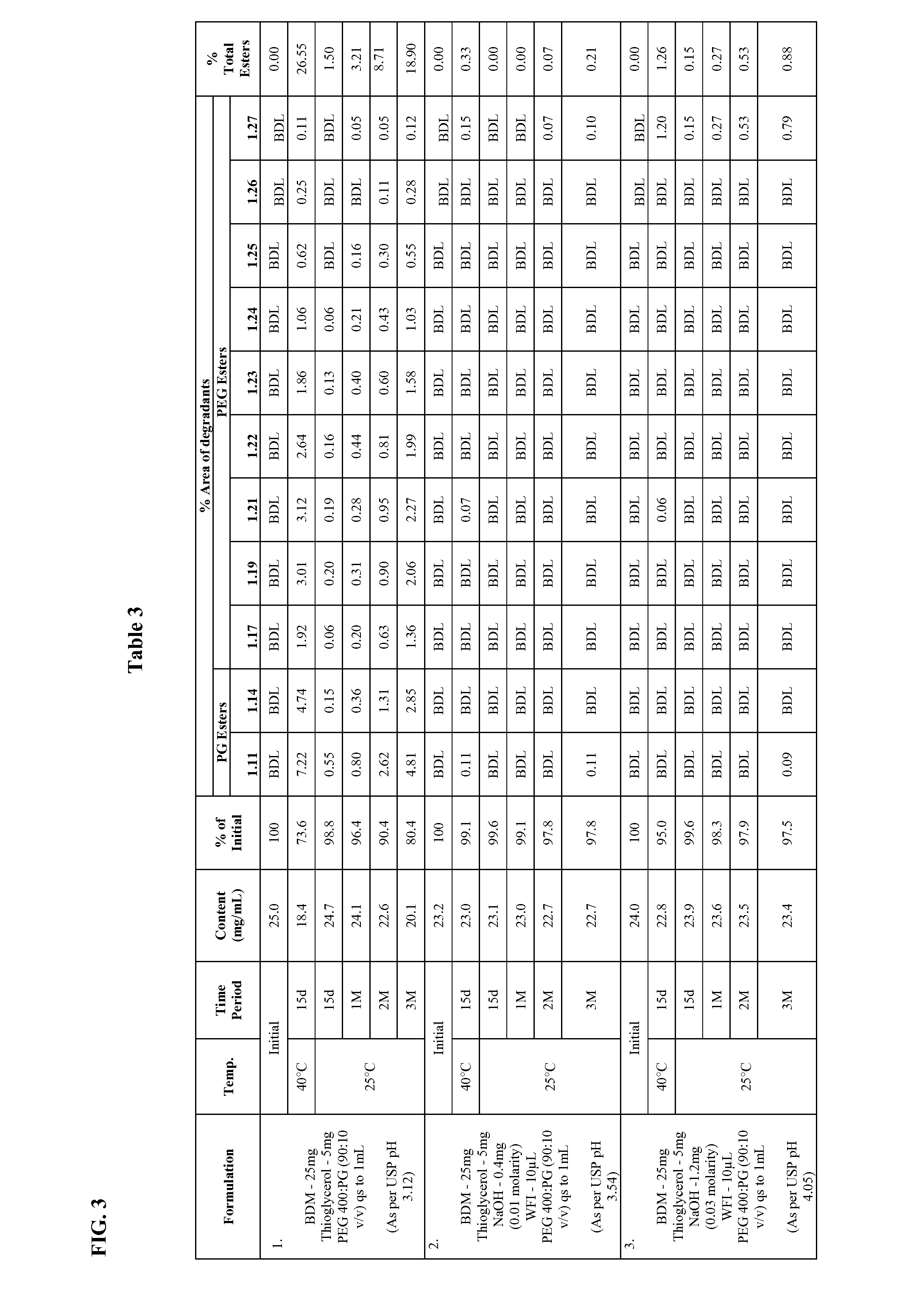
Long term storage stable bendamustine-containing compositions are disclosed. The compositions can include bendamustine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable fluid contains a mixture of PEG and PG; an organic or inorganic compound in an amount sufficient to obtain a pH of from about 6.0 to about 11 for the polyethylene glycol, as measured using USP monograph for polyethylene glycol; and optionally an antioxidant. The bendamustine-containing compositions have less than about 5% total esters, on a normalized peak area response (“PAR”) basis as determined by high performance liquid chromatography (“HPLC”) at a wavelength of 223 nm, after at least about 15 months of storage at a temperature of from about 5° C. to about 25° C.
Owner:EAGLE PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Organic and inorganic compound fertilizer
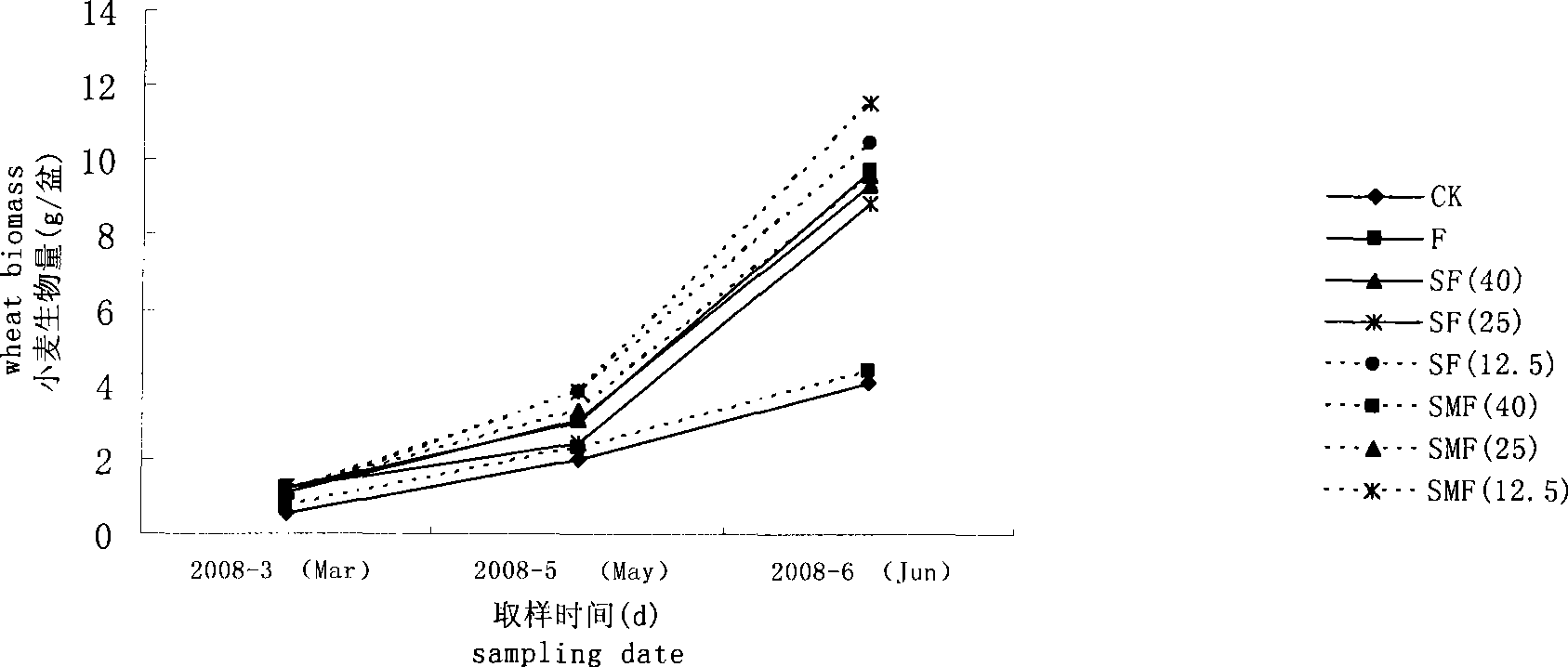
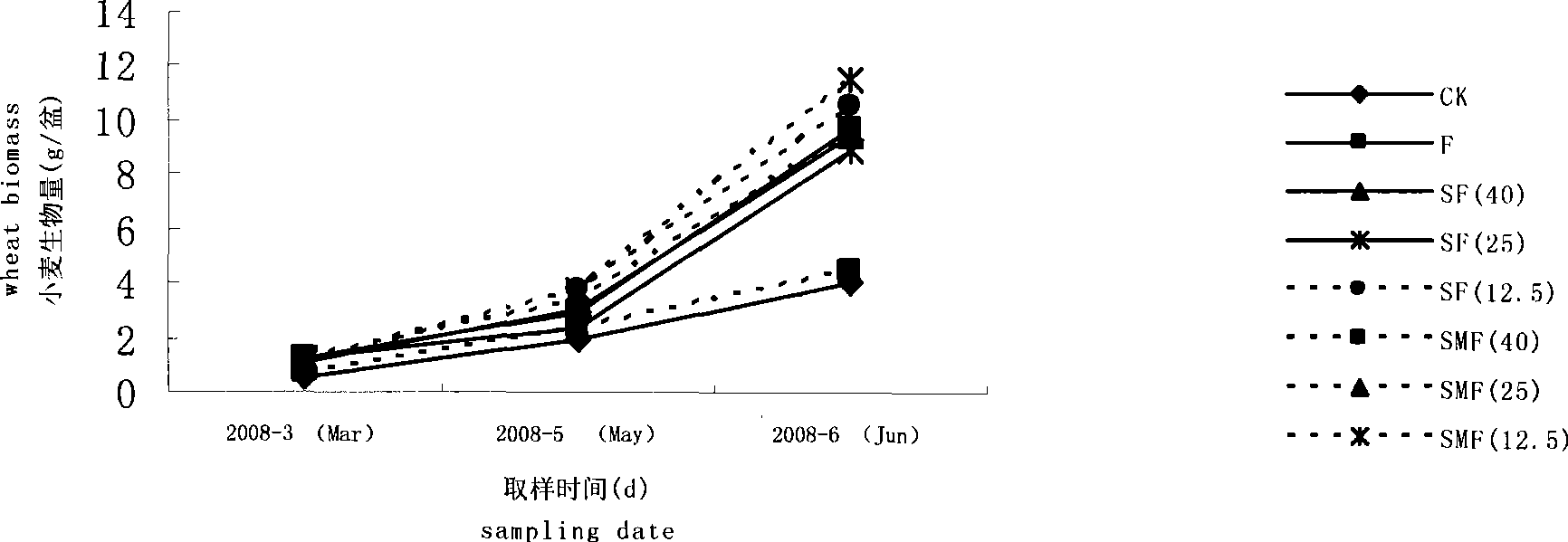
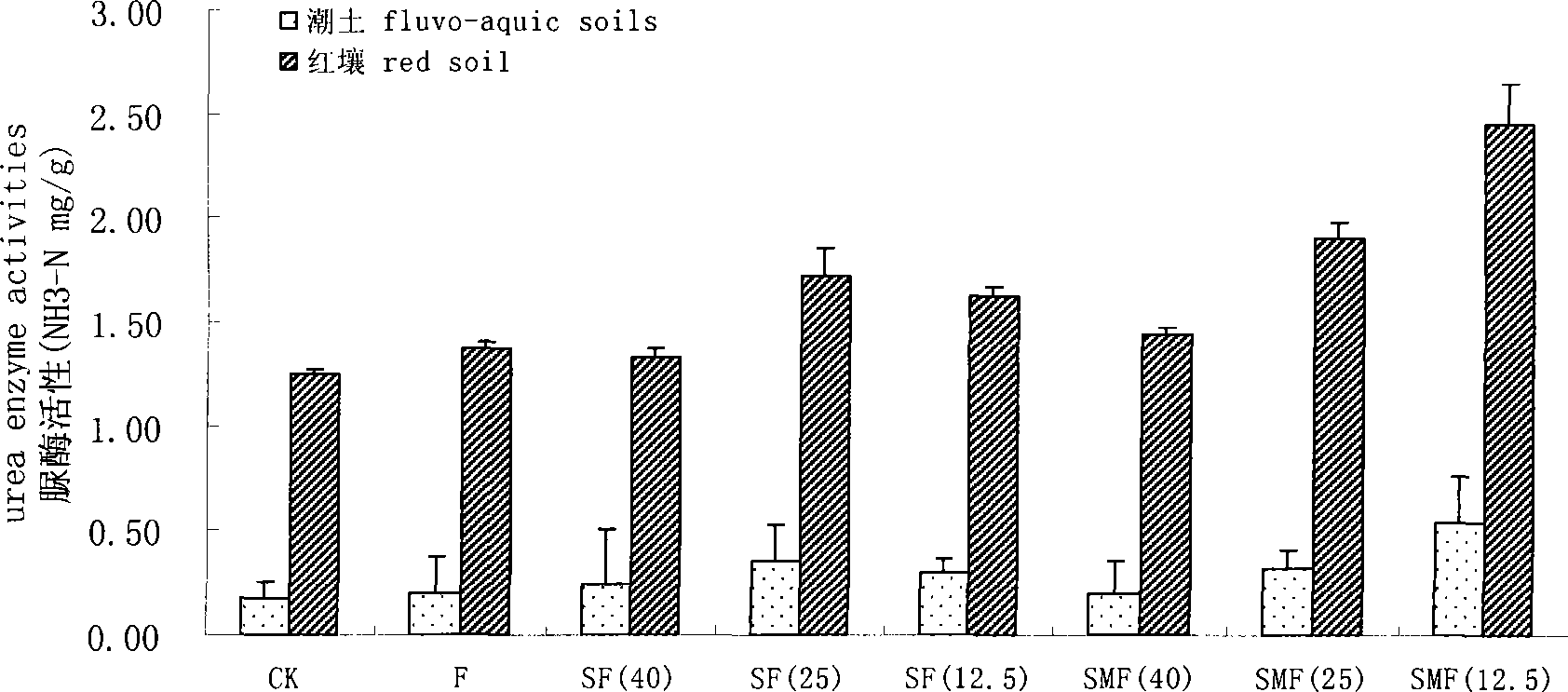
The invention relates to an organic-inorganic composite fertilizer, which consists of straws, excrements and fertilizers. By weight, in the composite fertilizer, the ratio of N, P2O5 and K2O is 10 to 35:8 to 12:5 to 8, and the ratio of C and N is 10:15. The organic-inorganic composite fertilizer has very obvious effects for improving biomass of wheat and increasing readily available nutrient of soil, urease activity, microbial biomass in the carbon-nitrogen aspect.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microstructured high-temperature hybrid material, its composite material and method of making
This invention provides a hybrid material that exhibits strength, stiffness and ability to resist high temperatures. This hybrid material essentially consists of component A and component B. Component A is selected from the group consisting of inorganic compounds, oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides, and combinations thereof. Component B is selected from the group comprising elemental carbon, inorganic compounds, oxides, carbides, nitrides, borides, and combinations thereof. Component B comprises a plurality of units, each of the units substantially exhibiting a shape, such that this shape substantially exhibits a long dimension and a short dimension, with the short dimension being in a direction that is essentially perpendicular to the direction of the long dimension and the short dimension being in the range from 0.1 nm to 0.5 μm. Each of the units of component B is substantially in contact with and substantially bonded to at least one of the units of component A.
Owner:CHUNG DEBORAH D L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com